Patents
Literature
106 results about "Quadrupole field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
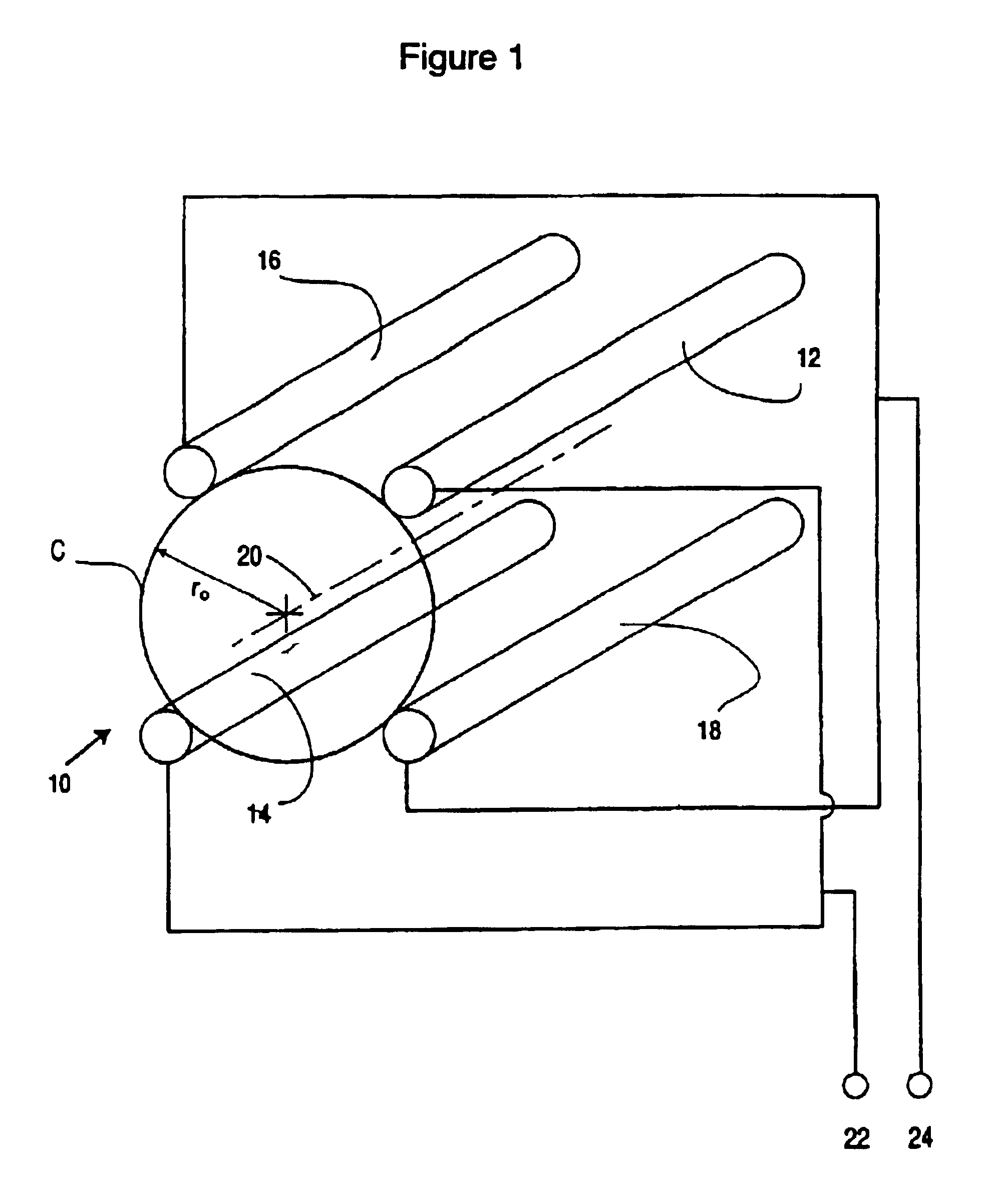
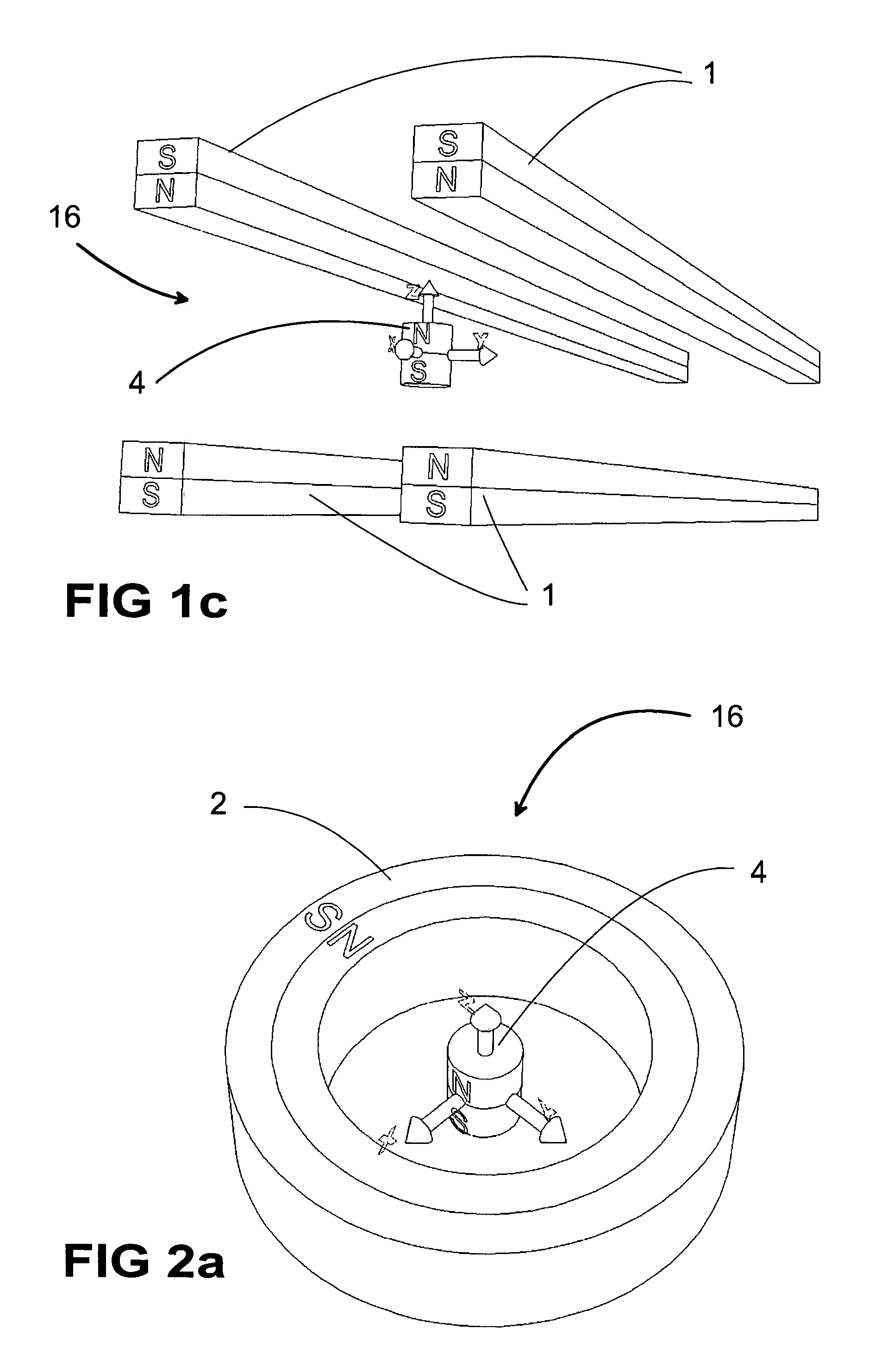
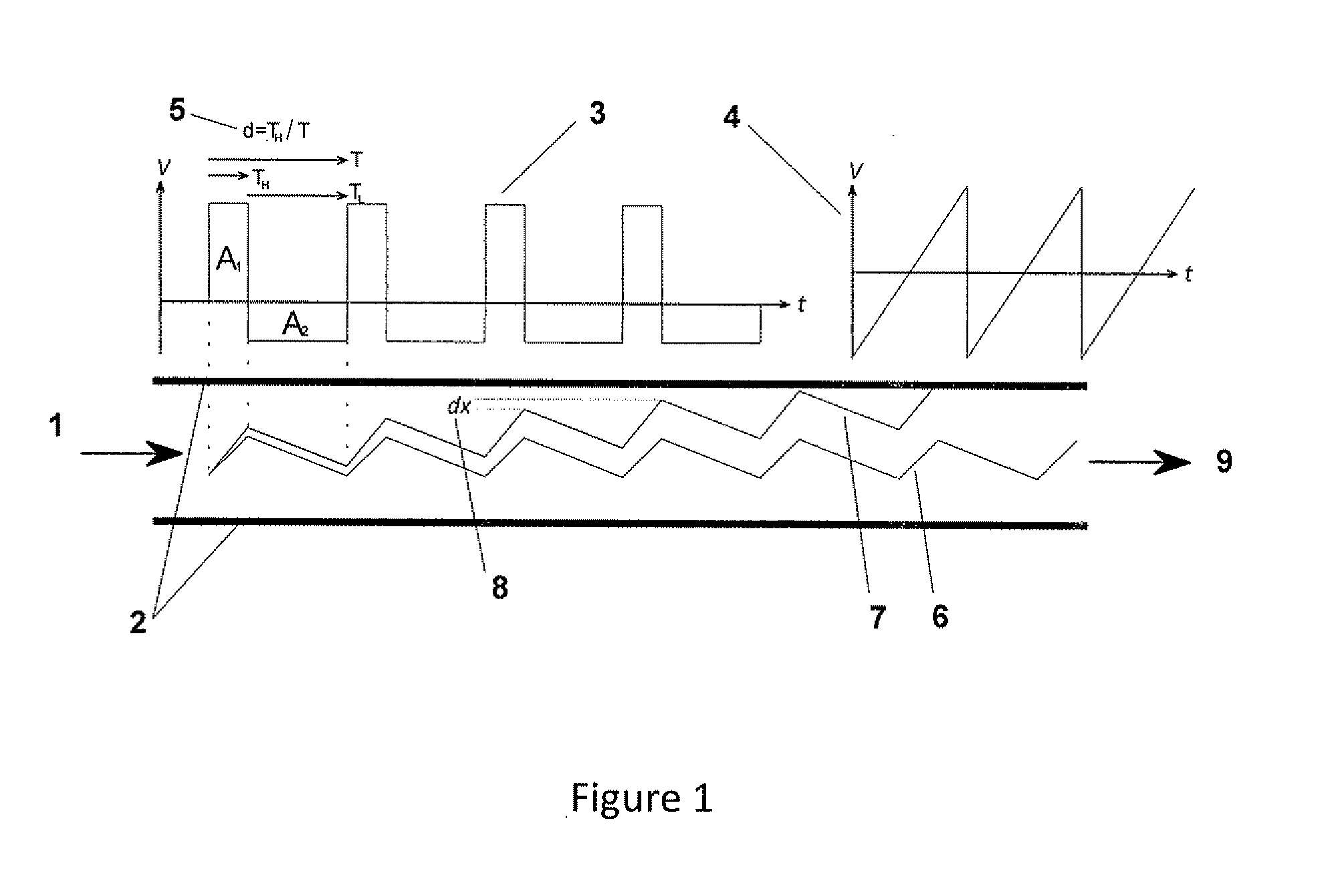
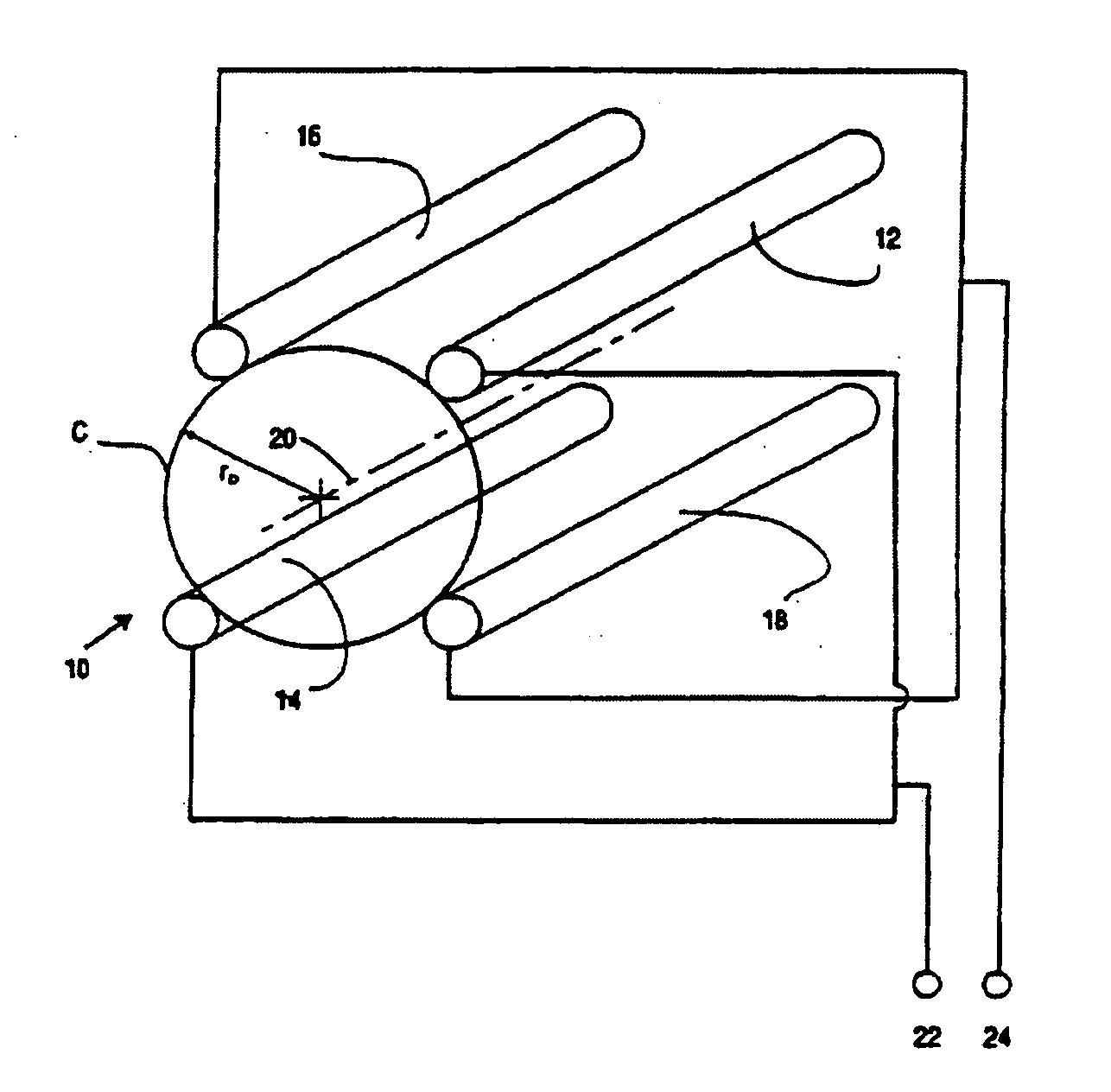
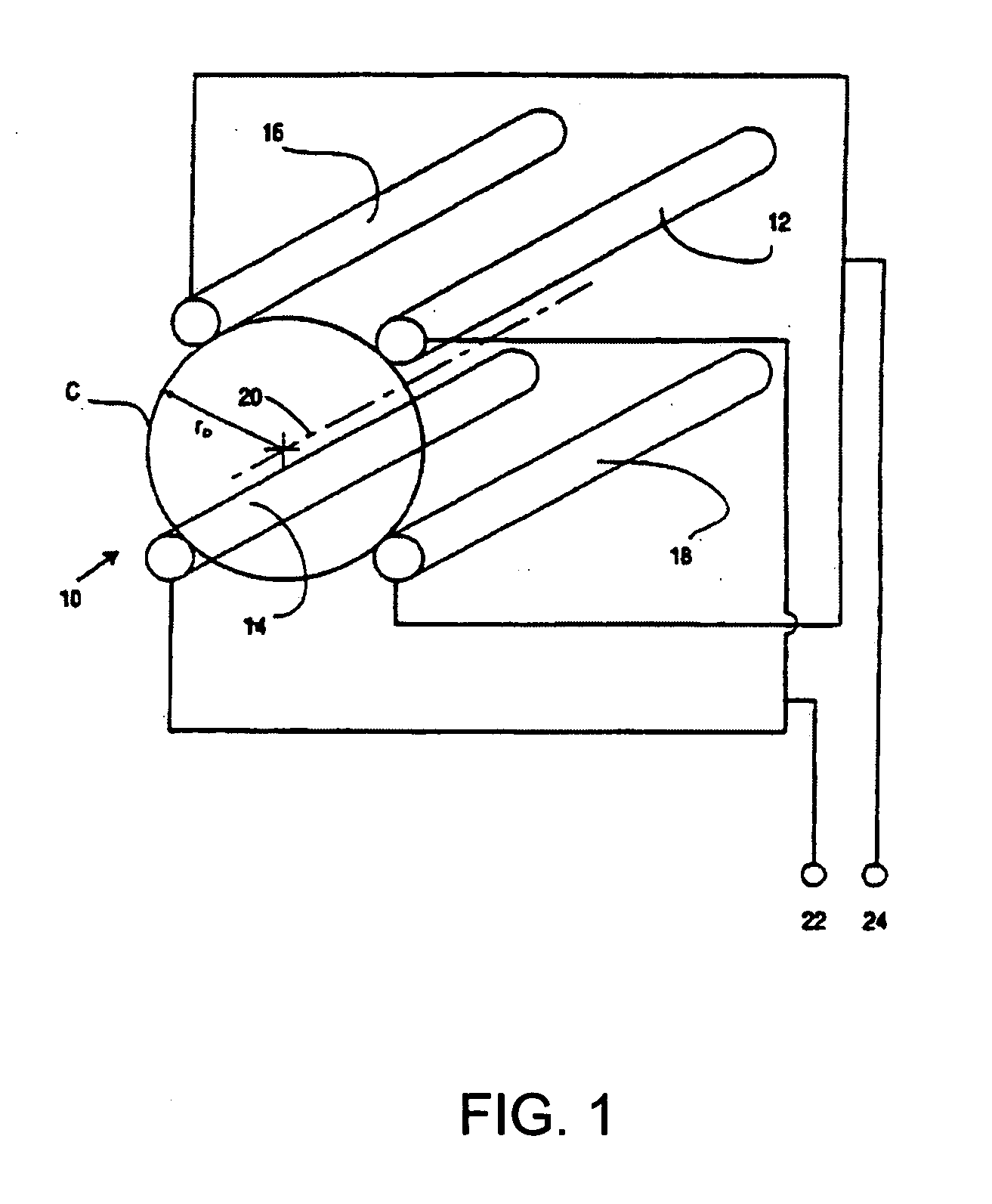
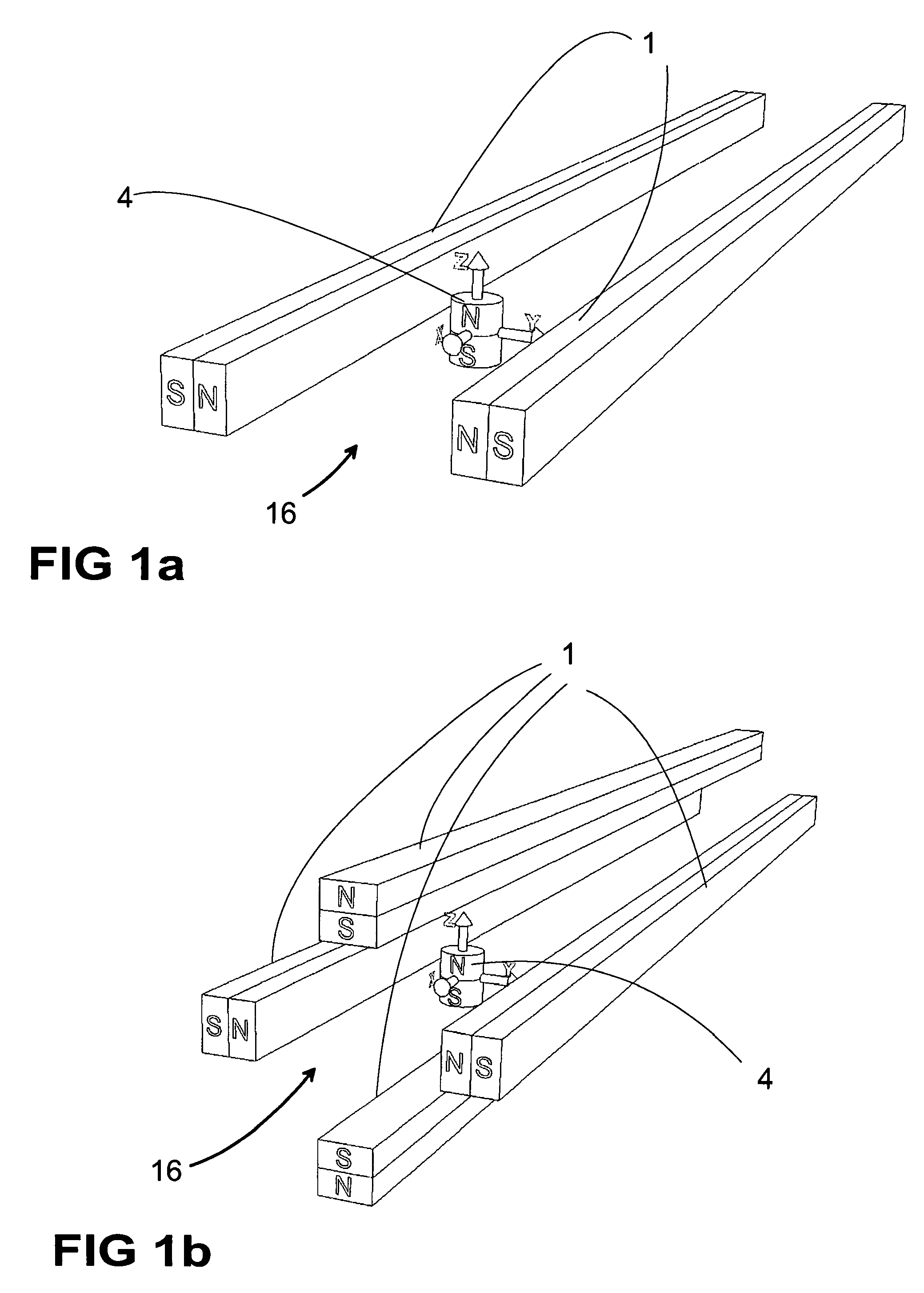
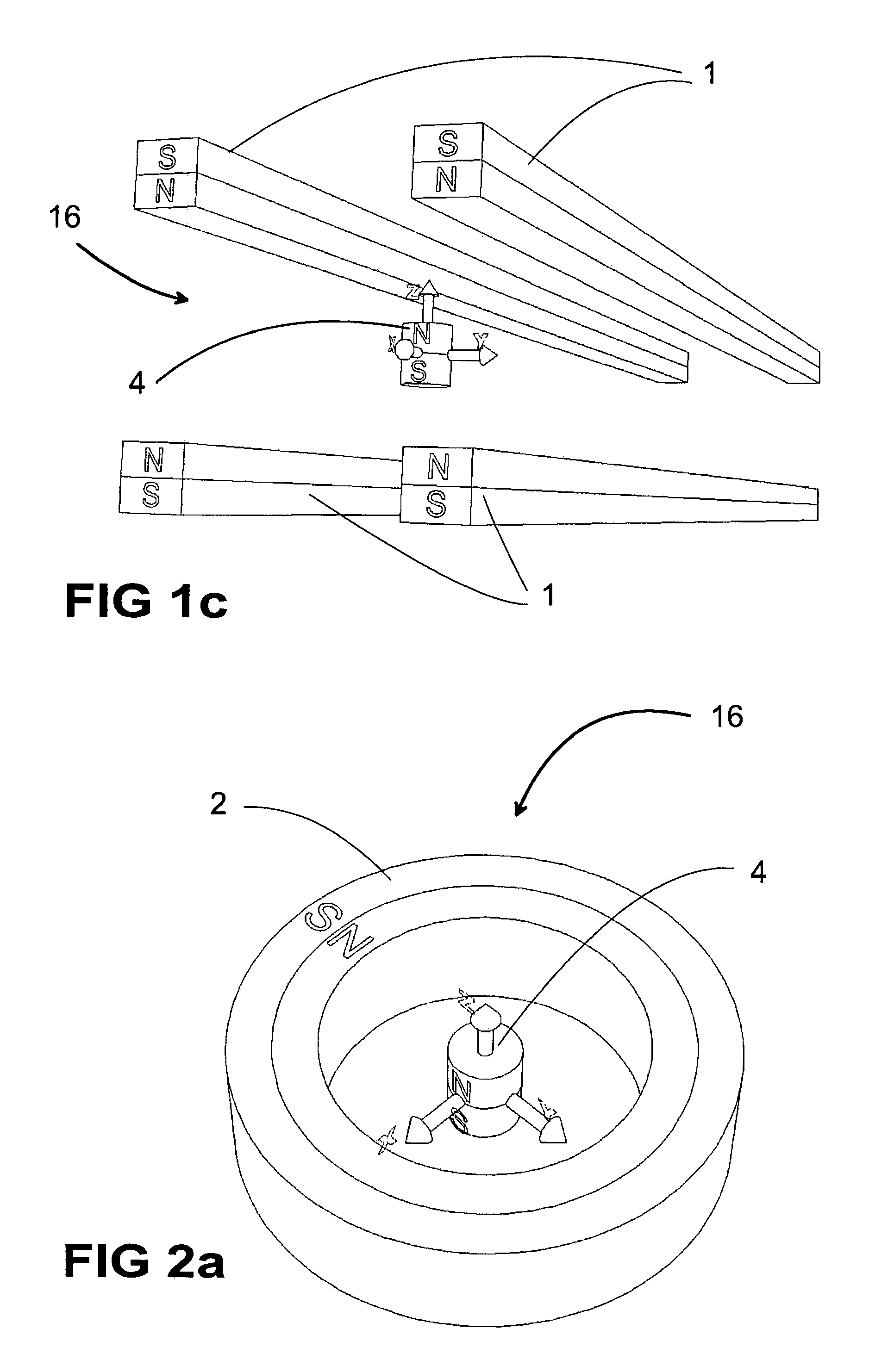
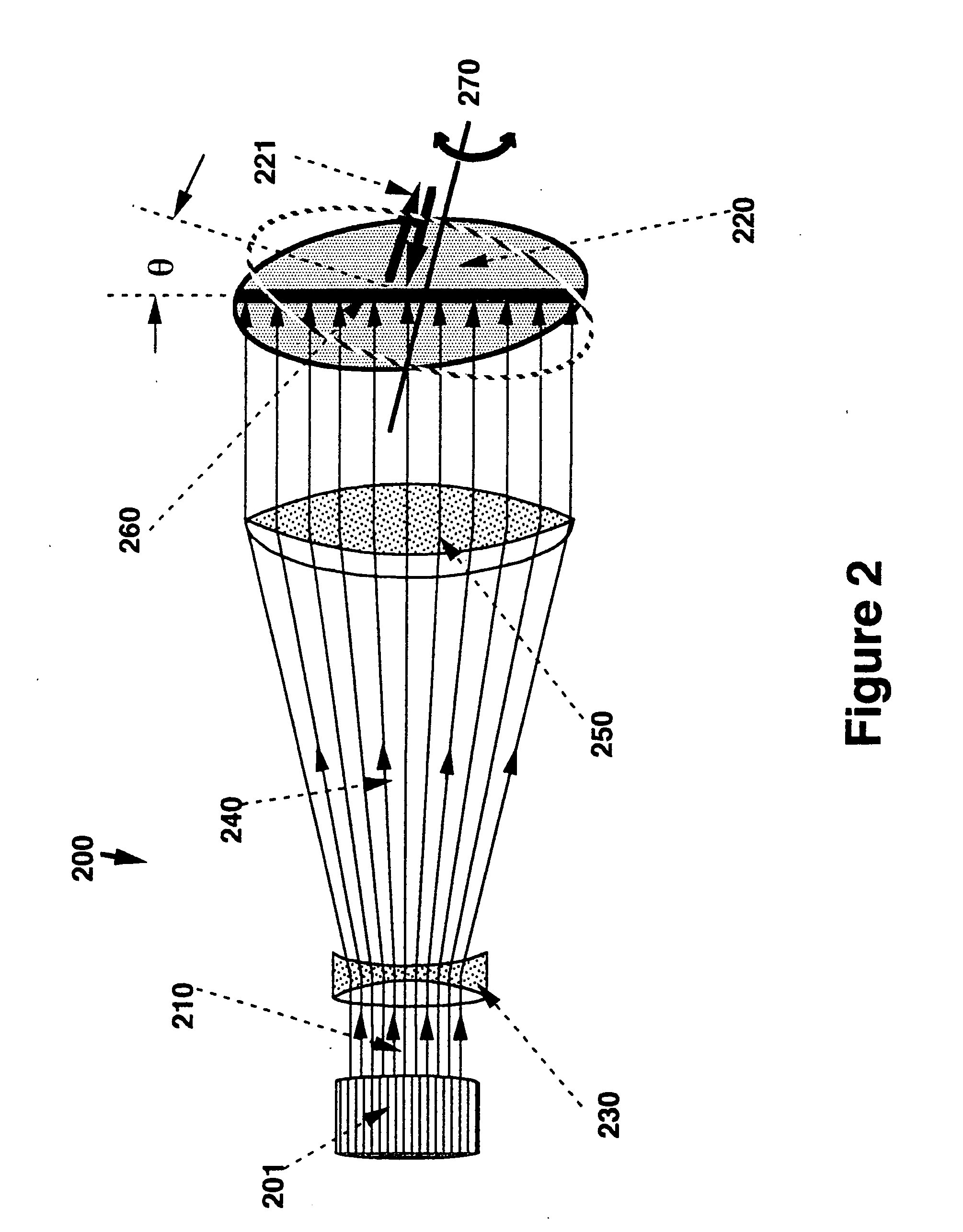
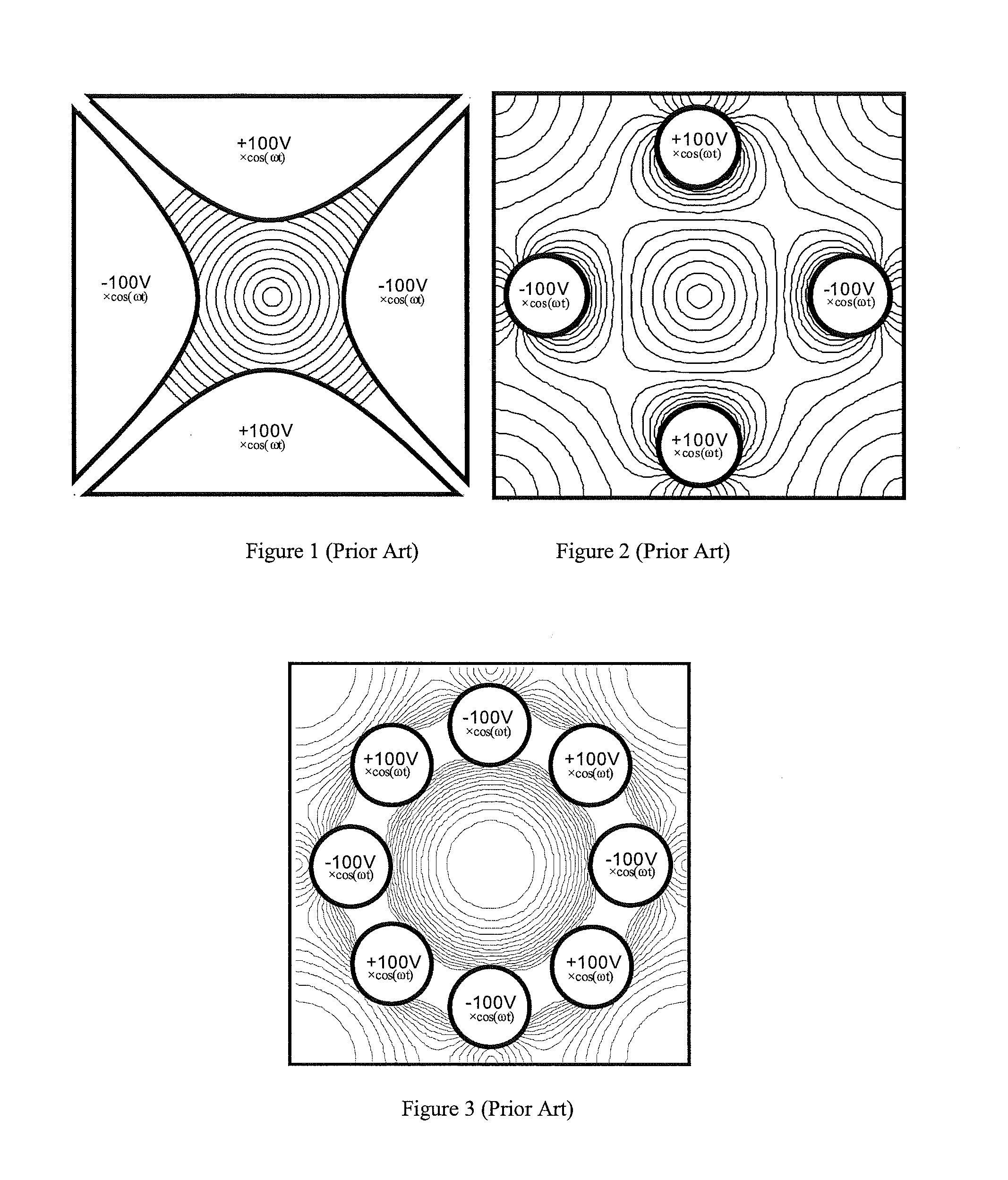
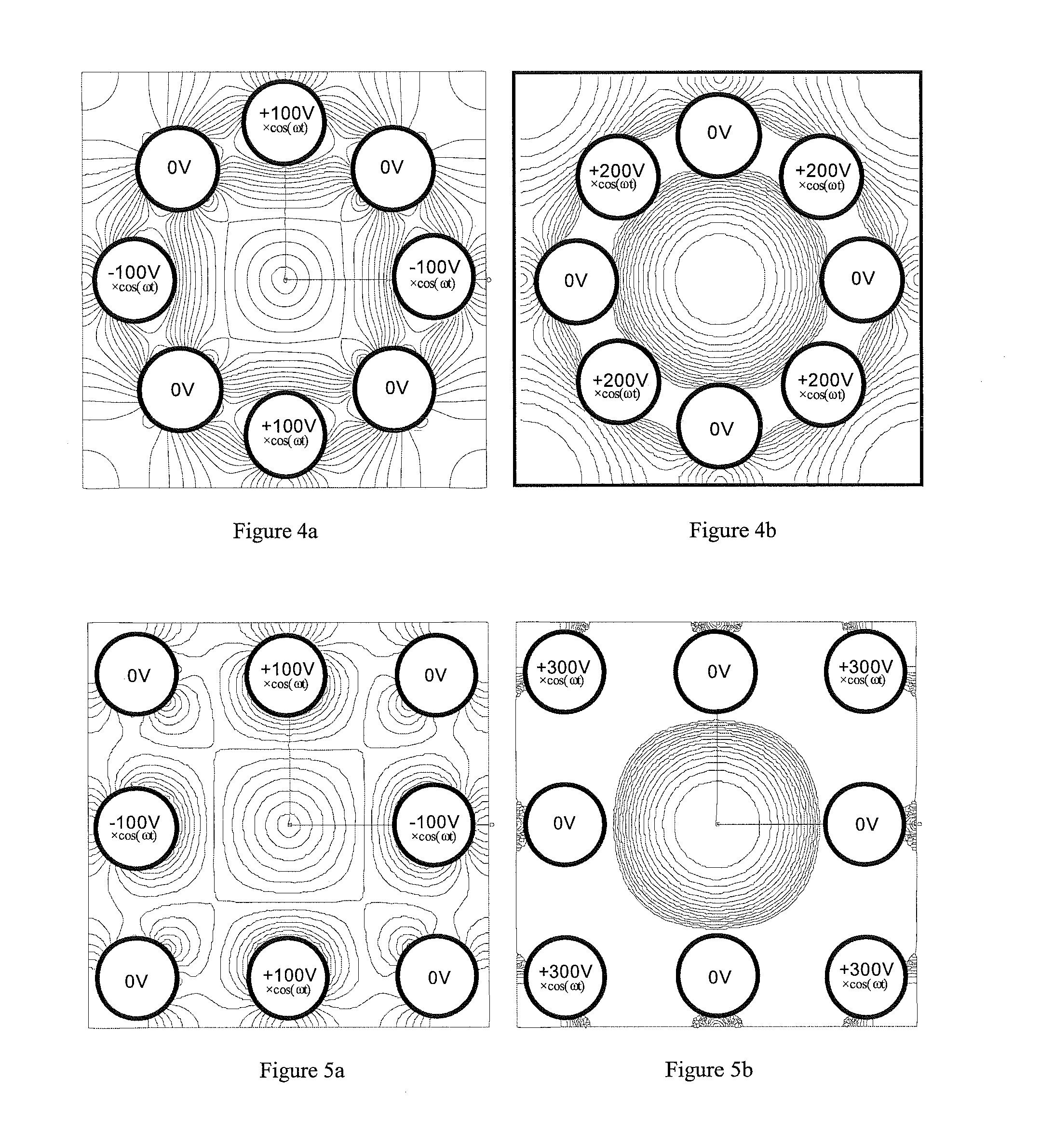
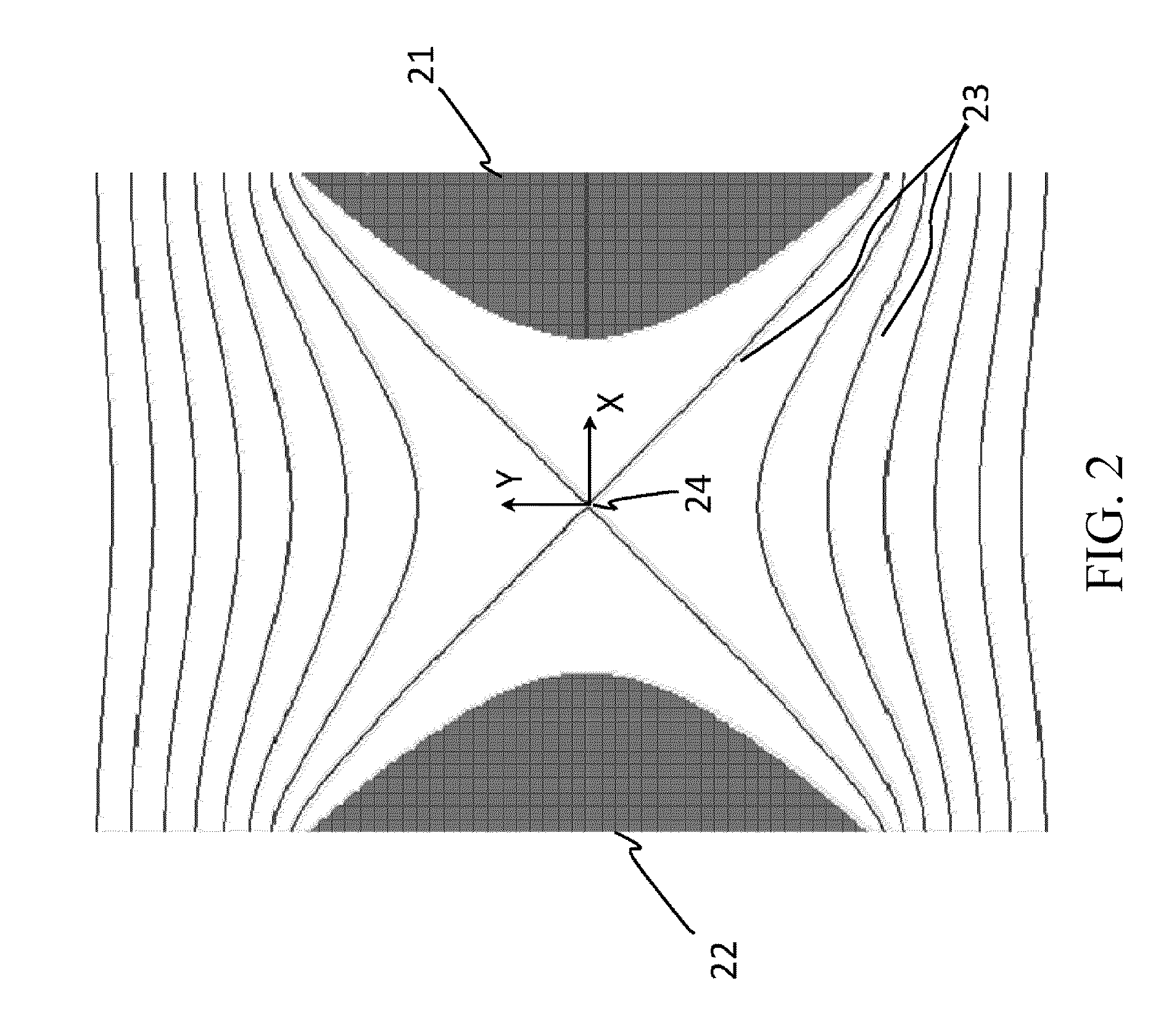
Quadrupole Magnetic Field. Two properly spaced coils with currents in the same direction can produce a useful magnetic field geometry in the Helmholtz coil arrangement. Also useful is the arrangement obtained by reversing one of the coils to produce a magnetic quadrupole field.
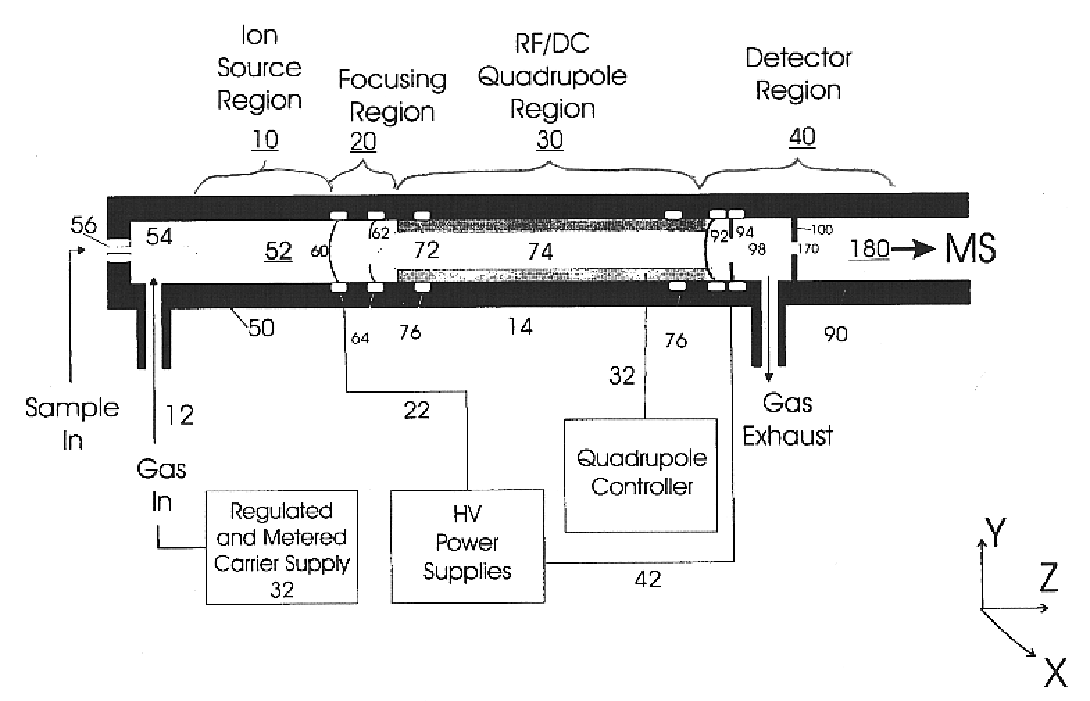
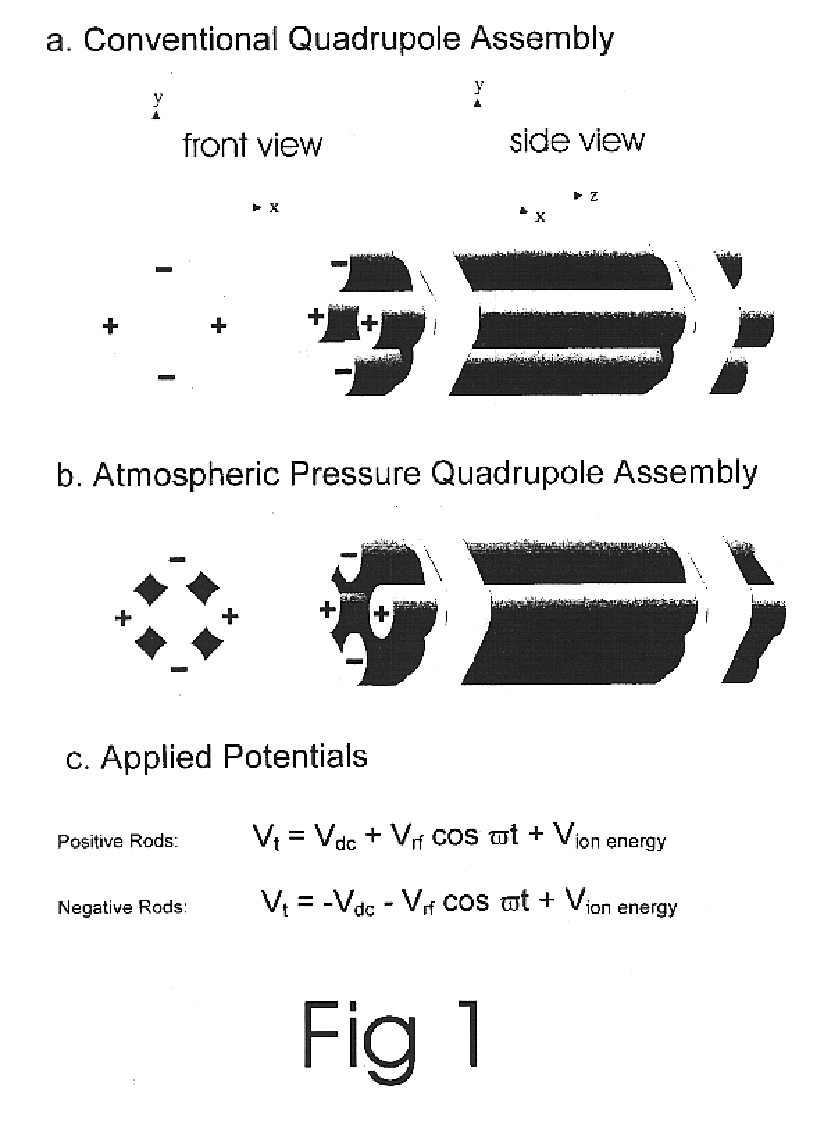
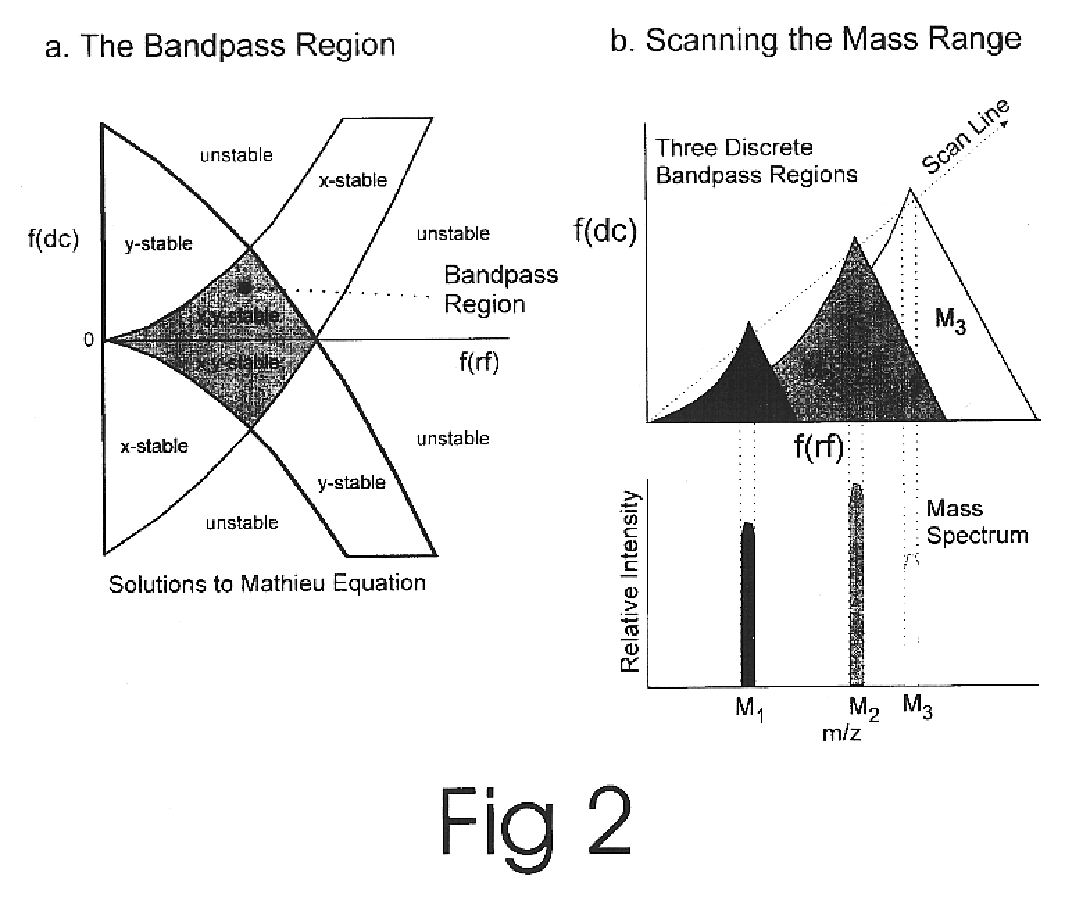
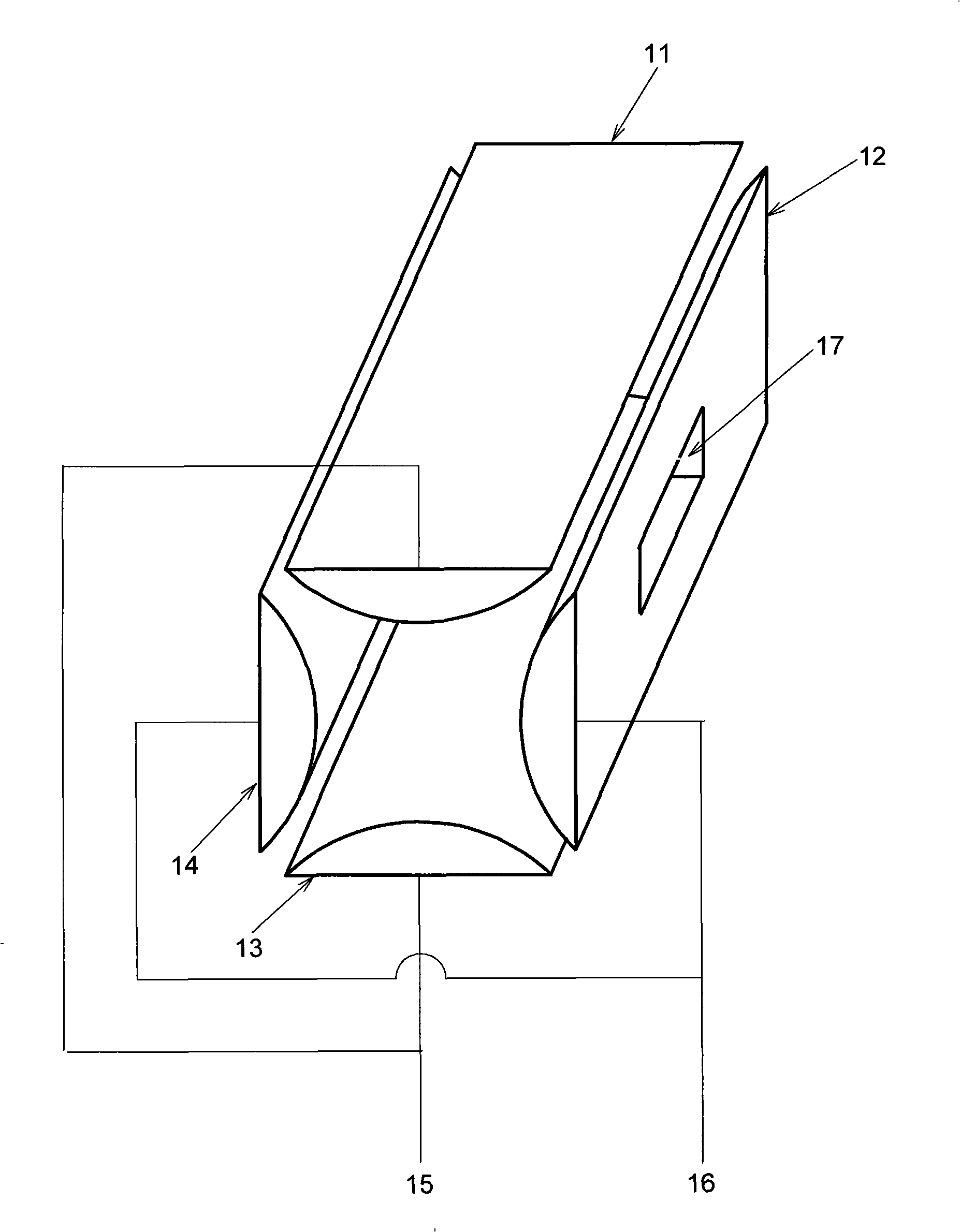
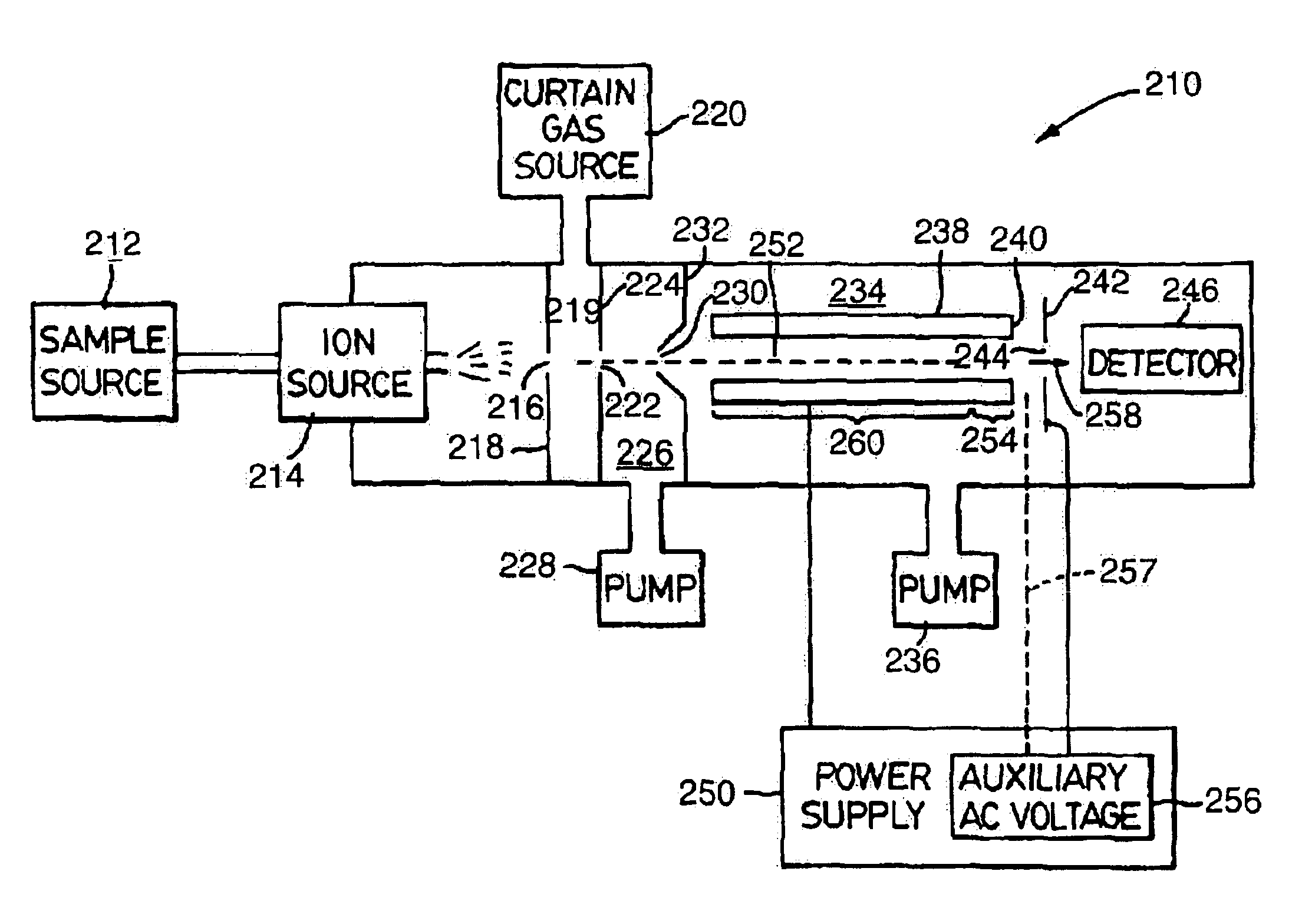
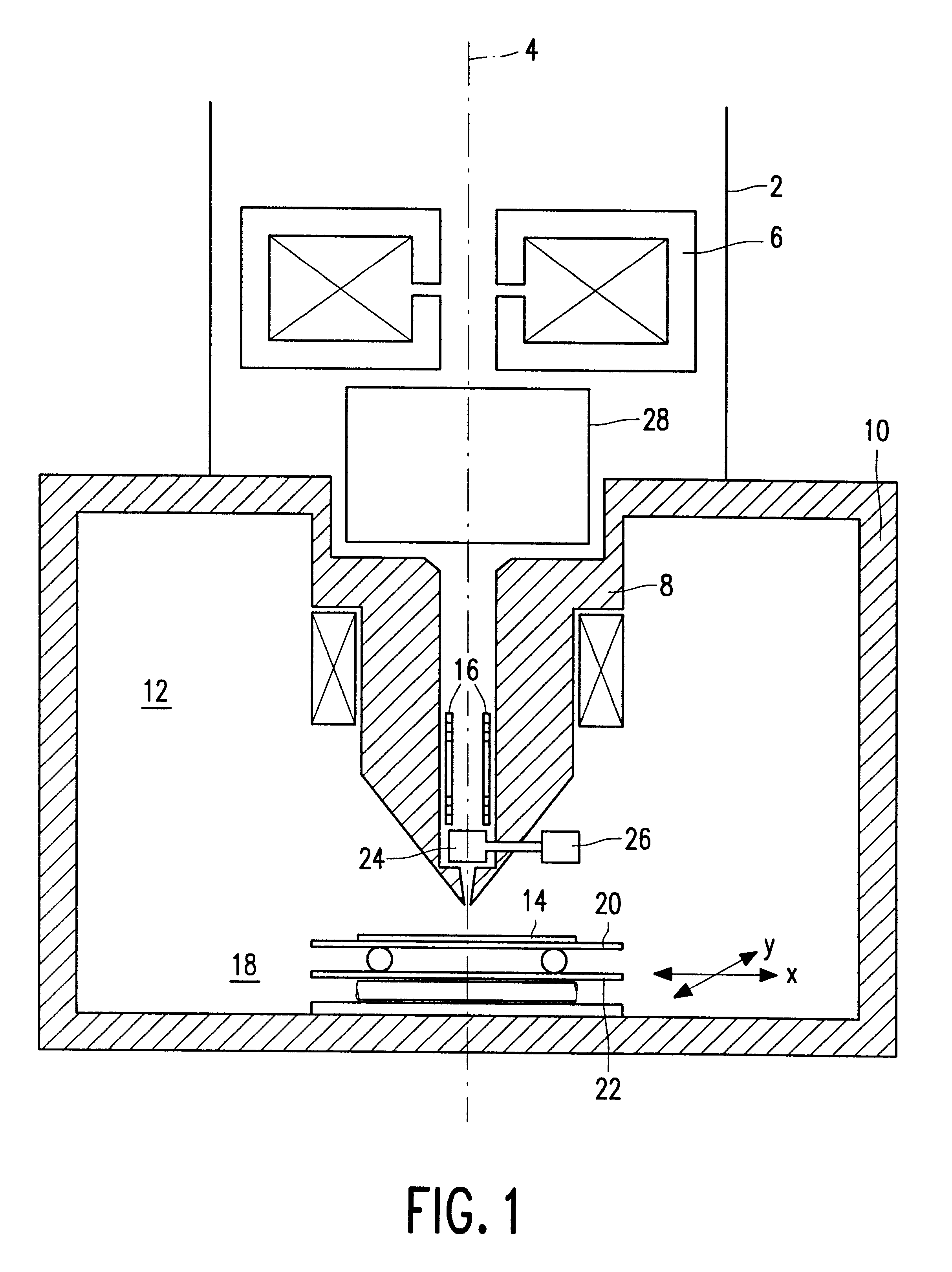
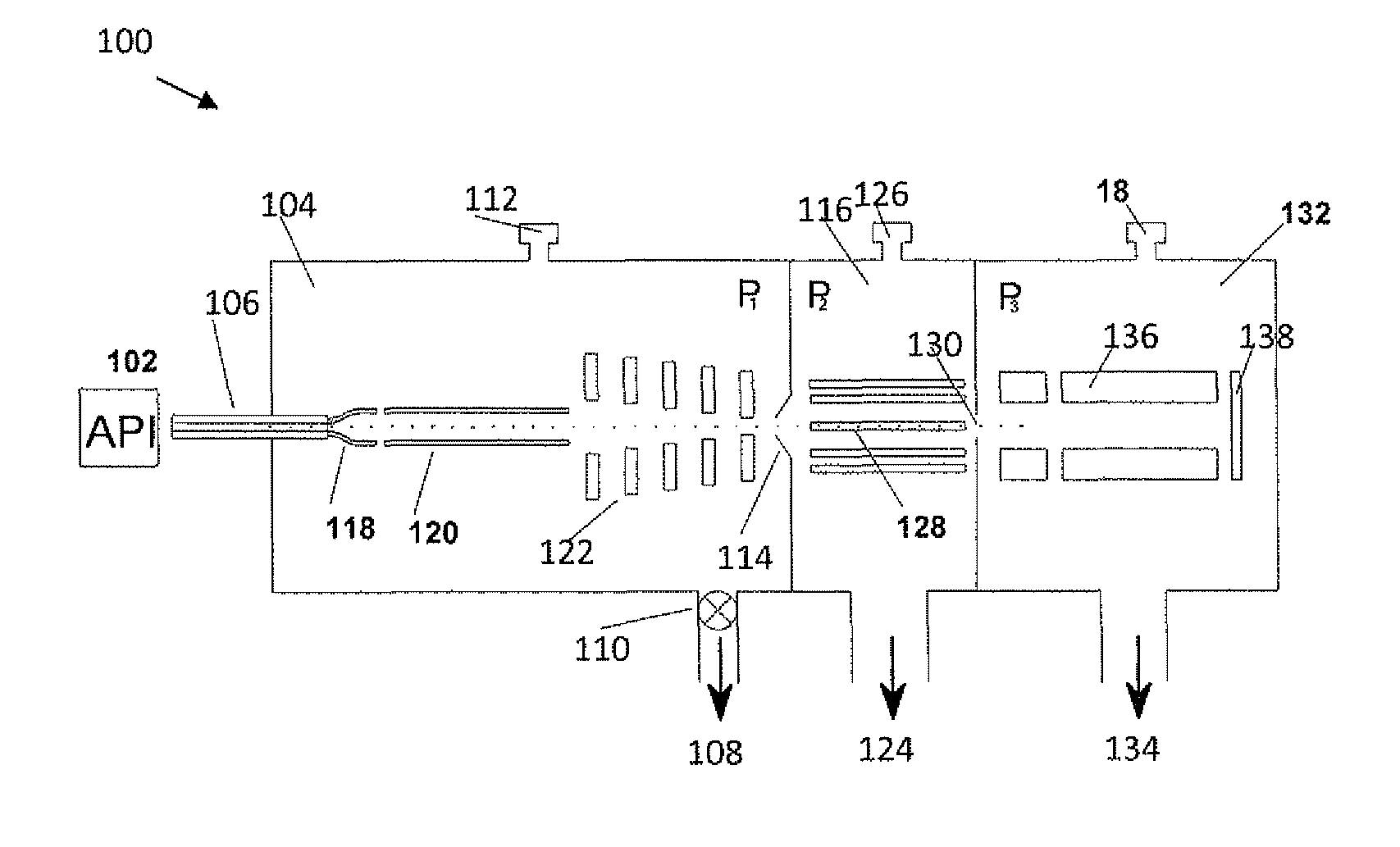
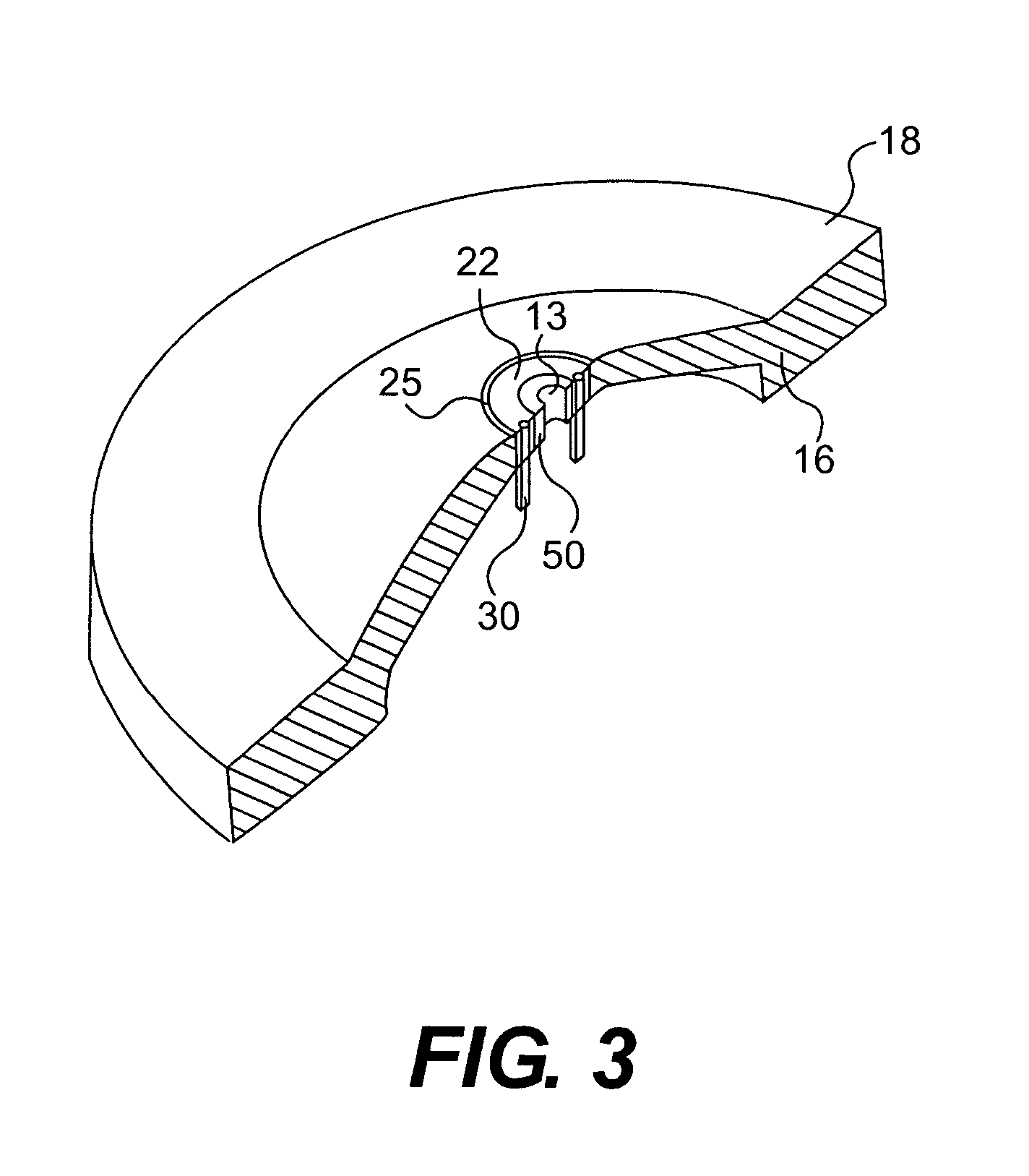
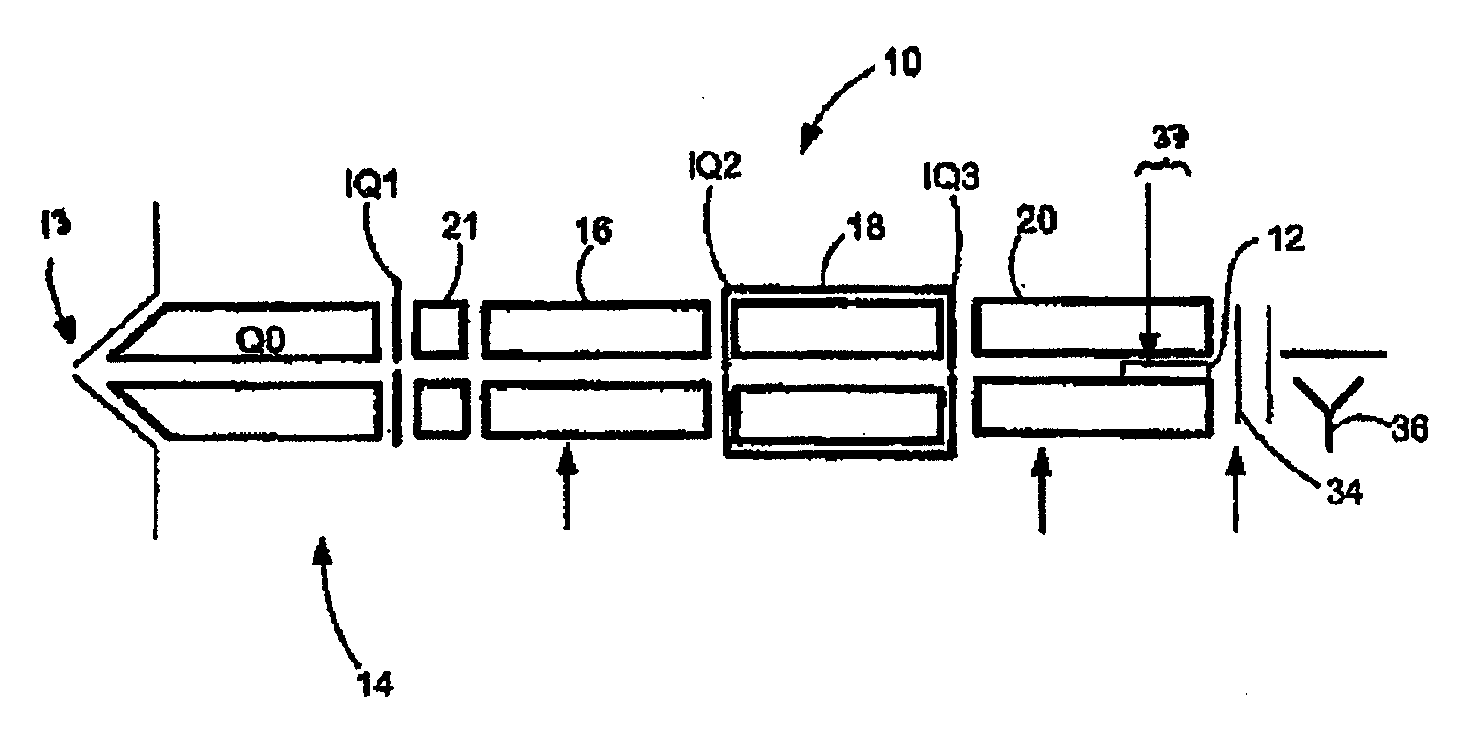
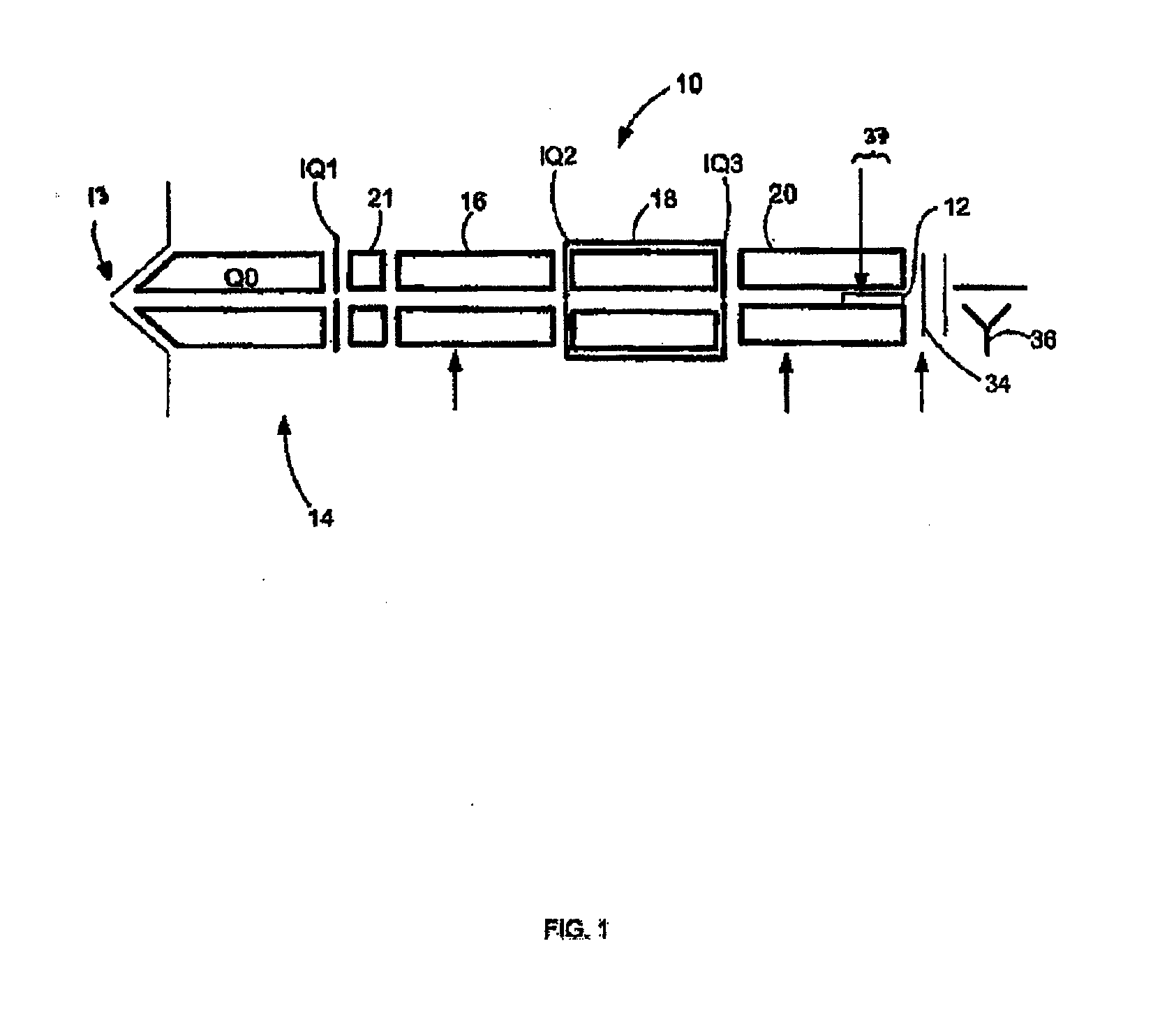
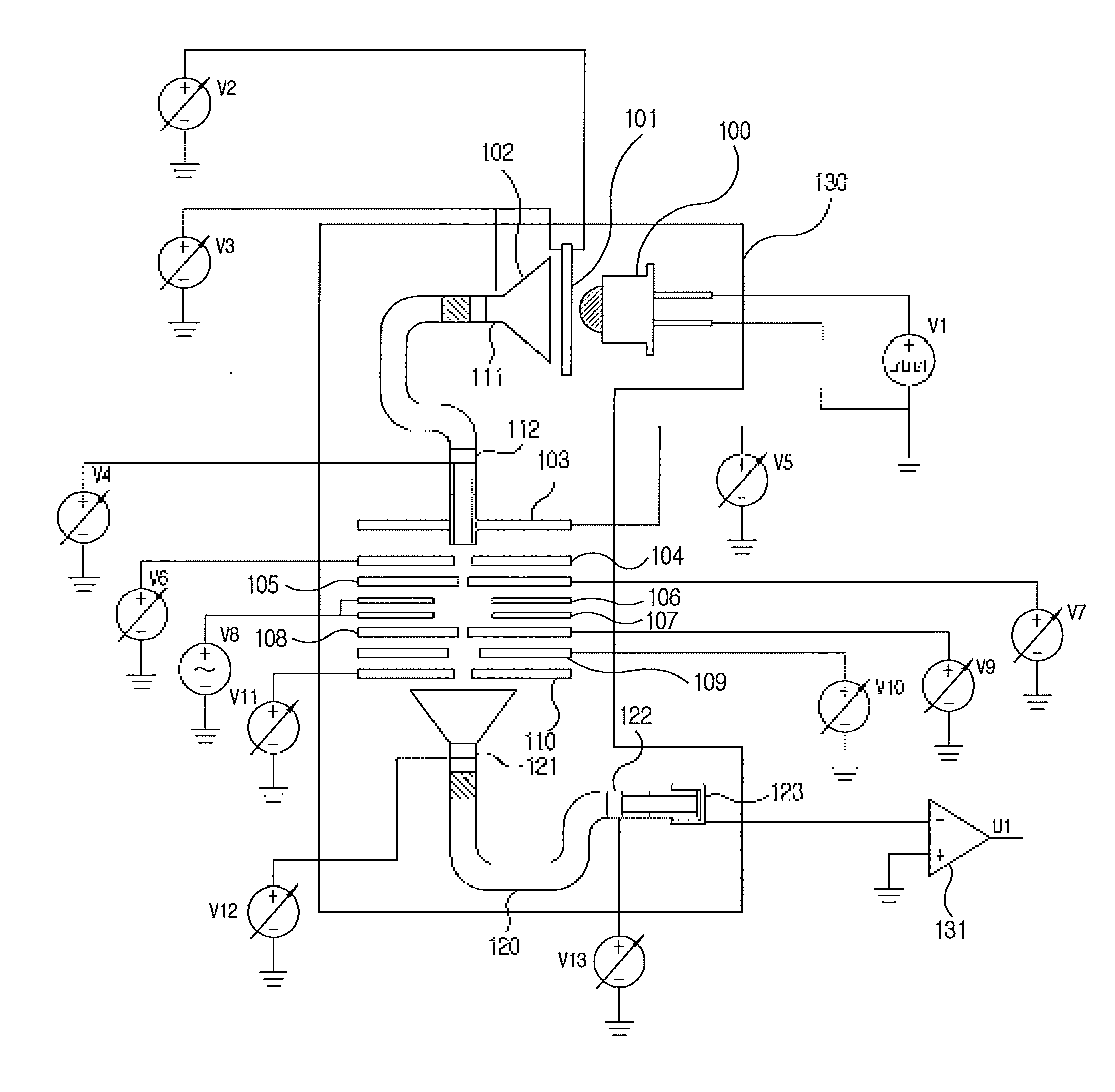
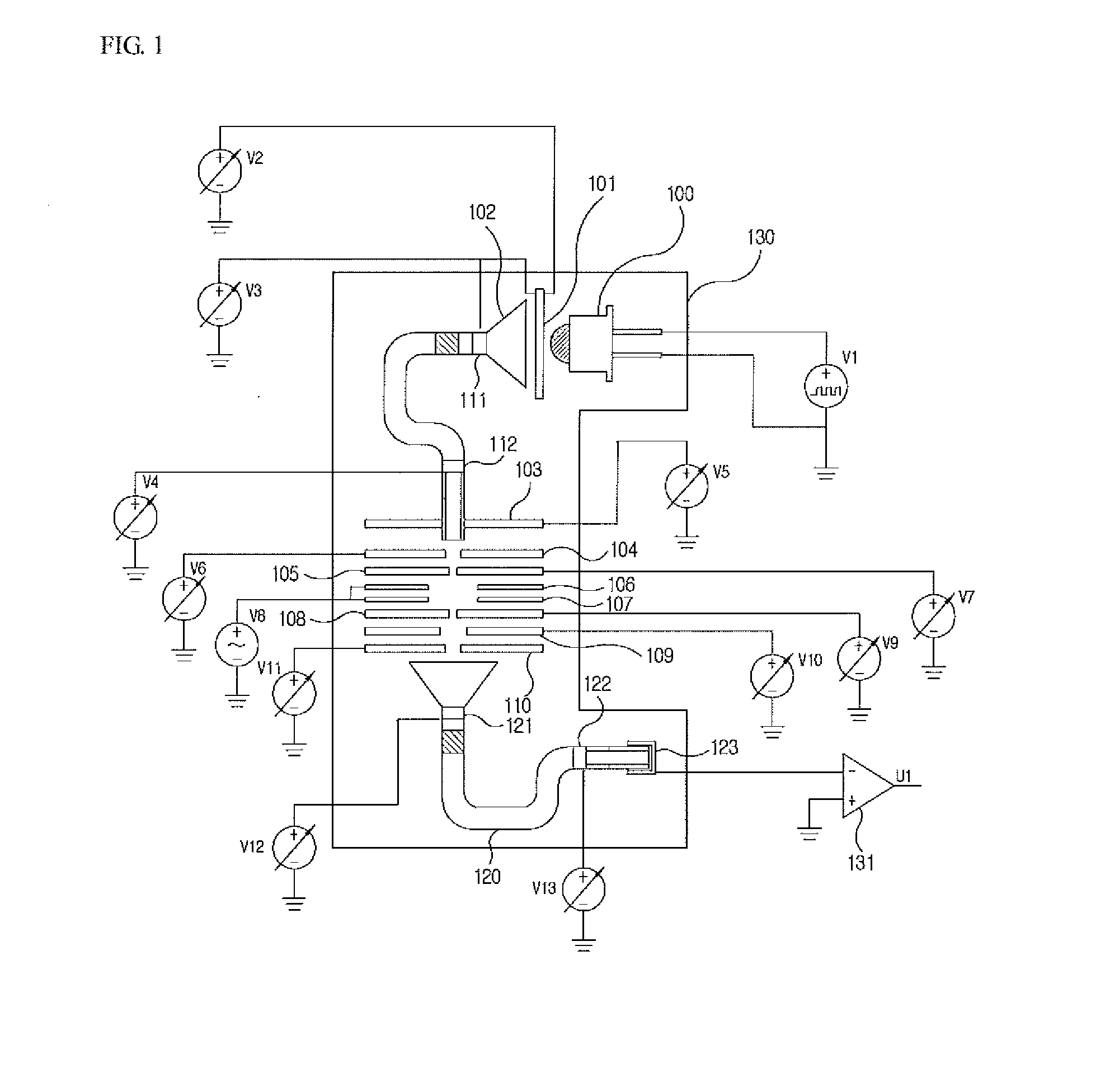
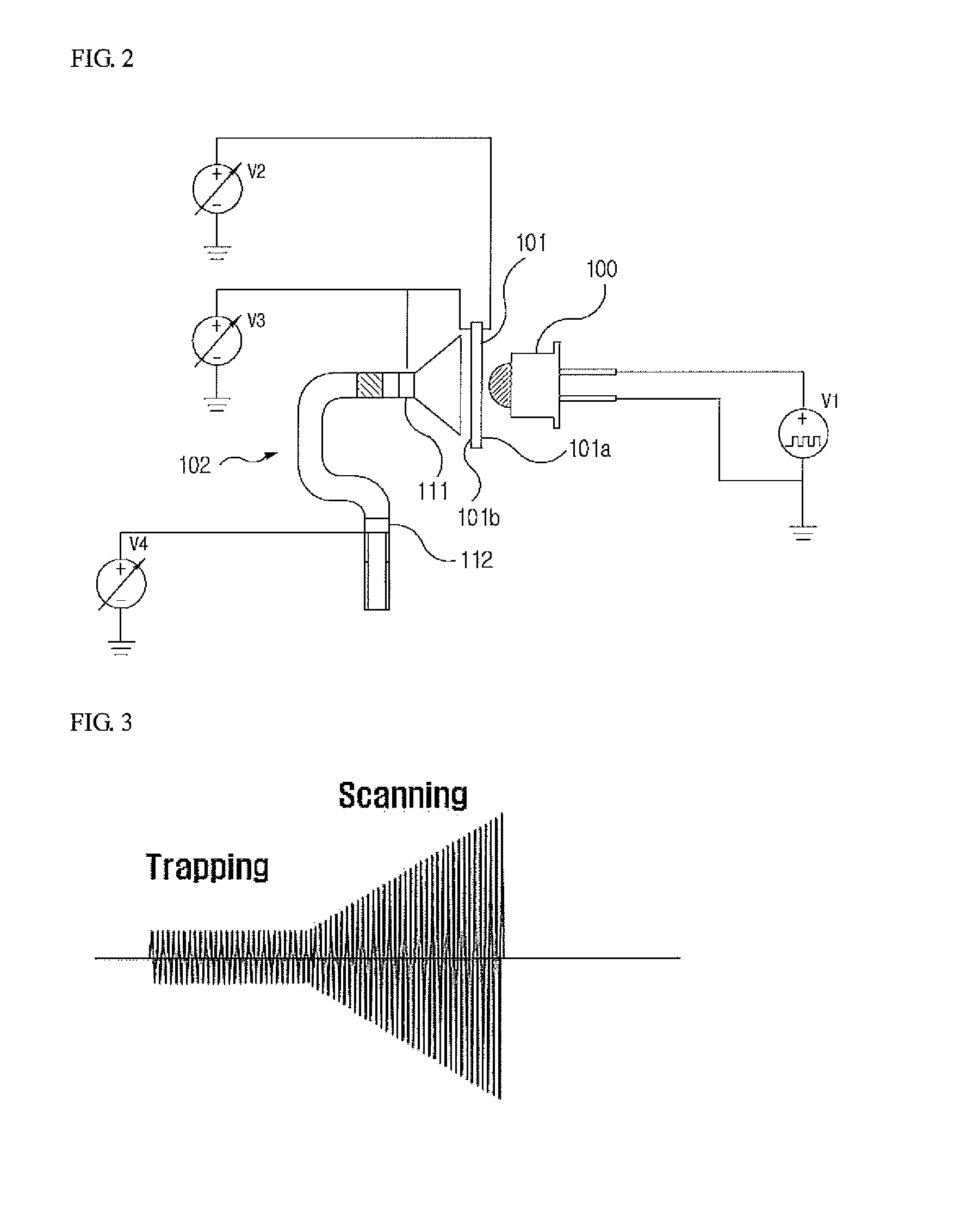
Apparatus and method for focusing and selecting ions and charged particles at or near atmospheric pressure
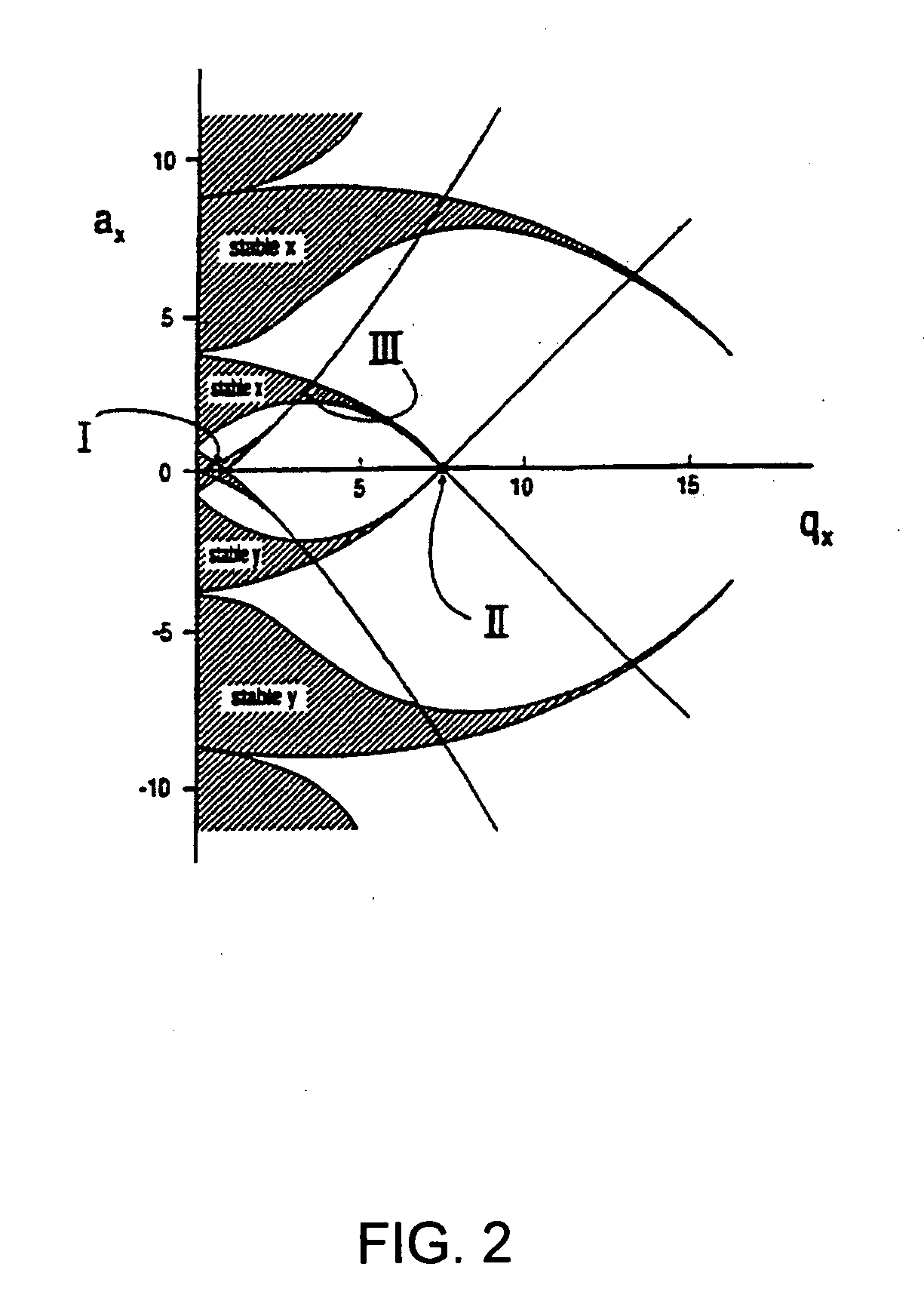
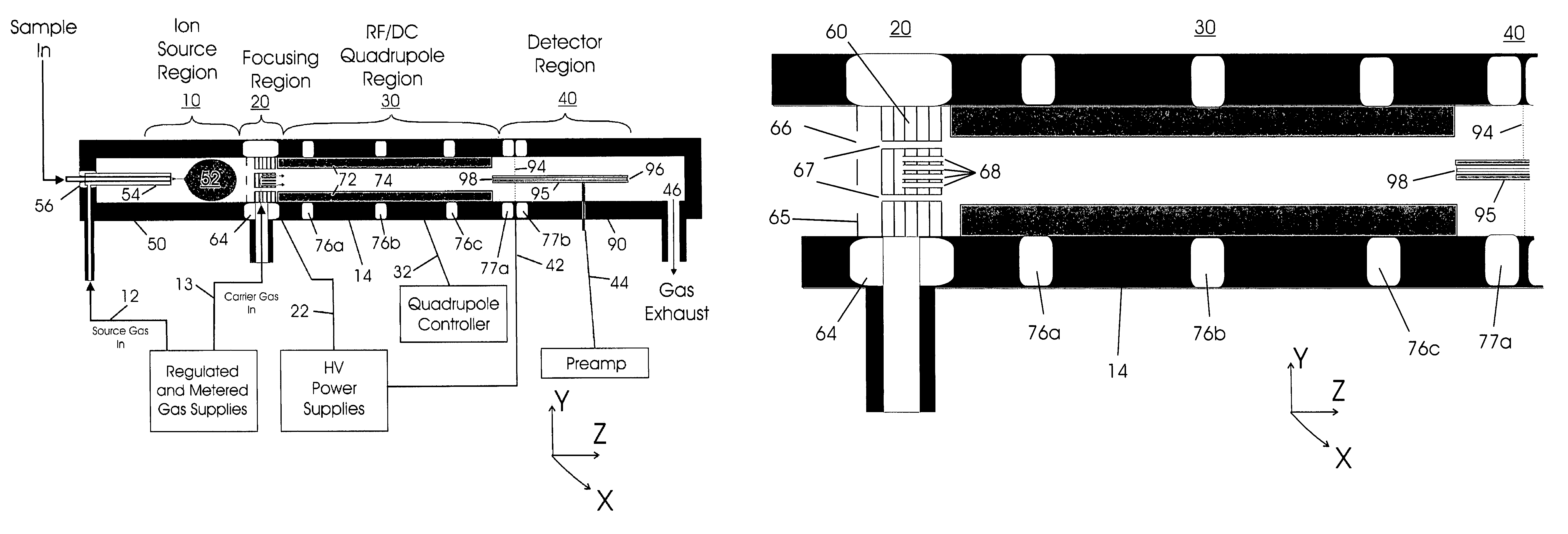
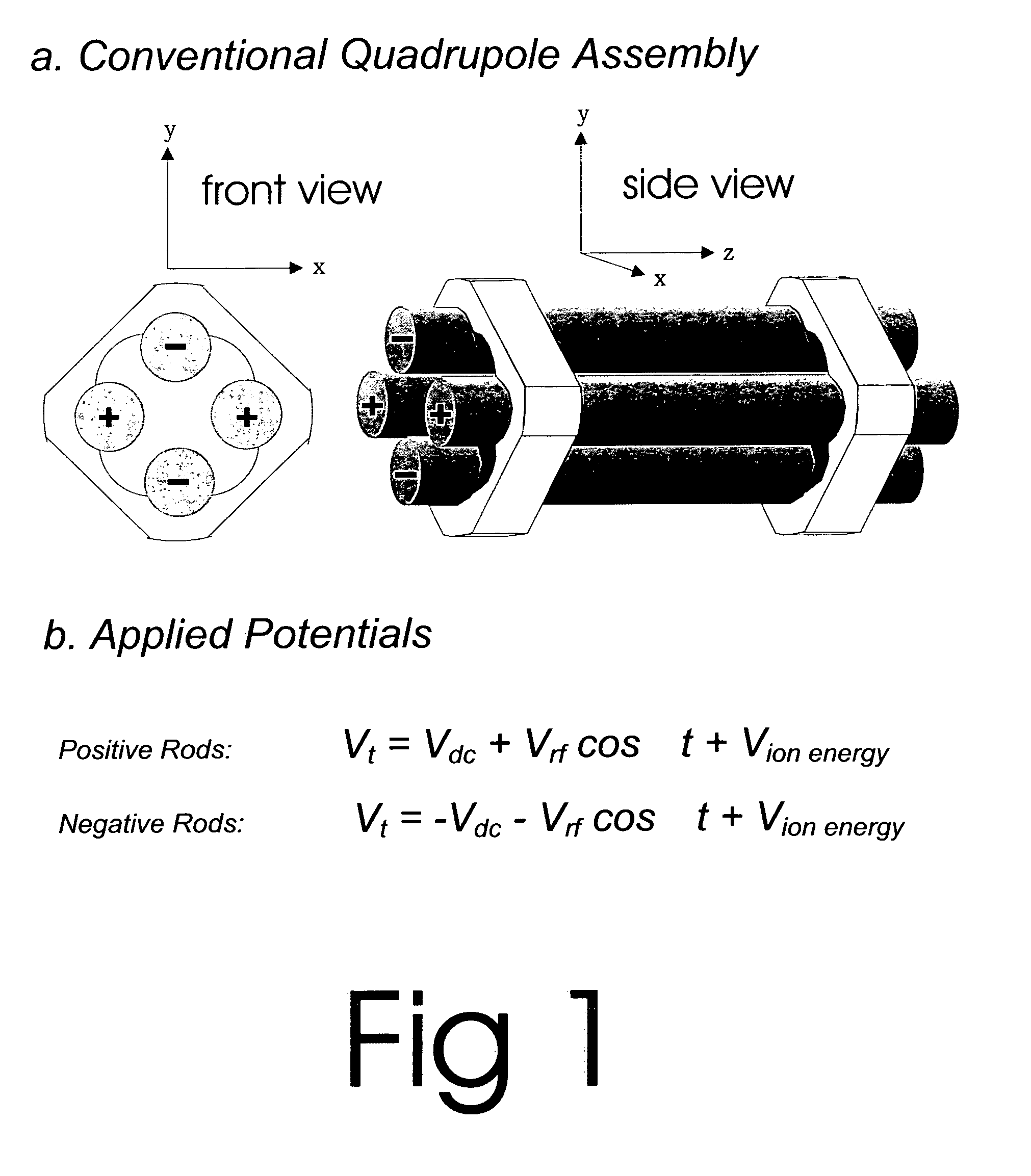
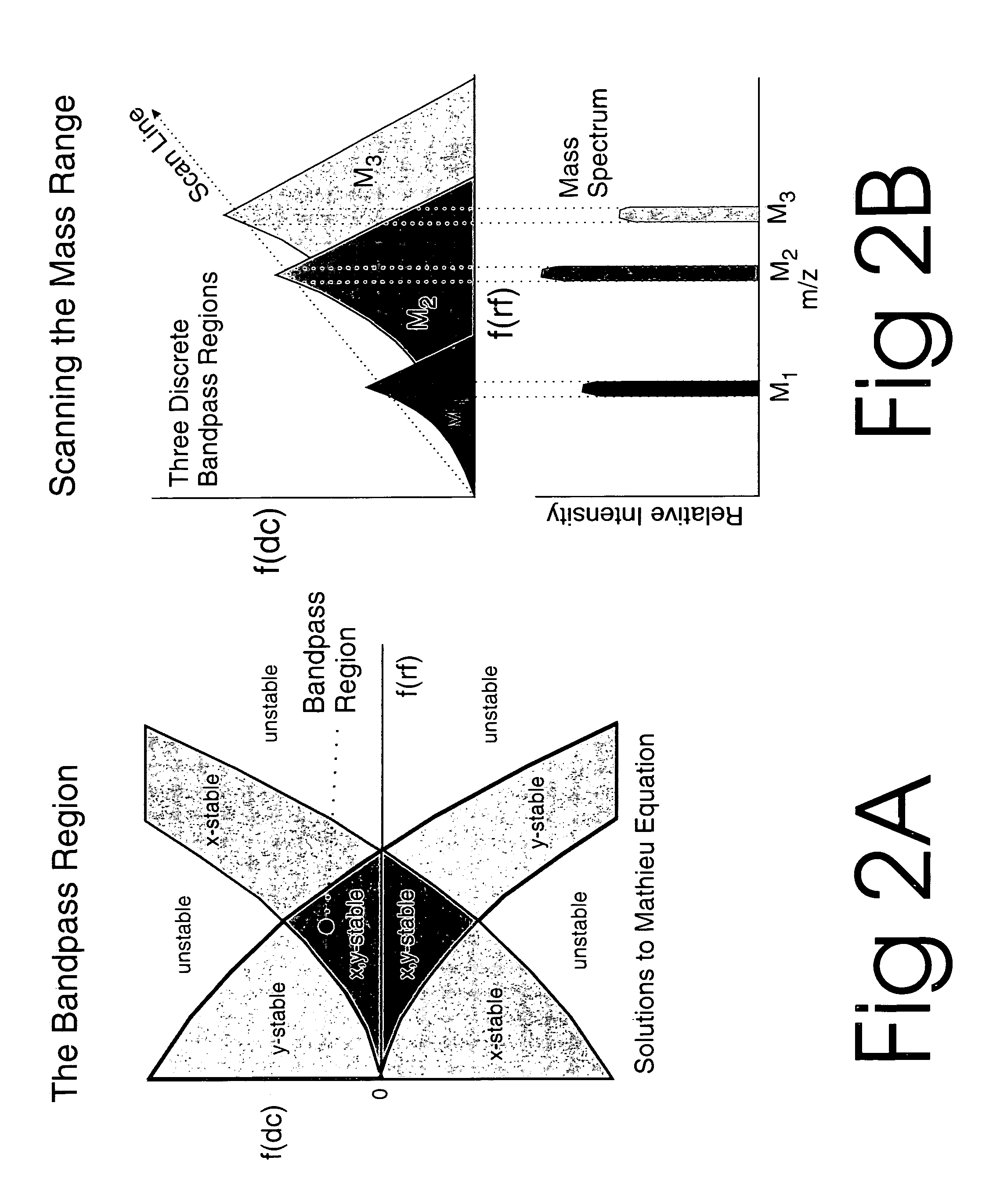
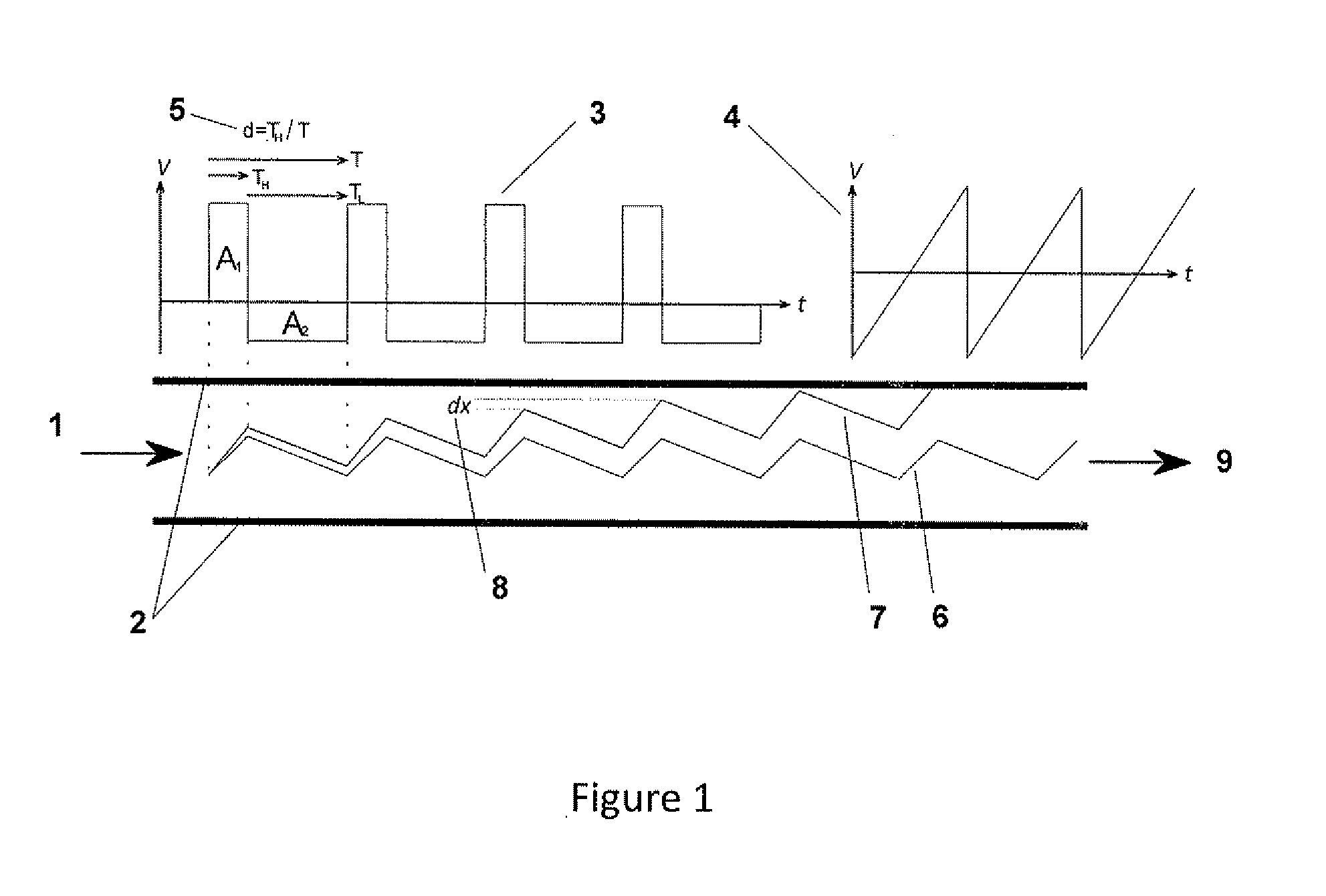
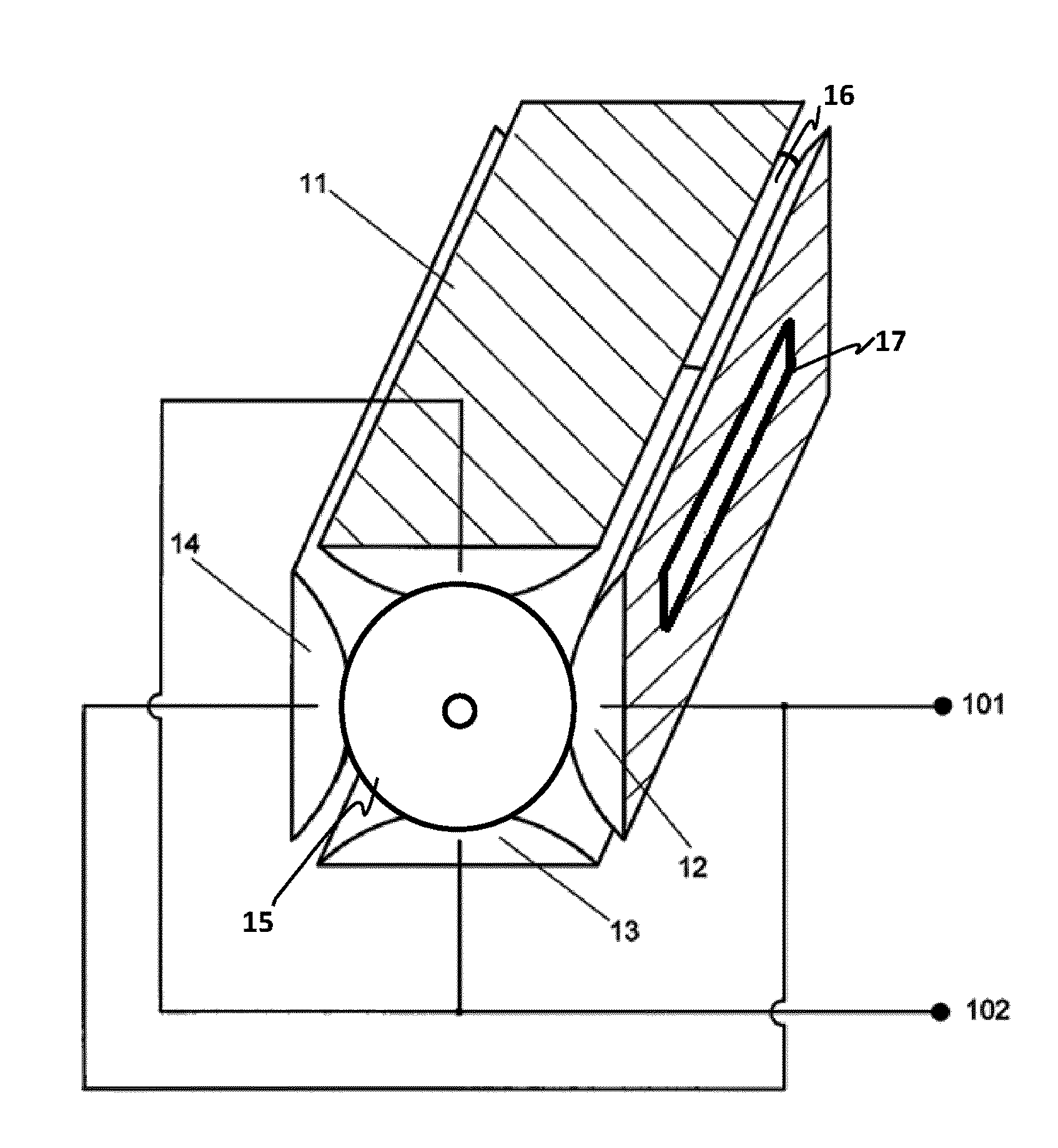
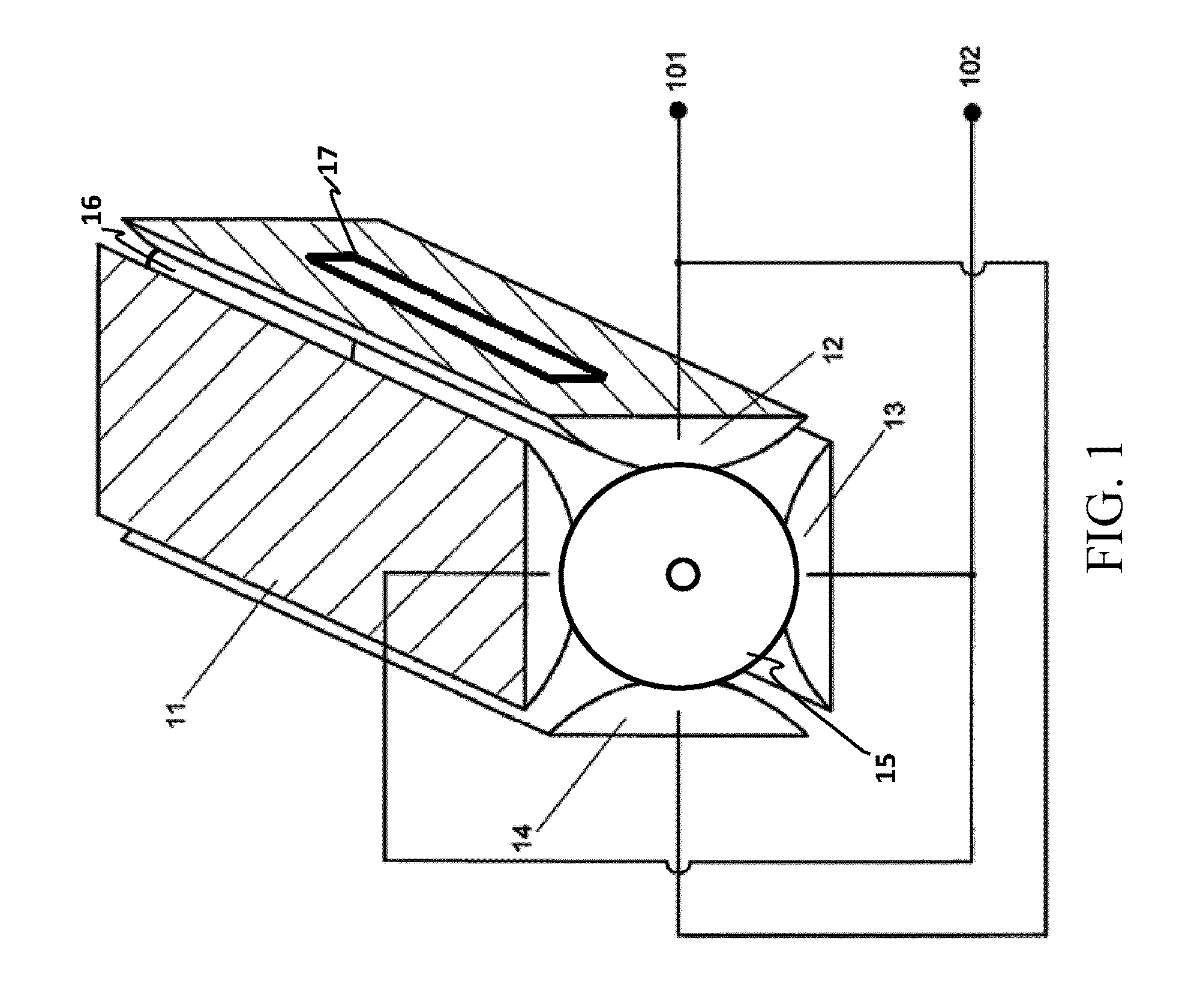
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for focusing, separating, and detecting gas-phase ions using the principles of quadrupole fields, substantially at or near atmospheric pressure. Ions are entrained in a concentric flow of gas and travel through a high-transmission element into a RF / DC quadrupole, through a second high-transmission element, and then impact on an ion detector, such as a faraday plate; or through an aperture with subsequent identification by a mass spectrometer. Ions with stable trajectories pass through the RF / DC quadrupole while ions with unstable trajectories drift off-axis collide with the rods and are lost. Embodiments of this invention are devices and methods for focusing, separating and detecting gas-phase ions without the need for a vacuum chamber when coupled to atmospheric ionization sources.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
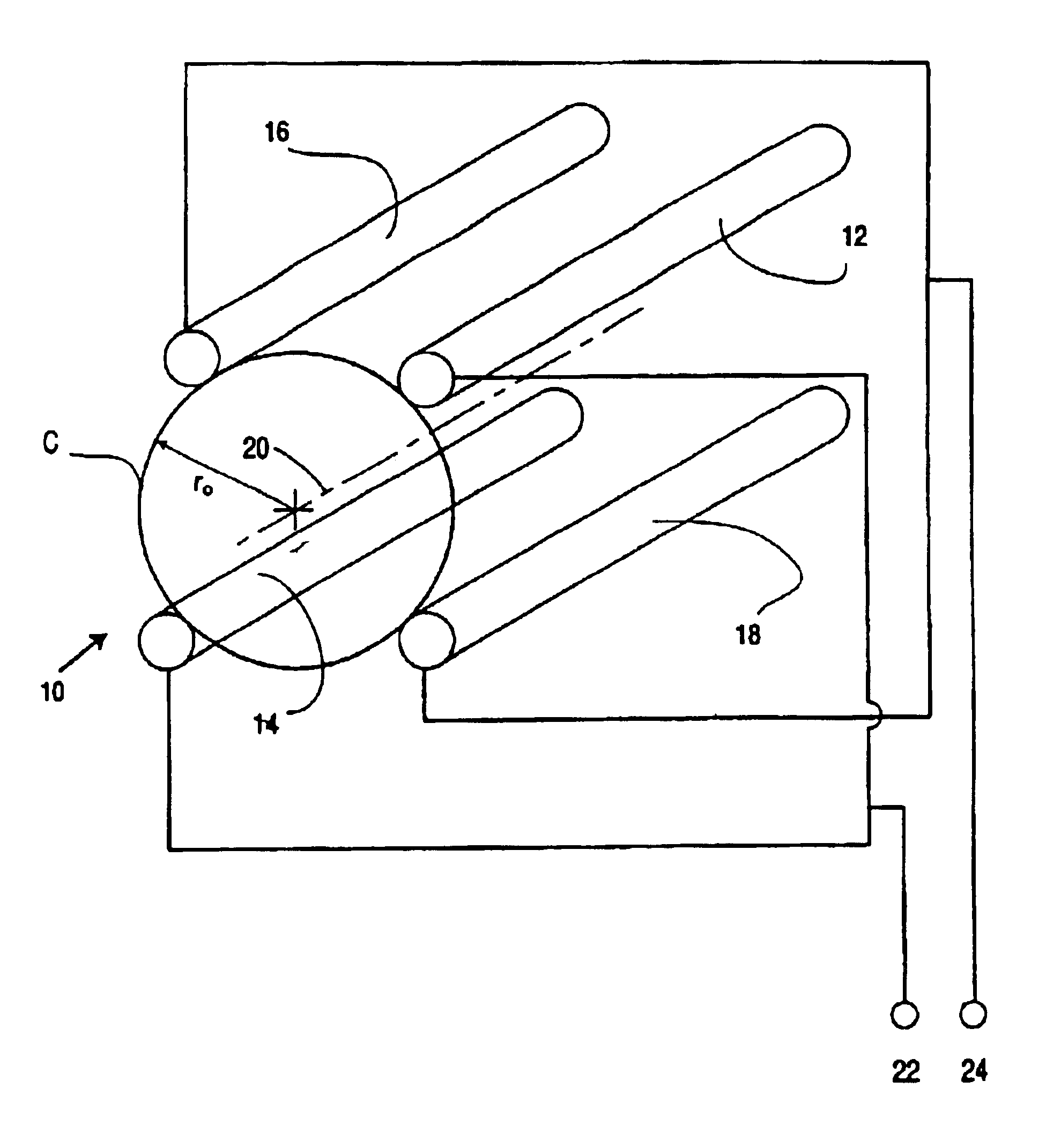
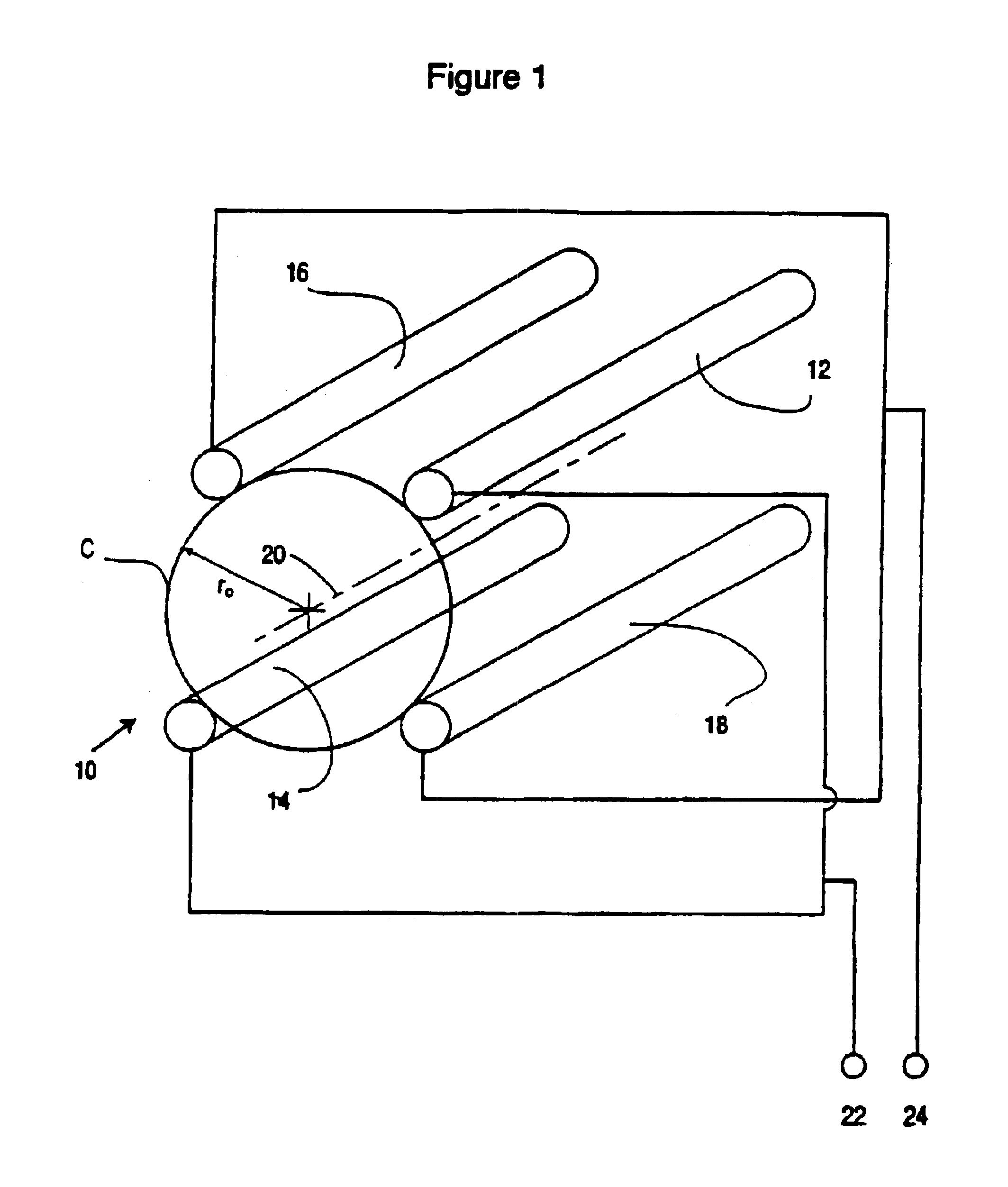
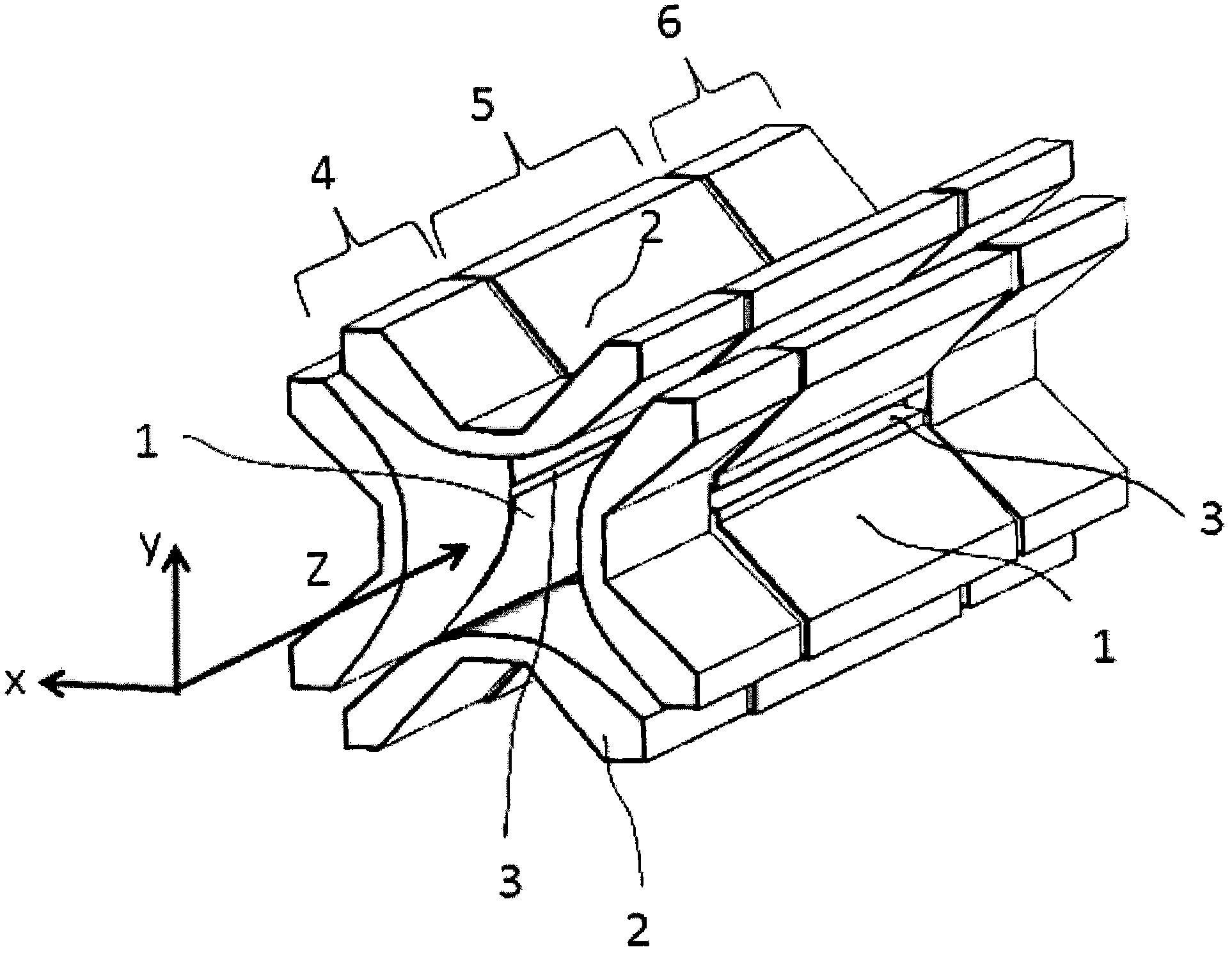
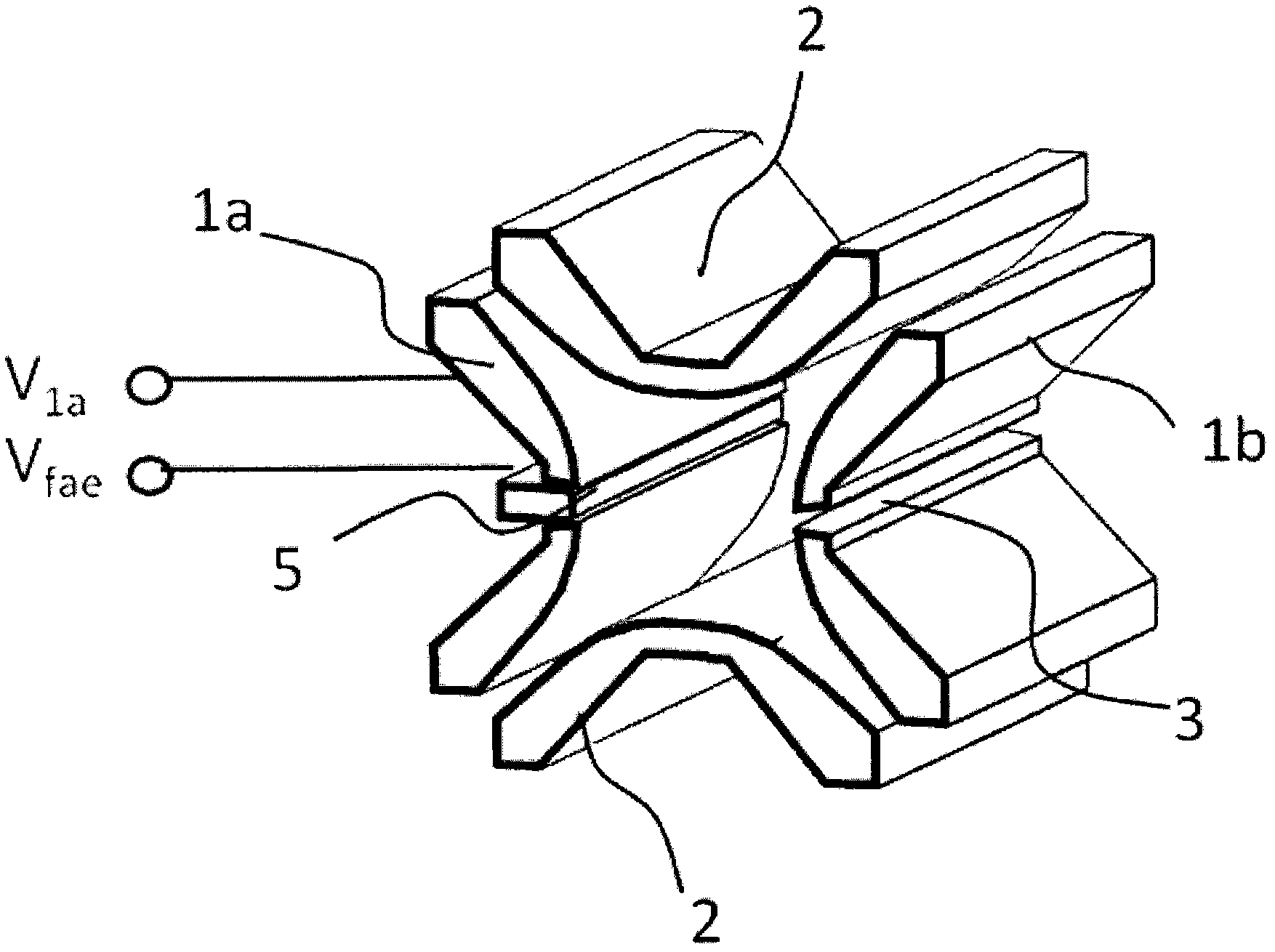
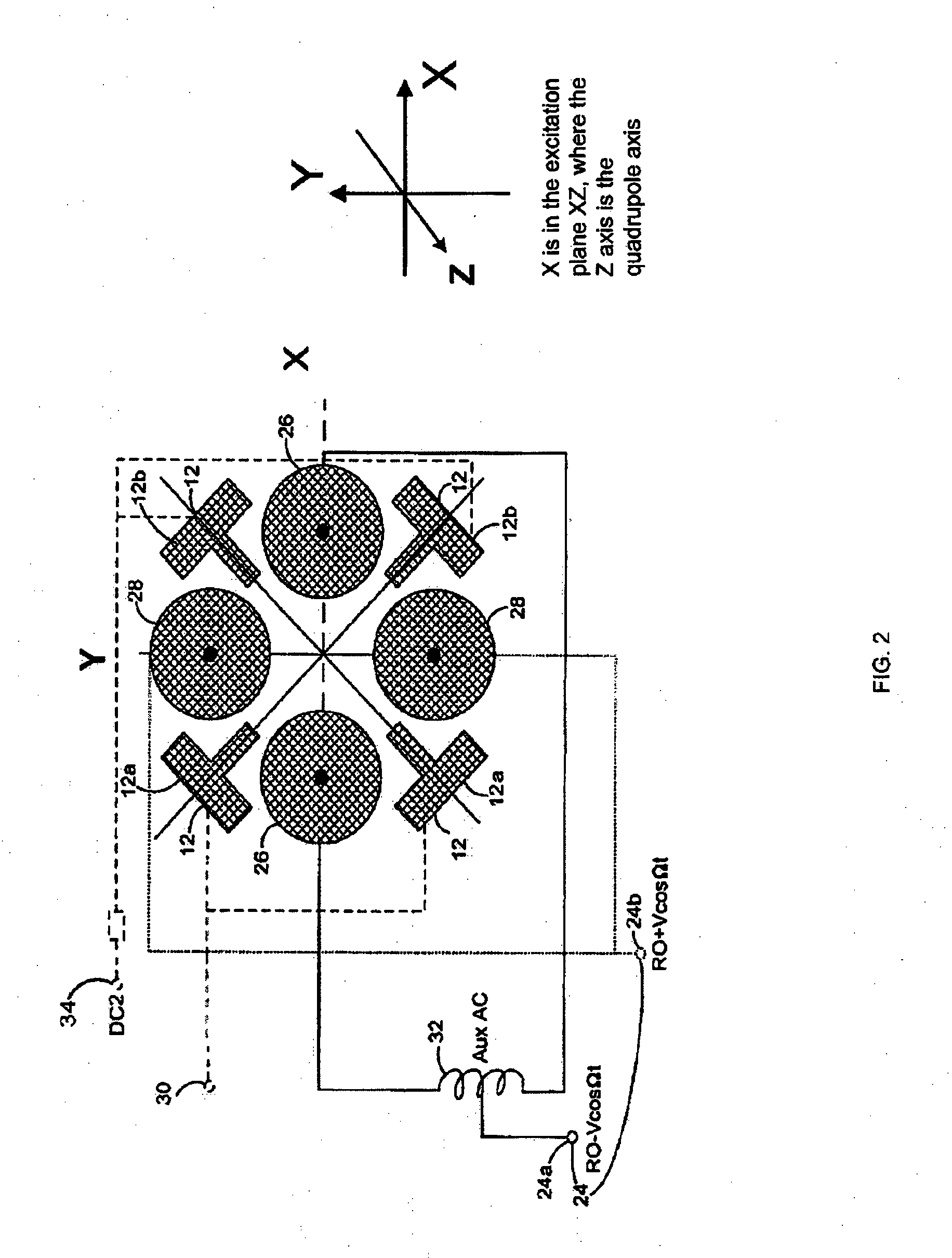
Geometry for generating a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field
InactiveUS6897438B2Trajectory stabilizationIncrease kinetic energyStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsQuadrupole fieldHarmonic
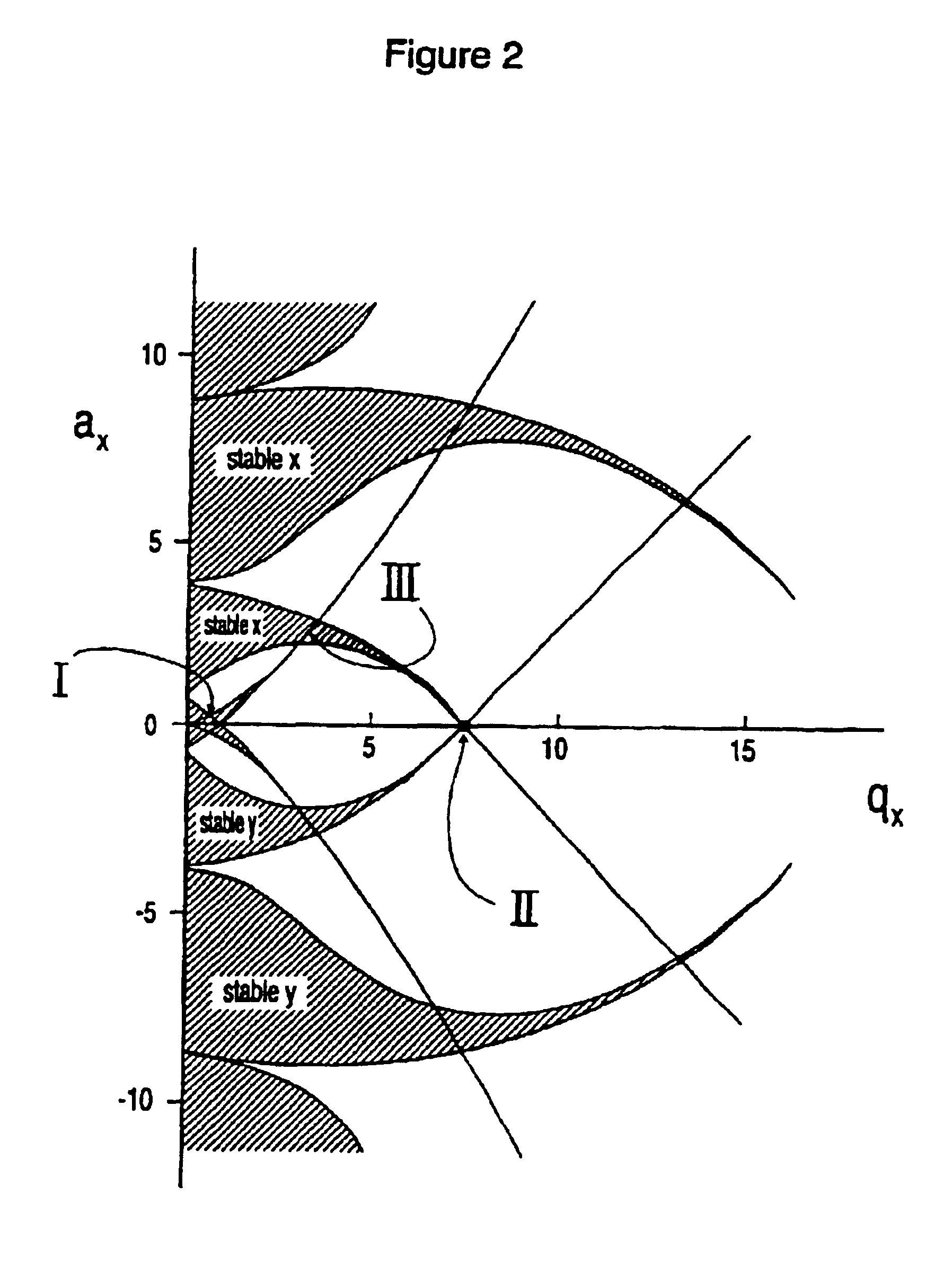
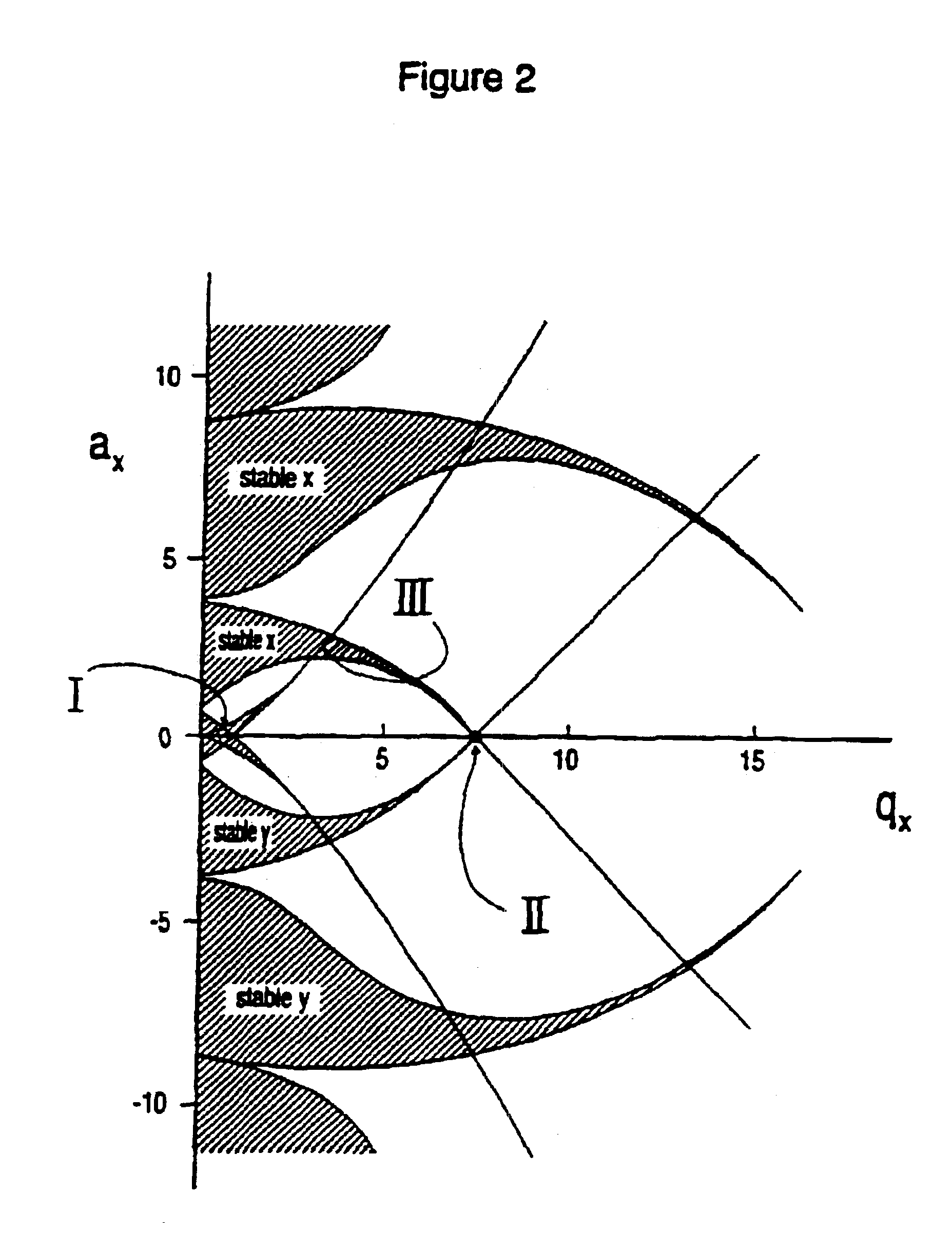
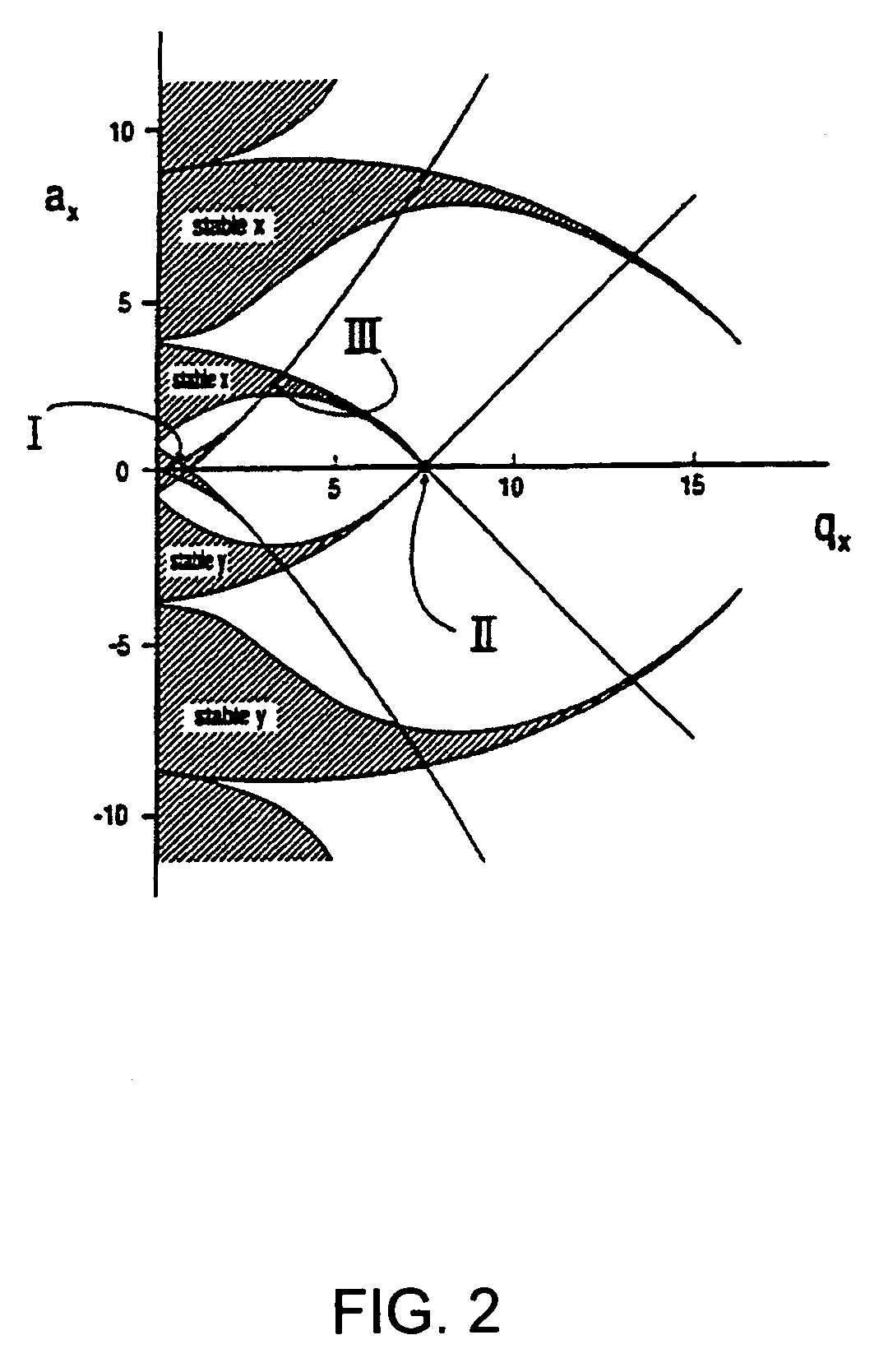
A method and apparatus for manipulating ions using a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field, and a method of manufacturing an apparatus for manipulating ions using a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field are described. The field has a quadrupole harmonic with amplitude A2, an octopole harmonic with amplitude A4, and higher order harmonics with amplitudes A6 and A8. The amplitude A8 is less than A4. The A4 component of the field is selected to improve the performance of the field with respect to ion selection and ion fragmentation. The selected A4 component can be added by selecting a degree of asymmetry under a 90° rotation about a central axis of the quadrupole. The degree of asymmetry is selected to be sufficient to provide the selected A4 component.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
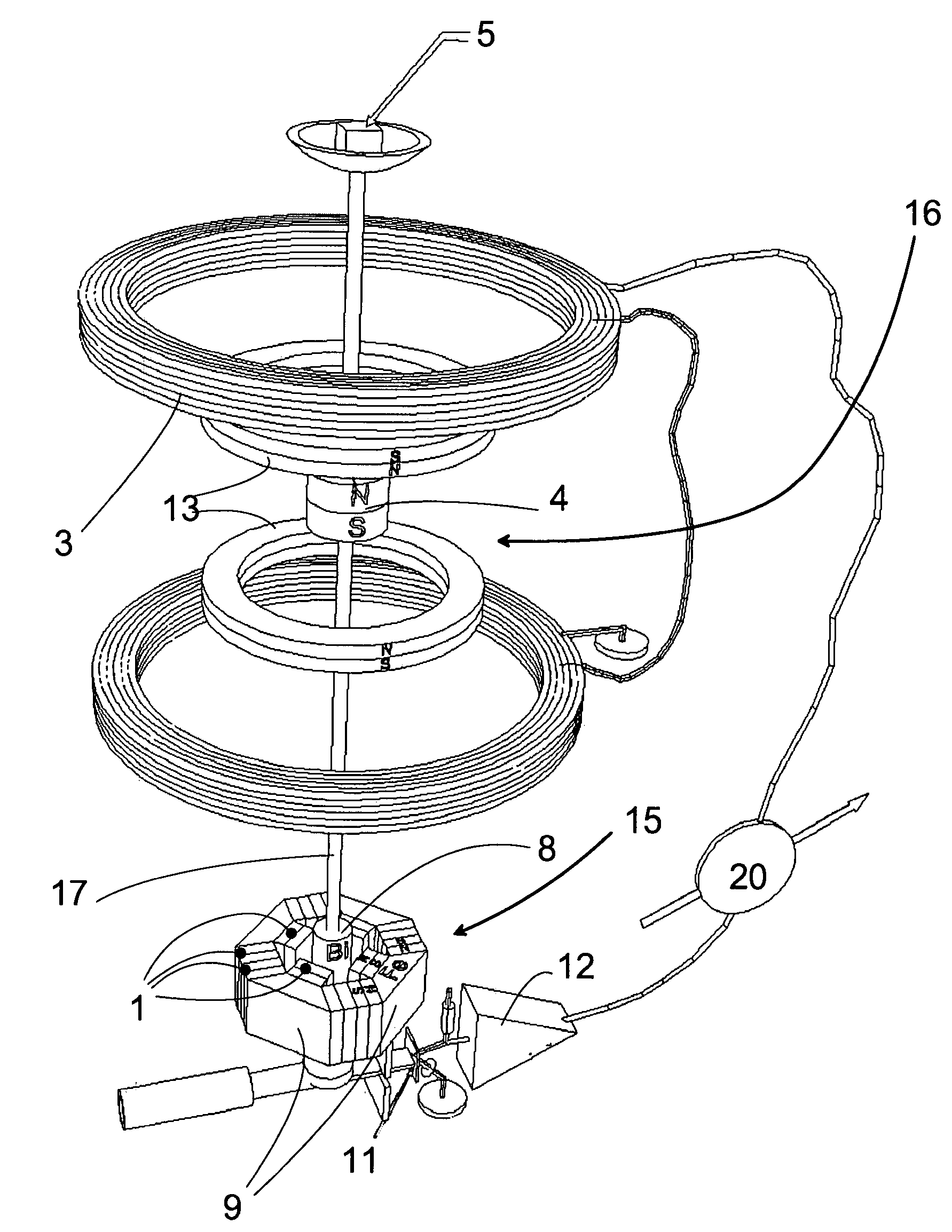
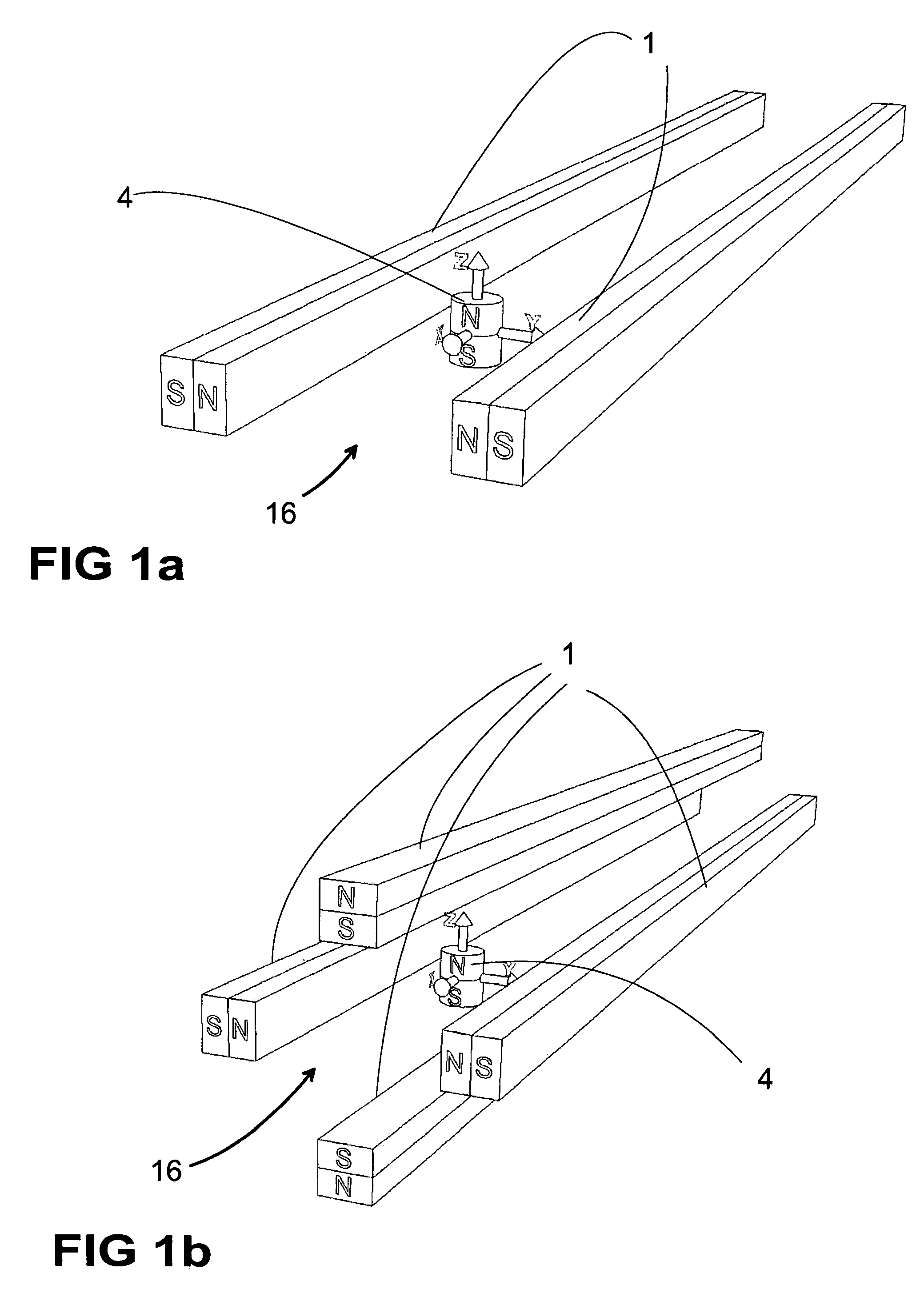
Magnetic Levitation System
ActiveUS20090160279A1Easy to solveMagnetic bearingsMechanical energy handlingQuadrupole fieldMagnetic dipole
A magnetic levitation system for supporting an object against gravity by a supporting force includes a permanent-magnet dipole aligned in a vertical position and coupled to the object, a supporting-field generator and a stabilization system. The supporting-field generator generates a supporting force on the permanent-magnet dipole via a supporting field. The supporting field is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional magnetic quadrupole field so that the supporting force is independent of a position of the dipole. The stabilization system constrains the dipole against movements in at least one horizontal direction, and includes a diamagnetic element coupled to the dipole and arranged below the dipole, and a stabilizing-field generator generating a second two-dimensional or three-dimensional stabilizing field to restore said diamagnetic element to a position where the field strength of the stabilizing field has a local minimum.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Controlling the characteristics of implanter ion-beams
InactiveUS6933507B2Eliminating magnetic short circuitsAccurate shapeStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldAngle of incidence
A method and apparatus satisfying growing demands for improving the precision of angle of incidence of implanting ions that impact a semiconductor wafer and the precision of ribbon ion beams for uniform doping of wafers as they pass under an ion beam. The method and apparatus are directed to the design and combination together of novel magnetic ion-optical transport elements for implantation purposes. The design of the optical elements makes possible: (1) Broad-range adjustment of the width of a ribbon beam at the work piece; (2) Correction of inaccuracies in the intensity distribution across the width of a ribbon beam; (3) Independent steering about both X and Y axes; (4) Angle of incidence correction at the work piece; and (5) Approximate compensation for the beam expansion effects arising from space charge. In a practical situation, combinations of the elements allow ribbon beam expansion between source and work piece to 350 millimeter, with good uniformity and angular accuracy. Also, the method and apparatus may be used for introducing quadrupole fields along a beam line.
Owner:PURSER KENNETH H +2
Method for cascade mass spectrometry by using multiple ion traps
InactiveCN101320016AHigh sensitivityImprove analysis efficiencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometersQuadrupole fieldIon trap mass spectrometry
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Ion analysis apparatus and method of use
ActiveUS20120056085A1Easy to modifyImprove performanceTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionQuadrupole fieldSystem configuration
The present invention is concerned with an ion analysis apparatus for conducting differential ion mobility analysis and mass analysis. In embodiments, the apparatus comprises a differential ion mobility device in a vacuum enclosure of a mass spectrometer, located prior to the mass analyser, wherein the pumping system of the apparatus is configure to provide an operating pressure of 0.005 kPa to 40 kPa for the differential ion mobility device, and wherein the apparatus includes a digital asymmetric waveform generator that provides a waveform of frequency of 50 kHz to 25 MHz. Examples demonstrate excellent resolving power and ion transmission. The ion mobility device can be a multipole, for example a 12-pole and radial ion focusing can be achieved by applying a quadrupole field to the device in addition to a dipole field.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method and apparatus for providing two-dimensional substantially quadrupole fields having selected hexapole components
ActiveUS20050067564A1Simple methodIncrease kinetic energyStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldHarmonic
A method and apparatus for manipulating ions using a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field, and a method of manufacturing and operating an apparatus for manipulating ions using a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field are described. The field has a quadrupole harmonic with amplitude A2 and a hexapole harmonic with amplitude A3. The amplitude A3 of the hexapole component of the field is selected to improve the performance of the field with respect to ion selection and ion fragmentation.
Owner:MDS CO LTD +2
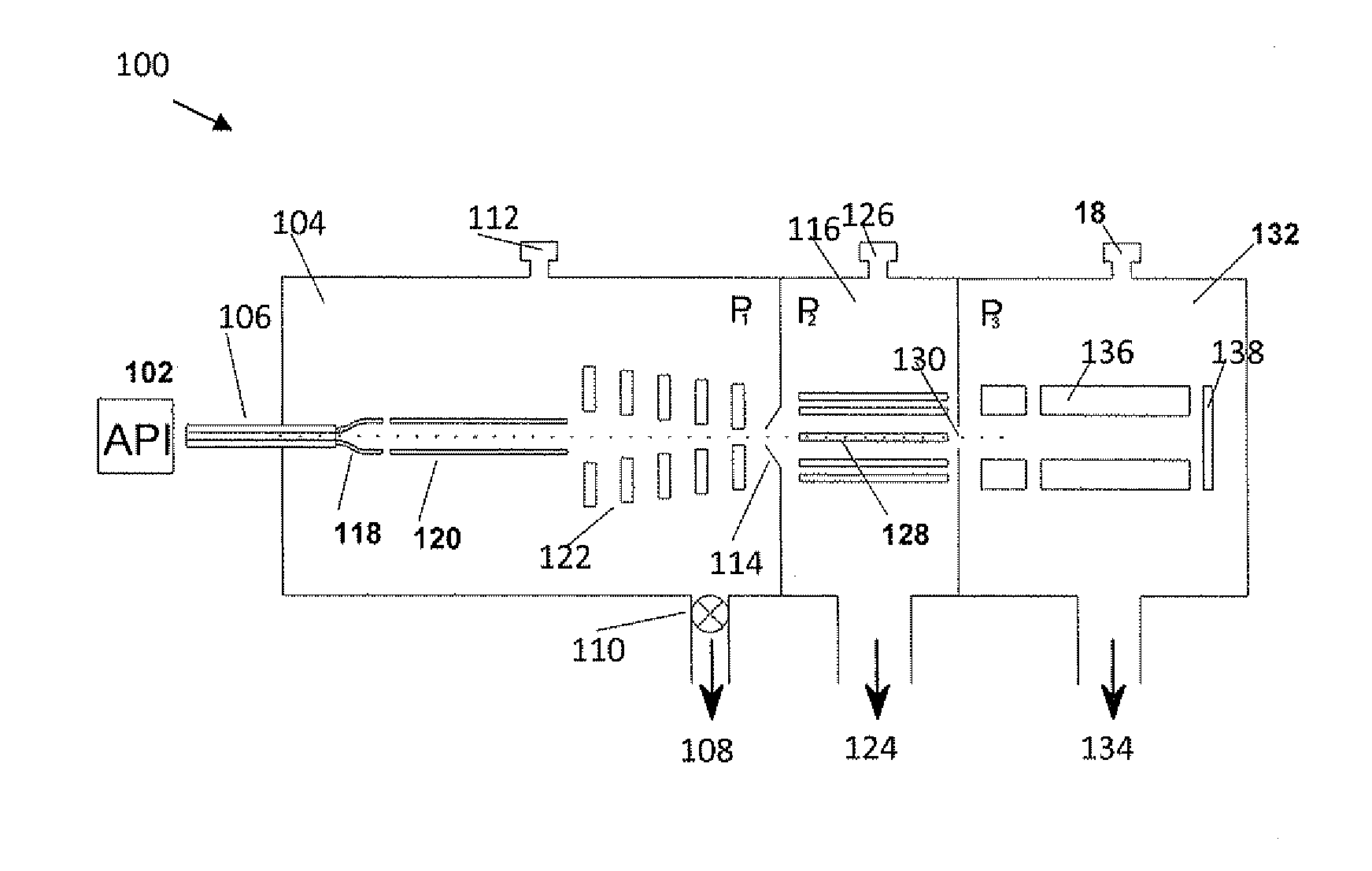
Atmosperic pressure quadrupole analyzer
InactiveUS7312444B1Precise processThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersQuadrupole fieldGas phase
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for focusing, separating, and detecting gas-phase ions using the principles of electrohydrodynamic quadrupole fields at high pressures, at or near atmospheric pressure. Ions are entrained in a concentric flow of gas and travel through a high-transmission element into a RF / DC quadrupole, exiting out of the RF / DC quadrupole, and then impacting on an ion detector, such as a faraday plate; or through an aperture or capillary tube with subsequent identification by a mass spectrometer. Ions with stable trajectories pass through the RF / DC quadrupole while ions with unstable trajectories drift off-axis collide with the rods and are lost. Alternatively, detection of ions with unstable trajectories can be accomplished by allowing the ions to pass through the rods and be detected by an off-axis detector. Embodiments of this invention are devices and methods for focusing, separating, and detecting gas-phase ions at or near atmospheric pressure, when coupled to mass spectrometers.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Axial ejection with improved geometry for generating a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field
InactiveUS7045797B2Simple methodStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsQuadrupole fieldHarmonic
A mass spectrometer having an elongated rod set, and a method of operating same. The rod set has an entrance end, an exit end and a longitudinal axis. Ions are admitted into the entrance end of the rod set. At least some of the ions are trapped in the rod set by producing a barrier field at an exit member adjacent to the exit end of the rod set and by producing an RF field between the rods of the rod set adjacent at least the exit end of the rod set. The RF and barrier fields interact in an extraction region adjacent to the exit end of the rod set to produce a fringing field. Ions in the extraction region are energized to mass selectively eject at least some ions of a selected mass to charge ratio axially from the rod set past the barrier field. The RF field is a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field having a quadrupole harmonic with amplitude A2, an octopole harmonic with amplitude A4, and a hexadecapole harmonic with amplitude A8. A8 is less than A4, and A4 is greater than 0.1% of A2.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
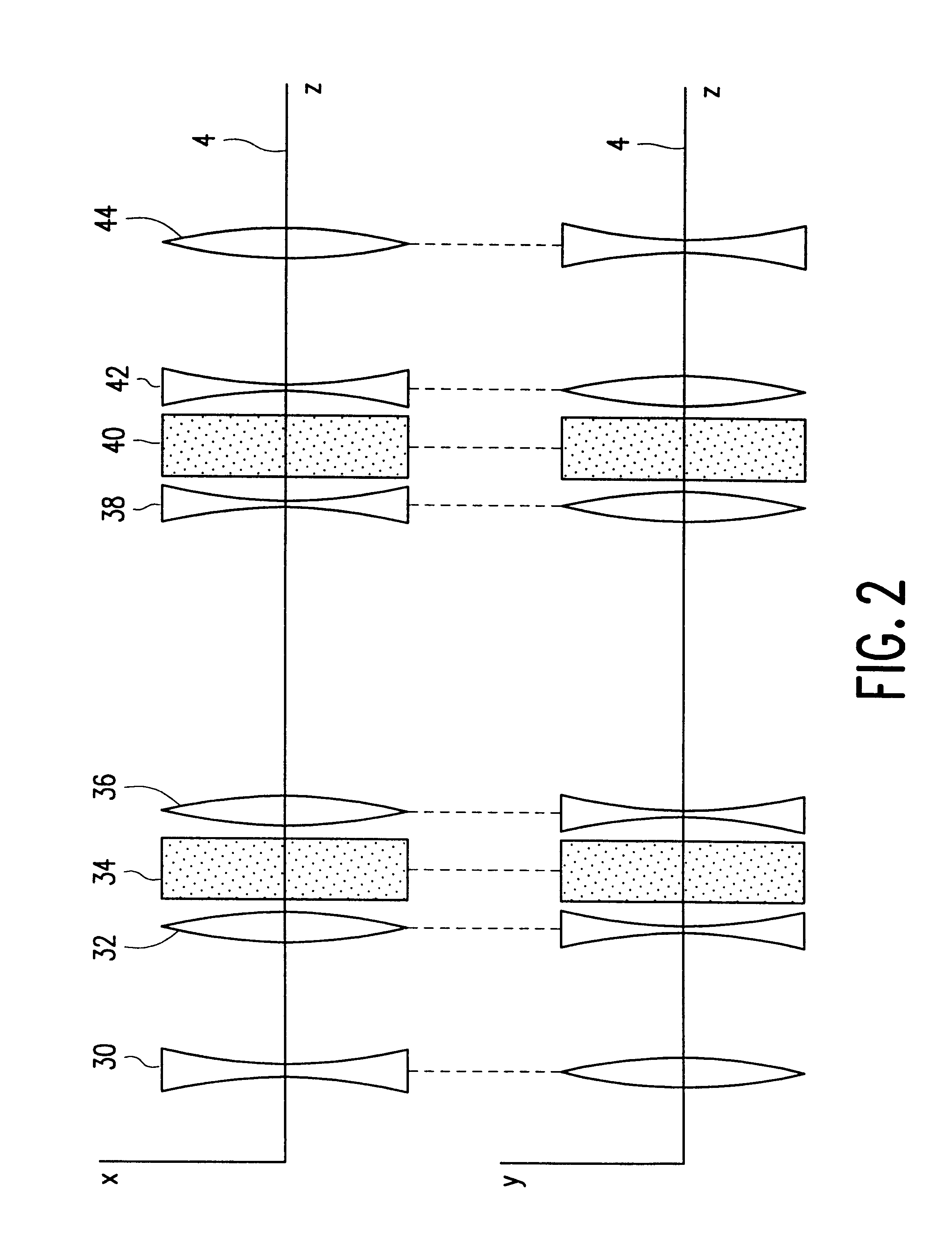
Electrostatic device for correcting chromatic aberration in a particle-optical apparatus
InactiveUS6184975B1Reduce errorsStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldImage resolution
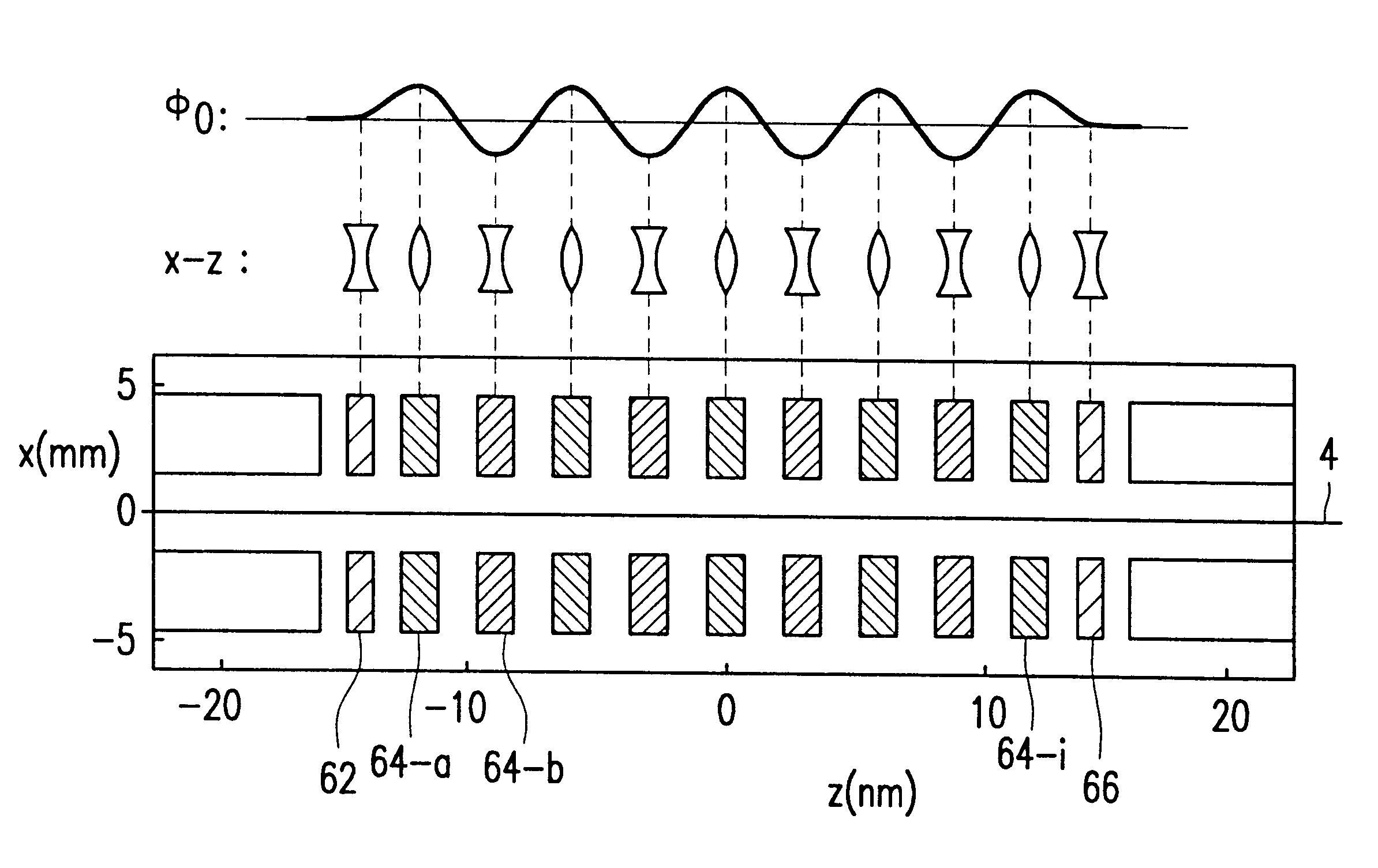
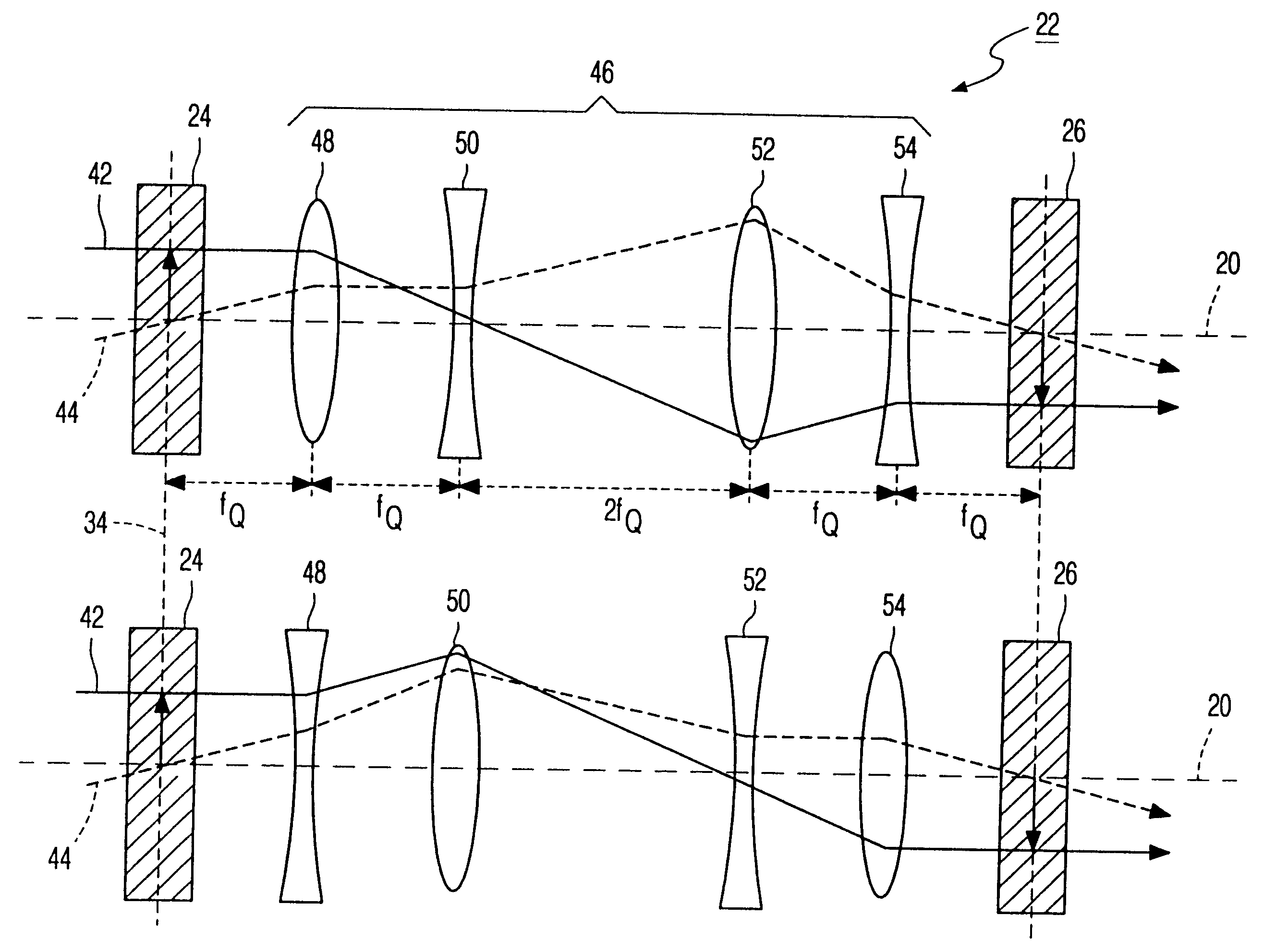
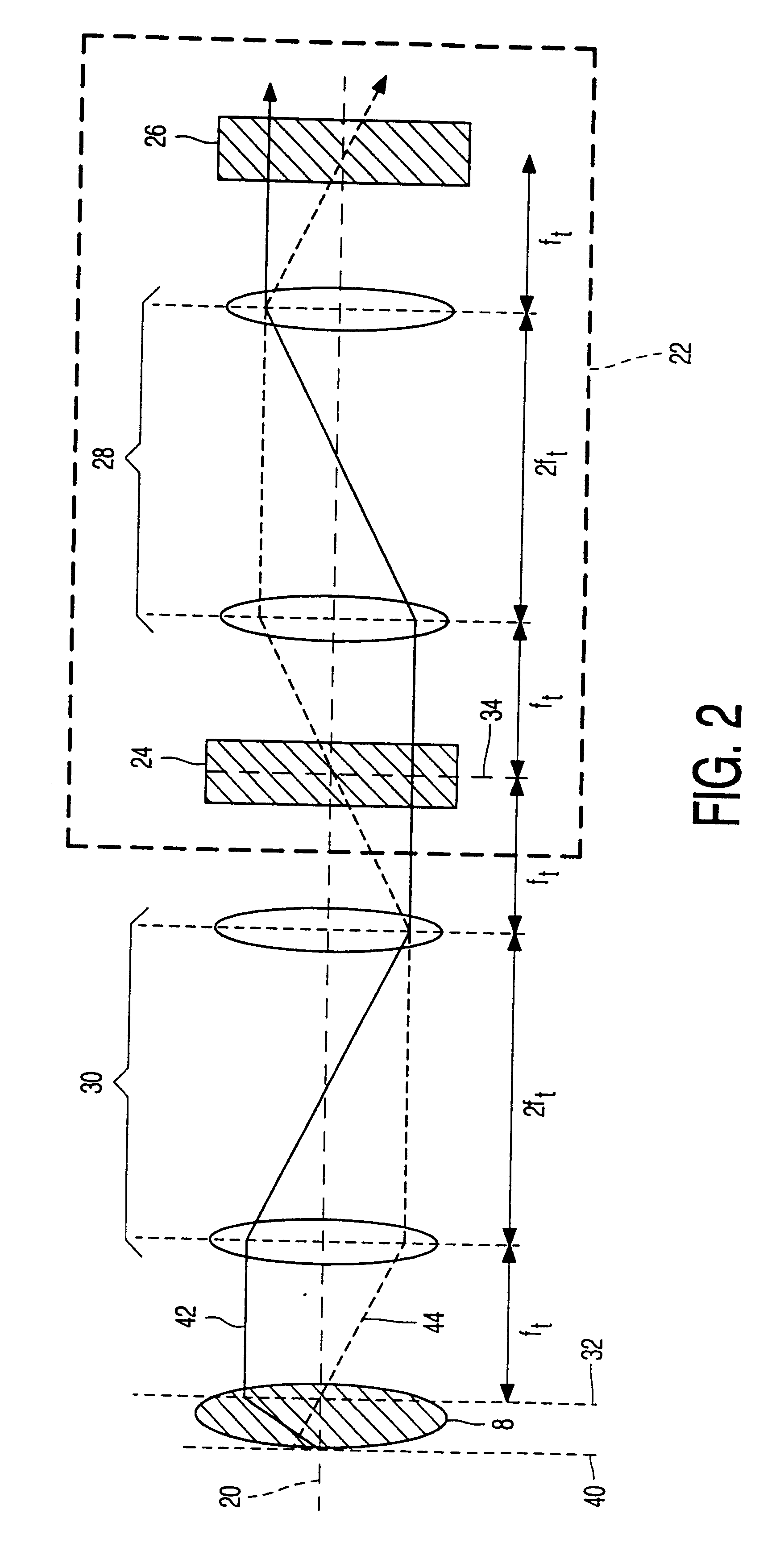
Electron-optical rotationally symmetrical lenses inevitably suffer from chromatic aberration which often determines the resolution limit at low acceleration voltages. This lens defect cannot be eliminated by compensation by means of rotationally symmetrical fields. In order to improve the resolution nevertheless, it has already been proposed to correct the chromatic aberration by means of a corrector (28) provided with two correction elements (34, 40). Each correction element consists of a number of quadrupole fields. Using the known corrector, it has been found that the chromatic magnification error is inadmissibly high. In order to solve this problem, the correction elements in the corrector according to the invention are provided with at least five layers of electrodes (60-a, 60-b, 60-c, 60-d) which produce quadrupole fields. Because of the strong periodicity of the electron paths in the correcting quadrupole fields, the chromatic magnification error is limited sufficiently (or even reduced to zero) so as to allow the use of the corrector for practical purposes.
Owner:FEI CO
Method and apparatus for providing two-dimensional substantially quadrupole fields having selected hexapole components
ActiveUS7141789B2Increase kinetic energySimple methodStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldHarmonic
A method and apparatus for manipulating ions using a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field, and a method of manufacturing and operating an apparatus for manipulating ions using a two-dimensional substantially quadrupole field are described. The field has a quadrupole harmonic with amplitude A2 and a hexapole harmonic with amplitude A3. The amplitude A3 of the hexapole component of the field is selected to improve the performance of the field with respect to ion selection and ion fragmentation.
Owner:MDS CO LTD +2
Correction device for correcting the lens defects in particle-optical apparatus
InactiveUS6329659B1Significant manufacturingSignificant organizational advantageThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersQuadrupole fieldImage resolution
Electron-optical rotationally symmetrical lenses inevitably suffer from spherical and chromatic aberration which often impose a limit on the resolution. These lens defects cannot be eliminated by compensation by means of rotationally symmetrical fields. In order to enhance the resolution nevertheless, it has already been proposed to correct the spherical aberration by means of a correction device provided with two hexapoles (24, 26) and two rotationally symmetrical transmission lens systems (28, 30). Each transmission lens system in the known correction device consists of two lenses. According to the invention, one or both transmission lens systems can be replaced by a respective system (46) of four quadrupoles (48, 50, 52, 54), without the correction capability being reduced or only hardly so. If the two central quadrupoles (50, 52) of the quadrupole system (46) forming part of the correction device (22) are also arranged to produce electric quadrupole fields, the chromatic aberration of the lens to be corrected can also be corrected.
Owner:FEI COMPANY
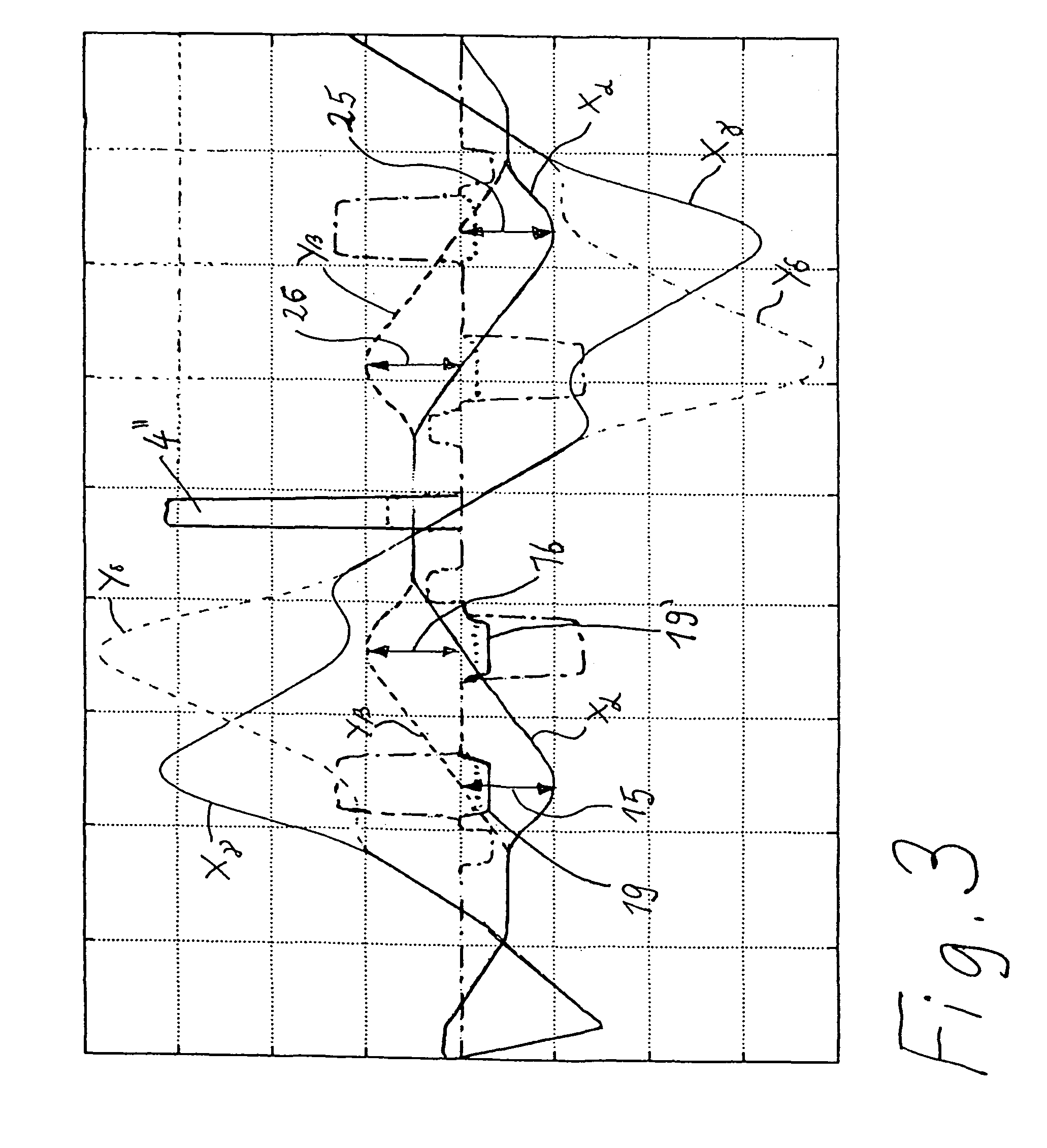
Corrector for correcting first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree
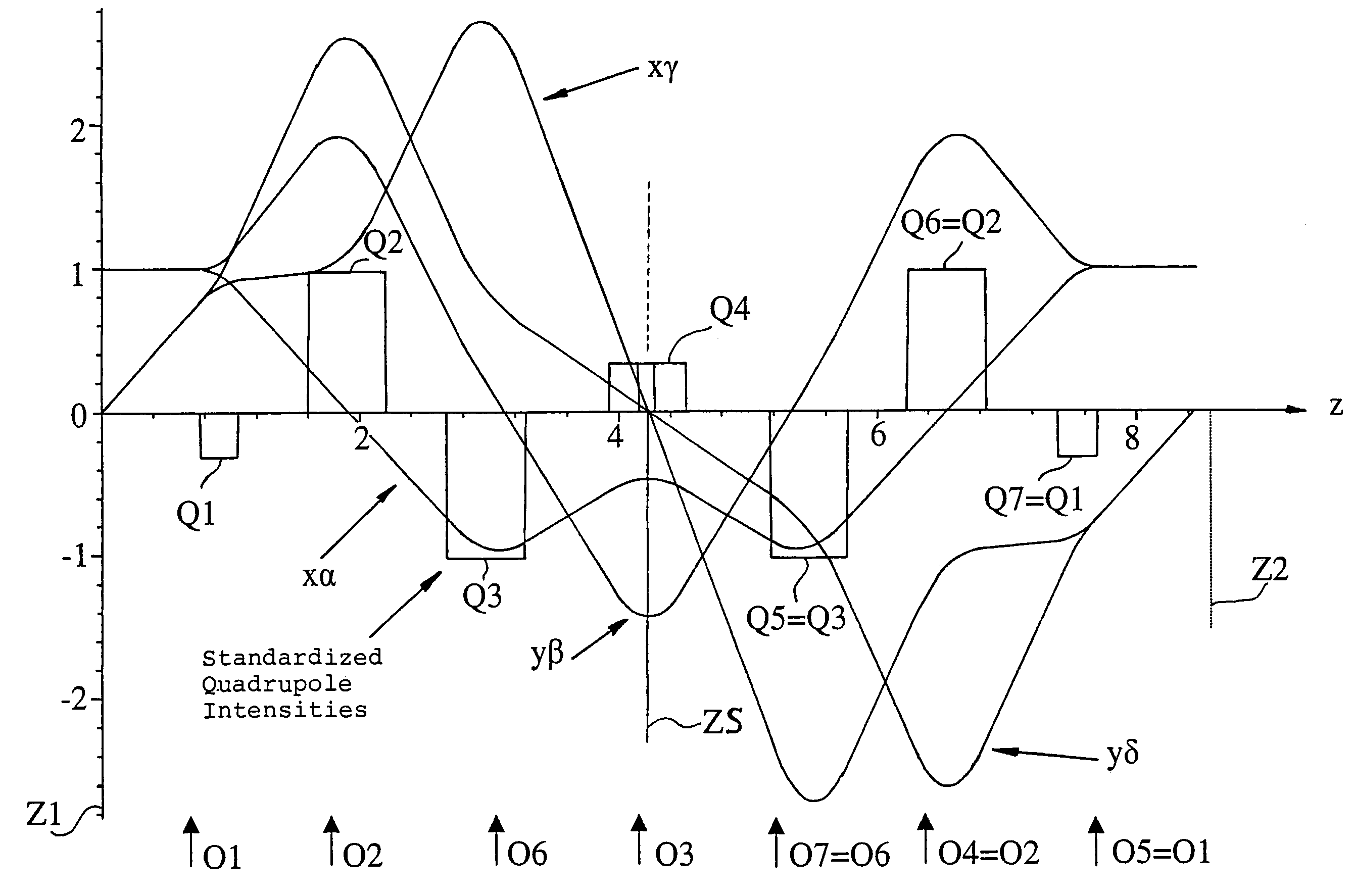
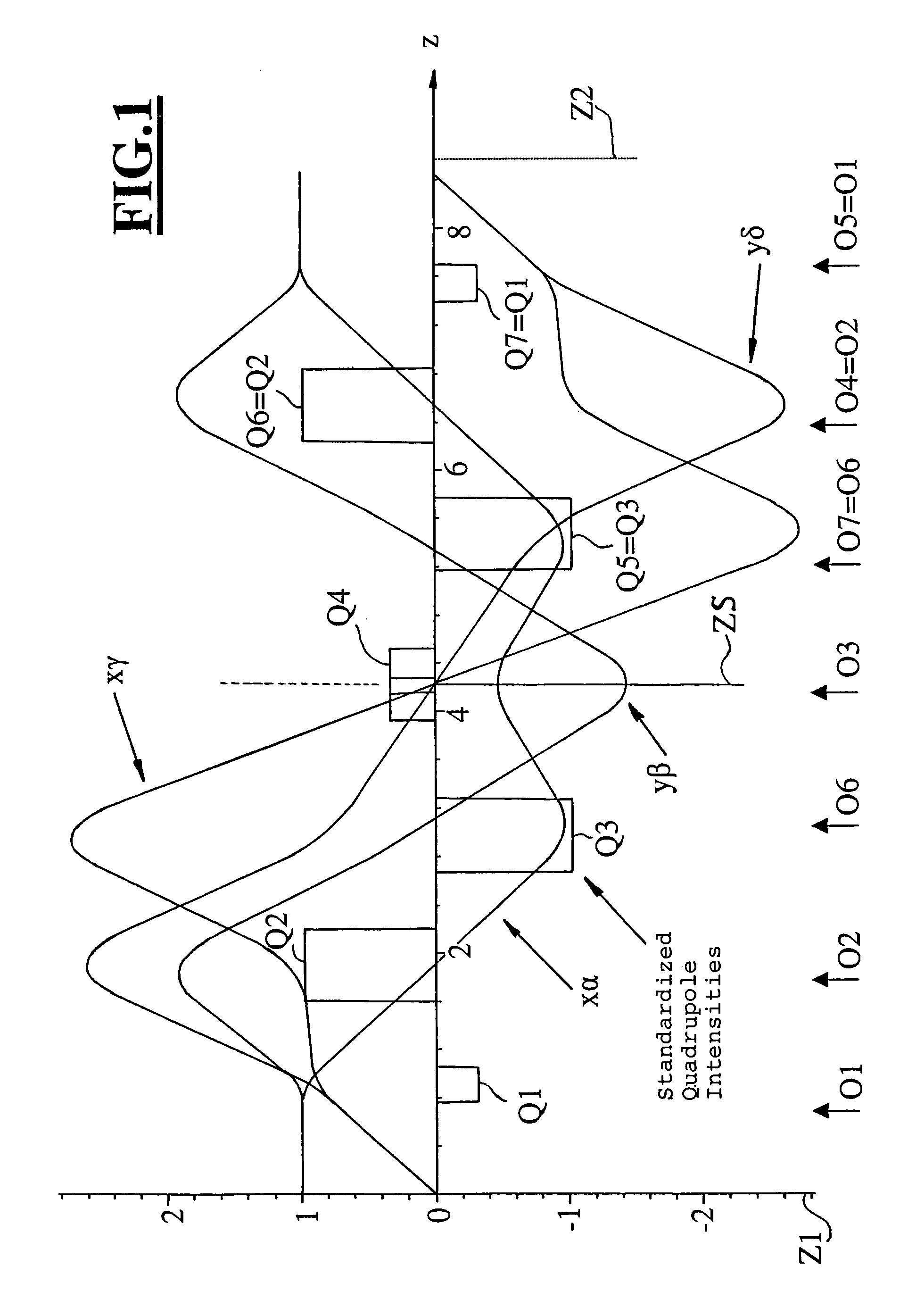
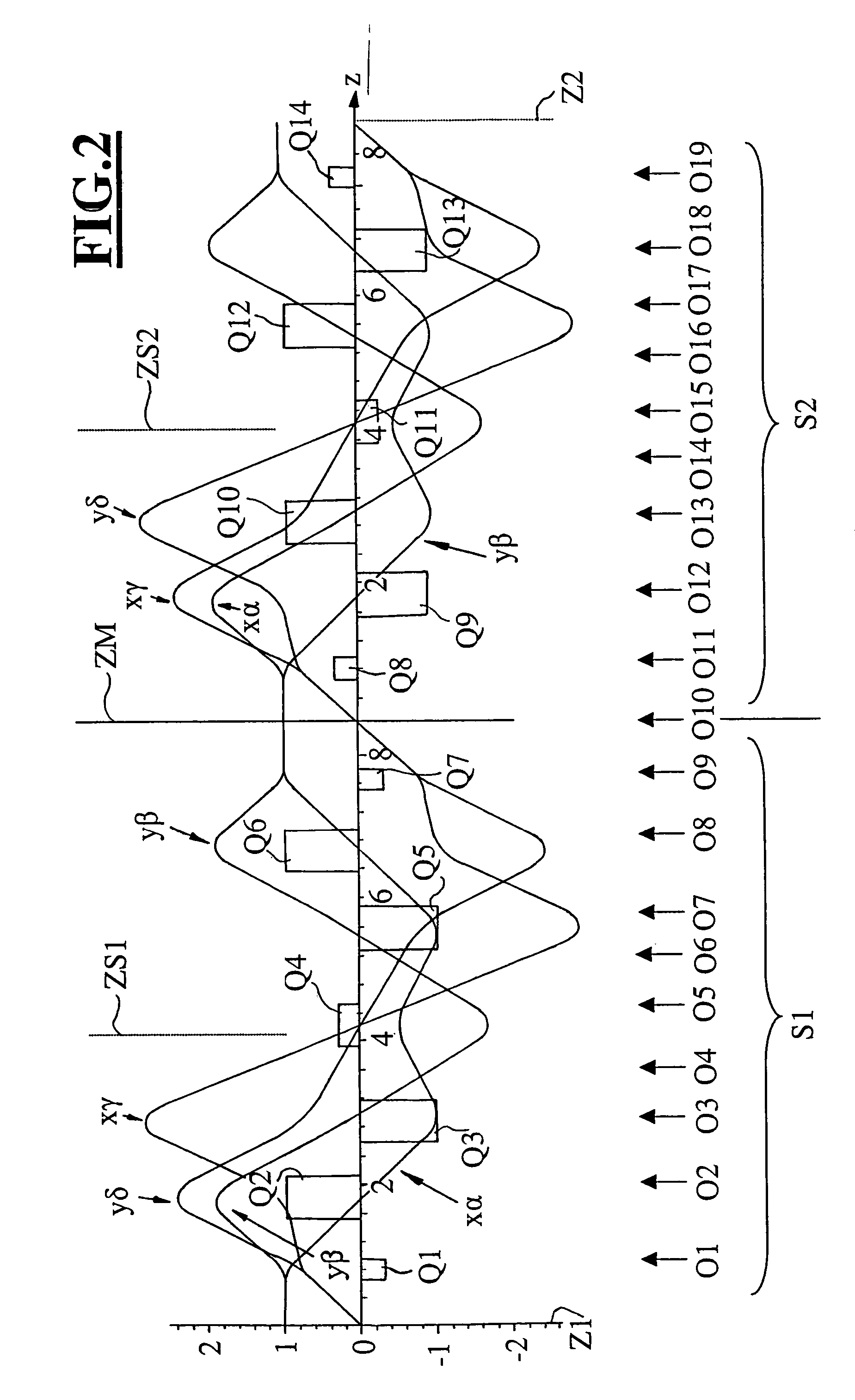
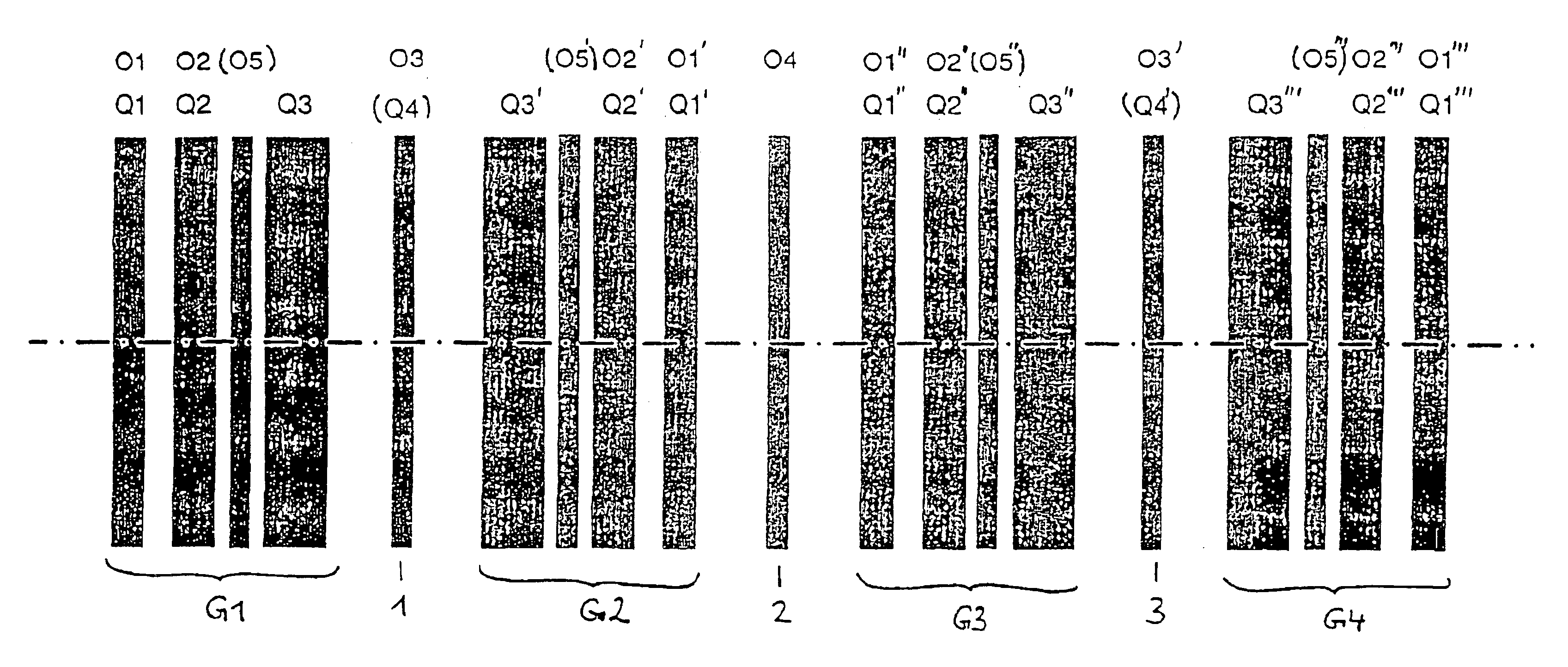
InactiveUS7012262B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesQuadrupole fieldElectron
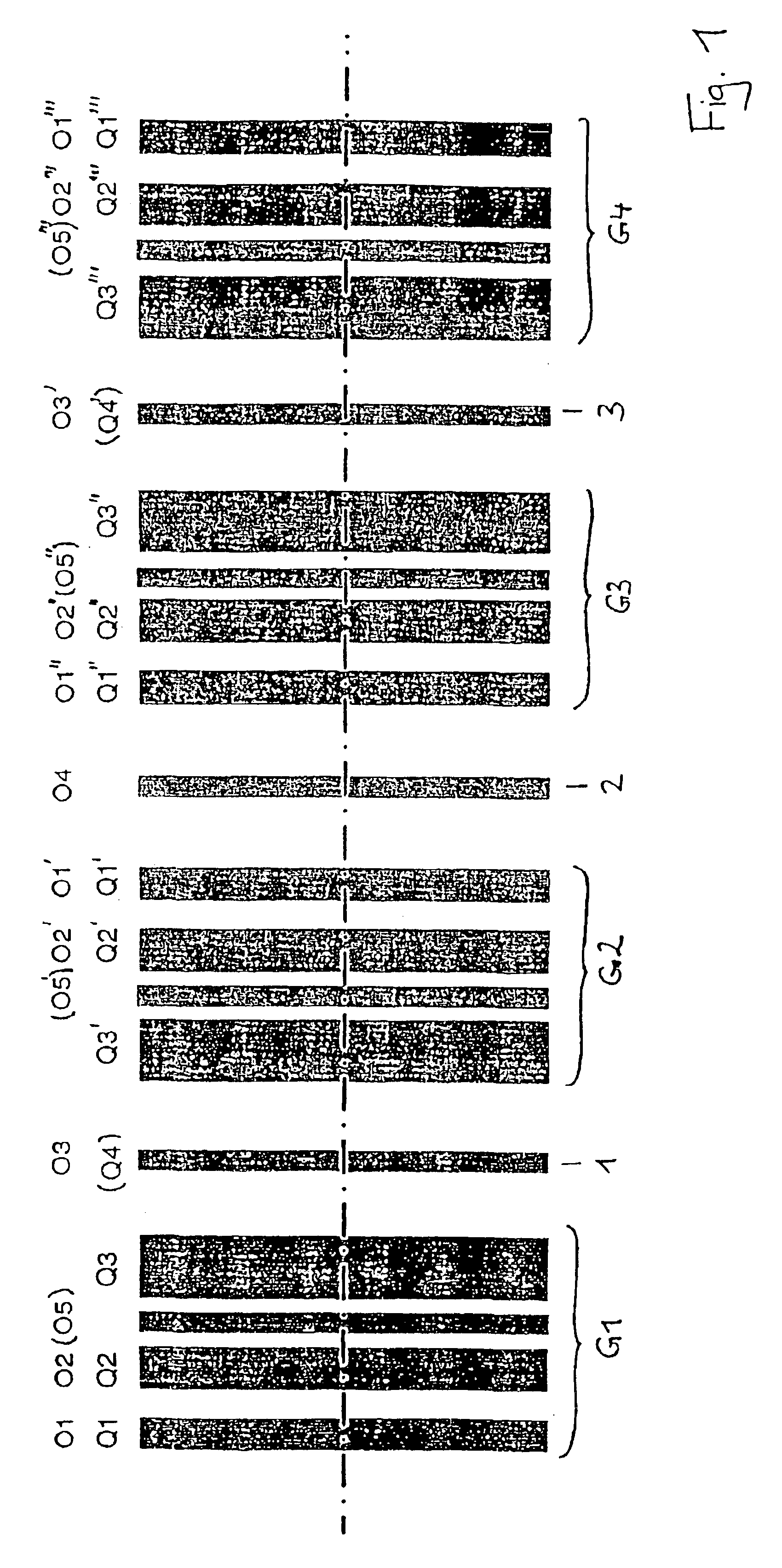
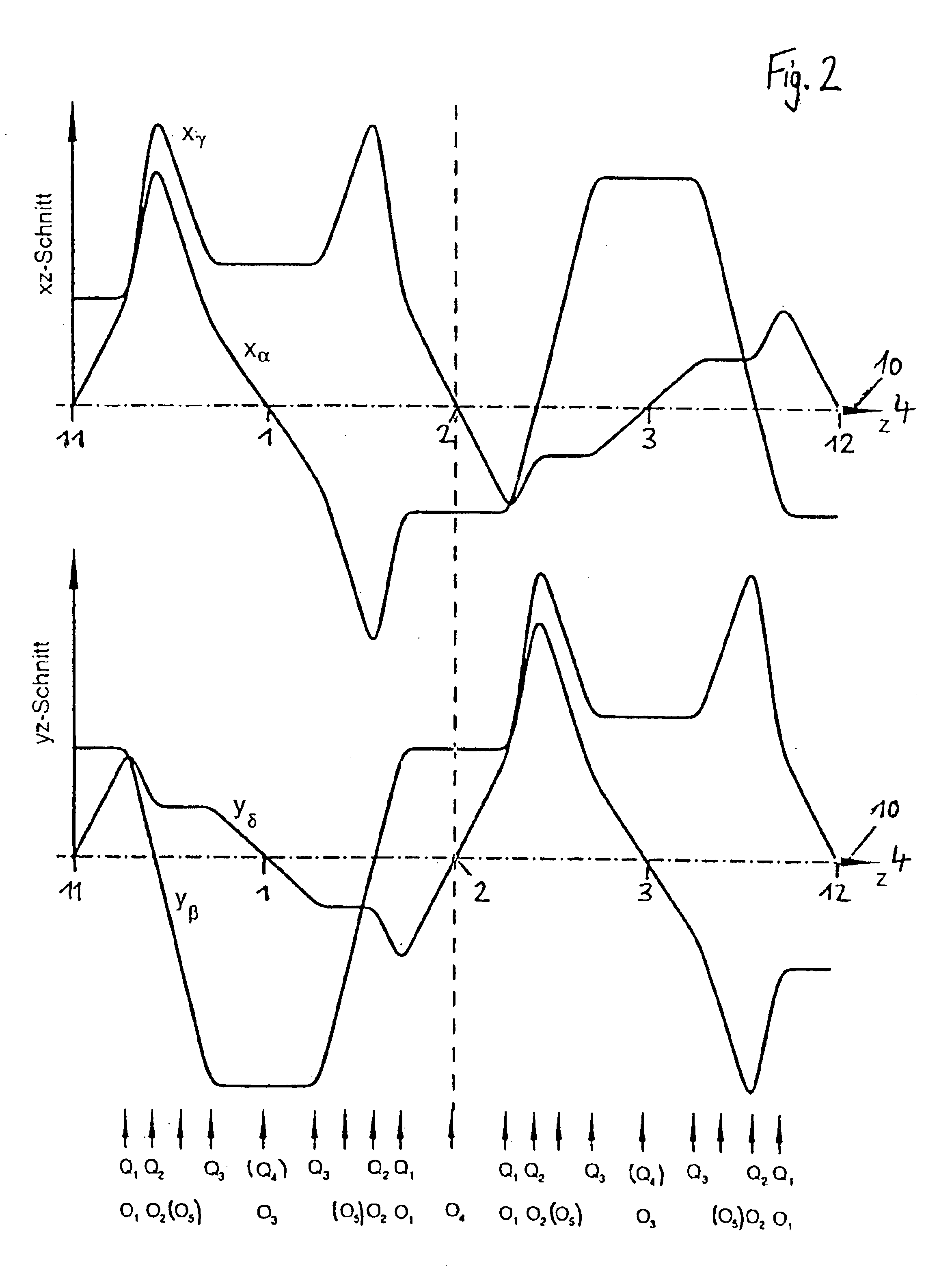
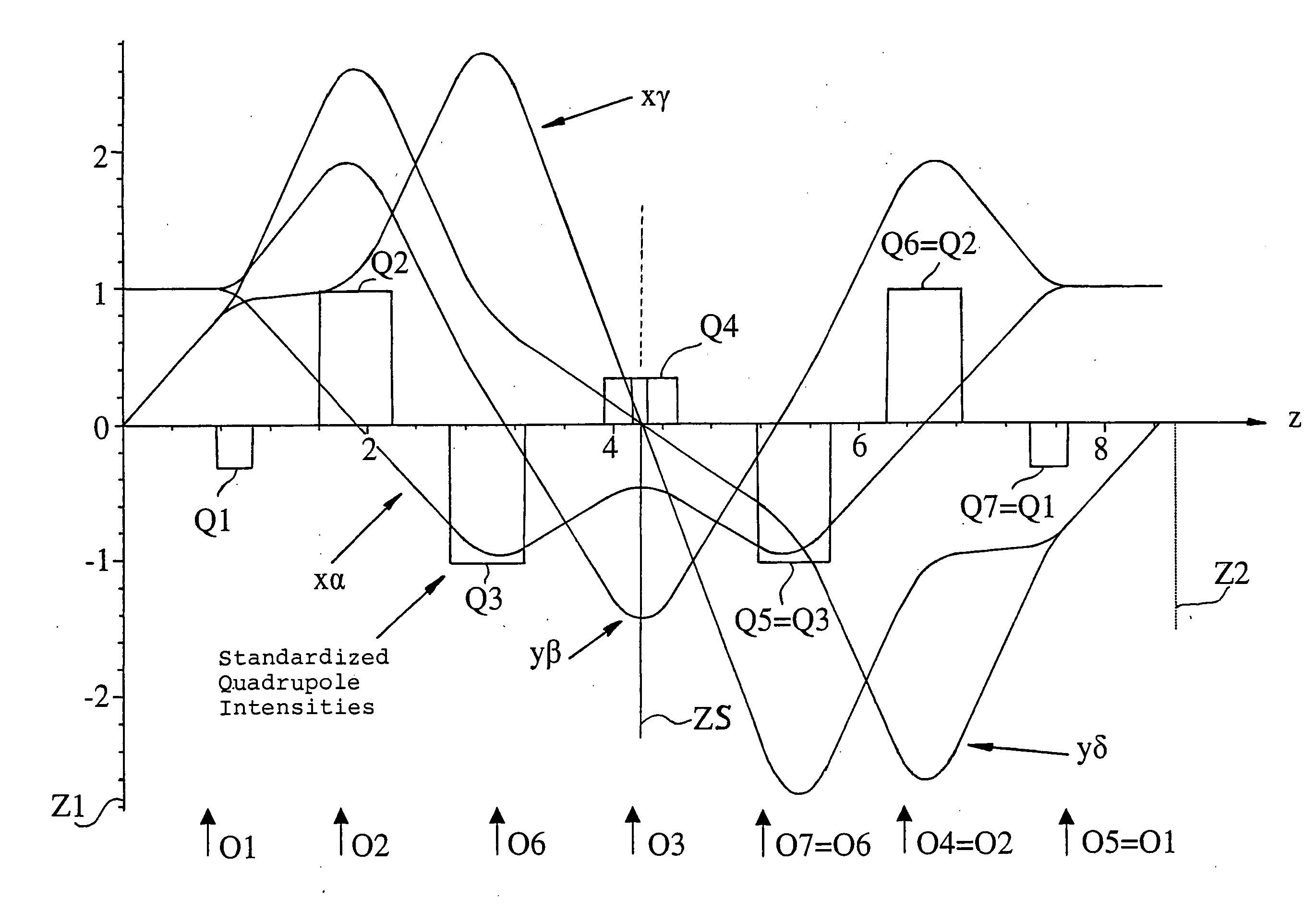
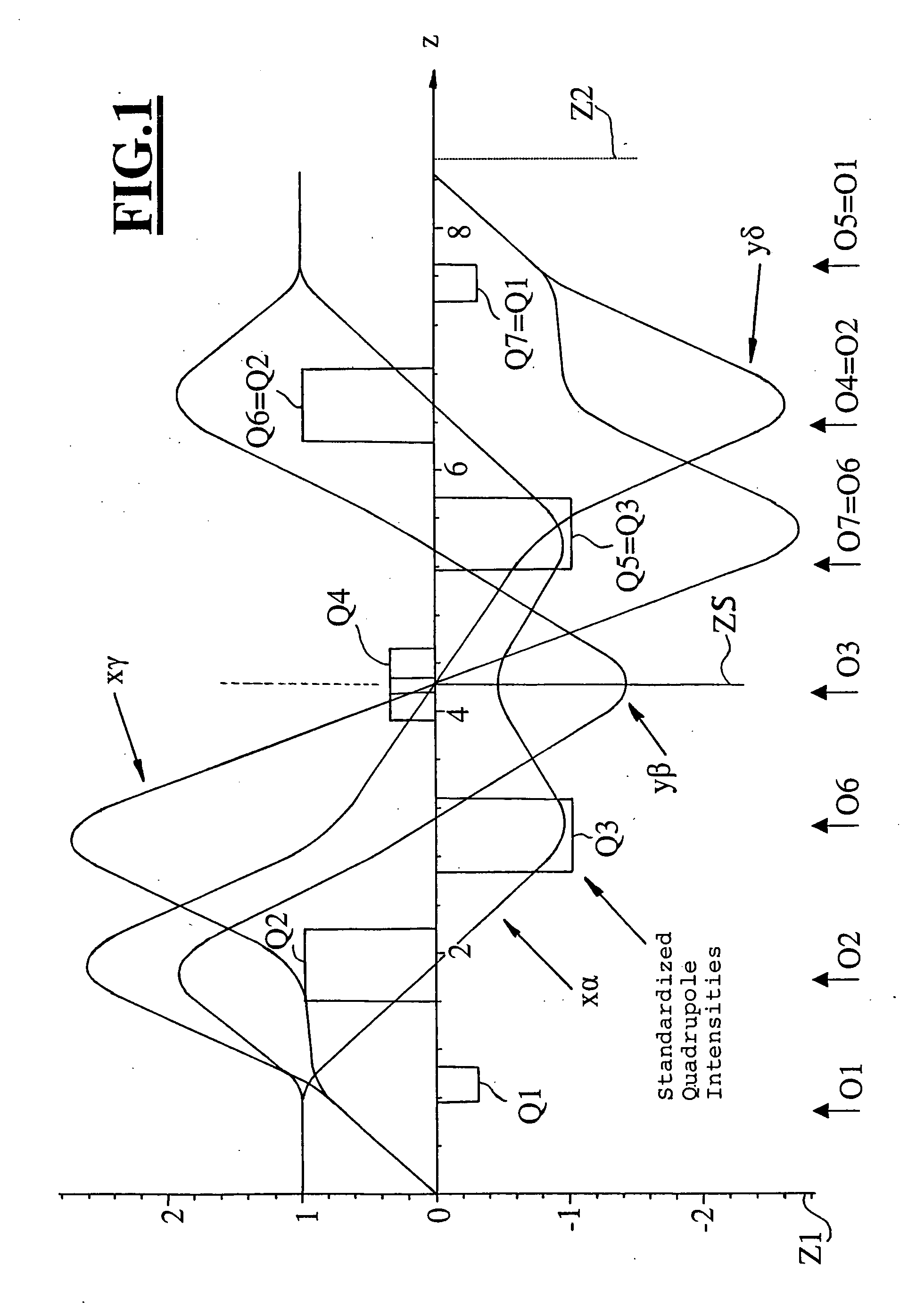
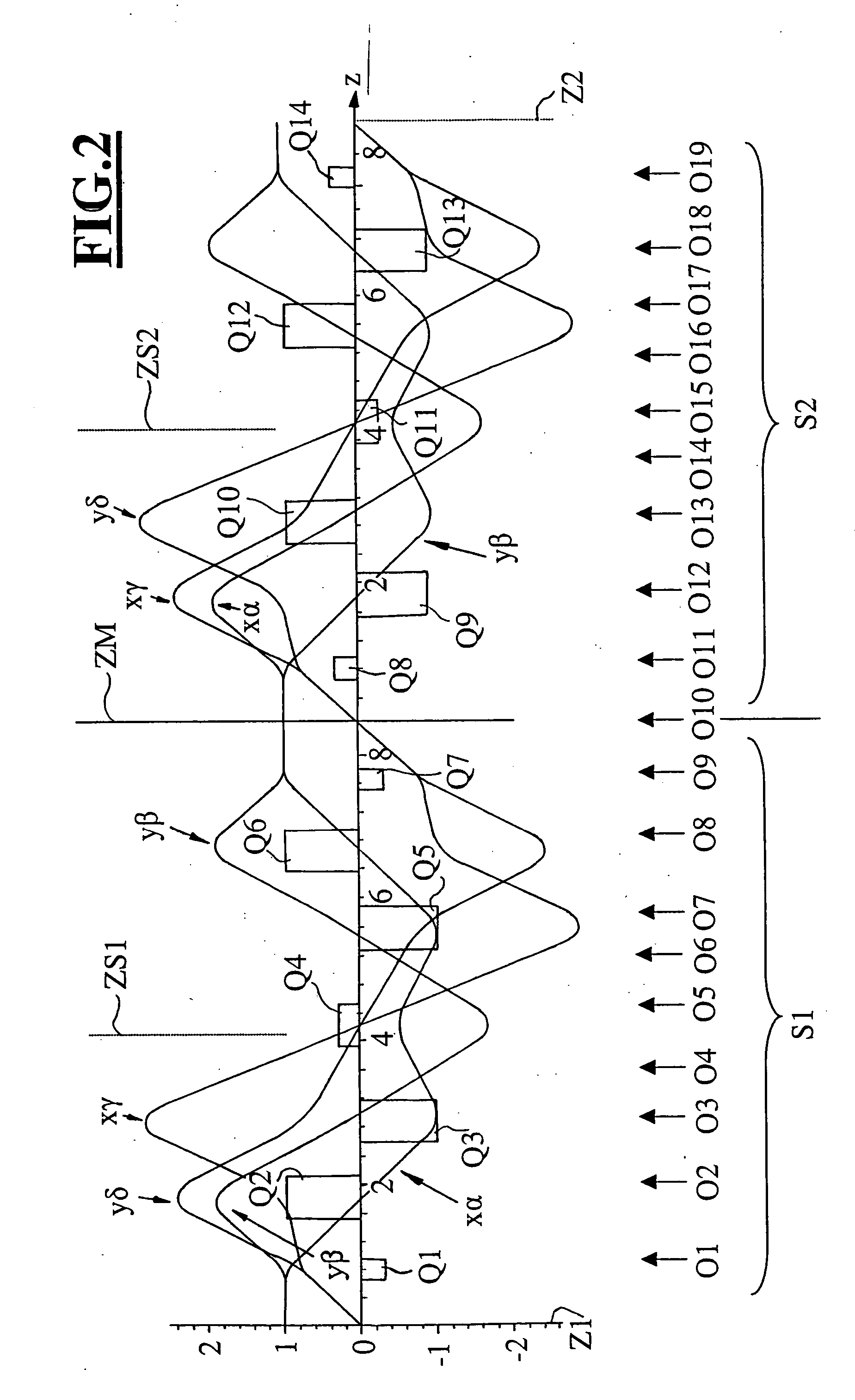
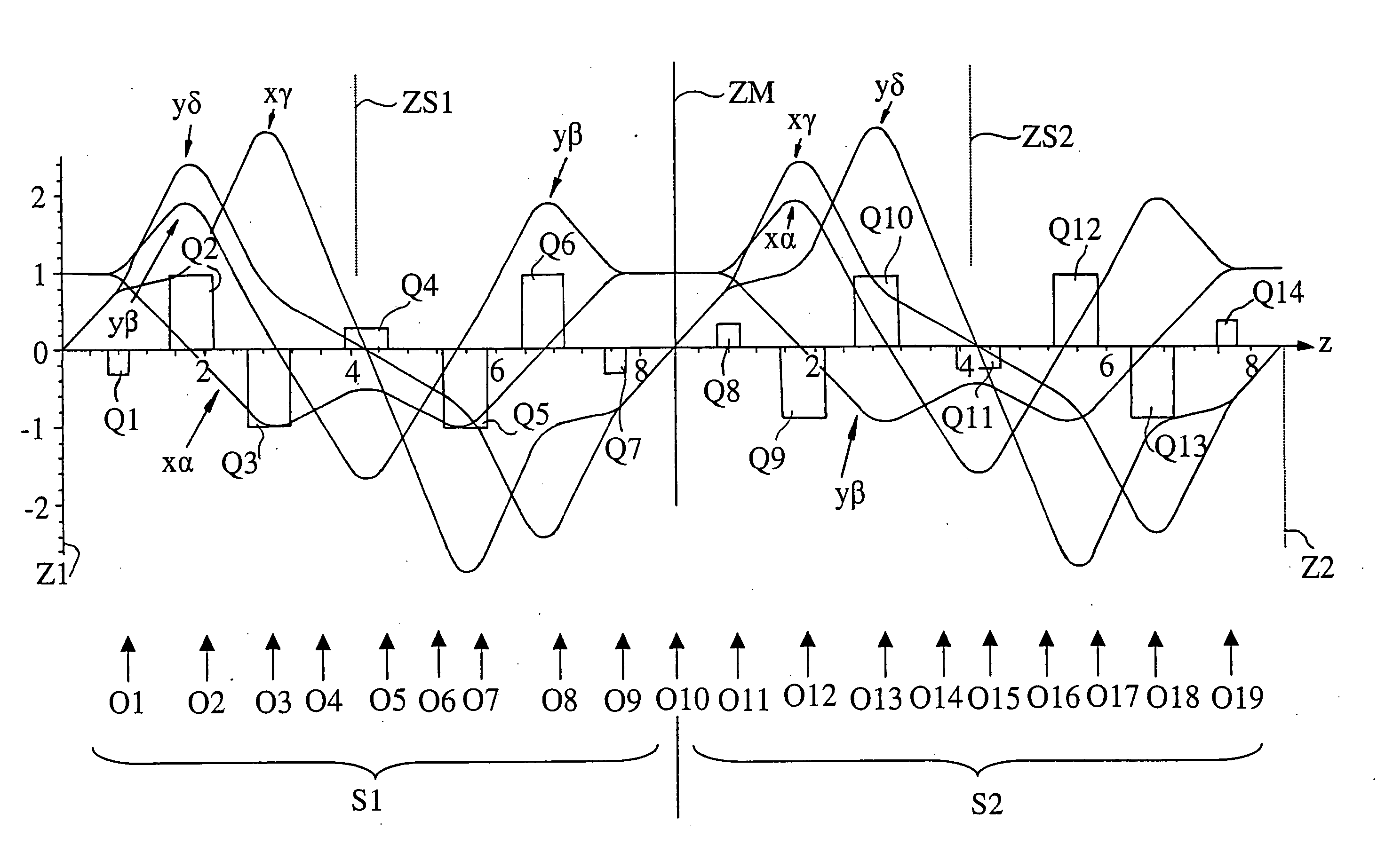
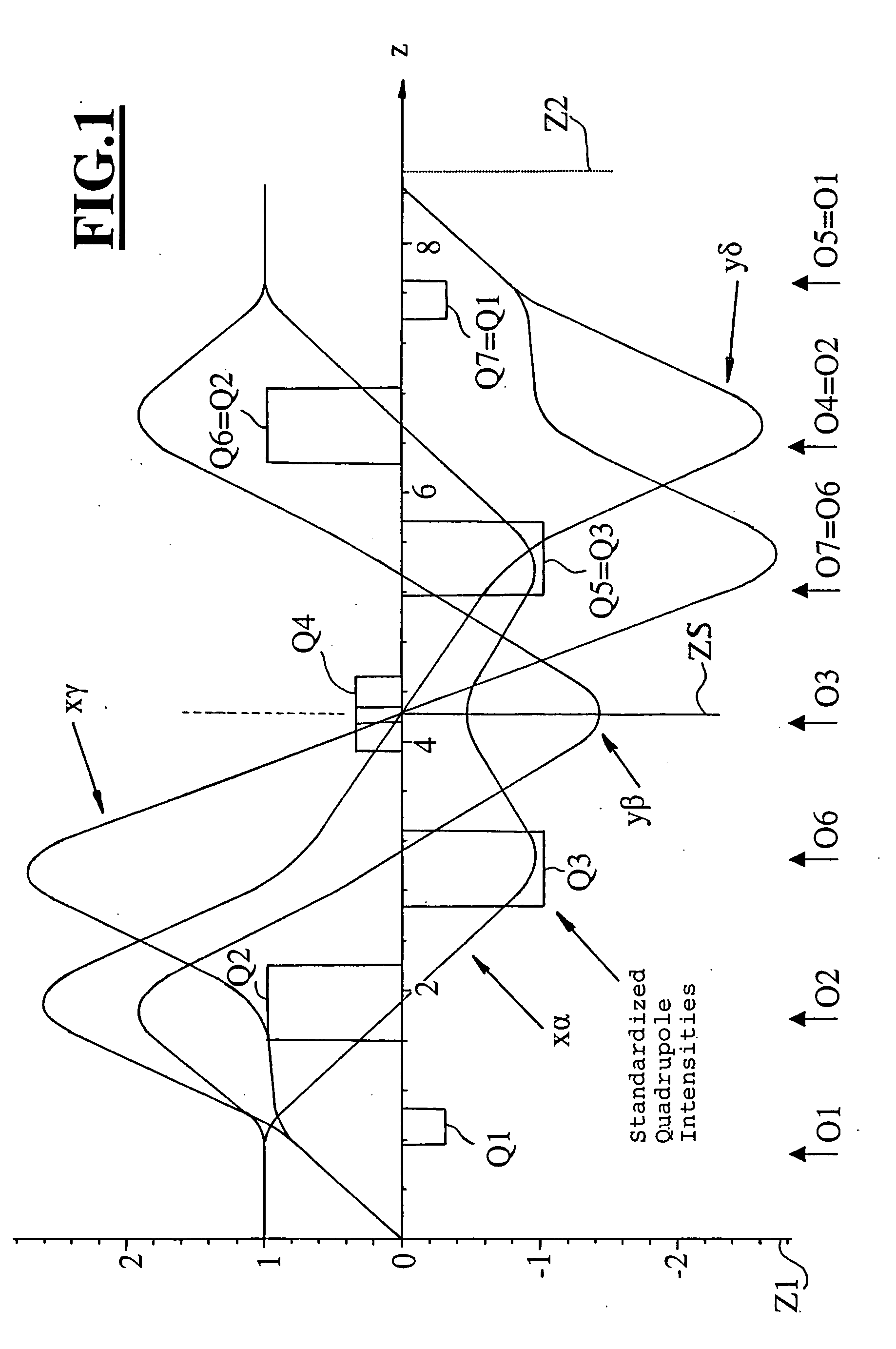
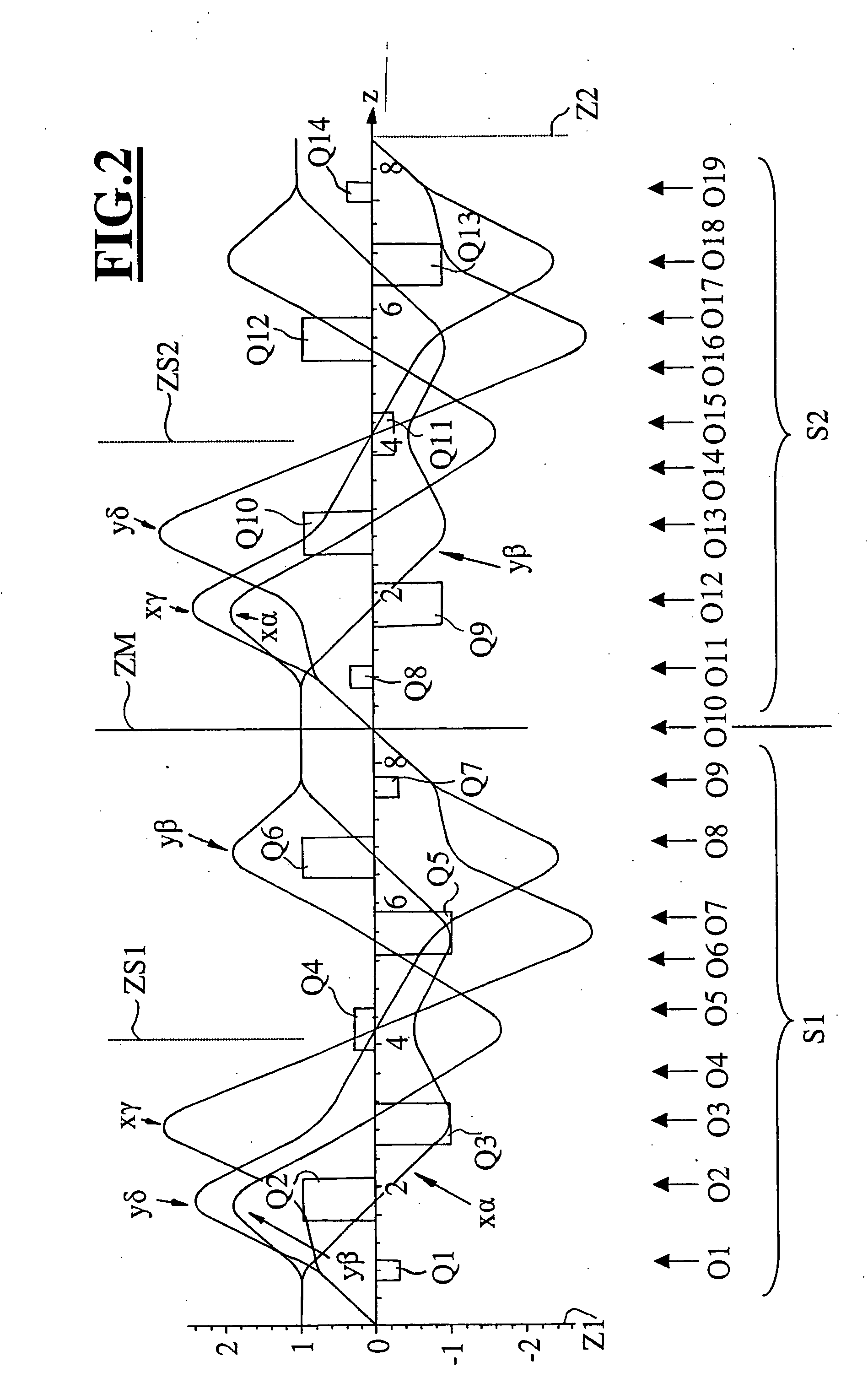
The invention is directed to a corrector for correcting energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the first degree as well as third-order spherical aberrations of electron-optical lens systems. The corrector includes at least one quadropole septuplet (S1) having seven quadrupoles (Q1 to Q7). The quadrupoles are mounted symmetrically to a center plane (ZS) so as to permit excitation along a linear axis. The corrector furthermore includes at least five octopoles (O1 to O7) which can be excited within the quadrupole septuplet. In an advantageous embodiment, two quadrupole septuplets are mounted in series one behind the other. The quadrupole fields of the two quadrupole septuplets are excited antisymmetrically to a center plane lying between the two quadrupole septuplets. With such a system, all geometric third-order aberrations and additional energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the third degree and geometric fifth-order aberrations of a lens system can be corrected in addition to the axial and off-axial first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
Ion analysis apparatus and method of use
ActiveUS8610054B2Easy to modifyImprove performanceStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionSpectrometerAtomic physics
The present invention is concerned with an ion analysis apparatus for conducting differential ion mobility analysis and mass analysis. In embodiments, the apparatus comprises a differential ion mobility device in a vacuum enclosure of a mass spectrometer, located prior to the mass analyzer, wherein the pumping system of the apparatus is configure to provide an operating pressure of 0.005 kPa to 40 kPa for the differential ion mobility device, and wherein the apparatus includes a digital asymmetric waveform generator that provides a waveform of frequency of 50 kHz to 25 MHz. Examples demonstrate excellent resolving power and ion transmission. The ion mobility device can be a multipole, for example a 12-pole and radial ion focusing can be achieved by applying a quadrupole field to the device in addition to a dipole field.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Ion trap with built-in field-modifying electrodes and method of operation
ActiveUS7279681B2Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryQuadrupole field
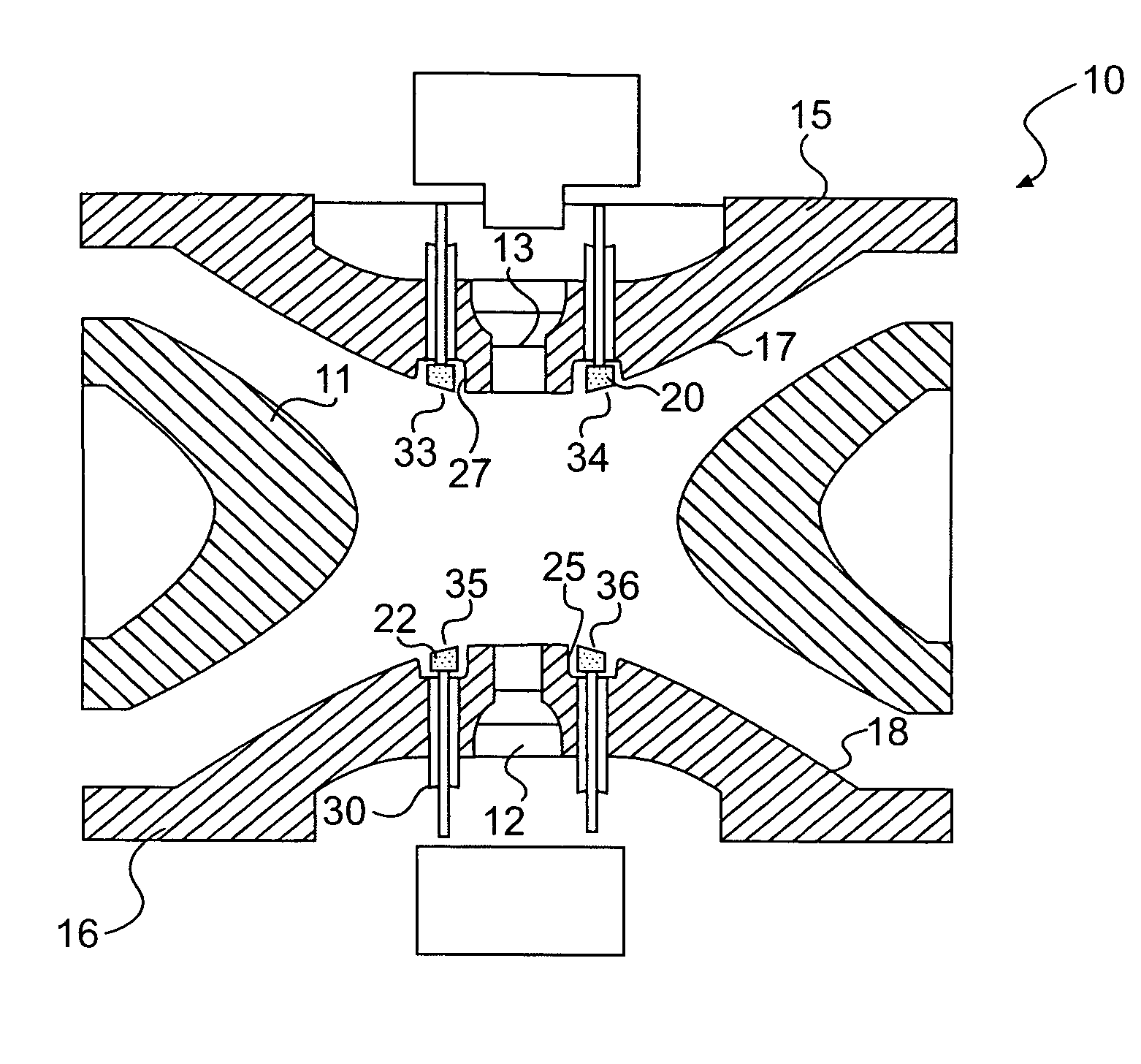
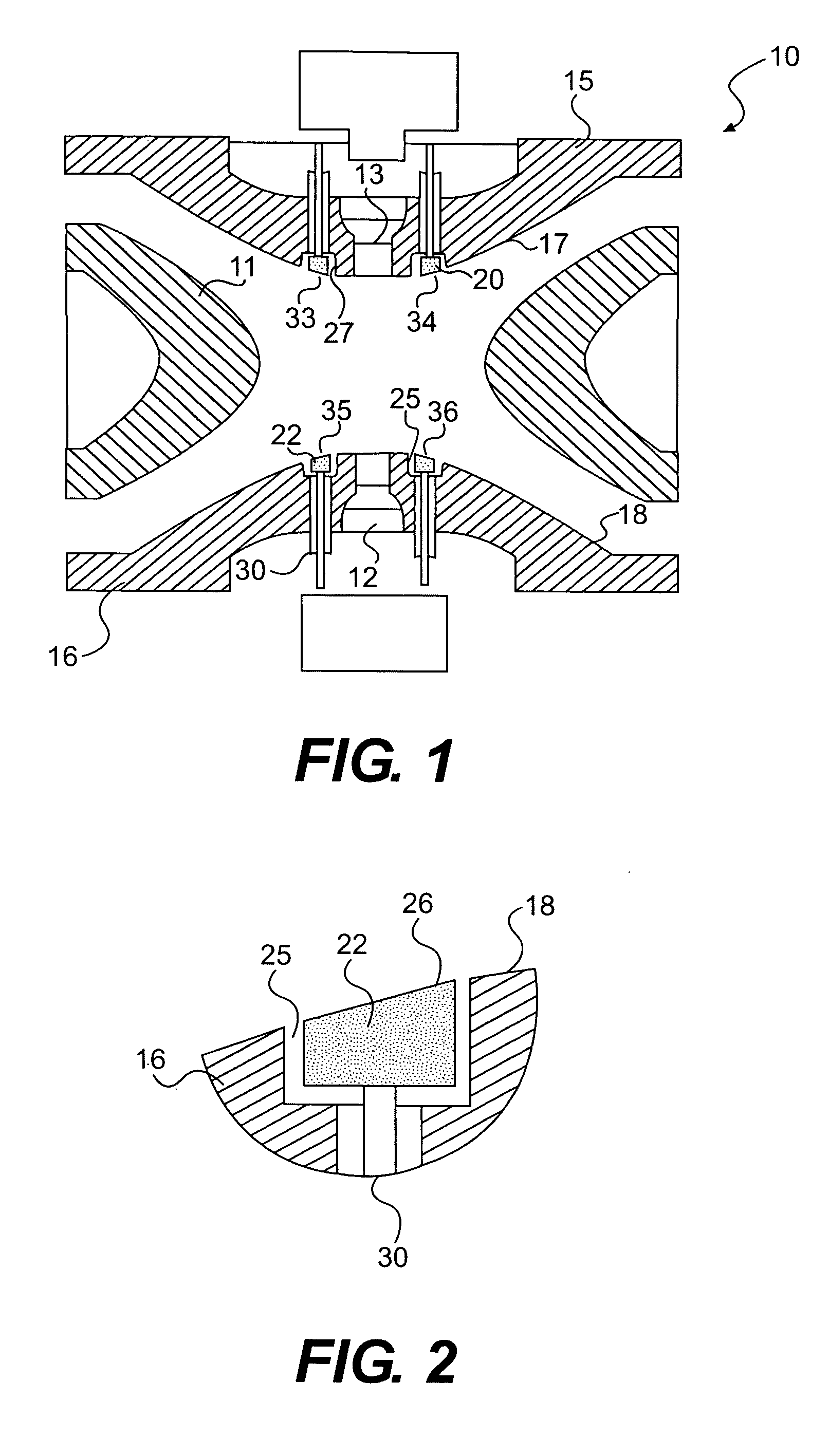
An apparatus and method for correcting deviations in a quadrupole field in a quadrupole ion trap is provided. More specifically the invention provides for correction electrodes positioned in at least one primary quadrupole electrode and a method of using the correction electrodes to provide a field correction potential.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Linear ion trap analyzer
ActiveCN102231356AIncrease the efficiency of one-way extractionMass spectrometersQuadrupole fieldIon trap mass spectrometry
The invention relates to a linear ion trap analyzer. The linear ion trap analyzer comprises an ion trapping space surrounded by a plurality of cylinder electrodes, wherein high frequency voltage is applied to at least one part of cylinder electrodes so as to generate a radial trapping electric field which mainly has two dimensional quadrupole fields in the trapping space; at least one ion leading-out slot is formed on an ion trap in the direction perpendicular to a center axis, and an alternating electric field for exciting dipoles is overlapped in the direction; a strip-type field regulating electrode is arranged in a slit in the cylinder electrode right opposite to the ion leading-out slot, or in the gap between two cylinder electrodes; and the voltage on the field regulating electrode is set as the sum of all or one part of the high frequency voltage on the adjacent cylinder electrode and direct current (DC) voltage, and the DC voltage can be regulated as required. By setting the field regulating electrode and regulating the DC voltage, one or more aims of optimizing a field form in a linear ion trap and influencing ion motion characteristics during resonance excitation can be fulfilled.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Scanning Systems for Particle Cancer Therapy
ActiveUS20140163301A1Little functionSmall sizeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyQuadrupole fieldParticle beam
A particle beam to treat malignant tissue is delivered to a patient by a gantry. The gantry includes a plurality of small magnets sequentially arranged along a beam tube to transfer the particle beam with strong focusing and a small dispersion function, whereby a beam size is very small, allowing for the small magnet size. Magnets arranged along the beam tube uses combined function magnets where the magnetic field is a combination of a bending dipole field with a focusing or defocusing quadrupole field. A triplet set of combined function magnets defines the beam size at the patient. A scanning system of magnets arranged along the beam tube after the bending system delivers the particle beam in a direction normal to the patient, to minimize healthy skin and tissue exposure to the particle beam.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Magnetic levitation system
A magnetic levitation system for supporting an object against gravity by a supporting force includes a permanent-magnet dipole aligned in a vertical position and coupled to the object, a supporting-field generator and a stabilization system. The supporting-field generator generates a supporting force on the permanent-magnet dipole via a supporting field. The supporting field is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional magnetic quadrupole field so that the supporting force is independent of a position of the dipole. The stabilization system constrains the dipole against movements in at least one horizontal direction, and includes a diamagnetic element coupled to the dipole and arranged below the dipole, and a stabilizing-field generator generating a second two-dimensional or three-dimensional stabilizing field to restore said diamagnetic element to a position where the field strength of the stabilizing field has a local minimum.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Energy filter and electron microscope
An energy filter with reduced aberration. The energy filter has a first stage of filter for receiving an electron beam entering along the optical axis and for focusing the beam in one direction vertical to the optical axis and a second stage of filter positioned along the optical axis behind the first stage of filter. The beam once focused by the first stage of filter is made to enter the second stage of filter. In the second stage of filter, the orbit of the electron beam is inverted with respect to the focal point. The two stages of filters are identical in length taken along the optical axis. The first and second stages of filters have electric and magnetic quadrupole fields, respectively, along the optical axis. These quadrupole fields make an angle of 45 degrees to the optical axis to achieve astigmatic focusing.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Corrector
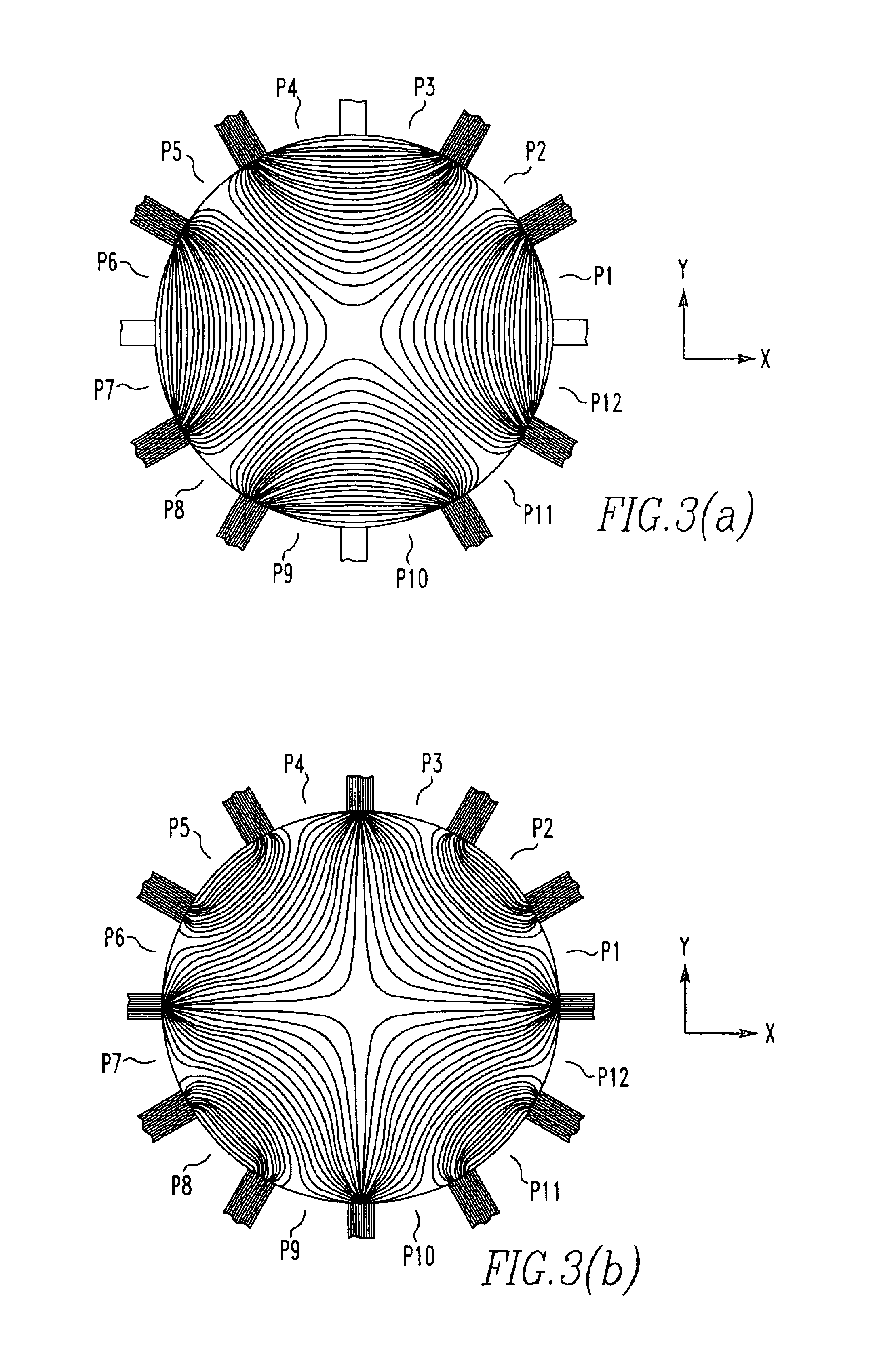
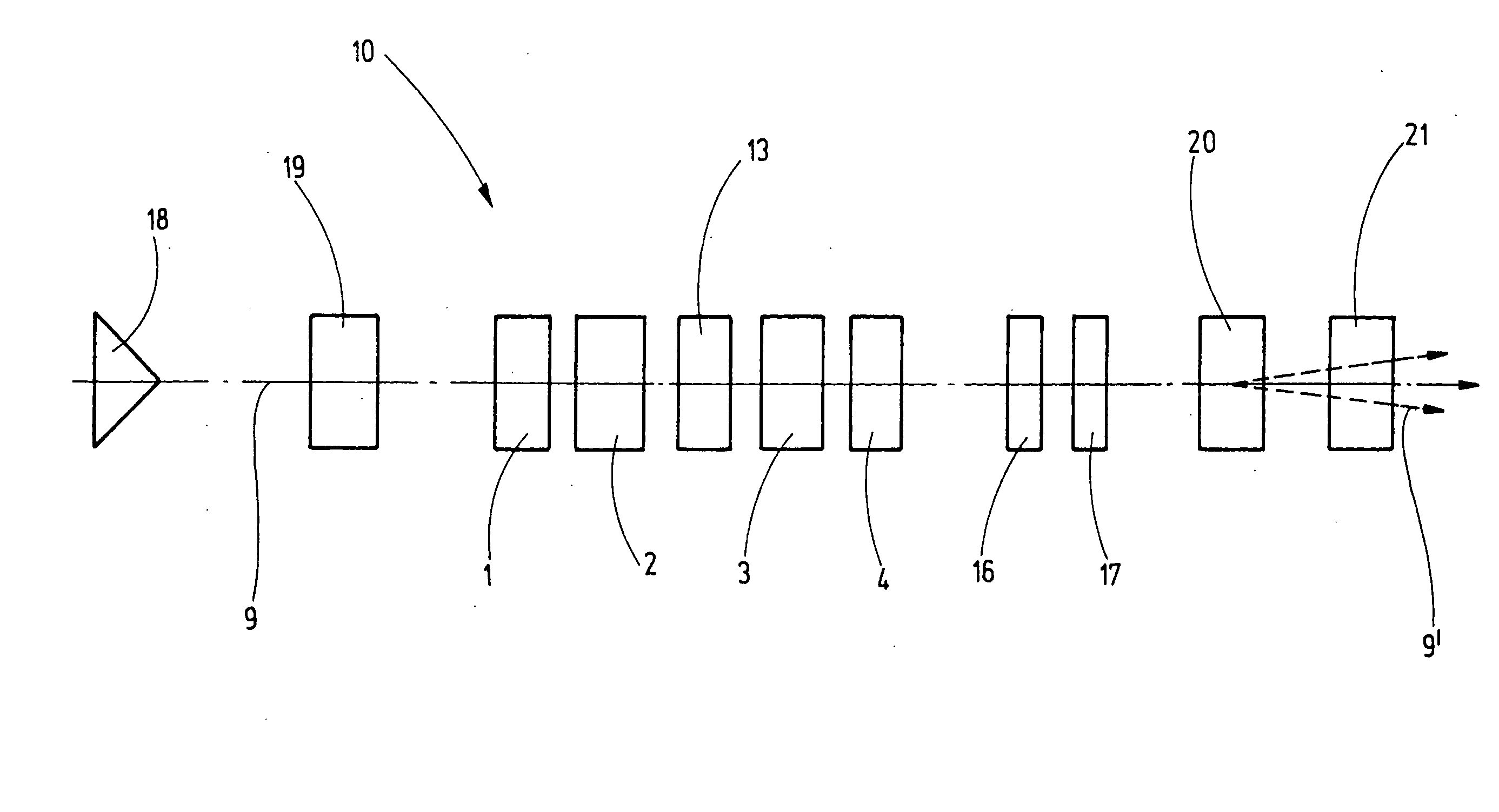
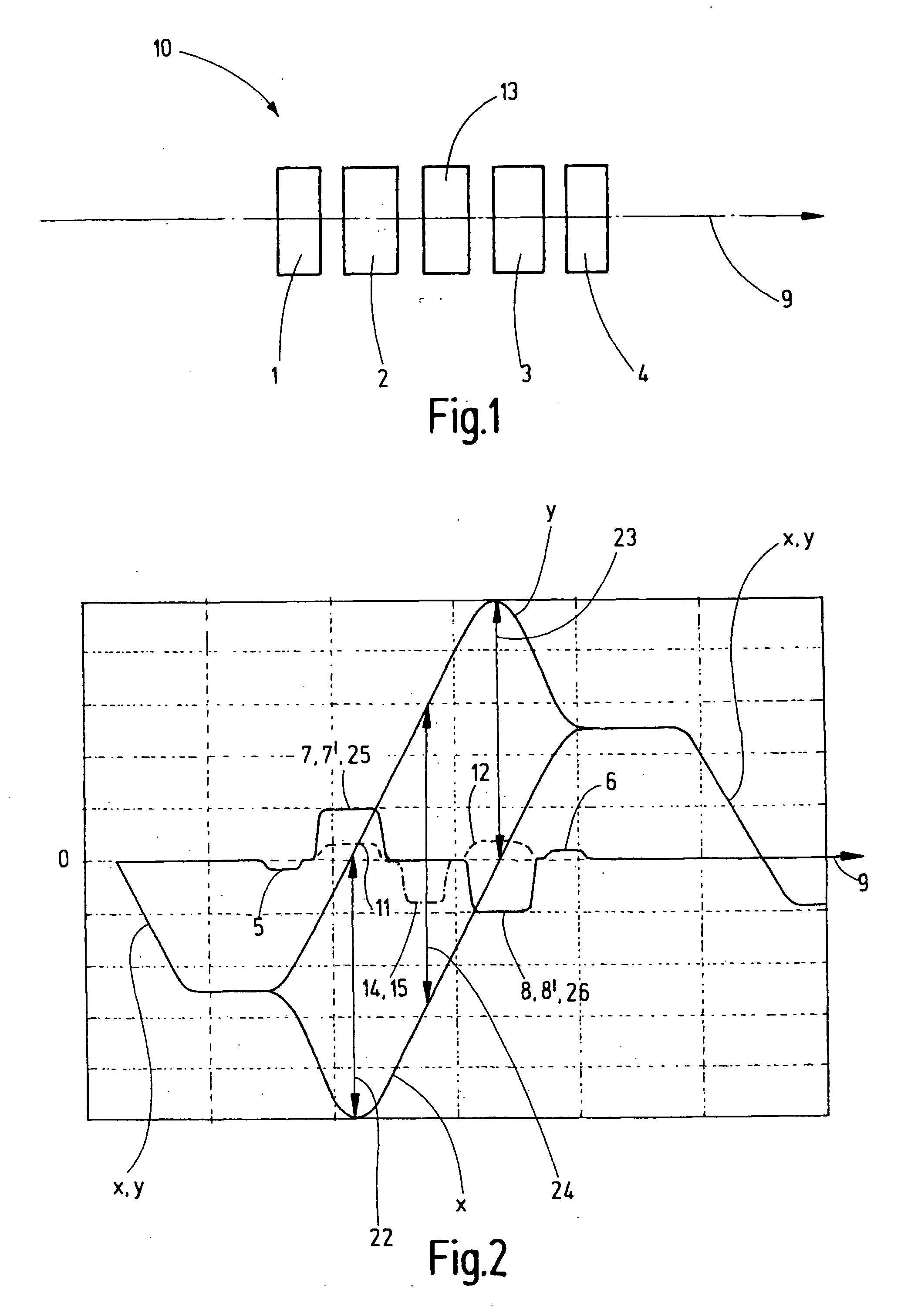
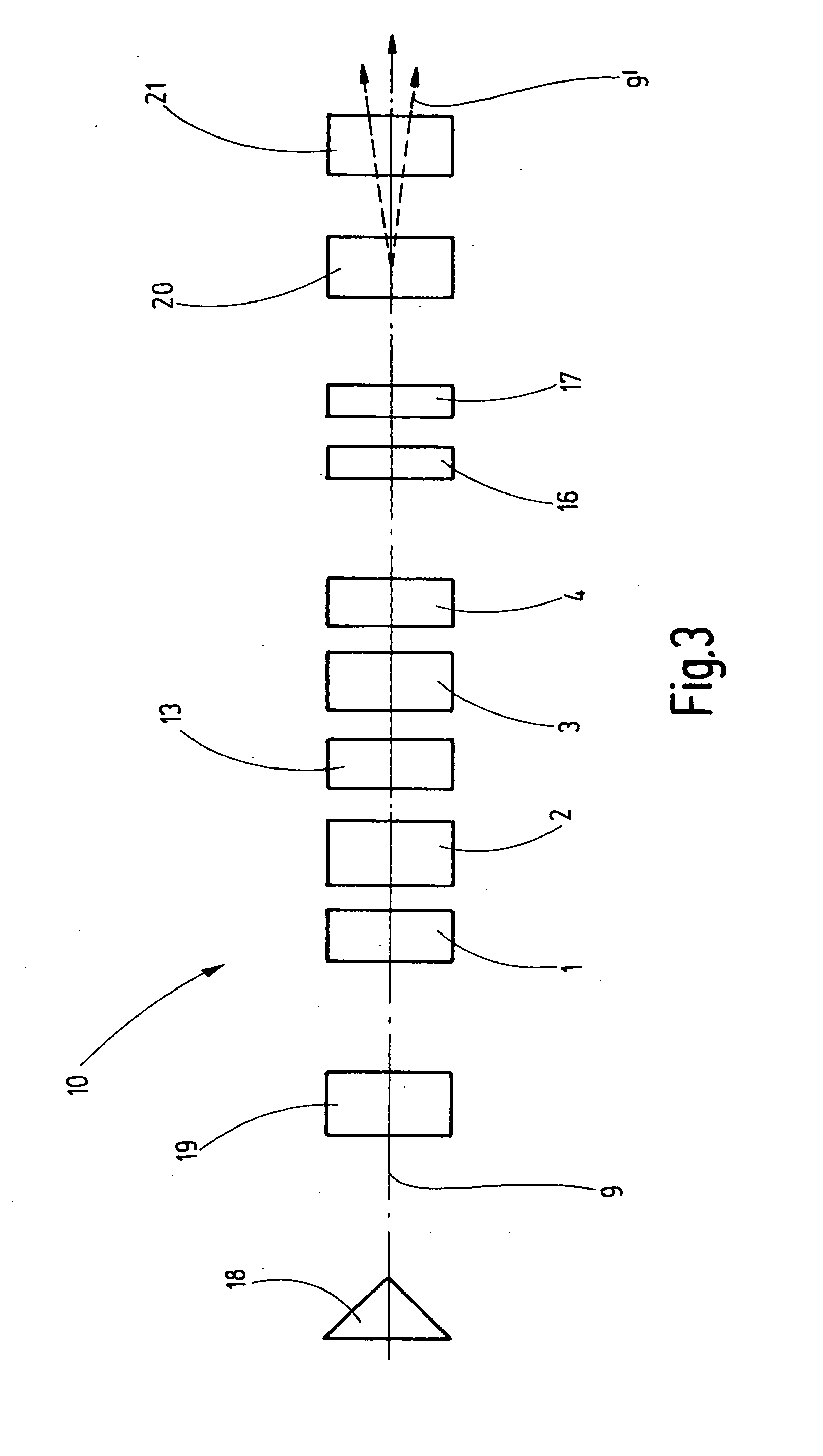
ActiveUS20090101818A1Avoid causingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldScanning electron microscope
The invention concerns a corrector (10) for chromatic and aperture aberration correction in a scanning electron microscope or a scanning transmission electron microscope, comprising four multipole elements (1, 2, 3, 4) which are consecutively disposed in the optical path (9), the first (1) and fourth (4) of which are used to generate quadrupole fields (5, 6) and the second (2) and third (3) of which are used to generate octupole fields (11, 12) and quadrupole fields (7, 7′, 8, 8′), wherein the latter are superposed magnetic (7, 8) and electric (7′, 8′) fields, and wherein the quadrupole fields (5, 6, 7, 8) of all four multipole elements (1, 2, 3, 4) are successively rotated with respect to one another through 90°. Elimination of errors up to fifth order can be realized with a corrector (10) of this type in that the second (2) and the third (3) multipole elements are designed as twelve-pole elements, and an additional twelve-pole element (13) is inserted between the second (2) and the third (3) multipole element, and is loaded with current and / or voltage, such that an octupole field (14) is generated that is superposed by a twelve-pole field (15).
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
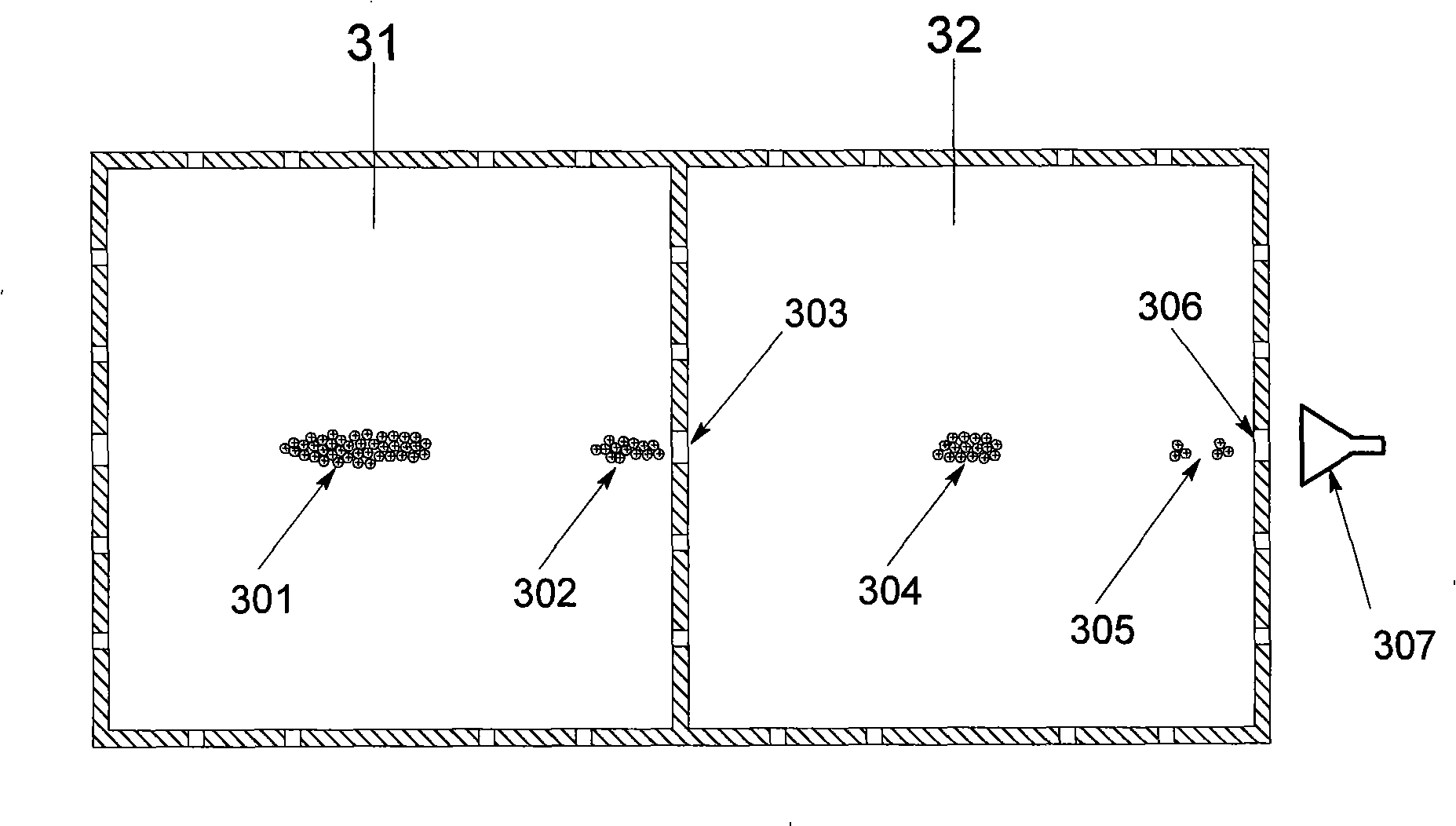
Methods and systems for providing a substantially quadrupole field with significant hexapole and octapole components
A system and method involving processing ions in a linear ion trap are provided, involving a two-dimensional asymmetric substantially quadrupole field having a hexapole and octopole component.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
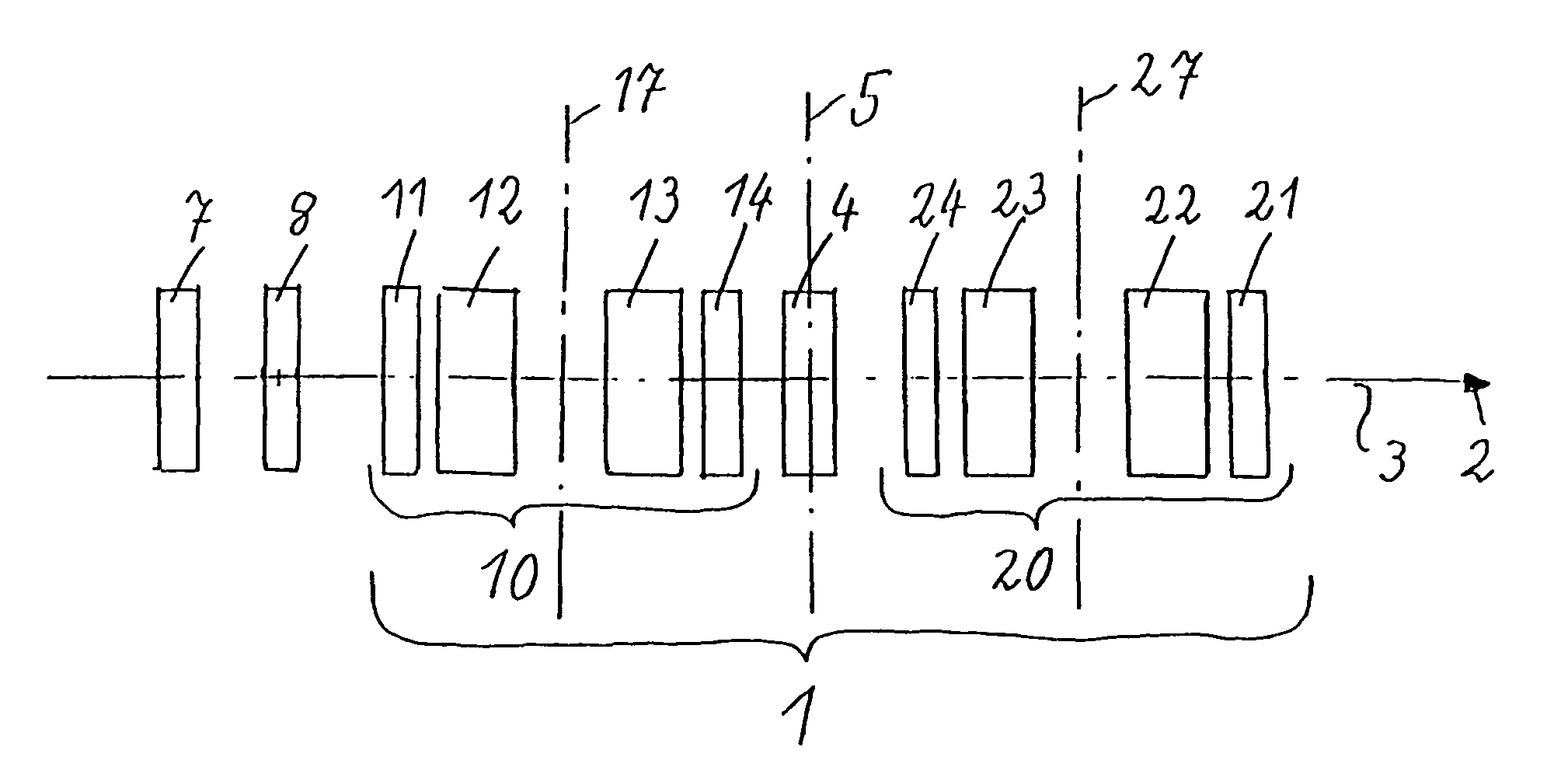
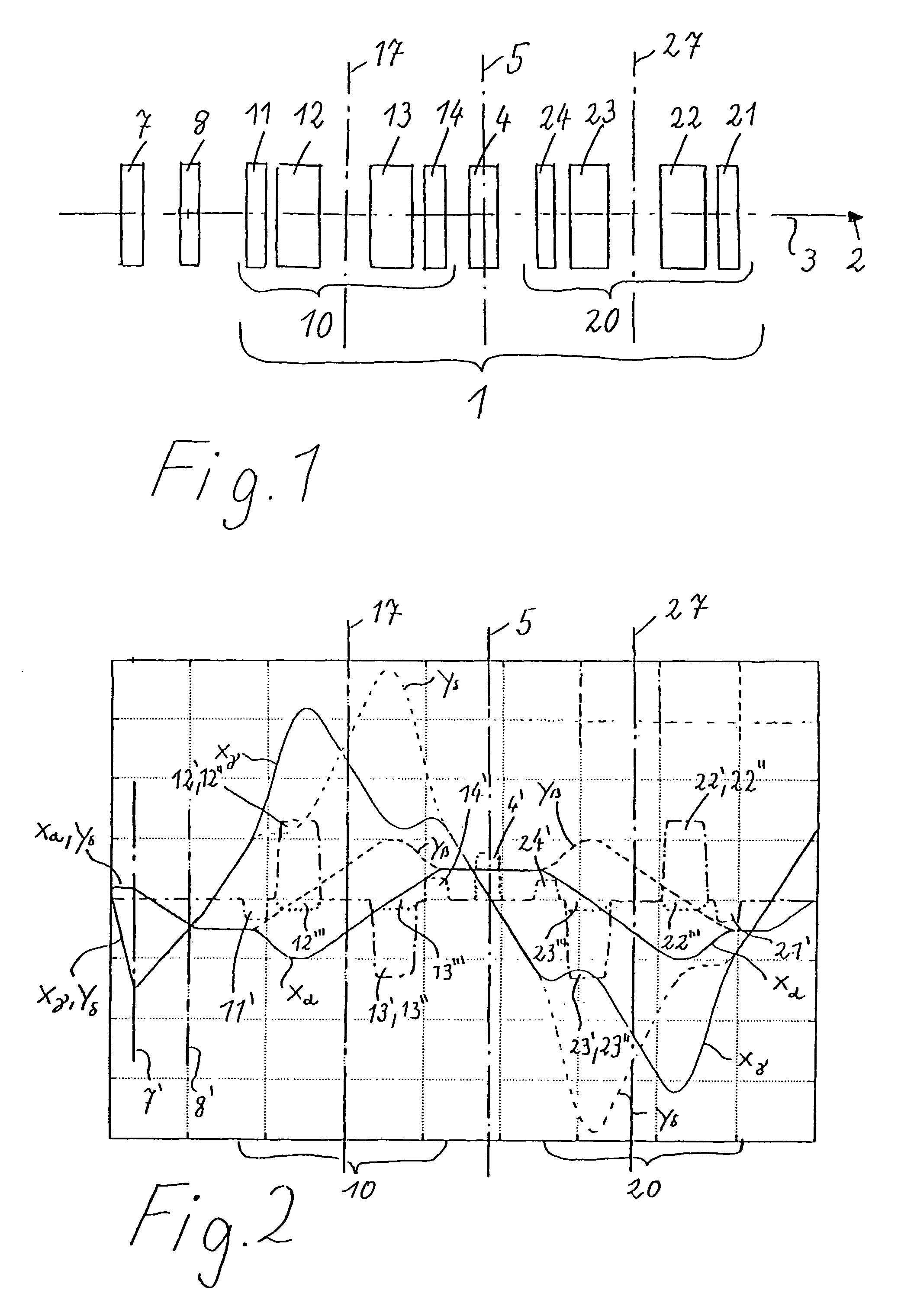
Corrector for axial and off-axial beam paths
InactiveUS7807965B2Eliminate astigmatismEliminate aberrationsStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationQuadrupole fieldOptical axis
A corrector (1) for the axial and off-axial beam path of a particle-optical system, comprises a first (10) and a second (20) correction piece, which are disposed one behind the other in the beam path (2) on an optical axis (3). Each correction piece (10, 20) comprises four successive multipole elements (11, 12, 13, 14; 24, 23, 22, 21) disposed symmetrically with respect to a center plane (5) and with the following fields: wherein the first (11; 24) and the fourth (14; 21) multipole elements of the multipole elements (11, 12, 13, 14; 24, 23, 22, 21) are used to generate quadrupole fields (11′, 14′; 24′, 21′) and the second (12; 23) and third (13; 22) are used to generate octupole fields (12′″, 13′″; 23′″,22′″) and quadrupole fields (12′, 13′; 23′,22′), wherein the latter are superposed magnetic (12′, 13′; 23′, 22′) and electric fields (12″, 13″; 23″, 22″), wherein the quadrupole fields (11′, 12′, 13′, 14′; 24′, 23′, 22′, 21′) of all four multipole elements (11, 12, 13, 14; 24, 23, 22,21) are rotated from one to the next through 90°. An astigmatism of third order is corrected by a central multipole element disposed in the center plane and generating an octupole field.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
Controlling the characteristics of implanter ion-beams
ActiveUS20050242294A1Eliminating magnetic short circuitsAccurate shapeElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansQuadrupole fieldAngle of incidence
A method and apparatus satisfying growing demands for improving the precision of angle of incidence of implanting ions that impact a semiconductor wafer and the precision of ribbon ion beams for uniform doping of wafers as they pass under an ion beam. The method and apparatus are directed to the design and combination together of novel magnetic ion-optical transport elements for implantation purposes. The design of the optical elements makes possible: (1) Broad-range adjustment of the width of a ribbon beam at the work piece; (2) Correction of inaccuracies in the intensity distribution across the width of a ribbon beam; (3) Independent steering about both X and Y axes; (4) Angle of incidence correction at the work piece; and (5) Approximate compensation for the beam expansion effects arising from space charge. In a practical situation, combinations of the elements allow ribbon beam expansion between source and work piece to 350 millimeter, with good uniformity and angular accuracy. Also, the method and apparatus may be used for introducing quadrupole fields along a beam line.
Owner:PURSER KENNETH H +2
Mass spectrometric ion storage device for different mass ranges
ActiveUS20130075602A1High yieldIsotope separationRadio frequency spectrometersQuadrupole fieldAnalyte
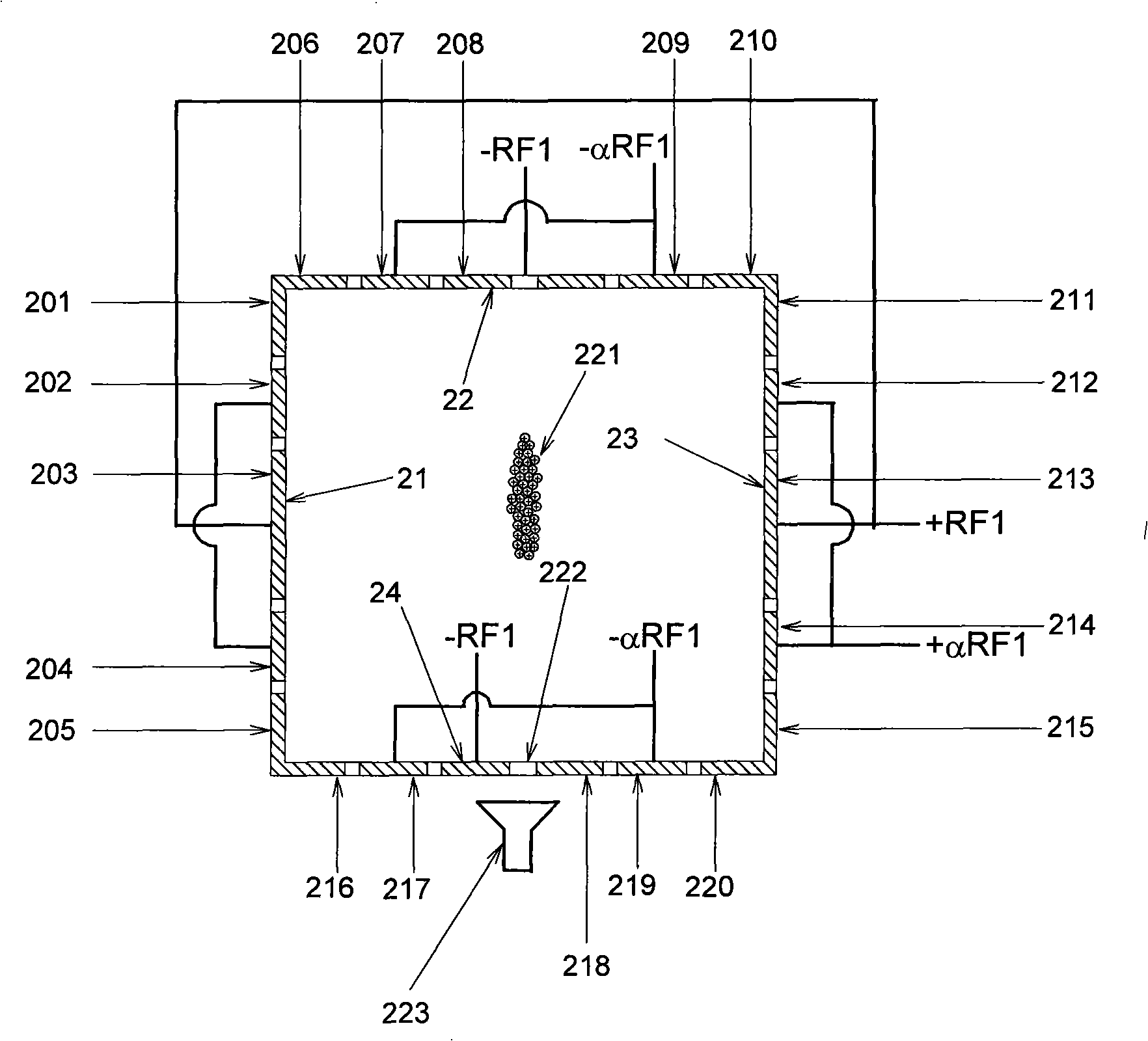
The invention relates to devices and methods for the storage of ions in mass spectrometers. The invention proposes the generation and superposition of two multipole fields of different order, independent of each other, in an RF multipole rod system. In an embodiment with eight pole rods, for example, it is thus possible to jointly store low-energy electrons in a central RF quadrupole field, which effectively acts only on electrons and holds them together radially, on the one hand, and multiply charged heavy positive ions in an RF octopole field, which effectively acts only on the ions, on the other hand, in order to fragment the positive ions by electron capture dissociation (ECD). In a different embodiment, multiply charged positive analyte ions and suitable negative reactant ions can react with each other in an octopole field by electron transfer dissociation (ETD) with a high fragmentation yield, and the fragment ions can subsequently be bundled by a transition to a quadrupole field to form a fine ion beam, which can leave the multipole rod system axially. A mixture of hexapole and dodecapole systems is also possible.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Ion trap mass spectrometer using cold electron souce
ActiveUS20150162178A1Easy to adjustIncrease ionization rateSamples introduction/extractionElectron/ion optical arrangementsQuadrupole fieldIon trap mass spectrometry
The present invention relates to an ion trap mass spectrometer using a cold electron source, in a production of a portable mass spectrometer, in which a microchannel plate (MCP) module is used, initial electrons are induced by injecting ultraviolet photons emitted from an ultraviolet diode to a front surface of the MCP module, electron beams amplified from the electrons are amplified using a channeltron electron multiplier (CEM), the amplified electron beams are accurately adjusted and injected into an ion trap, thus increasing the amplification rate, and since a quadrupole field is used as an ion filter which returns the initially injected electrons to the inside of an ion trap mass separator, the ionization rate increases.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Optical particle corrector
InactiveUS6888145B2Low stability requirementsLarge image aberrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansQuadrupole fieldReverse order
An optical particle corrector with a straight optical axis for eliminating color and aperture aberrations in optical particle lenses includes multipole elements in the form of electric and / or magnetic quadrupole and octupole elements. There are at least twelve quadrupole elements and ten octupole elements, in which three quadrupole elements and two octupole elements are assembled into a group. These groups are arranged successively along the straight optical axis, in which a first symmetrical plane is defined between the first and second groups, a second symmetrical plane is defined between the second and third groups and a third symmetrical plane is defined between the third and fourth groups. The multipole elements from one group to another correspond to each other in pairs, in which the multipole elements of the corresponding following group are positioned in reverse order along the straight optical axis in comparison with the corresponding multipole elements of the preceding group. The structure and refractive powers of the multipole elements that correspond to each other are mirror-symmetrically configured relative to the corresponding symmetrical plane between the groups. At least two of the quadrupole elements generate electric-magnetic quadrupole fields, in which the quadrupole element are, preferably, arranged in a mirror-symmetrical manner relative to the second, or to all, symmetrical planes. An additional octupole element is arranged in the first and third symmetrical planes. The corrector enables the transmission of extremely large image fields, while the optical quality remains the same due to the fact image aberrations outside the axis can be corrected.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
Corrector for correcting first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree
InactiveUS20050023480A1Aberration correctionStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationQuadrupole fieldEnergy dependent
The invention is directed to a corrector for correcting energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the first degree as well as third-order spherical aberrations of electron-optical lens systems. The corrector includes at least one quadropole septuplet (S1) having seven quadrupoles (Q1 to Q7). The quadrupoles are mounted symmetrically to a center plane (ZS) so as to permit excitation along a linear axis. The corrector furthermore includes at least five octopoles (O1 to O7) which can be excited within the quadrupole septuplet. In an advantageous embodiment, two quadrupole septuplets are mounted in series one behind the other. The quadrupole fields of the two quadrupole septuplets are excited antisymmetrically to a center plane lying between the two quadrupole septuplets. With such a system, all geometric third-order aberrations and additional energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the third degree and geometric fifth-order aberrations of a lens system can be corrected in addition to the axial and off-axial first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
Corrector for correcting first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree
InactiveUS20060102848A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesQuadrupole fieldEnergy dependent
The invention is directed to a corrector for correcting energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the first degree as well as third-order spherical aberrations of electron-optical lens systems. The corrector includes at least one quadropole septuplet (S1) having seven quadrupoles (Q1 to Q7). The quadrupoles are mounted symmetrically to a center plane (ZS) so as to permit excitation along a linear axis. The corrector furthermore includes at least five octopoles (O1 to O7) which can be excited within the quadrupole septuplet. In an advantageous embodiment, two quadrupole septuplets are mounted in series one behind the other. The quadrupole fields of the two quadrupole septuplets are excited antisymmetrically to a center plane lying between the two quadrupole septuplets. With such a system, all geometric third-order aberrations and additional energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the third degree and geometric fifth-order aberrations of a lens system can be corrected in addition to the axial and off-axial first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST GMBH
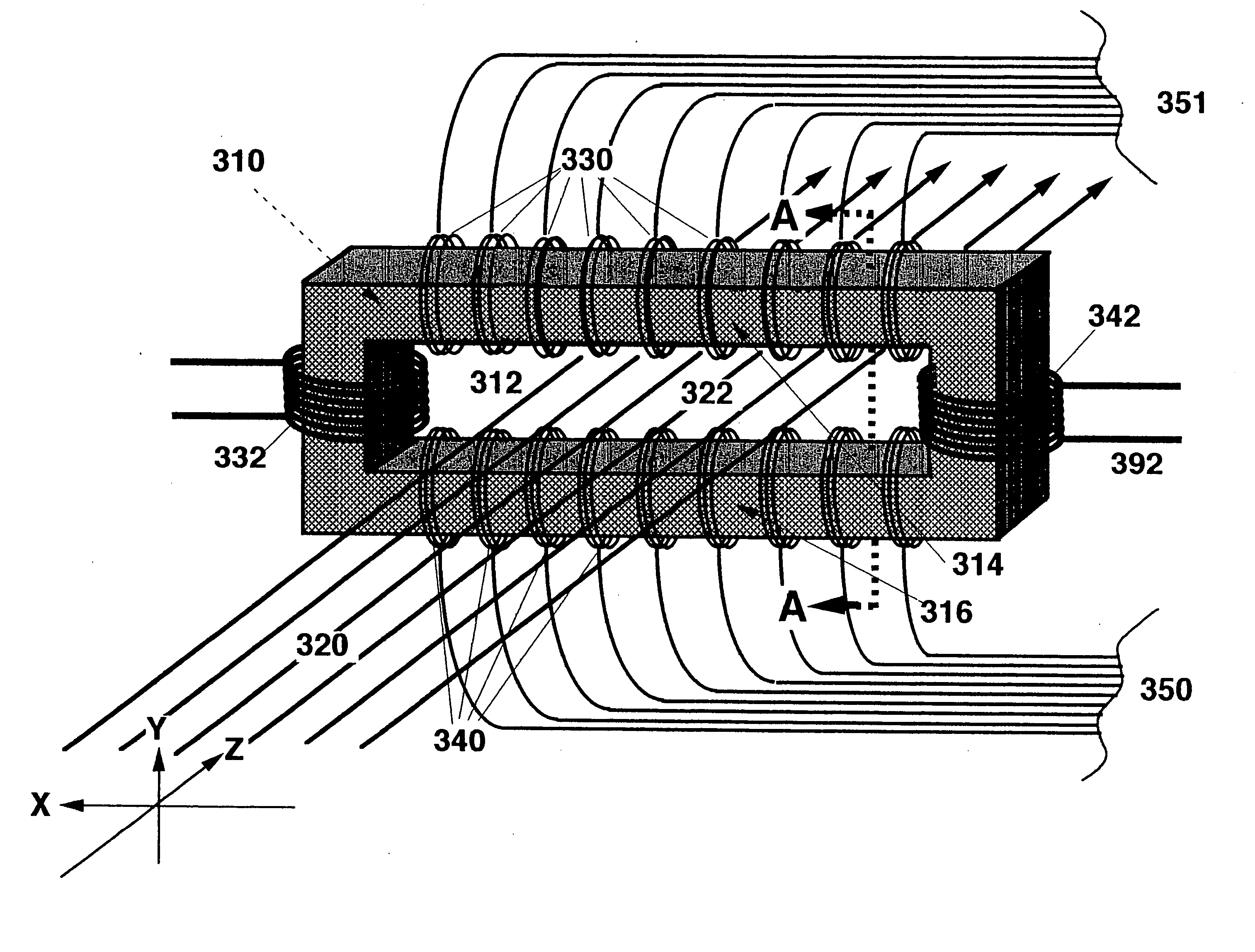
Liner ion beam bonding apparatus and array structure thereof
ActiveUS20150170898A1Improve analytical abilityQuality improvementStability-of-path spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsQuadrupole fieldSection plane
A linear ion beam bonding apparatus and an array structure thereof, comprising a pair of primary radiofrequency electrodes (501 and 502) extending along the axial direction and oppositely arranged on two sides of the central axis of the linear ion beam bonding apparatus. Section patterns on different section planes of each of the primary radiofrequency electrodes (501 and 502) and perpendicular to the central axis are all kept symmetric via a primary symmetric plane (506) of the central axis. Radiofrequency voltages attached to the primary radiofrequency electrodes (501 and 502) are of identical phases. An ion extraction groove (84) is arranged on at least one of the primary radiofrequency electrodes (501 and 502), while at least one pair of auxiliary electrodes (503 and 505) are arranged on two sides of the pair of primary radiofrequency electrodes (501 and 502). The auxiliary electrodes (503 and 505) are arranged in duality to the primary symmetric plane (506). At least one of the auxiliary electrodes (503 and 505) is provided with a finite number of symmetric planes (507), while a minimal angle greater than 0 degrees and less than 90 degrees is provided between each symmetric plane (507) and the symmetric plane (506) of the primary radiofrequency electrodes (501 and 502). By means of this, a quadrupole field component of an ion beam bonding radiofrequency electric field within the ion beam bonding apparatus is strengthened.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB SHANGHAI
Chromatic aberration corrector and electron microscope
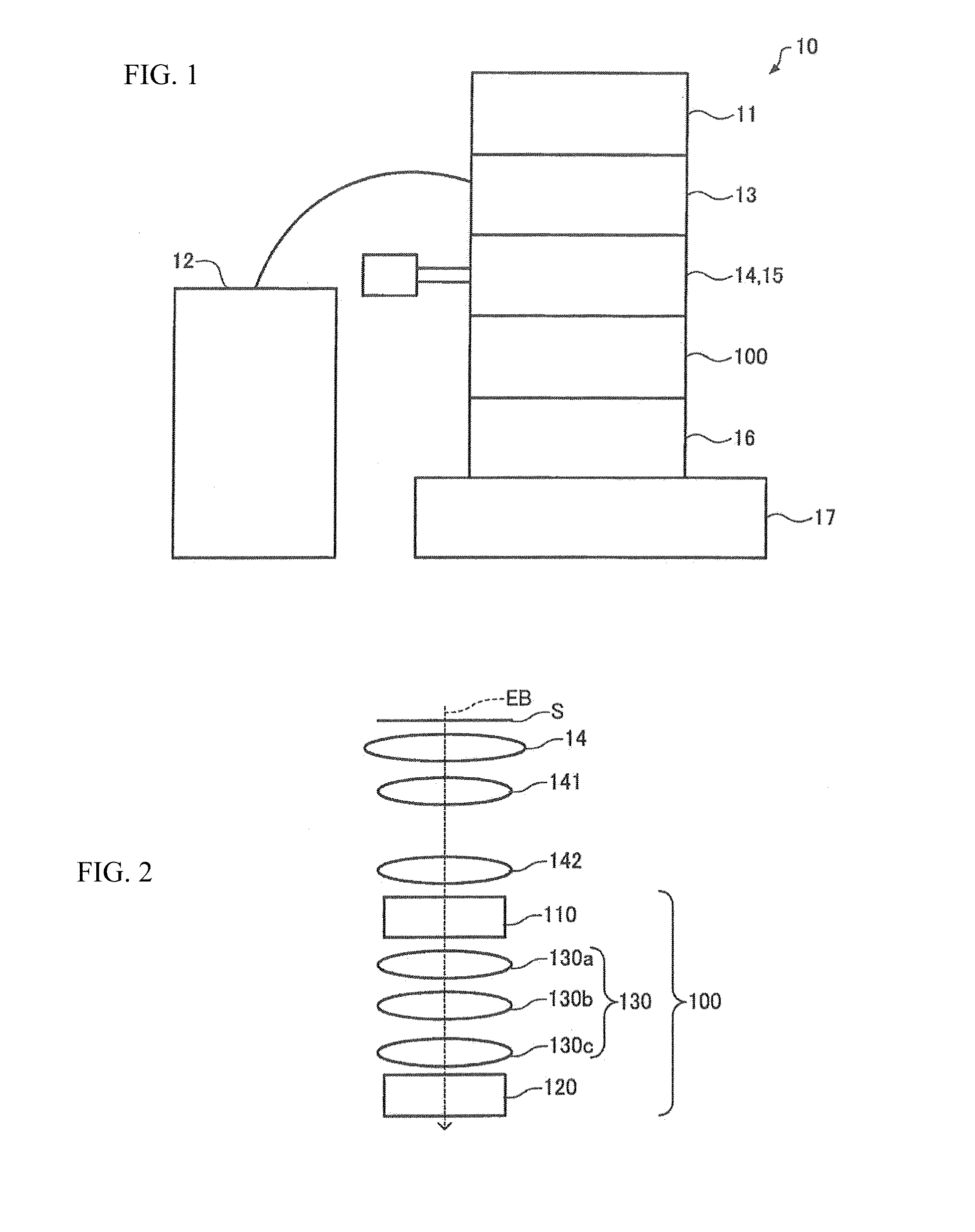
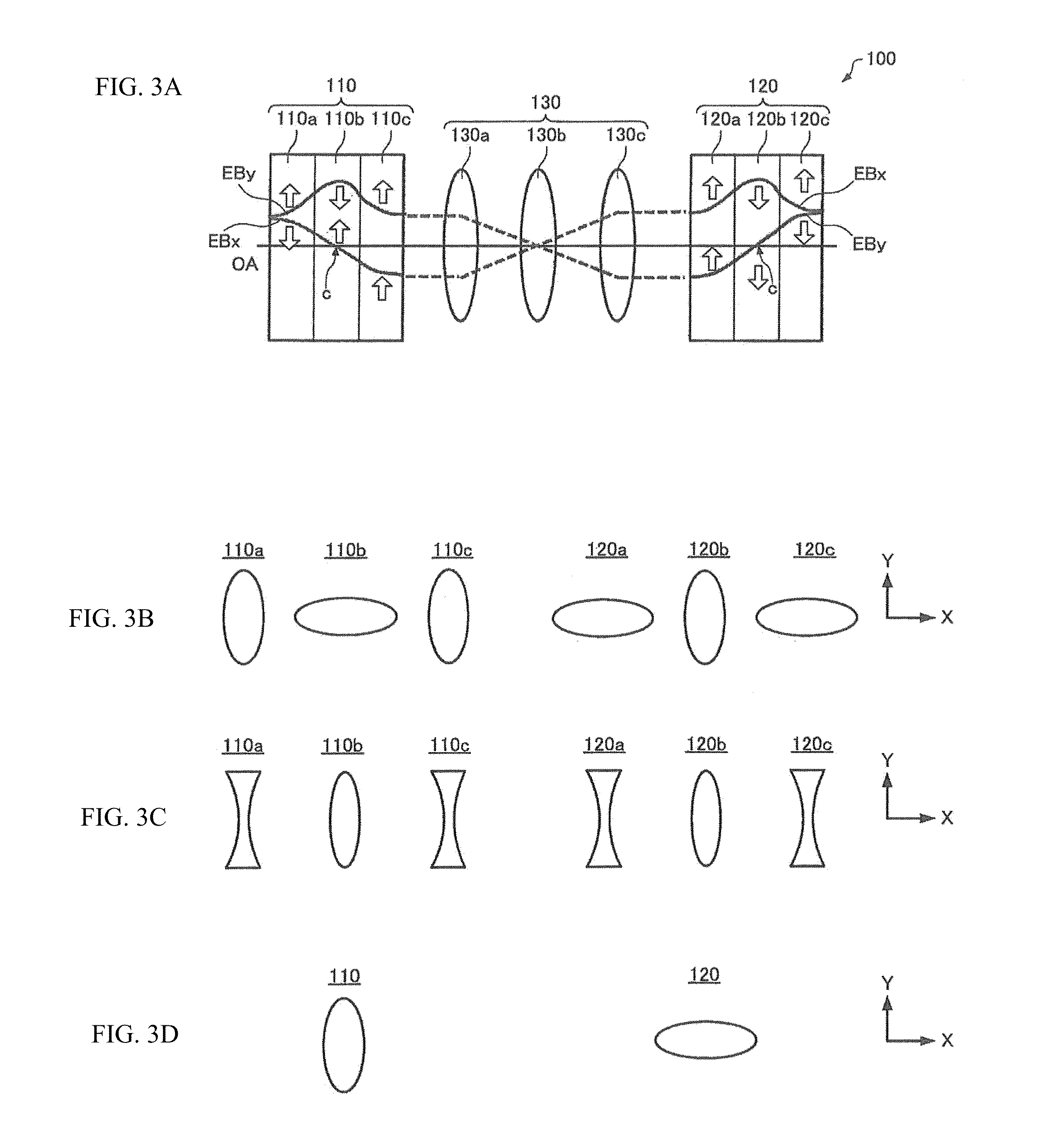
ActiveUS20140158901A1Shorten the lengthReduce thicknessStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuadrupole fieldOptical axis
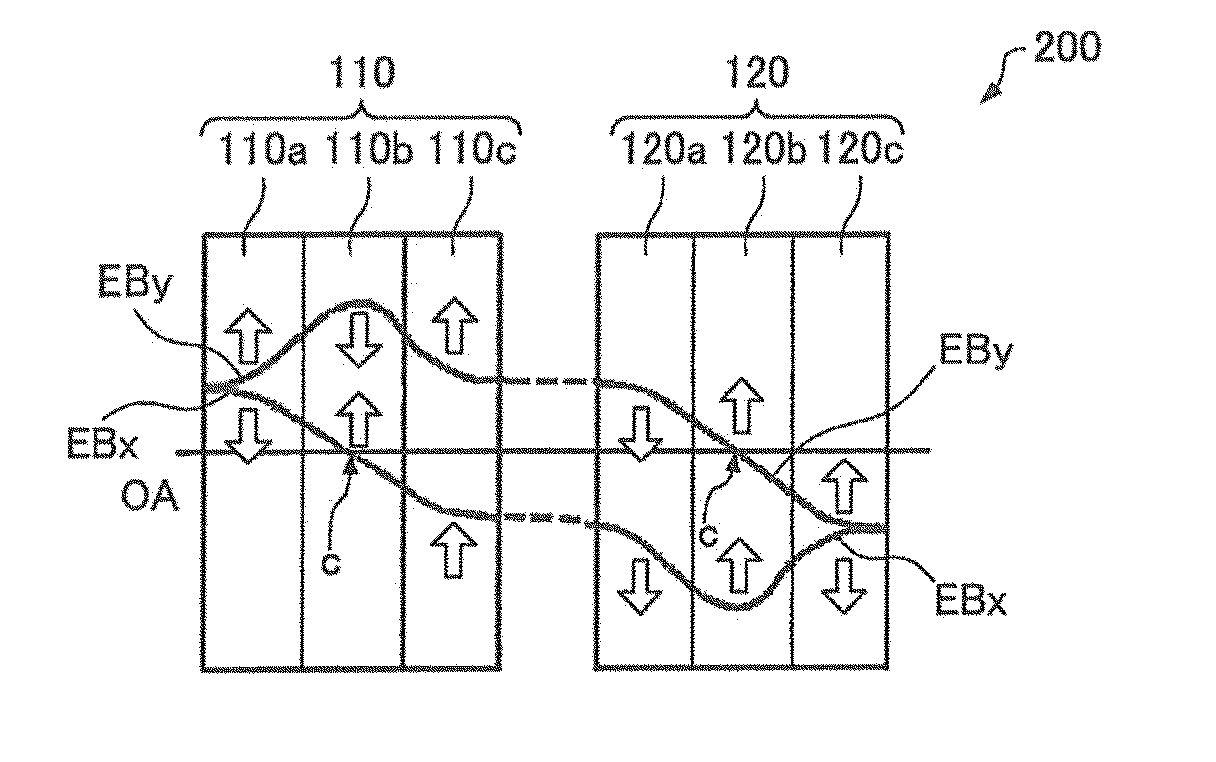
The chromatic aberration corrector (100) has a first multipole element (110) for producing a first electromagnetic field and a second multipole element (120) for producing a second electromagnetic field. The first multipole element (110) first, second, and third portions (110a, 110b, 110c) arranged along an optical axis (OA) having a thickness and producing a quadrupole field in which an electric quadrupole field and a magnetic quadrupole field are superimposed. In the first and third portions (110a, 110c), the electric quadrupole field is set stronger than the magnetic quadrupole field. In the second portion (110b), the magnetic quadrupole field is set stronger than the electric quadrupole field. The second portion (110b) produces a two-fold astigmatism component that is opposite in sign to two-fold astigmatism components produced by the first portion (110a) and third portion (110c).
Owner:JEOL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com