Patents
Literature
42 results about "Energy dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Energy dependence in general refers to either mankind's general dependence on primary or secondary energy for energy consumption (fuel, transport, automation, etc.). In a narrower sense, it may describe the dependence of one country on energy resources from another country.
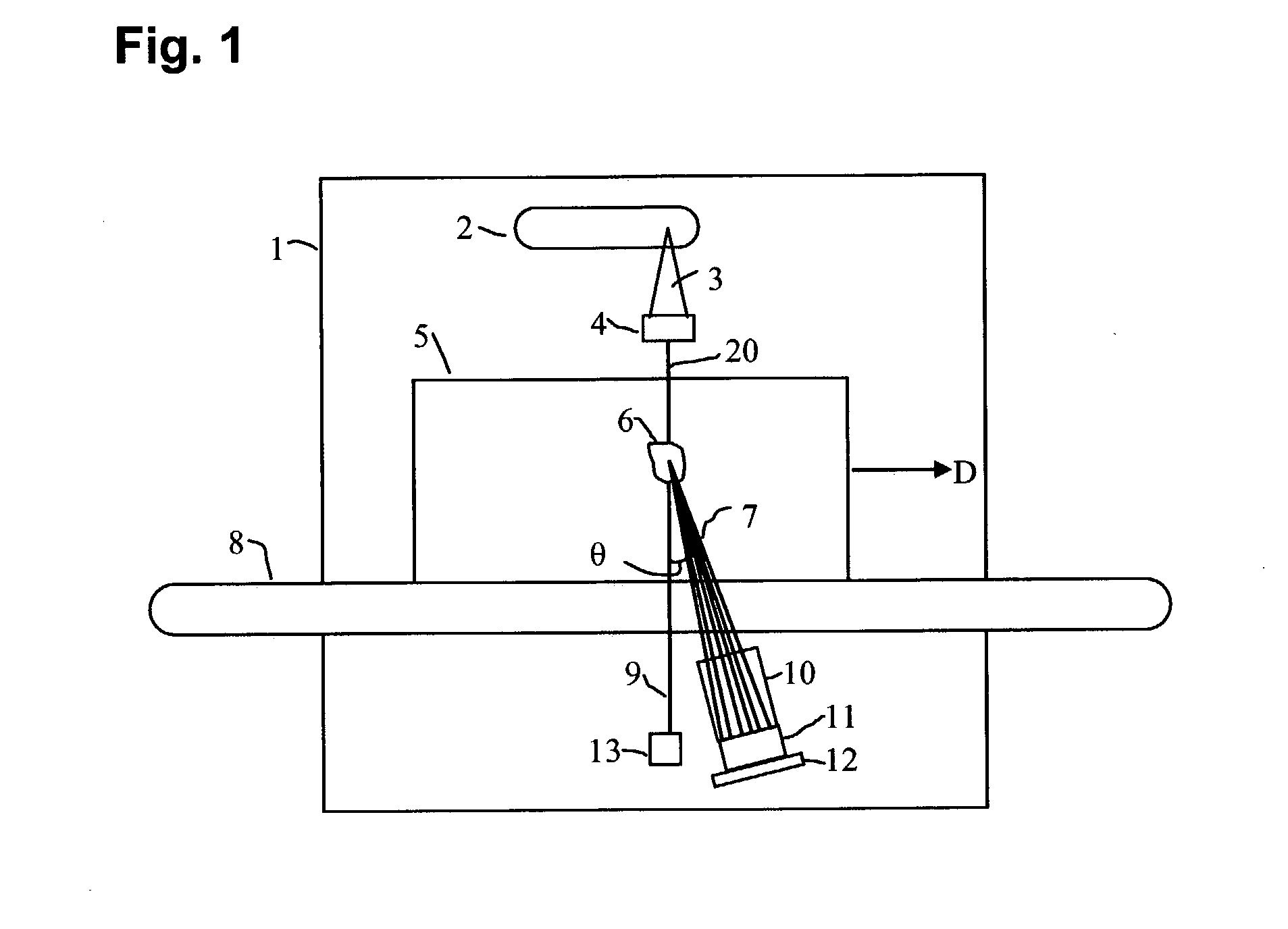
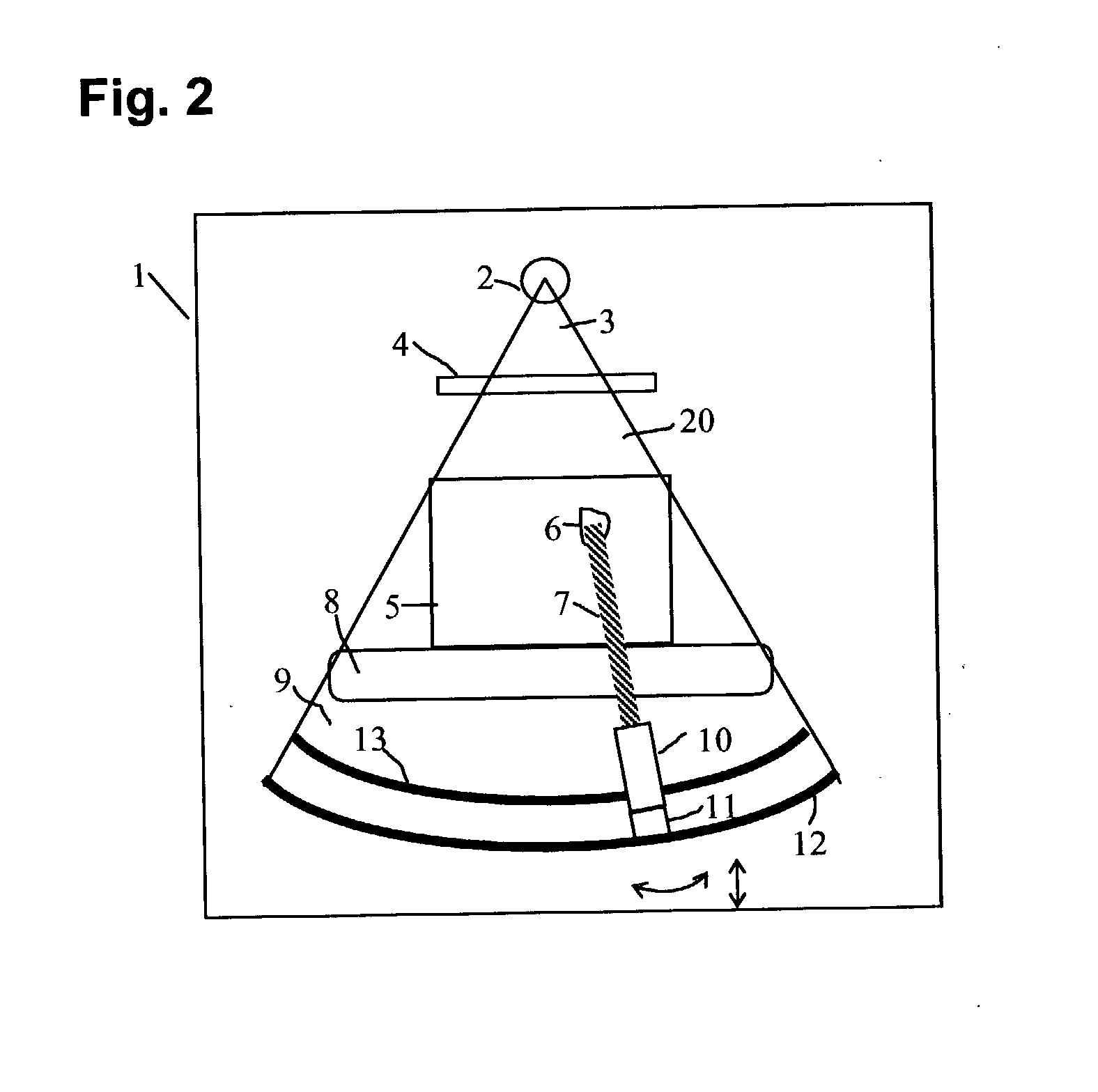
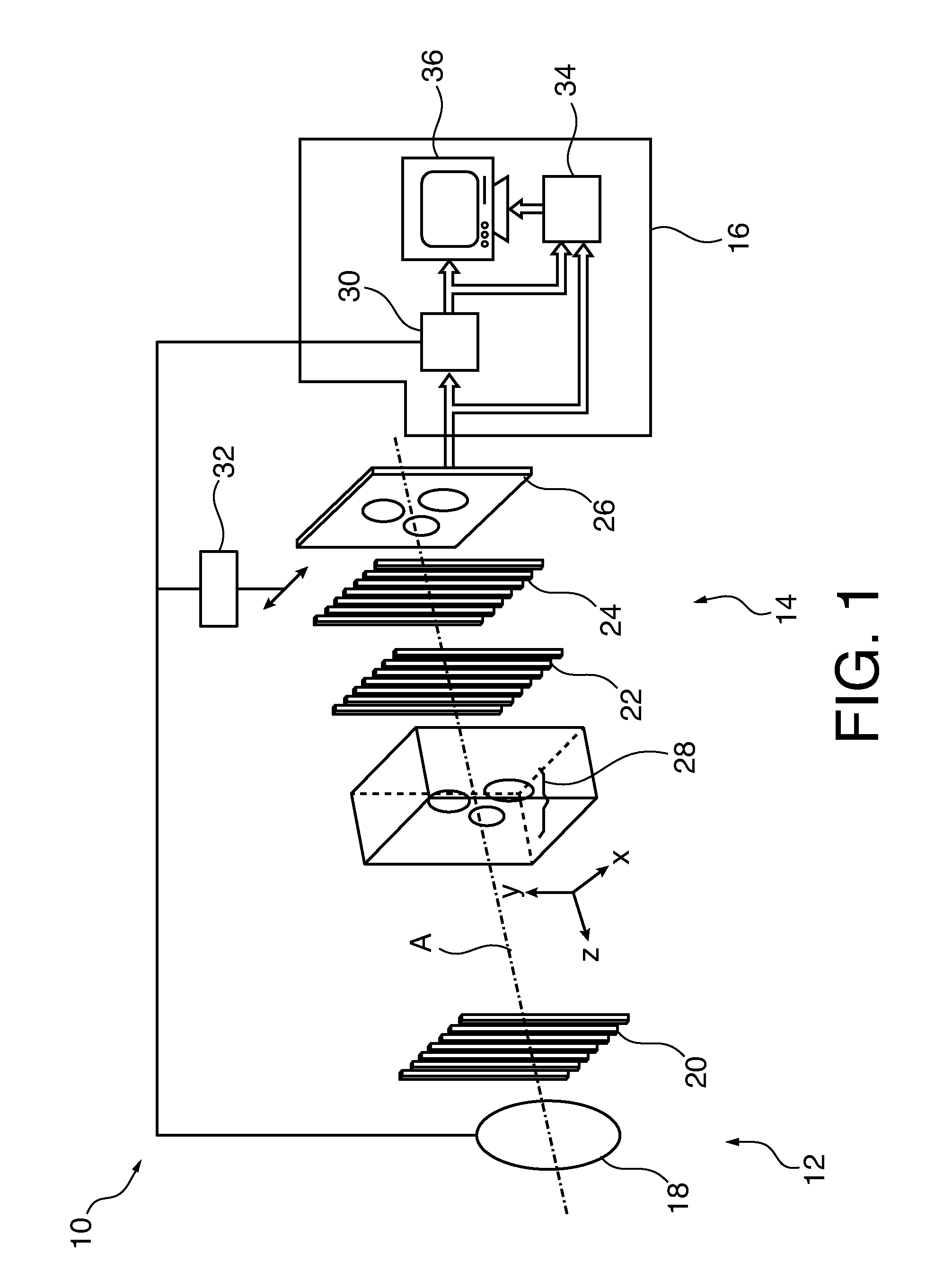
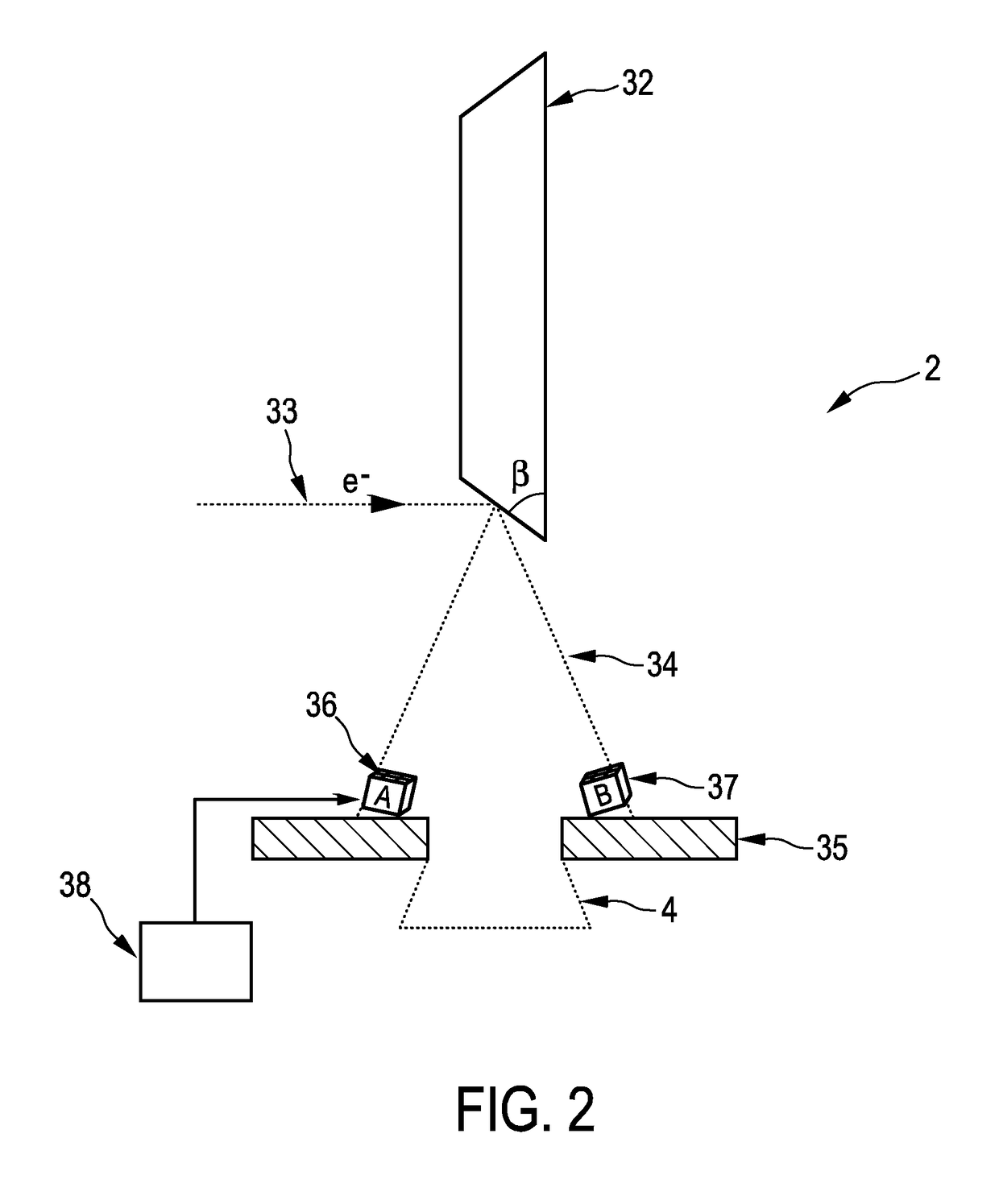
X-ray inspection system for detecting explosives and other contraband
InactiveUS7092485B2Rapidly and accurately discriminates among different substancesQuick checkUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayExplosive material
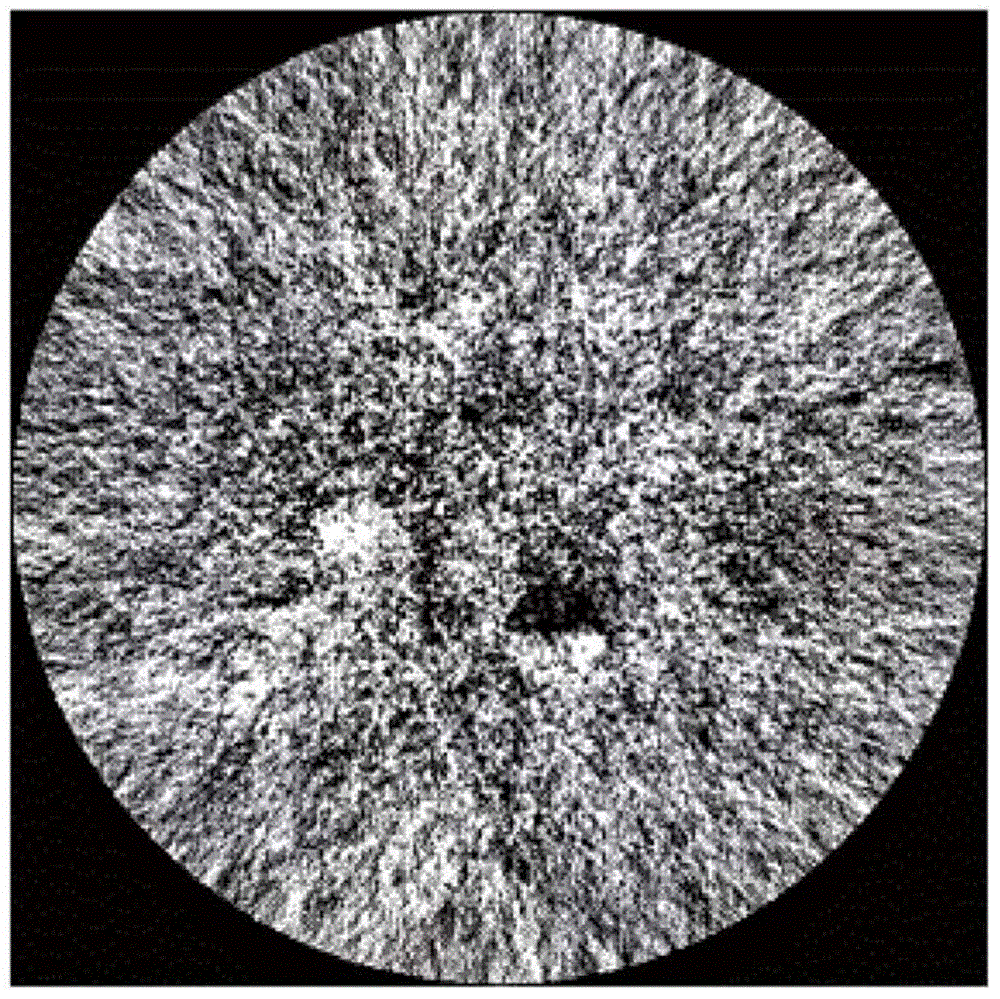
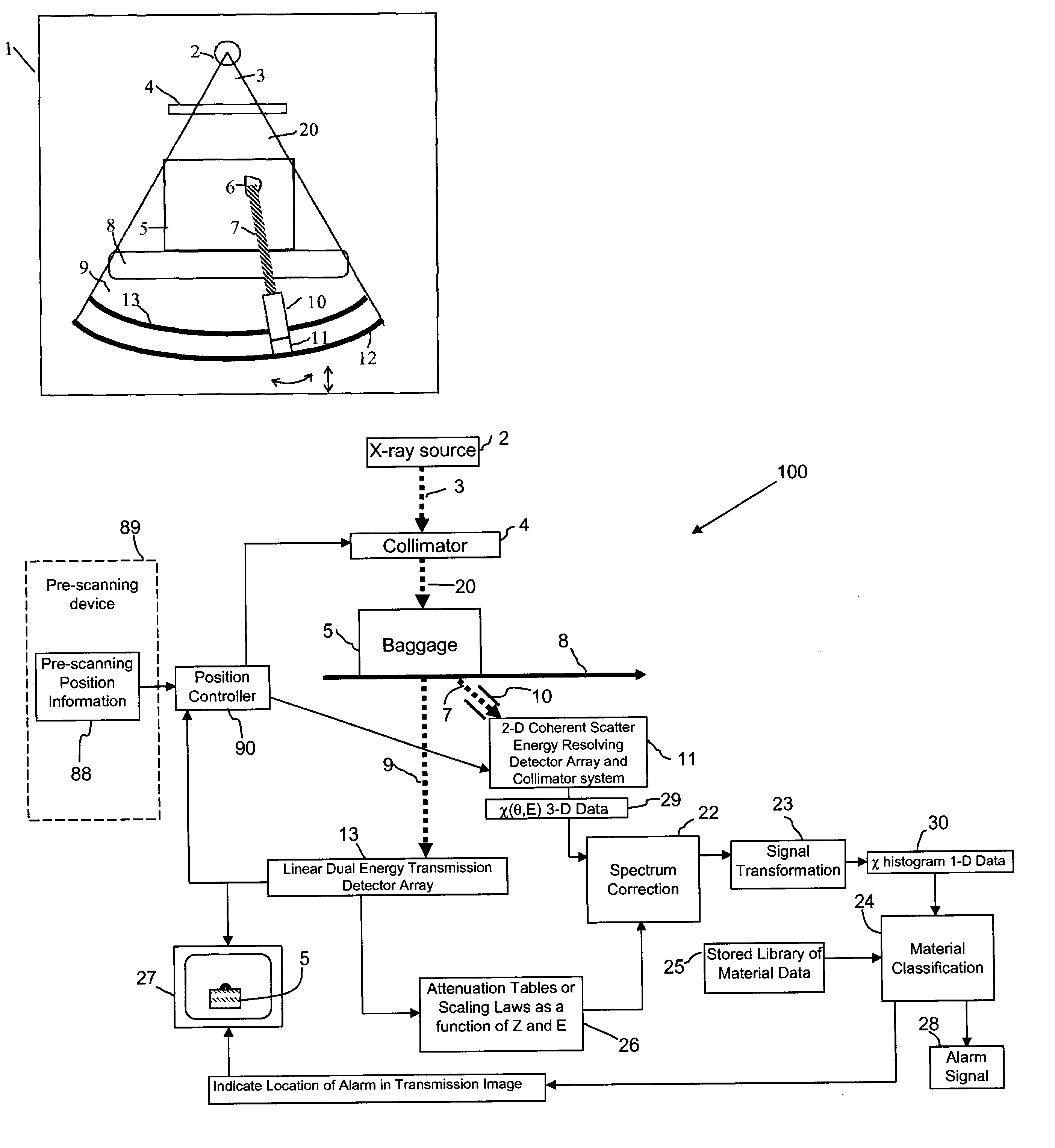
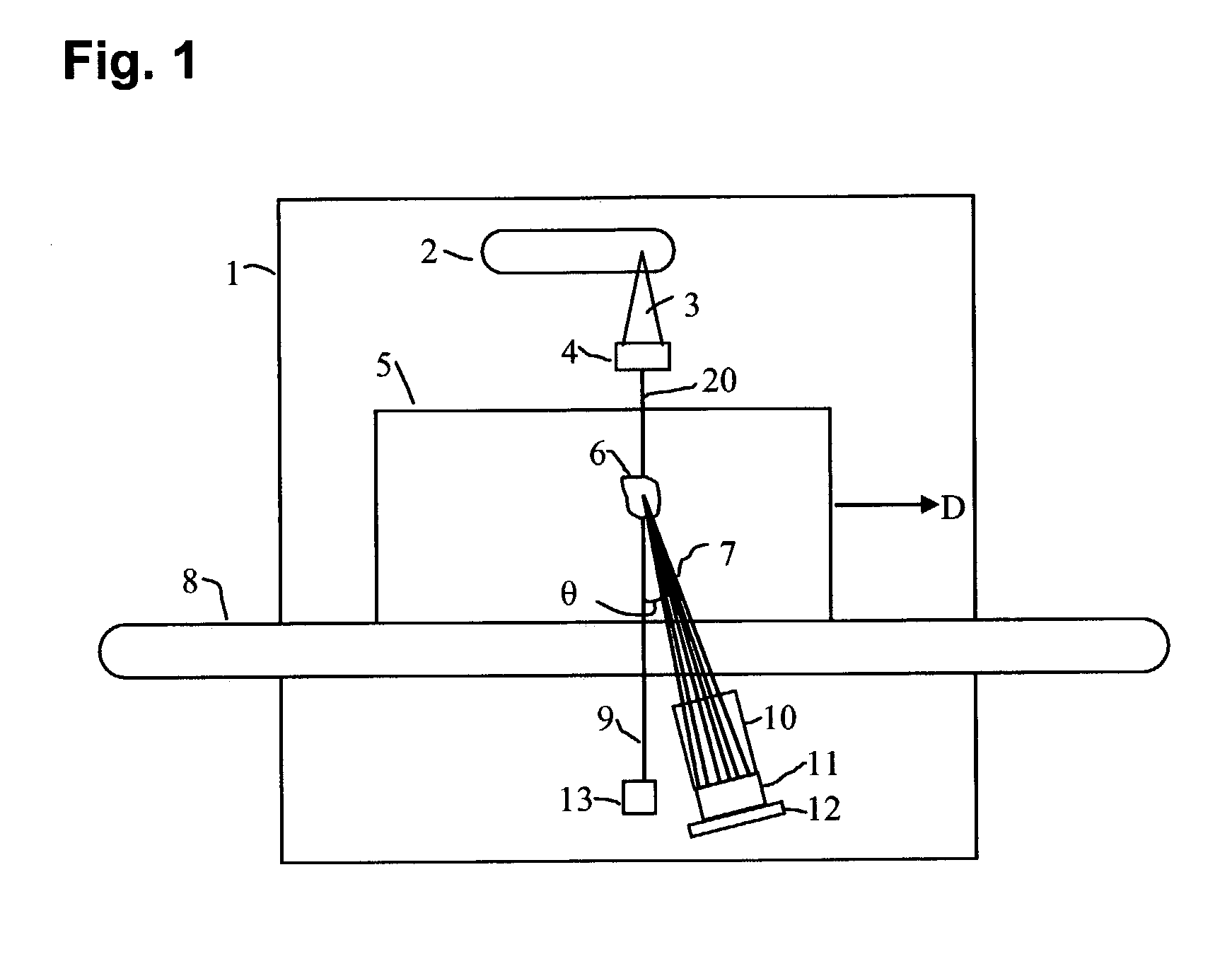
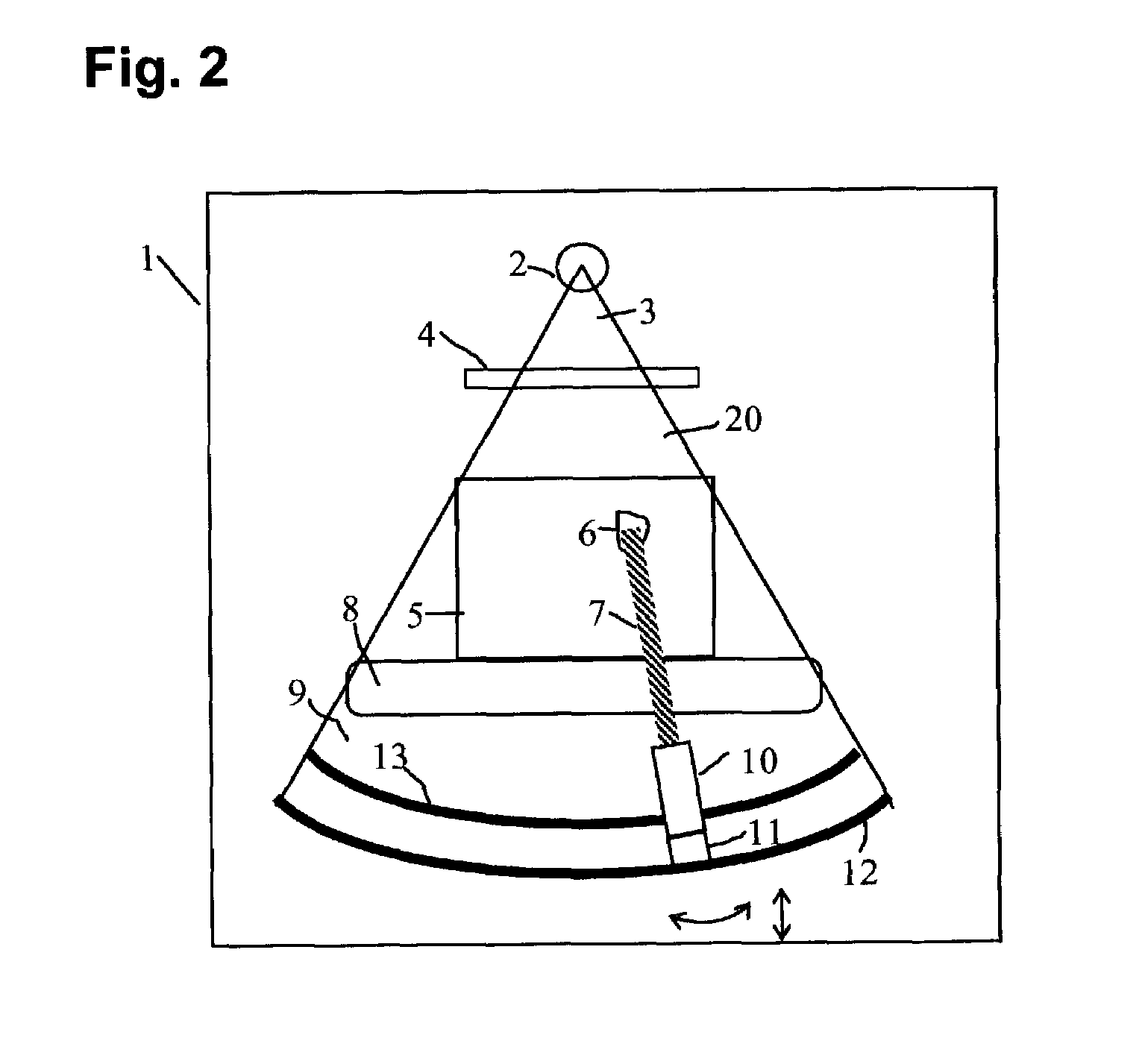
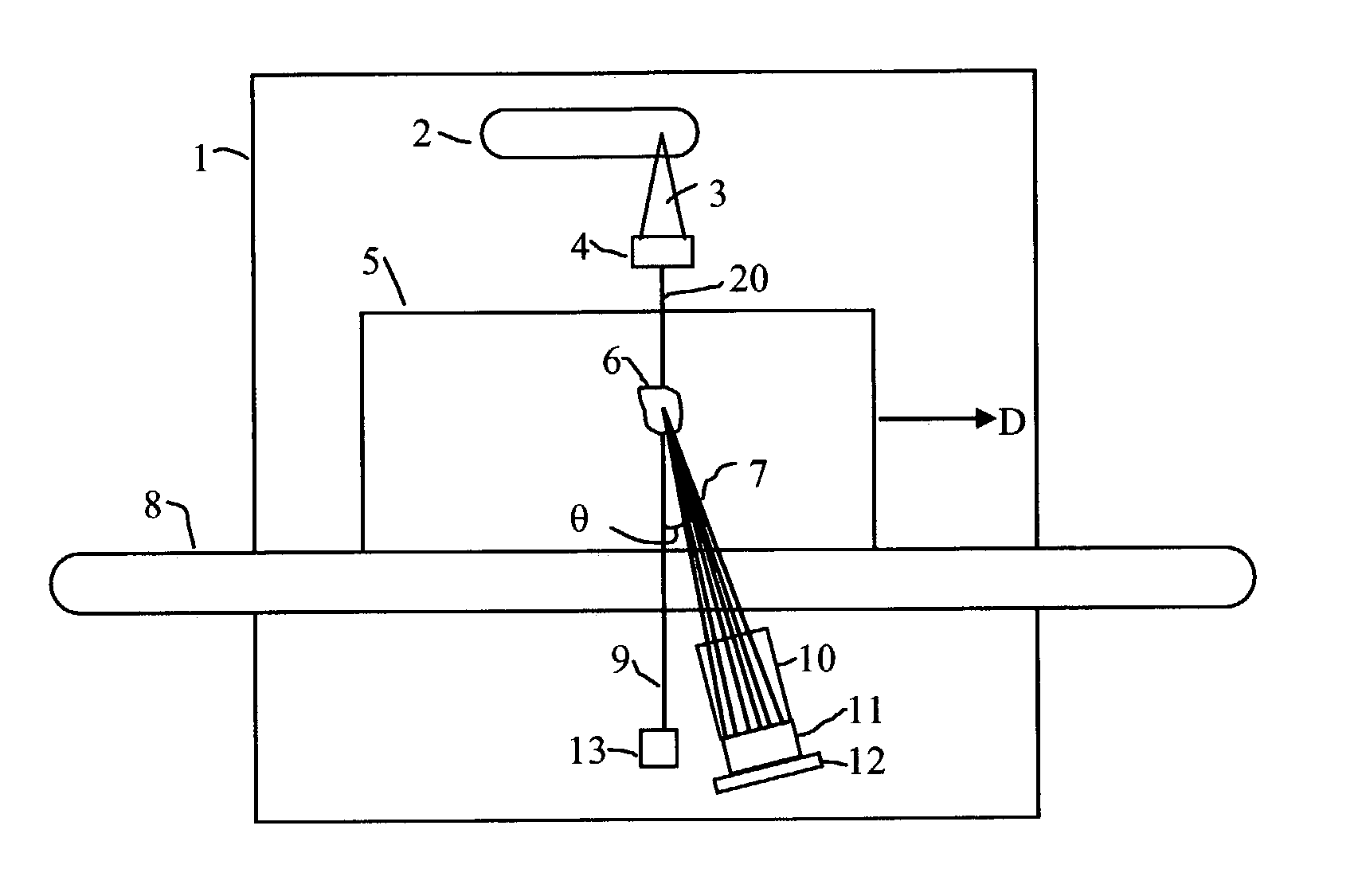
A baggage scanning system and method employ combined angular and energy dispersive x-ray scanning to detect the presence of a contraband substance within an interrogation volume of a baggage item. The interrogation volume is illuminated with penetrating, polychromatic x-rays in a primary fan beam from a source such as a tungsten-anode x-ray tube. An energy-dependent absorption correction is determined from measurement of the attenuation of the fan beam at a plurality of different energies. Radiation coherently scattered by substances in the interrogation volume is detected by an energy-resolved x-ray detector operated at a plurality of scattering angles to form a plurality of scattering spectra. Each scattering spectrum is corrected for energy-dependent absorption and the corrected spectra are combined to produce a scattering pattern. The experimental scattering pattern is compared with reference patterns that uniquely characterize known contraband substances. The system and method can locate and identify a wide variety of contraband substances in an accurate, reliable manner. The system provides for automated screening, with the result that vagaries of human performance are virtually eliminated. False alarms and the need for hand inspection are reduced and detection efficacy is increased.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
X-ray inspection system for detecting explosives and other contraband
InactiveUS20060140340A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayExplosive material
A baggage scanning system and method employ combined angular and energy dispersive x-ray scanning to detect the presence of a contraband substance within an interrogation volume of a baggage item. The interrogation volume is illuminated with penetrating, polychromatic x-rays in a primary fan beam from a source such as a tungsten-anode x-ray tube. An energy-dependent absorption correction is determined from measurement of the attenuation of the fan beam at a plurality of different energies. Radiation coherently scattered by substances in the interrogation volume is detected by an energy-resolved x-ray detector operated at a plurality of scattering angles to form a plurality of scattering spectra. Each scattering spectrum is corrected for energy-dependent absorption and the corrected spectra are combined to produce a scattering pattern. The experimental scattering pattern is compared with reference patterns that uniquely characterize known contraband substances. The system and method can locate and identify a wide variety of contraband substances in an accurate, reliable manner. The system provides for automated screening, with the result that vagaries of human performance are virtually eliminated. False alarms and the need for hand inspection are reduced and detection efficacy is increased.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
Inferential measurement of photoelectric absorption cross-section of geologic formations from neutron-induced, gamma-ray spectroscopy
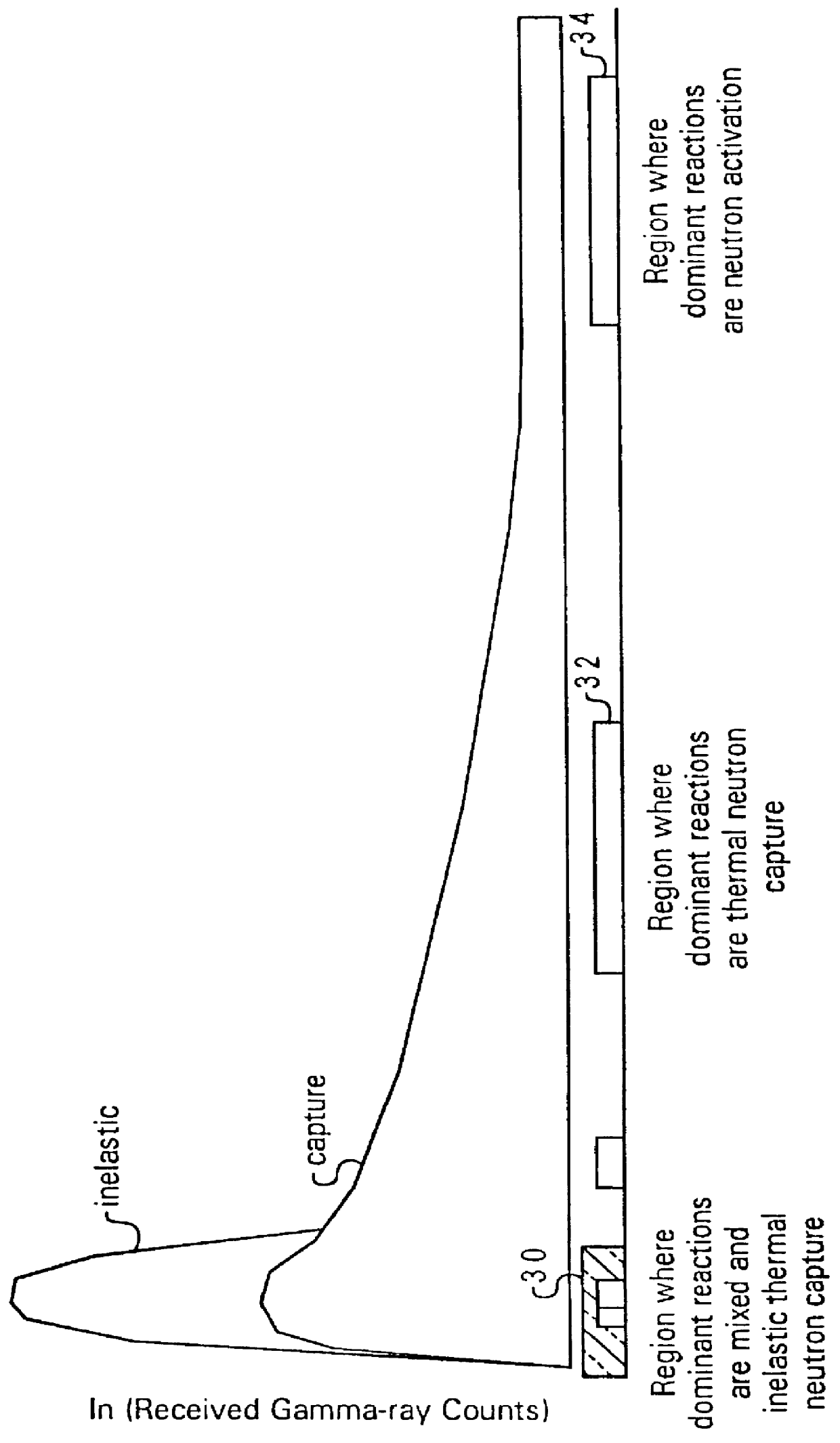
A method for inferring the photoelectric absorption of a formation by directly mapping spectroscopic measurements of gamma rays induced in the formation using a fast neutron source. The mapping is accomplished by creating a polynomial function based on counts of gamma-ray events in the gamma-ray energy spectrum; the coefficients of the polynomial function are determined in known calibration environments, and the value of the polynomial is the inferred photoelectric absorption parameter. The spectroscopic measurements are preferably generated by sorting gamma-ray counts of the gamma-ray spectrum into a plurality of energy-dependent channels, and measuring these gamma-ray energy distributions during different portions of the firing cycle where different types of dominant gamma-ray production reactions occur.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
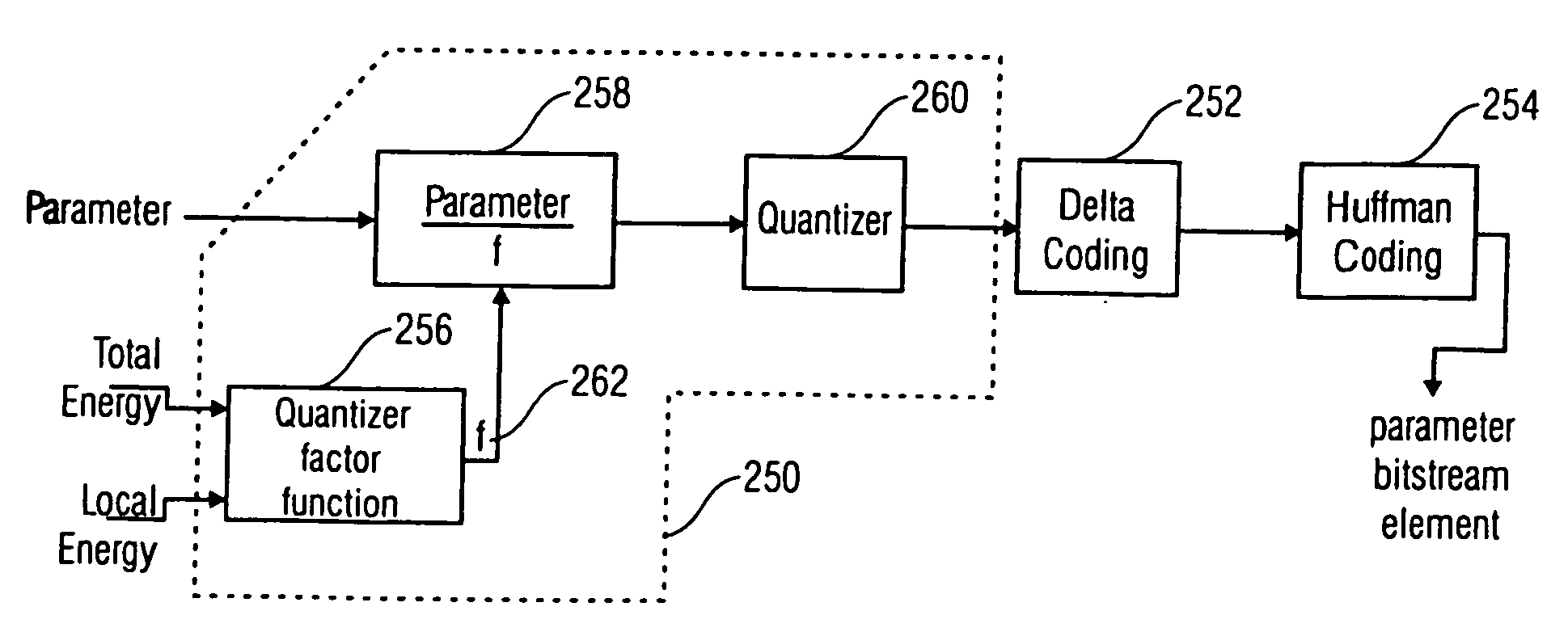
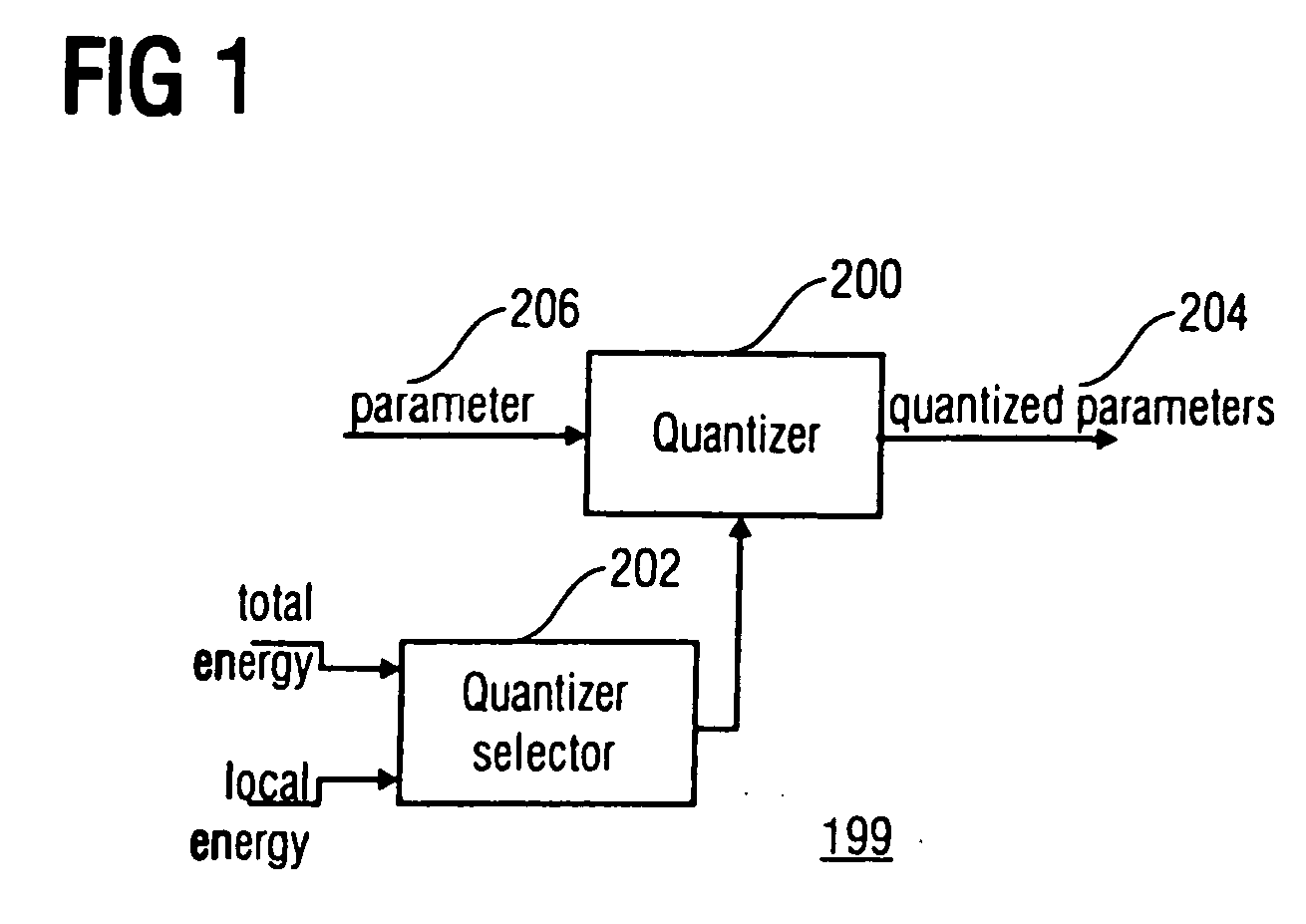
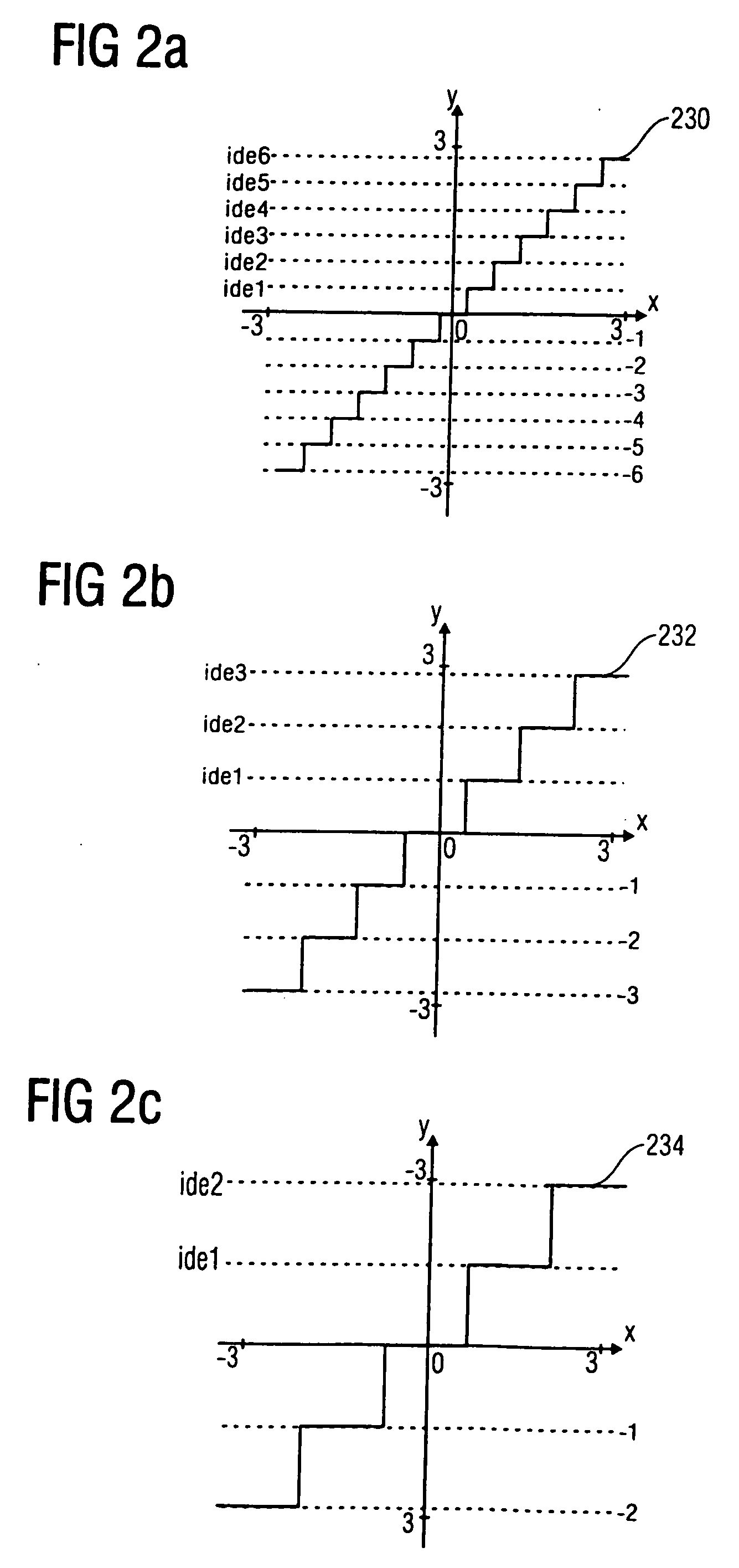
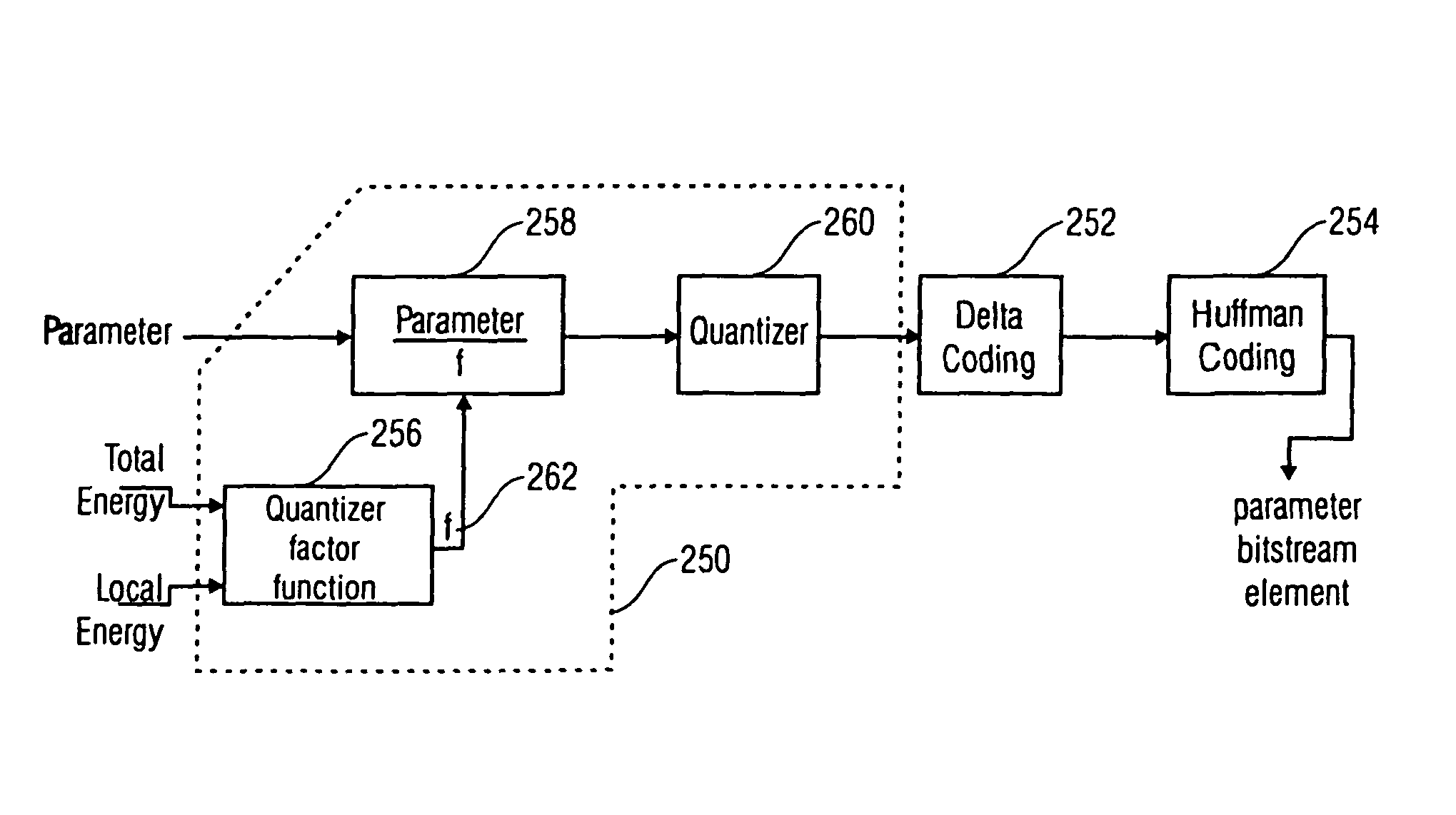
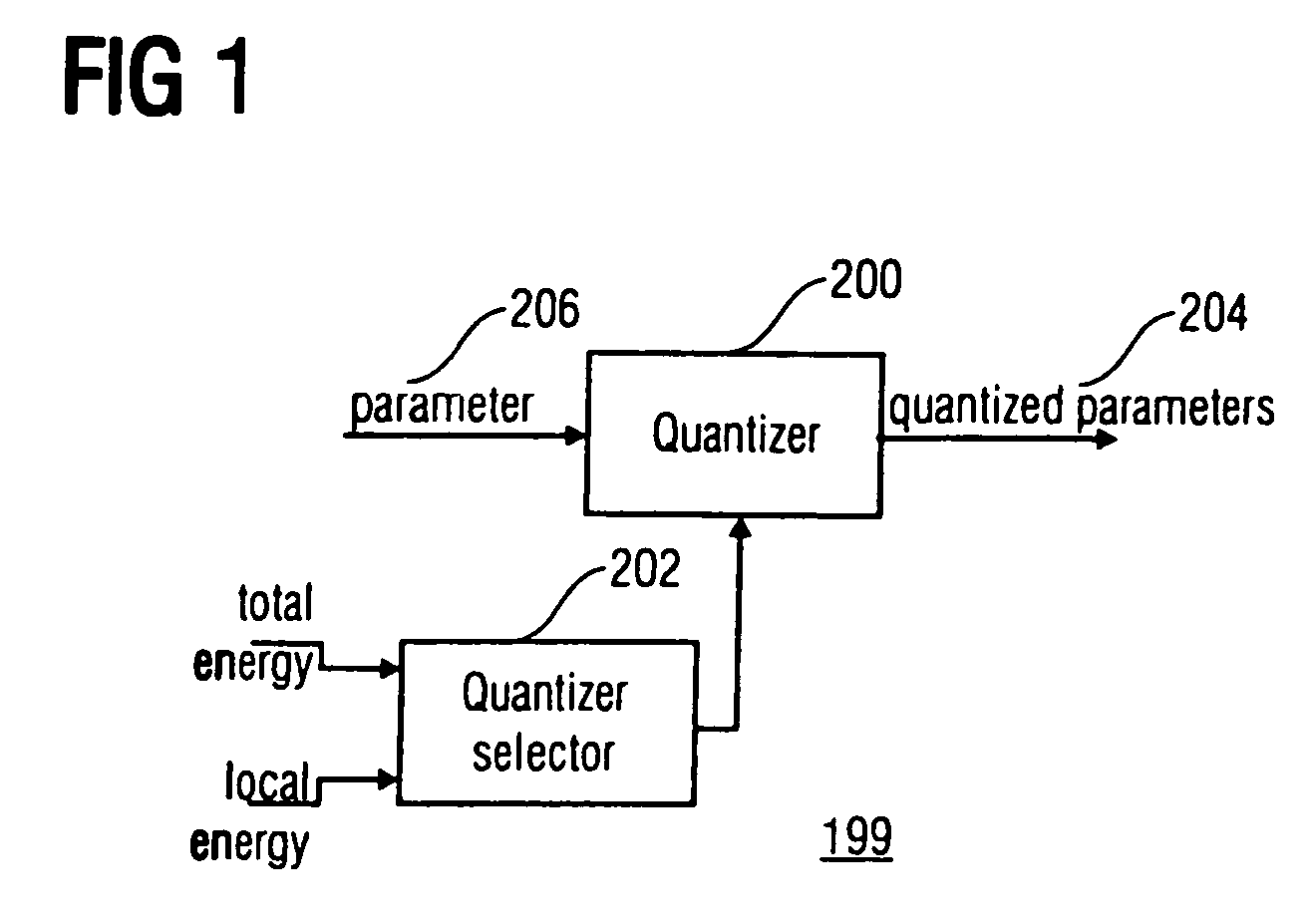
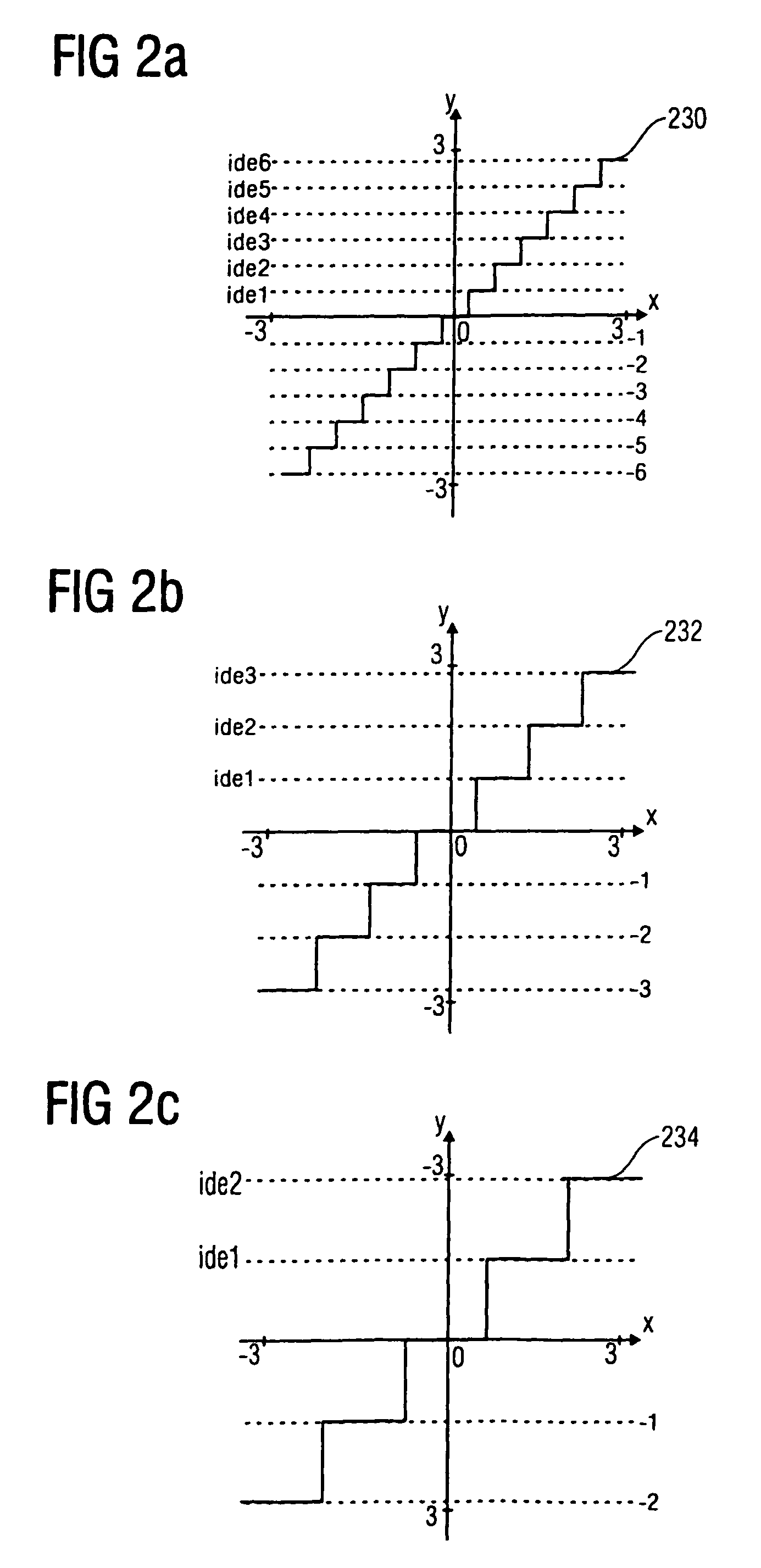
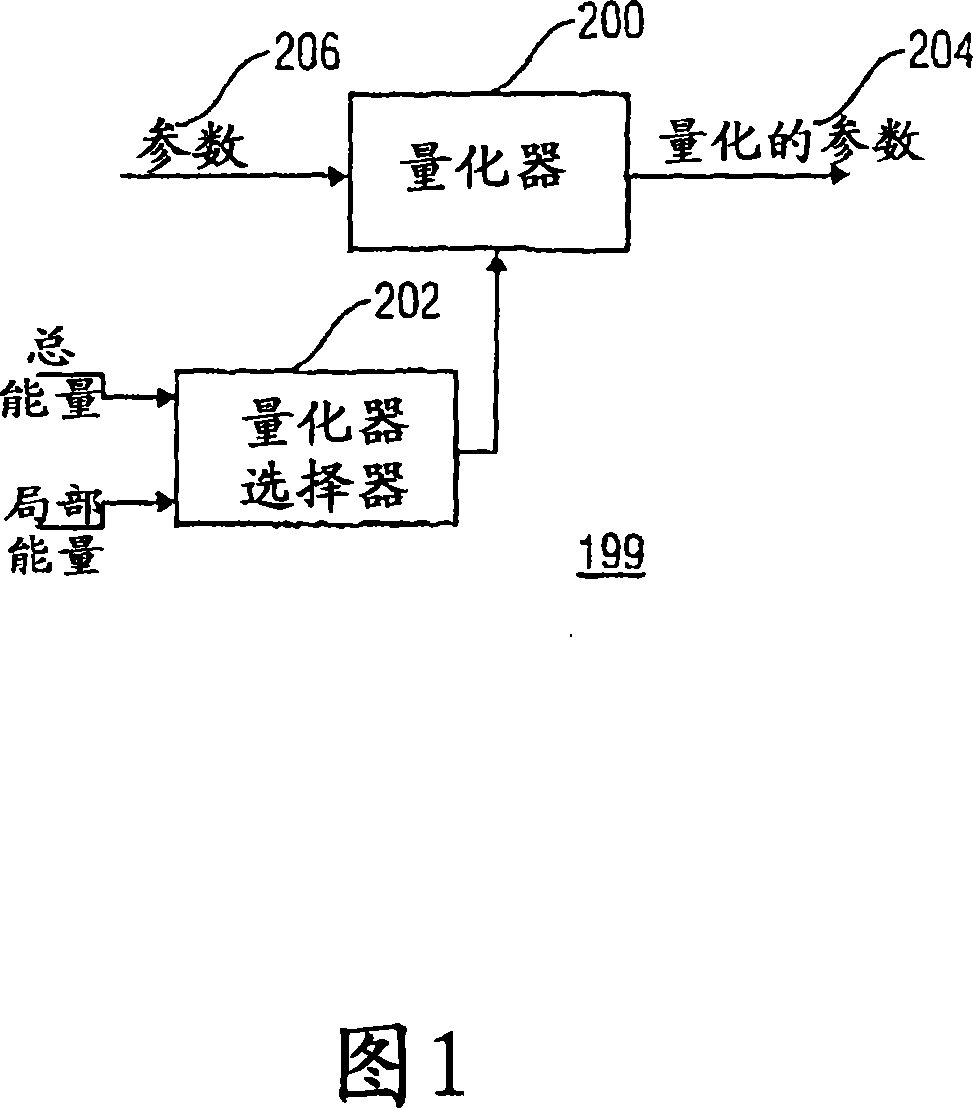
Energy dependent quantization for efficient coding of spatial audio parameters
ActiveUS20070016416A1Quantized more efficientlyEfficiently quantizedSpeech analysisCode conversionEnergy measurePsychoacoustics
Parameters being a measure for a characteristic of a channel or of a pair of channels, wherein the parameter is a measure for a characteristic of the channel or of the pair of channels with respect to another channel of a multi-channel signal can be quantized more efficiently using a quantization rule that is generated based on a relation of an energy measure of the channel or the pair of channels and an energy measure of the multi-channel signal. With generation of the quantization rule taking into account a psycho acoustic approach, the size of an encoded representation of the multi-channel signal can be decreased by coarser quantization without significantly disturbing the perceptual quality of the multi-channel signal when reconstructed from the encoded representation.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +2
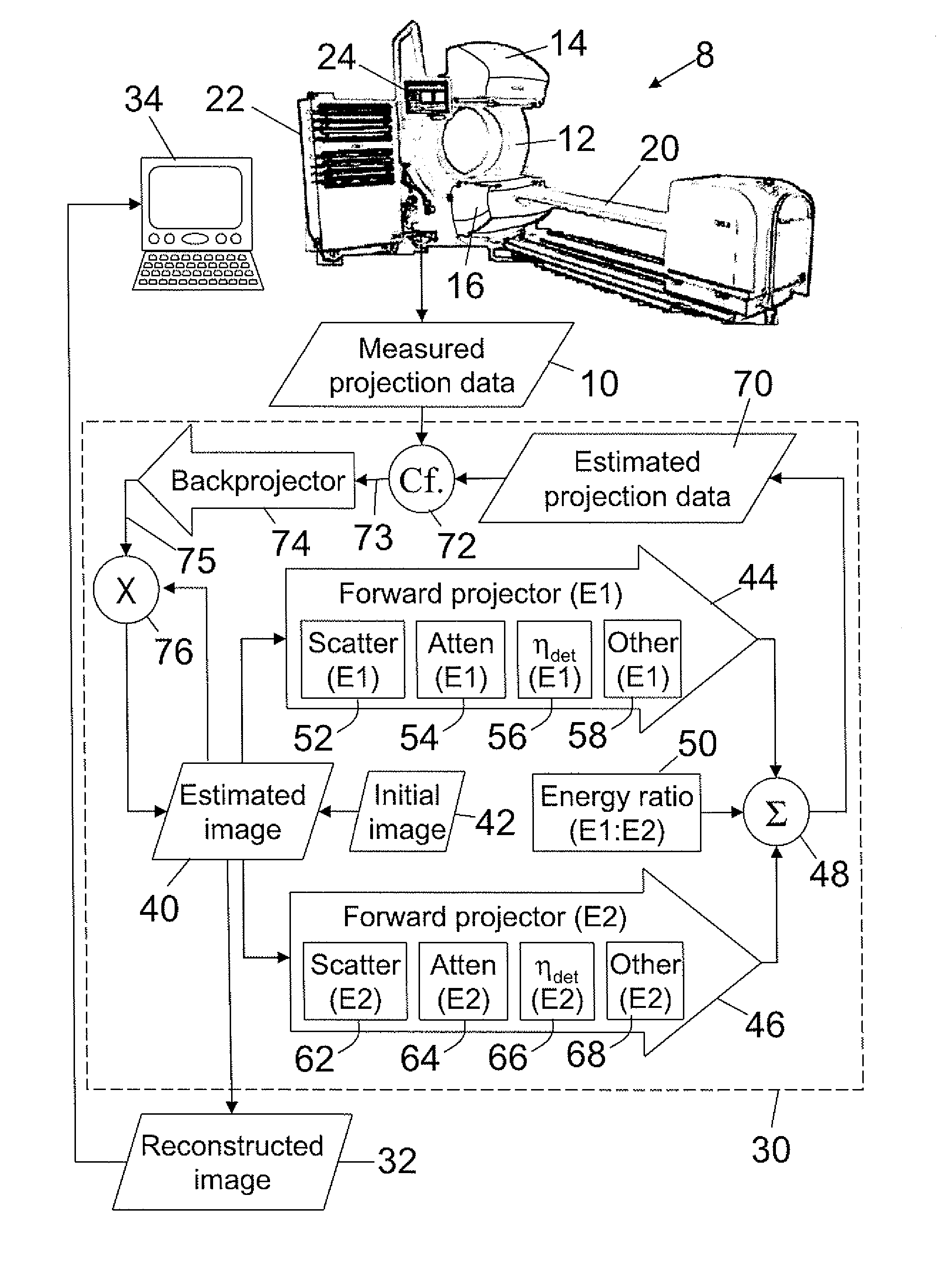
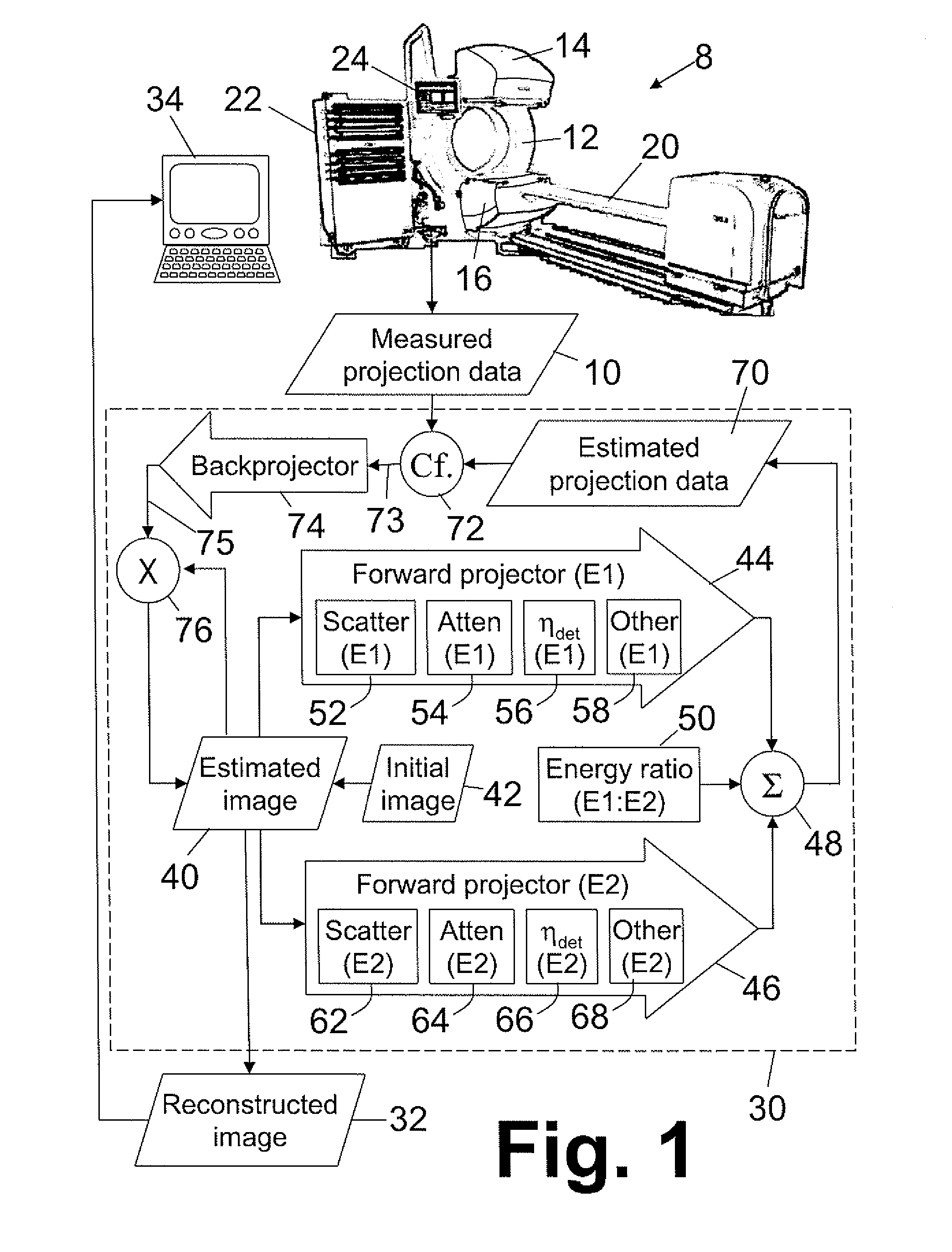
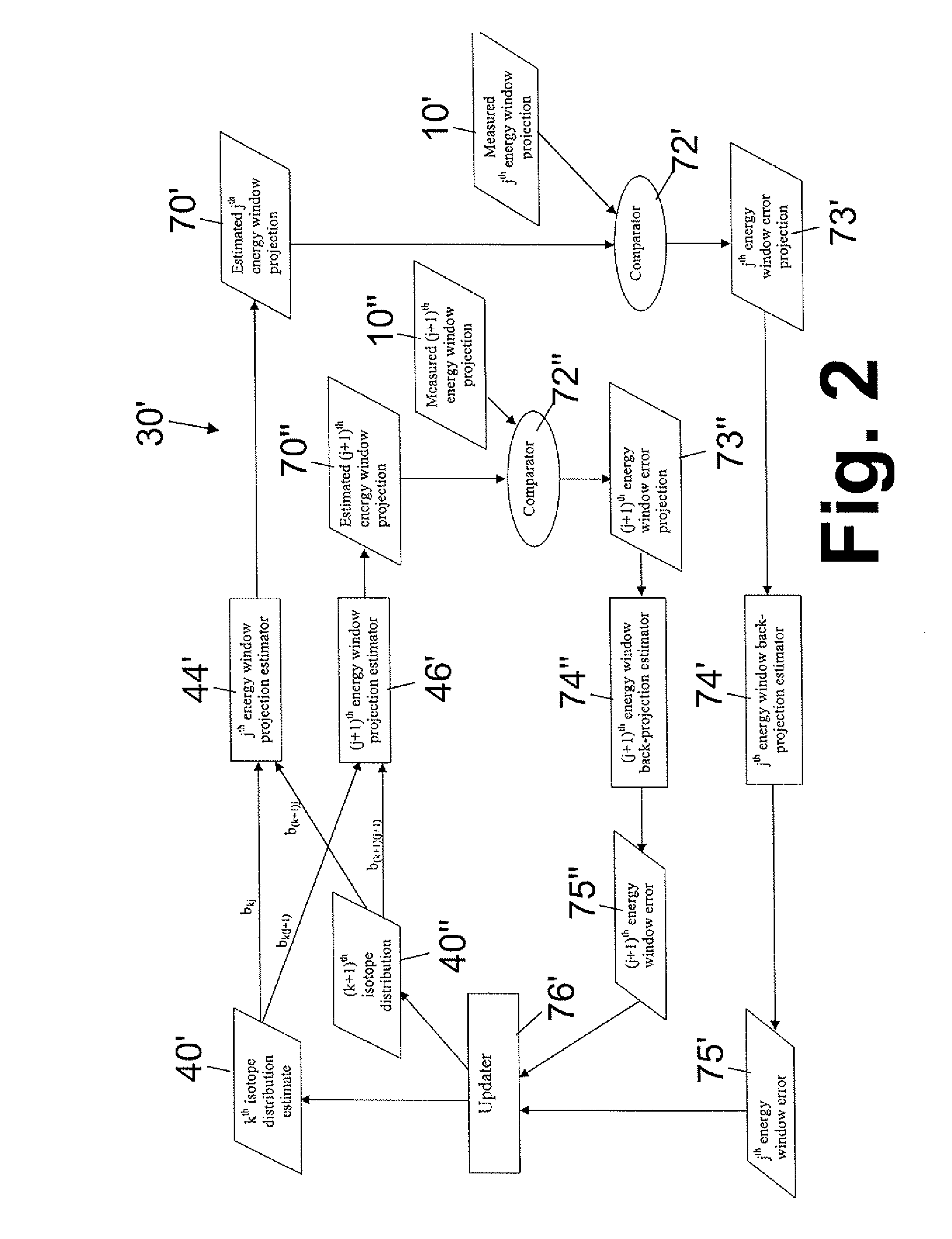
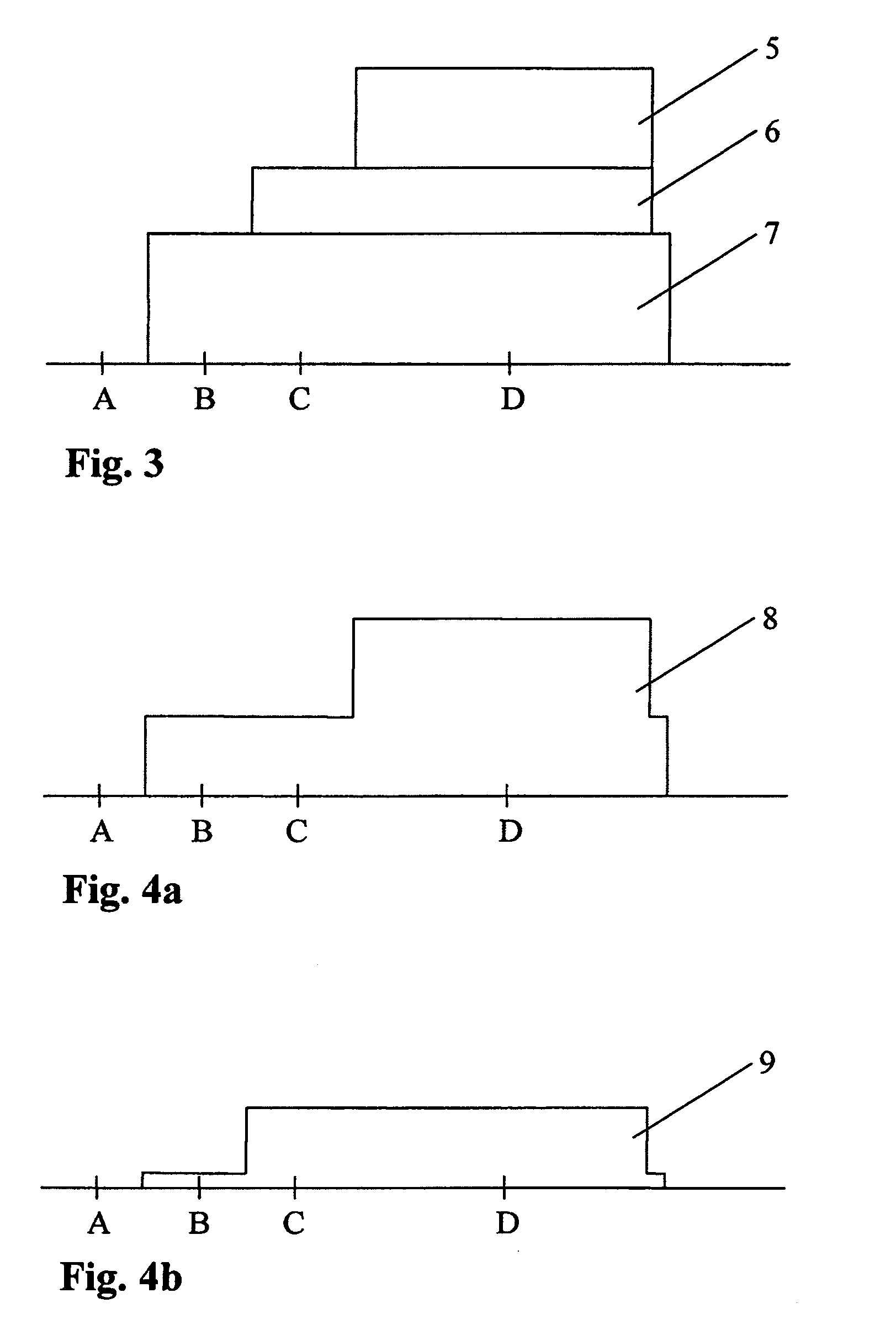
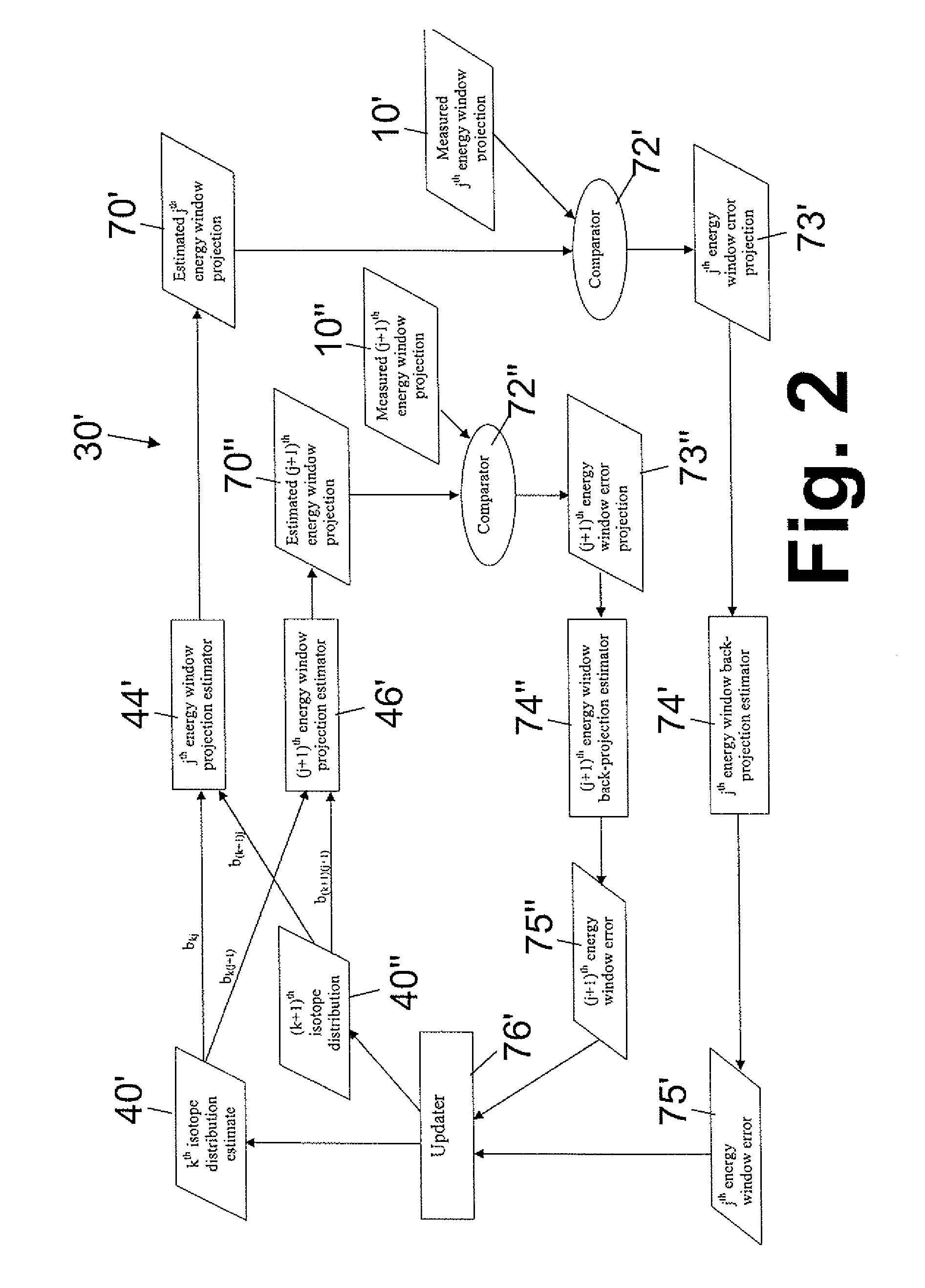
Iterative reconstruction of multiple-peak isotope images
ActiveUS20070183642A1Improving Image Reconstruction AccuracyAccurate placementReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionIsotopeEnergy dependent
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Energy dependent quantization for efficient coding of spatial audio parameters
ActiveUS8054981B2Quantized more efficientlyEfficiently quantizedSpeech analysisCode conversionPsychoacousticsEnergy measure
Parameters being a measure for a characteristic of a channel or of a pair of channels, wherein the parameter is a measure for a characteristic of the channel or of the pair of channels with respect to another channel of a multi-channel signal can be quantized more efficiently using a quantization rule that is generated based on a relation of an energy measure of the channel or the pair of channels and an energy measure of the multi-channel signal. With generation of the quantization rule taking into account a psycho acoustic approach, the size of an encoded representation of the multi-channel signal can be decreased by coarser quantization without significantly disturbing the perceptual quality of the multi-channel signal when reconstructed from the encoded representation.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +2
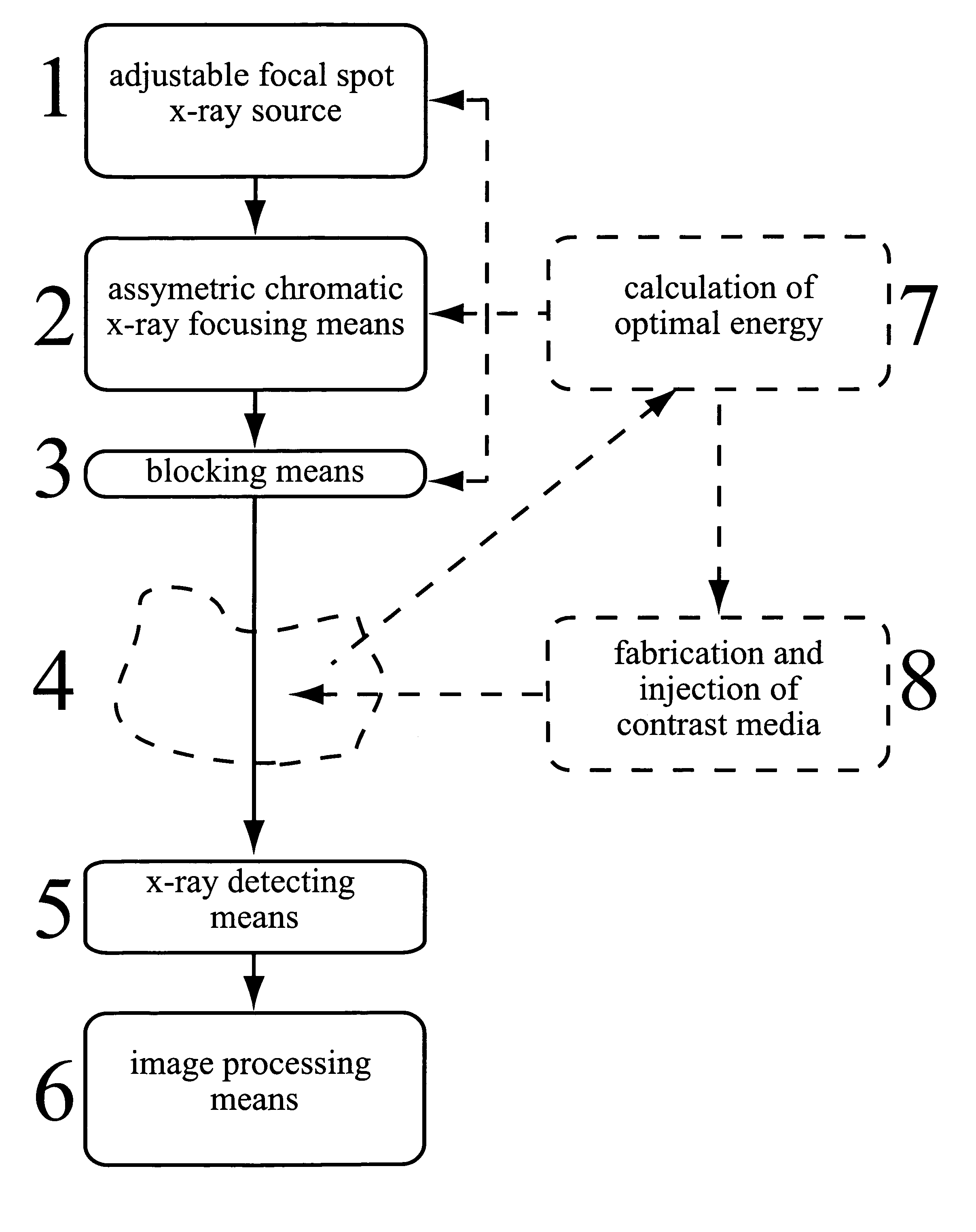
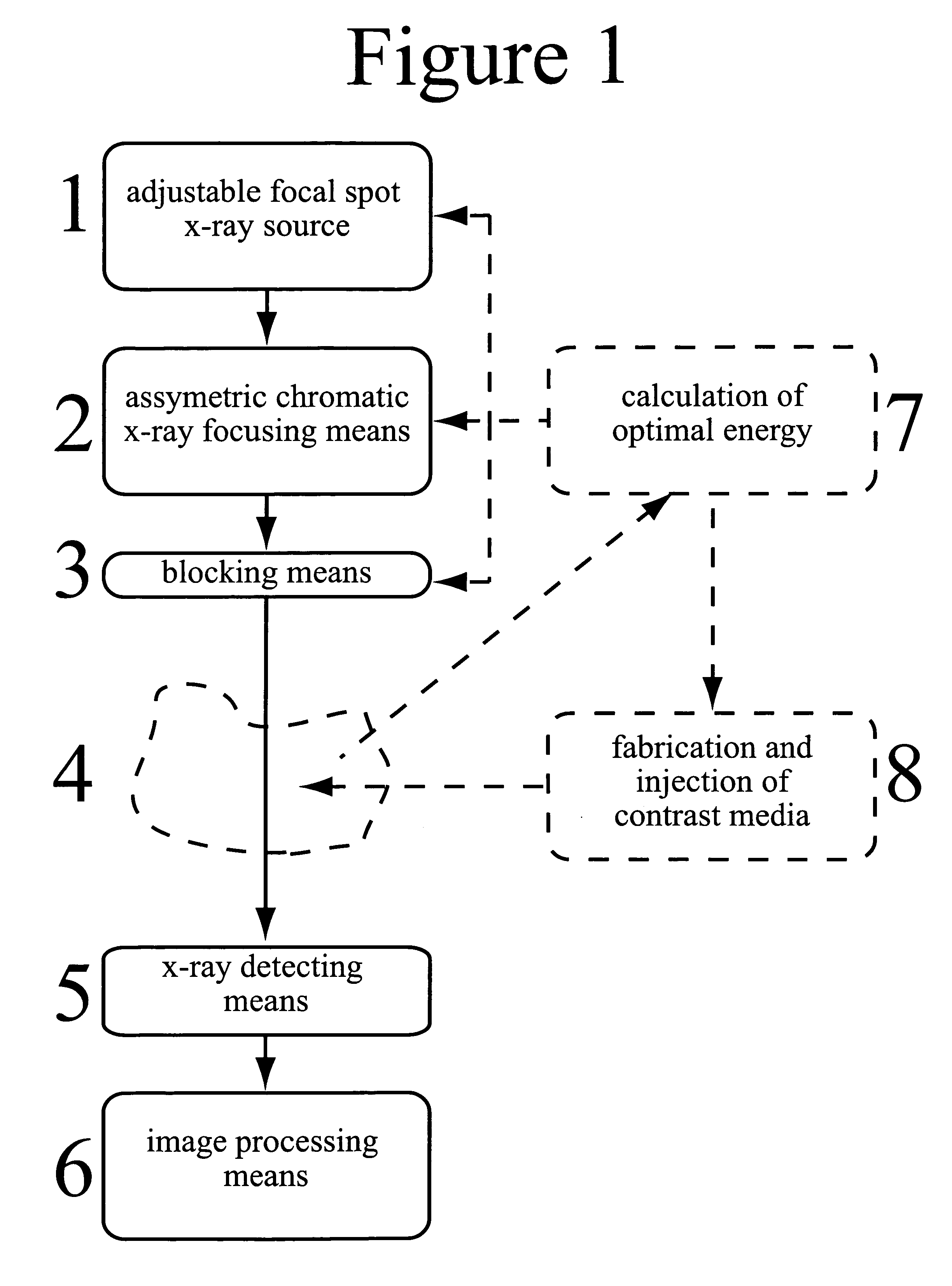
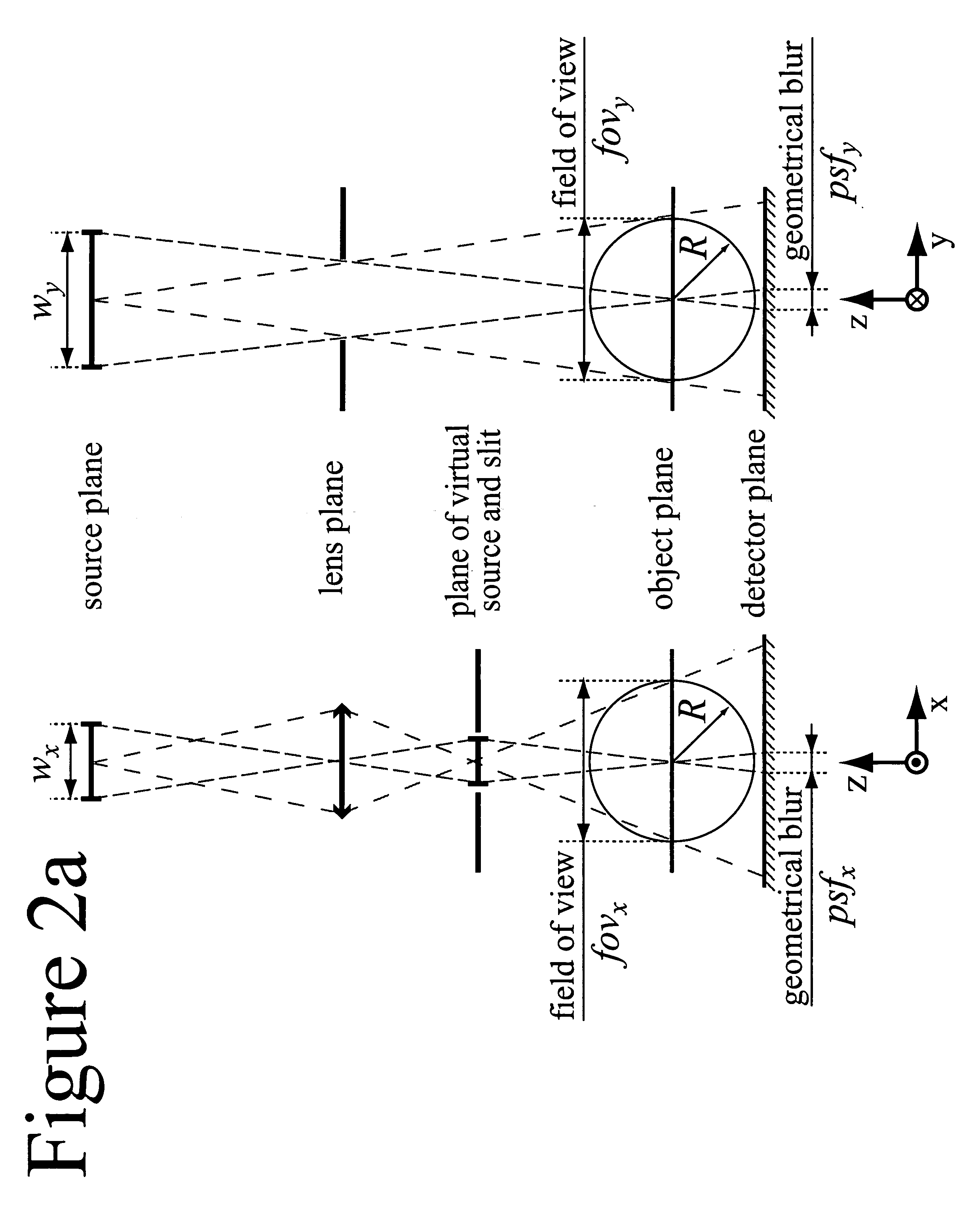
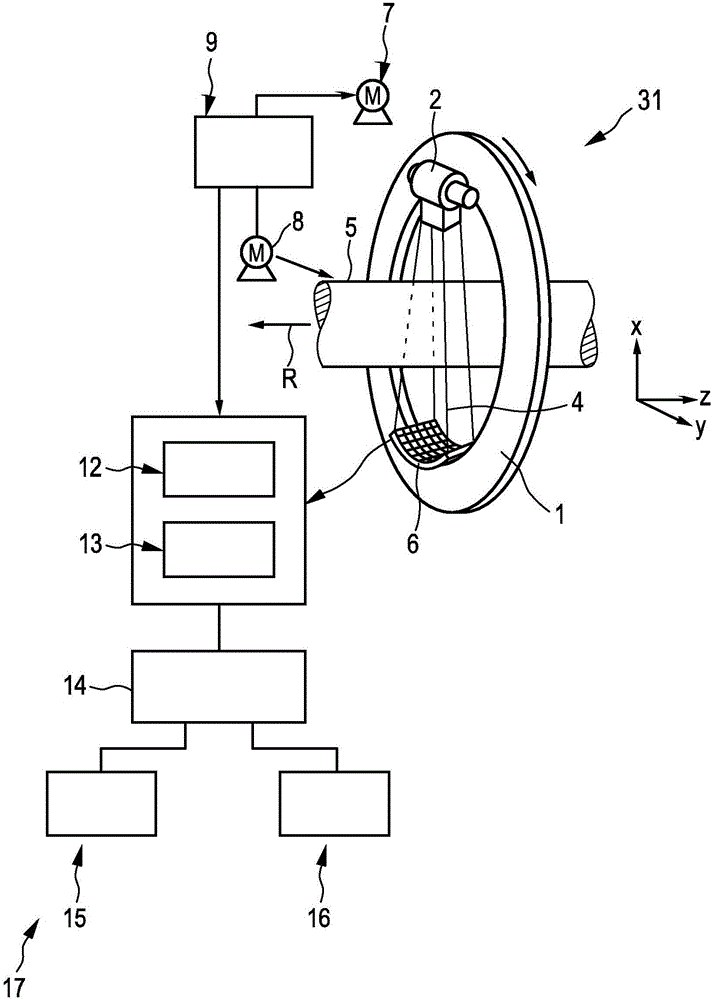
X-ray imaging arrangement
InactiveUS20070121784A1Compensation effectIncrease contrastTomographyAngiographySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)X-ray optics
An x-ray system for narrow bandwidth imaging of in particular small objects is provided. X-radiation from an x-ray source (1) is focused by chromatic x-ray optics (2) on an x-ray energy dependent distance from the optics. Asymmetric focusing of the x-ray optics is compensated for by choosing an asymmetric focal spot of the source. The energy selective focusing makes possible blocking unwanted x-ray energies (3) from reaching an object (4). In that way optimization of the energy according to the size of the object can be done to minimize dose and maximize signal-to-noise ratio (7). Furthermore, a critical edge subtraction image can be obtained at the object dependent optimal energy if the object is injected with a contrast agent having an absorption edge close to the optimal energy (8). Radiation is registered (5) and processed (6) to combine structural and energy subtraction images.
Owner:SECTRA MAMEA
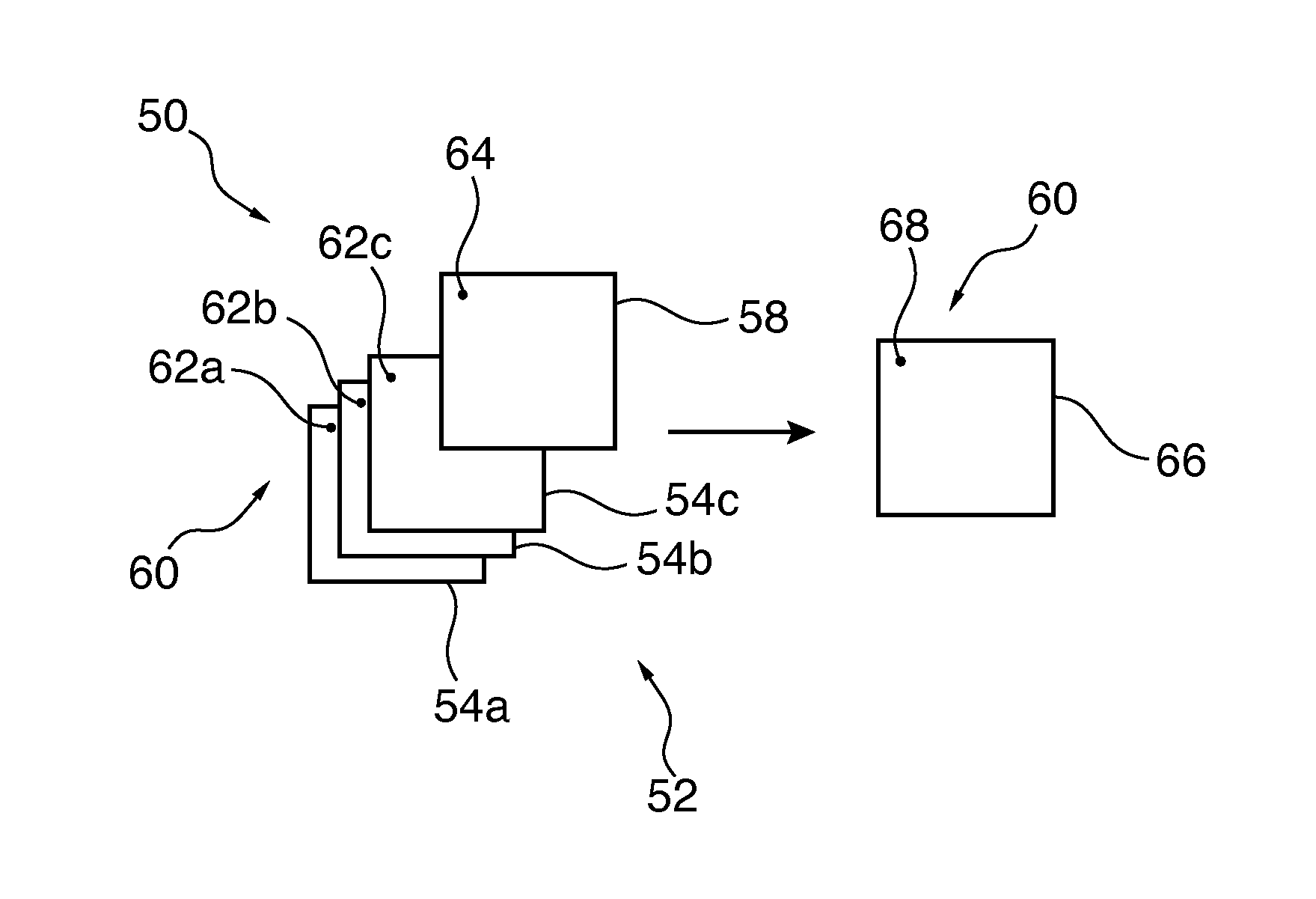
Differential phase contrast imaging with energy sensitive detection
ActiveUS9430832B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDifferential phaseComputational physics
For correcting differential phase image data 52, differential phase image data 52 acquired with radiation at different energy levels is received, wherein the differential phase image data 52 comprises pixels 60, each pixel 60 having a phase gradient value 62a, 62b, 62c for each energy level. After that an energy dependent behavior of phase gradient values 62a, 62b, 62c of a pixel 60 is determined and a corrected phase gradient value 68 for the pixel 60 is determined from the phase gradient values 62a, 62b, 62c of the pixel 60 and a model for the energy dependence of the phase gradient values 62a, 62b, 62c.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Corrector for correcting first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree
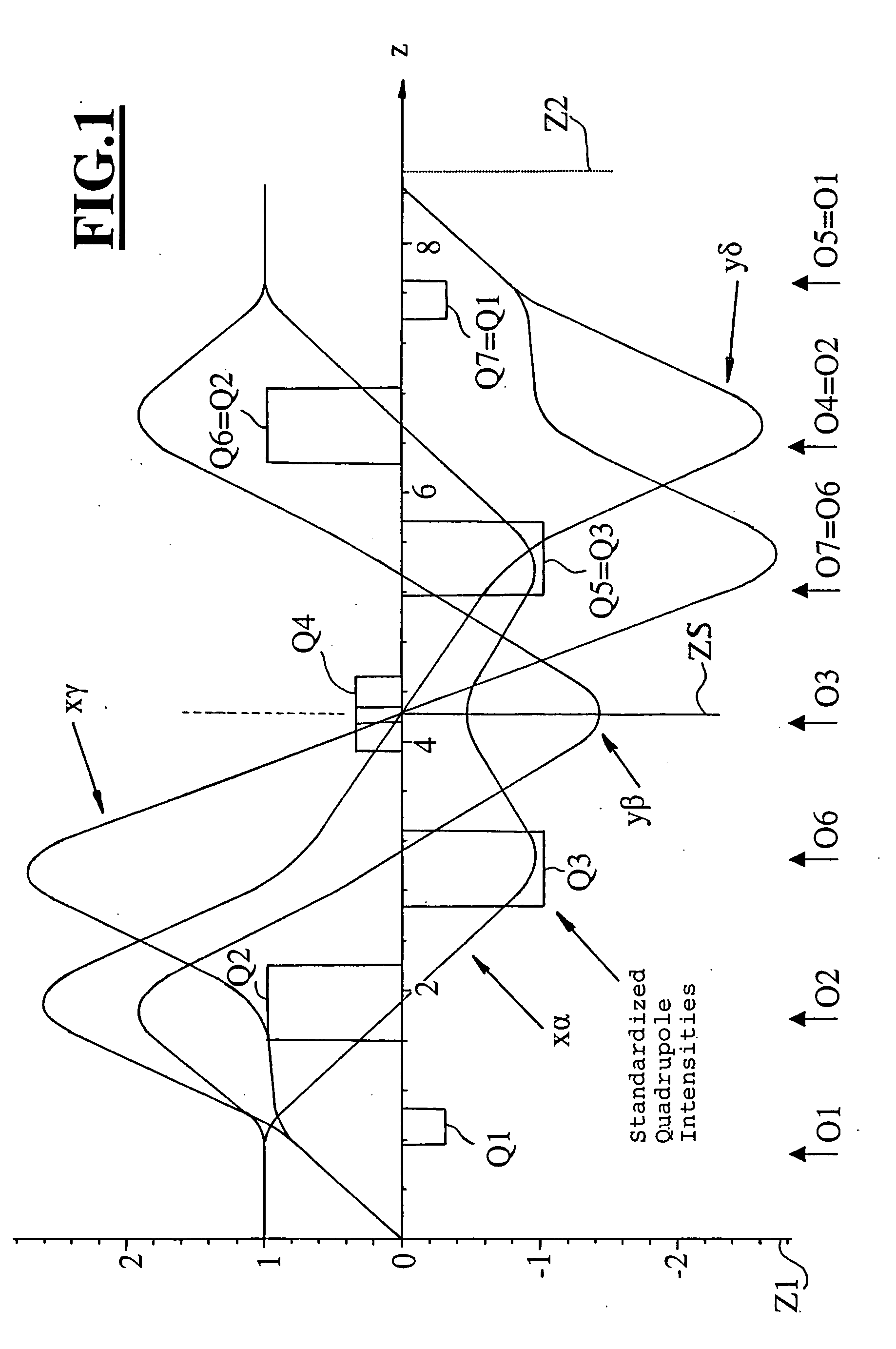
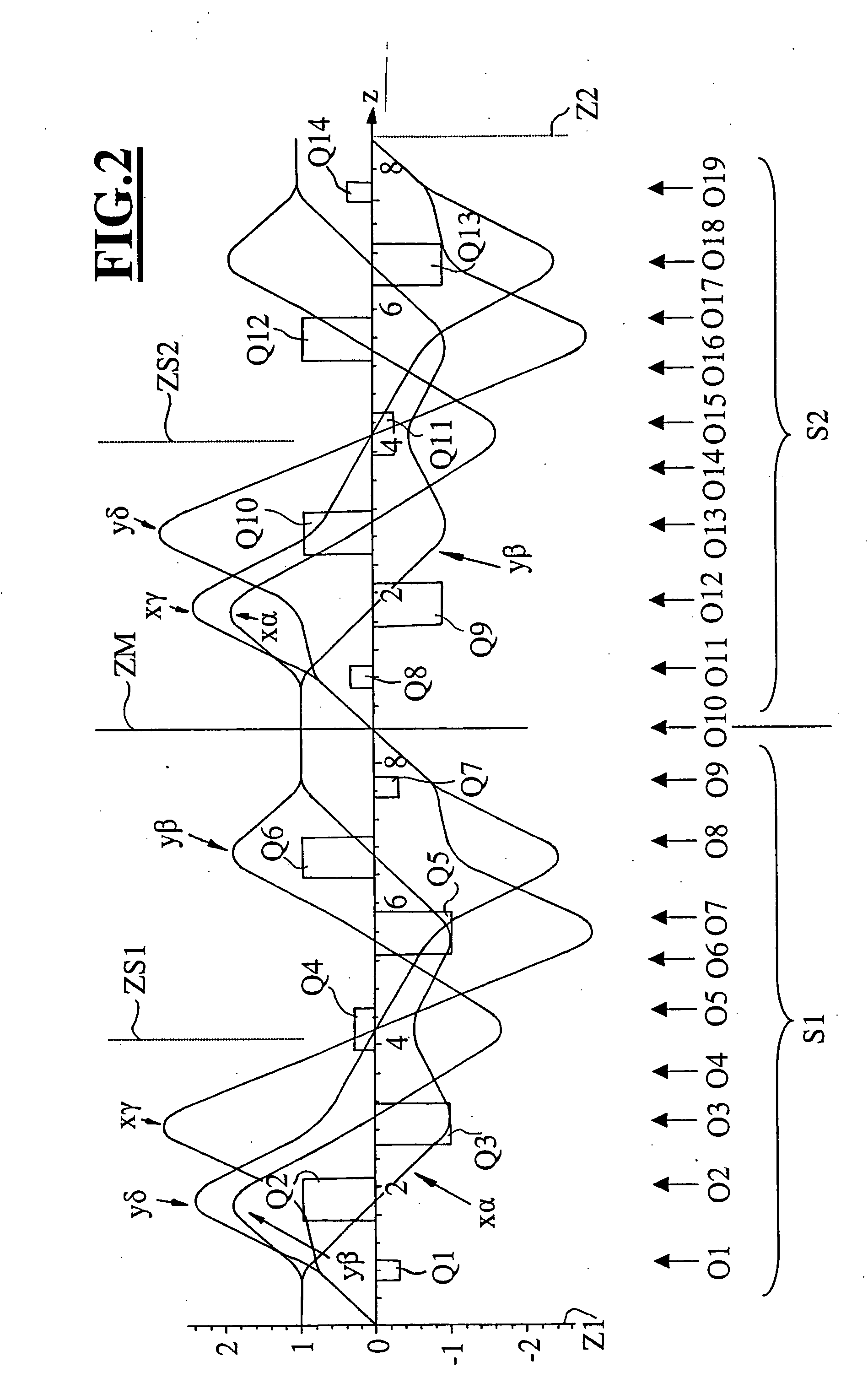
InactiveUS20050023480A1Aberration correctionStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationQuadrupole fieldEnergy dependent
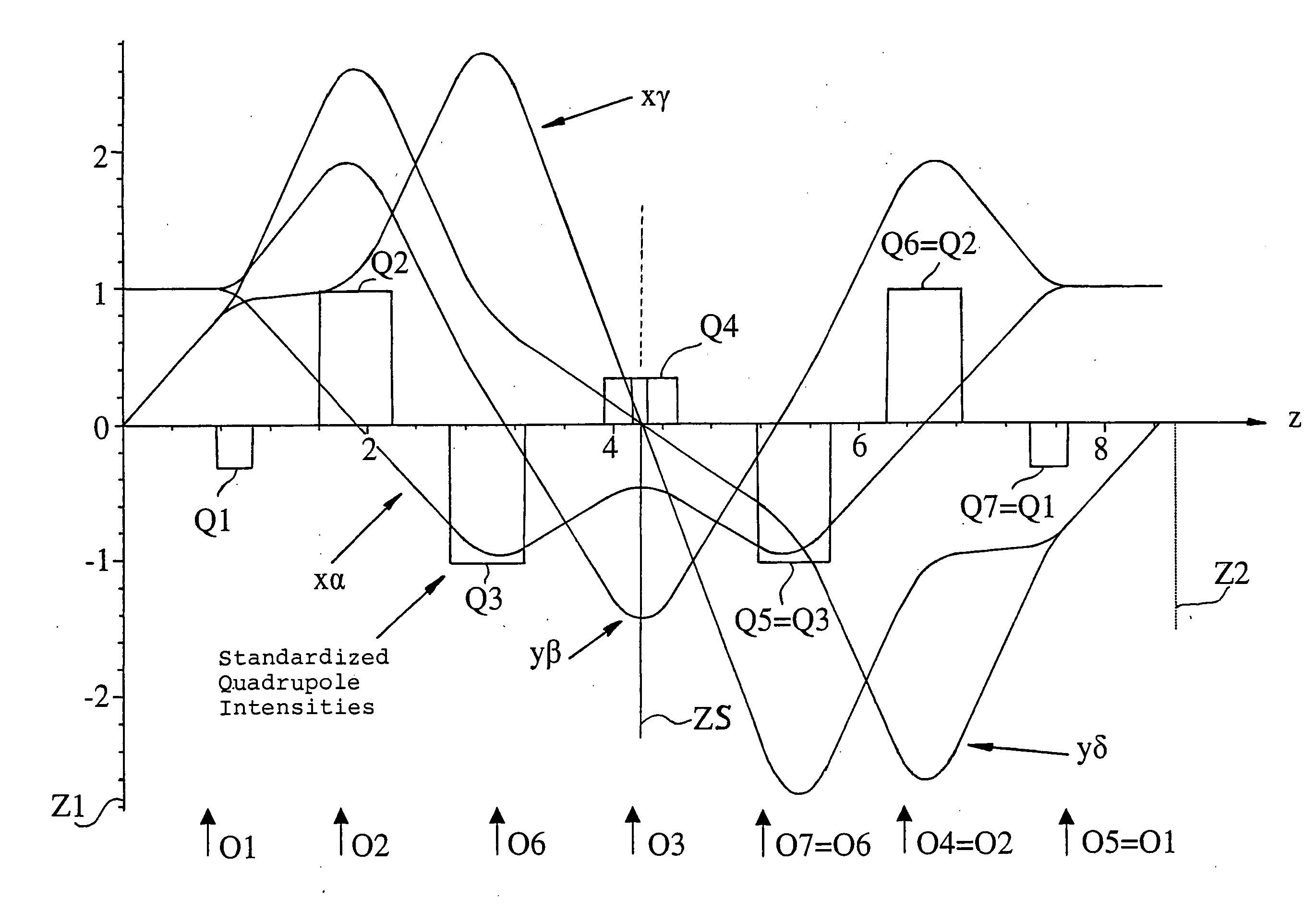
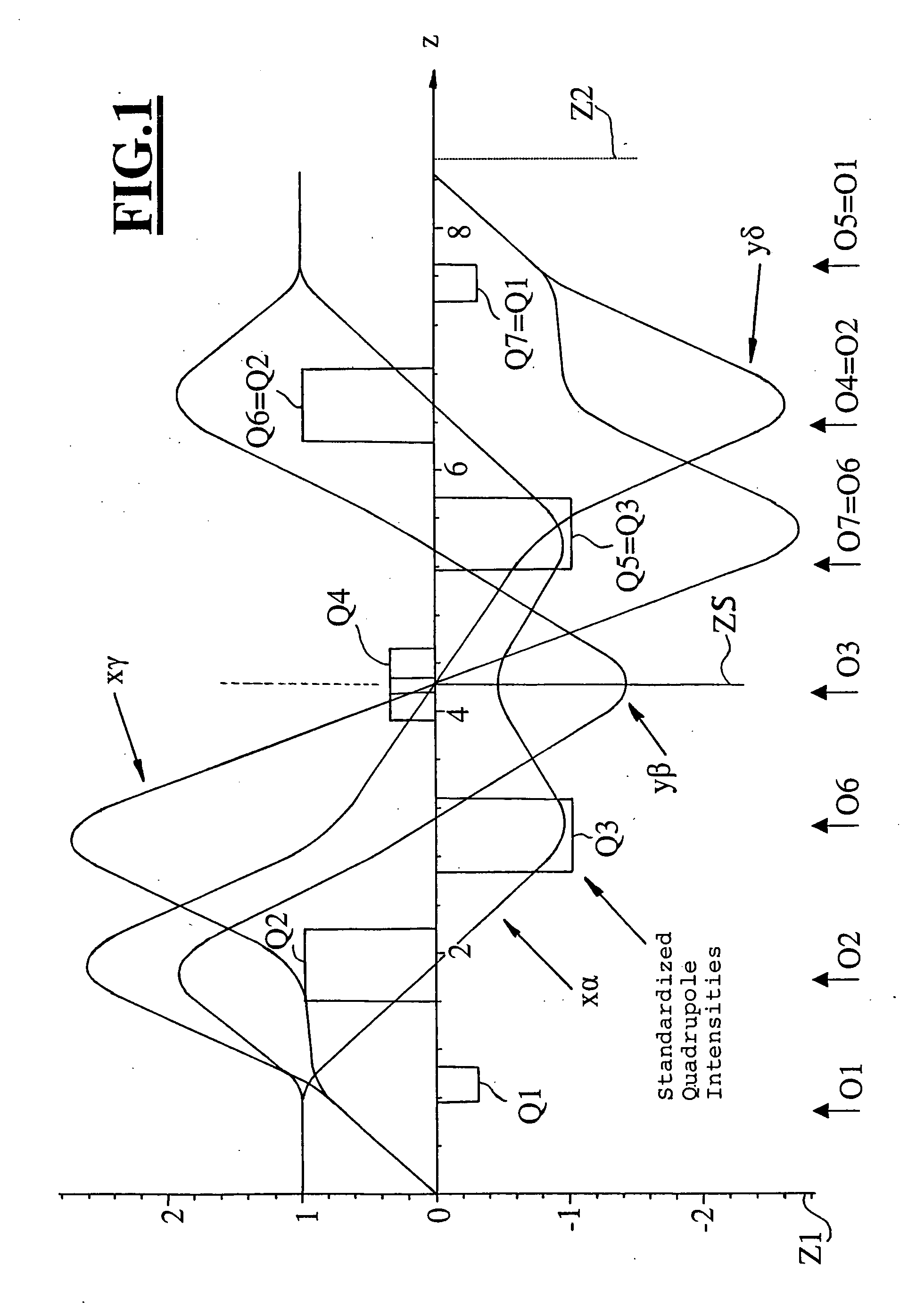
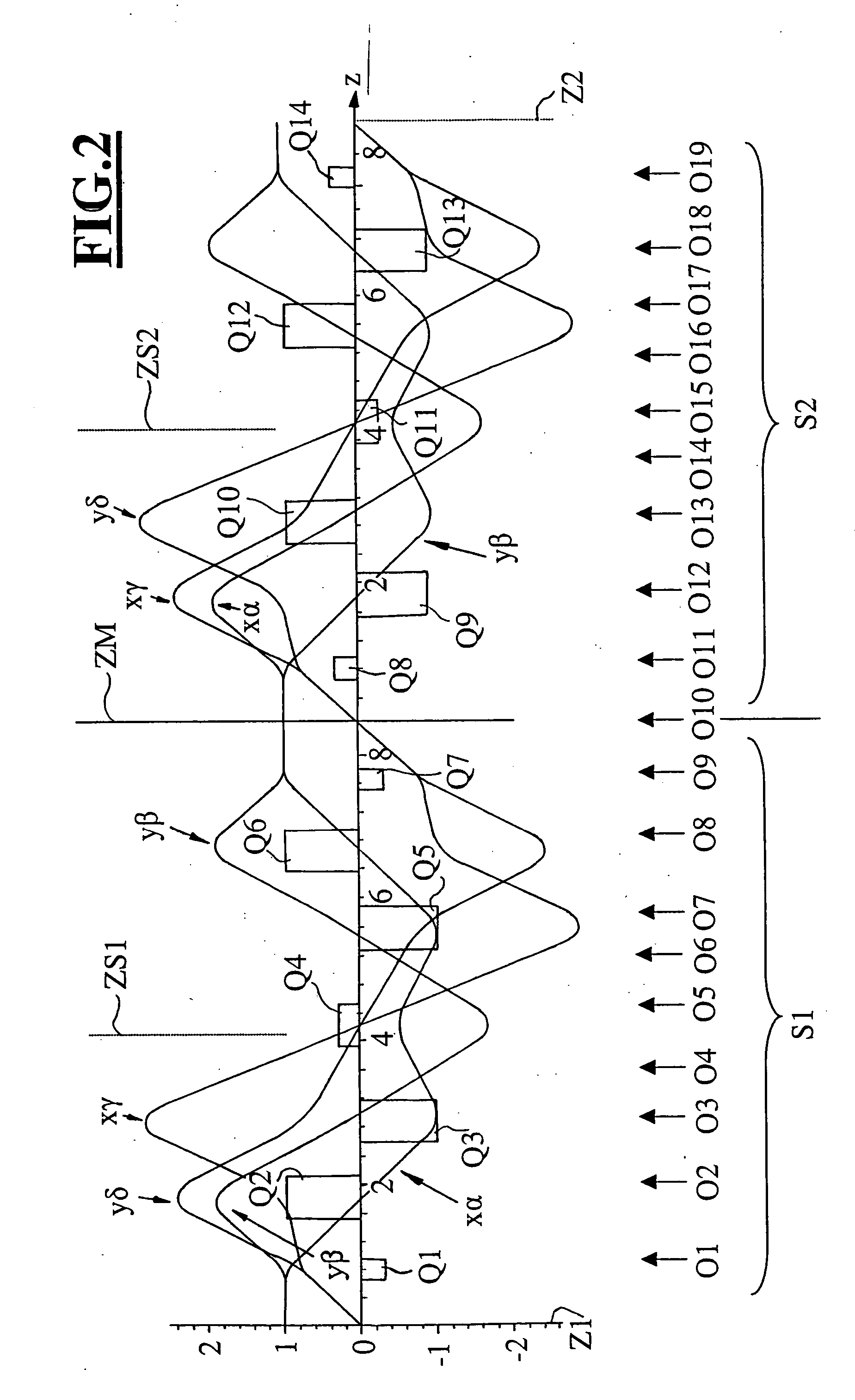
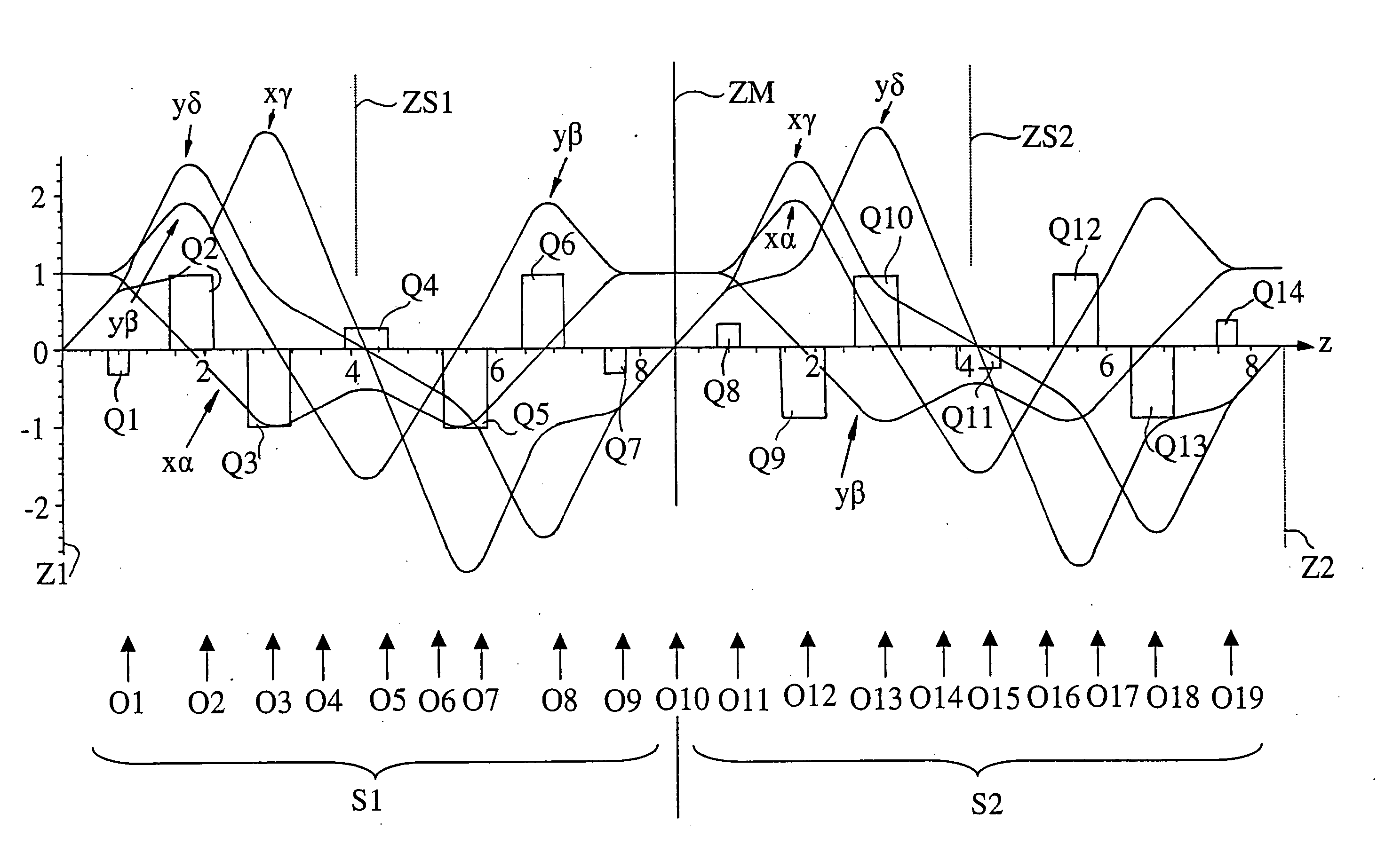
The invention is directed to a corrector for correcting energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the first degree as well as third-order spherical aberrations of electron-optical lens systems. The corrector includes at least one quadropole septuplet (S1) having seven quadrupoles (Q1 to Q7). The quadrupoles are mounted symmetrically to a center plane (ZS) so as to permit excitation along a linear axis. The corrector furthermore includes at least five octopoles (O1 to O7) which can be excited within the quadrupole septuplet. In an advantageous embodiment, two quadrupole septuplets are mounted in series one behind the other. The quadrupole fields of the two quadrupole septuplets are excited antisymmetrically to a center plane lying between the two quadrupole septuplets. With such a system, all geometric third-order aberrations and additional energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the third degree and geometric fifth-order aberrations of a lens system can be corrected in addition to the axial and off-axial first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
Corrector for correcting first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree
InactiveUS20060102848A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesQuadrupole fieldEnergy dependent
The invention is directed to a corrector for correcting energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the first degree as well as third-order spherical aberrations of electron-optical lens systems. The corrector includes at least one quadropole septuplet (S1) having seven quadrupoles (Q1 to Q7). The quadrupoles are mounted symmetrically to a center plane (ZS) so as to permit excitation along a linear axis. The corrector furthermore includes at least five octopoles (O1 to O7) which can be excited within the quadrupole septuplet. In an advantageous embodiment, two quadrupole septuplets are mounted in series one behind the other. The quadrupole fields of the two quadrupole septuplets are excited antisymmetrically to a center plane lying between the two quadrupole septuplets. With such a system, all geometric third-order aberrations and additional energy-dependent first-order aberrations of the third degree and geometric fifth-order aberrations of a lens system can be corrected in addition to the axial and off-axial first-order chromatic aberrations of the first degree.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST GMBH
Neutron detector and dose rate meter using beryllium-loaded materials
ActiveUS20180299570A1High energyHigh sensitivityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron doseDose rate
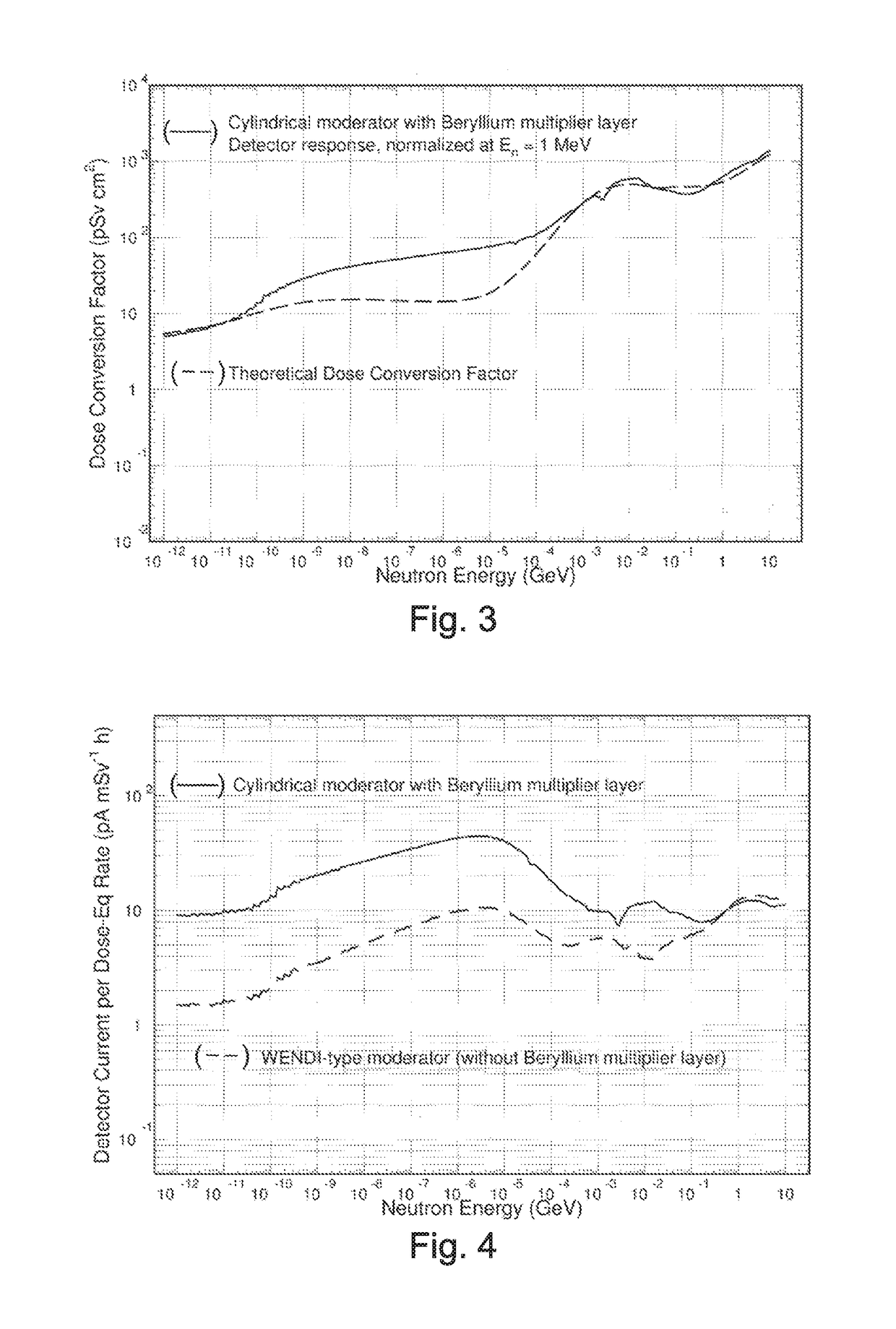
An apparatus and method for improving the sensitivity and energy response of neutron detectors and neutron dose rate meters. A beryllium layer is added to neutron detector moderators to improve the sensitivity of the detector. Energy dependence of the sensitivity is optimized by controlling the amount of beryllium in the moderator and by specifying the geometrical design parameters. The beryllium layer, in combination with additional material layers in the moderator, makes the detector response function correspond to the theoretical one in a wide range of energies. Response parameters of the neutron dose rate meter are within 20% of the theoretical response function in the neutron energy range from 500 keV to 10 GeV, and also in the energy range corresponding to thermal neutrons (about 1-100 meV).
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
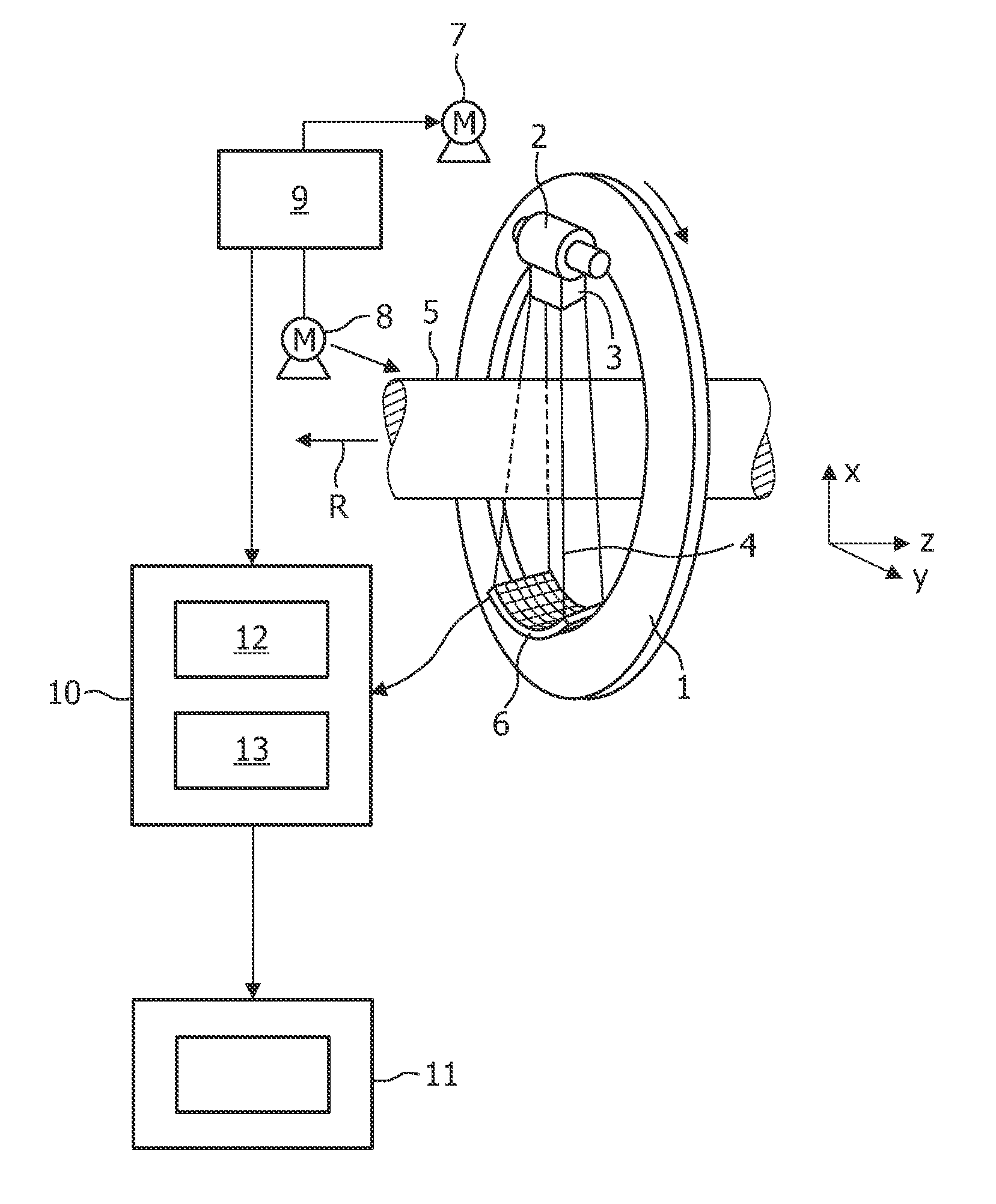
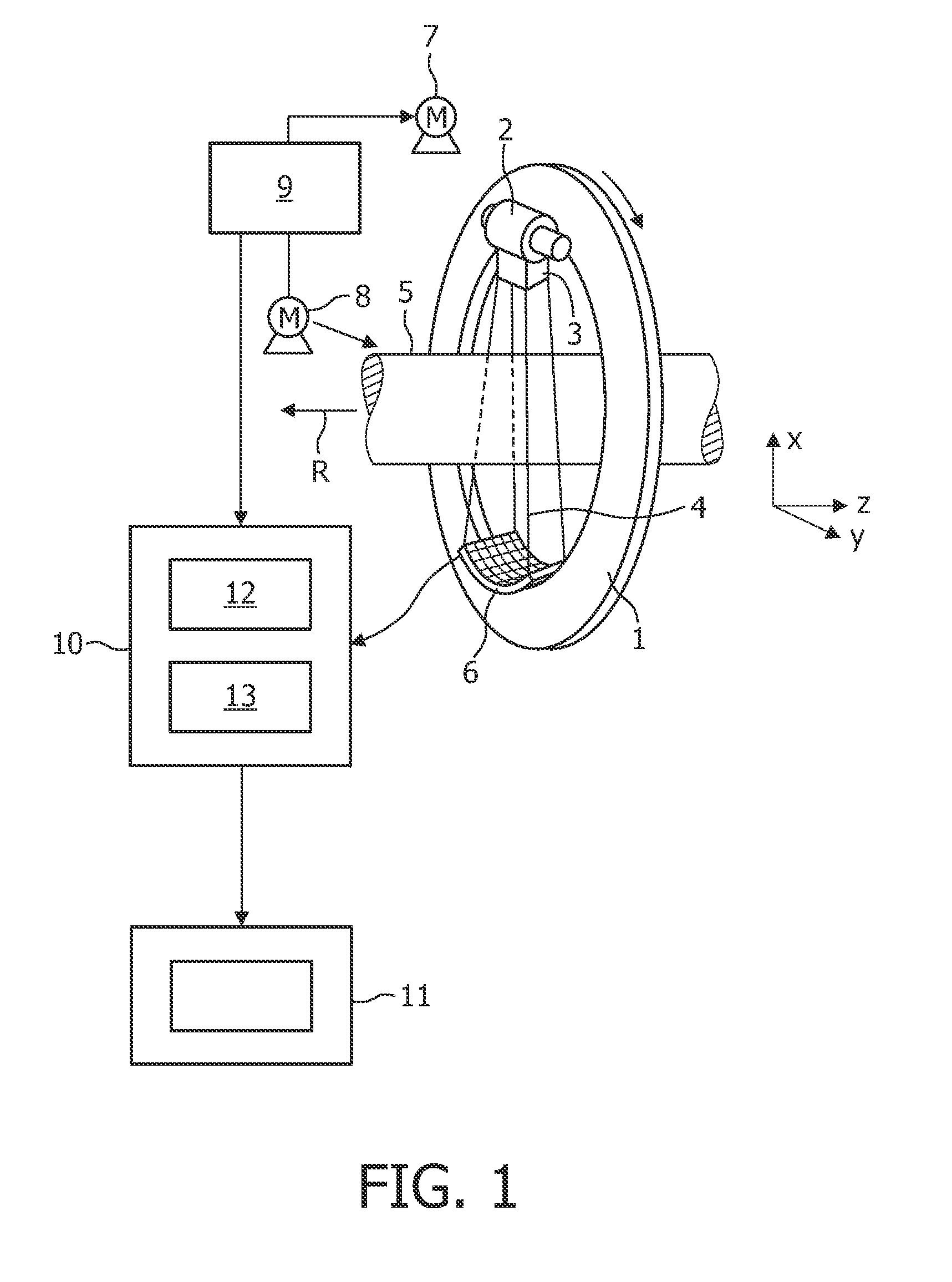
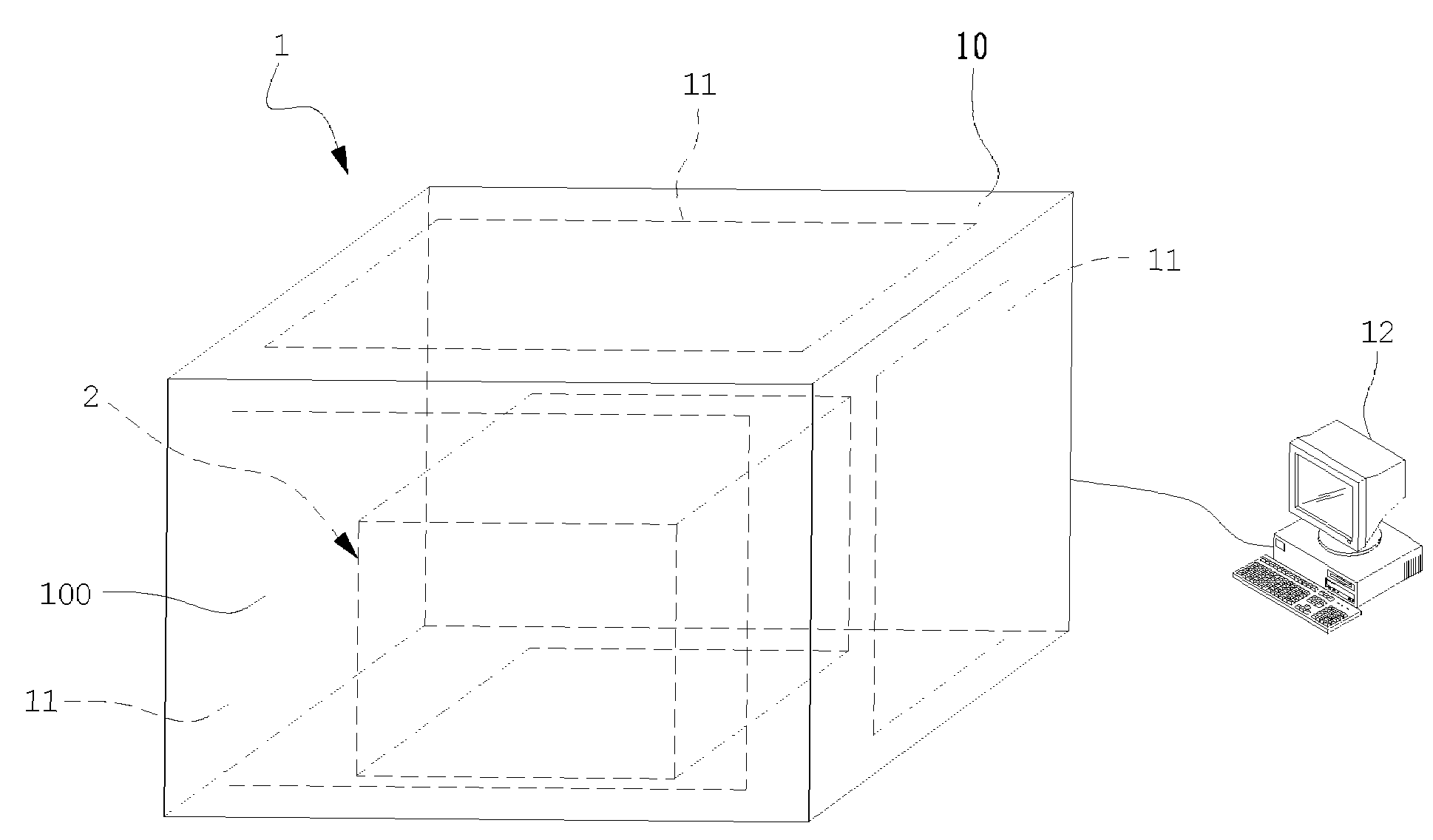
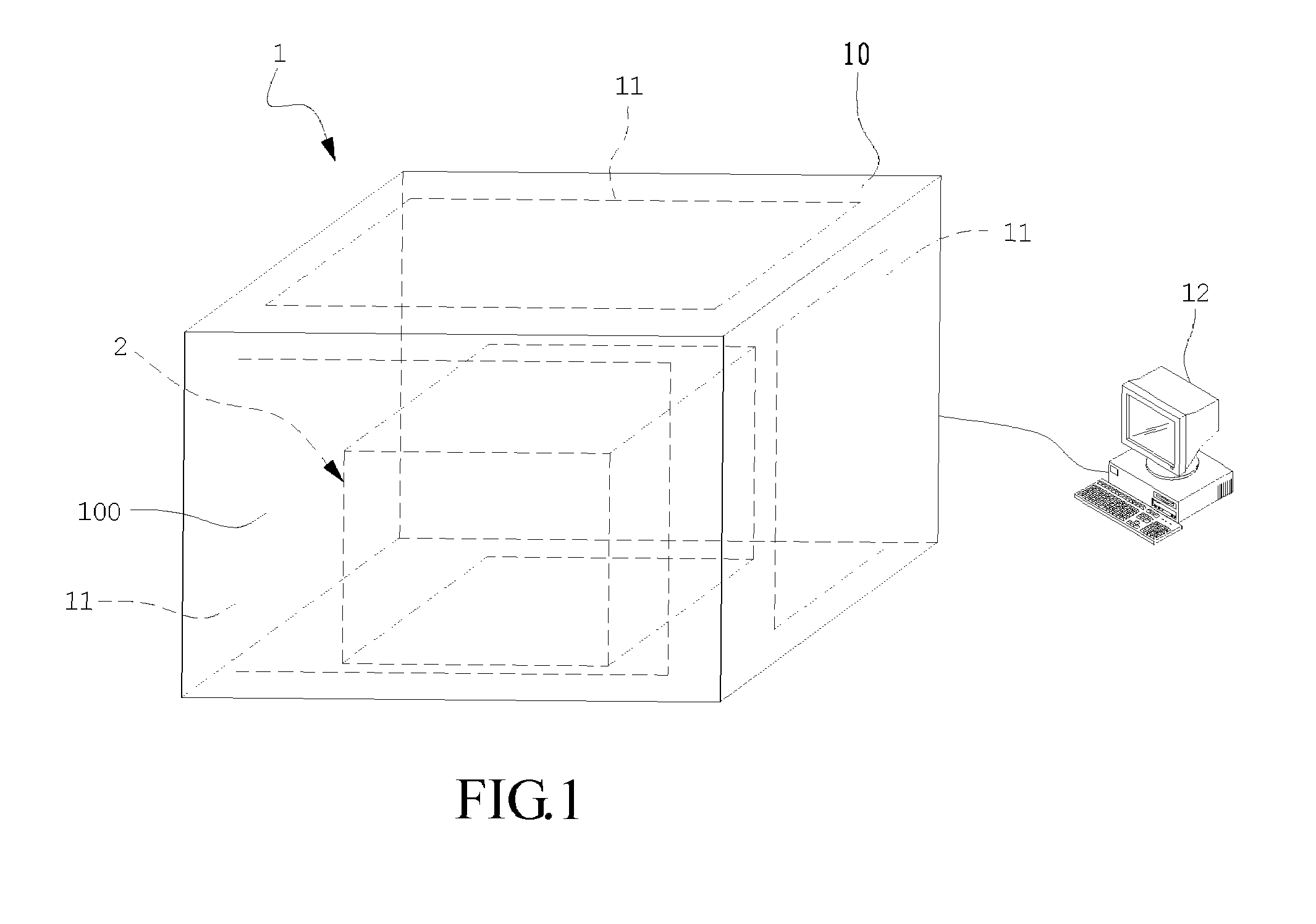
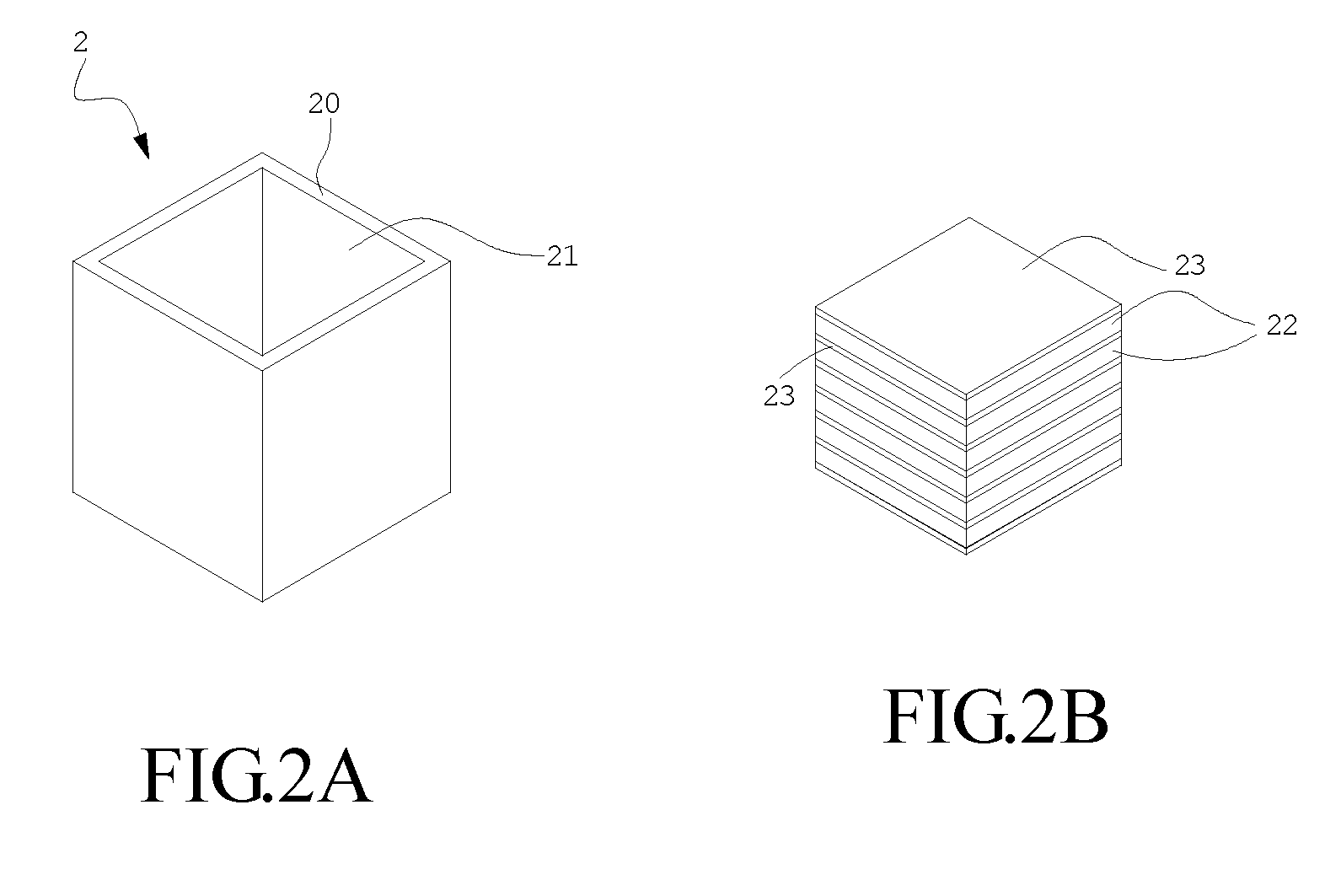
Volume Calibration Phantom and Calibration Method Thereof
A volume calibration phantom is disclosed in the present invention, which comprises a container; a plurality of plates stacking up inside the container; and at least one slab of radioactive source, each of which is disposed between the adjacent plates and comprises a plurality of radionuclides. With the volume calibration phantoms, the present invention further provides a calibration method which is an improvement over conventional calibration methods of space geometric center point source and relative penetration factor ratios. The method comprises the steps of generating a calibration curve of density vs. counting efficiency corresponding to the several different volume calibration phantoms; calculating the density of a radioactive waste specimen to obtain a corresponding radioactive activity according to the calibration curve, and then revising the corresponding radioactive activity according to the energy dependency and equation of gamma gross radioactivity for multiple radionuclides so as to obtain the correct gamma gross radioactivity of the radioactive waste specimen. By means of the method disclosed in the present invention, a precise and accurate result can be obtained.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
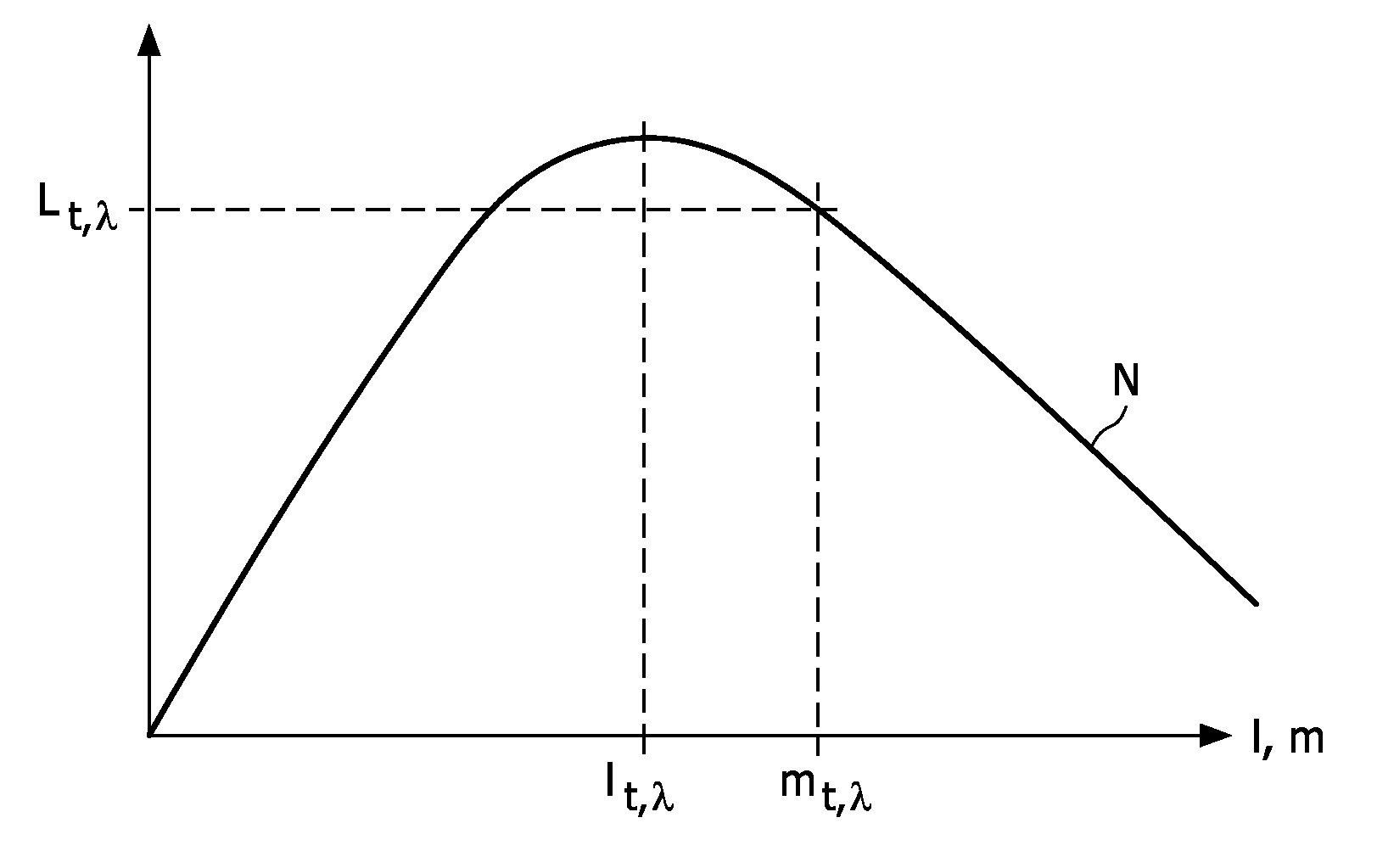
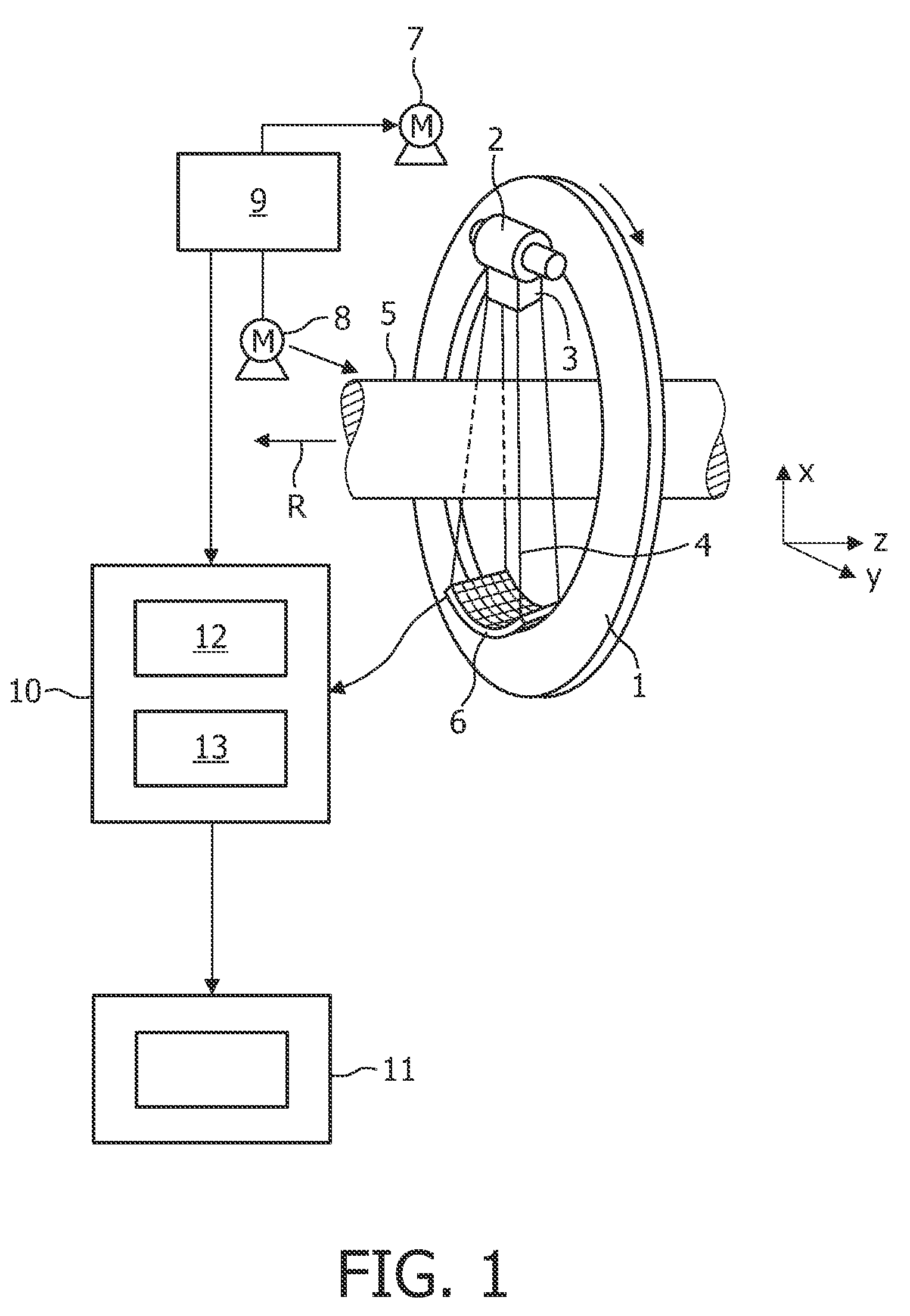
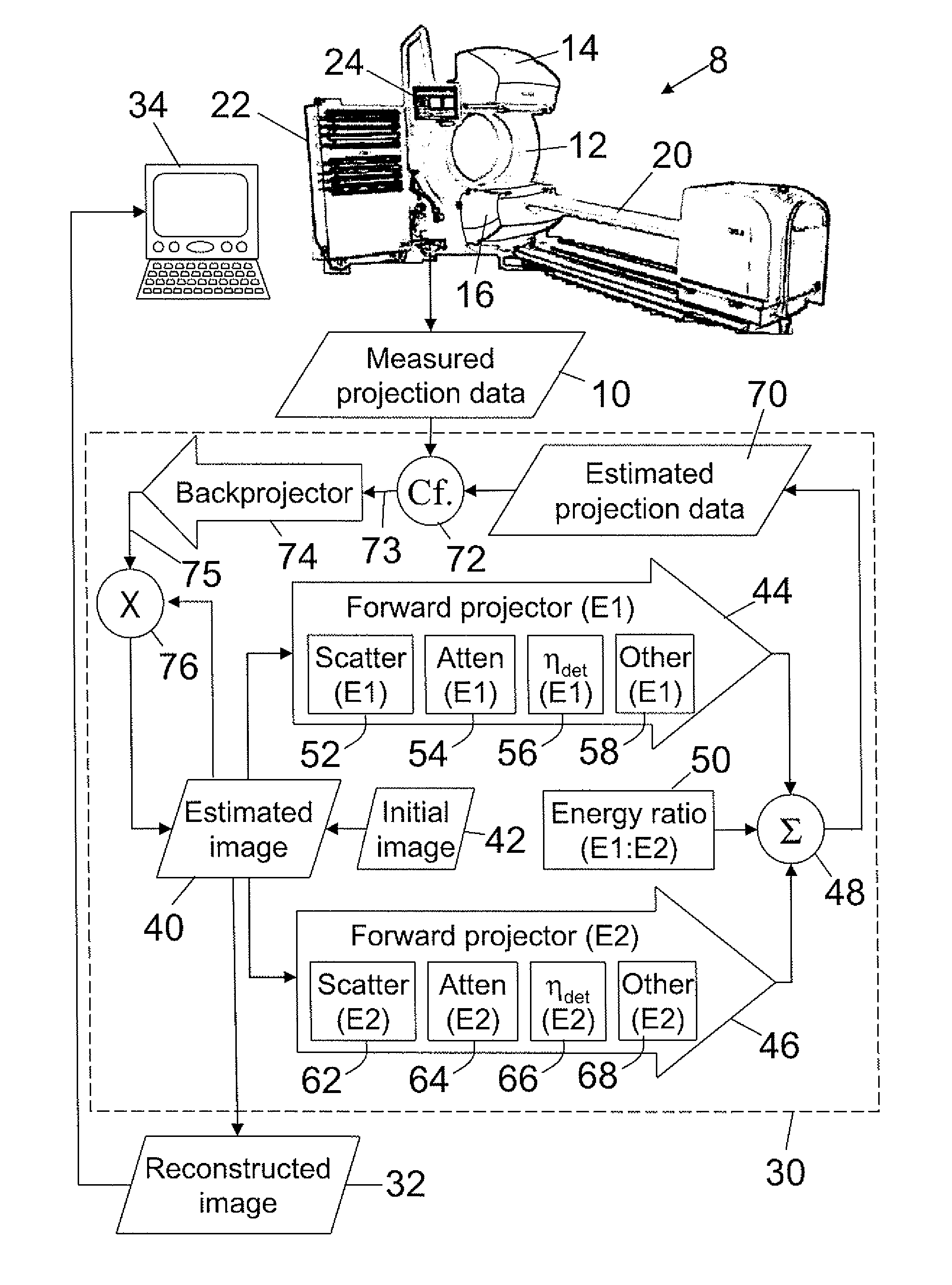
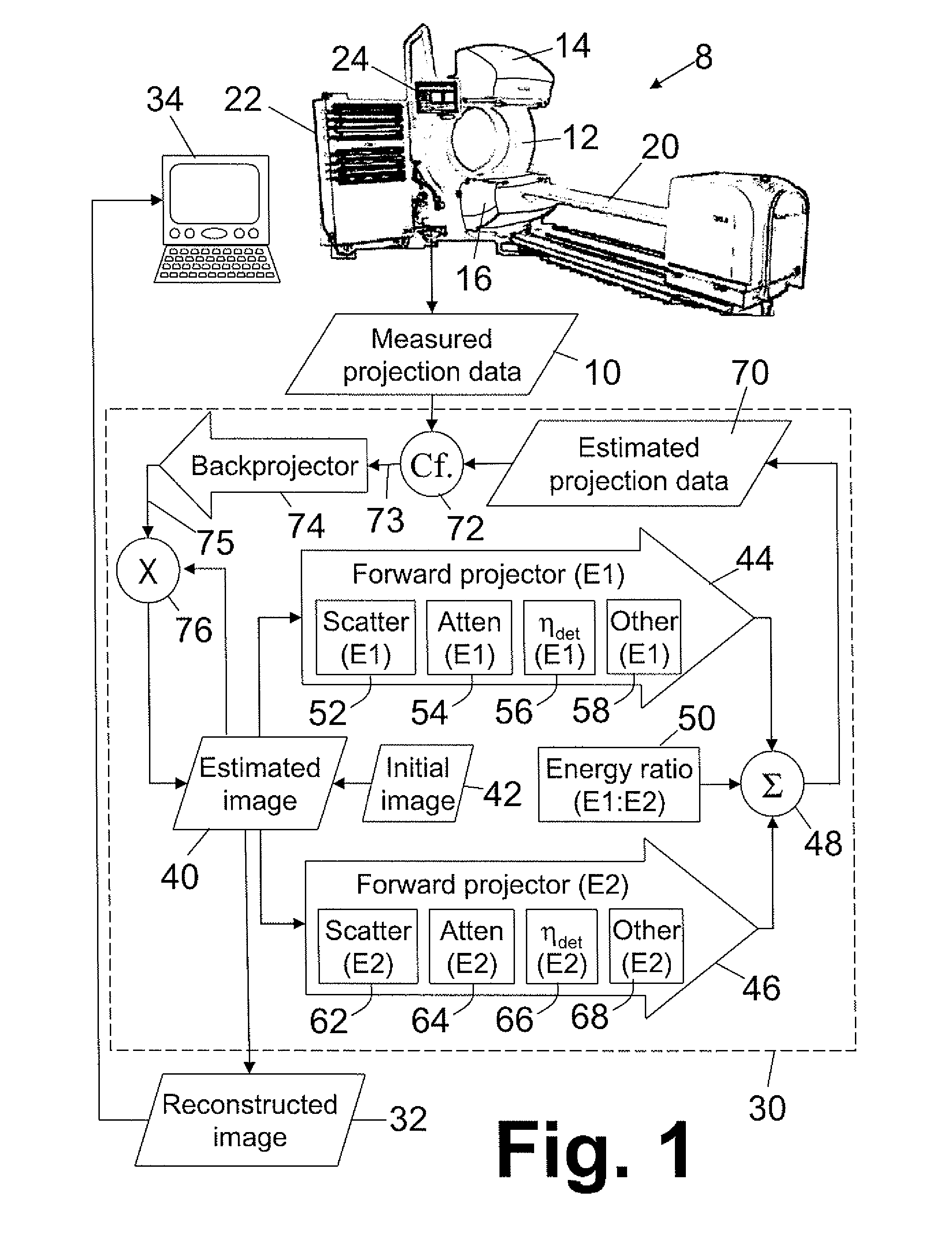
Imaging system for imaging a region of interest from energy-dependent projection data
InactiveUS7924968B2Reduce biasImage degradationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationEnergy dependent
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Energy dependent quantization for efficient coding of spatial audio parameters
Parameters being a measure for a characteristic of a channel or of a pair of channels, wherein the parameter is a measure for a characteristic of the channel or of the pair of channels with respect to another channel of a multi-channel signal can be quantized more efficiently using a quantization rule that is generated based on a relation of an energy measure of the channel or the pair of channels and an energy measure of the multi-channel signal. With generation of the quantization rule taking into account a psycho acoustic approach, the size of an encoded representation of the multi-cha nnel signal can be decreased by coarser quantization without significantly disturbing the perceptual quality of the multi-channel signal when reconstructed from the encoded representation.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +2
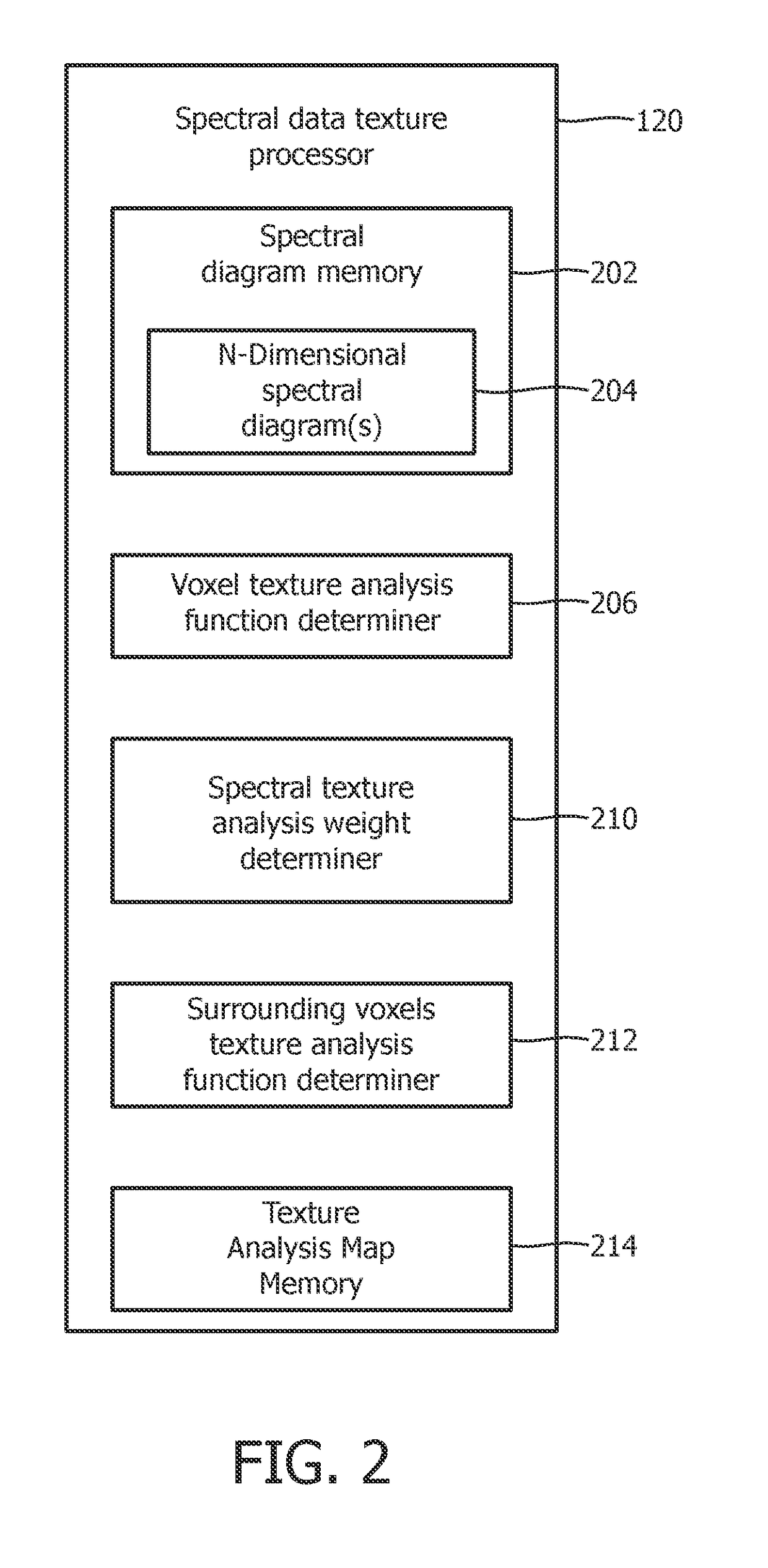
Texture analysis map for image data
ActiveUS20170243364A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionMulti dimensionalEnergy dependent
A method includes obtaining at least a first energy dependent spectral image volume and a second different energy dependent spectral image volume from reconstructed spectral image data. The method further includes generating a multi-dimensional spectral diagram that maps, for each voxel, a value of the first energy dependent spectral image volume to a corresponding value of the second energy dependent spectral image volume. The method further includes generating a set of spectral texture analysis weights from the multi-dimensional spectral diagram. The method further includes retrieving a set of texture analysis functions, which are generated as a function of voxel intensity and voxel gradient value from a co-occurrence matrix histogram. The method further includes generating a texture analysis map through a texture analysis of the reconstructed spectral image data with the set of texture analysis functions and the set of spectral texture analysis weights and visually presenting the texture analysis map.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
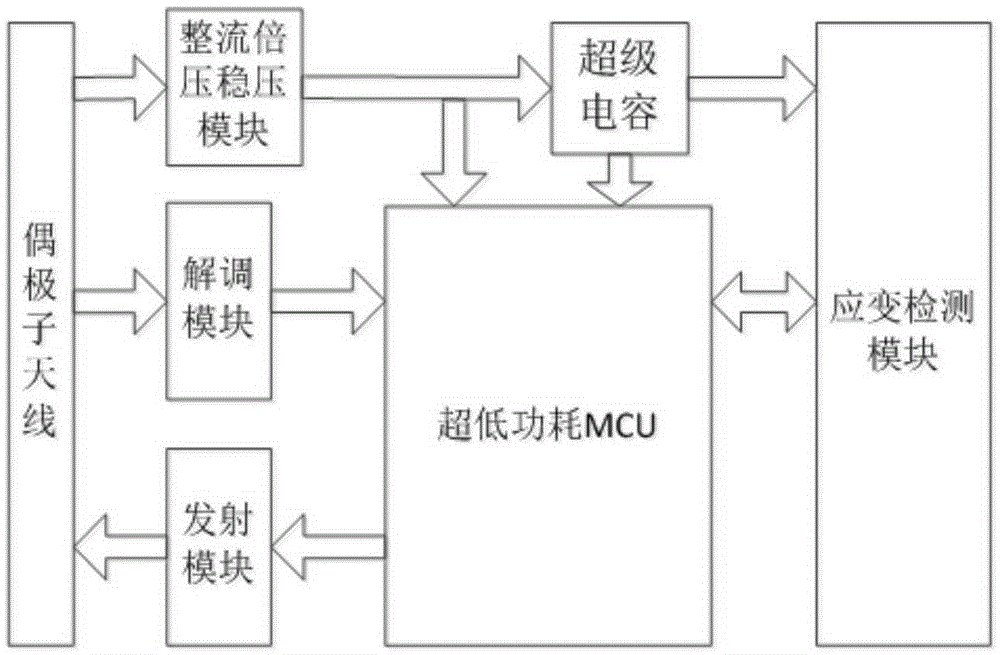
Ultra-low power consumption passive structural strain monitoring device
InactiveCN105318823AReduce volumeEasy to deployElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementCapacitanceWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses an ultra-low power consumption passive structural strain monitoring device, comprising a radio frequency front end, an ultra-low power consumption MCU, a strain detection module and a super-capacitor, wherein the radio frequency front end comprises a dipole antenna, a rectification voltage-multiplying voltage stabilization module, a demodulation and an emission module. The device can be embedded in a building structure to collect structural strain parameters, return structural strain change information to a reader in a wireless communication mode, and solve the problems of energy dependence and inconvenience of structural stain monitoring based on the wireless sensor network technology; in addition, the device does not need batteries for power supply, and can work for a long time without extra maintenance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Drum-type volume source calibration phantom and calibration method thereof
ActiveUS7479628B1AccuracyCalibration apparatusX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentModification factorCounting efficiency
A drum-type volume source calibration phantom is provided, which comprises a drum-type container; a plurality of plate groups stacking up inside the drum-type container, at least one slab of radioactive source, each of which is disposed between the adjacent plate groups and comprises a plurality of radionuclides. The present invention further provides a calibration method that starts by the step of providing a radioactivity test for each drum-type volume calibration phantom. Then, a calibration relationship of density vs. counting efficiency corresponding to the several different drum-type volume source calibration phantoms is performed in a waste curie monitor. Finally, a characteristic of photonic energy dependency is measured for a modification factor.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR ENERGY RES NUCLEAR ENERGY COUNCIL EXECUTIVE YUAN
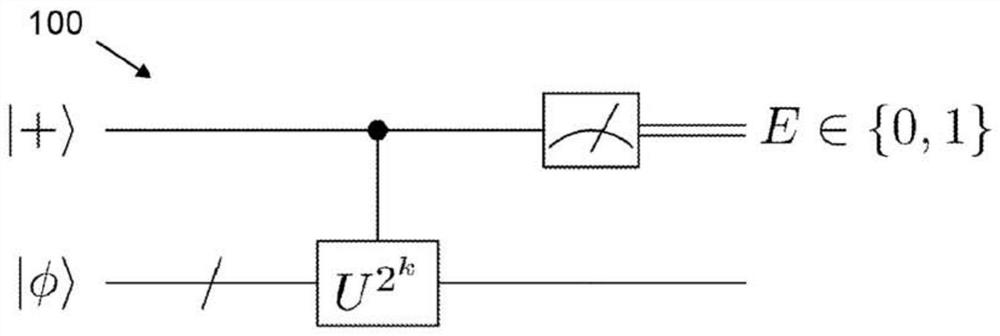
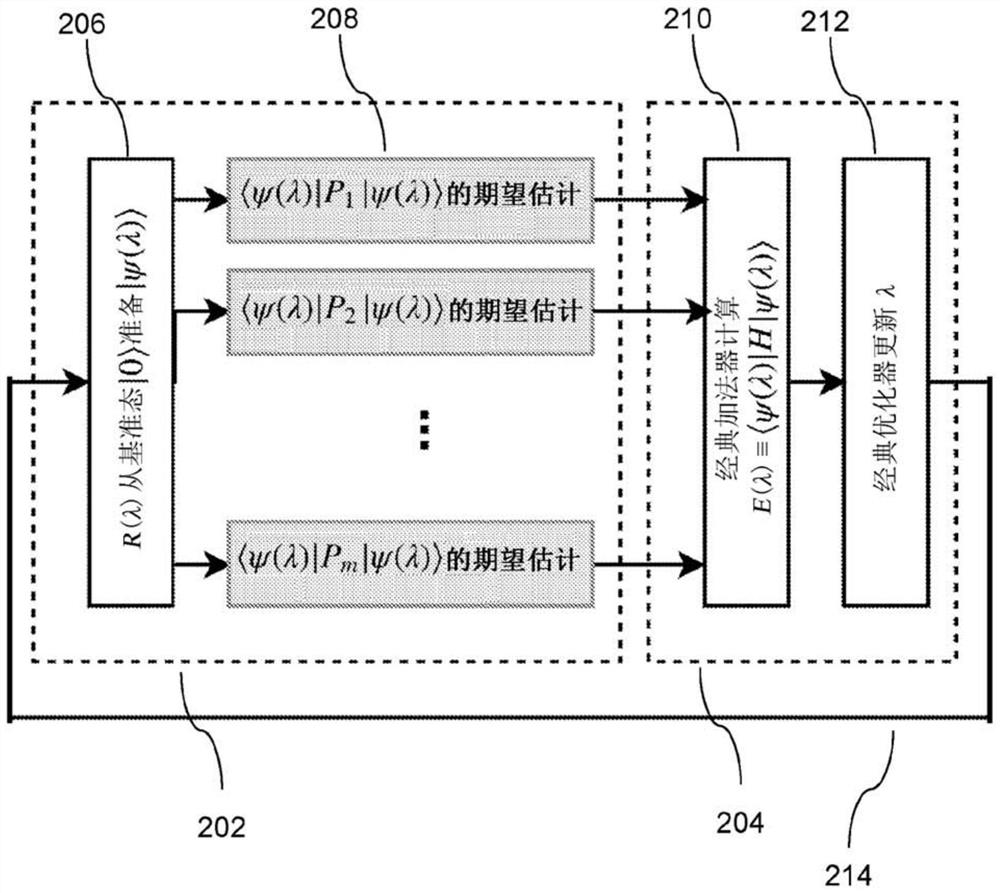
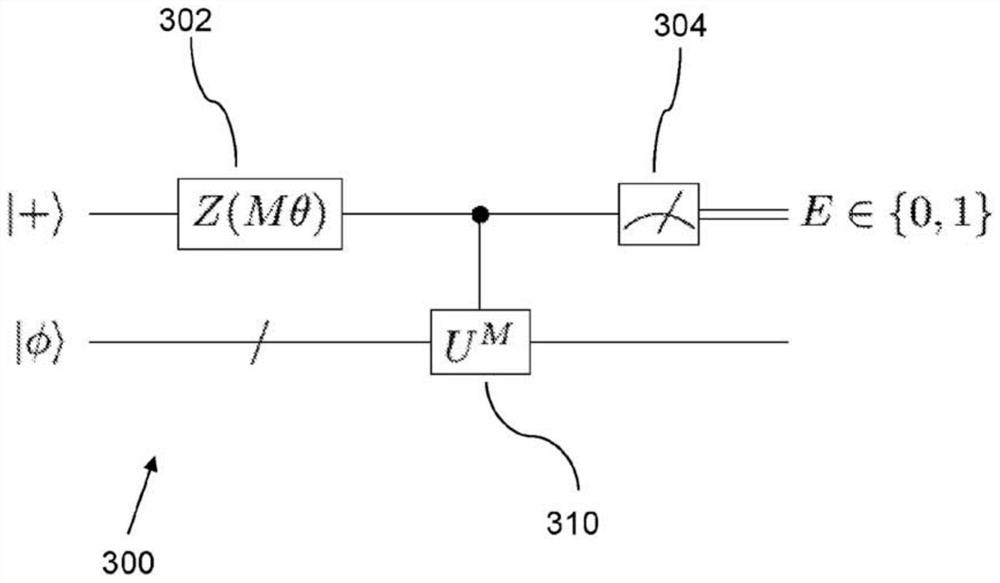
A method of determining a state energy
There is provided a method for determining an energy level of a physical system using a quantum computer, wherein the energy level of the physical system is described by the summation of a plurality of summands. The method comprises performing an energy estimation routine which comprises preparing an ansatz trial state using an arrangement of quantum gates, wherein the ansatz trial state has a trial state energy dependent on a trial state variable, and estimating an expectation value of each summand respectively. The estimating comprises constructing, based on the arrangement of quantum gates,an initial quantum circuit to operate on the ansatz trial state and further comprises performing a summand expectation value determination sub- routine a plurality of times in an iterative process. The energy estimation routine further comprises summing the expectation value estimates of each summand to determine an estimate for the trial state energy. The method further comprises determining theenergy level of the physical system by applying an optimisation procedure to the energy estimation routine, wherein the optimisation procedure comprises iteratively updating the trial state variableand performing the energy estimation routine a plurality of times to determine a respective trial state energy for each of a plurality of different ansatz trial states.
Owner:河道研究有限公司
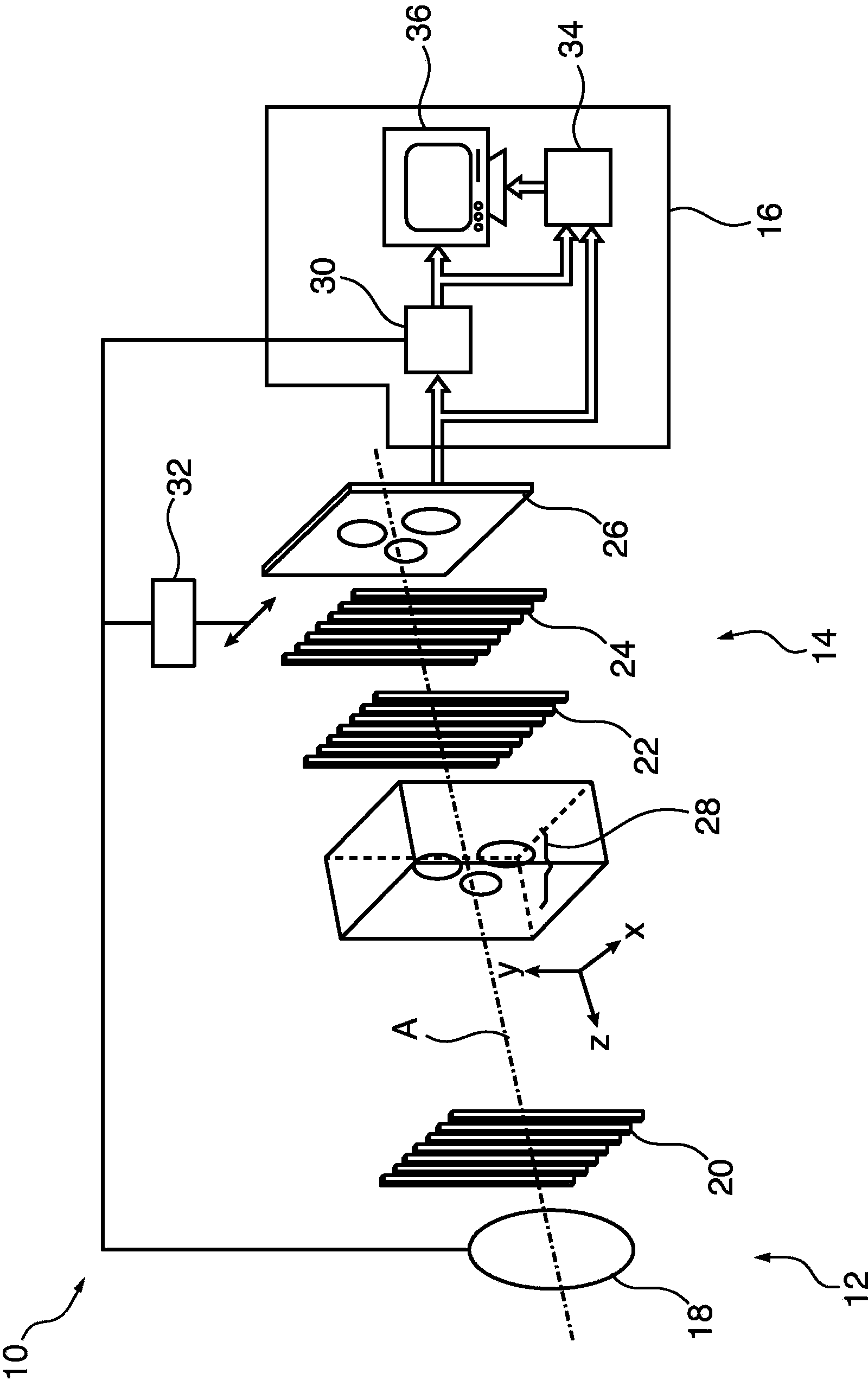
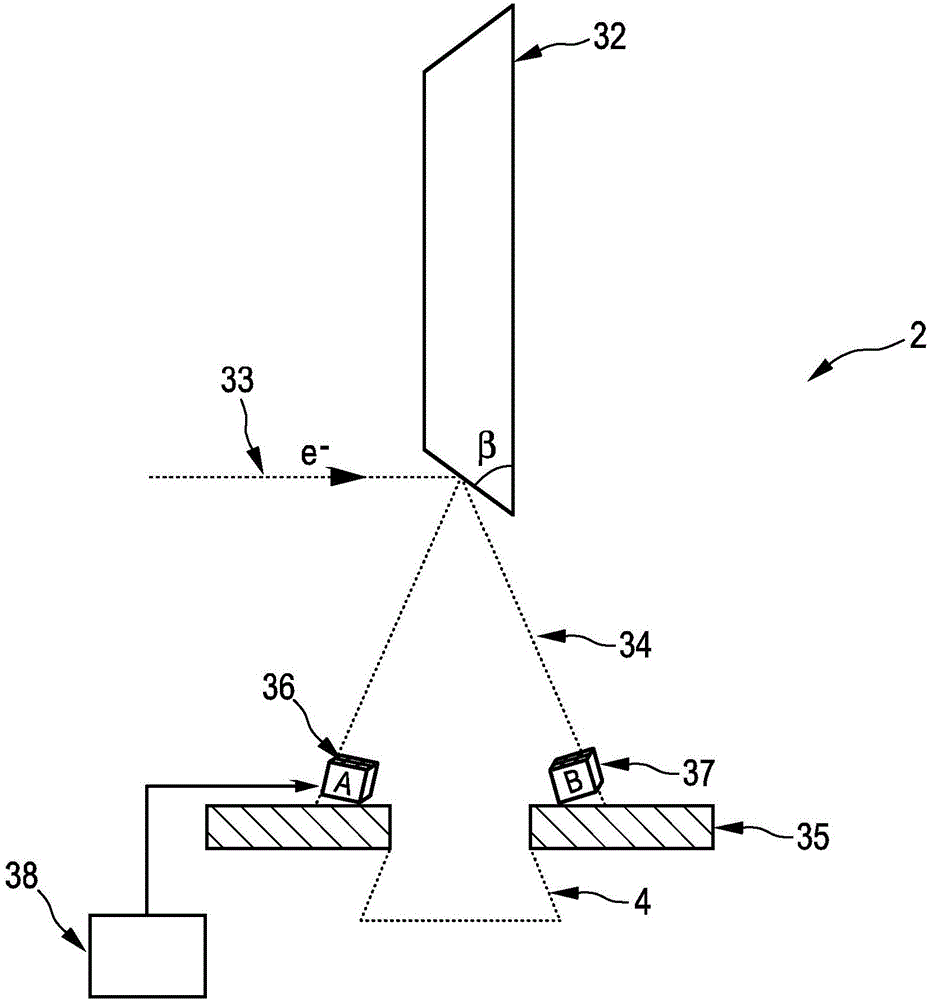
Method for improving the ability to recognize materials in an X-ray inspection system, and X-ray inspection system
ActiveUS8311309B2Easy to identifySuppressing contourMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionSoft x rayX-ray
A method for improving the ability to recognize materials in an X-ray inspection system is provided that includes the steps of recording at least two absorption X-ray images of an object to be examined at different energies, mathematically modeling the object by a number of layers assuming a particular material for each layer, wherein an absorption value describes the absorptivity of a layer, the number of layers is less than or equal to the number of X-ray images and at least one layer is assumed to be a material to be recognized during the inspection, decomposing the absorption value of each layer into a path-dependent factor and an energy-dependent factor, calculating the path-dependent factors for all layers from the absorption X-ray images using the absorption equation, calculating at least one synthetic image from the sum of all layers of the product of the absorption values and the weighting factors, evaluating the synthetic image.
Owner:SMITHS HEIMANN
Iterative reconstruction of multiple-peak isotope images
ActiveUS7865005B2Accurate placementReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionIsotopeMachine learning
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
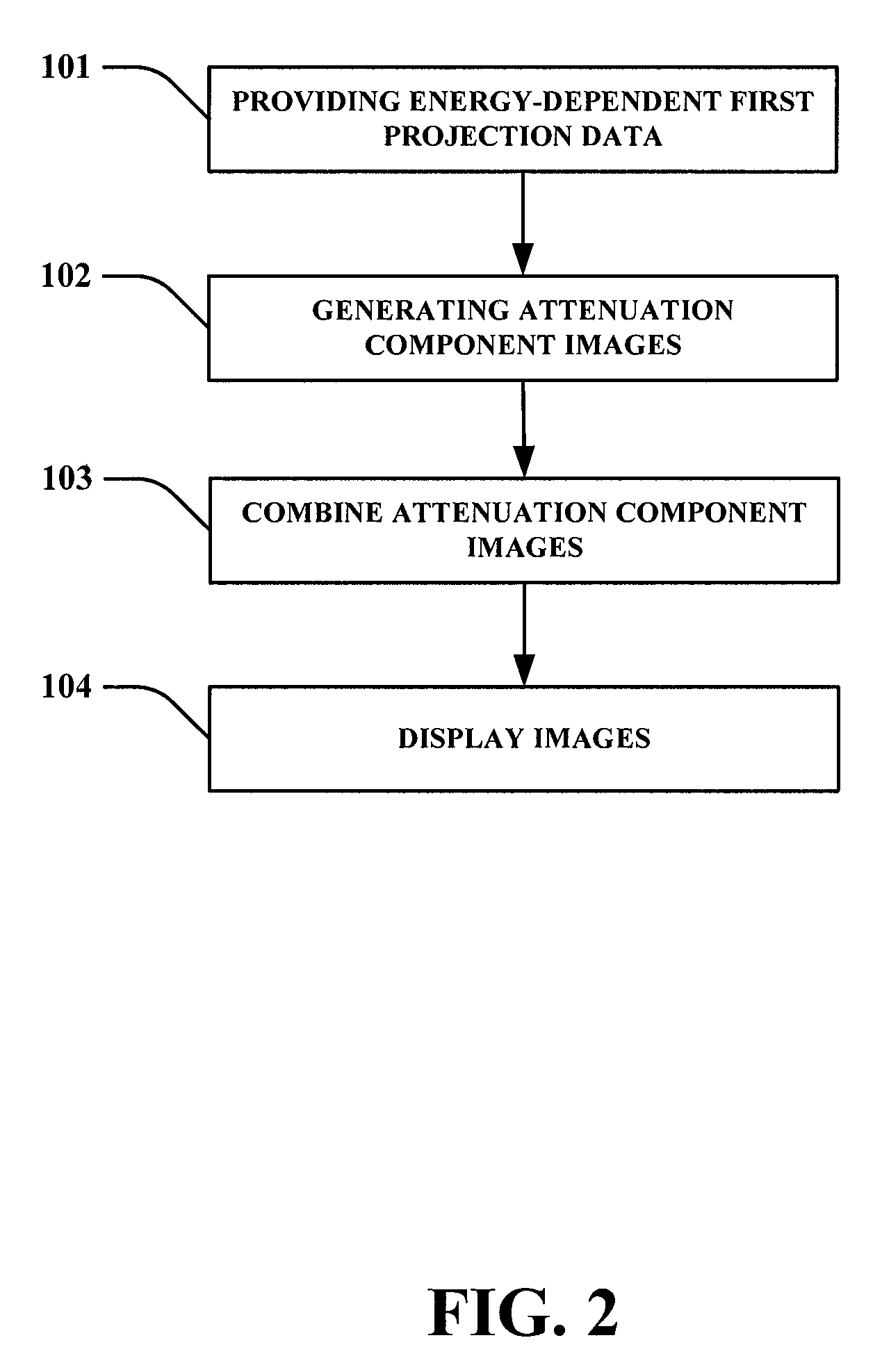
Imaging system for imaging a region of interest from energy-dependent projection data
InactiveUS20100091946A1Large signal to noise ratioReduce artifactsReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationComputer science
The invention relates to an imaging system for imaging a region of interest from energy-dependent projection data, wherein the imaging system comprises a projection data providing unit (1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8) for providing energy-dependent first projection data of the region of interest. The imaging system comprises further an attenuation component image generation unit (12) for generating attenuation component images of the region of interest by generating energy-dependent second projection data using a model in which the projection data depend on attenuation component images. The component image generation unit (12) is adapted for generating the attenuation component images such that deviations of the second projection data from the first projection data are reduced.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Differential phase contrast imaging with energy sensitive detection
ActiveCN103918005AImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionDifferential phaseComputational physics
For correcting differential phase image data 52, differential phase image data 52 acquired with radiation at different energy levels is received, wherein the differential phase image data 52 comprises pixels 60, each pixel 60 having a phase gradient value 62a, 62b, 62c for each energy level. After that an energy dependent behavior of phase gradient values 62a, 62b, 62c of a pixel 60 is determined and a corrected phase gradient value 68 for the pixel 60 is determined from the phase gradient values 62a, 62b, 62c of the pixel 60 and a model for the energy dependence of the phase gradient values 62a, 62b, 62c.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
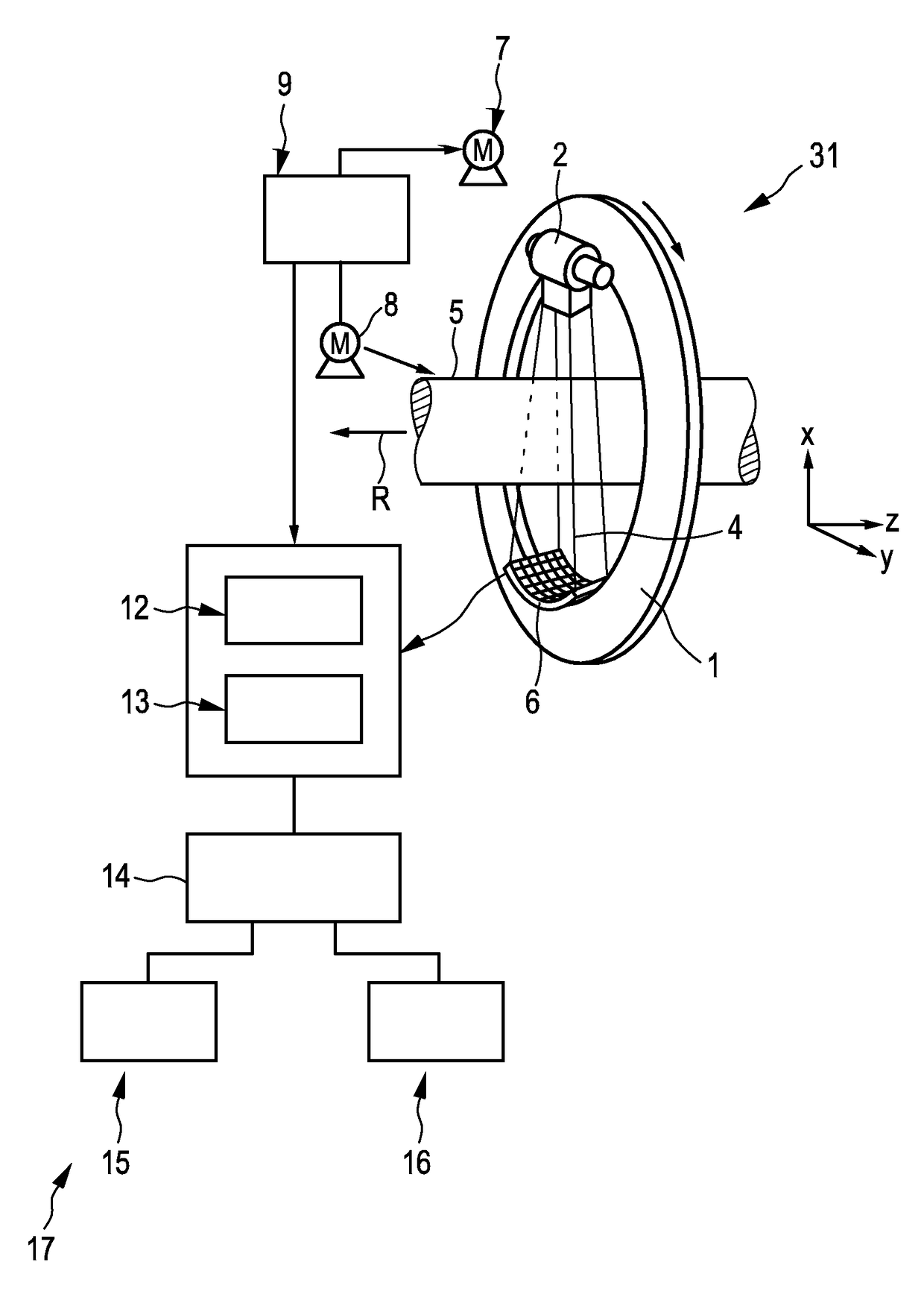
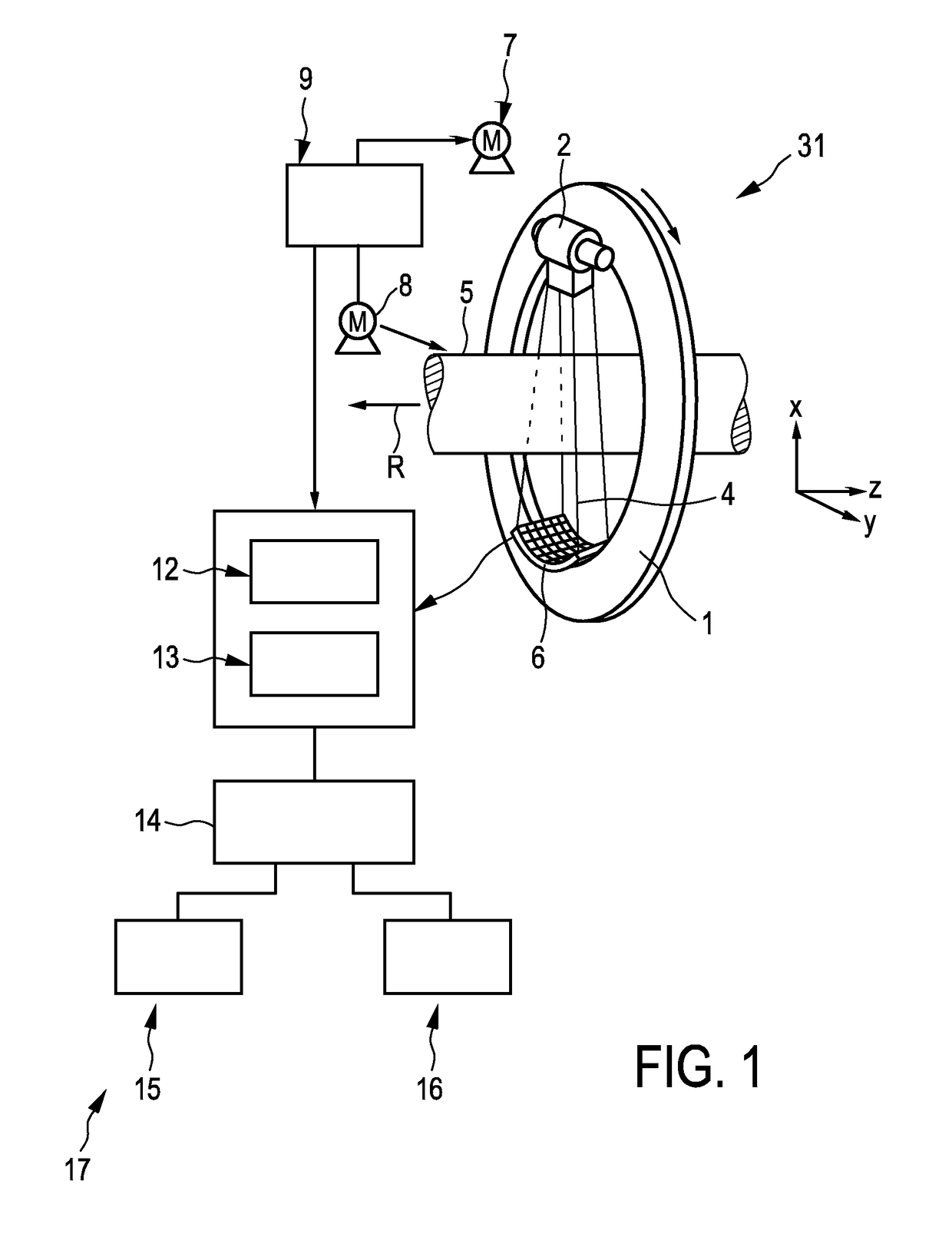
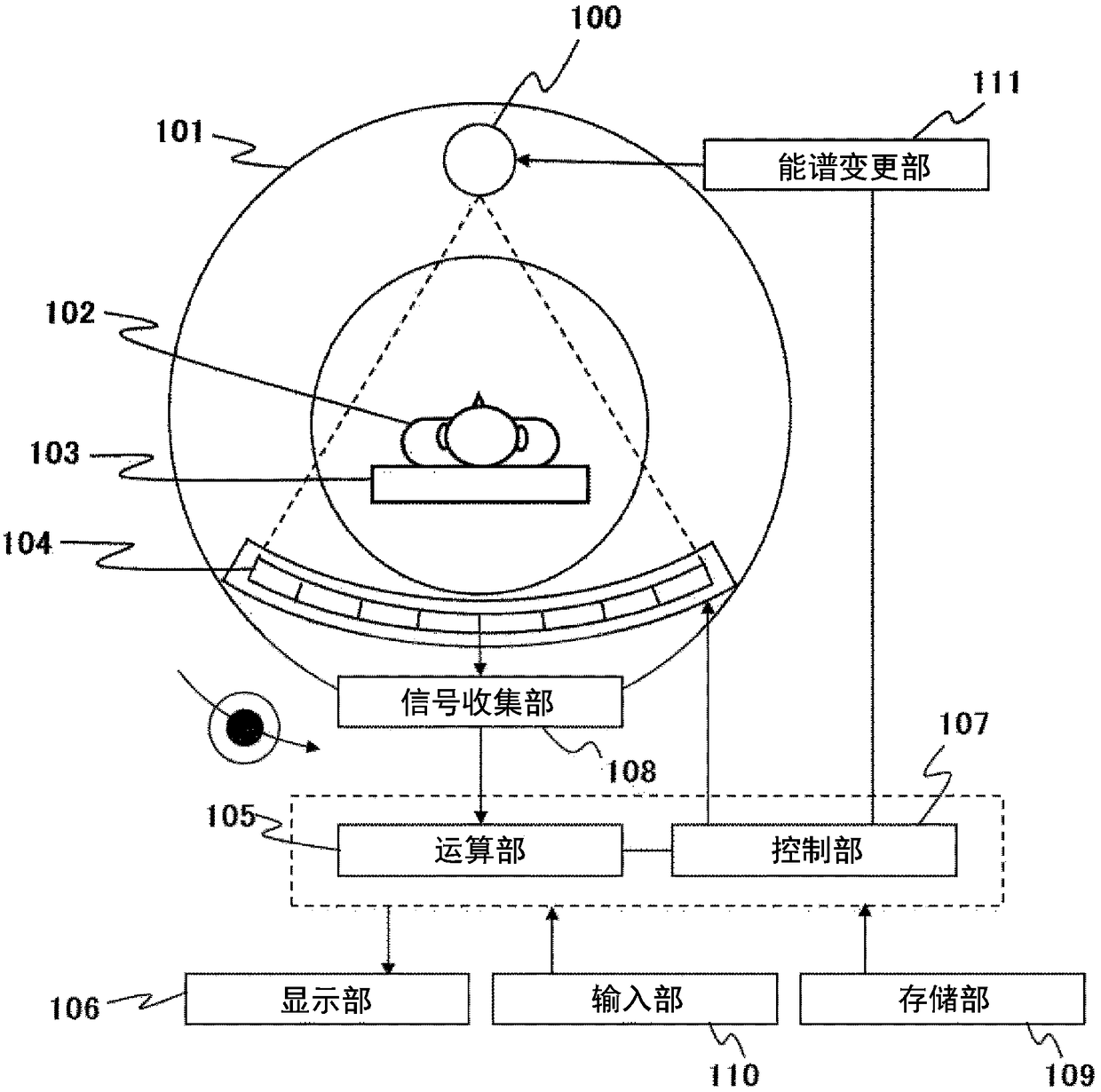
System for generating spectral computed tomography projection data
ActiveUS9833202B2Quality improvementImprove image qualityRadiation diagnostic image/data processingComputerised tomographsSpectral projectionComputing tomography
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Multiple layer charge-coupled photovoltaic device
ActiveUS20150303341A1Increase powerImprove efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesTrappingPhotonics
A structure composed of multiple layers that consist of 7 stages of photon and electron management, enhancement, and conversion for the purposes of photovoltaic applications is described. The invention consists of one or more layers comprised of: 1) an energy dependent up and down conversion layer optimized for a particular wavelength such as infrared; 2) a layer for multiple implementations of light capturing and trapping; 3) a layer for photonic and plasmonic enhancement of captured and trapped light; 4) a layer for converting photons to electrons; 5) a layer for multiplying electrons; 6) a layer for storing generated electrons; and 7) a layer for using electrons for power. One or more layers may serve simultaneous purposes.
Owner:ALLEN AARON RICHARD
Volume calibration phantom and calibration method thereof
A volume calibration phantom comprises a container; a plurality of plates stacking up inside the container; and at least one slab of radioactive source, each of which is disposed between the adjacent plates and comprises a plurality of radionuclides. With the volume calibration phantoms, the present invention further provides a calibration method which is an improvement over conventional calibration methods of space geometric center point source and relative penetration factor ratios. The method comprises the steps of generating a calibration curve of density vs. counting efficiency corresponding to the several different volume calibration phantoms; calculating the density of a radioactive waste specimen to obtain a corresponding radioactive activity according to the calibration curve, and then revising the corresponding radioactive activity according to the energy dependency and equation of gamma gross radioactivity for multiple radionuclides so as to obtain the correct gamma gross radioactivity of the radioactive waste specimen.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Method and x-ray system for generating a phase contrast image
InactiveCN104427938ADetermine Absorption BehaviorMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHealth-index calculationSoft x rayUltrasound attenuation
A method and an X-ray system are disclosed for generating a phase contrast image of an examination object. In an embodiment, the distribution of an electron density in the examination object is determined by defining energy-dependent attenuation values for X-radiation with at least two different X-ray energy spectra, phase-shift values are obtained from the previously determined electron density distribution, and a phase contrast image is generated from the calculated phase-shift values.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
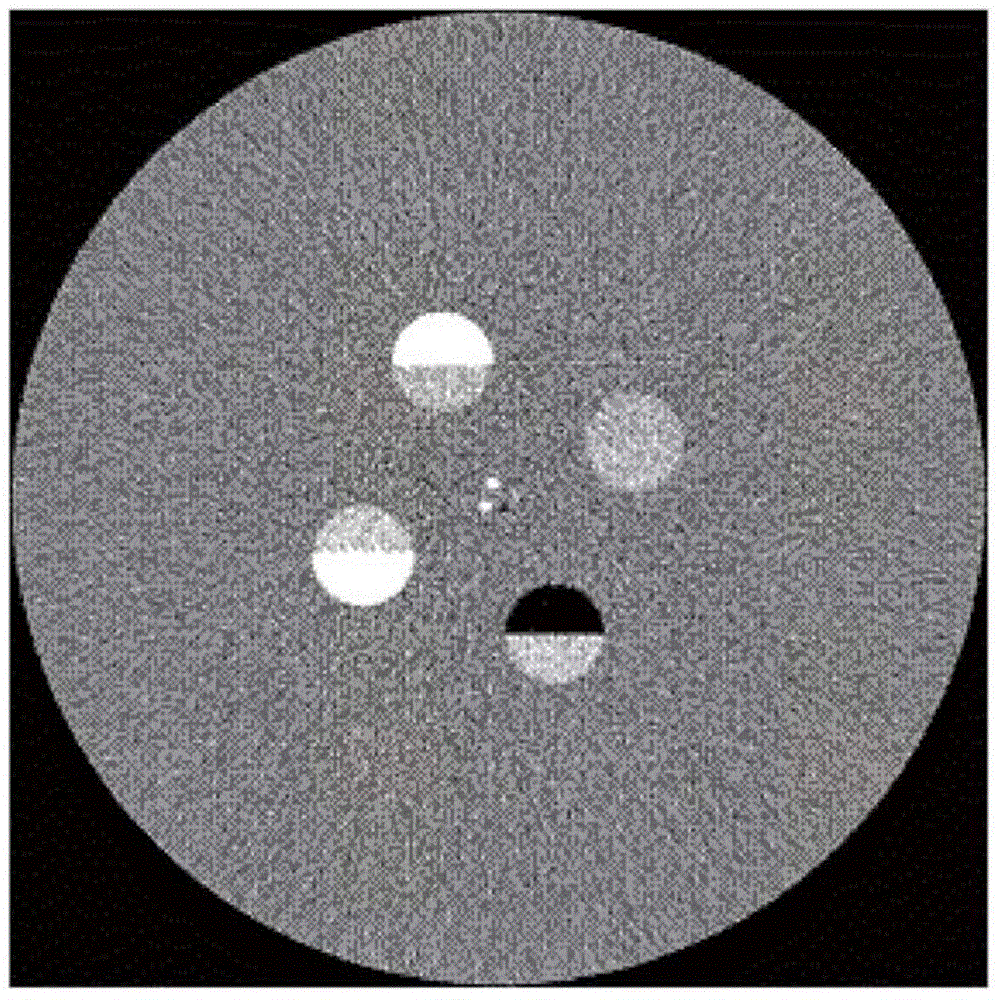
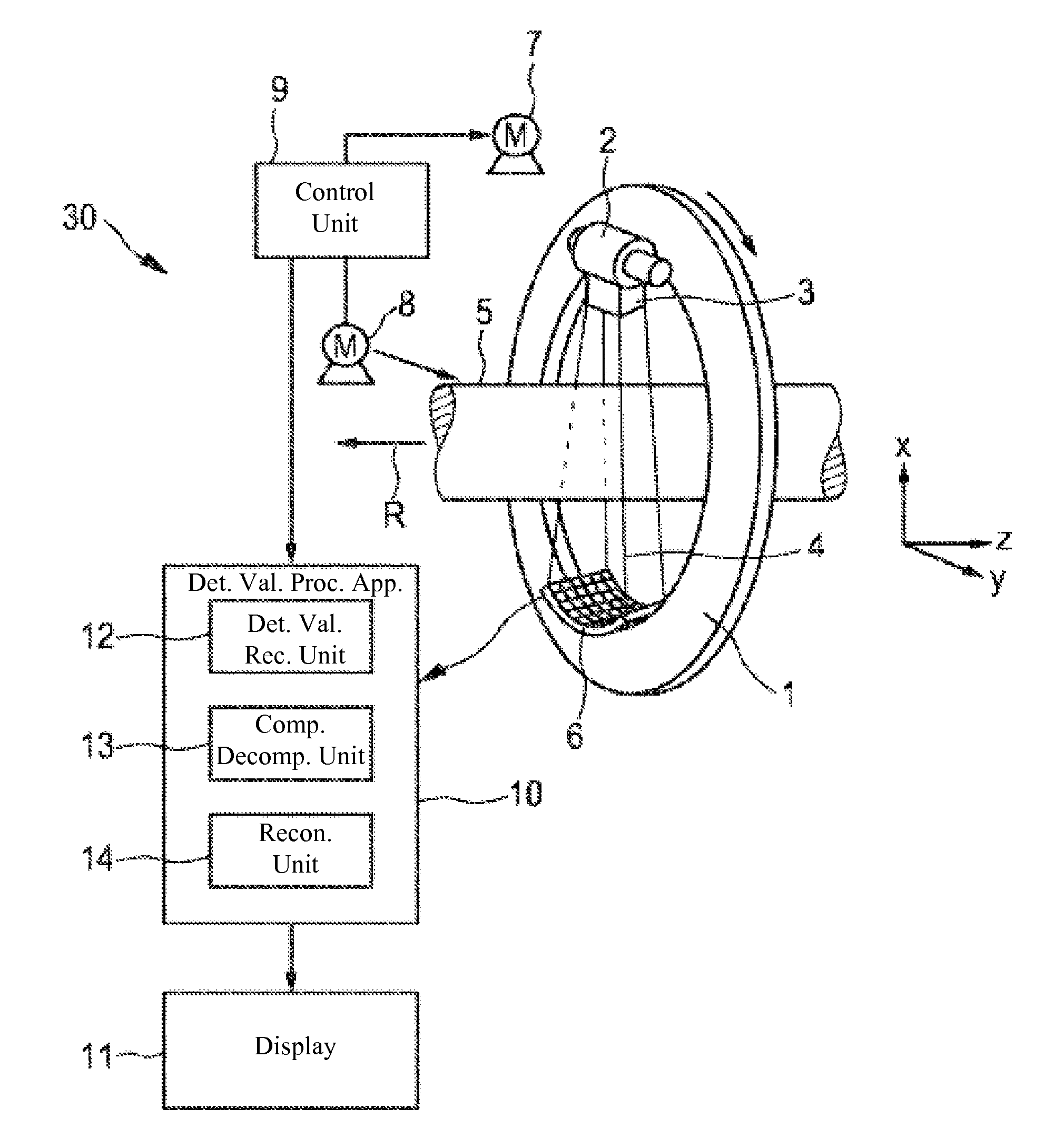
Detection values processing apparatus
ActiveUS9316601B2Quality improvementReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasound attenuationDecomposition
The invention relates to a detection values processing apparatus. Energy-dependent detection values are provided, which are indicative of polychromatic radiation (4) after having traversed an examination zone (5). The radiation is filtered by a filter (15) which comprises K-edge filter material. A component decomposition technique is applied to the detection values for determining K-edge attenuation values being first component attenuation values, which are indicative of an attenuation caused by the K-edge filter material, and additional component attenuation values, which are indicative of an attenuation caused by additional components of the examination zone, wherein an image of the examination zone is reconstructed from the additional component attenuation values. An image can therefore be reconstructed, which is not adversely affected by the filter, because the K-edge attenuation values are not used for reconstructing the image. This can improve the quality of the reconstructed image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Eyi chusystem for generating spectral computed tomography projection data
ActiveCN105939667ARadiation diagnostic image/data processingComputerised tomographsSpectral projectionComputing tomography
The invention relates to a system (31) for generating spectral computed tomography projection data. A spectral projection data generation device (6) comprising an energy-resolving detector generates spectral computed tomography projection databased on polychromatic radiation (4), which has been provided by a radiation device (2), after having traversed an examination zone (5), and a reference values generation device generates energy-dependent reference values based on radiation, which has not traversed the examination zone. A spectral parameter providing unit (12) provides a spectral parameter being indicative of a spectral property of the radiation device based on the energy-dependent reference values. In particular, spectral properties of the radiation device can be monitored over time, wherein this information can be used for, for instance, correcting the spectral computed tomography projection data, and / or, if undesired spectral properties of the radiation device are indicated, triggering a replacement of the radiation device.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
X-ray ct data processing device and x-ray ct device comprising same
ActiveCN108135560AEasy to quantifyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionX-rayEnergy dependent
The purpose of the present invention is, when carrying out multi-energy photography with an energy-separation detector and creating an image in which a subject is separated into a plurality of standard substances, to estimate the appropriateness of posited standard substances and determine with good precision that appropriate standard substances are present in said subject. An X-ray CT data processing device, which processes CT data which is acquired in each of a plurality of detected energy ranges and creates a reconstructed image which is separated into prescribed standard substances, comprises: a standard substance data computation unit which, using different combinations of a plurality of instances of the CT data, computes, for each of a plurality of standard substances, physical quantities which are not energy-dependent, creating a plurality of instances of standard substance data for the same standard substance; and an appropriateness determination index creation unit which, on the basis of the plurality of instances of standard substance data which the standard substance data computation unit has computed, creates an index for determining the appropriateness of the standardsubstance.
Owner:HITACHI HEALTHCARE MFG LTD
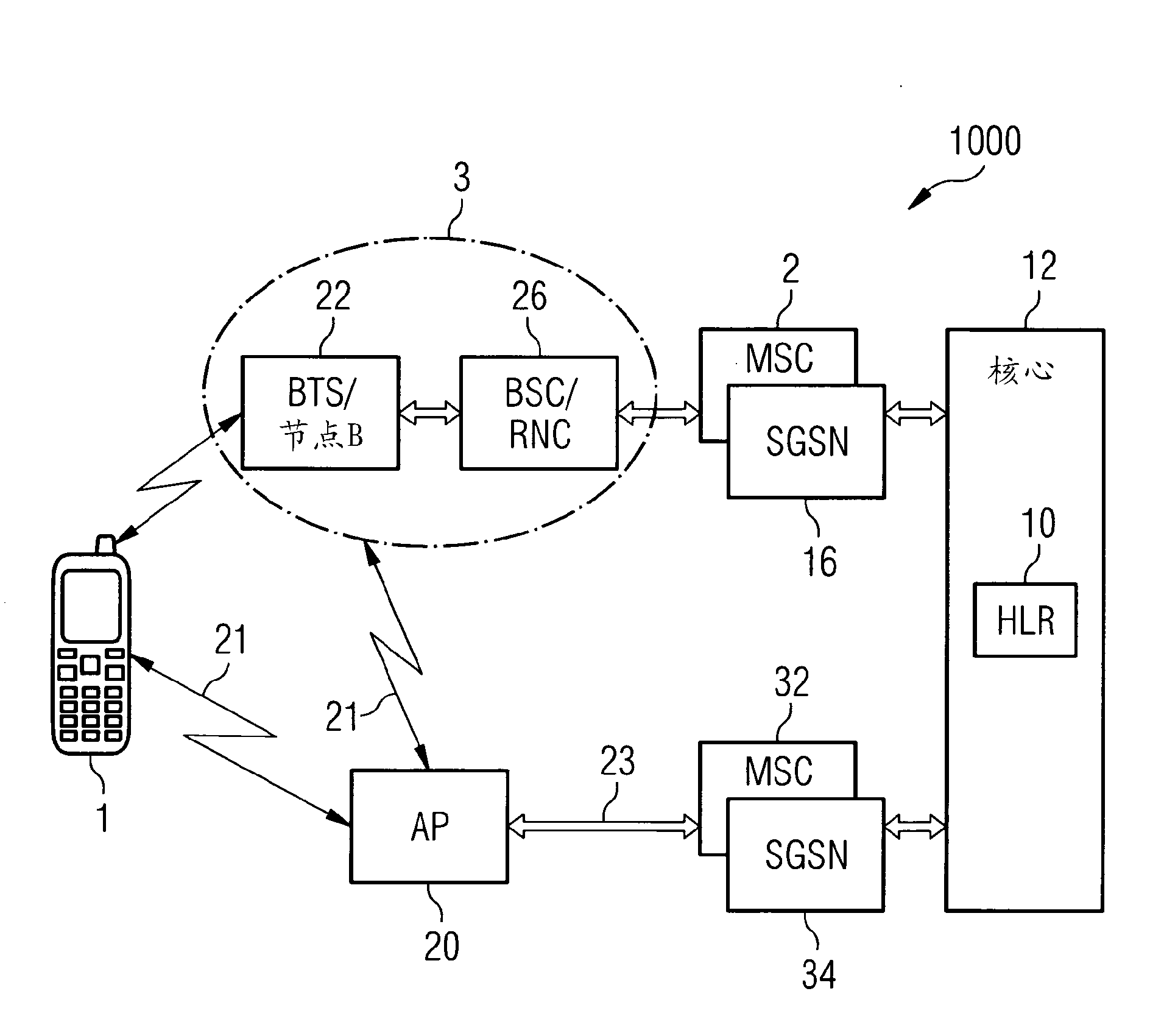
Method and network device for managing resource allocation
InactiveCN102396258APower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications networkResource allocation
A method and network device for managing resource allocation in at least one network device (3, 20) of a plurality of network devices in a mobile telecommunications network (1000) comprising the steps of: - determining at least one energy dependent parameter in relation to each of the at least one network devices; and - using the at least one determined energy-dependent parameter to make a resource allocation determination.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com