Patents
Literature
955 results about "X ray irradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
X-ray irradiation. Renewable, non-isotope, ionizing radiation and radiotherapy. X-ray irradiators are becoming a widely used tool in small animal research as they represent a direct replacement or alternative to traditional gamma irradiators.
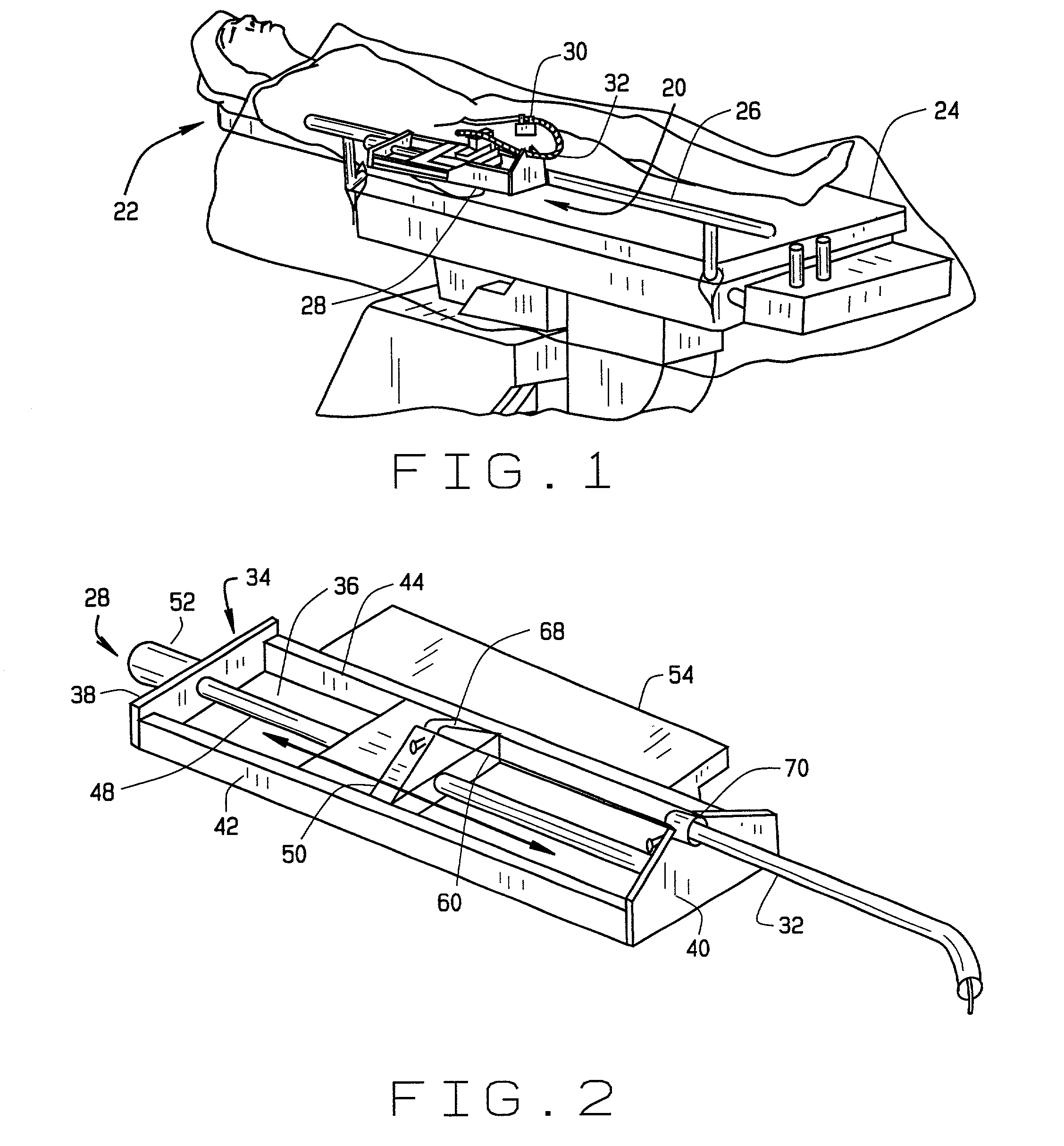
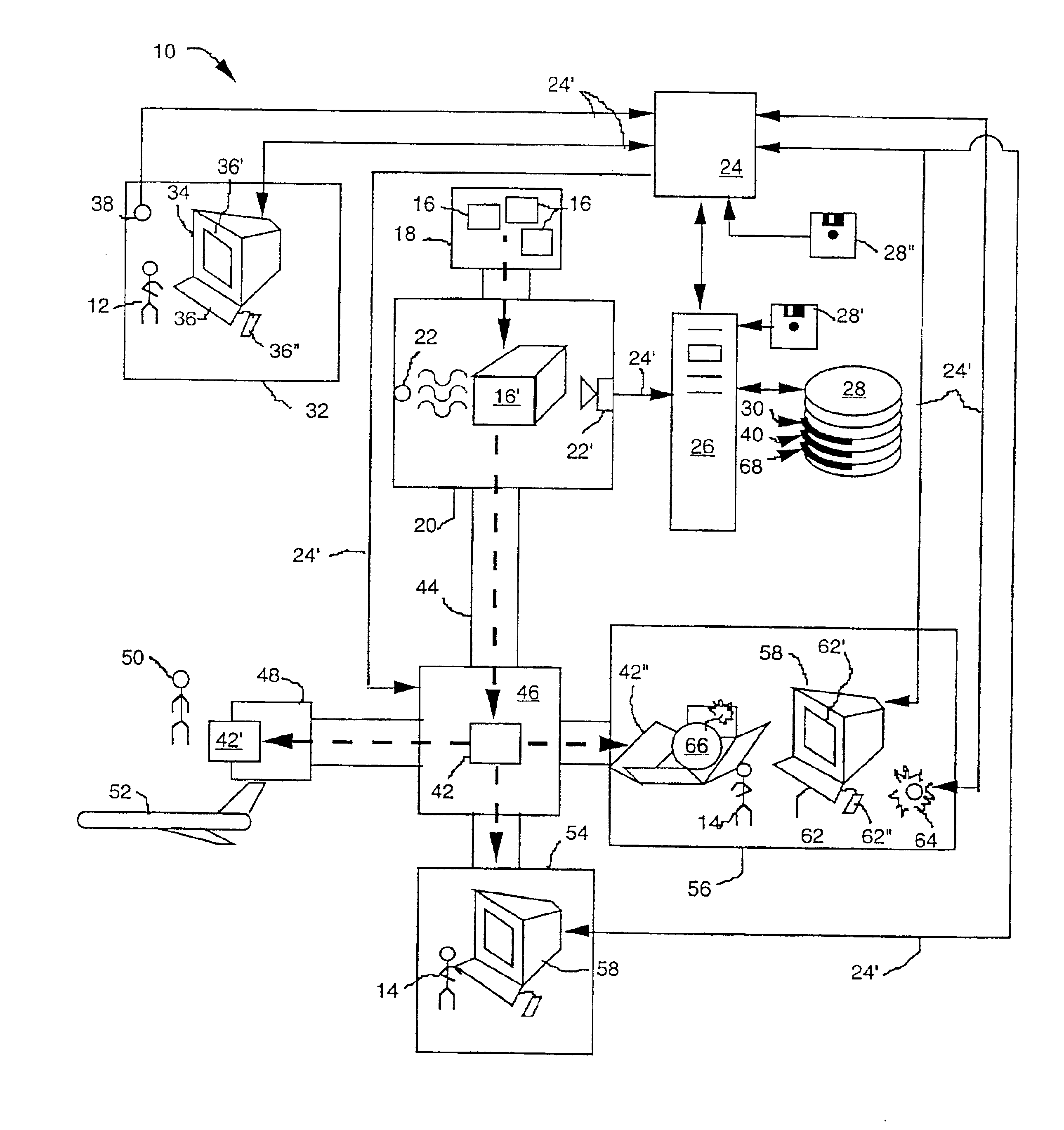
System and methods for advancing a catheter
InactiveUS7276044B2Reduce repeated x-ray exposureReduce X-ray exposureEar treatmentSurgical needlesControl systemEngineering
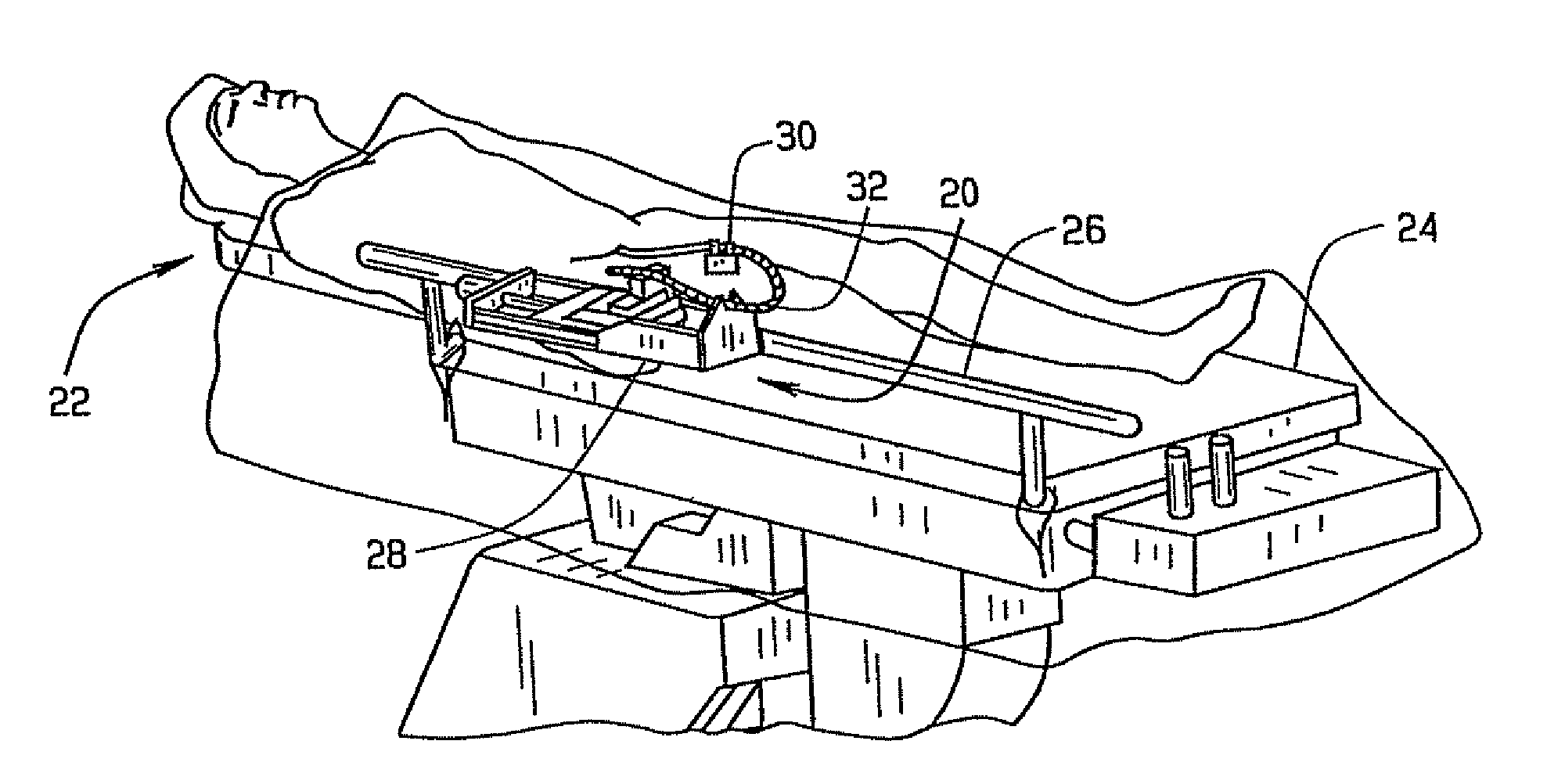
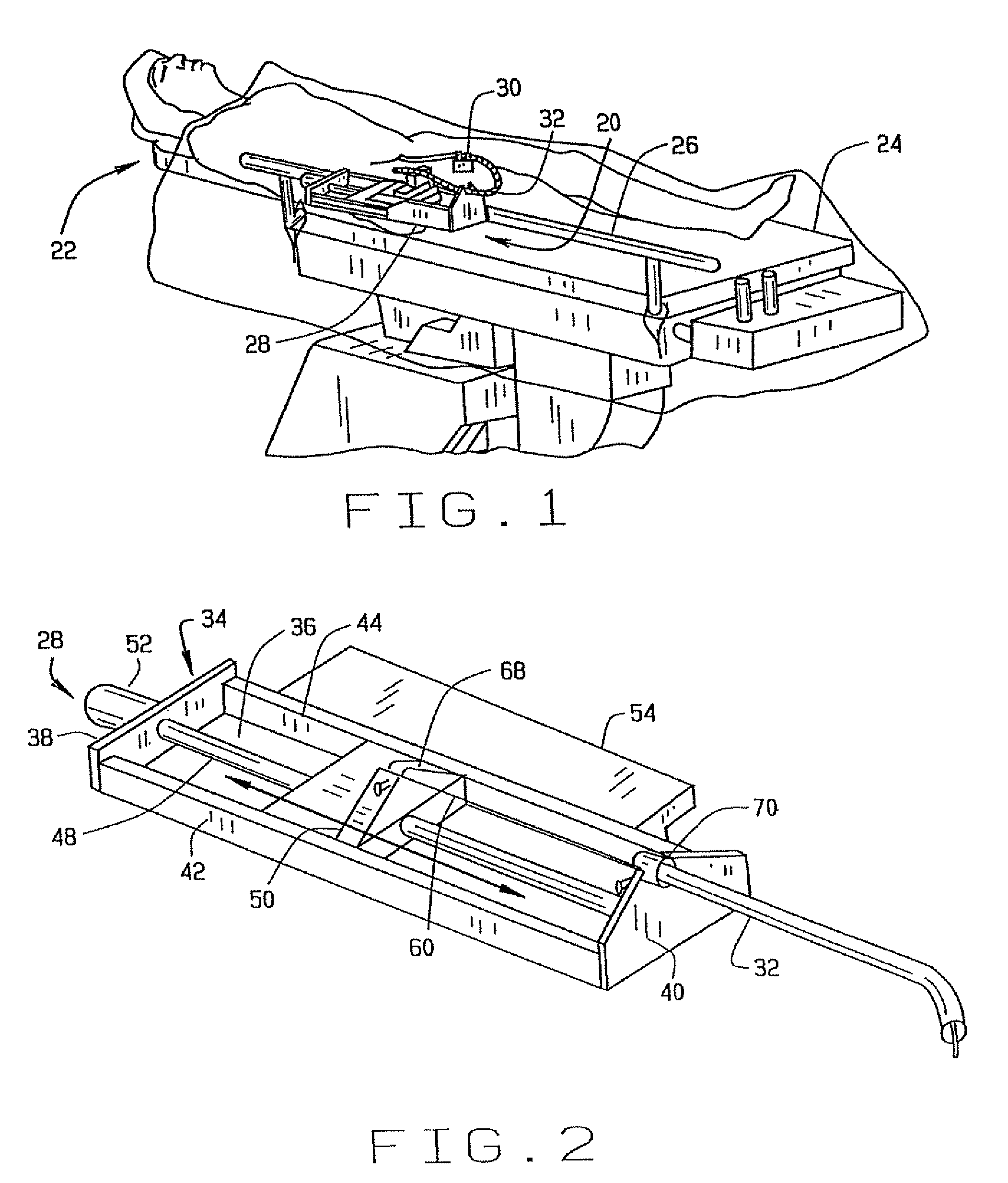
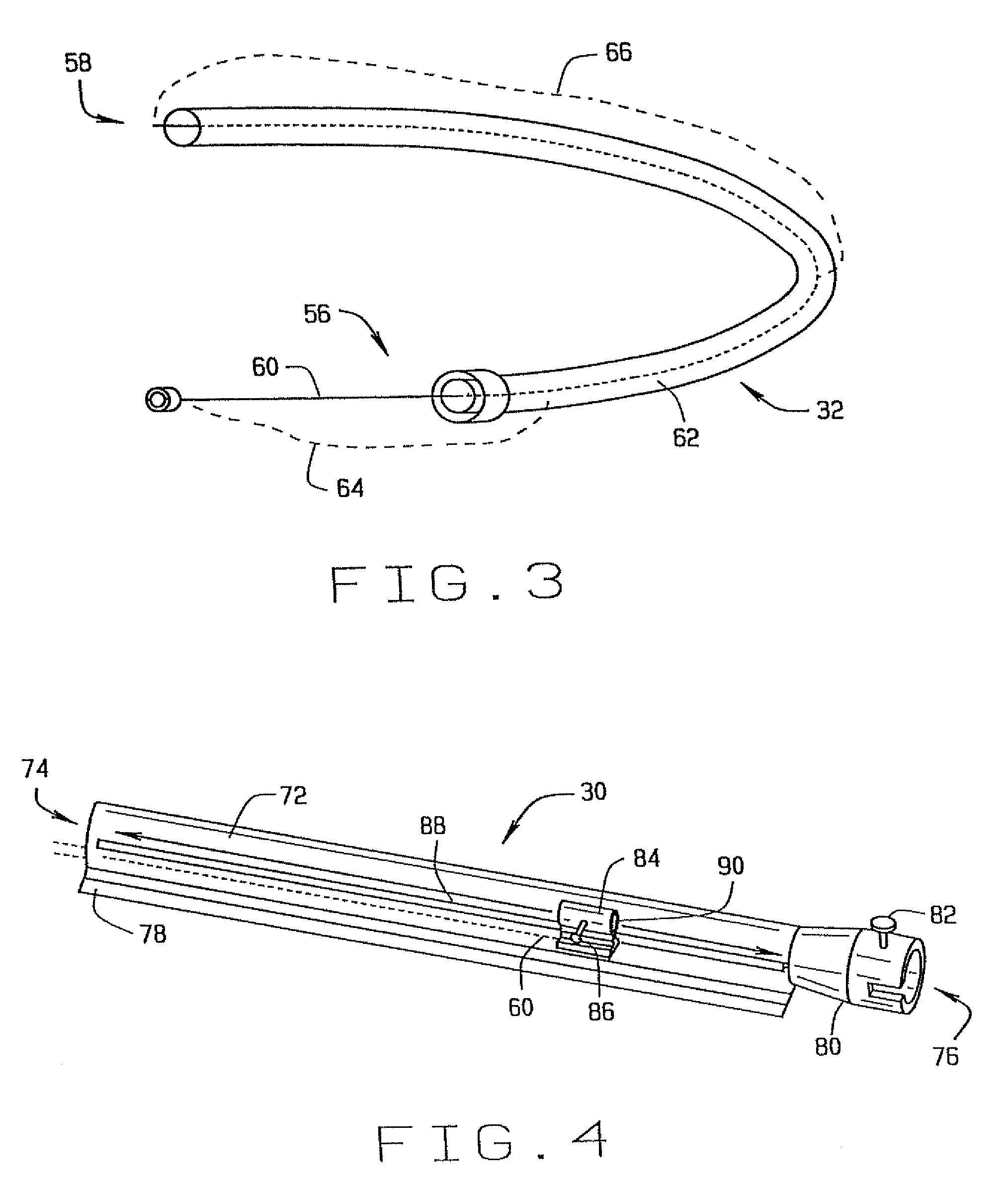
An advancer system is described for moving an elongate medical device within a body. The system includes a drive unit having a motor. The drive unit is configured to translate movement of the motor to the device so as to alternately advance and retract the device relative to the body. The advancer system also includes a user-operable control system configured to control the drive unit. The control system can interface with a magnetic navigation system. The above-described system allows an operating physician to control catheter advancement and retraction while remaining outside an x-ray imaging field. Thus the physician is freed from repeated x-ray exposure.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
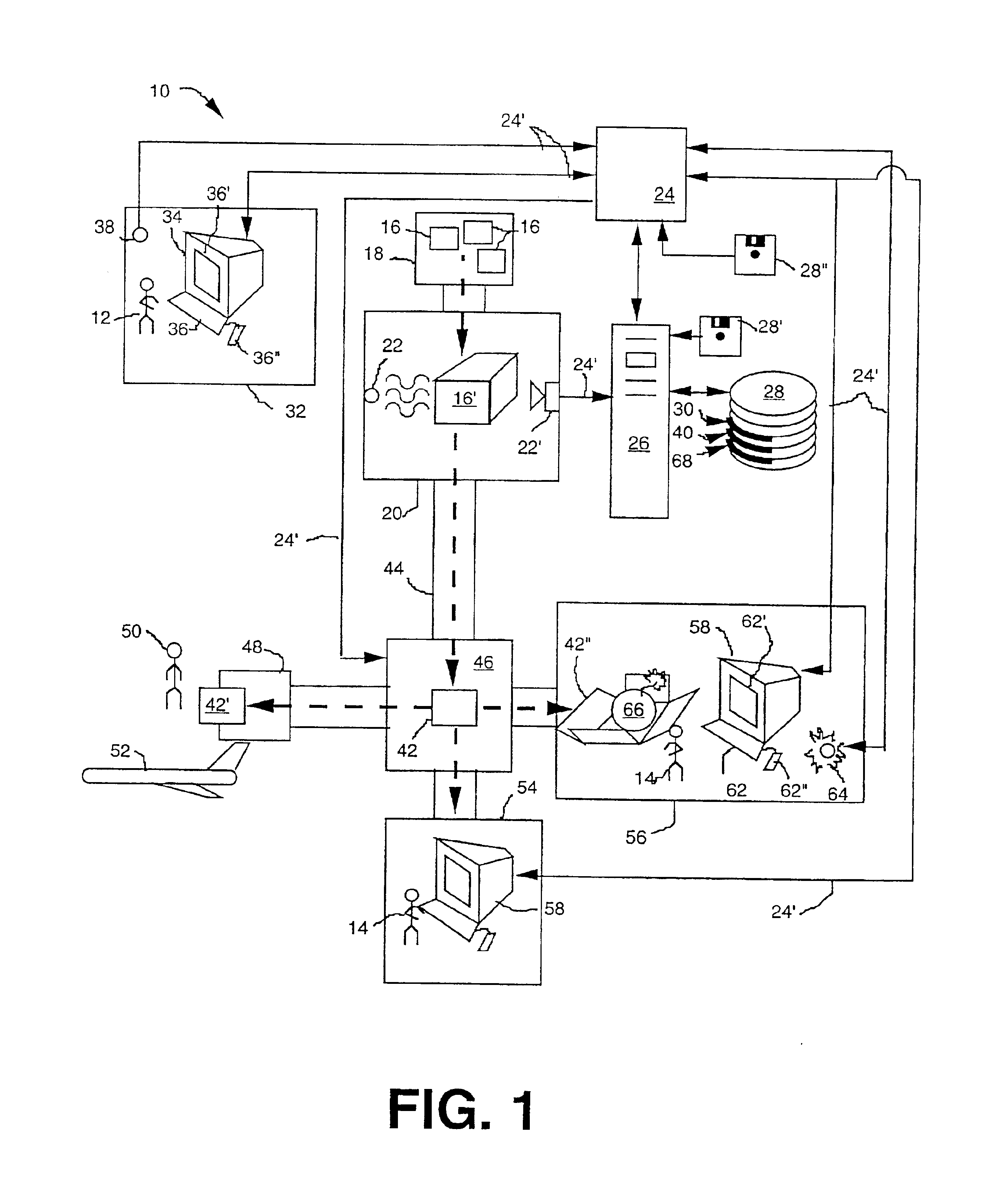
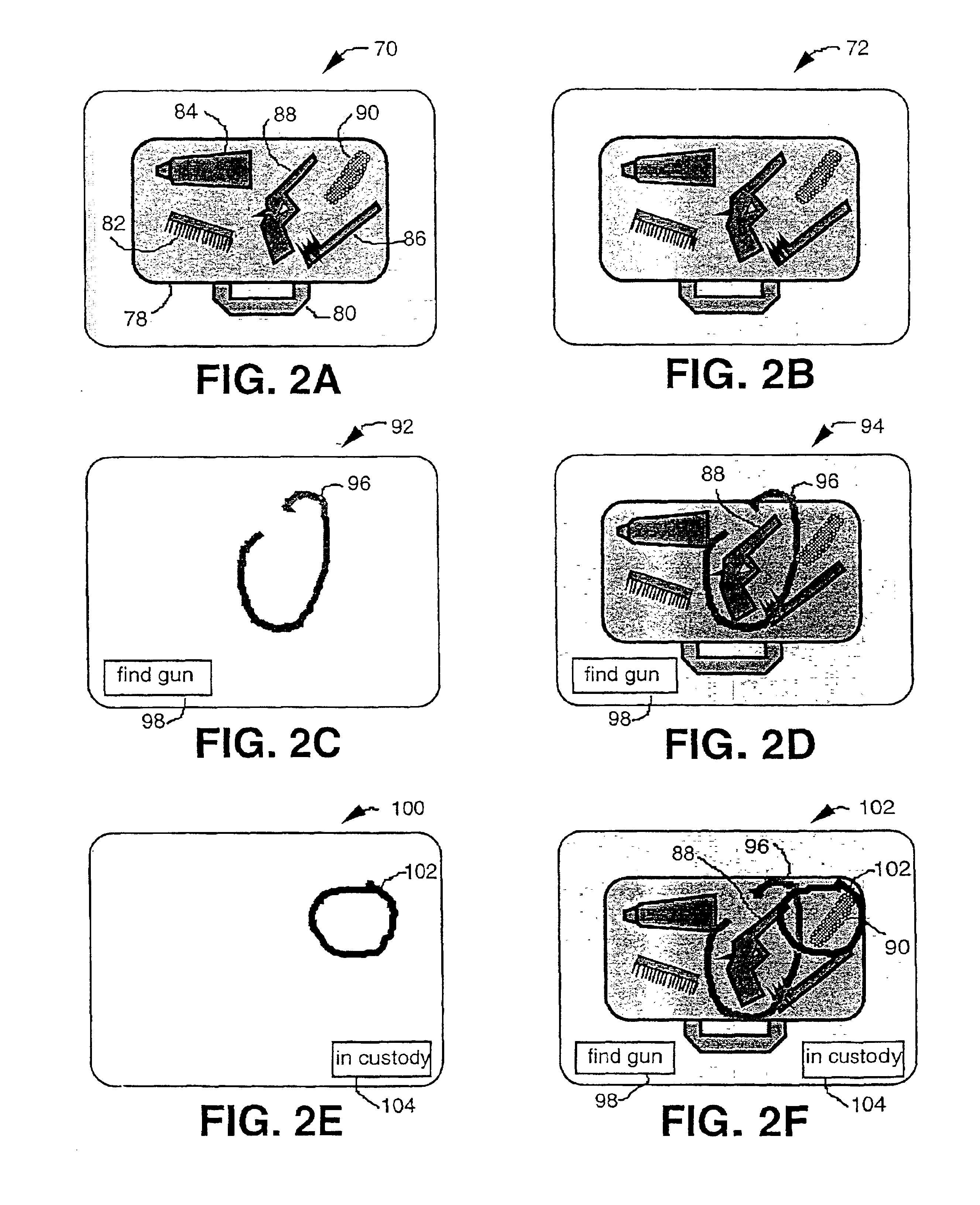
Generation and distribution of annotation overlays of digital X-ray images for security systems
InactiveUS6839403B1Material analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionX-rayData treatment
An image display storage and retrieval system provides a mechanism to transmit x-ray images of parcels to one or more remote workstations. The images may be annotated at these workstations to specifically identify articles to be targeted for more thorough investigation. The image display storage and retrieval system comprises an x-ray image source to illuminate a parcel with x-rays, scan the received x-ray pattern produced from the x-rays passing through the parcel, and digitize the x-ray image of the parcel, an initial screening station where images are initially received and may be annotated, an inspection station where the images (with or without annotation) and parcels to be inspected are received, an optional parcel path switch to direct parcels to either a clearance station or an inspection station, a data storage and retrieval device to record and retrieve images, a data processor to receive the images and a data network connecting the initial screening station, the inspection station, the optional path switch, the data storage and retrieval device and the data processor so as to enable the exchange of data.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
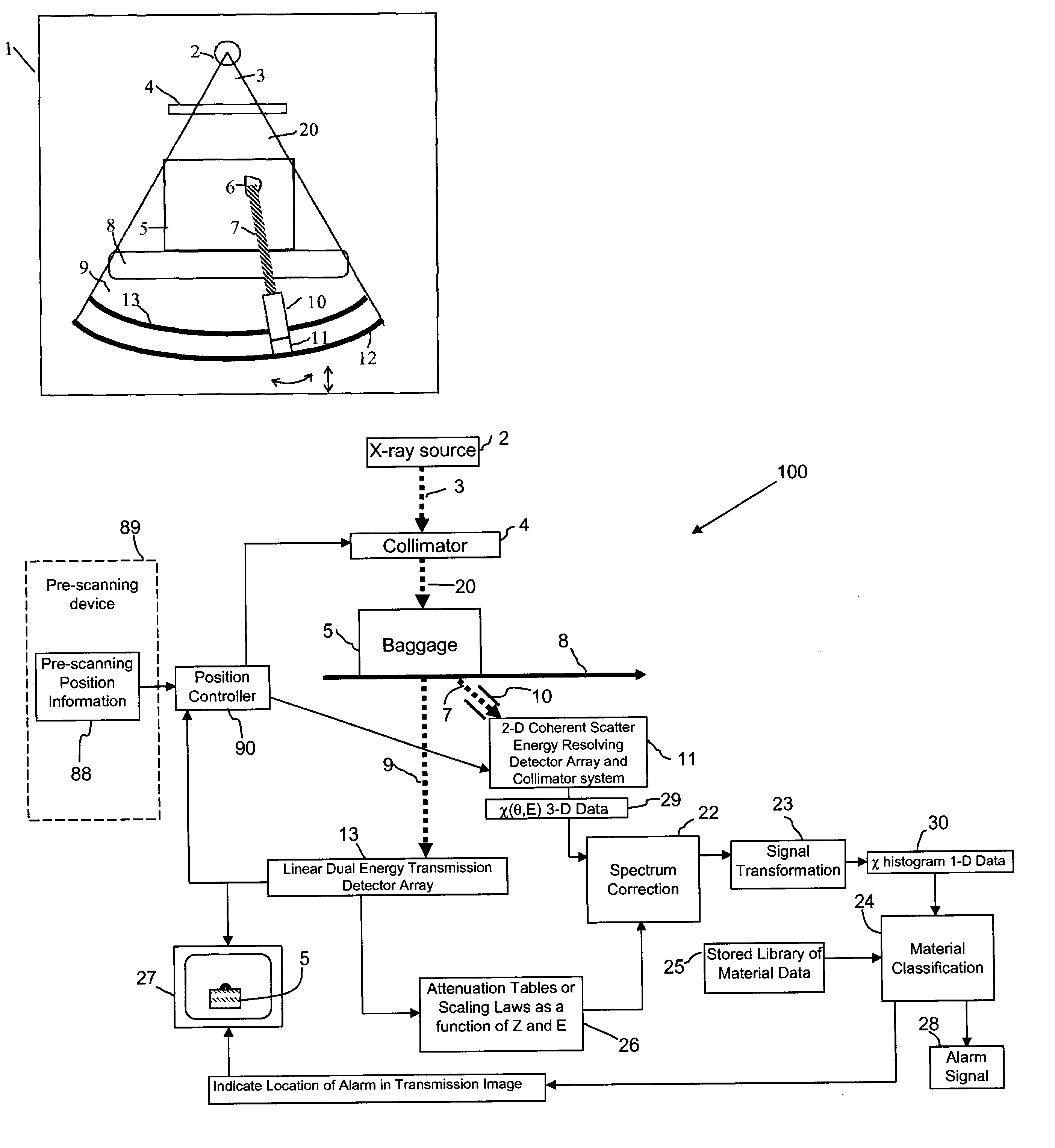
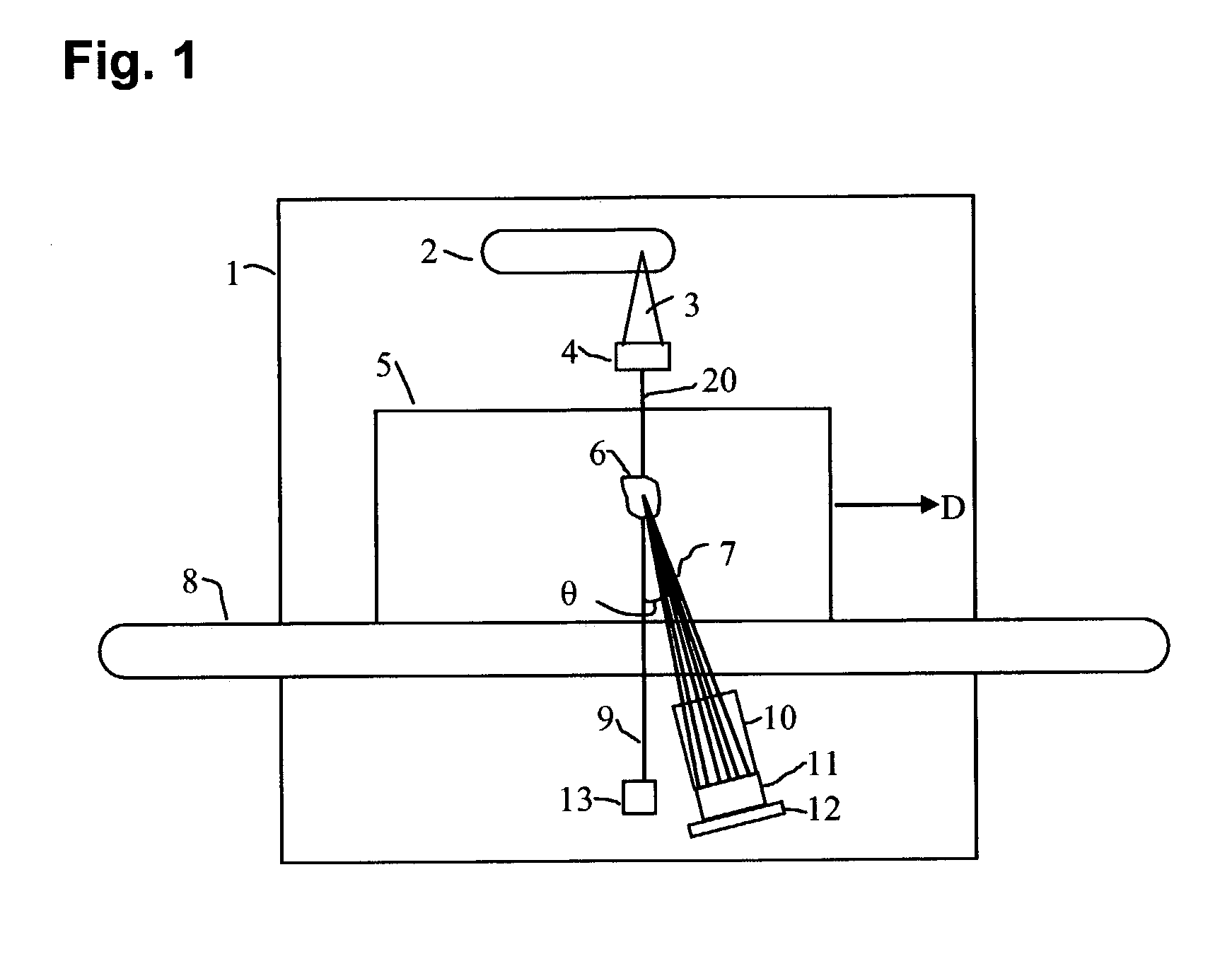
X-ray inspection system for detecting explosives and other contraband
InactiveUS7092485B2Rapidly and accurately discriminates among different substancesQuick checkUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayExplosive material
A baggage scanning system and method employ combined angular and energy dispersive x-ray scanning to detect the presence of a contraband substance within an interrogation volume of a baggage item. The interrogation volume is illuminated with penetrating, polychromatic x-rays in a primary fan beam from a source such as a tungsten-anode x-ray tube. An energy-dependent absorption correction is determined from measurement of the attenuation of the fan beam at a plurality of different energies. Radiation coherently scattered by substances in the interrogation volume is detected by an energy-resolved x-ray detector operated at a plurality of scattering angles to form a plurality of scattering spectra. Each scattering spectrum is corrected for energy-dependent absorption and the corrected spectra are combined to produce a scattering pattern. The experimental scattering pattern is compared with reference patterns that uniquely characterize known contraband substances. The system and method can locate and identify a wide variety of contraband substances in an accurate, reliable manner. The system provides for automated screening, with the result that vagaries of human performance are virtually eliminated. False alarms and the need for hand inspection are reduced and detection efficacy is increased.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
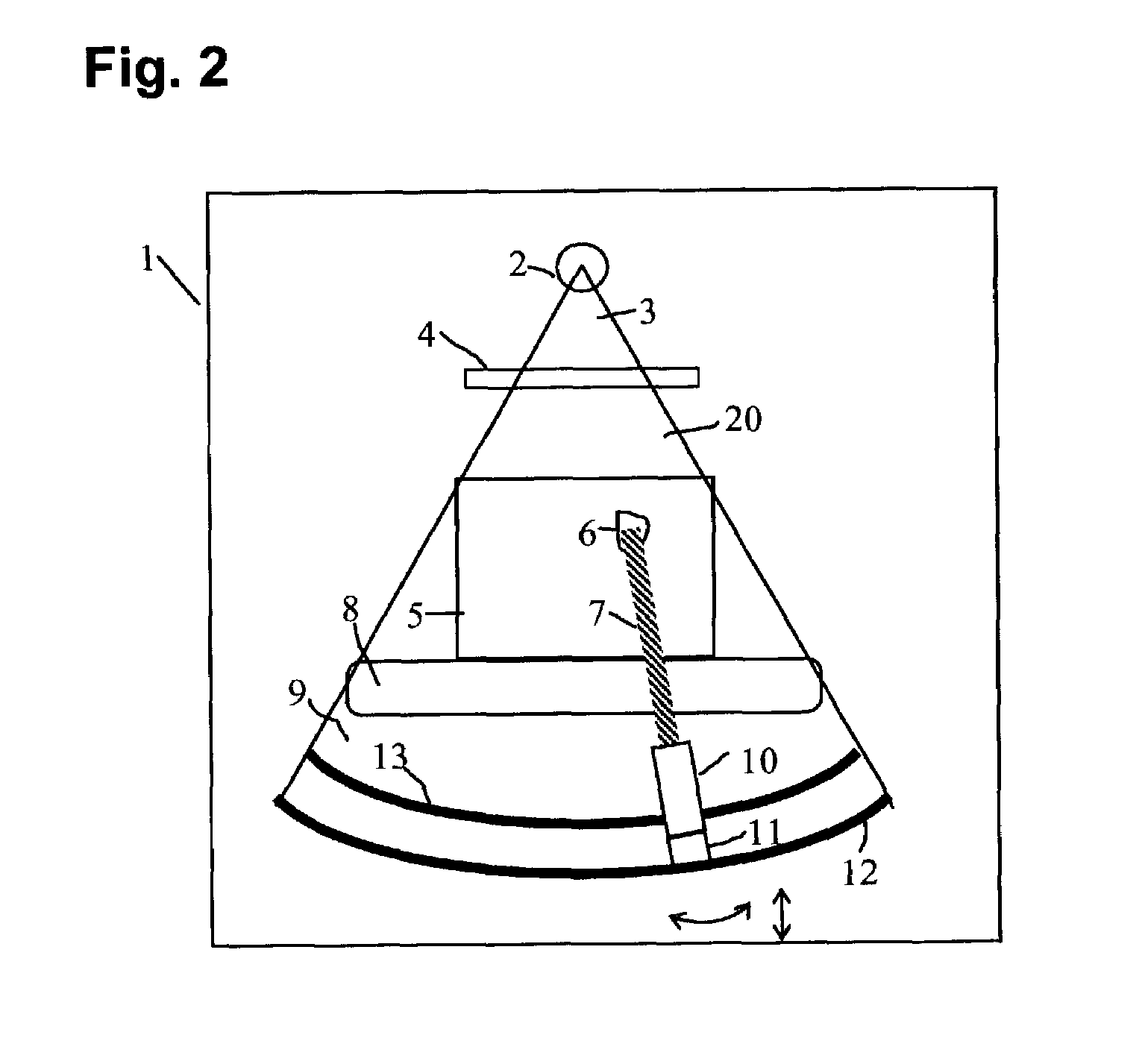
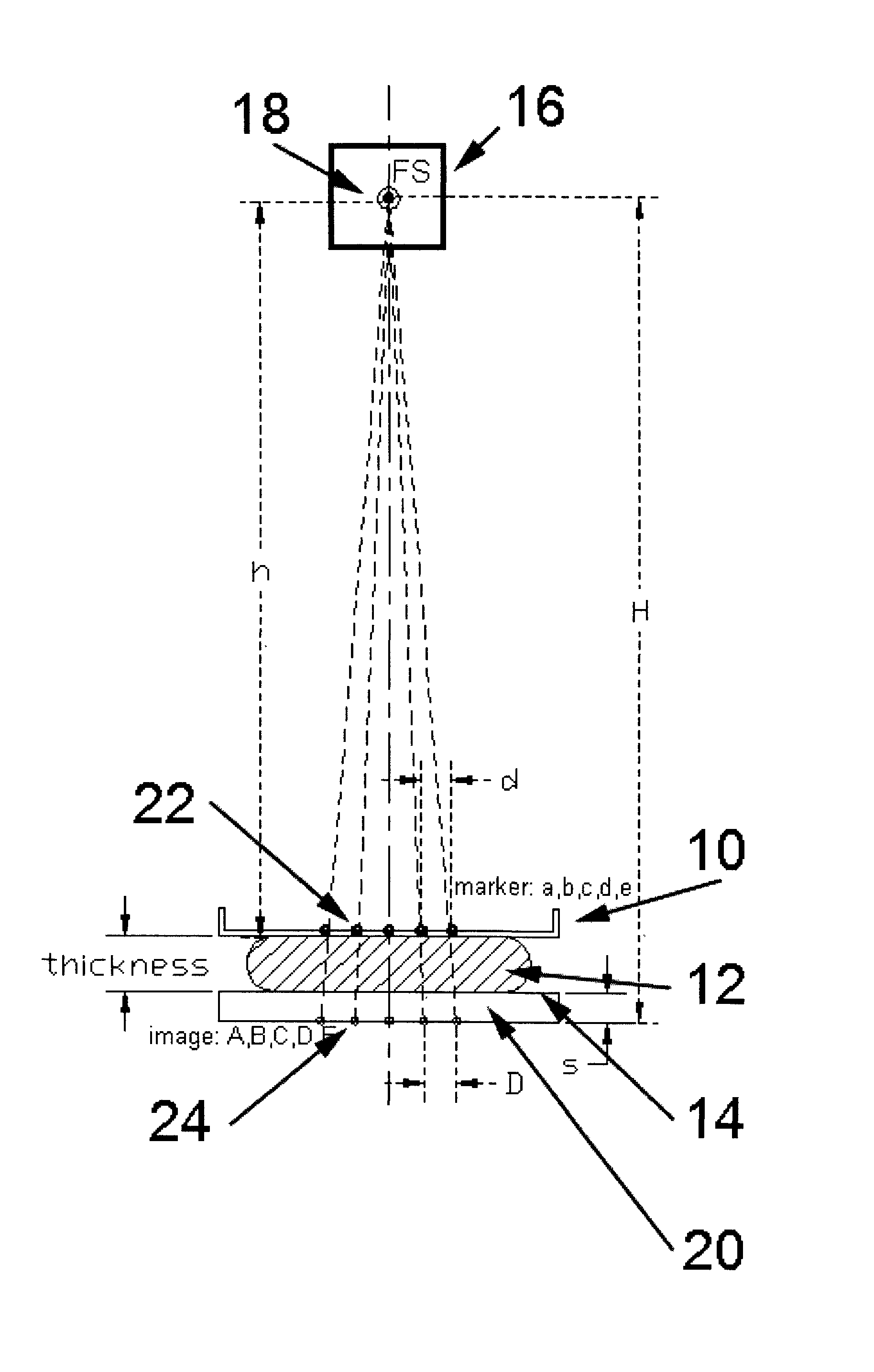
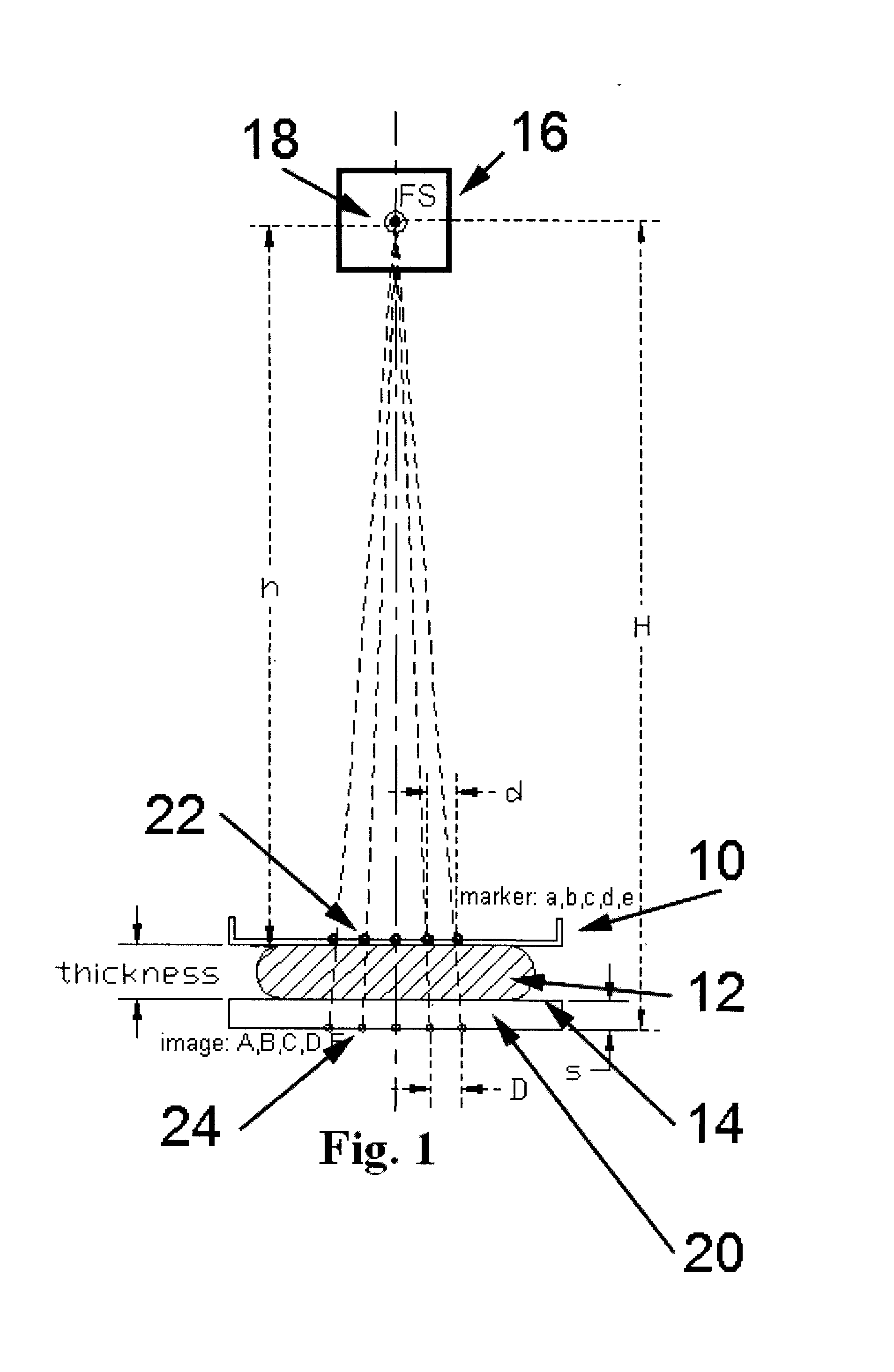
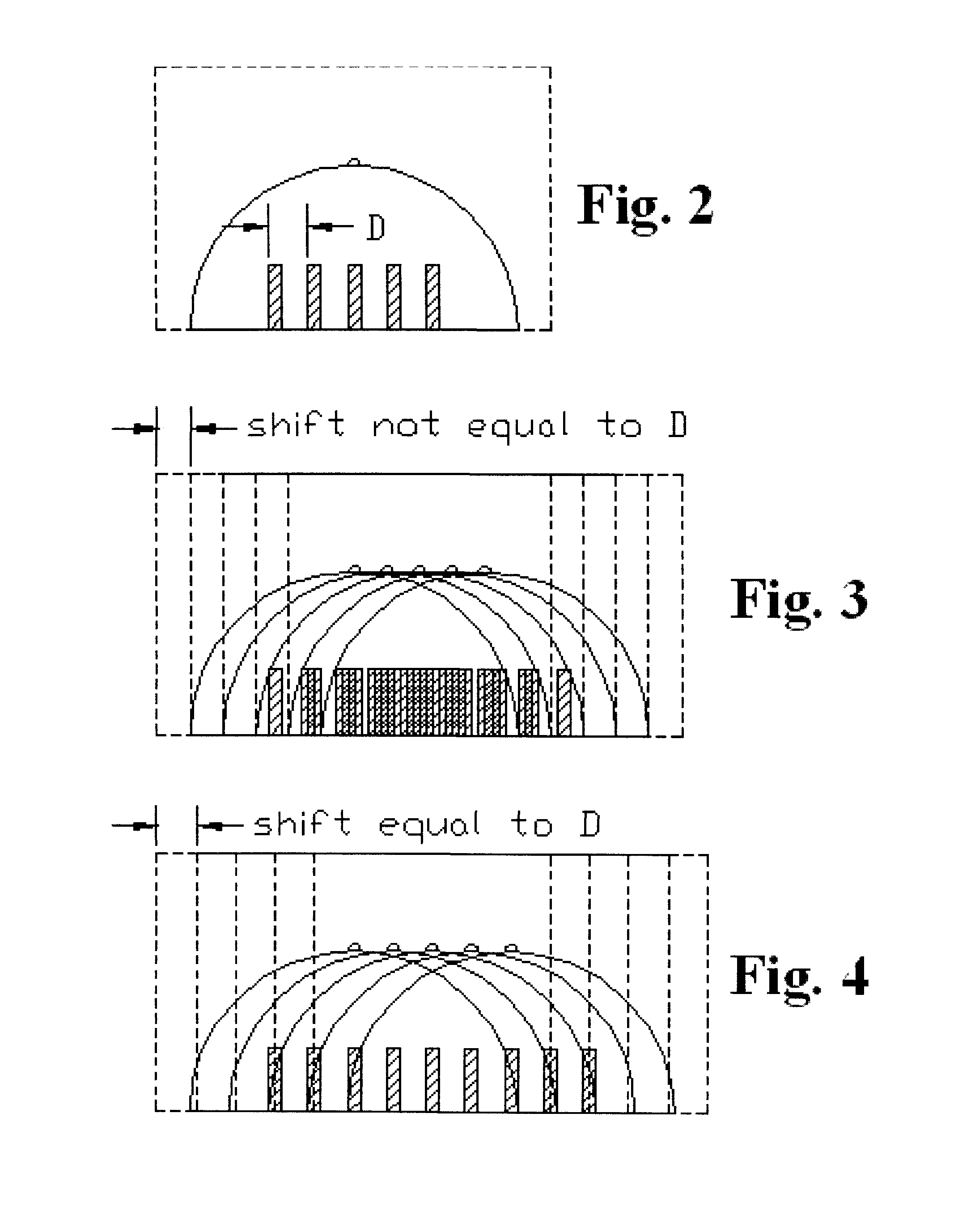
X-ray imaging with X-ray markers that provide adjunct information but preserve image quality
ActiveUS20090268865A1Enhance the imageIncrease distancePatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringTomosynthesisSoft x ray
A method and an apparatus for estimating a geometric thickness of a breast in mammography / tomosynthesis or in other x-ray procedures, by imaging markers that are in the path of x-rays passing through the imaged object. The markings can be selected to be visible or to be invisible when the composite markings / breast image is viewed in clinical settings. If desired, the contribution of the markers to the image can be removed through further processing. The resulting information can be used determining the geometric thickness of the body being x-rayed and thus setting imaging parameters that are thickness-related, and for other purposes. The method and apparatus also have application in other types of x-ray imaging.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Method for surgical navigation utilizing scale-invariant registration between a navigation system and a localization system
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
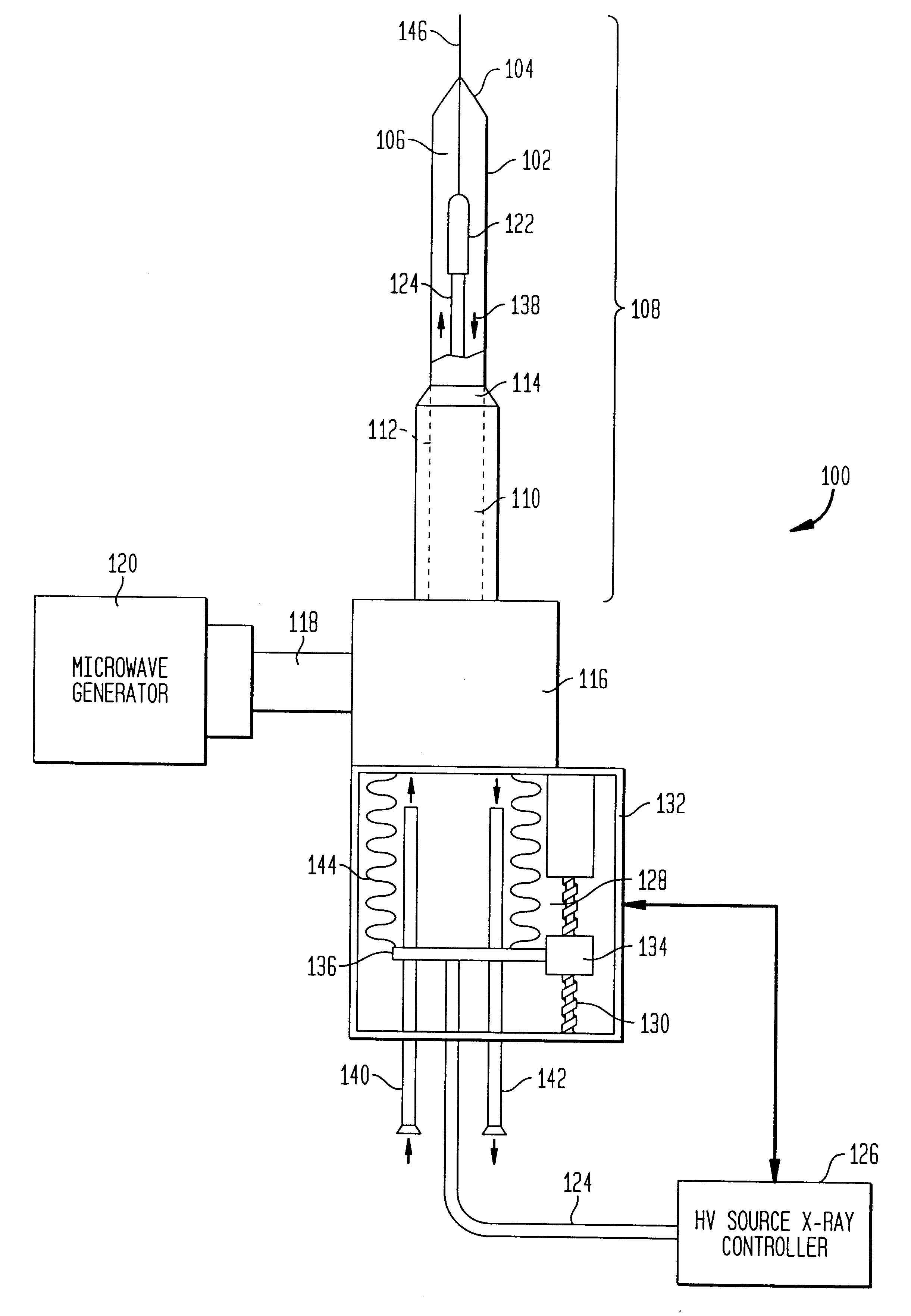
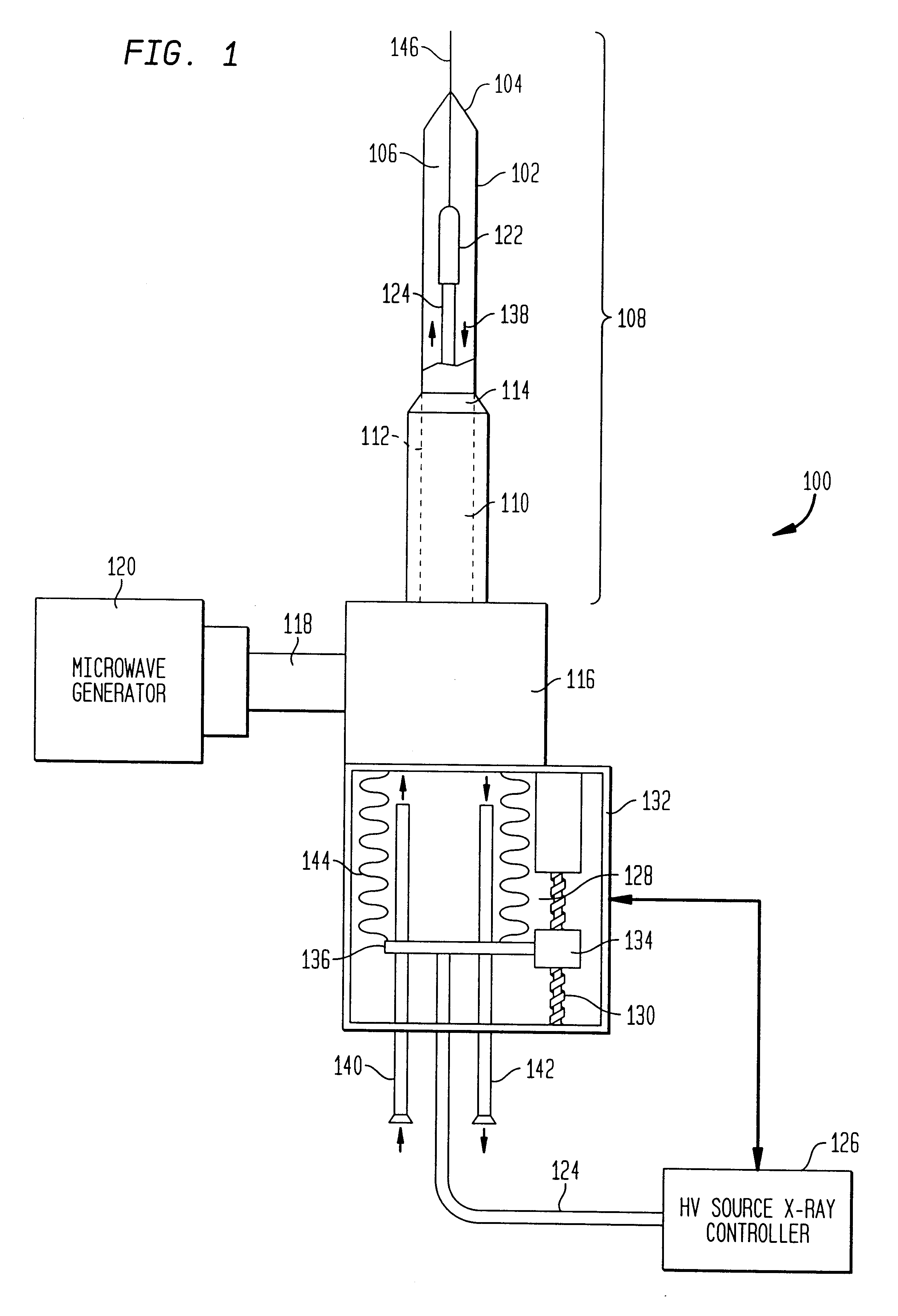
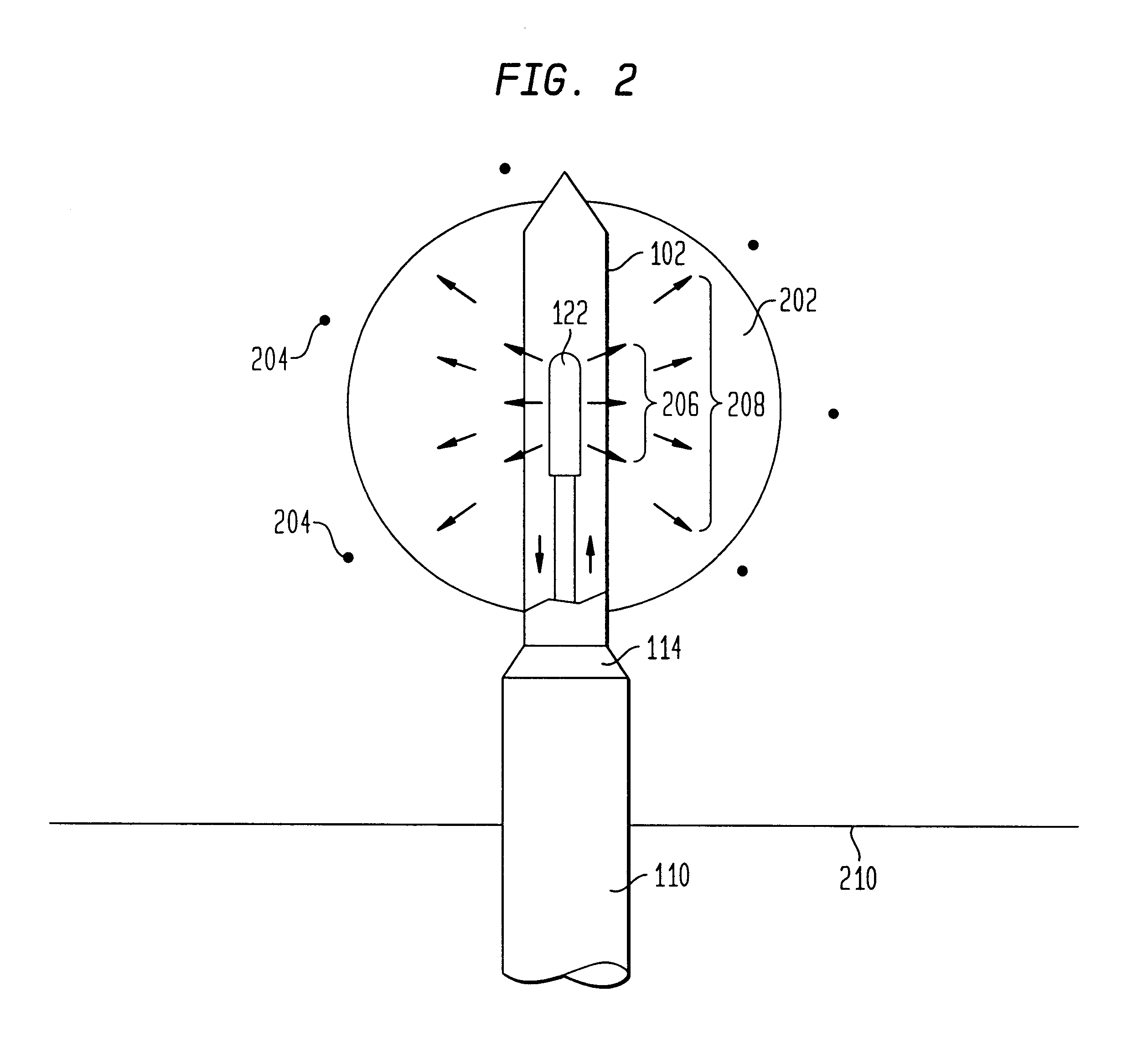
Apparatus and method for treatment of malignant tumors
InactiveUS6866624B2Increase powerIncrease temperatureElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyAbnormal tissue growthBrachytherapy
The present invention relates to a device for simultaneously treating a tumor or cancerous growth with both hyperthermia and X-ray radiation using brachytherapy. The device includes a needle-like introducer serving as a microwave antenna. Microwaves are emitted from the introducer to increase the temperature of cancerous body tissue. The introducer is an inner conductor of a coaxial cable. The introducer contains a hollow core which houses an X-ray emitter. The X-ray emitter is connected to a high voltage miniature cable which extends from the X-ray emitter to a high voltage power source. The X-ray emitter emits ionizing radiation to irradiate cancerous tissue. A cooling system is included to control the temperature of the introducer. Temperature sensors placed around the periphery of the tumor monitor the temperature of the treated tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Method for surgical navigation utilizing scale-invariant registration between a navigation system and a localization system
ActiveUS20060058646A1Precise NavigationAccurate operationImage analysisCatheterLocalization systemDisplay device
A system for navigating a medical device through the lumens and cavities in an operating region in a subject, comprising an imaging system for displaying an image of the operating region, including a representation of the distal end of the medical device in the operating region. The system also includes a localization system for determining the position of the medical device in a frame of reference translatable to the displayed image. Finally, the system includes an algorithm for evaluating one or more rotation matrix using a cost function to determine an optimum rotation matrix for performing transformation of a vector in the local frame of the localization system to that of the reference frame of the navigation system. The rotation matrix can then provide a scale invariant transformation or “registration” of the coordinate systems of the localization system and the navigation system. This allows navigation to be performed to a significant extent from the localization system display alone, which avoids the frequent x-ray irradiation that occurs during the use of fluoro imaging for navigation purposes.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
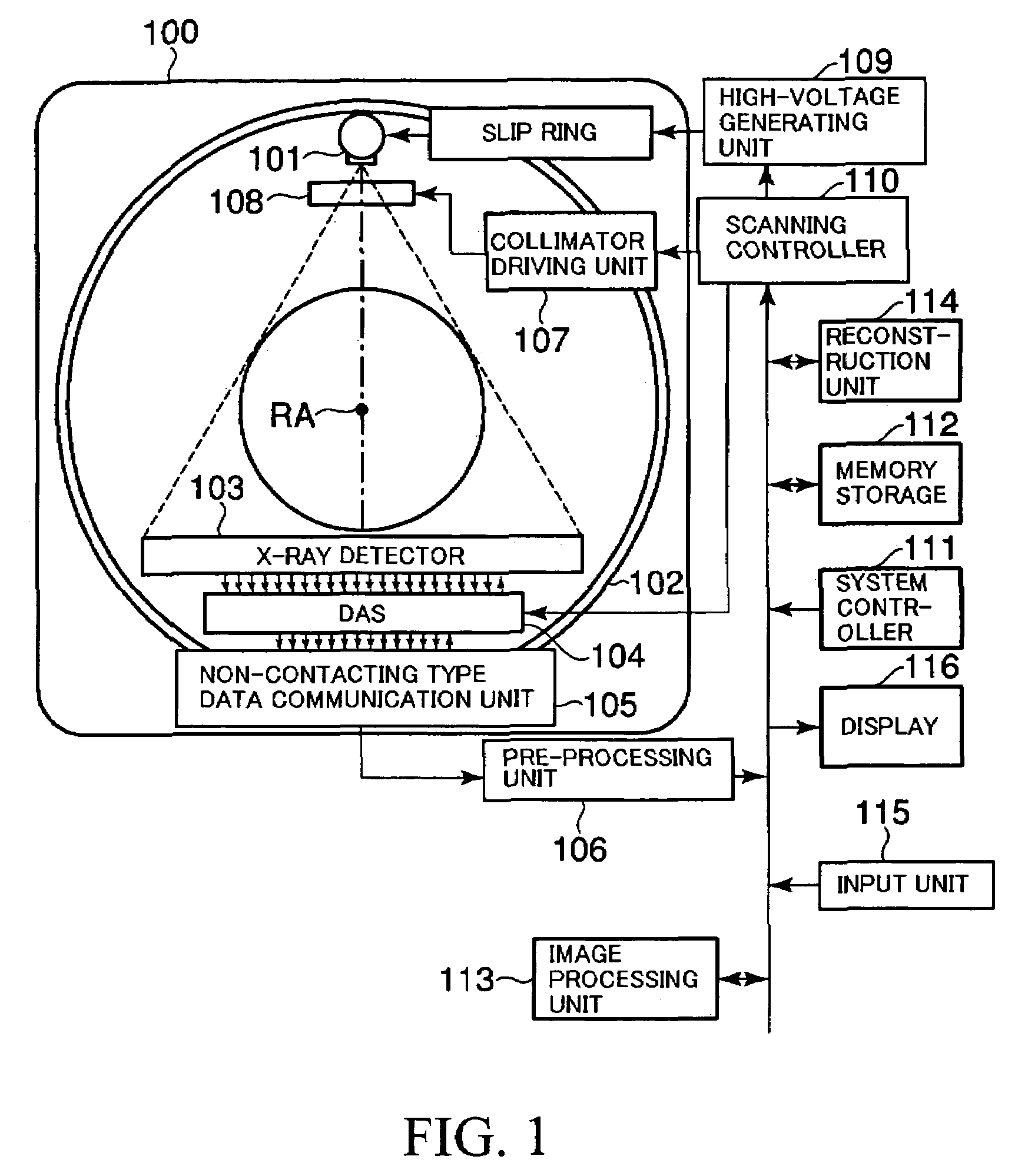
X-ray CT apparatus
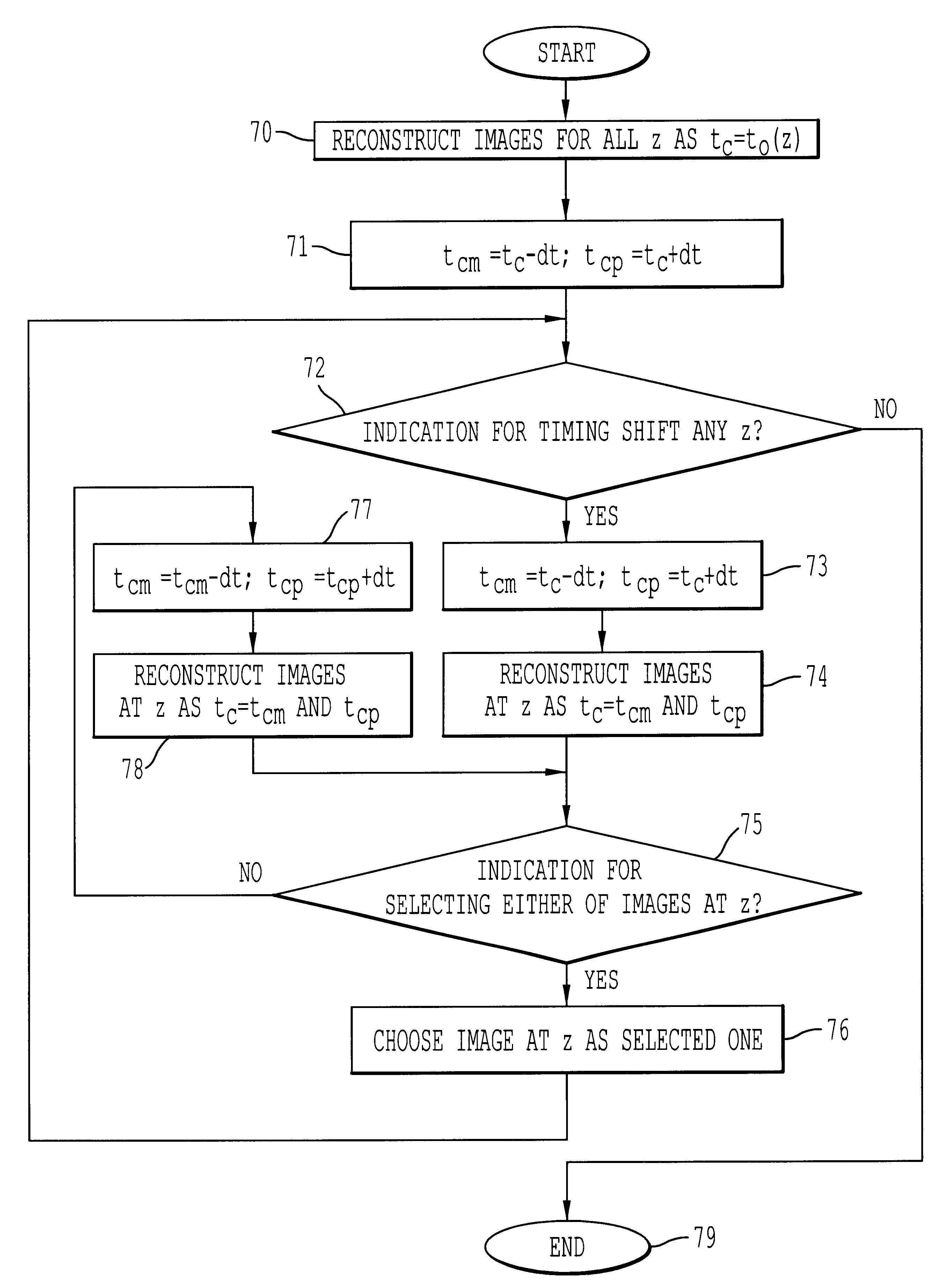
An X-ray CT apparatus includes a plurality of X-ray irradiation sources and a plurality of X-ray detection units. Timing of irradiation of X-ray is shifted by each X-ray irradiation source, the detection unit separately obtains projection data and scatter correction data. In a scatter correction unit, scatter correction is performed based on the projection data and the scatter correction data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
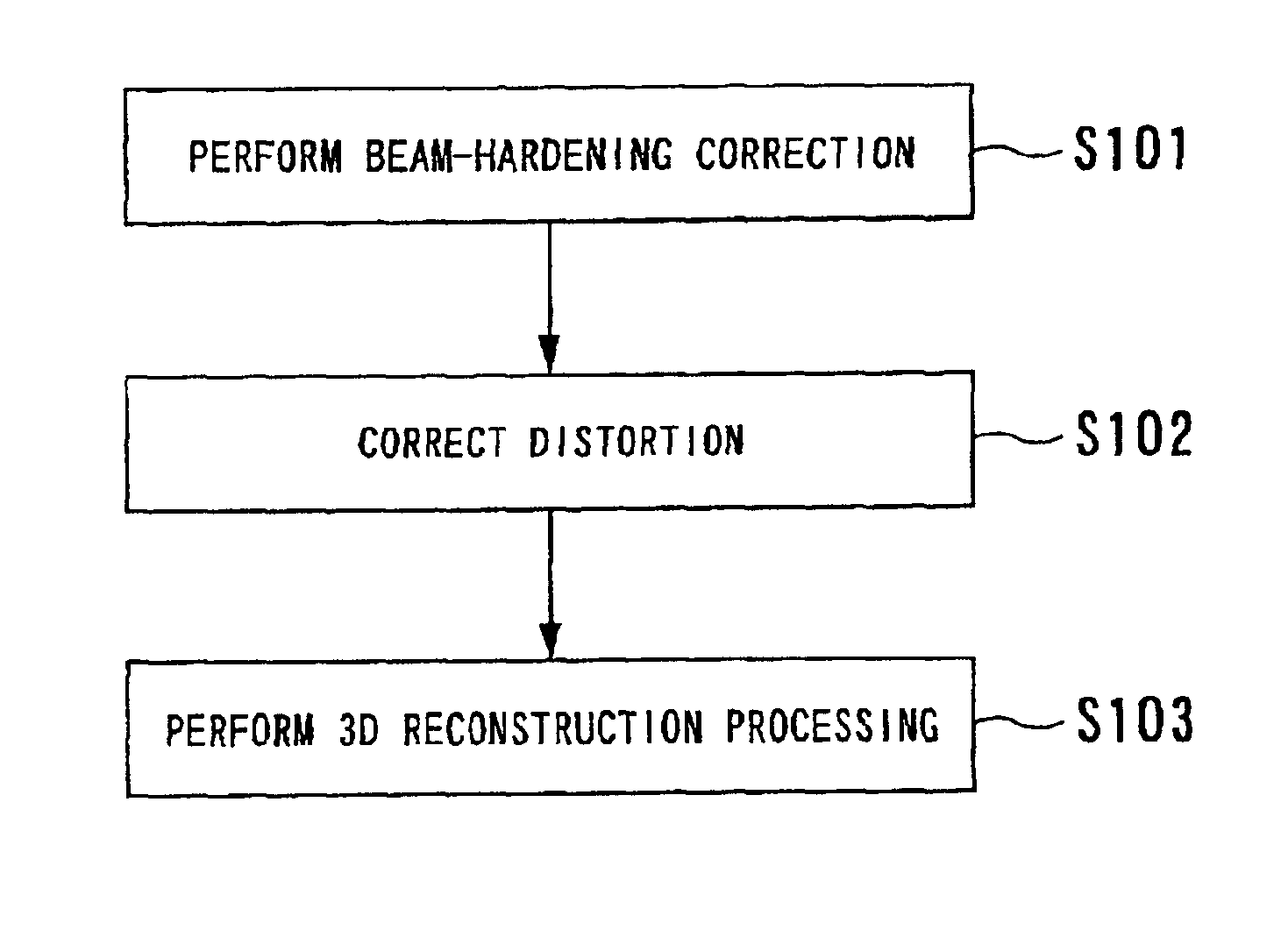
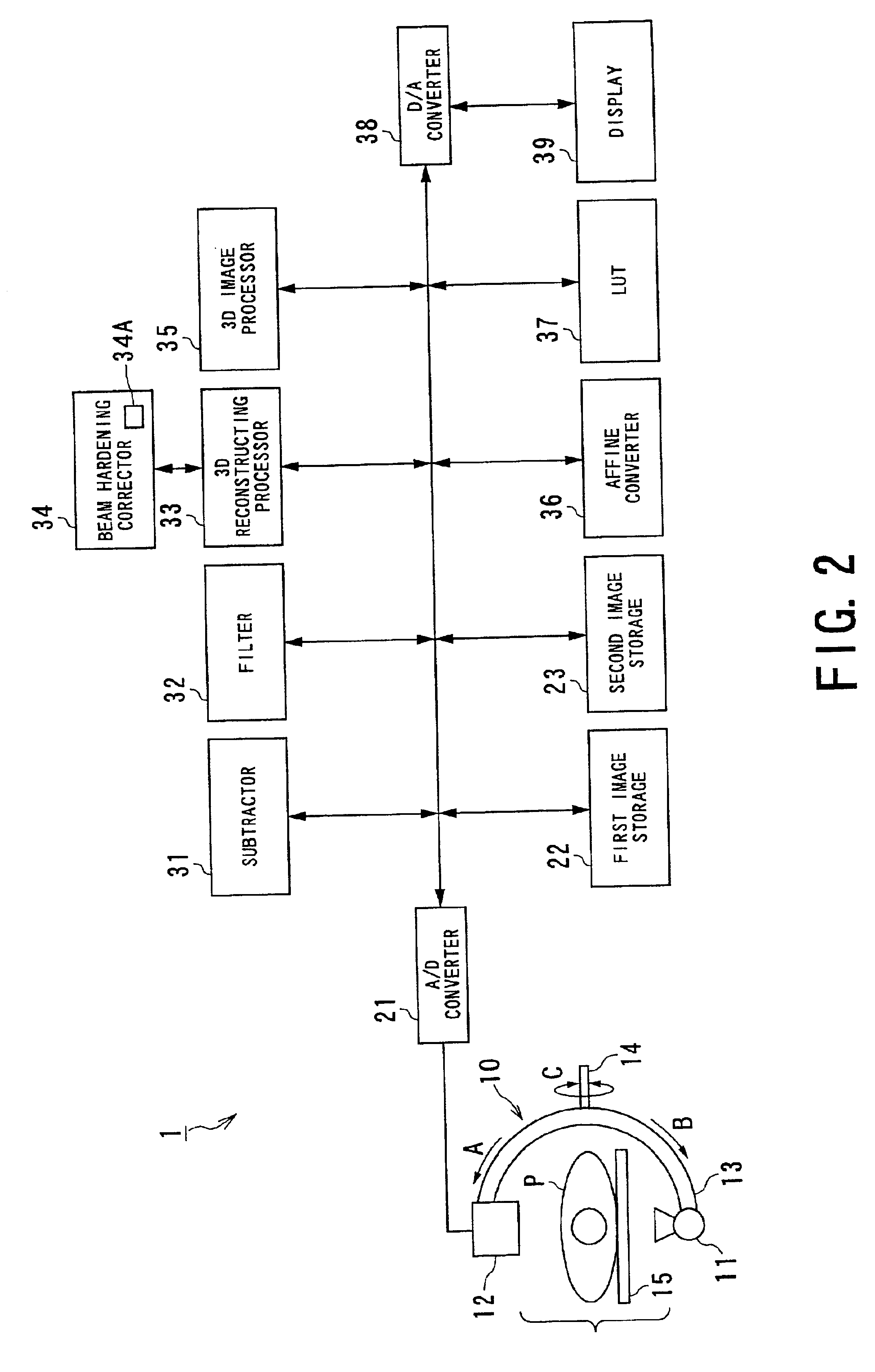
Image processing involving correction of beam hardening
InactiveUS6845142B2Avoid artifactsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSoft x rayImaging processing
An image processing apparatus is provided for processing a plurality of sets of projection data acquired by radiating an X-ray onto an object in a multitude of directions. The apparatus has a correcting unit and a reconstructing unit. The correcting unit corrects the projection data with regard to beam hardening of the projection data. The beam hardening is caused due to a contrast agent injected into the object. For example, the correcting unit includes a correction table defining a correcting value to a change in densities of a region in which the contrast agent is present and corrects the projection data on the basis of the correcting value obtained from the correction table. The reconstructing unit reconstructs the corrected projection data into an image of the object. Thus, artifacts due to beam hardening resultant from use of the contrast agent can be avoided.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Radiation imaging apparatus, system and method as well as program
InactiveUS20070125952A1Avoid it happening againSimple configurationTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansSignal processing circuitsX-ray
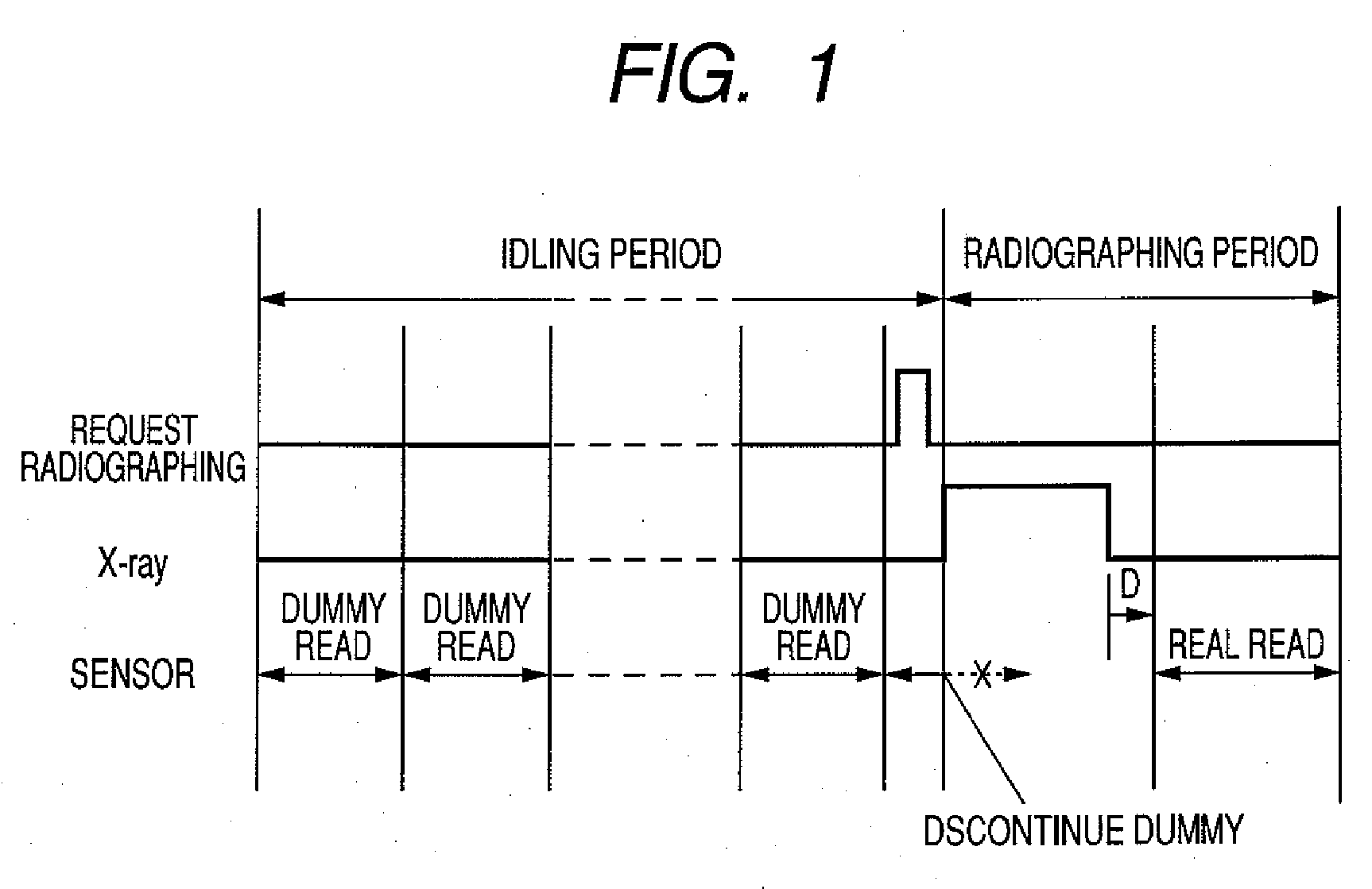
An object hereof is to restrain occurrence of artifact in an acquired radiation image with comparatively simple configuration without providing wiring between a radiation source and a radiation imaging apparatus to thereby obtain a radiation image with extremely good quality. Therefore, a controller selectively carries out real read operation of reading an electric signal obtained by activating a drive circuit from a signal processing circuit unit in case of detecting X-ray irradiation with an X-ray detecting circuit and dummy read operation of reading an electric signal obtained by activating a drive circuit from a signal processing circuit unit in case of detecting X-ray non-irradiation with an X-ray detecting circuit; discontinues the dummy read operation at the time of detecting the start of X-ray irradiation with the X-ray detecting unit in dummy read operation; and starts real read operation at the time of detecting the finish of X-ray irradiation with the X-ray detecting unit.
Owner:CANON KK
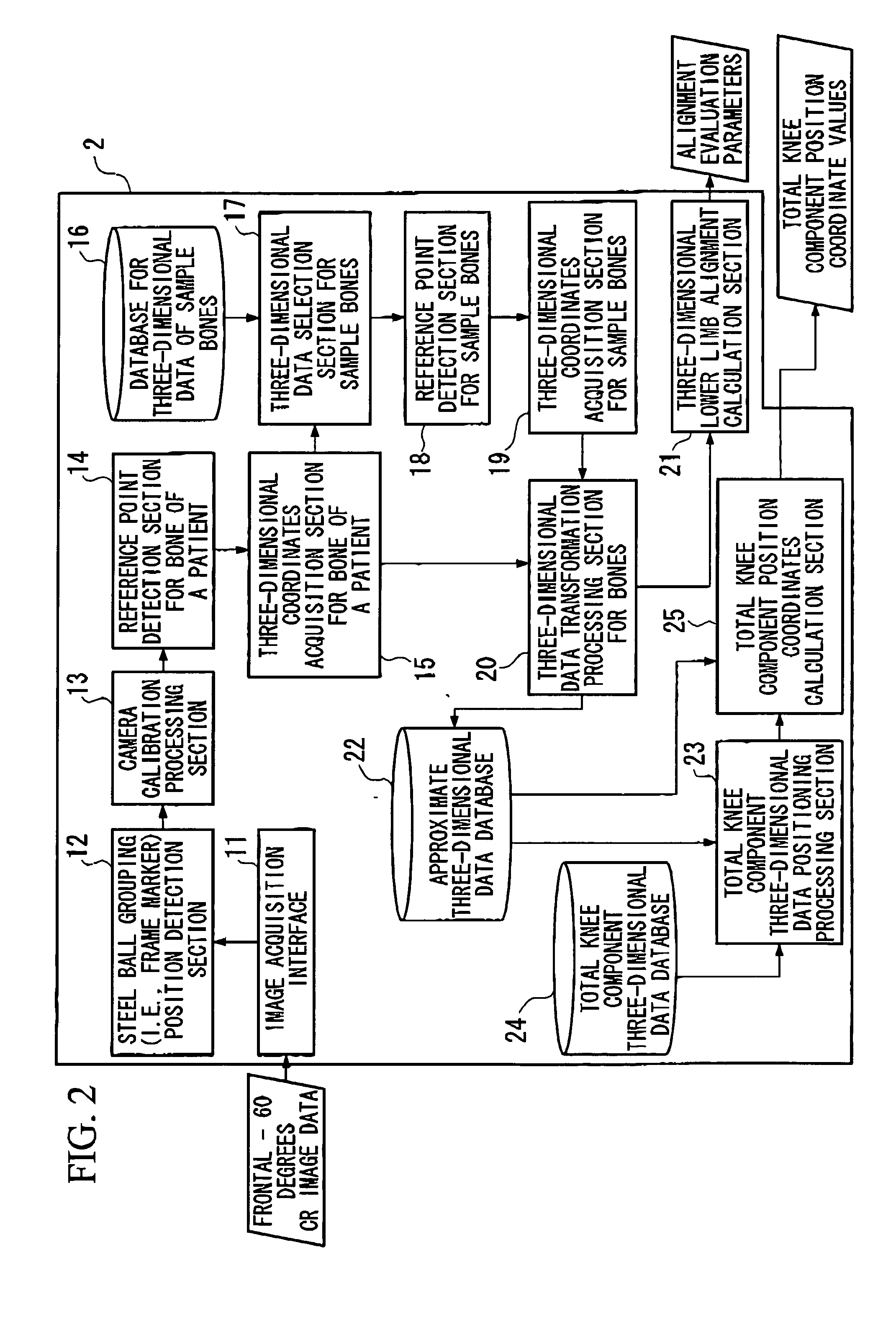
Calculation method, calculation program and calculation system for information supporting arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050256389A1Accurately determineAddressing slow performanceImage enhancementImage analysisKnee JointX-ray
The present invention provides an arthroplasty supporting information calculation method for supporting diagnoses of a patient with knee disordered and total joint replacement to a total knee component, and an arthroplasty supporting information calculation program, and an arthroplasty supporting information calculation system. In an arthroplasty supporting terminal of the present invention, photographed X-ray images are acquired using X-ray irradiation mechanisms and a dedicated cassette base, Approximate three-dimensional data of a patient's bones is then created by transforming a display image of three-dimensional data of CT of the patient and / or sample bones to match the X-ray image in which the patient's bones are photographed. Three-dimensional coordinate values are then determined for this approximate three-dimensional data of the patient's bones. From these three-dimensional coordinate values, parameters are determined for evaluating positional relationships between at least two bones. The position of the display image of the three-dimensional data of a total knee component is then adjusted to match the display image of the approximate three-dimensional data of the patient's bones based on the three-dimensional coordinate values. The position of the total knee component is then calculated as anatomical coordinate values that represent the positions of at least two bones.
Owner:NIIGATA MACHINE TECHNO CO LTD +1
Computed tomography system and method
InactiveUS6466640B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDose ReducedComputed tomography
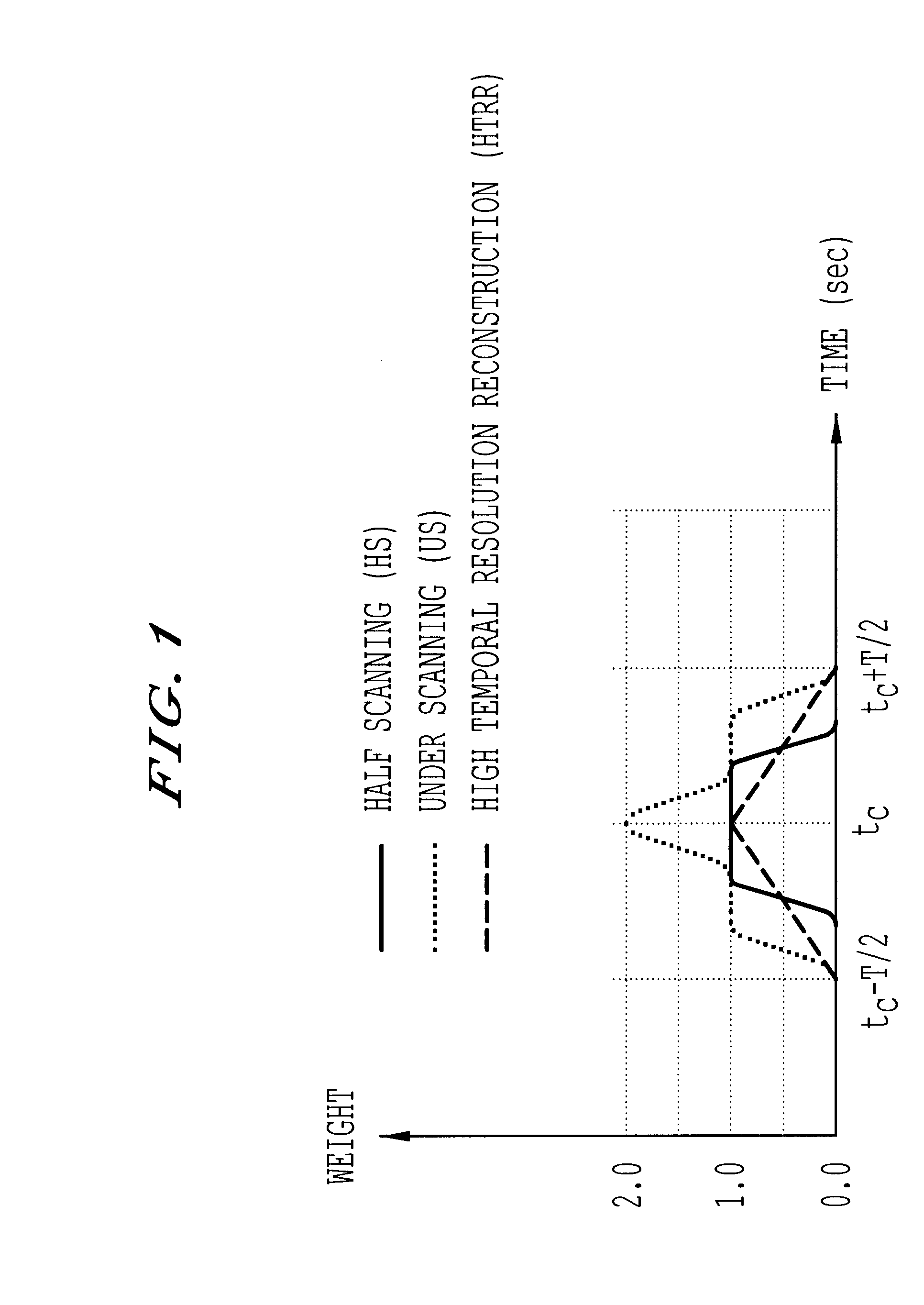
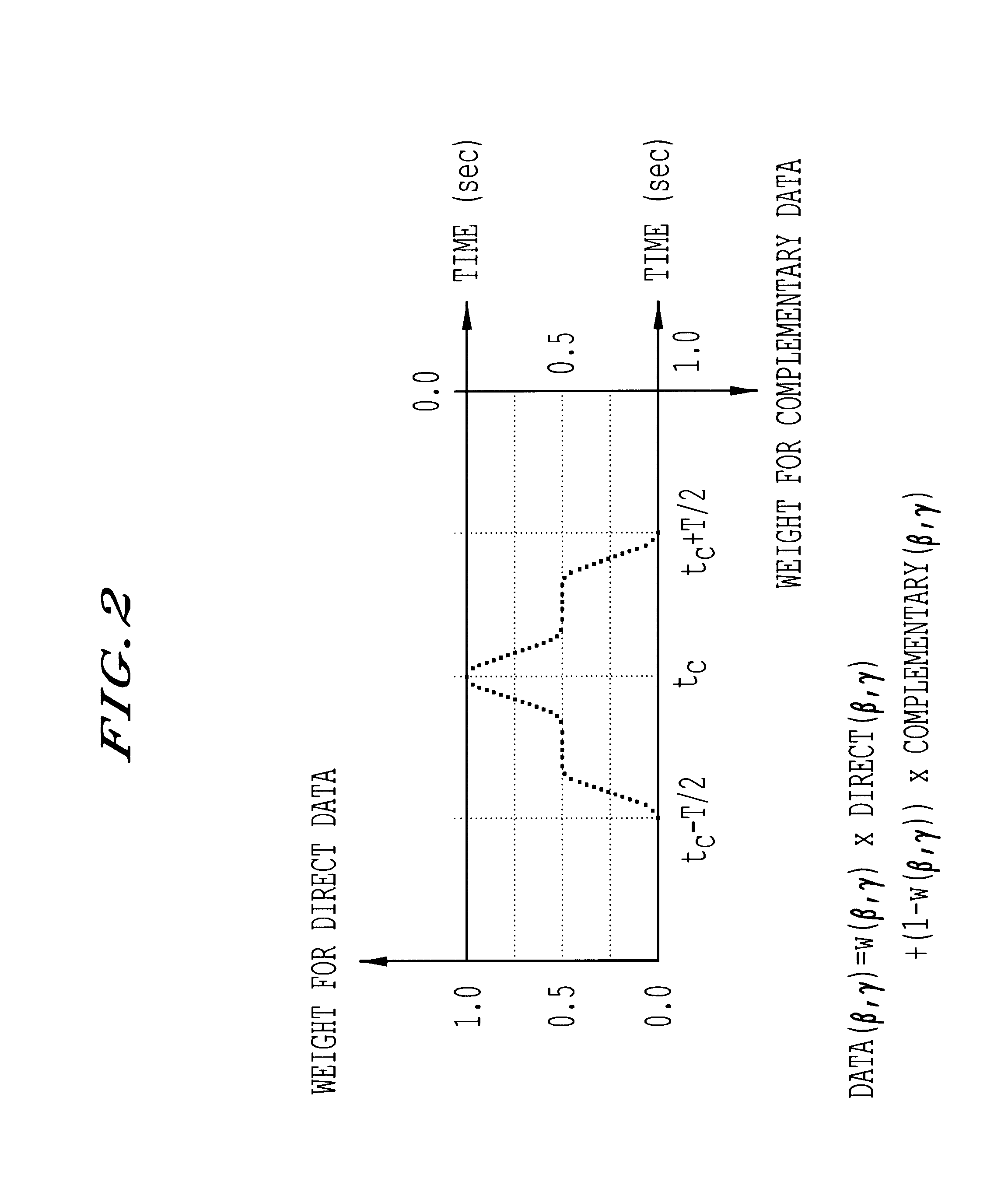
Method and system for computed tomography. Data is collected by irradiating a subject with x-rays. The data is interpolated and then weighted based upon the data collection time. The interpolated and weighted data is then used to reconstruct the image using fan beam reconstruction. The weighting function may by shifted in time. Signals may be obtained from the subject and used to control exposure, reduce the dose and provide automatic volumetric cardiac reconstruction. The method and system can increase the temporal and spatial resolution, and reconstruct images at different timing.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and methods for advancing a catheter
An advancer system is described for moving an elongate medical device within a body. The system includes a drive unit having a motor. The drive unit is configured to translate movement of the motor to the device so as to alternately advance and retract the device relative to the body. The advancer system also includes a user-operable control system configured to control the drive unit. The control system can interface with a magnetic navigation system. The above-described system allows an operating physician to control catheter advancement and retraction while remaining outside an x-ray imaging field. Thus the physician is freed from repeated x-ray exposure.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
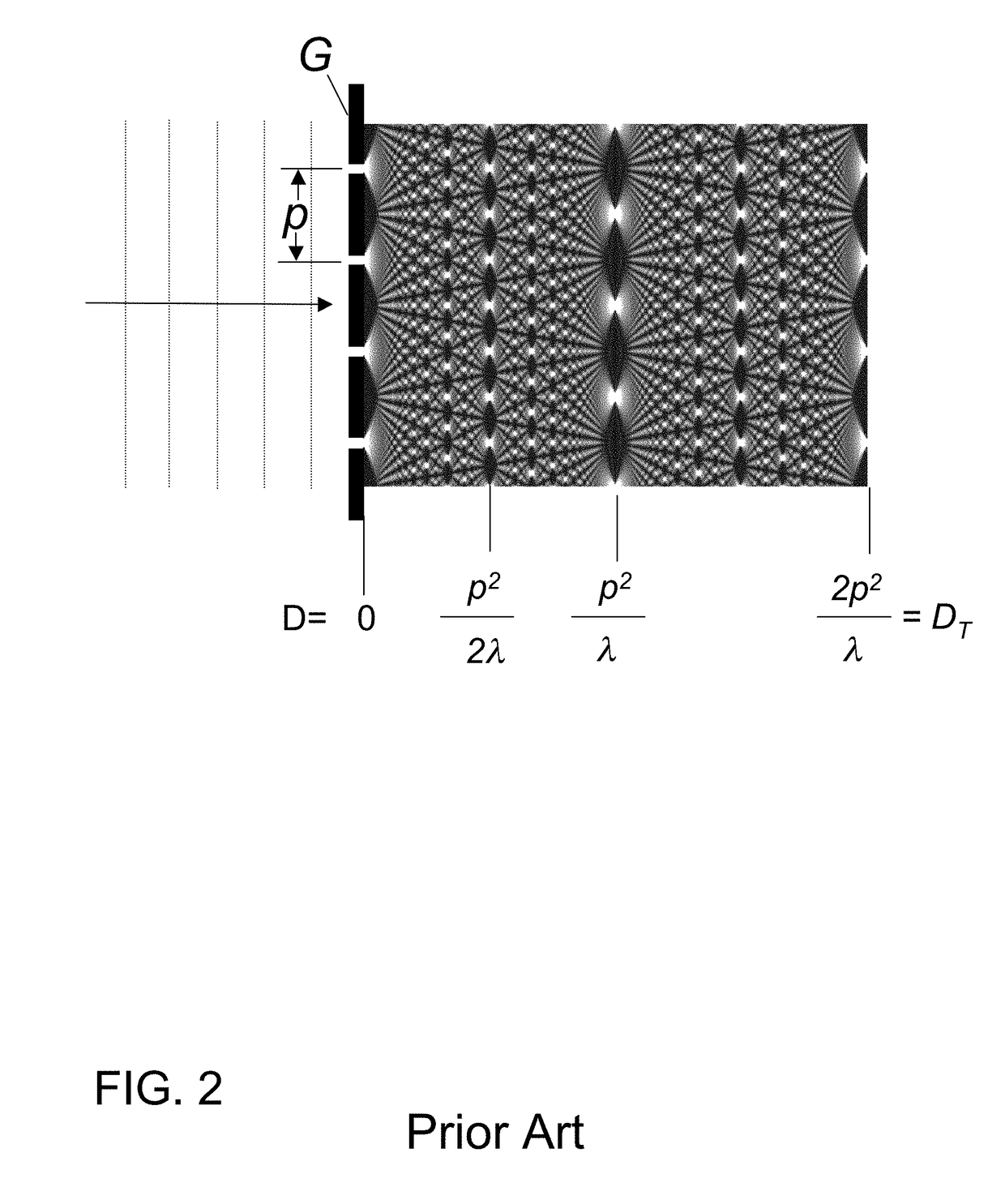
X-ray irradiation apparatus and x-ray exposure apparatus
An x-ray irradiation apparatus and x-ray exposure apparatus provide improved x-ray generation. The x-ray irradiation apparatus includes a target material feed-out device to provide a target material in a feed-out direction to a specified target position and a laser to provide laser light to the specified target position to cause the target material to emit x-rays. In some configurations, an x-ray generation position control device may be used to determine and control a position of x-ray generation, a rotary mechanism may be operatively connected to the target material feed-out device to axially rotate the target material feed-out device about the feed-out direction, and / or a target feed-out control device may be used to detect and control the position of the target material feed-out device.
Owner:NIKON CORP
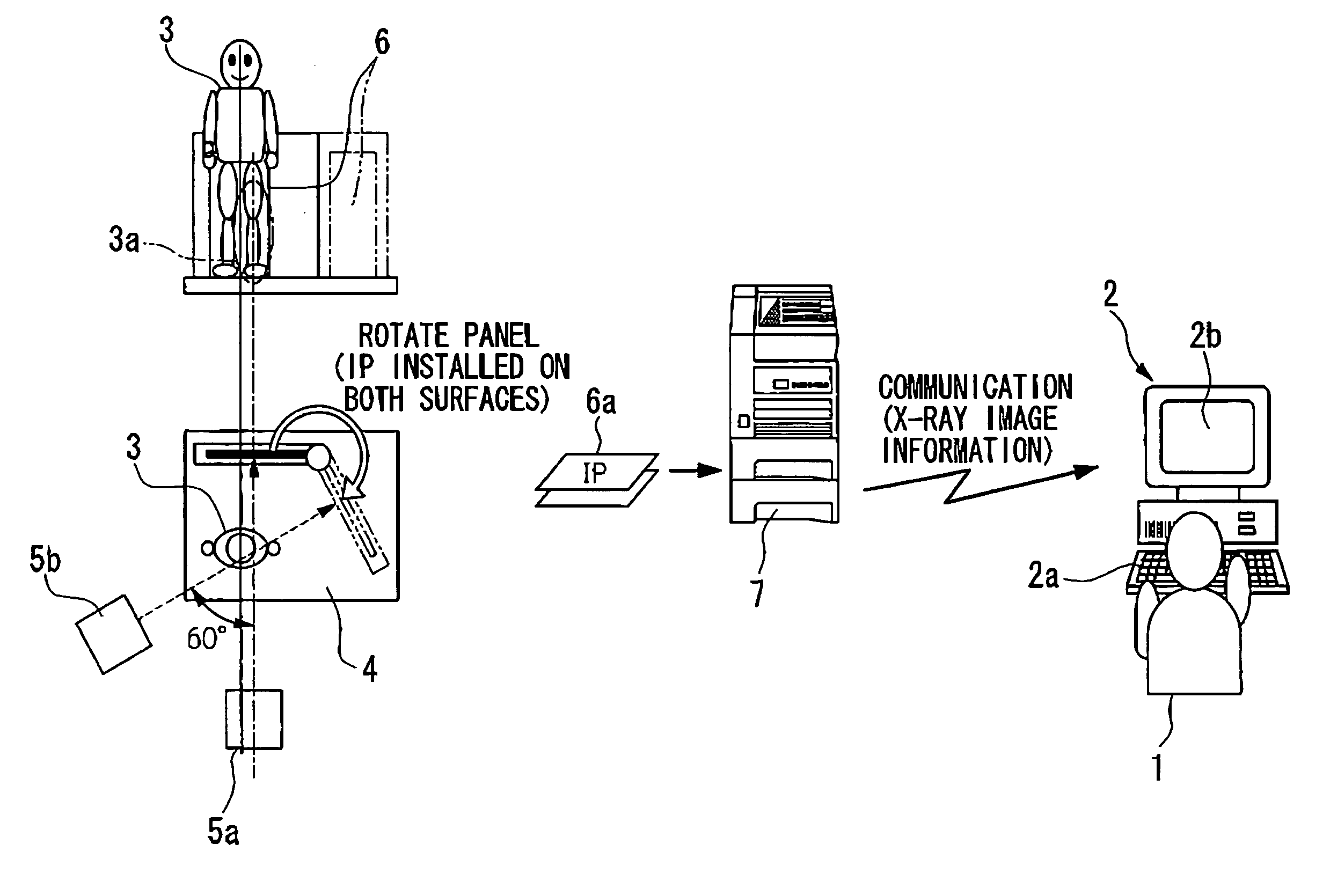
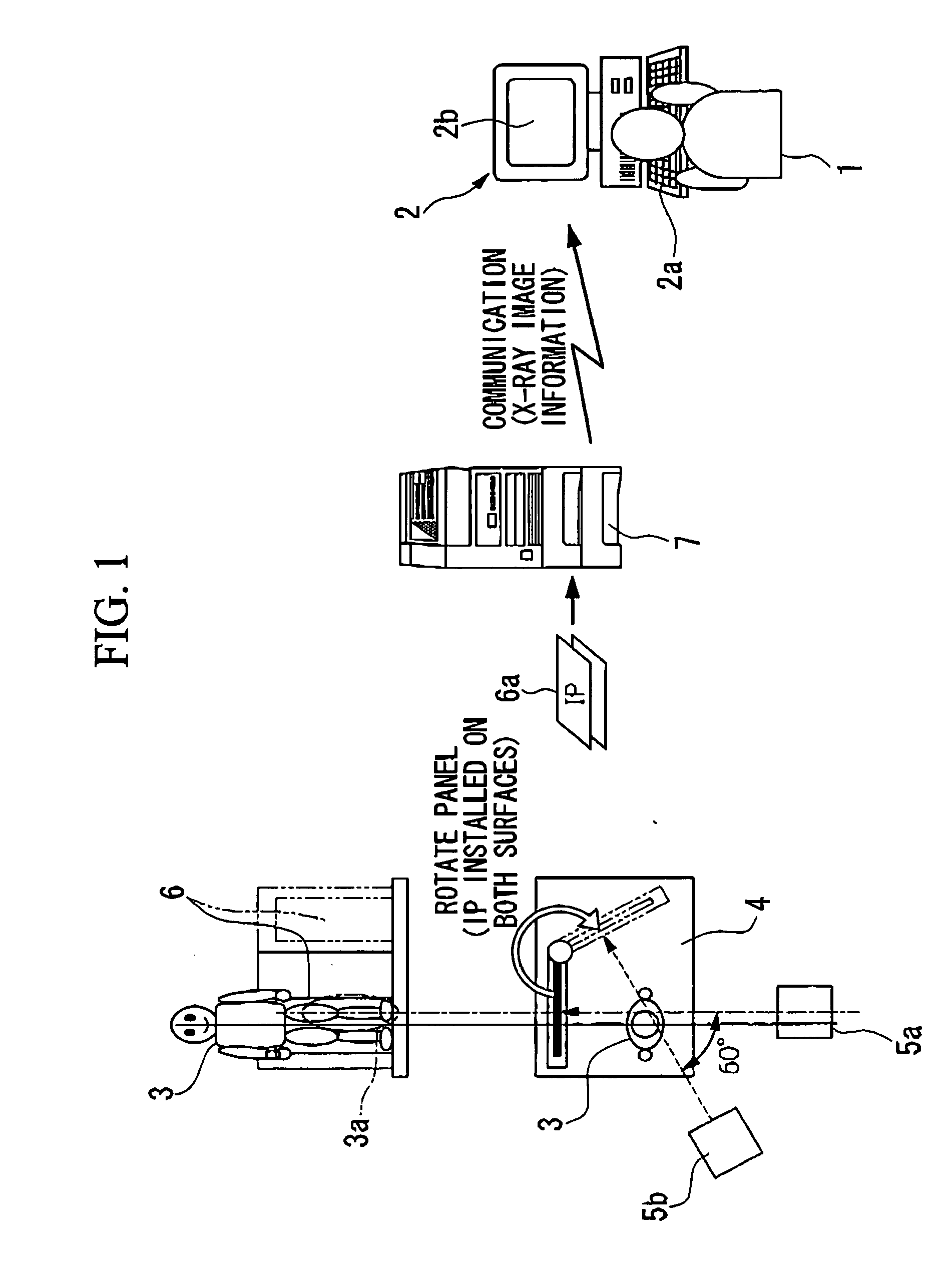
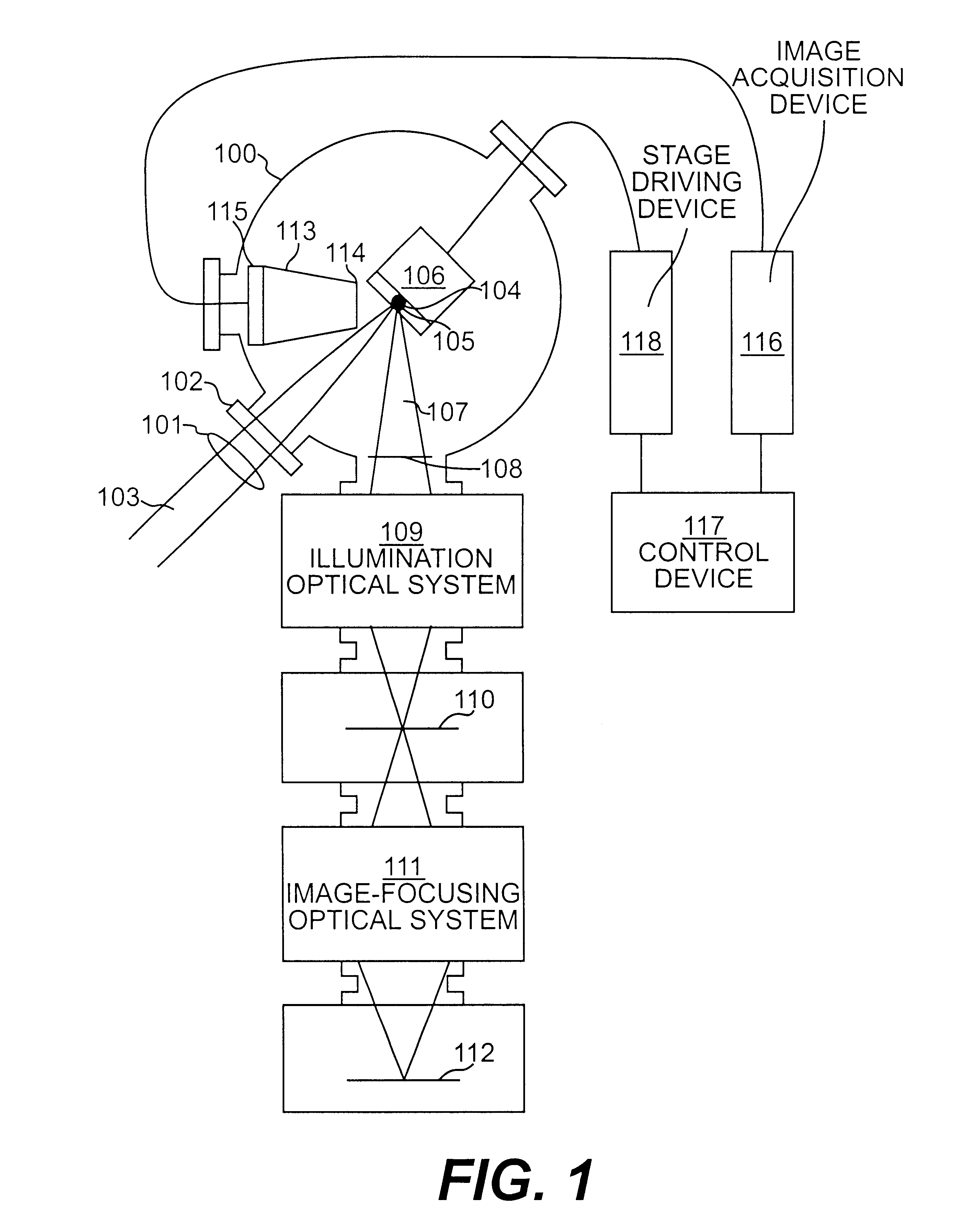
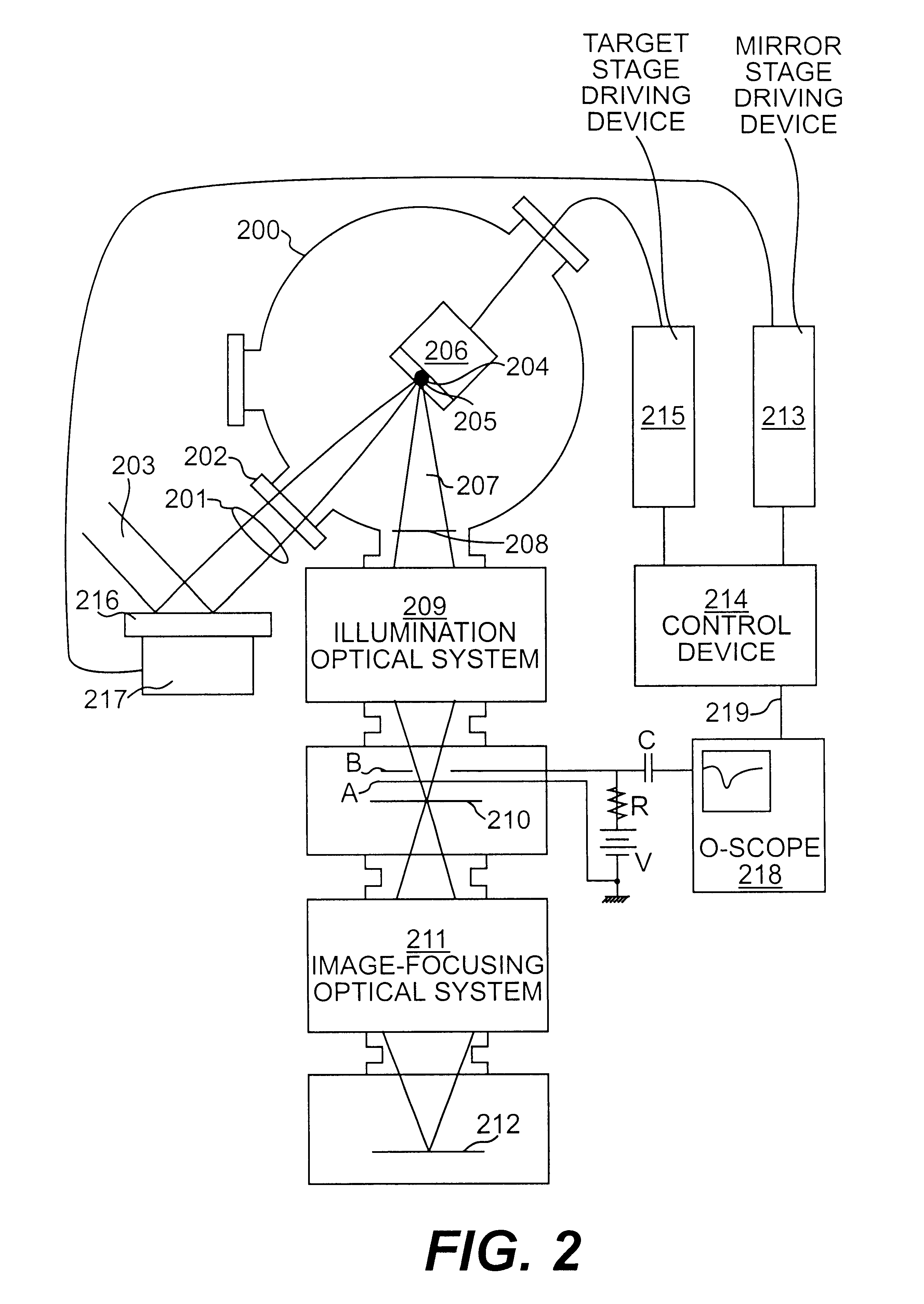
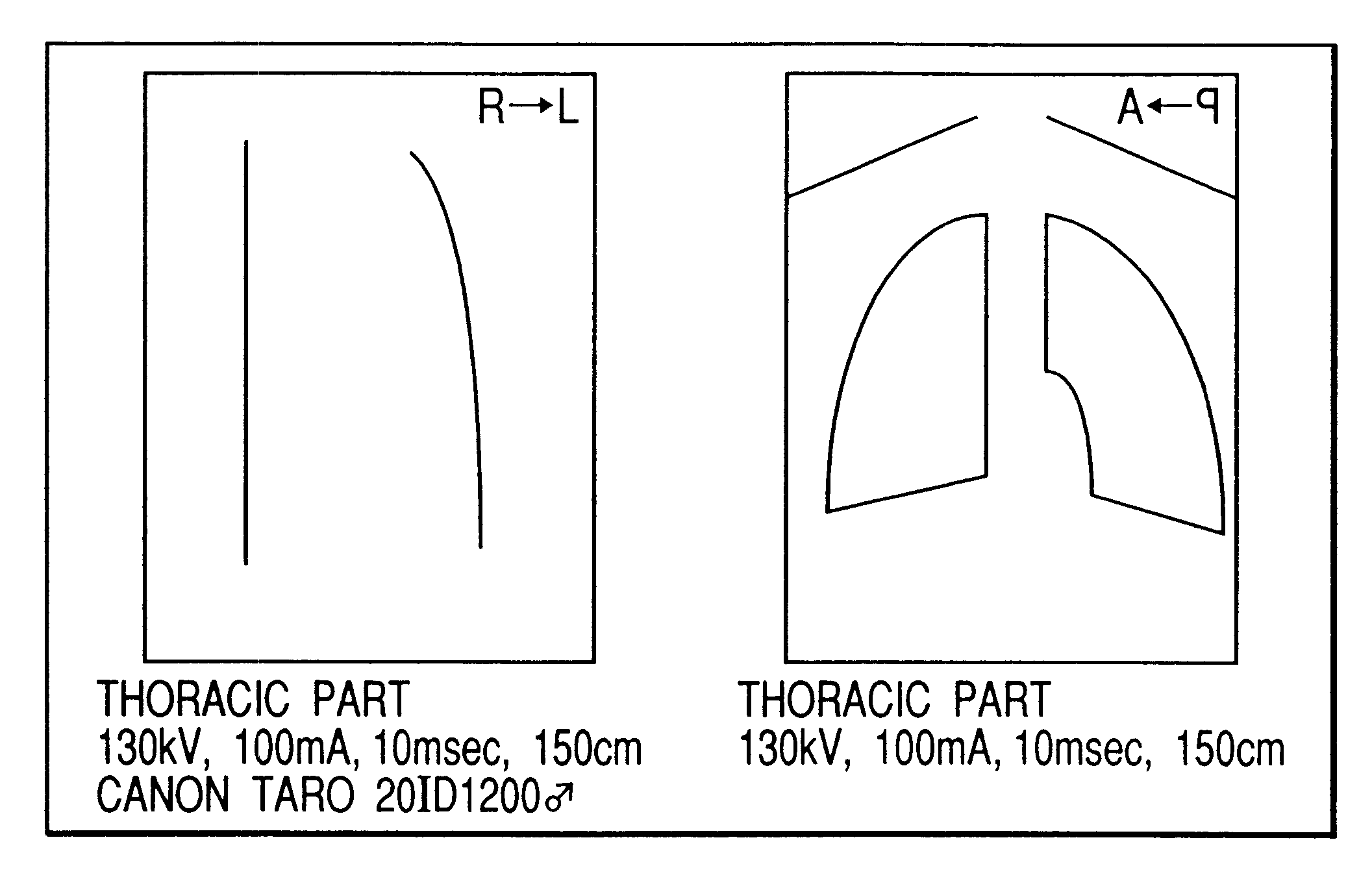
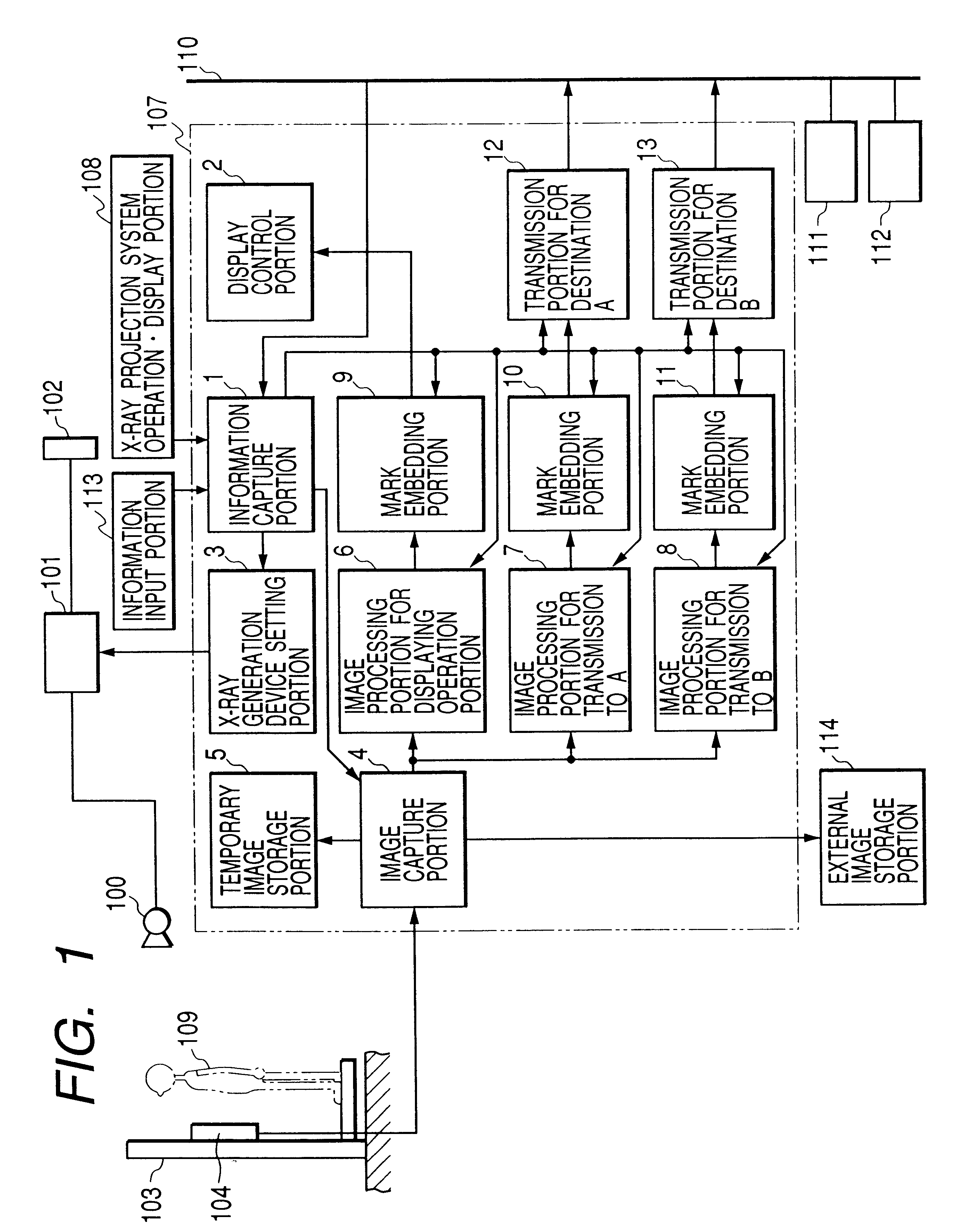
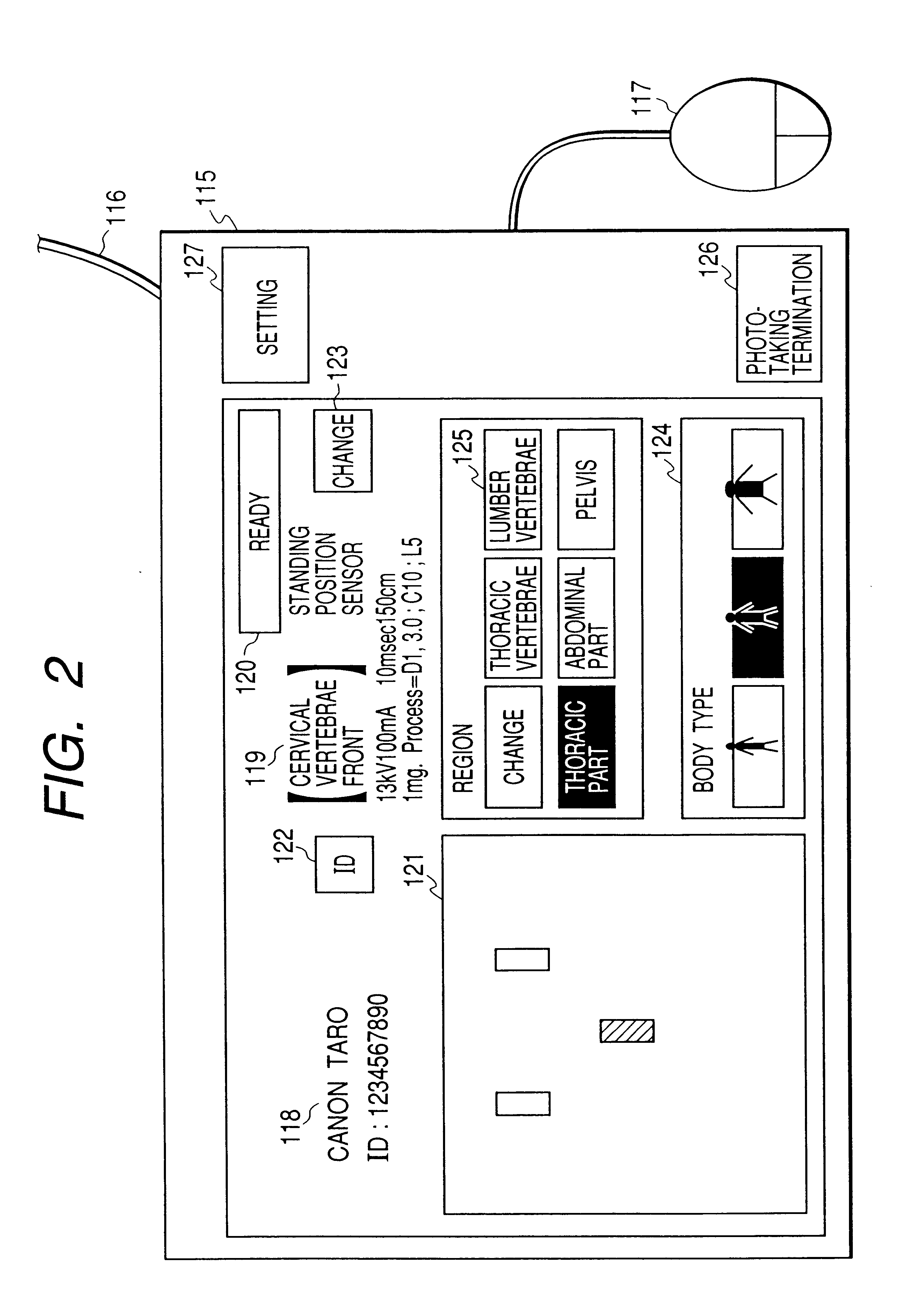
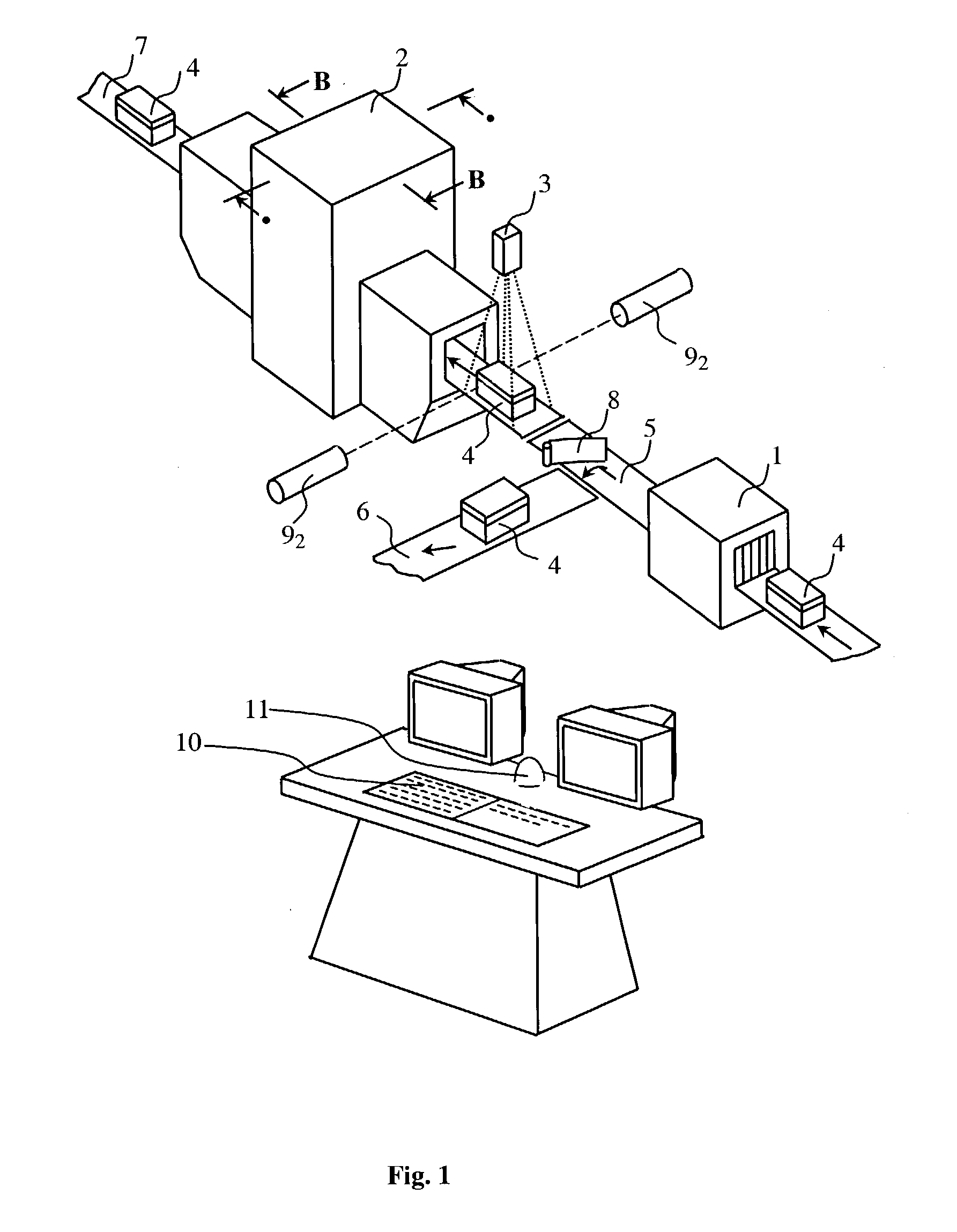
X-ray photo-taking system, X-ray photo-taken image display method, and storage medium
This invention provides an X-ray photo-taking system, X-ray photo-taken image display method, and storage medium by which an operator can readily understand the position (right, left, or center) of a photo-taking region of an object to be examined, the X-ray irradiation direction, and the photo-taking attitude only by monitoring an X-ray image, and by which text information is narrowed down to patient information and photo-taking information to make these pieces of information easy to see. The system includes an information capture portion for symbolizing the direction of an object to be examined during photo-taking, the photo-taking direction, the position of a photo-taking region, and the photo-taking attitude, a mark embedding portion for embedding a mark in a portion of an image, a display control portion for displaying the X-ray photo-taken image in which the mark is embedded by the mark embedding portion, and a transmission portion for transmitting the X-ray photo-taken image in which the mark is embedded by the mark embedding portion to a network.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray CT apparatus
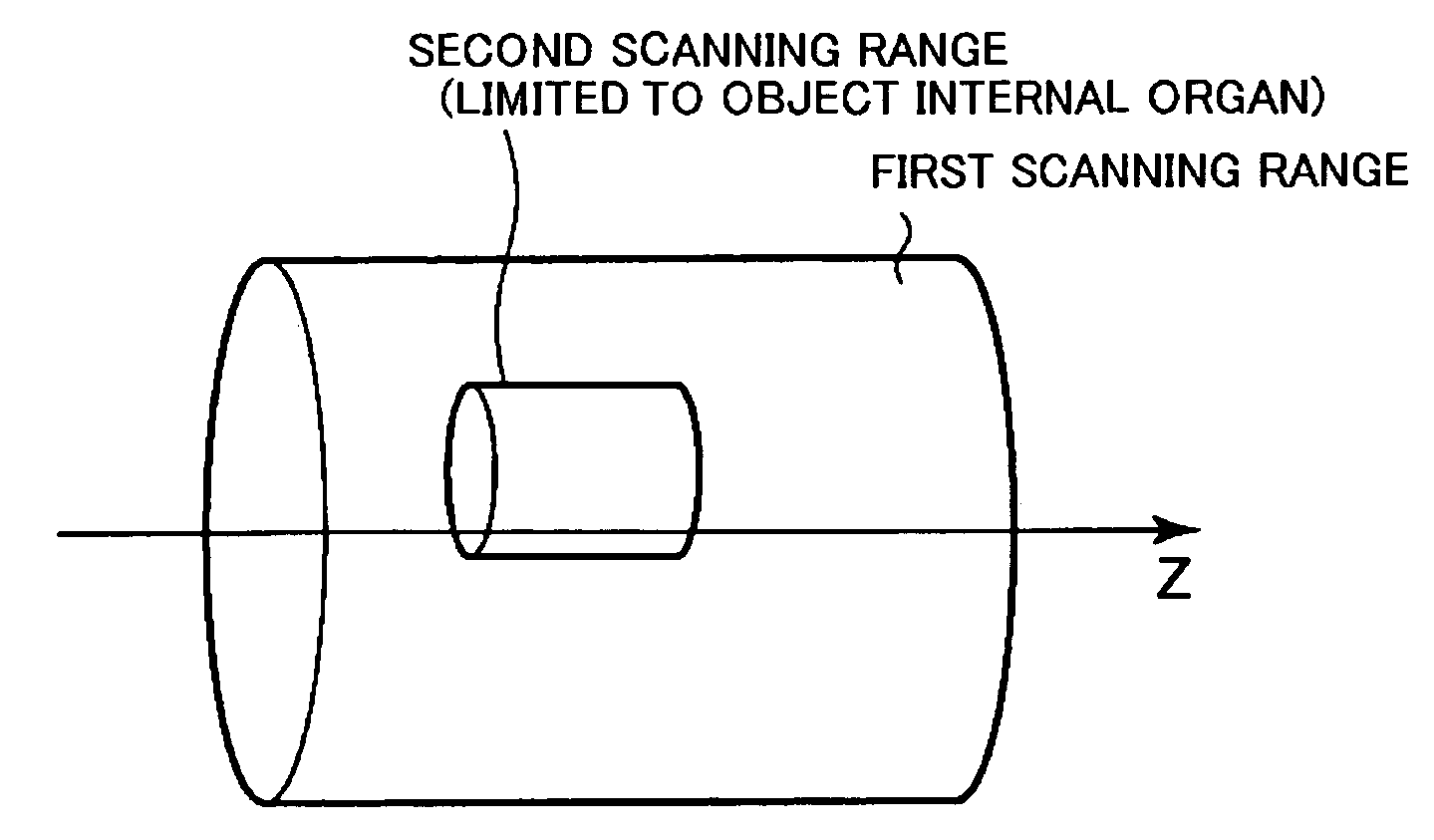
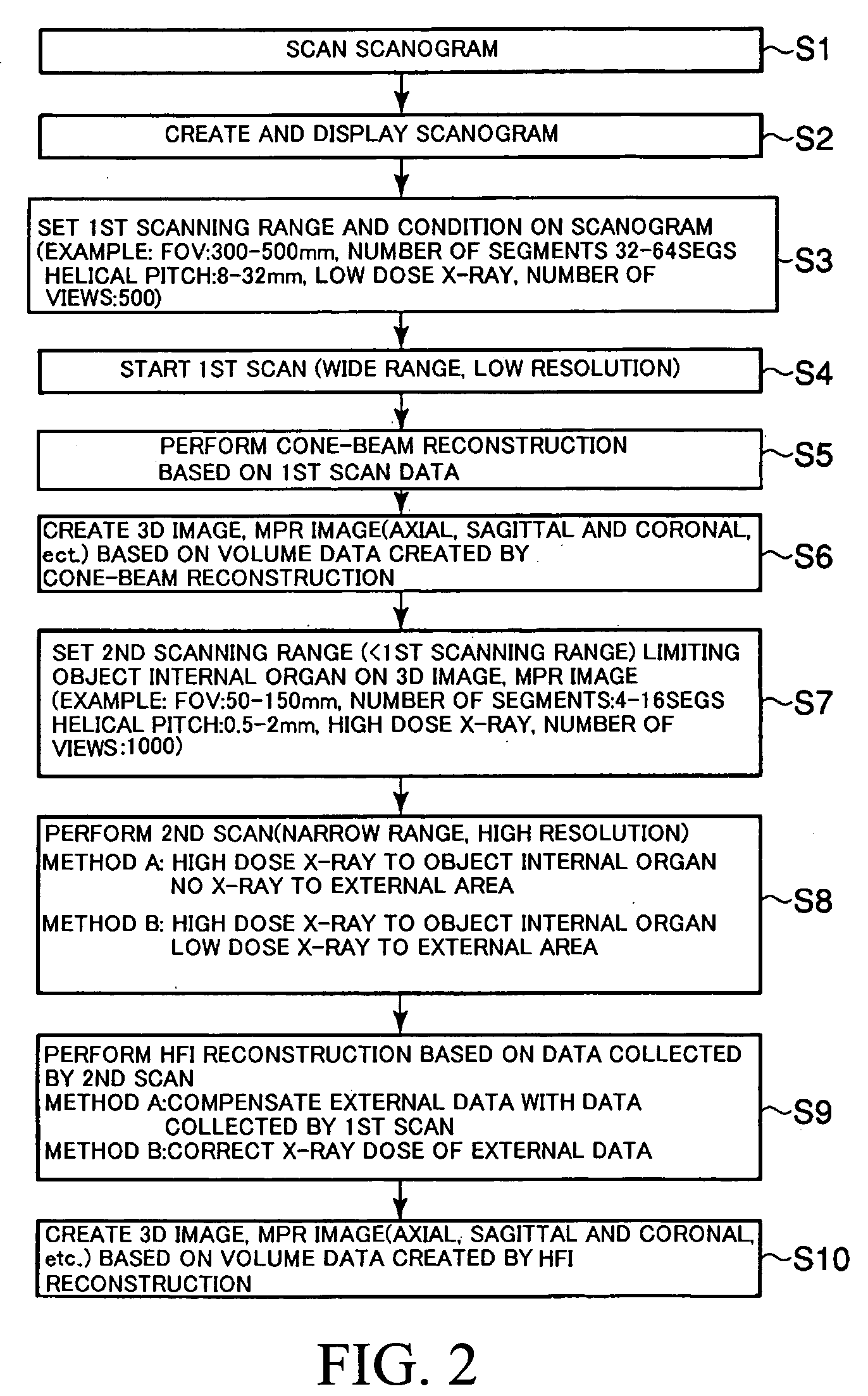
InactiveUS7113569B2Reduce X-ray doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayImaging processing
An X-ray CT apparatus, as one example, includes at least one X-ray irradiation source configured to irradiate an X-ray to a volume of interest, at least one X-ray detector including a plurality of detection element segments configured to detect the X-ray penetrated through the volume of interest, at least one collimator configured to create an opening that is movable in at least one of a slice direction and a channel direction, at least one image processing part configured to extract a portion of the volume data, a controller configured to set the opening of the at least one collimator to a second opening size according to a cylinder-like second scanning range that is set to limit the volume of interest and configured to perform a second scan, and at least one reconstruction part configured to reconstruct image data based on data collected by the second scan.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
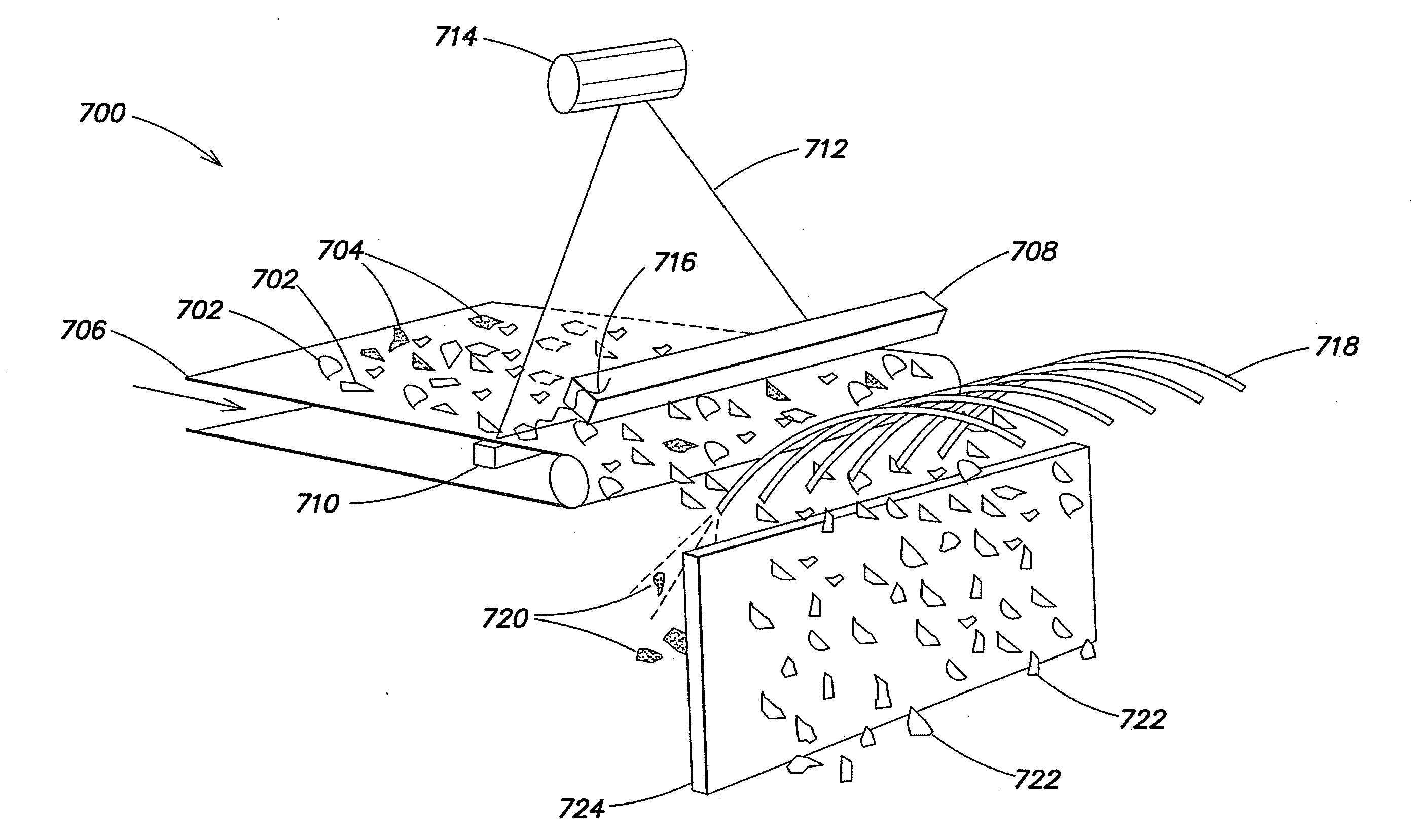
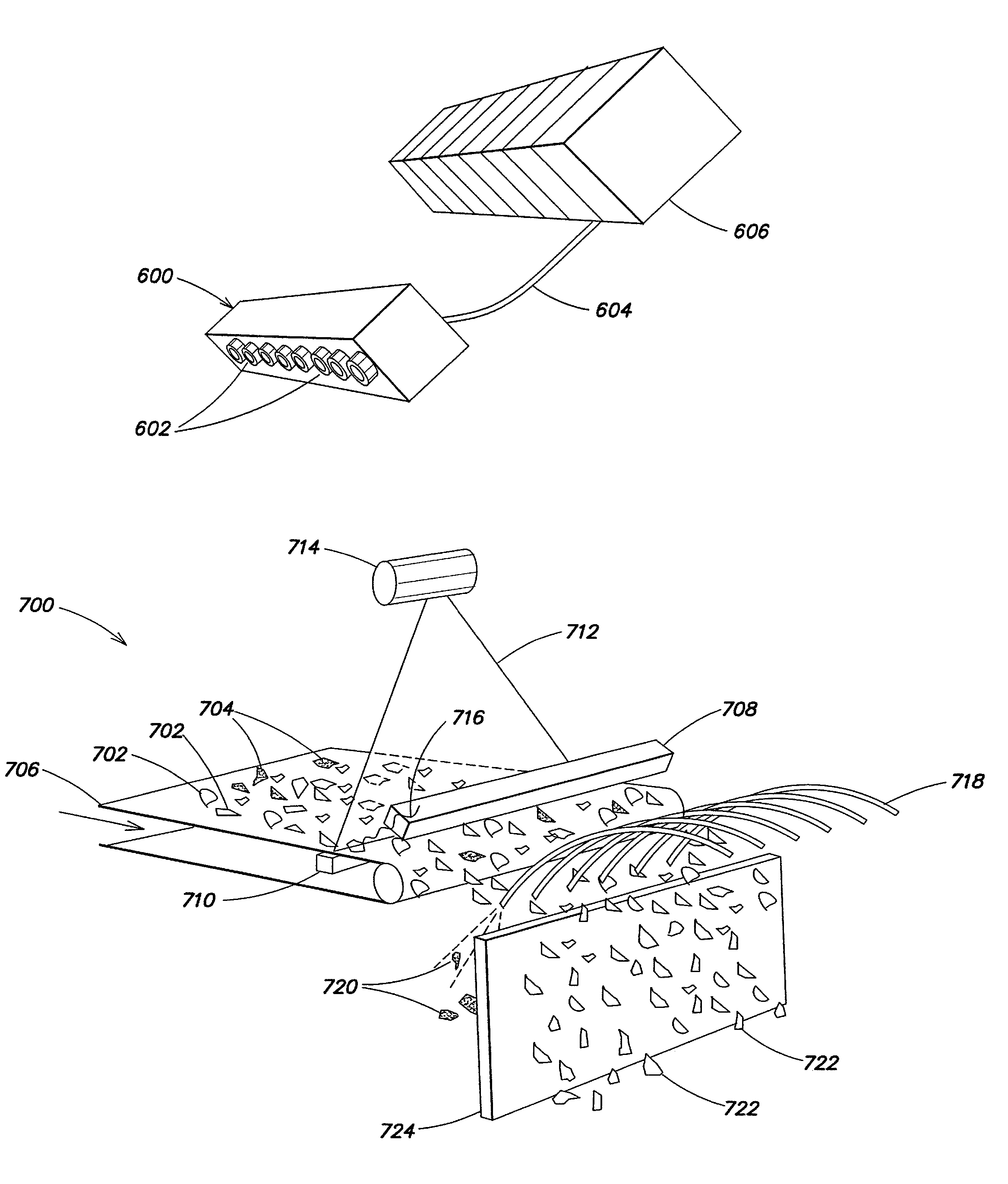
Material sorting technology
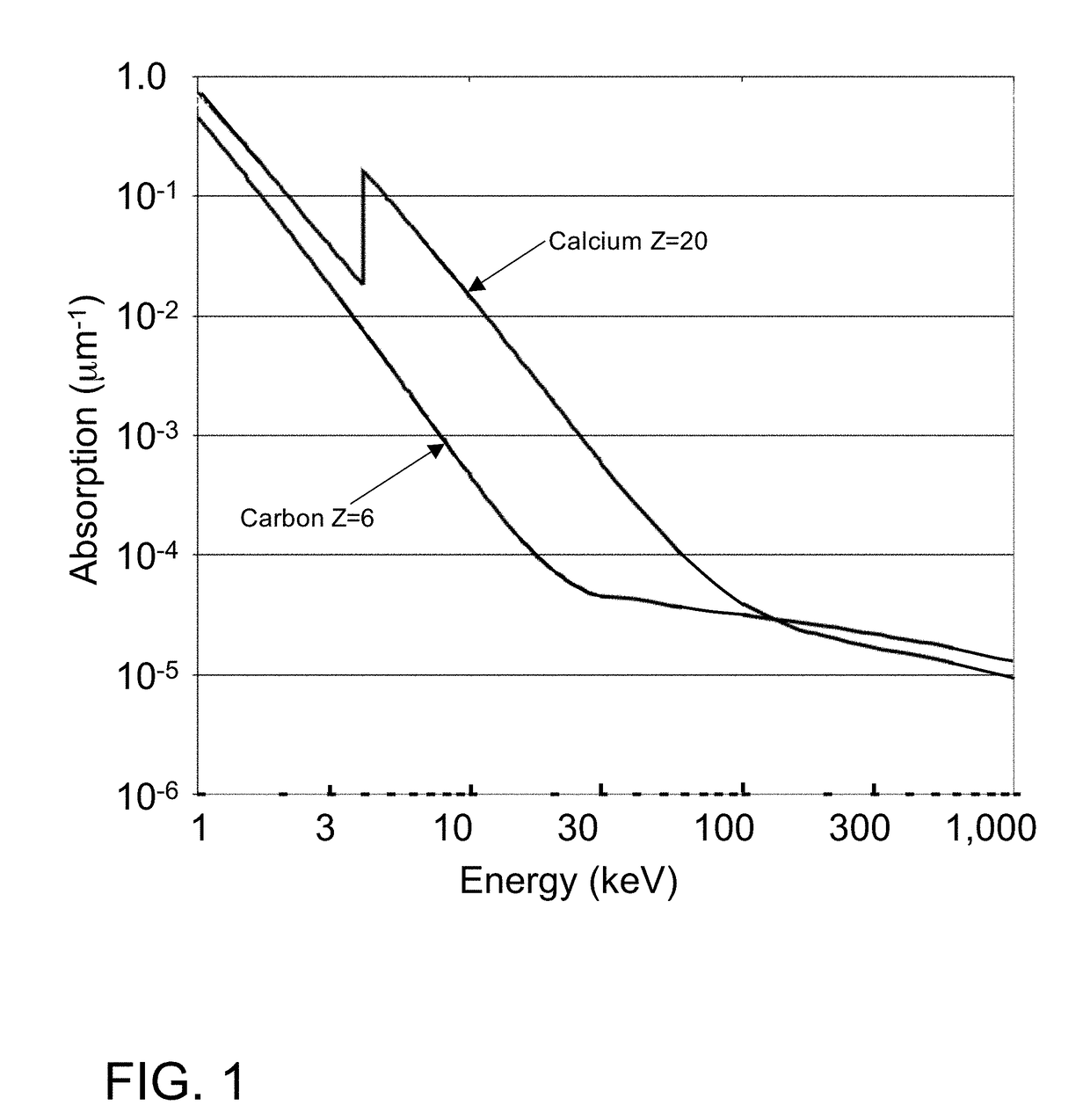
InactiveUS20130079918A1X-ray spectral distribution measurementDigital data processing detailsX-rayDetector array
Systems for sorting materials, such as those made of metal, are described. The systems may operate by irradiating the materials with x-rays and then detecting fluoresced x-rays, transmitted x-rays, or both. Detection of the fluoresced x-rays may be performed using an x-ray fluorescence detector array. The systems may be configured to provide high throughput sorting of small pieces of materials.
Owner:SPECSTREETCARET
X-ray method for the measurement, characterization, and analysis of periodic structures
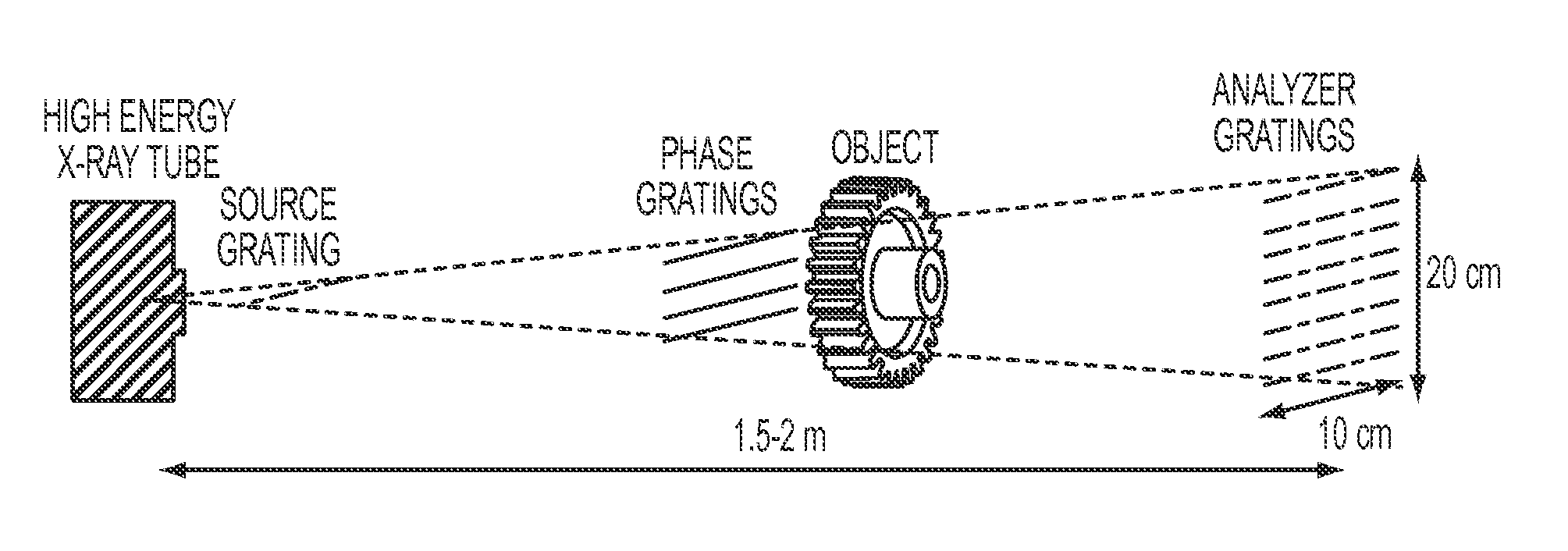
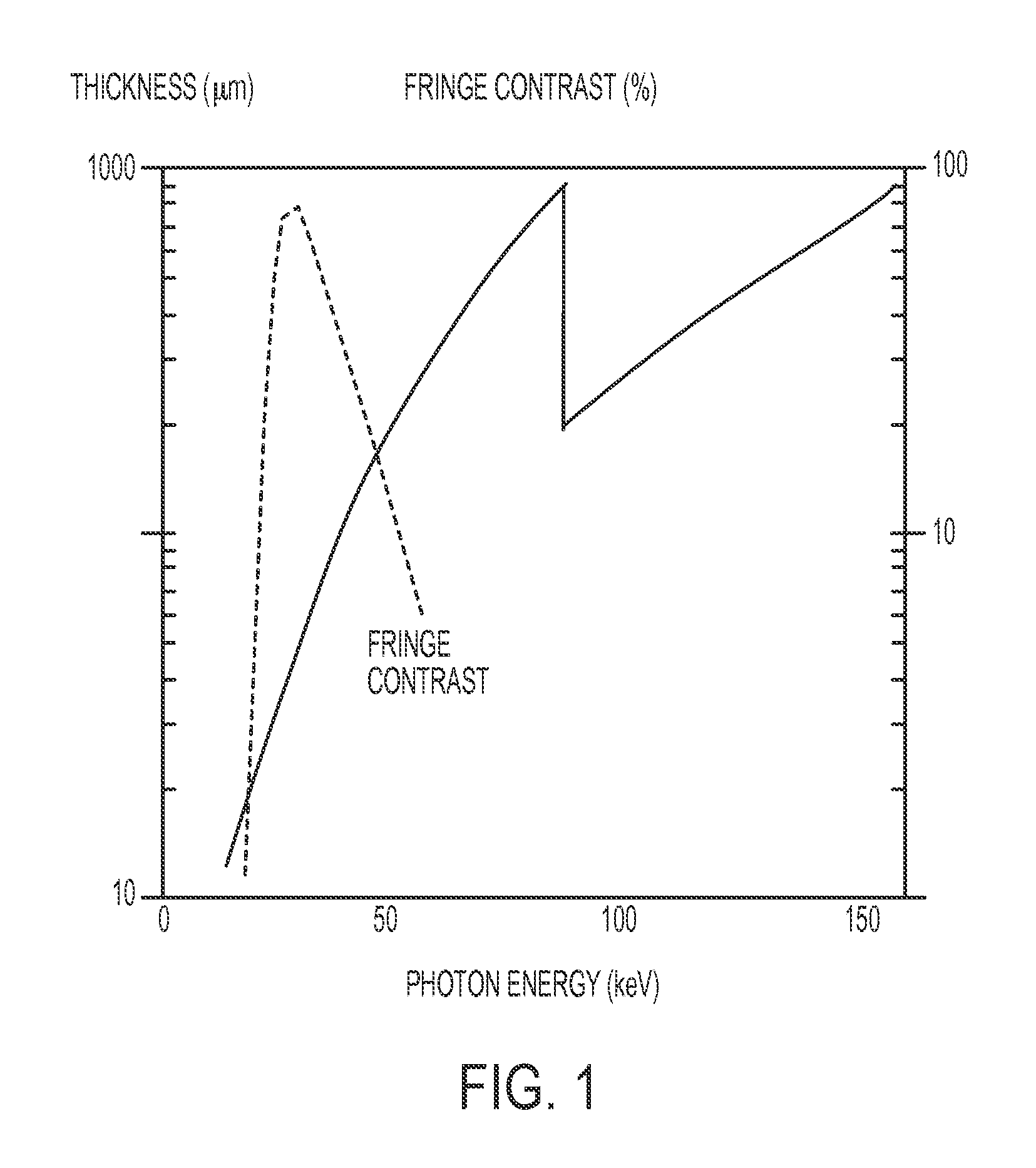
ActiveUS20150260663A1Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Periodic spatial patterns of x-ray illumination are used to gather information about periodic objects. The structured illumination may be created using the interaction of a coherent or partially coherent x-ray source with a beam splitting grating to create a Talbot interference pattern with periodic structure. The object having periodic structures to be measured is then placed into the structured illumination, and the ensemble of signals from the multiple illumination spots is analyzed to determine various properties of the object and its structures. Applications to x-ray absorption / transmission, small angle x-ray scattering, x-ray fluorescence, x-ray reflectance, and x-ray diffraction are all possible using the method of the invention.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Fluidized Bed Device
InactiveUS20090123665A1Good hygroscopicityVulnerable to moistureLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingFluidized bedX-ray
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Radiation imaging apparatus, radiation imaging system, and program
InactiveUS20070080299A1Accurate and high-S/N-ratio X-ray radiographic imageObtain goodSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansX-rayRadiation imaging
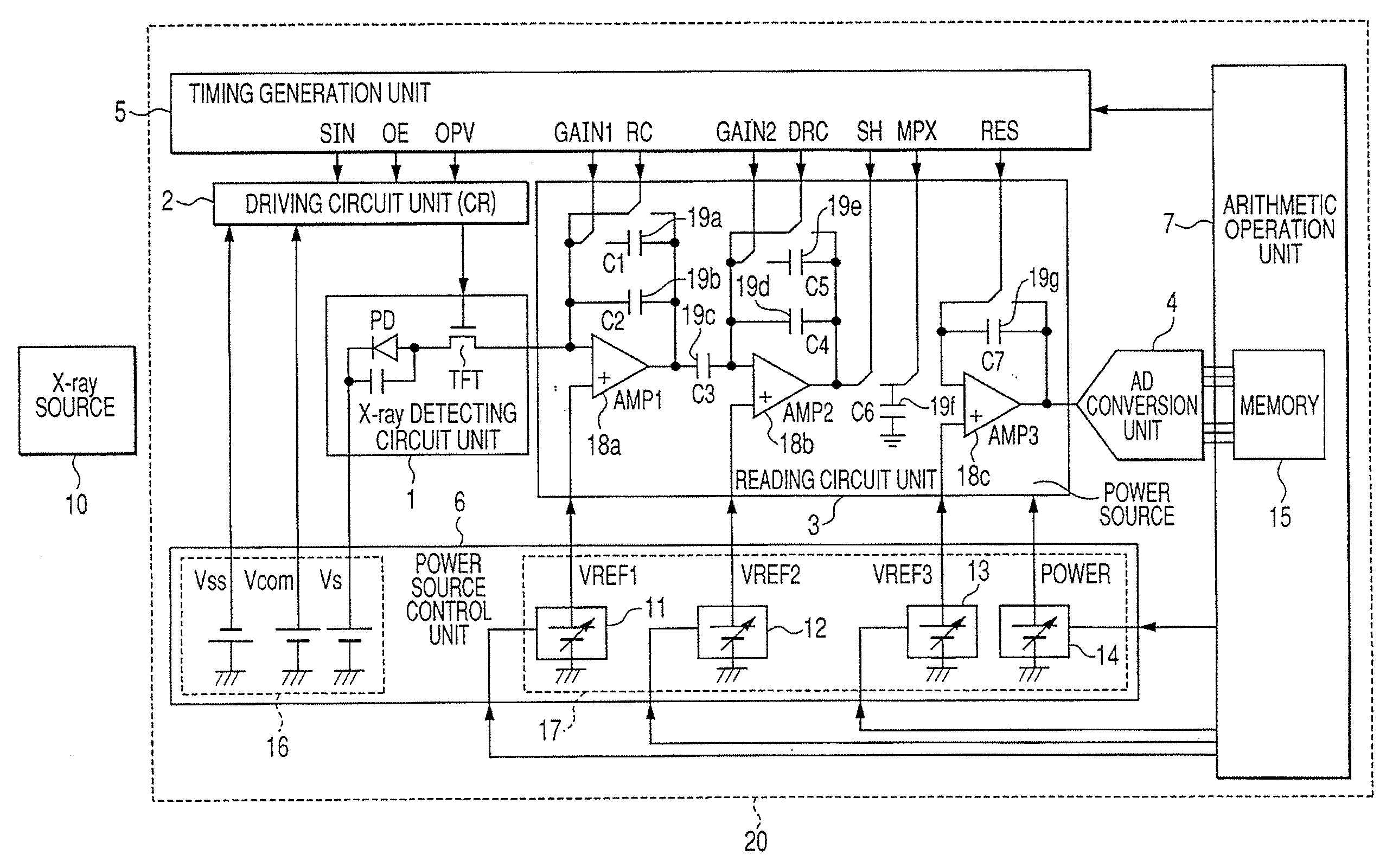
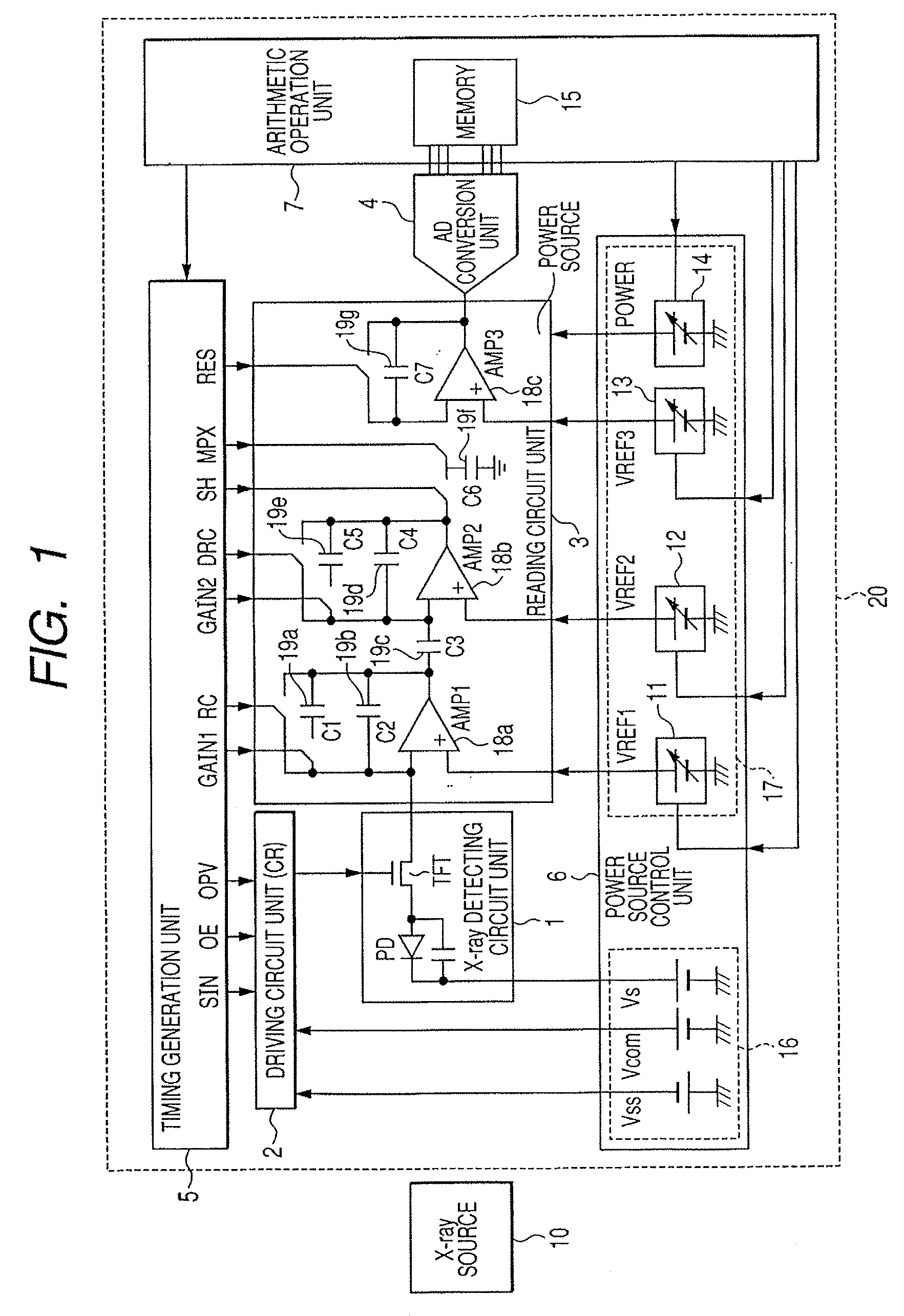
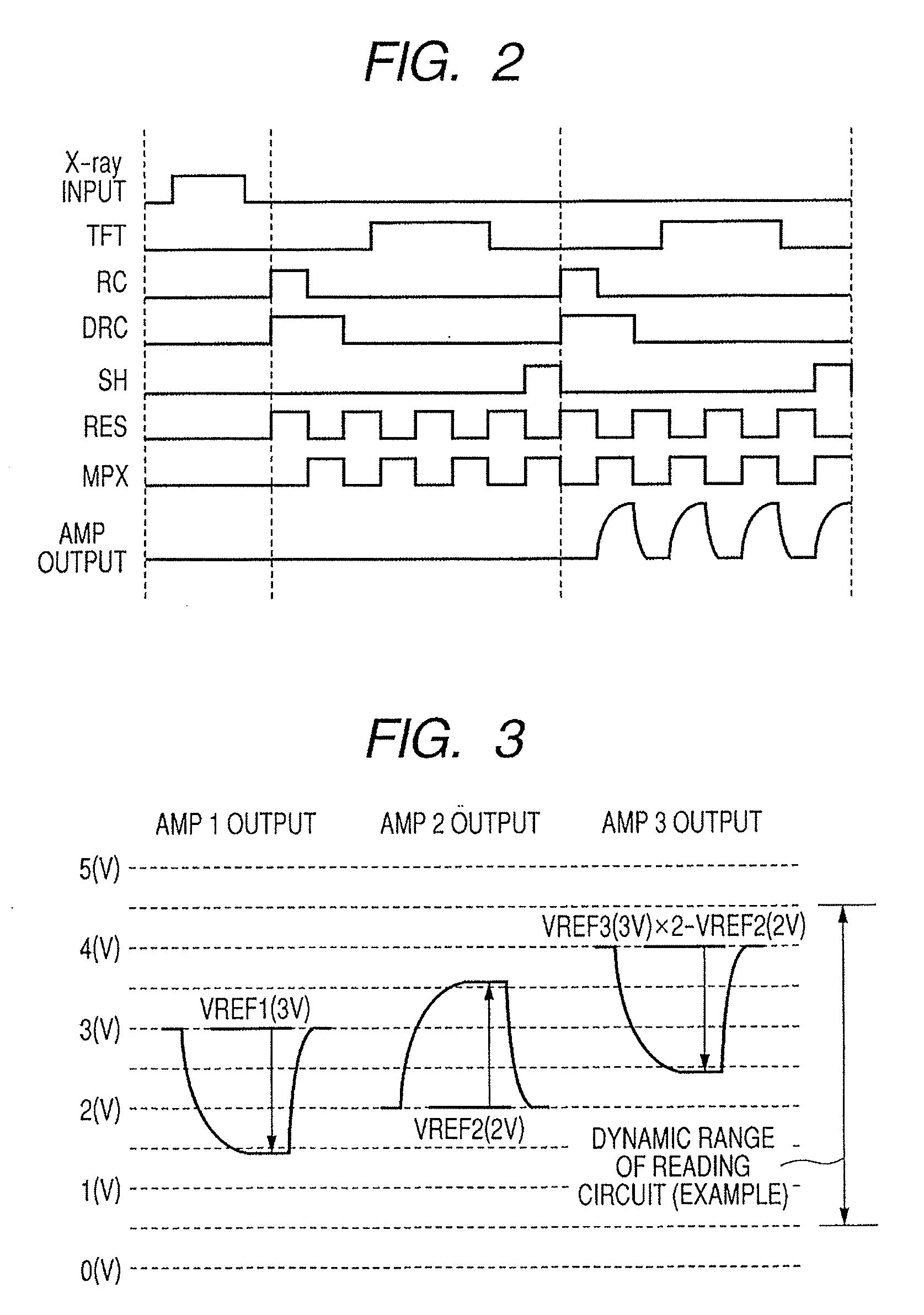
It is made possible that, in accordance with a plurality of radiographing modes such as the still image radiographing mode and the moving image radiographing mode, the outputs both in the irradiation period and in the non-irradiation period are made to fall within the dynamic range of the radiographing system, whereby an accurate, high-S / N-ratio X-ray radiographic image is obtained. For that purpose, in accordance with the plurality of radiographing modes, an arithmetic operation unit adjusts a power source to control voltage to be applied to a reading circuit unit or an Analogue-Digital conversion unit, such that, in each of the radiographing modes, both an electric signal in the X-ray irradiation period and an electric signal in the X-ray non-irradiation period fall within the dynamic ranges of the reading circuit unit and the Analogue-Digital conversion unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Decellularized Tissue and Method of Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20070244568A1Improve efficiencyGood effectMammal material medical ingredientsProsthesisUltravioletSolvent
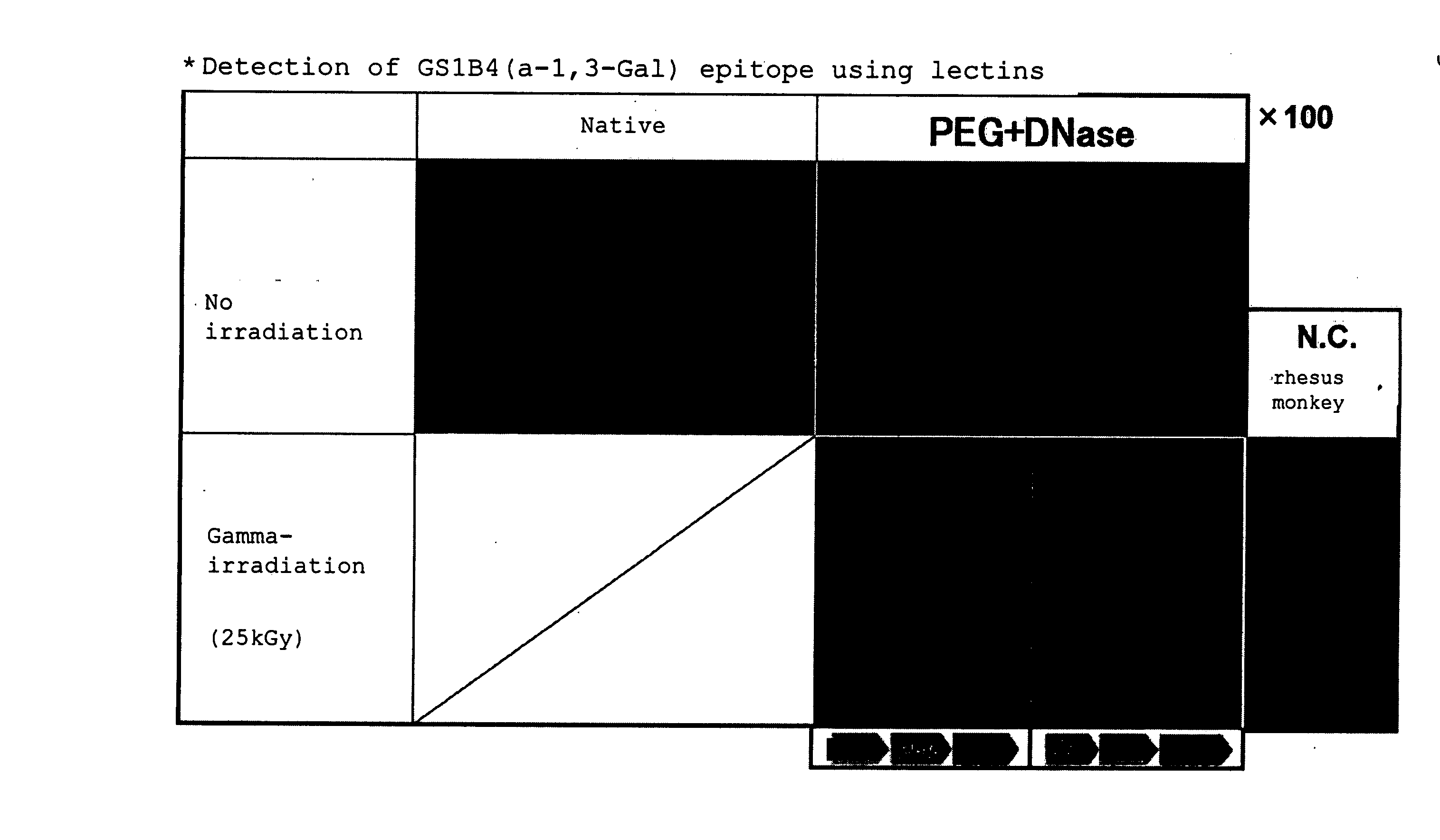
Decellularization of tissue by means of an amphipathic solvent a well-established practice. However, situations exist where the provision of enhanced decellularization is preferred. There is a demand for treating methods for coping with such situations. Thus, it is intended to provide a method for enhancing decellularization. The method comprises not only the immersing of a tissue in a solution containing an amphiphilic molecule in non-micellar form (for example, 1,2-epoxide polymer) but also performing a radical reaction (for example, treatment selected from the group consisting of exposure to gamma-ray irradiation, ultraviolet irradiation, a free radical supply source, ultrasonication, electron beam irradiation, and X-ray irradiation).
Owner:CARDIO +1
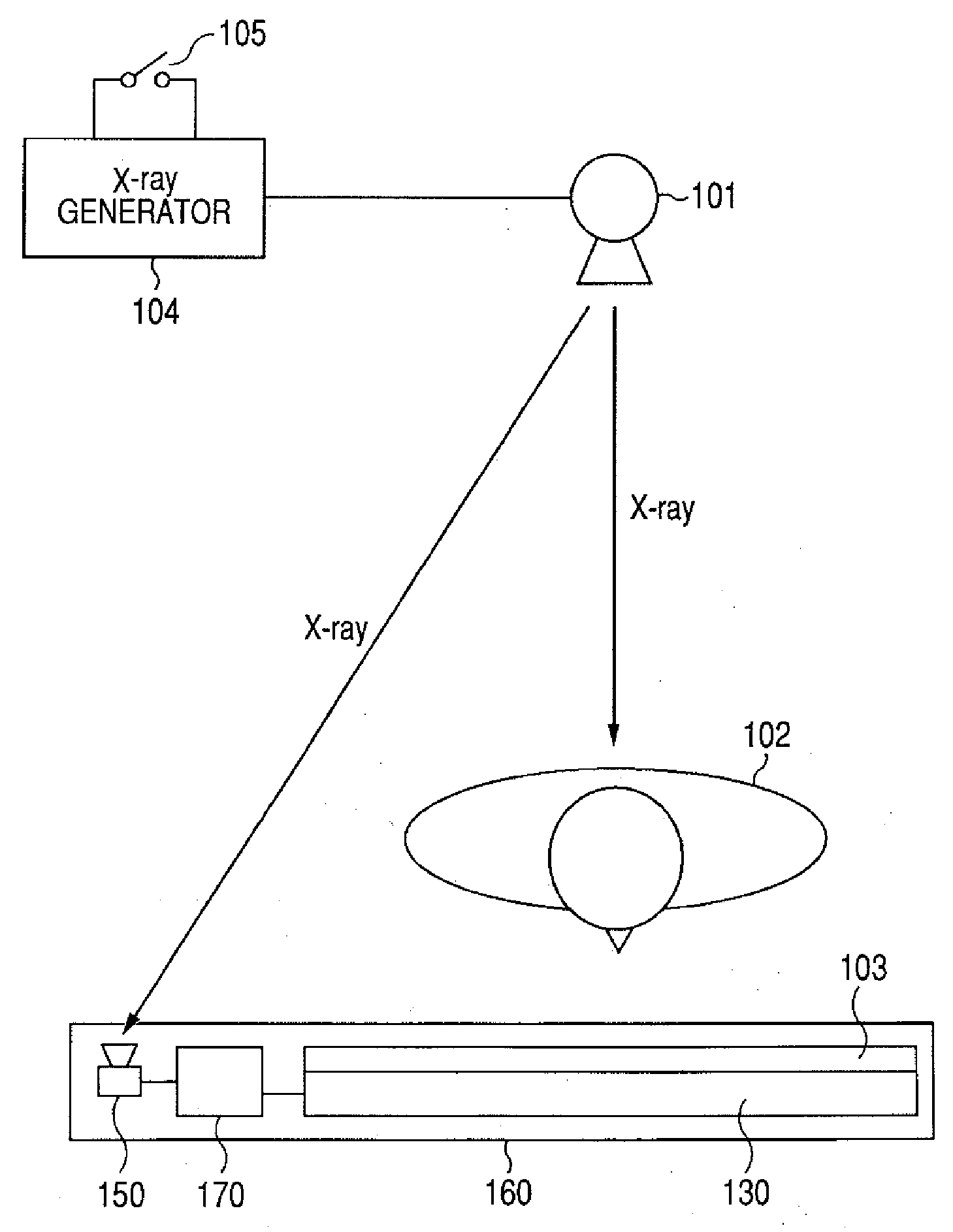
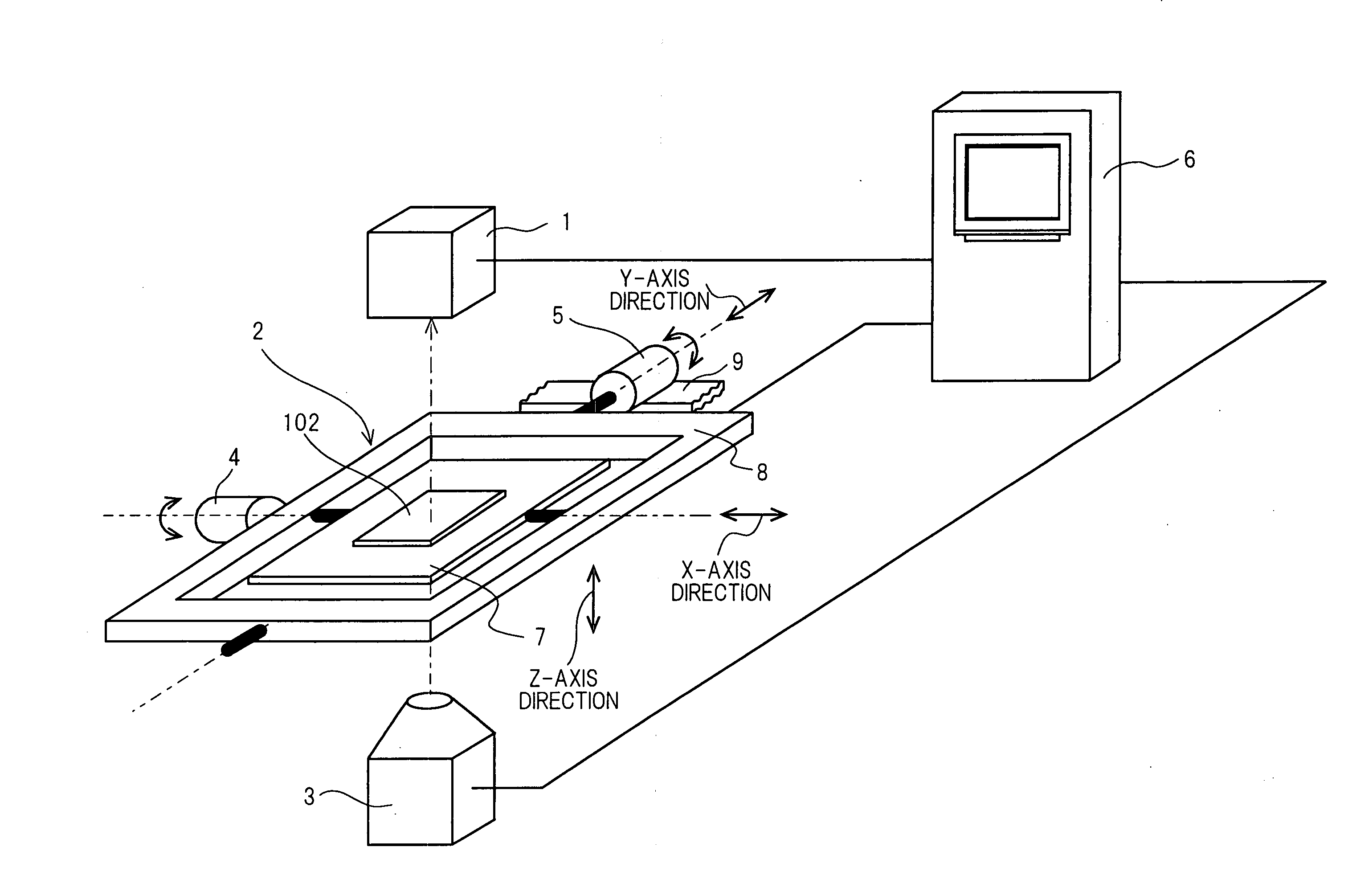
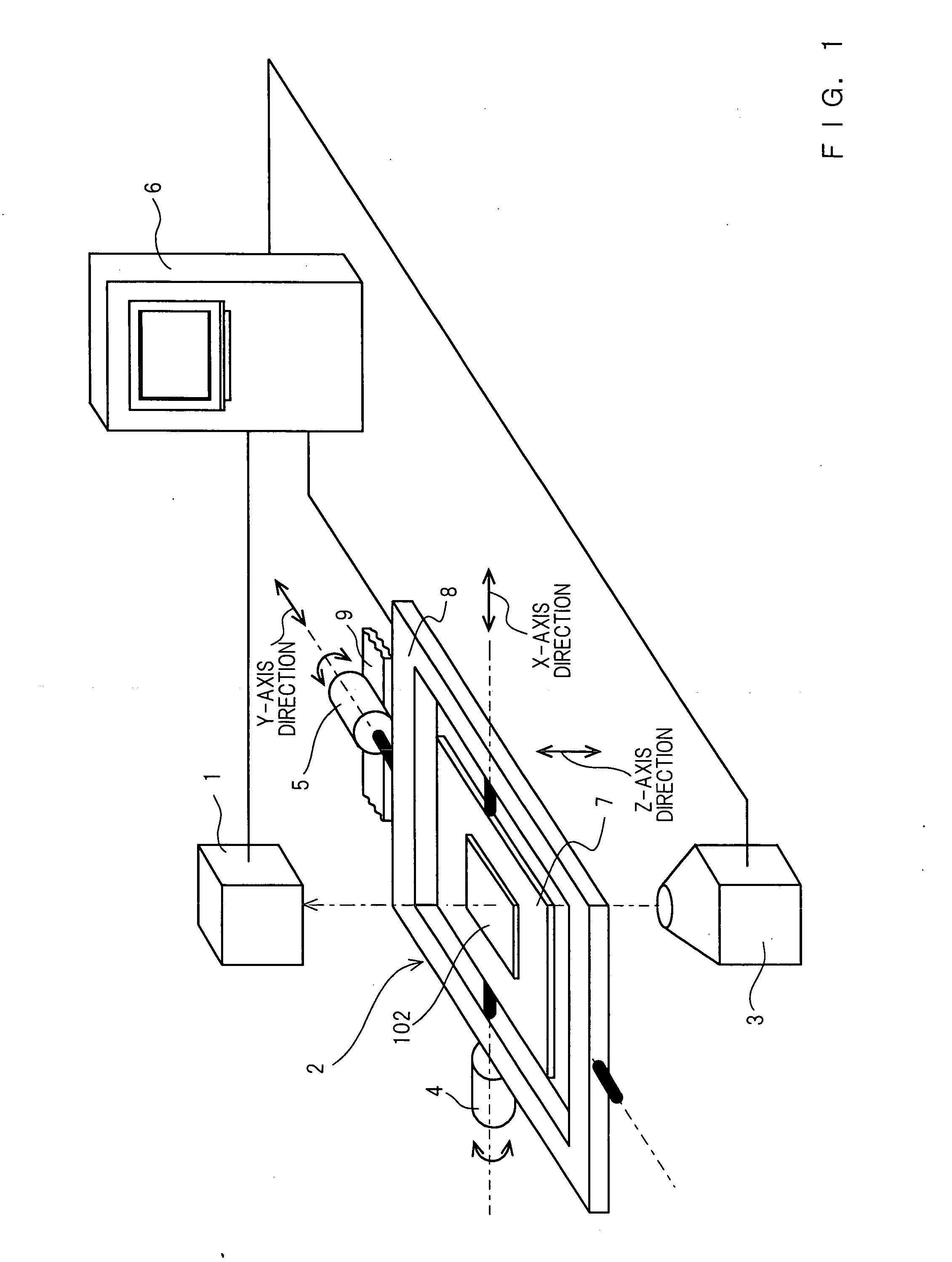
X-ray inspection apparatus and X-ray inspection method
InactiveUS20050074088A1High-density packagingLow costRadiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-rayX ray image
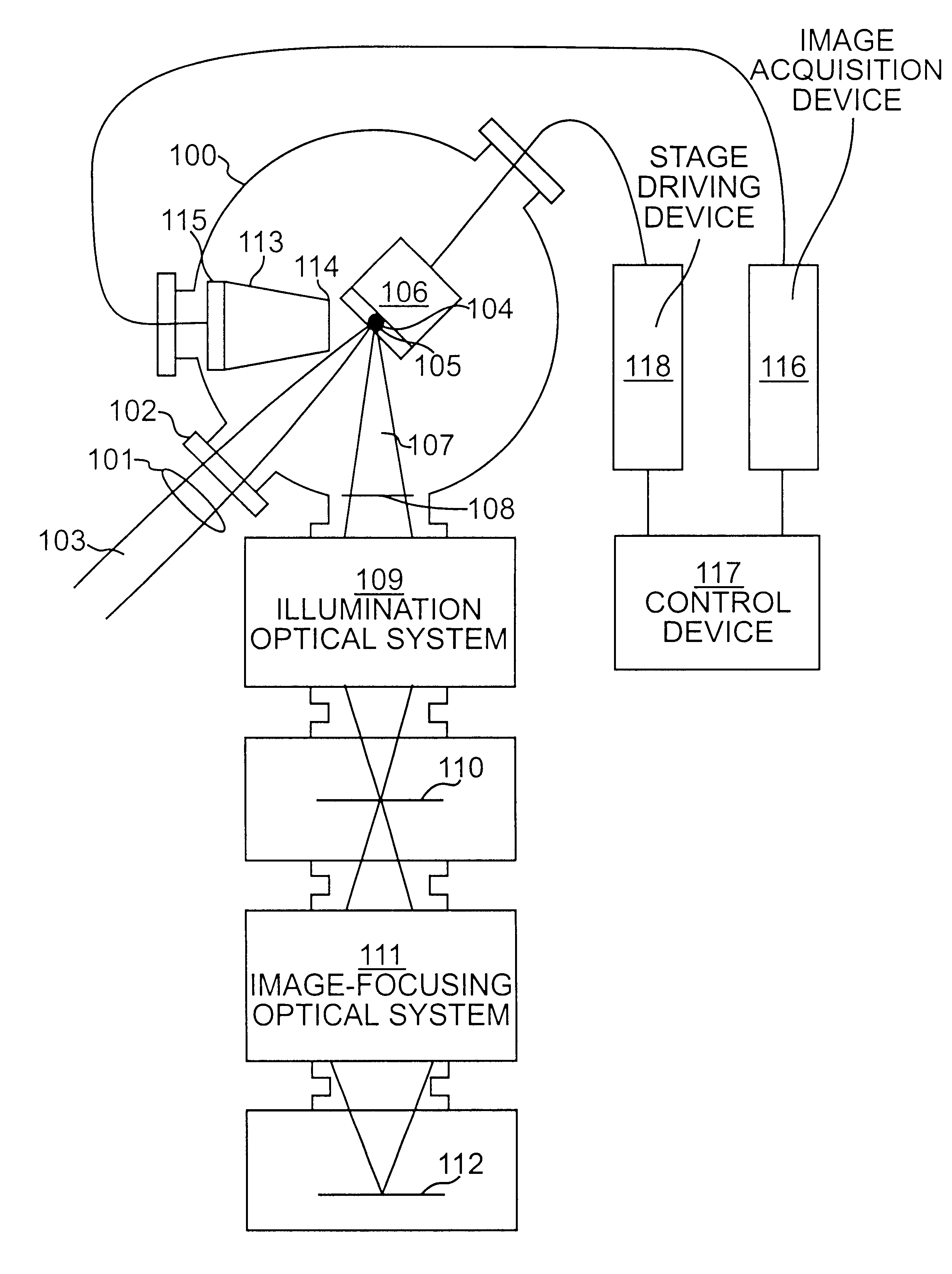
The X-ray inspection device and the X-ray inspection method according to the present invention are configured to hold an object to be inspected irradiated with an X-ray from an X-ray irradiation device, uses a swinging device for performing swinging motion of tilting the object to be inspected at an arbitrary angle and in an arbitrary direction, images the X-ray that passes through the object to be inspected in an X-ray detection device and extracts data of a desired cross section from the X-ray image of the X-ray detection device in a control device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
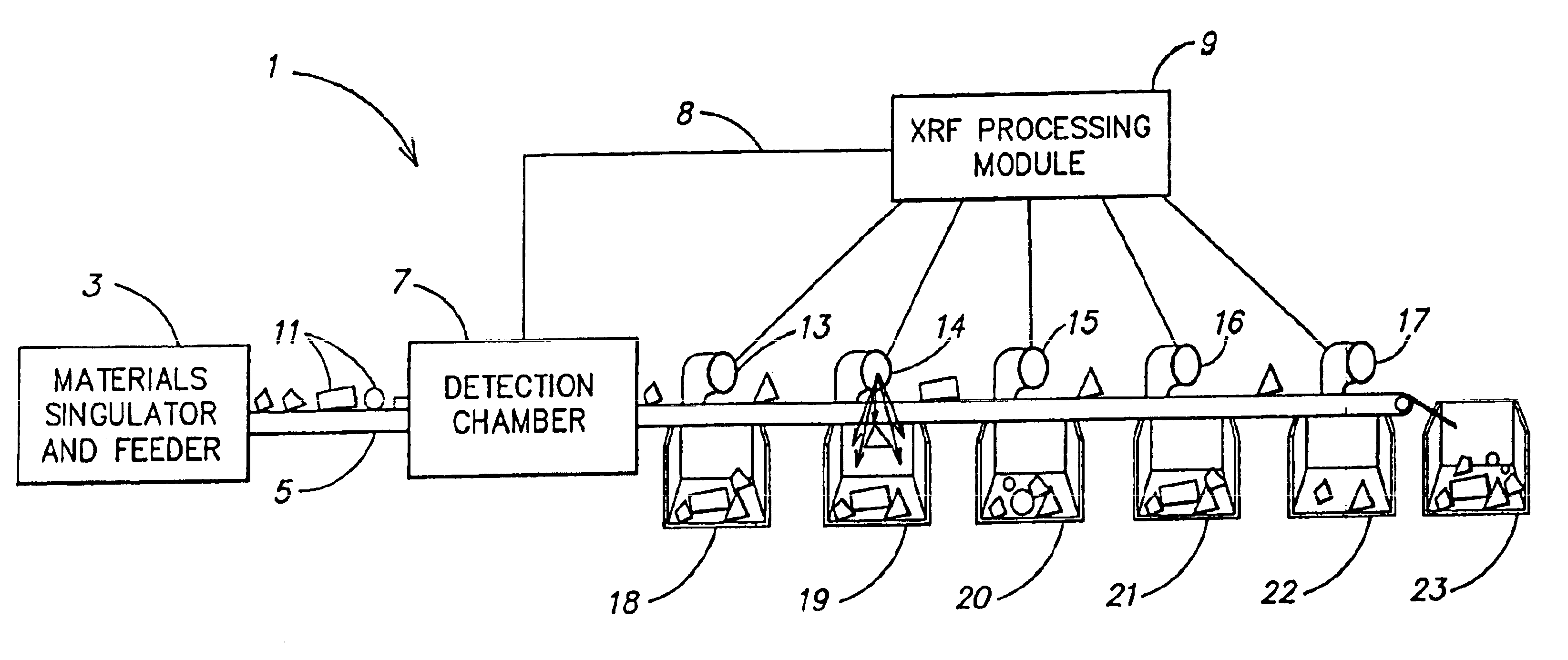
Apparatus for detecting foreign matter with high selectivity and high sensitivity by image processing
InactiveUS6023497AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsForeign matterX-ray
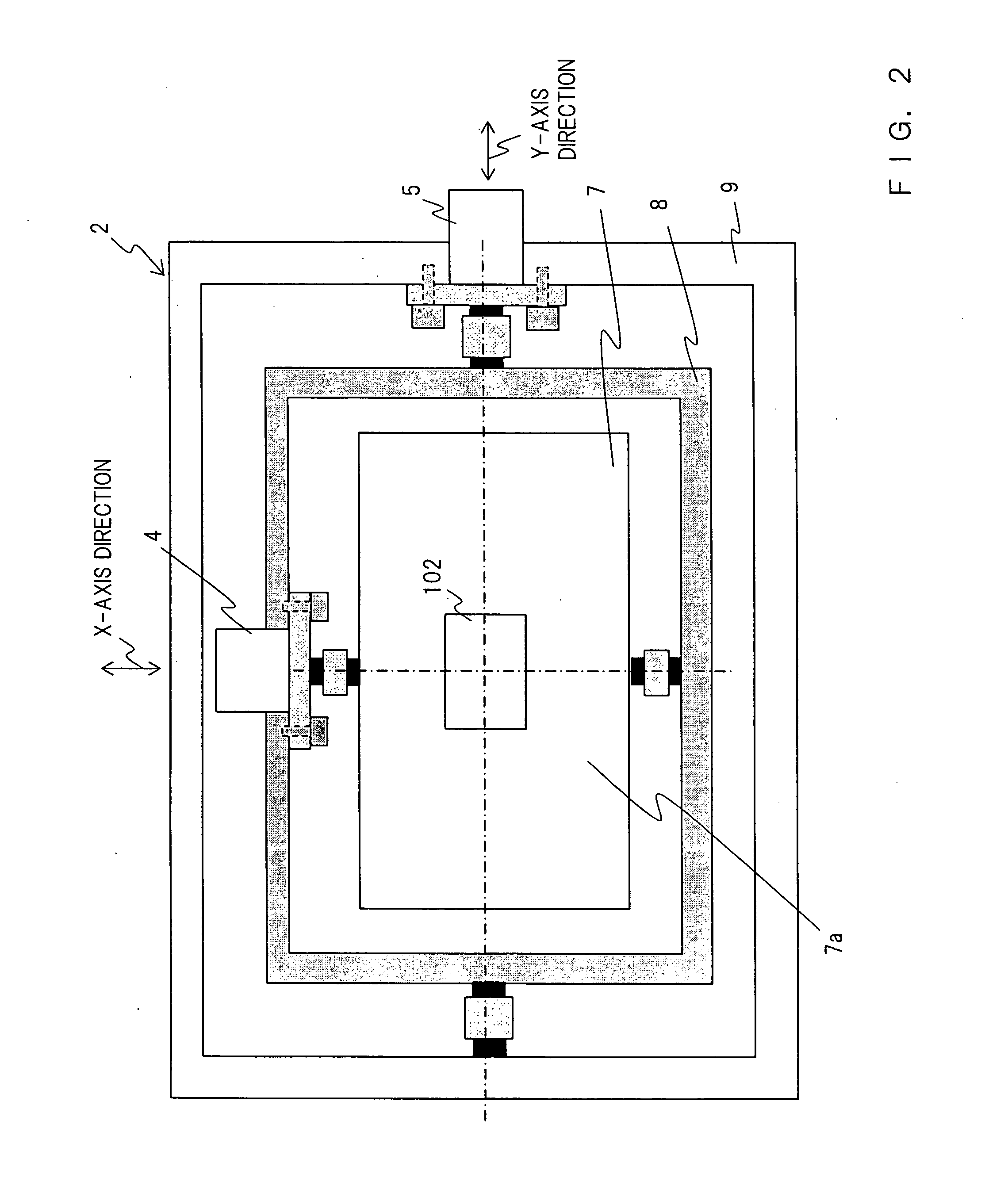
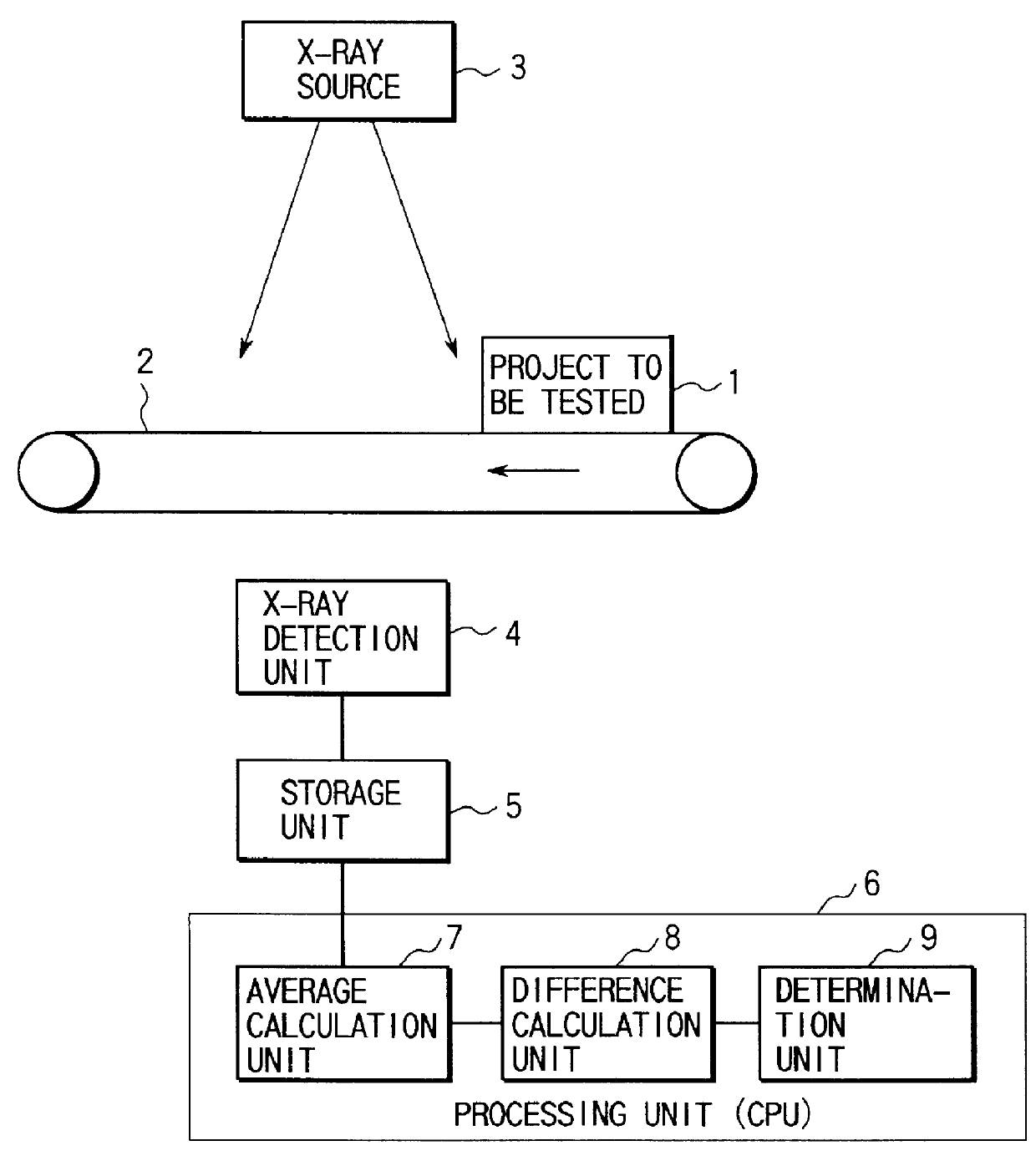
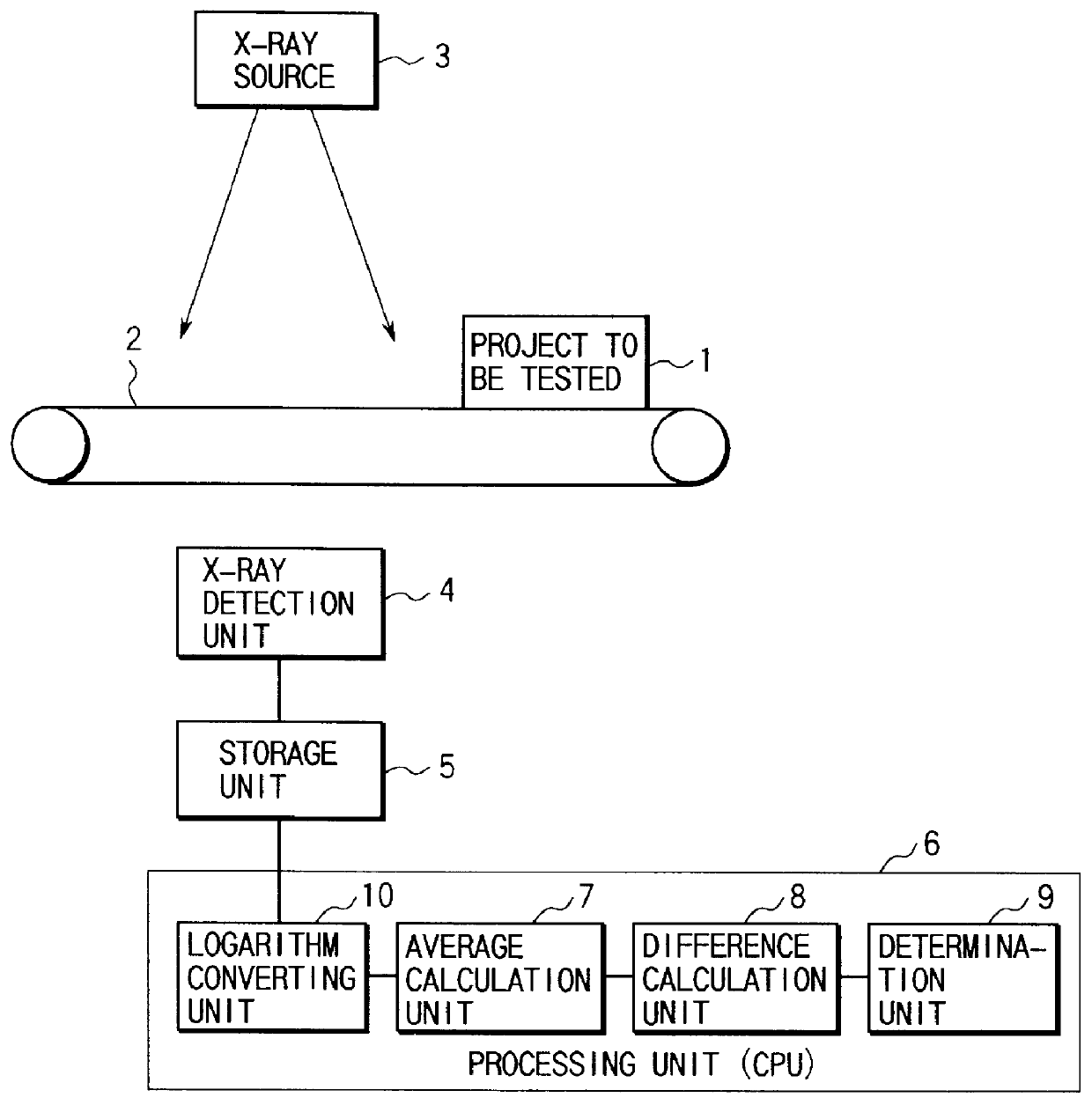
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03778 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 17, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 17, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 11456 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 19, 1998This invention provides a contaminant-detecting apparatus having high selectivity and high sensitivity against a contaminant. A product (1) is conveyed to a point where it is irradiated by x-rays from source (3). An x-ray detector (4), having a predetermined detection unit width in a direction perpendicularly intersecting the conveying direction, then detects the x-rays transmitted through the product. A storage unit (5) stores a two-dimensional distribution of x-ray intensity detected by the x-ray detector as a transmission image in units of pixels. An average calculation unit (7) performs a sum-or-product operation of a kernel, which is equal to or larger than 7x7 pixels, (9x9 or 11x11), and equal to or smaller than (a pixel count corresponding to +E,fra 1 / 2+EE the predetermined x-ray detection unit width)x(pixel count corresponding to +E,fra 1 / 2+EE the predetermined x-ray detection unit width), and includes a target pixel, in units of pixels of the transmission image stored in the storage unit by using a predetermined coefficient matrix, thereby calculating the weighted average over the kernel. A difference calculation unit (8) calculates the difference between the x-ray intensity of the target pixel of the transmission image stored in the storage unit and the weighted average over the kernel of the target pixel which is calculated by the difference calculation unit. A determination unit (9) compares the difference calculated by the difference calculation unit with predetermined criteria, thereby determining presence / absence of a contaminant in the product to be tested.
Owner:ANRITSU SANKI SYSTEM CO LTD
Method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation
InactiveUS20030147484A1Increases radiation levelReduce riskConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron irradiationX-ray
A method for detecting an explosive in an object under investigation involves the initial X-ray irradiation of the object under investigation, e.g. a piece of luggage or mailing, and forming its X-ray images; using the X-ray images to detect areas with a high density of organic materials and identifying articles therein; determining the location, dimensions and supposed mass of an unidentified article; determining and forming a directional pattern of the neutron radiator corresponding to the dimensions of the unidentified article. The method further includes subsequent thermal neutron irradiation of the area with the unidentified article; recording gamma-ray quanta having the energy of 10.8 MeV and cascade gamma-ray quanta with energies of 5.534 and 5.266 MeV by at least two gamma-ray detectors; counting of simultaneously recorded pairs of cascade gamma-ray quanta; determination of the overall gamma-ray intensity, taking into account weight factors in readings of the detectors; determination of the threshold value for the overall gamma-ray intensity basing on the supposed mass of explosive being detected; and making a decision in the event the threshold value of overall gamma-ray intensity is exceeded. When checking small-size objects, the neutron irradiation step is preceded by replacing the ambient air by a gaseous medium not containing nitrogen.
Owner:SCI & TECHN CENT RATEC
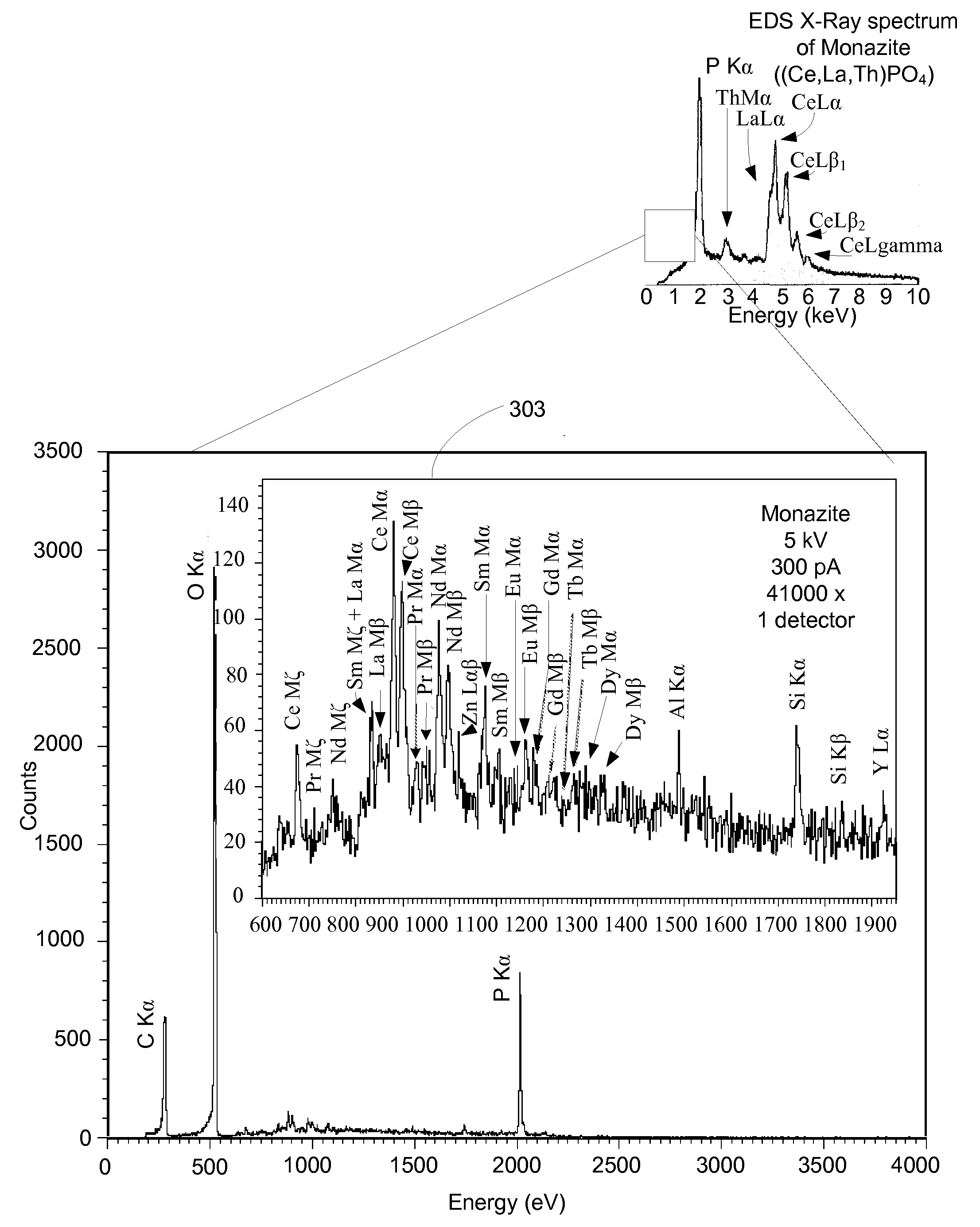
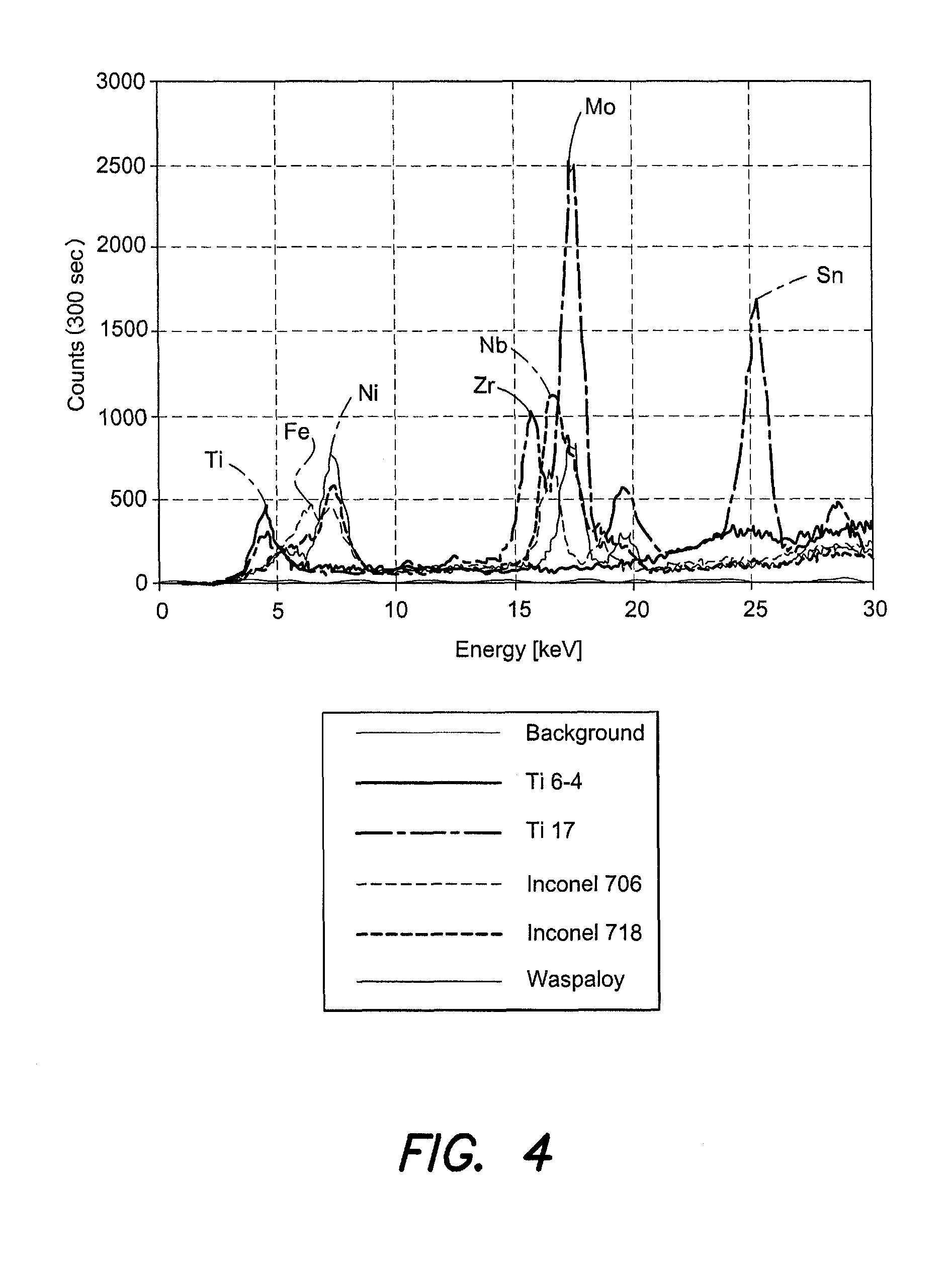
Microcalorimetry for x-ray spectroscopy
ActiveUS20110064191A1High resolution mappingSolve the lack of resolutionThermometer detailsX-ray spectral distribution measurementBeam energySpectrometer
An improved microcalorimeter-type energy dispersive x-ray spectrometer provides sufficient energy resolution and throughput for practical high spatial resolution x-ray mapping of a sample at low electron beam energies. When used with a dual beam system that provides the capability to etch a layer from the sample, the system can be used for three-dimensional x-ray mapping. A preferred system uses an x-ray optic having a wide-angle opening to increase the fraction of x-rays leaving the sample that impinge on the detector and multiple detectors to avoid pulse pile up.
Owner:FEI CO
X-ray illuminators with high flux and high flux density
InactiveUS9449781B2Heat generationIncrease electron densityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesDesign for XFluorescence
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray illumination that have an x-ray brightness several orders of magnitude greater than existing x-ray technologies. These may therefore useful for applications such as trace element detection or for micro-focus fluorescence analysis. The higher brightness is achieved in part by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of microstructures of one or more selected x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment of the targets with higher electron density or higher energy electrons, which leads to greater x-ray flux. The high brightness / high flux x-ray source may then be coupled to an x-ray optical system, which can collect and focus the high flux x-rays to spots that can be as small as one micron, leading to high flux density.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
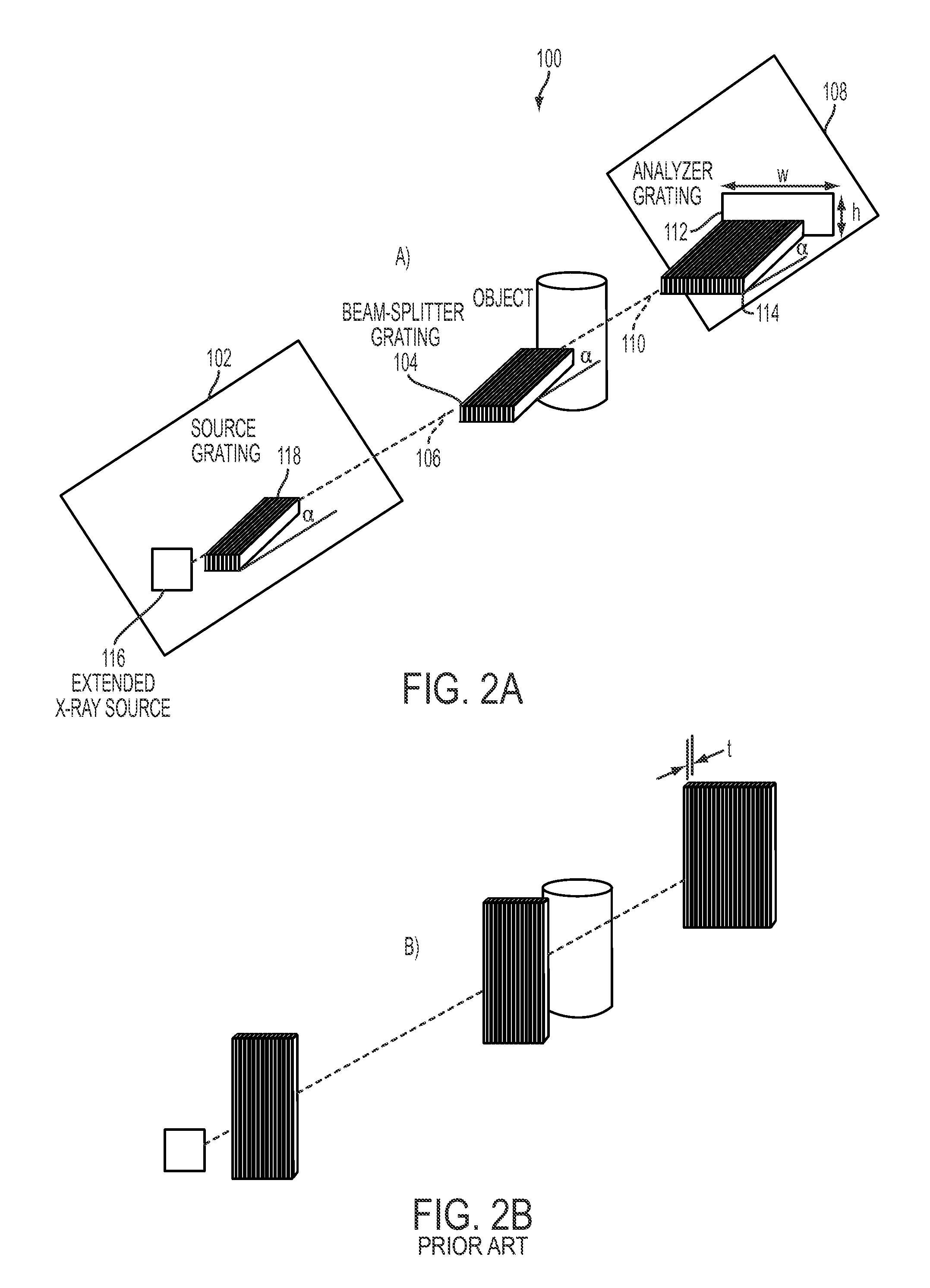
Differential phase contrast x-ray imaging system and components
A differential phase contrast X-ray imaging system includes an X-ray illumination system, a beam splitter arranged in an optical path of the X-ray illumination system, and a detection system arranged in an optical path to detect X-rays after passing through the beam splitter.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High speed materials sorting using x-ray fluorescence
InactiveUS6888917B2Accuracy of compromisedSpeed of compromisedX-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansSpectral patternSoft x ray
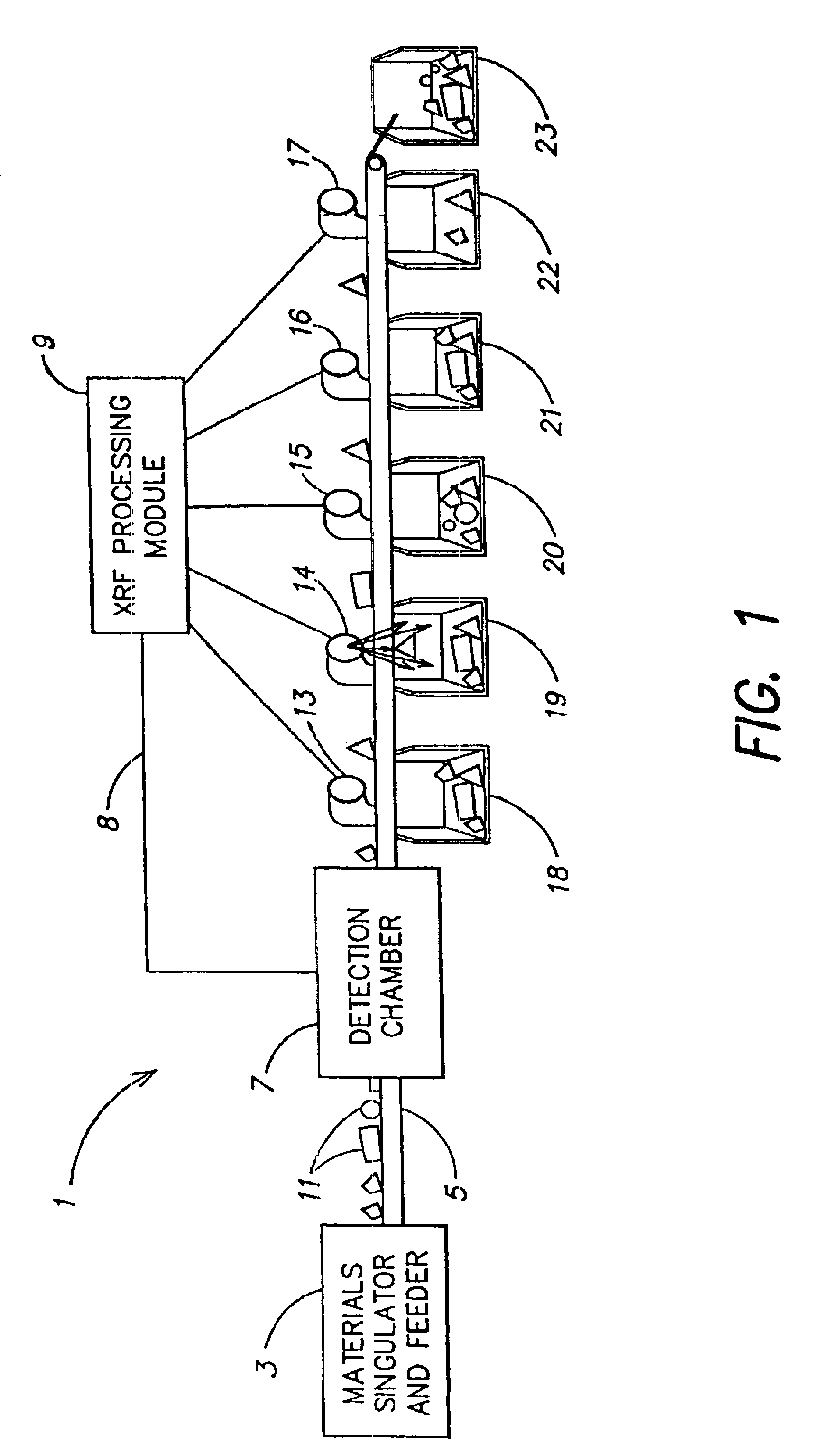
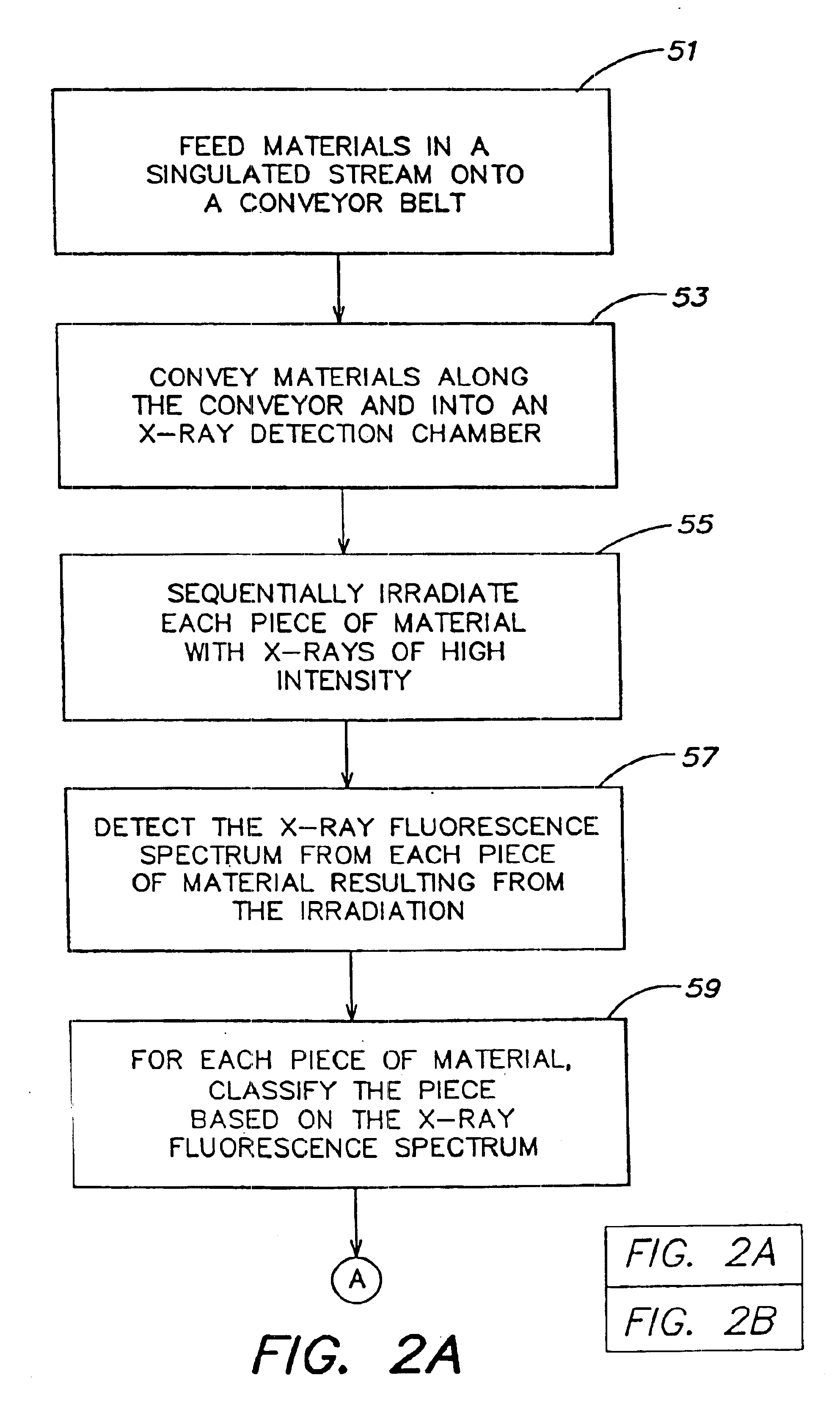
A system and process for classifying a piece of material of unknown composition at high speeds, where the system connected to a power supply. The piece is irradiated with first x-rays from an x-ray source, causing the piece to fluoresce x-rays. The fluoresced x-rays are detected with an x-ray detector, and the piece of material is classified from the detected fluoresced x-rays. Detecting and classifying may be cumulatively performed in less than one second. An x-ray fluorescence spectrum of the piece of material may be determined from the detected fluoresced x-rays, and the detection of the fluoresced x-rays may be conditioned such that accurate determination of the x-ray fluorescence spectrum is not significantly compromised, slowed or complicated by extraneous x-rays. The piece of material may be classified by recognizing the spectral pattern of the determined x-ray fluorescence spectrum. The piece of material may be flattened prior to irradiation and detection. The x-ray source may irradiate the first x-rays at a high intensity, and the x-ray source may be an x-ray tube.
Owner:SPECSTREETCARET
X-ray method for the measurement, characterization, and analysis of periodic structures
ActiveUS9874531B2Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Material sorting technology
InactiveUS8855809B2X-ray spectral distribution measurementDigital data processing detailsX-rayDetector array
Systems for sorting materials, such as those made of metal, are described. The systems may operate by irradiating the materials with x-rays and then detecting fluoresced x-rays, transmitted x-rays, or both. Detection of the fluoresced x-rays may be performed using an x-ray fluorescence detector array. The systems may be configured to provide high throughput sorting of small pieces of materials.
Owner:SPECSTREETCARET
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com