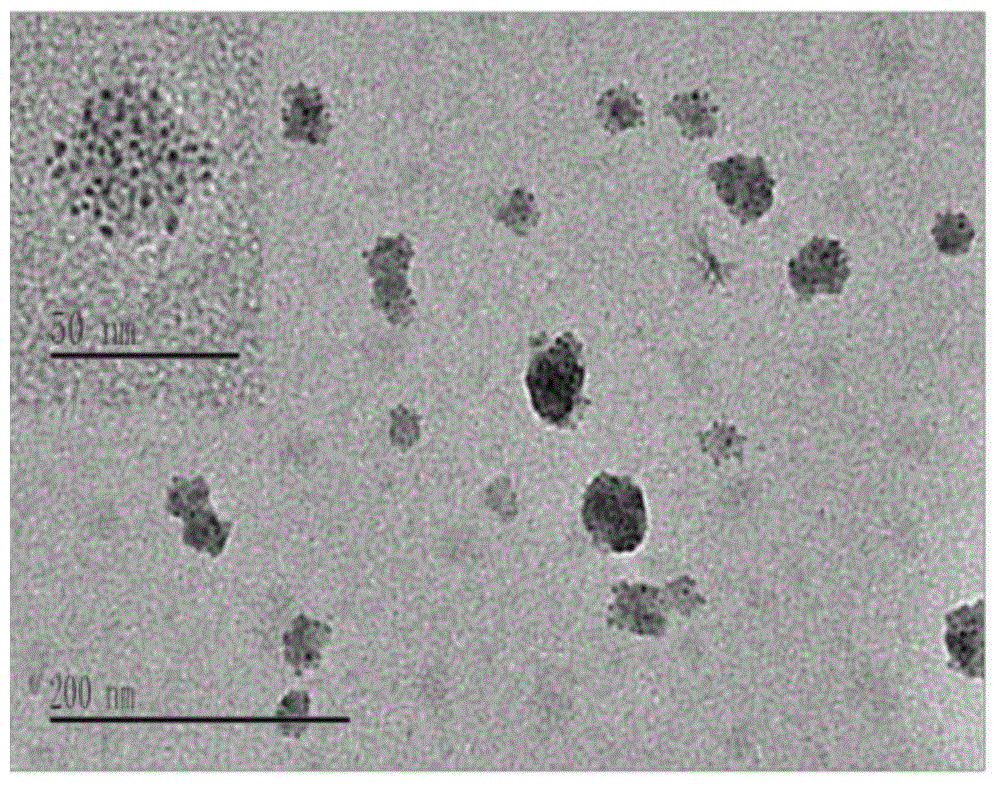
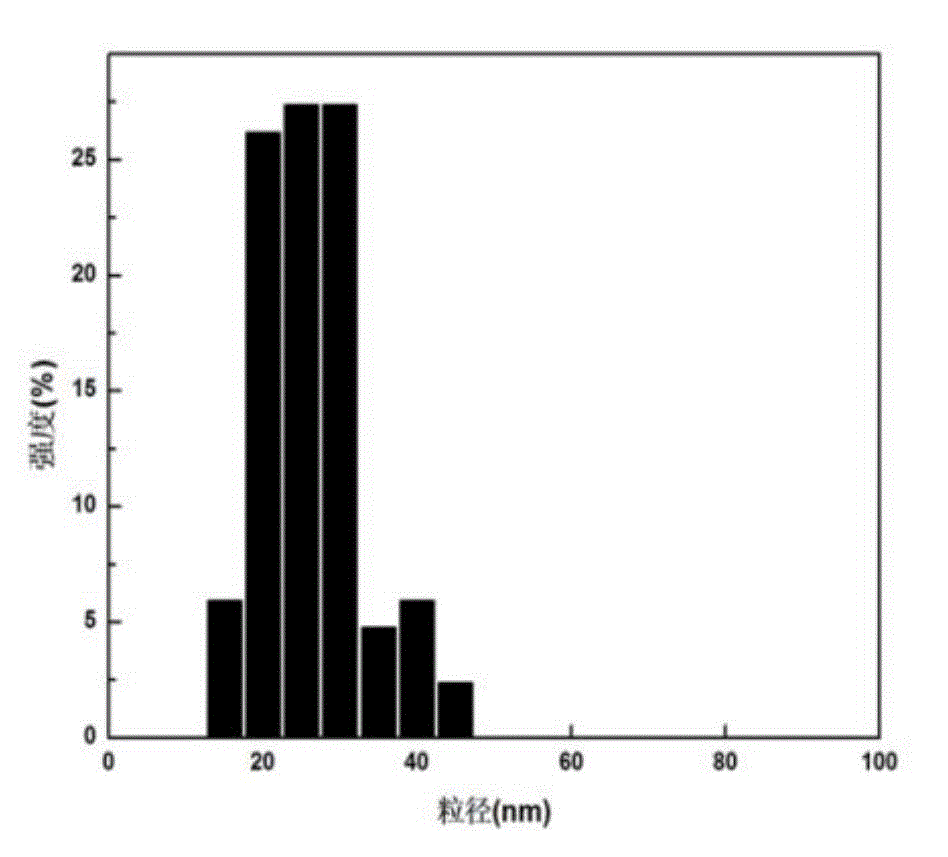
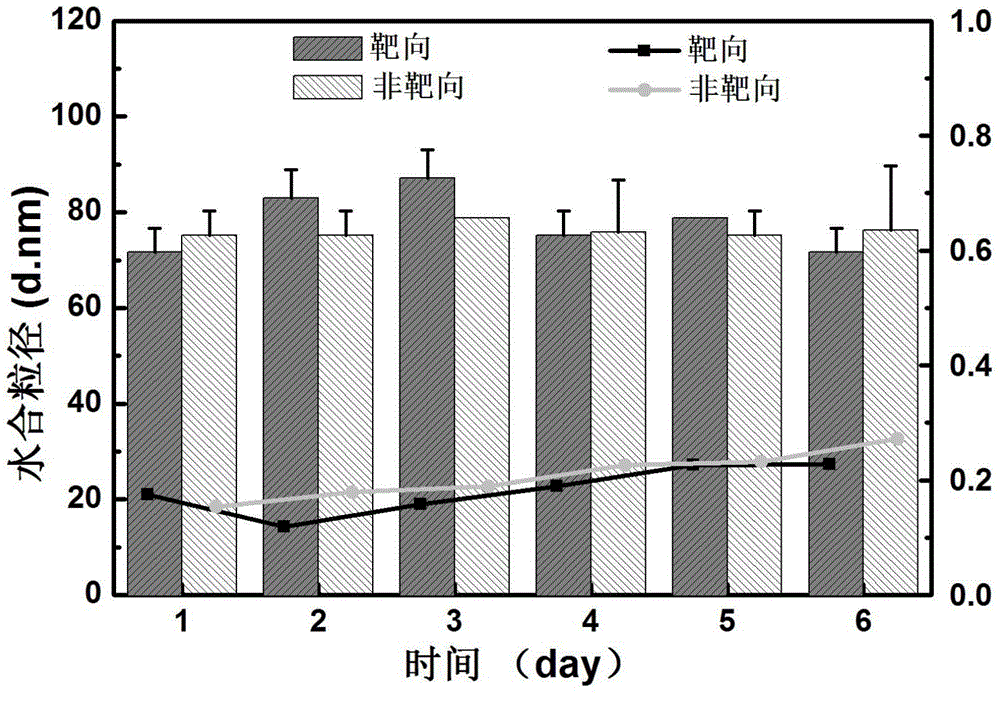
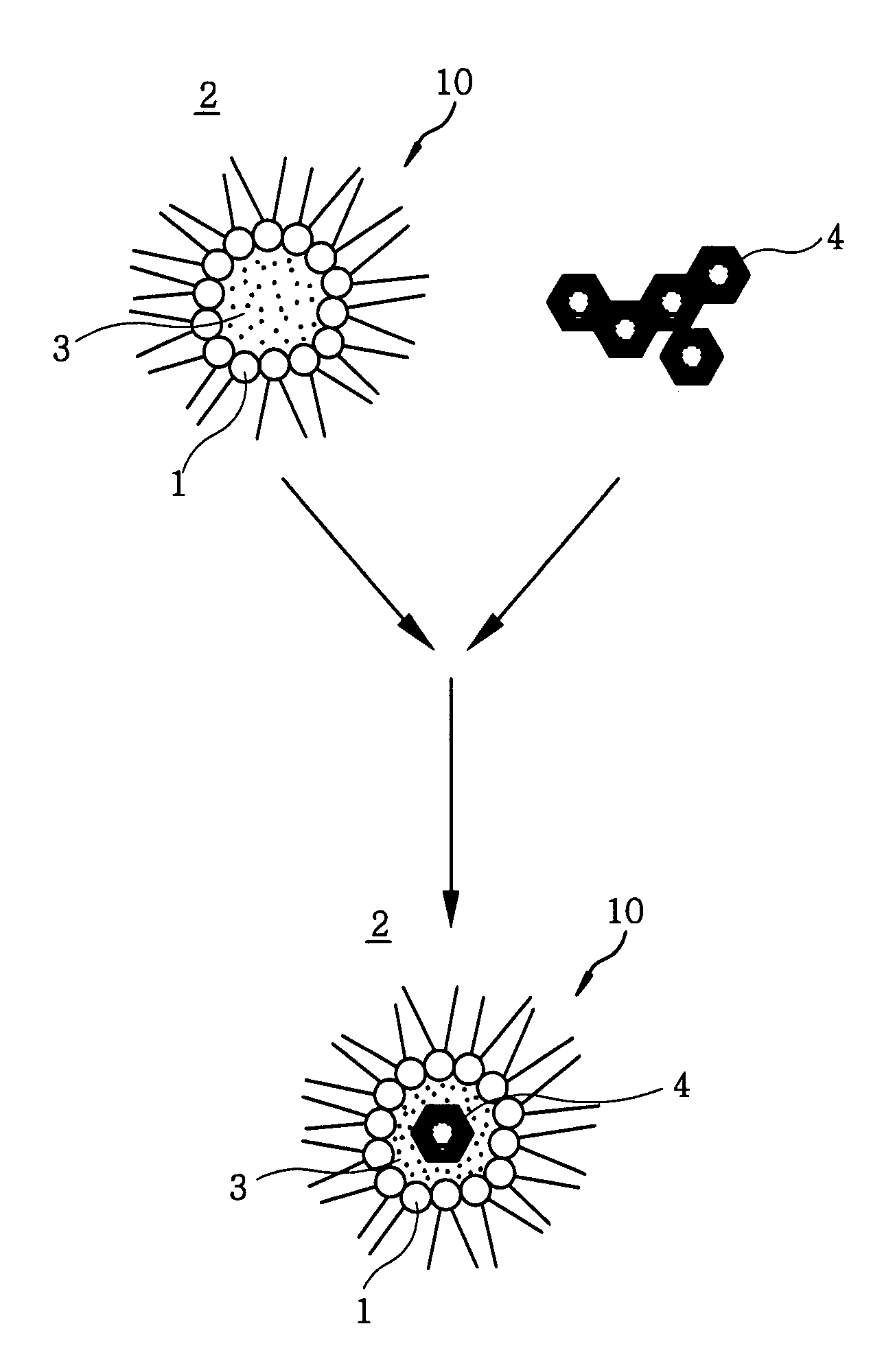
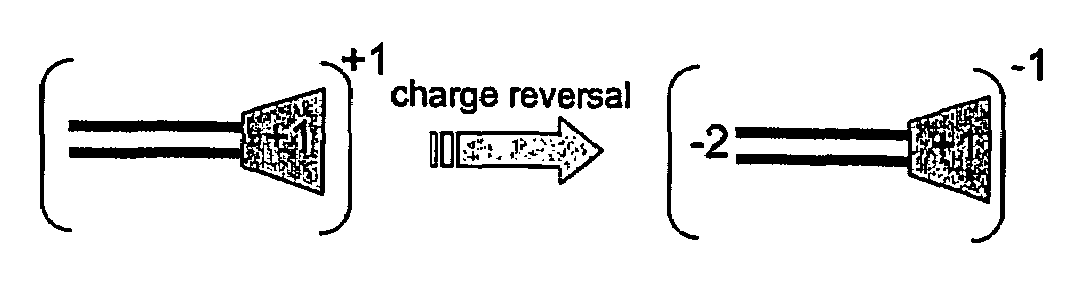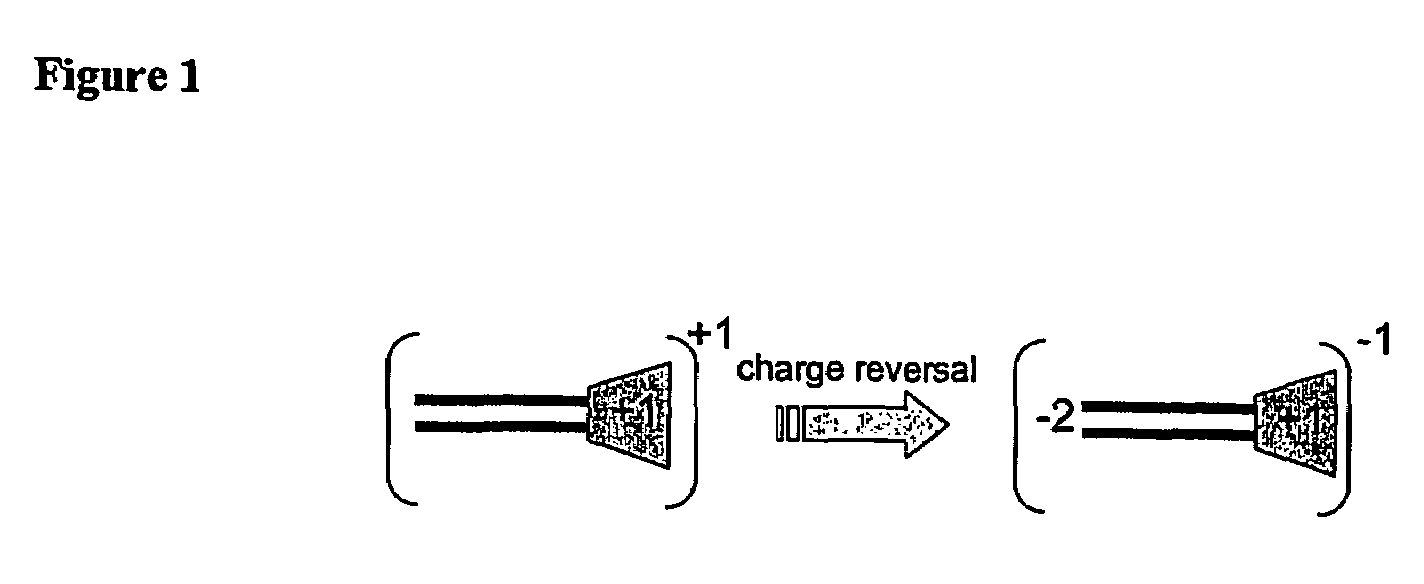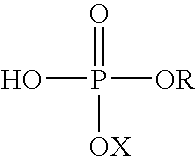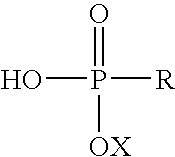Patents
Literature
220 results about "Amphiphilic molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of amphiphilic. : of, relating to, or being a compound (such as a surfactant) consisting of molecules having a polar water-soluble group attached to a water-insoluble hydrocarbon chain; also : being a molecule of such a compound.
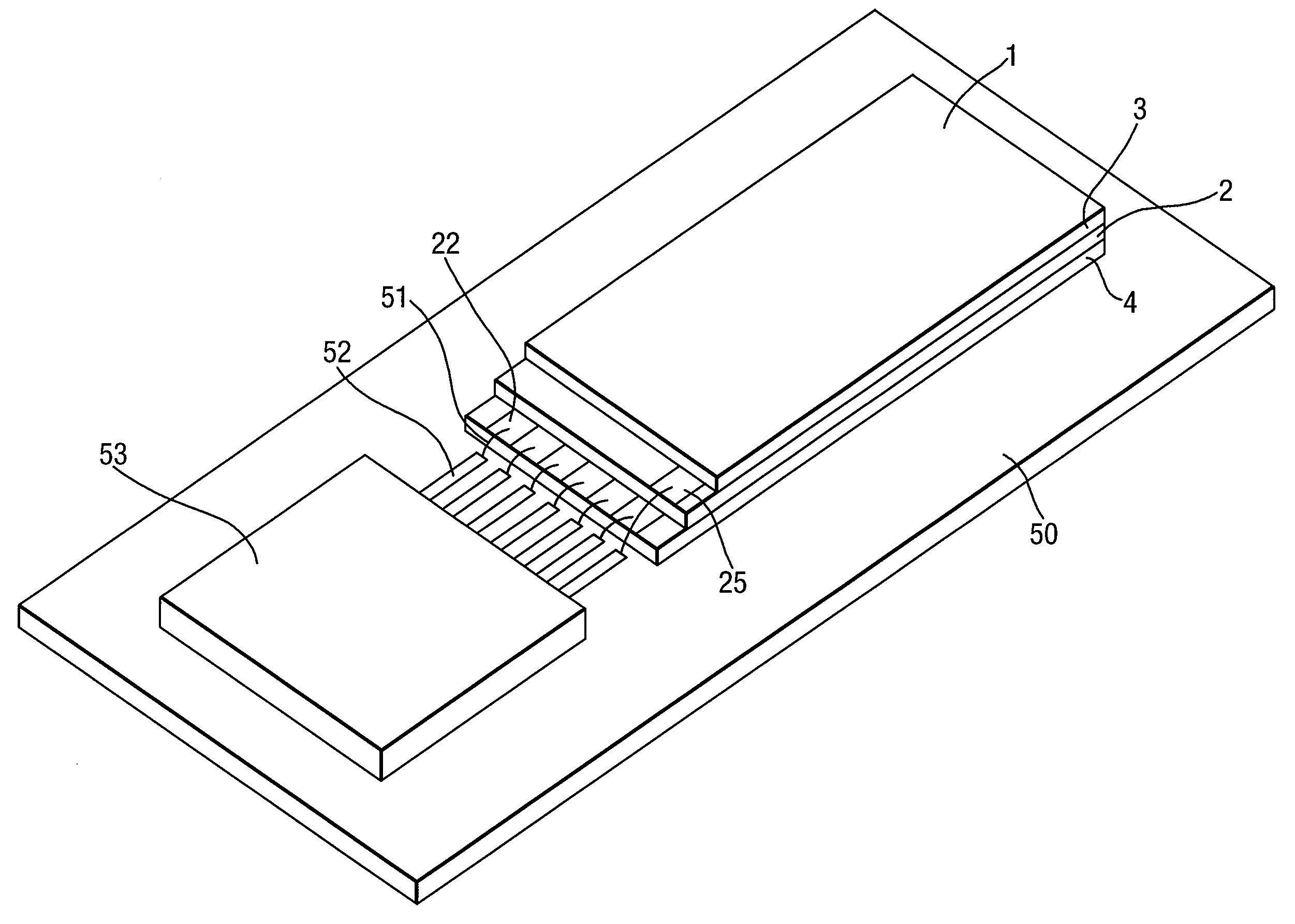
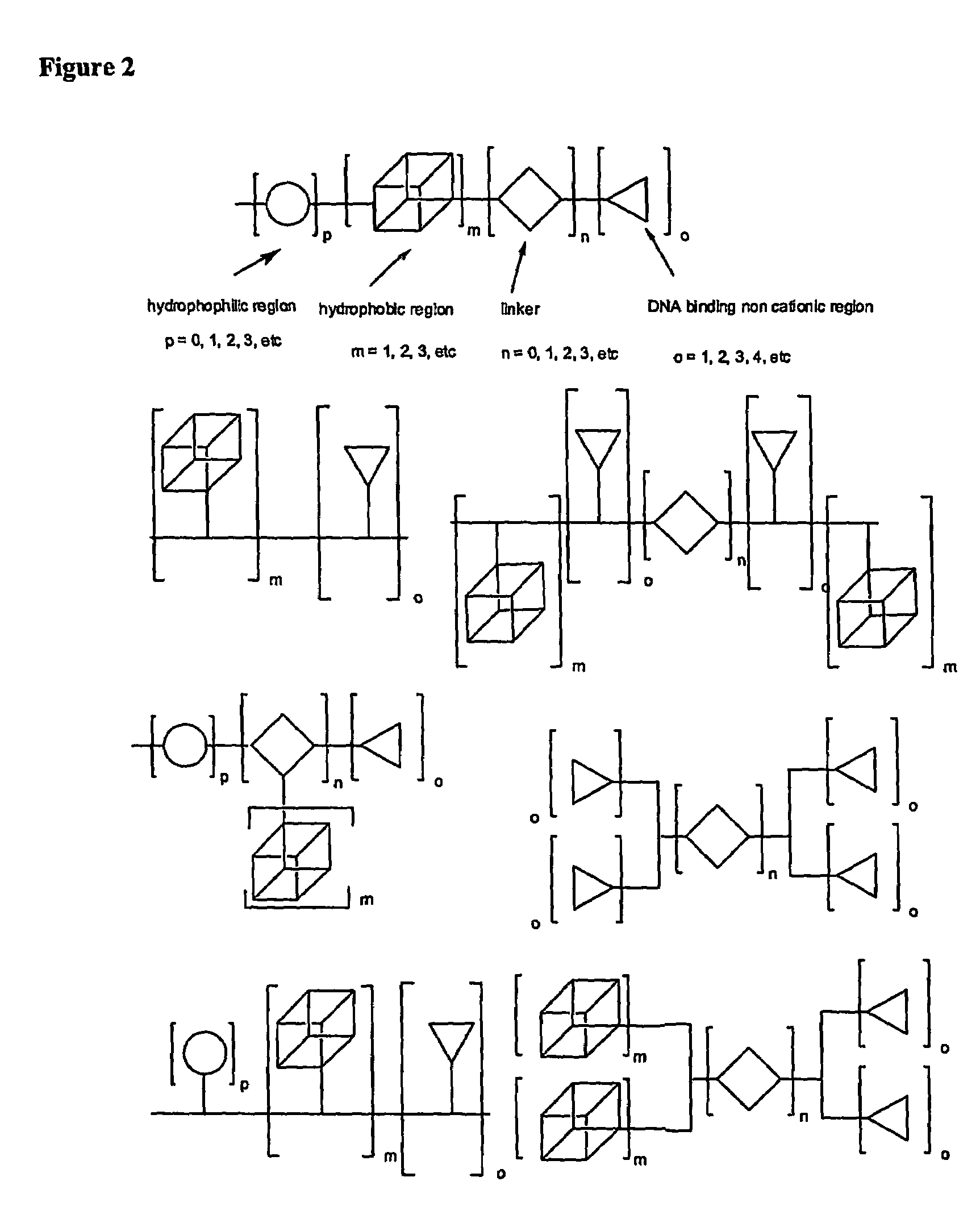
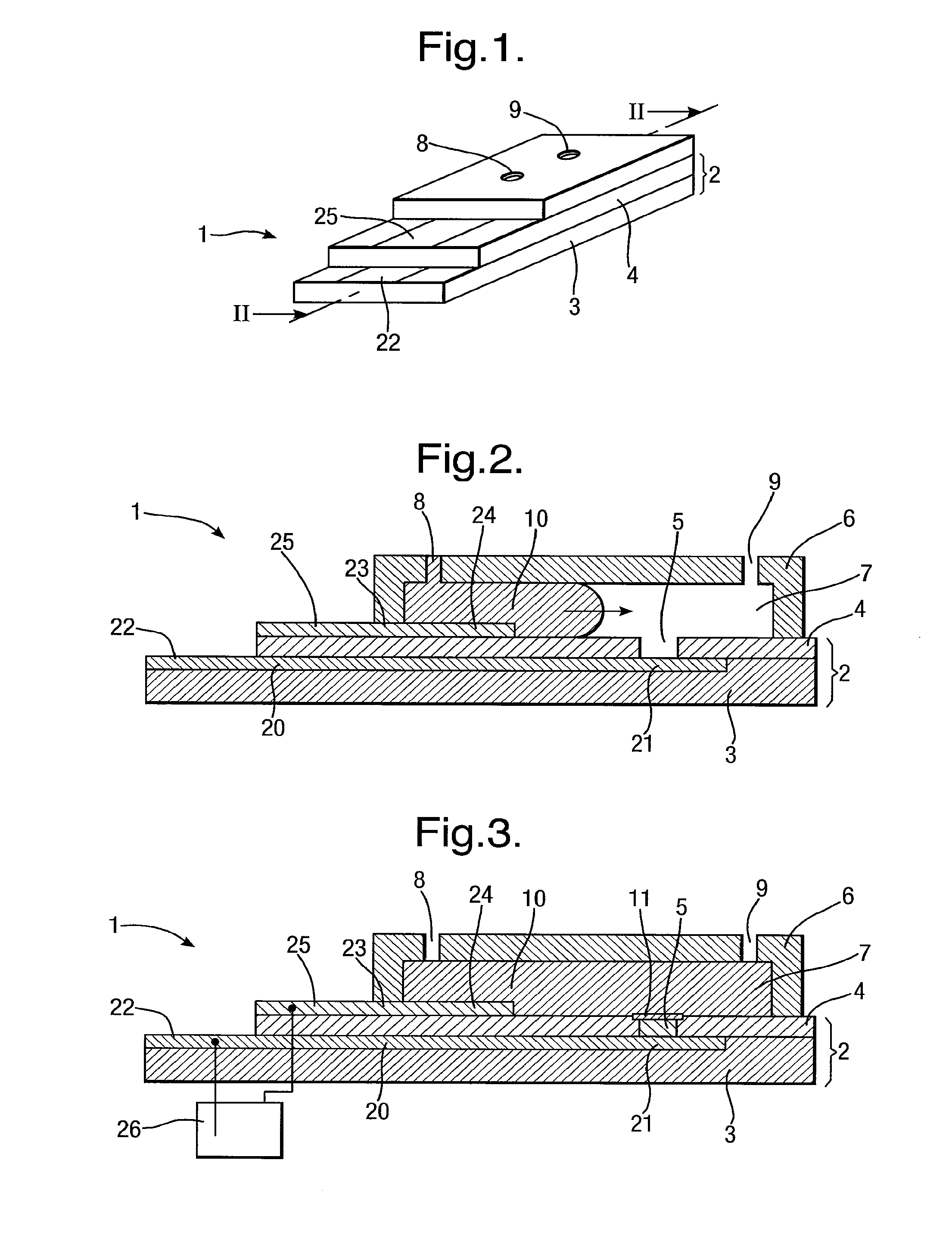
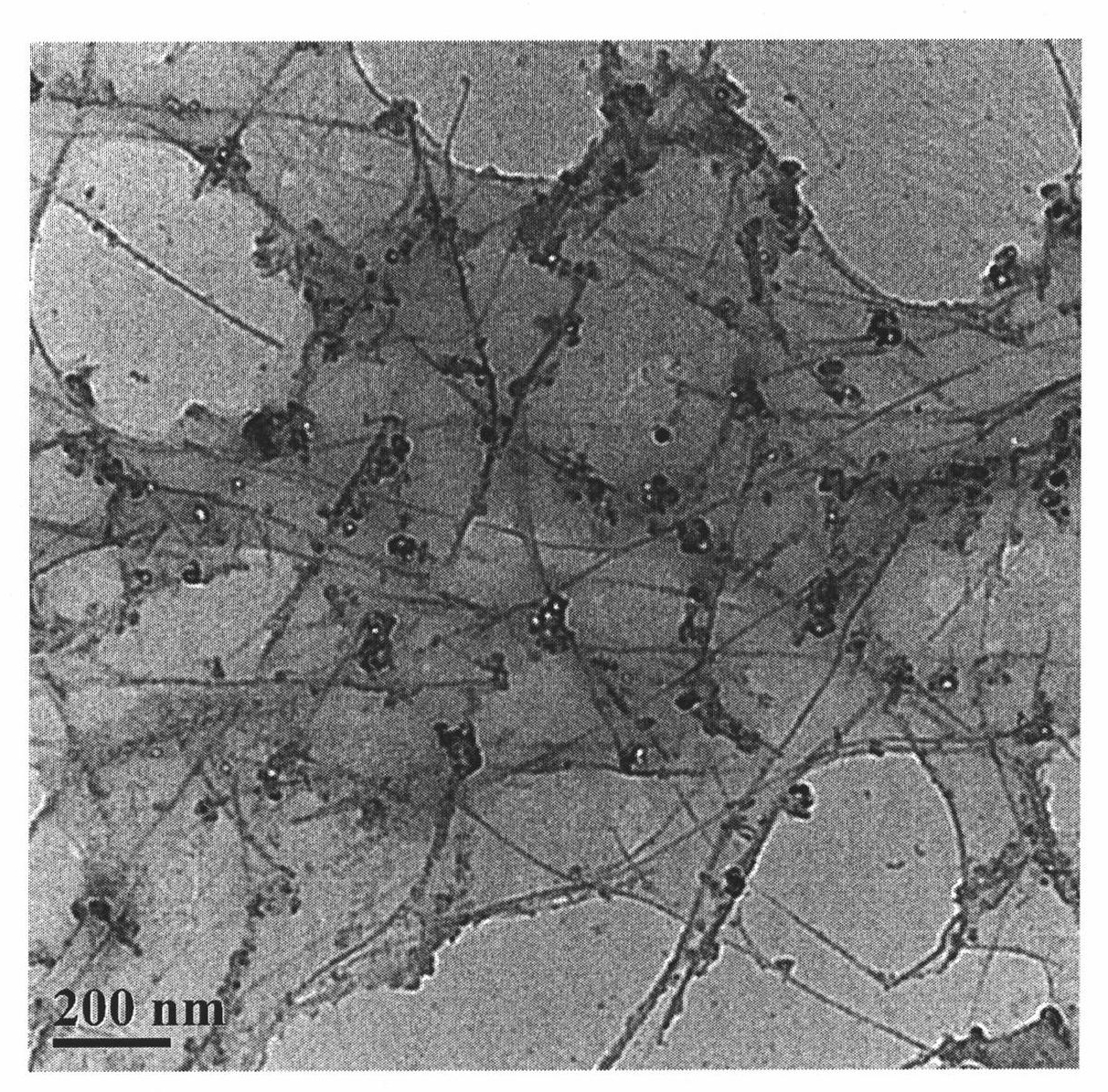
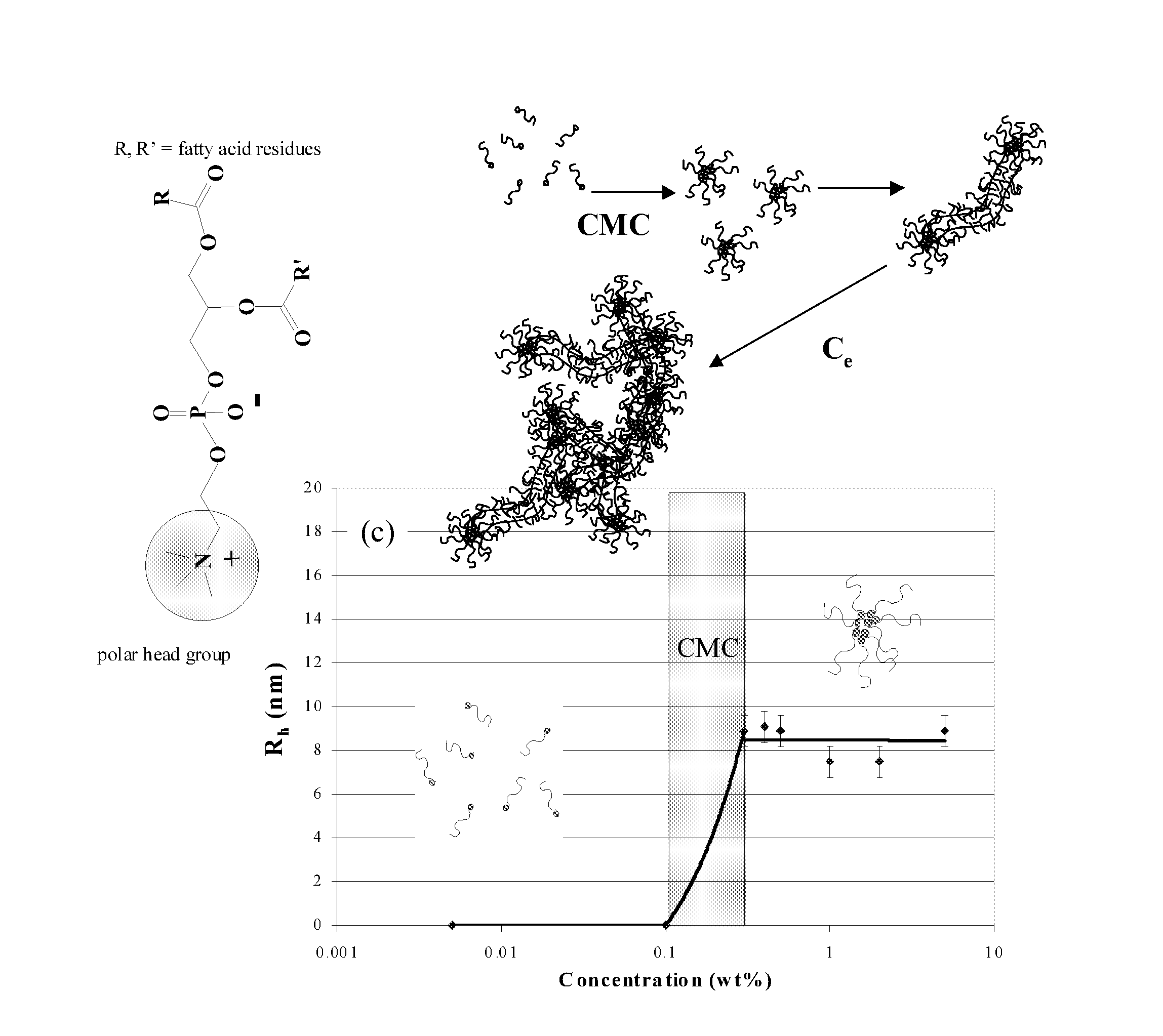
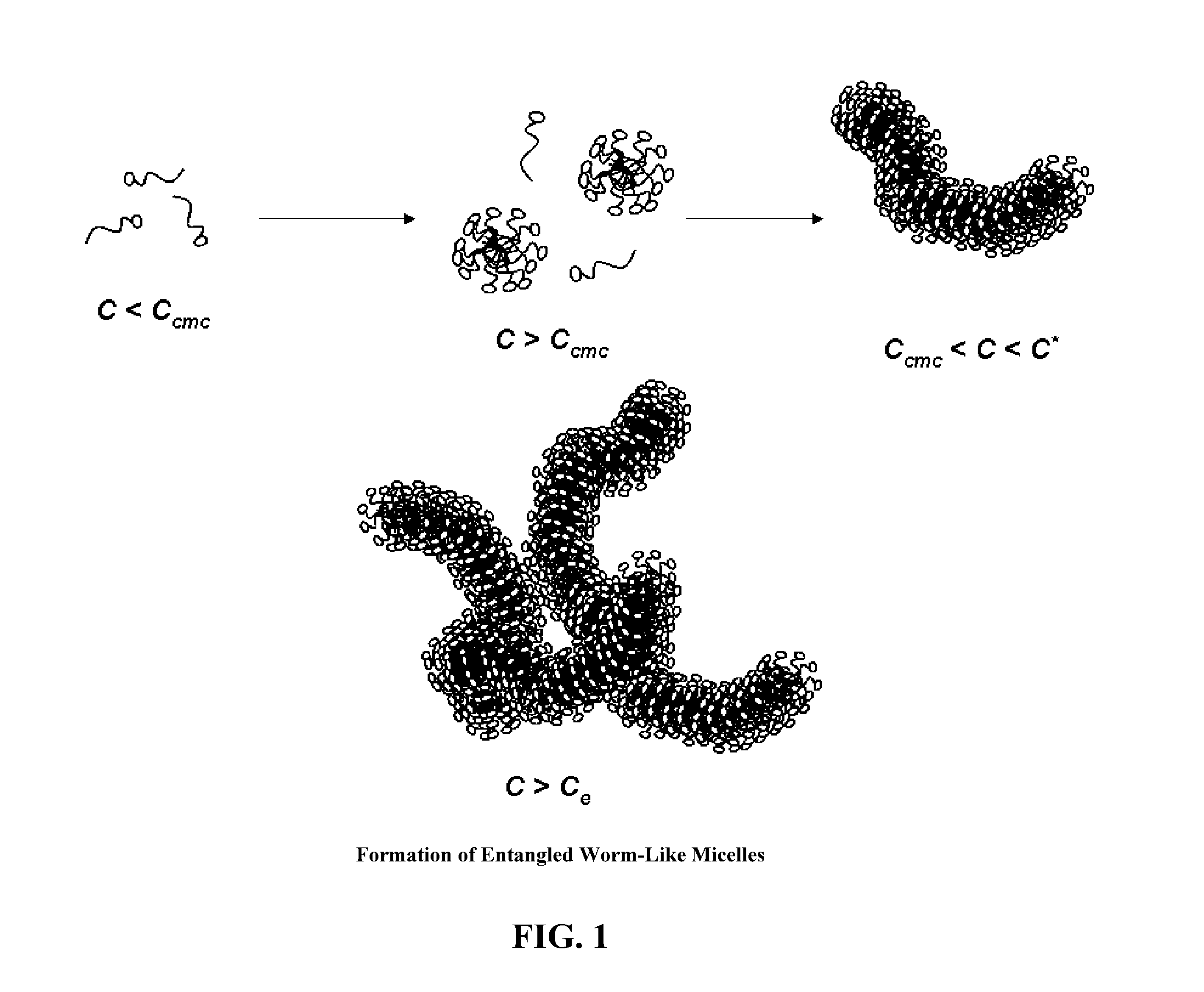
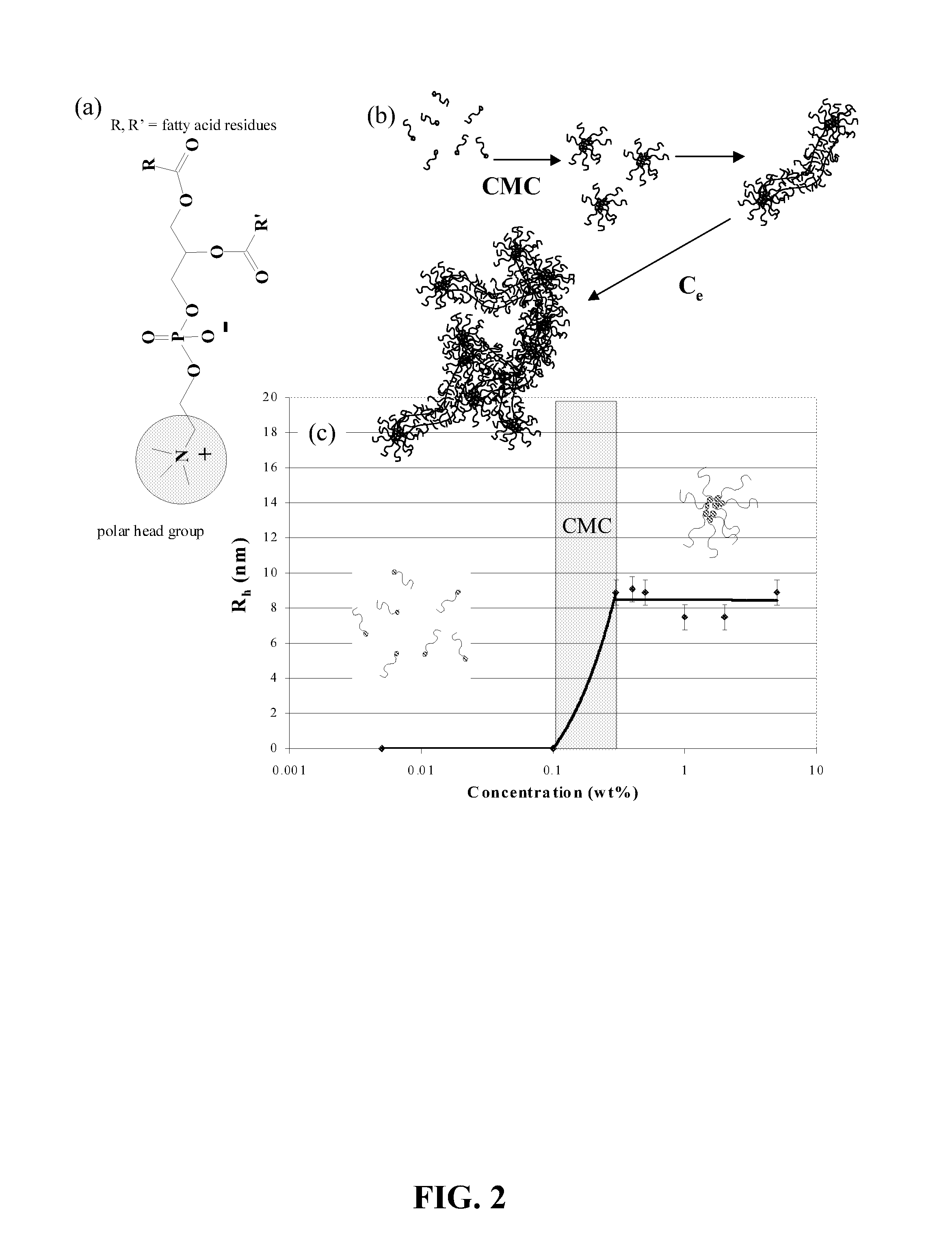
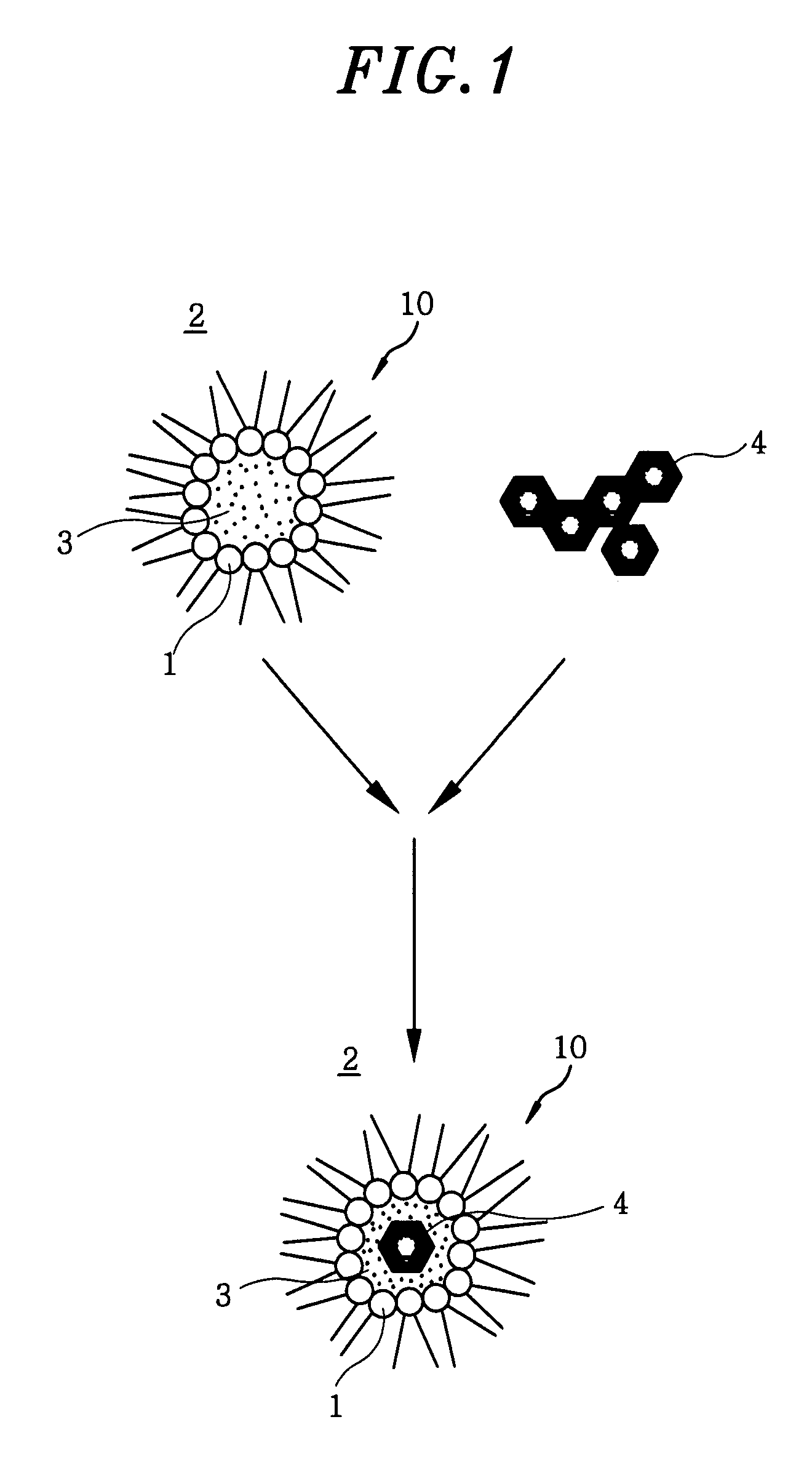
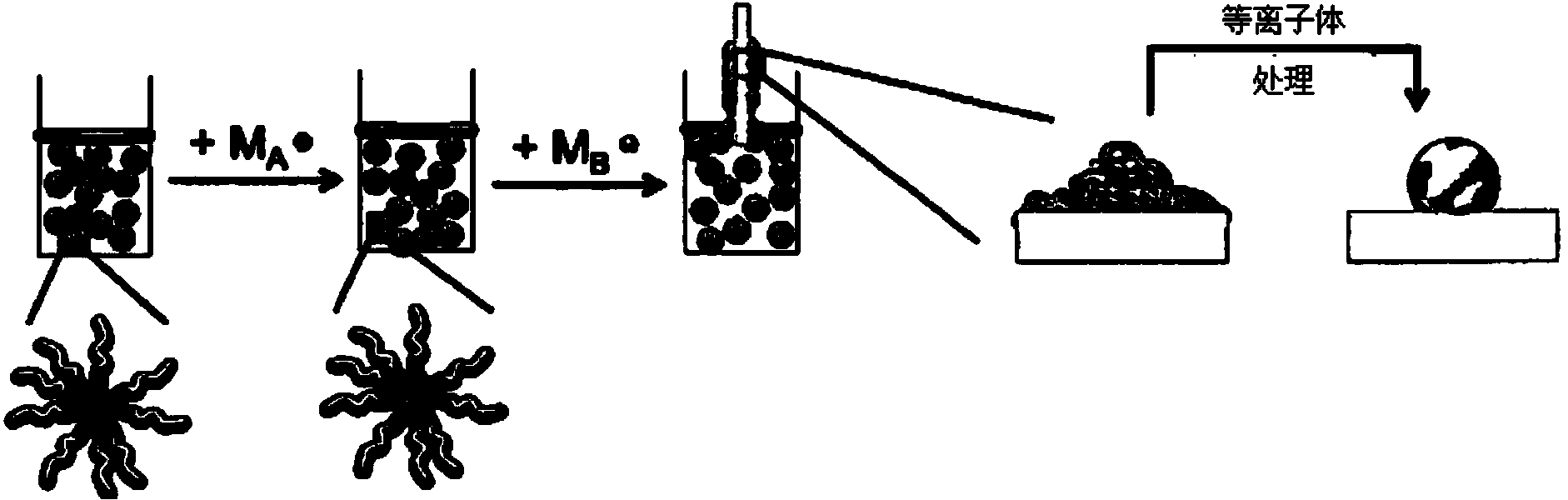
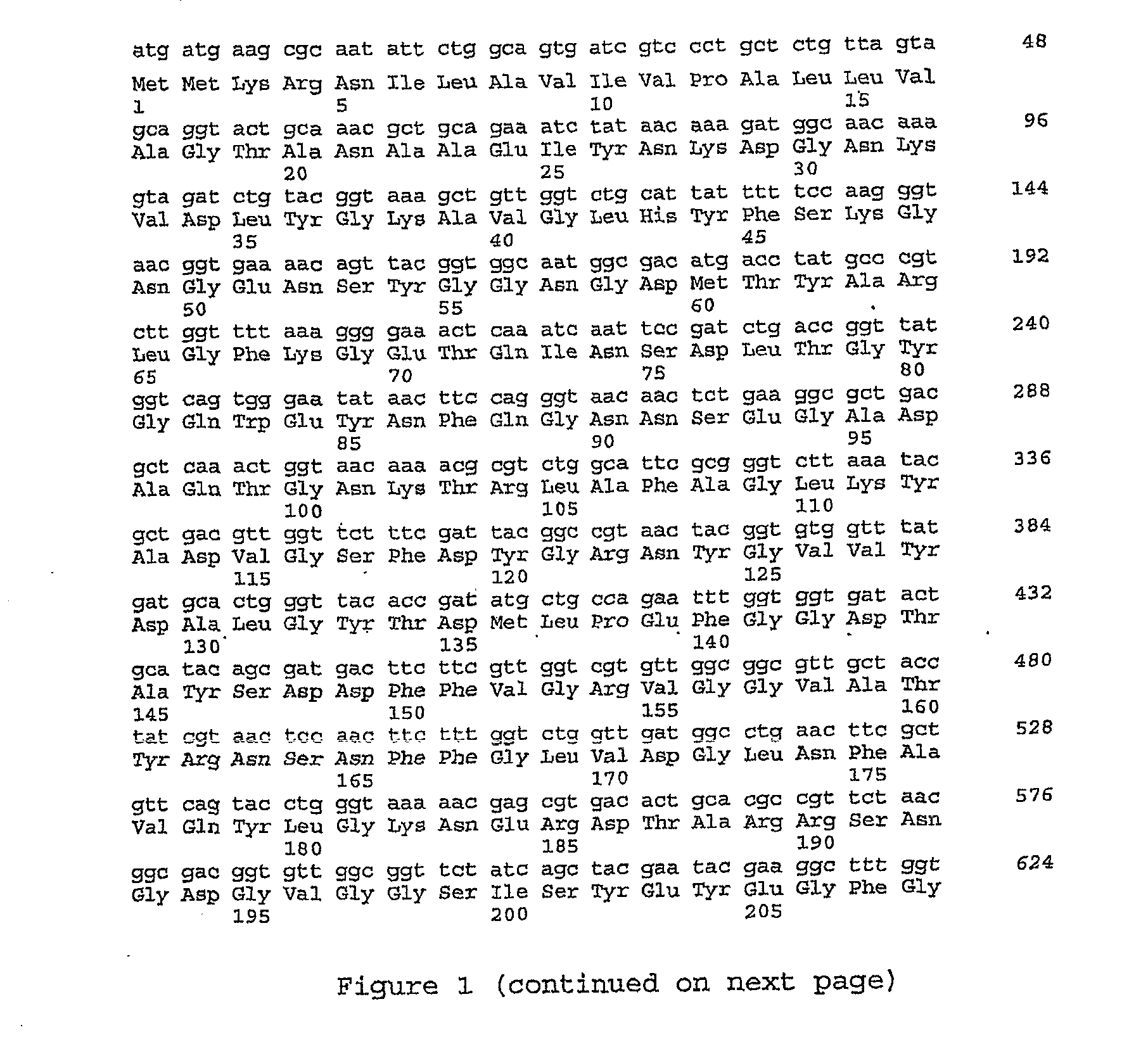
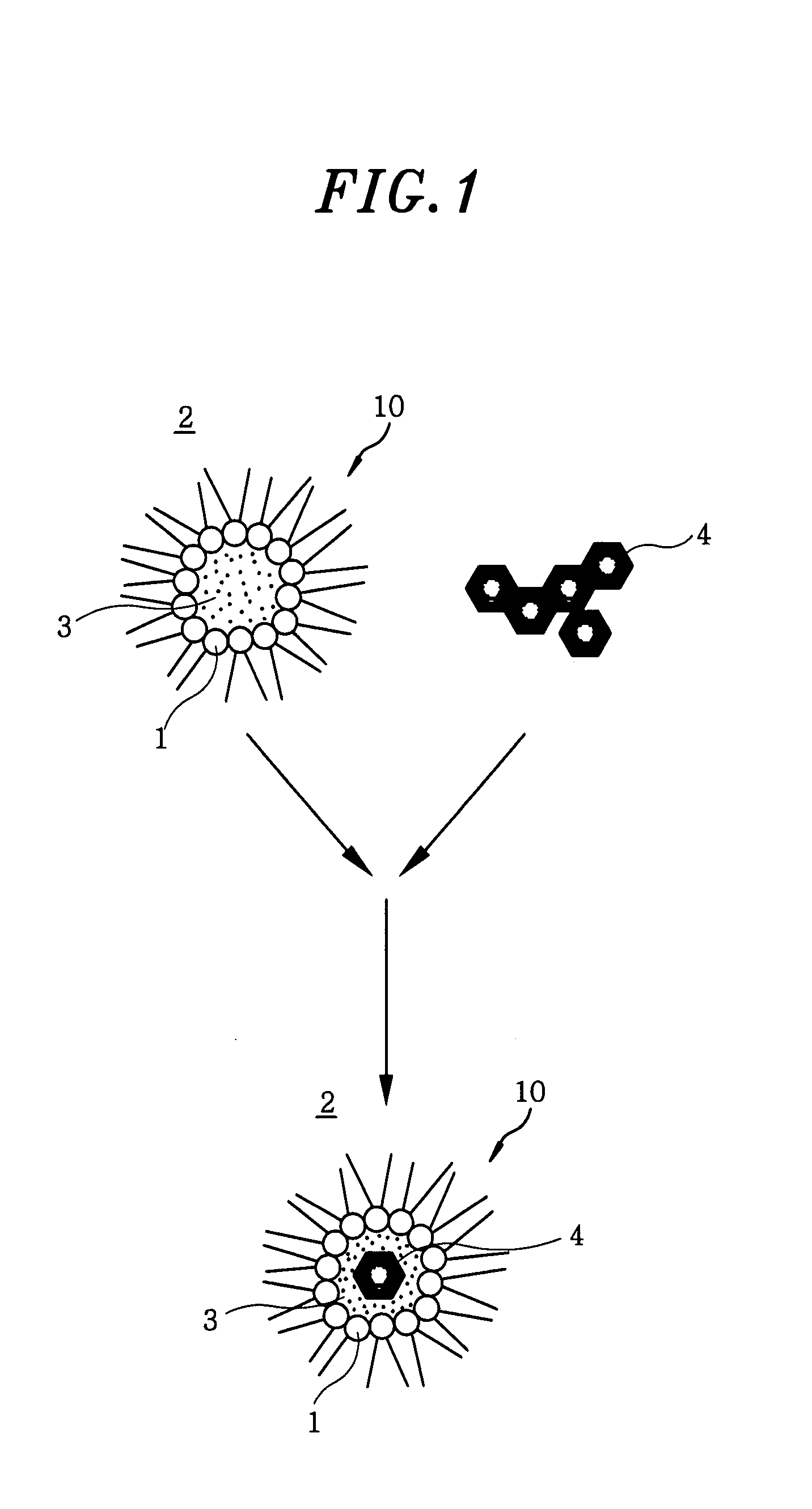
Formation of Layers of Amphiphilic Molecules
InactiveUS20090167288A1Reducing ionic flowReduce sensitivitySemi-permeable membranesMicrobiological testing/measurementConductive materialsPre treatment
To form a layer separating two volumes of aqueous solution, there is used an apparatus comprising elements defining a chamber, the elements including a body of non-conductive material having formed therein at least one recess opening into the chamber, the recess containing an electrode. A pre-treatment coating of a hydrophobic fluid is applied to the body across the recess. Aqueous solution, having amphiphilic molecules added thereto, is flowed across the body to cover the recess so that aqueous solution is introduced into the recess from the chamber and a layer of the amphiphilic molecules forms across the recess separating a volume of aqueous solution introduced into the recess from the remaining volume of aqueous solution.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Molecules for Gene Delivery and Gene Therapy, and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20090221684A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGenetic Materials
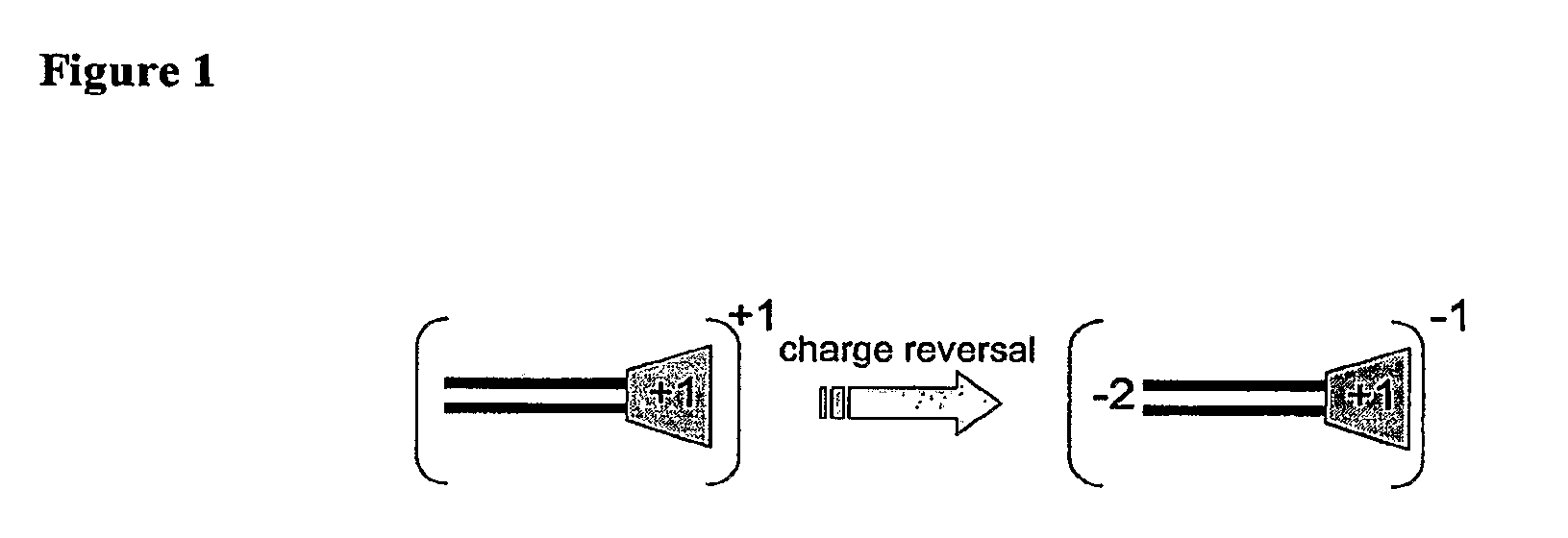
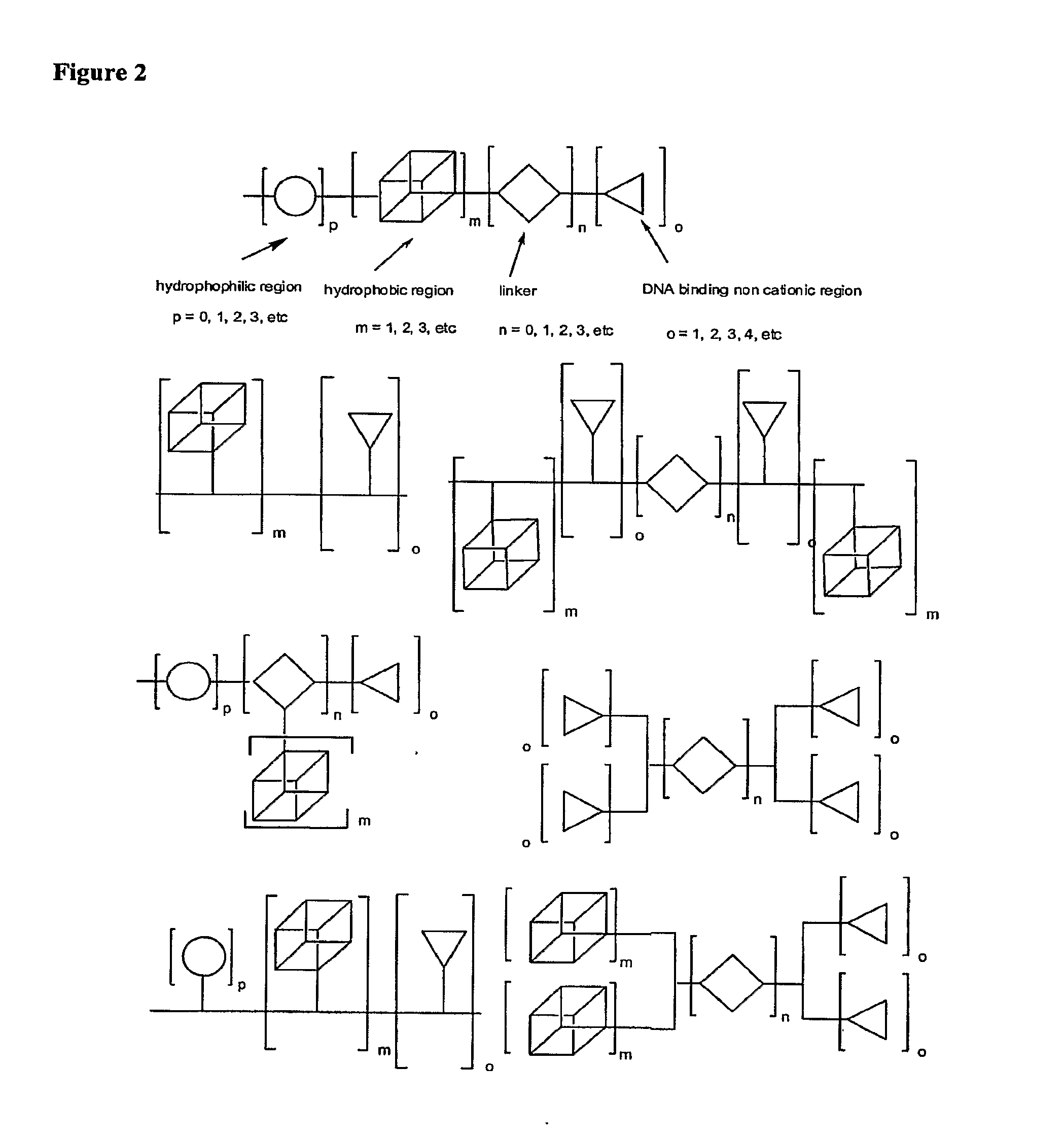
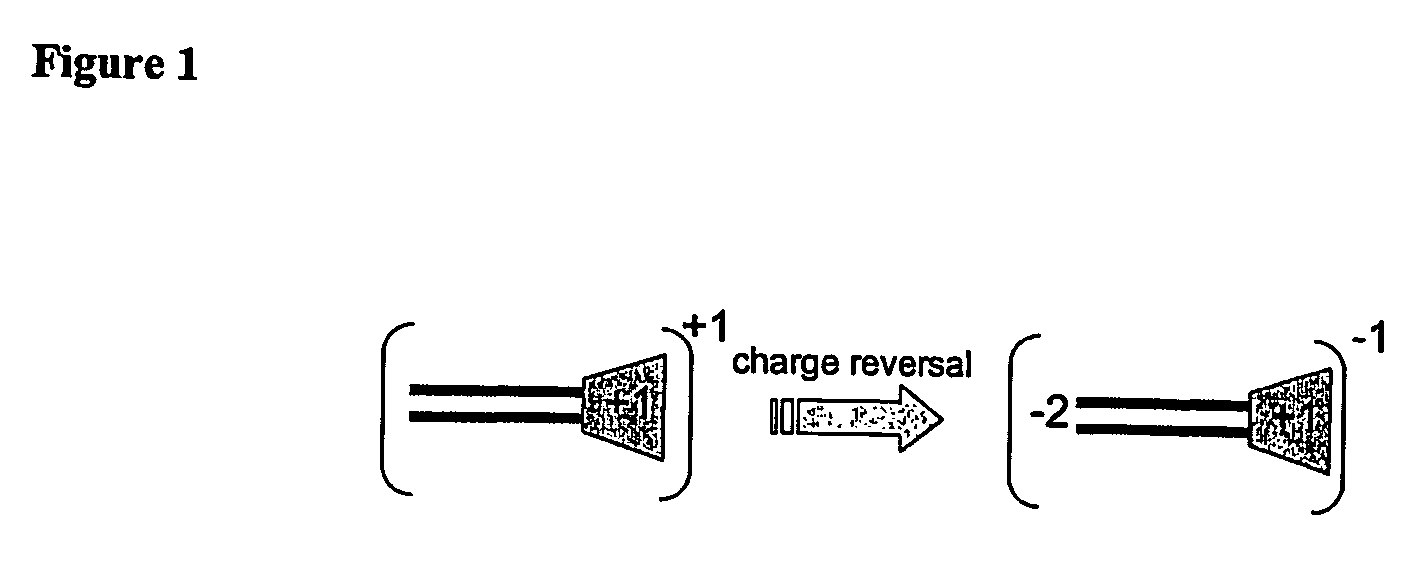
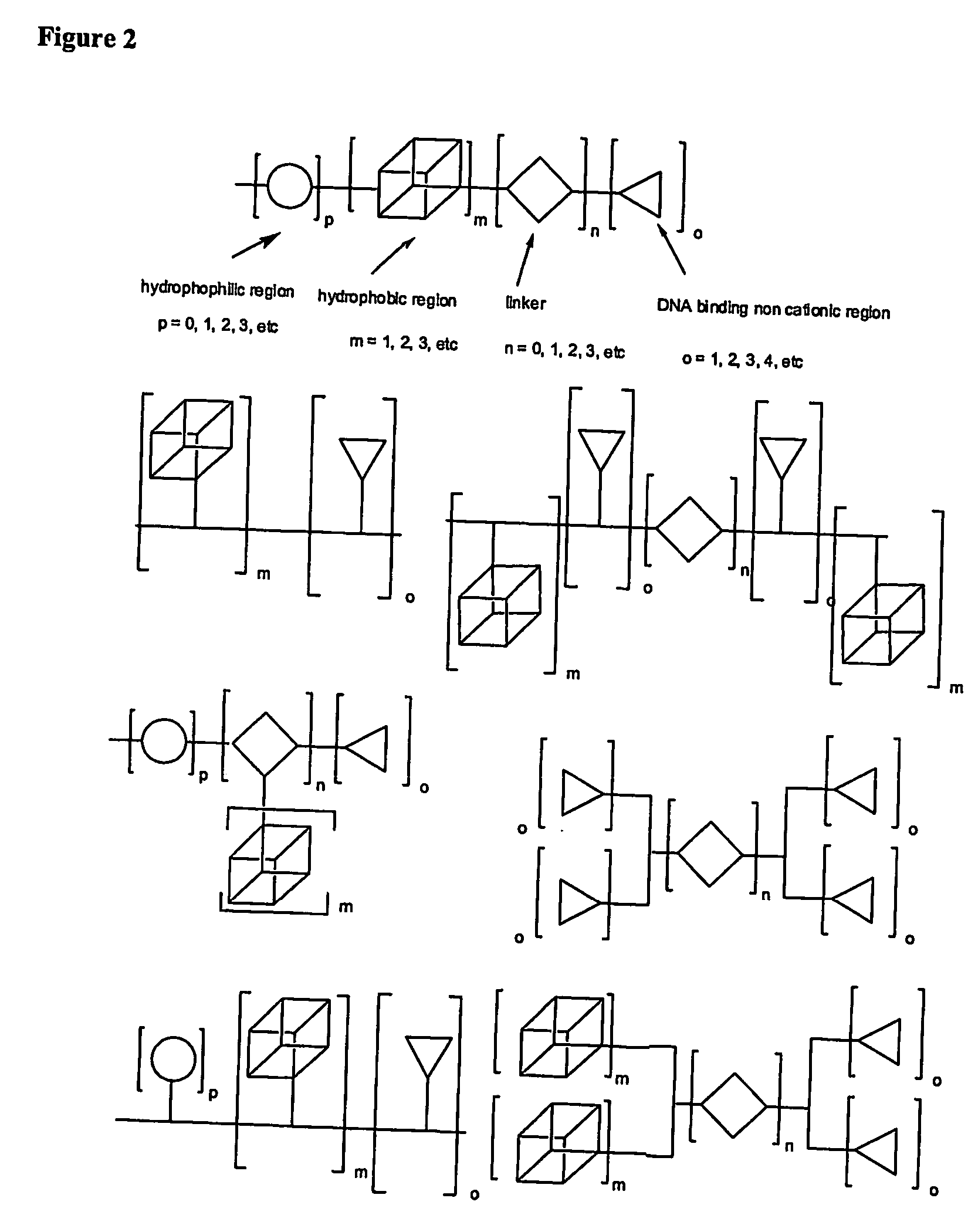
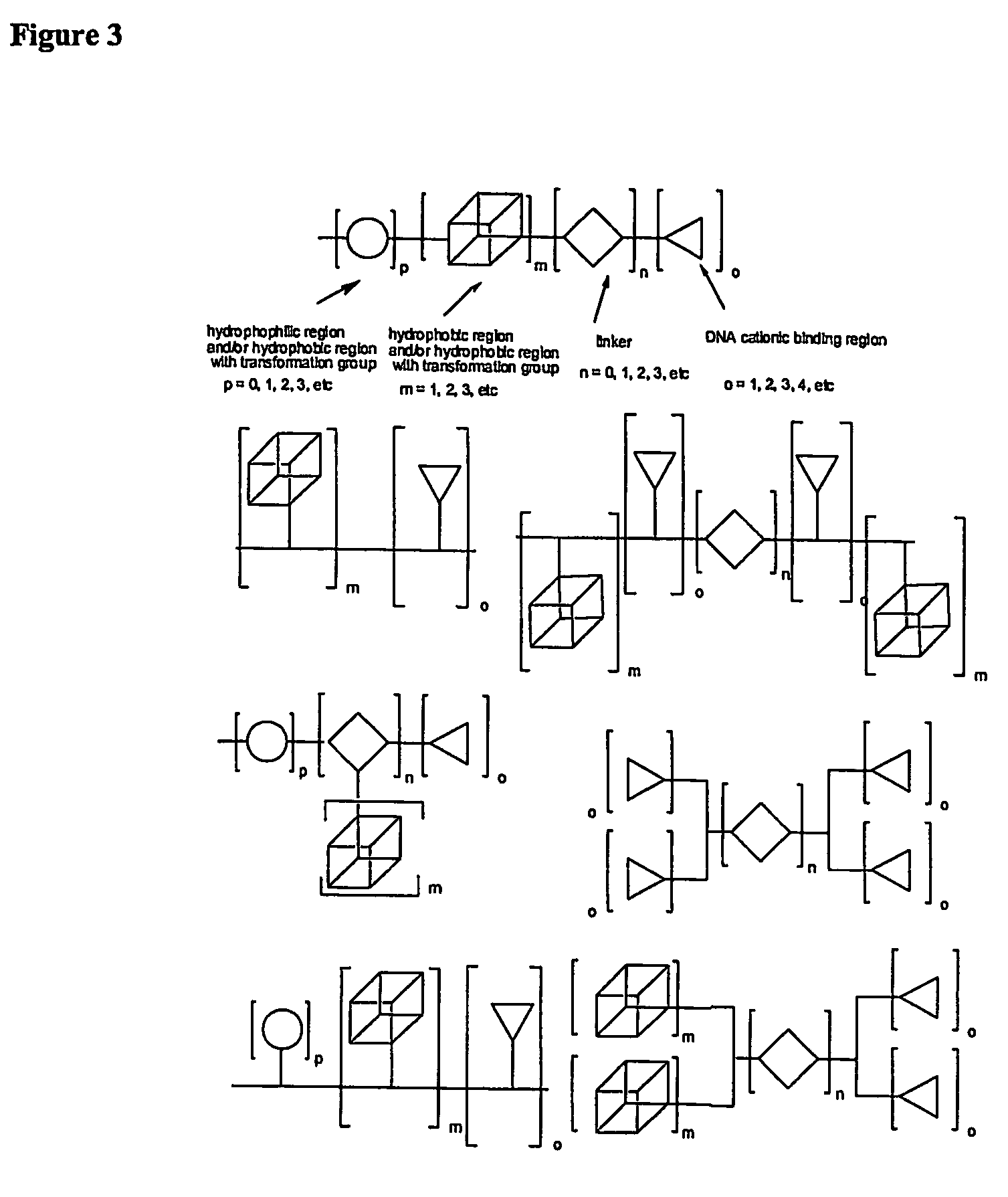
One aspect of the present invention relates to a synthetic non-viral vector composition for gene therapy. Another aspect of the invention relates to the use of the composition for in vitro, ex vivo and / or in vivo transfer of genetic material. The invention also encompasses a pharmaceutical composition (useful for delivery of nucleic acids to a cell), containing a non-cationic amphiphilic molecule or macro-molecule; or a cationic amphiphilic molecule or macromolecule that transforms from a cationic entity to an anionic, neutral, or zwitterionic entity upon a chemical, photochemical, or biological reaction. Another aspect of the invention relates to multicationic compounds that are composed of three or more amino acids. The present invention also relates to the use of the pharmaceutical composition for delivery of nucleic acids to a cell. Moreover, the invention encompasses the non-viral vector compositions tethered to a surface. The surface-tethered compositions are useful for the delivery of nucleic acids to cells in contact with the surface. An additional embodiment of the invention relates to a hydrogel comprising a composition of the invention, and methods of using same for the delivery of genetic material to a cell.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Functional synthetic molecules and macromolecules for gene delivery
The present invention describes a synthetic non-viral vector composition for gene therapy and the use of such compositions for in vitro, ex vivo and / or in vivo transfer of genetic material. The invention proposes a pharmaceutical composition containing 1) a non-cationic amphiphilic molecule or macromolecule and its use for delivery of nucleic acids or 2) a cationic amphiphilic molecule or macromolecule that transforms from a cationic entity to an anionic, neutral, or zwitterionic entity by a chemical, photochemical, or biological reaction and its use for delivery of nucleic acids. Moreover this invention describes the use of these non-viral vector compositions in conjunction with a surface to mediate the delivery of nucleic acids. An additional embodiment is the formation of a hydrogel with these compositions and the use of this hydrogel for the delivery of genetic material. A further embodiment of this invention is the use of a change in ionic strength for the delivery of genetic material.
Owner:FIFTH BASE
Porous carbon structures and methods
Methods for making porous articles are described, along with articles and structures which can be made by these methods. The methods typically involve polymerization of a carbon-containing precursor in the presence of an amphiphilic molecular structure, followed by carbonization to make a final product. Articles of the invention are generally porous, carbon-containing, and can have one or any number of features including crystallinity, electrical conductivity, and porosity of a specific and advantageous nature.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Decellularized Tissue and Method of Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20070244568A1Improve efficiencyGood effectMammal material medical ingredientsProsthesisUltravioletSolvent
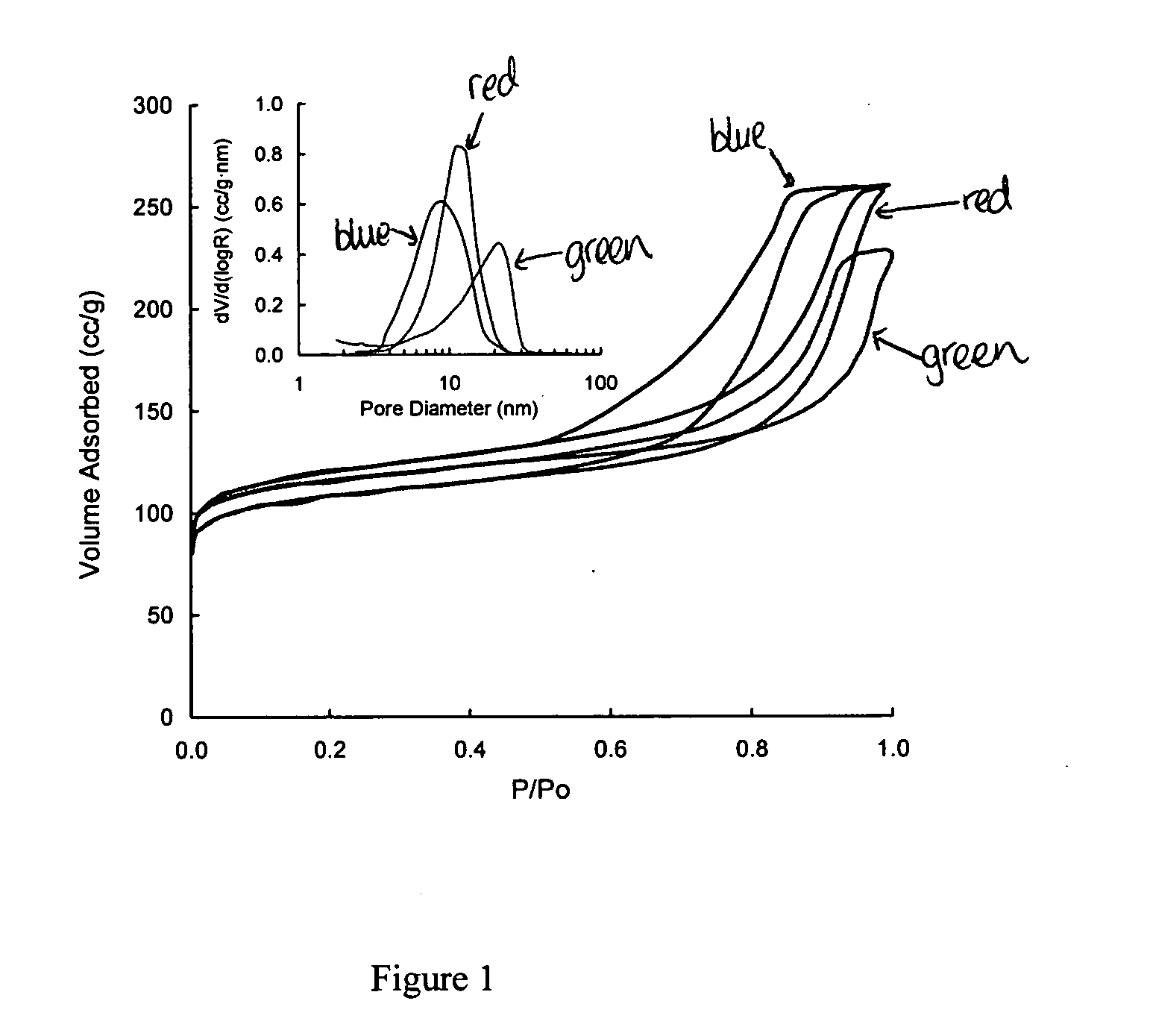
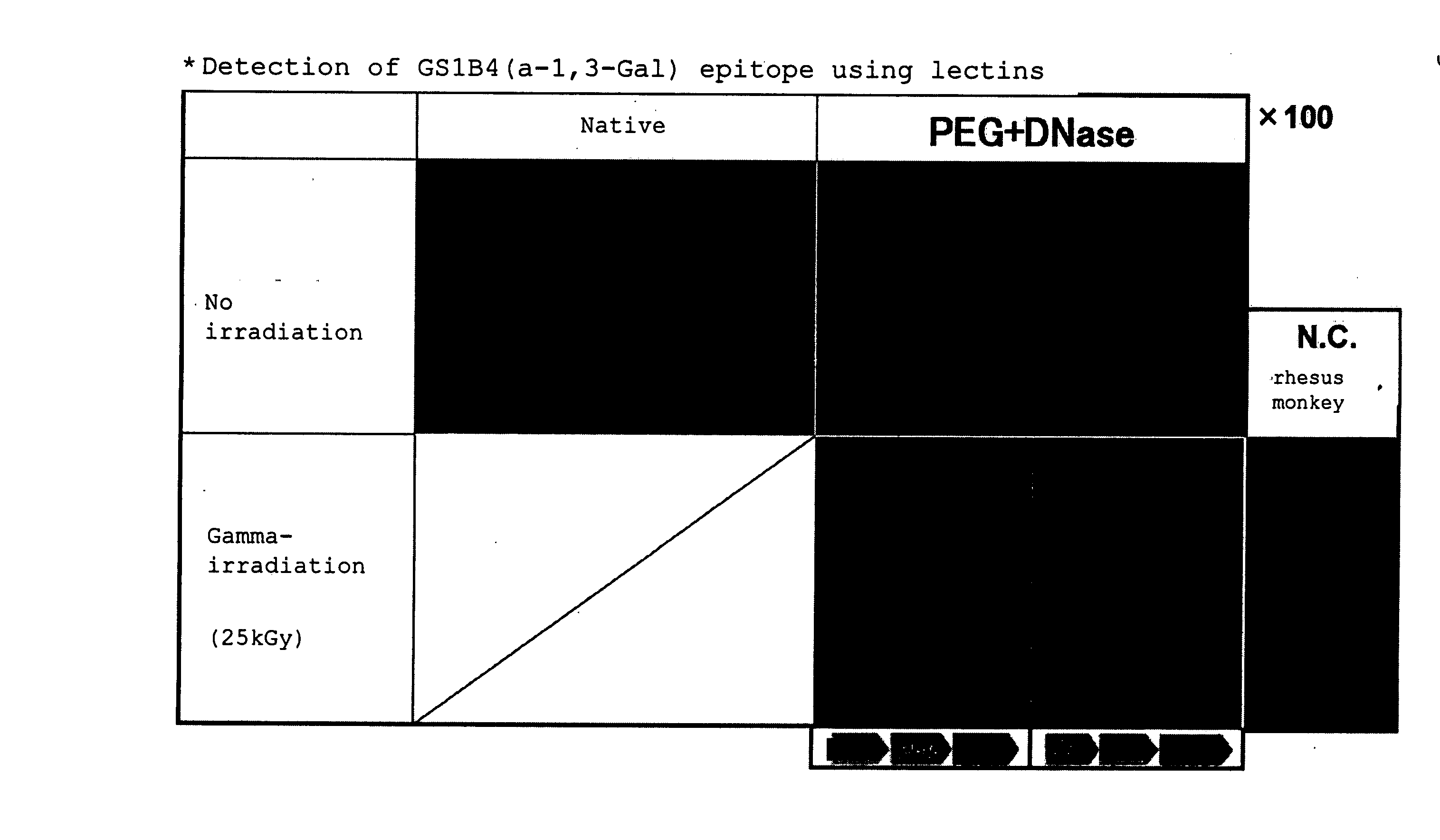
Decellularization of tissue by means of an amphipathic solvent a well-established practice. However, situations exist where the provision of enhanced decellularization is preferred. There is a demand for treating methods for coping with such situations. Thus, it is intended to provide a method for enhancing decellularization. The method comprises not only the immersing of a tissue in a solution containing an amphiphilic molecule in non-micellar form (for example, 1,2-epoxide polymer) but also performing a radical reaction (for example, treatment selected from the group consisting of exposure to gamma-ray irradiation, ultraviolet irradiation, a free radical supply source, ultrasonication, electron beam irradiation, and X-ray irradiation).
Owner:CARDIO +1
Functional synthetic molecules and macromolecules for gene delivery
The present invention describes a synthetic non-viral vector composition for gene therapy and the use of such compositions for in vitro, ex vivo and / or in vivo transfer of genetic material. The invention proposes a pharmaceutical composition containing 1) a non-cationic amphiphilic molecule or macromolecule and its use for delivery of nucleic acids or 2) a cationic amphiphilic molecule or macromolecule that transforms from a cationic entity to an anionic, neutral, or zwitterionic entity by a chemical, photochemical, or biological reaction and its use for delivery of nucleic acids. Moreover this invention describes the use of these non-viral vector compositions in conjunction with a surface to mediate the delivery of nucleic acids. An additional embodiment is the formation of a hydrogel with these compositions and the use of this hydrogel for the delivery of genetic material. A further embodiment of this invention is the use of a change in ionic strength for the delivery of genetic material.
Owner:FIFTH BASE
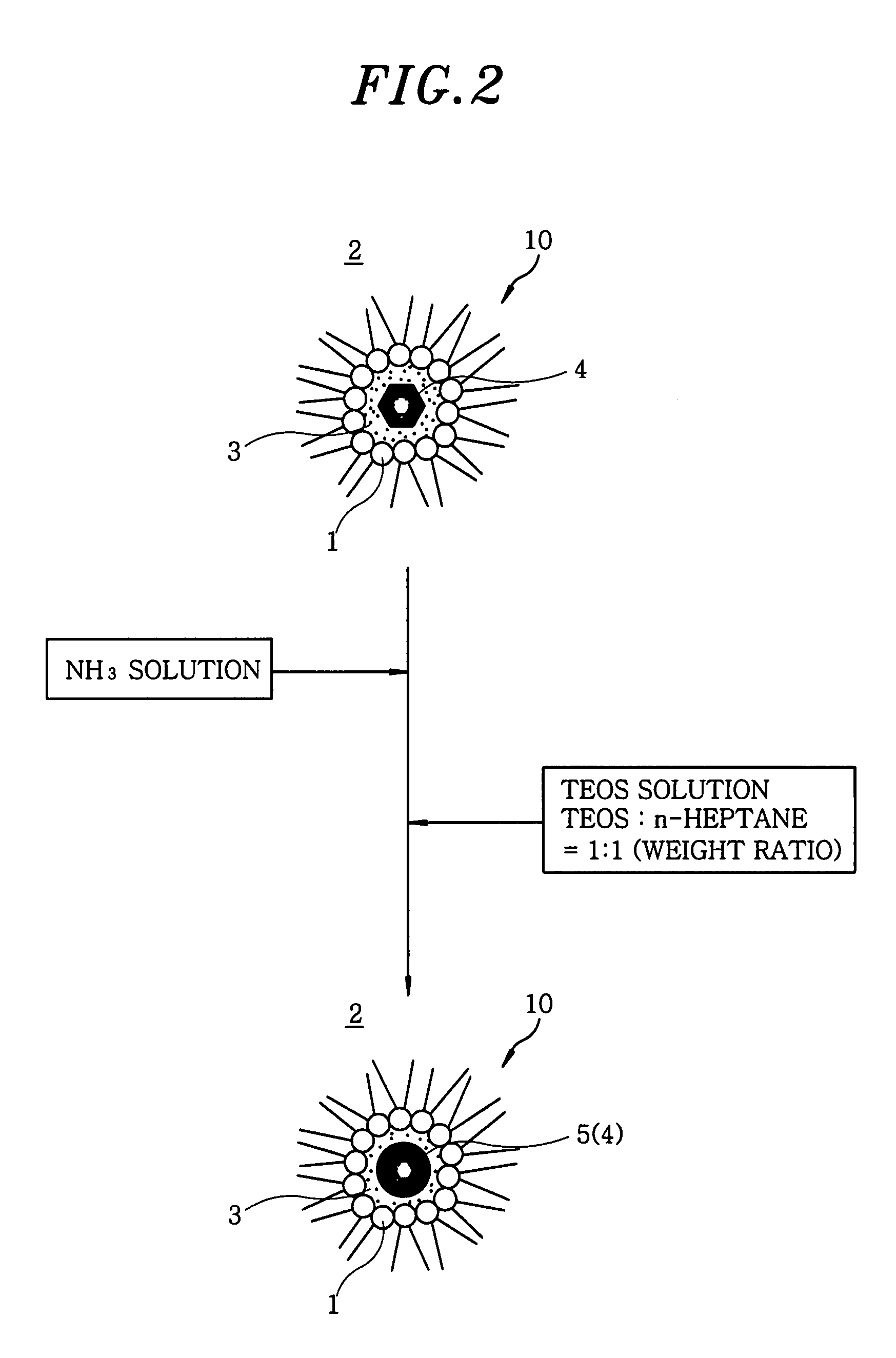
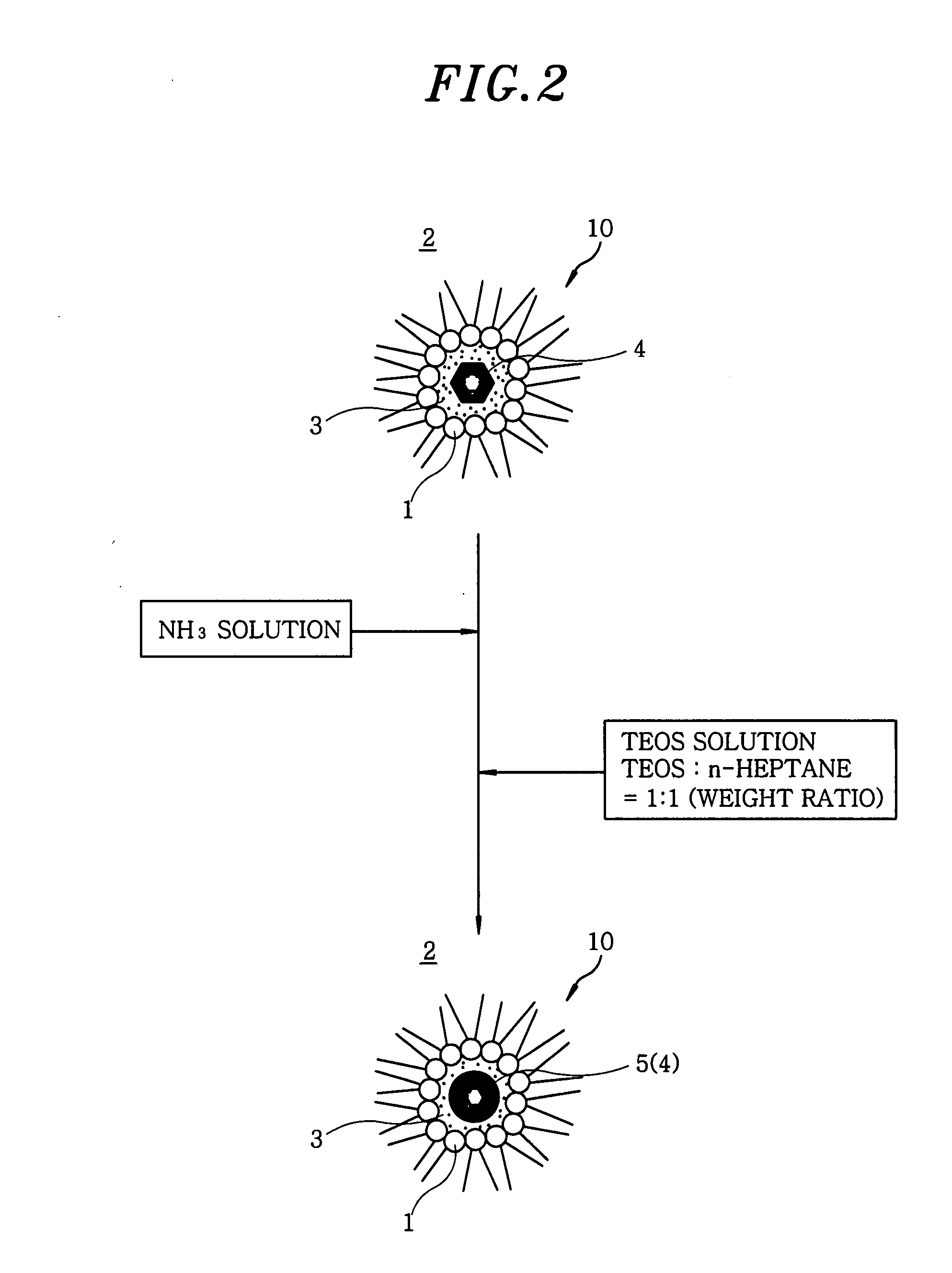
Formation of layers of amphiphilic molecules
InactiveUS20140329693A1Quality improvementImplementation is particularly straightforwardSemi-permeable membranesMicrobiological testing/measurementConductive materialsPre treatment
To form a layer separating two volumes of aqueous solution, there is used an apparatus comprising elements defining a chamber, the elements including a body of non-conductive material having formed therein at least one recess opening into the chamber, the recess containing an electrode. A pre-treatment coating of a hydrophobic fluid is applied to the body across the recess. Aqueous solution, having amphiphilic molecules added thereto, is flowed across the body to cover the recess so that aqueous solution is introduced into the recess from the chamber and a layer of the amphiphilic molecules forms across the recess separating a volume of aqueous solution introduced into the recess from the remaining volume of aqueous solution.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Polymersomes and related encapsulating membranes
InactiveUS7217427B2Easy to measureMaintaining semi-permeabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAqueous solutionMembrane configuration
The present invention provides biocompatible vesicles comprising semi-permeable, thin-walled encapsulating membranes which are formed in an aqueous solution, and which comprise one or more synthetic super-amphiphilic molecules. When at least one super-amphiphile molecule is a block copolymer, the resulting synthetic vesicle is termed a “polymersome.” The synthetic, reactive nature of the amphiphilic composition enables extensive, covalent cross-linking of the membrane, while maintaining semi-permeability. Cross-linking of the polymer building-block components provides mechanical control and long-term stability to the vesicle, thereby also providing a means of controlling the encapsulation or release of materials from the vesicle by modifying the composition of the membrane. Thus, the encapsulating membranes of the present invention are particularly suited for the reliable, durable and controlled transport, delivery and storage of materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Ultrastable Particle-Stabilized Foams and Emulsions
ActiveUS20090325780A1Cheap methodLong-term stabilityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologySolubilityEmulsion
Described is a method to prepare wet foams exhibiting long-term stability wherein colloidal particles are used to stabilize the gas-liquid interface, said particles being initially inherently partially lyophobic particles or partially lyophobized particles having mean particle sizes from 1 nm to 20 μm. In one aspect, the partially lyophobized particles are prepared in-situ by treating initially hydrophilic particles with amphiphilic molecules of specific solubility in the liquid phase of the suspension.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Block co-polymer worm micelles and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20050180922A1Increase the diameterUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideOrganic solventIn vivo
Provided are worm-like micelles, capable of encapsulating at least one encapsulant, wherein each worm-like micelle comprises one or more wholly synthetic, polymeric, super-amphiphilic molecules that self assemble in aqueous solution, without organic solvent or post assembly polymerization; and wherein at least one of said super-amphiphilic molecules is a hydrophilic block copolymer, the weight fraction (w) of which, relative to total copolymer molecular weight, directs assembly of the amphiphilic molecules into the worm-like micelle of up to one or more microns in length, and determines its stability, flexibility and convective responsiveness. Also provide are methods of preparing and methods of using the worm-like micelles, particularly when loaded with one or more encapsulants. The loaded worm-like micelles of the present invention are particularly suited for the stable and controlled transport, delivery and storage of materials, either in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Functional associative coatings for nanoparticles
InactiveUS7906147B2Readily and efficiently optimizing propertyAvoid interactionPowder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAmphiphileNanoparticle
Described herein are nanoparticles that are coated with a bilayer of molecules formed from surface binding molecules and amphiphatic molecules. The bilayer coating self assembles on the nanoparticles from readily available materials / molecules. The modular design of the bilayer coated nanoparticles provides a means for readily and efficiently optimizing the properties of the bilayer coated nanoparticle compositions. Also described herein are uses of such nanoparticles in medicine, laboratory techniques, industrial and commercial applications.
Owner:NANOPROBES
Polymersomes and related encapsulating membranes
InactiveUS20050048110A1Easy to measureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryAqueous solutionStructural unit
The present invention provides biocompatible vesicles comprising semi-permeable, thin-walled encapsulating membranes which are formed in an aqueous solution, and which comprise one or more synthetic super-amphiphilic molecules. When at least one super-amphiphile molecule is a block copolymer, the resulting synthetic vesicle is termed a “polymersome.” The synthetic, reactive nature of the amphiphilic composition enables extensive, covalent cross-linking of the membrane, while maintaining semi-permeability. Cross-linking of the polymer building-block components provides mechanical control and long-term stability to the vesicle, thereby also providing a means of controlling the encapsulation or release of materials from the vesicle by modifying the composition of the membrane. Thus, the encapsulating membranes of the present invention are particularly suited for the reliable, durable and controlled transport, delivery and storage of materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
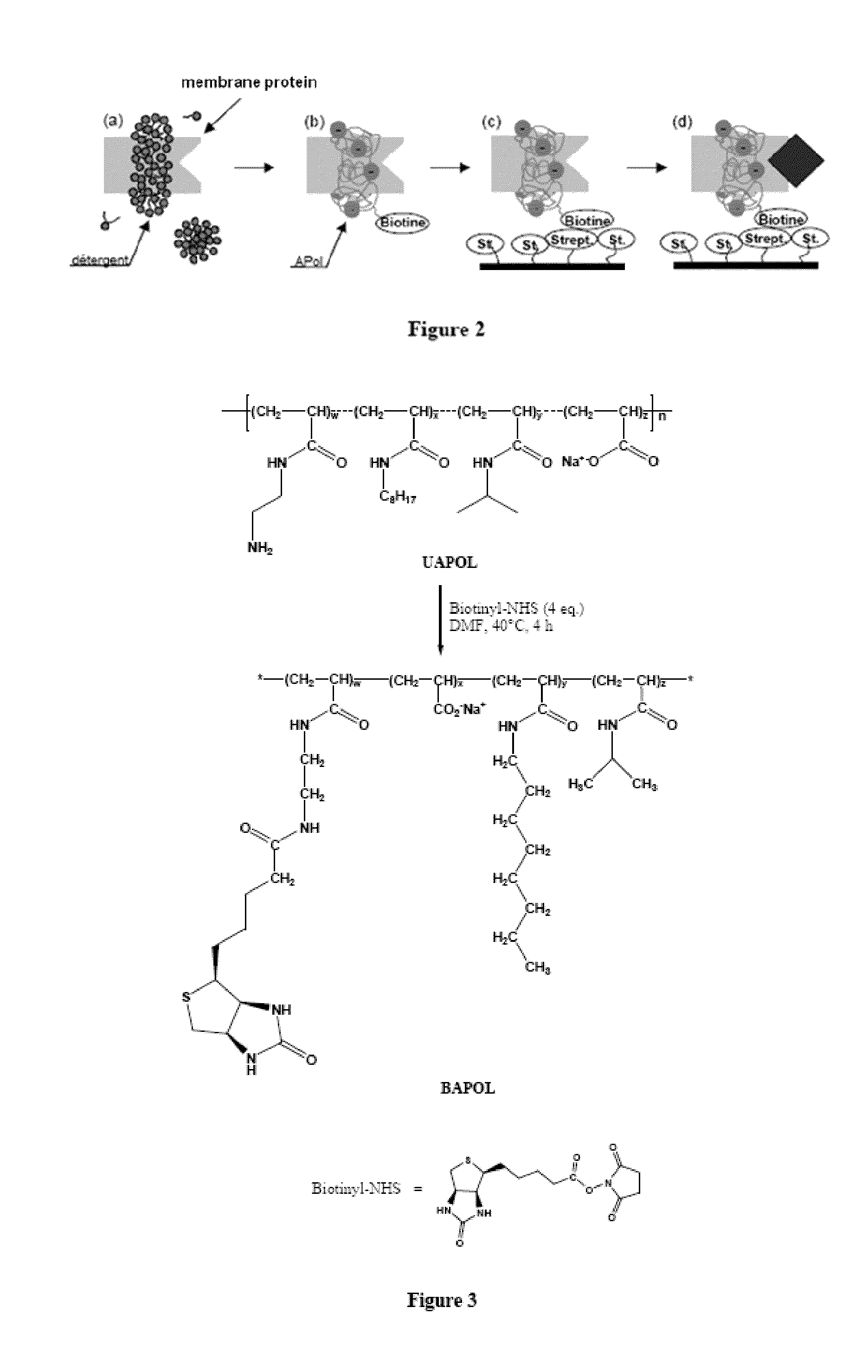
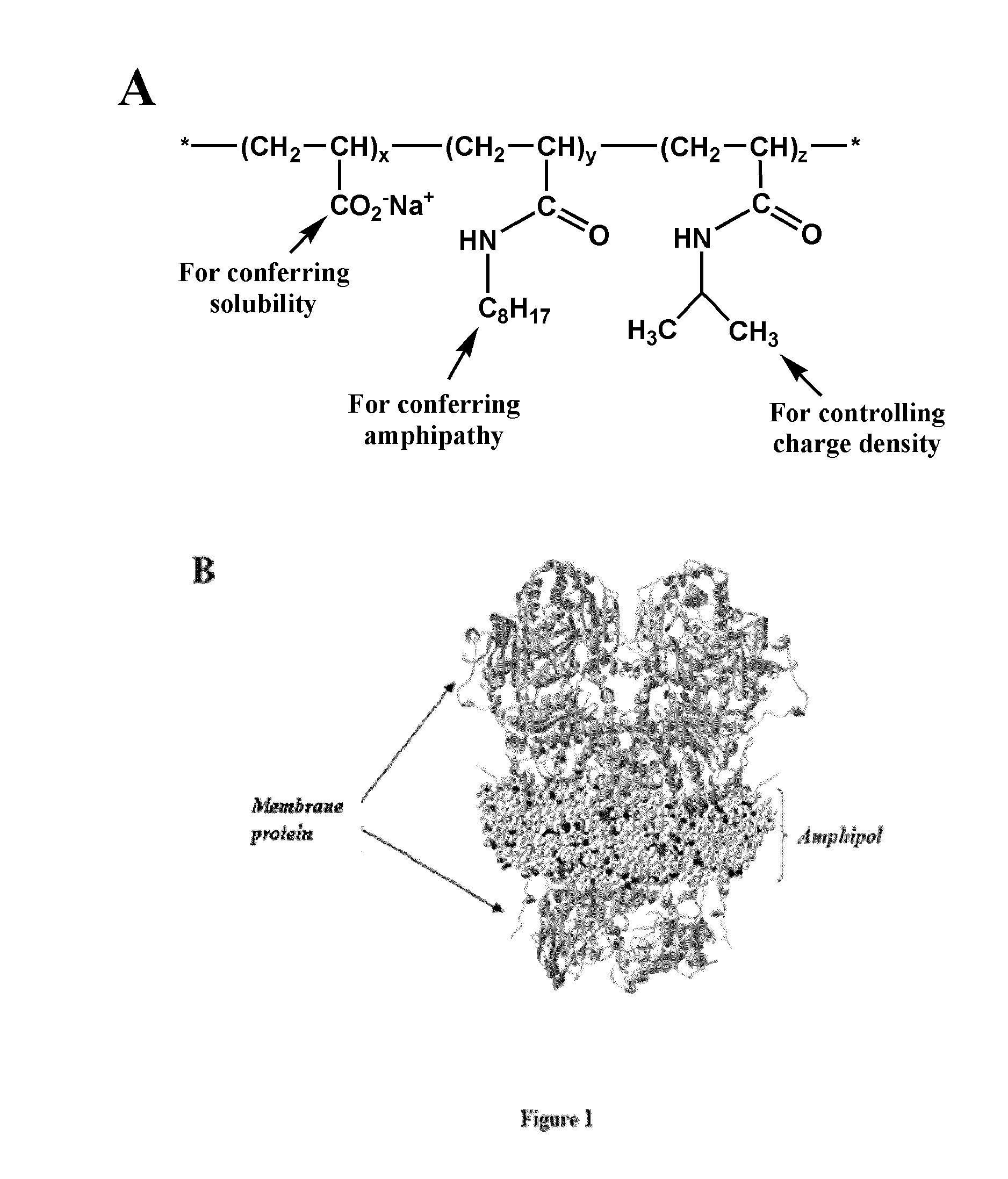
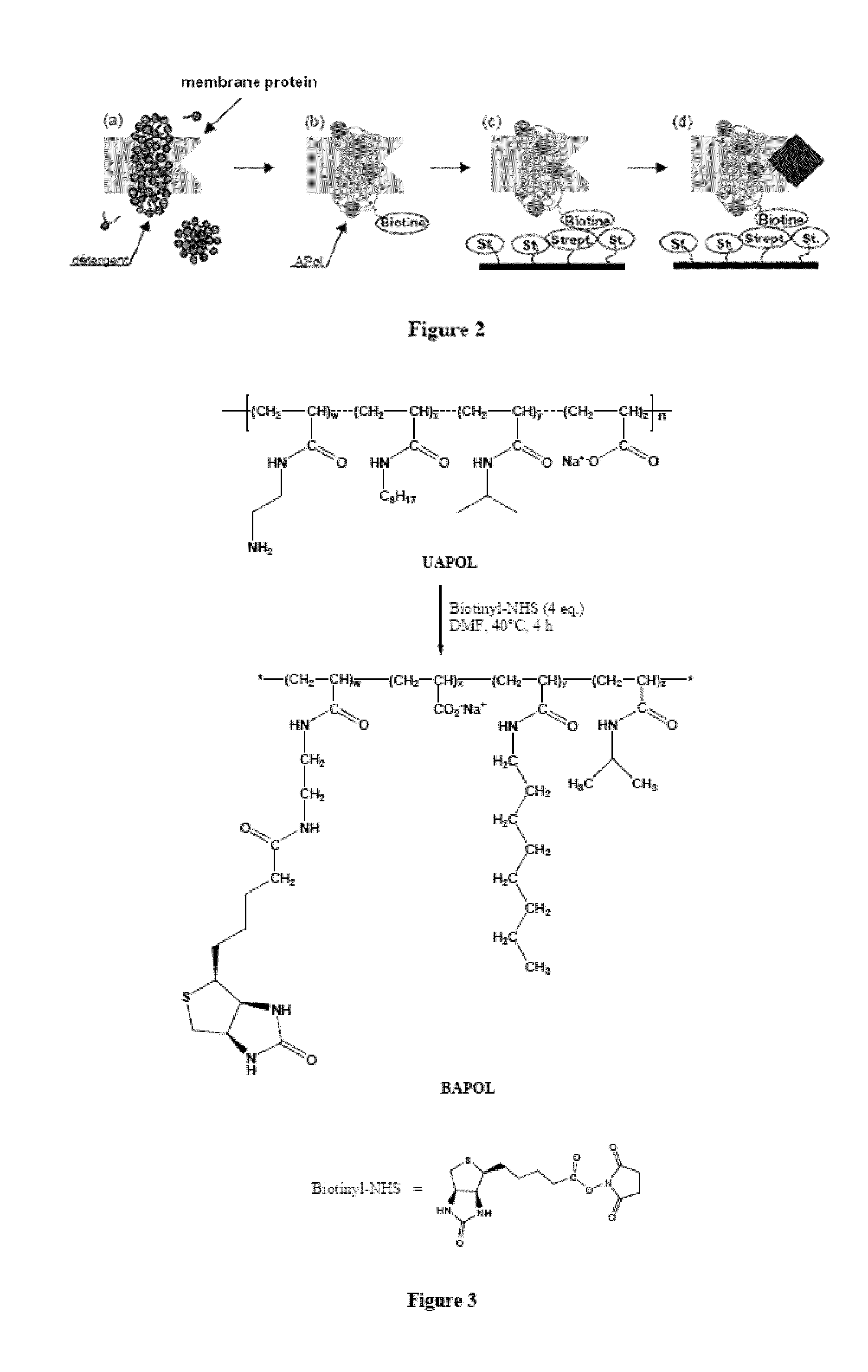
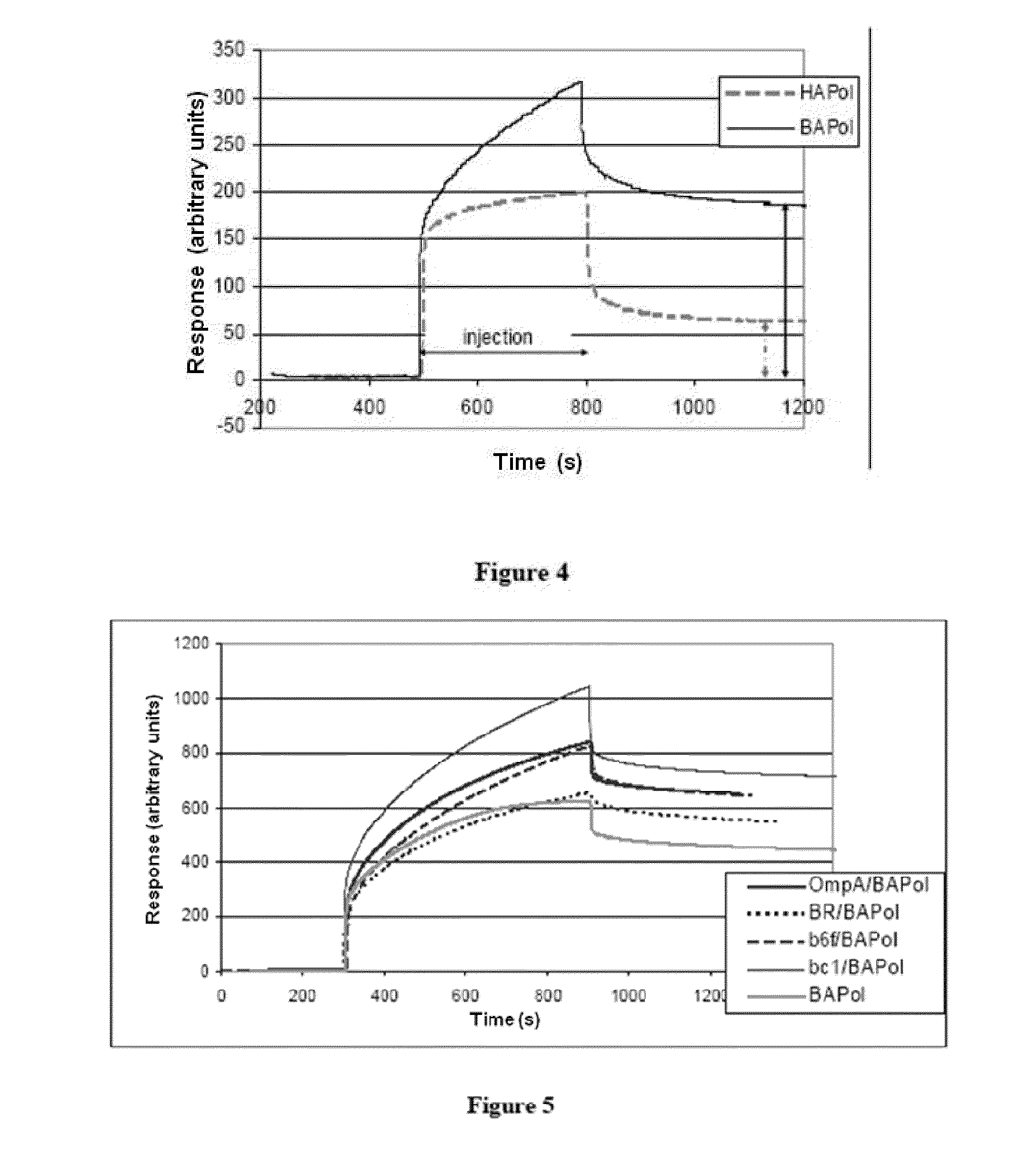
Immobilization of membrane porteins onto supports via an amphiphile
ActiveUS20090275066A1High yieldEasy to processPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningAmphiphileCell Membrane Proteins
The invention pertains to the field of membrane protein immobilization onto supports. It relates to a product comprising a support and at least one membrane protein attached to the surface thereof, characterized in that said membrane protein is attached to said support using an amphiphilic molecule with which said membrane protein is complexed. It also relates to a process for preparing such product, as well as to various applications in the fields of diagnosis, drug design and biotechnologies. It further relates to a kit, together with a functionalized amphiphilic molecule, for preparing a product according to the invention comprising a support and an amphiphilic molecule, wherein the amphiphilic molecule and the support interact through a hydrophobic bond, an ionic bond, a specific bond or a covalent bond.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Immobilization of membrane proteins onto supports via an amphiphile
ActiveUS8207263B2High yieldEasy to processMicrobiological testing/measurementPaper coatingCell Membrane ProteinsDrug design
The invention pertains to the field of membrane protein immobilization onto supports. It relates to a product comprising a support and at least one membrane protein attached to the surface thereof, characterized in that said membrane protein is attached to said support using an amphiphilic molecule with which said membrane protein is complexed. It also relates to a process for preparing such product, as well as to various applications in the fields of diagnosis, drug design and biotechnologies. It further relates to a kit, together with a functionalized amphiphilic molecule, for preparing a product according to the invention comprising a support and an amphiphilic molecule, wherein the amphiphilic molecule and the support interact through a hydrophobic bond, an ionic bond, a specific bond or a covalent bond.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Method needing no vacuum process to prepare organic polymer solar cell
InactiveCN101661994ASimple manufacturing processImprove production efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTin dioxideIndium
The invention provides a method needing no vacuum process to prepare an organic polymer solar cell. Indium oxide-tin dioxide (ITO) modified by zinc oxide (ZnO) or titanium oxide (TiO2) and the like, or tin dioxide (FTO) substrate doped with fluorine are taken as a cathode of the battery, and a polymer electrode with high conductivity is taken as an anode of the battery so as to compose the solar cell structure; a layer of hydrophobic polymer active layer modified by self-assembled amphiphilic molecules on water and oil is added between the active layer and the polymer electrode so that the surface of the active layer changes from hydrophobic to hydrophile, thus leading the solution of the water-soluble polymer electrode material with high conductivity to form an electrode film with good film-forming capability on the active layer; the whole preparation process of the solar cell is completed by a solution wet method, the method avoids the defects that in the vacuum evaporating and plating process of the metal electrode, the cost is high, the equipment dependency is strong, the process is complex, the energy consumption is high and the preparation in large area is difficult, furthermore, the method effectively simplifies the preparation process of the device.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
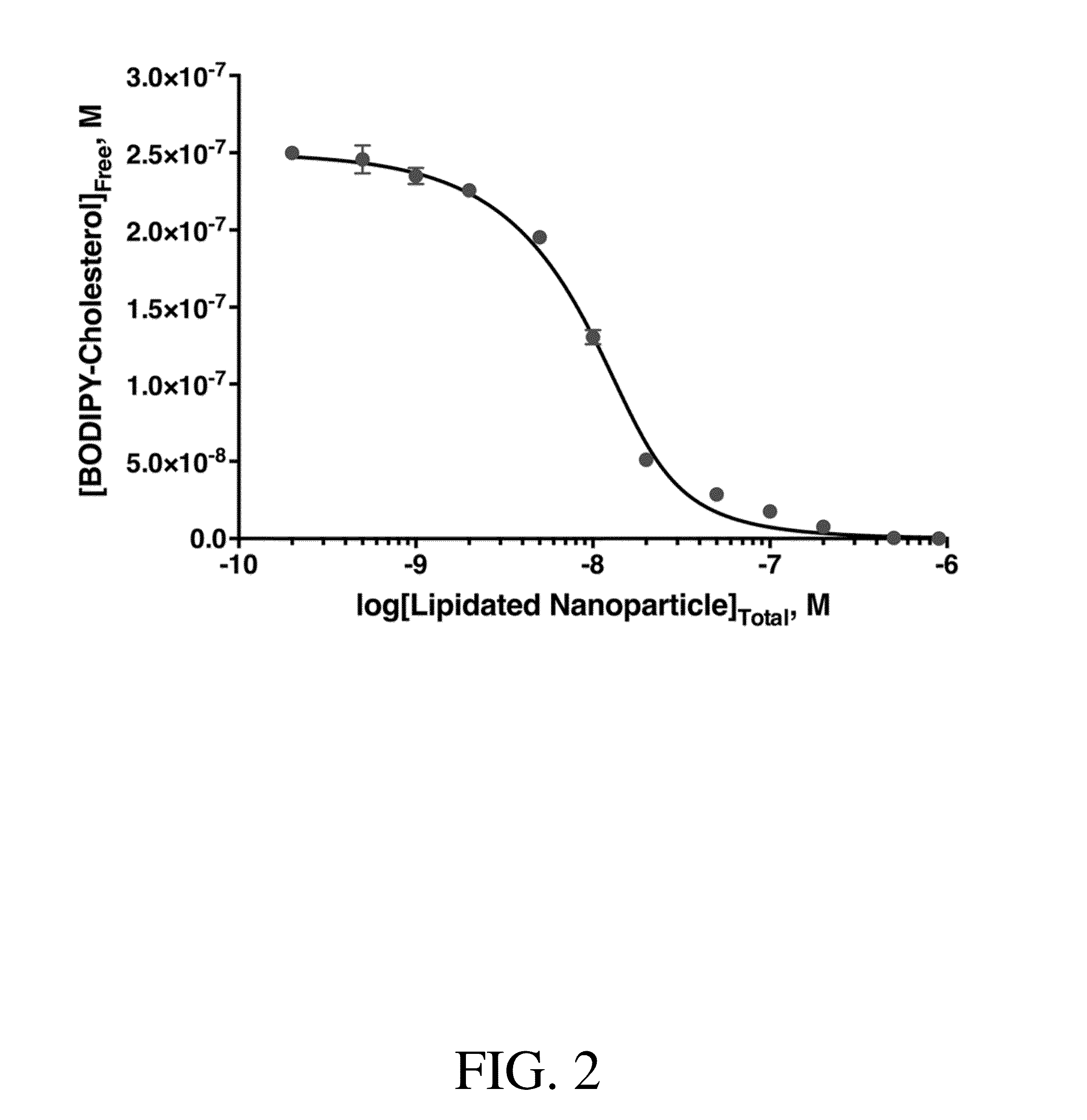
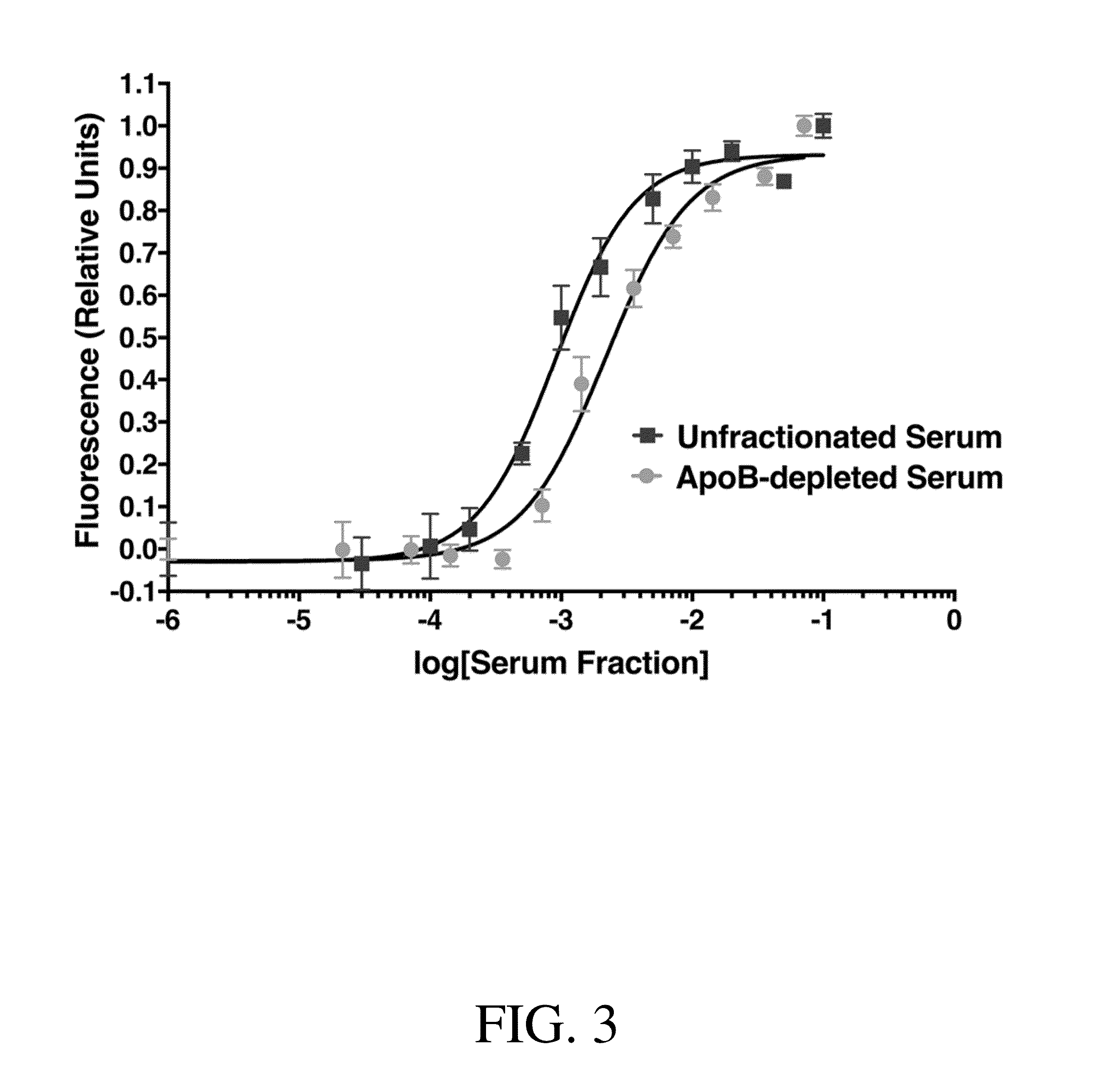
Assays for measuring binding kinetics and binding capacity of acceptors for lipophilic or amphilphilic molecules
ActiveUS20160274134A1Increase volumeEnhanced signalDisease diagnosisBiological testingCell freeNanoparticle
Aspects of the invention relate to methods for measuring the binding constant of a lipophilic or amphiphilic molecule acceptor for a lipophilic or amphiphilic molecule. Methods involve rapid, cell-free competition assays including a labeled lipophilic or amphiphilic molecule and nanoparticle.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
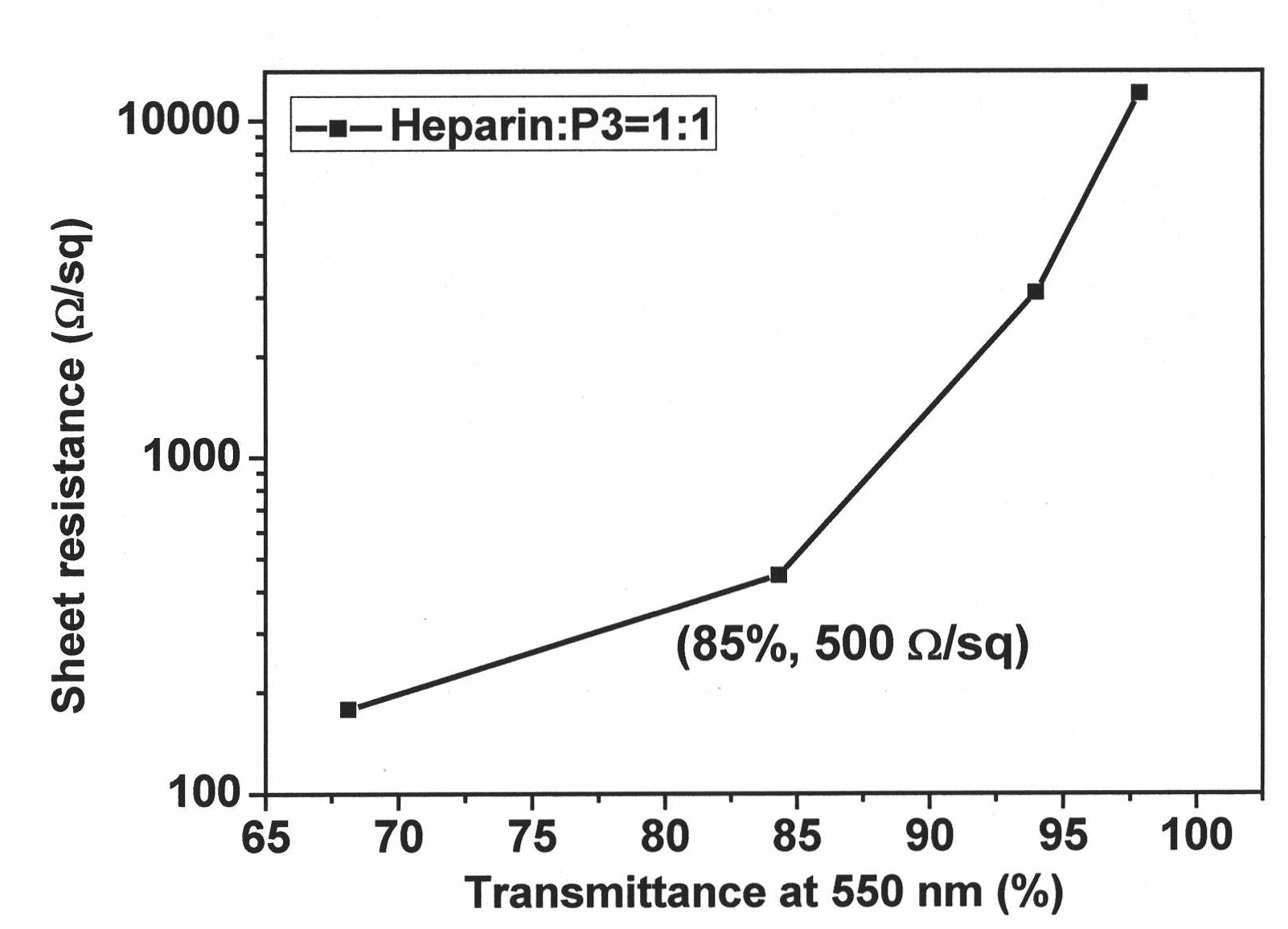
Dispersant for dispersing carbon nano-tube and preparation method of carbon nano-tube film
InactiveCN101773801AImprove performanceEasy to removeNanostructure manufactureTransportation and packagingElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh concentration
The invention provides a method for dispersing a carbon nano-tube by degradable biological molecules and further preparing a carbon nano-tube film having low sheet resistance or having low sheet resistance and high transmittance in high production efficiency. The method is characterized in that the selected biological molecules are amphiphilic molecules with both lipophilic structure, such as long carbon chain frames and the like and hydrophilic groups, such as SO3-, PO4-, COO-, -OH and the like, thus having strong dispersing ability towards the carbon nano-tube. The suspension of the carbon nano-tube which is dispersed by the biological molecules has high concentration, small control size and good stability, and the required amount of the dispersant is far less than that of the traditional dispersant, such as SDS, SDBS and the like, thus reducing the contact resistance greatly introduced by the dispersant, and therefore, the prepared carbon nano-tube film has excellent electrical conductivity. The biological molecules basically have no absorption in a visible region, thus having little influence on the transmittance of the film. Moreover, the biological molecules are degradable and are easy to be removed from the film, thus providing an effective approach to further improve the electrical conductivity of the film.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
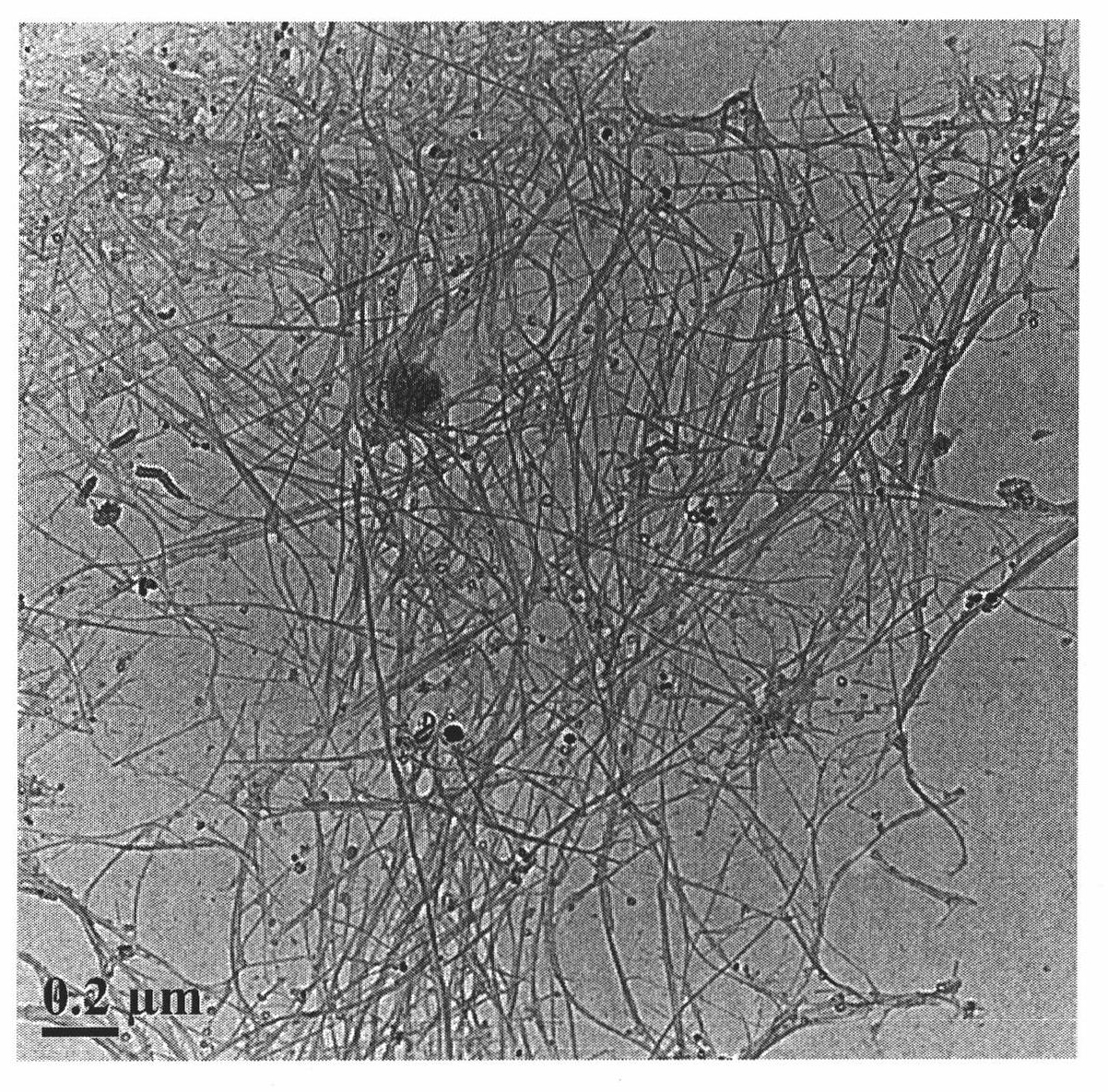
Amphiphilic Fibers and Membranes and Processes for Preparing Them
The present invention relates to the fields of chemistry and biology and more particularly to the field of biomaterials. The present invention includes amphiphilic fibers and membranes, which can be used for biomembranes and biocompatible devices. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing amphiphilic fibers and membranes from solutions comprising amphiphilic molecules. More particularly, the present invention relates to processes for preparing fibers and membranes from electrospinning solutions comprising amphiphilic molecules. The present invention further provides fibers and nonwoven membranes comprising amphiphilic fibers chosen from anionic surfactants, cationic surfactants, nonionic surfactants, phospholipids, sulfobetaines, lyotropic liquid crystalline molecules, and / or block copolymers. Electrospun fibers offer the potential for direct fabrication of biologically based, high-surface-area membranes without the use of multiple synthetic steps, complicated electrospinning designs, or post-processing surface treatments. Polymeric phospholipids, for example, have been shown to be attractive candidates for blood purification membranes, artificial heart valves and organs, and other prosthetics, including other biocompatible devices.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Tumor-targeted nuclear magnetic resonance/fluorescence dual-mode imaging contrast agent, preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN106390143AUniform particle size distributionImprove stabilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetTumor targeting
The present invention provides a tumor-targeted nuclear magnetic resonance / fluorescence dual-mode imaging contrast agent, preparation and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the contrast agent is nanometer micro-particles formed by self-assembling a nuclear magnetic resonance amphiphilic molecule, a near-infrared fluorescent dye amphiphilic molecule and a tumor targeting amphiphilic molecule in a solution, can stably exists under a physiological pH value condition, can be specifically accumulated at a tumor site in a targeting manner, can significantly enhance the intensity of the MRI signal and the near-infrared fluorescence signal at a tumor lesion site, can improve the specificity and the sensitivity of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and near infrared fluorescence imaging scanning, and is expected to be adopted as the contrast agent for fluorescence guidance during tumor resection surgeries and postoperative nuclear magnetic resonance monitoring.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dispersion of carbon nanoparticles and core-shell type carbon nanoparticles, and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS7648765B2Convenient coatingEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentOrganic solventCarbon Nanoparticles
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Non-Polymeric Compositions for Controlled Drug Delivery
InactiveUS20100034801A1Prevent and minimize phase separationMaintain physical stabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideControl mannerPolymer
The present invention provides a novel liquid composition suitable for in-situ formation of a depot system to deliver a bioactive substance in a controlled manner. The composition of the present invention comprises: (a) a hydrophobic non-polymeric carrier material; (b) a water miscible biocompatible organic solvent that dissolves the hydrophobic non-polymeric material; (c) an ionic complex that is formed between an amphiphilic molecule and a bioactive substance having a net charge at neutral pH in water. The present invention also provides a method of manufacturing and use of the composition thereof.
Owner:FORESEE PHARMA CO LTD
Substrate surface structured with thermally stable metal alloy nanoparticles, method for preparing the same and uses thereof, in particular as catalyst
InactiveCN103747870AImprove the immunityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsSolventNanostructure
The invention relates to a method for preparing a substrate surface structured with thermally stable metal alloy nanoparticles. The method comprises providing a micellar solution of amphiphilic molecules such as organic diblock or multiblock copolymers in a suitable solvent; loading the micelles of said micellar solution with metal ions of a first metal salt; loading the micelles of said micellar solution with metal ions of at least one second metal salt; depositing the metal ion-loaded micellar solution onto a substrate surface to form a (polymer) film comprising an ordered array of (polymer) domains; co-reducing the metal ions contained in the deposited domains of the (polymer) film by means of a plasma treatment to form an ordered array of nanoparticles consisting of an alloy of the metals used for loading the micelles on the substrate surface.The invention also provides a nanostructured substrate surface obtainable by said method as well as the use of said nanostructured substrate surface as a catalyst.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
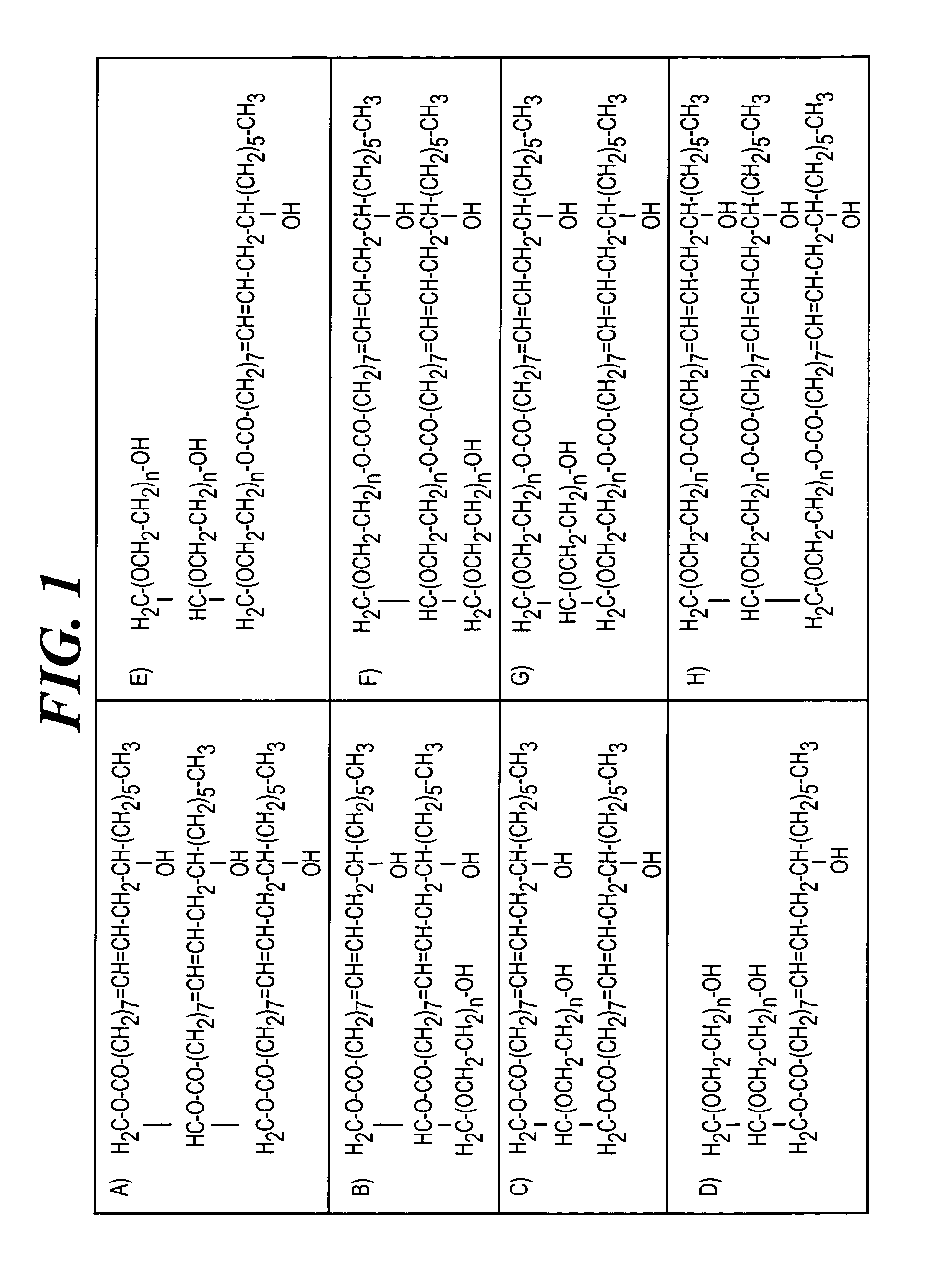
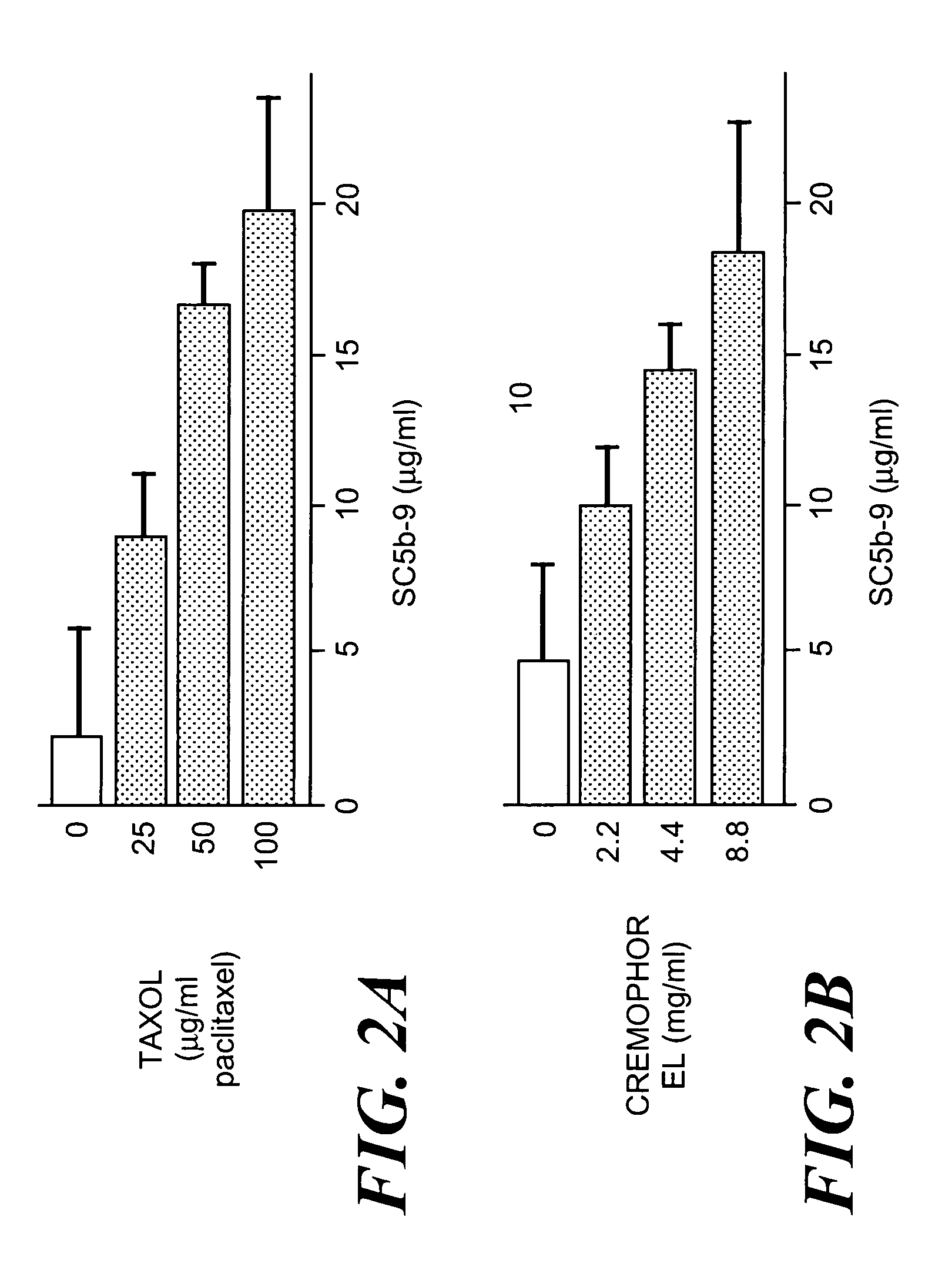
Method of inhibiting side effects of pharmaceutical compositions containing amphiphilic vehicles or drug carrier molecules
A method is provided for inhibiting or preventing toxicity and other unwanted effects (a) caused by solvents for pharmaceuticals which solvents or emulsifier which contain amphiphilic molecules such as polyethoxylated oils or a derivative thereof, or (b) caused by a drug in a vehicle containing amphiphilic molecules such as phopholipids or derivative thereof, emptying a complement inhibitor. Drug compositions containing amphiphilic molecules, or derivatives thereof and a complement inhibitor, and pharmaceutical compositions including a drug, solvent or carrier containing amphiphilic molecules or derivatives thereof, and a complement inhibitor are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
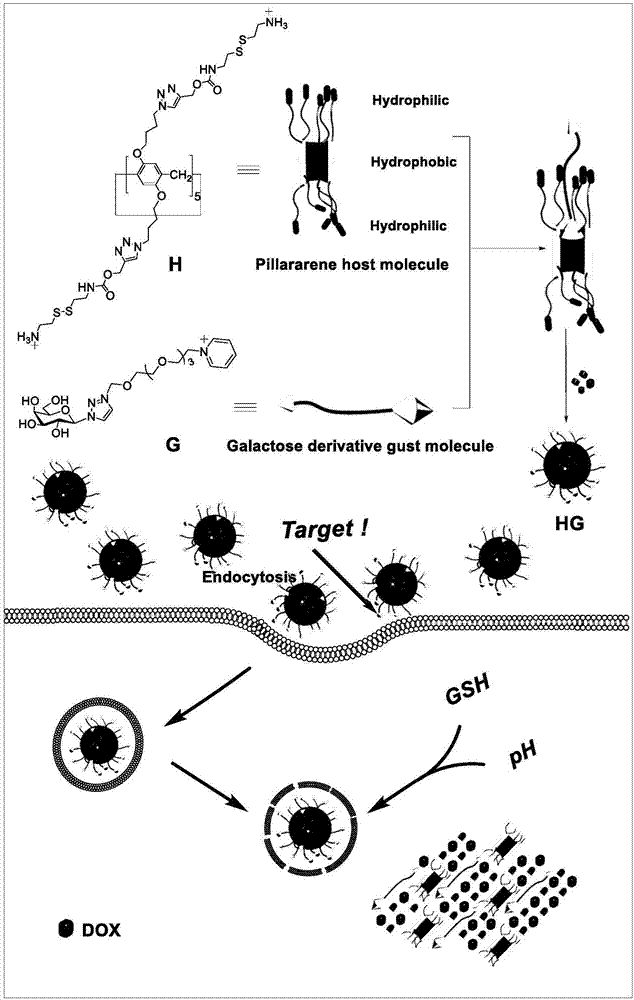
Targeted pH-GSH dual-response multifunctional nano-vesicle drug loading system
InactiveCN107536803APromote ruptureIncrease lethalityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellDual response
The invention relates to a targeted pH-GSH dual-response multifunctional nano-vesicle drug loading system. By using cystamine functionalized column [5] aromatic hydrocarbon with pH-GSH dual responsiveness as a host molecule and using a pyridinium modified galactose derivative as a guest molecule, glycosyl-functionalized column [5] aromatic hydrocarbon amphiphilic molecule is prepared through the host-guest interaction; nano-vesicle is formed in a solution through hydrophilic and hydrophobic effect; and an anti-cancer drug is encapsulated in the vesicle cavity so as to construct the targeted pH-GSH dual-response multifunctional nano-vesicle drug loading system. As the surface of vesicle contains galactosyl, biocompatibility of the system can be remarkably raised. Meanwhile, galactosyl can interact with specific galactose binding protein overexpressed on the surface of hepatoma carcinoma cell to realize targeted selective access to cancer cell so as to rapidly release an anti-cancer drugin the cancer cell and raise lethality of cancer cell.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Biosensor
InactiveUS20110111985A1High densityImprove responsePeptide librariesLiquid surface applicatorsHydrophilic coatingCoupling
The invention provides a product comprising: a membrane-spanning protein; a lipid membrane formed from amphiphilic molecules and membrane-spanning protein molecules; and a substrate: characterised in that the membrane protein is directly coupled to the substrate. The invention also provides a method for producing such a product which i) comprises treating a substrate with a hydrophilic coating agent; providing at least one membrane-spanning protein; iii) bringing the protein into contact with the treated substrate under conditions for the coupling of the protein directly to the treated substrate; iv) adding amphiphilic molecules to the protein-coupled substrate to form a lipid membrane. The product is useful for biosensors, protein arrays and the like.
Owner:PORVAIR SCI
Pressure-sensitive adhesive composition, pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, pressure-sensitive adhesive member and image display, and method for peeling off optical film from an image display and method for removing display panel from image display
ActiveUS20110008552A1Stable adhesive characteristicThe process is simple and fastLiquid crystal compositionsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesDisplay devicePolymer
The pressure-sensitive adhesive composition of the invention includes a base polymer; and amphiphilic molecule particles that have an aggregate structure of amphiphilic molecules having hydrophilic group and hydrophobic group in the same molecule. The pressure-sensitive adhesive has stable adhesive characteristics and can be reduced in adhesive strength in a desired manner depending on how it is to be used.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Dispersion of carbon nanoparticles and core-shell type carbon nanoparticles, and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20080032135A1Convenient coatingEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentOrganic solventCarbon Nanoparticles
A dispersion of carbon nanoparticles is prepared by monodispersing carbon nanoparticles in water droplets of a reverse micelle solution in which the water droplets are coated with amphiphilic molecules and dispersed in an organic solvent. In a method of preparing the dispersion of carbon nanoparticles, carbon nanoparticles and a monodispersion function material, e.g., ammonia, for imparting a polarity to surfaces of the carbon nanoparticles are added to the reverse micelle solution. The solution is then stirred, so that the carbon nanoparticles whose surfaces have the polarity are monodispersed in the water droplets of the reverse micelle solution. Further, a metal alkoxide is added to the solution and then stirring them, so that the surfaces of the carbon nanoparticles are coated with oxide of the metal.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
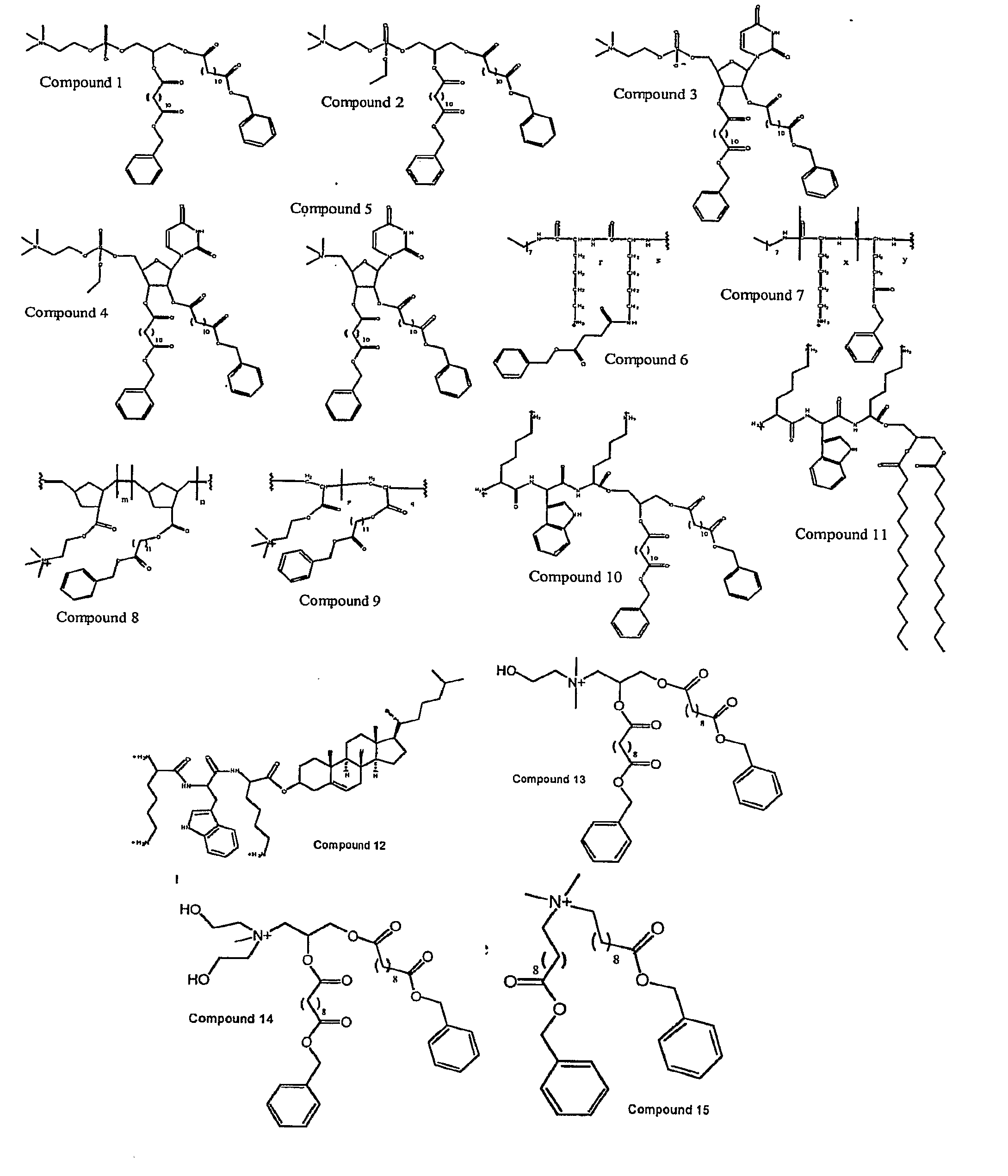
Amphiphilic molecules with aggregation-induced emission effects, preparing method thereof and uses of the amphiphilic molecules
InactiveCN105348176AHigh and stable luminous efficiencyGood water solubilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum efficiencyAggregation-induced emission
The invention discloses amphiphilic molecules with aggregation-induced emission effects, a preparing method thereof and uses of the amphiphilic molecules. The general structure of the amphiphilic molecules is shown as a formula I (with n being any integer from 9 to 13). The amphiphilic molecules are prepared by a two-step reaction process, wherein the process includes 1) modifying tetraphenyl ethylene with long alkyl chains by a coupling reaction and 2) refluxing the product of the former reaction in pyridine to obtain the amphiphilic molecules. The amphiphilic molecules are extremely low in critical aggregation concentration, high in aggregate fluorescence quantum efficiency, low in working concentration and good in biocompatibility. When the amphiphilic molecules are used as chromophores and applied to cell imaging, both contrast and distinguishability are high. The amphiphilic molecules have a wide application prospect when being used as fluorescence probes.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
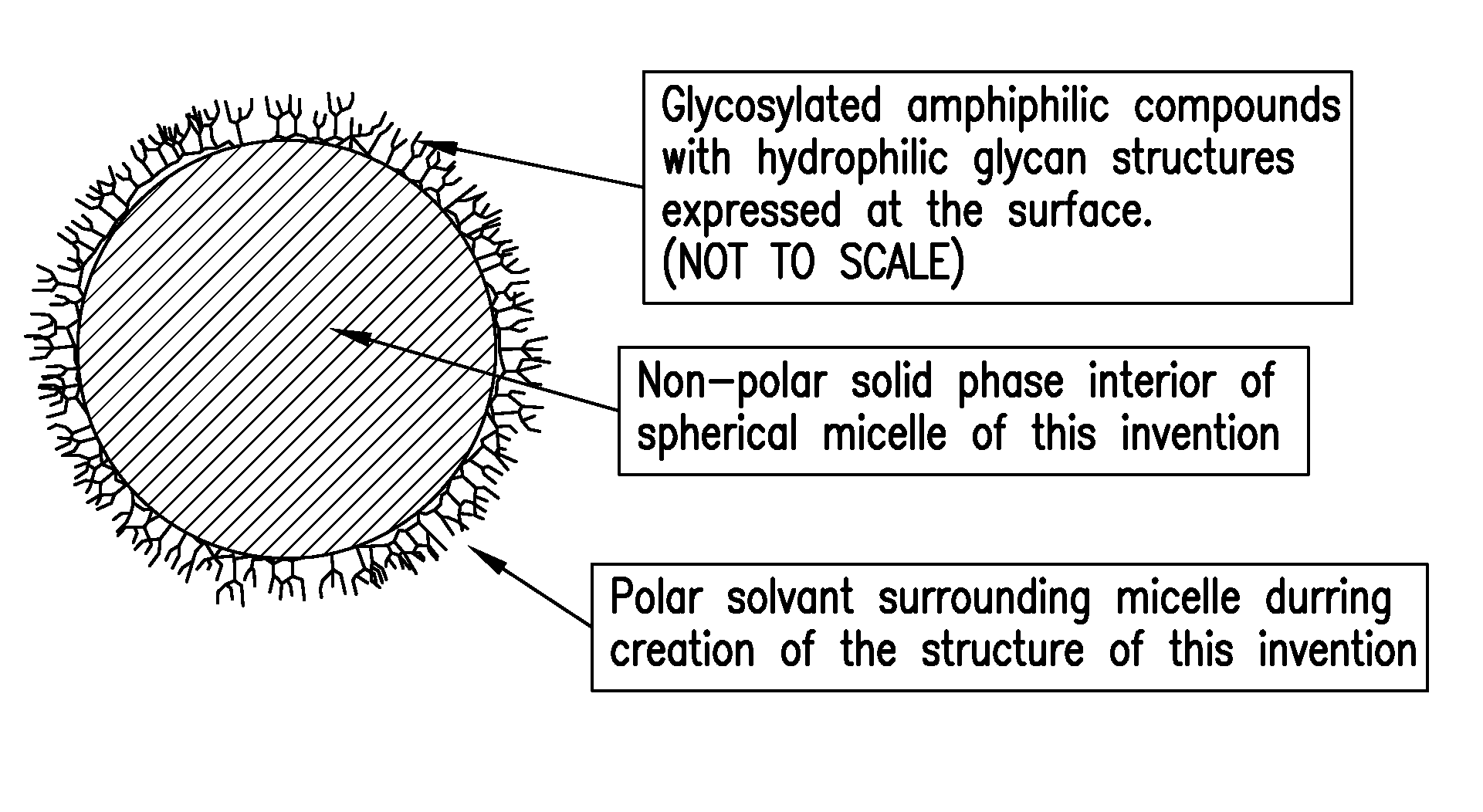
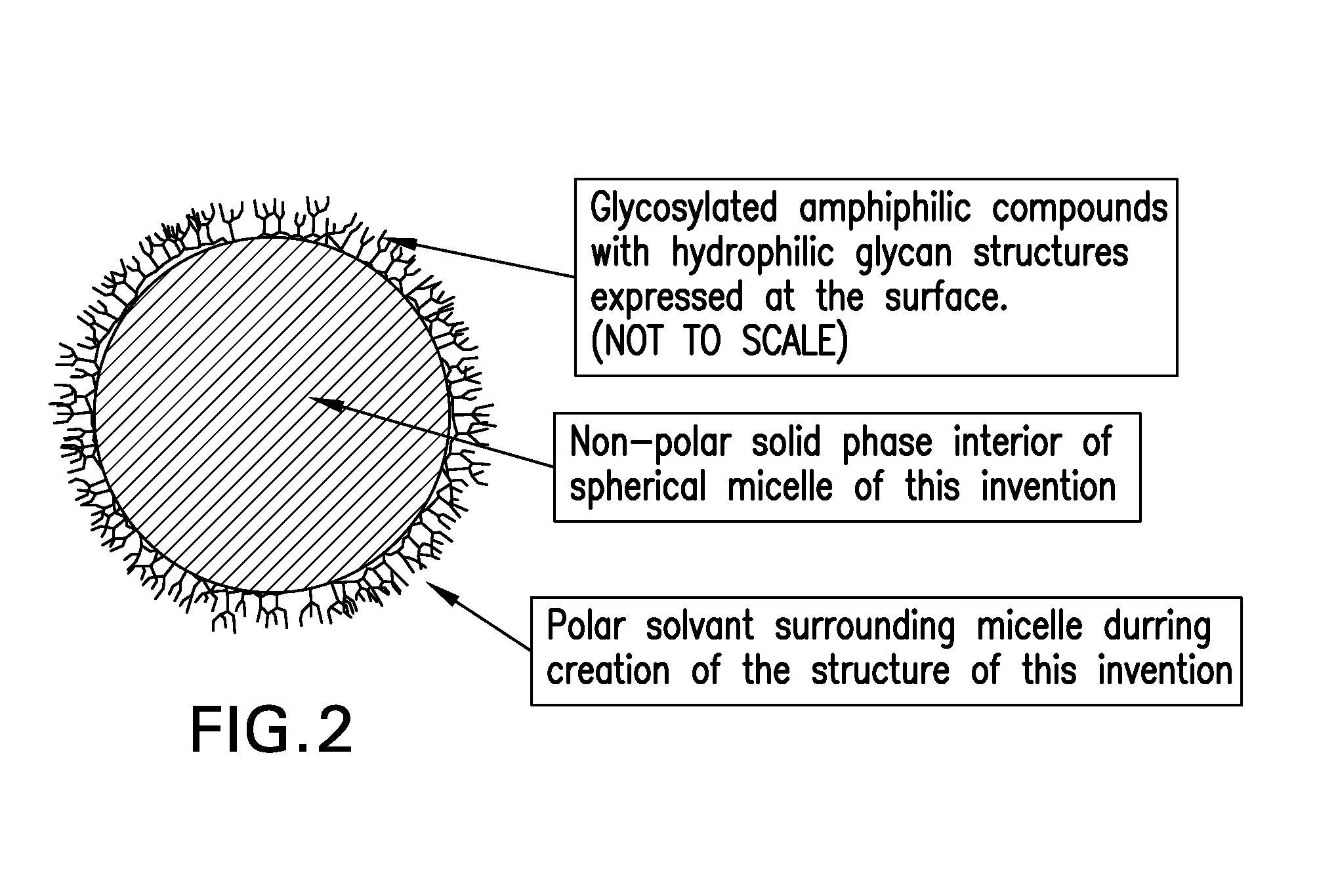
Solid State Membranes with Surface-Embedded Glycosylated Amphiphilic Molecules and Micelles Formed Therefrom
InactiveUS20080305348A1Good biocompatibilityAvoid immune responseSolvent extractionLayered productsChemical ligationSolvent
Disclosed herein are glycosylated amphiphilic molecules composed of hydrophobic “tails” and hydrophilic “heads” that self align to form a membrane at the interface of a polar solvent and a non-polar liquid or a solid. The present invention is directed to a solid state membrane, typically a thin film, composed of a non-polar solid material having the hydrophobic “tail” of a glycosylated amphiphilic molecule embedded in or linked to its surface such that the hydrophilic “head” protrudes from the solid surface and presents useful properties to the surrounding environment. A membrane or film in accordance with the present invention is produced when a non-polar liquid, in the presence of a polar solvent and an amphiphilic biological compound, undergoes a transformation from liquid to solid, through thermal, chemical or radiative means, with the resultant effect that the amphiphilic molecule is affixed or “locked” to the surface, more particularly the hydrophobic ends of the amphiphilic compounds are mechanically or chemically linked to or embedded in the non-polar solid. The membrane and micelles produced therefrom remain stable even in the absence of the polar solvent, thereby allowing the hydrophilic components of the amphiphilic compounds to present useful properties at the surface thereof.
Owner:SPEDDEN RICHARD H
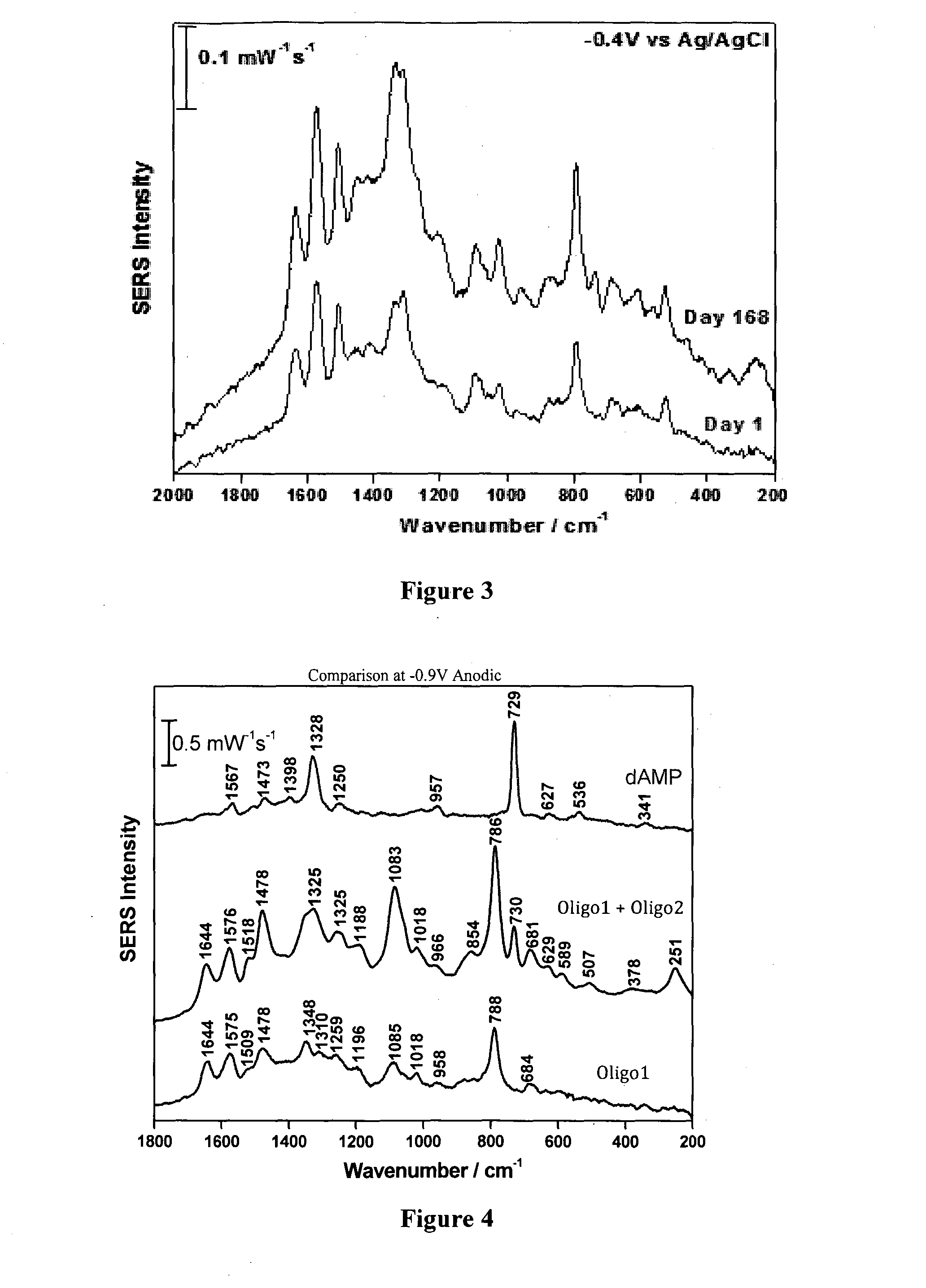
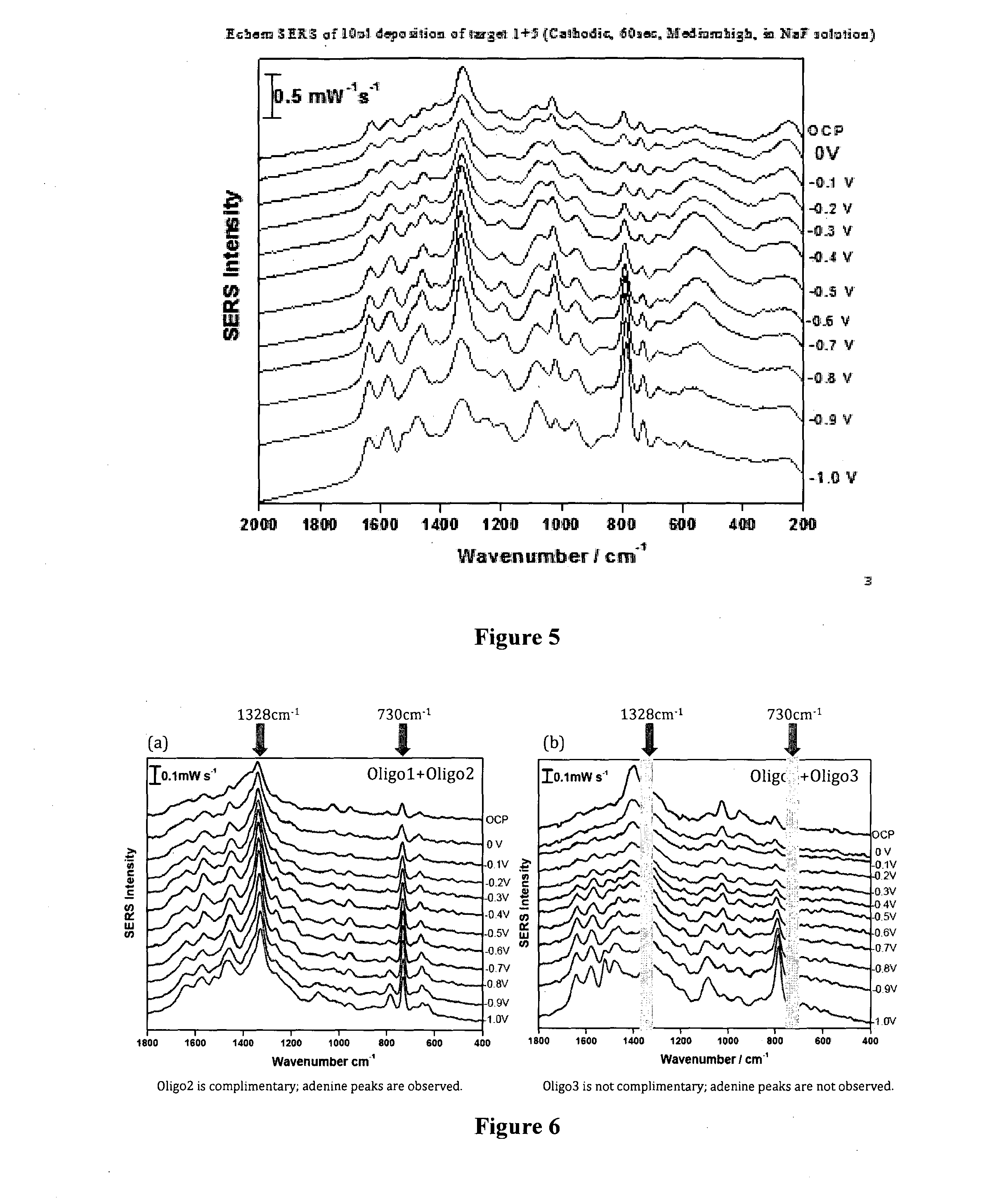
Method of detecting and/or qualifying an analyte in a biological sample
ActiveUS20140302492A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAptamerAnalyte
An aptamer-based SERS detection technique that directly monitors an aptamer-analyte capture event by generating spectroscopic information regarding the identity of the analyte that has been bound to the aptamer from a complex biological sample. A reproducible SERS spectrum is measured for an aptamer-analyte complex formed on a metal surface and this spectral information is used directly to identify the specific aptamer-analyte complex and optionally also to quantify the analyte in the sample, thus enabling discrimination between true and false positives in quantitative analyte assays on complex biological samples. In one embodiment the aptamer is attached directly to the metal surface and surrounded by a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of amphiphilic molecules. In an alternative embodiment the metal surface is coated with a SAM and the aptamer is attached to the amphiphilic molecules of the SAM.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com