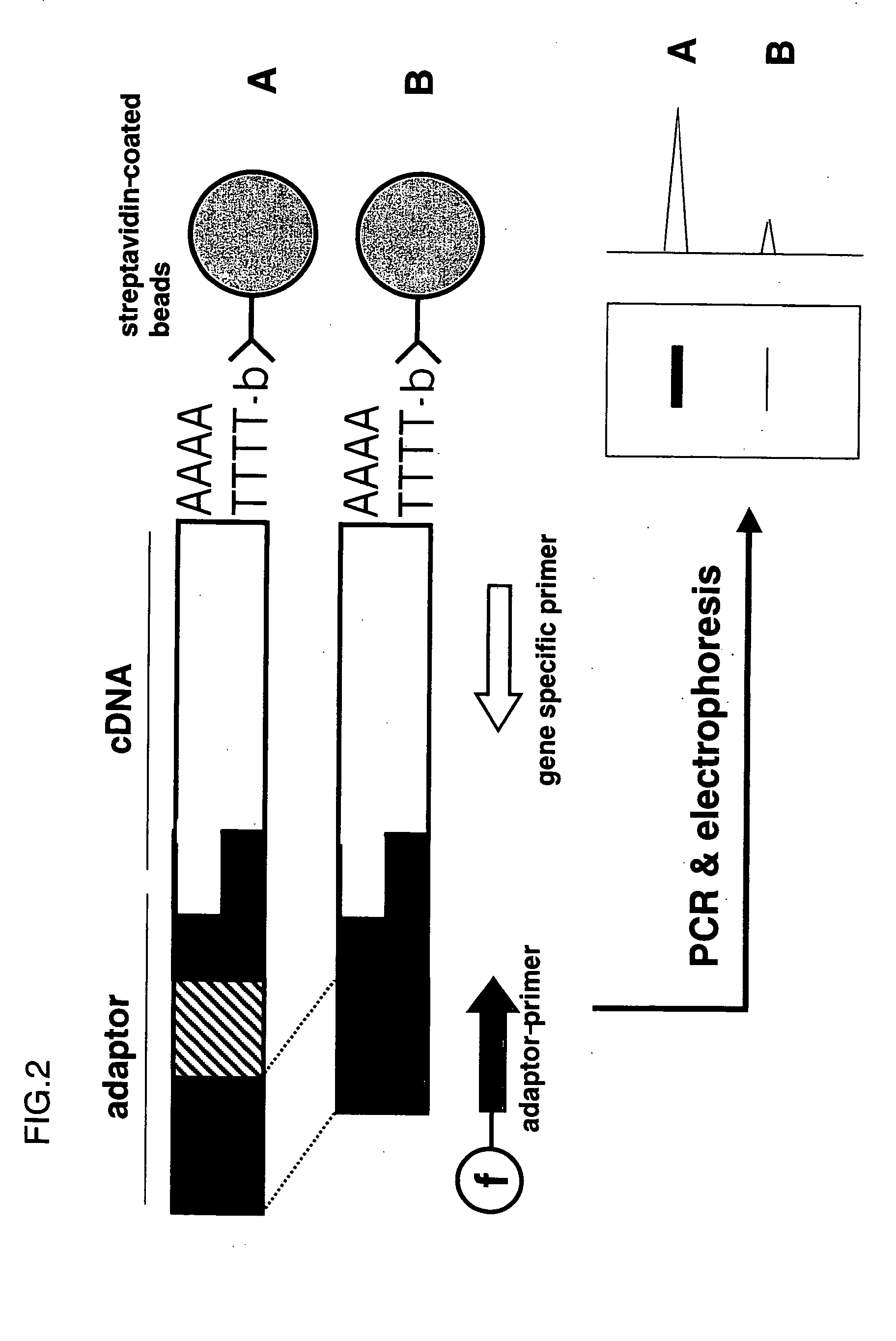
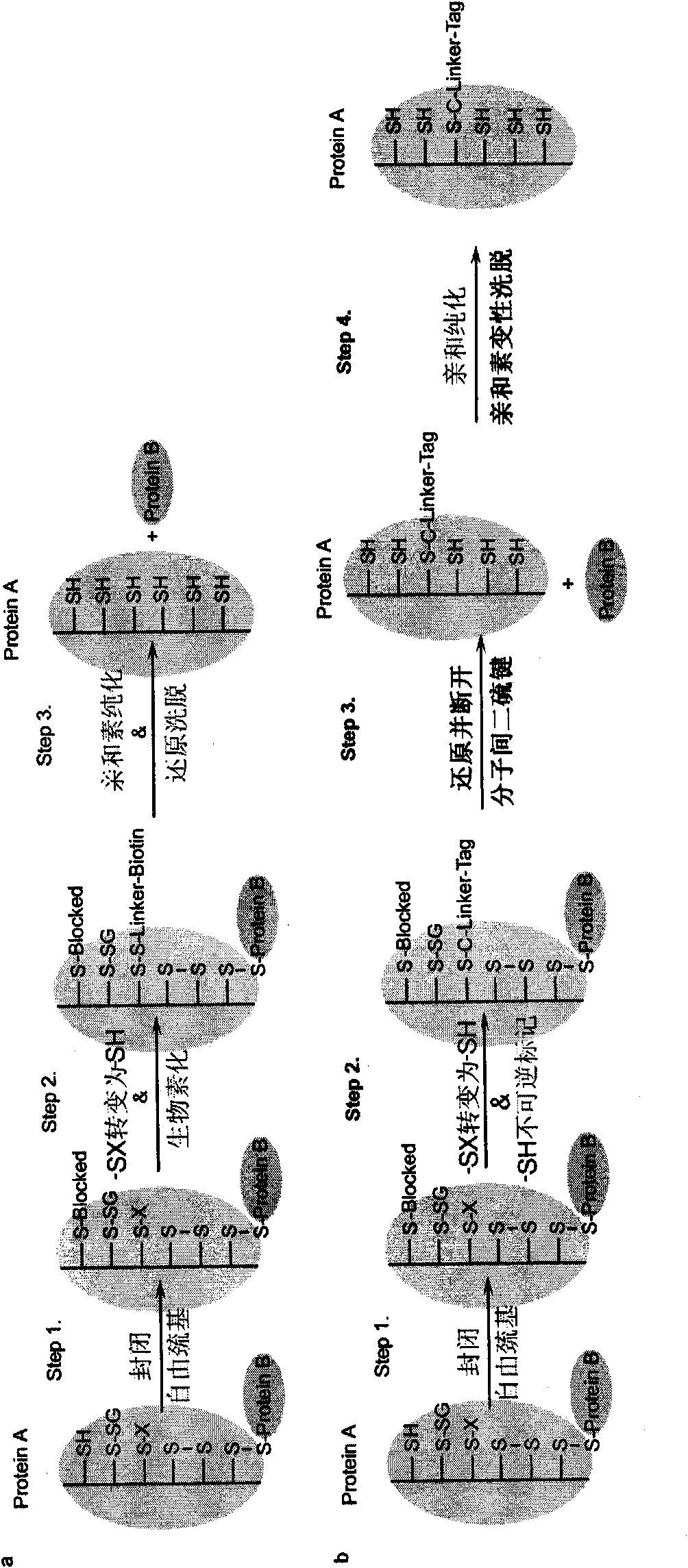
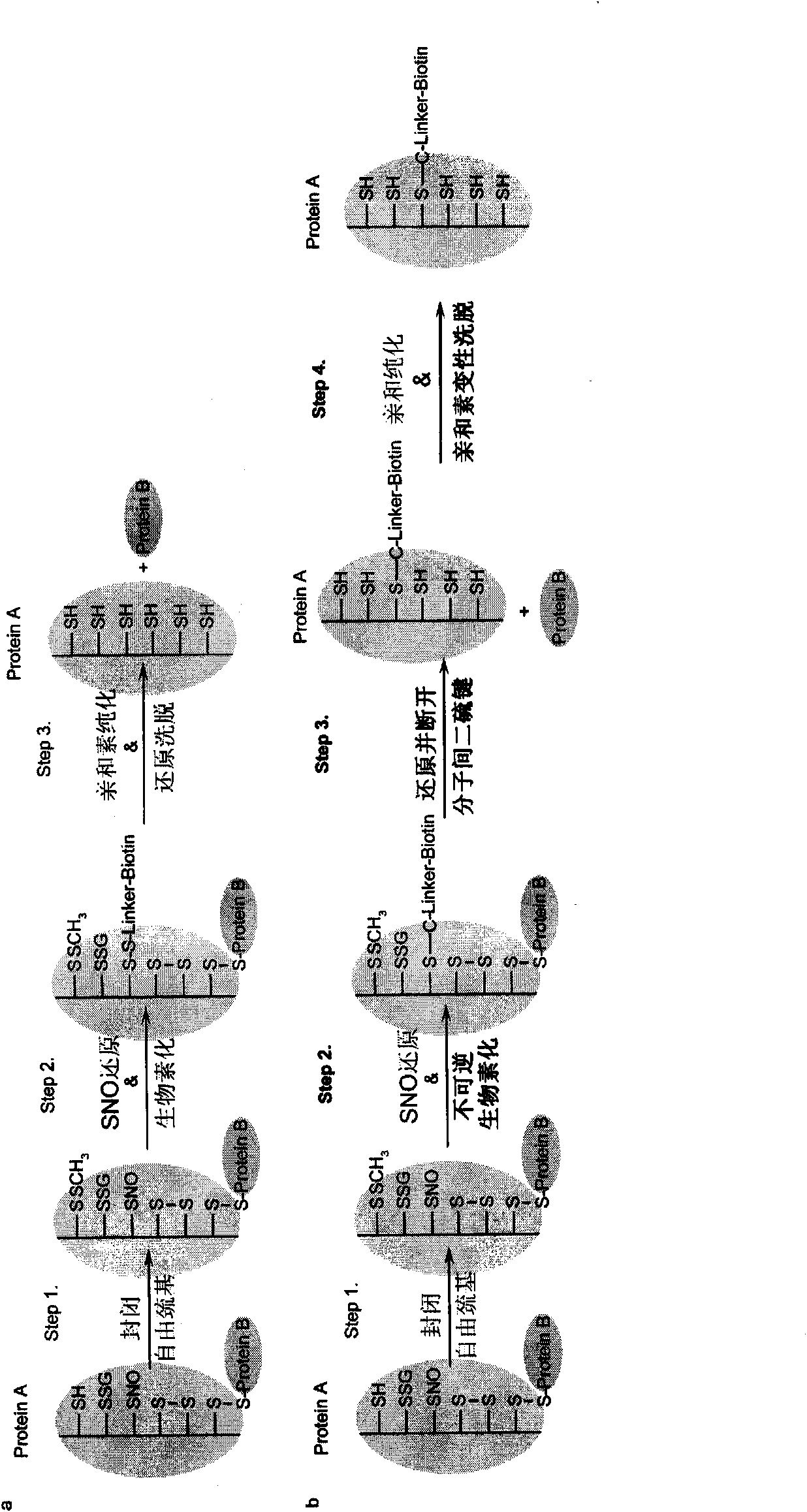
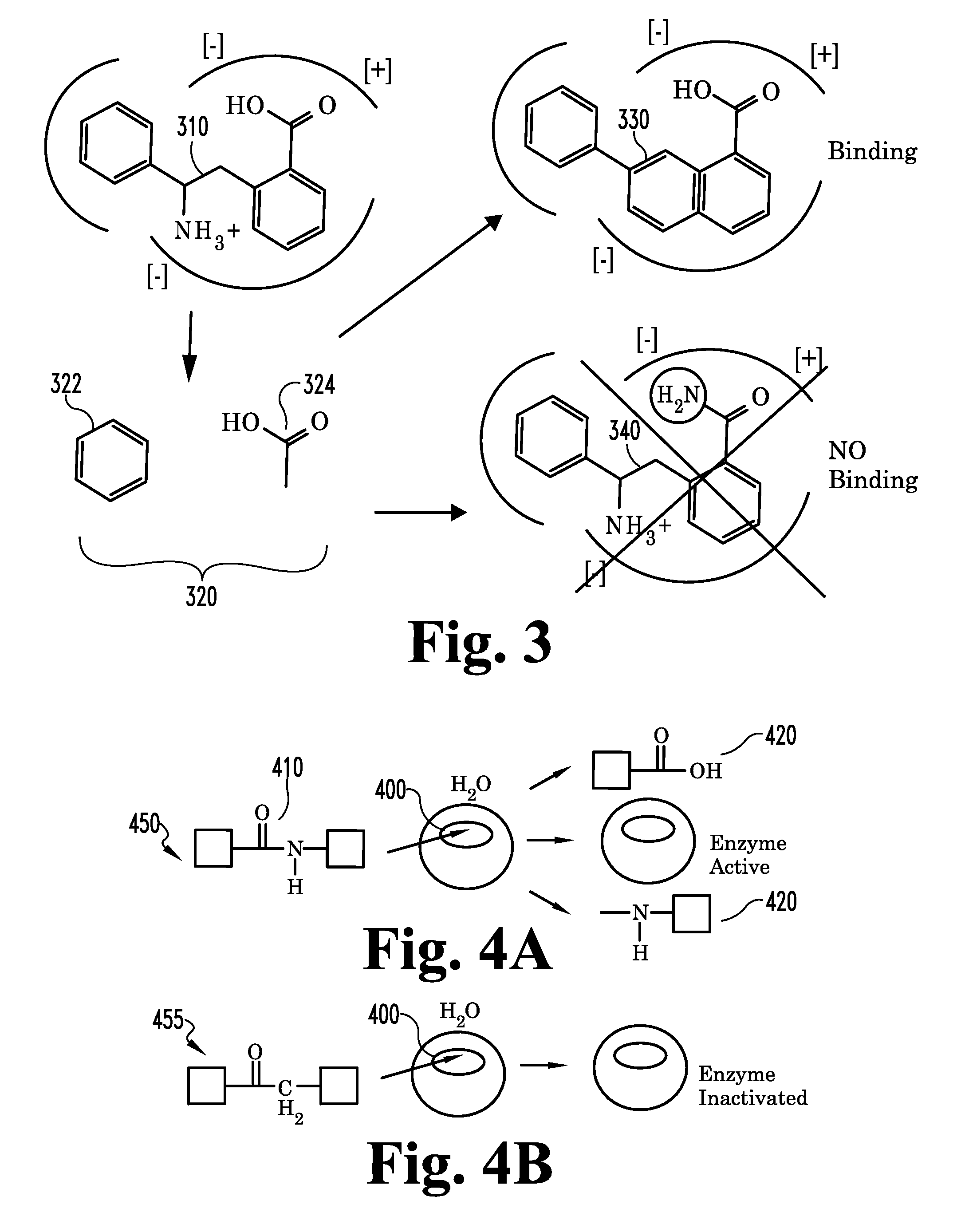
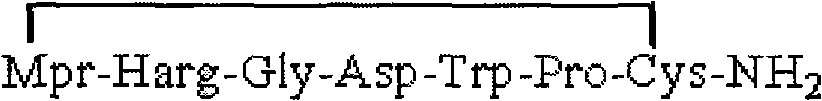Patents
Literature
369 results about "Drug design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
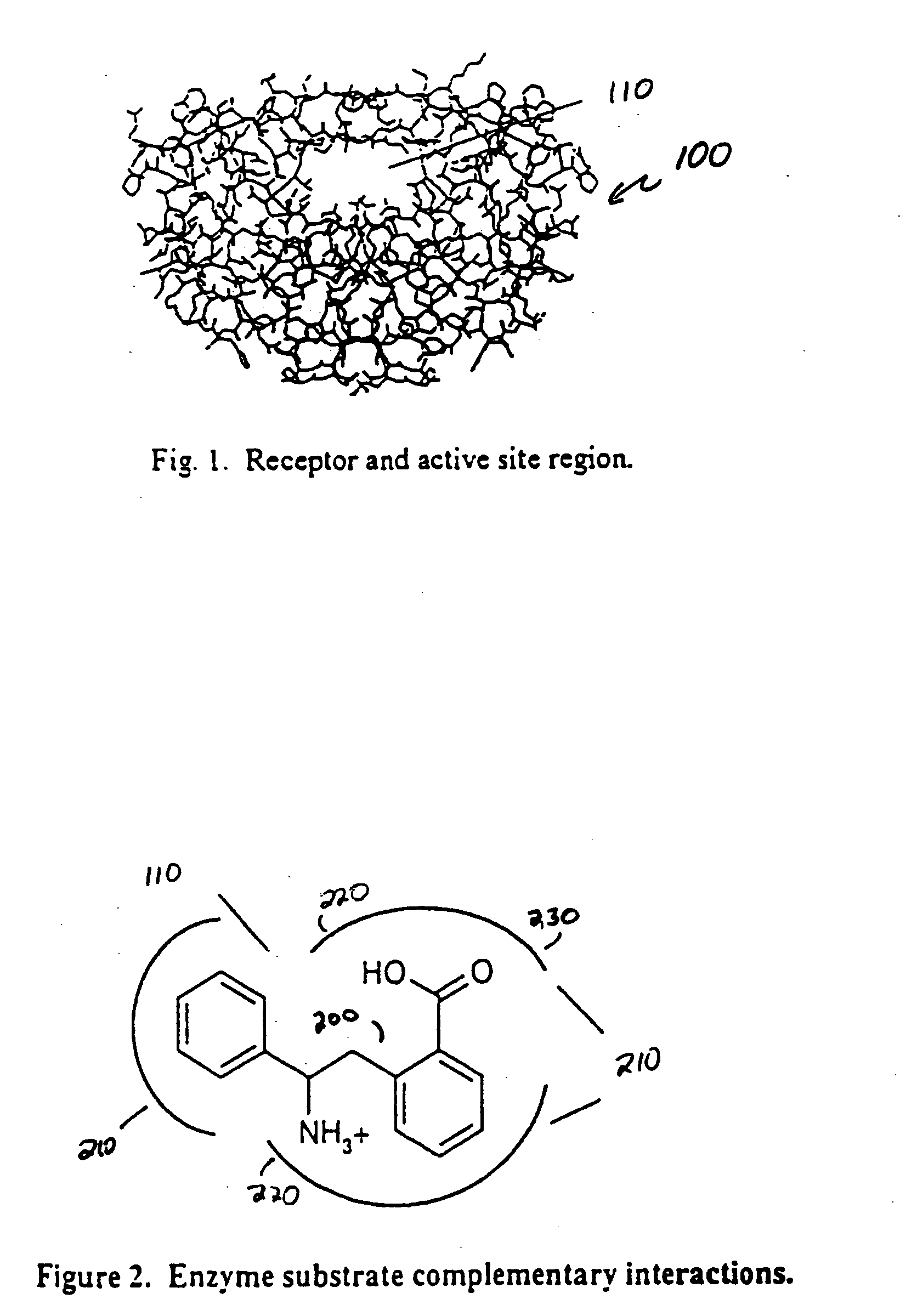
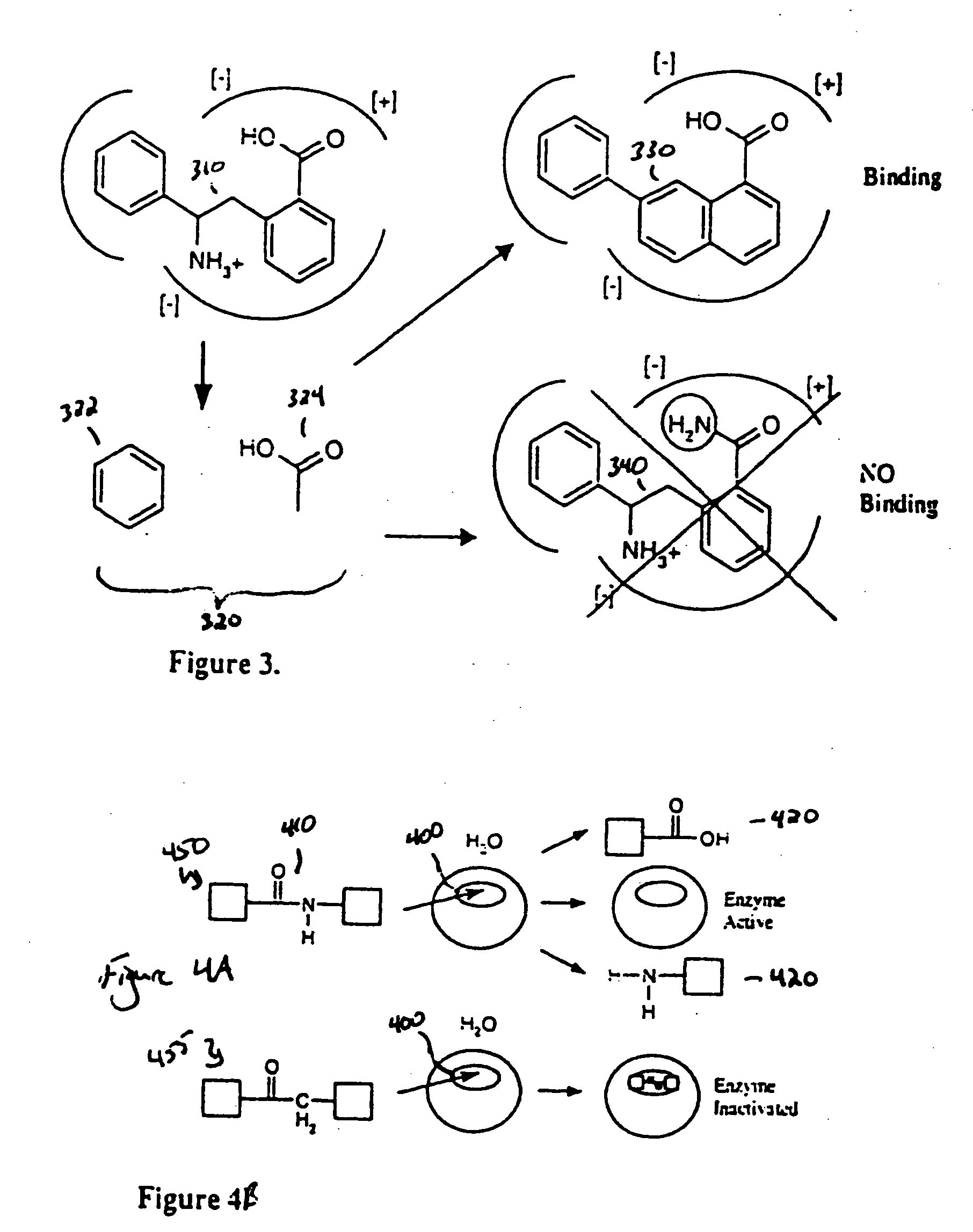
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals including peptides and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.
Cyclodextrin polymers for carrying and releasing drugs
This invention discloses methods for preparing compositions of cyclodextrin polymers for carrying drugs and other active agents. Methods are also disclosed for preparing cyclodextrin polymer carriers that release drugs under controlled conditions. The invention also discloses methods for preparing compositions of cyclodextrin polymer carriers that are coupled to biorecognition molecules for targeting the delivery of drugs to their site of action. The advantages of the water soluble (or colloidal) cyclodextrin polymer carrier are: (1) Drugs can be used that are designed for efficacy without conjugation requirements. (2) It will allow the use of drugs designed solely for efficacy without regard for solubility. (3) Unmodified drugs can be delivered as macromolecules and released within the cell. (4) Drugs can be targeted by coupling the carrier to biorecognition molecules. (5) Synthesis methods are independent of the drug to facilitate multiple drug therapies.
Owner:KOSAK KENNETH M
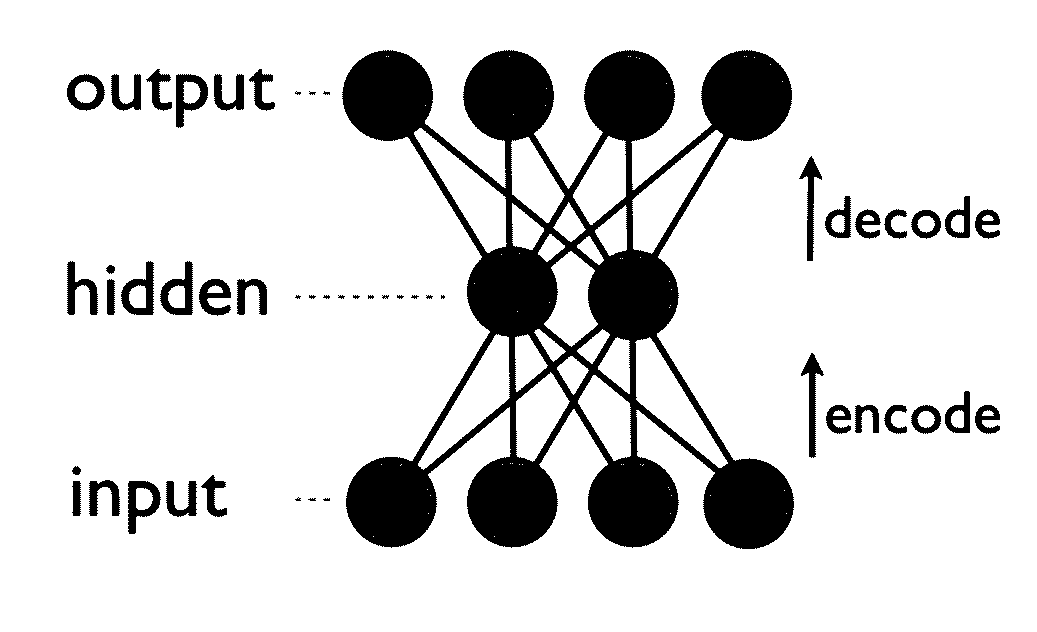
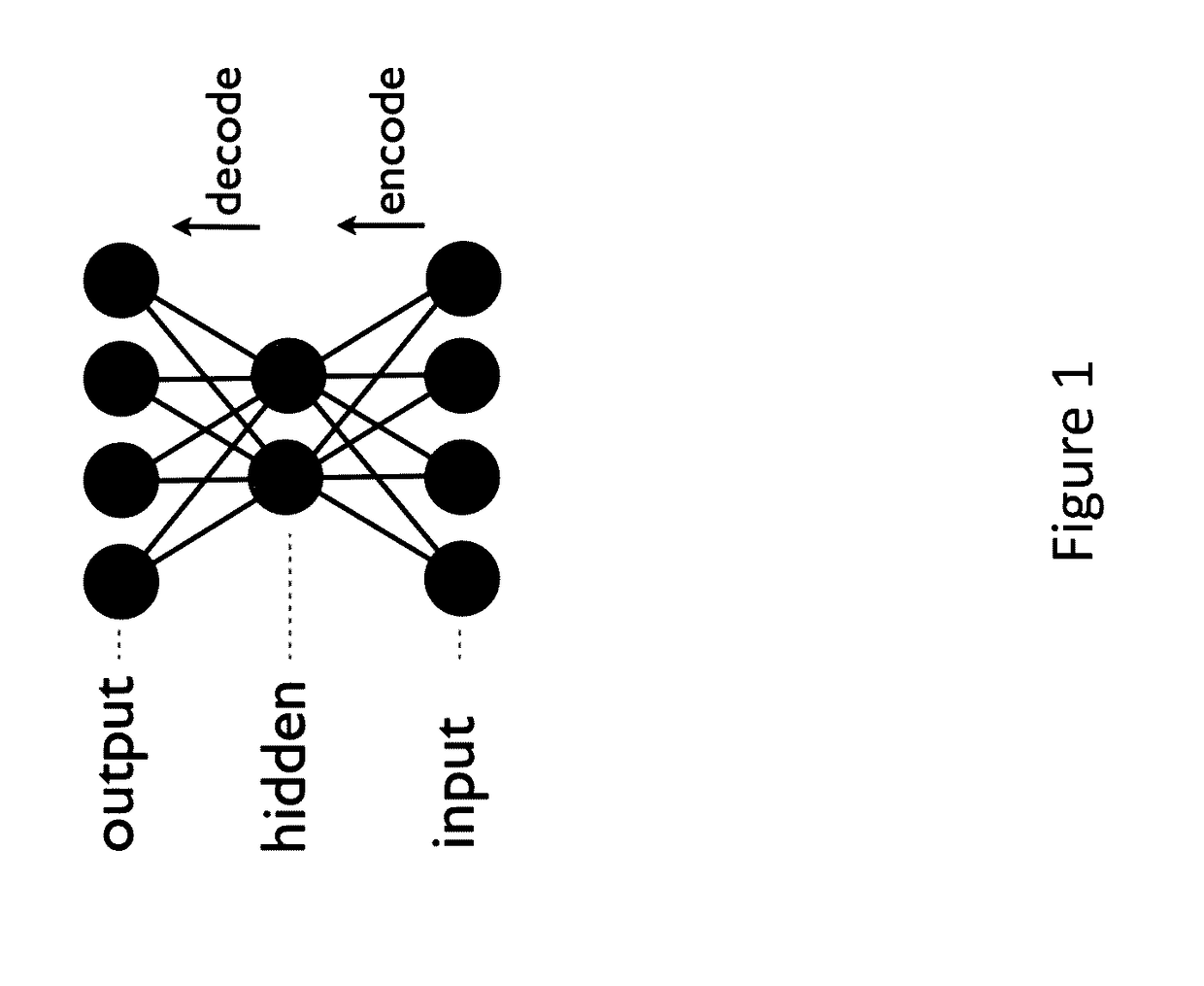
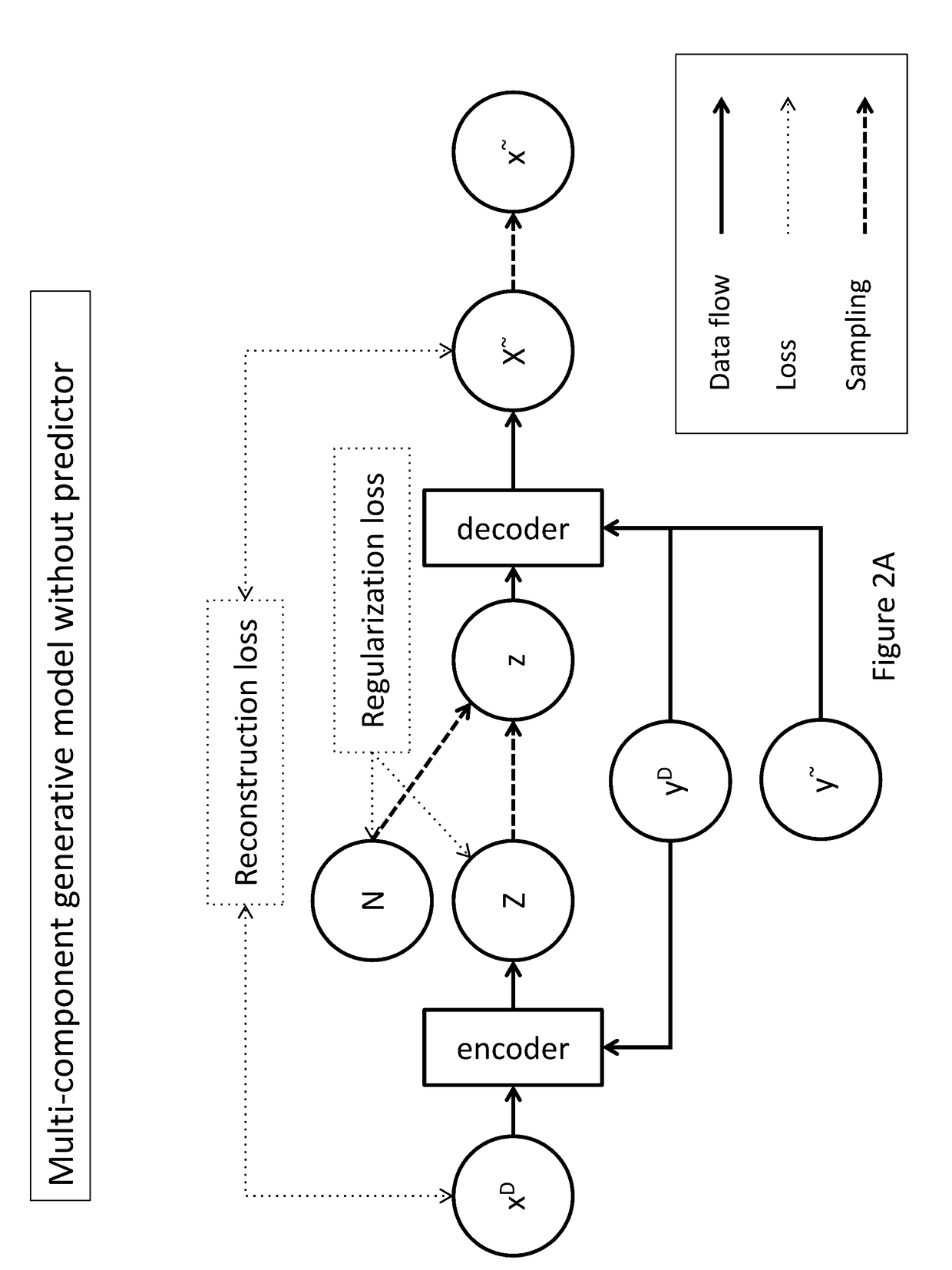
Generative machine learning systems for drug design
ActiveUS20170161635A1Minimizing reconstruction errorMinimize loss functionMolecular designProbabilistic networksChemical compoundStudy methods
In various embodiments, the systems and methods described herein relate to generative models. The generative models may be trained using machine learning approaches, with training sets comprising chemical compounds and biological or chemical information that relate to the chemical compounds. Deep learning architectures may be used. In various embodiments, the generative models are used to generate chemical compounds that have desired characteristics, e.g. activity against a selected target. The generative models may be used to generate chemical compounds that satisfy multiple requirements.
Owner:PREFERRED NETWORKS INC
Compositions and method for regulating apoptosis
ActiveUS6992063B2Suppress programmed cell deathRelieve suppressionTripeptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsInhibitor of apoptosisApoptosis
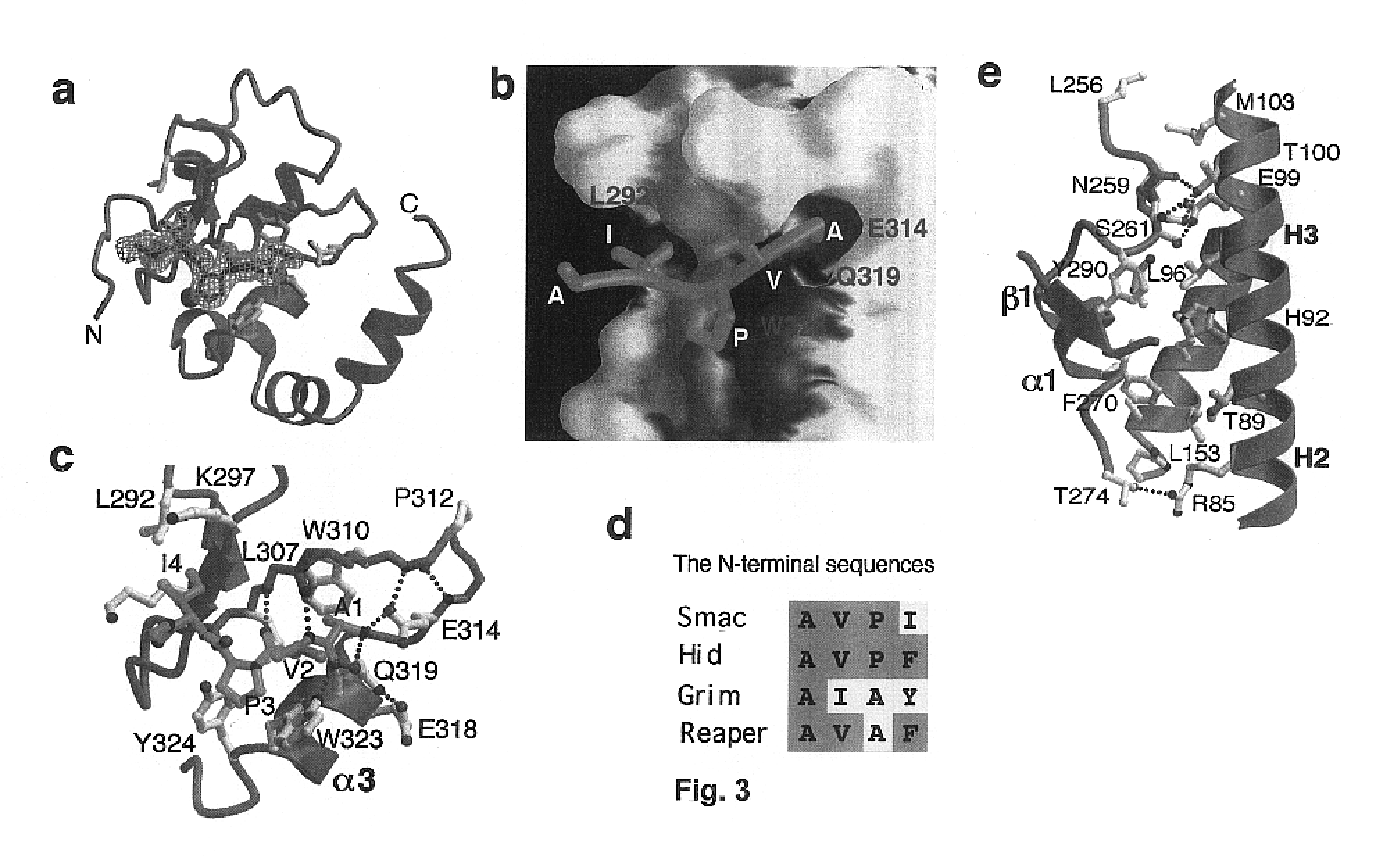
Peptides and peptidomimetics capable of modulating apoptosis through their interaction with cellular IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) are disclosed. The peptides and mimetics are based on the N-terminal tetrapeptide of IAP-binding proteins, such as Smac / DIABLO, Hid, Grim and Reaper, which interact with a specific surface groove of IAP. Also disclosed are methods of using these peptides and peptidomimetics for therapeutic purposes and for rational drug design.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Crystal of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha prolyl hydroxylase
The crystal structure of ligand-bound EGLN1 catalytic domain of prolyl hydroxylase is disclosed. These coordinates are useful in computer aided drug design for identifying compounds that regulate EGLN1 prolyl hydroxylase and thereby regulate HIF-regulated disorders.
Owner:AKEBIA THERAPEUTICS
Quantum mechanics based method for scoring protein-ligand interactions
The present invention provides for the first time a quantum mechanics-based method for scoring protein-ligand interactions and binding affinity predictions, using quantum mechanical Hamiltonians and / or a combined quantum mechanical / molecular mechanical approach, and Poisson-Boltzmann (PB)-based solvation methods. Also provided is a method for using quantum mechanics to describe the enthalpic and solvation effects of binding. The method comprises comparing the calculated binding affinities to experimental values in order to measure the success of the method. The methods disclosed herein may further be used to score protein and drug or protein and inhibitor interactions. The present method can predict the free energy of binding of protein-ligand complexes with high accuracy so as to enable lead optimization, thus serving as a powerful tool in computational drug design.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method of predicting cancer
InactiveUS20050260572A1Reduce intensityReduce weightMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsOncologyMalignancy
The invention relates to a cancer predicting method and a drug design method. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for predicting cancer which is useful for the genetic diagnosis for evaluating the malignancy of cancer. The invention also relates to a method for designing a drug based on the result of the above prediction method.
Owner:DNA CHIP RES +1
Specific detection method of protein or polypeptide cysteine sulfydryl modification and application thereof
ActiveCN101893634AMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingSpecific detectionProtein insertion
The invention relates to a specific detection method of protein or polypeptide cysteine sulfydryl related modification under the condition that the interference of the intermolecular disulfide bond is removed, a kit for executing the method and application of the kit in screening new physiopathology related endogenous targets or exogenous protein or polypeptide targets of cysteine sulfydryl related modification, screening drugs designed to regulate the protein or polypeptide cysteine sulfydryl related modification and detecting content of cysteine sulfydryl related modification in samples.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
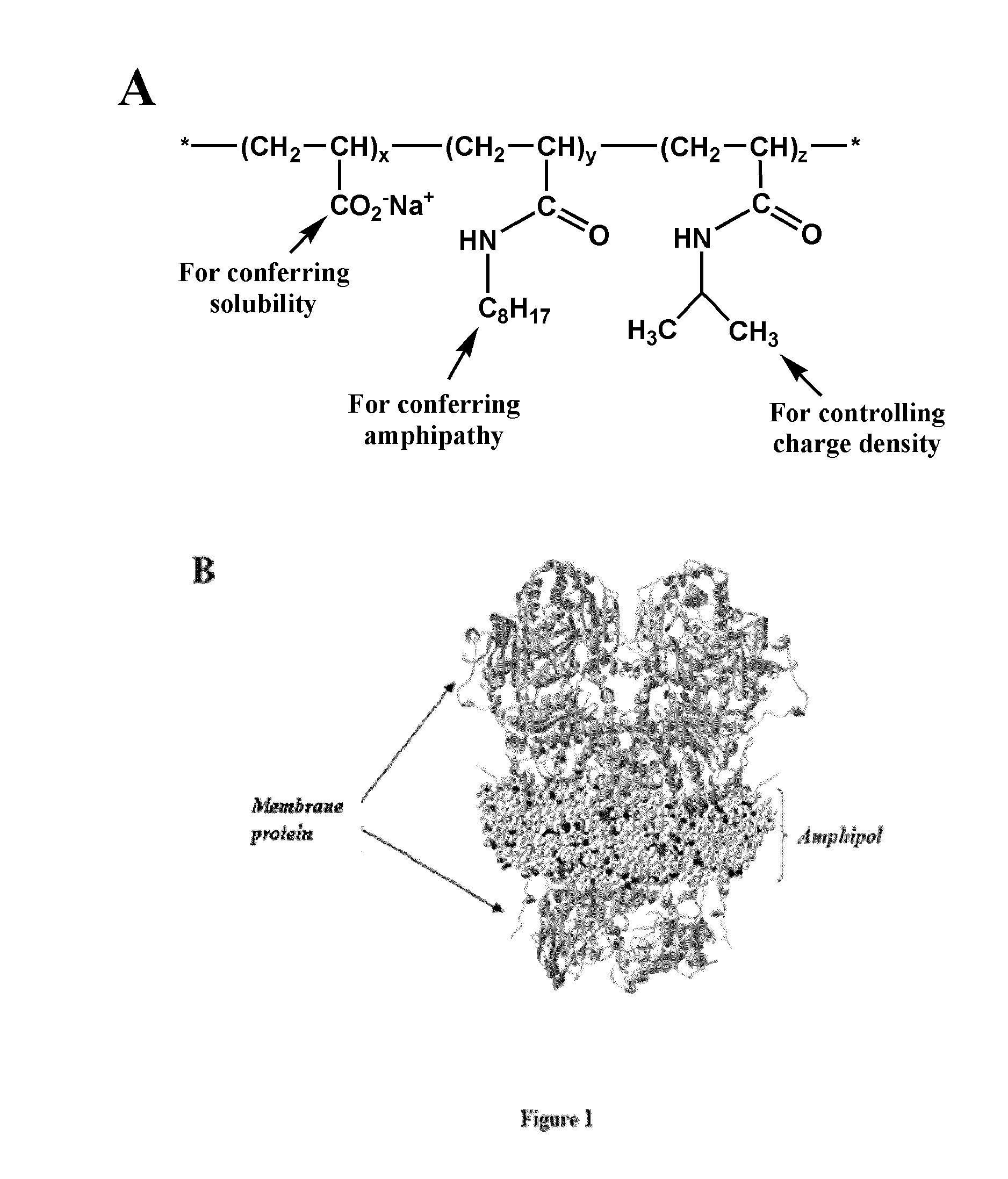
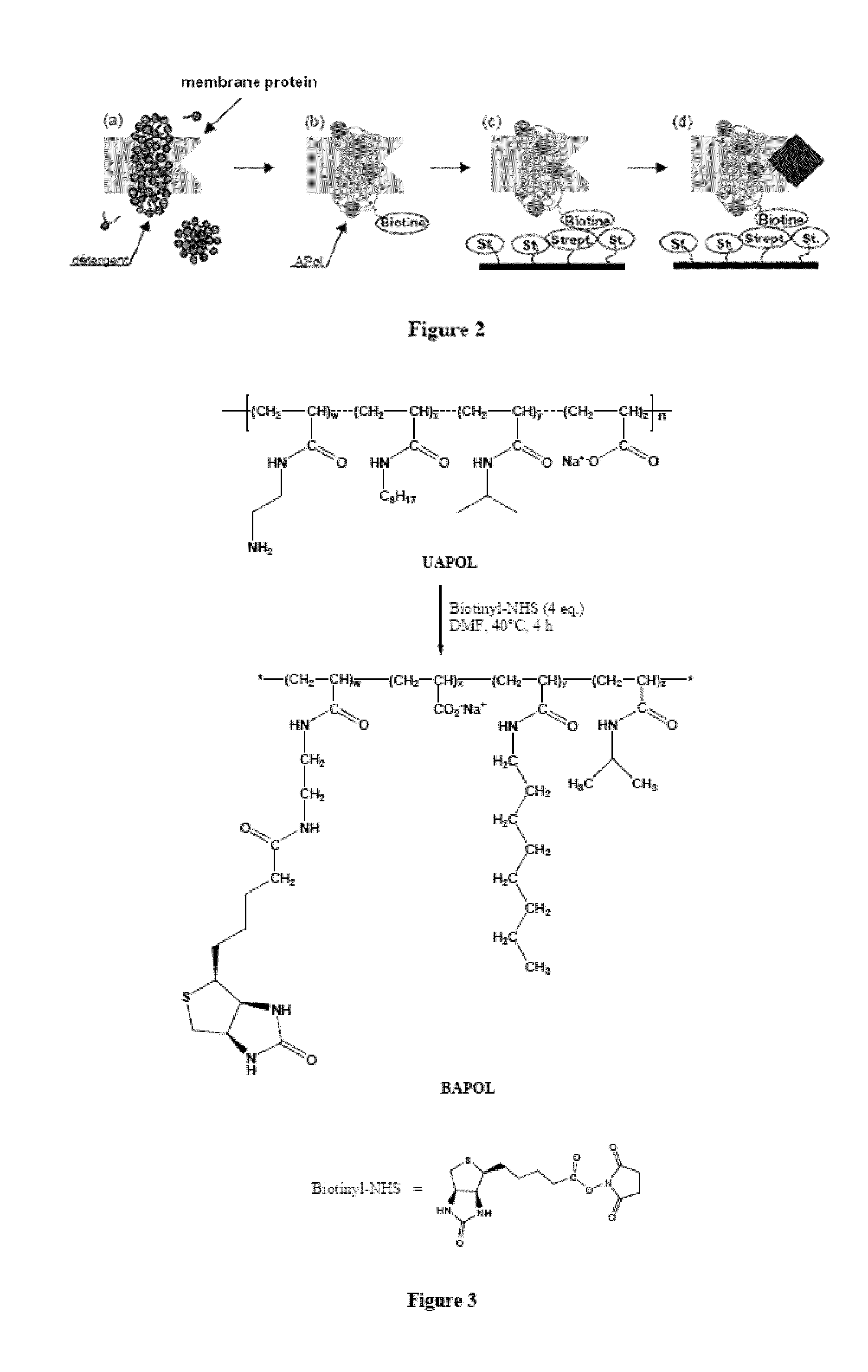
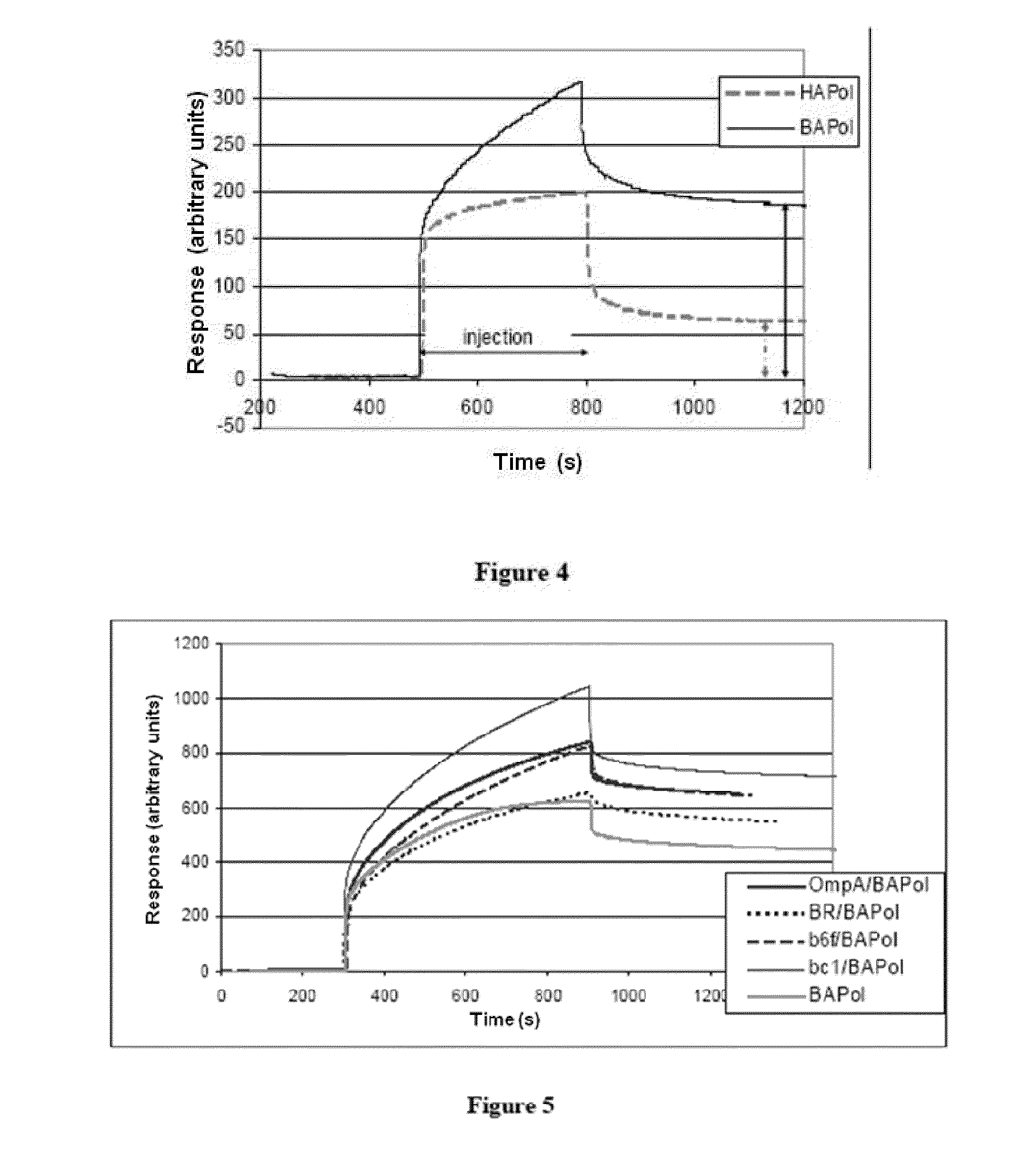
Immobilization of membrane porteins onto supports via an amphiphile
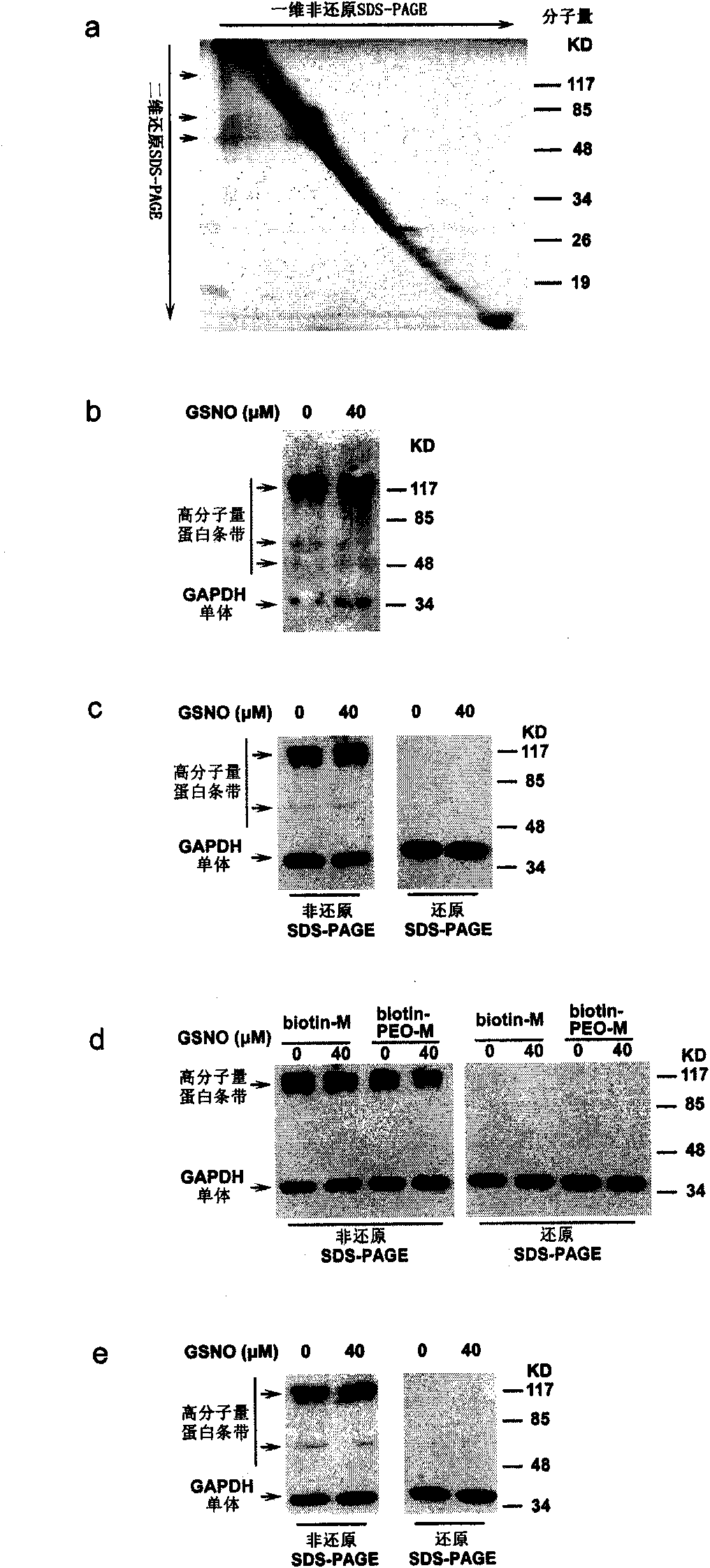
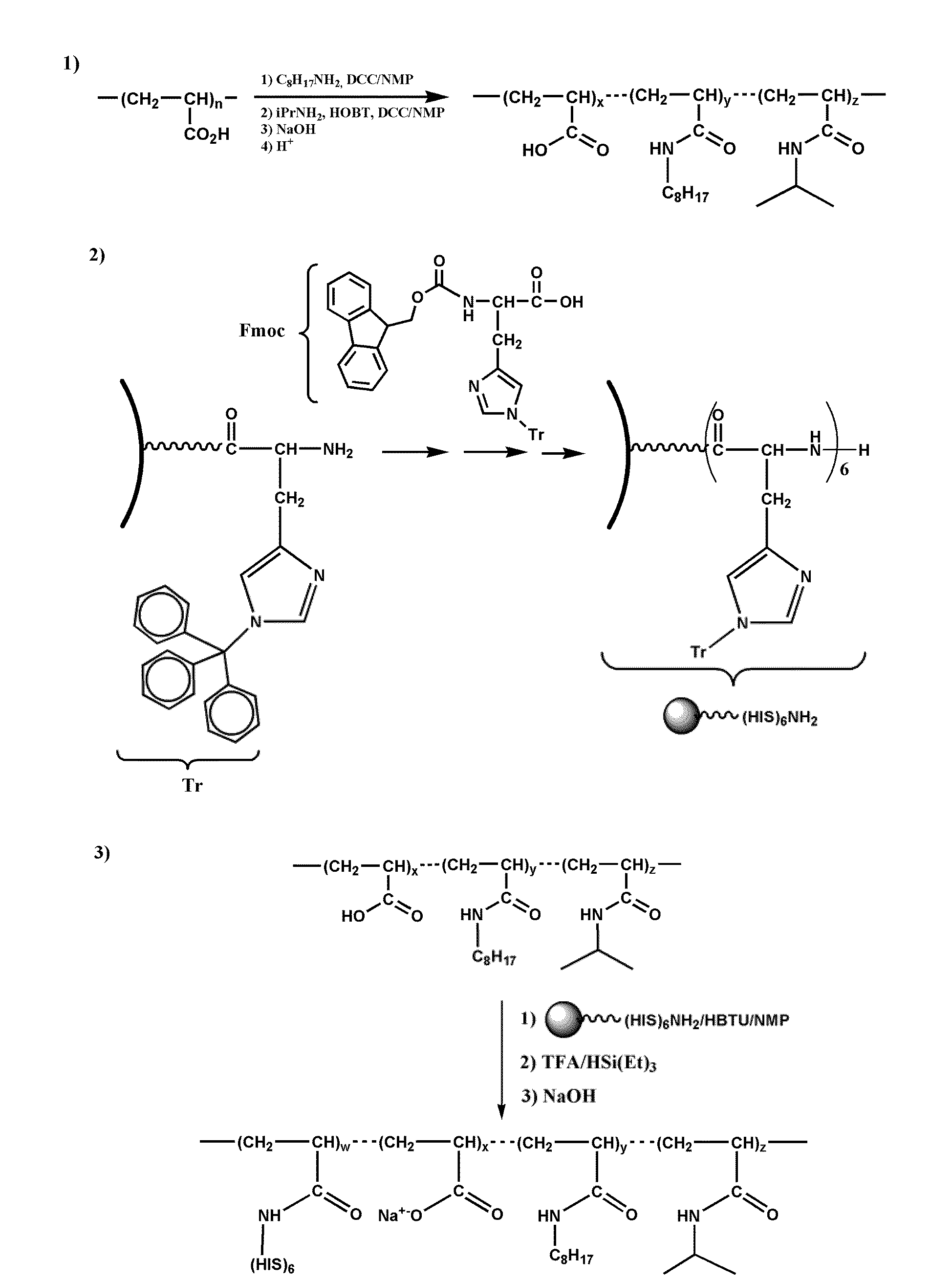
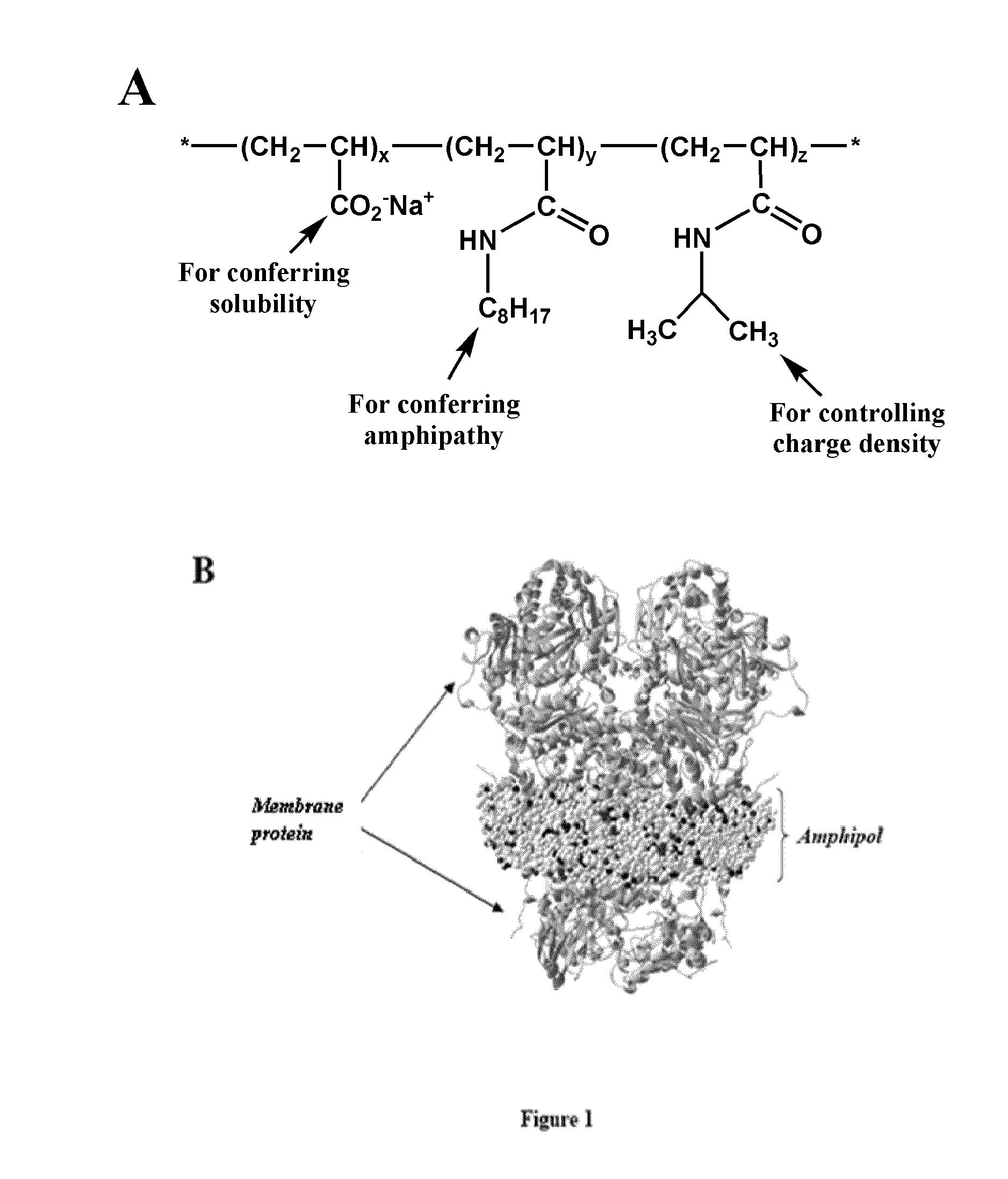
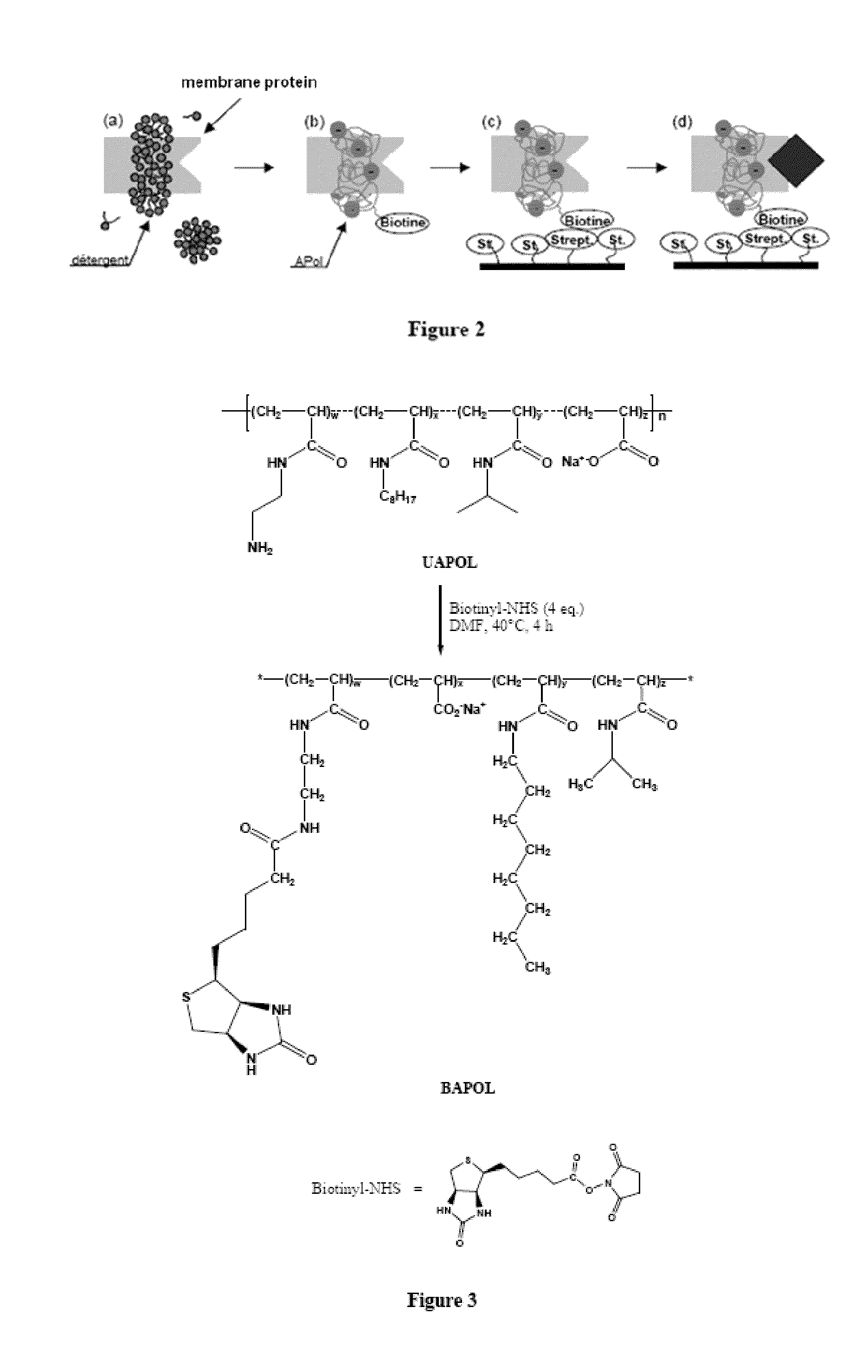
ActiveUS20090275066A1High yieldEasy to processPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningAmphiphileCell Membrane Proteins
The invention pertains to the field of membrane protein immobilization onto supports. It relates to a product comprising a support and at least one membrane protein attached to the surface thereof, characterized in that said membrane protein is attached to said support using an amphiphilic molecule with which said membrane protein is complexed. It also relates to a process for preparing such product, as well as to various applications in the fields of diagnosis, drug design and biotechnologies. It further relates to a kit, together with a functionalized amphiphilic molecule, for preparing a product according to the invention comprising a support and an amphiphilic molecule, wherein the amphiphilic molecule and the support interact through a hydrophobic bond, an ionic bond, a specific bond or a covalent bond.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Modified surface antigen
Novel proteins that constitute modified forms of a Neisseria meningitidis surface antigen and encoding nucleic acids are provided. The modified surface proteins are characterized by having deletions of non-conserved amino acids, and thereby being capable of eliciting cross-protective immune responses against Neisseria meningitidis. The invention extends to the use of the modified surface antigens in diagnostics, in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and in the design and / or screening of medicaments. The modified surface antigens are particularly useful in vaccines which effectively immunize against a broader spectrum of N. meningitidis strains than would be expected from a corresponding wild-type surface antigen.
Owner:QUEENSLAND THE UNIV OF
Inhibitors for extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking domains and uses therefor
InactiveUS20070066616A1Inhibit cell proliferationReduce cell proliferationBiocideAnimal repellantsExtracellular signalComputer aid
Provided herein are compounds and methods of using compounds that selectively inhibit binding to one or more docking domain regions of an extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) to inhibit in a cell having an extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. Such methods may be used to inhibit cell proliferation of a neoplastic cell, to treat a cancer and further may be used in conjunction with administration of an anticancer drug at a reduced dosage to treat a cancer with a concomitant reduction in toxicity to an individual receiving the treatment. Also provided is a method to design and screen for compounds to inhibit binding within the extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking domain region, using at least in part computer-aided drug design modeling.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL +1
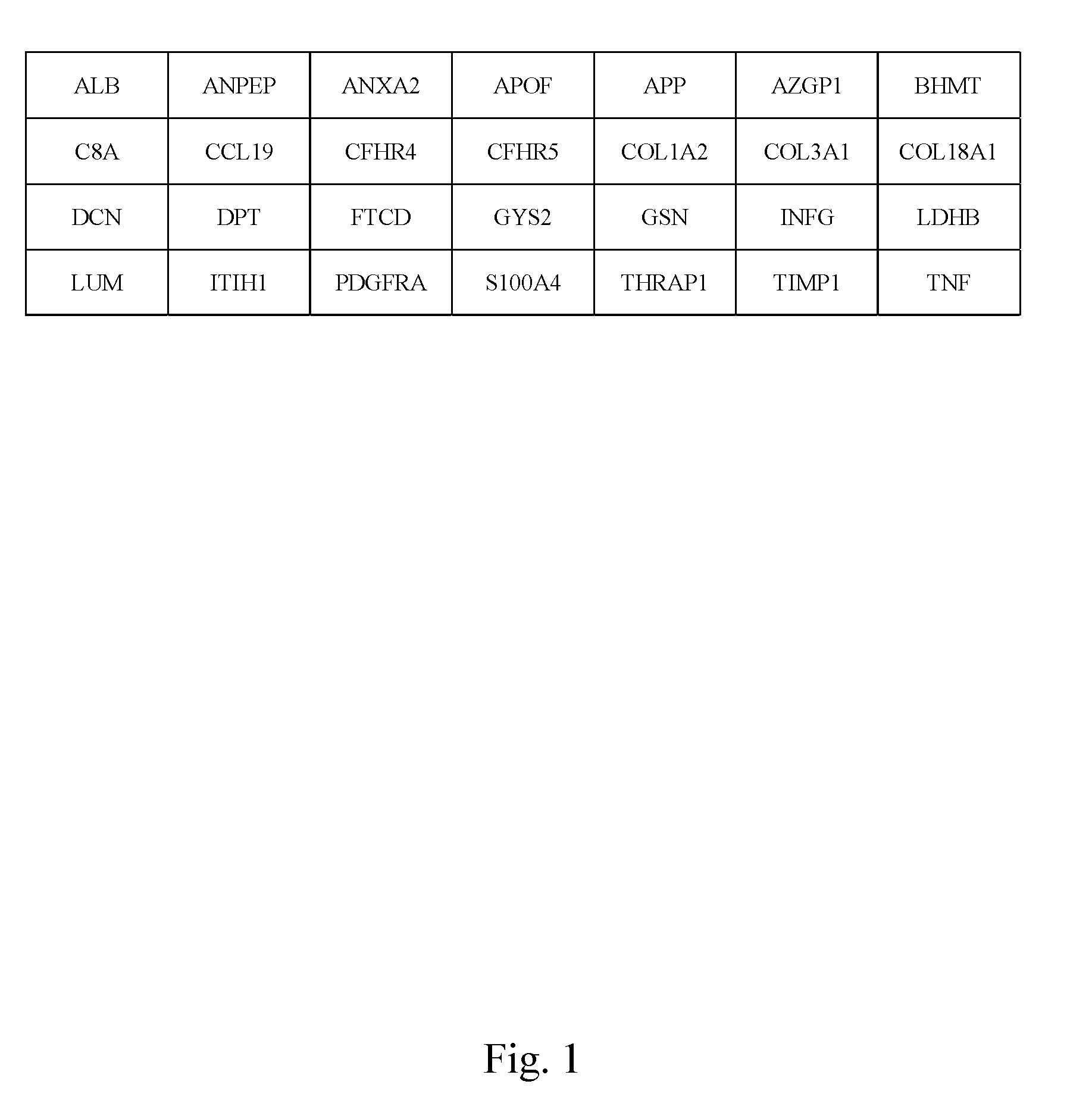
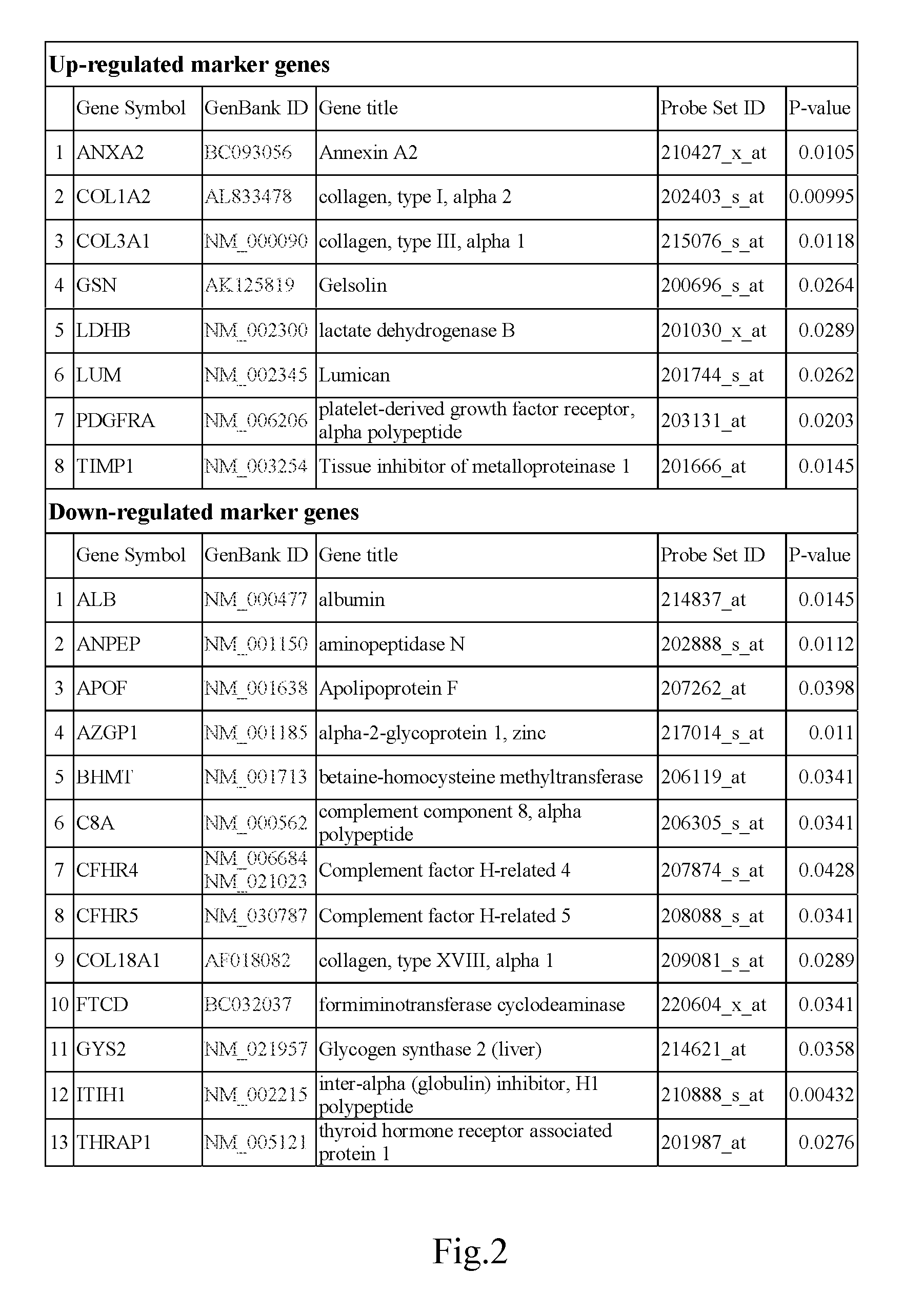
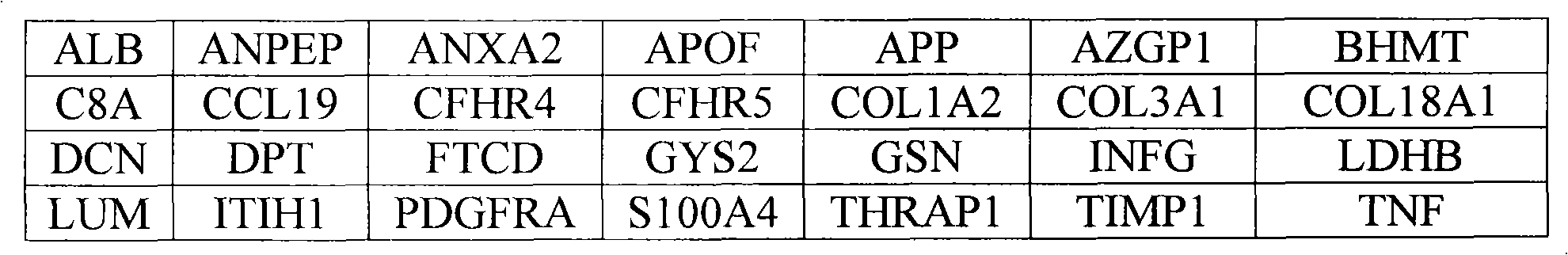
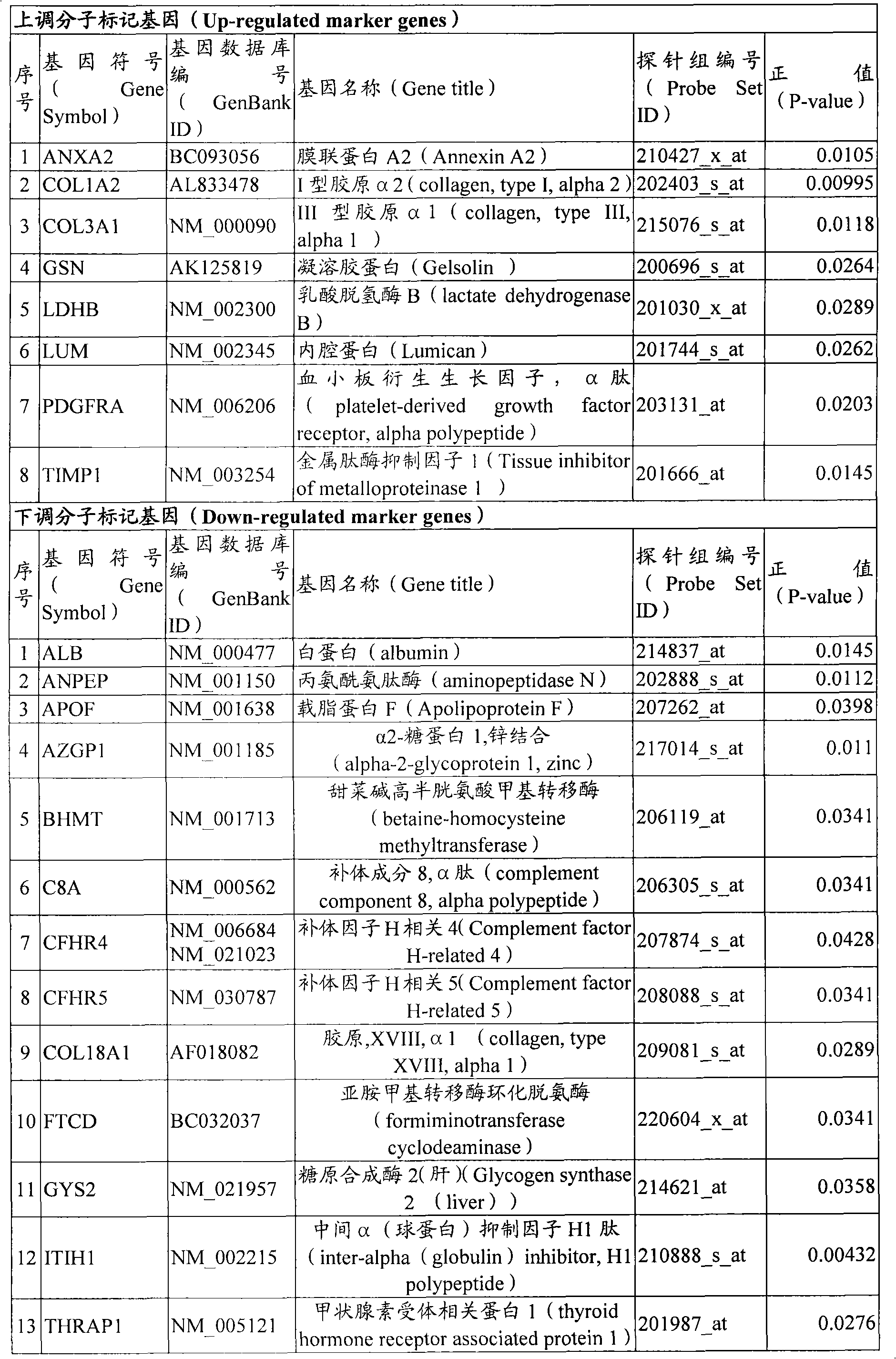
Markers identified for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and the microarray panel thereof
InactiveUS20080161203A1Cure and slow down liver fibrosis progressionSlow curingPeptide librariesHydrolasesCFHR5Biology
In the present invention, the markers identified for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and the microarray panel thereof comprise at least one of the following proteins / genes:8 up-regulated genes such asANXA2; COL1A2; COL3A1; GSN; LDHB; LUM; PDGFRA and TIMP1.13 down-regulated genes such asALB; ANPEP; APOF; AZGP1; BHMT C8A; CFHR4; CFHR5; COL18A1; FTCD; GYS2; ITIH1, and THRAP1.9 therapeutic targets such as PDGFRA; S100A4; COL3A1; CCL19; DCN; DPT; APP; TNF; and INFG.The present invention is capable of screening markers for the early warning of the occurrence for severe fibrosis or cirrhosis and potentially targets for drug design.
Owner:VITA GENOMICS
Immobilization of membrane proteins onto supports via an amphiphile
ActiveUS8207263B2High yieldEasy to processMicrobiological testing/measurementPaper coatingCell Membrane ProteinsDrug design
The invention pertains to the field of membrane protein immobilization onto supports. It relates to a product comprising a support and at least one membrane protein attached to the surface thereof, characterized in that said membrane protein is attached to said support using an amphiphilic molecule with which said membrane protein is complexed. It also relates to a process for preparing such product, as well as to various applications in the fields of diagnosis, drug design and biotechnologies. It further relates to a kit, together with a functionalized amphiphilic molecule, for preparing a product according to the invention comprising a support and an amphiphilic molecule, wherein the amphiphilic molecule and the support interact through a hydrophobic bond, an ionic bond, a specific bond or a covalent bond.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
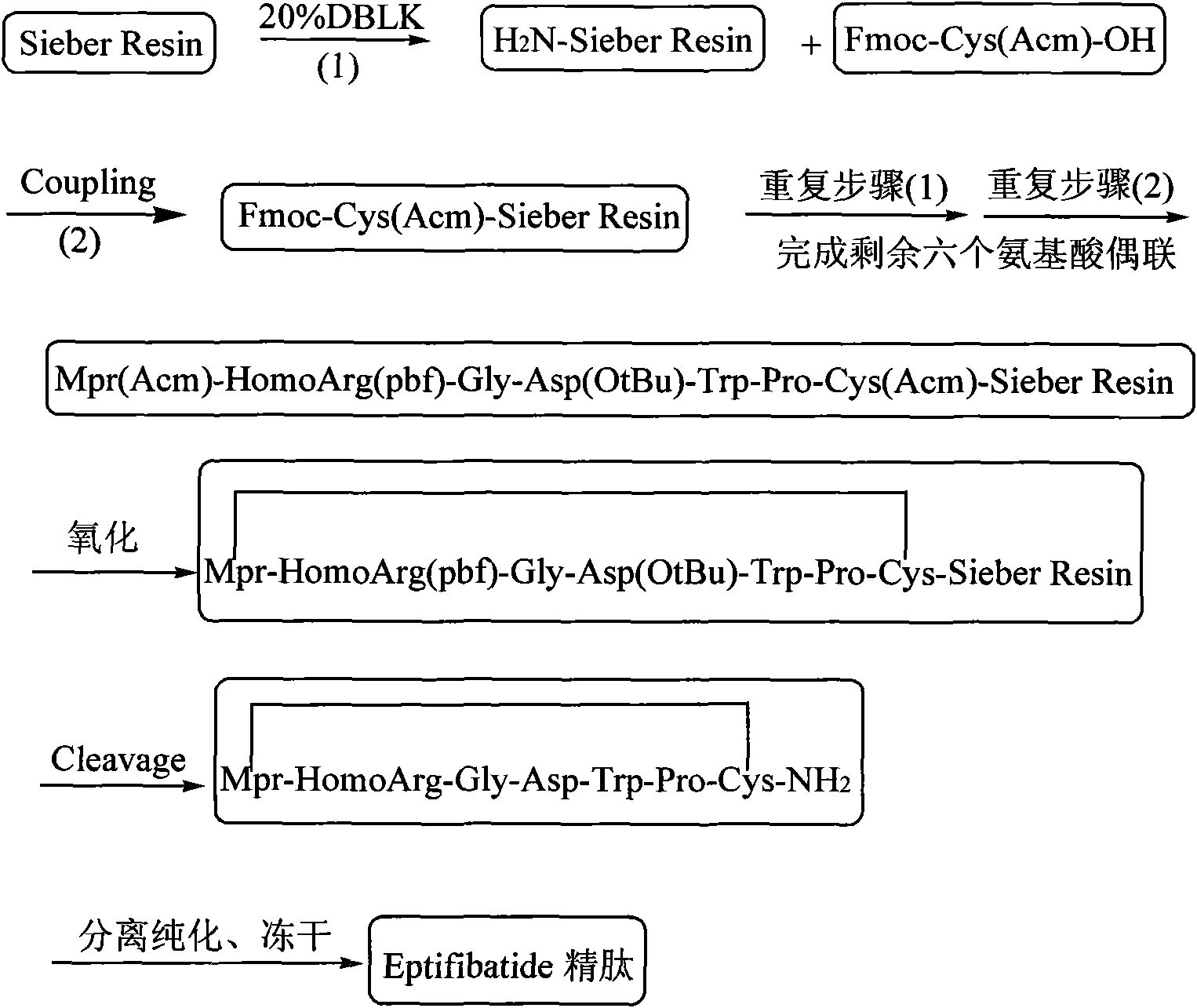
Method for preparing Eptifibatide with solid phase method
InactiveCN101538316AMild reaction conditionsReduce pollutionPeptide preparation methodsBlood disorderSide chainCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing Eptifibatide with a solid phase method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) selecting Sieber resin to remove Fmoc, and obtaining H2N-Sieber resin; 2) adopting Fmoc / tBu solid phase method to couple and synthesize linear peptide Eptifibatide-Sieber resin with full protective lateral chains in sequence; 3) conducting solid phase oxidation to the resin, and obtaining oxidant peptide Eptifibatide-Sieber resin with full protective lateral chains; 4) cutting the resin and removing the lateral chain protection, and obtaining crude product of Eptifibatide; and 5) conducting separation and purification, and breeze drying by a freeze dryer, and obtaining refined Eptifibatide peptide. The technology is characterized by simple operation, easy post treatment, less investment of raw material, low cost, high yield and the like, and has considerable economical and practical value and wide application prospect in the field of polypeptide drug design and synthesis simultaneously.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
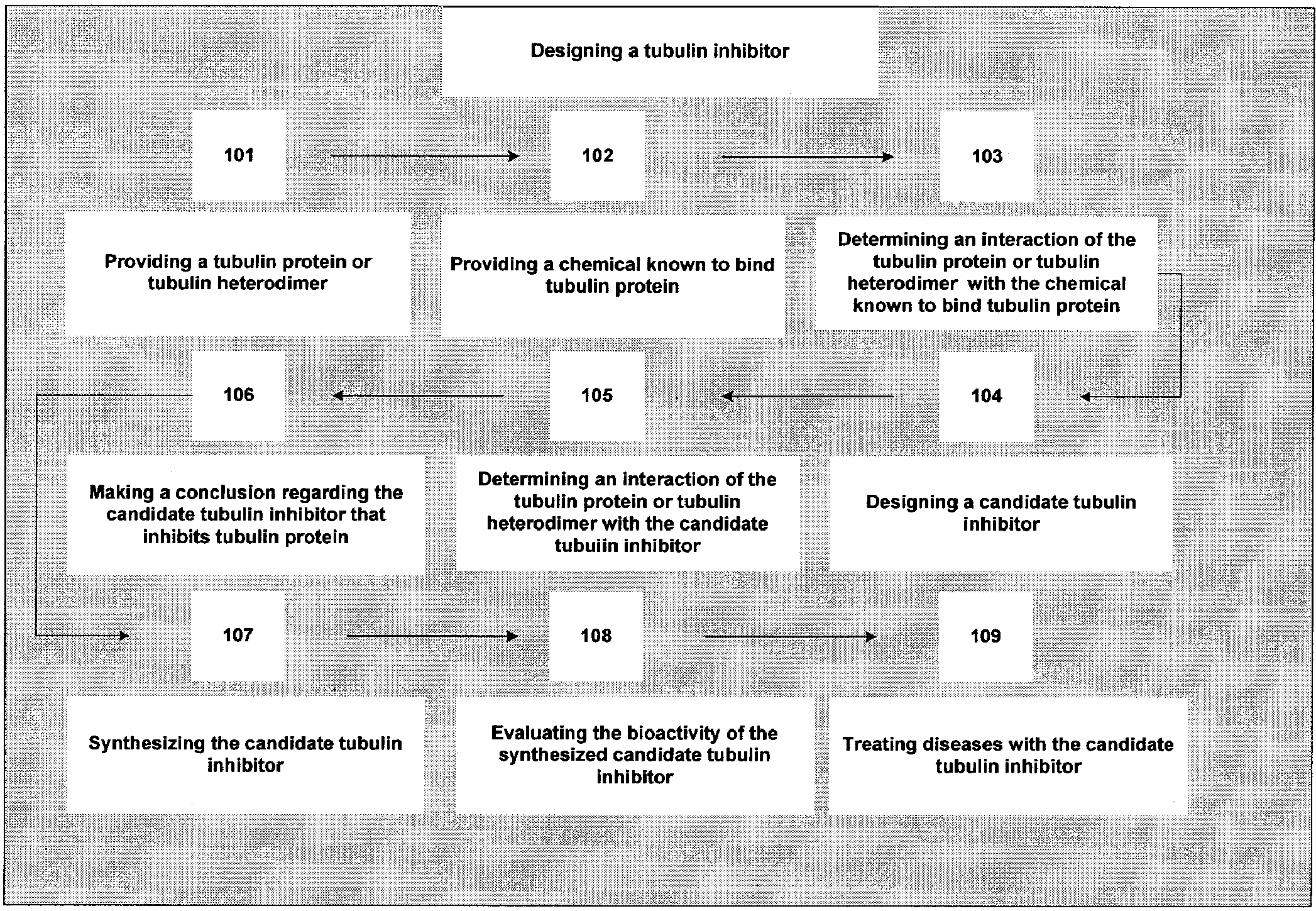
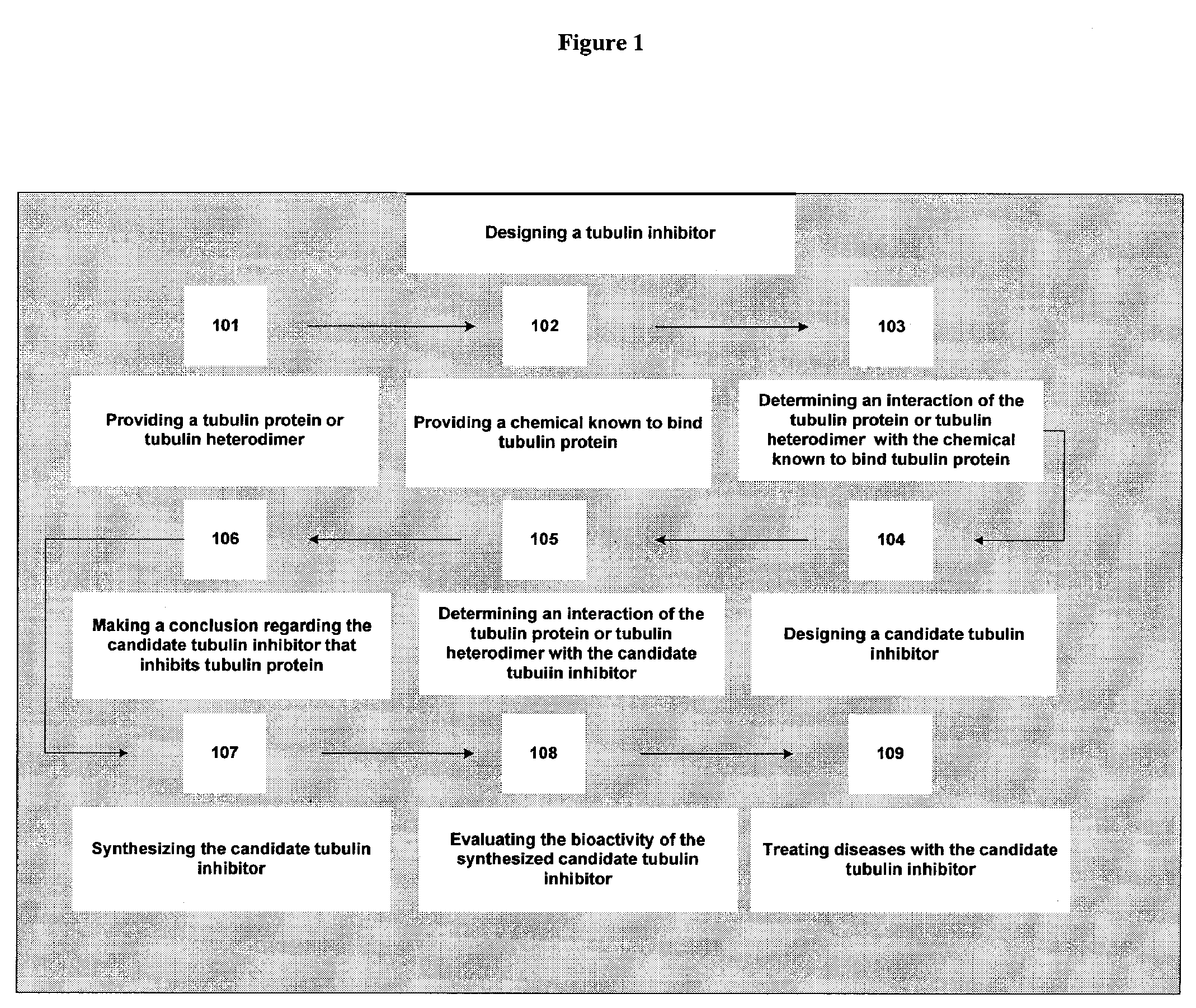
Drug design for tubulin inhibitors, compositions, and methods of treatment thereof
The present invention relates to a computer-assisted method of a designing of a tubulin inhibitor comprising: a) determining an interaction between a tubulin protein and a chemical known to bind the tubulin protein by evaluating a binding of the tubulin protein to the chemical known to bind the tubulin protein; b) based on the interaction, designing a candidate tubulin inhibitor; c) determining an interaction between the tubulin protein and the candidate tubulin inhibitor by evaluating a binding of the tubulin protein to the candidate tubulin inhibitor; and d) concluding that the candidate tubulin inhibitor inhibits the tubulin protein wherein the conclusion is based on the interaction of step c). The invention also provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases with the candidate tubulin inhibitors.
Owner:BIPAR SCI INC
Methods of determining ligand residue binding affinity
InactiveUS20050123993A1Biological testingSpecial data processing applicationsBinding siteInteraction energy
Methods and systems for determining the affinity between polypeptide amino acid residues and one or more molecular fragments, and for using the affinity values to aid in drug design including a computer simulation which calculates the interaction energy between a polypeptide and at least one molecular fragment. An affinity value is then assigned to at least one fragment and residue pair if the fragment is in the vicinity of the residue. Affinity values are used to rank fragments, build ligands and determine binding sites.
Owner:LOCUS PHARMA INC
Method for predicting binding free energy of protein and ligand based on progressive neural network
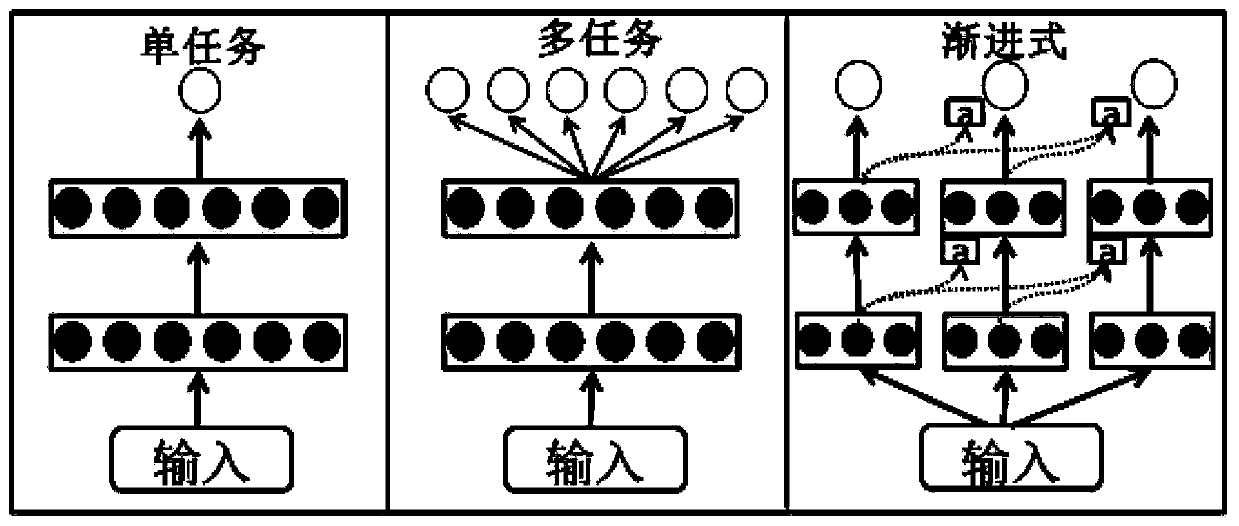
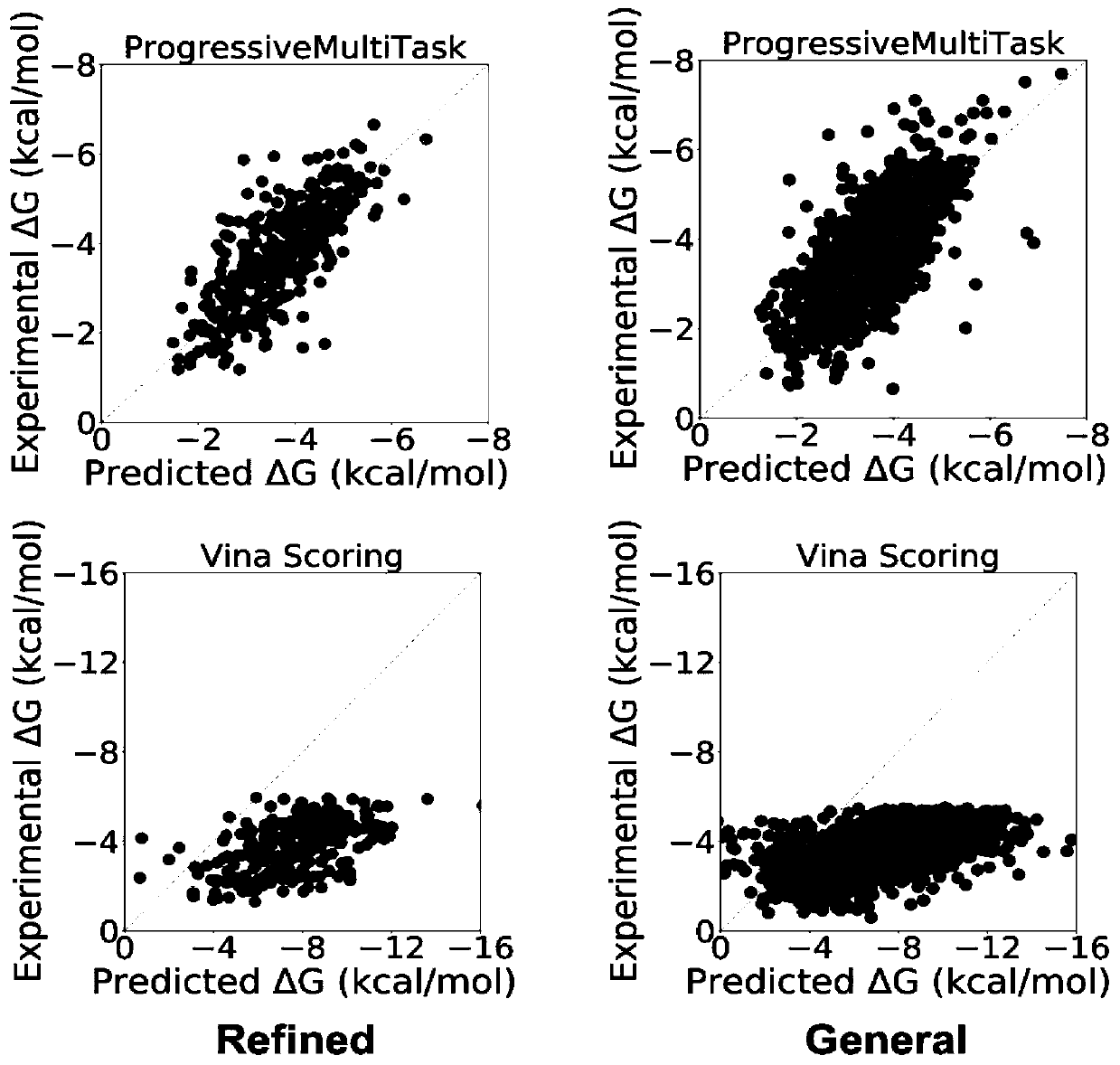
ActiveCN110910951APrevent overfittingImprove generalization abilityProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmTest set
The invention discloses a method for predicting the binding free energy of protein and ligand based on a progressive neural network, and belongs to the technical field of computer-aided drug design. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a pdb file from a PDBbind database, establishing local database, acquiring an amino acid molecule within 4.5 angstroms in the protein binding pocket by takingthe ligand molecule as a center, performing extended connectivity fingerprint calculation, carrying out SPLIF fingerprint calculation, searching for the number of salt bridges and hydrogen bonds between protein and ligand molecules, converting the structural information of the protein and the ligand into a one-dimensional tensor, and establishing a training set, a verification set and a test set;training the progressive neural network by using the training set; optimizing and searching hyper-parameters for prediction; through comparison with a molecular docking result, obtaining a higher Pearson correlation coefficient. According to the invention, the technical problem of how to convert a three-dimensional structure of protein and ligand molecules into tensors which are easy to calculateby a computer and input the tensors into the progressive neural network for training and optimization is solved, and the calculation rate and the prediction accuracy are greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Regulators of protein misfolding and aggregation and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20070204352A1Increase in protein misfoldingPromote aggregationCompound screeningNervous disorderCell AggregationsNucleotide
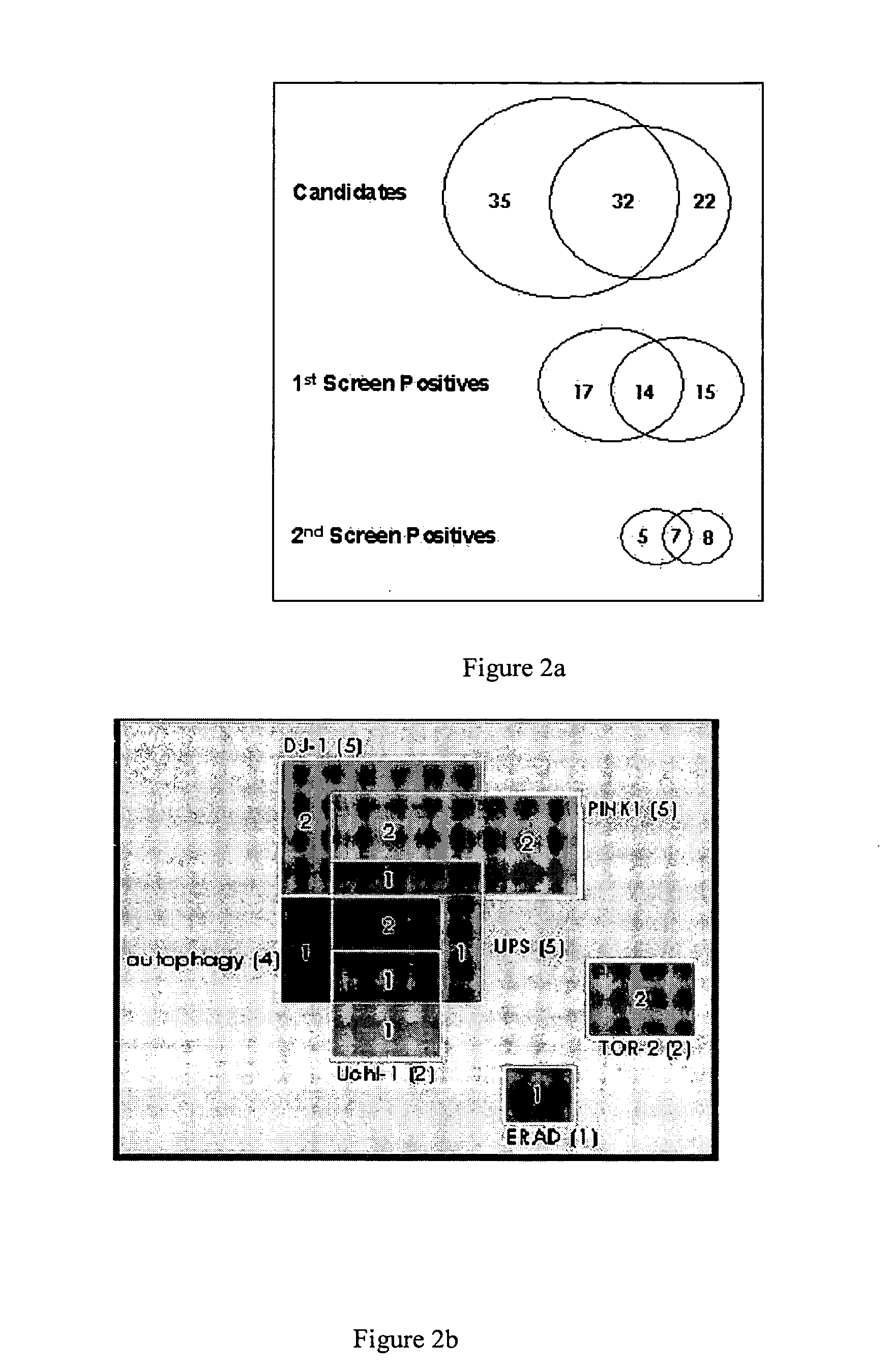
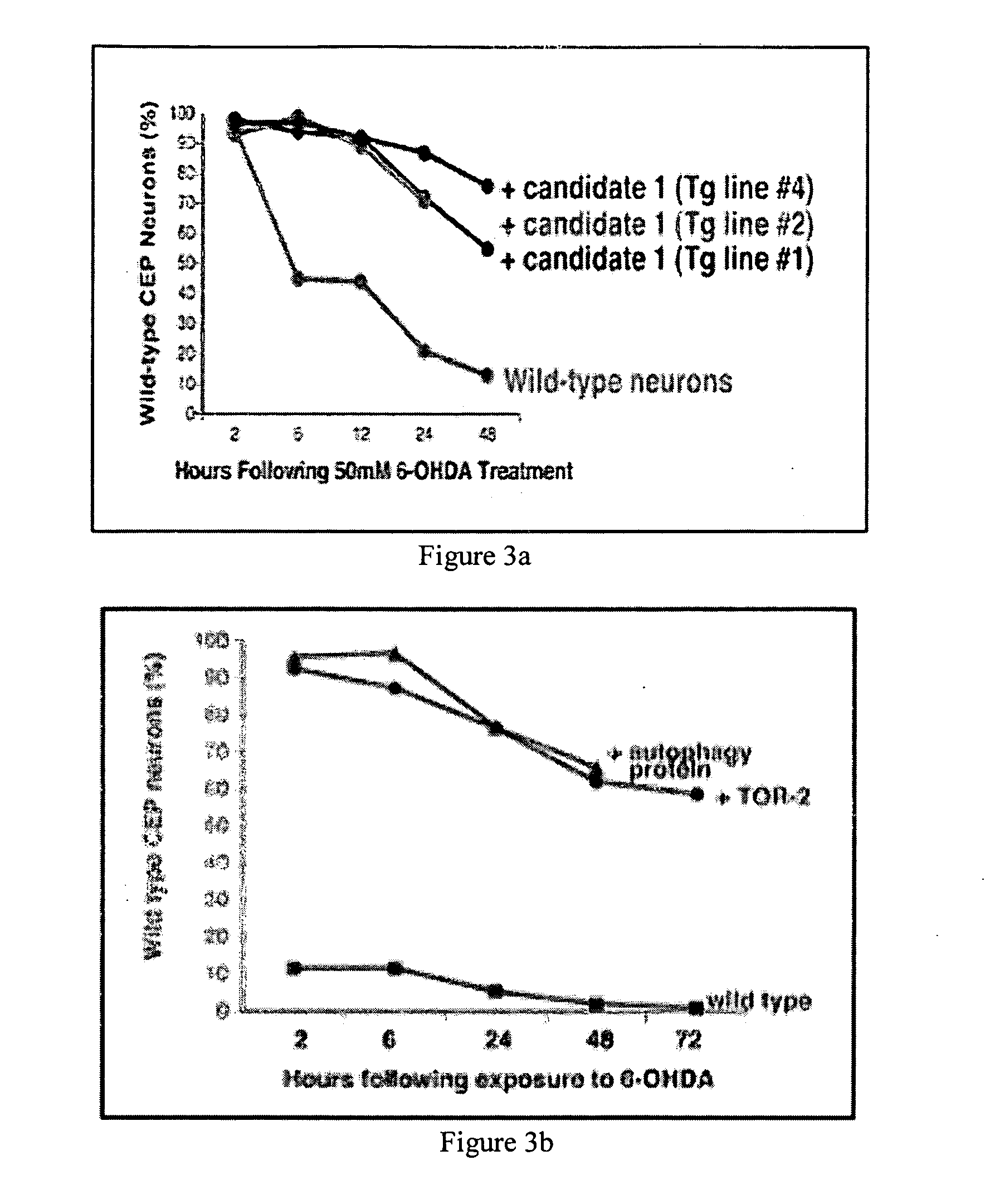
Polynucleotide molecules and the proteins encoded by the molecules, diagnostic and treatment methods for neurological disorders characterized by protein aggregation are provided. Genes are described herein that affect the misfolding of, and subsequent aggregation of, aggregation-prone proteins such as alpha-synuclein and have implications for the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases related to protein aggregation such as Parkinson's disease. Knockdown of expression of the genes described herein using RNAi results in alpha-synuclein protein aggregation in a C. elegans model of protein aggregation. Dopaminergic neuroprotection after exposure to the neurotoxin 6-OHDA or overexpression of alpha-synuclein may also be provided by overexpression of proteins. Knowledge of genes relating to protein misfolding and aggregation provides powerful means to develop diagnostic screening methods, mutation analysis and drug design information for the development of novel therapeutic and neuroprotective compounds to treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
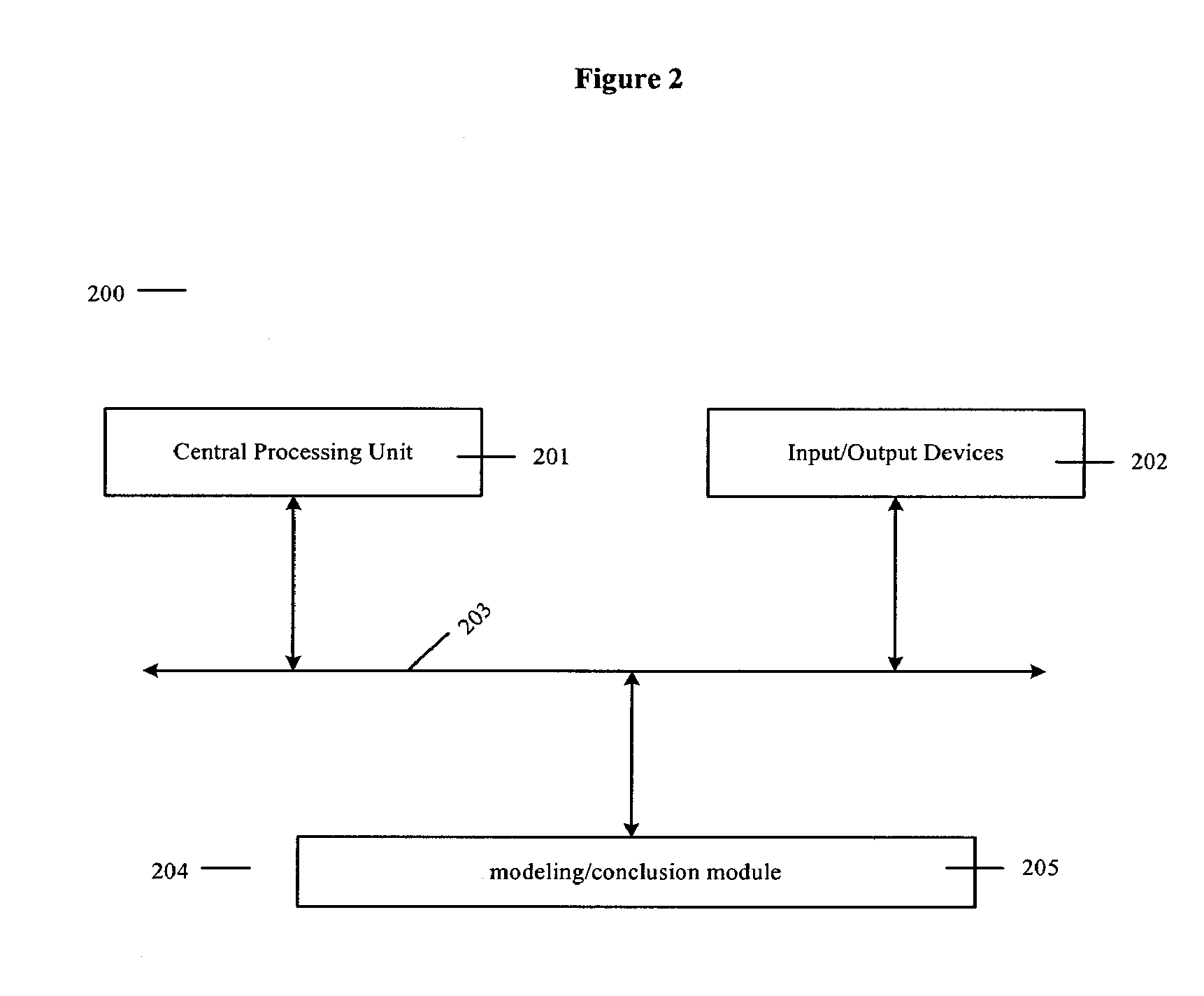
System and method for improved computer drug design
InactiveUS20060041414A1Rapid minimizationWeaken energyMolecular designChemical structure searchComputer-aidedComputer aid
A system and method for computer-aided drug design employs adaptive sampling and iterative fitting of mult-atomic subunits. The iterative fitting is performed by successive perturbation of the location of the multi-atomic subunits in directions that reduces potential energy.
Owner:DRUG DESIGN METHODOLOGIES
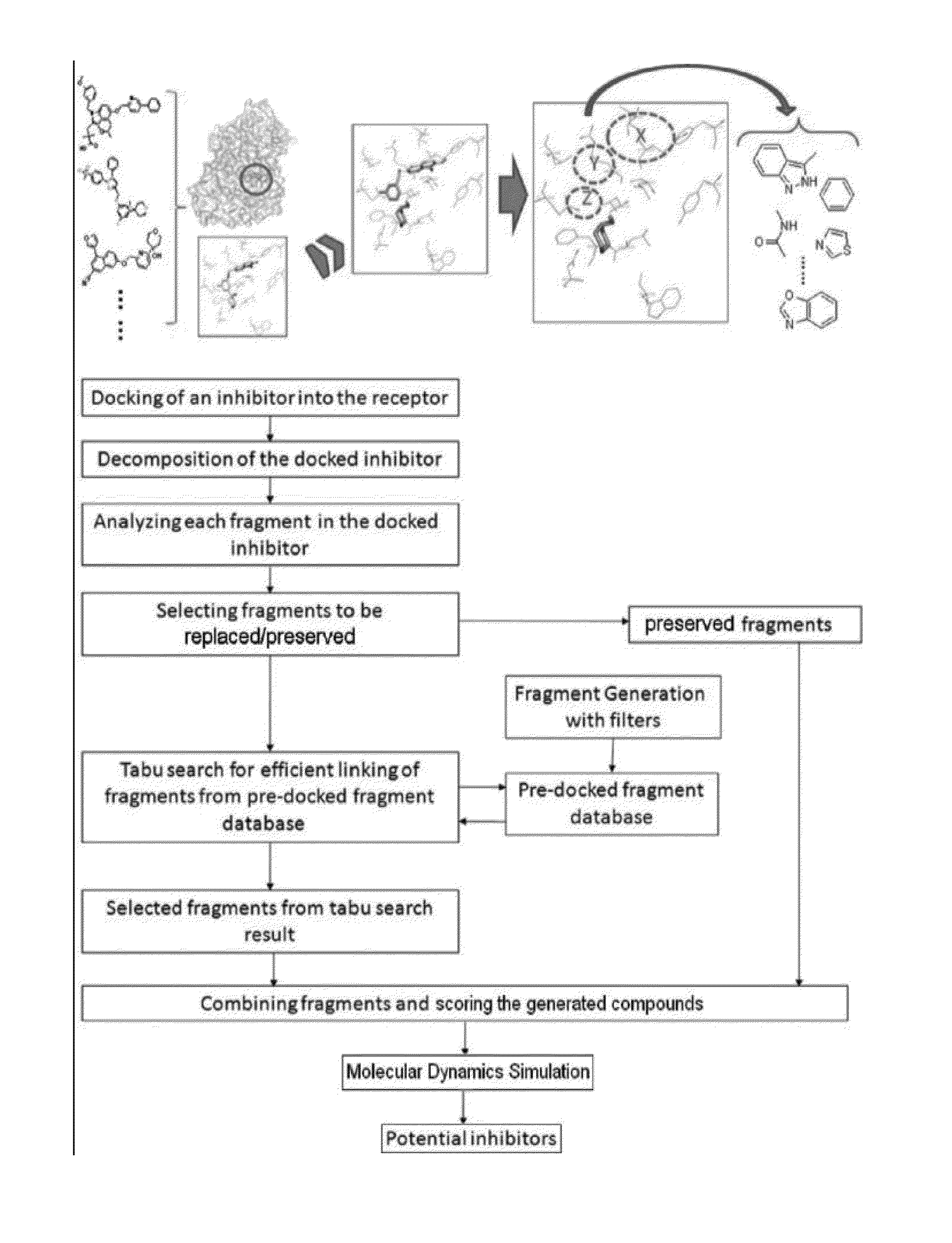
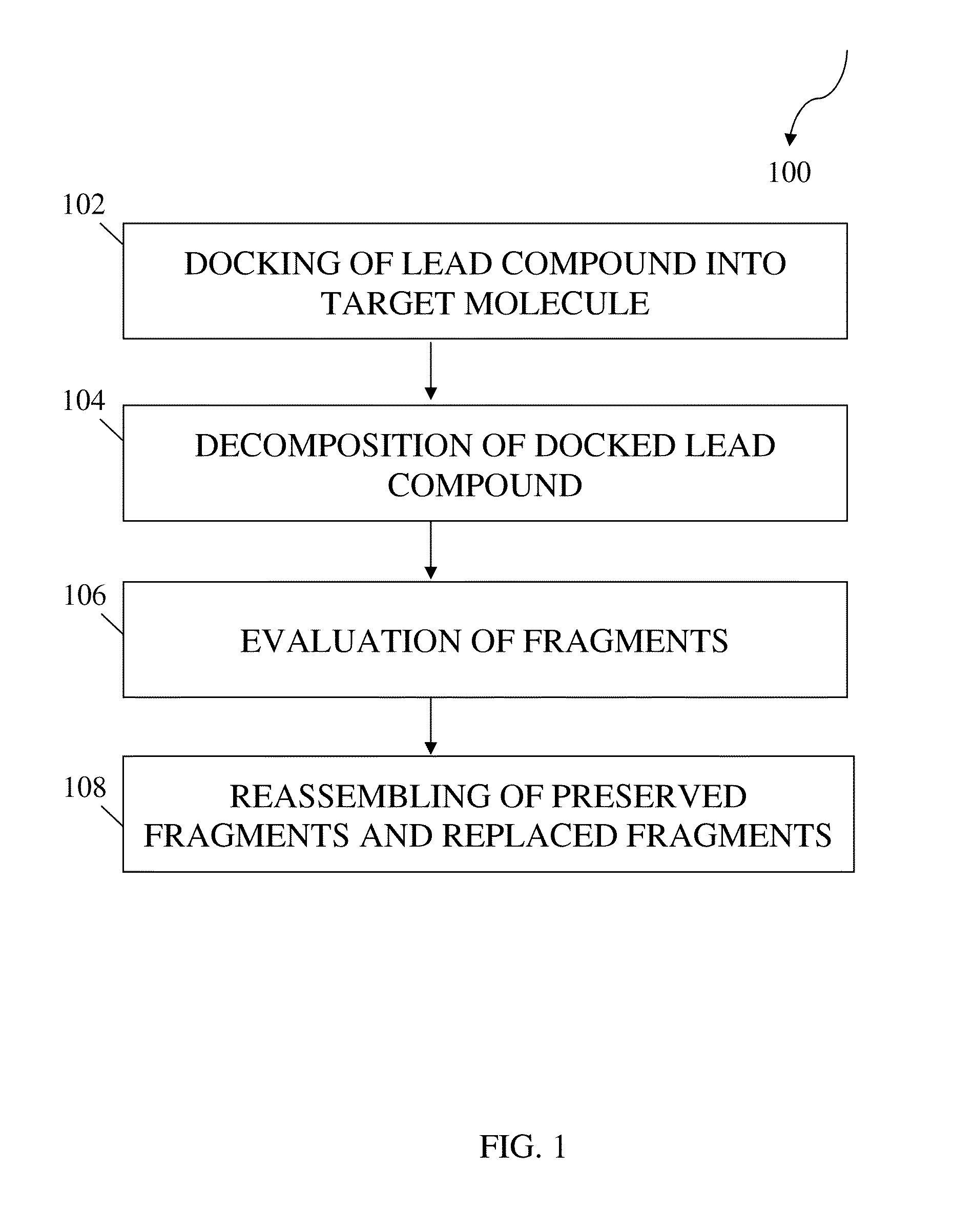
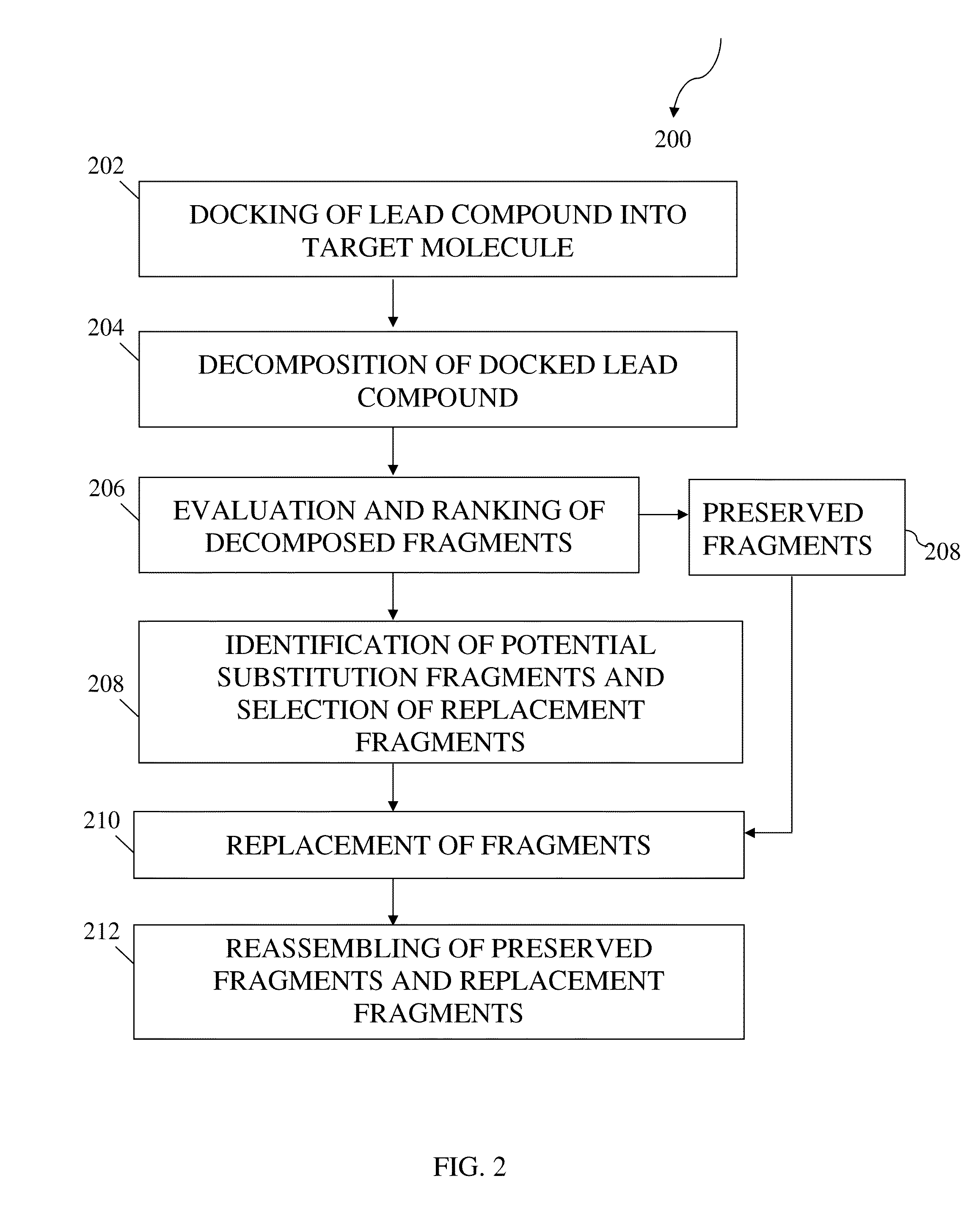
Structure-based fragment hopping for lead optimization and improvement in synthetic accessibility
InactiveUS20130226549A1Molecular designAnalogue computers for chemical processesReaction ruleChemical reaction
The invention develops a computer-aided drug design method and system to optimize a lead through structure-based drug design with synthetic accessibility. In this invention, two systems of the structure-based lead optimization are developed and implemented: 1) LeadOp (“short for lead optimization”)—an algorithm that performs lead optimization through structure-based fragment hopping method; and 2) LeadOp+R (short for “lead optimization with synthetic accessibility based on chemical reaction route”)—an algorithm that performs lead optimization with synthetic accessibility. LeadOp algorithm provides users to optimize a lead compound with various combinations of fragments with stronger binding based on group efficiency, generating lead with stronger potency. Furthermore, LeadOp+R provides an advantage in the selection of the new fragment to be assembled, which was identified based on the group efficiency calculated in the active site and reaction rule.
Owner:TSENG YUFENG J
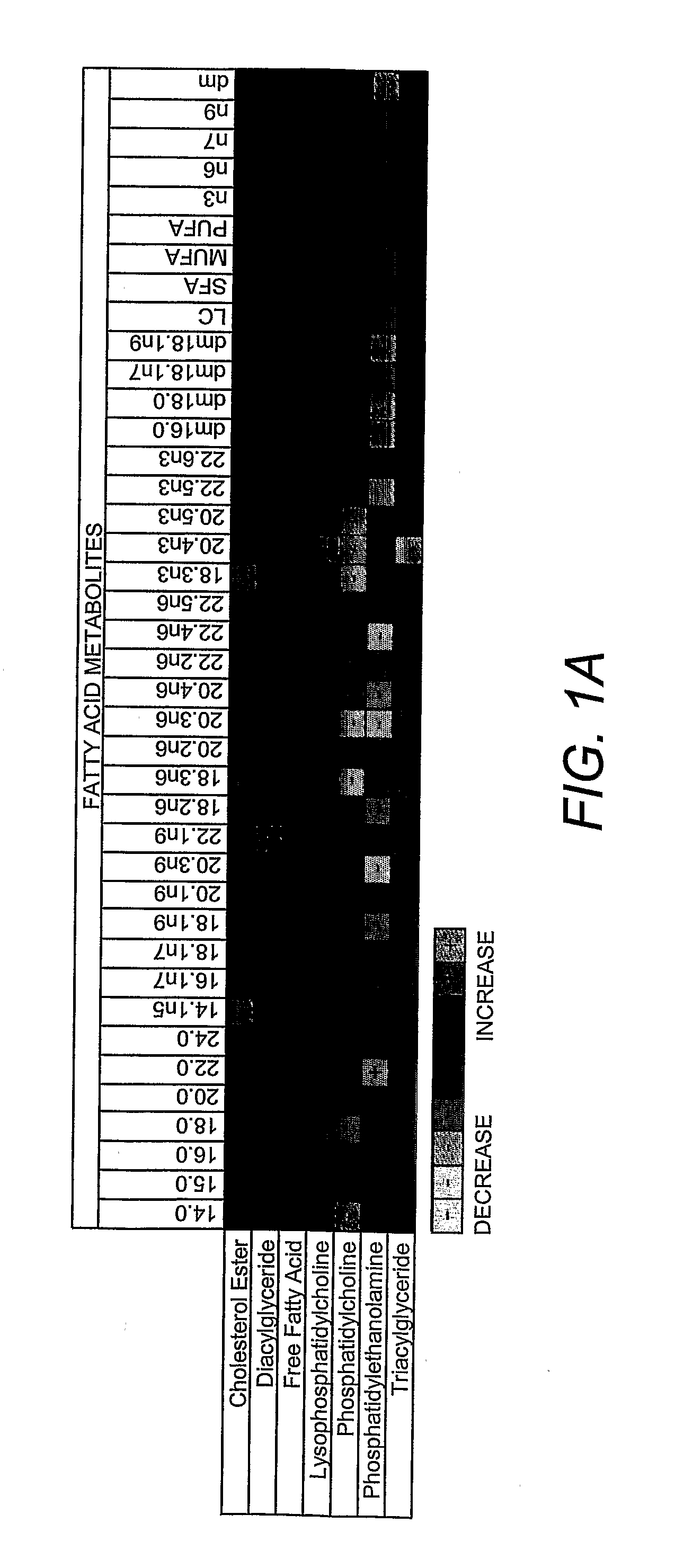
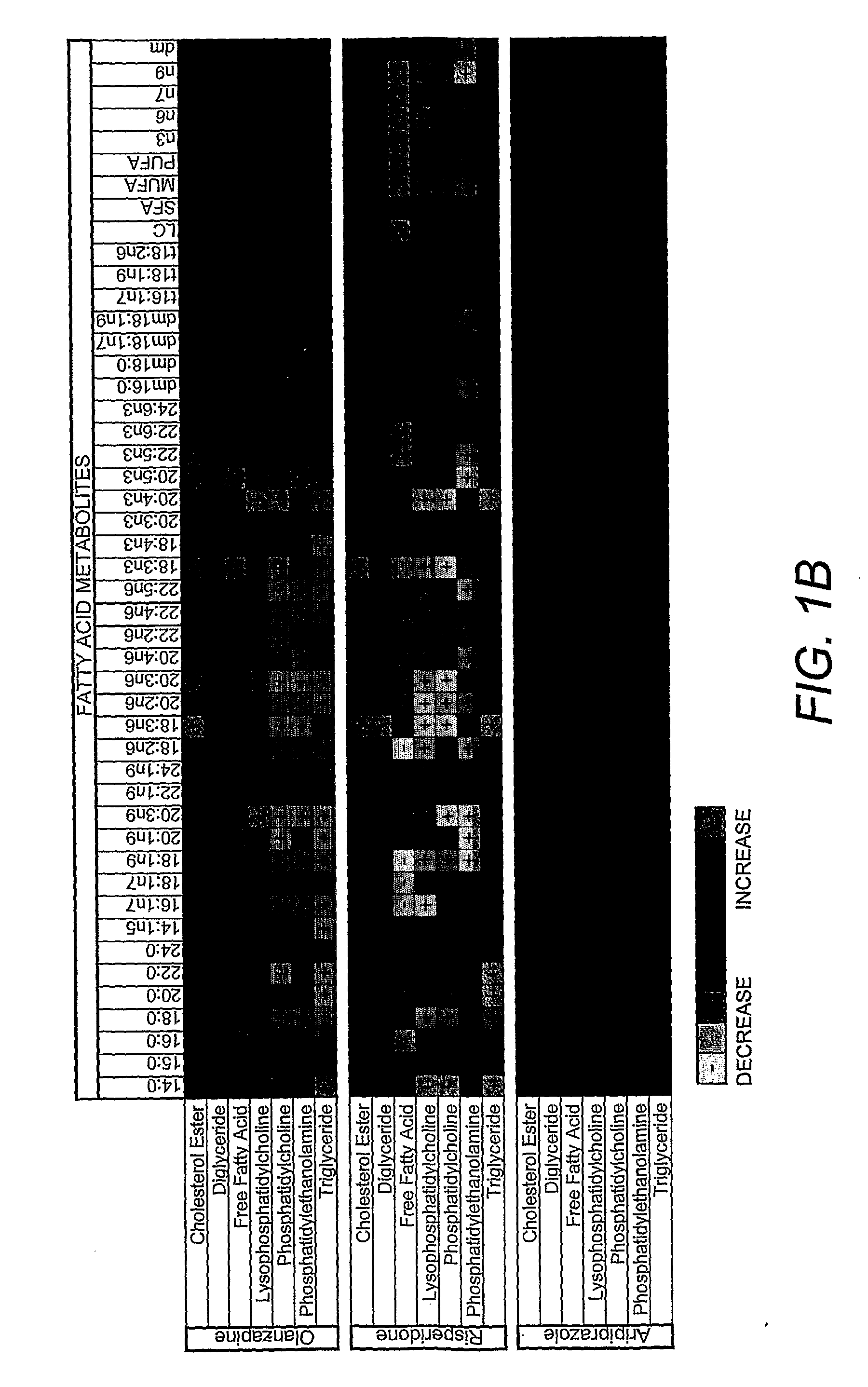
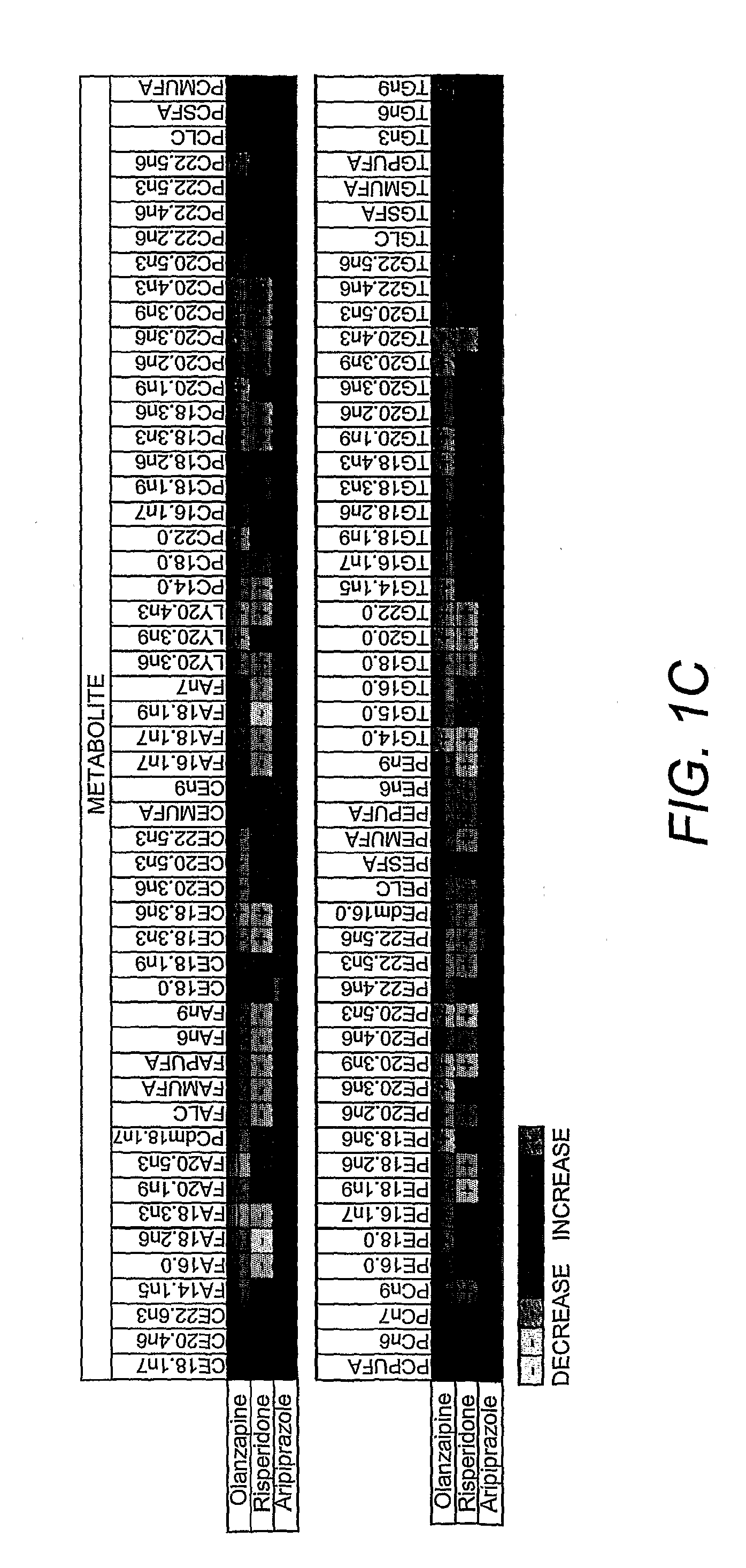
Lipidomics approaches for central nervous system disorders
InactiveUS20090305323A1Less metabolic side effectEasy to determineMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseLipid formation
The present invention has utilized the power of lipidomics to profile lipid metabolites and to characterize changes in lipid metabolism as they relate to CNS disorders. Lipidomic signatures can guide the development of diagnostic, prognostic and surrogate markers for CNS disorders; identification of new targets for drug design based on highlighted perturbed pathways; stratify patients with CNS disorders as to which pathways are impaired, and facilitate the determination of which patients with CNS disorders are candidates for a particular therapy, i.e. provide the tools for a personalized approach to therapy; identify which patients are responding or are developing side effects to a treatment; design of modified antipsychotics that have less metabolic side effects and enhanced activity; overcome the lag phase in response to some treatments; and find better combination therapies for CNS disorders that target the pathways that are impaired (e.g., impairments in lipid and / or carbohydrate metabolism).
Owner:TRUE HEALTH IP LLC +2
System and method for improved computer drug design
InactiveUS7801685B2Rapid minimizationWeaken energyMolecular designChemical structure searchComputer-aidedEngineering
A system and method for computer-aided drug design employs adaptive sampling and iterative fitting of multi-atomic subunits. The iterative fitting is performed by successive perturbation of the location of the multi-atomic subunits in directions that reduces potential energy.
Owner:DRUG DESIGN METHODOLOGIES
Molecule making for identifying liver fibrosis and hepatic cirrhosis and micro-array system plate thereof
InactiveCN101275951AIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBiological testingProtein insertionLiver fibrosis
The present invention provides a molecular mark for determining liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and a micro-array system board thereof. The invention at least comprises one in 28 proteins or at least comprises one in the genes encoding these proteins. Among these proteins or genes, 8 members are upper regulatory genes, 13 members are lower regulatory genes, and the rest 9 members are treating target. The invention is a molecular mark with filtering capacity to warn the generation of severe liver fibrosis or cirrhosis. The molecular mark of the invention is also a target which has latent capacity for the medicament design.
Owner:VITA GENOMICS
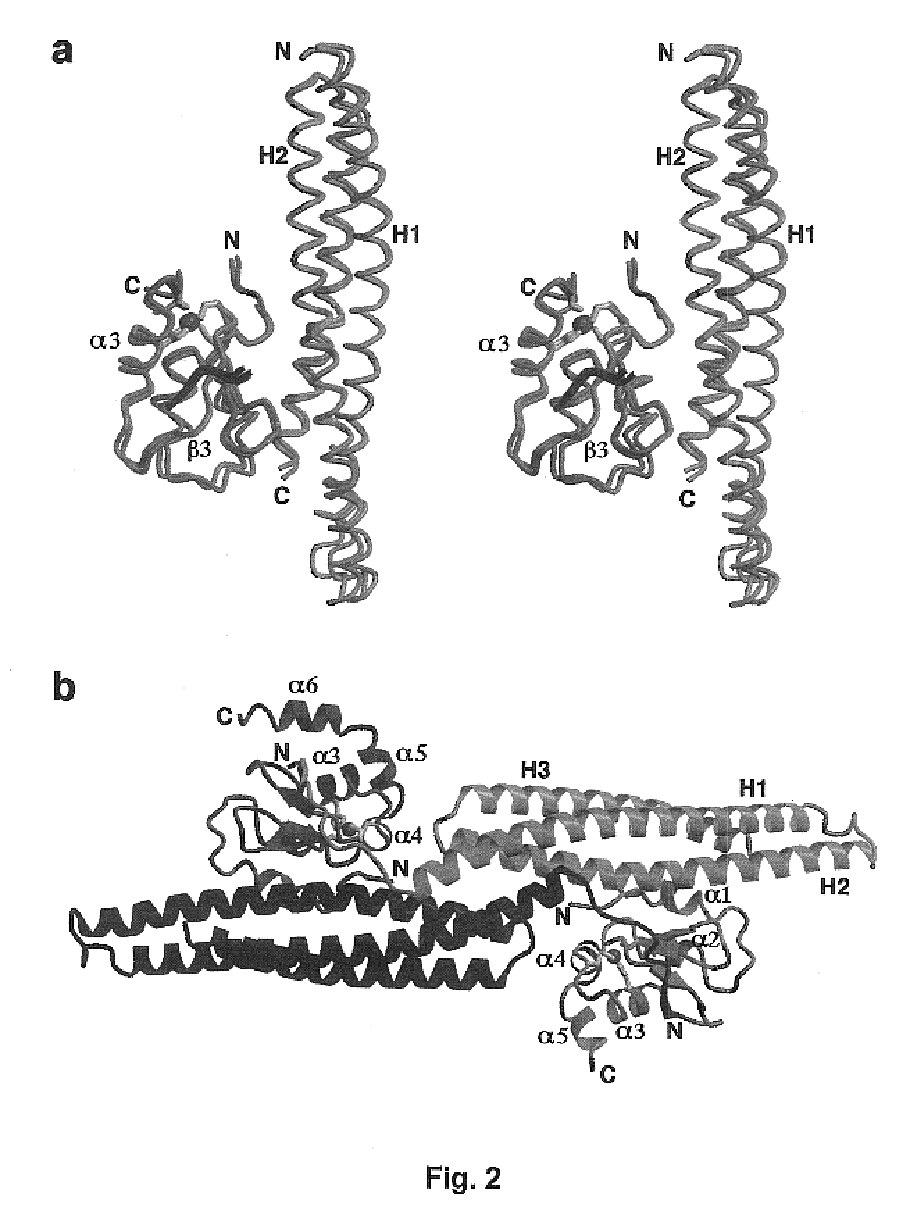
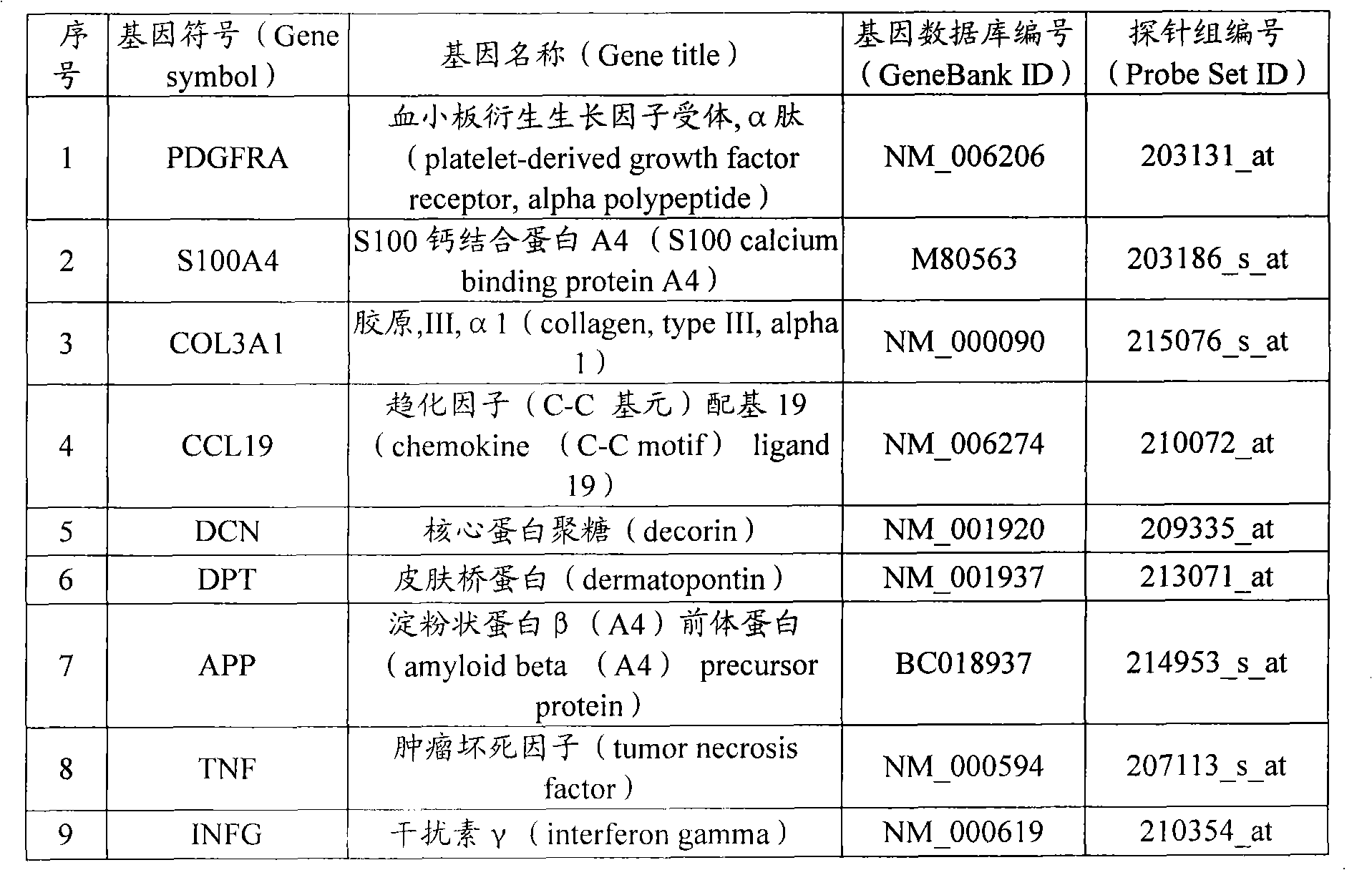
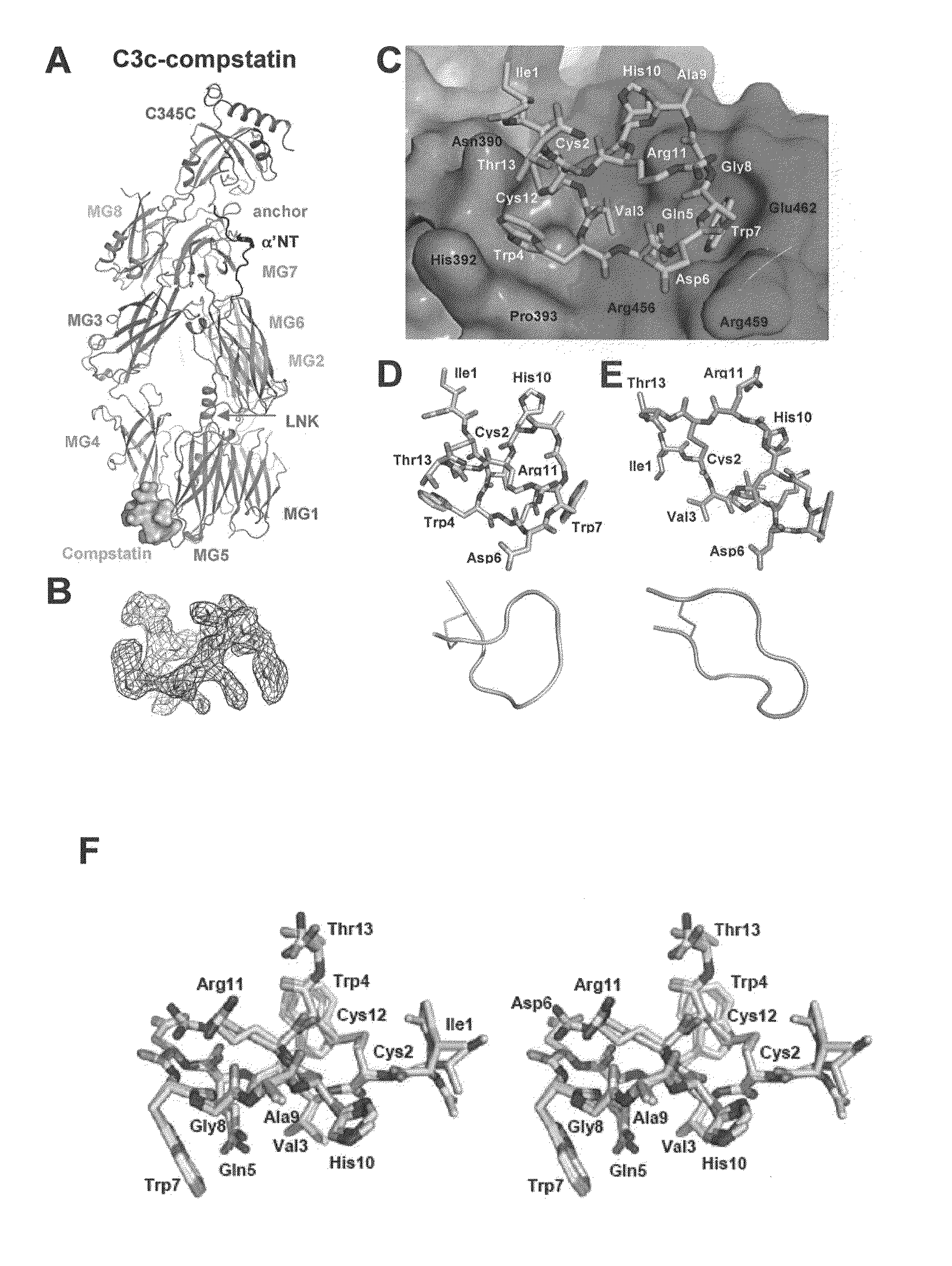
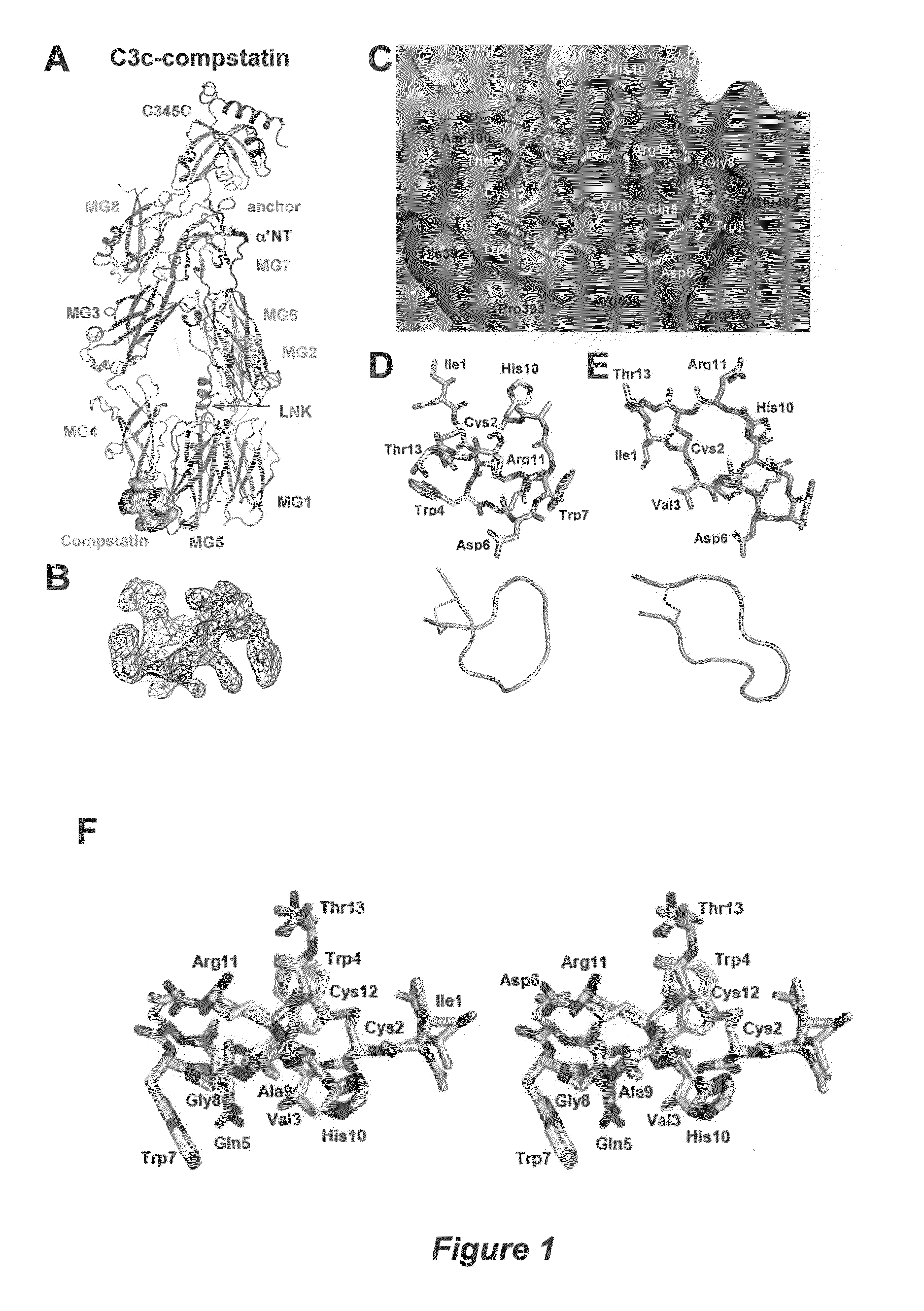
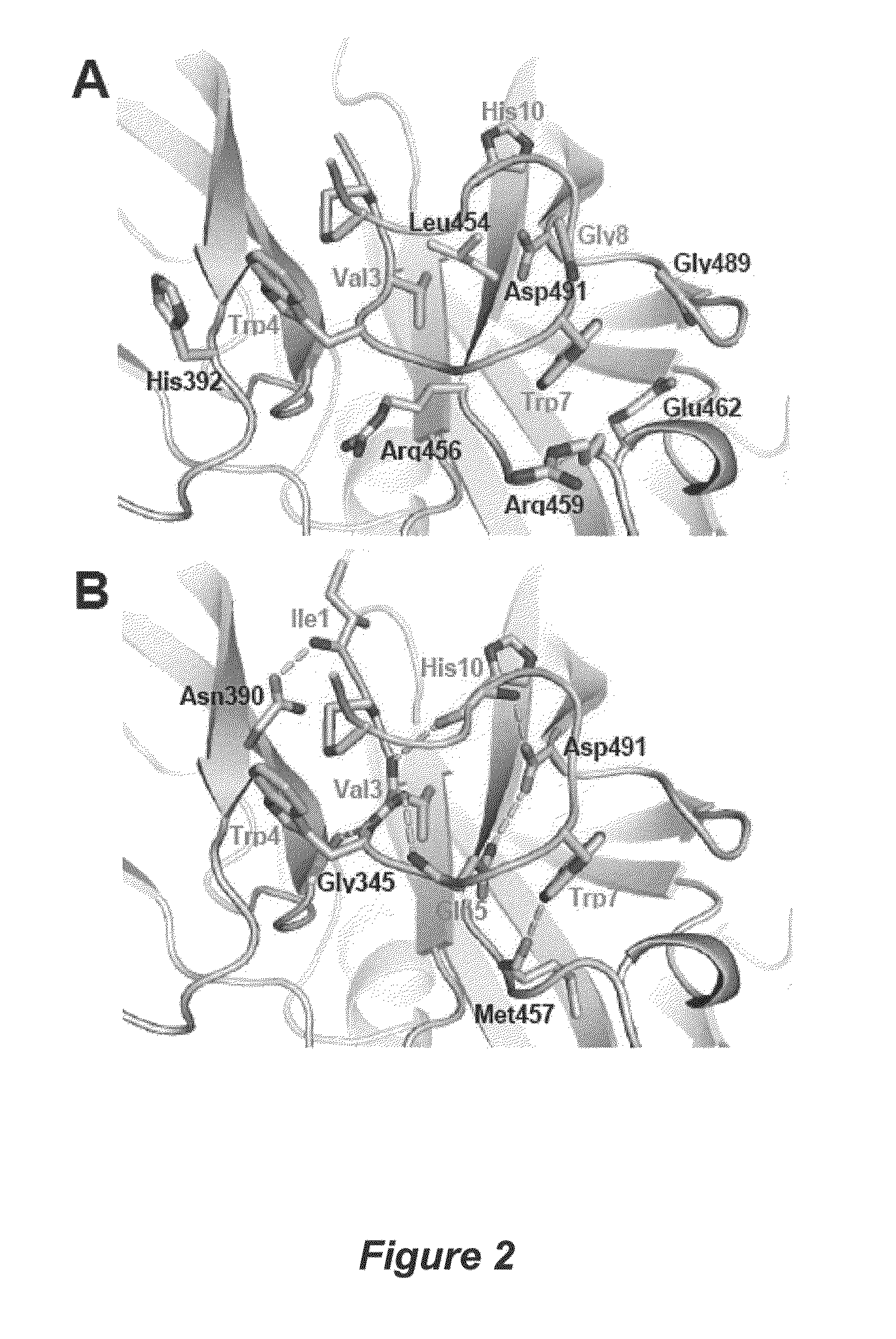
Structure of compstatin-C3 complex and use for rational drug design
The structure of C3c in complex with the complement inhibitor, compstatin, and use of this information for rational design or identification of complement-inhibiting drugs are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Use of zwitterionic polysaccharides for the specific modulation of immune processes
InactiveUS20090317410A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsThree Dimensional Molecular StructureBiology
The invention relates to three-dimensional molecular structure determination of polymers, three-dimensional computer molecular modeling, rational drug design, and immunomodulatory polymers. In particular the invention is directed to immunomodulatory polymers, as well as to methods for designing, selecting, and screening therapeutic agents having immunomodulatory activity.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Transforming growth factor beta crystals
InactiveUS6294656B1Improve concentrationPrevent penetrationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganism based processesOxidizing agentCrystallization
The invention concerns TGF-beta in a crystalline form which shows no adsorption or less adsorption to the walls of vials than the soluted TGF-beta and which is more stable towards oxidative agents than the soluted form. TGF-beta crystals of the invention can be used for structure determination and for drug design and for the production of a slow release pharmaceutical preparation.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
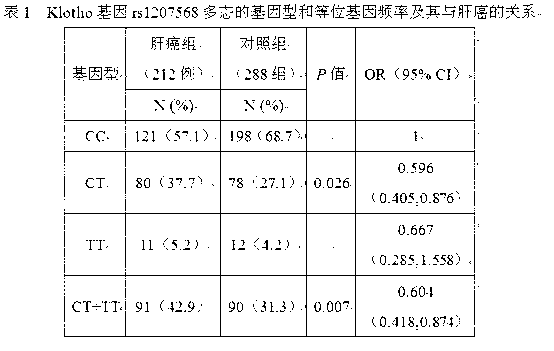
Hepatocellular carcinoma-related klotho gene single-nucleotide polymorphism and its construction method and use
InactiveCN102796820AConducive to screeningEasy to solveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationKlothoNucleotide
The invention provides hepatocellular carcinoma-related klotho gene single-nucleotide polymorphism and its construction method and use. The hepatocellular carcinoma-related klotho gene single-nucleotide polymorphism and its construction method have the advantages that 1, through a detection method provided by the invention, polymorphism of a single nucleotide located in an exon 4 area of a human klotho gene can be detected fast and simply and it is diagnosed that if an individual has susceptibility of hepatocellular carcinoma so that the hepatocellular carcinoma-susceptible population screening and hepatocellular carcinoma prevention are promoted; 2, a T allele point of rs648202 is used as a drug design target point for drug screening so that an active molecule adjusting a klotho gene expression level is selected and development of a novel antitumor drug is promoted; 3, through primer sequences and HaeIII endonuclease provided by the invention, simple, efficient and specific detection of rs648202 polymorphism is realized; and 4, according to hepatocellular carcinoma-related klotho gene single-nucleotide polymorphism, a hepatocellular carcinoma genetic diagnosis kit can be constructed.
Owner:黄曙 +1
Protein kinase inhibitors comprising ATP mimetics conjugated to peptides or pertidomimetics
InactiveUS20050026840A1High activityHigh selectivityBiocideNervous disorderPTK InhibitorsAutoimmune condition
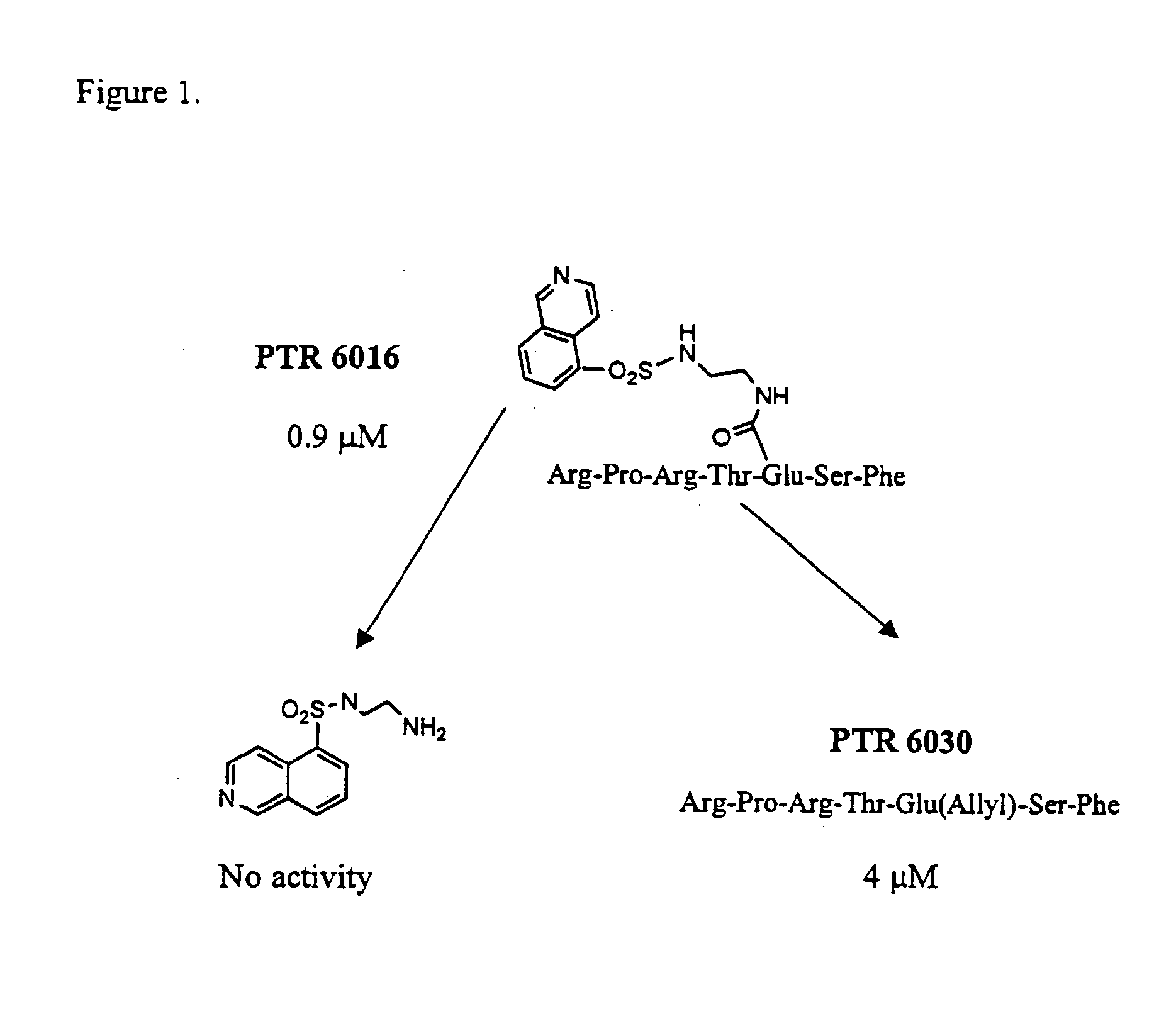
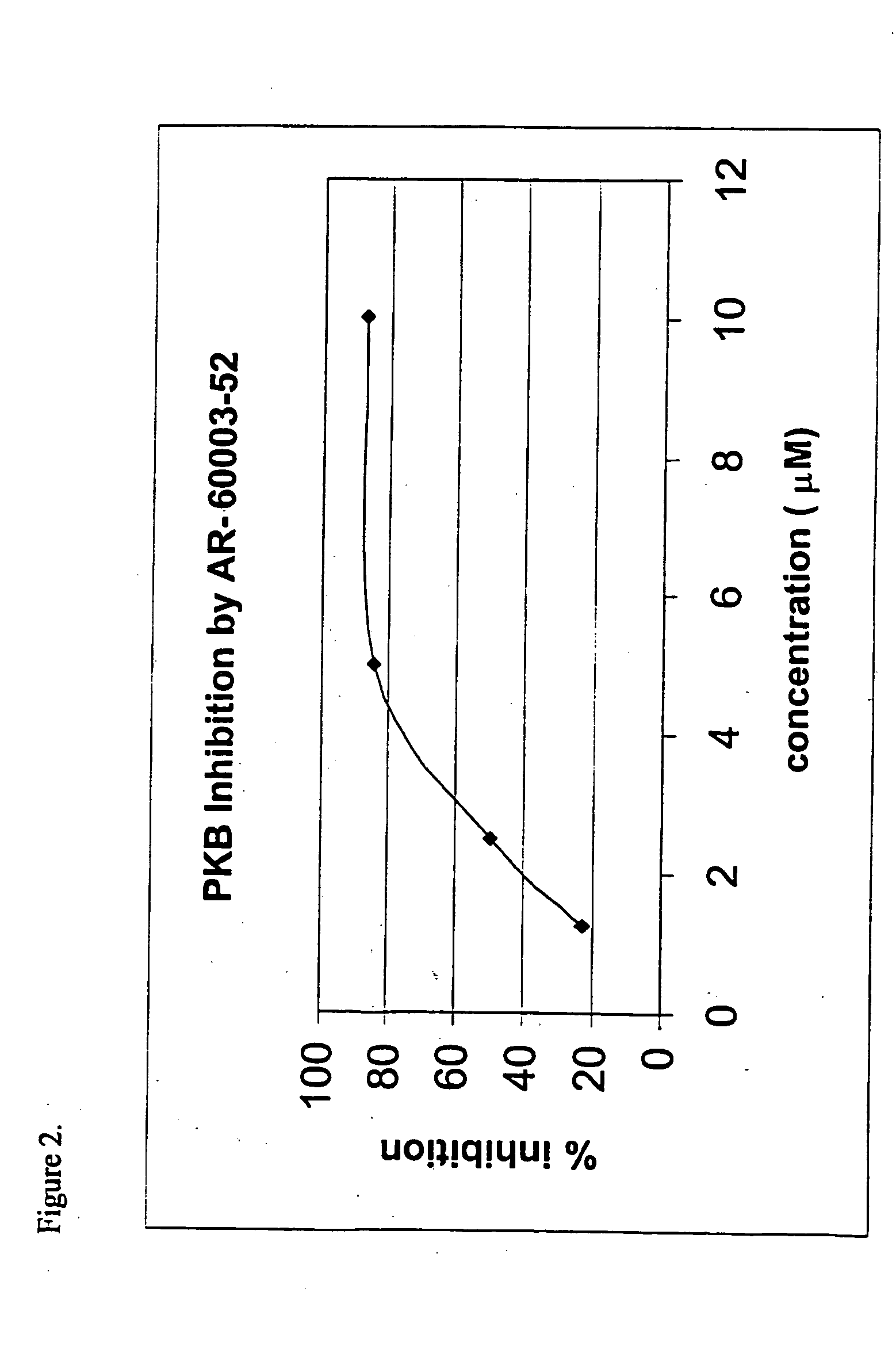
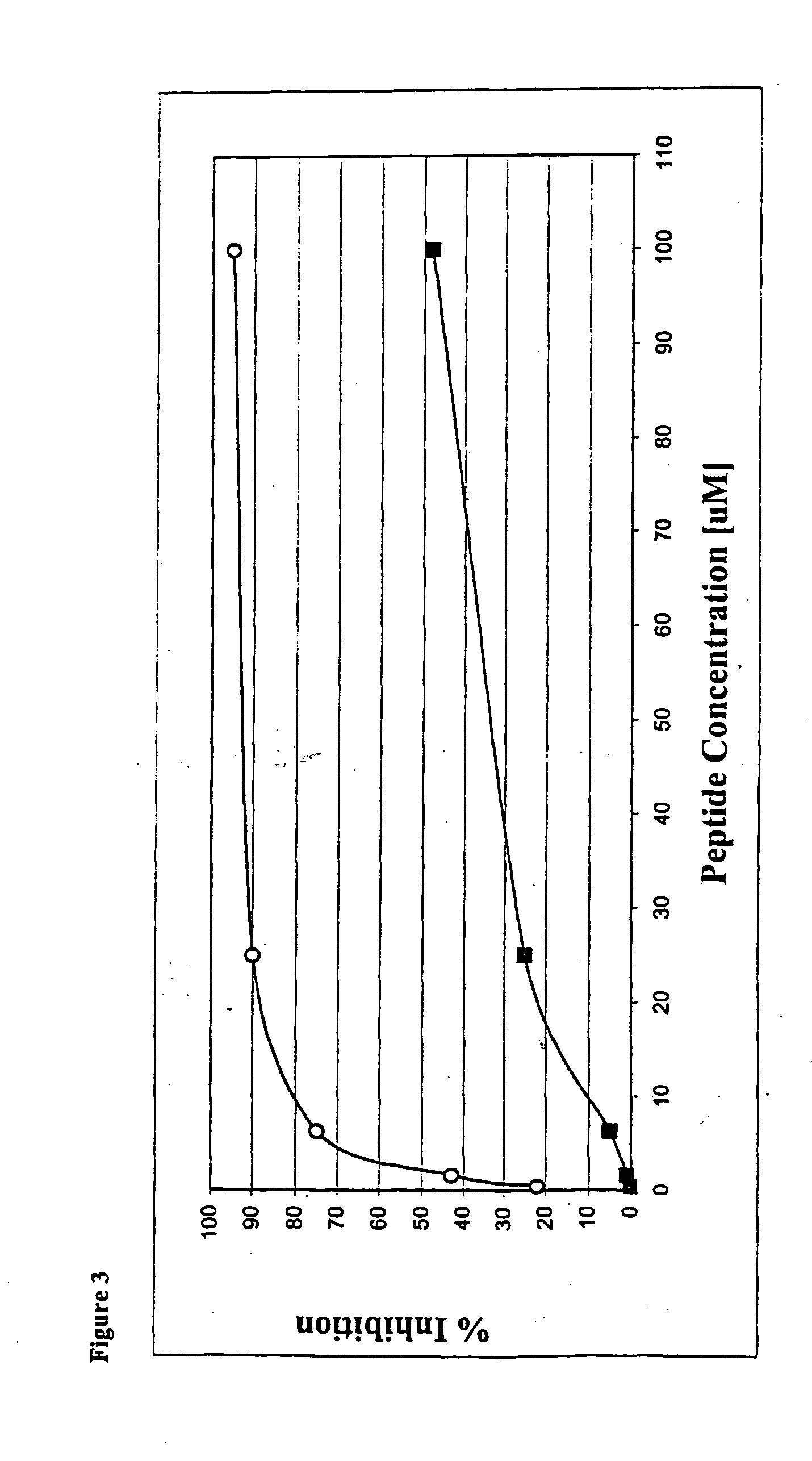
The present invention provides small molecules having high affinity to the ATP binding site of protein kinases, which are conjugated to apeptide or peptidomimetic moiety which mimics the substrate of PKB. The chimeric compounds according to the present invention preferably serve as PKB inhibitors with improved activity and selectivity. Novel ATP mimetic compounds, particularly isoquinoline derivatives, conjugated with peptides or peptidomimetics are useful as inhibitors of protein kinases for experimental, medical, and drug design purposes. Furthermore, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these protein kinase inhibitors, and methods of using such compositions for treatment and diagnosis of cancers, diabetes, cardiovascular pathologies, hemorrhagic shock, obesity, inflammatory diseases, diseases of the central nervous system, and autoimmune disease, are disclosed.
Owner:CUREGENICS
Anti-aging micrornas
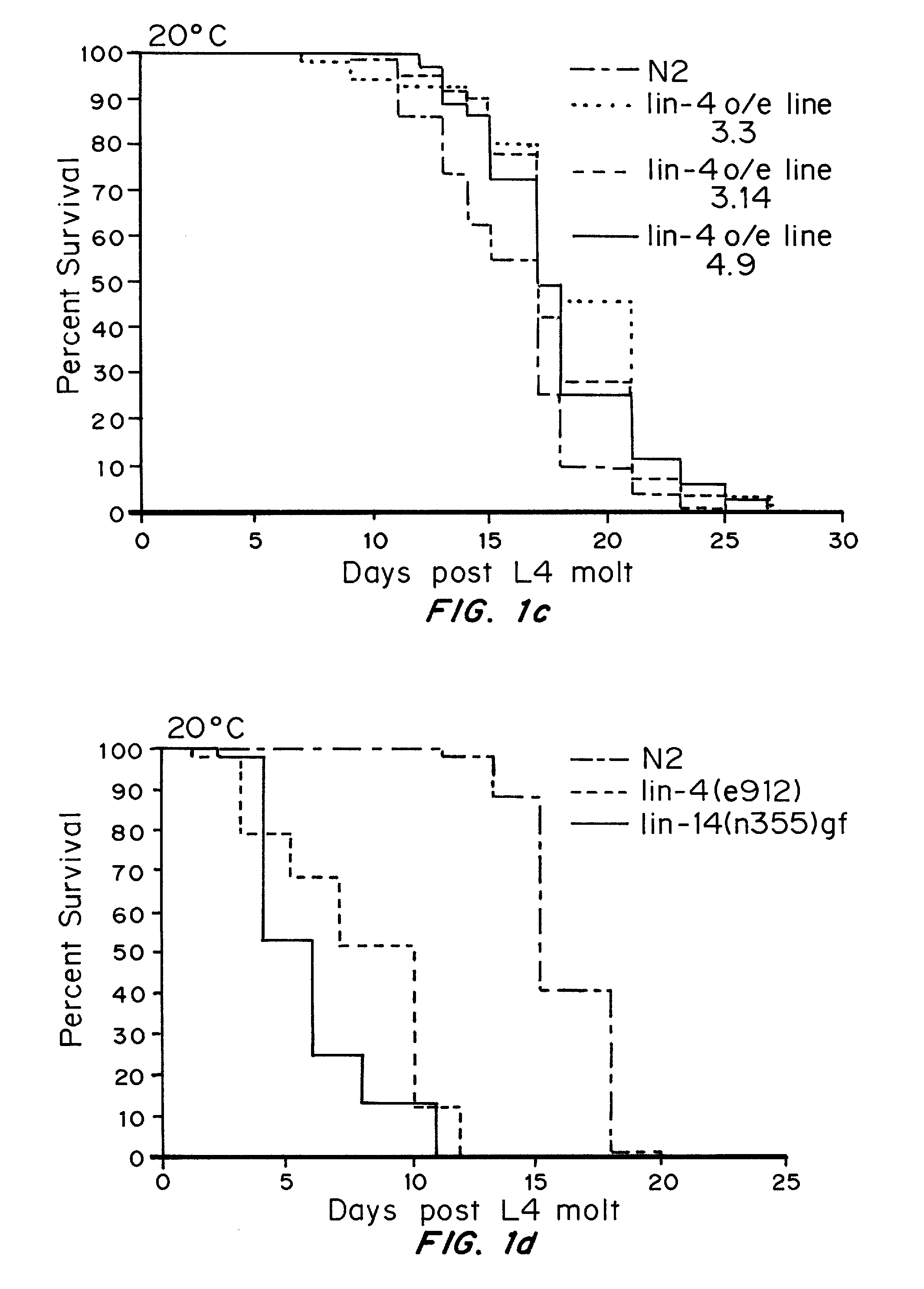
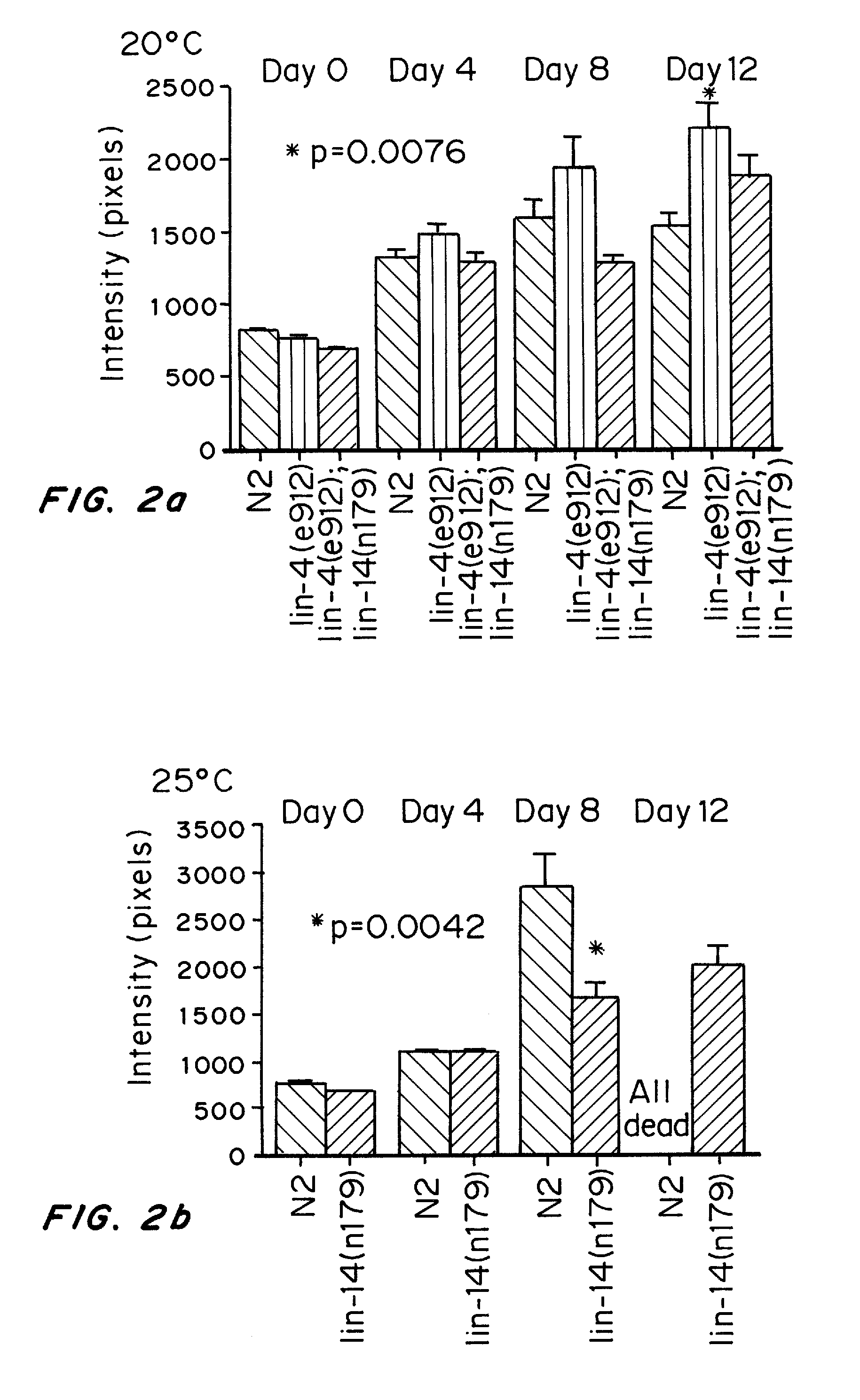
ActiveUS20070287678A1Avoiding characteristicTreating and slowing effectCompound screeningNervous disorderAge related diseaseDrug target
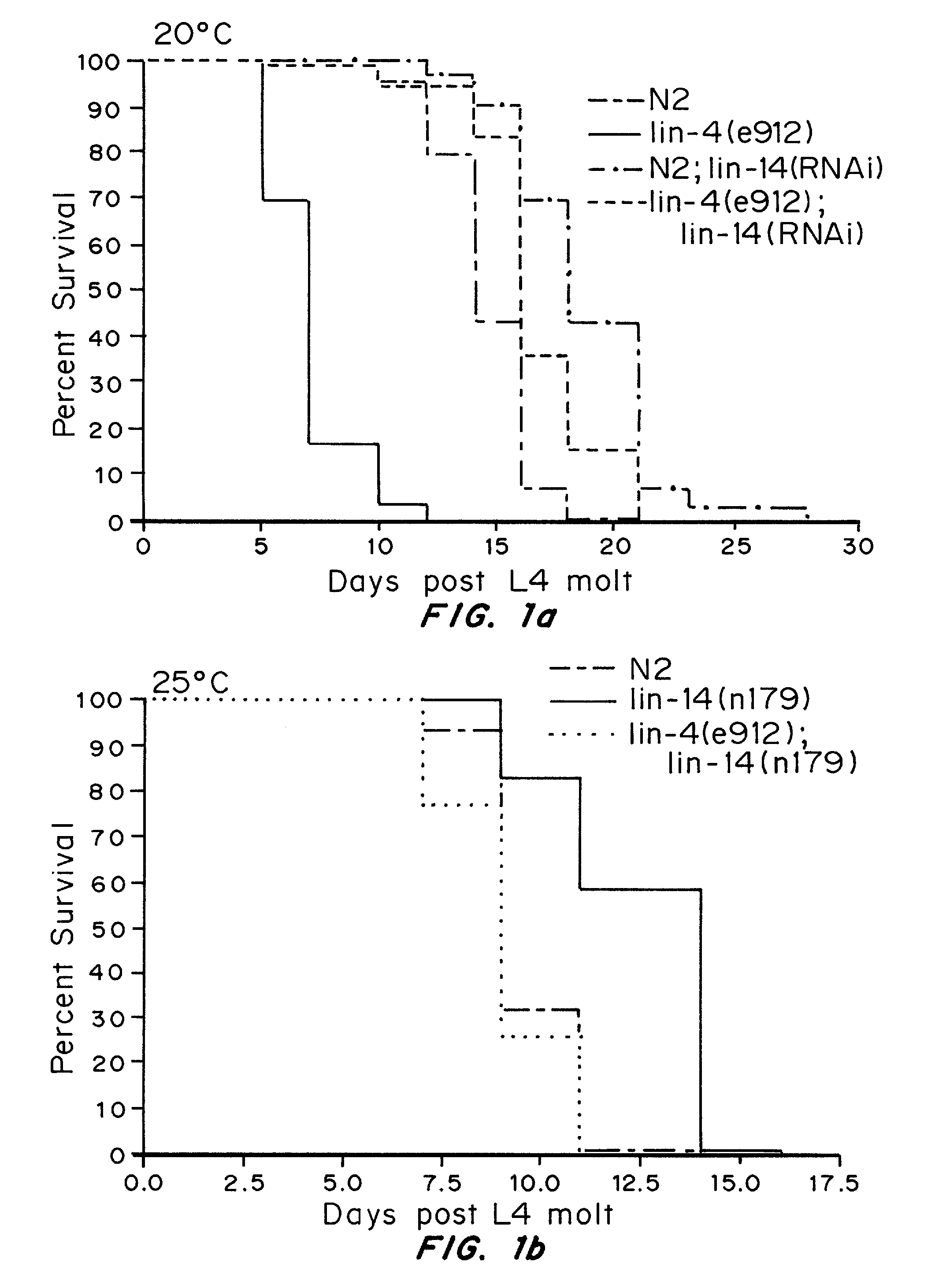
Methods and compositions for modulating aging genes or their targets for the treatment or prevention of senescence or symptoms thereof have been developed based on the discovery of naturally occurring inhibitory nucleic acids, in particular lin-4 miRNA, that downregulate genes involved in senescence, lifespan, or age-related disorders. Representative aging genes include, but are not limited to lin-4, lin-14, let-7, lin-28, egl-35 and lin-42. Methods for identifying modulators of aging genes and targets of aging genes are also provided. The disclosed compositions are useful as diagnostics. These can be used in assays to compare genes in normal individuals, with those who are aging well or who demonstrate early senescence, and with those who have age-related disorders such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. The genes can be used to study the pathways and mechanisms involved in aging and age-related disorders. These genes can be used as drug targets, or in drug design, to develop drugs that can inhibit one or more characteristics of senescence or age-related disorders. These compositions should be effective therapies for treating or slowing the effects of one or more symptoms or characteristics of age-related disorders resulting from activation or over-expression of aging genes. Compositions that alter the expression of particular aging genes affecting the insulin-like signal pathway are described. Suitable compositions described herein include, inhibitory nucleic acids and small molecules, in particular miRNA.
Owner:YALE UNIV
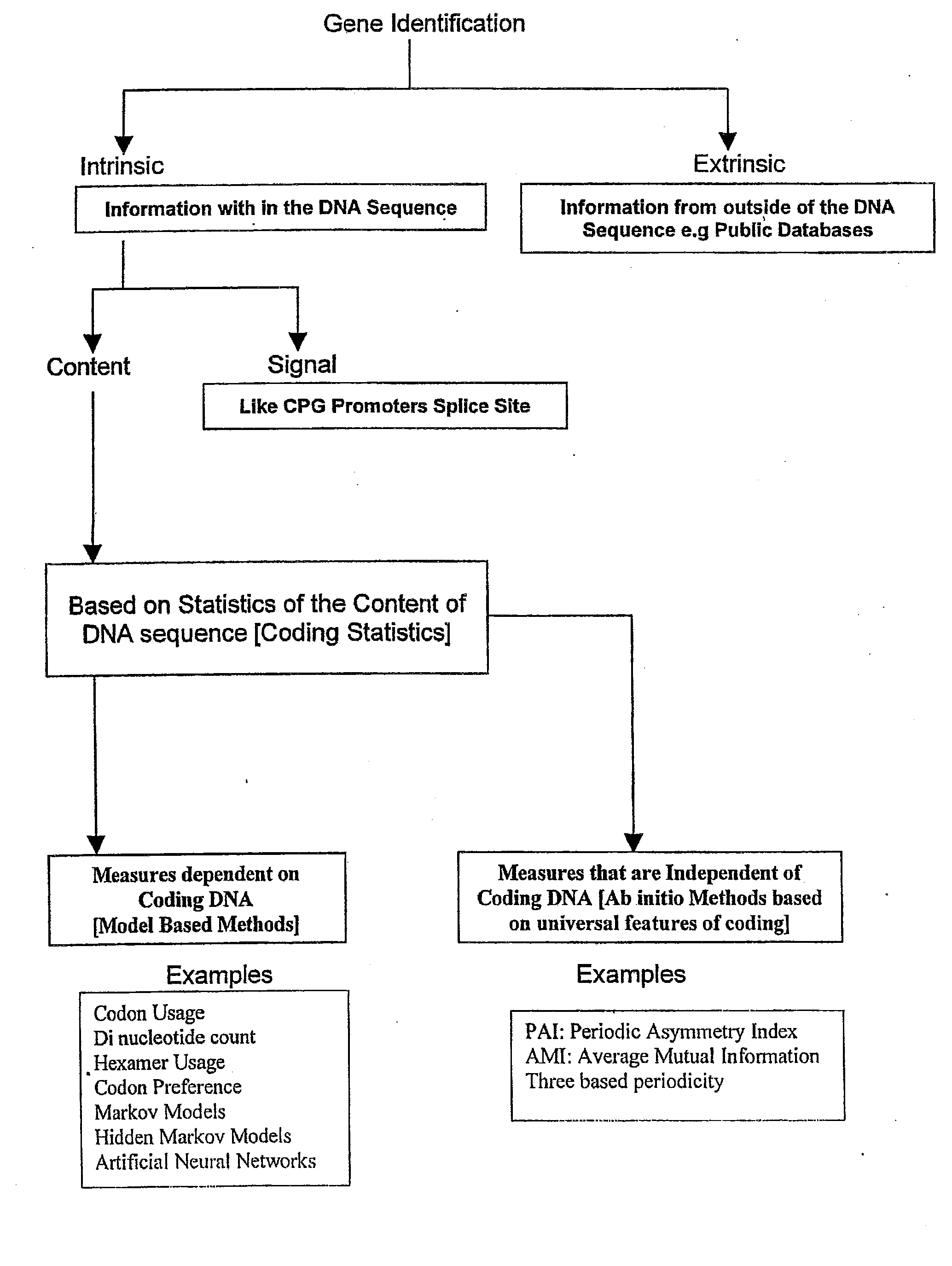
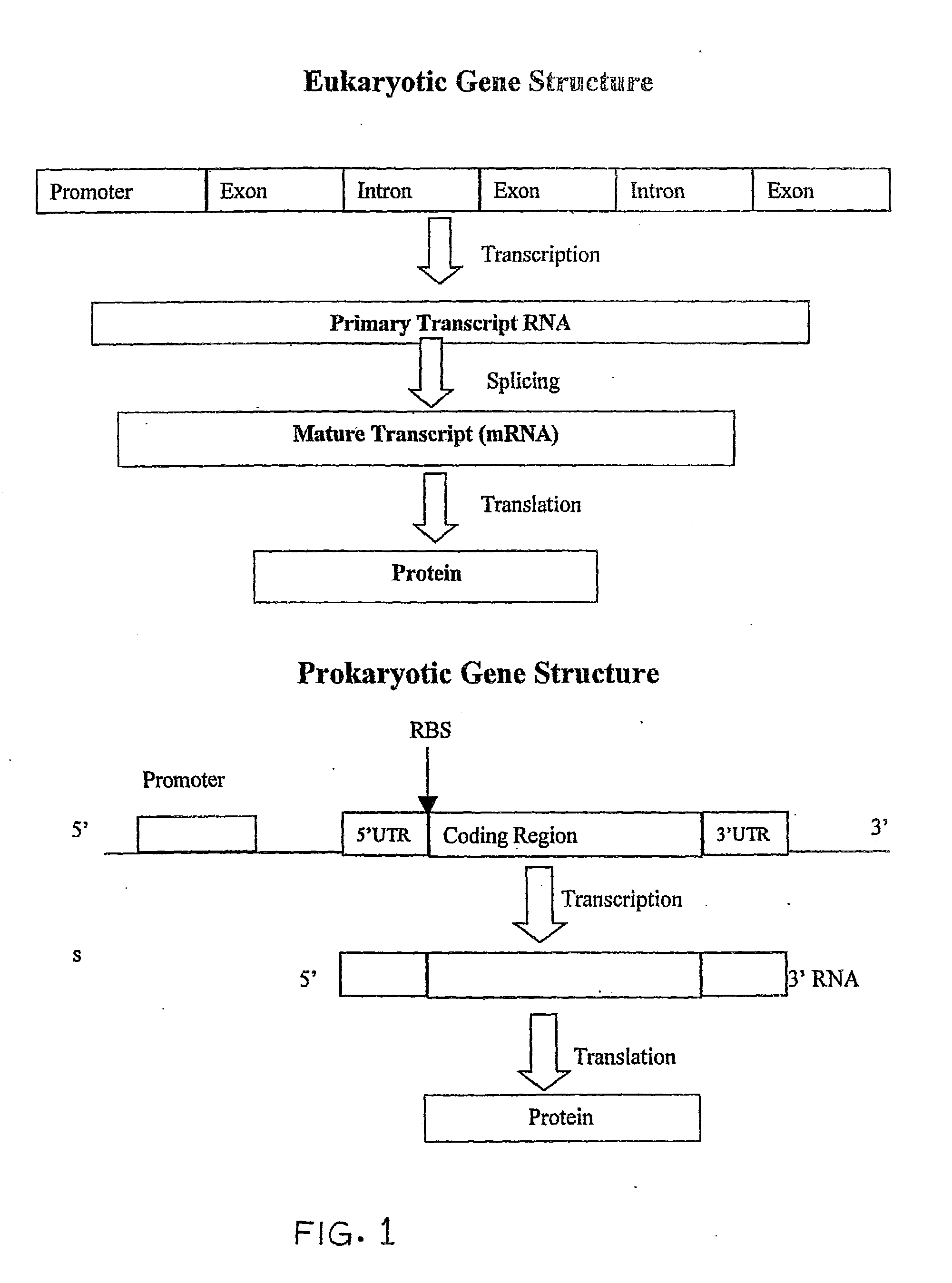
System and method for analysis of a DNA sequence by converting the DNA sequence to a number string and applications thereof in the field of accelerated drug design
InactiveUS20110040488A1Eliminating open reading frame biasBiological testingSequence analysisNew medicationsPharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to a system and a method for analysis of a DNA sequence by converting the DNA sequence into a unique number string using a genomic number system in order to extract and / or analyze biological information. The invention is particularly useful in the development of new drugs or active chemical agents.
Owner:MASCON GLOBAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com