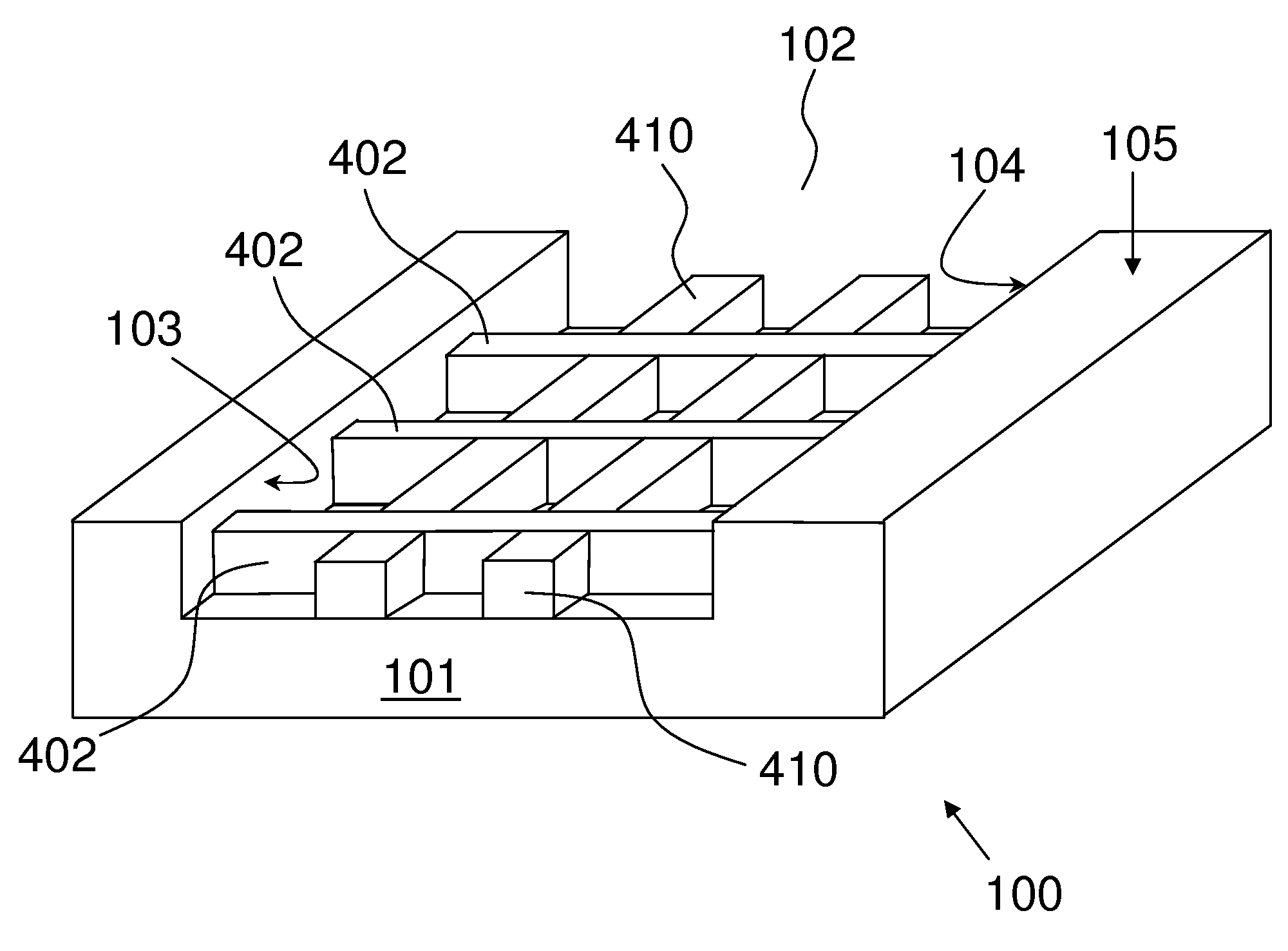
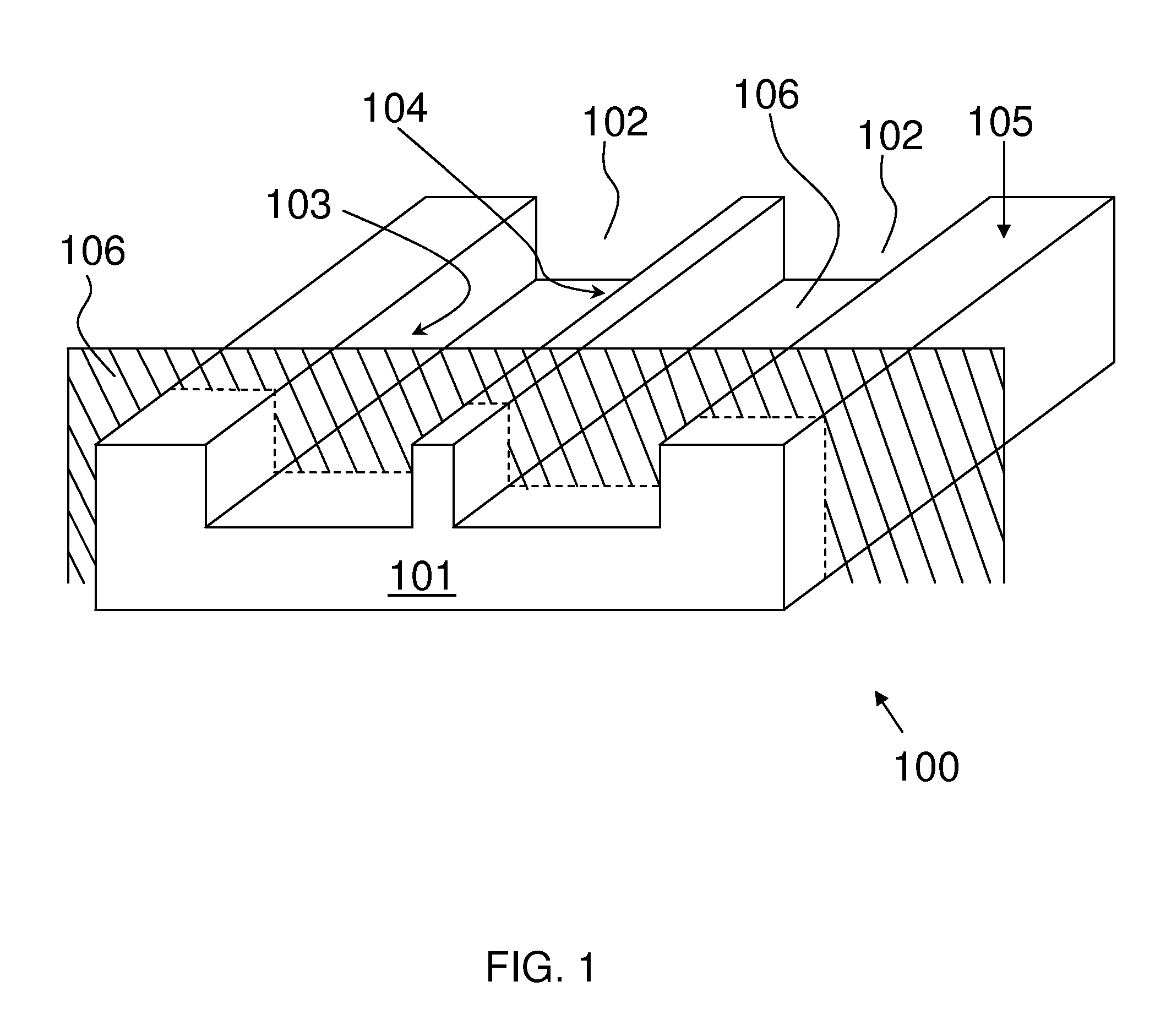
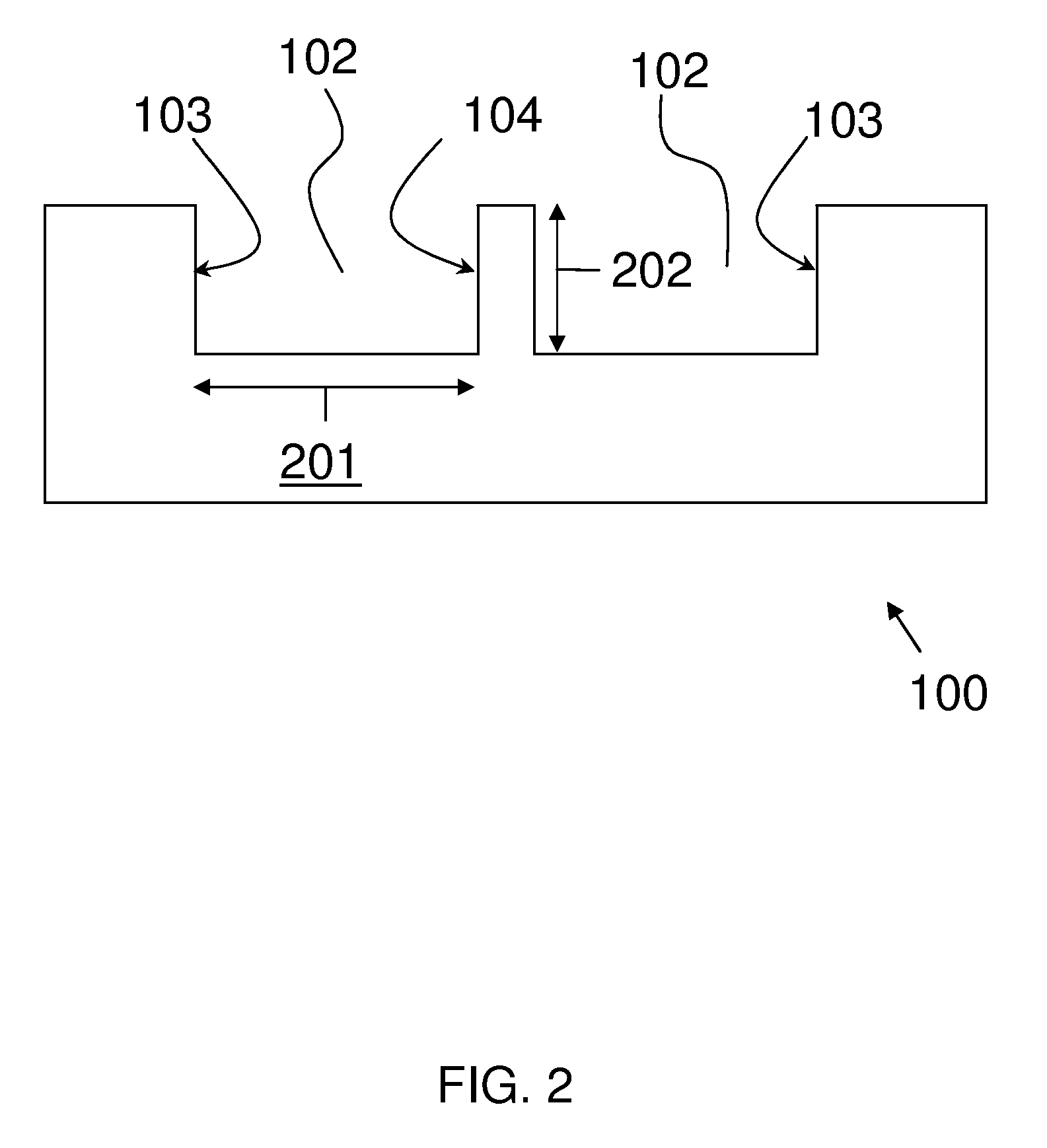
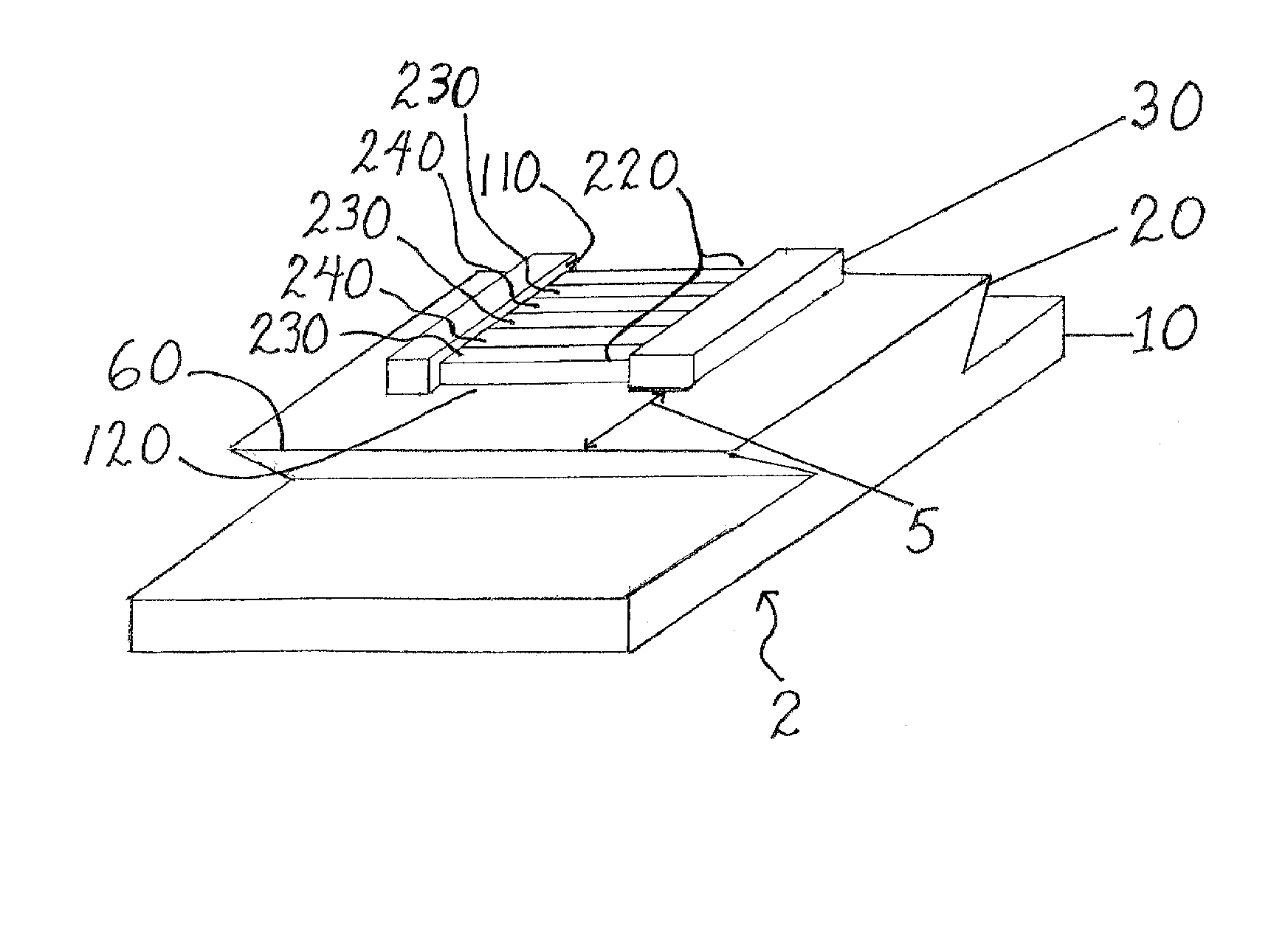
Patents
Literature
607 results about "Self assemble" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
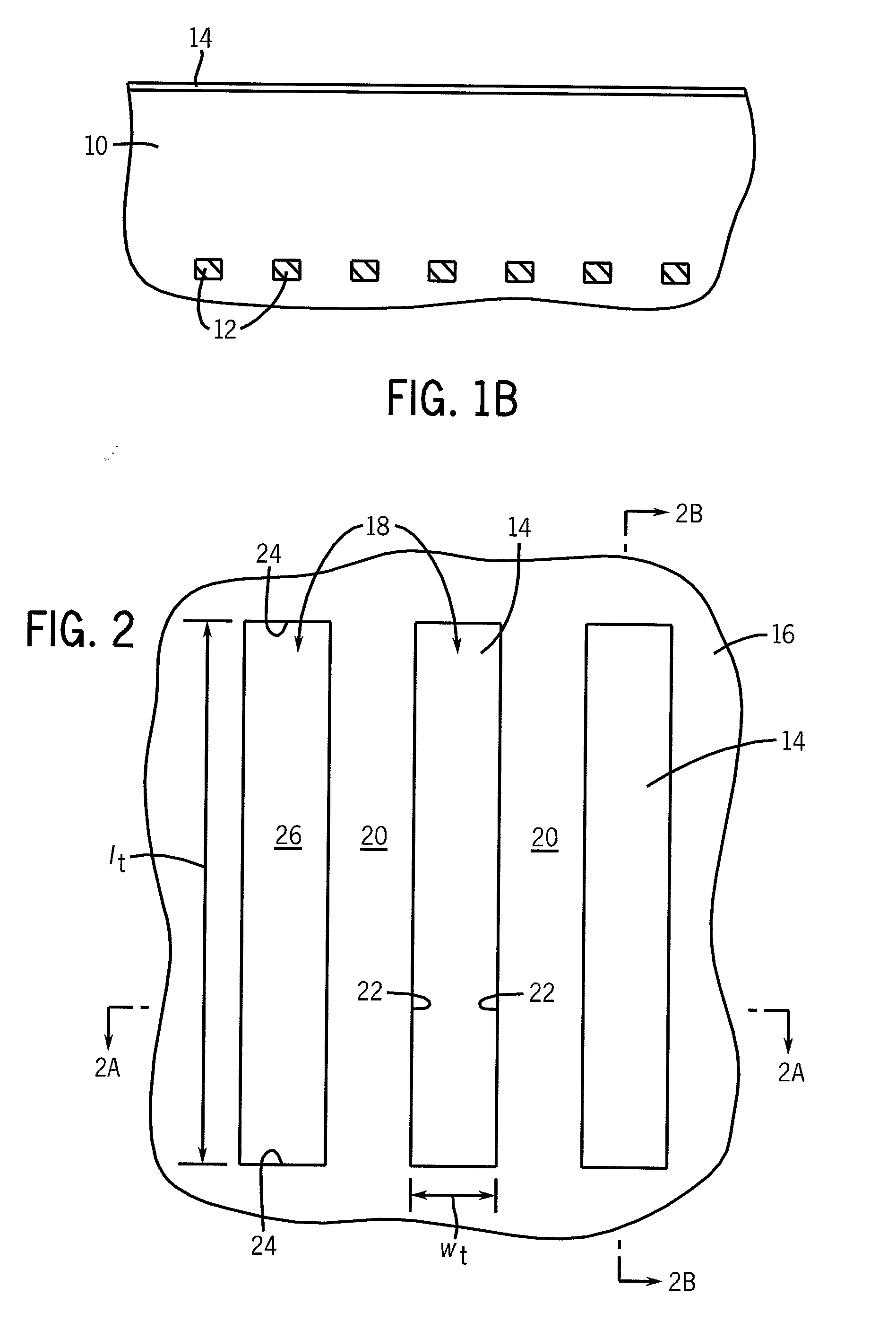
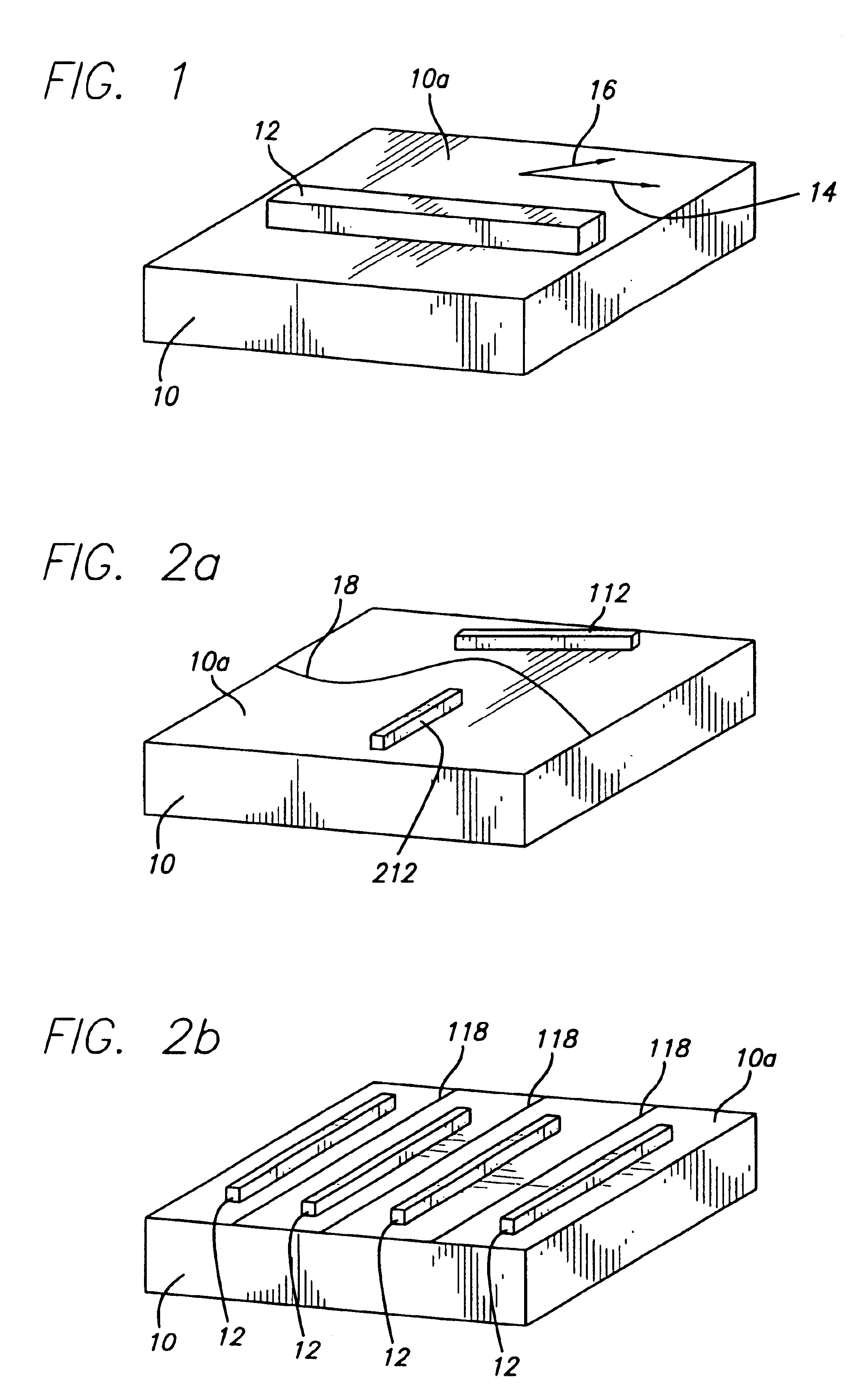
Method for selective deposition of a thin self-assembled monolayer
ActiveUS20060128142A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf-assembled monolayerSelf assemble
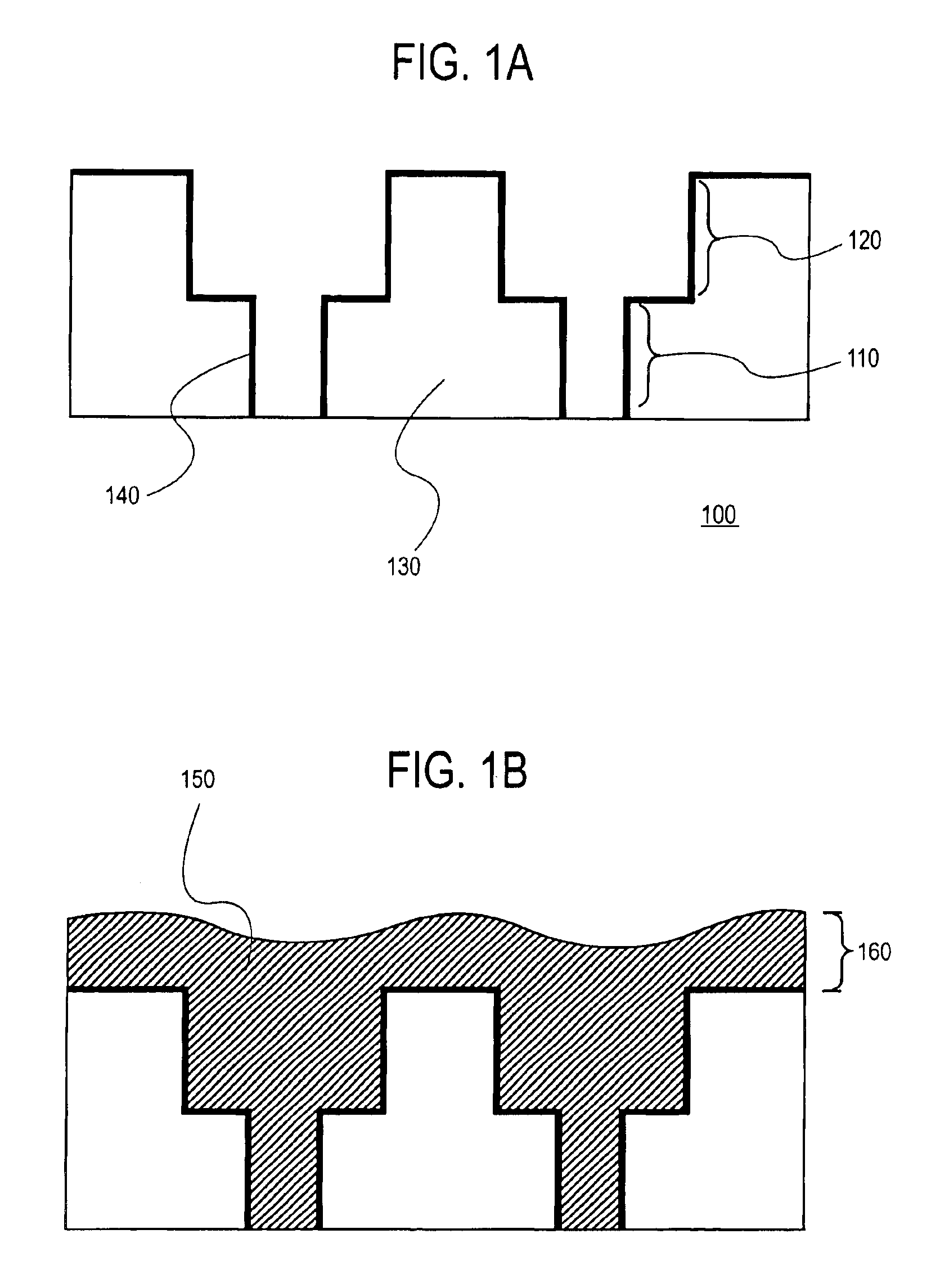
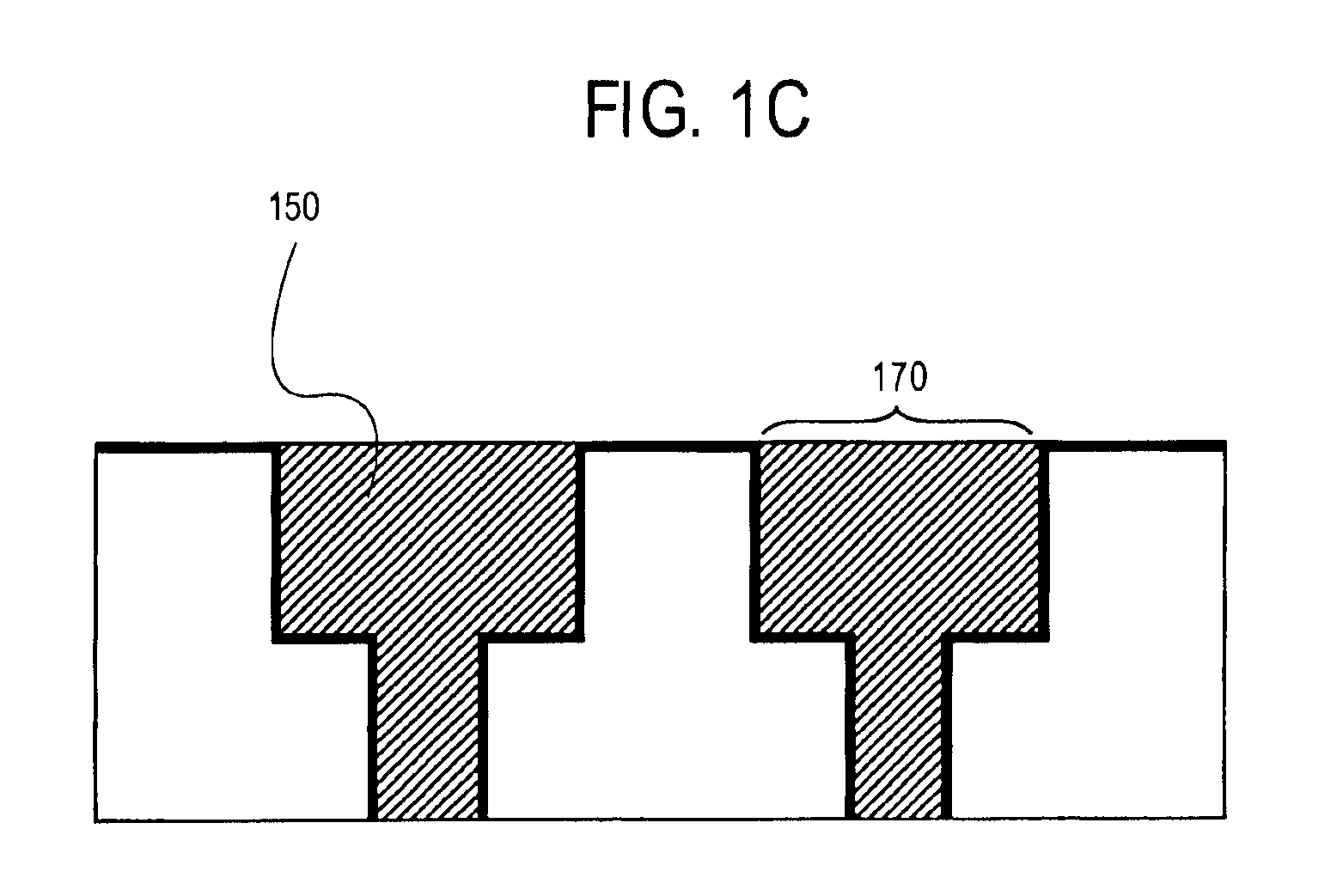
A method for selective deposition of self-assembled monolayers to the surface of a substrate for use as a diffusion barrier layer in interconnect structures is provided comprising the steps of depositing a first self-assembled monolayer to said surface, depositing a second self-assembled monolayer to the non-covered parts of said surface and subsequently heating said substrate to remove the first self-assembled monolayer. The method of selective deposition of self-assembled monolayers is applied for the use as diffusion barrier layers in a (dual) damascene structure for integrated circuits.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
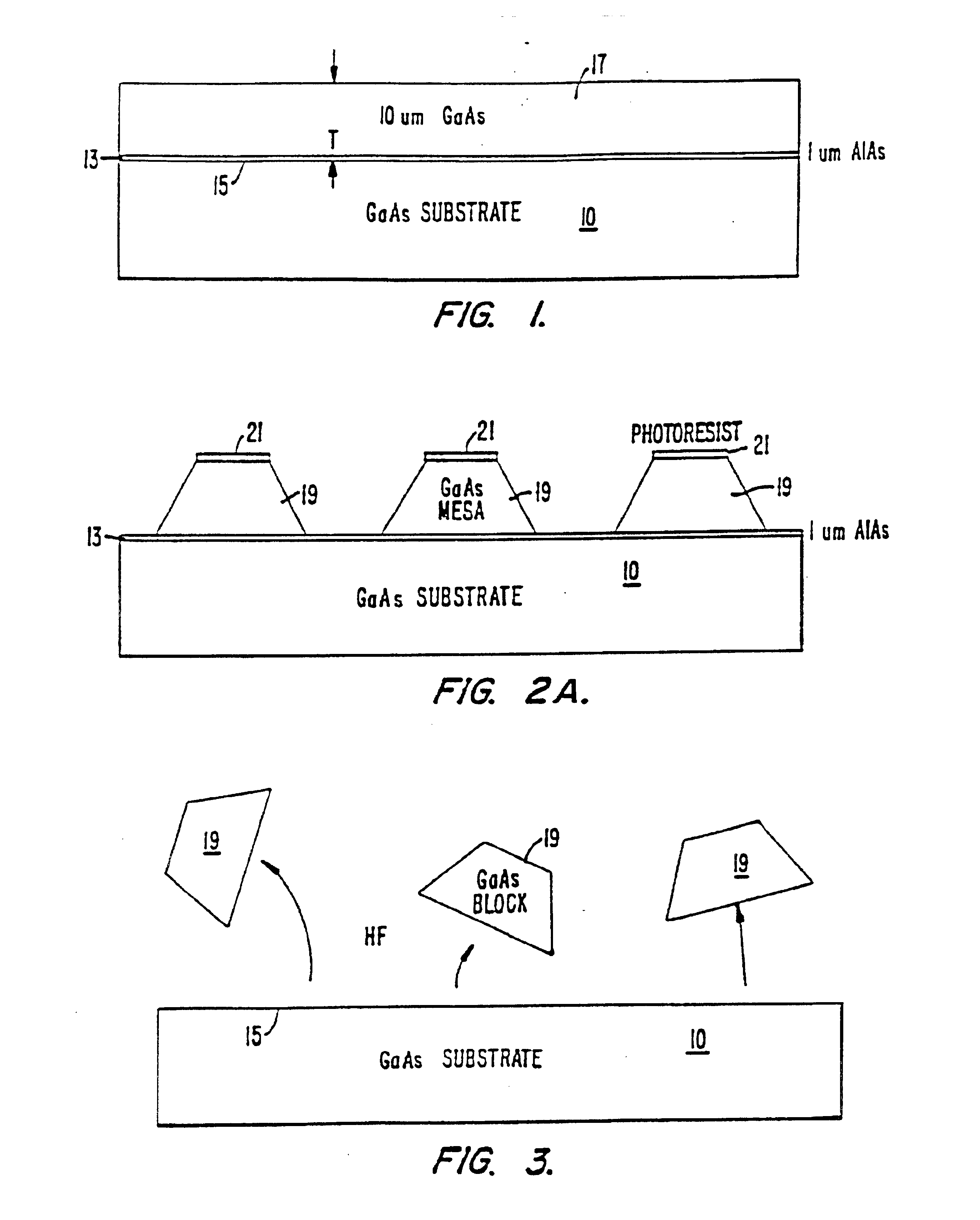
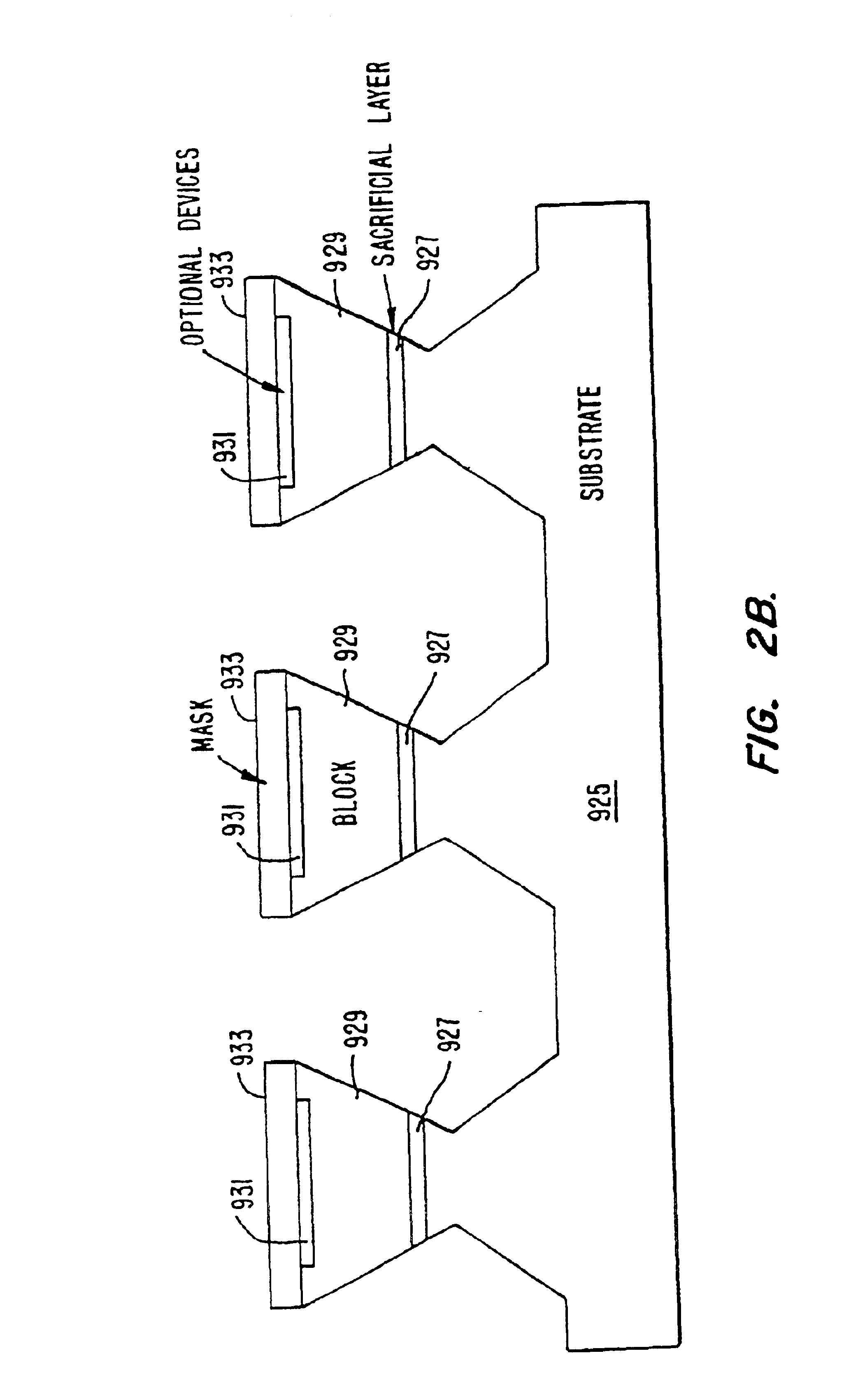
Method and apparatus for fabricating self-assembling microstructures
InactiveUS6864570B2Promote circulationEvenly distributedTransistorSemiconductor laser arrangementsFluid transportSelf assemble
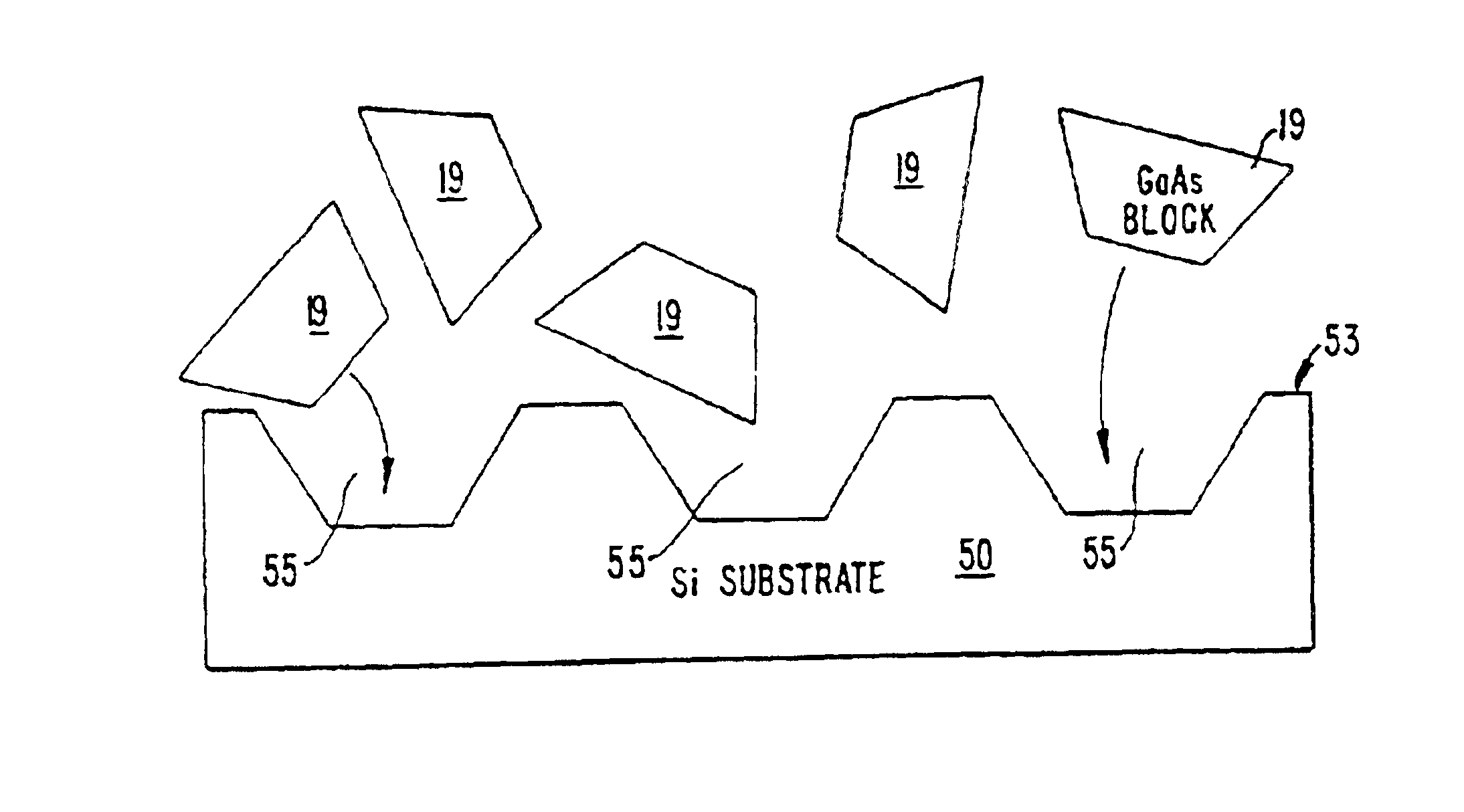
A method and apparatus for assembling microstructures onto a substrate through fluid transport. The microstructures being shaped blocks self-align into recessed regions located on a substrate such that the microstructure becomes integral with the substrate. The improved method includes a step of transferring the shaped blocks into a fluid to create a slurry. Such slurry is then dispensed evenly or circulated over the top surface of a substrate having recessed regions thereon. The microstructure via the shape and fluid tumbles onto the surface of the substrate, self-aligns, and engages into a recessed region.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
One-Dimensional Arrays of Block Copolymer Cylinders and Applications Thereof
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Formation of nanoscale wires
InactiveUS6773616B1Improve crystal qualityMinimizes environmental toxic chemicals usageNanotechPolycrystalline material growthNanowireMicrometer scale
Self-organized, or self-assembled, nanowires of a first composition may be used as an etching mask for fabrication of nanowires of a second composition. The method for forming such nanowires comprises: (a) providing an etchable layer of the second composition and having a buried insulating layer beneath a major surface thereof; (b) growing self-assembled nanowires on the surface of the etchable layer; and (c) etching the etchable layer anisotropically down to the insulating layer, using the self-assembled nanowires as a mask. The self-assembled nanowires may be removed or left. In either event, nanowires of the second composition are formed. The method enables the formation of one-dimensional crystalline nanowires with widths and heights at the nanometer scale, and lengths at the micrometer scale, which are aligned along certain crystallographic directions with high crystal quality. Further, the method of the present invention avoids traditional lithography methods, minimizes environmental toxic chemicals usage, simplifies the manufacturing processes, and allows the formation of high-quality one-dimensional nanowires over large areas.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and method using self-assembled nano structures in the design and fabrication of an integrated circuit micro-cooler
ActiveUS7109581B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNano structuringSelf assemble
Heat sink structures employing carbon nanotube or nanowire arrays to reduce the thermal interface resistance between an integrated circuit chip and the heat sink are disclosed. Carbon nanotube arrays are combined with a thermally conductive metal filler disposed between the nanotubes. This structure produces a thermal interface with high axial and lateral thermal conductivities.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Registered structure formation via the application of directed thermal energy to diblock copolymer films
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nano-sized self-assembled liquid dilutable vehicles
Owner:NUTRALEASE
Alternating Self-Assembling Morphologies of Diblock Copolymers Controlled by Variations in Surfaces
Methods for fabricating sublithographic, nanoscale microstructures arrays including openings and linear microchannels utilizing self-assembling block copolymers, and films and devices formed from these methods are provided. In some embodiments, the films can be used as a template or mask to etch openings in an underlying material layer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
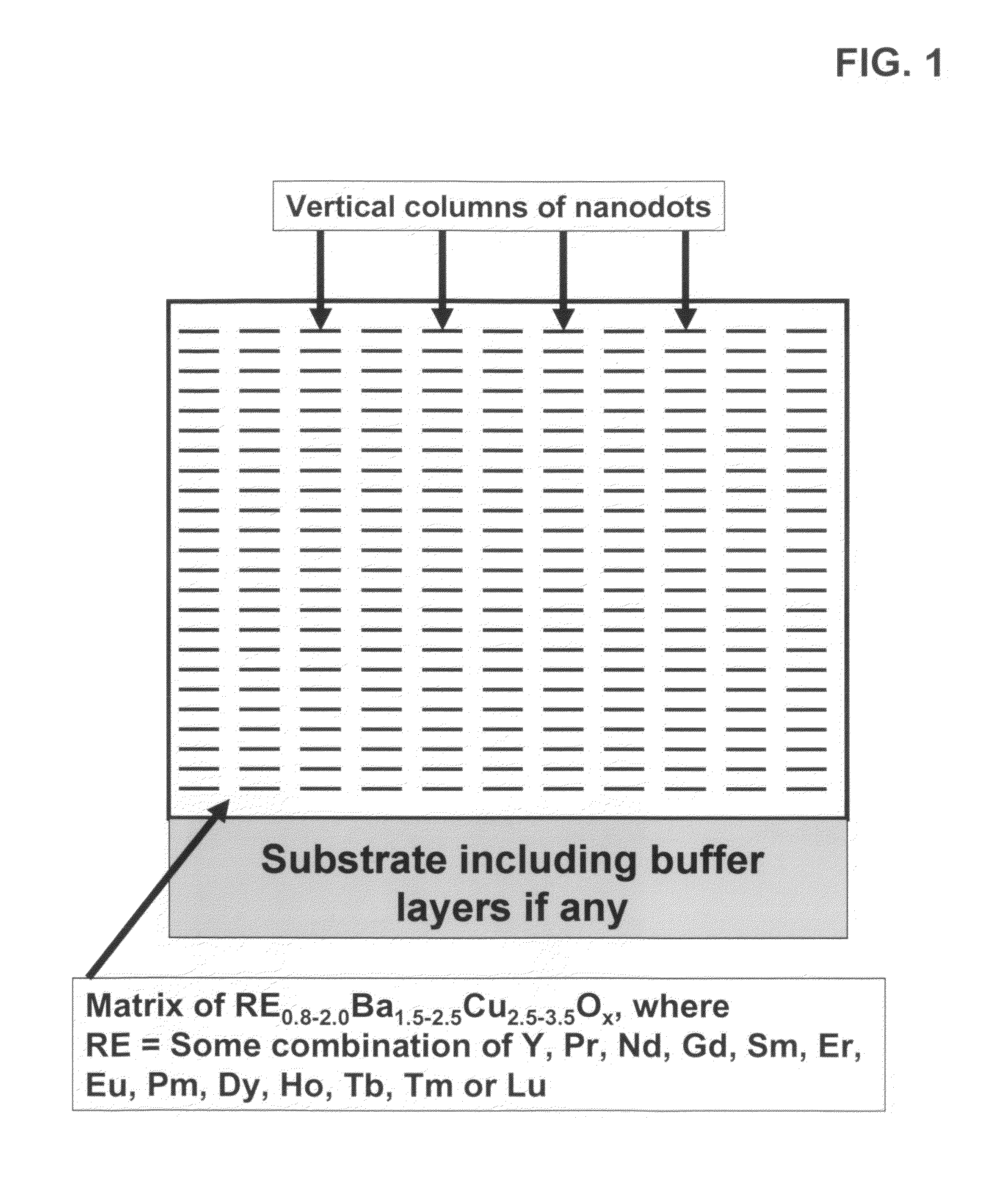
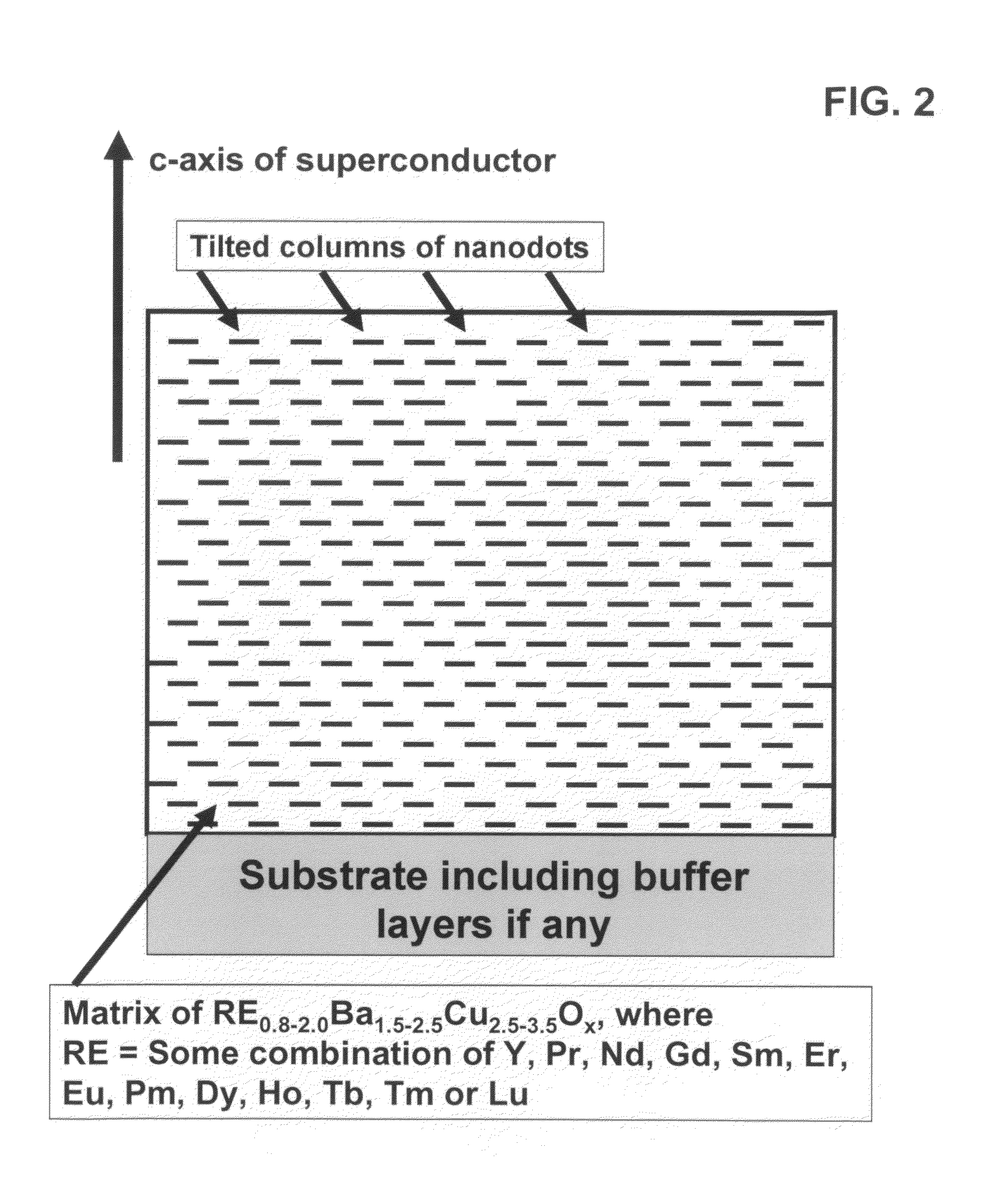
High performance devices enabled by epitaxial, preferentially oriented, nanodots and/or nanorods
ActiveUS20080176749A1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionNanodotPhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate same with self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods of a single or multicomponent material within another single or multicomponent material for use in electrical, electronic, magnetic, electromagnetic, superconducting and electrooptical devices is disclosed. Self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods are ordered arrays wherein ordering occurs due to strain minimization during growth of the materials. A simple method to accomplish this when depositing in-situ films is also disclosed. Device applications of resulting materials are in areas of superconductivity, photovoltaics, ferroelectrics, magnetoresistance, high density storage, solid state lighting, non-volatile memory, photoluminescence, thermoelectrics and in quantum dot lasers.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Self-assembled electrical networks
Techniques for self assembly of macro-scale objects, optionally defining electrical circuitry, are described, as well as articles formed by self assembly. Components can be joined, during self-assembly by minimization of free energy, capillary attraction, or a combination.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
One-dimensional arrays of block copolymer cylinders and applications thereof
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Selective deposition using hydrophobic precursors
ActiveUS20170323776A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSelf-assembled monolayerGas phase
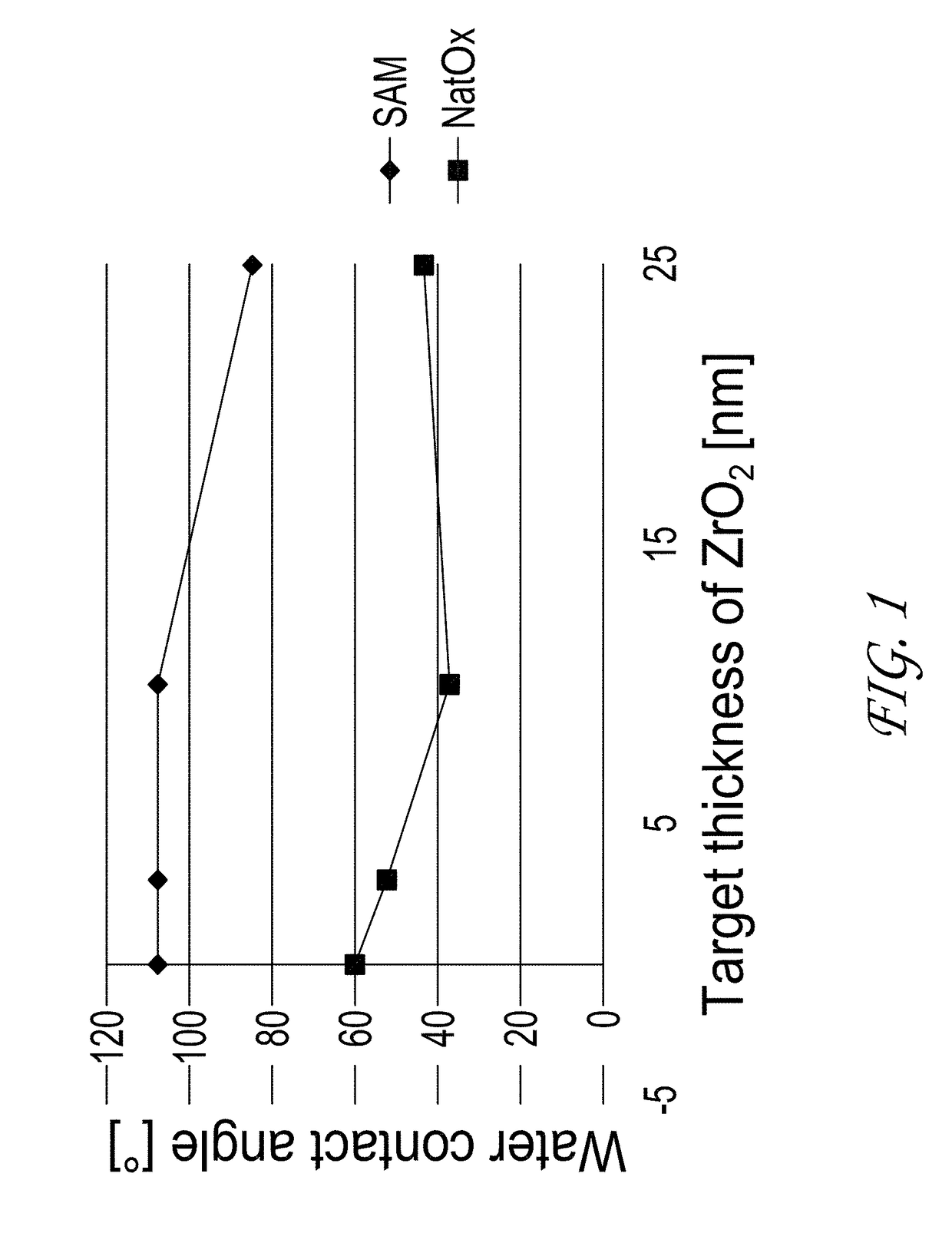
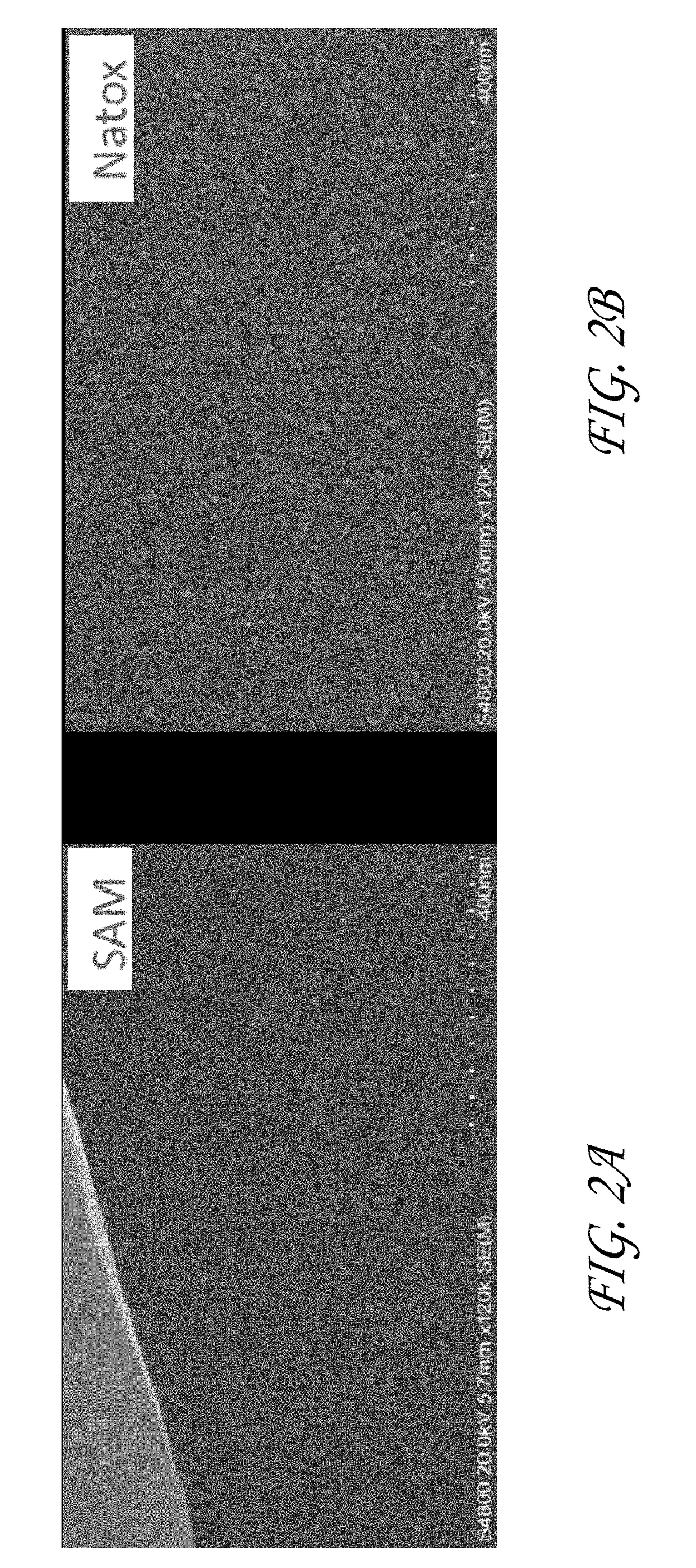
Vapor deposition processes are provided in which a material is selectively deposited on a first surface of a substrate relative to a second organic surface. In some embodiments a substrate comprising a first surface, such as a metal, semi-metal or oxidized metal or semi-metal is contacted with a first vapor phase hydrophobic reactant and a second vapor phase reactant such that the material is deposited selectively on the first surface relative to the second organic surface. The second organic surface may comprise, for example, a self-assembled monolayer, a directed self-assembled layer, or a polymer, such as a polyimide, polyamide, polyuria or polystyrene. The material that is deposited may be, for example, a metal or metallic material. In some embodiments the material is a metal oxide, such as ZrO2 or HfO2. In some embodiments the vapor deposition process is a cyclic chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process or an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. In some embodiments the material is deposited on the first surface relative to the second surface with a selectivity of greater than about 50%, greater than about 60%, greater than about 70%, greater than about 80%, greater than about 90% or greater than about 95%.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Self-assembling cell aggregates and methods of making engineered tissue using the same
A composition comprising a plurality of cell aggregates for use in the production of engineered organotypic tissue by organ printing. A method of making a plurality of cell aggregates comprises centrifuging a cell suspension to form a pellet, extruding the pellet through an orifice, and cutting the extruded pellet into pieces. Apparatus for making cell aggregates comprises an extrusion system and a cutting system. In a method of organ printing, a plurality of cell aggregates are embedded in a polymeric or gel matrix and allowed to fuse to form a desired three-dimensional tissue structure. An intermediate product comprises at least one layer of matrix and a plurality of cell aggregates embedded therein in a predetermined pattern. Modeling methods predict the structural evolution of fusing cell aggregates for combinations of cell type, matrix, and embedding patterns to enable selection of organ printing processes parameters for use in producing an engineered tissue having a desired three-dimensional structure.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
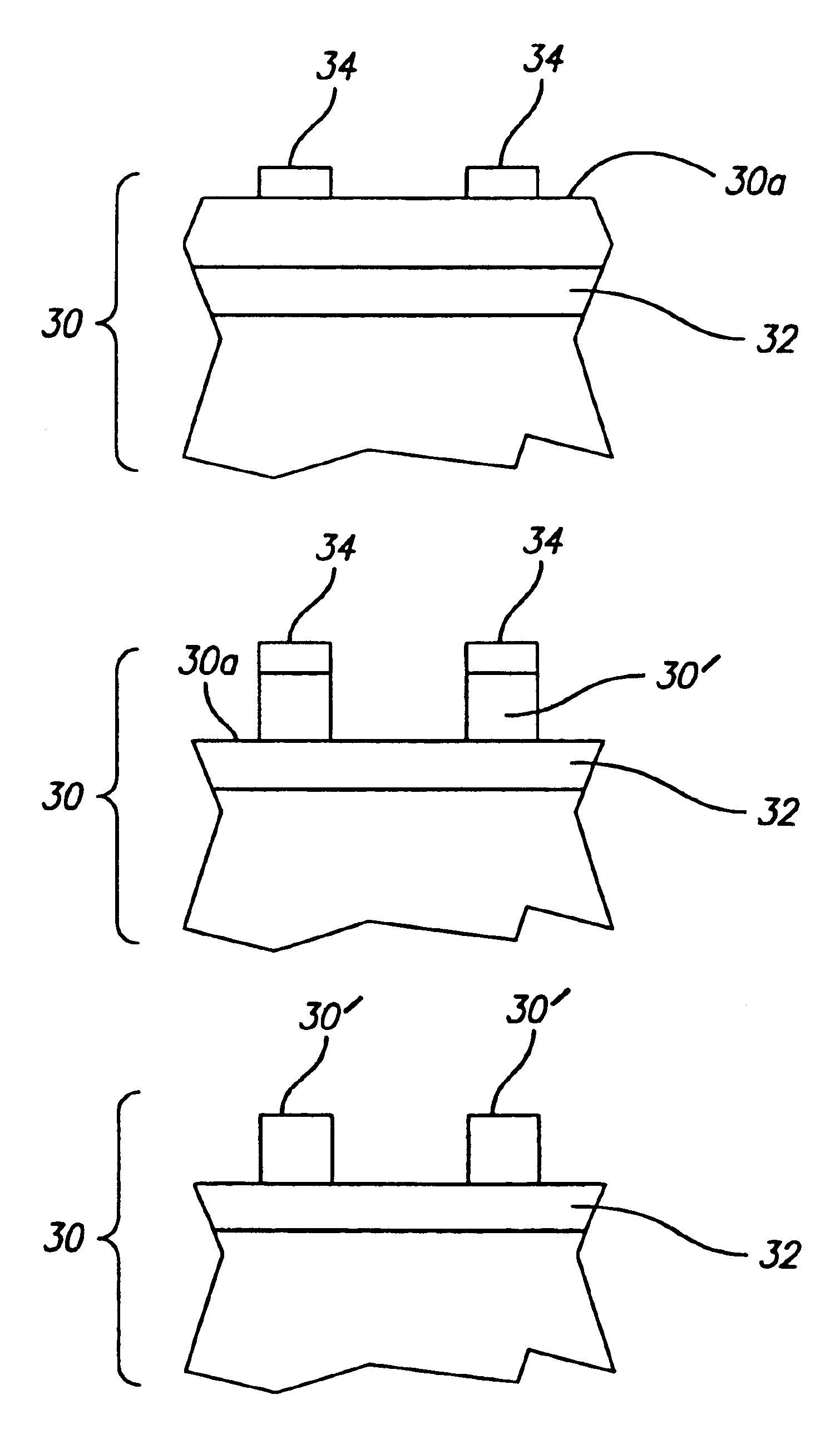
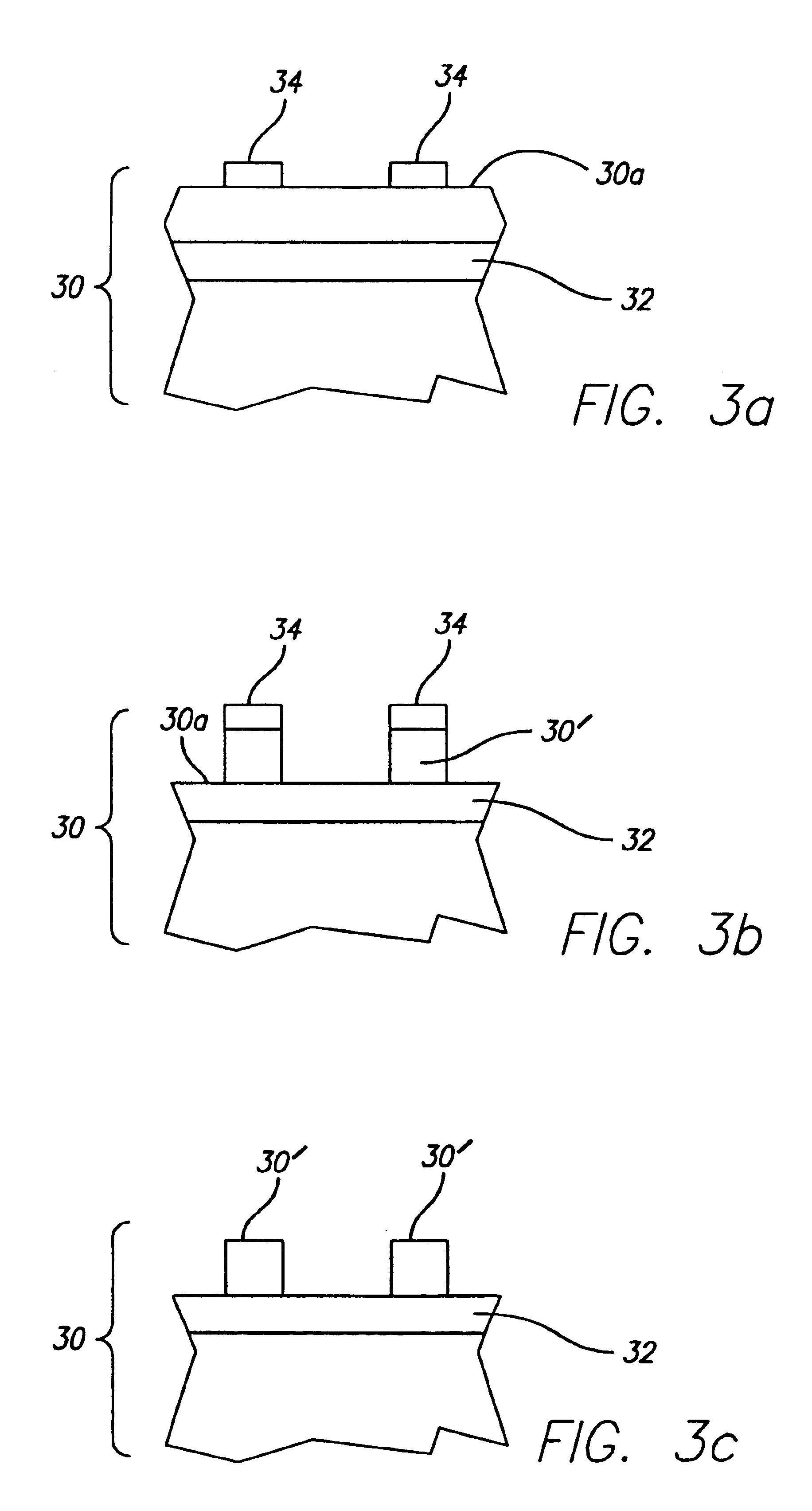
Method to increase electromigration resistance of copper using self-assembled organic thiolate monolayers
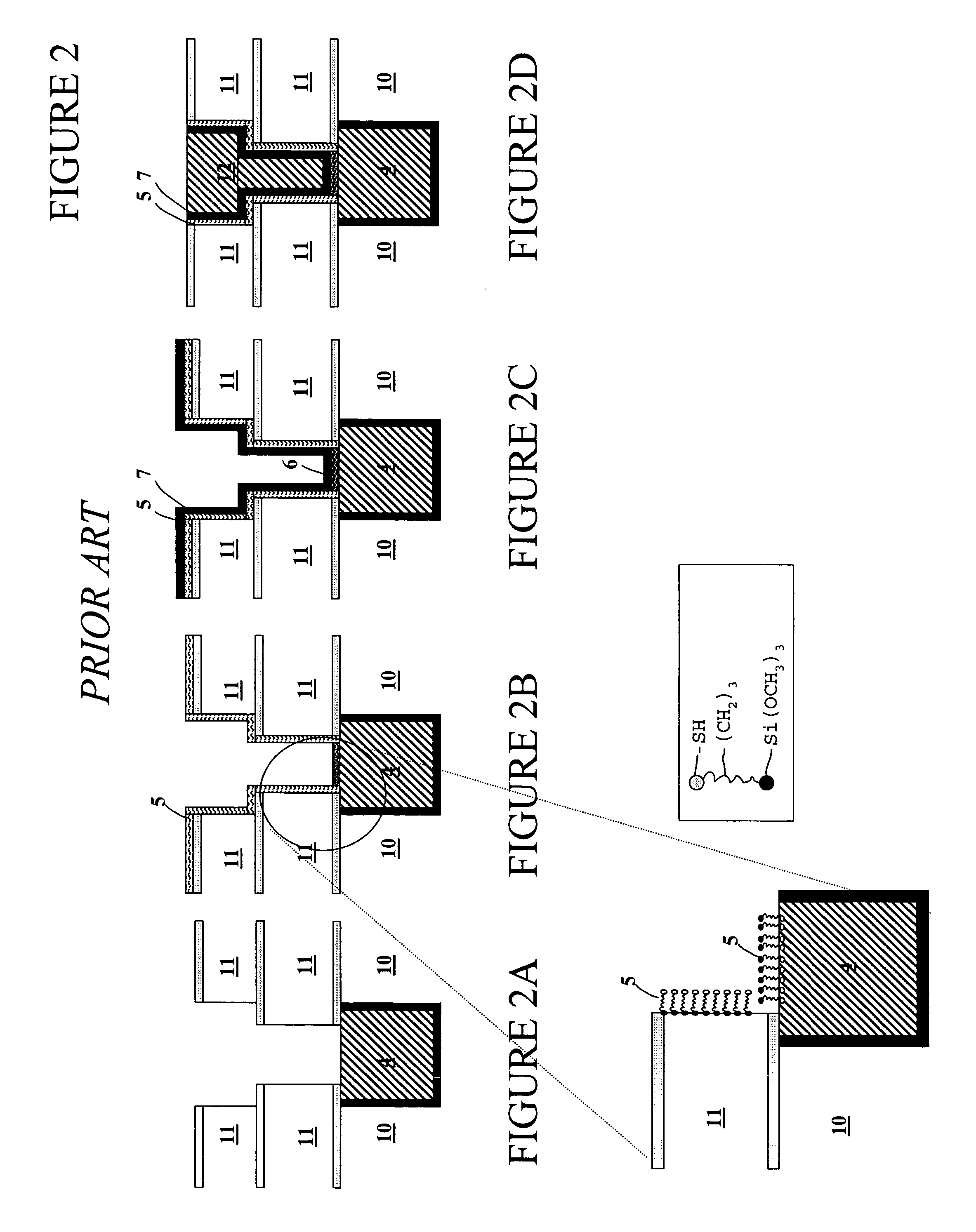
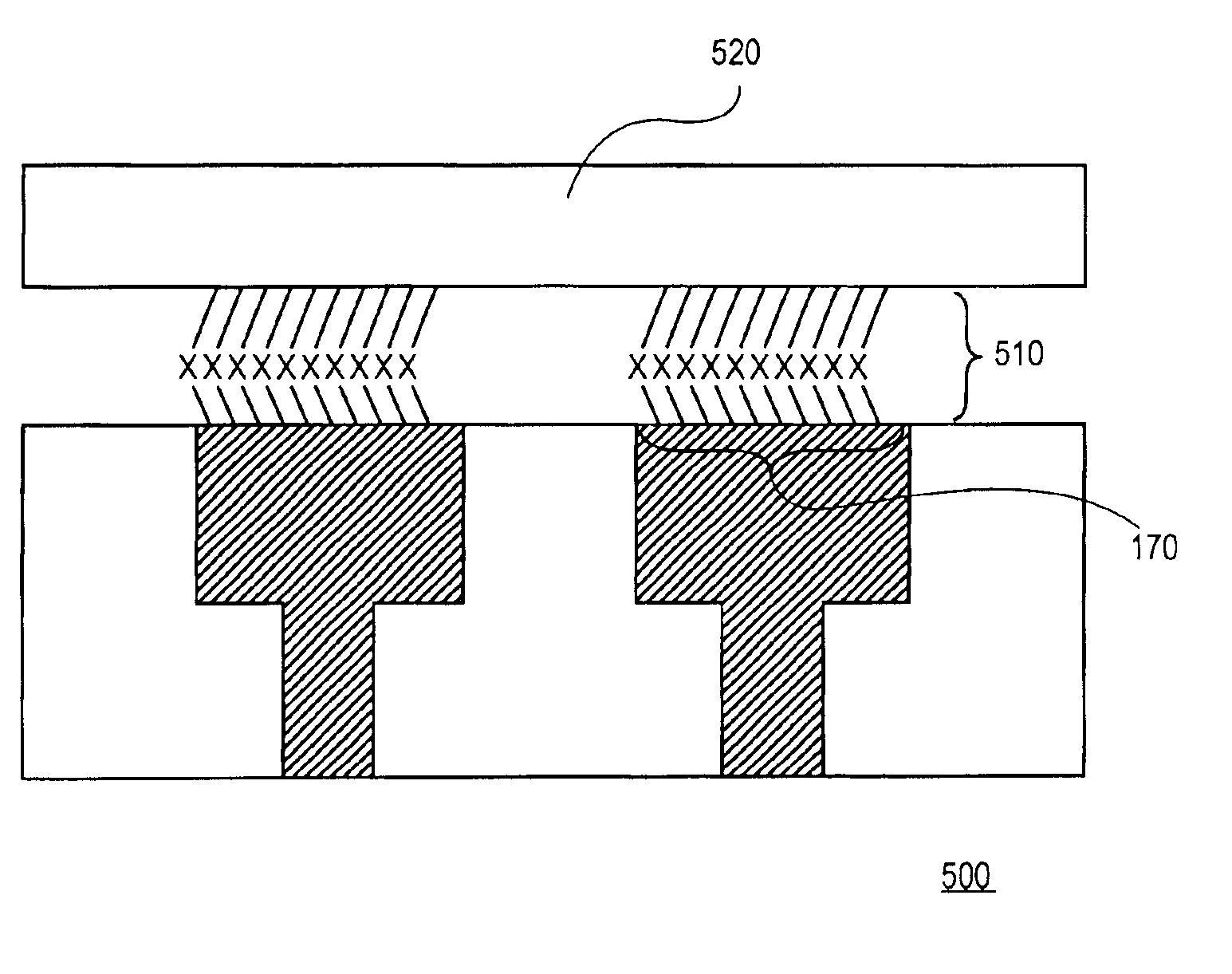
Methods and solutions for forming self assembled organic monolayers that are covalently bound to metal interfaces are presented along with a device containing a self assembled organic monolayer. Embodiments of the present invention utilize self assembled thiolate monolayers to prevent the electromigration and surface diffusion of copper atoms while minimizing the resistance of the interconnect lines. Self assembled thiolate monolayers are used to cap the copper interconnect lines and chemically hold the copper atoms at the top of the lines in place, thus preventing surface diffusion. The use of self assembled thiolate monolayers minimizes the resistance of copper interconnect lines because only a single monolayer of approximately 10 Å and 20 Å in thickness is used.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Orienting, positioning, and forming nanoscale structures
ActiveUS20080233343A1Material nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurface layerSelf assemble
Methods and a structure. A first film of a first block copolymer is formed inside a trough integrally disposed on an energetically neutral surface layer of a substrate. Line-forming microdomains are assembled of the first block copolymer, and form first self-assembled structures within the first film normal to the sidewalls and parallel to the surface layer. At least one microdomain is removed from the first film such that oriented structures remain in the trough oriented normal to the sidewalls and parallel to the surface layer. A second film of a second block copolymer is formed inside the trough. Line-forming microdomains are assembled of the second block copolymer, and form second self-assembled structures within the second film oriented normal to the oriented structures and parallel to the sidewalls. A second method and a structure are also provided.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method of positioning patterns from block copolymer self-assembly
InactiveUS7560141B1Material nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurface layerSelf assemble
A method of controlling both alignment and registration (lateral position) of lamellae formed from self-assembly of block copolymers, the method comprising the steps of obtaining a substrate having an energetically neutral surface layer comprising a first topographic “phase pinning” pattern and a second topographic “guiding” pattern; obtaining a self-assembling di-block copolymer; coating the self-assembling di-block copolymer on the energetically neutral surface to obtain a coated substrate; and annealing the coated substrate to obtain micro-domains of the di-block copolymer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for preparing silicon nano-pillar array based on nanosphere etching technology
InactiveCN102633230AQuality improvementHigh feasibilityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingNano structuringSelf assemble
A method for preparing a silicon nano-pillar array based on nanosphere etching technology relates to a Si nano-structure. The method comprises the following steps of: after cleaning a silicon slice, performing activation treatment on the silicon slice by means of a reactive ion etching system, thereby obtaining a silicon slice surface with hydrophilicity; self-assembling single-layer polystyrene nanospheres on a silicon substrate by a spin coating method; regulating and controlling the diameters of the single-layer polystyrene nanospheres by means of the reactive ion etching system, thereby obtaining the single-layer polystyrene nanospheres different in diameter; taking the single-layer polystyrene nanospheres as masks, performing etching by means of the masks and by inductively coupled plasma etching technology, and performing etching and sidewall protection by alternately using SF6 and C4F8; and removing the masks and by-products produced in the etching process by using an organic reagent, thus finally obtaining the silicon nano-pillar array.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fabrication method for arranging ultra-fine particles
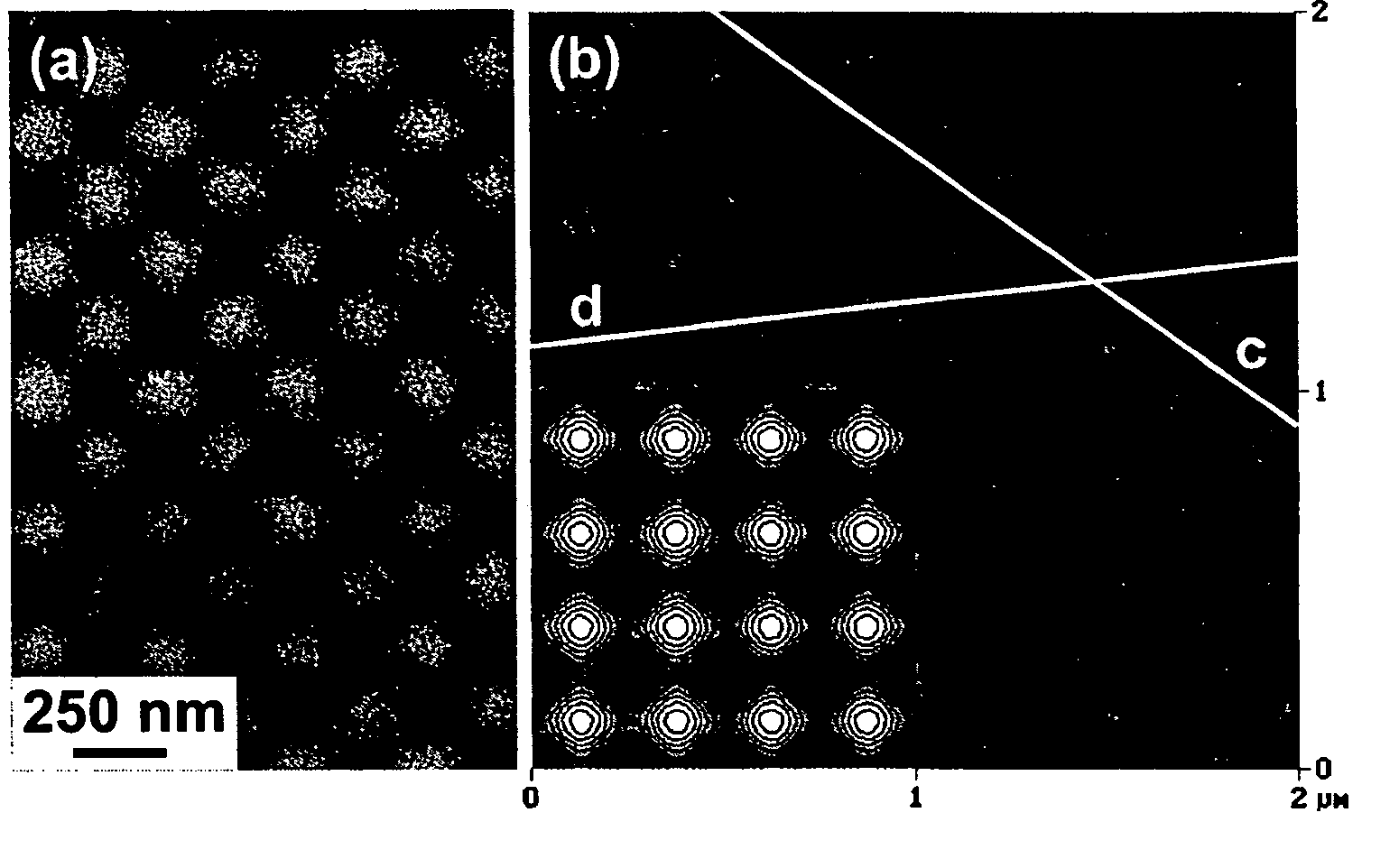
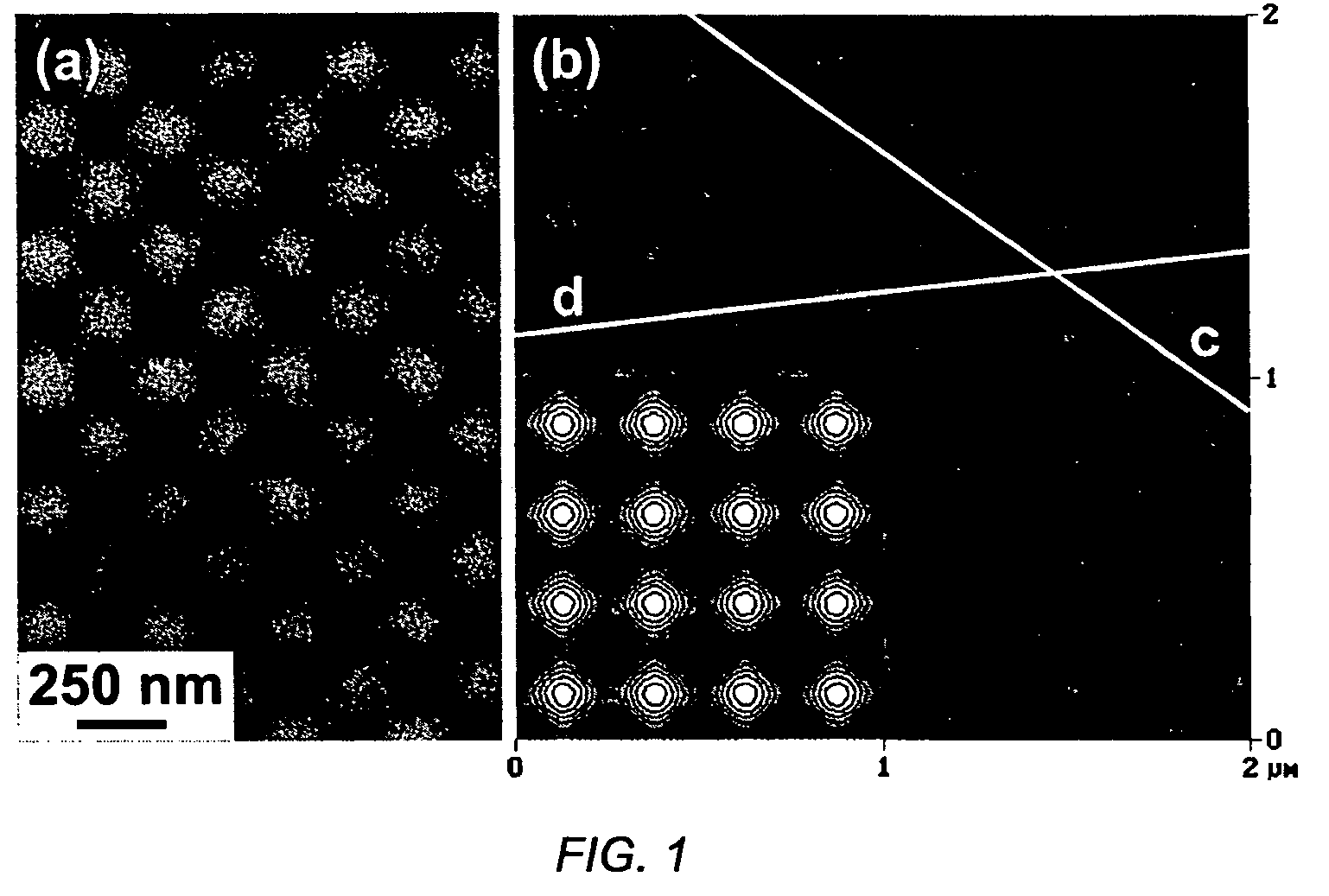
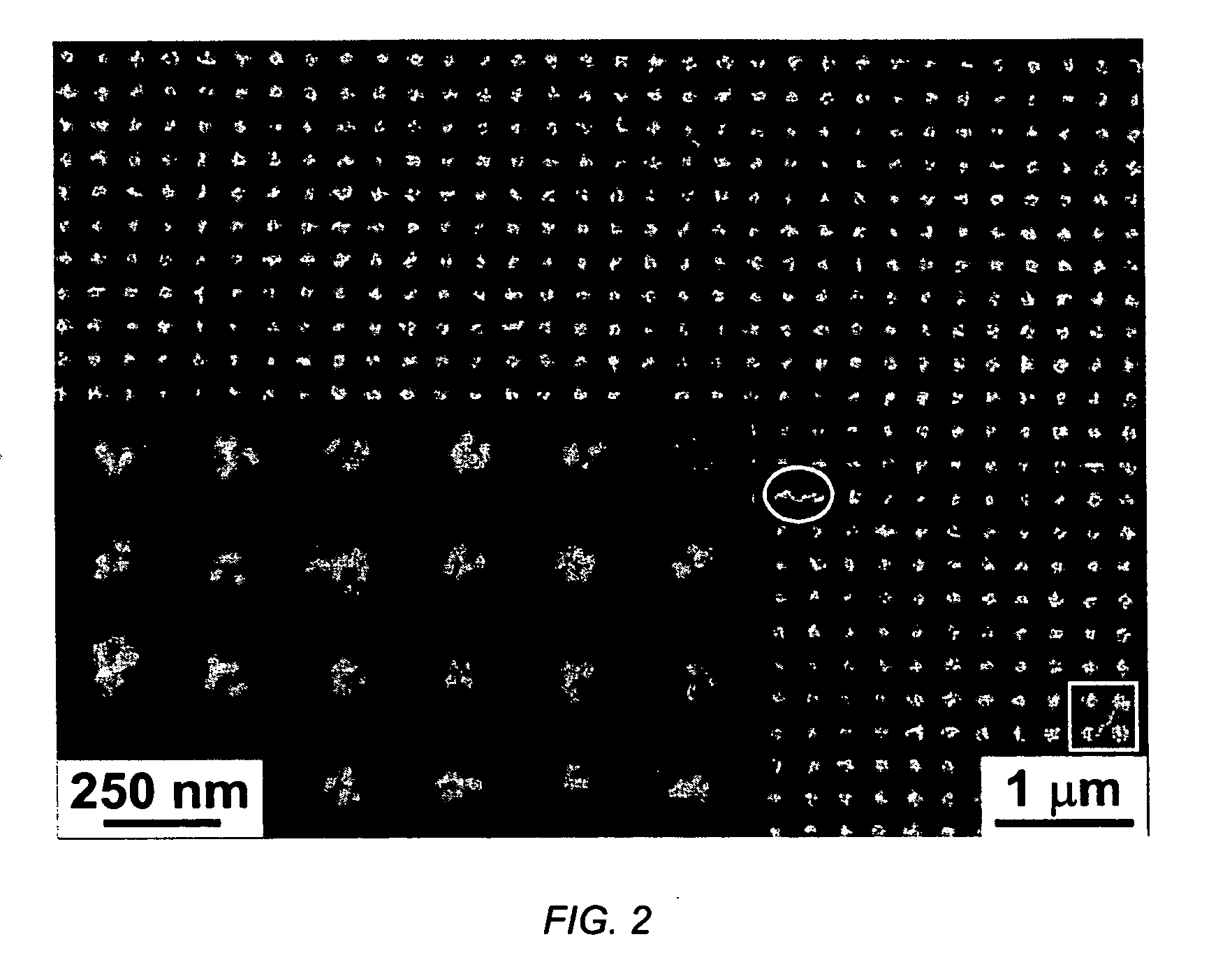
A method and resultant device, in which metal nanoparticles are self-assembled into two-dimensional lattices. A periodic hole pattern (wells) is fabricated on a photoresist substrate, the wells having an aspect ratio of less than 0.37. The nanoparticles are synthesized within inverse micelles of a polymer, preferably a block copolymer, and are self-assembled onto the photoresist nanopatterns. The nanoparticles are selectively positioned in the holes due to the capillary forces related to the pattern geometry, with a controllable number of particles per lattice point.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Graphoepitaxial self-assembly of arrays of downward facing half-cylinders
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Molecular imprinting photonic crystal for detecting glucose
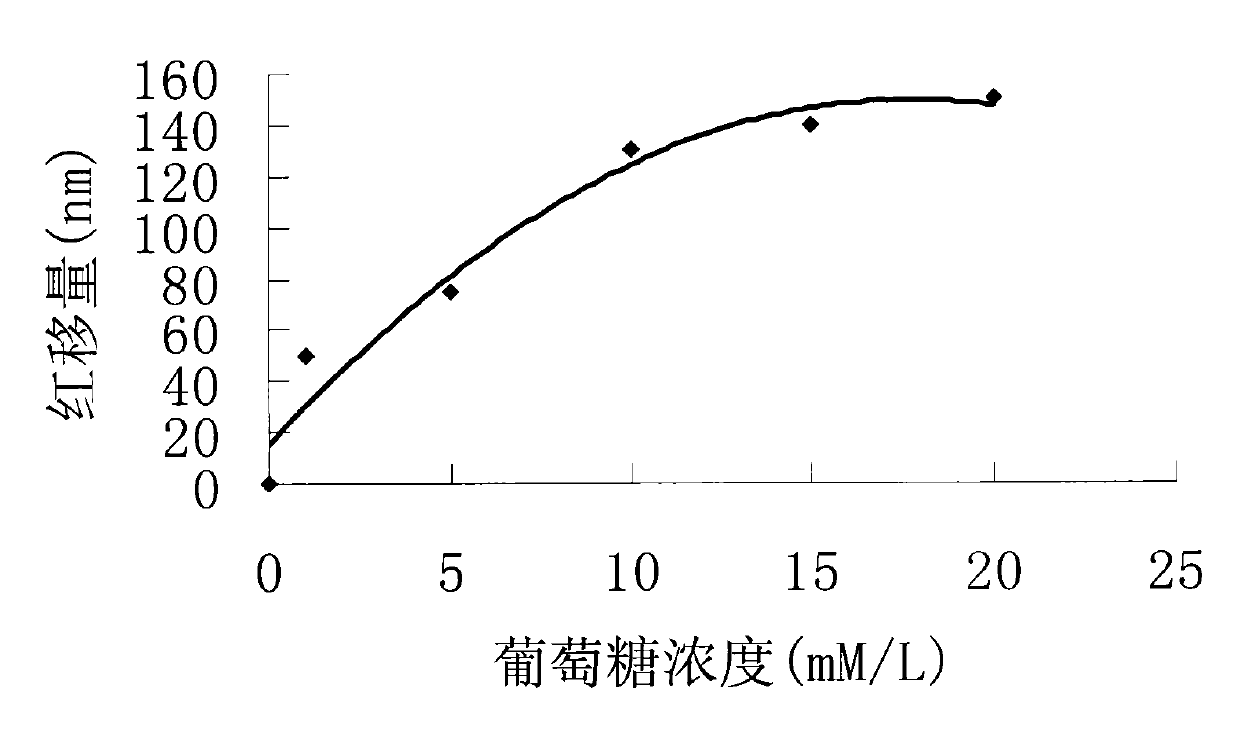
InactiveCN101793996ALarge redshiftReal-time detectionColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical light guidesPhotonic crystalSelf assemble
The invention relates to a molecular imprinting photonic crystal for detecting glucose, which belongs to the technical field of applied chemistry and clinical analysis test. A method comprises the following steps: firstly, inserting a substrate subjected to hydrophilic treatment into PMMA colloidal pellet solution, and self-assembling pellets on the substrate to obtain a three-dimensional photonic crystal template; secondly, dripping molecular imprinting pre-polymerization solution on the edge of the three-dimensional photonic crystal template, and thermally polymerizing the template; and finally, cleaning the glucose imprinting template to obtain a glucose molecular imprinting photonic crystal template. The molecular imprinting photonic crystal has specific glucose adsorption performance, enables direct observation of the change, and fulfills the aim of real-time, quick and convenient detection.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Amorphous silicon sensor with micro-spring interconnects for achieving high uniformity in integrated light-emitting sources
InactiveUS20030057533A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLaser arrayLed array
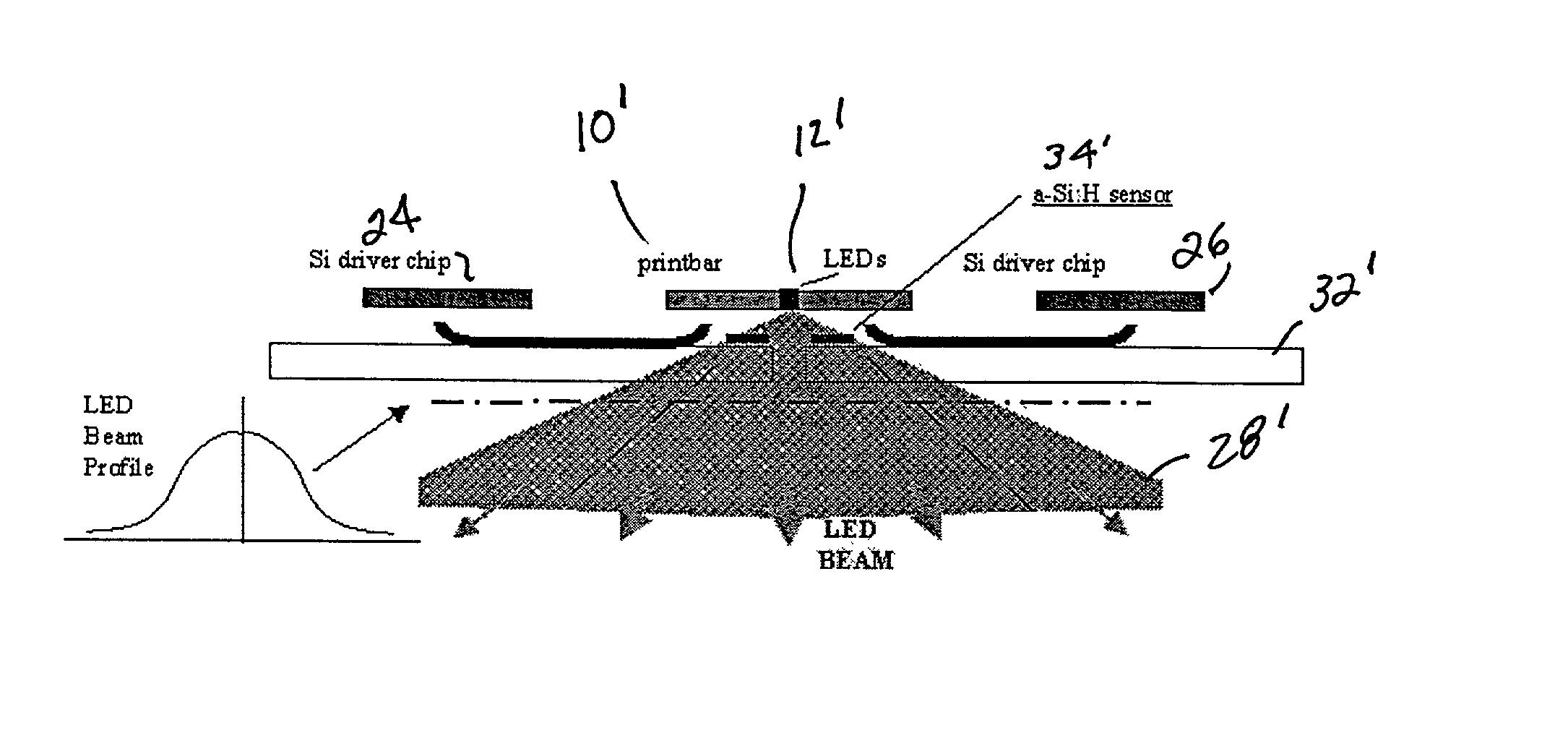
A hybrid structure or device is provided wherein carried on a single substrate is at least one micro-spring interconnect having an elastic material that is initially fixed to a surface of the substrate, an anchor portion which is fixed to the substrate surface and a free portion. The spring contact is self-assembling in that as the free portion is released it moves out of the plane of the substrate. Also integrated on the substrate is a sensor having an active layer and contacts. The substrate and sensor may be formed of materials which are somewhat partially transparent to light at certain infrared wavelengths. The integrated sensor / spring contact configuration may be used in an imaging system to sense output from a light source which is used for image formation. The light source may be a laser array, LED array or other appropriate light source. The sensor is appropriately sized to sense all or some part of light from the light source. The sensor may also be sufficiently transparent so that light is not blocked from its emission path, with a contrast ratio such that it only absorbs a small fraction of light passing therethrough. An additional characteristic is that the manufacturing process is compatible with the manufacturing process for the micro-spring interconnects. Data from the sensor is used as light source correction information. This information is provided to a calibration configuration which allows for calibration of high-speed systems.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Air gap structure having protective metal silicide pads on a metal feature
ActiveUS20090140428A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSalicideSelf assemble
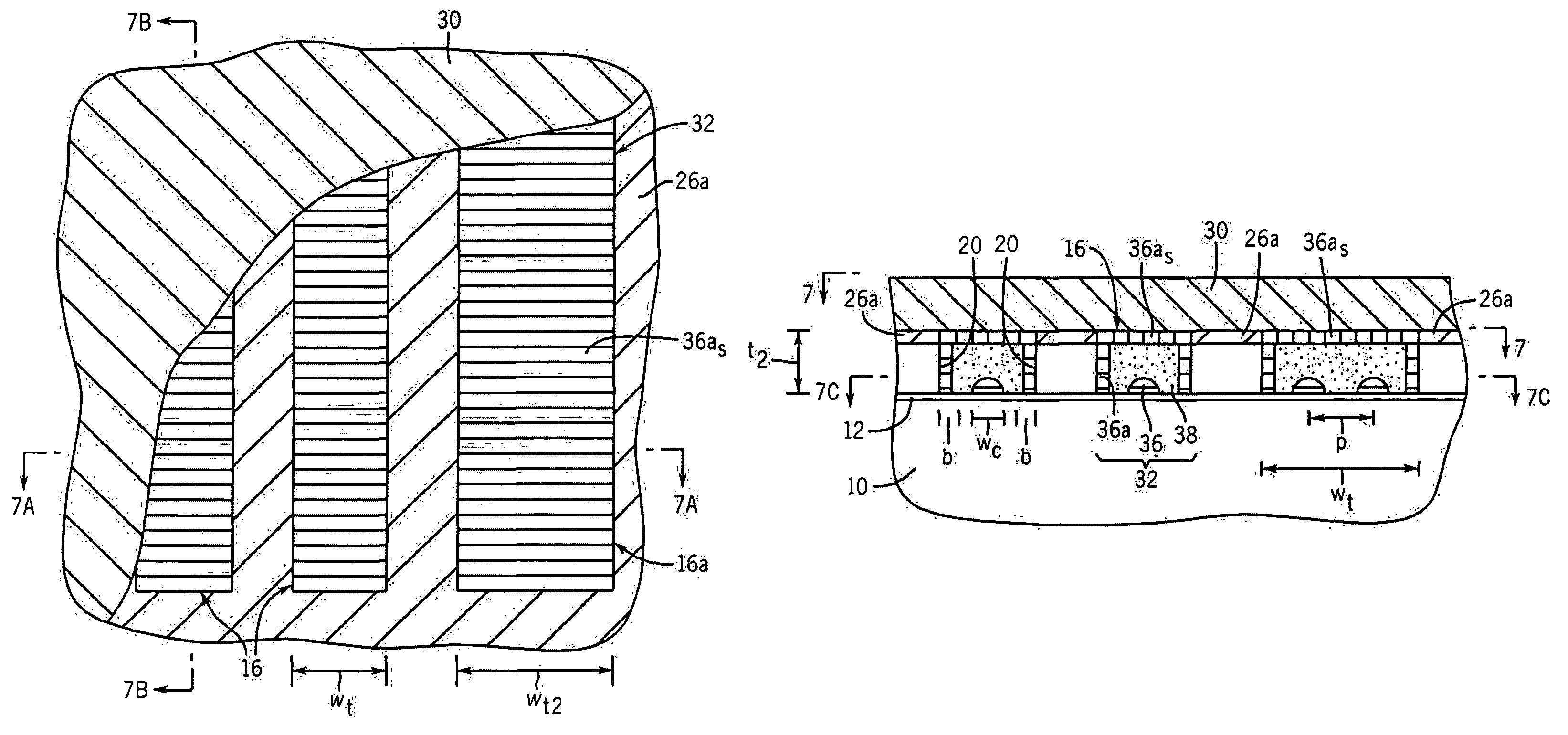
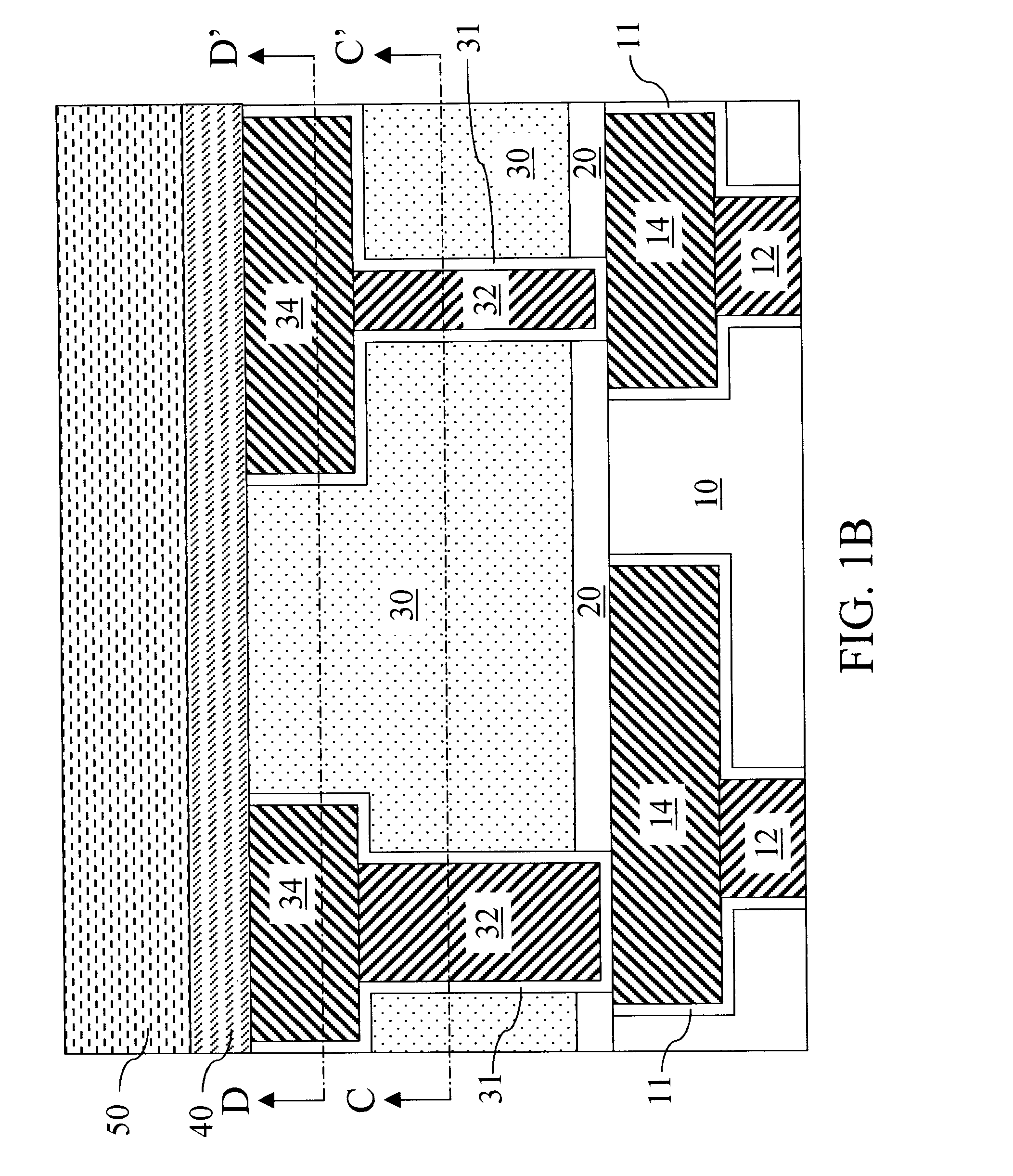
A hard mask is formed on an interconnect structure comprising a low-k material layer and a metal feature embedded therein. A block polymer is applied to the hard mask layer, self-assembled, and patterned to form a polymeric matrix of a polymeric block component and containing cylindrical holes. The hard mask and the low-k material layer therebelow are etched to form cavities. A conductive material is plated on exposed metallic surfaces including portions of top surfaces of the metal feature to form metal pads. Metal silicide pads are formed by exposure of the metal pads to a silicon containing gas. An etch is performed to enlarge and merge the cavities in the low-k material layer. The metal feature is protected from the etch by the metal silicide pads. An interconnect structure having an air gap and free of defects to surfaces of the metal feature is formed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for reducing tip-to-tip spacing between lines
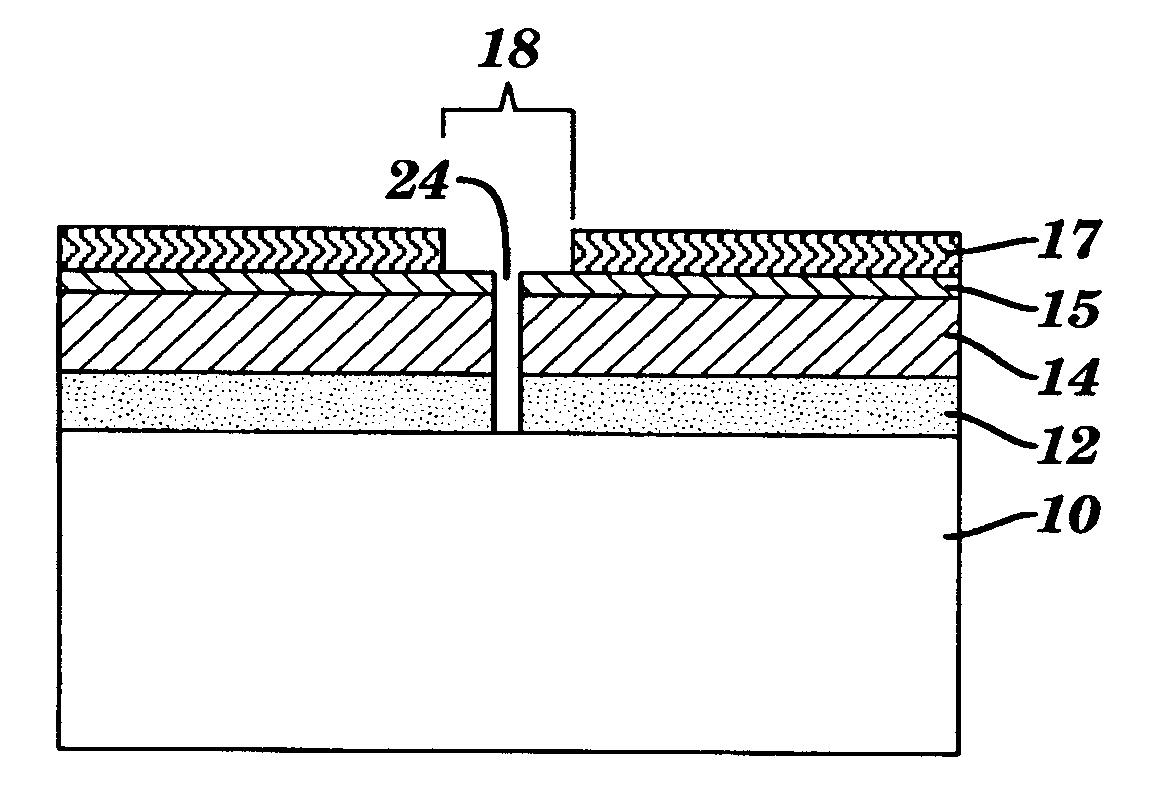
ActiveUS20100178615A1Reducing tip-to-tip spacingNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf assemblePhotolithography
This invention provides a method for reducing tip-to-tip spacing between lines using a combination of photolithographic and copolymer self-assembling lithographic techniques. A mask layer is first formed over a substrate with a line structure. A trench opening of a width d is created in the mask layer. A layer of a self-assembling block copolymer is then applied over the mask layer. The block copolymer layer is annealed to form a single unit polymer block of a width or a diameter w which is smaller than d inside the trench opening. The single unit polymer block is selectively removed to form a single opening of a width or a diameter w inside the trench opening. An etch transfer process is performed using the single opening as a mask to form an opening in the line structure in the substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
A method for preparing electrostatically self-assembled drug carried layer
The invention provides a method for preparing an electrostatically self-assembled drug carried layer. The method includes (1) performing surface modification pretreatment on a medical apparatus; (2) performing charge load surface pretreatment on the medical apparatus to form charge, which is the same to the charge carried by a first weak polyelectrolyte, on the surface of the medical apparatus; (3) preparing solution of a second weak polyelectrolyte and solution of a third weak polyelectrolyte, dissolving a drug in the second weak polyelectrolyte solution or the third weak polyelectrolyte solution; (4) soaking the medical apparatus with charge carried surface in the second weak polyelectrolyte solution, taking out, washing; (5) soaking the medical apparatus in the third weak polyelectrolyte solution, taking out, washing; and (6) repeating the step (4) and the step (5) alternately to form alternate electrostatically self-assembled drug carried layer with a desired drug density on the surface of the medical apparatus. The drug is included in the weak polyelectrolyte molecule layer.
Owner:LIFETECH SCIENTIFIC (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
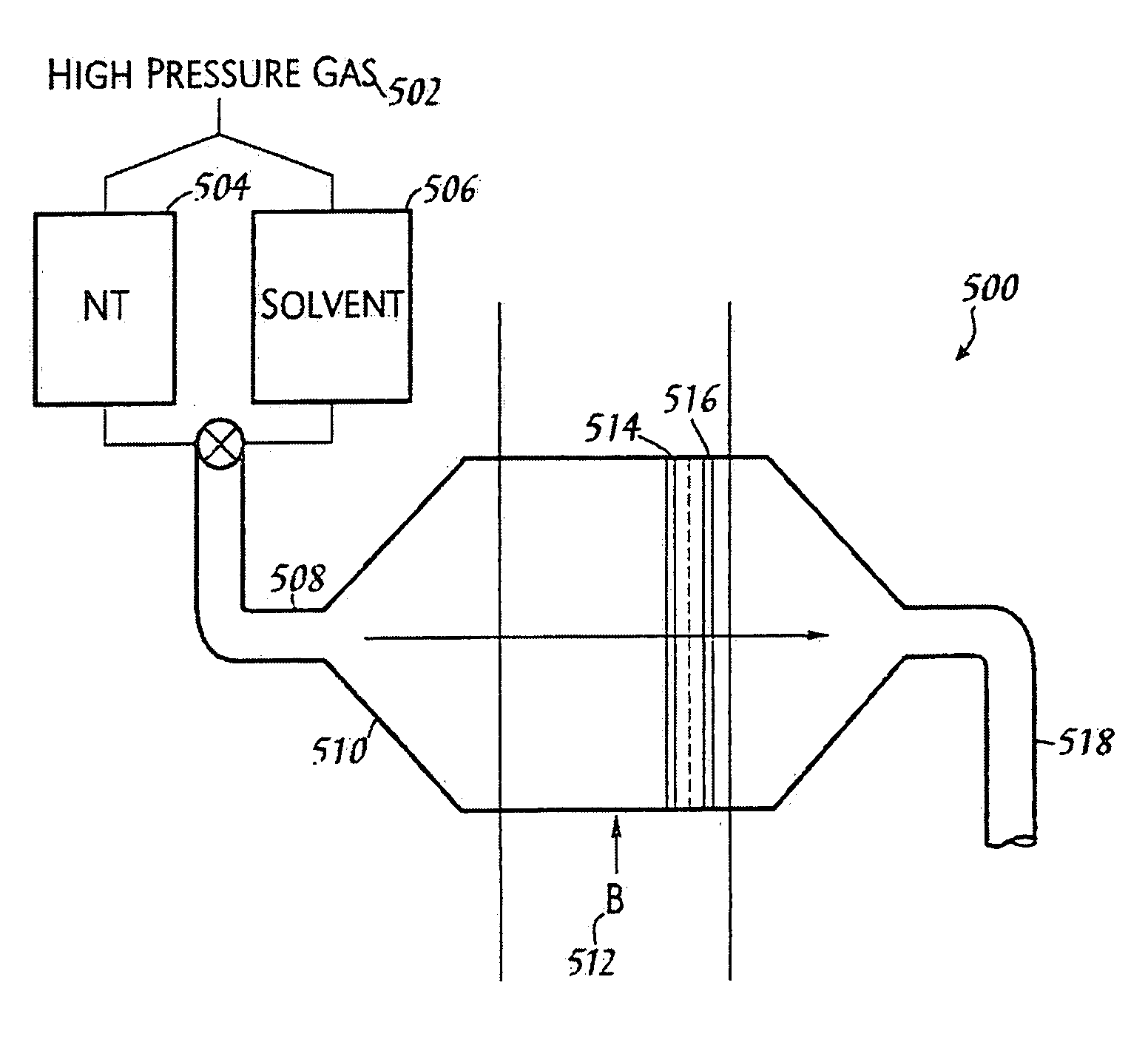
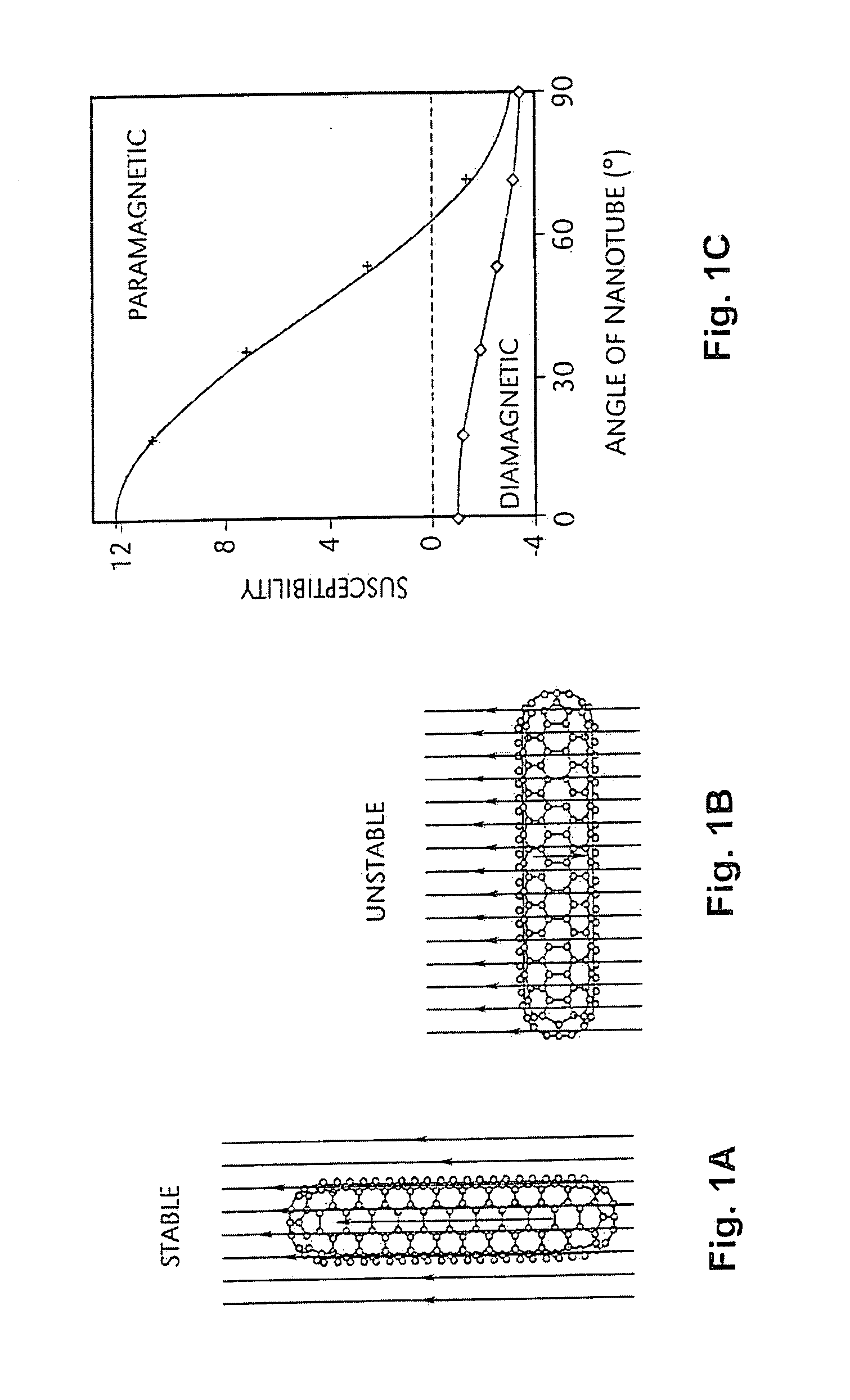
Macroscopic ordered assembly of carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20080210370A1Firmly assembledMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNear neighborMicroscopic scale
The present invention is directed to the creation of macroscopic materials and objects comprising aligned nanotube segments. The invention entails aligning single-wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) segments that are suspended in a fluid medium and then removing the aligned segments from suspension in a way that macroscopic, ordered assemblies of SWNT are formed. The invention is further directed to controlling the natural proclivity or nanotube segments to self assemble into or ordered structures by modifying the environment of the nanotubes and the history of that environment prior to and during the process. The materials and objects are “macroscopic” in that they are large enough to be seen without the aid of a microscope or of the dimensions of such objects. These macroscopic ordered SWNT materials and objects have the remarkable physical, electrical, and chemical properties that SWNT exhibit on the microscopic scale because they are comprised of nanotubes, each of which is aligned in the same direction and in contact with its nearest neighbors. An ordered assembly of closest SWNT also serves as a template for growth of more and larger ordered assemblies. An ordered assembly further serves as a foundation for post processing treatments that modify the assembly internally to specifically enhance selected material properties such as shear strength, tensile strength, compressive strength, toughness, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Nanoporous structures produced from self-assembling molecules
Methods for producing nanoporous structures are provided. In the subject methods, two or more, e.g., first and second, different types of self-assembling molecules are combined with each other under conditions sufficient to produce a composite ordered structure from the two or types of molecules. A feature of two or more molecules that are combined in this first step is that a portion of the molecules include cross-linking functionalities not found in the other portion of the molecules. The resultant self-assembled composite structure is then subjected to conditions sufficient for cross-linking of the portion of the molecules that includes the cross-linking functionalities to produce a stabilized composite structure. Finally, the remaining non-cross-linked molecules of the stabilized composite structure are separated from the stabilized composite structure to produce a nanoporous structure. Also provided are nanoporous structures produced according to the subject methods, articles of manufacture that include the same, as well as kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
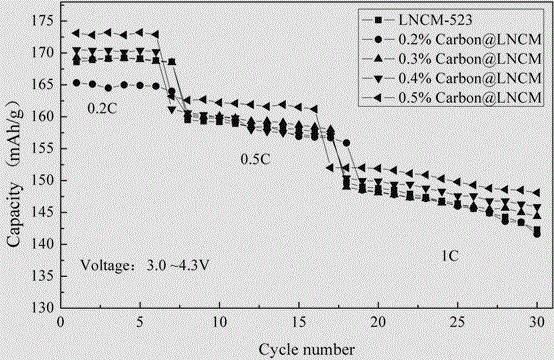
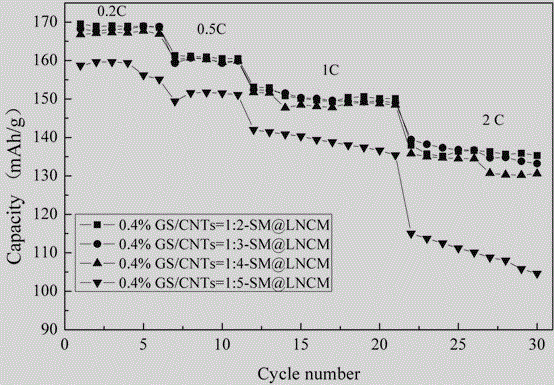
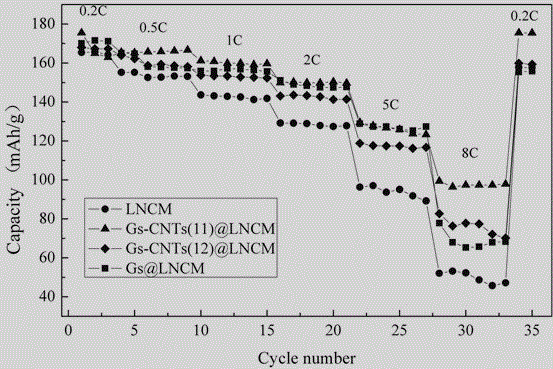
Coupled carbon nano tube-graphene composite three-dimensional network structure-coated ternary material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105070888AImprove conductivityIncrease the diffusion coefficientMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesManganeseCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to the technical field of battery materials, in particular to a coupled carbon nano tube-graphene composite three-dimensional network structure-coated ternary material and a preparation method thereof. According to the coupled carbon nano tube-graphene composite three-dimensional network structure-coated ternary material, a nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material, carbon nano tubes and graphene are taken as raw materials; and the ternary material is characterized by being prepared by the following steps: with polyvinyl pyrrolidone as a dispersing agent, through a liquid-phase self-assembling method, simultaneously connecting the graphene and the carbon nano tubes with a silane coupling agent to form a three-dimensional network structure; and evenly dispersing the coupled carbon nano tube-graphene composite material and the nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material through a physical method, coating the surface of the nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material, and sintering the nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary material in an inert atmosphere, so as to obtain the evenly coated product. The product provided by the invention has the advantages of high specific discharge capacity, long cycle life and simplicity in preparation process; and large-scale production is easy to realize.
Owner:SHANDONG YUHUANG NEW ENERGY TECH +1
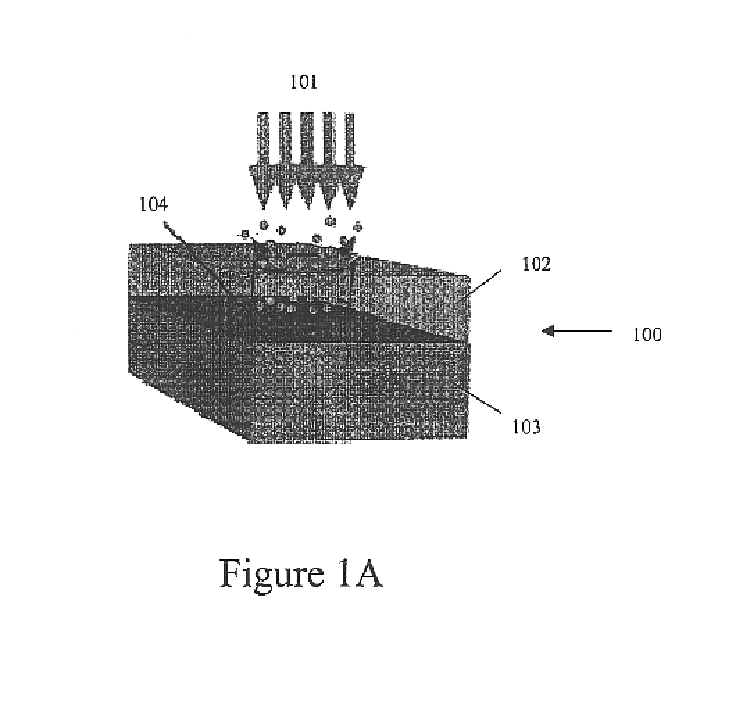
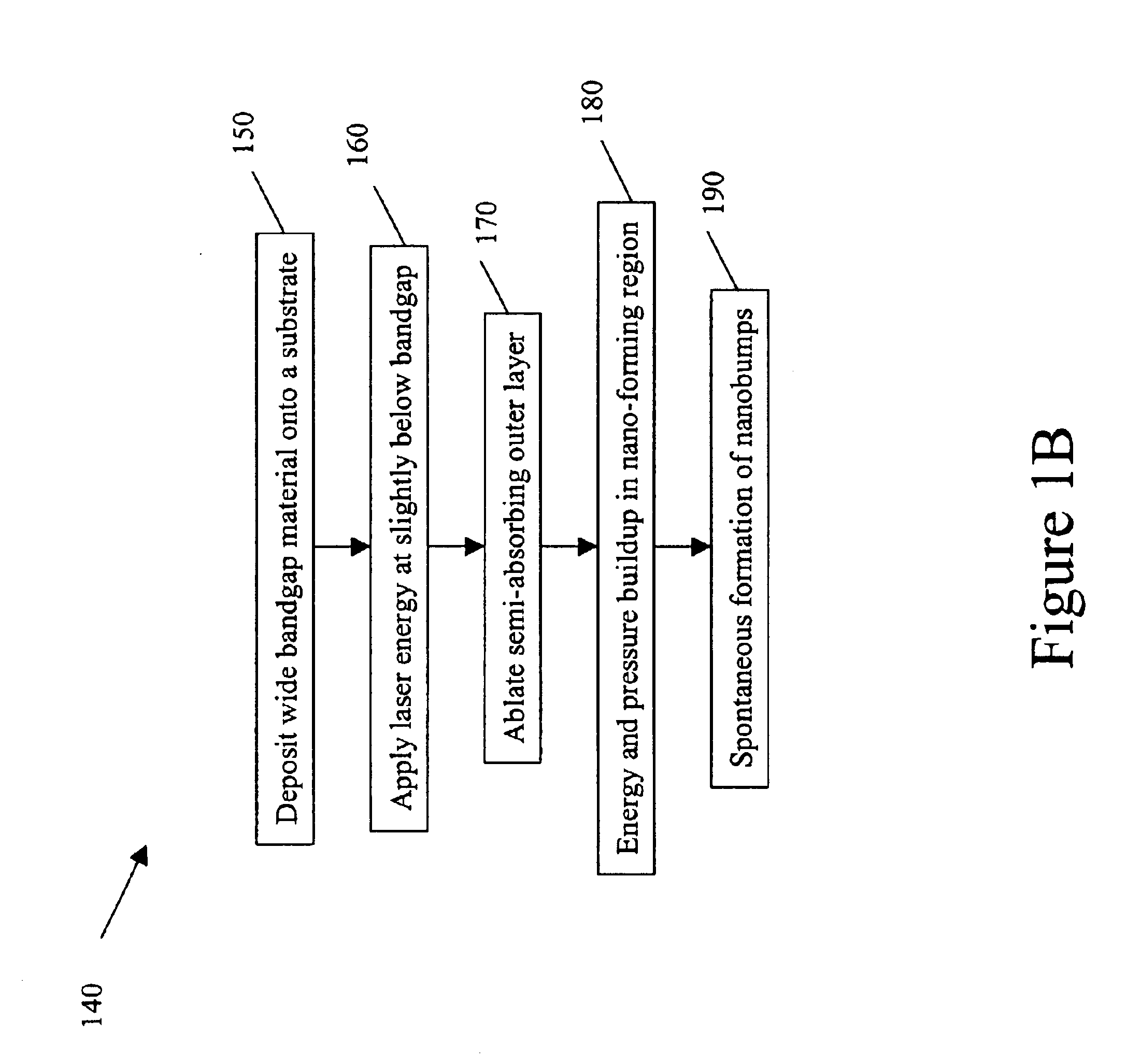
Self-assembled nanobump array stuctures and a method to fabricate such structures
InactiveUS6853075B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanomagnetismSelf assembleNanometre
A self-assembled nanobump array structure including a semi-absorbing outer layer provided on at least one nanobump-forming substrate layer, the semi-absorbing outer layer configured to ablate slowly to allow an applied laser energy to be transmitted to the at least one nanobump-forming substrate layer, in which the self-assembled nanobump array structure is formed by an energy and a pressure buildup occurring in the at least one nanobump-forming substrate layer.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
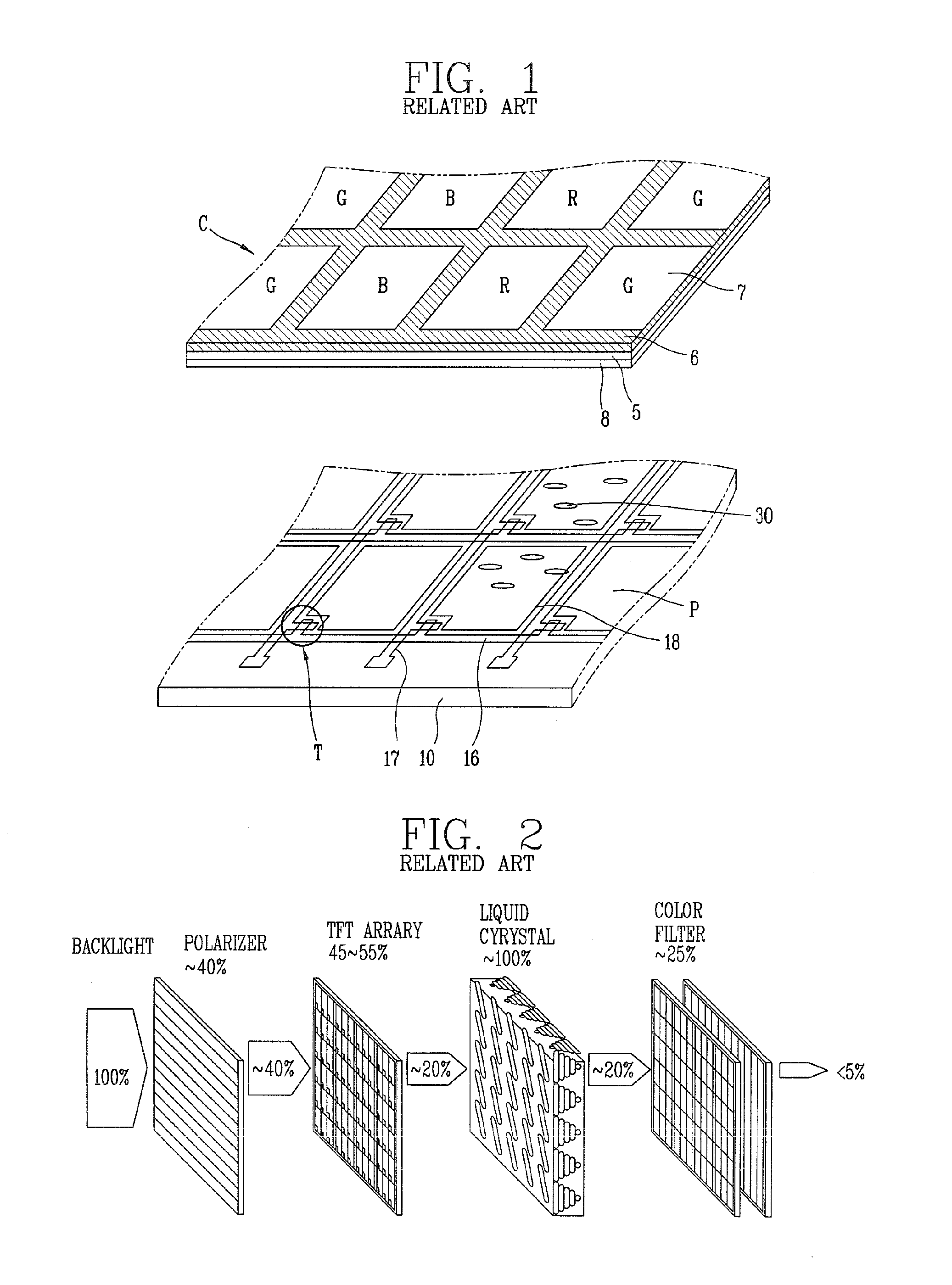
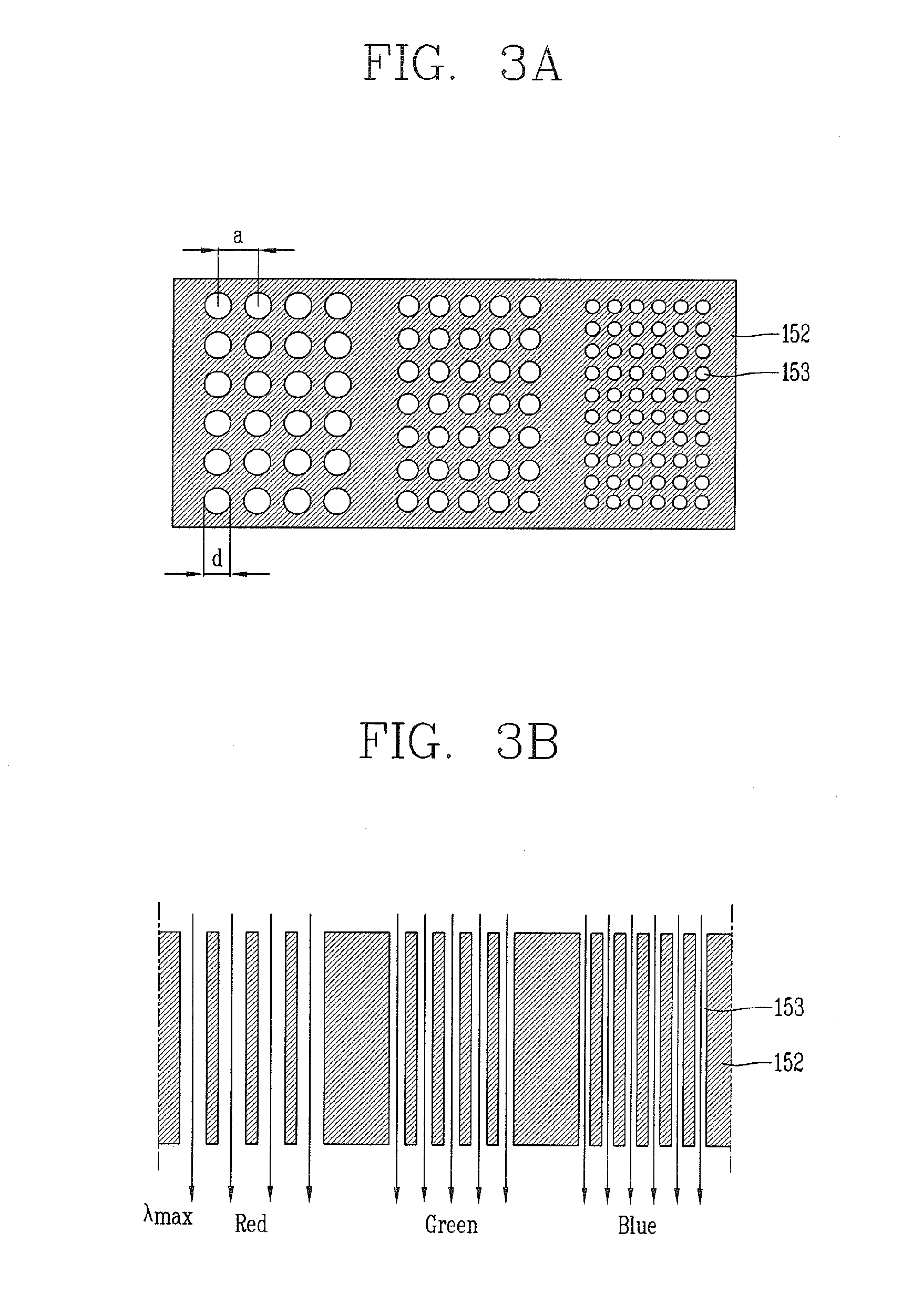
NANO patterning method and methods for fabricating surface plasmon color filter and liquid crystal display device using the same
ActiveUS20110269364A1Increase the aperture ratioEnhancing transmittance rateRecording apparatusDecorative surface effectsThiolLiquid-crystal display
Disclosed are a nano patterning method for fabricating a surface plasmon color filter having a transmissive pattern which selectively transmits light of specific wavelengths, and methods for fabricating a surface plasmon color filter and a liquid crystal display (LCD) device using the same. Used are a stamp which provides a partial electrification region, and a template, thiol-terminated nanospheres which can be self-assembled, thereby fabricating nano holes having a two-dimensional period and arranged in a hexagonal lattice. This may be applied onto a large area of a substrate, and may implement simplified processes and reduced fabrication costs.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
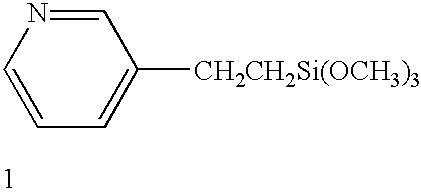
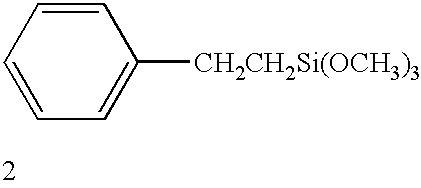
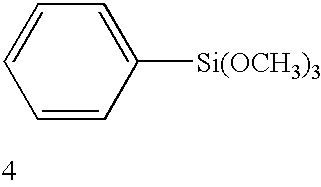
Self-assembled near-zero-thickness molecular layers as diffusion barriers for Cu metallization
InactiveUS20020105081A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDiffusionSelf assemble
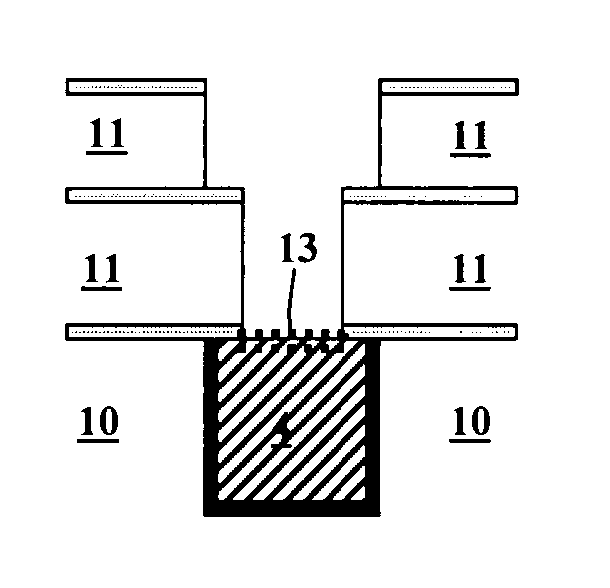
The present invention provides a diffusion barrier in an integrated circuit. The diffusion barrier comprises a self-assembled monolayer. The diffusion barrier is preferably less than 5 nm thick; more preferably it is less than 2 nm thick. The self-assembled monolayer typically contains an aromatic group at its terminus.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com