Patents
Literature
459 results about "Micrometer scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
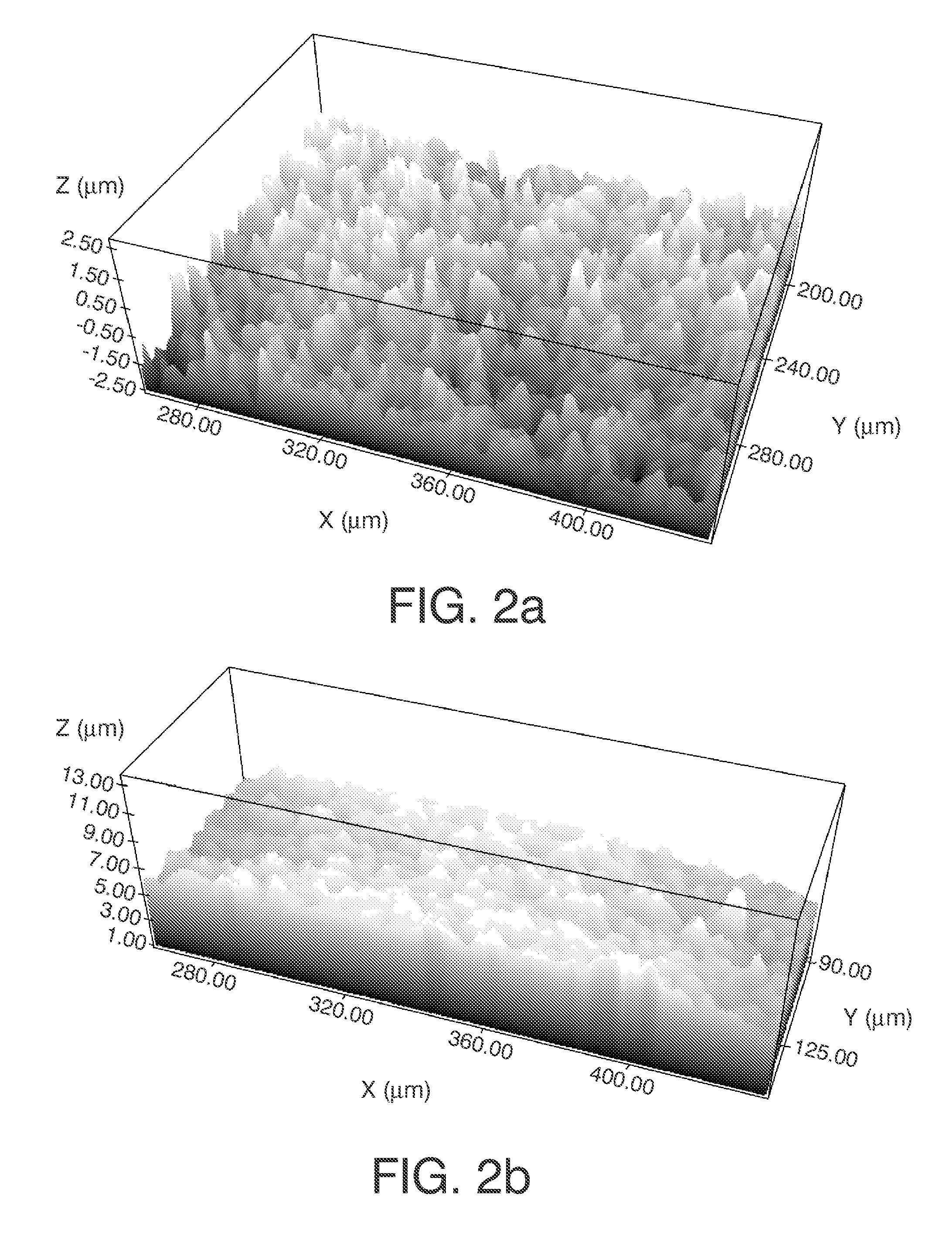
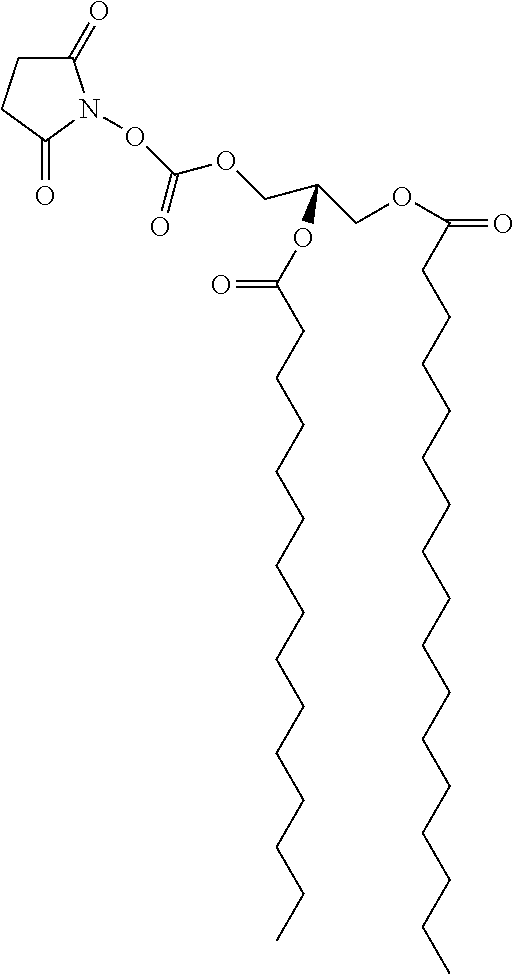
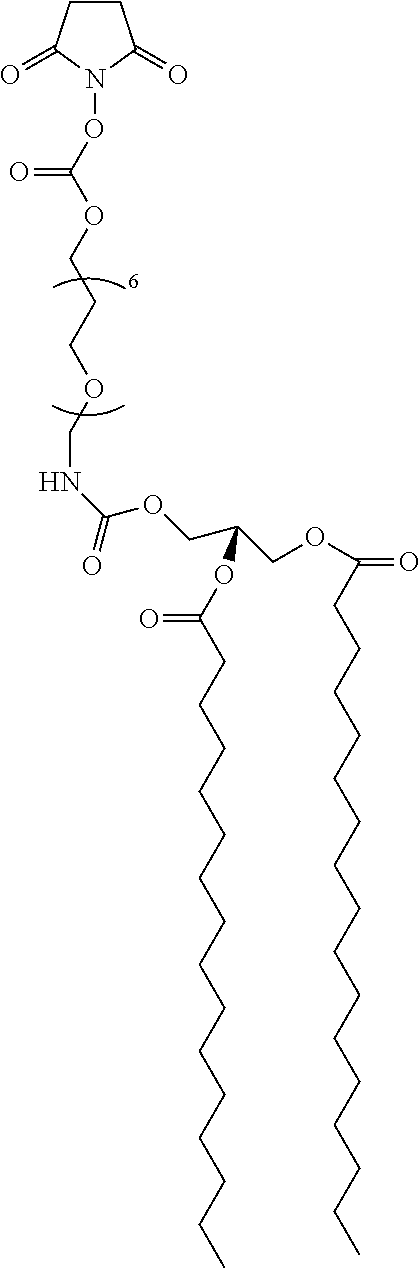
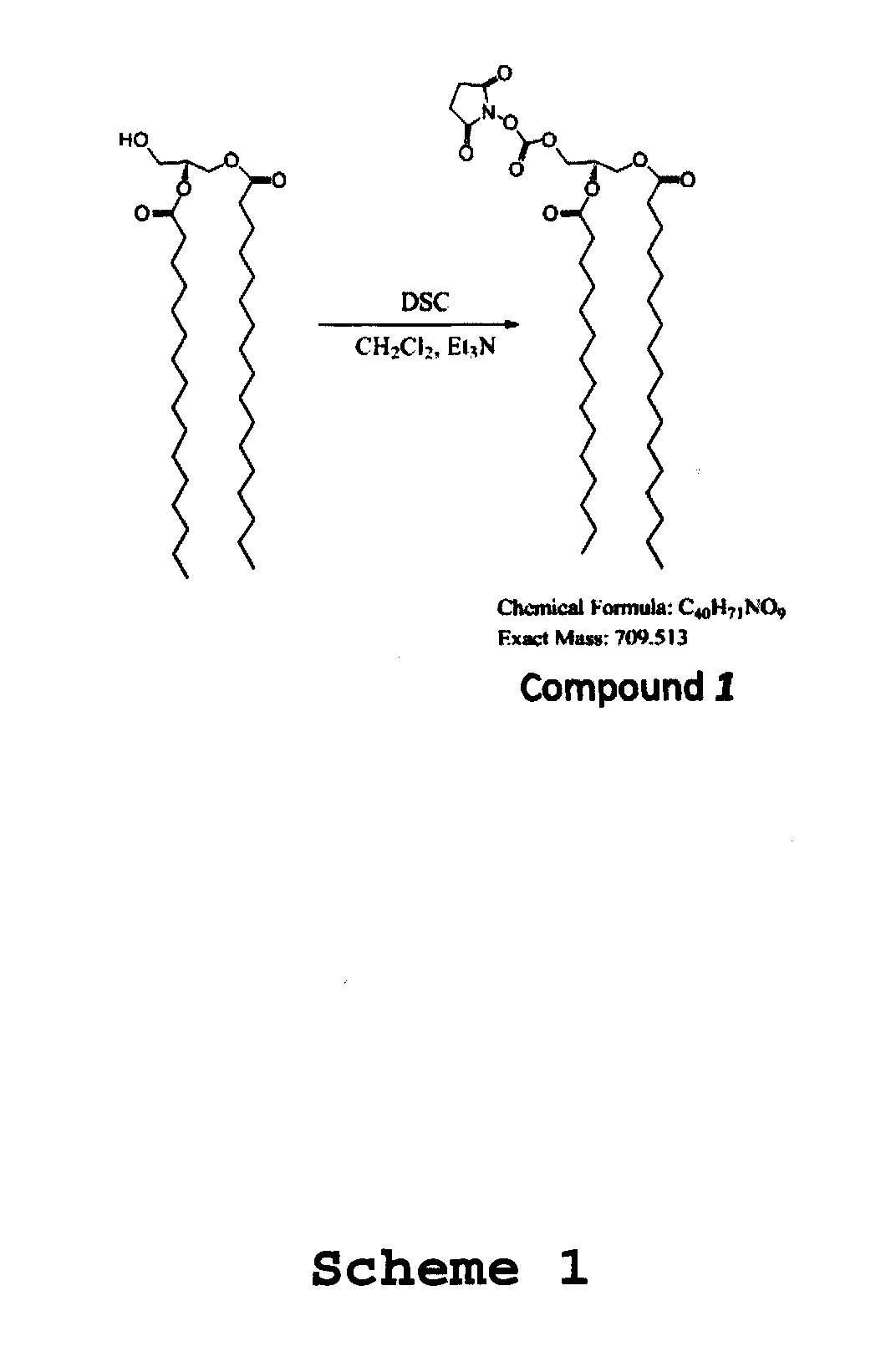
Micrometers have two scales: a primary scale, on the barrel or sleeve, and a secondary scale, on the thimble. Values are taken from each of these scales and combined to make the total measurement. A micrometer uses a calibrated screw or thread (found internally on the spindle) for measurement.
Apparatus and methods for plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of polymer coatings
Apparatuses and methods are described that involve the deposition of polymer coatings on substrates. The polymer coatings generally comprise an electrically insulating layer and / or a hydrophobic layer. The hydrophobic layer can comprise fused polymer particles have an average primary particle diameter on the nanometer to micrometer scale. The polymer coatings are deposited on substrates using specifically adapted plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition approaches. The substrates can include computing devices and fabrics.
Owner:LIQUIPEL IP
Formation of nanoscale wires
InactiveUS6773616B1Improve crystal qualityMinimizes environmental toxic chemicals usageNanotechPolycrystalline material growthNanowireMicrometer scale
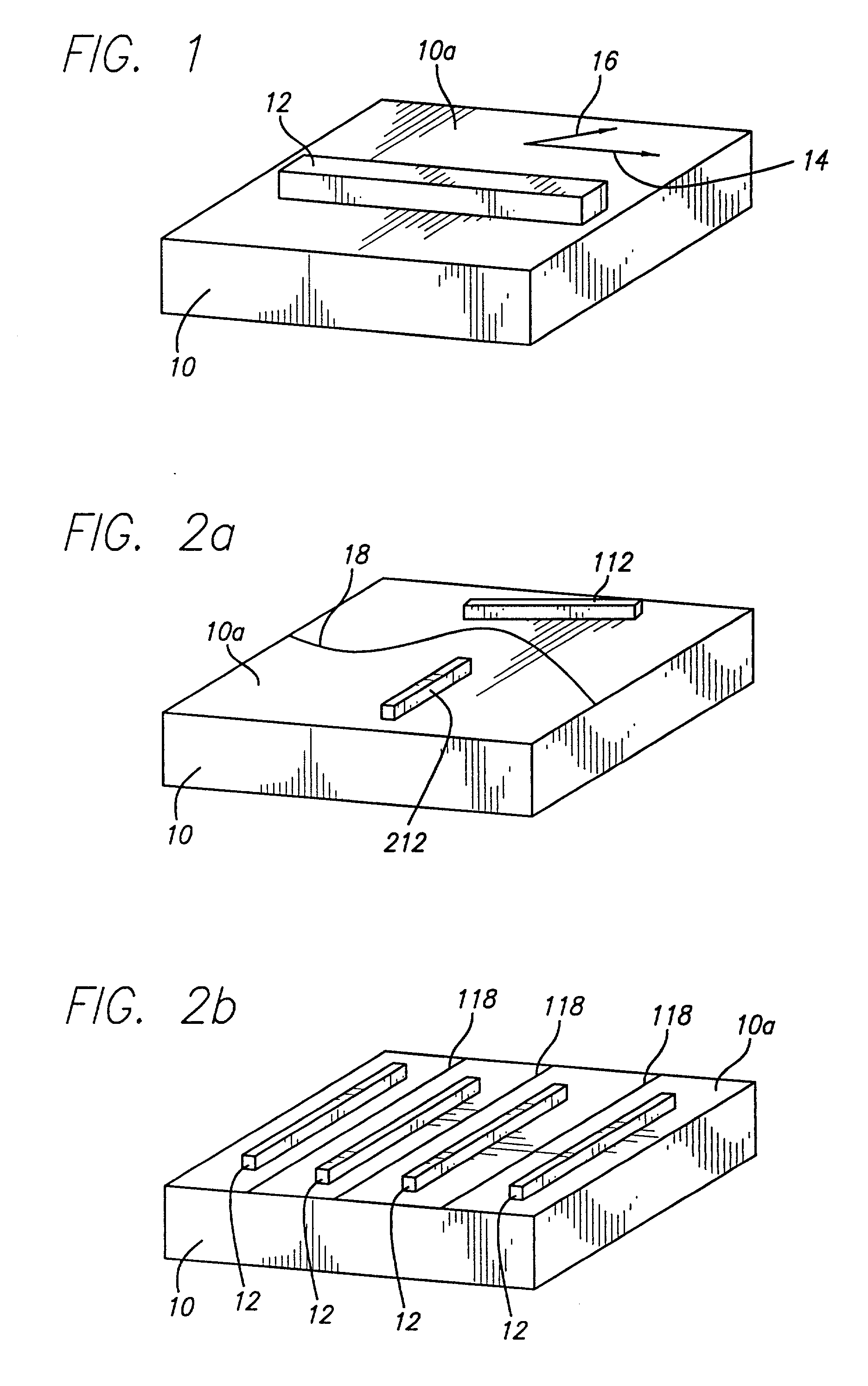
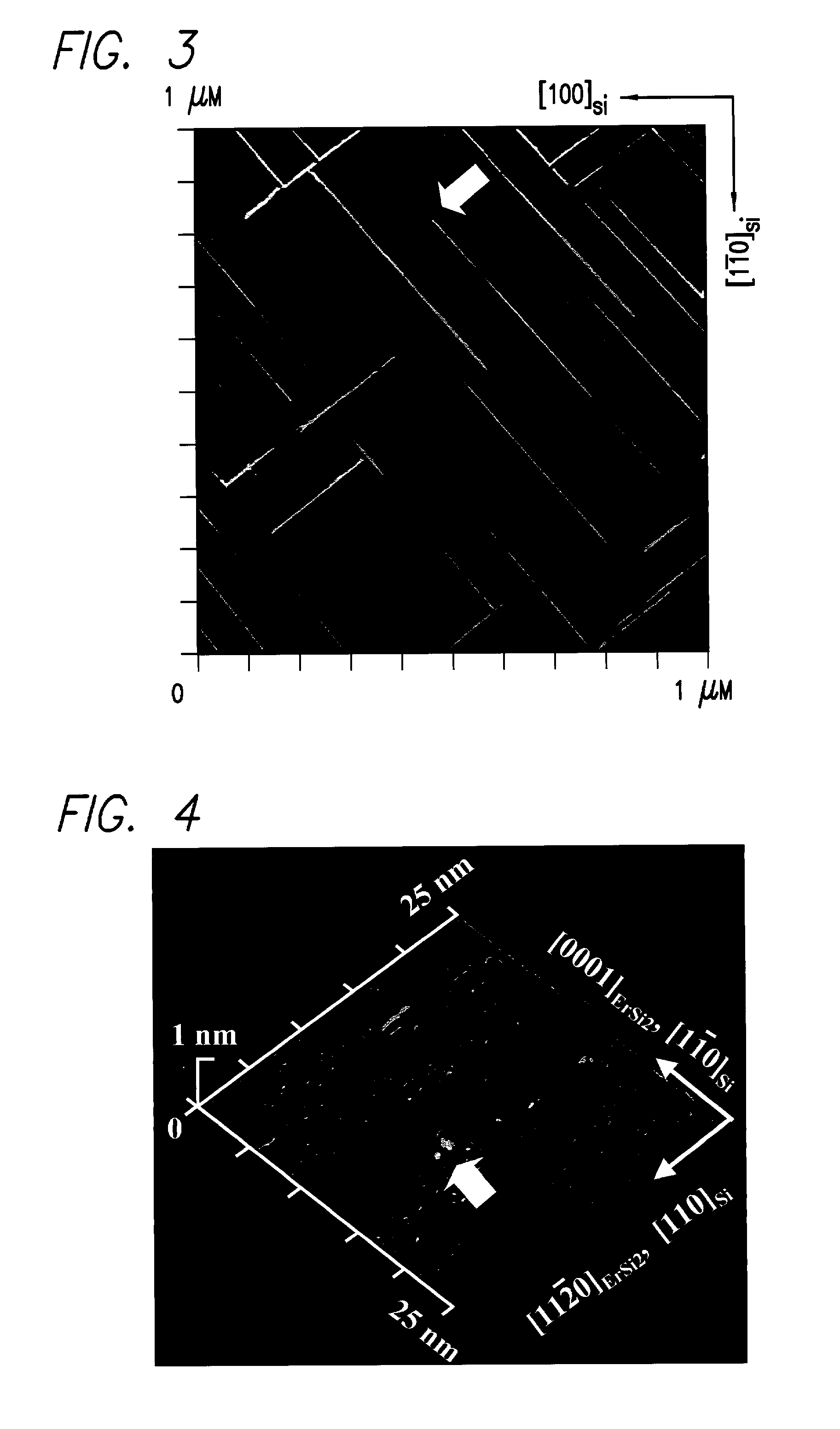
Self-organized, or self-assembled, nanowires of a first composition may be used as an etching mask for fabrication of nanowires of a second composition. The method for forming such nanowires comprises: (a) providing an etchable layer of the second composition and having a buried insulating layer beneath a major surface thereof; (b) growing self-assembled nanowires on the surface of the etchable layer; and (c) etching the etchable layer anisotropically down to the insulating layer, using the self-assembled nanowires as a mask. The self-assembled nanowires may be removed or left. In either event, nanowires of the second composition are formed. The method enables the formation of one-dimensional crystalline nanowires with widths and heights at the nanometer scale, and lengths at the micrometer scale, which are aligned along certain crystallographic directions with high crystal quality. Further, the method of the present invention avoids traditional lithography methods, minimizes environmental toxic chemicals usage, simplifies the manufacturing processes, and allows the formation of high-quality one-dimensional nanowires over large areas.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Nanoporous inorganic membranes and films, methods of making and usage thereof
InactiveUS20110139707A1Easy to integrateWell knownSemi-permeable membranesPaper/cardboard articlesMicrometer scaleIrradiation
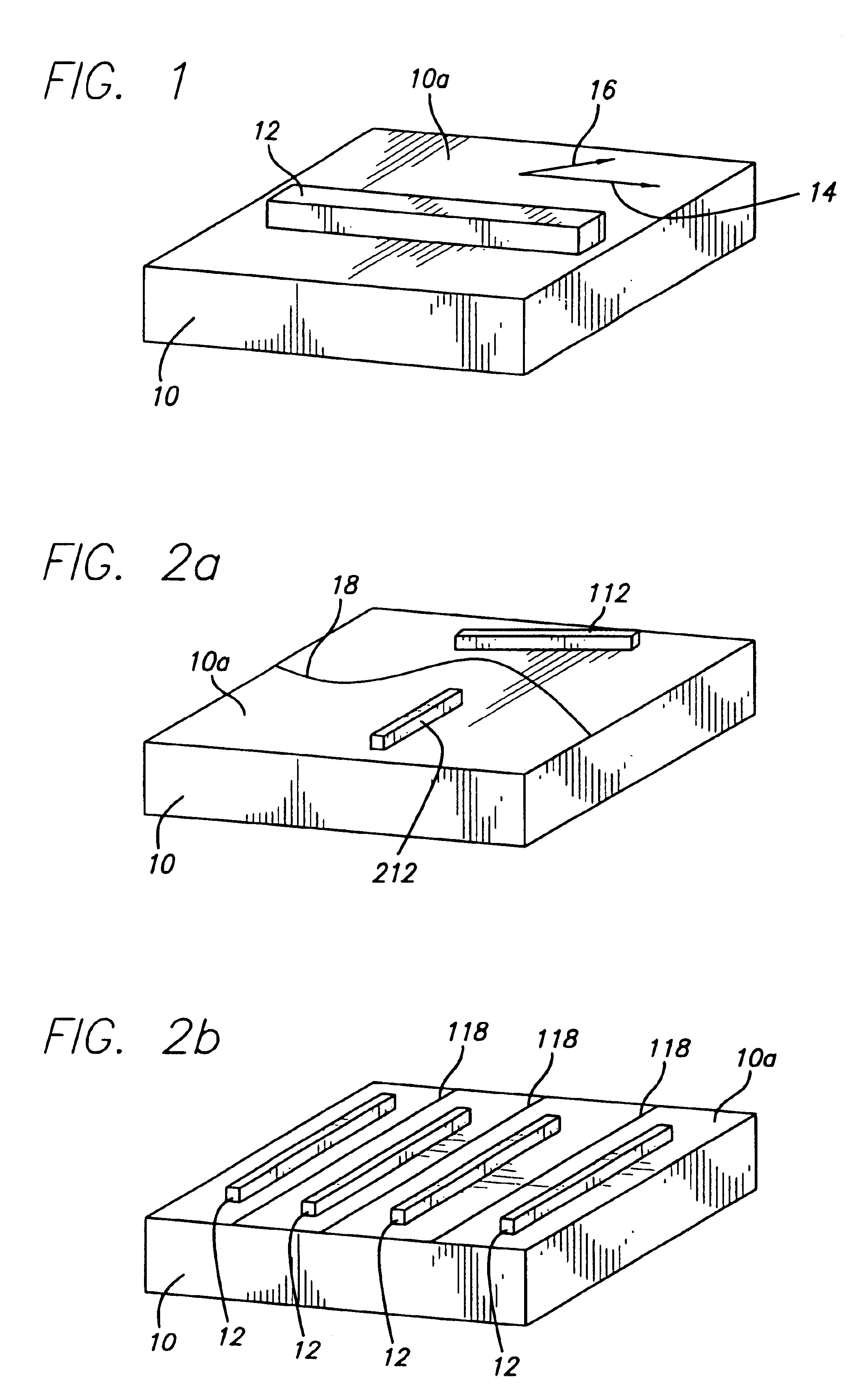
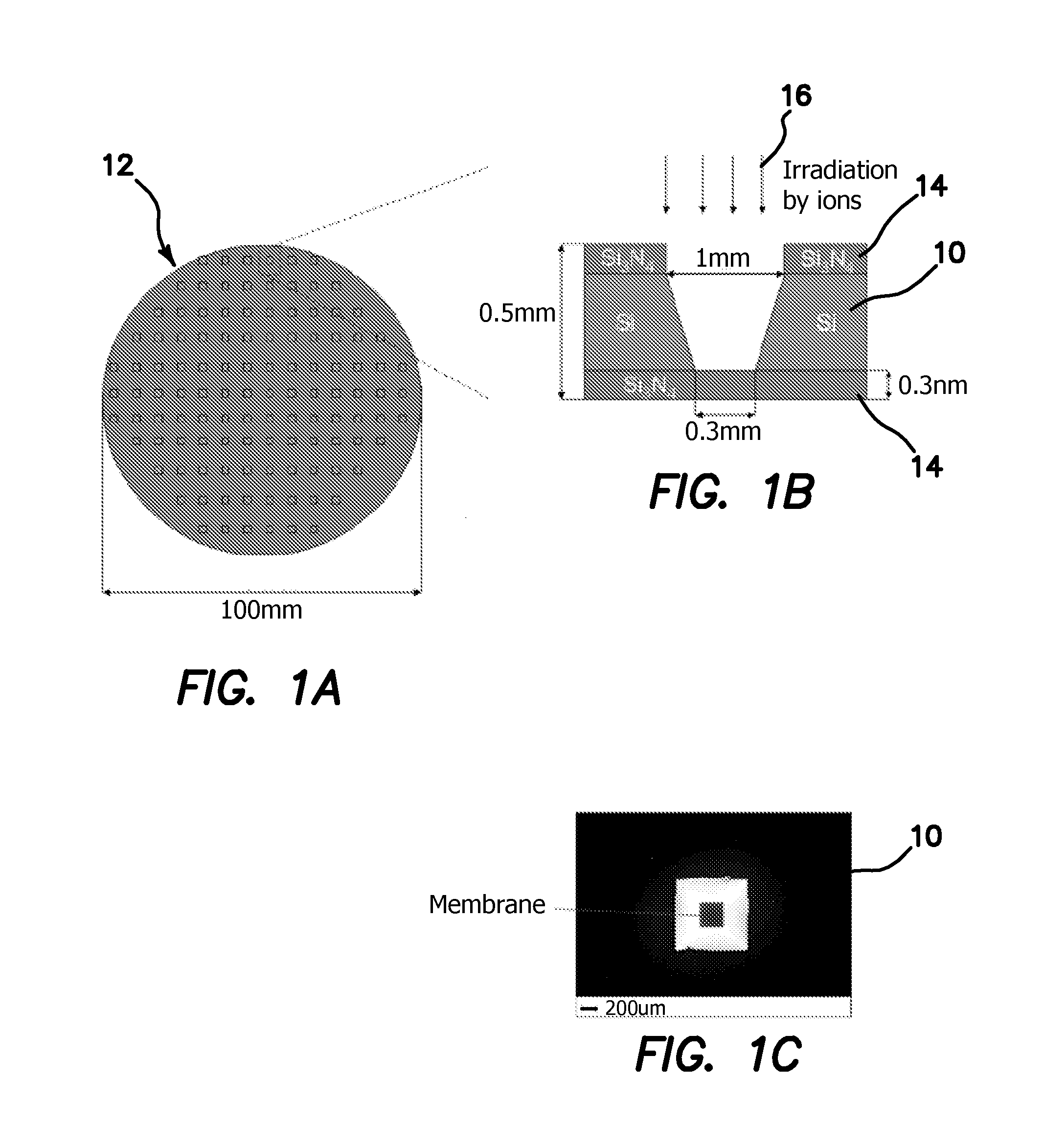
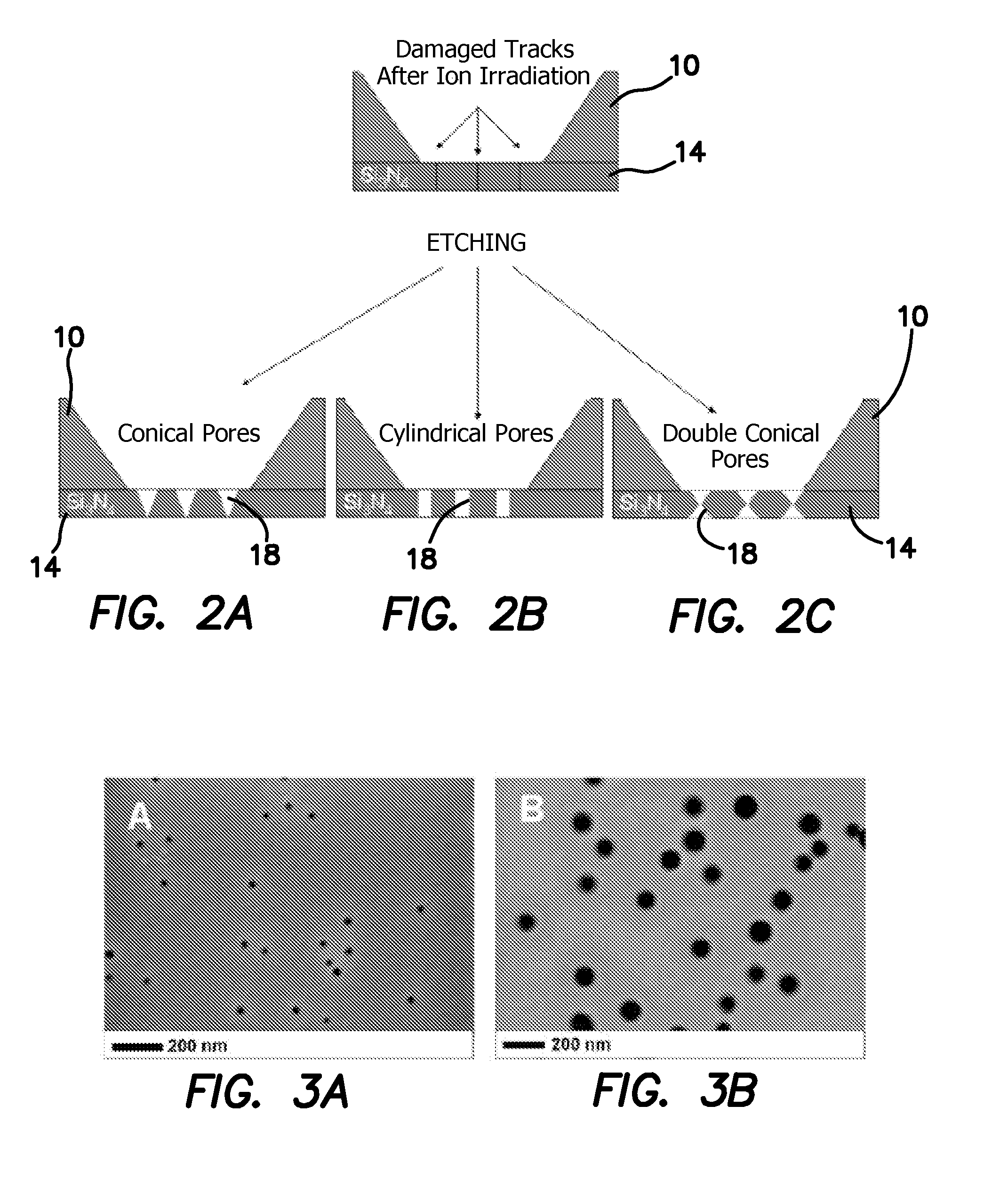
A method for fabricating isolated pores in an inorganic membrane includes the steps of patterning the inorganic membrane to selectively expose a portion of the membrane, forming a plurality of tracks of material damage in the exposed portion of the inorganic membrane by irradiation with energetic ions, and chemically etching the track damaged material to define the pores through the inorganic membrane with a predetermined geometrically defined cross sectional shape and with a controlled diameter range from less than 1 nanometer and up to micrometer scale.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Underwater super-oleophobic oil-water separation mesh membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102716676AFast separationEasy to separateSemi-permeable membranesPolymer scienceVegetable oil
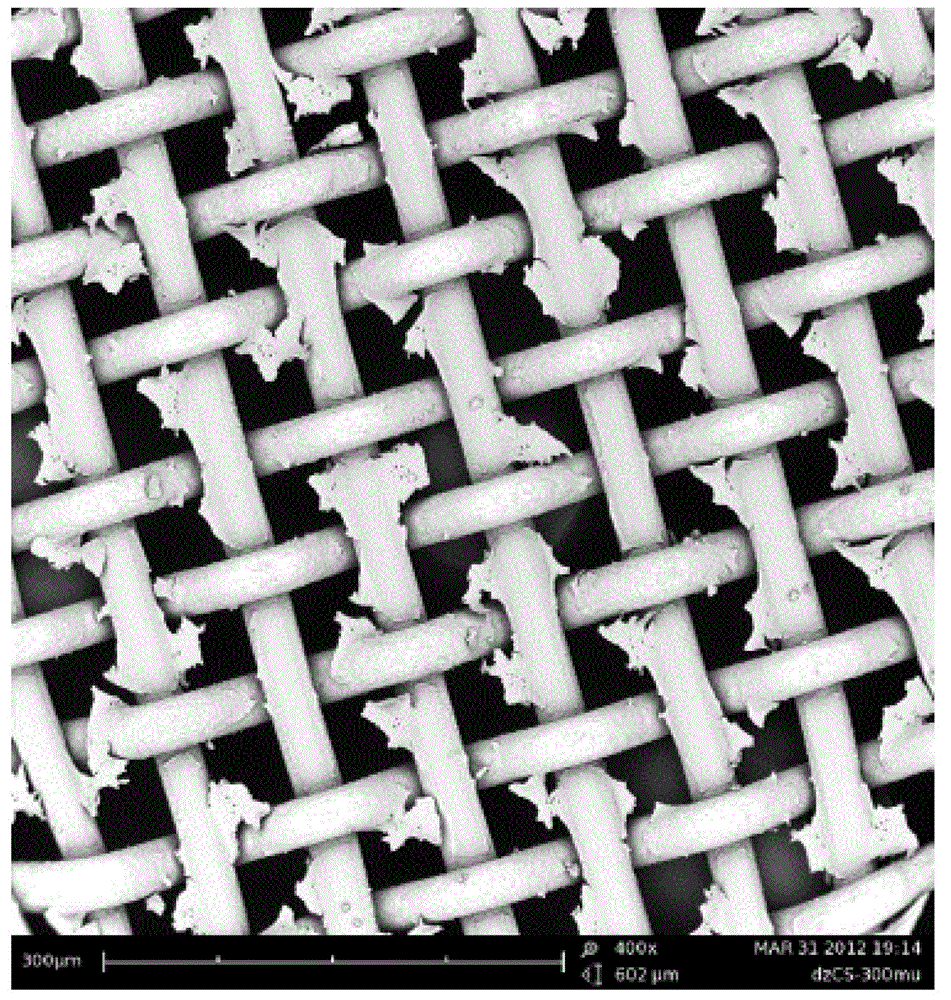
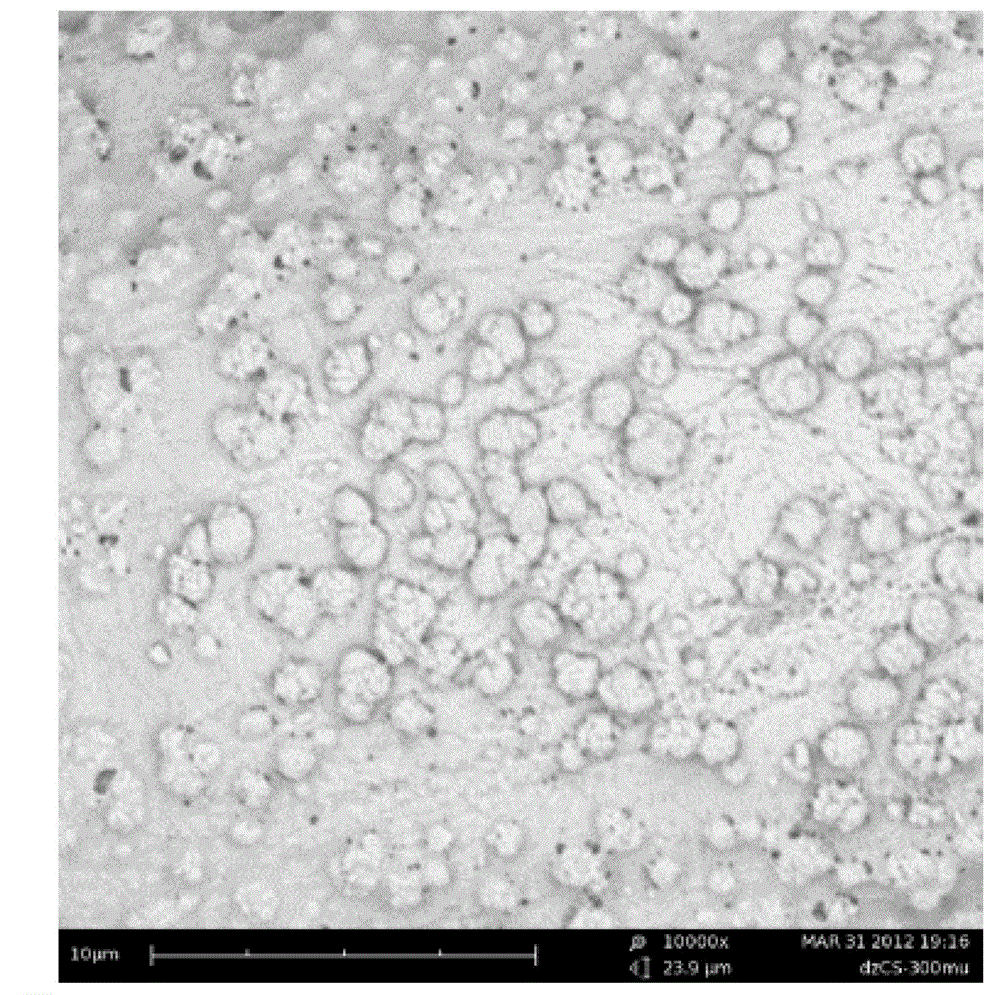
The invention discloses an underwater super-oleophobic oil-water separation mesh membrane and a preparation method thereof. The oil-water separation mesh membrane is prepared by coating a micron-thickness chitosan-based polymer coating layer on the mesh wire of a fabric mesh with 100-400 meshes. The oil-water separation mesh membrane is provided with micrometer-scale meshes and the chitosan-based polymer coating layer is provided with protruding structures with a nanoscale width. The preparation method of the oil-water separation mesh membrane comprises the following steps of: (1) cleaning and drying the fabric mesh; (2) dissolving a chitosan-based polymer in acid solution and stirring evenly to obtain mixed solution; (3) immersing the cleaned and dried fabric mesh in the mixed solution, taking out and drying the fabric mesh; and (4) immersing the fabric mesh obtained by the step (3) in alkaline solution, taking out and drying the fabric mesh to obtain the oil-water separation mesh membrane. The oil-water separation mesh membrane provided by the invention has the advantages of large water flux, high oil-water separation speed and good oil-water separation effect, is applicable to treatment of sewage with high oil content, and has good separation effect on normal hexane, petroleum ether, dichloroethane, benzene, animal and vegetable oils and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for measuring thermal conductivity
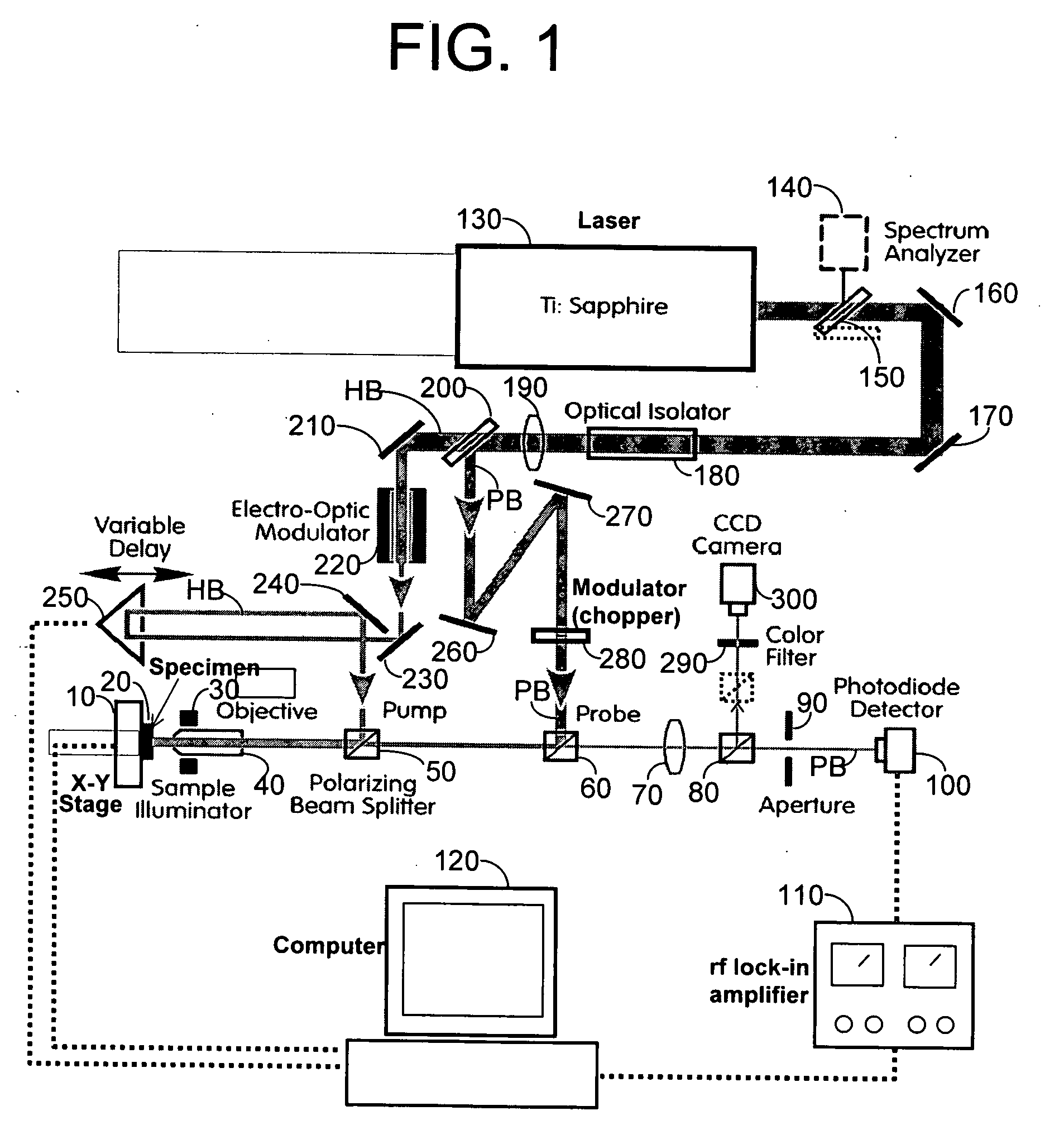
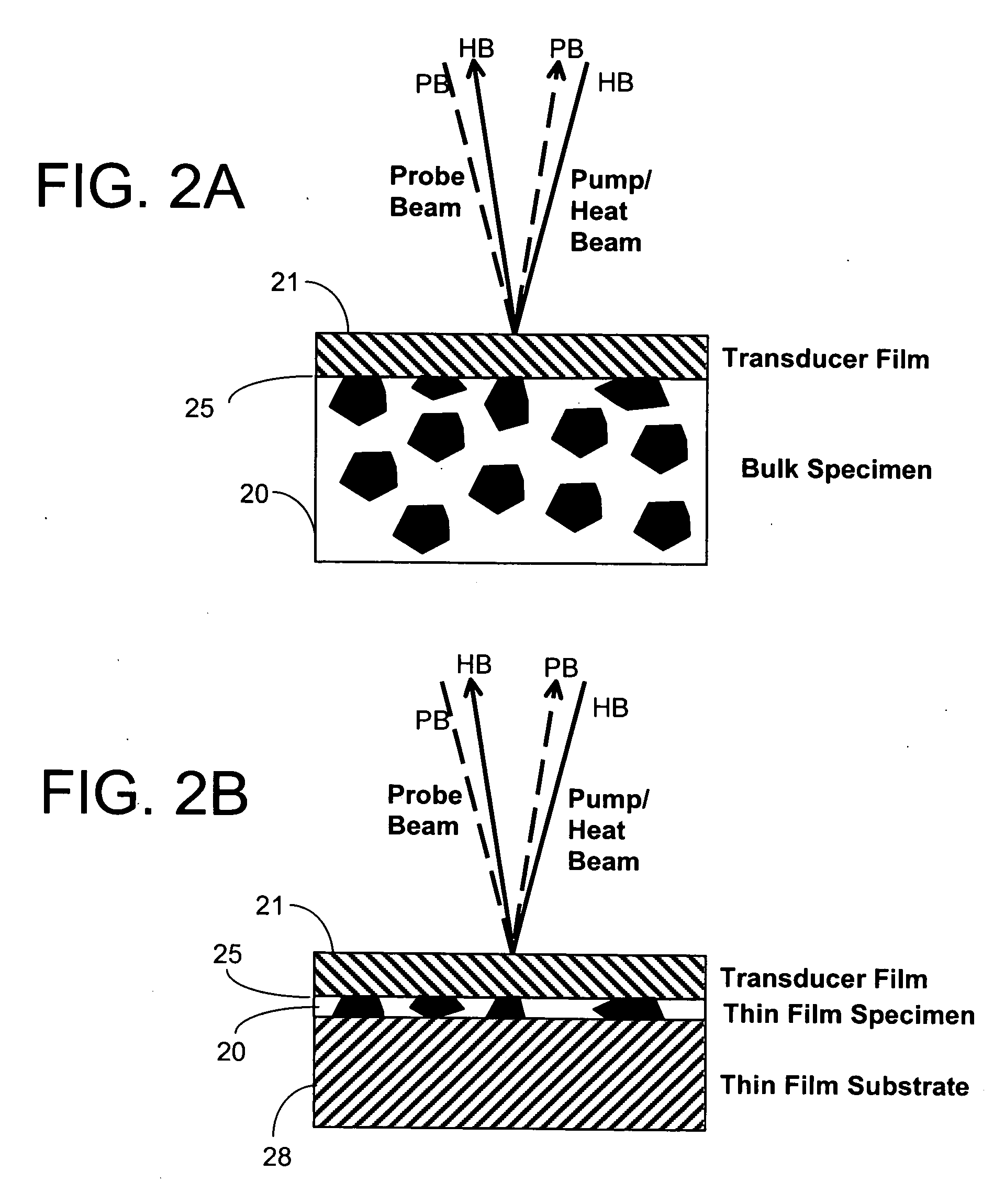
InactiveUS20060222043A1Increase heightLow thermal conductivityThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityFemtosecond pulsed laserPump probe
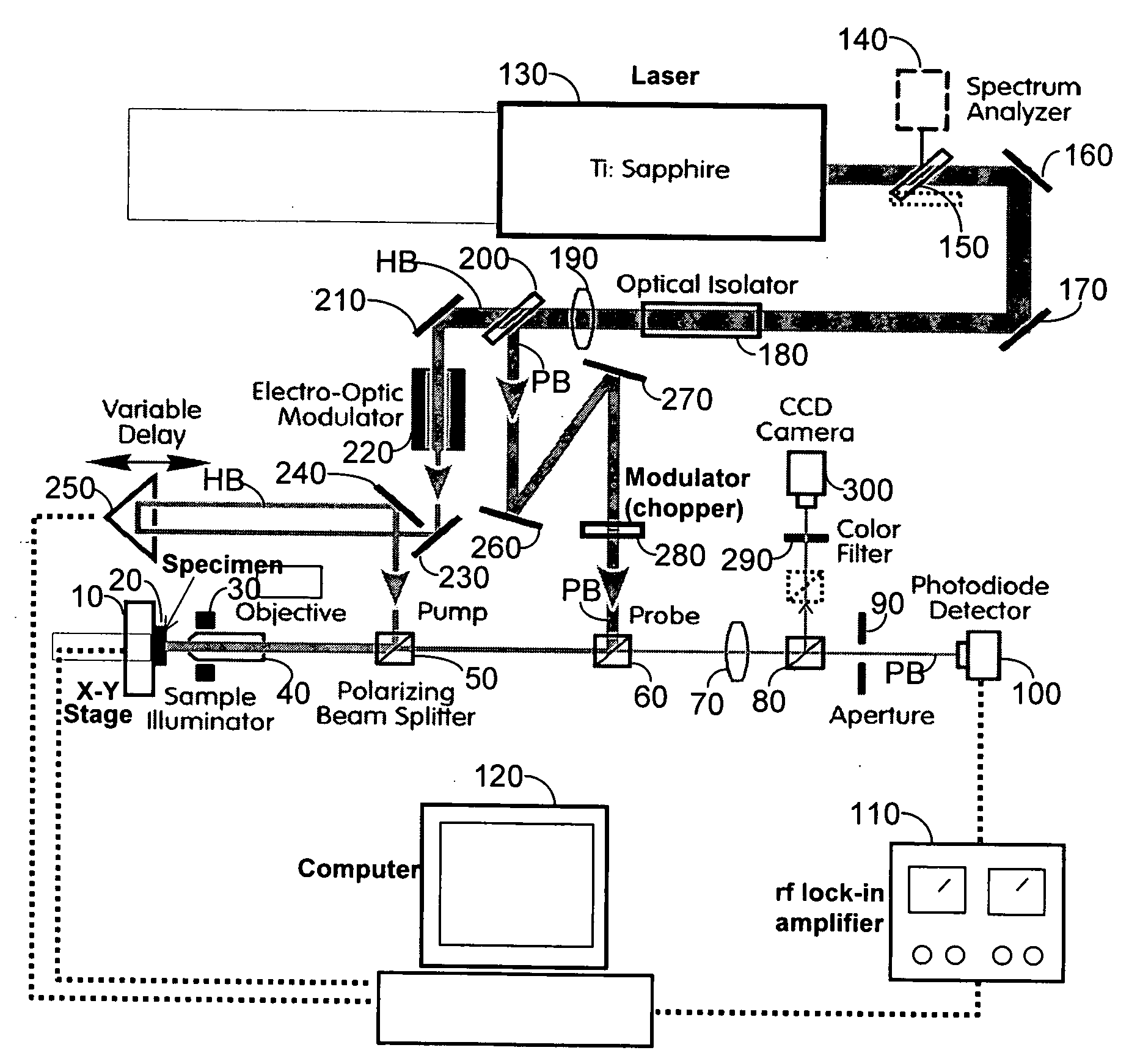
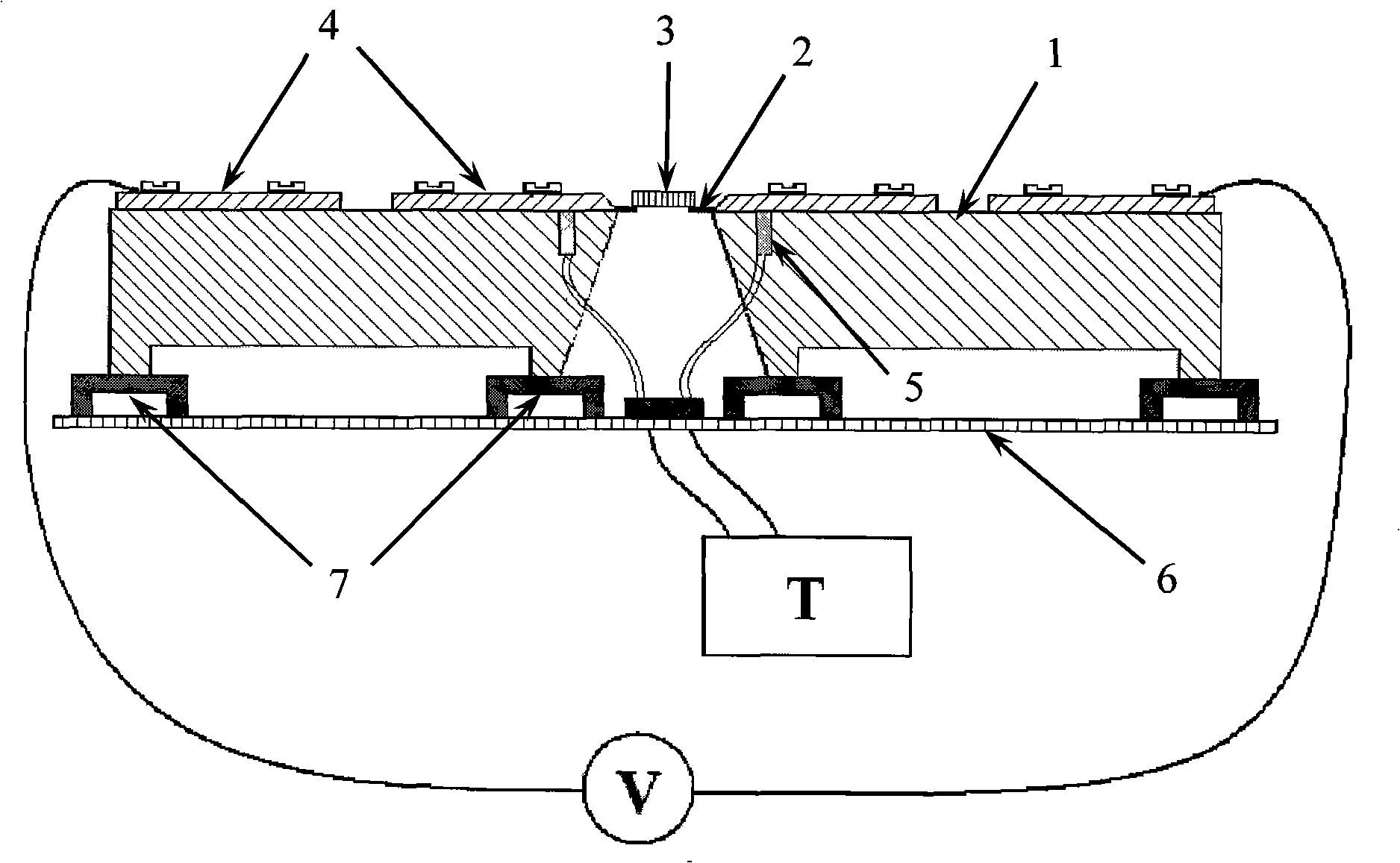
An apparatus and method for measuring and mapping thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity at micrometer scale resolution. The apparatus and method utilize a mode-locked femtosecond pulsed laser in a pump-probe configuration to analyze time-domain thermoreflectance of a specimen to evaluate its thermal conductivity in micro-scale, so that, if desired, an image of thermal conductivity distribution of micro-scale regions may be obtained therefrom. A multi-layer, complete three-dimensional model that takes into account the entire three-dimensional heat flow in cylindrical coordinates enables micro-scale measurements to be made at an accuracy of about 90% of well-accepted values.
Owner:CAHILL DAVID GERARD
Method for obtaining a surface of titanium-based metal implant to be inserted into bone tissue
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a surface of a titanium-based metal implant intended to be inserted into bone tissue, comprising: (a) projecting particles of aluminium oxide under pressure on the external area of the implant; (b) chemically treating the sandblasted external area of the implant with an acid composition comprising sulfuric acid and hydrofluoric acid; and (c) thermally treating the sandblasted external area of the implant by heating at a temperature of 200-450° C. for 15-120 min. The invention likewise defines a metal implant having said surface. The surface thus obtained has good micrometer-scale roughness with a suitable morphology, as well as a composition which is virtually free of impurities and a thickness which is approximately three times the thickness of conventional surfaces, which characteristics provide it with very good osseointegration properties.
Owner:PHIBO DENTAL SOLUTIONS
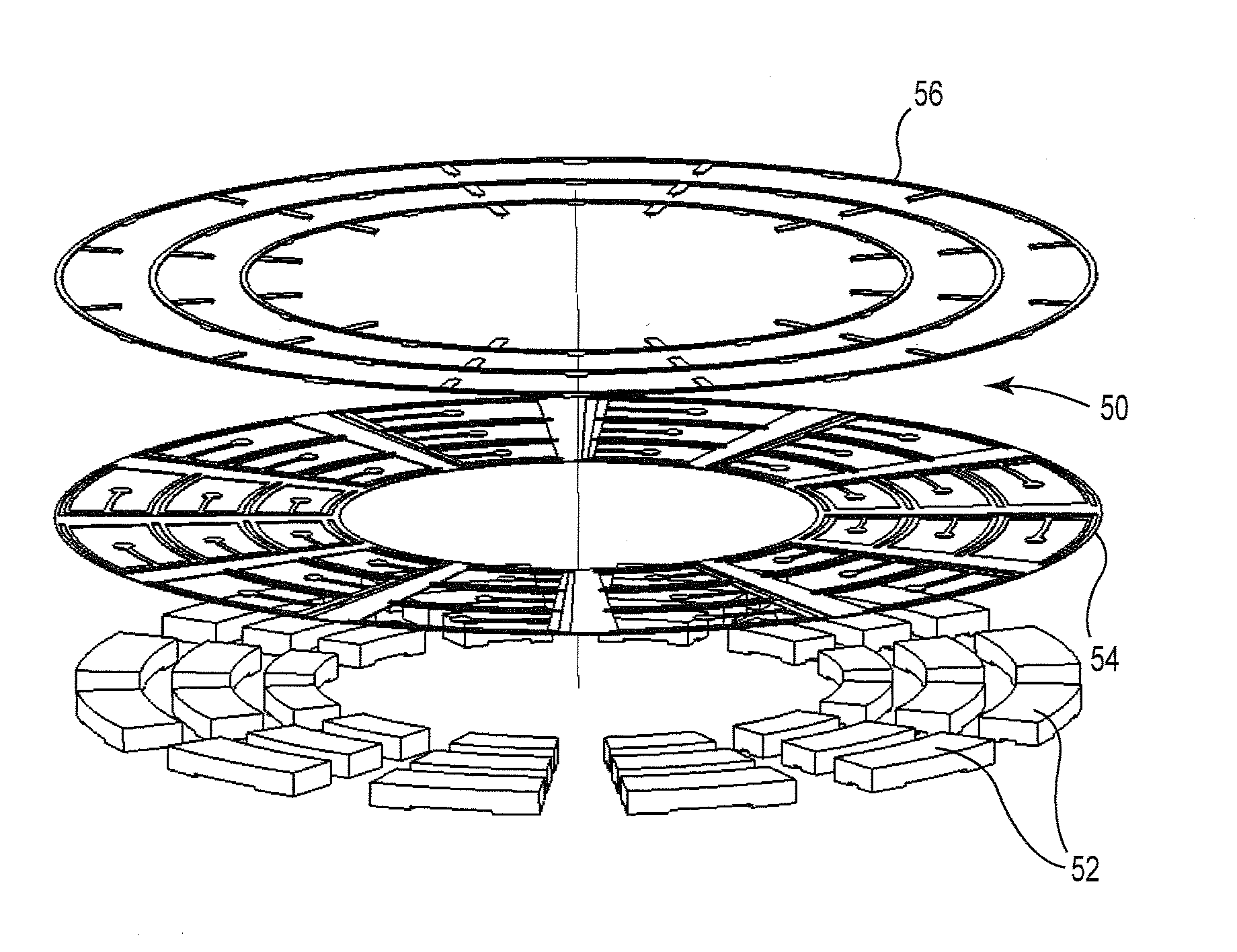
Ion trap in a semiconductor chip
ActiveUS7411187B2Particle separator tubesDigital data processing detailsMicrometer scaleSemiconductor chip
A micrometer-scale ion trap, fabricated on a monolithic chip using semiconductor micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technology. A single 111Cd+ ion is confined, laser cooled, and the heating measured in an integrated radiofrequency trap etched from a doped gallium arsenide (GaAs) heterostructure. Single 111Cd+ qubit ions are confined in a radiofrequency linear ion trap on a semiconductor chip by applying a combination of static and oscillating electric potentials to integrated electrodes. The electrodes are lithographically patterned from a monolithic semiconductor substrate, eliminating the need for manual assembly and alignment of individual electrodes. The scaling of this structure to hundreds or thousands of electrodes is possible with existing semiconductor fabrication technology.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY +1
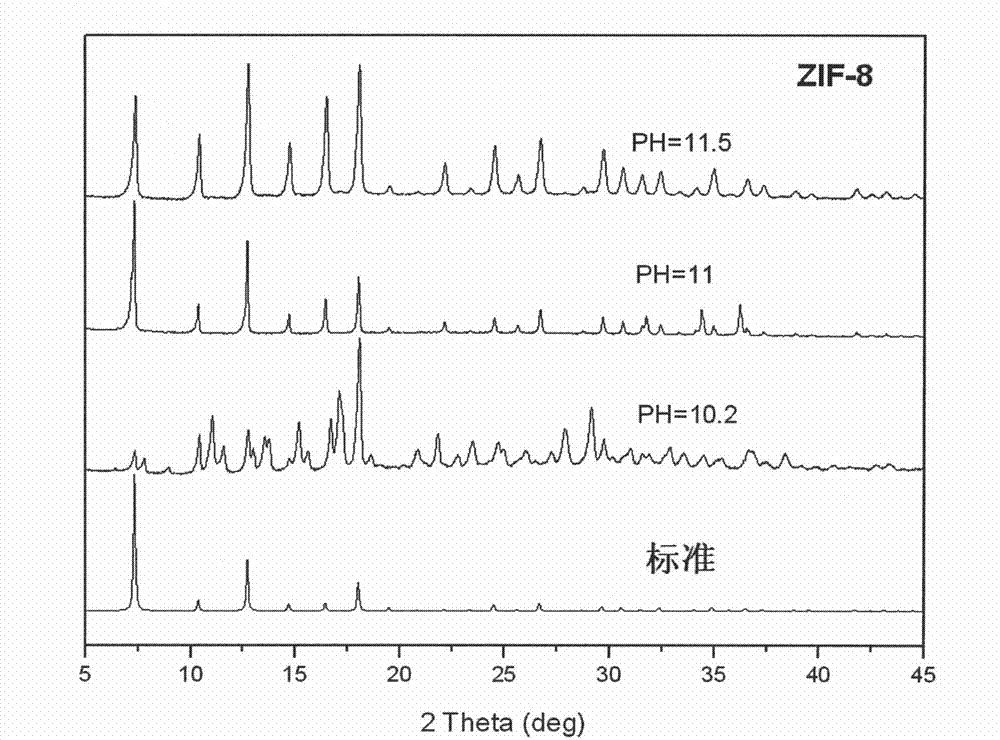
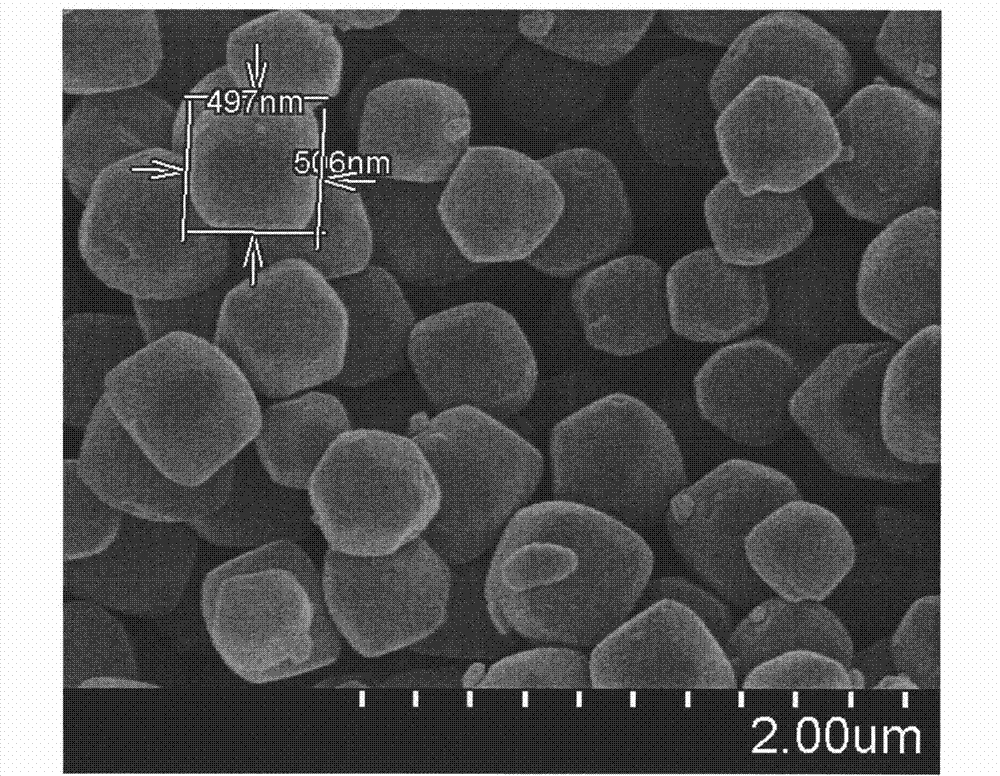
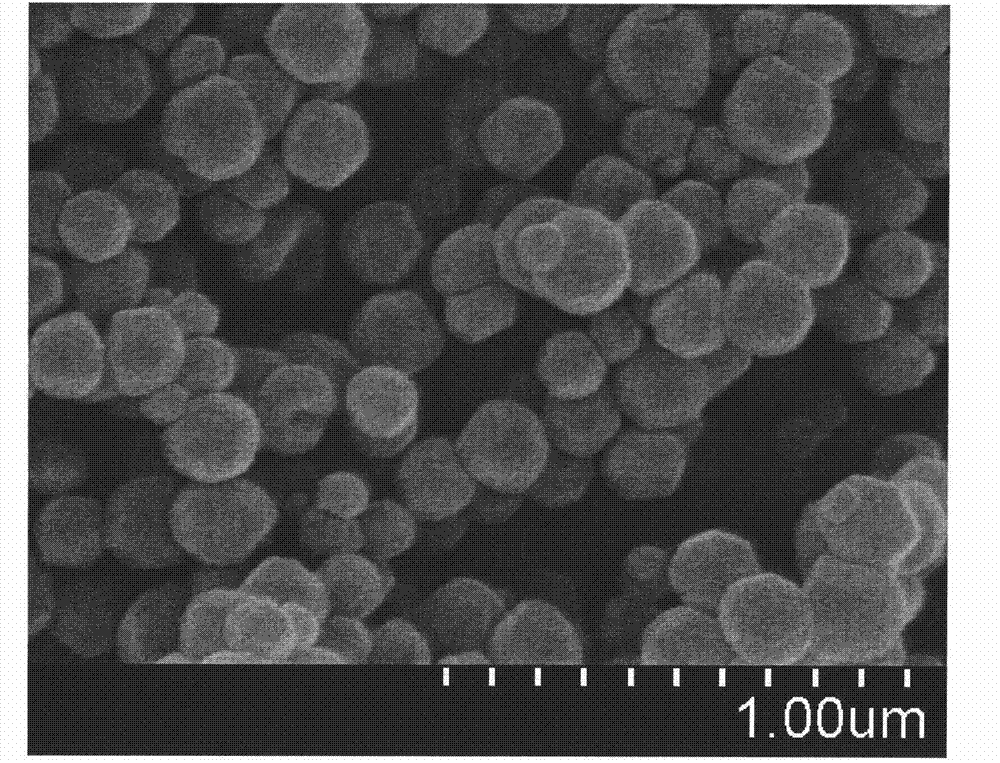
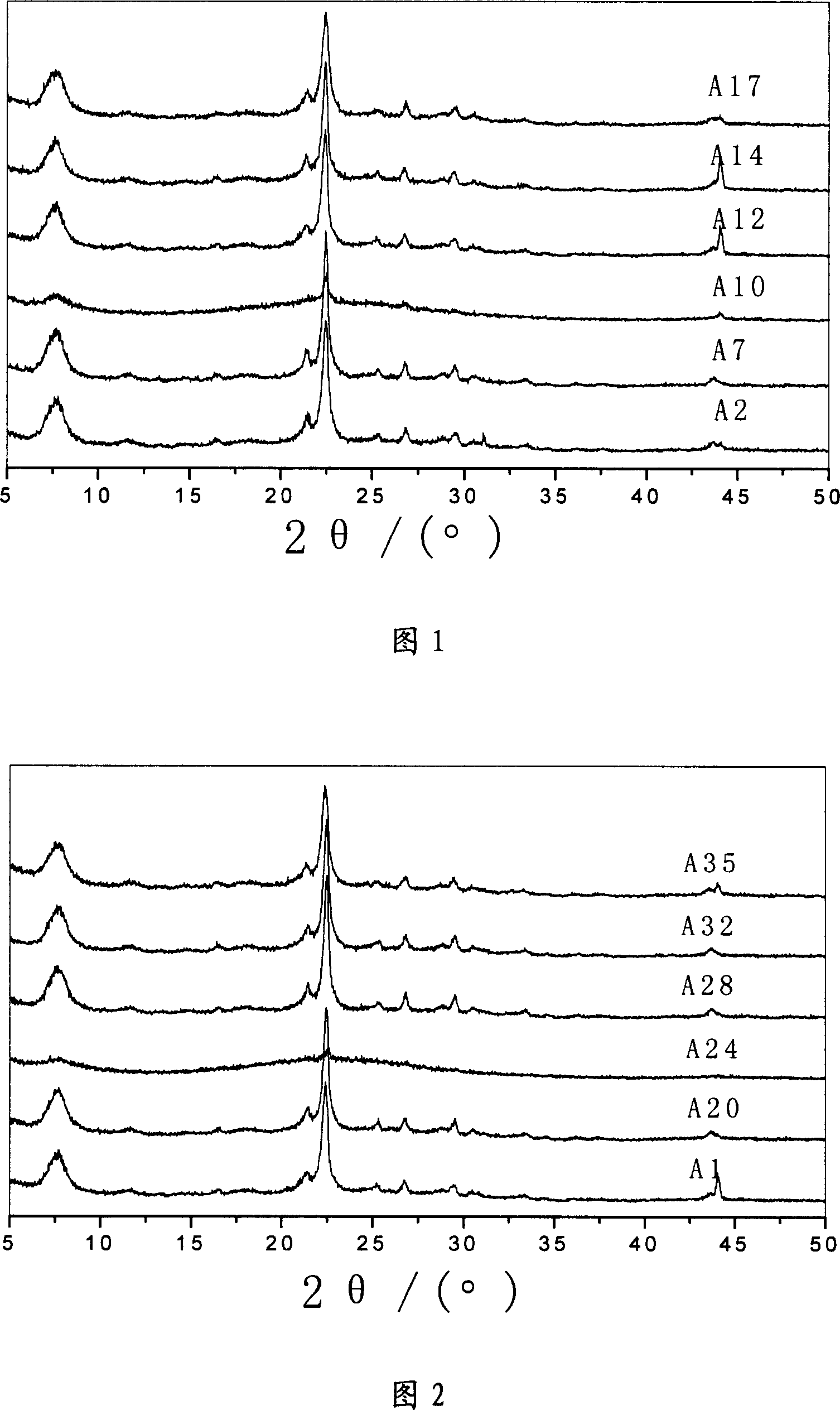
Preparation method of nanometer-to-micrometer scale zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs)
ActiveCN102731538AGood lookingPromotes deprotonationCobalt organic compoundsZinc organic compoundsOrganic fluidSolvent
The invention which belongs to the technical field of new materials relates to a synthetic method of ZIFs, and concretely discloses a method for synthesizing nanometer / micrometer scale ZIFs based on imidazole and its derivatives at room temperature in a concise, efficient and green manner. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a single imidazole ligand or a mixture of two imidazole ligands in water or an organic liquid to form a solution, adding an alkaline substance to adjust the pH value of the solution, adding a metal salt to form a reaction system, and reacting to obtain the nanometer or micrometer scale ZIFs. The method which allows routine reactants to be utilized and the alkaline substance to be added to adjust the pH value of the system has the advantages of ligand application amount reduction, controllable product size, and high purity of the nanometer / micrometer scale ZIFs. The synthetic method has the characteristics of cheap and easily available raw materials and solvent, and no pollution, and has important meanings to the production and the application of the ZIFs.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for preparing beta zeolite with multilevel pore canals
ActiveCN101003378AEasy to operateShorten the diffusion distanceMolecular sieve catalystsCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesPressure decreaseMicrometer scale
This invention discloses a method for preparing multi-level porous beta-zeolite. The method comprises: soaking monolithic silica gel column in sucrose solution, drying, polymerizing, carbonizing to obtain C-Si composite, wetting the C-Si composite with a mixed solution of Al source, inorganic alkali, organic amine and water, crystallizing, and recovering the product. In this method, carbon material can effectively protect the porous structure of monolithic silica gel column from damage during crystallization process. The obtained beta-zeolite has multi-level pores, including micrometer-scale macropores, mesopores and micropores. The macropores can shorten the diffusion distances of reactive molecules, reduce the pressure decrease of the equipment, raise the unit processing capacity of the equipment, and make the adjustment and control of the product selectivity easier. The mesopores can provide large inner specific surface area, which is meaningful to the catalytic reaction of macromolecules.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Ion trap in a semiconductor chip
ActiveUS20070040113A1Particle separator tubesDigital data processing detailsIon trap mass spectrometryMicrometer scale
A micrometer-scale ion trap, fabricated on a monolithic chip using semiconductor micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) technology. A single 111Cd+ ion is confined, laser cooled, and the heating measured in an integrated radiofrequency trap etched from a doped gallium arsenide (GaAs) heterostructure. Single 111Cd+ qubit ions are confined in a radiofrequency linear ion trap on a semiconductor chip by applying a combination of static and oscillating electric potentials to integrated electrodes. The electrodes are lithographically patterned from a monolithic semiconductor substrate, eliminating the need for manual assembly and alignment of individual electrodes. The scaling of this structure to hundreds or thousands of electrodes is possible with existing semiconductor fabrication technology.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY +1
Micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure and preparation method and device thereof
ActiveCN103046088AEvenly distributedUniform detachmentMaterial nanotechnologyCellsMicro nanoHeat treated
The invention relates to the preparation of a porous surface, and discloses a micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure and a preparation method and a preparation device thereof. The preparation method for the micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure is a method for electro-deposition by a hydrogen template method, takes red copper as an anode and a cathode substrate, and includes: performing electro-deposition by taking red copper as an anode and a cathode substrate, and the mixture consisting of the H2SO4 and CuSO4 aqueous solution and additives as the electro-deposition solution to obtain an electro-deposition sample, soaking the electro-deposition sample with deionized water and ethanol and then drying to obtain the micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure; and thermally treating the obtained micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure to enhance the mechanical performance of the micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure. The device for preparing the micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure comprises an electro-deposition tank, an electro-deposition solution, a direct current power supply, a cathode substrate and an anode. The preparation method is simple to operate, and low in cost, and the micro-nano composite porous copper surface structure is controllable; and by the method, a micro-nano composite structure formed by superposing a micrometer scale aperture structure and a wall nano dendrites structure can be prepared, and the aperture of the structure is gradually increased and the structure is uniform.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method to grow self-assembled epitaxial nanowires
InactiveUS20030008505A1Surface cleaningQuality improvementNanotechDecorative surface effectsNanowireLattice mismatch
Self-assembled nanowires are provided, comprising nanowires of a first crystalline composition formed on a substrate of a second crystalline composition. The two crystalline materials are characterized by an asymmetric lattice mismatch, in which in the interfacial plane between the two materials, the first material has a close lattice match (in any direction) with the second material and has a large lattice mismatch in all other major crystallographic directions with the second material. This allows the unrestricted growth of the epitaxial crystal in the first direction, but limits the width in the other. The nanowires are grown by first selecting the appropriate combination of materials that fulfill the foregoing criteria. The surface of the substrate on which the nanowires are to be formed must be cleaned in order (1) to ensure that the surface has an atomically flat, regular atomic structure on terraces and regular steps and (2) to remove impurities. Finally, epitaxial deposition of the first crystalline material on the cleaned surface is performed, thereby forming the self-assembled nanowires. Thus, one-dimensional epitaxial crystals are obtained with widths and heights at the nanometer scale, and lengths at the micrometer scale, which are aligned along certain crystallographic directions with high crystal quality.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and system for measuring quasi one-dimensional nano-material Seebeck coefficient
InactiveCN101354388AGet real attributesGood repeatabilityMaterial thermal analysisPotential differenceMicrometer scale
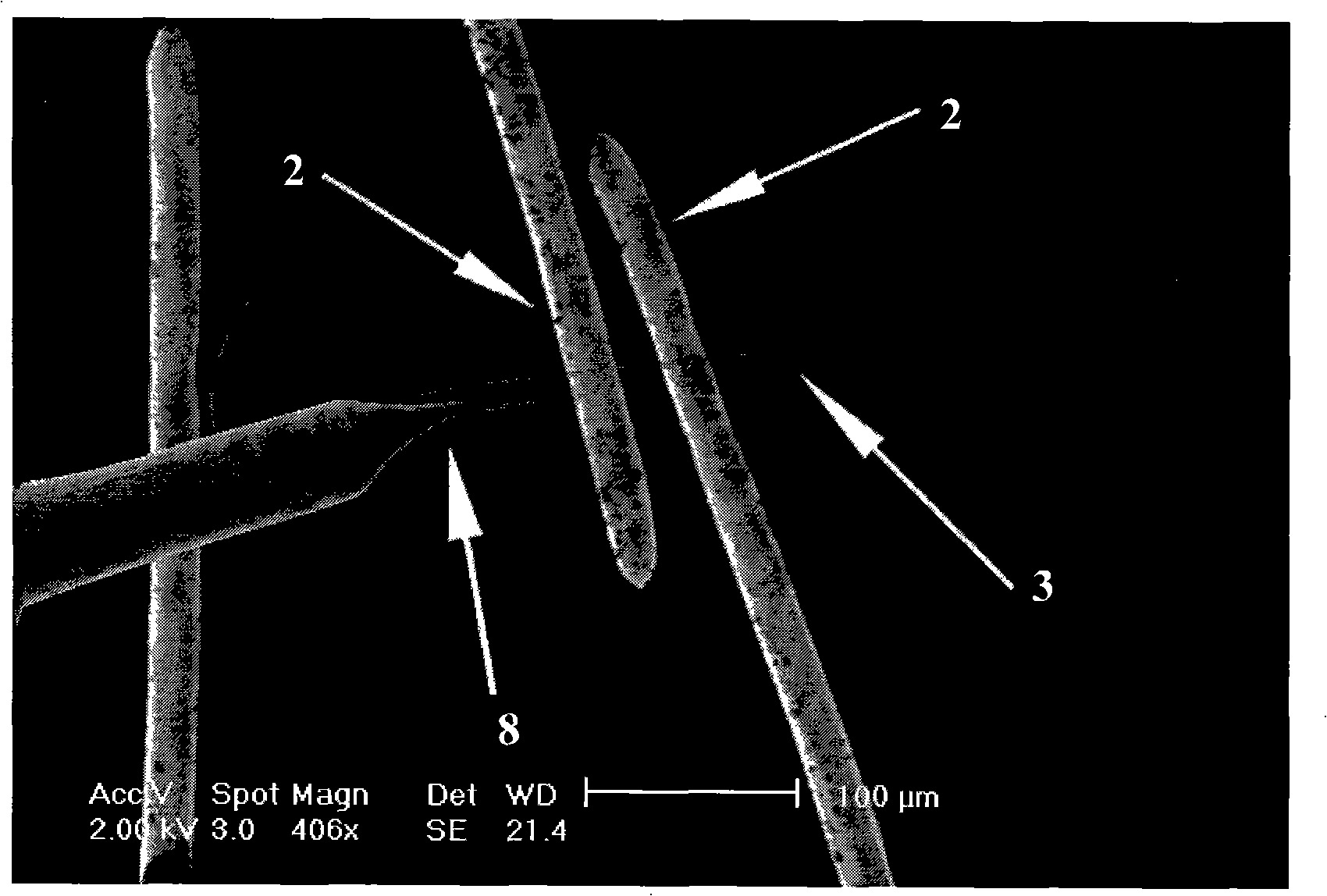
The invention discloses a method and a system that are used for measuring the Seebeck coefficient of a quasi-one-dimensional nano material; two line transition electrodes with micrometer-scaled cross sections are respectively contacted with two centimeter-scaled block metal electrodes, a nano probe system is utilized for leading a single rod of the quasi-one-dimensional nano material to be detected to be connected with the two transition electrodes, temperature difference between the two block metal electrodes is altered, and the temperature difference and corresponding potential difference between the two electrodes are simultaneously measured, thus obtaining the Seebeck coefficient of the quasi-one-dimensional nano material. The corresponding testing system comprises three parts of an experimental platform, a temperature altering device and a data collecting and processing device. The method and the system solve the problem of the contact transition between the centimeter-scaled electrodes and the nano sample to be detected through the micrometer-scaled transition electrodes, utilize the nano probe system for installing the nano material, and lead the nano material not to be randomly dispersed at two sides of the electrodes, thus improving experimental success rate, controllability and reliability; and the provided measuring system has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and easy popularization and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
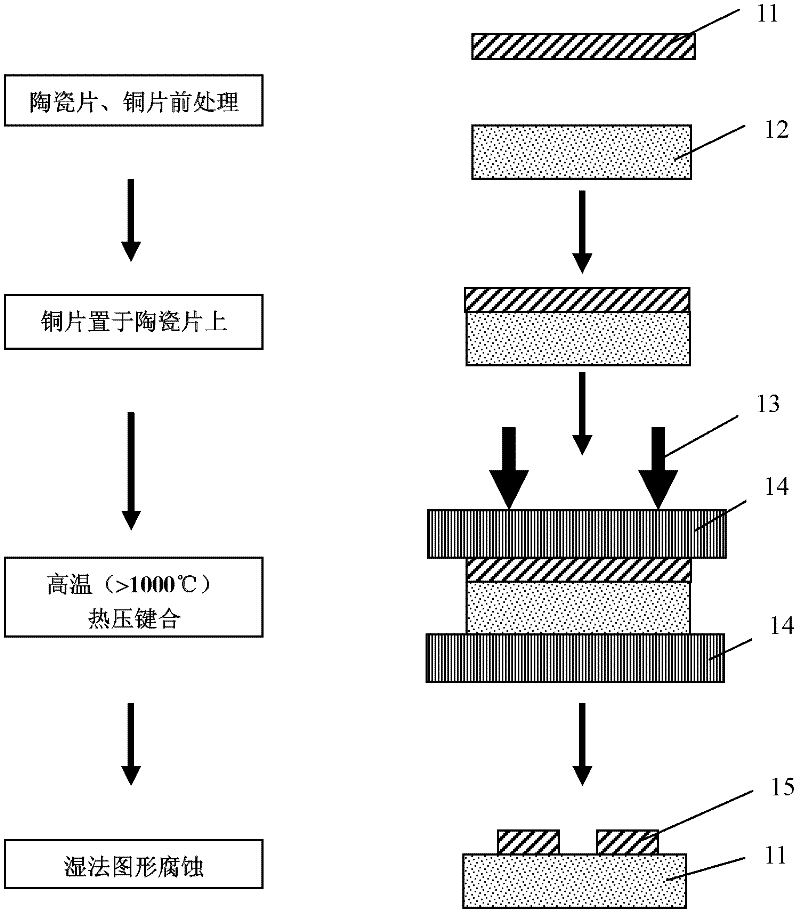
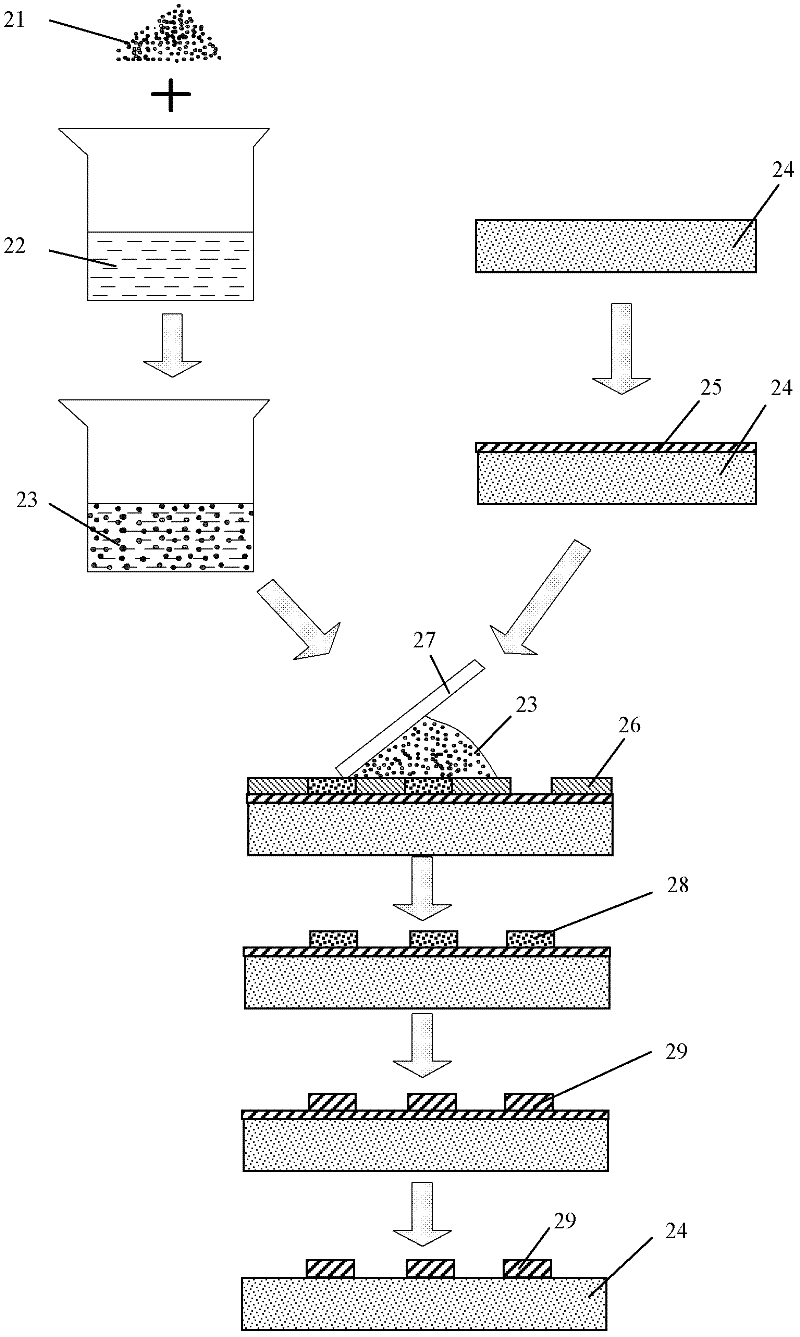
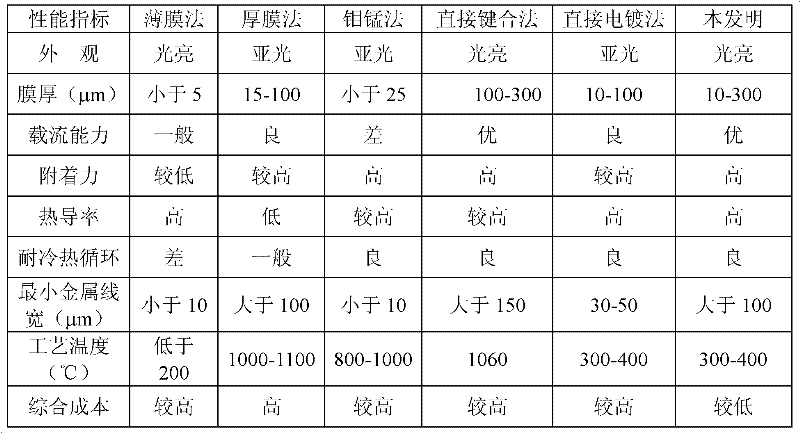
Method for preparing metallized ceramic substrate by low-temperature sintering
The invention provides a method for preparing a metallized ceramic substrate by low-temperature sintering. The method comprises completely mixing metal nanopowder with an organic matter to obtain metal nanopaste; and printing the metal nanopaste on the surface of a ceramic substrate by screen printing process to form a metal paste layer, and sintering at a certain temperature in an atmosphere to obtain the final product with a single-sided or double-sided metal layer. For the nanoscale effect, high-strength bonding between metal and ceramic is realized at a relatively low temperature. Compared with the prior thick film method (in which metal particles have diameter of micrometer scale) and DBC (direct bonded copper) art, the method has low temperature condition, and is particularly suitable for batch preparation of metallized ceramic substrates. The prepared metallized ceramic substrate has good performance including large adhesion and small thermal stress.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
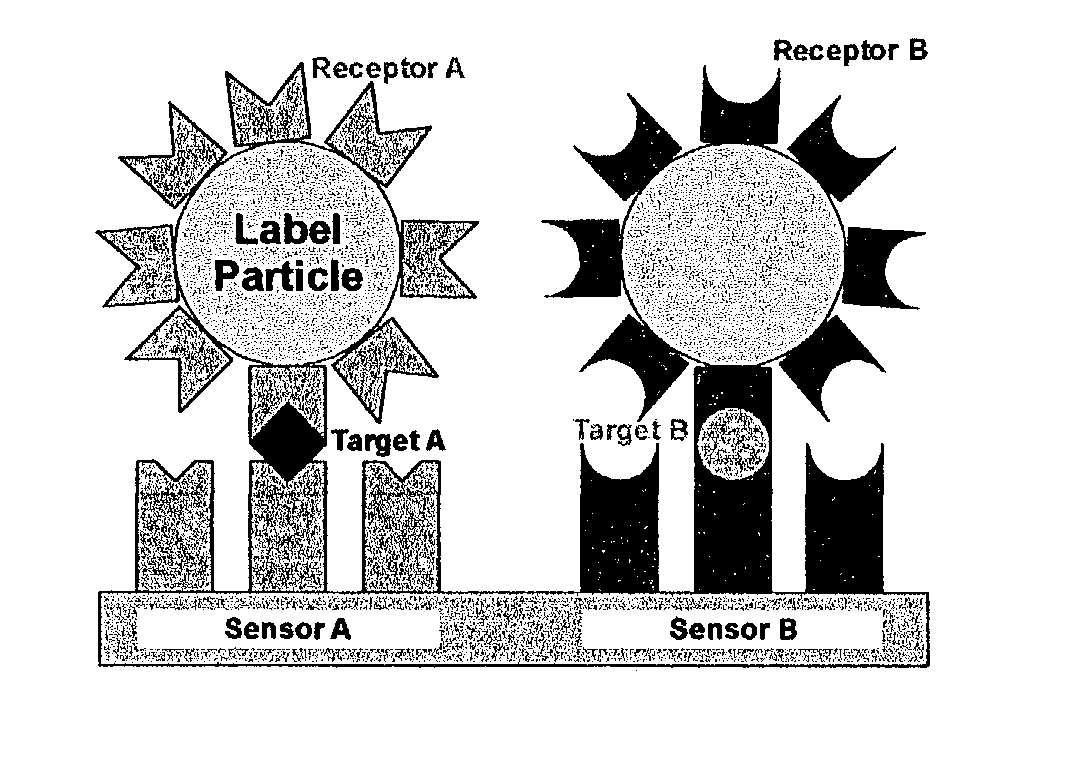
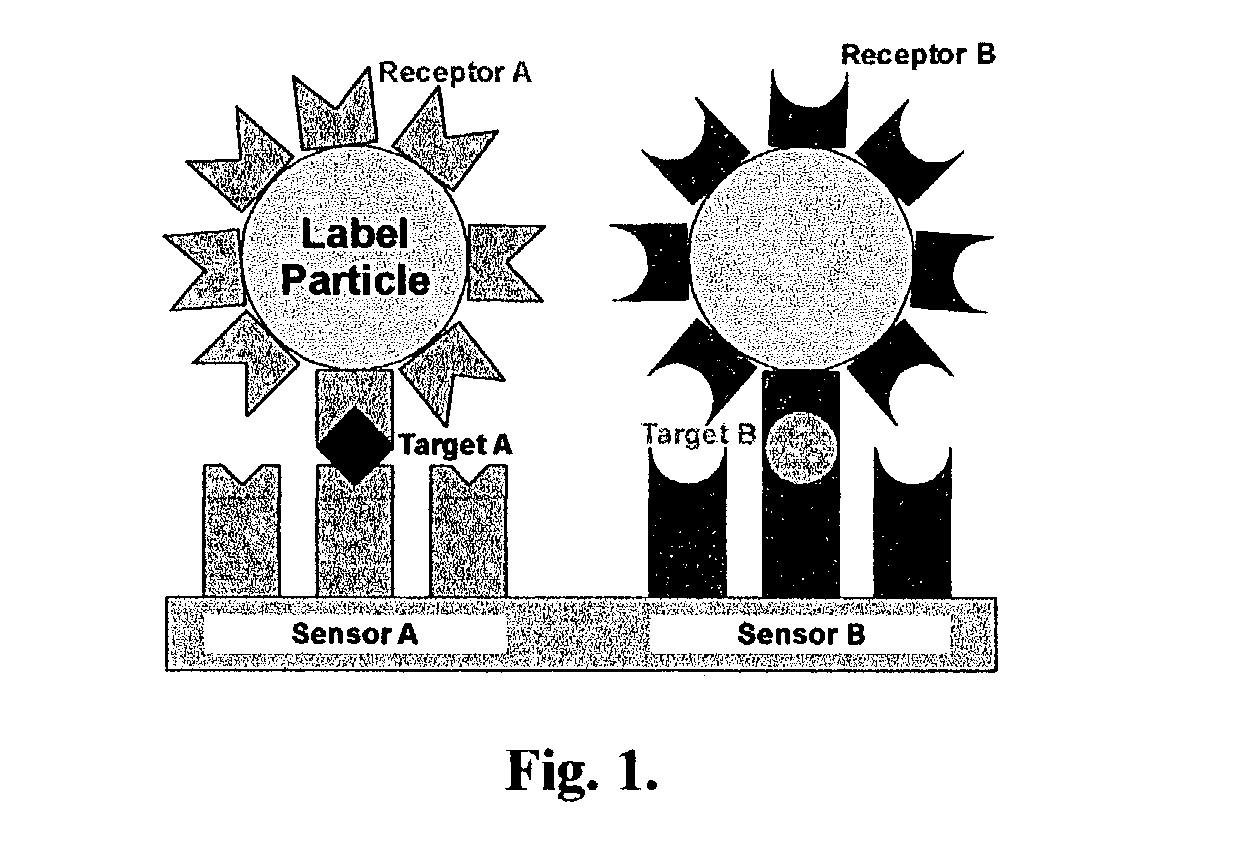
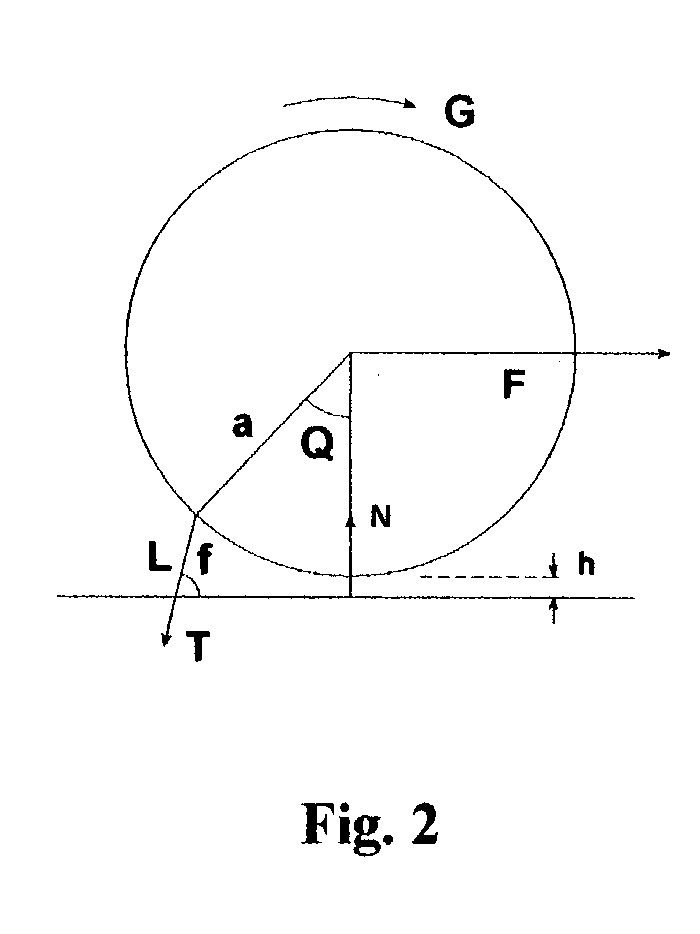
Fluidic force discrimination
InactiveUS20040253744A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrometer scaleUltimate tensile strength
This invention describes a method of using controlled fluidic forces to improve the performance of a biochemical binding assay where a target molecule is captured by specific molecular recognition onto a substrate surface with an affinity coating, and then labeled with a detectable micrometer-scale particle using a second specific molecular recognition reaction with the target. By using specific ranges of label sizes and laminar flow conditions, controlled fluidic forces can be applied to the label particles in order to selectively remove molecules bound to a surface according to their binding strength, and thereby increase the ratio of specifically bound labels to more weakly attached non-specifically bound labels. This method can be used with a wide variety of label types and associated detection methods, improving the sensitivity and selectivity of a broad range of binding assays.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
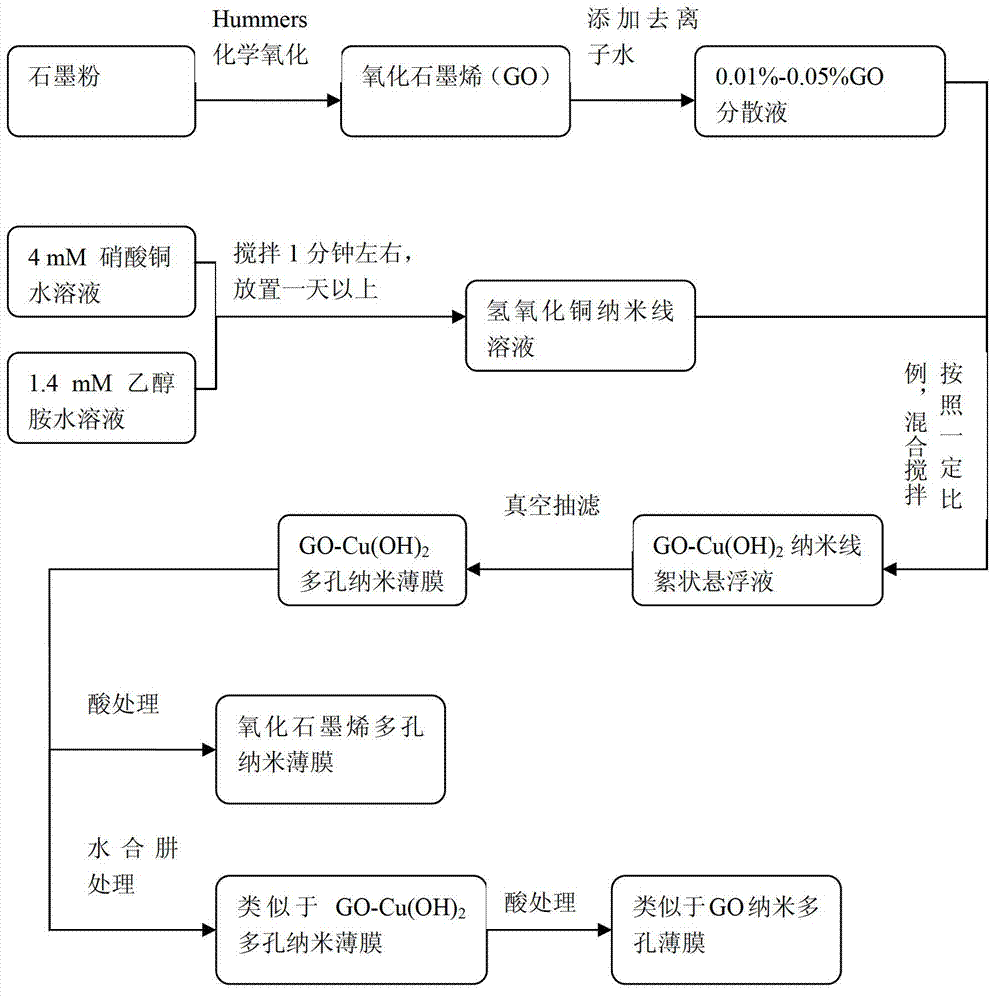
Method for preparing graphene oxide base porous film by using metal hydroxide nanowires and graphene oxide, and application of graphene oxide base porous film
InactiveCN102814124AImprove mechanical propertiesGood chemical stabilitySemi-permeable membranesCopper oxides/halidesEthylenediamineNanowire
The present invention discloses a method for preparing a graphene oxide base porous film by using metal hydroxide nanowires and graphene oxide, and an application of the graphene oxide base porous film. According to the present invention, a chemical oxidation ultrasonic dispersion method is adopted to prepare a diluent negatively charged graphene oxide (GO) dispersion liquid with a content of 0.01-0.05%; the GO dispersion liquid is mixed with a positively charged metal hydroxide nanowire solution with a concentration of 0.15-1.2 mM, wherein the diameter is nanometer scale, and the length is micrometer scale; stirring is performed for 5-30 minutes; vacuum suction filtration (negative pressure of 50-85 kPa) is performed on a polycarbonate porous film; a hydrazine hydrate treatment is performed for 5-60 minutes; and an acid (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3) or a complexing agent ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) is adopted to remove the metal hydroxide nanowires to obtain a nanometer GO porous separation film formed by the left pores through removing the nanowires, wherein molecules with a molecular weight of about 350 daltons can be effectively separated with the separation film. The graphene oxide base porous film prepared by the method of the present invention has a separation performance similar to a nanometer graphene oxide separation film, and further is a porous separation film with good separation efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and systems to predict fatigue life in aluminum castings
InactiveUS20090276166A1Accurately fatigue propertyAccurate of fatigue propertyPlug gaugesDigital computer detailsCrazingCasting defect
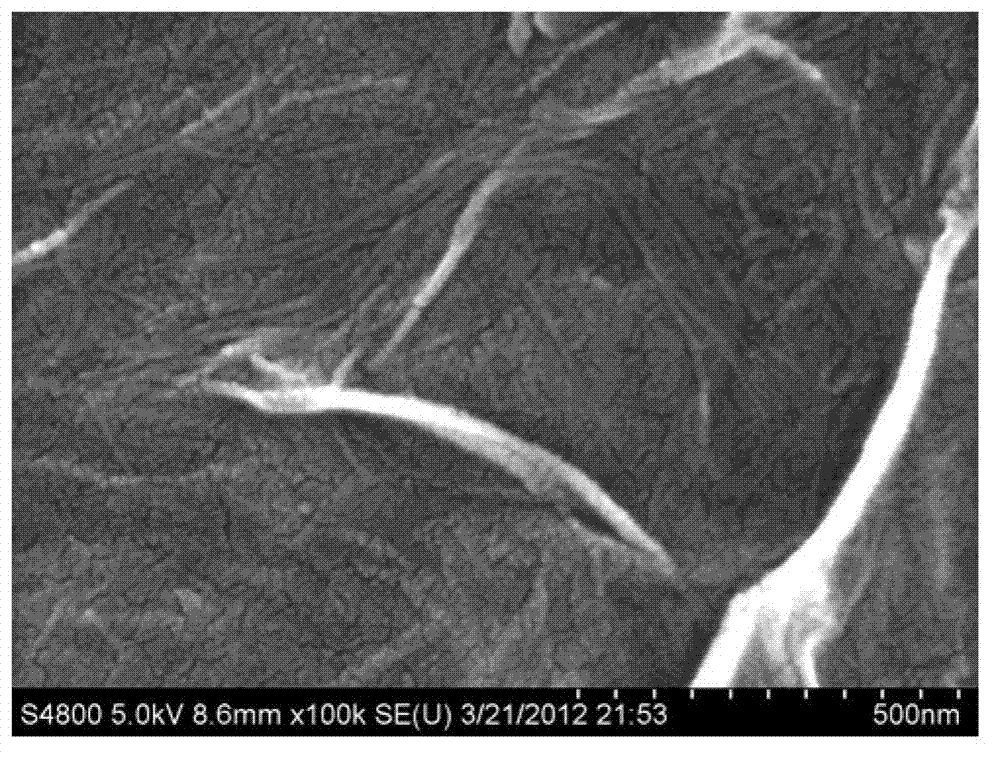
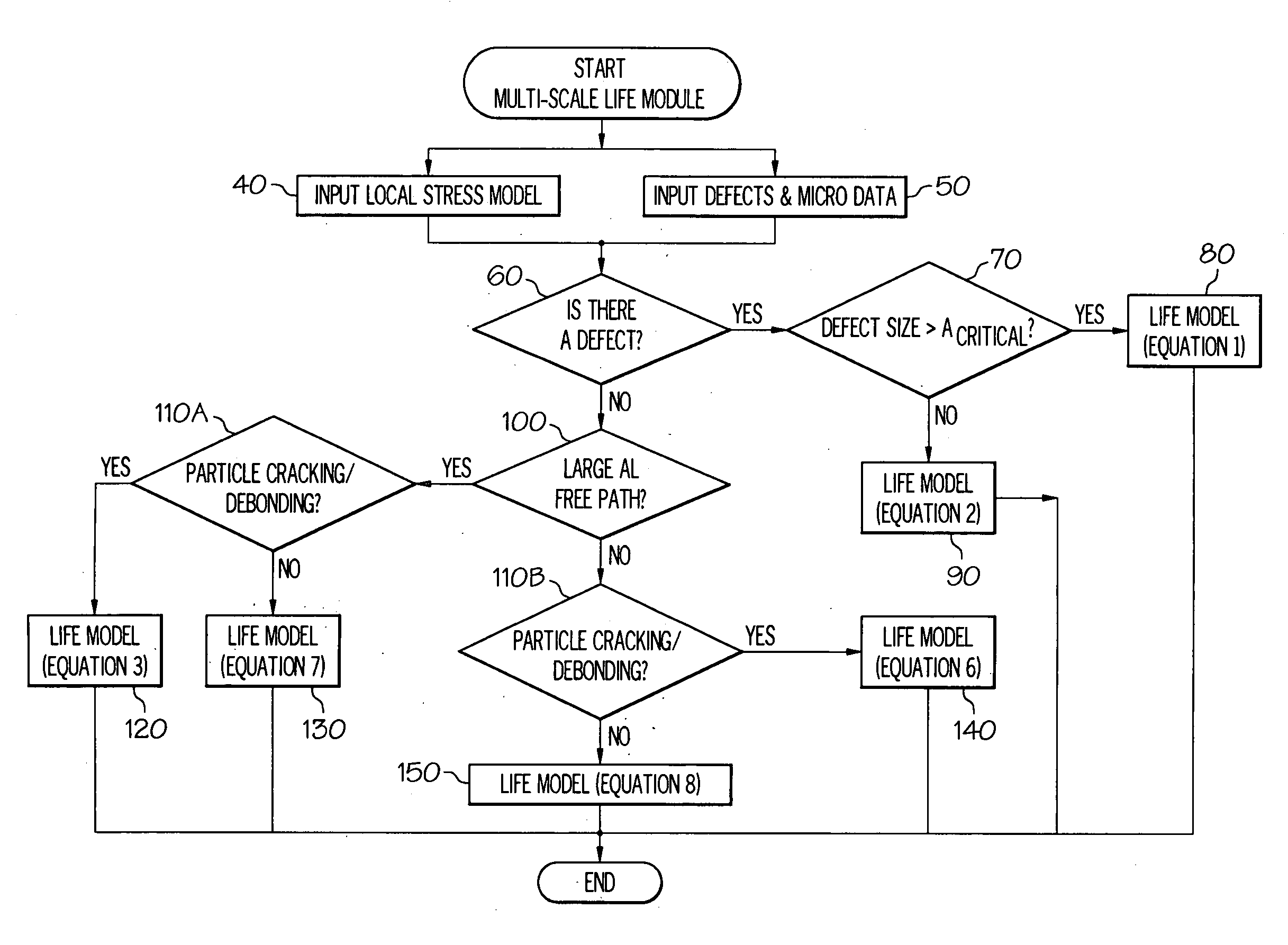
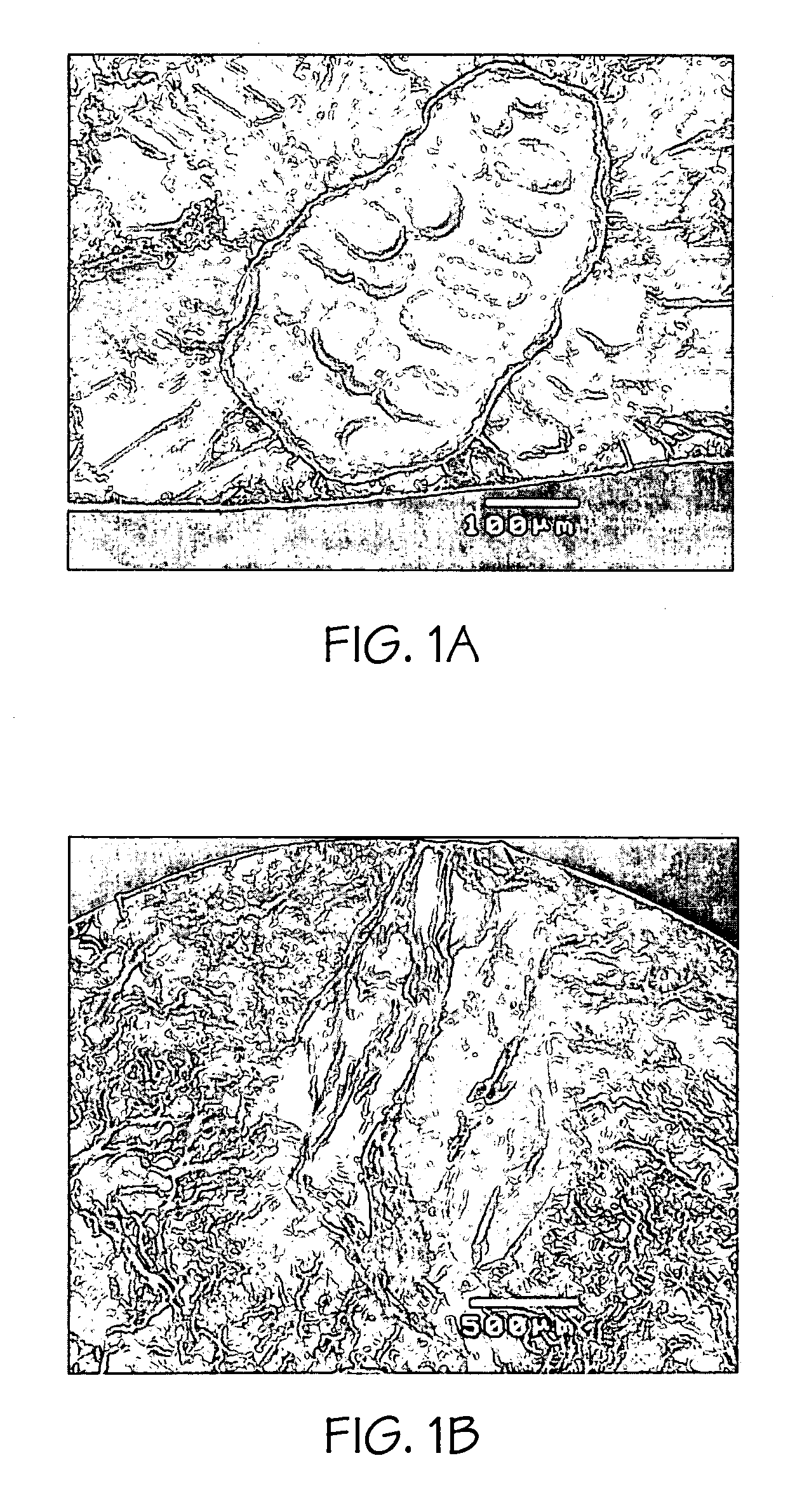
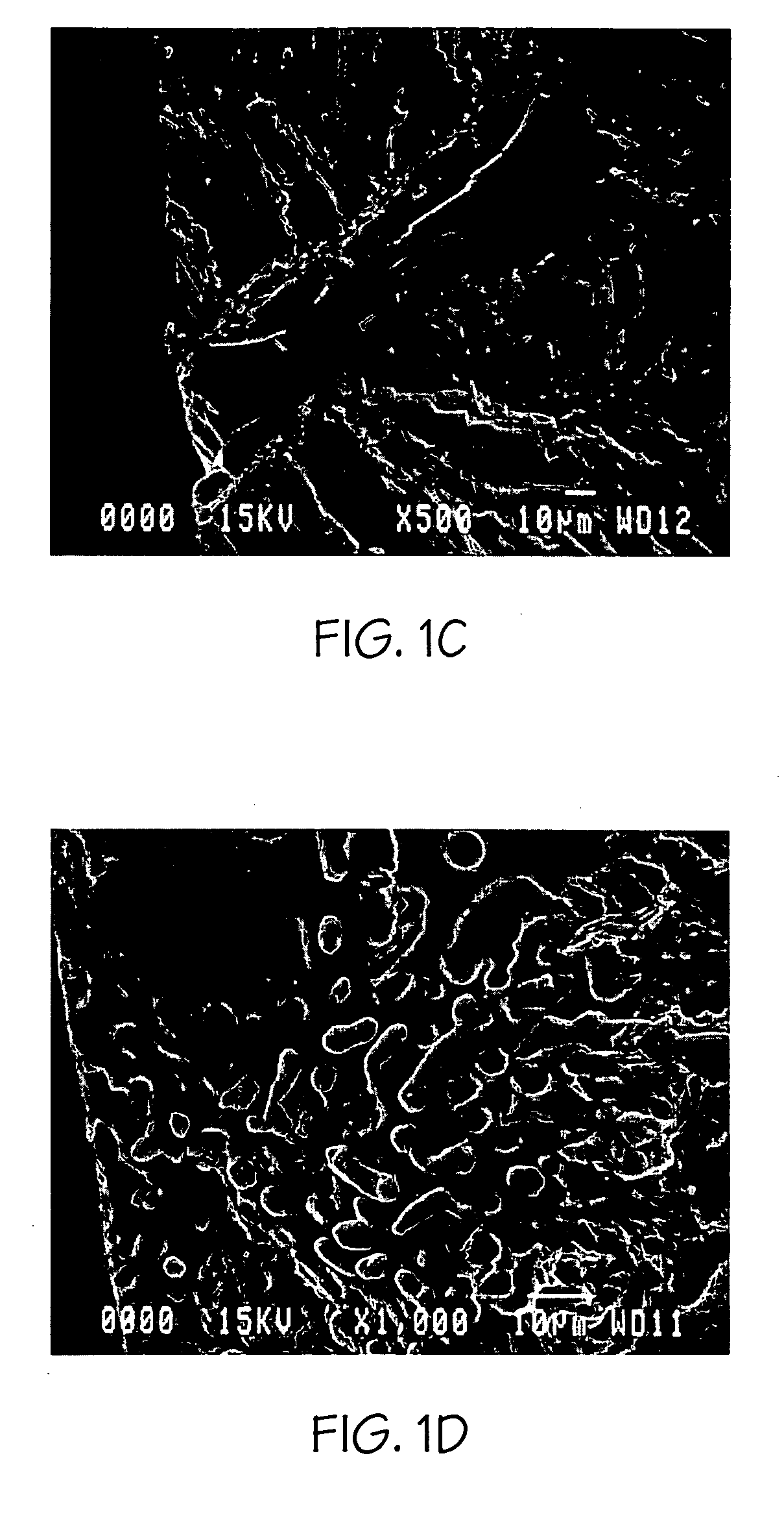
Methods and systems of predicting fatigue life in aluminum castings that combines extreme values of both casting flaws and microstructures with multiscale life models. The multiscale life models account for differing fatigue crack initiation based on the size scale of the defect and microstructure features, including provisions for generally millimeter scale casting flaws, generally micrometer scale second phase particles by cracking or debonding, or submicrometer scale dislocation interactions with precipitates which form persistent slip bands. In the presence of casting flaws, the fatigue initiation life is negligible and the total fatigue life is spent in propagation of a fatigue crack from such flaws. In the absence of casting flaws, however, the total fatigue life is spent in both crack initiation and propagation, except for the case where fatigue cracks initiate from large second phase particles in a coarse microstructure. The extreme values of casting flaws, second phase particles, mean free path through an aluminum matrix or grain sizes are obtained from extreme value statistics when two or three dimensional sizes of casting flaws and microstructure features are provided by either direct measurement or analytical prediction. The upper bound flaw or microstructure feature size is calculated by extreme value statistics.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
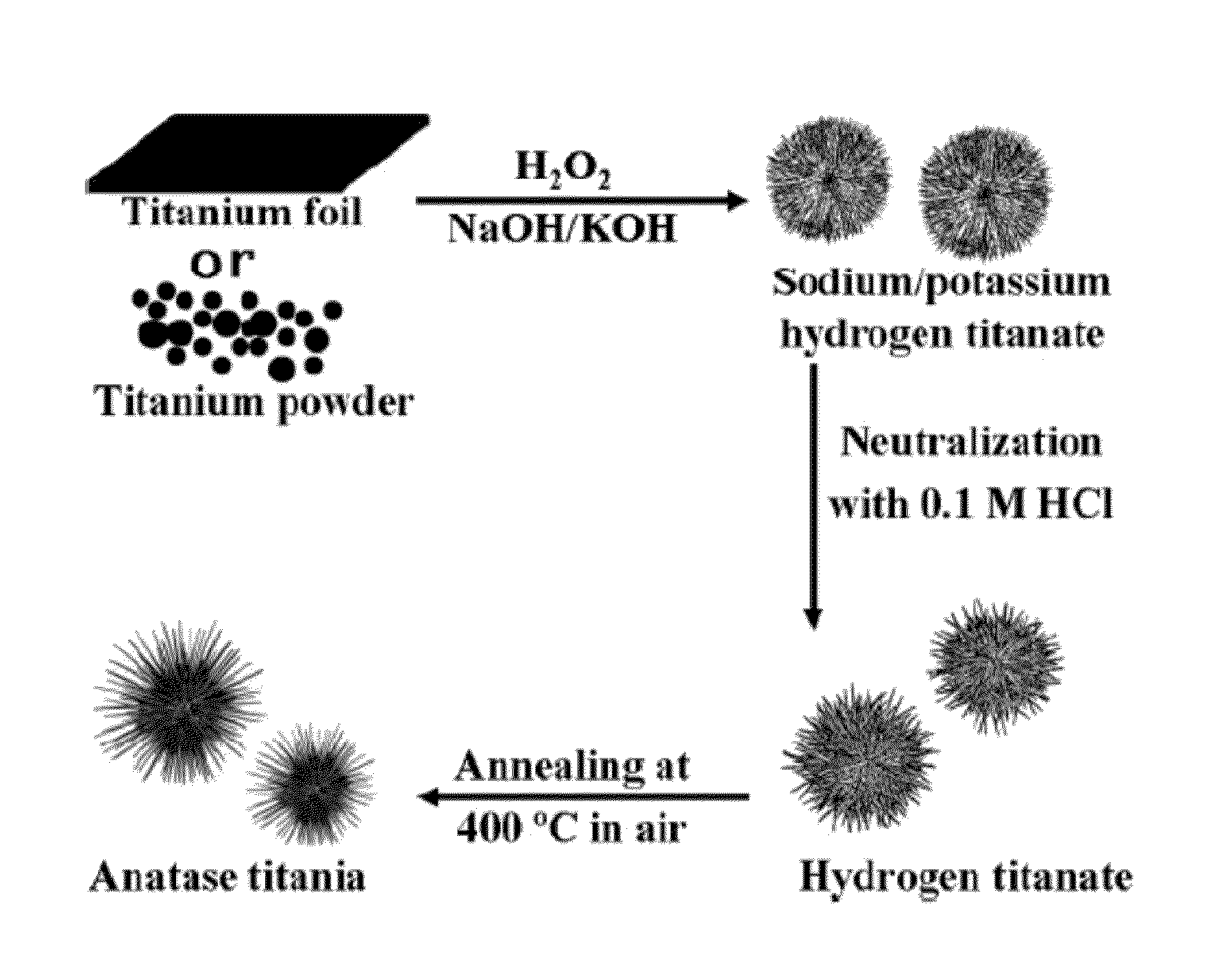
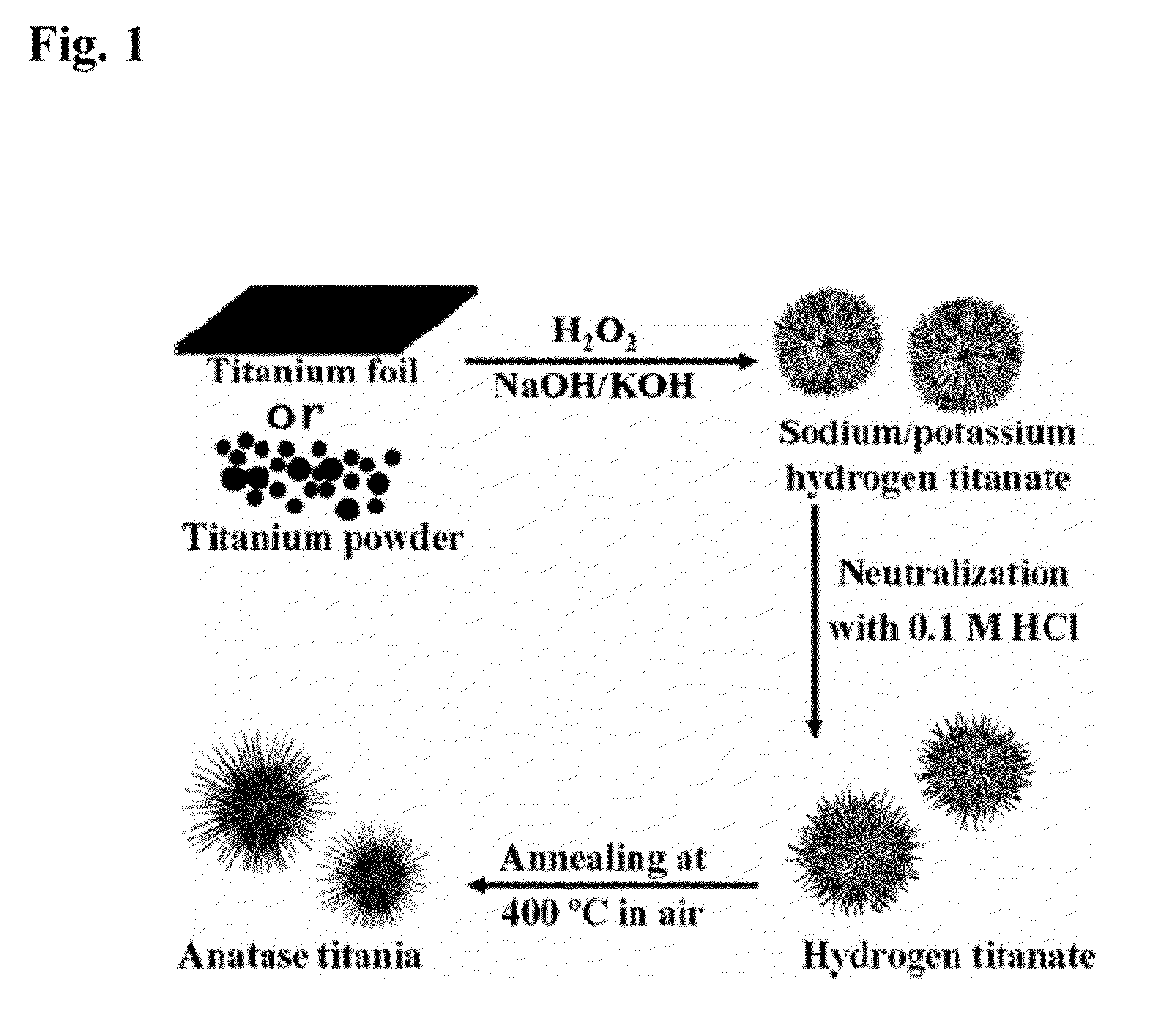
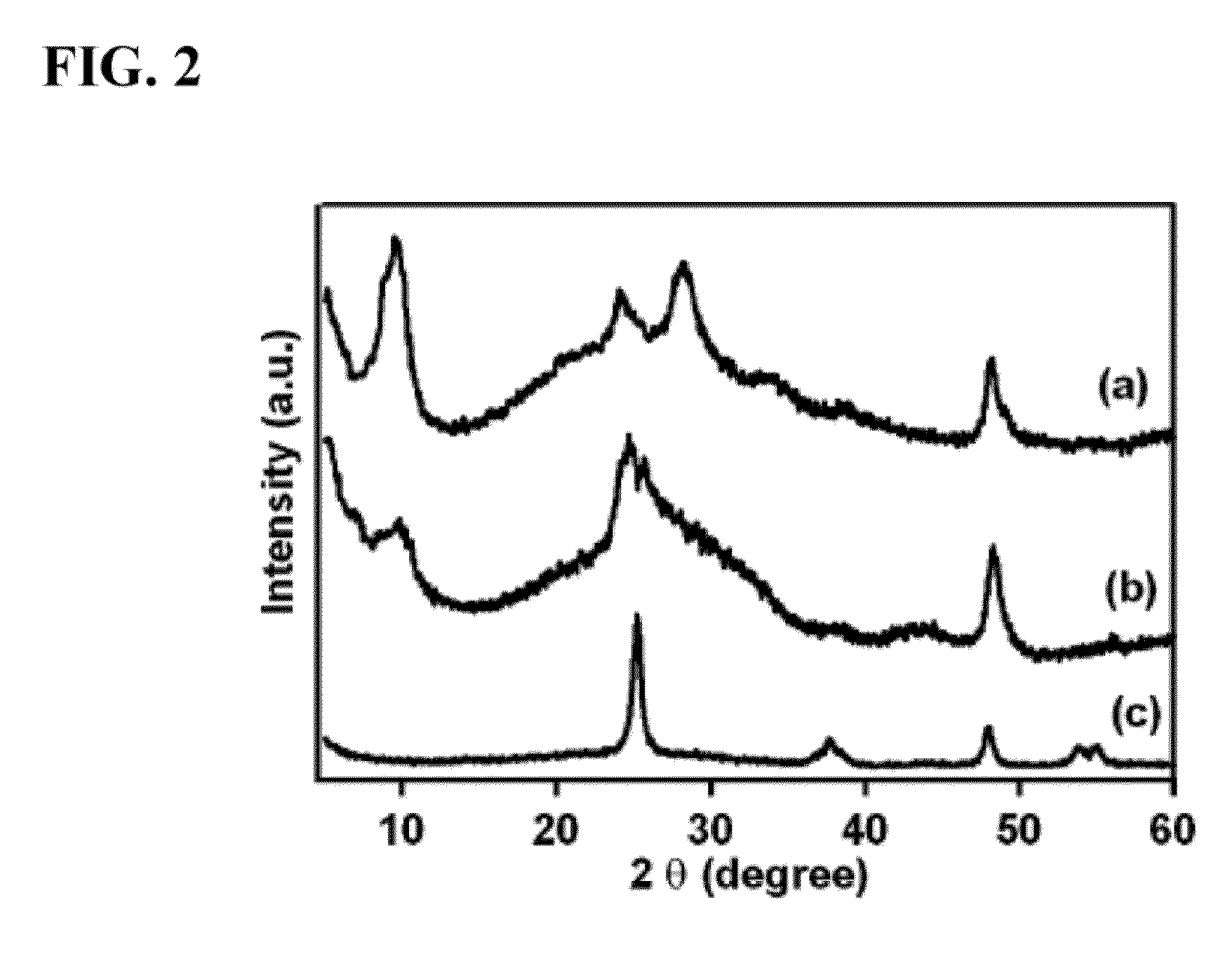
Titanate and titania nanostructures and nanostructure assemblies, and methods of making same
ActiveUS20130102458A1Improve scalabilityImprove photocatalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenMicrometer scaleTitanium
The invention relates to nanomaterials and assemblies including, a micrometer-scale spherical aggregate comprising: a plurality of one-dimensional nanostructures comprising titanium and oxygen, wherein the one-dimensional nanostructures radiate from a hollow central core thereby forming a spherical aggregate.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
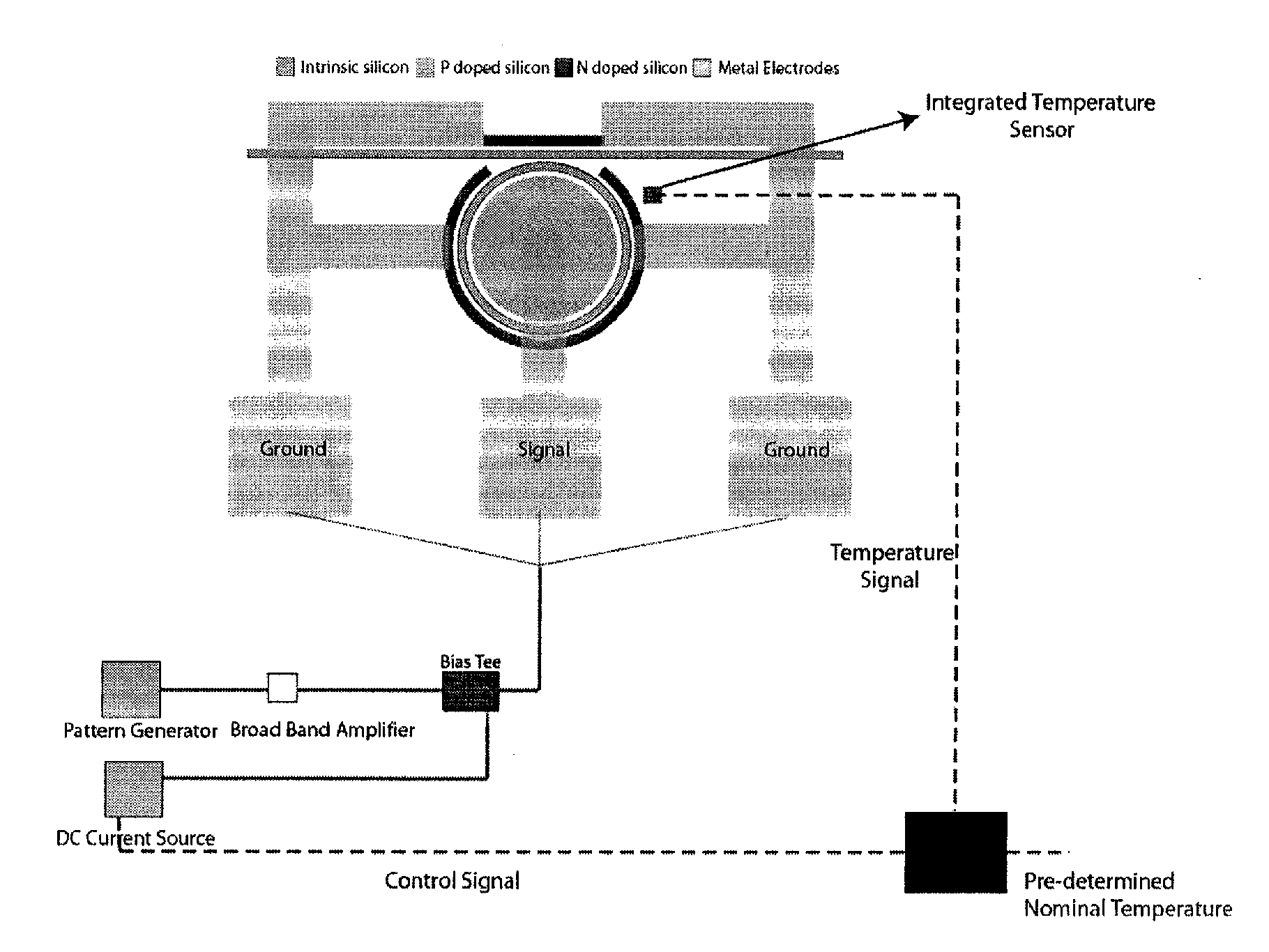
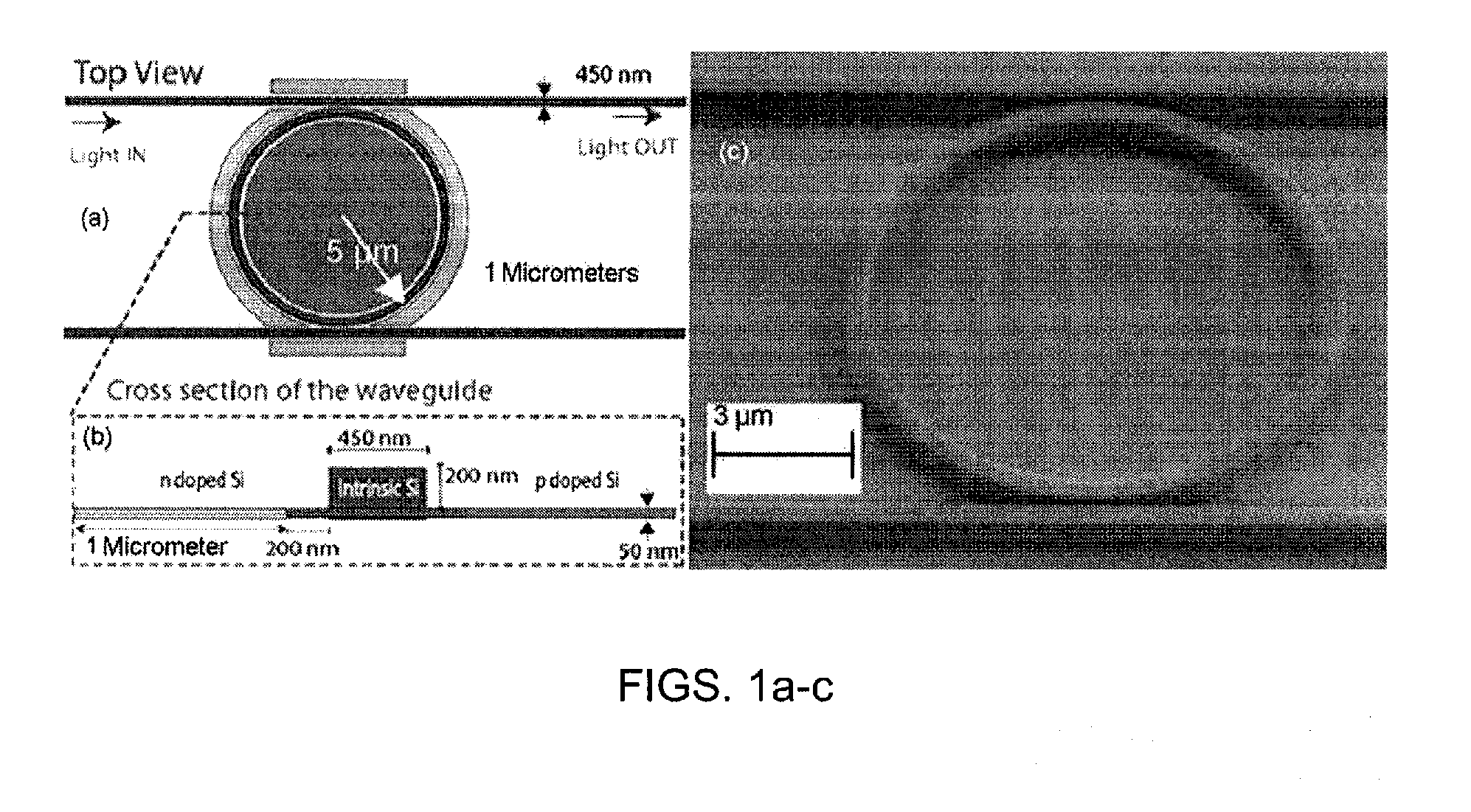
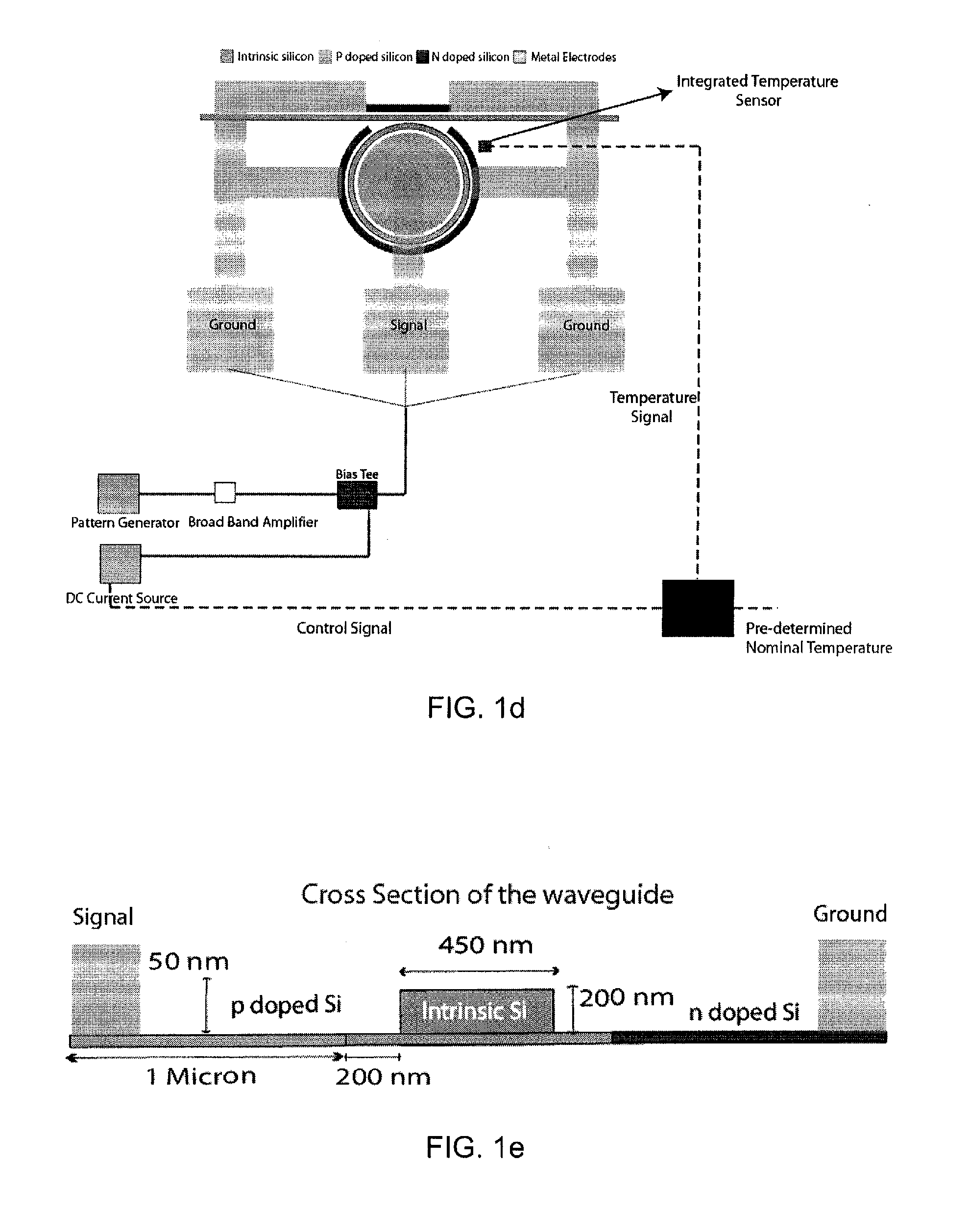
Apparatus and methods for wide temperature range operation of micrometer-scale silicon electro-optic modulators
ActiveUS20120062974A1Increase currentTotal current dropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsMicrometer scaleThermal variation
A thermally stabilized, high speed, micrometer-scale silicon electro-optic modulator is provided. Methods for maintaining desired temperatures in electro-optic modulators are also provided. The methods can be used to maintain high quality modulation in the presence of thermal variations from the surroundings. Direct current injection into the thermally stabilized electro-optic modulator is used to maintain the modulation performance of the modulator. The direct injected current changes the local temperature of the thermally stabilized electro-optic modulator to maintain its operation over a wide temperature range.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
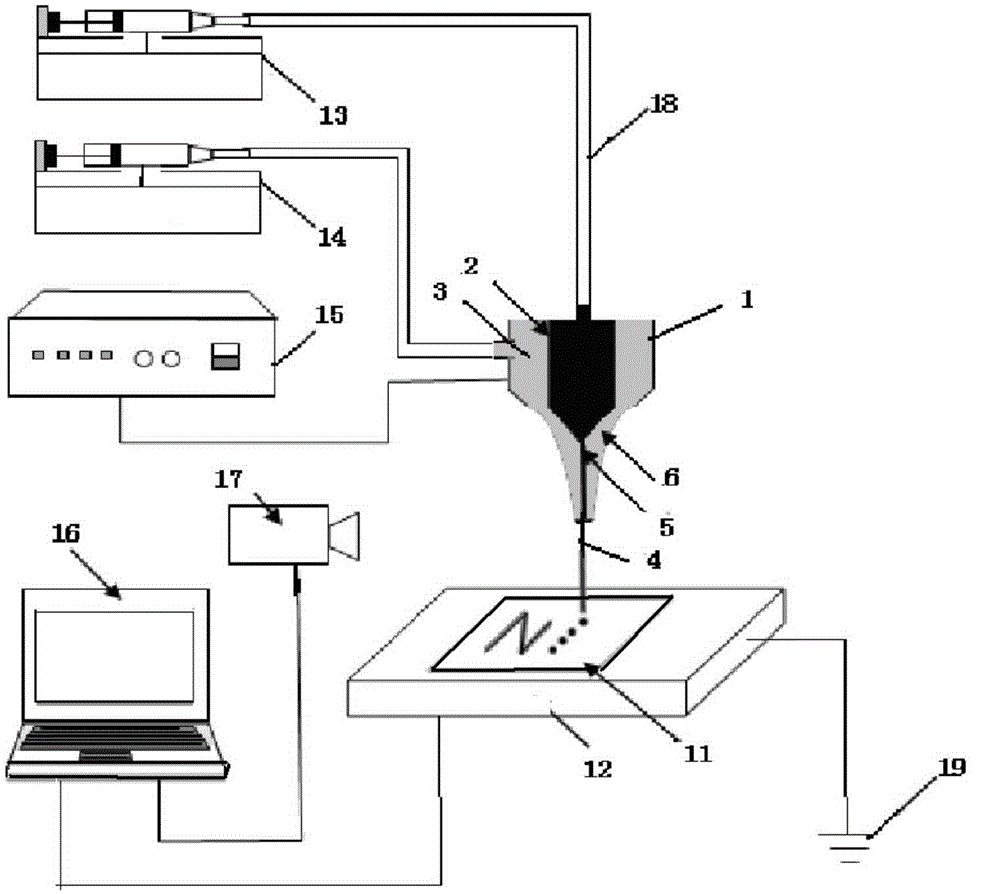
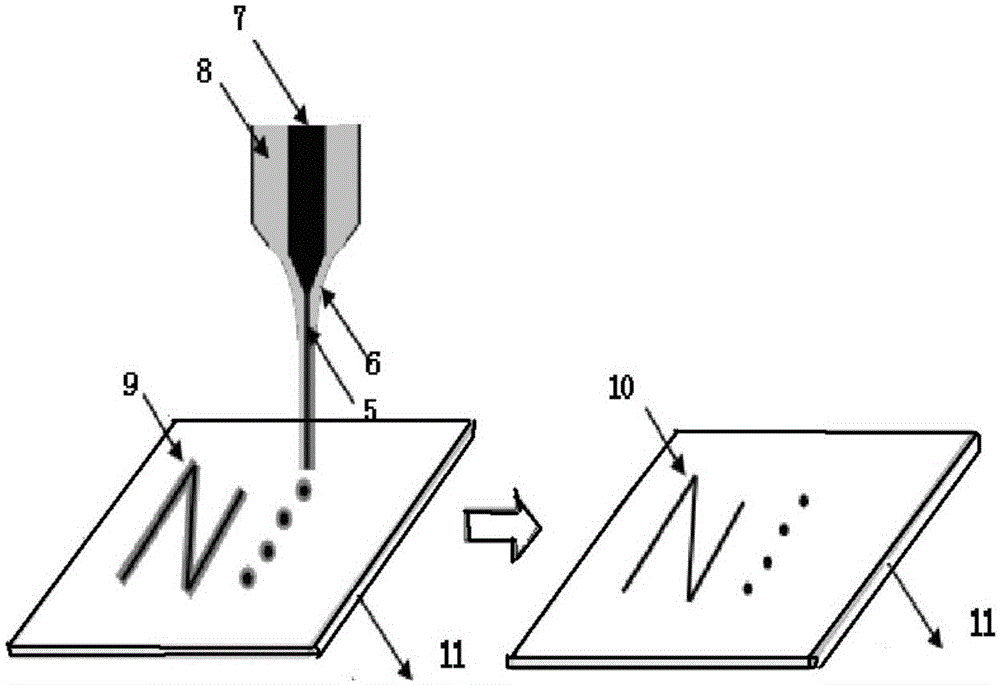
Coaxial focusing electro stream printing method
ActiveCN105058786AAdaptableStrong interferenceAdditive manufacturing apparatusJet flowMicrometer scale
The invention relates to a coaxial focusing electro stream printing method, belongs to the technical field of advanced manufacture and relates to a coaxial focusing electro stream printing method. According to the method, in the coaxial focusing electro stream printing process, two kinds of liquid are contained in a coaxial focusing electro stream printing nozzle, one kind of the liquid is a required forming material called inner function liquid, and the other kind of the liquid is an auxiliary material called outer liquid; the outer liquid and the inner function liquid are not dissolved mutually, and the viscosity of the outer liquid is larger than that of the inner function liquid. The coaxial focusing electro stream printing nozzle forms coaxial focusing jet flow with the two layers of liquid during printing and prints a bi-layer structure on a substrate; and finally, an outer printing material is removed to obtain an inner function structure. The method has the characteristics of being high in printing resolution, material adaptability and microenvironment disturbance resistance and is capable of achieving high-resolution patterned printing through a spray needle of micrometer scales at normal temperatures and pressures.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Manufacturing method of metal and plastic combination body and combination body
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a metal and plastic combination body. The method comprises the steps that an aluminum or aluminum alloy base body is provided; a solution is used for soaking and corroding of the aluminum or aluminum alloy base body; the soaked and corroded aluminum or aluminum alloy base body is subjected to electrochemistry corrosion, water solution of sodium bicarbonate is used as electrolyte, a multi-hole layer which is provided with a plurality of corrosion holes is formed on the surface of the aluminum or aluminum alloy base body, the plurality of corrosion holes comprise holes with nanoscale diameters and holes with micrometer-scale diameters, the corrosion holes are communicated in a mutual-staggering mode so that a three-dimension network multi-hole structure of the multi-hole layer is formed; fused plastic is injected on the surface of the multi-hole layer, and the metal and plastic combination body is formed. The method is simple in technology and environmental-friendly, and the combination body manufactured with the method is high in combining strength of metal and the plastic. The invention further provides the metal and plastic combination body manufactured with the method.
Owner:UR IND MATERIALS LANGFANG CO LTD
Coaxial measuring tool and measuring method
InactiveCN1624422APrecise positioningReduce labor intensityUsing optical meansMicrometer scaleLight pipe
The invention relates to the measuring tool set up and method for axiality of axial line of axial line of main engine of ship and basis points of head and tail , The measuring tool set up includes two same light pipes on the head and tail, two light targets and four supports of light targets, two target plates supports of head and tail, two base tool set up and micrometer ordination axis of inside diameter. The measuring steps are as follows: the target plate supports of the head and tail are put separately on basis points of head and tail of the ship, telescope is used to build a axial line of head and tail; the light targets are separately installed on the front and back ends of head and tail light pipes in the main axis pipe, the telescope is used to adjust the support of head and tail light pipes , making the center of light targets on head and tail light pipes on the axial line of head and tail ; the final orientation basis points of axial line is used to process the light pipes; the telescope is used to mark the axial line of head and tail of main axial hole and by the difference of the middle point of axial line, is acquired. Its advantages are accurate orientation of main axial, high efficiency.
Owner:中国船舶集团渤海造船有限公司
Methods for making microarrays and their uses
ActiveUS20140274771A1Limiting scale and degreeAvoid wastingPeptide librariesLibrary screeningFluorescenceSurface binding
The present invention provides microarrays that can be analysed by more than one technique using a non-covalent ligand attachment strategy to solid supports such as indium tin oxide (ITO) covered transparent glass slides. This provides, inter alia, glycan arrays on a micrometer scale which allow multimodal readout by MALDI-Tof-MS, fluorescence and optical microscopy. Glycans functionalized with a C5-aminolinker were attached in situ on a picomolar scale to a hydrophobic tag bound to this surface, thus avoiding the wasteful off-chip ligand tagging of other approaches. Glycan arrays prepared using this methodology were analysed both with a fluorescence scanner and by on-chip MALDI-mass spectrometry in a series of glycomics experiments specifically requiring a multimodal readout.
Owner:ASOCIACION CENT DE INVESTIGACION COOP & BIOMATERIALES - CIC BIOMAGUNE
Methods and apparatuses for the development of microstructured nuclear fuels
ActiveUS7521007B1Ensure uniform motionLow costFuel elementsNuclear energy generationChemical vapor depositionMaterials science
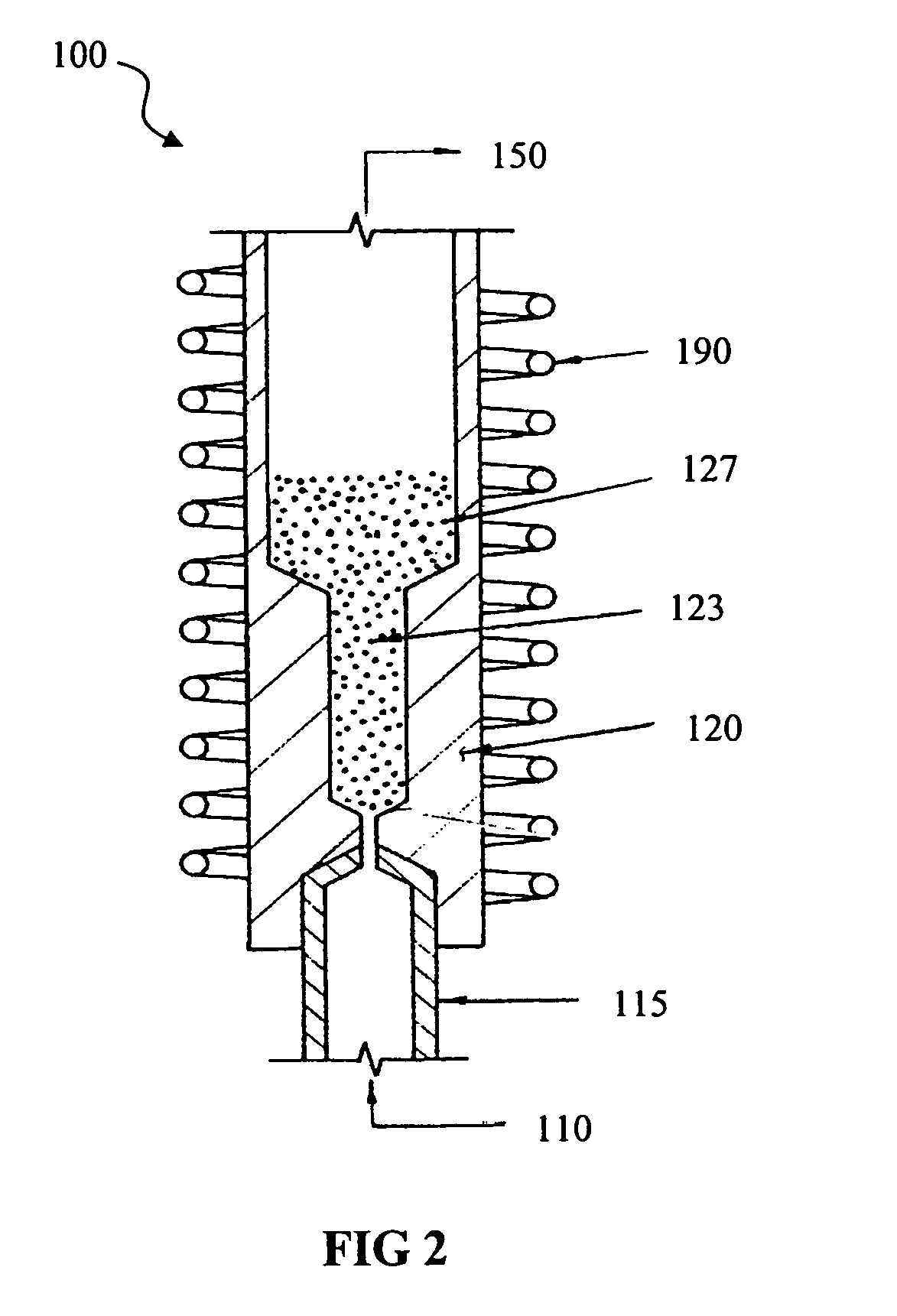
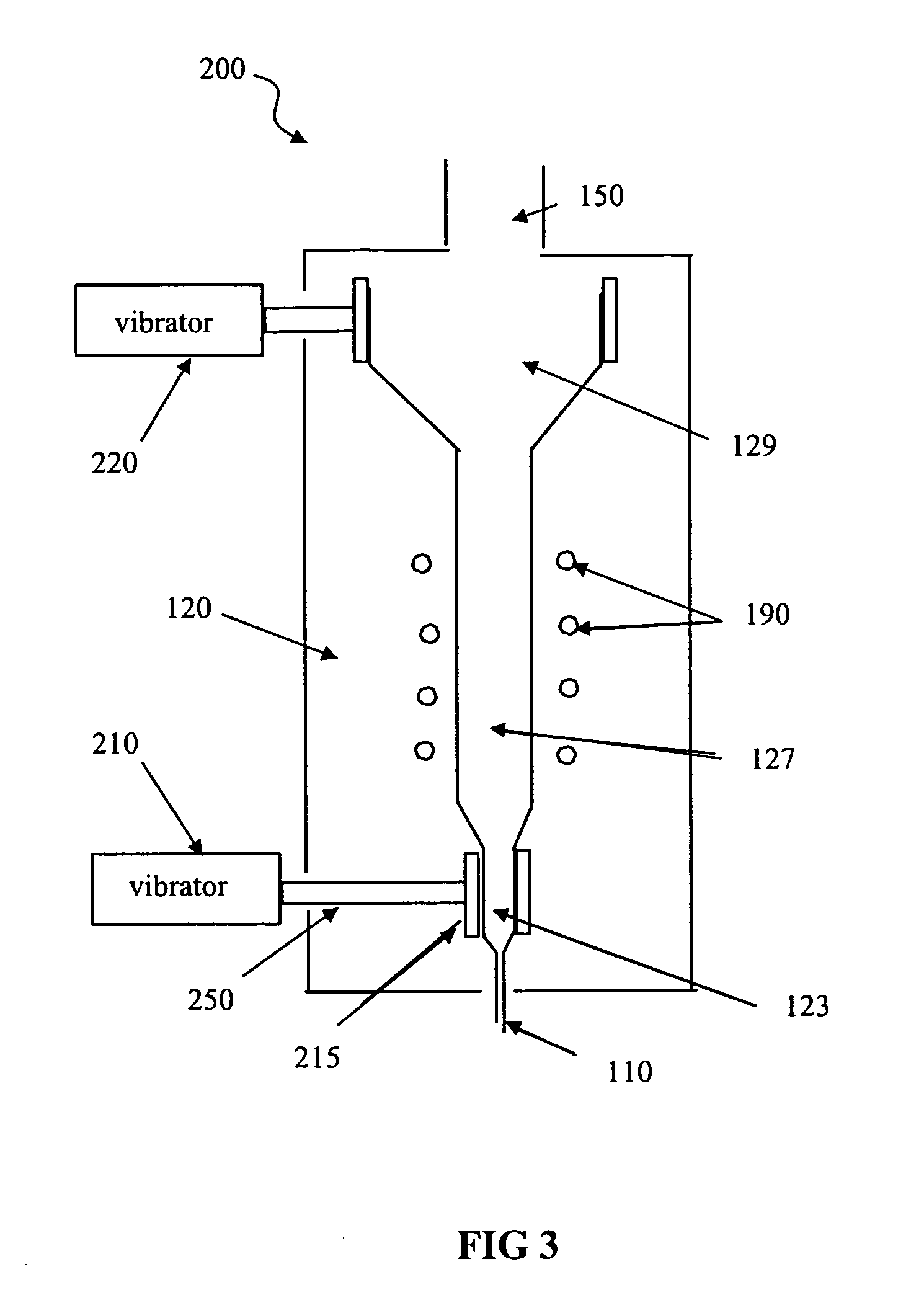
Microstructured nuclear fuel adapted for nuclear power system use includes fissile material structures of micrometer-scale dimension dispersed in a matrix material. In one method of production, fissile material particles are processed in a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) fluidized-bed reactor including a gas inlet for providing controlled gas flow into a particle coating chamber, a lower bed hot zone region to contain powder, and an upper bed region to enable powder expansion. At least one pneumatic or electric vibrator is operationally coupled to the particle coating chamber for causing vibration of the particle coater to promote uniform powder coating within the particle coater during fuel processing. An exhaust associated with the particle coating chamber and can provide a port for placement and removal of particles and powder. During use of the fuel in a nuclear power reactor, fission products escape from the fissile material structures and come to rest in the matrix material. After a period of use in a nuclear power reactor and subsequent cooling, separation of the fissile material from the matrix containing the embedded fission products will provide an efficient partitioning of the bulk of the fissile material from the fission products. The fissile material can be reused by incorporating it into new microstructured fuel. The fission products and matrix material can be incorporated into a waste form for disposal or processed to separate valuable components from the fission products mixture.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Micrometer-scale glucose sensor microelectrode
ActiveCN103462615ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGlucose sensorsMicrometer scale
The invention relates to the field of detecting instruments, in particular to a micrometer-scale glucose sensor microelectrode. The micrometer-scale glucose sensor microelectrode comprises a substrate, a working electrode and a counter electrode, the front portion of the substrate is a working area, the working electrode and the counter electrode are located in the working area, the maximum diameter of the cross section of the working area is less than or equal to 1 millimeter, PADs in one-to-one correspondence to the electrodes are arranged at the tail of the substrate, and each of the working electrode and the counter electrode is connected with the corresponding PAD through a lead. The electrodes are reasonably distributed on the planar or columnar insulating substrate and width of each electrode or cross-sectional diameter of each columnar electrode is limited to effectively reduce size of the electrode, so that rejection reaction of receptors is reduced.
Owner:MEDTRUM TECH
Preparation method and application of cobalt sulfur compound
ActiveCN104993132AWide range of sourcesHigh specific capacityCobalt sulfidesCell electrodesSemiconductor materialsSolar cell
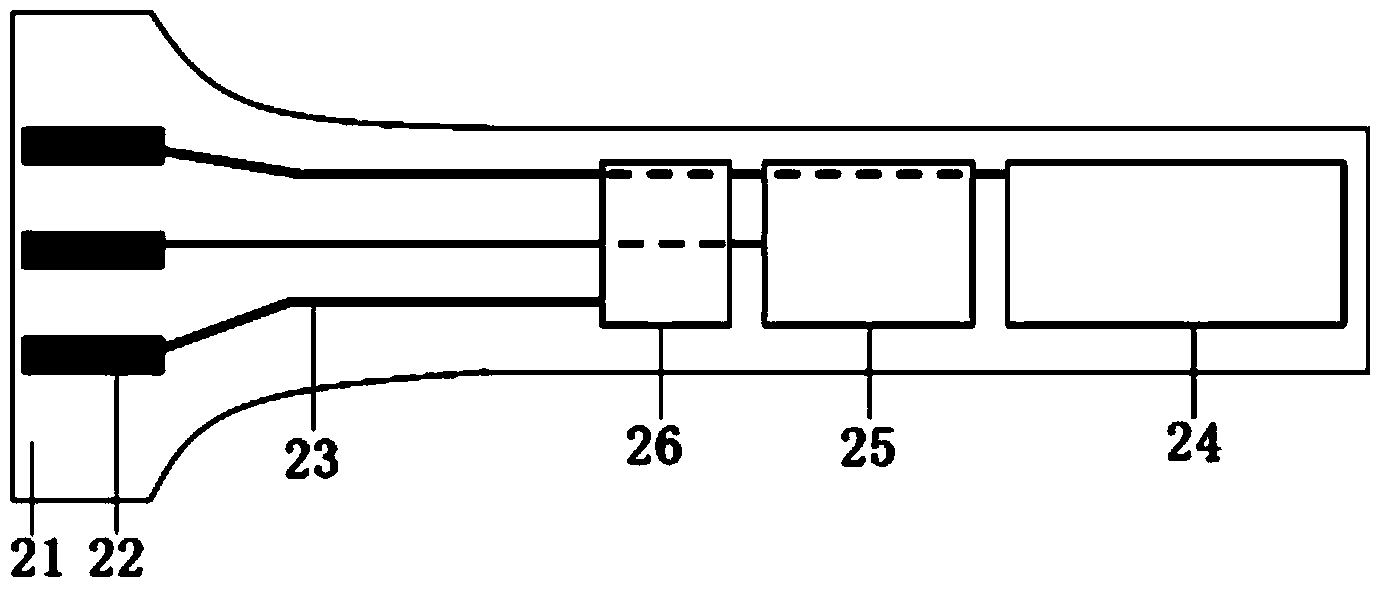
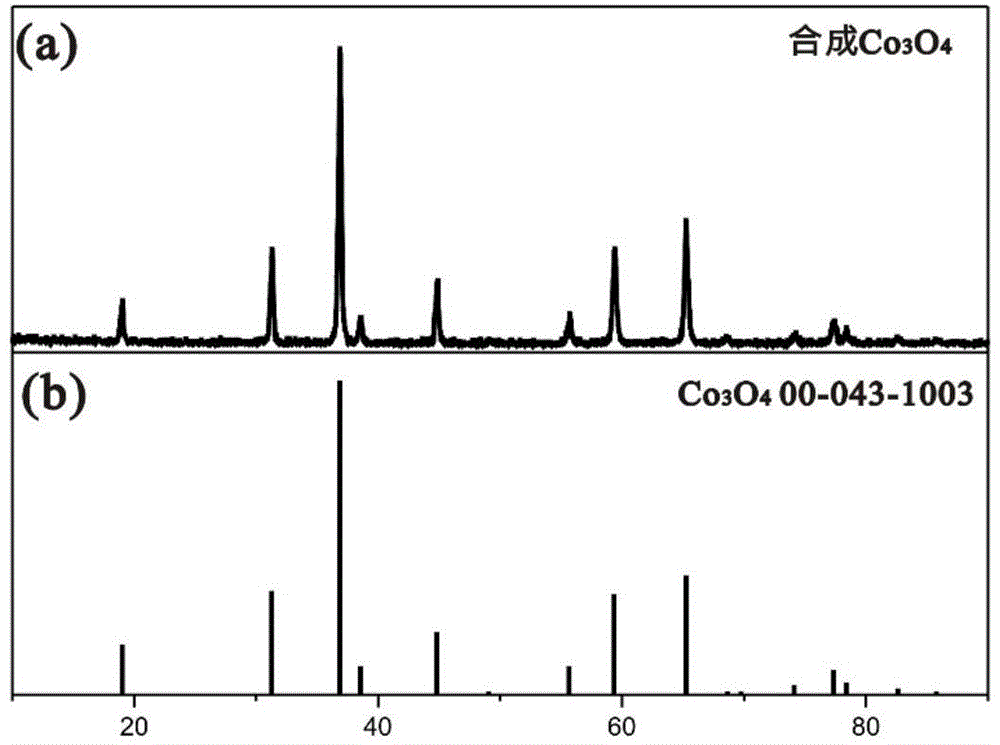
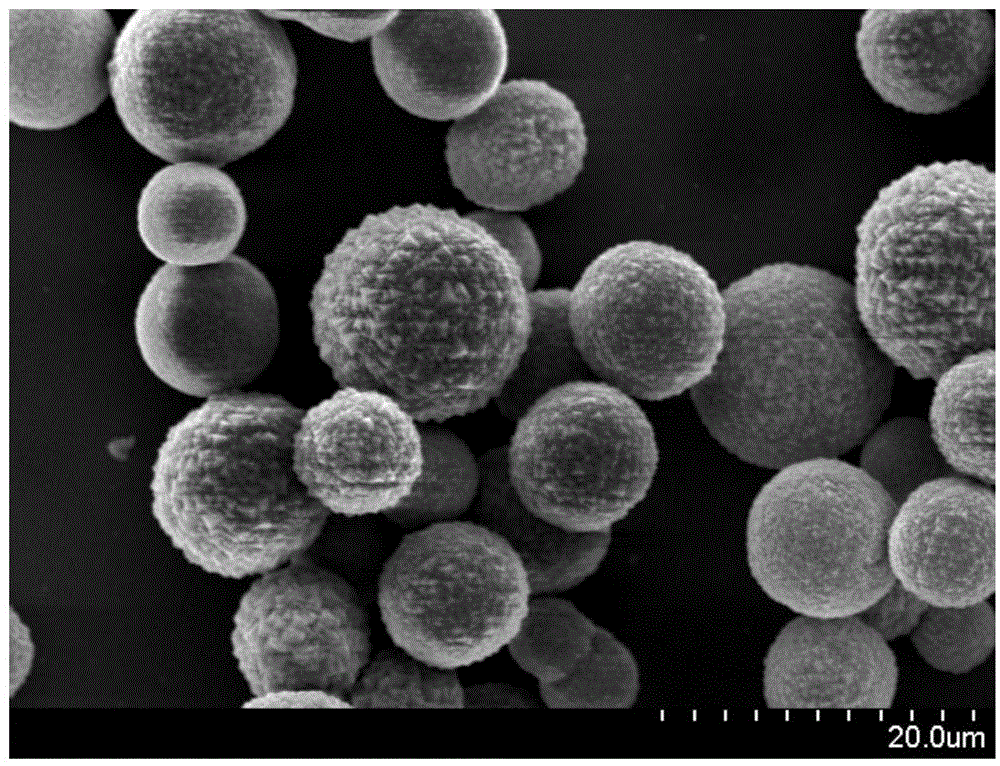
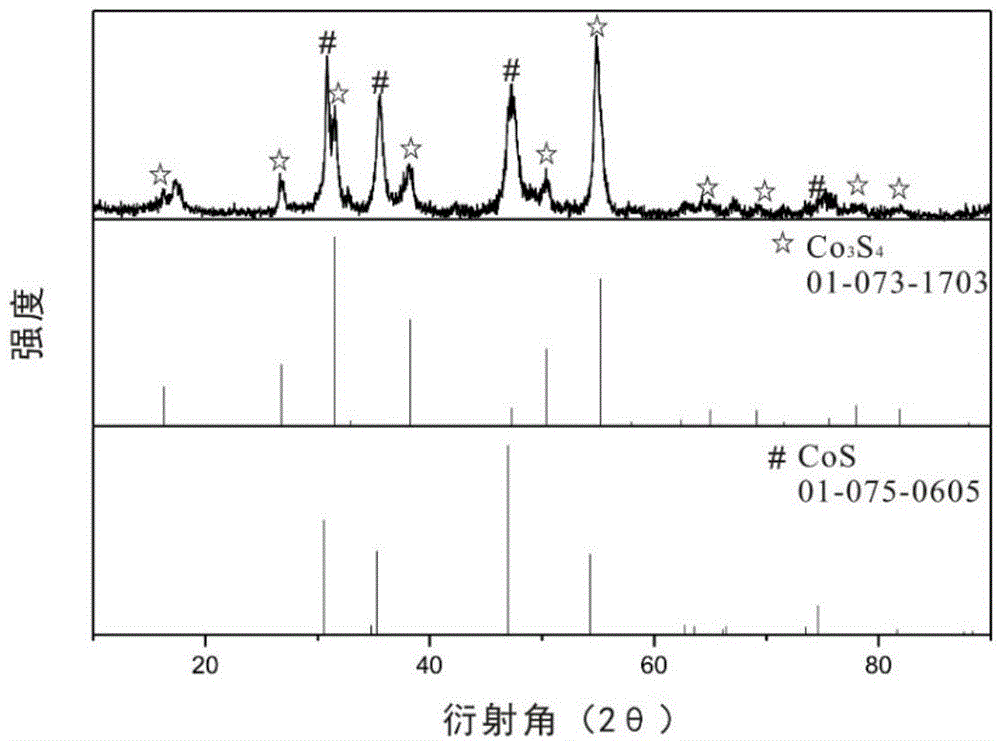
Relating to cobalt sulfur compounds, the invention provides a preparation method and application of a cobalt sulfur compound. The method includes: dissolving a water soluble cobalt source and urea in a mixed solvent to form a solution, carrying out reaction to obtain cobalt carbonate, performing calcinations to obtain a cobalt oxide, and reacting the cobalt oxide with a sulfur source in a reducing atmosphere to obtain a micrometer-scale cobalt sulfur compound. The micrometer-scale cobalt sulfur compound can be spherical cobalt sulfur compound or lamellar square-like cobalt sulfur compound, and the obtained cobalt sulfur compound can be Co9S8, CoS, Co3S4 and CoS2, etc. The cobalt sulfur compound prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention can be applied as an electrode active material in preparation of secondary battery electrodes. According to the invention, specific shape cobalt sulfide can be prepared, is low in synthesis cost and has high tap density, and can be applied to secondary battery electrode materials, optical parametric oscillators, semiconductor materials, solar cells and other aspects.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Array of abrasive members with resilient support
An abrasive article having an array of abrasive members with an elastomeric support that permits each abrasive member to move independently in at least pitch and roll. Each abrasive member maintains a fluid bearing (air is the typical fluid) with the substrate. The abrasive members are capable of selectively engaging with nanometer-scale and / or micrometer-scale height variations and micrometer-scale and / or millimeter-scale wavelengths of waviness, on the surfaces of substrates. The spacing and pitch of the abrasive members can be adjusted to follow the topography of the substrate to remove a generally uniform layer of material; to engage with the peaks on the substrate to remove target wavelengths of waviness; and / or to remove debris and contamination from the surface of the substrate.
Owner:RDC HLDG
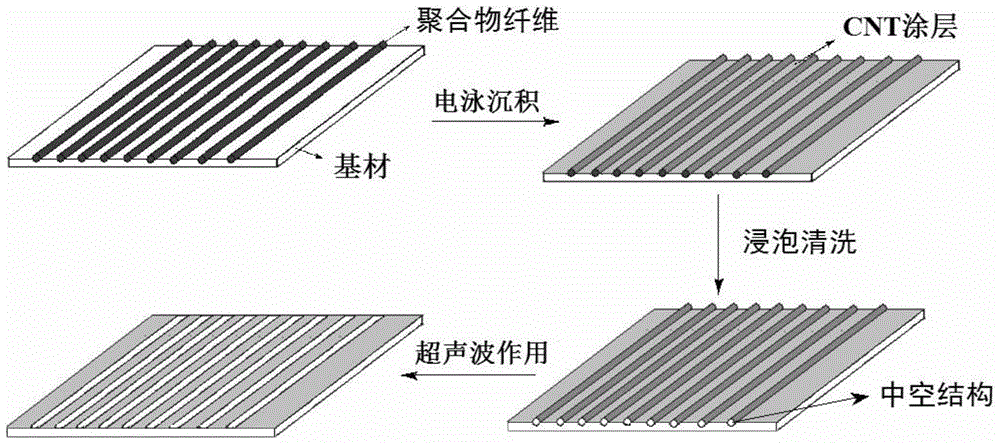
Nerve conduit material having topological structure and modified by CNT/conducting polymer composite coating and preparation method of nerve conduit material
The invention provides a nerve conduit material having a topological structure and modified by a CNT (Carbon Nano Tube) / conducting polymer composite coating and a preparation method of the nerve conduit material. With electro-spun polymer fibers as templates, CNTs are deposited on the surface of a substrate by use of an electrophoresis method so as to form a three-dimensional porous network CNT coating, next, solvent cleaning and ultrasonic stripping are carried out to form the CNT coating with a directional groove structure, then a conducting polymer is deposited by use of electro-chemical impulse polymerization, and the conducting polymer is coaxially wound around the surface of the CNT bundle to form the nerve conduit material modified by the CNT / conducting polymer composite coating having the directional groove structure. The surface of the nerve conduit material has two layers in the topological structure: at micrometer scale, the coating is provided with a patterned micrometer-scale groove for guiding the rearrangement of a neural cytoskeleton; at nanometer scale, the coating is provided with a nanometer-scale porous network structure for guaranteeing the physical conditions for the attachment and growth of nerve cells and excellent electrochemical properties of the nerve conduit.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
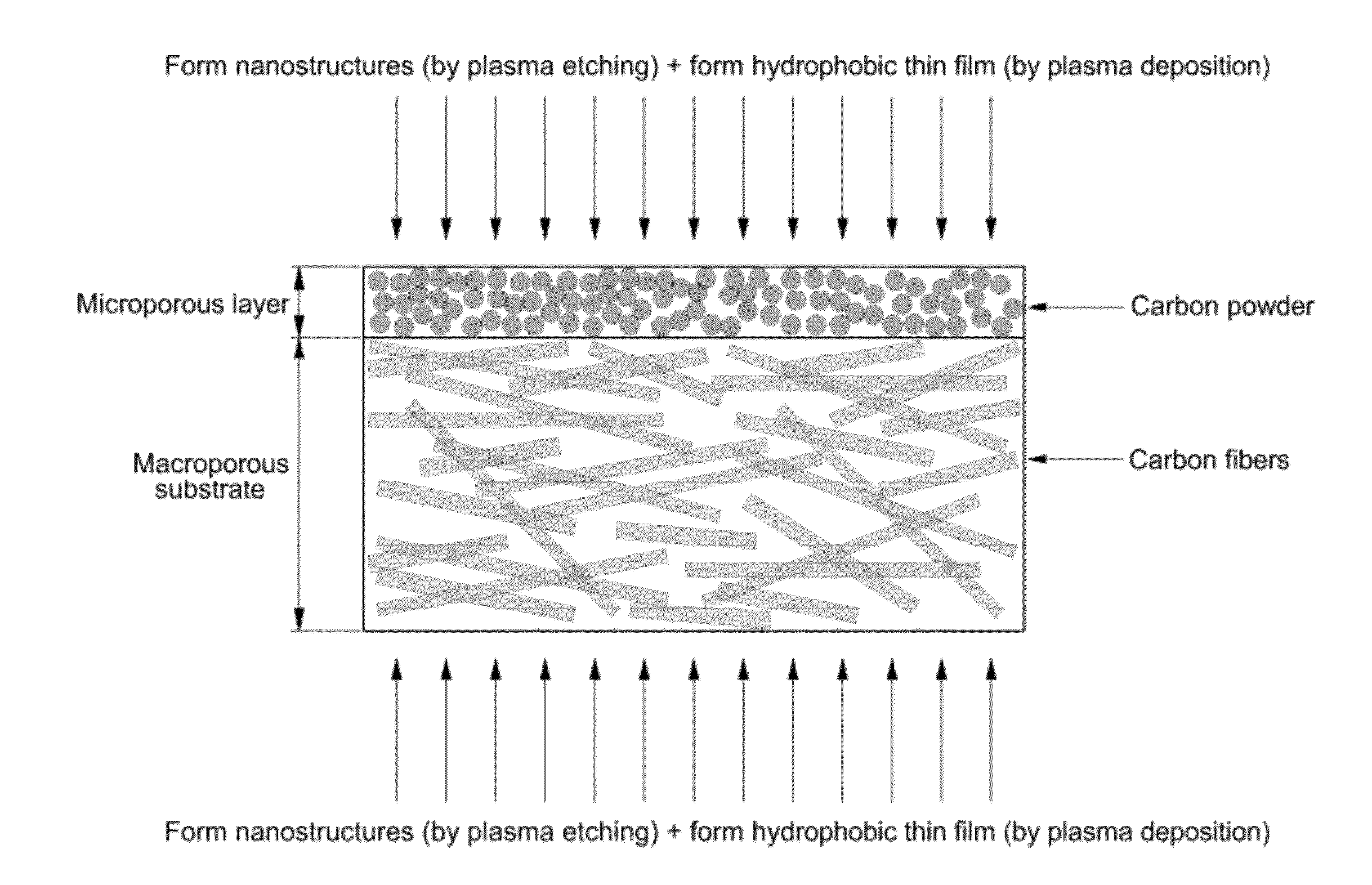
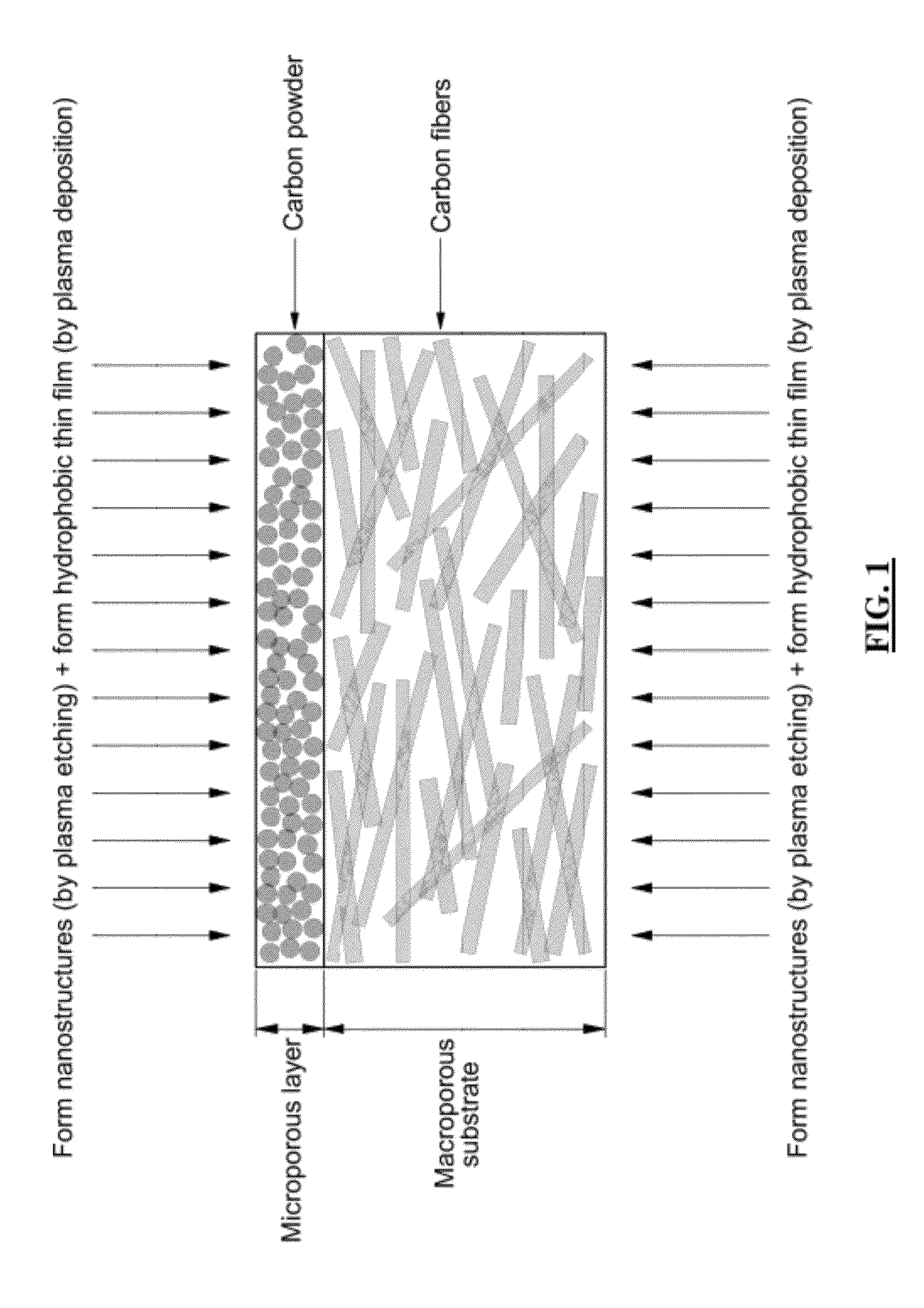
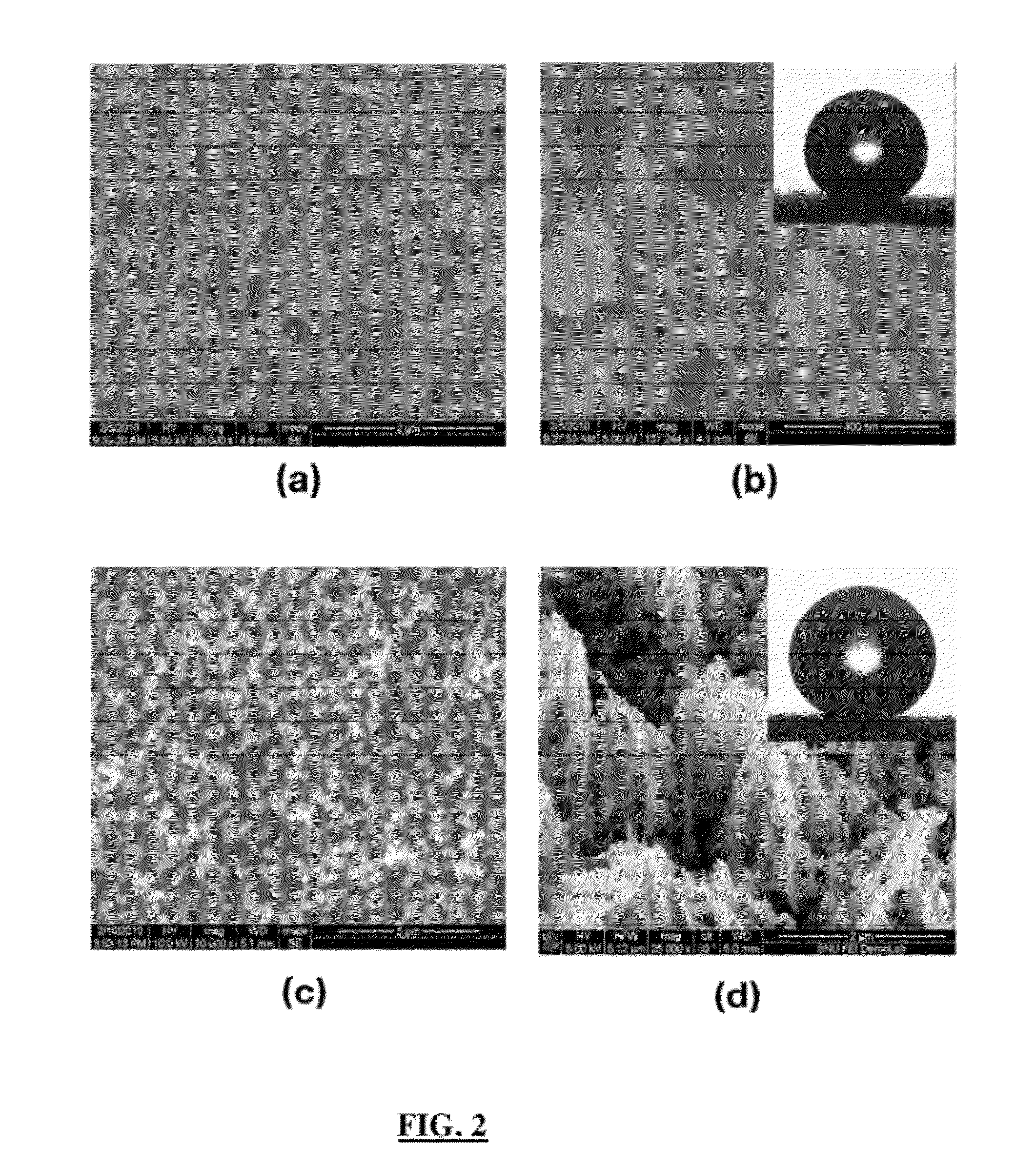
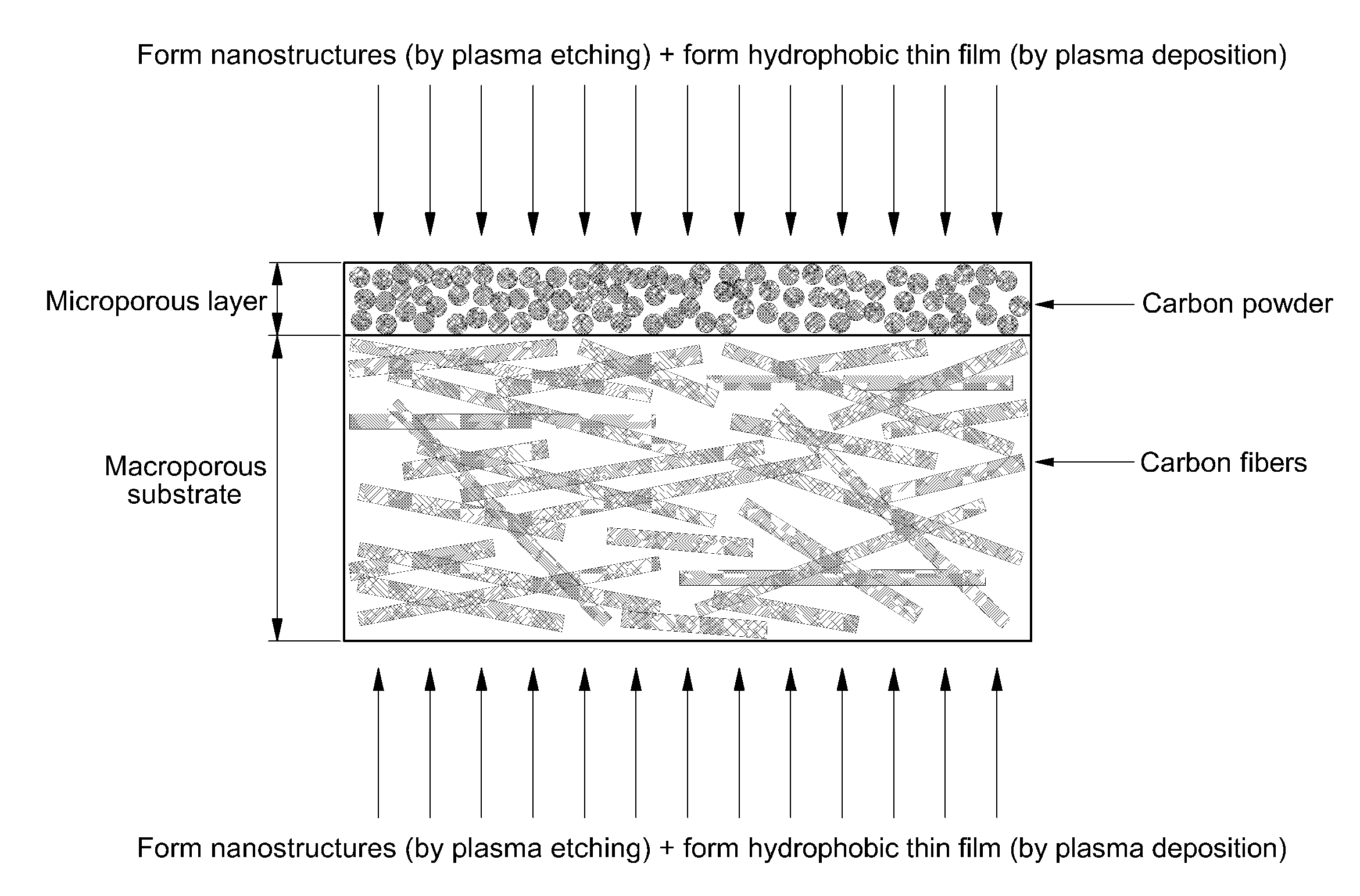
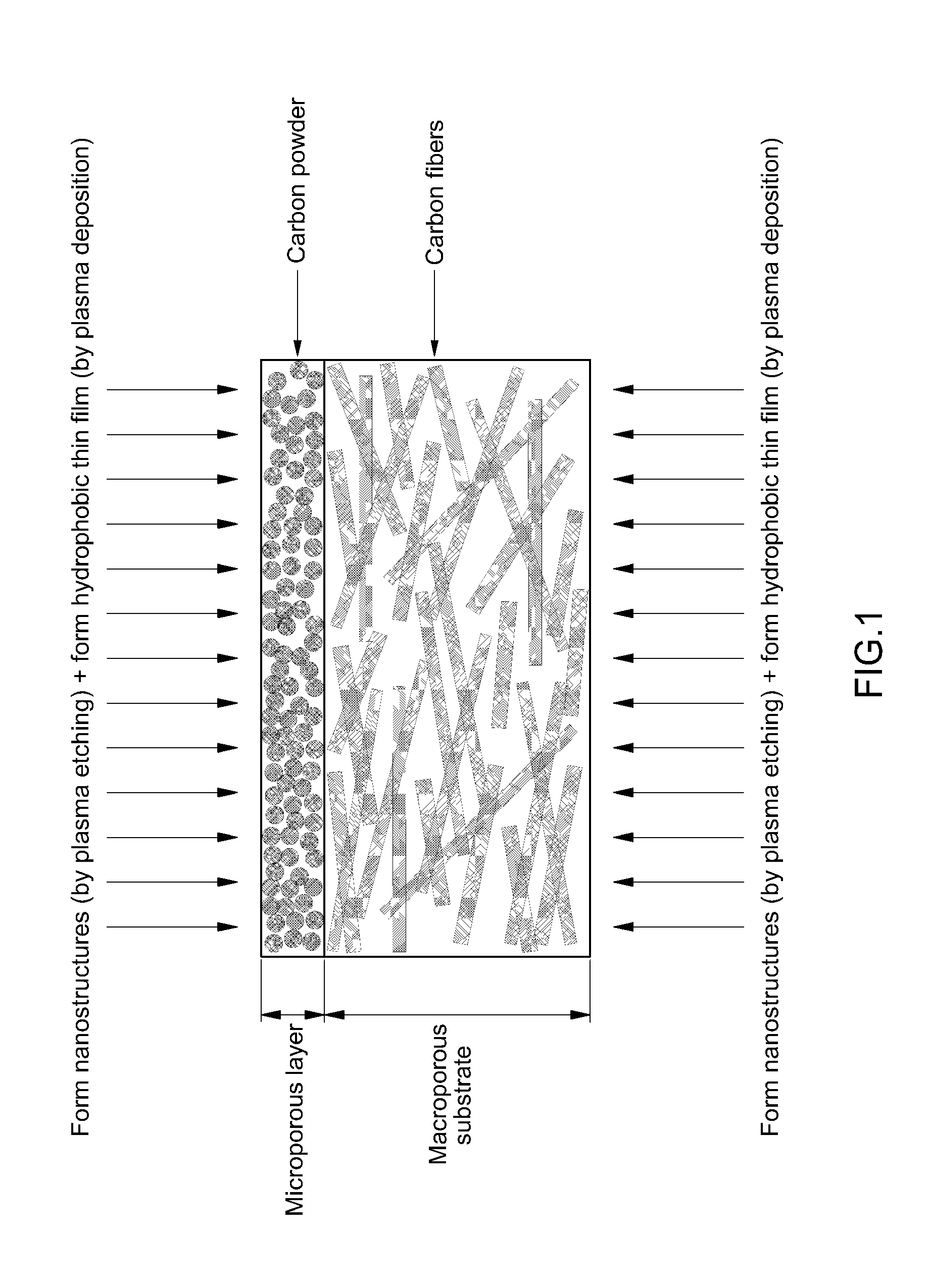
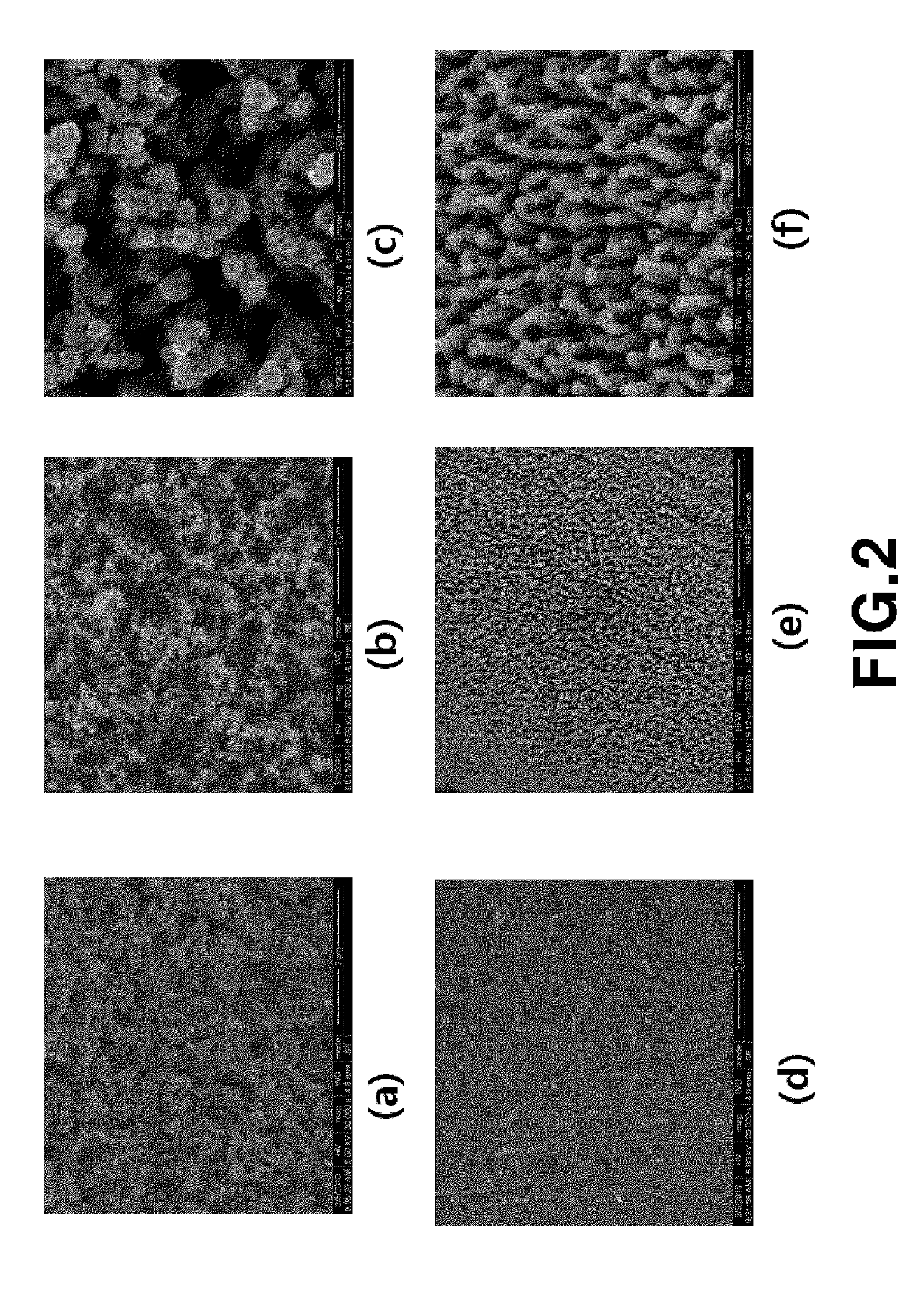
Porous medium with increased hydrophobicity and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120276335A1Improve hydrophobicityEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsElectrochemical responseMicro nano
The present invention provides a porous medium with increased hydrophobicity and a method of manufacturing the same, in which a micro-nano dual structure is provided by forming nanoprotrusions with a high aspect ratio by performing plasma etching on the surface of a porous medium with a micrometer-scale surface roughness and a hydrophobic thin film is deposited on the surface of the micro-nano dual structure, thus significantly increasing hydrophobicity. When this highly hydrophobic porous medium is used as a gas diffusion layer of a fuel cell, it is possible to efficiently discharge water produced during electrochemical reaction of the fuel cell, thus preventing flooding in the fuel cell. Moreover, it is possible to sufficiently supply reactant gases such as hydrogen and air (oxygen) to a membrane electrode assembly (MEA), thus improving the performance of the fuel cell.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Fuel cell with enhanced mass transfer characteristics
ActiveUS20130089807A1Enhanced mass transfer characteristicReduce floodingSolid electrolytesNanotechElectrochemical responseMicro nano
Disclosed is a fuel cell with enhanced mass transfer characteristics in which a highly hydrophobic porous medium, which is prepared by forming a micro-nano dual structure in which nanometer-scale protrusions with a high aspect ratio are formed on the surface of a porous medium with a micrometer-scale roughness by plasma etching and then by depositing a hydrophobic thin film thereon, is used as a gas diffusion layer, thereby increasing hydrophobicity due to the micro-nano dual structure and the hydrophobic thin film. When this highly hydrophobic porous medium is used as a gas diffusion layer for a fuel cell, it is possible to reduce water flooding by efficiently discharging water produced by an electrochemical reaction of the fuel cell and to improve the performance of the fuel cell by facilitating the supply of reactant gases such as hydrogen and air (oxygen) to a membrane-electrode assembly (MEA).
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com