Patents
Literature
208 results about "Mean free path" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
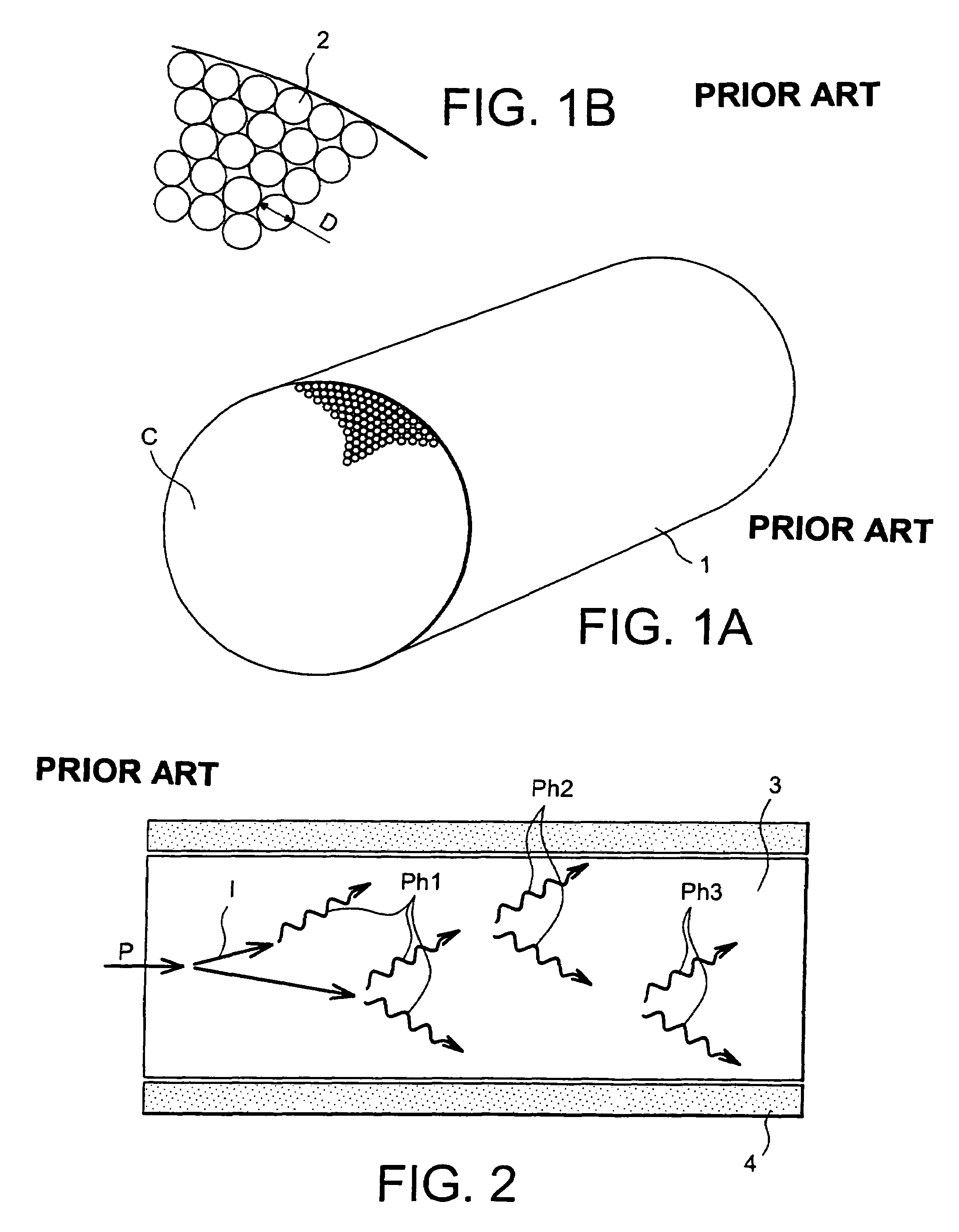
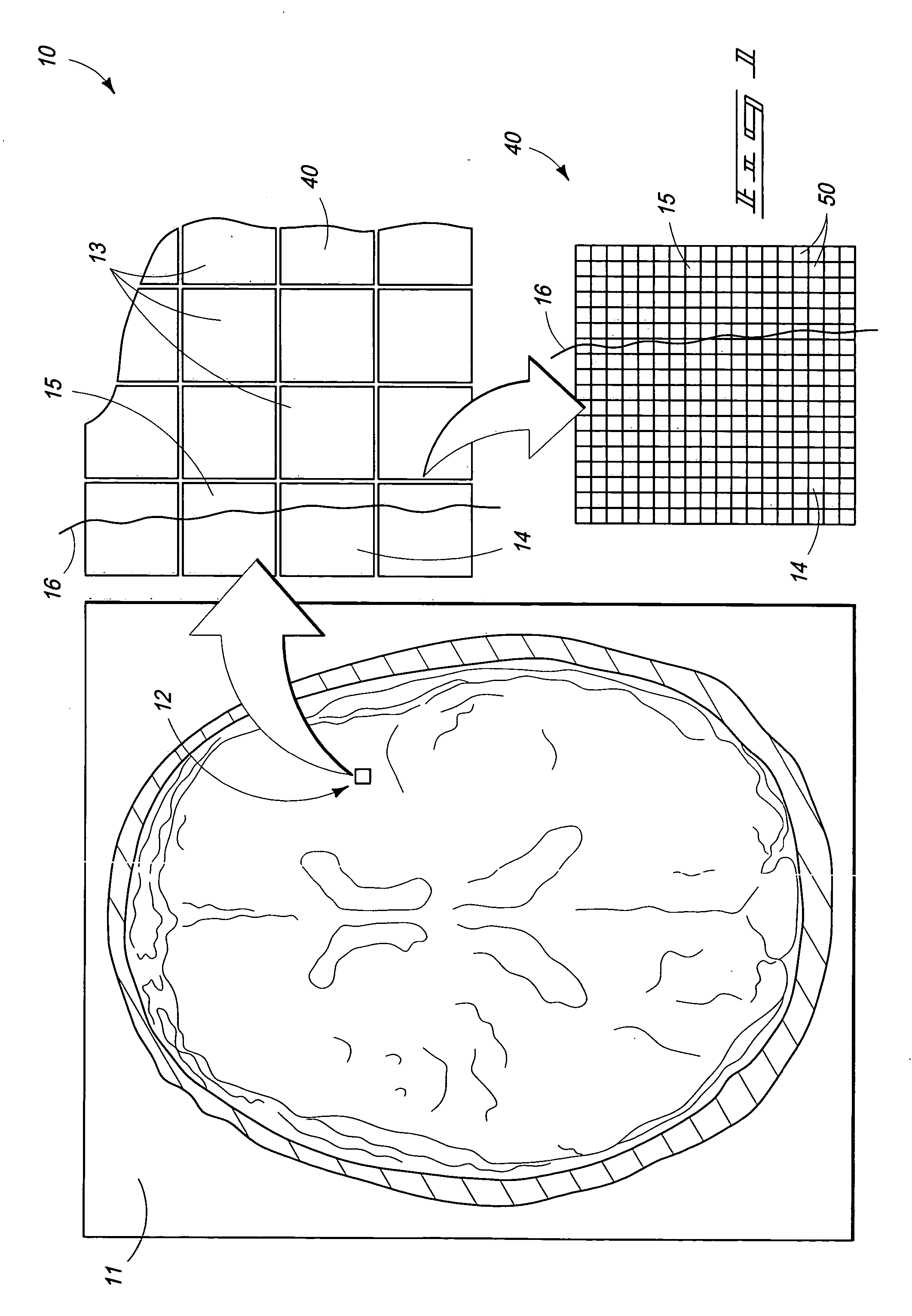
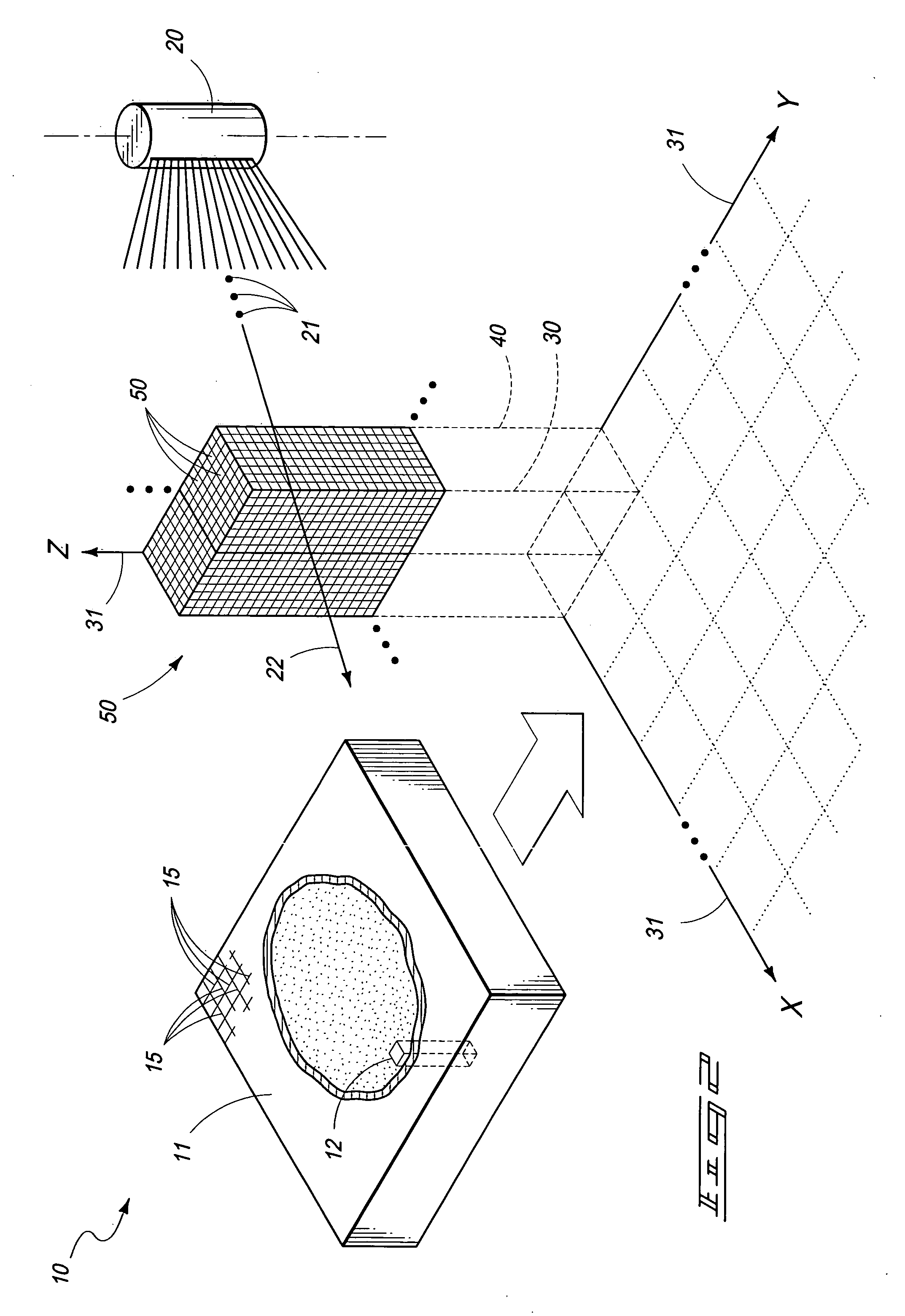
In physics, the mean free path is the average distance travelled by a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, a photon) between successive impacts (collisions), which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.
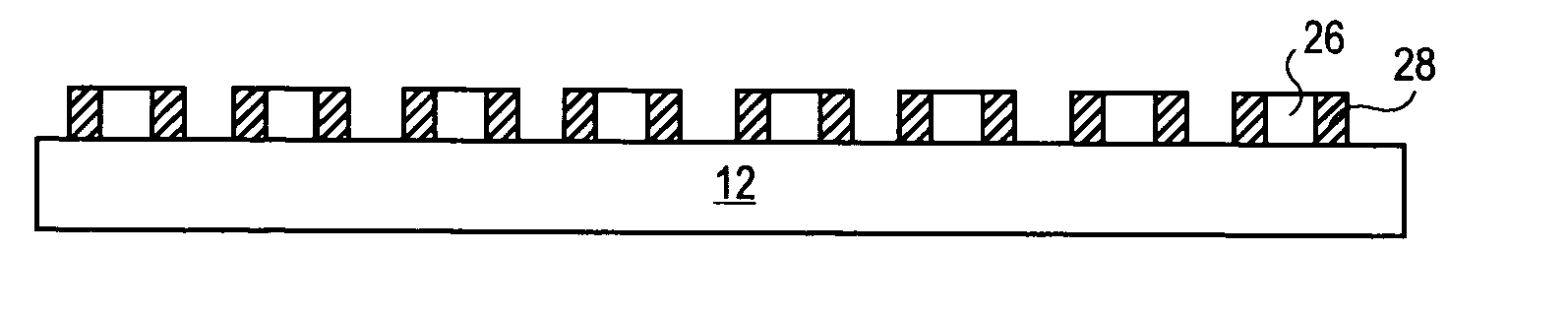
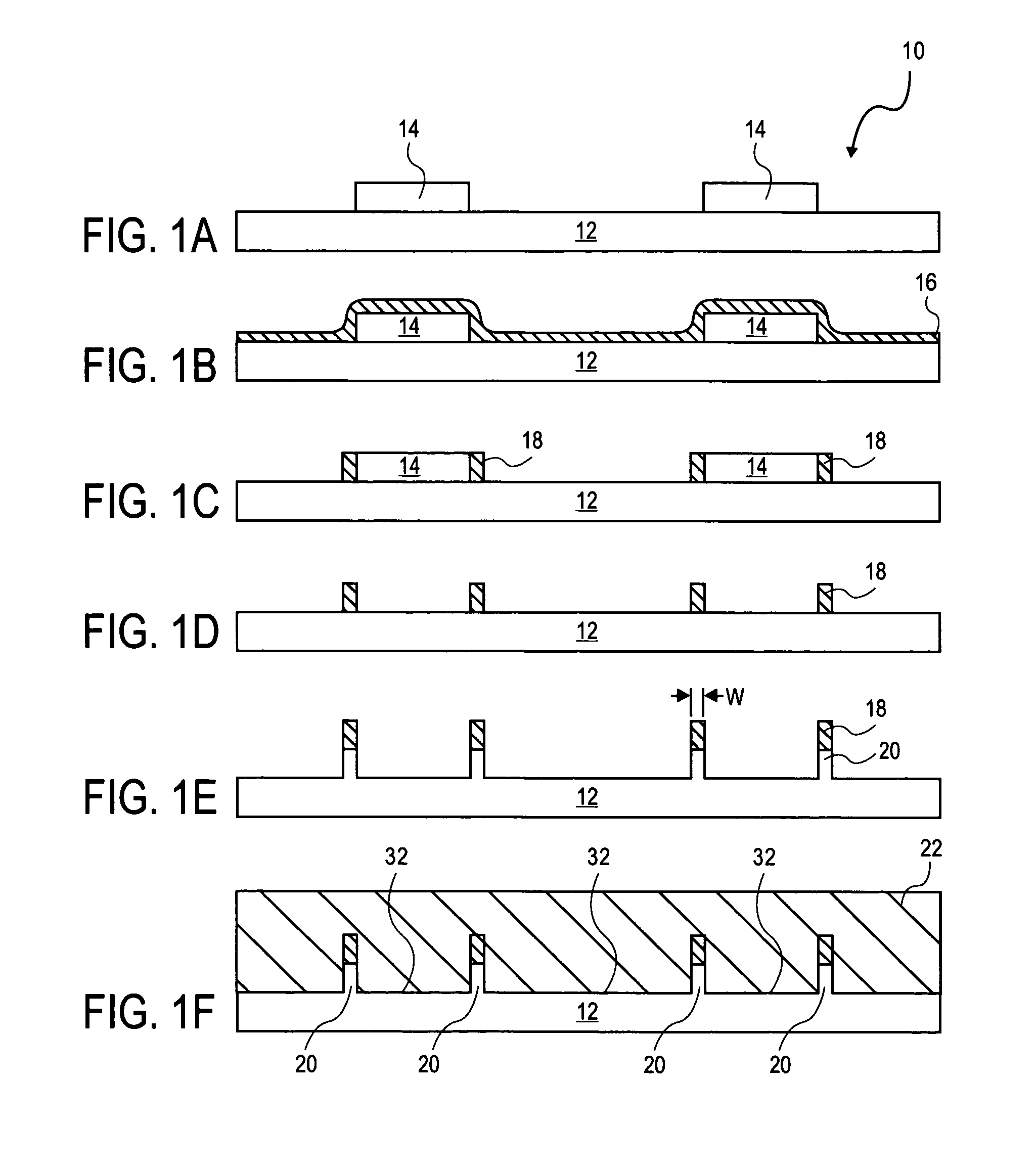
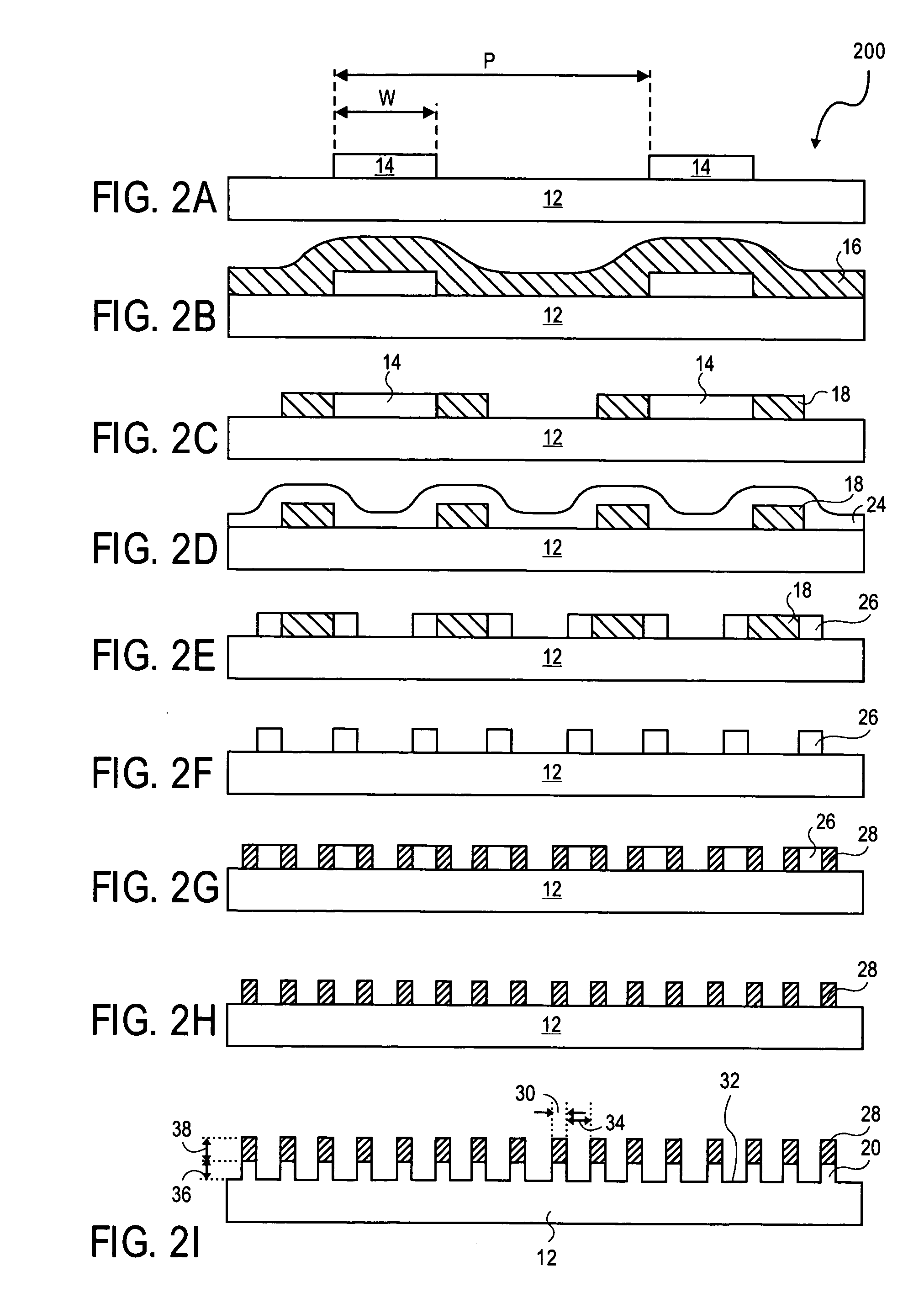
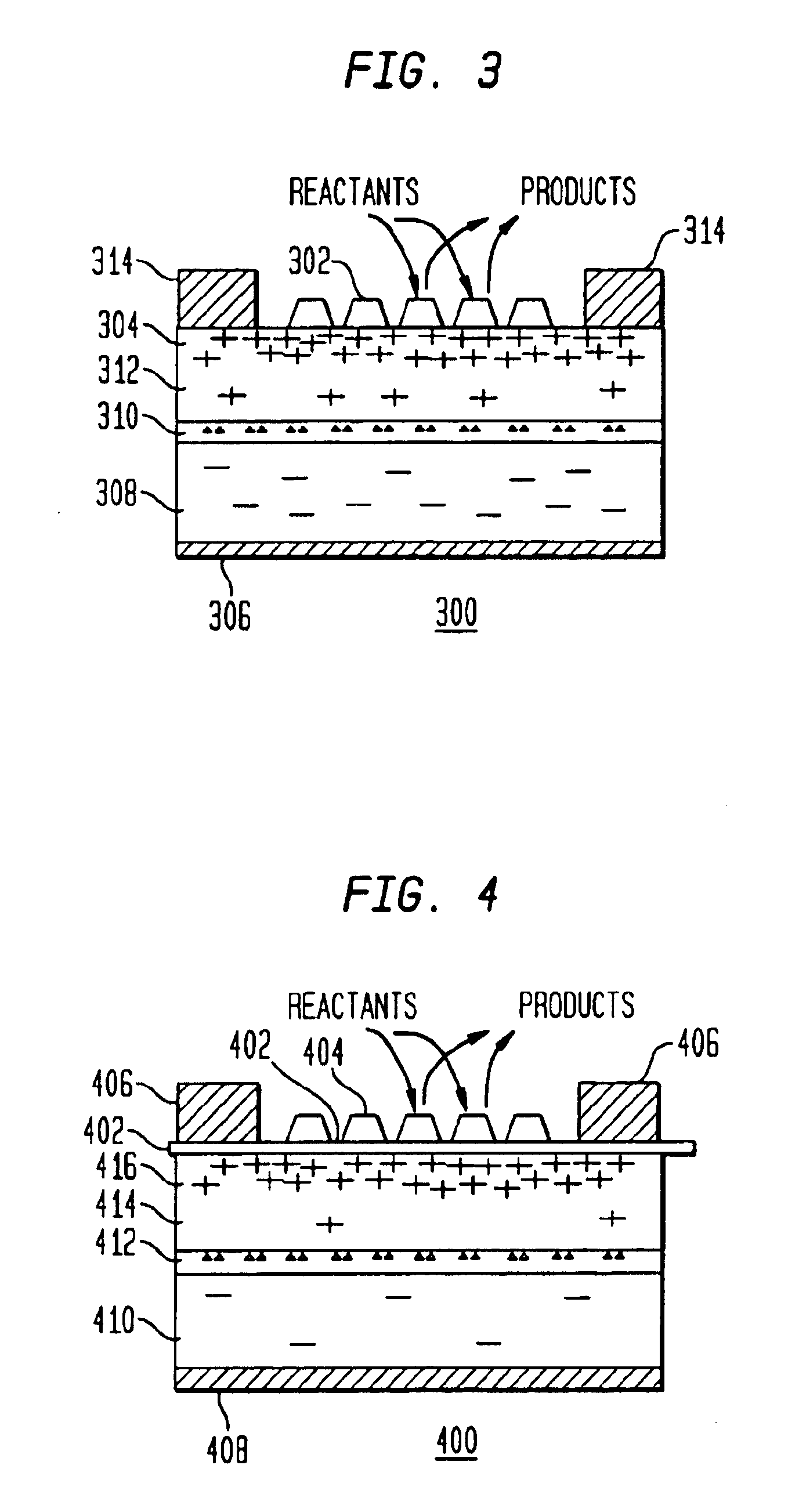
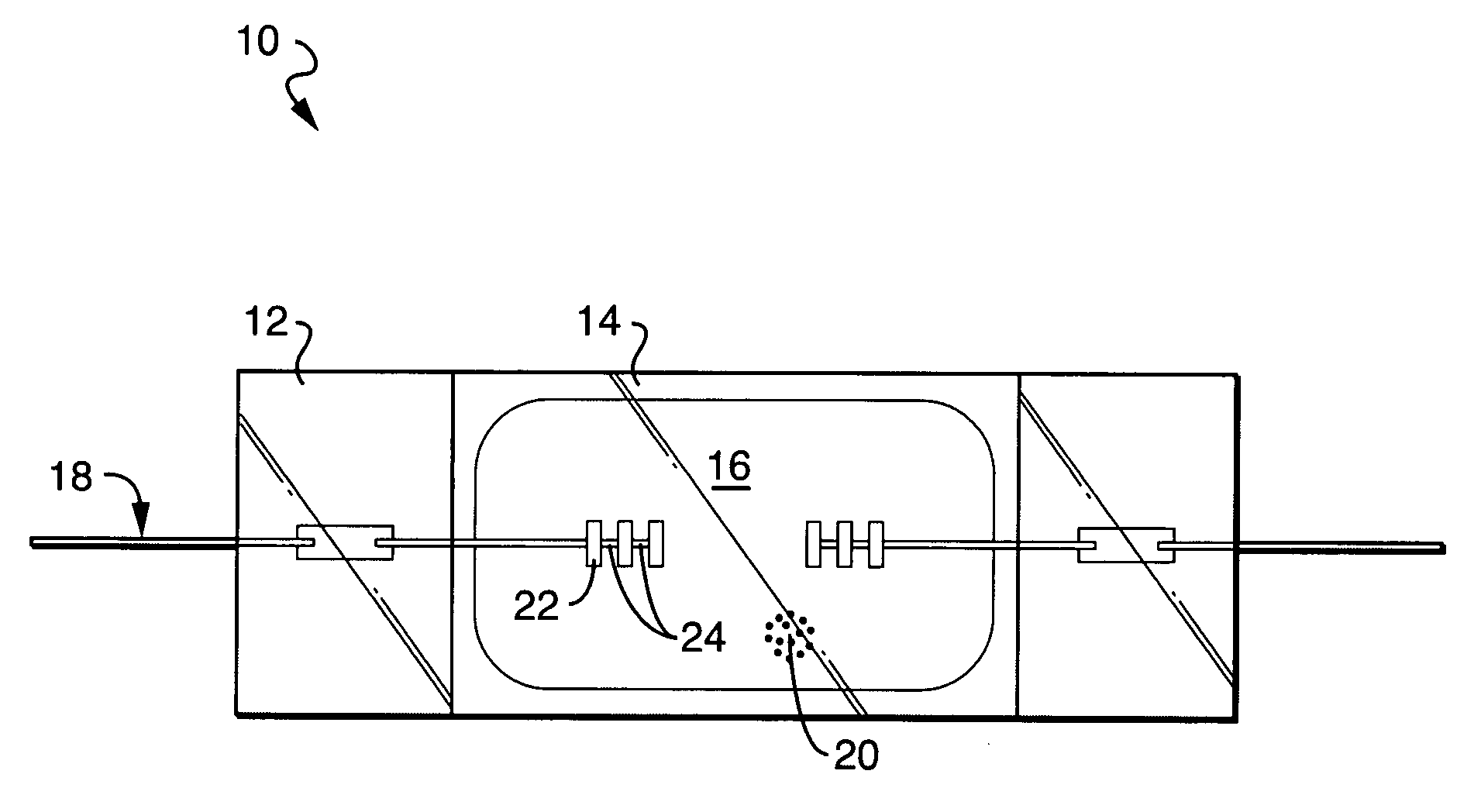
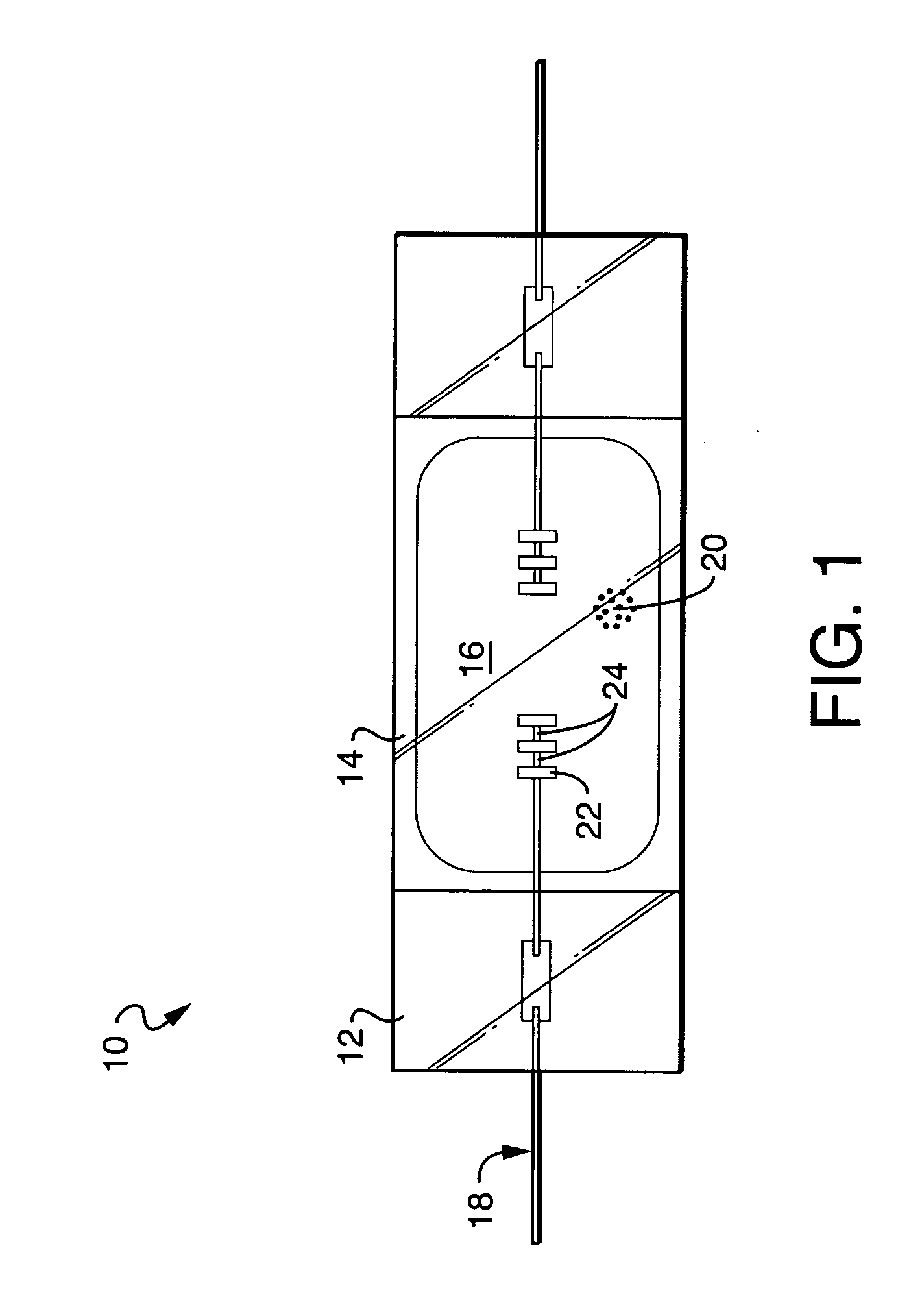
Quantum wire gate device and method of making same
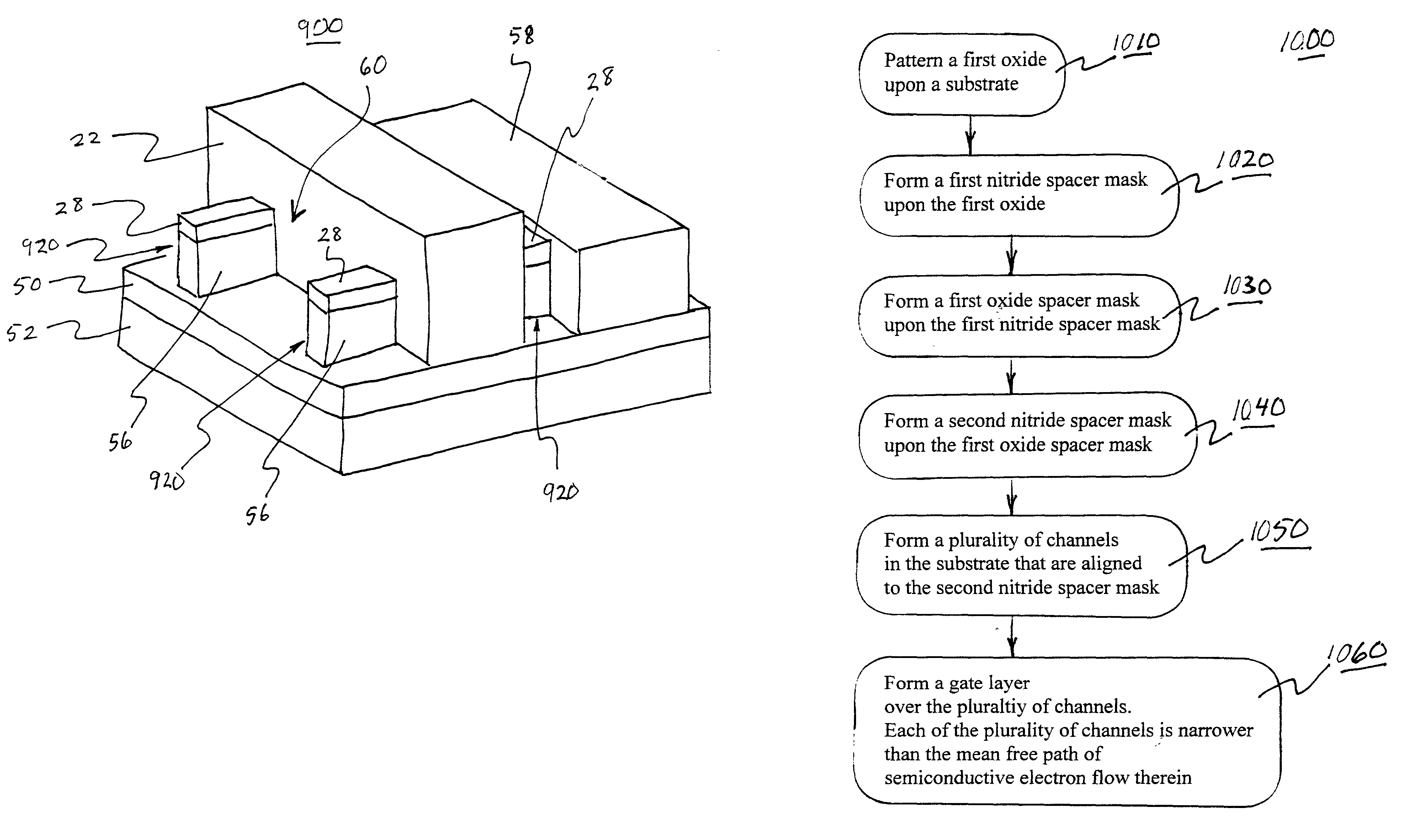
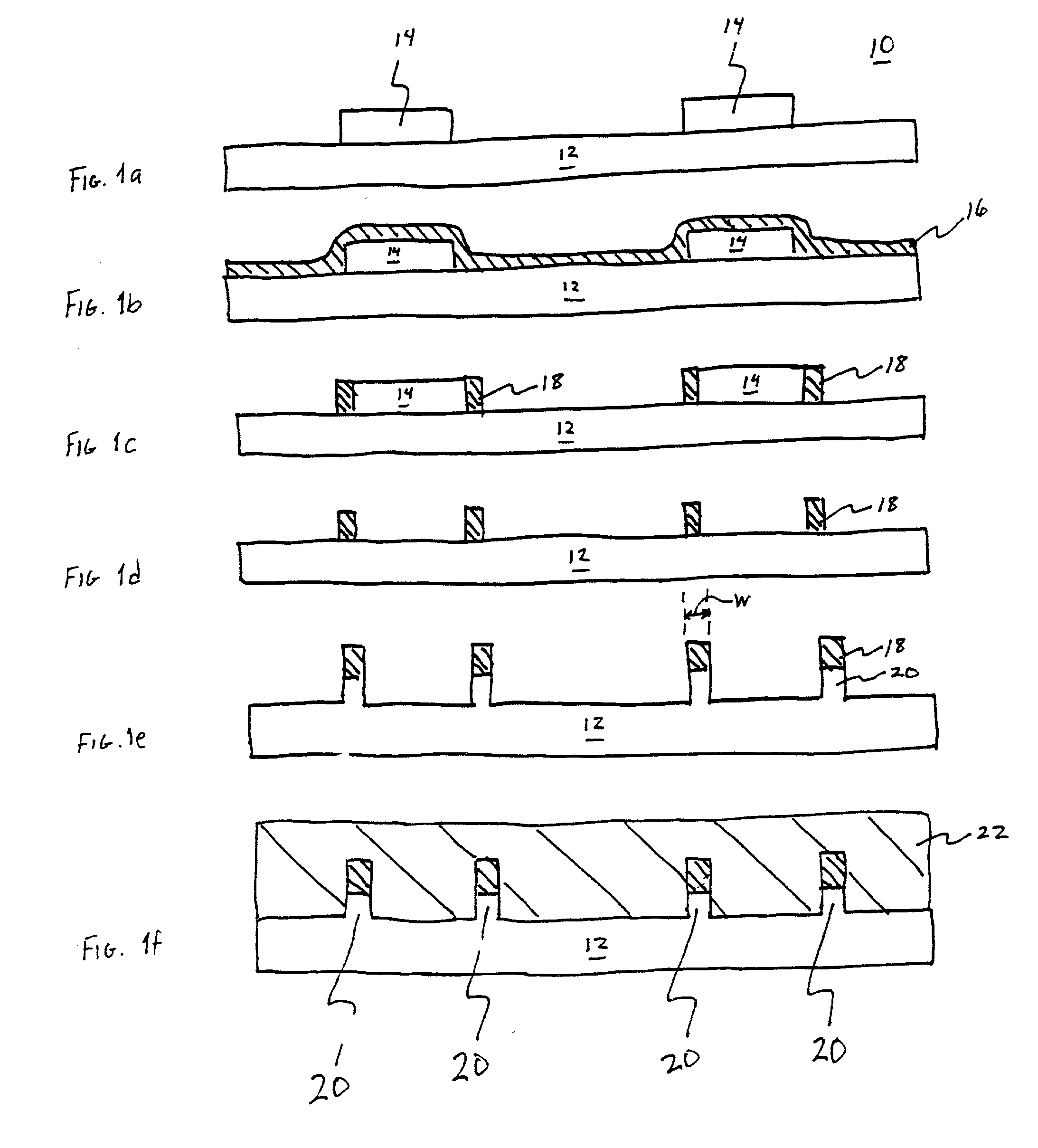
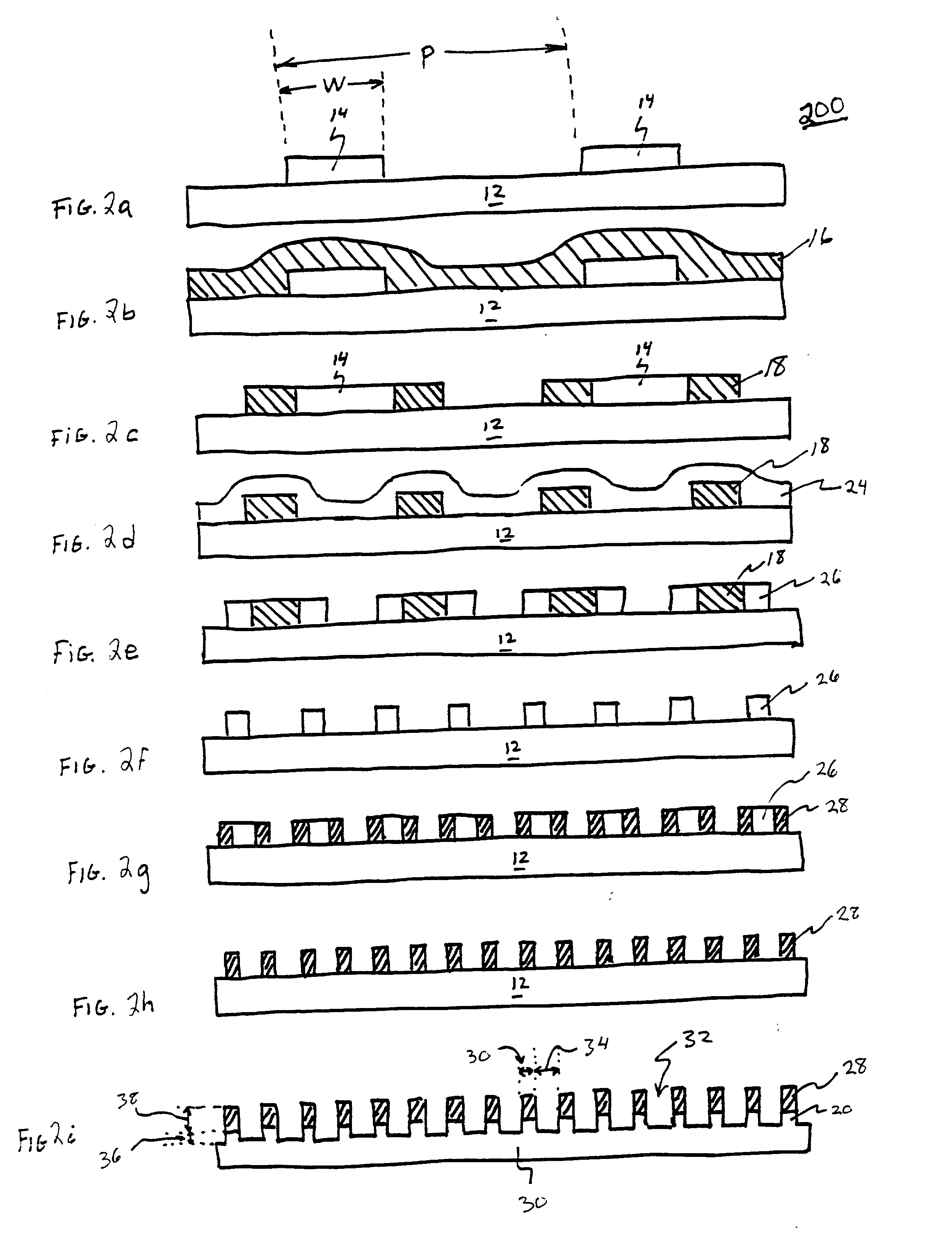
The present invention relates to a method of forming a quantum wire gate device. The method includes patterning a first oxide upon a substrate. Preferably the first oxide pattern is precisely and uniformly spaced to maximize quantum wire numbers per unit area. The method continues by forming a first nitride spacer mask upon the first oxide and by forming a first oxide spacer mask upon the first nitride spacer mask. Thereafter, the method continues by forming a second nitride spacer mask upon the first oxide spacer mask and by forming a plurality of channels in the substrate that are aligned to the second nitride spacer mask. A dielectric is formed upon the channel length and the method continues by forming a gate layer over the plurality of channels. Because of the inventive method and the starting scale, each of the plurality of channels is narrower than the mean free path of semiconductive electron flow therein.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multifocal imaging systems and method
InactiveUS20070057211A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLow noiseGrating
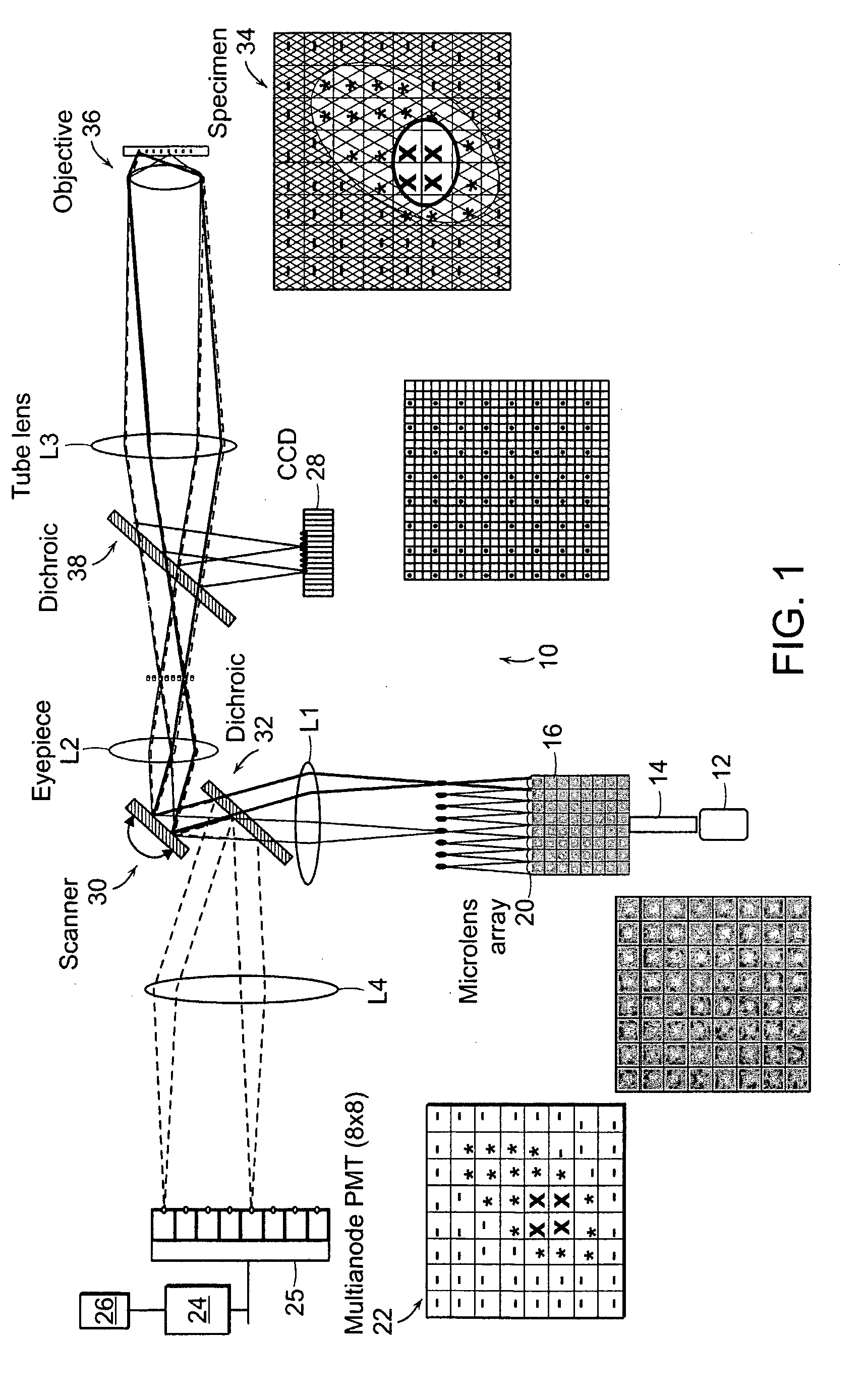
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and compositions for optimizing interfacial properties of magnetoresistive sensors
InactiveUS6828897B1Minimize electromigrationExtended service lifeNanomagnetismFixed microstructural devicesMean free pathElectronegativity
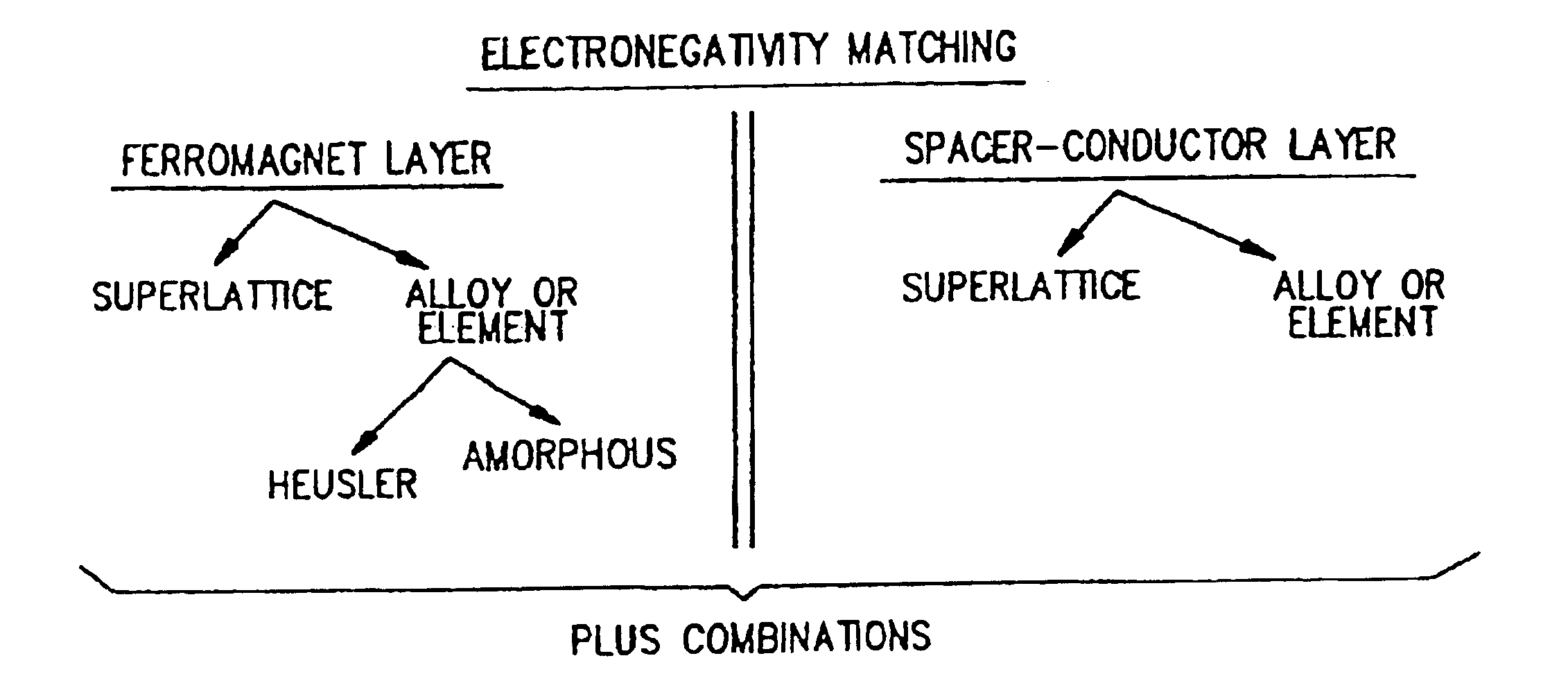
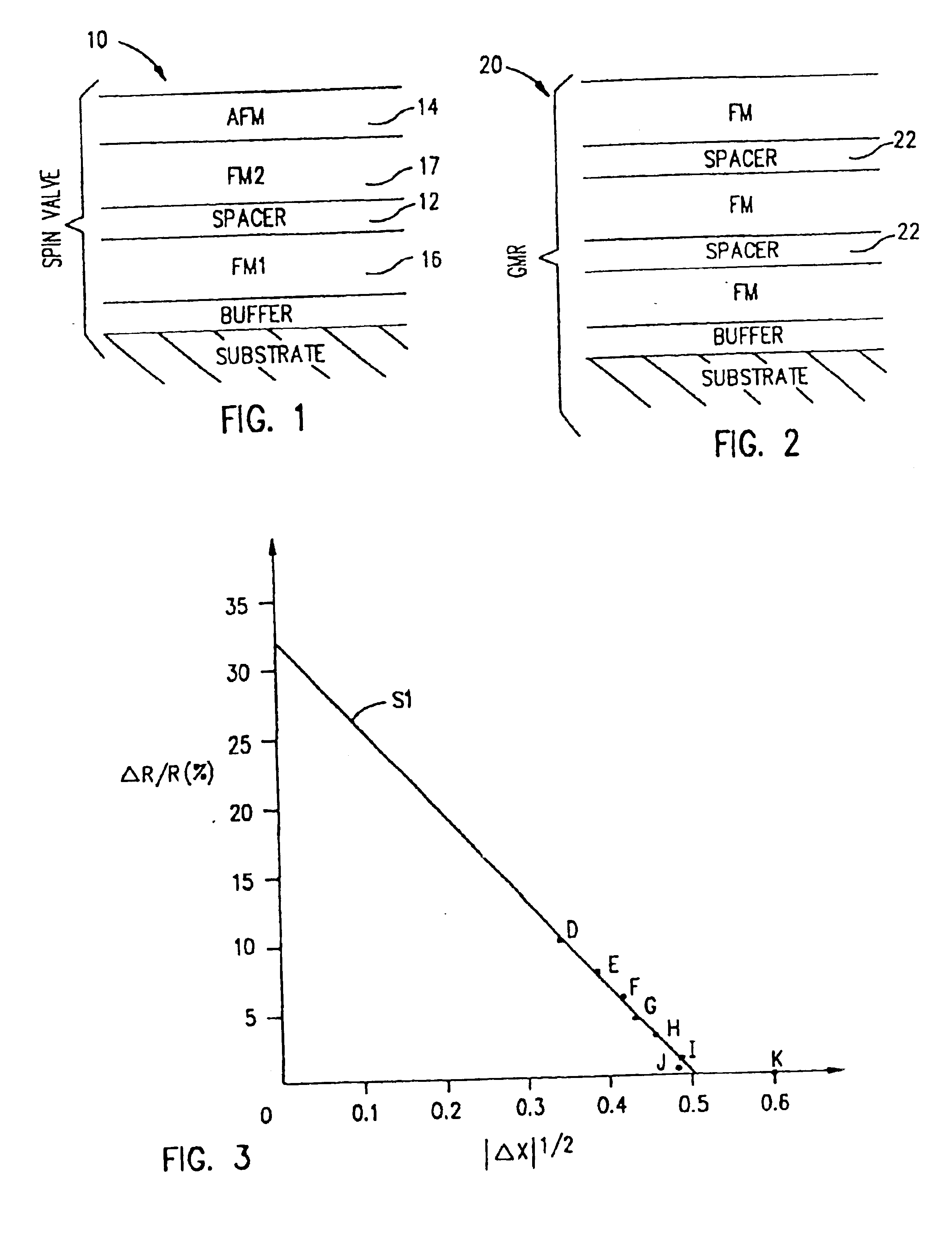
A method for maximizing the interfacial properties of magnetoresistive sensors, such as spin valve and GMR sensors used in storage devices, comprises selecting the materials for ferromagnetic layers and for electrically conductive spacers that are interposed between the ferromagnetic layers. The electronegativities of the selected materials are substantially matched so that an absolute value of the differences in electronegativities is minimized. The conductive spacer material provides a relatively low resistivity and a large mean free path. The sensors experience greater chemical and thermal stability, are corrosion resistant, and realize an increased signal output.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and device for determining a light transport parameter in a biological matrix
ActiveUS7315752B2Easy to separateEasy to useDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsMean free pathLight irradiation
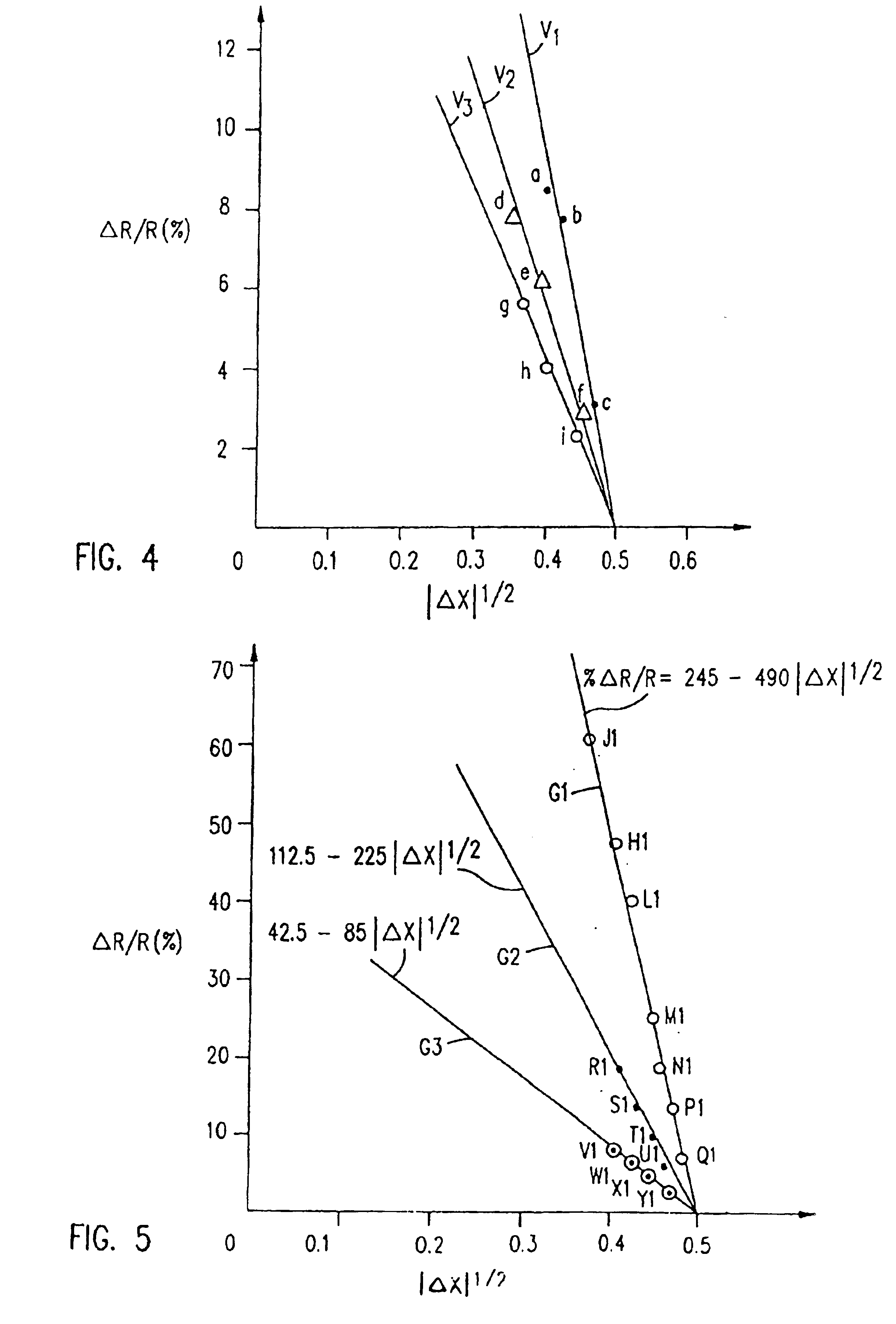
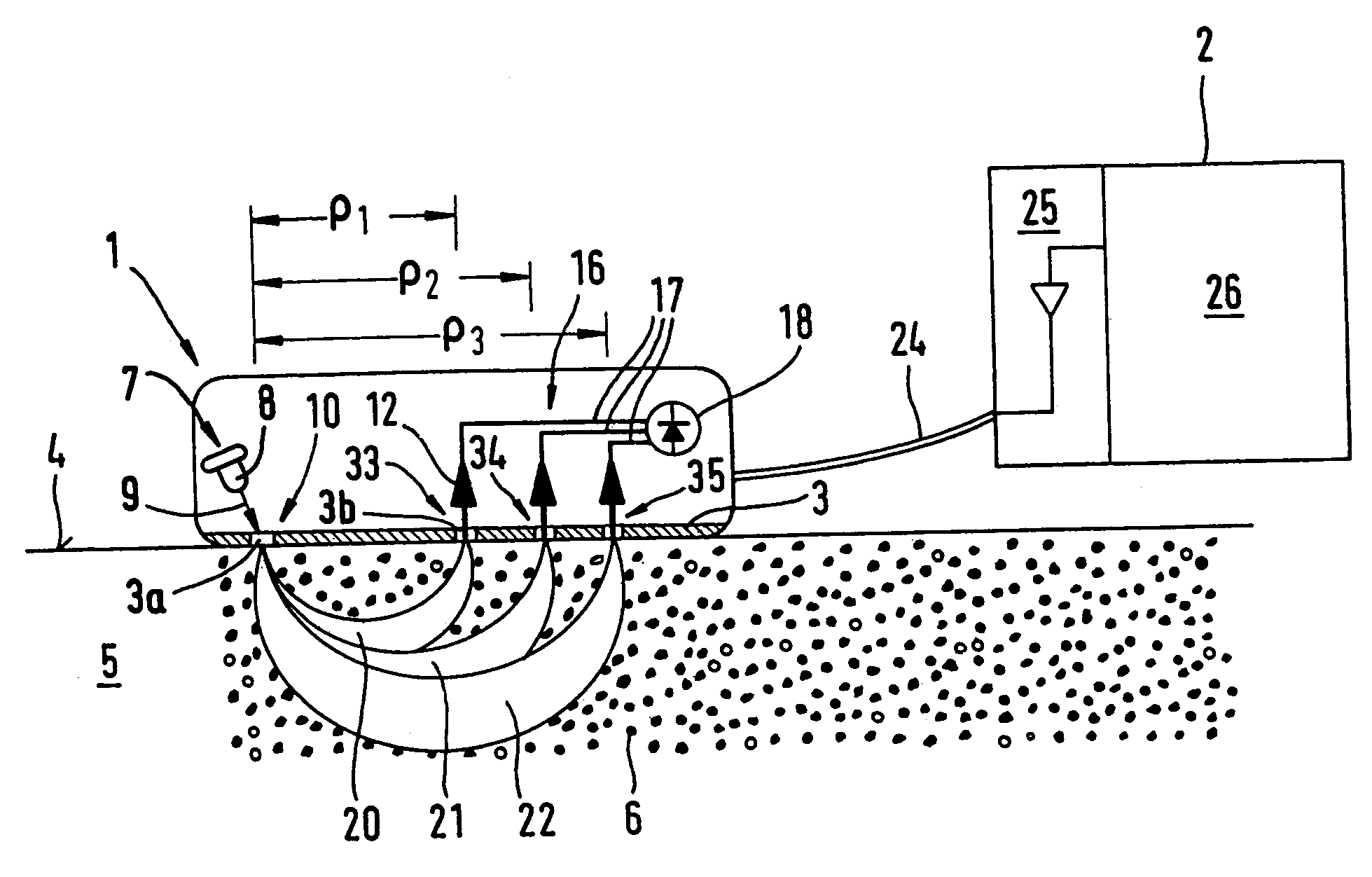
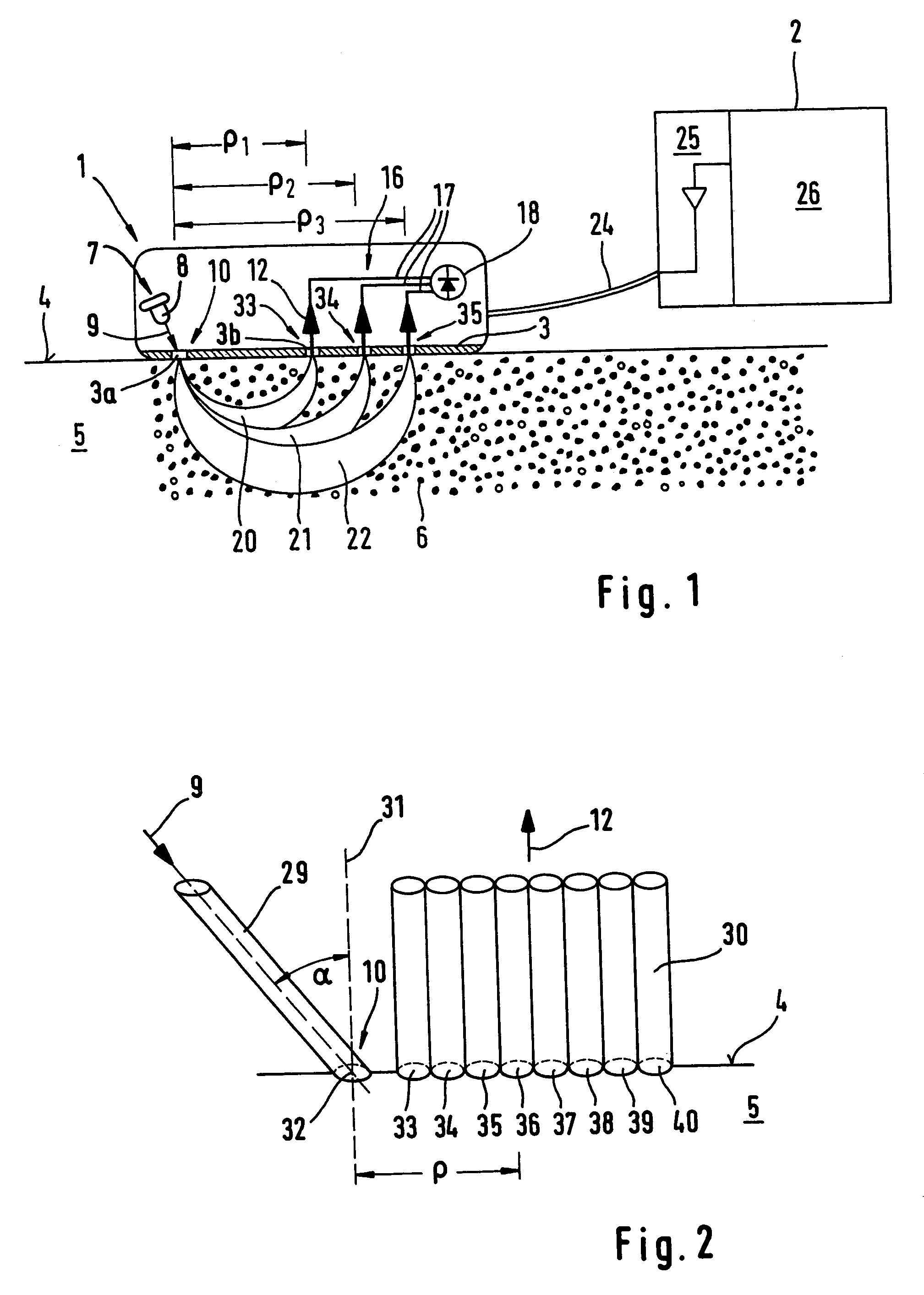
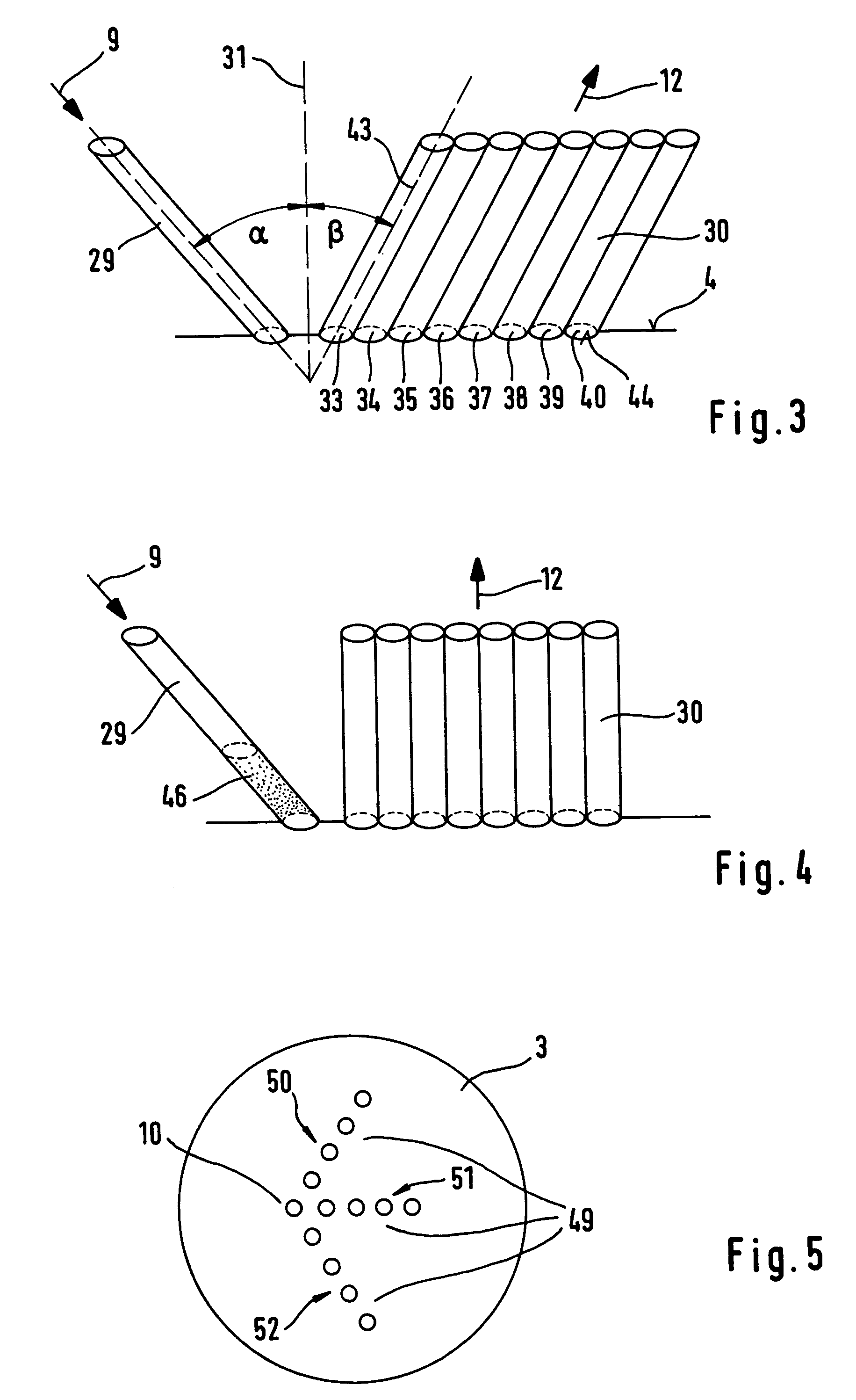
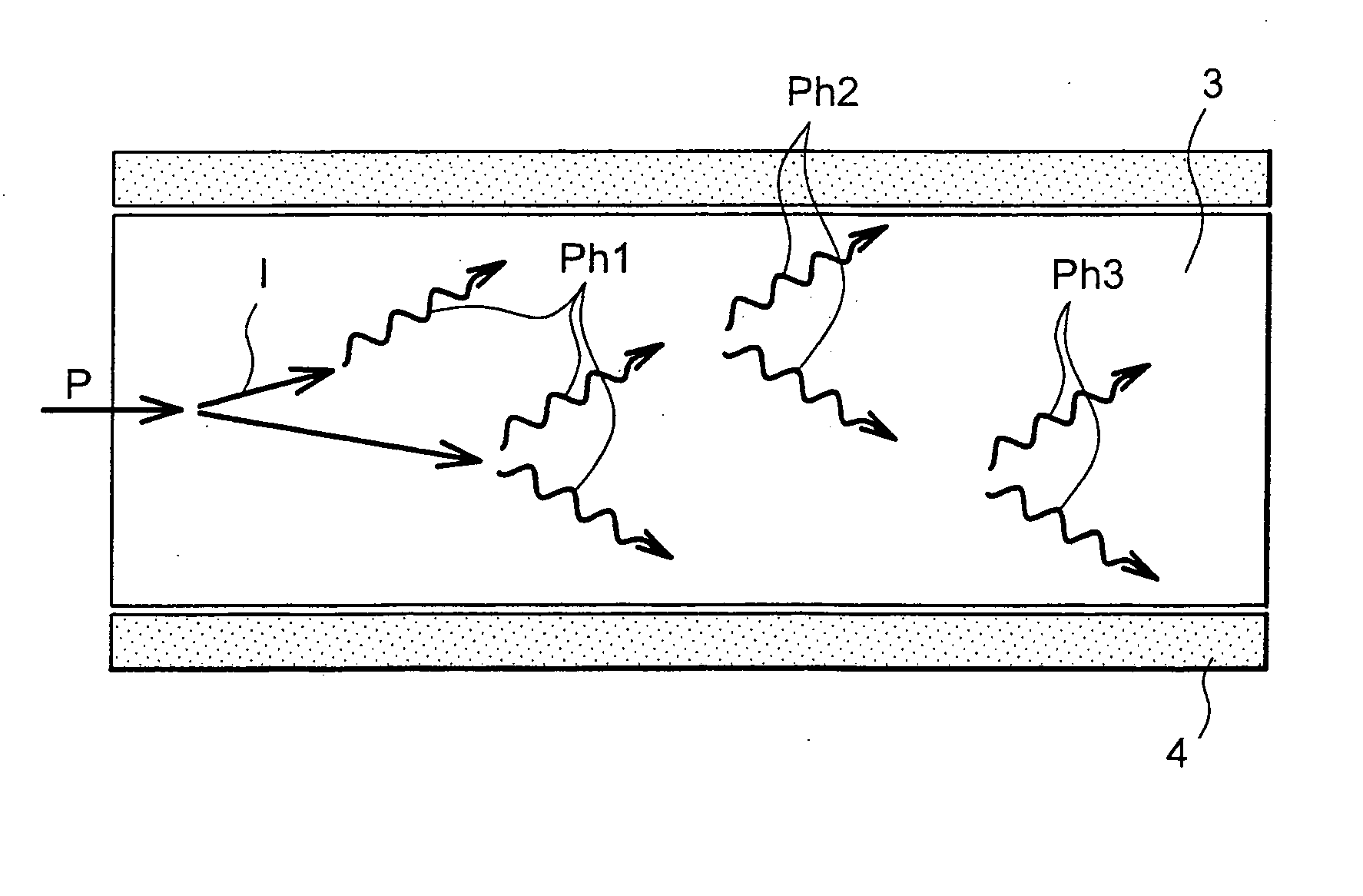
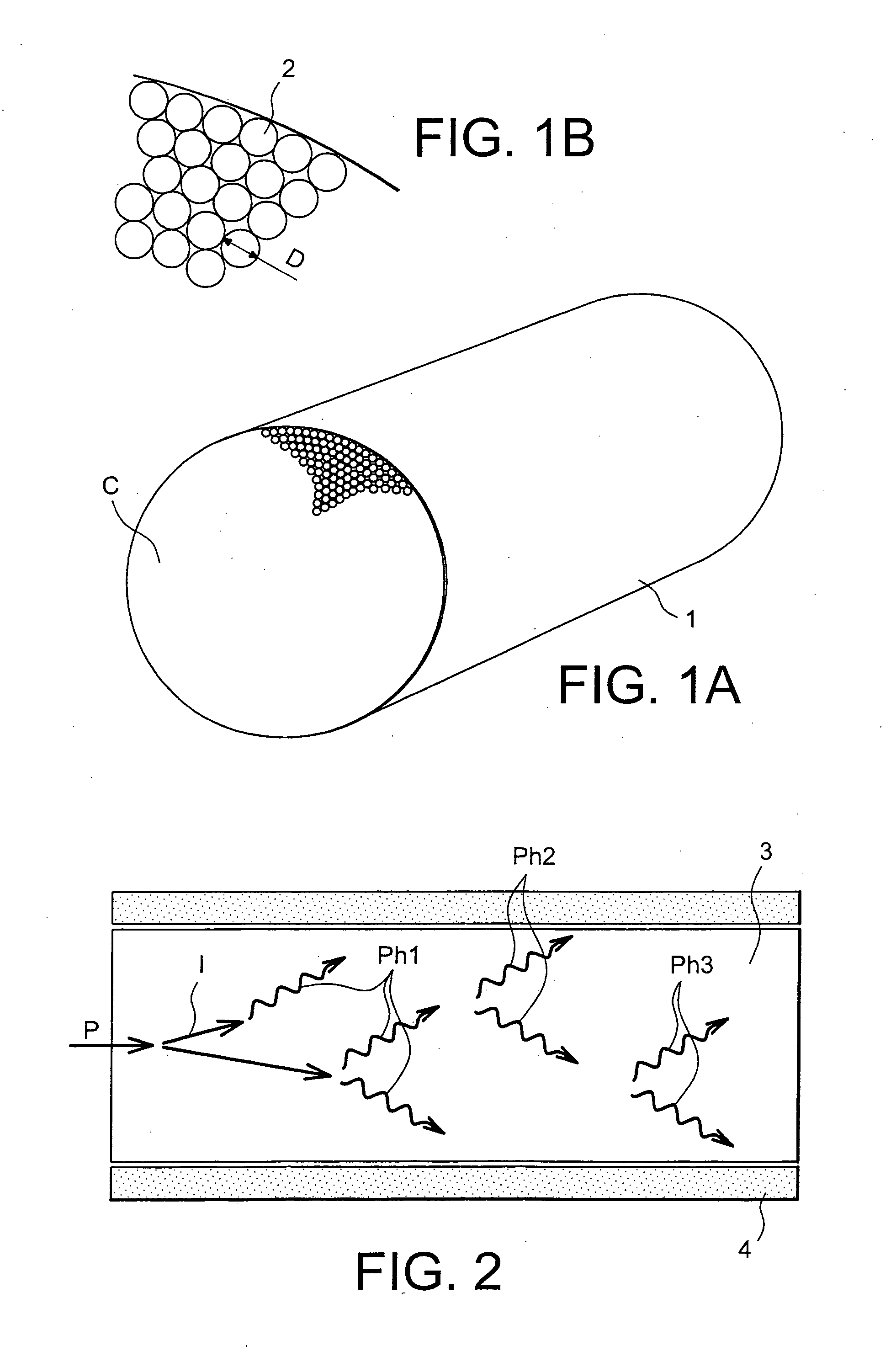
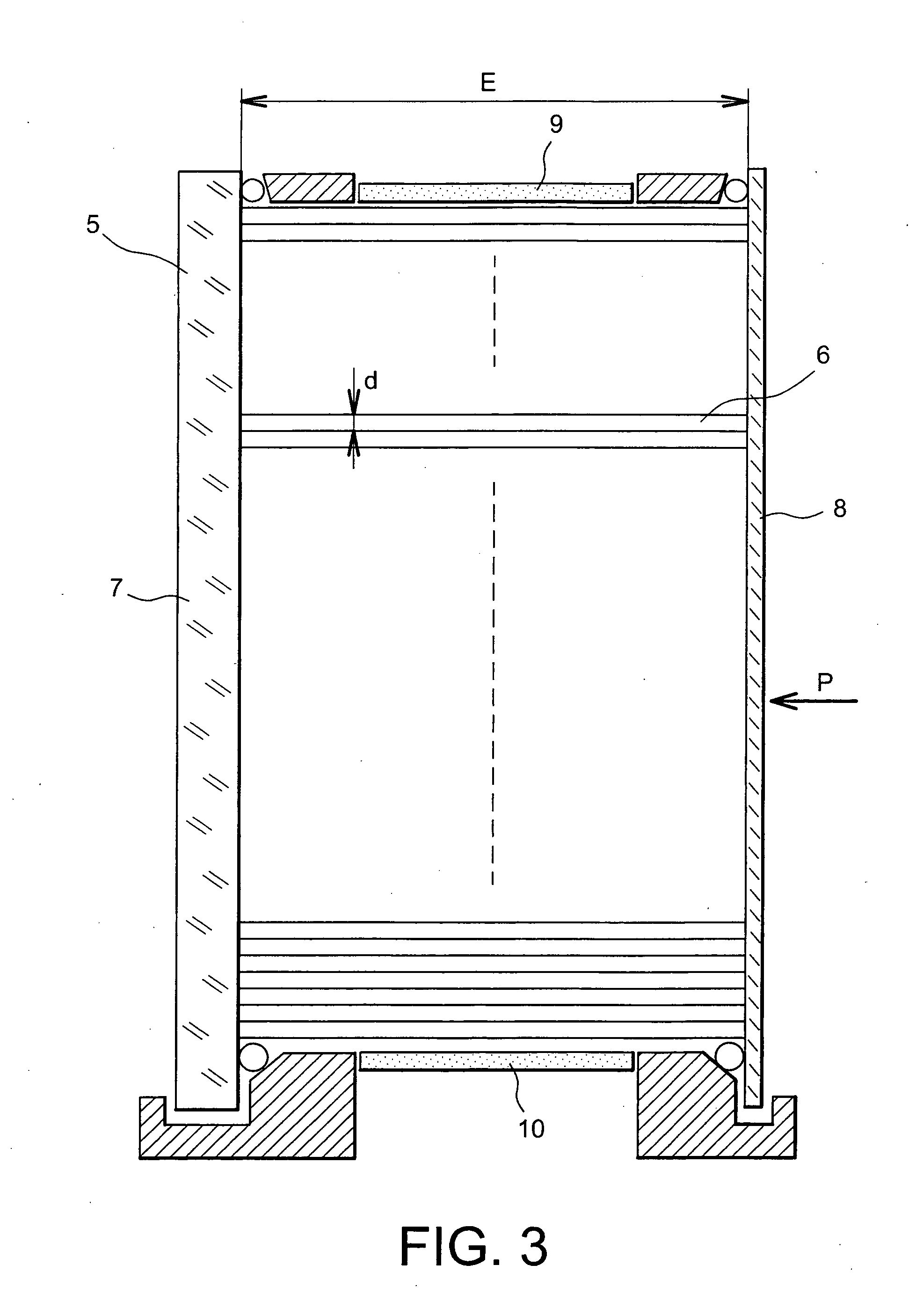
A method for the selective determination of the scattering index μs of a scattering biological matrix, in particular for the purpose of non-invasive determination of the concentration of glucose in the skin, by means of detection measurements, in each of which light in the form of primary light (9) is irradiated into the biological matrix (5) and an intensity measurement value of secondary light (12) exiting at a detection site (33-40) that is located at different measuring distances (ρ) from the respective light irradiation site (10) during the detection measurements is measured. In order to improve the quality and selectivity of the determination of μs, the primary light is irradiated obliquely at an angle between 5° and 85° using a contacting light-guiding element. In at least two detection measurements, the measuring distance (ρ) between the respective light irradiation site (10) and the respective detection site (33-40) corresponds to no more than five times the mean free path length of the light propagating in the biological matrix.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
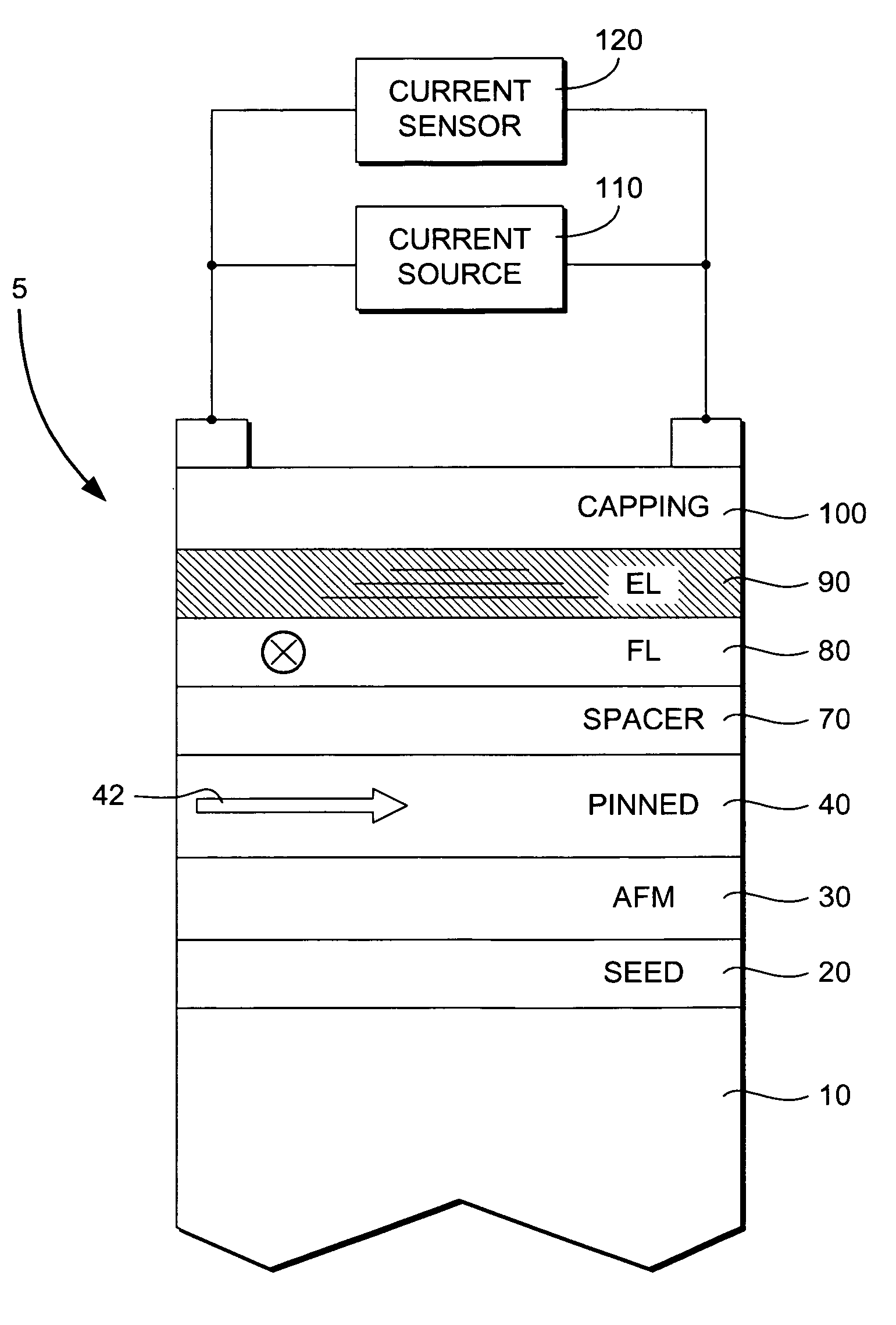
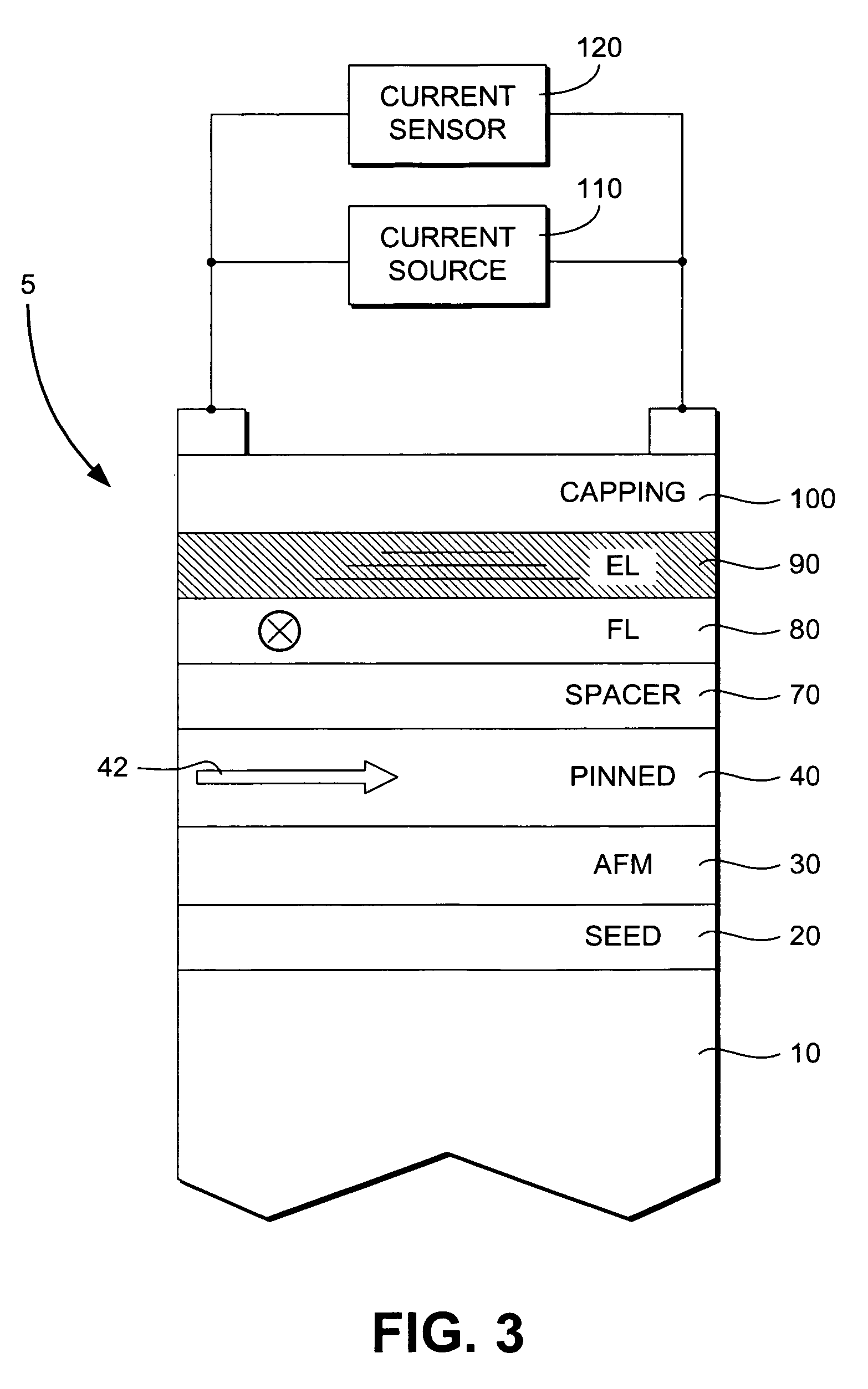
Spin valve sensor having a nonmagnetic enhancement layer adjacent an ultra thin free layer
InactiveUS7196880B1Effective bias point controlReduce thicknessNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMean free pathElectronic properties
A spin valve device includes a non-magnetic enhancement layer adjacent an ultra thin free layer. The thickness of the free layer may be less than the mean free path of a conduction electron through the free layer. The GMR ratio is significantly improved for free layer thicknesses below 50 Å. The enhancement layer allows electrons to travel longer in their spin state before encountering scattering sites. The electronic properties of the enhancement layer material can be matched with the adjacent free layer without creating a low resistance shunt path. Because the free layer may be made ultra thin and the enhancement layer is formed of a nonmagnetic material, less magnetic field is required to align the free layer, allowing for improved data density. Also, the enhancement layer allows for effective bias point control by shifting sensor current density distribution.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and means for capture and long-term sequestration of carbon dioxide
InactiveUS20090081096A1High heat of reactionHigh regeneration energyCombination devicesGas treatmentSolubilityAmbient pressure
The invention teaches a practical method of recovering CO2 from a mixture of gases, and sequestering the captured CO2 from the atmosphere for geologic time as calcium carbonate and provides a CO2 scrubber for carbon capture and sequestration. CO2 from the production of calcium oxide is geologically sequestered. A calcium hydroxide solution is produced from the environmentally responsibly-produced calcium oxide. The CO2 scrubber incorporates an aqueous froth to maximize liquid-to-gas surface area and time-of-contact between gaseous CO2 and the calcium hydroxide solution. The CO2 scrubber decreases the temperature of the liquid and the mixed gases, increases ambient pressure on the bubbles and vapor pressure inside the bubbles, diffuses the gas through intercellular walls from relative smaller bubbles with relative high vapor pressure into relative larger bubbles with relative low vapor pressure, and decreases the mean-free-paths of the CO2 molecules inside the bubbles, in order to increase solubility of CO2 and the rate of dissolution of gaseous CO2 from a mixture of gases into the calcium hydroxide solution.The CO2 scrubber recovers gaseous CO2 directly from the atmosphere, from post-combustion flue gas, or from industrial processes that release CO2 as a result of process. CO2 reacts with calcium ions and hydroxide ions in solution forming insoluble calcium carbonate precipitates. The calcium carbonate precipitates are separated from solution, and sold to recover at least a portion of the cost of CCS.
Owner:WESTEC ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS
High conductance plasma containment structure
InactiveUS6051100AExcellent plasma confinement propertyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMean free pathEngineering
Plasma containment is achieved within a region by a containment plate while gas is allowed to flow through this region by openings in the plate. The openings in the plate are larger in two of the cross-sectional dimensions parallel to the plate surface than the thickness of the dark space or plasma sheath. This plasma containment plate allows high conductance for conditions including those of long molecular mean free path and thick material deposits on the interior chamber of the plasma reactor.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
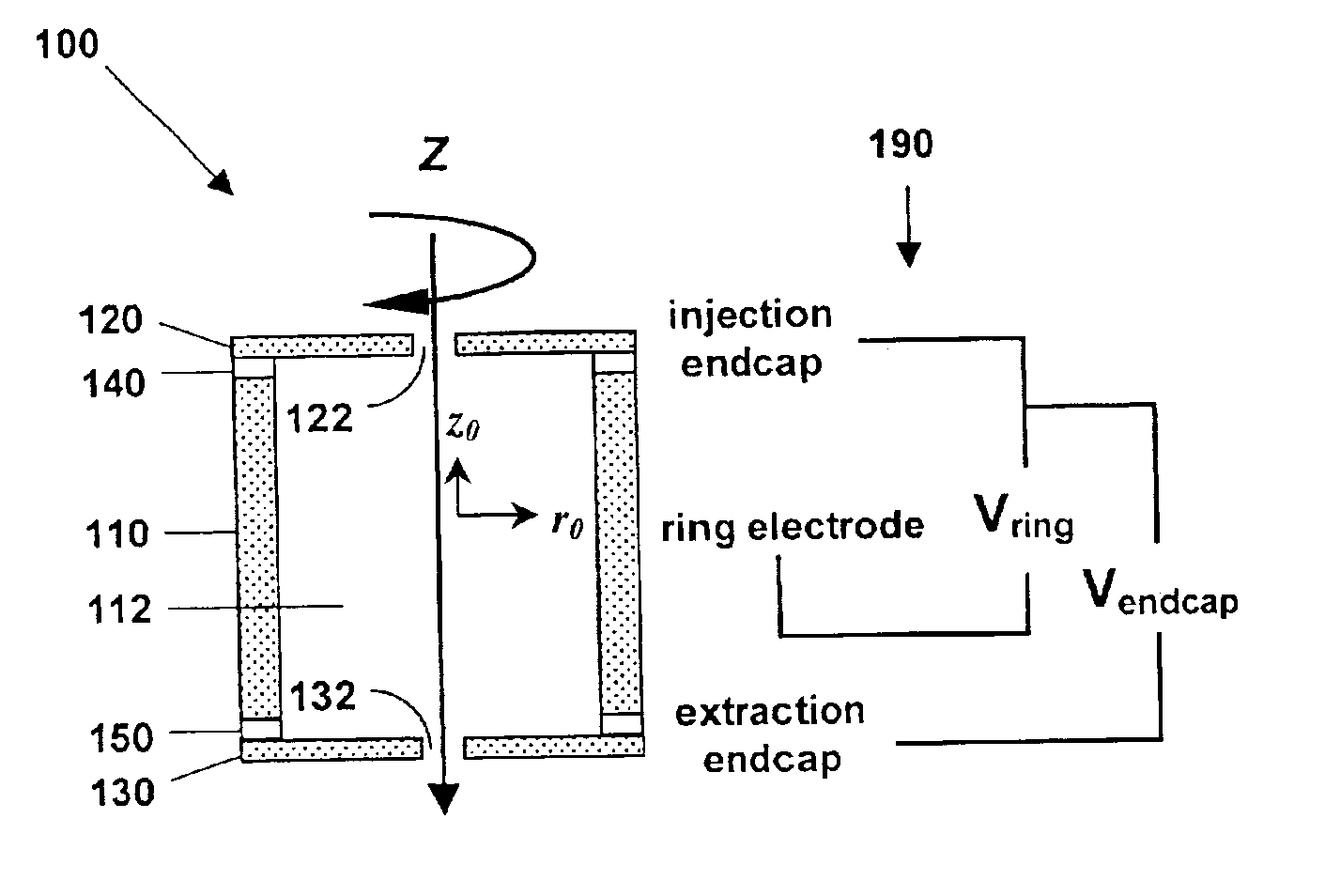
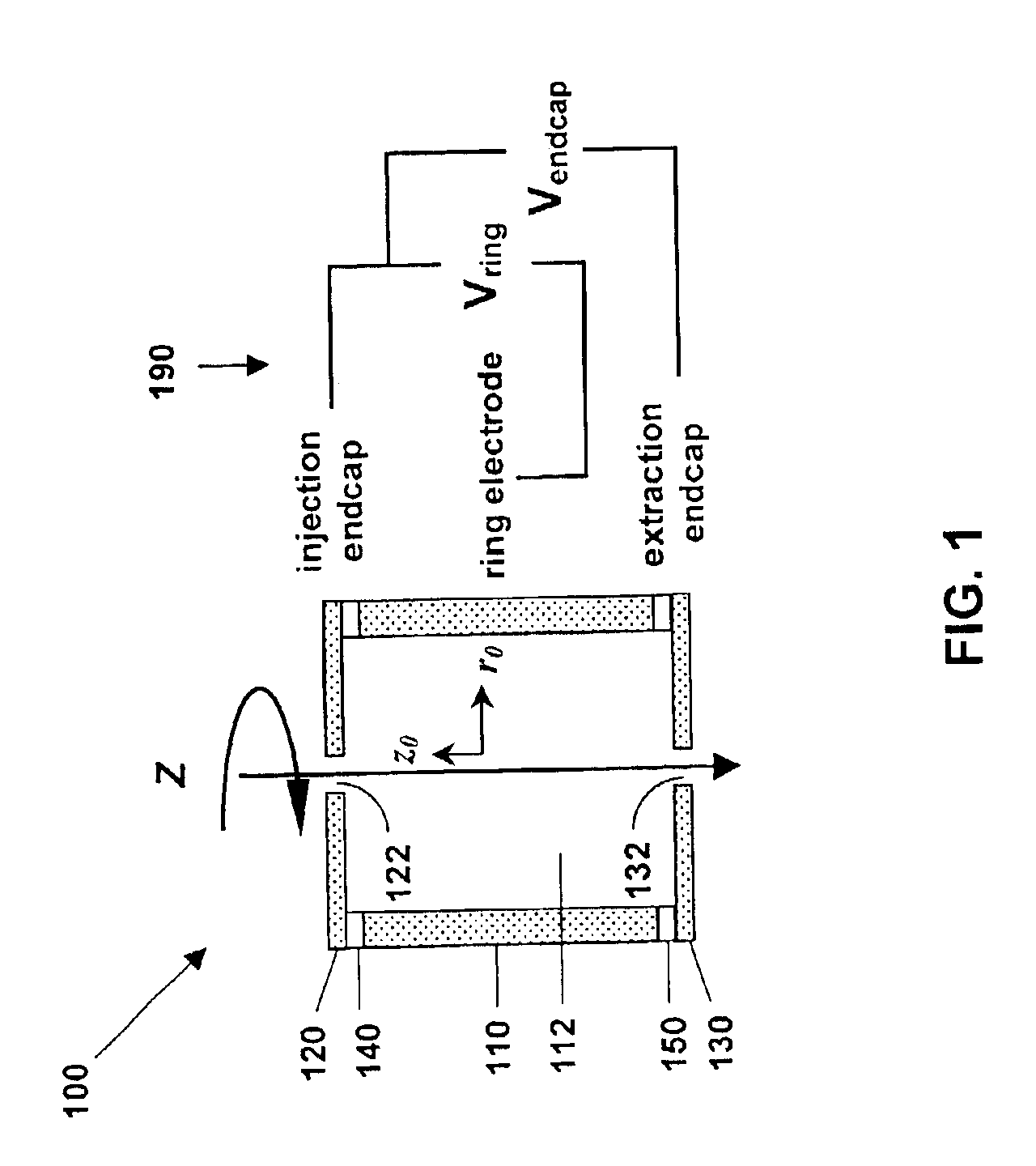
Microfabricated cylindrical ion trap
InactiveUS6870158B1Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationManufacturing cost reductionHigh pressure
A microscale cylindrical ion trap, having an inner radius of order one micron, can be fabricated using surface micromachining techniques and materials known to the integrated circuits manufacturing and microelectromechanical systems industries. Micromachining methods enable batch fabrication, reduced manufacturing costs, dimensional and positional precision, and monolithic integration of massive arrays of ion traps with microscale ion generation and detection devices. Massive arraying enables the microscale cylindrical ion trap to retain the resolution, sensitivity, and mass range advantages necessary for high chemical selectivity. The microscale CIT has a reduced ion mean free path, allowing operation at higher pressures with less expensive and less bulky vacuum pumping system, and with lower battery power than conventional- and miniature-sized ion traps. The reduced electrode voltage enables integration of the microscale cylindrical ion trap with on-chip integrated circuit-based rf operation and detection electronics (i.e., cell phone electronics). Therefore, the full performance advantages of microscale cylindrical ion traps can be realized in truly field portable, handheld microanalysis systems.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Mems based multi-polar electrostatic chuck
InactiveUS20050041364A1Effective clampingEasy to controlEmergency protective arrangement detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMean free pathSemiconductor
The present invention is directed to a semiconductor processing apparatus and a method for clamping a semiconductor substrate and controlling a heat transfer associated therewith. According to one aspect of the present invention, a multi-polar electrostatic chuck and associated method is disclosed which provides a controlled and uniform heat transfer coefficient across a surface thereof. The multi-polar electrostatic chuck comprises a semiconductor platform having a plurality of protrusions that define gaps therebetween, wherein a distance or depth of the gaps is uniform and associated with a mean free path of the cooling gas therein. The electrostatic chuck is permits a control of a backside pressure of a cooling gas within the plurality of gaps to thus control a heat transfer coefficient of the cooling gas. The plurality of protrusions further provide a uniform contact surface, wherein a contact conductivity between the plurality of protrusions and the substrate is controllable and significantly uniform across the substrate.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Thermoelectric semiconductor compound and method of making the same
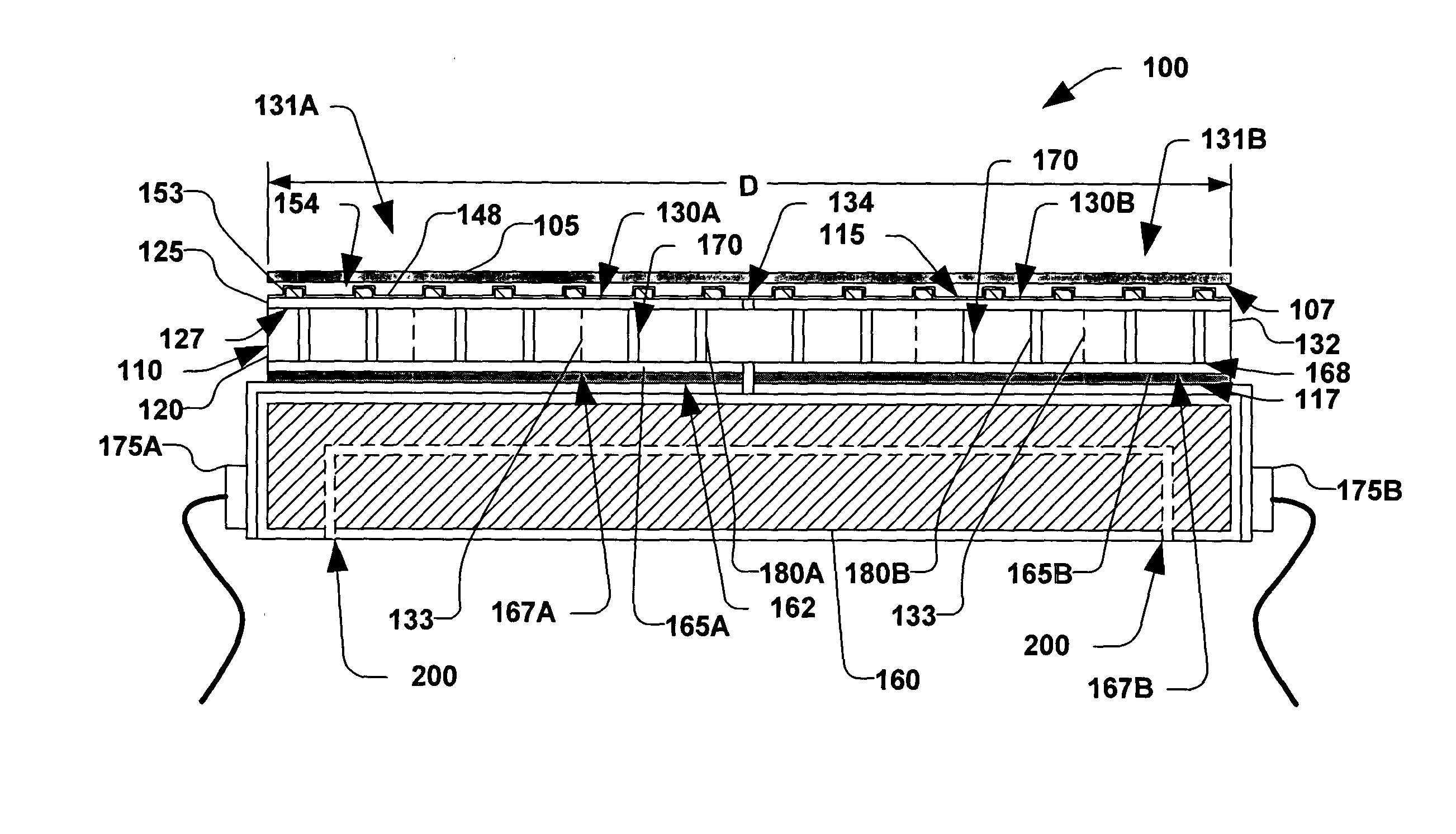
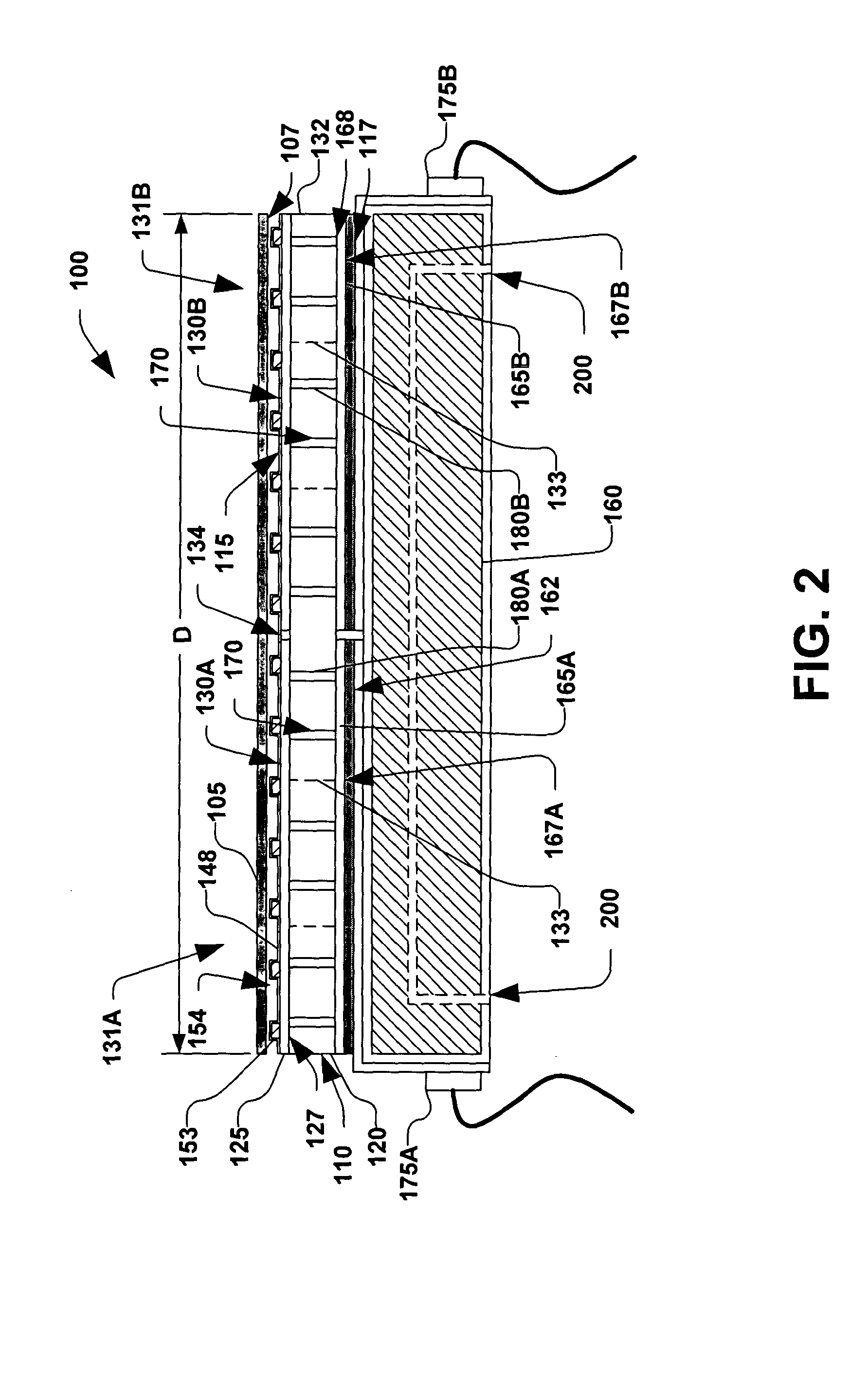
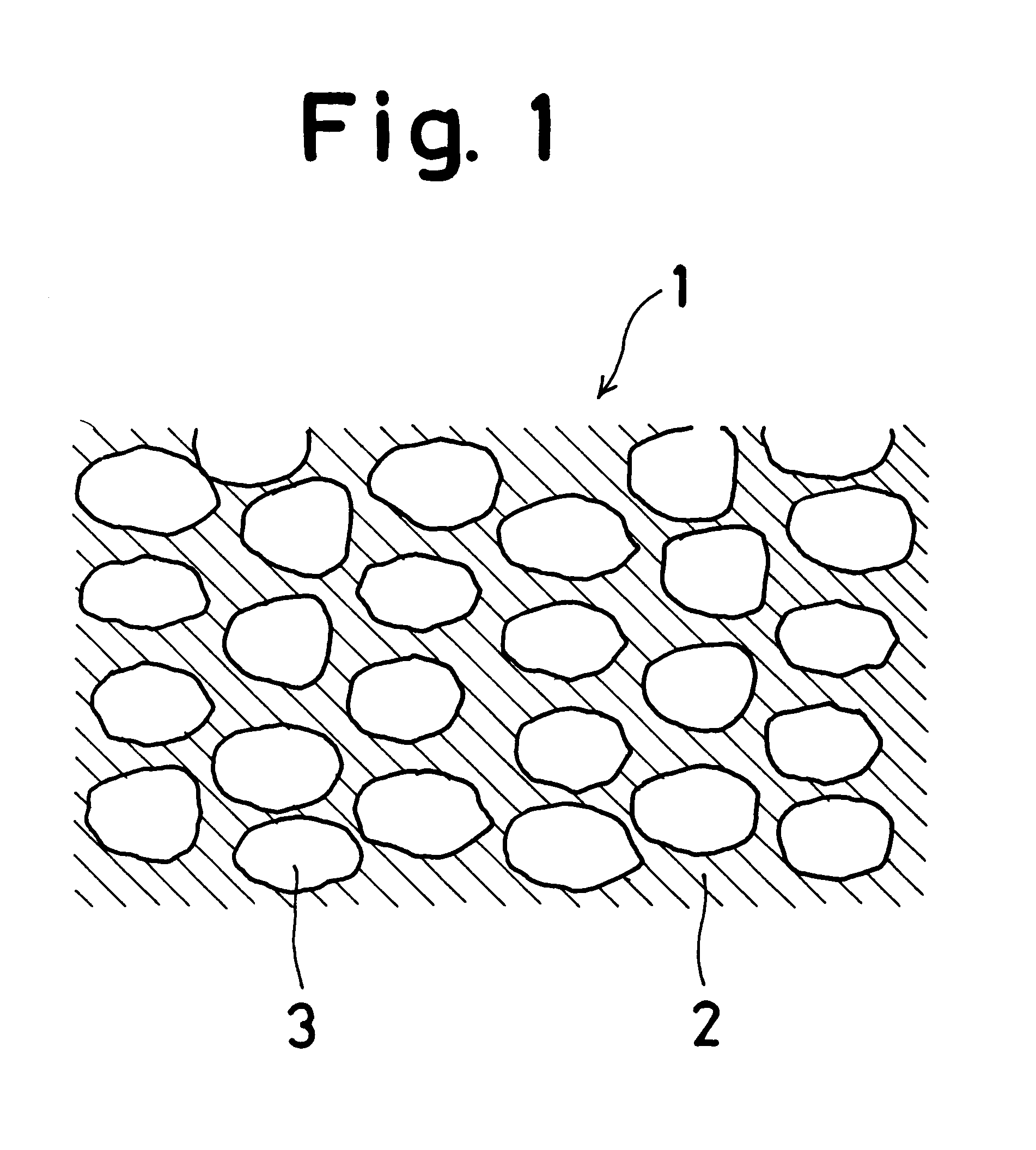
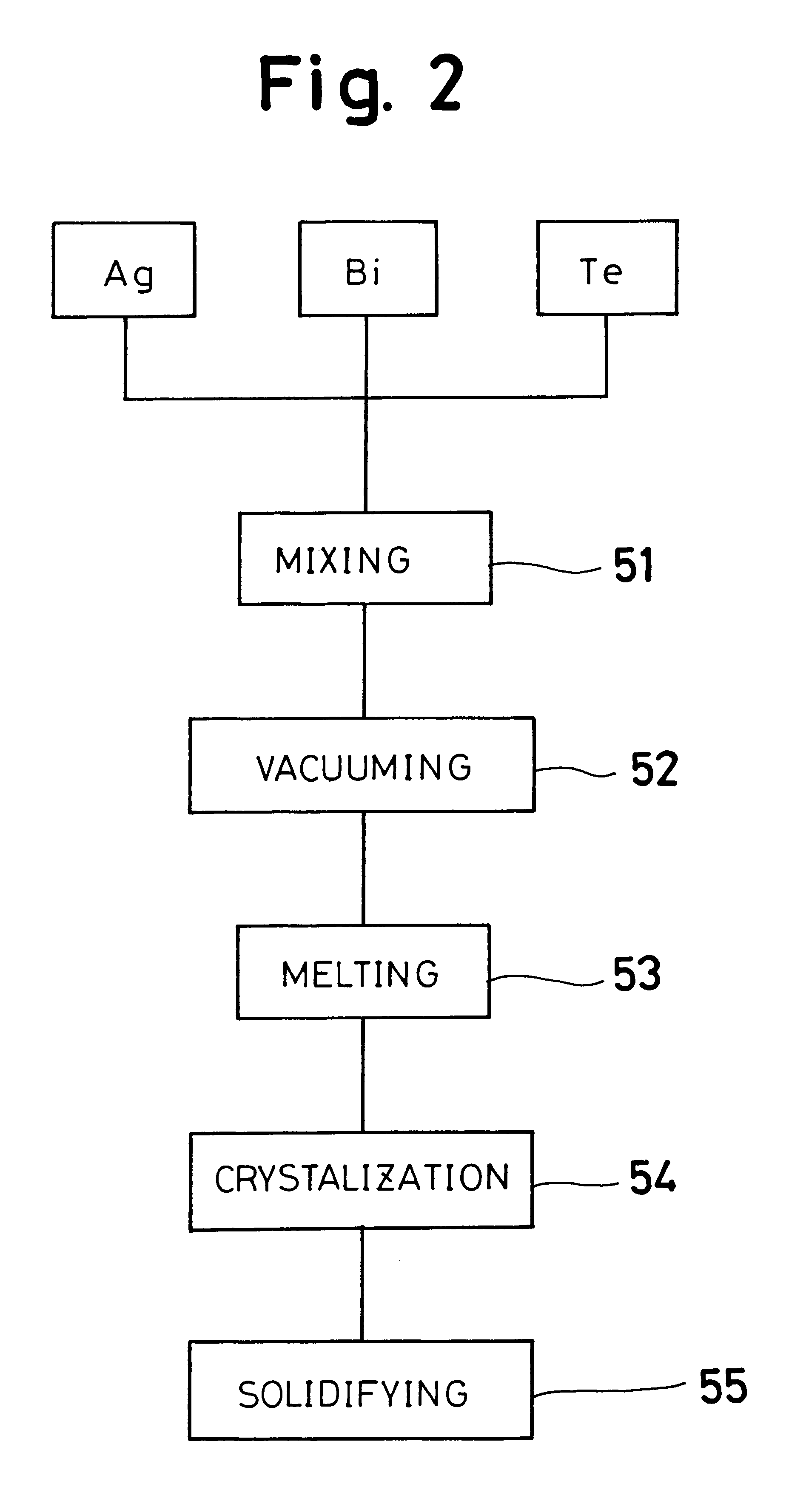
InactiveUS6225548B1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsMean free pathSingle crystal
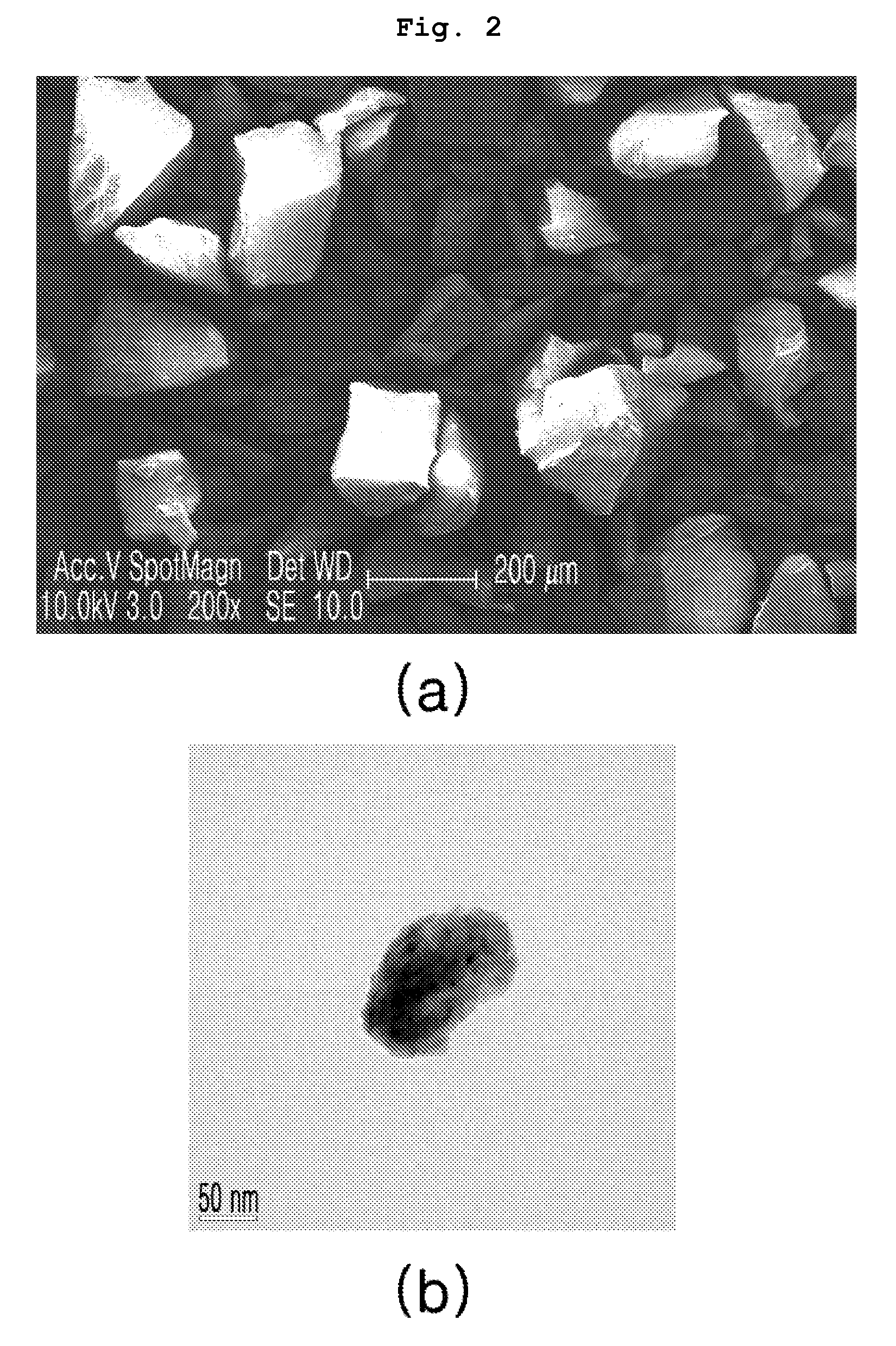
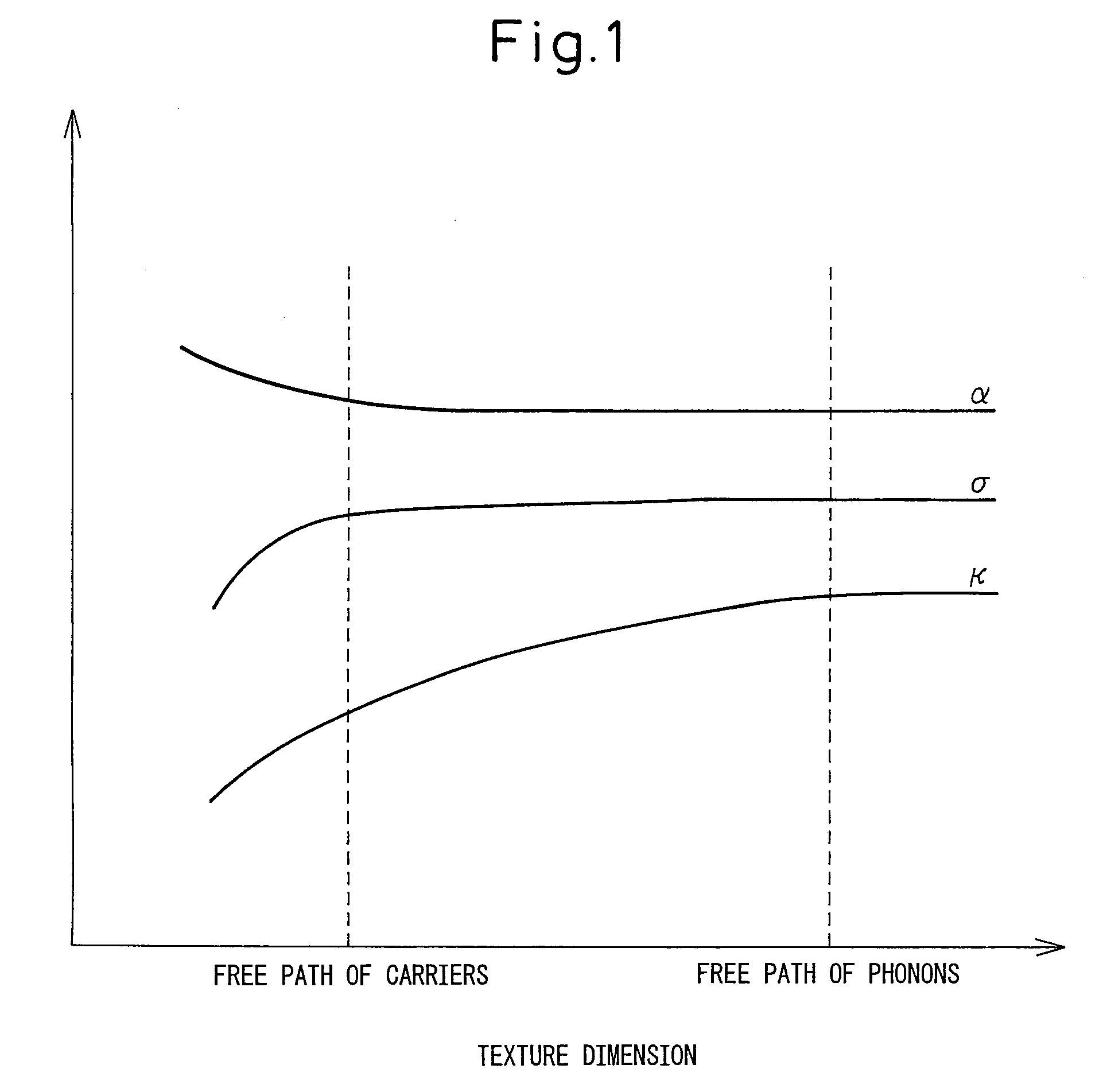
A thermoelectric semiconductor compound is provided whose performance index Z is remarkably improved without sacrificing Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity or thermal conductivity. The thermoelectric semiconductor compound includes a first thermoelectric semiconductor which is in the form of matrix and a second thermoelectric semiconductor which is in the form of particles dispersed in the matrix. The first thermoelectric semiconductor and the second thermoelectric semiconductor have a common element. The average diameter D of the dispersed particles complies with a formula of A<D<B, where A is the mean free path of a carrier in a single crystal of the second thermoelectric semiconductor and B is the mean free path of a long wave length phonon in the single crystal of the second thermoelectric semiconductor. A method for making the a thermoelectric semiconductor compound is provided.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Apparatus and method for plasma treatment
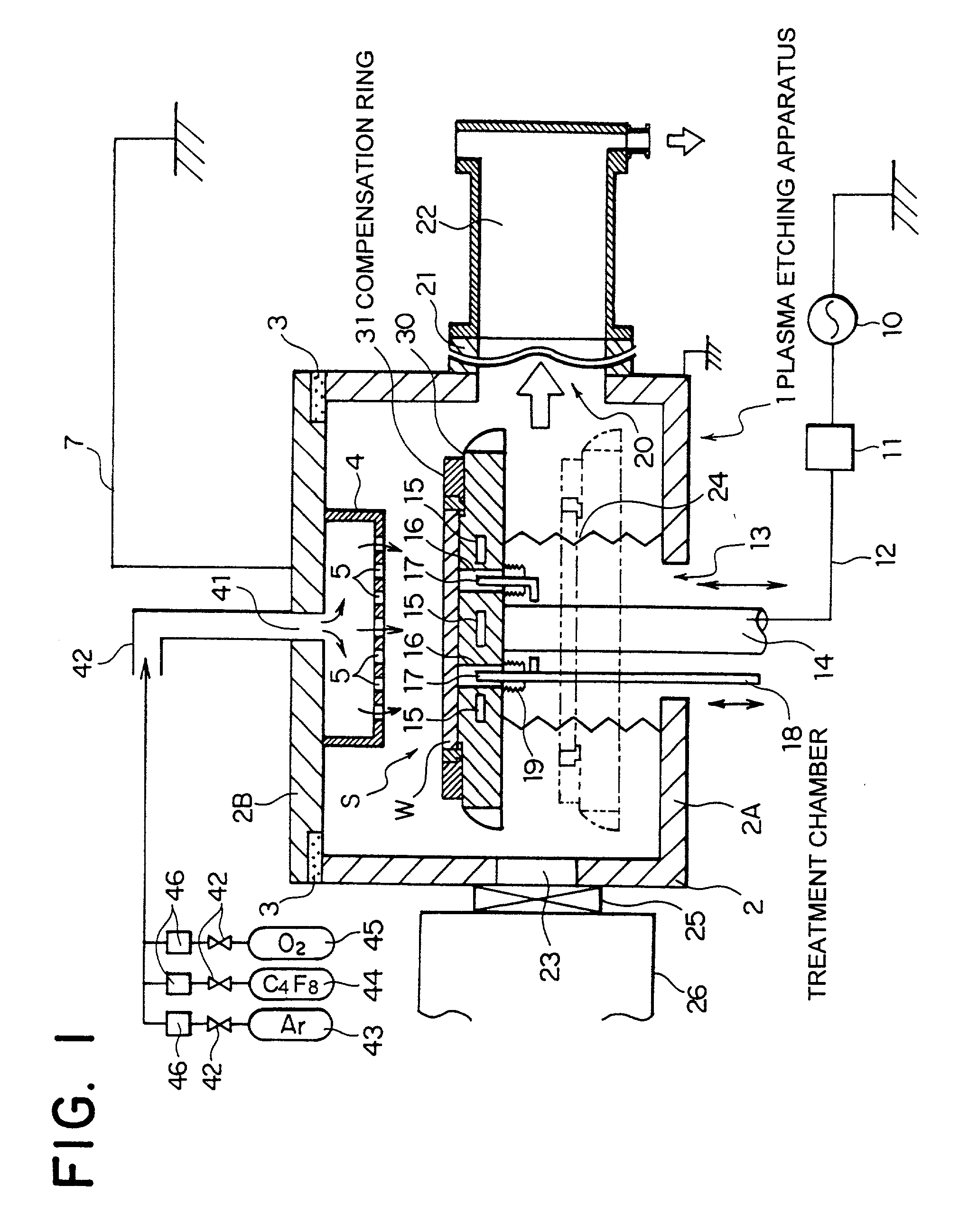
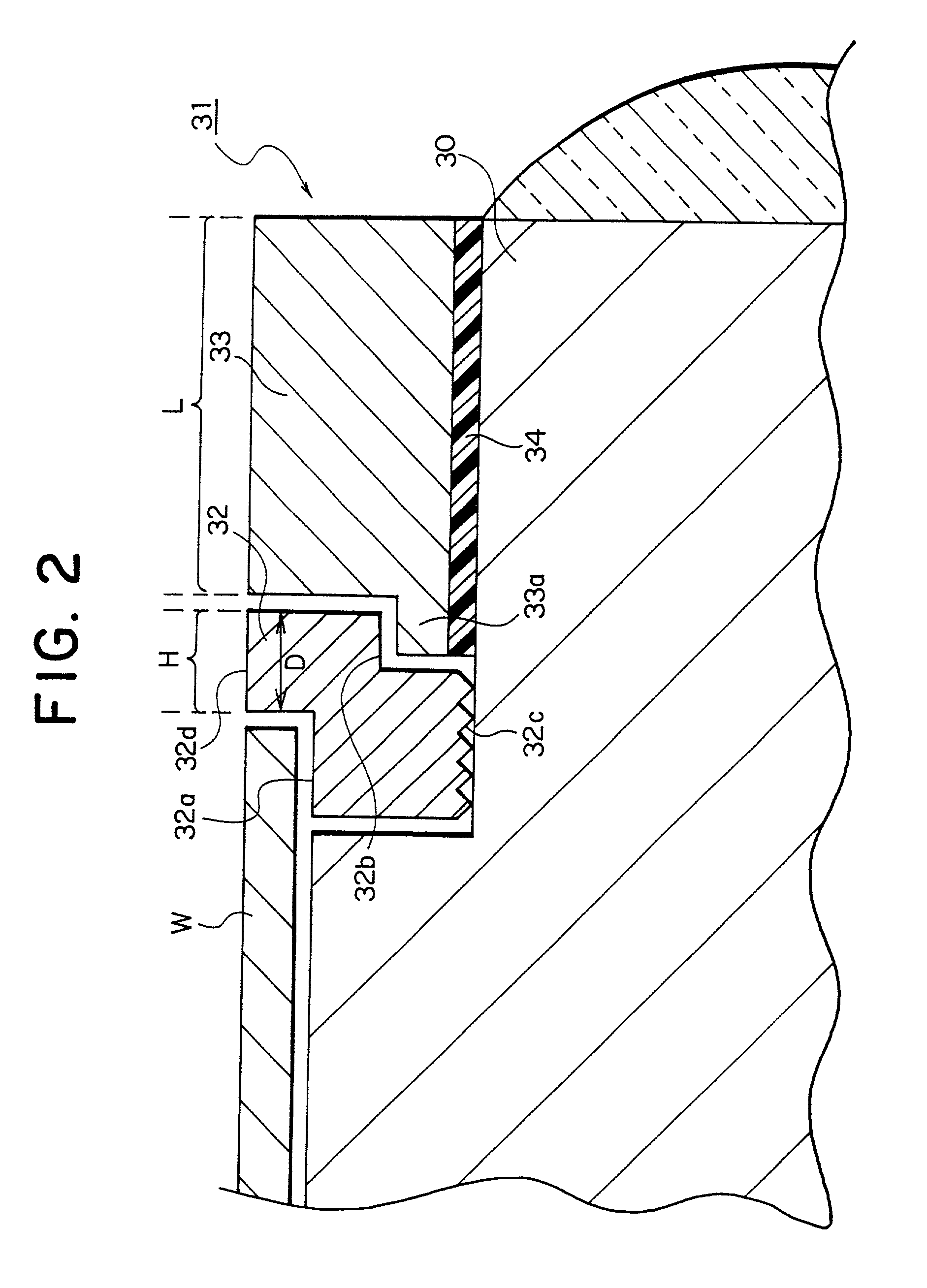
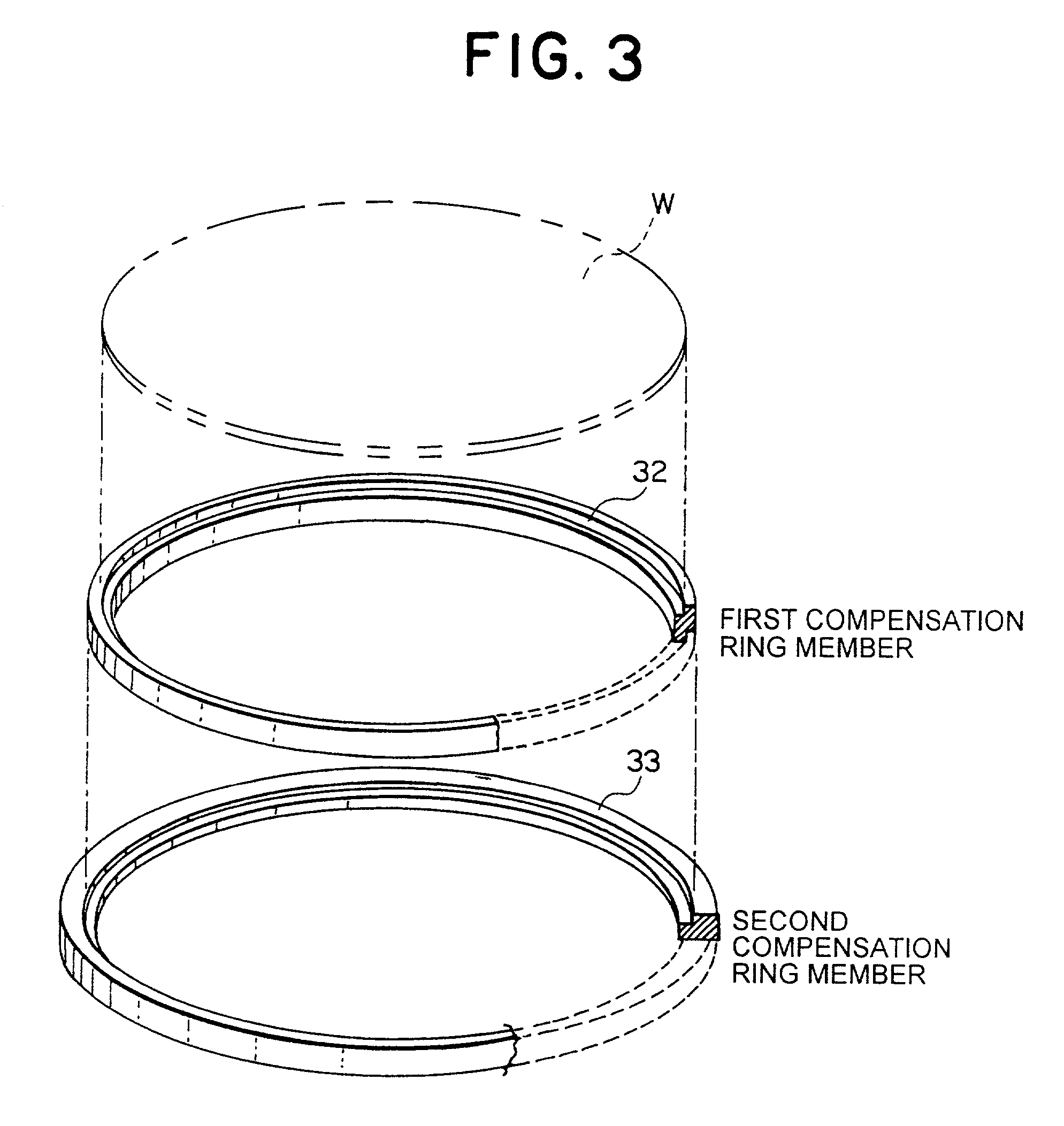
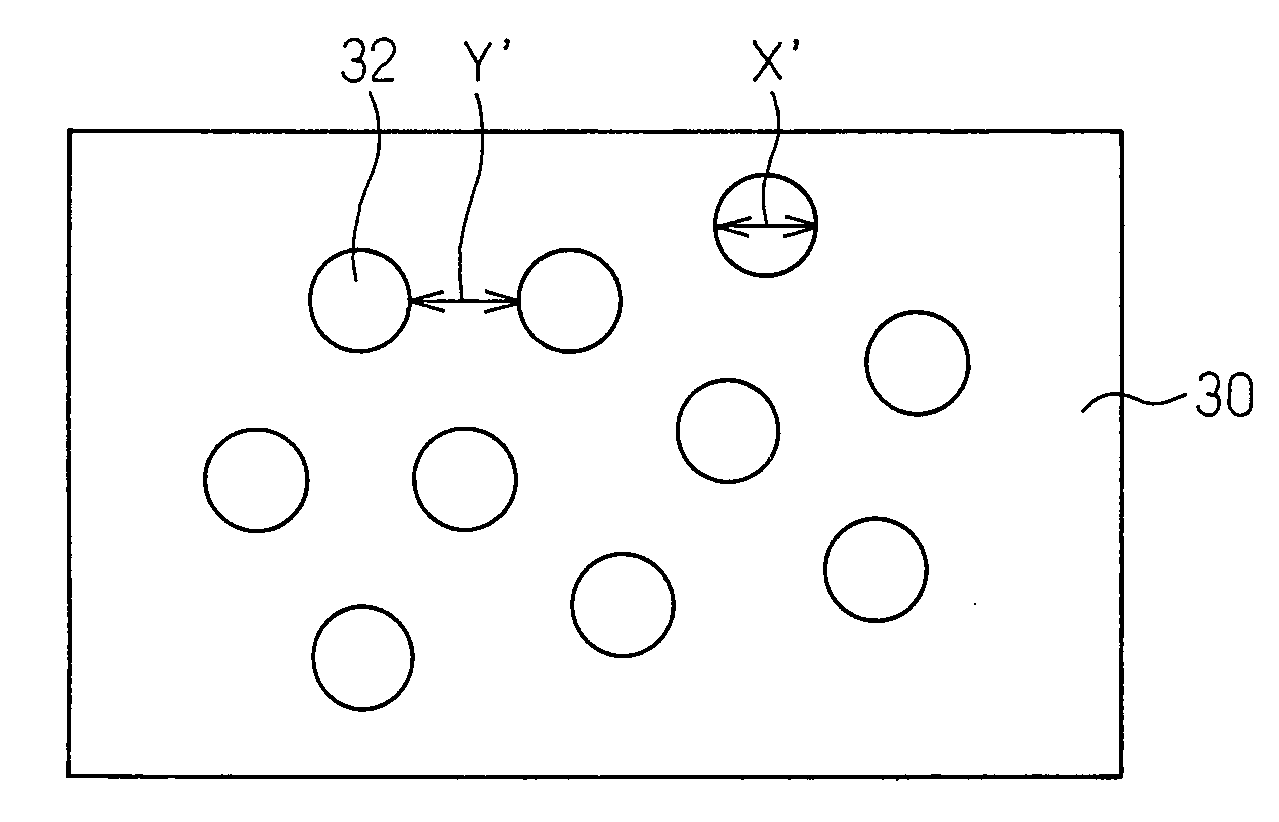
A compensation ring 31 disposed to surround a periphery of a wafer W on a susceptor 30 is concentrically divided into an inside first compensation ring member 32 and an outside second compensation ring member 33. A width of a first compensation ring member 32 is made such thin as one to three times mean free path of treatment gas molecules, thereby suppressing heat transfer between a susceptor 30 and a second compensation ring member 33. A base of a second compensation ring member, through a layer of conductive silicone rubber 34, is made to come into an intimate contact with an upper surface of a susceptor 30, thus helping to cool.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
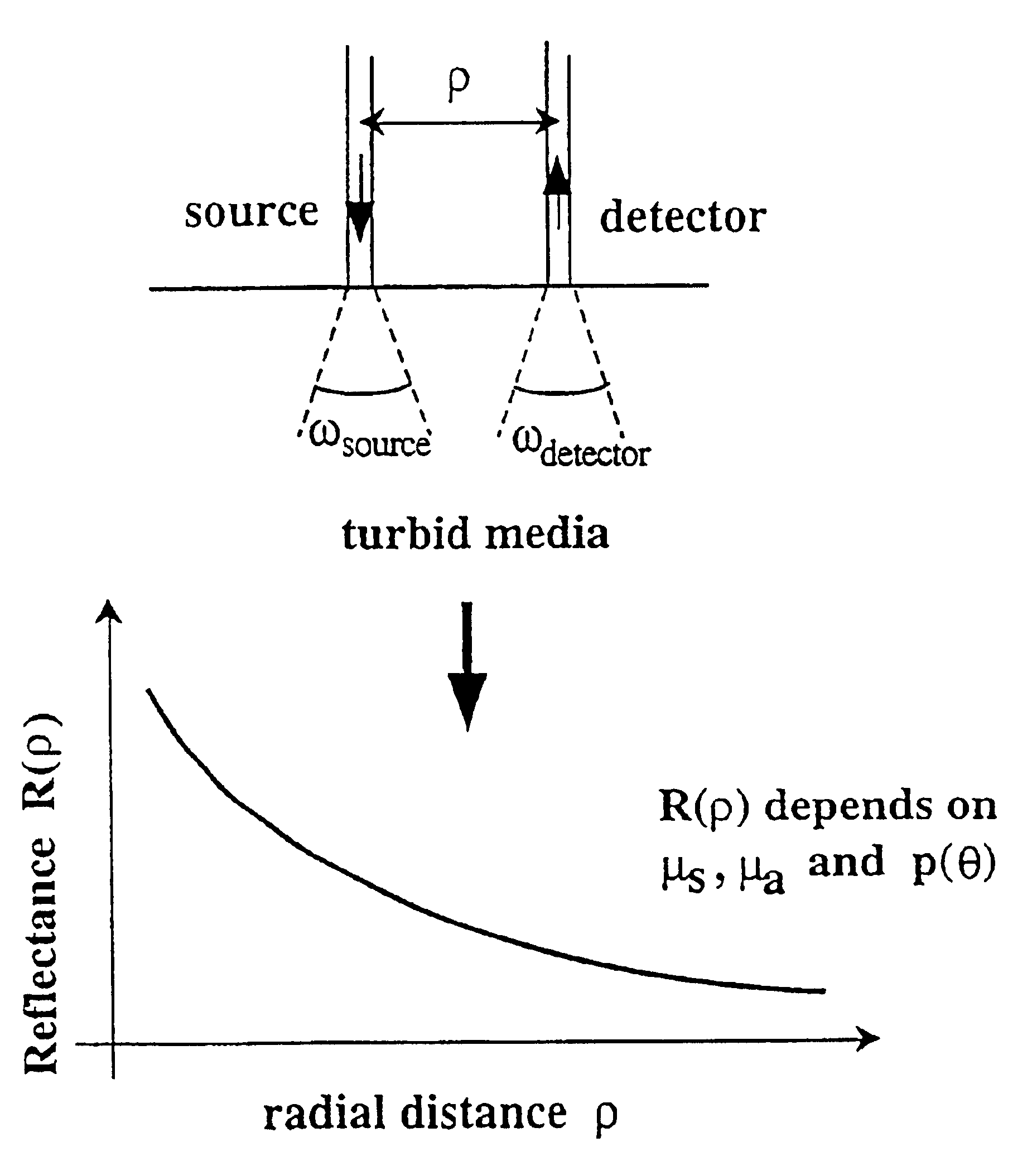
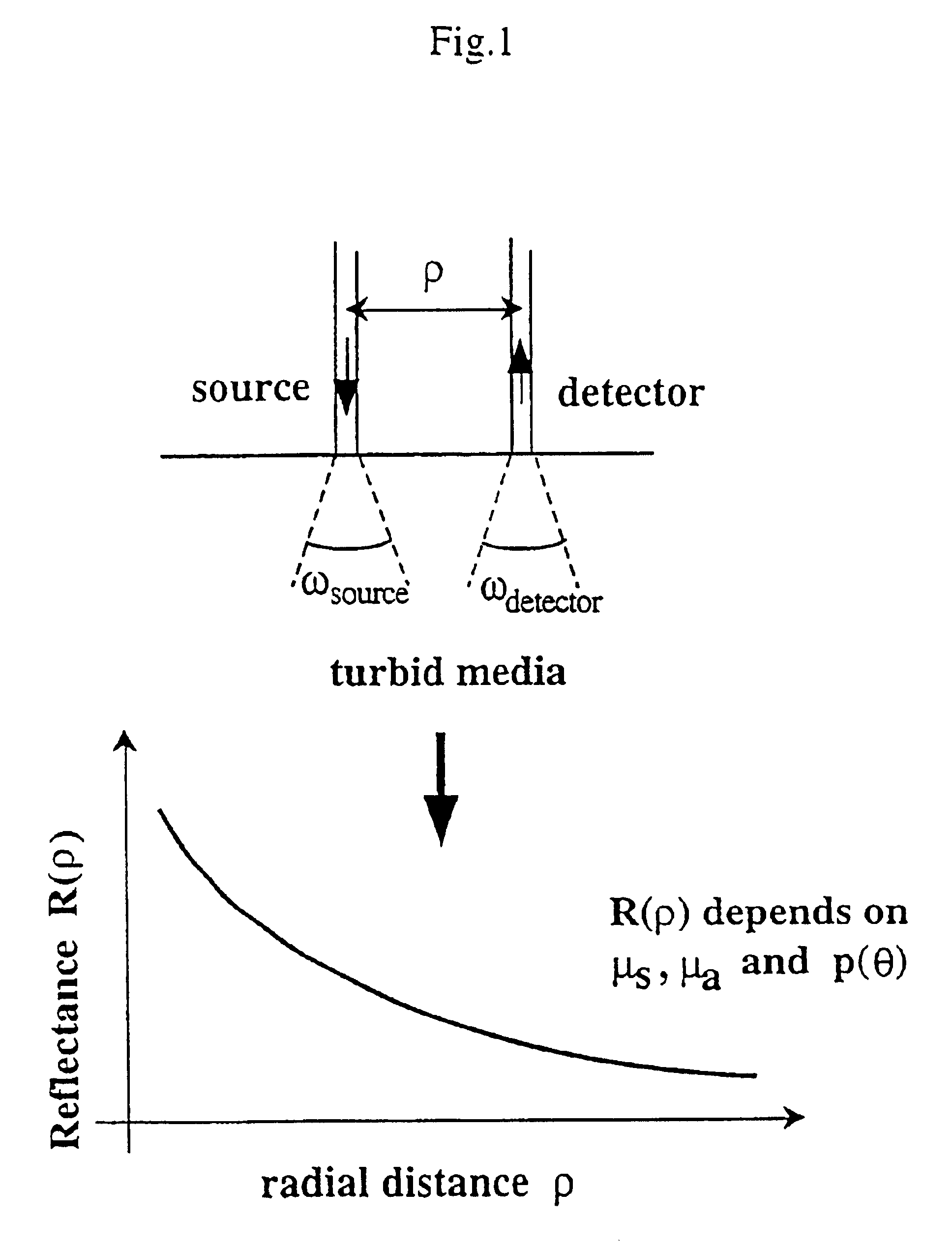
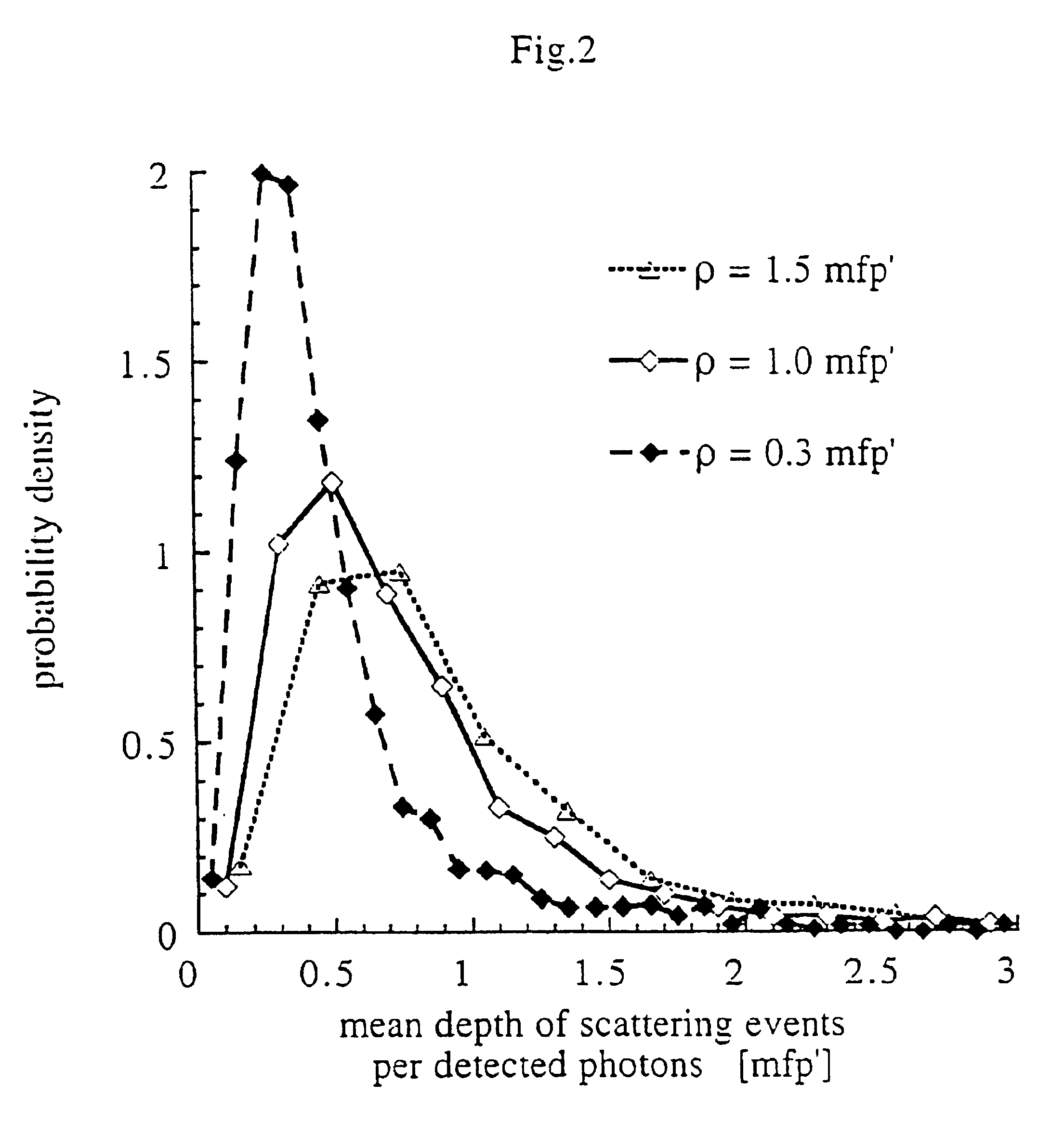
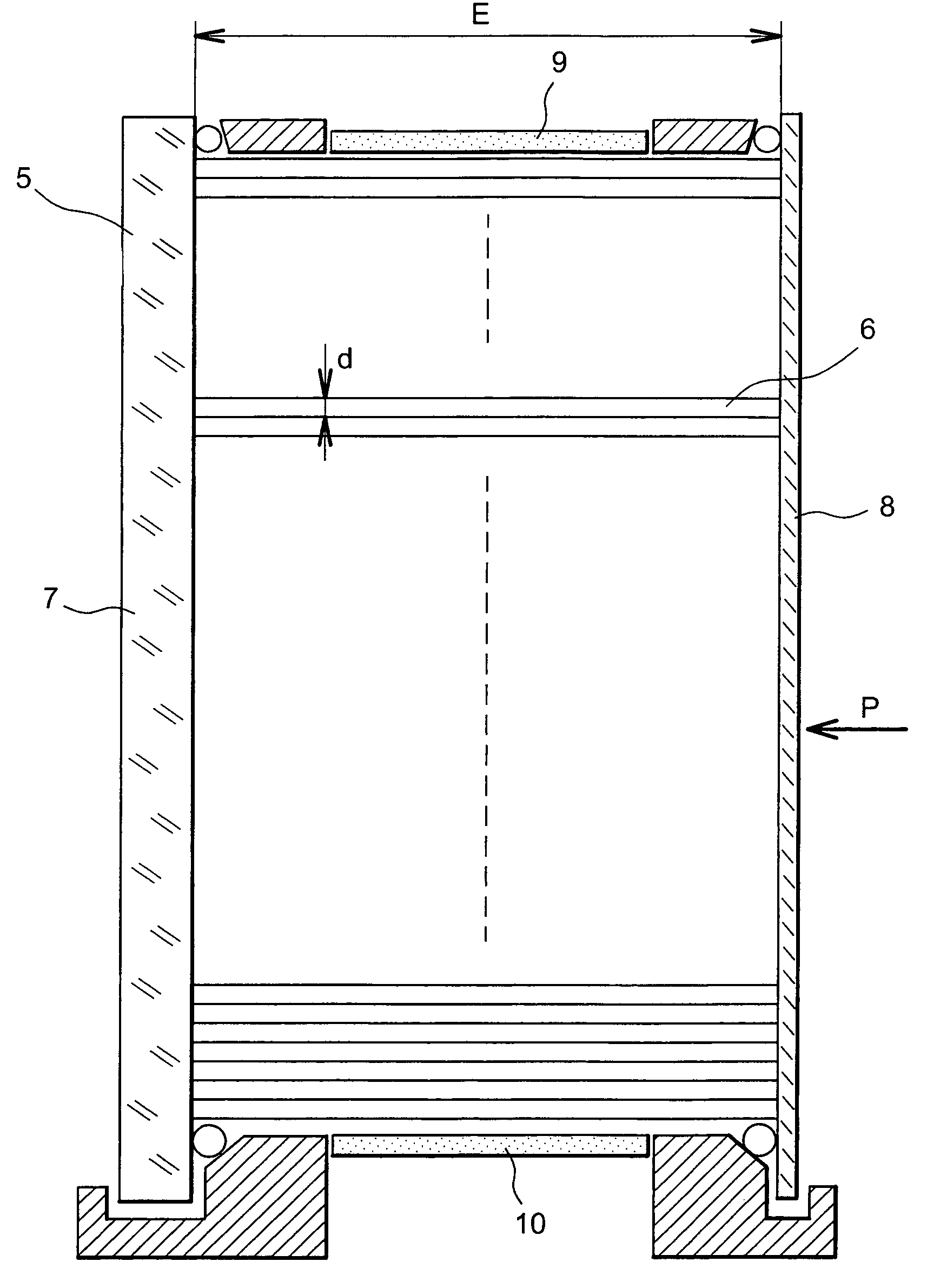
Method and apparatus for measuring locally and superficially the scattering and absorption properties of turbid media
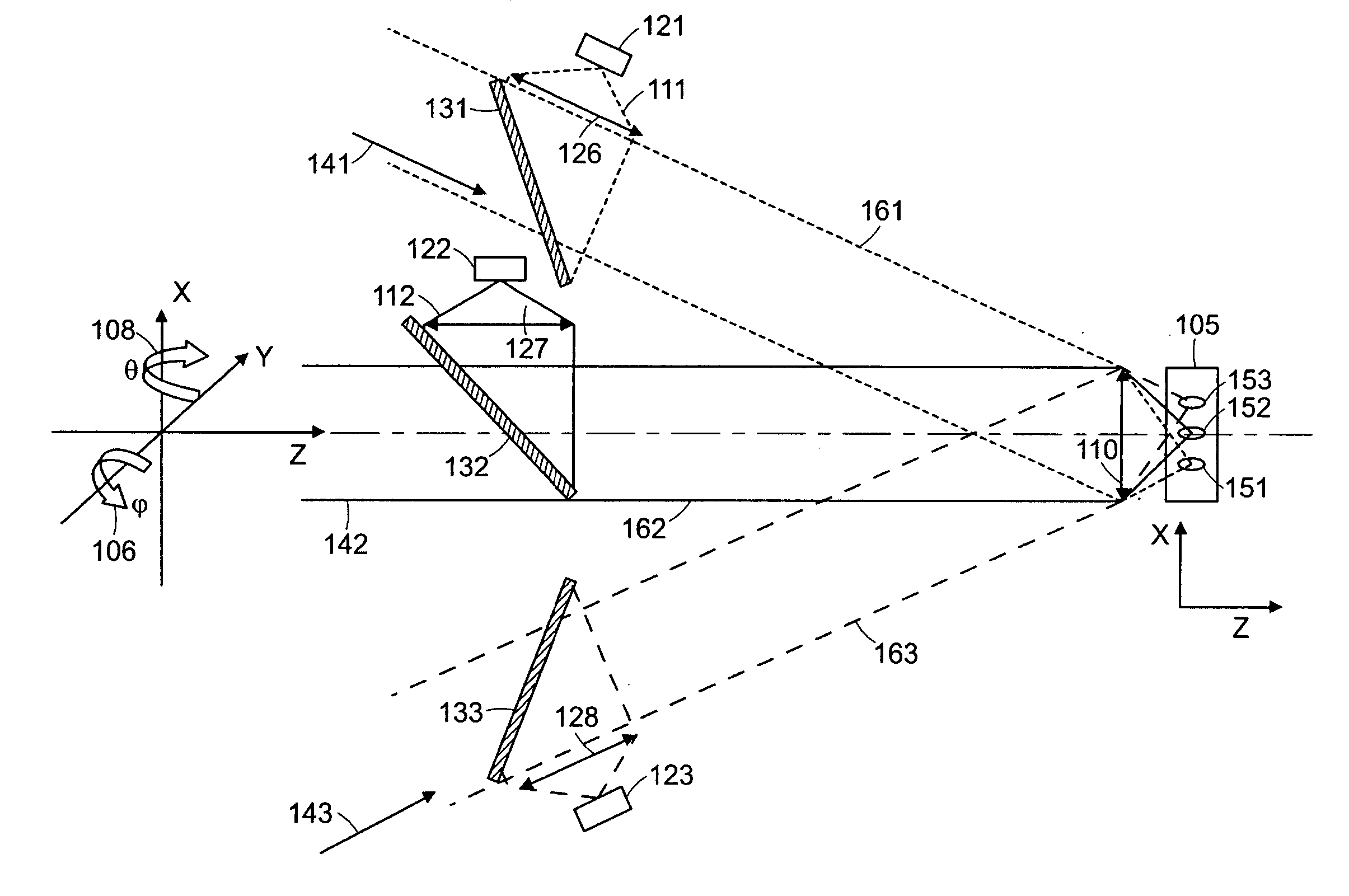
We present a method and apparatus for local and superficial measurement of the optical properties of turbid media. The depth probed is on the order of 1 transport mean free path of the photon. The absorption coefficient, reduced scattering coefficient and the phase function parameter γ=(1−g2) / (1−g1) are optical parameters computed from a single measurement of the spatially resolved reflectance close to the source. Images of superficial structures of the medium can be obtained by performing multi-site measurements. An important application of this technique is the characterization of biological tissues, for example for medical diagnostic purposes. Measurements on biological tissues can be achieved using a probe of diameter less than 2 mm, and the average volume probed is on the order of 1 mm3. Separate images of absorption and tissue structure can be achieved with a resolution of approximately one transport mean free path of the considered tissue.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Quantum wire gate device and method of making same
The present invention relates to a method of forming a quantum wire gate device. The method includes patterning a first oxide upon a substrate. Preferably the first oxide pattern is precisely and uniformly spaced to maximize quantum wire numbers per unit area. The method continues by forming a first nitride spacer mask upon the first oxide and by forming a first oxide spacer mask upon the first nitride spacer mask. Thereafter, the method continues by forming a second nitride spacer mask upon the first oxide spacer mask and by forming a plurality of channels in the substrate that are aligned to the second nitride spacer mask. A dielectric is formed upon the channel length and the method continues by forming a gate layer over the plurality of channels. Because of the inventive method and the starting scale, each of the plurality of channels is narrower than the mean free path of semiconductive electron flow therein.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Two-dimensional ionising particle detector
InactiveUS7238951B2Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberMean free path
A two-dimensional ionising particle detector including a matrix of detecting fibers, each detecting fiber forming a pixel of the detector. Each detecting fiber is composed of a glass capillary filled with a liquid scintillator for which the chemical composition is chosen such that an average free path of primary scintillation photons is negligible compared with a diameter of the capillary. The detector is applicable, for example, to high resolution particle imagery.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Solid state surface catalysis reactor
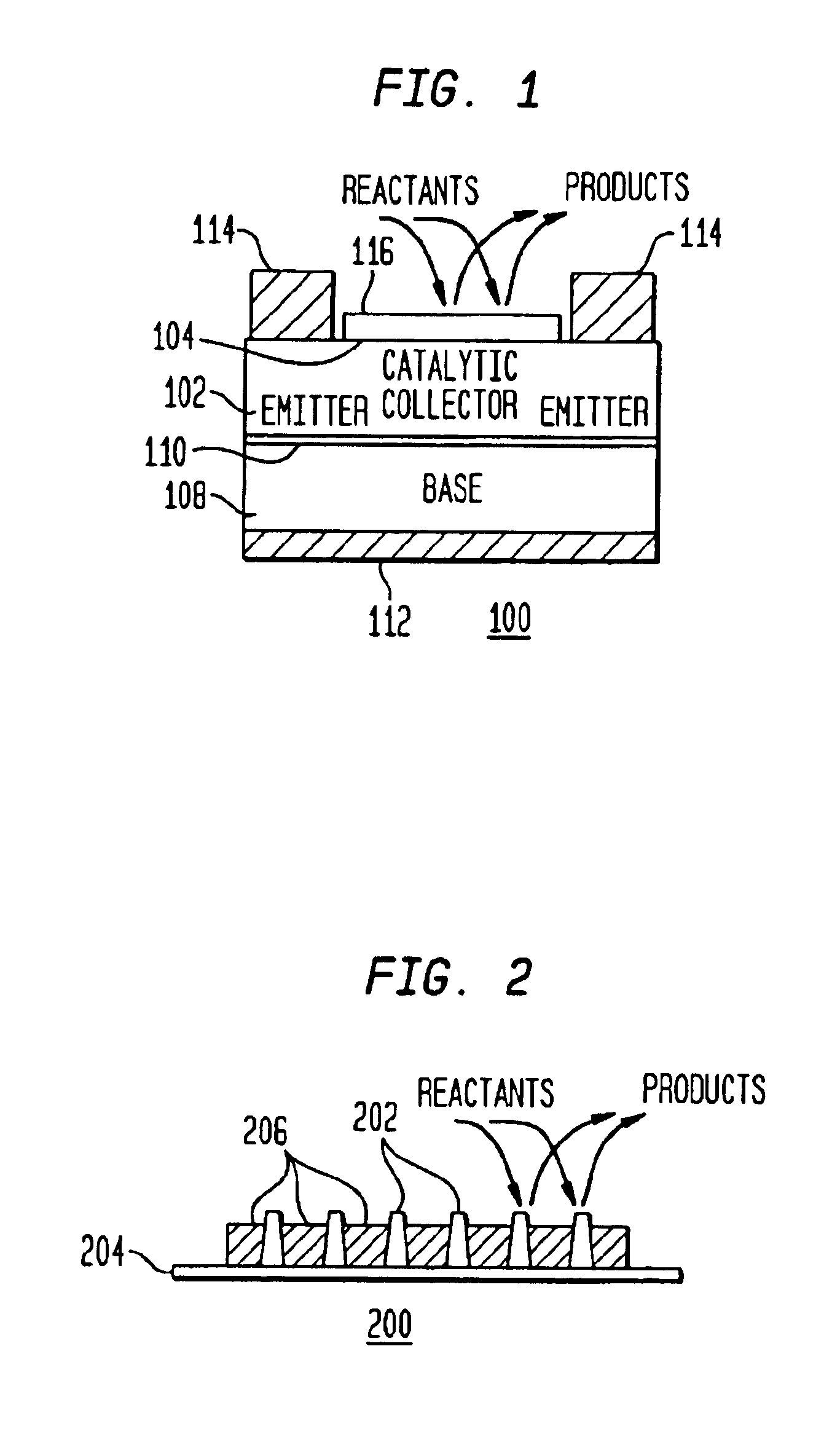
InactiveUS6916451B1Physical/chemical process catalystsPhotovoltaicsChemical reactionElectric generator
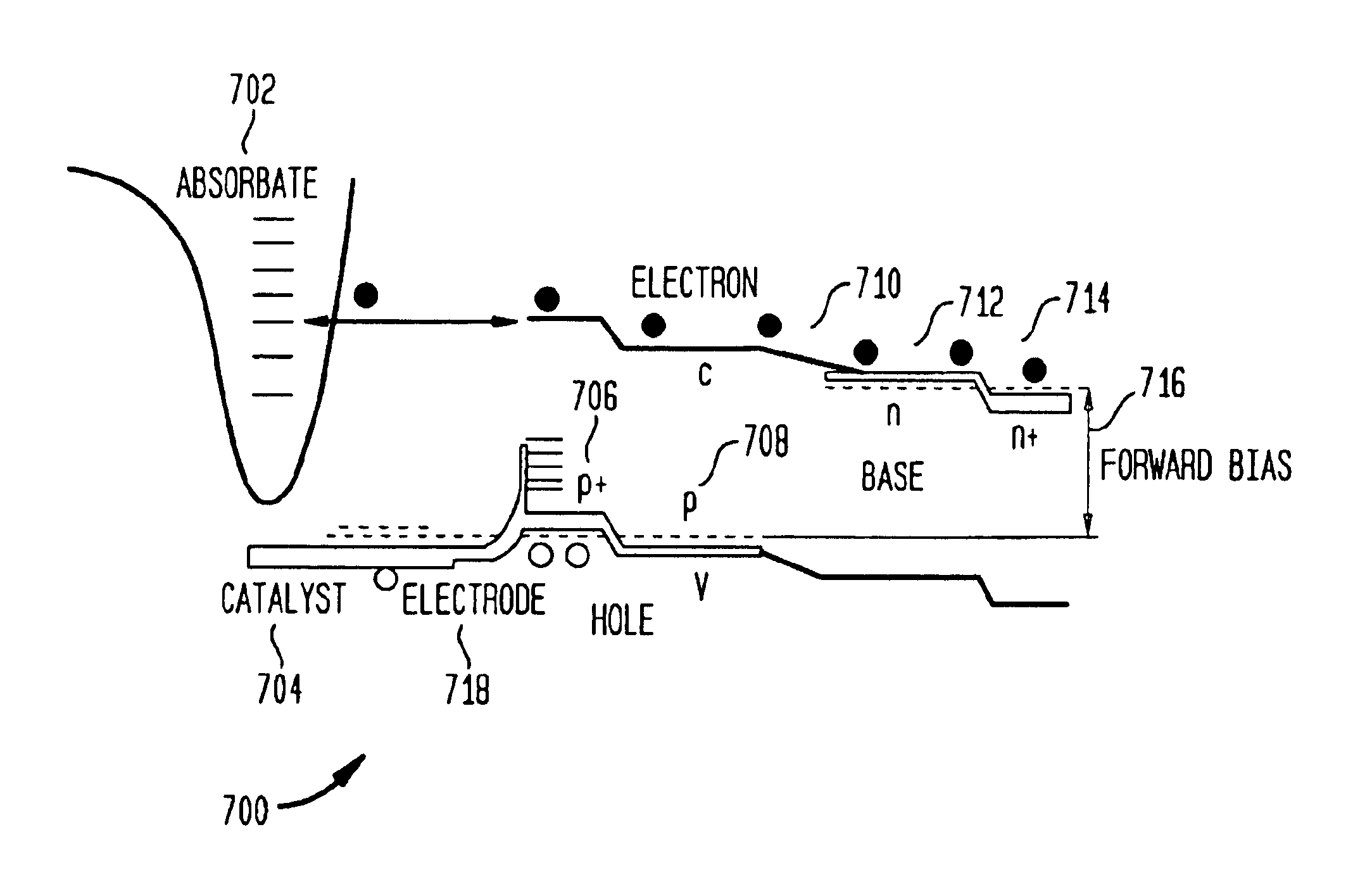
A method and apparatus to stimulate chemical reactions on a catalyst surface using electricity, and the reverse process to convert energy released from chemical reactions into electricity. A reversible emitter generates electrons which are injected into reactants on the catalyst surface, exciting chemically reactive vibrational resonances. Hot electrons created in the emitter region of a semiconductor junction diffuse to the co-located collector region and catalyst surface. Catalyst clusters or films bonded on the collector surface transfer the hot electrons to or from the catalyst surface having adsorbed reactants. The dimension of the catalyst-collector is less than the energy mean free path of hot electrons. The hot electrons excite reactant vibrations before thermalizing with the substrate lattice thereby accelerating reactions. The hot electrons are also generated by the same reactions on a catalyst surface. The method and apparatus is reversible and may be operated as an electric generator using chemical reactions.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
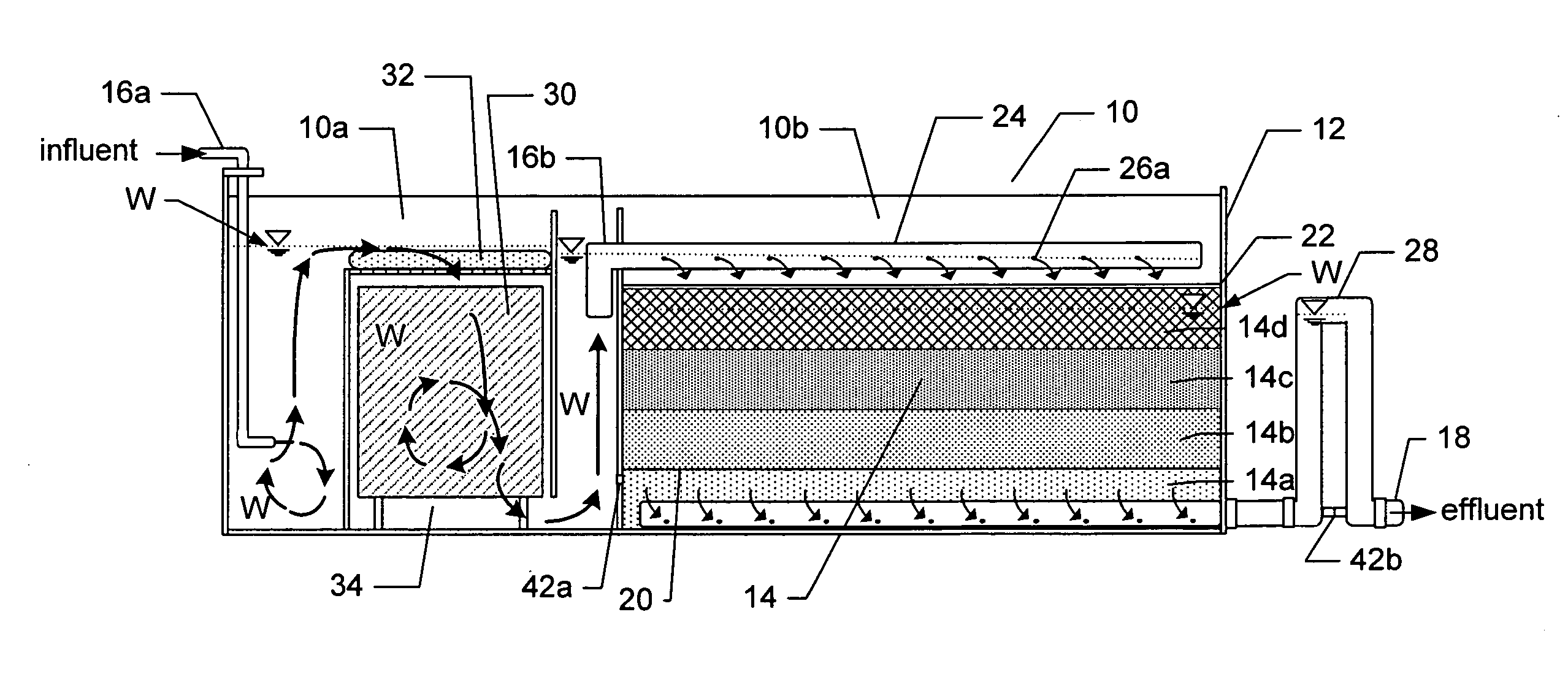
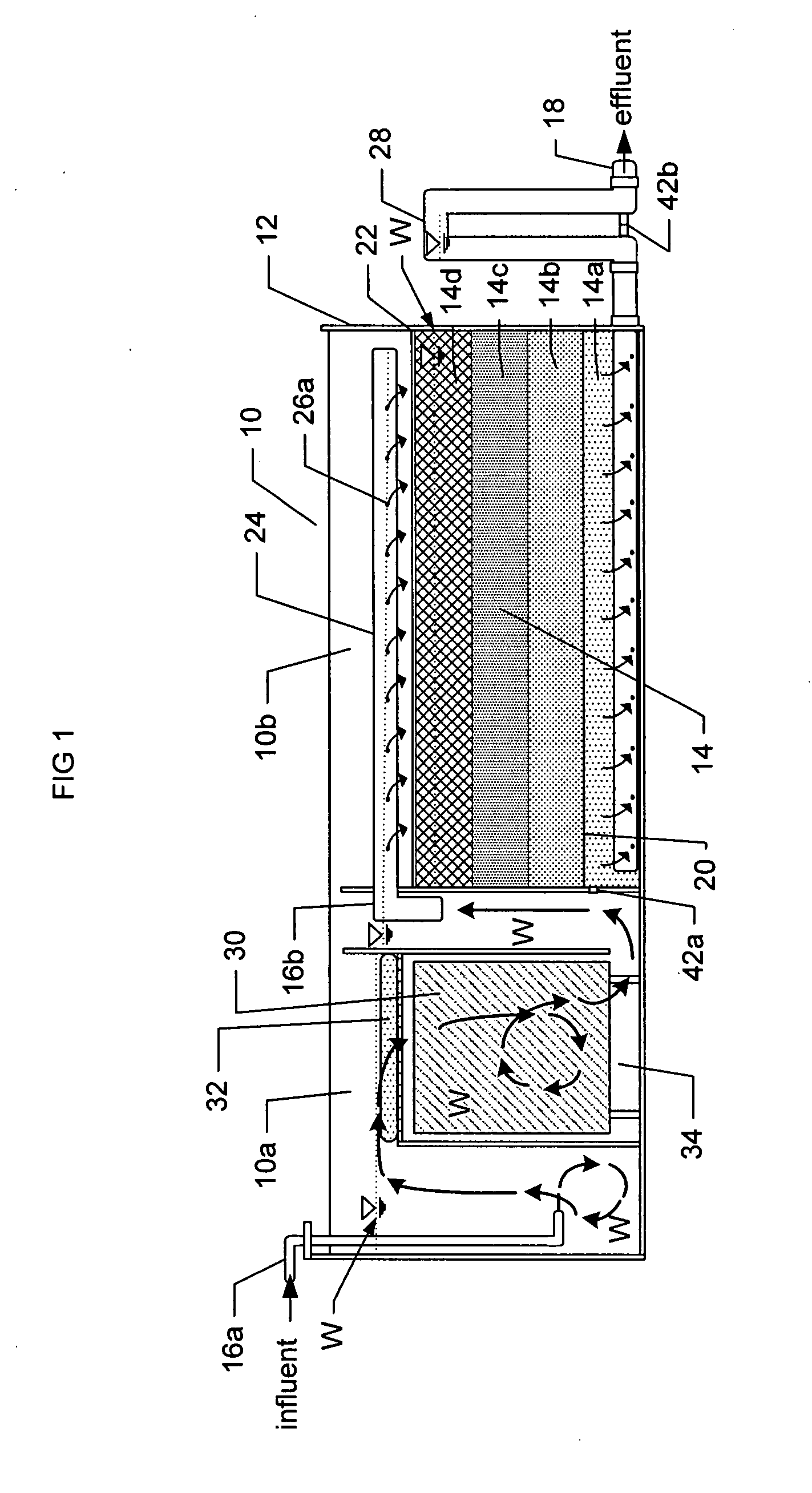
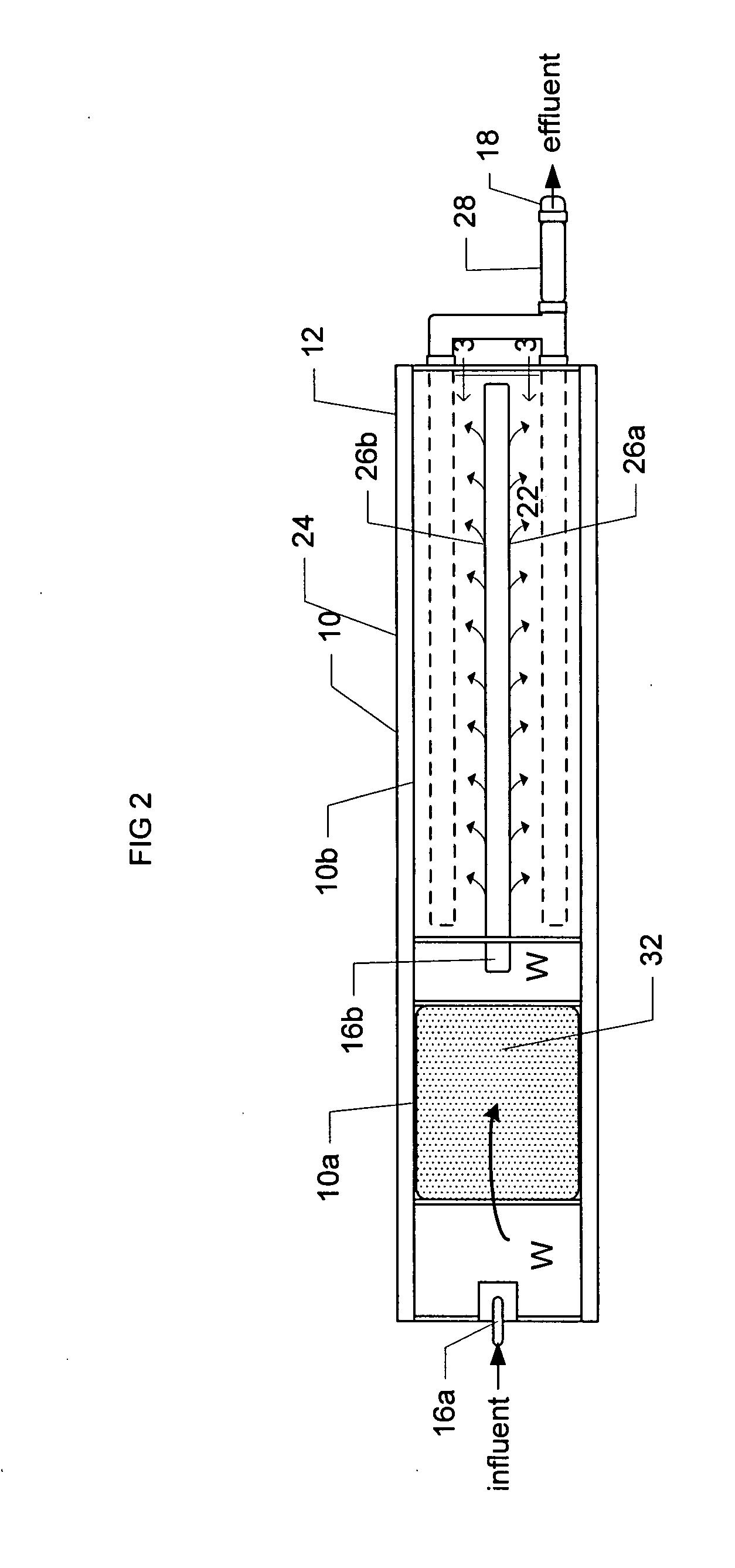
Passive stormwater management apparatus and system
ActiveUS20090101555A1Easy to cleanCost-effective and extremely effective in removingGeneral water supply conservationTreatment involving filtrationMean free pathParticulates
A stormwater inlet near an upper edge of a layered filter media vessel is equipped with a distribution header that ensures effective use of the surface area of the filter media by providing plural spaced streams of stormwater thereat, each at a point of impact having its energy dissipated by a layer of material that covers the upper layered filter media surface. The stormwater inflow is metered to control the stormwater pollutant removal process kinetics, thereby slowing the mean free path of the stormwater therethrough and optimizing pollutant capture. The water level within the vessel is height adjustable manually by a pivot arm in the form of a standing column of water coupled to the water within the container. Weep conduits are provided to slowly drain down the standing water in the system between storm events, simplifying maintenance and promoting best removal of pollutants from first-flush storm events. Stormwater pretreatment, e.g. by use of an oleophilic agent or a pH-buffering agent, is provided. Filter media are easily cleaned, as by scraping and / or adding filter media material when existing material's particulate capture capacity is exhausted.
Owner:NEWTERRA CORP INC
Adhesion by plasma conditioning of semiconductor chip surfaces
InactiveUS6869831B2Improve adhesionClean the polymer surfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPolymeric surfaceMean free path
A plasma conditioning method of improving the adhesion between an integrated circuit chip, having active and passive surfaces, the active surface polymer-coated and having a plurality of electrical coupling members, and an insulating underfill material. The method comprises the steps of positioning a wafer having a plurality of integrated circuits, including the coupling members, in a vacuum chamber of a plasma apparatus so that the polymer-coated surface faces the plasma source. Next, a plasma is initiated; the ion mean free path is controlled so that the ions reach the wafer surface with predetermined energy. The wafer surface is then exposed to the plasma for a length of time sufficient to roughen the polymer surface, clean the polymer surface from organic contamination and improve the surface affinity to adhesion. The adhesion ability of this surface to organic underfill material is thus enhanced.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Spin-valve thin-film magnetic element and method for making the same
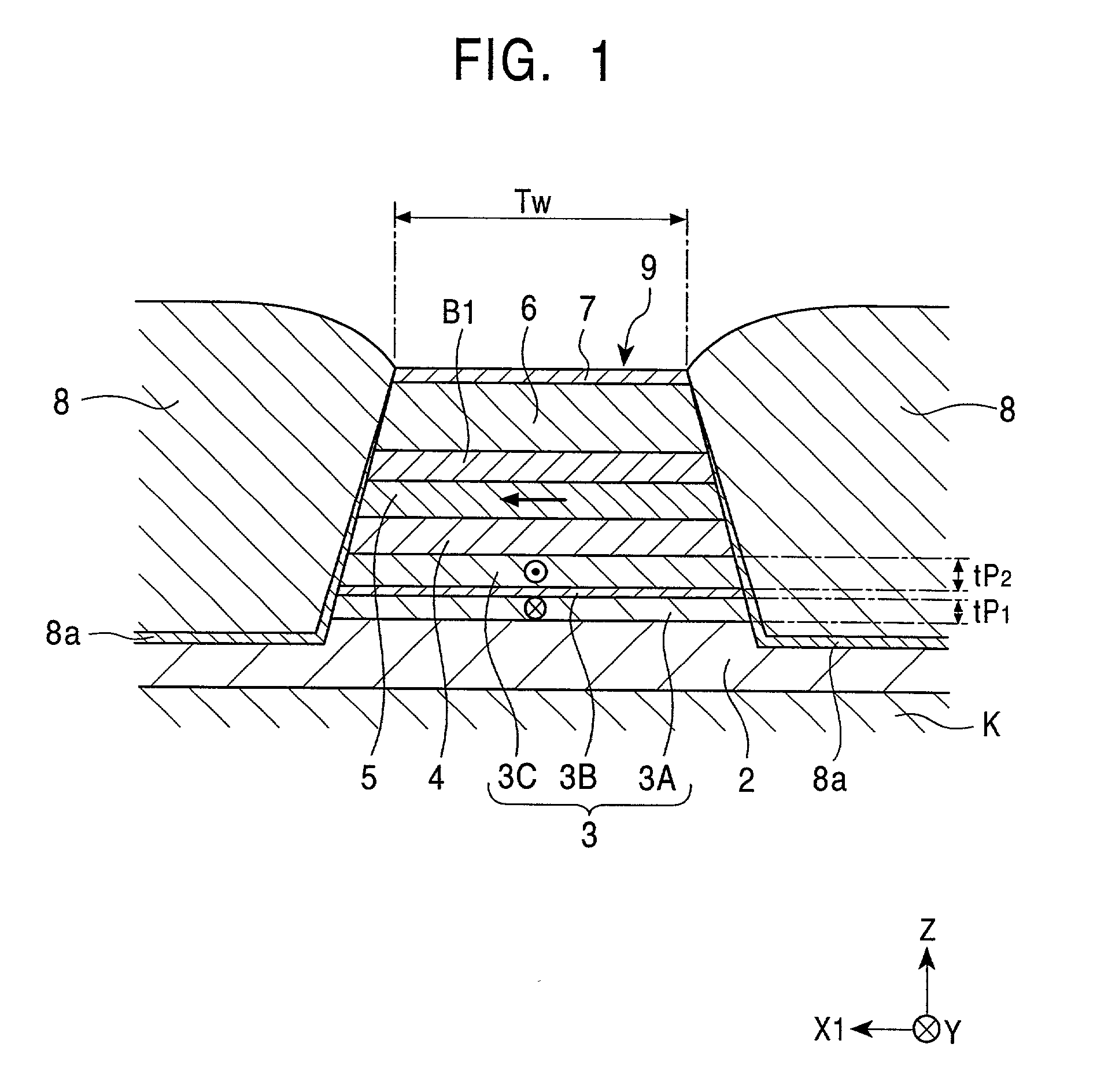
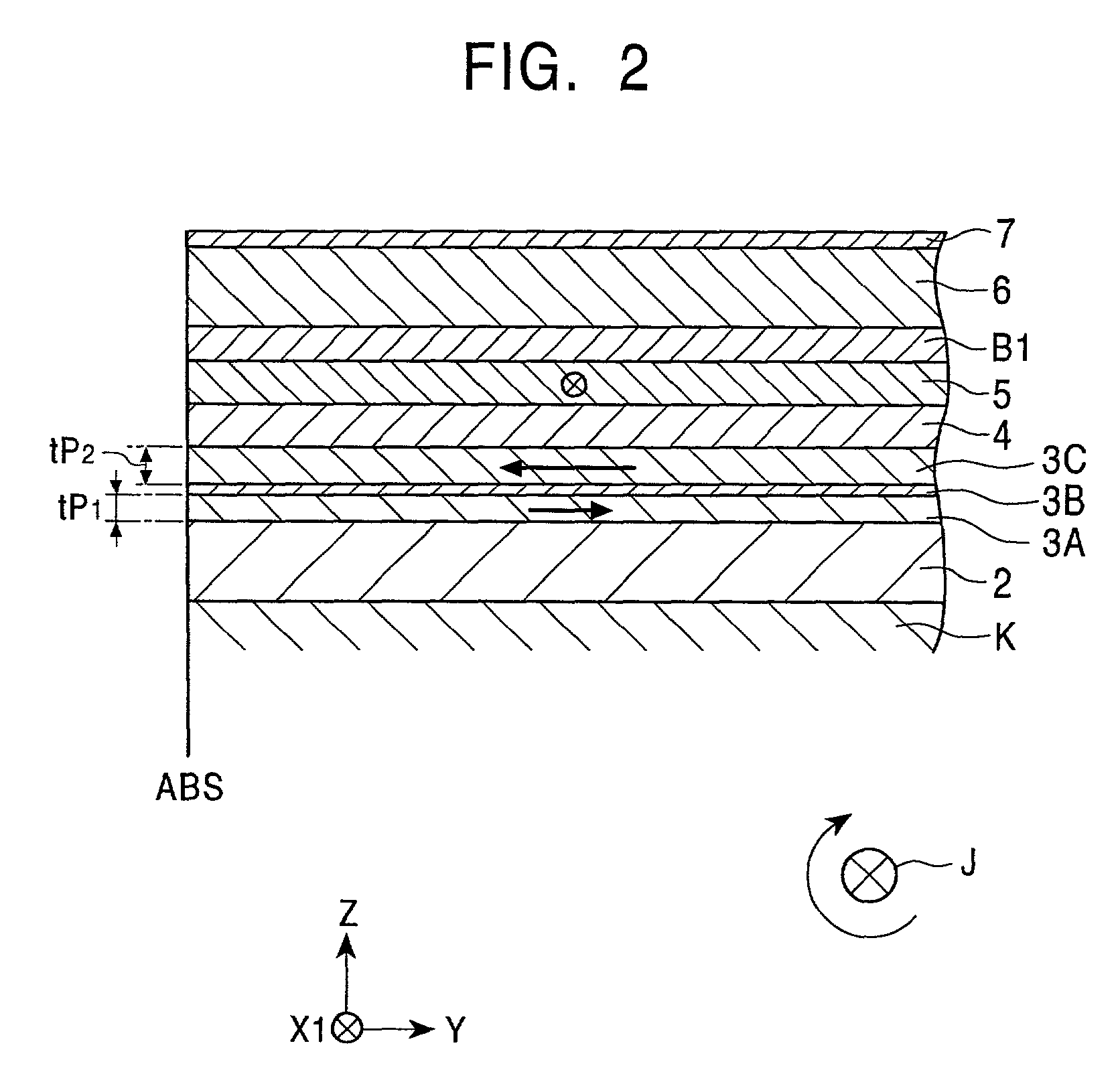
A spin-valve thin-film magnetic element includes a substrate, a composite formed thereon, and electrode layers formed on both sides of the composite. The composite includes an antiferromagnetic layer, a pinned magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic conductive layer, a free magnetic layer, a mean-free-path-extending layer, and an exchange bias layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer may be a back layer or a mirror reflective layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer extends the mean free path of spin-up conduction electrons in the spin-valve thin-film magnetic element. This spin-valve thin-film magnetic element meets trends toward a narrower track width.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Deep ultraviolet light emitting diode
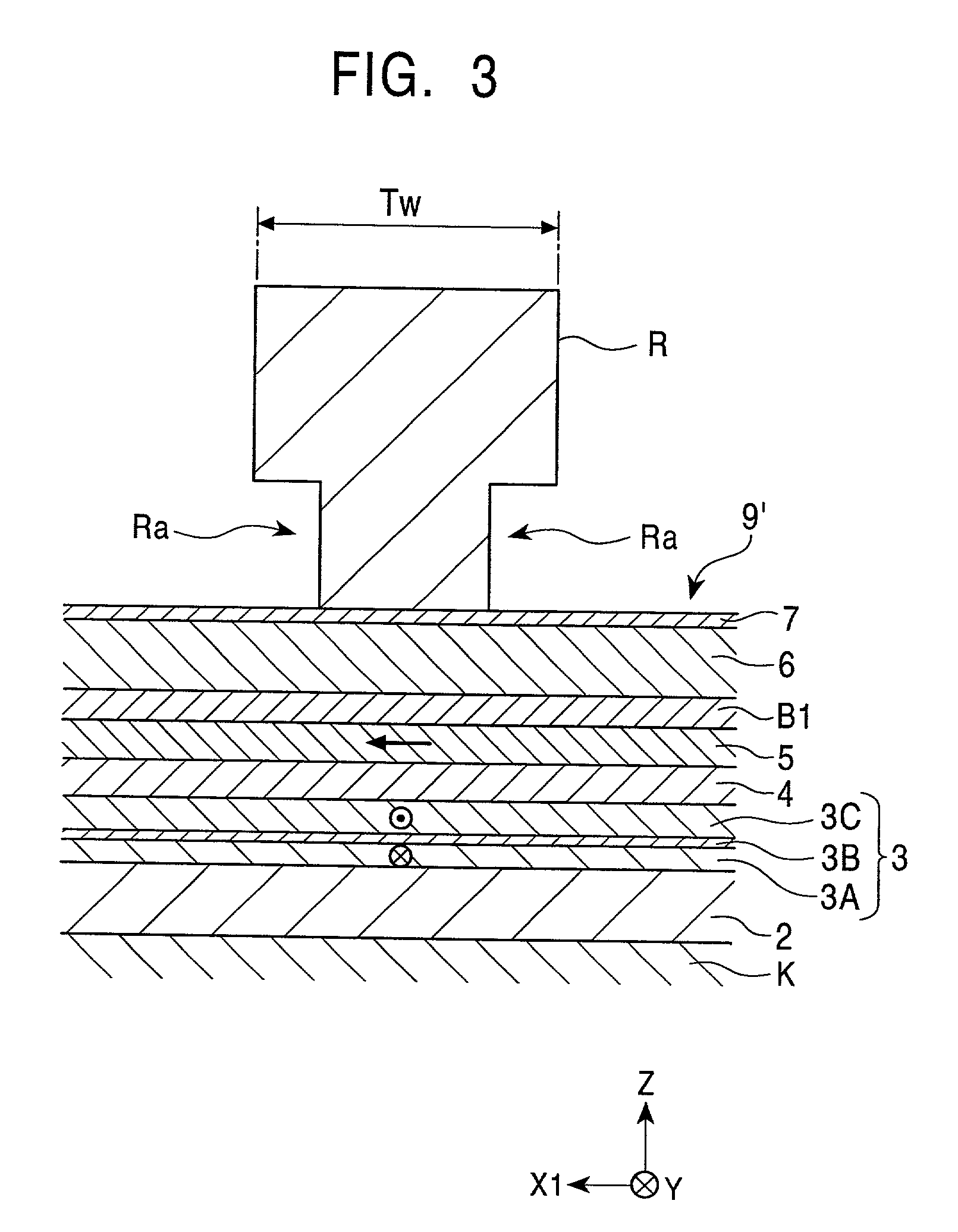
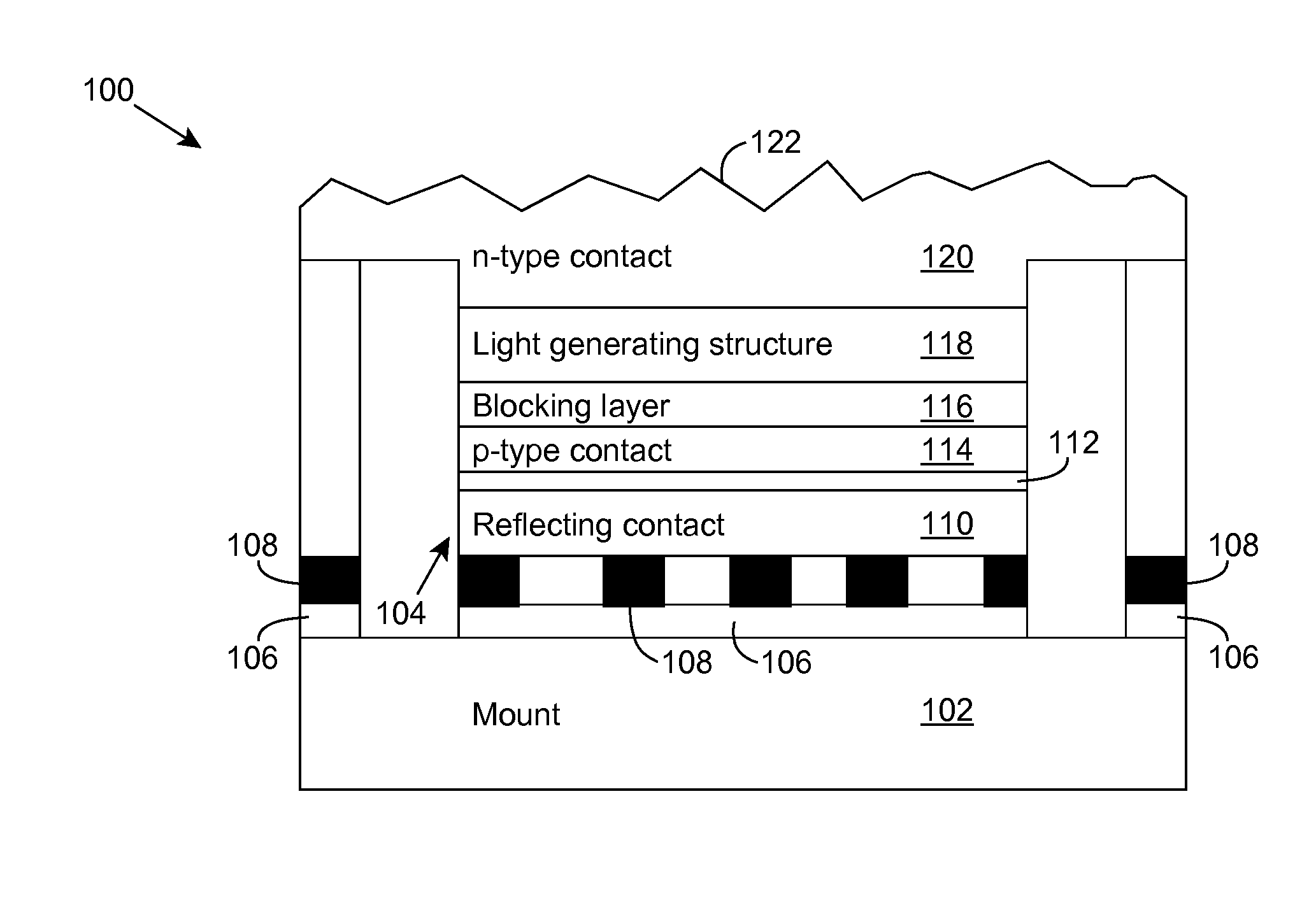
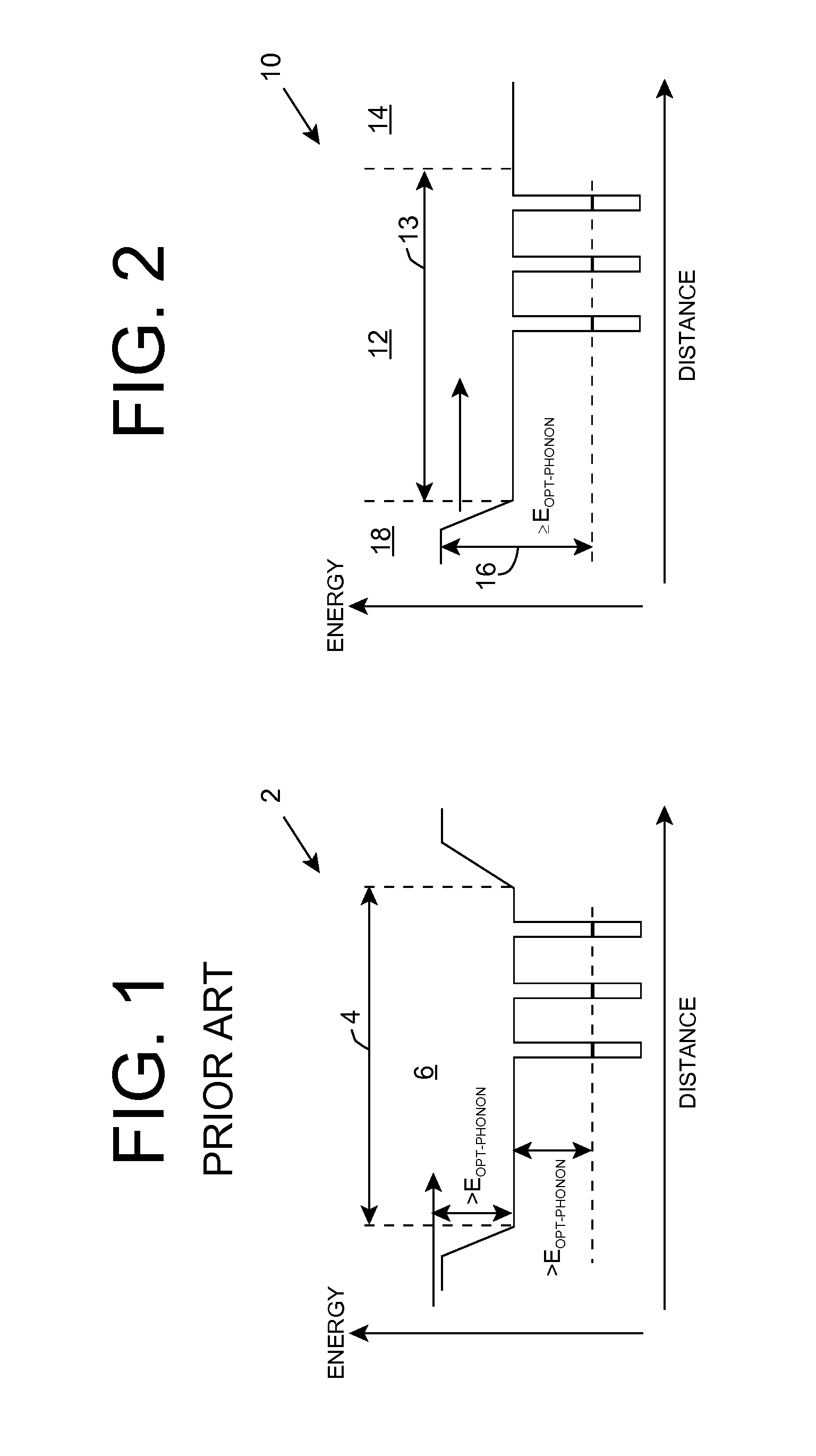
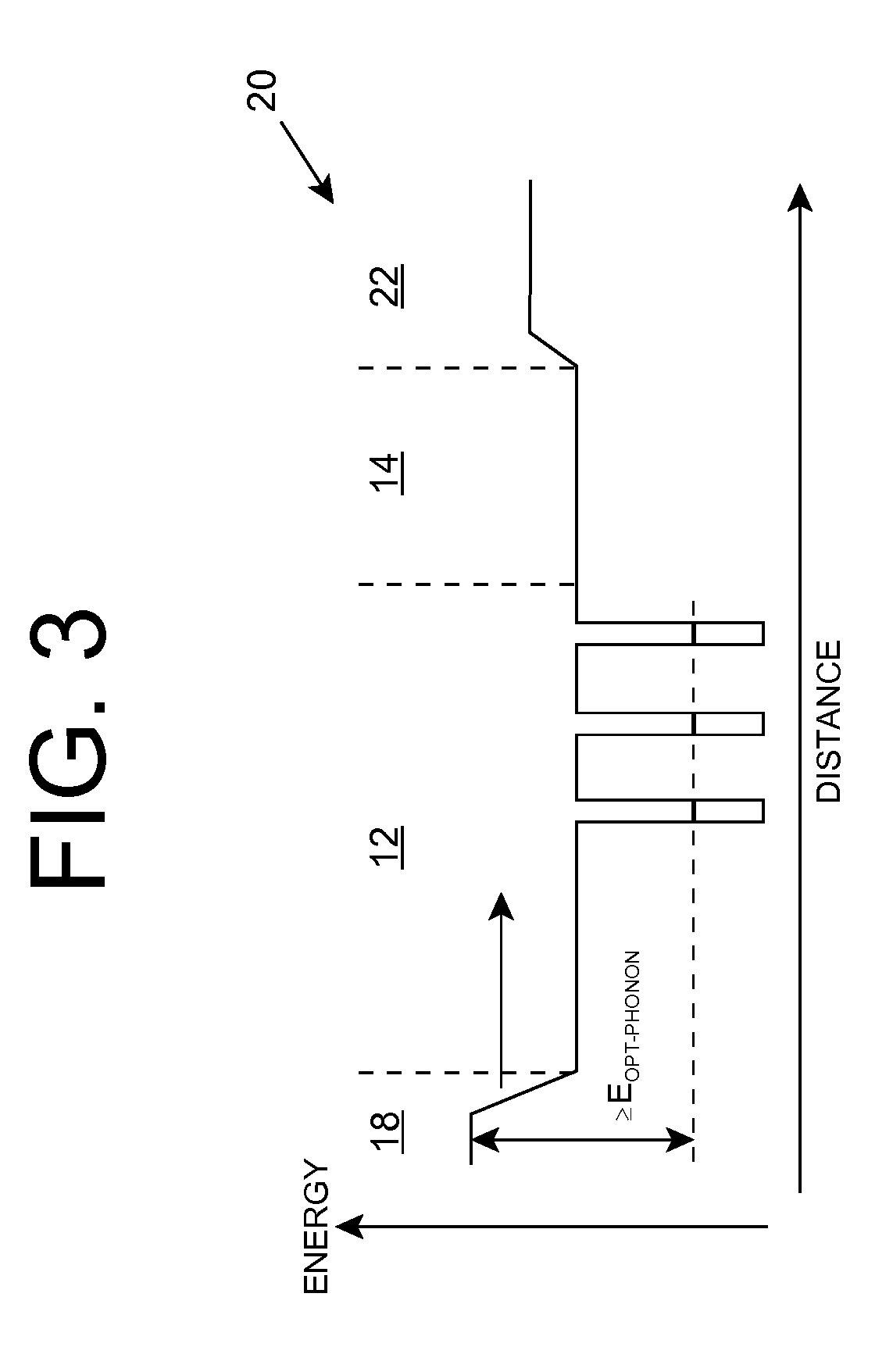
A light emitting diode is provided, which includes an n-type contact layer and a light generating structure adjacent to the n-type contact layer. The light generating structure includes a set of quantum wells. The contact layer and light generating structure can be configured so that a difference between an energy of the n-type contact layer and an electron ground state energy of a quantum well is greater than an energy of a polar optical phonon in a material of the light generating structure. Additionally, the light generating structure can be configured so that its width is comparable to a mean free path for emission of a polar optical phonon by an electron injected into the light generating structure. The diode can include a blocking layer, which is configured so that a difference between an energy of the blocking layer and the electron ground state energy of a quantum well is greater than the energy of the polar optical phonon in the material of the light generating structure. The diode can include a composite contact, including an adhesion layer, which is at least partially transparent to light generated by the light generating structure and a reflecting metal layer configured to reflect at least a portion of the light generated by the light generating structure.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Methods and systems to predict fatigue life in aluminum castings
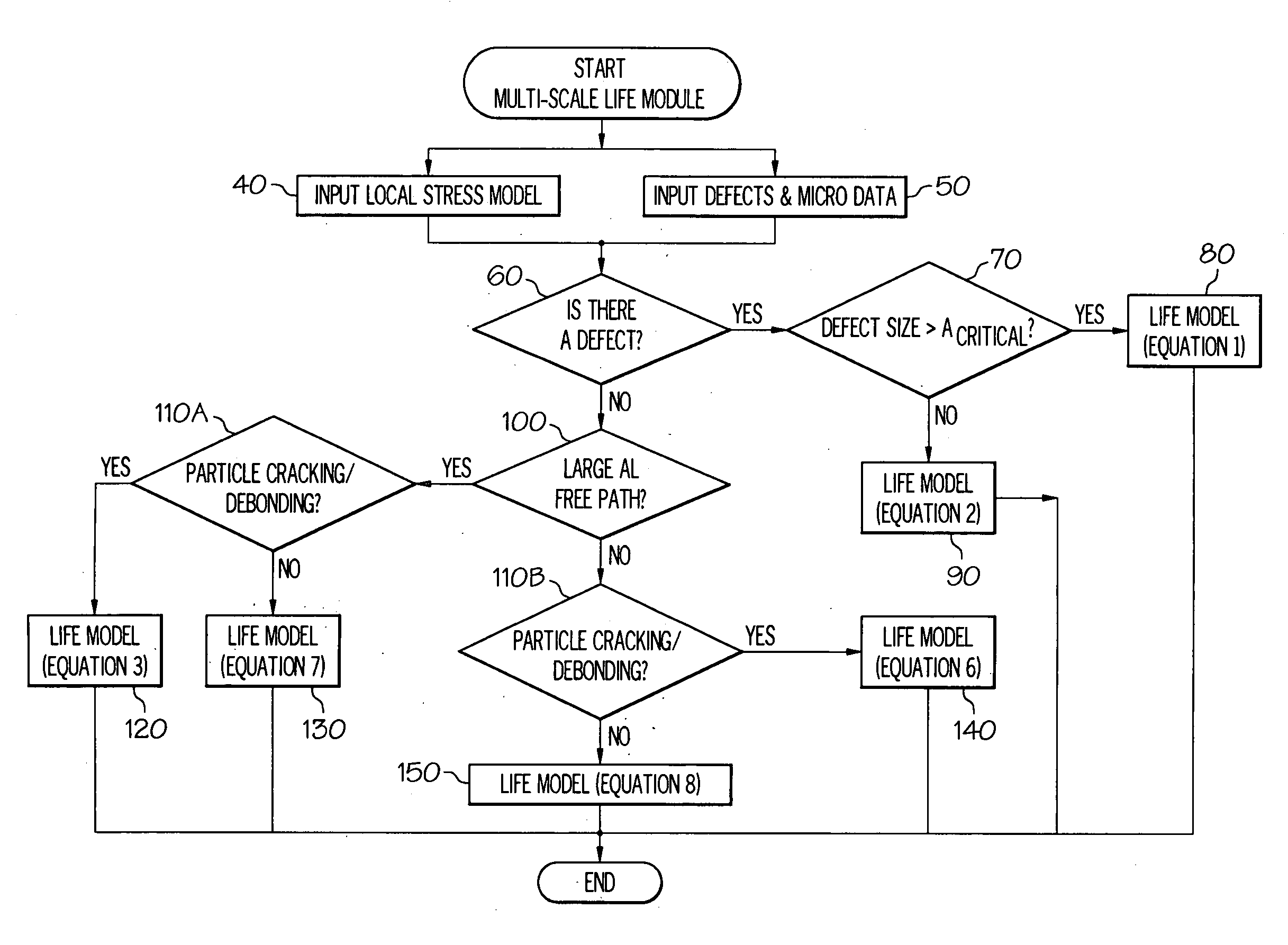
InactiveUS20090276166A1Accurately fatigue propertyAccurate of fatigue propertyPlug gaugesDigital computer detailsCrazingCasting defect
Methods and systems of predicting fatigue life in aluminum castings that combines extreme values of both casting flaws and microstructures with multiscale life models. The multiscale life models account for differing fatigue crack initiation based on the size scale of the defect and microstructure features, including provisions for generally millimeter scale casting flaws, generally micrometer scale second phase particles by cracking or debonding, or submicrometer scale dislocation interactions with precipitates which form persistent slip bands. In the presence of casting flaws, the fatigue initiation life is negligible and the total fatigue life is spent in propagation of a fatigue crack from such flaws. In the absence of casting flaws, however, the total fatigue life is spent in both crack initiation and propagation, except for the case where fatigue cracks initiate from large second phase particles in a coarse microstructure. The extreme values of casting flaws, second phase particles, mean free path through an aluminum matrix or grain sizes are obtained from extreme value statistics when two or three dimensional sizes of casting flaws and microstructure features are provided by either direct measurement or analytical prediction. The upper bound flaw or microstructure feature size is calculated by extreme value statistics.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Radiation shielding members including nano-particles as a radiation shielding material and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20100102279A1Increase the probability of collisionImproved Radiation Shielding PerformanceOther chemical processesBlast furnace componentsPorosityMaterials science
Disclosed is a radiation shielding member having improved radiation absorption performance, including 80.0˜99.0 wt % of a polymer matrix or metal matrix and 1.0˜20.0 wt % of a radiation shielding material in the form of nano-particles having a size of 10˜900 nm as a result of pulverization, wherein the radiation shielding material is homogeneously dispersed in the matrix through powder mixing or melt mixing after treatment with a surfactant which is the same material as the matrix or which has high affinity for the matrix. A preparation method thereof is also provided. This radiation shielding member including the nano-particles as the shielding material further increases the collision probability of the shielding material with radiation, compared to conventional shielding members including micro-particles, thus reducing the mean free path of radiation in the shielding member, thereby exhibiting superior radiation shielding effects. At the same density, the shielding member has reduced thickness and volume and is thus lightweight. The porosity of the shielding member is minimized, thereby preventing the deterioration of shielding effects and properties of the shielding member and realizing applicability in spent fuel managing transport / storage environments and the like.
Owner:GIPS CO LTD
Thermoelectric conversion material and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20090314324A1Reliable suppressionDispersion limitedThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsMean free pathNanoparticle
A thermoelectric conversion material wherein at least a part of the insulating material contained in the thermoelectric conversion material has a particle size not larger than a mean free path of the phonons in the insulating material or wherein a dispersion gap of the insulating material is not larger than a mean free path of the phonons in the thermoelectric conversion material, and a method of producing the thermoelectric conversion material comprising the steps of forming composite nano particles by reducing and precipitating starting particles of a thermoelectric conversion material on the nano particles constituted by an insulating material, followed by a heat treatment to coat the nano particles with the thermoelectric conversion material; and packing and sintering the composite nano particles.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
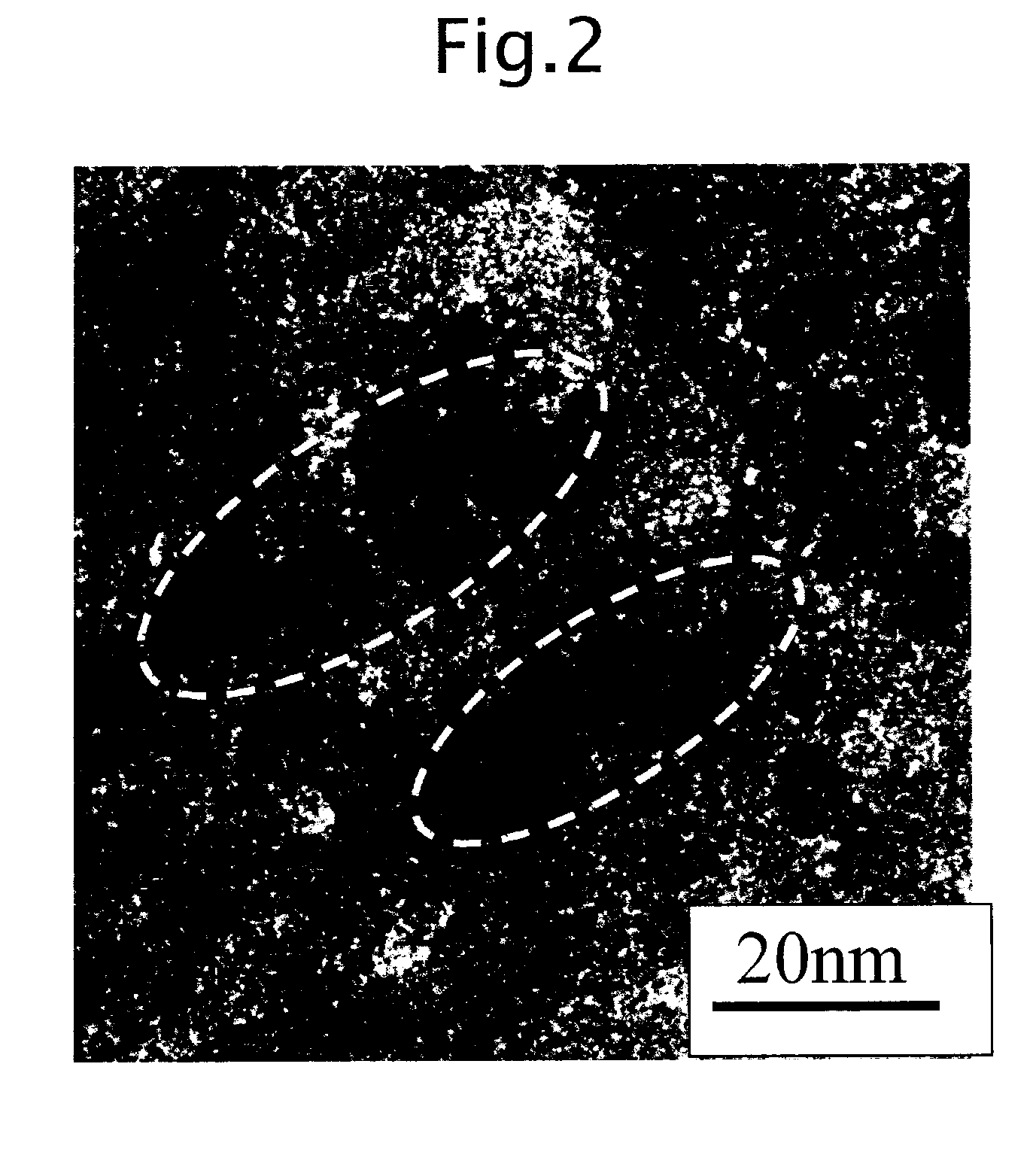
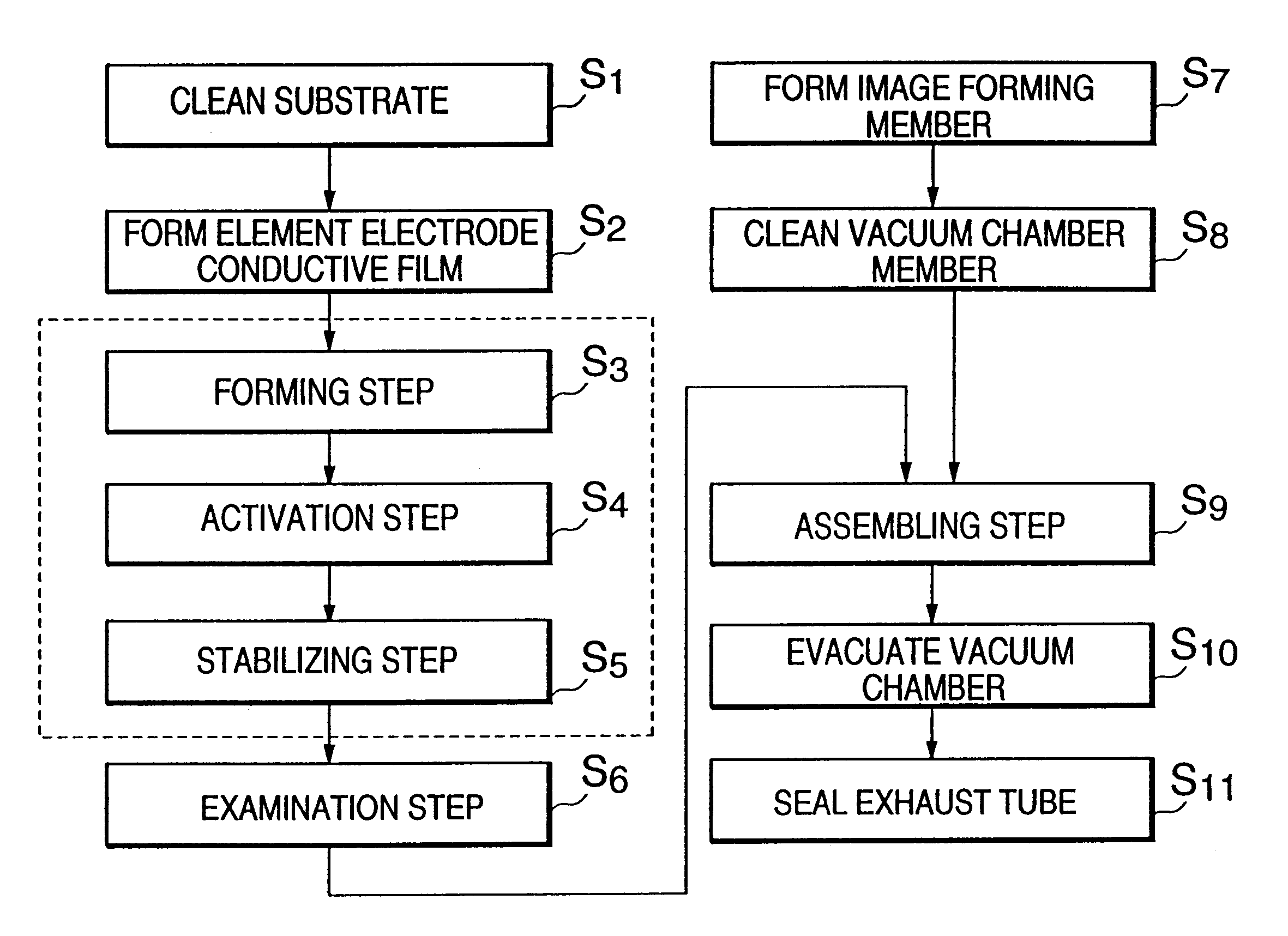
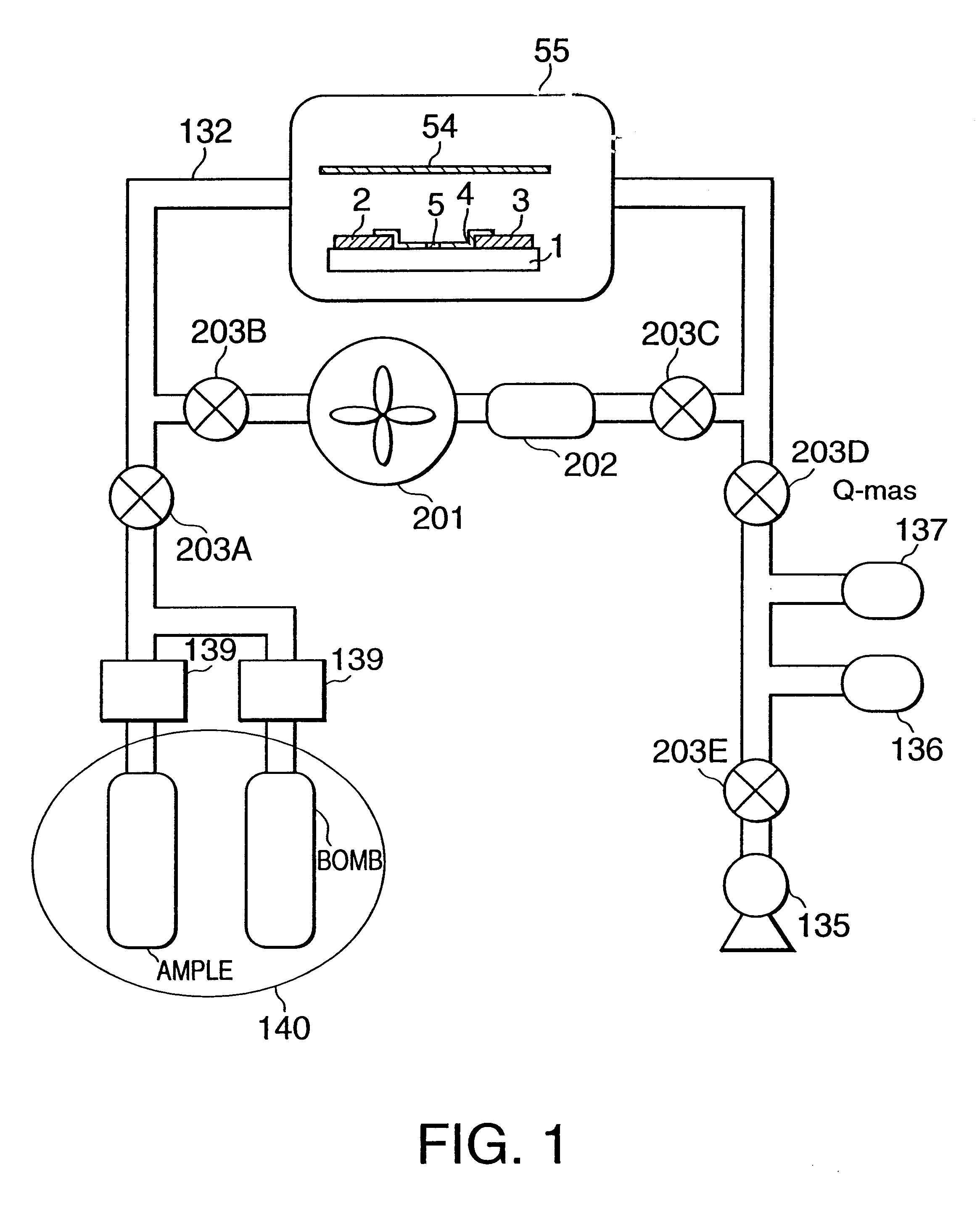
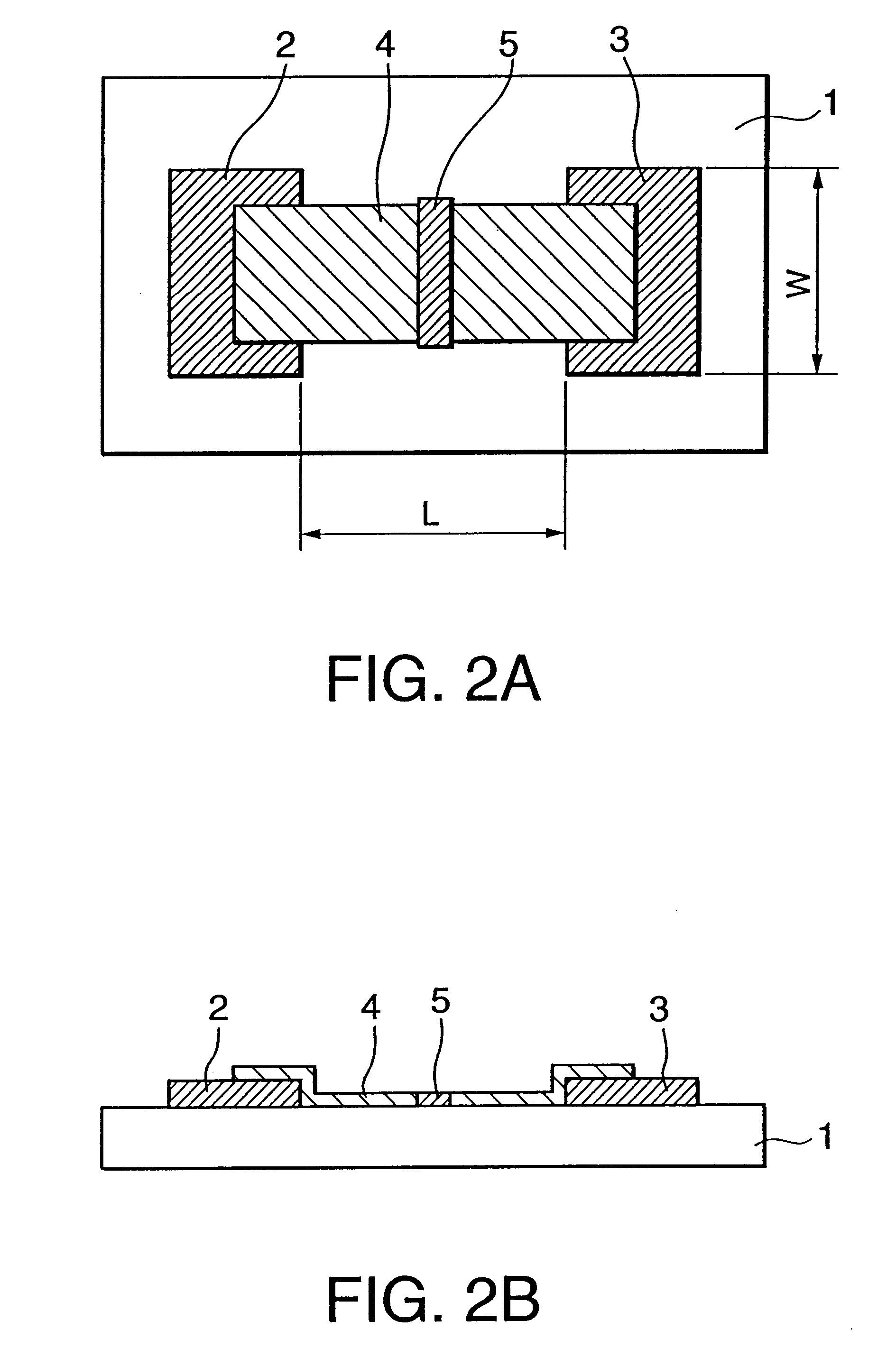
Electron source manufacturing method, and image forming apparatus method
A method of manufacturing an electron source with electron emitting elements is provided. The method has a process of depositing a deposit substance in an area including at least an area of the electron emitting element from which area electrons are emitted. The depositing process is performed in an atmosphere of a gas containing at least a source material of the deposit substance, the gas having a mean free path allowing the gas to take a viscous flow state.
Owner:CANON KK
Two-dimensional ionising particle detector
InactiveUS20050161611A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberMean free path
A two-dimensional ionising particle detector including a matrix of detecting fibers, each detecting fiber forming a pixel of the detector. Each detecting fiber is composed of a glass capillary filled with a liquid scintillator for which the chemical composition is chosen such that an average free path of primary scintillation photons is negligible compared with a diameter of the capillary. The detector is applicable, for example, to high resolution particle imagery.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for preparing thermal barrier coating
ActiveCN102212786AImprove thermal shock resistanceExtend your lifeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingBiological activationPhonon
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thermal barrier coating. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a deposition matrix is bombarded by ion beams while a deposition coating is evaporated by electron beams, the steam energy of the electron beams is about 0.1-1 electron volts, and the energy is not enough to well migrate atoms in the process of depositing the coating; and the energy of the ion beams can reach thousands of electron volts, and the energy is enough to interfere growth of columnar crystals to increase crystal boundaries and crystal sub-boundaries and enlarge or increase microscopic holes so as to reduce phonon and photon scattering mean free path and reduce the thermal conductivity of the thermal barrier coating. The energy of vaporous clouds can be increased through activation ionization effects of ions; and compared with the conventional EB-PVD (Electron Beam Physical Vapour Deposition), the method can ensure that same performances can be achieved at low deposition temperature; furthermore, forms, structures and stresses of the columnar crystals can be also adjusted and controlled through ion assisted deposition, and thus, the service life ofthe thermal barrier coating can be prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
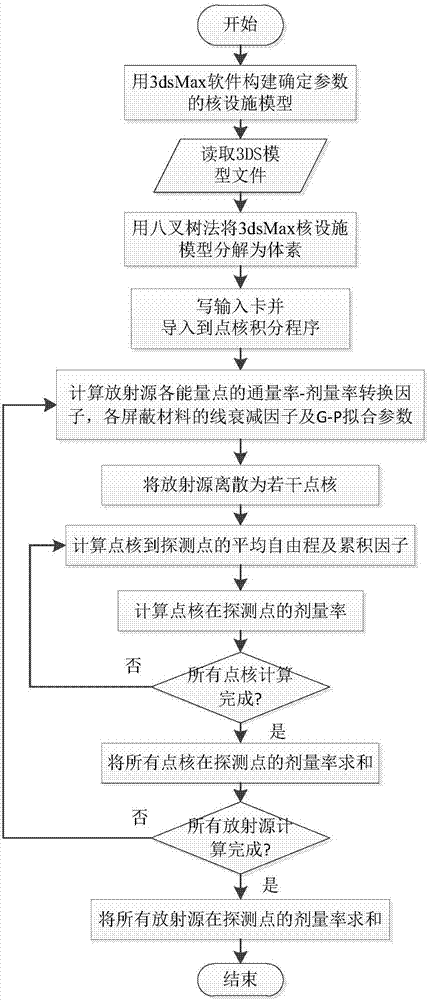
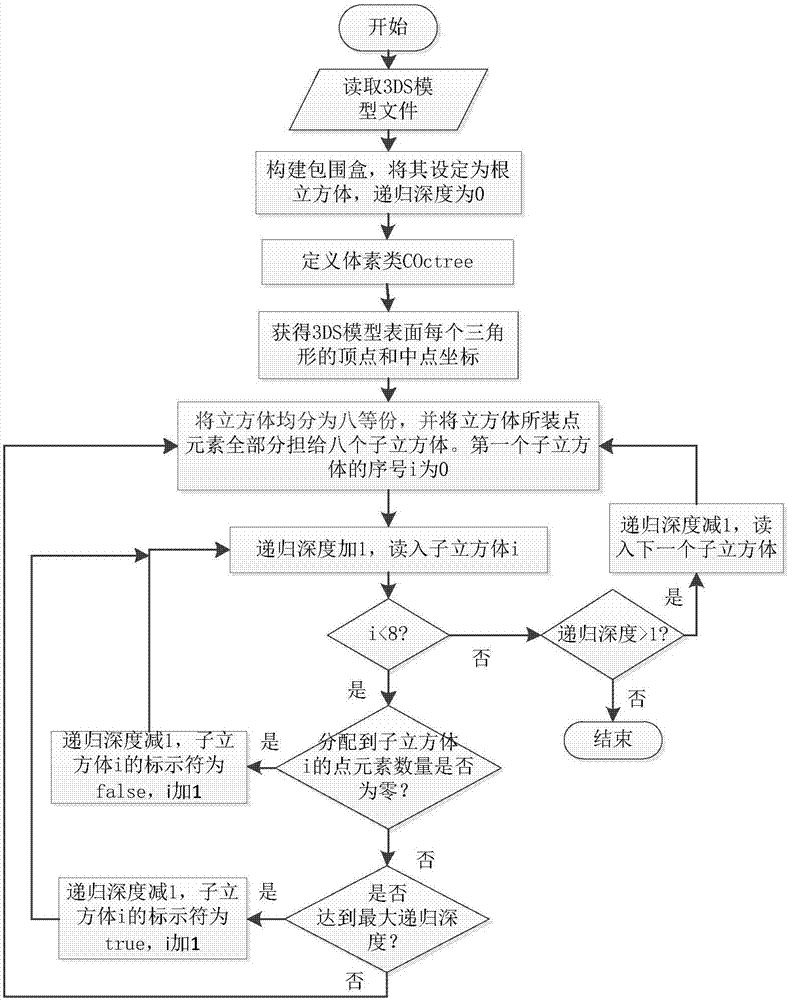
3dsMax-based nuclear facility model radiation field dosage simulation method
ActiveCN107194103AQuick assignmentRealize radiation field dose calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsVoxelDecay factor
The invention provides a 3dsMax-based nuclear facility model radiation field dosage simulation method. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a model by 3dsMax software according to determined nuclear facility parameters, and storing a file in a 3DS format; importing a 3DS nuclear facility model file and obtaining model parameters; decomposing the 3dsMax nuclear facility model into voxels by using an octree method; writing determined voxel parameters and material information into an input card; importing the input card into a point nuclear integration program; calculating an accumulation factor; calculating a mean free path, in a radiation field, of a gamma ray; establishing a flux rate-dosage rate conversion factor, quality decay factors of chemical elements and materials and a single-layer accumulation factor database by utilizing an SQLite database engine; carrying out combined operation on a box by using a Boolean connective operator, and constructing a complicated radiation field geometric structure; and calculating a three-dimensional radiation field dosage by using a point nuclear integration method. The method provided by the invention is capable of realizing radiation field dosage calculation of complicated 3dsMax nuclear facility models with sizes, materials and energy parameters.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Field emission microelectronic device
InactiveUS20080001513A1Discharge tube main electrodesTubes without control meansMean free pathField electron emission
A nano-scaled field emission electronic device includes a substrate, a cathode electrode, and an anode electrode. The cathode electrode is placed on the substrate and has an emitter. The anode electrode is positioned opposite to and spaced from the cathode electrode. The nano-scaled field emission electronic device further has at least one kind of inert gas filled therein. The following condition is satisfied: h<λe, wherein h indicates a distance between a tip of the emitter and the anode electrode, and λe indicates an average free path of an electron in the inert gases. More advantageously, the following condition is satisfied:h<λe_10.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Slotted electrode for high intensity discharge lamp
InactiveUS20060208635A1Reduce evaporationEasy maintenanceElectrode assembly support/mounting/spacing/insulationSolid cathode detailsMean free pathGas composition
Operation of an HID lamp may be improved by forming a glow generating recess on an exterior side the electrode. The lamp may be of standard construction with a light transmissive lamp envelope having a wall defining an enclosed volume. At least one electrode assembly is extended in a sealed fashion from the exterior of the lamp through the lamp envelope wall to be exposed at an inner end of the electrode assembly to the enclosed volume. A metal halide lamp fill is enclosed with an inert fill gas. The inner end of the electrode is formed with a recess having a least spanning dimension S and a recess depth of D where S is greater the electron ionization mean free path but less than twice the cathode fall plus negative glow distances, throughout the glow discharge phase of starting, for the chosen fill gas composition and pressure (cold).
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Method for tracking the movement of a particle through a geometric model for use in radiotherapy
InactiveUS20060058636A1Improve developmentFast trackDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMean free pathDosimetry radiation
A method for tracking the movement of a particle through a geometric model so as to facilitate the development of a dosimetry plan includes providing a particle with a short mean free path length; providing a geometric model which has a boundary which separates regions of the geometric model having different densities and / or compositions; arranging a first plurality of substantially uniform volume elements having a predetermined size into the geometric model; and arranging a second plurality of substantially uniform volume elements having a predetermined size less than that of the first plurality of substantially uniform volume elements, and in overlaying relation relative to the first plurality of substantially uniform volume elements.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Super-resolution spectral imaging system and super-resolution spectral imaging method based on scattering medium
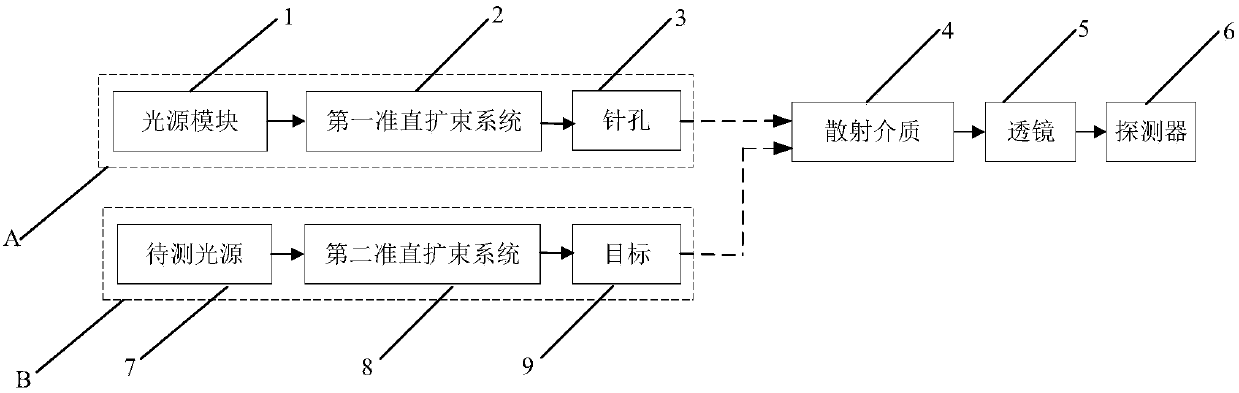
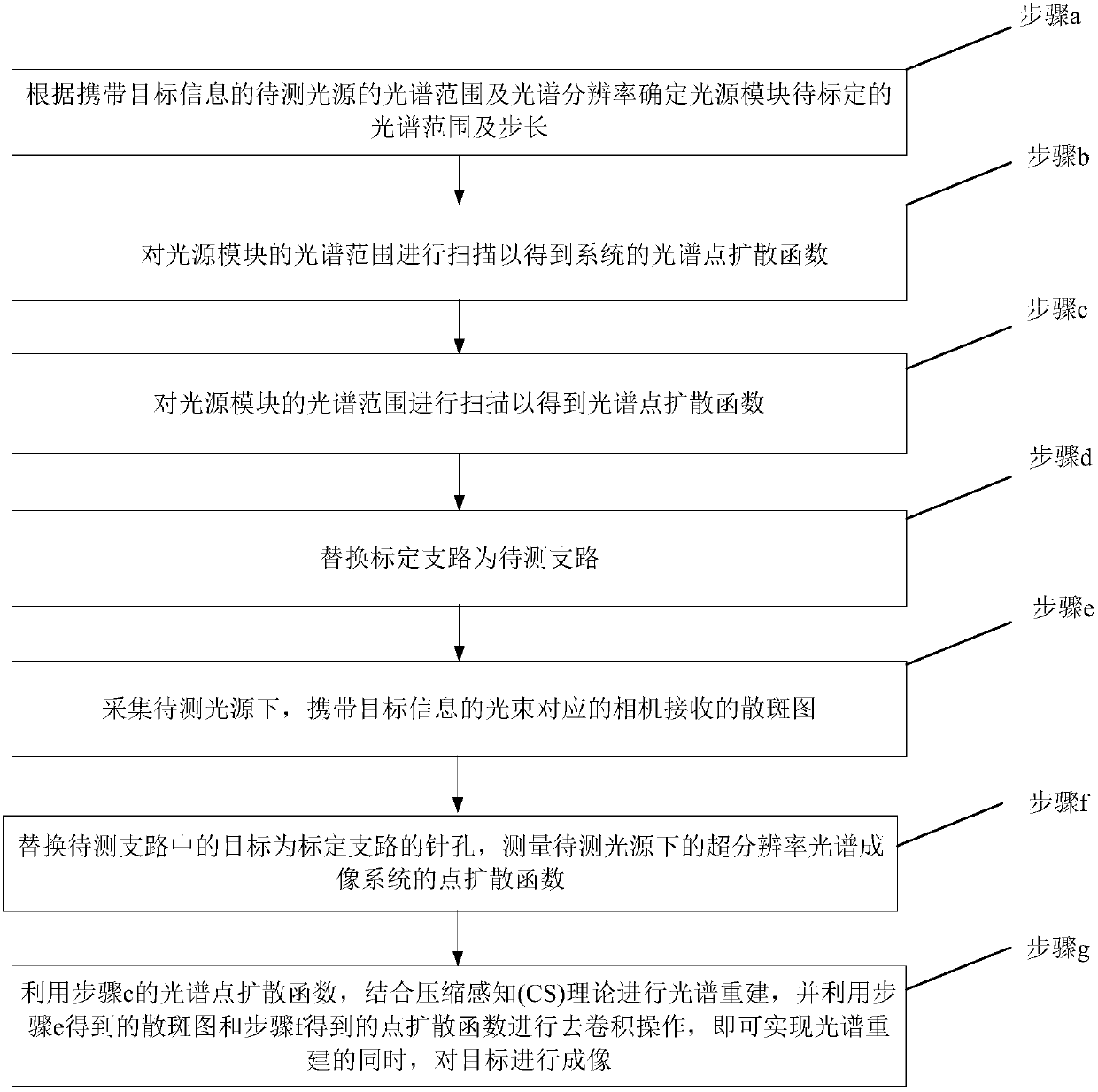
ActiveCN107907483AEnable Spectral MeasurementsAchieve target imagingColor/spectral properties measurementsPoint spreadMean free path
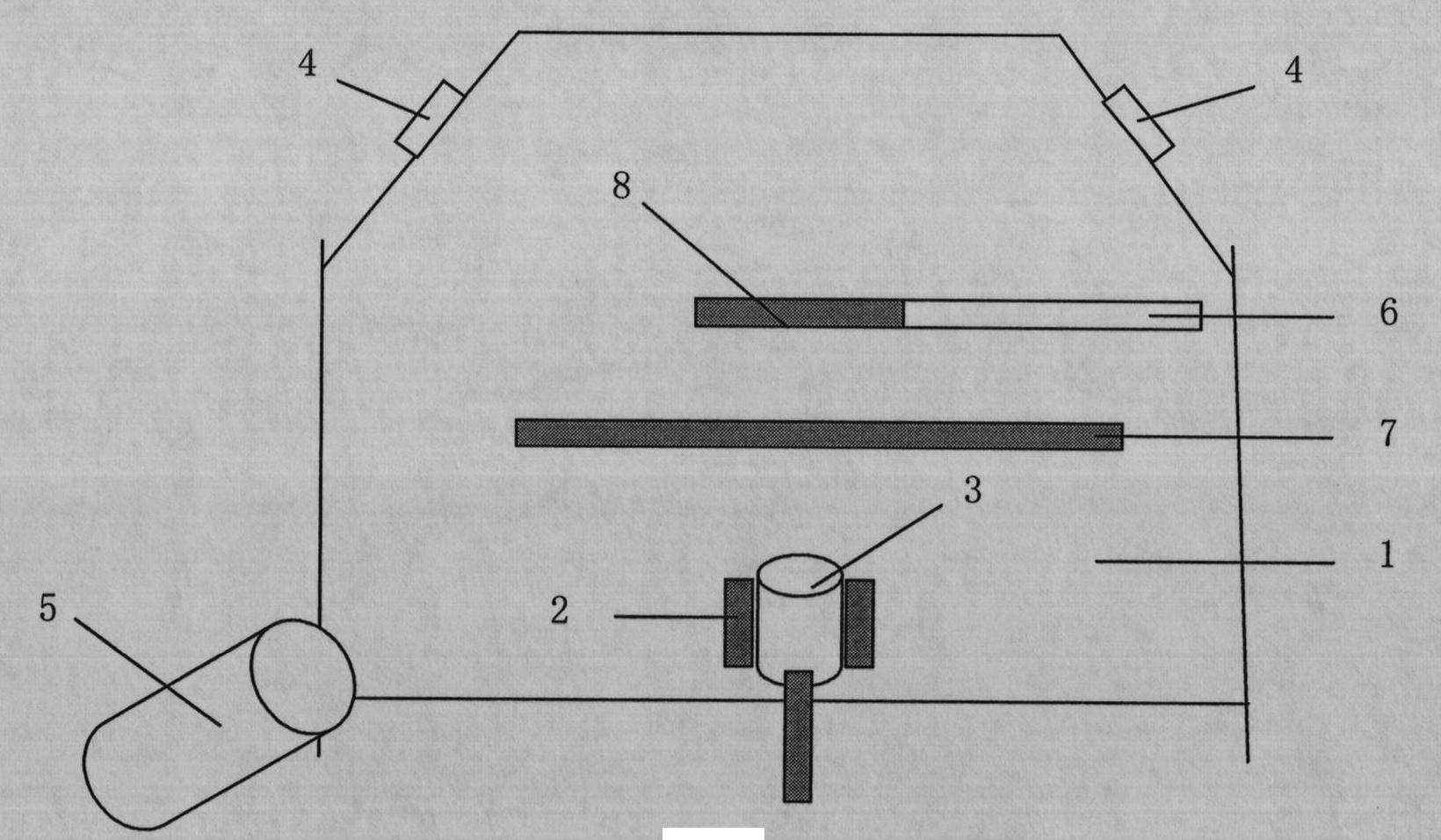
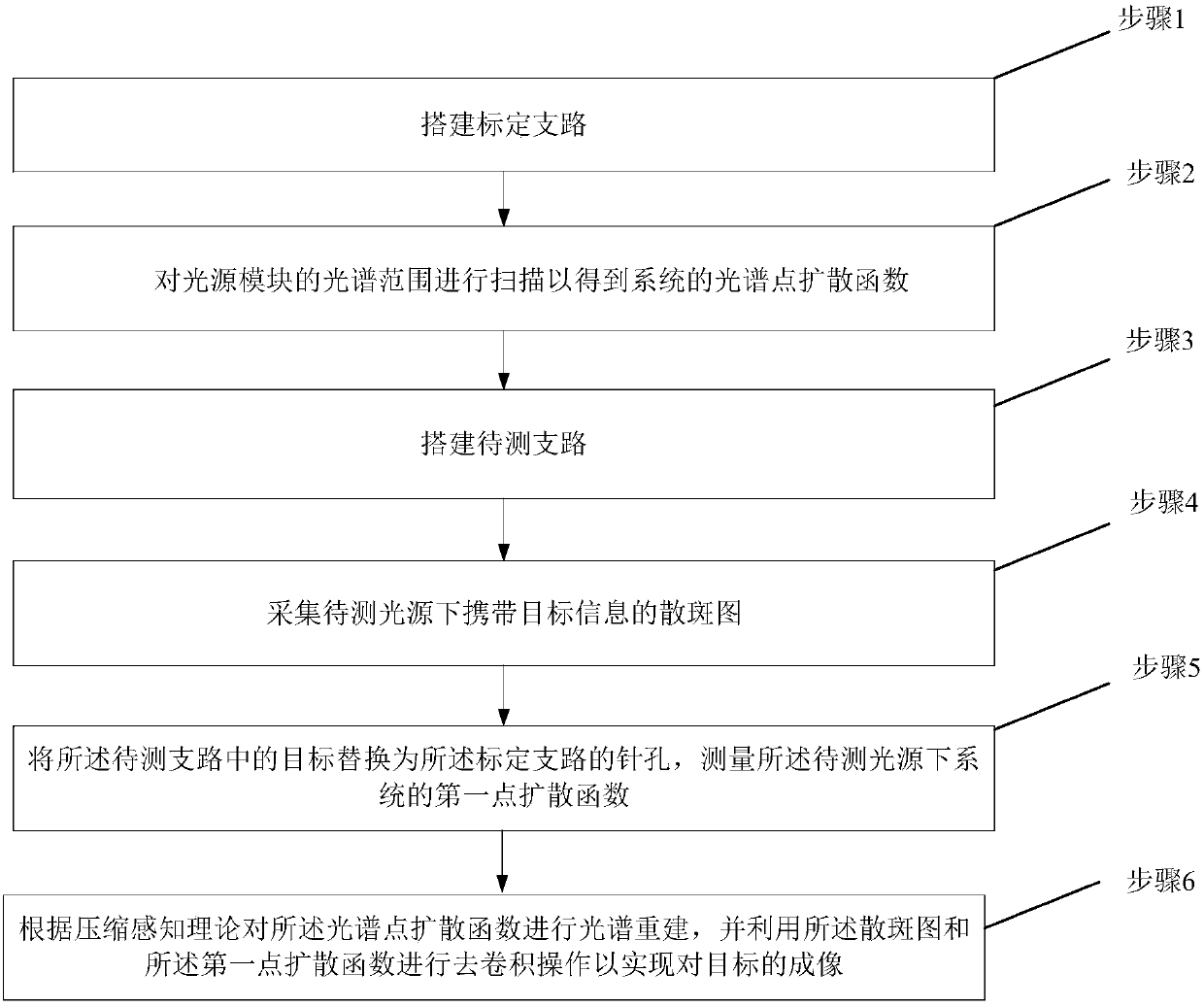
The present invention relates to a super-resolution spectral imaging system and a super-resolution spectral imaging method based on a scattering medium. The super-resolution spectral imaging system comprises a calibration branch A, a scattering medium 4, a lens 5, a detector 6 and a branch B to be detected, wherein the calibration branch A comprises a light source module 1, a first collimation beam expansion system 2 and a pinhole 3, and the branch B to be detected comprises a light source 7 to be detected, a second collimation beam expansion system 8 and a target 9. According to the embodiments of the present invention, the point spread functions of the system are measured when the light source module outputs different wavelengths so as to construct the spectral point spread function (SPSF), the spectral reconstruction is achieved by using the compressed sensing (CS) method while the scattering medium with the appropriate scattering mean free path is matched, and the speckle receivedby the camera is subjected to convolution removing by using the point spread function corresponding to the wavelength of the light source to be detected, such that the maximum super-resolution imagingcan be achieved without the increase of the complexity of the system; and the super-resolution spectral imaging system has advantages of simple structure, easy control, low component cost, strong anti-disturbance capability and wide application field.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com