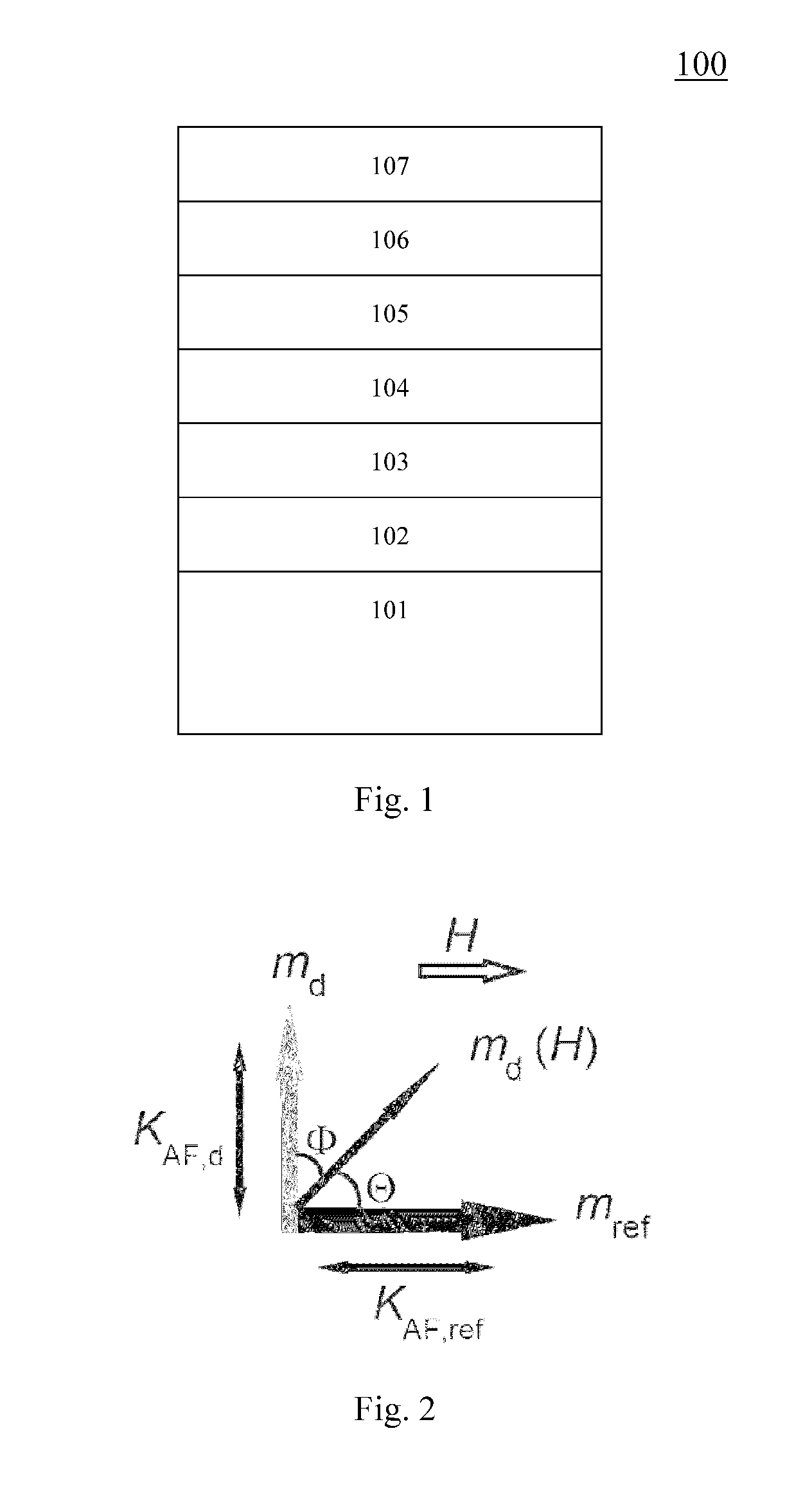
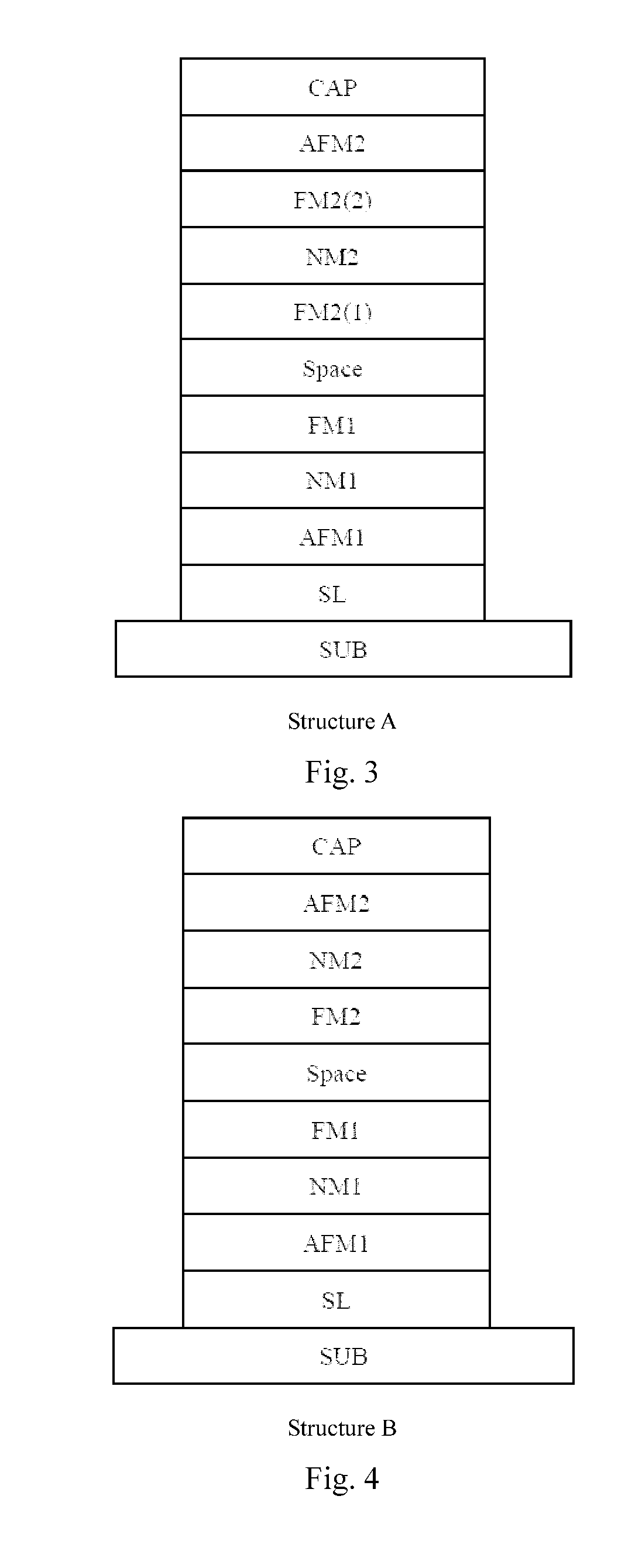
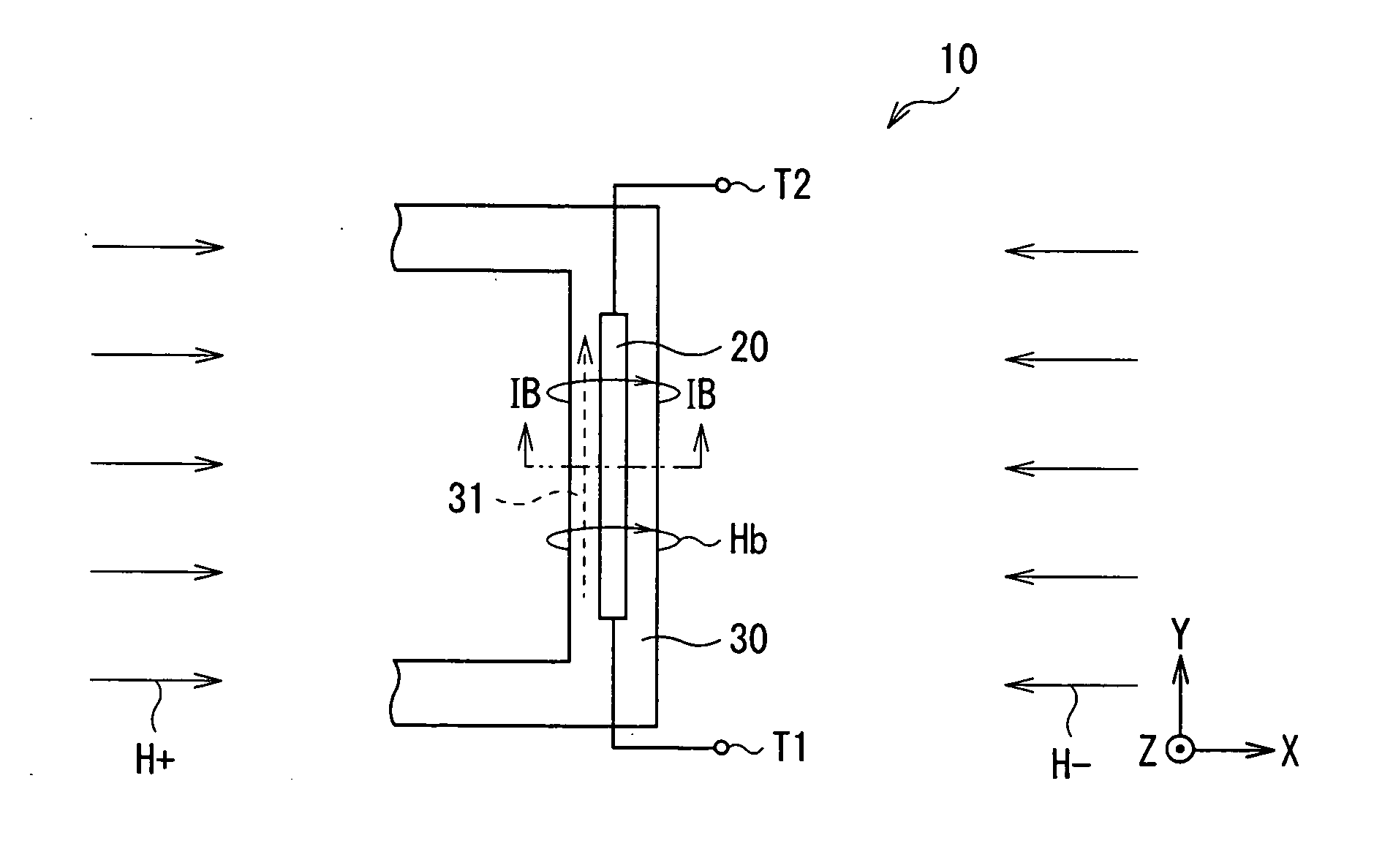
Patents
Literature
166 results about "Exchange bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
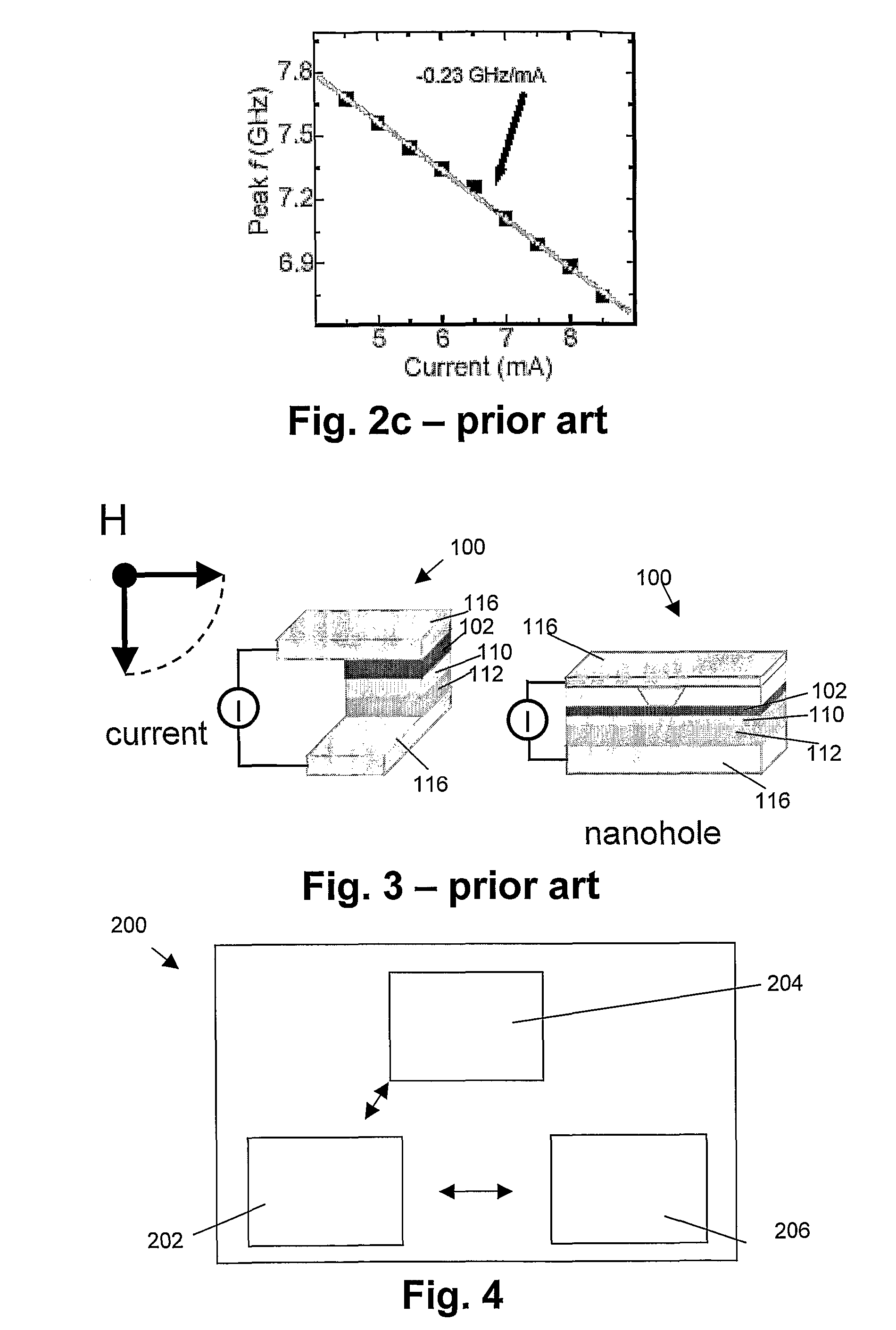
Exchange bias or exchange anisotropy occurs in bilayers (or multilayers) of magnetic materials where the hard magnetization behavior of an antiferromagnetic thin film causes a shift in the soft magnetization curve of a ferromagnetic film. The exchange bias phenomenon is of tremendous utility in magnetic recording, where it is used to pin the state of the readback heads of hard disk drives at exactly their point of maximum sensitivity; hence the term "bias."
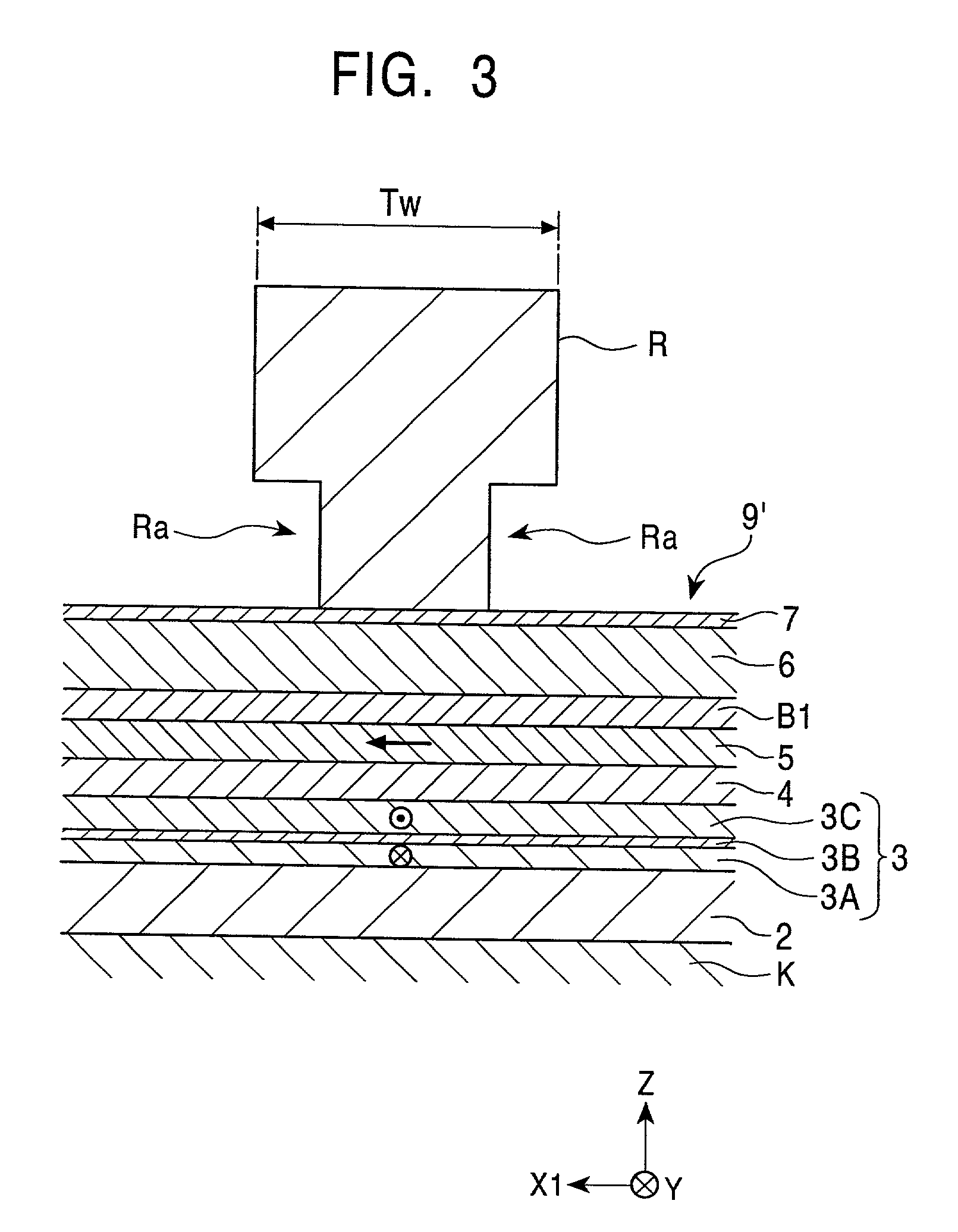
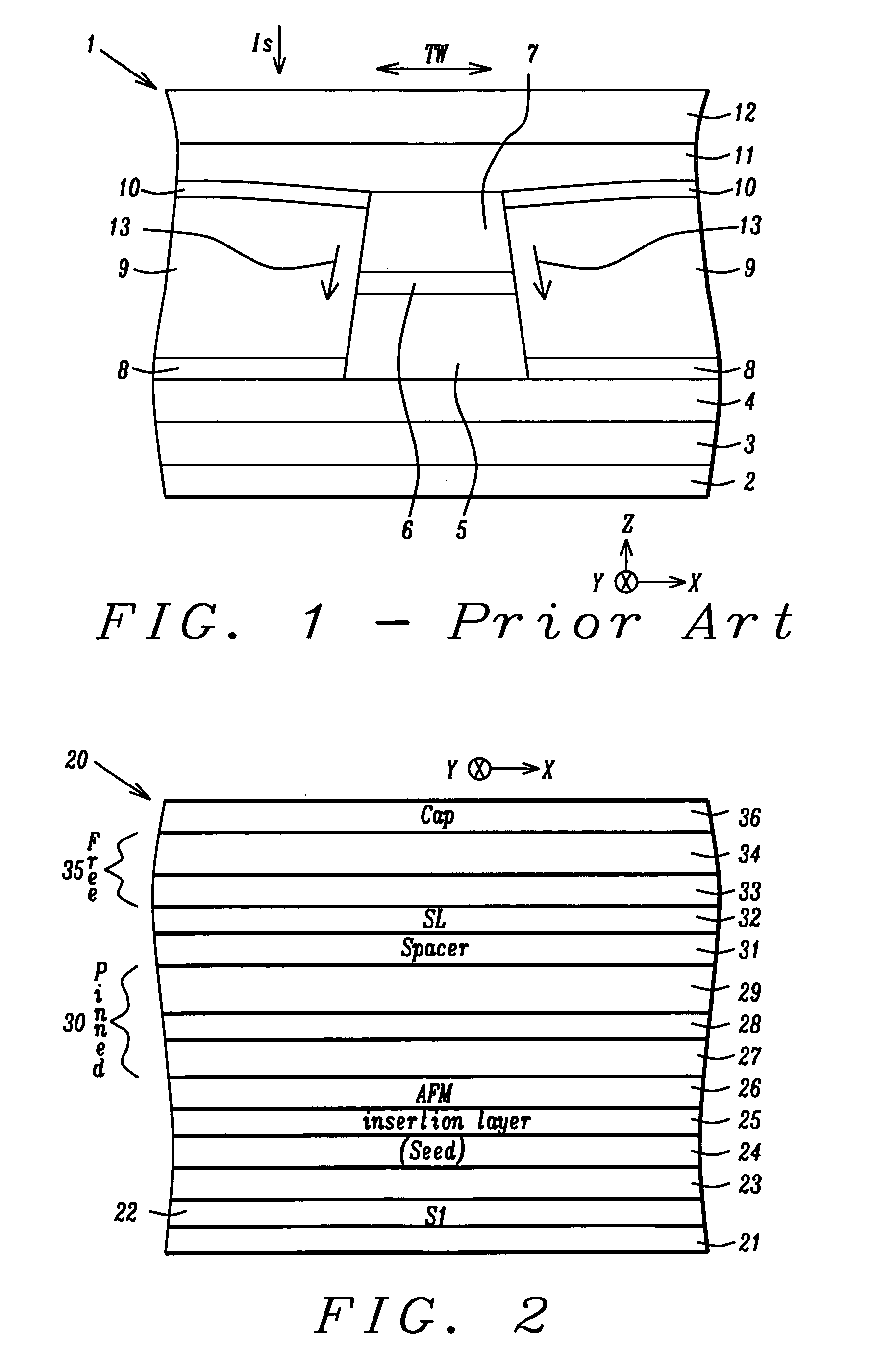
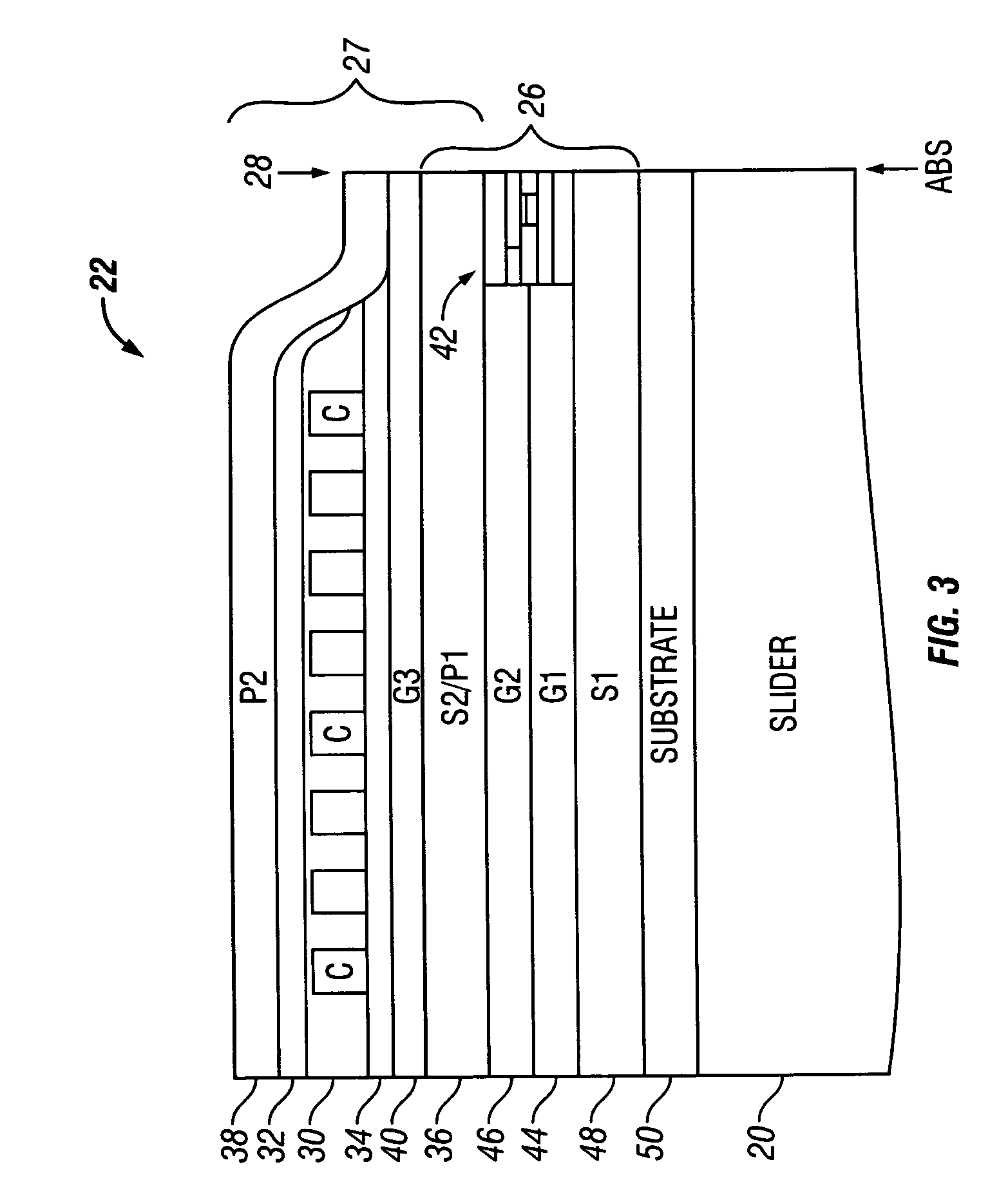
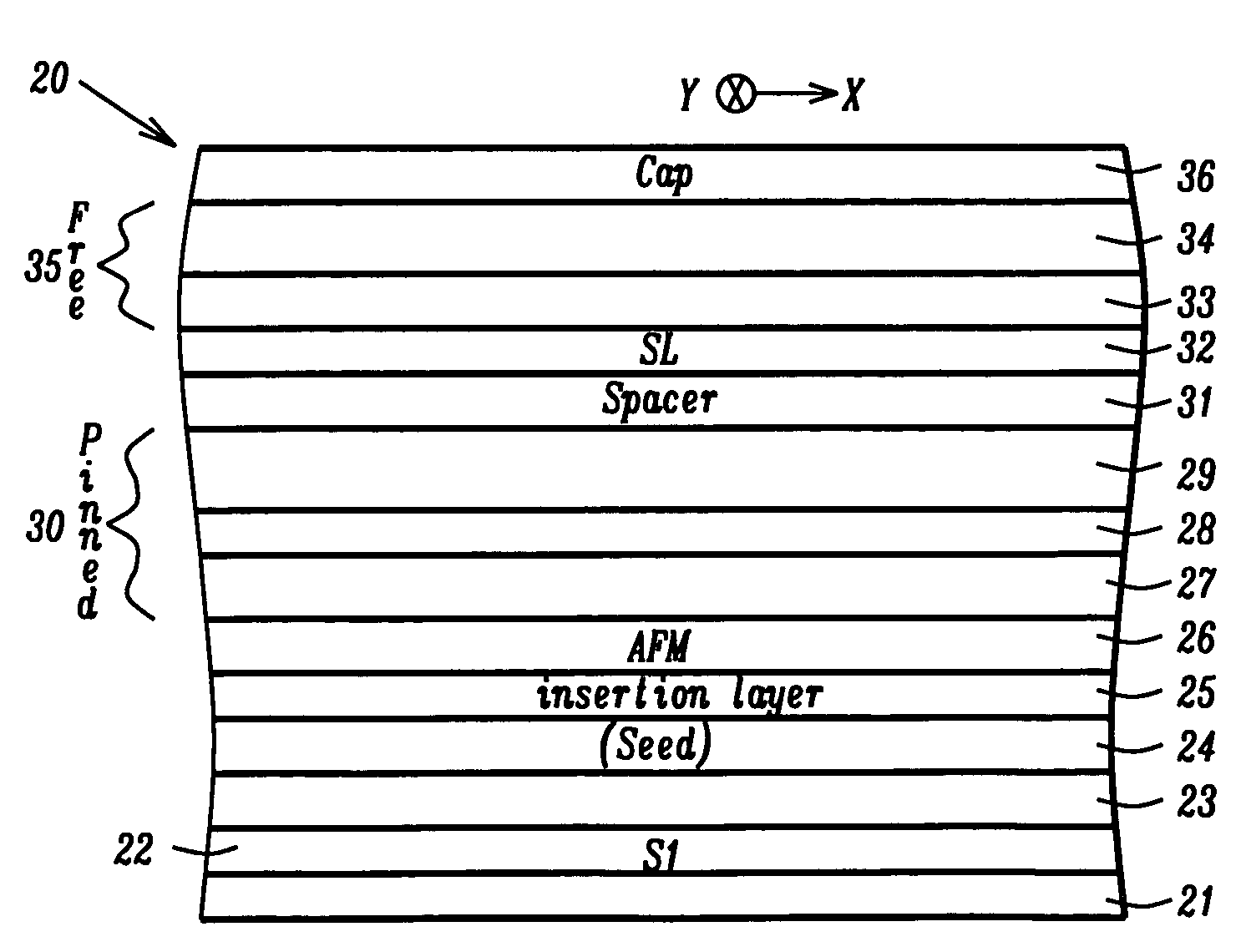
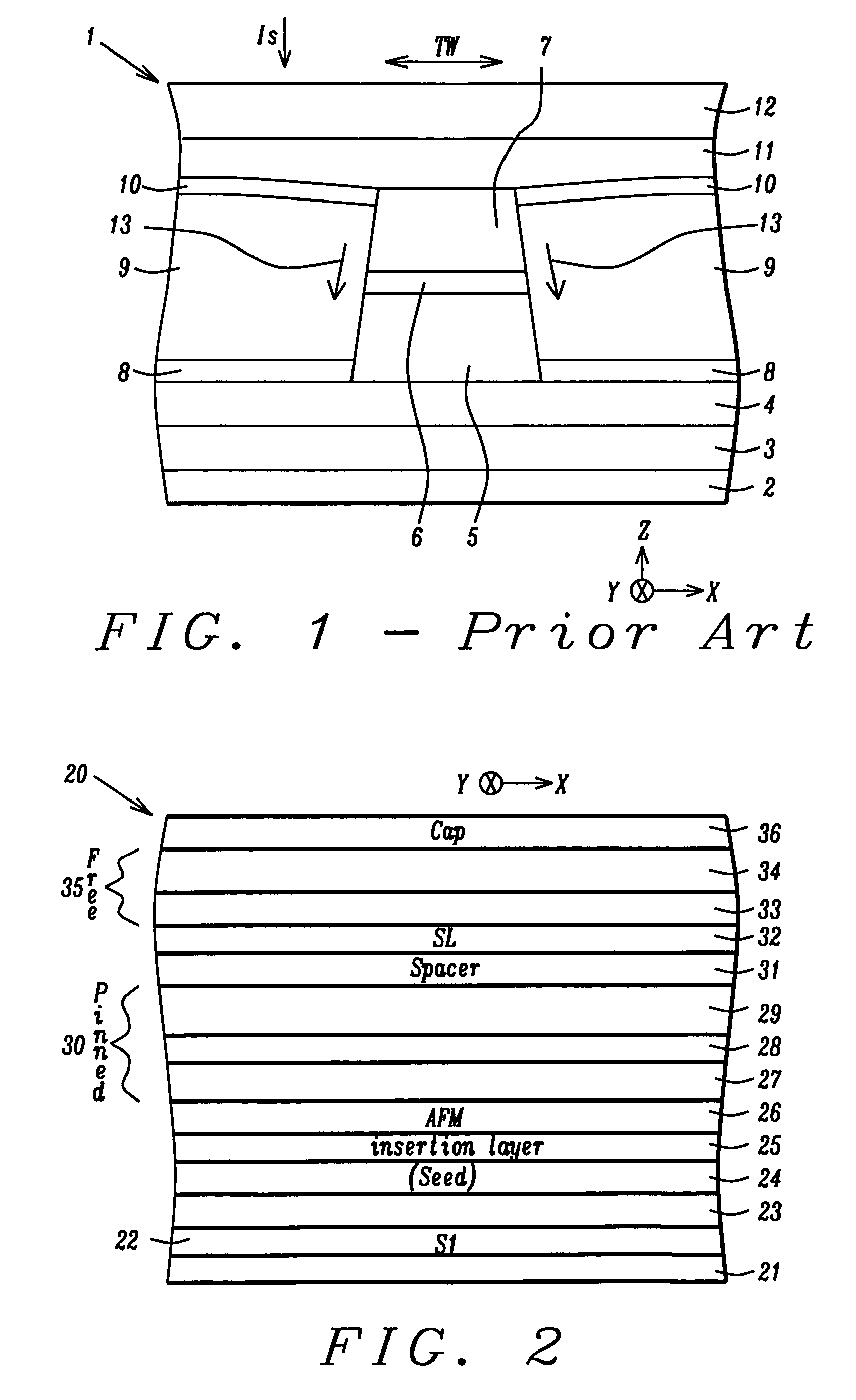
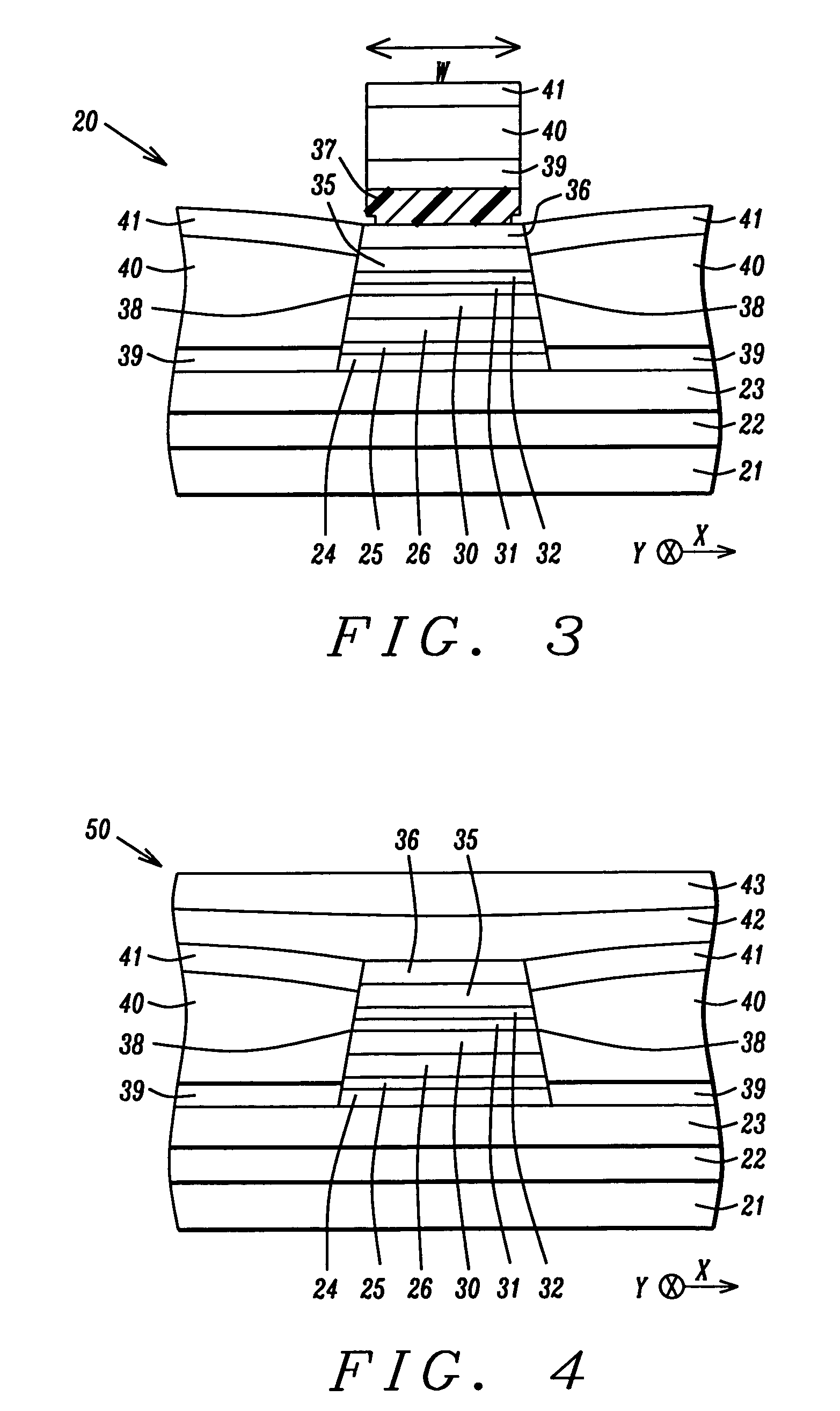
Top spin valve with improved seed layer
InactiveUS6687098B1Improved exchange bias fieldNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismEngineeringHigh resistivity
The present invention provides an improved top spin valve and method of fabrication. In the preferred embodiment of the top spin valve of the present invention, a seed layer is formed of non-magnetic material having the elements Ni and Cr. In the preferred embodiments, the seed layer material has an ion milling rate comparable to that of the free layer material. This allows free layer sidewalls to be formed with shorter tails, improving free layer-to-magnetic bias layer junction, thus improving free layer domain structure and track width. In one embodiment, the seed layer may have NiFeCr, with Cr from about 20% to 50%. In another embodiment, the seed layer may have NiCr, with about 40%. Some embodiments may have the seed layer formed on an optional Ta pre-seed layer. Such embodiments provide an improved fcc (111) texture particularly for NiFe and for NiFe / CoFe free layers grown on a seed layer improving spin valve performance, and especially in embodiments having very thin NiFe free layers, ultra thin NiFe free layers, and free layers without NiFe, such as a free layer of CoFe. Such a seed layer can improve AFM pinning layer texture to improve the exchange bias, thus providing better thermal stability. Such a seed layer also provides high resistivity and can improve the magnetostriction of adjacent NiFe free layer material or improve the soft properties of an adjacent CoFe free layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Novel process and structure to fabricate CPP spin valve heads for ultra-hing recording density
InactiveUS20050201022A1Enhanced Specular ReflectionIncrease bulk scatteringNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismDopantSpins
A CPP-GMR spin value sensor structure with an improved MR ratio and increased resistance is disclosed. All layers except certain pinned layers, copper spacers, and a Ta capping layer are oxygen doped by adding a partial O2 pressure to the Ar sputtering gas during deposition. Oxygen doped CoFe free and pinned layers are made slightly thicker to offset a small decrease in magnetic moment caused by the oxygen dopant. Incorporating oxygen in the MnPt AFM layer enhances the exchange bias strength. An insertion layer such as a nano-oxide layer is included in one or more of the free, pinned, and spacer layers to increase interfacial scattering. The thickness of all layers except the copper spacer may be increased to enhance bulk scattering. A CPP-GMR single or dual spin valve of the present invention has up to a threefold increase in resistance and a 2 to 3% increase in MR ratio.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
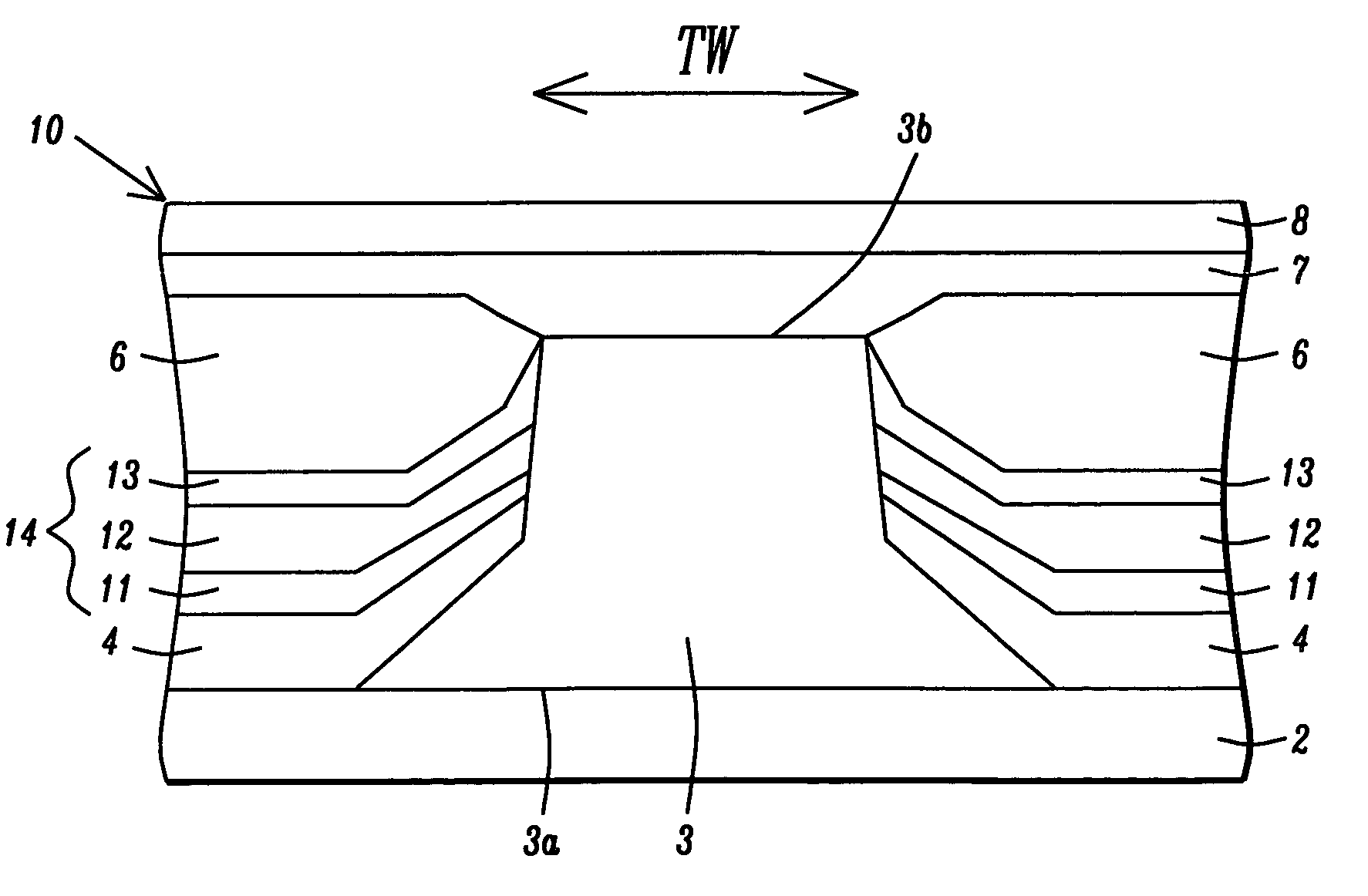
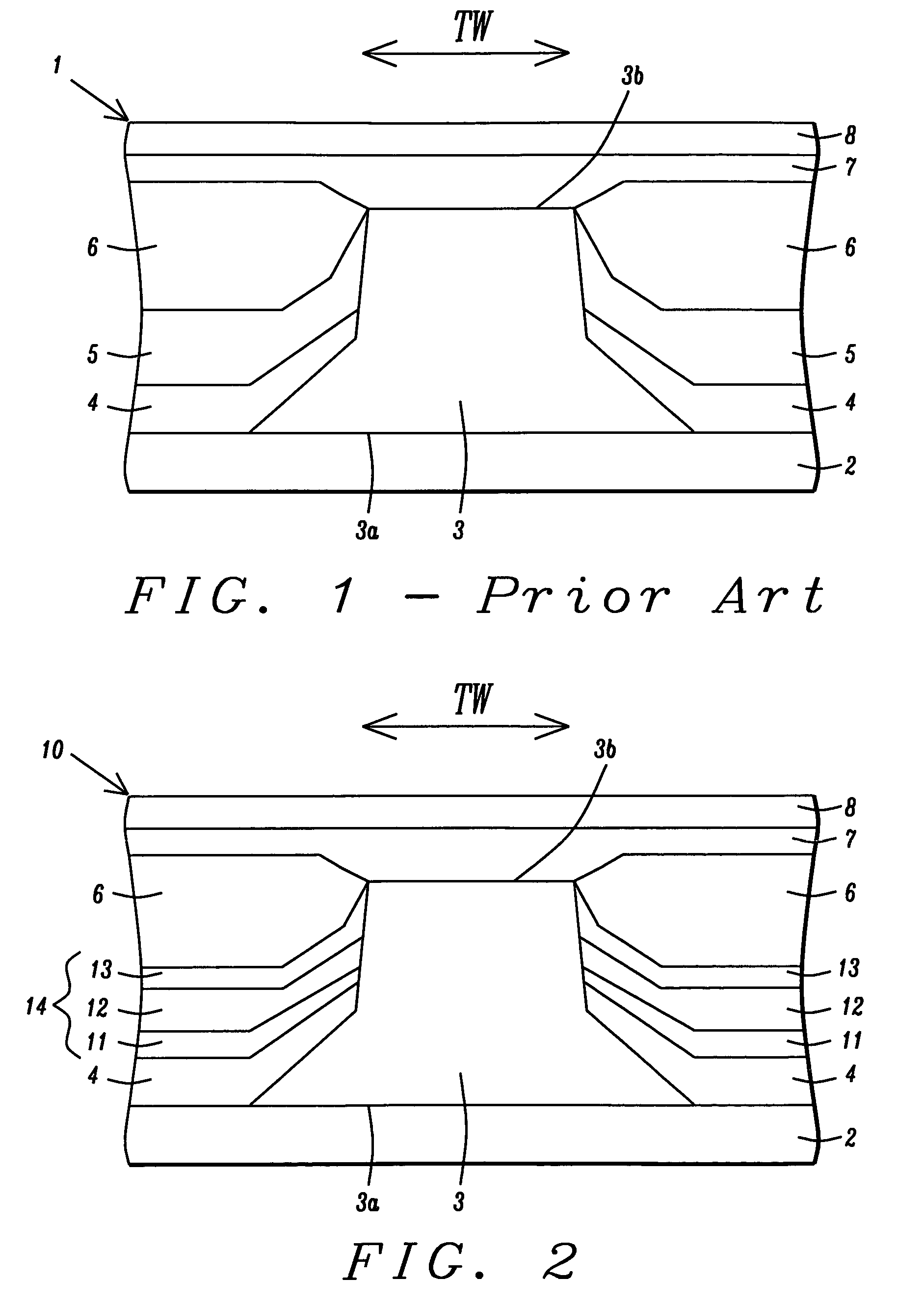
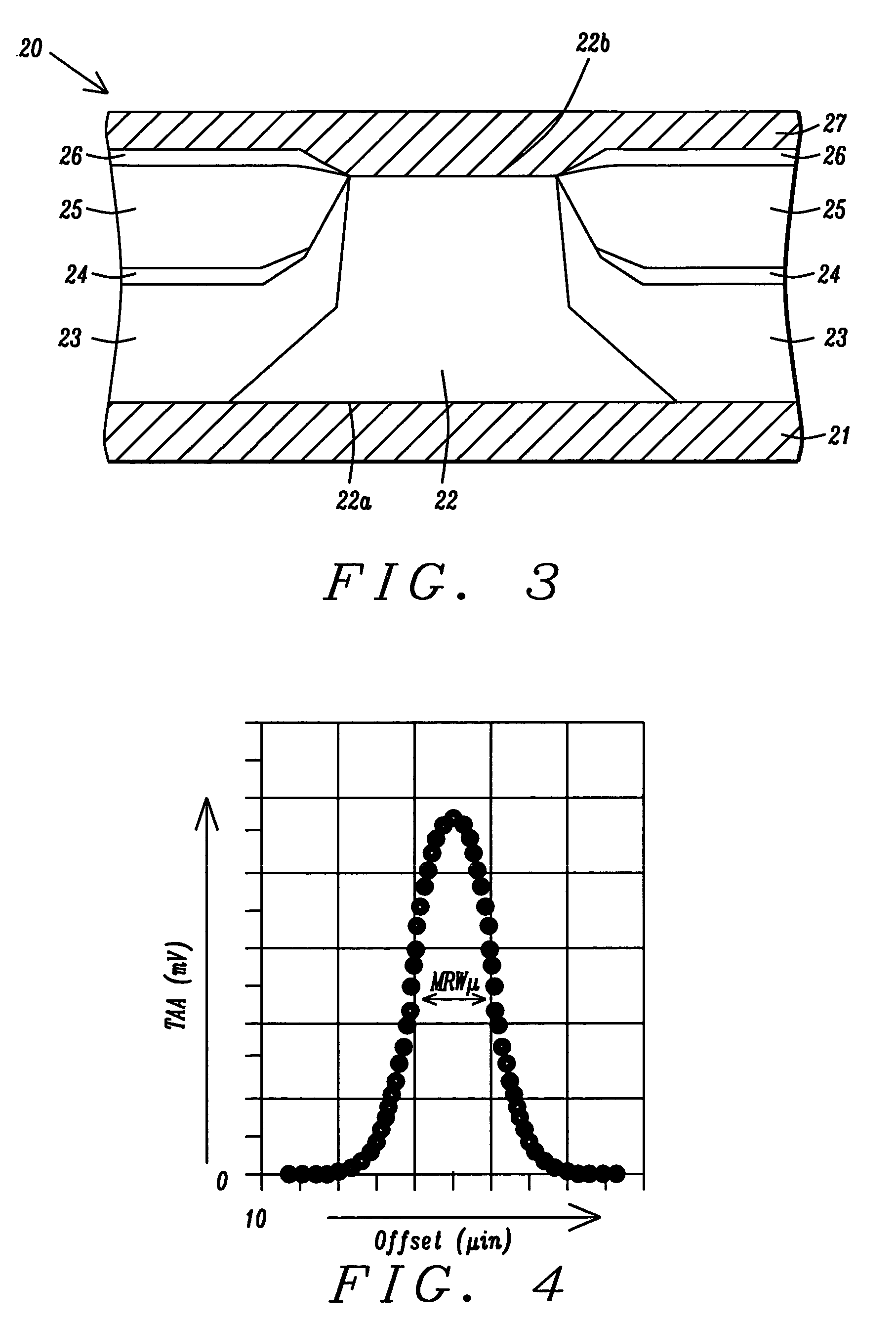
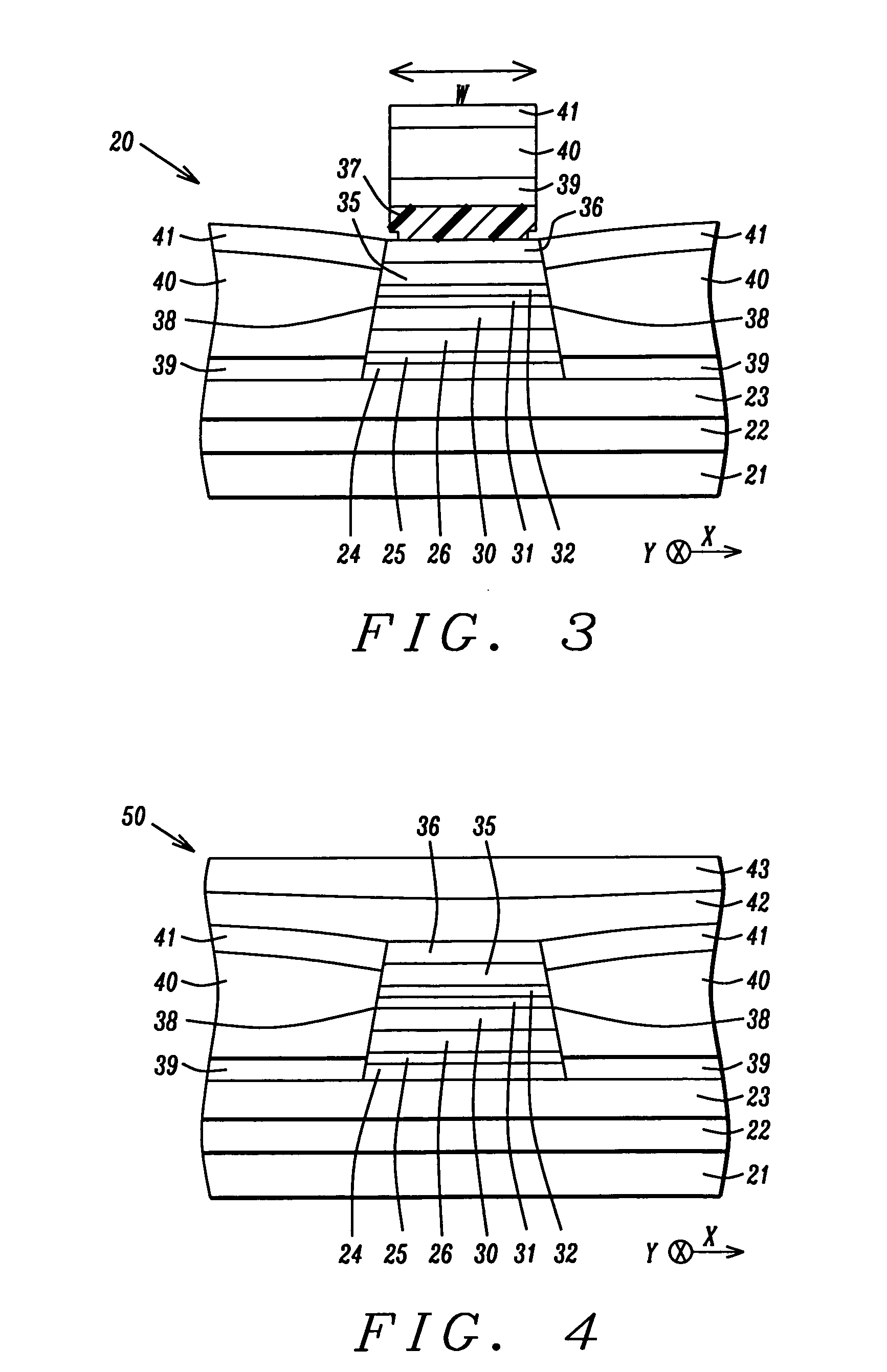
Abutted exchange bias design for sensor stabilization
InactiveUS7283337B2Hard structureSuppresses side-lobesRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsIn planeSelf-stabilization
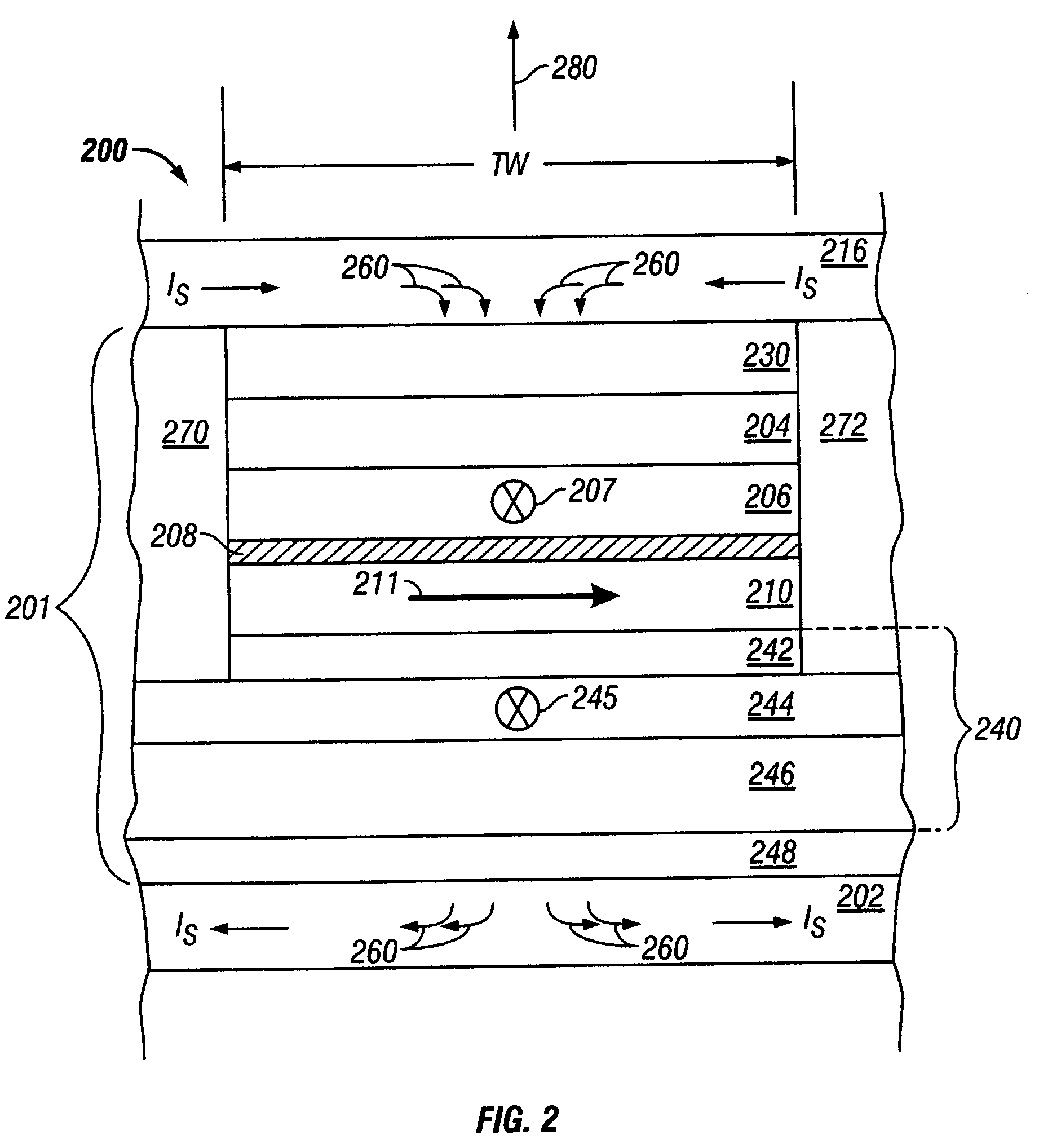
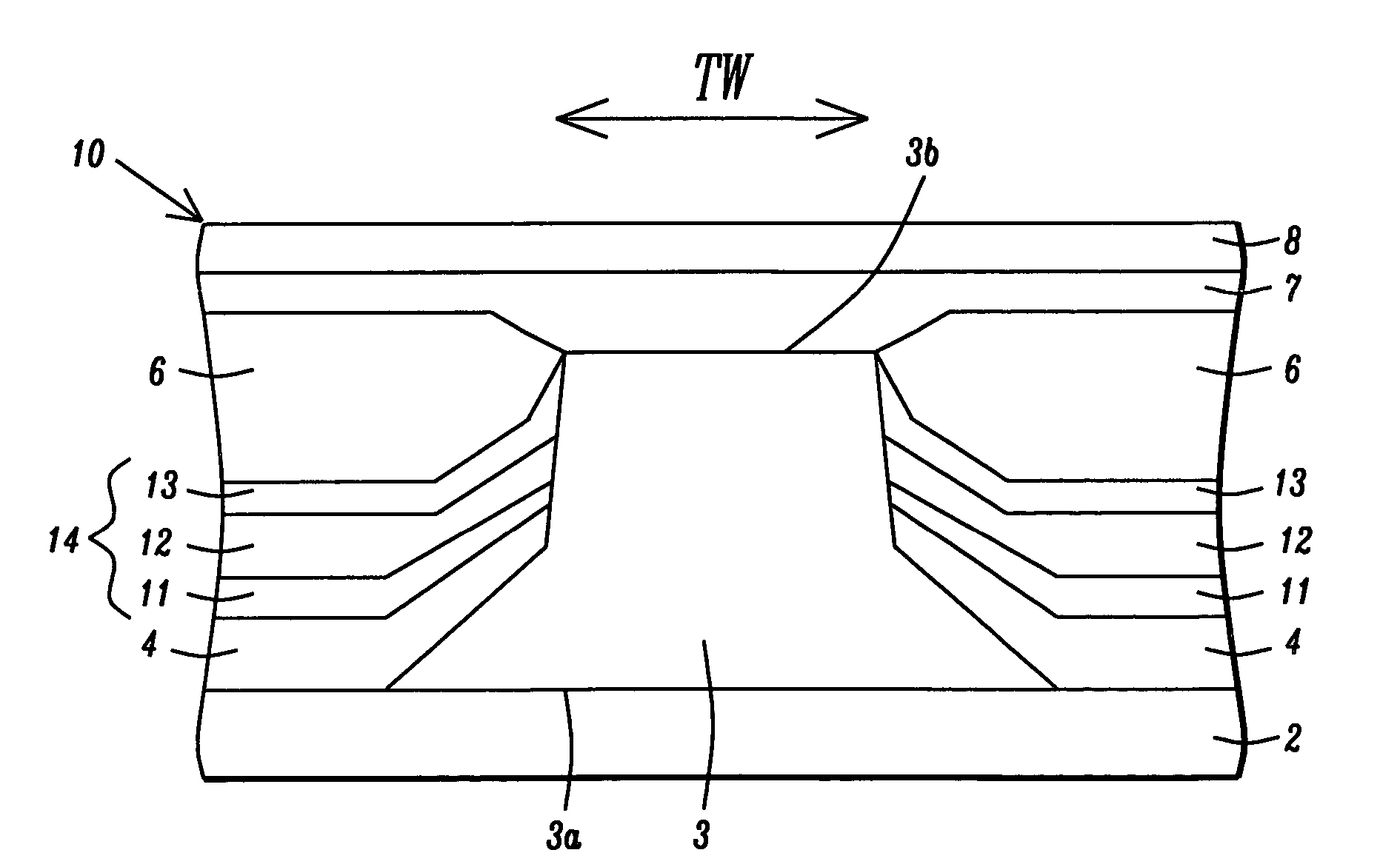
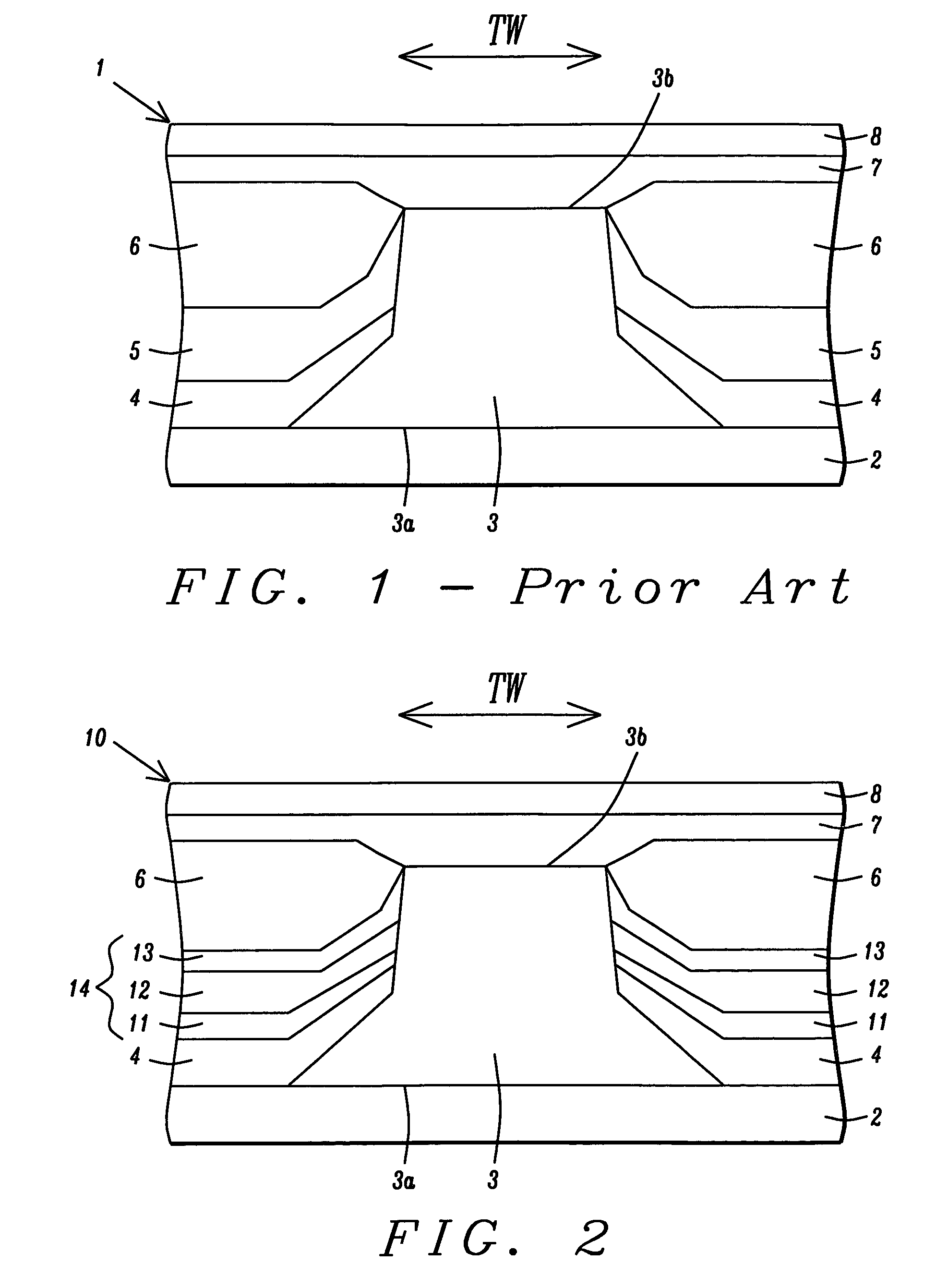
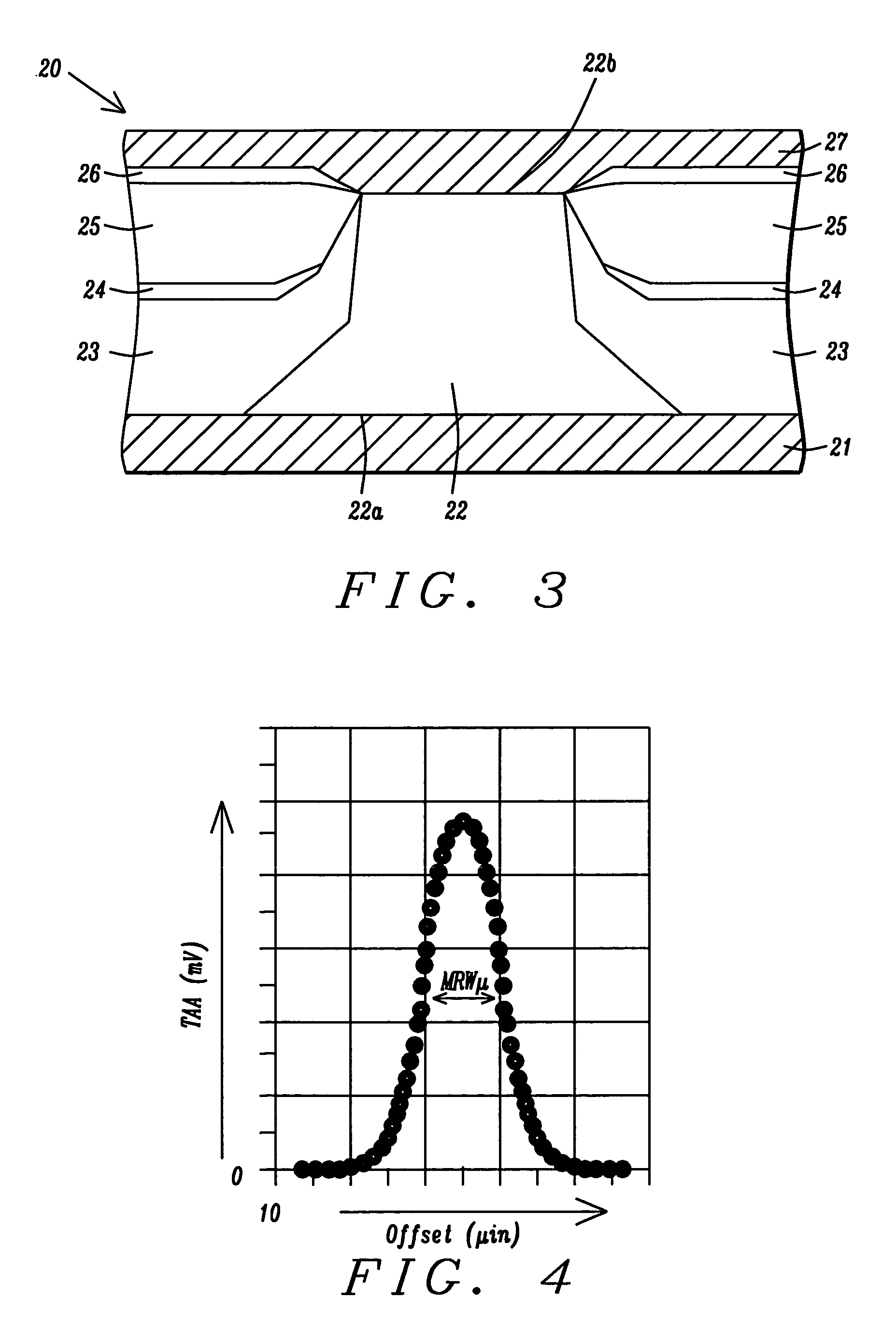
A hard bias (HB) structure for biasing a free layer in a MR sensor within a magnetic read head is comprised of a main biasing layer with a large negative magnetostriction (λS) value. Compressive stress in the device after lapping induces a strong in-plane anisotropy that effectively provides a longitudinal bias to stabilize the sensor. The main biasing layer is formed between two FM layers, and at least one AFM layer is disposed above the upper FM layer or below the lower FM layer. Additionally, there may be a Ta / Ni or Ta / NiFe seed layer as the bottom layer in the HB structure. Compared with a conventional abutted junction exchange bias design, the HB structure described herein results in higher output amplitude under similar asymmetry sigma and significantly decreases sidelobe occurrence. Furthermore, smaller MRWu with a similar track width is achieved since the main biasing layer acts as a side shield.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Process and structure to fabricate CPP spin valve heads for ultra-high recording density
InactiveUS7256971B2Raise the ratioIncrease resistanceNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismDopantElectrical resistance and conductance
A CPP-GMR spin value sensor structure with an improved MR ratio and increased resistance is disclosed. All layers except certain pinned layers, copper spacers, and a Ta capping layer are oxygen doped by adding a partial O2 pressure to the Ar sputtering gas during deposition. Oxygen doped CoFe free and pinned layers are made slightly thicker to offset a small decrease in magnetic moment caused by the oxygen dopant. Incorporating oxygen in the MnPt AFM layer enhances the exchange bias strength. An insertion layer such as a nano-oxide layer is included in one or more of the free, pinned, and spacer layers to increase interfacial scattering. The thickness of all layers except the copper spacer may be increased to enhance bulk scattering. A CPP-GMR single or dual spin valve of the present invention has up to a threefold increase in resistance and a 2 to 3% increase in MR ratio.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Monolithic reference full bridge magnetic field sensor
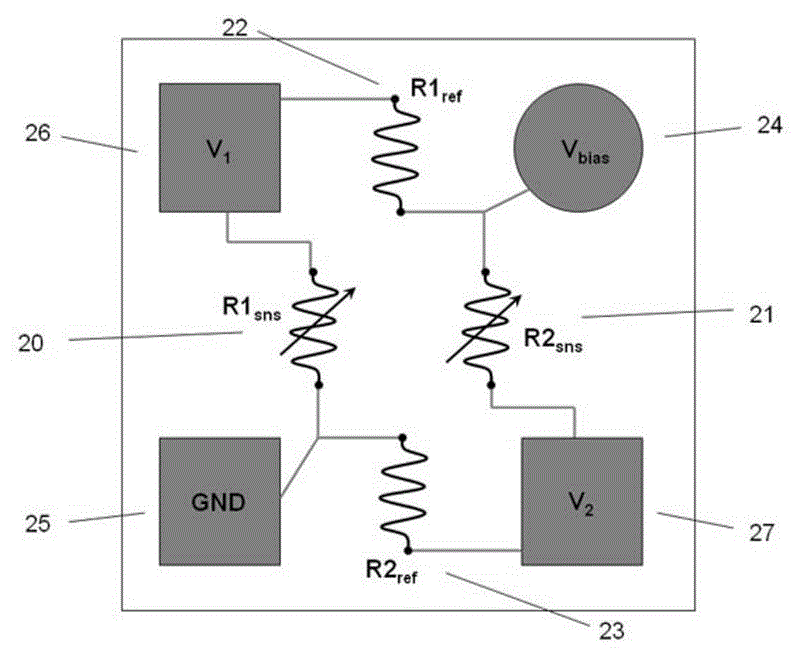
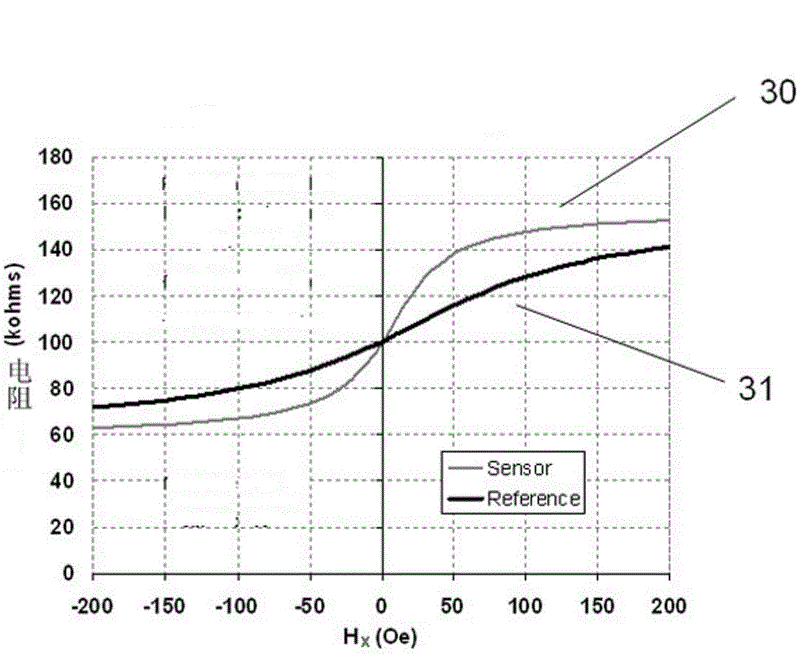
ActiveCN102621504AImprove linearityMagnetic measurementsGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetoMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a monolithic reference full bridge magnetic field sensor. The magnetic field sensor is a Wheatstone bridge formed by a magneto-resistor reference element and a sensing element. Both a sensing arm and a reference arm are magnetic tunnel junction resistance or giant magnetoresistance material. According to the invention, the sensitivity of the sensing element and the reference element are adjusted through one or one set of magnetic bias combination, exchange bias, magnetic shielding or shape anisotropy performance. In addition, bridge output offset and symmetry can be optimized through presetting and adjusting a resistance value ratio of the reference element to the sensing element. Through using the technology, the magnetic field sensor presents excellent temperature stability, low offset voltage and excellent voltage symmetry.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
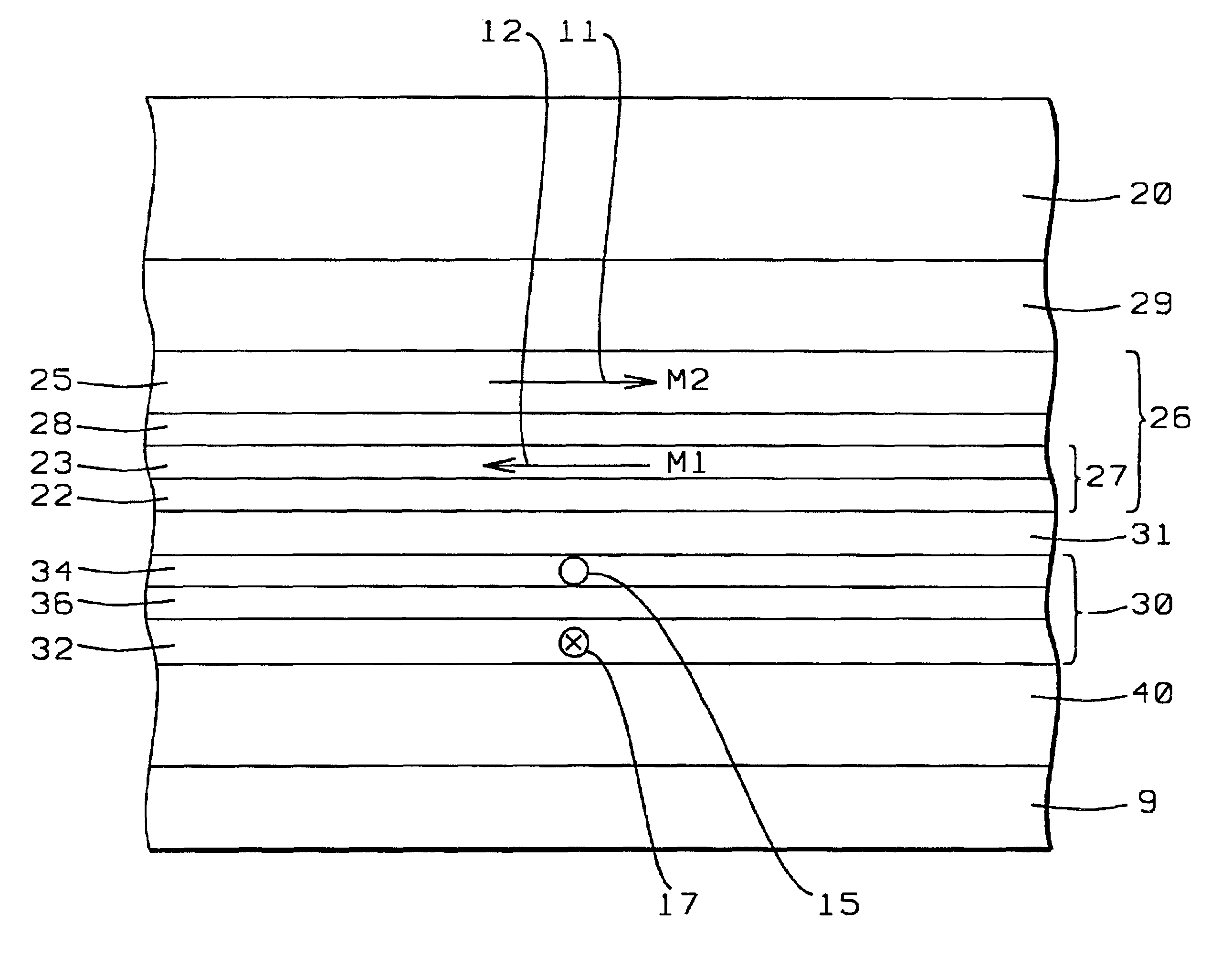
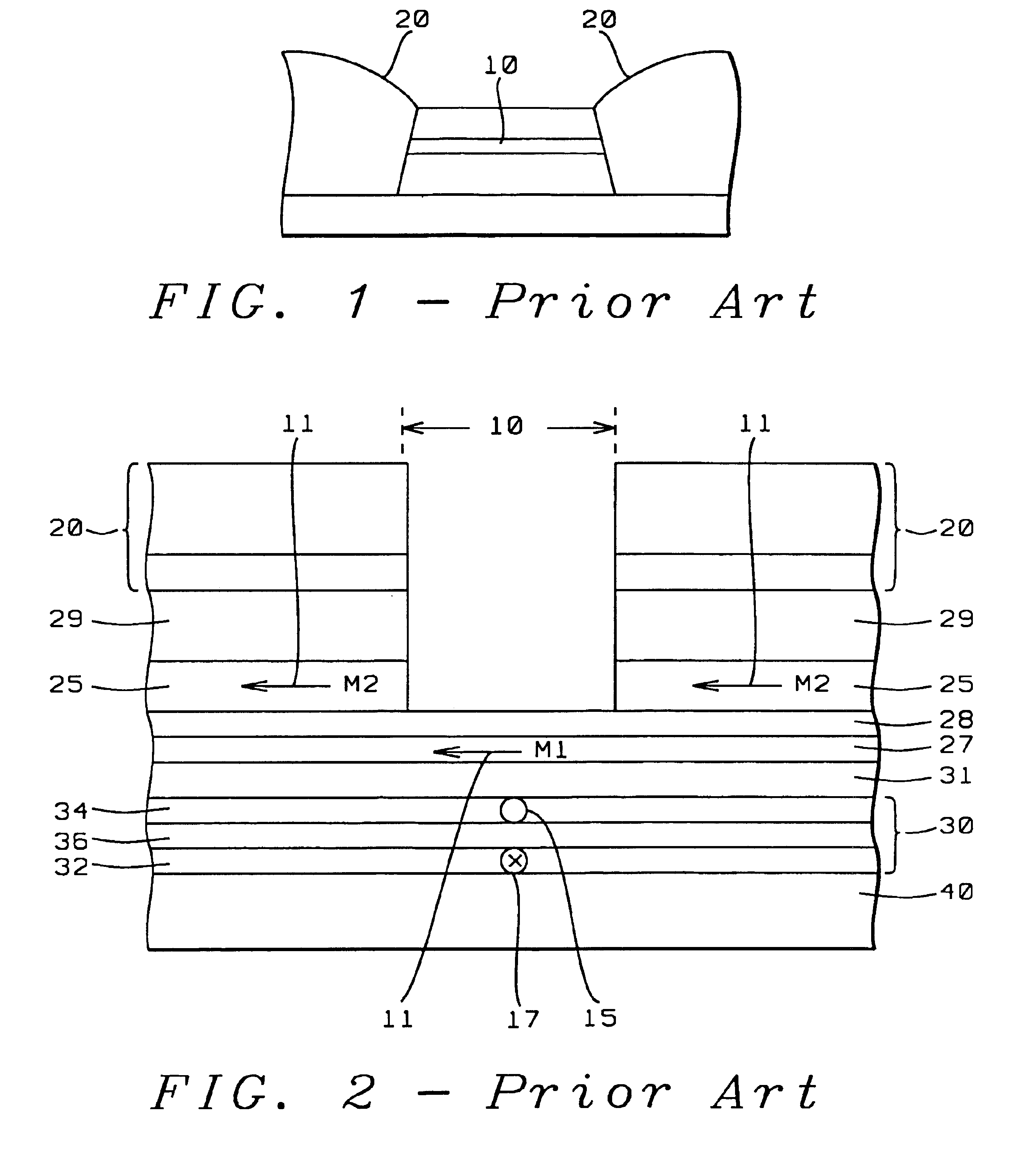
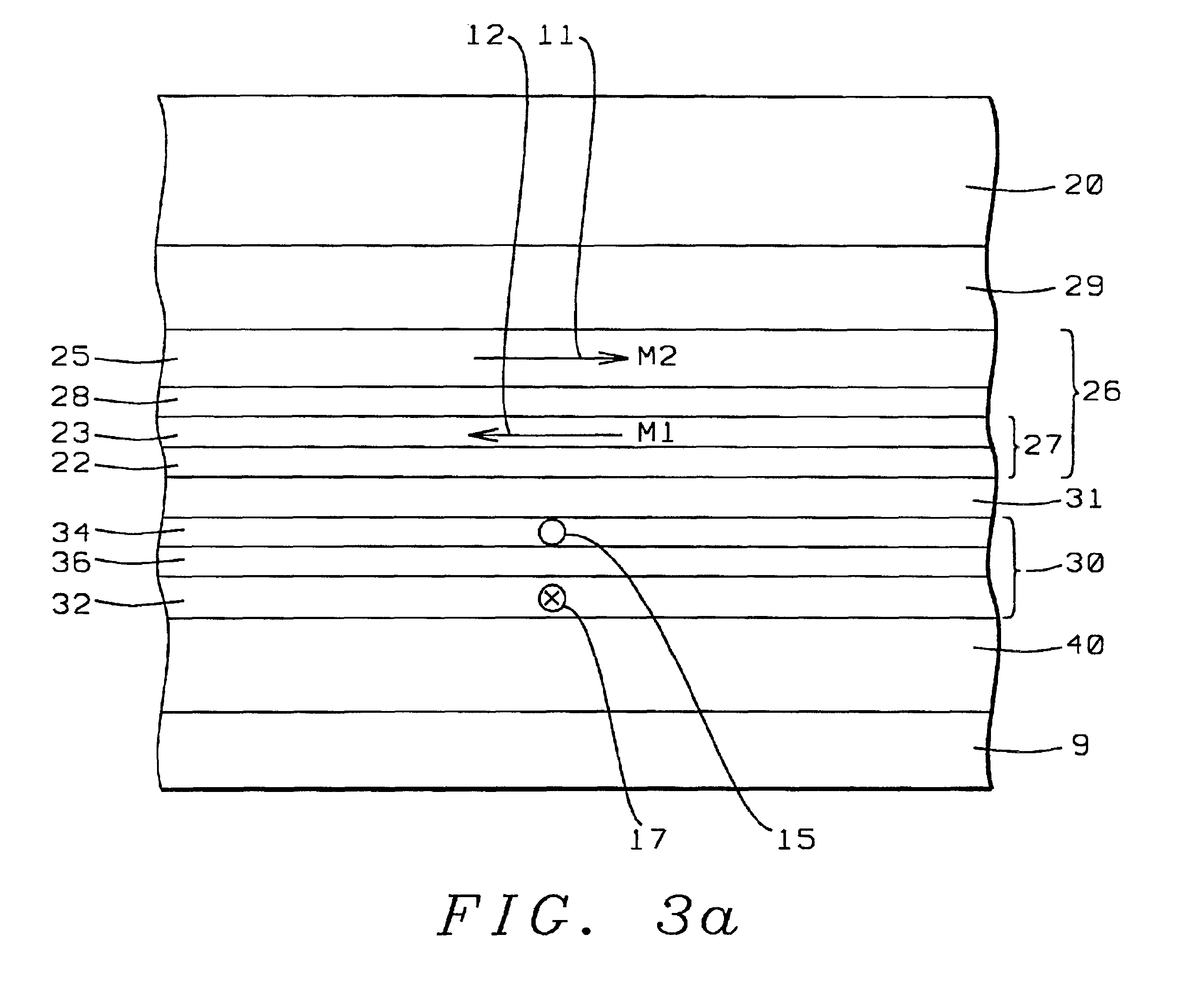
Spin valve sensor with exchange biased free layer and antiparallel (AP) pinned layer pinned without a pinning layer
InactiveUS20030179515A1Improved magnetostrictionImprovement factorNanoinformaticsHeads using thin filmsEngineeringLateral extension
A spin valve sensor includes an antiparallel (AP) pinned layer structure which is self-pinned without the assistance of an antiferromagnetic (AFM) pinning layer. A free layer of the spin valve sensor has first and second wing portions which extend laterally beyond a track width of the spin valve sensor and are exchange coupled to first and second AFM pinning layers. Magnetic moments of the wing portions of the free layer are pinned parallel to the ABS and parallel to major planes of the layers of the sensor for magnetically stabilizing the central portion of the free layer which is located within the track width.
Owner:IBM CORP
A kind of magnetic nanometer multilayer film for magnetic sensor and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN102270736ASimple manufacturing processReduce manufacturing costNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsNon magneticControllability
The invention discloses a magnetic nano-multilayers structure and the method for making it. The multilayer film includes-sequentially from one end to the other end-a substrate, a bottom layer, a magnetic reference layer, a space layer, a magnetic detecting layer and a cap layer. The, up-stated structure is for convert the information of the rotation of the magnetic moment of the magnetic detecting layer into electrical signals. The magnetic detecting layer is of a pinning structure to react to the magnetic field under detection. On the other hand, the invention sandwiches an intervening layer between the AFM and the FM to mitigate the pinning effect from the exchange bias. Moreover, the thickness of the intervening layer is adjustable to control the pinning effect from the exchange bias. The controllability ensures that the magnetic moments of the magnetic reference layer and the magnetic detecting layer remain at right angles to each other when the external field is zero. The invention achieves a GMR or TMR magnetic sensor exhibiting a linear response and by tuning the thickness of the non-magnetic metallic layer, the sensitivity as well as the detecting range of the devices can be tuned easily.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spin valve sensor with exchange biased free layer and antiparallel (AP) pinned layer pinned without a pinning layer
InactiveUS6865062B2Improve stabilityHigh amplitude read outputNanoinformaticsHeads using thin filmsLateral extensionEngineering
A spin valve sensor includes an antiparallel (AP) pinned layer structure which is self-pinned without the assistance of an antiferromagnetic (AFM) pinning layer. A free layer of the spin valve sensor has first and second wing portions which extend laterally beyond a track width of the spin valve sensor and are exchange coupled to first and second AFM pinning layers. Magnetic moments of the wing portions of the free layer are pinned parallel to the ABS and parallel to major planes of the layers of the sensor for magnetically stabilizing the central portion of the free layer which is located within the track width.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
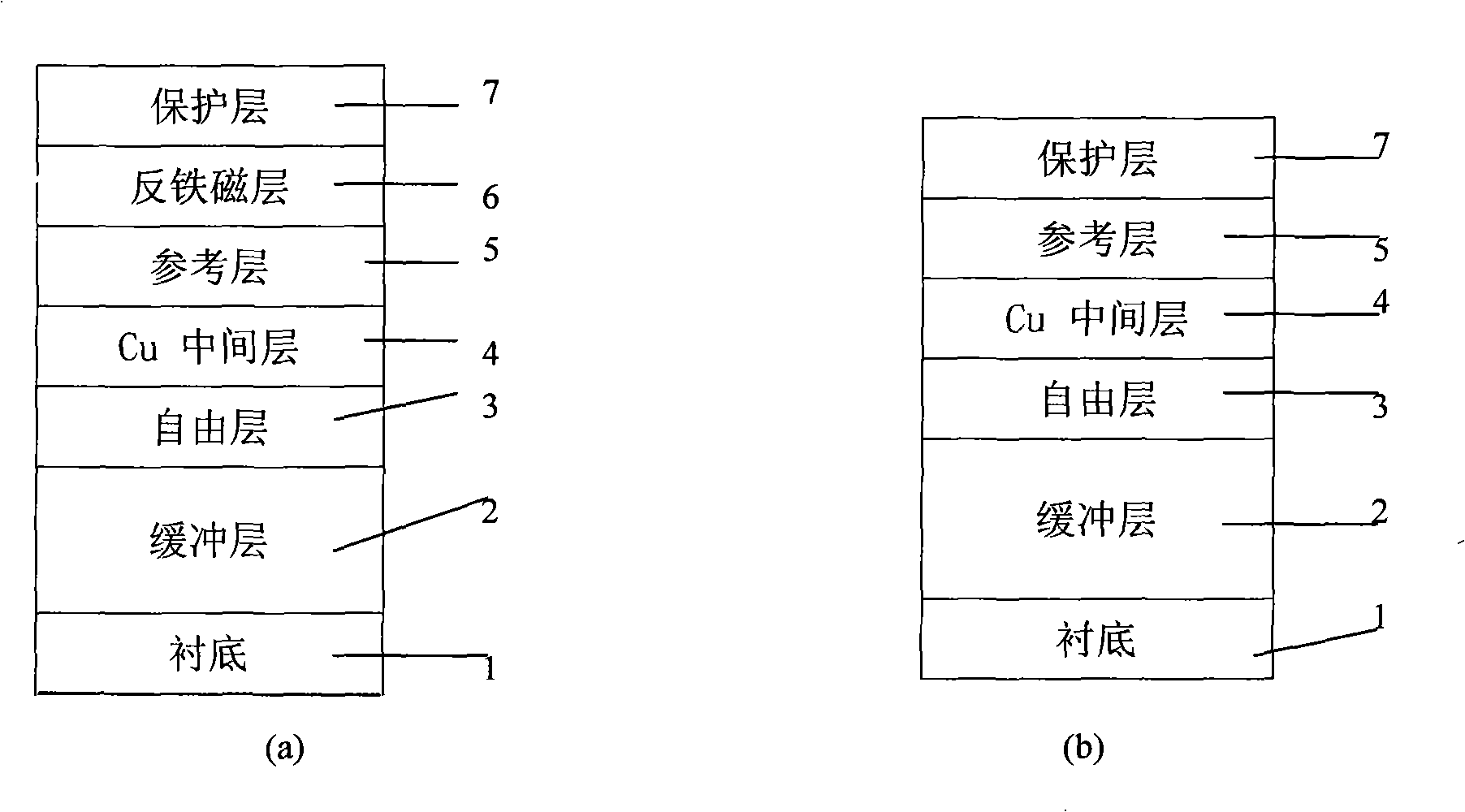
Spin-valve thin-film magnetic element and method for making the same
A spin-valve thin-film magnetic element includes a substrate, a composite formed thereon, and electrode layers formed on both sides of the composite. The composite includes an antiferromagnetic layer, a pinned magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic conductive layer, a free magnetic layer, a mean-free-path-extending layer, and an exchange bias layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer may be a back layer or a mirror reflective layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer extends the mean free path of spin-up conduction electrons in the spin-valve thin-film magnetic element. This spin-valve thin-film magnetic element meets trends toward a narrower track width.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Method for fabricating a patterned synthetic longitudinal exchange biased GMR sensor
InactiveUS6857180B2Reduce contribution of signal AStabilizing bias pointNanomagnetismElectrical transducersMagnetizationExchange bias
Patterned, longitudinally and transversely antiferromagnetically exchange biased GMR sensors are provided which have narrow effective trackwidths and reduced side reading. The exchange biasing significantly reduces signals produced by the portion of the ferromagnetic free layer that is underneath the conducting leads while still providing a strong pinning field to maintain sensor stability. In the case of the transversely biased sensor, the magnetization of the free and biasing layers in the same direction as the pinned layer simplifies the fabrication process and permits the formation of thinner leads by eliminating the necessity for current shunting.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetic Tunnel Junction Device and Method of Manufacturing the Same
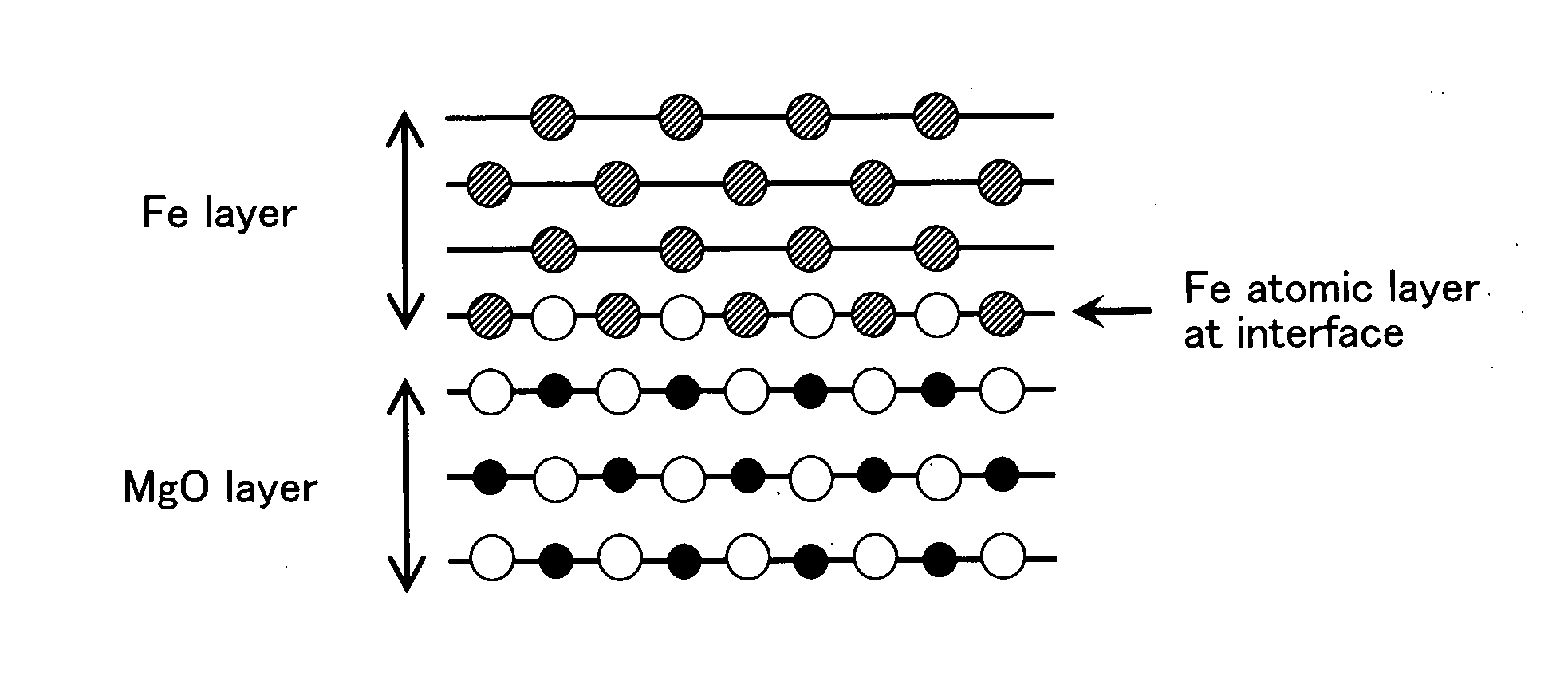
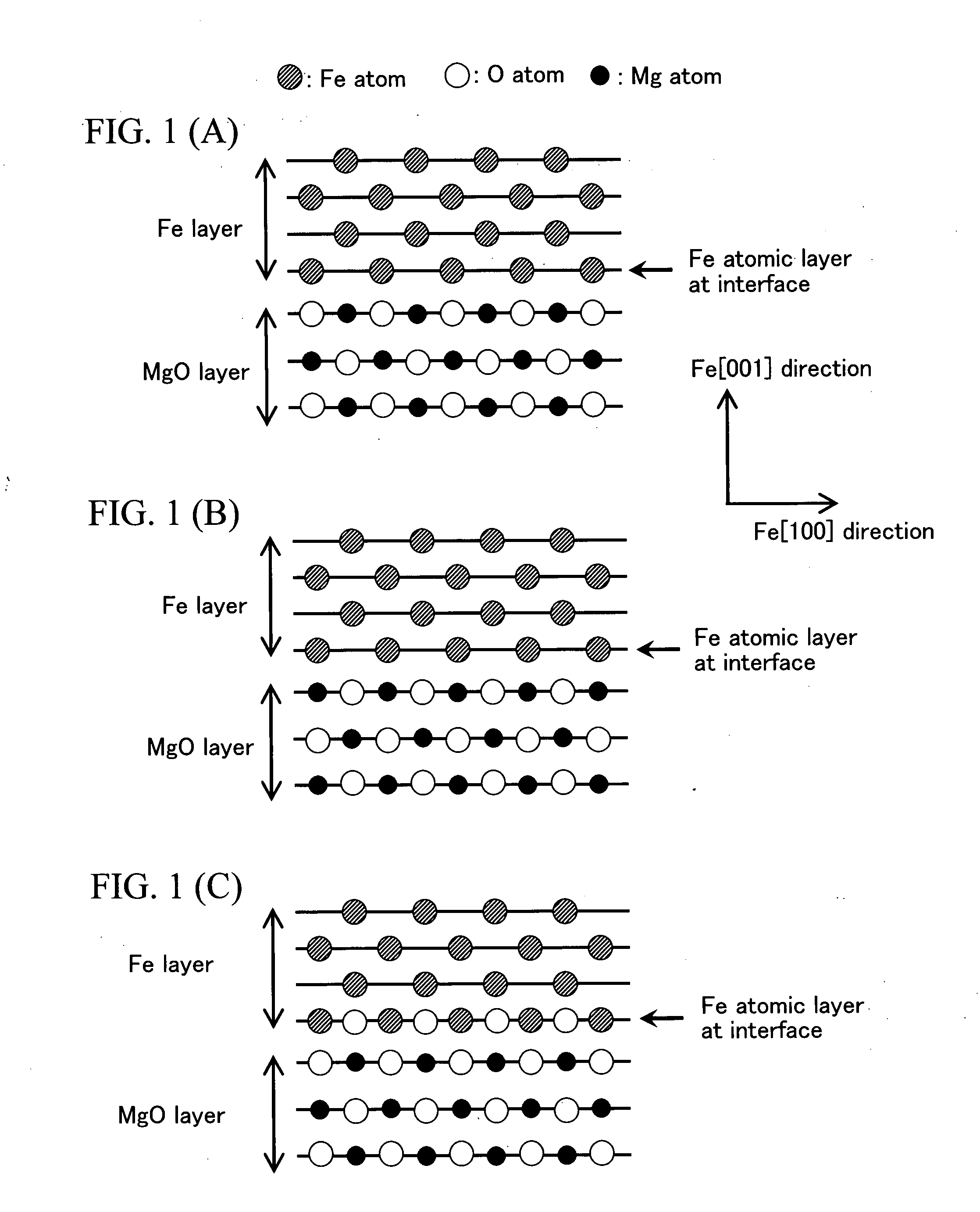
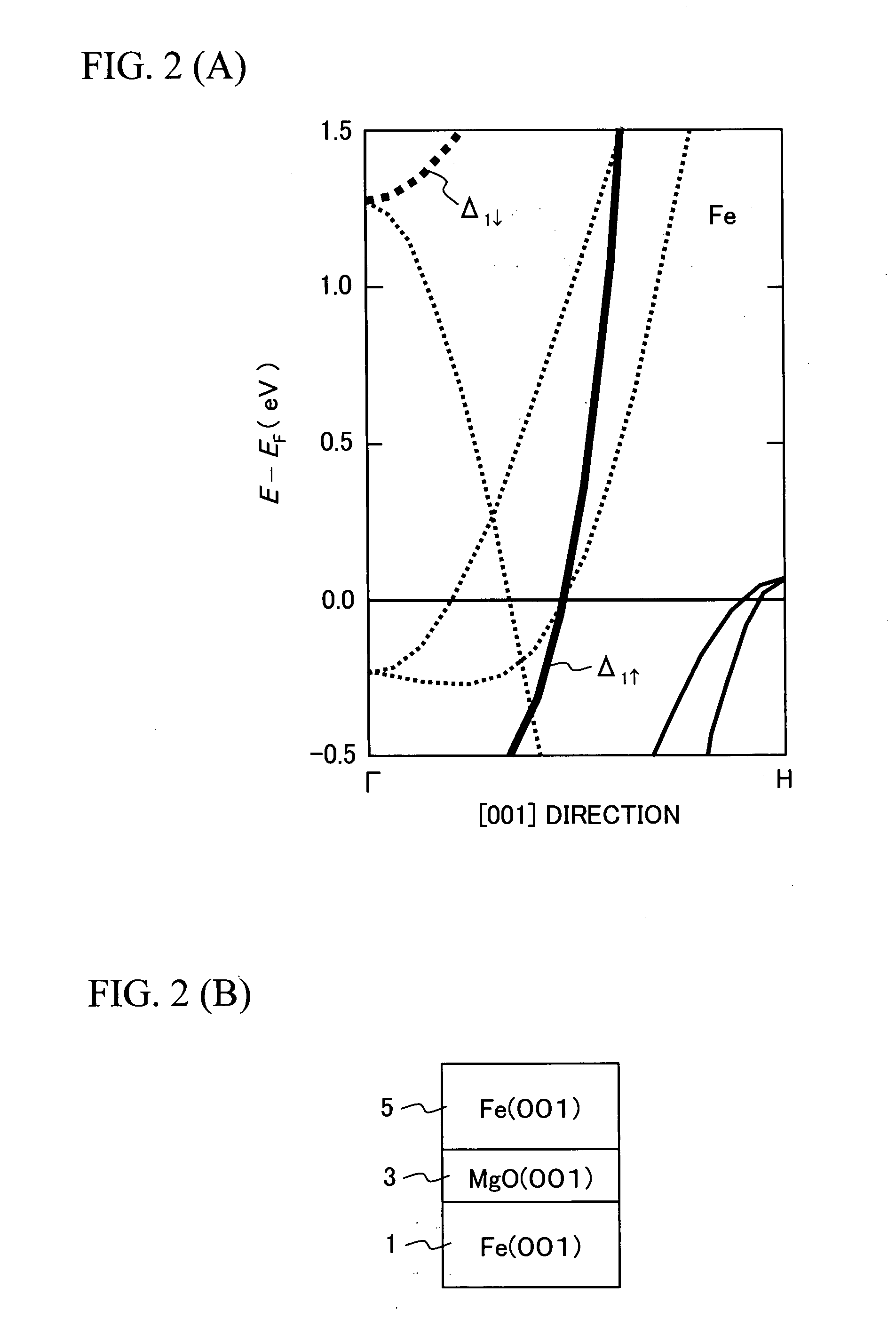
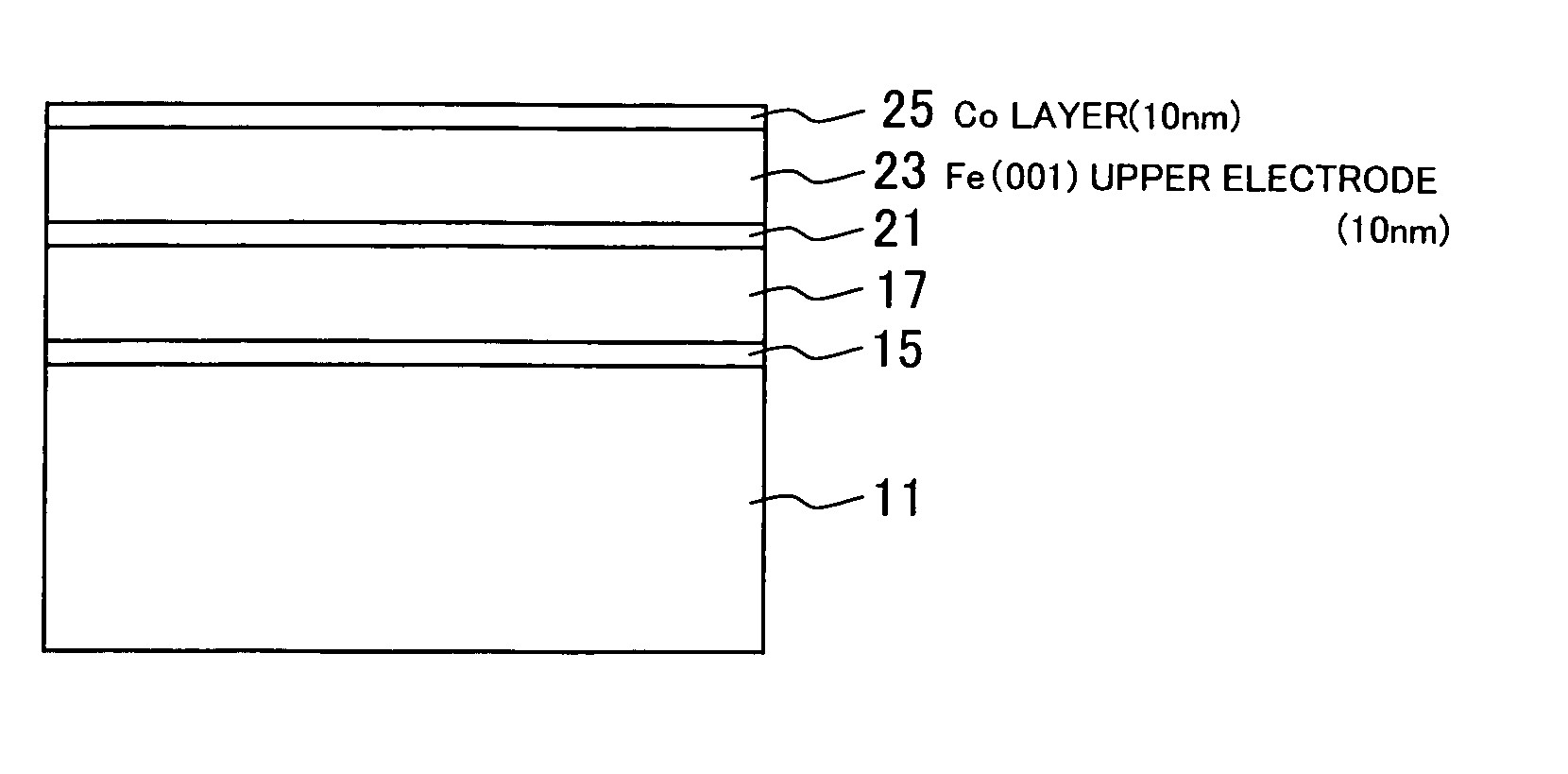
InactiveUS20070258170A1Increases tunneling probabilityIncreased reluctanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationRoom temperature
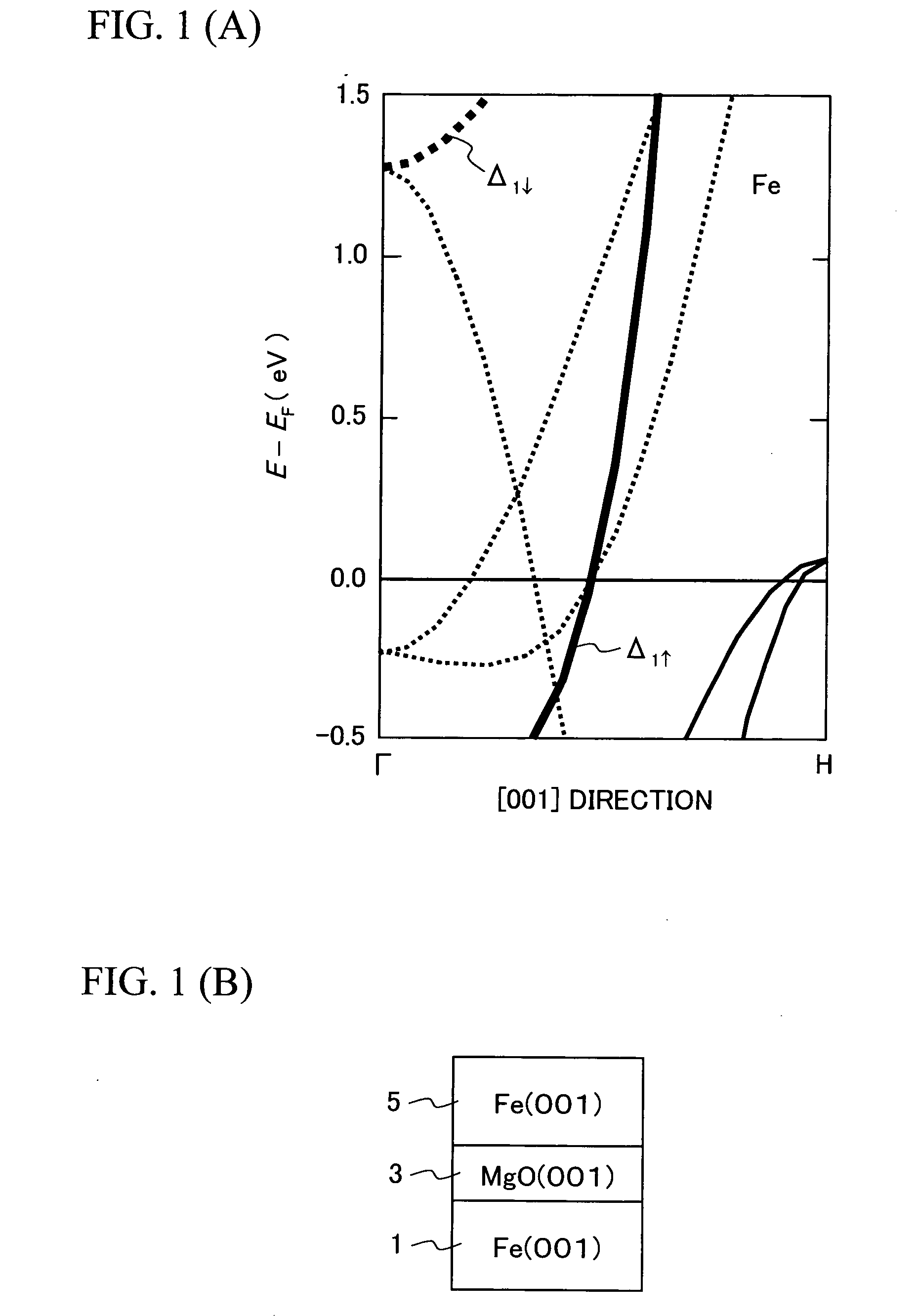
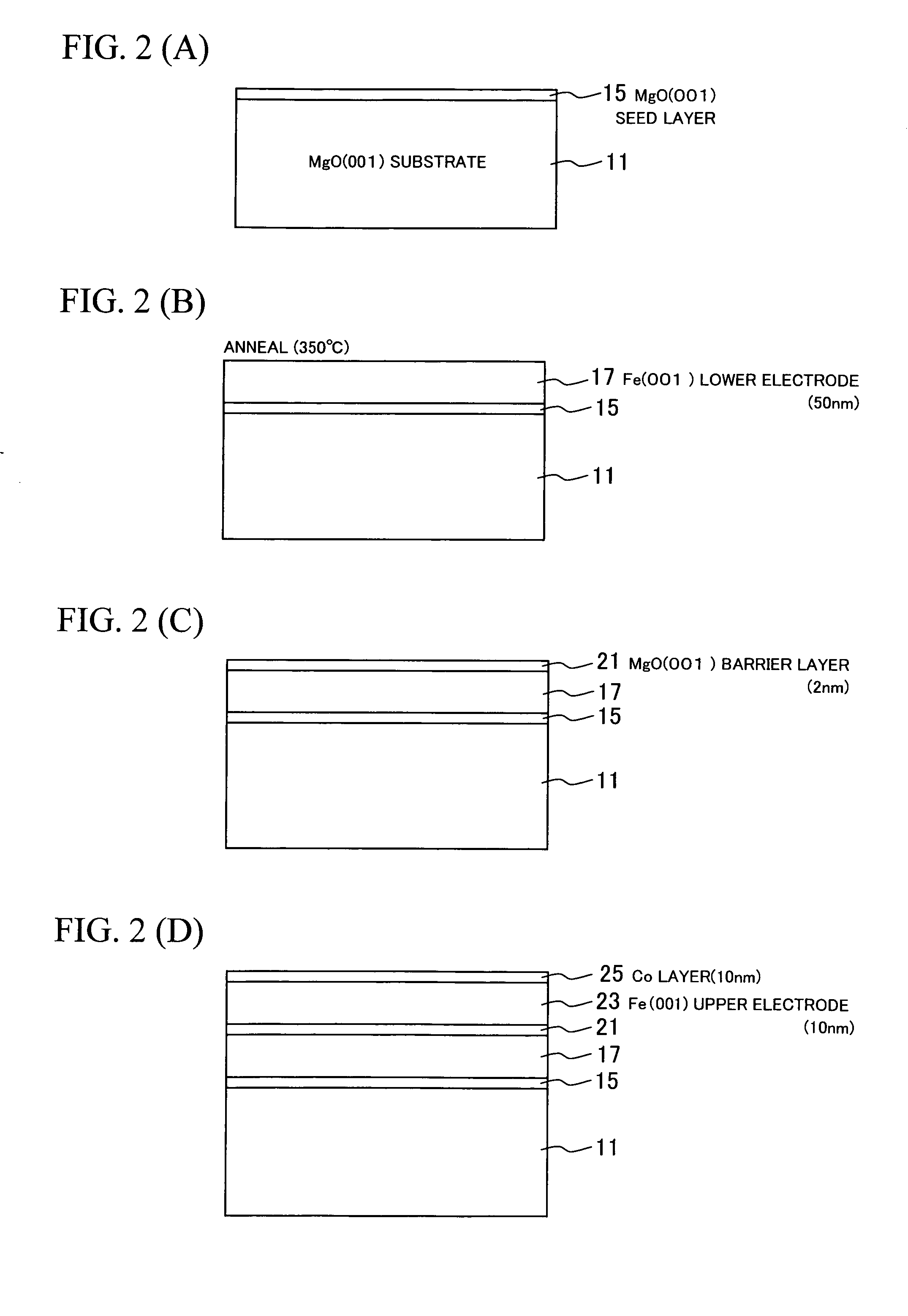
A single-crystalline MgO (001) substrate 11 is prepared, and then an epitaxial Fe (001) lower electrode (first electrode) 17 with a thickness of 50 nm is grown on a MgO (001) seed layer 15 at room temperature. Annealing is then performed in ultrahigh vacuum (2×10−8 Pa) at 350° C. A 2-nm thick MgO (001) barrier layer 21 is epitaxially grown on the Fe (001) lower electrode (first electrode) 17 at room temperature, using electron beam evaporation of MgO. A Fe (001) upper electrode (second electrode) 23 with a thickness of 10 nm is then grown on the MgO (001) barrier layer 21 at room temperature, successively followed by the deposition of a IrMn layer 25 with a thickness of 10 nm on the Fe (001) upper electrode (second electrode) 23. The IrMn layer 25 is used for realizing an antiparallel magnetization alignment by giving an exchange-biasing field to the upper electrode 23. Thereafter, the above-prepared sample is subjected to microfabrication so as to obtain a Fe (001) / MgO (001) / Fe (001) MTJ device with an enhanced MR ratio.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
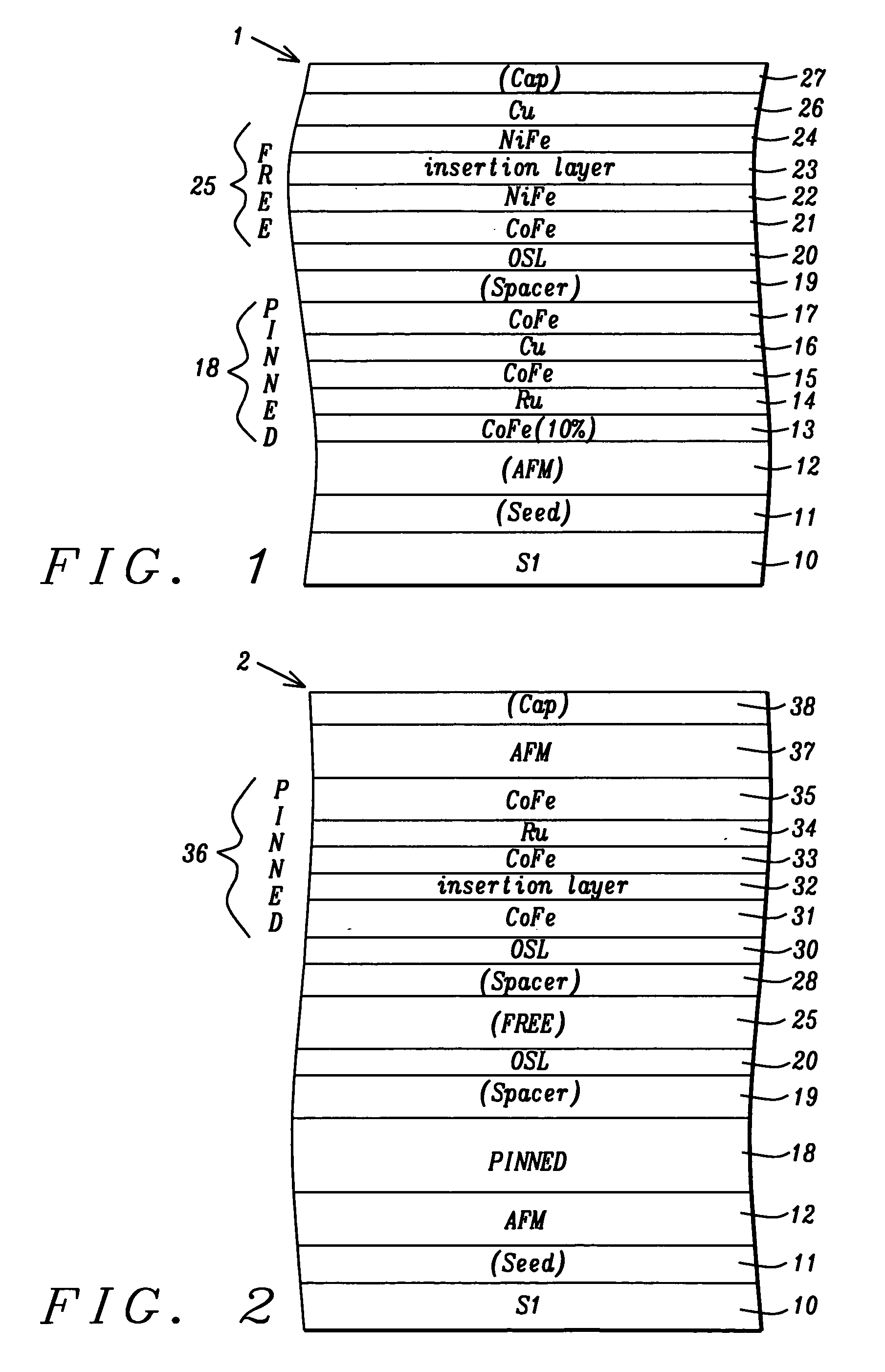
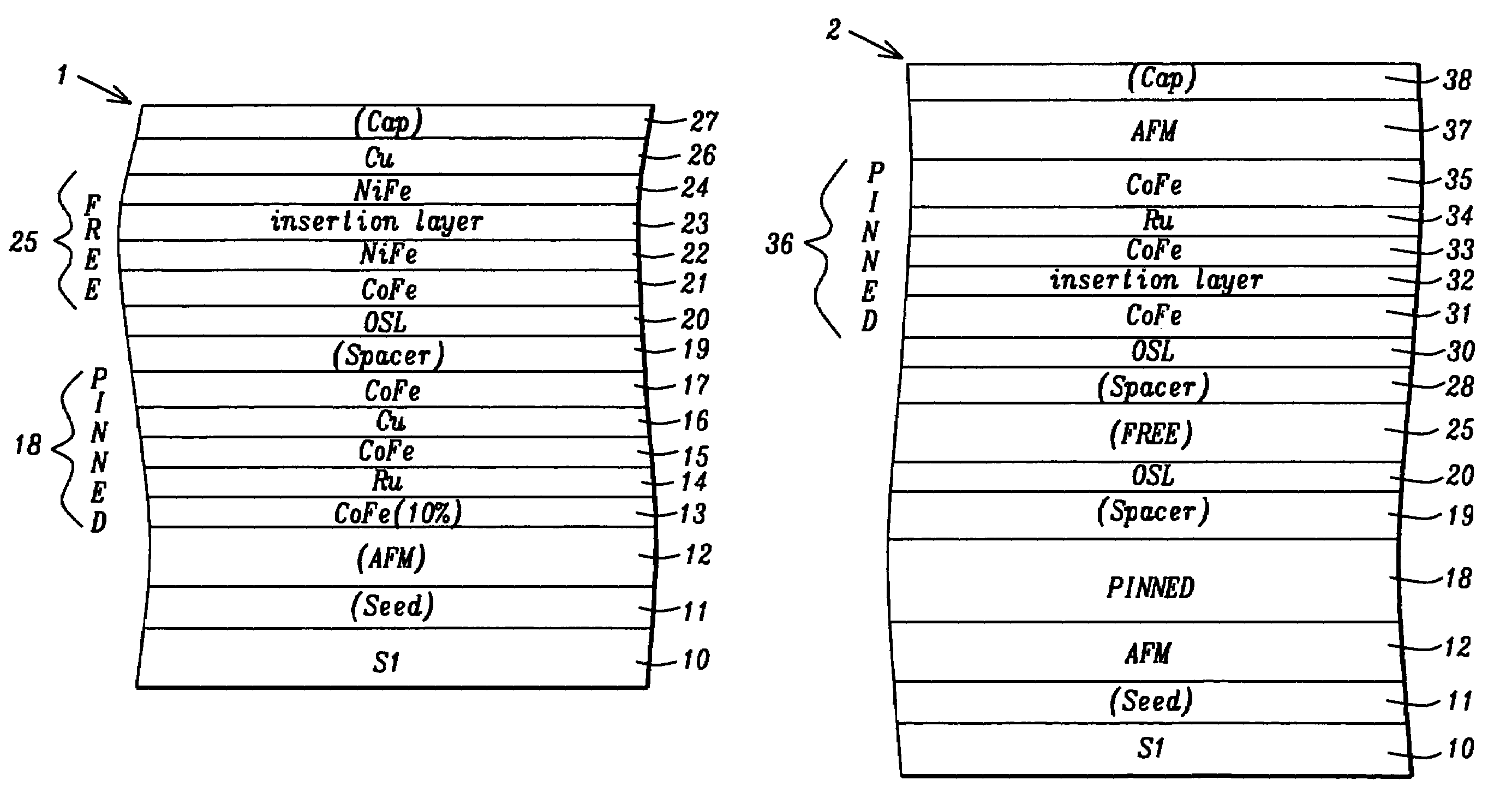
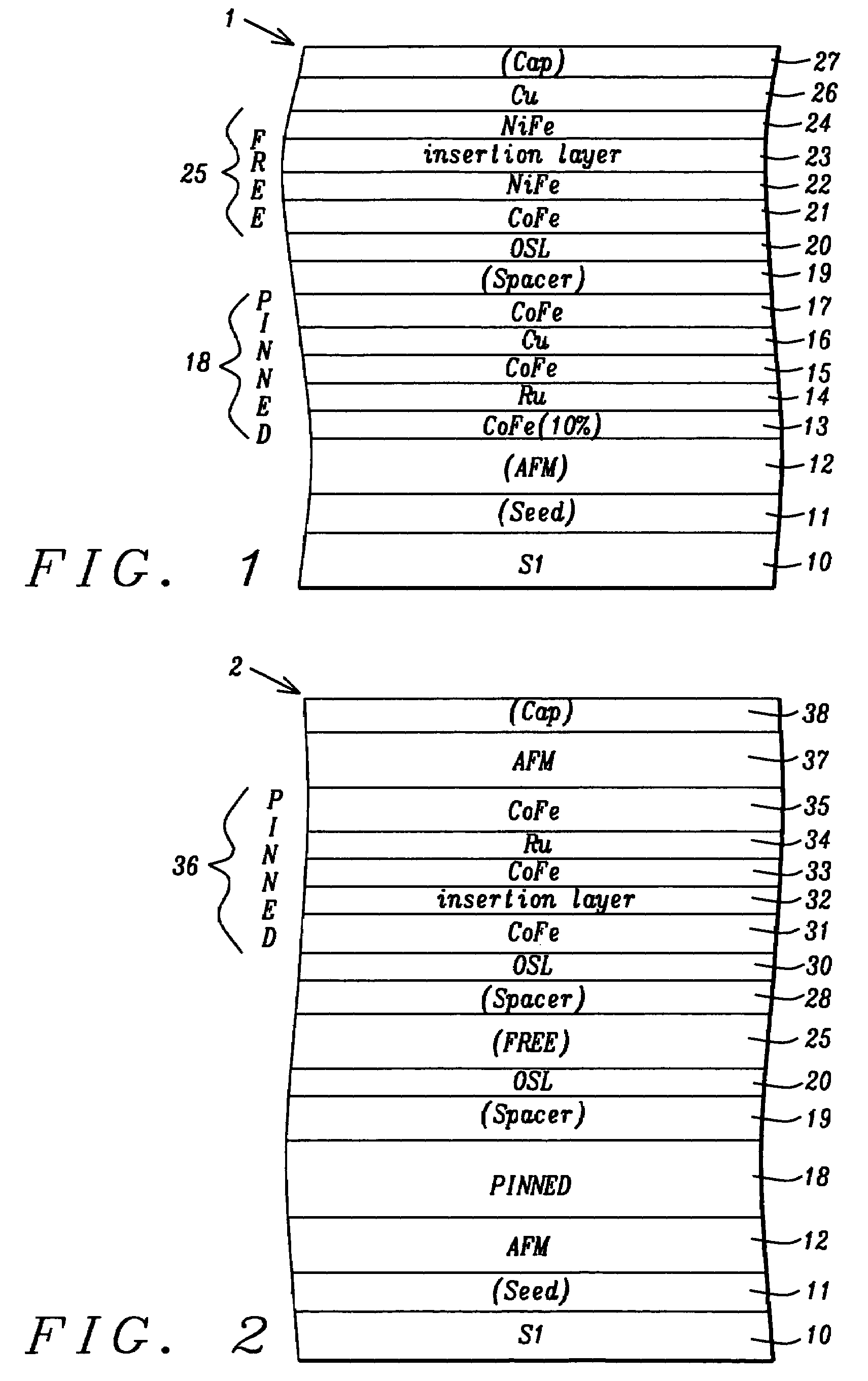
CoFe insertion for exchange bias and sensor improvement
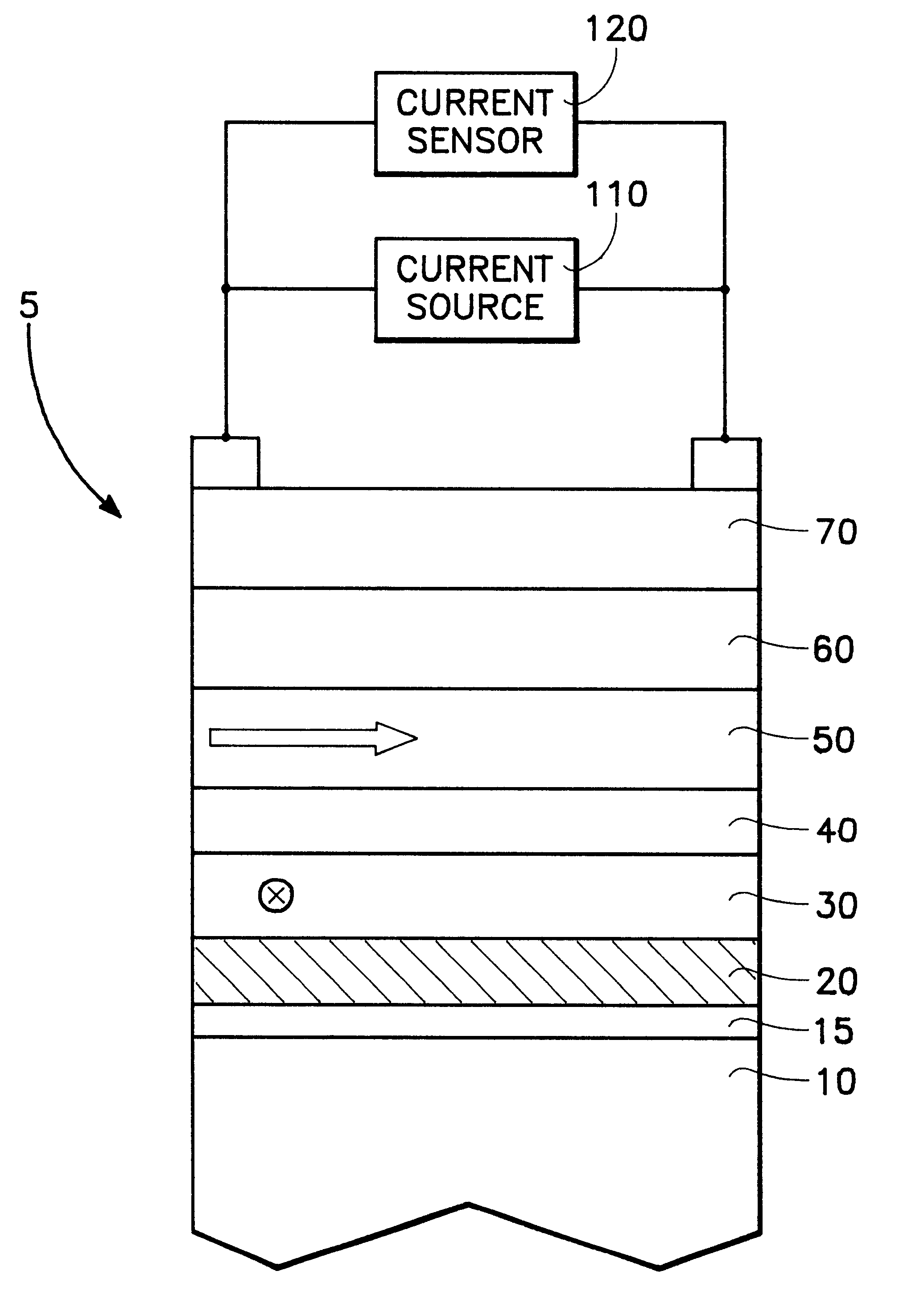
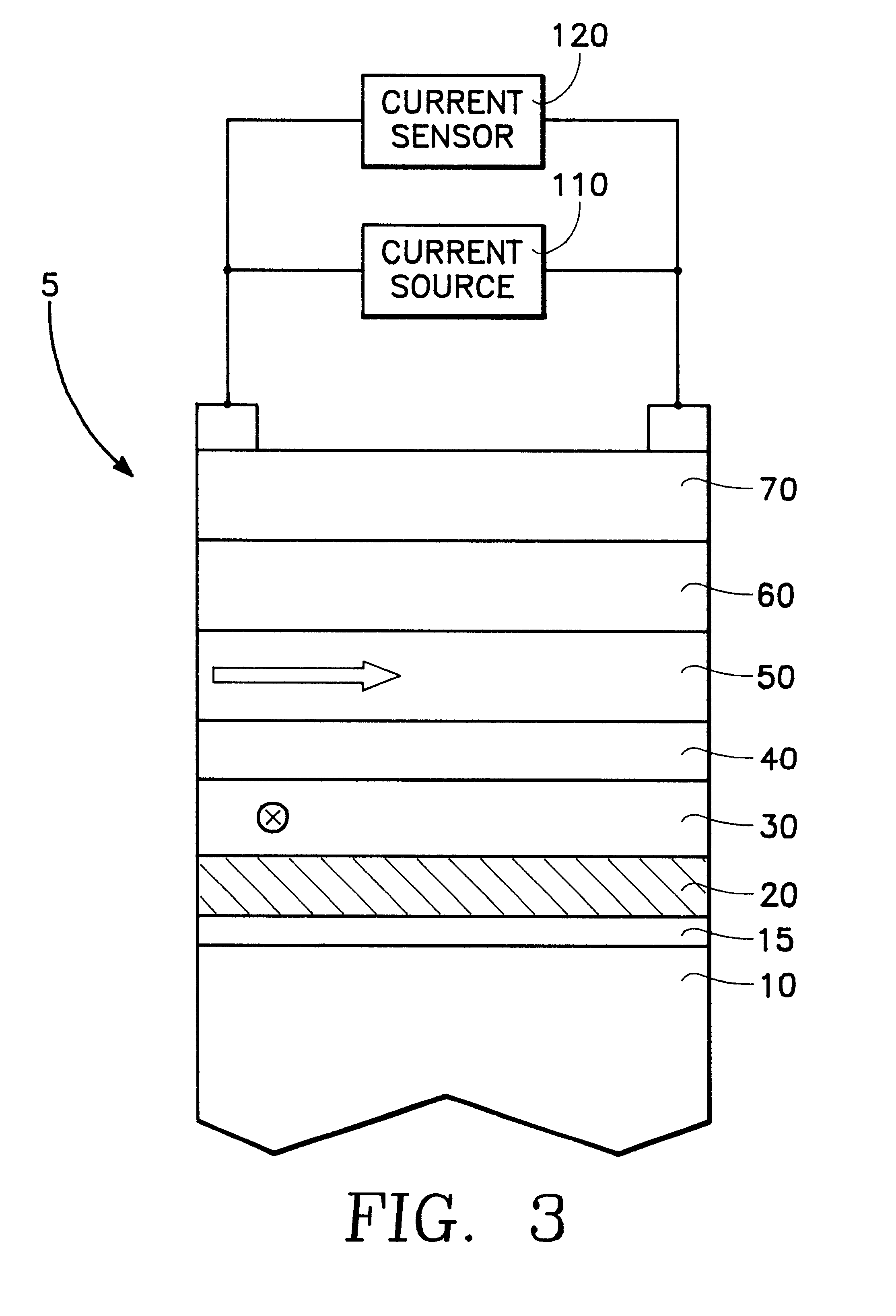
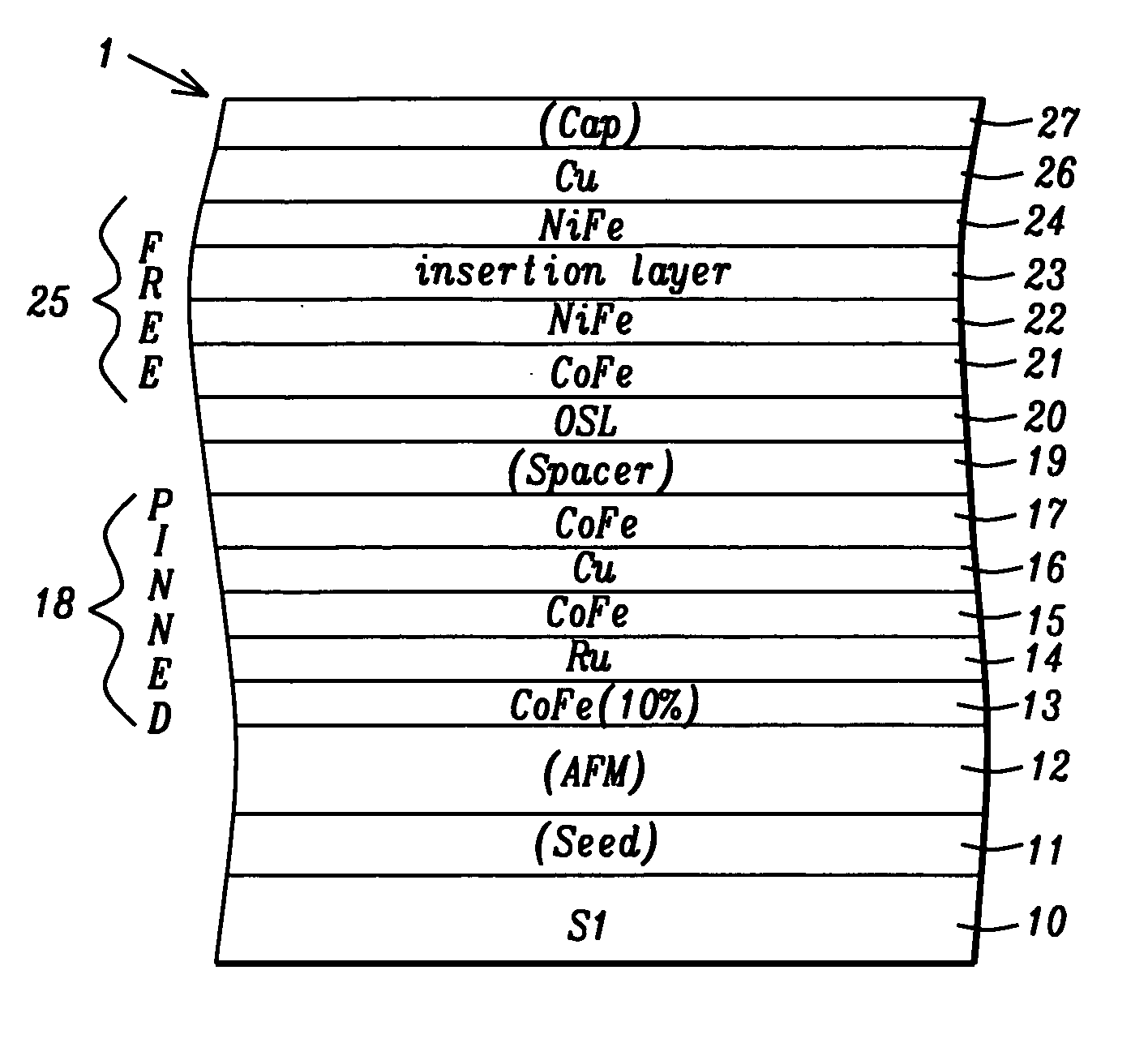
ActiveUS20060061915A1Improved GMR ratioReduce couplingNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSputter depositionExchange bias
A GMR spin value structure with improved performance and a method for making the same is disclosed. A key feature is the incorporation of a thin ferromagnetic insertion layer such as a 5 Angstrom thick CoFe layer between a NiCr seed layer and an IrMn AFM layer. Lowering the Ar flow rate to 10 sccm for the NiCr sputter deposition and raising the Ar flow rate to 100 sccm for the IrMn deposition enables the seed layer to be thinned to 25 Angstroms and the AFM layer to about 40 Angstroms. As a result, HEX between the AFM and pinned layers increases by up to 200 Oe while the Tb is maintained at or above 250° C. When the seed / CoFe / AFM configuration is used in a read head sensor, a higher GMR ratio is observed in addition to smaller free layer coercivity (HCF), interlayer coupling (HE), and HK values.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
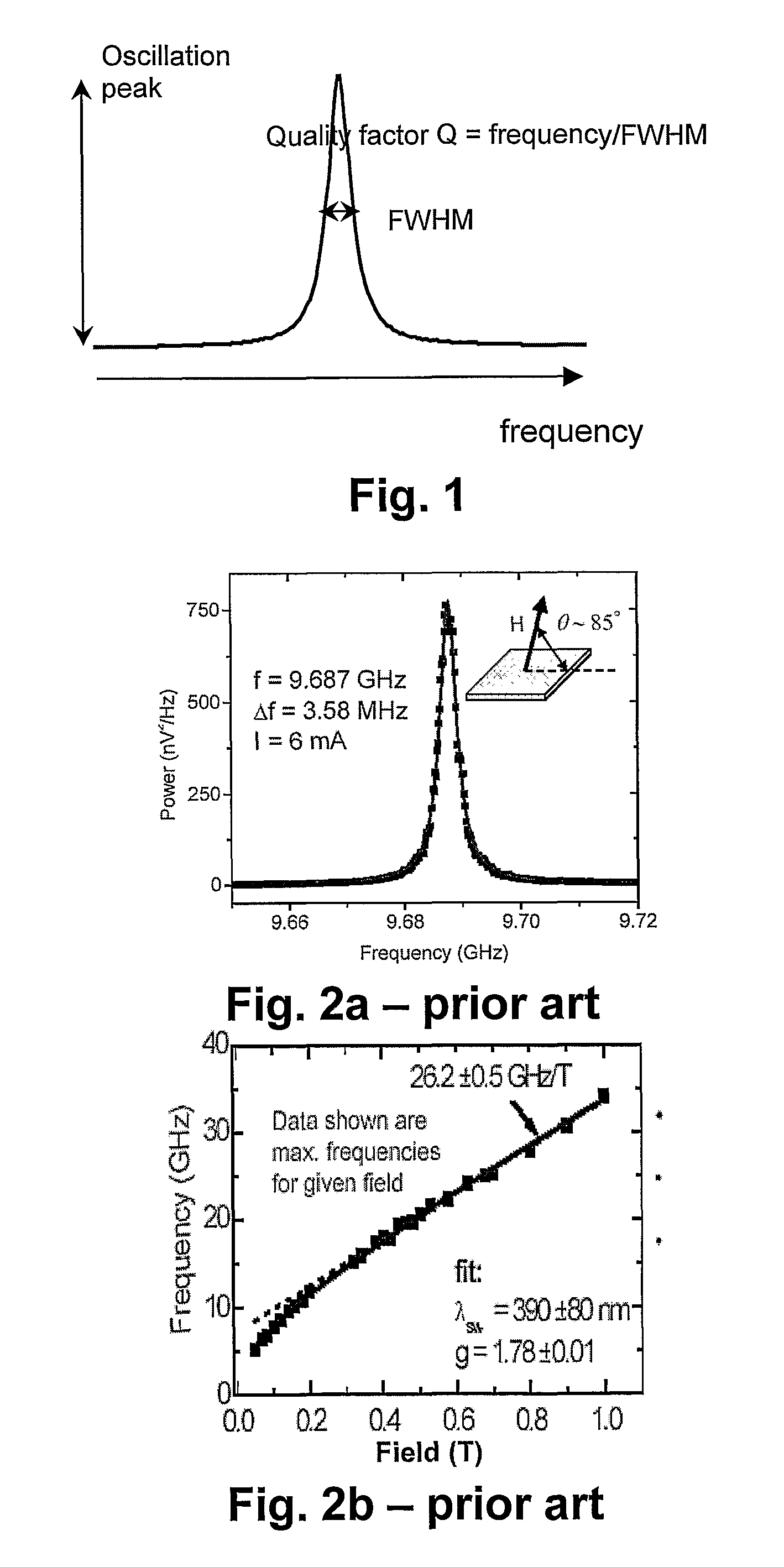
Fully Integrated Tuneable Spin Torque Device For Generating An Oscillating Signal And Method For Tuning Such Apparatus
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film and element, magnetoresistive sensor using same, magnetic apparatus, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20050019610A1Reduced effectivenessPrevent oxidationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsNon magneticOxygen
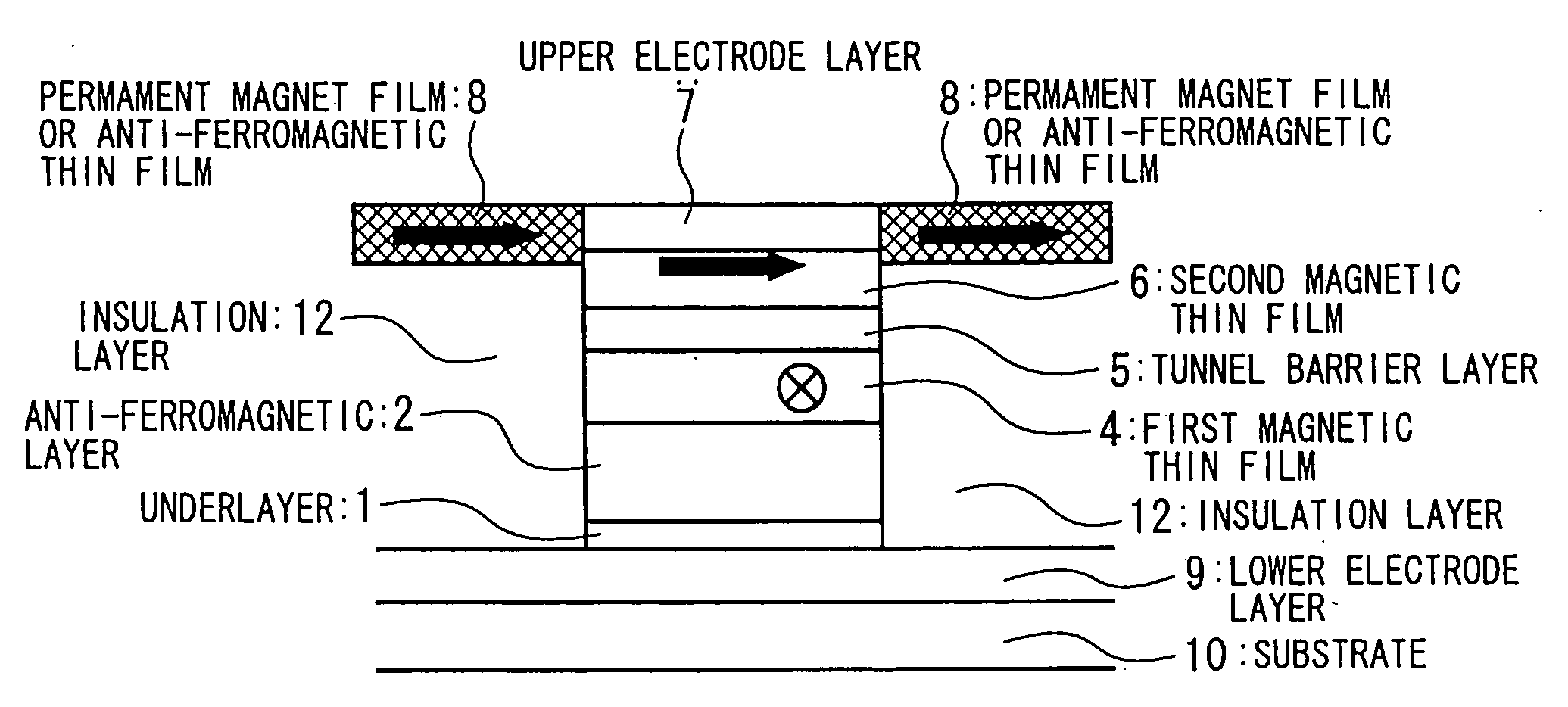
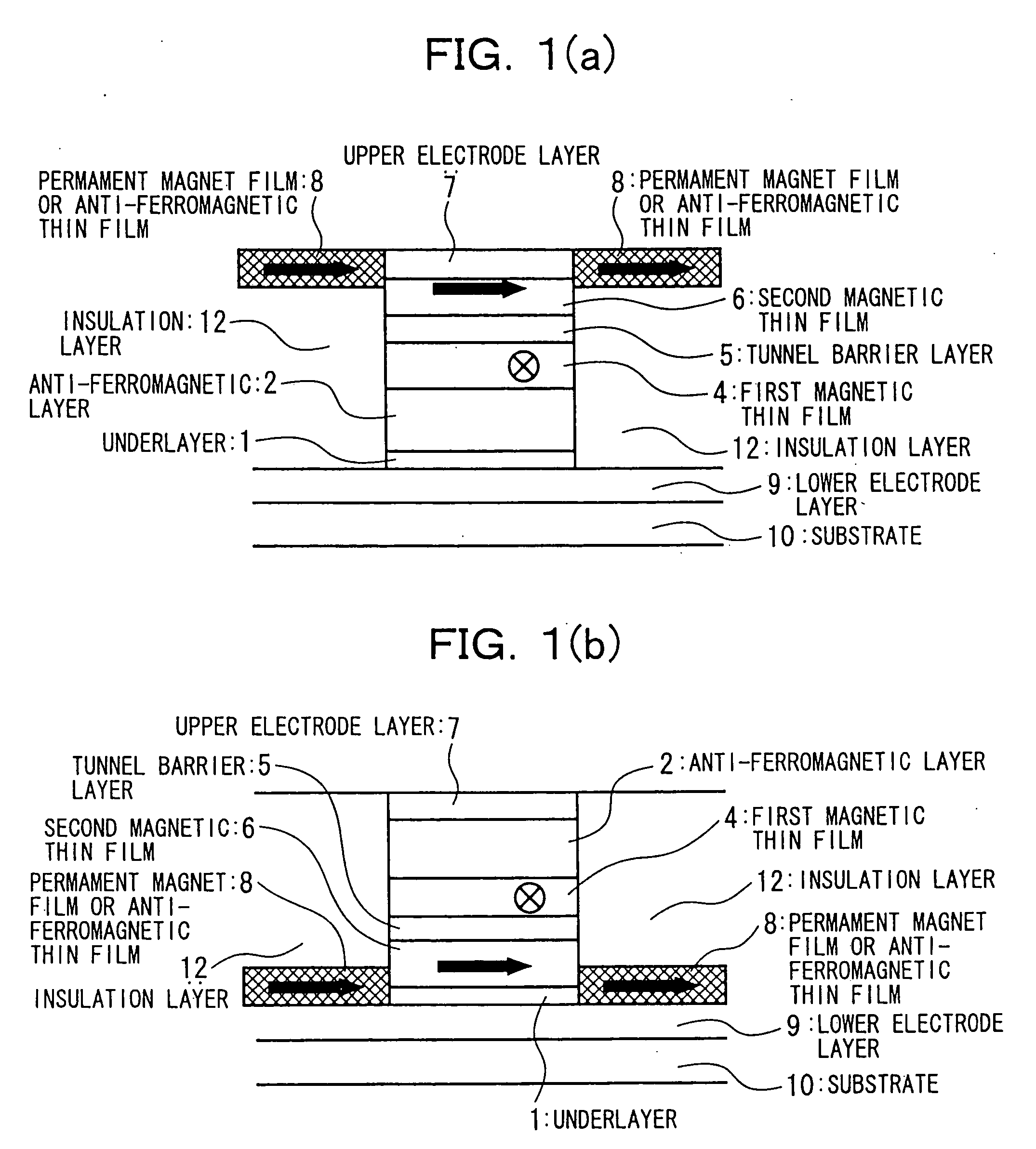
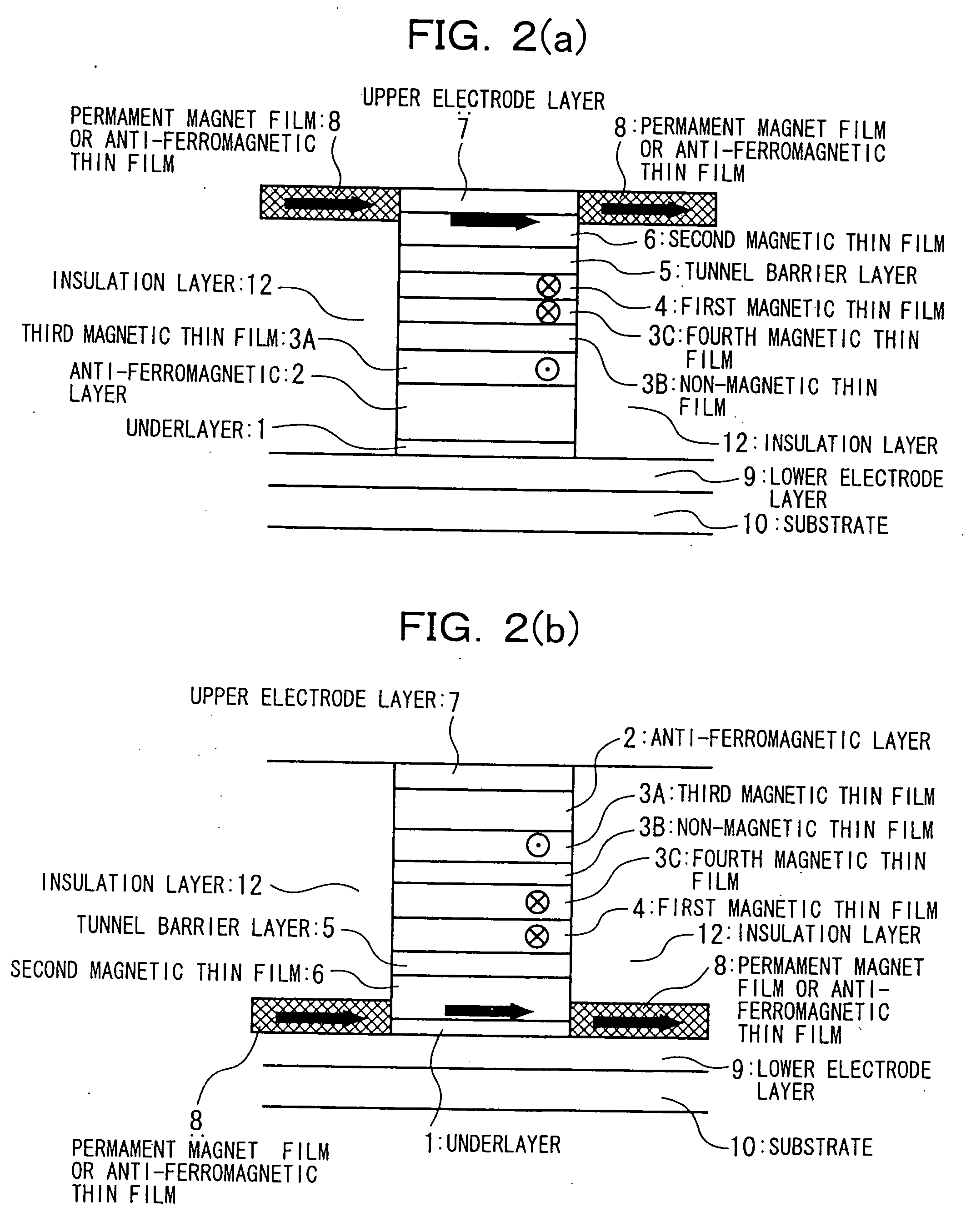
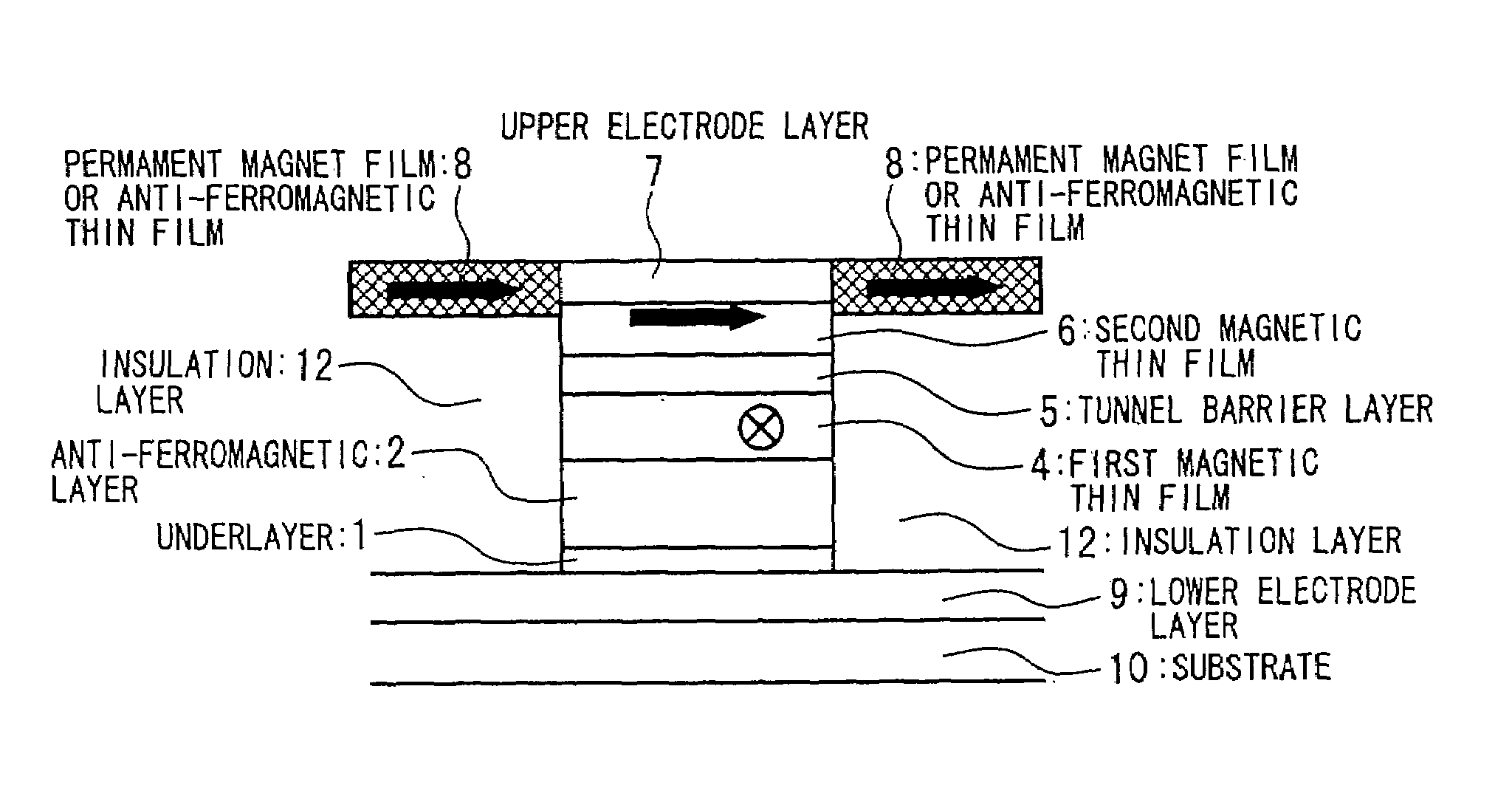
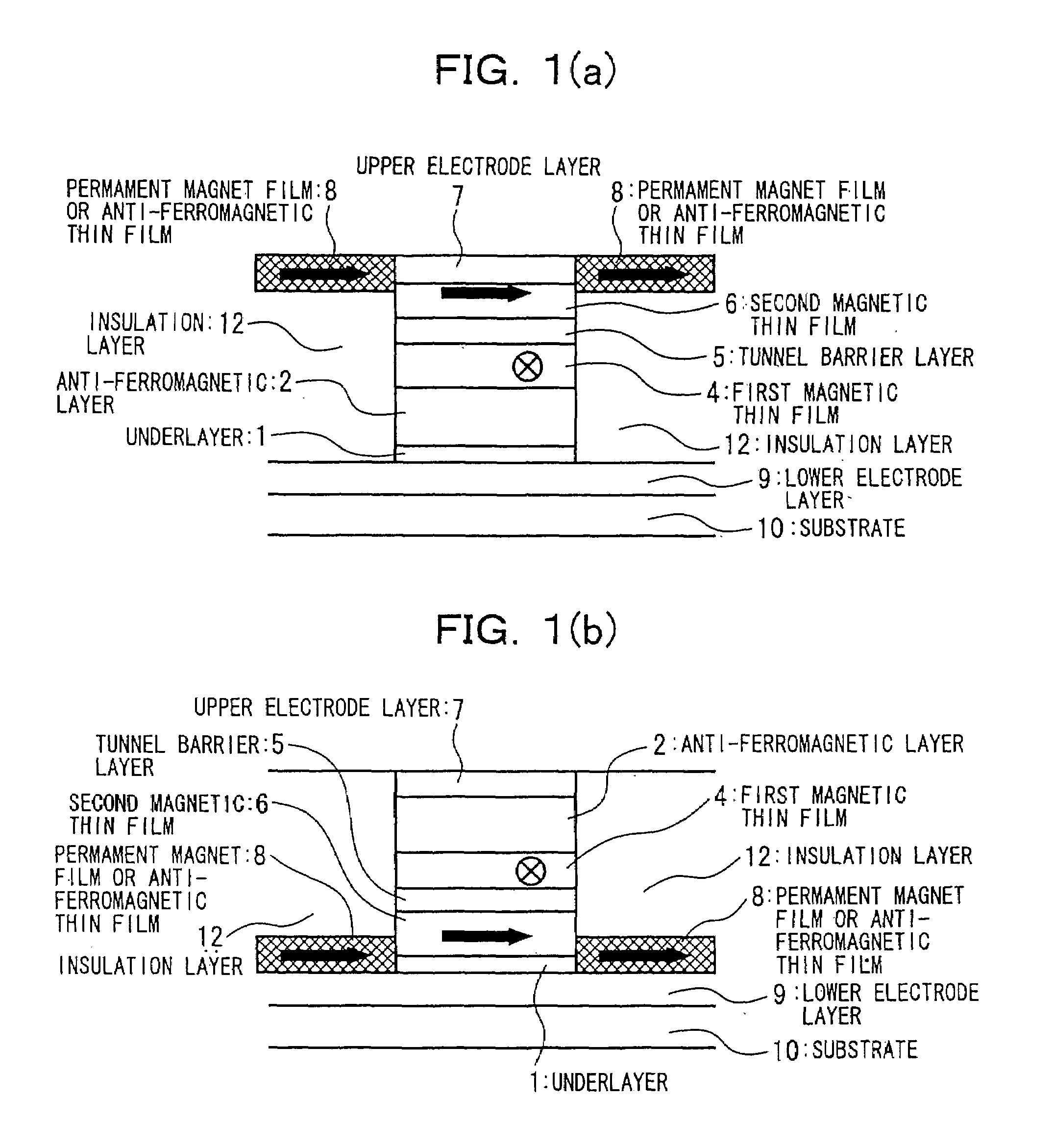
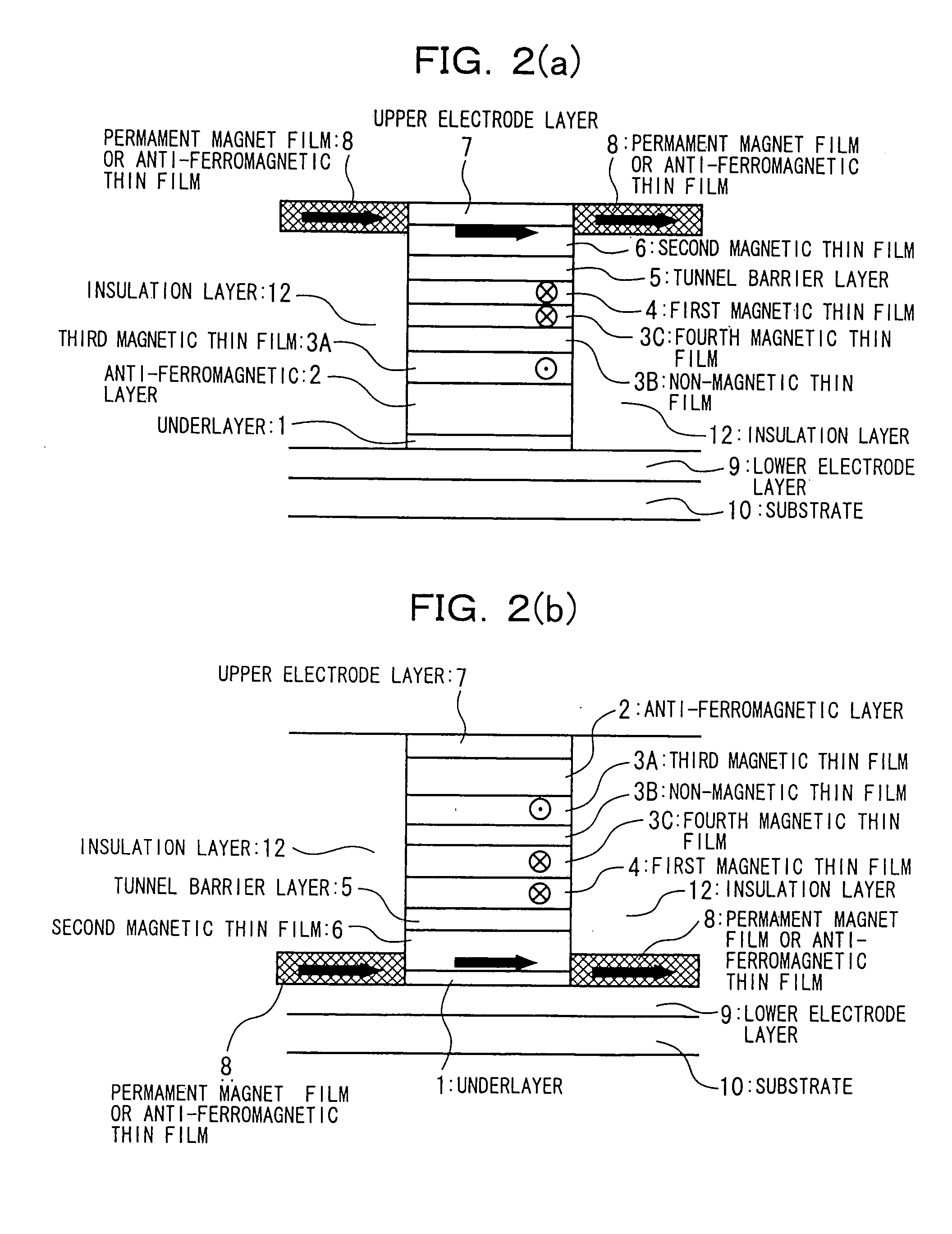
In a spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film in which a magnetic thin film to which an exchange bias is applied by exchange coupling via an anti-ferromagnetic thin film and a magnetic thin film that detects a magnetic field are laminated, a magnetic thin film or an anti-ferromagnetic thin film (PtMn, PdMn, NiMn) is laminated onto an underlayer (Ta, Zr, Hf), the surface roughness thereof being in the range from 0.1 to 5 Angstroms. A means used to control the surface roughness introduces into the film growing chamber oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, or a gas mixture thereof into a vacuum of 10−6 Torr to 10−9 Torr, reduces the substrate temperature to 0° C. or lower during film growth, or oxidizes an underlayer. The lower electrode layer material used is a film laminate of a high-permeability amorphous magnetic material and a non-magnetic metallic layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetic nano-multilayers for magnetic sensors and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20130099780A1Reduced strengthSimple manufacturing processNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsNon magneticControllability
The invention discloses a magnetic nano-multilayers structure and the method for making it. The multilayer film includes—sequentially from one end to the other end—a substrate, a bottom layer, a magnetic reference layer, a space layer, a magnetic detecting layer and a cap layer. The, up-stated structure is for convert the information of the rotation of the magnetic moment of the magnetic detecting layer into electrical signals. The magnetic detecting layer is of a pinning structure to react to the magnetic field under detection. On the other hand, the invention sandwiches an intervening layer between the AFM and the FM to mitigate the pinning effect from the exchange bias. Moreover, the thickness of the intervening layer is adjustable to control the pinning effect from the exchange bias. The controllability ensures that the magnetic moments of the magnetic reference layer and the magnetic detecting layer remain at right angles to each other when the external field is zero. The invention achieves a GMR or TMR magnetic sensor exhibiting a linear response and by tuning the thickness of the non-magnetic metallic layer, the sensitivity as well as the detecting range of the devices can be tuned easily.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic sensing device and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20060002031A1InhibitionReduce noiseRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsHysteresisMagnetization
The present invention provides a magnetic sensing device capable of stably sensing a signal magnetic field with high sensitivity by suppressing occurrence of hysteresis to reduce 1 / f noise. A magnetic sensing device has a stacked body including a pinned layer having a magnetization direction pinned to a predetermined direction (Y direction), a free layer having a magnetization direction which changes according to an external magnetic field and, when the external magnetic field is zero, becomes parallel to the magnetization direction of the pinned layer, and an intermediate layer sandwiched between the pinned layer and the free layer. The thickness of the intermediate layer is set so that an exchange bias magnetic field becomes positive. Consequently, the magnetization directions are stabilized. When read current is passed in a state where an external magnetic field is applied in a direction orthogonal to the magnetization direction of the pinned layer, occurrence of hysteresis in the relation between a change in the external magnetic field and a resistance change can be suppressed. As a result, 1 / f noise is suppressed and a signal magnetic field can be stably sensed with high sensitivity.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Current-perpendicular-to-plane magnetoresistive sensor with free layer stabilized by in-stack orthogonal magnetic coupling
InactiveUS20050207070A1Reduce parasitic resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeCoupling
A magnetically-coupled structure has two ferromagnetic layers with their in-plane magnetization directions coupled orthogonally across an electrically-conducting spacer layer that induces the direct orthogonal magnetic coupling. The structure has application for in-stack biasing in a current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP) magnetoresistive sensor. One of the ferromagnetic layers of the structure is a biasing ferromagnetic layer and the other ferromagnetic layer is the sensor free layer. An antiferromagnetic layer exchange-couples the biasing layer to fix its moment parallel to the moment of the sensor pinned layer. This allows a single annealing step to be used to set the magnetization direction of the biasing and pinned layers. The electrically-conducting spacer layer, the biasing layer and the antiferromagnetic layer that exchange-couples the biasing layer may all extend beyond the edges of the sensor stack.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Novel abutted exchange bias design for sensor stabilization
InactiveUS20060198059A1Hard structureSuppresses side-lobesRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsIn planeOrbit
A hard bias (HB) structure for biasing a free layer in a MR sensor within a magnetic read head is comprised of a main biasing layer with a large negative magnetostriction (λS) value. Compressive stress in the device after lapping induces a strong in-plane anisotropy that effectively provides a longitudinal bias to stabilize the sensor. The main biasing layer is formed between two FM layers, and at least one AFM layer is disposed above the upper FM layer or below the lower FM layer. Additionally, there may be a Ta / Ni or Ta / NiFe seed layer as the bottom layer in the HB structure. Compared with a conventional abutted junction exchange bias design, the HB structure described herein results in higher output amplitude under similar asymmetry sigma and significantly decreases sidelobe occurrence. Furthermore, smaller MRWu with a similar track width is achieved since the main biasing layer acts as a side shield.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
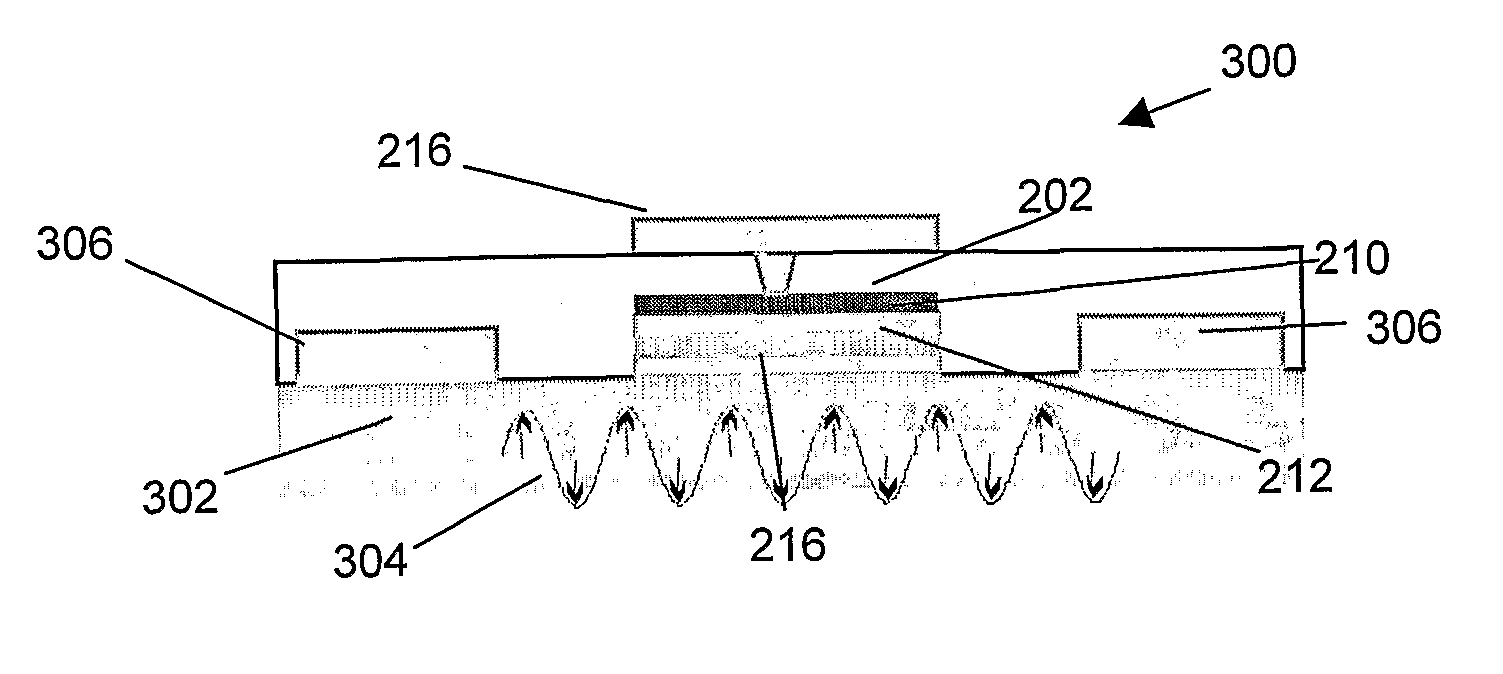
Self aligned magnetoresistive flux guide read head with exchange bias underneath free layer
A magnetoresistive sensor for use in a data storage device has a recessed sensing element (magnetic tunnel junction, CPP spin valve, etc.) with an exchange biased sensing ferromagnetic (free) layer, and a flux guide that magnetically connects the sensing element to a sensing surface of the sensor. The free layer is selectively exchange biased by a layer of exchange bias material placed under non-active regions of the free layer that lie outside the sensing element and flux guide track widths. The flux guide is provided by extending the free layer from a forward edge of the sensing element to the sensor surface. Advantageously, the sensing element and the flux guide have equal track width so that magnetic flux directed from the flux guide into the sensing element is not diluted with consequent loss of sensitivity.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Magnetic tunnel junction device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060176735A1Great magnetoresistanceThe implementation process is simpleMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageMagnetizationEvaporation
The MR ratio of an MTJ device is increased. A single-crystalline MgO (001) substrate 11 is prepared, and then an epitaxial Fe (001) lower electrode (first electrode) 17 with a thickness of 50 nm is grown on a MgO (001) seed layer 15 at room temperature. Annealing is then performed in ultrahigh vacuum (2×10−8 Pa) at 350° C. A 2-nm thick MgO (001) barrier layer 21 is epitaxially grown on the Fe (001) lower electrode (first electrode) 17 at room temperature, using electron beam evaporation of MgO. A Fe (001) upper electrode (second electrode) 23 with a thickness of 10 nm is then grown on the MgO (001) barrier layer 21 at room temperature, which is successively followed by the deposition of a Co layer 21 with a thickness of 10 nm on the Fe (001) upper electrode (second electrode) 23. The Co layer 21 is used for realizing an antiparallel magnetization alignment by enhancing an exchange bias magnetic field of the upper electrode 23. Thereafter, the above-prepared sample is subjected to microfabrication so as to obtain a Fe (001) / MgO (001) / Fe (001) MTJ device. The density of dislocation defects that exist at the interface between one of the first or the second Fe (001) layer and the single-crystalline MgO (001) layer is not more than 25 to 50 defects / μm.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
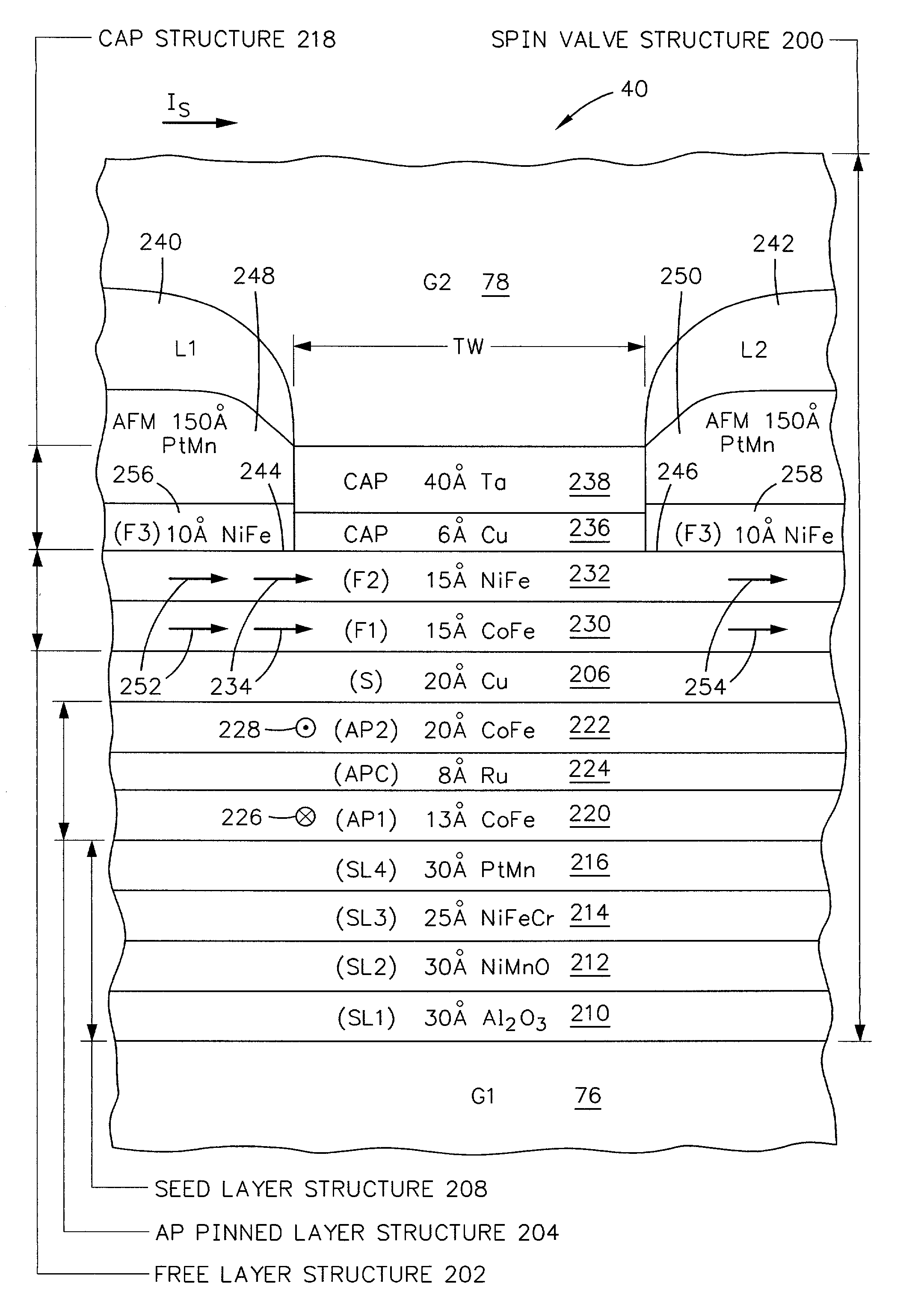
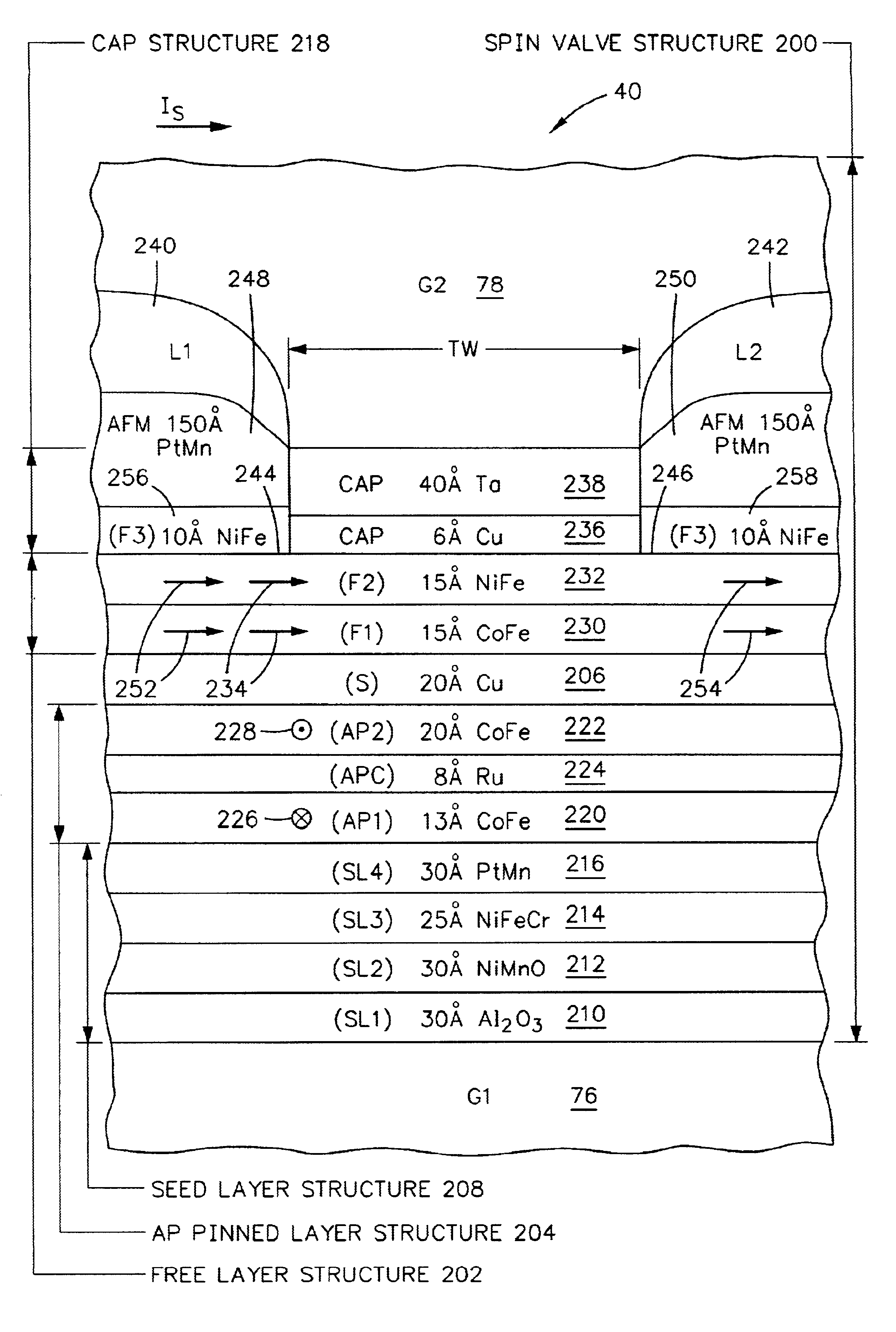
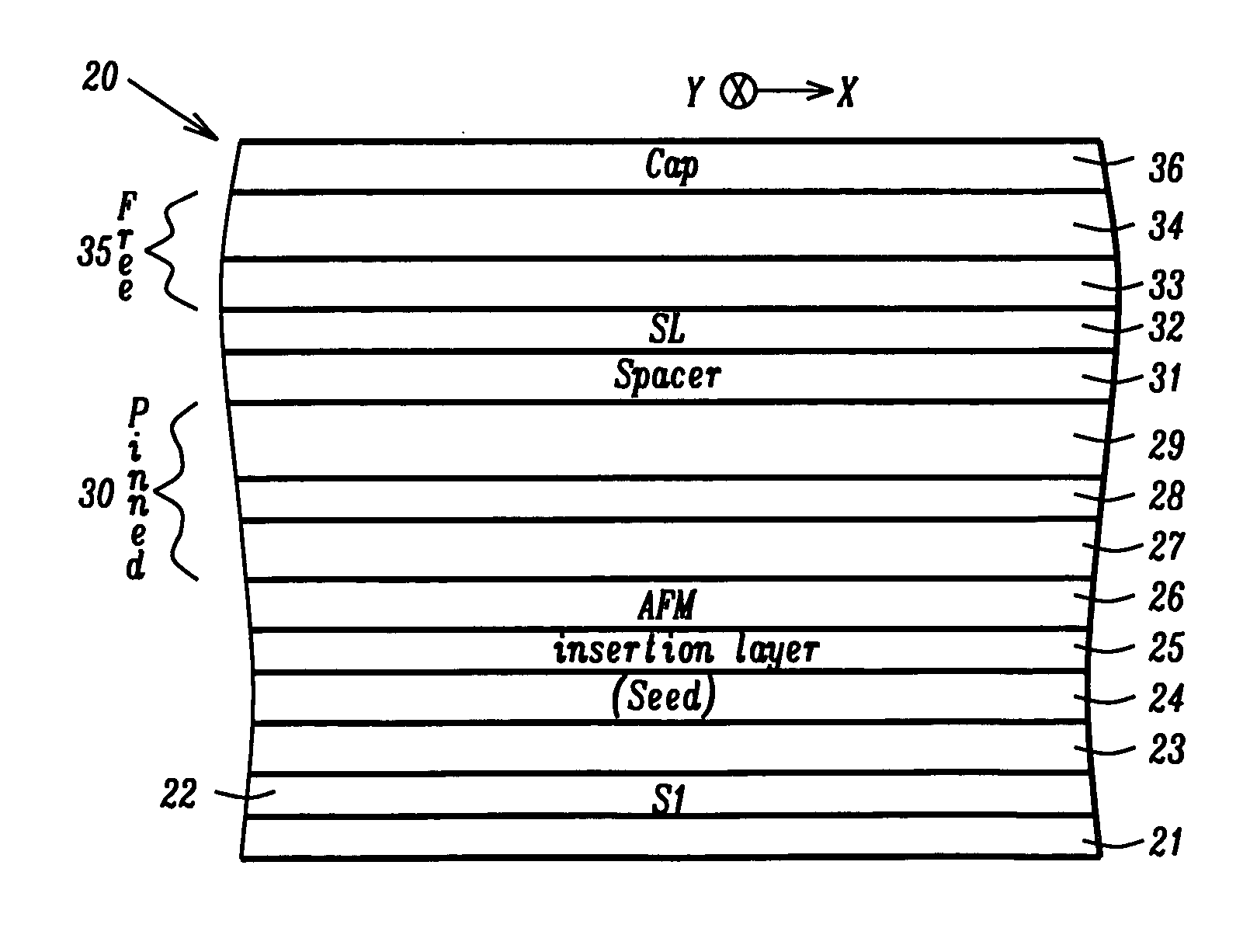
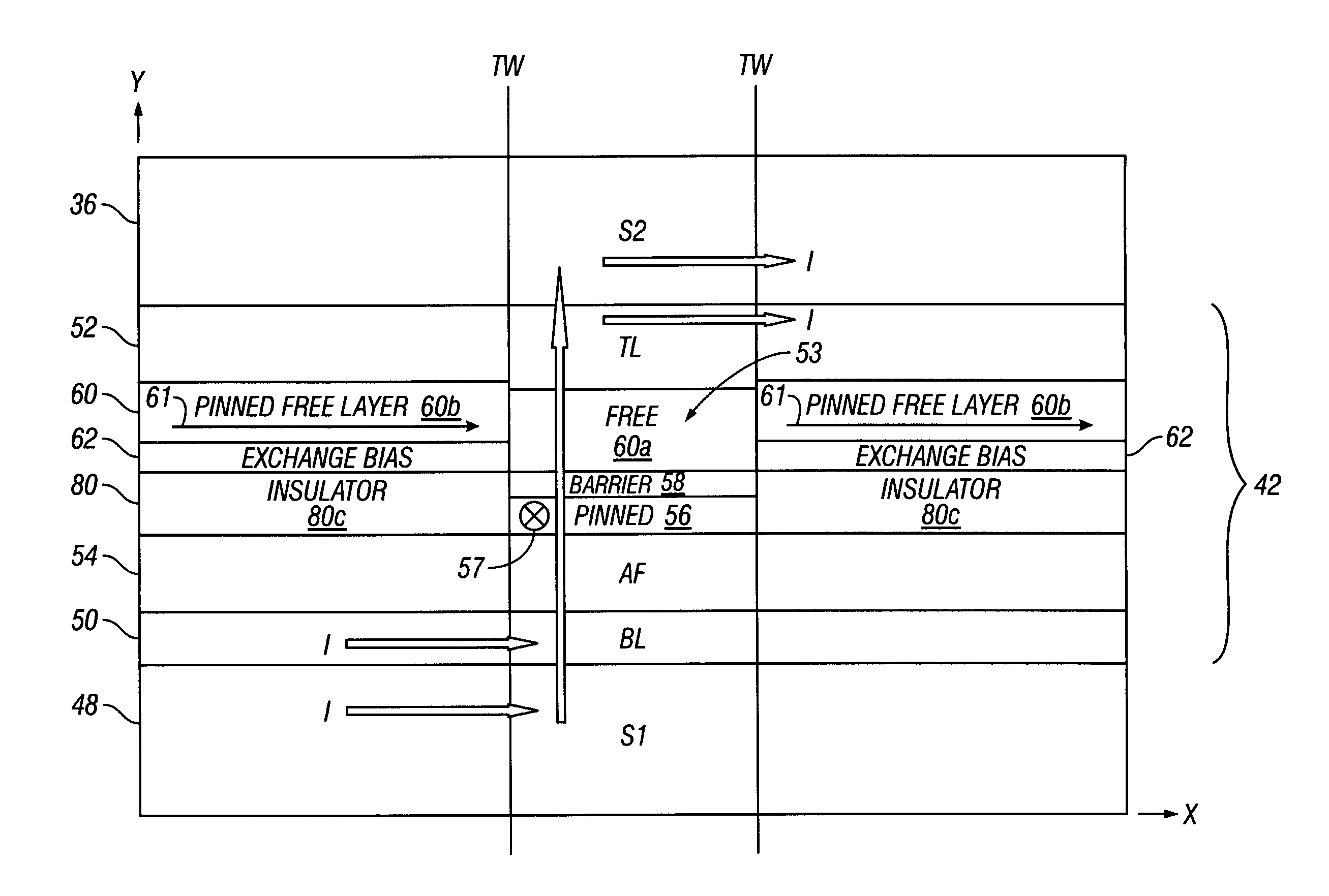
High resolution magnetic read head using top exchange biasing and/or lateral hand biasing of the free layer
ActiveUS8451567B2High resolutionImprove performanceElectrical transducersMagnetic measurementsExchange biasHigh resolution
A CPP (Current Perpendicular to Plane) MR (Magnetoresistive) read head and its method of fabrication includes a patterned CPP MR sensor stack having a SAF (Synthetic Antiferromagnetic) free layer structure that is longitudinally biased by the combination of an exchange biasing layer formed over the sensor stack and hard biasing layers that are formed adjacent to the patterned sides of the stack. The combination provides the stack with high resolution reading capabilities without the necessity for a narrow read gap formed by closely spaced top and bottom shields. Sixteen embodiments are described that provide different versions of the exchange biasing layer, different positions of the hard biasing layers and different patternings of the CPP MR sensor stack.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetic memory using single domain switching by direct current
InactiveUS20060028863A1Eliminate crosstalkMinimize magnetostatic interactionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageStatic random-access memoryMagnetic memory
A method for implementing miniaturization of magnetic random access memory (MRAM) and a magnetic memory using single domain switching by direct current are provided. The magnetic memory preferably includes a half-circle or U-shaped architecture with an exchange biasing pad, such as a FeMn exchange biasing pad that effectively generates a head-to-head magnetization configuration. The magnetic memory also includes nanometer scale notches in order to minimize magnetostatic interaction between a single domain memory element and the spin current sources and to effectively trap the magnetic domain wall. Reading the bit can be carried out by anisotropic magnetoresistance, or by other means of determining the magnetization orientation through resistance measurements, such as a spin valve or a magnetic tunneling junction.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Cross-track shielding in a GMR head
Owner:MAXTOR
Exchange coupling film capable of improving playback characteristics
InactiveUS6873500B2Improve wettabilityImprove smoothnessNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismExchange biasAtomic physics
A seed layer is formed containing Cr and an element X (wherein the element X is Fe, Ni, etc.) on a substrate layer formed from Ta, etc. At this time, the compositional ratio of the aforementioned Cr is specified to be 80 at % or more, and the seed layer is formed to have a film thickness of 20 Å or more, but 130 Å or less. According to this, the wettability of the seed layer surface can be improved remarkably compared to that heretofore attained, the unidirectional exchange bias magnetic field and rate of resistance change in the fixed magnetic layer can be increased, and it becomes possible to make the smoothness of the surface of each layer on the aforementioned seed layer excellent.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Double exchange bias field type spinning valve
InactiveCN101471420AWiden the high resistance areaImprove stabilityMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGiant magnetoresistanceHigh resistance
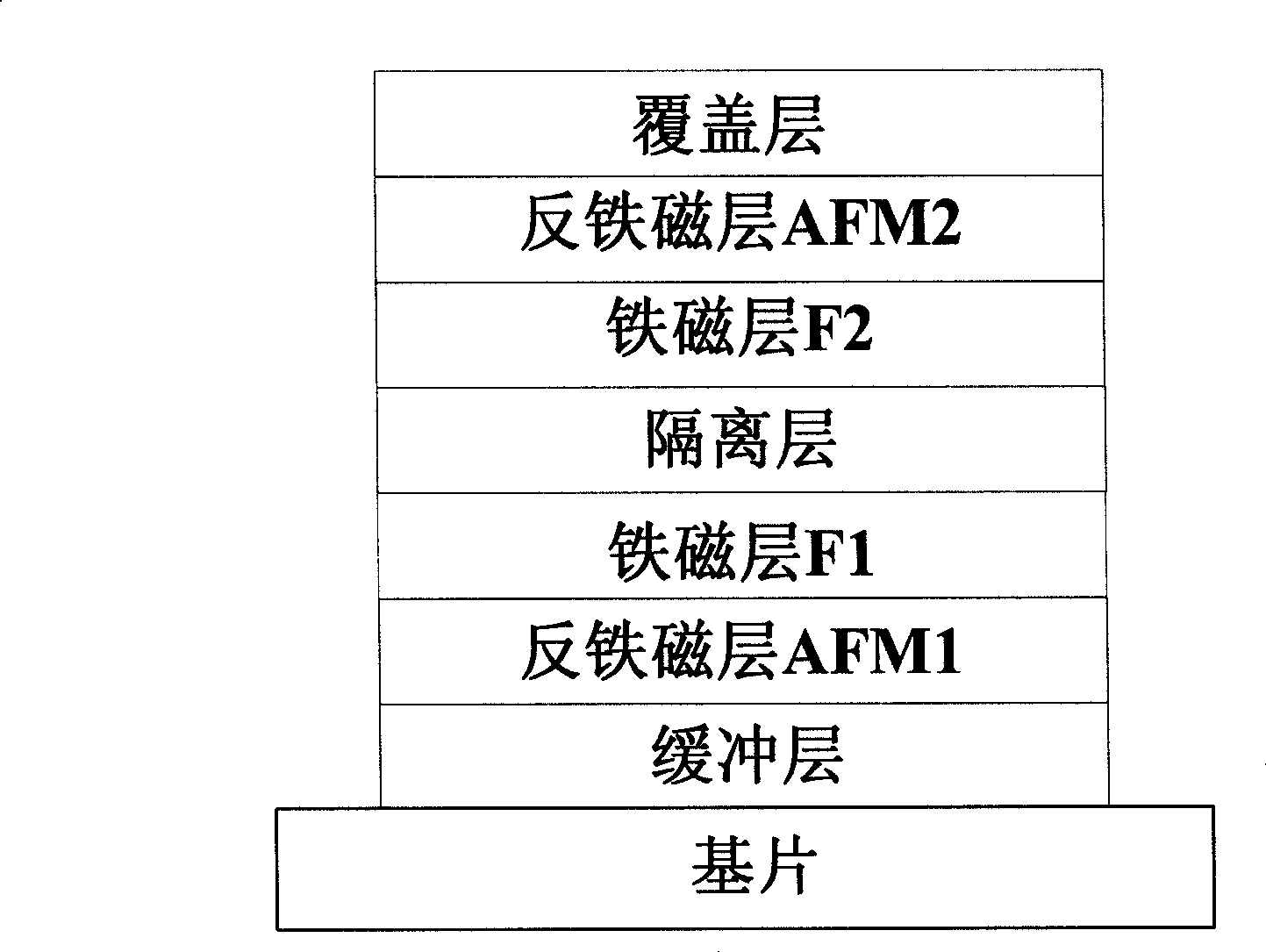
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials and devices and relates to a magnetic recording technology, in particular to an exchange bias field-type spin valve. The invention provides a double exchange bias field-type spin valve, which is composed of a substrate, a buffer layer, an antiferromagnetic layer AFM1, a ferromagnetic layer F1, a separator, a ferromagnetic layer F2, an antiferromagnetic layer AFM2 and a coating layer, wherein an exchange bias field Hex1 is generated between the antiferromagnetic layer AFM1 and the ferromagnetic layer F1 along the membrane surface; and an exchange bias filed Hex2 in the opposite direction to Hex1 is also generated between the antiferromagnetic layer AFM2 and the ferromagnetic layer F2 along the membrane surface. Due to the double exchange bias field, the exchange bias field range of the spin valve can be expanded at room temperature so as to widen the high-resistance region of the spin valve, thereby facilitating the improvement of the stability of the exchange bias field-type spin valve in information storage or other applications. In addition, the double exchange bias field-type spin valve can be fabricated at room temperature without high-temperature annealing, and has the advantages of good membrane stability and high giant magnetoresistance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Perpendicular magnetic recording media with laminated soft magnetic underlayer
InactiveUS20060093865A1Suppress magnetic domain noiseImprove write performanceRecord information storageMagnetic recordingNon magneticRecording layer
A recording medium including a perpendicular magnetic recording layer and a laminated SUL formed on a substrate is provided. The SUL includes an antiferromagnetic layer interposed between laminated structures including a magnetic layer, a non-magnetic layer and a magnetic layer. The layers may each have a thickness of 20 nm or less and the layers below the antiferromagnetic layer may be thinner than the layers on the antiferromagnetic layer. The laminated structures formed on and below the antiferromagnetic layer have unidirectional magnetic anisotropies set in the opposite radial direction to each other by an exchange bias. As a result, media magnetic domain noise can be diminished.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CoFe insertion for exchange bias and sensor improvement
ActiveUS7564658B2Raise the ratioEnhance TbNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSputter depositionExchange bias
A GMR spin value structure with improved performance and a method for making the same is disclosed. A key feature is the incorporation of a thin ferromagnetic insertion layer such as a 5 Angstrom thick CoFe layer between a NiCr seed layer and an IrMn AFM layer. Lowering the Ar flow rate to 10 sccm for the NiCr sputter deposition and raising the Ar flow rate to 100 sccm for the IrMn deposition enables the seed layer to be thinned to 25 Angstroms and the AFM layer to about 40 Angstroms. As a result, HEX between the AFM and pinned layers increases by up to 200 Oe while the Tb is maintained at or above 250° C. When the seed / CoFe / AFM configuration is used in a read head sensor, a higher GMR ratio is observed in addition to smaller free layer coercivity (HCF), interlayer coupling (HE), and HK values.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Self-rotation valve with vertical magnetic anisotropy
InactiveCN101320616AMagnetically anisotropicMeet application requirementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPolarizabilitySpin valve
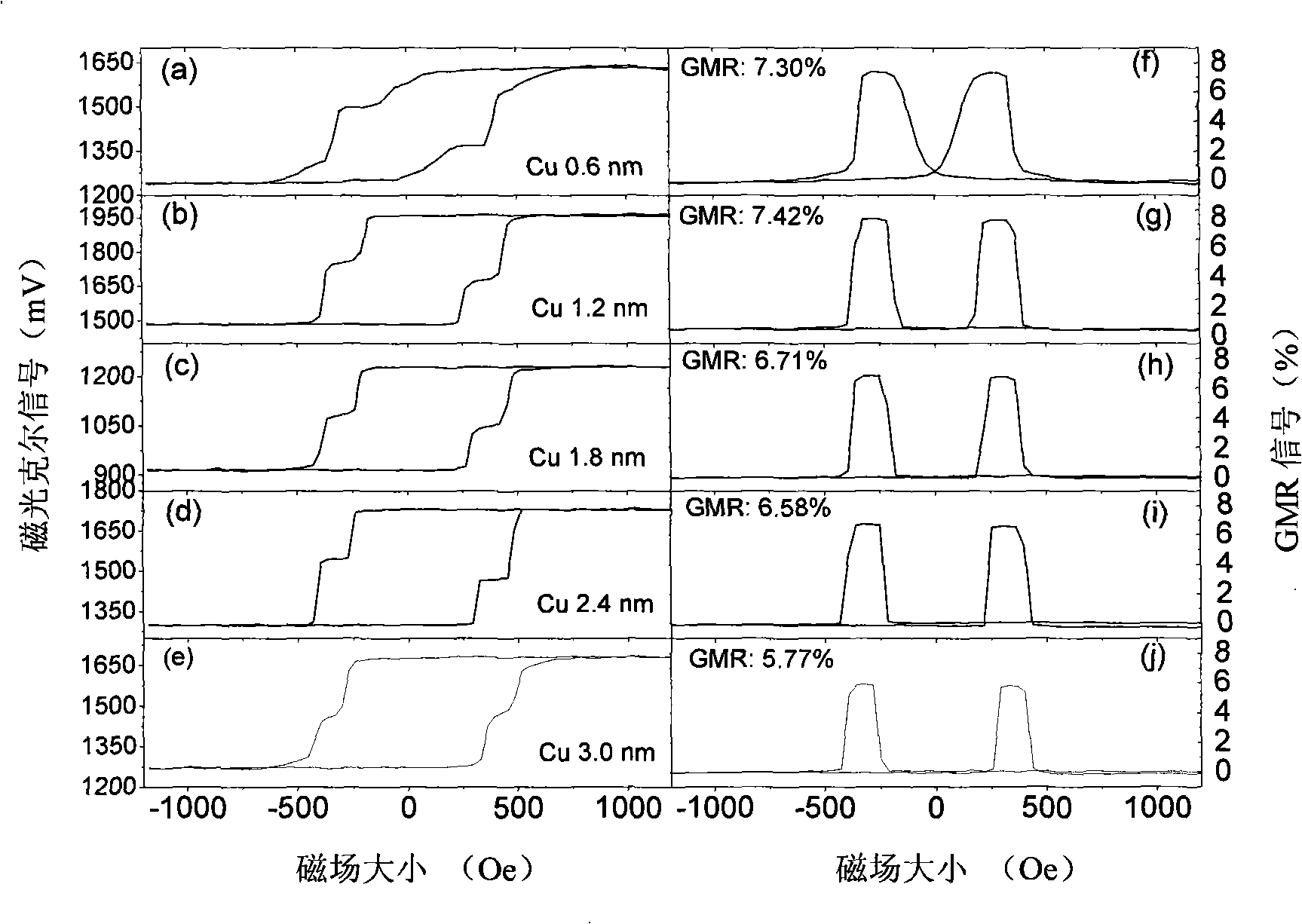
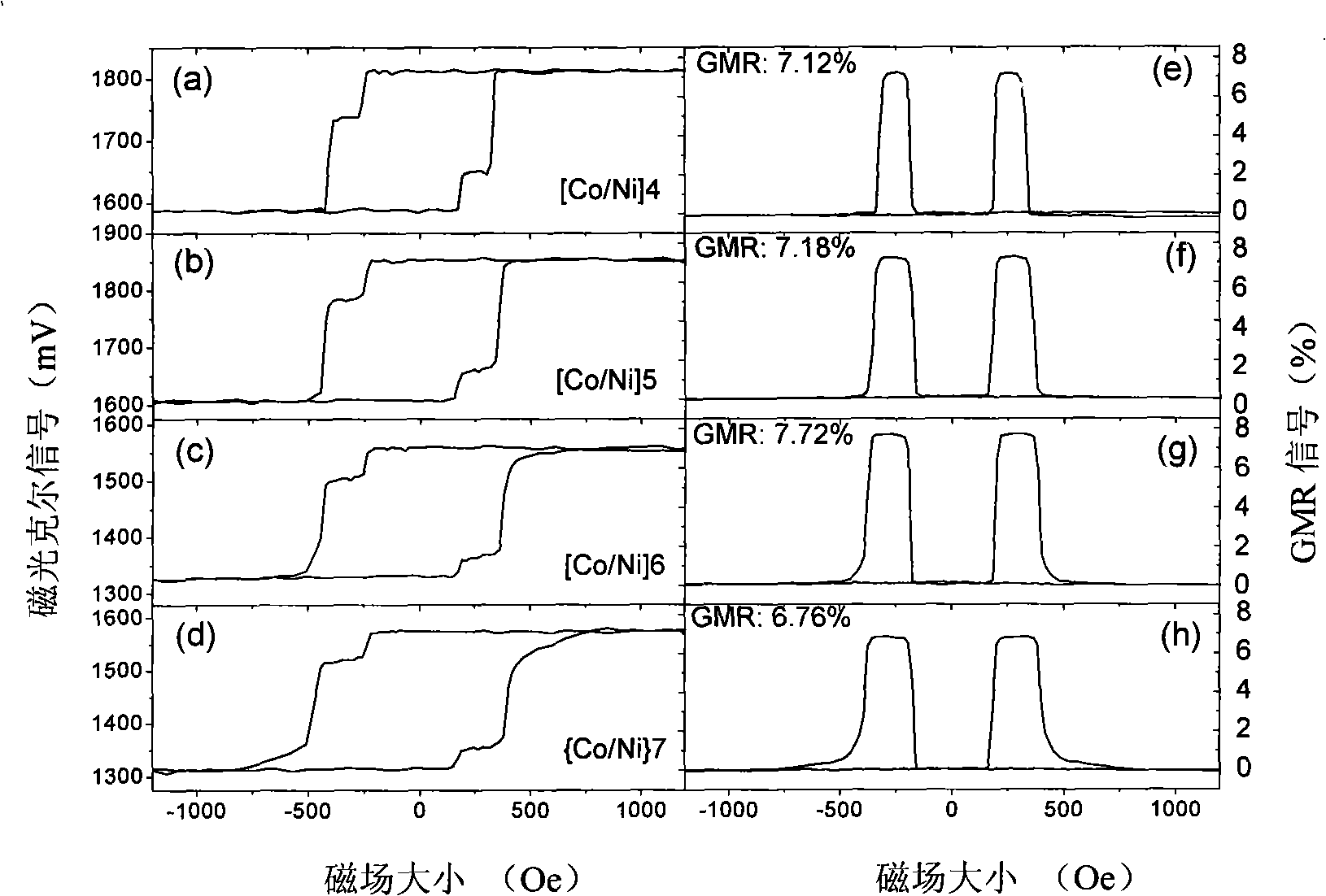
This invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic recording, specifically is a spin valve with vertical magnetic anisotropy. Ferromagnetic layers of upper, middle and lower adopt Co / Ni multi-layer film structure and are made by utilizing a method of magnetron sputtering to deposit under the normal temperature. The Co / Ni multi-layer film includes the feature of a preferred direction of magnetization vertical with a film surface because of larger surface and interface anisotropy, and the properties, such as the coefficient of the magnetic vertical anisotropy, the coercive force can be modulated through thicknesses, periodicity and buffer layer of layers of Co, Ni. In addition, Co and Ni are the magnetic materials and have bigger spin polarizability. A whole spin valve and a pseudo spin valve GMR signal can achieve 5 / 4 to 7.7%; and the exchange bias field of the whole spin valve can achieve more than 4500e, and the thermal stability can achieve 250 degrees centigrade. This invention has an important application value in the computer hard disk reading head, MRAM and the other spin electronic apparatuses.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
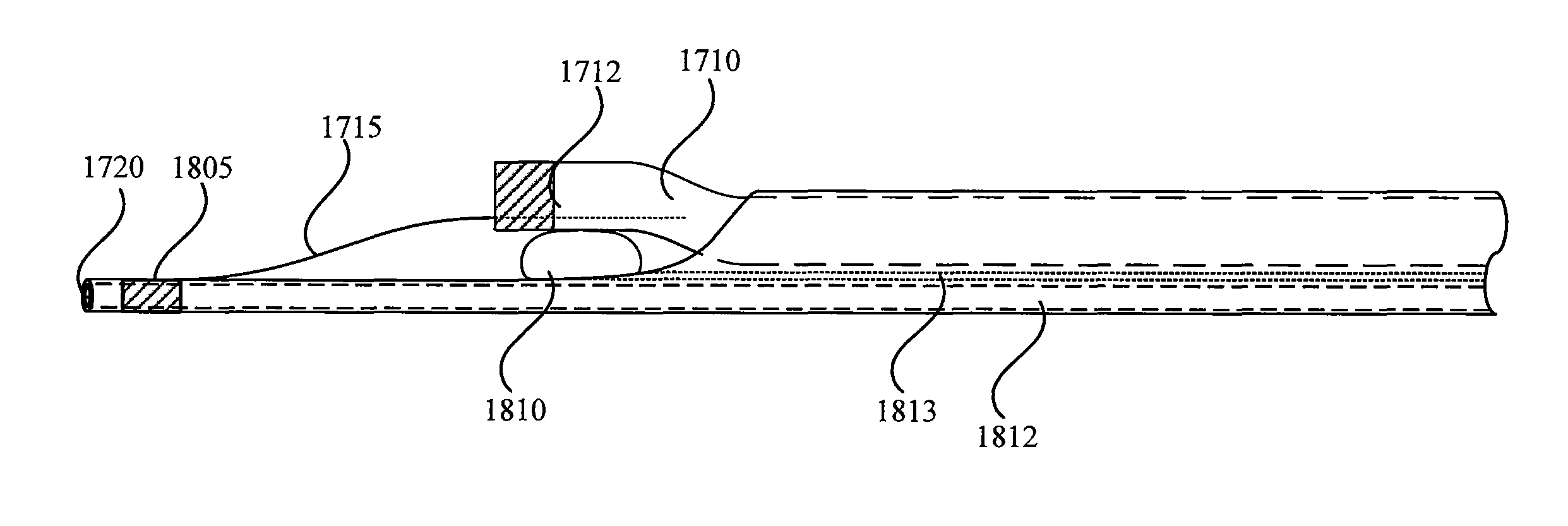
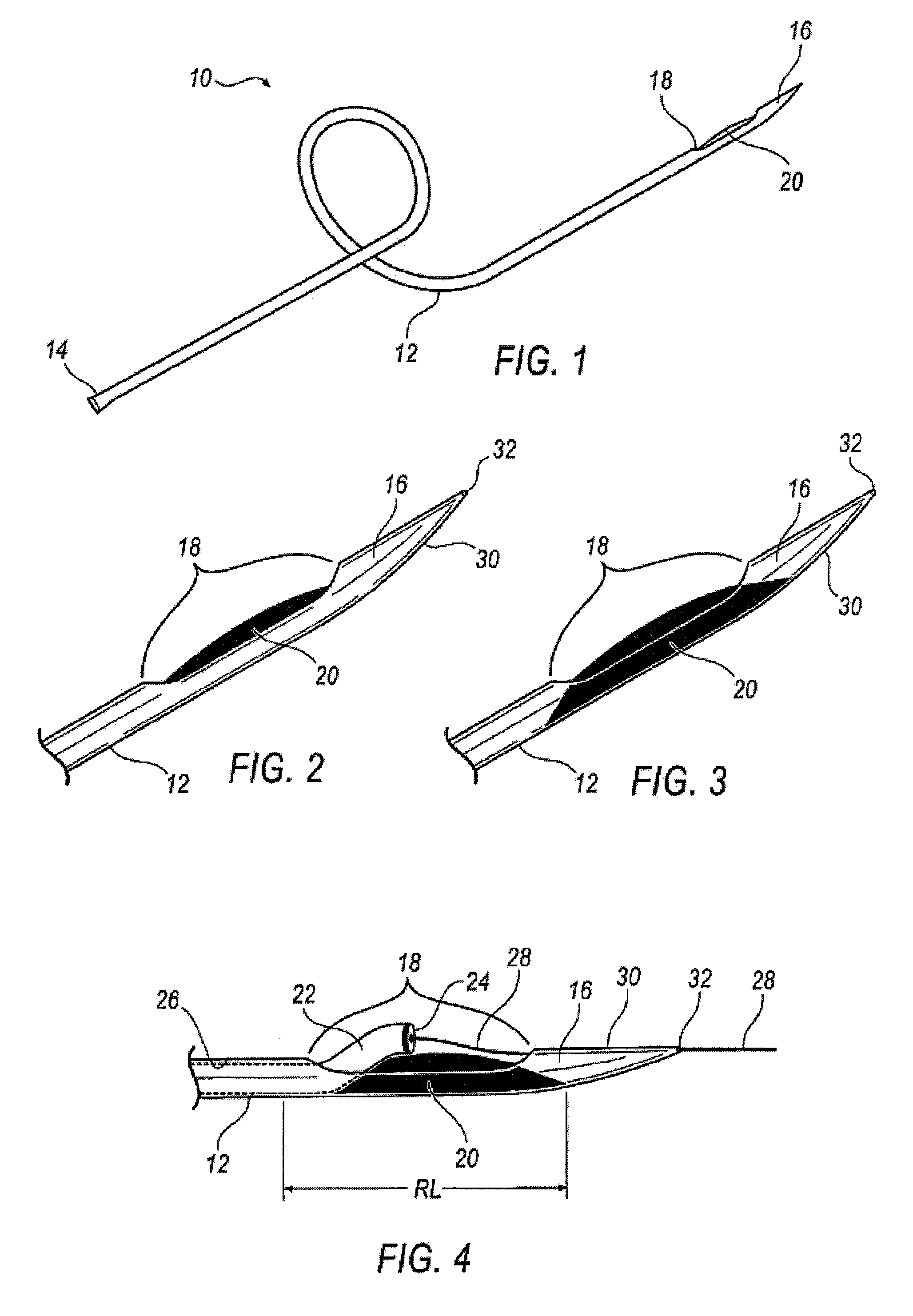
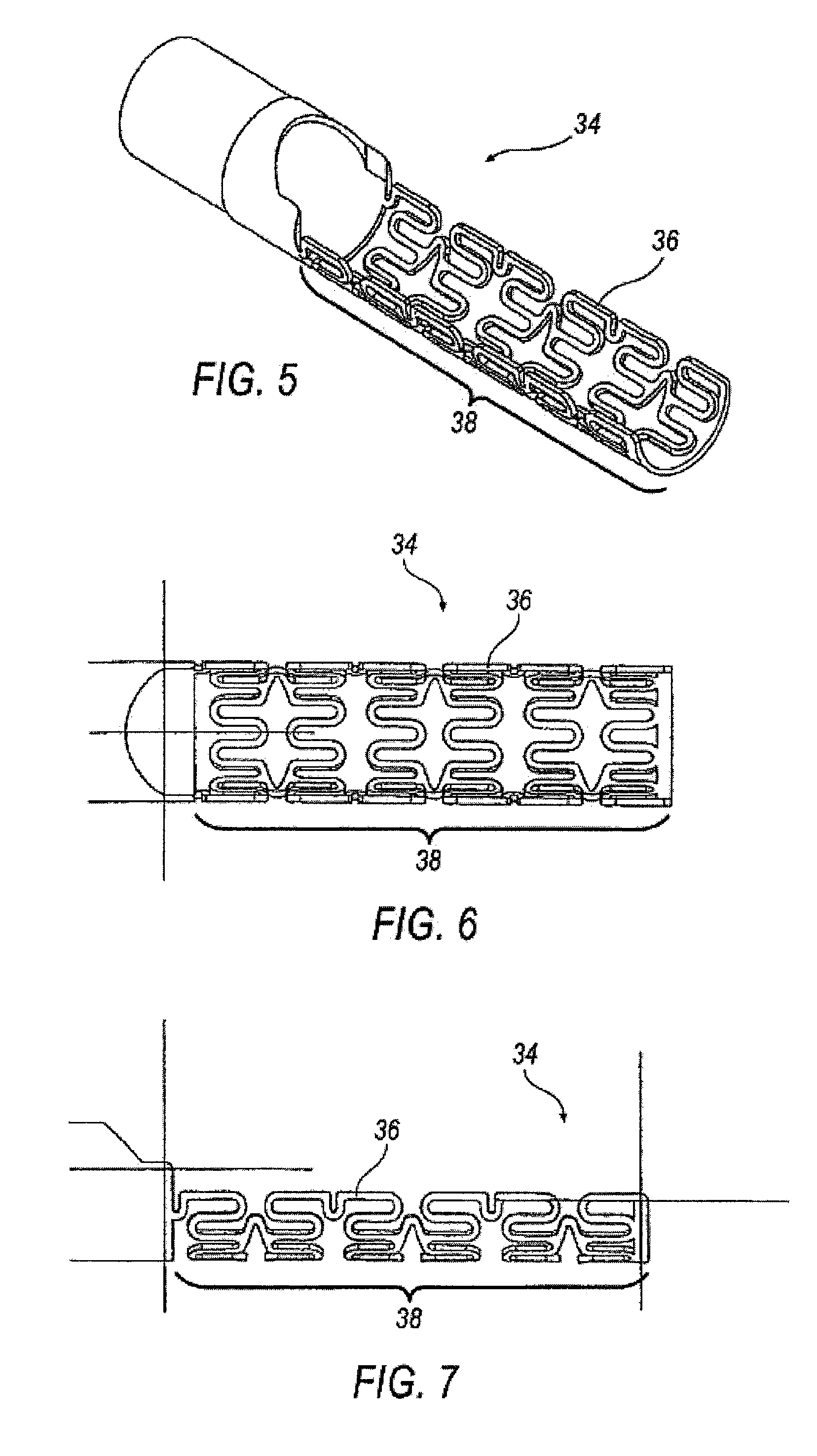
Rapid exchange bias laser catheter design
Embodiments of a balloon biasing laser catheter are provided. In some embodiments, the laser catheter may include a distal tip that extends from the distal end of the catheter from a point near the light guide aperture. The distal tip may be disposed at the periphery of the catheter. In some embodiments, a balloon may be disposed between the light guide aperture and the distal tip, such that the a light guide extending from the aperture may be disposed proximate with the distal tip having the balloon in between. A retaining wire may be coupled with the distal tip and slidably coupled with the light guide. The retaining wire may keep the light guide biased relatively parallel with the distal tip and / or the catheter body when the balloon is inflated. The light guide may include a guidewire lumen the extends to the distal end of the distal tip.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film and element, magnetoresistive sensor using same, magnetic apparatus, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7160572B2Reduced effectivenessPrevent oxidationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsNitrogen gasOxygen
In a spin tunnel magnetoresistive effect film in which a magnetic thin film to which an exchange bias is applied by exchange coupling via an anti-ferromagnetic thin film and a magnetic thin film that detects a magnetic field are laminated, a magnetic thin film or an anti-ferromagnetic thin film (PtMn, PdMn, NiMn) is laminated onto an underlayer (Ta, Zr, Hf), the surface roughness thereof being in the range from 0.1 to 5 Angstroms. A means used to control the surface roughness introduces into the film growing chamber oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, or a gas mixture thereof into a vacuum of 10−6 Torr to 10−9 Torr, reduces the substrate temperature to 0° C. or lower during film growth, or oxidizes an underlayer. The lower electrode layer material used is a film laminate of a high-permeability amorphous magnetic material and a non-magnetic metallic layer.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com