Patents
Literature
1064 results about "Casting defect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
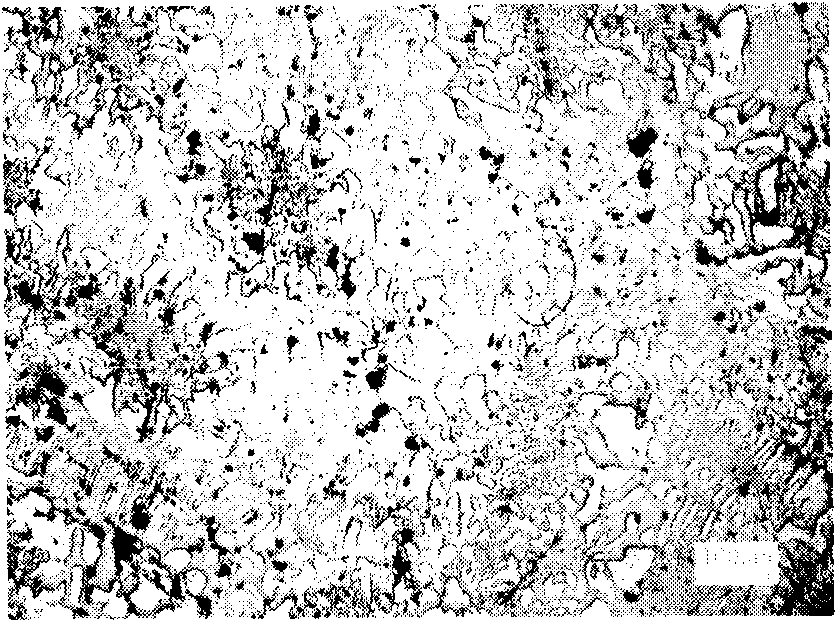
A casting defect is an undesired irregularity in a metal casting process. Some defects can be tolerated while others can be repaired, otherwise they must be eliminated. They are broken down into five main categories: gas porosity, shrinkage defects, mold material defects, pouring metal defects, and metallurgical defects.
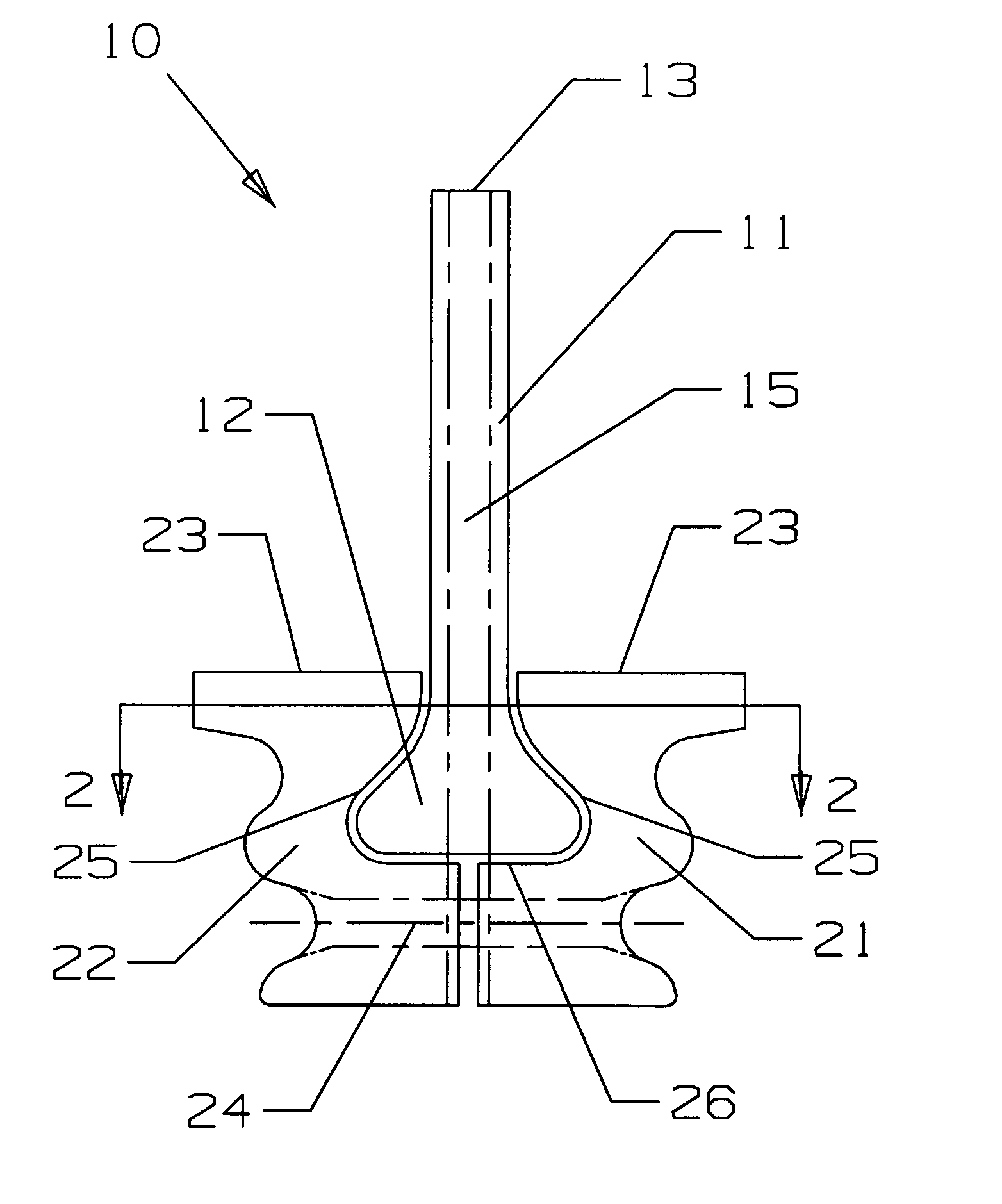
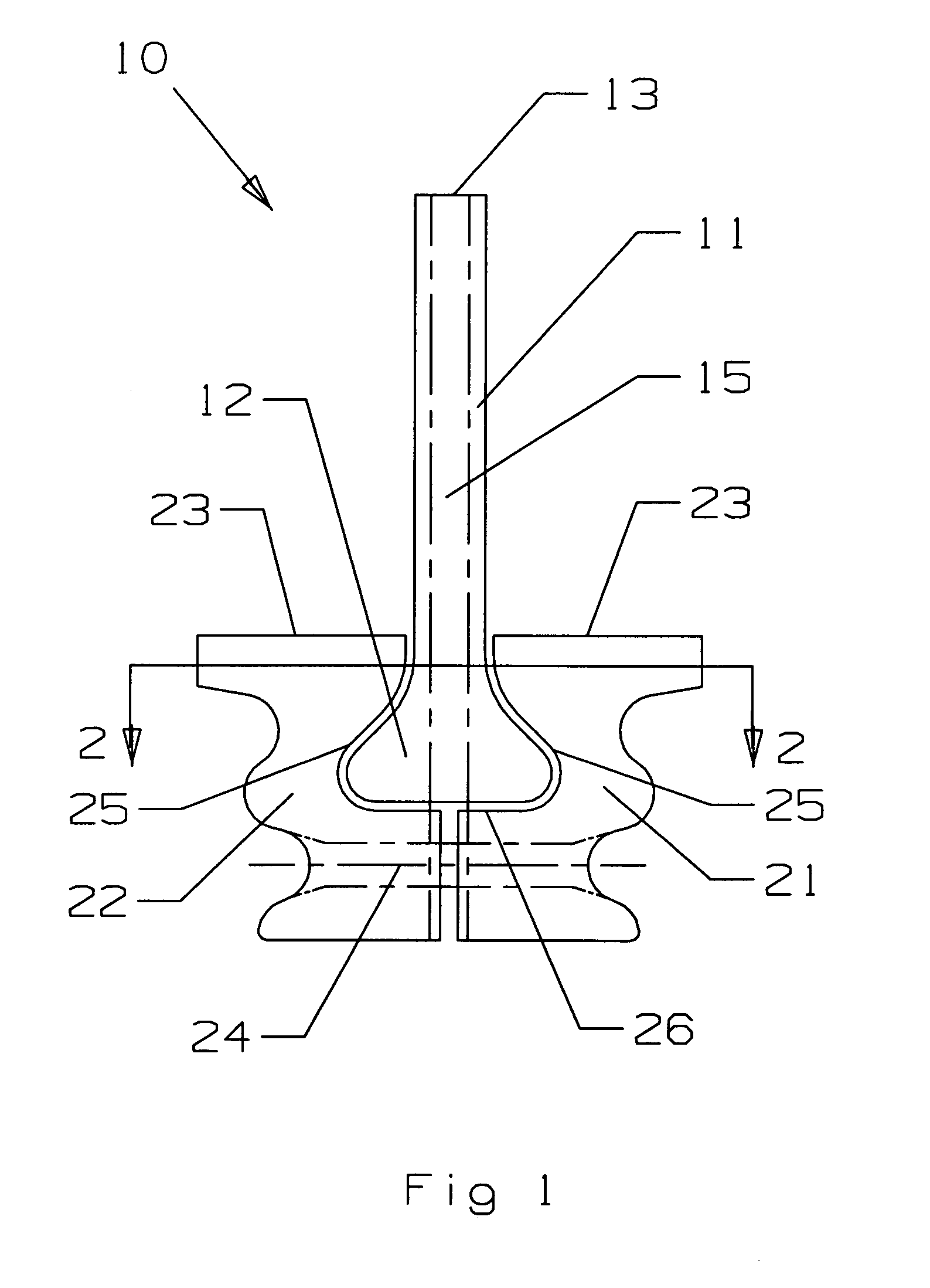
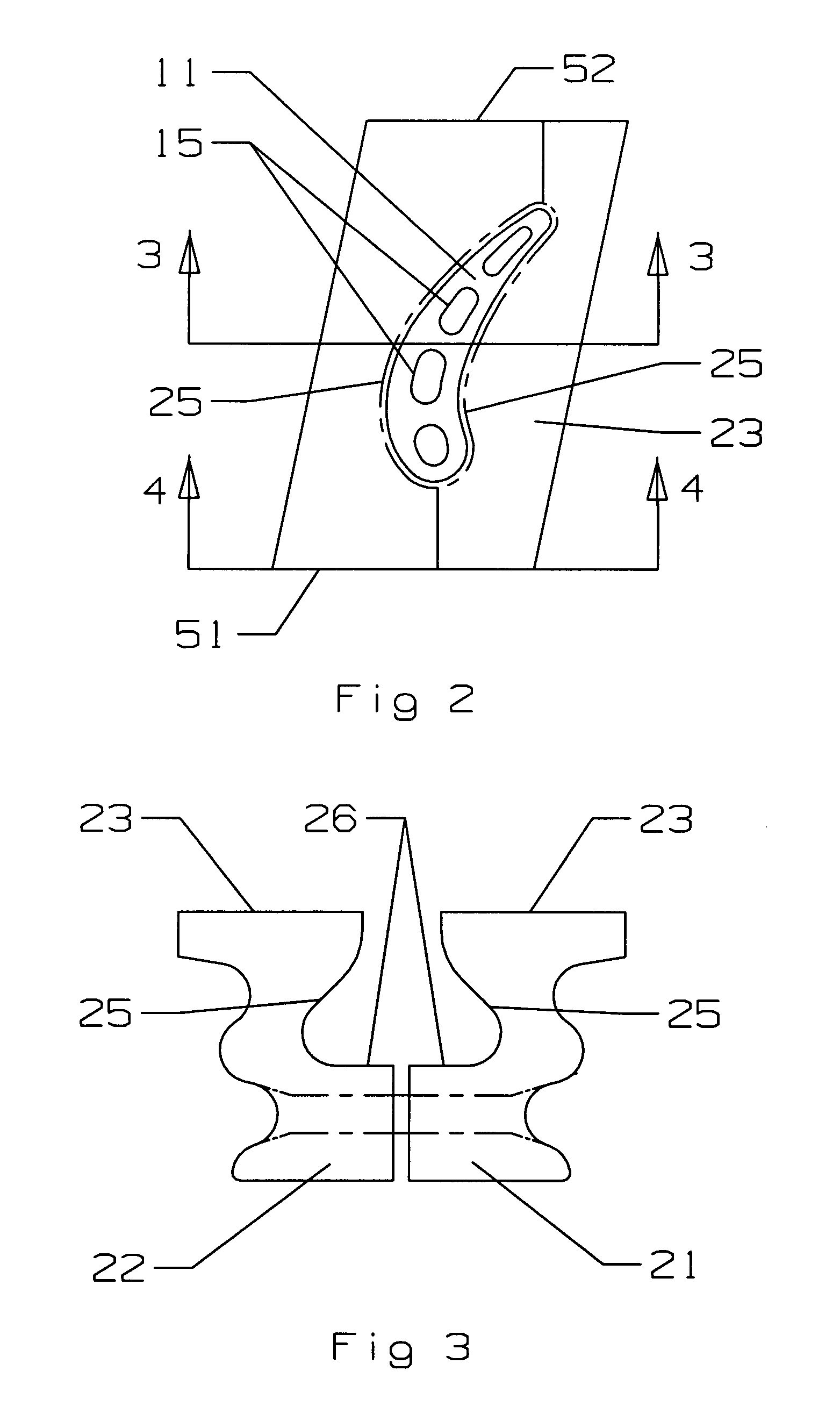
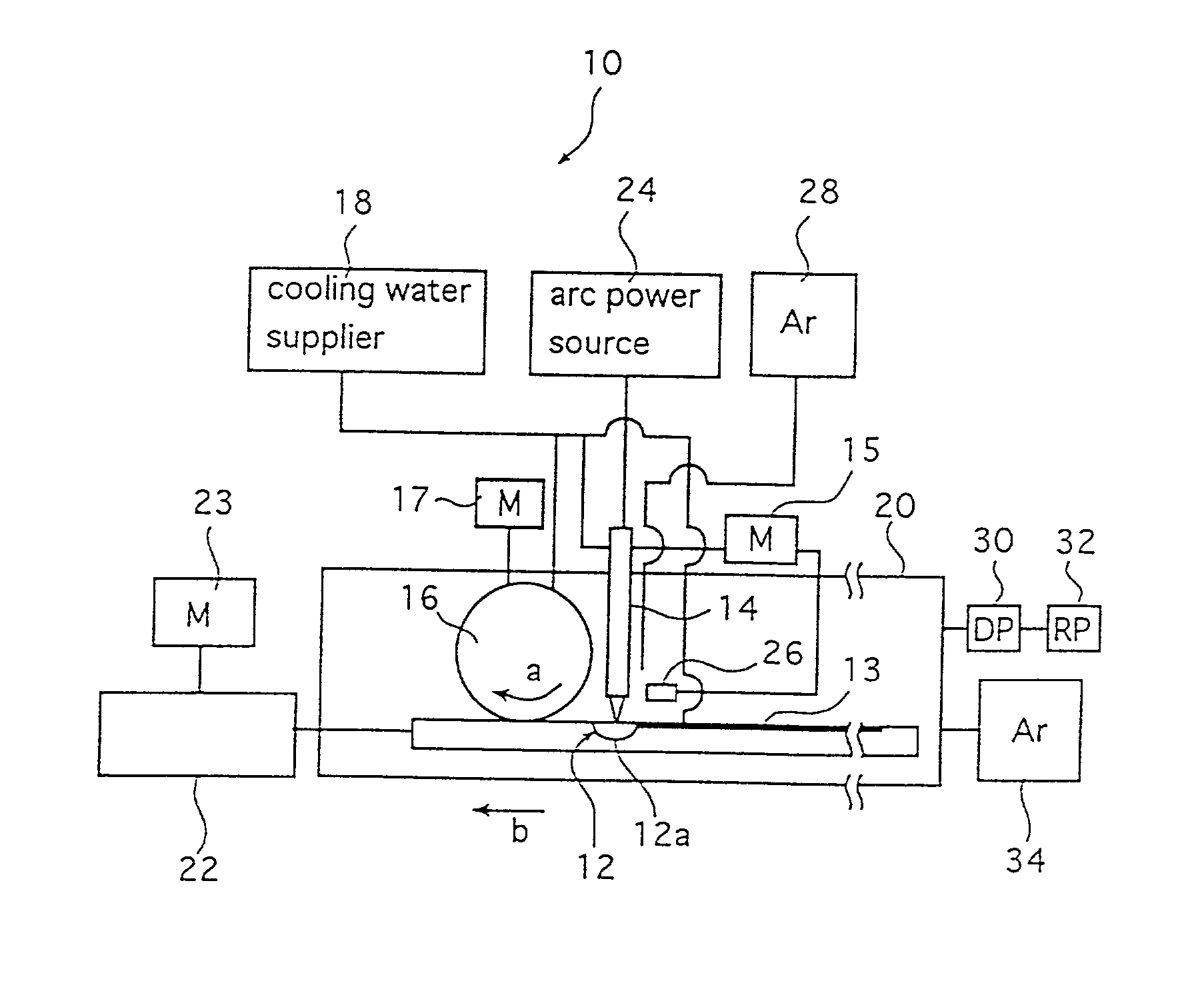
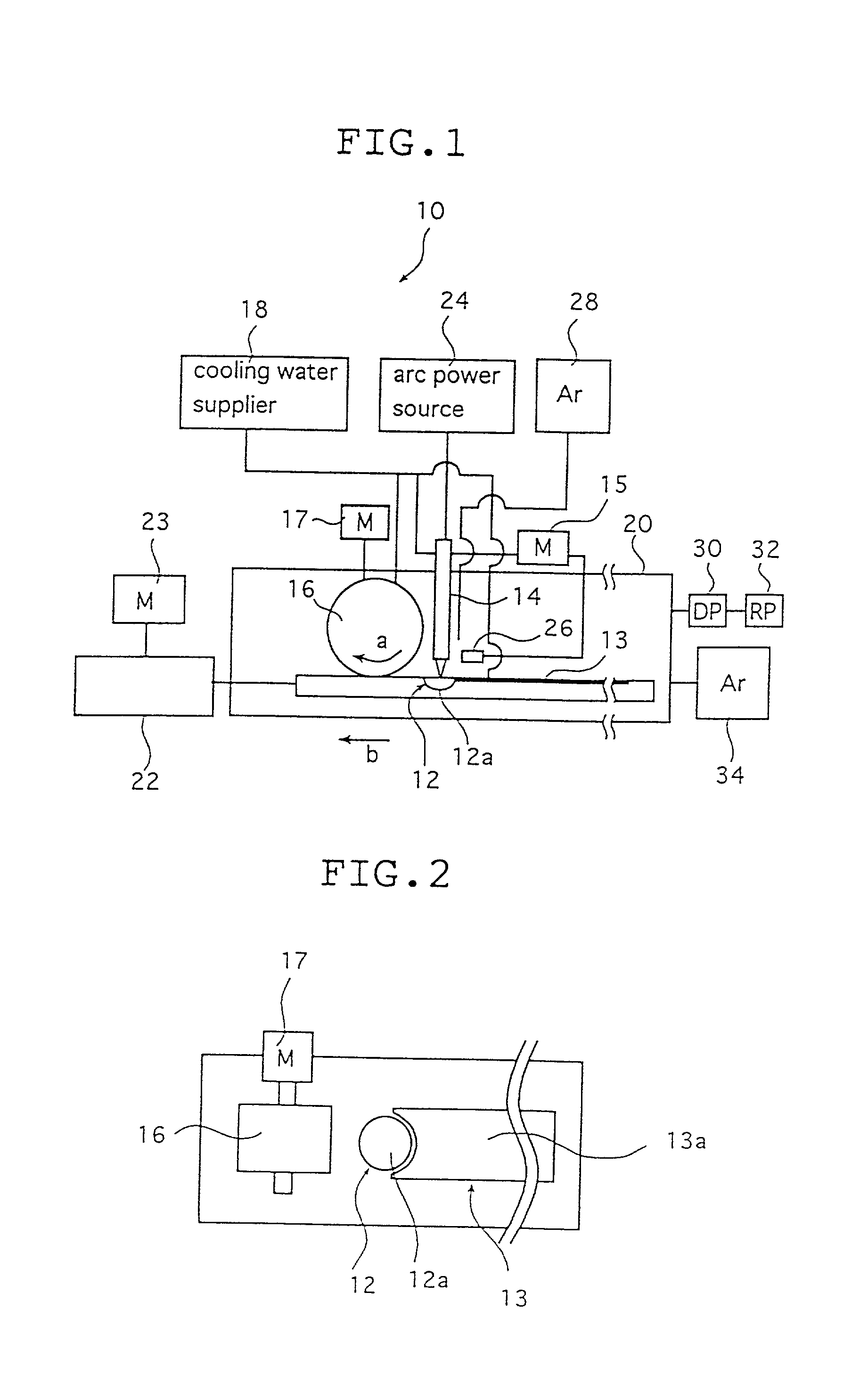
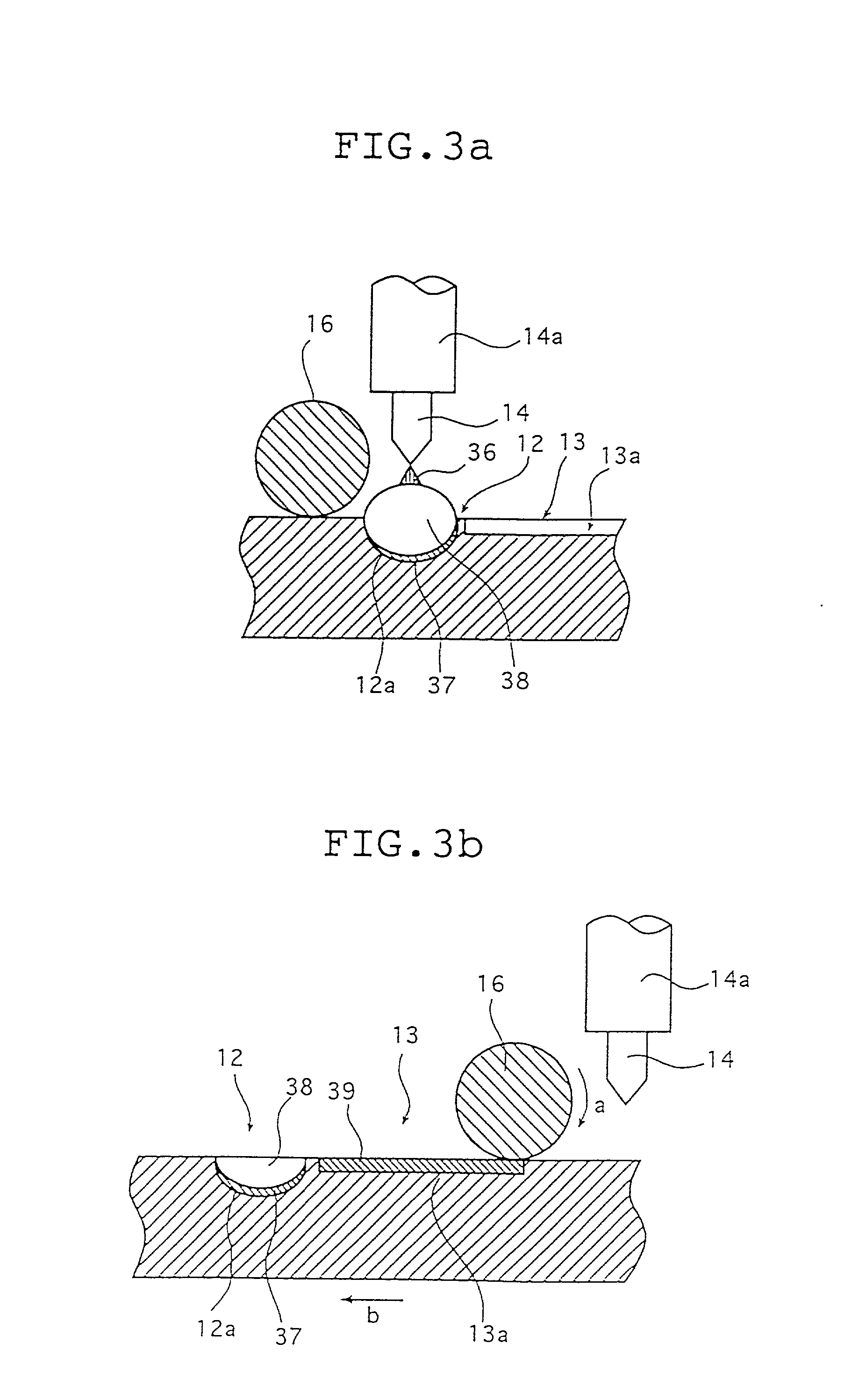
Integral turbine blade and platform
InactiveUS7972113B1Reduce defective castingIncrease mechanical fatiguePropellersRotary propellersTurbine bladeSingle crystal
A turbine blade for a gas turbine engine, in which the turbine blade includes an airfoil portion with a root having a dovetail shape, and two platform halves that include a dovetail shaped opening within the platform halves to secure the blade root within the platform halves when fastened together. The platform halves have an outer fir tree shaped surface so that the blade assembly can be inserted into a slot within a rotor disk. the blade is uncoupled from the platform in the invention so that the airfoil can be made from a single crystal material with low casting defects because the platform is not cast with the airfoil. the two platform halves include the openings with side walls that are curved to follow the contour of the airfoil root so that the airfoil is secured within the platform halves against all directions of movement. An annular groove extends around the platform opening to provide for a seal to produce a seal between the high pressure cooling air supply passage within the platform and the lower pressure hot gas flow passing through the blade.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
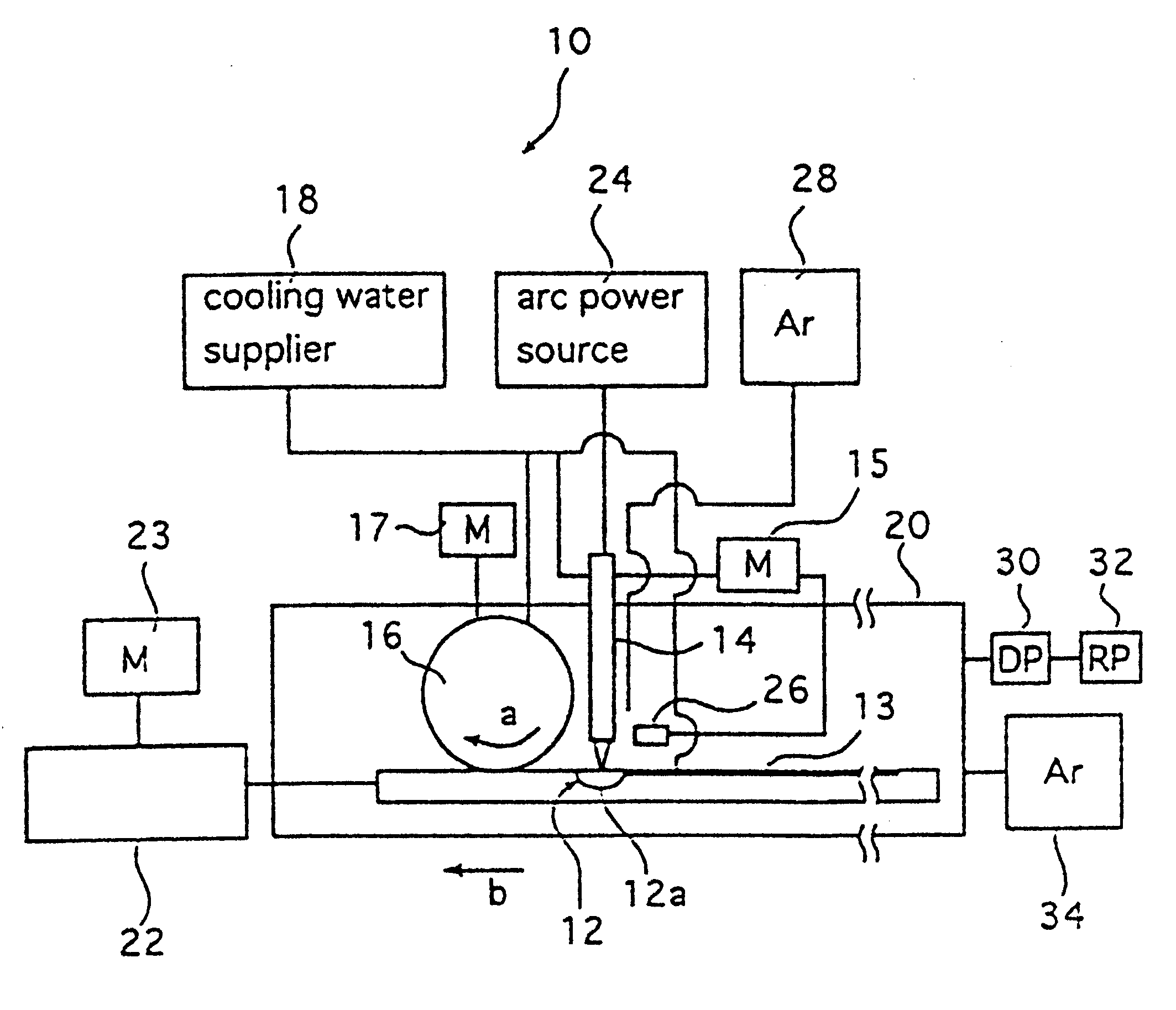
Process and apparatus for producing metallic glass
InactiveUS6427753B1Simple processGood strength performanceFoundry mouldsFoundry coresHigh energyHearth
A process and an apparatus for producing metallic glass which are capable of producing a bulk amorphous alloy of desired shape, in particular, a bulk amorphous alloy of desired final shape are provided. In the present invention, the molten metal at a temperature above the melting point is selectively cooled at a rate higher than the critical cooling rate, and the product comprises single amorphous phase which is free from the crystalline phase formed by the development of crystal nuclei through nonuniform nucleation. The present invention is capable of producing the bulk amorphous alloy which is free from casting defects such as cold shuts and which has excellent strength properties in a simple process at a high reproducibility. Accordingly, a bulk metallic glass of desired shape is produced by filling a metal material in a hearth; melting the metal material by using a high-energy heat source which is capable of melting the metal material; pressing the molten metal at a temperature above the melting point of the metal material to deform the molten metal into the desired shape by at least one of compressive stress and shear stress at a temperature above the melting point, while avoiding the surfaces of the molten metal cooled to a temperature below the melting point of the metal material from meeting with each other during the pressing; and cooling the molten metal at a cooling rate higher than the critical cooling rate of the metal material simultaneously with or after the deformation to produce the bulk metallic glass of desired form.
Owner:MAKABE GIKEN
Cast aluminum-silicon alloy for engine cylinder head and heat treatment process
InactiveCN102071341AImprove room temperature performanceHigh tensile strengthChemical compositionSilicon alloy
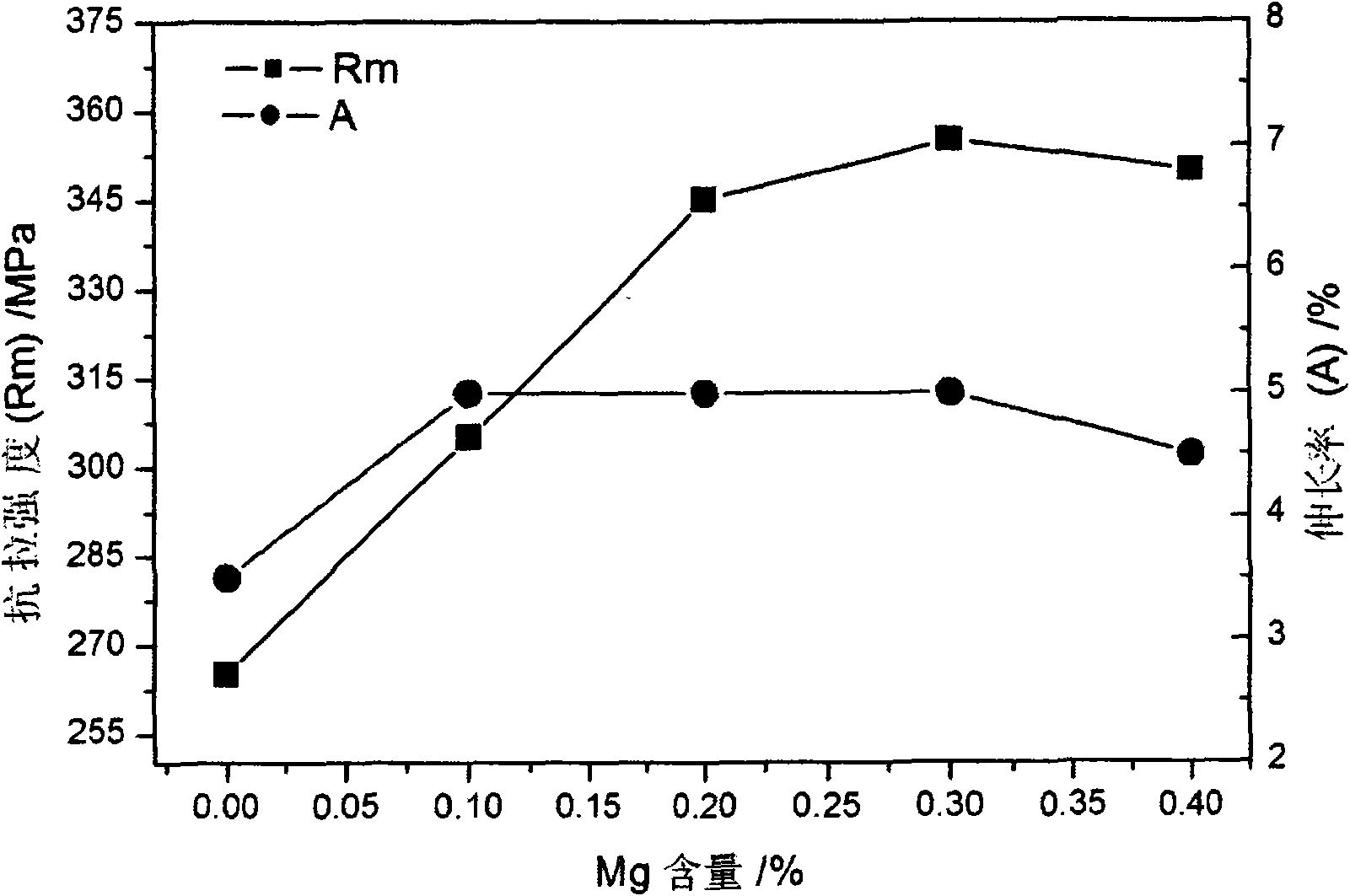
The invention relates to a cast aluminum-silicon alloy for an engine cylinder head and a heat treatment process. The alloy comprises the following chemical ingredients in percentage by weight: 5.0 to 7.0 percent of Si, 3.0 to 4.0 percent of Cu, 0.2 to 0.4 percent of Mg, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of Mn, 0.10 to 0.20 percent of Zr, 0.15 to 0.25 percent of Ti, 0.01 to 0.05 percent of B, 0.02 to 0.09 percent of Sr, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of rare earth (RE), less then 0.3 percent of Fe and the balance Al, wherein the rare earth (RE) adopts mixed rare earth. The heat treatment process comprises the following steps: carrying out primary solution at a temperature between 490 DEG C and 505 DEG C, and carrying out heat insulation for 4 to 6h; carrying out secondary solution at a temperature between 510 DEG C and 525 DEG C, carrying out heat insulation for 6 to 10h, and carrying out quenching by hot water of 60 to 80 DEG C; and carrying out aging treatment with parameters of the aging temperature being 155to 165 DEG C and the heat insulation time being 5 to 9h, and carrying out cooling in the air. All alloy elements of the cast aluminum-silicon alloy provided by the invention are reasonably matched, good mechanical performance is realized, at a normal temperature, the tensile strength reaches 325 to 355MPa, the tensile stretch is 2.5 to 5.5 percent, at a high temperature of 250 DEG C, the tensile strength reaches 240 to 270MPa, and the tensile stretch is 3.0 to 5.5 percent, after the heating processing technology, the heat resistance performance of the alloy is improved, and the casting defect is reduced.
Owner:NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP CORP
Horizontal continuous light alloy casting process and apparatus with cooperation of power ultrasound wave and low frequency electromagnetic wave
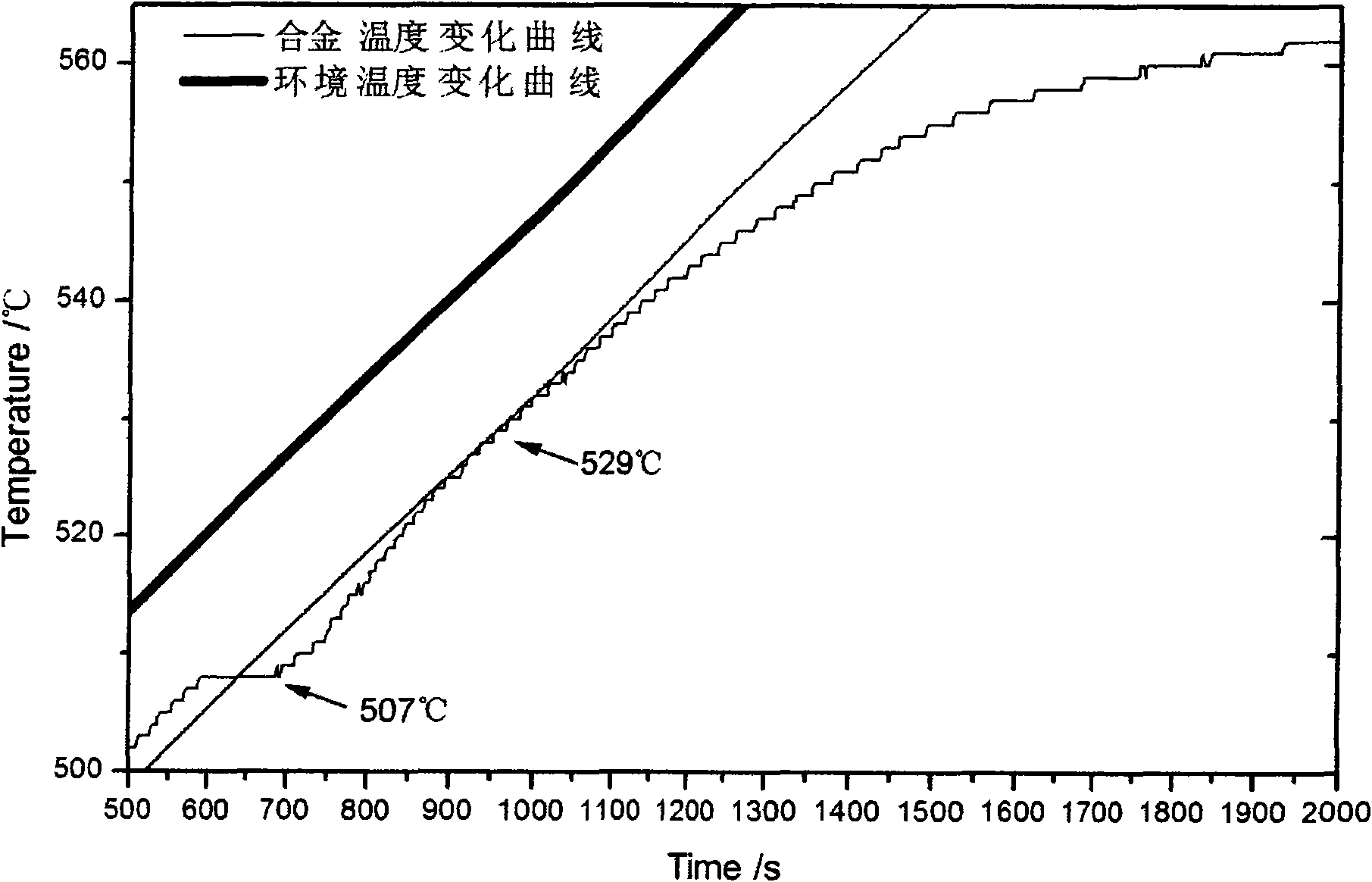
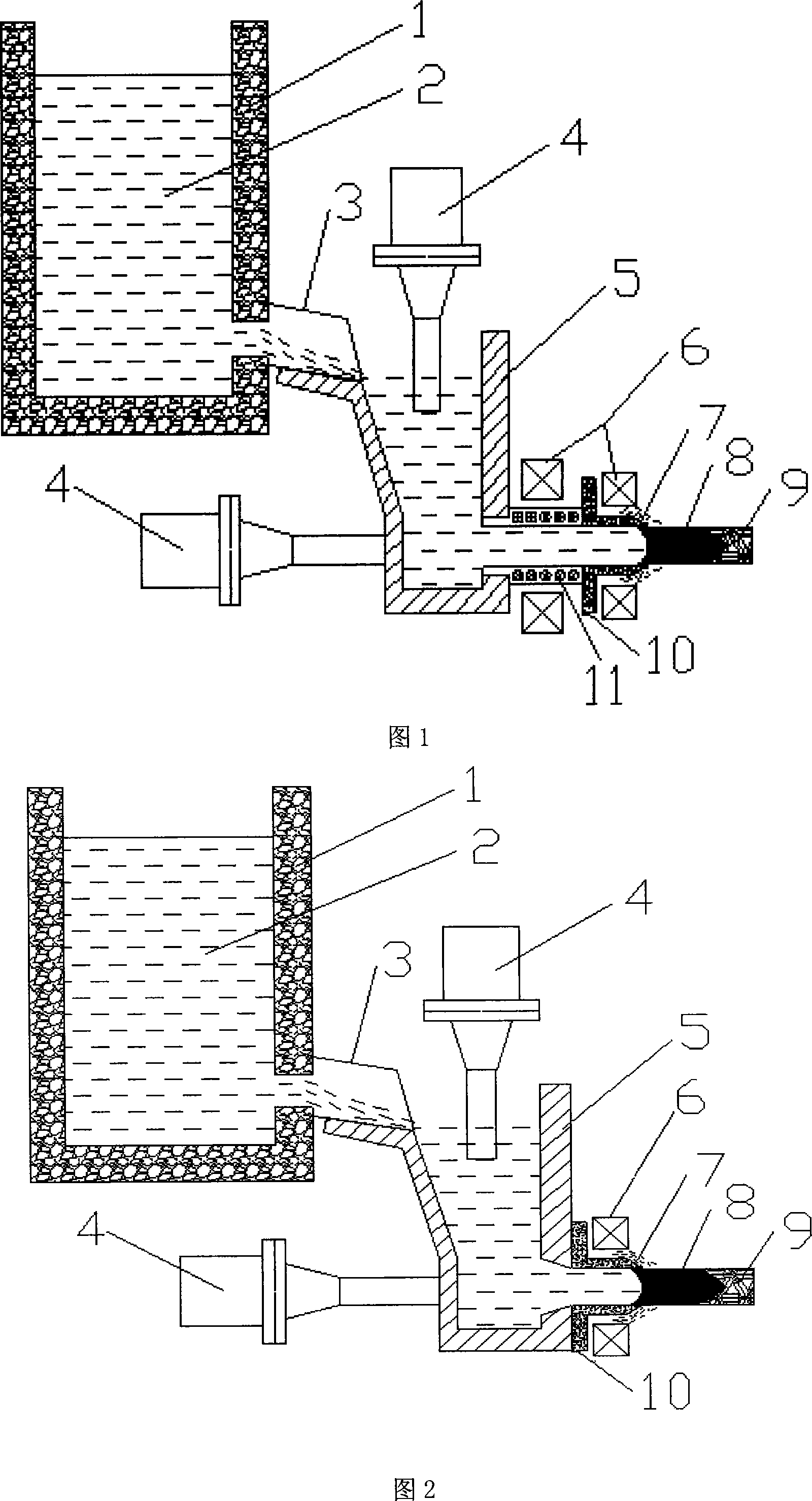
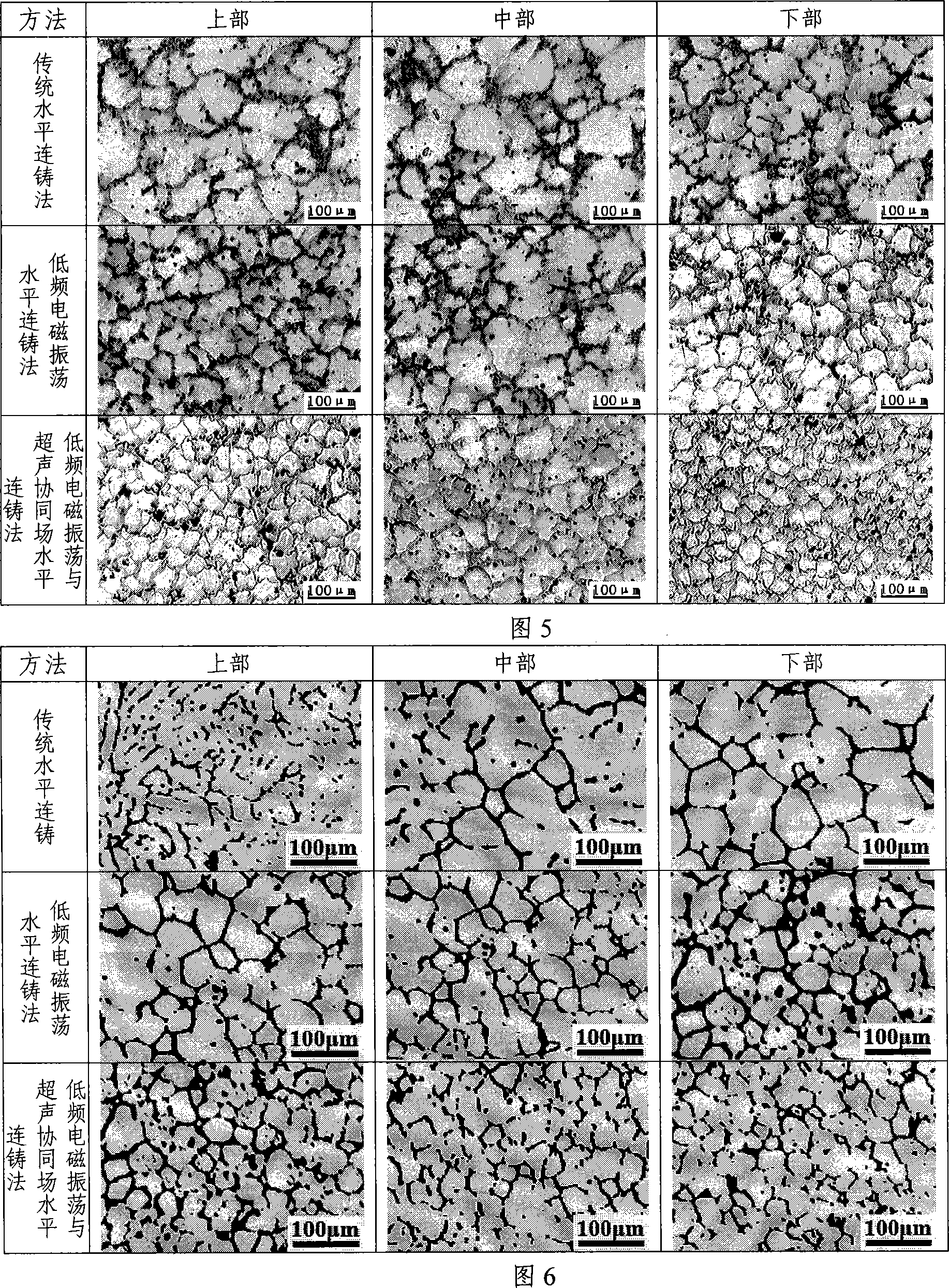
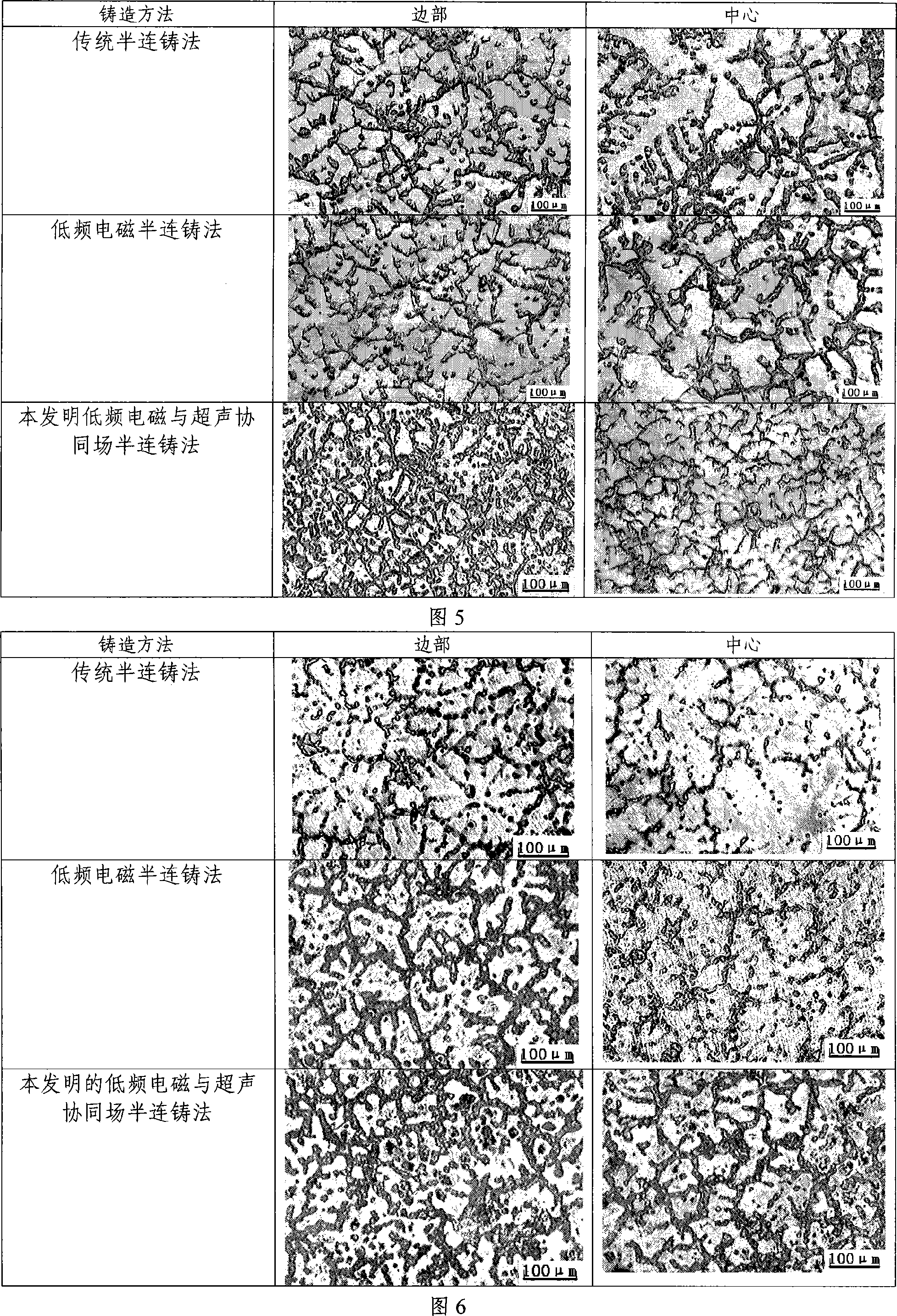
The present invention is horizontal continuous light alloy casting process and apparatus with cooperation of power ultrasonic wave and low frequency electromagnetic wave. In the continuous casting apparatus, one set of exciting windings is set inside the water jacket and applied with AC power to produce low frequency electromagnetic field, or one set of exciting windings is set inside the water jacket while one other set of exciting windings is set between the crystallizer and the pouring basket to produce electromagnetic fields. At the same time, one ultrasonic rod is inserted into the crystallizer to apply power ultrasonic field during casting. The present invention can reduce the temperature gradient in casting blank solidification, alter liquid hole shape, raise the homogeneity of the casting blank and raise casting blank quality.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Process and apparatus for producing metallic glass
InactiveUS20020100573A1Simple processGood strength performanceFoundry mouldsFoundry coresHigh energyAlloy
A process and an apparatus for producing metallic glass which are capable of producing a bulk amorphous alloy of desired shape, in particular, a bulk amorphous alloy of desired final shape are provided. In the present invention, the molten metal at a temperature above the melting point is selectively cooled at a rate higher than the critical cooling rate, and the product comprises single amorphous phase which is free from the crystalline phase formed by the development of crystal nuclei through nonuniform nucleation. The present invention is capable of producing the bulk amorphous alloy which is free from casting defects such as cold shuts and which has excellent strength properties in a simple process at a high reproducibility. Accordingly, a bulk metallic glass of desired shape is produced by filling a metal material in a hearth; melting the metal material by using a high-energy heat source which is capable of melting the metal material; pressing the molten metal at a temperature above the melting point of the metal material to deform the molten metal into the desired shape by at least one of compressive stress and shear stress at a temperature above the melting point, while avoiding the surfaces of the molten metal cooled to a temperature below the melting point of the metal material from meeting with each other during the pressing; and cooling the molten metal at a cooling rate higher than the critical cooling rate of the metal material simultaneously with or after the deformation to produce the bulk metallic glass of desired form.
Owner:MAKABE GIKEN
Low pressure casting process for aluminum alloy cylinder part
The invention discloses a low pressure casting process for an aluminum alloy cylinder part. The aluminum alloy used by the method comprises the following materials in percentage by mass: 6.0 to 7.0 percent of Si, 0.3 to 0.5 percent of Mg, 0.1 to 0.2 percent of Ti, 0.05 to 0.15 percent of Fe and the balance of Al. After melting, thining, modification, and refining, the materials are subjected to low pressure casting and pouring; and after low pressure casting process of liquid lifting, filling, pressure maintaining and pressure releasing, the materials form a cast in a die cavity; and after a cast blank is subjected to solution treatment, and heat treatment of incomplete artificial aging, the cast has the advantages that: the texture is compact, casting defects such as pores, shrinkage porosity, shrinkage cavity, slag inclusion, and the like are avoided, the quality of the cast is improved; meanwhile, the working allowance of the cast is less, so the material utilization is improved and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:王宏波
Method of producing amorphous alloy excellent in flexural strength and impact strength
A molten alloy was pressure-solidified under a pressure exceeding one atmospheric pressure to eliminate casting defects. The molten alloy was solidified by applying a cooling rate difference to the surface and the interior of the molten alloy to allow a compressive stress layer to remain on the surface of the amorphous alloy ingot and a tensile stress layer in the interior portion. Thus, a amorphous alloy sheet having a thickness of 1 mm or more and excellent in bending strength and impact strength is obtained.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Vertical semi-continuous light alloy ingot casting process and apparatus with cooperation of power ultrasound wave and low frequency electromagnetic wave
InactiveCN101020229AReduced lateral temperature gradientImprove uniformityElectromagnetic fieldIngot casting
The present invention is vertical semi-continuous light alloy casting process and apparatus with cooperation of power ultrasonic field and low frequency electromagnetic field. During casting, one low frequency electromagnetic field acting on the surface of metal molt and one power ultrasonic field acting on the crystallizer axis part are applied simultaneously. The present invention can reduce the transverse temperature gradient in casting blank solidification, alter liquid hole shape, raise the homogeneity of the casting blank and raise casting blank quality.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Copper base alloy, and cast ingot and parts to be contacted with liquid
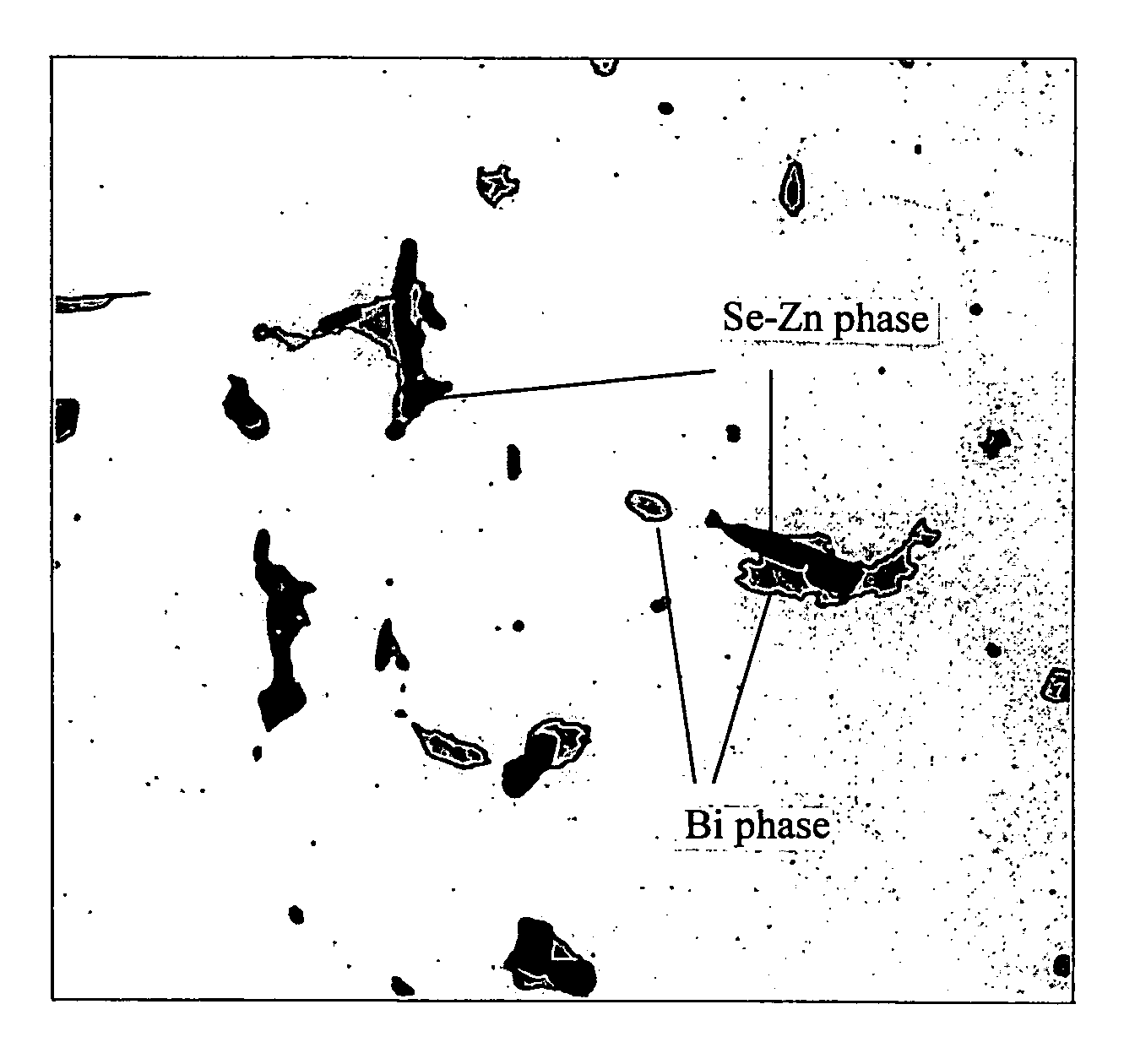
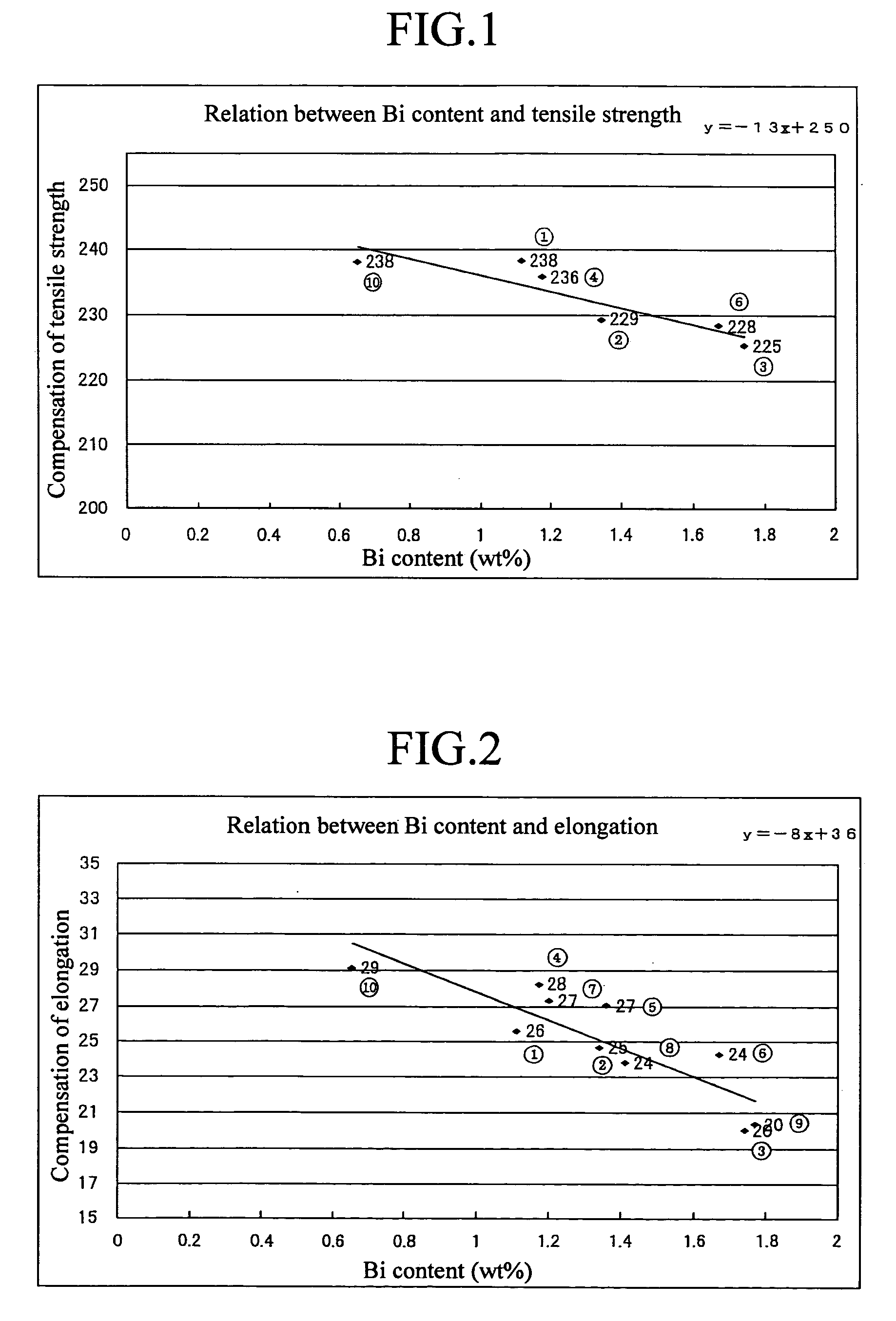
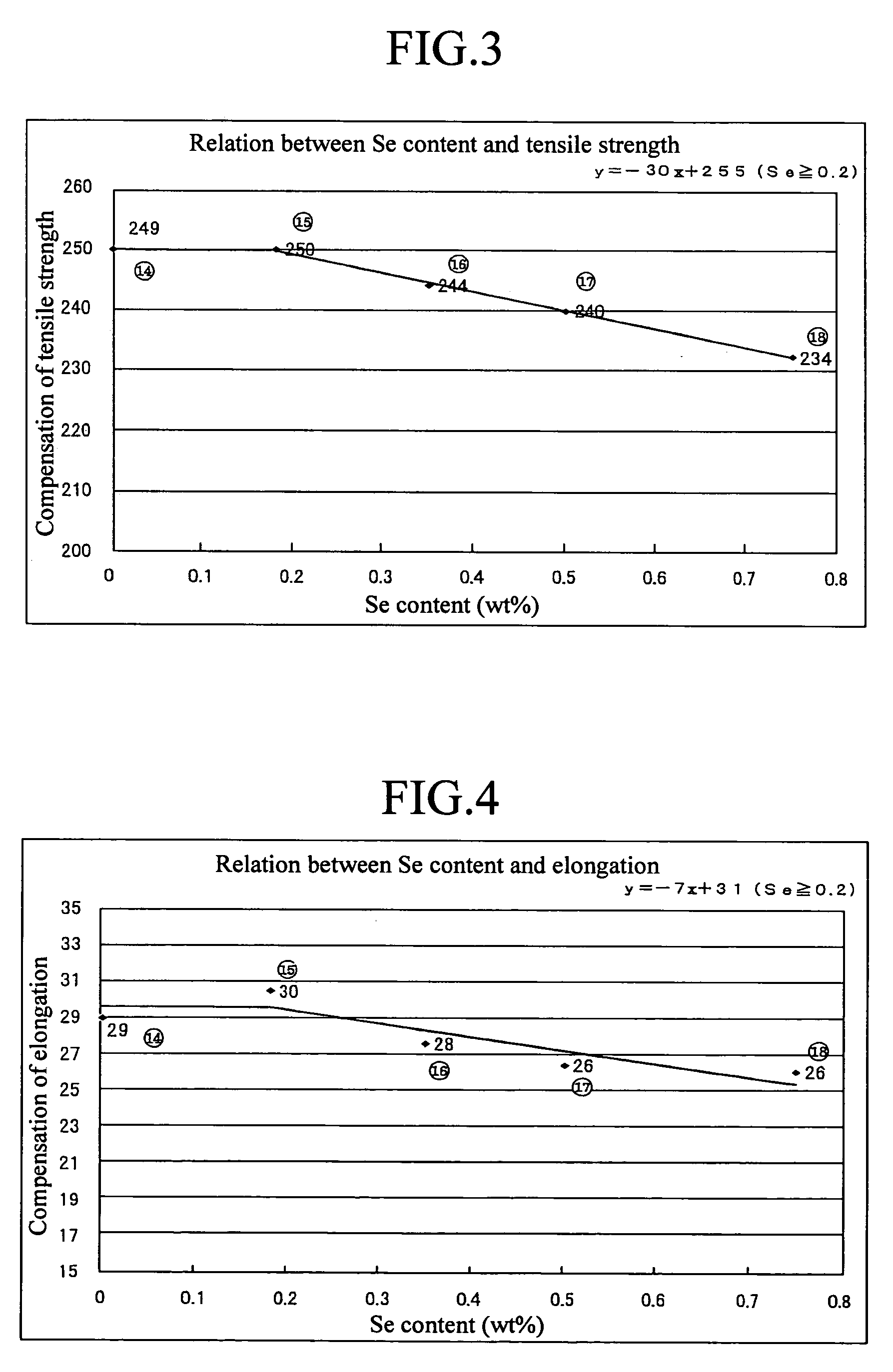
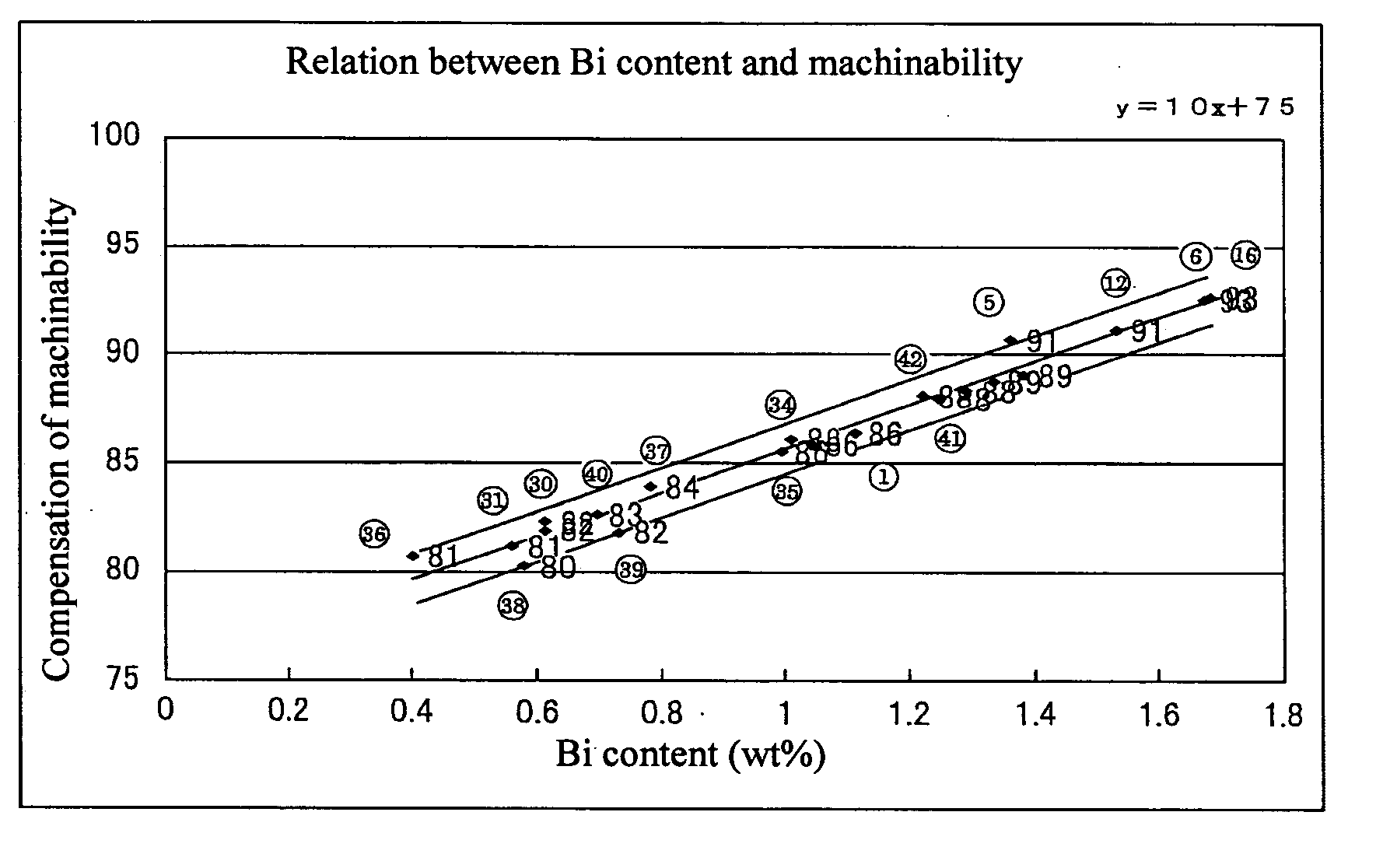
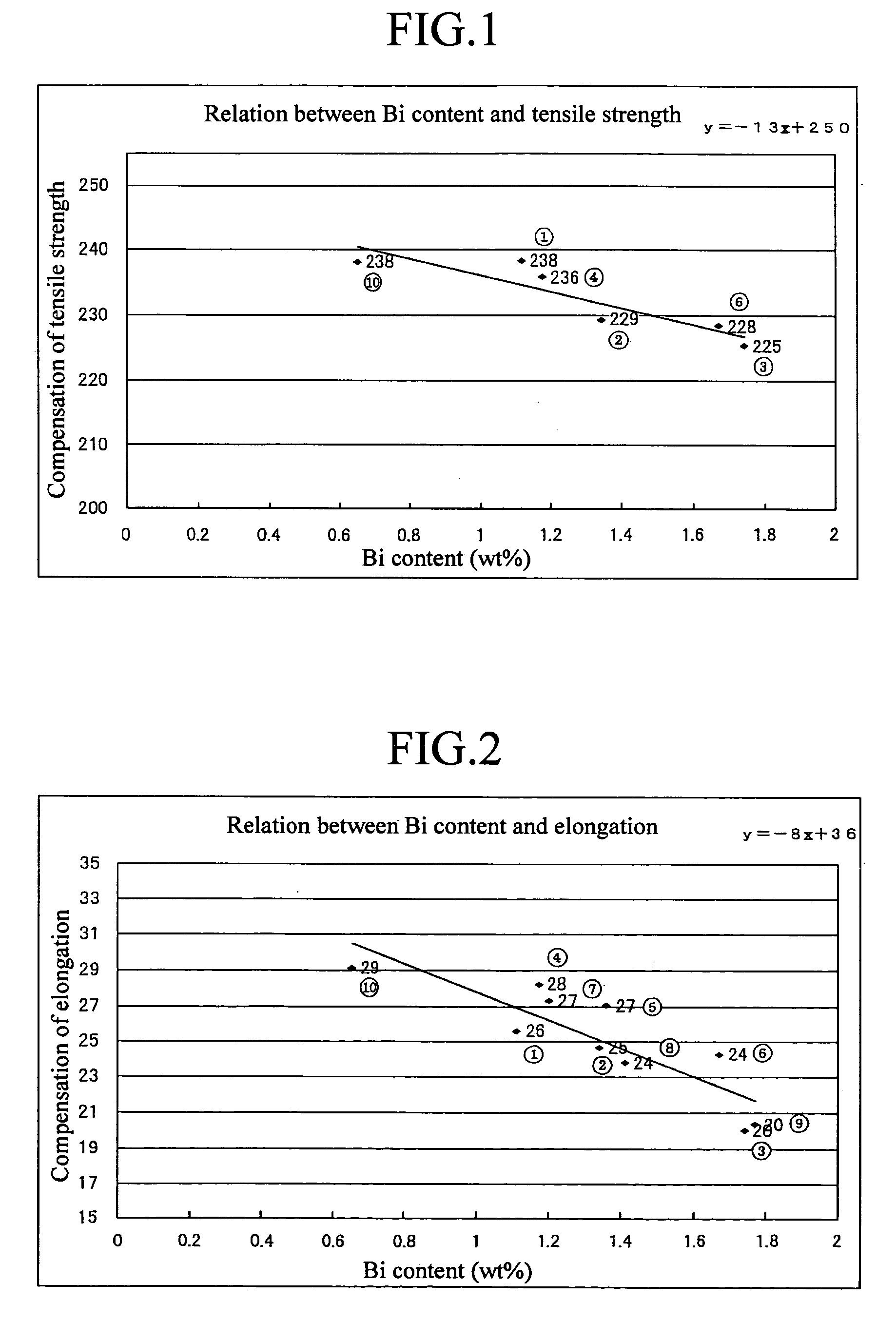
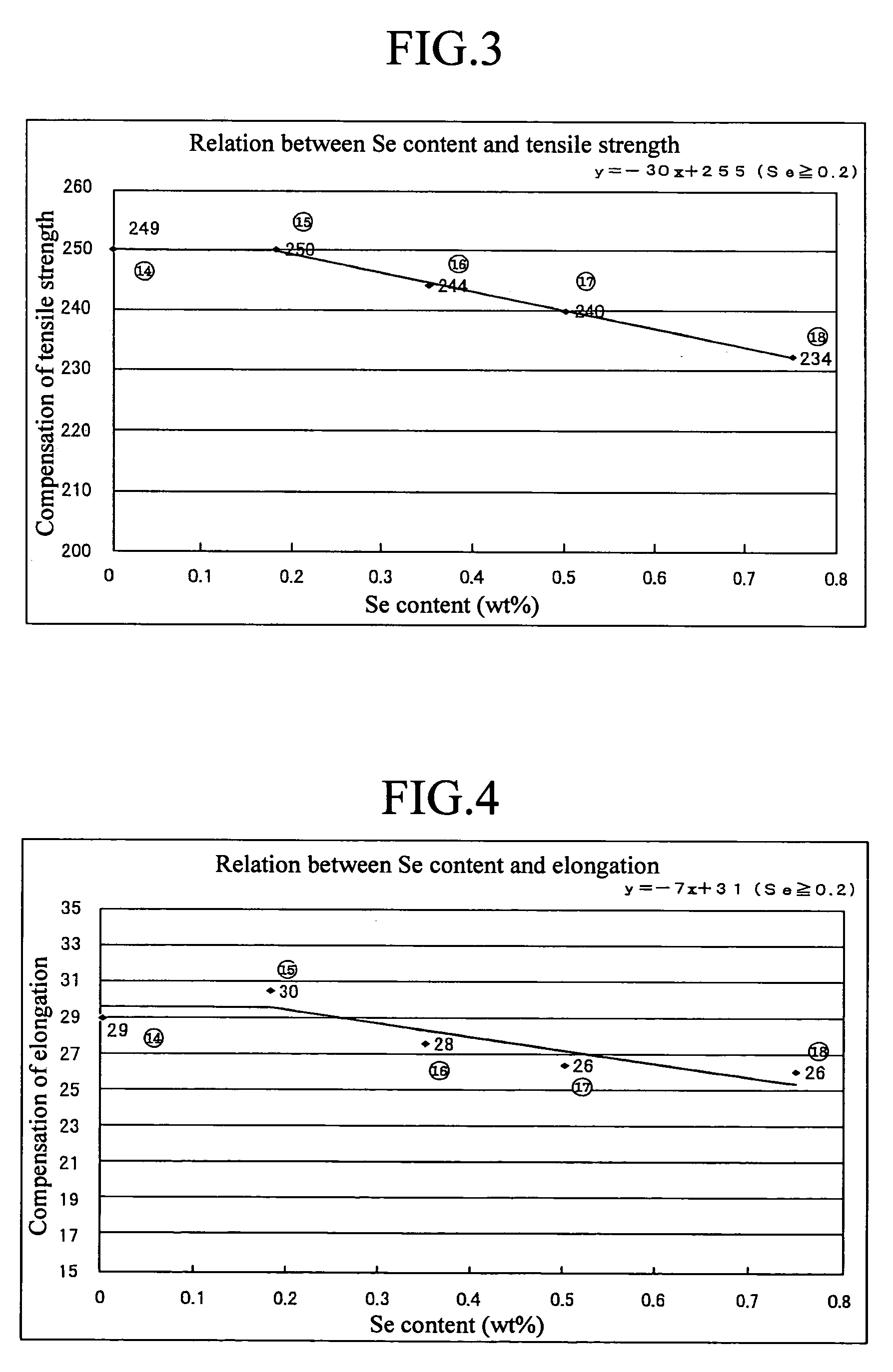
By exactly comprehending the true properties of the rare elements (such as Bi and Se) which are alternative components for Pb, the alloy is enabled to secure machinability equal to the bronze alloy (CAC406) generally used hitherto and acquire mechanical properties at least equal to the CAC406 as well in spite of a decrease in the content of the rare elements (such as Bi and Se) in the alloy. Further, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of casting defects by elucidating the unresolved influence of the decrease of the alternative components (such as Bi and Se) for Pb on the wholesomeness of a casting. Moreover, it is possible, by decreasing the rare elements, to produce a copper-based alloy containing rare elements at a low cost and to provide a cast ingot and a liquid-contacting part each using the alloy. The copper-based alloy, and the cast ingot and liquid-contacting part each using the alloy individually contain at least 2.8 to 5.0 wt % of Sn, 0.4 to 3.0 wt % of Bi and satisfying 0<Se≦0.35 wt % to enable securing prescribed machinability and wholesomeness of a casting and exalt mechanical properties thereof.
Owner:KITZ CORP
Visible casting method
ActiveCN1631579AGood casting processAvoid entrainmentCasting safety devicesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSystems designX-ray
Owner:中科西王特钢有限公司
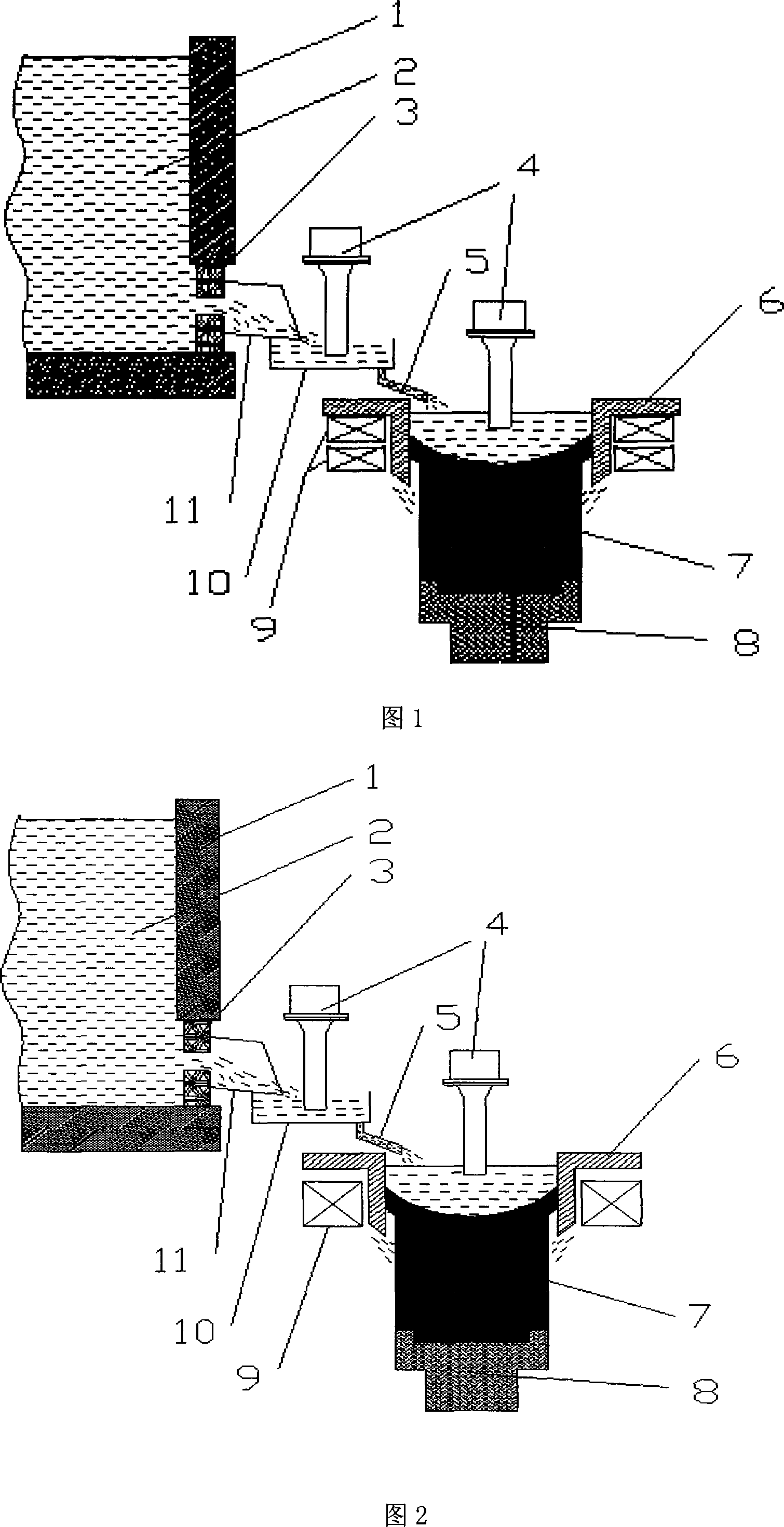
Casting method for hub and water mist cooling device used in casting method
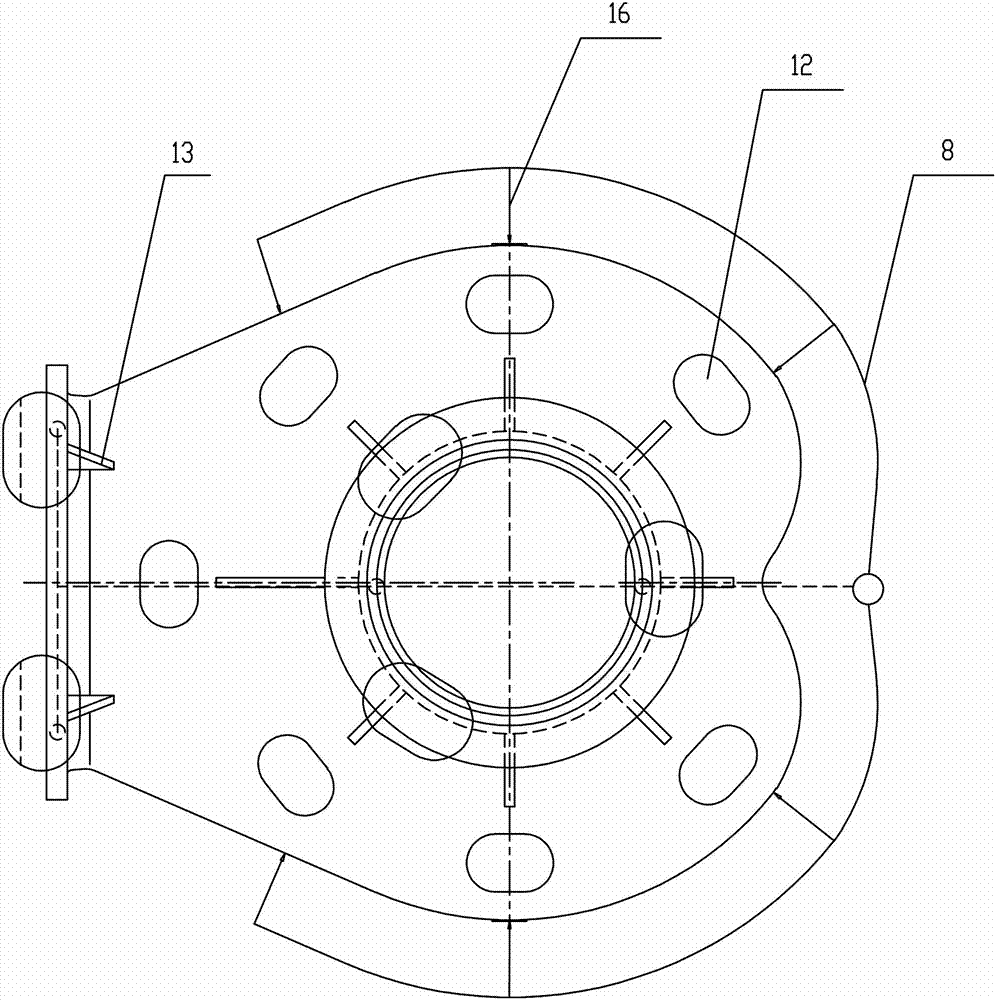
InactiveCN102416444AAvoid Bubble ProblemsAvoid casting defects such as shrinkage porosityFoundry mouldsFoundry coresEllipseRoom temperature
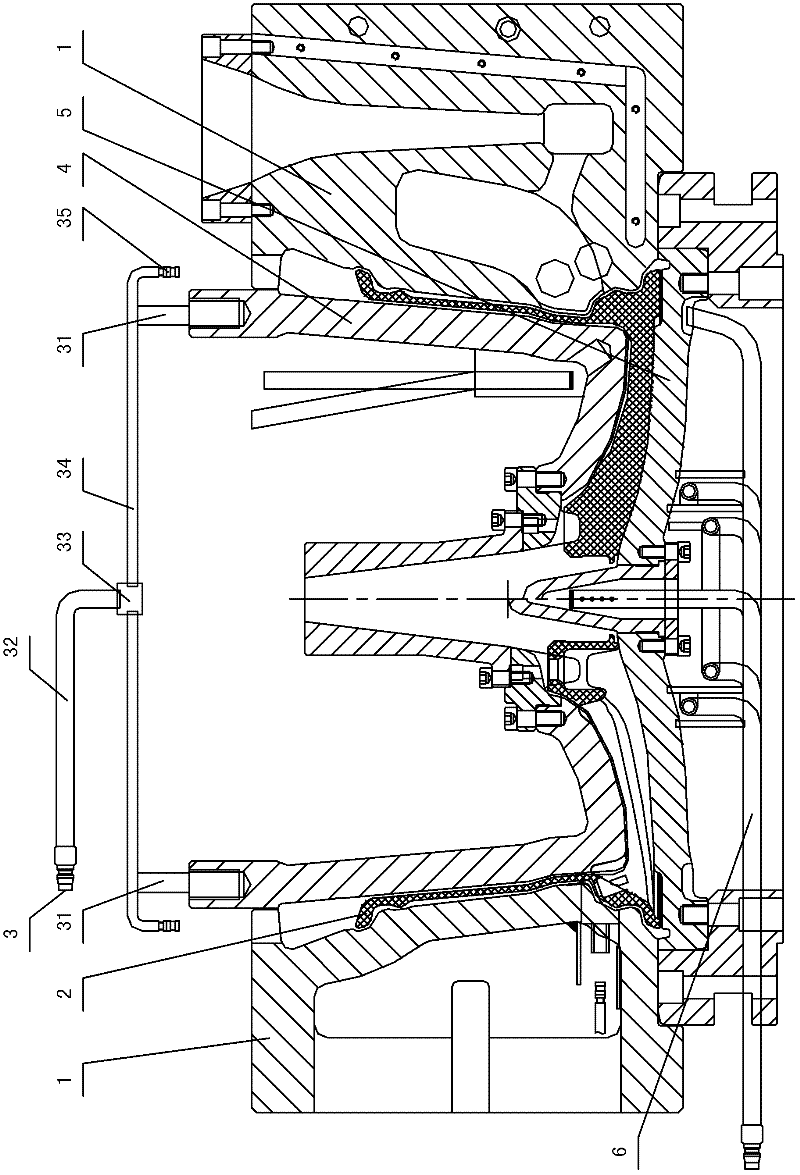
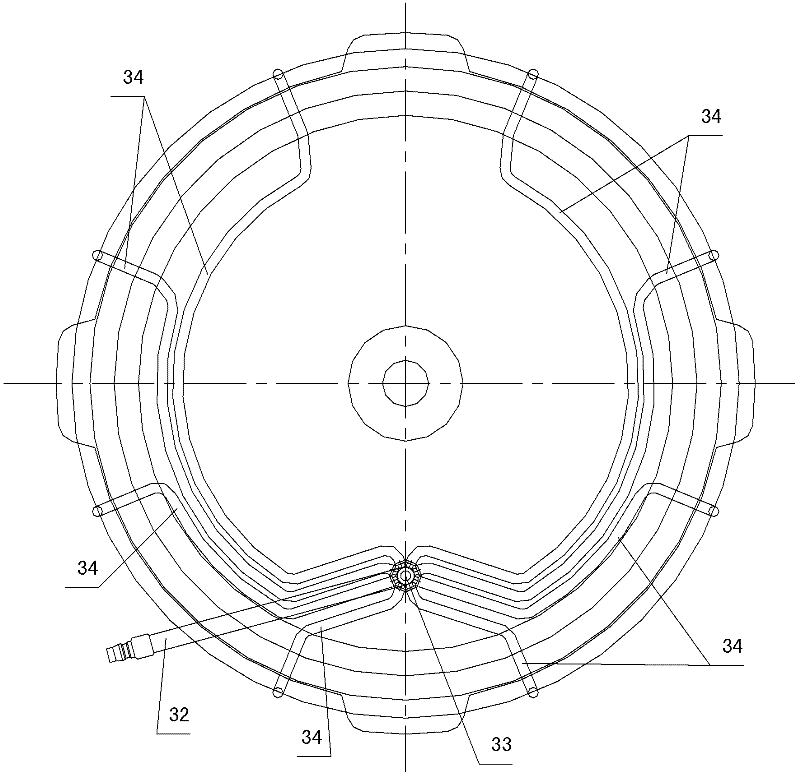
The invention discloses a casting method for a hub, which comprises the following steps of: 1) arranging a mold and a cooling device on a casting machine; 2) casting liquid aluminum water into a cavity of the mold; 3) performing primary cooling by using a water cooling device (6), and opening a side mold (1); 4) starting a water mist cooling device (3), and ensuring that the water mist cooling device (3) is directly aligned with the edge part of a hub casting (2) and performs water mist cooling; 5) cooling to room temperature, and stripping; 6) demolding. In the water mist cooling device usedin the casting method, one end of a mist pipe is communicated with a mist source, the other end of the mist pipe is communicated with a mist spray head (35), the mist pipe is fixed on the top of an upper mold (4) through a connecting bracket (31), and the mist spray head (35) is positioned above the edge part of the hub casting (2). Therefore, casting defects such as shrinkage and the like on theedge of the upper end of the hub are overcome; in addition, an ellipse is difficult to form after a rim at the uppermost end of the casting is demolded.
Owner:NINGBO CANDONG MOLD TECH +1
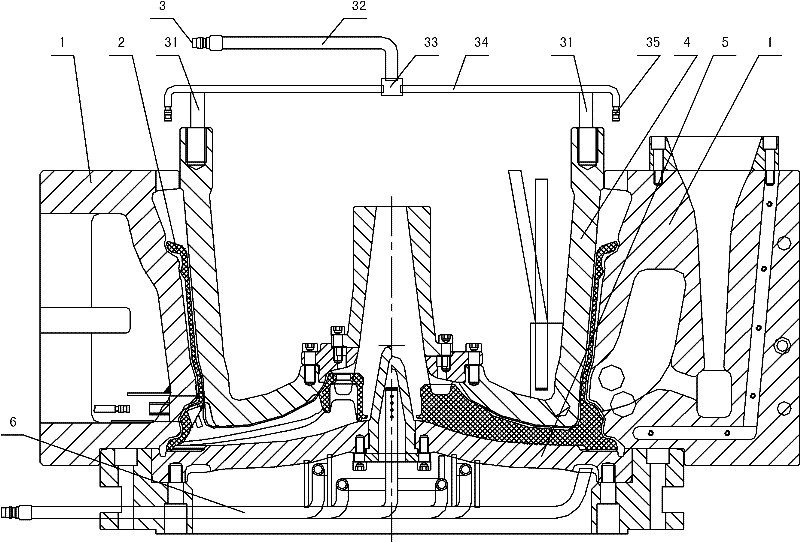
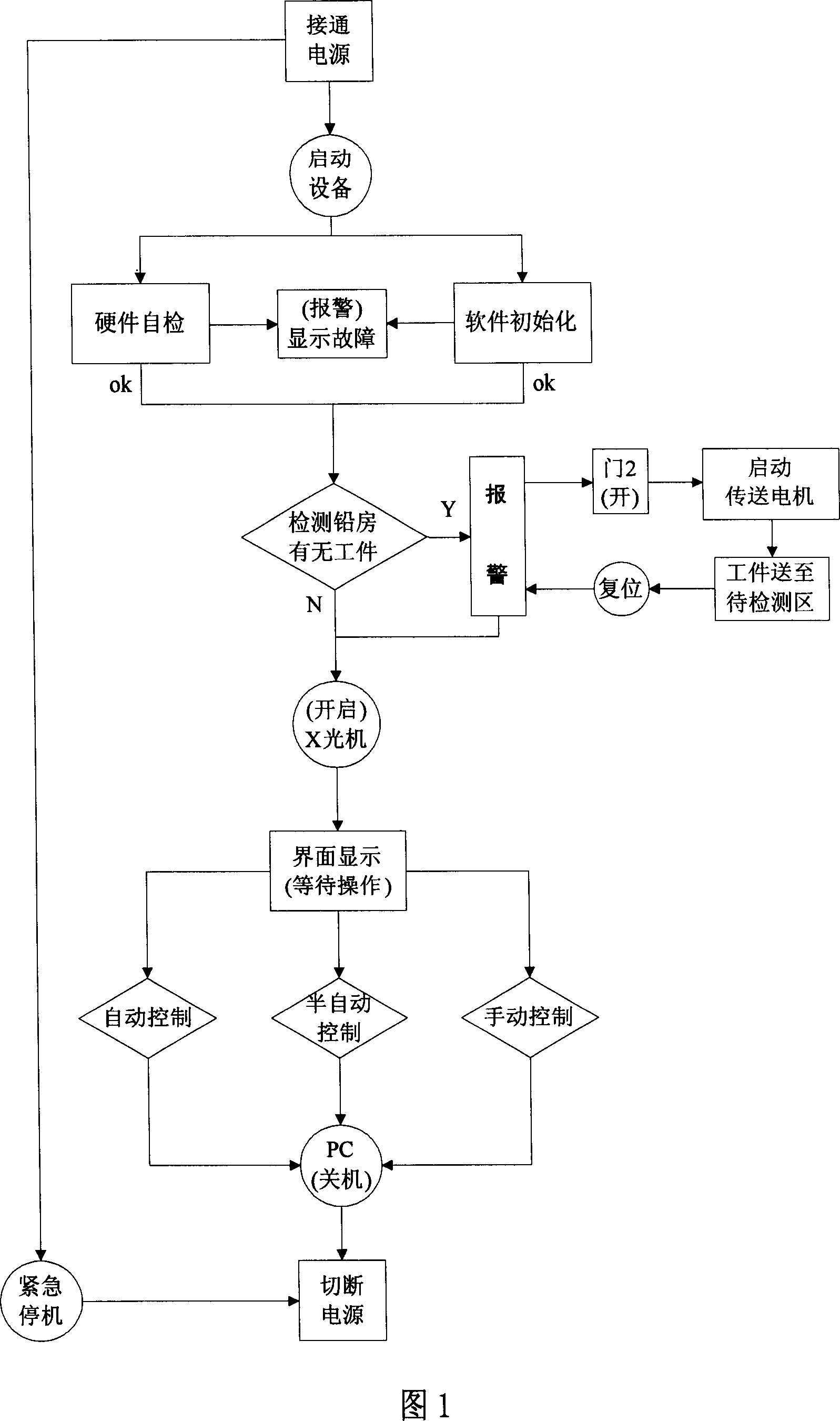
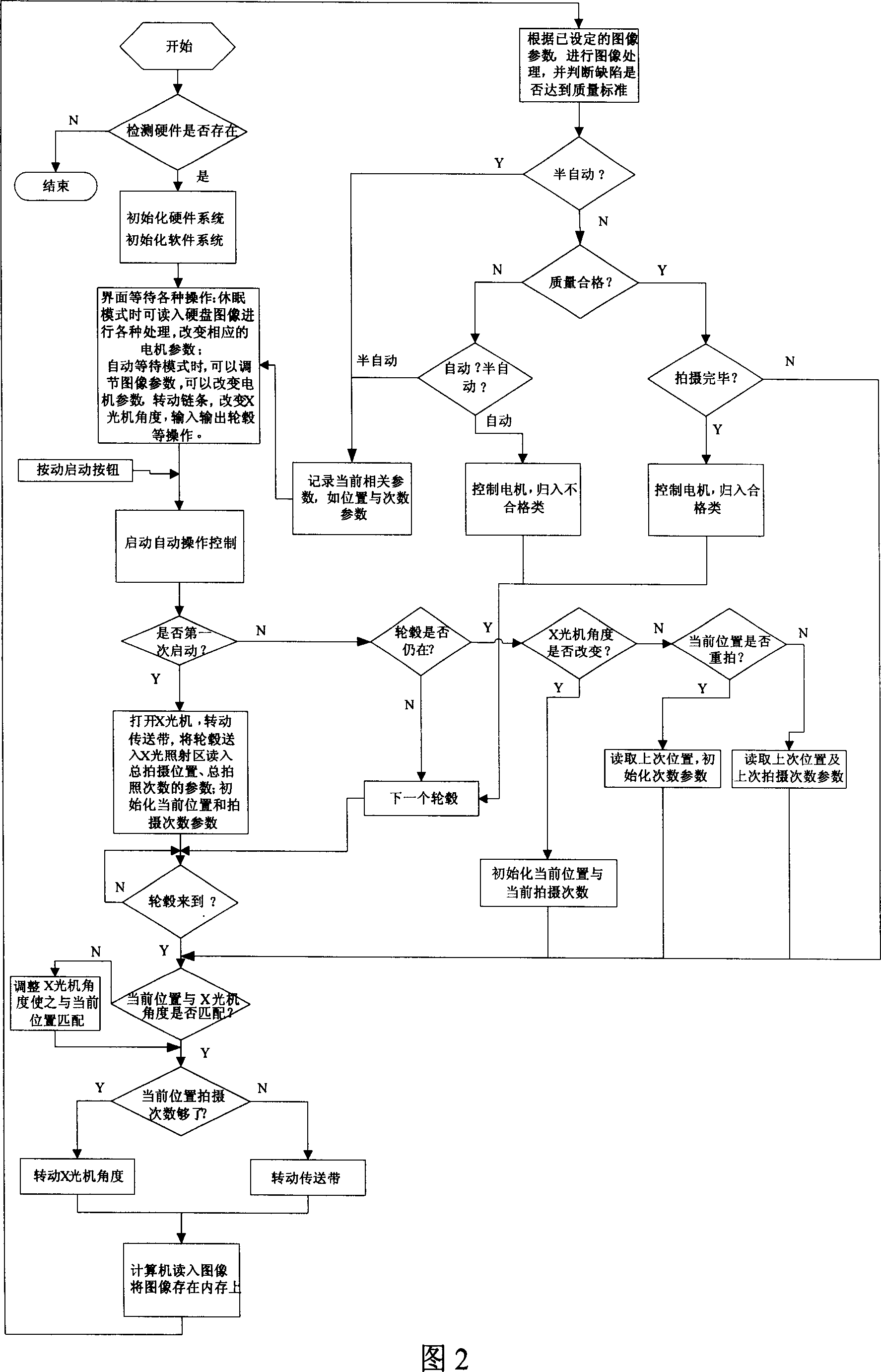
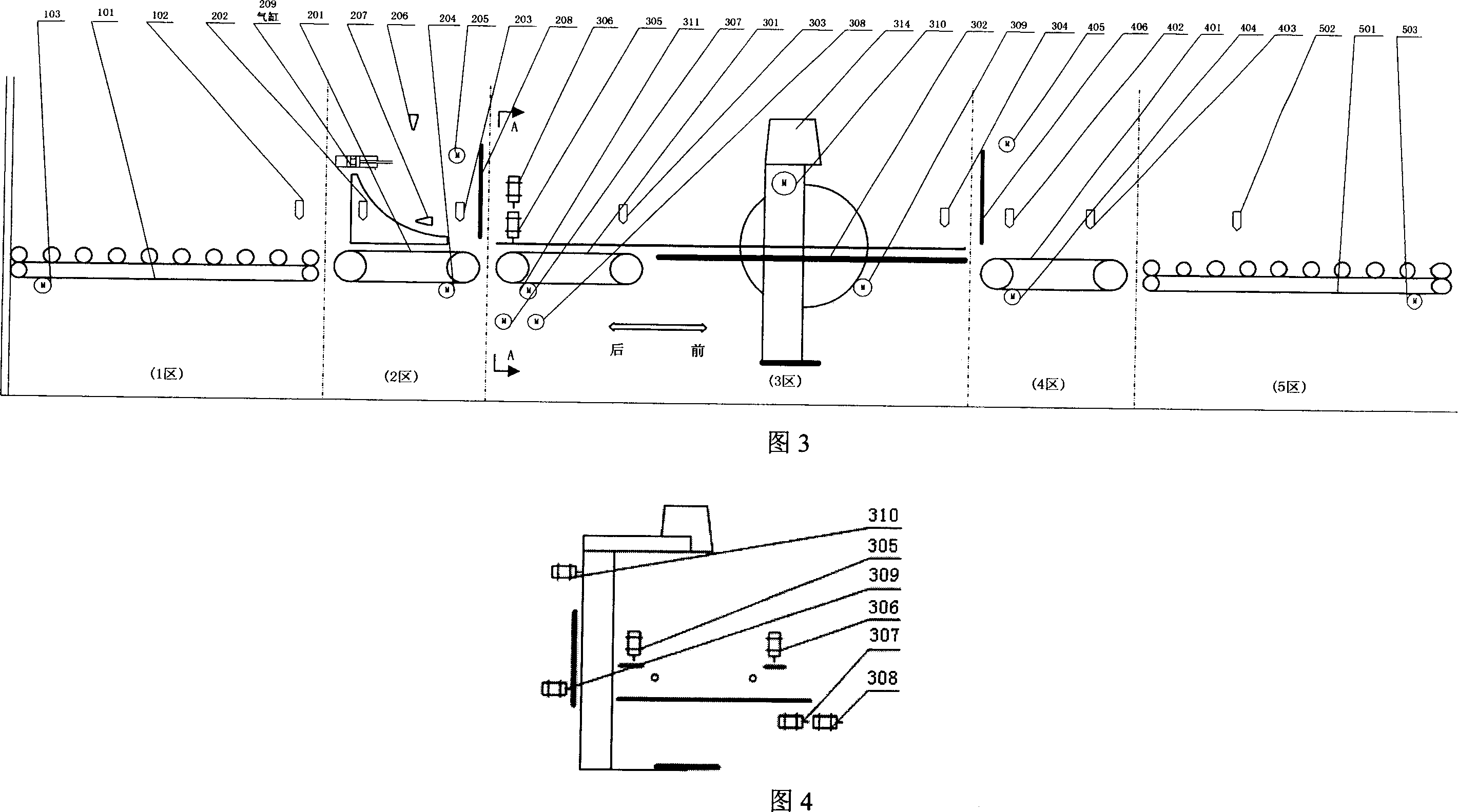
Automatic decting method and device for wheel hub casting fault based on image understanding
InactiveCN101021491AFully automatedSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationLight pipeControl system
The invention discloses an automatic detecting method and device of wheel hub casting defect based on image comprehension. It uses PLC controlling system to control moving and rotating of wheel hub and moving of X light pipe precisely. Parameters of PLC controlling system are set by detecting software of wheel hub casting defect in PC. Utilize X light to shoot images of wheel hub on different positions which are also set by the detecting software. Detecting software adopts detecting algorithm to distinguish wheel hub casting defect automatically. Detecting method contains manual, semi-automatic or automatic detecting program for selecting. The system has high precision and good stability, which improves automatic level of wheel hub detecting and the objectivity of detecting standards greatly.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
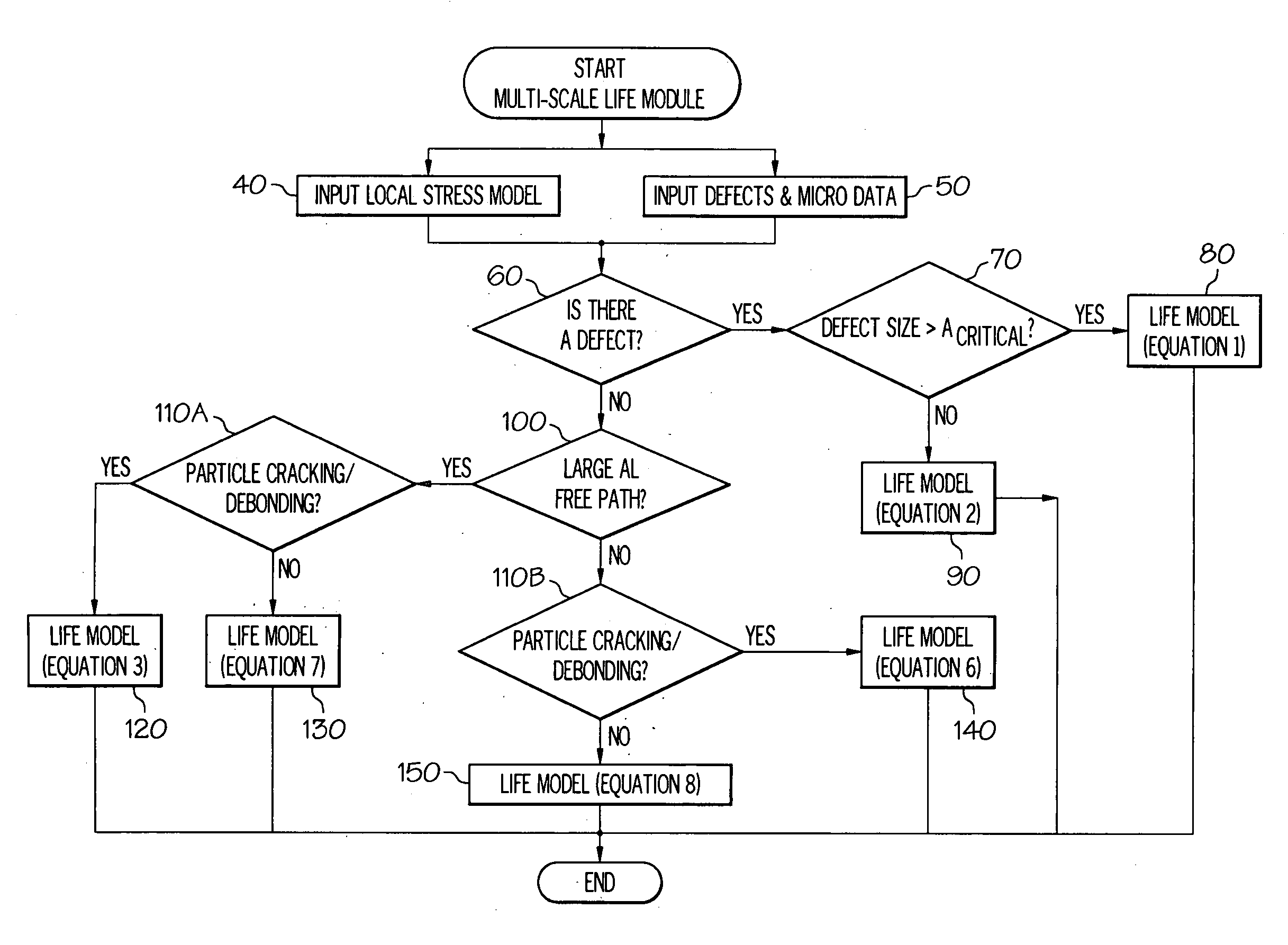
Methods and systems to predict fatigue life in aluminum castings
InactiveUS20090276166A1Accurately fatigue propertyAccurate of fatigue propertyPlug gaugesDigital computer detailsCrazingCasting defect
Methods and systems of predicting fatigue life in aluminum castings that combines extreme values of both casting flaws and microstructures with multiscale life models. The multiscale life models account for differing fatigue crack initiation based on the size scale of the defect and microstructure features, including provisions for generally millimeter scale casting flaws, generally micrometer scale second phase particles by cracking or debonding, or submicrometer scale dislocation interactions with precipitates which form persistent slip bands. In the presence of casting flaws, the fatigue initiation life is negligible and the total fatigue life is spent in propagation of a fatigue crack from such flaws. In the absence of casting flaws, however, the total fatigue life is spent in both crack initiation and propagation, except for the case where fatigue cracks initiate from large second phase particles in a coarse microstructure. The extreme values of casting flaws, second phase particles, mean free path through an aluminum matrix or grain sizes are obtained from extreme value statistics when two or three dimensional sizes of casting flaws and microstructure features are provided by either direct measurement or analytical prediction. The upper bound flaw or microstructure feature size is calculated by extreme value statistics.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for manufacturing blank of pipe clamp
InactiveCN105728648AAchieve productionSave materialFoundry mouldsFoundry coresMolding machineCasting defect
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a blank of a pipe clamp and belongs to the field of construction. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a pipe clamp precoated sand mold is designed and manufactured according to a design drawing of the pipe clamp; 2, the precoated sand mold of the pipe clamp is placed on an automatic molding machine, and a precoated sand pouring sand shell model and a sand core model are manufactured; 3, pouring is carried out; and 4, a casting is taken out and cleaned. The method has the beneficial effects that production of the blank of the pipe clamp can be efficiently achieved, materials and manpower can be saved, and the mechanical machining amount can be reduced; and casting defects can be reduced, the yield is increased, and automatic production can be easily achieved.
Owner:YUZHOU KUNLUN MOLD CO LTD
Casting method for large thin-wall valve body steel casting
ActiveCN103506580AImprove production efficiencyReduce manufacturing costFoundry mouldsFoundry coresPhysical modelCasting defect
A casting method for a large thin-wall valve body steel casting comprises the following steps: 1, manufacturing a composite physical model: manufacturing an upper half valve body external mold, a lower half valve body external mold, the overall frame of a second core box, and an irregular-shaped section template; filling a mixed filler between the frame and the section template; tamping, smoothly trimming the filler; performing natural curing after the dimensional requirement is met; 2, sand mulling; 3, modeling and core manufacturing; 4, painting, mounting the core, and combining boxes; 5, smelting and casting; 6, performing post-treatment. The large thin-wall valve body steel casting is prepared through the steps. The casting method adopting the composite model can improve the model manufacturing efficiency, saves wood, and reduces the model manufacturing cost; through the adoption of stepped flat ingate system, as well as the manner that a chiller, a riser and compensation are combined, the thin-wall valve body steel casting is protected from fracture, insufficient casting, cold shut, wrinkling, and other casting defects, so as to realize the sequential solidification of the valve body steel casting, and meet the technical requirement of the valve body steel casting.
Owner:YICHANG MARINE DIESEL ENGINE
Method of removing casting defects
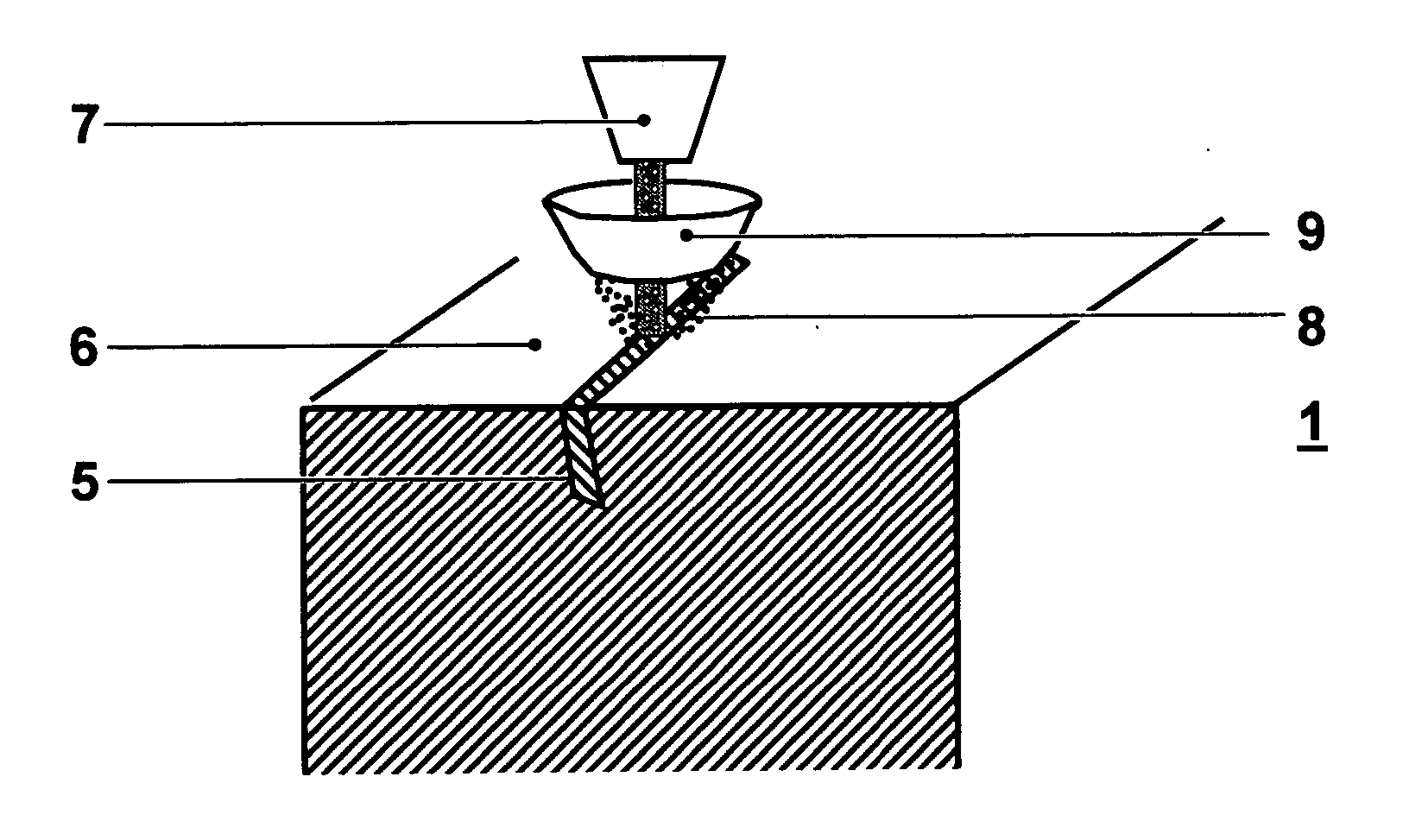
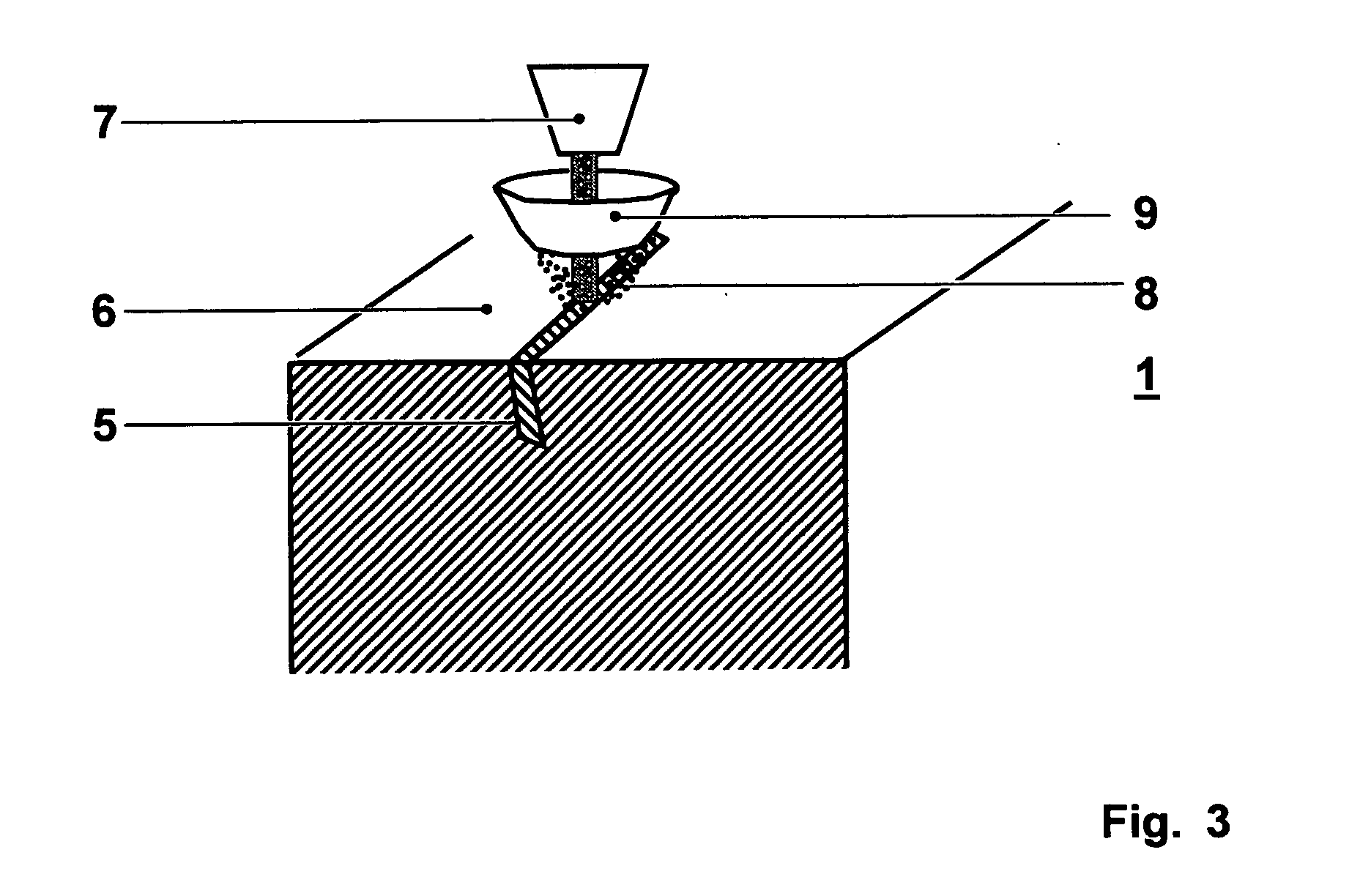
InactiveUS20050067065A1Easy and cost-effective mannerFree from defectTurbinesPolycrystalline material growthCasting defectMaterials science
A method for removing casting defects (5) from an article (1) with an oriented microstructure can include locating at least one casting defect (5) and melting the casting defect (5) locally by a heat source (7) to a depth at least as great as the casting defect (5) itself. The molten material can then be solidified epitaxially with respect to the surrounding oriented microstructure of the article (1) in a way that the resulting solidified area is substantially free of any defect.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Copper base alloy, and cast ingot and parts to be contacted with liquid
By exactly comprehending the true properties of the rare elements (such as Bi and Se) which are alternative components for Pb, the alloy is enabled to secure machinability equal to the bronze alloy (CAC406) generally used hitherto and acquire mechanical properties at least equal to the CAC406 as well in spite of a decrease in the content of the rare elements (such as Bi and Se) in the alloy. Further, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of casting defects by elucidating the unresolved influence of the decrease of the alternative components (such as Bi and Se) for Pb on the wholesomeness of a casting. Moreover, it is possible, by decreasing the rare elements, to produce a copper-based alloy containing rare elements at a low cost and to provide a cast ingot and a liquid-contacting part each using the alloy. The copper-based alloy, and the cast ingot and liquid-contacting part each using the alloy individually contain at least 2.8 to 5.0 wt % of Sn, 0.4 to 3.0 wt % of Bi and satisfying 0<Se≦0.35 wt % to enable securing prescribed machinability and wholesomeness of a casting and exalt mechanical properties thereof.
Owner:KITZ CORP
Grain fining agent for casting aluminium alloy, preparation process and application thereof
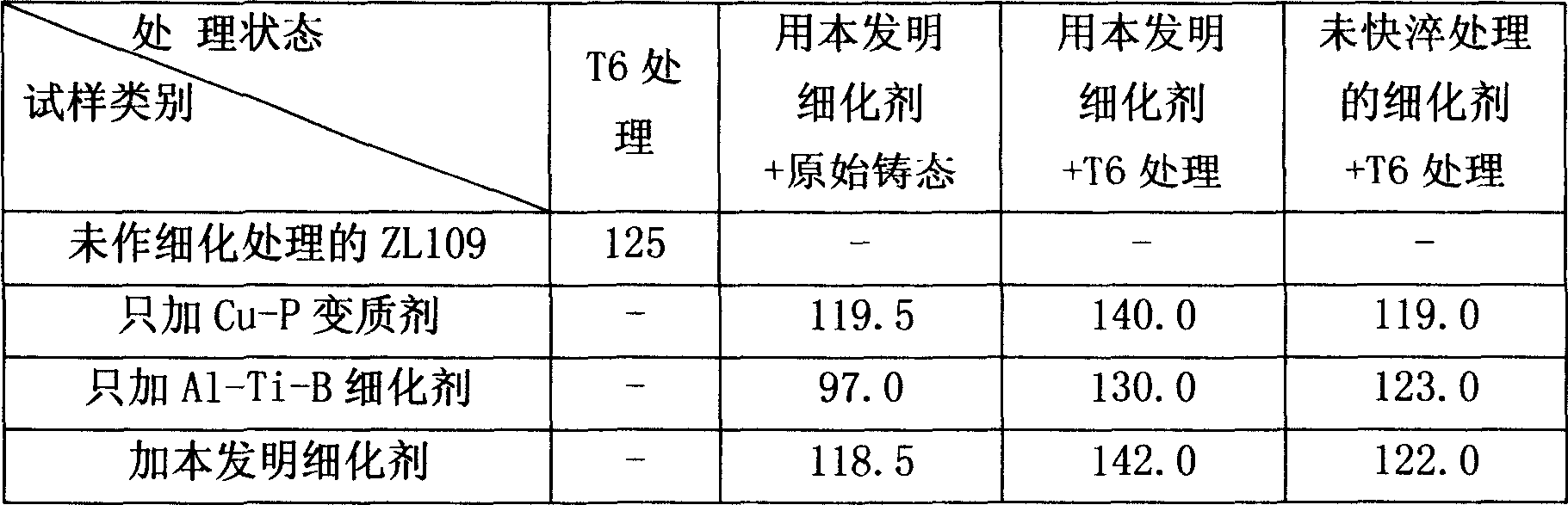
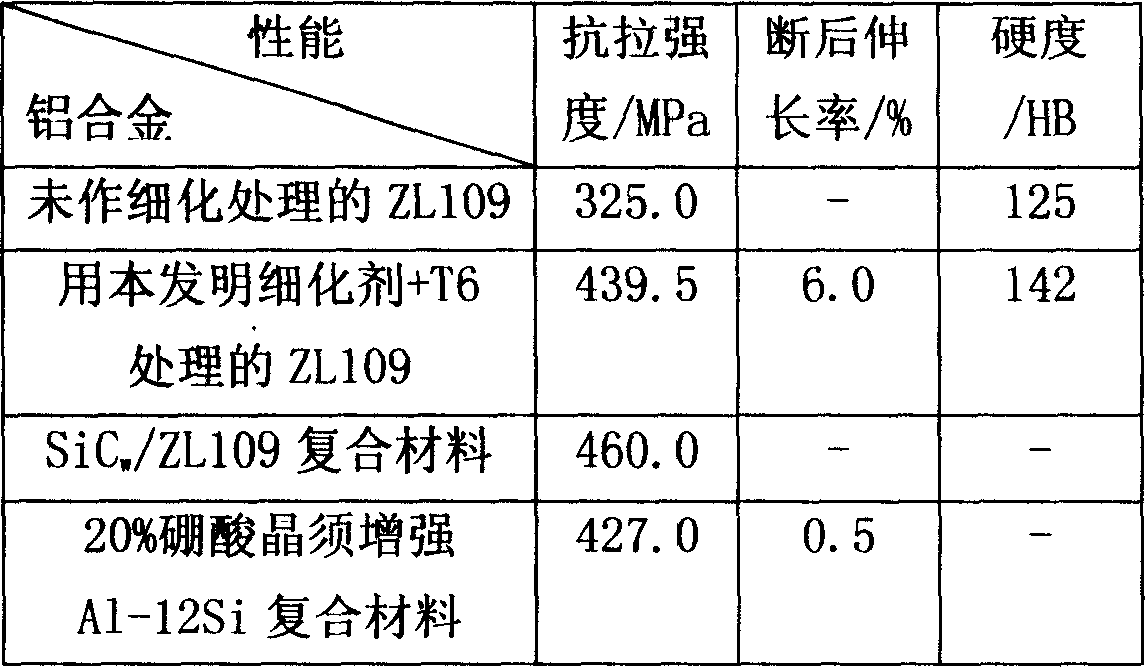
This invention relates to the crystal grain refining agent which is used to produce aluminium alloy and the method of preparation and application thereof. It is composed of intermediate alloy Cu-P and Al-Ti-B and the crystal grain refine reagent has nanometer crystal band, the weight ratio of the alloy Cu-P to alloy Al-Ti-B is 0.35-0.45:0.65-0.55, the average thickness of bank is 0.3-0.6mm, and the average width is 0.4-1.2mm. The bank is made by quickly quenching flailing. It can be applied to the plunger of the combustion engine by melting metal casting. During the production of aluminium alloy by melting metal, the primary crystal silicon and eutectic silicon can be refined by adding into the crystal grain refine reagent, this increases the energy of interface, so it can decrease the flaw of casting, the over-all properties of the aluminium alloy can be increased. At last, the mechanical property of plunger which is made of aluminium alloy, the abrasion of it and the lifetime of it can improve distinctly.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Core assembly pouring device for cylinder block casting in automobile engine
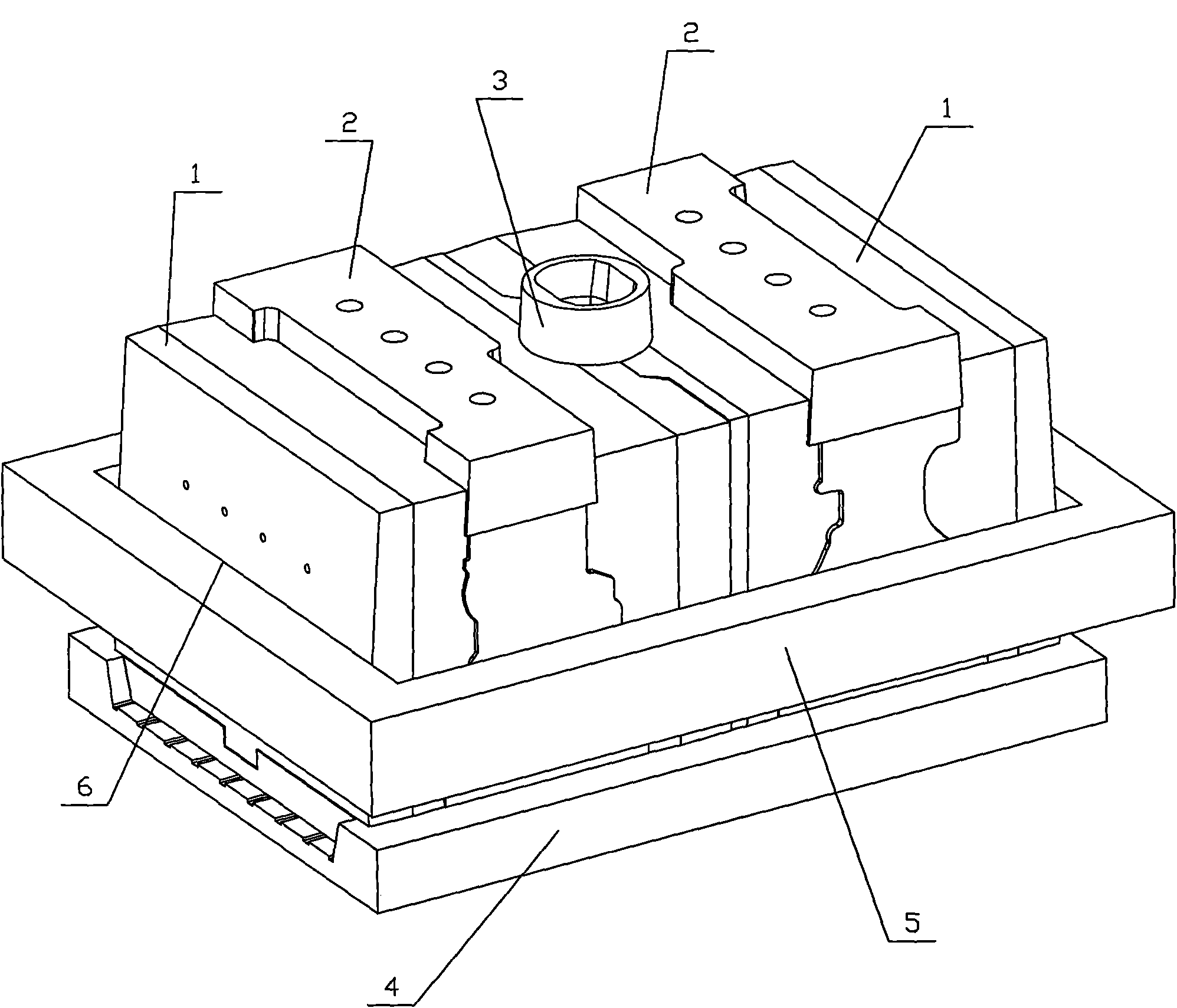
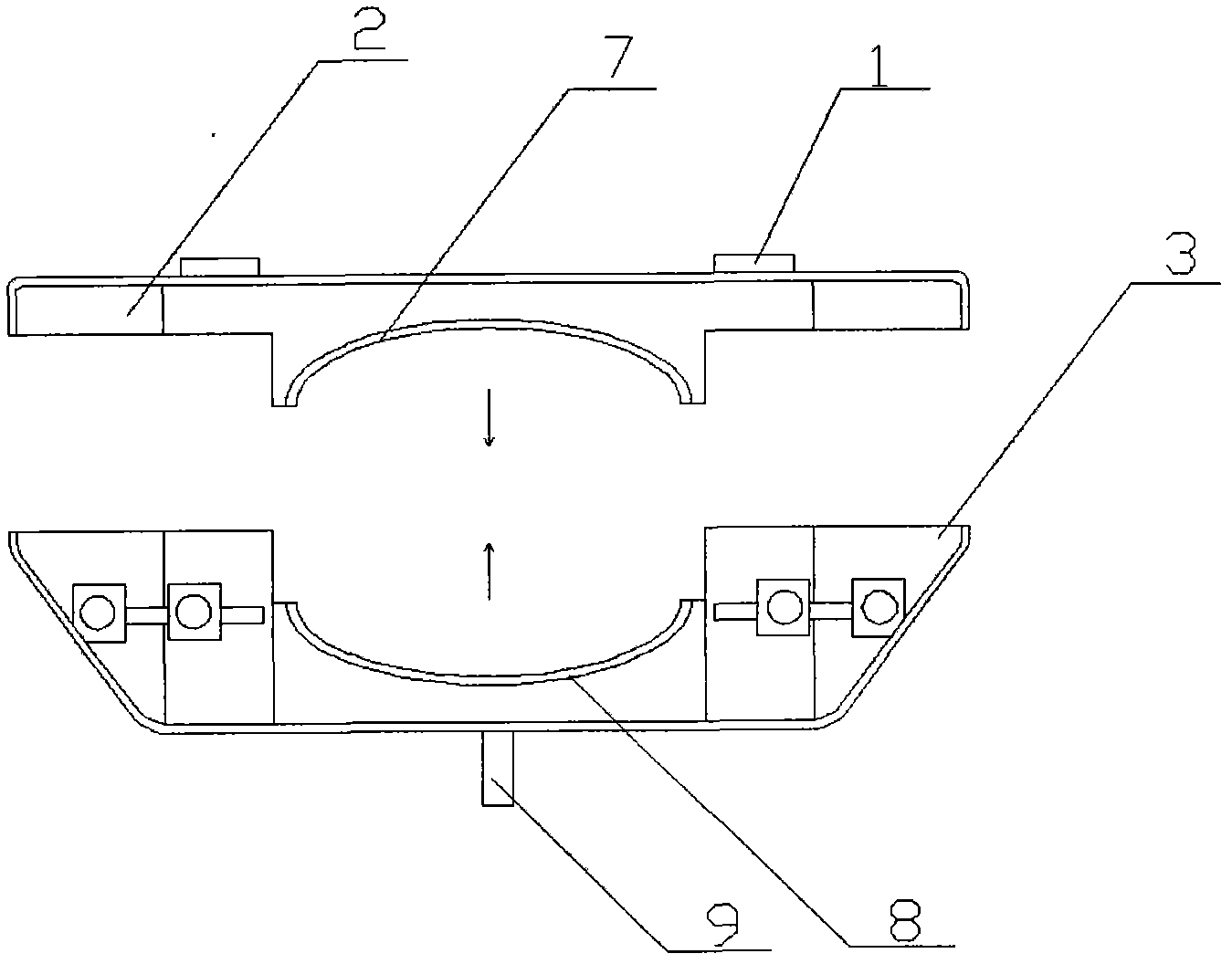
InactiveCN101817060ASolve the deformationReduce in quantityFoundry mouldsFoundry coresEngineeringCylinder block
The invention discloses a core assembly pouring device for a cylinder body casting in an automobile engine, comprising a base plate (4), two raiser cores (2), a sprue core (3), sand core assemblies (1) and a locking device (5), wherein the sand core assemblies (1) are connected on the base plate (4) and are locked by the locking device (5), the raiser core (2) and the sprue core (3) are located on the two adjacent sand core assemblies (1) which are clamped on the base plate (4), and the locking device (5) is sleeved and pressed outside the two sand core assemblies (1). By adopting the structure, the sand core of the cylinder body consists of a plurality of sand cores, and each sand core is composed of a plurality of small sand cores, thus reducing the size of each sand core, being beneficial to the forming of the sand cores and reducing casting defects of castings; and meanwhile, the number of the sand core assemblies is two, e.g. one die generates two castings, thus greatly improving production efficiency.
Owner:宁波强盛机械模具有限公司
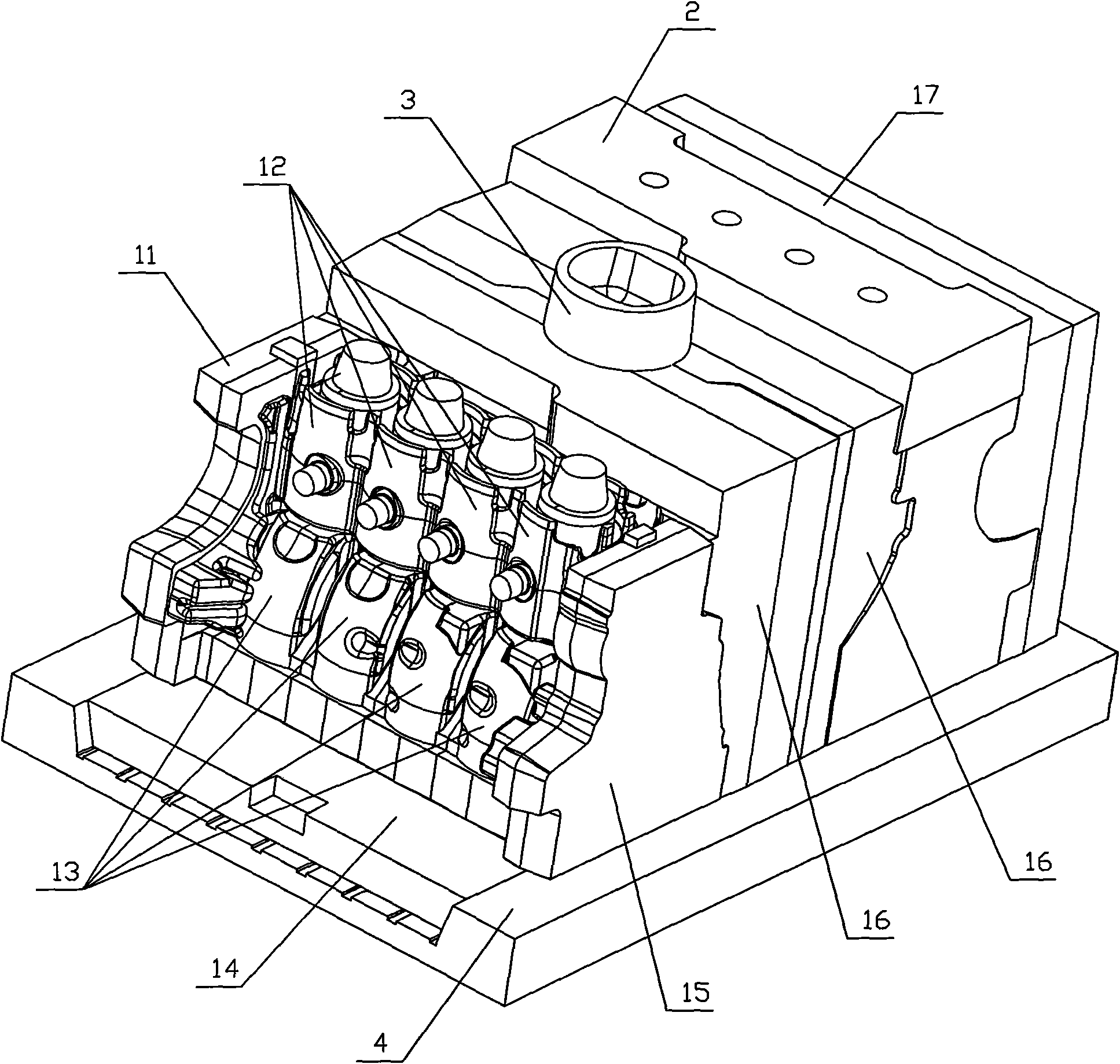
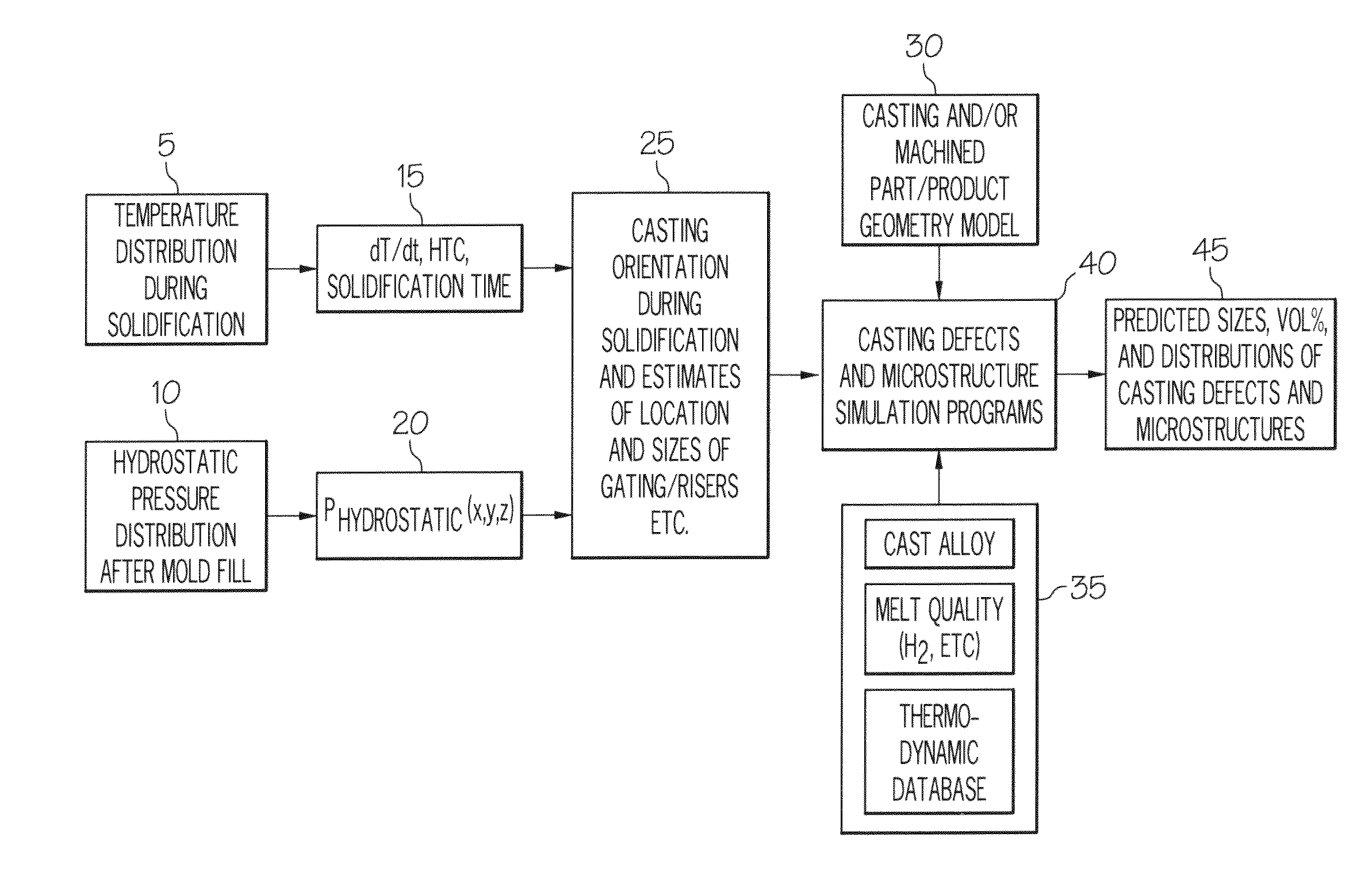
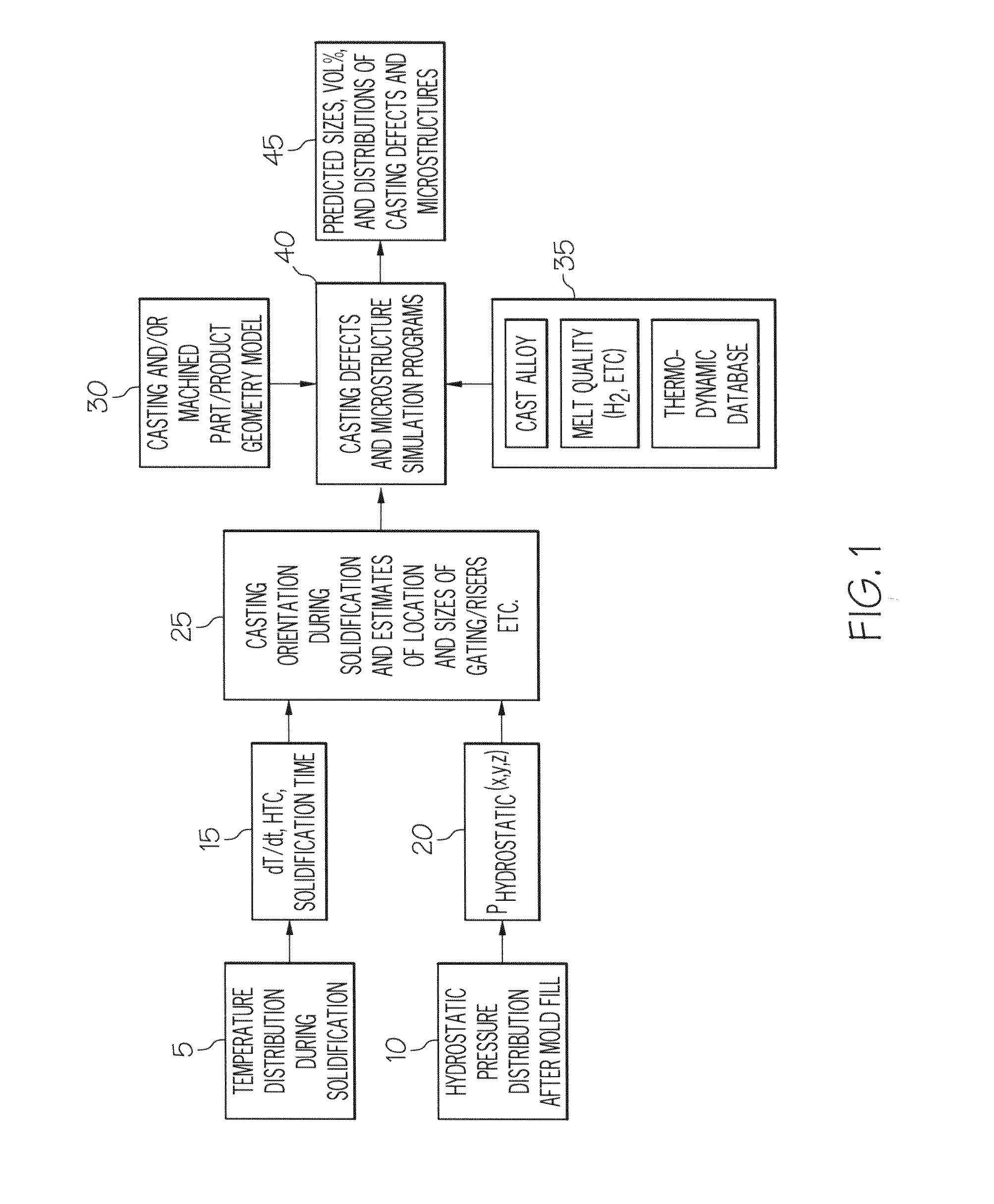
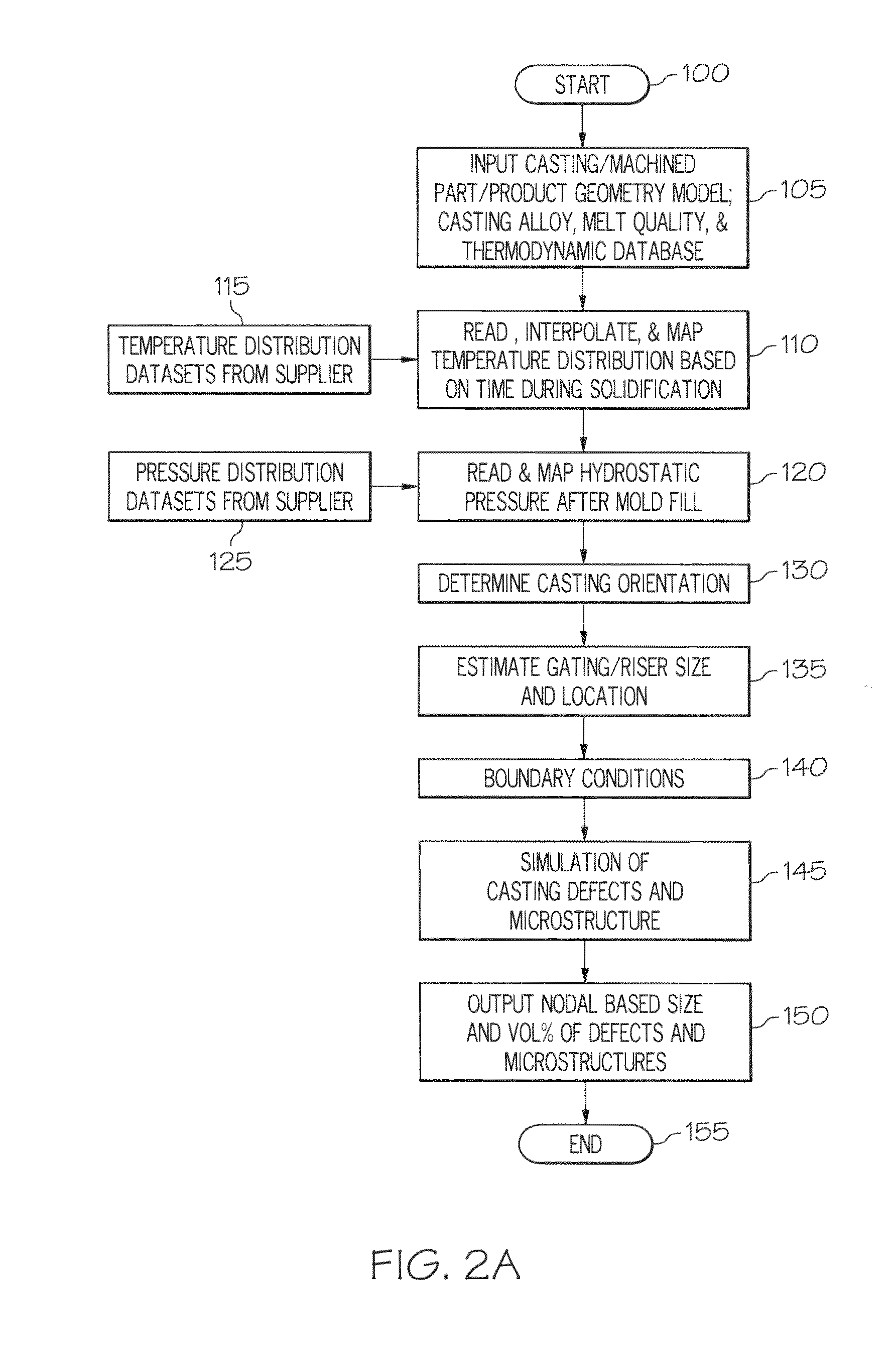
Method for simulating casting defects and microstructures of castings
ActiveUS20110144788A1Accurate durability analysisCasting safety devicesAnalogue computers for control systemsCasting defectMaterials science
Systems for predicting casting defects and microstructure in suppliers / vendors' castings for part / system durability analysis without knowing the details of the casting layout and casting gating and riser design as well as casting process parameters are provided. The systems involve the use of an integrated pore growth and interdendritic flow model. Methods of predicting casting defects and microstructures of a part without knowing the details of the casting layout and casting gating and riser design as well as casting process parameters and articles of manufacture are also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Thermal couple protector tube processing technique
The invention relates to a process for producing protecting pipes of thermocouples, which is composed of three parts of a process for producing cores, a process for dip-coating and a process for combining boxes to cast. The invention comprises firstly, producing sand cores in a wood-made box which is composed of an upper half and a lower half, arranging sand cores which are produced into an iron slot which contains coating materials and dip-coating, reserving after drying, lastly, arranging the sand cores which are dip-coated with the coating materials on an upper sand box and a lower sand box, molding closely, and casting, finishing steps of cutting, hole-filling and wire-coning on a turning machine after polishing, and obtaining qualified protecting pipes of the thermocouples. The invention has the advantages that firstly, a plurality of common casting defects can be avoided and eliminated, finished product rate is increased from 70% to 95%, secondly, the preciseness of casts can be increased greatly, un-straightness is 0.5%, and the tolerance of wall thickness is +-1.5, thirdly, mechanical processing has good performance with non hard points which are easy to appear on thin-wall casts and hard phases of carbides, the conditions of surface electric plating and enamels are good with no tiny defects such as needle holes which affect electric plating, enamels and sand holes, and fourthly, the finished product rate of casting processes can reach 85%.
Owner:西安鑫龙机械铸造有限公司
Method for casting low speed diesel engine cylinder cap for large cylinder diameter boat
ActiveCN103212672AStable foundry productionReduce manufacturing costFoundry mouldsFoundry coresLow speedCasting defect
The invention discloses a method for casting a low speed diesel engine cylinder cap for a large cylinder diameter boat, which comprises the following steps: (1) compiling casting processes: designing a joint surface and a cast system according to a progressive solidification principle; (2) making a wood mold; (3) moulding; (4) melting the poured melt; (5) pouring a casting; (6) insulating and cooling; (7) dismantling mold and cleaning; (8) tempering. The cylinder cap obtained by the casting method does not have casting defects, thereby achieving the technology requirement for casting the cylinder cap. The invention method can substantially reduce the production cost and shorten the production period, and guarantee the stable casting production of the low speed diesel engine cylinder cap for the large cylinder diameter boat in the precondition that formaldehyde and other harmful gases do not generated for polluting environments.
Owner:ANHUI MAGANG HEAVY MASCH MFG CO LTD
Surfacing-free centrifugal combined ultra-high anti-abrasion roll squeezer roller sleeve and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103008050AImprove toughnessWith super high wear-resistant outer layerGrain treatmentsTransitional RegionPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a surfacing-free centrifugal combined ultra-high anti-abrasion roll squeezer roller sleeve and a manufacturing method thereof. The roller sleeve comprises a roller sleeve body, wherein the roller sleeve body has a double-layer structure with an inner high-flexibility layer and an outer high abrasion resistance layer; and cast textures are arranged on the surface of the high abrasion resistance layer of the roller sleeve body. The roller sleeve has the characteristics that under the action of centrifugal force, the compactness of the roller sleeve is high, and metallurgical bonding of the inner layer and the outer layer is fully realized; a transitional region is smooth; by control over a cast organization subjected to 'less oxidization' thermal treatment, when the ultra-high abrasion resistance of the outer layer and the high flexibility of the core part are guaranteed, the impact resistance of the outer layer is improved; the centrifugally cast textures are basically the same as that of the outer layer; under the action of the centrifugal force, heavy points in steel liquid are subjected to offshoring segregation, so that the abrasion resistance of the textures is slightly higher than that of the outer layer; due to full metallurgical bonding under the action of the centrifugal force, casting defects such as cracks, impurities and air holes areavoided; ineffective forms such as falling and stripping which are caused by welding micro cracks are completely eliminated; the roller sleeve is maintenance free all the time; the production period is short; and large-scale production is realized.
Owner:河北奥木森陶瓷辊套有限公司
Cast Al-Si alloy
The cast Al-Si alloy consists of Si 11.0-13.5 wt%, Mg 0.15-0.55 wt%, Sr 0.015-0.080 wt%, B 0.010-0.050 wt%, Cu <0.20 wt%, Fe <0.20 wt%, Zn <0.10 wt%, Mn <0.10 wt%, Ti <0.10 wt%, each of other impurity<0.05 wt%, total impurity content<0.15 wt%, and Al the rest. The cast Al-Si alloy has Si content near the eutectic point of the alloy, and its alloy liquid has excellent flowability, powerful shrink feeding capacity, low gas absorption and less casting defaults. The cast Al-Si alloy has high toughness and lowered casting mold cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High-chromium cast iron composite inoculant, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a high-chromium cast iron composite inoculant, a preparation method and an application thereof, in particular to cast iron alloy containing chromium. The high-chromium cast iron composite inoculant is a nanocrystalline high-chromium cast iron composite inoculant containing rare-earth ferrosilicon and ferroboron. The high-chromium cast iron composite inoculant comprises Fe-Ce-Si-Ca intermediate alloy and Fe-B intermediate alloy, wherein the weight ratio between the Fe-Ce-Si-Ca intermediate alloy and the Fe-B intermediate alloy is 1:0.07-0.13. The nanocrystalline crystal grains of the inoculant are less than 100nm, the inoculant is a flaky inoculant obtained by carrying out melt fast-quenching processing on raw materials which comprise commercially purchased rare-earth ferrosilicon and commercially purchased ferroboron, the inoculant is used for carrying out crystal grain and tissue refining processing on the tissue of the high-chromium cast iron alloy of high-chromium cast iron wear parts used for engineering machinery, the processing method is a metal melt casting method, the casting defect of the existing casting technology of the high-chromium cast iron alloy is overcame, and matrix crystal grains and cementite phases are obviously refined, so that the overall mechanical properties of the high-chromium cast iron alloy are obviously improved.
Owner:TIANJIN LIXINSHENG ADVANCED CASTING
Automobile hub isothermal forging and spinning forming process
InactiveCN102814621AReduce consumptionHigh precisionMetal-working apparatusWheelsTemperature controlCasting defect
The invention relates to an automobile hub isothermal forging and spinning forming process which mainly overcomes casting defects of proneness to shrinkage and looseness, low mechanical property and the like of a traditional metal mold casting blank forming method and overcomes the shortcoming that an automobile hub is large in machining allowance, high in production cost and difficult in wide application. The technical scheme includes that the process includes: cutting an aluminum alloy rod to a blank; preheating the blank to the temperature of 460 DEG C to 500 DEG C and then keeping the temperature for 1 hour; forging and pressing the blank for 3-4 times under a forging press to manufacture a pre-forging blank; preheating a die; placing the pre-forging blank into the forging die (controlling the die temperature at 400-450 DEG C) under a 1500t forging press, and performing isothermal forging for 2-3 times again to enable an aluminum alloy hub to be formed primarily; and spinning for precise forming. By the forming process, product manufacturing precision and strength are enhanced, and the forming process belongs to precise forming and is capable of effectively saving production cost and improving mechanical property of the hub.
Owner:韦光东
Method for producing ultrahigh pressure switch pressure-bearing aluminum alloy tanks under low pressure through V method
ActiveCN102941333ASpeed up the flowReduce scour forceFoundry mouldsFoundry coresVacuum castingUltra high pressure
The invention discloses a method for producing ultrahigh pressure switch pressure-bearing aluminum alloy tanks under low pressure through a V method in the technical field of vacuum casting, which comprises the following processing steps: jig manufacture, low-temperature gating system manufacture, upper tank molding, lower tank molding, lower core mould assembling, casting and pressure removing and picking. The method solves the defects of slag inclusion, pores, pinholes and the like of cast caused by intensive scouring of molten metal to cast, and simultaneously can solve the problems that the cavity casting system occupies excessive molten metal, and particularly the product yield of cast with low wall thickness and large size is low.
Owner:NANYANG HUISEN PRECISION INSTR CASTING
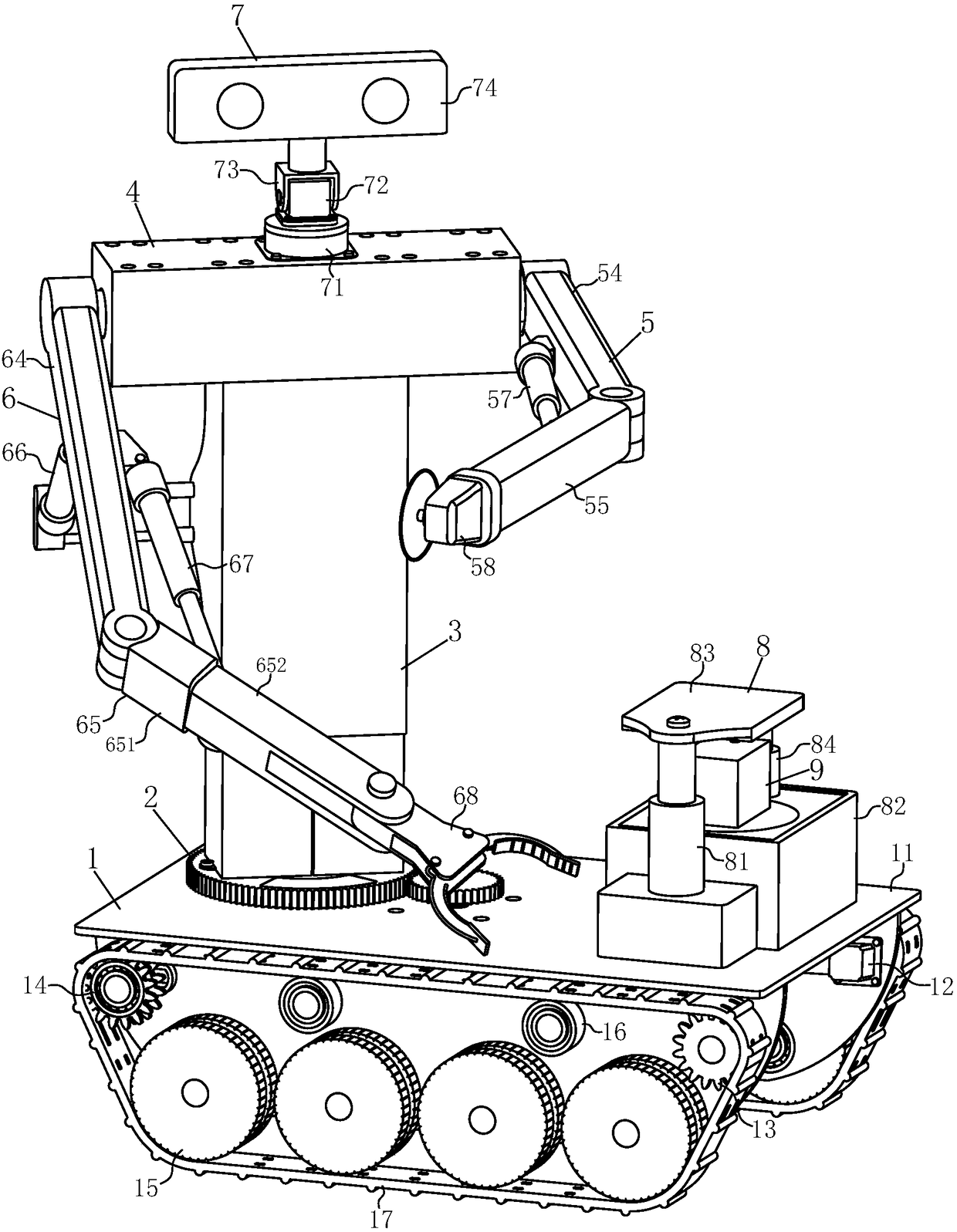
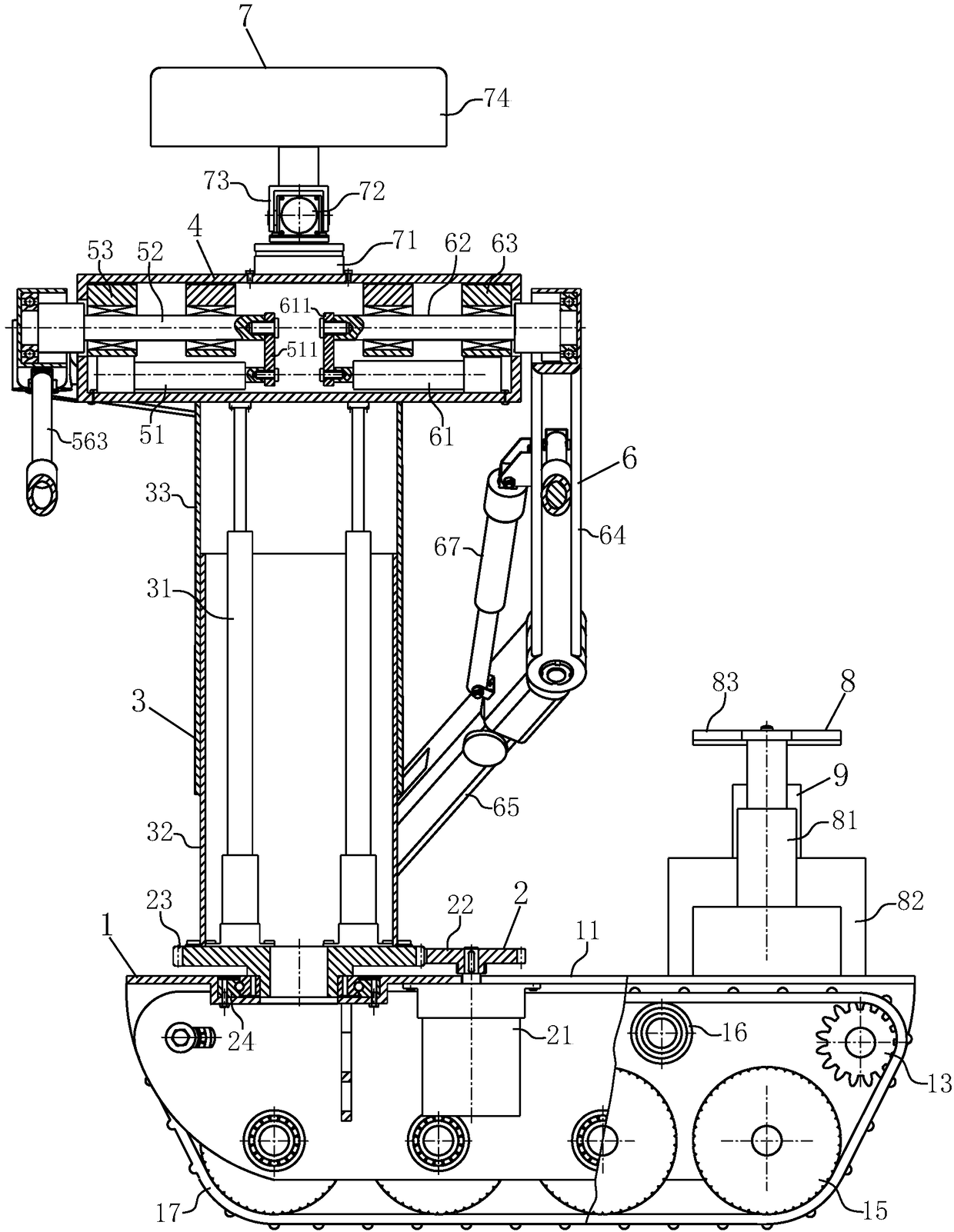
Double-arm casting sampling detection robot
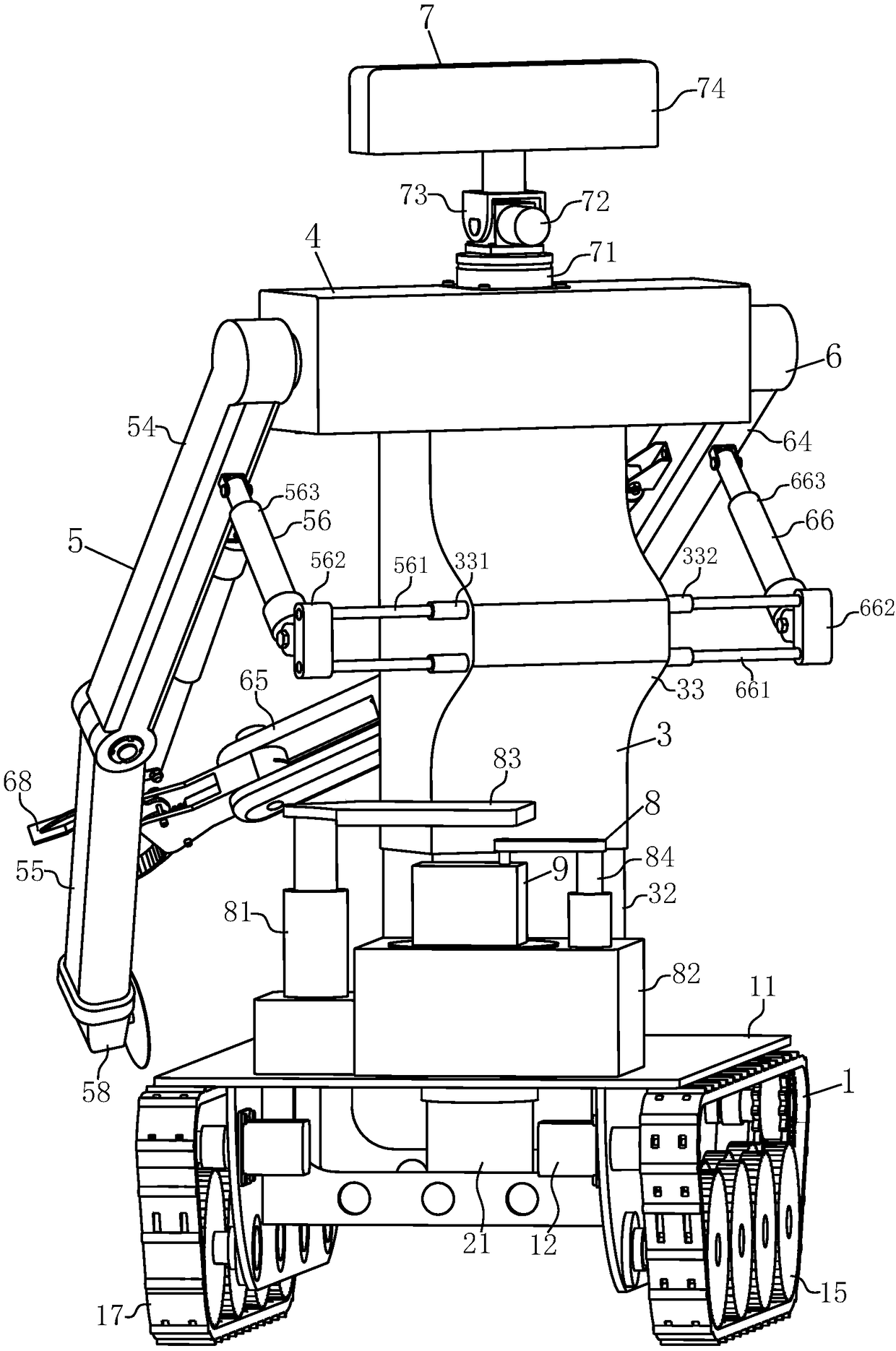
PendingCN108393894ALong distanceAvoid damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSimulationBinocular stereo
The invention discloses a double-arm casting sampling detection robot. The double-arm casting sampling detection robot comprises a moving platform, a waist rotating device, a lifting machine body, a shoulder support, a left work arm, a right work arm, a binocular stereo-vision system and a detection device. The moving platform is a walking mechanism and a bearing platform of the double-arm castingsampling detection robot, the waist rotating device and the lifting machine body can separately realize rotating and lifting adjusting functions, and the left work arm and the right work arm which are installed on the shoulder support are separately used for clamping castings and cutting castings. Three dimension scanning and component analysis testing are carried out in the detection device, andthe binocular stereo-vision system is used for obtaining field images and performing tasks such as navigation, target recognition and measurement. The double-arm casting sampling detection robot is used in casting production for replacing manual sampling, geometric parameter measurement, casting defect, component analysis and the like to the castings and samples; and the double-arm casting sampling detection robot has the advantages of high degree of automation, high adaptability and fast and convenient properties, can overcome the technical defects of existing detection devices and is more suitable for popularization.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
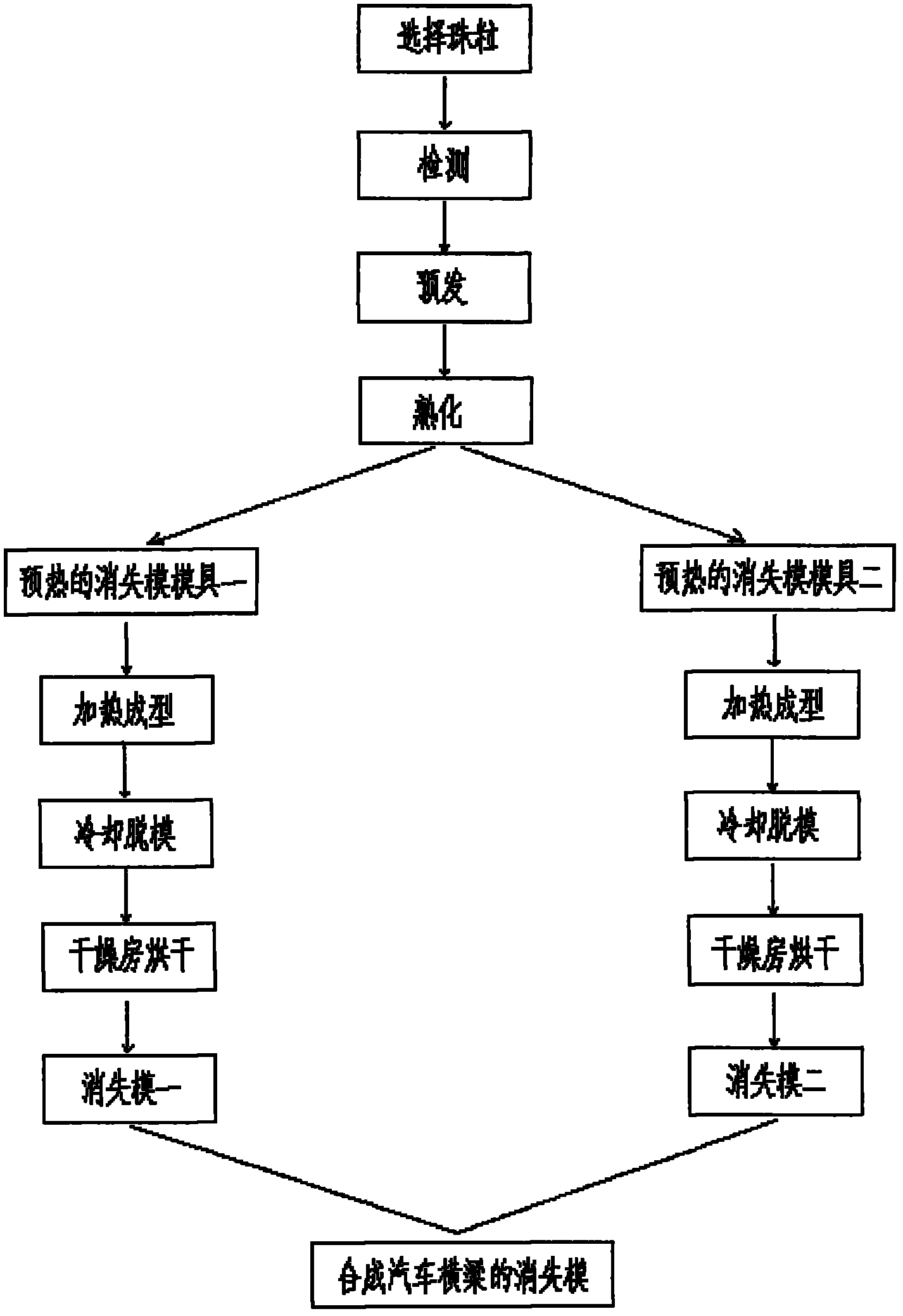
Method for manufacturing automobile cross beam lost foam and using method
InactiveCN102009123ASolution to short lifeReduce or eliminate cleanupFoundry mouldsFoundry coresCasting defectMoisture
The invention provides a method for manufacturing an automobile cross beam lost foam. The method comprises the following steps of: a, selecting proper STMMA beads, and detecting moisture and volatile content of the beads; b, pre-expanding: fully removing the redundant moisture from an intermittent steam pre-expander through a steam-water separation device, and then delivering the STMMA beads intothe intermittent steam pre-expander; c, curing: controlling the curing time of the beads to be between 12 and 48 hours; d, filling the cured beads into a lost foam die, and cooling and molding to obtain a lost foam I and a lost foam II; e, delivering the lost foams into a drying room; and f, inserting and connecting the lost foam I and the lost foam II together to synthesize the automobile cross beam lost foam. The method has simple process; the lost foam die has a reasonable structure; the method has low cost and high production efficiency; and the produced automobile cross beam has smooth surface and low casting defect rate.
Owner:青岛顺联集装箱部件制造有限公司
Workblank manufacturing method of automobile brake disc
InactiveCN105458184AAchieve productionSave materialFoundry mouldsMoulding machinesSand castingCasting defect
The invention discloses a workblank manufacturing method of an automobile brake disc, and belongs to the field of automobile accessory manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, according to design paper of the brake disc, and a precoated sand shell mold and a sand core mold are designed and manufactured; secondly, the sand shell mold or sand core mold is placed on a sand shell or sand core automatic forming machine to manufacture a precoated sand casting sand shell model and a sand core model; thirdly, pouring is carried out; and fourthly, a casting is taken out and cleaned. The beneficial effects that production of the brake disc workblank can be efficiently achieved, materials and manpower are saved, mechanical allowance is reduced, casting defects are reduced, the yield is improved, and automation production is easily achieved are achieved.
Owner:YUZHOU KUNLUN MOLD CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com