Patents
Literature
1026results about "Casting safety devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
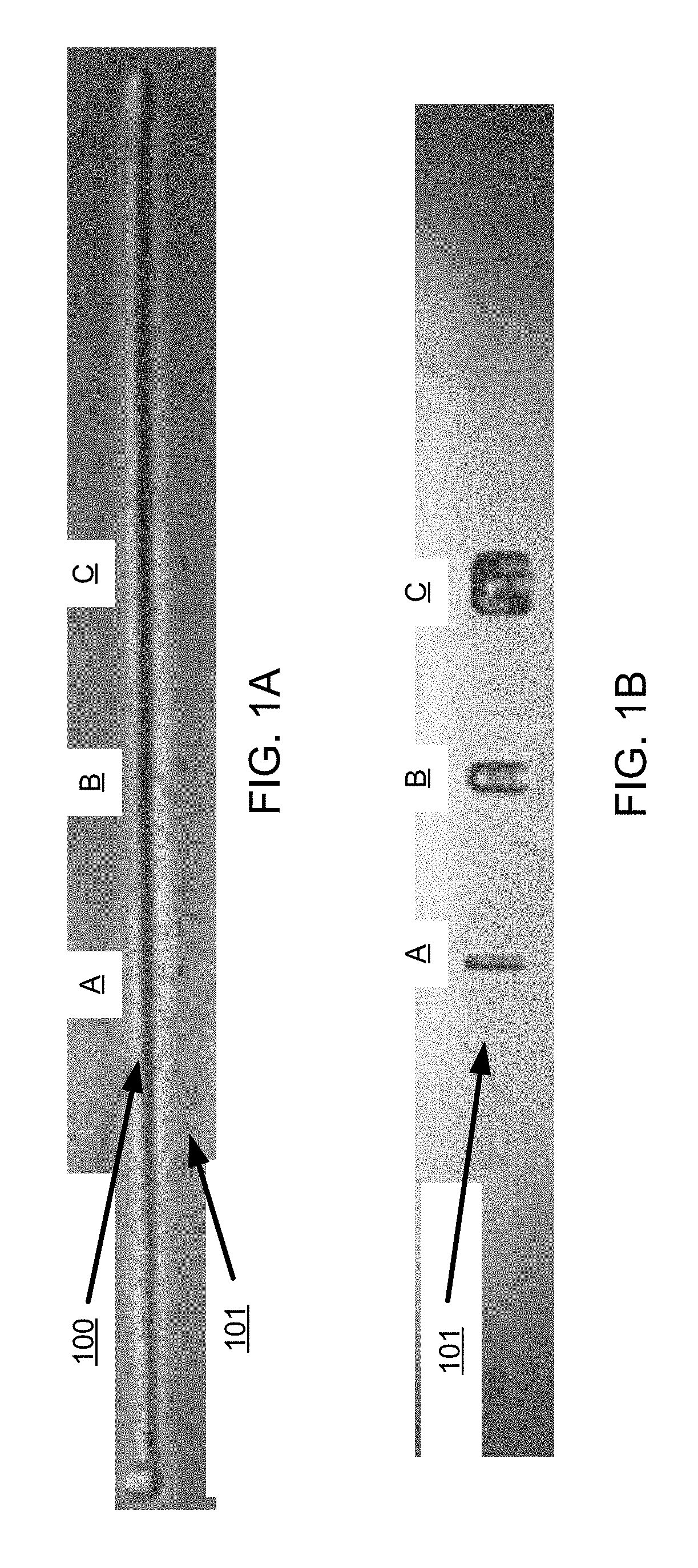
Rapid prototype casting
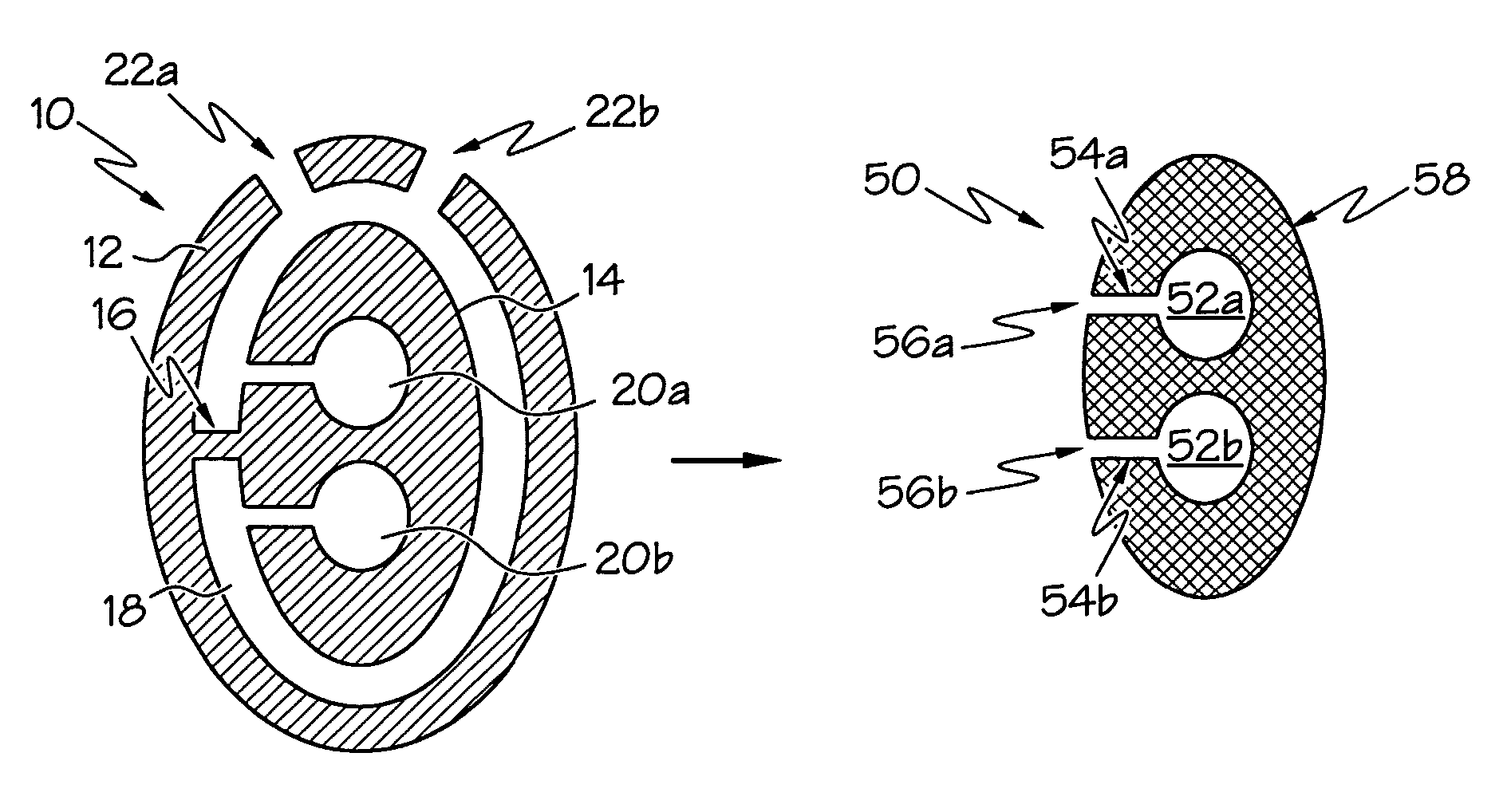
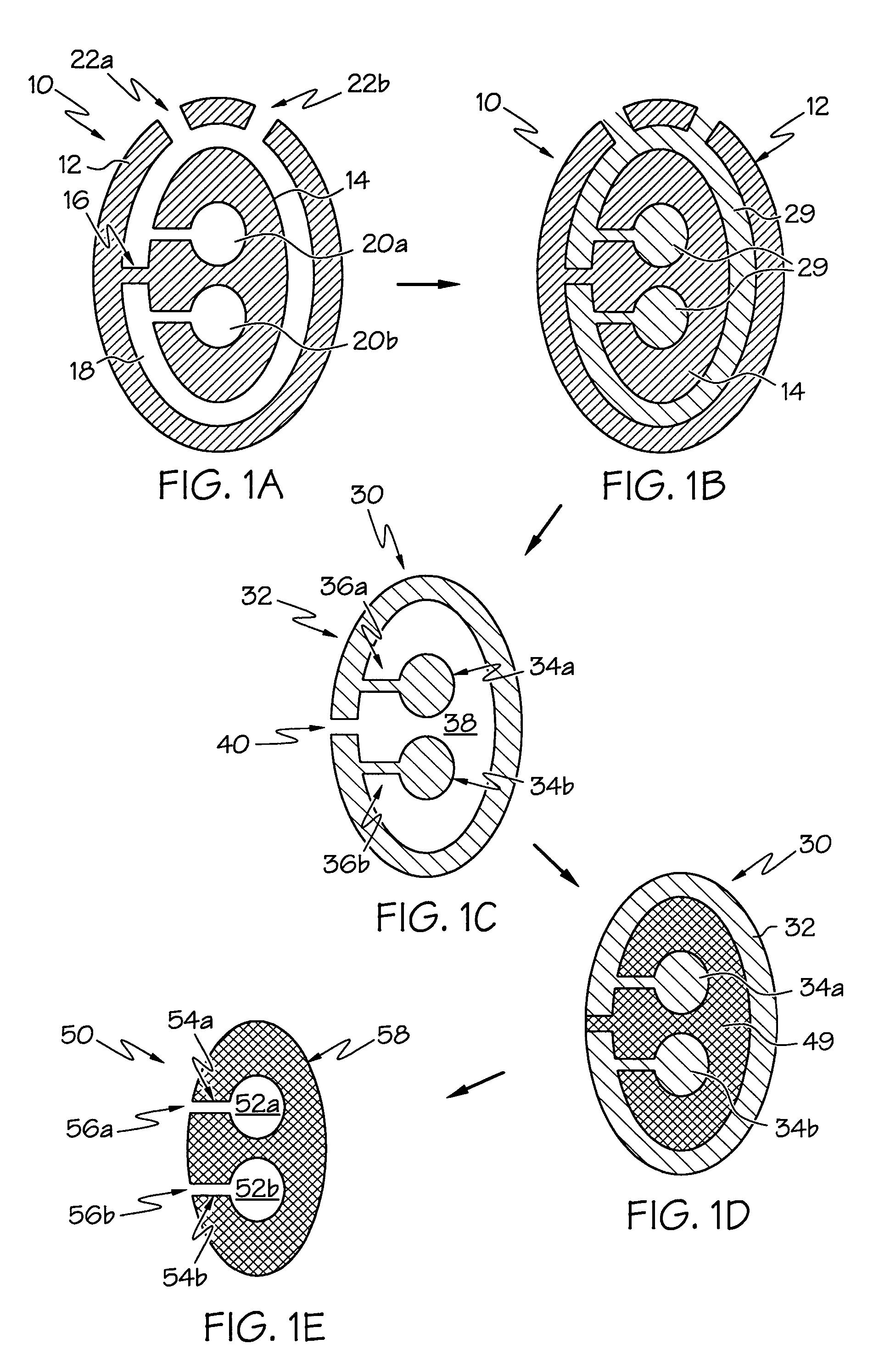
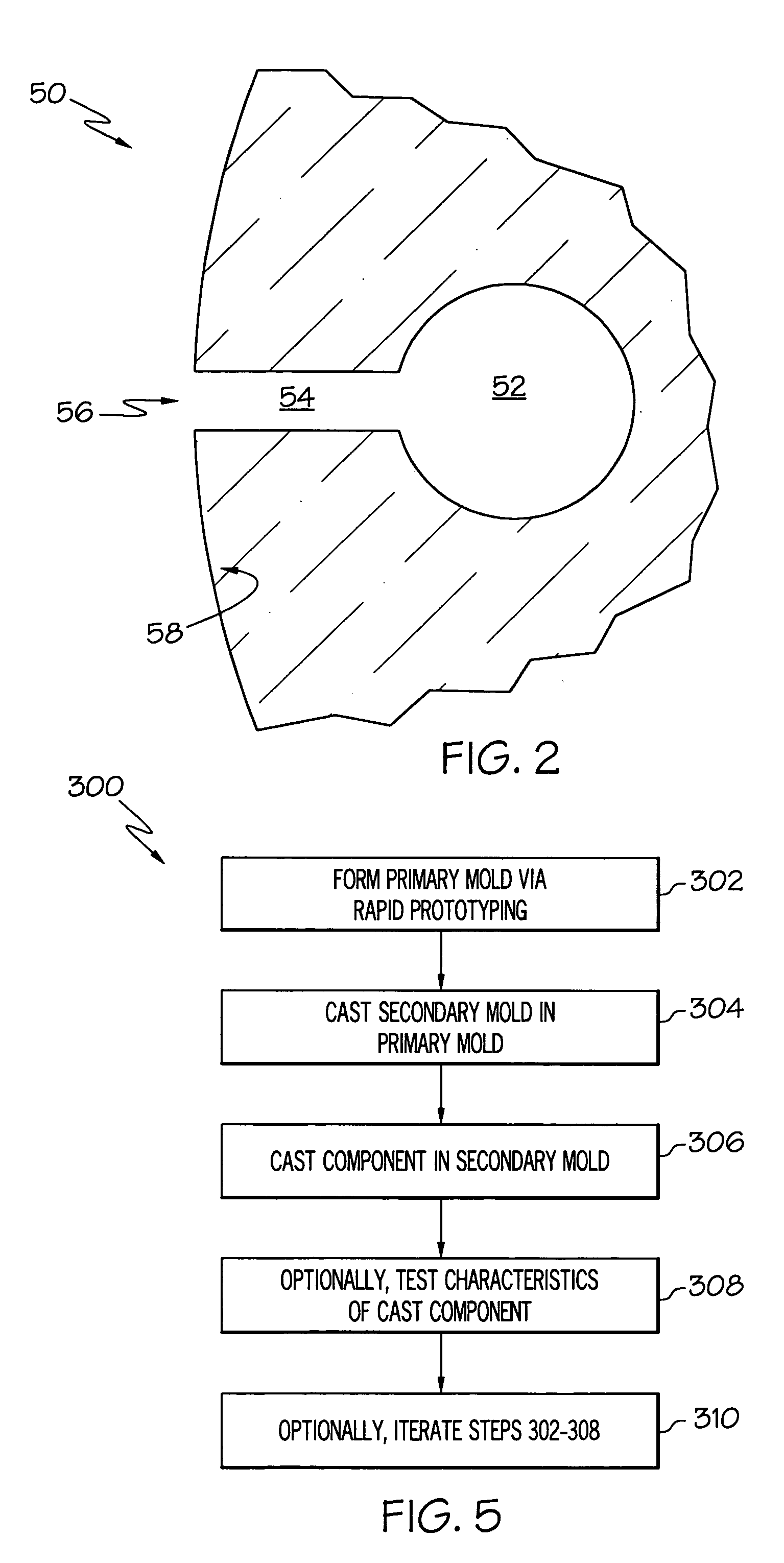
Methods for rapid prototype casting metal components, wherein the metal components are cast in a secondary ceramic mold, the secondary ceramic mold is cast in a primary mold, and the primary mold is formed by rapid prototyping or rapid manufacturing. The secondary ceramic mold may comprise a one-piece integral shell and core(s), and the metal components may have at least one hollow portion or void therein, such as a hollow airfoil for a gas turbine engine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Systems and methods for computationally developing manufacturable and durable cast components
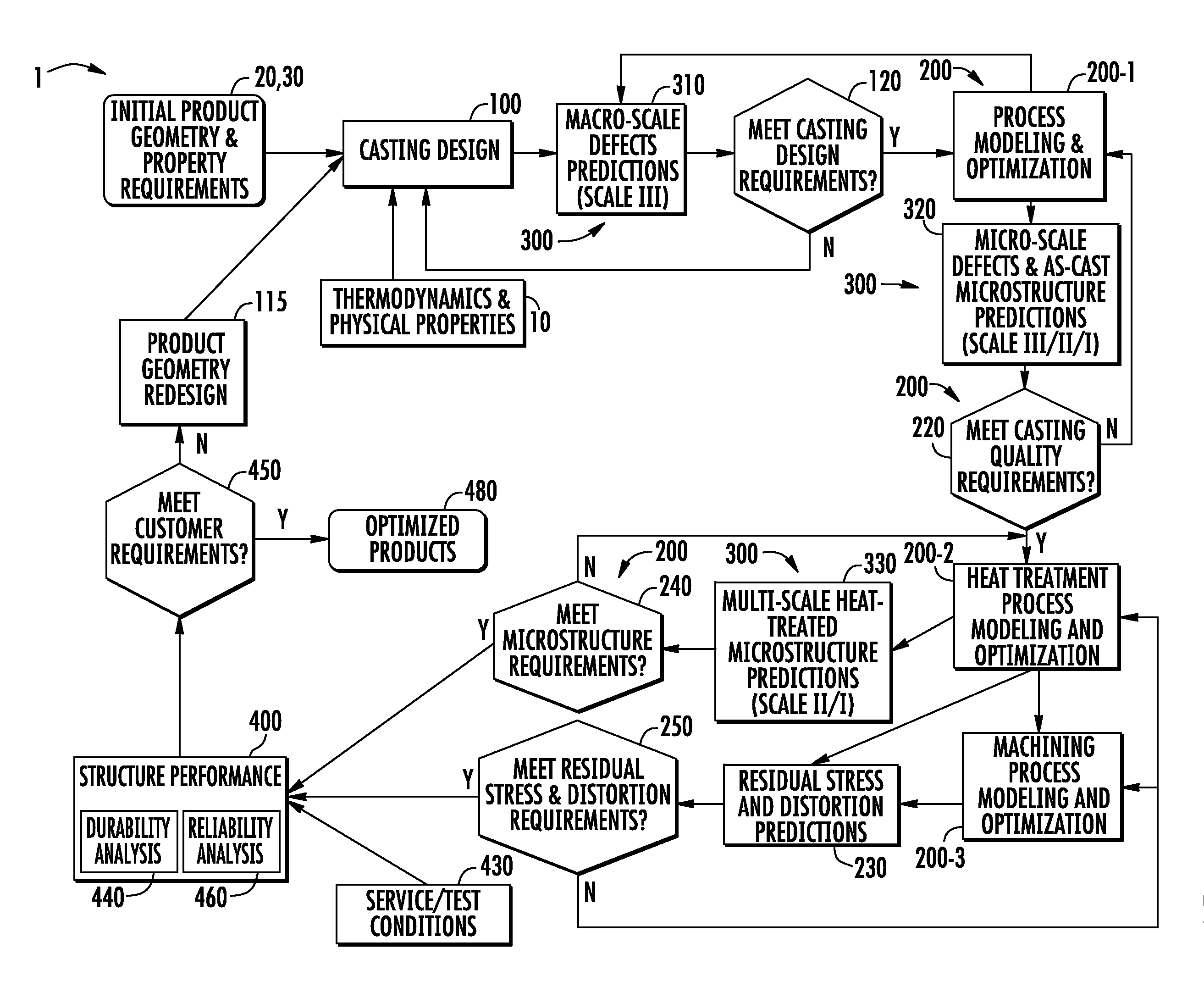
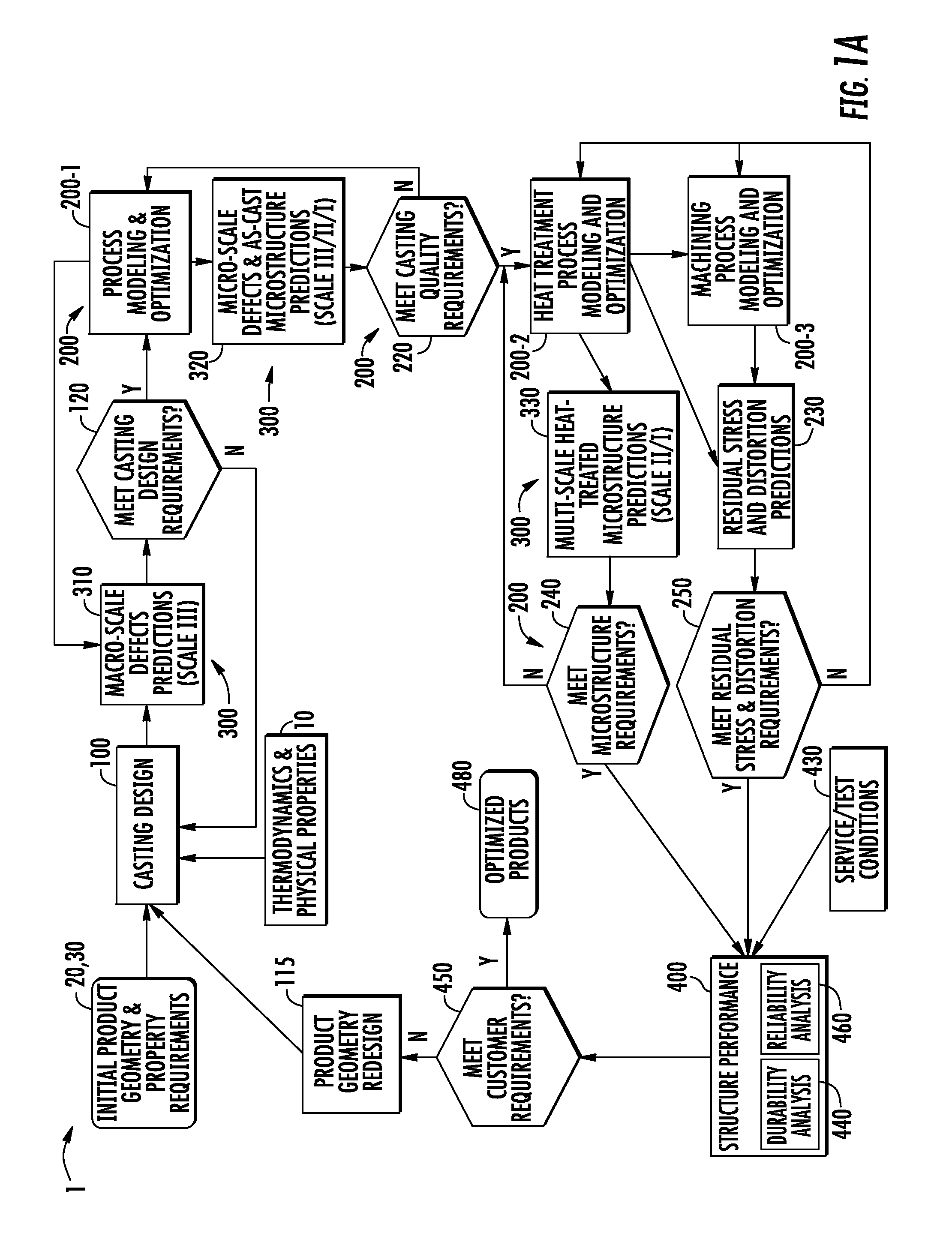
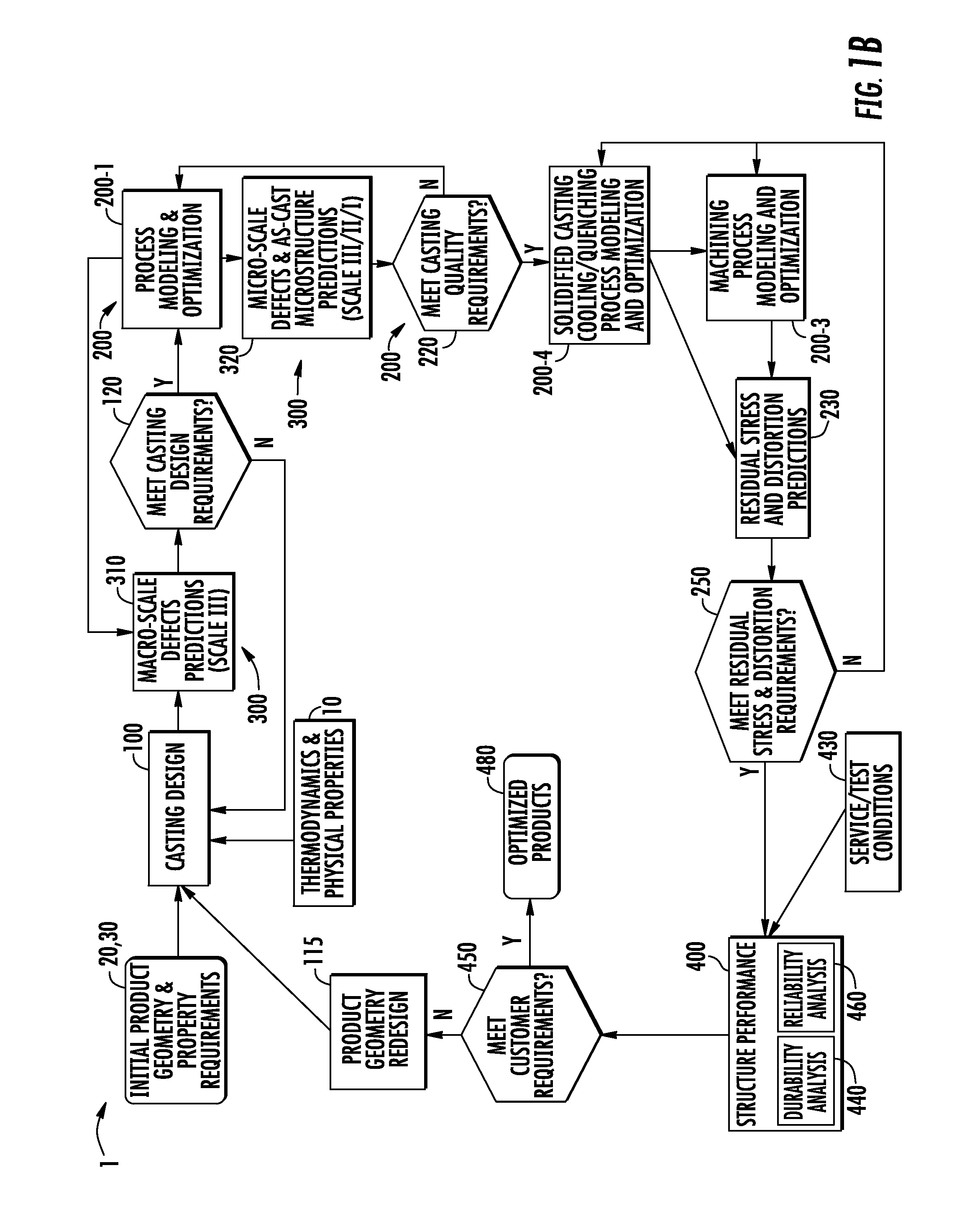
A method and system for optimizing a simulated casting of a light weight alloy component. The simulation includes passing component design data through various computational modules relating to casting designs, process modeling and optimization, material microstructure and defects and product performance. Variations in microstructure and defects across various very small size scales are extended to increasingly larger scales to permit structural performance calculations of the cast component to take such non-uniformities into consideration. At least some of the modules employ an expert system-based approach to achieve the optimized results. The results can be compared to end user needs to determine if redesign of the part geometry or manufacturing process is needed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method, apparatus, computer readable storage medium and computer program for forming an object
InactiveUS20110042031A1Polycrystalline material growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer programFreezing point
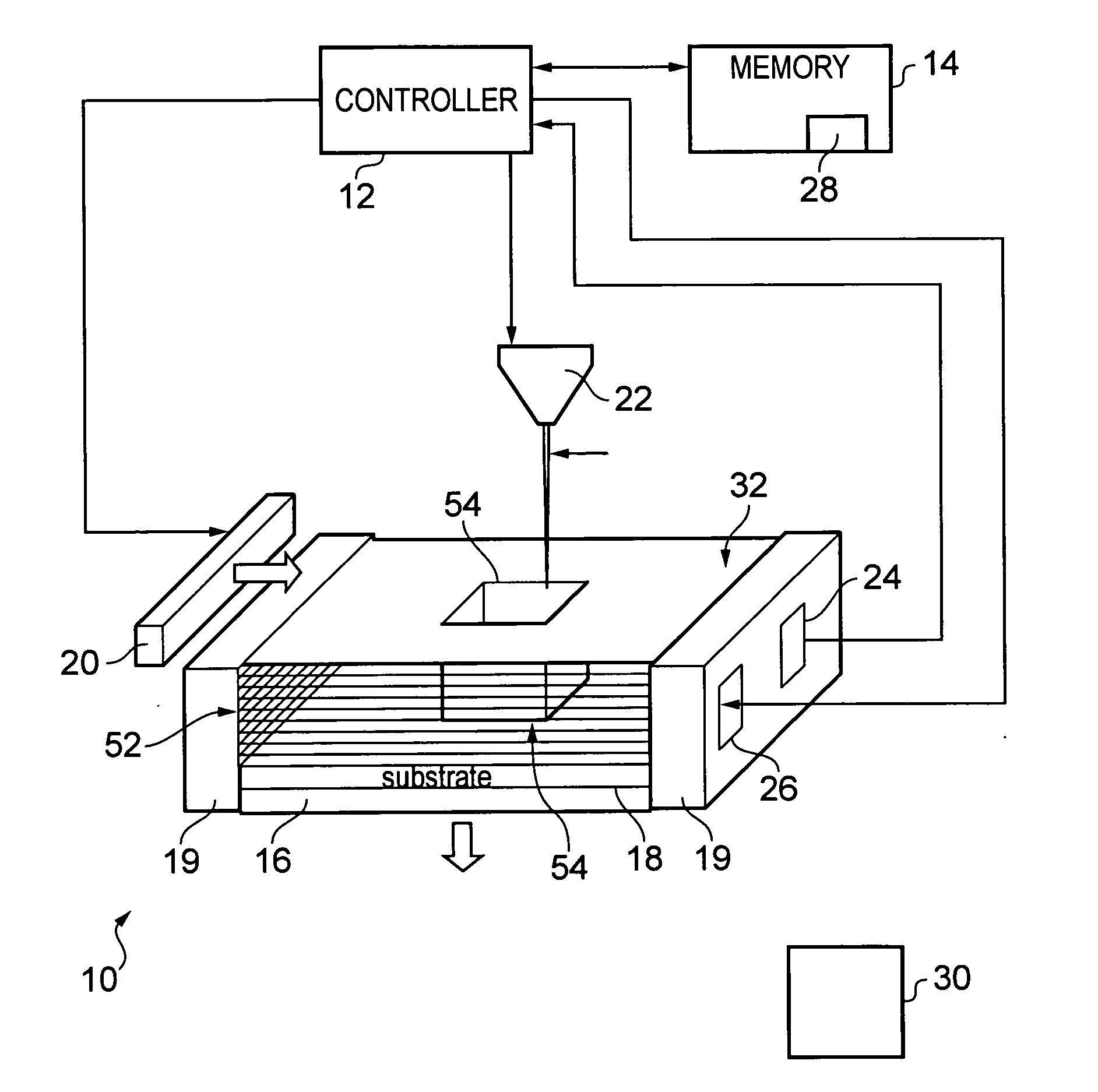
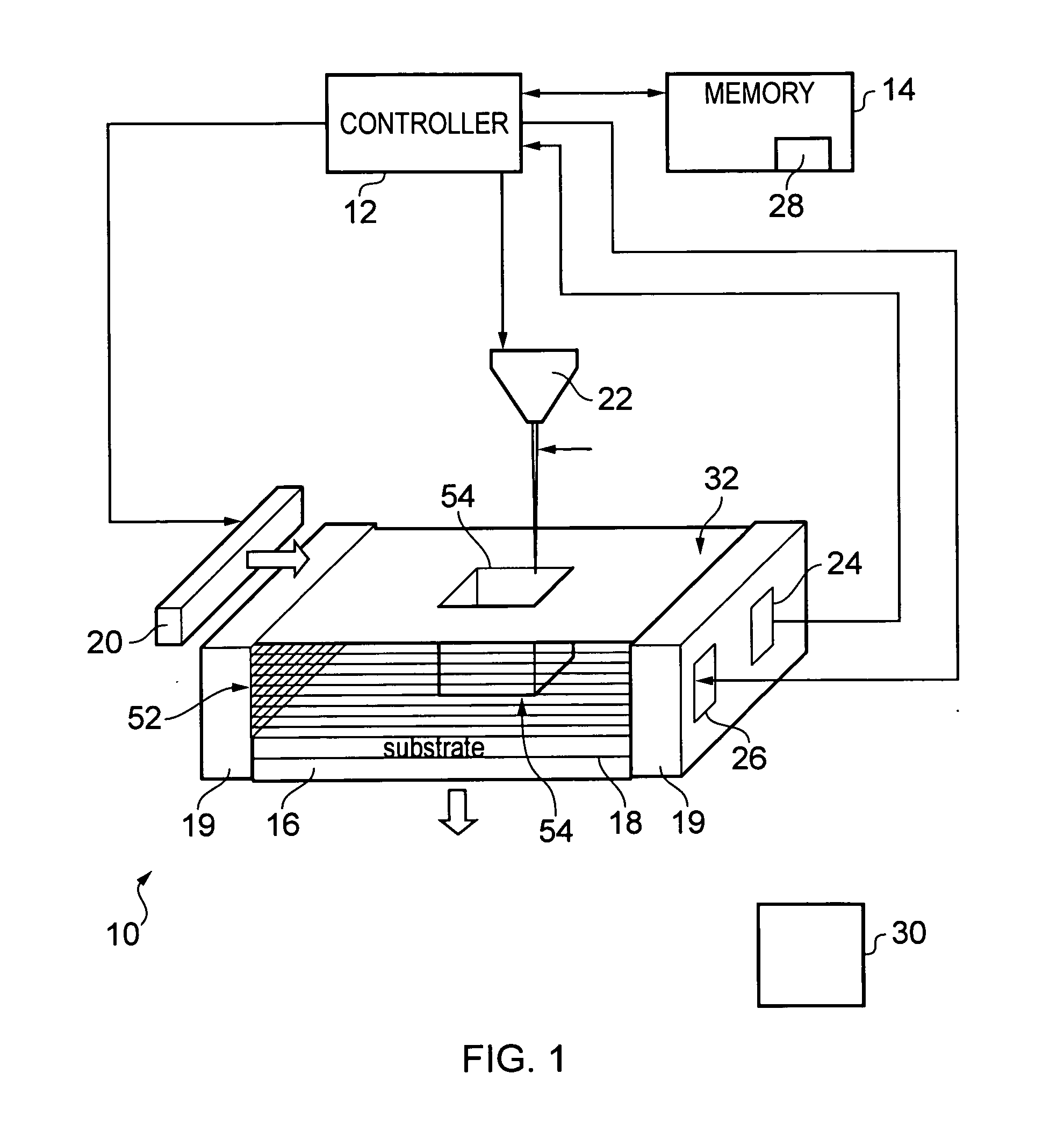
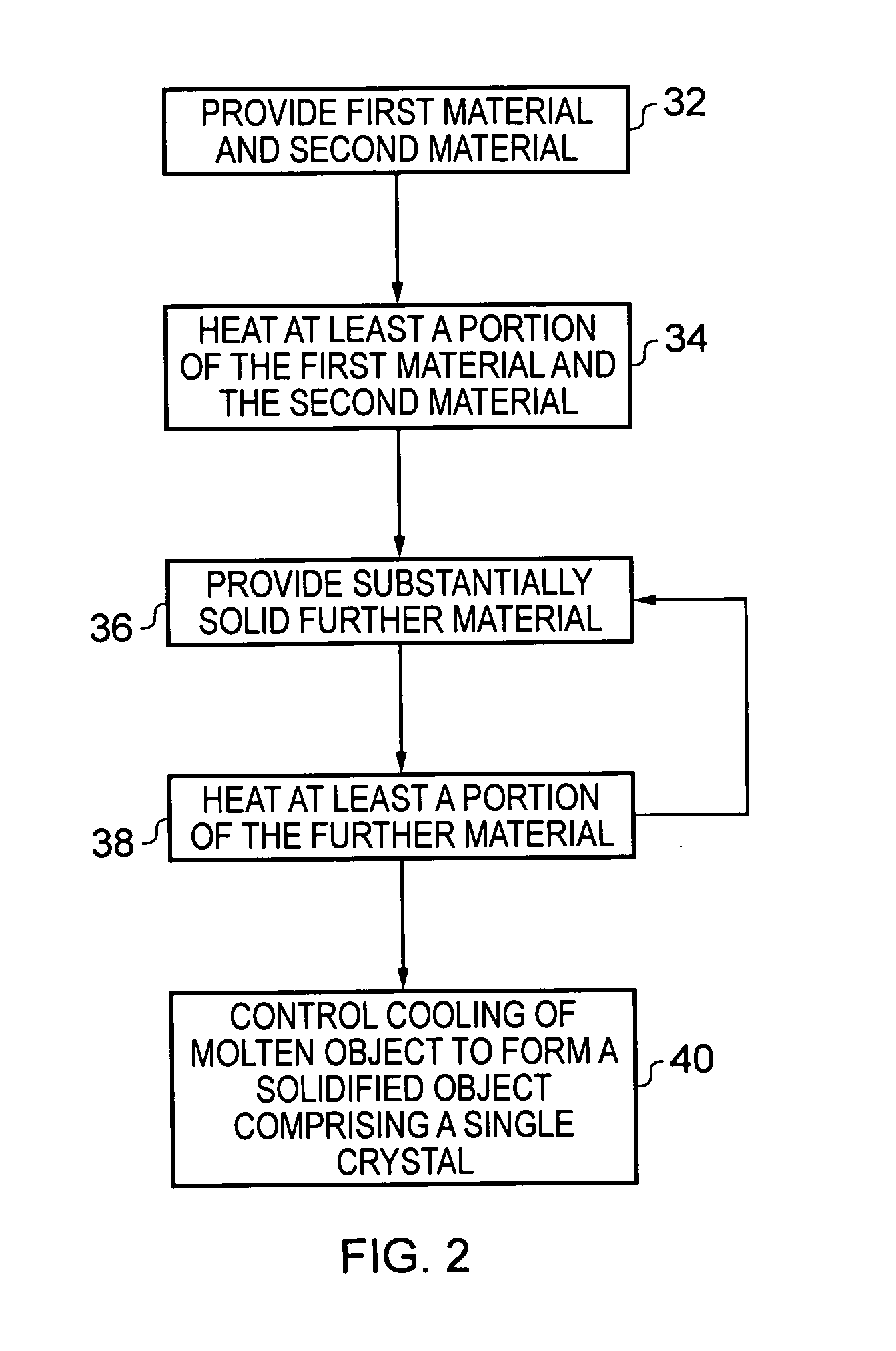
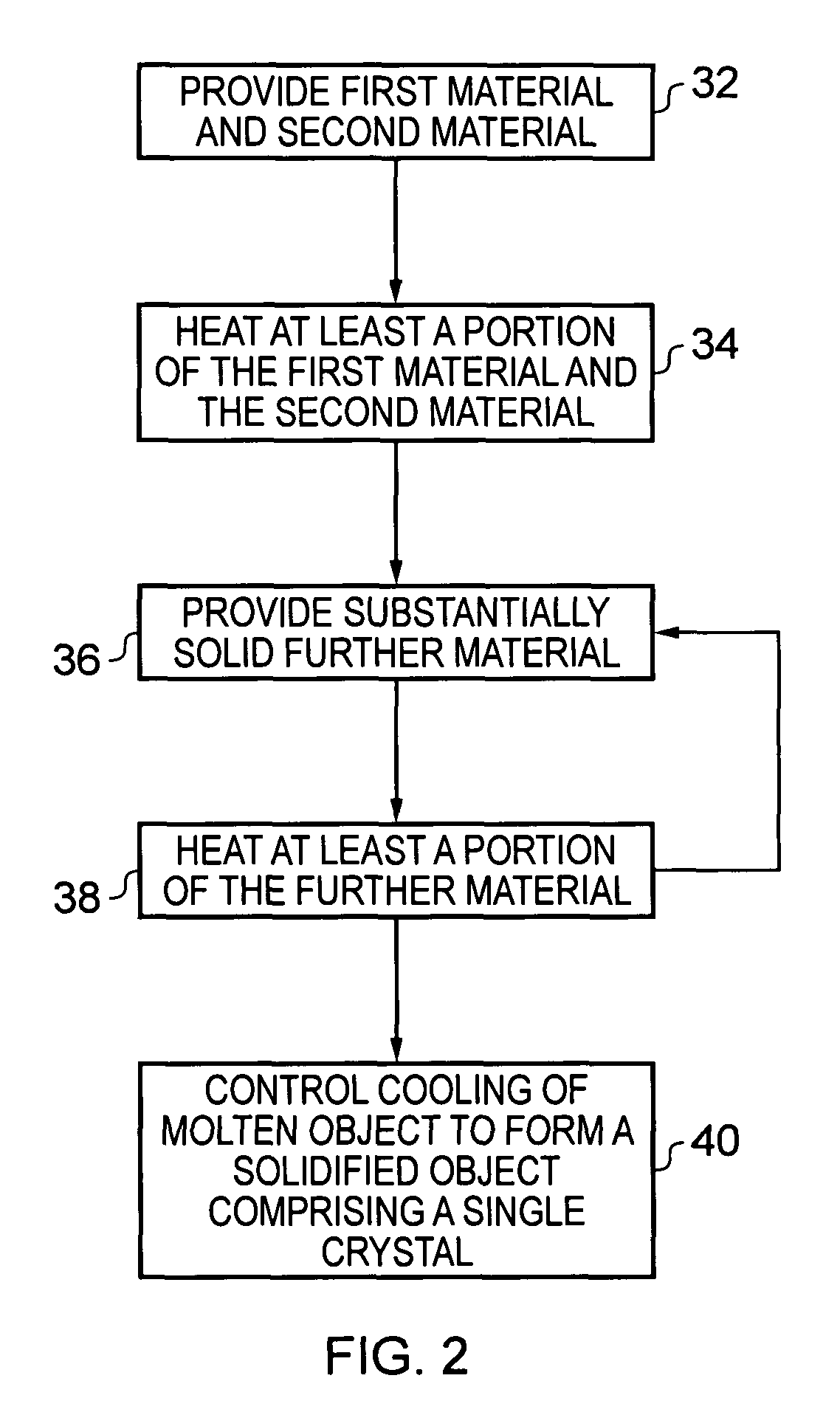
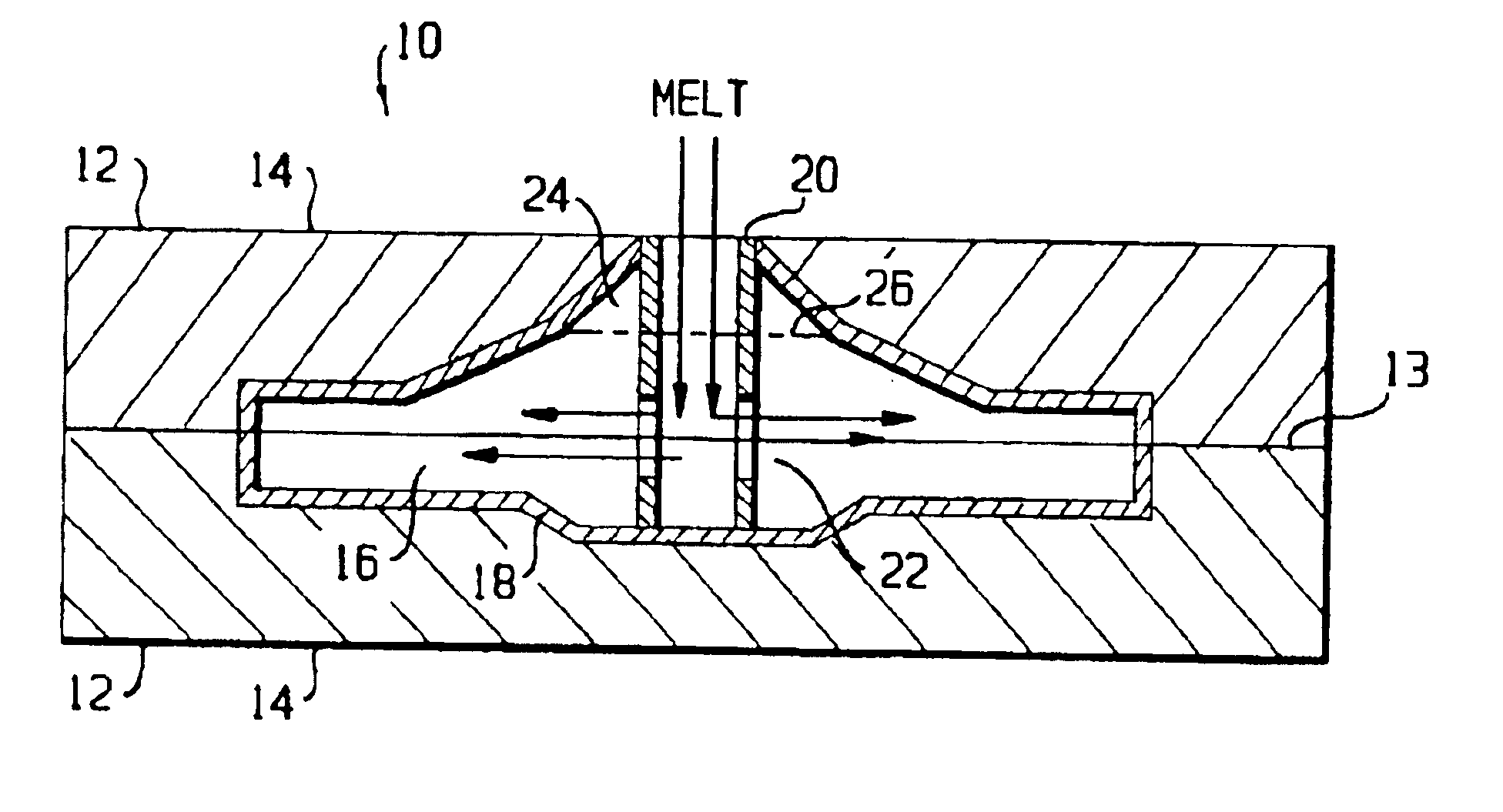
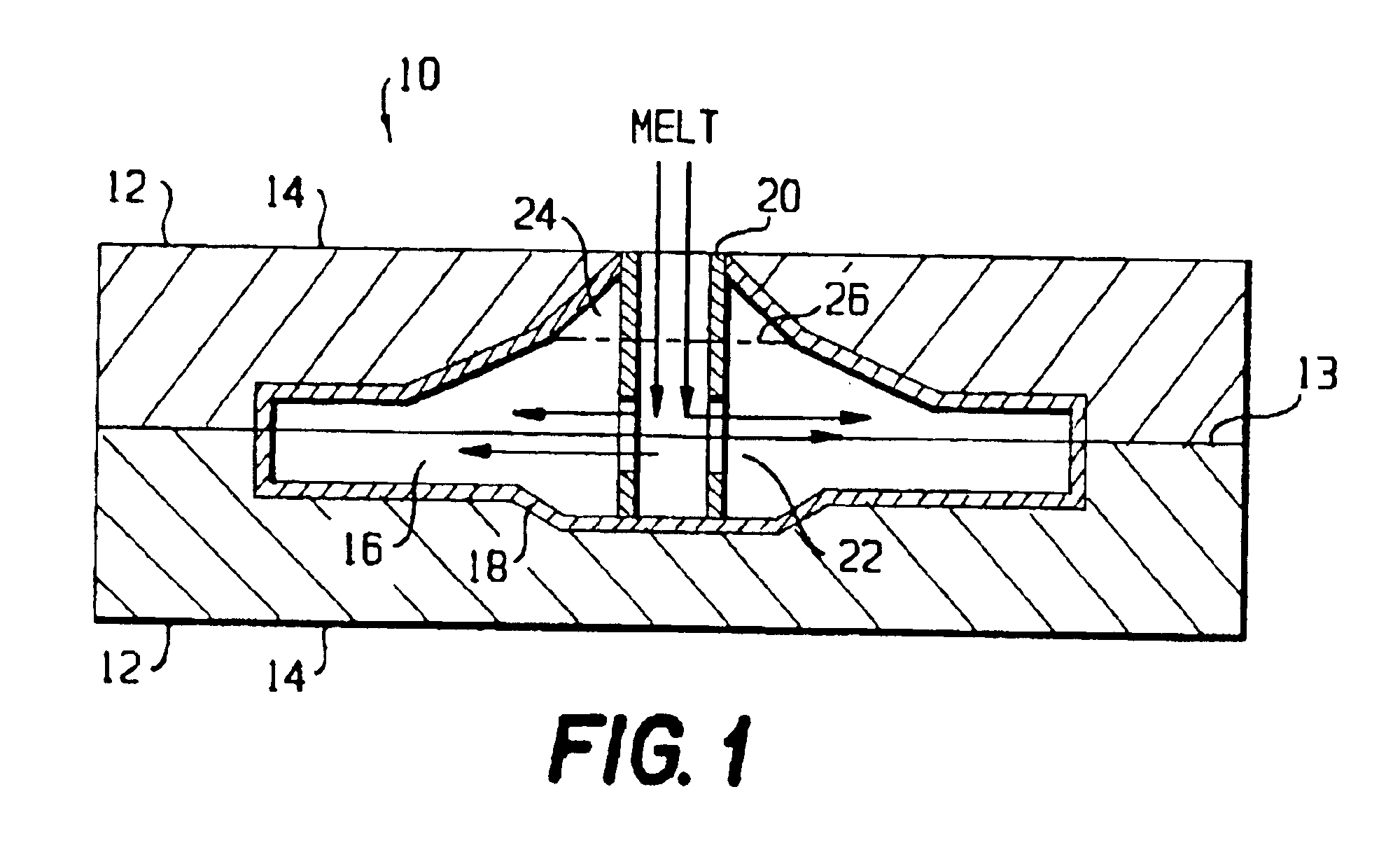
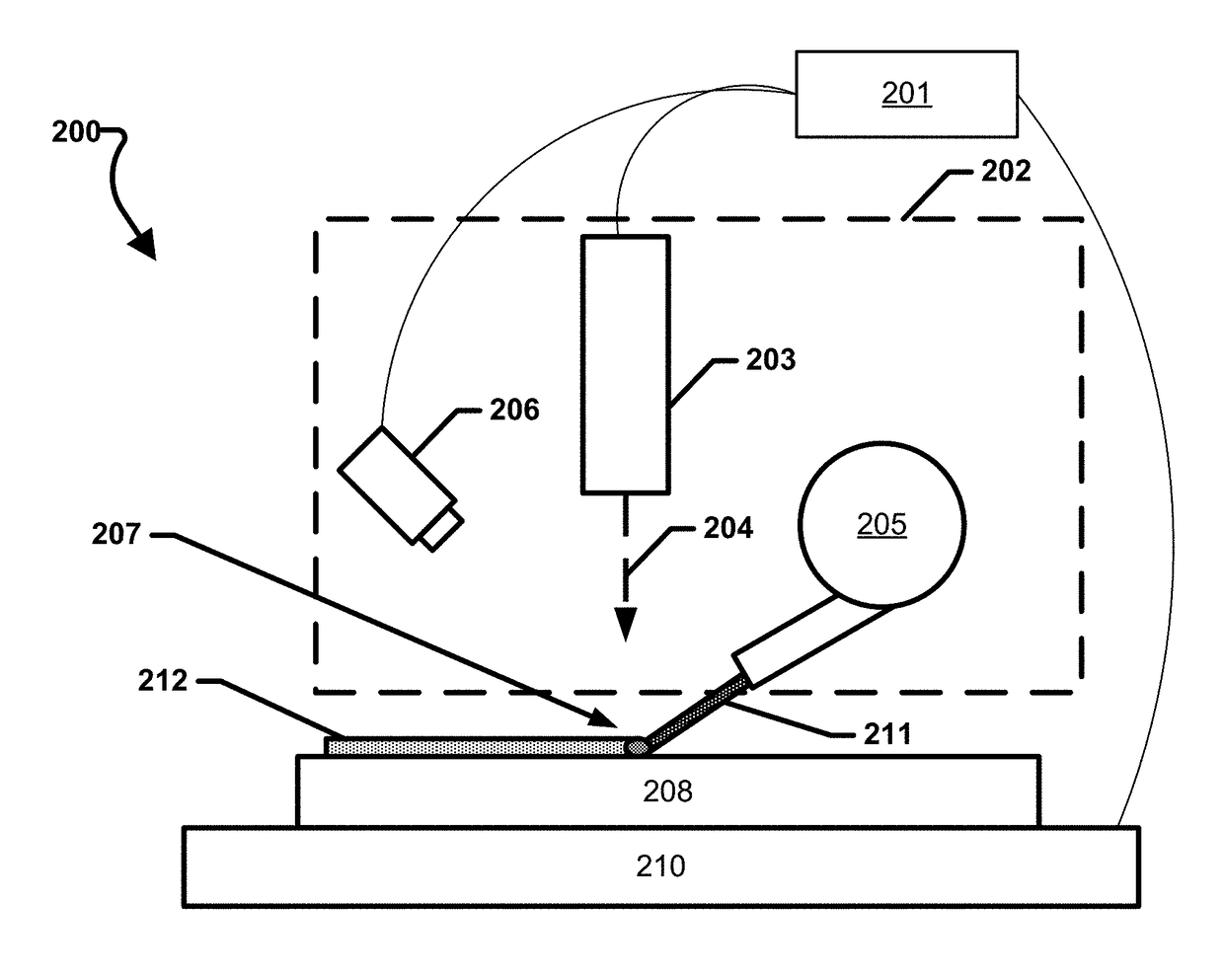
A method for forming an object, including providing at least a first material having a melting point at a first temperature and a second material having a melting point at a second temperature; heating at least a portion of the first and second materials above the first and second temperatures to form a substantially molten alloy, the molten alloy having a solidifying point at a third temperature, the third temperature being less than the first temperature and the second temperature; and providing substantially solid further material to at least a portion of the molten alloy, the further material having a melting point at a temperature greater than the third temperature.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD
Combined metallic bonding and molding for electronic assemblies including void-reduced underfill
ActiveUS20090291524A1Small sizeReducing joint misalignmentCasting safety devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDielectric membrane
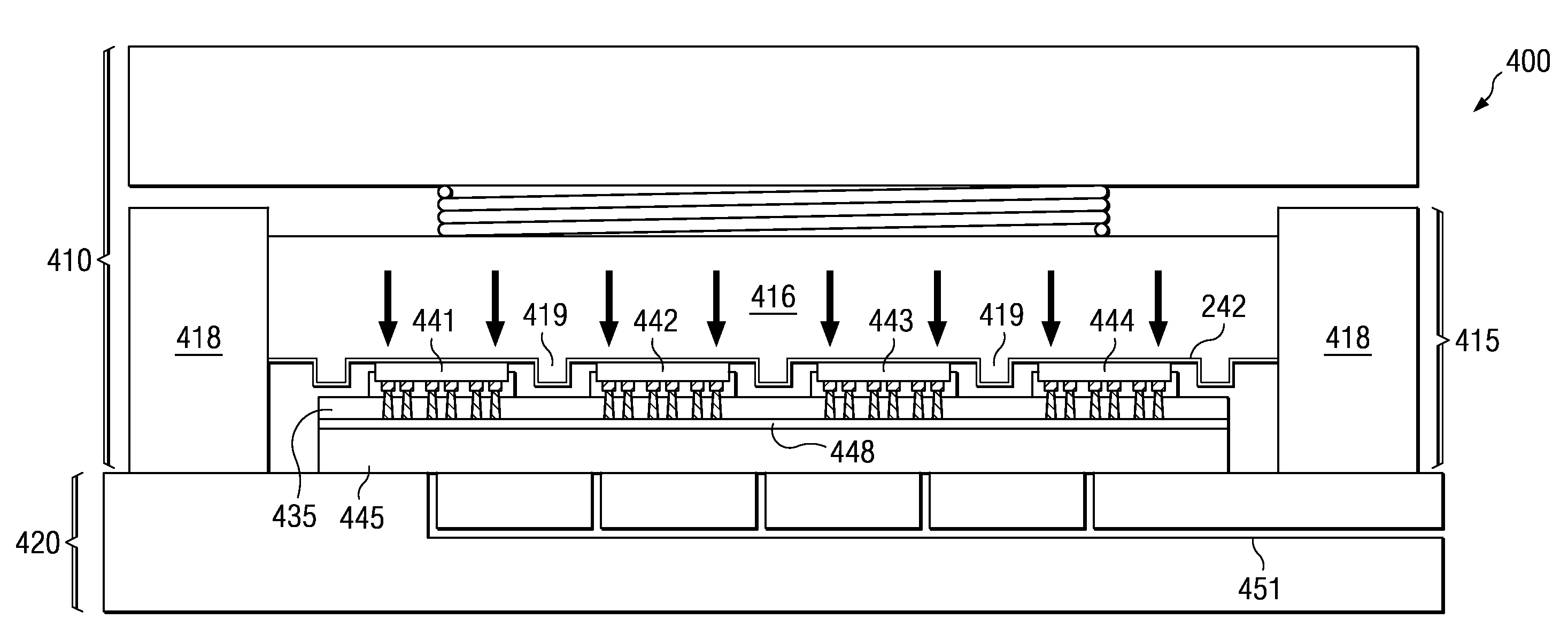
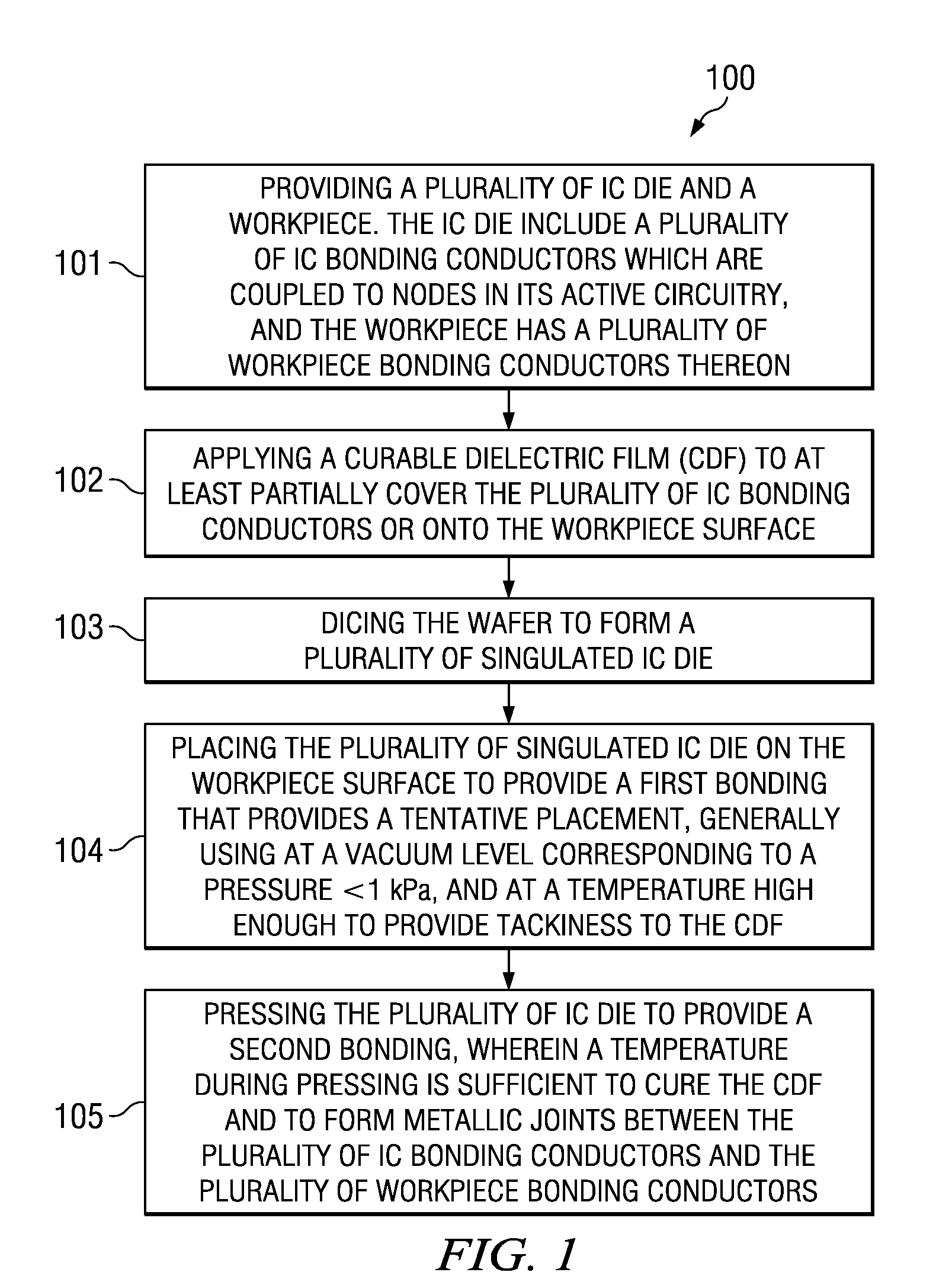
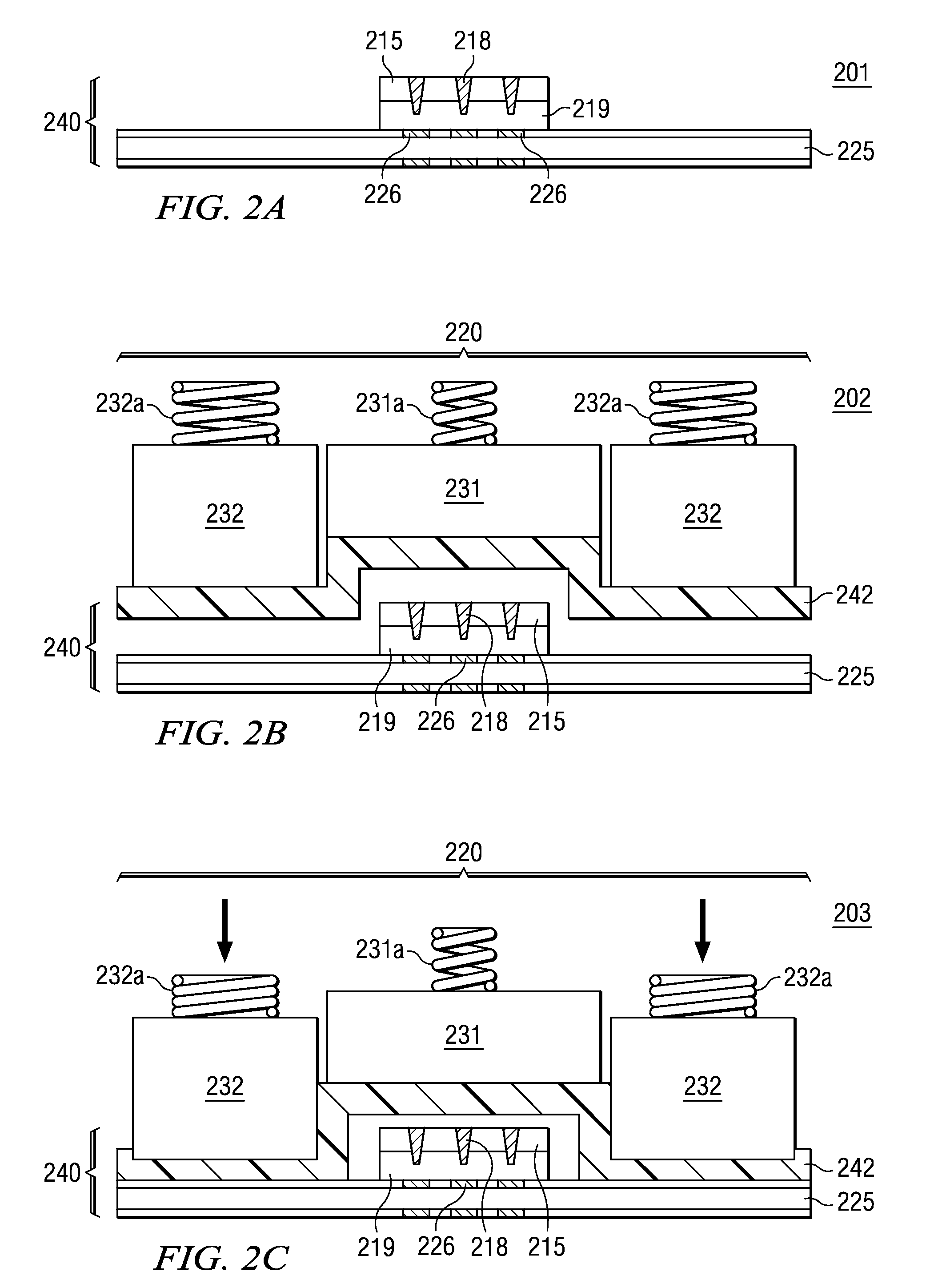
A method for forming electronic assemblies includes providing a plurality of IC die each having IC bonding conductors and a workpiece having workpiece bonding conductors. A curable dielectric film is applied to the IC bonding conductors or the workpiece surface. The plurality of IC die are placed on the workpiece surface so that the plurality of IC bonding conductors are aligned to and face the plurality of workpiece bonding conductors to provide a first bonding. The placing is performed at a vacuum level corresponding to a pressure <1 kPa, and at a temperature sufficient to provide tackiness to the curable dielectric film. The plurality of IC die are then pressed to provide a second bonding. A temperature during pressing cures the curable dielectric film to provide an underfill and forms metallic joints between the plurality of IC bonding conductors and the plurality of workpiece bonding conductors.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
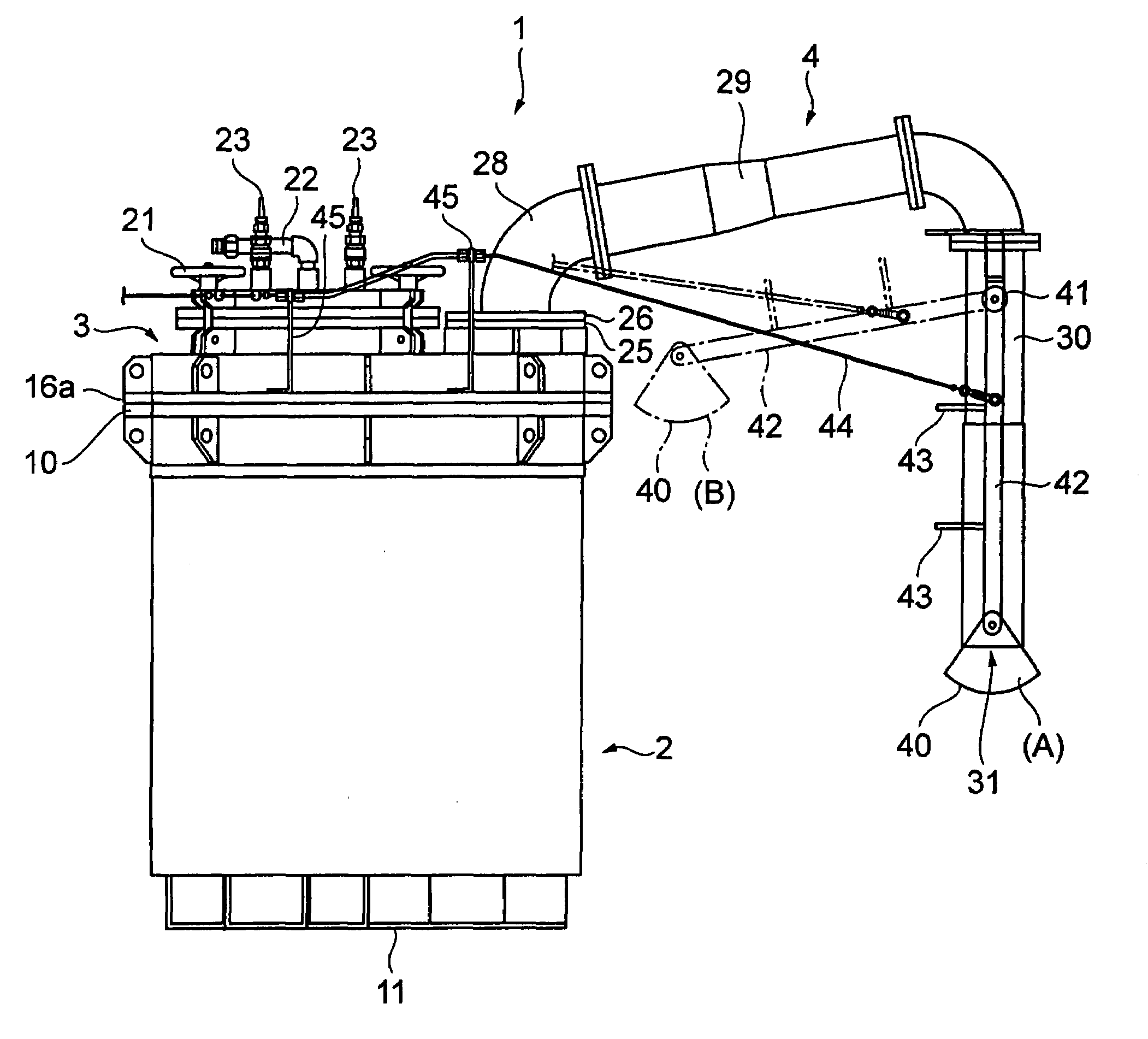
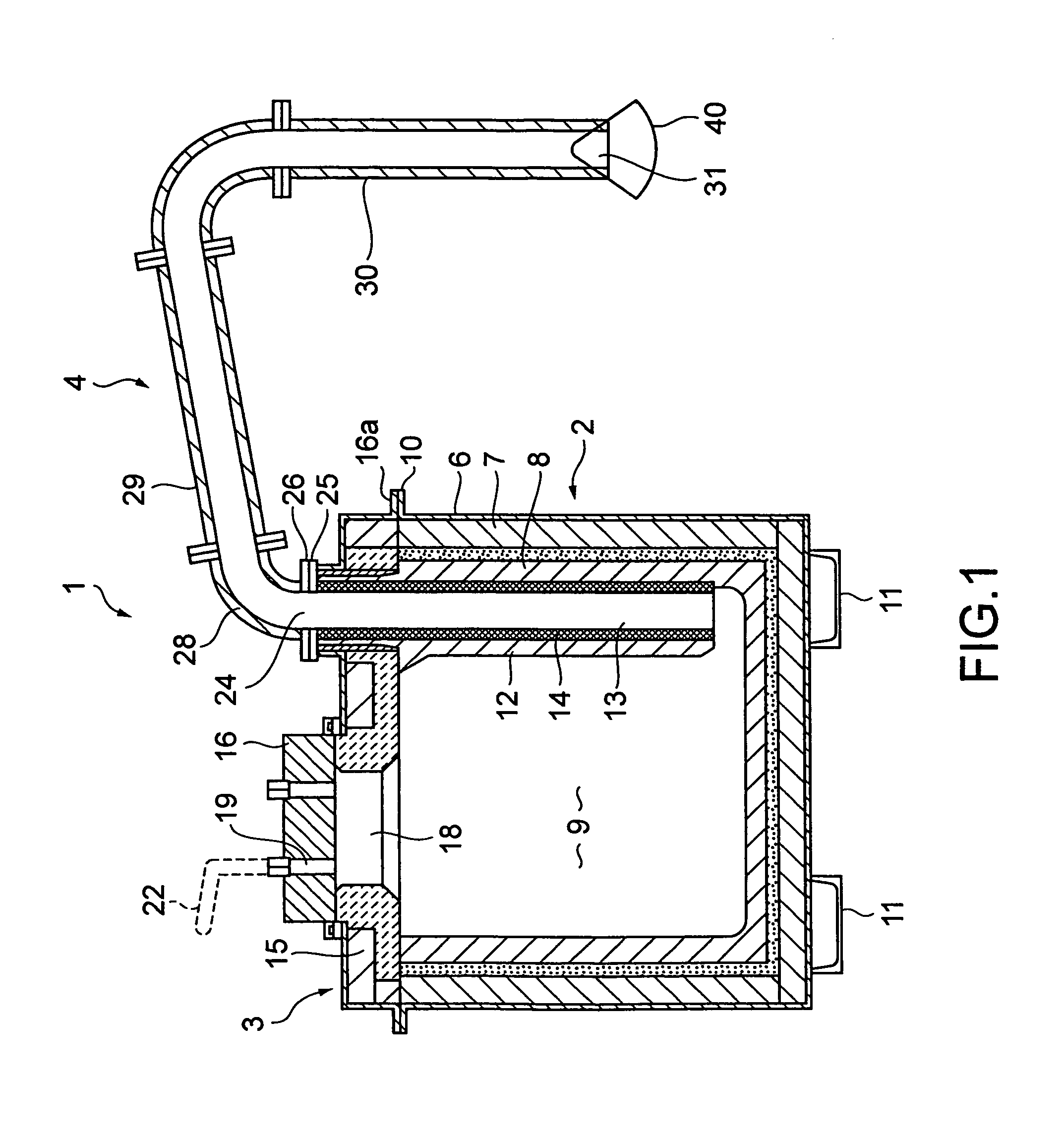
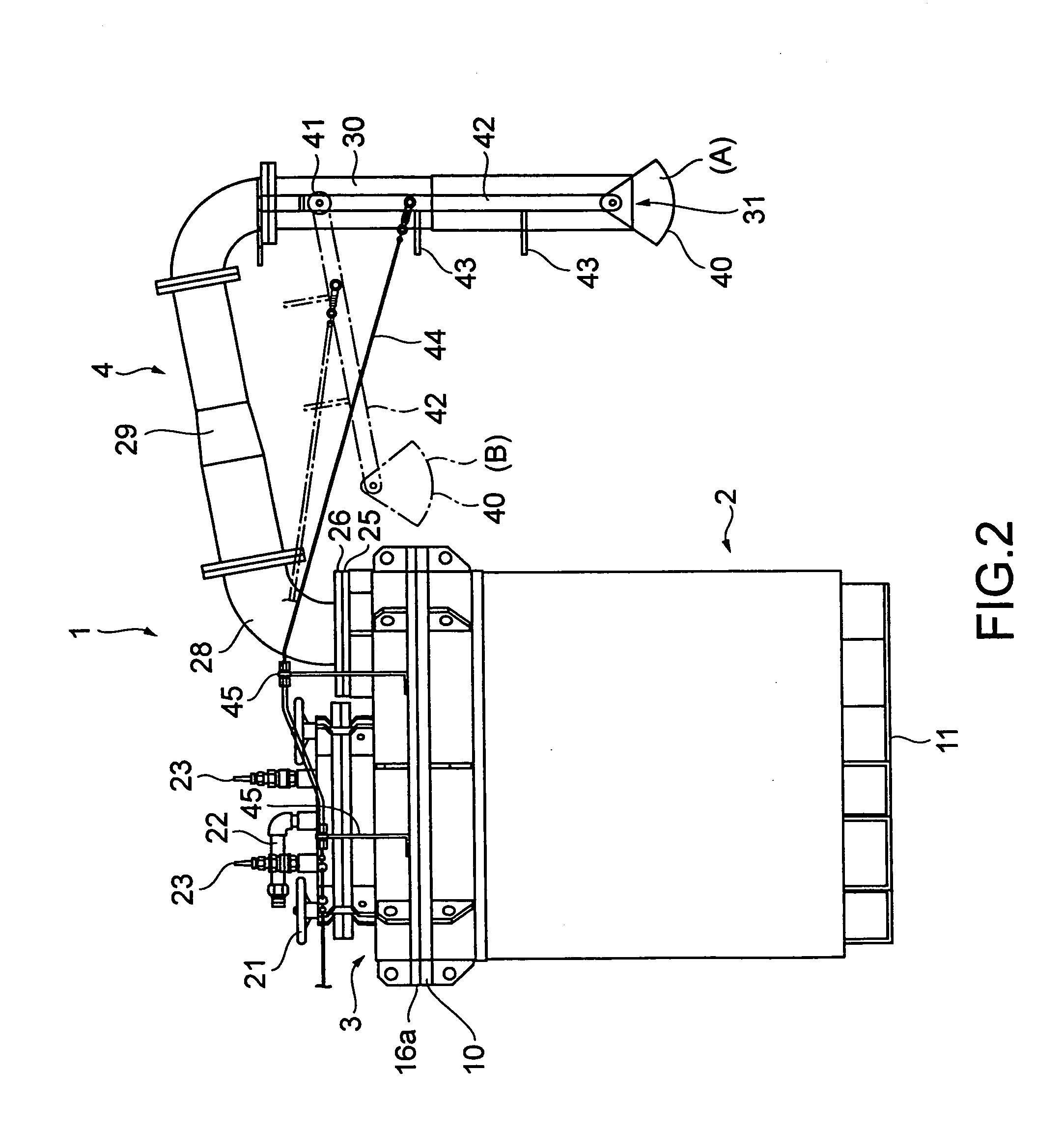
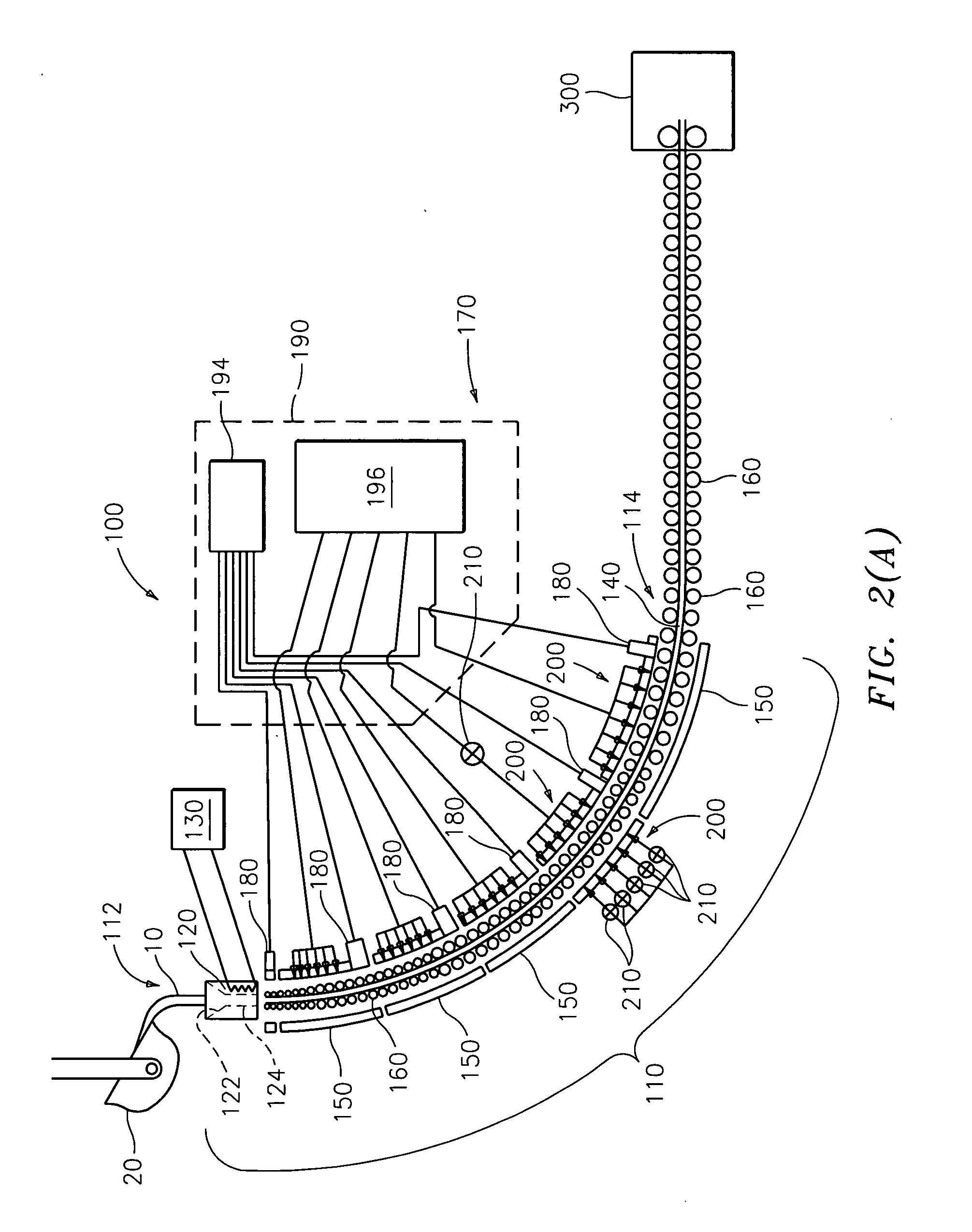
System for supplying molten metal, container and a vehicle
InactiveUS7481966B2Low costMelt-holding vesselsMolten metal supplying equipmentsWire rodHermetic seal
A molten metal supplying system comprising a container having a main body capable of being hermetically sealed and having a passage through which compressed gas is received, a pipe having an outlet supplying molten metal in the container to the outside, the outlet downwardly extending, a reception dish receiving the molten metal capable of being placed below the pipe outlet, a holding member having a fulcrum to the pipe rotatably holding the reception dish, a wire with a first and second end, the first end connected to the reception dish or holding member, a pair of channel members at the outer bottom of the container main body, and a vehicle having a fork that can be inserted and removed from the channel members, a carriage on which the fork is mounted, a lift mechanism for lifting up and down the carriage, and a wire pull and return mechanism mounted on the carriage pulling and returning the wire with it's second end.
Owner:HOEI SHOKAI CO LTD
Molding and casting machine
ActiveUS20080135205A1Improved swing movementEasy to adjustPig casting plantsCasting safety devicesMolding machineSand casting
Disclosed is a sand casting molding machine for double indexing molds in a mold string. The machine can include a shot chamber having sand, a swingable squeeze head, a lateral squeeze head, a core setter, a mold hold down, a mold retention device and a mold string conveyor.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP WAUPACA
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in anisotropic pyrolytic graphite molds under vacuum
Molds are fabricated having a substrate of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, and having a mold cavity coated with pyrolytic graphite. The molds may be made by making the substrate (main body) of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, by, for example, isostatic or vibrational molding, machining the substrate to form the mold cavity, and coating the mold cavity with pyrolytic graphite via a chemical deposition process. The molds may be used to make various metallic alloys such as nickel, cobalt and iron based superalloys, stainless steel alloys, titanium alloys and titanium aluminide alloys into engineering components by melting the alloys in a vacuum or under a low partial pressure of inert gas and subsequently casting the melt in the graphite molds under vacuum or low partial pressure of inert gas.
Owner:SANTOKU CORP
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in refractory metals and refractory metal carbides coated graphite molds under vacuum
InactiveUS20050016706A1Quality improvementImprove mechanical propertiesCasting safety devicesFoundry mouldsSuperalloyTitanium carbide
Molds are fabricated having a substrate of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, and having a mold cavity coated with a refractory metal such as W or Re or a refractory metal carbide such as TaC or HfC. The molds may be made by making the substrate (main body) of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, by, for example, isostatic or vibrational molding, machining the substrate to form the mold cavity, and coating the mold cavity with titanium carbide via either chemical deposition or plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition, magnetron sputtering or sputtering. The molds may be used to make various metallic alloys such as nickel, cobalt and iron based superalloys, stainless steel alloys, titanium alloys and titanium aluminide alloys into engineering components by melting the alloys in a vacuum or under a low partial pressure of inert gas and subsequently casting the melt in the graphite molds under vacuum or low partial pressure of inert gas.
Owner:SANTOKU AMERICA
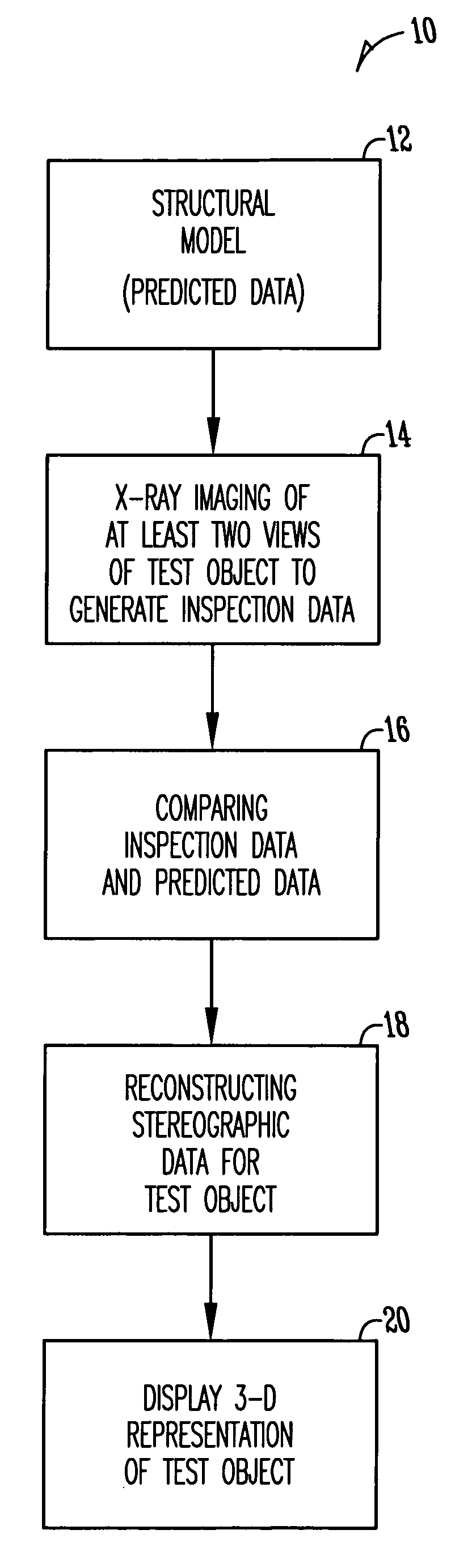
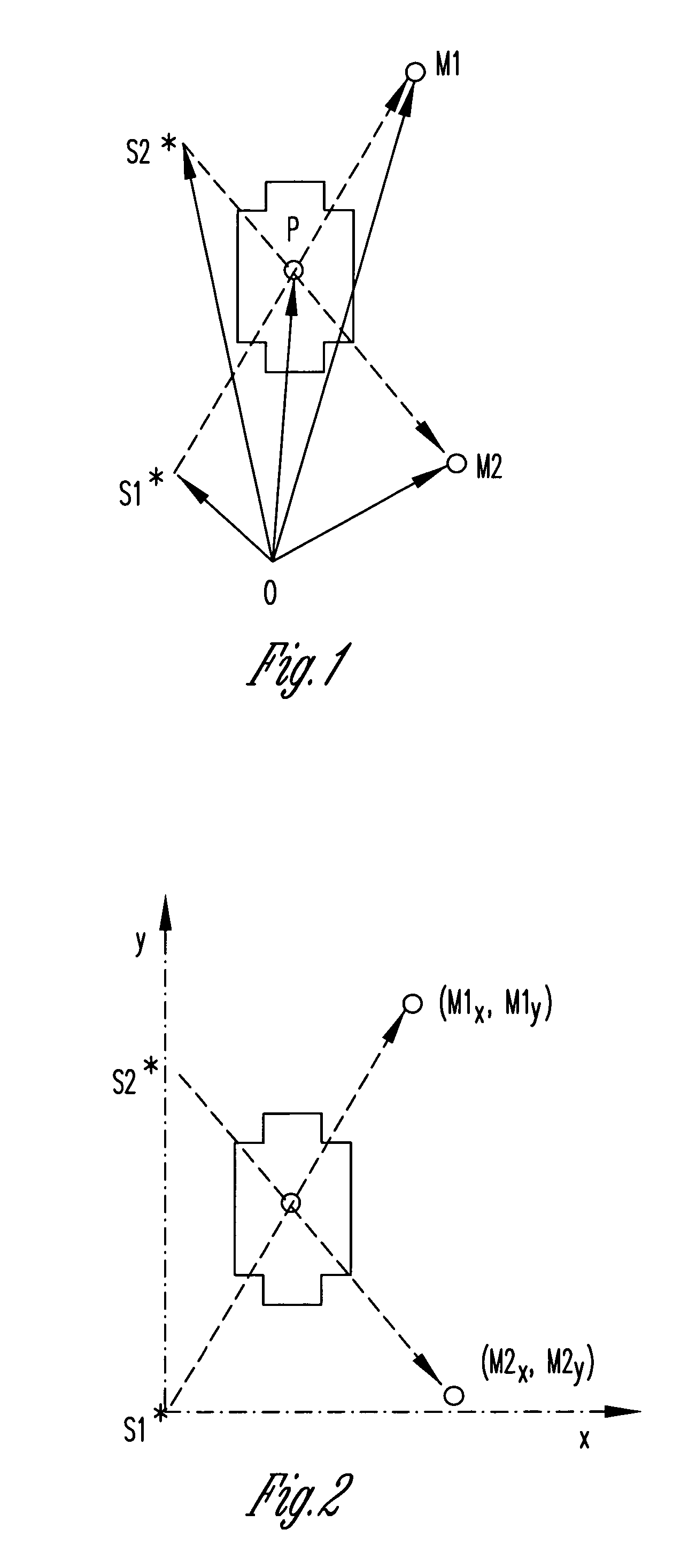
Model-assisted reconstruction of volumetric data
The present invention is a method for inspecting objects. The method includes obtaining a structural model of a first object, the model providing dimensions and material properties for the first object, inspecting a second object to provide inspection data for at least two views of a structure of the second object, comparing inspection and predicted data based on the structural model of the first object and a simulation of the inspection process, reconstructing stereographic data for the second object based on the structural model of the first object and contributions of the inspection data of the second object. In another embodiment, where there is a structural model of an object, the object can be subjected to a dynamic process and the object is inspected throughout the process.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for forming an object
InactiveUS8186414B2Polycrystalline material growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusFreezing pointMelting point
A method for forming an object, including providing at least a first material having a melting point at a first temperature and a second material having a melting point at a second temperature; heating at least a portion of the first and second materials above the first and second temperatures to form a substantially molten alloy, the molten alloy having a solidifying point at a third temperature, the third temperature being less than the first temperature and the second temperature; and providing substantially solid further material to at least a portion of the molten alloy, the further material having a melting point at a temperature greater than the third temperature.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in refractory metals and refractory metal carbides coated graphite molds under vacuum
InactiveUS6986381B2Quality improvementImprove mechanical propertiesCasting safety devicesFoundry mouldsTitanium carbideSuperalloy
Owner:SANTOKU AMERICA
System and Method for In-Situ Characterization and Inspection of Additive Manufacturing Deposits Using Transient Infrared Thermography
ActiveUS20170297095A1Improve defect contrast within imageAdditive manufacturing apparatusCasting safety devicesManufacturing engineeringThermography
Systems and methods are provided for the real time inspection of additive manufacturing deposits using infrared thermography. Various embodiments may enable the measurement of material properties and the detection of defects during the additive manufacturing process. Various embodiments may enable the characterization of deposition quality, as well as the detection of deposition defects, such as voids, cracks, disbonds, etc., as a structure is manufactured layer by layer in an additive manufacturing process. Various embodiments may enable quantitative inspection images to be archived and associated with the manufactured structure to document the manufactured structure's structural integrity.
Owner:NASA
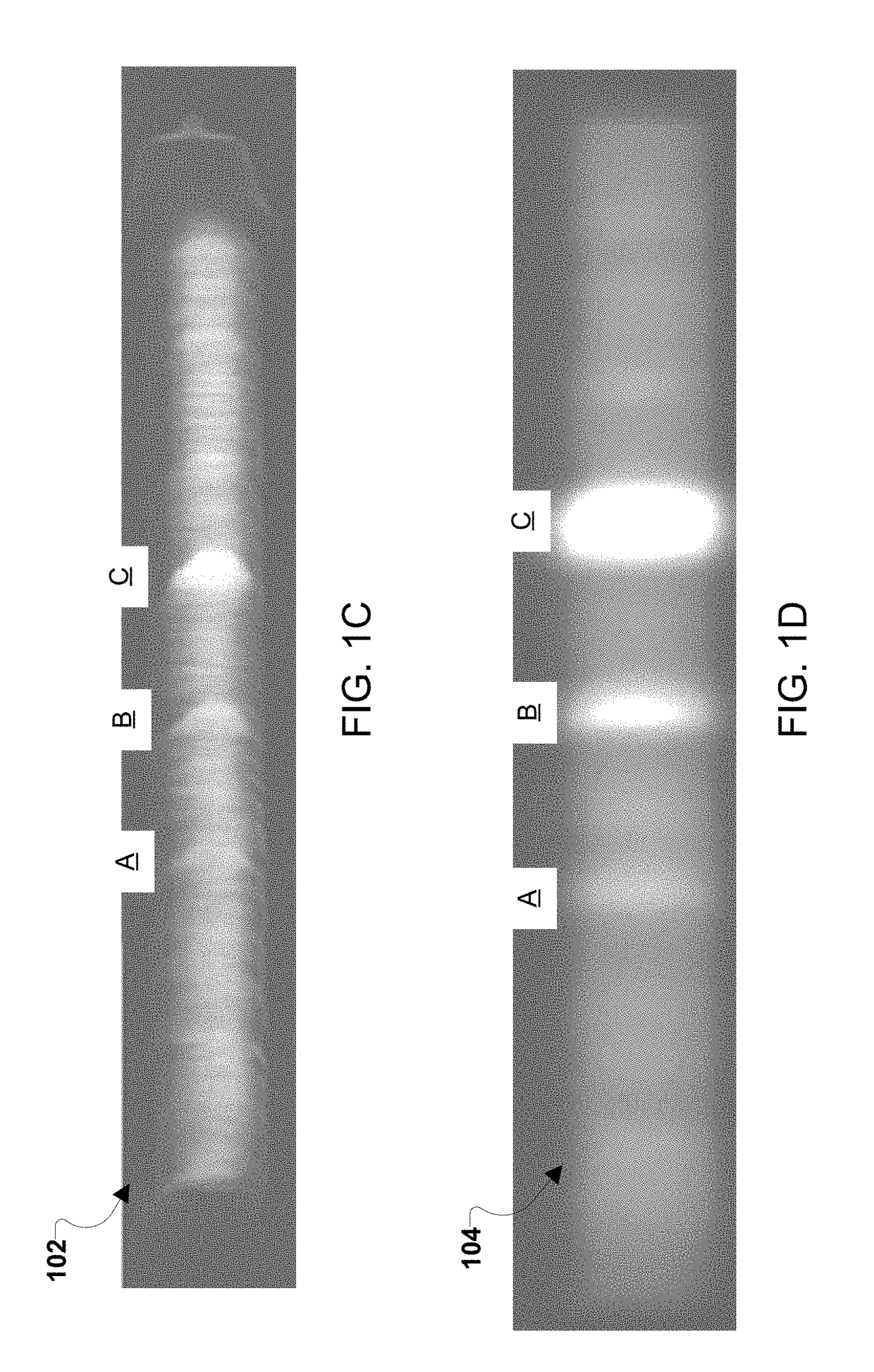
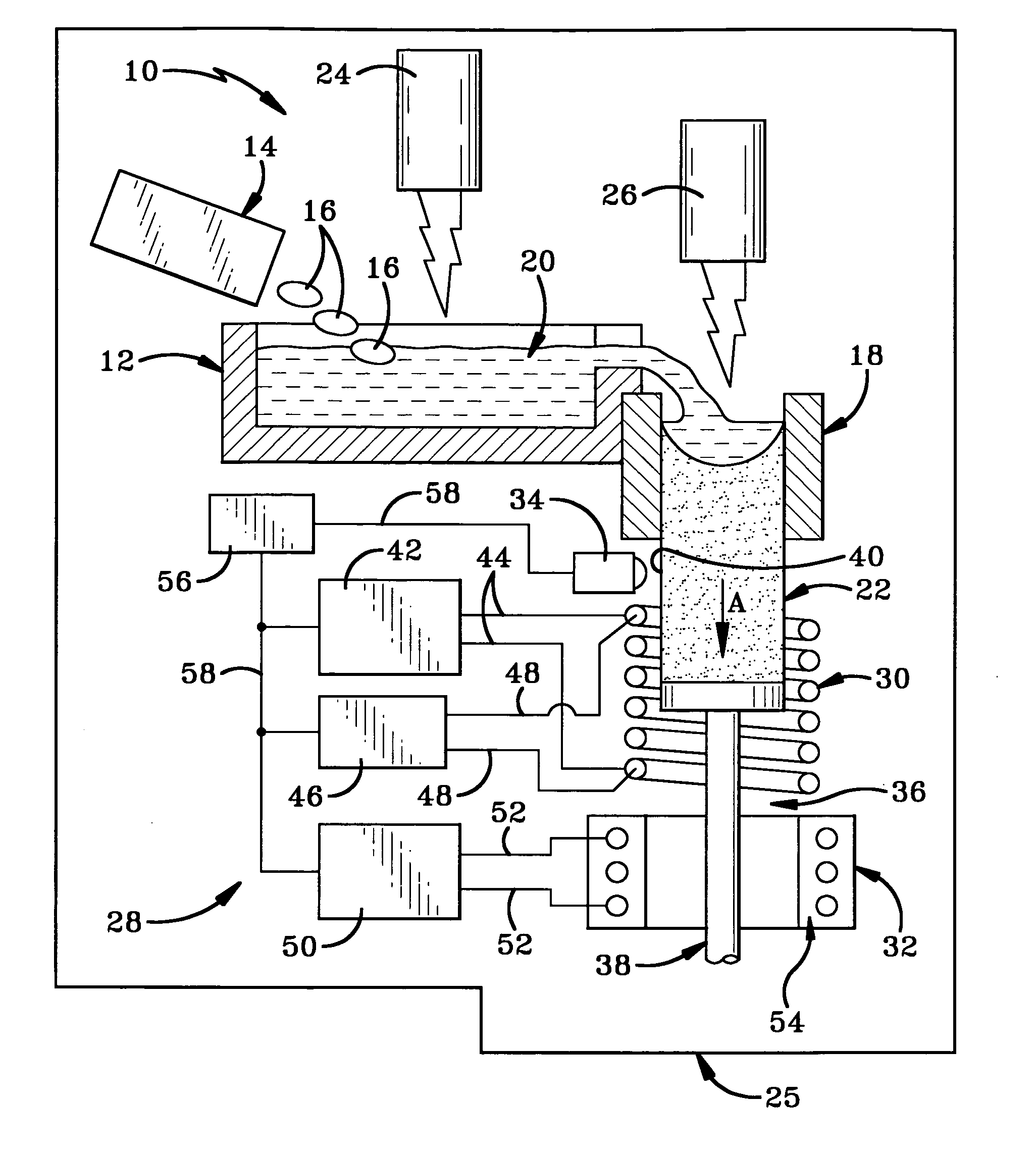
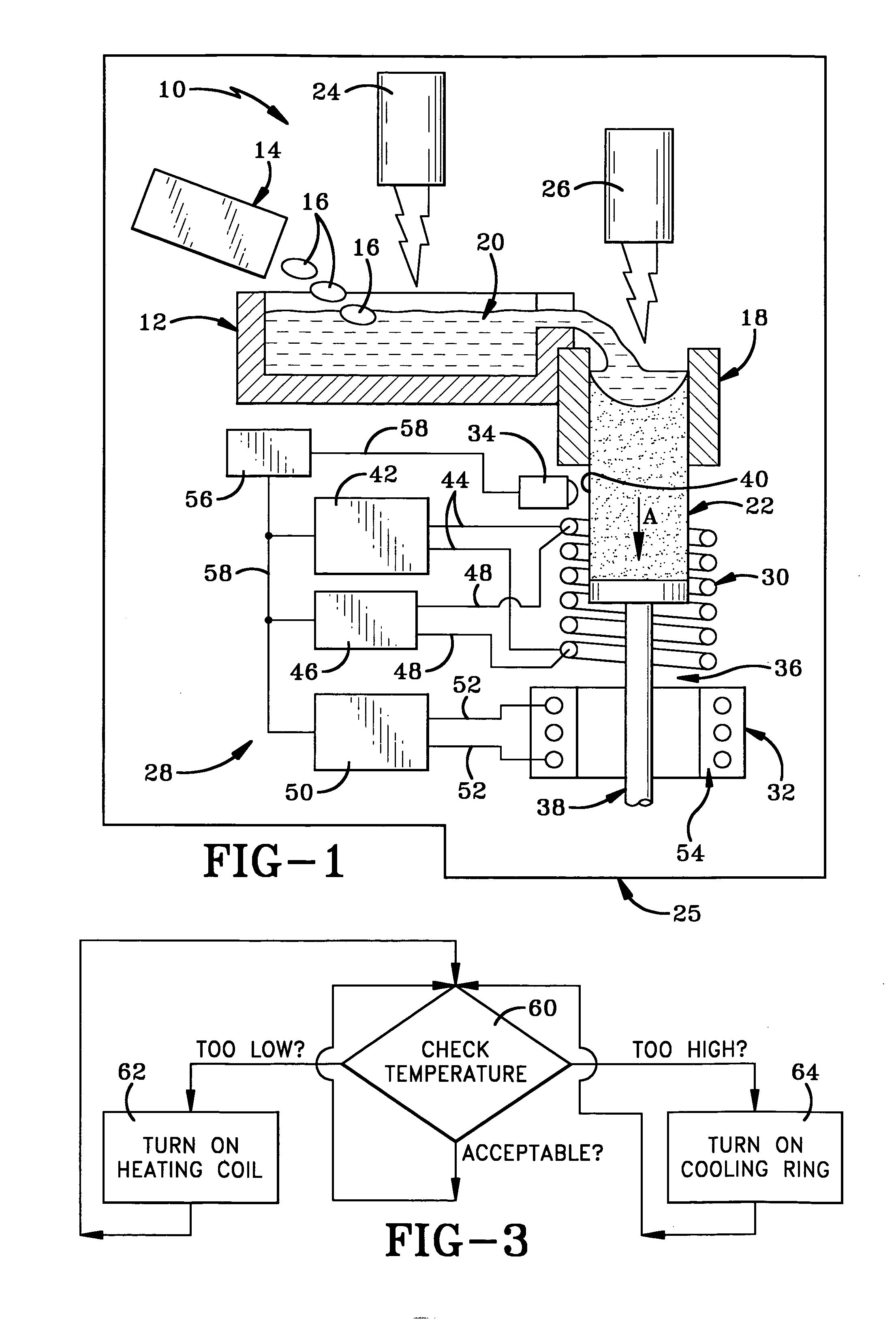
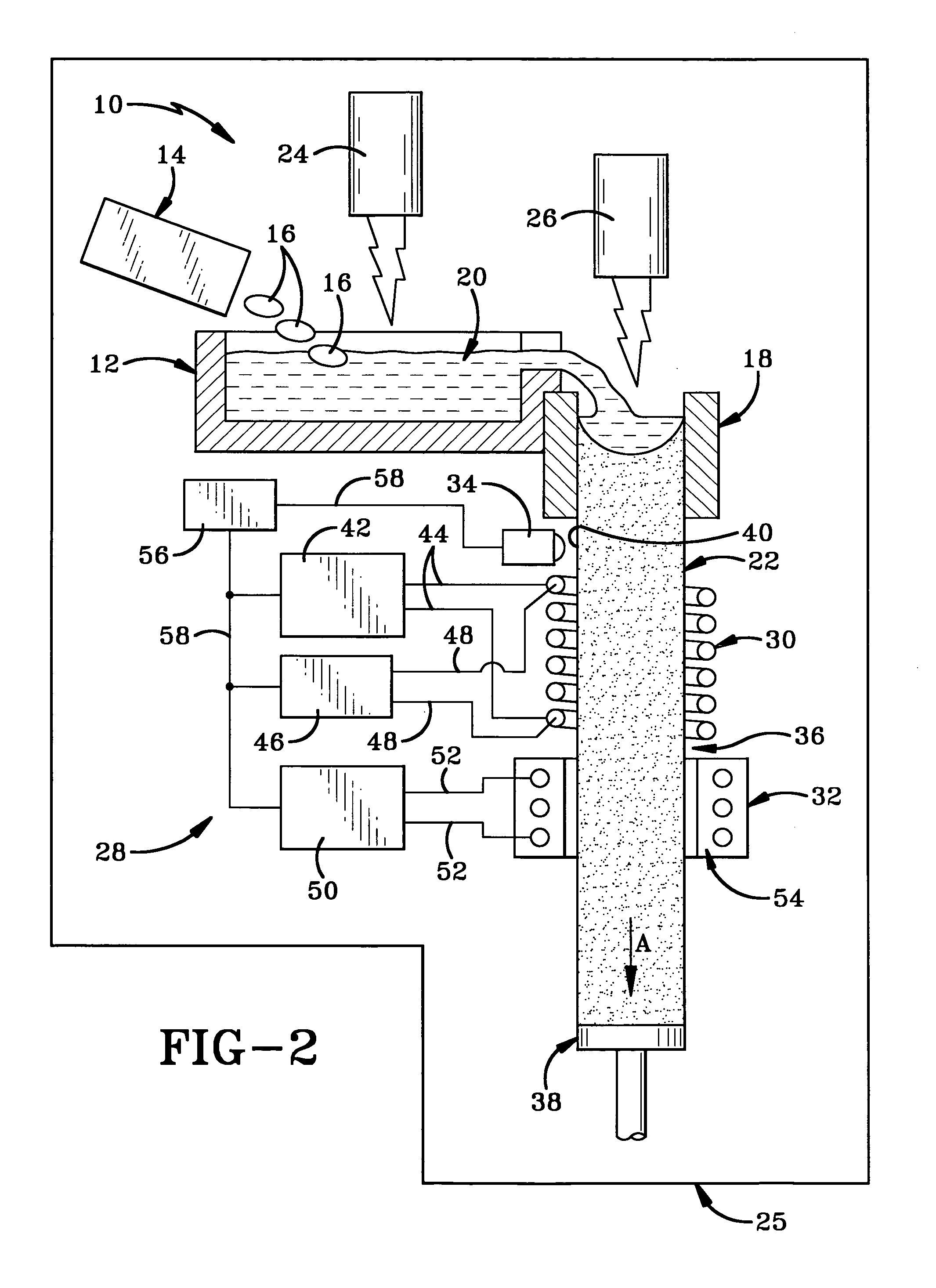
Method and apparatus for temperature control in a continuous casting furnace
ActiveUS20080035298A1Lighting and heating apparatusCasting safety devicesTemperature controlCasting mold
A continuous casting furnace includes a temperature control mechanism for controlling the temperature of a metal cast as it exits a continuous casting mold in order to provide improved characteristics of the metal cast. The temperature control mechanism includes a temperature sensor for sensing the temperature of the metal cast, and a heat source and cooling device for respectively heating and cooling the metal cast in light of the temperature of the metal cast. A control unit determines if the temperature of the metal cast is within a predetermined range and controls the heat source and cooling device accordingly. The heat source may double as a cooling device or the cooling device may be separate from the heat source.
Owner:HOWMET AEROSPACE INC
Visible casting method
ActiveCN1631579AGood casting processAvoid entrainmentCasting safety devicesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSystems designX-ray
Owner:中科西王特钢有限公司
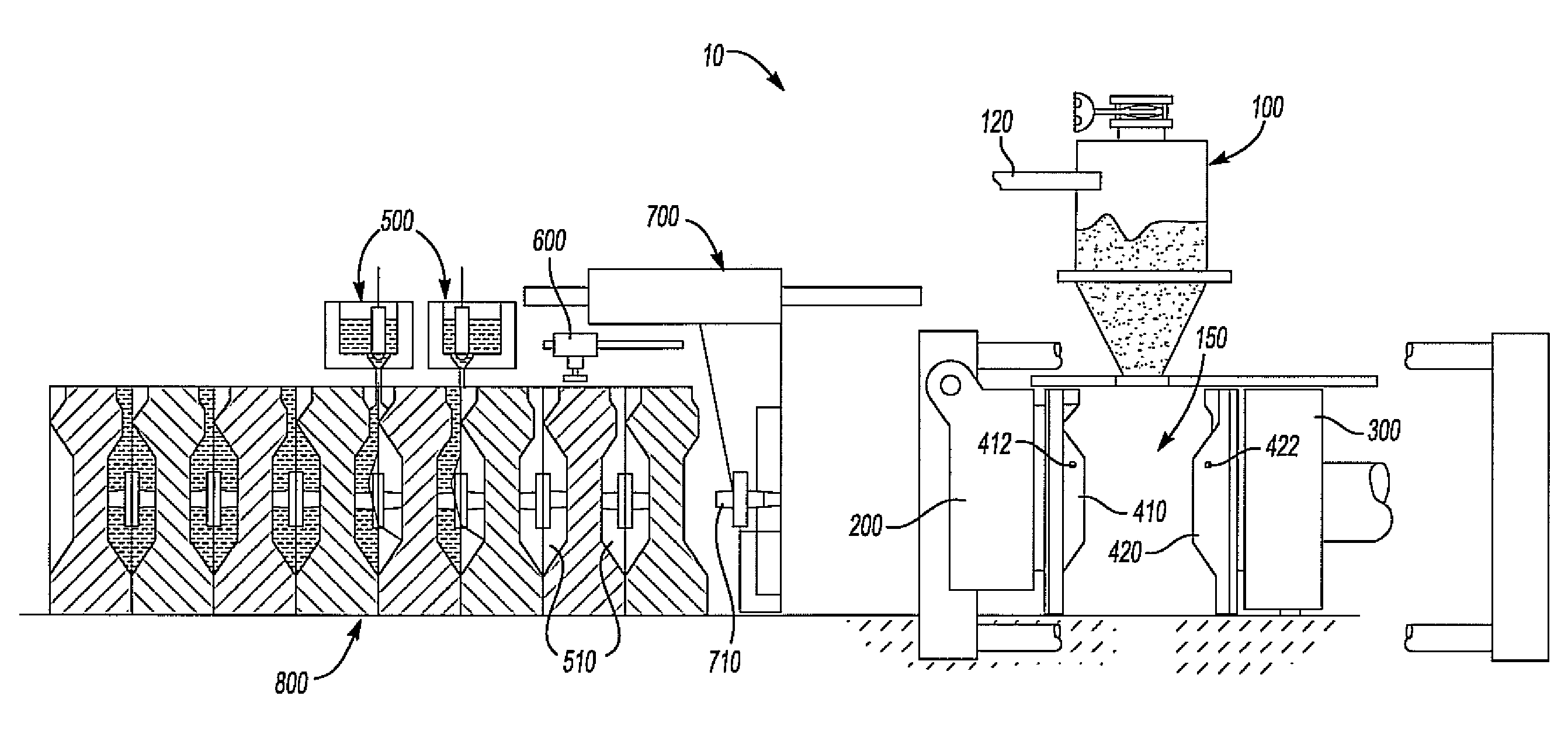
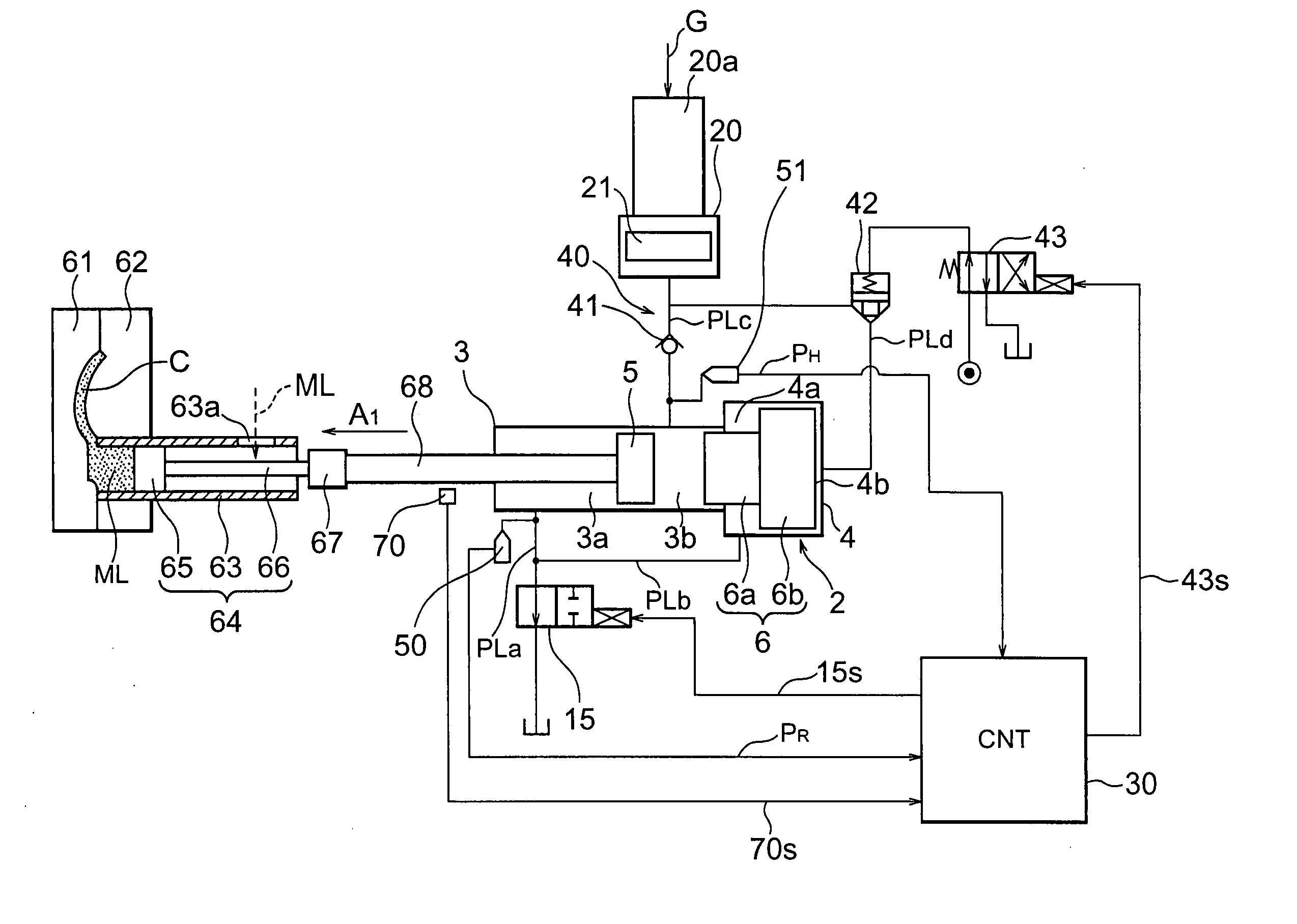
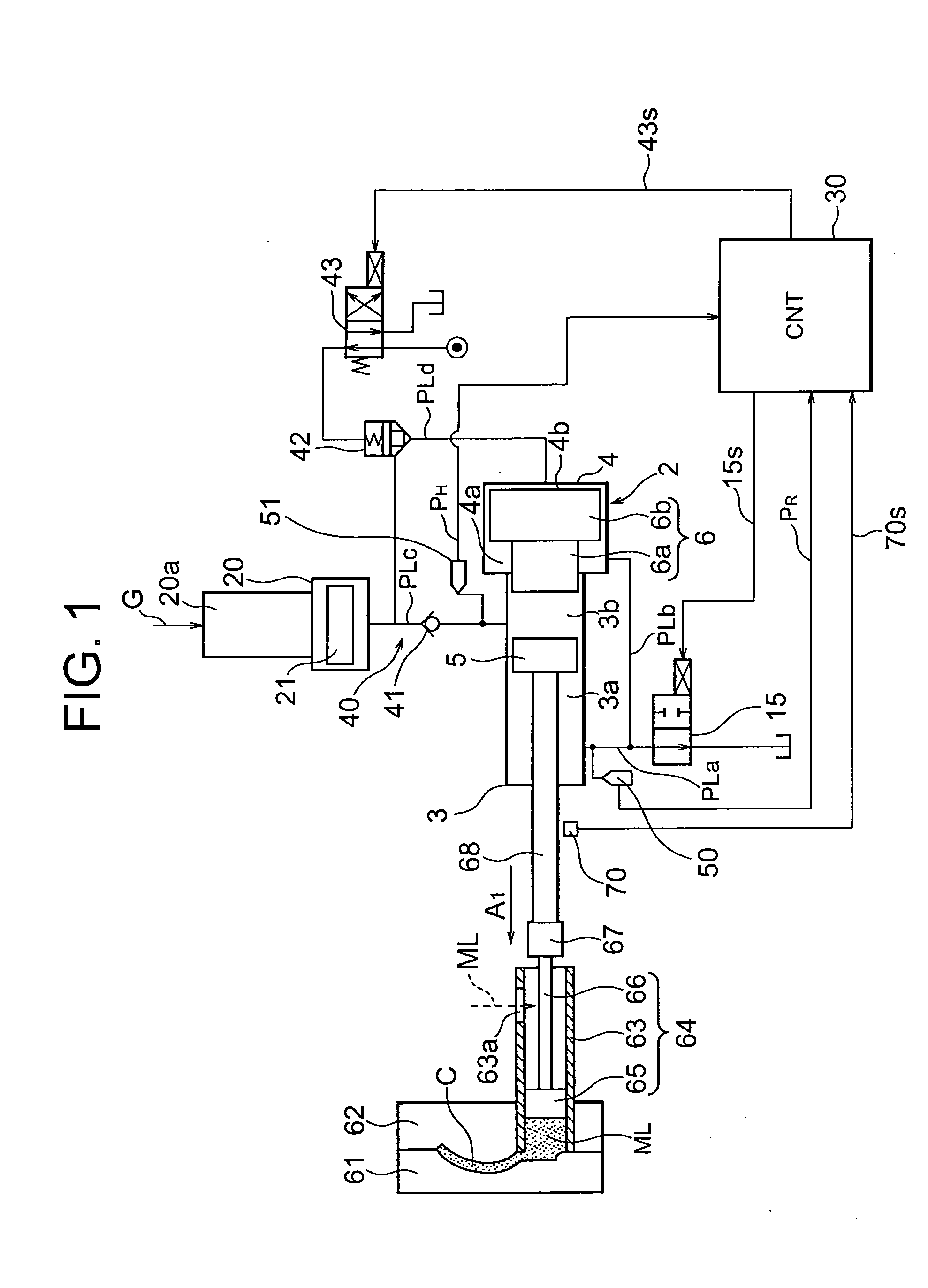
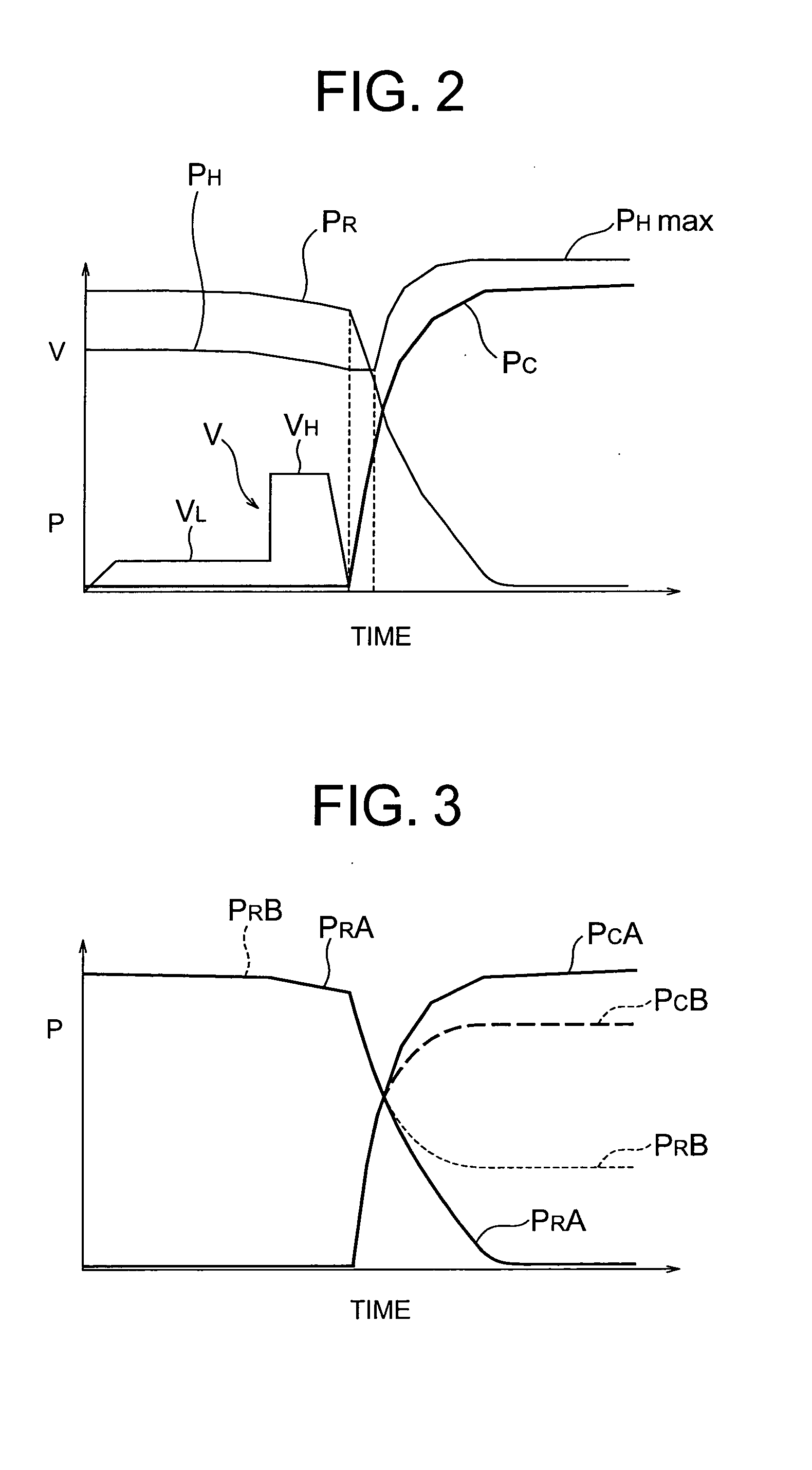
Injection system and casting method of die casting machine
An injection system of a die casting machine giving the necessary casting pressure without adjusting the accumulator side, provided with an injection cylinder including an injection piston linked with the injection plunger and a booster piston arranged behind the injection piston, an accumulator for supplying a pressurized liquid of a predetermined pressure, a liquid pressure circuit for supplying the pressurized liquid from the accumulator to the injection cylinder, driving the injection piston, then driving the booster piston, a control valve for controlling a flow rate of the pressurized liquid discharged from the front side of the injection piston of the injection cylinder so as to control a flow rate of the injection piston, and controlling the pressure of the pressurized liquid at the front side of the injection piston by the timing of closing the control valve to determine the final value of the casting pressure.
Owner:TOSHIBA MASCH CO LTD
Method for centralized monitoring of continuous casting production working procedure of steel-smelting
InactiveCN101152668AAvoid confictIncrease productivityCasting safety devicesTotal factory controlData informationManagement information systems
The invention relates to a remote control method for whole process of industrial production and mainly solves the technical problem that the prior monitoring method has single object and cannot cover the whole production flow. A focusing monitor method for steel-making continuous casting production comprises the following steps: a. establishment of computer monitor network, firstly, network of management information system and procedure control system for every production unit can be established, TCP / IP protocol is adopted, interface tablet is established, and communication between various systems sends and receives treatment in the way of array; b. establishment of working procedure control flow, working procedure is arrayed in the order of logistics according to the position of production unit and then working procedure control flow is formed; c. monitoring of production flow, program information tablet is established and association between every program can be established, and then overall monitoring can be conducted; d. dynamic data adjustment, data updating of production program information can be conducted according to practical production information of every production unit; e. real time monitor of work procedure control flow, working procedure control flow gets dynamic data information from production program information and establishes connection through every production unit; f. determination of product quality. The invention can be used for remote control of the whole flow of steel-making continuous casting.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Axle from a seamless tube for railroad vehicles, and a process for manufacturing an axle from a seamless steel tube for railroad vehicles
ActiveUS20100308612A1Reduce weightHigh tensile strengthRailway vehiclesFurnace typesChemical compositionUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates to an axle forged from seamless tubes, with a chemical composition suitable to guarantee high fatigue strength, improved yield strength and tensile strength, and having reduced weight for use on railroad vehicles. The present invention further relates to a process of manufacturing the axle forged from seamless steel tube with high fatigue strength, improved yield strength and tensile strength, and having reduced weight for use on railroad vehicles, which is produced from pig iron or scrap, casting, reheating furnace, perforation of billets, elongation of perforated billets, hollow finishing, forging and finish machining, which includes a supporting and centering chamfer at the inner edge of the inspection bore of the end and smooth recess in the entrance of the threaded bores.
Owner:V & M DO BRASIL
Monitoring method for a continuous casting mould including building up a database
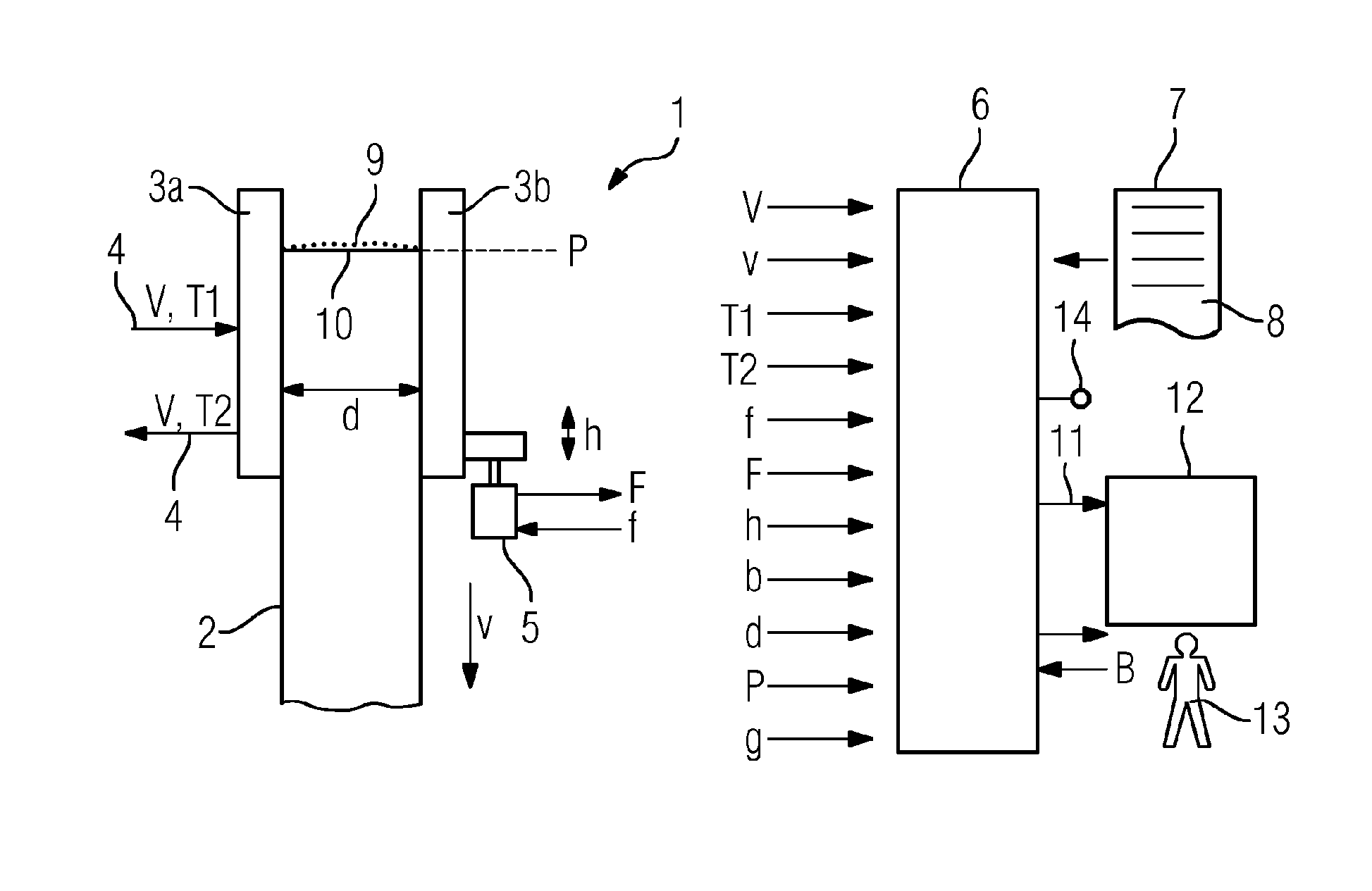
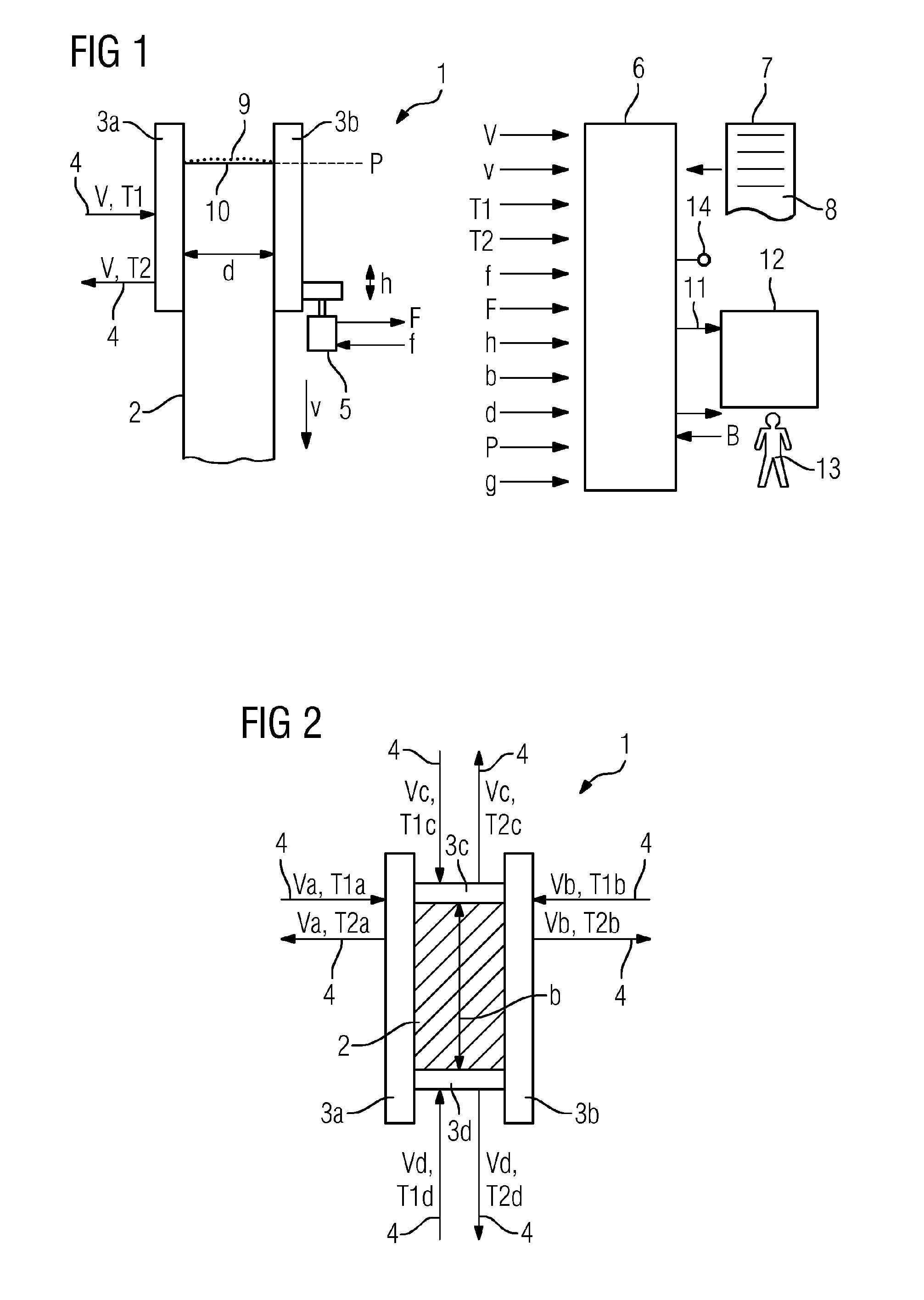
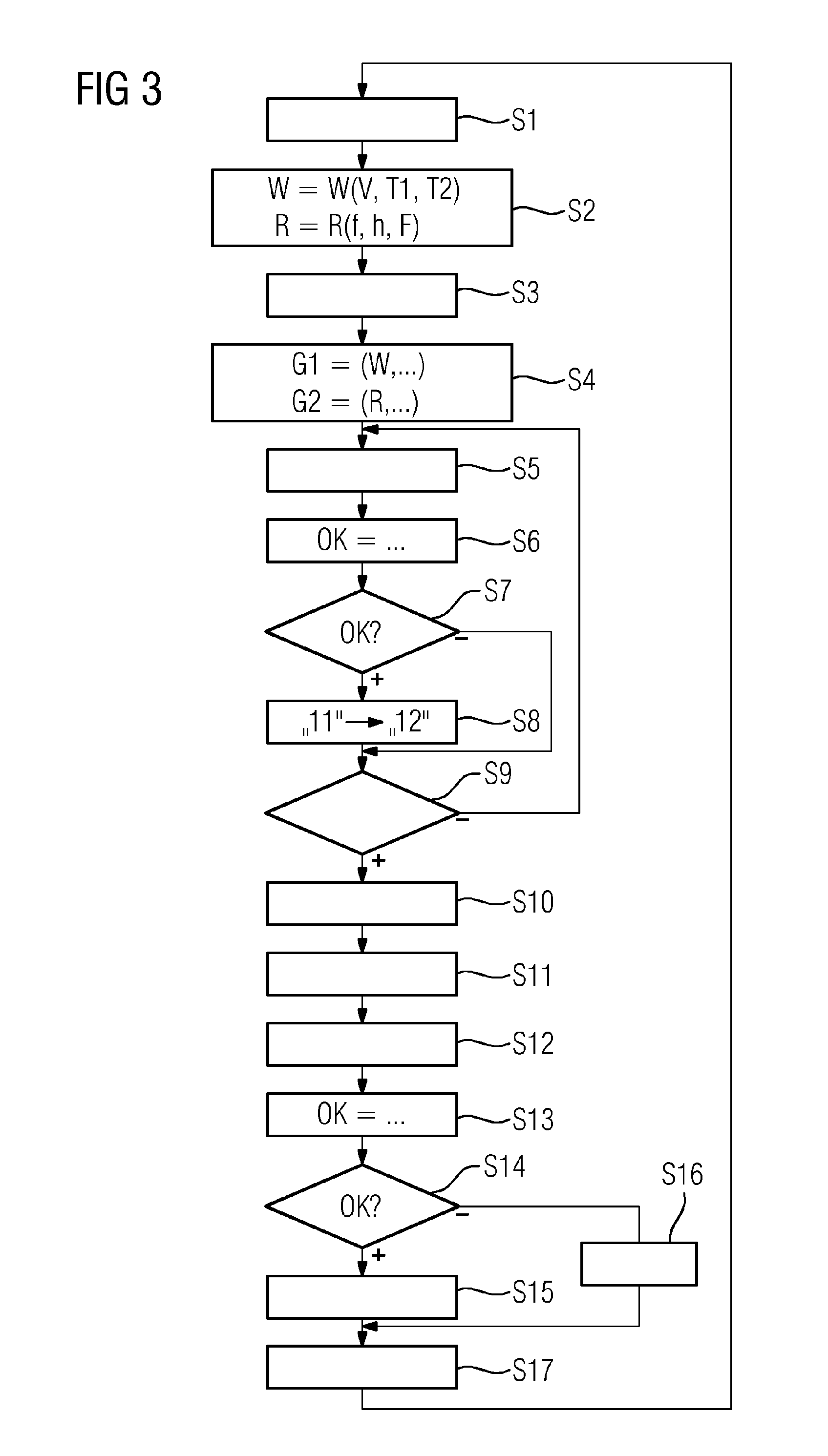
InactiveUS20150314368A1Casting safety devicesMould controlling devicesStability criterionMaterials science
A monitoring device (6) records variables that are characteristic of operating parameters of a continuous casting mold (1) for casting a metal strand (2). The monitoring device (6) records at least some of the characteristic variables by independently performing measurements during the casting of the metal strand (2). The monitoring device (6) forms groups (G1, G2) of operating parameters and independently tests whether the operating parameters of the respective group (G1, G2) satisfy a respective predetermined stability criterion. The monitoring device (6) accepts the operating parameters into a database (12). The monitoring device (6) determines those data records (11) contained in the database (12) that coincide in their input variables with the basic operating parameters and determines admissible operating parameter ranges for supplementary operating parameters. The monitoring device (6) independently tests whether the supplementary operating parameters lie within the admissible operating parameter ranges.
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH AUSTRIA GMBH
Feeding System for Semi-Solid Metal Injection
InactiveUS20110108231A1Avoid impuritiesIncrease the lengthCasting safety devicesMetal alloyReciprocating motion
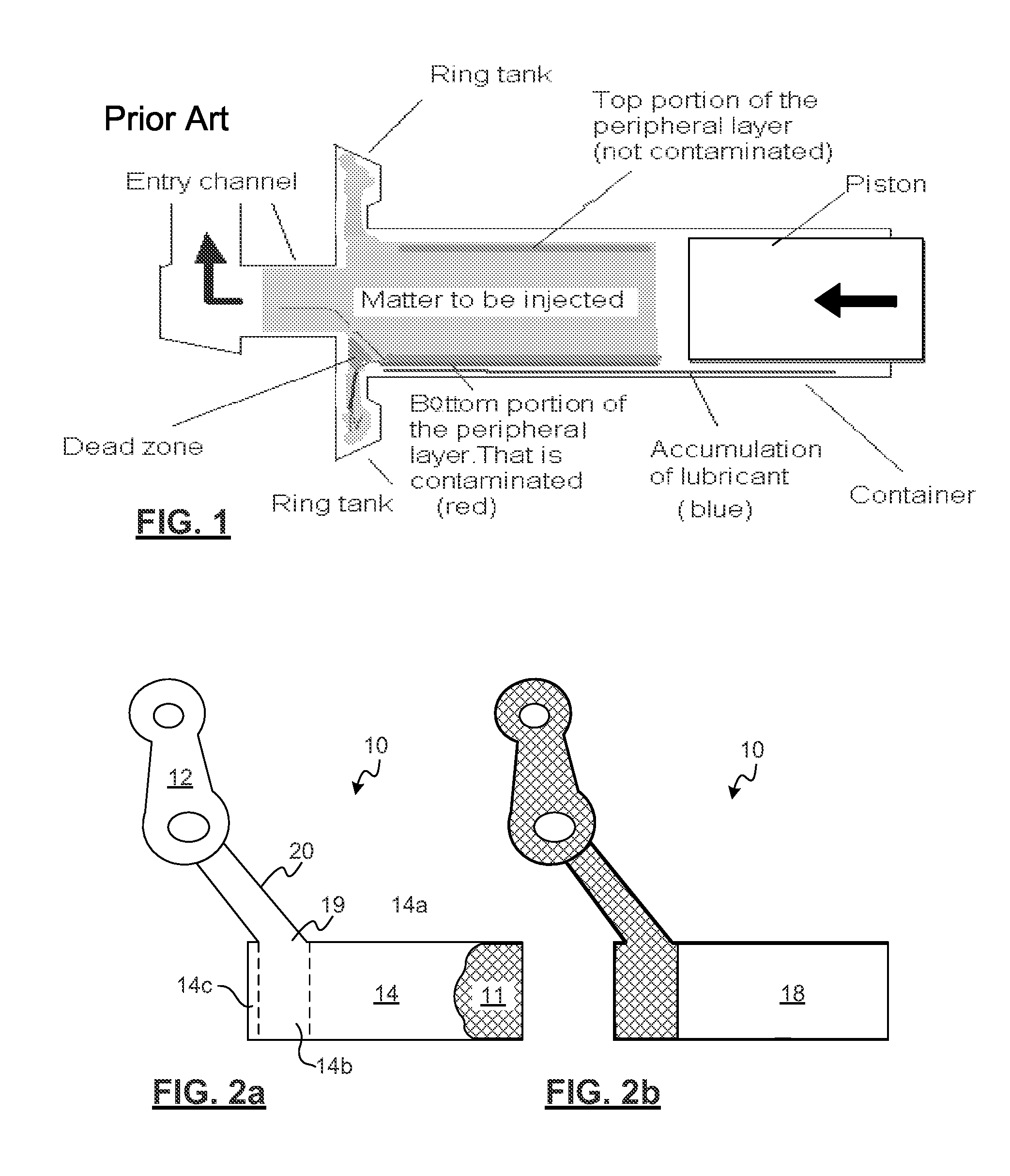
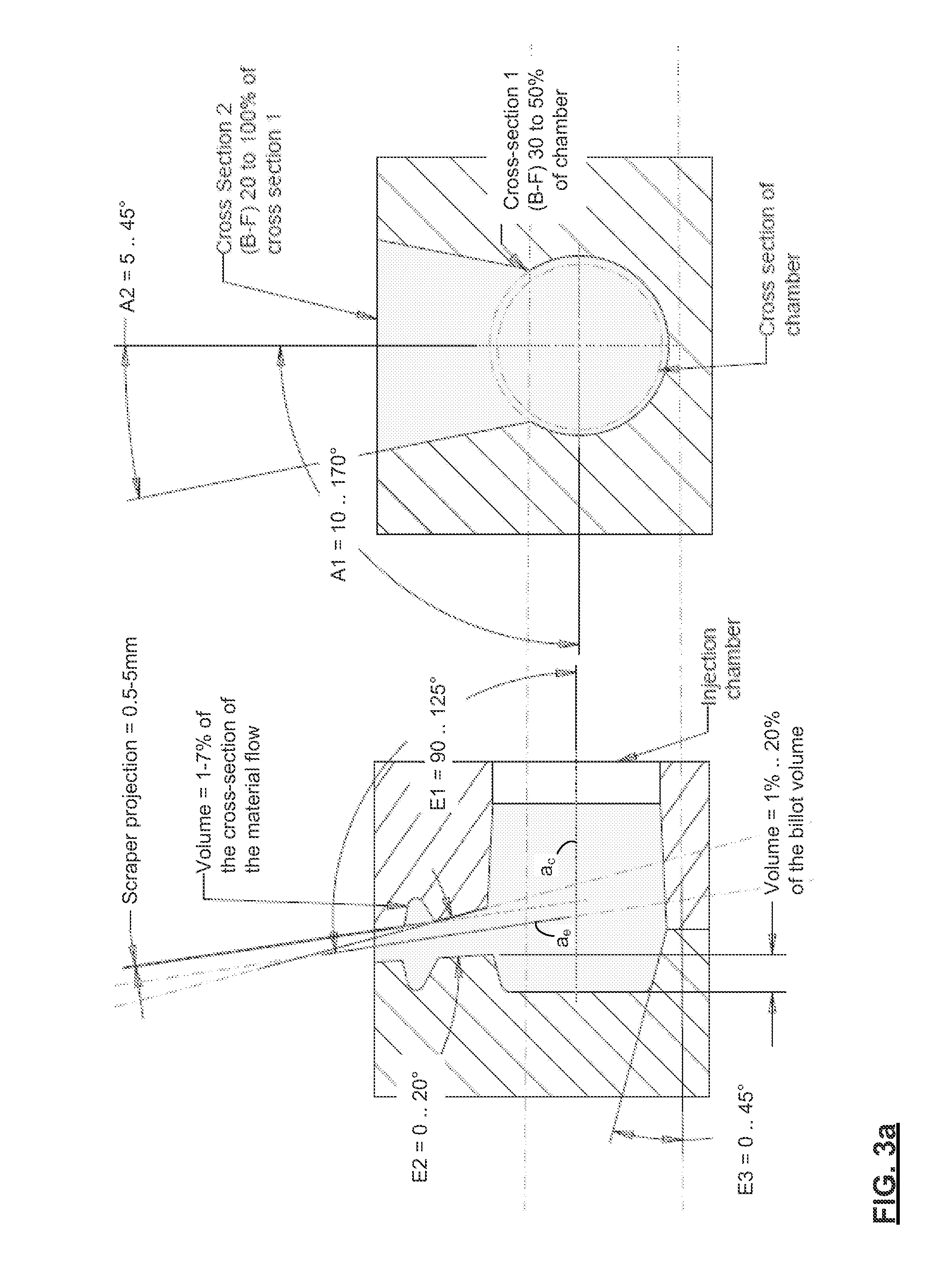
A semi-solid metal alloy injection feed system for reduced inclusion injection moulding comprises a substantially closed injection chamber for containing a billet of semi-solid metal alloy, and thrusting the billet through the injection chamber into a mould, wherein the injection chamber has a first section defined by a wall with an inner contour for mating with a bearing surface for reciprocating motion of the bearing surface within the first section, along a center axis of the injection chamber; and the injection chamber has an outlet in fluid communication with the mould, the outlet provided at an opening in the injection chamber that is offset with respect to the center axis, and is disposed at an angle of 90° to 125° from the center axis. There is no neck or throttling between the chamber and the outlet. A butt end trap is preferably formed that requires inclusions that are principally on a bottom side of the injector to travel a relatively long ways to enter the outlet.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
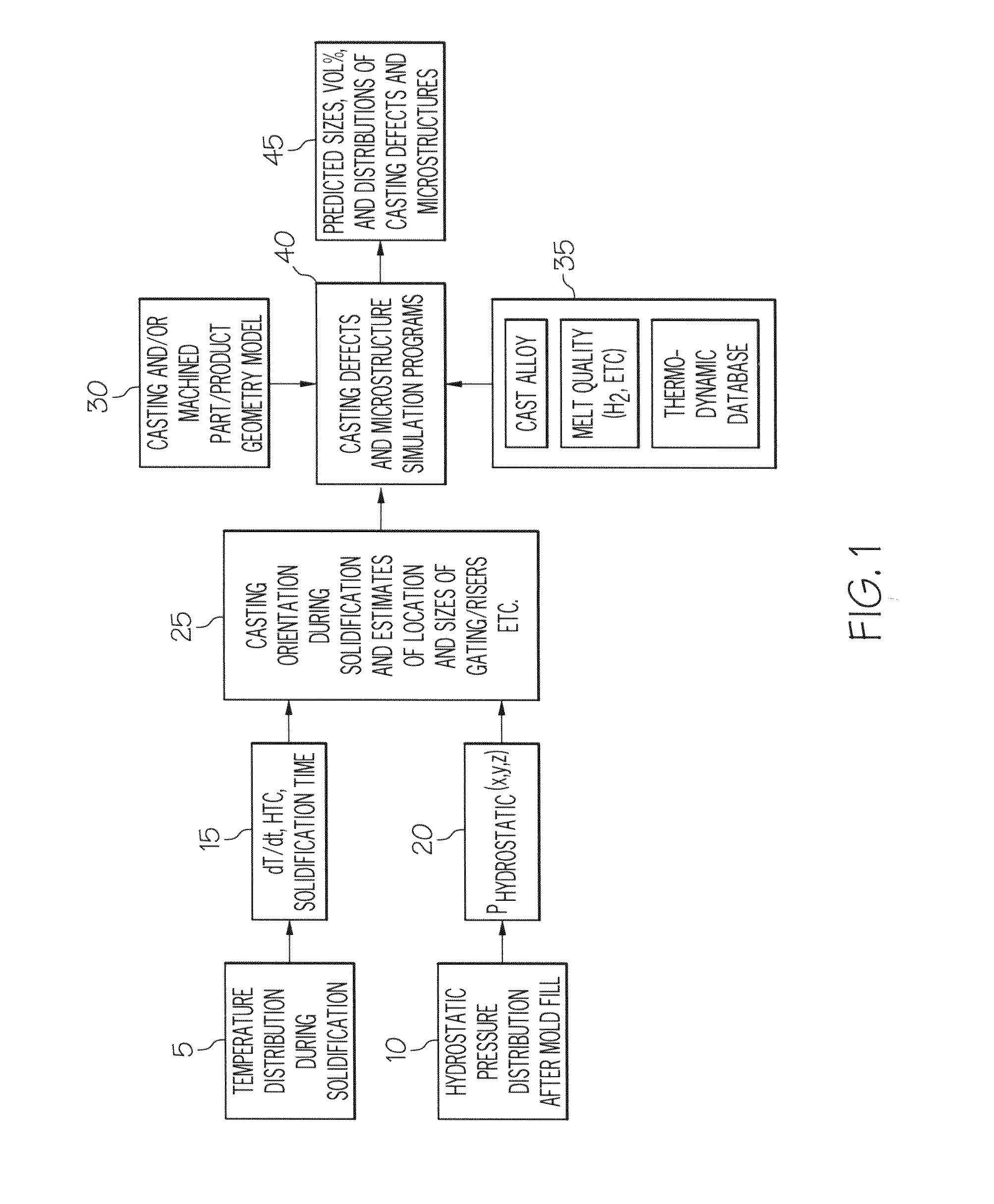
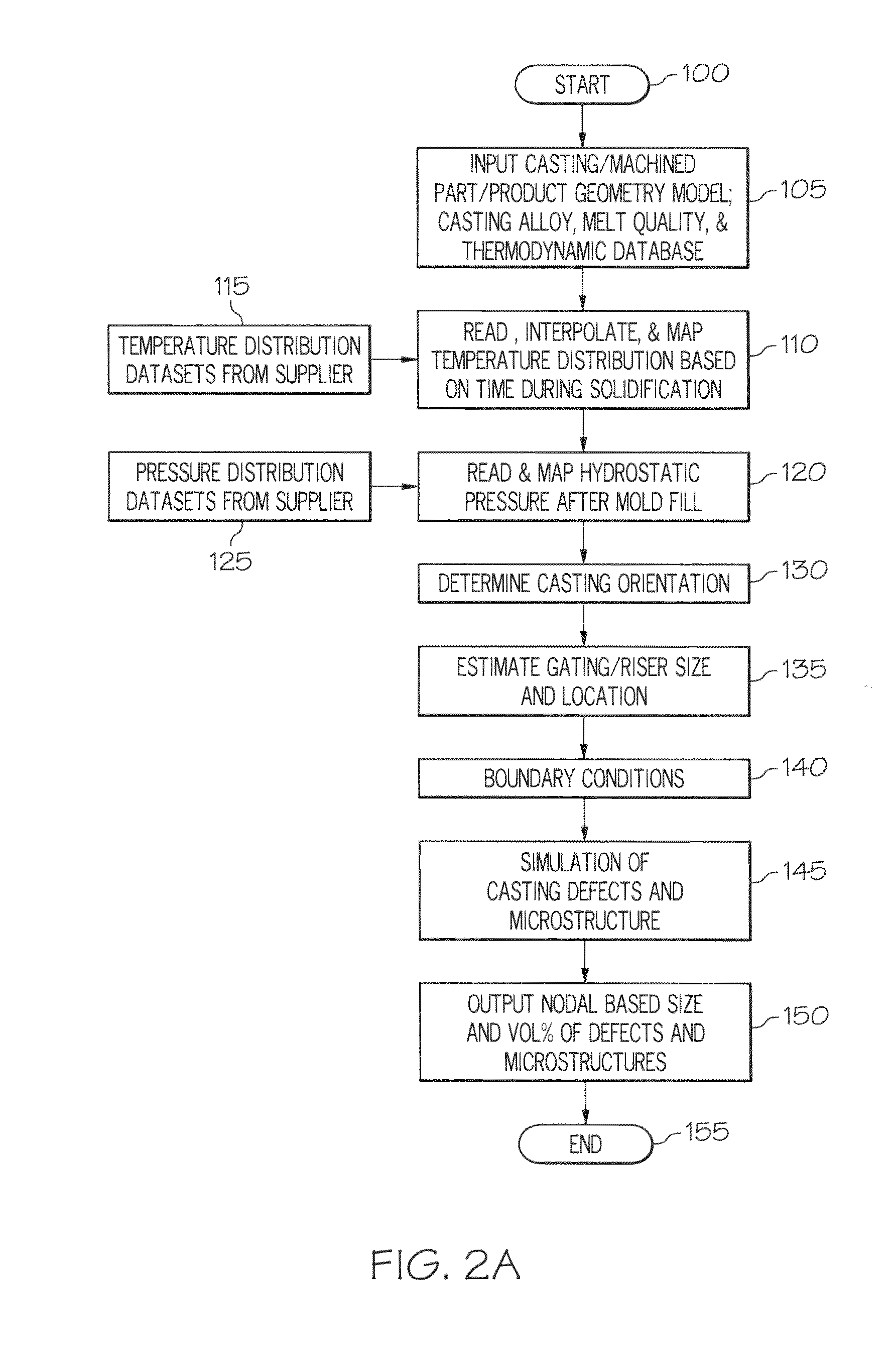
Method for simulating casting defects and microstructures of castings
ActiveUS20110144788A1Accurate durability analysisCasting safety devicesAnalogue computers for control systemsCasting defectMaterials science
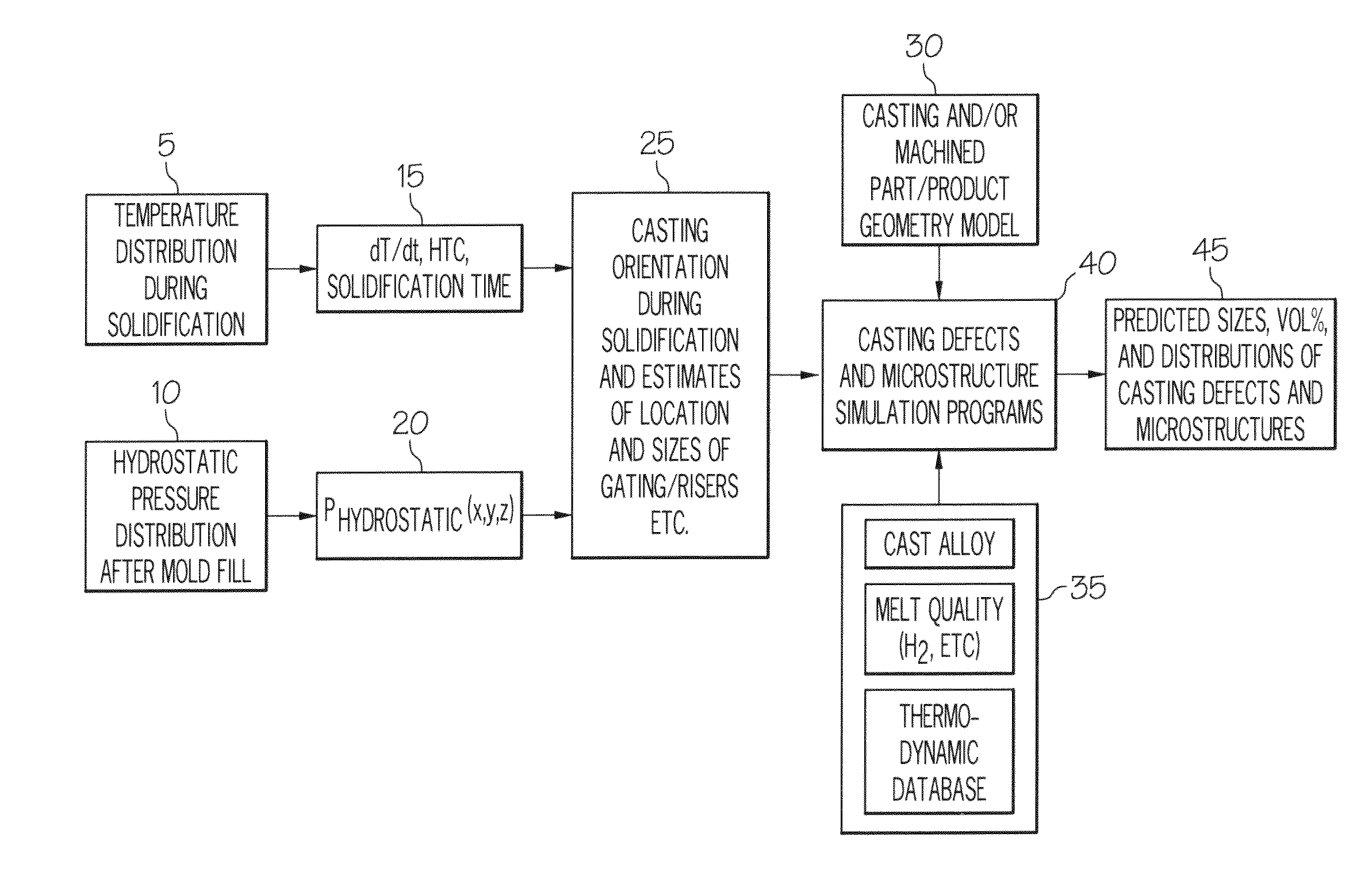
Systems for predicting casting defects and microstructure in suppliers / vendors' castings for part / system durability analysis without knowing the details of the casting layout and casting gating and riser design as well as casting process parameters are provided. The systems involve the use of an integrated pore growth and interdendritic flow model. Methods of predicting casting defects and microstructures of a part without knowing the details of the casting layout and casting gating and riser design as well as casting process parameters and articles of manufacture are also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for founding main regulation valve body of steam turbine
InactiveCN101081432AAddressing deficiencies created by packingSolving Difficult-to-Production ProblemsCasting safety devicesFoundry mouldsMechanical propertyHeat treated
The present invention is process of casting valve body of main steam regulating valve for steam turbine and belongs to the field of metal casting technology. The casting process includes one vertical casting step and two steps of heat treatment to eliminate shrinkage faults. The casting process can produce casting of valve body with high mechanical performance.
Owner:JIANGSU LEADER PRECISION MACHINERY
Device and a method for continuous casting
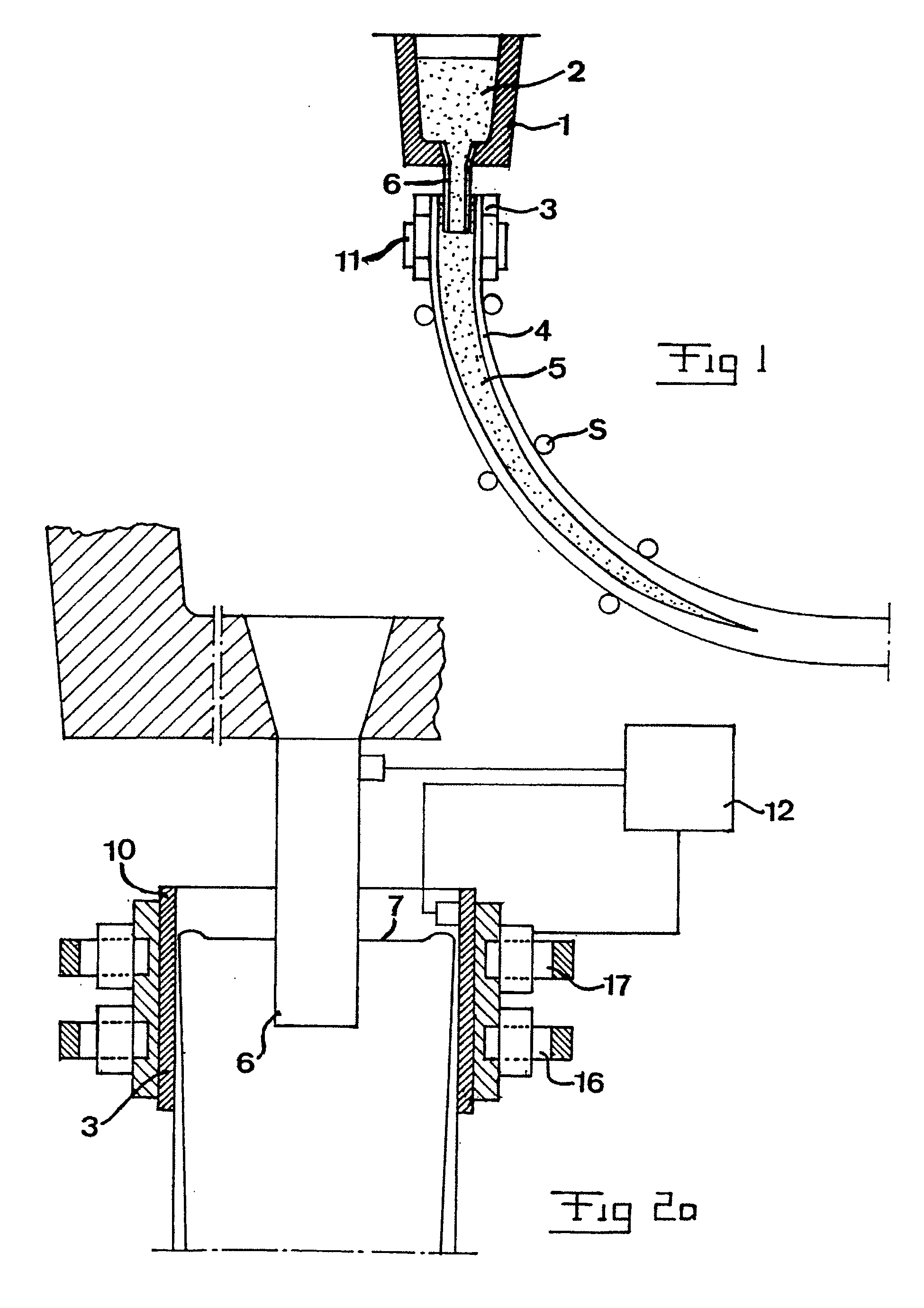
InactiveUS20050039876A1Promote resultsUniform and stable temperatureCasting safety devicesMetallurgyMolten metal
An apparatus for continuous casting of metals has members (16) adapted to generate a stationary magnetic field of a variable strength over substantially the entire horizontal cross section of the mould from one long side to the other long side close to, or below, the region for supply of molten metal at a distance below the upper surface of the molten metal. There are also members (17) adapted to generate a variable magnetic field in the area of the upper surface in a region that is centrally located with respect to said cross section and close to a region for supply of molten metal. A unit (12) is adapted to control said magnetic members (16, 17) to generate, independently of each other, magnetic fields with an appearance that is dependent on the value prevailing of one or more predetermined casting parameters.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Process for preparing the walls of a mold for molding or shaping to make them ready for the next molding cycle
In a process for preparing the mold walls (12a, 12b) of a mold (12, 12) for the molding or shaping of a molded part after completion of the molding cycle and after removal of the molded part from the mold (12) to make the mold walls ready for the next molding cycle, the tempering of the mold walls (12a, 12b) and the coating of the walls with mold wall treatment agent are carried out independently of each other, i.e., without any time overlap, and in a controlled manner, preferably in a program-controlled manner. To apply the coating, preferably a spray element with centrifugal atomization and air control is used, the mold walls preferably being coated with essentially solvent-free mold wall treatment agent.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Large-scale shaft products vertical casting and repairing device and using method
The invention relates to a large scale axle kind product vertical casting and restoration apparatus and a use method thereof, belonging to mechanical fields. A frame is fastened with an operation table and a frame station and is movably connected with a mobile arm, a temperature holding pot is fastened with the operation table and a base and is screwed connected with a guide tube, a leak protection pot is fastened with the operation table and the frame station and the base, and the operation table is fastened with the frame station and the base, a column is fasened with the operation table and the base and is movably connected with a lifting table which is connected with a center shaft by bearing and is fastened with an electric machine. The center shaft is connected with a gear box of the electric machine and is connected with a chuck by key. The center shaft, basic parts and a location tip of the mobile arm are provided for supporting. The chuck is buckled with the basic parts. The frame station, a crystallizer, an inductor, and a pouring cup are connected with each other by flanges. The crystallizer is covered by a liner, and the basic parts are covered by a seal ring and a leak protection groove. The pouring cup is inlayed with a thermocouple, the basic parts are fastened with a fixture, an upper lock loop and a lower lock loop. A product / a restoration product can be obtained by treating, assembling, processing, stopping process and post-treating the basic parts, which is applicable for casting or repairing the axle kind product, with high quality.
Owner:MCC CAPITAL ENGINEERING & RESEARCH +1
Molding and casting machine
ActiveUS7806161B2Easy to moveEasy to adjustPig casting plantsCasting safety devicesMolding machineSand casting
Disclosed is a sand casting molding machine for double indexing molds in a mold string. The machine can include a shot chamber having sand, a swingable squeeze head, a lateral squeeze head, a core setter, a mold hold down, a mold retention device and a mold string conveyor.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP WAUPACA
Method and system for tracking and positioning continuous cast slabs
ActiveUS20080264598A1Keep in touchReduce thicknessCasting safety devicesMould controlling devicesControl signalComputer vision
A system and method for tracking and positioning a continuous cast strand in a casting plant. Lateral positions and, optionally, elevational positions of a cast strand are monitored by sensors as casting proceeds and are fed to a computer-based system as corresponding position information where the information is stored as associated data. The computer-based system processes the associated data and generates corresponding control signals which are used to control at least one correcting device to maintain desired orientation of the cast strand as casting proceeds.
Owner:NUCOR CORP
Active temperature feedback control of continuous casting
InactiveUS20070251663A1Uniform surface temperatureImprove efficiencyTemperature control using plurality of sensorsCasting safety devicesEngineeringFeedback control
The invention includes a system, method and machine readable program for dynamically controlling the casting of a material. Generally, the systems and methods described herein include an active control feedback system or aspects thereof including a temperature sensing device that is well-suited for the harsh environment of the interior of a caster such as a caster for casting metal. Temperature measurement can be accomplished either directly or indirectly. The system is configured to compare the measured temperature with an ideal casting temperature. The temperature sensing device is operably coupled to a cooling device that modulates a flow of coolant to dynamically cool the material being cast. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, the cooling device includes a plurality of nozzles for delivering one or more cooling fluids to the material being cast.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE +1
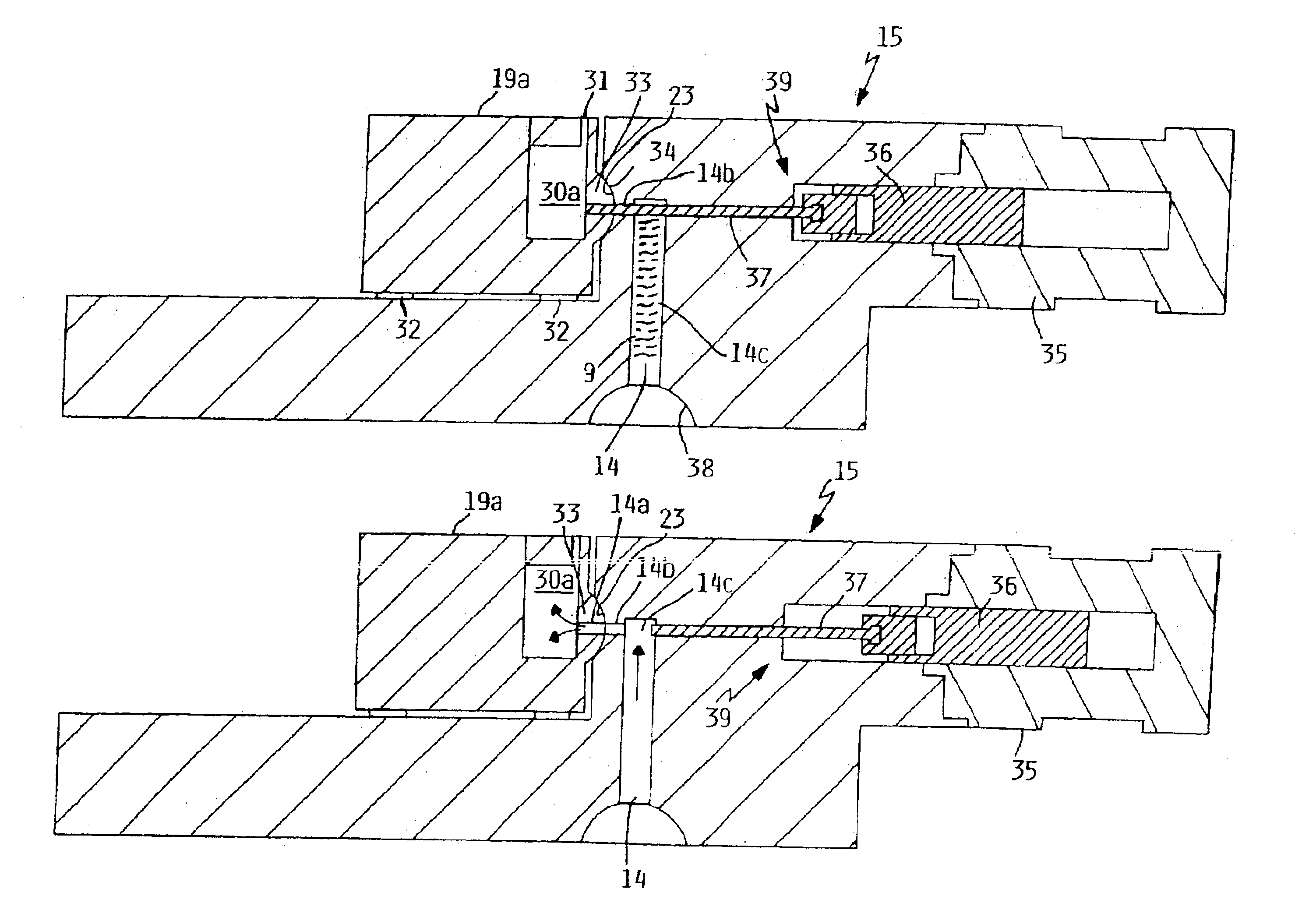
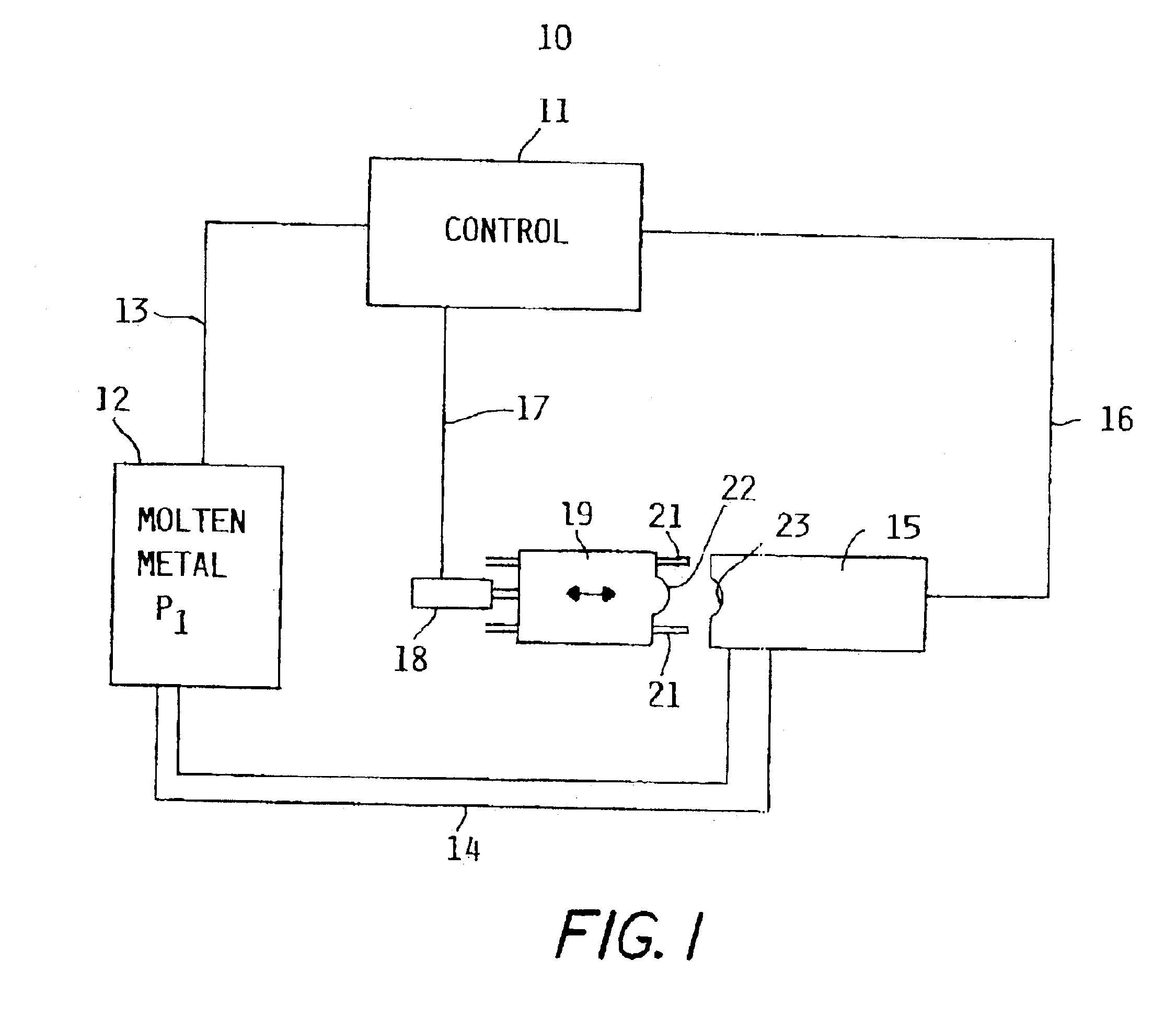
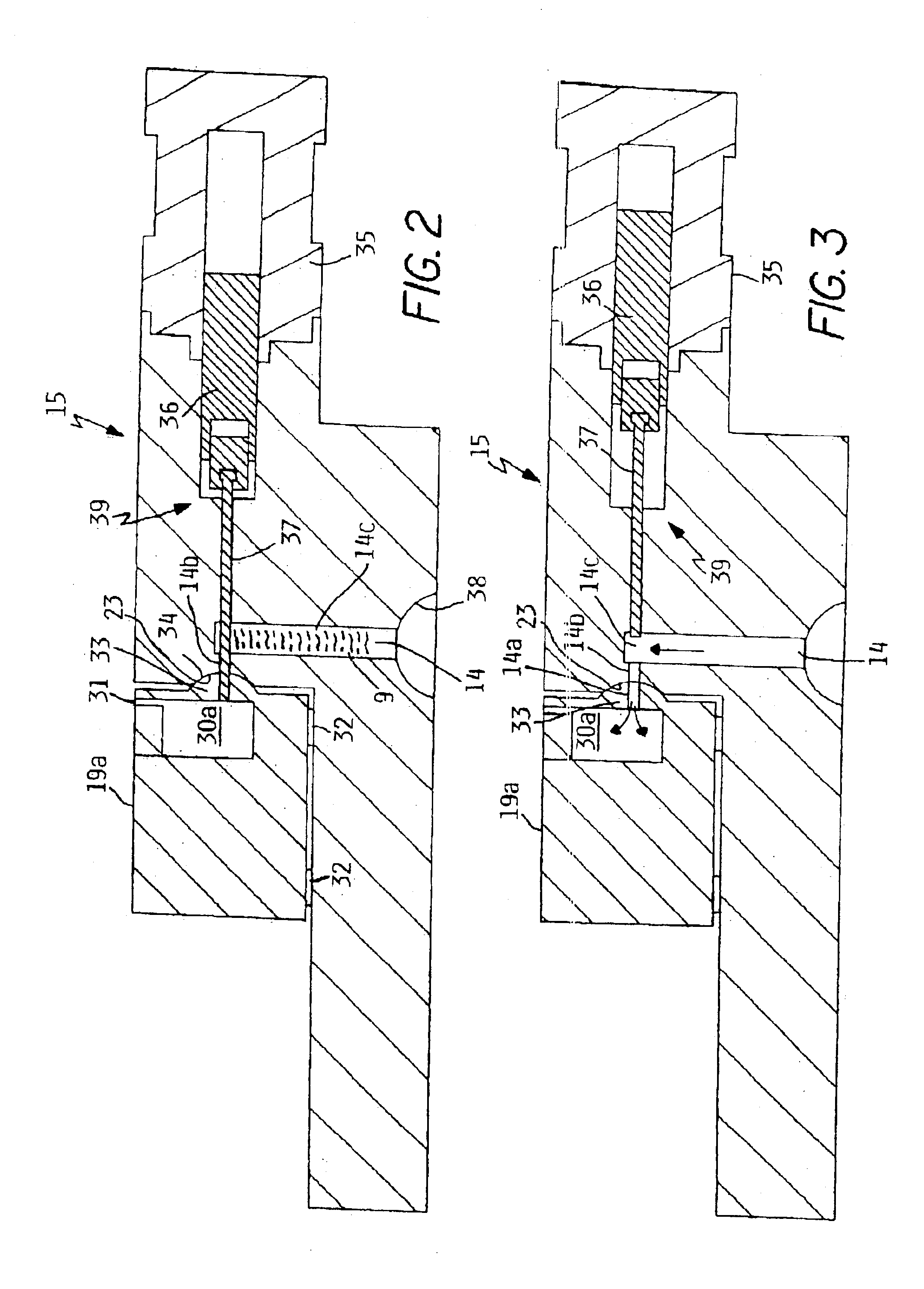
Apparatus and method of forming parts
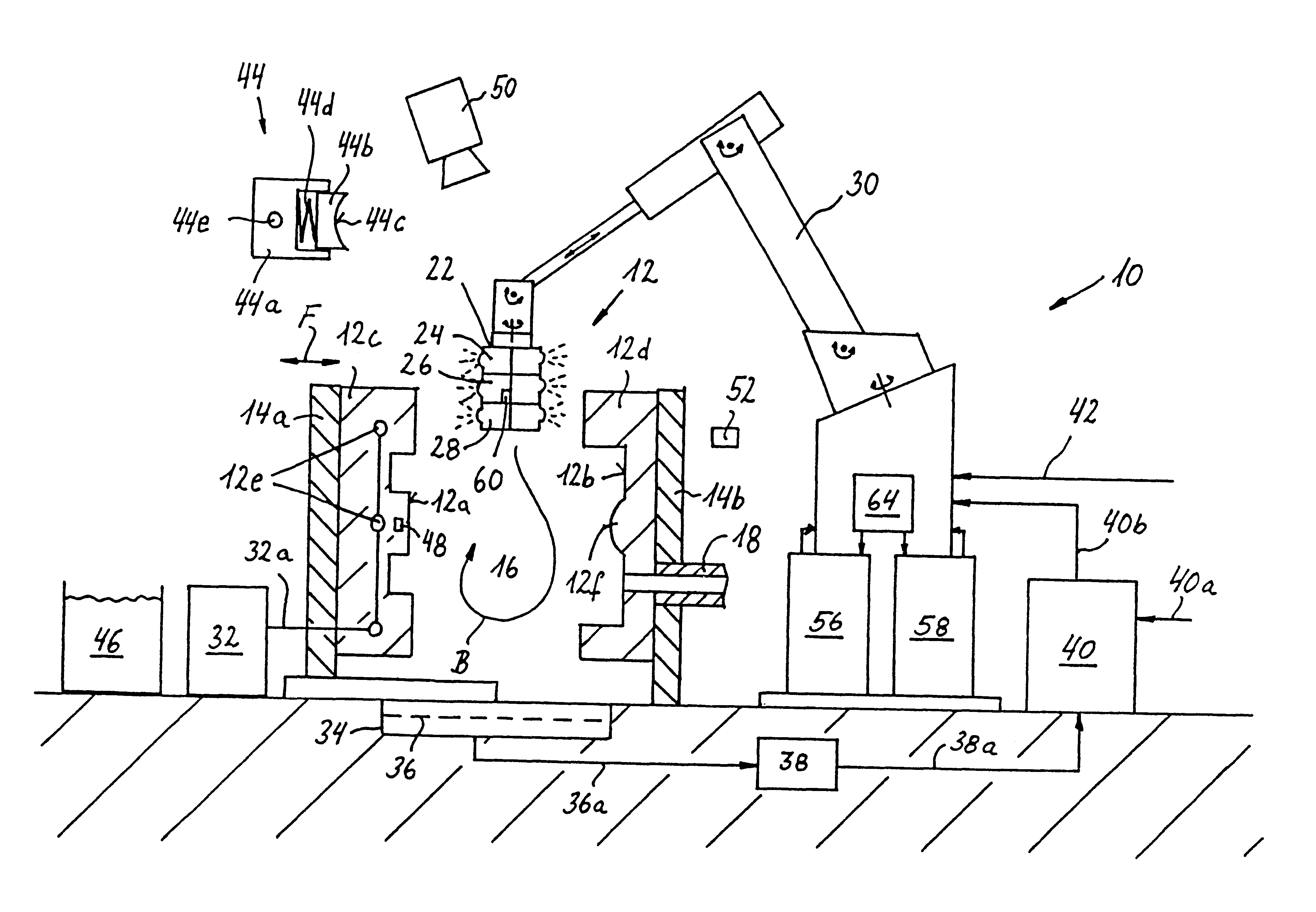
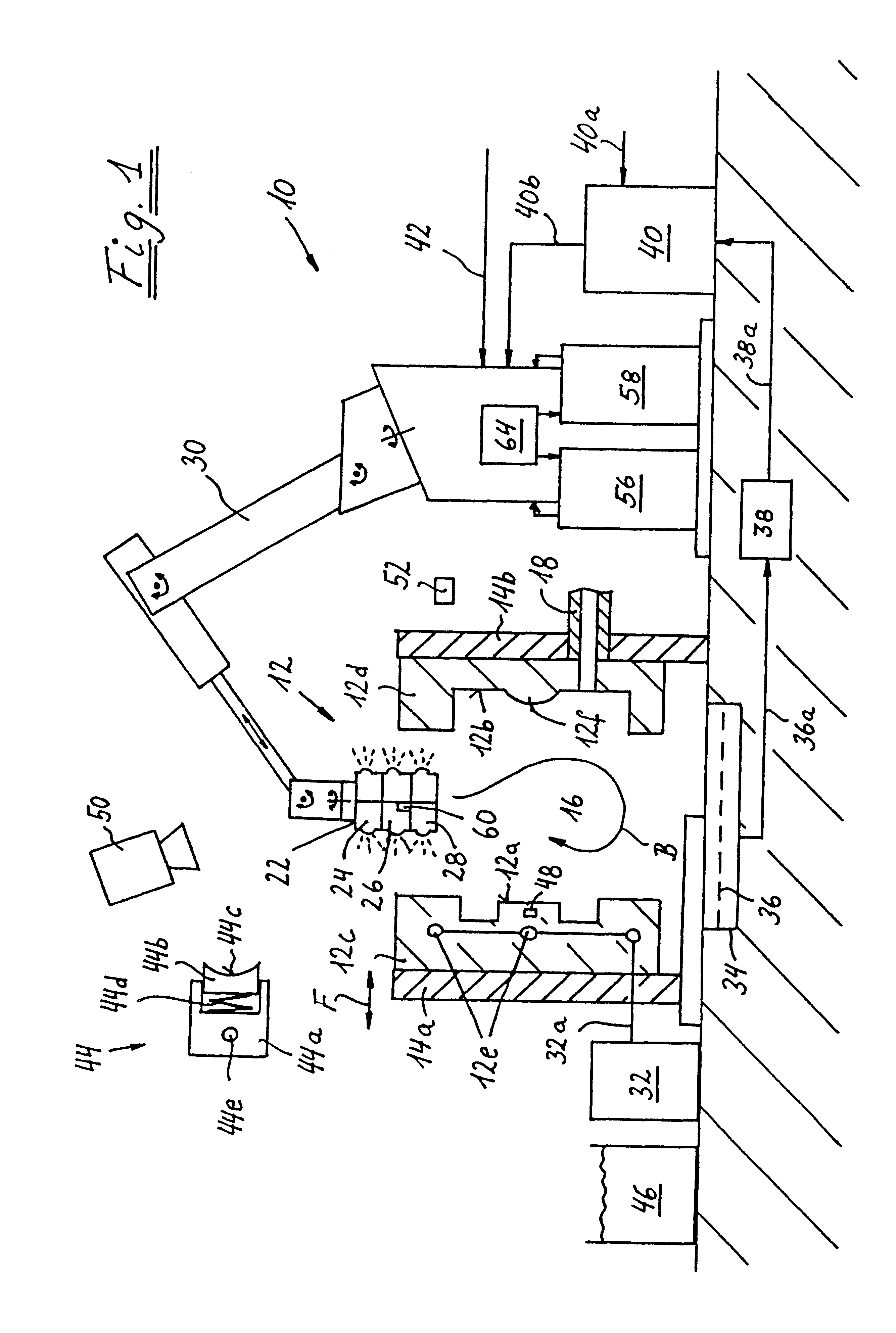
InactiveUS6896031B2Minimizes shrinkageAvoid enteringMolten metal pouring equipmentsMolten metal supplying equipmentsMolten stateCasting
A closed system and method that includes a source of pressurizeable molten lead connected to a mold having a mold cavity therein with the mold maintainable at sufficiently low temperature so that a charge of molten lead located in the mold cavity solidifies to thereby form a solidified casting in the mold cavity. A housing having a runner, is maintainable at sufficiently high temperature to maintain the molten lead in a molten state so that the mold cavity can be refilled with a fresh charge molten lead when a solidified casting is removed therefrom without introducing air to the closed system. A shut-off valve, having an open position to allow a charge of molten lead to flow into the mold cavity and a closed position to prevent molten lead from flowing out of the runner as the molten lead in mold cavity solidifies with the shut-off valve configurable to intensify the pressure of the lead in the mold cavity.
Owner:WATER GREMLIN
Automated spray form cell
InactiveUS6640878B2High sensitivityAccurate distributionMolten spray coatingCasting safety devicesStress inducedAutomotive industry
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
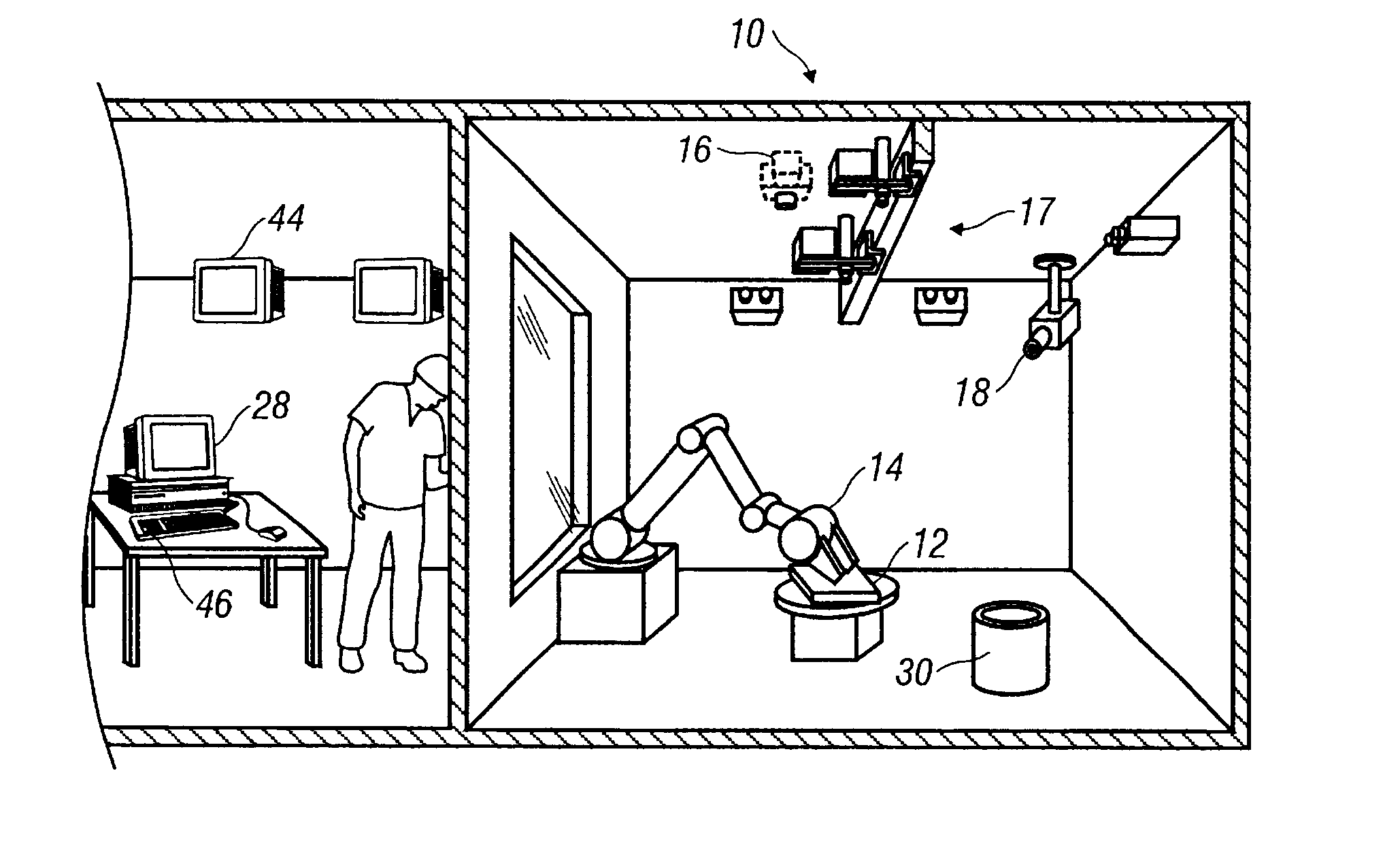
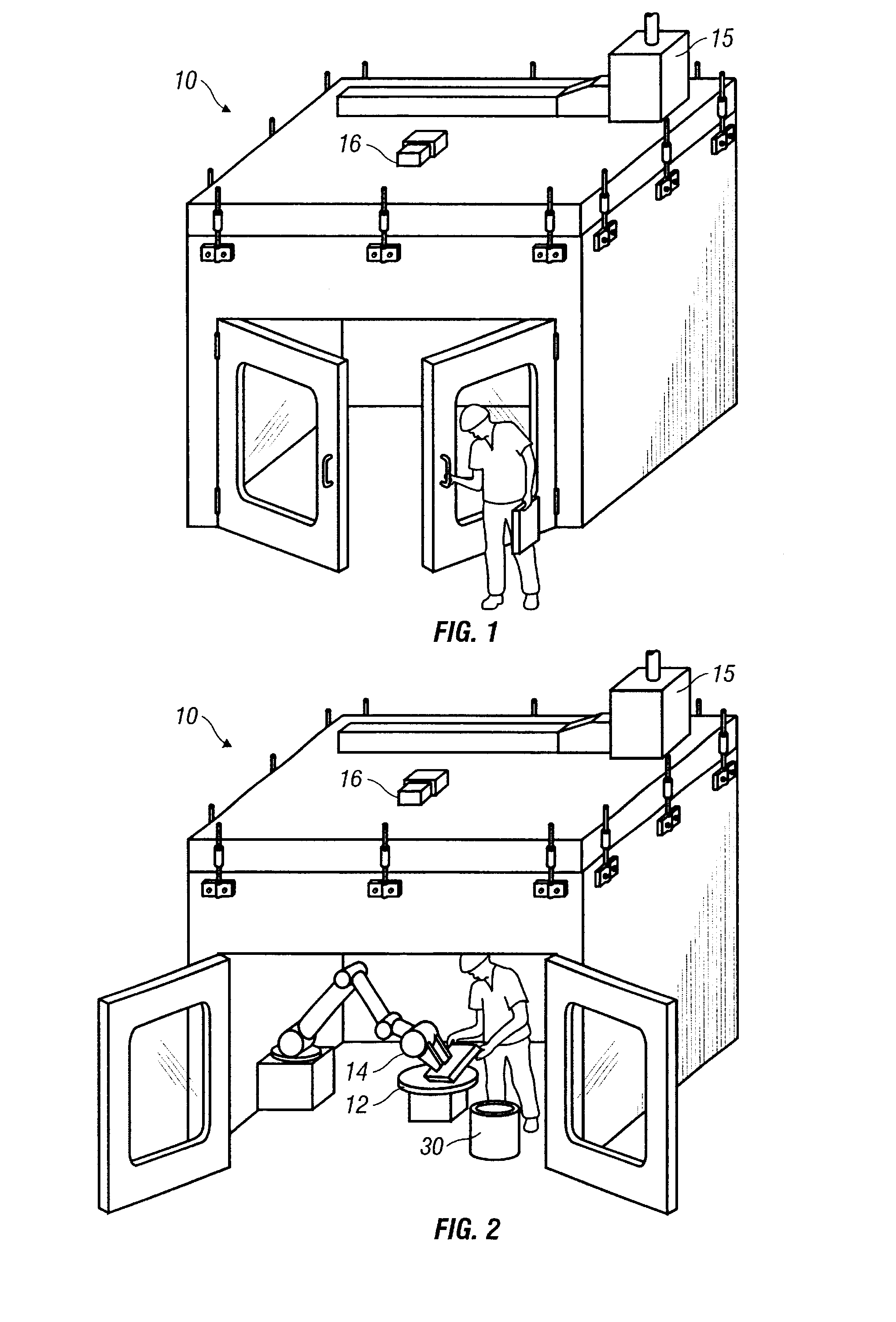
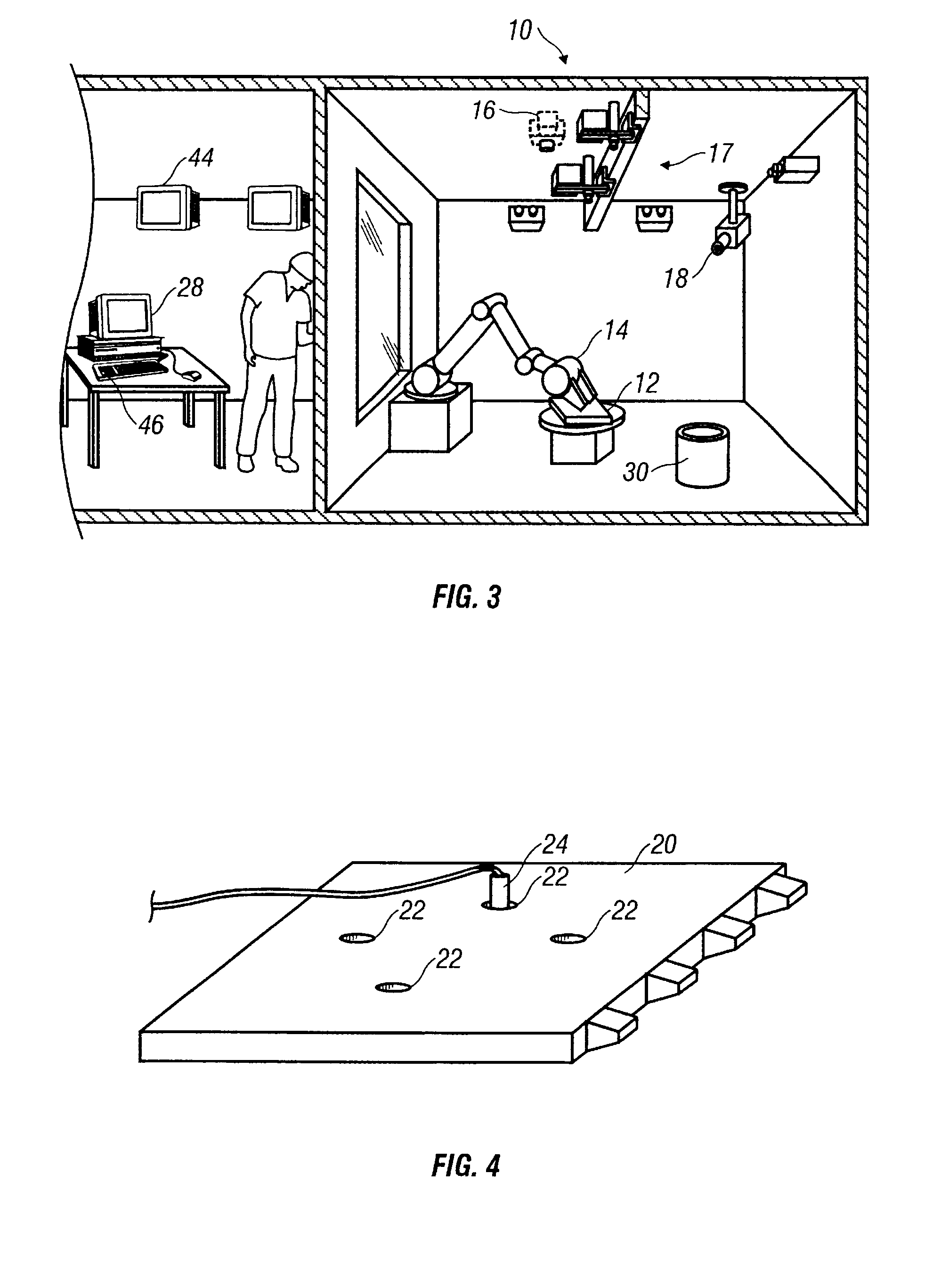
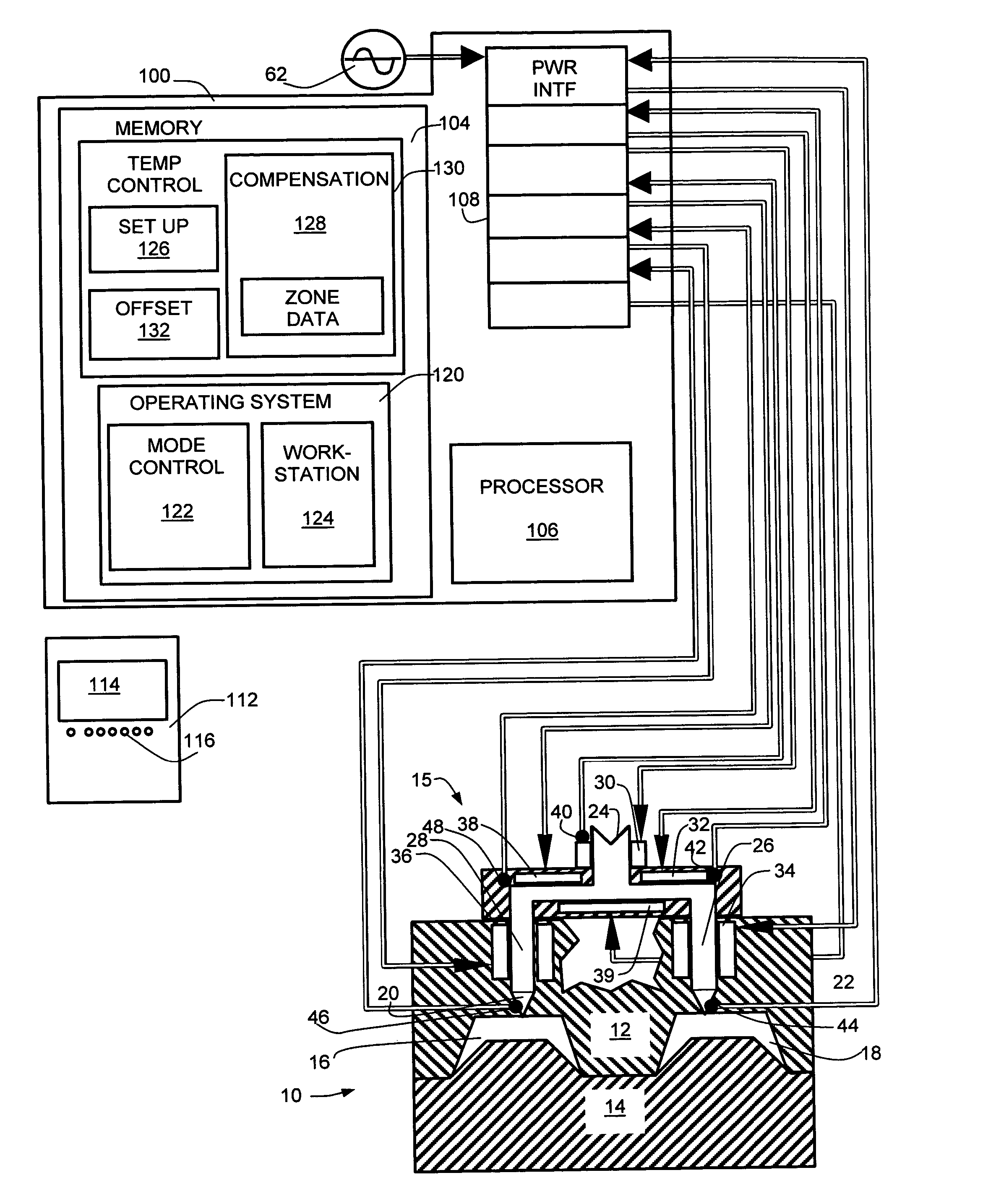
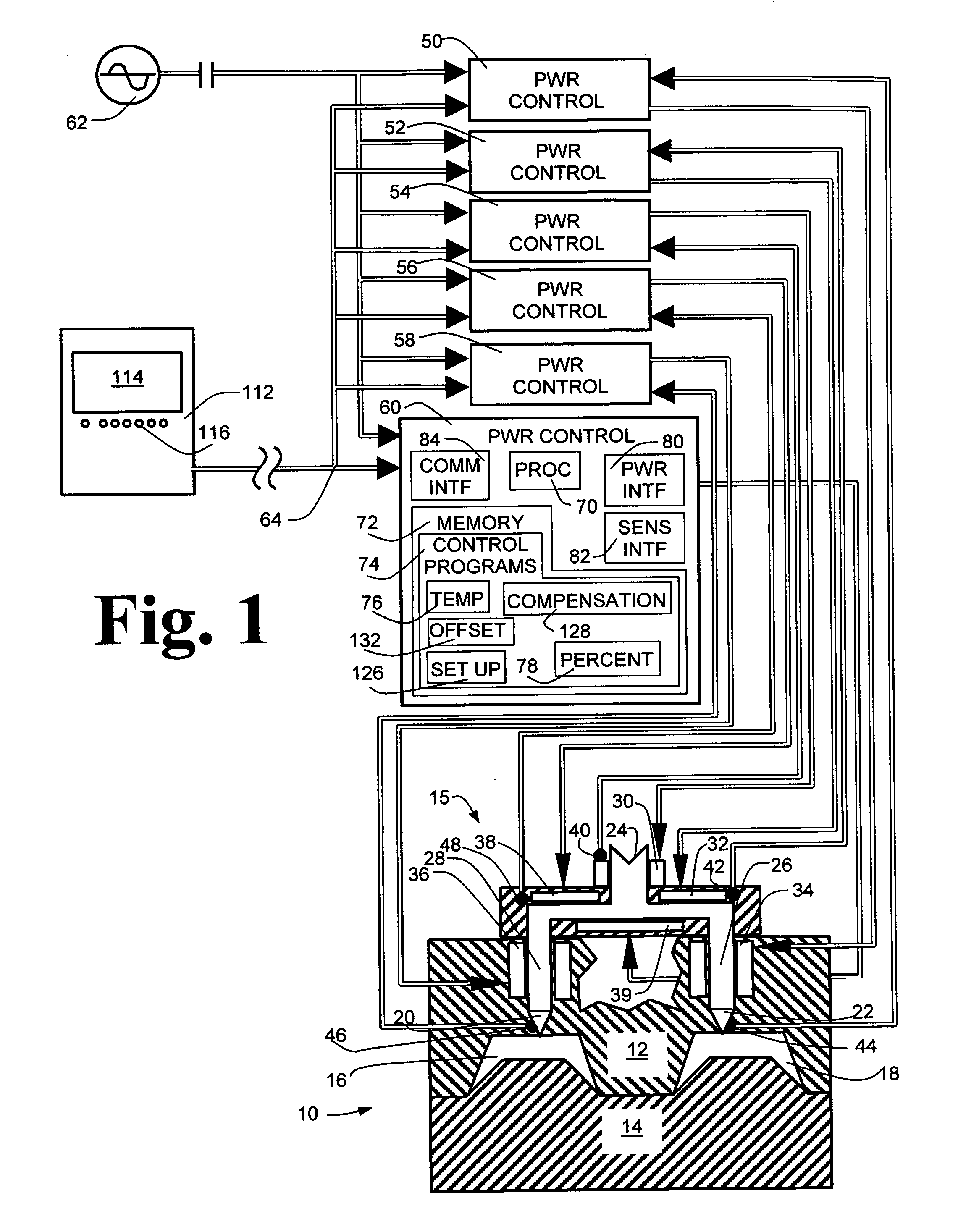
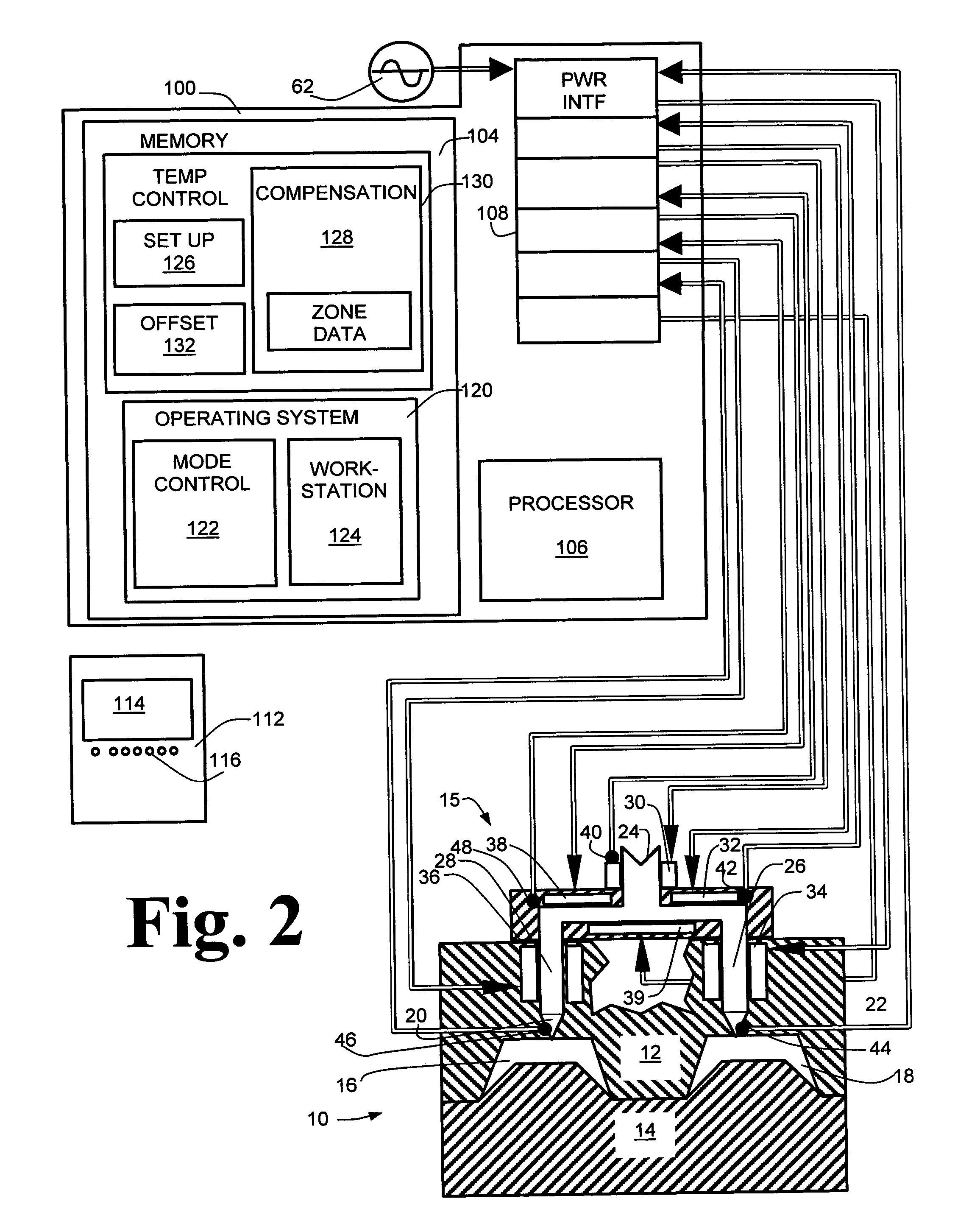
Temperature control
ActiveUS7020540B2Temperatue controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementTemperature controlControl zone
A method and apparatus are disclosed for controlling temperature of a plant comprising plural temperature control zones, wherein an effective control parameter for a first zone for which a signal representing measured temperature is available is produced according to an algorithm relating measured temperature, a desired temperature and a control parameter associated with a device affecting temperature in the first temperature control zone, the effective control parameter is summed with an offset value representing a proportional offset of the effective control parameter of a second temperature control zone relative to the effective control parameter of the first temperature control zone and the result is applied to control a device affecting temperature in the second temperature control zone. Advantageously, the offset value comprises a fixed amount and a variable amount, the variable amount accounting for dynamic differences in temperature control characteristics of the first and second temperature control zones.
Owner:D M E CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com