Patents
Literature
2169 results about "Design data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for document processing
ActiveUS8910870B2Record carriers used with machinesSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcodeDocument preparation
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to document processing, and more particularly to systems and methods that can utilize relative positions between the content of the document and a decodable indicia affixed to the document. In one embodiment, indicia reading terminals are provided that include an imaging module for capturing a frame of image data of a document. The document can include one or more decodable indicia such as a form barcode and various content fields, which delineate particular content of the document. The form barcode can include information respecting the form design and form design data. This information can be used to process the content of the document such as by providing coordinates or similar location and positioning metrics for use in processing the content of the document. In one example, the frame of image data is analyzed to identify the form barcode, from which the relative location of the content fields can be discerned without extensive processing of the frame of image data.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
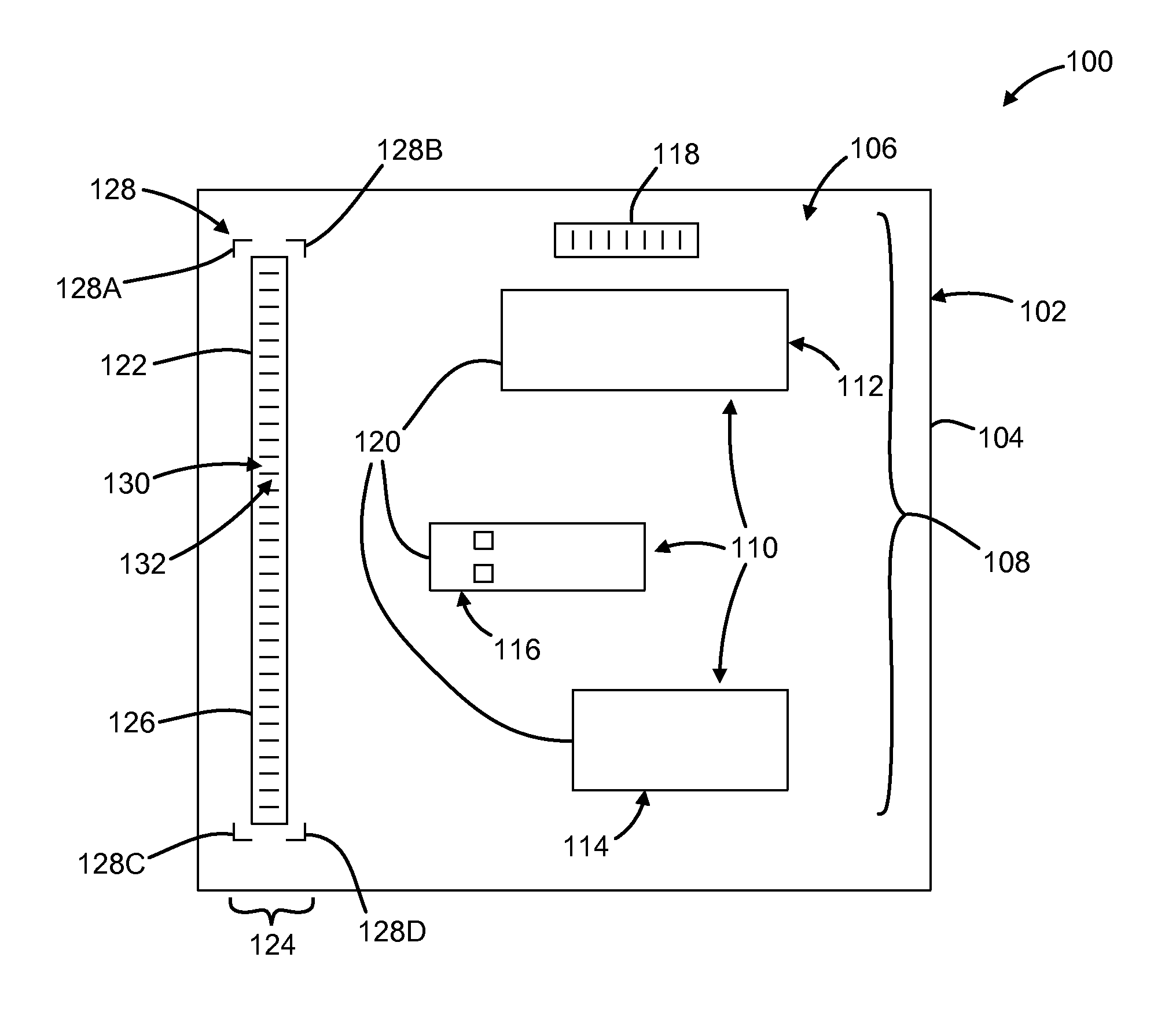
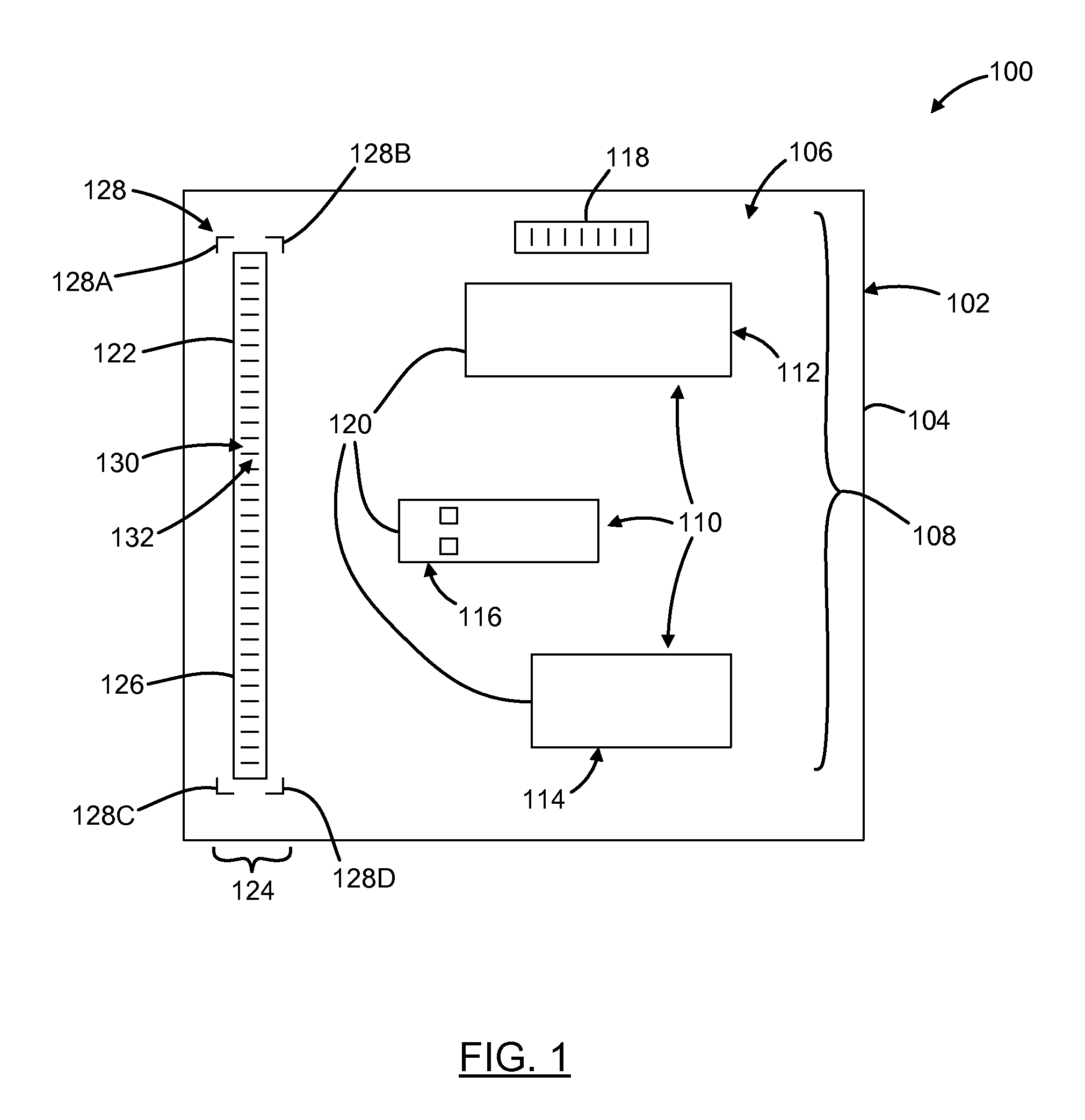
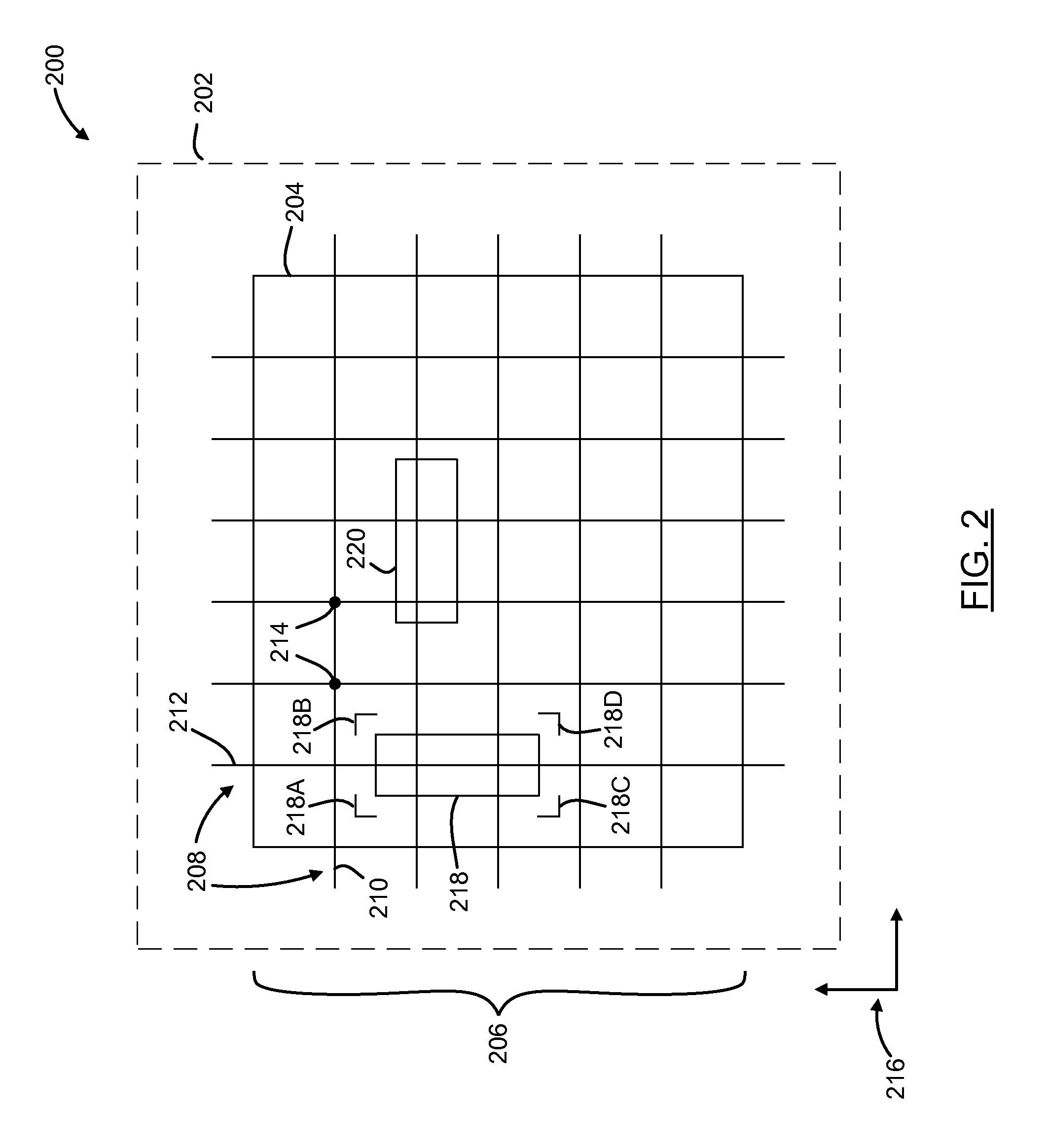
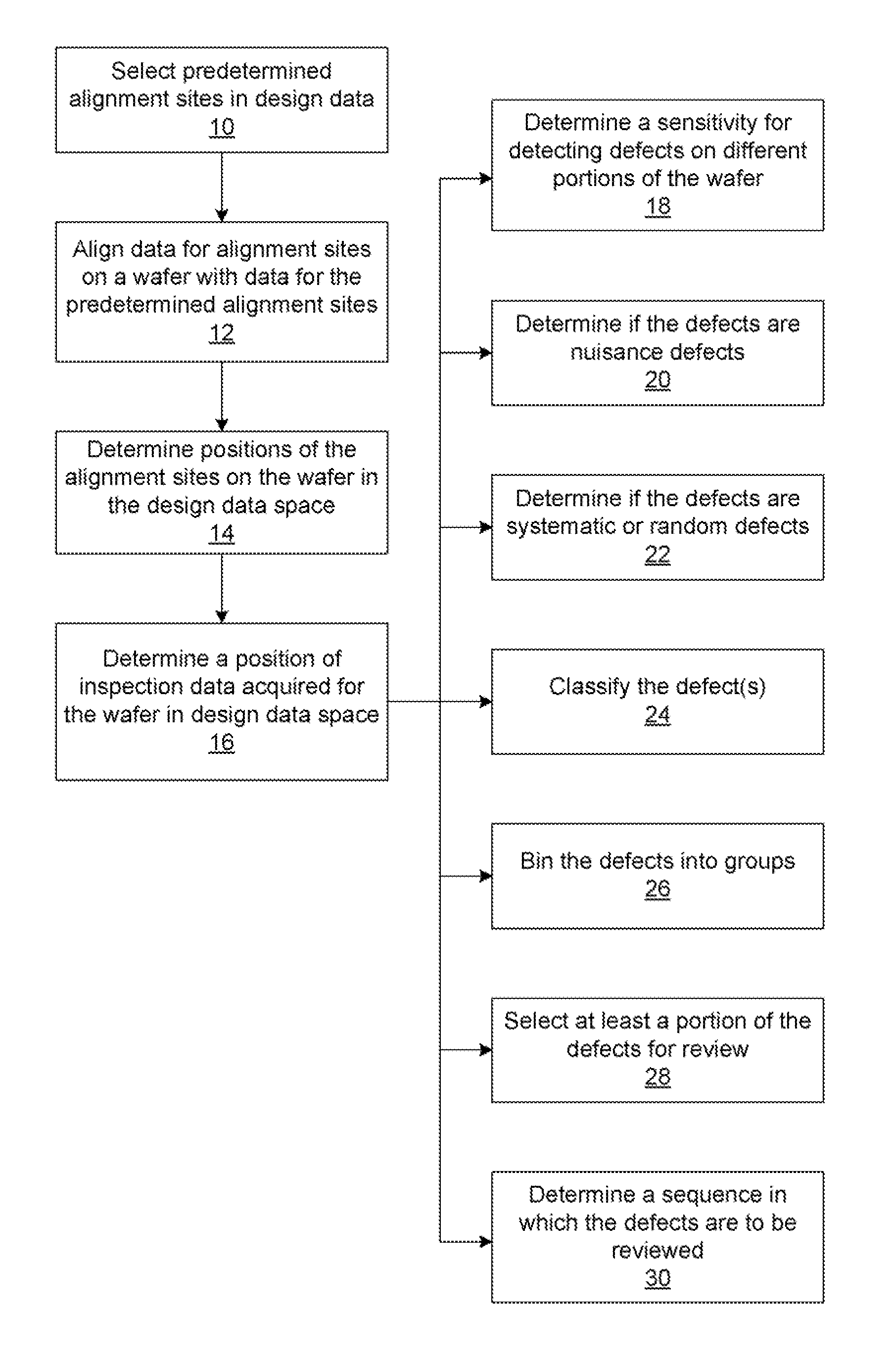
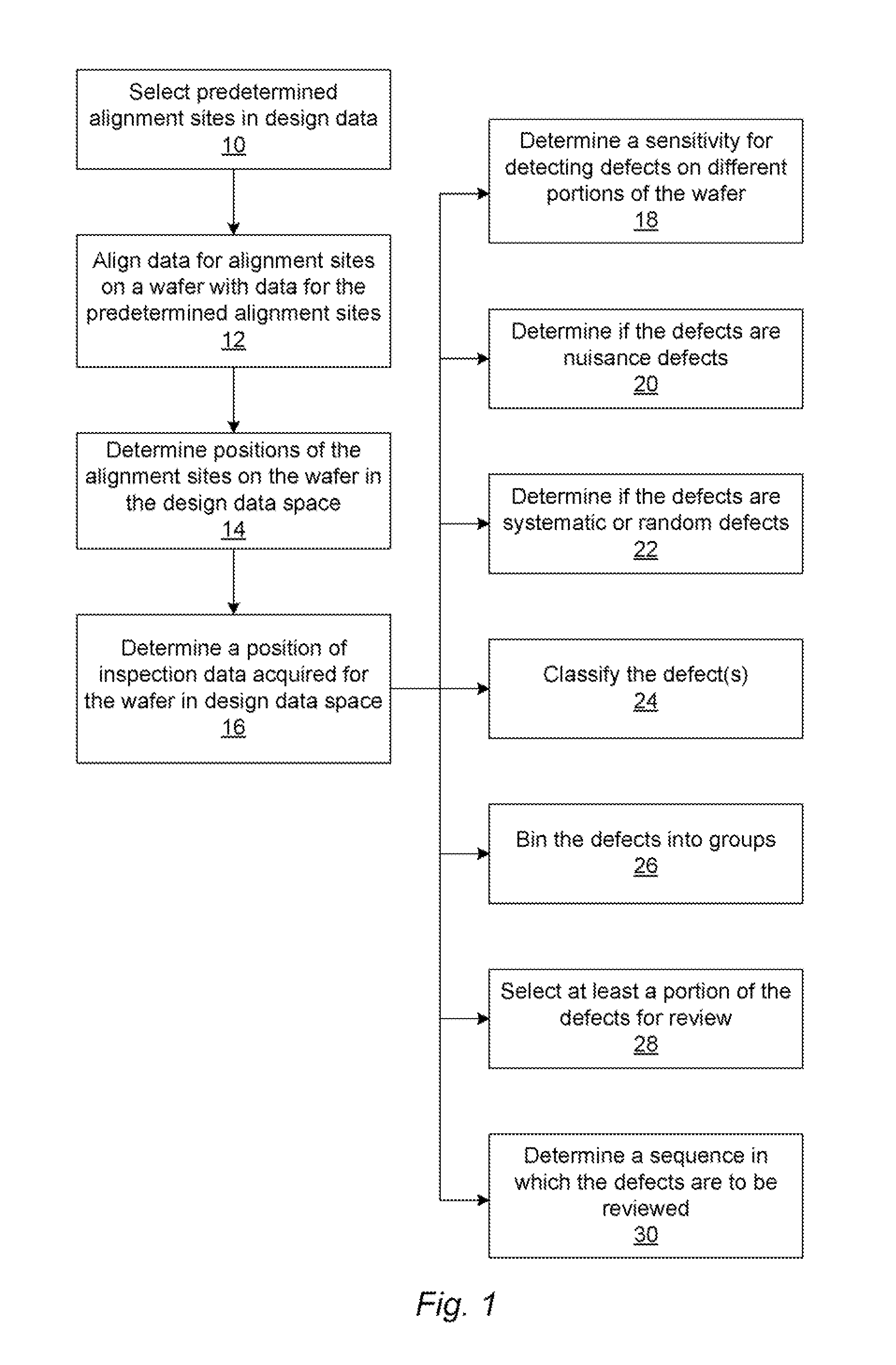
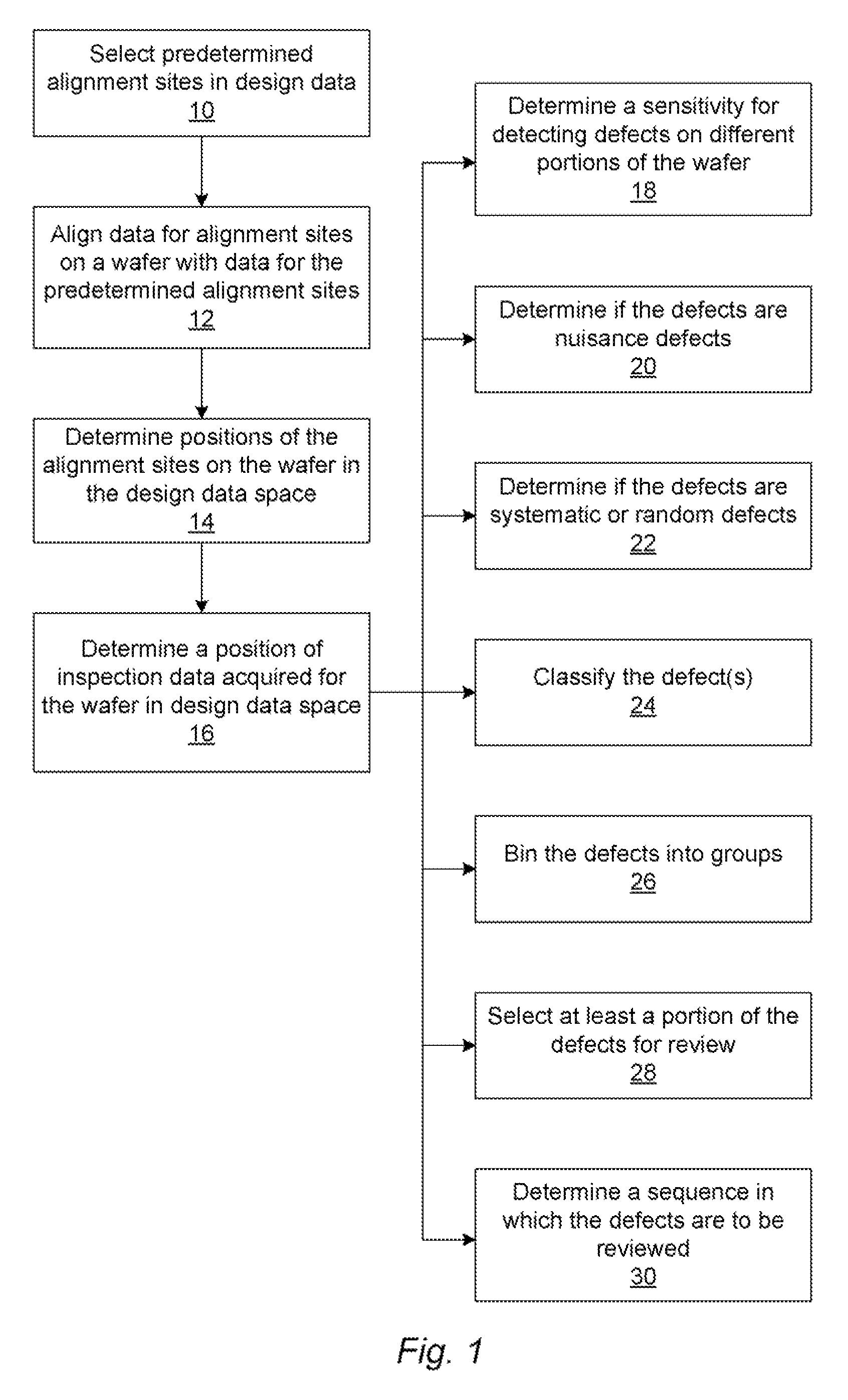
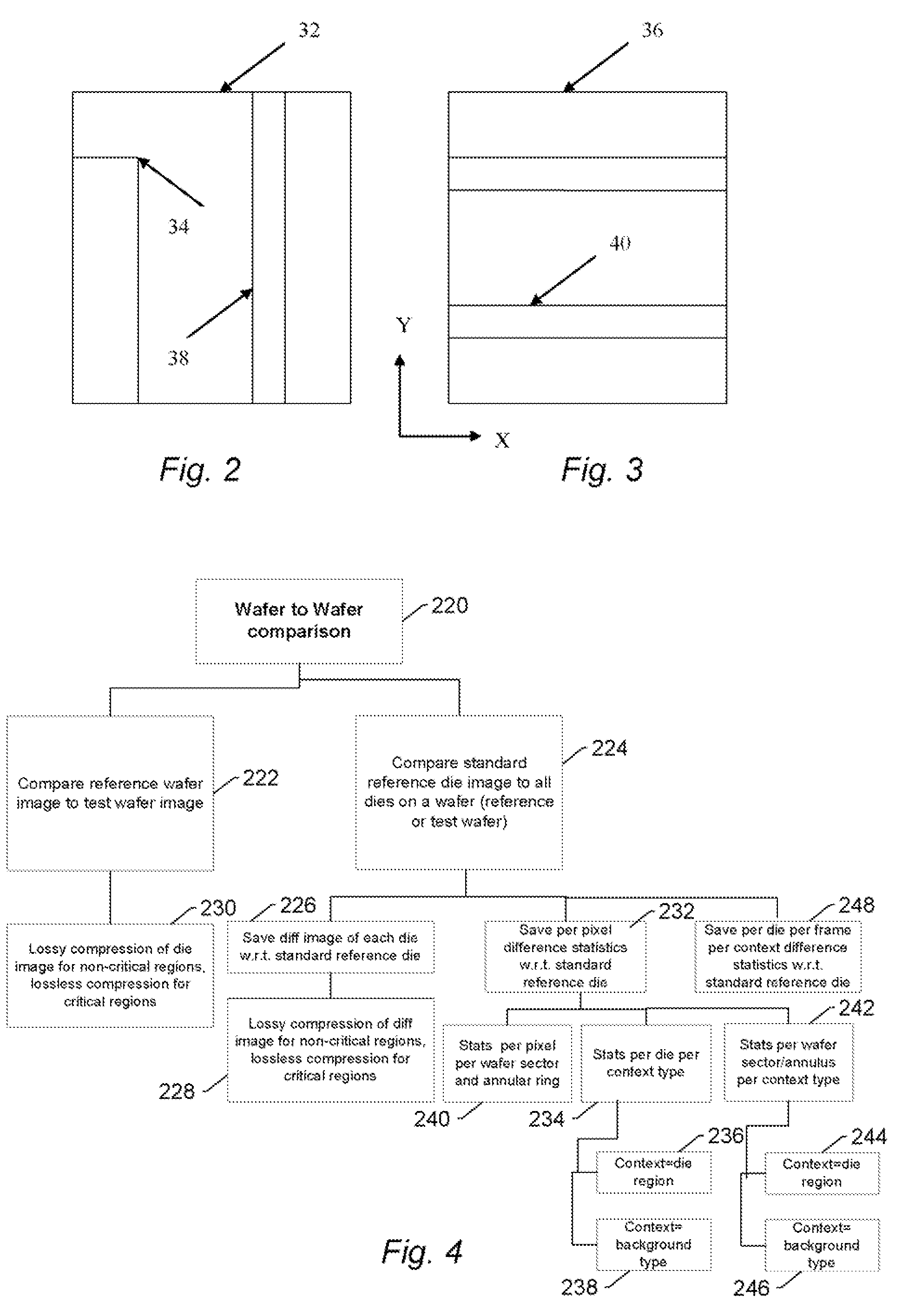
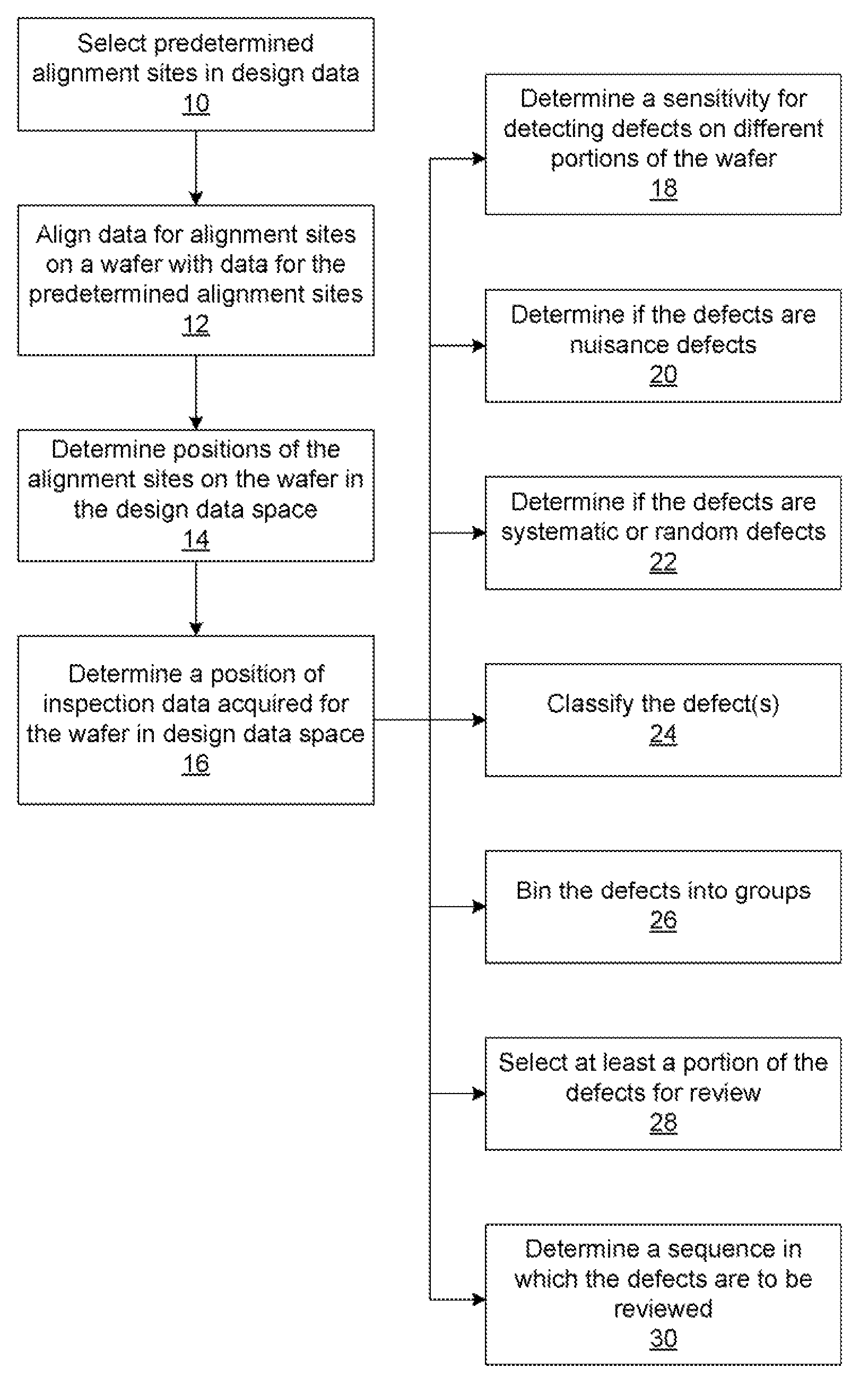
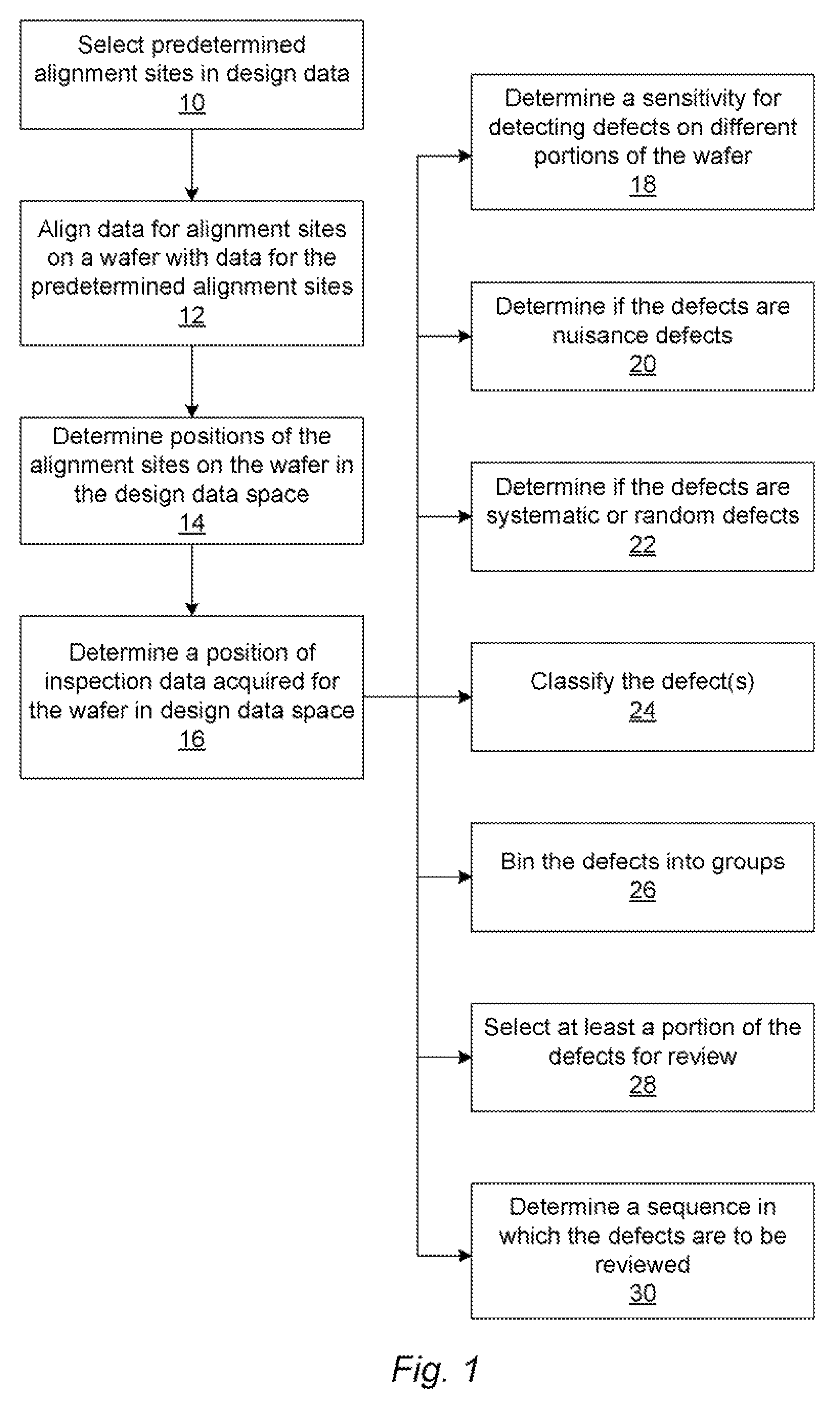
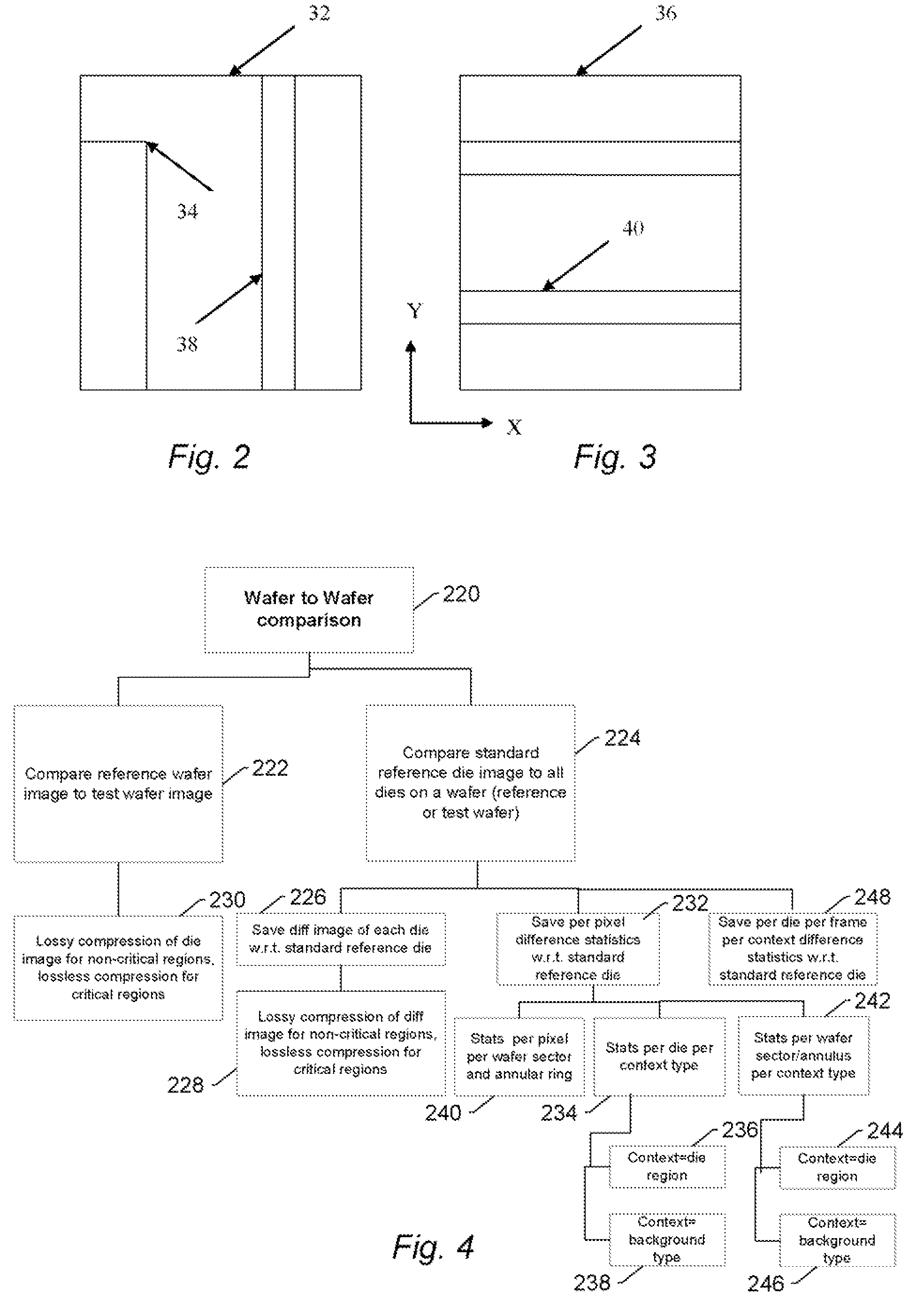
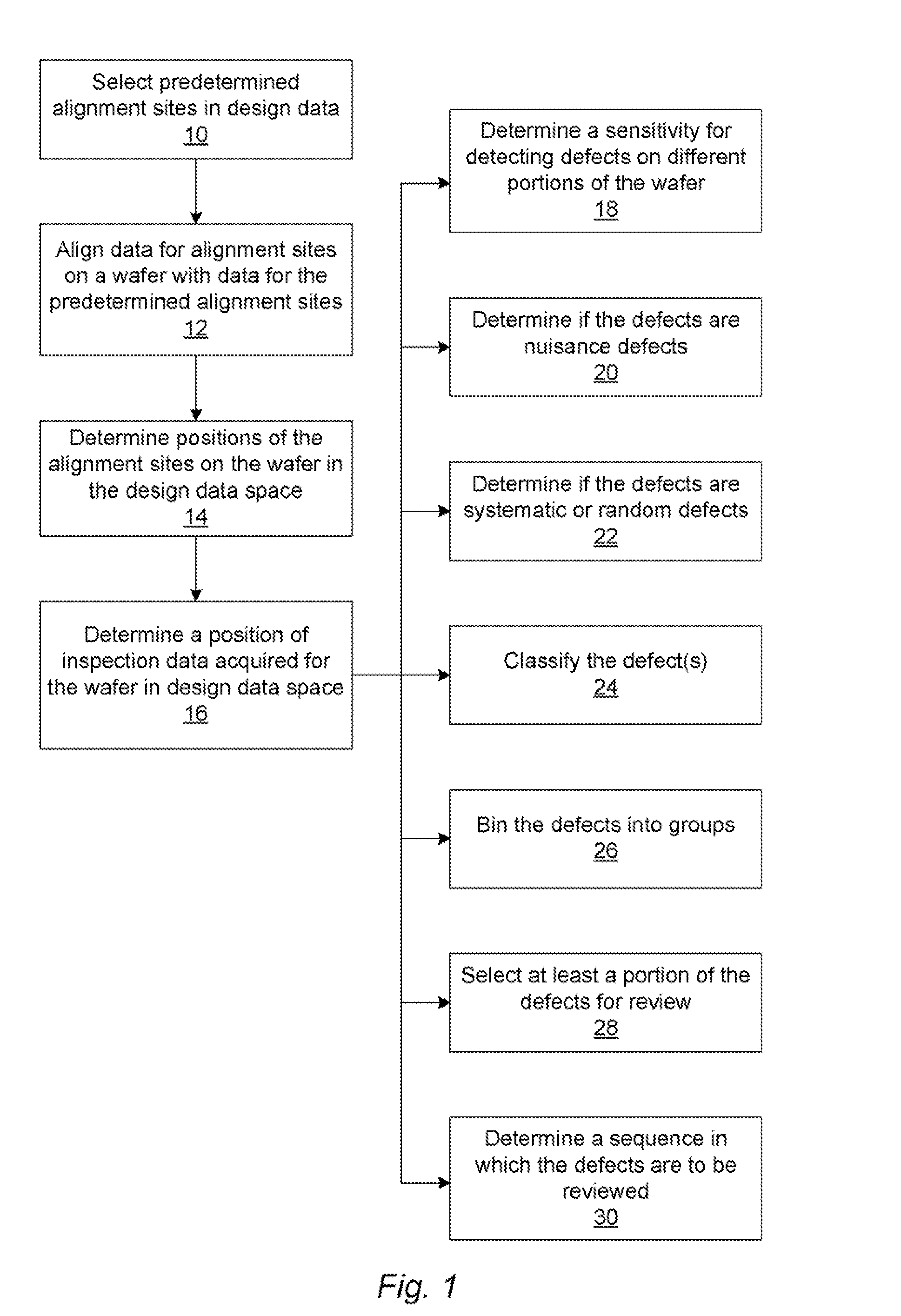
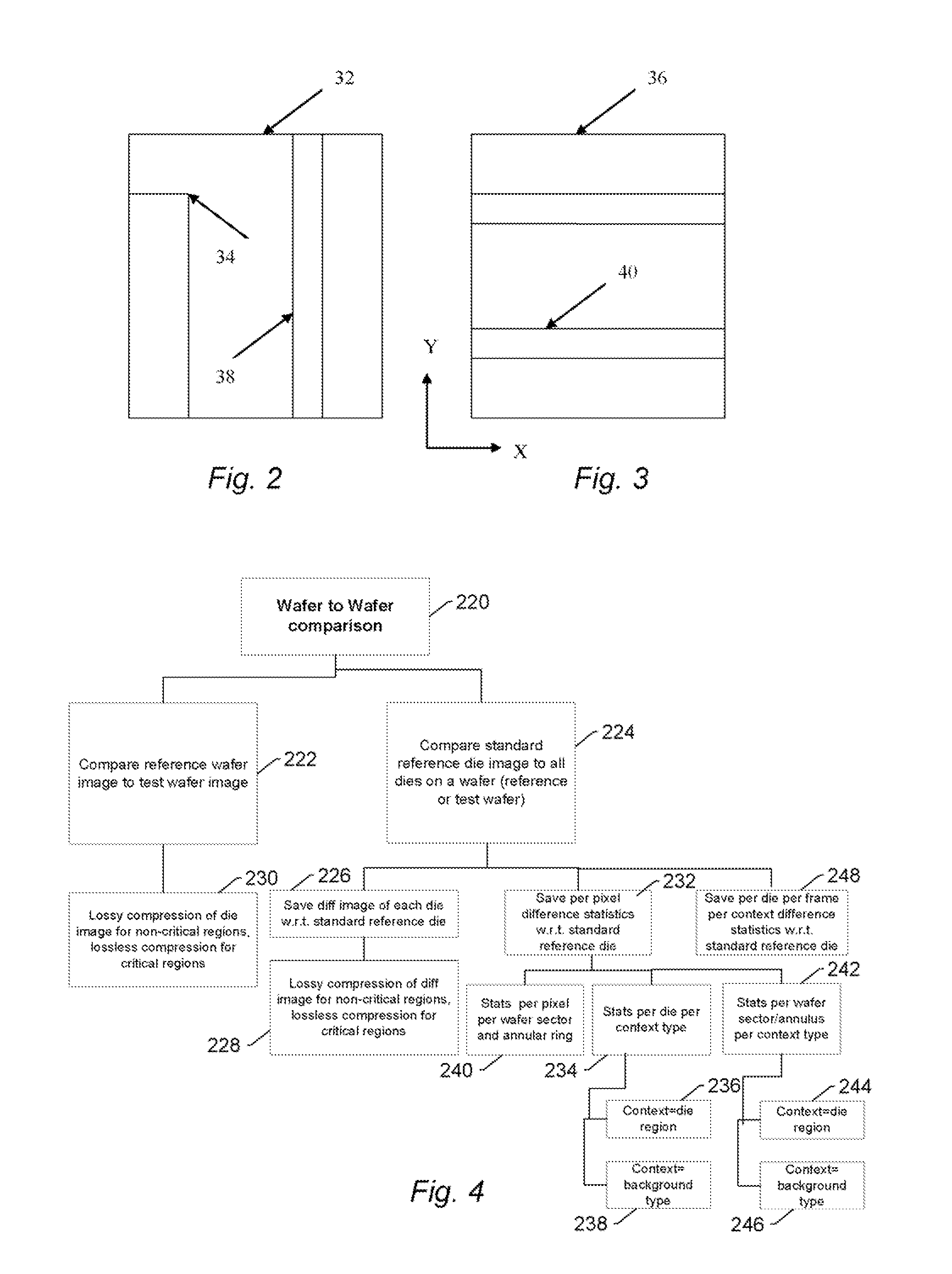
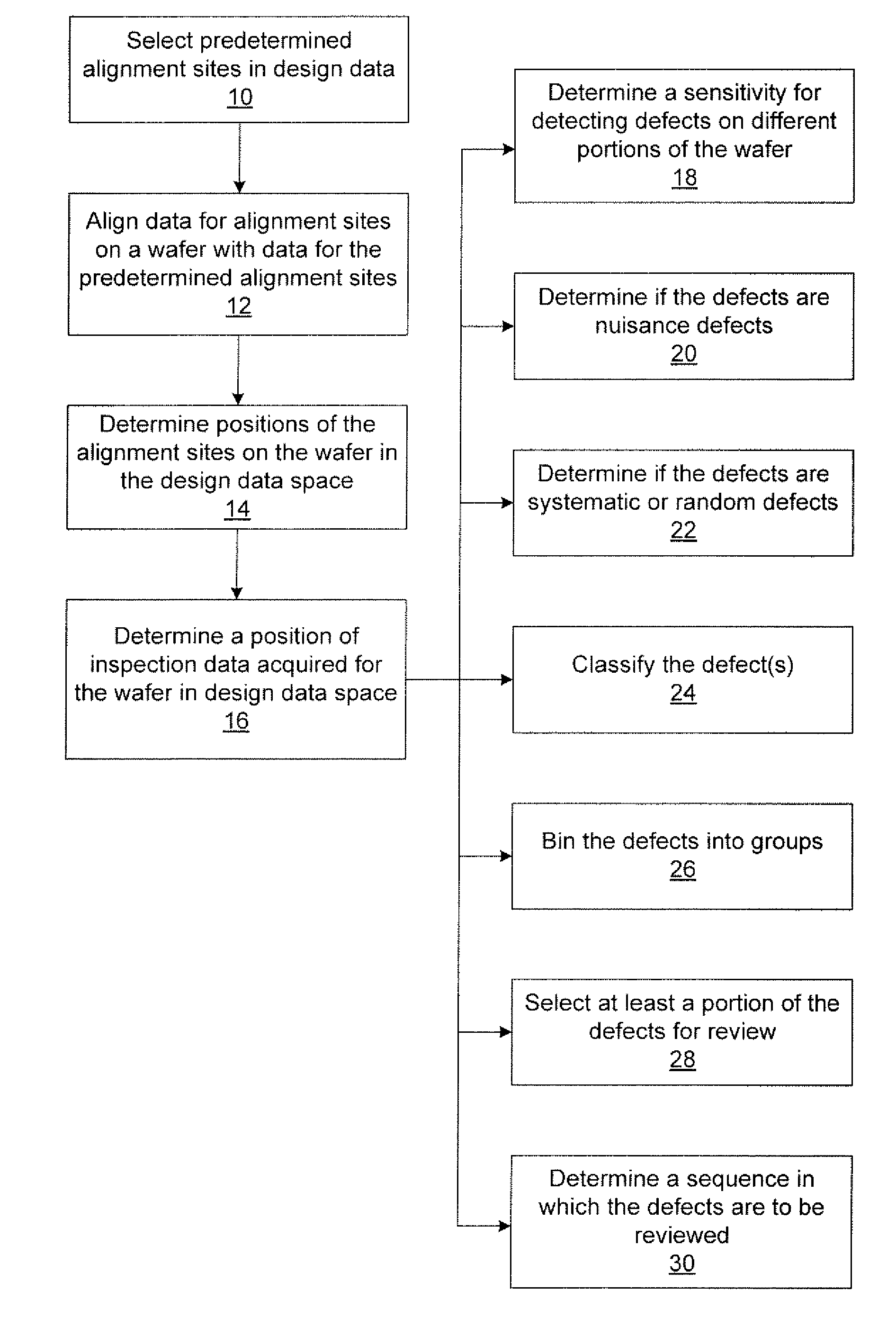
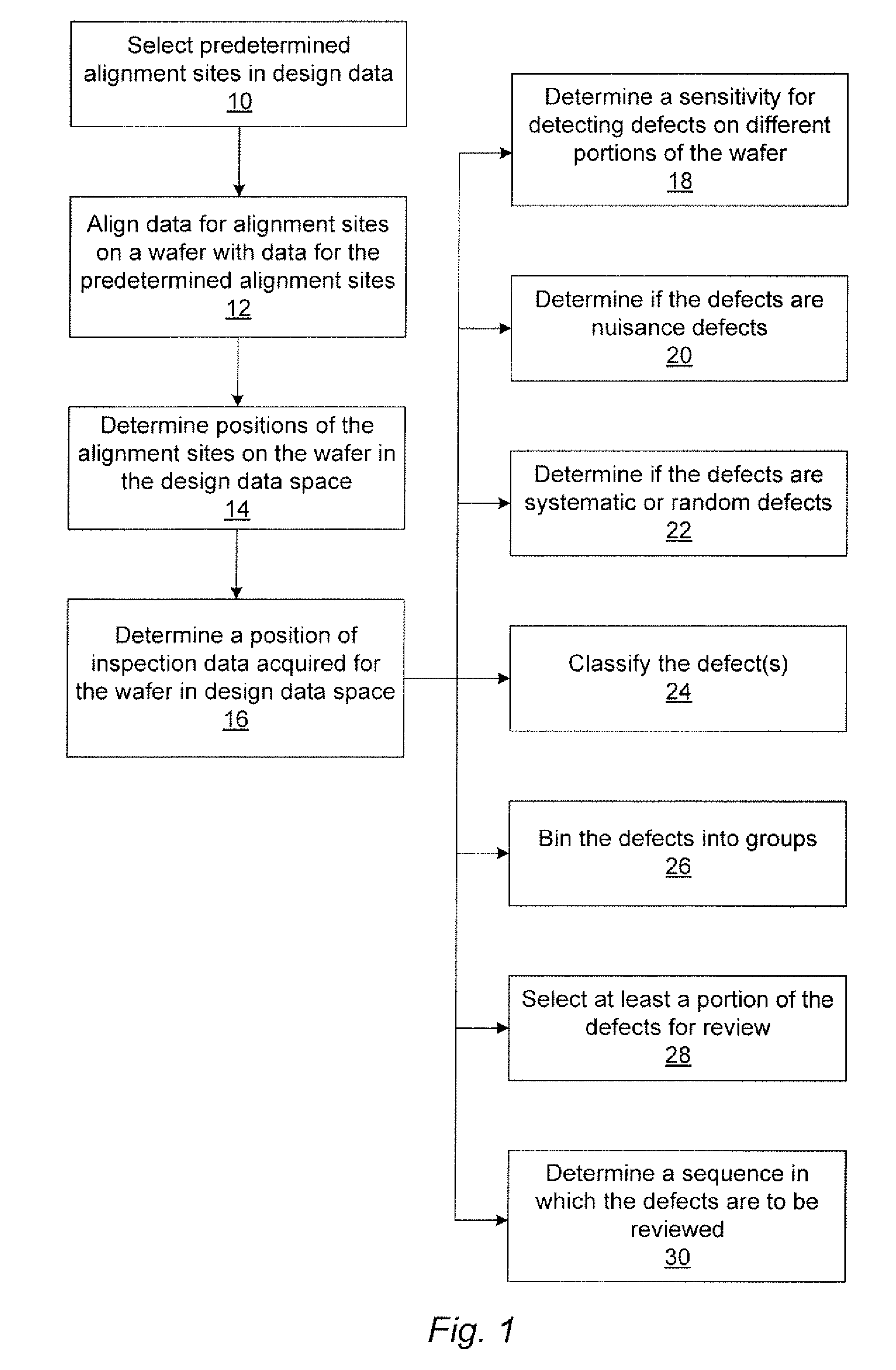
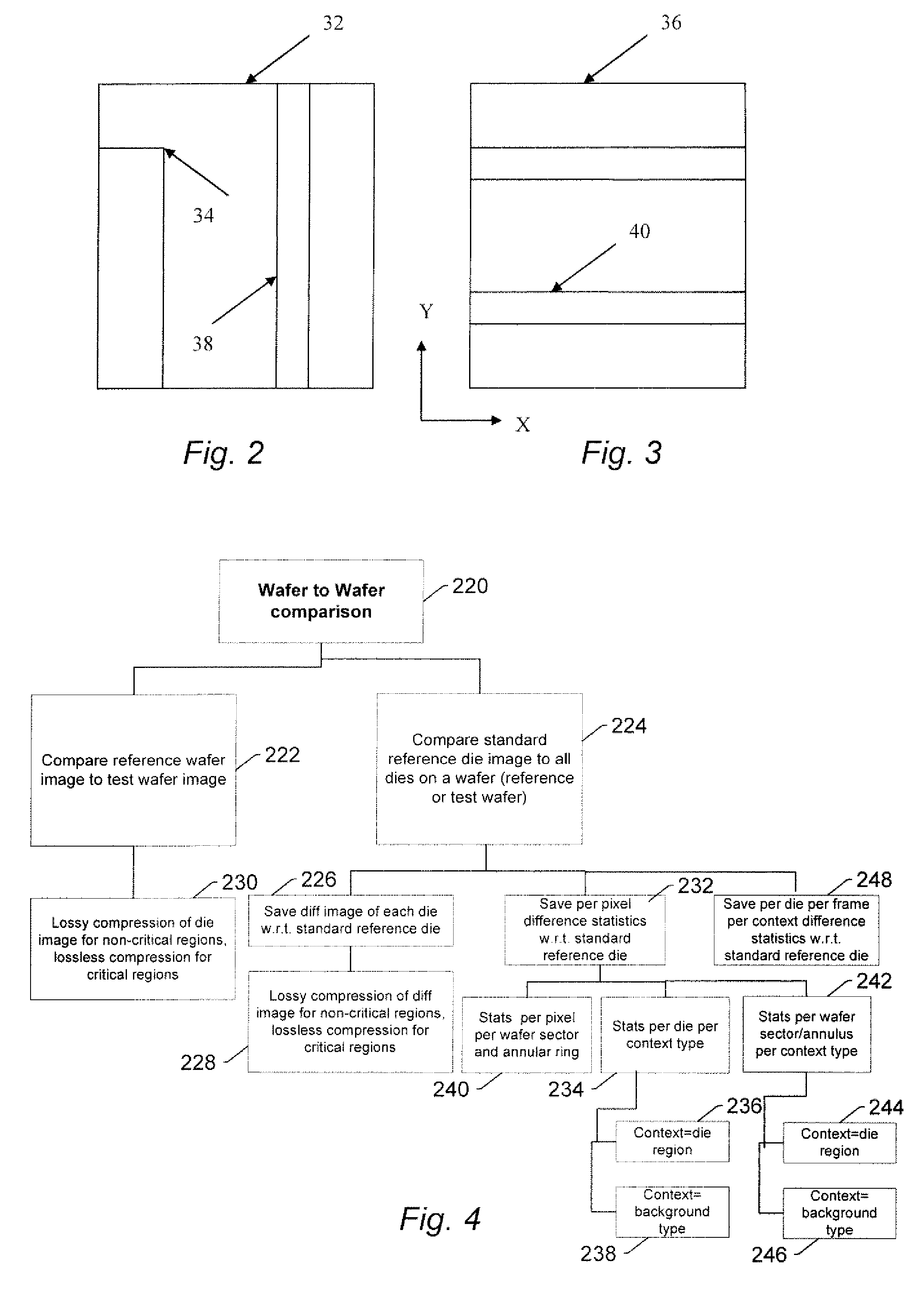
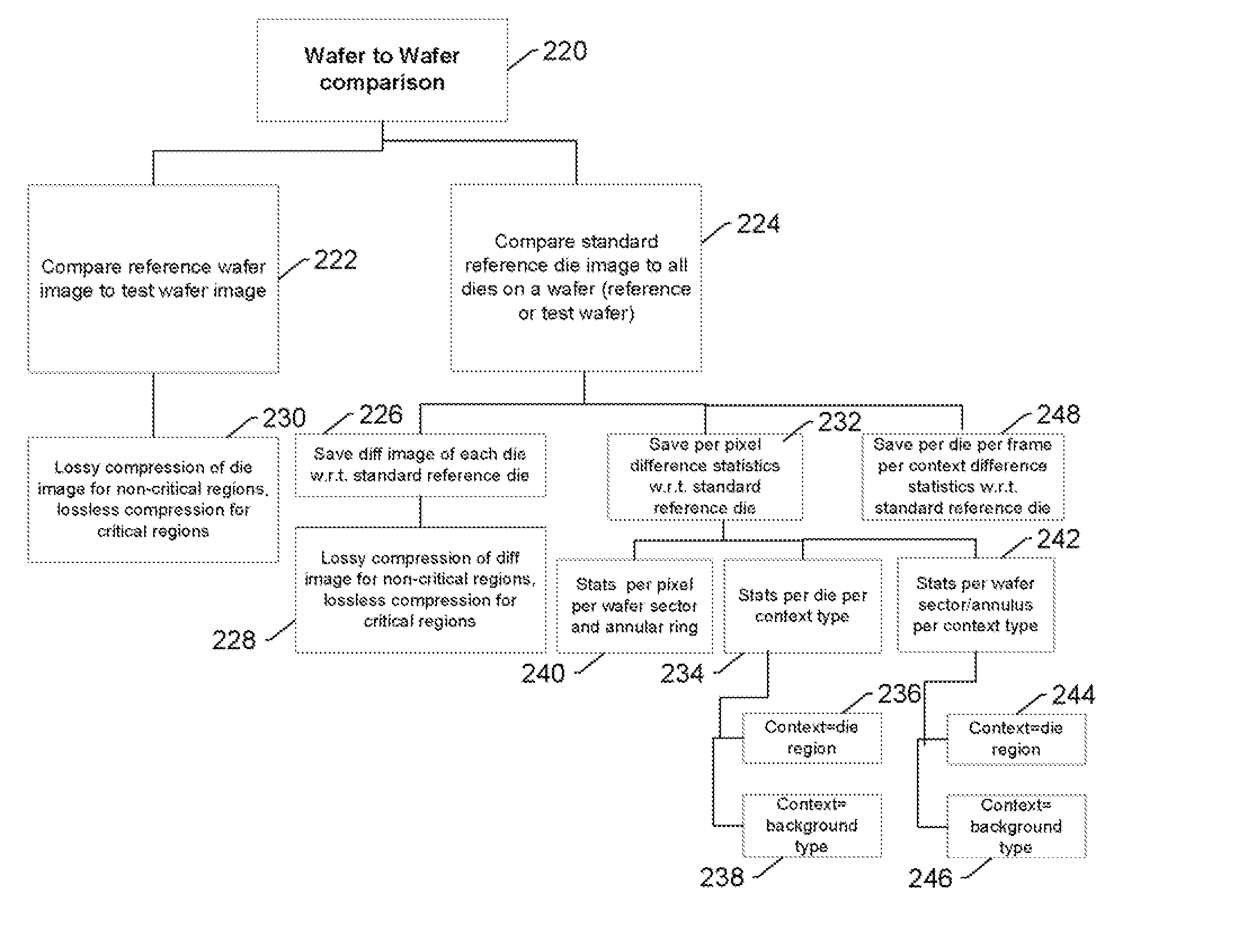
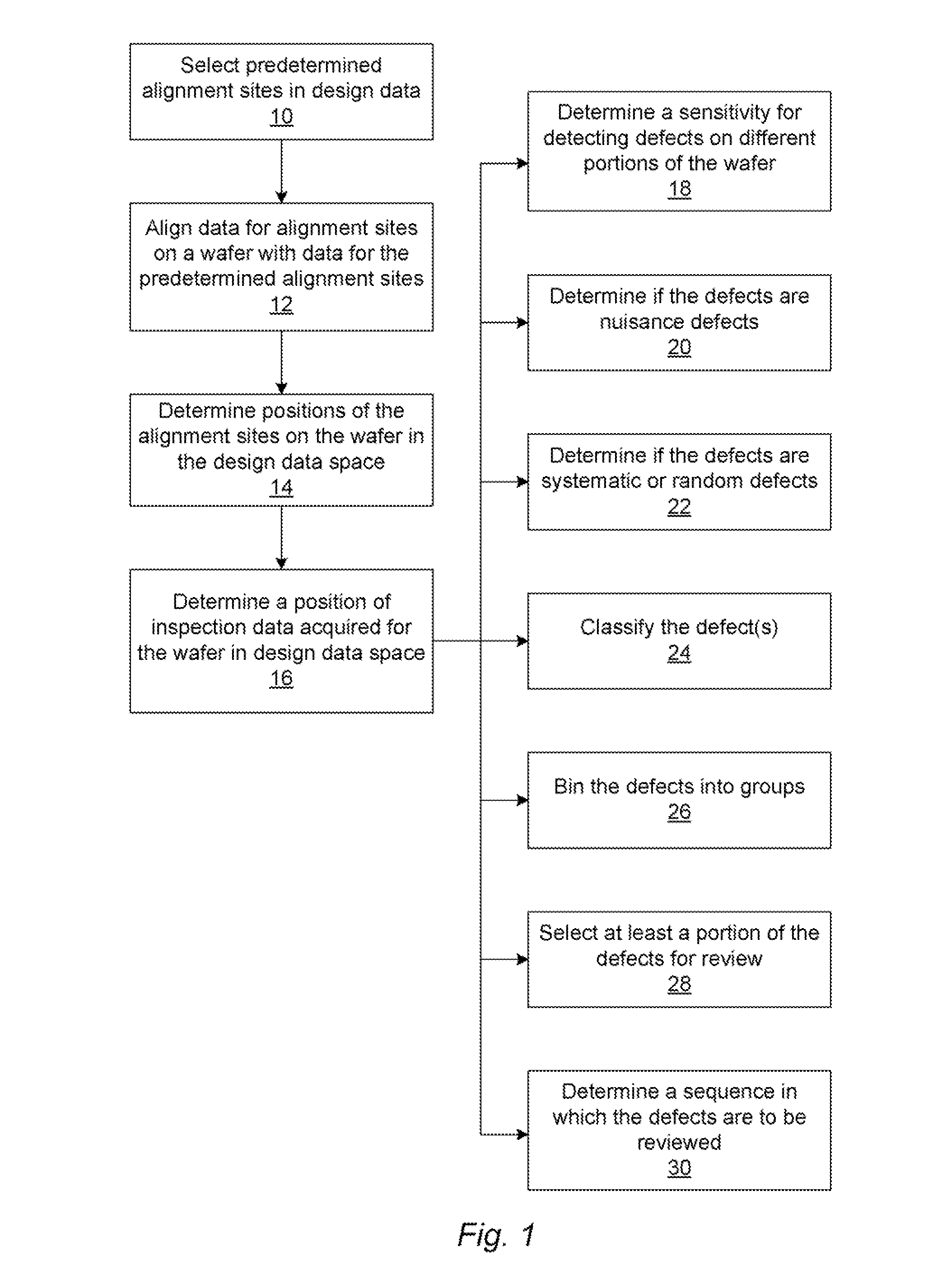
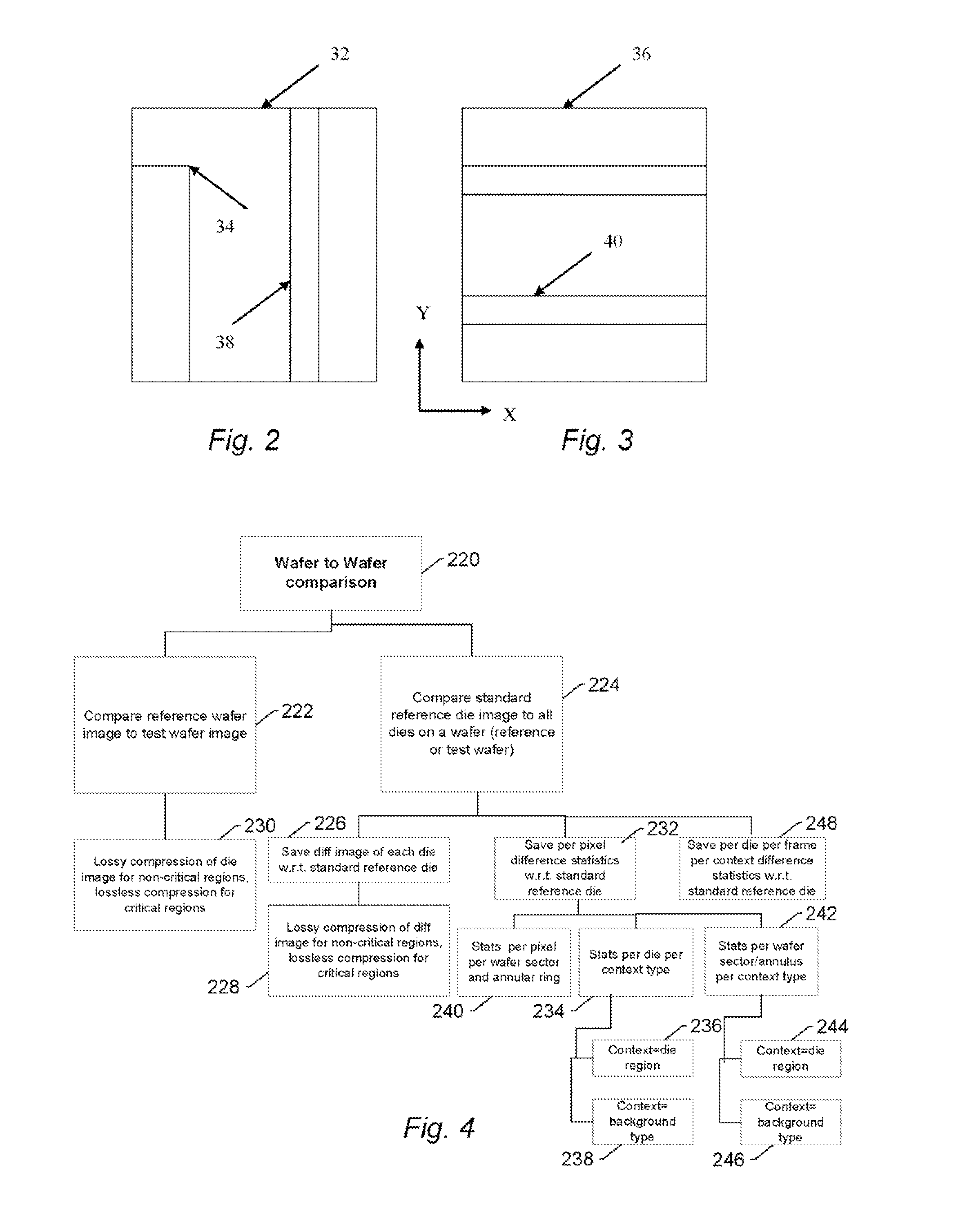
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS20070288219A1Increase catch rateReduce errorsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceDesign data
Various methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data are provided. One computer-implemented method for binning defects detected on a wafer includes comparing portions of design data proximate positions of the defects in design data space. The method also includes determining if the design data in the portions is at least similar based on results of the comparing step. In addition, the method includes binning the defects in groups such that the portions of the design data proximate the positions of the defects in each of the groups are at least similar. The method further includes storing results of the binning step in a storage medium.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS7570796B2Reduce errorsImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceDesign data
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS7676077B2Reduce errorsImprove defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringDesign data
Various methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data are provided. One computer-implemented method for determining a position of inspection data in design data space includes aligning data acquired by an inspection system for alignment sites on a wafer with data for predetermined alignment sites. The method also includes determining positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in design data space based on positions of the predetermined alignment sites in the design data space. In addition, the method includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer by the inspection system in the design data space based on the positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in the design data space. In one embodiment, the position of the inspection data is determined with sub-pixel accuracy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for storing multiple levels of design data in a common database
InactiveUS6505328B1Increase flexibilityEasy to integrateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designGraphicsLogic circuit design
Owner:MAGMA DESIGN AUTOMATION
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS20070156379A1Increase catch rateImprove signal-to-noise ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringDesign data
Various methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data are provided. One computer-implemented method for determining a position of inspection data in design data space includes aligning data acquired by an inspection system for alignment sites on a wafer with data for predetermined alignment sites. The method also includes determining positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in design data space based on positions of the predetermined alignment sites in the design data space. In addition, the method includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer by the inspection system in the design data space based on the positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in the design data space. In one embodiment, the position of the inspection data is determined with sub-pixel accuracy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
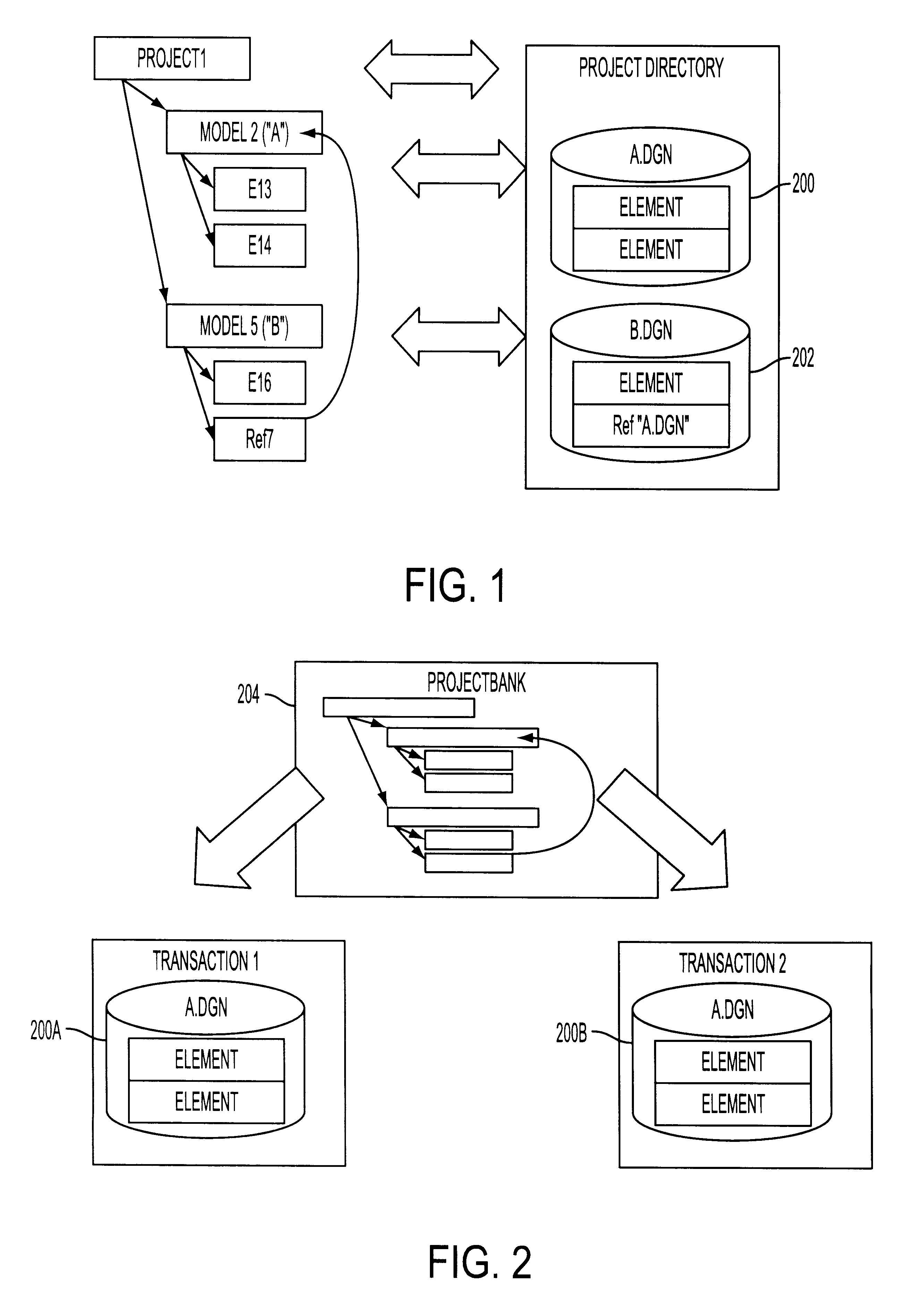
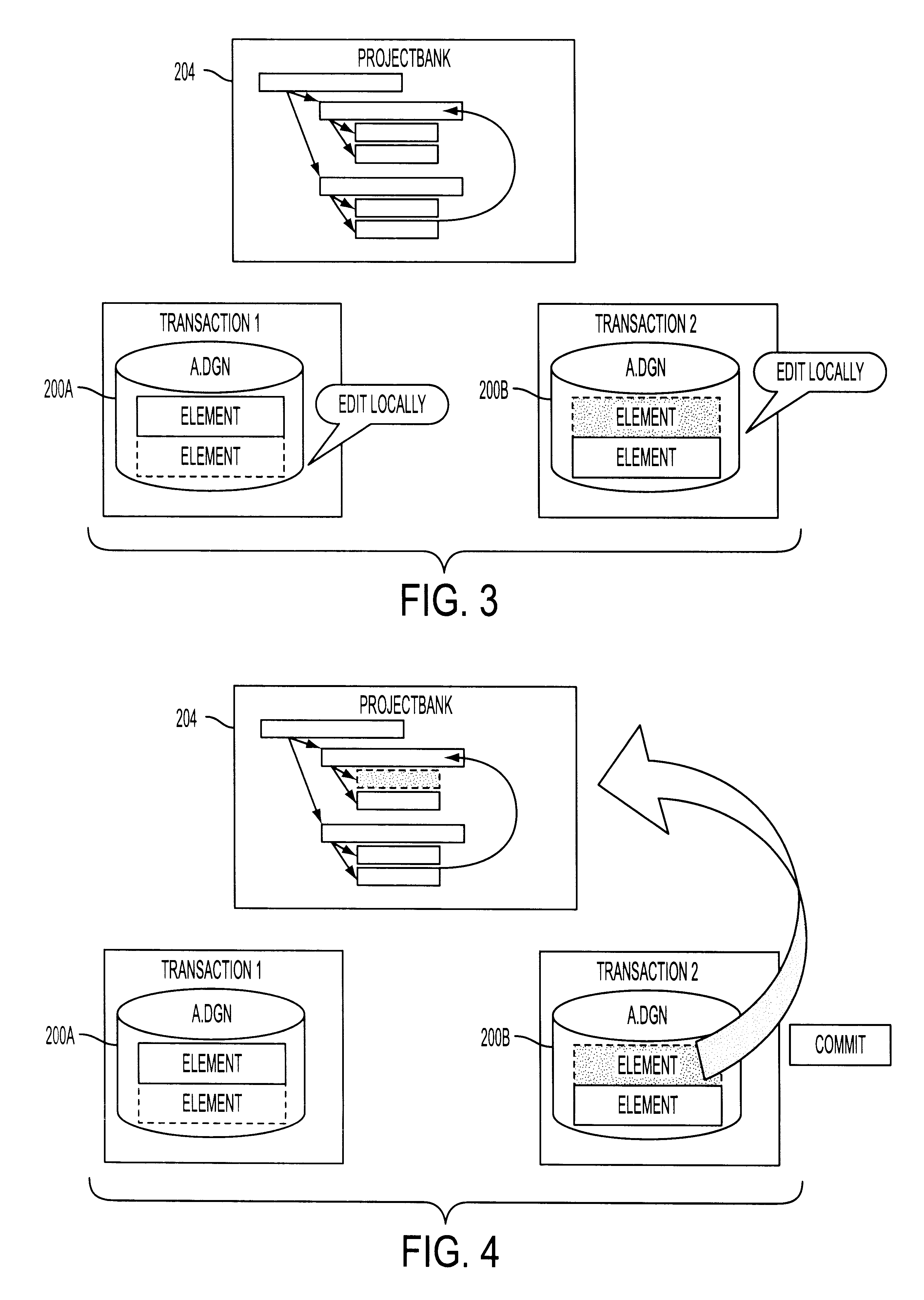
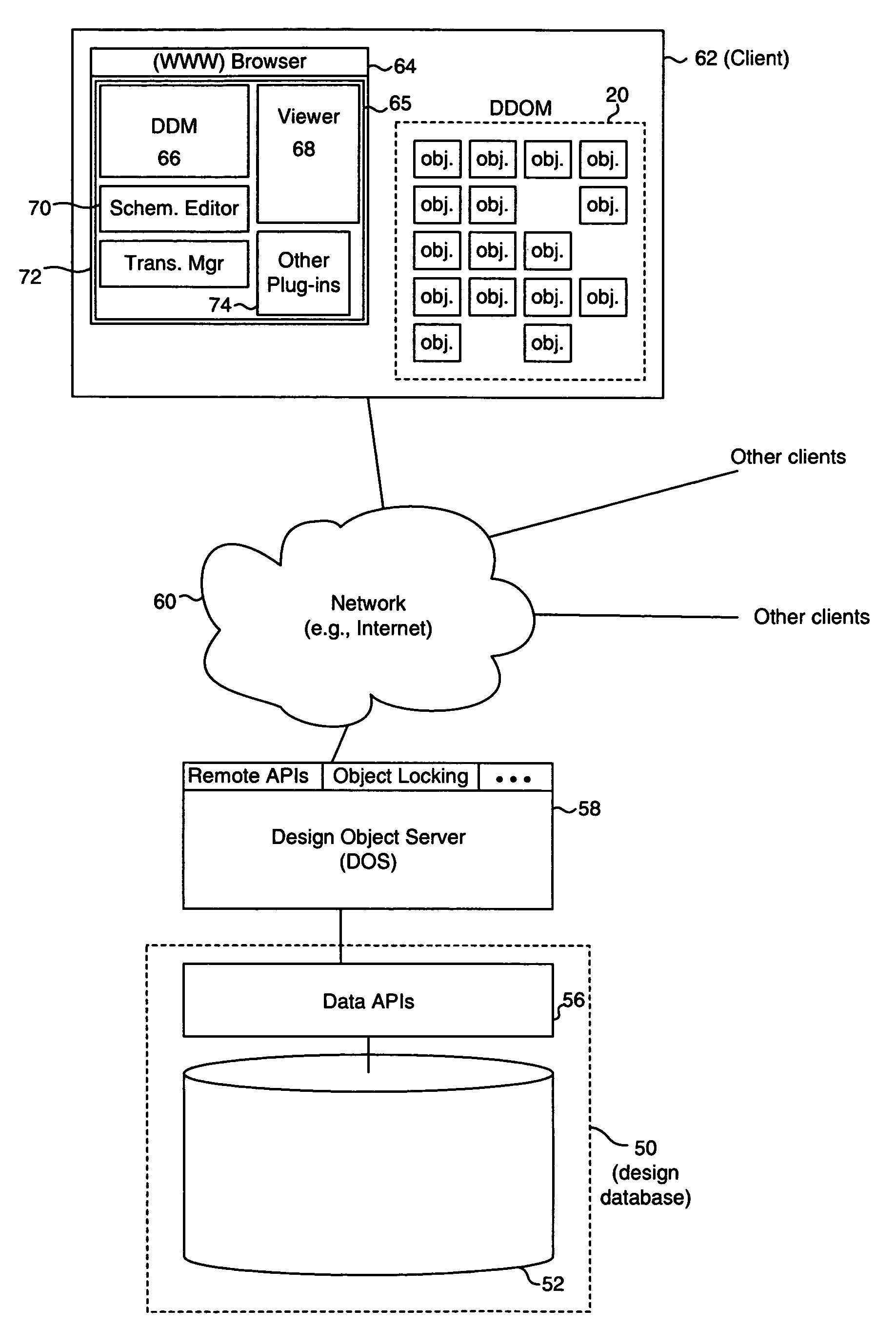
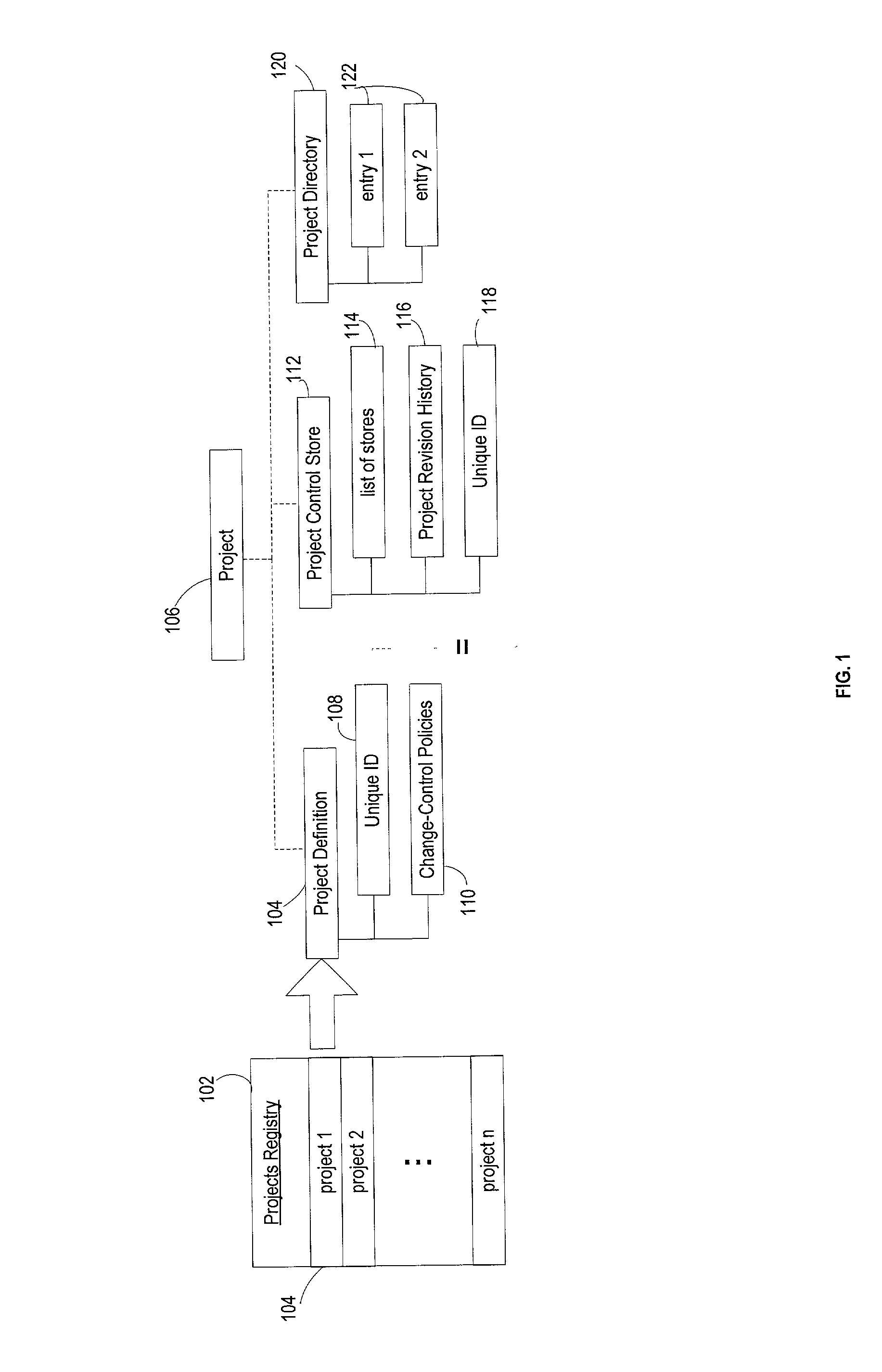
System for collaborative engineering using component and file-oriented tools
InactiveUS6341291B1Improve the level ofHigh currentData processing applicationsCAD network environmentSoftware engineeringIdenticon
Conventional file-based engineering design data for an engineering model are represented by a plurality of components. Each component has a unique identifier, a set of fields, each field having a data type and a data value, and a program which interprets and modifies the fields. The plurality of components are stored in a repository of a server. The repository also stores a history of any changes made to the components. A plurality of client computers are bidirectionally connected to the server. Each client computer may obtain the current version of the components and may send locally edited versions of the components back to the server to replace the current versions in the repository. At the client computer, the user interacts with the components using conventional file-based software. Before locally edited versions of the components are committed to the server to replace the current versions, a synchronization and merging process occurs whereby the latest version of the components are downloaded to the client computer and are compared to the locally edited version of the components to detect resolvable (compatible) and unresolvable (incompatible) conflicts therebetween. The commit process is performed only if no unresolvable conflicts exist between the two versions of the components. To facilitate translation between file-based data and components, a schema is written to "wrap" each of the engineering file formats. Each schema is a set of classes that capture all of the information in the file-based data.
Owner:BENTLEY SYST INC
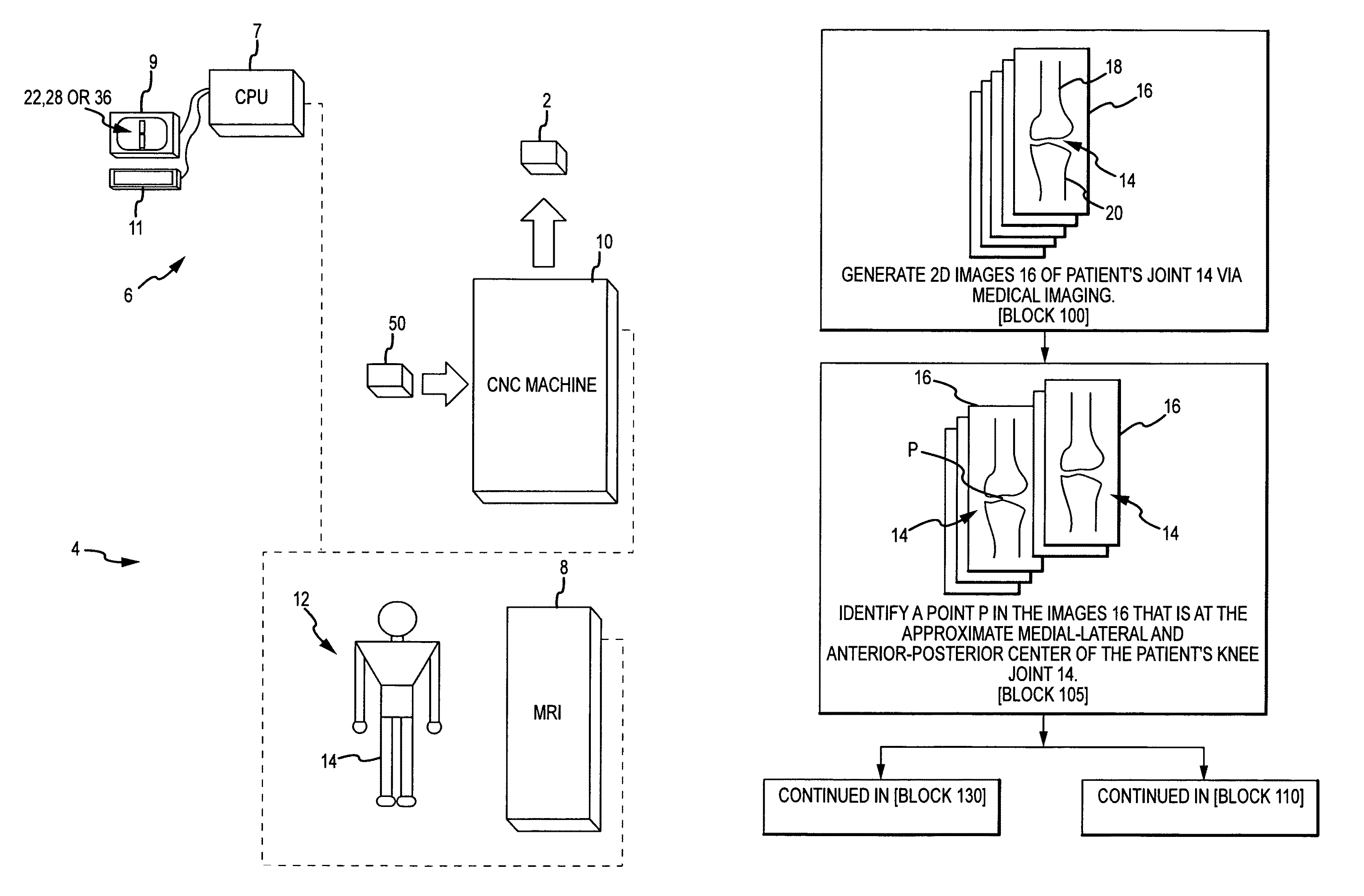
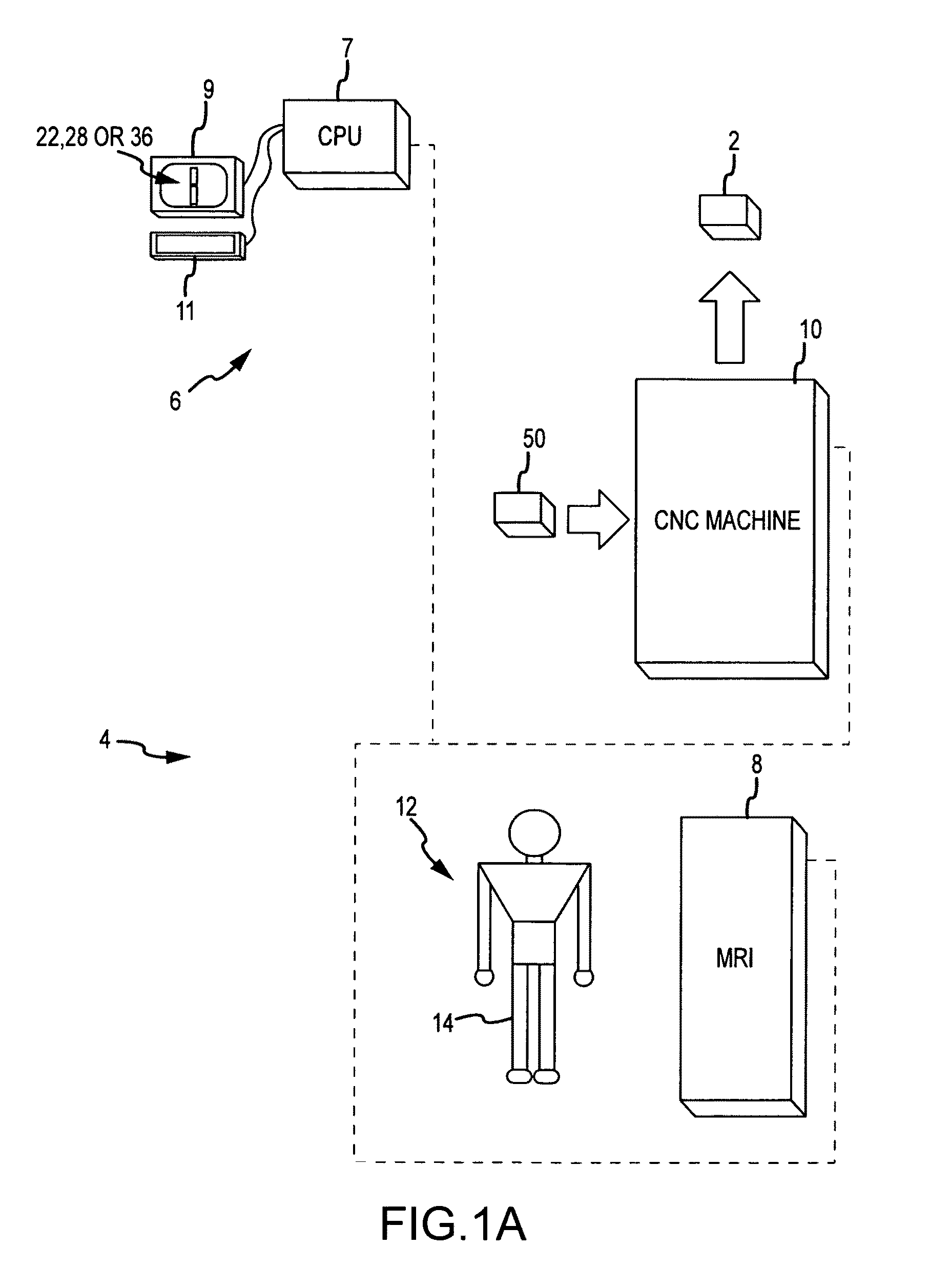
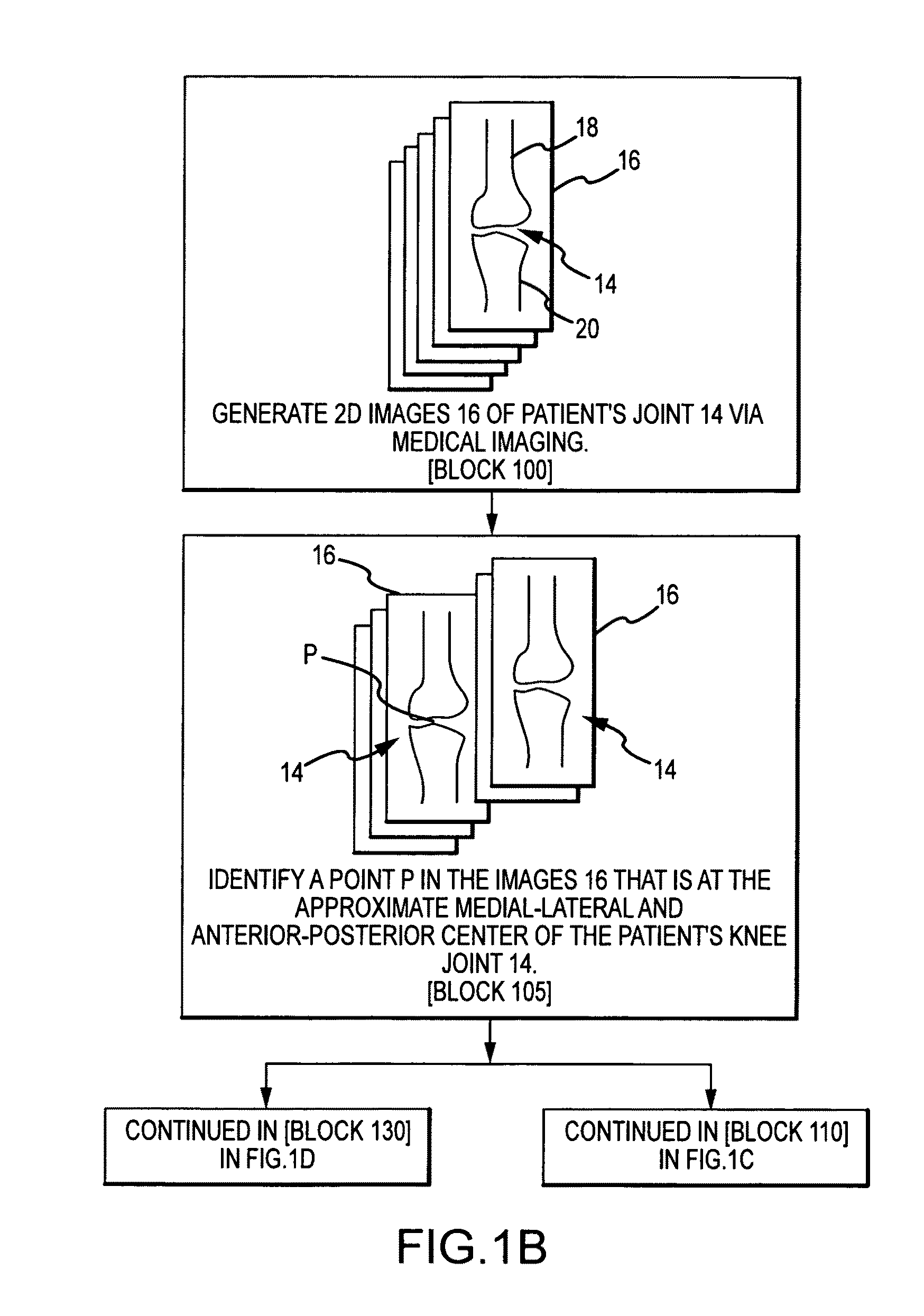
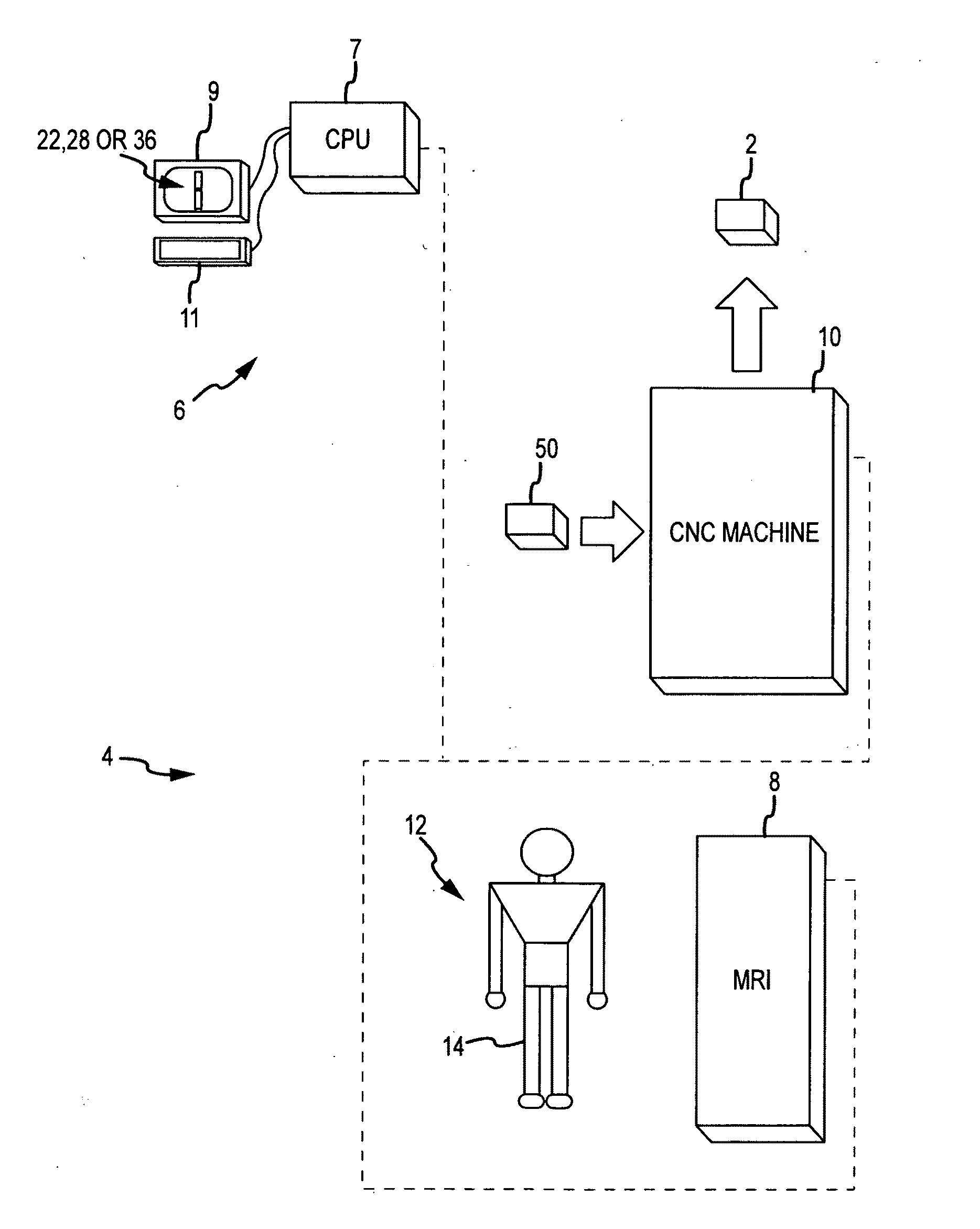
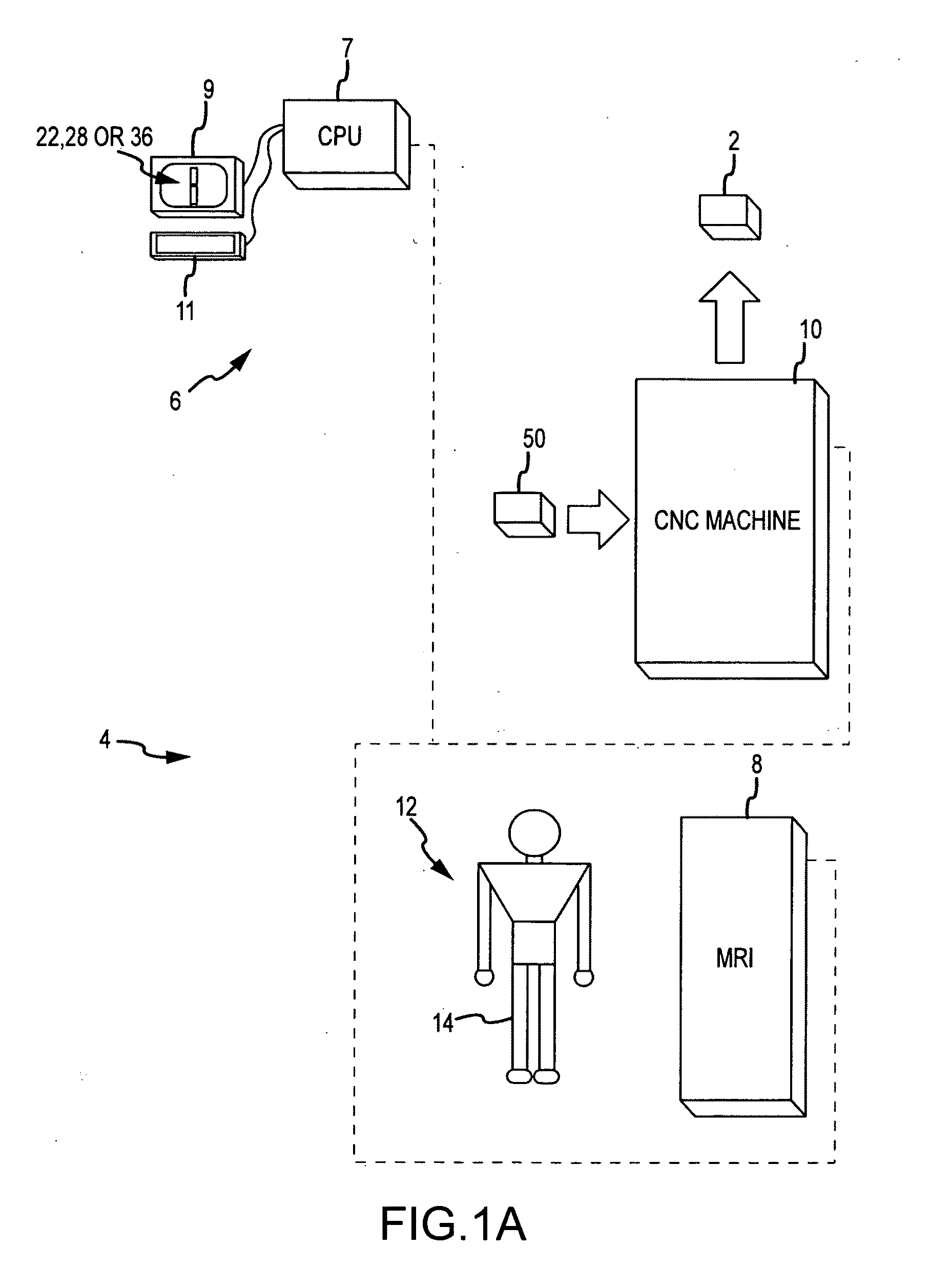
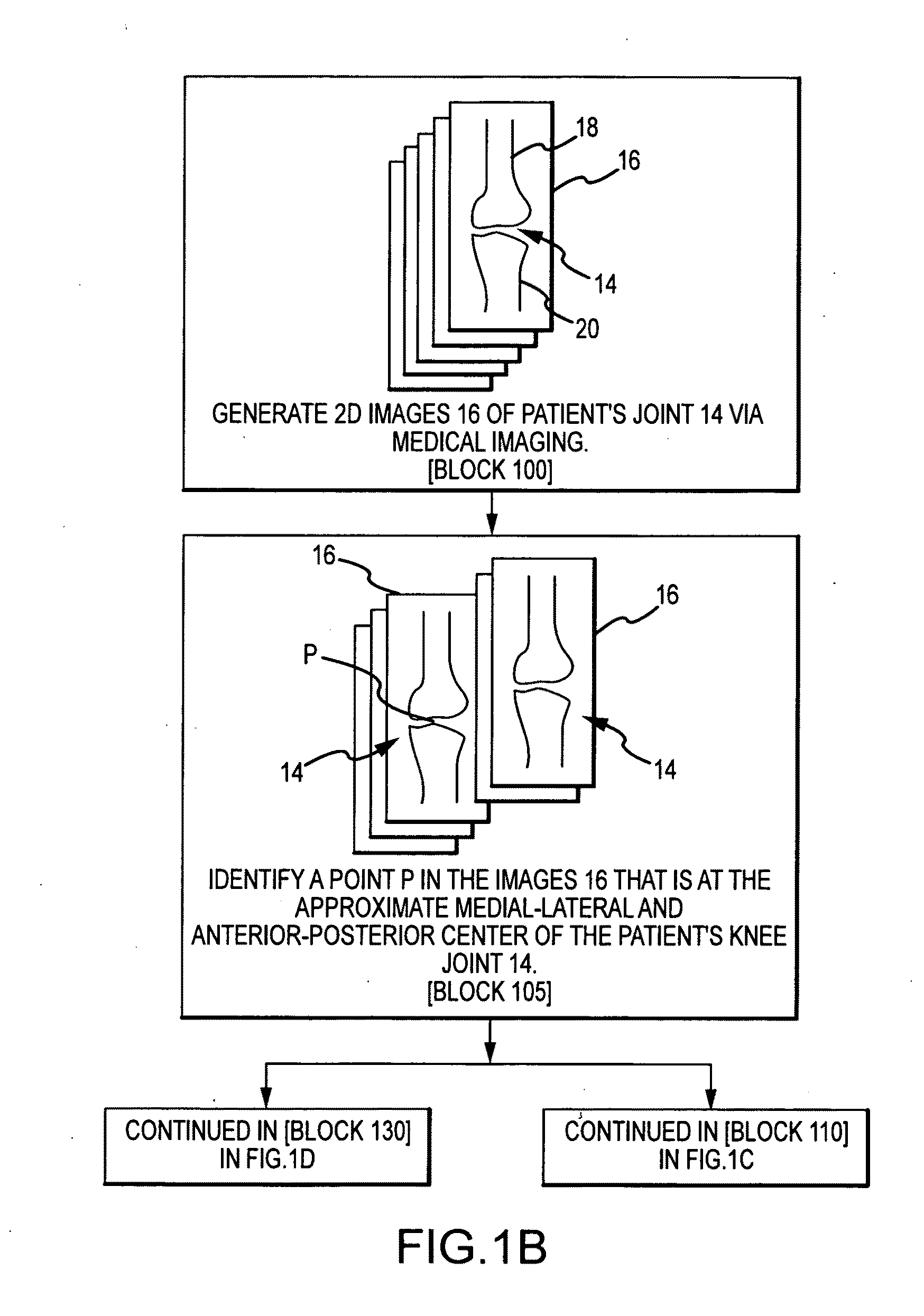
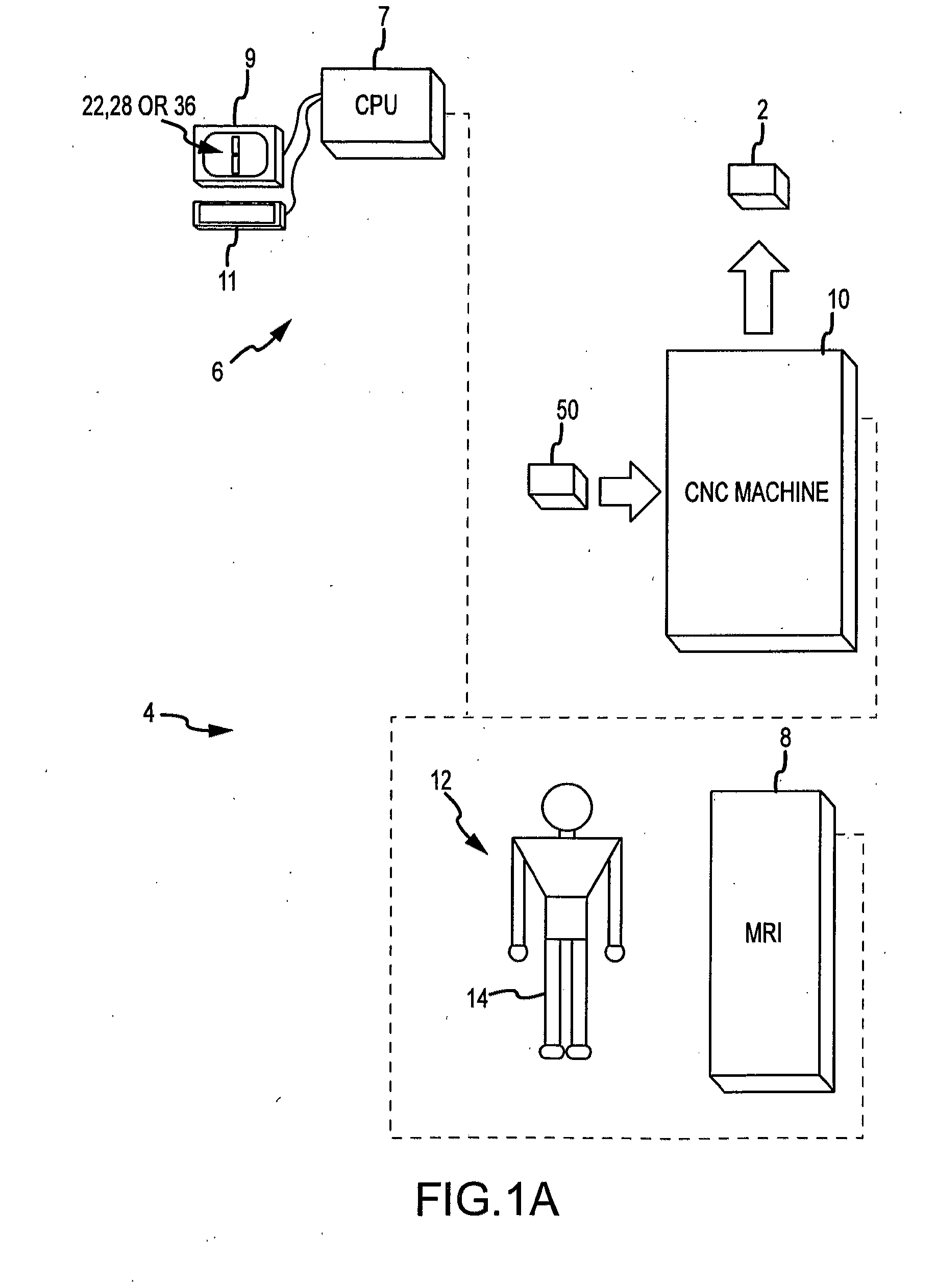
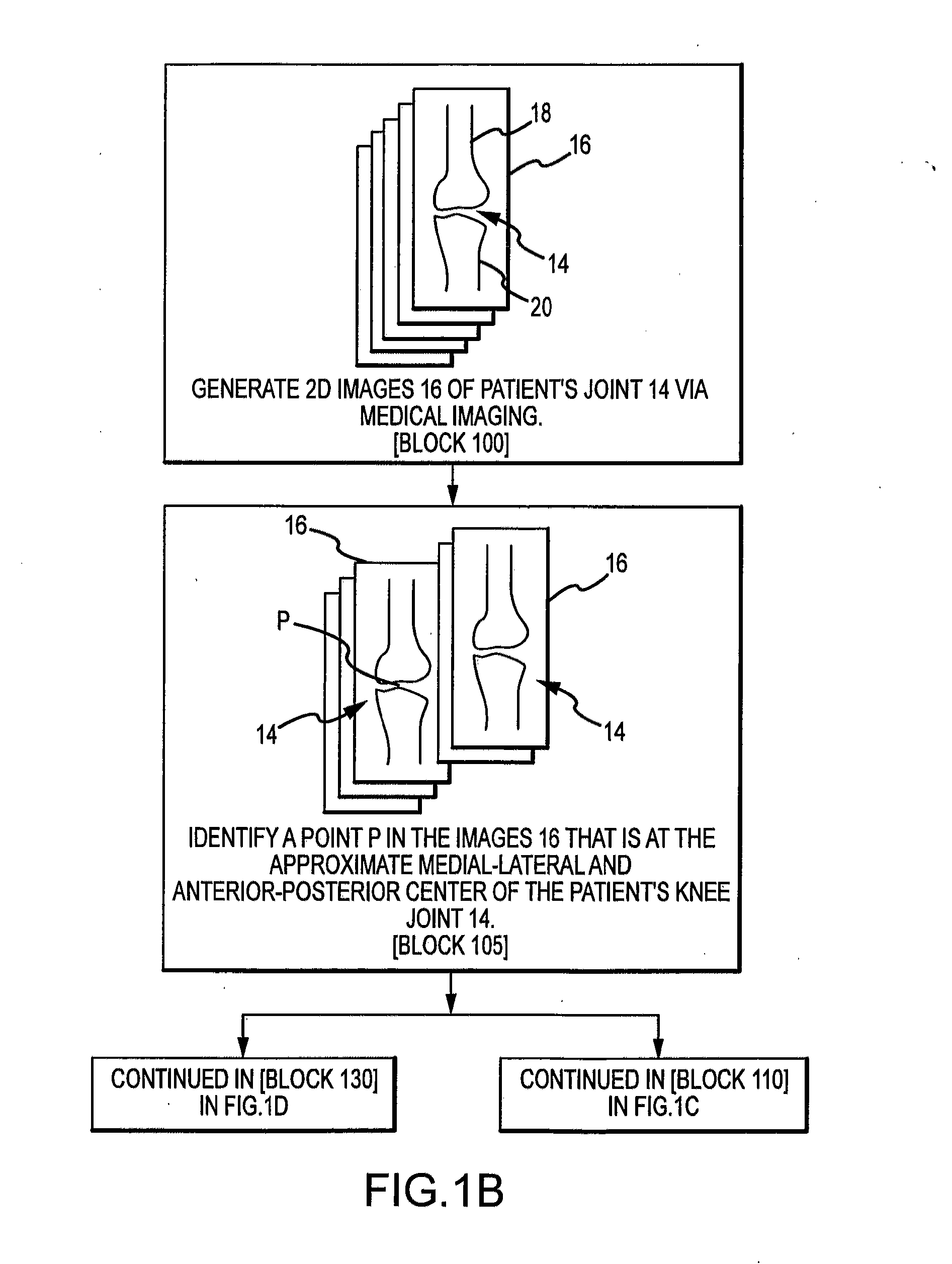
System and method for image segmentation in generating computer models of a joint to undergo arthroplasty
ActiveUS8160345B2Details involving processing stepsImage enhancementMedical imagingImage segmentation
A custom arthroplasty guide and a method of manufacturing such a guide are disclosed herein. The guide manufactured includes a mating region configured to matingly receive a portion of a patient bone associated with an arthroplasty procedure for which the custom arthroplasty guide is to be employed. The mating region includes a surface contour that is generally a negative of a surface contour of the portion of the patient bone. The surface contour of the mating region is configured to mate with the surface contour of the portion of the patient bone in a generally matching or interdigitating manner when the portion of the patient bone is matingly received by the mating region. The method of manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide includes: a) generating medical imaging slices of the portion of the patient bone; b) identifying landmarks on bone boundaries in the medical imaging slices; c) providing model data including image data associated with a bone other than the patient bone; d) adjusting the model data to match the landmarks; e) using the adjusted model data to generate a three dimensional computer model of the portion of the patient bone; f) using the three dimensional computer model to generate design data associated with the custom arthroplasty guide; and g) using the design data in manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
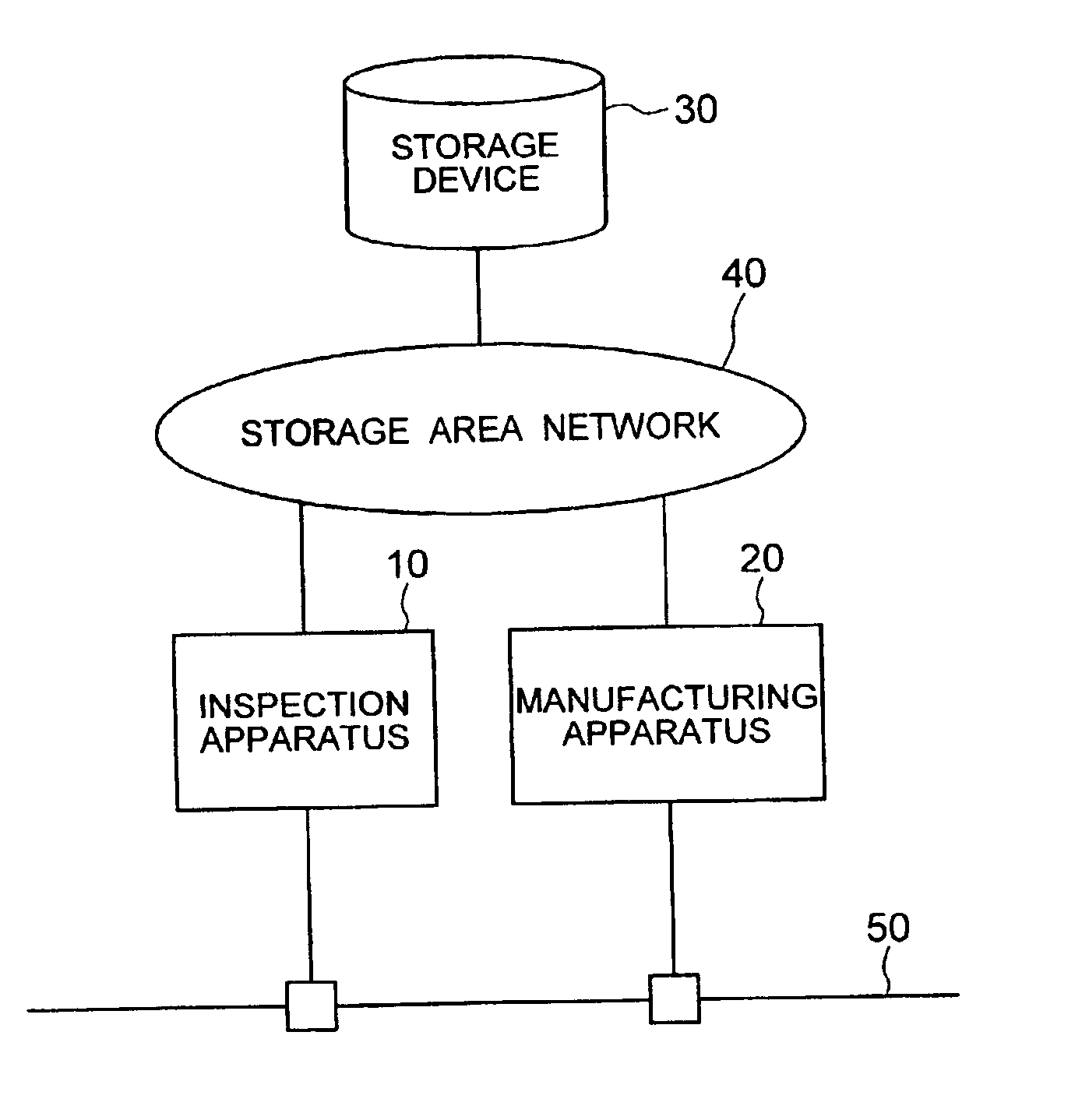
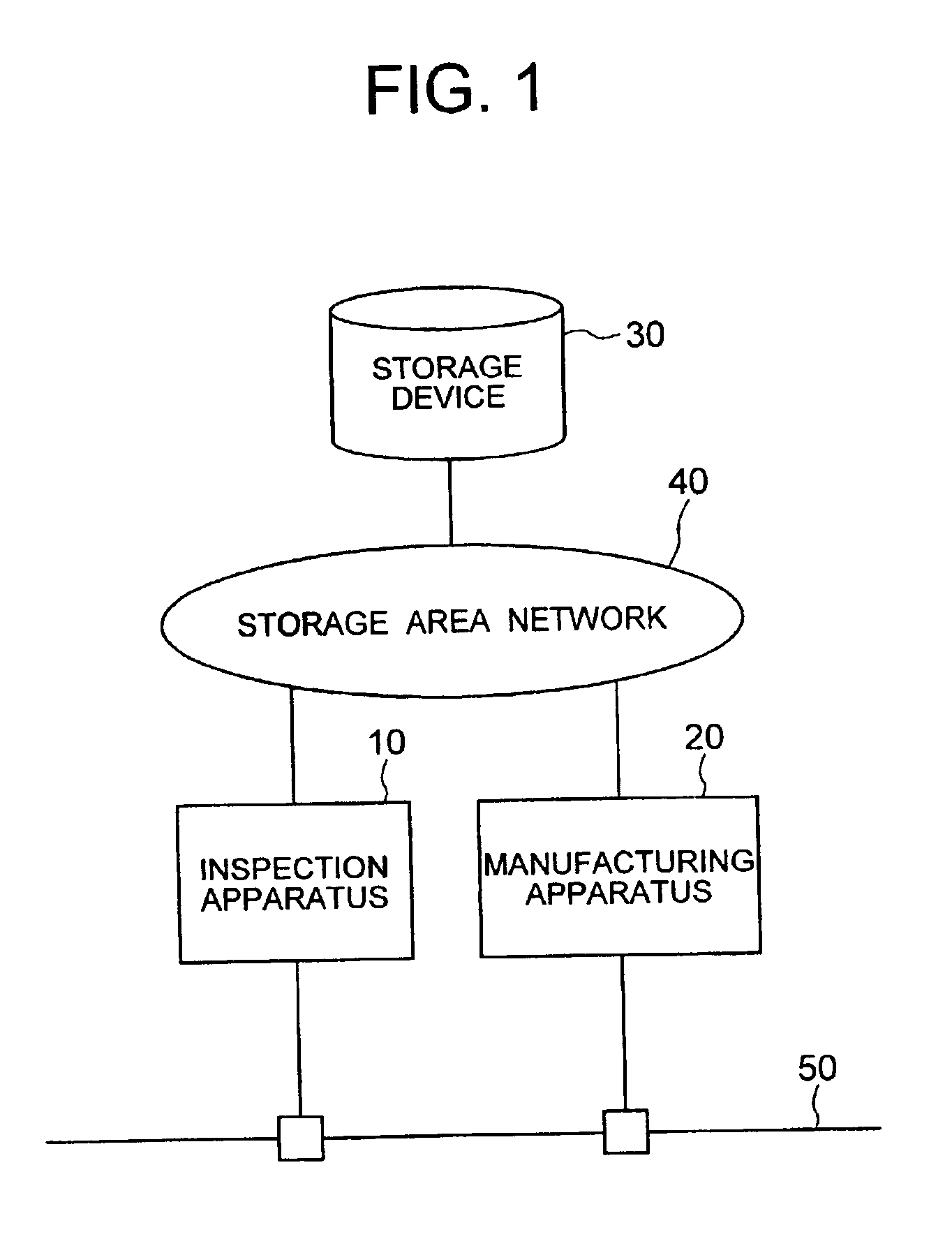
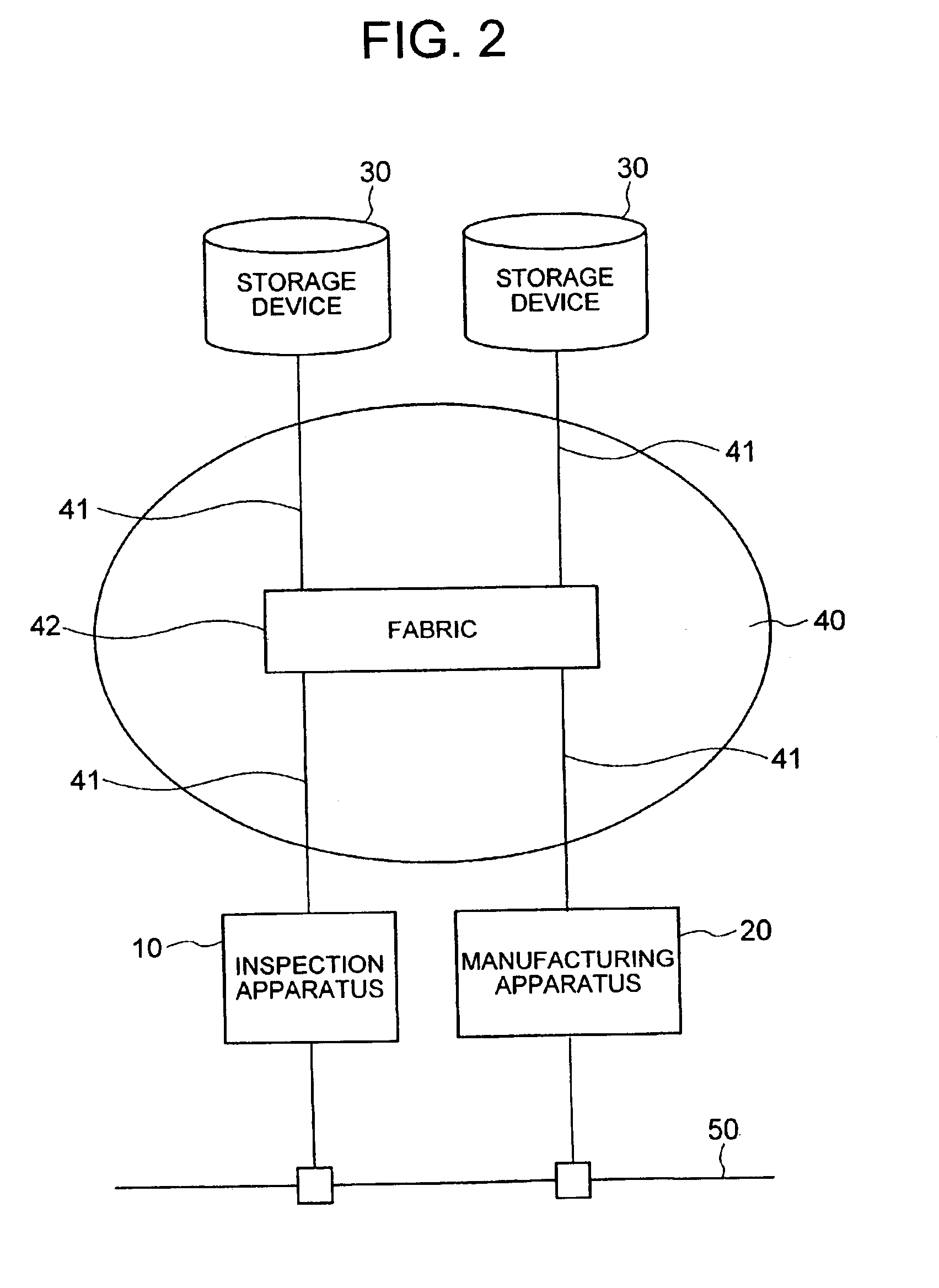
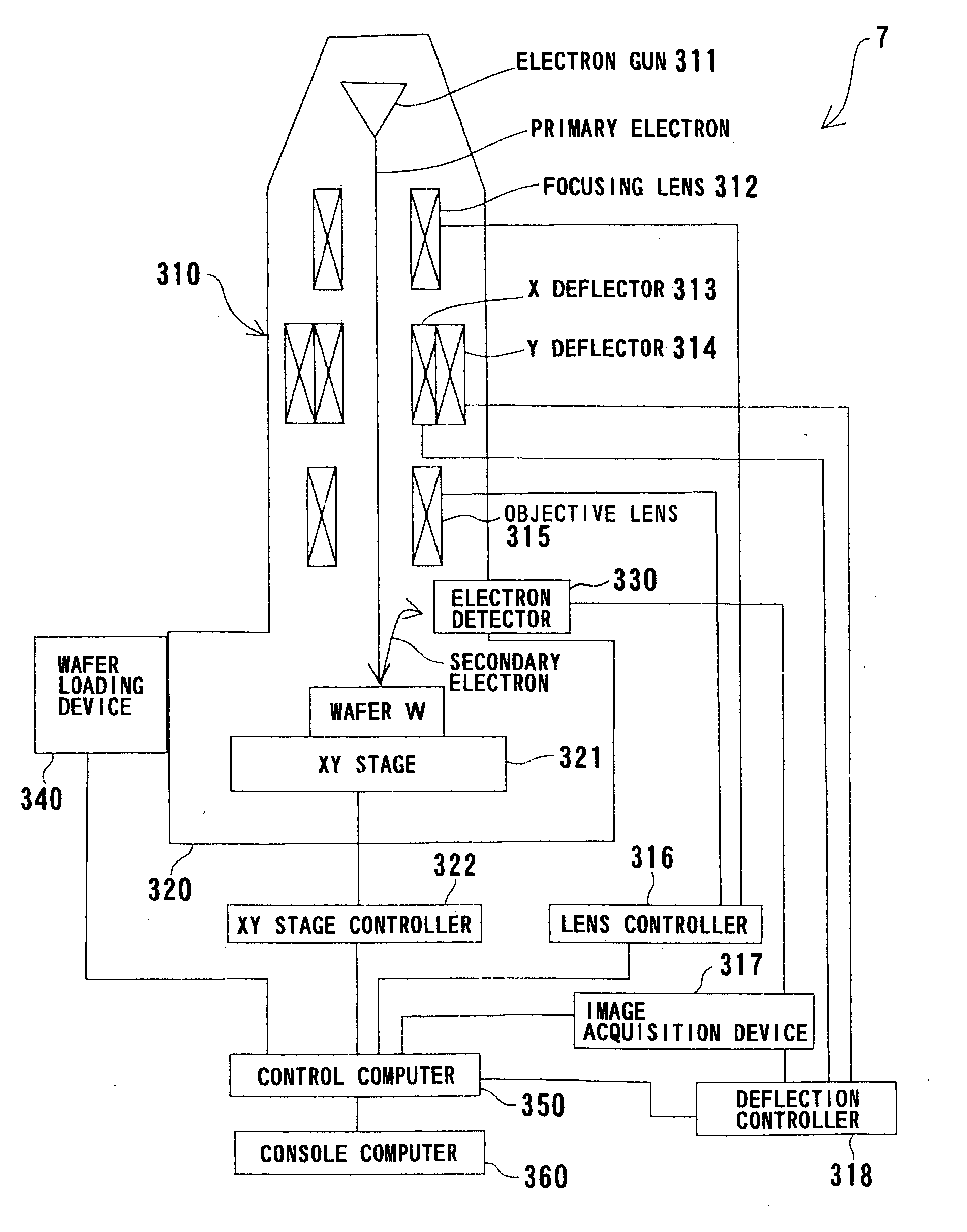
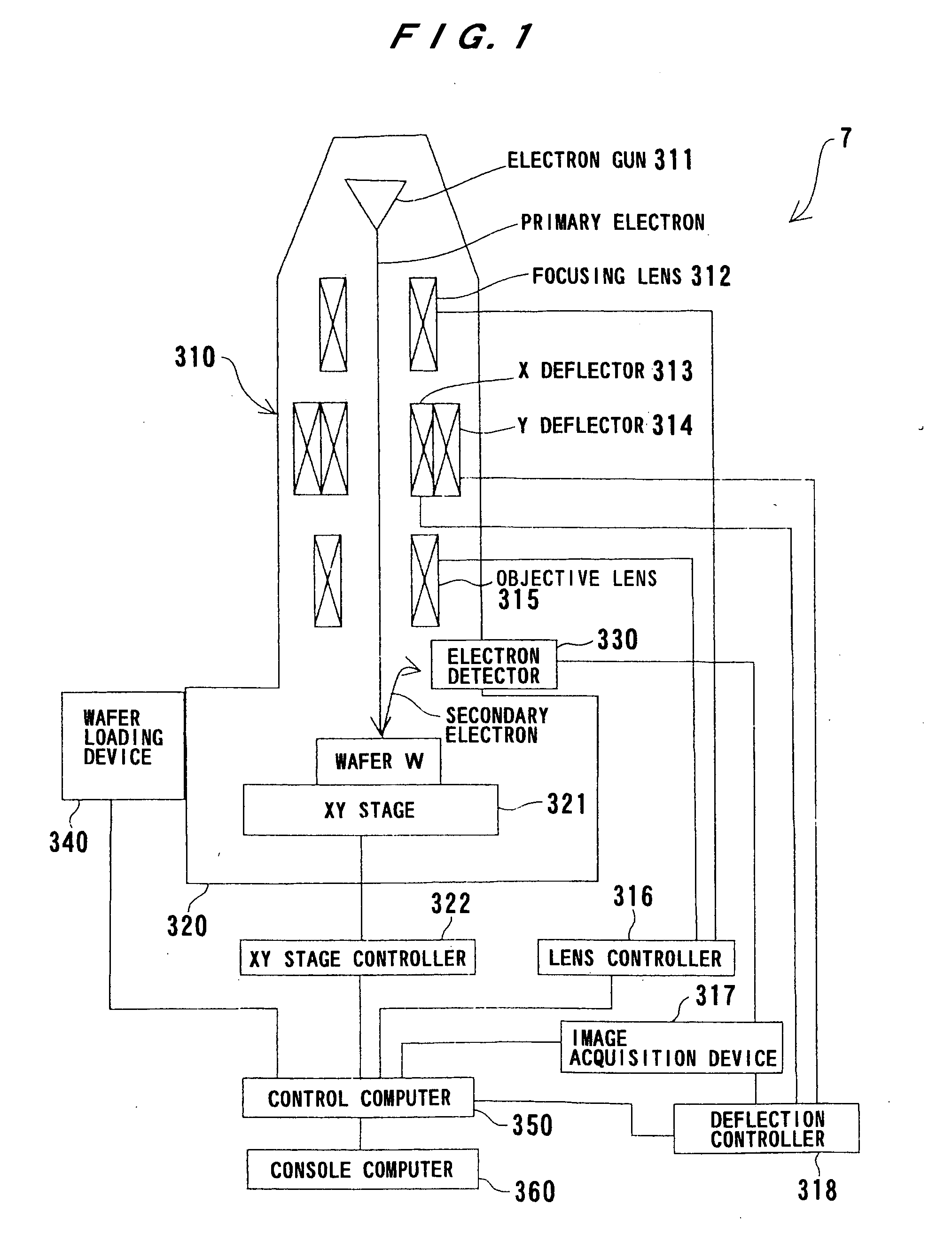
Semiconductor production system
InactiveUS6850854B2Improve system throughputIncrease in sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingStorage area networkObservation unit
A semiconductor production system has a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus having an exposure unit, a control unit for controlling the exposure unit and a storage device; a semiconductor inspection apparatus having an observation unit, a control unit for controlling the observation unit and a storage device; and a storage device commonly used by the semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and the semiconductor inspection apparatus. The manufacturing apparatus, the inspection apparatus and the commonly used storage device are interconnected via a storage area network. With the semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and the storage device linked together via the storage area network, a large volume of image data or design data can be communicated at high speed, thus improving the system throughput.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and systems for determining a position of inspection data in design data space
Various methods and systems for determining a position of inspection data in design data space are provided. One computer-implemented method includes determining a centroid of an alignment target formed on a wafer using an image of the alignment target acquired by imaging the wafer. The method also includes aligning the centroid to a centroid of a geometrical shape describing the alignment target. In addition, the method includes assigning a design data space position of the centroid of the alignment target as a position of the centroid of the geometrical shape in the design data space. The method further includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer in the design data space based on the design data space position of the centroid of the alignment target.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
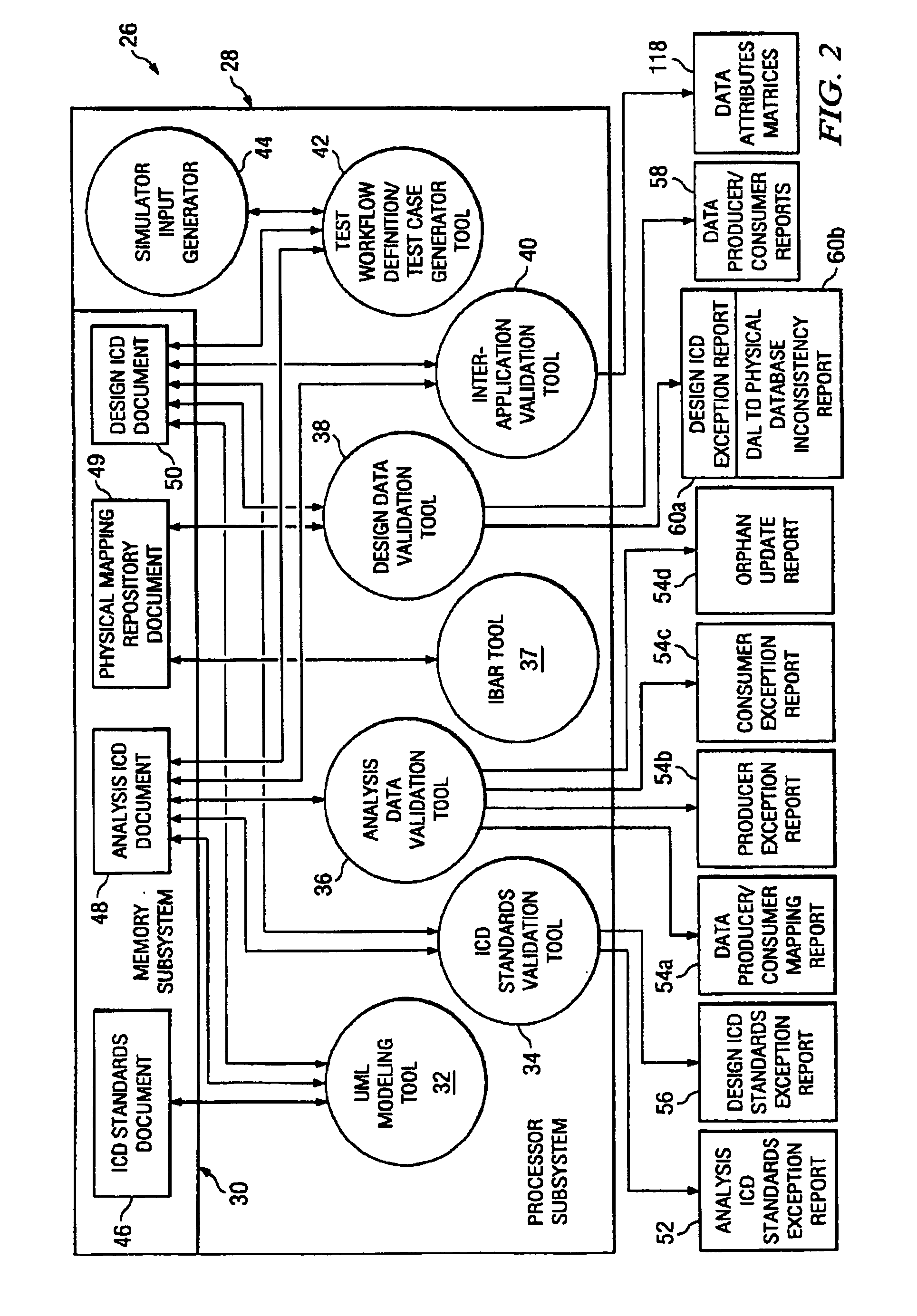
Design data validation tool for use in enterprise architecture modeling
InactiveUS7203929B1Requirement analysisSpecific program execution arrangementsData validationSequence diagram
A selected scenario of a design ICD document for an integrated enterprise is validated by examining each IDL call of each sequence diagram forming part of the selected scenario. A list of data attributes contained in one or more of the IDL calls are generated and each IDL call associated therewith is generated. A physical location to which each such IDL call is mapped is then associated with the IDL call. By analyzing the IDL calls and associated physical locations on a data attribute-by-data attribute basis, inconsistencies in the physical mapping of the data attributes to the databases forming an IIS for the integrated enterprise may be identified and subsequently corrected.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
System and method for image segmentation in generating computer models of a joint to undergo arthroplasty
ActiveUS20110282473A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsImage segmentationMedical imaging
A custom arthroplasty guide and a method of manufacturing such a guide are disclosed herein. The guide manufactured includes a mating region configured to matingly receive a portion of a patient bone associated with an arthroplasty procedure for which the custom arthroplasty guide is to be employed. The mating region includes a surface contour that is generally a negative of a surface contour of the portion of the patient bone. The surface contour of the mating region is configured to mate with the surface contour of the portion of the patient bone in a generally matching or interdigitating manner when the portion of the patient bone is matingly received by the mating region. The method of manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide includes: a) generating medical imaging slices of the portion of the patient bone; b) identifying landmarks on bone boundaries in the medical imaging slices; c) providing model data including image data associated with a bone other than the patient bone; d) adjusting the model data to match the landmarks; e) using the adjusted model data to generate a three dimensional computer model of the portion of the patient bone; f) using the three dimensional computer model to generate design data associated with the custom arthroplasty guide; and g) using the design data in manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
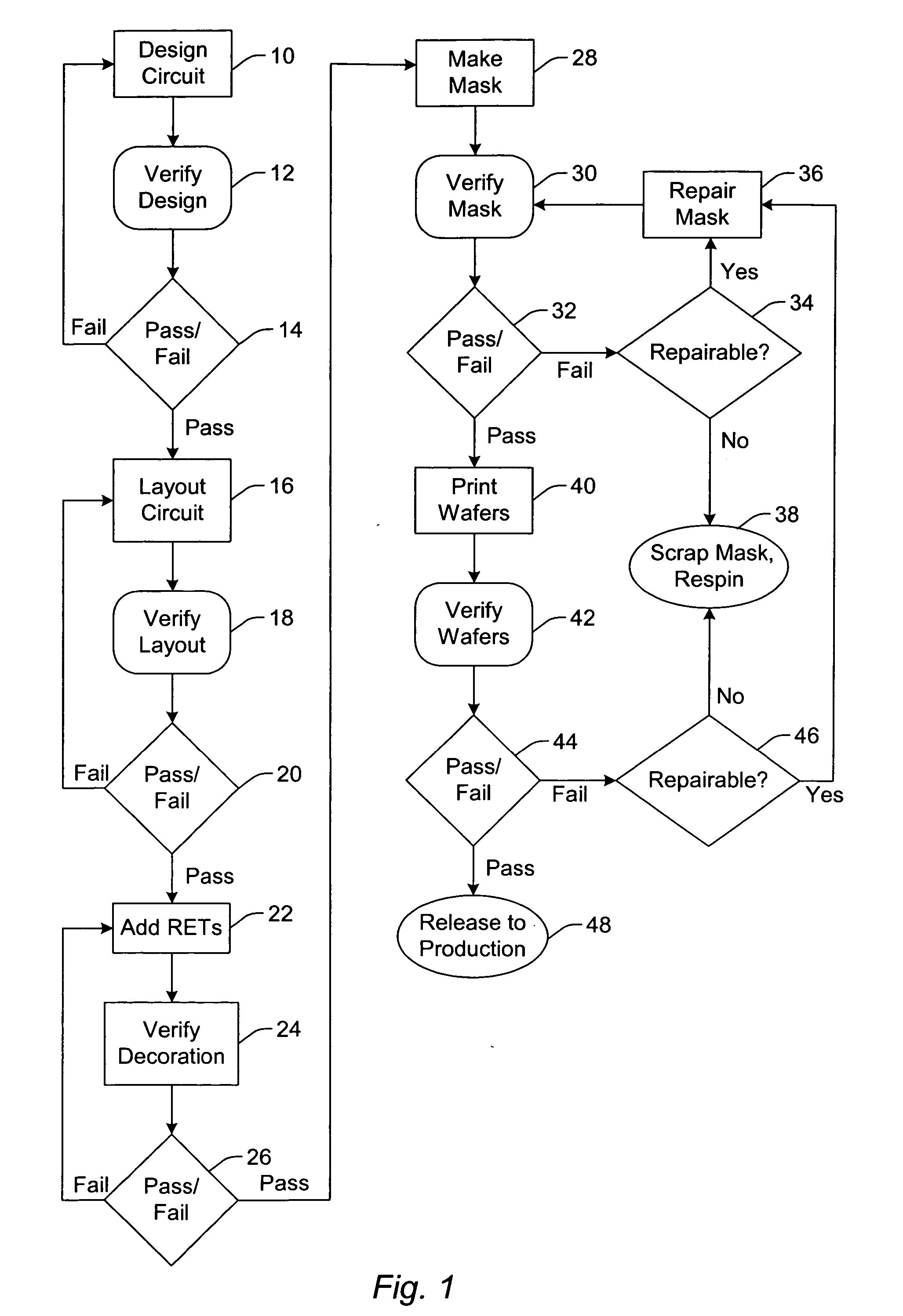
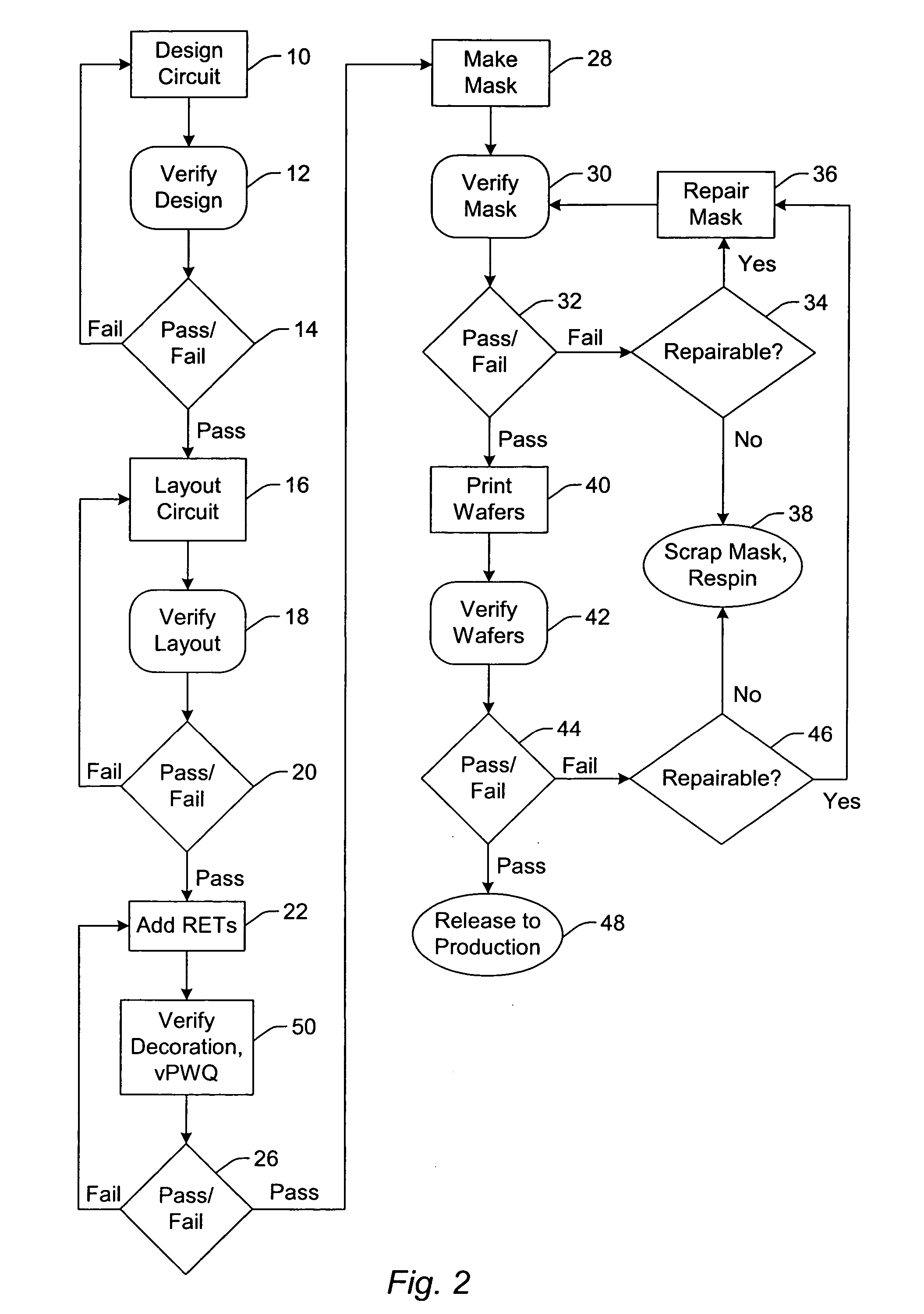
Auto correction of error checked simulated printed images
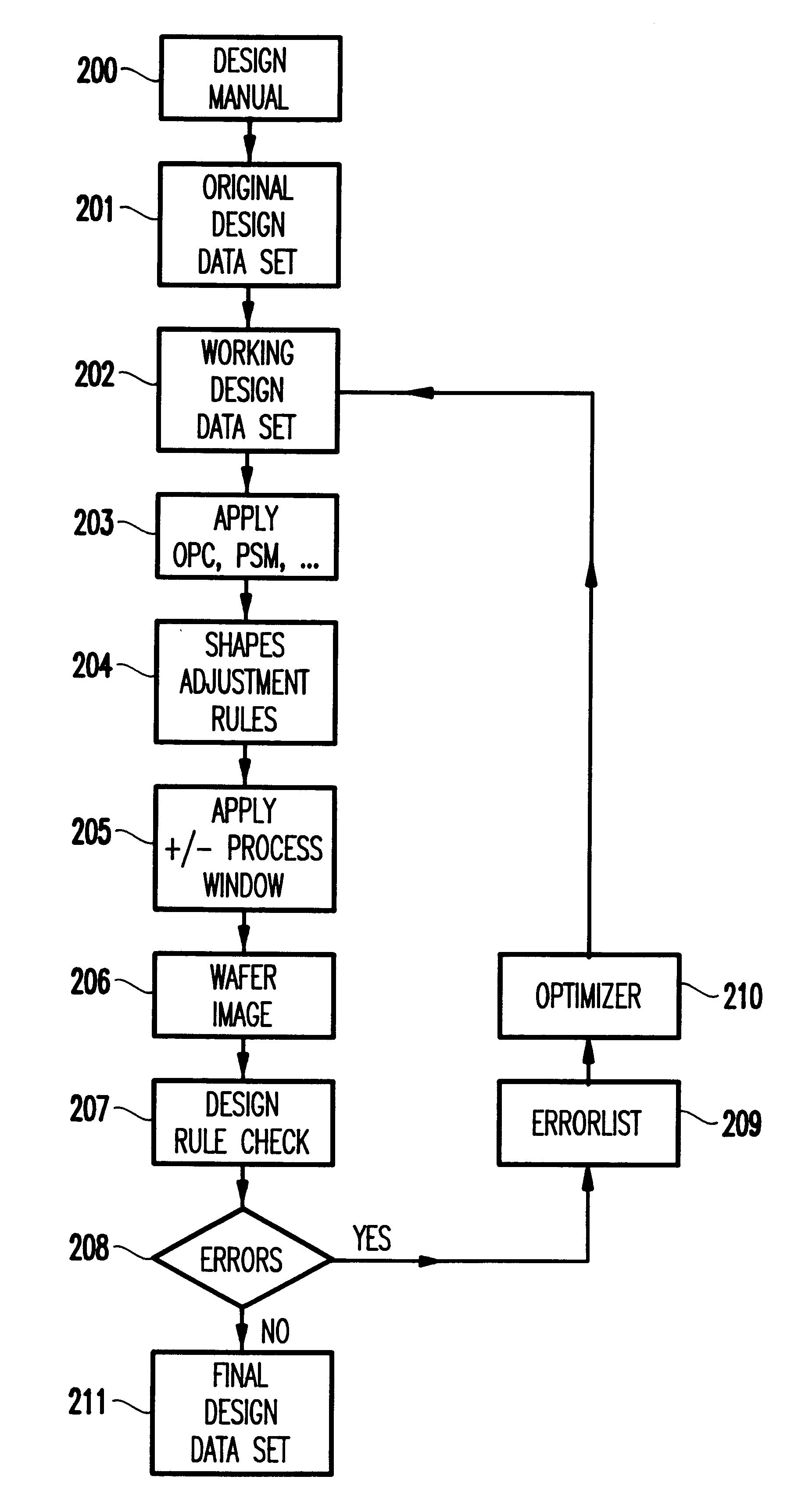
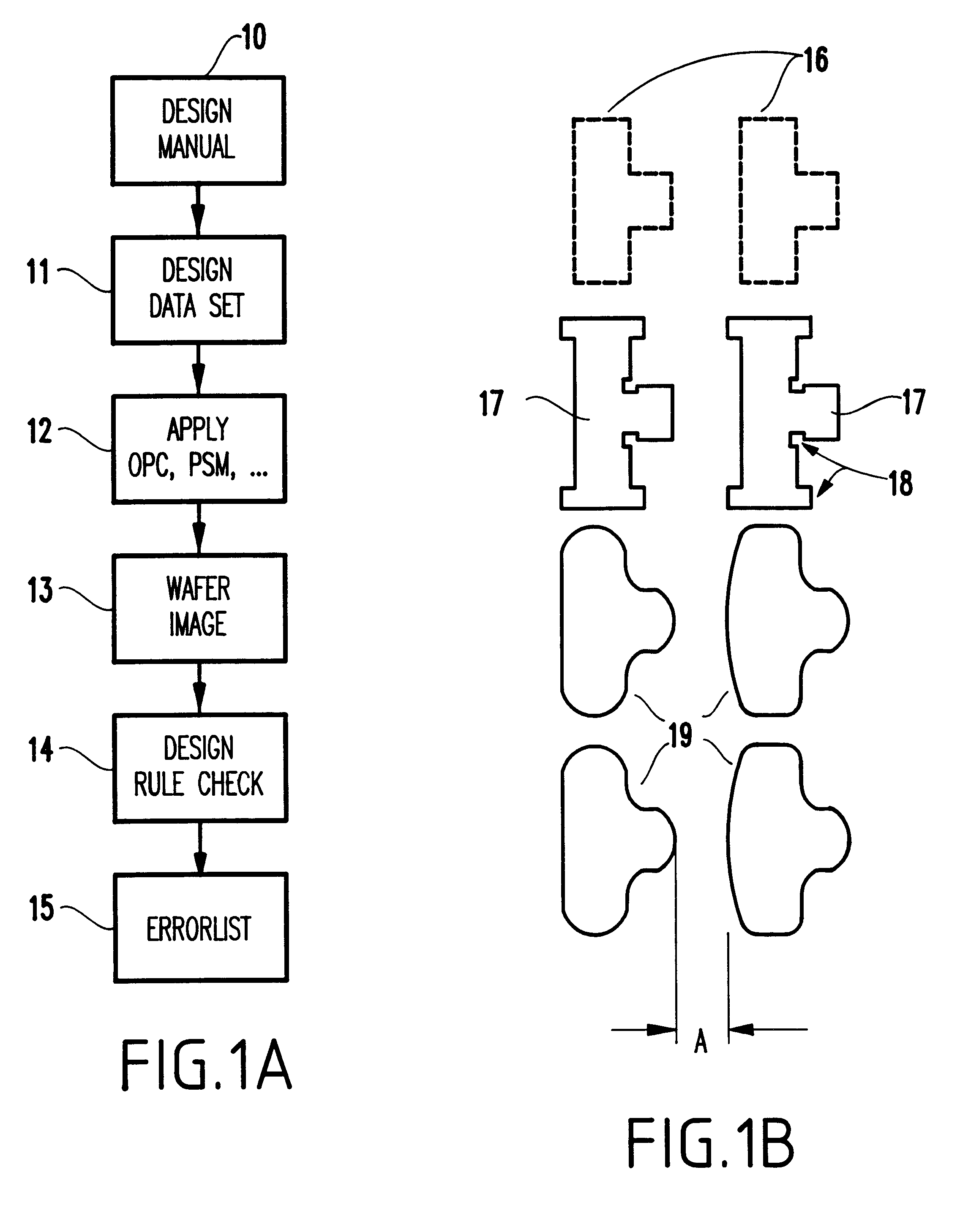
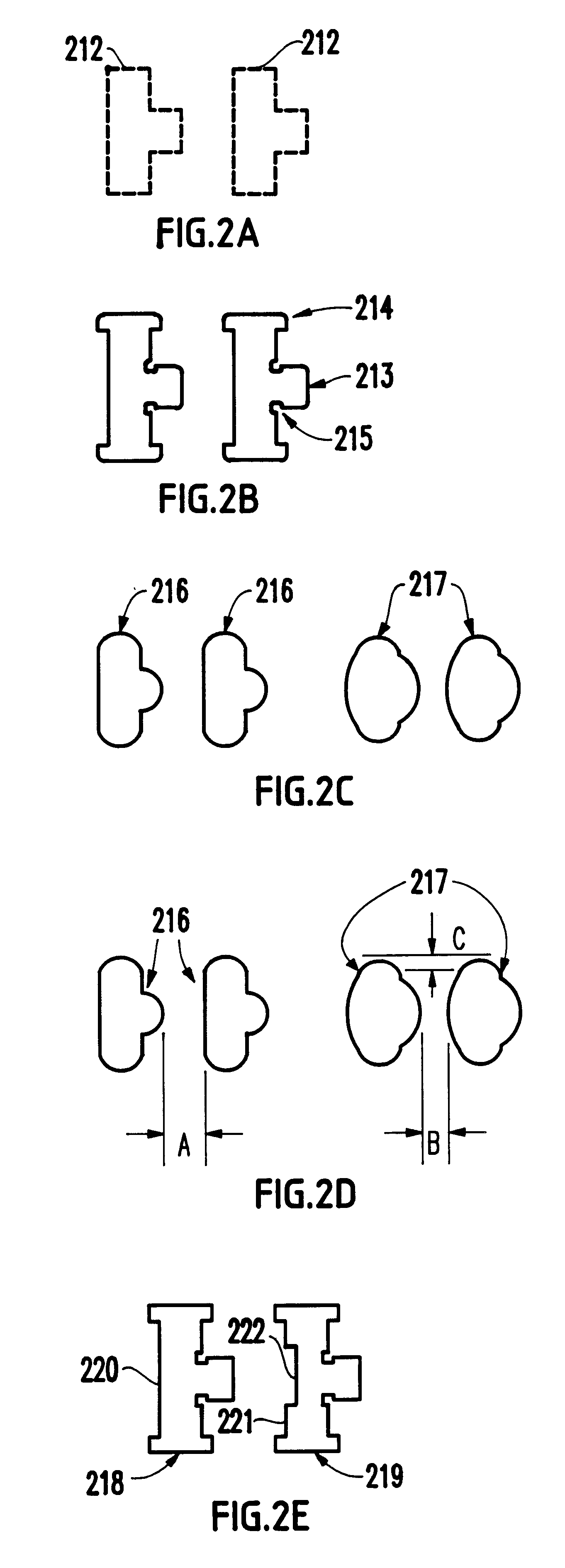
A method and computer system are provided for checking integrated circuit designs for design rule violations. The method may include generating a working design data set, creating a wafer image data set, comparing the wafer image data set to the design rules to produce an error list and automatically altering the working design data set when the comparing indicates a design rule violation. The method further automatically repeats the creating, the comparing and the automatically altering until no design rule violations occur or no solution to the errors exists.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for image segmentation in generating computer models of a joint to undergo arthroplasty
ActiveUS20120192401A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsImage segmentationMedical imaging
A custom arthroplasty guide and a method of manufacturing such a guide are disclosed herein. The method of manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide includes: a) generating medical imaging slices of the portion of the patient bone; b) identifying landmarks on bone boundaries in the medical imaging slices; c) providing model data including image data associated with a bone other than the patient bone; d) adjusting the model data to match the landmarks; e) using the adjusted model data to generate a three dimensional computer model of the portion of the patient bone; f) using the three dimensional computer model to generate design data associated with the custom arthroplasty guide; and g) using the design data in manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
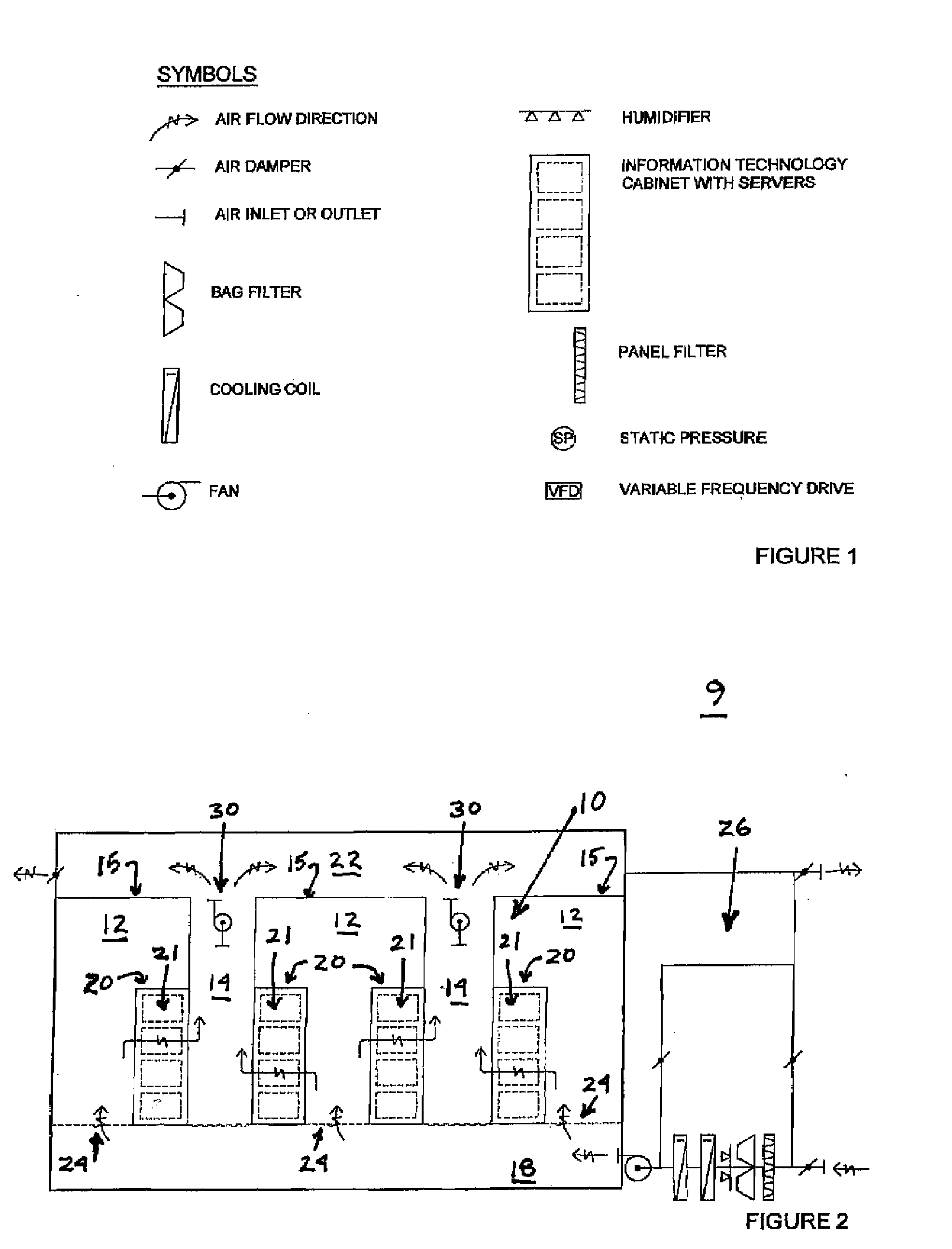
Cool design data center
ActiveUS20080185446A1Easy to solveAvoid uneven loadLighting and heating apparatusElectrical apparatus contructional detailsAir managementAir volume
An improved solution for cooling a data center is provided. In an embodiment of the invention, a data center design that combines physical segregation of hot and cold air streams together with a data hall variable air volume system is provided. The invention is a data center design that resolves air management issues of re-circulation, bypass and load balance. Bypass is airflow supplied by the cooling units that directly returns without cooling servers. Recirculation airflow is server discharge warm air that returns directly without being cooled. Load balance is supplying the required server airflow. An embodiment includes physical segregation of cold and hot air streams and by providing variable air volume to match server load. Air segregation is done by enclosing the hot aisle end and above the cabinets. The air conditioning system provides variable air volume to the data hall (cold side) to meet server demands. The cooling plant consists of variable-air-volume air-cooling system, which cools air by air free cooling (economizer) and is supplemented with mechanical cooling in the warmer seasons.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Marine seismic survey method and system
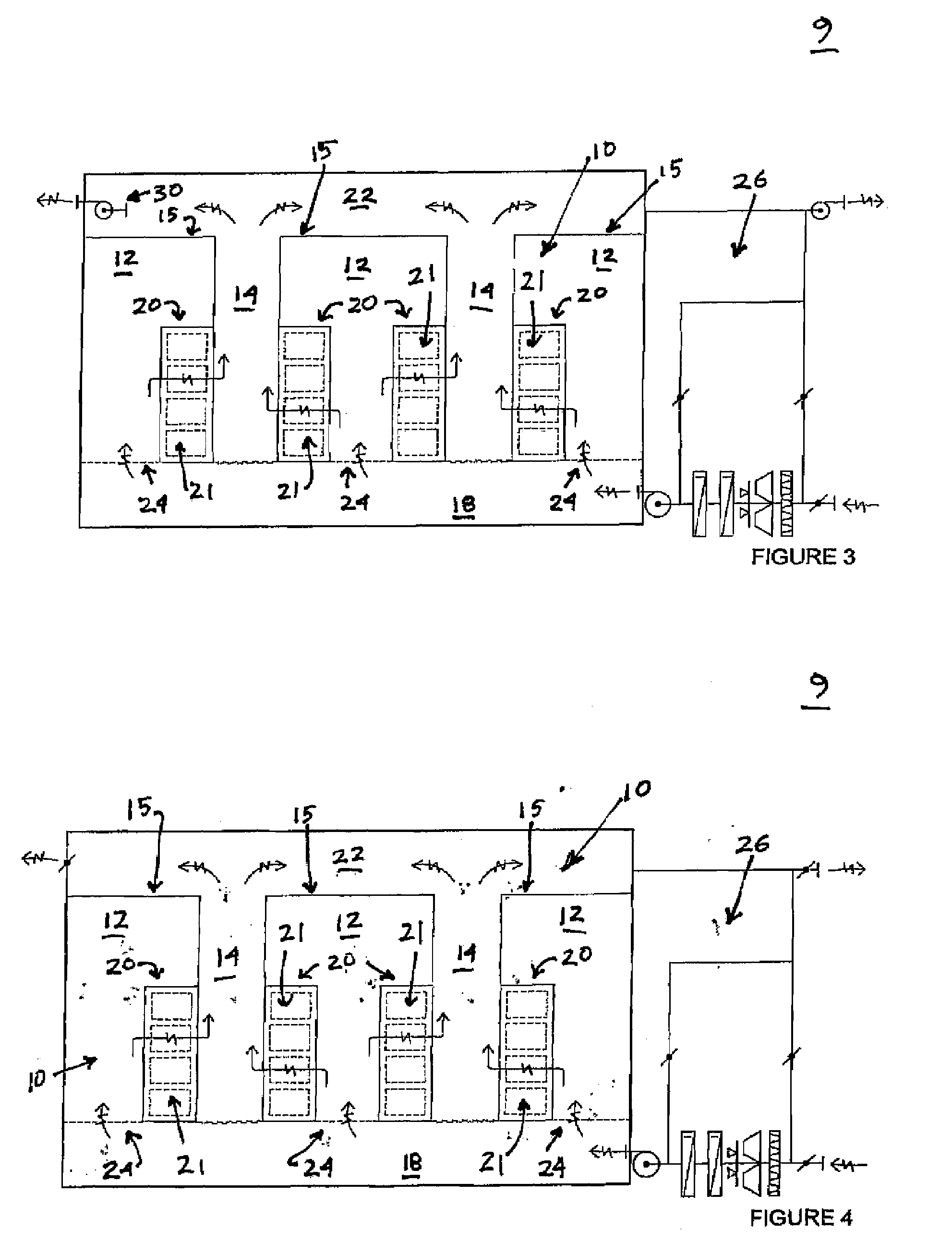
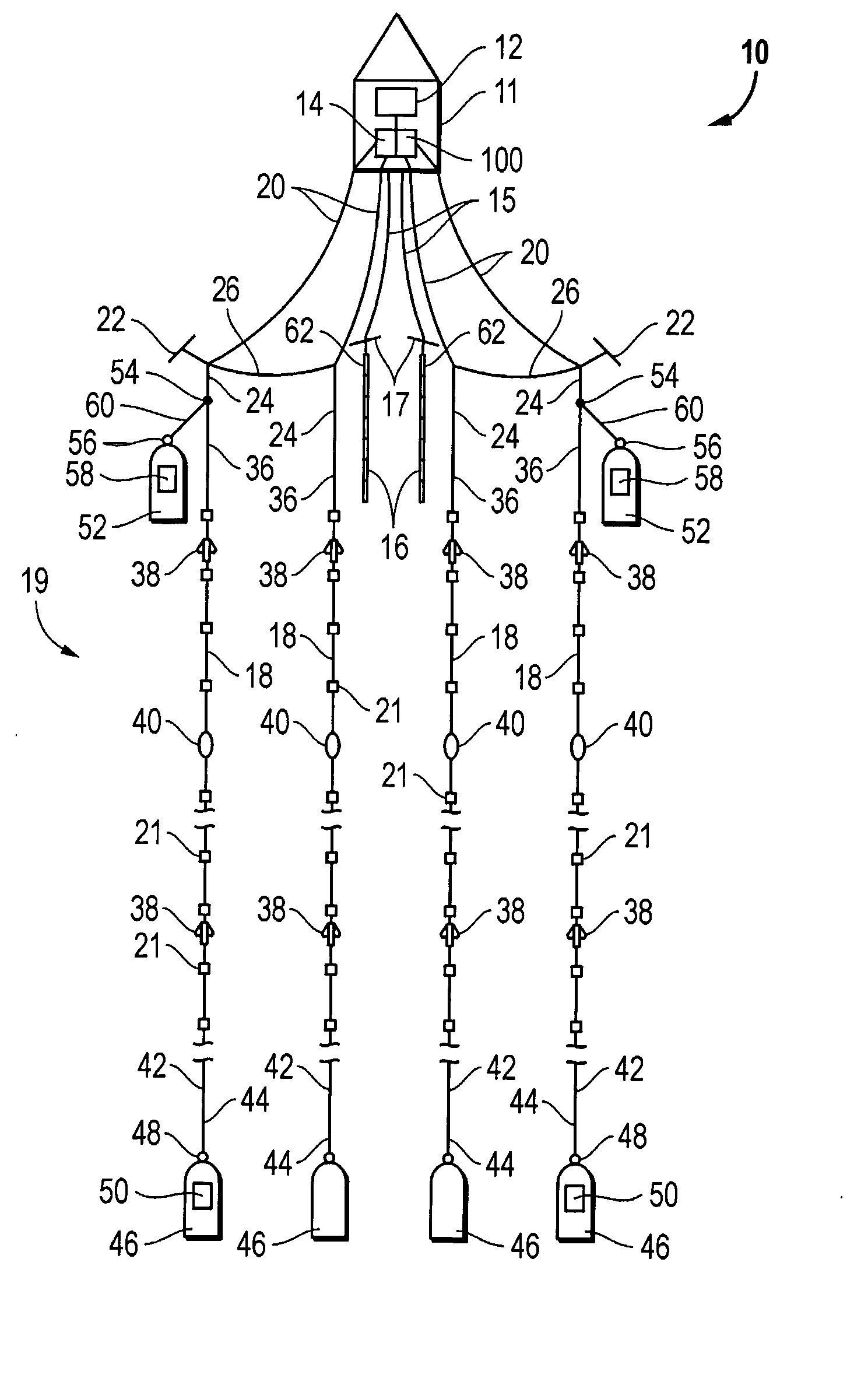
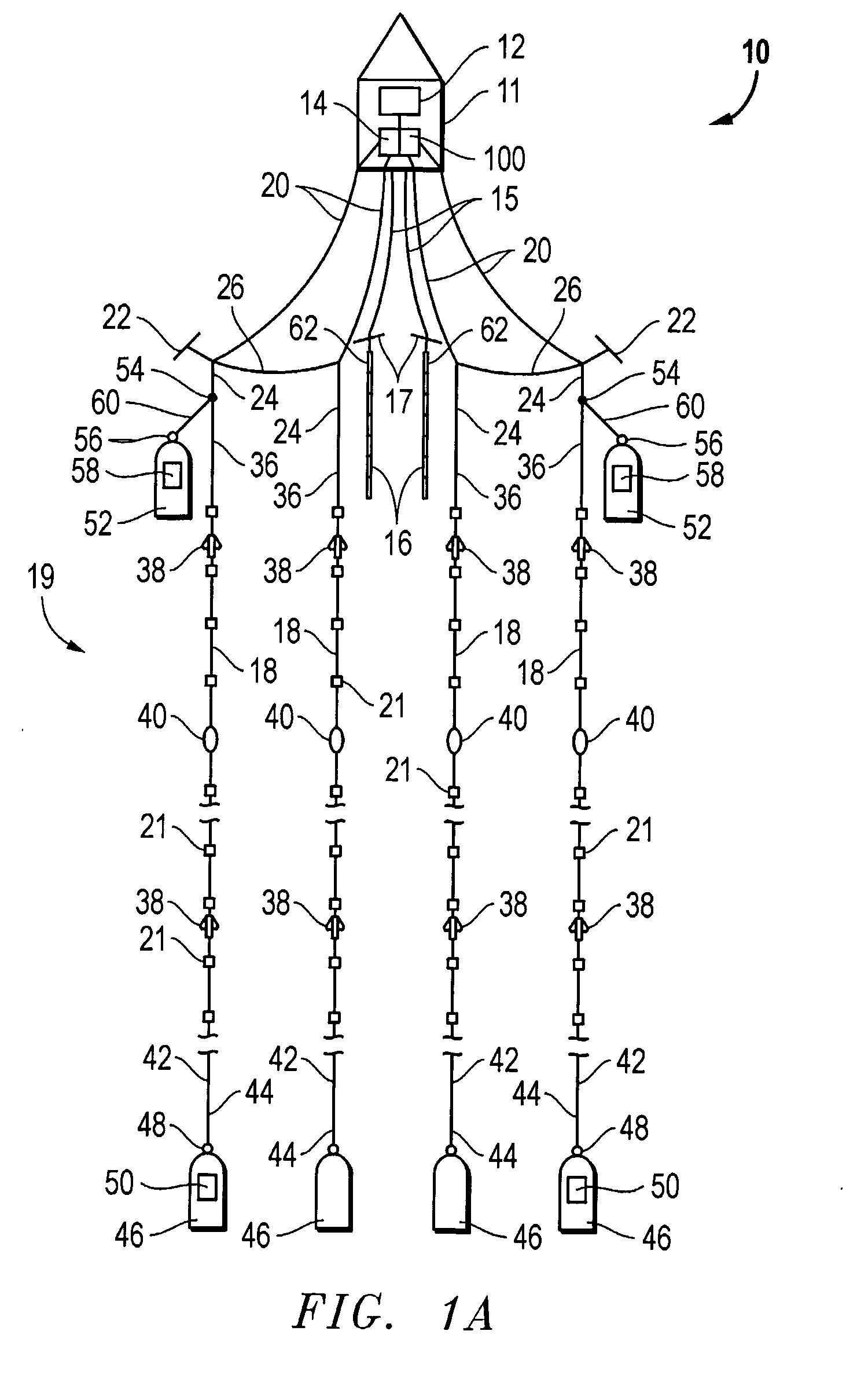
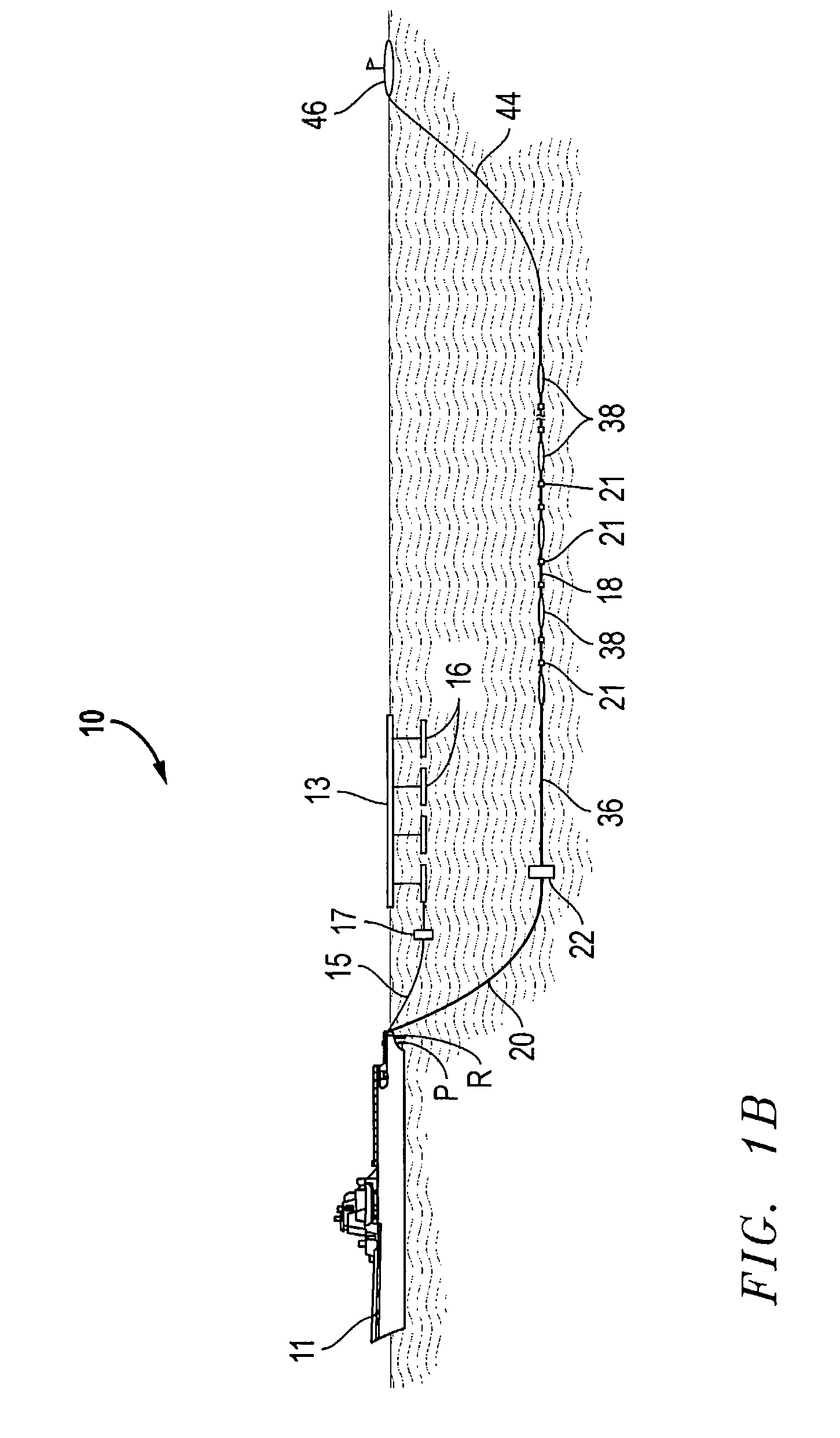
ActiveUS20090141587A1Reduce non-productive timeSeismic signal recordingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyEnvironmental data
An inventive method provides for control of a seismic survey spread while conducting a seismic survey, the spread having a vessel, a plurality of spread control elements, a plurality of navigation nodes, and a plurality of sources and receivers. The method includes the step of collecting input data, including navigation data for the navigation nodes, operating states from sensors associated with the spread control elements, environmental data for the survey, and survey design data. The positions of the sources and receivers are estimated using the navigation data, the operating states, and the environmental data. Optimum tracks for the sources and receivers are determined using the position estimates and a portion of the input data that includes at least the survey design data. Drive commands are calculated for at least two of the spread control elements using the determined optimum tracks. The inventive method is complemented by an inventive system.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
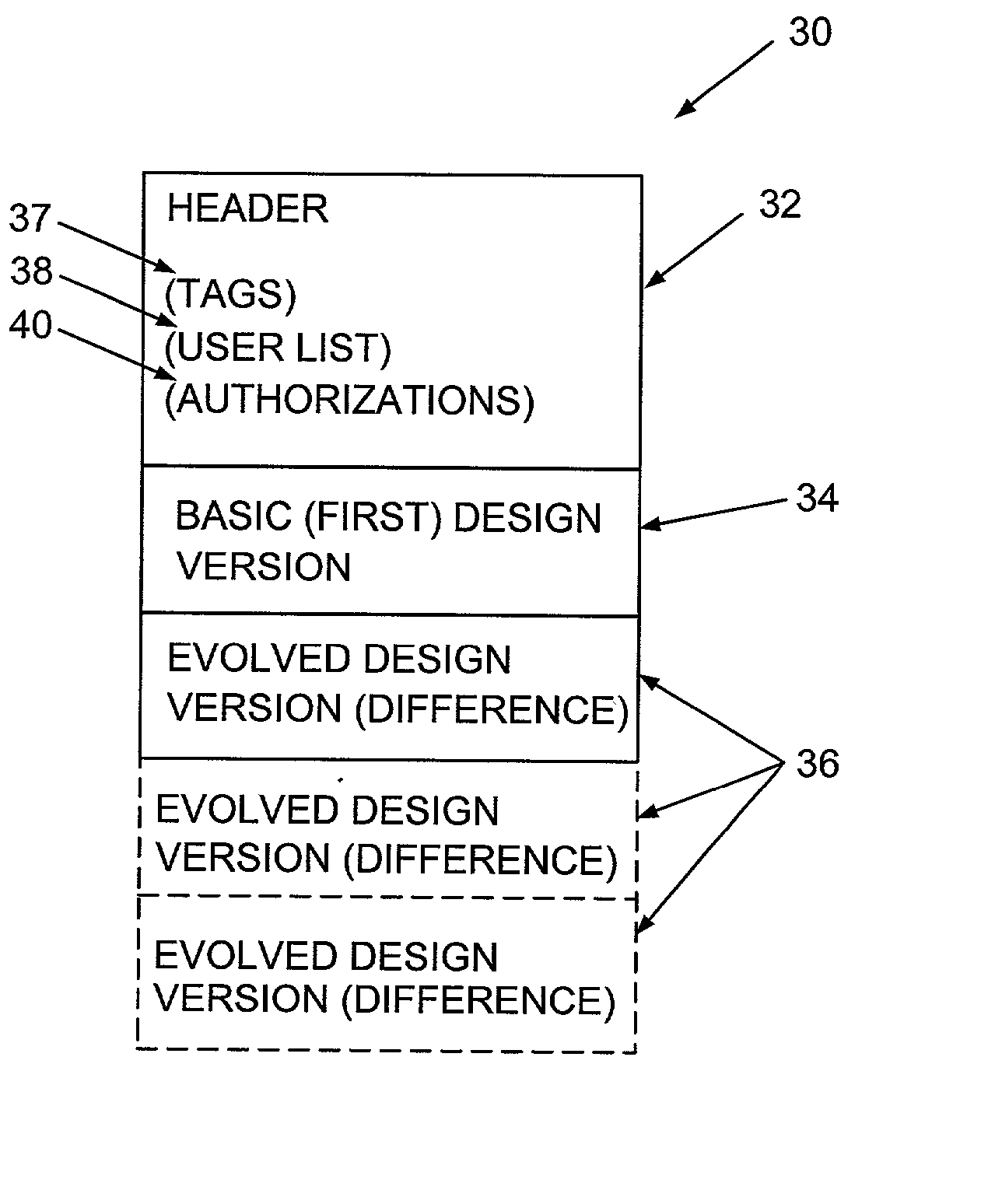
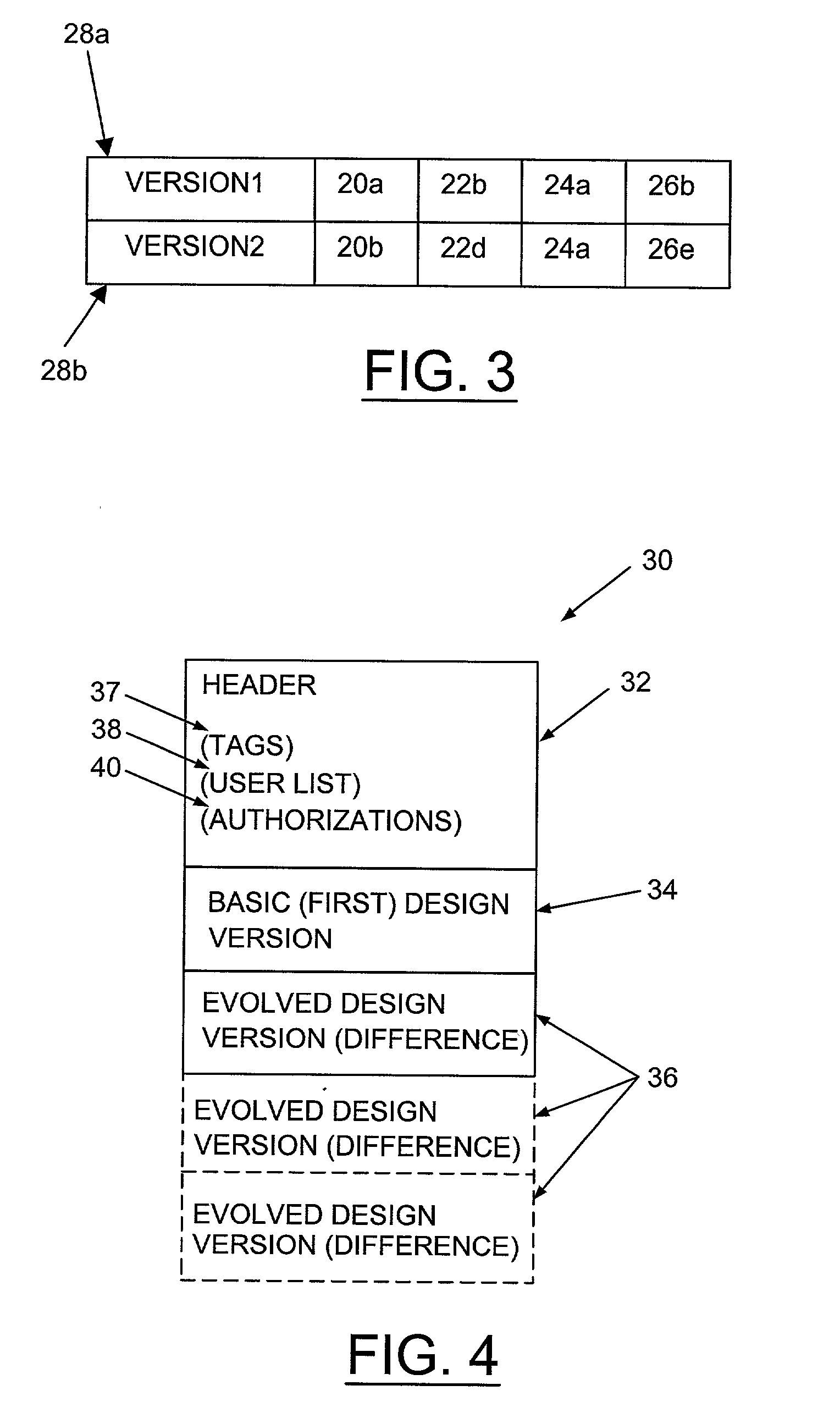
Revision control for database of evolved design
InactiveUS20030212718A1Data processing applicationsComputer security arrangementsAuthorizationDatabase
The invention relates to a method of controlling access to a database of a design. The method may comprise the step of identifying a version of the design by a first identifier, allocating first authorization information to the first identifier, and controlling access to the database. The first authorization information may indicate a permission of one or more users to access information in the database in respect of the first identifier. The access may be controlled in accordance with the first authorization information.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
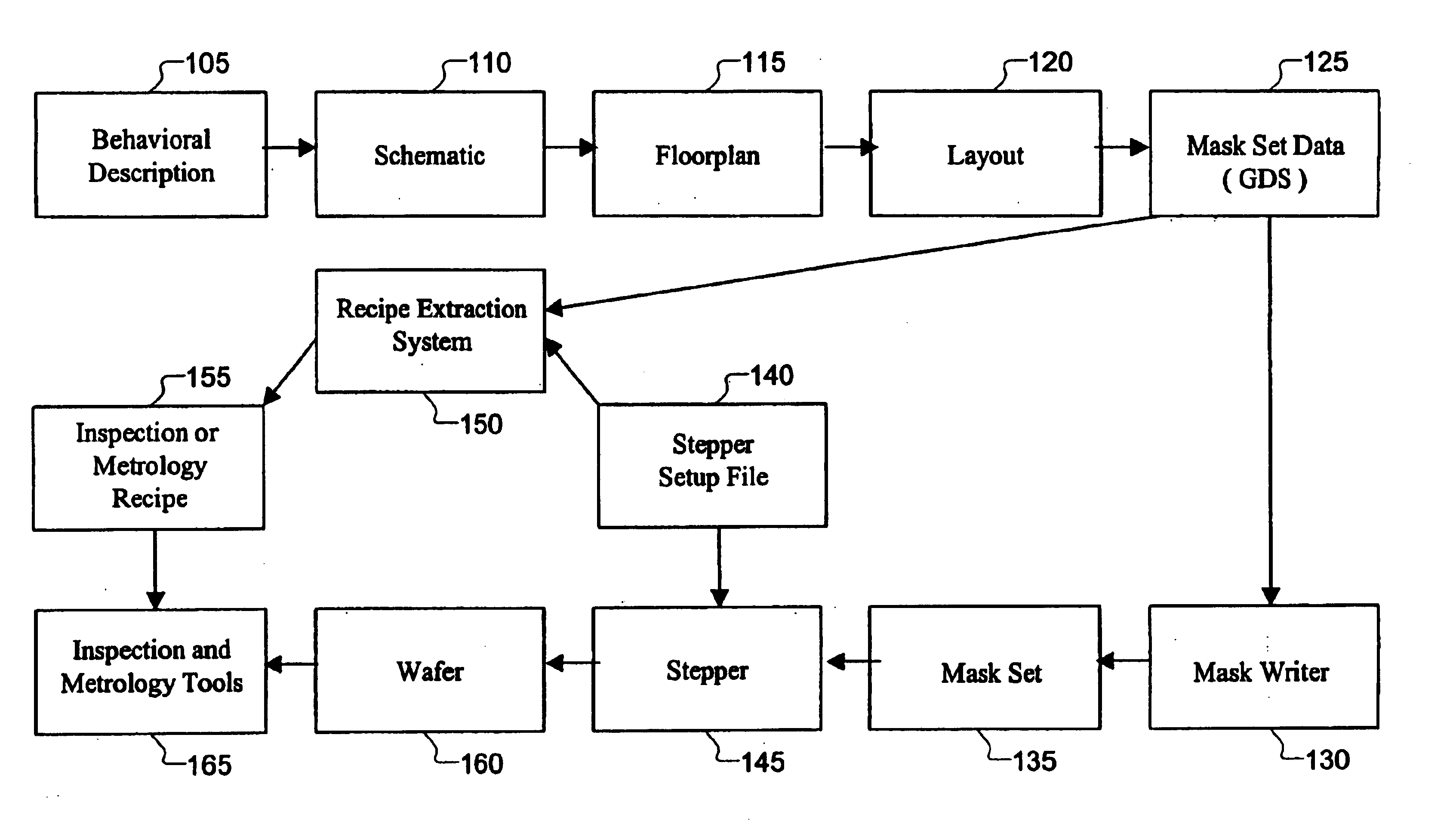
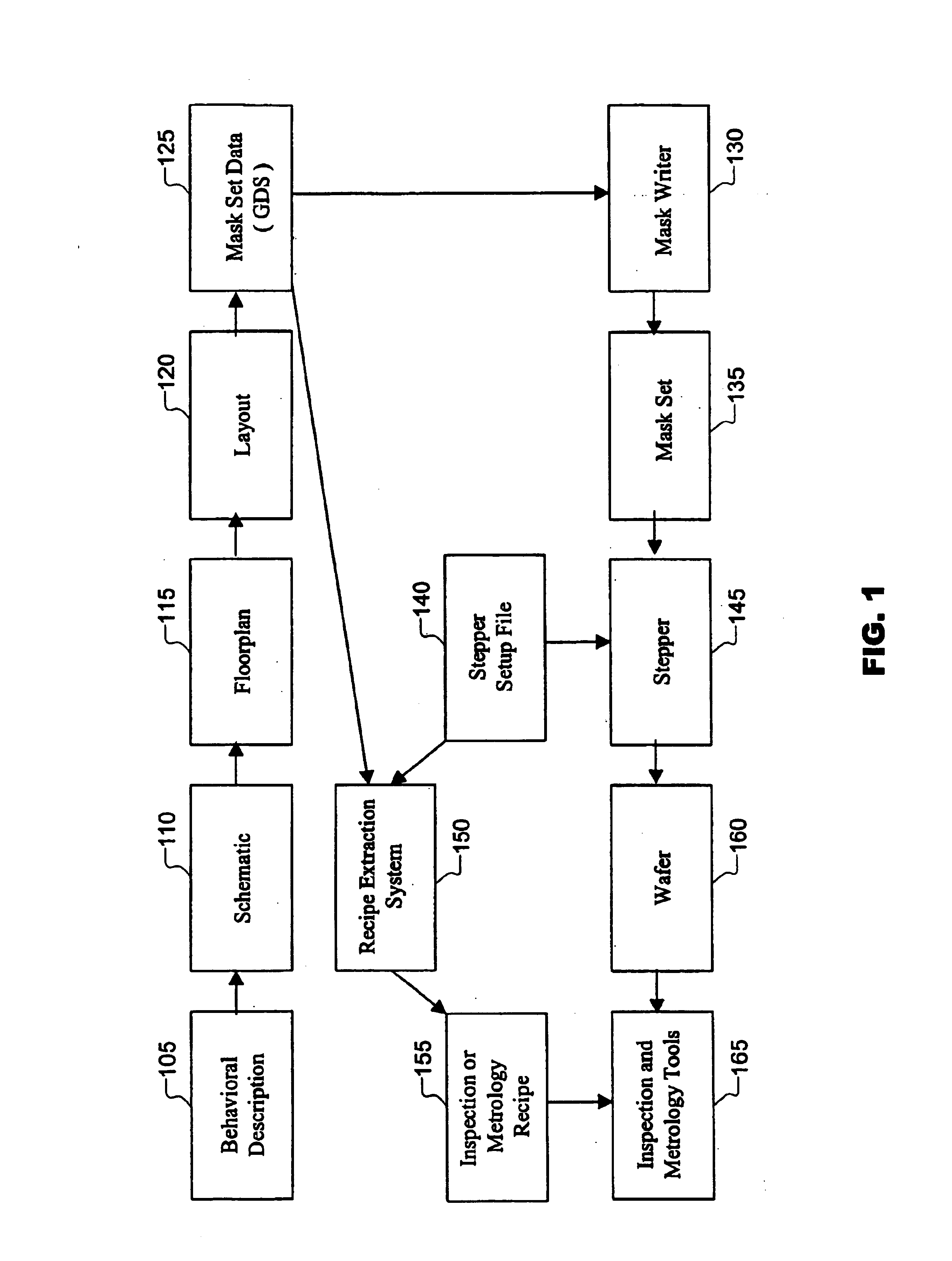
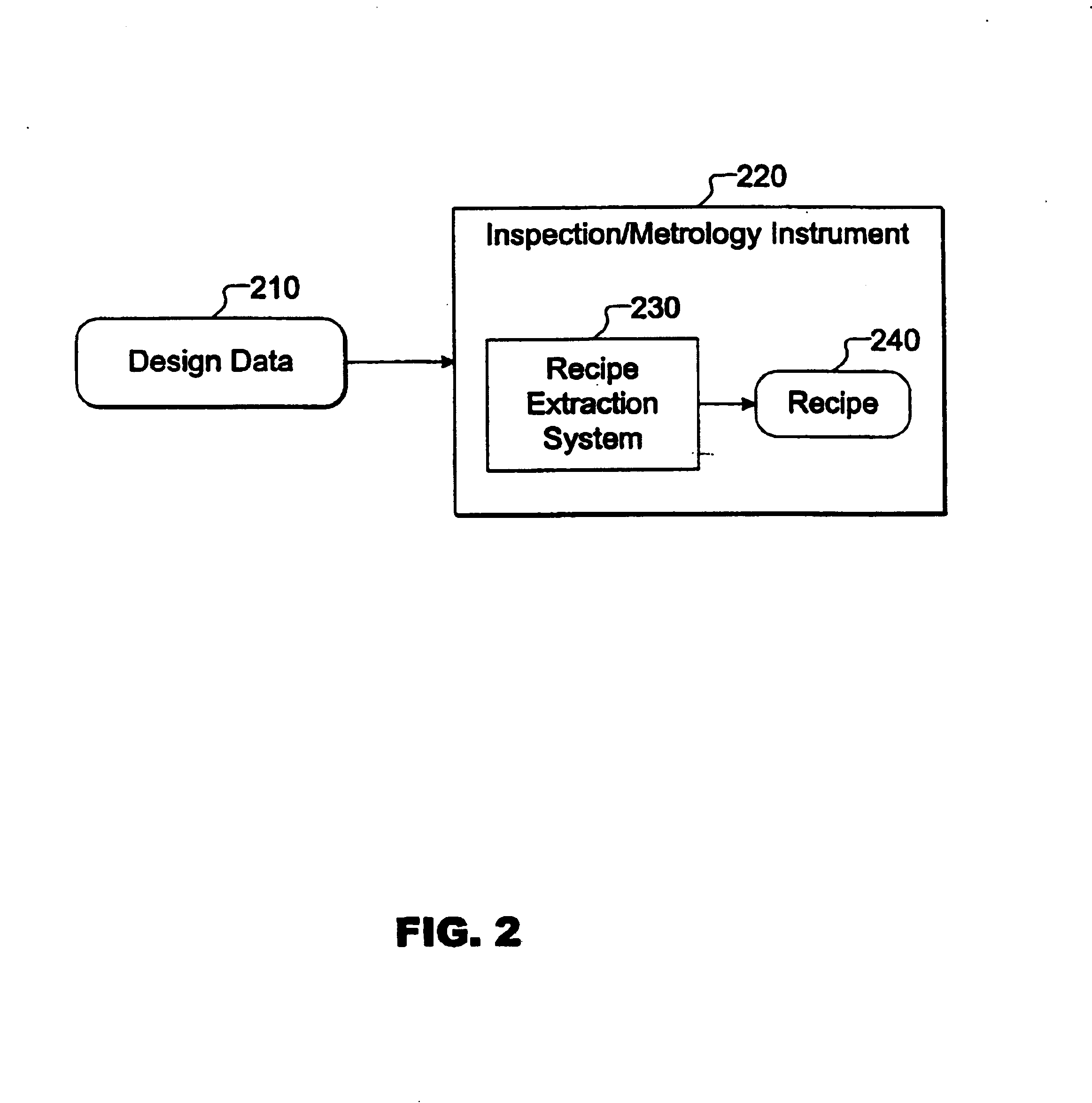
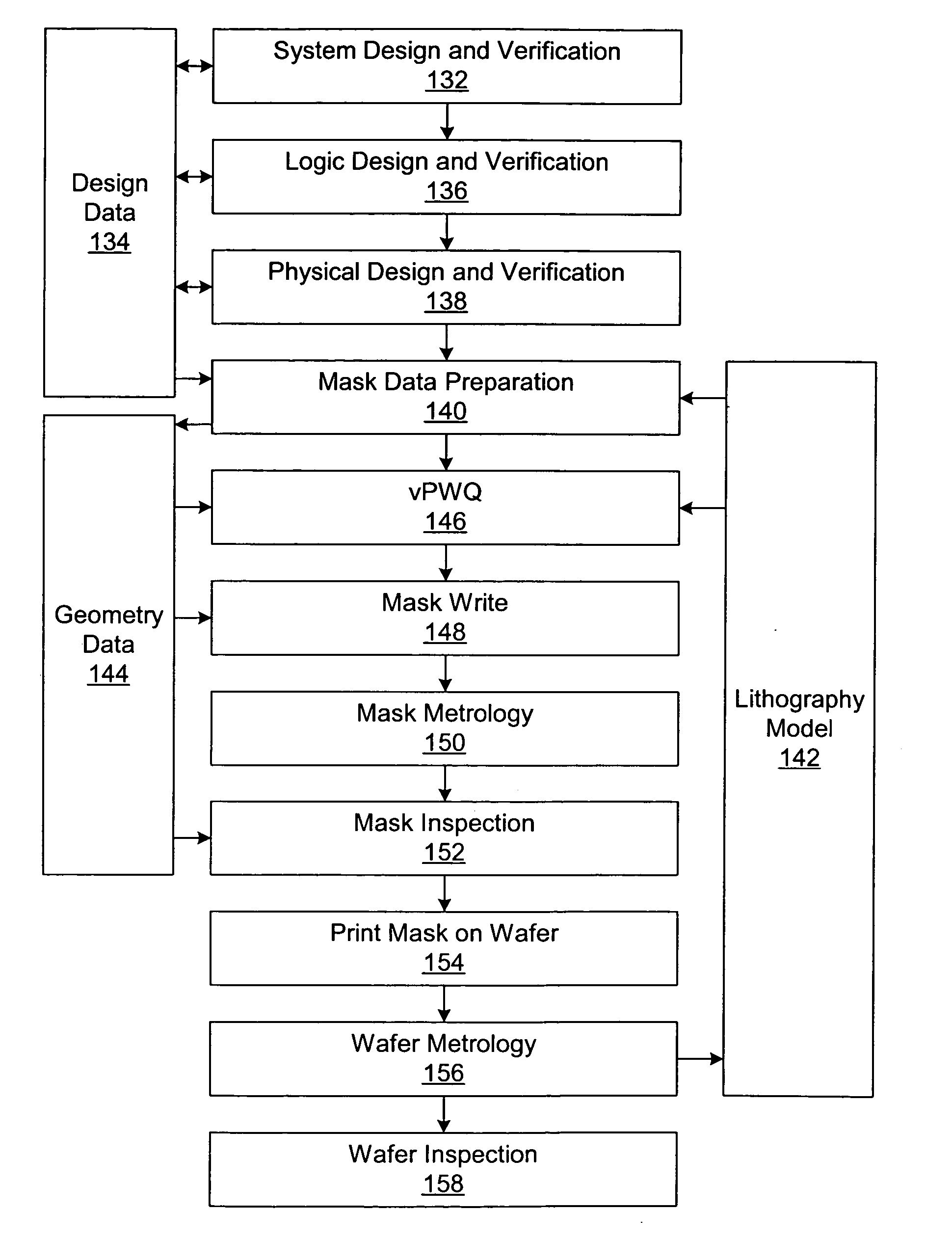
Design driven inspection or measurement for semiconductor using recipe
InactiveUS6886153B1Reduces instrument setup timeReduce setup timeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMetrologySemiconductor
Design driven inspection / metrology methods and apparatus are provided. A recipe is a set of instructions including wafer processing parameters, inspection parameters, or control parameters for telling an inspection / metrology system how to inspect / measure a wafer. Design data is imported into a recipe extraction system that recognizes instances of target structures and configures recipe parameters accordingly, thereby reducing manual instrument setup time, improving inspection / measurement accuracy, and improving fabrication efficiency.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
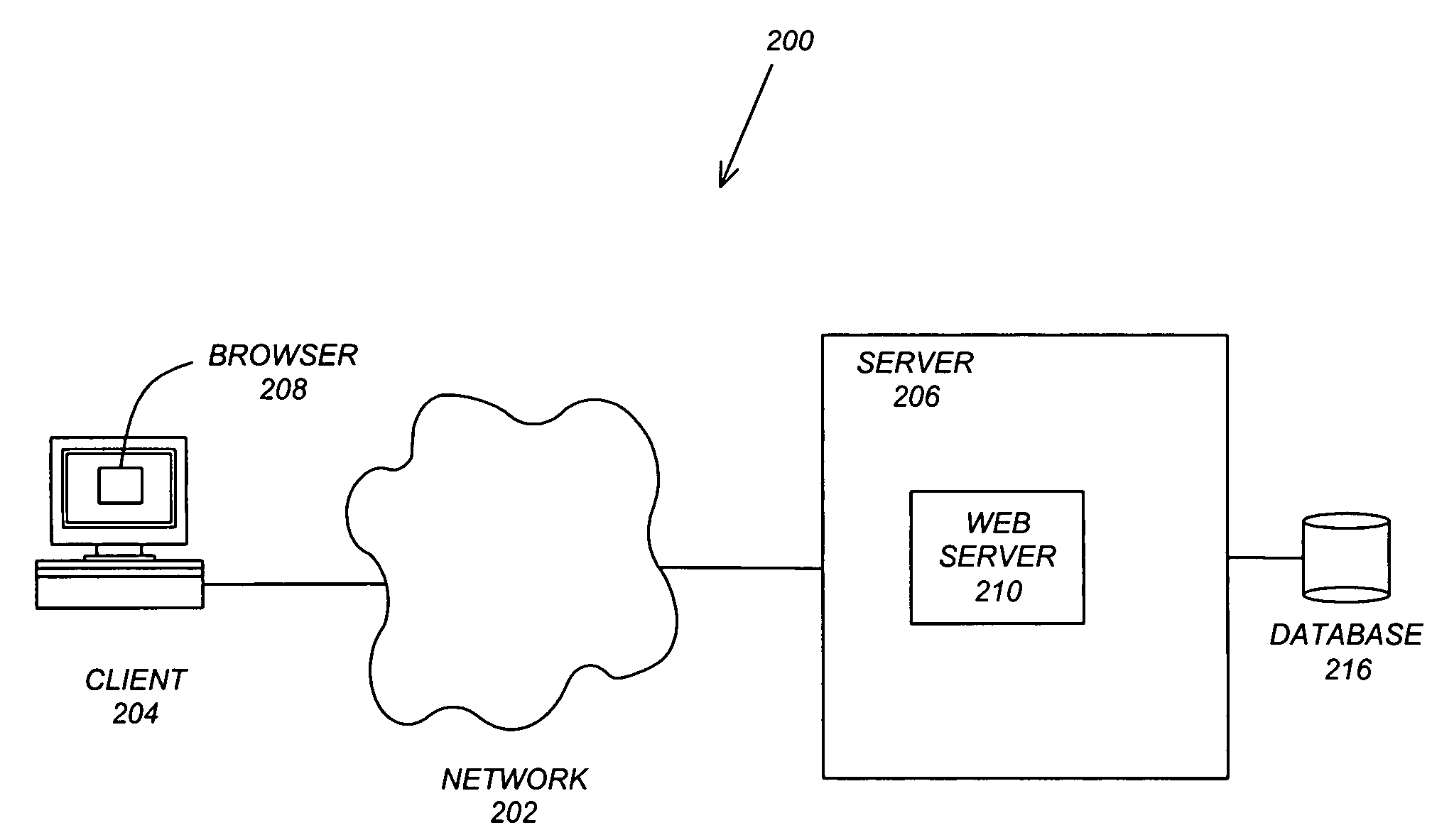
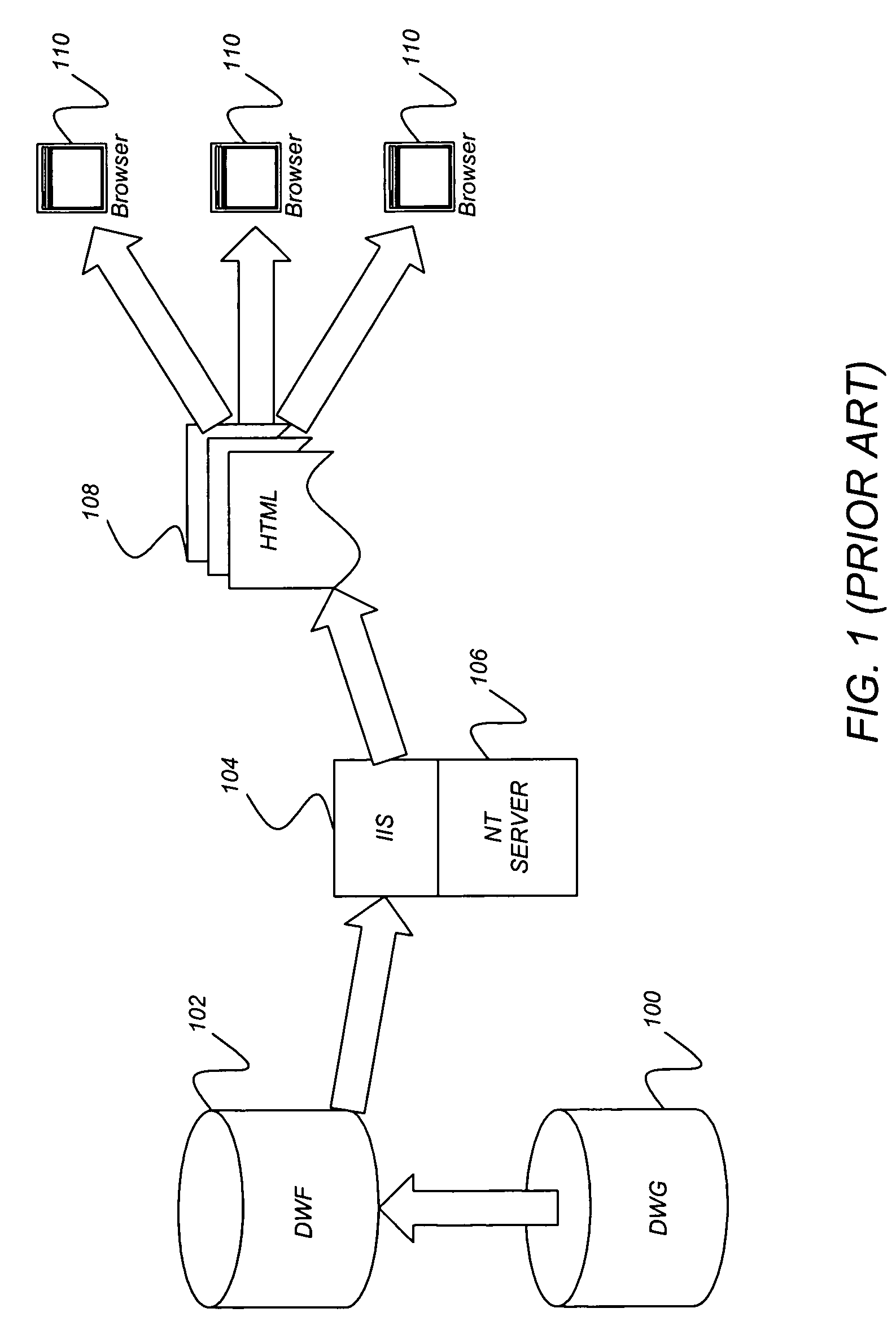
Method and apparatus for providing access to drawing information
InactiveUS7047180B1Improve automationImprove the level ofData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsWeb siteWeb browser
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for automating the finding and serving of CAD design data is disclosed. One or more embodiments of the invention increase the level of access and automation possible with design data. One or more embodiments of the invention provide a server comprised of various components including an information extraction component, a search component, and a conversion component. The various components provide users with enhanced access to drawing and design data. One or more embodiments of the invention also provide programmable, scriptable components that can query, filter, manipulate, merge, and translate design drawing data using the Web browser interface. Further, Web site administrators can use the present invention to dynamically index and publish design drawing data.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Generating simulated output for a specimen
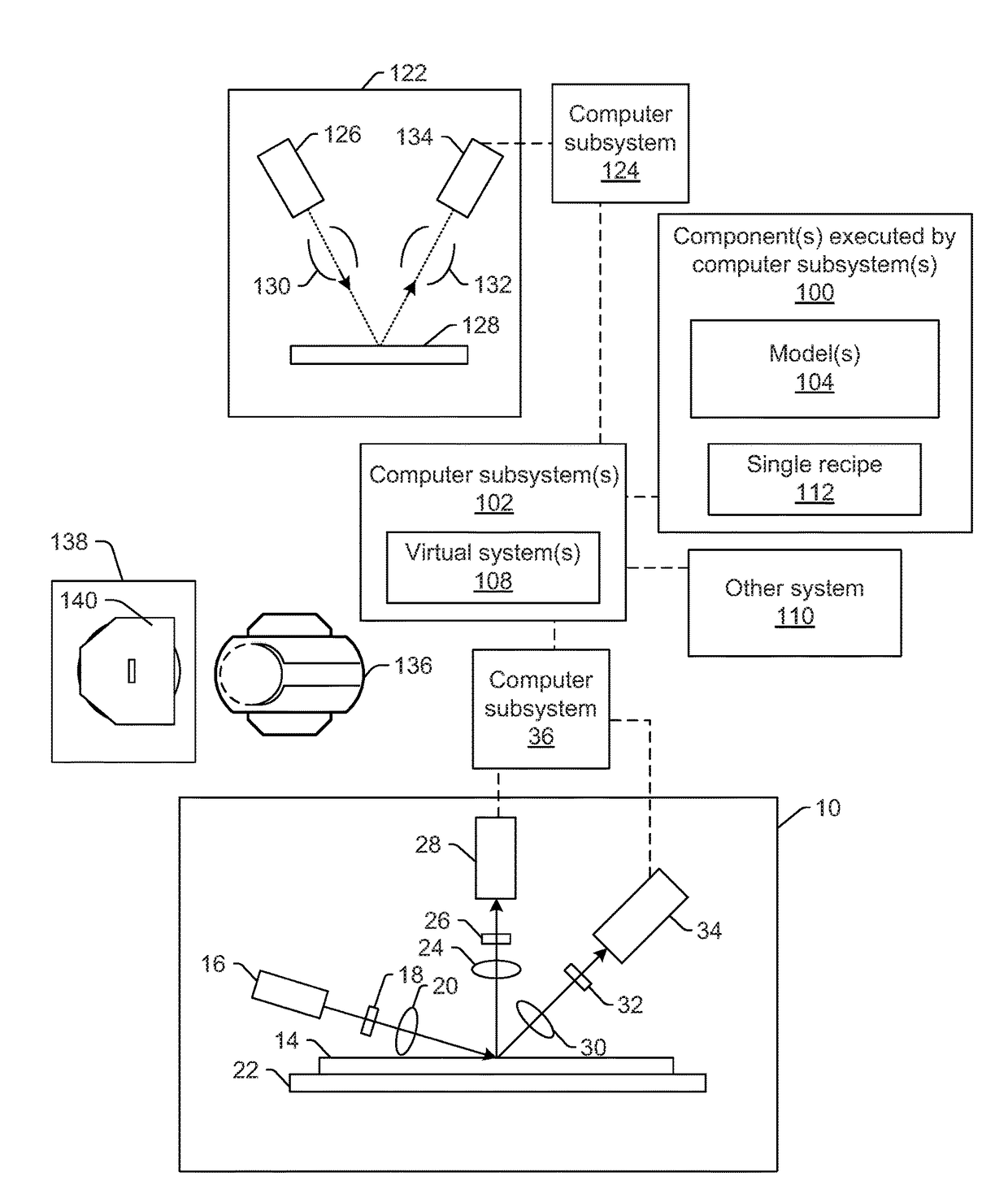
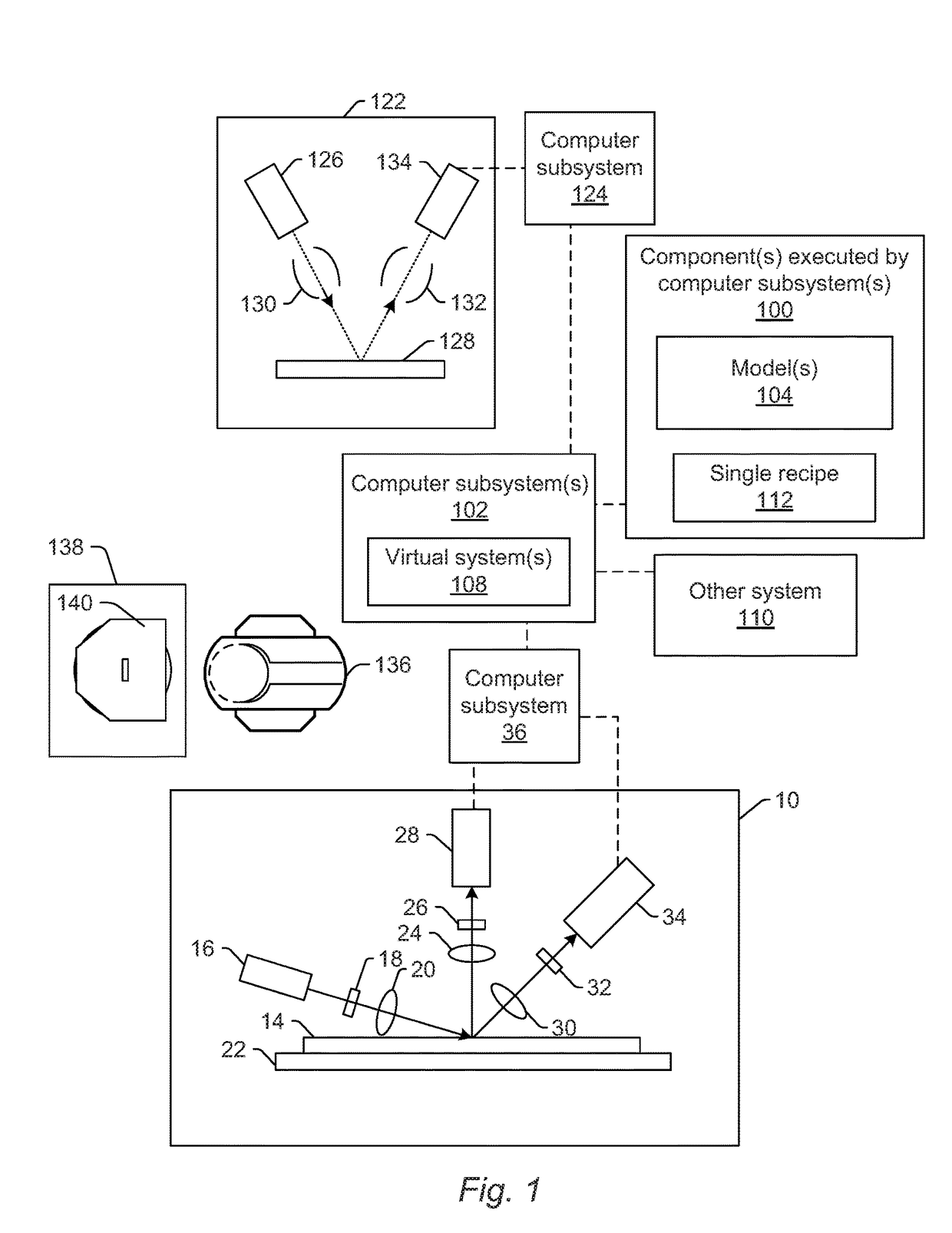
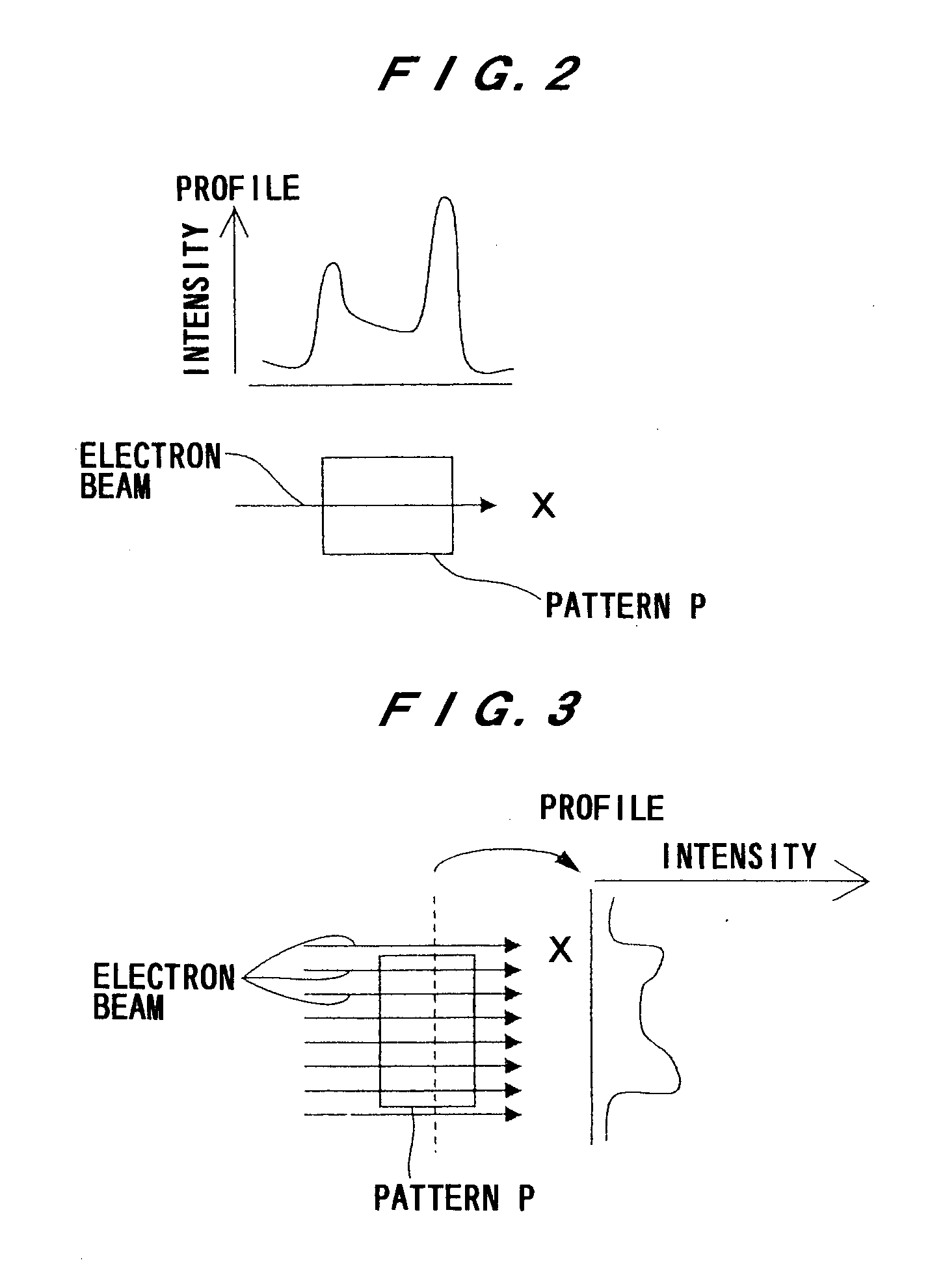
Methods and systems for generating simulated output for a specimen are provided. One method includes acquiring information for a specimen with one or more computer systems. The information includes at least one of an actual optical image of the specimen, an actual electron beam image of the specimen, and design data for the specimen. The method also includes inputting the information for the specimen into a learning based model. The learning based model is included in one or more components executed by the one or more computer systems. The learning based model is configured for mapping a triangular relationship between optical images, electron beam images, and design data, and the learning based model applies the triangular relationship to the input to thereby generate simulated images for the specimen.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS20090297019A1Reduce errorsImprove defectsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceDesign data
Various methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data are provided. One computer-implemented method for binning defects detected on a wafer includes comparing portions of design data proximate positions of the defects in design data space. The method also includes determining if the design data in the portions is at least similar based on results of the comparing step. In addition, the method includes binning the defects in groups such that the portions of the design data proximate the positions of the defects in each of the groups are at least similar. The method further includes storing results of the binning step in a storage medium.
Owner:KLA CORP
Computer-implemented methods for detecting defects in reticle design data
ActiveUS20060236294A1Market predictionsDetecting faulty computer hardwareManufacturing technologyImage detection
Computer-implemented methods for detecting defects in reticle design data are provided. One method includes generating a first simulated image illustrating how the reticle design data will be printed on a reticle using a reticle manufacturing process. The method also includes generating second simulated images using the first simulated image. The second simulated images illustrate how the reticle will be printed on a wafer at different values of one or more parameters of a wafer printing process. The method further includes detecting defects in the reticle design data using the second simulated images. Another method includes the generating steps described above in addition to determining a rate of change in a characteristic of the second simulated images as a function of the different values. This method also includes detecting defects in the reticle design data based on the rate of change.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Pattern inspection apparatus and method
A pattern inspection apparatus is used for inspecting a pattern, such as semiconductor integrated circuit (LSI), liquid crystal panel, and a photomask by using an image of the pattern to-be-inspected and design data for fabricating the pattern to-be-inspected. The pattern inspection apparatus includes a reference pattern generation device for generating a reference pattern represented by one or more lines from design data, an image generation device for generating the image of the pattern to-be-inspected, a detecting device for detecting an edge of the image of the pattern to-be-inspected, and an inspection device for inspecting the pattern to-be-inspected by comparing the edge of the image of the pattern to-be-inspected with the one or more lines of the reference pattern.
Owner:TASMIT INC
Computer-implemented methods, processors, and systems for creating a wafer fabrication process
InactiveUS20060161452A1Market predictionsDetecting faulty computer hardwareWafer fabricationEngineering
Computer-implemented methods, processors, and systems for creating a wafer fabrication process are provided. One computer-implemented method includes determining individual error budgets for different parameters of the wafer fabrication process based on an overall error budget for the wafer fabrication process and simulated images that illustrate how reticle design data will be printed on a wafer at different values of the different parameters. The method also includes creating the wafer fabrication process based on the overall error budget and the individual error budgets.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Distributed electronic design automation environment
InactiveUS20060101368A1Readily apparentCAD network environmentComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionWeb browserConfigfs
PCB Logical design data is stored in a database according to a connectivity-based data model. Circuit functional blocks, inputs and outputs of functional blocks, and signals are stored as separate data structures. Those structures may be edited by users at separate clients during concurrent editing sessions. Profile data for each of multiple users specifies logical design data elements accessible by, and PCB design software to be provided to, that user. The PCB design software may be plug-ins executable within a web browser at a client, and the client computers may communicate with the database via the Internet. Layout data may also be stored in the database, with elements of the layout data mapped to elements of the logical design data. Constraint data may also be stored in the database, with elements of the constraint data being mapped to elements of the layout data.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Distributed electronic design automation environment
ActiveUS7546571B2CAD network environmentComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionWeb browserDesign software
PCB Logical design data is stored in a database according to a connectivity-based data model. Circuit functional blocks, inputs and outputs of functional blocks, and signals are stored as separate data structures. Those structures may be edited by users at separate clients during concurrent editing sessions. Profile data for each of multiple users specifies logical design data elements accessible by, and PCB design software to be provided to, that user. The PCB design software may be plug-ins executable within a web browser at a client, and the client computers may communicate with the database via the Internet. Layout data may also be stored in the database, with elements of the layout data mapped to elements of the logical design data. Constraint data may also be stored in the database, with elements of the constraint data being mapped to elements of the layout data.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
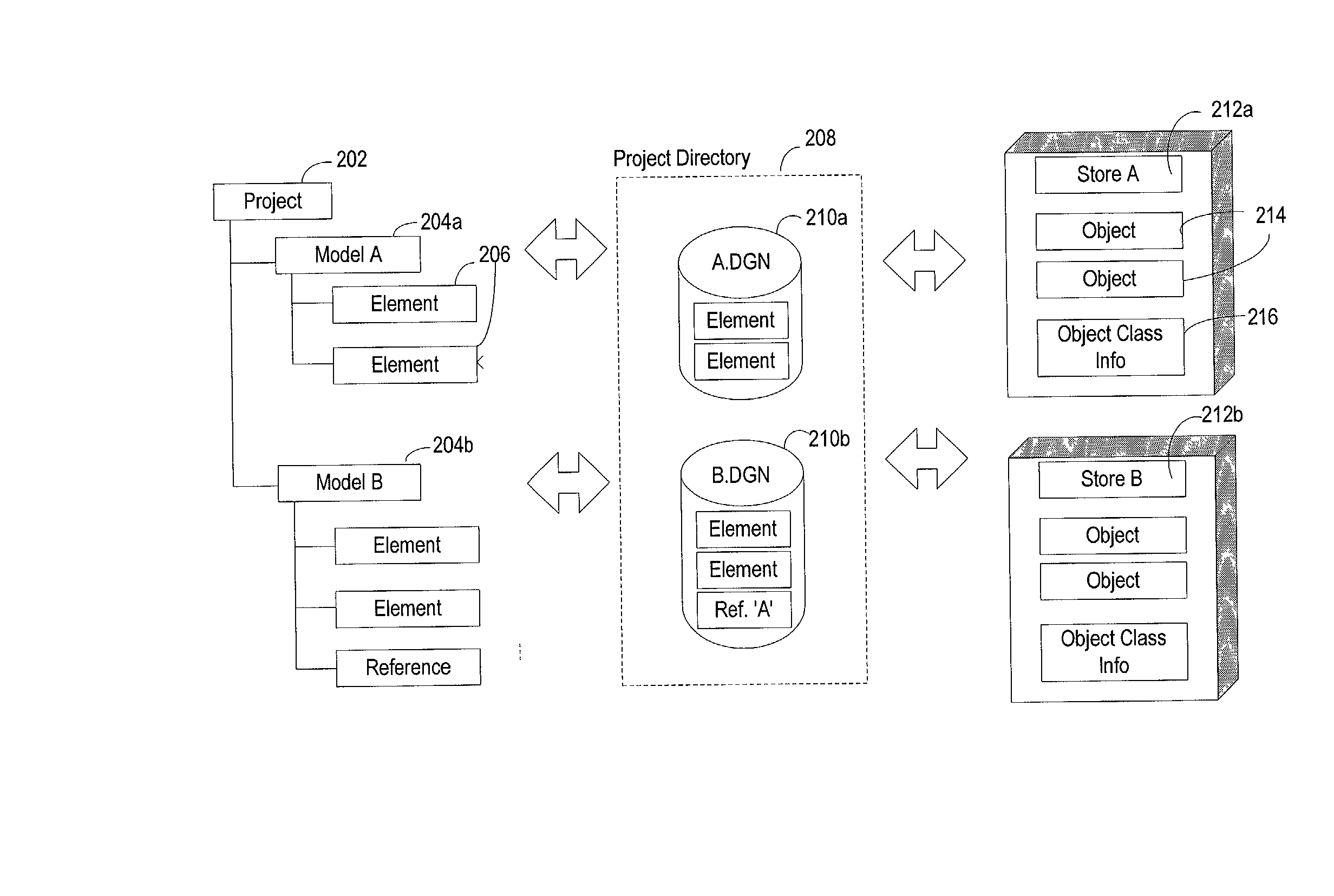
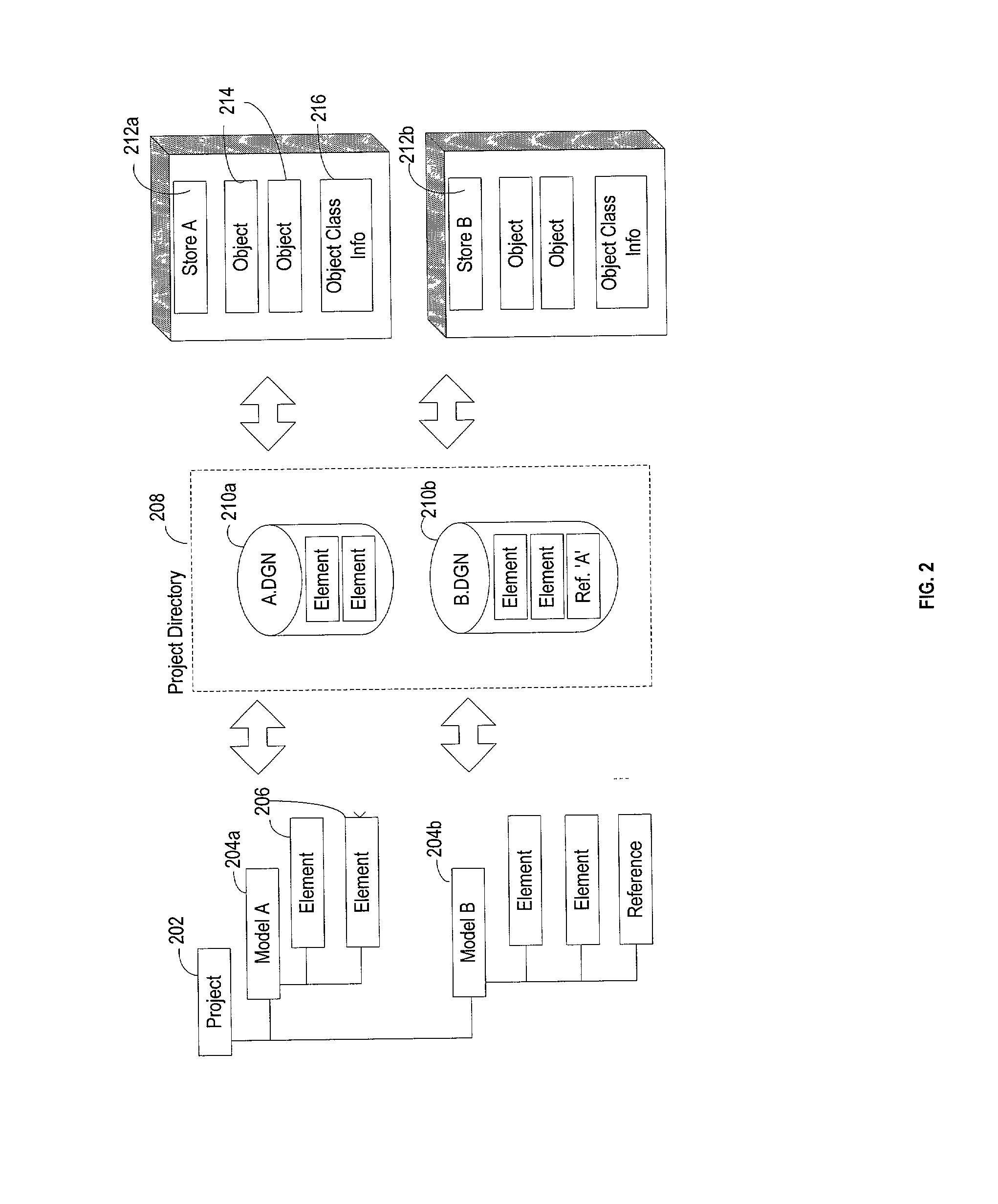
System, method and computer program product for collaborative engineering using component and file oriented tools
InactiveUS20020029218A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSoftware engineeringClient-side
Conventional file-based engineering design data for an engineering model are represented by a plurality of components. The plurality of components are kept in stores, which reside on servers. Each store contains the components that correspond to the elements of one design file. The stores also maintain a history of changes made to the components. A plurality of client computers are bidirectionally connected to the servers. Each client computer may obtain the current version of the components and may send locally edited versions of the components back to the servers to replace the current versions in the stores. At the client computer, the user interacts with the components using conventional file-based software. Before the locally edited versions of the components are committed to the servers to replace the current versions, a synchronization and merging process occurs whereby the latest version of the components are downloaded to the client computer and are compared to the locally edited version of the components to detect resolvable (compatible) and unresolvable (incompatible) conflicts. The commit process is performed only if no unresolvable conflicts exist between the two versions of the components. To facilitate translation between file-based data and components, a schema is written to "wrap" each of the engineering file formats. Each schema is a set of classes that capture all of the information in the file-based data.
Owner:BENTLEY SYST INC
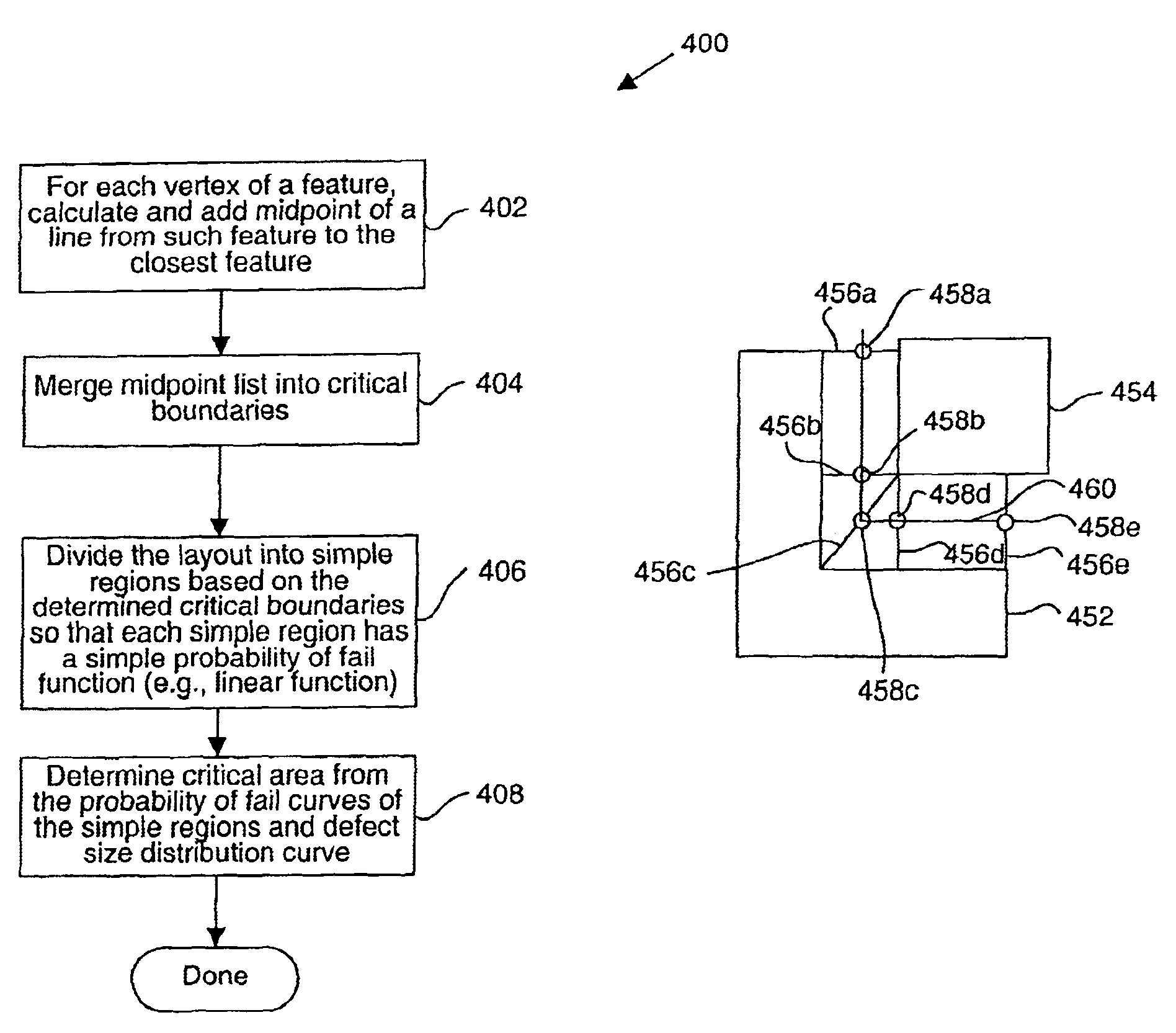
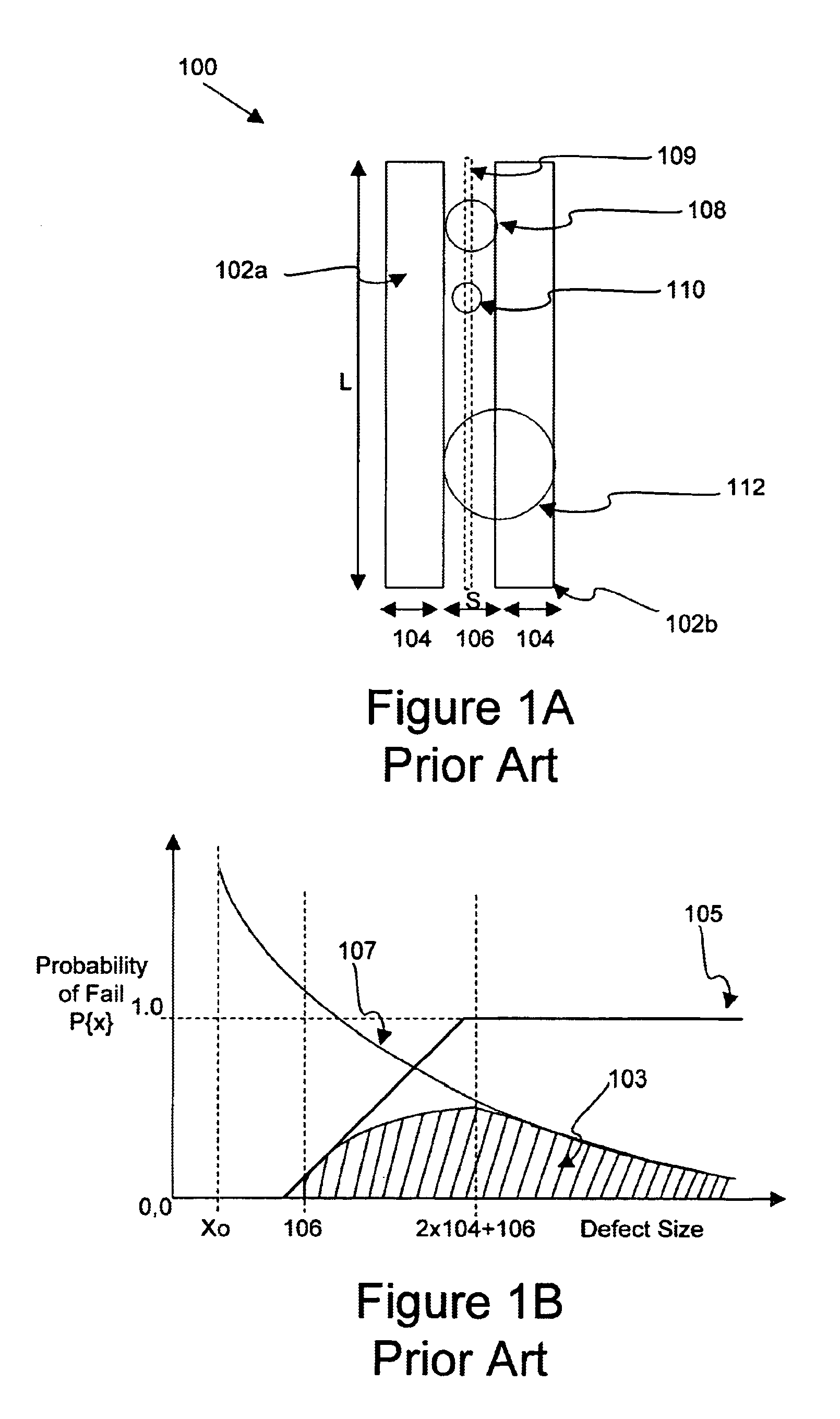
Apparatus and methods for determining critical area of semiconductor design data
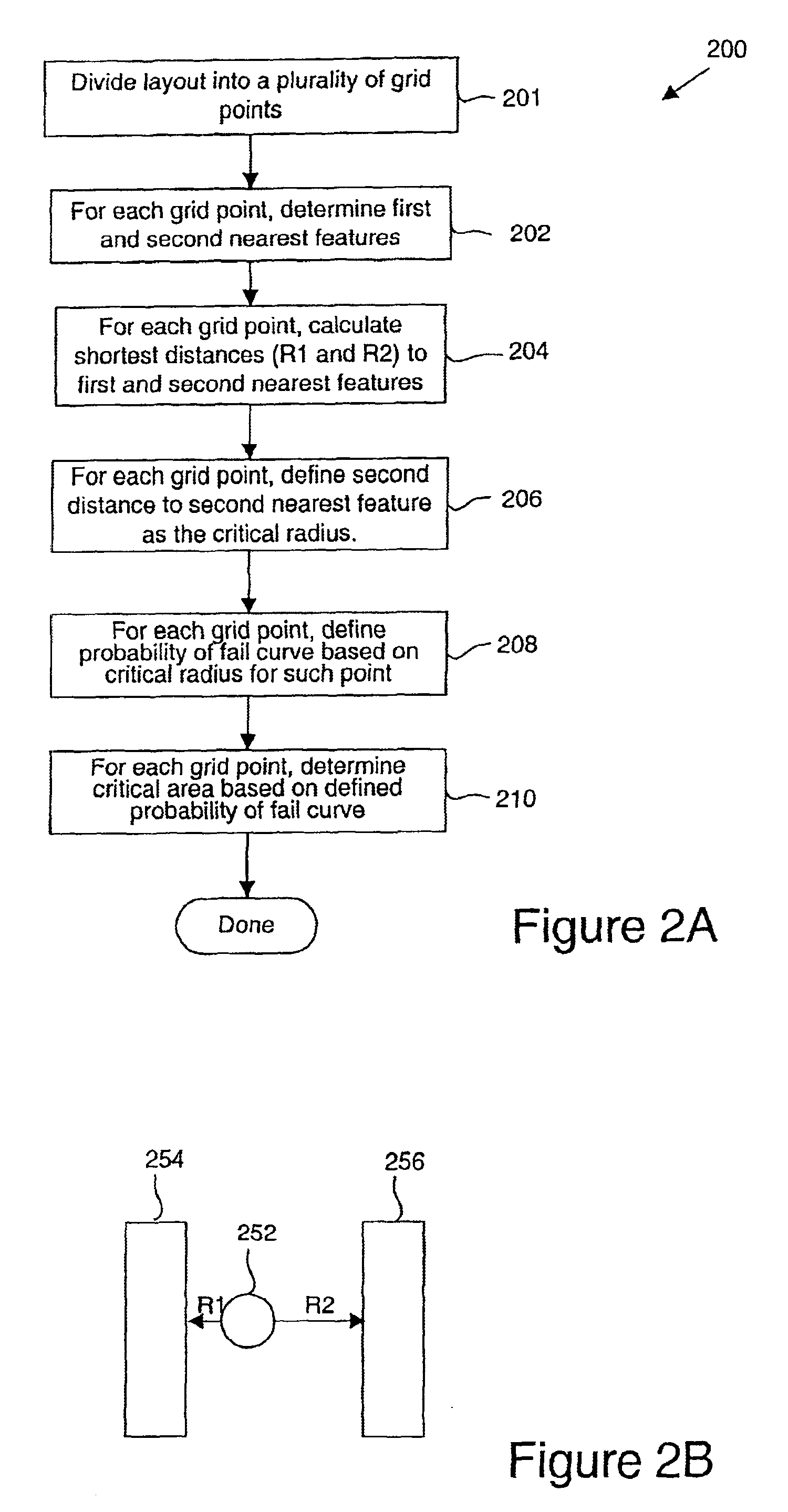
InactiveUS6948141B1Electric discharge tubesDetecting faulty computer hardwareMiddle lineComputer science
Disclosed are mechanisms for efficiently and accurately calculating critical area. In general terms, a method of determining a critical area for a semiconductor design layout is disclosed. The critical area is utilizable to predict yield of a semiconductor device fabricated from such layout. A semiconductor design layout having a plurality of features is first provided. The features have a plurality of polygon shapes which include nonrectangular polygon shapes. Each feature shape has at least one attribute or artifact, such as a vertex or edge. A probability of fail function is calculated based on at least a distance between two feature shape attributes or artifacts. By way of example implementations, a distance between two neighboring feature edges (or vertices) or a distance between two feature edges (or vertices) of the same feature is first determined and then used to calculate the probability of fail function. In a specific aspect, the distances are first used to determine midlines between neighboring features or midlines within a same feature shape, and the midlines are then used to determine the probability of fail function. A critical area of the design layout is then determined based on the determined probability of fail function. In specific implementations, the defect type is a short type defect or an open type defect. In a preferred implementation, the features may have any suitable polygonal shape, as is typical in a design layout.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
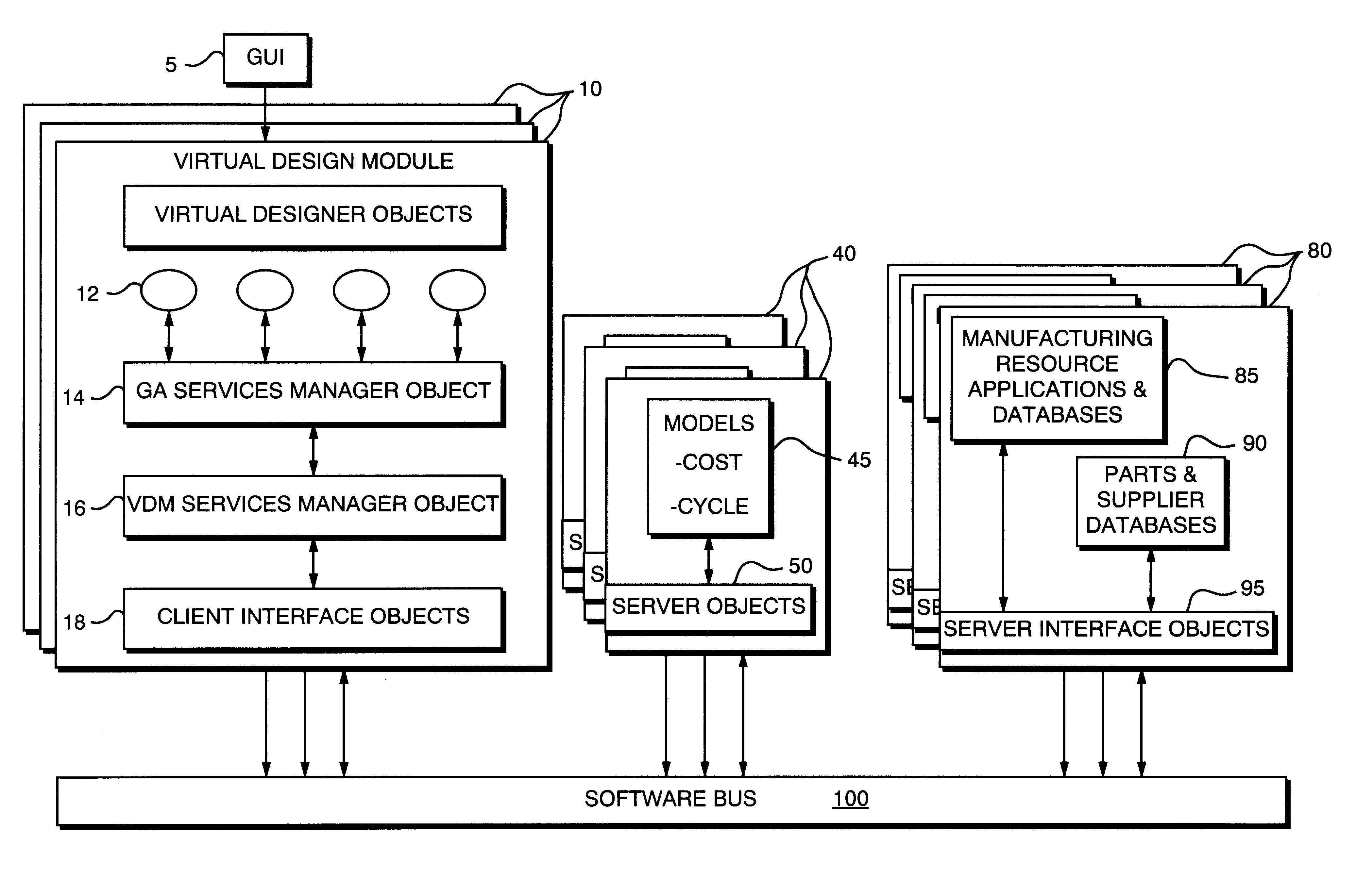
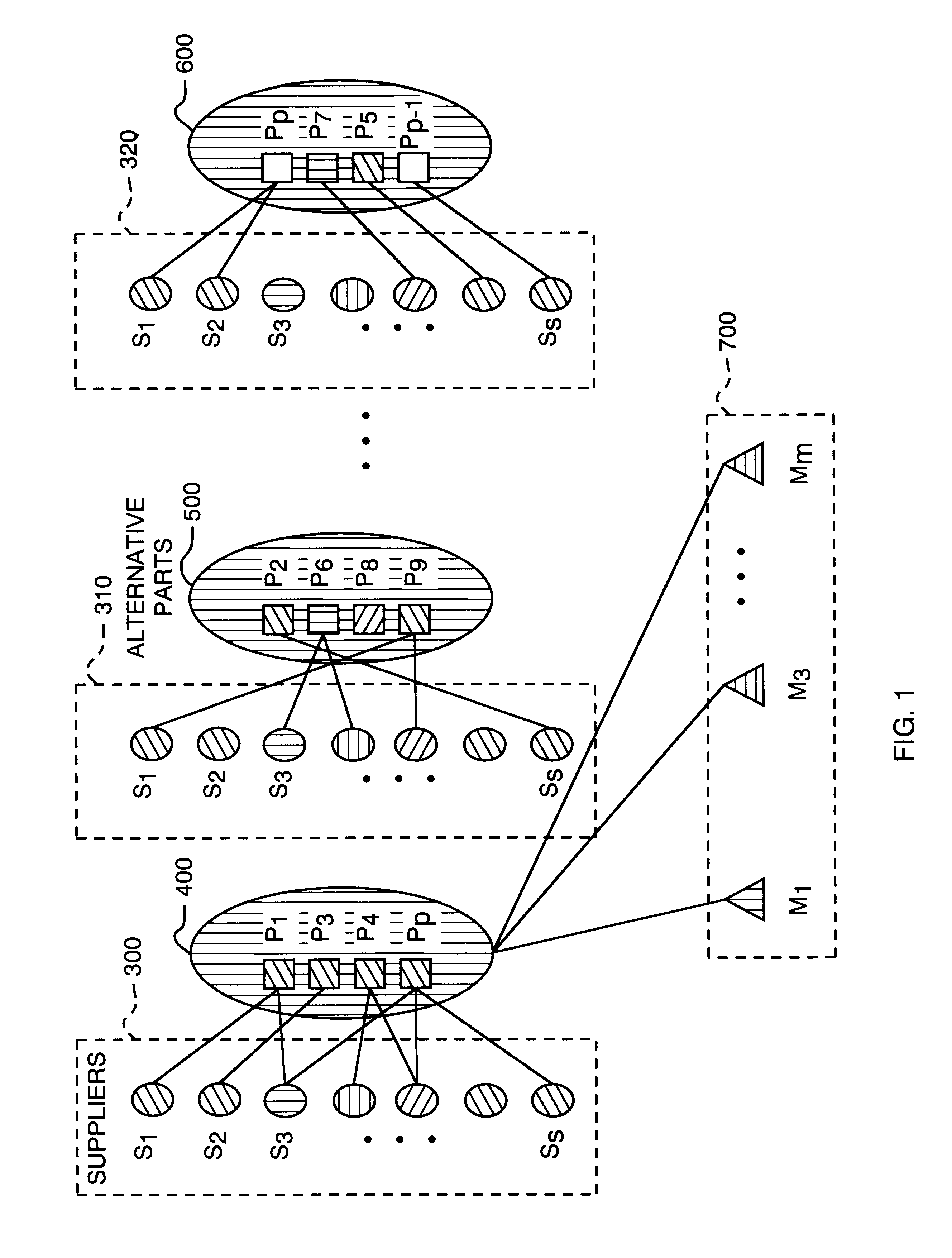
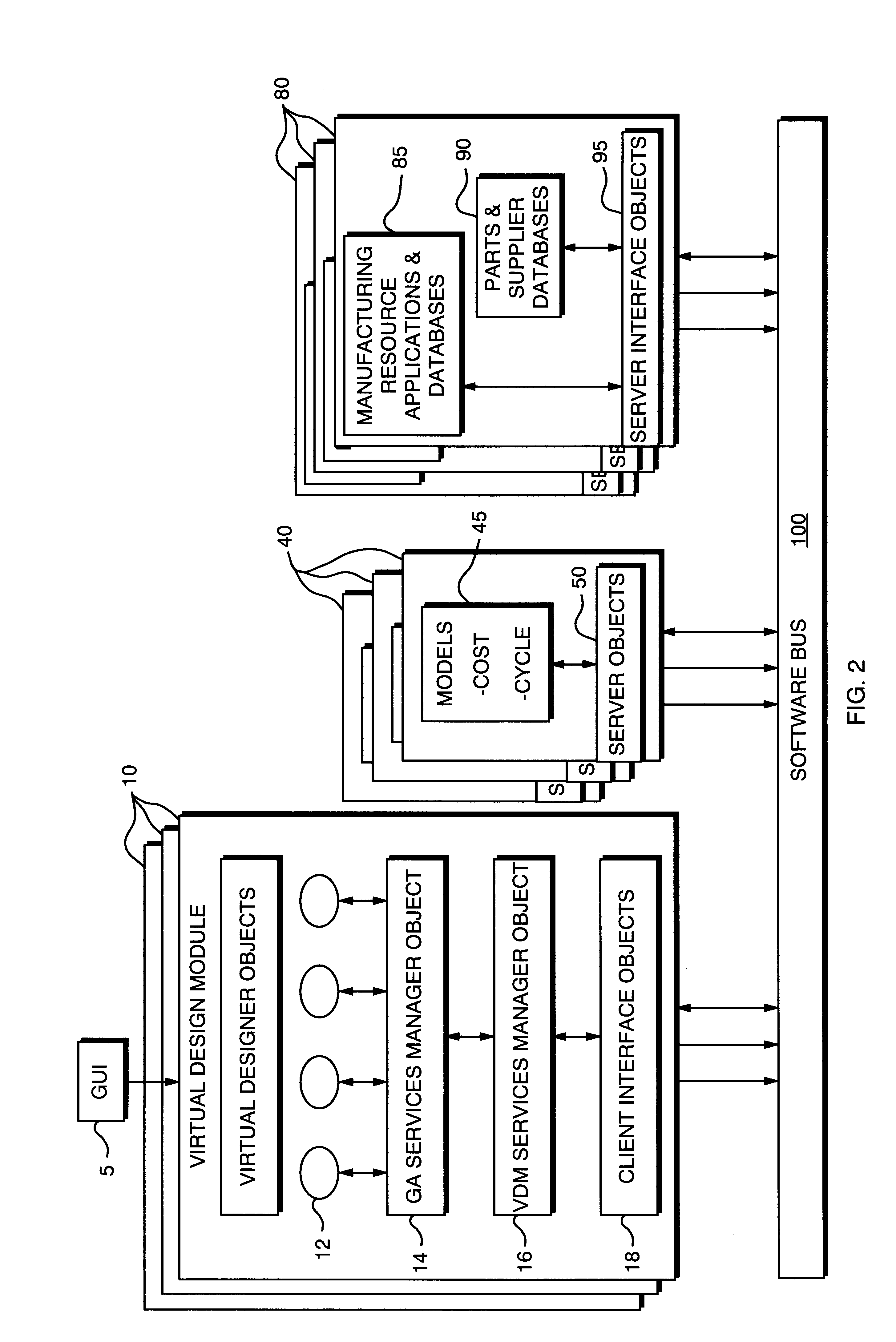
Virtual design module
A Virtual Design Module (VDM) used in a networked design environment generates manufactured product designs that are near optimal in terms of cost and production cycle time by using design data files containing alternative parts and manufacturers information. Numerous product design alternatives are considered and evaluated in terms of design-manufacturing-parts-supplier feasibility and real-time information on cost and production cycle time for realization. The VDM generates a population of new designs with appropriate board design information to allow for design-manufacturer-supplier decision making and determines the feasibility of each member of the current generation of designs and rejects designs that are not feasible. The VDM triggers Mobile Software Agents (MSA) that obtain data for parts availability, cost, lead time and manufacturer data for manufacturing availability, cost and lead time for each feasible member of the current generation of designs and return the data. In one application for printed circuit board design, the VDM evaluates each member of the current generation of designs by calculating cost, lead-time and value using a J function. The VDM then improves board designs through selection and use of board design modifiers. The process continues until optimized designs are obtained. Optimized board designs are output as results to an operator.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
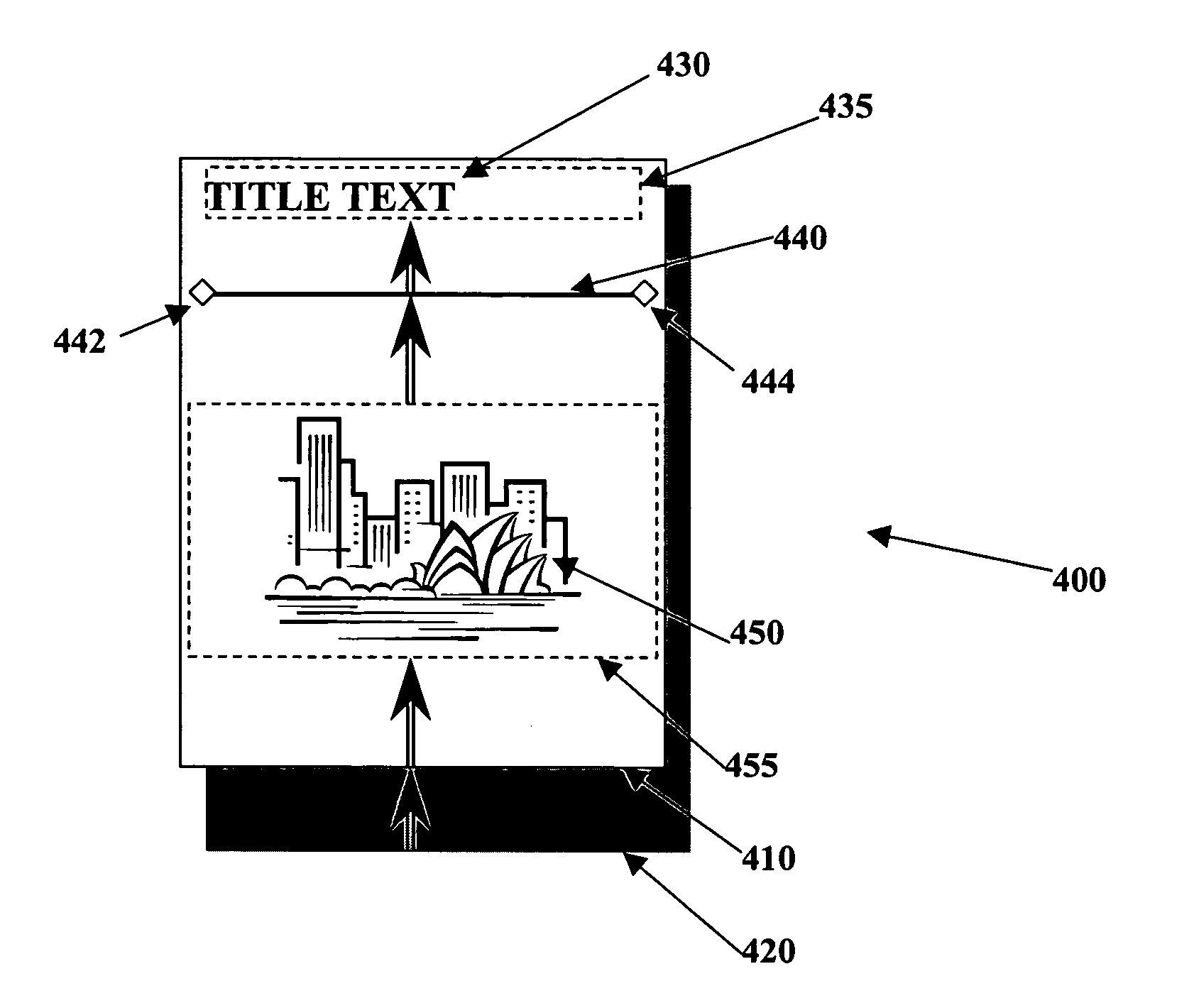
Method of formatting documents
ActiveUS7272789B2Flexible designFlexible presentationNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsRating system
Owner:TYPEFI SYST PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com