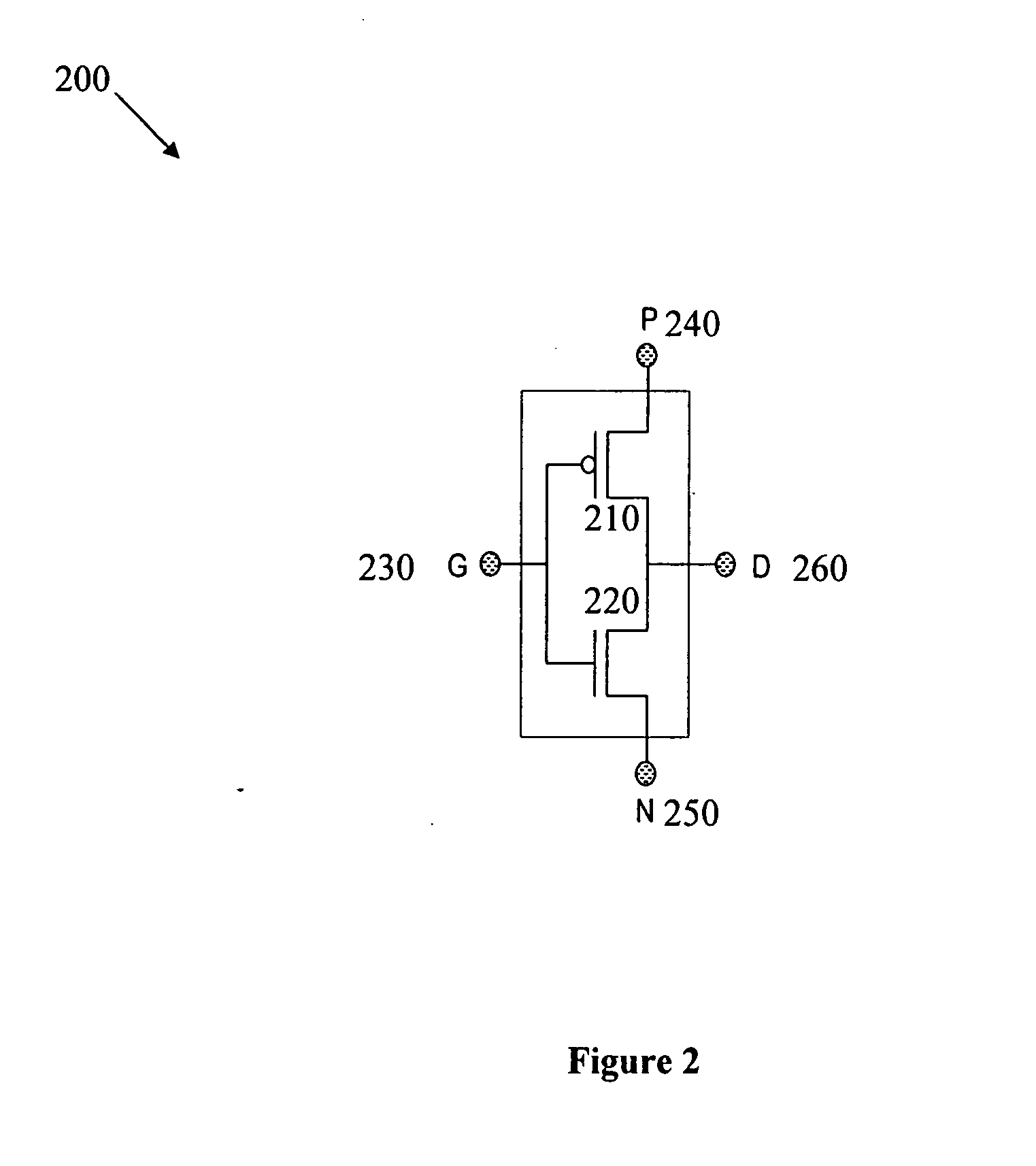
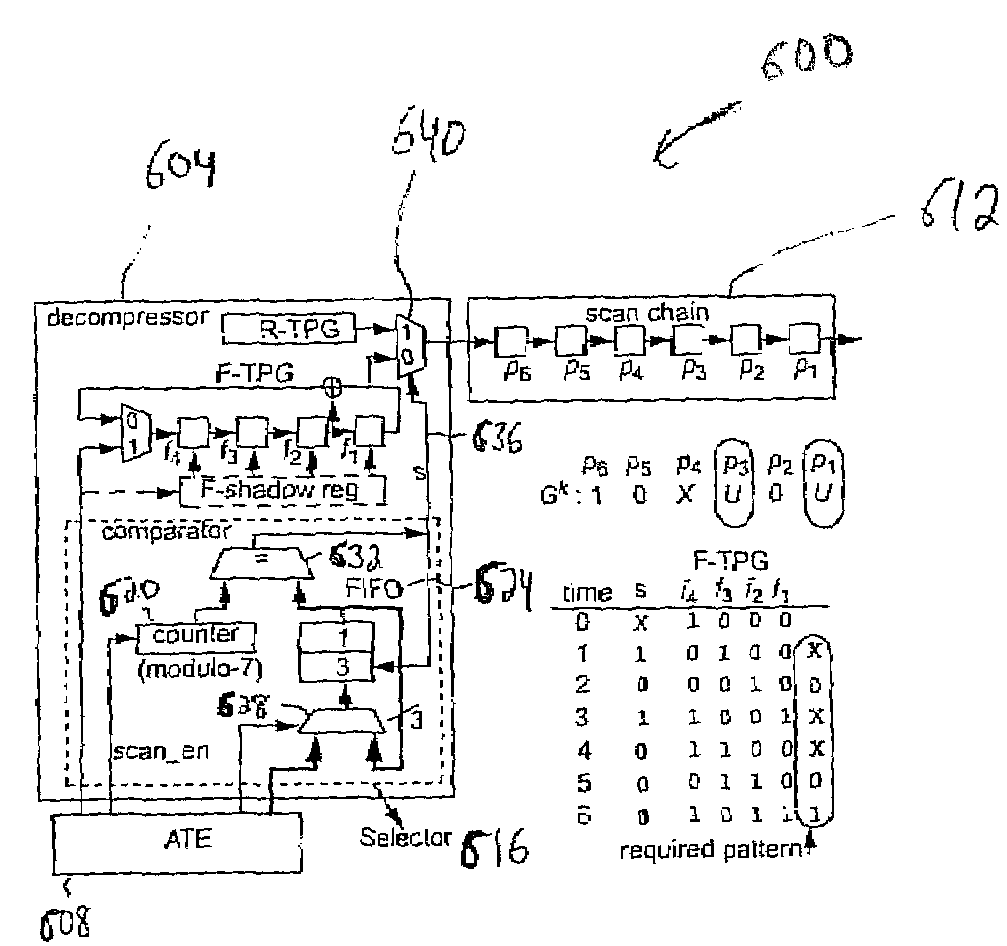
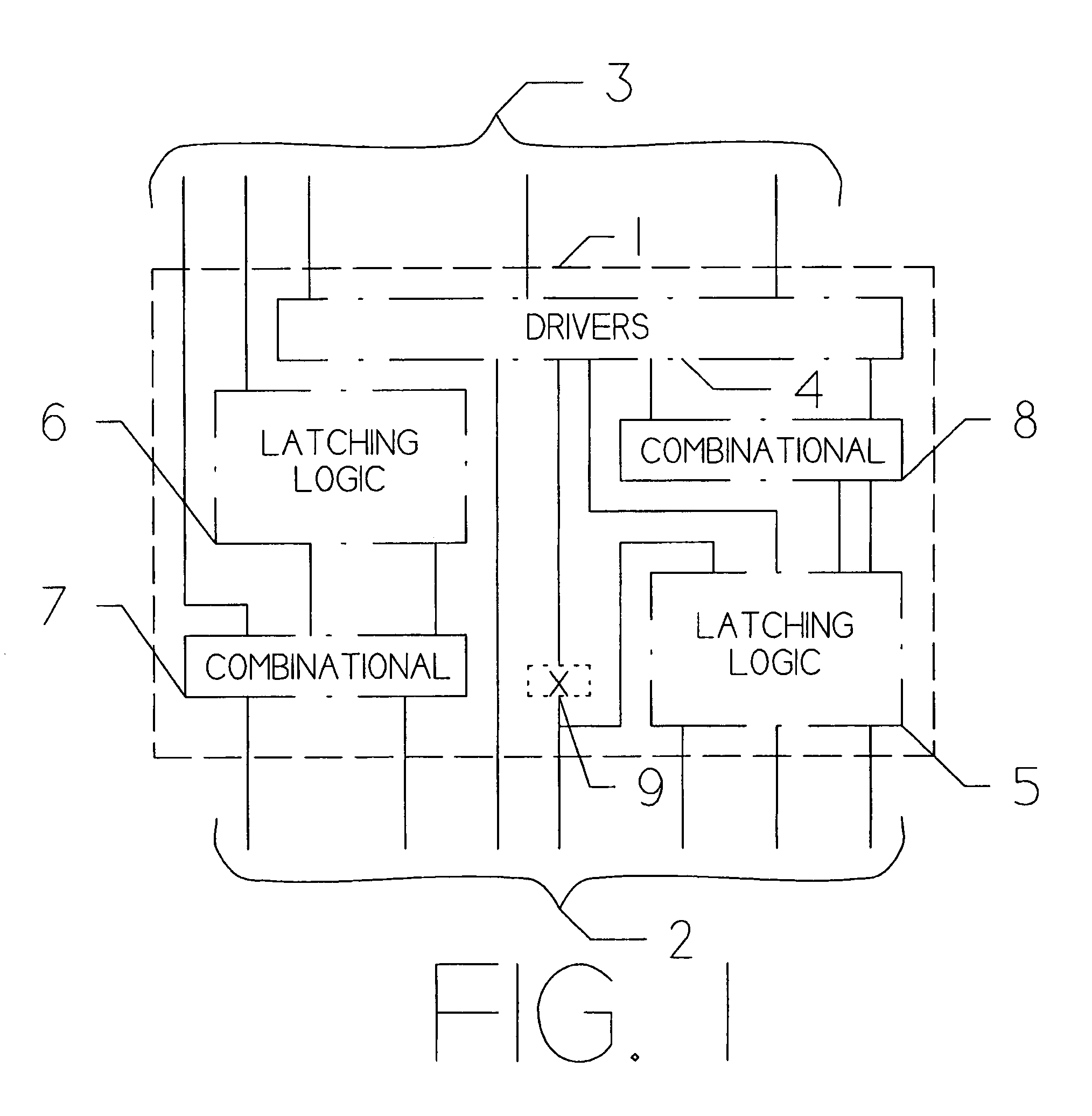
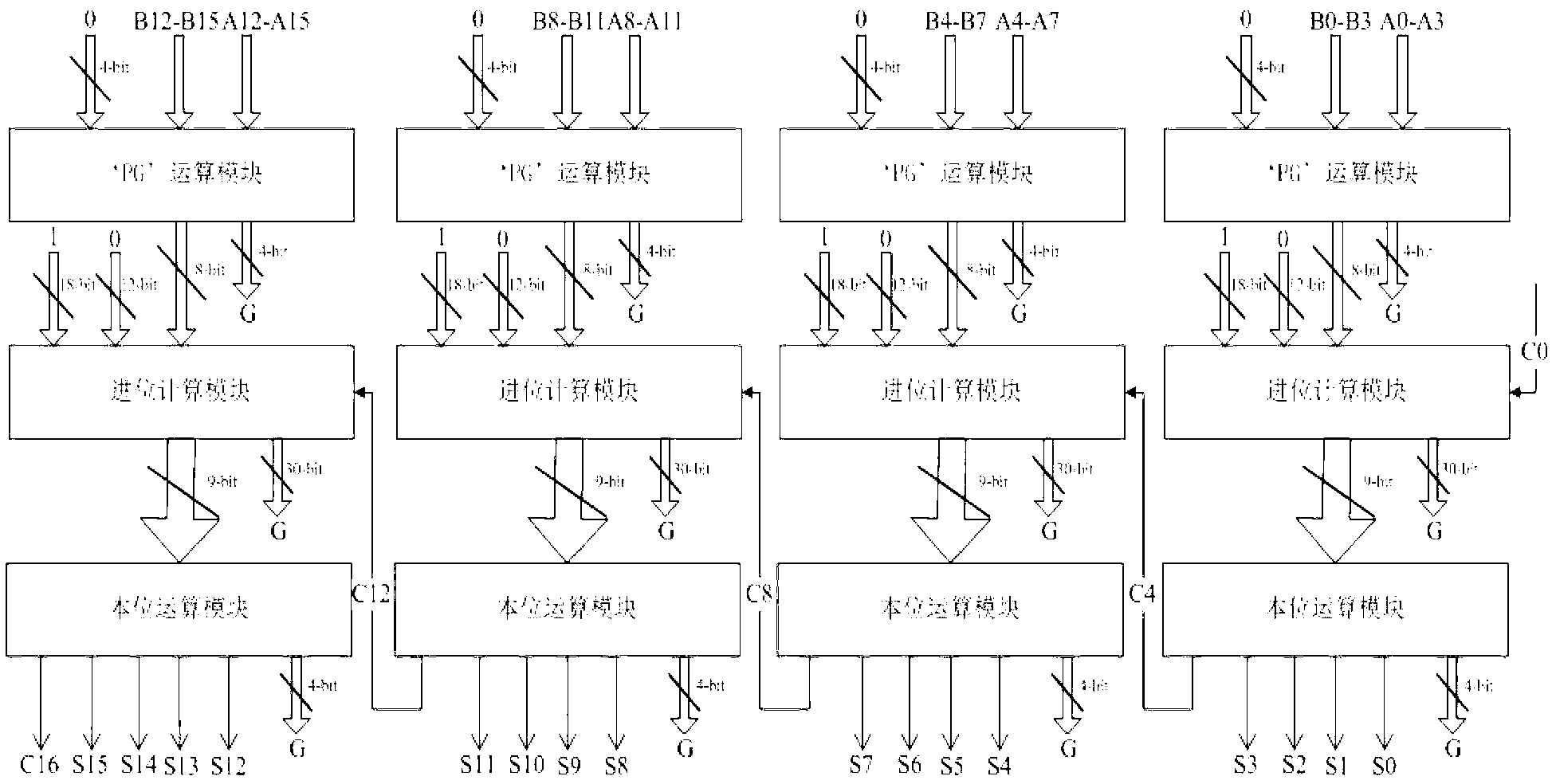Patents
Literature
91 results about "Logic circuit design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
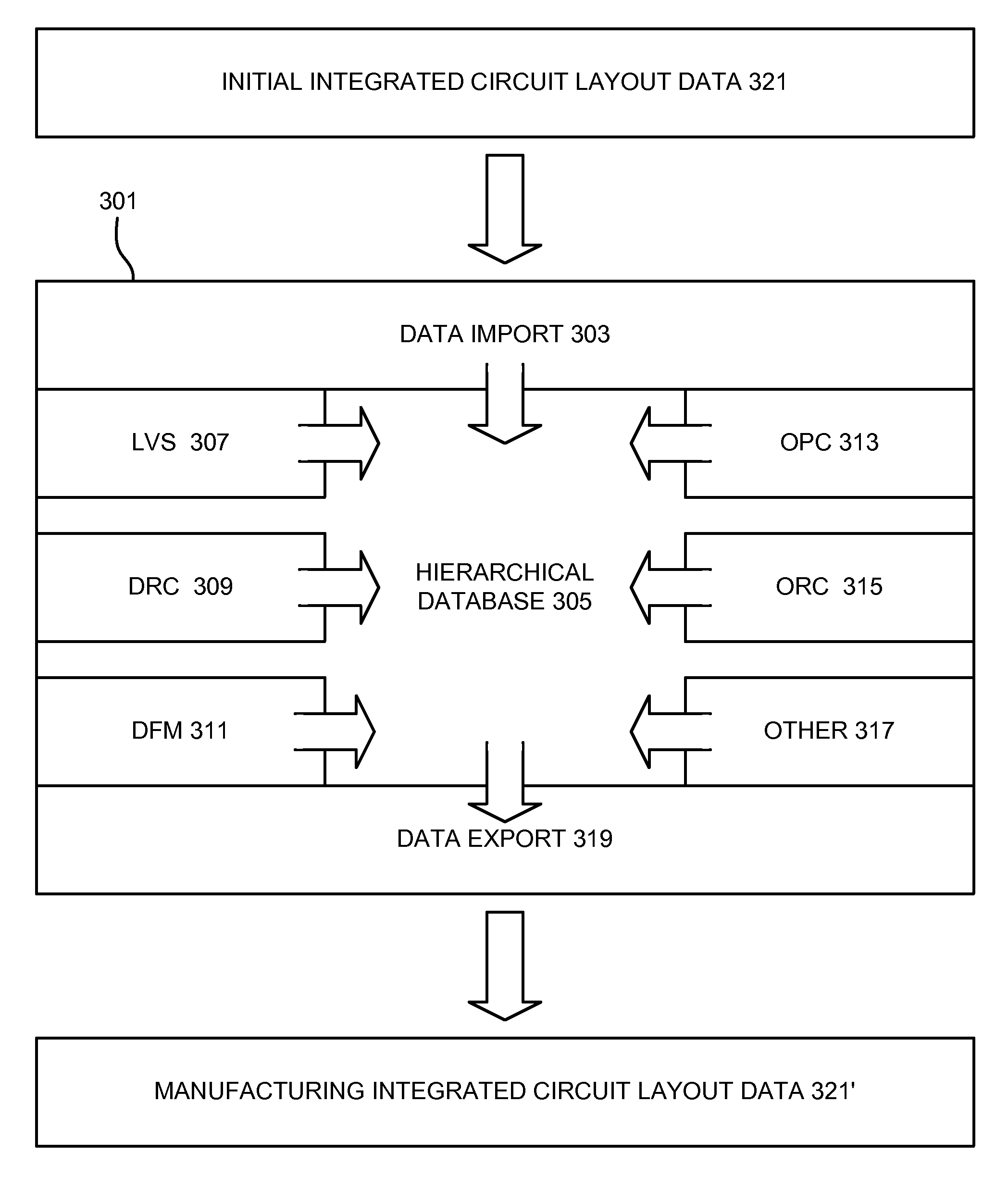
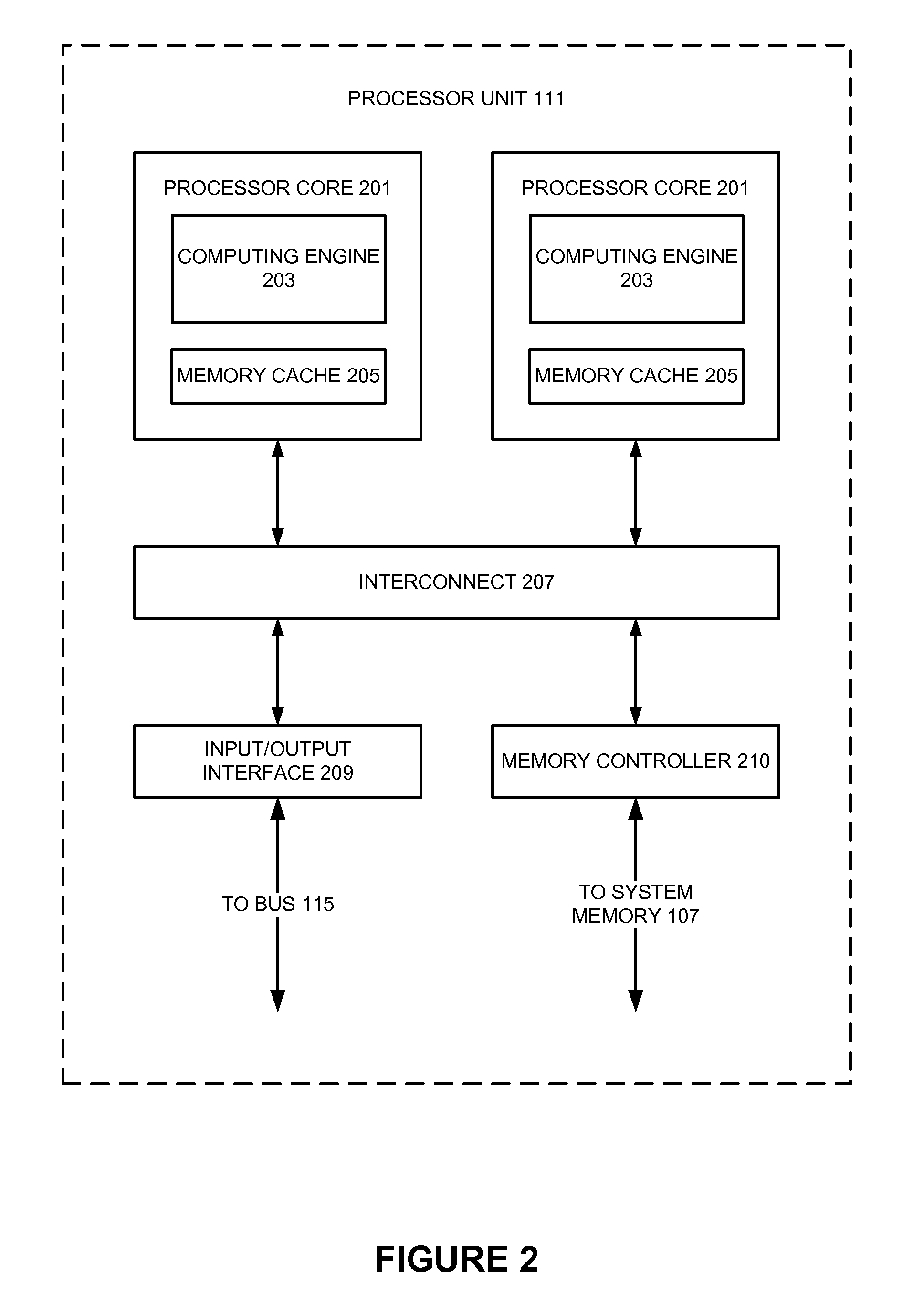
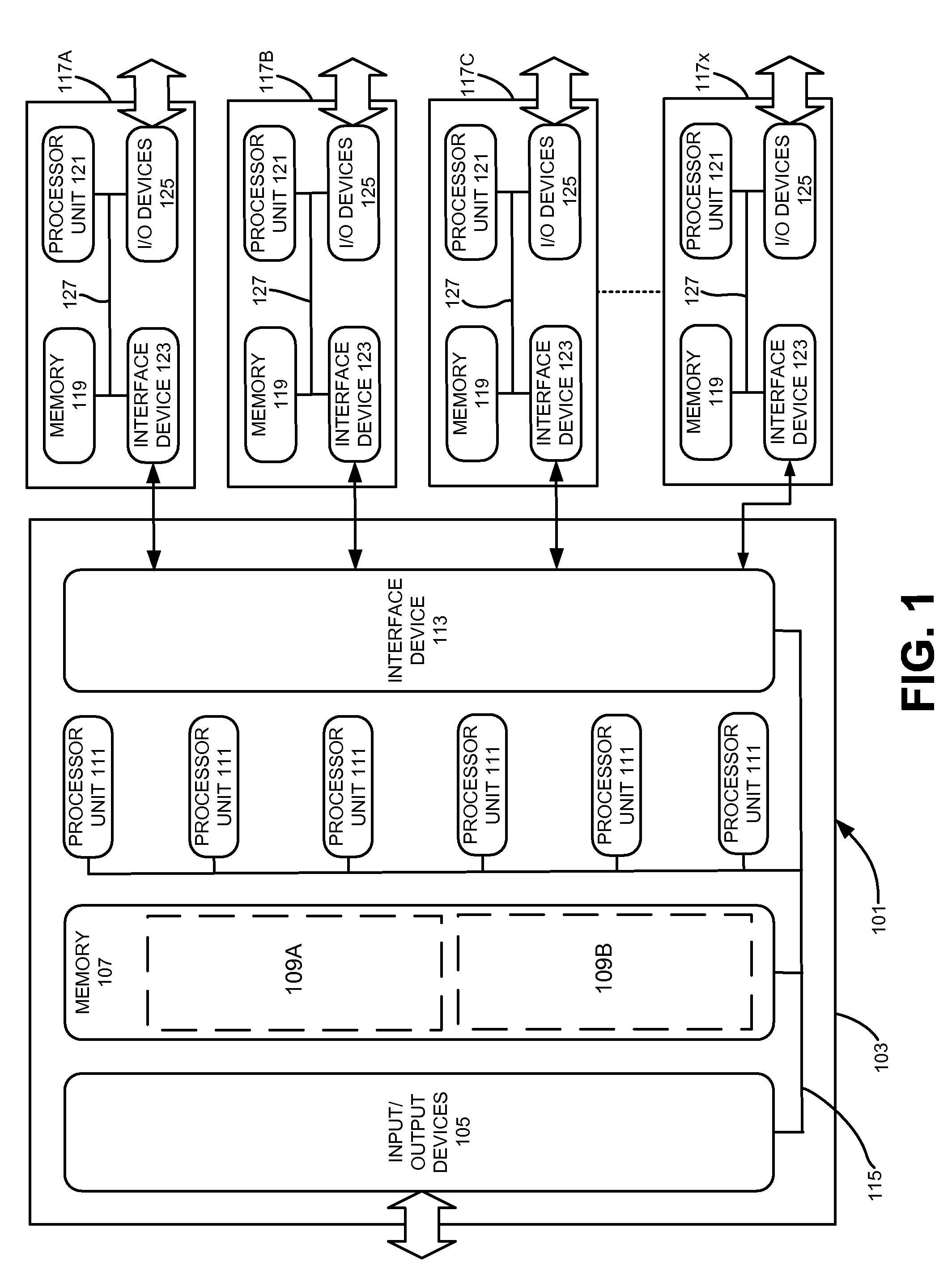
Method for storing multiple levels of design data in a common database
InactiveUS6505328B1Increase flexibilityEasy to integrateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designGraphicsLogic circuit design
Owner:MAGMA DESIGN AUTOMATION
Method and apparatus for high-speed parsing of network messages
InactiveUS6892237B1Efficient analysisIncrease speedMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksPattern matchingRandom access memory
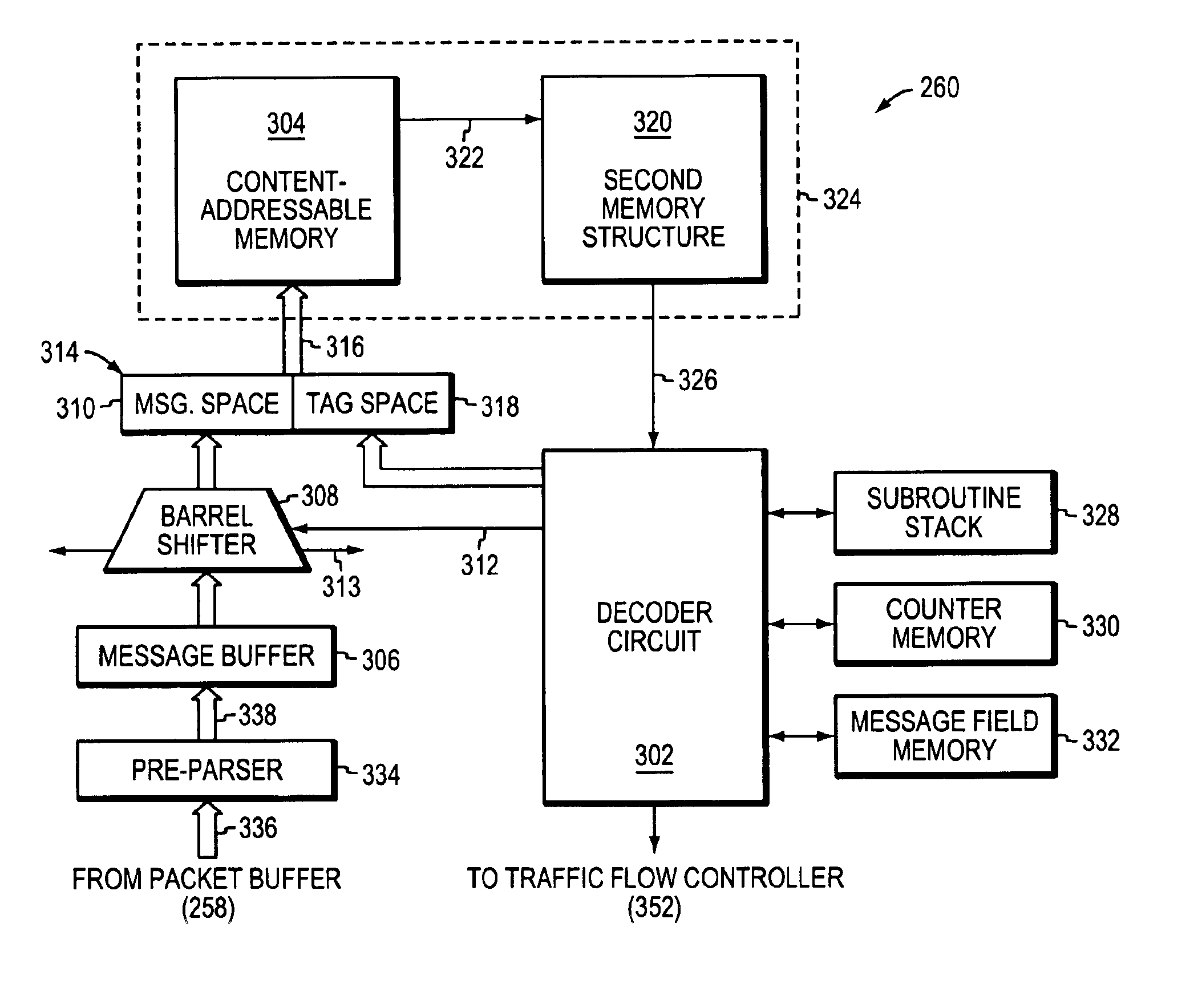
A programmable pattern matching engine efficiently parses the contents of network messages for regular expressions and executes pre-defined actions or treatments on those messages that match the regular expressions. The pattern matching engine is preferably a logic circuit designed to perform its pattern matching and execution functions at high speed, e.g., at multi-gigabit per second rates. It includes, among other things, a message buffer for storing the message being evaluated, a decoder circuit for decoding and executing corresponding actions or treatments, and one or more content-addressable memories (CAMs) that are programmed to store the regular expressions used to search the message. The CAM may be associated with a second memory device, such as a random access memory (RAM), as necessary, that is programmed to contain the respective actions or treatments to be applied to messages matching the corresponding CAM entries. The RAM provides its output to the decoder circuit, which, in response, decodes and executes the specified action or treatment.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
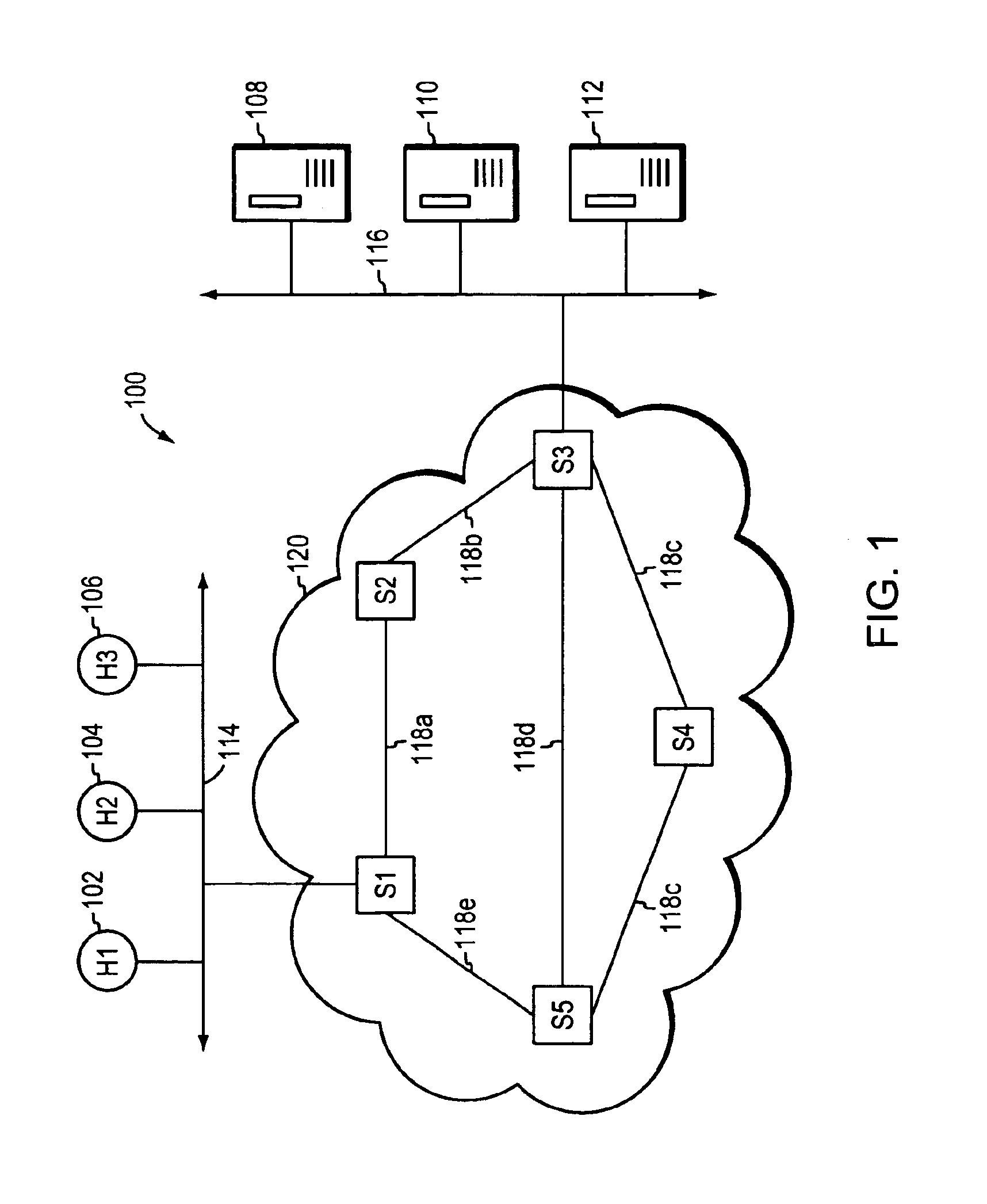
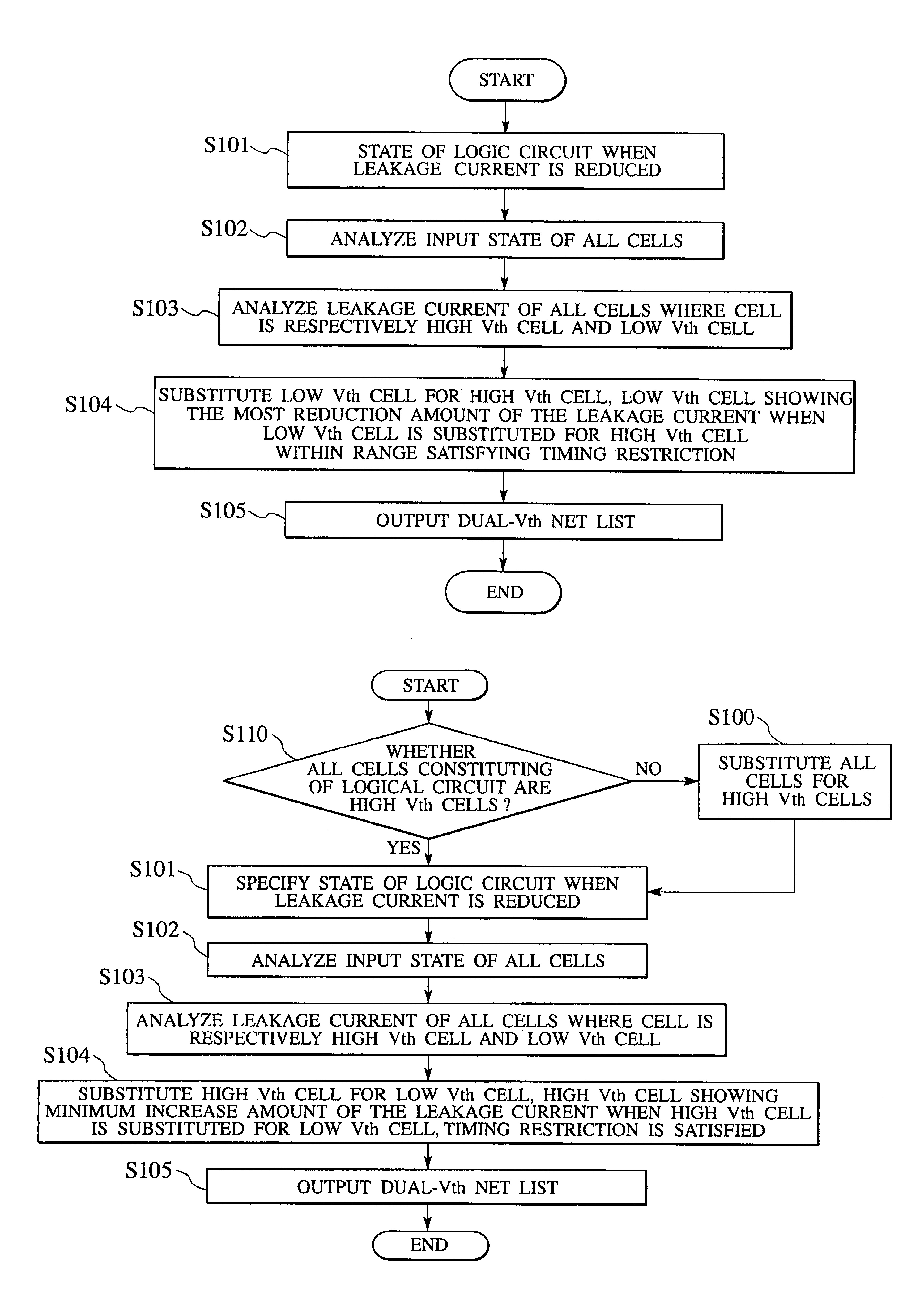
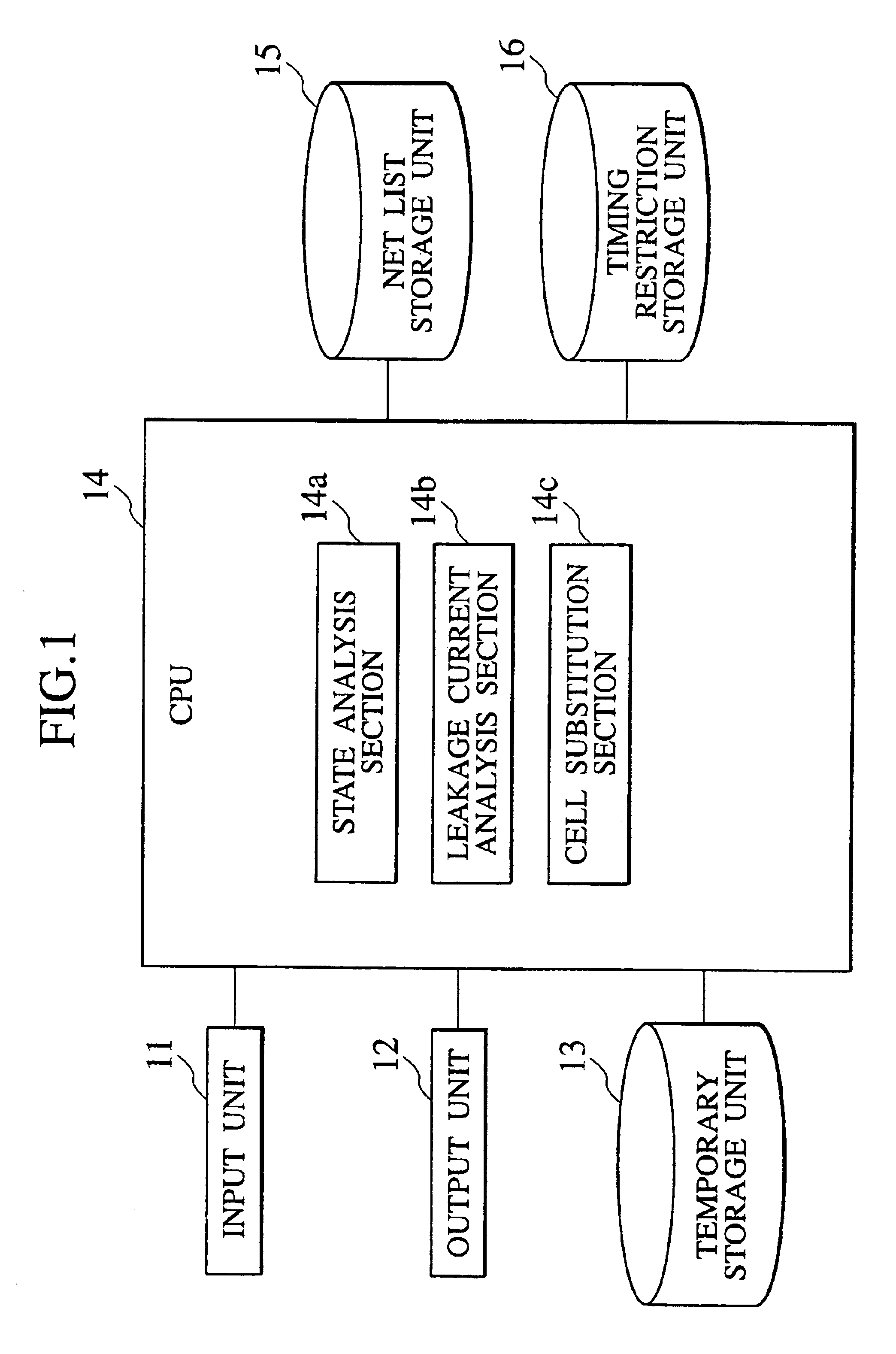
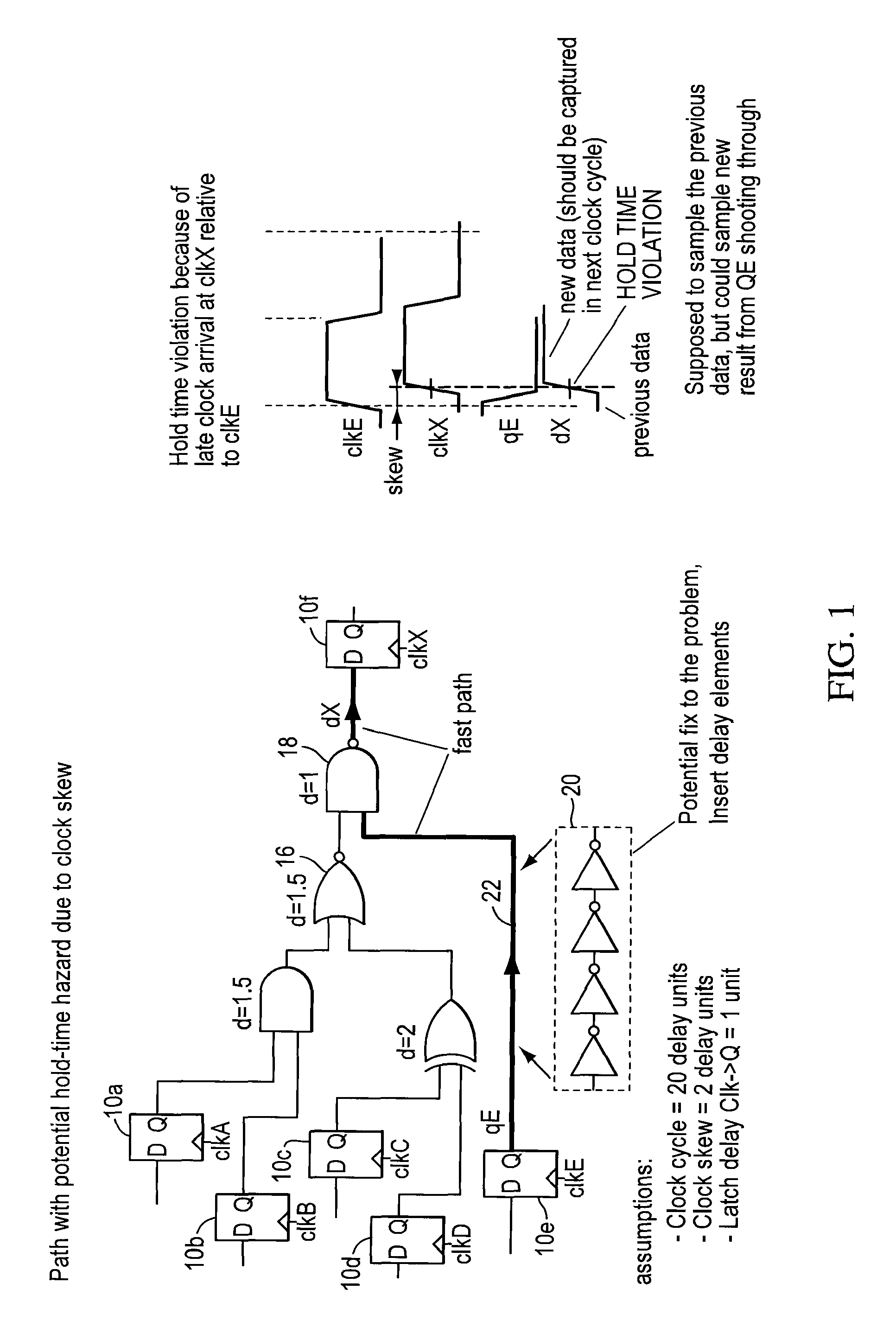
Logic circuit design equipment and method for designing logic circuit for reducing leakage current
A logic circuit design equipment and a logic circuit design method include analyzing input states of all of first cells, respectively, analyzing leakage currents of all of first cells in a case where each first cell is high Vth cell showing a small leakage current at a low speed operation and low Vth cell showing a large leakage current at a high speed operation, respectively, and substituting the first cells for second cells within a range satisfying a timing restriction. Herein, a threshold of the second cell is different from a threshold of the first cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
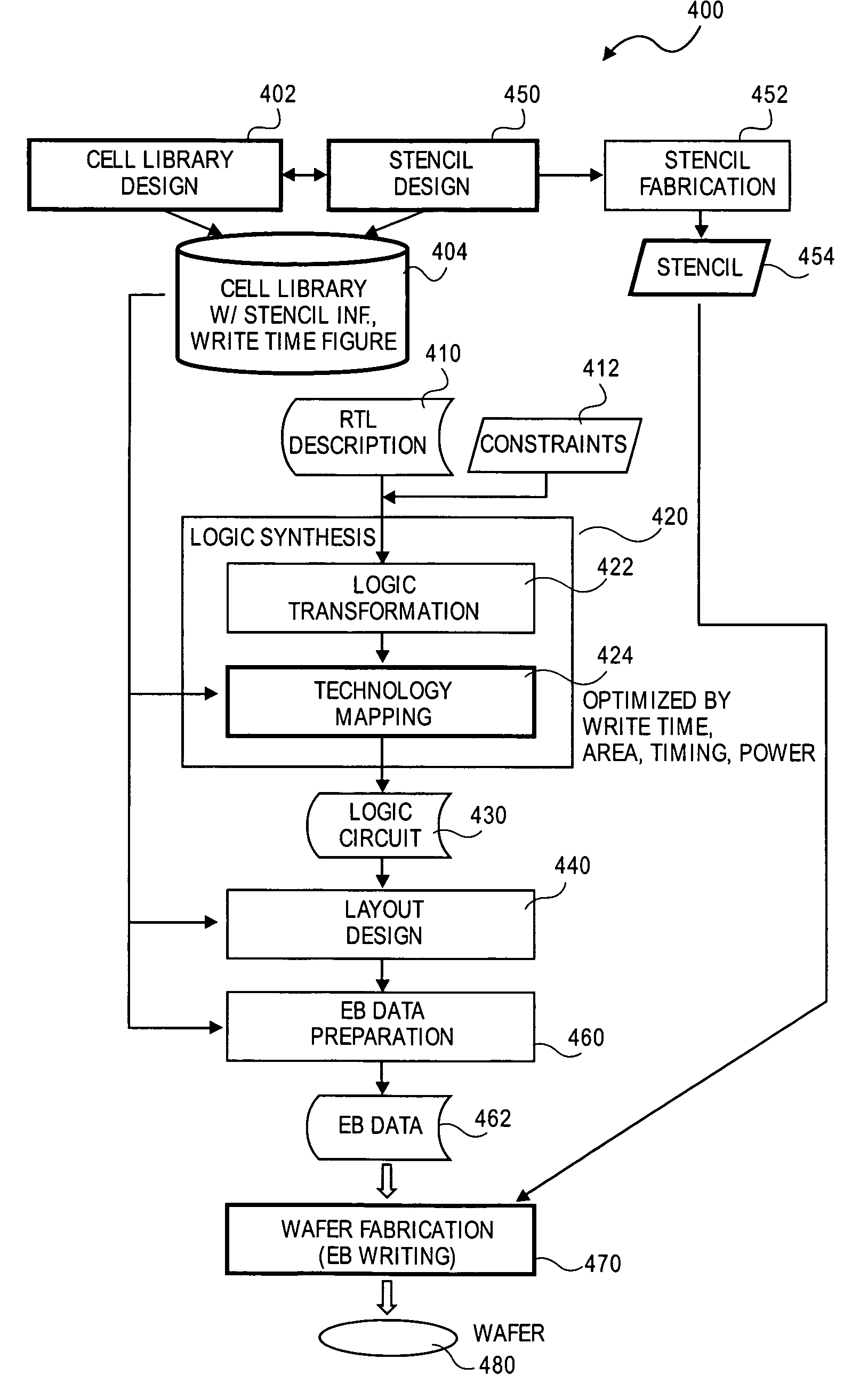
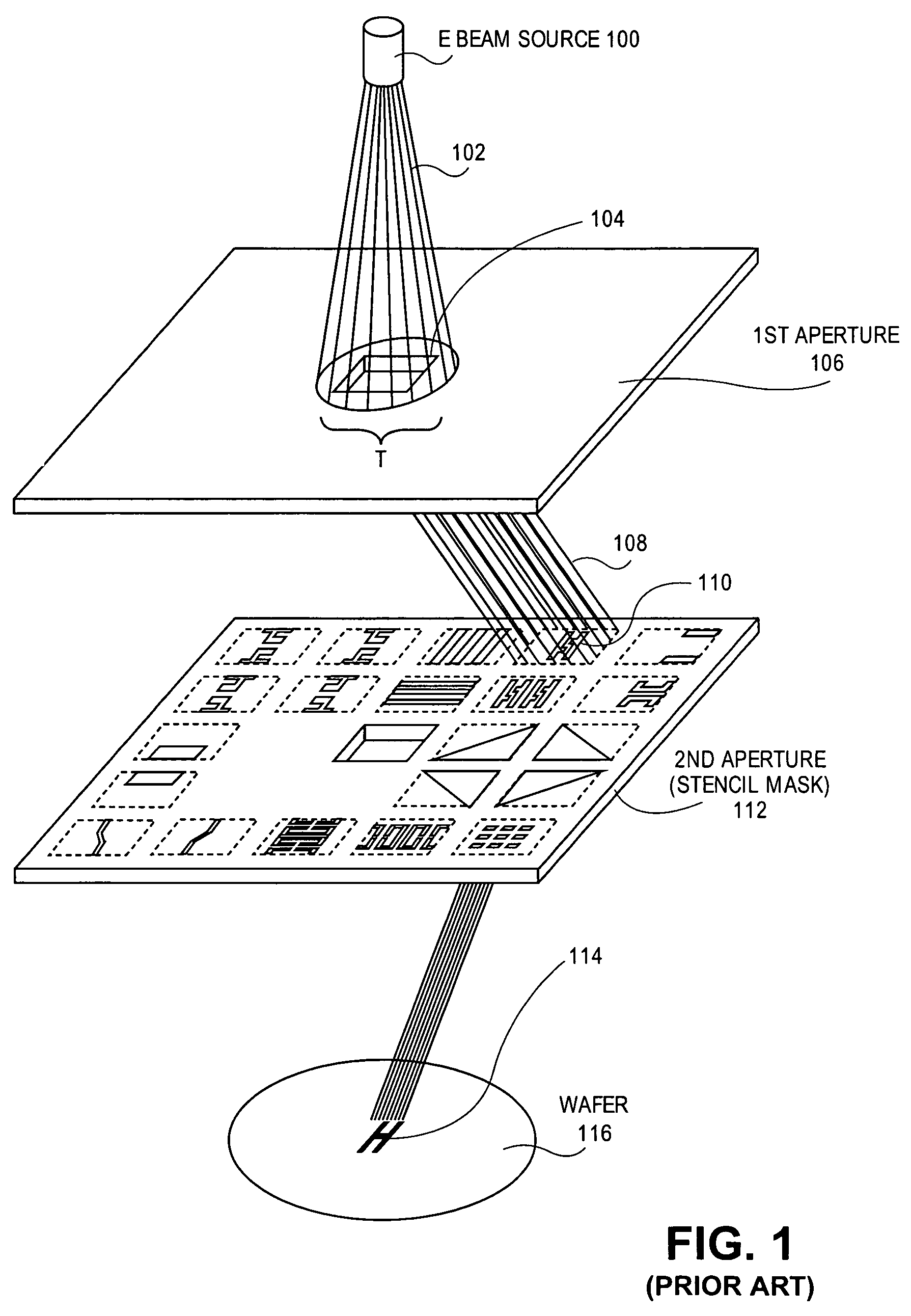
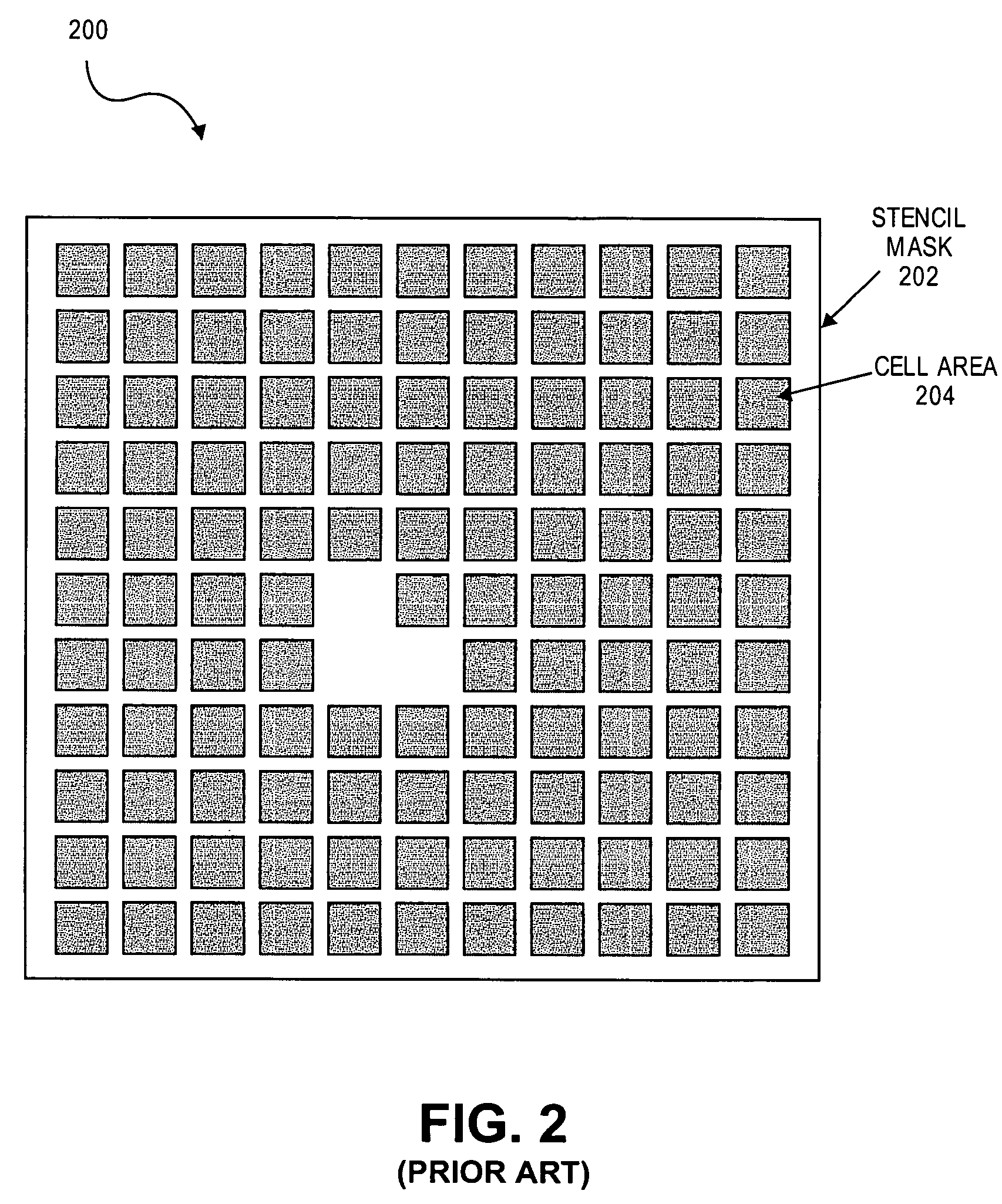
Method and system for logic design for cell projection particle beam lithography
InactiveUS20080128637A1Short EB writing timeShorten write timeElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsCell patternLithographic artist
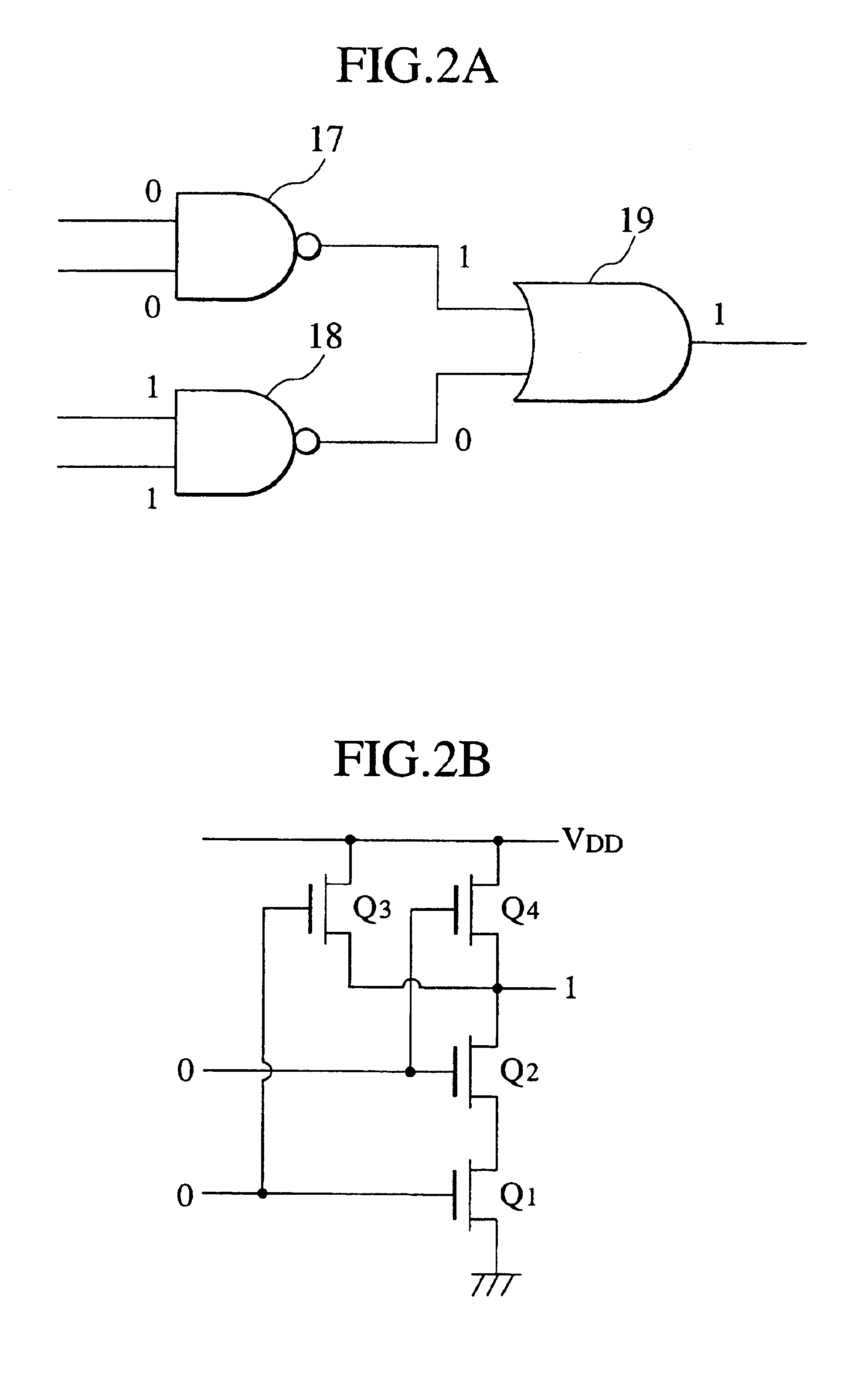
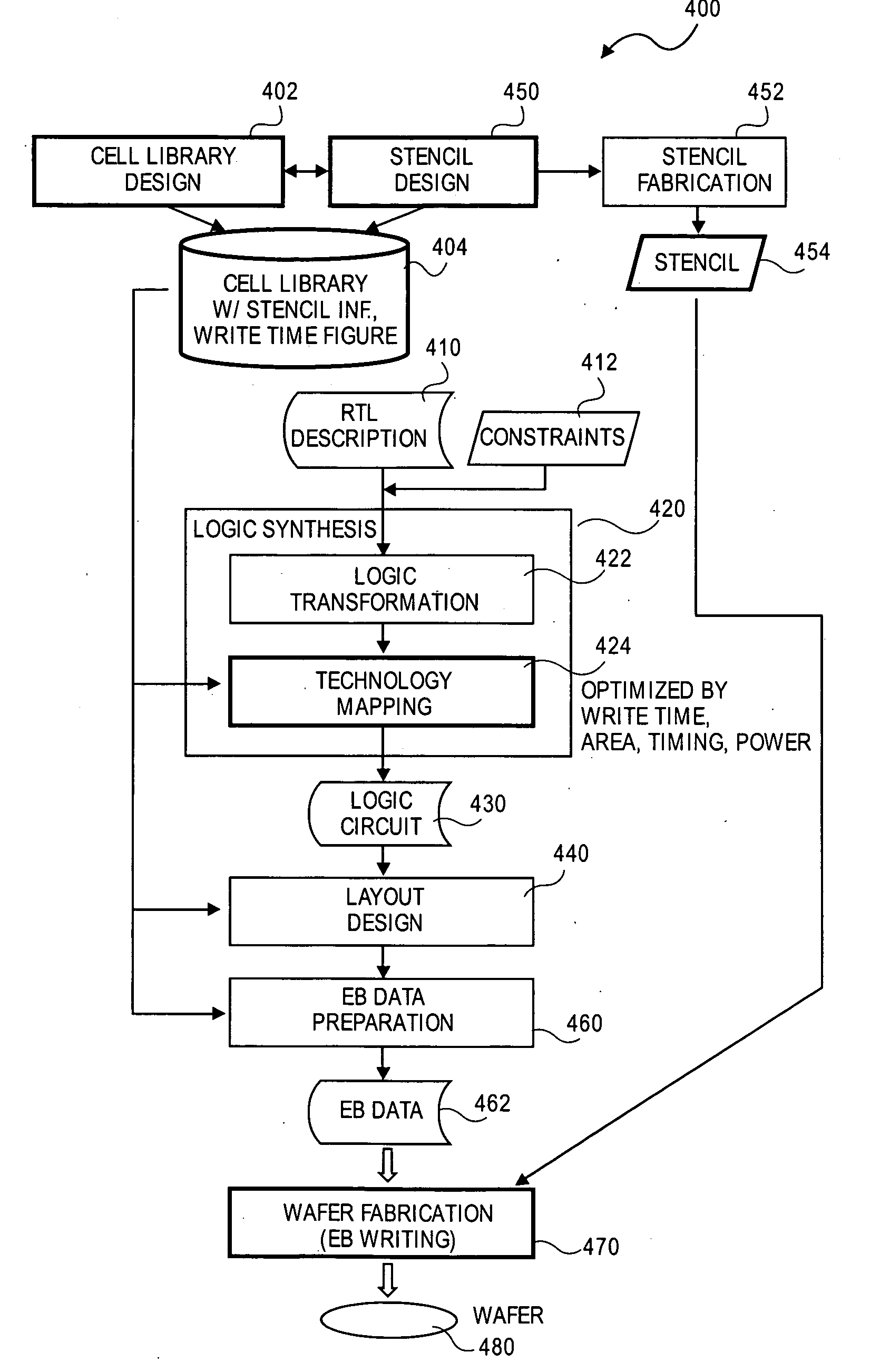
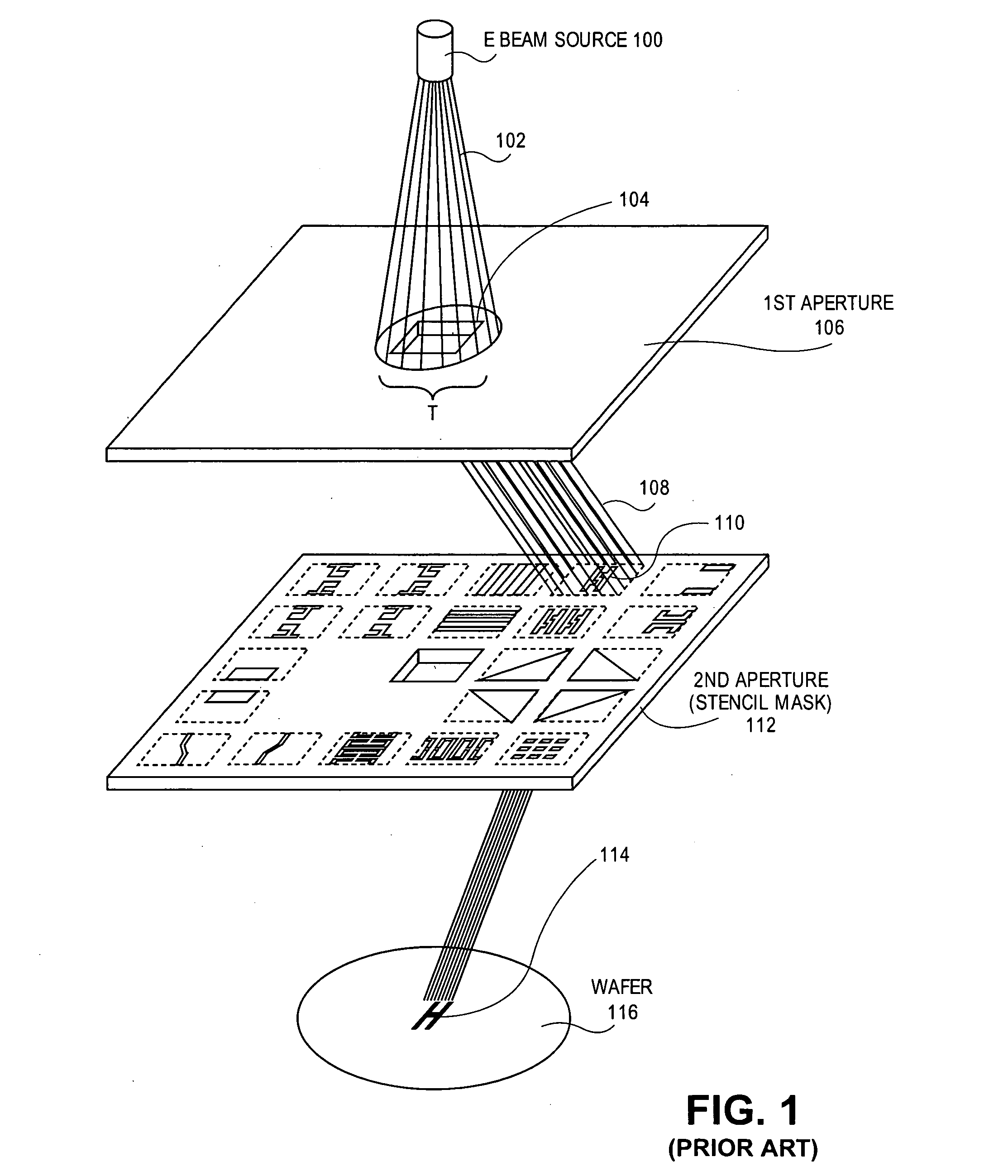
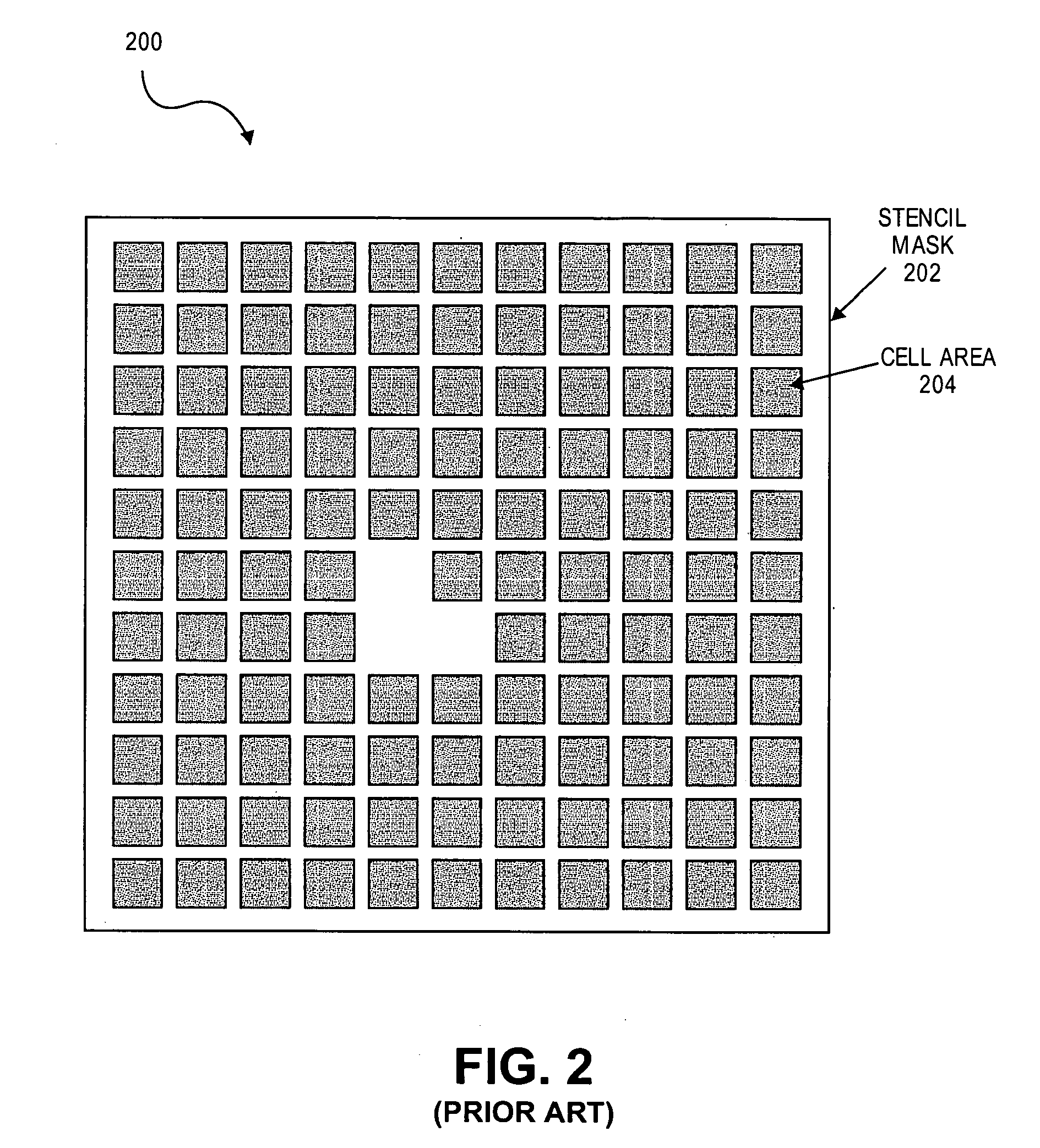
A method for particle beam lithography, such as electron beam (EB) lithography, includes predefining a stencil design having a plurality of cell patterns with information from a cell library, fabricating the stencil design, synthesizing a functional description into a logic circuit design after predefining the stencil design so that one or more characteristics of the stencil design are considered during synthesizing of the functional description into the logic circuit design, optimizing the logic circuit design, generating a layout design from the optimized logic circuit design, and forming the logic circuit on a substrate according to the stencil design and the layout design.
Owner:D2S
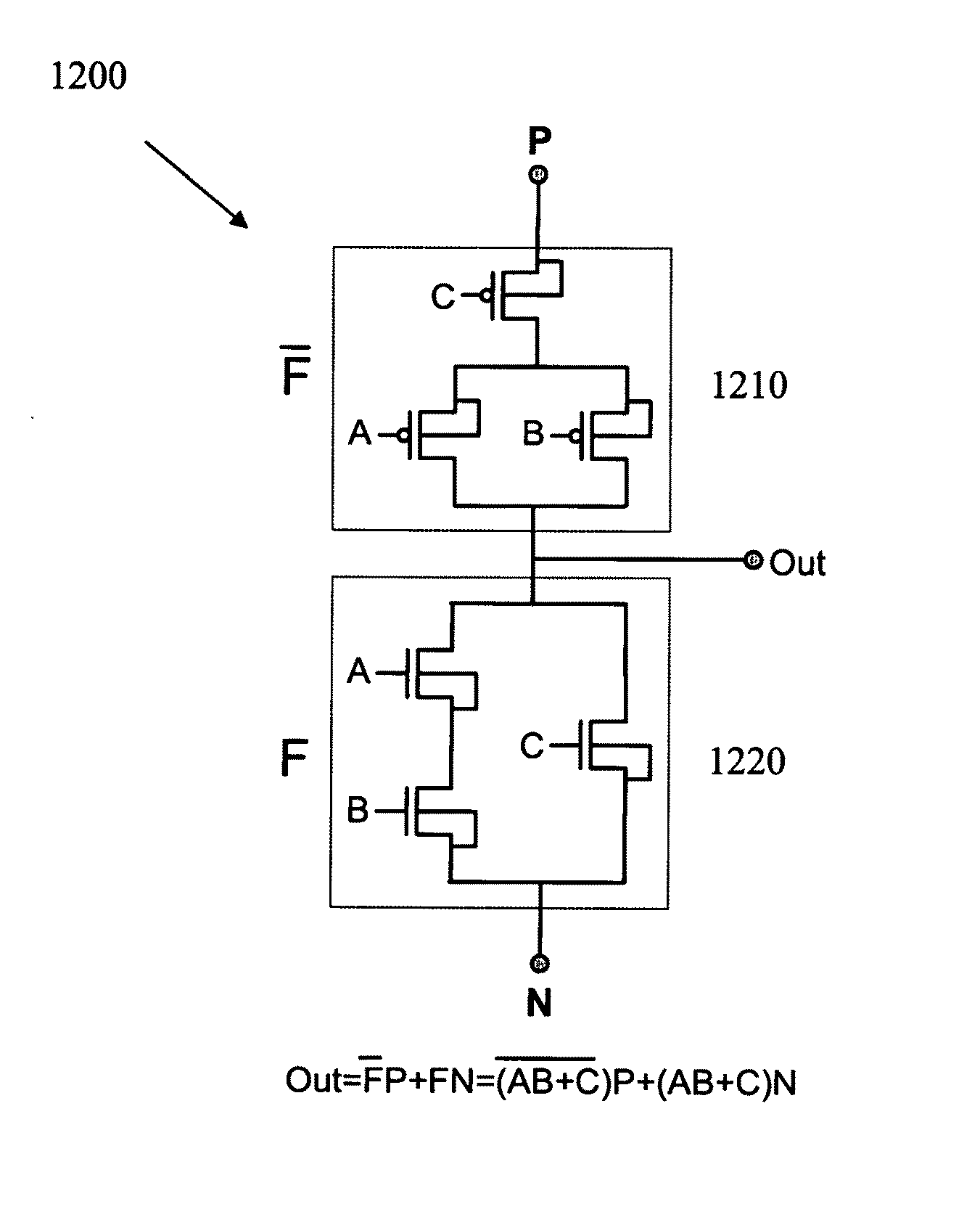
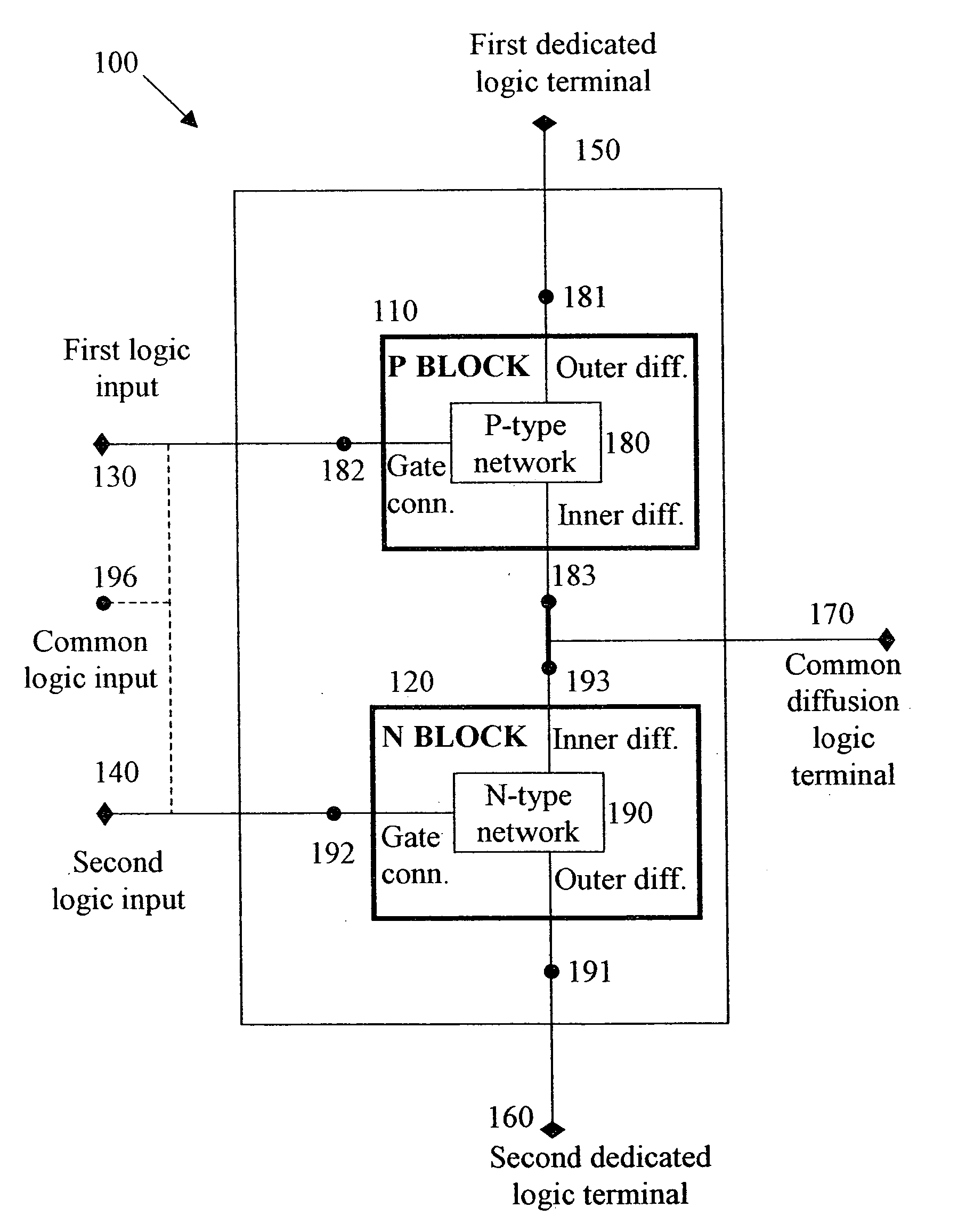
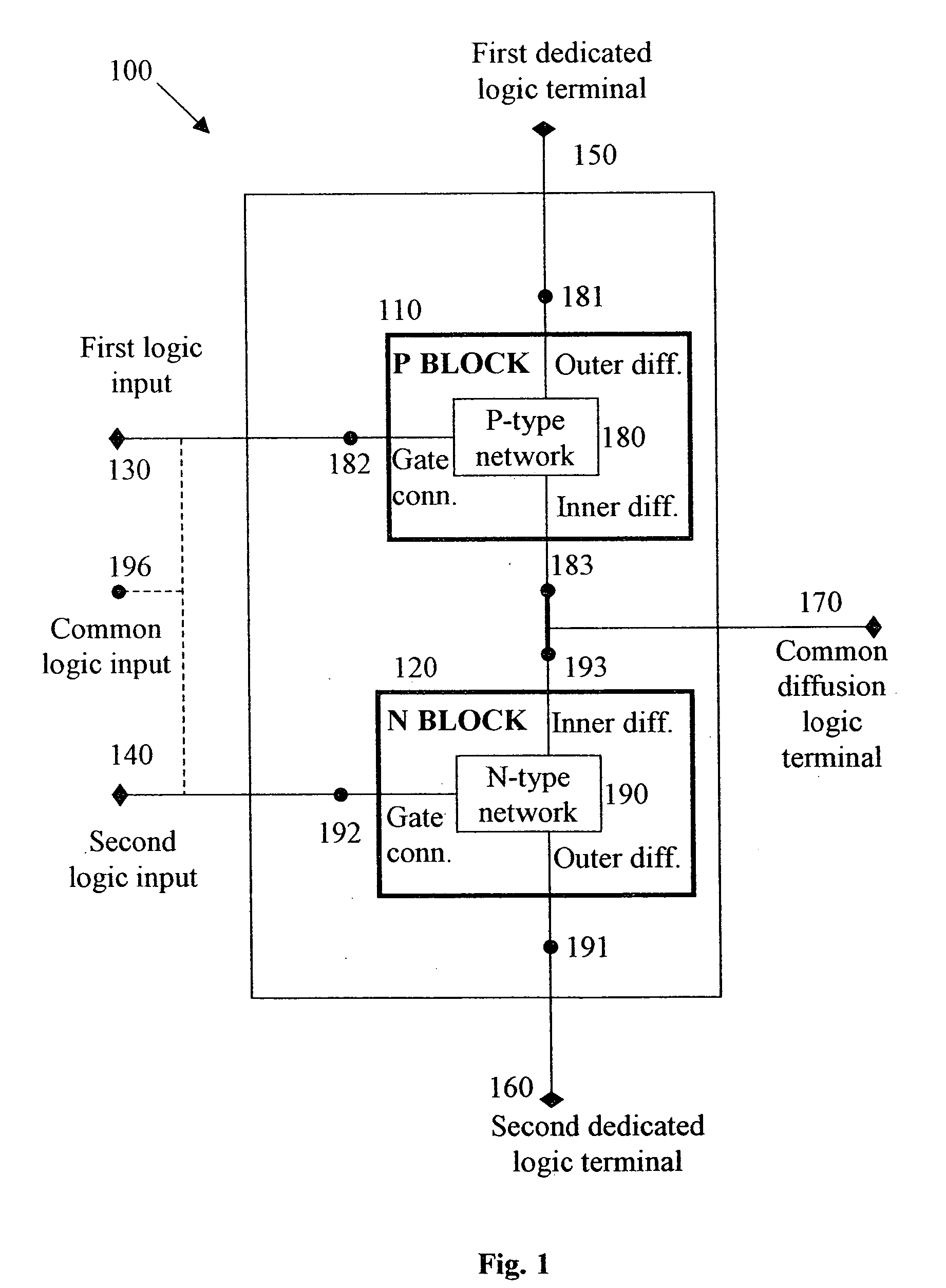
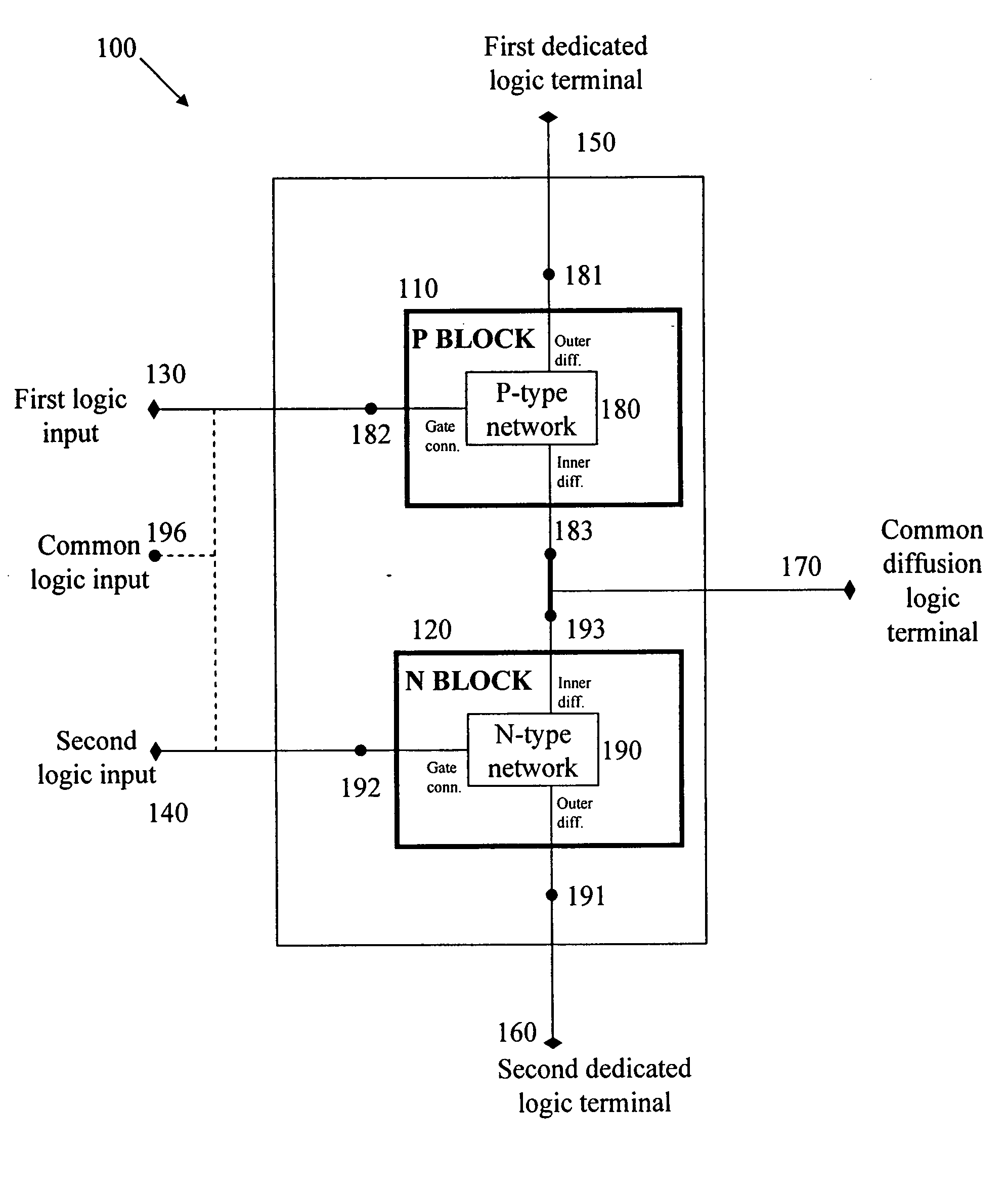
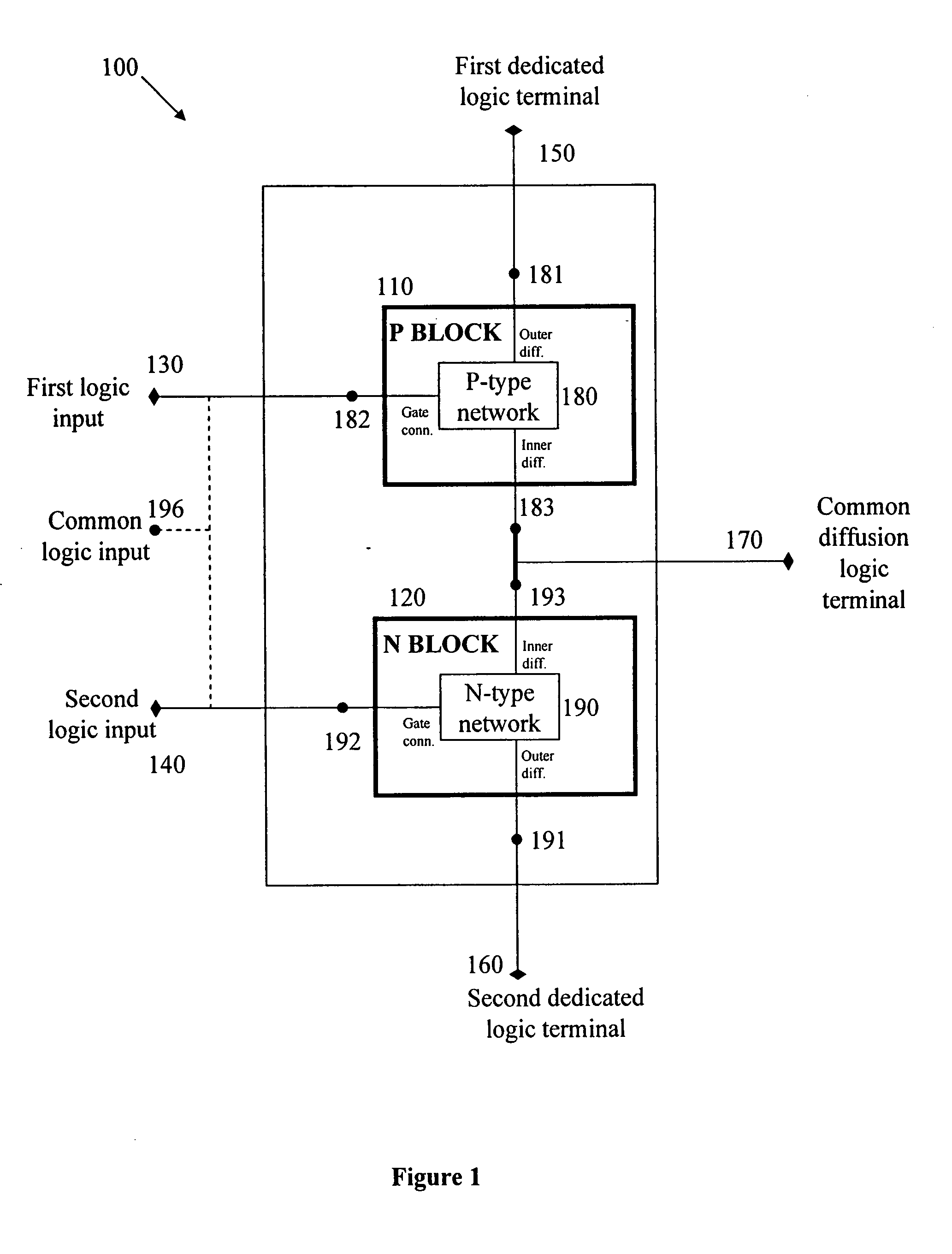
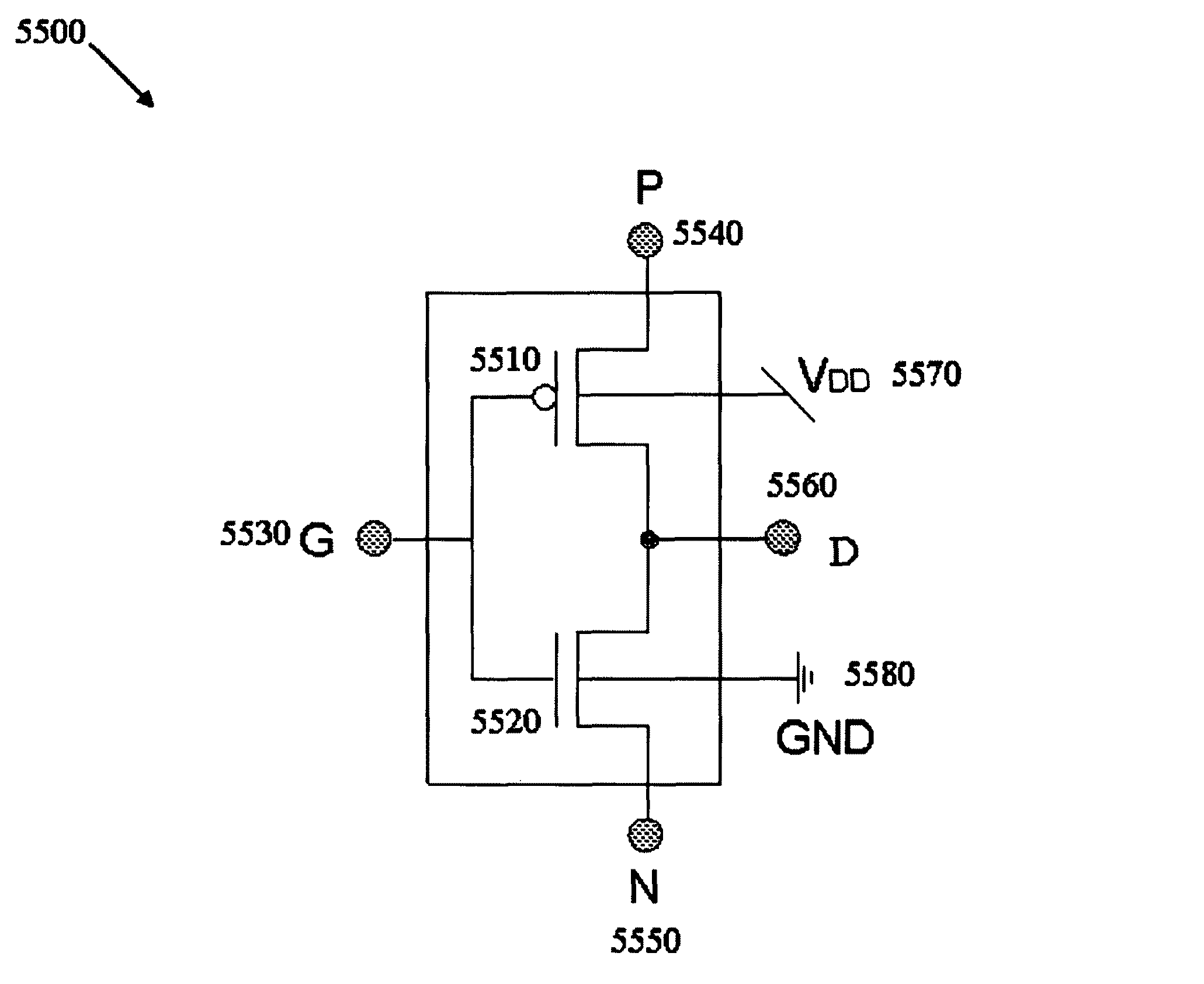
Logic Circuit and Method of Logic Circuit Design
InactiveUS20100231263A1Fast and versatileReduce areaLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringLogic circuit design
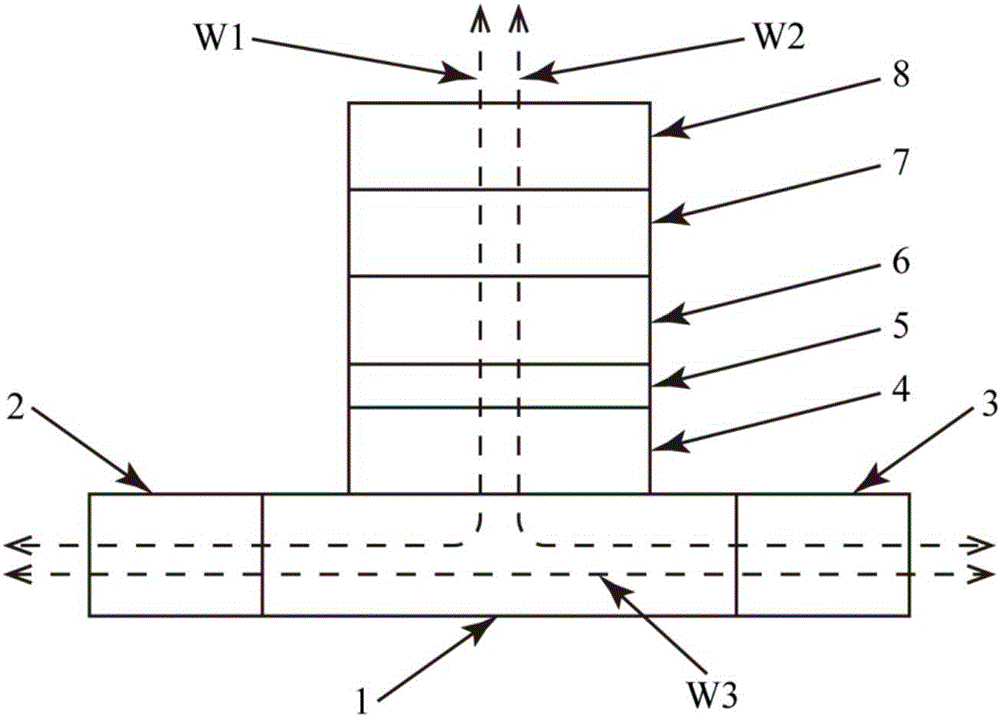
A complementary logic circuit contains a first logic input, a second logic input, a first dedicated logic terminal, a second dedicated logic terminal, a high-voltage terminal configured for connection to a high constant voltage a low-voltage terminal configured for connection to a low constant voltage, a p-type transistor, and an n-type transistor. The p-type transistor has an outer diffusion connection, a gate connection, an inner diffusion connection, and a bulk connection. The n-type transistor has an outer diffusion connection, a gate connection, an inner diffusion connection, and a bulk connection. The first dedicated logic terminal is connected to the outer diffusion connection of the p-type transistor, the second dedicated logic terminal is connected to the outer diffusion connection of the n-type transistor, the inner diffusion connection of the p-type transistor and the inner diffusion connection of the n-type transistor is connected to form a common diffusion logic terminal, the high-voltage terminal is connected to the bulk connection of the p-type transistor, and the low-voltage terminal is connected to the bulk connection of the n-type transistor.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
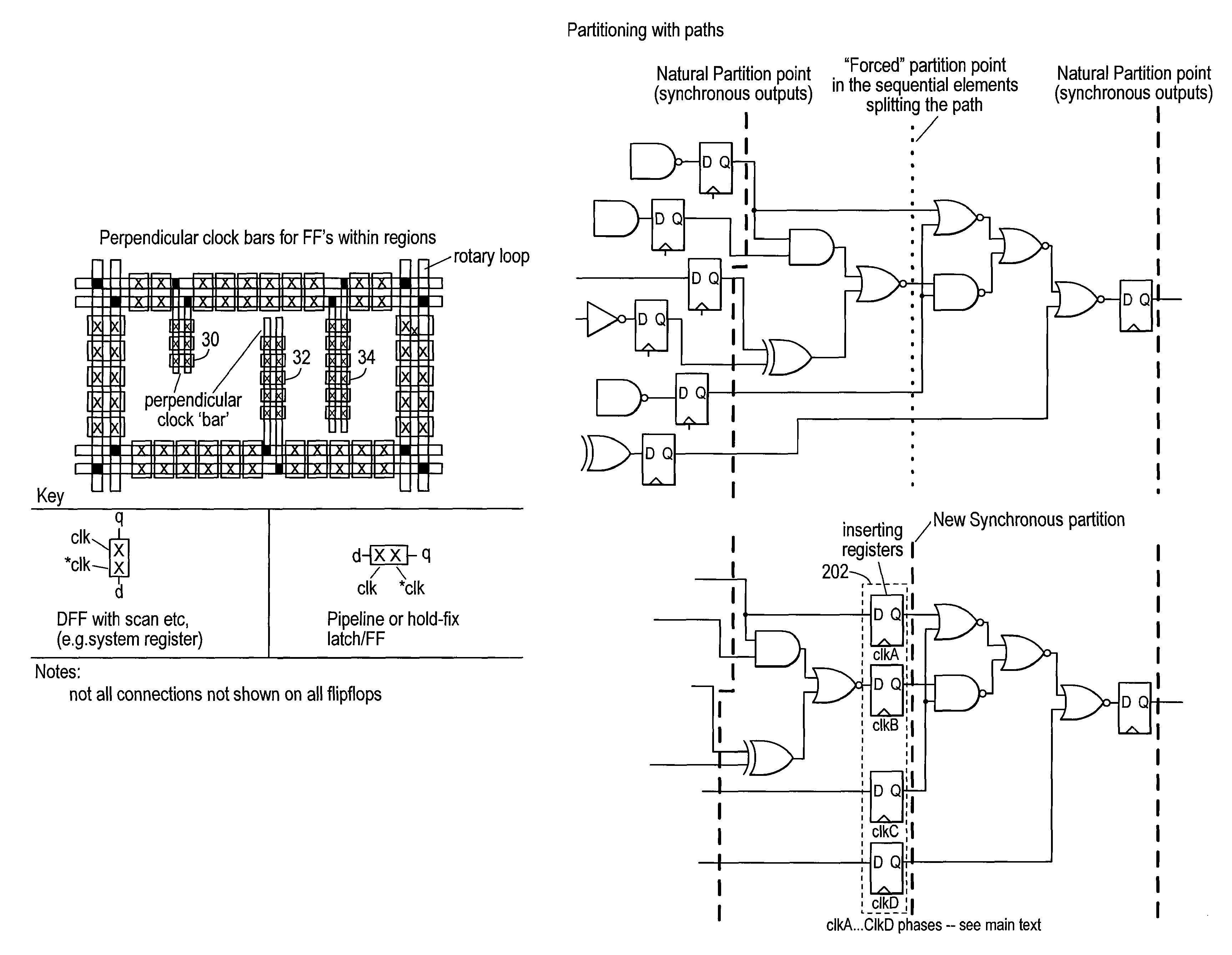
Rotary clock synchronous fabric
Methods for generating a design for logic circuitry using rotary traveling wave oscillators (RTWOs) are described. A plurality of RTWOs are is arranged into an array of rows and columns. Adjacent elements in the array are interconnected so that the clocks in adjacent element are phase synchronous. Clocked devices are placed along the signal path of each array element and each is connected to one of the multiple phases provided by the RTWO element. The logic circuitry, described by a netlist, is divided into a number of partitions and each of these partitions is mapped to one of the array elements. The logic circuitry of the partition is then placed within or about the element of the array to which the partition is mapped and the circuitry in the partition is connected between the clocked devices in the element of the array, according to the net list.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
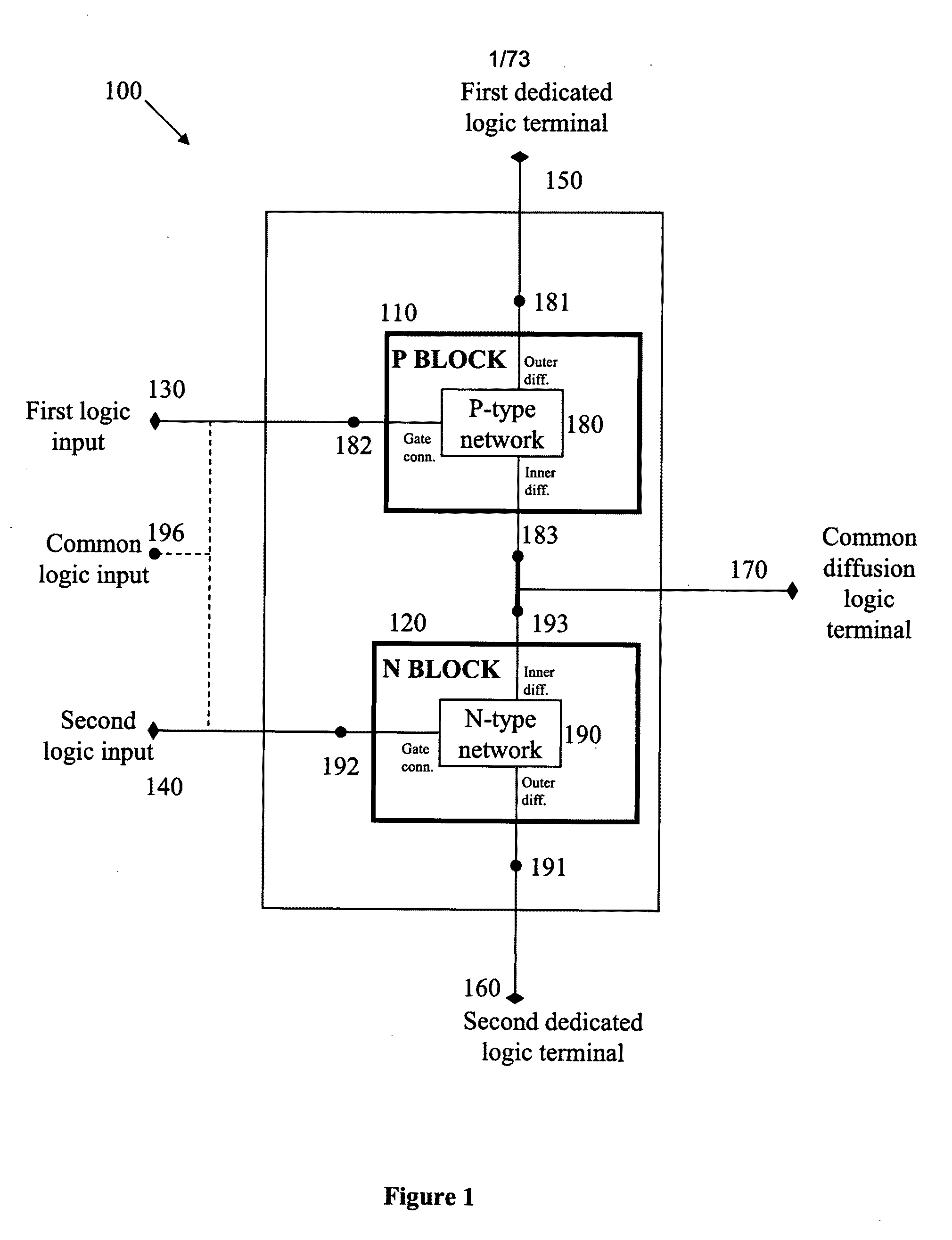
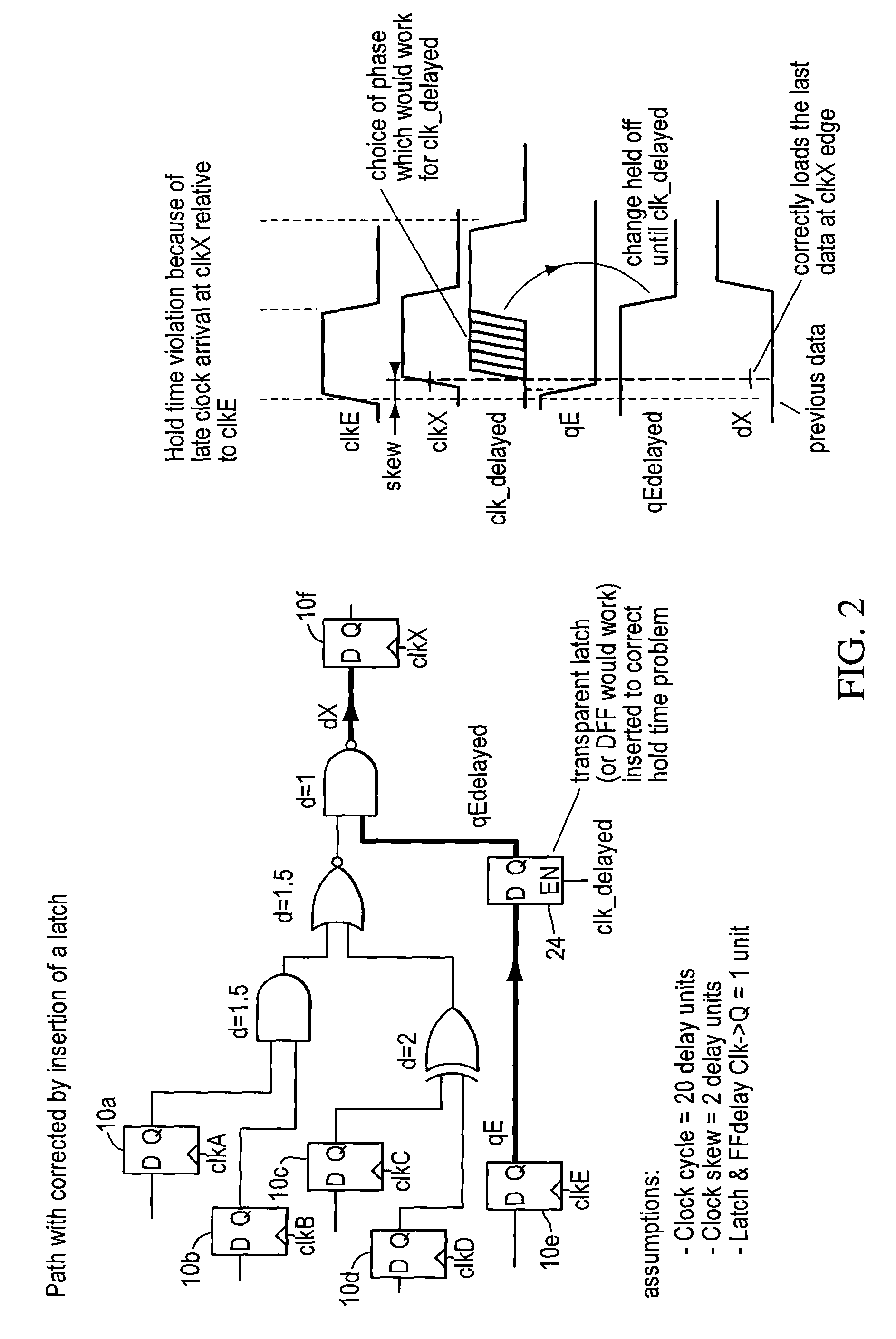
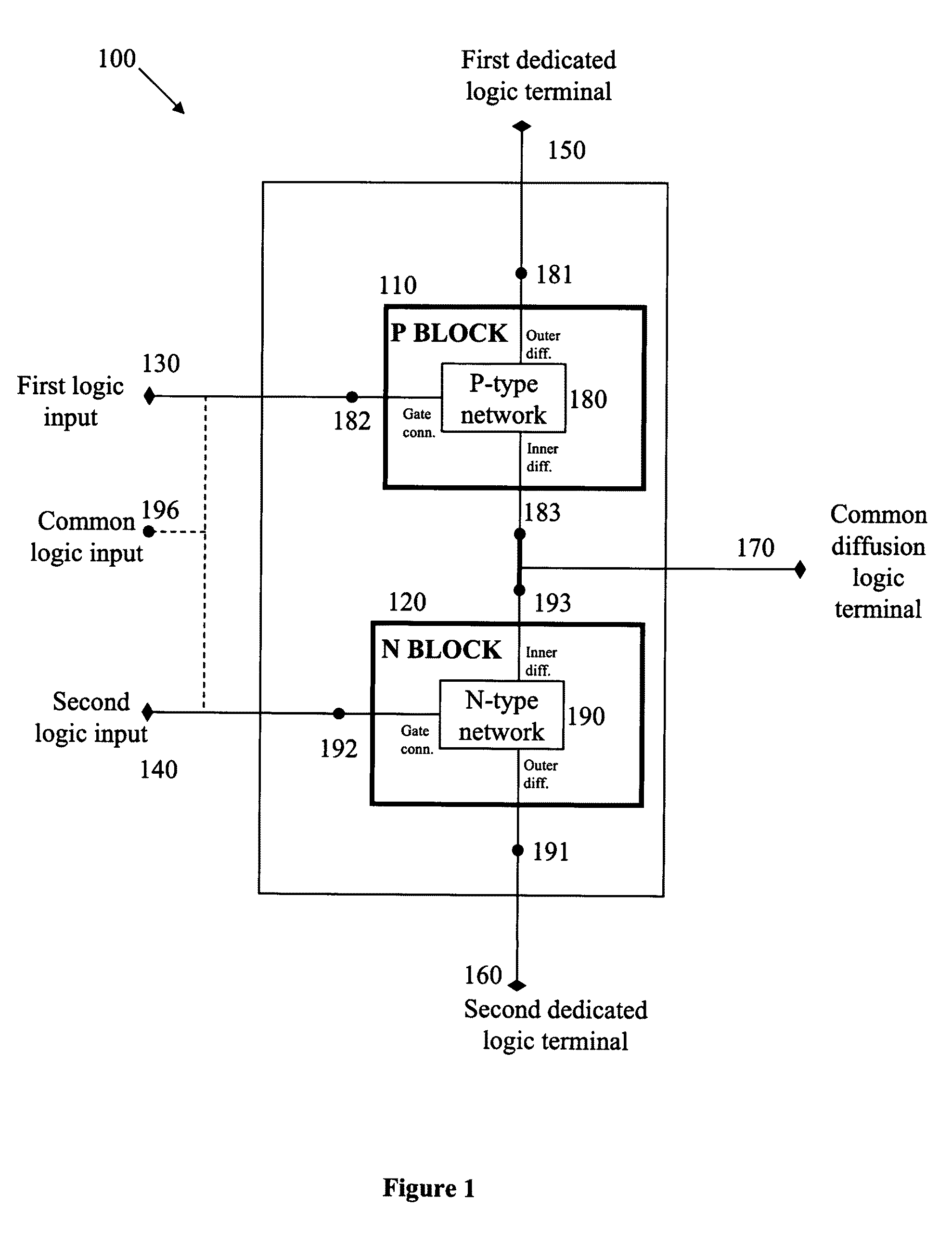
Logic circuit and method of logic circuit design
ActiveUS20040130349A1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionComputer aided designTelecommunicationsLogic circuit design
A complementary logic circuit contains a first logic input, a second logic input, a first dedicated logic terminal, a second dedicated logic terminal, a first logic block, and a second logic block. The first logic block consists of a network of p-type transistors for implementing a predetermined logic function. The p-type transistor network has an outer diffusion connection, a first network gate connection, and an inner diffusion connection. The outer diffusion connection of the p-type transistor network is connected to the first dedicated logic terminal, and the first network gate connection of the p-type transistor network is connected to the first logic input. The second logic block consists of a network of n-type transistors which implements a logic function complementary to the logic function implemented by the first logic block. The n-type transistor network has an outer diffusion connection, a first network gate connection, and an inner diffusion connection. The outer diffusion connection of the n-type transistor network is connected to the second dedicated logic terminal, and the first network gate connection of the n-type transistor network is connected to the second logic input. The inner diffusion connections of the p-type network and of the n-type network are connected together to form a common diffusion logic terminal.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
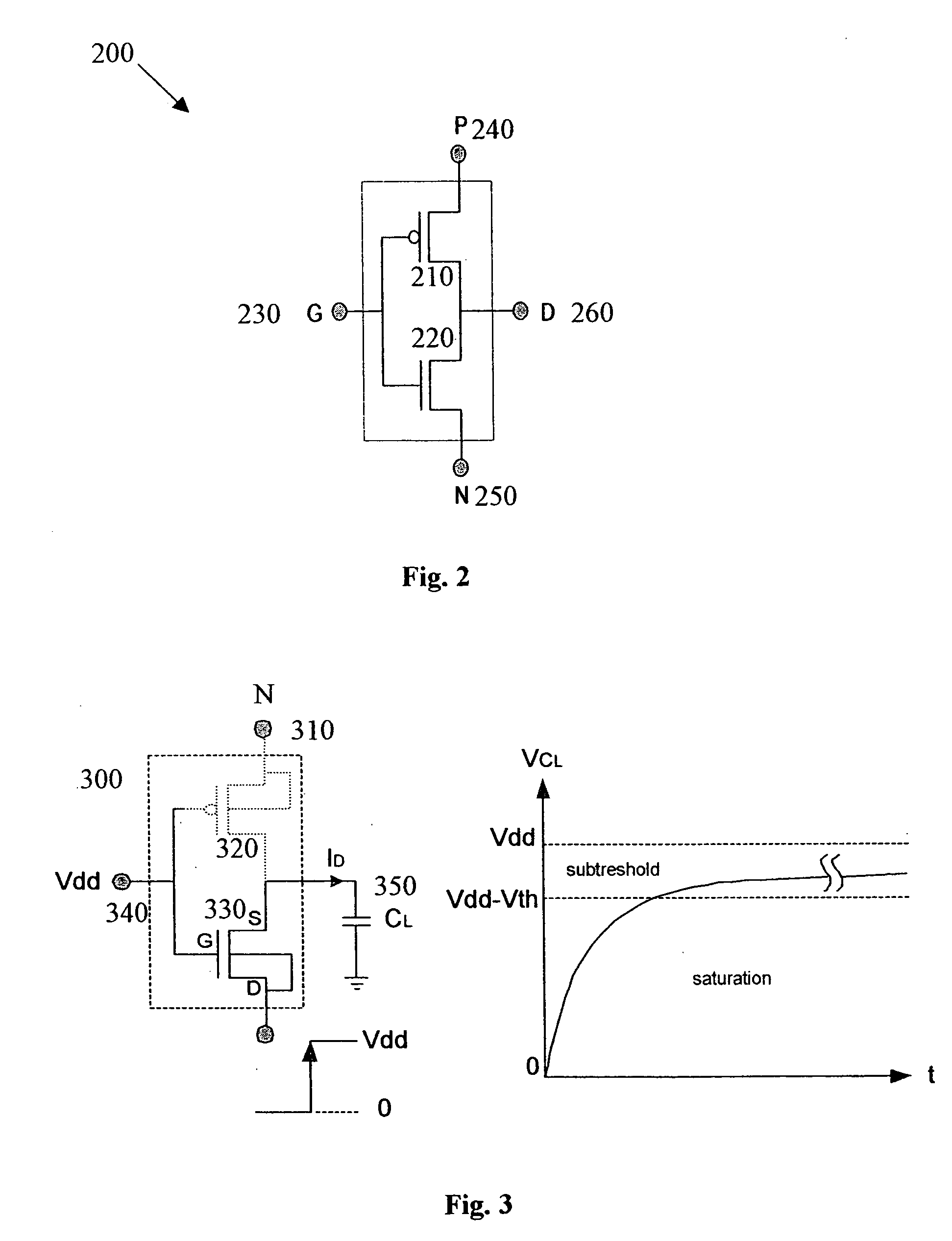
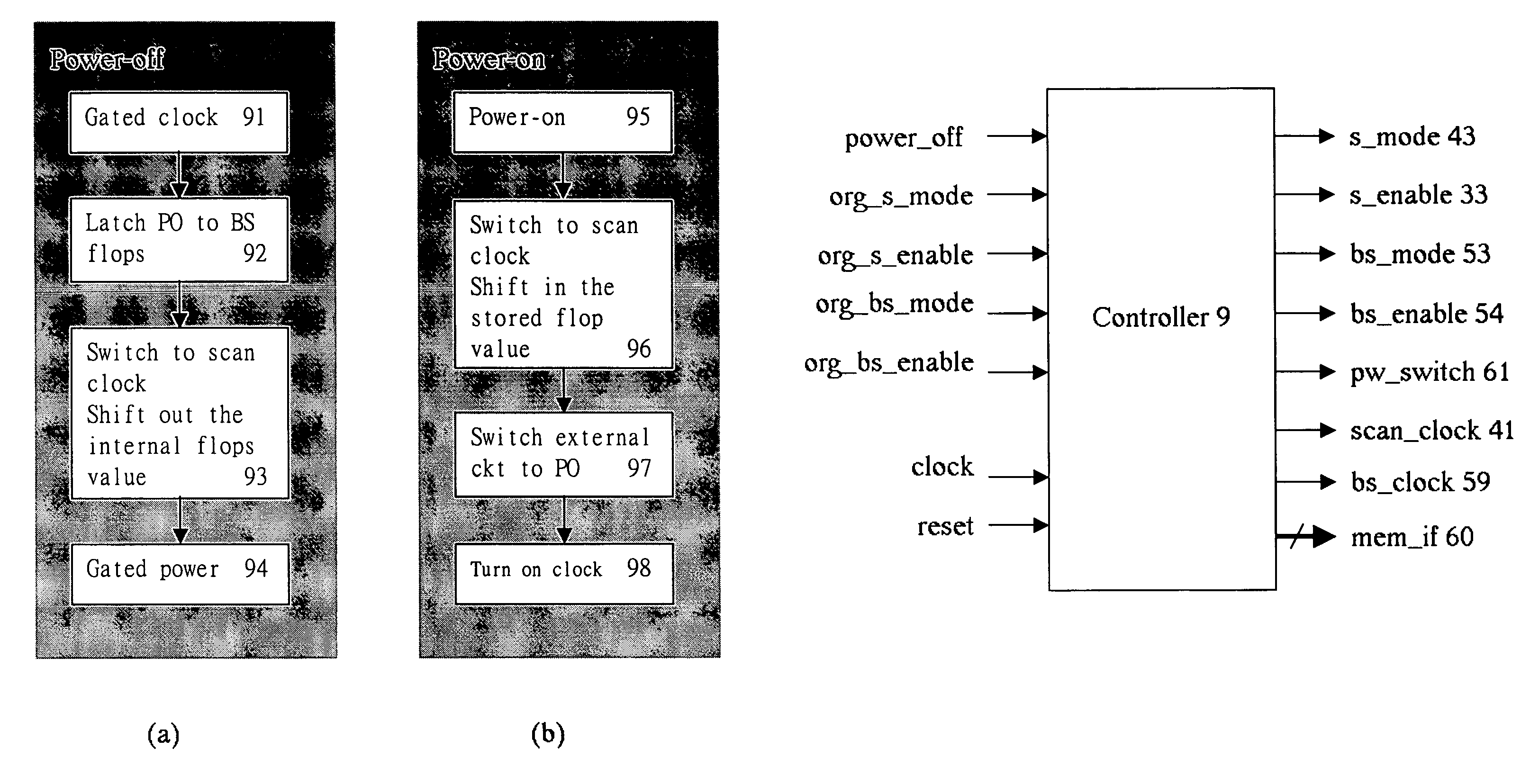
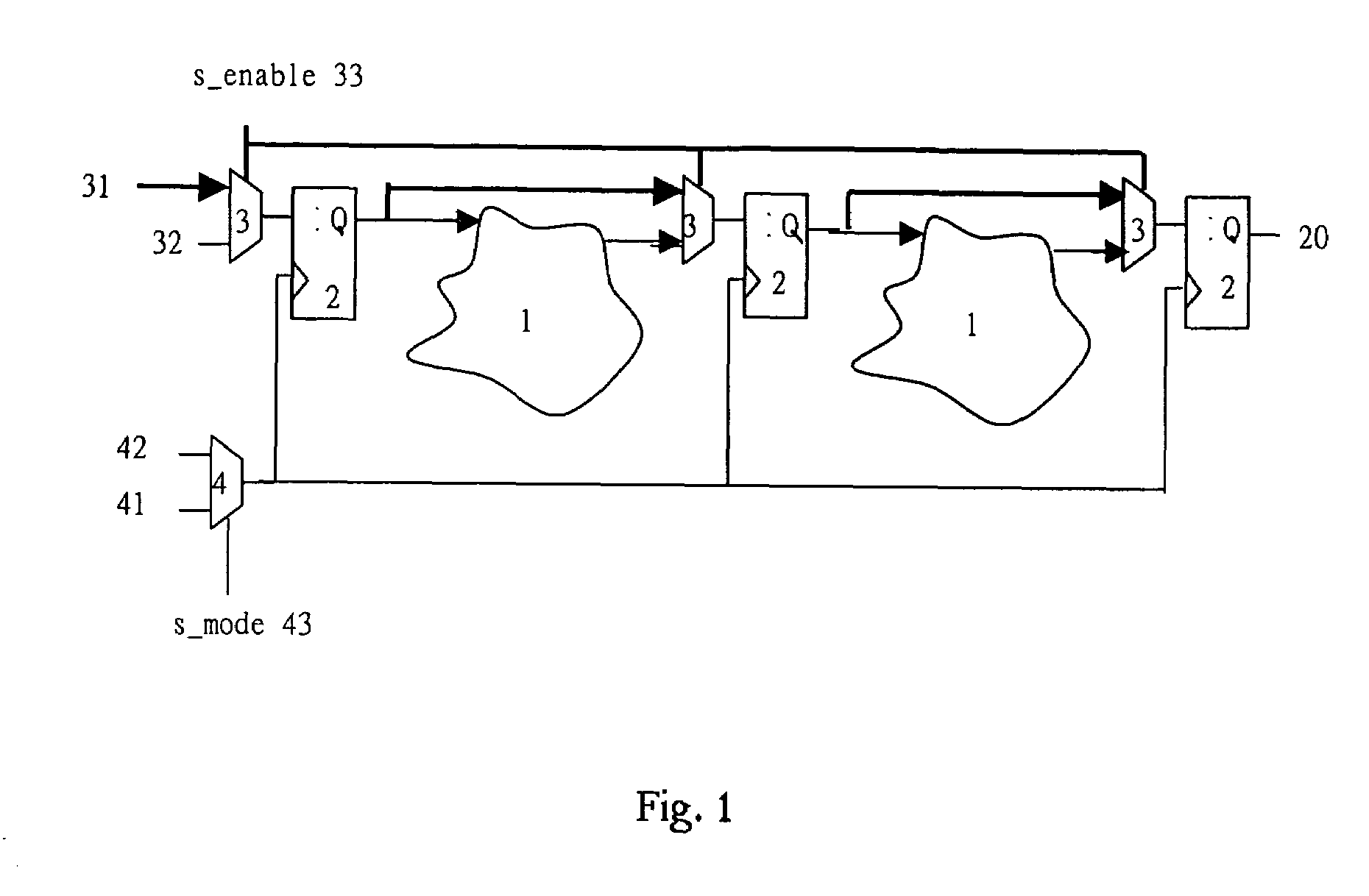
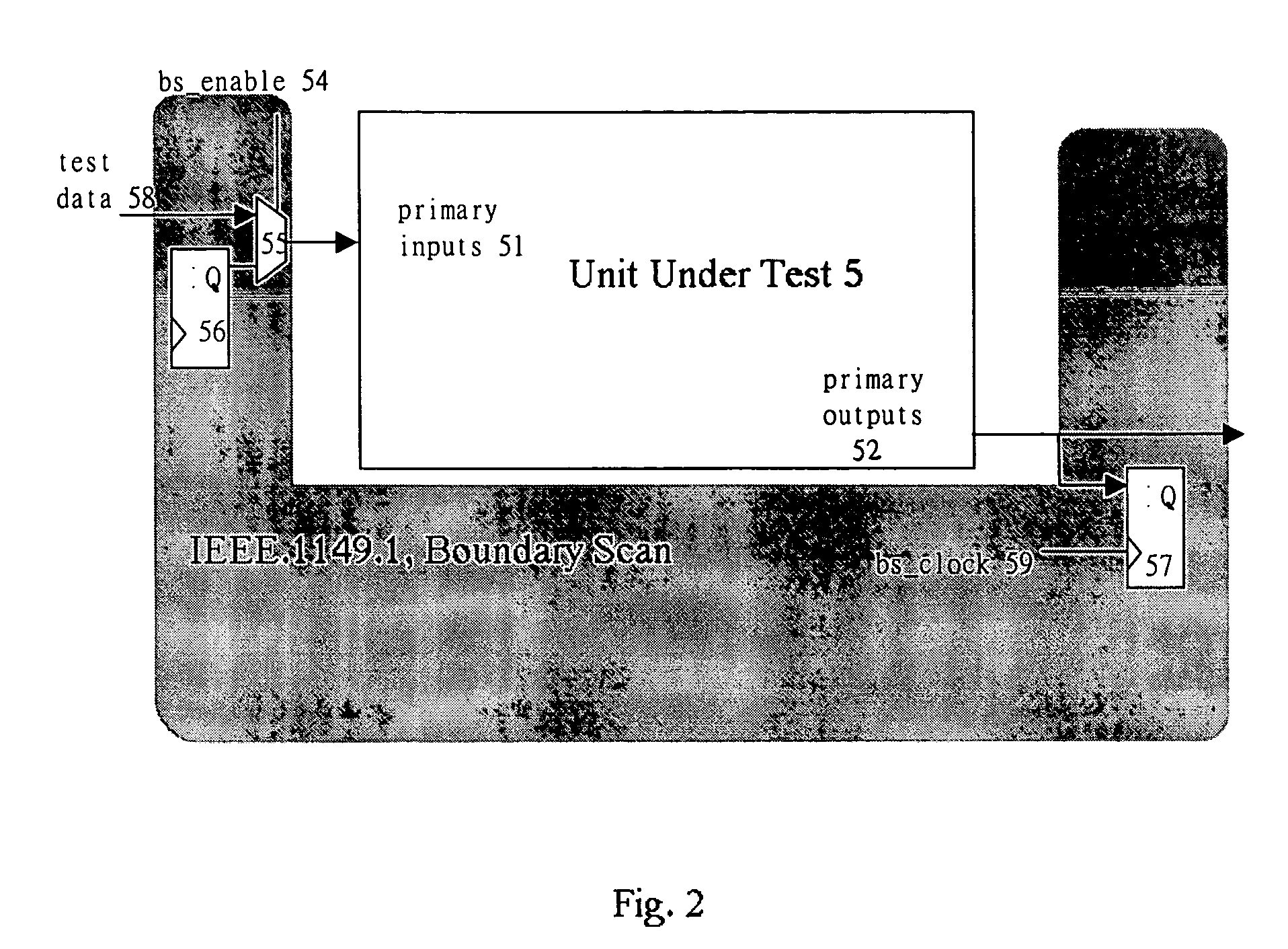
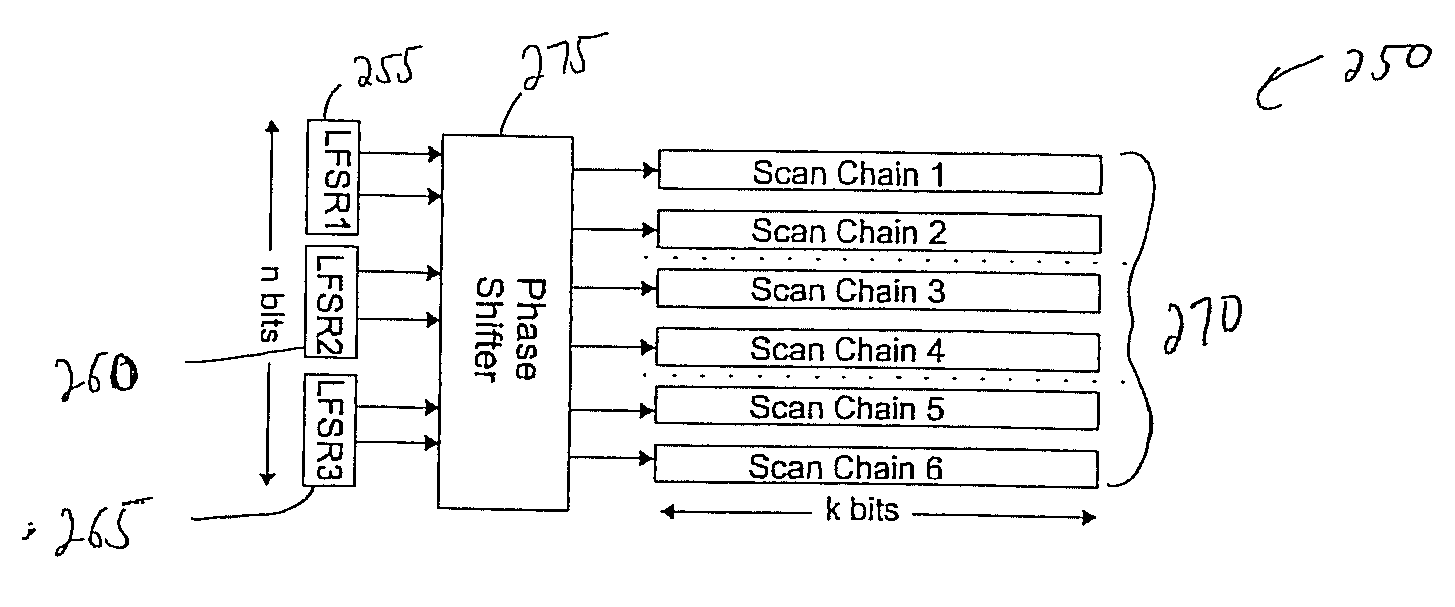
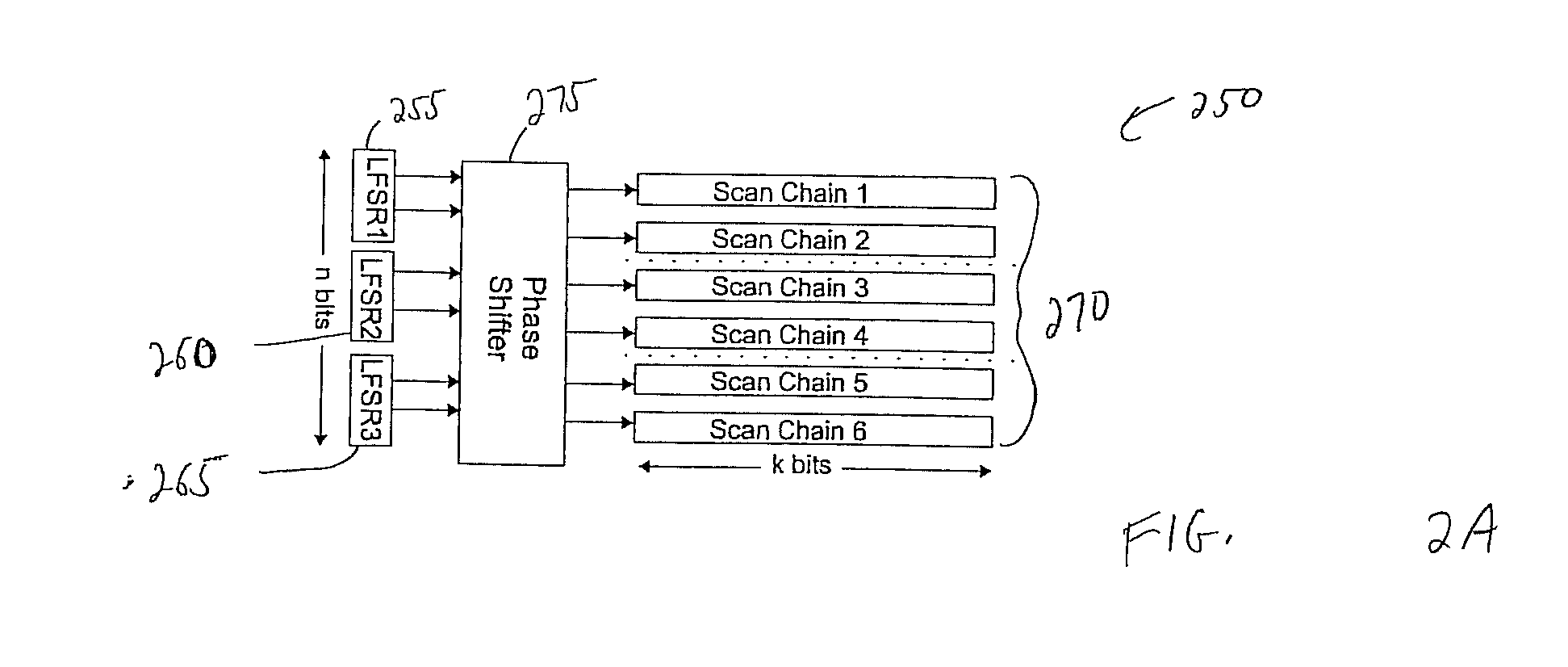
Method of using scan chains and boundary scan for power saving
InactiveUS7392447B2Reduce hardware overheadSave powerEnergy efficient ICTElectronic circuit testingInternal memoryExternal storage
Owner:PRINCETON TECH CORP
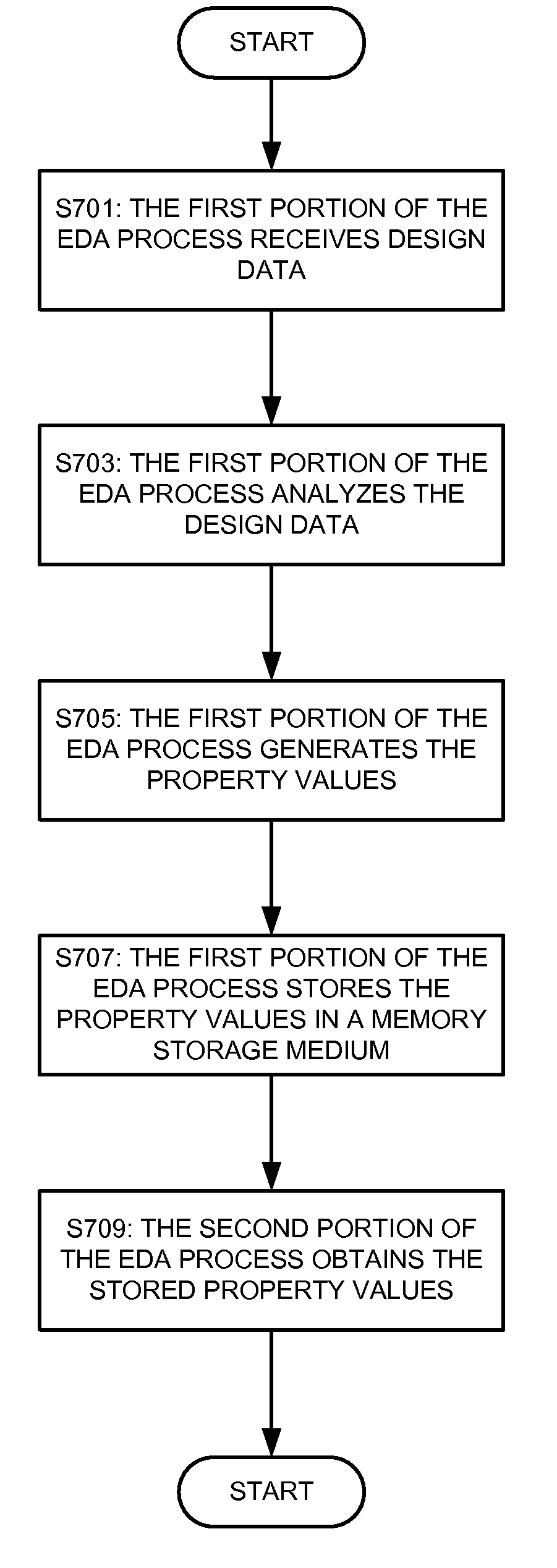
Properties In Electronic Design Automation
InactiveUS20080115096A1Easily calculateComputer aided designTotal factory controlComputer architectureLogic circuit design
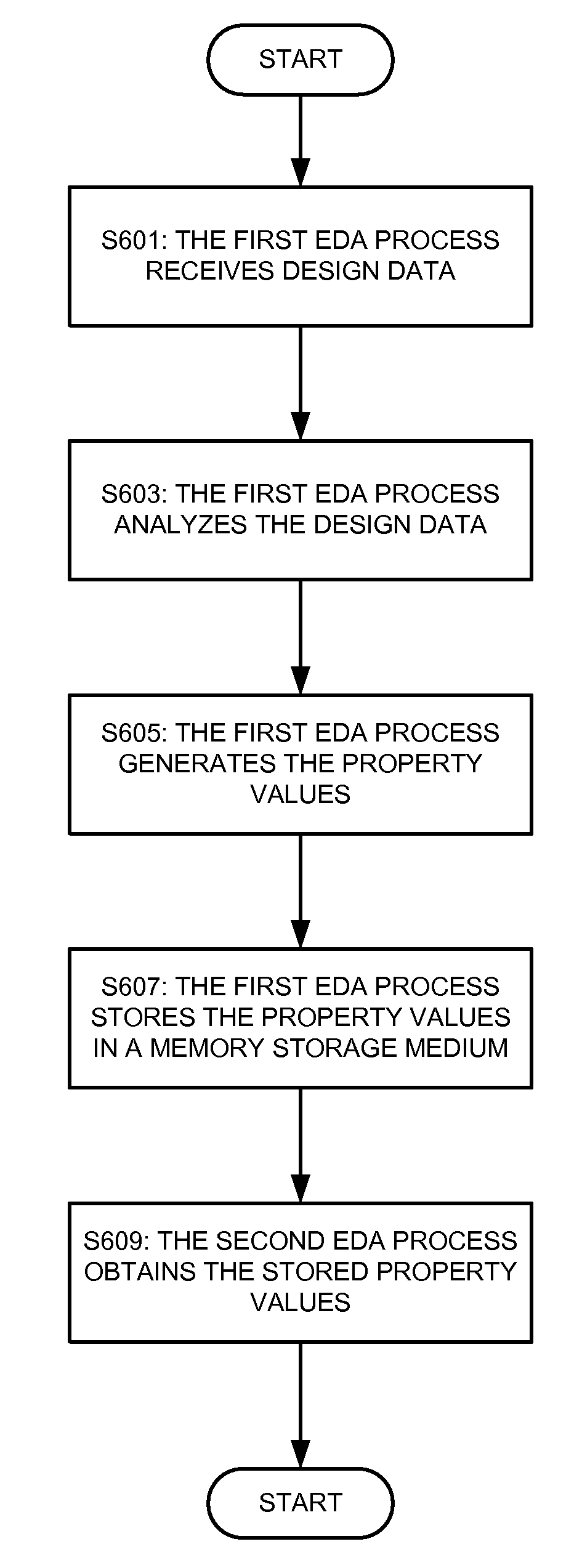
One or more properties can be associated with a design object in a microdevice design. The design object may be an object in a physical layout design for a microdevice, such as a geometric element in a layout design. The design object also may be a collection of geometric elements in a layout design, such as a net, a cell in a hierarchical design, or even a collection of all of the geometric elements in a layer of a design. Still further, the design object may even be an item in a logical circuit design, such as a net in a logical circuit design for an integrated circuit. The values of one or more properties may be statically assigned for or dynamically generated during a design process performed by an electronic design automation tool. A property may be assigned a constant value or a value defined by an equation or other type of script that includes one or more variables. A property may be simple, where the definition of the property's value is not dependent upon the value of any other properties. Alternately, a property may be a compound property, where the definition of the property's value incorporates another, previously-determined property value. Still further, a property may be an alternative property, where the property is assigned one value definition under a first set of conditions and assigned another value definition under a second set of conditions. A first electronic design automation process may generate one or more property values. The generated property values then can be passed to another electronic design automation process in the design analysis flow for its use.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
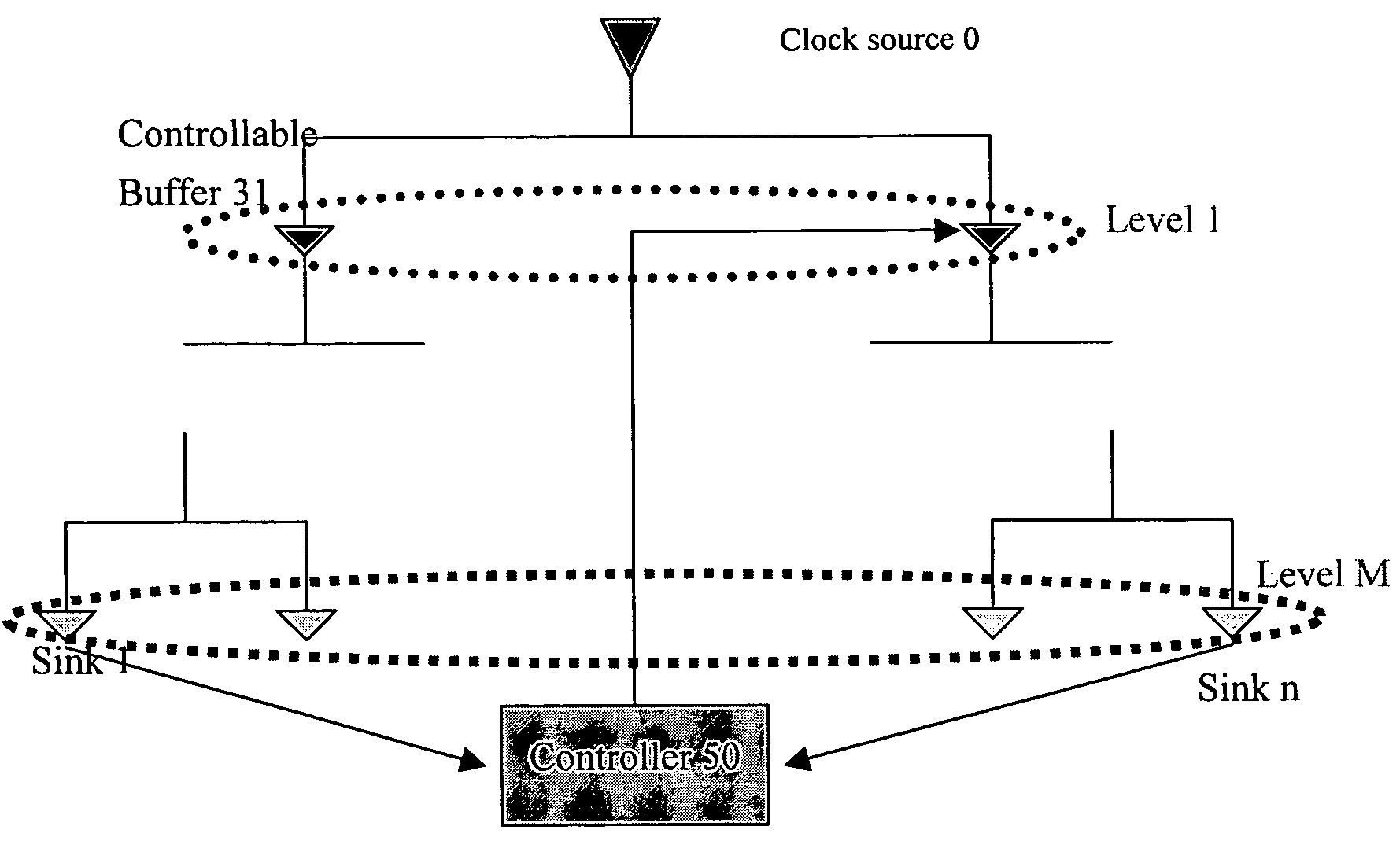
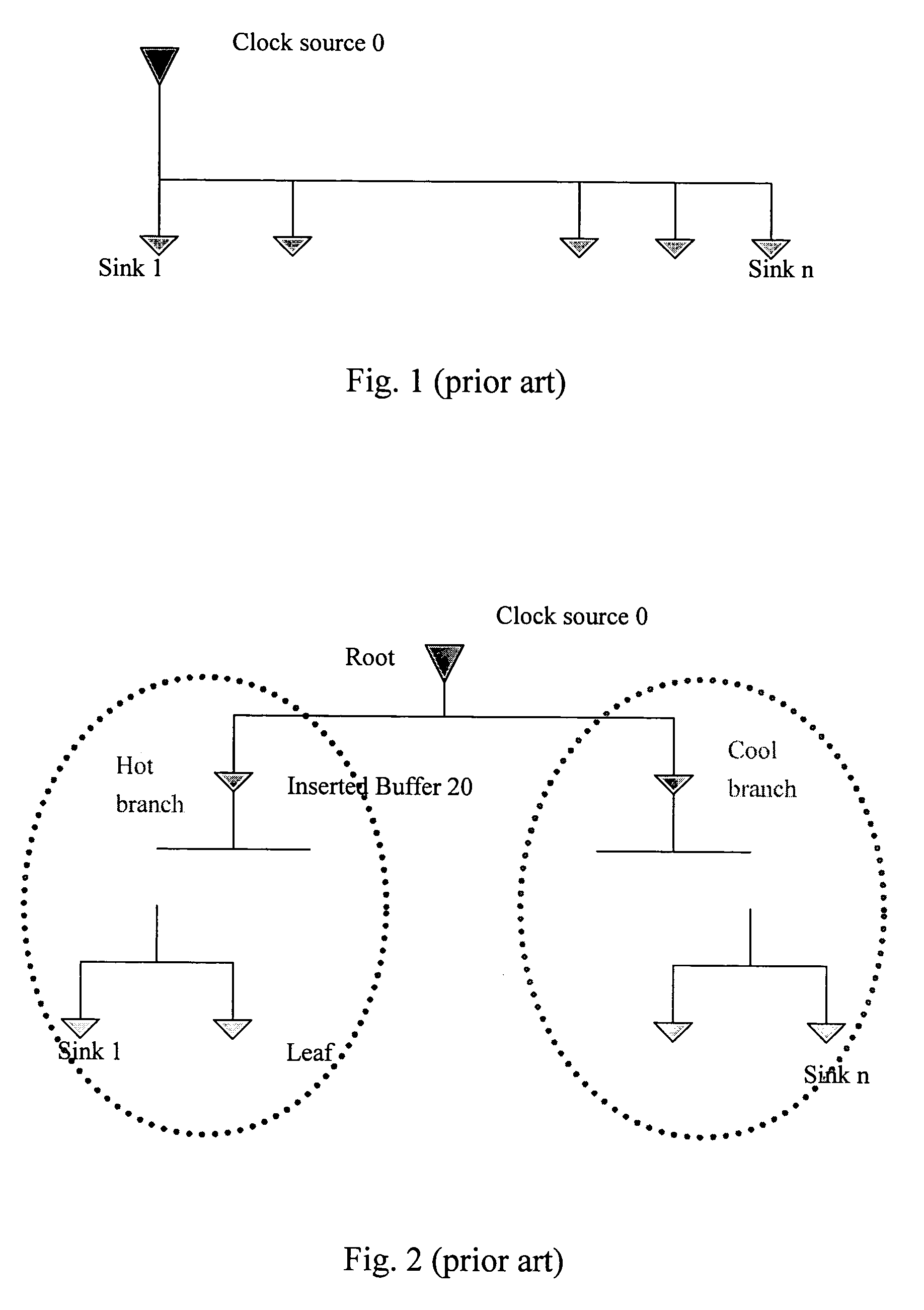
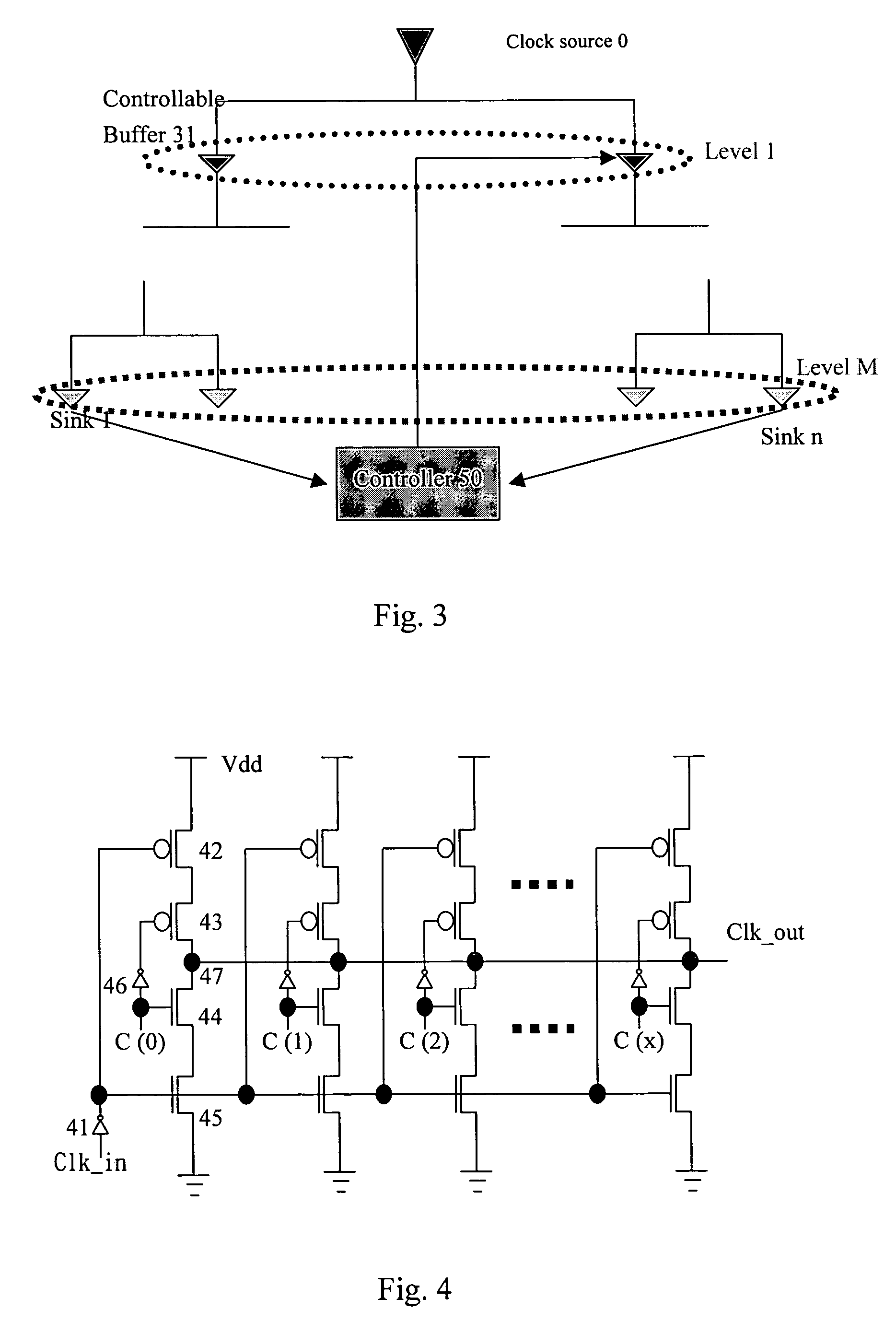
Method for dynamic balancing of a clock tree
InactiveUS7042269B2Excessively generatedSolid-state devicesElectric pulse generatorTime delaysClock tree
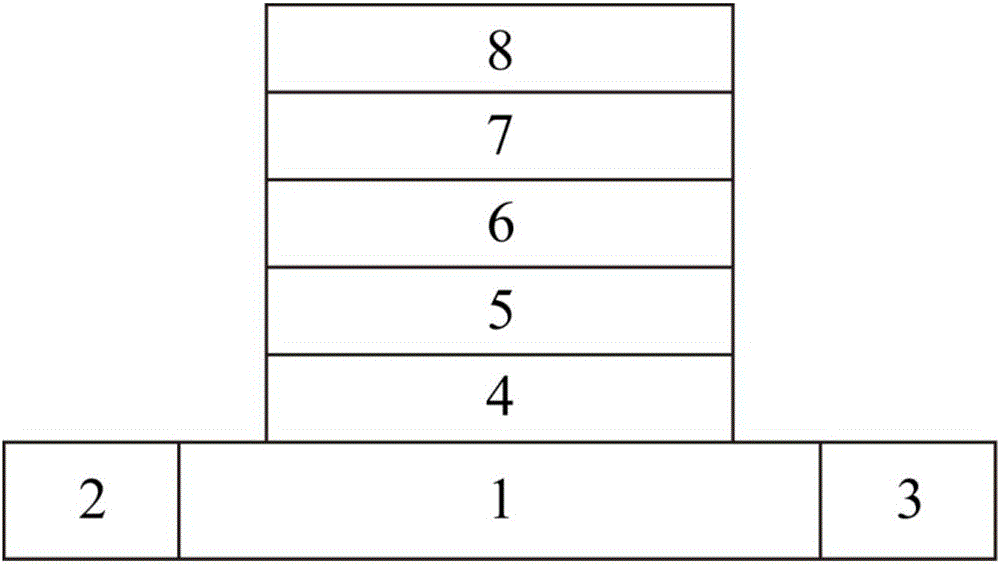
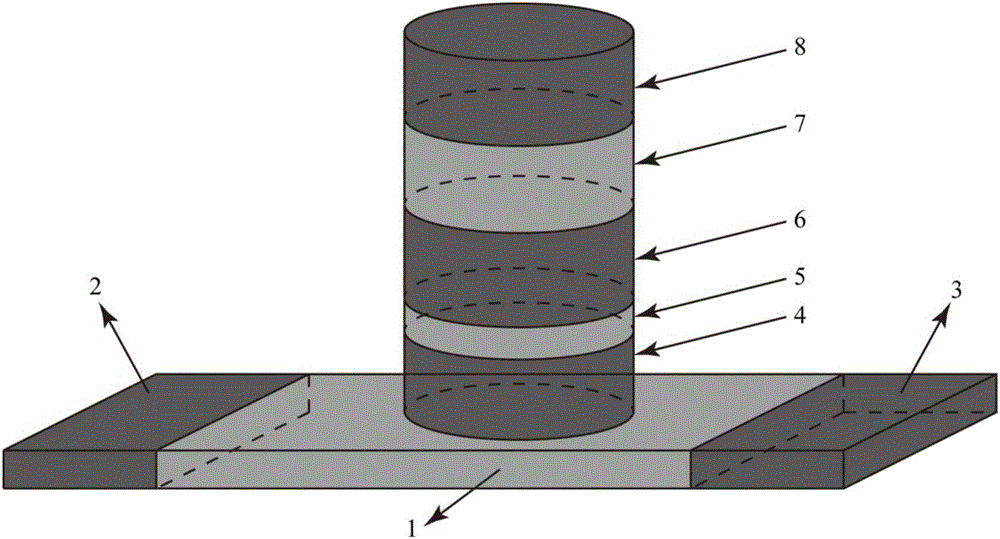
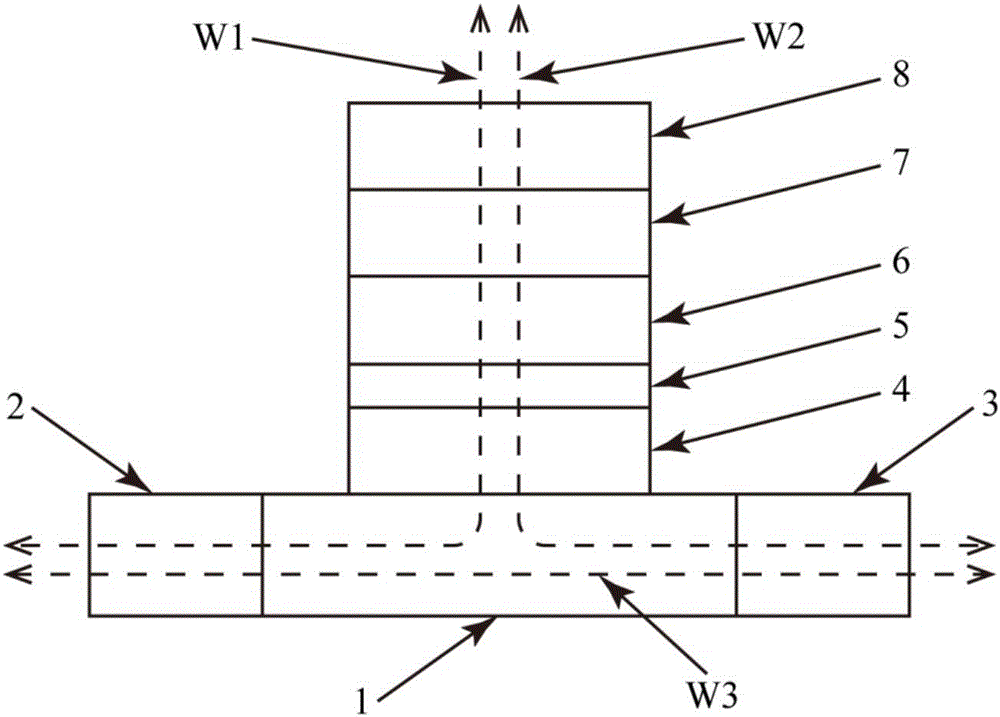
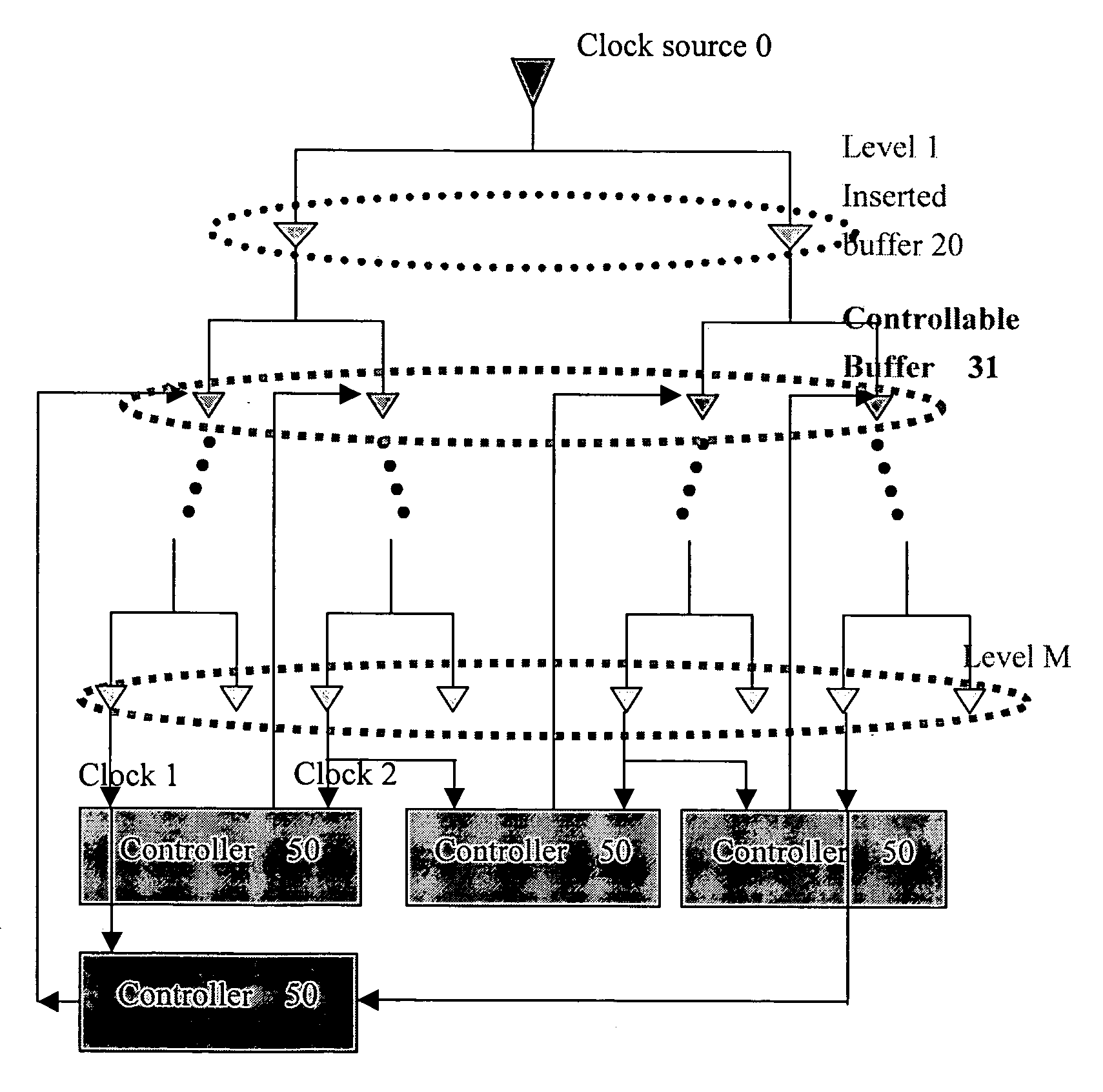
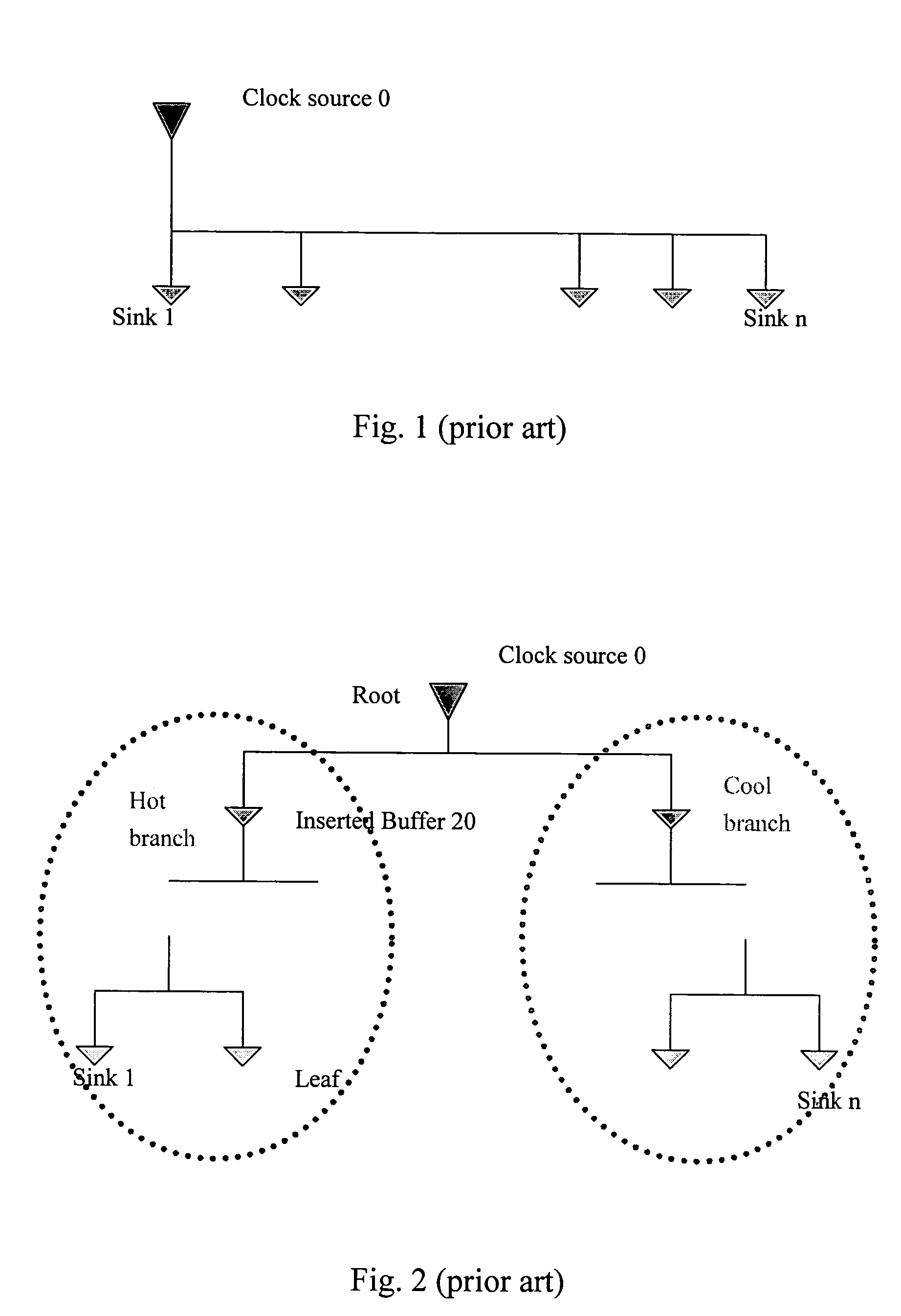
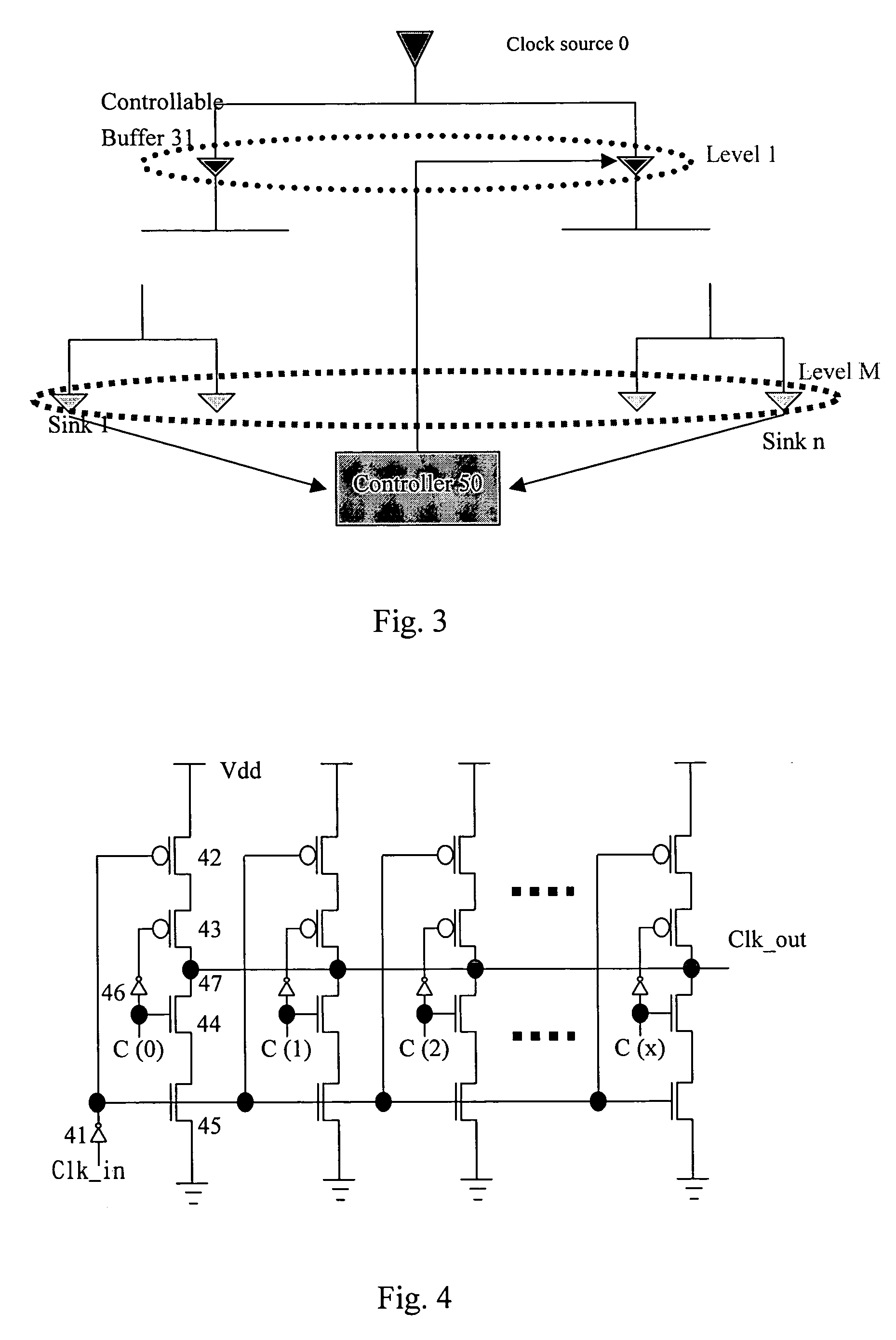
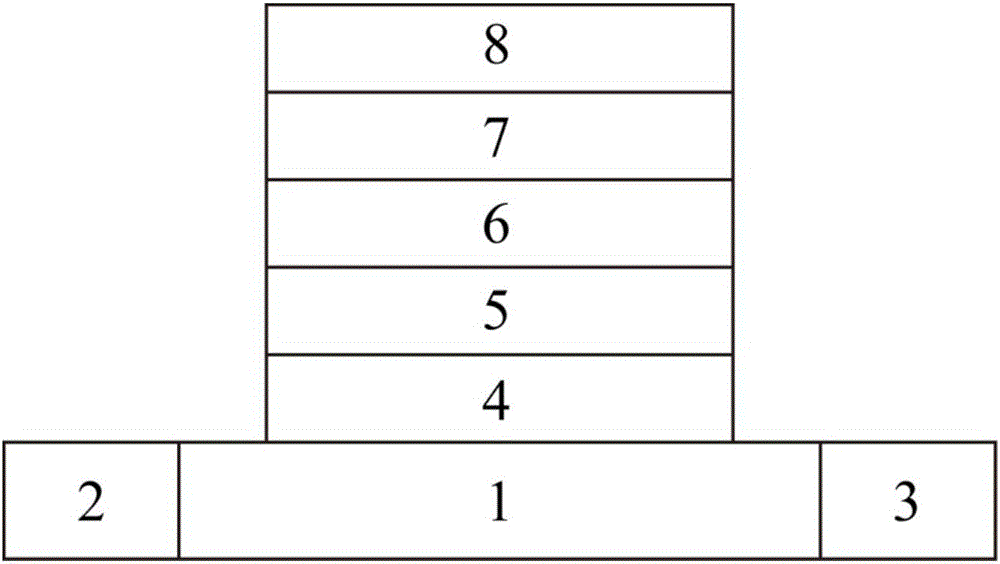
The present invention provides a method to balance a clock tree dynamically. A controllable buffer is inserted in a specific level of a clock tree, and a controller is provided for adjusting two clocks with different skew by controlling the PMOS / NMOS arrangements in the controllable buffer so as to generate more current for compensating the time delay of slow clock to a sink. This method effectively suppressed the clock skew generated by the voltage drop or the temperature variations in the synchronous logic circuit design.
Owner:PRINCETON TECH CORP
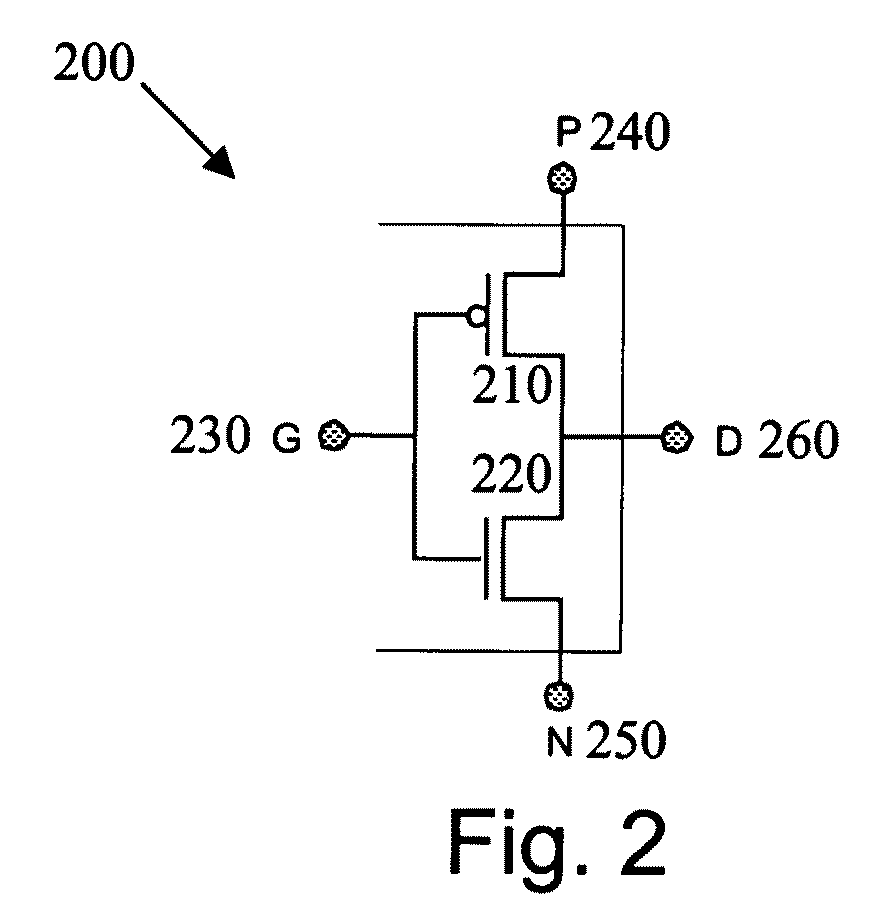
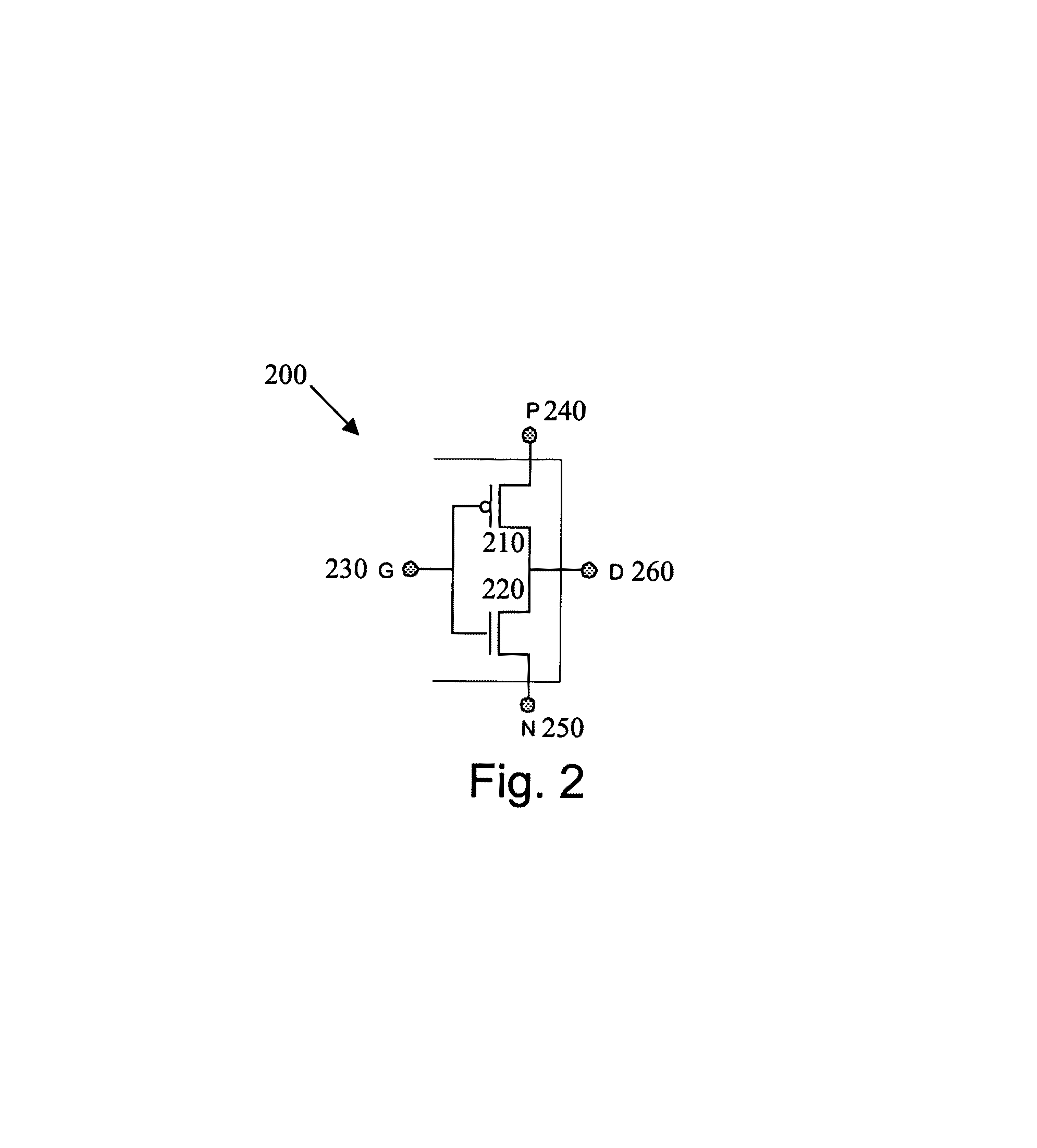
Logic circuit and method of logic circuit design
InactiveUS20070261015A1Reduce areaReduce total powerProgram controlComputer aided designDiffusionLogic circuit design
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method and apparatus for testing logic circuit designs
InactiveUS7484151B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionLogic circuit designEngineering
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for storing multiple levels of design data in a common database
InactiveUS20020188922A1Improve efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designGraphicsLogic circuit design
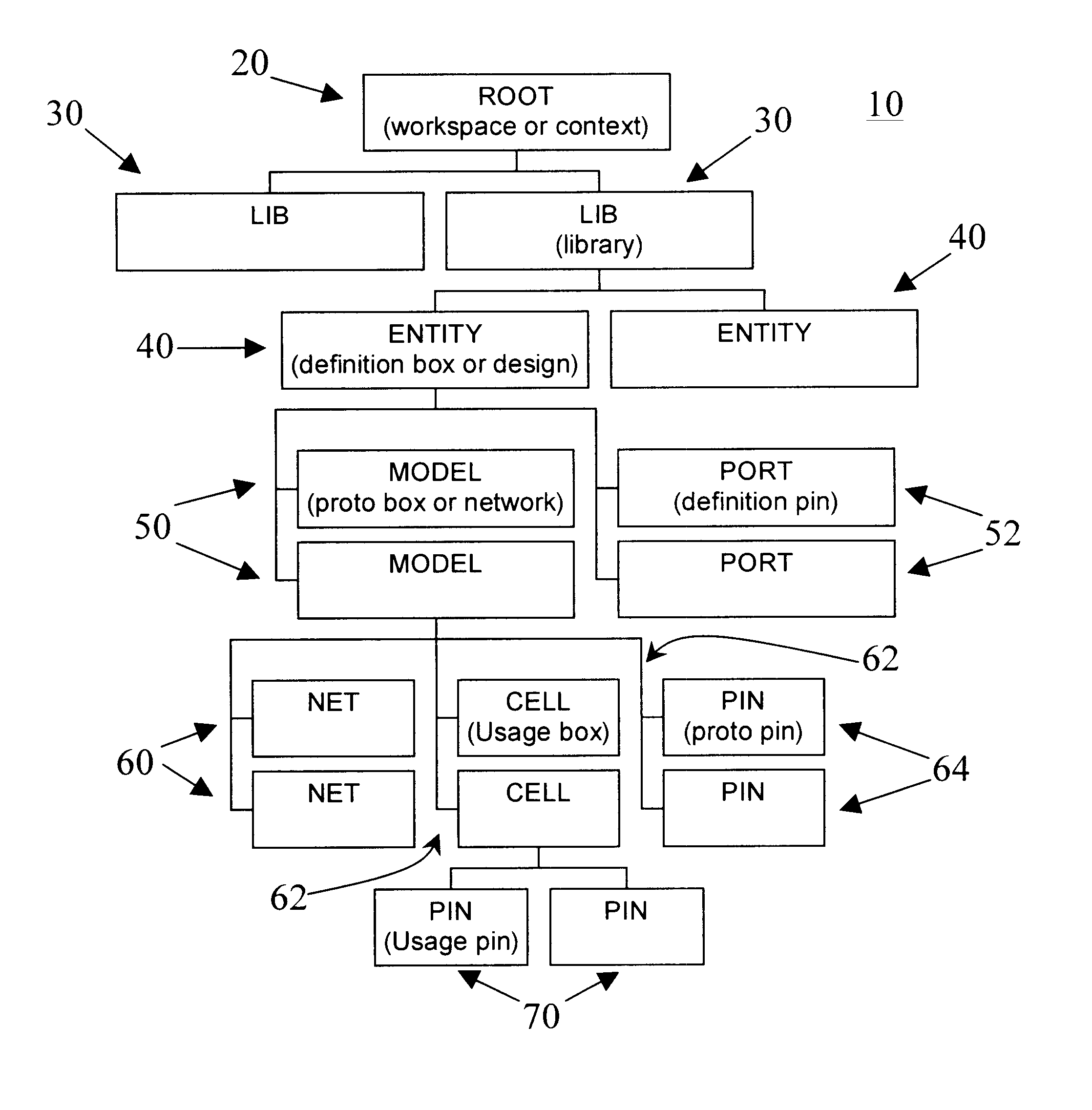
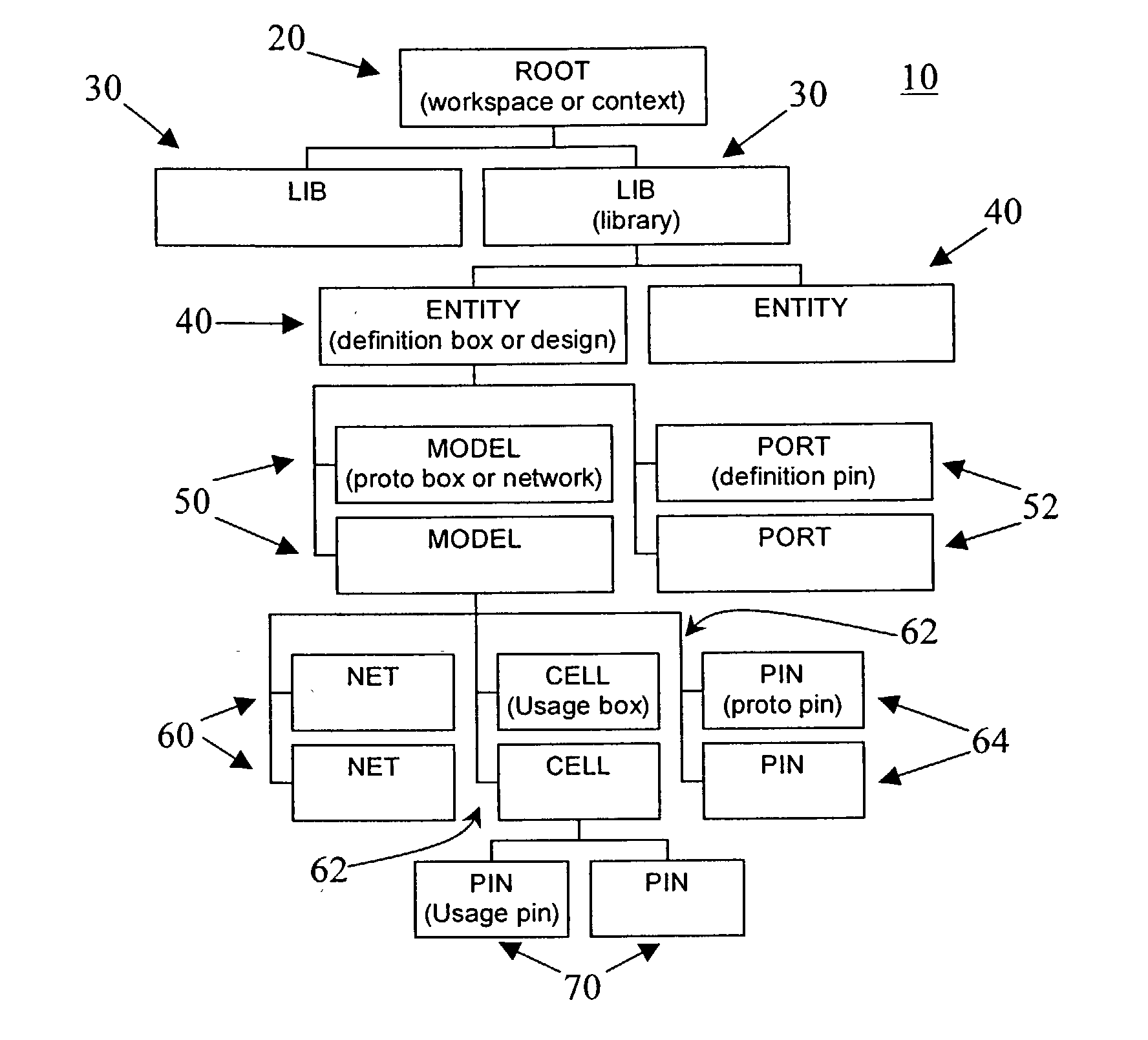
An automated logic circuit design system uses a common database to store design data at different states of the design process, including data-flow graphs, netlists and layout descriptions. In this way, the need to translate circuit descriptions between tools is eliminated, thus leading to increased speed, flexibility and integration. The common database includes entities, models, cells, pins, busses and nets. The data-flow graphs are stored as graphs, the nodes in a graph as cells, and the edges as busses. Physical design data is available by storing the cells in a model in a KD tree. This allows queries on cells in the netlist located in the layout within arbitrary areas.
Owner:MAGMA DESIGN AUTOMATION
Method and apparatus for choosing tests for simulation and associated algorithms and hierarchical bipartite graph data structure
ActiveUS7315973B1Wasting resourceOvercome disadvantagesElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceLogic circuit design
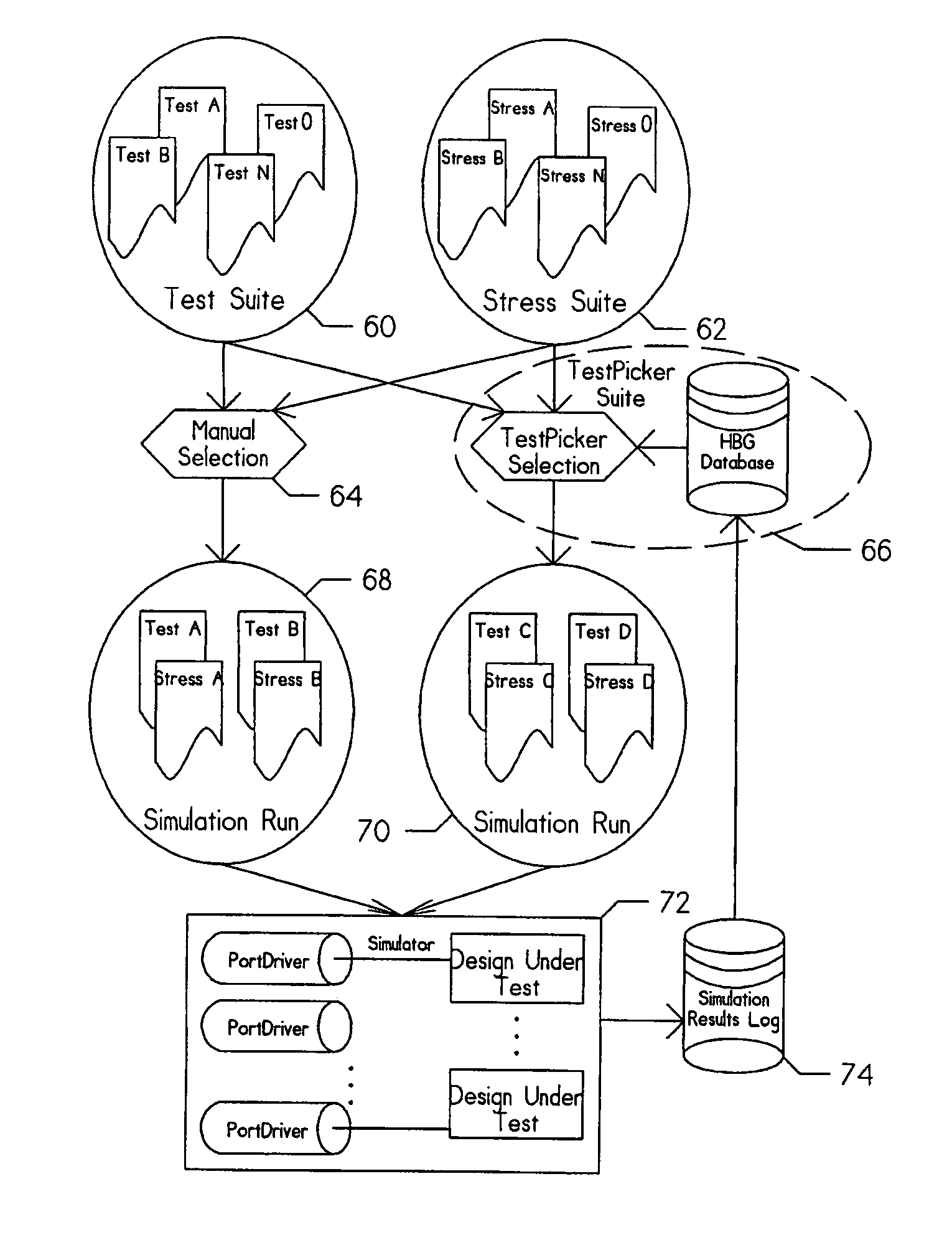
An apparatus for and method of generating test cases for testing simulated logic circuit designs. The test cases are basically generated automatically in a random fashion, manually, or using some combination of automatic and manual techniques. Each test case has a corresponding success indication. These test cases are provided to the simulated logic design for execution. Following execution, each test case is rated pass or fail by comparison of the result with the corresponding success indication and a reason for failure is recorded for each failure. A significantly smaller list of test cases is prepared by eliminating test cases which do not have a unique reason for failure. The smaller list of test cases is then presented for a simulation run which requires substantially less simulator time and substantially less manual analysis of the results.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Properties In Electronic Design Automation
InactiveUS20080141193A1Easily calculateComputer aided designTotal factory controlComputer architectureLogic circuit design
One or more properties can be associated with a design object in a microdevice design. The design object may be an object in a physical layout design for a microdevice, such as a geometric element in a layout design. The design object also may be a collection of geometric elements in a layout design, such as a net, a cell in a hierarchical design, or even a collection of all of the geometric elements in a layer of a design. Still further, the design object may even be an item in a logical circuit design, such as a net in a logical circuit design for an integrated circuit. The values of one or more properties may be statically assigned for or dynamically generated during a design process performed by an electronic design automation tool. A property may be assigned a constant value or a value defined by an equation or other type of script that includes one or more variables. A property may be simple, where the definition of the property's value is not dependent upon the value of any other properties. Alternately, a property may be a compound property, where the definition of the property's value incorporates another, previously-determined property value. Still further, a property may be an alternative property, where the property is assigned one value definition under a first set of conditions and assigned another value definition under a second set of conditions. A first electronic design automation process may generate one or more property values. The generated property values then can be passed to another electronic design automation process in the design analysis flow for its use.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Method and system for logic design for cell projection particle beam lithography
A method for particle beam lithography, such as electron beam (EB) lithography, includes predefining a stencil design having a plurality of cell patterns with information from a cell library, fabricating the stencil design, synthesizing a functional description into a logic circuit design after predefining the stencil design so that one or more characteristics of the stencil design are considered during synthesizing of the functional description into the logic circuit design, optimizing the logic circuit design, generating a layout design from the optimized logic circuit design, and forming the logic circuit on a substrate according to the stencil design and the layout design.
Owner:D2S
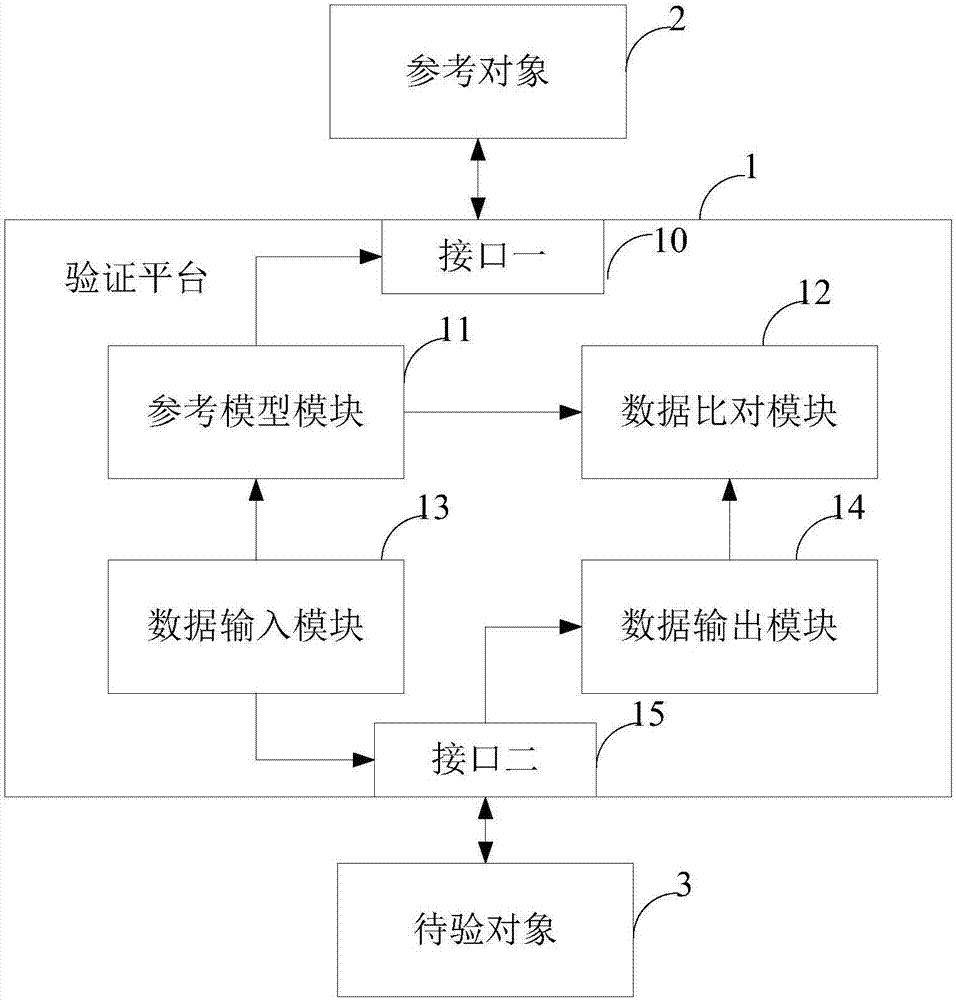
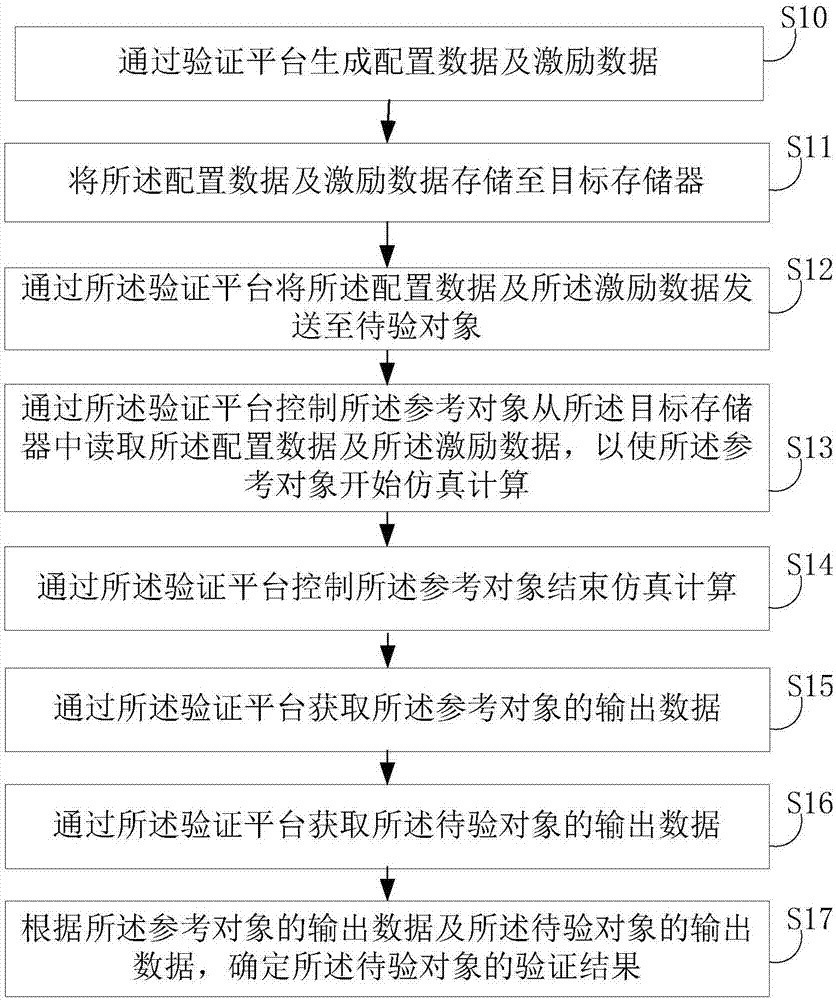
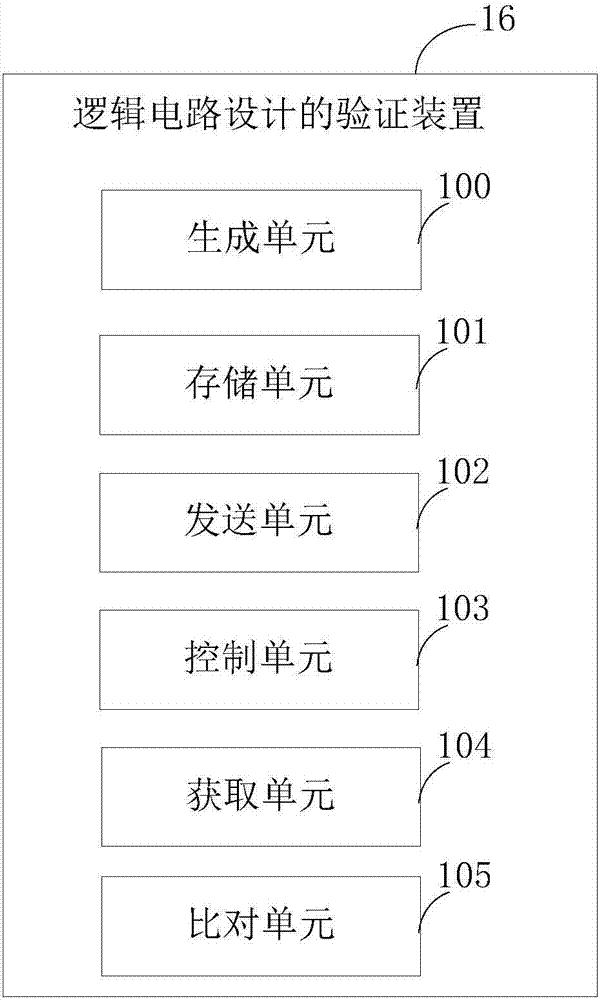
Method and device for verifying logic circuit design, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN107247859AStrong scalabilityImprove reusabilitySpecial data processing applicationsValidation methodsLogic circuit design
Owner:SHENZHEN INTELLIFUSION TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Properties In Electronic Design Automation
ActiveUS20080115097A1Easily calculateComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureLogic circuit design
One or more properties can be associated with a design object in a microdevice design. The design object may be an object in a physical layout design for a microdevice, such as a geometric element in a layout design. The design object also may be a collection of geometric elements in a layout design, such as a net, a cell in a hierarchical design, or even a collection of all of the geometric elements in a layer of a design. Still further, the design object may even be an item in a logical circuit design, such as a net in a logical circuit design for an integrated circuit. The values of one or more properties may be statically assigned for or dynamically generated during a design process performed by an electronic design automation tool. A property may be assigned a constant value or a value defined by an equation or other type of script that includes one or more variables. A property may be simple, where the definition of the property's value is not dependent upon the value of any other properties. Alternately, a property may be a compound property, where the definition of the property's value incorporates another, previously-determined property value. Still further, a property may be an alternative property, where the property is assigned one value definition under a first set of conditions and assigned another value definition under a second set of conditions. A first electronic design automation process may generate one or more property values. The generated property values then can be passed to another electronic design automation process in the design analysis flow for its use.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
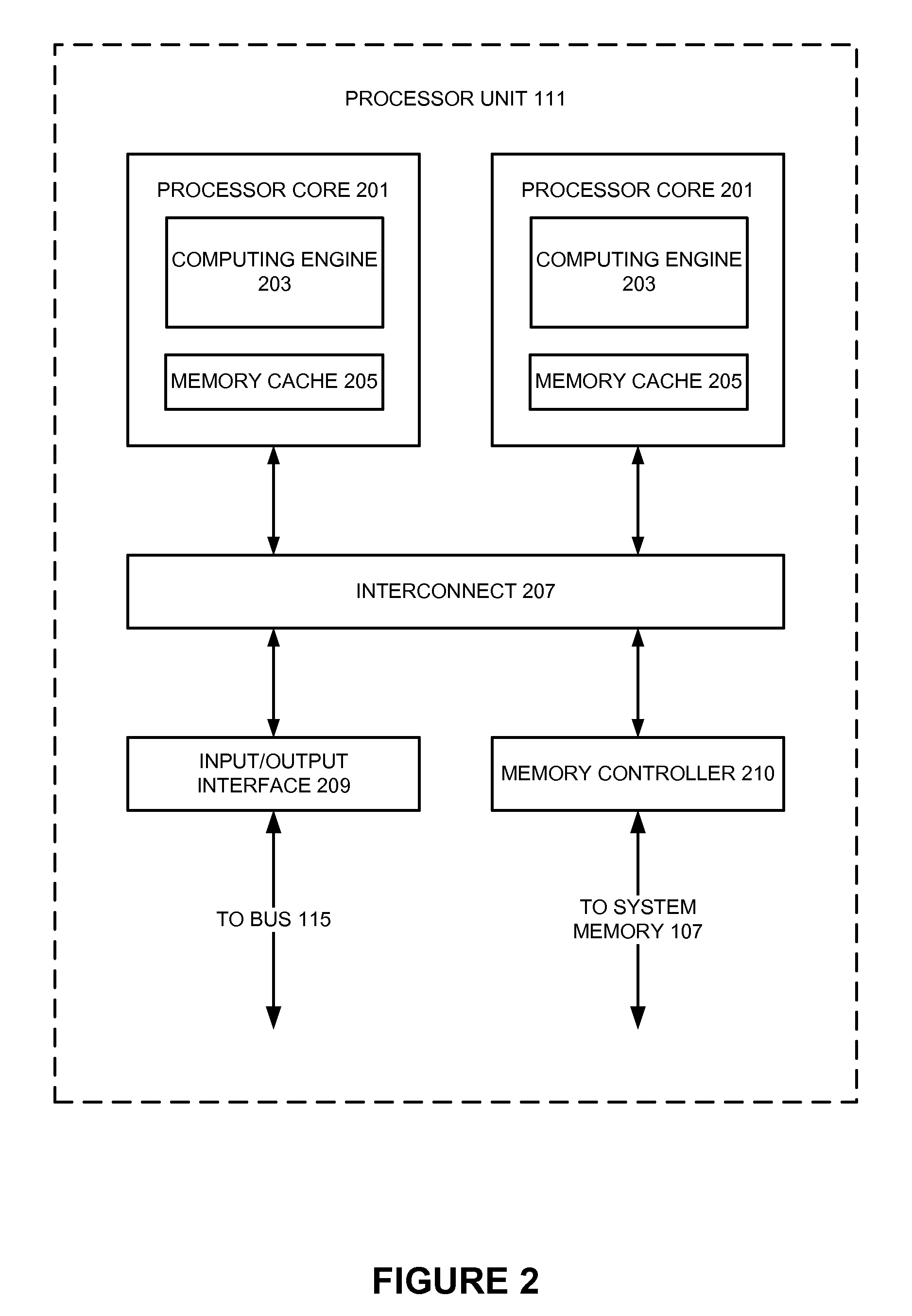
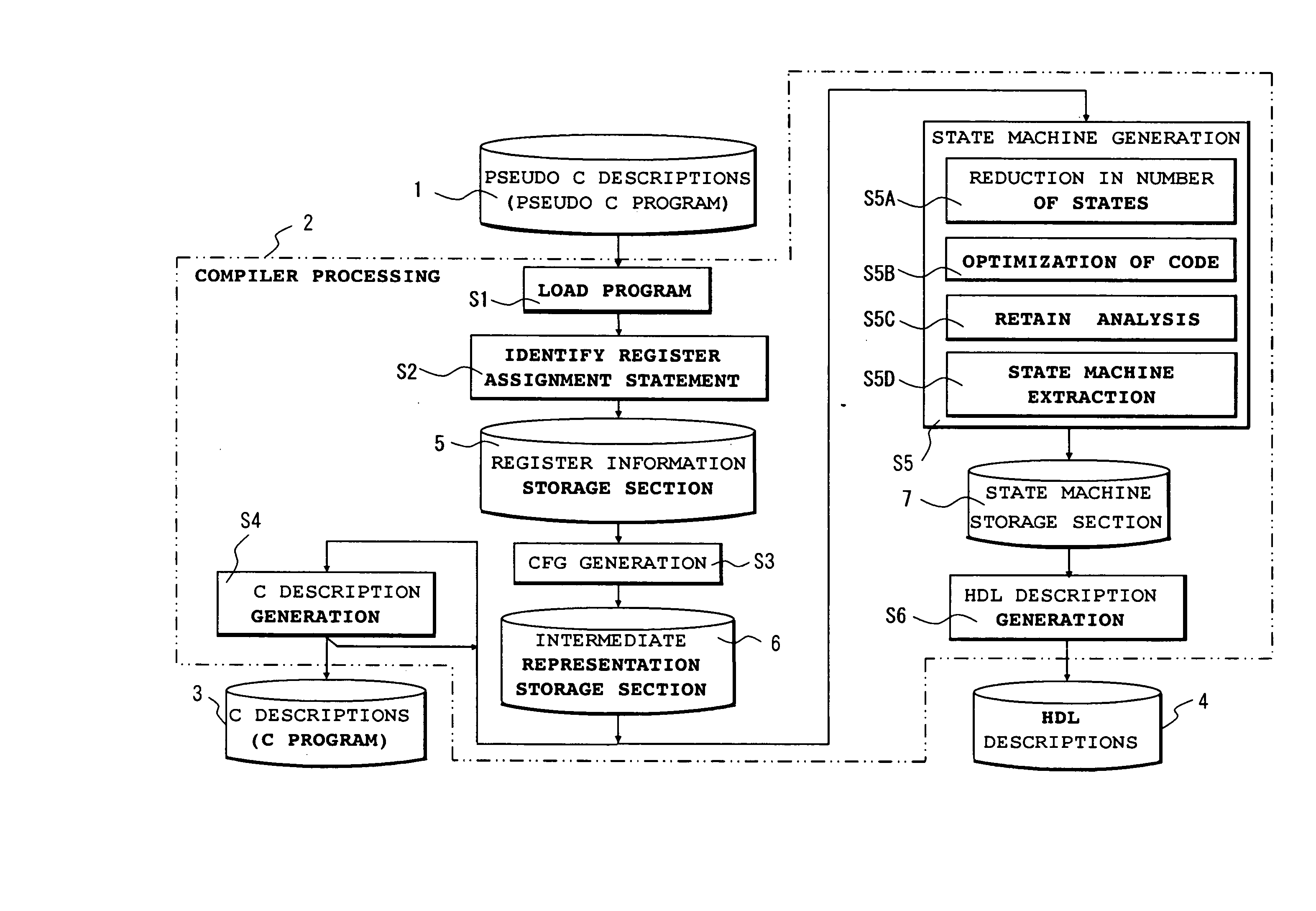
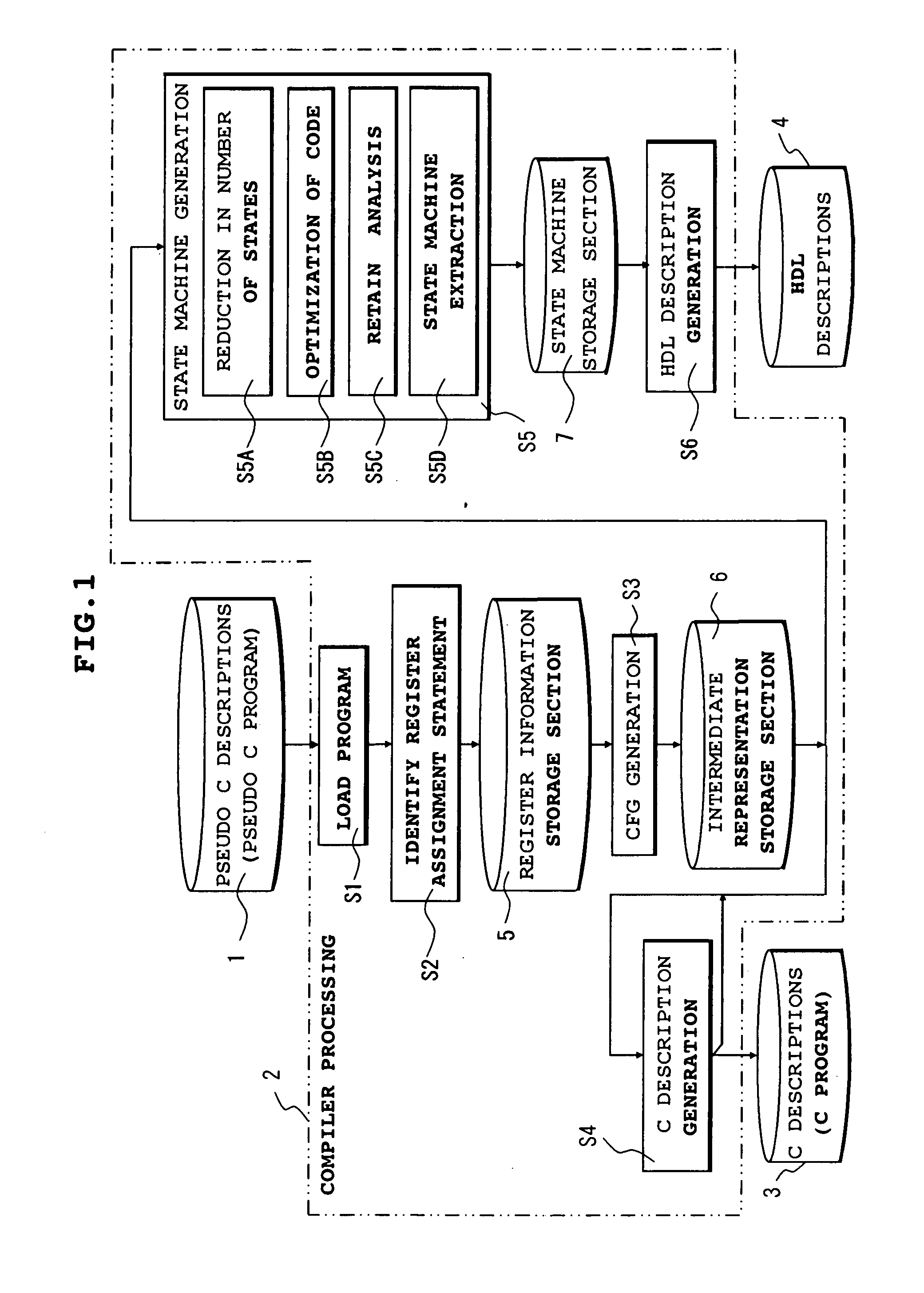
Compiler and logic circuit design method
InactiveUS20080098336A1Reduce in quantityDegraded in termCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic circuit designRegister assignment
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
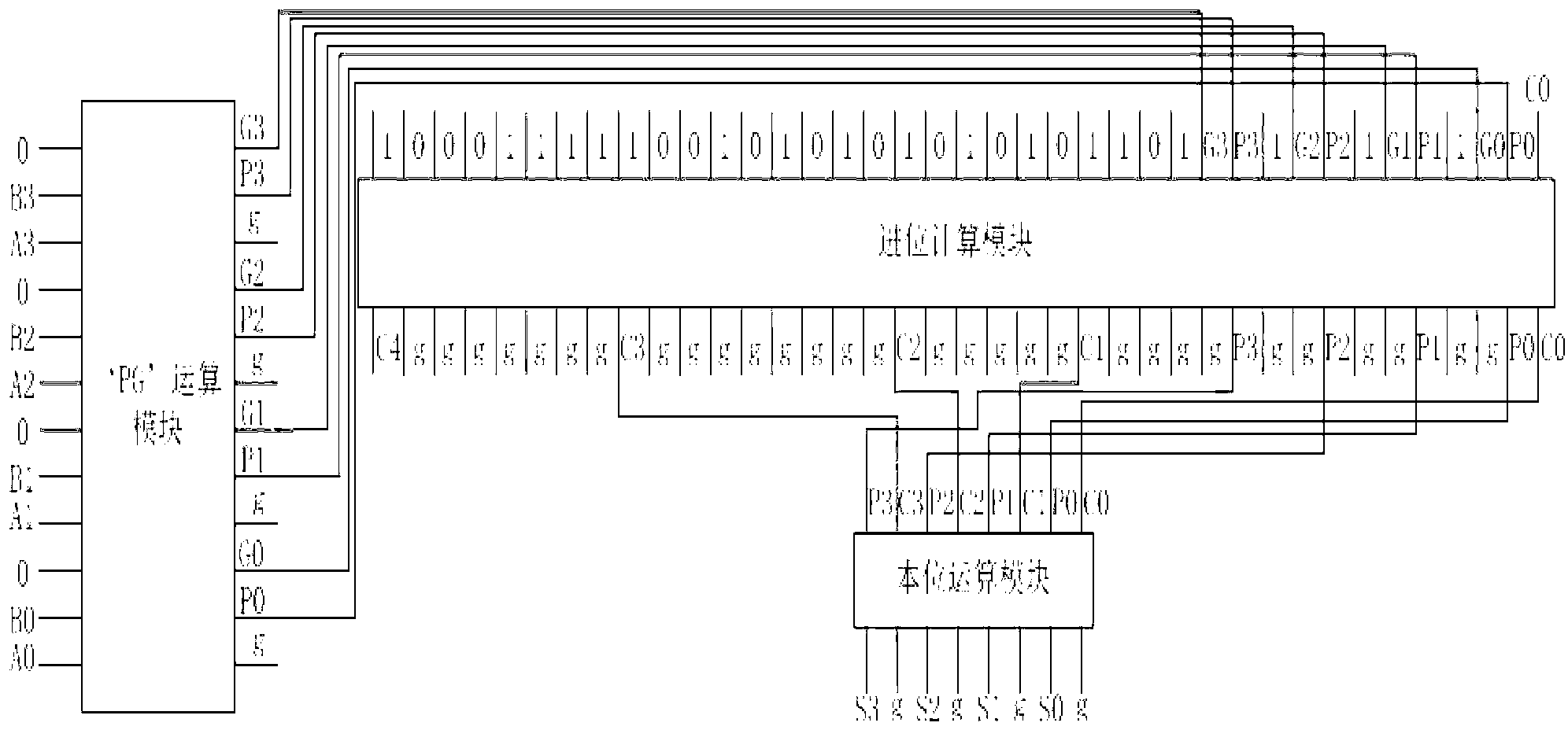
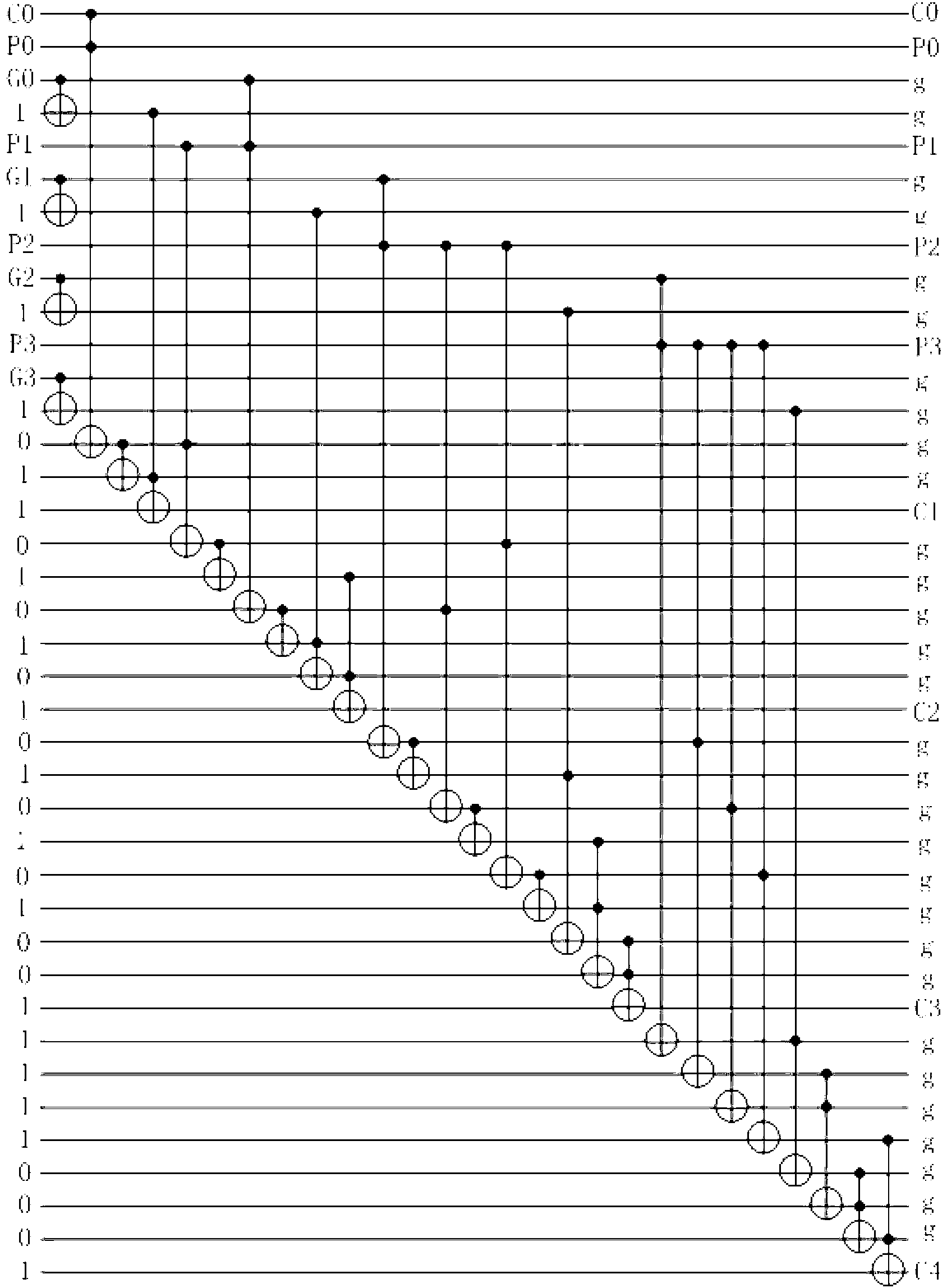
Reversible-logic-based 16-bit carry look-ahead adder
The invention discloses a 16-bit carry look-ahead adder based on reversible logic and relates to the microelectronic technical field. The adder is formed by cascading of four stages of 4-bit reversible carry look-ahead adders. The 4-bit reversible carry look-ahead adder at each stage calculates 4-bit in-place calculation results of the stage and corresponding carry outputs respectively; a first carry output, a second carry output and a third carry output are respectively input into a corresponding carry input end of the 4-bit reversible carry look-ahead adder of the next stage to serve as a carry input, and a fourth carry output serves as a carry output of a 16-bit reversible carry look-ahead adder. According to the 16-bit carry look-ahead adder, a reversible logic design method is used for achieving the 16-bit carry look-ahead adder, the circuit delay can be reduced greatly, and simultaneously, by following the reversible logic circuit design, energy losses can be reduced, and circuit losses can even be completely eradicated.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
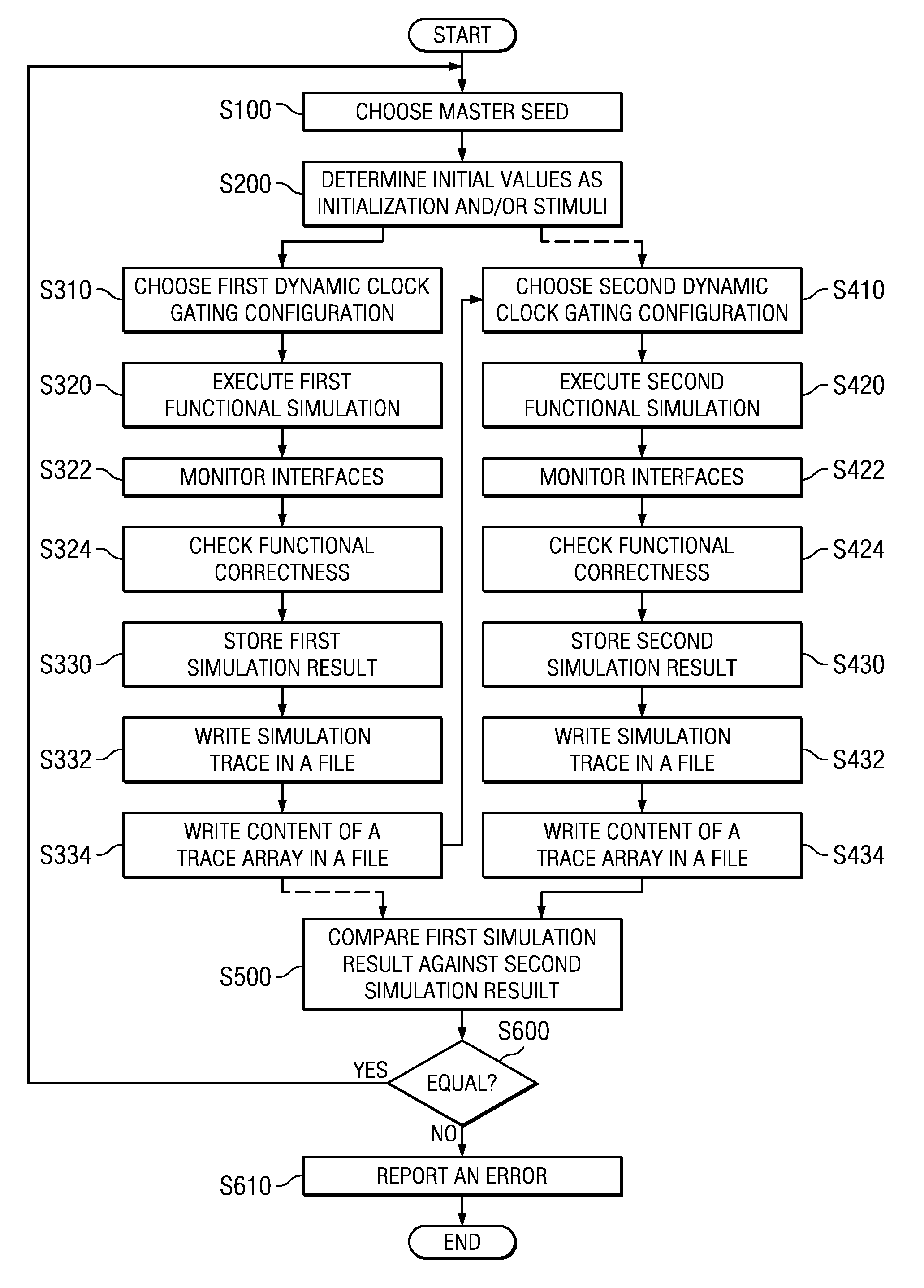
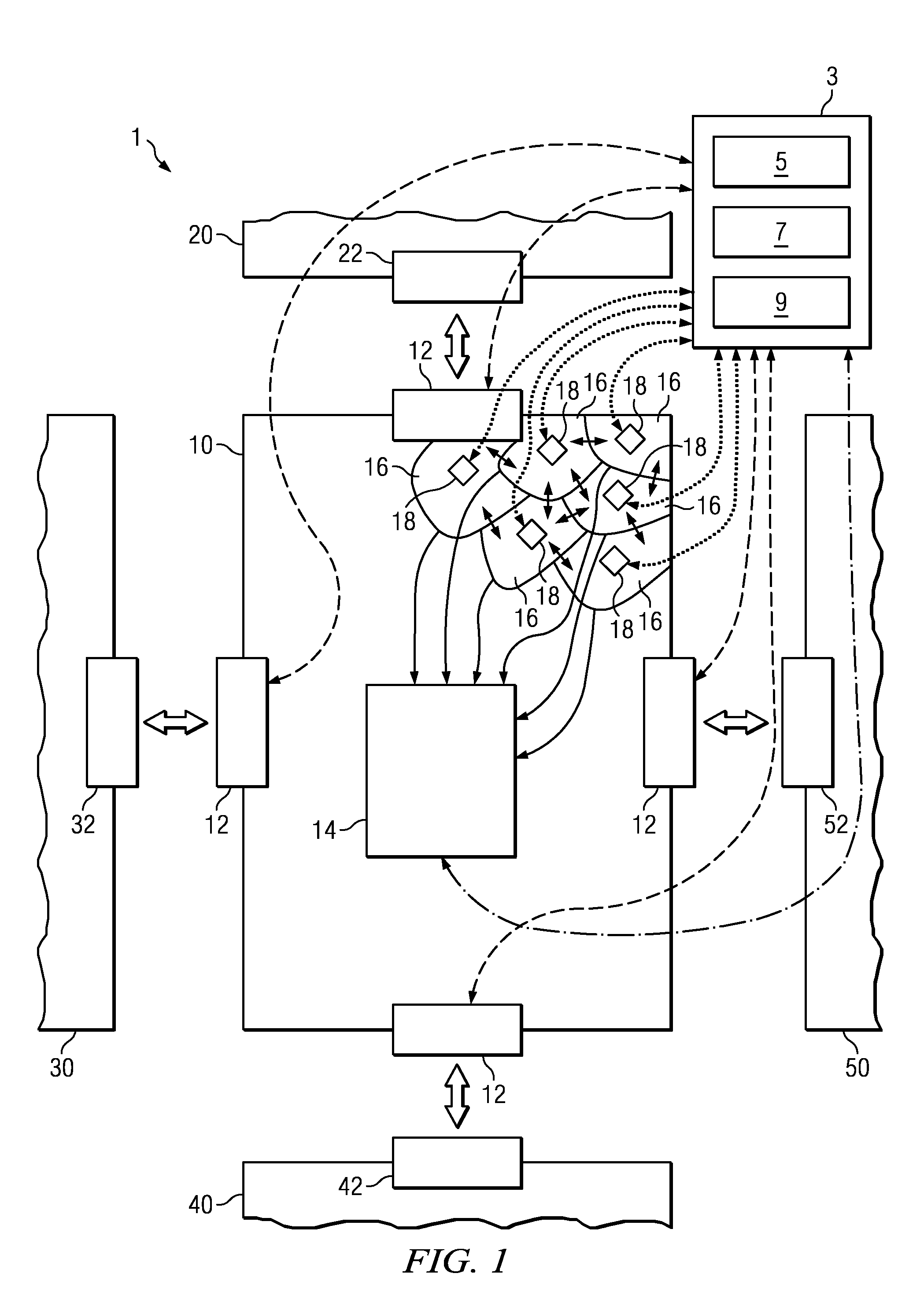
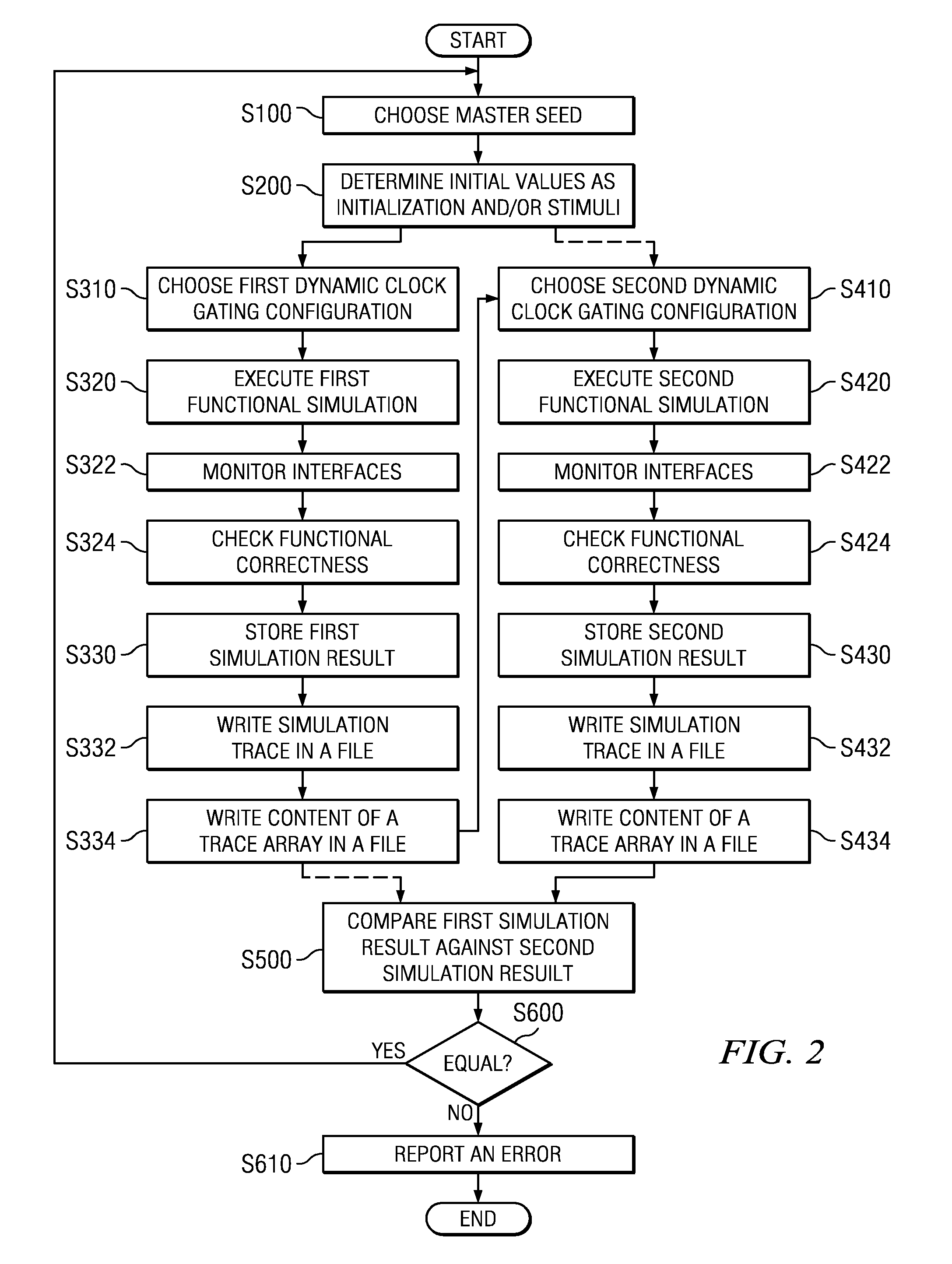
Method, System, Computer Program Product, and Data Processing Program for Verification of Logic Circuit Designs Using Dynamic Clock Gating
InactiveUS20110066988A1Guaranteed functionDetect changeDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designComputer hardwareLogic circuit design
A method and system for verifying a logic circuit design using dynamic clock gating is disclosed. The method comprises choosing at least one master seed to determine initial values as initialization for said logic circuit and / or stimuli data for at least one interface of said logic circuit, choosing at least two different dynamic clock gating configurations for every chosen master seed, executing a functional simulation with said logic circuit for every chosen dynamic clock gating configuration by using said determined initialization and / or stimuli data based on a corresponding master seed, comparing simulation results of functional simulations against each other executed with said logic circuit for at least two different chosen dynamic clock gating configurations, and reporting an error if said at least two simulation results are not identical.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
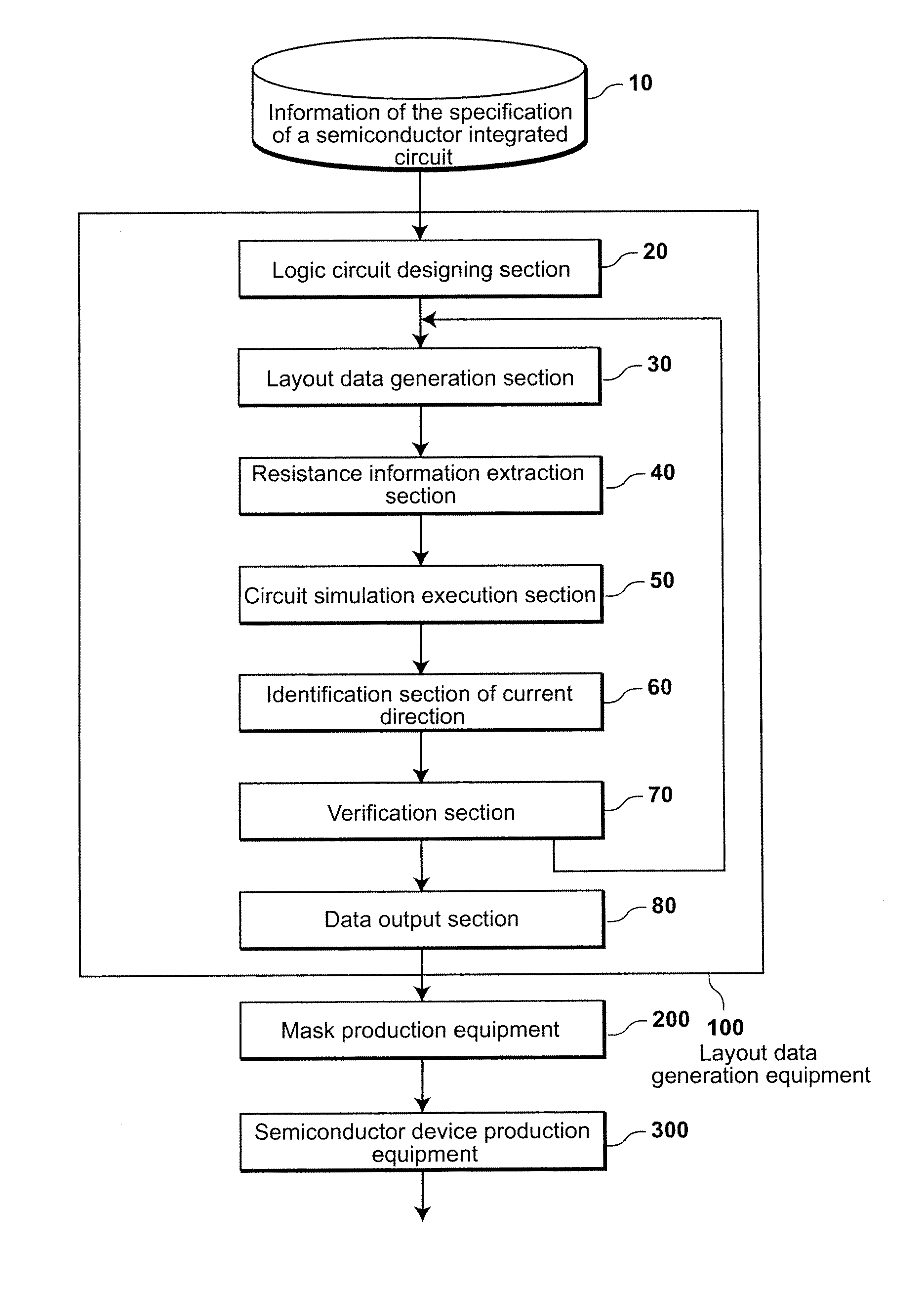
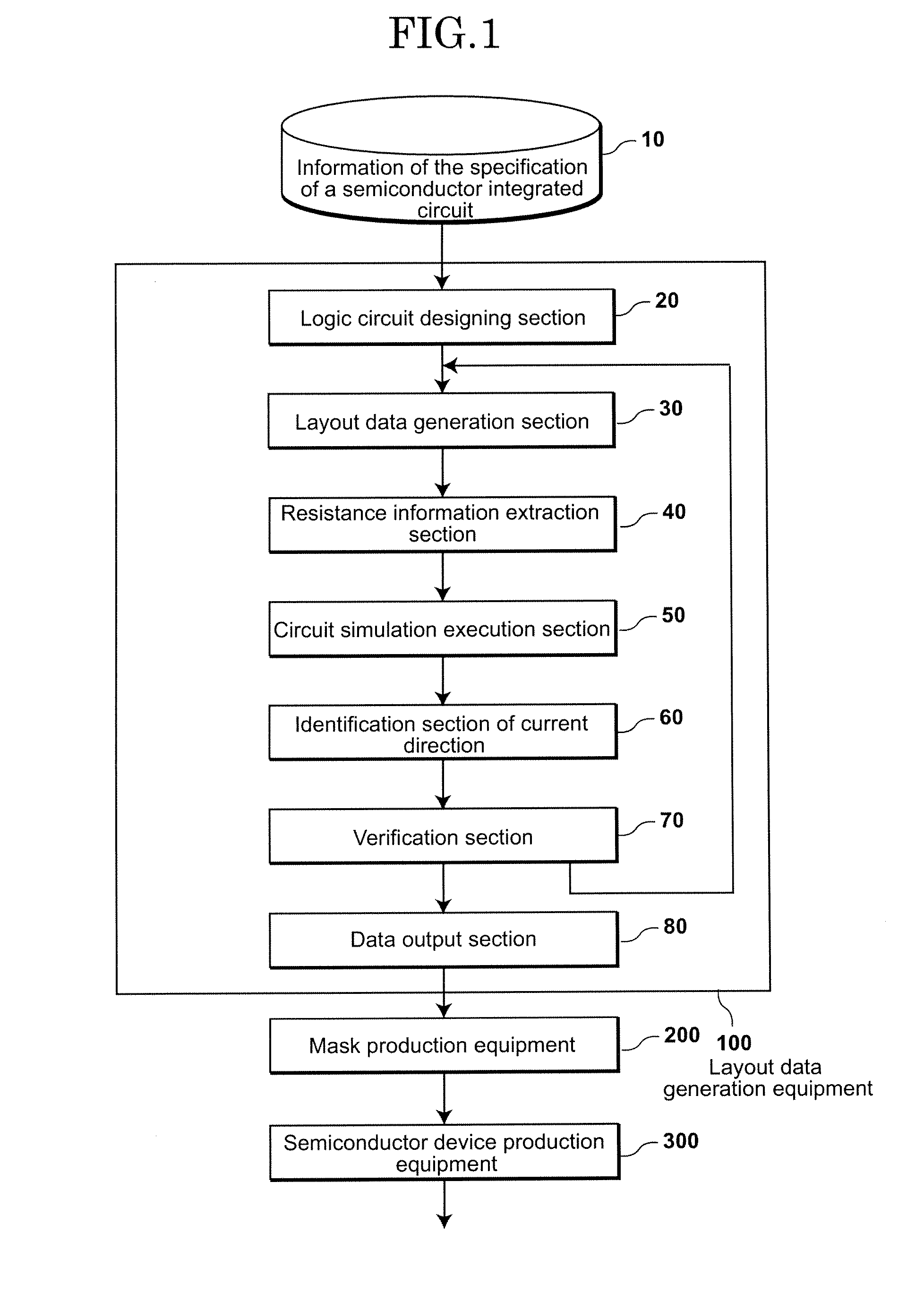
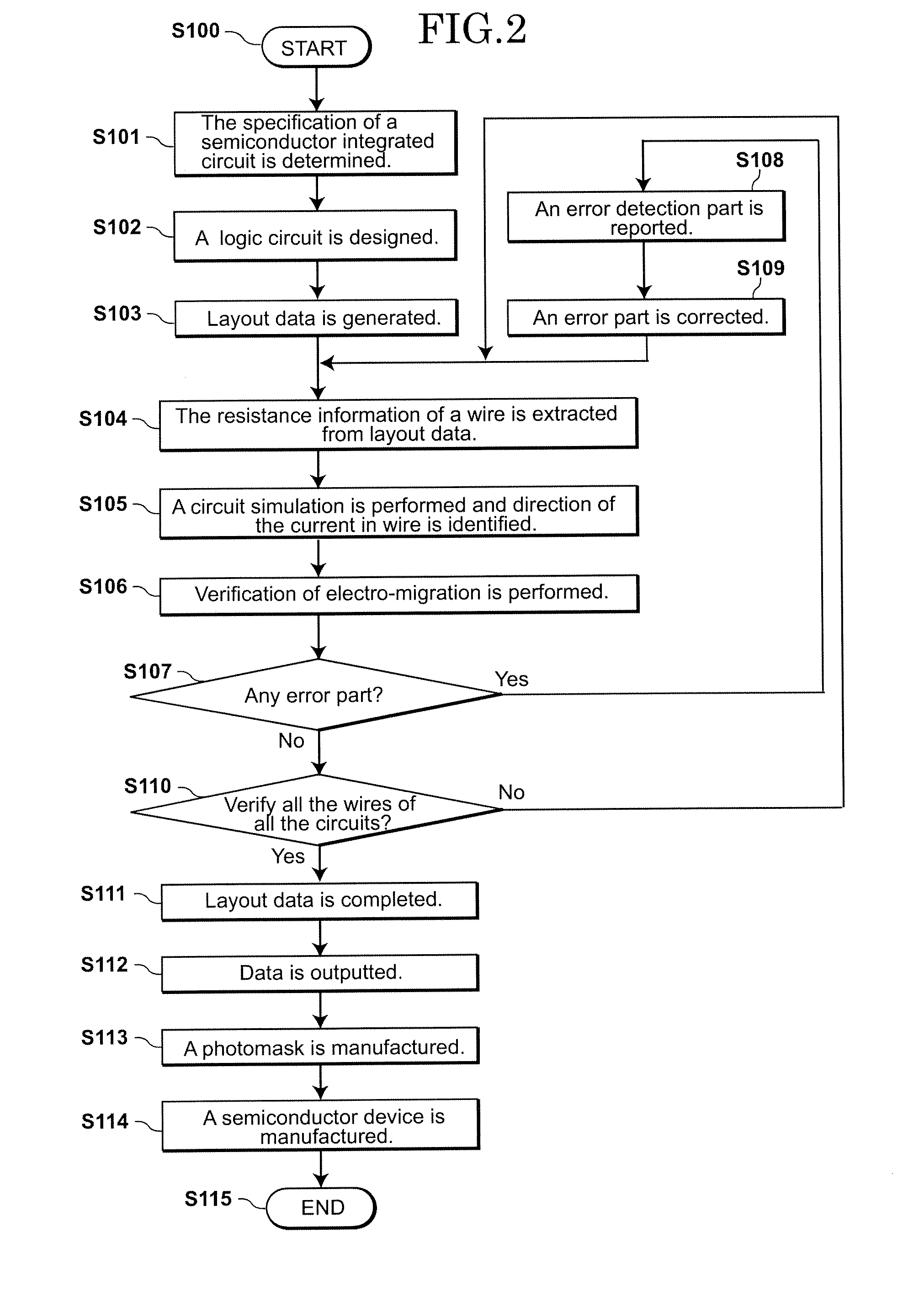
Layout data generation equipment of semiconductor integrated circuit, data generation method and manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080141196A1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic circuit designEngineering
A layout-data generation equipment includes a logic circuit designing section which designs a logic circuit based on information of the specifications of a semiconductor integrated circuit, a layout-data generation section which creates layout-data based on the logic circuit, a resistance information extraction section which extracts resistance information of a wire from the layout-data, a circuit simulation execution section which executes a circuit simulation, an identification section of current direction which identifies a direction of a current in the wire based on the resistance information of a wire and an execution result of the circuit simulation, a verification section which verifies whether layout-data of the wire breaks a design rule, the design rule being extracted from the information of the specifications of a semiconductor integrated circuit and the verification section generates this verification result, and a data output section which outputs the layout-data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Circuit for dynamic switching of a buffer threshold
InactiveUS6198308B1Reduce degradationReduce sensitivitySwitching accelaration modificationsThreshold modification in field effect transistorsPropagation delayThreshold potential
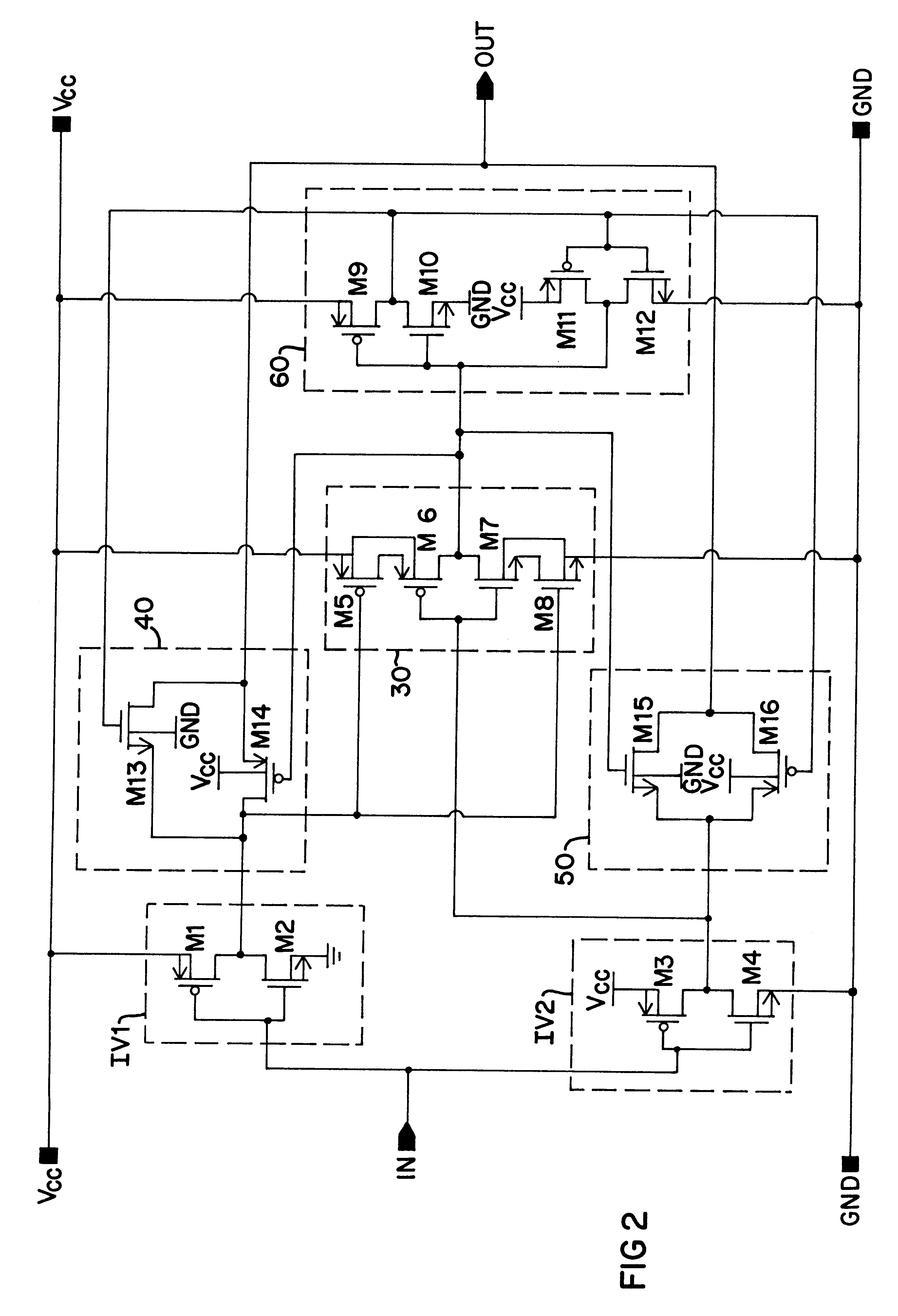
A buffer circuit for providing dynamic threshold control. The buffer circuit includes a pair of input inverters designed with different skewed threshold potential characteristics. The outputs of the skewed inverters are directed to a logic circuit designed to select either the faster or the slower signal received from the two inverters for transmission to passgate devices coupled to the respective inverters. Only one of the passgate devices is enabled to ensure that only one of the output signals from the two inverters is propagated through the buffer. A latch is preferably connected between the logic circuit and the two passgate devices to maintain the states of the inverters and the logic circuit. The circuit can be designed to define the threshold potential at which switching will occur so as to reduce propagation delay or increase it as desired. It is therefore possible using the circuit to increase transmission rates with minimal affect on signal noise.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
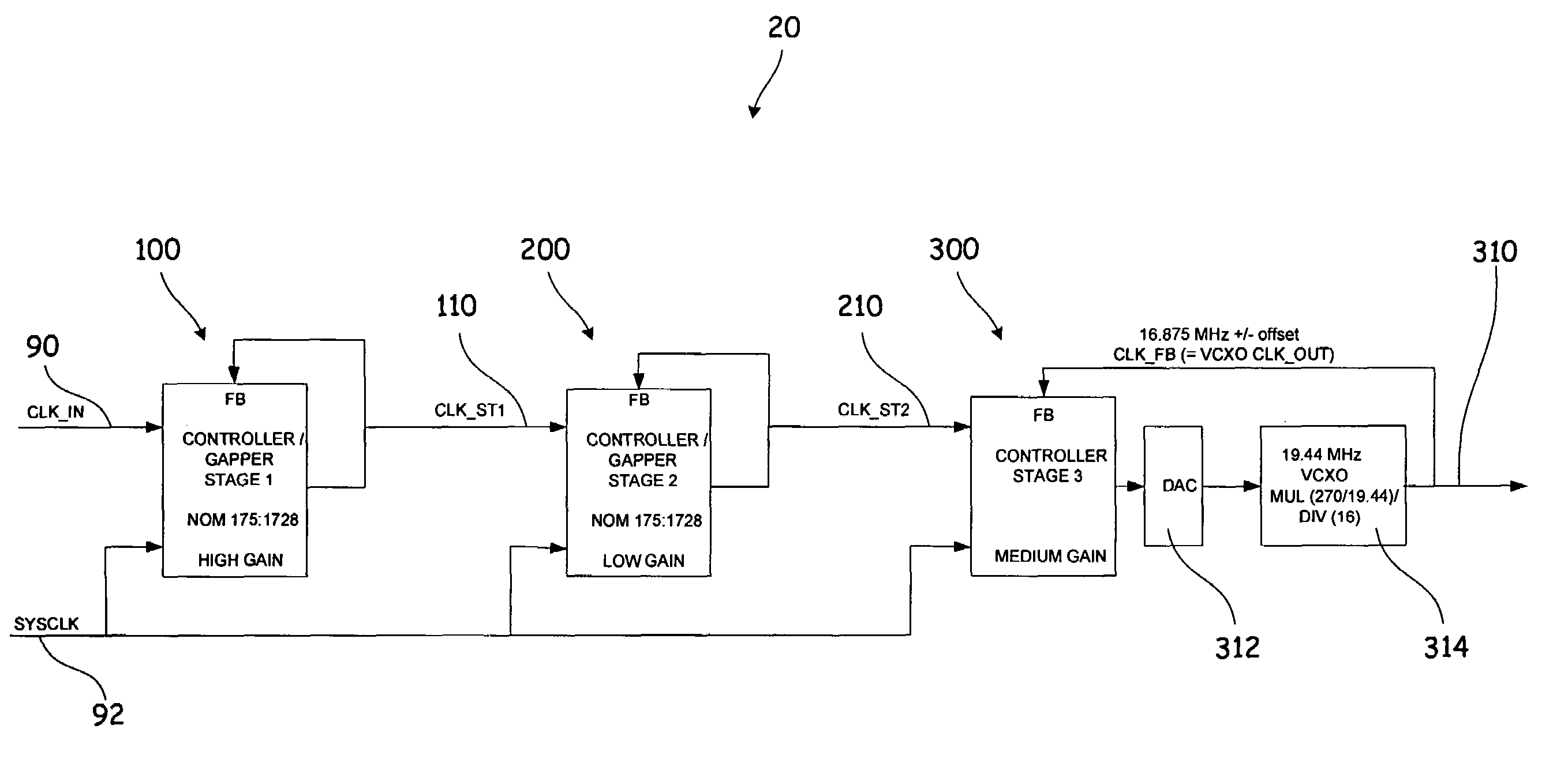
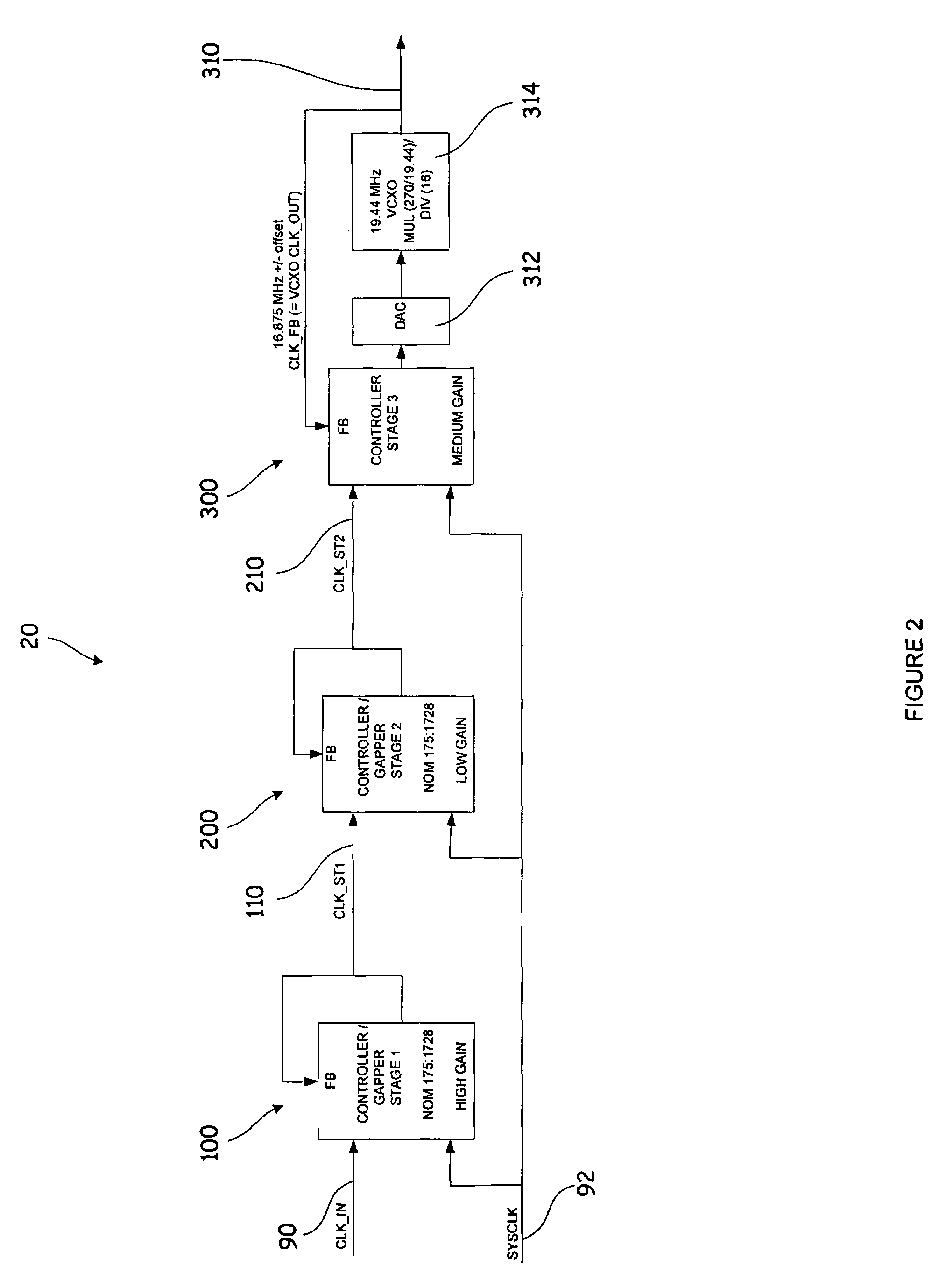
System and method for an adaptable timing recovery architecture for critically-timed transport applications
InactiveUS7733999B2Removing or filtering unwanted jitter and wanderRemove jitter and wanderPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexGate arrayLogic circuit design
The present invention provides a timing recovery architecture and circuit for recovering the clock timing from a received signal in critically-timed transport applications. The present invention further relates to a timing recovery architecture and circuit for removing network-induced clock jitter and wander that occurs in a transport network during asynchronous mapping techniques, bit and / or byte-stuffing techniques, or traditional pointer adjustment schemes associated with traditional PDH (pleisiosynchronous digital hierarchy), SDH (synchronous digital hierarchy), and packet-based networks. The timing recovery circuit may be implemented in a logic circuit such as programmable, digital FPGA (field programmable gate array) logic, or alternatively in standard cell or gate-array ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit) technology, or like logic circuit design.
Owner:CIENA
Low-power-consumption magnetic multi-resistance-state memory cell
ActiveCN106654002ARealize multi-resistive storageSimple designMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionLogic circuit designProcess complexity
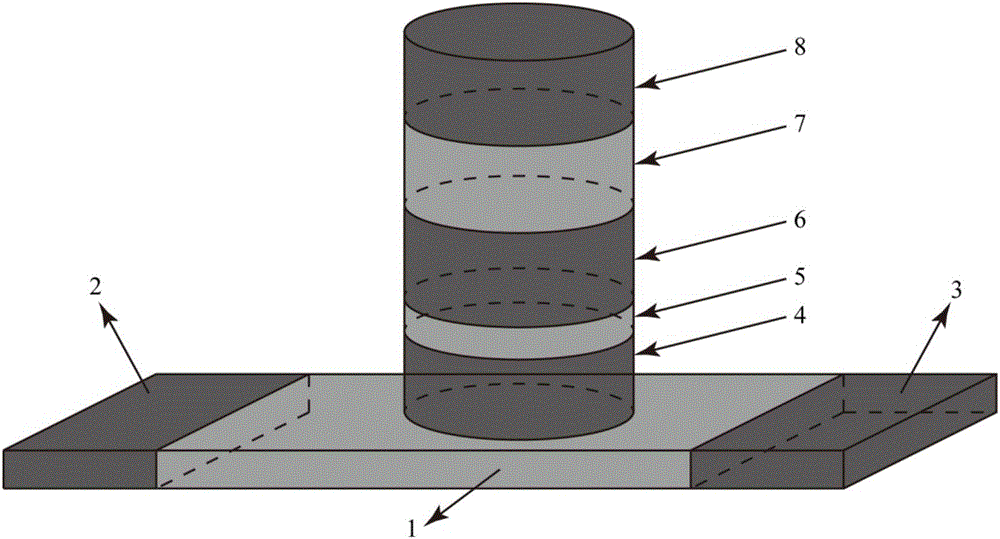
The invention provides a low-power-consumption magnetic multi-resistance-state memory cell. The low-power-consumption magnetic multi-resistance-state memory cell successively comprises an anti-ferromagnetic strip film, a first ferromagnetic metal, a first oxide, a second ferromagnetic metal, a first synthetic anti-ferromagnetic layer and a first electrode from bottom to top. The thickness of the anti-ferromagnetic strip film is 0-20 nm. The thickness of the first ferromagnetic metal is 0-3 nm. The thickness of the first oxide is 0-2 nm. The thickness of the second ferromagnetic metal is 0-3 nm. The thickness of the first synthetic anti-ferromagnetic layer is 0-20 nm. The thickness of the first electrode is 10-200 nm. The two ends of the anti-ferromagnetic strip film are respectively plated with a second electrode and a third electrode. Five layers of materials arranged above the anti-ferromagnetic strip film form material magnetic tunnel junctions. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the multi-resistance-state storage can be realized. The low-power-consumption magnetic multi-resistance-state memory cell can be applied not only to the fields of single-bit memory and logic operation, but also the fields of brain-like calculation and the like. Data are written by adopting a unidirectional current, so that the design of memories and logic circuits is simplified. The integration level of circuits is improved and the power consumption of the memory cell is reduced. The process complexity and the manufacturing cost are reduced. Moreover, data are written by using different branches, so that the write operations of different data are independently optimized and designed.
Owner:致真存储(北京)科技有限公司
Method for dynamic balancing of a clock tree
InactiveUS20060006917A1Excessively generatedSolid-state devicesElectric pulse generatorComputer architectureTime delays
The present invention provides a method to balance a clock tree dynamically. A controllable buffer is inserted in a specific level of a clock tree, and a controller is provided for adjusting two clocks with different skew by controlling the PMOS / NMOS arrangements in the controllable buffer so as to generate more current for compensating the time delay of slow clock to a sink. This method effectively suppressed the clock skew generated by the voltage drop or the temperature variations in the synchronous logic circuit design.
Owner:PRINCETON TECH CORP
Low-power-consumption magnetic storage unit
ActiveCN106449970ASimple designHighly integratedMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic storageLogic circuit design
The invention discloses a low-power-consumption magnetic storage unit which consists of six layers from bottom to top, that is, a heavy metal stripy film of 0-20nm thick, a first ferromagnetic metal layer of 0-3nm thick, a first oxide layer of 0-2nm thick, a second ferromagnetic metal layer of 0-3nm thick, a first synthesized antiferromagnetic layer of 0-20nm thick and a first electrode of 10-20nm thick, wherein two ends of the heavy metal stripy film are respectively plated with a second electrode and a third electrode; the five layers of substances above the heavy metal stripy film form magnetic tunnel junctions. According to the low-power-consumption magnetic storage unit, data can be written through one-way current, so that design of a memory and a logic circuit can be simplified, the circuit integration degree is increased, the power consumption of the storage unit is reduced, and the complexity and the manufacturing cost of processes can be reduced; as data are written through different branches, writing operation of different data can be independently optimized and designed conveniently.
Owner:致真存储(北京)科技有限公司
Logic circuit and method of logic circuit design
InactiveUS8004316B2Fast and versatileReduce areaLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSpecial data processing applicationsLow voltageLogic circuit design
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method and Apparatus for Testing Logic Circuit Designs
InactiveUS20070113129A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionLogic circuit designTester device
Disclosed is a logic testing system that includes a decompressor and a tester in communication with the decompressor. The tester is configured to store a seed and locations of scan inputs and is further configured to transmit the seed and the locations of scan inputs to the decompressor. The decompressor is configured to generate a test pattern from the seed and the locations of scan inputs. The decompressor includes a first test pattern generator, a second test pattern generator, and a selector configured to select the test pattern generated by the first test pattern generator or the test pattern generated by the second test pattern generator using the locations of scan inputs.
Owner:NEC CORP
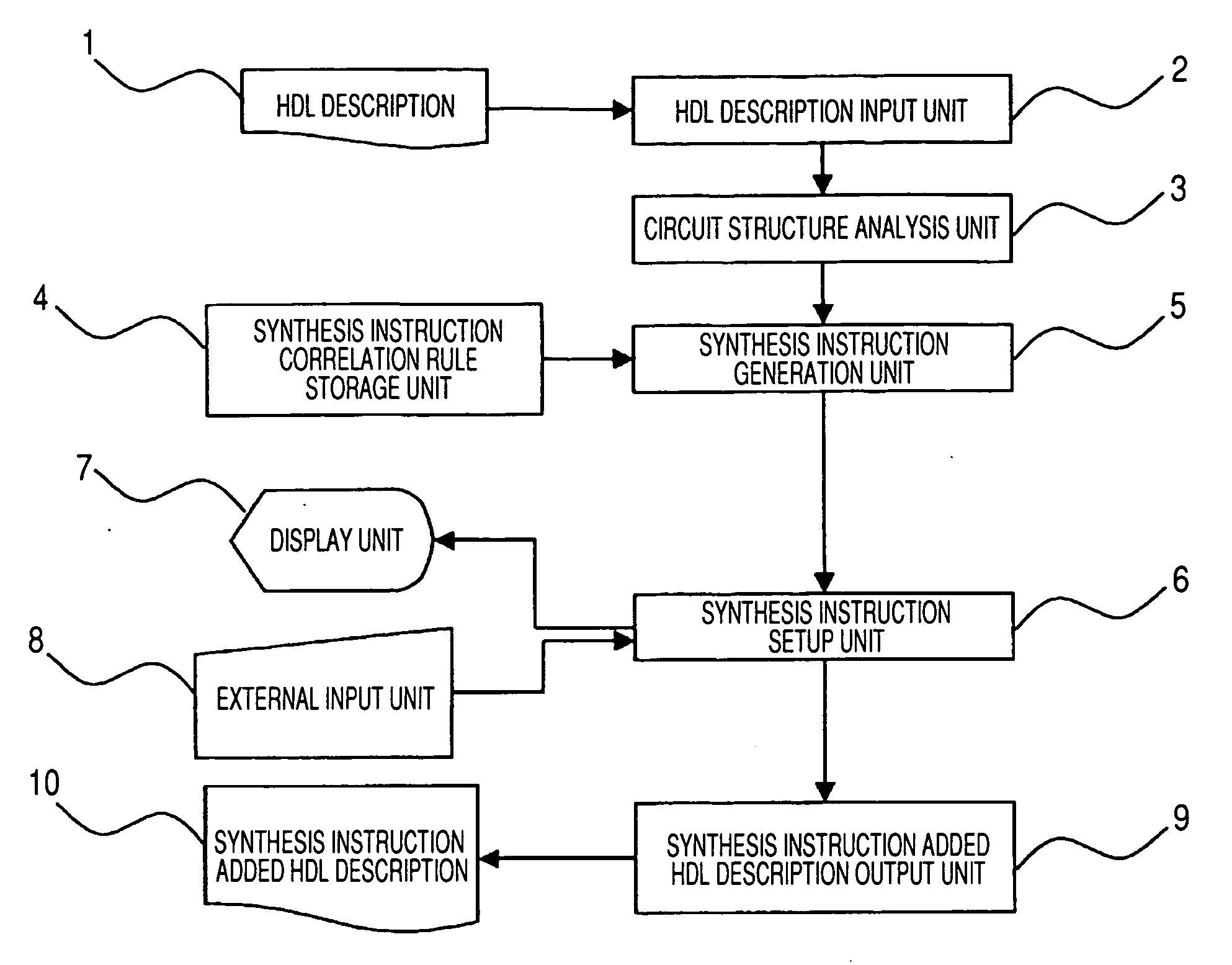
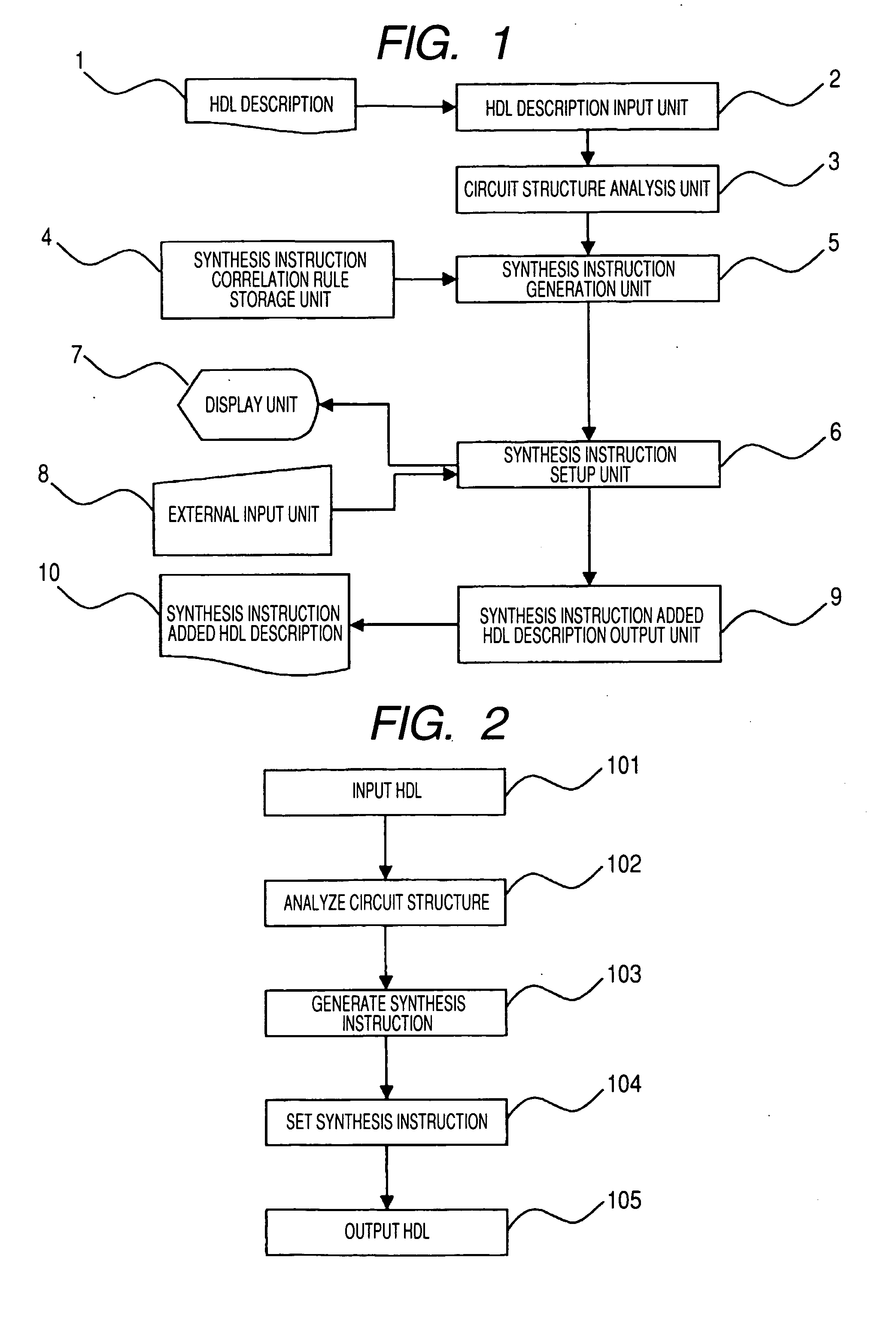
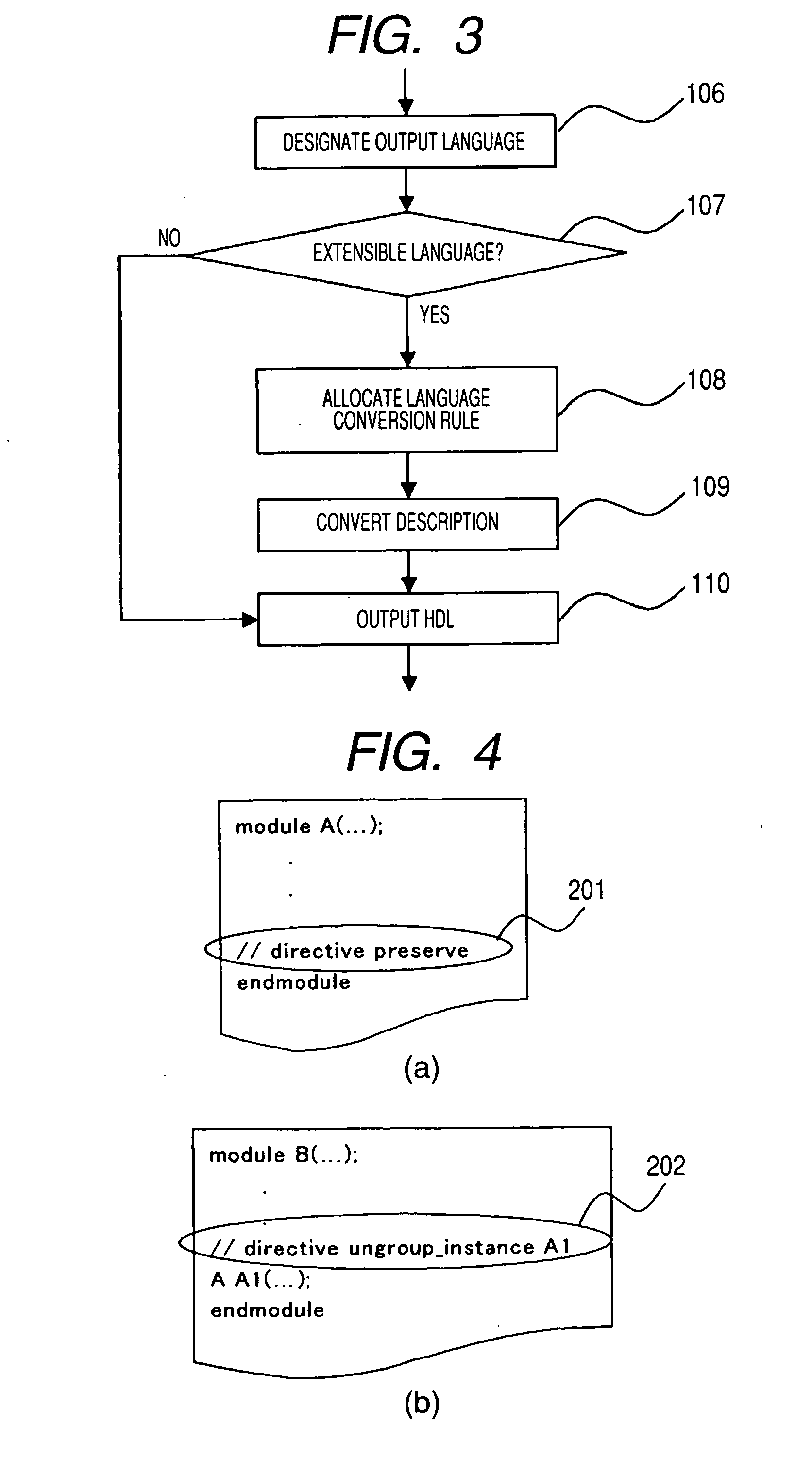
Logic circuit design support apparatus, and logic circuit design support method employing this apparatus
InactiveUS20070083844A1Simple preparation processReduce in quantityCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStructure analysisMultiplexer
A circuit structure analysis unit performs structure analysis for logic circuit information, obtained from an HDL description, and acquires analysis results for function parts, such as a register, an operation unit and a multiplexer. A synthesis instruction generation unit compares the analysis results with a synthesis instruction correlation rule, and automatically generates a synthesis instruction to control a logic synthesis method. Finally, an HDL description output unit outputs a synthesis instruction added HDL description, wherein a synthesis instruction is inserted into the original HDL description. When the synthesis instruction added HDL description is employed in the logic synthesis, starting at the top hierarchical level, a synthesis instruction for the logic circuit is not required in a synthesis execution script.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com