Patents
Literature
597 results about "Clock skew" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
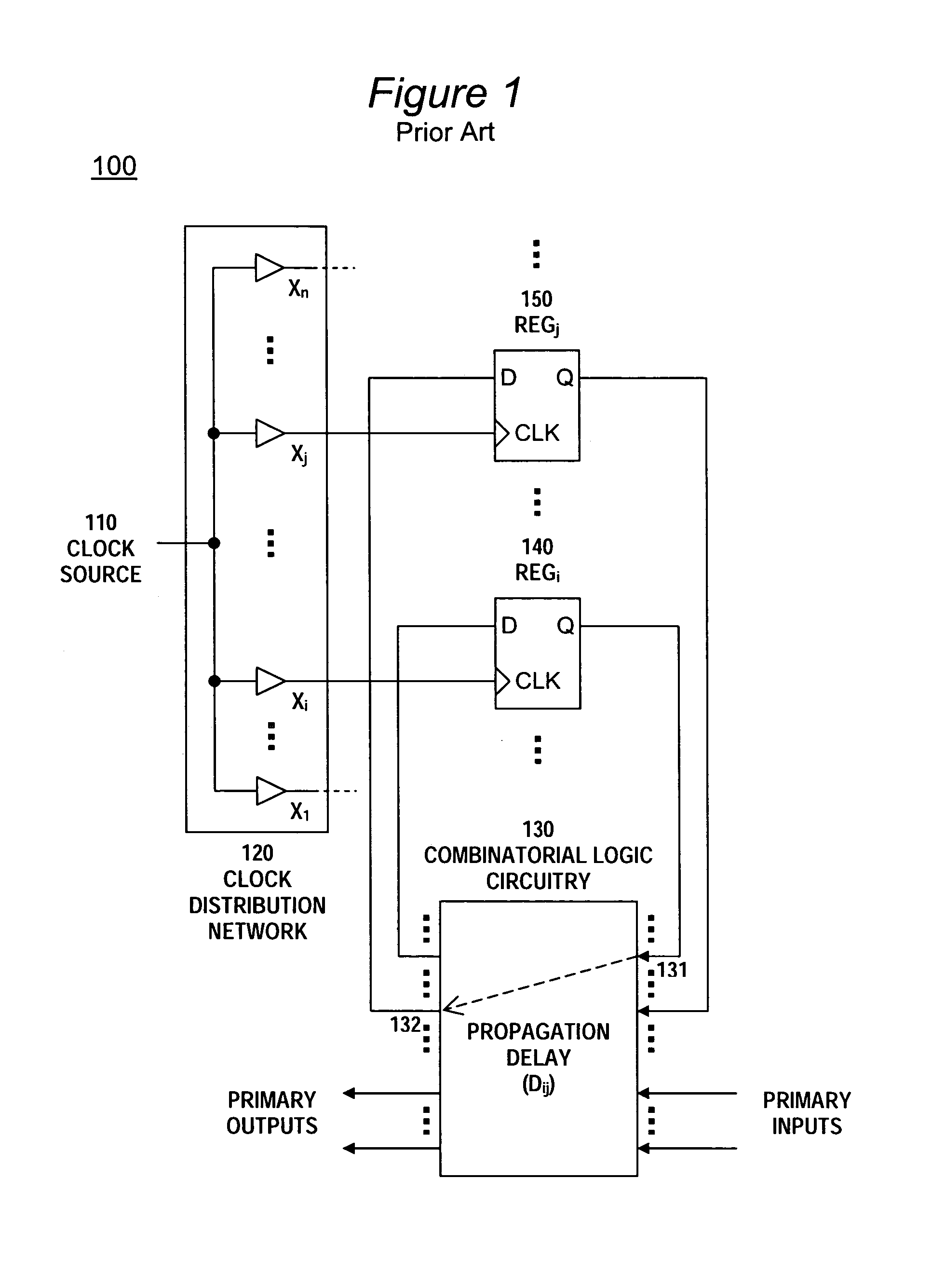
Clock skew (sometimes called timing skew) is a phenomenon in synchronous digital circuit systems (such as computer systems) in which the same sourced clock signal arrives at different components at different times. The instantaneous difference between the readings of any two clocks is called their skew.
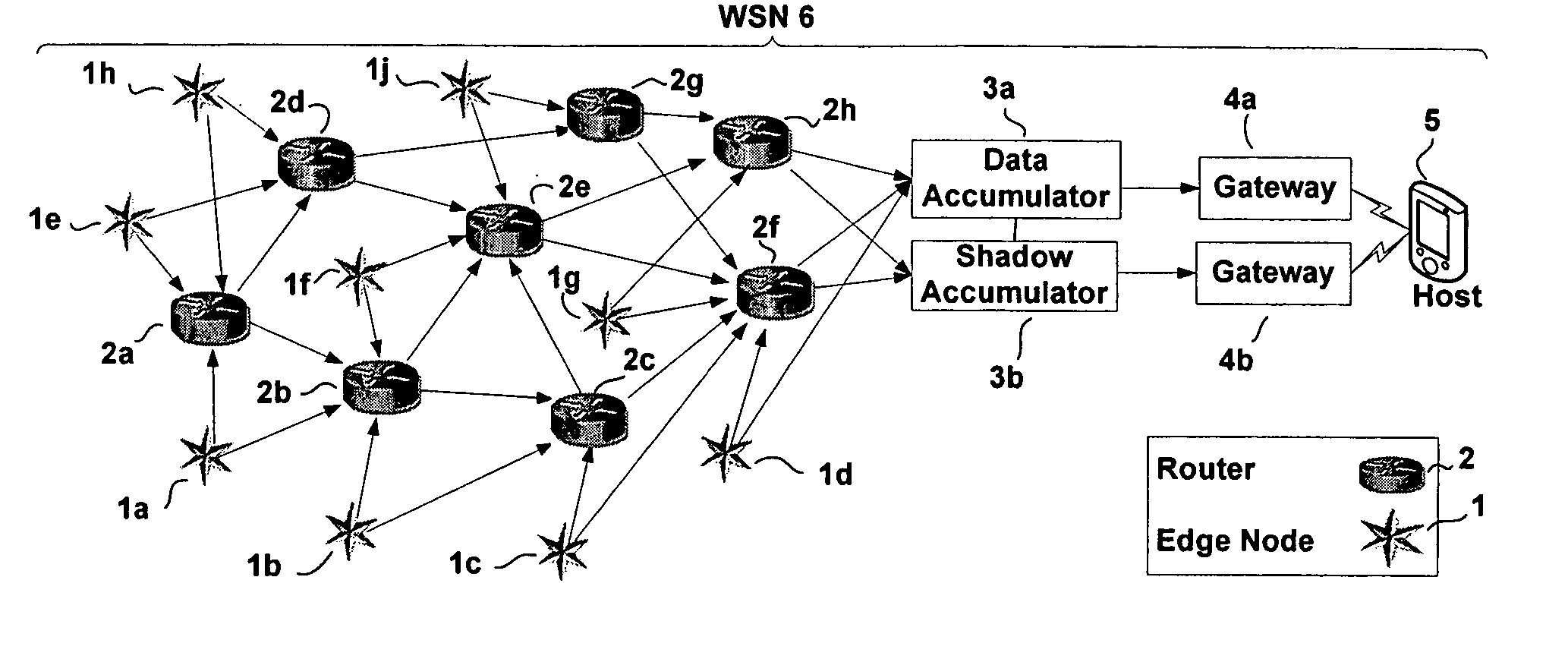
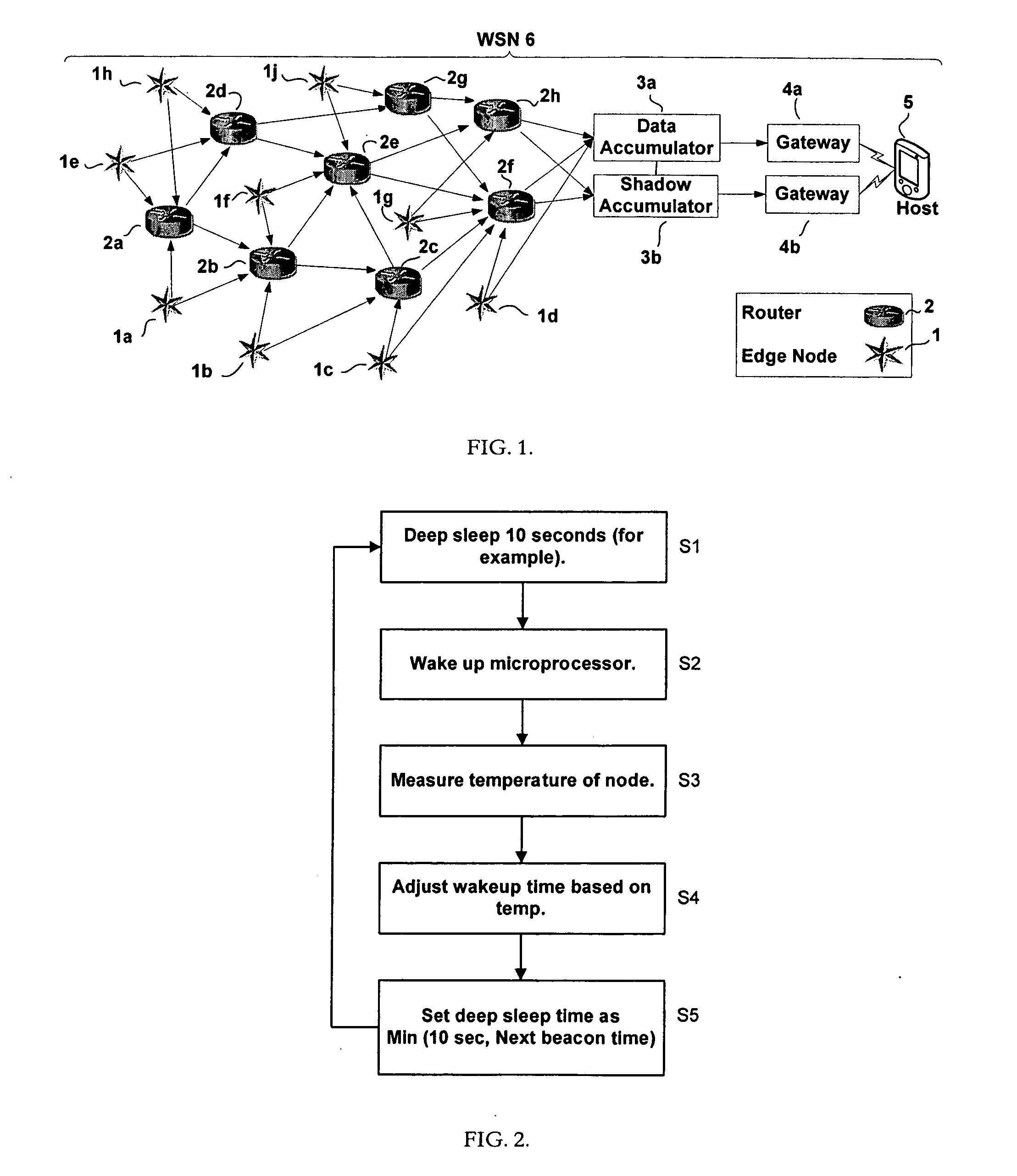
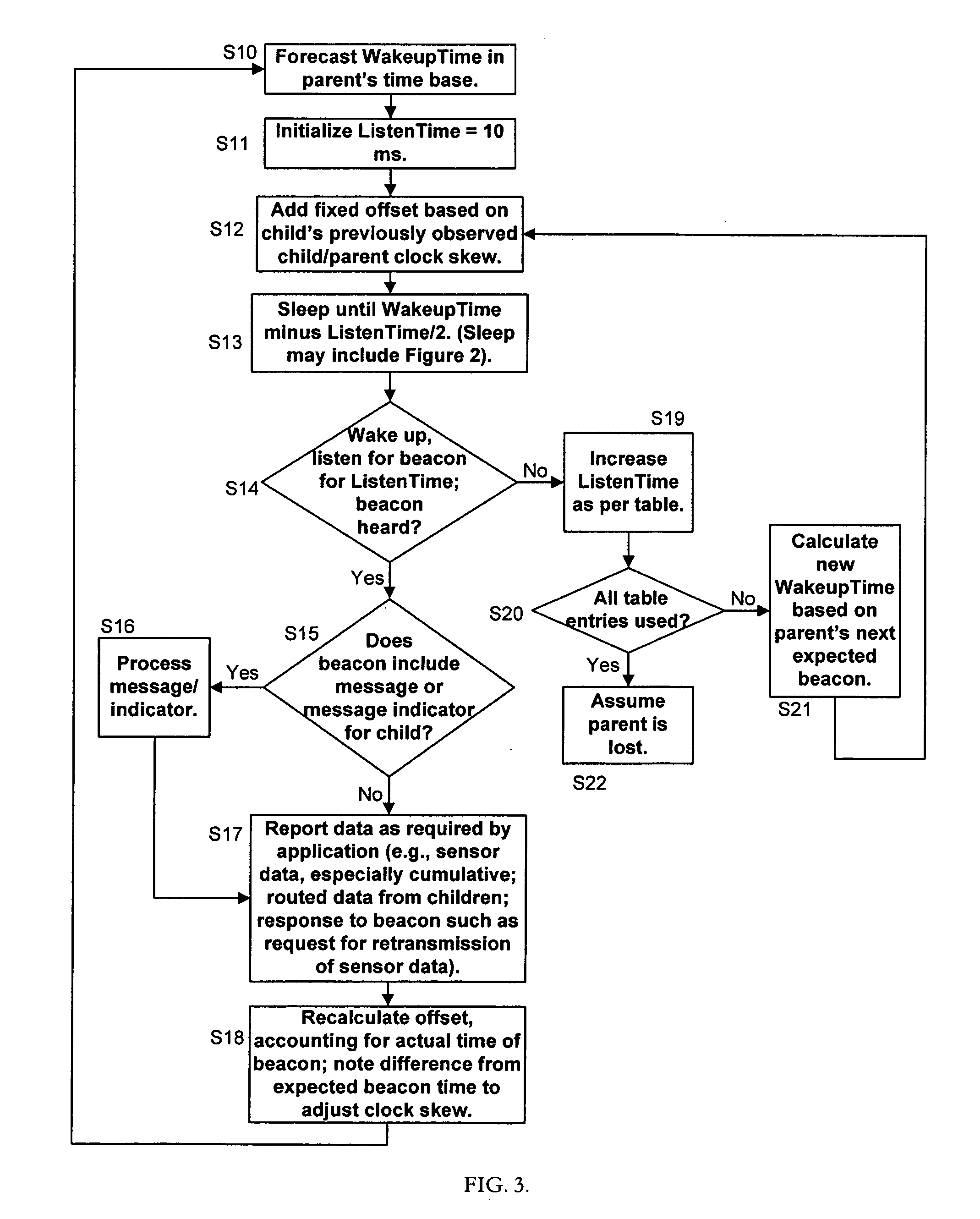
Method for reporting and accumulating data in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS20060187866A1Affect operationAffect abilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime managementEdge node
A method and apparatus for coordinating communication in a wireless sensor network may include a plurality of nodes, such as routers, edge nodes, data accumulators and / or gateways. Time management functions, such as determining an elapsed time, may be controlled based on a detected temperature, e.g., a temperature detected at a node, and / or based on a detected clock skew between two or more clocks in two or more different devices. Accurate time management may allow for devices to more accurately coordinate communication instances, e.g., communication that occurs at periodic wake up times. A cluster head, such as a data accumulator, may be associated with a network after its initial formation and cause nodes in the network to alter their hierarchy in the network, thereby making the cluster headaccumulator a parent to nodes in the network. Nodes having a relatively lower hop count may have a higher battery capacity than nodes having a higher hop count.
Owner:YOKOGAWA USA +1
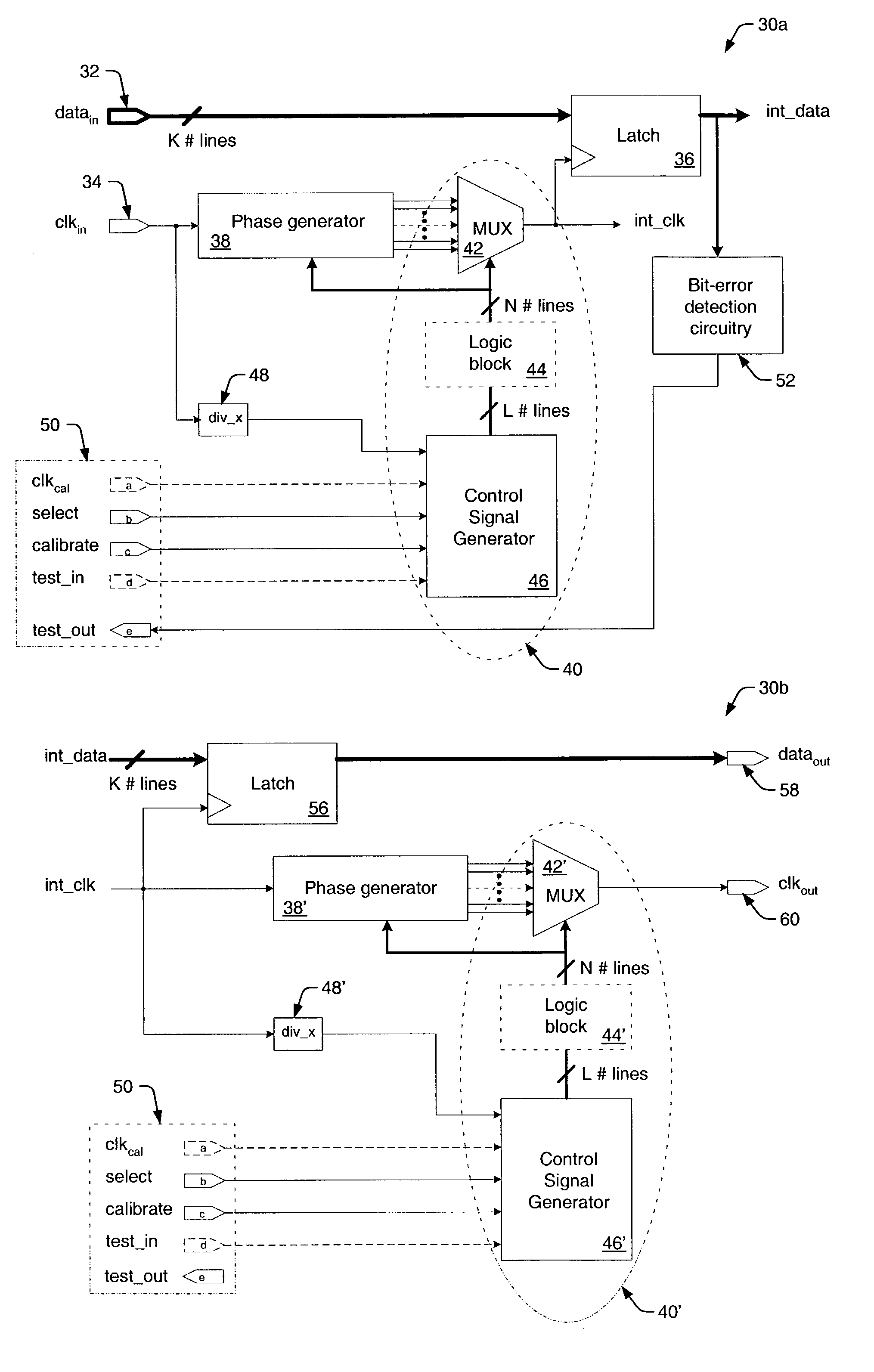
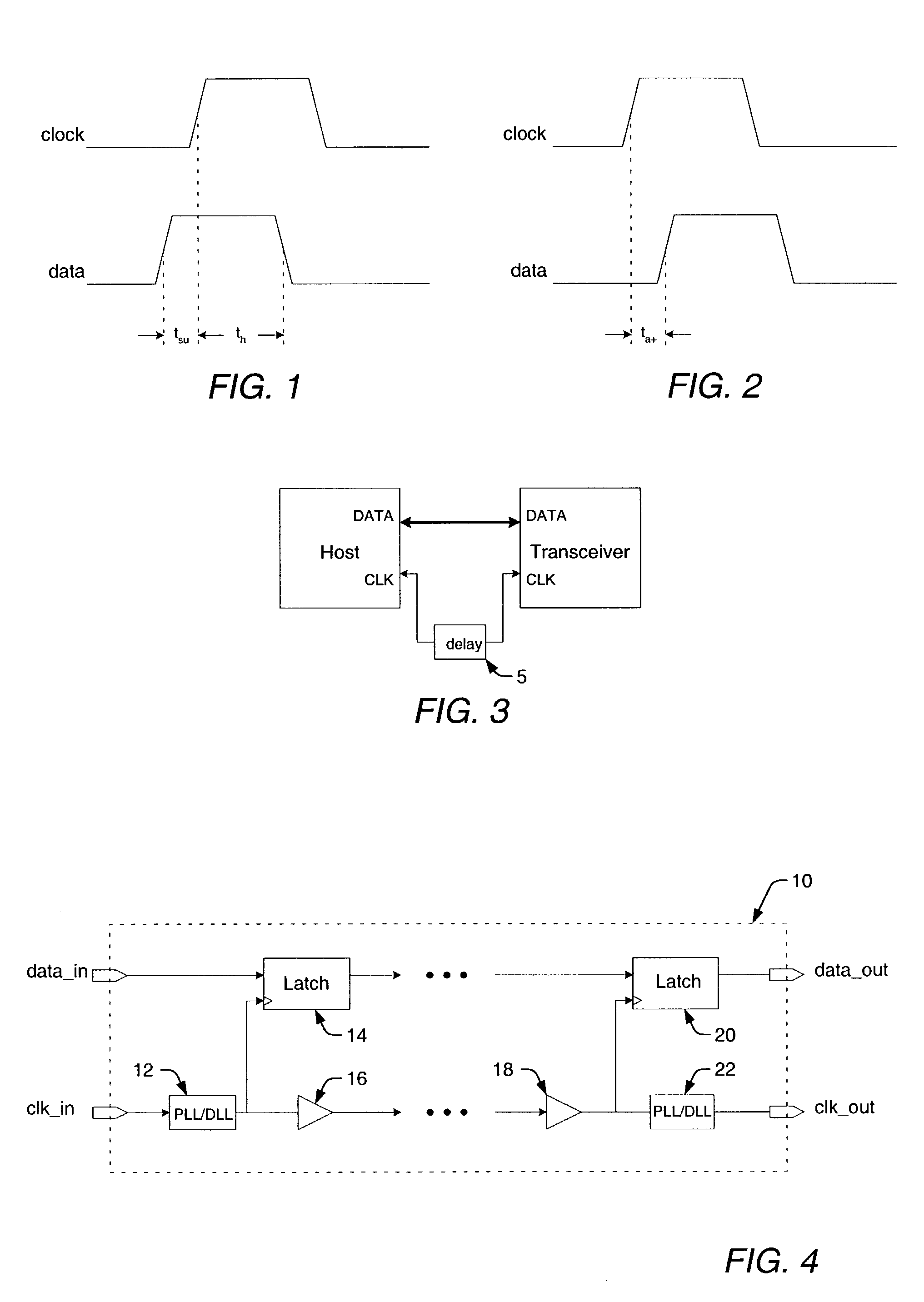
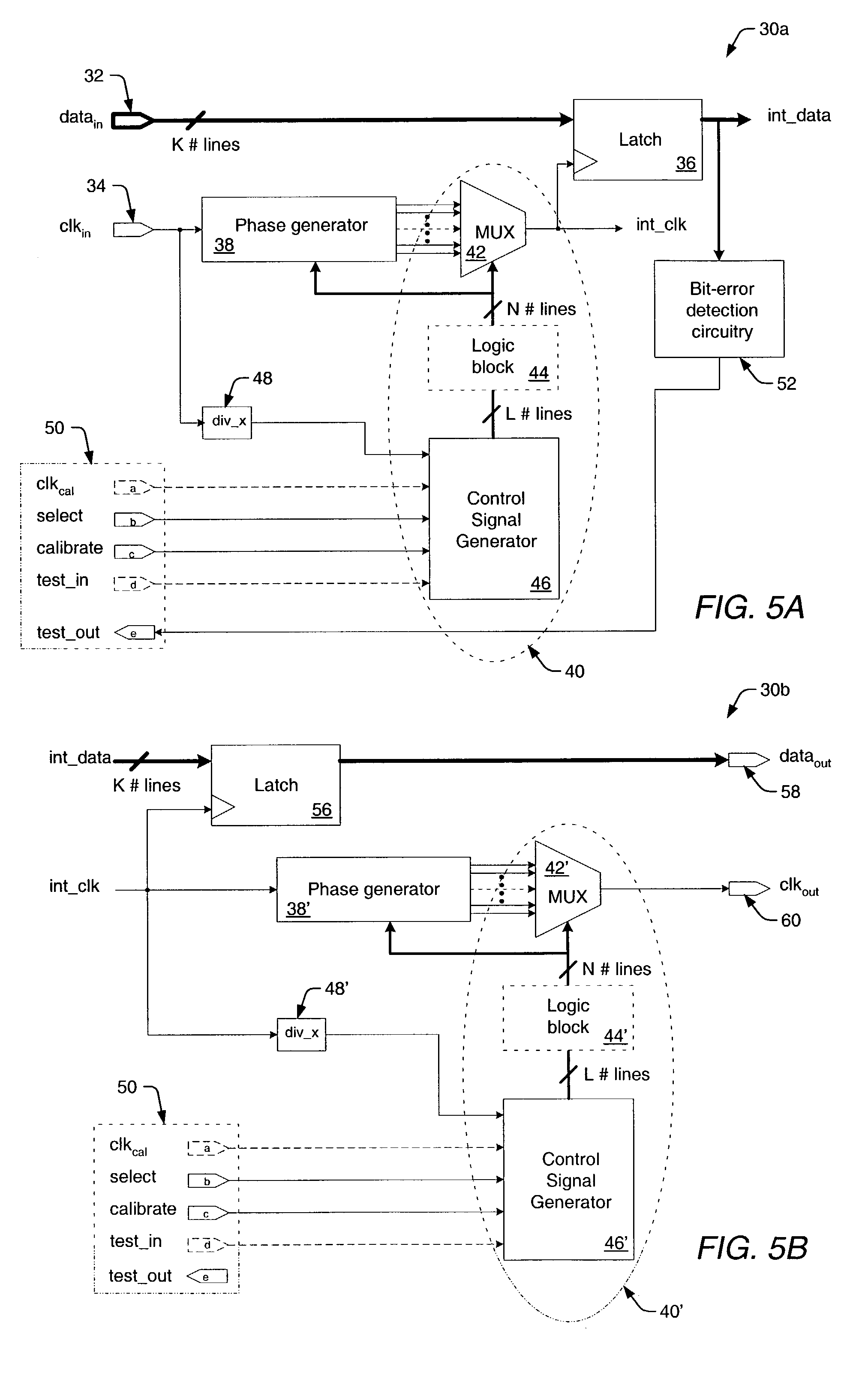
Parallel data interface and method for high-speed timing adjustment
InactiveUS7069458B1Accurate samplingMinimize clock skewPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingAccess timeTime delays
A parallel data interface and method is provided herein, which adjusts a timing relationship of a clock signal to not only minimize clock skew, but to also compensate for noise components that may affect one or more paths of a parallel data bus. In some embodiments, the parallel data interface includes a first phase generator coupled to generate a first plurality of time delay pulses, and a first phase selector adapted to select one of the first plurality of time delay pulses to adjust the timing of a clock signal to sample each and every one of the plurality of data signals between minimum setup and hold time thresholds. In some embodiments, the parallel data interface includes a second phase generator coupled to generate a second plurality of time delay pulses, and a second phase selector adapted to select one of the second plurality of time delay pulses to adjust the timing of the clock signal to output the plurality of data signals from the data interface at least an amount of time (i.e., an access time) after the adjusted clock transition is output from the data interface.
Owner:RPX CORP
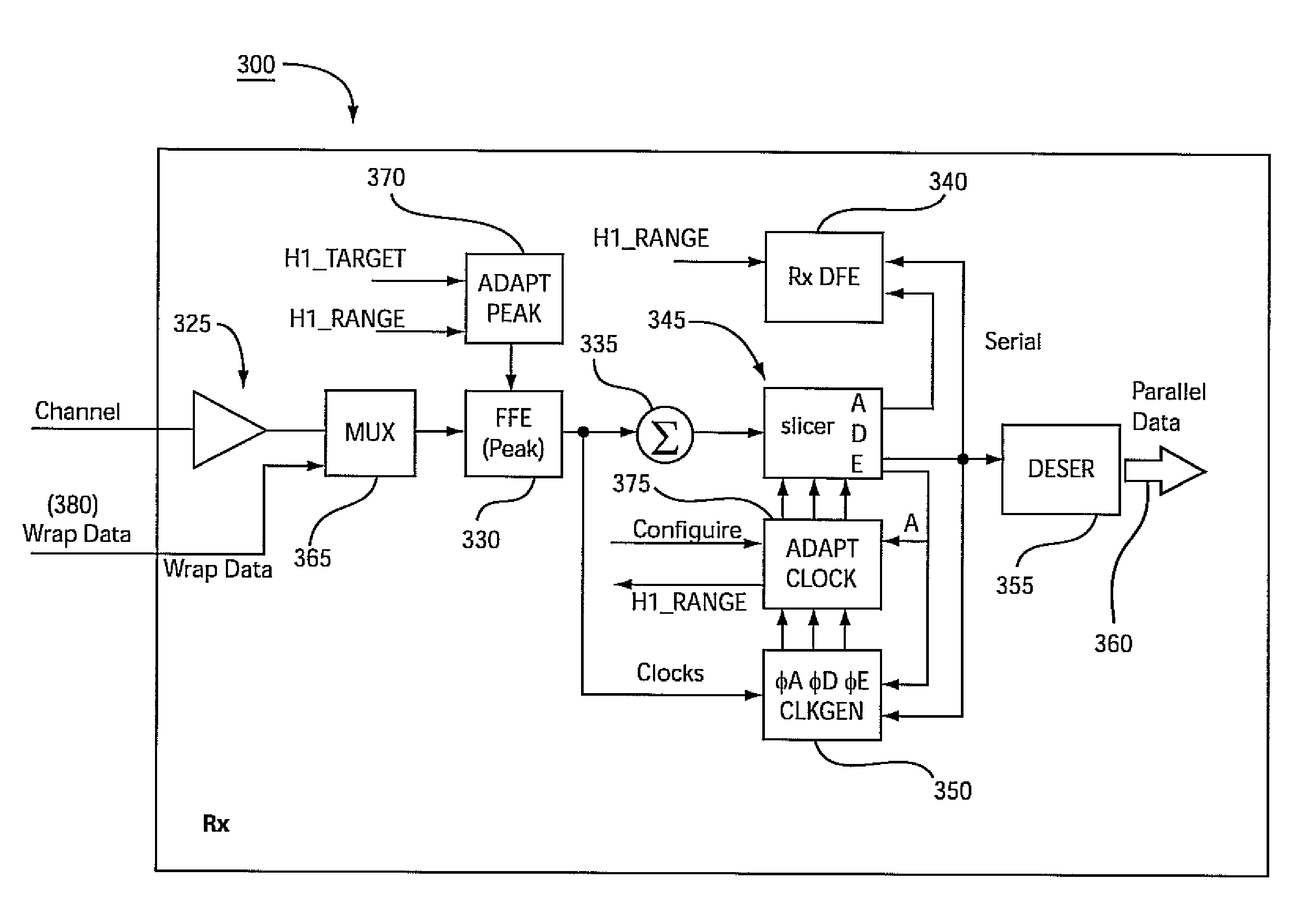
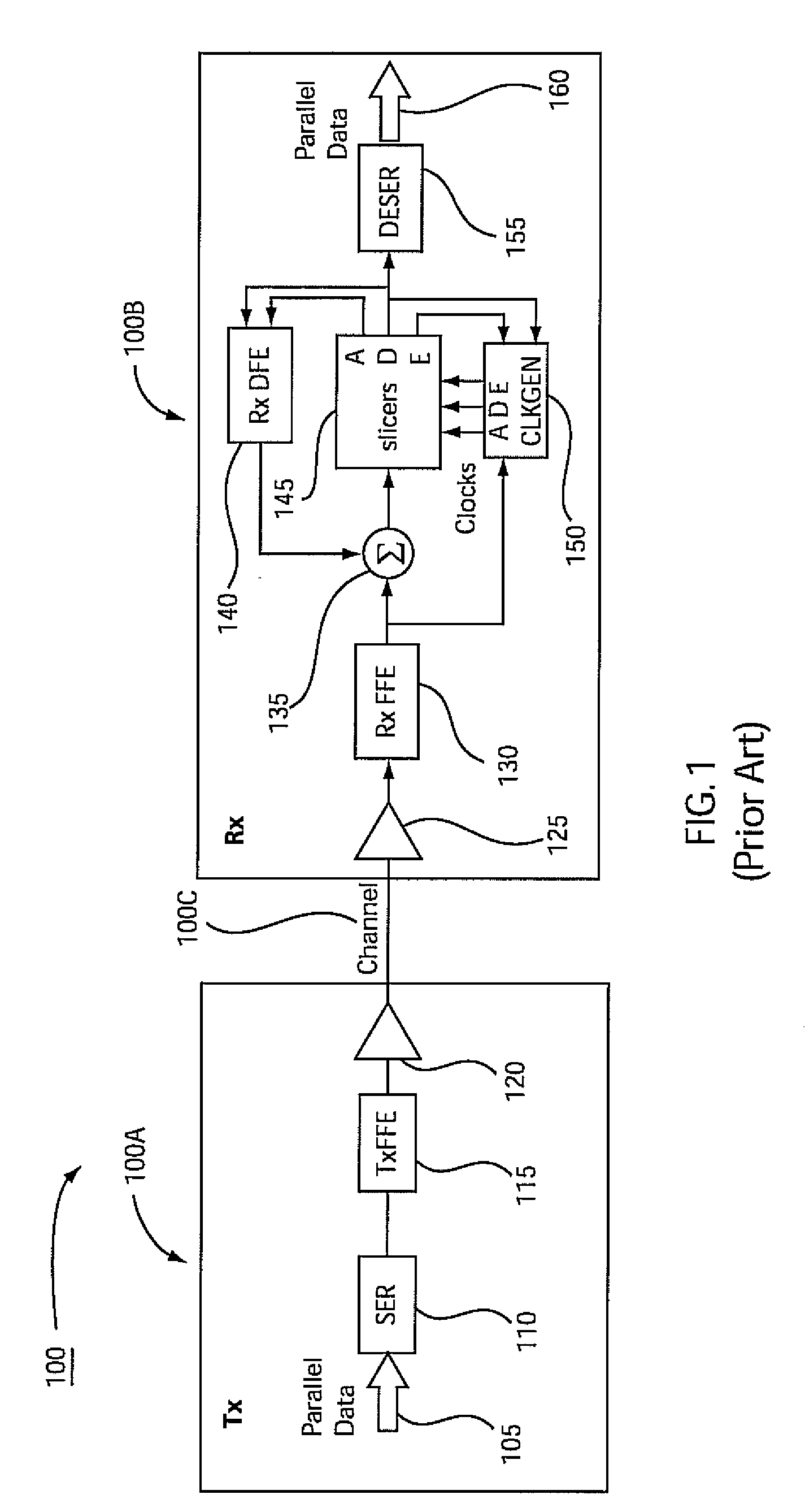
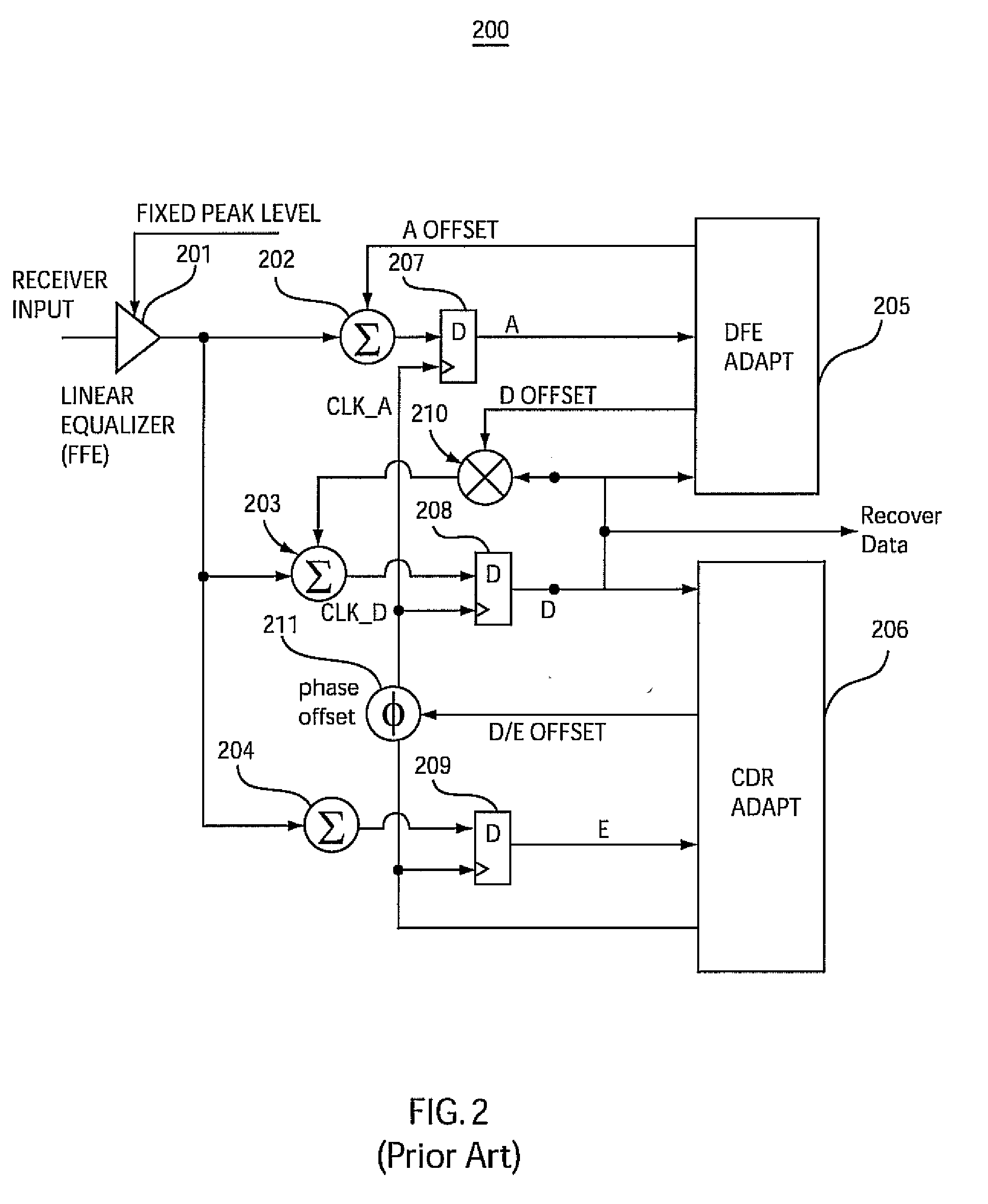
Adaptive clock and equalization control systems and methods for data receivers in communications systems
ActiveUS20100046683A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCommunications systemControl system
Systems and methods for adaptive clock and equalization control are provided for data receivers, which are based on a “closed loop” sampling clock framework that employs controllable and dynamically adapted time offsets on both local data and amplitude clocks. The controllable clock offsets are dynamically adapted using signal processing methods adapted to achieve optimum sampling of data and amplitude sampling clock signals to accurately detect data bits and optimize system equalization settings, including, decision-feedback equalizer and / or an optional linear equalizer preceding a decision-feedback equalizer.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
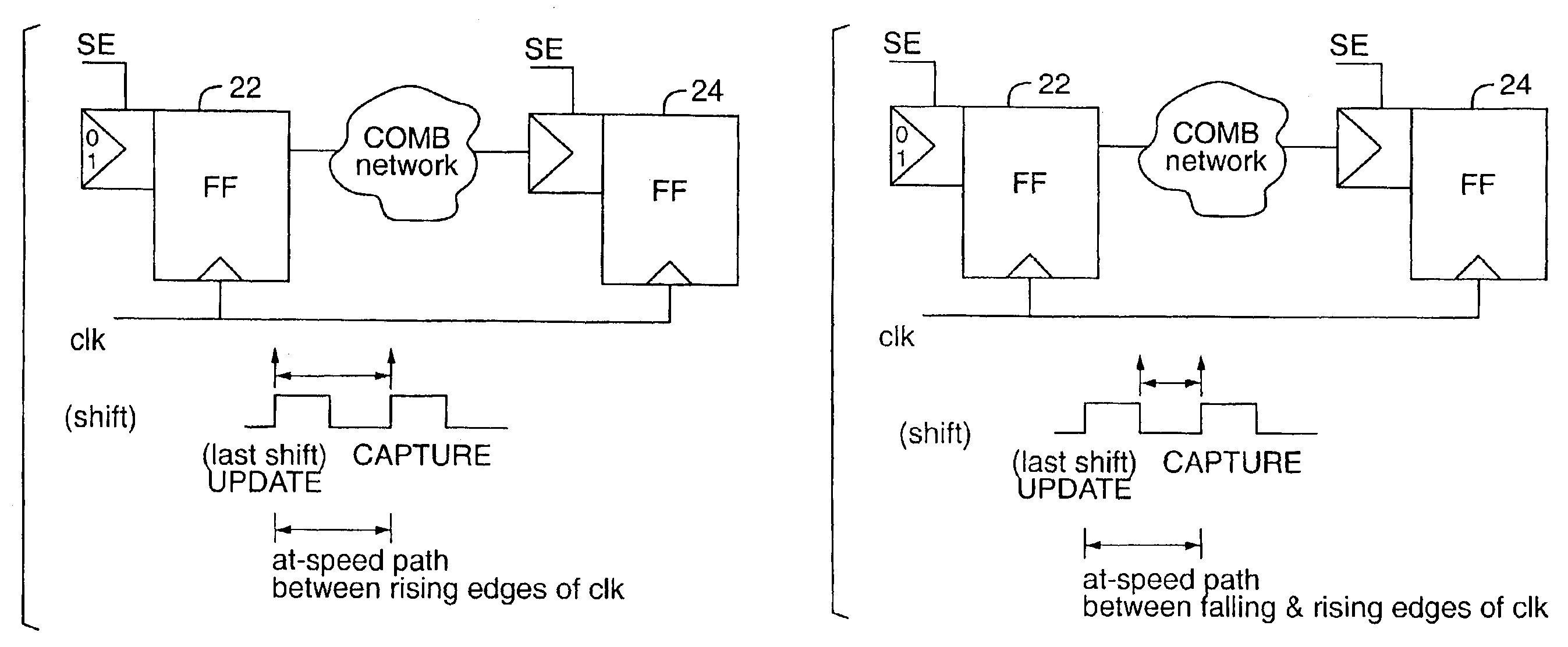
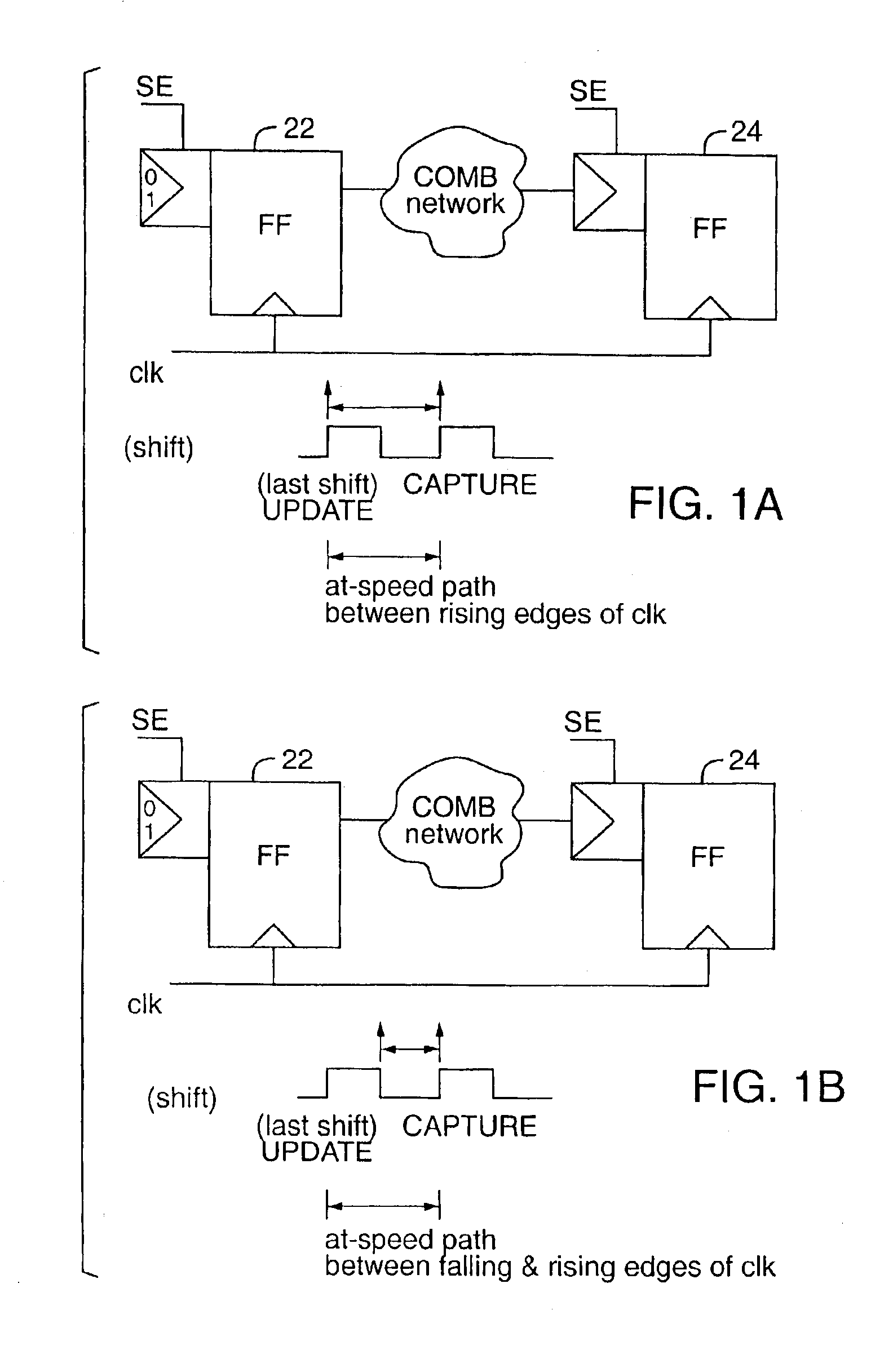
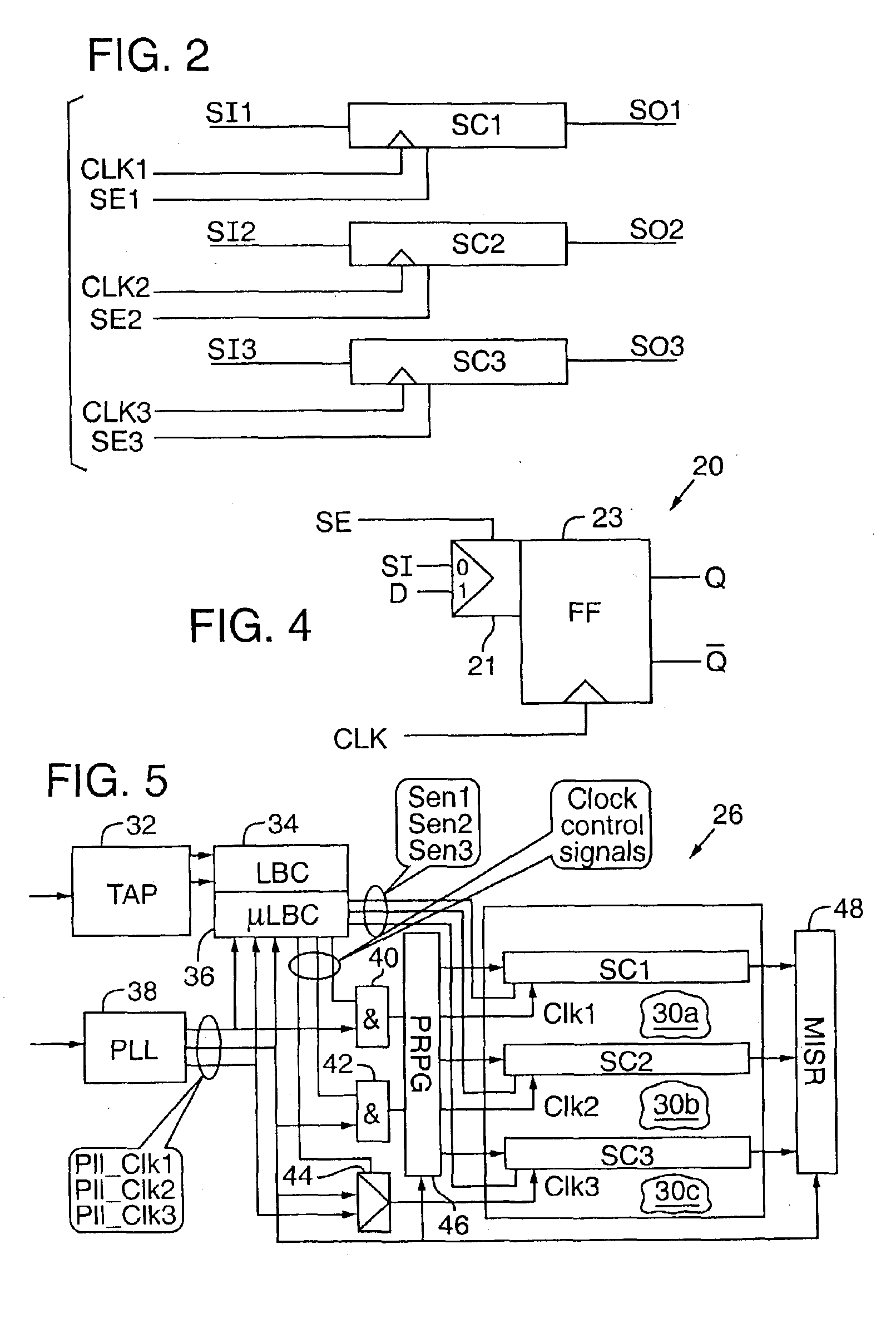
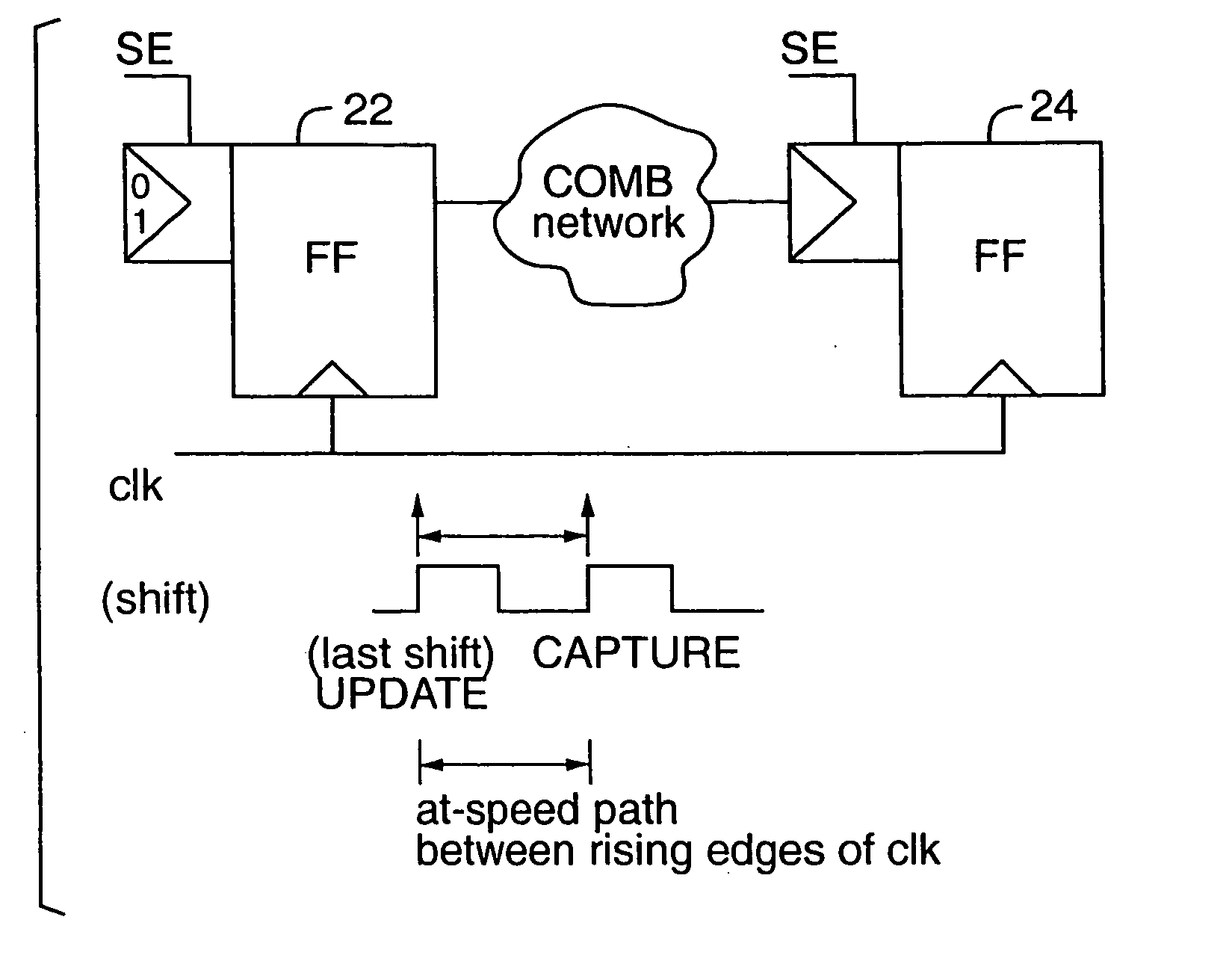
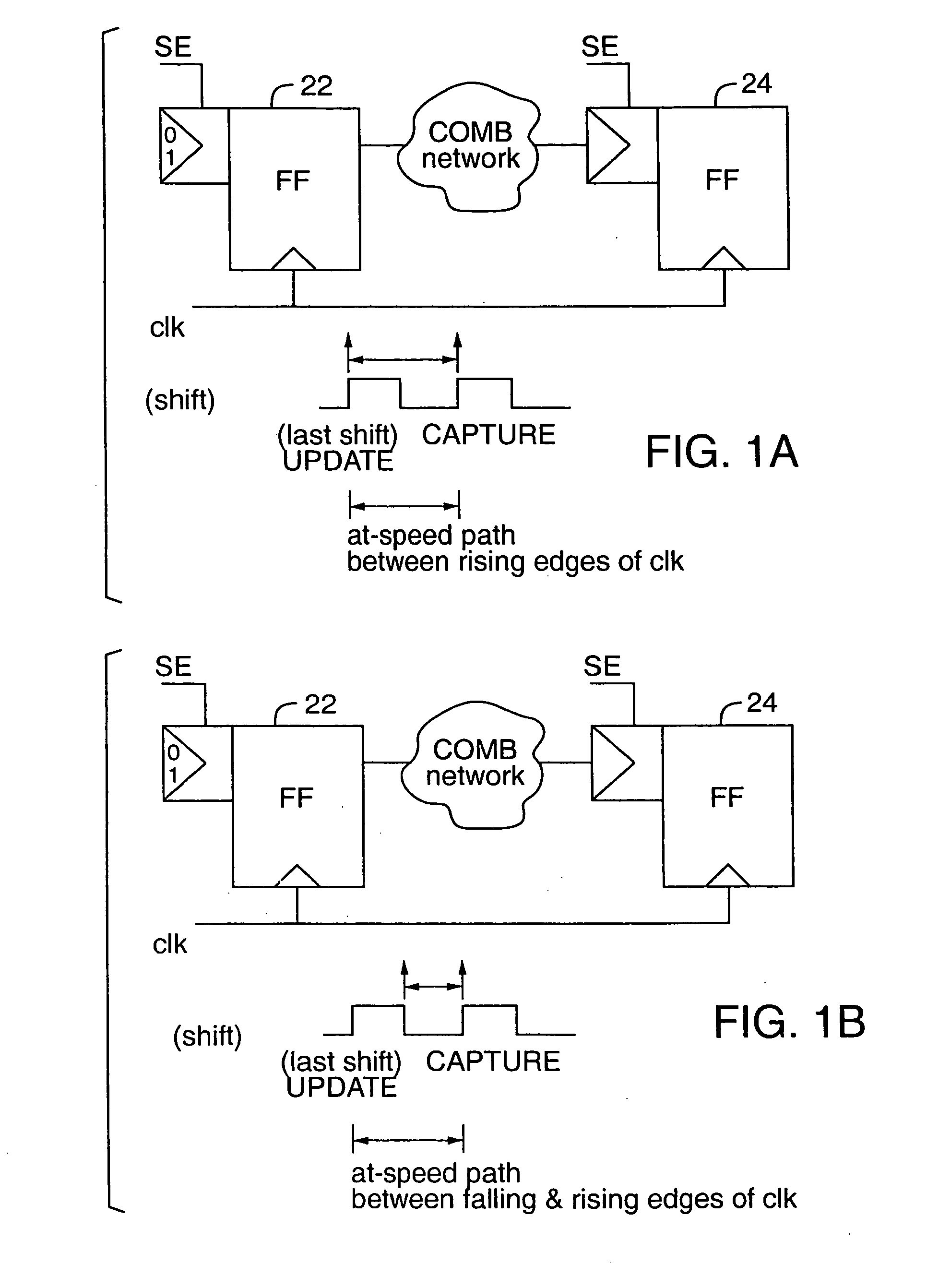
Method and apparatus for at-speed testing of digital circuits
InactiveUS6966021B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionMulti inputProcessor register
A scheme for multi-frequency at-speed logic Built-In Self Test (BIST) is provided. This scheme allows at-speed testing of very high frequency integrated circuits controlled by a clock signal generated externally or on-chip. The scheme is also applicable to testing of circuits with multiple clock domains which can be either the same frequency or different frequency. Scanable memory elements of the digital circuit are connected to define plurality of scan chains. The loading and unloading of scan chains is separated from the at-speed testing of the logic between the respective domains and may be done at a faster or slower frequency than the at-speed testing. The BIST controller, Pseudo-Random Pattern Generator (PRPG) and Multi-input Signature Register (MISR) work at slower frequency than the fastest clock domain. After loading of a new test pattern, a clock suppression circuit allows a scan enable signal to propagate for more that one clock cycle before multiple capture clock is applied. This feature relaxes the speed and skew constraints on scan enable signal design. Only the capture cycle is performed at the corresponding system timing. A programmable capture window makes it possible to test every intra- and inter-domain at-speed without the negative impact of clock skew between clock domains.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
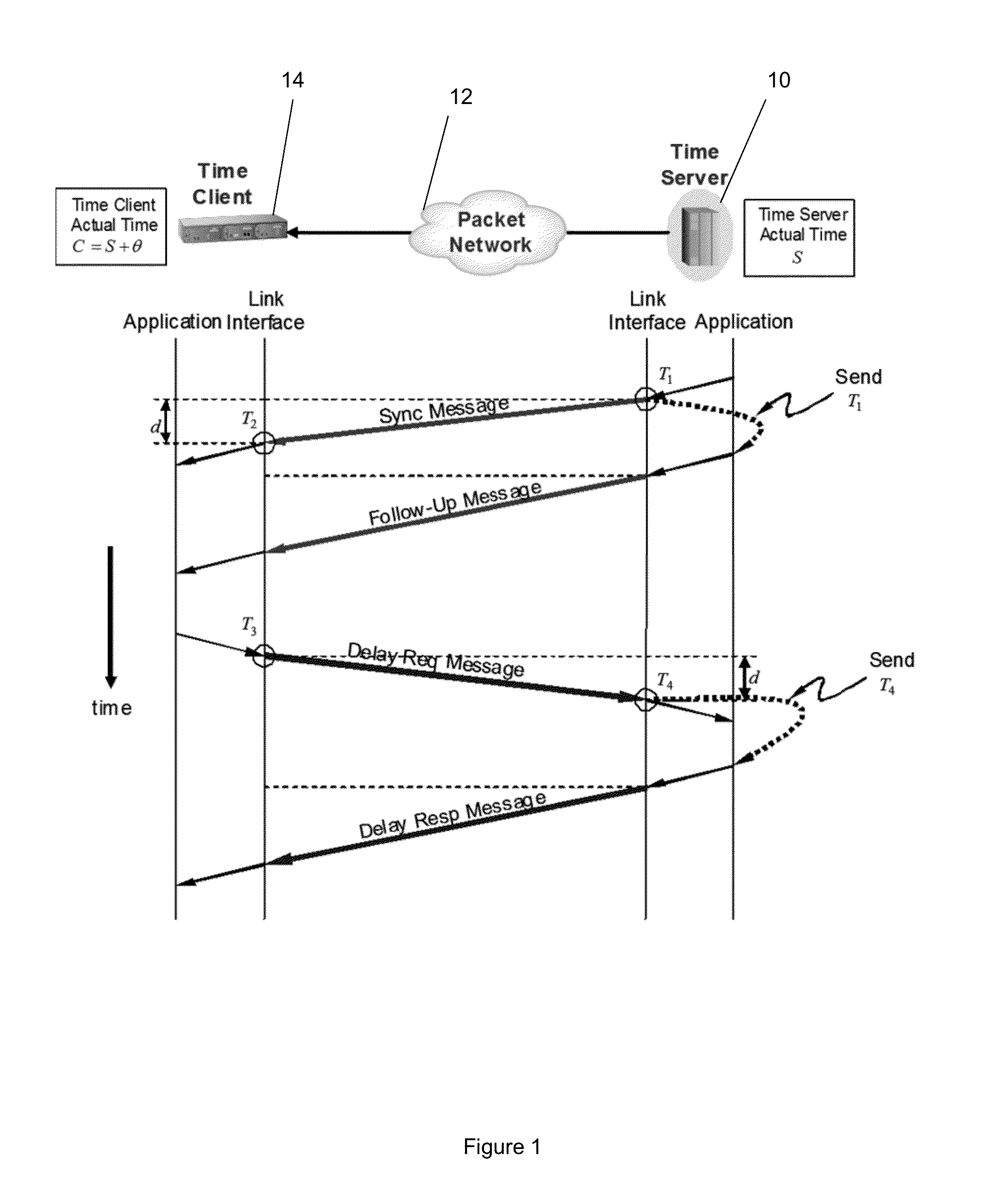
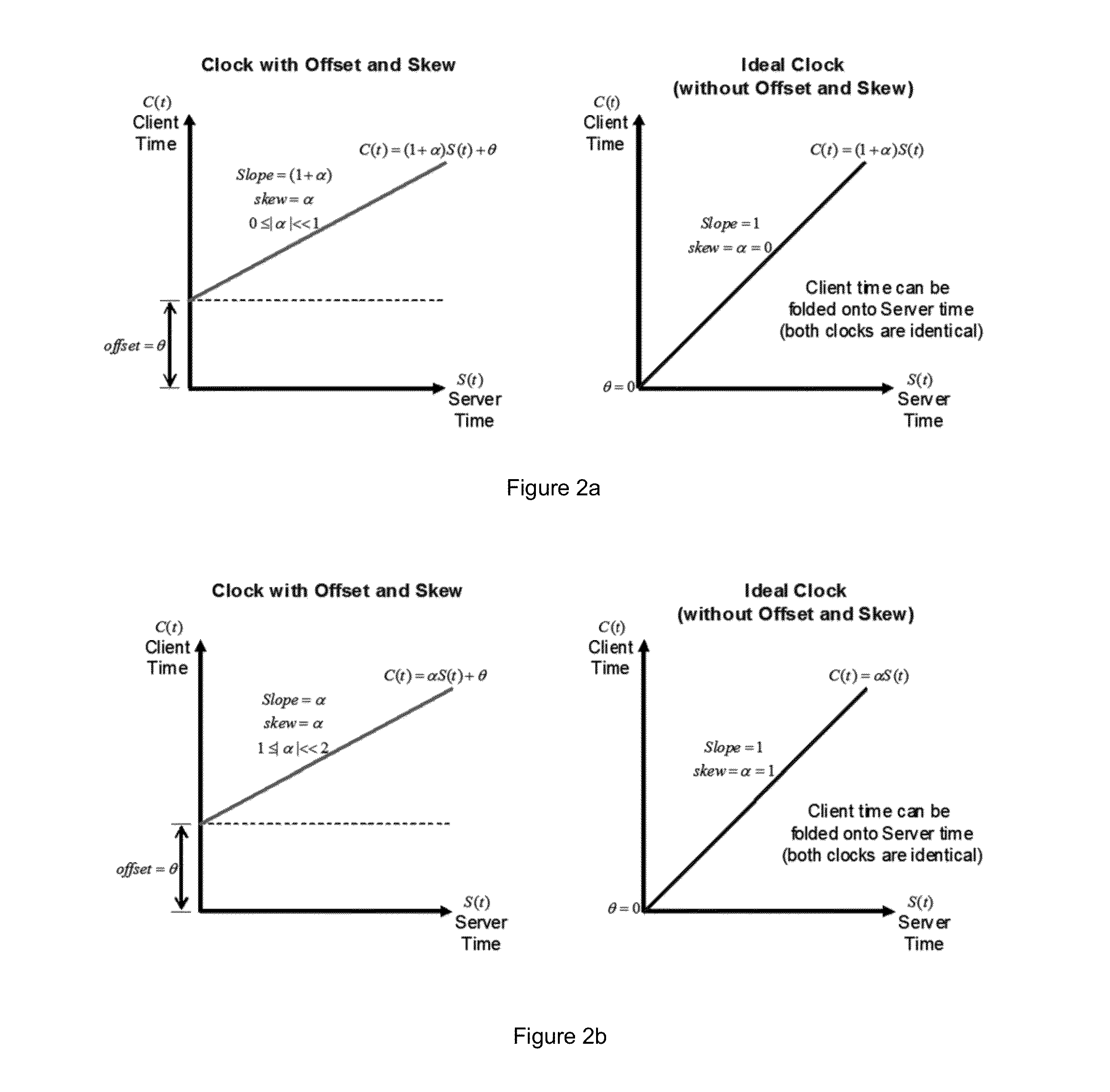
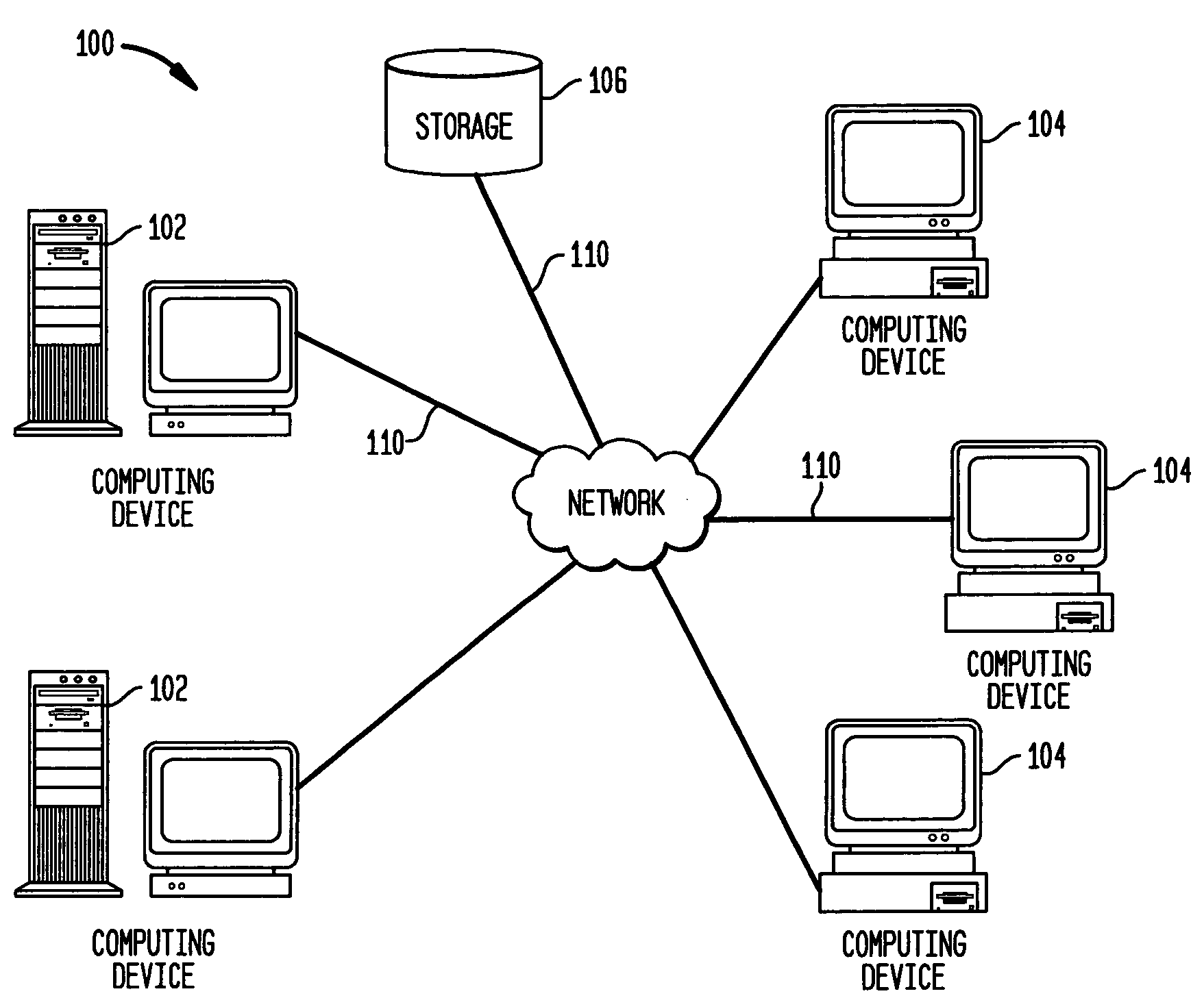
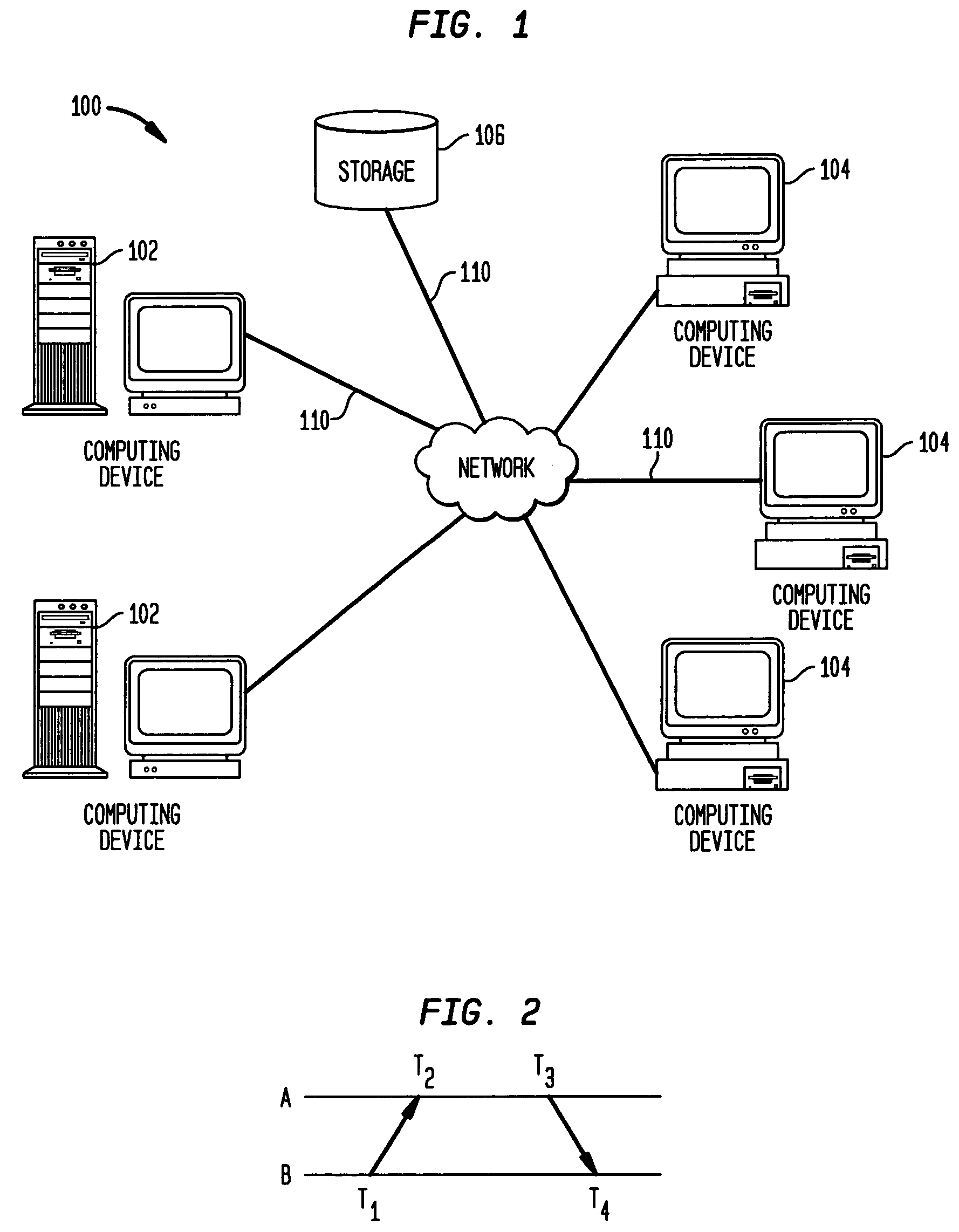
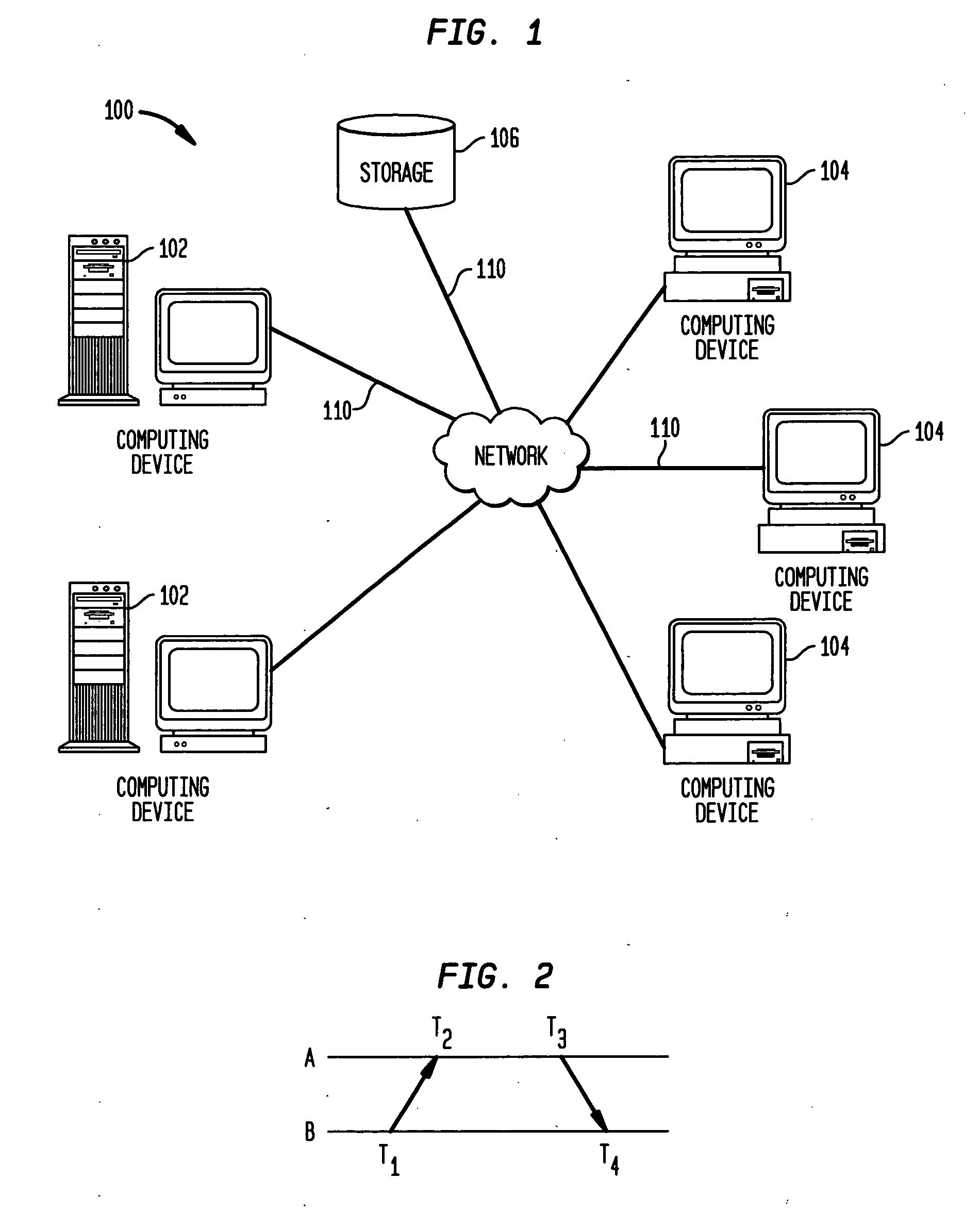
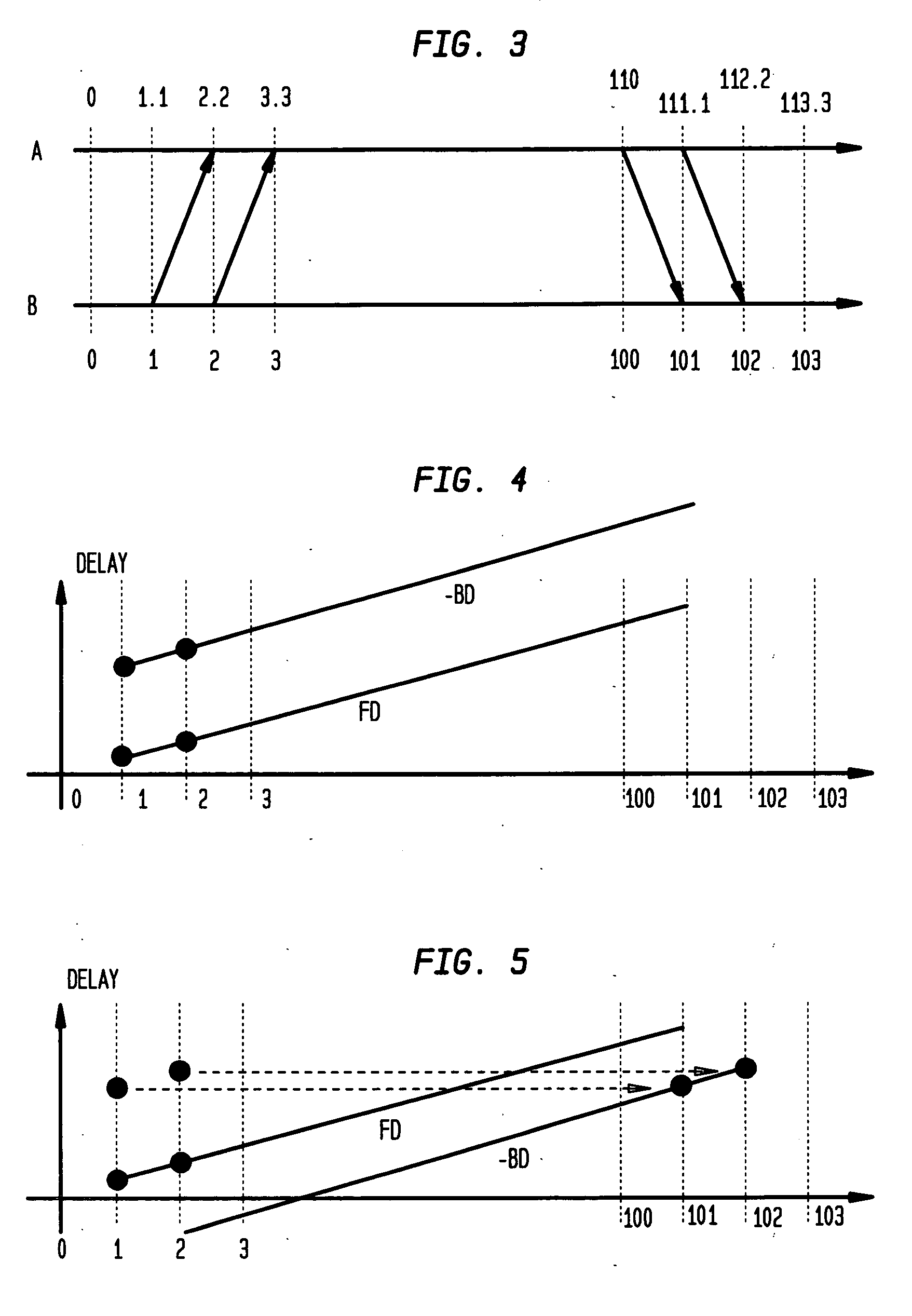
Method and system for clock skew and offset estimation
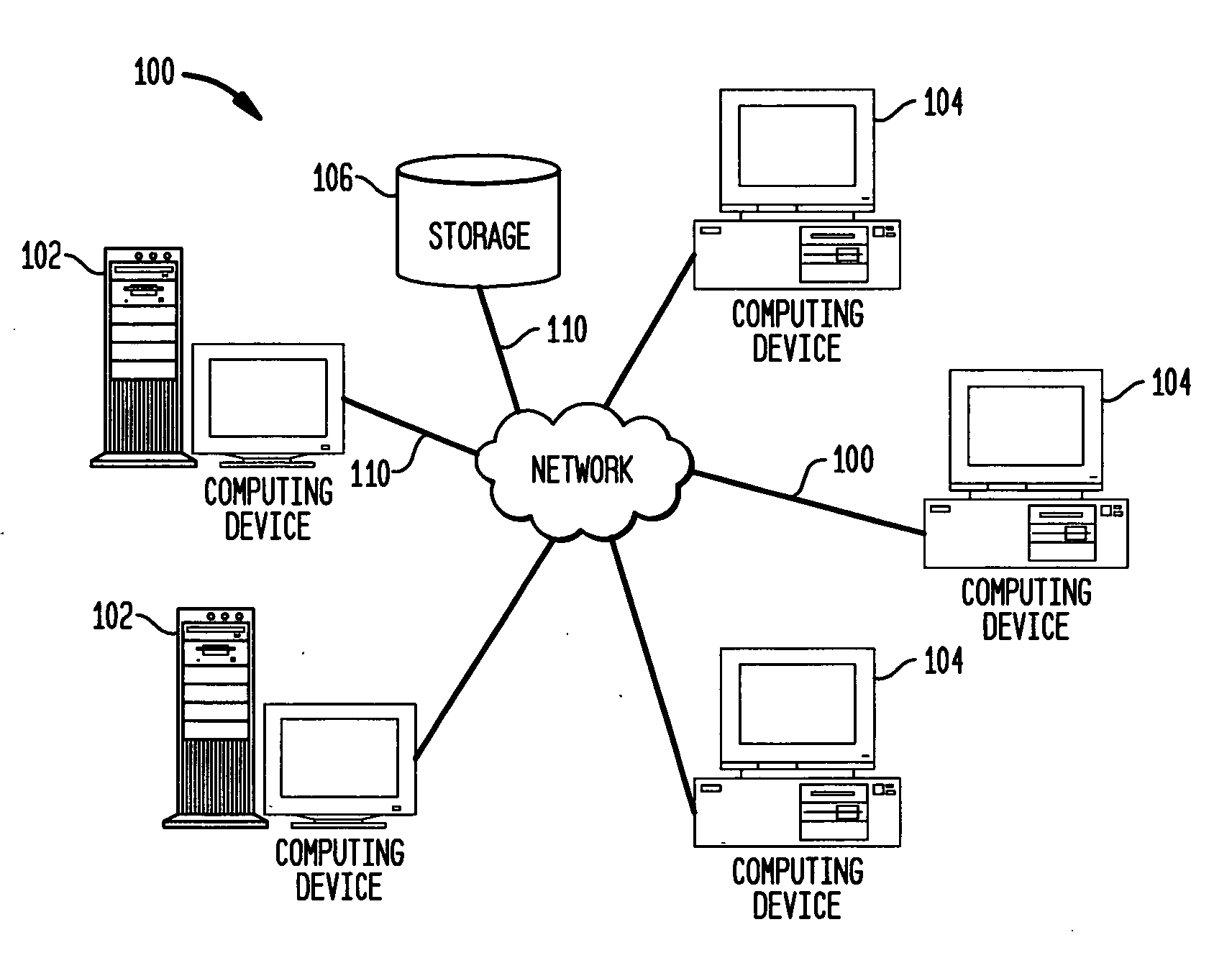
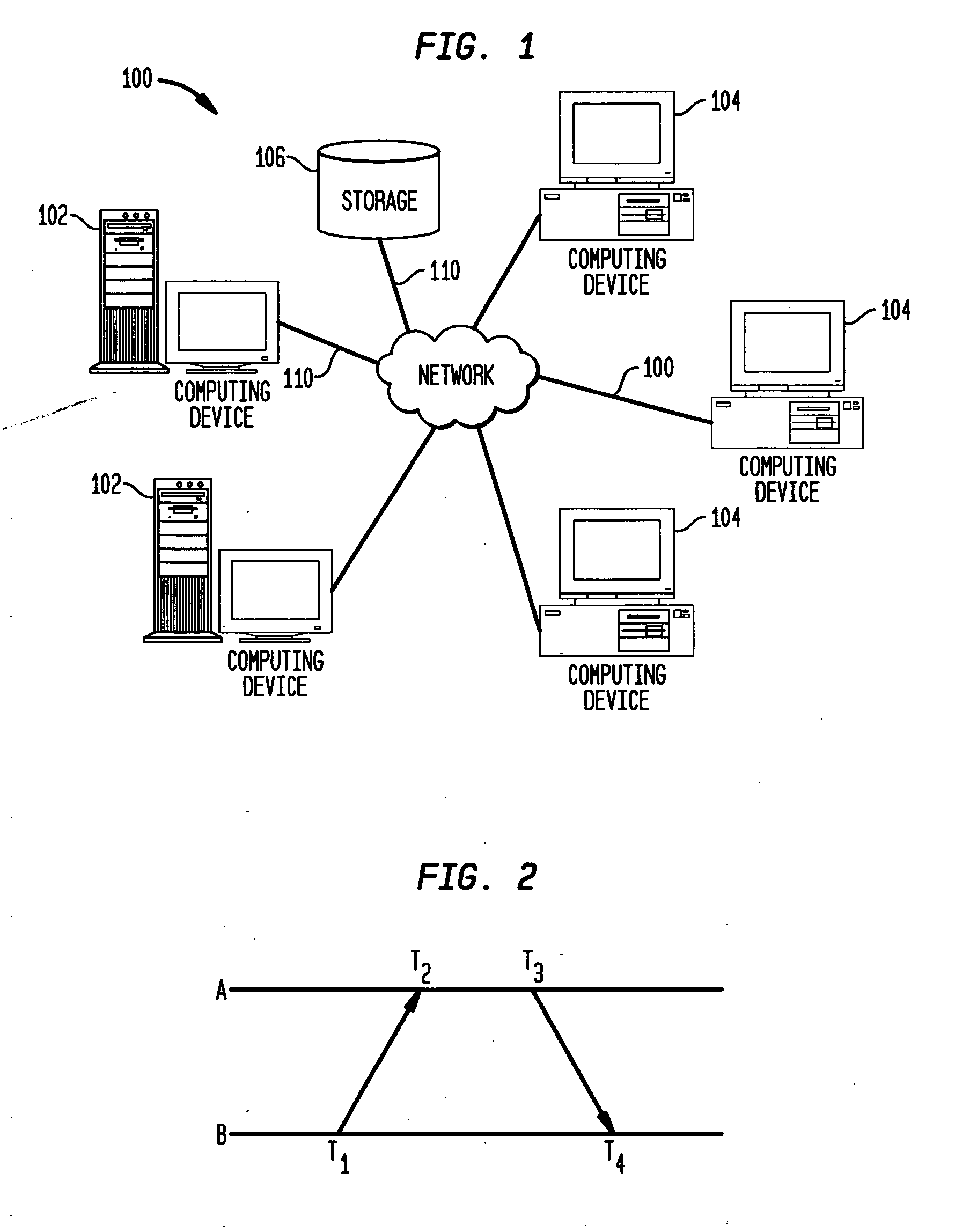
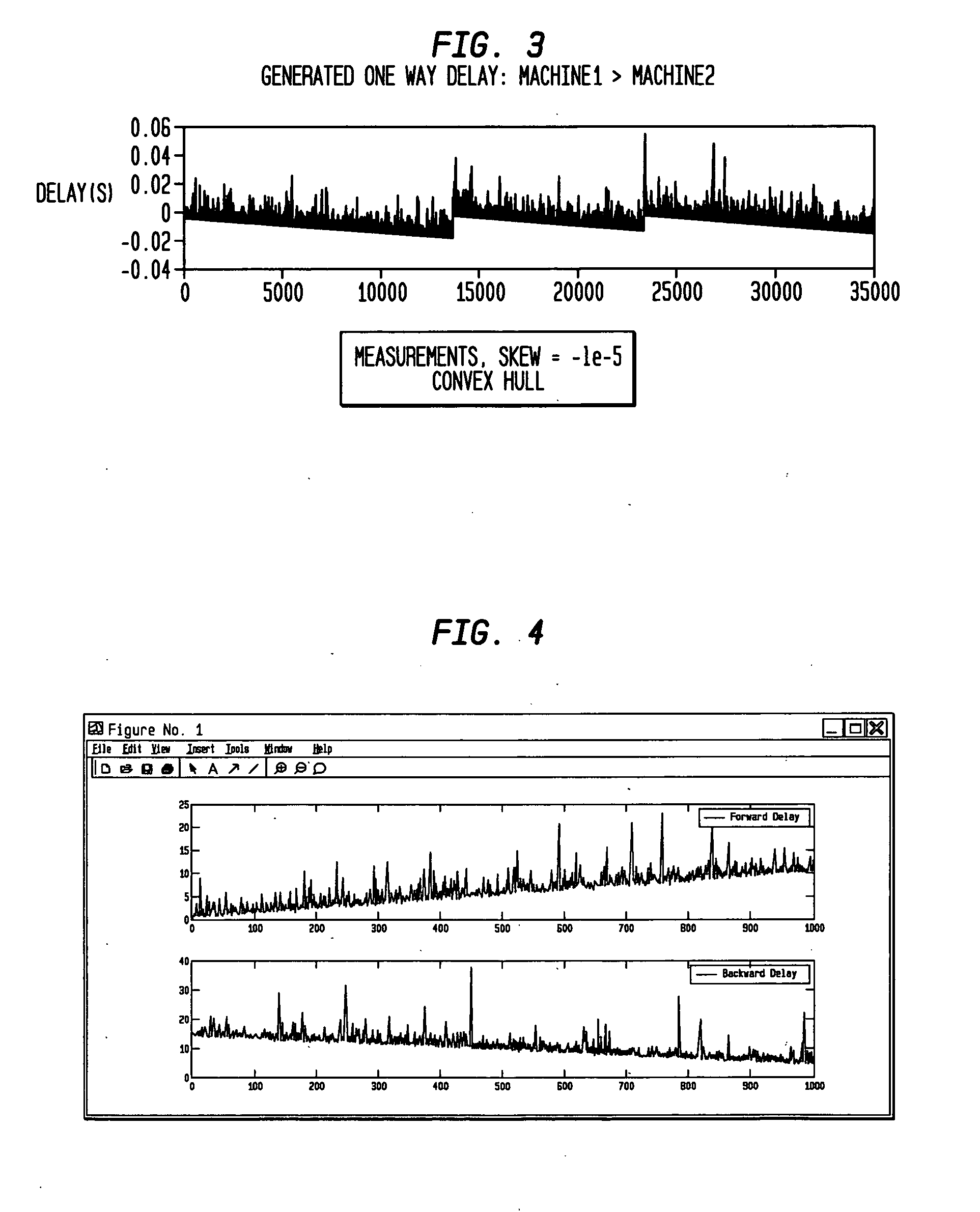
Disclosed are a method and system for estimating the skew and offset between two clocks in a computer system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a first set of data values representing a forward delay between the first and second clocks, and obtaining a second set of data values representing a negative backward delay between the first and second clocks. The method comprises the further steps of forming a lower convex hull for said first set of data values, and forming an upper convex hull, above the lower convex hull, for said second set of data values. The clock offset and the skew between said first and second clocks are estimated using those convex hulls. In a preferred embodiment, this estimation is made by identifying a best clock line between the first and second convex hulls.
Owner:IBM CORP
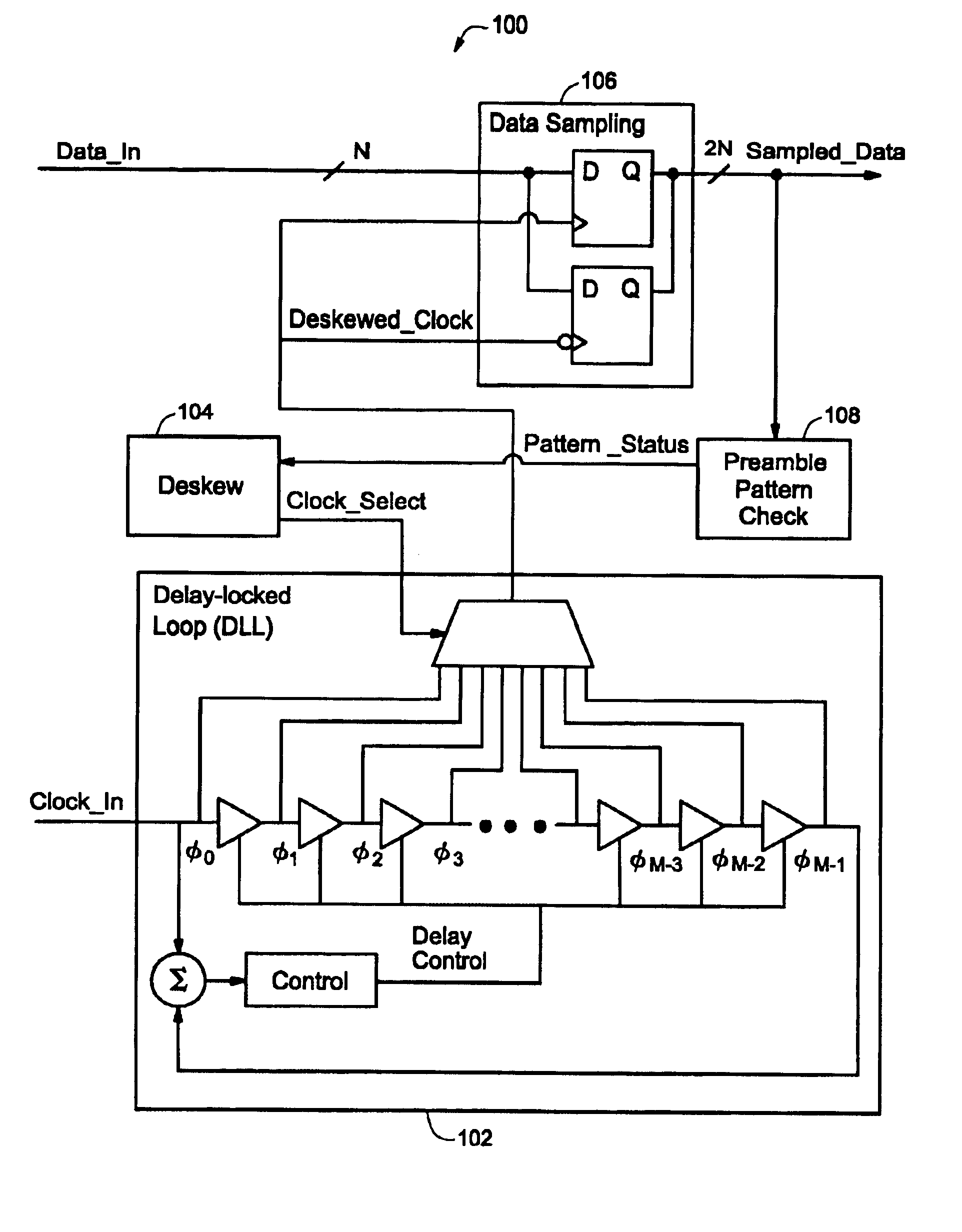
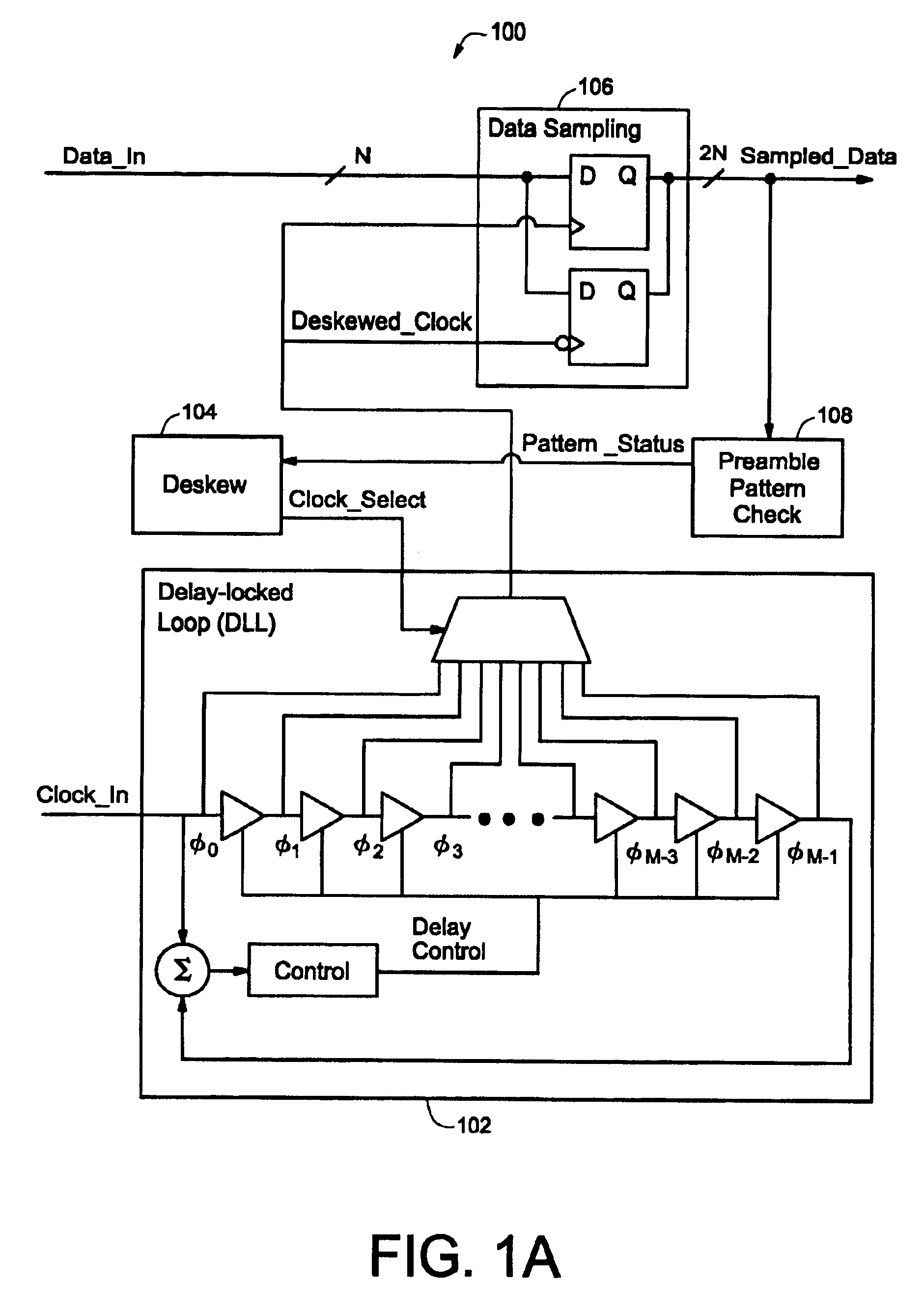
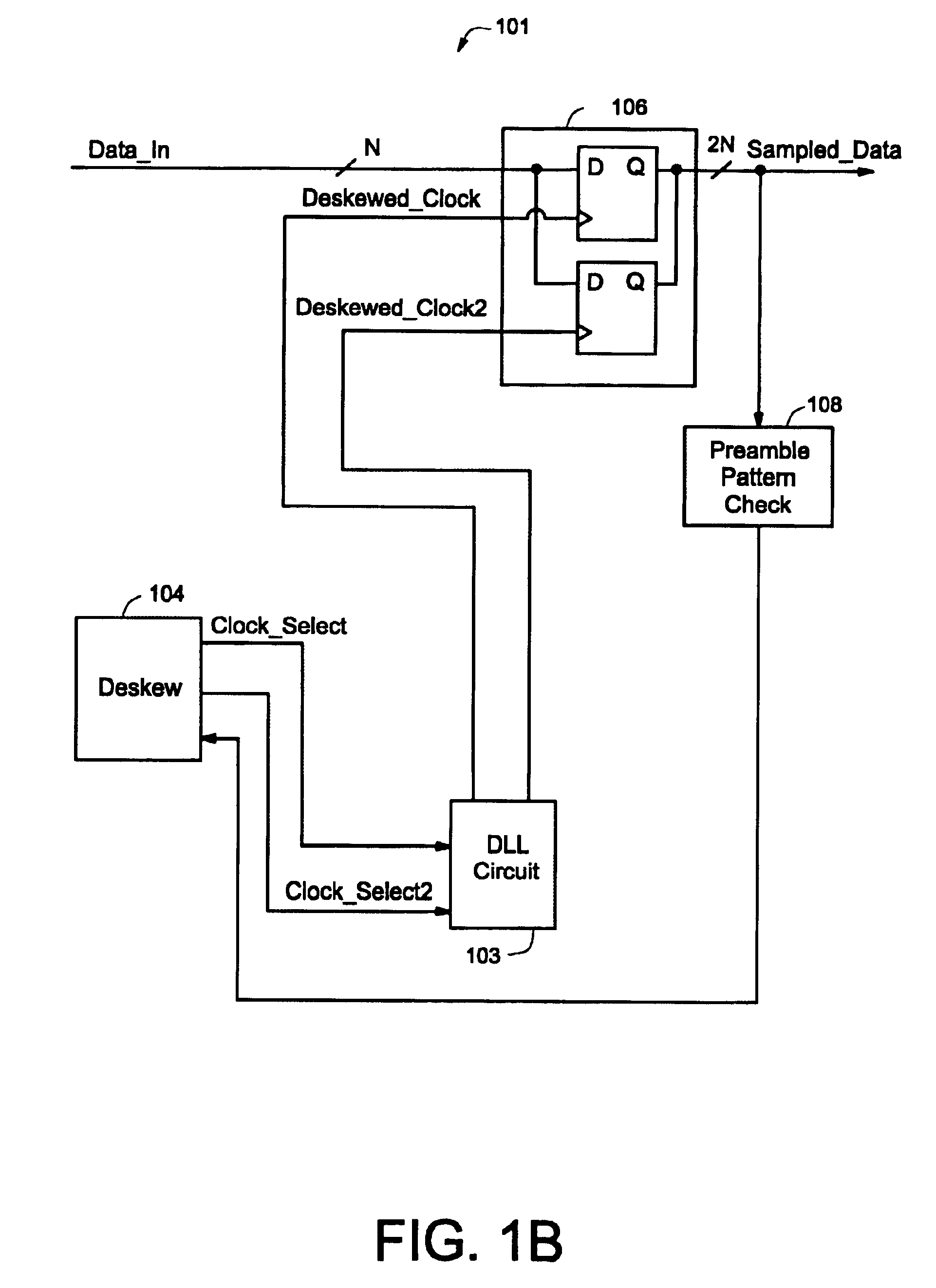
Clock deskew protocol using a delay-locked loop
InactiveUS6861886B1Synchronisation information channelsPulse automatic controlDelay-locked loopClock phase
A data / clock deskewing methodology uses a delay-locked loop (DLL) circuit. The DLL circuit generates a number of clock phases in response to an input clock, where each clock phase is delayed relative to the input clock signal. The clock phases are used to sample data from a data line. The sampled data is checked against a preamble pattern (a sequence of known data). A digital deskew control block selects one of the clock phases after analyzing the results of preamble pattern check such that subsequently received data is sampled with the appropriately selected clock phase.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
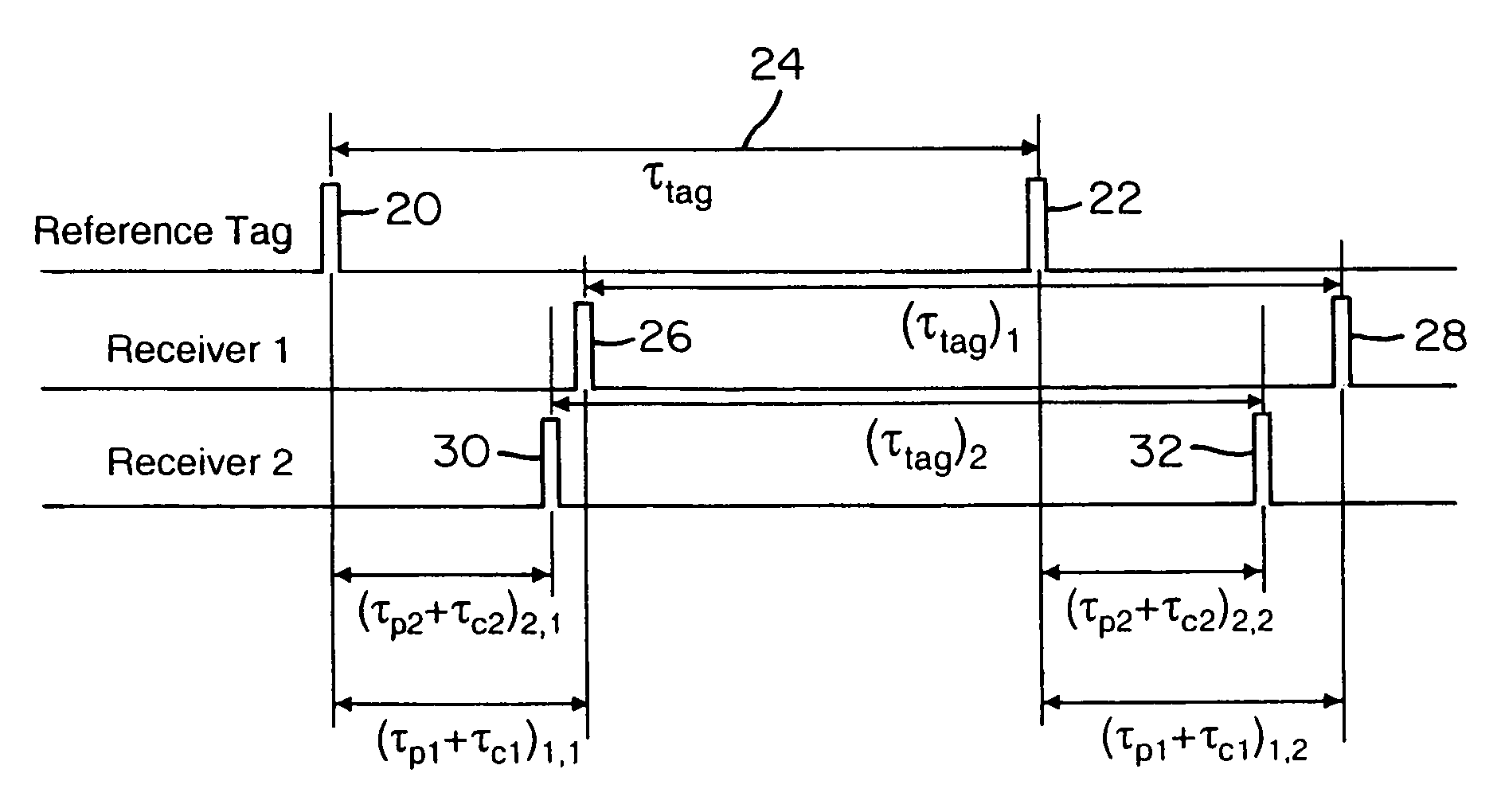
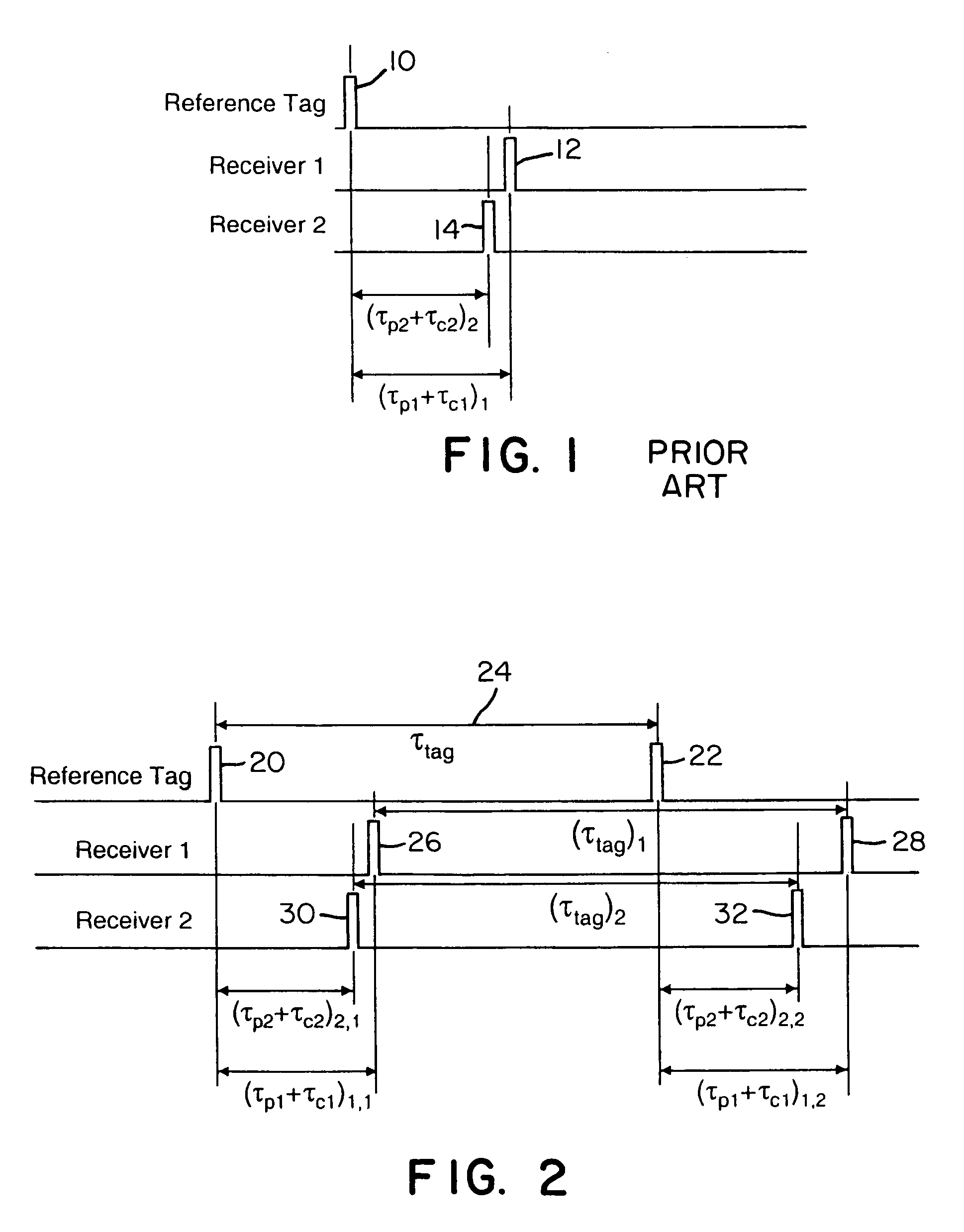
Wireless time reference system and method
ActiveUS7492316B1Accurate measurementDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationClock rateReference intervals
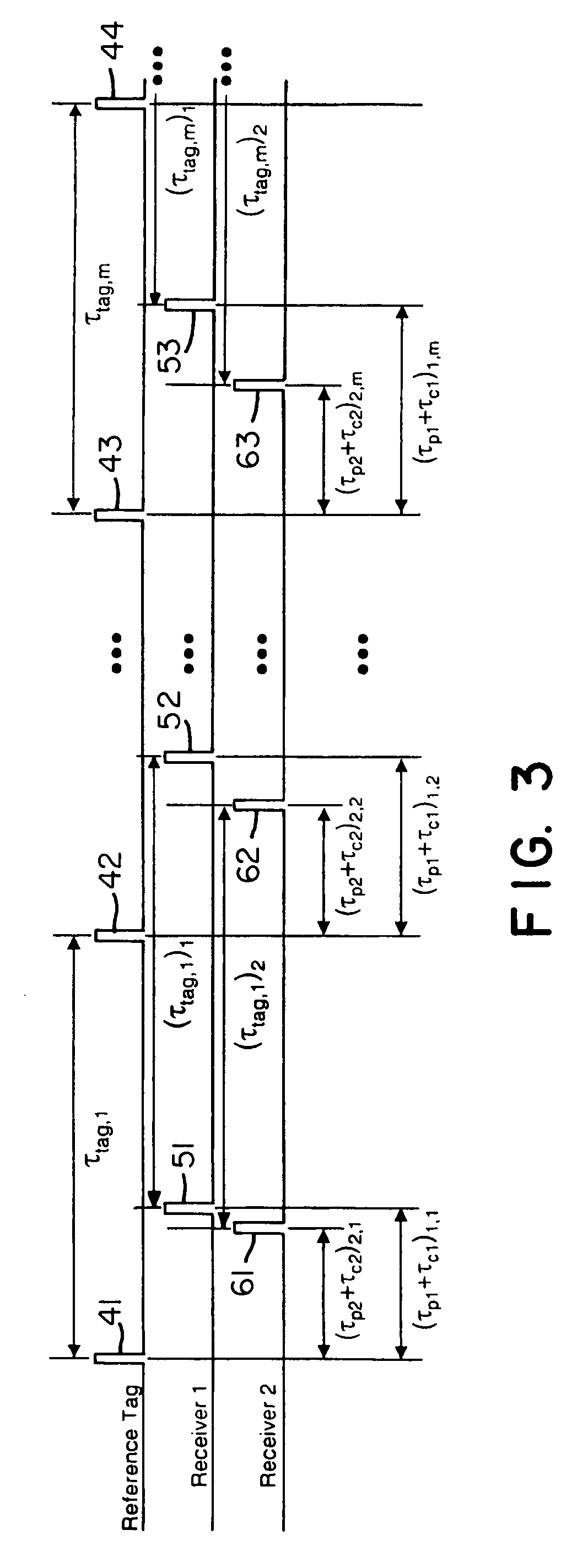
Instead of normalizing time reference of independent spatially-located clocks using a reference tag transmission from known location, the present invention uses an interarrival time interval between a pulse pair of UWB pulses as a timing metric. Thus, a method of synchronizing spatially-located clock or normalizing time indications thereof comprises transmitting a UWB pulse pair, determining at first and second monitoring stations a respective count value indicative of a locally measured time interval between received pulse pairs, determining a ratio between clock counts of first and second monitoring stations, and utilizing the ratio to determine clock skew, e.g., a timing correction to be applied to respective local clocks of the monitoring stations. A corresponding system comprises a reference tag transmitter that transmits a pulse pair of UWB pulses to define a time reference interval, a first independent receiver that receives the pulse pair to generate a first count value indicative an interarrival interval between the pulse pair, a second independent receiver that receives the pulse pair to similarly generate a second count value, and a processor hub responsive to the count values to determine a ratio corresponding to the ratio of respective clock frequencies of the first and second receiver clocks. Once the correction is applied, time-of-arrival information from object tag transmissions may be used to determine object location with sub-foot position accuracies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Asymmetric multiprocessor
InactiveUS20070283128A1Increase freedomLoad minimizationEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerExecution controlClock phase
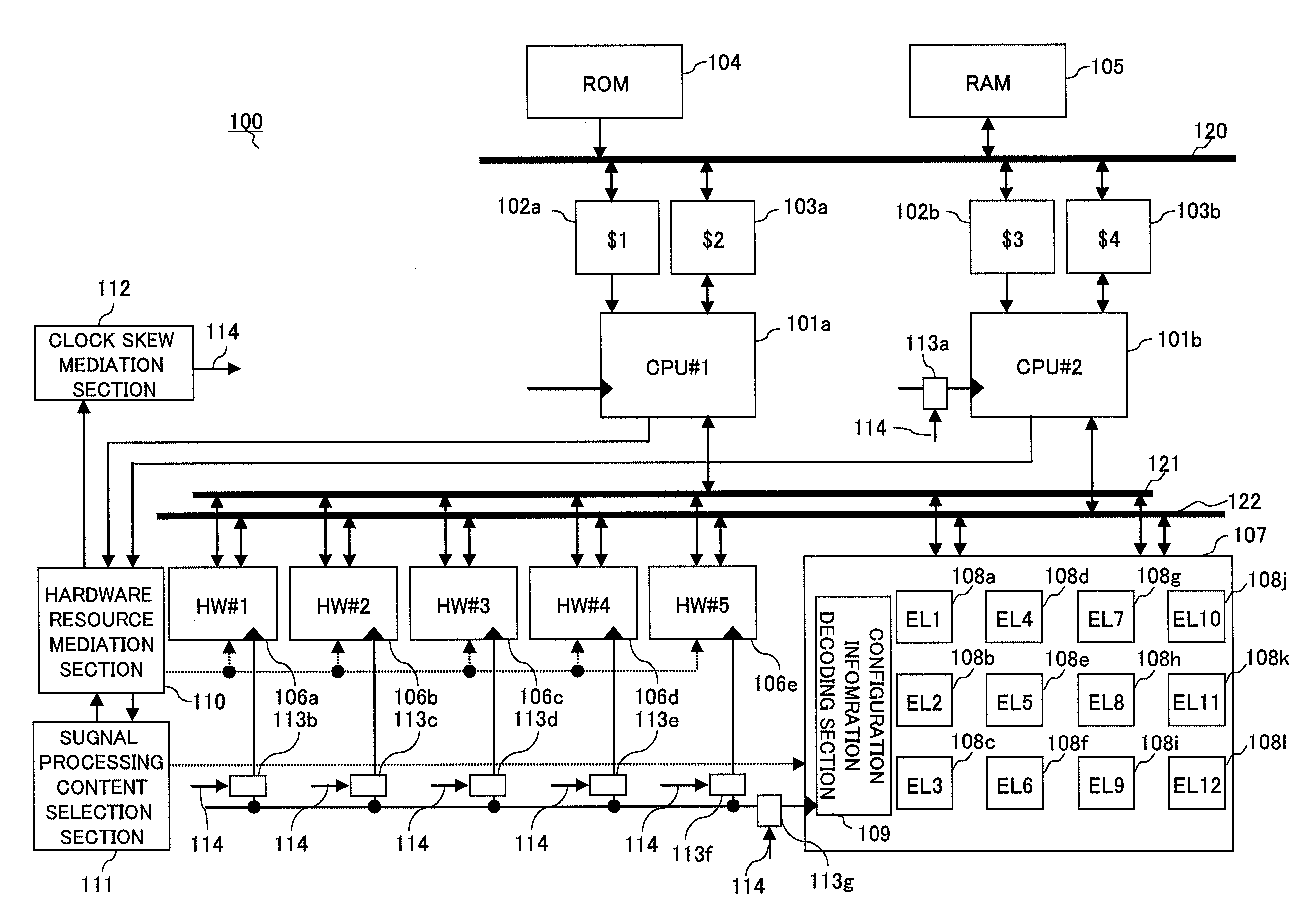
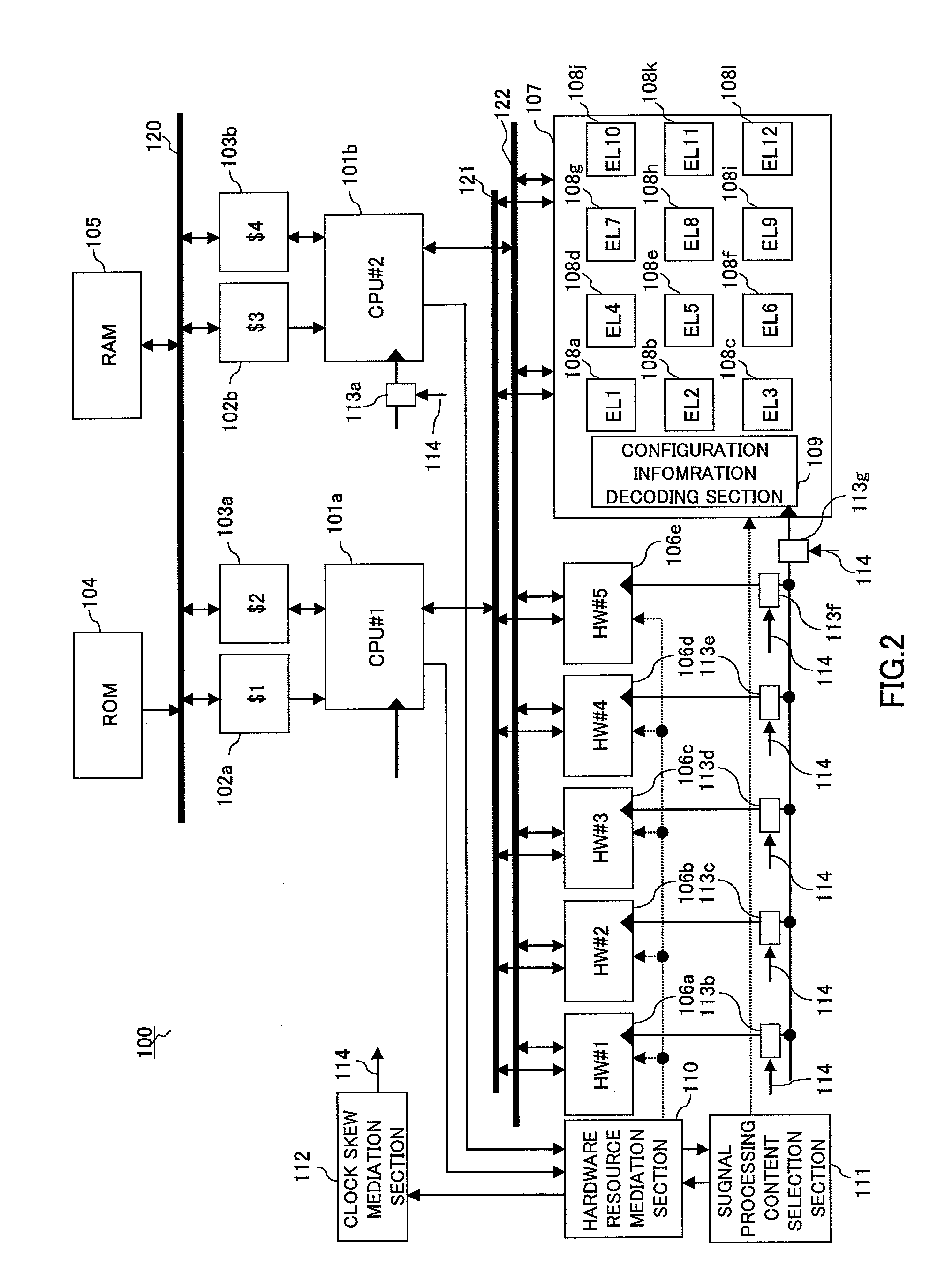
An asymmetric multiprocessor capable of increasing the degree of freedom of distributed processing, minimizing the processing load on each processor (CPU), and achieving a large reduction in power consumption by reducing the operating frequency or lowering the power supply voltage. Asymmetric multiprocessor (100) includes a hardware resource mediation section (110) that mediates request signals requesting permission to use arbitrary hardware accelerators from CPU cores (101a and 101b) ; a signal processing content selection section (111) that selects signal processing content of dynamically reconfigurable signal processor section (107) connected as a slave; a clock skew mediation section (112) that performs control to arbitrarily shift a clock phase relationship among groups; and clock delay generation sections (113a through 113g) that delay a clock signal based on clock skew selection enable signal (114).
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
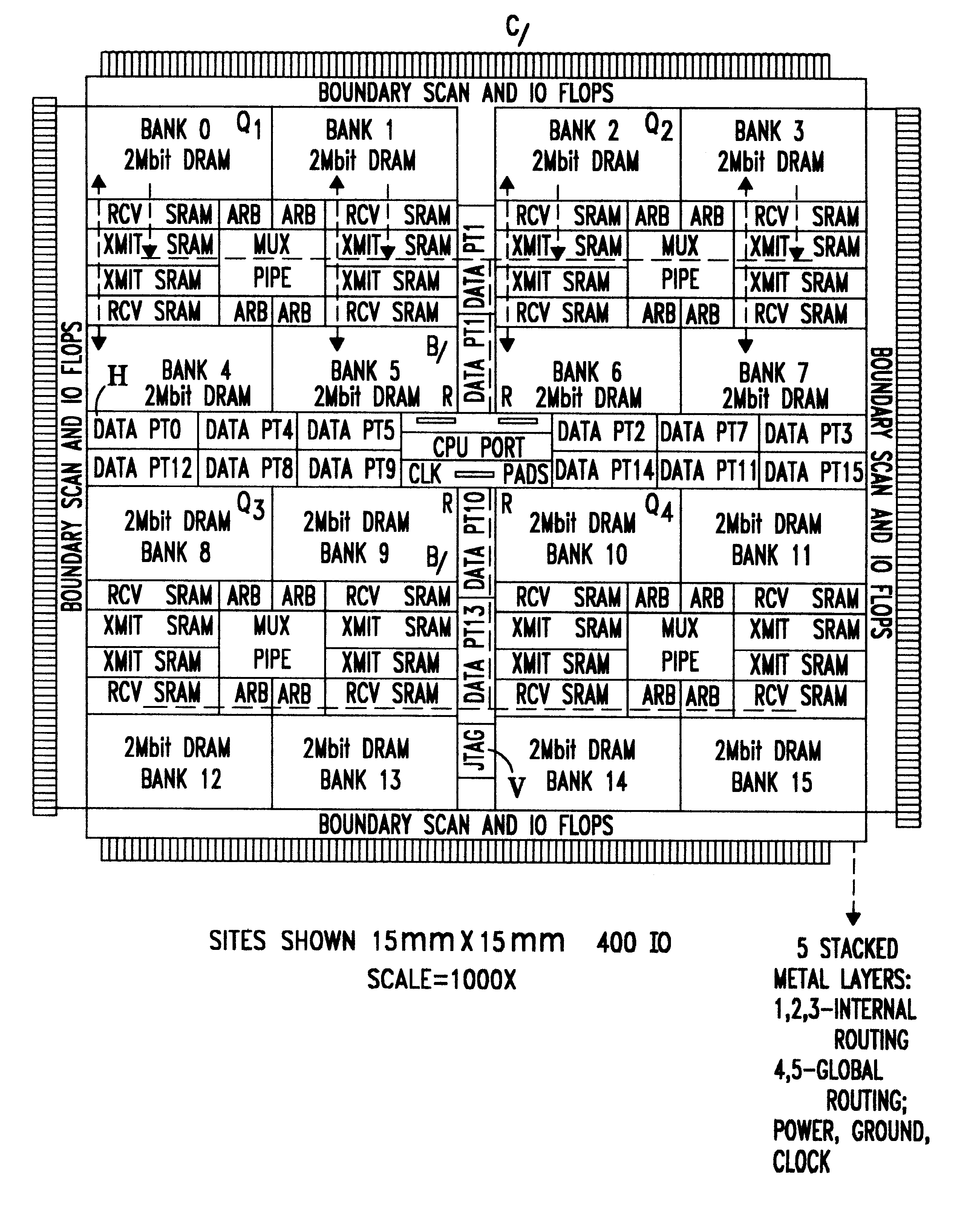
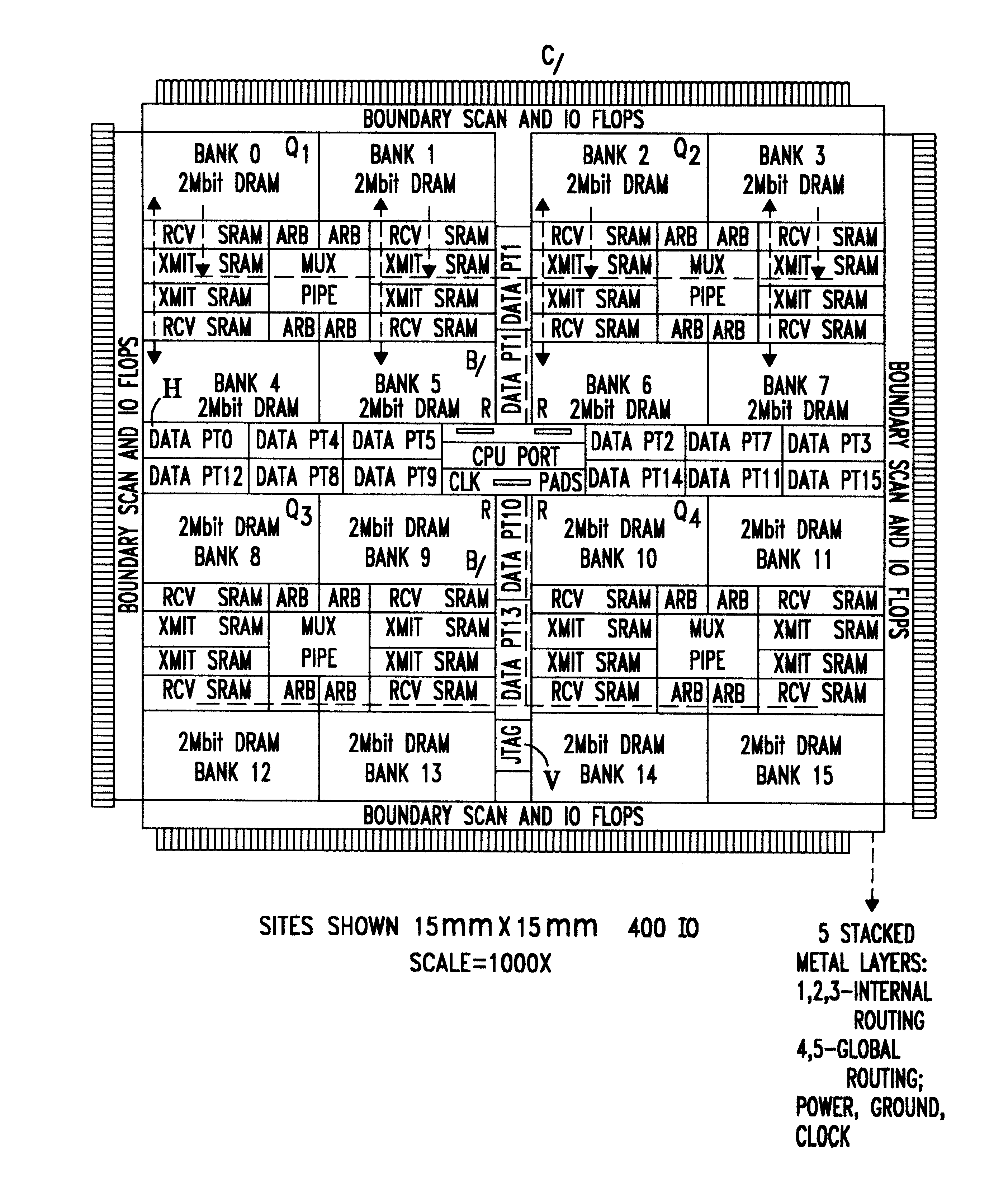
Chip layout for implementing arbitrated high speed switching access of pluralities of I/O data ports to internally cached DRAM banks and the like
InactiveUS6237130B1Guaranteed economic efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesData connectionData port
A novel chip layout for a network wherein pluralities of I / O data ports are each connected to transmit / receive SRAM buffer banks operable under arbitration units to access pluralities of internally cached DRAM banks via internal busses to enable switching data connections amongst all data ports through the appropriate buffers, the chip layout having, data ports substantially symmetrically placed with each data port connected to each arbitration unit and each transmit / receive buffer bank, and with each data port enabled to write into any DRAM bank, with the connections being effected such that each data port is substantially symmetric with respect to DRAM bank, arbitration unit and transmit / receive buffer banks and busses; and with timing clocks centrally placed on the chip to minimize clock skew by symmetric clock distribution.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS
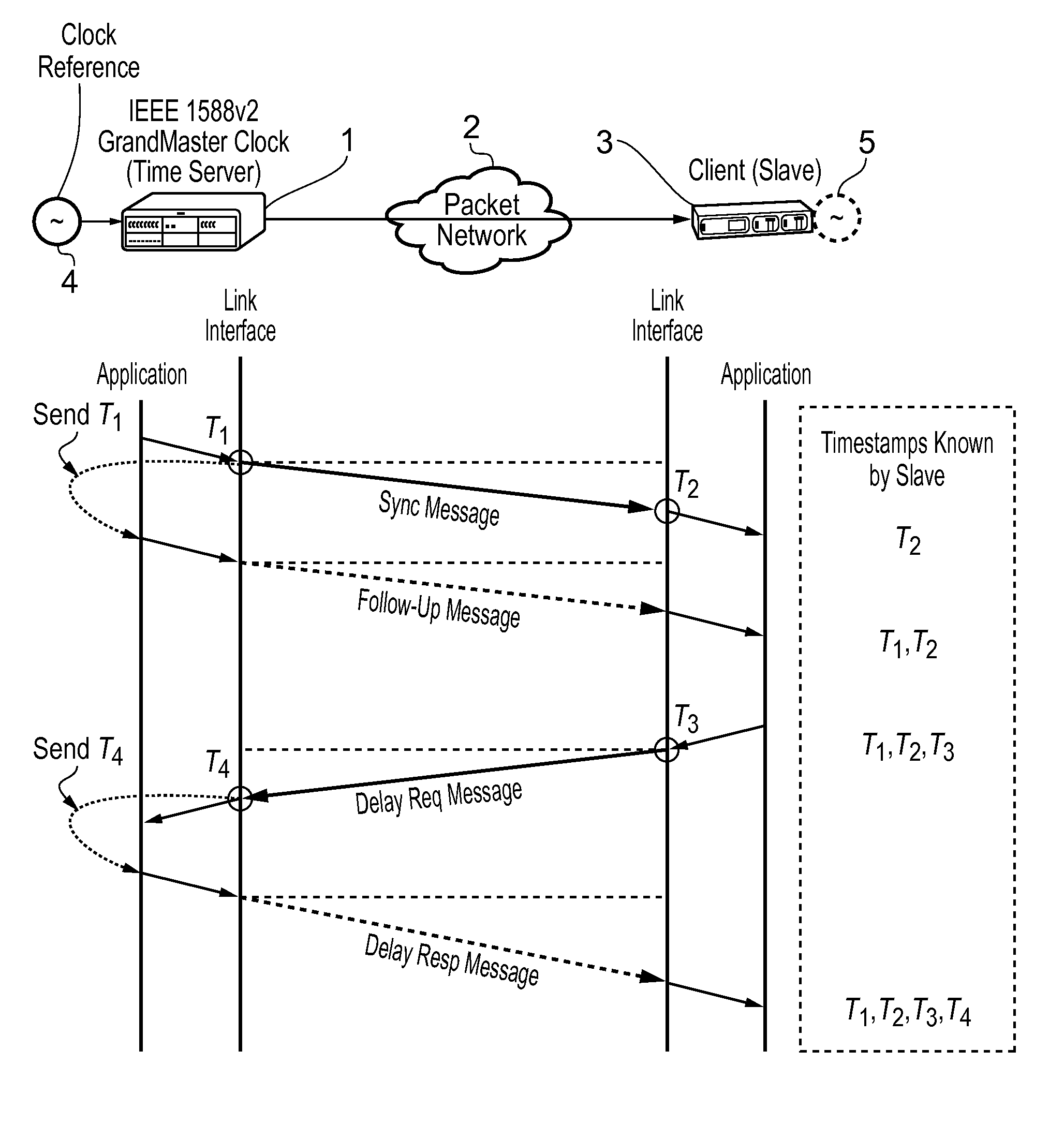
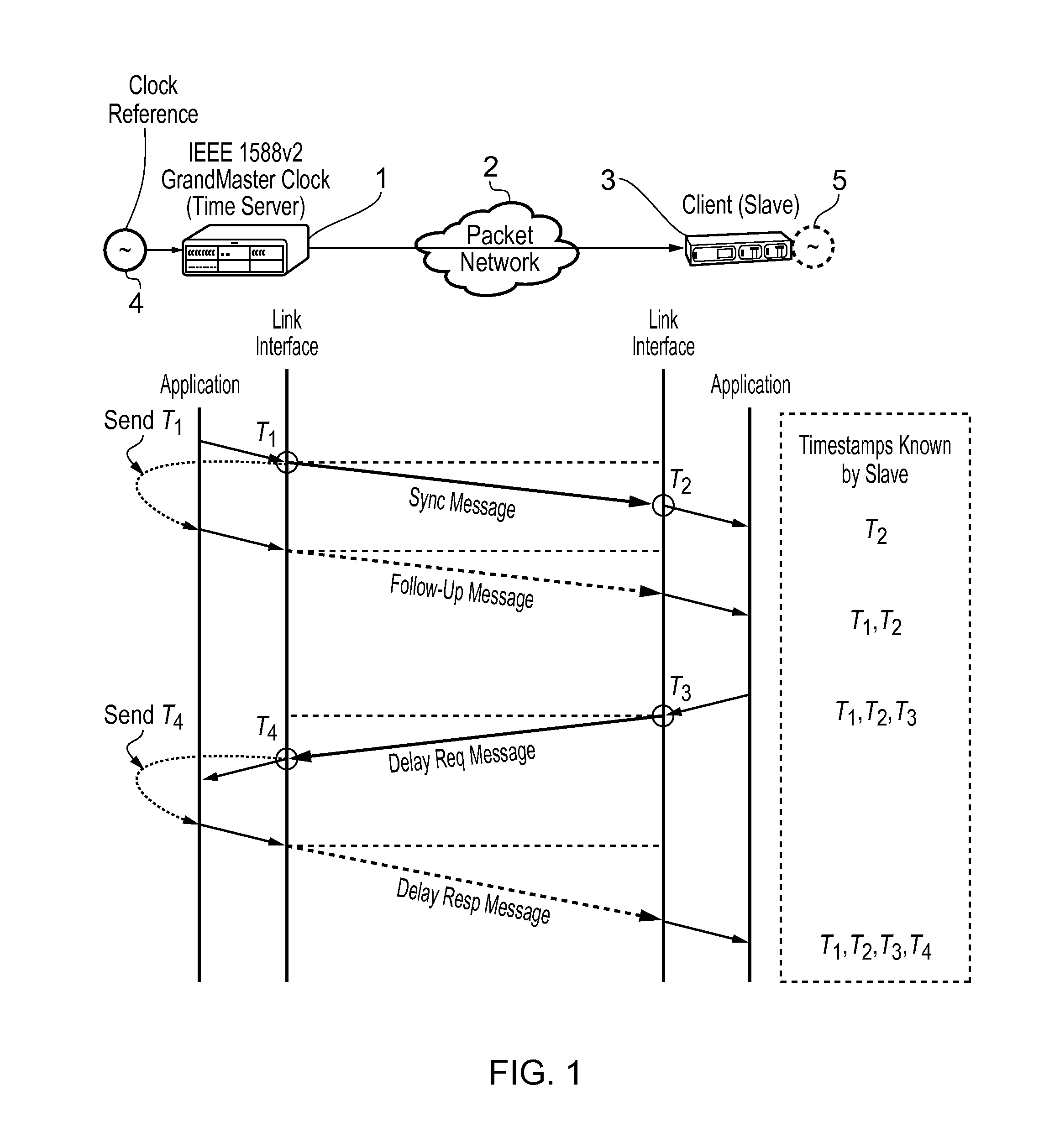
Method and devices for time and frequency synchronization using a phase locked loop
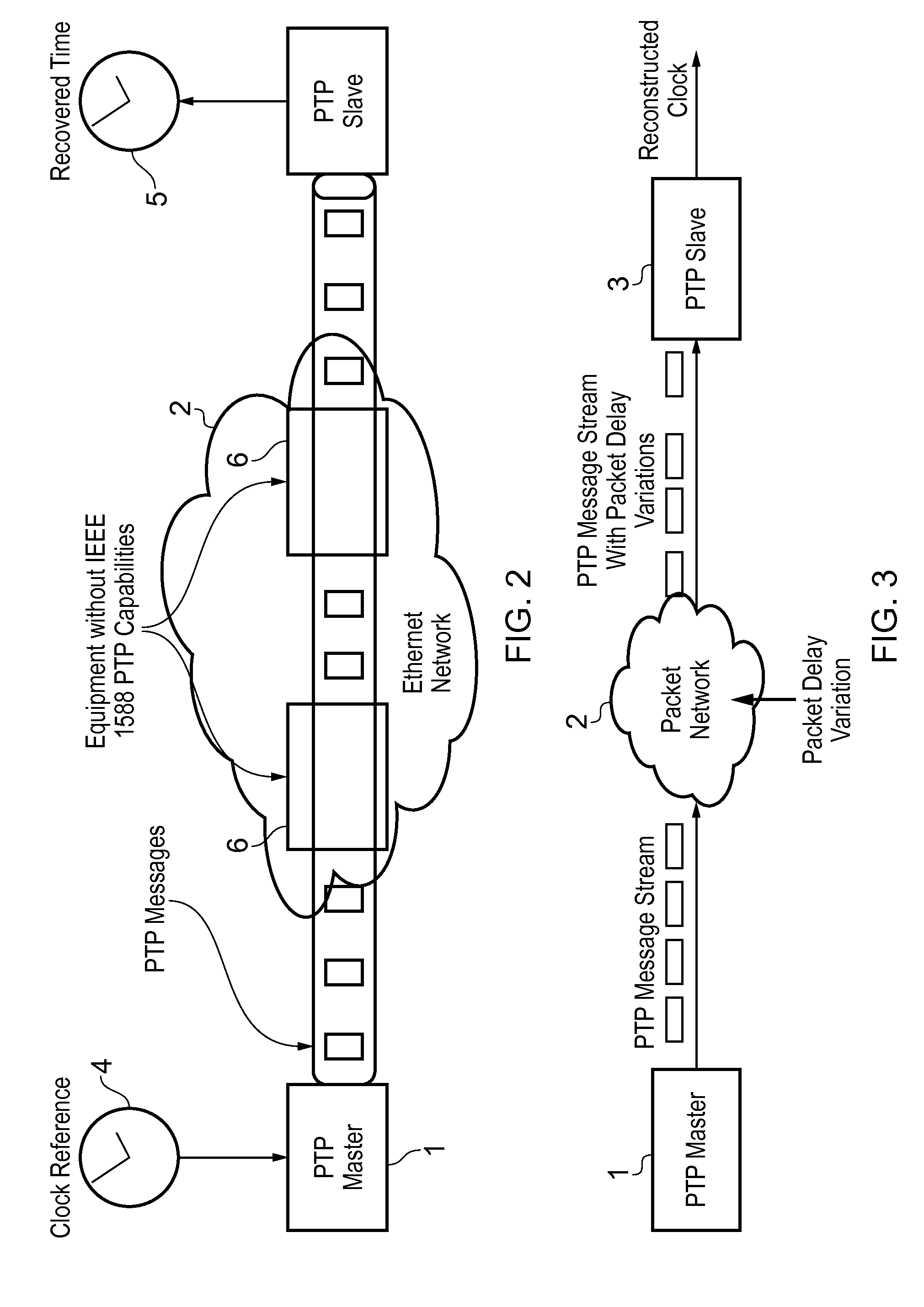
This invention relates to methods and devices for time and frequency synchronization, especially over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP). Timing protocol messages are exposed to artifacts in the network such as packet delay variations (PDV) or packet losses. Embodiments of the invention provide a digital phase locked loop (DPLL) based on direct digital synthesis to provide both time and frequency signals for use at the slave (time client). An example of this DPLL in conjunction with a recursive least squares mechanism for clock offset and skew estimation is also provided.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
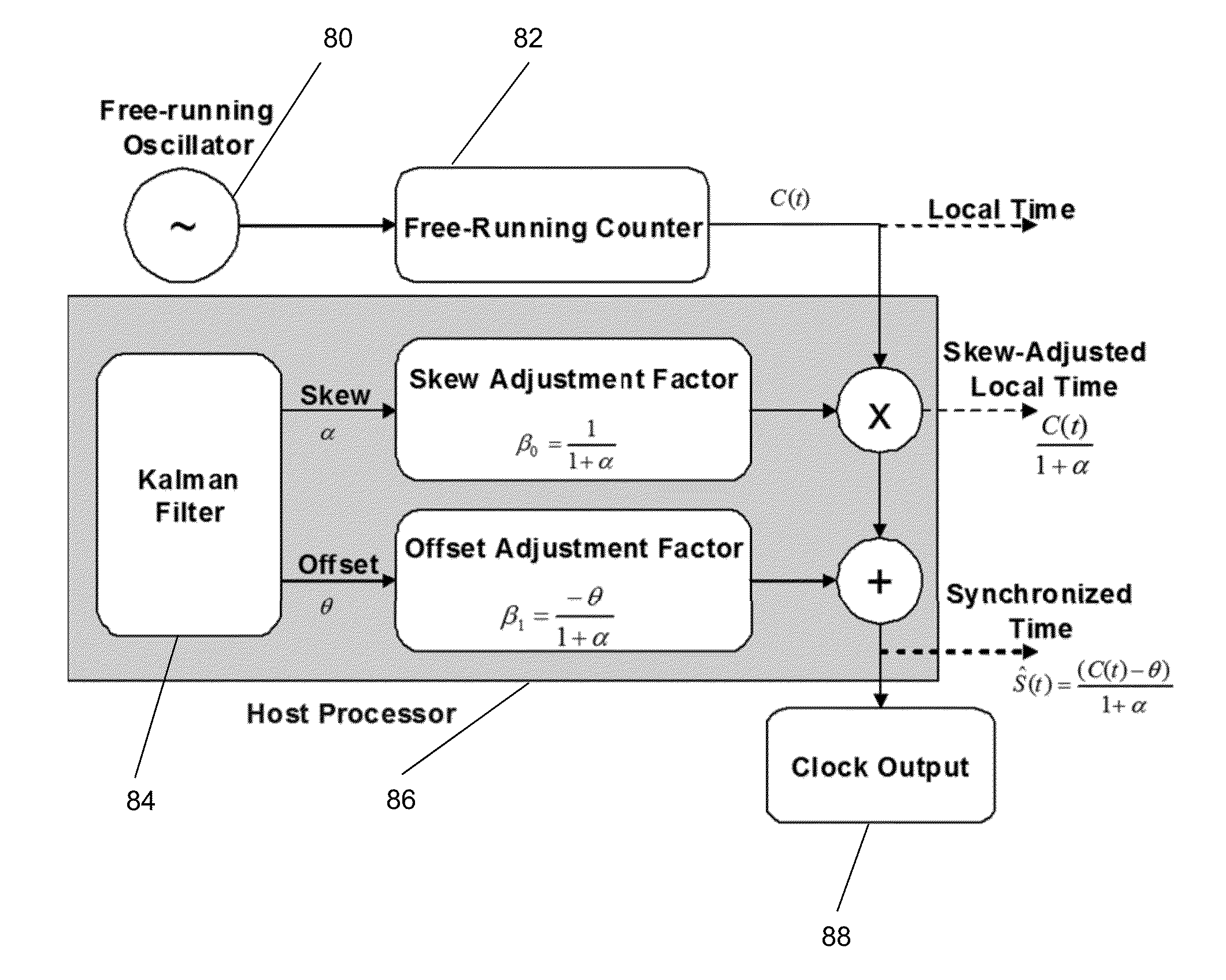
Method and system for clock offset and skew estimation
This invention relates to methods and devices for clock offset and skew estimation. The invention has particular application in the alignment of slave clocks to a master clock. In embodiments of the invention, the slave clock employs an independent free running clock and a recursive estimation technique to estimate the clock offset and clock skew between the slave and master clocks. The slave can then use the offset and skew to correct the free running clock to reflect an accurate image of the master clock.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
Method and system for the clock synchronization of network terminals
A method and system for network terminal clock synchronization includes determining a respective round trip delay time from a master terminal to each slave terminal and offsetting the clock of each slave terminal by an amount proportional to the respective determined round trip delay time such that the master terminal and each of the slave terminals have substantially the same point of reference in time. The method and system further include, in response to a trigger signal, determining a respective offset between the master clock of the master terminal and the clocks of each of the slave terminals and offsetting the clocks of each of the slave terminals by an amount proportional to the determined respective offset to synchronize the clocks of each of the slave terminals to the master clock of the master terminal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
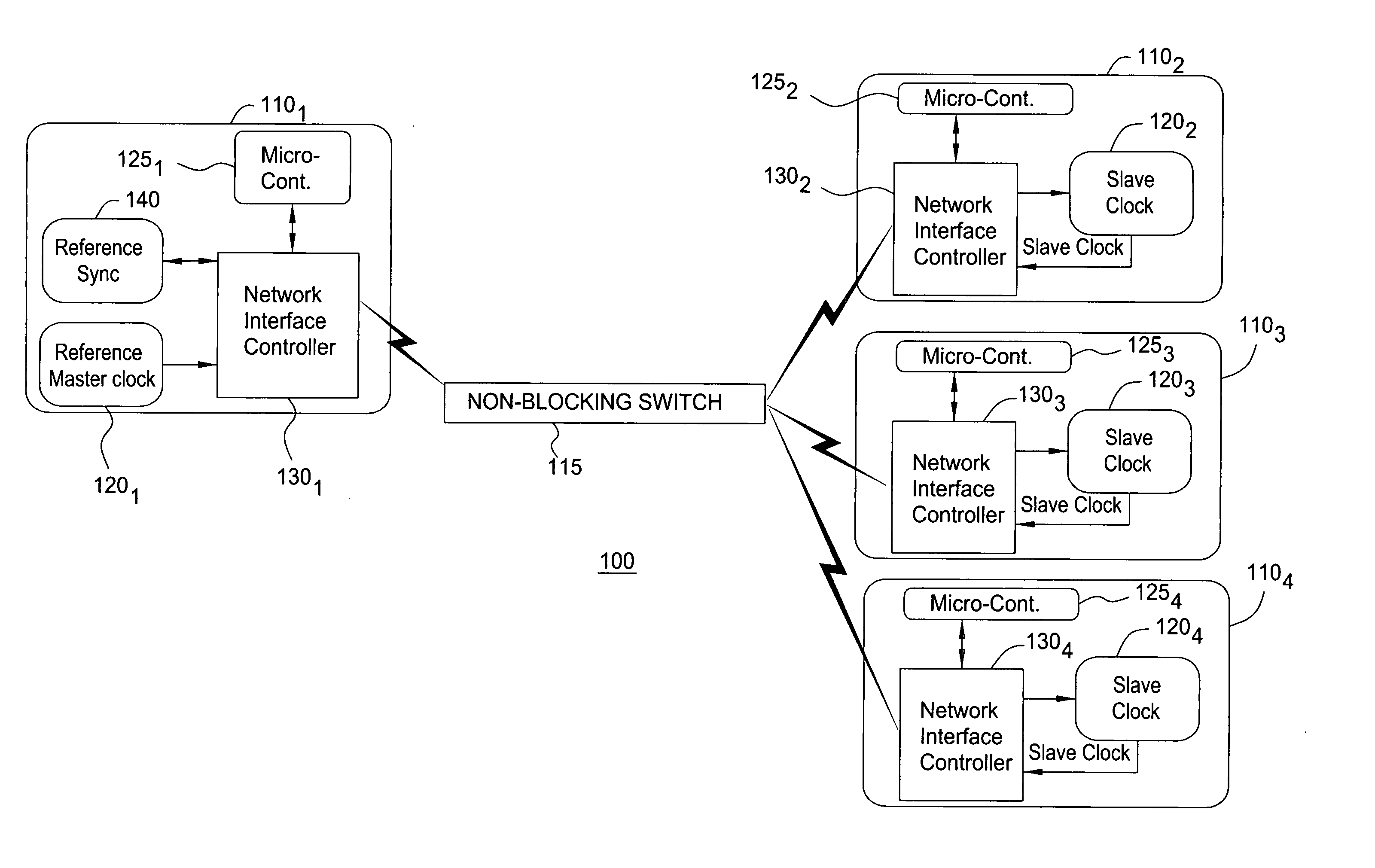
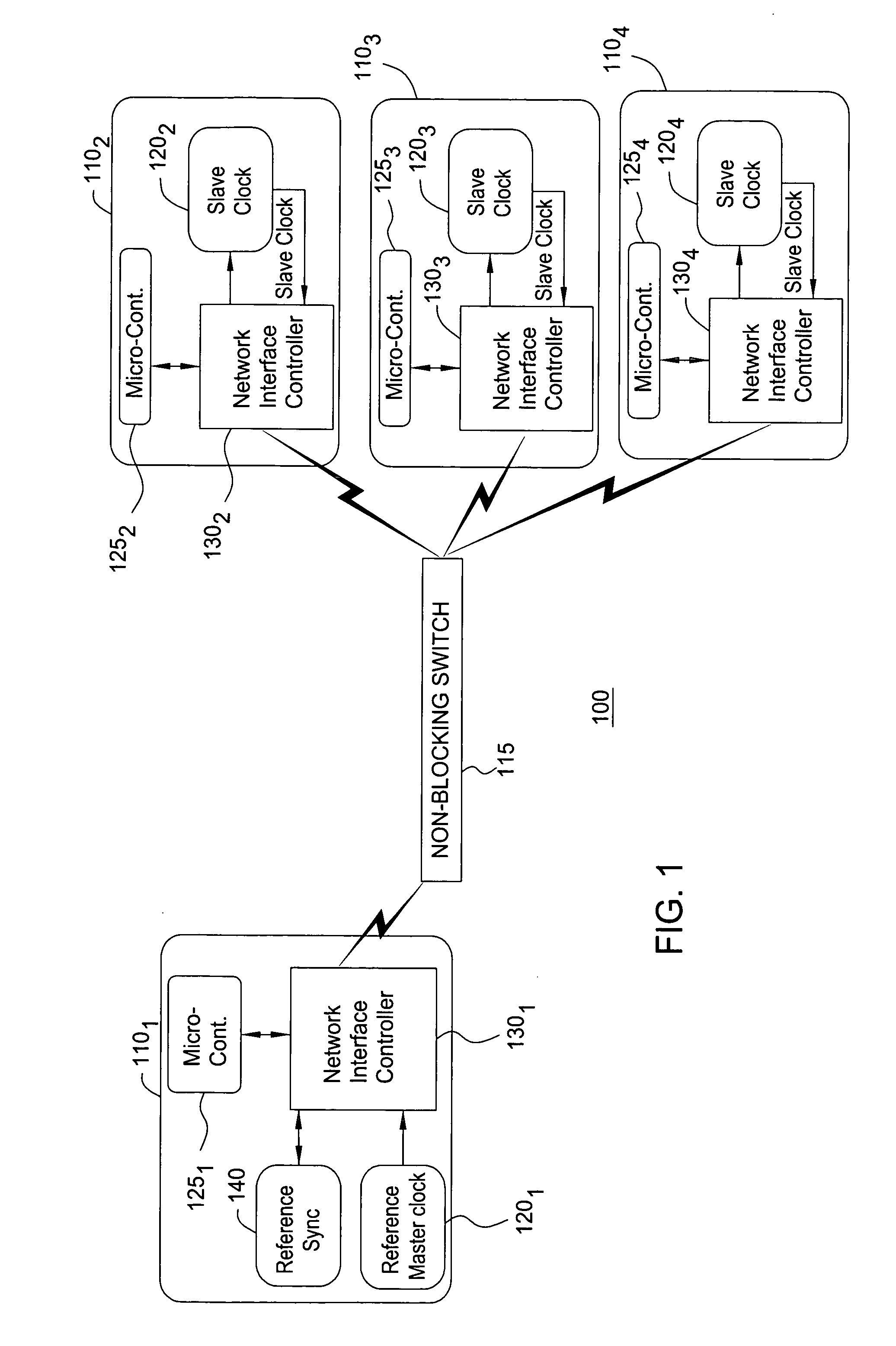
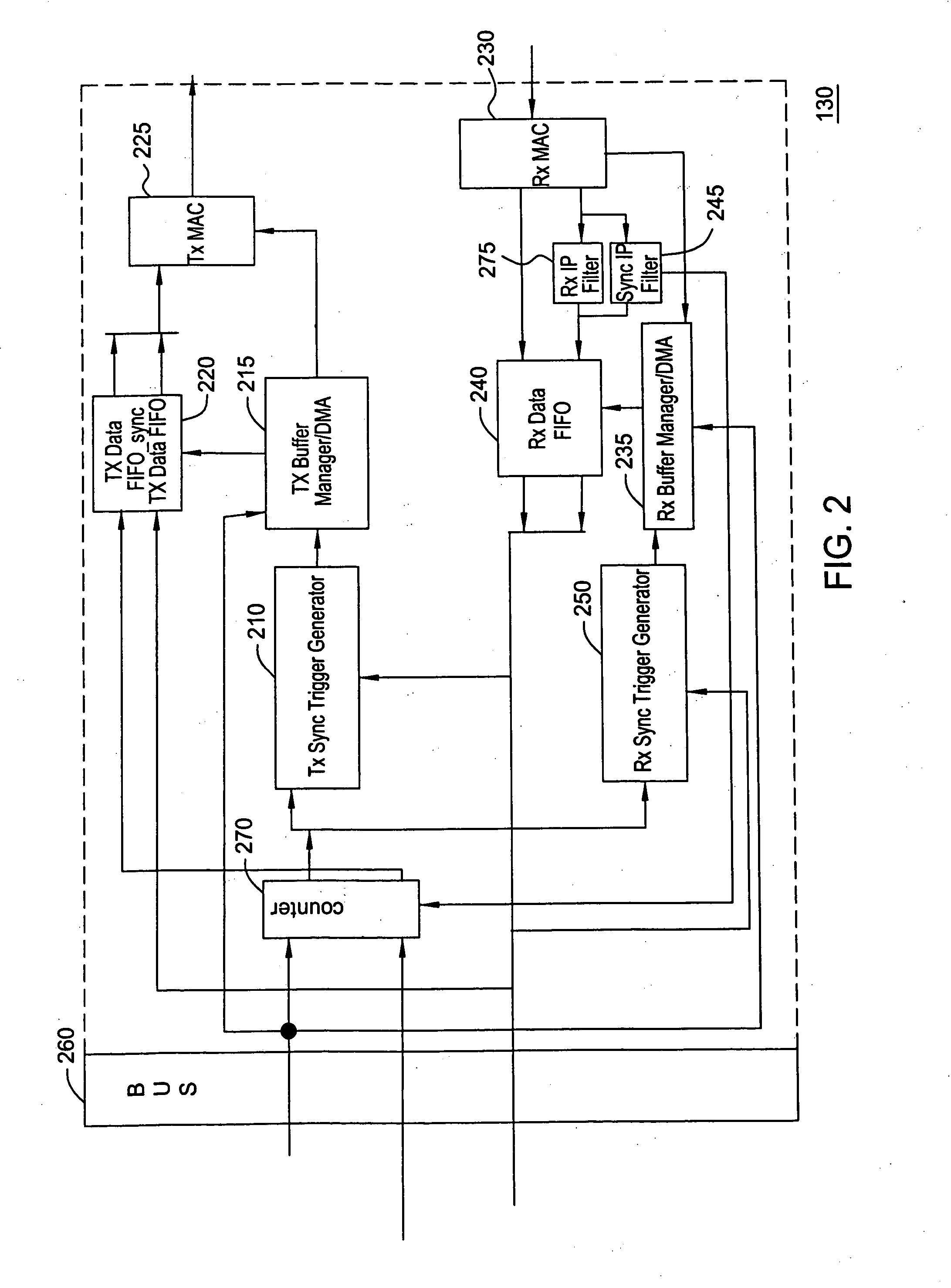
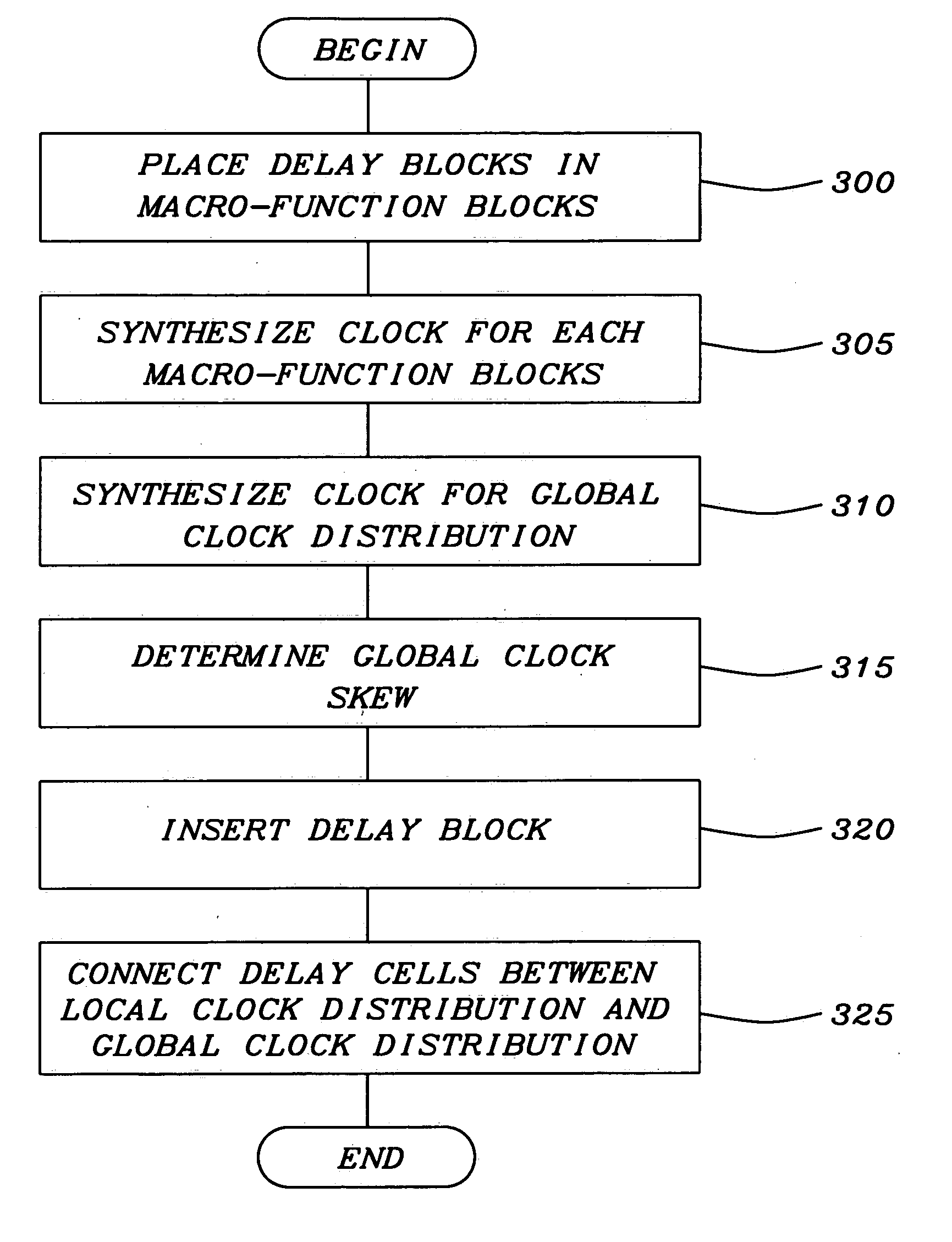
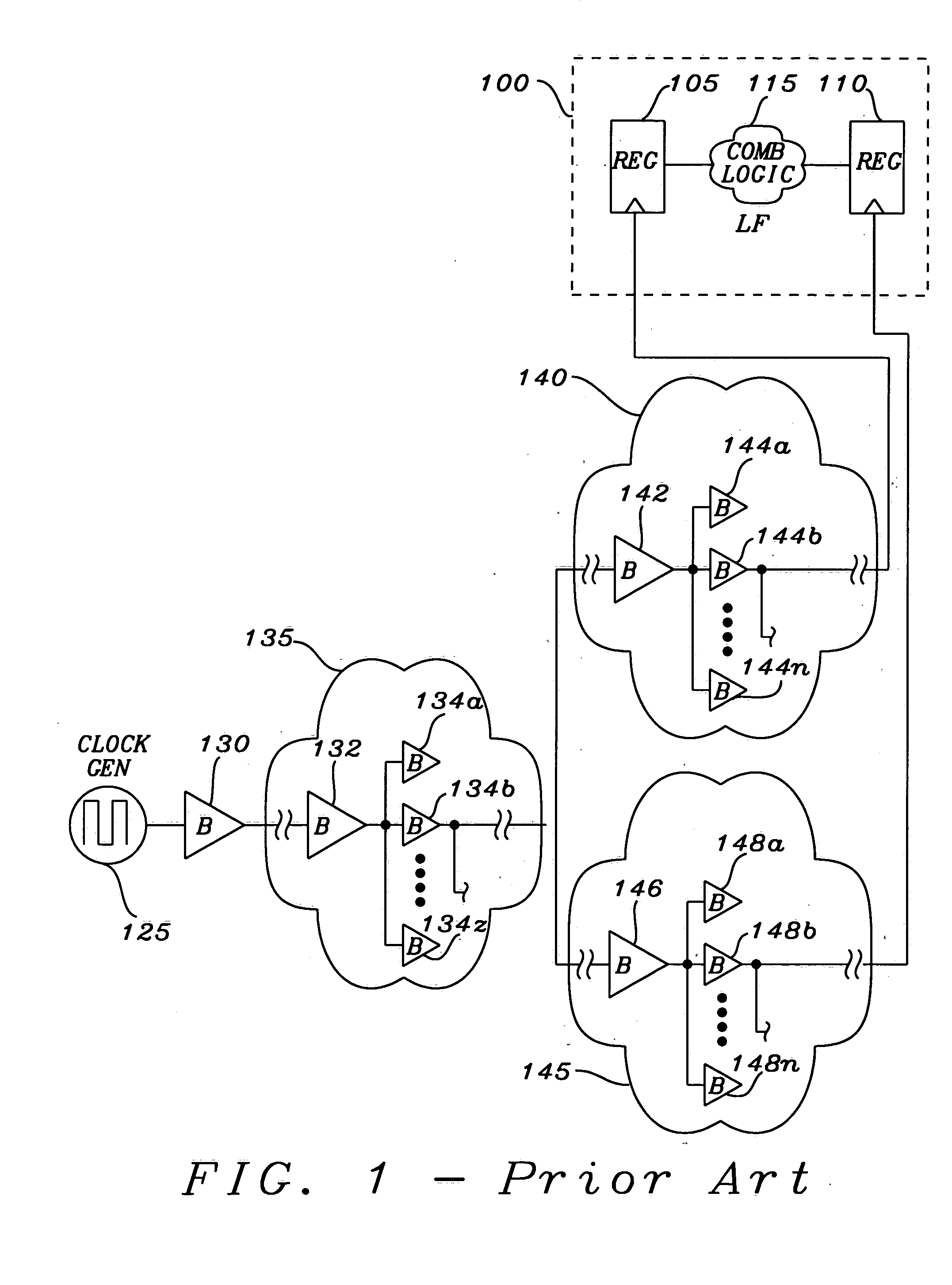
Methodology to optimize hierarchical clock skew by clock delay compensation
InactiveUS20050102643A1CAD circuit designGenerating/distributing signalsDistribution systemComputer science
A method for synthesizing a clock distribution system within an integrated circuit for compensating for clock skew within a global or top level clock distribution network begins with allocating at least one delaying circuit within each of functional circuits of the integrated circuit. An intra-functional clock distribution network is fabricated within each of the functional circuits. Once the intra-functional clock distribution network is fabricated, an inter-functional clock distribution network is constructed between each of the functional circuits. A clock skew for the inter-functional clock distribution network is determined. The clock skew is then compensated by inserting the delaying circuit at a terminal of the inter-function clock distribution network where each of the functional circuits is connected to the inter-functional clock distribution network.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
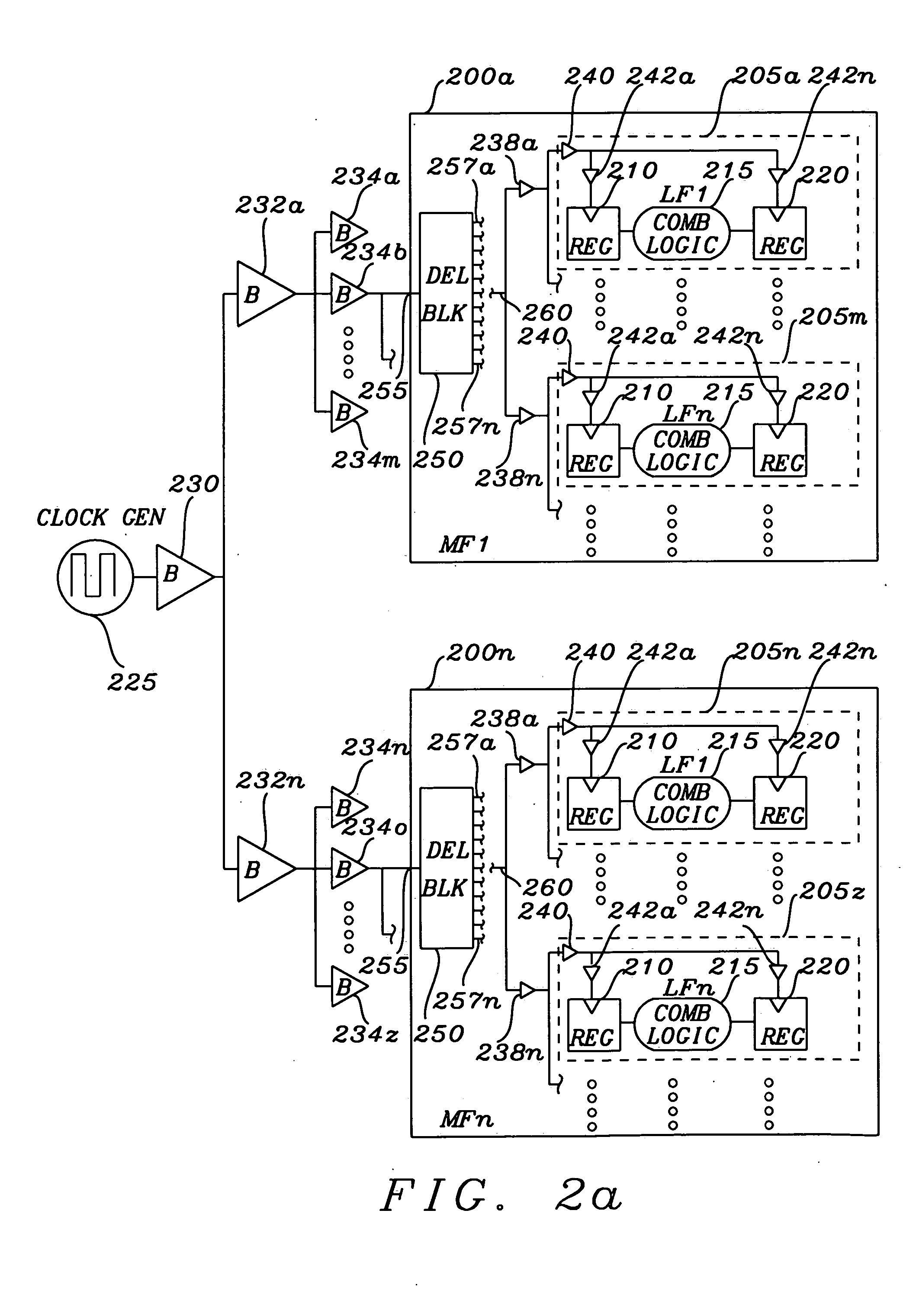
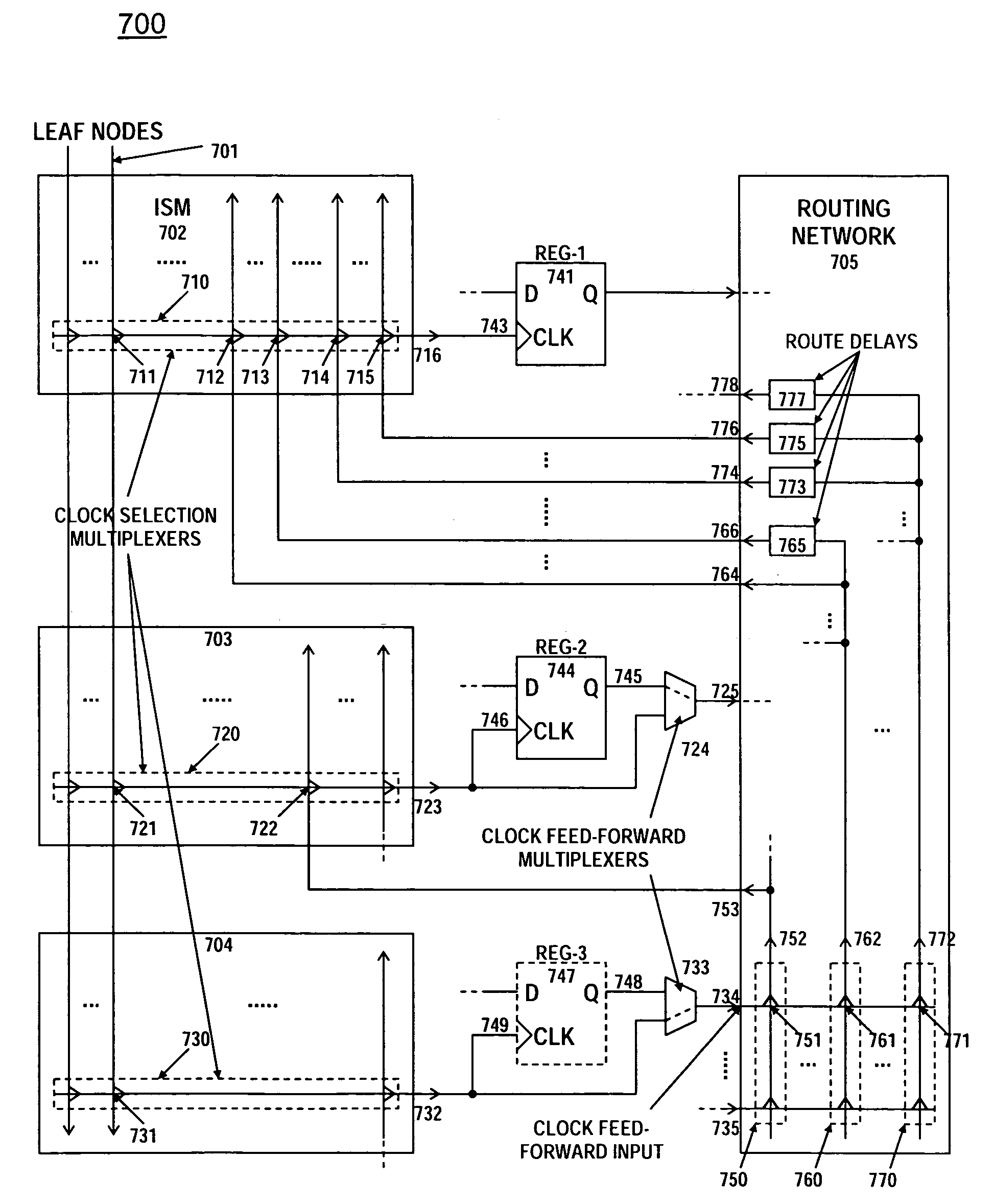
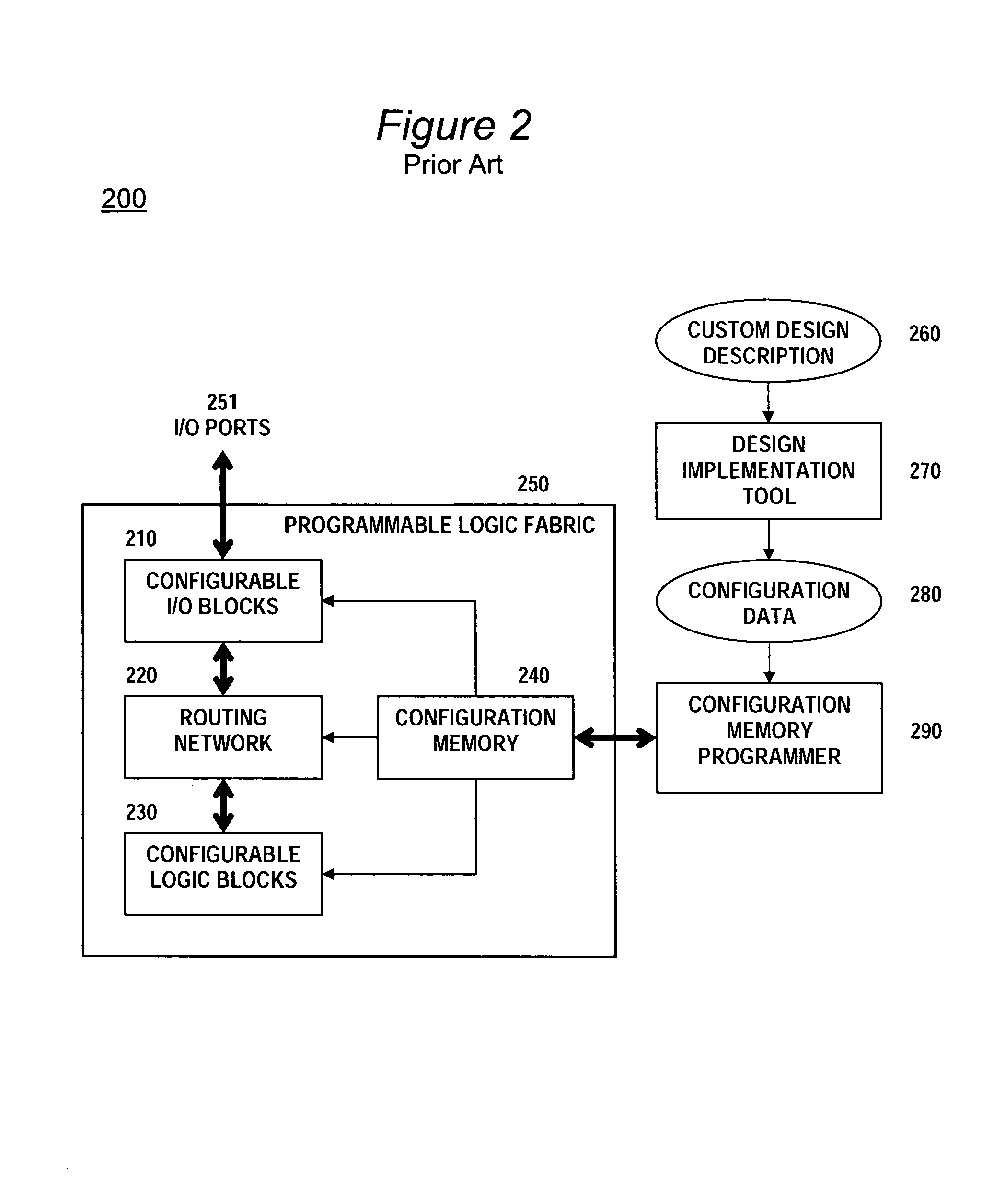
Apparatus and method for clock skew adjustment in a programmable logic fabric
InactiveUS7362135B1Minimize operating periodMinimize clock periodSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designProcessor registerProgrammable logic device
A programmable logic fabric includes configurable logic block (CLB) containing registers and combinatorial logic elements. An input switch matrix distributes incoming signals to CLB inputs or inputs of embedded logic elements including a register clock. A routing network allows a variety of routing paths with distinct delays to be selected to route the CLB outputs to the input switch matrices. Presented clock delay insertion architectures allow a leaf node of dedicated clock network and a register clock input can be alternatively routed through the routing network, thereby allowing for the generation of a variable amount of clock delay. Required clock delay for each register minimizing the clock period is computed by clock skew optimization program. A set of alternative clock routes is generated for each register clock where each route delay is close to the corresponding required delay while satisfying the monotone increasing conditions. Optimal clock route for each register clock can be efficiently selected from the alternative clock routes by an integer monotonic program to reduce the clock period of a custom design implemented in the fabric.
Owner:CHANG HYUN TAEK
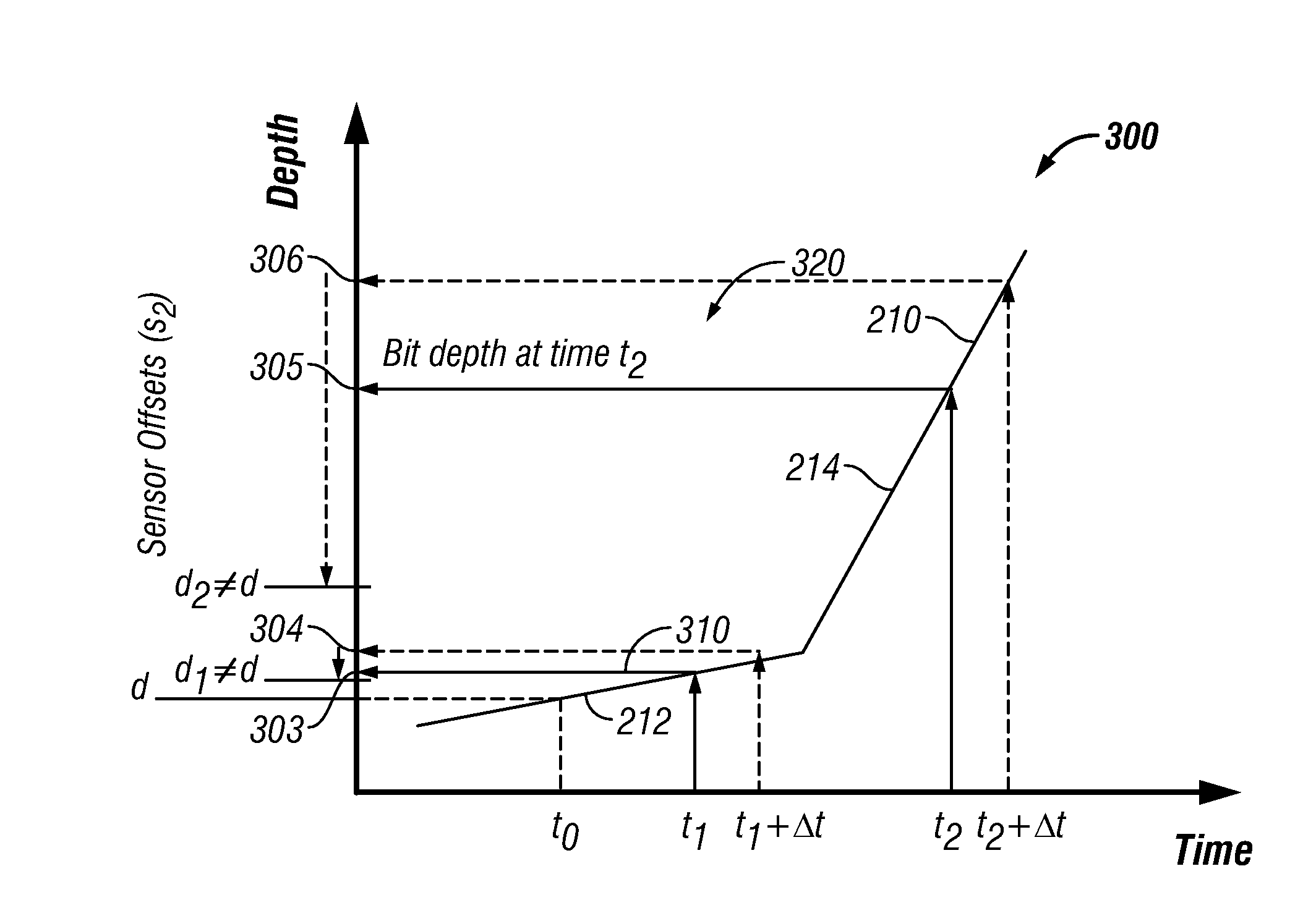
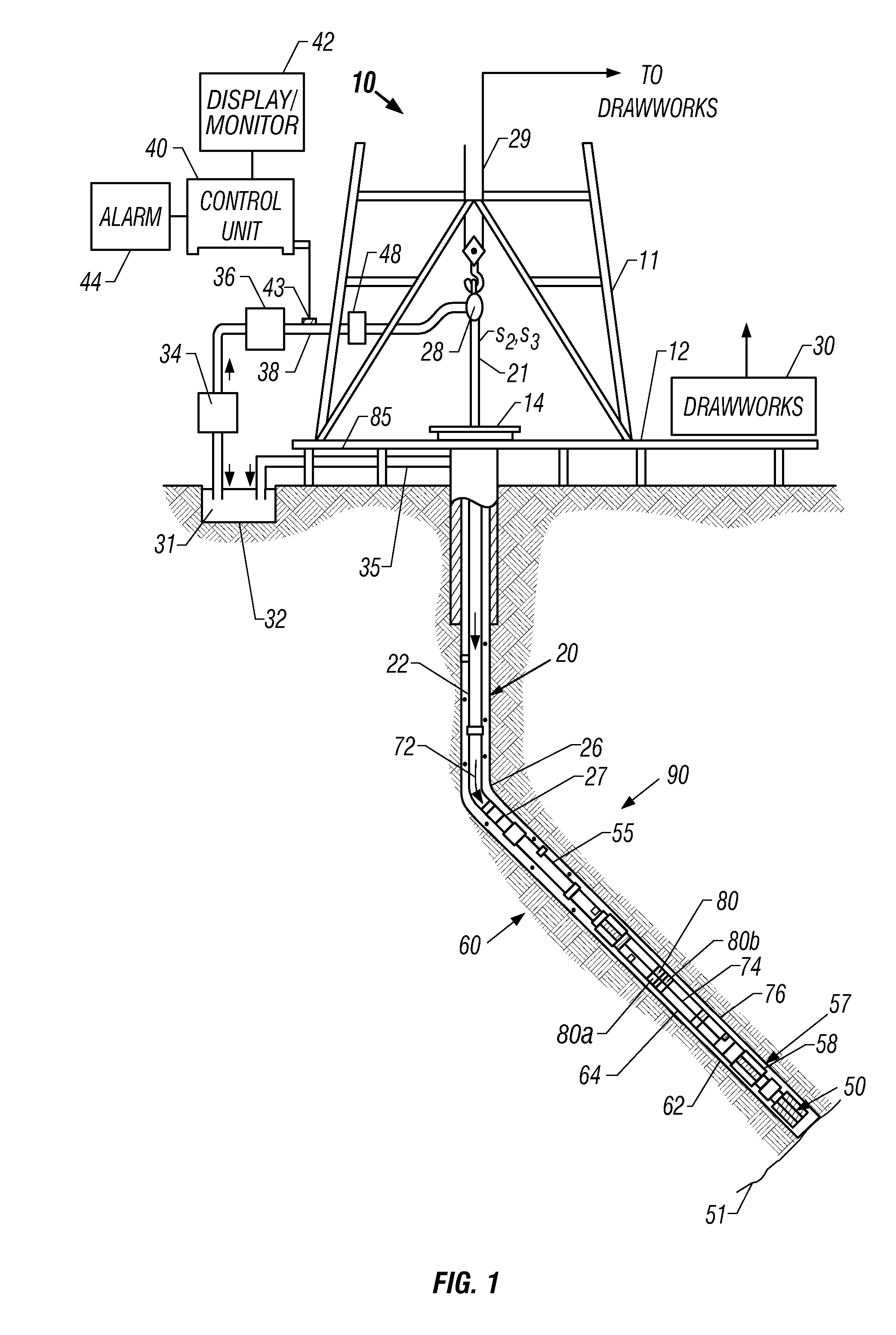
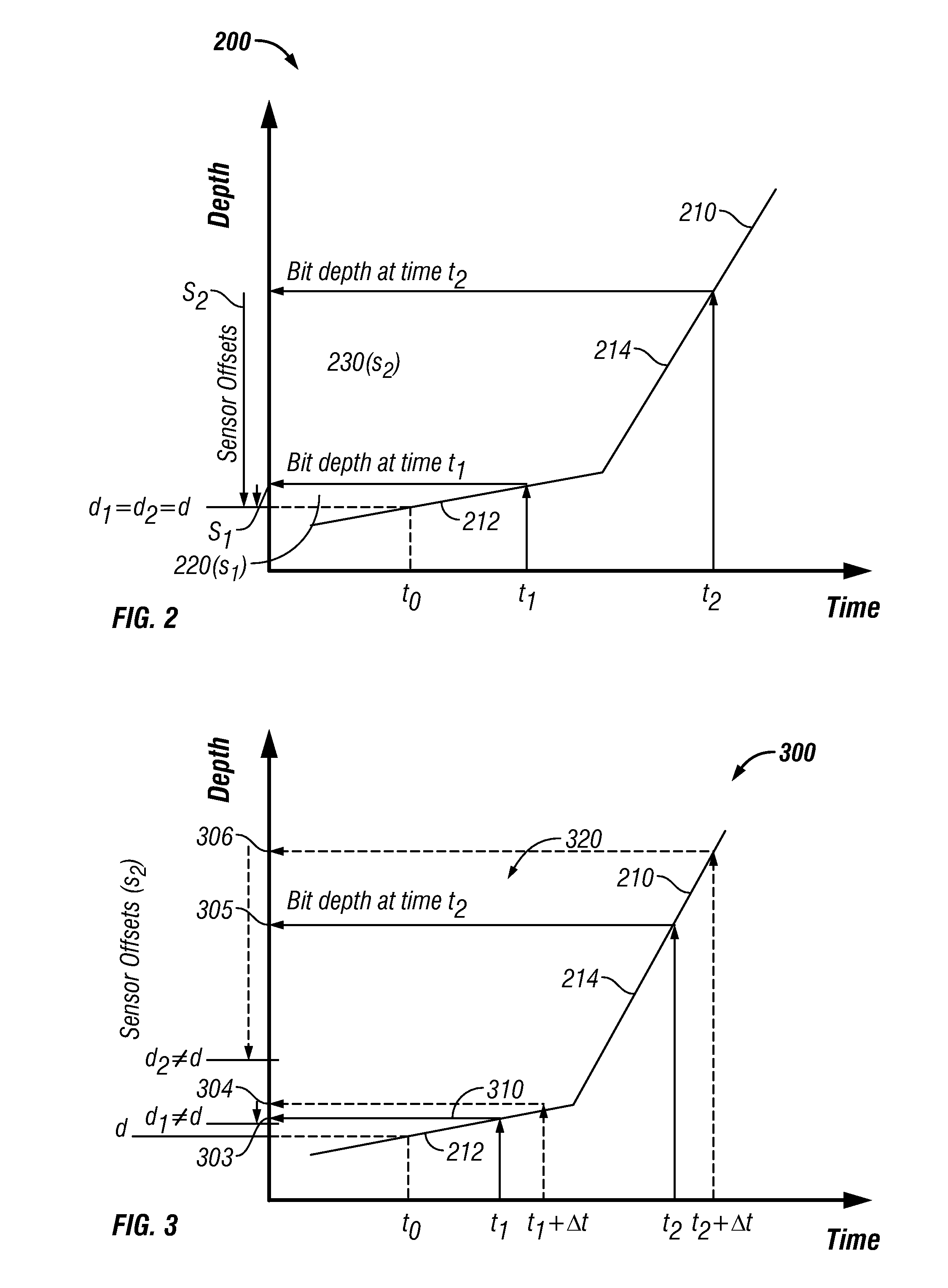
Apparatus and Method for Clock Shift Correction for Measurement-While-Drilling Measurements
The disclosure provides a method which includes transmitting signals over a time period between a downhole location and a surface location during drilling of a wellbore; recording the time of each signal at the surface using a surface clock and the time of each signal downhole using a downhole clock; and correcting the downhole measurements using the recorded times.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
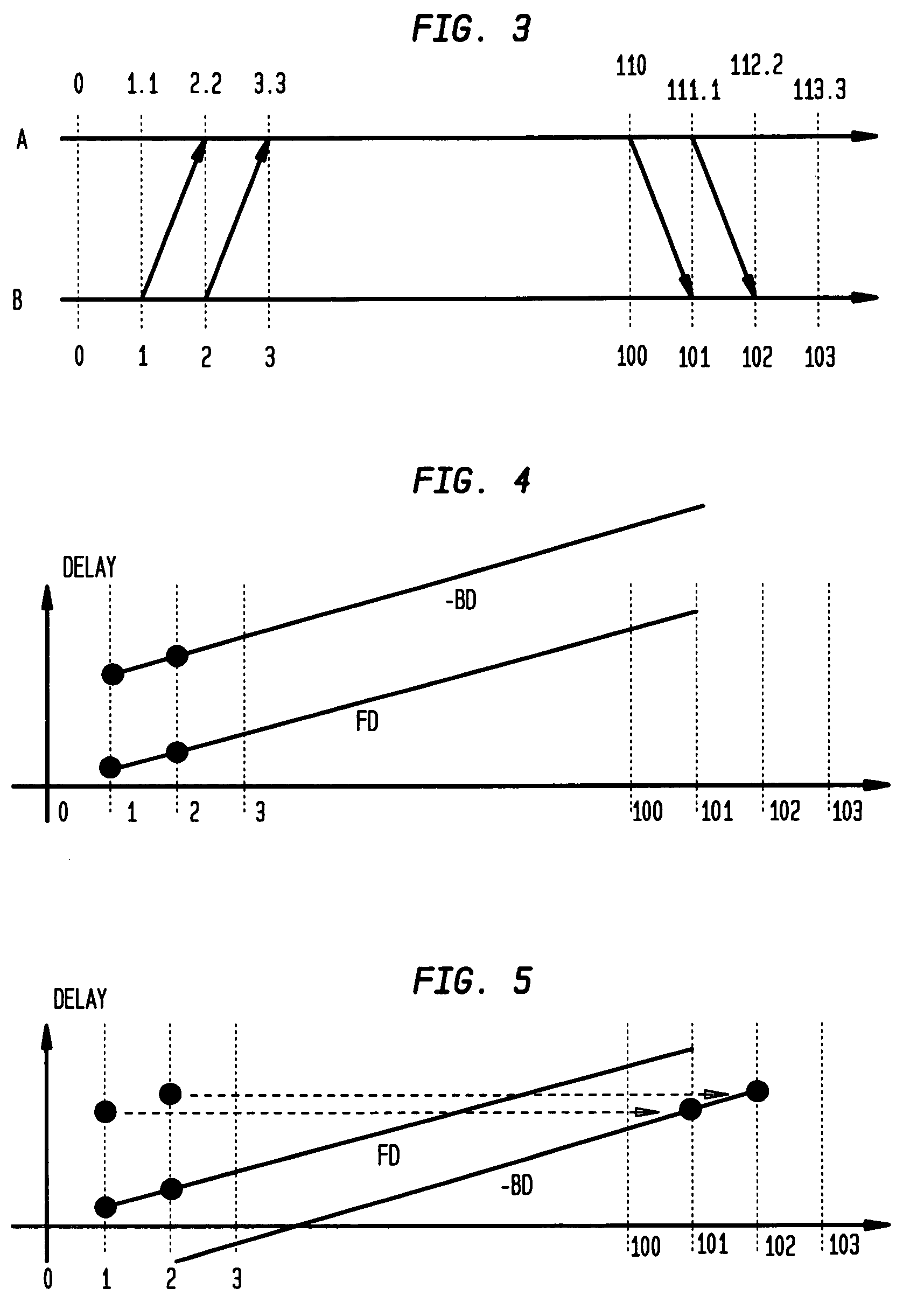
Method for calculating clock offset and skew
ActiveUS7475272B2Accelerated programError detection/correctionTime-division multiplexComputerized systemComputer science
Disclosed is a method for calculating clock offset and skew between two clocks in a computer system. The method comprises the steps of sending data packets from a first processing unit in the computer system to a second processing unit in the computer system, and sending the data packets from the second processing unit to the first processing unit. First, second, third and fourth time stamps are provided to indicate, respectively, when the packets leave the first processing unit, arrive at the second processing unit, leave the second processing unit, and arrive at the first processing unit. The method comprises the further steps of defining a set of backward delay points using the fourth time stamps, and calculating a clock offset between clocks on the first and second processing units and clock skews of said clocks using said set of backward delay points.
Owner:IBM CORP
Use of T4 timestamps to calculate clock offset and skew
ActiveUS20070061607A1Accelerated programError detection/correctionTime-division multiplexProcessing elementClock skew
Disclosed are a method and system for calculating clock offset and skew between two clocks in a computer system. The method comprises the steps of sending data packets from a first processing unit in the computer system to a second processing unit in the computer system, and sending the data packets from the second processing unit to the first processing unit. First, second, third and fourth time stamps are provided to indicate, respectively, when the packets leave the first processing unit, arrive at the second processing unit, leave the second processing unit, and arrive at the first processing unit. The method comprises the further steps of defining a set of backward delay points using the fourth time stamps, and calculating a clock offset between clocks on the first and second processing units and clock skews of said clocks using said set of backward delay points.
Owner:IBM CORP
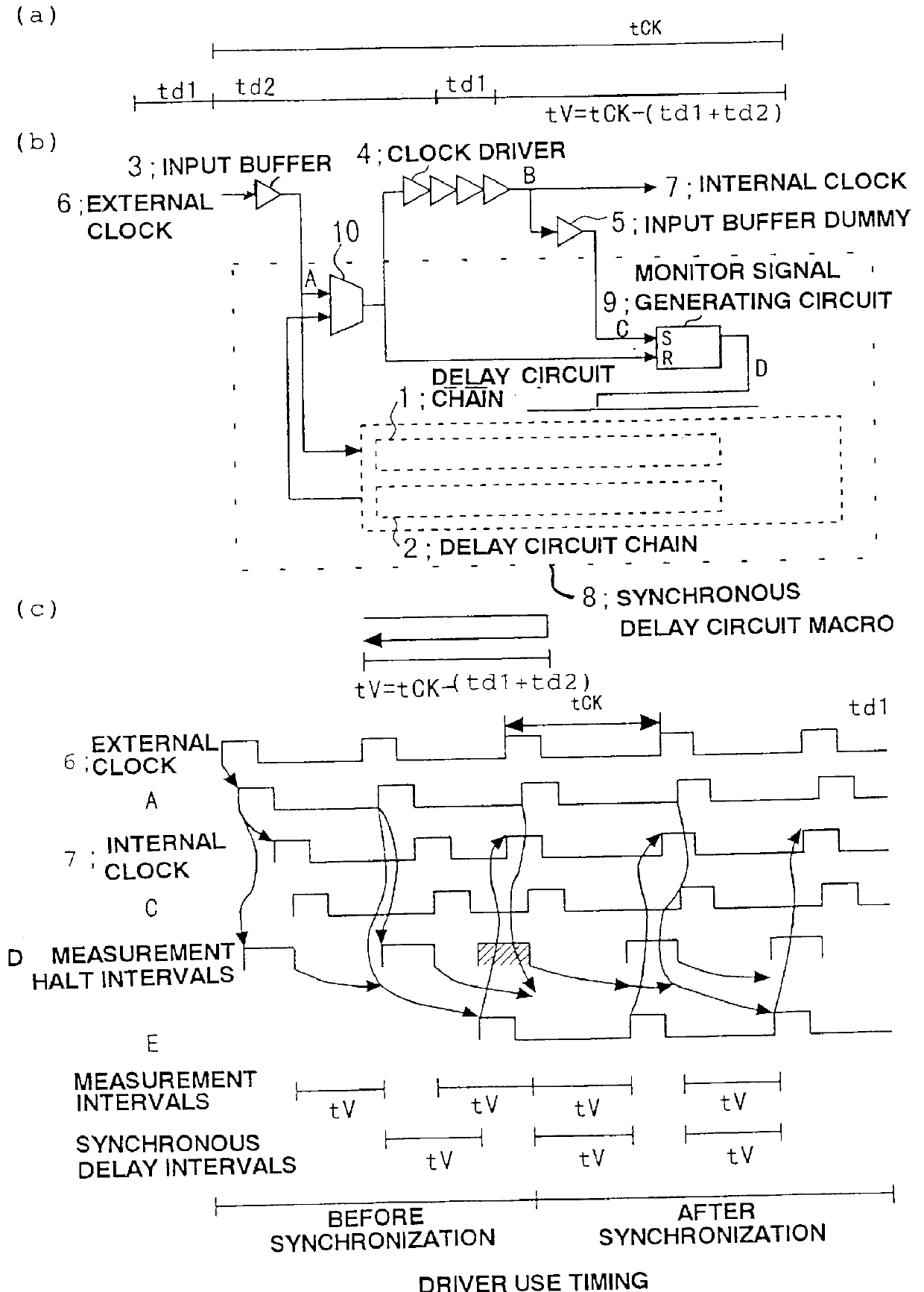
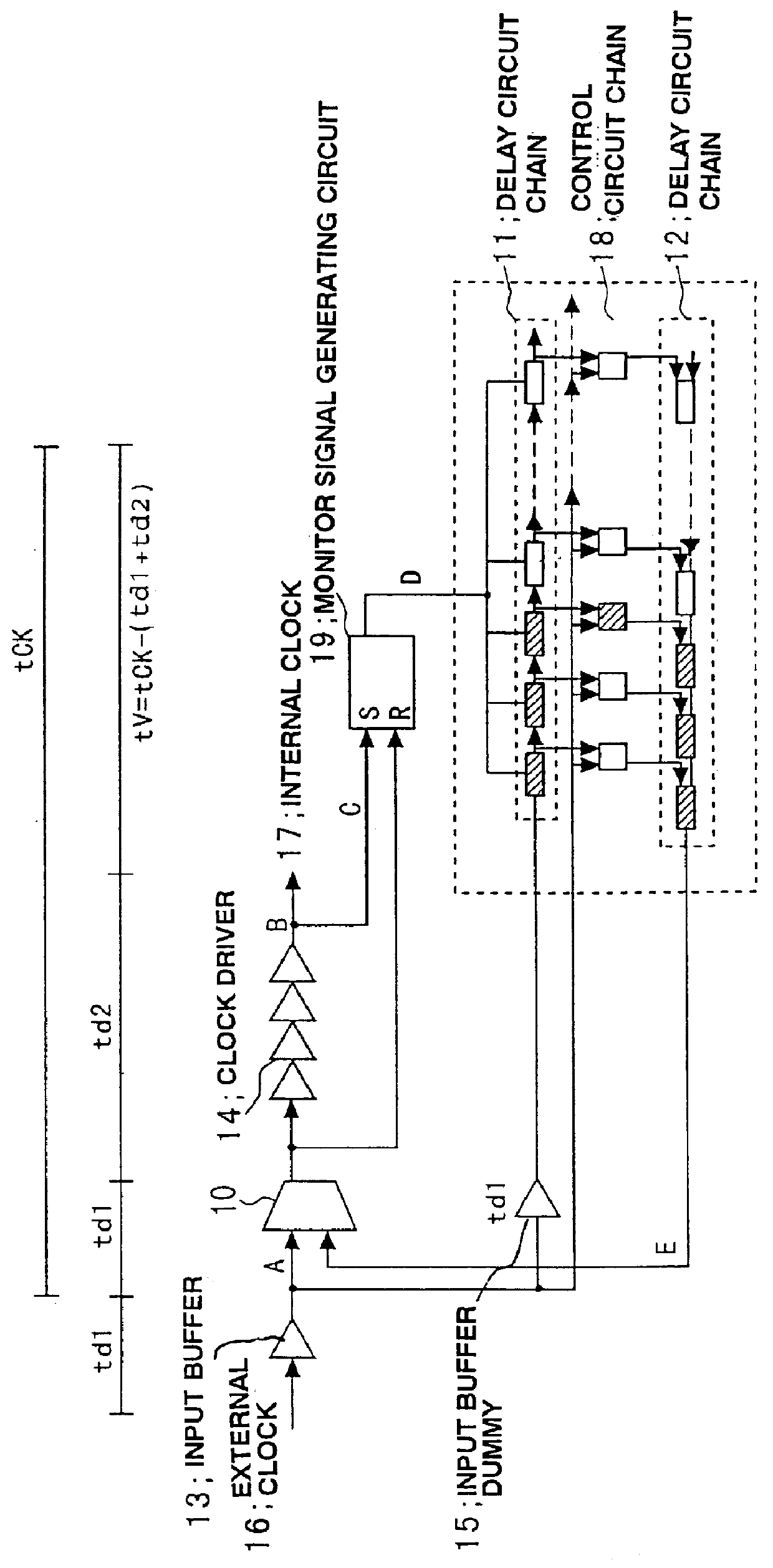
Synchronous delay circuit
InactiveUS6075395AEfficient and economical designPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsSoftware engineeringHemt circuits
A synchronous delay circuit contains a first delay circuit for propagating a pulse for a fixed period of time, a second delay circuit for passing the pulse over a length proportional to the length of the first delay circuit along the path that the pulse propagated, and a circuit for outputting a monitor signal when a clock period is propagating through a clock driver. The first delay circuit measures a clock period tCK, and the second delay circuit reconstructs the measured clock period. External clock signals travel through a path from an input buffer through a first switch of a clock driver. The time corresponding to a delay time of the input buffer (td1) and a delay time of the clock divider (td2) is subtracted from the clock period tCK producing a delay circuit with a delay of tCK-(td1+td2). When the clock pulse passes through the delay circuit whose delay is tCK-(td1+td2), the internal clock delay becomes equal to the clock cycle tCK. Thus, the internal clock is free of clock skew.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
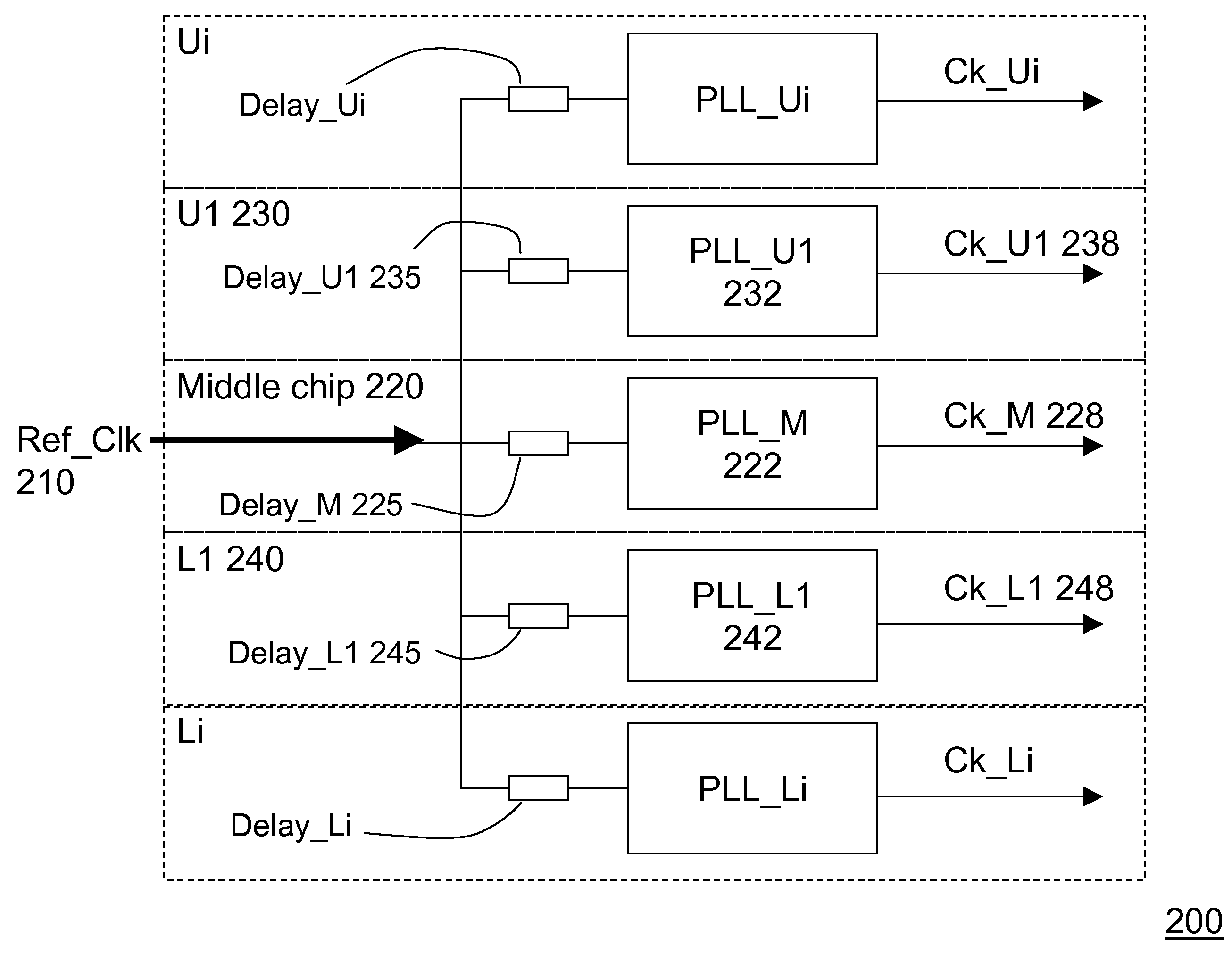
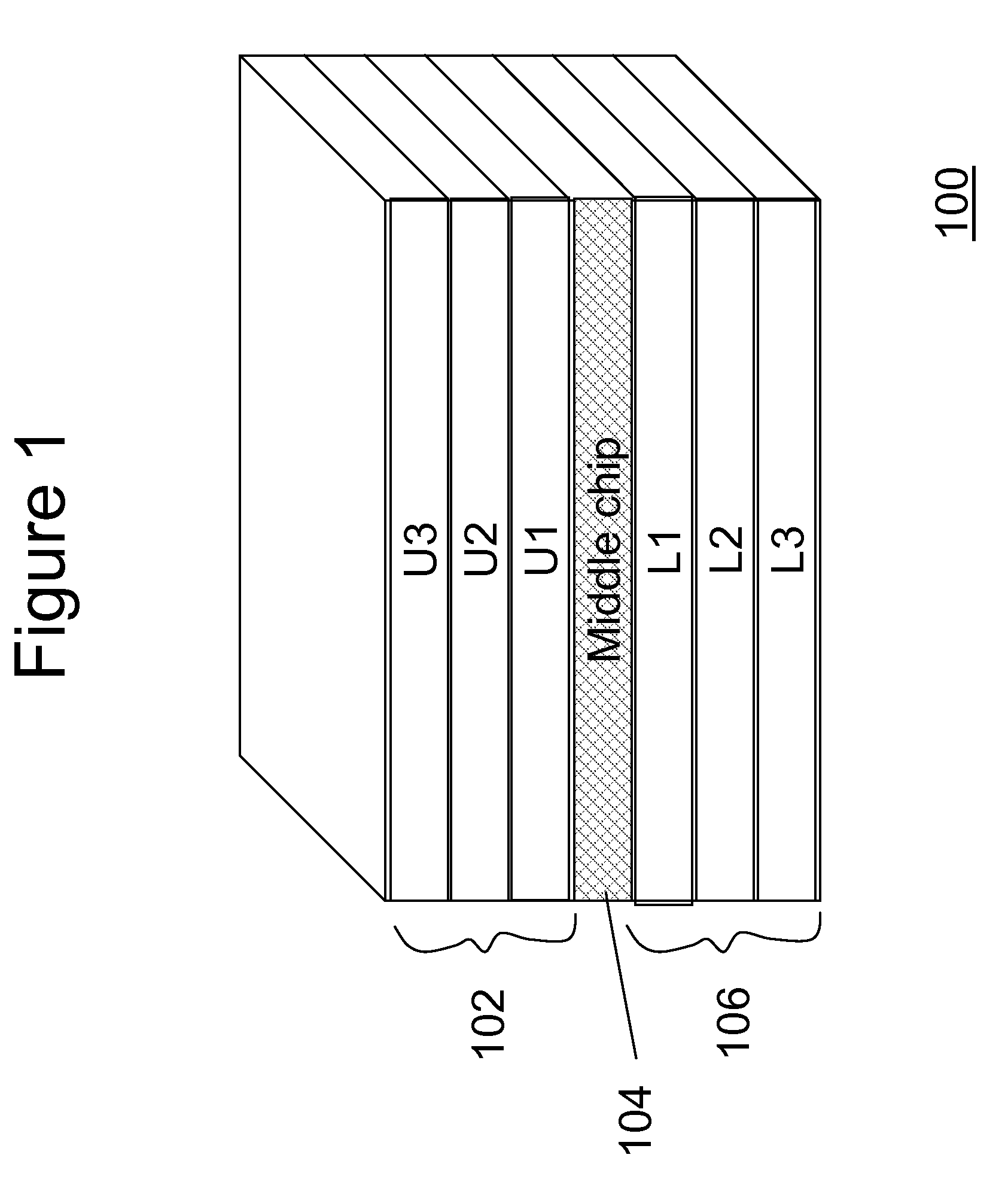
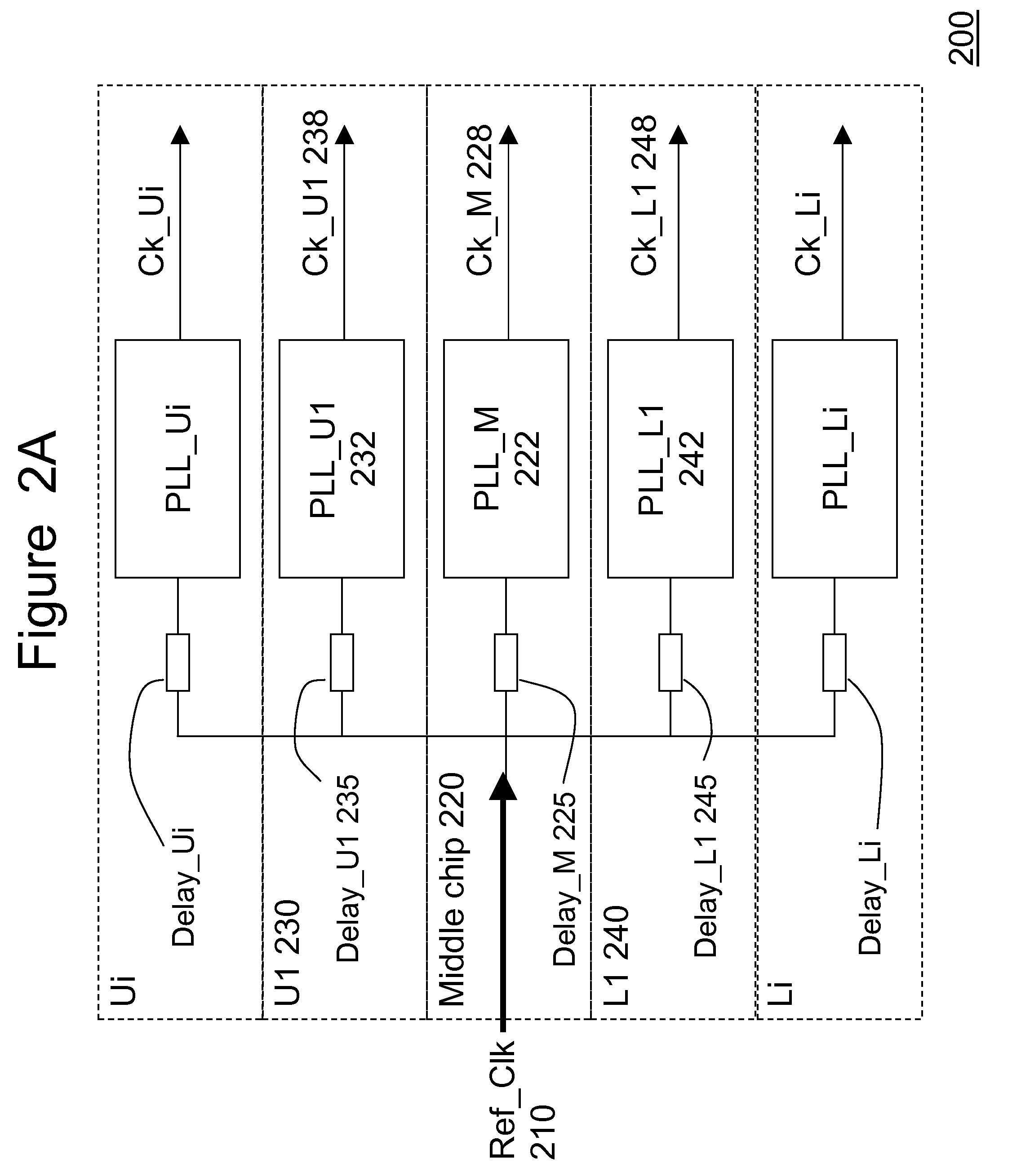
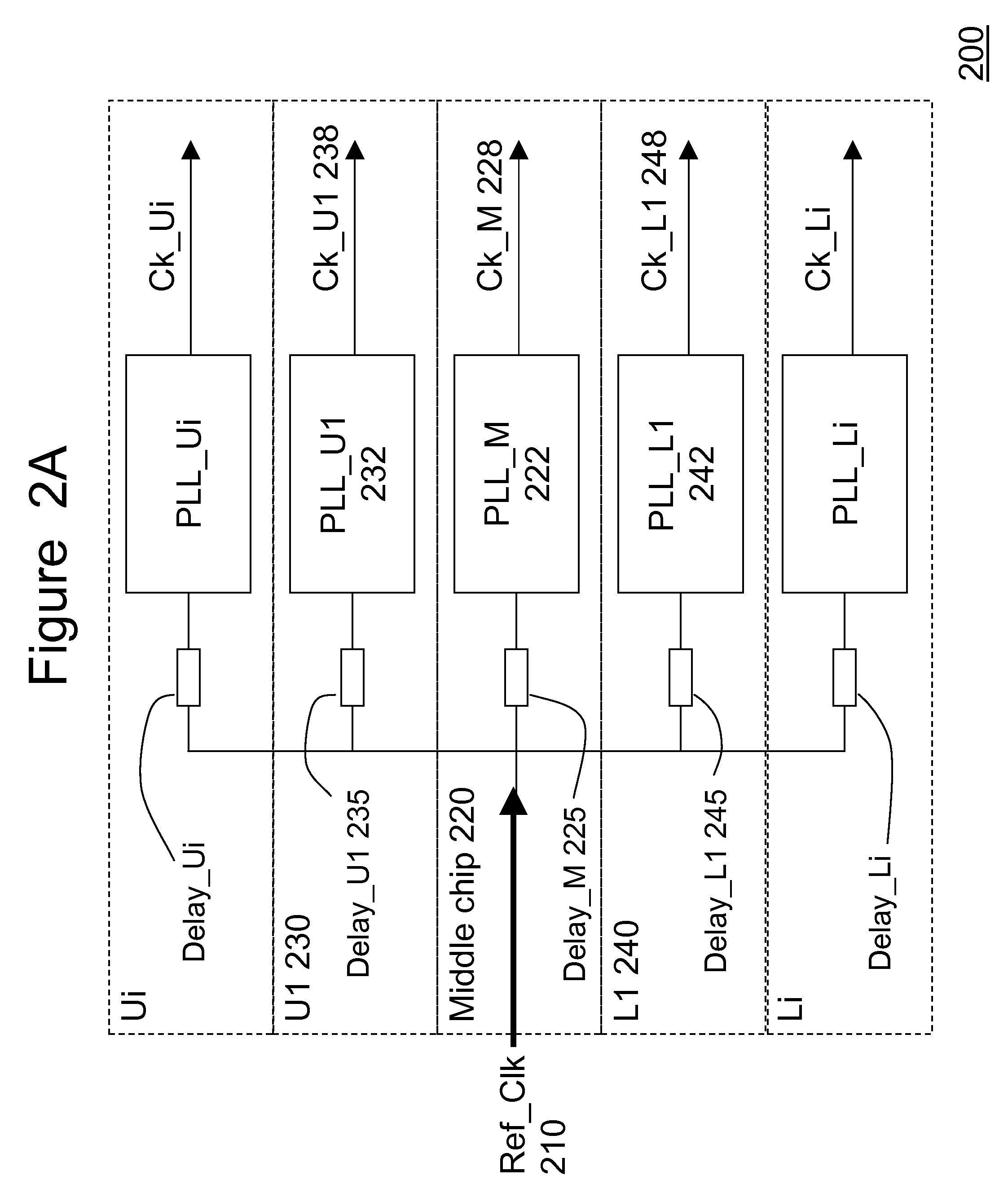
Three-dimensional chip-stack synchronization
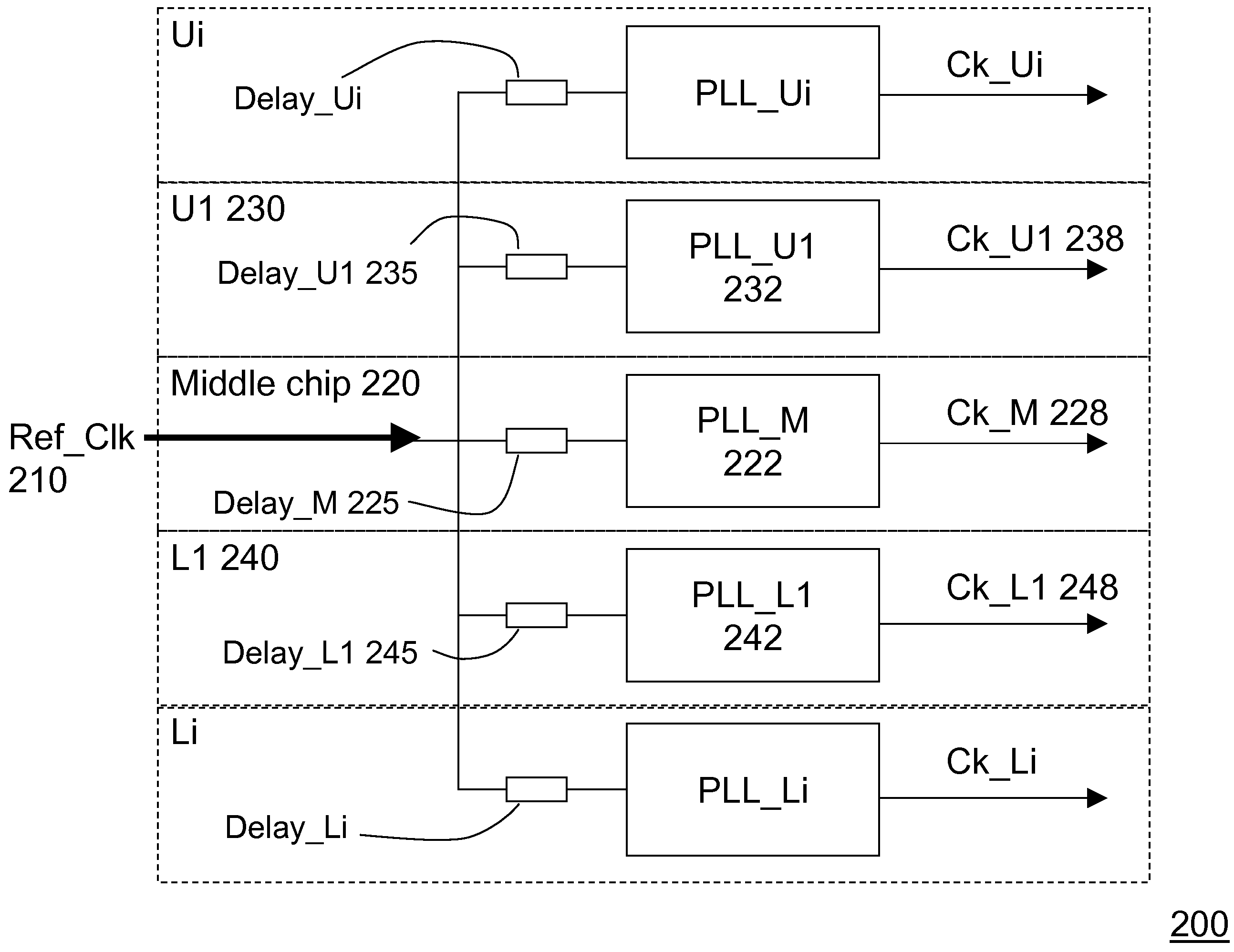
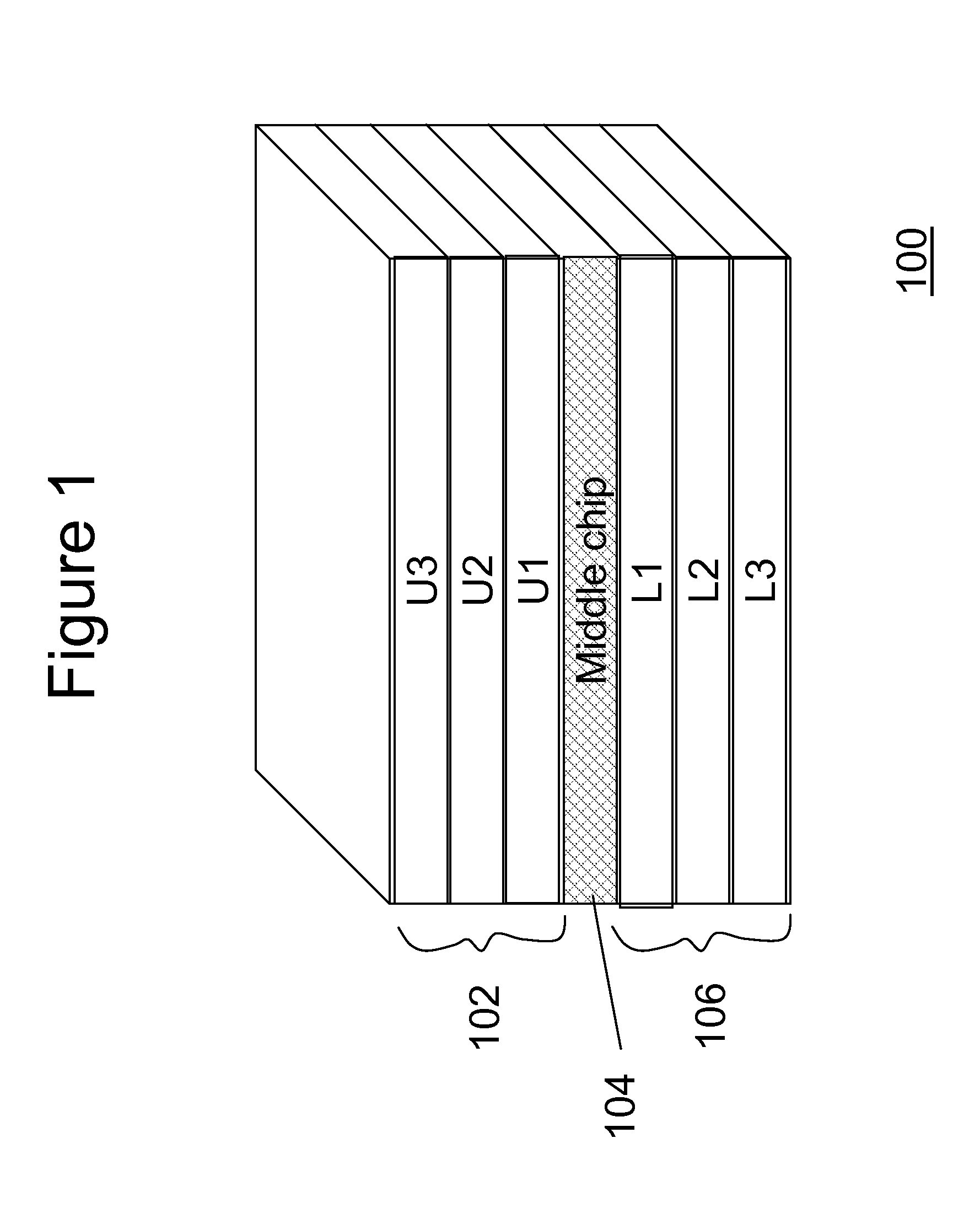
ActiveUS20100277210A1Minimizes clock skew clockMinimizes clock clock jitterPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesClock skewElectrical and Electronics engineering
a central reference clock is placed in a substantially middle chip of a 3-D chip-stack. The central reference clock is distributed to each child chip of the 3-D chip-stack, so that a plurality of clocks is generated for each individual chip in the 3-D-stack in a synchronous manner. A predetermined number of through-silicon-vias and on-chip wires are employed to form a delay element for each slave clock, ensuring that the clock generated for each child chip is substantially synchronized. Optionally, an on-chip clock trimming circuit is embedded for further precision tuning to eliminate local clock skews.
Owner:IBM CORP
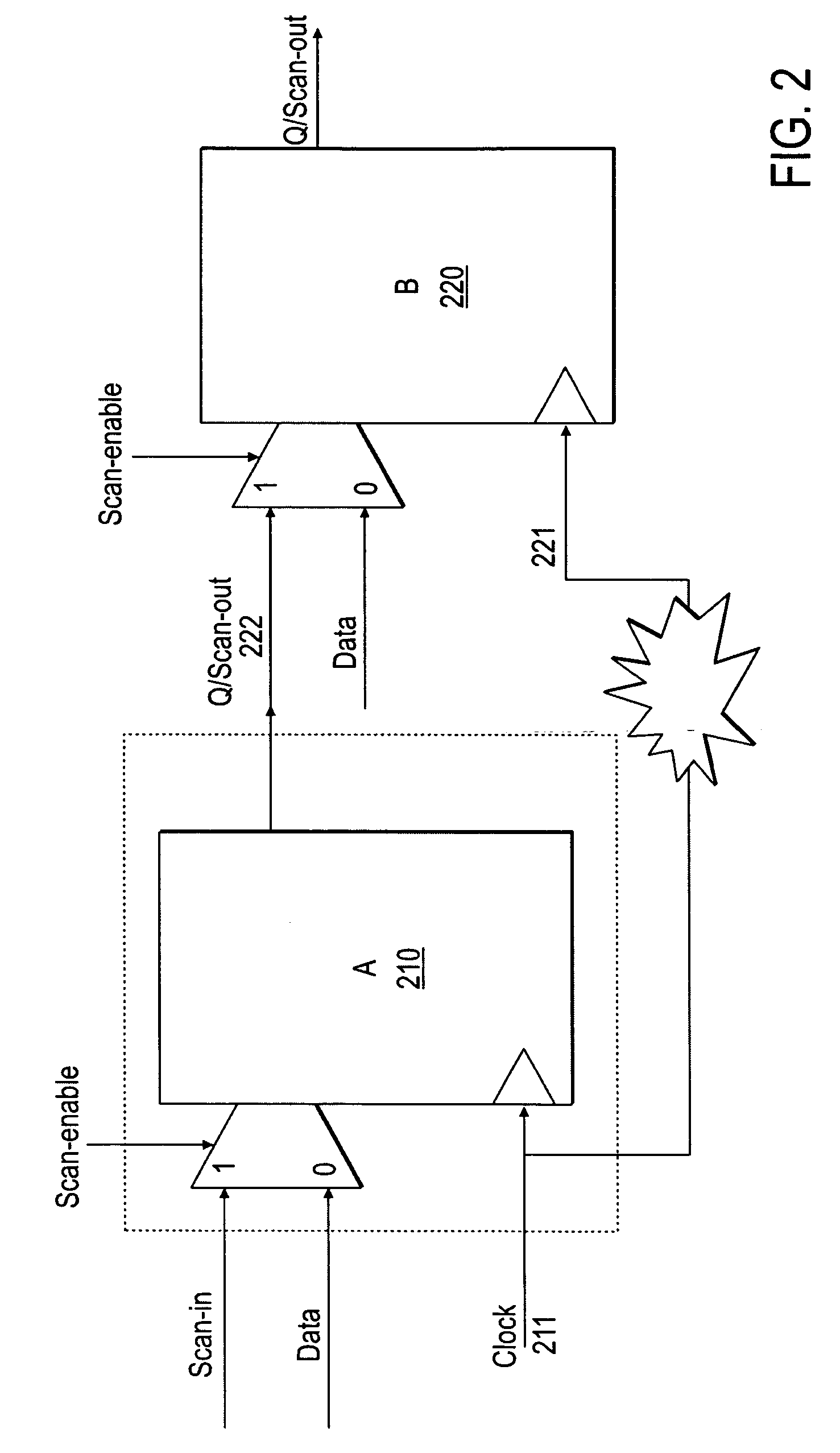
System and method for performing timing analysis, including error diagnosis, signal tracking and clock skew
InactiveUS6594806B1Increase circuit design flexibilityImprove design flexibilityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic timing analysisSignal tracking
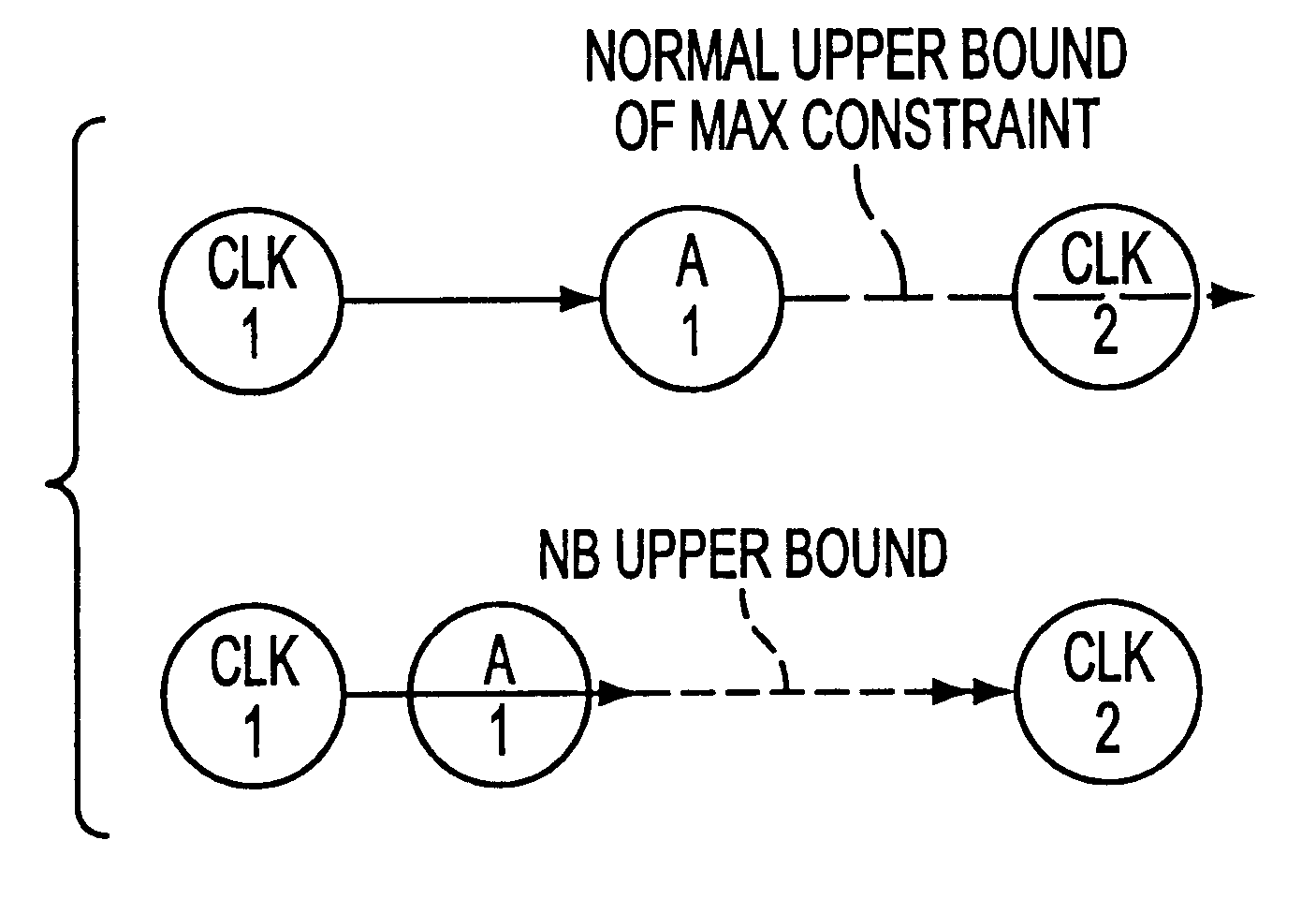
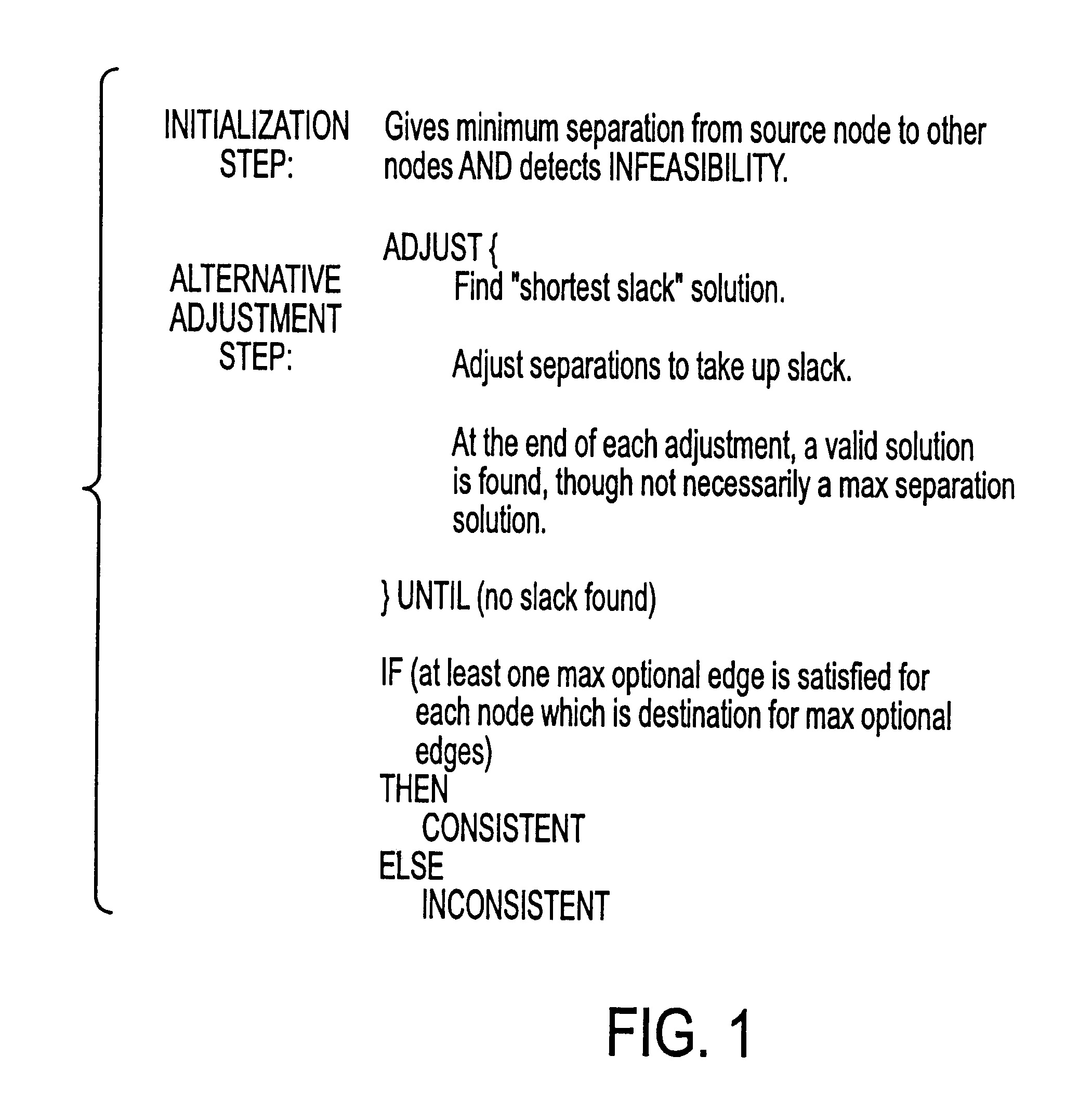
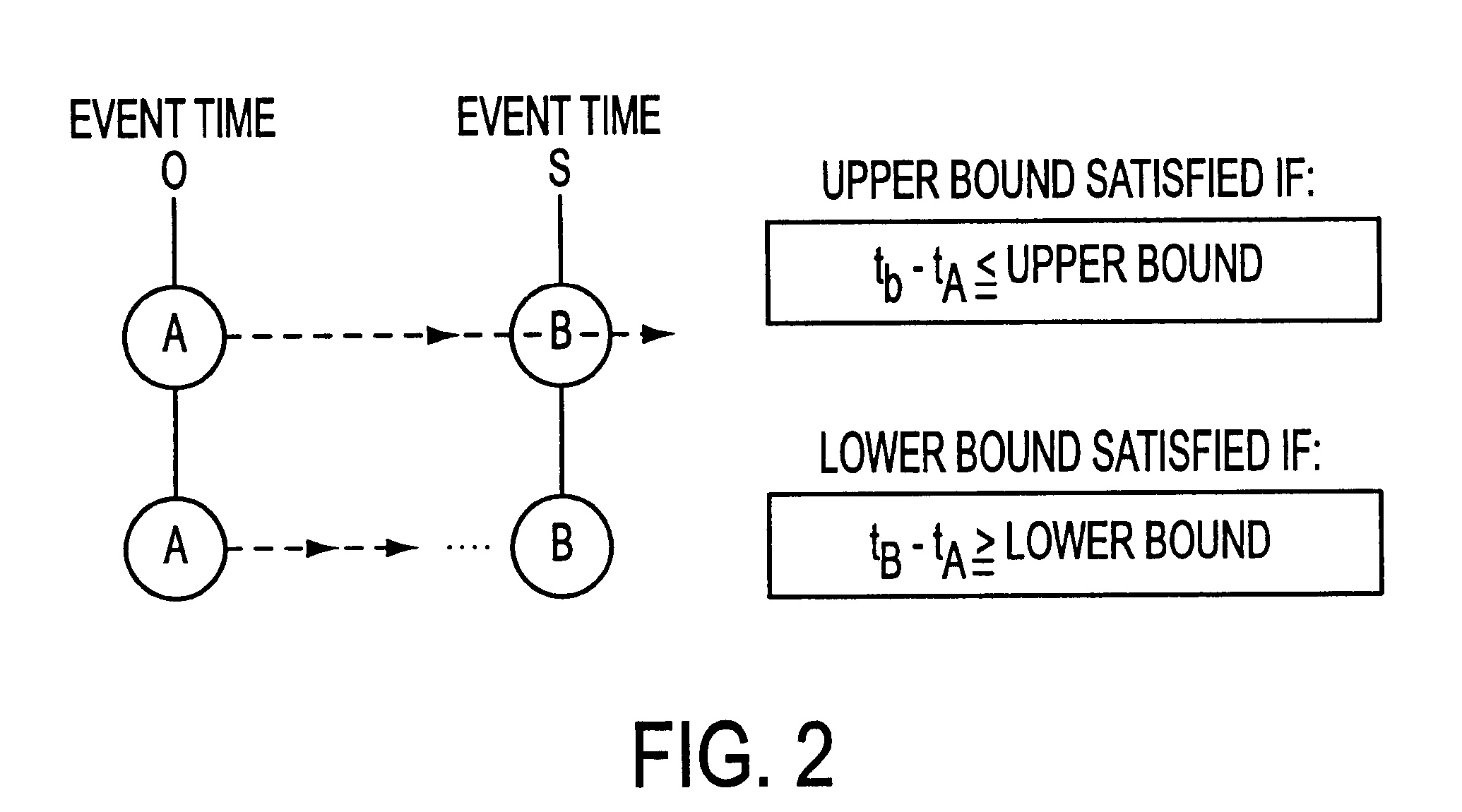
A method for performing timing analysis comprising inputting circuit timing information for a circuit, including temporal constraints between events of a desired circuit operation. A timing diagram representing the desired circuit operation, based on the circuit timing information is generater. All violated constraints within said timing diagram are identified. The method forces no violations of said violated constraints by designating the violated constraints as Non-Breakable (NB) constraints, such that a time difference from a source event to a destination event which defines said NB constraint is no less than a minimum bound and no more than a maximum bound of a linear constraint representing a timing requirement between the source and the destination events.
Owner:NEC CORP
Motion circuit and on-board driver circuit for liquid crystal display panel employing the motion circuit
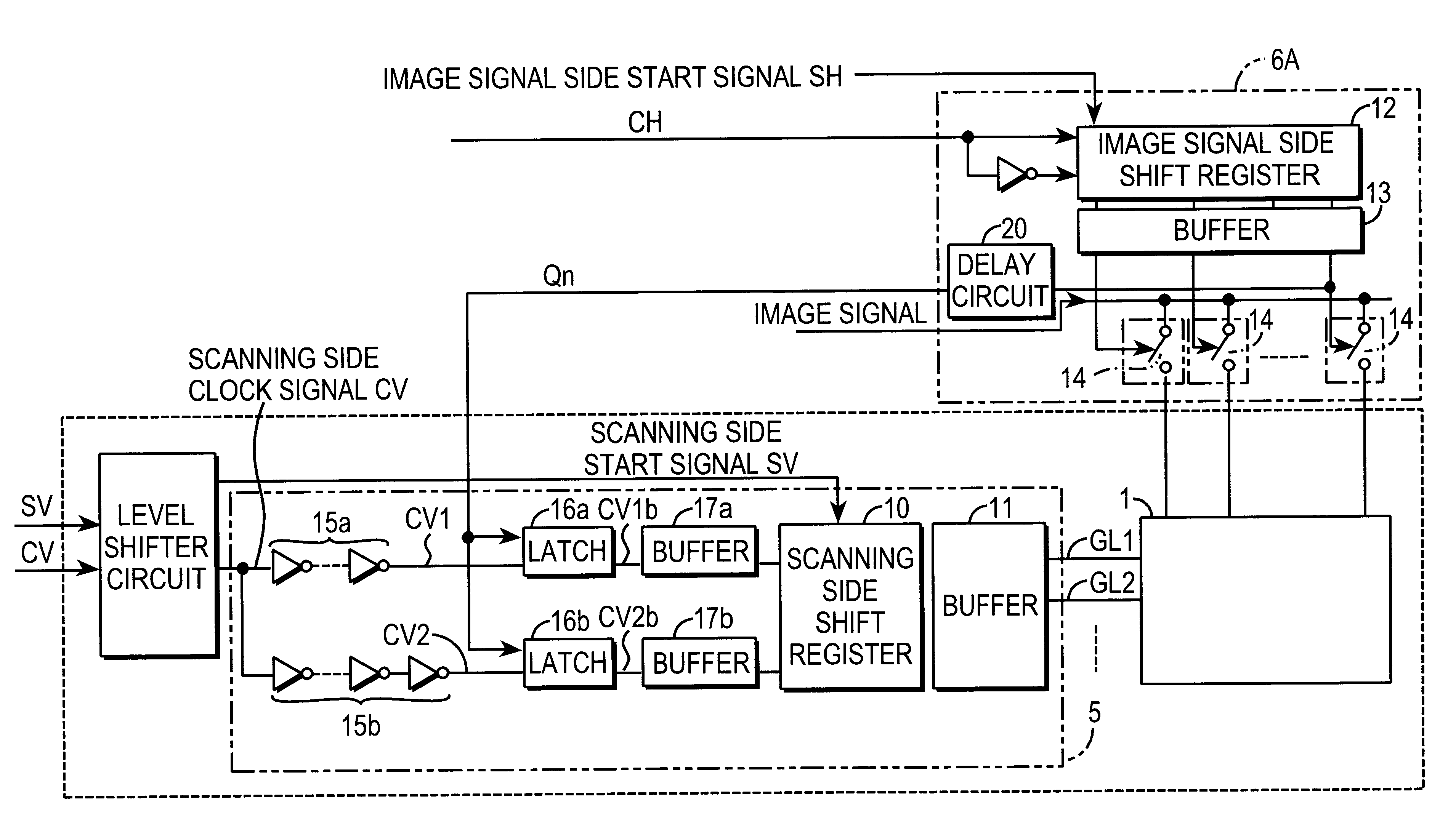
InactiveUS6373458B1Reduce generationStable circuit operations with no malfunctionsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageDriver circuitShift register
The motion circuit of the present invention is an on-board driver circuit which is composed of polycrystal silicon semiconductor layers formed on a substrate, and which is provided with a first latch circuit for latching one of a normal phase and reverse phase clock signals having a clock skew using a clock signal and for outputting it to a shift register, and a second latch circuit for latching the other one of the normal phase and reverse phase clock signals using a clock signal and for outputting to the shift register. The latch operations of the first and second latch circuits are timed to make the two clock signals have reverse polarities. Consequently, it is realized to provide a motion circuit performing stable circuit operations without malfunctions, by preventing the occurrence of the fail phenomenon due to a skew between the normal phase and reverse phase clock signals which drive the shift register. It is also realized to provide an on-board driver circuit for a liquid crystal display panel by employing the motion circuit.
Owner:TOSHIBA MATSUSHITA DISPLAY TECH
Three-dimensional chip-stack synchronization
ActiveUS7863960B2Clock skew is minimizedMinimizes the clock skew and clock jitterPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesSlave clockEngineering
A central reference clock is placed in a substantially middle chip of a 3-D chip-stack. The central reference clock is distributed to each child chip of the 3-D chip-stack, so that a plurality of clocks is generated for each individual chip in the 3-D-stack in a synchronous manner. A predetermined number of through-silicon-vias and on-chip wires are employed to form a delay element for each slave clock, ensuring that the clock generated for each child chip is substantially synchronized. Optionally, an on-chip clock trimming circuit is embedded for further precision tuning to eliminate local clock skews.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
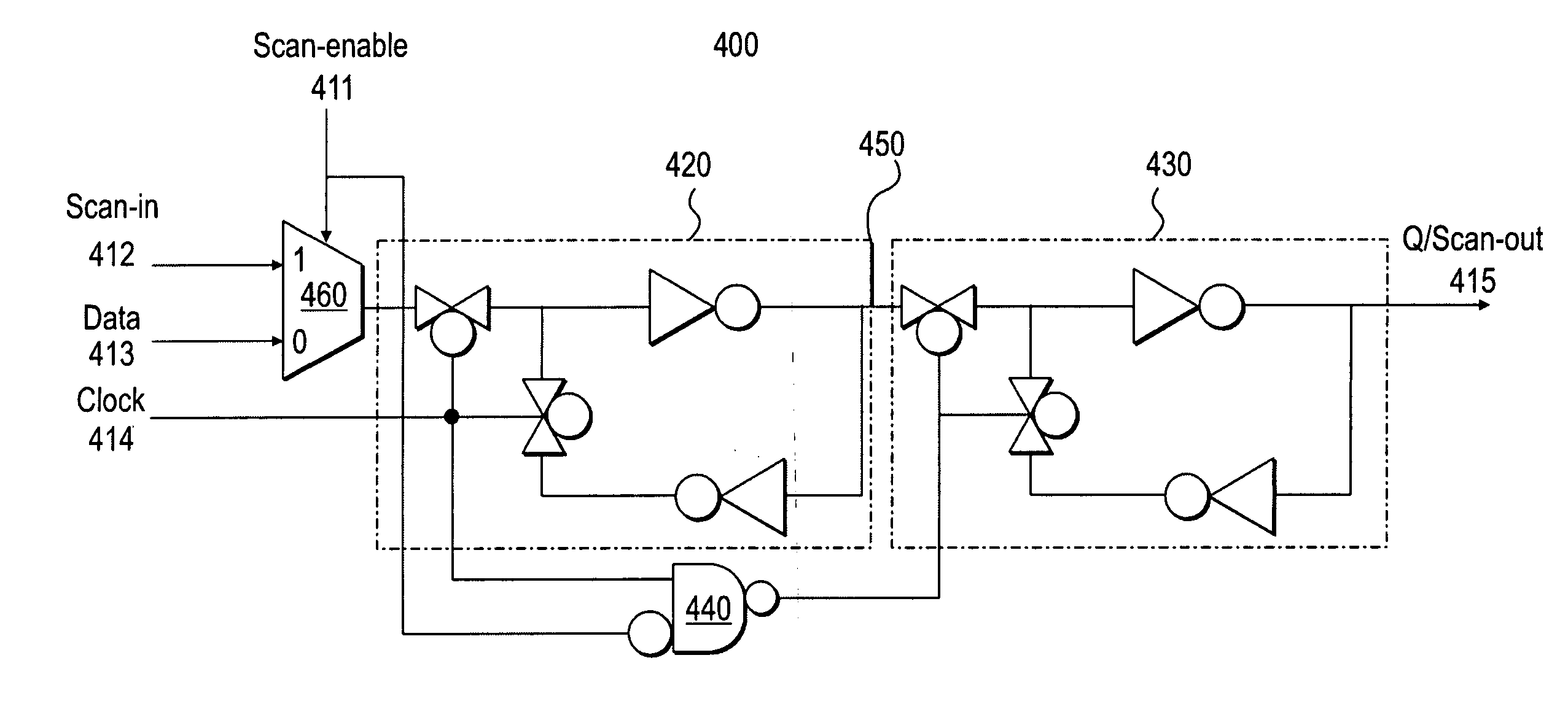
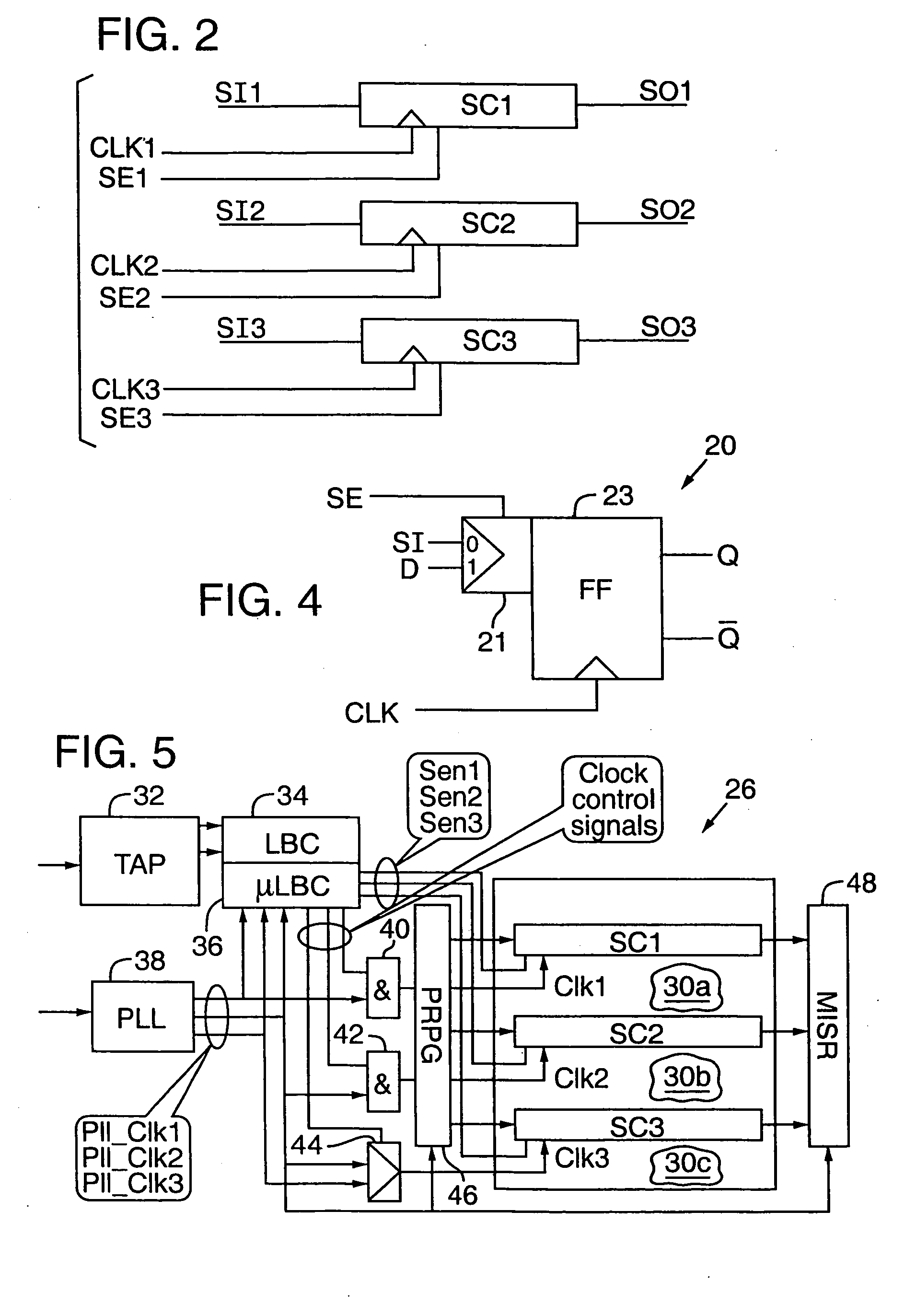
Method and system for clock skew independent scan register chains
InactiveUS20060095819A1Electronic circuit testingElectric pulse generatorClock networkComputer science
A method and system for system for clock skew independent scan chains are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method comprises connecting a plurality of mux-D scan registers in a chain configuration, wherein a first mux-D scan register of the plurality is associated with a first clock network, and a second mux-D scan register of the plurality is associated with a second clock network. The plurality of mux-D scan registers have a scan mode. The first mux-D scan register and the second mux-D scan register become clock skew independent by controlling a scan-enable signal and a clock signal.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and apparatus for at-speed testing of digital circuits
InactiveUS20060064616A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionMulti inputLogic built-in self-test
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
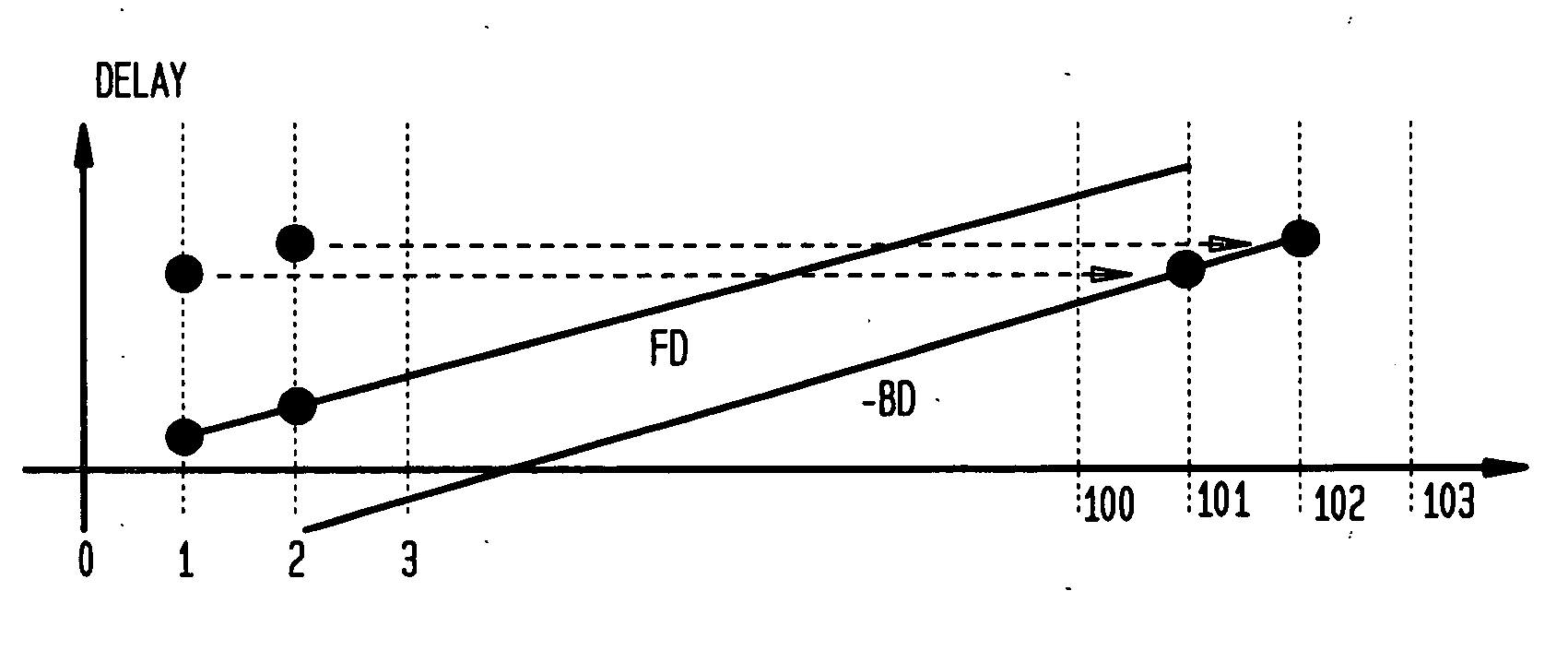
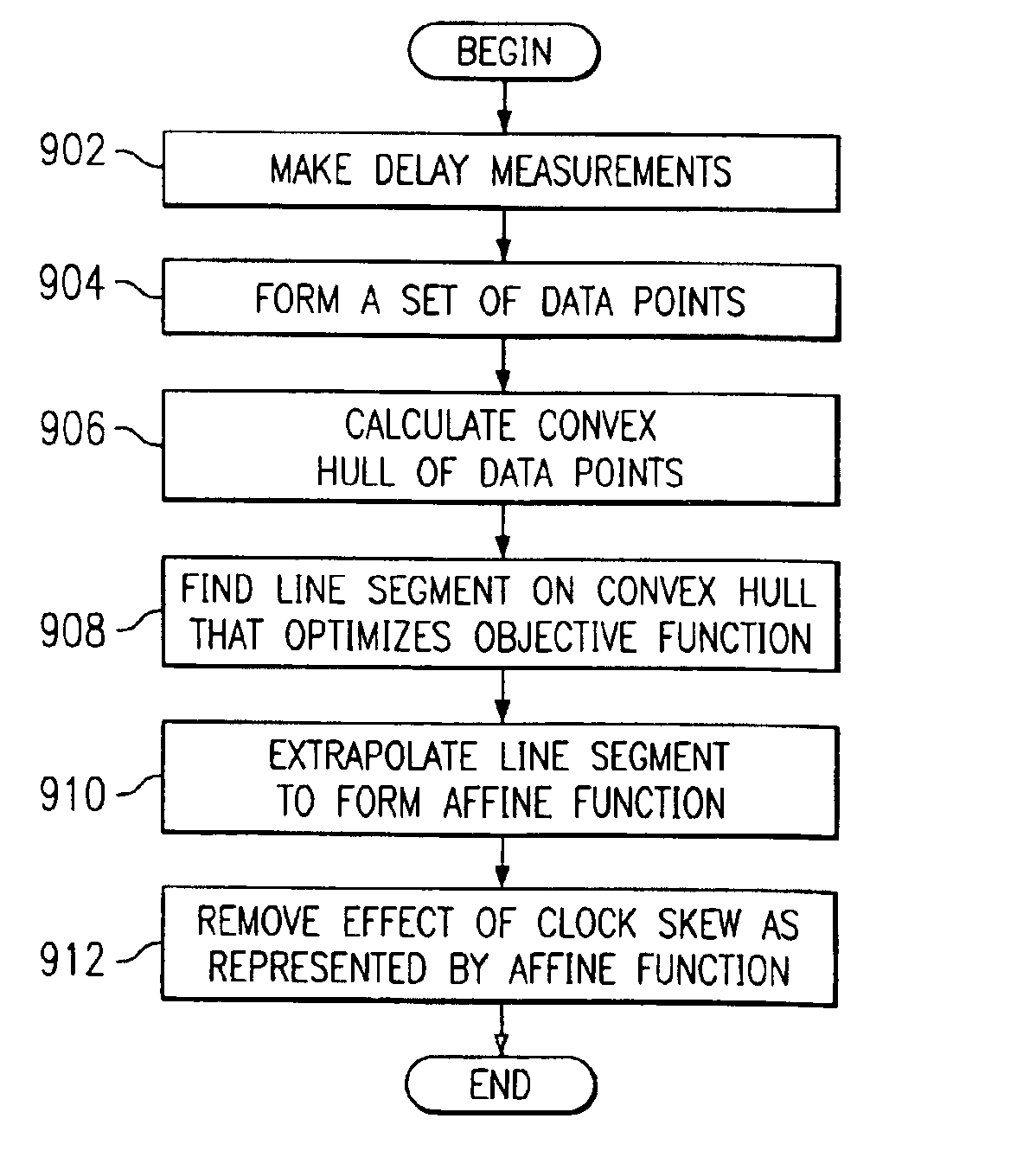
Clock synchronization with removal of clock skews through network measurements in derivation of a convext hull
InactiveUS6957357B2Optimize objective functionError detection/correctionVoltage-current phase angleData processing systemNetwork measurement
A method, computer program product, and data processing system for estimating and correcting the amount of clock skew in end-to-end network timing measurements is disclosed. Measured delays are combined with their time of measurement to create ordered pairs. These ordered pairs represent points within a Cartesian plane. The convex hull of these points is determined, and an optimal line segment from the resulting polygon is selected and extrapolated to create an affine function estimating clock skew over time. The optimal line segment of the polygon is one that optimizes a selected objective function. The objective function is selected so as to be an appropriate measurement of the accuracy of the resulting linear function as an estimate of the actual clock skew.
Owner:IBM CORP
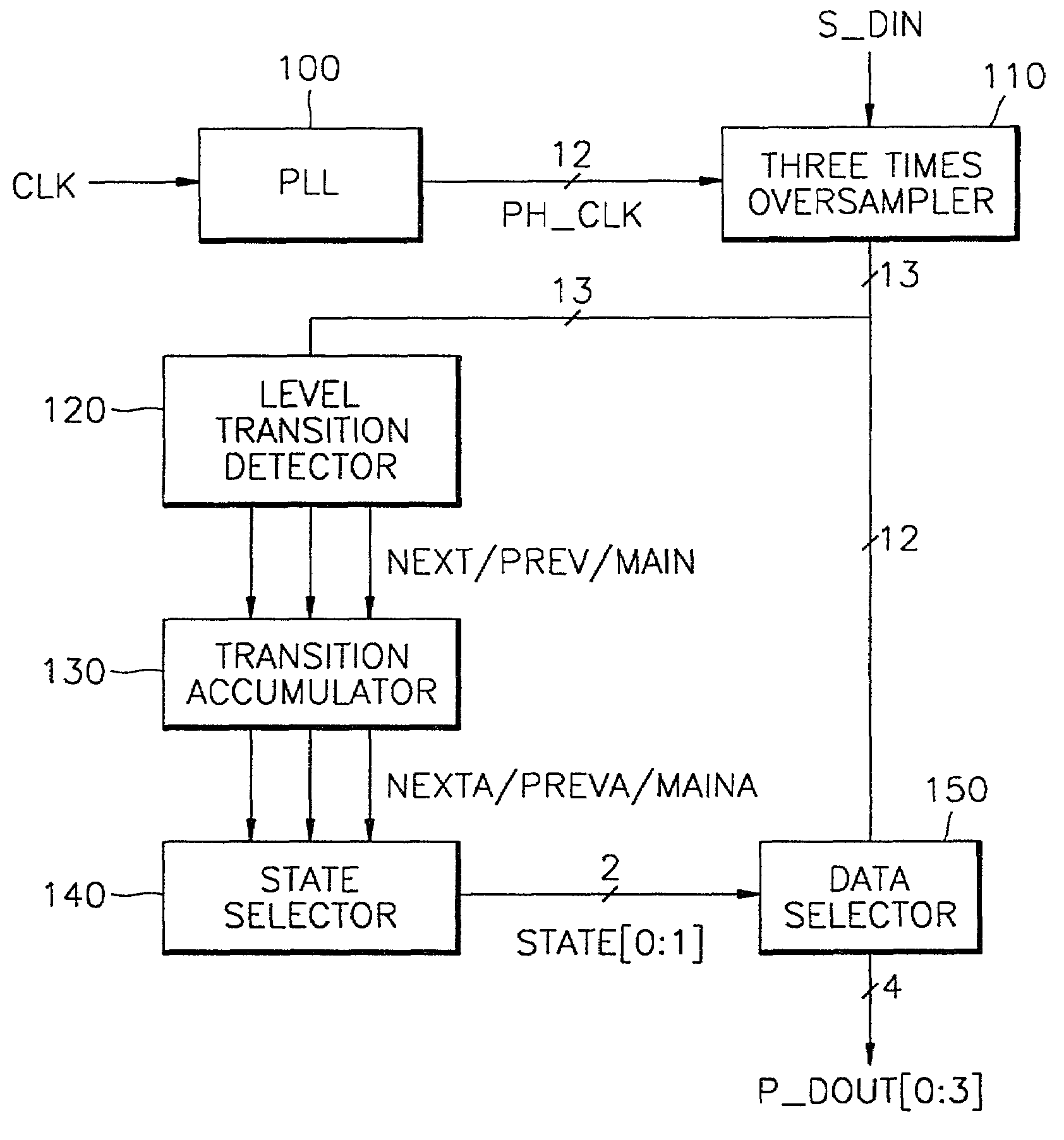
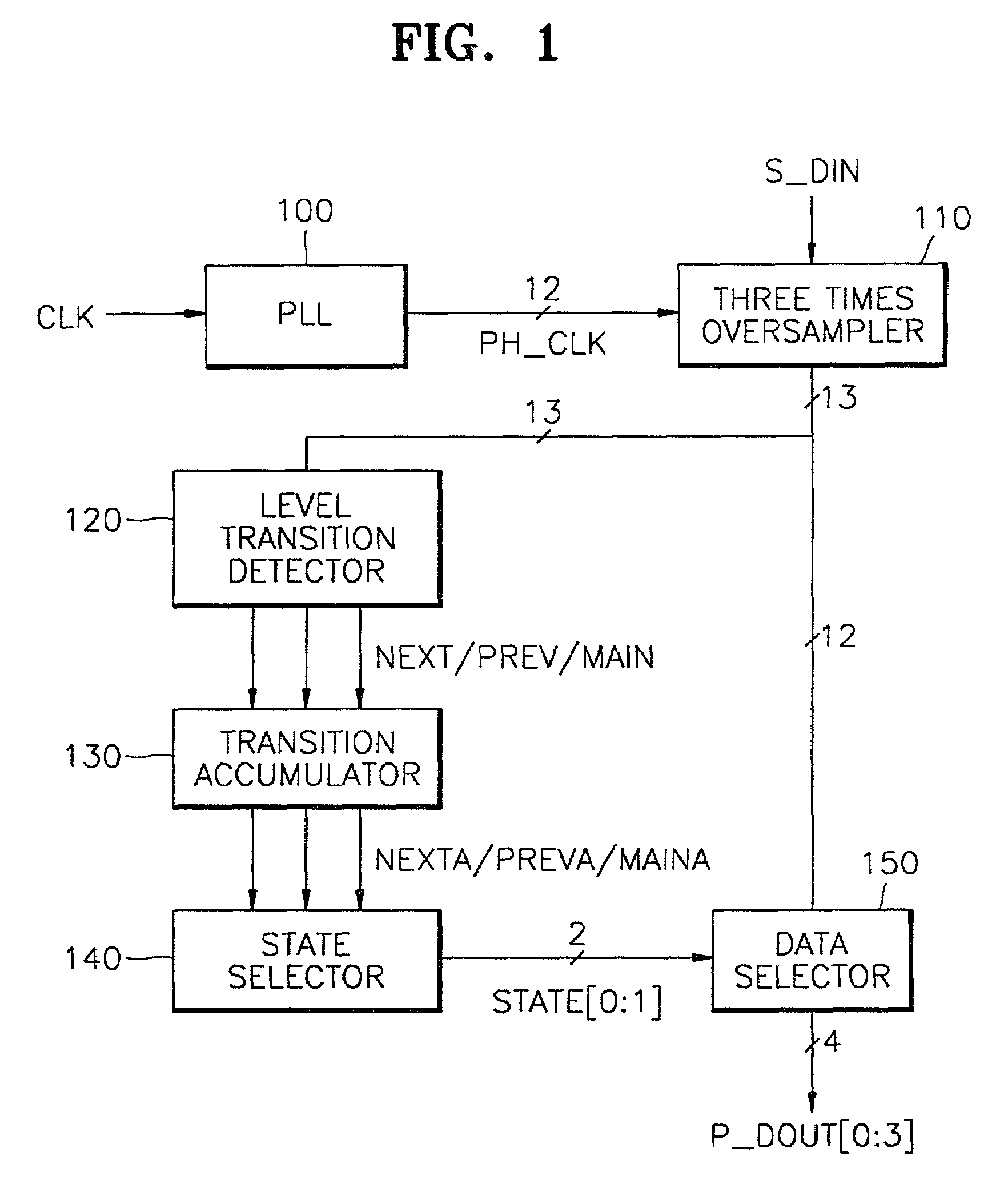
Data recovery apparatus and method for minimizing errors due to clock skew
InactiveUS6959058B2Data stabilityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMultiplexerComputer science
A data recovery apparatus for minimizing errors due to clock skew and a data recovery apparatus therefor are provided. The data recovery apparatus comprises a phase locked loop (PLL), an oversampler, a level transition detector, a transition accumulator, a state selector, and a data selector. The PLL generates a plurality of phase clock signals having different delay times, which signals are synchronized with an input clock signal. The oversampler 110 M (>1) times oversamples data serially input from the outside in response to the plurality of phase clock signals and outputs the oversampled result as a plurality of bit data items. The level transition detector receives the plurality of bit data output from the oversampler, detects the point of time at which the level transitions between adjacent bits and outputs the detection result as first through Mth transition signals. The transition accumulator accumulates the number of generations of the first through Mth transition signals output from the level transition detector and outputs a signal whose generation frequency is high as first through Mth transition accumulation signals. The state selector generates a state signal for selecting bit data items of corresponding positions among the plurality oversampling data items in response to the first through Mth transition accumulation signal. The data selector receives the oversampled plurality of bit data, selects bit data items of the sampling positions corresponding to the state signal, and outputs the selected bit data items in parallel. It is possible to minimize errors due to clock skew, which can be generated during the reproduction of data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for the clock synchronization of network terminals
A method and system for network terminal clock synchronization includes determining a respective round trip delay time from a master terminal to each slave terminal and offsetting the clock of each slave terminal by an amount proportional to the respective determined round trip delay time such that the master terminal and each of the slave terminals have substantially the same point of reference in time. The method and system further include, in response to a trigger signal, determining a respective offset between the master clock of the master terminal and the clocks of each of the slave terminals and offsetting the clocks of each of the slave terminals by an amount proportional to the determined respective offset to synchronize the clocks of each of the slave terminals to the master clock of the master terminal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Controller for clock skew determination and reduction based on a lead count over multiple clock cycles
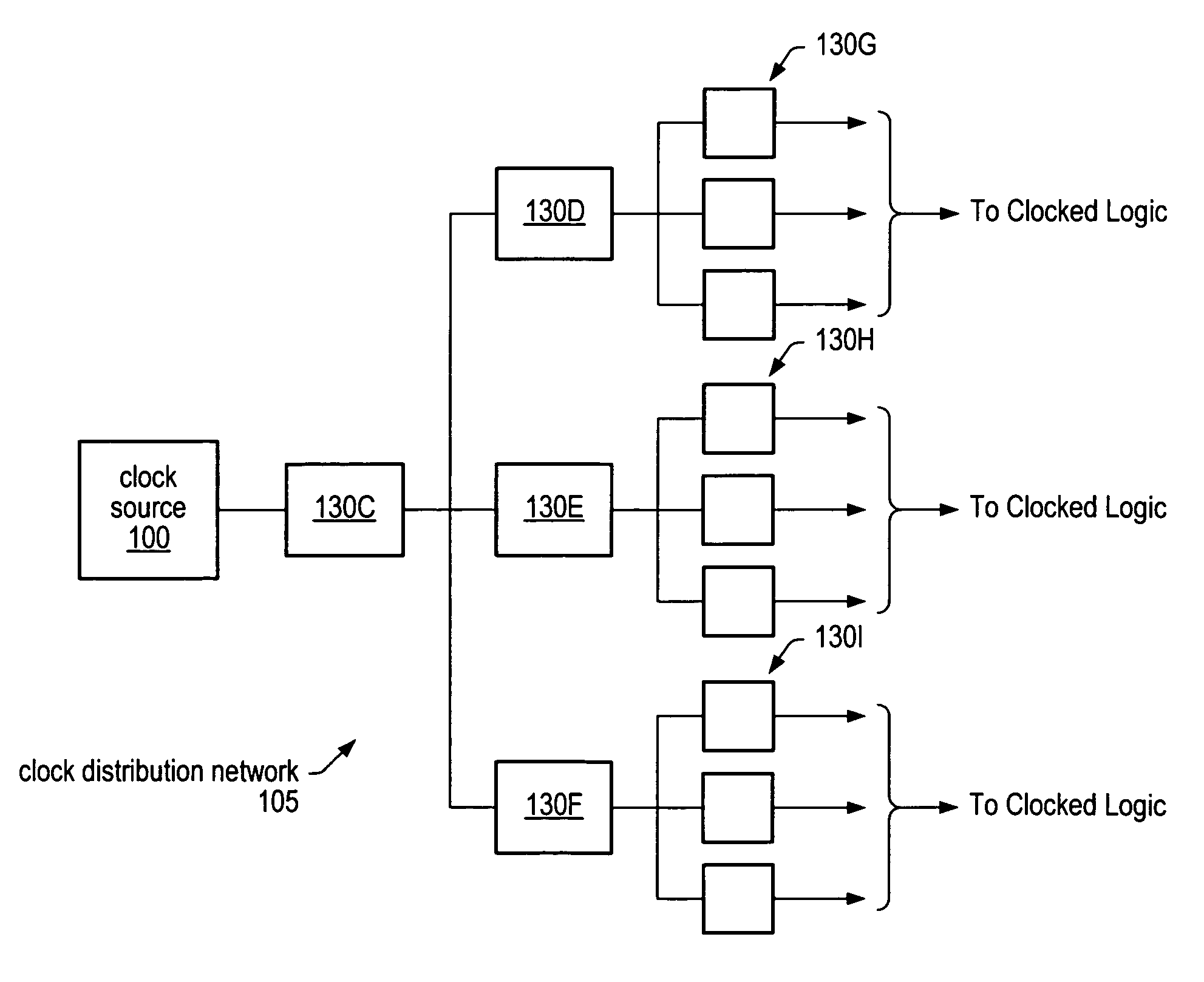
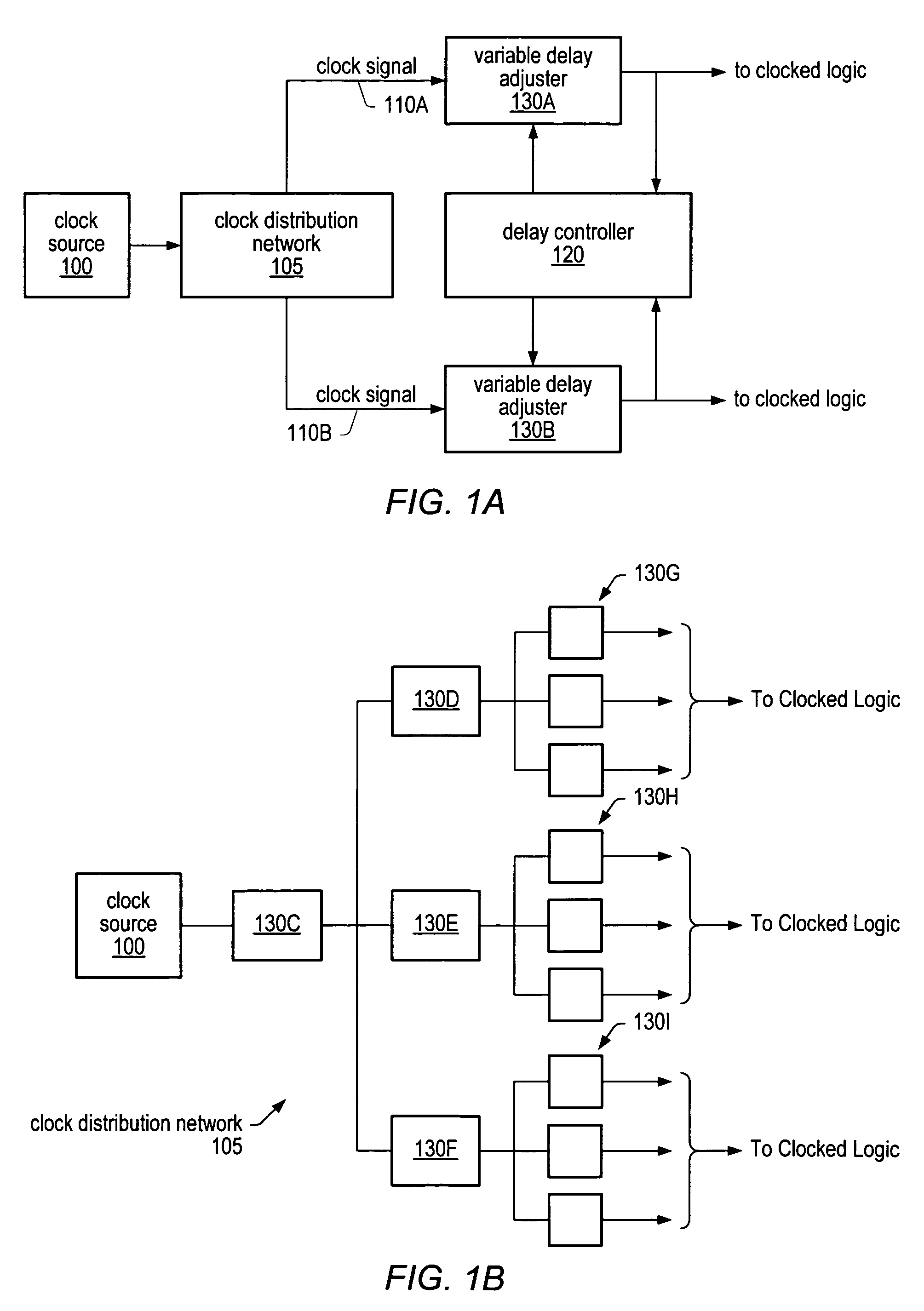
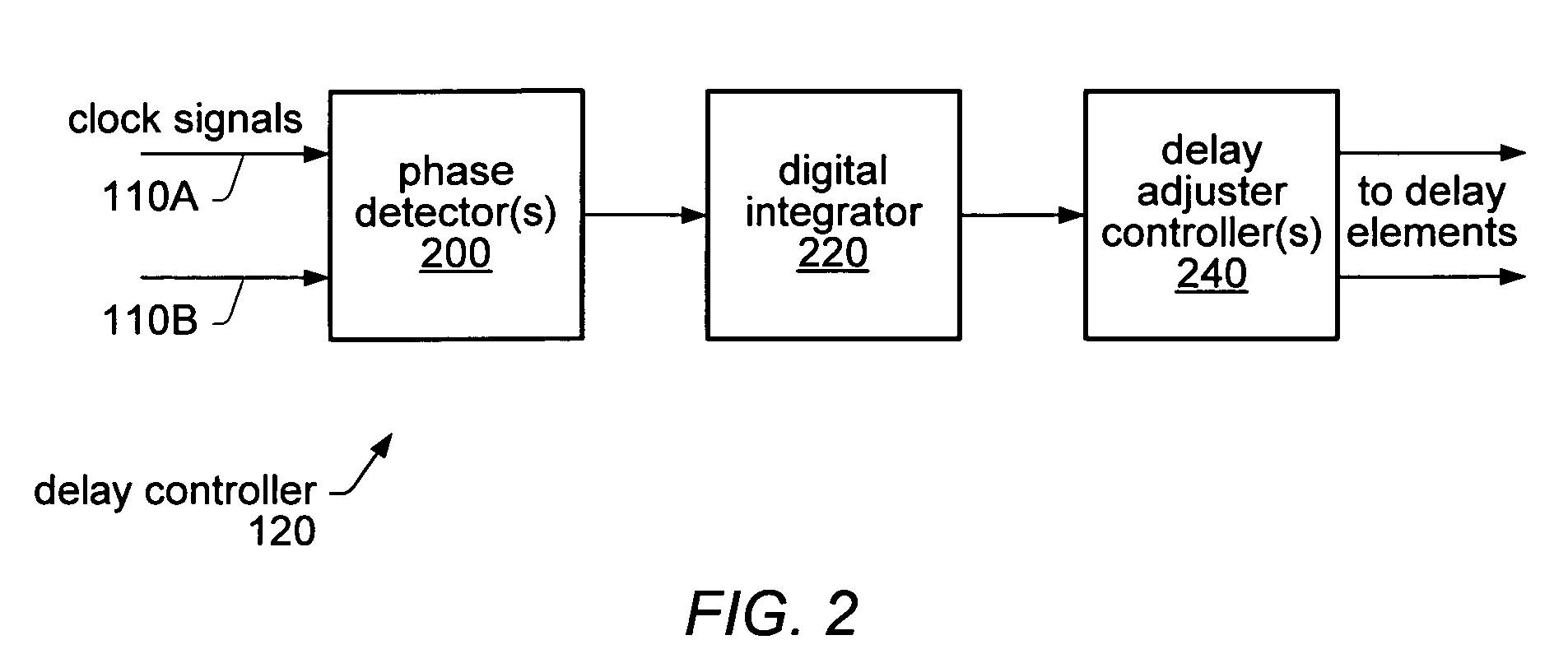
Clock skew may be detected measured and compensated for using phase detectors and variable delay adjusters. Phase detectors may be distributed throughout a clock distribution network and may be configured to analyze two clock signals to determine how often one signal leads the other. The output of the phase detectors may be measured and counted over a large number of clock cycles. The difference between the number of times one signal leads or lags behind the other may be used to determine the amount of delay to apply to the leading clock signal in order to minimize (reduce) skew between the two clock signals. The same techniques for detecting and measuring clock skew may also be used to detect and measure jitter in the clock signals. By configuring variable delay adjusters on clock signals, the amount of jitter in the clock signals can be measured or characterized.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Clock tree synthesis for low power consumption and low clock skew
InactiveUS20060053395A1Reduce power consumptionReduces clock skew of clock skewPower supply for data processingCAD circuit designSynthesis methodsClock tree synthesis
A method for low power clock tree synthesis using buffer insertion, removal and resizing for high-speed VLSI design is proposed. The developed tool can be embedded in the existing clock tree synthesis design flow to ensure satisfying both the specifying database constrains and the clock skew constrains. For a given clock tree netlist, the location information of buffers, the parameters of wires and the buffers' timing and power library are all included. The buffer delay and wire delay of the clock tree are calculated first. Then the feasible solution is solved if the input netlist is not feasible for the given constrains. Finally, a modified low power clock tree netlist, which satisfies the timing specifications, is obtained using our proposed method.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Techniques for graphical analysis and manipulation of circuit timing requirements
InactiveUS7580037B1Improve visualizationEasy extractionDigital variable displayDrawing from basic elementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
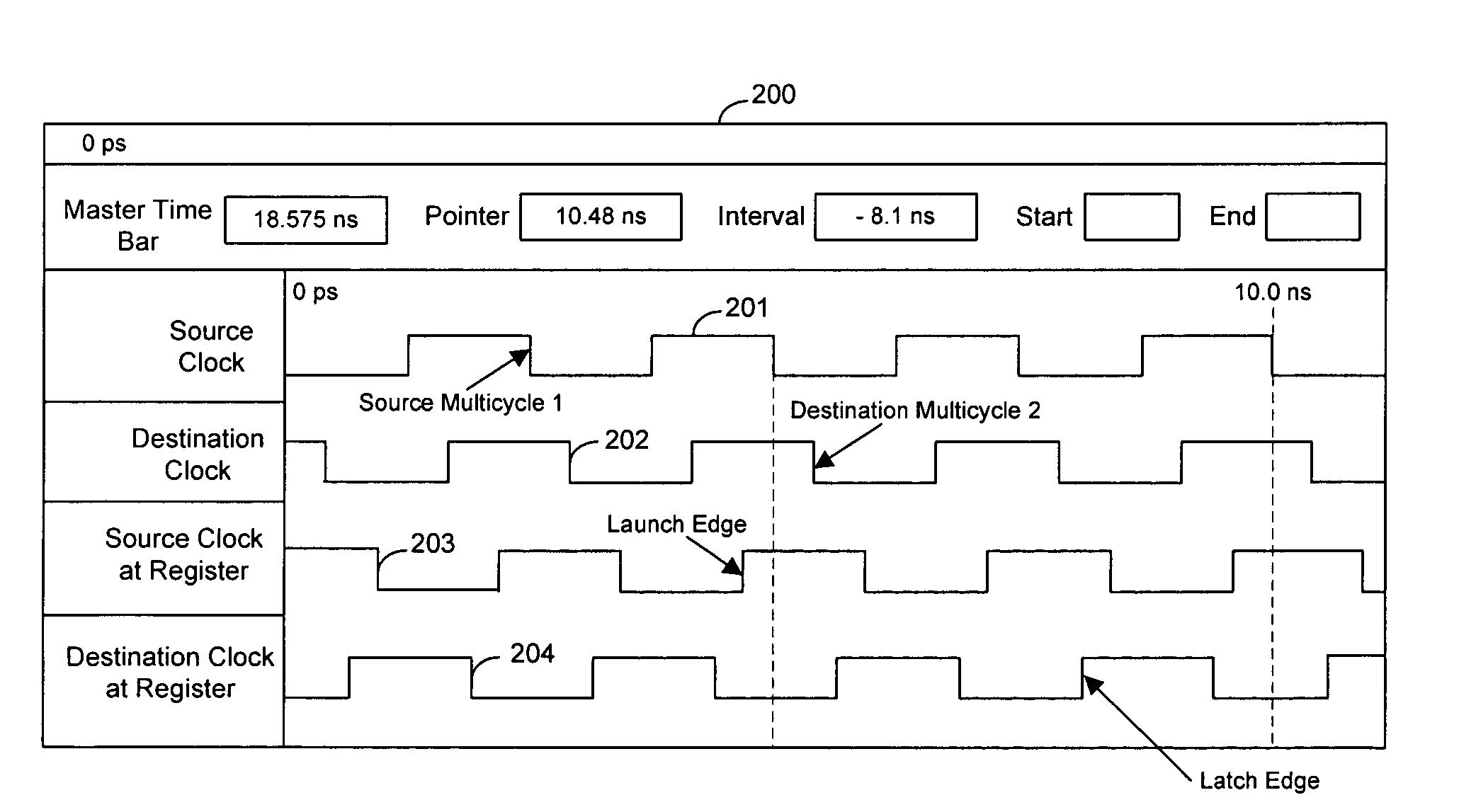
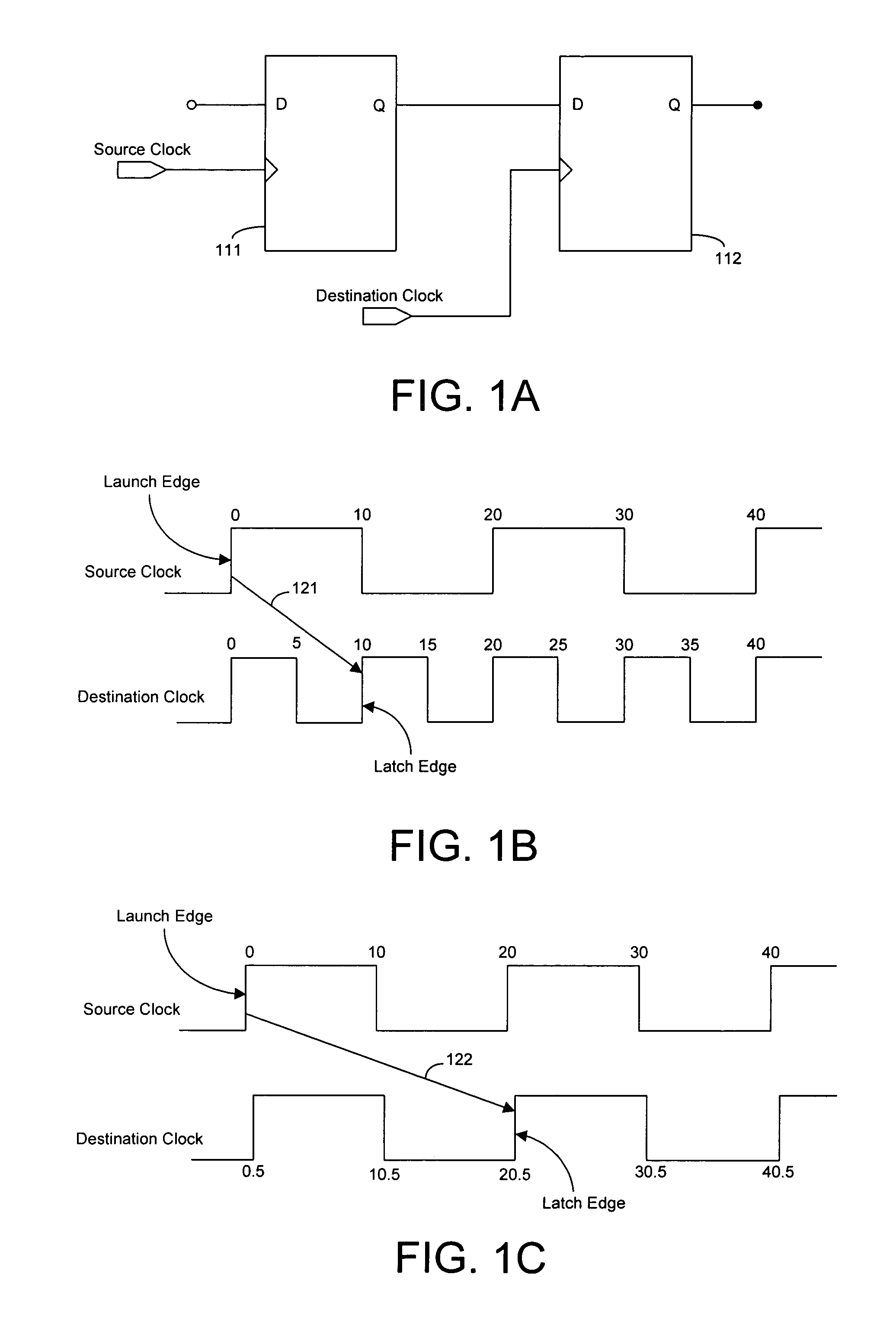
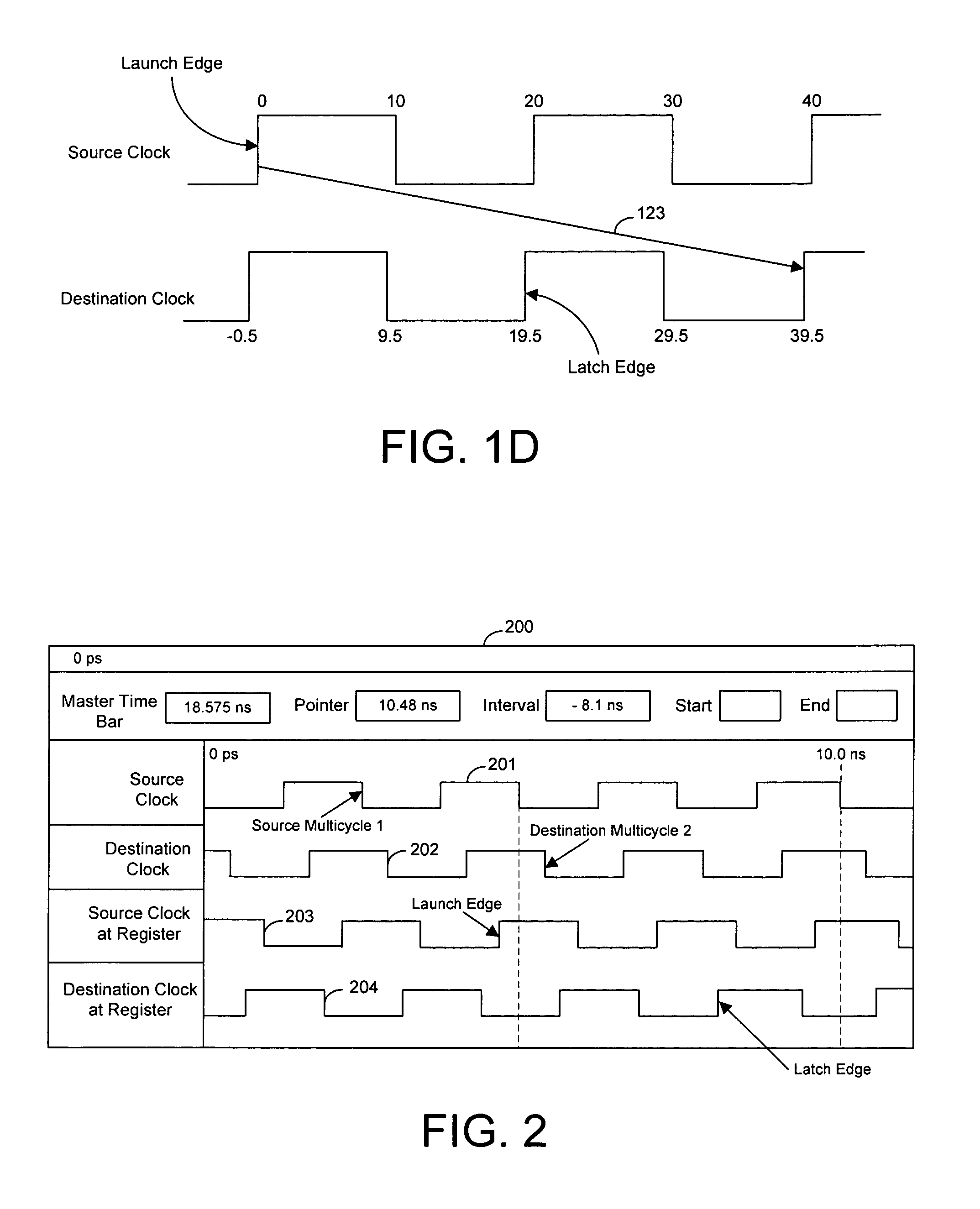
Techniques for organizing and displaying timing data derived from an EDA tool are provided that allows users to easily extract, analyze, and manipulate portions of the timing data relevant to particular user requirements. Relevant portions of signal waveforms are displayed on an interactive graphical user interface (GUI). Time points on the waveforms are marked with pointers so that users can easily visualize the relationships between different signals. A user can also extract relevant timing data from the EDA tool by manipulating the GUI. Manipulating and understanding circuit design requirements affects all of the design cycle and the quality of the final result from an EDA tool. A user can visualize all aspects of timing analysis on the GUI, such as clock skew, and the setup / hold relationship. A data entry approach is provided that can be used for natural and intuitive manipulation of various timing relationships.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com