Patents
Literature
40 results about "Round-trip delay time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
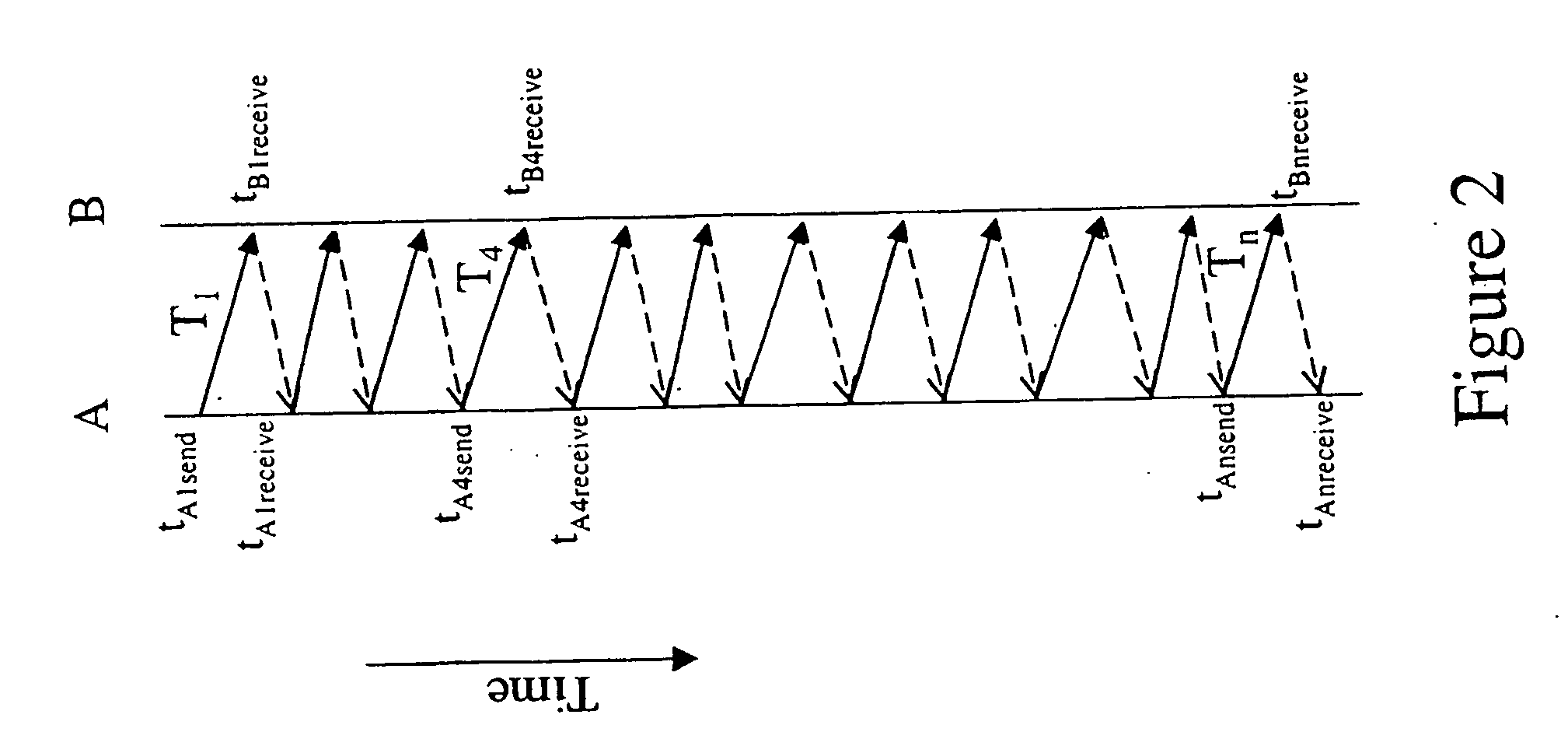
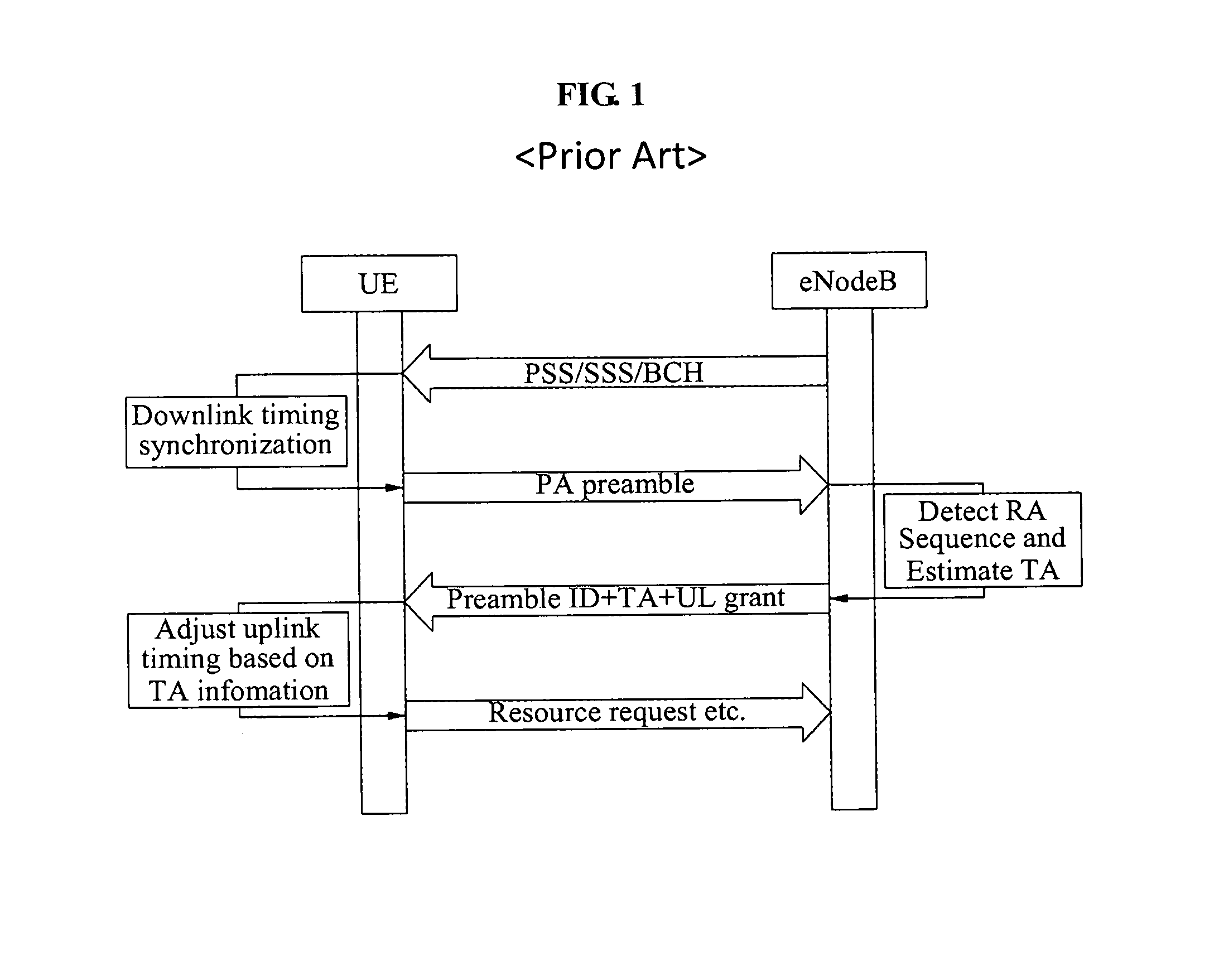
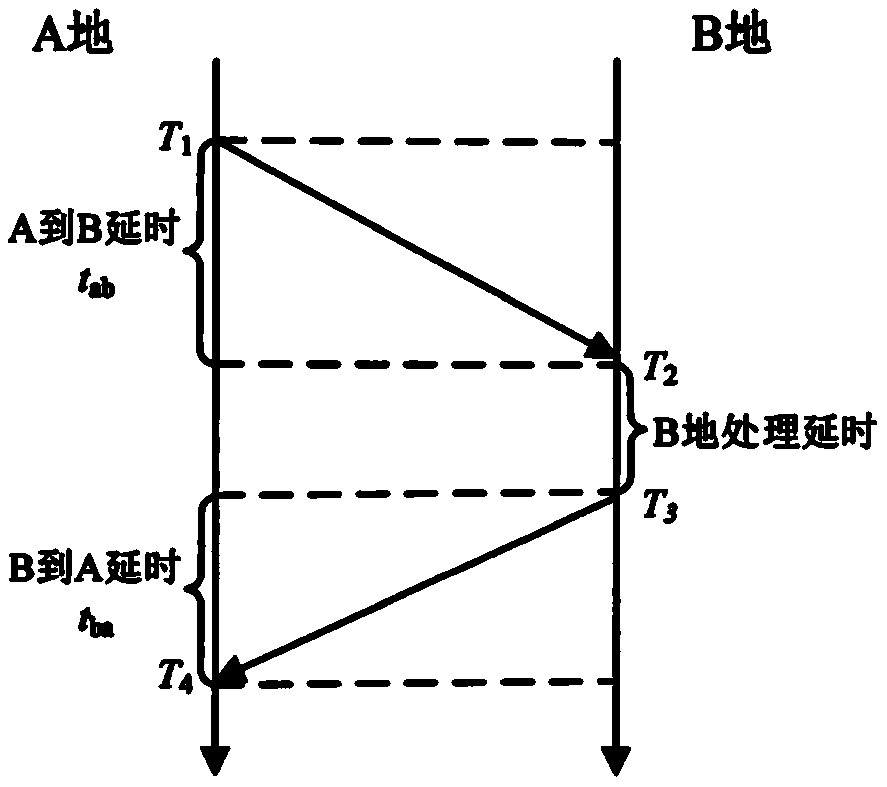
In telecommunications, the round-trip delay time (RTD) or round-trip time (RTT) is the length of time it takes for a signal to be sent plus the length of time it takes for an acknowledgement of that signal to be received. This time delay includes the propagation times for the paths between the two communication endpoints.
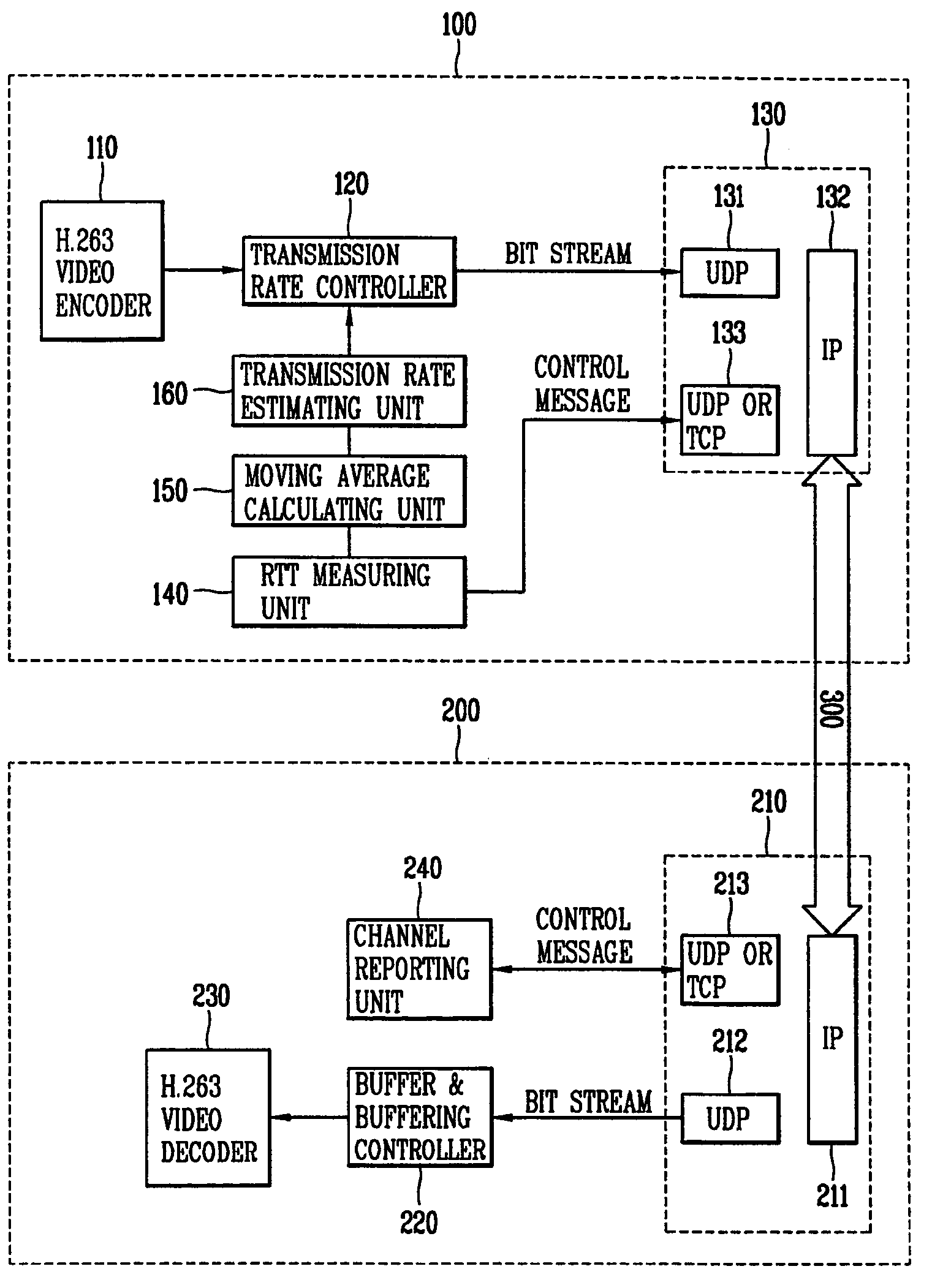
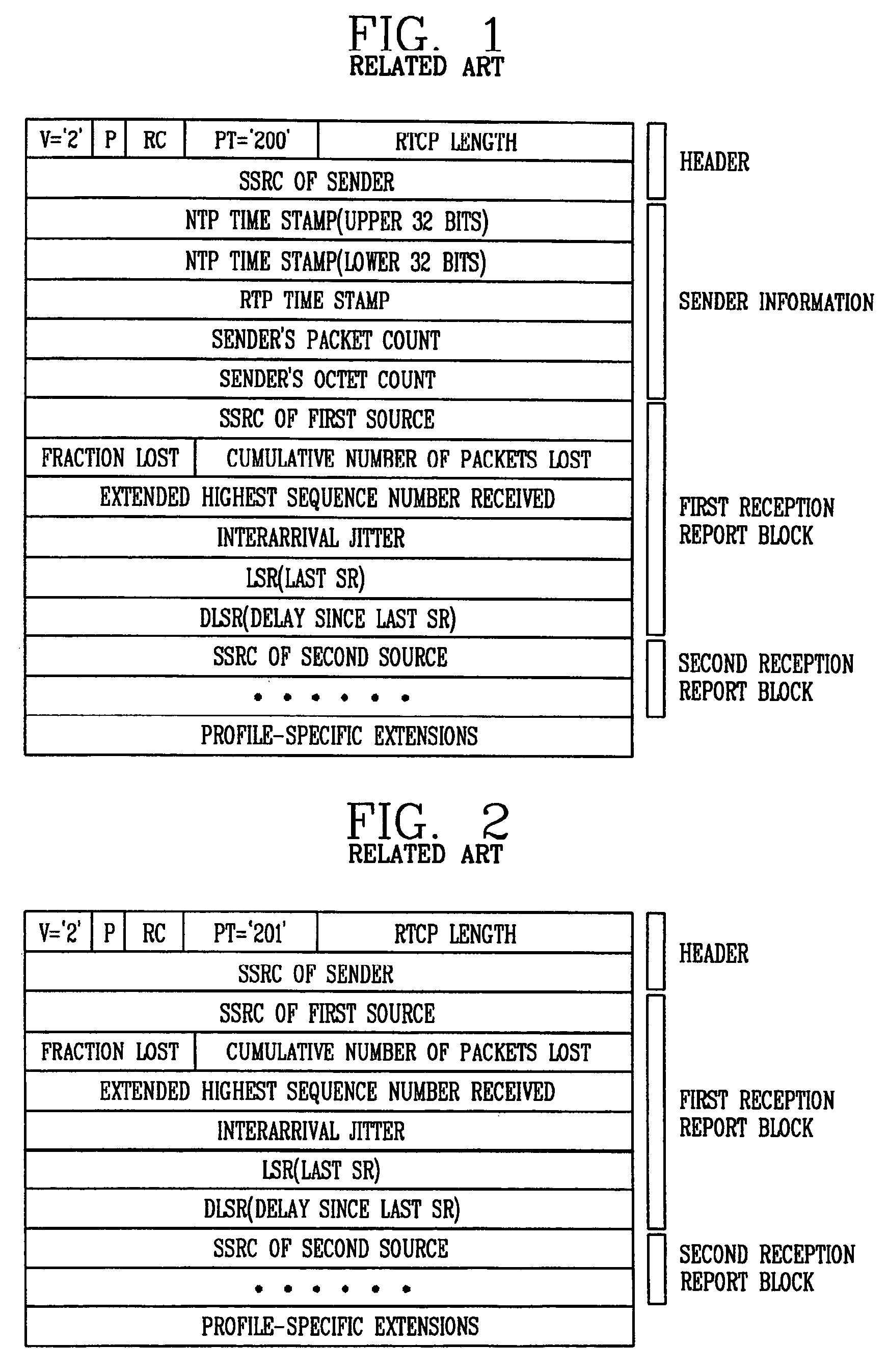
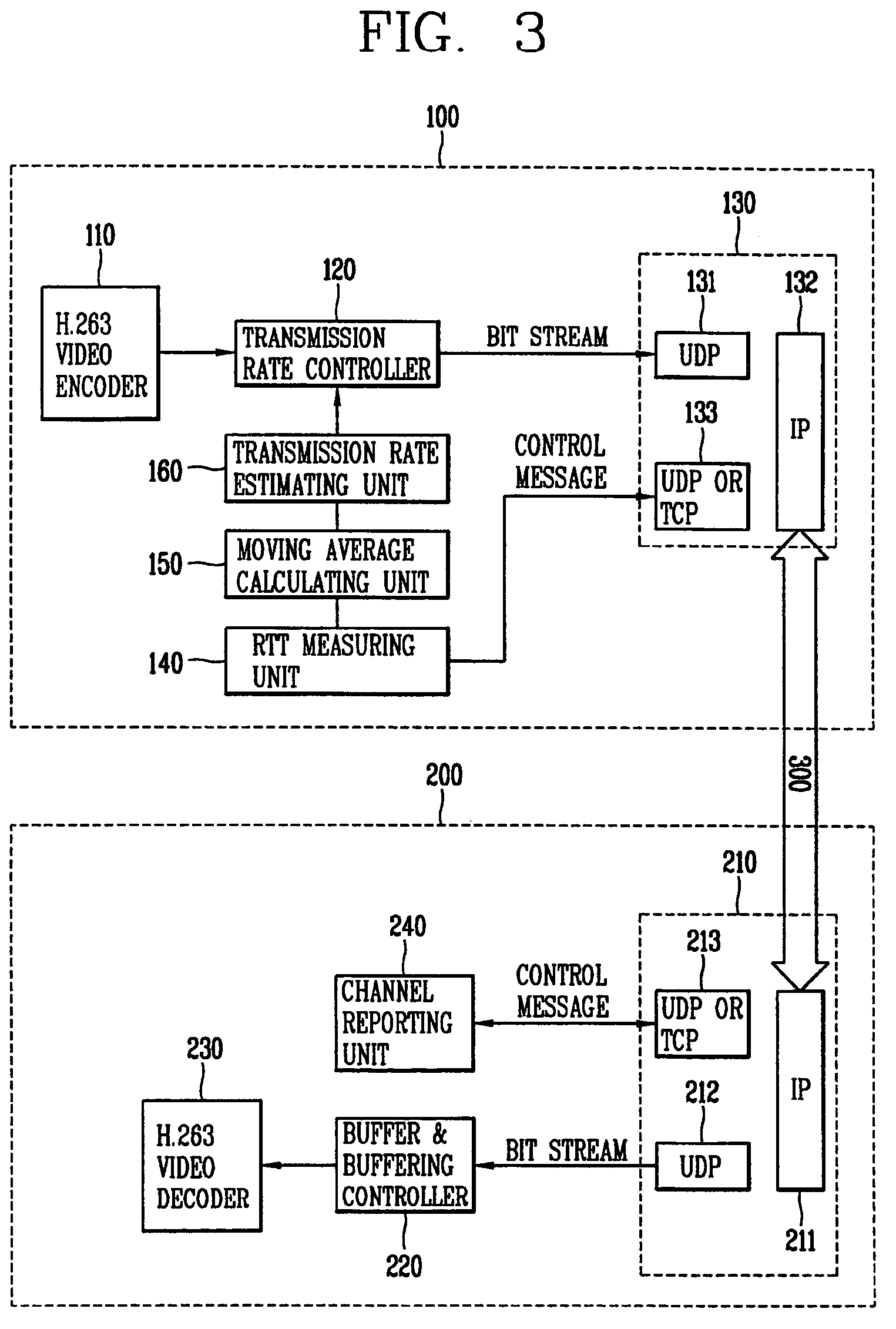
Roundtrip delay time measurement apparatus and method for variable bit rate multimedia data
InactiveUS7496040B2Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareVideo encoding
An apparatus for measuring a roundtrip delay time associated with communication of multimedia data is provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a video encoder for encoding multimedia data to produce encoded multimedia data; a transmission rate controller for controlling transmission rate of the encoded multimedia data according to an effective transmission rate; and a first sending / receiving unit for sending the multimedia data via a first channel.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
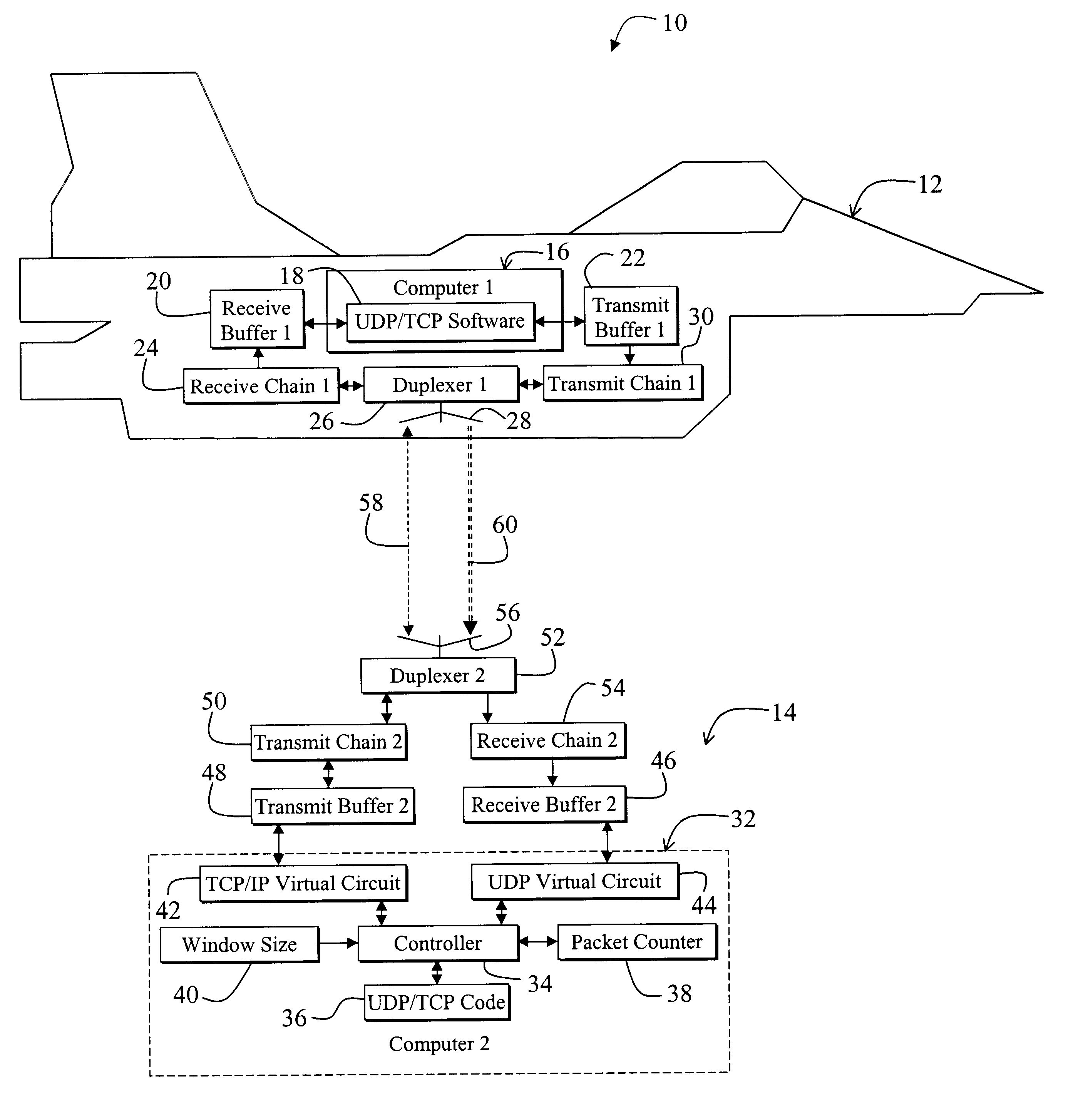
Effective protocol for high-rate, long-latency, asymmetric, and bit-error prone data links
InactiveUS6831912B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsLong latencyTelecommunications link
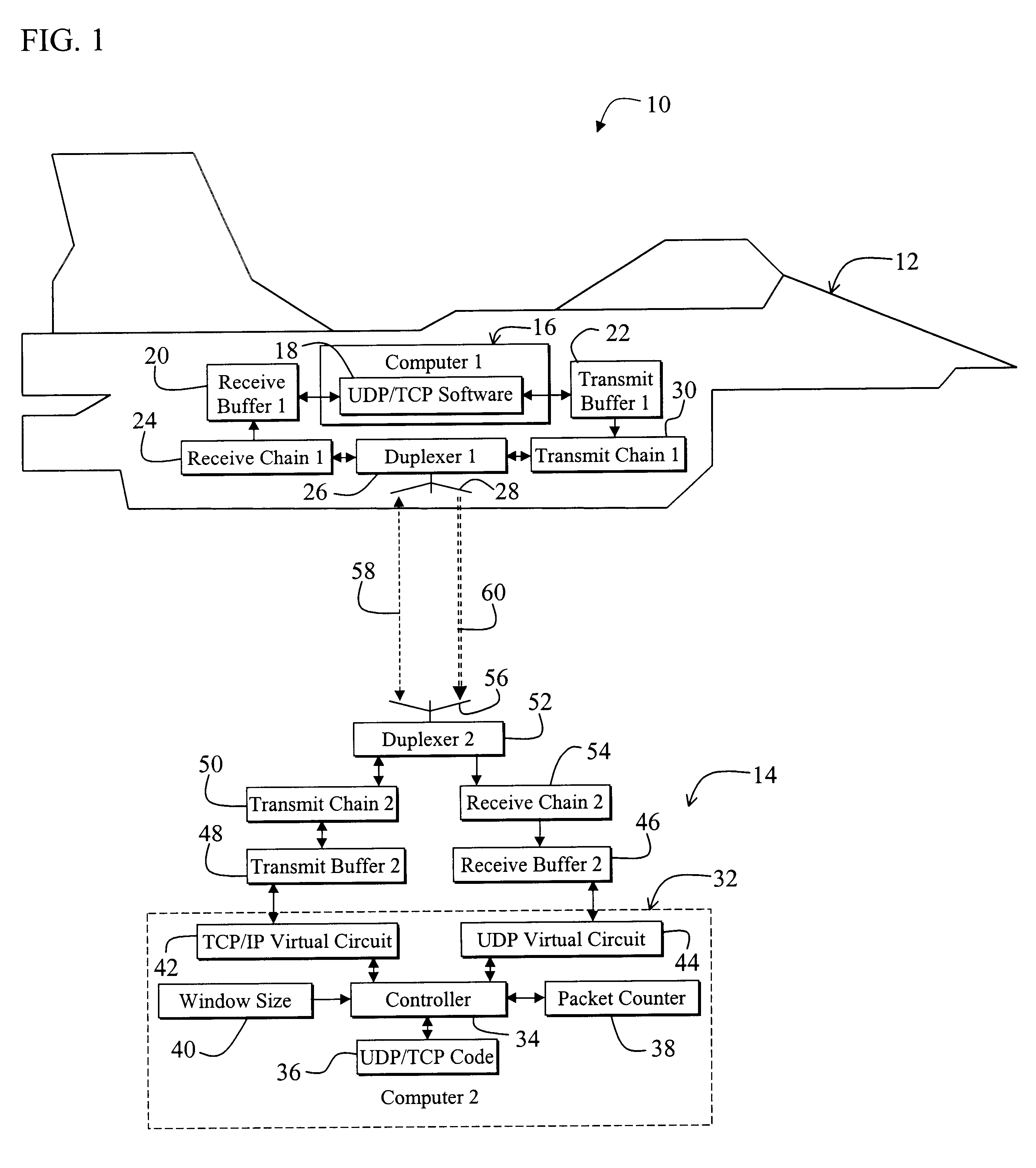
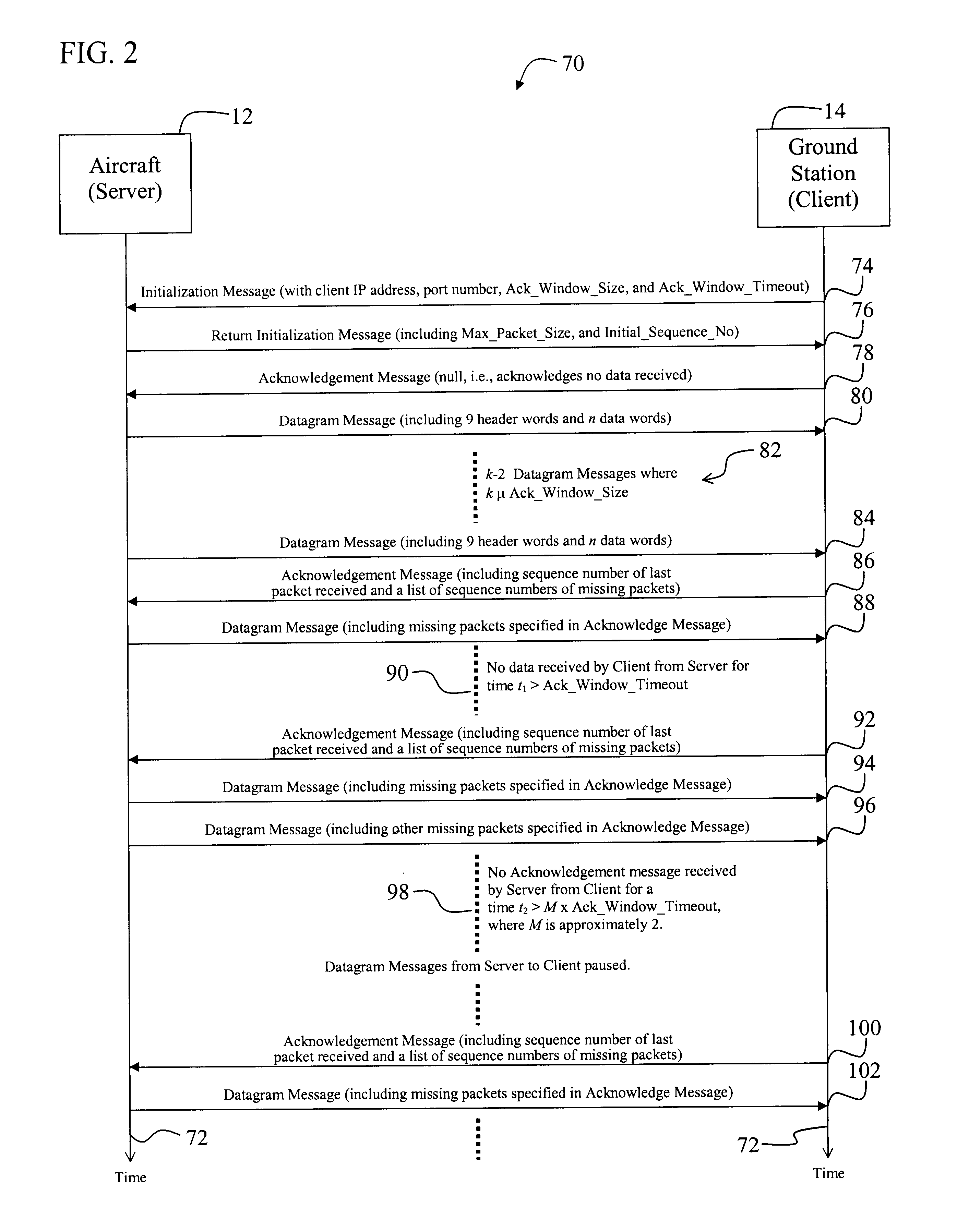
A system for efficiently and reliably communicating over a high-speed asymmetric communications link. The system includes a first mechanism for connecting a first device to a second device via a channel. A second mechanism delivers data packets over the channel from the first device to the second device. Each packet is associated with a window of packets. A third mechanism selectively employs the second mechanism to re-send data packets not received by the second device after each window of packets. The window of packets is sized in accordance with the bandwidth of the communications link between the first device and the second device, and the round trip delay time. In a specific embodiment, the first mechanism (includes Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) functionality on the first device and the second device for establishing a first TCP / IP link from the second device to the first device. The first mechanism also includes Universal Datagram Protocol (UDP) functionality on the first device and the second device for transferring UDP packets from the first device to the second device. The third mechanism sends acknowledgement messages from the second device to the first device specifying the packets not received by the second device. The system further includes a fourth mechanism for selectively disabling the second mechanism when first device does not receive an acknowledgement message after a predetermined time interval. The predetermined time interval is a function of a window timeout variable. The predetermined function is (M)x(window timeout), where M is approximately 2. The window timeout is greater than N multiplied by a number of packets included in the window of packets divided by the data rate of the communications link between the first device and the second device, here N is an integer greater than 1. N is between 3 and 10.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Communication terminal which perform low-delay communication by using a broadband line
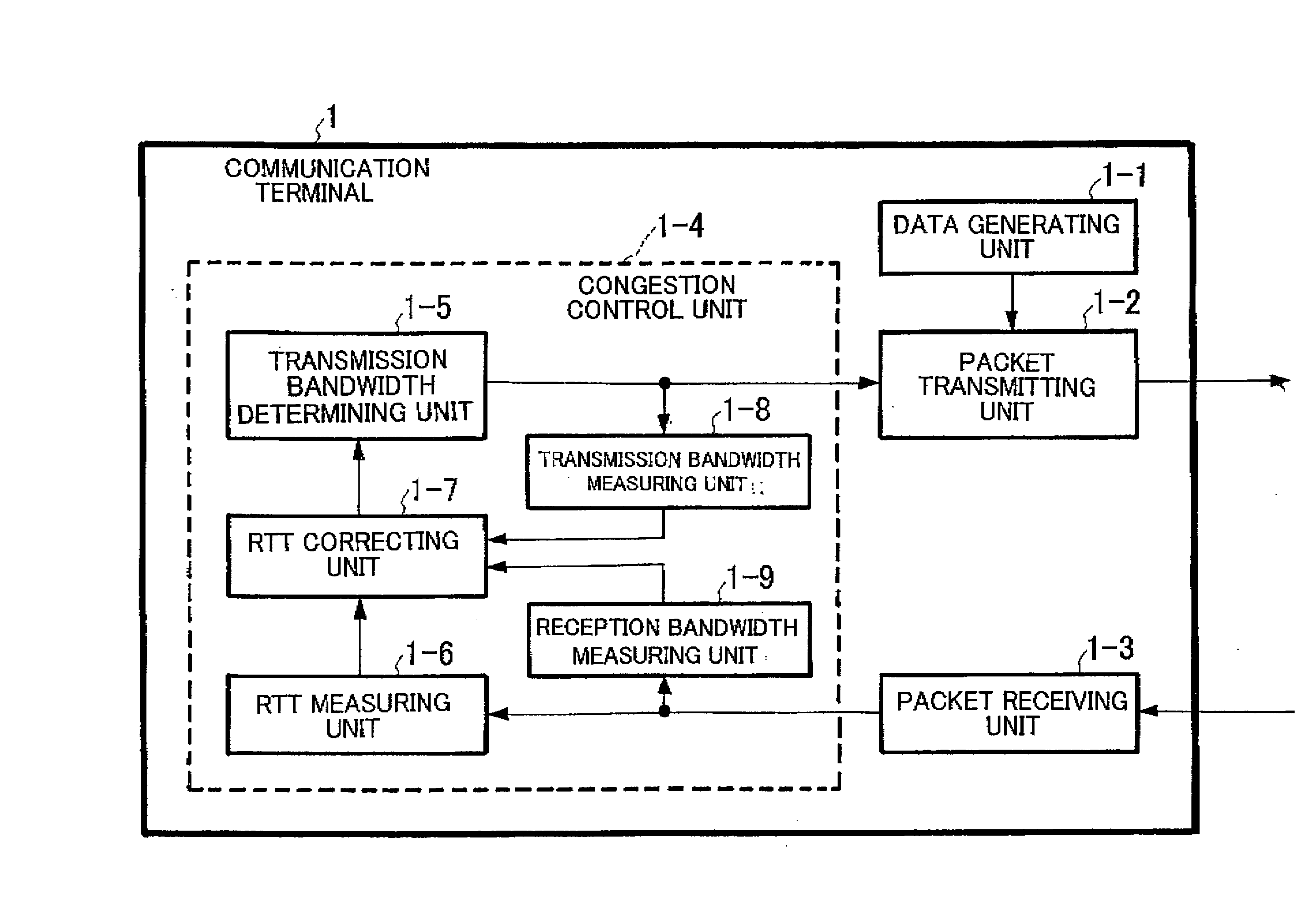
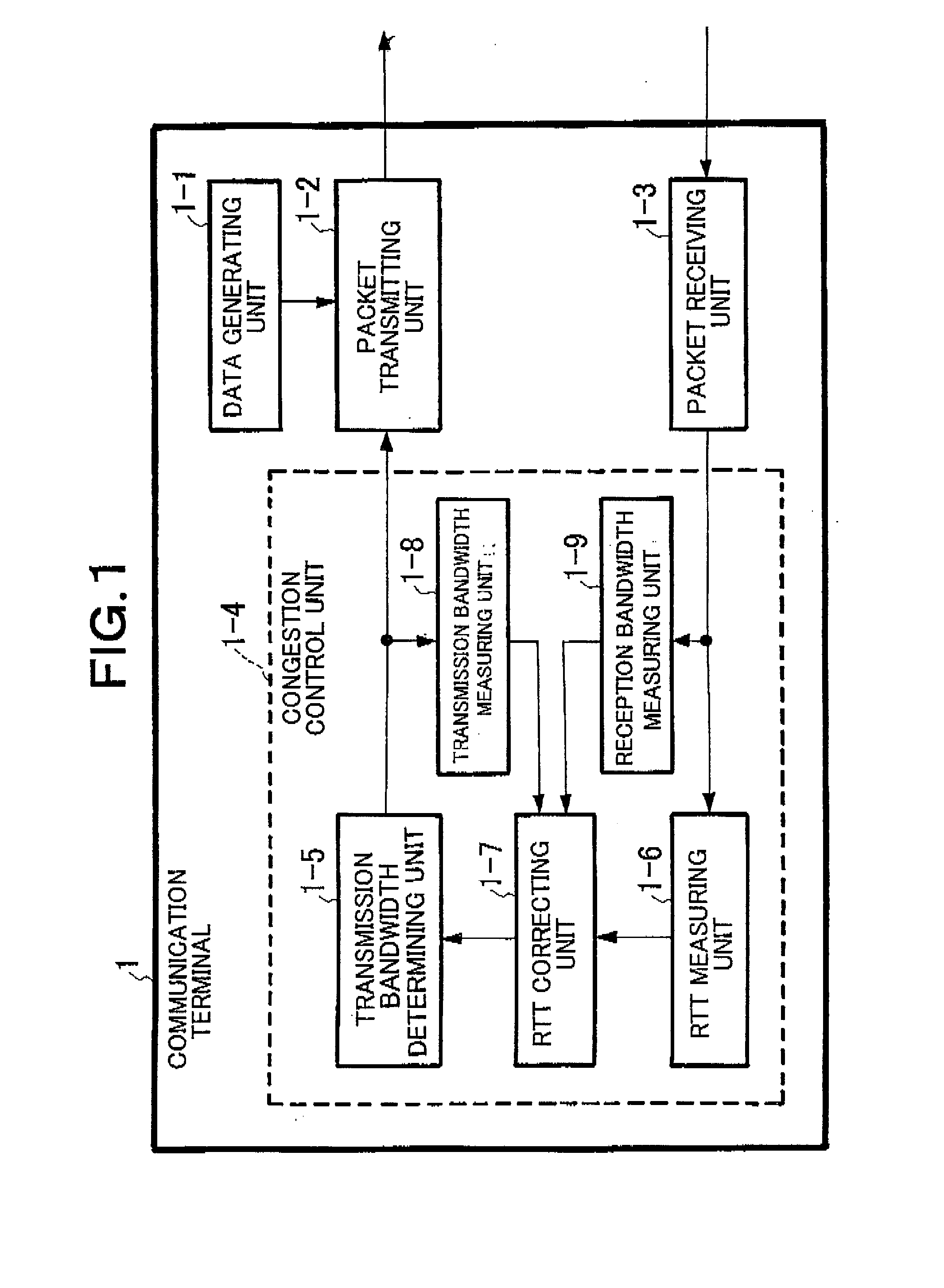
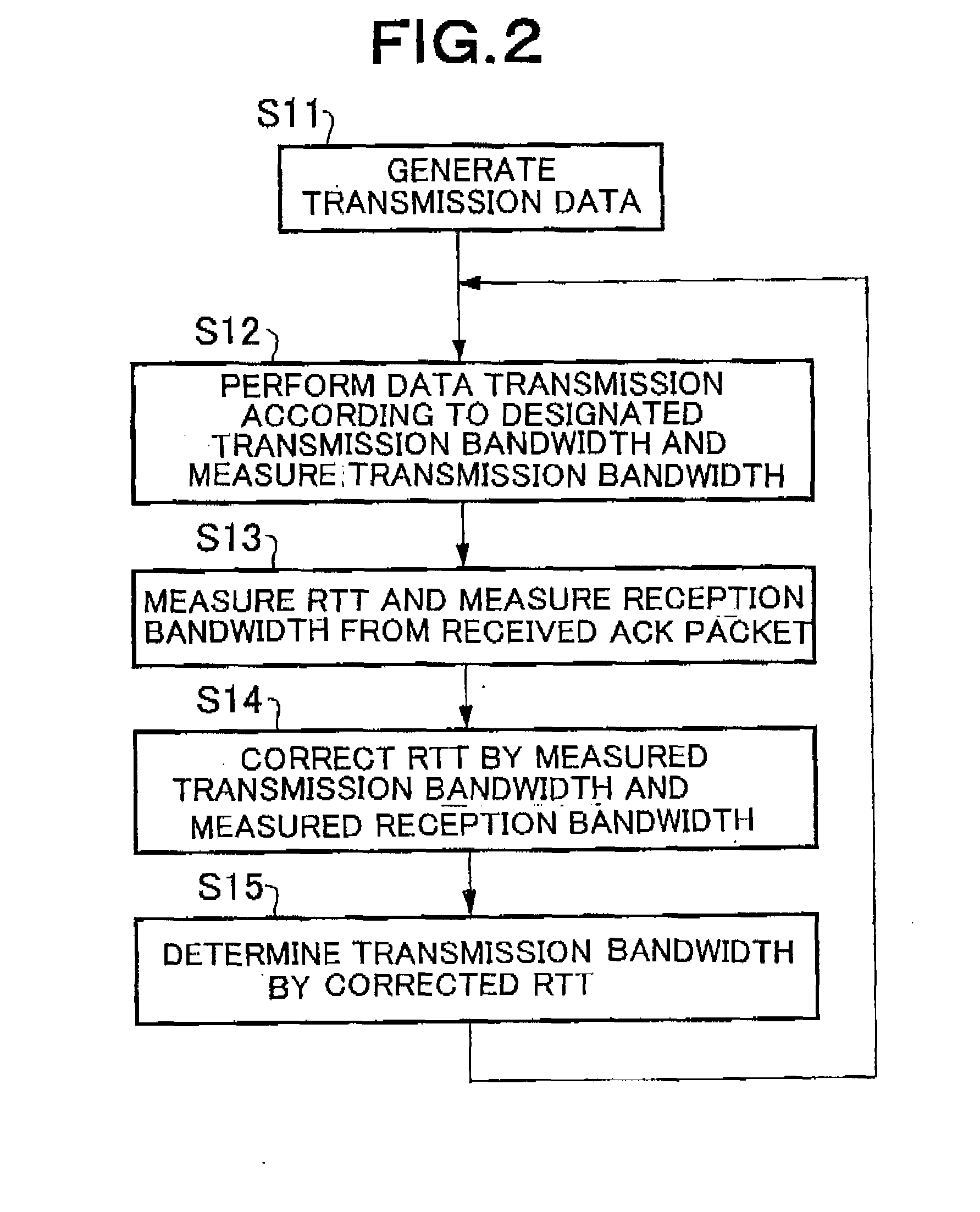
ActiveUS20080212480A1Reduce latencyExpand the transmission rangeError preventionTransmission systemsRound-trip delay timeDelayed time
A communication terminal which sets a communication session between a plurality of communication terminals through a network to perform data transmission and reception includes a measuring unit which measures round-trip delay time (RTT) or one-way delay time between the communication terminals for performing transmission and reception on the basis of the received acknowledgement, a reception bandwidth measuring unit which measures a reception bandwidth in a reception terminal of the communication terminals on the basis of the received acknowledgement, a correcting unit which corrects a value of the round-trip delay time or the one-way delay time by using at least the reception bandwidth, and a transmission bandwidth determining unit which determines a transmission bandwidth on the basis of the value of the corrected round-trip delay time or the corrected one-way delay time.
Owner:NEC CORP
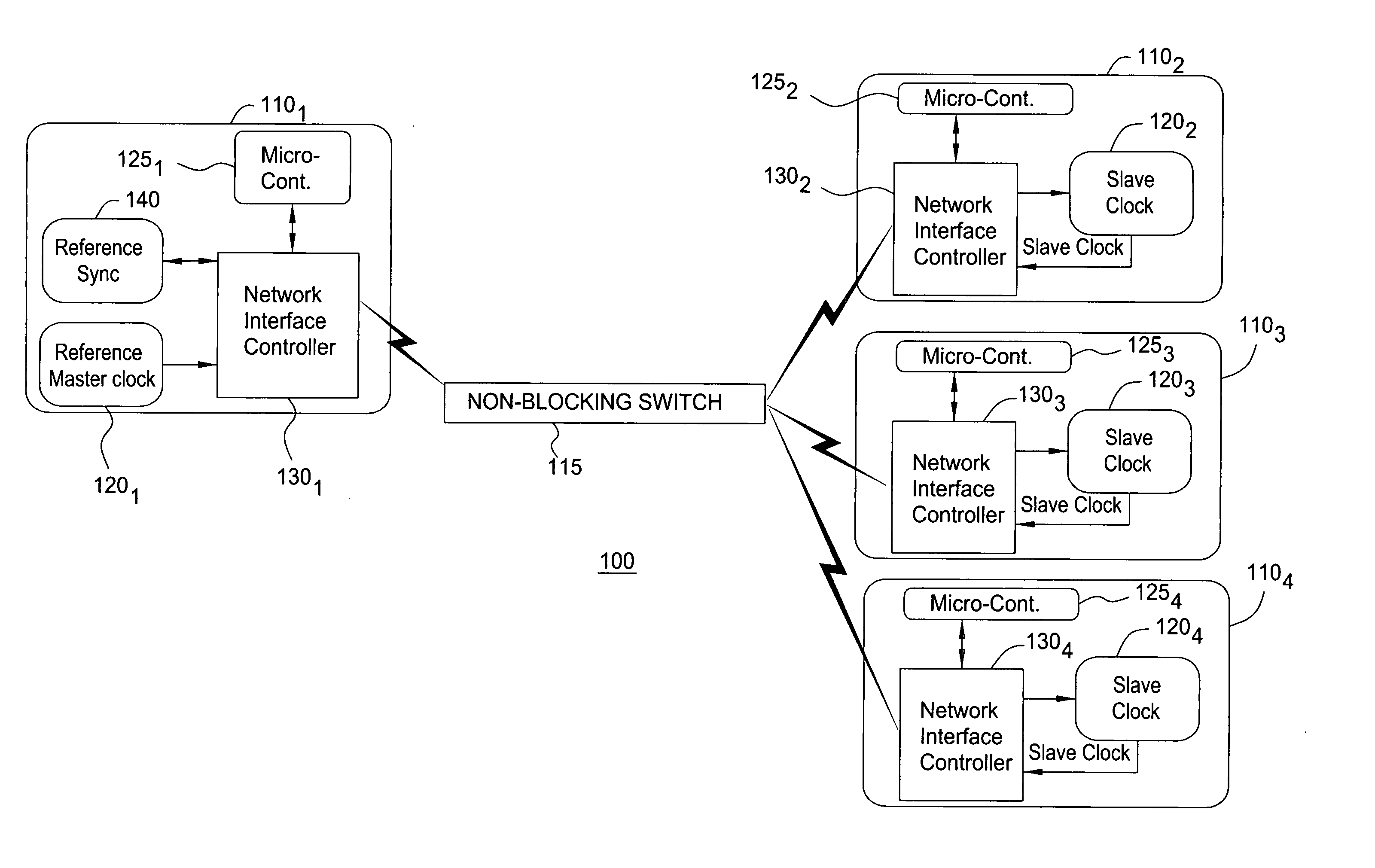
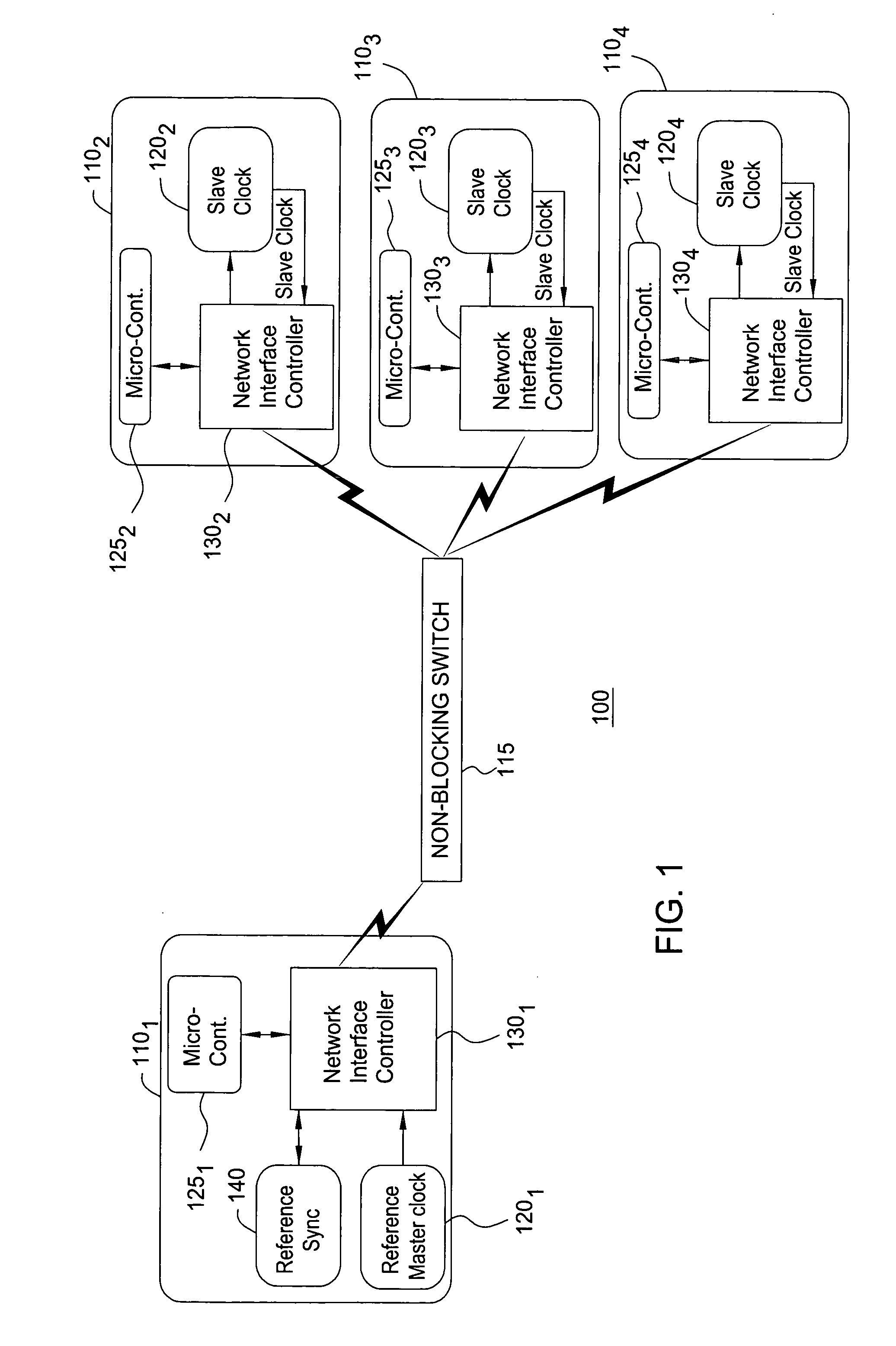
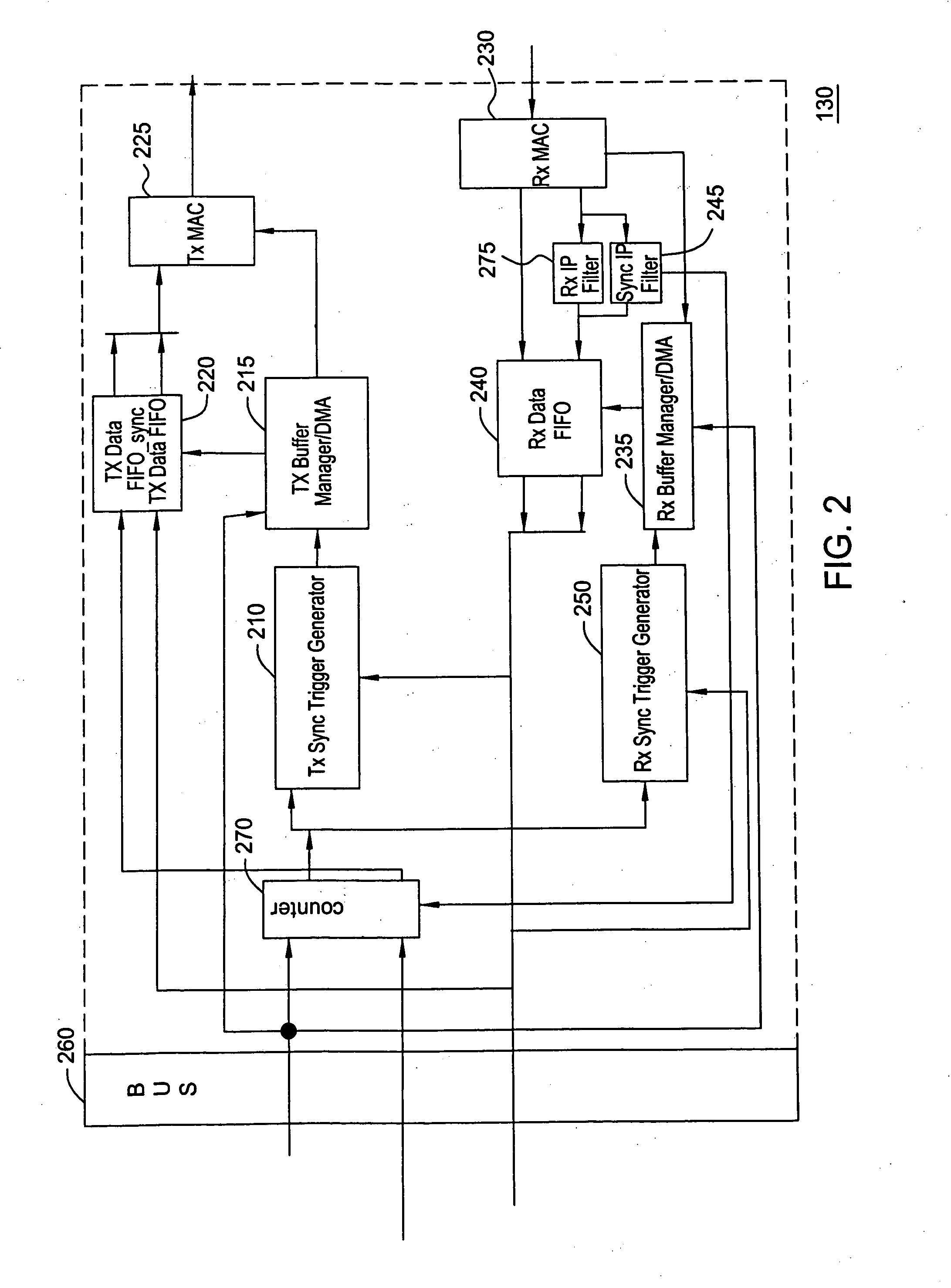
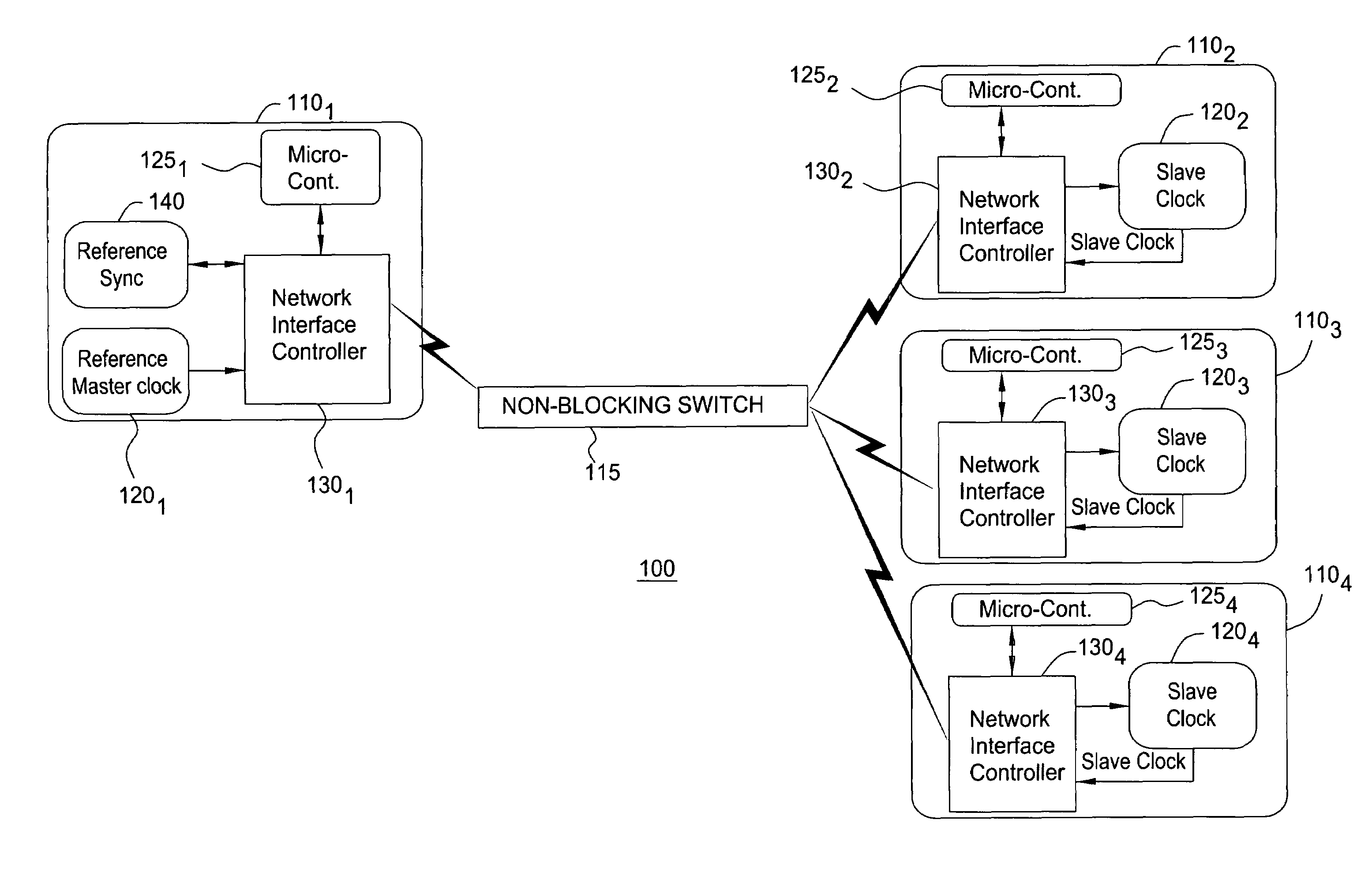
Method and system for the clock synchronization of network terminals
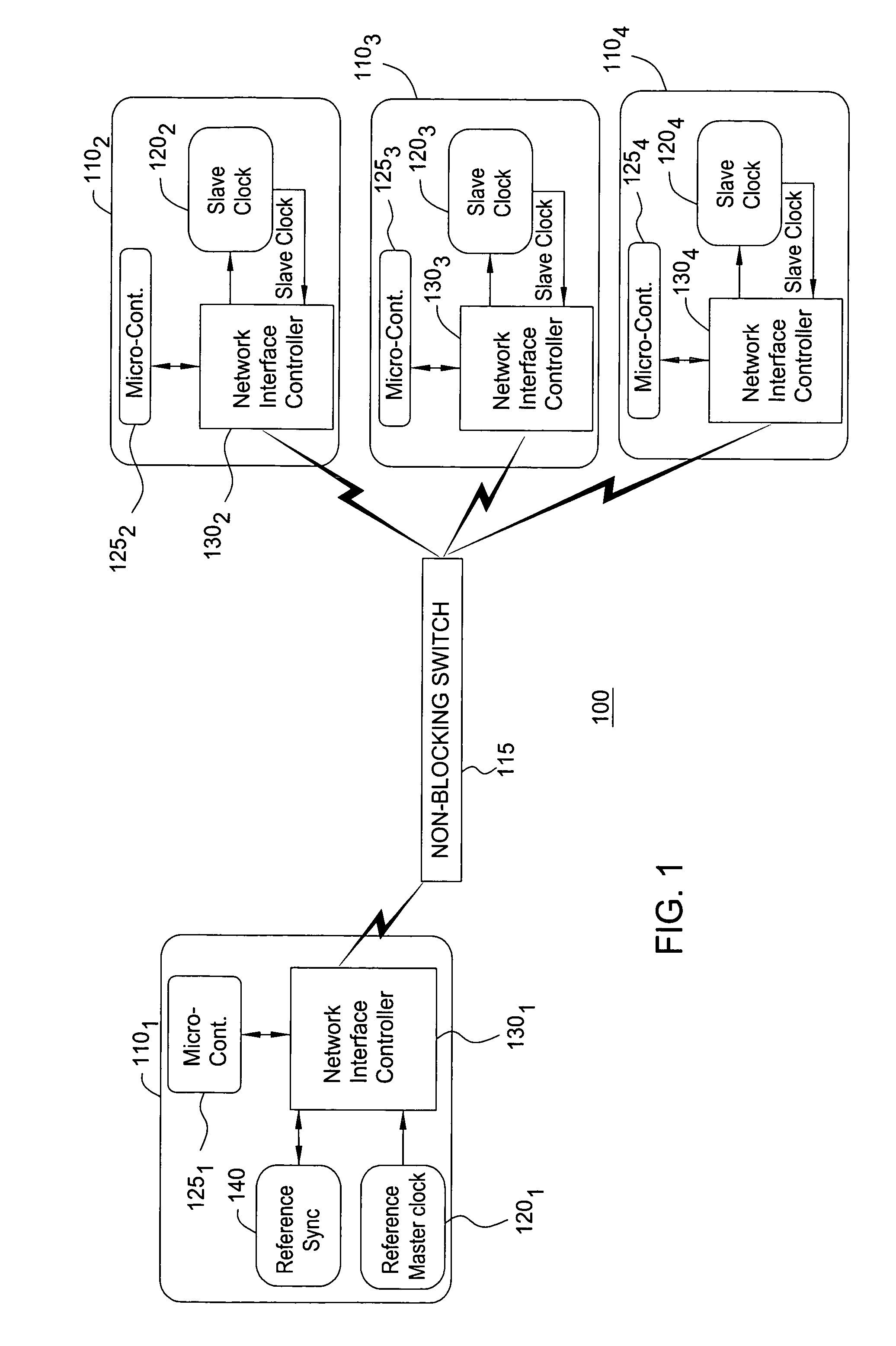
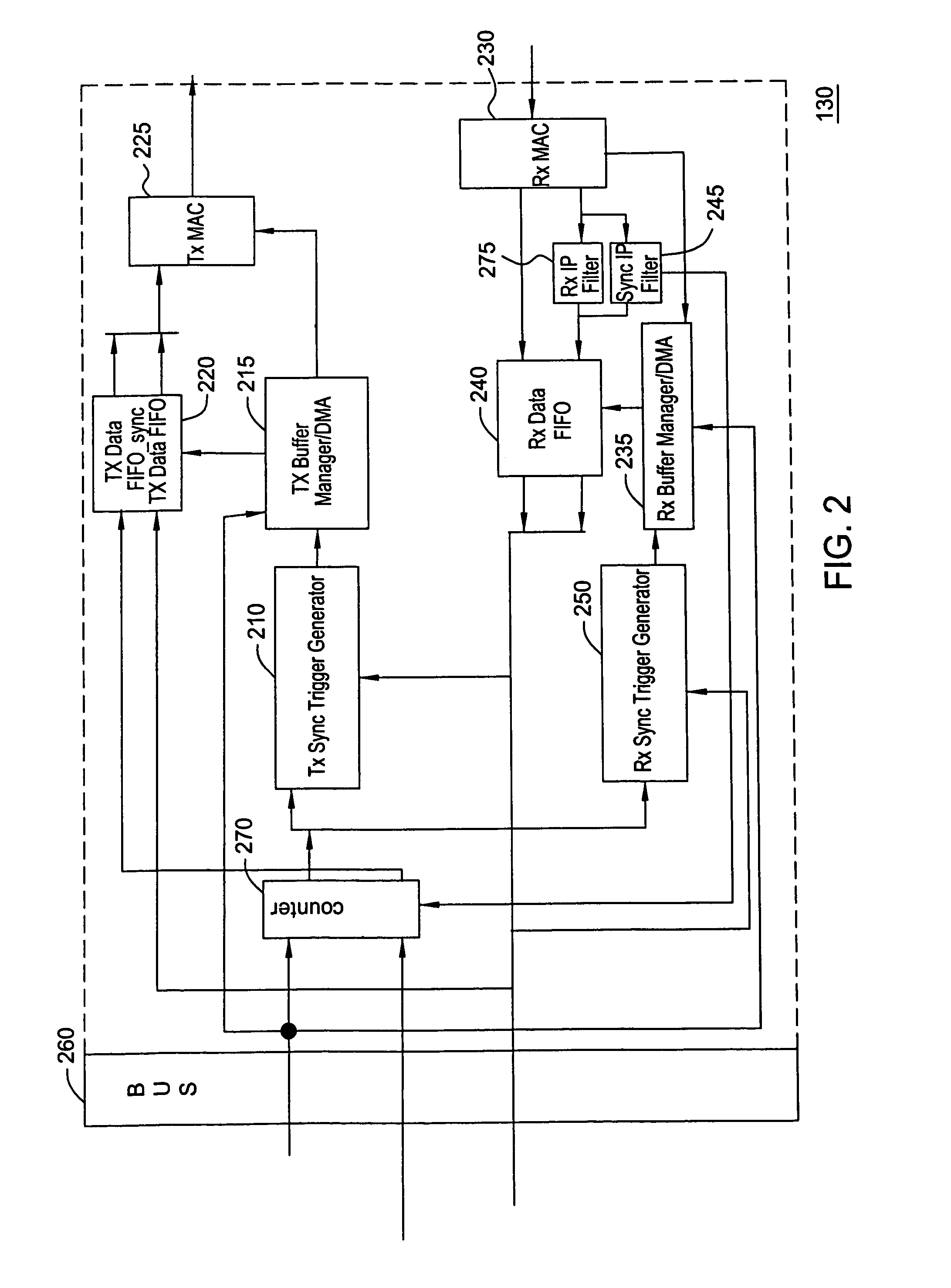
A method and system for network terminal clock synchronization includes determining a respective round trip delay time from a master terminal to each slave terminal and offsetting the clock of each slave terminal by an amount proportional to the respective determined round trip delay time such that the master terminal and each of the slave terminals have substantially the same point of reference in time. The method and system further include, in response to a trigger signal, determining a respective offset between the master clock of the master terminal and the clocks of each of the slave terminals and offsetting the clocks of each of the slave terminals by an amount proportional to the determined respective offset to synchronize the clocks of each of the slave terminals to the master clock of the master terminal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Virtual group maintenance and security
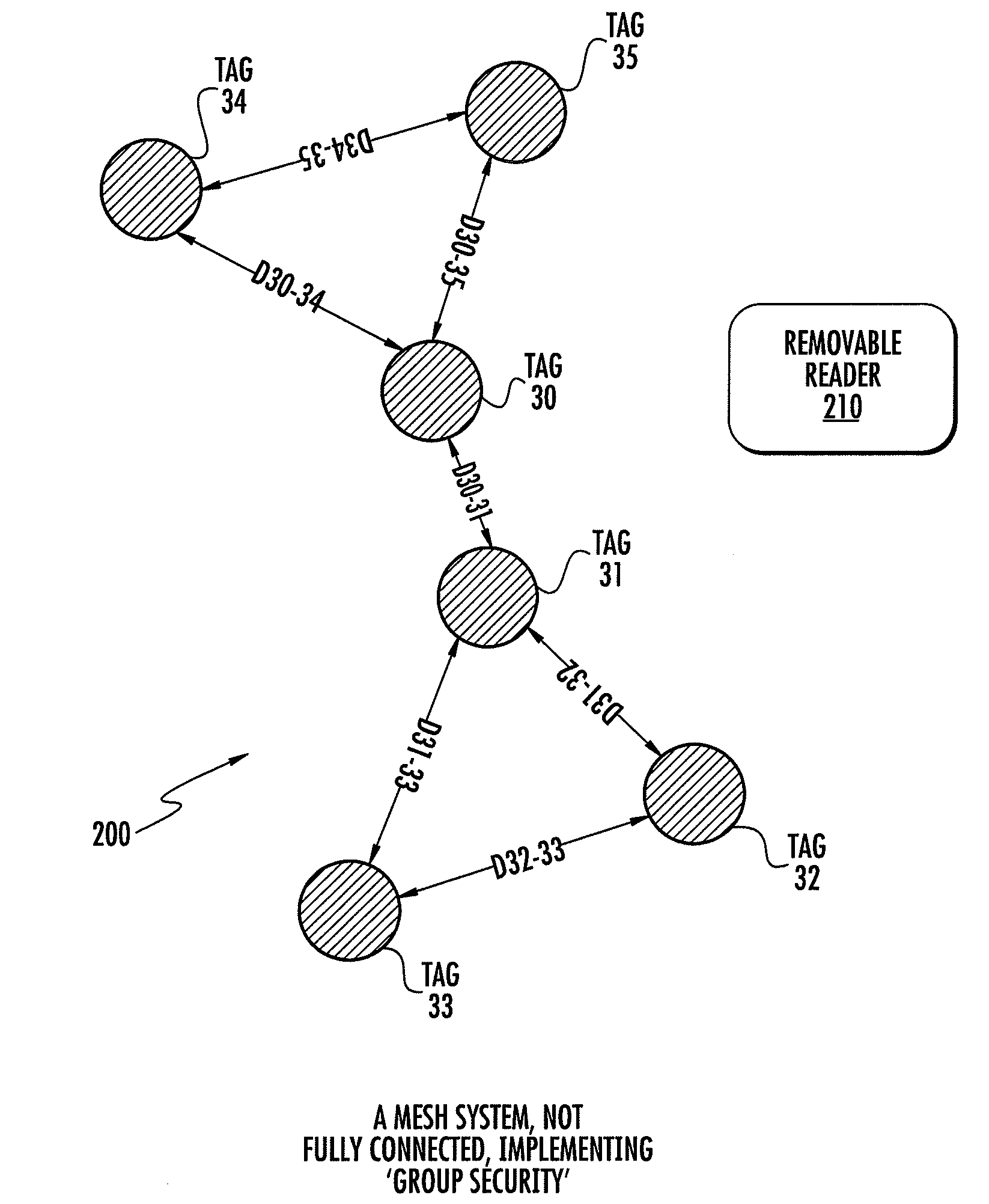
ActiveUS8169319B2Save battery powerElectric signal transmission systemsSubscribers indirect connectionTime delaysRound-trip delay time
A method of providing security and maintenance of a group of devices using a group of tags. Each of the tags is attached to a device and includes a radio frequency transceiver for intercommunicating using ultra-wide band signals. Using the intercommunication, distance between two of the tags is determined and an alarm is triggered when the distance is greater than a previously defined threshold distance. The distance is preferably determined by measuring a round trip delay time between the transmission of a transmitted signal to the other tag and reception of a response signal in response to the transmitted signal from the other tag. The distance is preferably determined by measuring a time delay between transmitting a unicast ultra-wide band message and receiving a unicast response message. The intercommunication preferably uses ultra-wide band signals which relay information regarding completeness of the group between the tags of the group. A configuration mechanism is typically used for configuring the group. Upon completing the configuration, the configuration mechanism, e.g. reader or monitor, may be removed and the tags maintain the group and provide security by the intercommunication between the tags. The tags are preferably synchronized to transmit and receive solely during a previously determined periodic sequence of time intervals.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Method and system for the clock synchronization of network terminals
A method and system for network terminal clock synchronization includes determining a respective round trip delay time from a master terminal to each slave terminal and offsetting the clock of each slave terminal by an amount proportional to the respective determined round trip delay time such that the master terminal and each of the slave terminals have substantially the same point of reference in time. The method and system further include, in response to a trigger signal, determining a respective offset between the master clock of the master terminal and the clocks of each of the slave terminals and offsetting the clocks of each of the slave terminals by an amount proportional to the determined respective offset to synchronize the clocks of each of the slave terminals to the master clock of the master terminal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Optical transmission system and synchronization method using time reference pulse
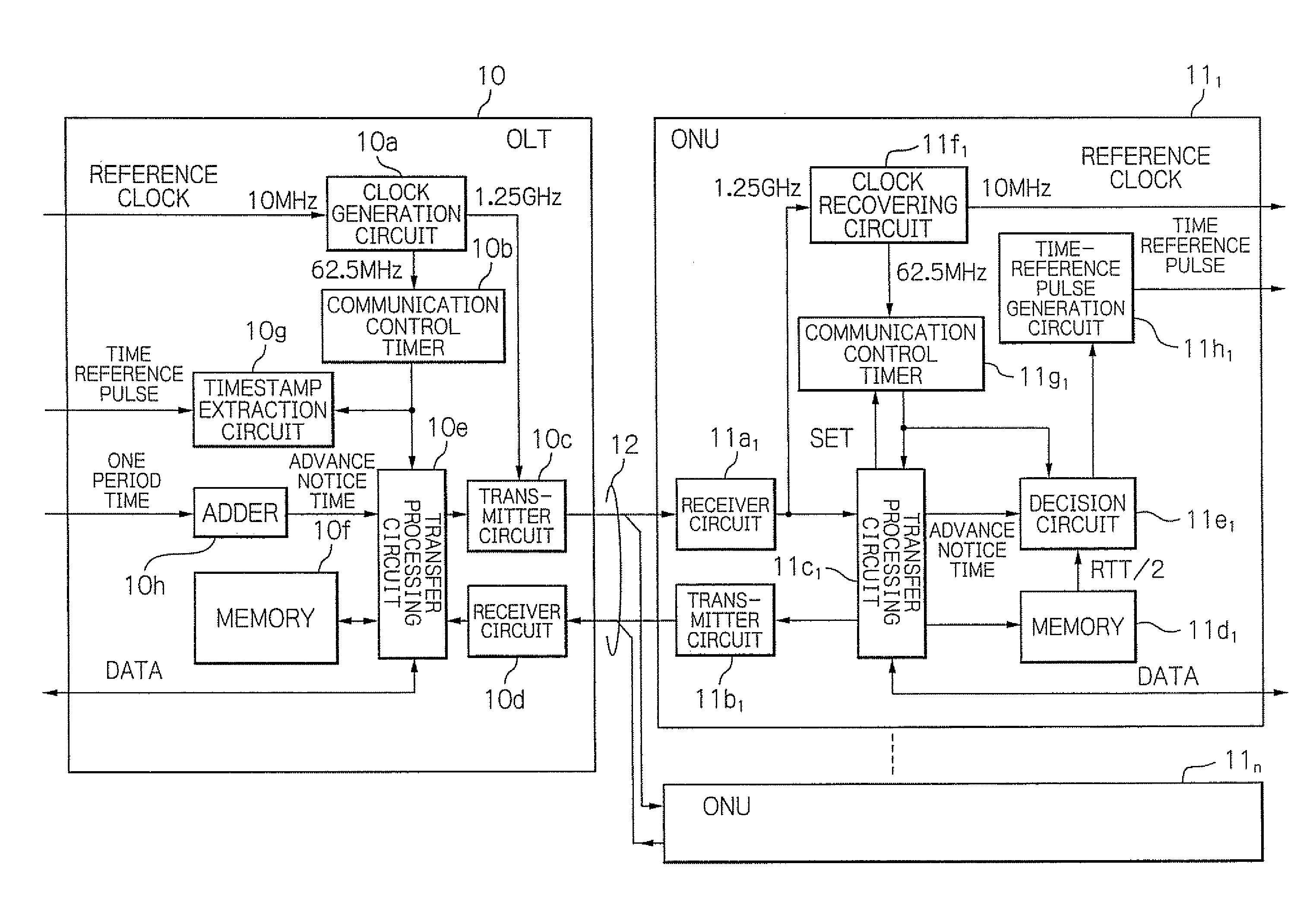
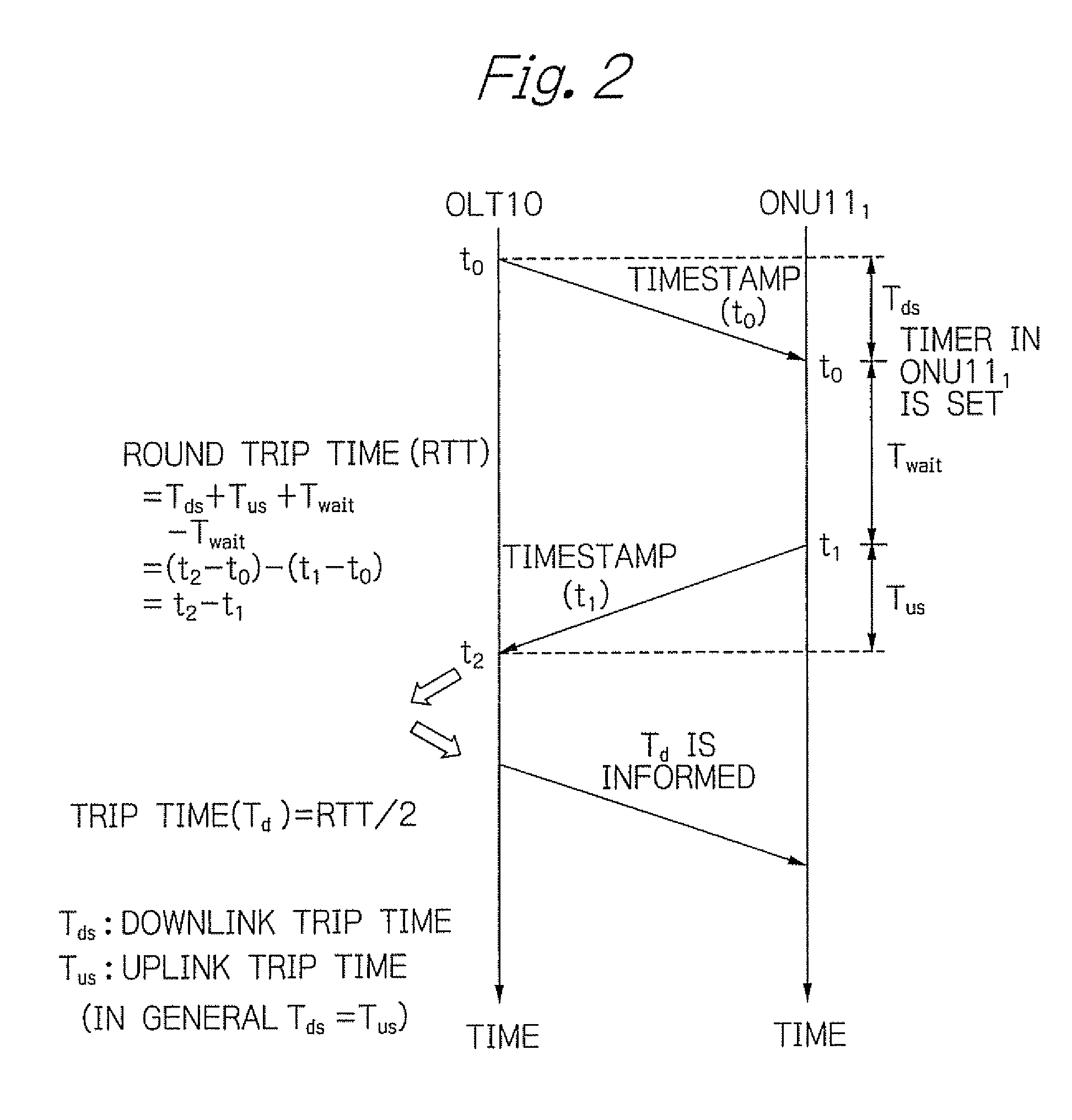
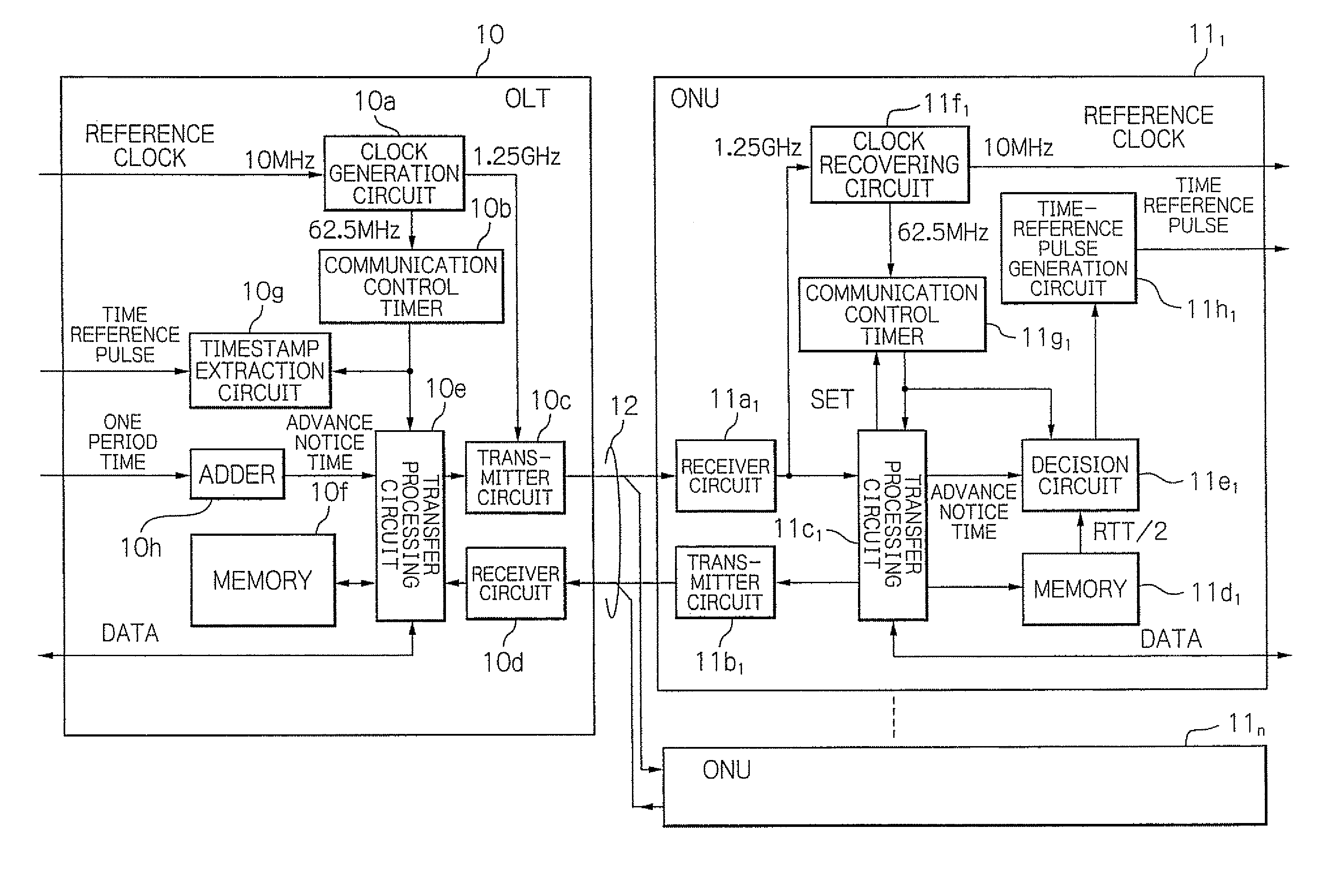
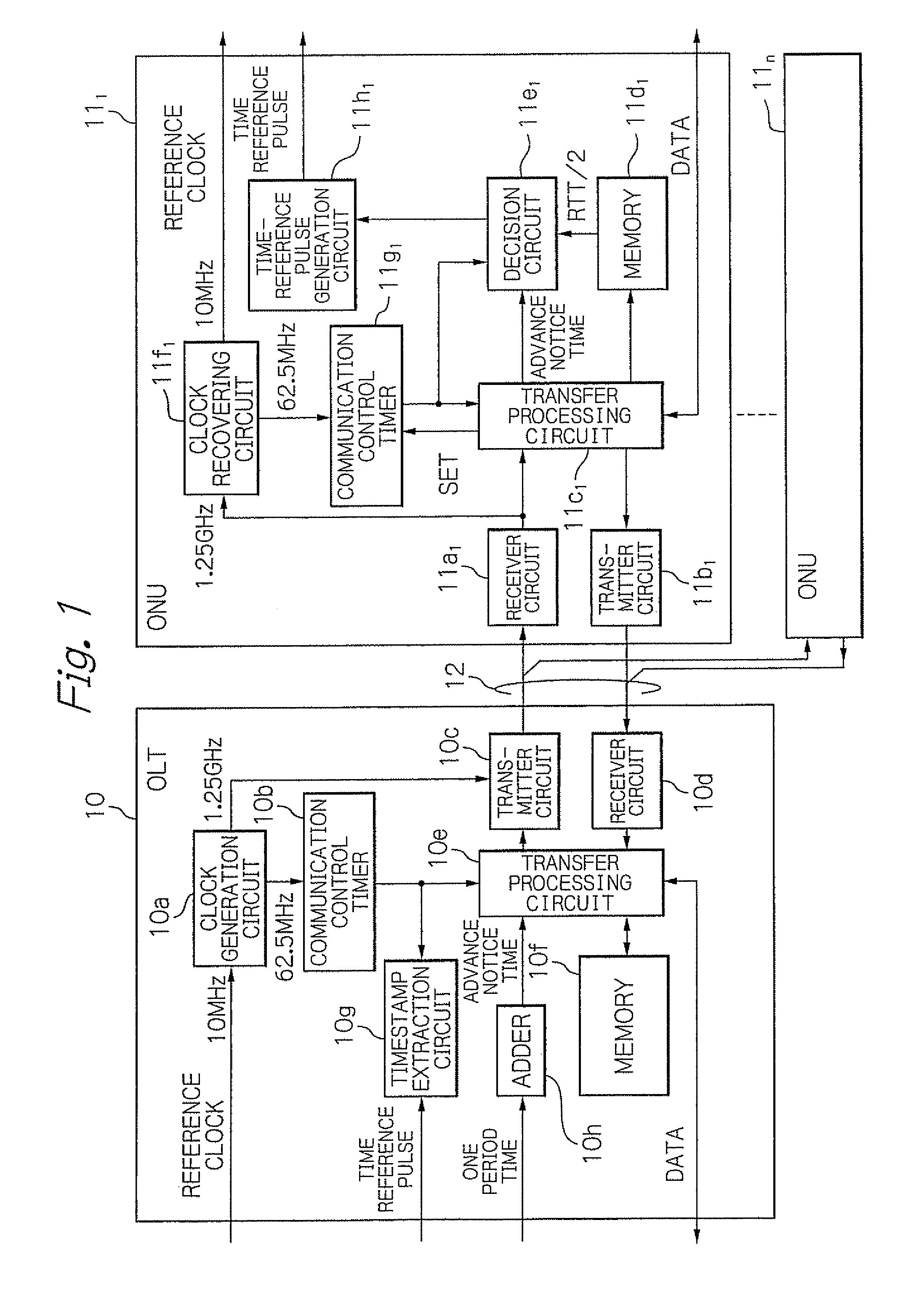
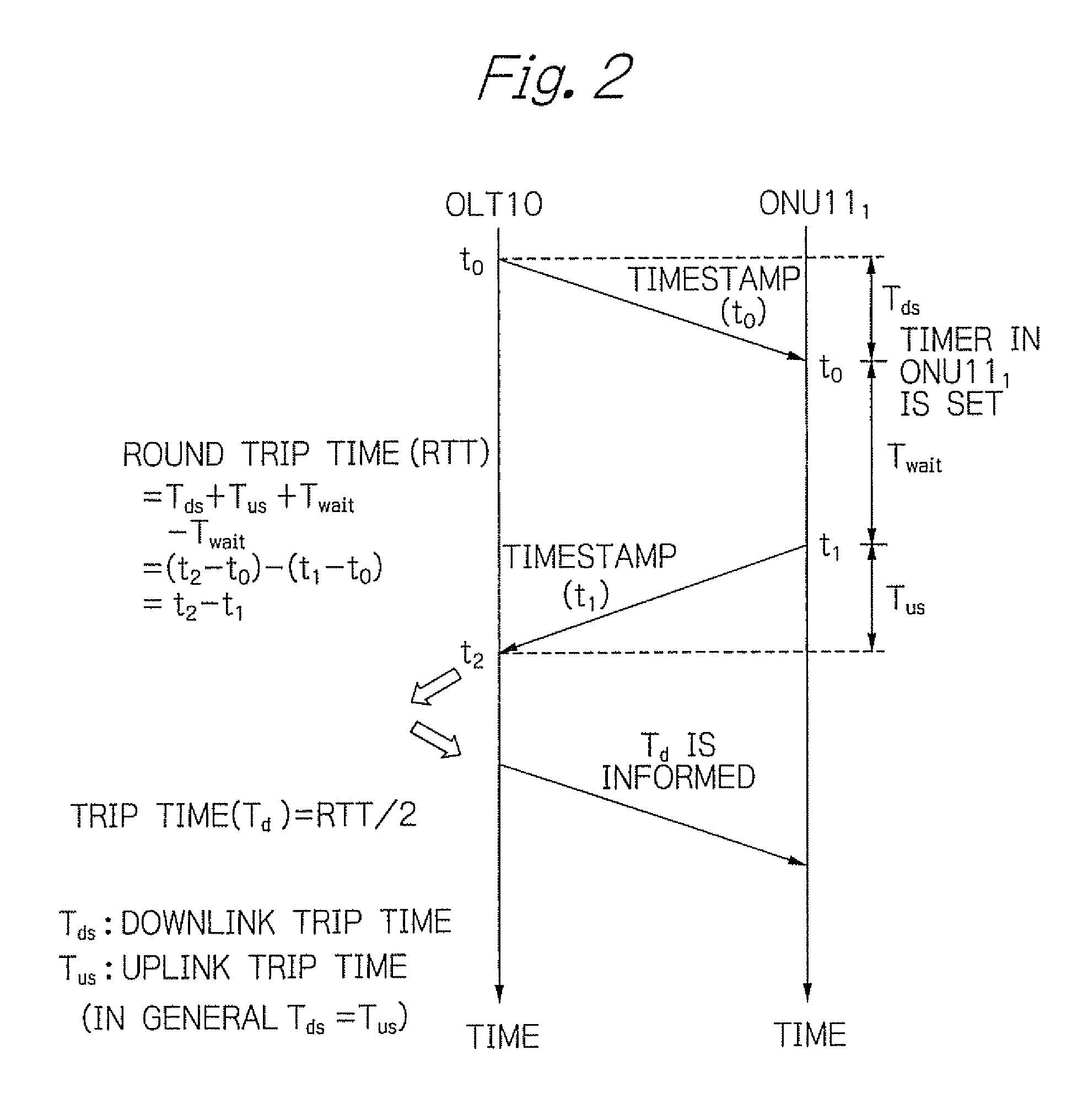
InactiveUS20090297164A1Rapid and accurate time-synchronizationSimple circuit structureMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime informationRound-trip delay time
An OLT includes a first transmitter and receiver unit for transmitting and receiving signals with ONUs, a first communication control timer, a measurement unit for measuring a round trip time (RTT) between the OLT and each of ONUs, an advance notice time generation unit for generating an advance notice time signal by adding a predetermined time to a time information that indicates a time in the first communication control timer in response to a first time reference pulse, and a unit for controlling the first transmitter and receiver unit to transmit the generated advance notice time signal to each of the ONUs, and to transmit signals indicating measured RTT / 2 to the respective ones of the ONUs.
Owner:KDDI CORP
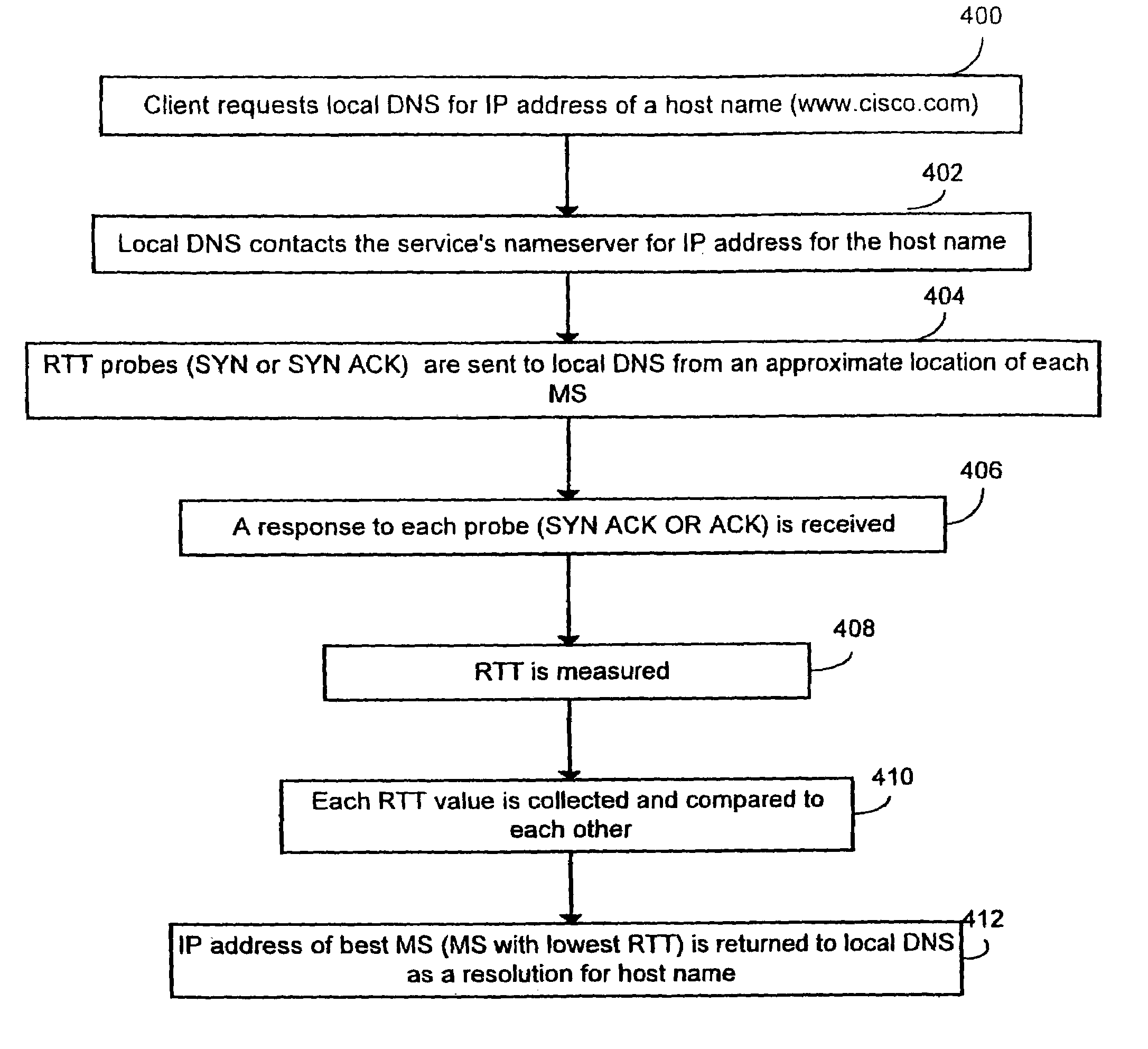
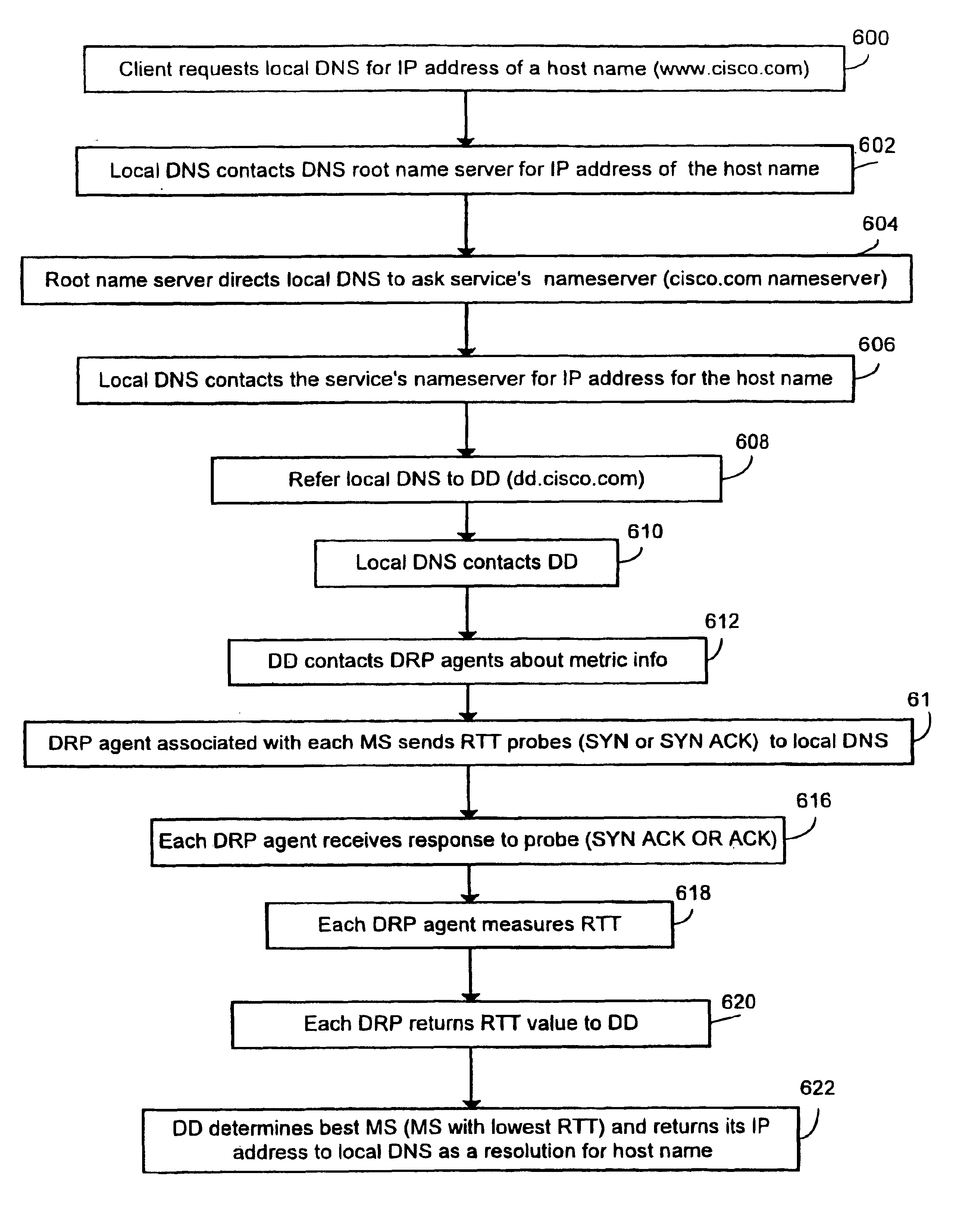
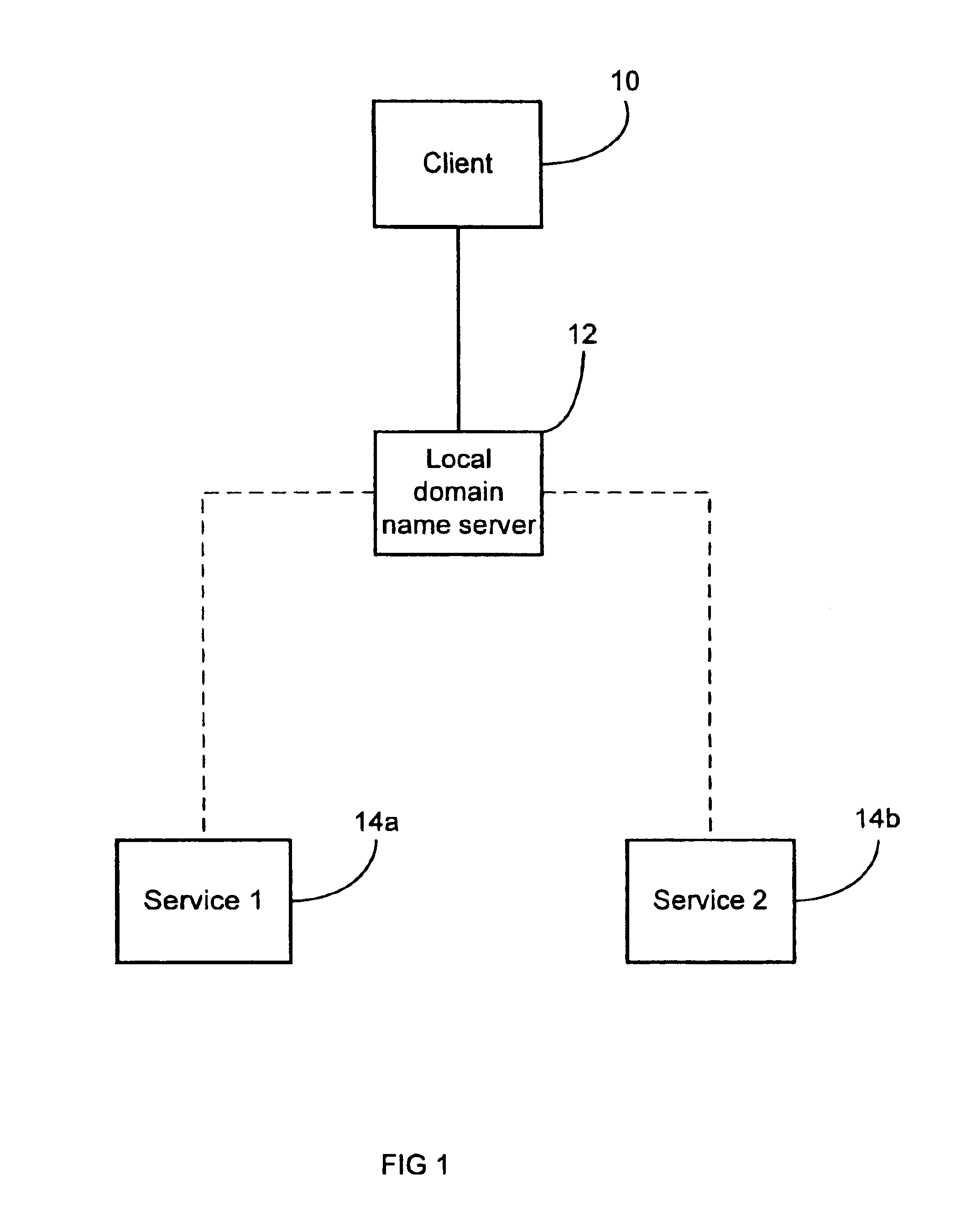
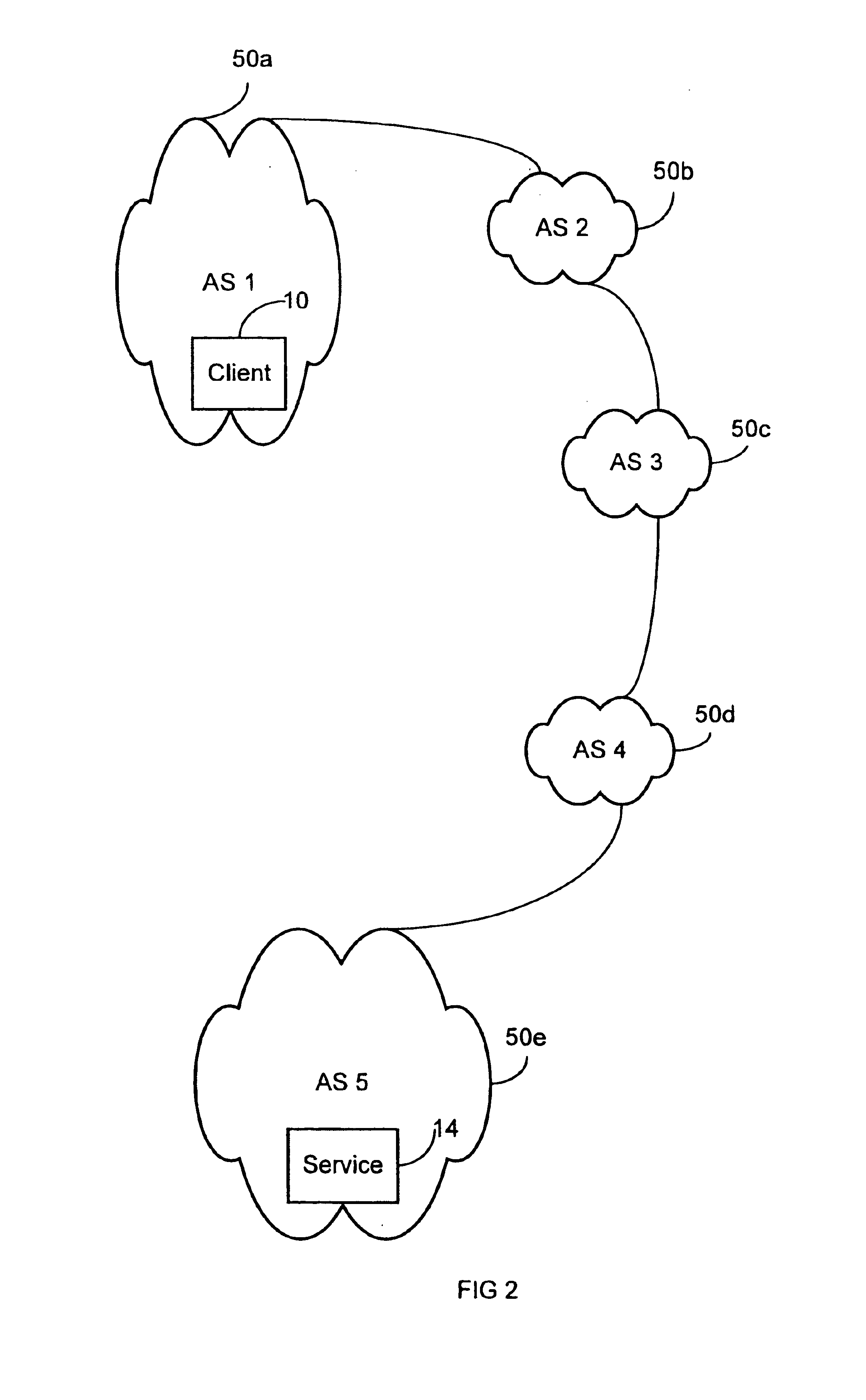
System and method for measuring round trip times in a network using a TCP packet
An embodiment of the present invention is a system and method for measuring round trip times in a network, such as the Internet, by utilizing a packet, such as a transmission control protocol (TCP) packet. The TCP packet may be a packet which is typically utilized during establishment of a reliable connection, such as a SYN or a SYN ACK. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a mirrored service is selected for a client by sending the TCP packet from an approximate location of each of the mirrored service to an approximate location of the client. A response is then received by each mirrored service from the approximate location of the client, and a round trip time for each mirrored service is measured from the time the TCP packet was sent to the time the response was received. The various round trip times of each mirrored service are compared with each other and a best round trip time, such as the shortest time, is selected. A mirrored service associated with the best round trip time is selected for use with the client.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for measuring round trip times in a network using a TCP packet
An embodiment of the present invention is a system and method for measuring round trip times in a network, such as the Internet, by utilizing a packet, such as a transmission control protocol (TCP) packet. The TCP packet may be a packet which is typically utilized during establishment of a reliable connection, such as a SYN or a SYN ACK. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a mirrored service is selected for a client by sending the TCP packet from an approximate location of each of the mirrored service to an approximate location of the client. A response is then received by each mirrored service from the approximate location of the client, and a round trip time for each mirrored service is measured from the time the TCP packet was sent to the time the response was received. The various round trip times of each mirrored service are compared with each other and a best round trip time, such as the shortest time, is selected. A mirrored service associated with the best round trip time is selected for use with the client.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
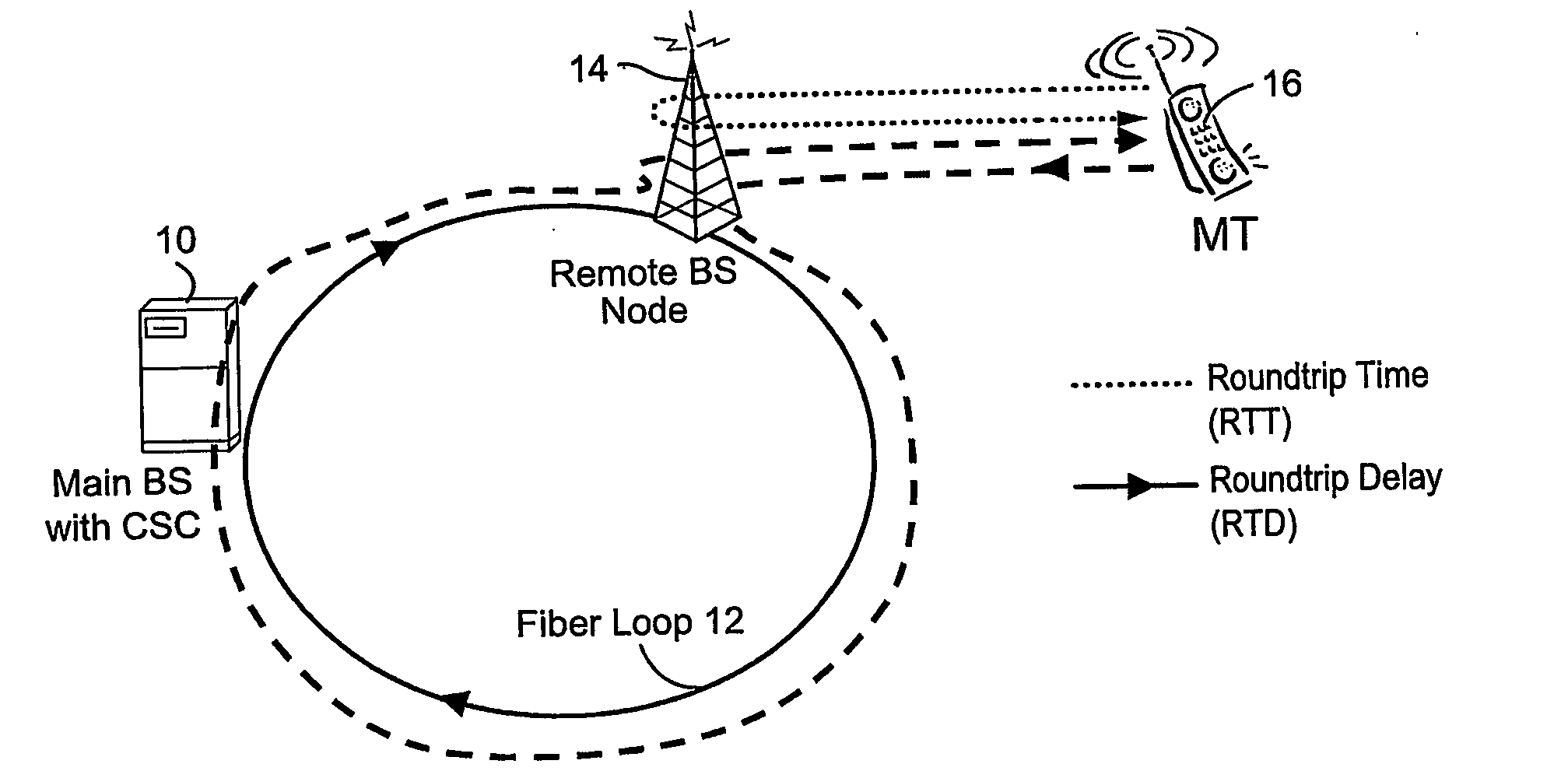
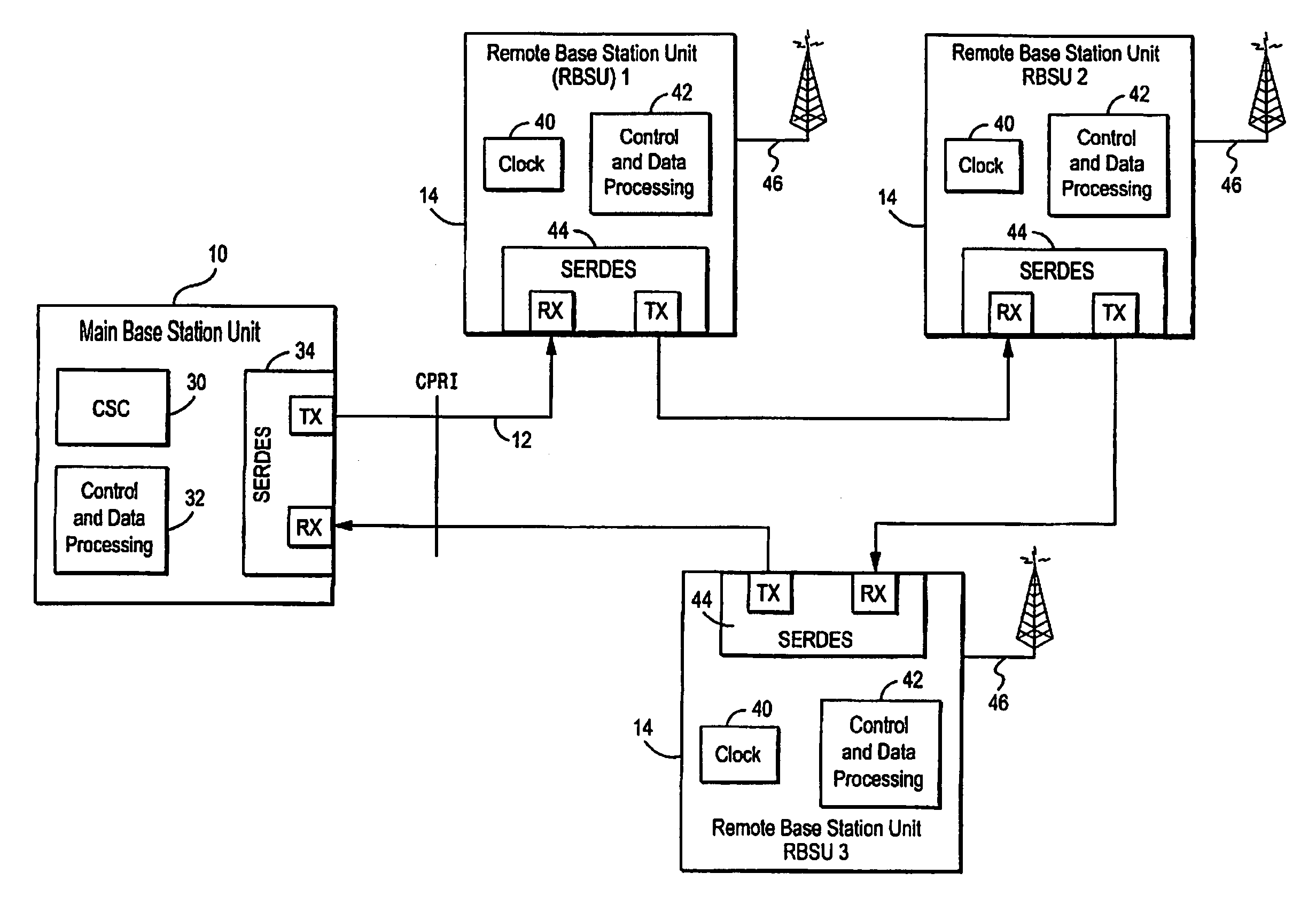
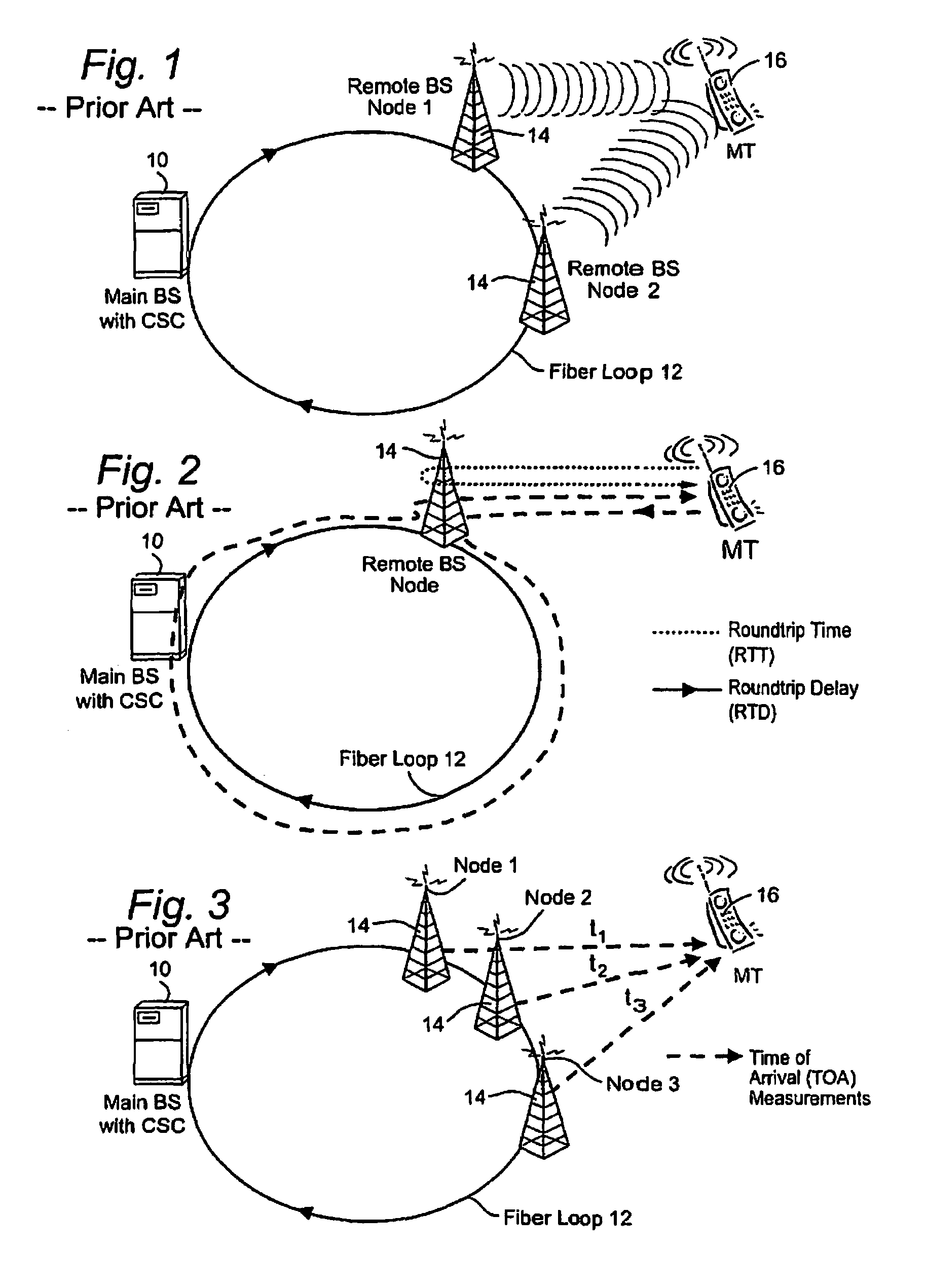
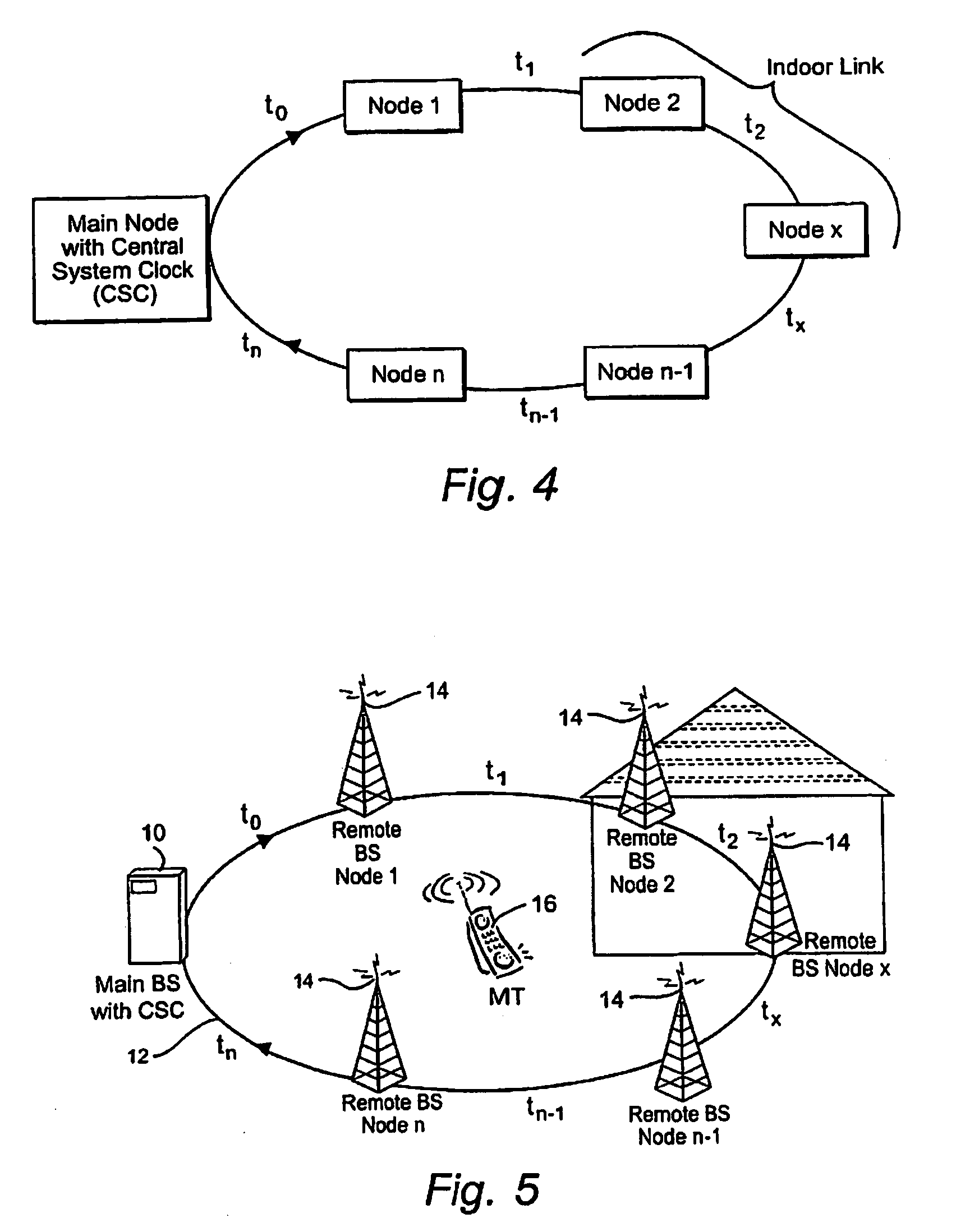
Temperature compensation for transmission between nodes coupled by a unidirectional fiber ring
InactiveUS20070127919A1Laser detailsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansDelayed timeRound-trip delay time
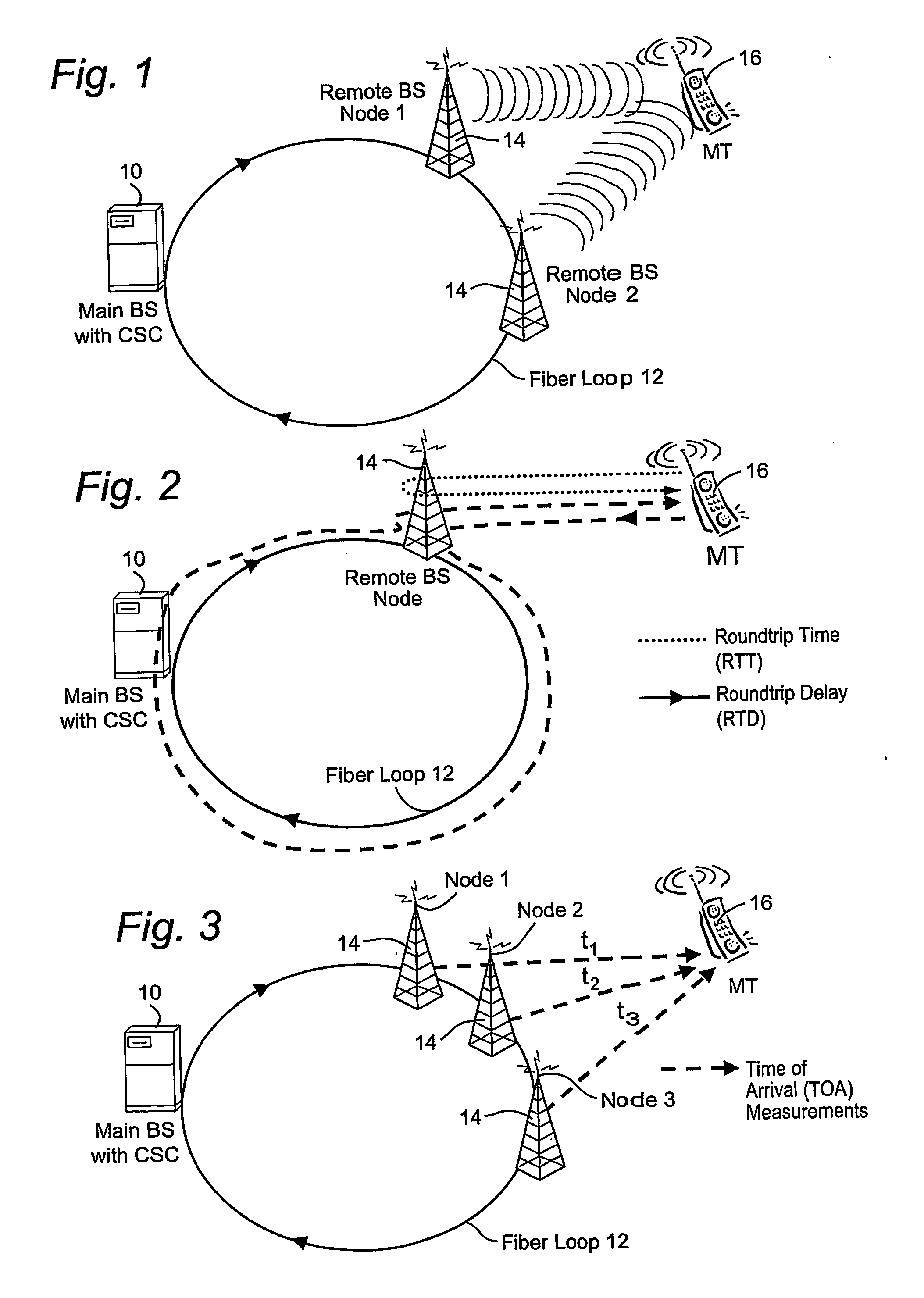
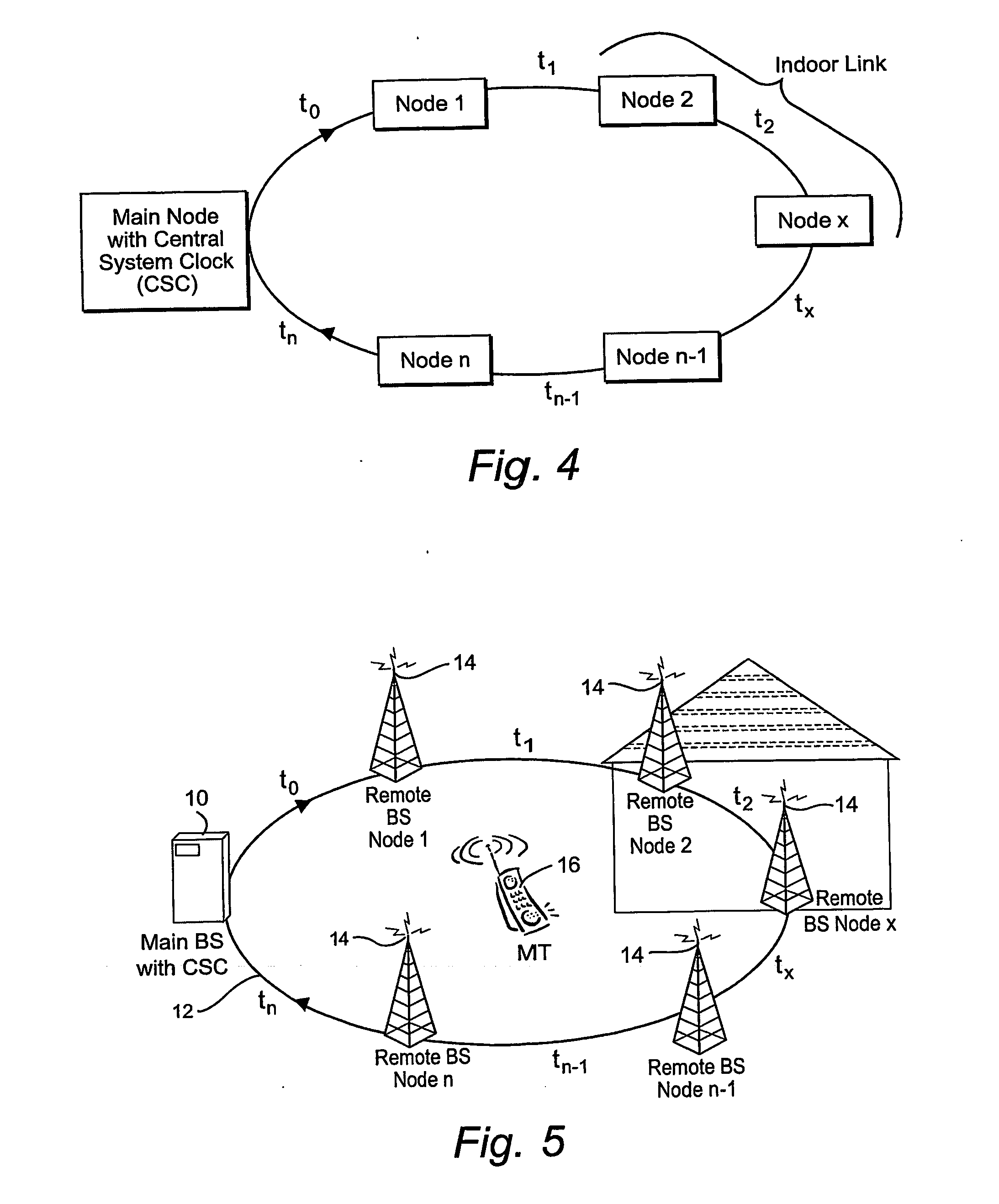
Transmissions over a unidirectional optical fiber coupling multiple nodes are compensated for temperature-induced effects. A round-trip delay time is determined for a signal sent from a first node to travel around the unidirectional optical fiber loop and be received back at the first node. That measured round-trip delay time is then used to account for temperature-induced effects on signal transmissions over the unidirectional optical fiber loop. This temperature compensation is particularly beneficial in applications that require a high level of timing accuracy.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for distributing a self-synchronized clock to nodes on a chip
InactiveUS7174475B2Eliminate needError detection/correctionSingle output arrangementsDelayed timeRound-trip delay time
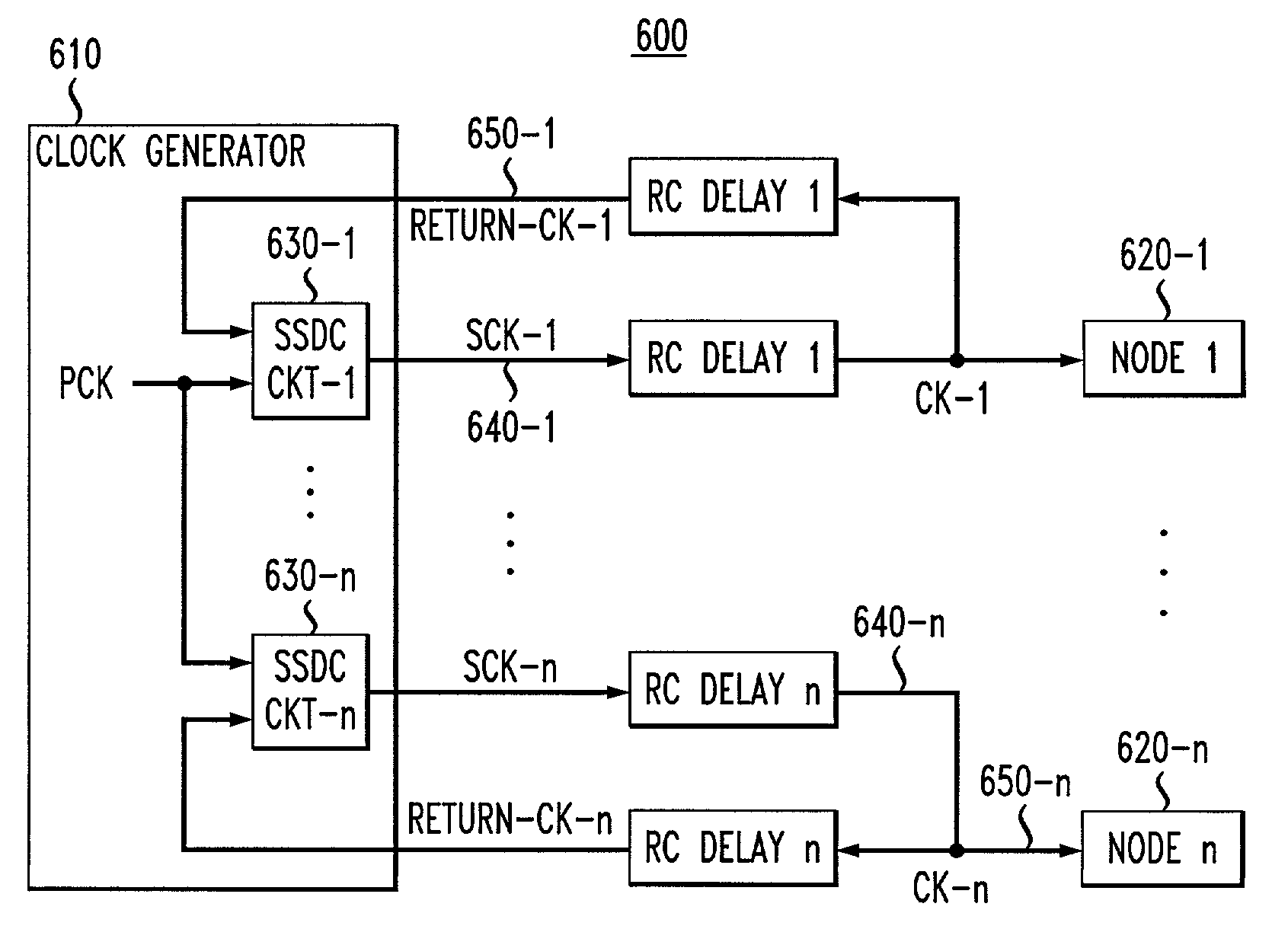
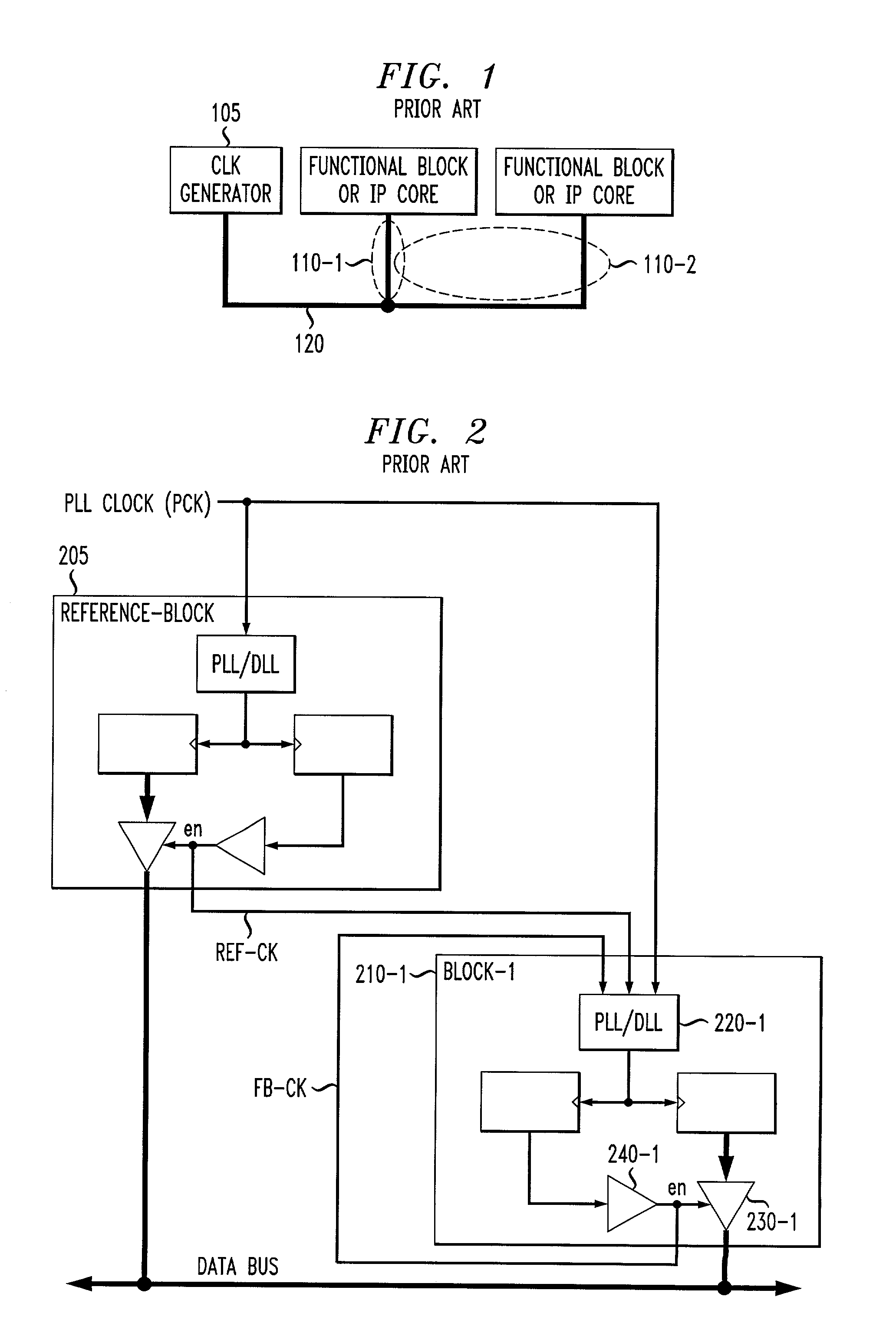
A method and apparatus are disclosed for dynamically reducing clock skew among various nodes on an integrated circuit. The disclosed clock skew reduction technique dynamically estimates the clock delay to each node and inserts a corresponding delay for each node such that the clock signals arriving at each node are all in phase with a global clock (or 180° out of phase). Delays attributable to both the wire RC delays and the clock buffer delays are addressed. A feedback path for the clock signal associated with each node allows the round trip travel time of the clock signal to be estimated. When the length of the feedback path matches the length of the primary clock path, the clock skew present at the corresponding node can be estimated as fifty percent (50%) of the round trip delay time. Dynamic adjustments to the delay control circuit are permitted as operating conditions shift. Clock signals arriving at individual nodes on the integrated circuit remain in phase with the global PLL clock (PCK), regardless of variations in the operating voltage or temperature (or both).
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
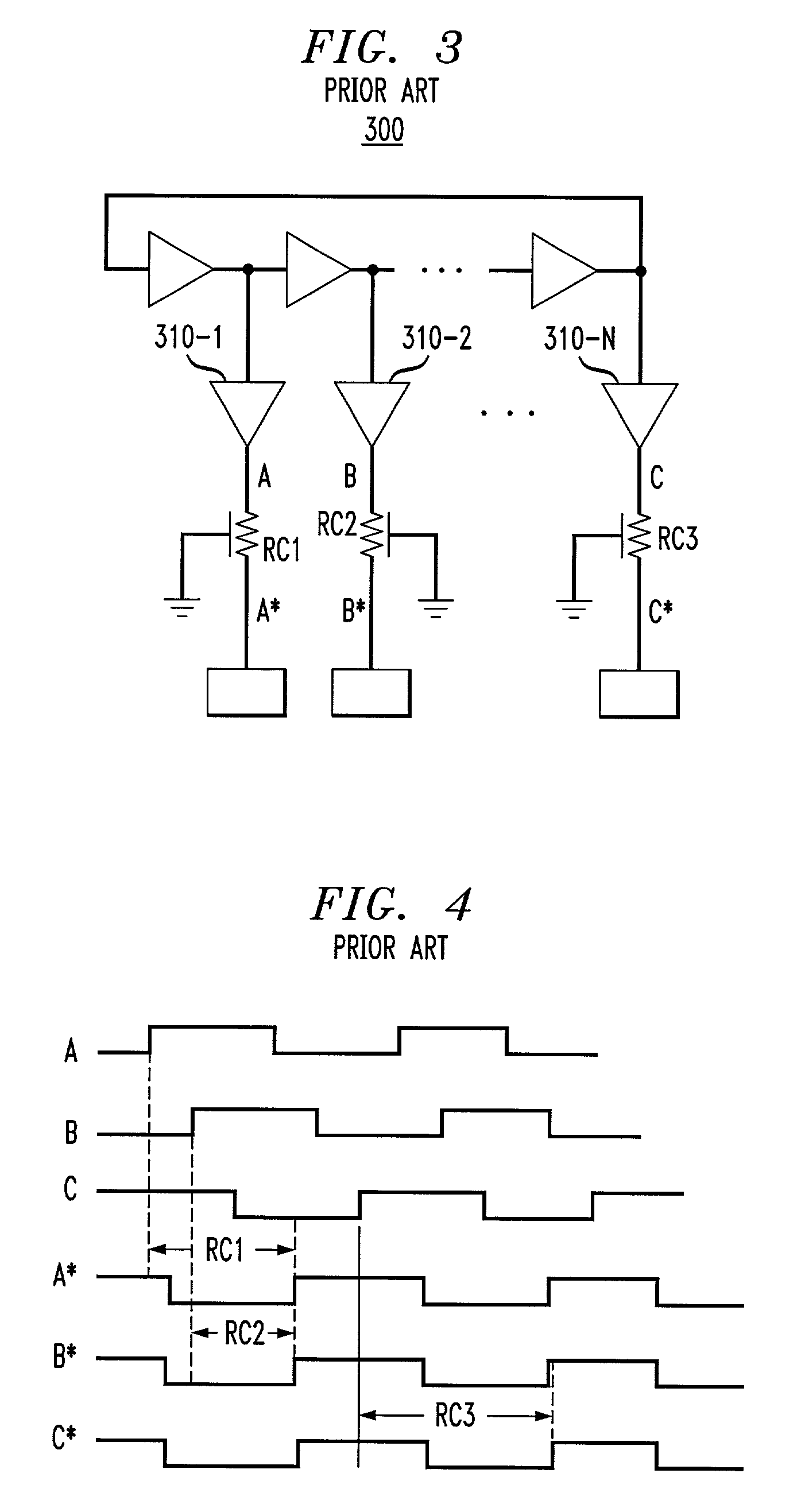
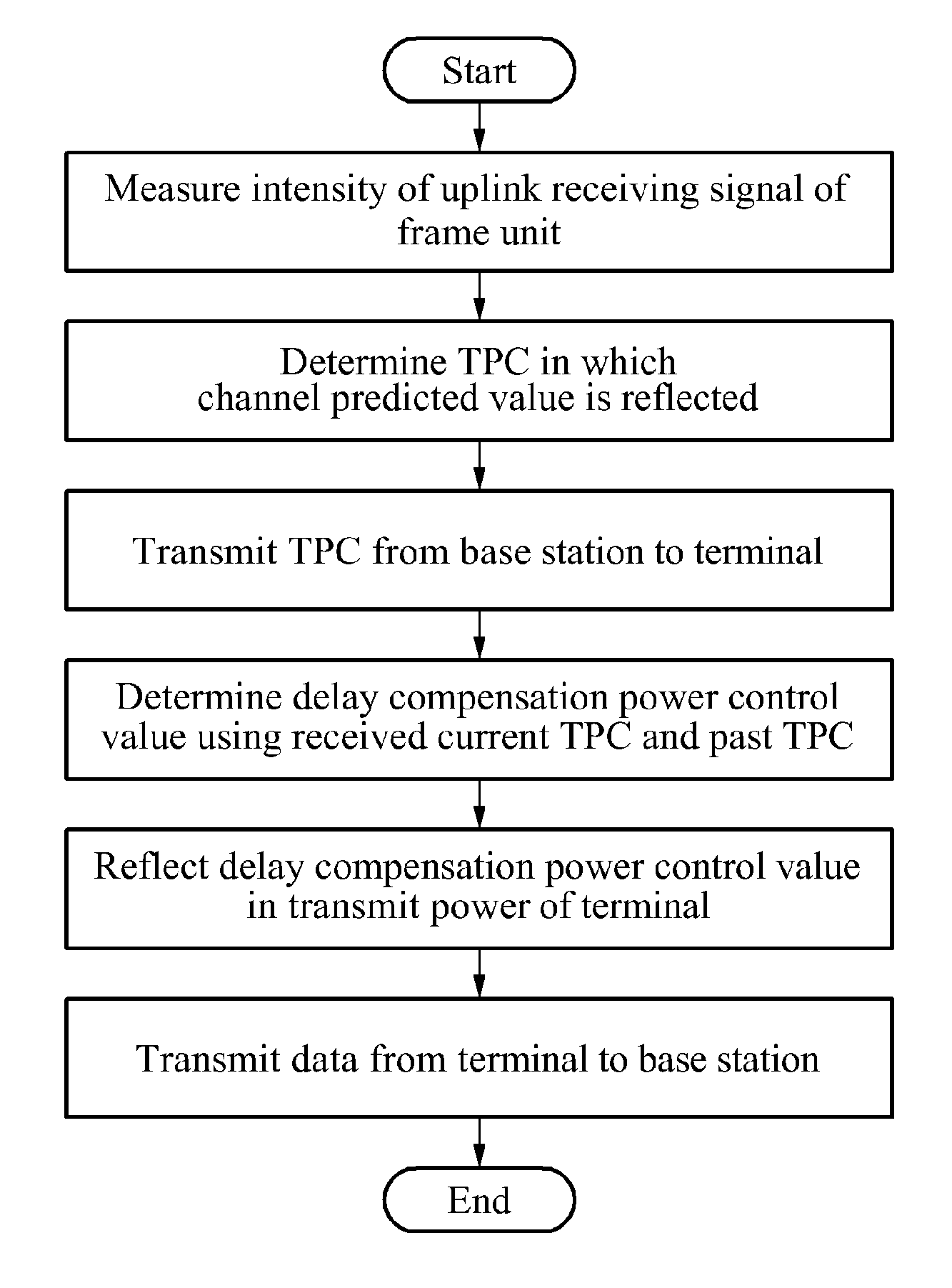
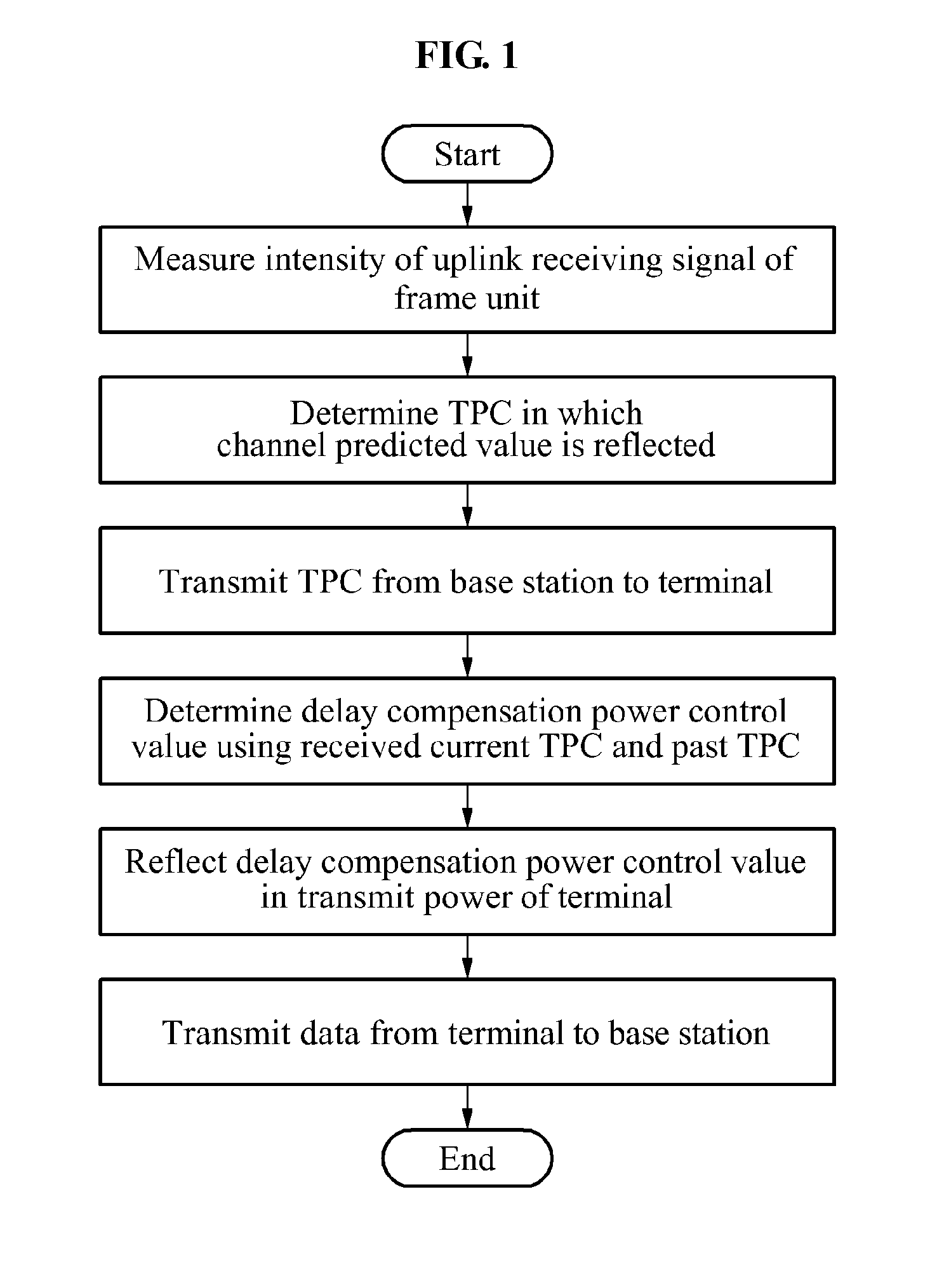
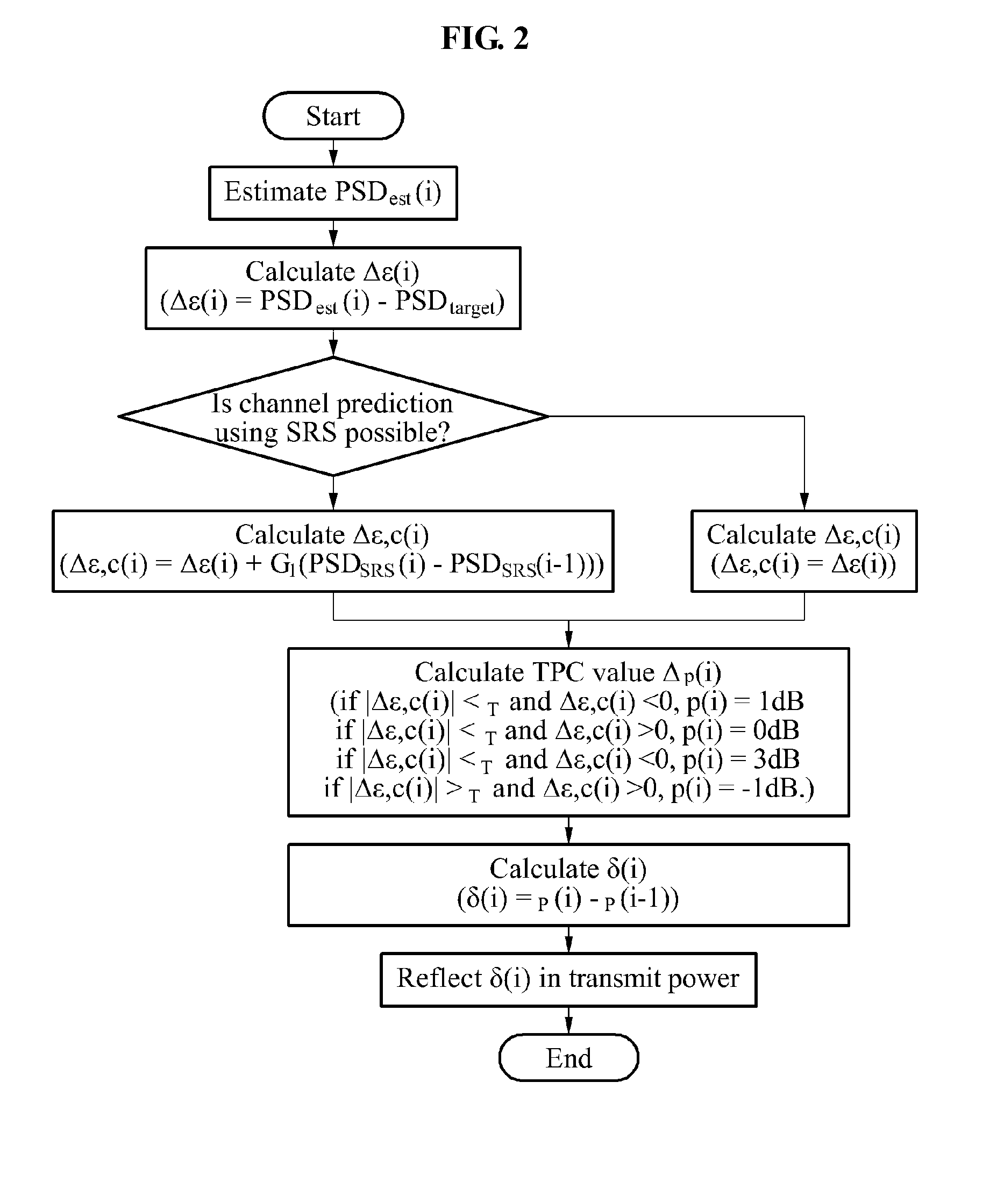
Methods for power control and link adapation in lte-based mobile communication system
InactiveUS20150126239A1Long delay timePower managementRadio transmissionTransmitted powerClosed loop
Provided is a power control and link adaptation method for compensating for a long round trip delay time and slow channel fading in a long term evolution (LTE)-based mobile communication system having a long round trip delay time, similar to a satellite mobile system, the method that may compensate for the long round trip delay time of the satellite mobile system in which a distance between a base station and a terminal is relatively long, when compared to a terrestrial LTE system, support a modulation and coding scheme (MCS) level requested by a terminal, by predicting a channel after the round trip delay time elapses, maintain compatibility within an existing LTE frame, by generating a transmit power control (TPC) instruction for an uplink closed-loop power control, on a frame by frame basis, and compensate for slow channel fading of the satellite mobile system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
High-throughput communication system, communication terminal, session relay, and communication protocol
InactiveUS20060114830A1Improve throughputEasy to useTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowCommunications system
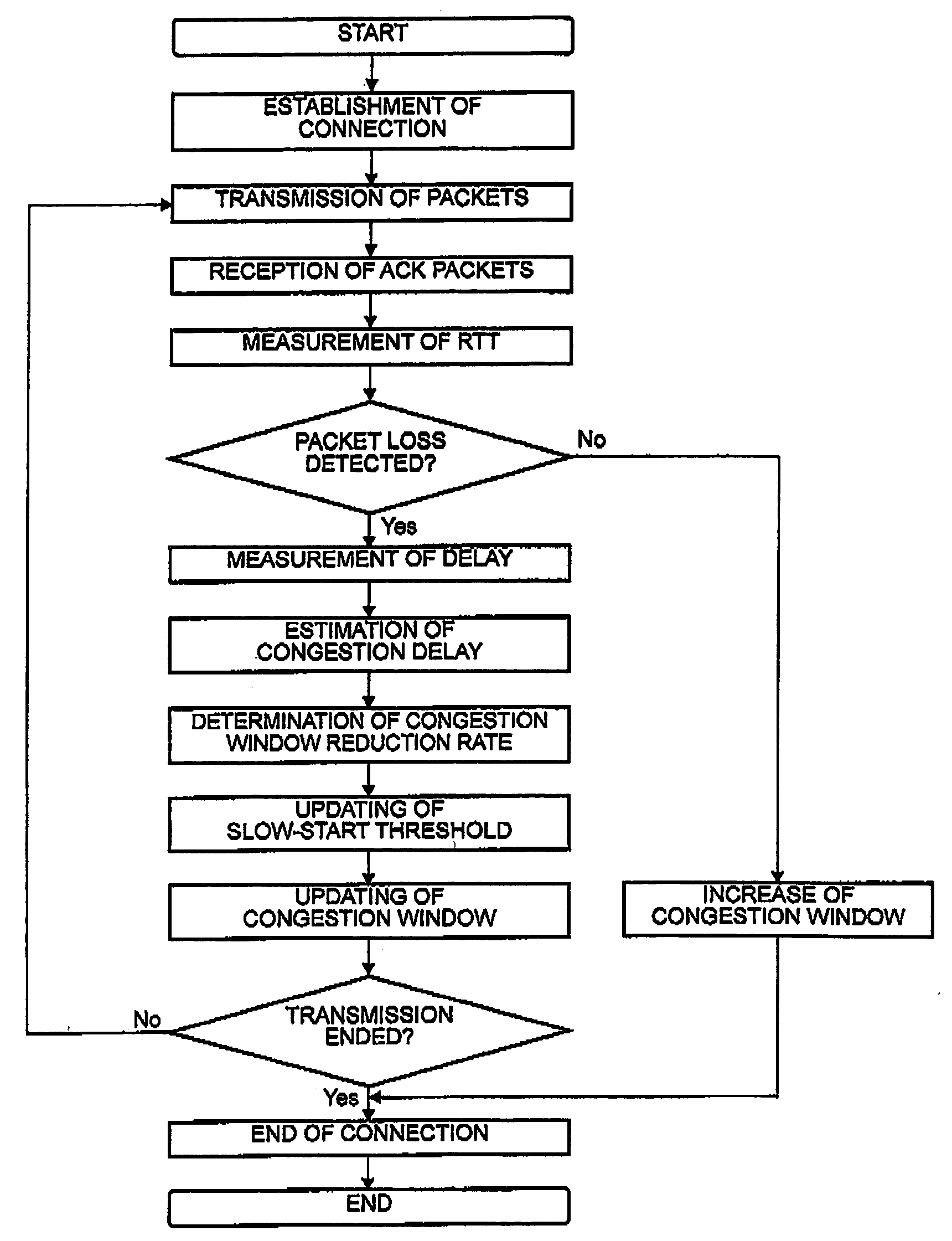
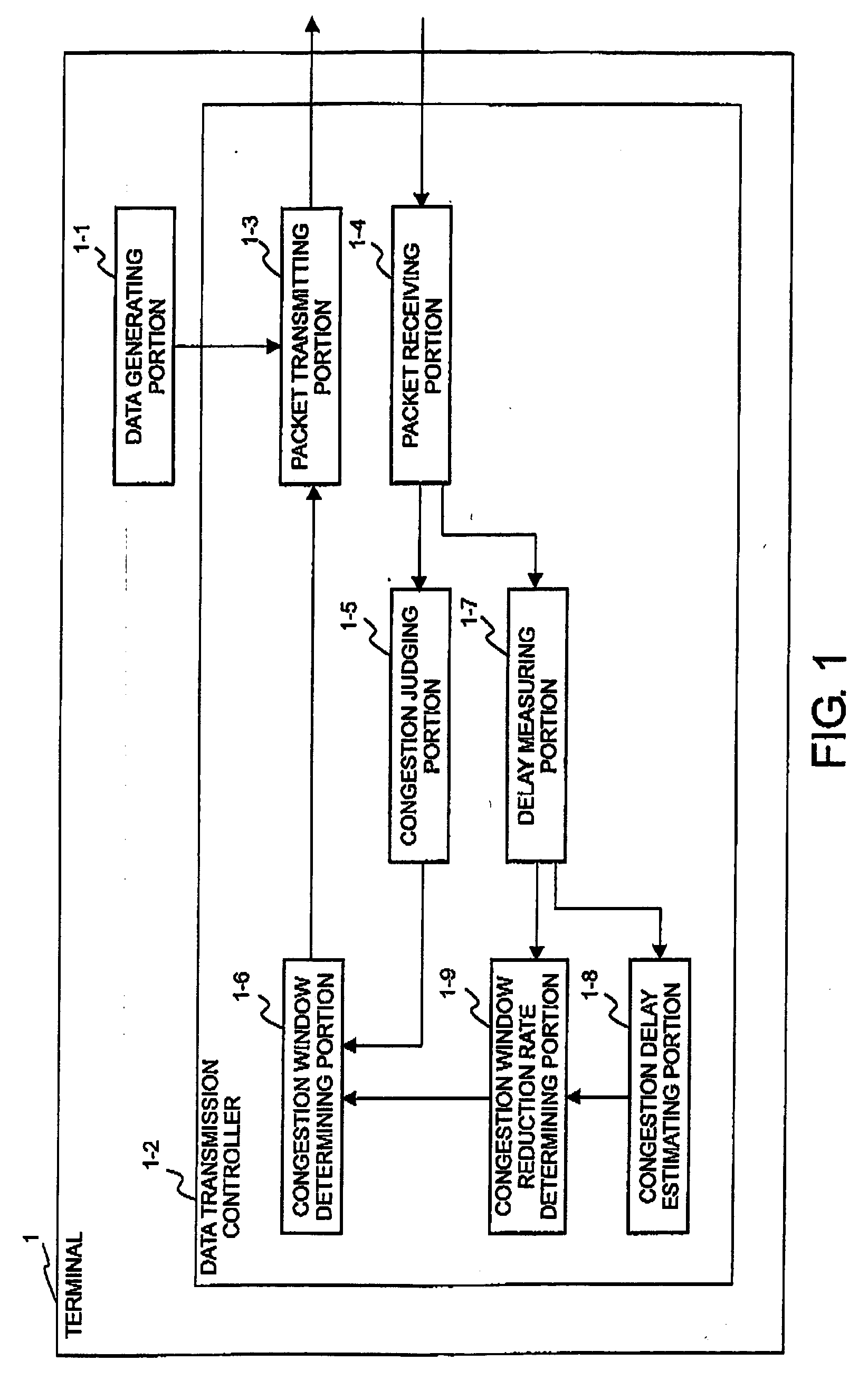
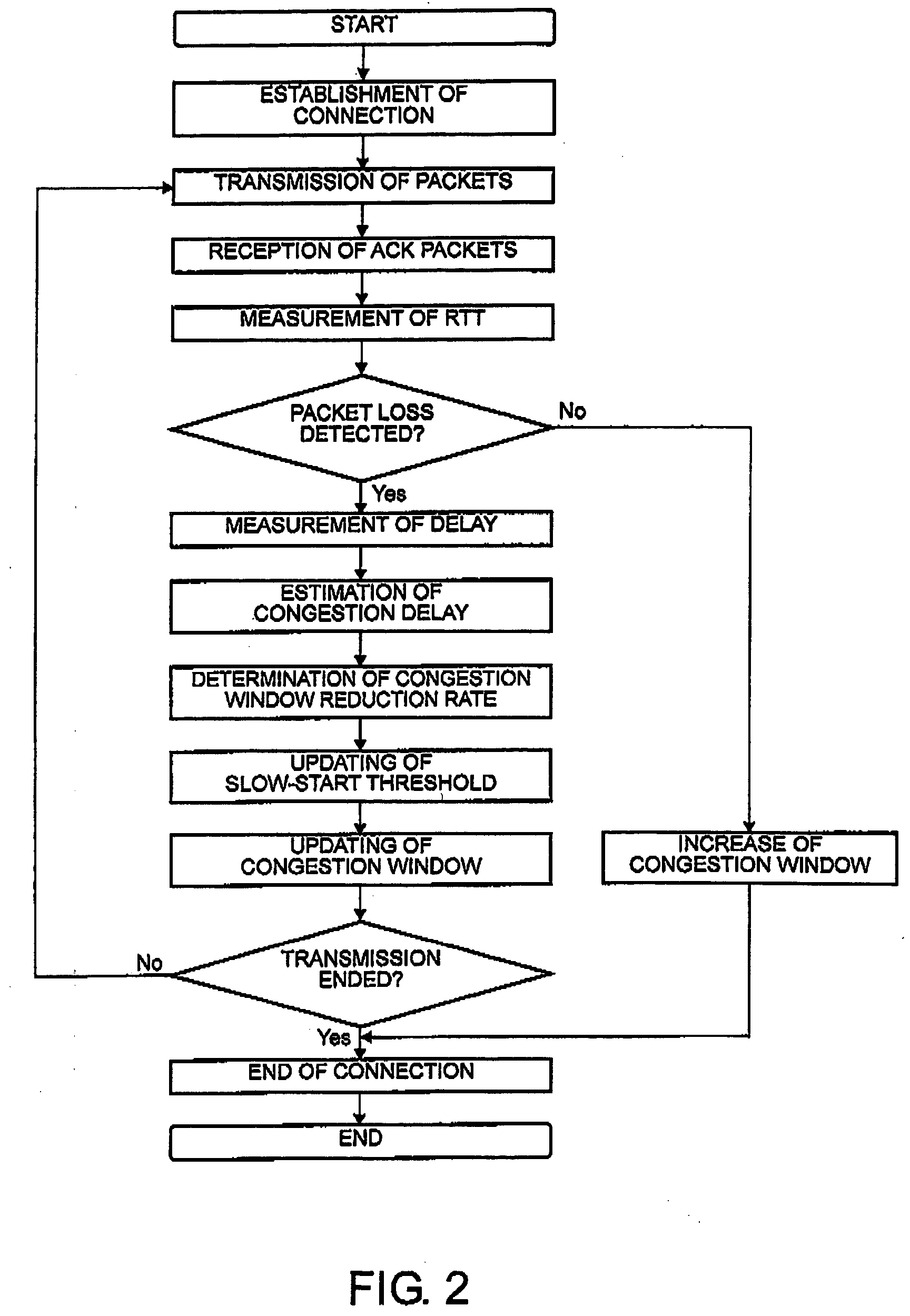
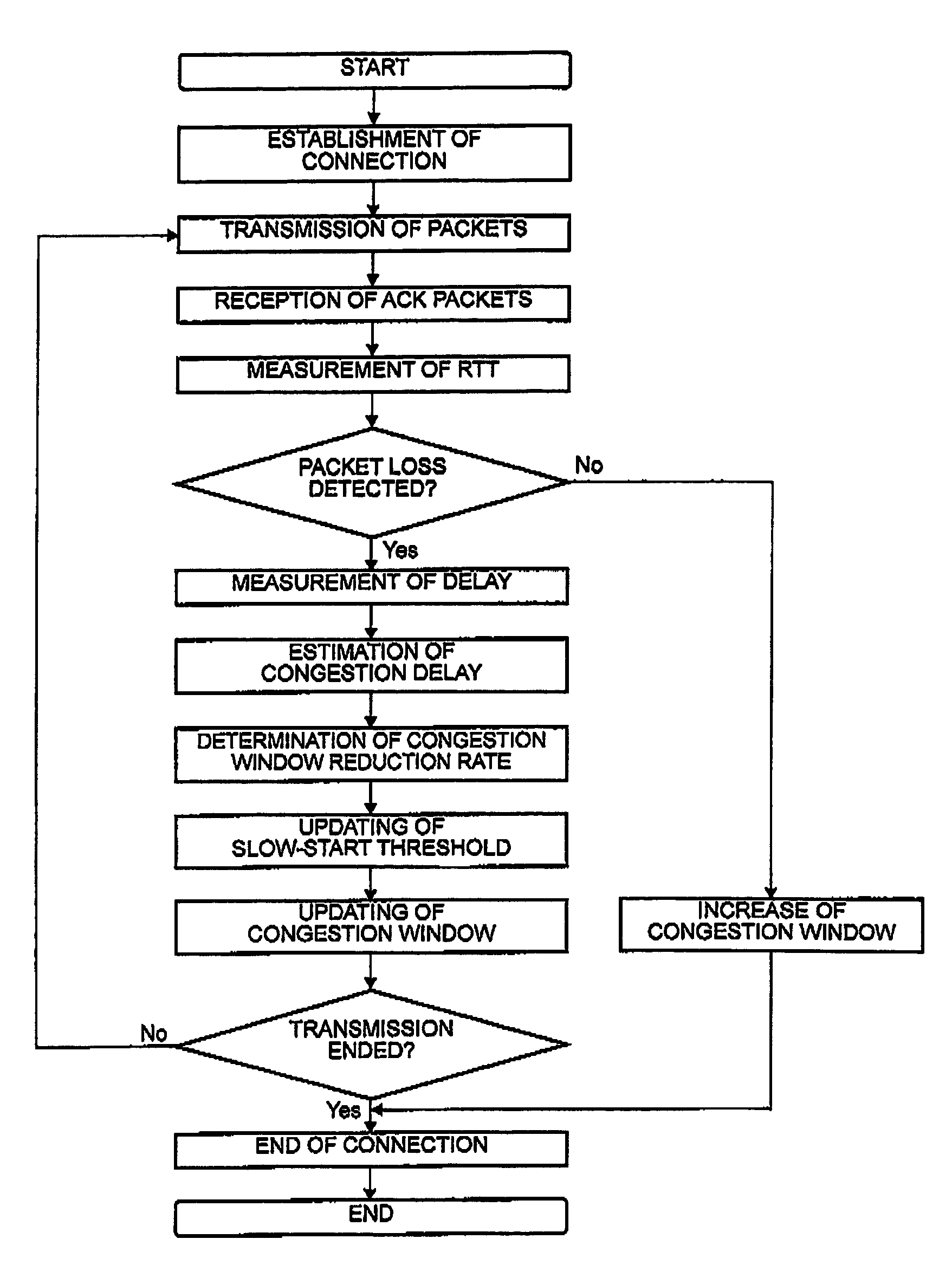
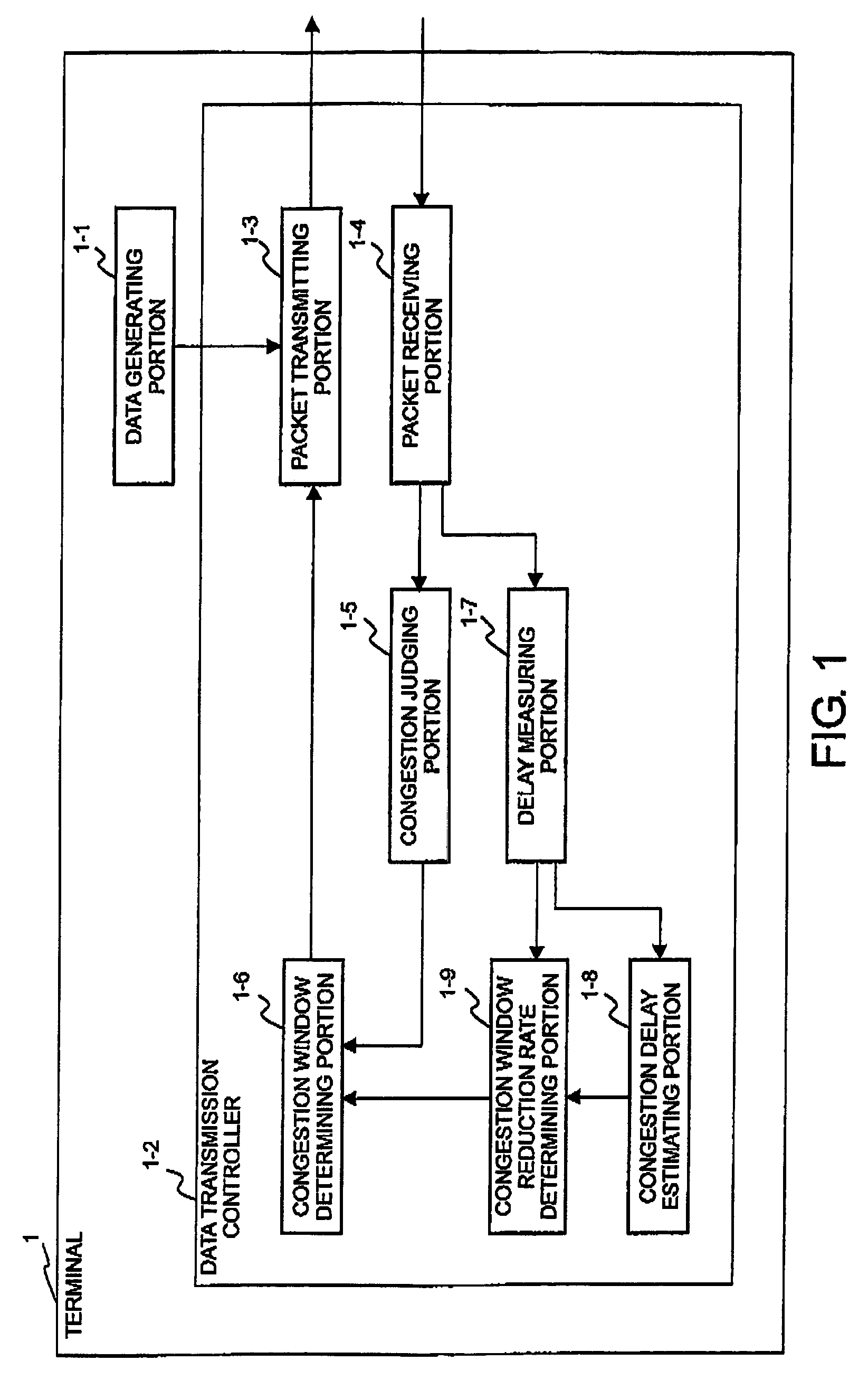
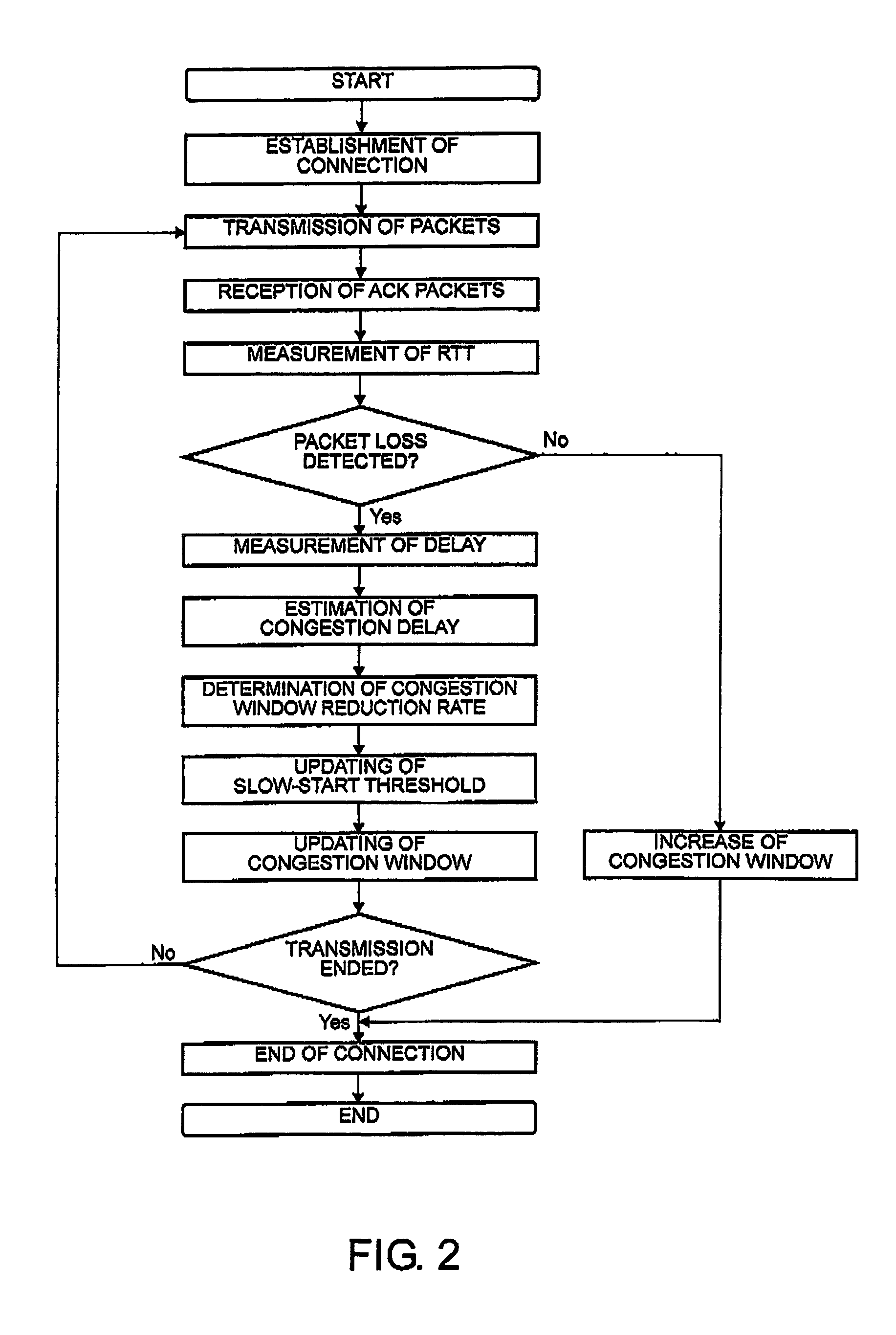
In a communication system for transmitting and receiving data between a plurality of terminals via a network through a session relay for relaying communication between the terminals, each of the terminals or the session relay measures a one-way or a round-trip delay time in the network, determines a threshold delay time at which network congestion is judged. With reference to a delay time upon detection of packet loss and the threshold delay time, estimation is made about the possibility that the packet loss results from congestion. A congestion window is changed with reference to the possibility upon detection of the packet loss.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Moving picture compression encoding transceiver apparatus
InactiveUS7609645B2Shorten the timeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverVideo encoding
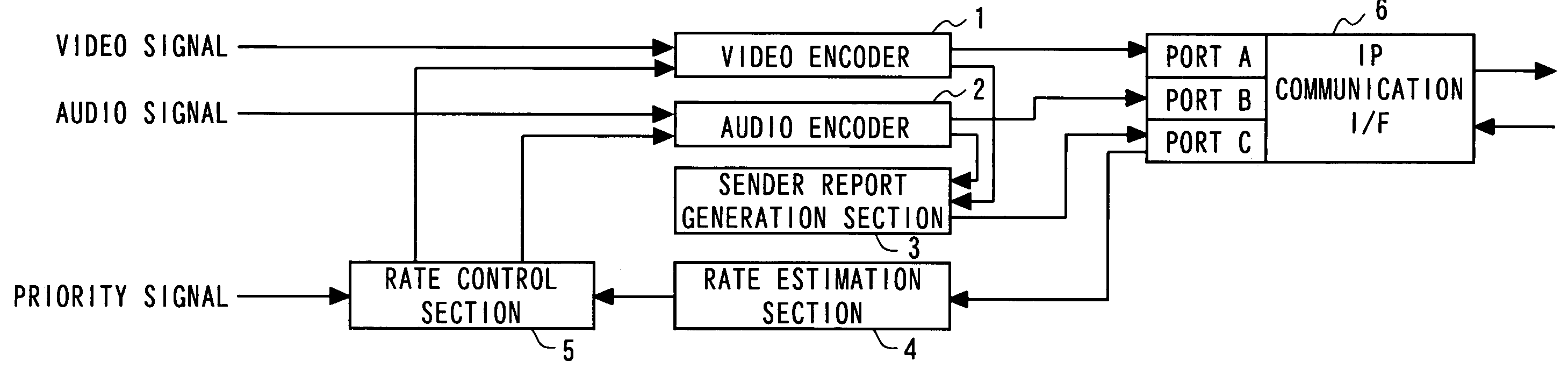
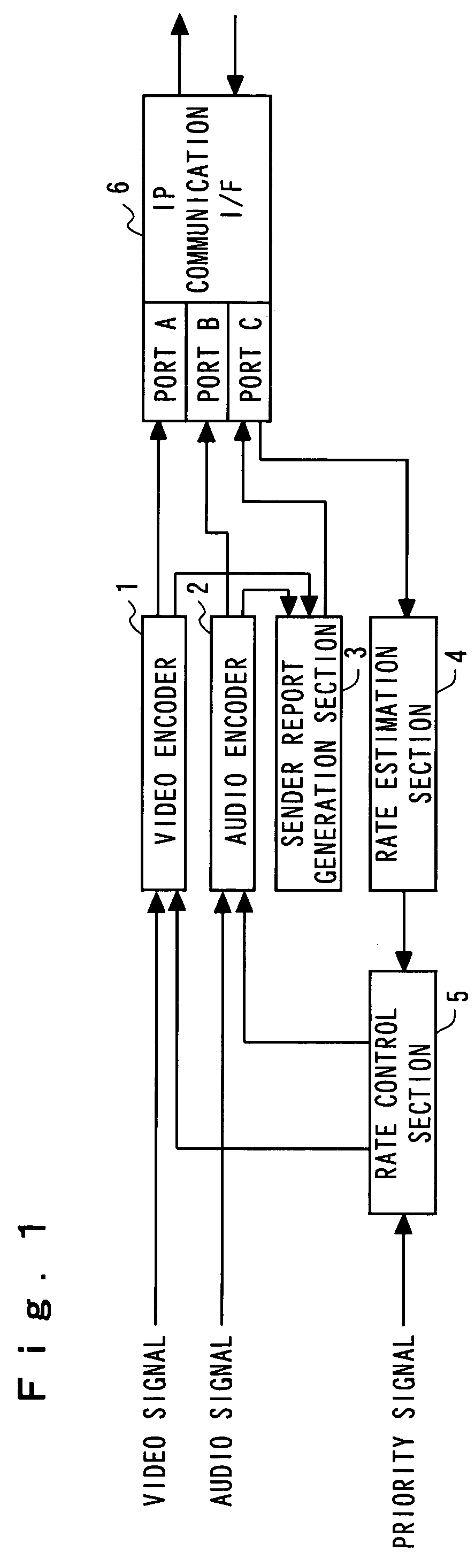
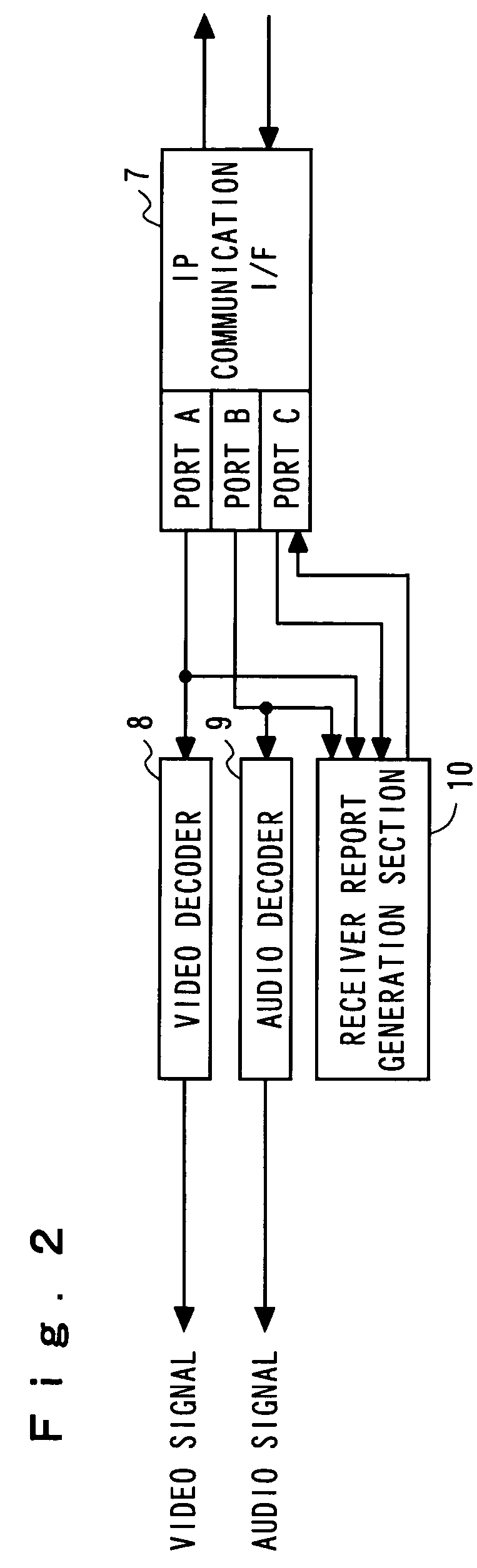
It is made possible to concretely estimate actual transmission bit rate in a frame of grasping a line state by using a report packet.Together with media packets encoded by a video encoder 1 and an audio encoder 2, a sender report packet generated by a sender report generation section 3 is sent to the transmission line. A receiver report packet is fed back from the receiver side. Each of the sender report packet and the receiver report packet includes report packets of two kinds differing in size. A rate estimation section 4 estimates transmission bit rate on the basis of round-trip delay time for the sender report packet and the receiver report packet each having a small size and round-trip delay time for the sender report packet and the receiver report packet each having a large size.
Owner:KDDI R&D LAB INC
High-throughput communication system, communication terminal, session relay, and communication protocol
InactiveUS7760638B2Improve throughputEasy to useTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowCommunications system
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Method of determining a timing offset between a first clock and a second clock in a communications network
InactiveUS7120090B2Mechanical clocksSynchronous motors for clocksRound-trip delay timeBroadcast communication network
Owner:UNIFY GMBH & CO KG
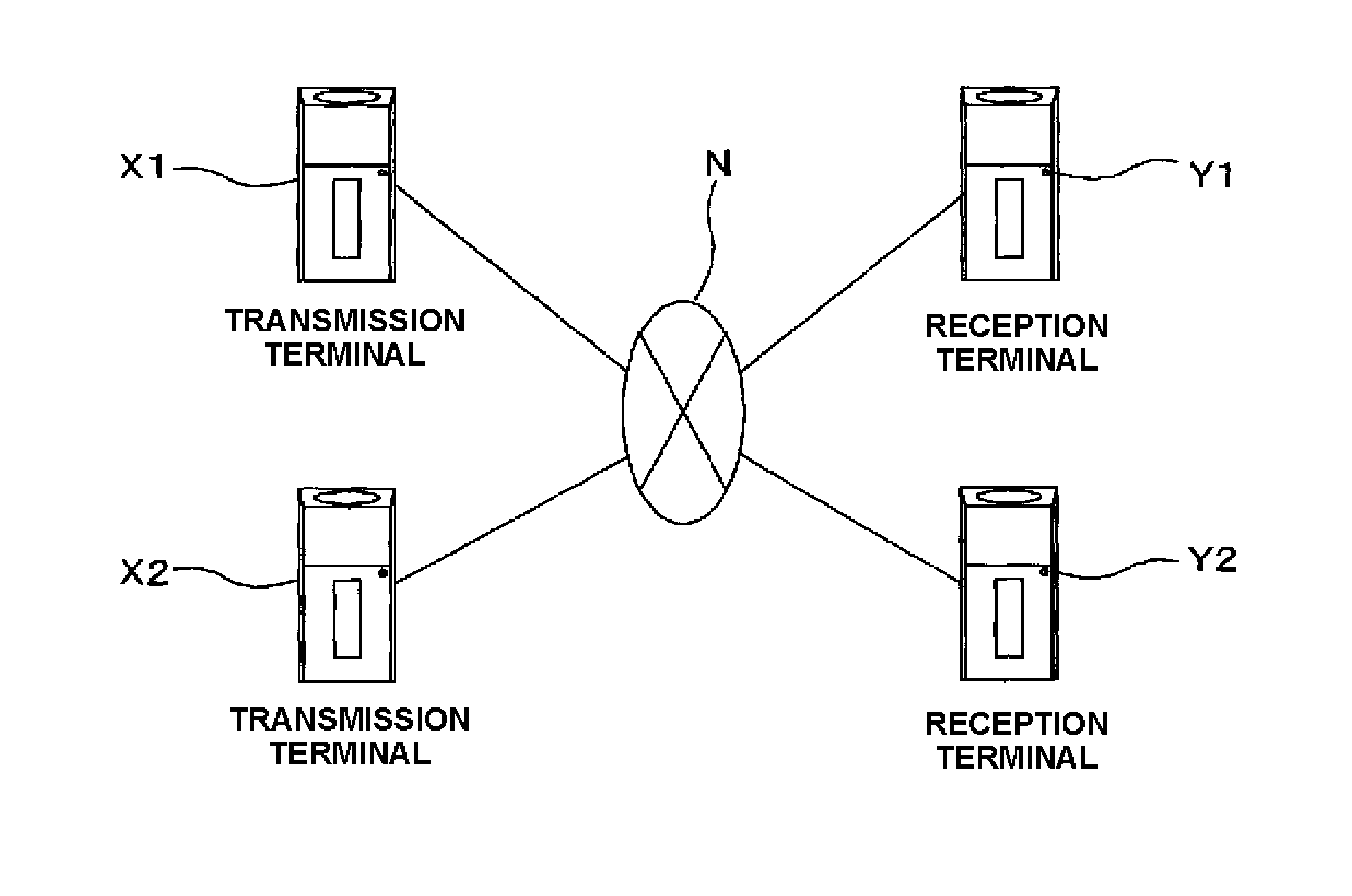
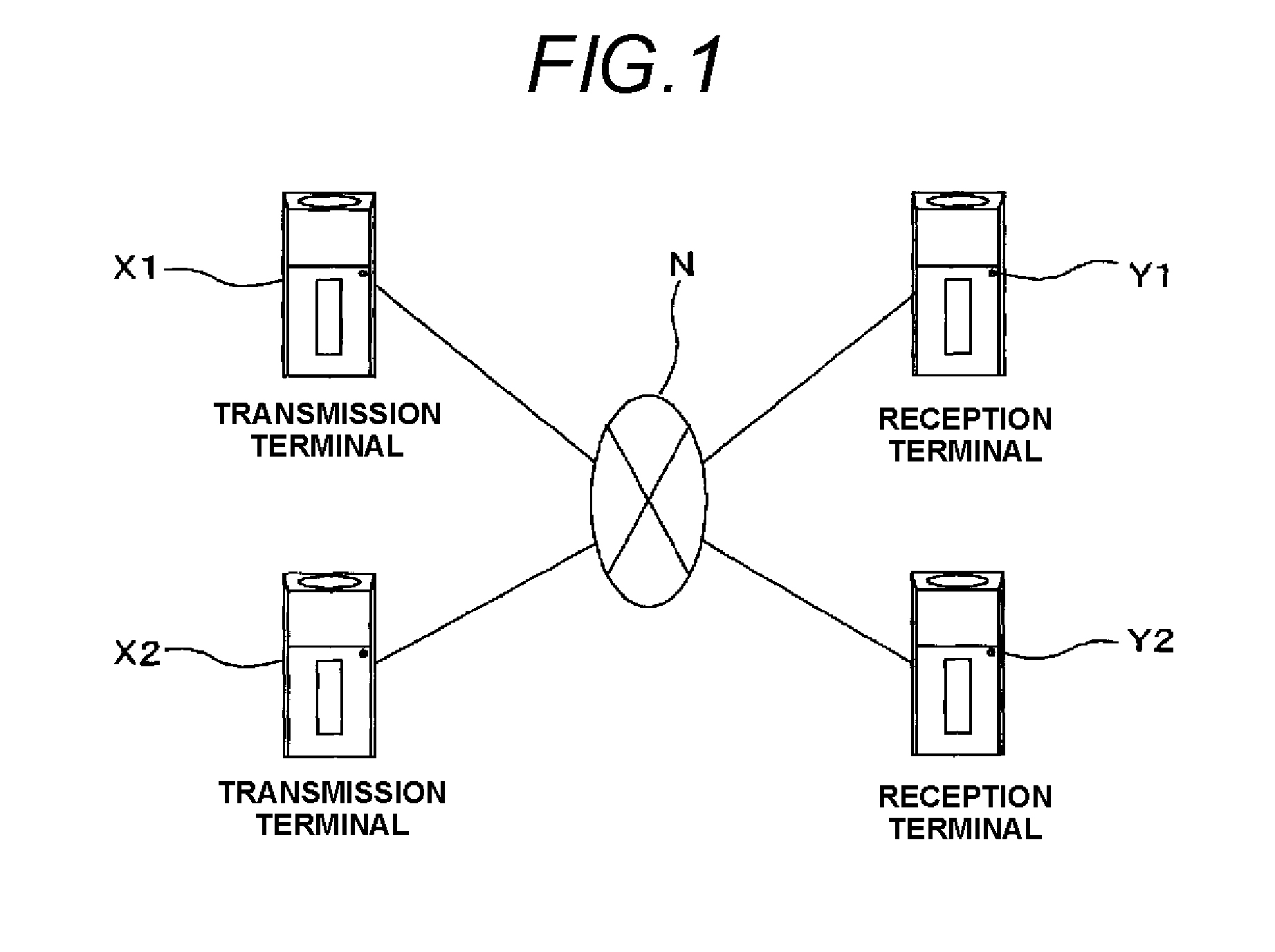
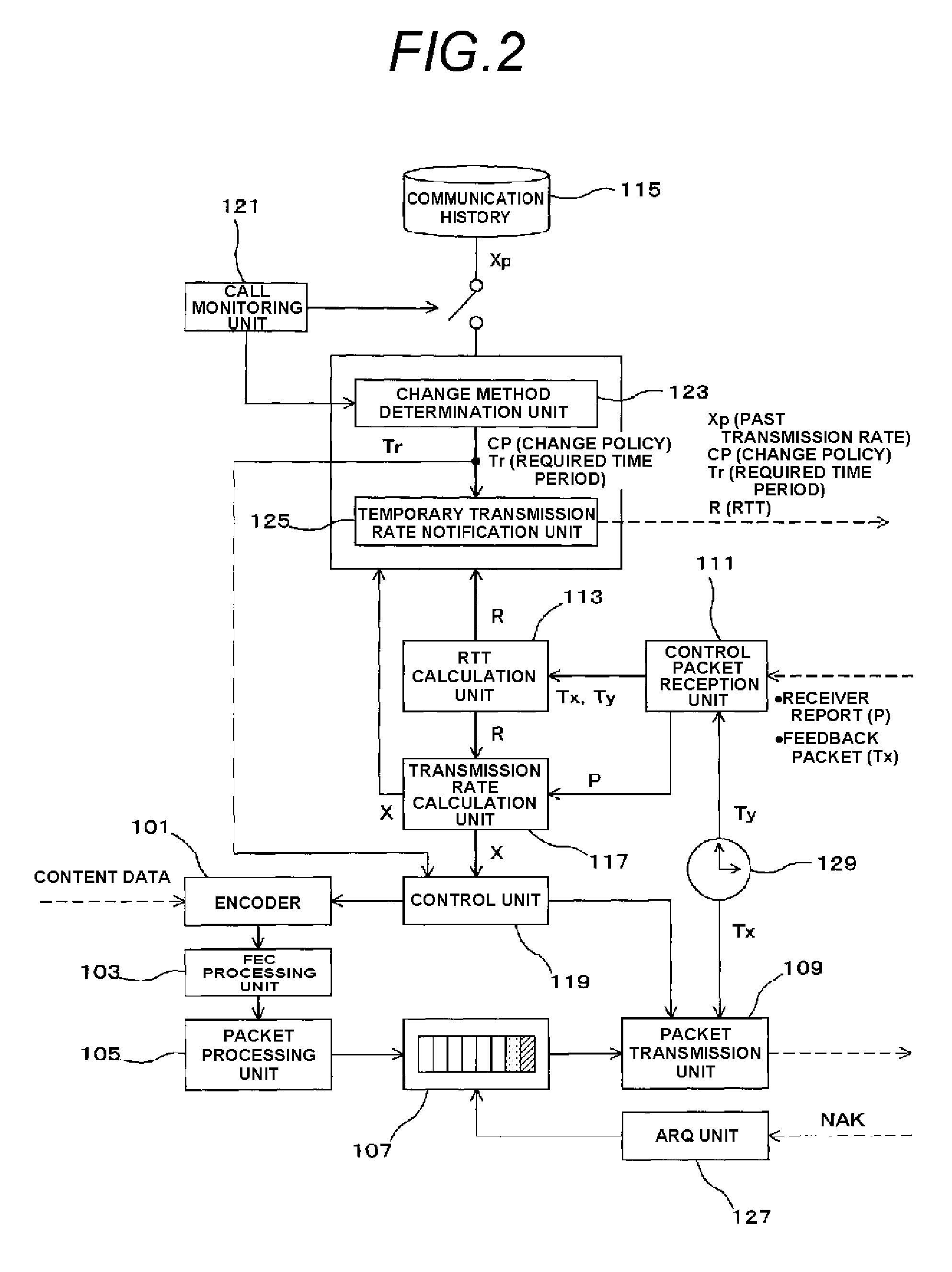
Transmission rate control device and transmission rate control method
ActiveUS20110170417A1Quick changeError preventionTransmission systemsRound-trip delay timeDelayed time
A first communication terminal which communicates with a second communication terminal through a best effort network includes: a communication history storage unit in which a communication history is stored for each of the communication terminals; and a round-trip delay time calculation unit which calculates a round-trip delay time that occurs in a communication with the second communication terminal. The second communication terminal includes a target loss event rate calculation unit which calculates a target loss event rate that is to be set by the first communication terminal in a communication with the second communication terminal, based on a past transmission rate that is recorded in the communication history and has been realized in the communication with the second communication terminal, and on the round-trip delay time that occurs in the communication with the second communication terminal. The first communication terminal changes a transmission rate which is set at the present time to a target transmission rate which is calculated based on the target loss event rate and the round-trip delay time. According to the transmission rate control device, when it is determined that the bandwidth that is estimated to be available in a communication through the network is rapidly changed, the transmission rate can be changed to a target bit rate in a short time period.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of determining a timing offset between a first clock and a second clock in a communications network
InactiveUS20060126437A1Mechanical clocksSynchronous motors for clocksRound-trip delay timeTransmission time
A system for determining a timing offset between a first clock and a second clock at respective first and second points in a communications network. A series of request signals is transmitted from the first point in the network to the second point in the network. A series of reply signals is transmitted from the second point in the network to the first point in the network. Each reply signal and a corresponding reply signal having a minimum round trip delay time are identified and a minimum single leg delay time is determined from the minimum round trip delay time. A timing offset between the clock values of the first clock and the second clock at a first instance is estimated, the estimation being based upon the minimum single leg delay time, and a transmission time and a reception time of one of the identified request signal and the corresponding reply signal, as given by the respective clocks at the transmission and reception points of the signal.
Owner:UNIFY GMBH & CO KG
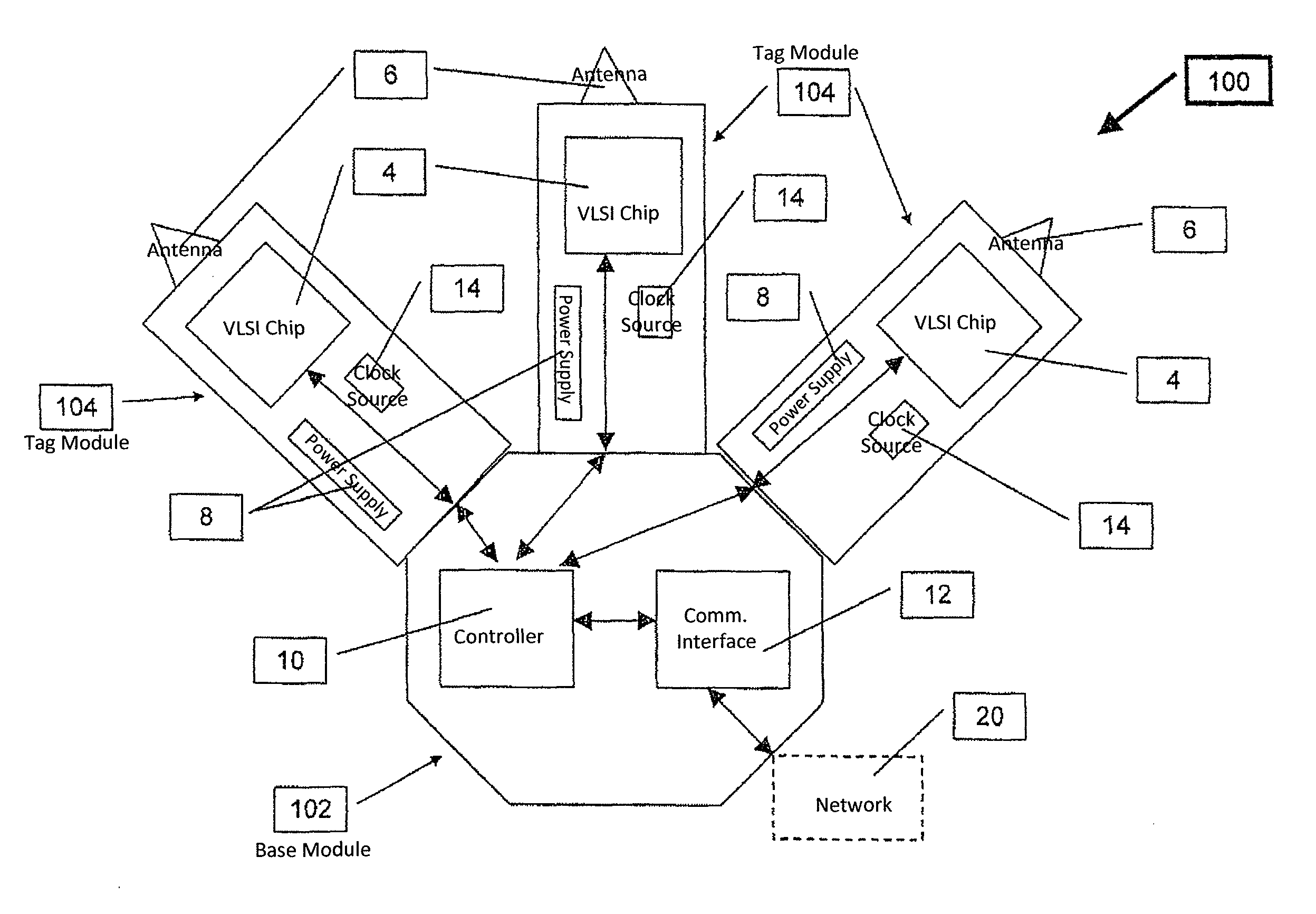
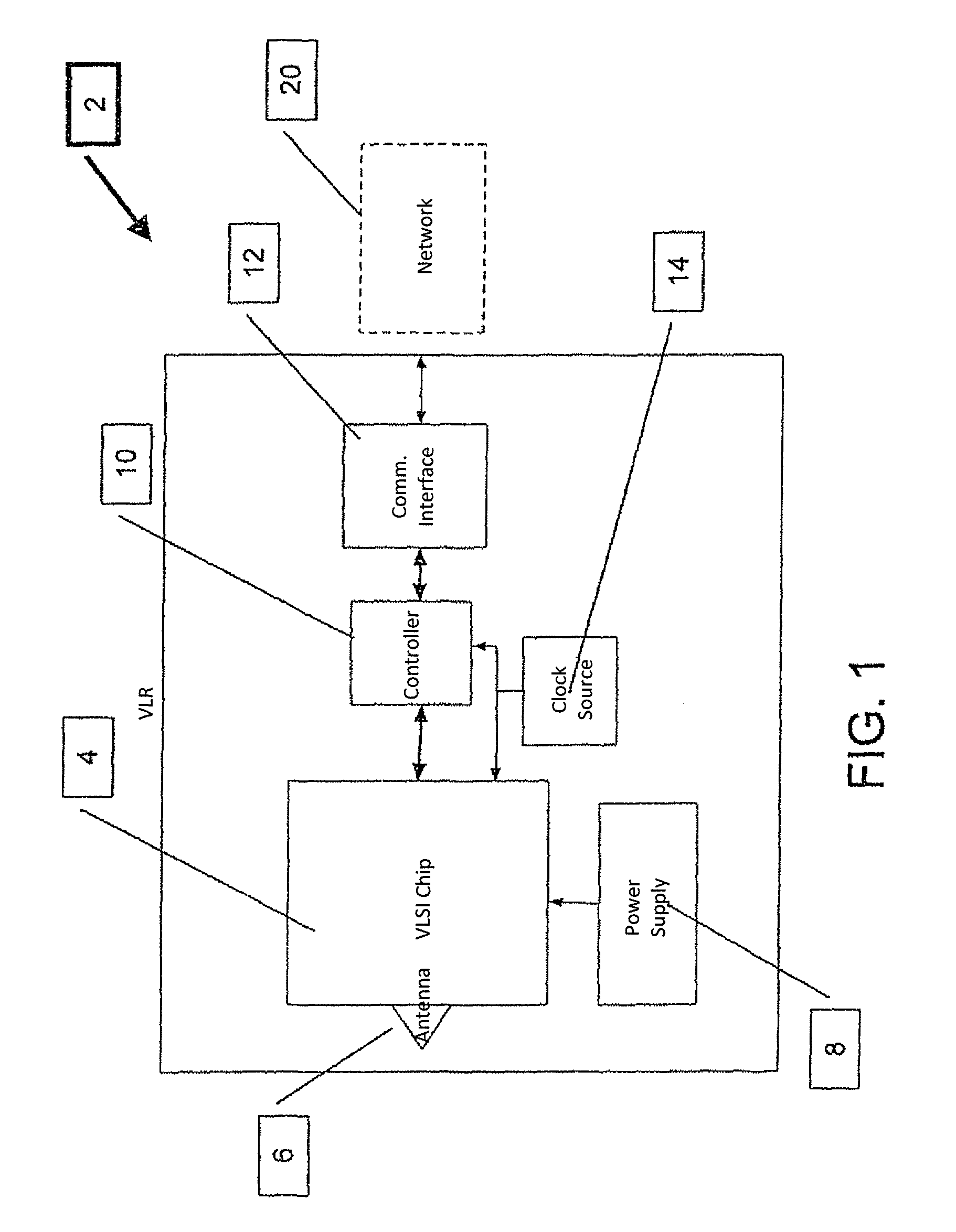
Array of very light readers for active RFID and location applications
ActiveUS20100164690A1Improve Backhaul reliabilityReduce collisionSensing record carriersSubscribers indirect connectionData packCommunication interface
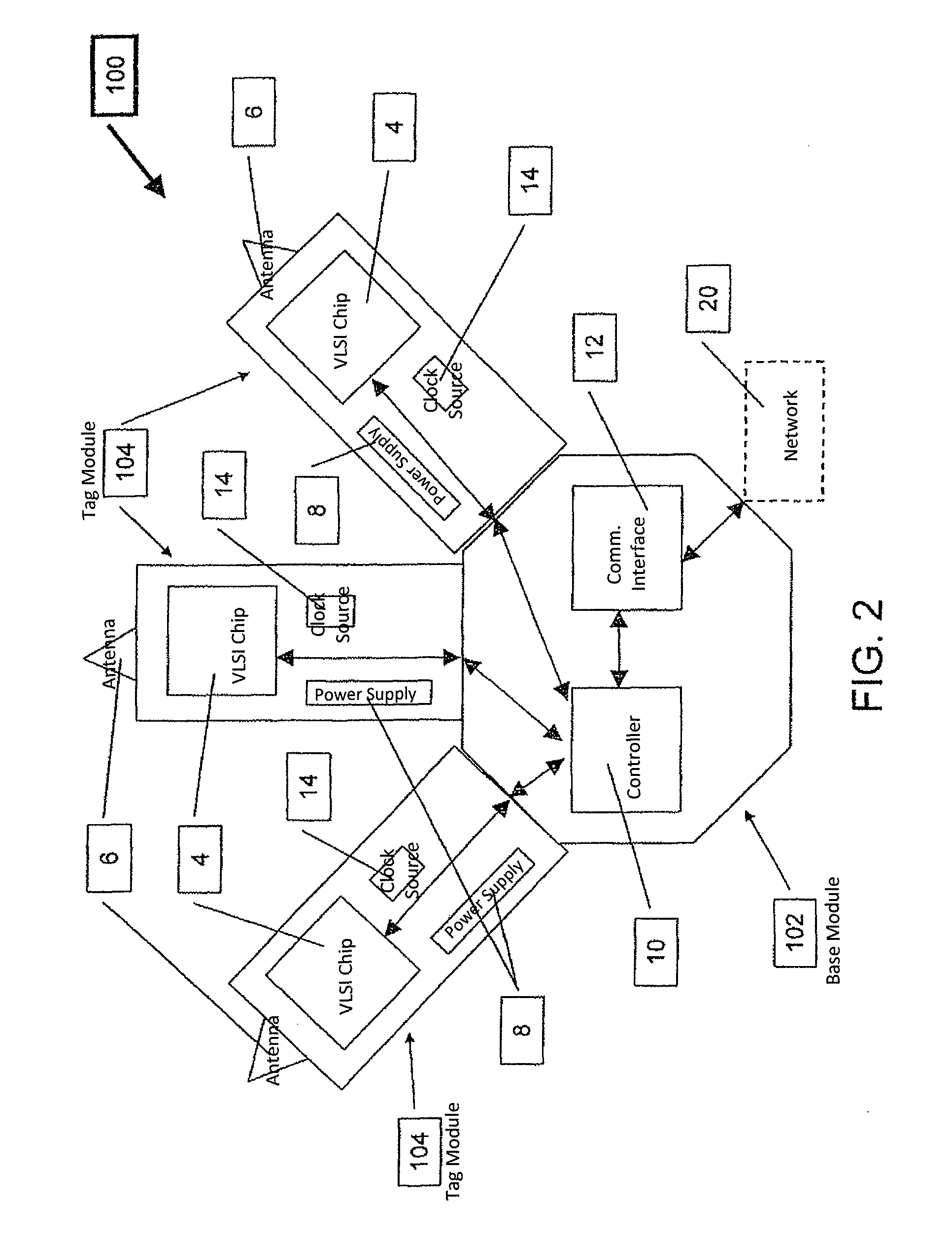
The Very Light Readers of the present invention are based on an augmented Tag circuit with a preferred embodiment including at least one VLSI chip integrating a UWB front end, digital transceiver, and possibly an internal controller; a UWB Antenna; a power supply; a controller configured to implement the Media Access Control protocol of the system; a Communication Interface subsystem for connection to the system network and a clock source. Also described is a system capable of reducing collision occurrence in a network for communicating between multiple readers and a plurality of RF Tags. Tags are configured to receive interrogation signals and transmit response signals. Readers are configured to transmit interrogation signals, receive response signals, estimate the quantity of responses received to an interrogation, determine the round trip delay time of each response and estimates whether a collision between responses has occurred. If so, the Reader transmits an additional interrogation signal. The Reader also transmits an acknowledgment packet to responding Tags so responding Tag will not answer again to that broadcast session. Other Readers in the network also receive the acknowledge packet and do not try again to reach the responding Tags, thereby lowering congestion directed toward Tags from multiple Reader transmissions.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
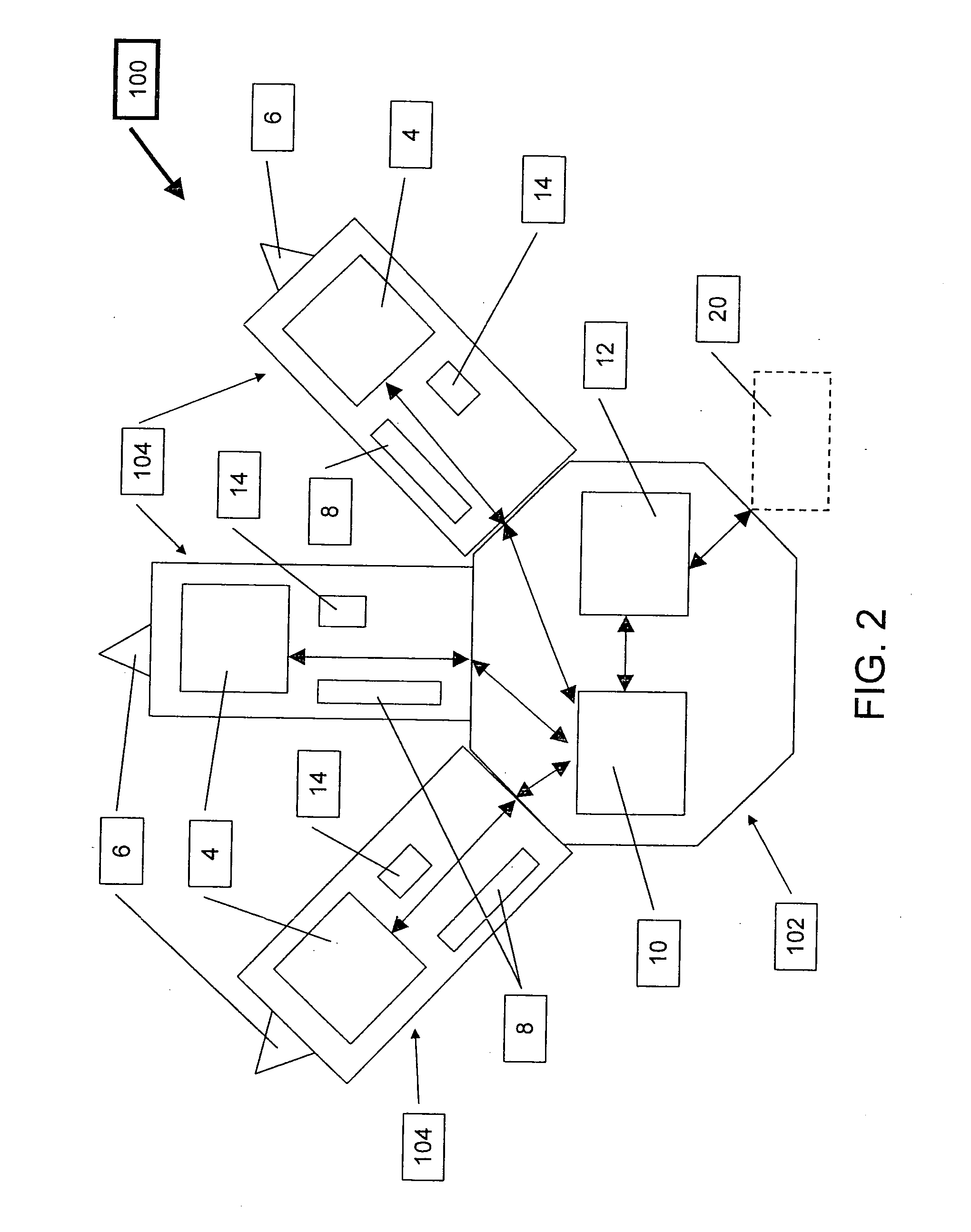
Communications terminal, communications method, and program and integrated circuit for communication
ActiveUS20120158818A1Quality improvementMultiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionRound-trip delay timeMulticast
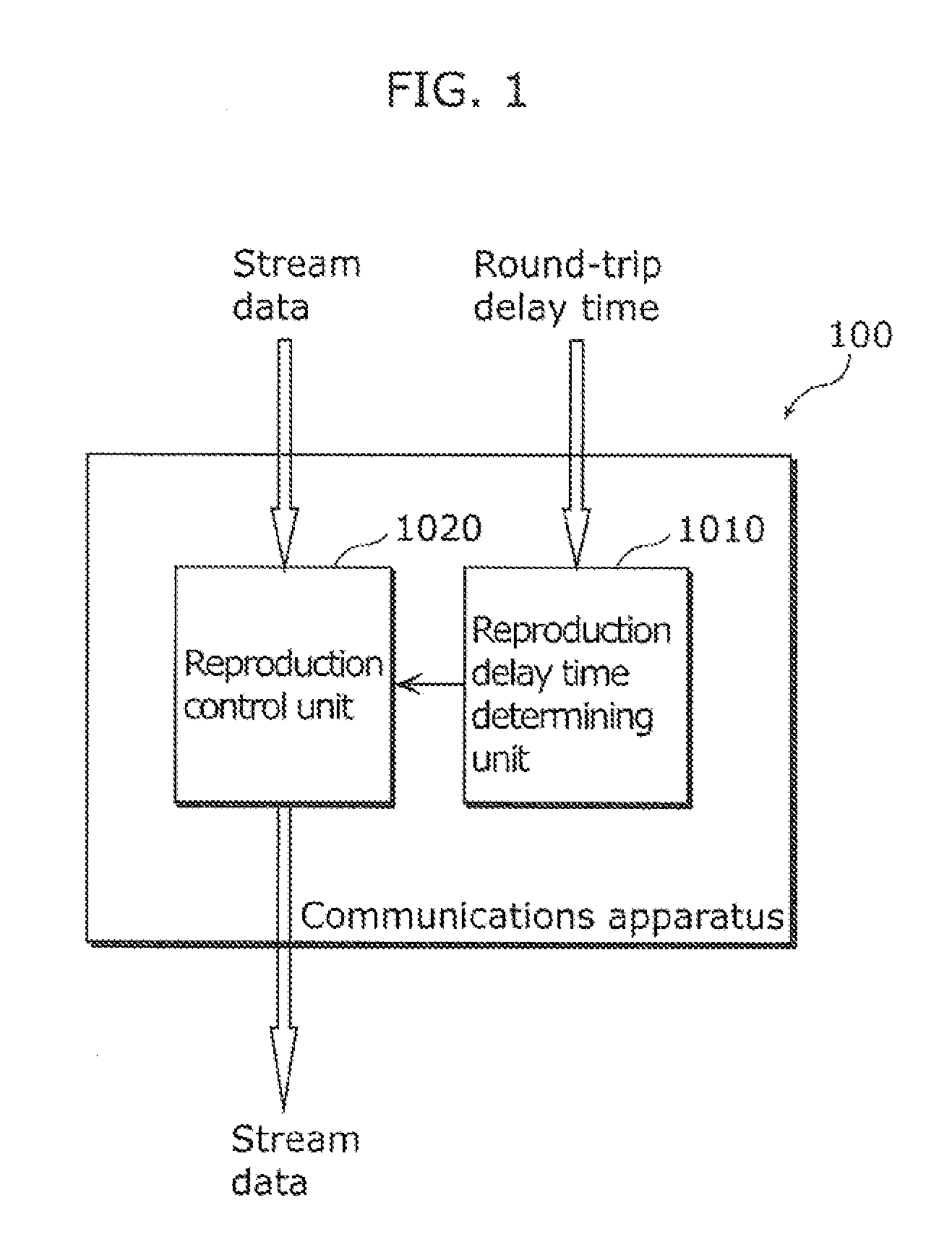
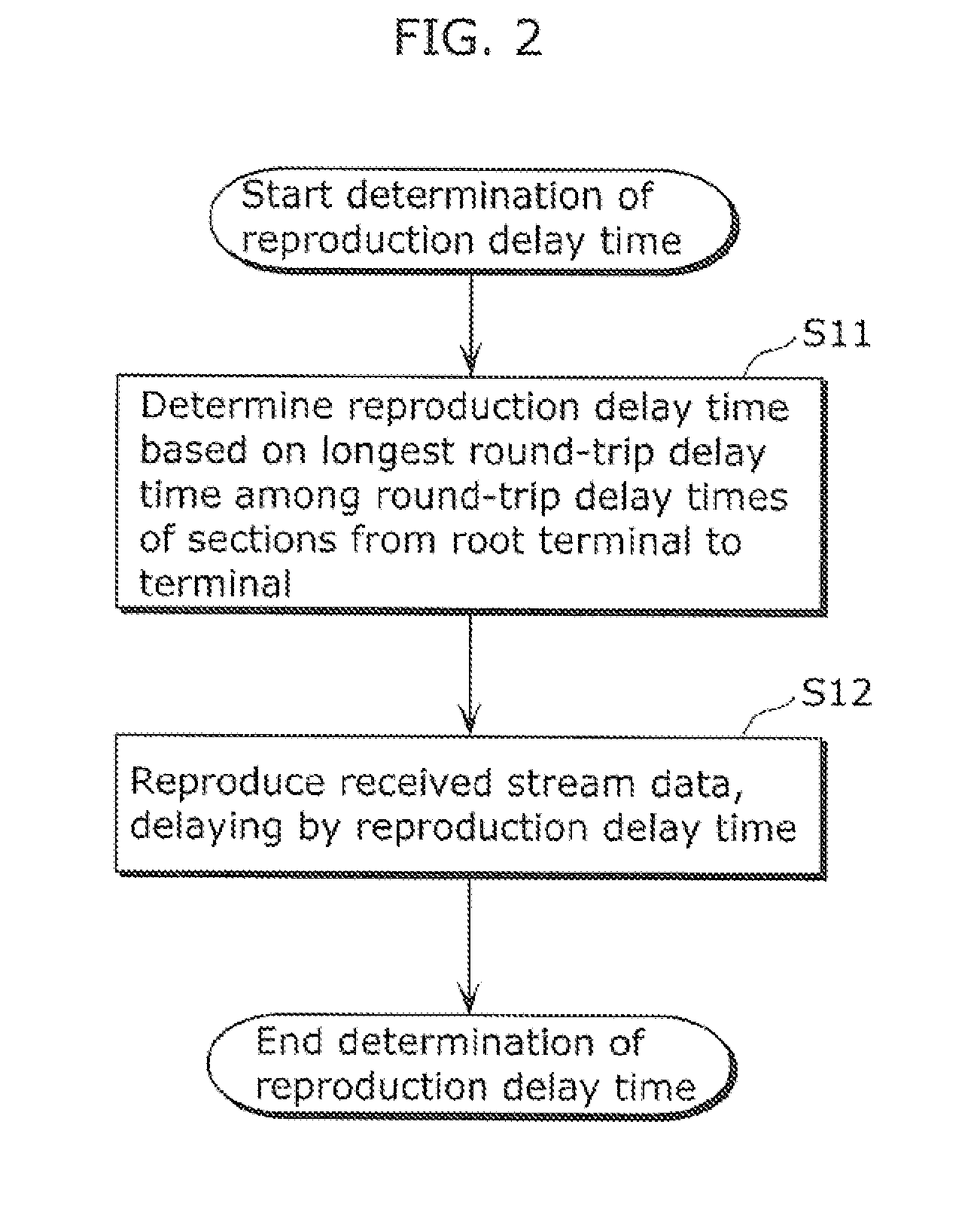
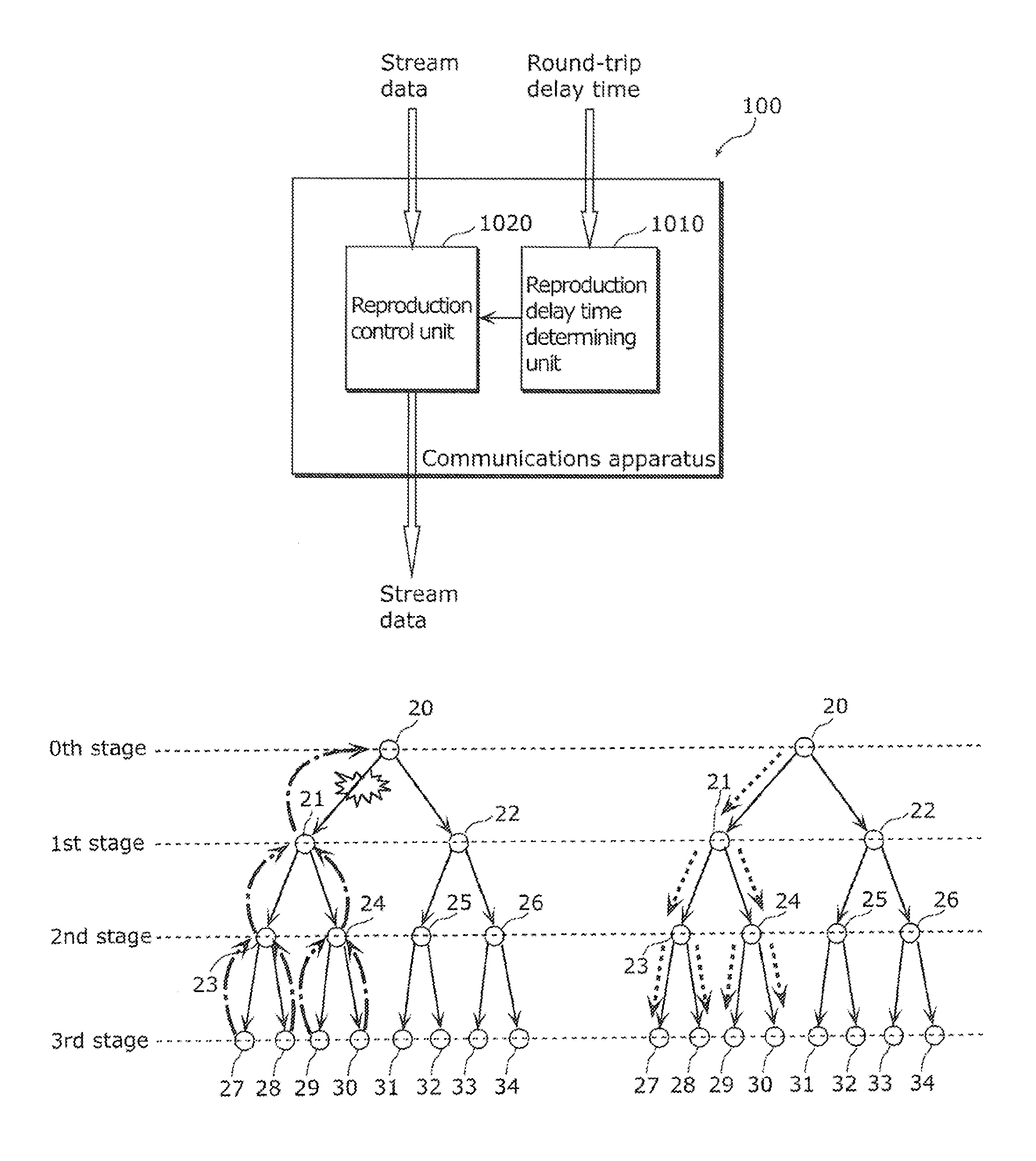
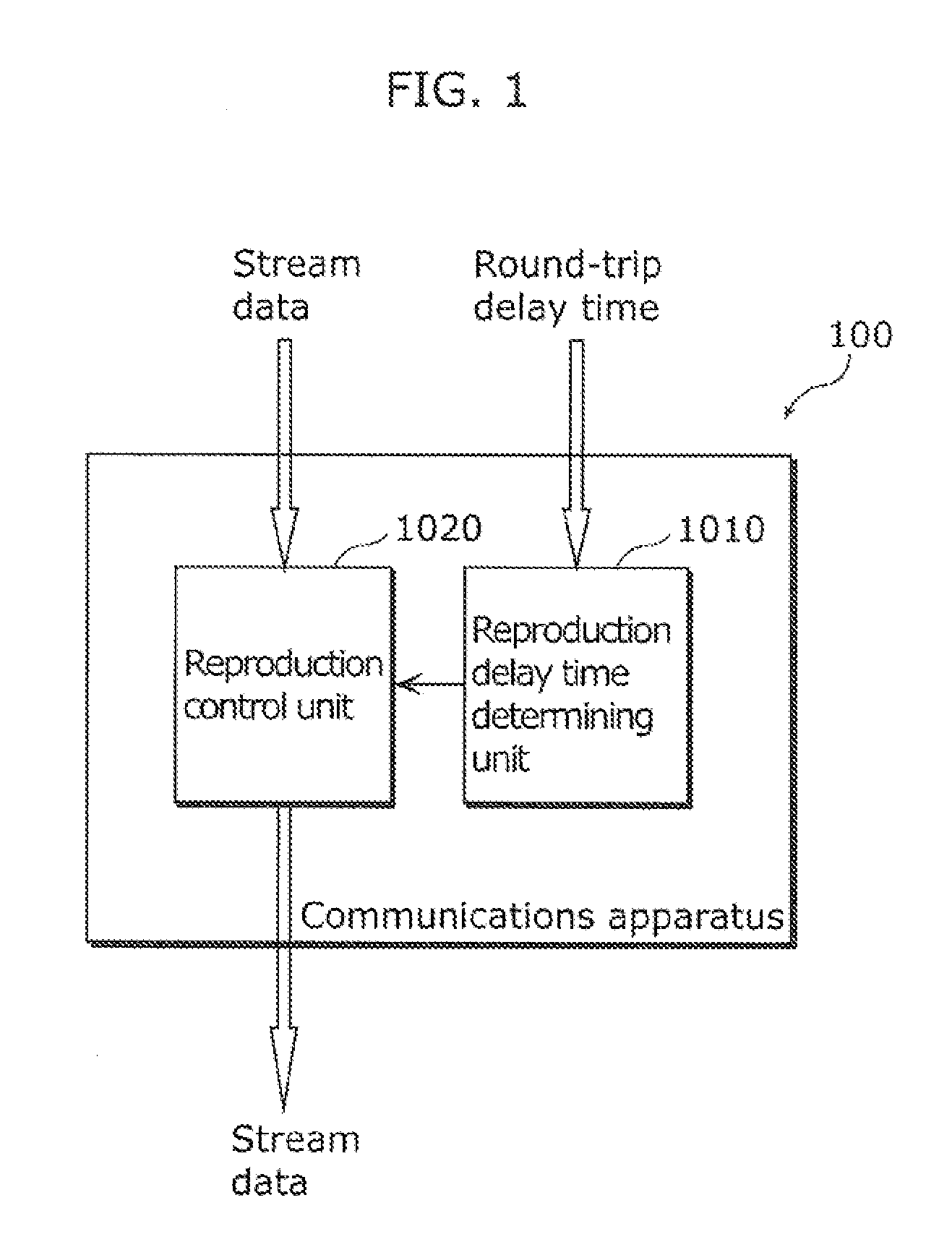
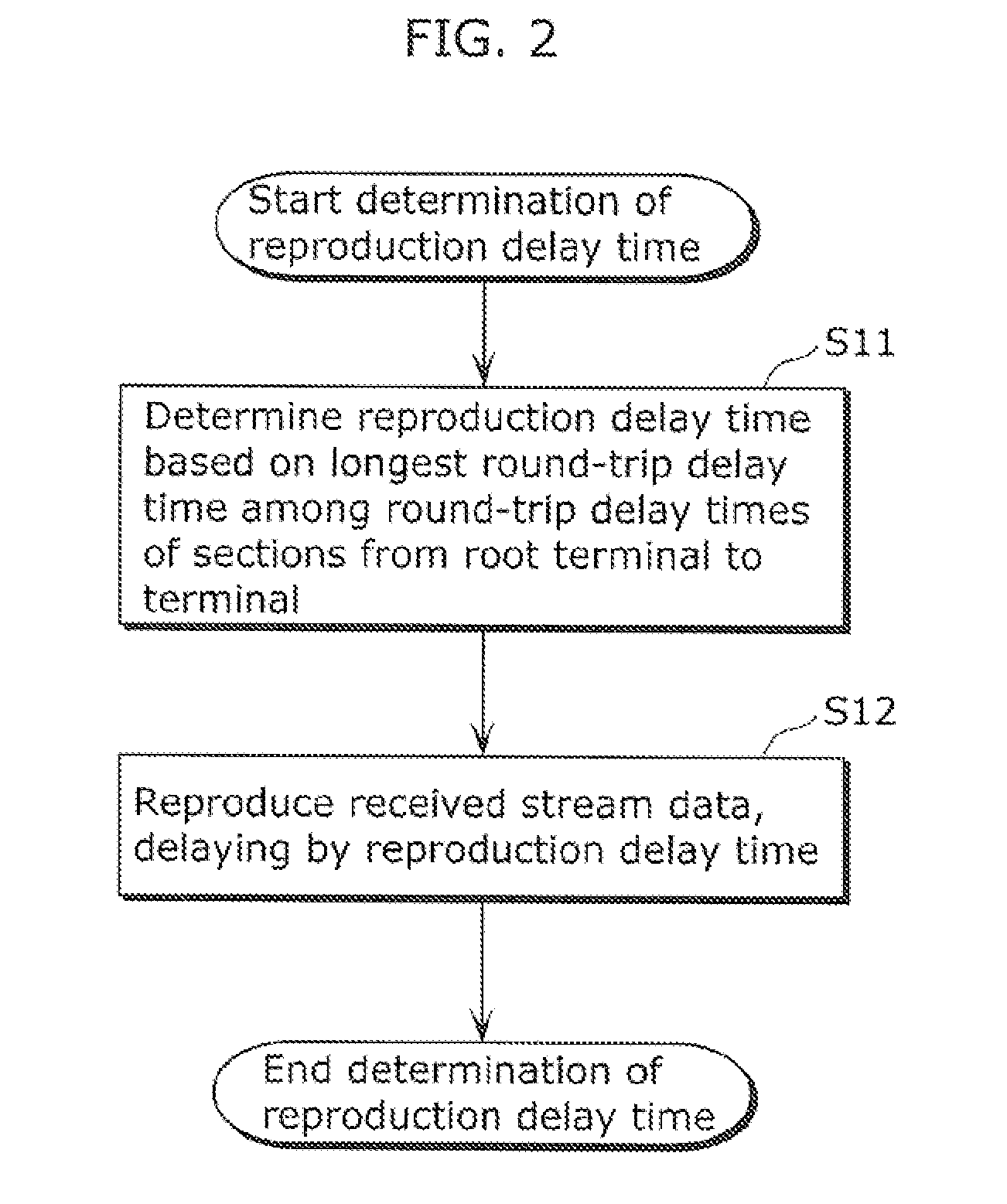
A communication terminal (100) is one of communication terminals each having one parent terminal and zero or more child terminals. The communication terminals form an Application Layer Multicast (ALM) tree to sequentially distribute retransmission data of stream data from the parent terminal to the child terminal. The communications terminal (100) includes: a reproduction delay time determining unit (1010) determining a reproduction delay time based on a longest round-trip delay time among round-trip delay times of sections between a root terminal and the communications terminal (100), each of the round-trip delay times being required for transmission and reception of data through one of the sections between two neighboring terminals of the communications terminals on the ALM tree; and a reproduction control unit (1020) reproducing the stream data received from the root terminal, with the stream data delayed by the reproduction delay time determined by the reproduction delay time determining unit (1010).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
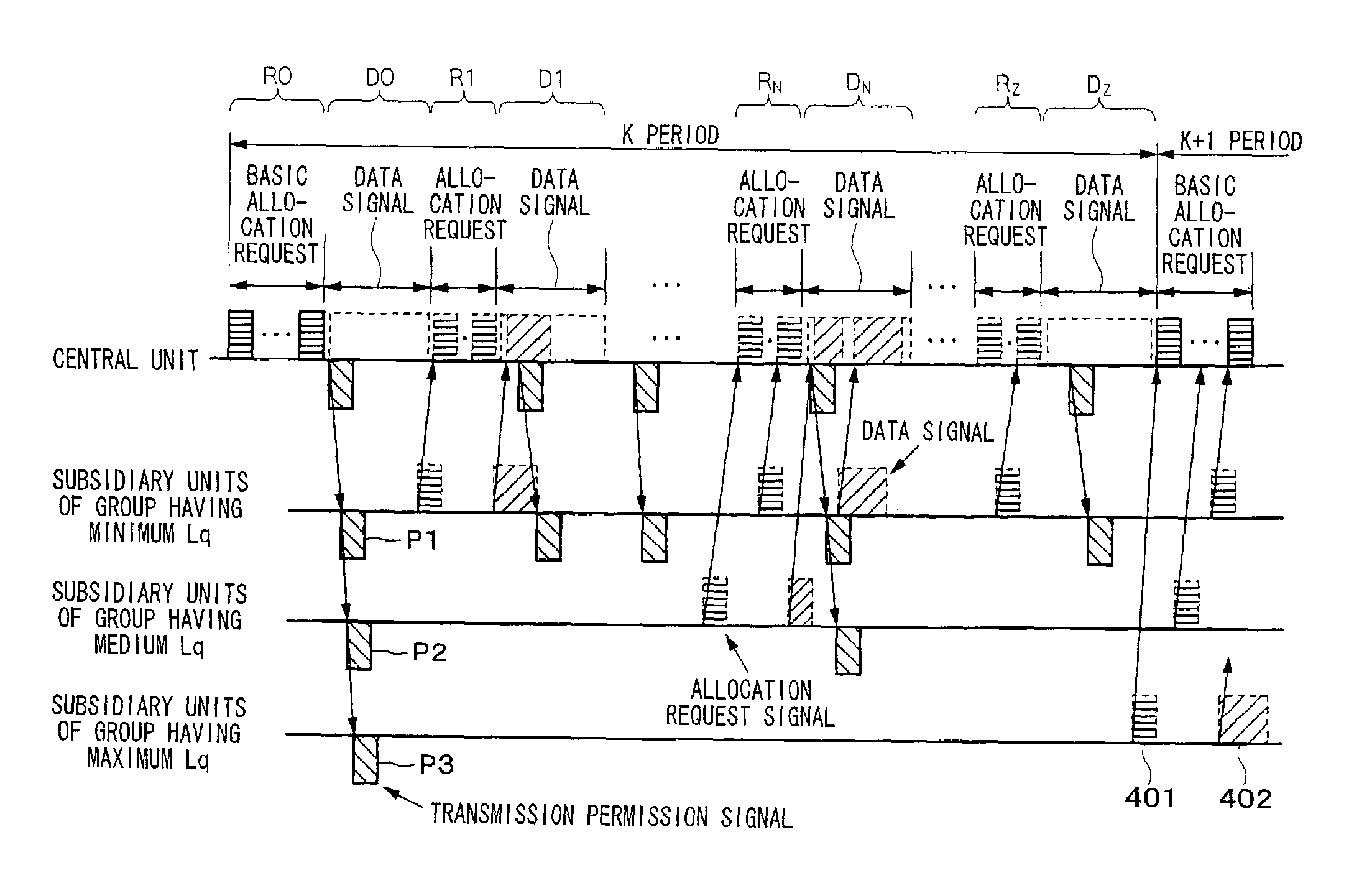
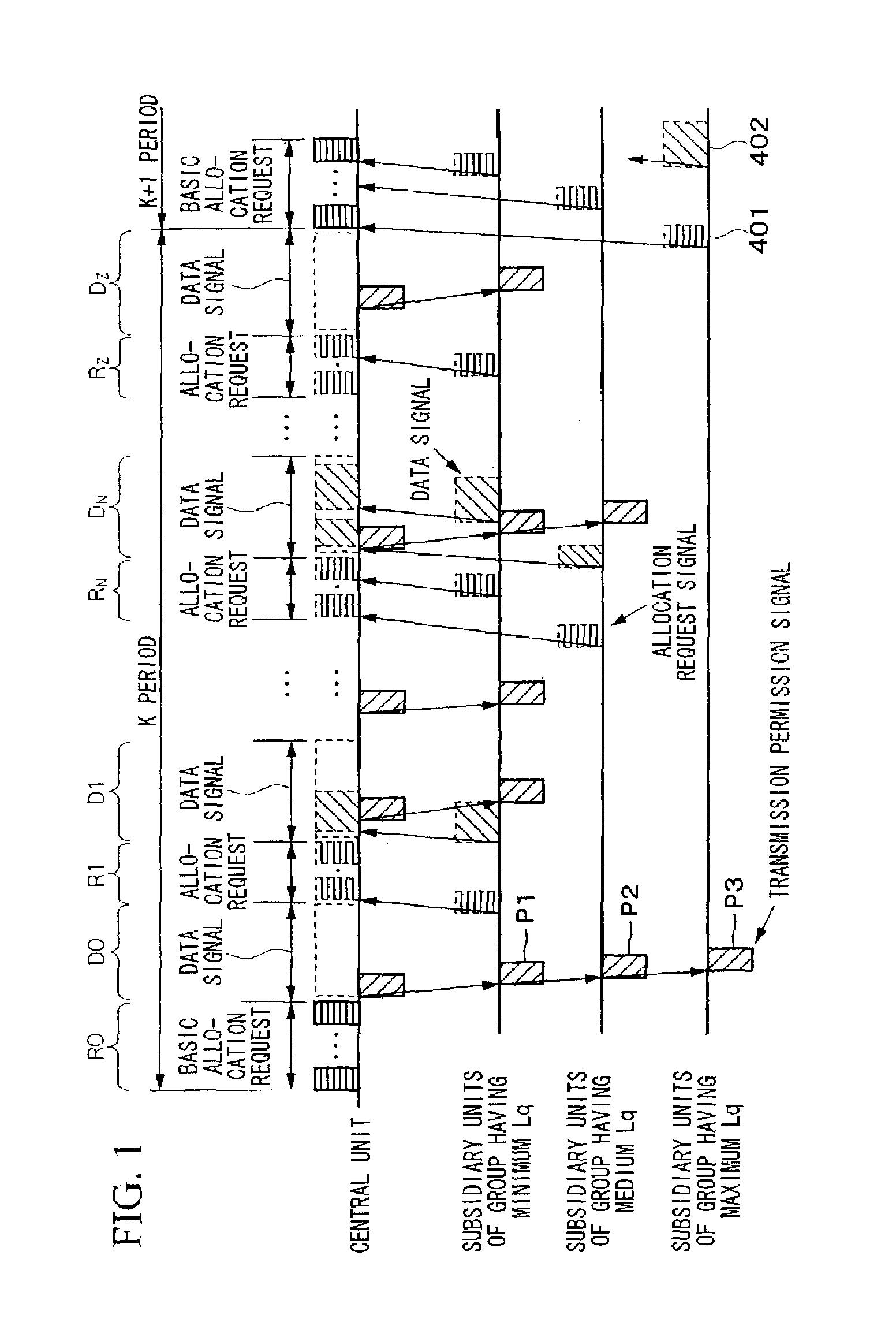
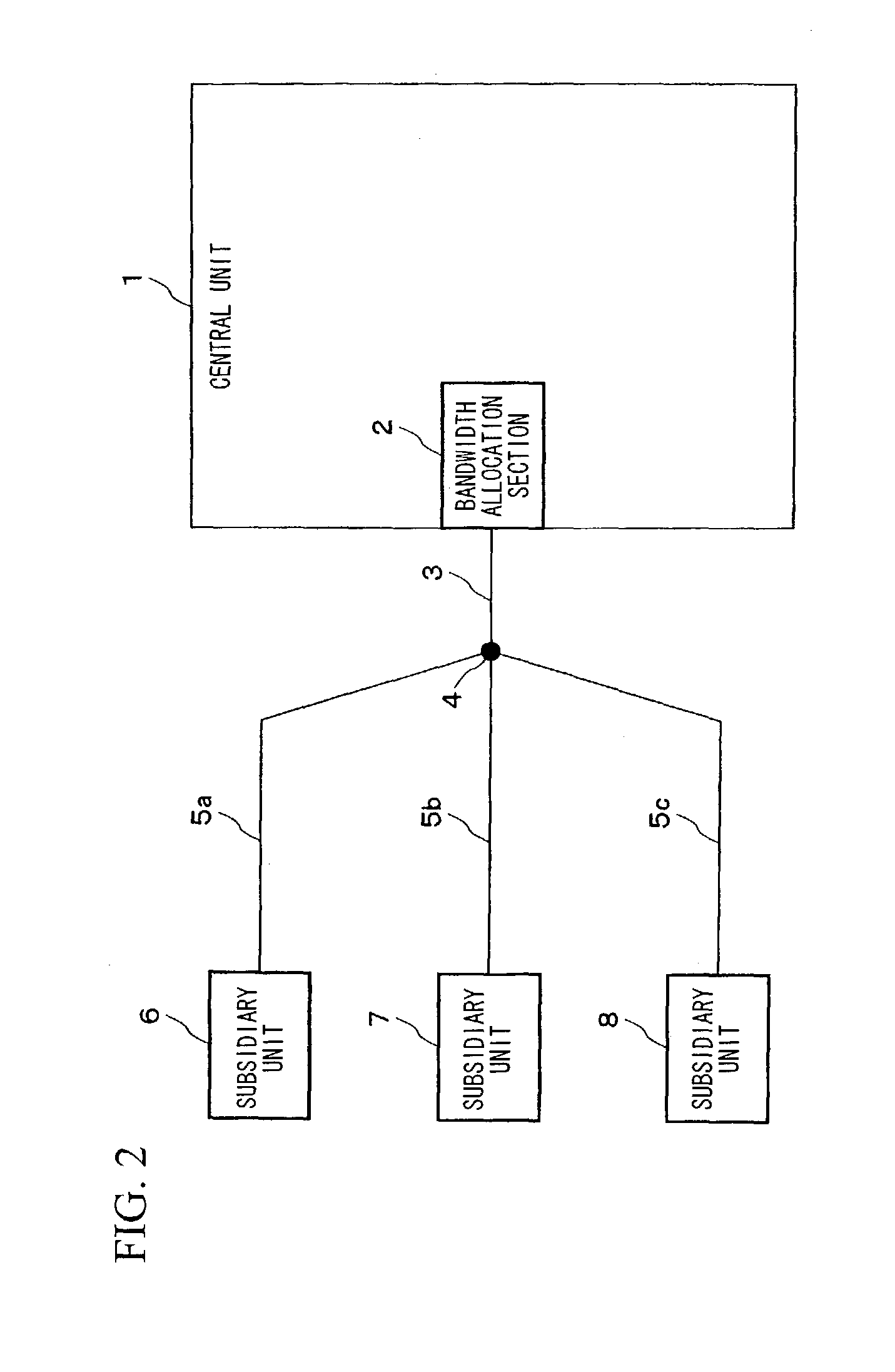
Bandwidth allocation method in point-to-multipoint communication system
ActiveUS7260116B2Easy to useReduce latencyTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexPropagation delayData signal
A bandwidth allocation method used in a point-to-multipoint communication system, for efficiently using the bandwidth while shortening delay time. A central unit quantizes round-trip propagation delay times of subsidiary units, groups the subsidiary units, assigns the same quantized round-trip delay time to the same group, and allocates allocation request signal bandwidths to the subsidiary units of the same group when receiving allocation requests within a predetermined period. Based on the quantized round-trip delay time, the bandwidths are located as close as possible while the bandwidths do not temporally overlap with each other and as temporally ahead as possible. Data signal bandwidths are also allocated to the subsidiary units of the same group, based on the quantized round-trip delay time and requested amounts of data, in a manner such that the bandwidths are located as temporally ahead as possible but temporally behind in comparison with the allocation request signal bandwidths.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
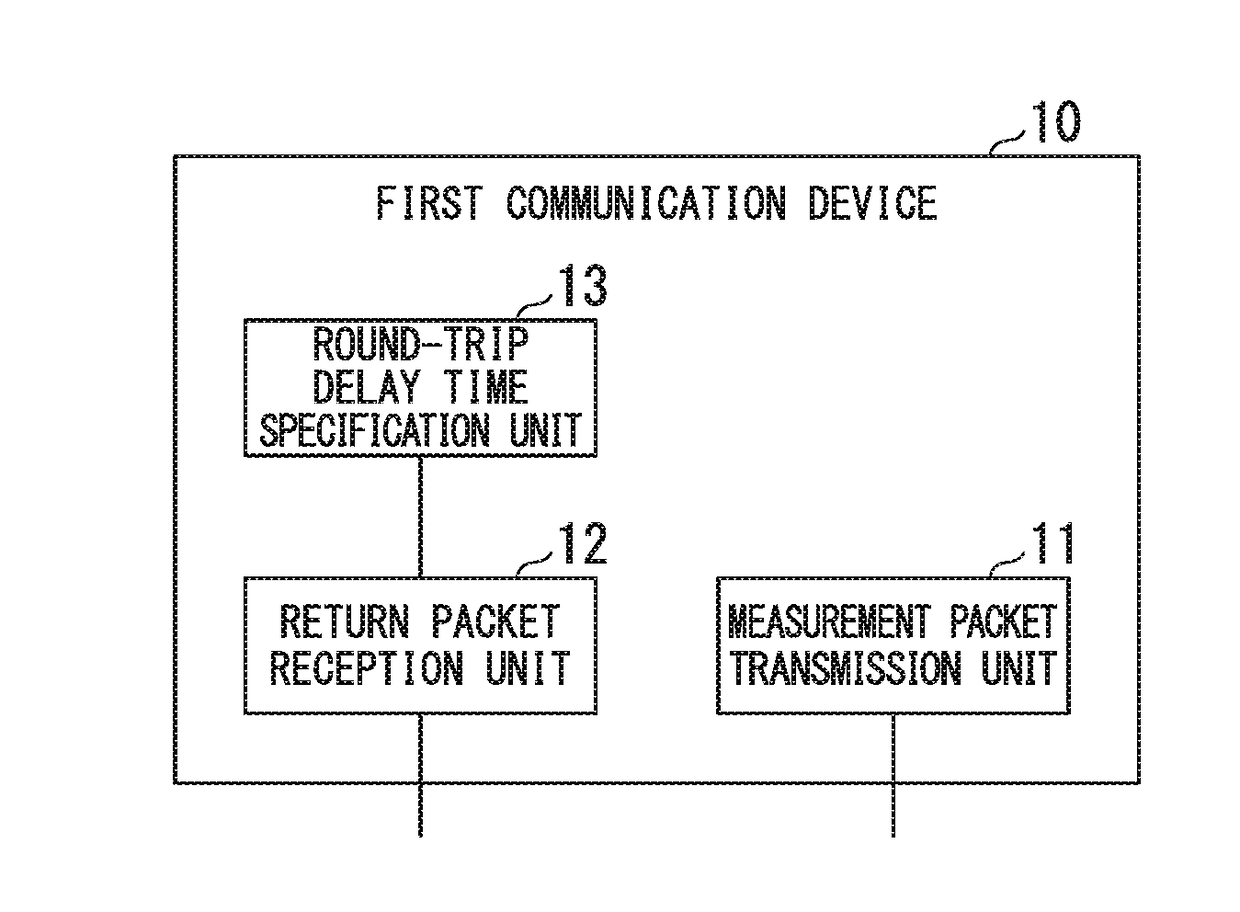
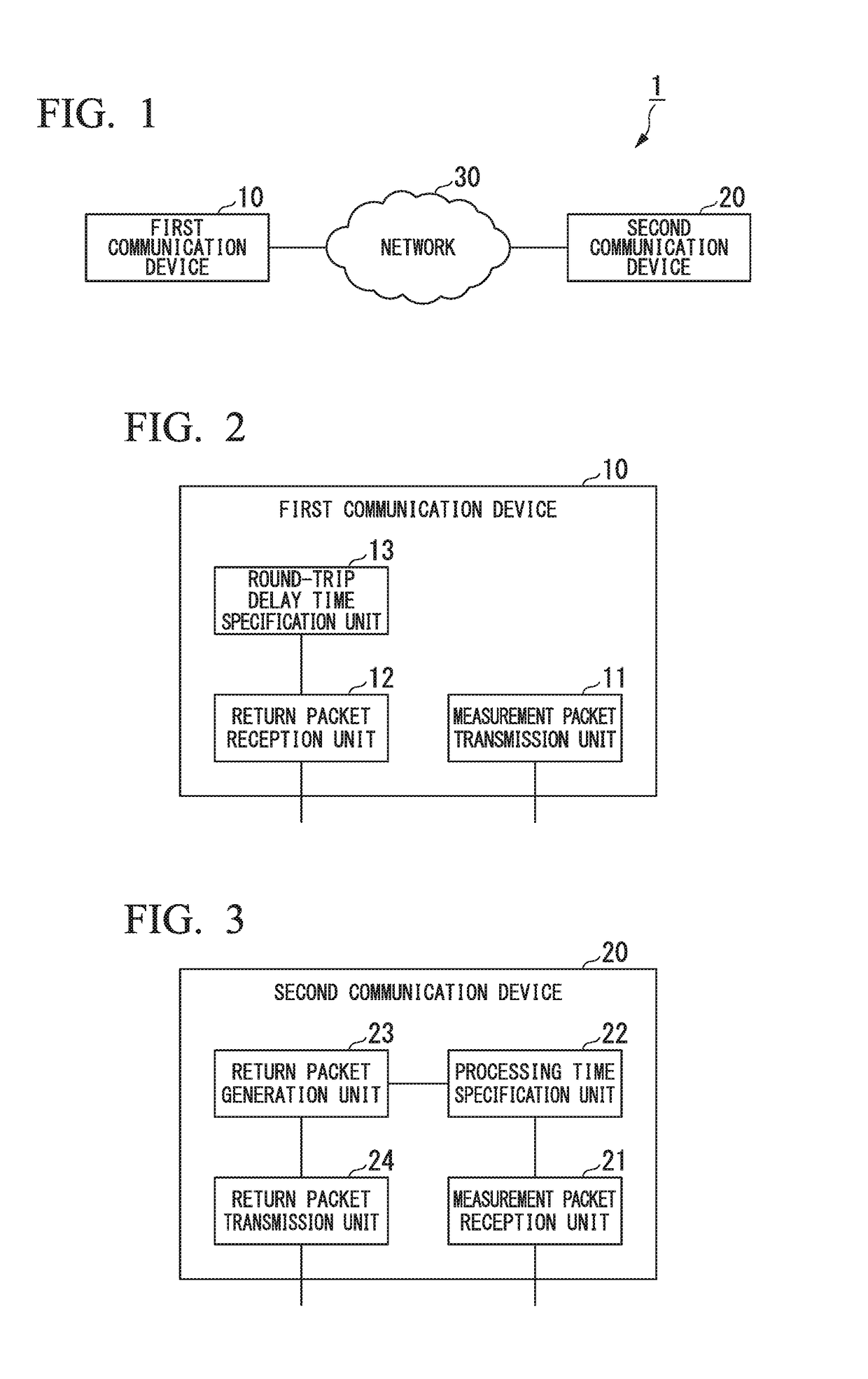
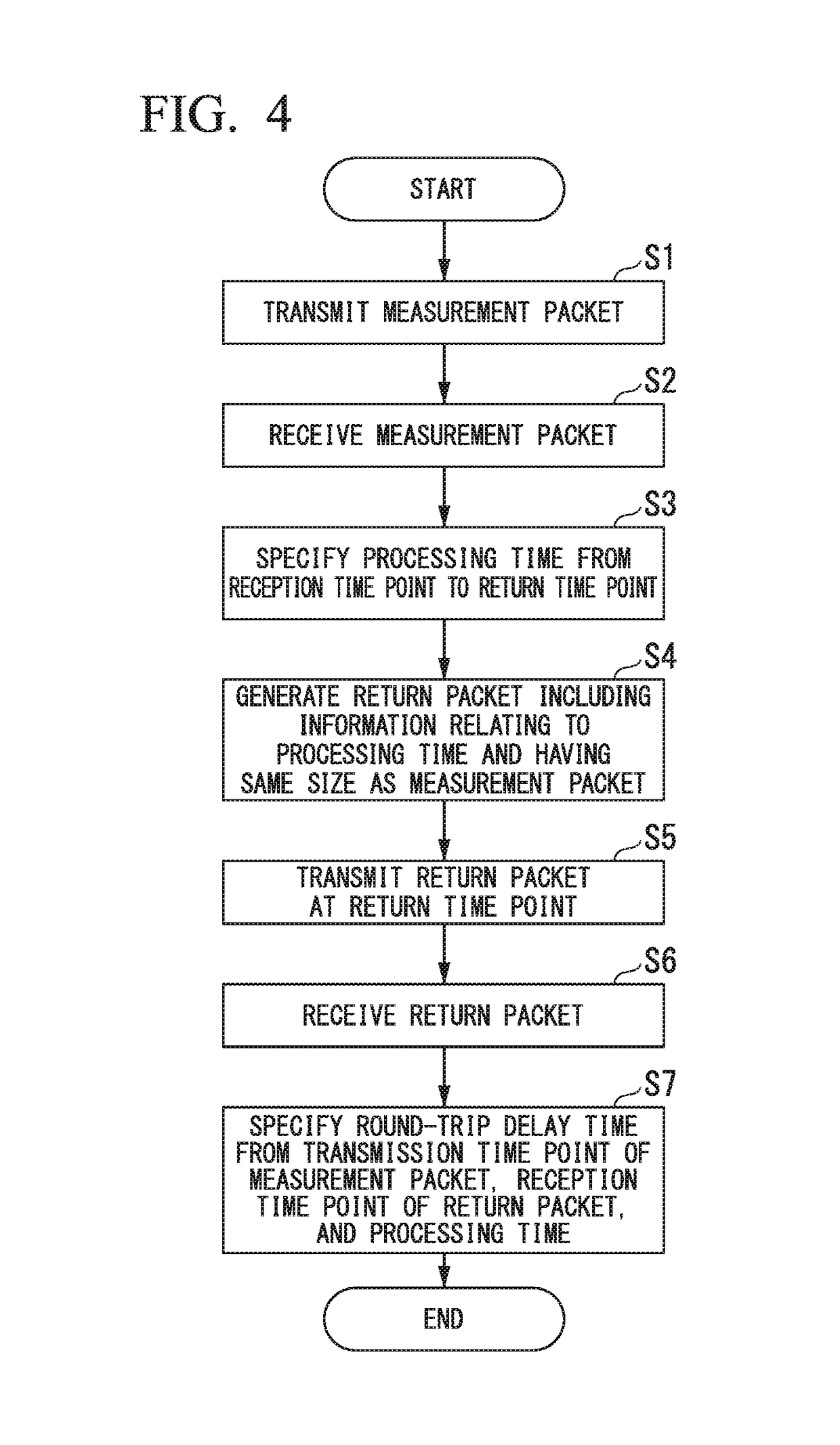
Round-trip delay time measurement system, round-trip delay time measurement method, return method, communication device, program, and data structure
ActiveUS20170353372A1Accurate measurementData switching networksRound-trip delay timeCommunication device
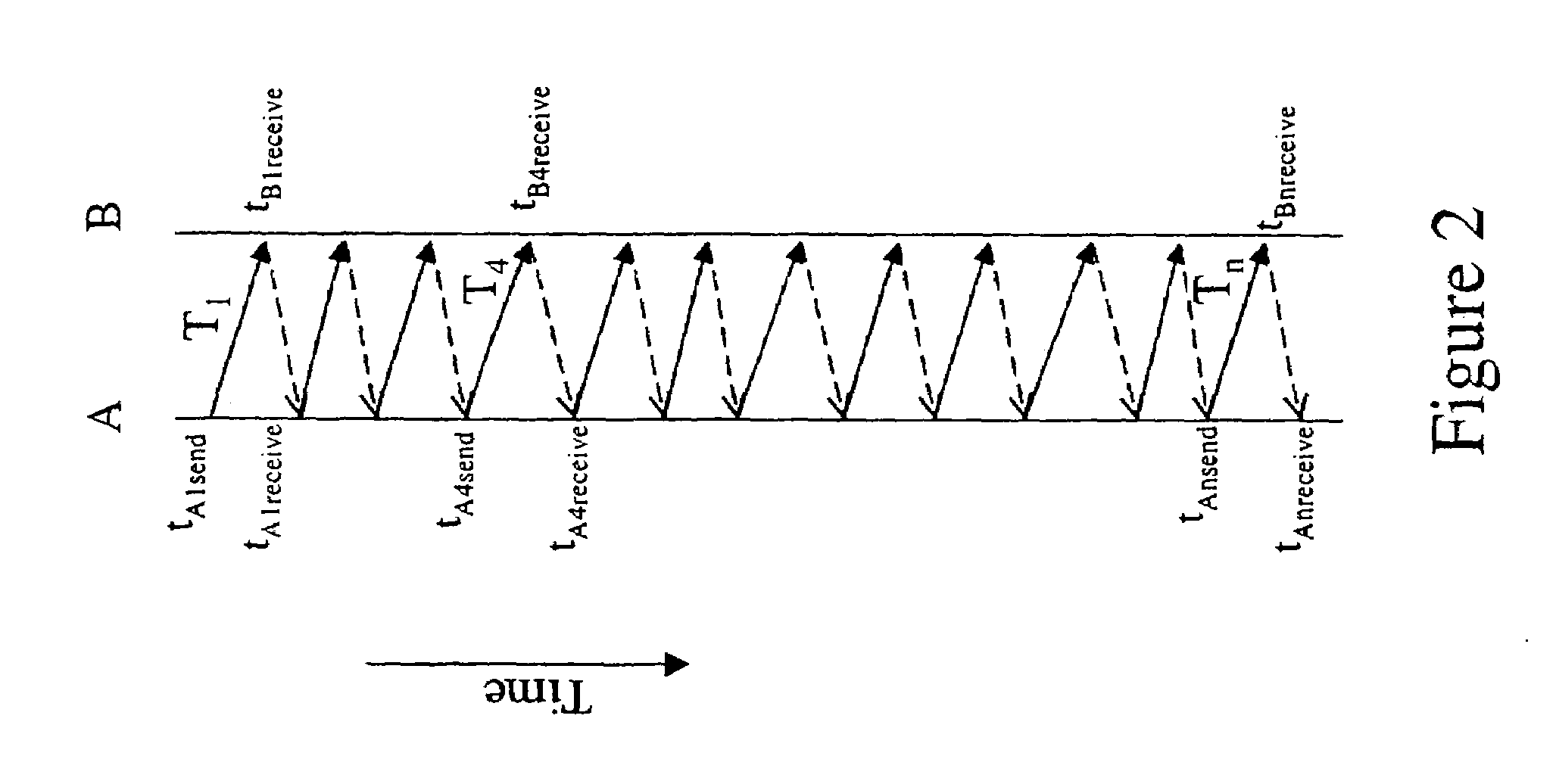
A communication device performs communication with an external device. The communication device includes: a measurement packet transmission unit that transmits a measurement packet at a first transmission time point; a return packet reception unit that receives a return packet at a second reception time point, the return packet being transmitted as a reply to the measurement packet at a second transmission time point by the external device, the return packet including information relating to a processing time indicating a duration from a first reception time point at which the measurement packet is received by the external device, to the second transmission time point, the return packet having a same packet size as the measurement packet; and a delay time specification unit that specifies, as a round-trip delay time, a duration obtained by subtracting the processing time from a duration from the first transmission time point to the second reception time point.
Owner:NEC CORP
Array of very light readers for active RFID and location applications
ActiveUS9307554B2Low costImprove rendering capabilitiesCo-operative working arrangementsSubscribers indirect connectionCommunication interfaceTransceiver
The Very Light Readers of the present invention are based on an augmented Tag circuit with a preferred embodiment including at least one VLSI chip integrating a UWB front end, digital transceiver, and possibly an internal controller; a UWB Antenna; a power supply; a controller configured to implement the Media Access Control protocol of the system; a Communication Interface subsystem for connection to the system network and a clock source. Also described is a system capable of reducing collision occurrence in a network for communicating between multiple readers and a plurality of RF Tags. Tags are configured to receive interrogation signals and transmit response signals. Readers are configured to transmit interrogation signals, receive response signals, estimate the quantity of responses received to an interrogation, determine the round trip delay time of each response and estimates whether a collision between responses has occurred. If so, the Reader transmits an additional interrogation signal. The Reader also transmits an acknowledgment packet to responding Tags so responding Tag will not answer again to that broadcast session. Other Readers in the network also receive the acknowledge packet and do not try again to reach the responding Tags, thereby lowering congestion directed toward Tags from multiple Reader transmissions.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Temperature compensation for transmission between nodes coupled by a unidirectional fiber ring
Transmissions over a unidirectional optical fiber coupling multiple nodes are compensated for temperature-induced effects. A round-trip delay time is determined for a signal sent from a first node to travel around the unidirectional optical fiber loop and be received back at the first node. That measured round-trip delay time is then used to account for temperature-induced effects on signal transmissions over the unidirectional optical fiber loop. This temperature compensation is particularly beneficial in applications that require a high level of timing accuracy.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Random access method and random access channel structure in mobile communication system having large cell radius
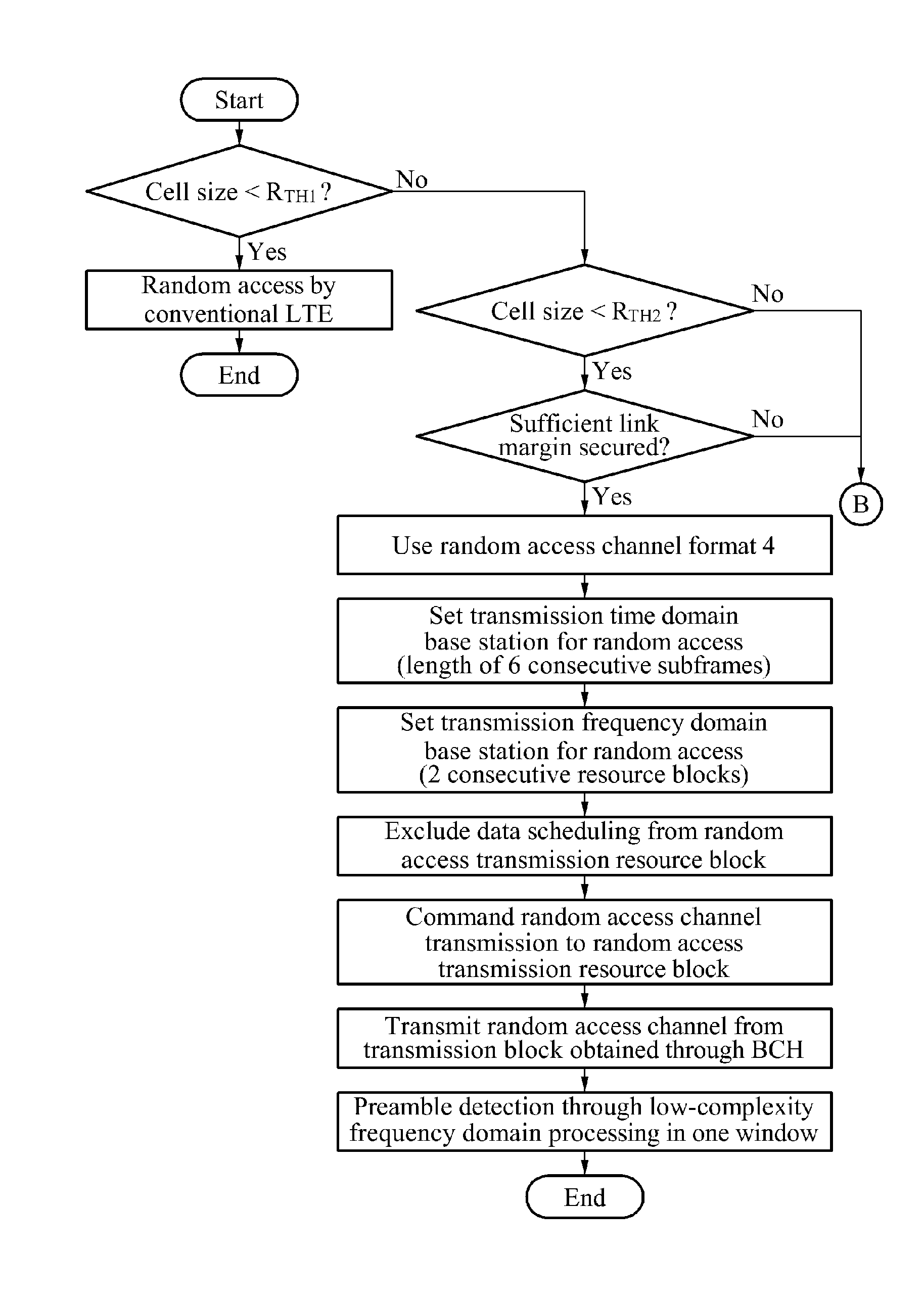
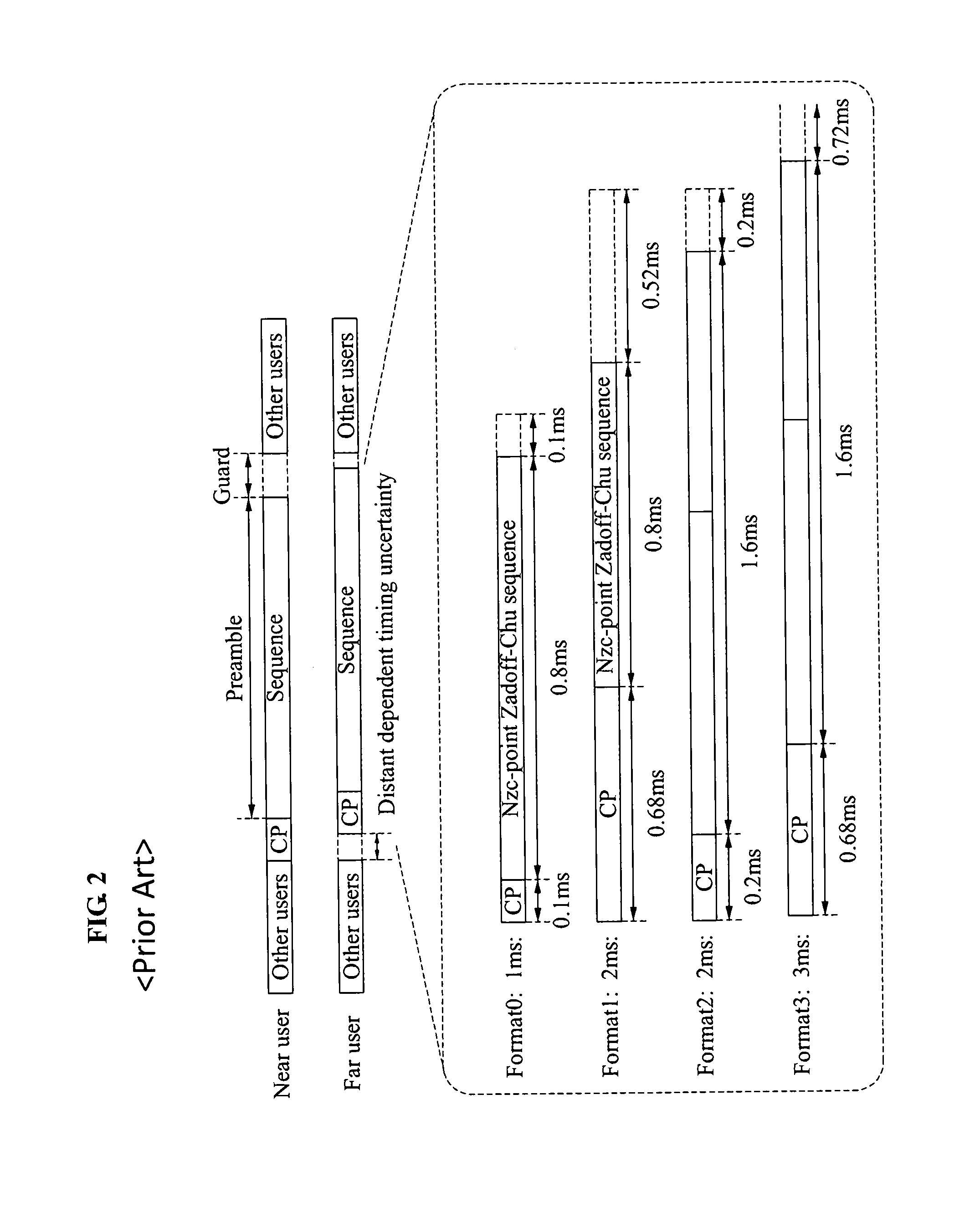
ActiveUS9538554B2Network traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionLink marginDelayed time
A random access method in a mobile communication system, the random access method for supporting random access with a cell size of about 100 kilometers (km) or more and a power limited terminal, and a preamble structure thereof are provided. While a conventional long term evolution (LTE) random access preamble sequence is reused, a difference in a round-trip delay time between terminals in a large cell area may be compensated. Additionally, since higher power transmission is achieved per bandwidth, a higher link margin may be secured. Also, compatibility with resource scheduling of the conventional LTE may be maintained. Random access may be supported in a large cell, and a preamble structure of a satellite mobile communication may be implemented based on terrestrial LTE.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Time synchronization method and system
ActiveCN110278049AHigh time accuracyImprove time synchronization accuracyTime-division multiplexTime deviationDelayed time
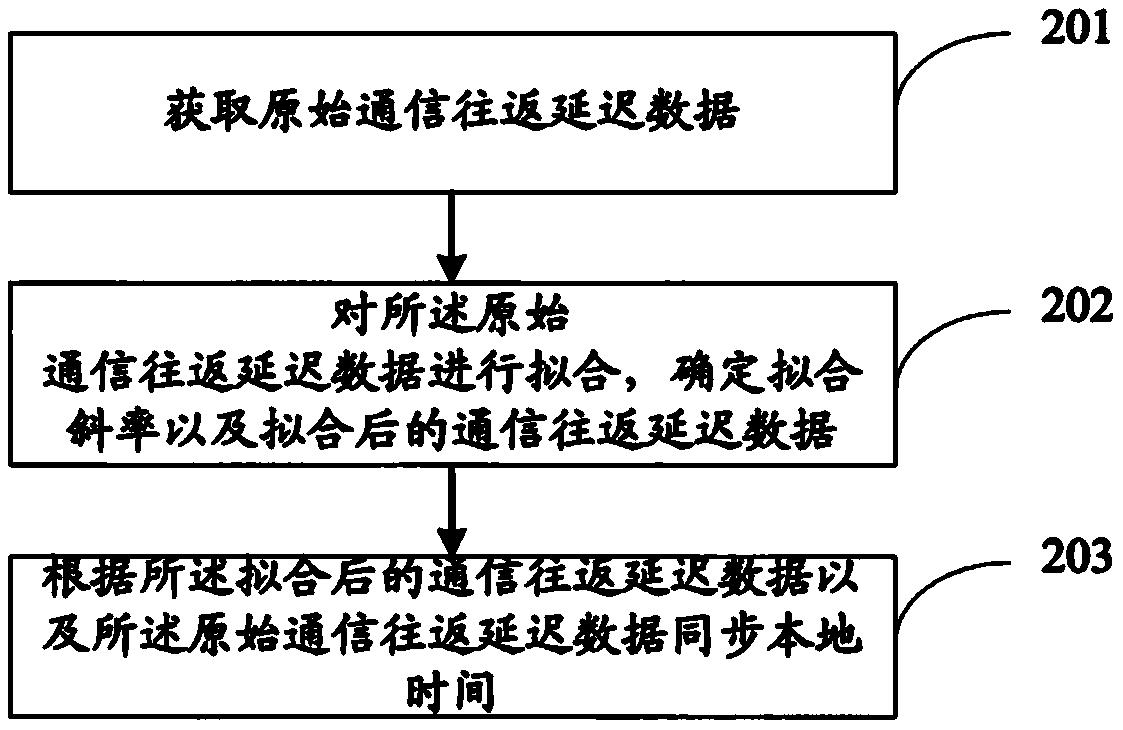
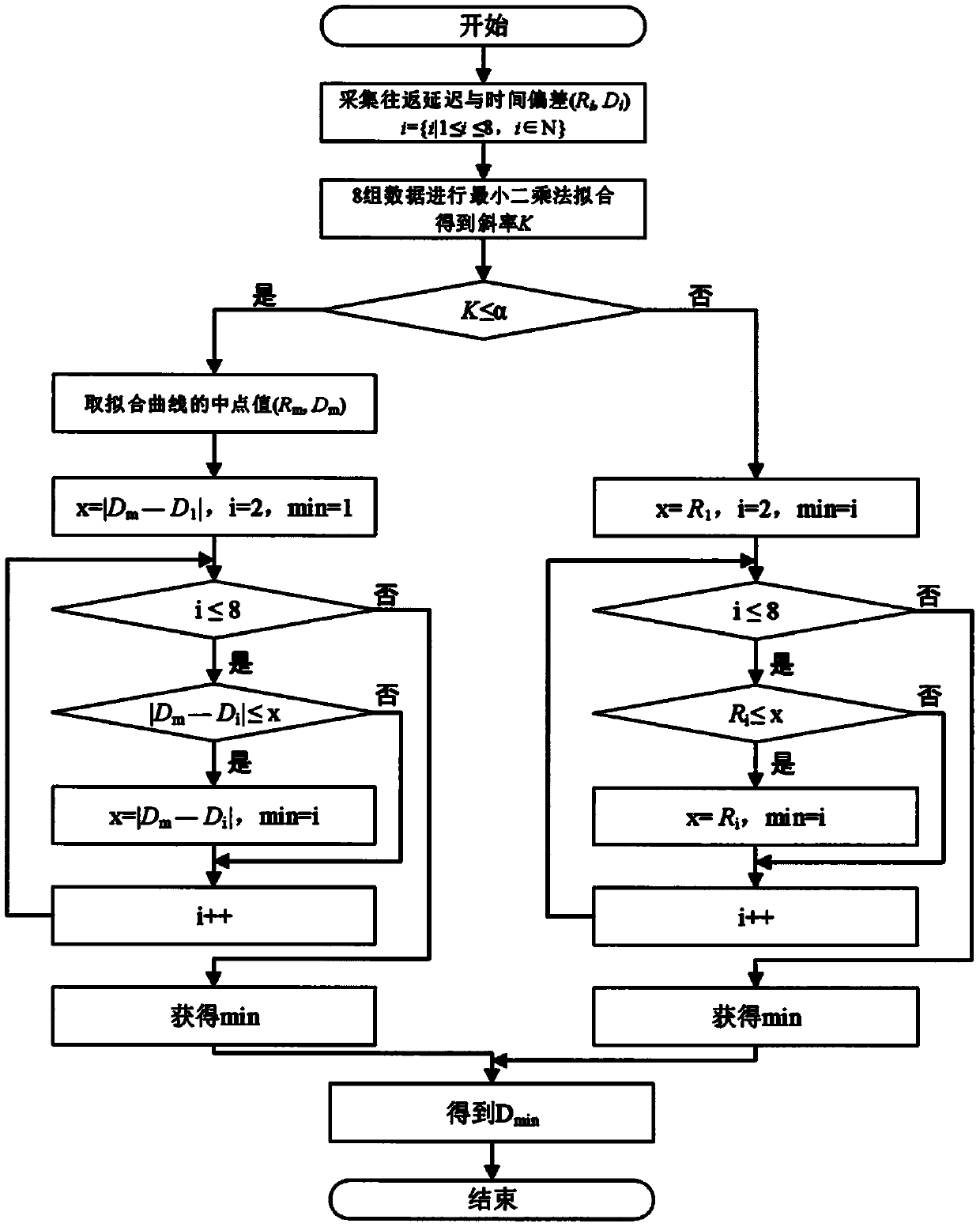
The invention discloses a time synchronization method and system. The time synchronization method comprises the following steps of acquiring the original communication round-trip delay data, wherein the original communication round-trip delay data comprises the original round-trip delay time and the original time deviation, and the original round-trip delay time and the original time deviation are in one-to-one correspondence; fitting the original communication round-trip delay data, and determining a fitting slope and the fitted communication round-trip delay data, wherein the fitted communication round-trip delay data comprises fitted round-trip delay time and fitted time deviation; and synchronizing the local time according to the fitted communication round-trip delay data and the original communication round-trip delay data. By adopting the time synchronization method and system provided by the invention, the network time service precision and the time synchronization precision can be improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU METROLOGY & TESTING INST
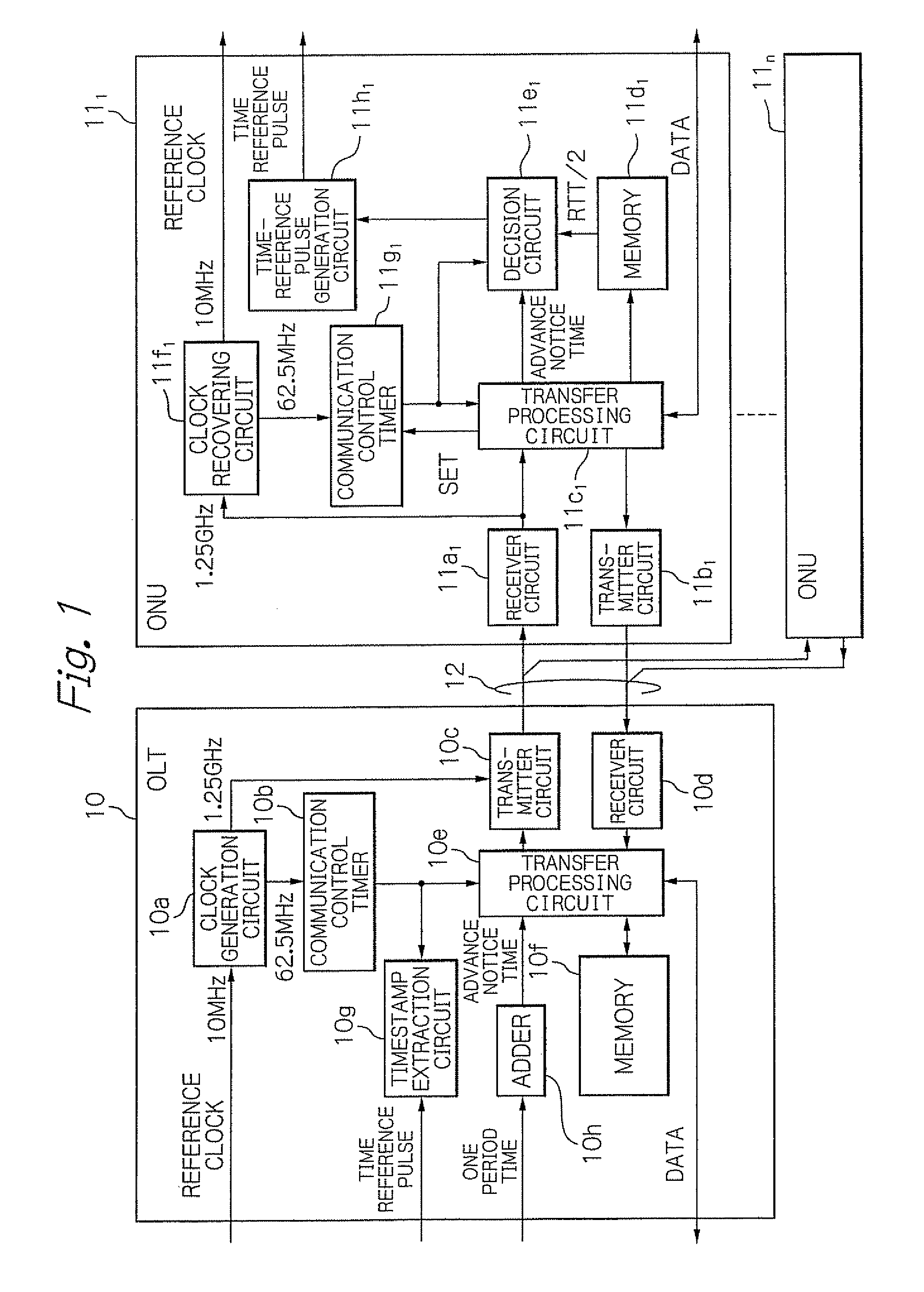
Optical transmission system and synchronization method using time reference pulse
InactiveUS8126333B2Rapid and accurate time-synchronizationSimple circuit structureMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime informationRound-trip delay time
An OLT includes a first transmitter and receiver unit for transmitting and receiving signals with ONUs, a first communication control timer, a measurement unit for measuring a round trip time (RTT) between the OLT and each of ONUs, an advance notice time generation unit for generating an advance notice time signal by adding a predetermined time to a time information that indicates a time in the first communication control timer in response to a first time reference pulse, and a unit for controlling the first transmitter and receiver unit to transmit the generated advance notice time signal to each of the ONUs, and to transmit signals indicating measured RTT / 2 to the respective ones of the ONUs.
Owner:KDDI CORP
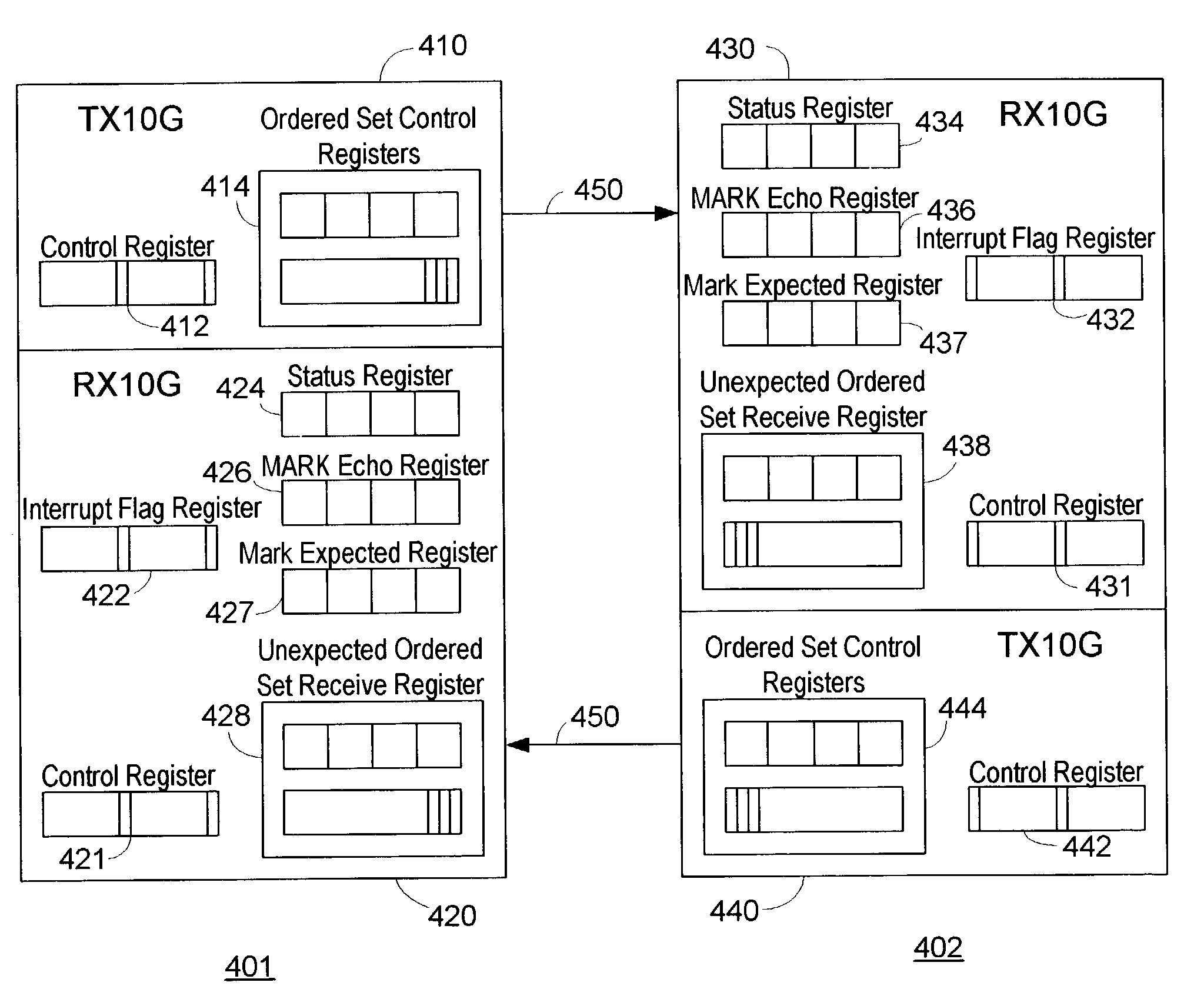
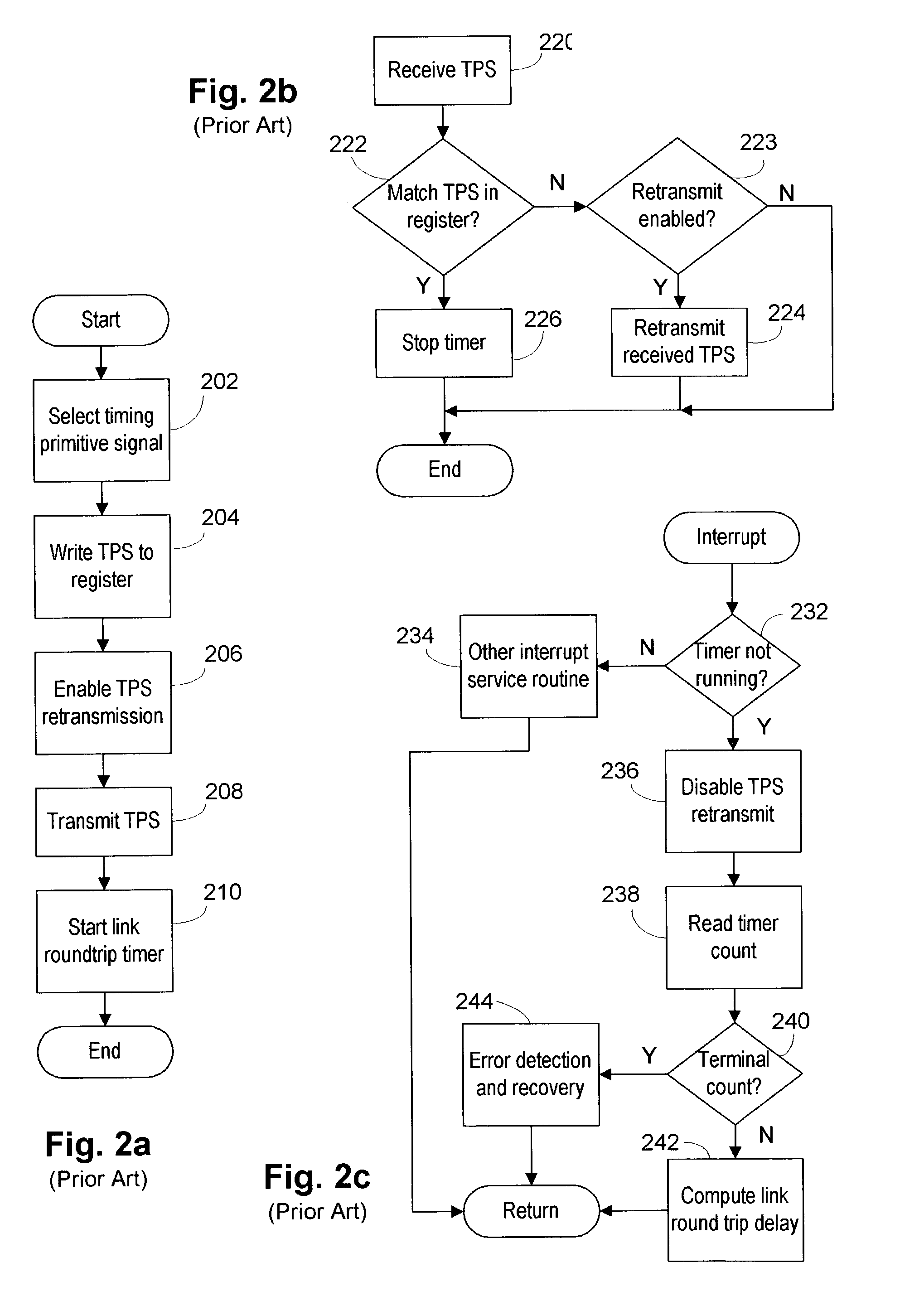
Method and apparatus for round trip delay measurement in a bi-directional, point-to-point, serial data channel
InactiveUS7286527B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsChannel network
The link round trip delay between two switches in a Fibre Channel network may be determined by sending a particular timing signal value from an originating switch to a responding switch. The responding switch may store the timing signal value in an “echo” register for comparison to subsequently received timing signals. The originating switch may then send the pre-selected timing signal to the responding switch while simultaneously starting a timer. When the responding switch receives the timing signal, it may compare the value of the received signal to that stored in its echo register. If the value, is the same, the responding switch may retransmit—i.e., echo—the timing signal to the originating switch. When the originating switch receives the echoed timing signal, it may stop its timer and compute the link round trip delay time. The computed link round trip delay time between the originating switch and the responding switch may be advantageously used in fabric routing algorithms.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Communications terminal, communications method, and program and integrated circuit for controlling a reproduction delay time in distributing a stream
ActiveUS9184928B2Quality improvementHigh-quality reproductionSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsStreaming dataTelecommunications
A communication terminal (100) is one of communication terminals each having one parent terminal and zero or more child terminals. The communication terminals form an Application Layer Multicast (ALM) tree to sequentially distribute retransmission data of stream data from the parent terminal to the child terminal. The communications terminal (100) includes: a reproduction delay time determining unit (1010) determining a reproduction delay time based on a longest round-trip delay time among round-trip delay times of sections between a root terminal and the communications terminal (100), each of the round-trip delay times being required for transmission and reception of data through one of the sections between two neighboring terminals of the communications terminals on the ALM tree; and a reproduction control unit (1020) reproducing the stream data received from the root terminal, with the stream data delayed by the reproduction delay time determined by the reproduction delay time determining unit (1010).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Long-distance access method based on LTE wireless communication technology
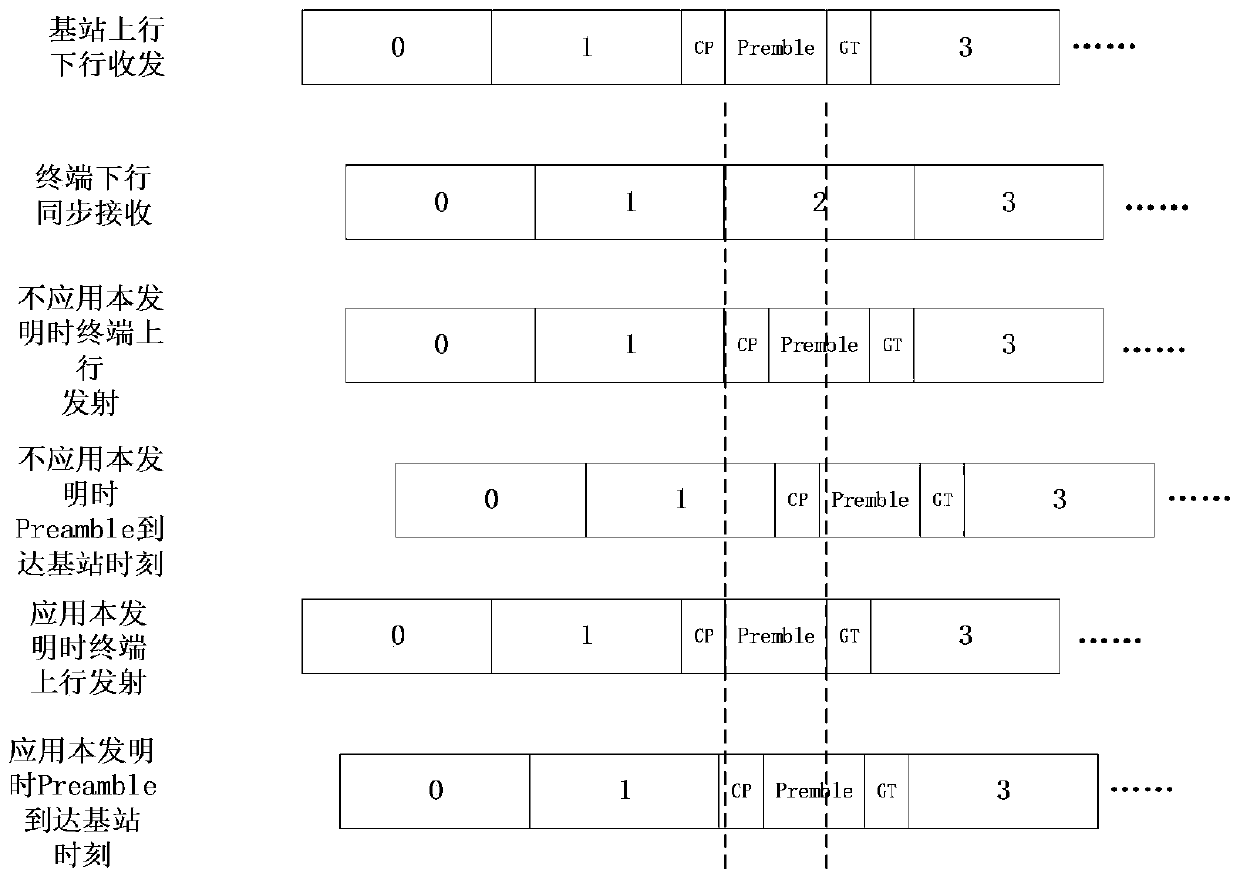
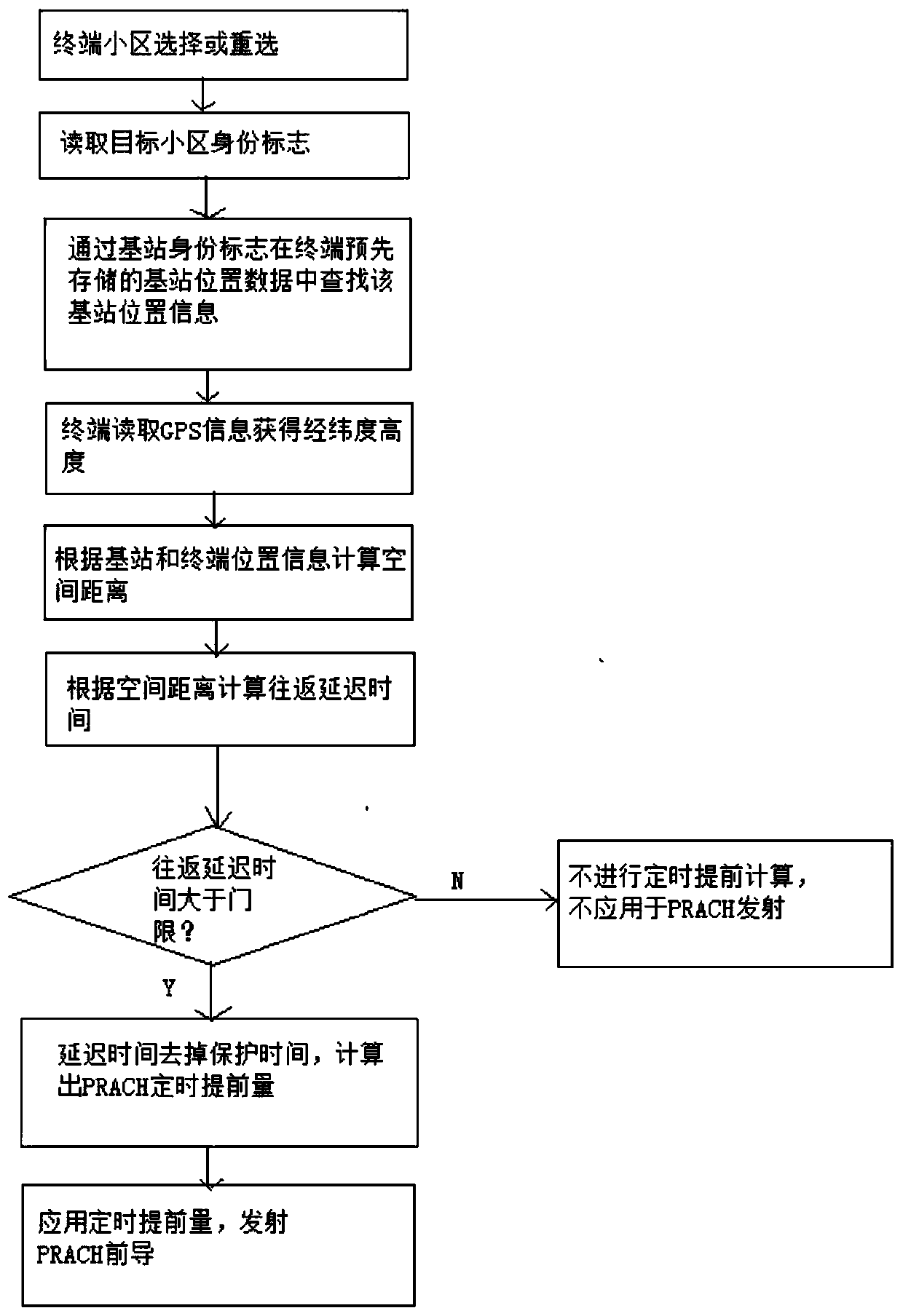
ActiveCN111132002AAchieve coverageAchieve accessLocation information based serviceRound-trip delay timeTiming advance
The invention belongs to the technical field of LTE wireless communication, and particularly relates to a long-distance access method based on an LTE wireless communication technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, storing LTE base station position information and community information in a terminal; 2, calculating a spatial linear distance between the terminal and the LTE base station by using the obtained information through the terminal; and 3, calculating the round-trip delay time by utilizing the space linear distance, and then calculating the timing advance value. An ultra-long-distance LTE community coverage and access process is realized, and an LTE system can obtain a maximum coverage effect with low time-frequency resource overhead.
Owner:北京长焜科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com