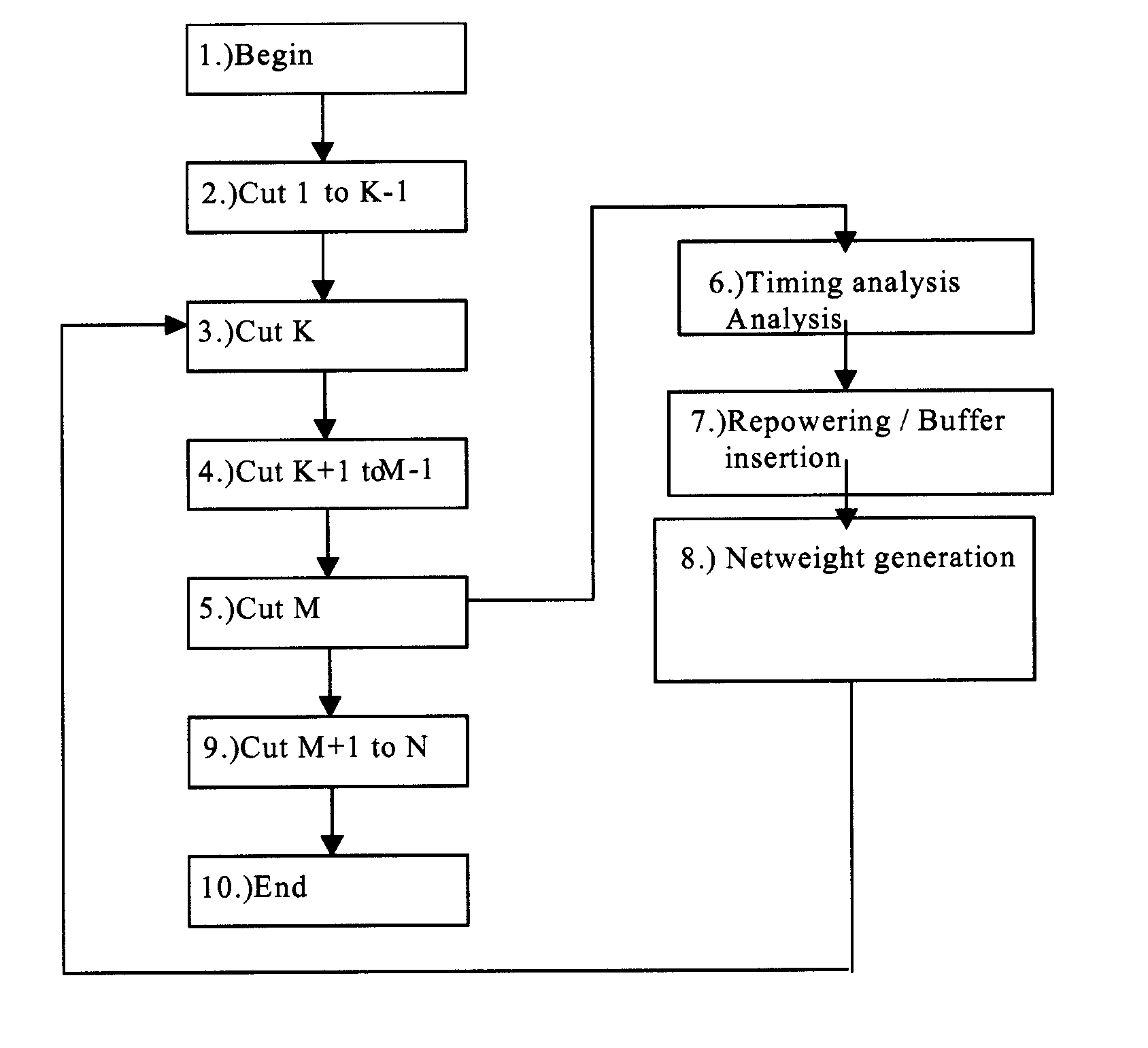
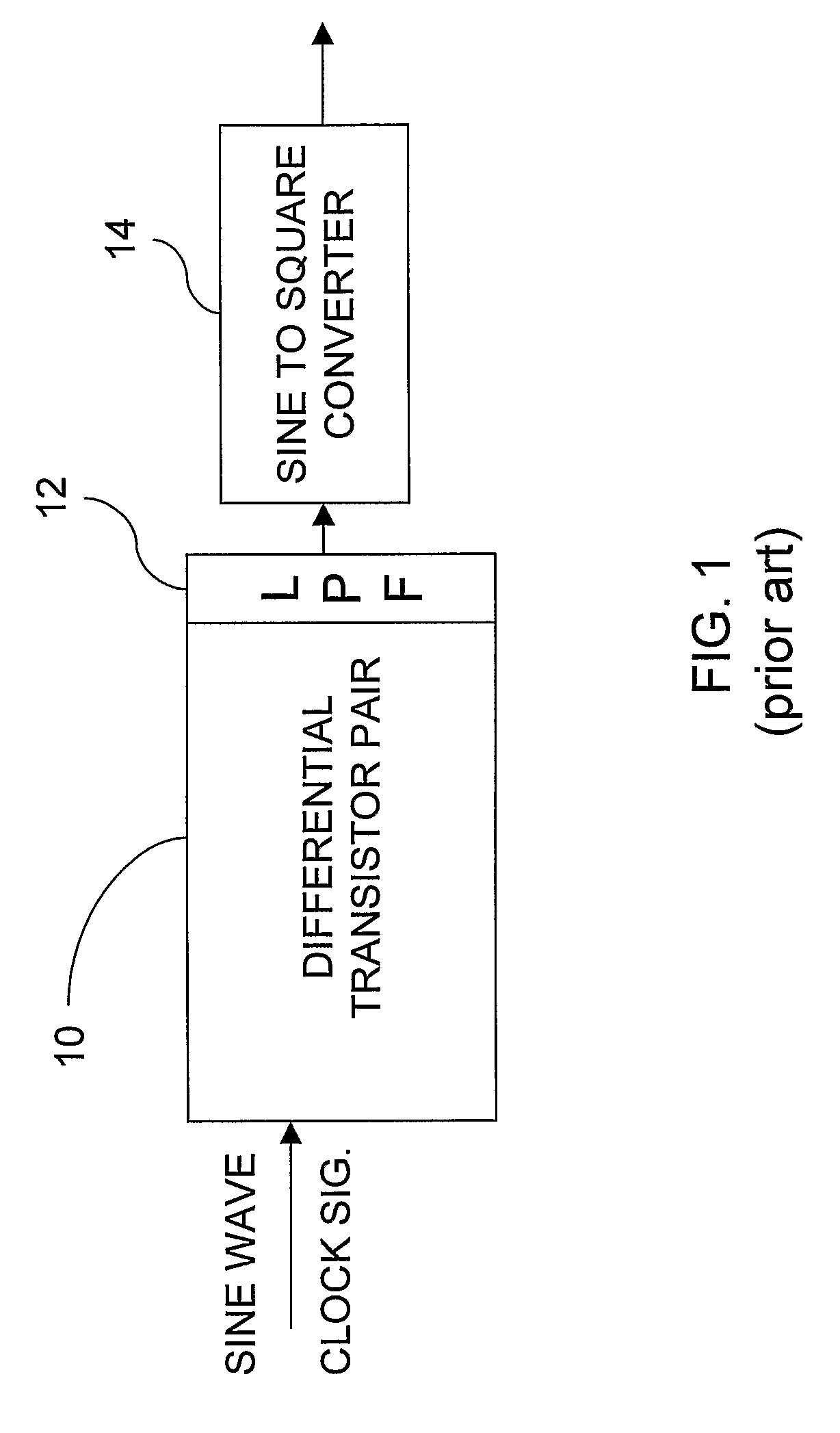
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Vlsi chip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
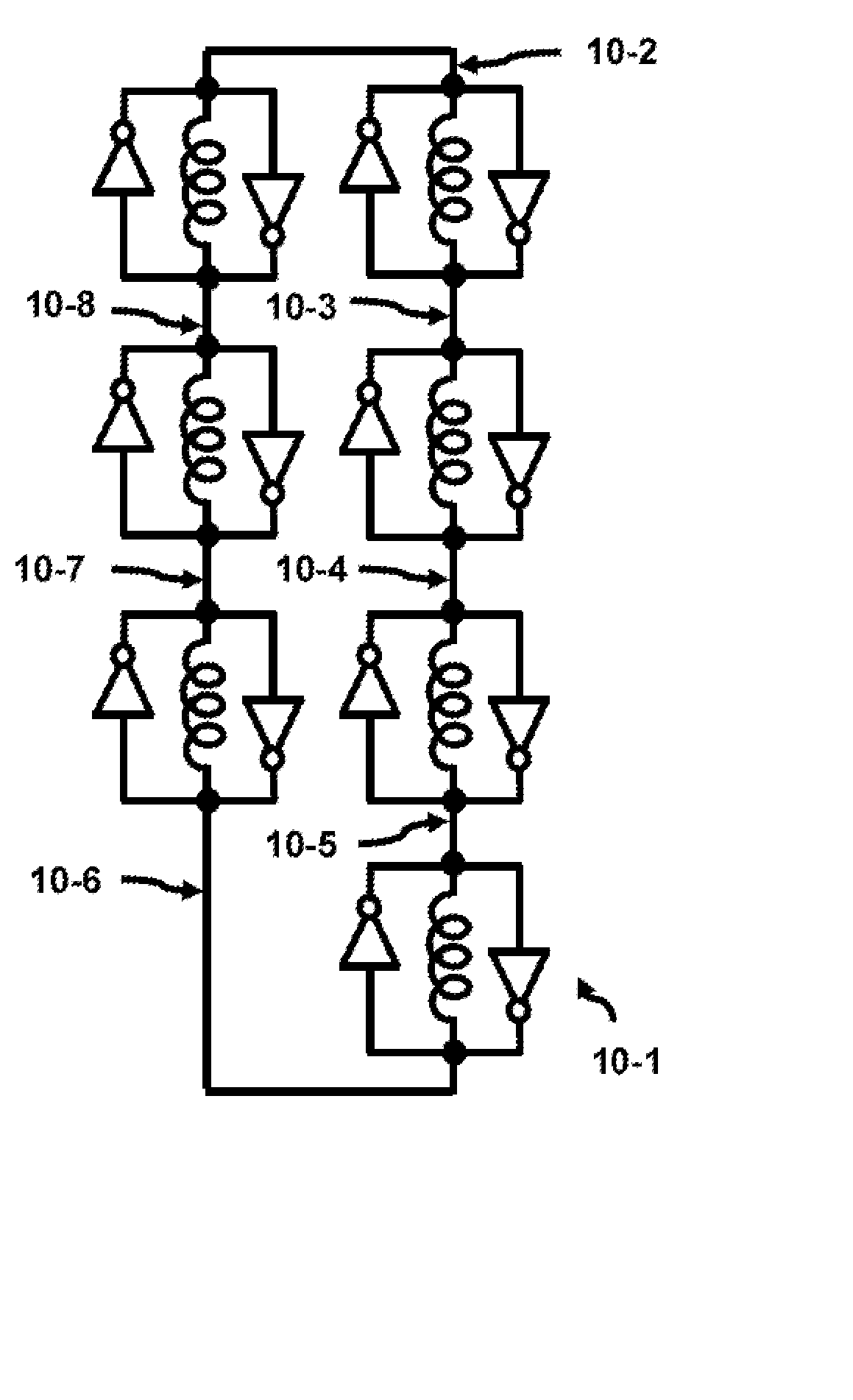
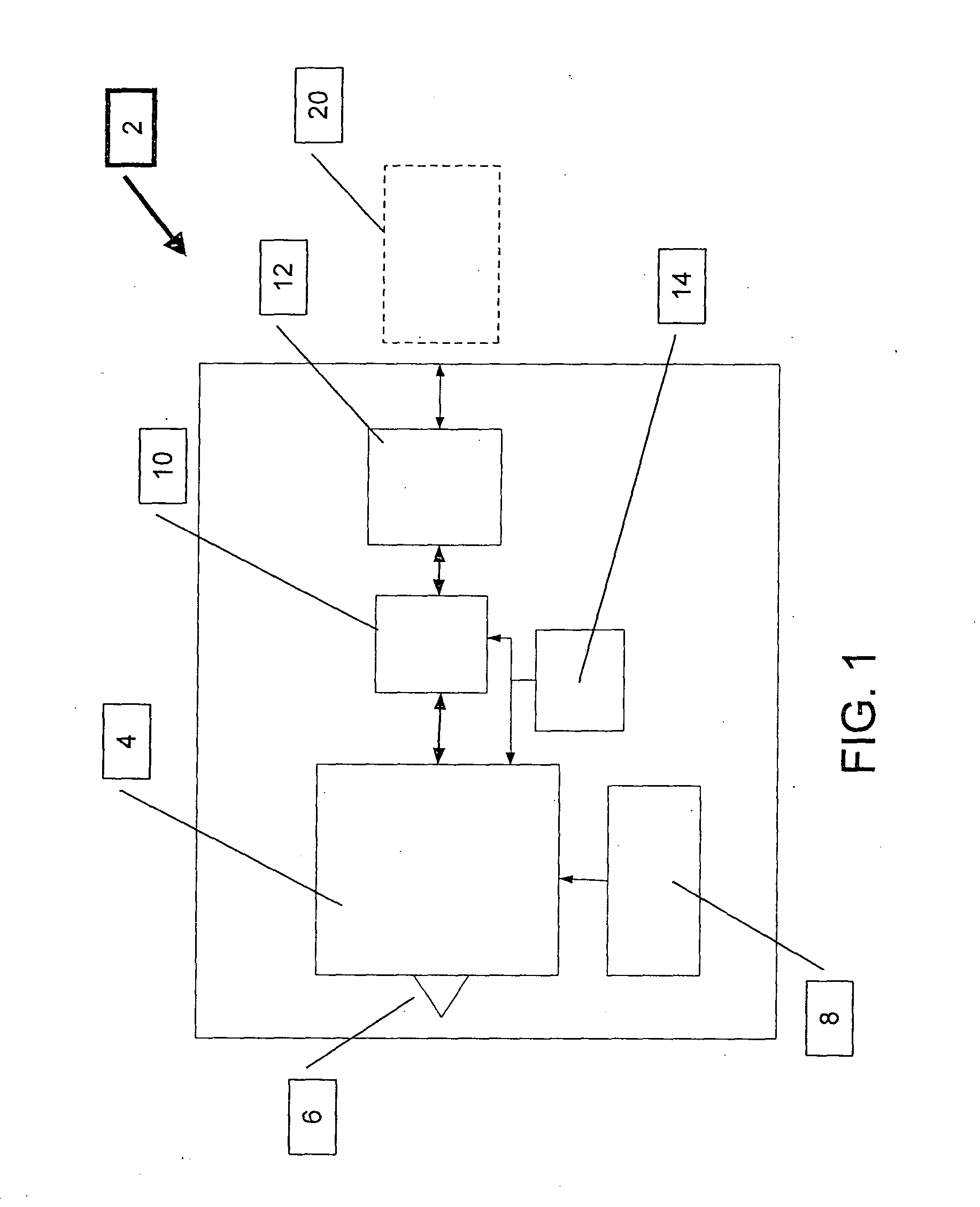
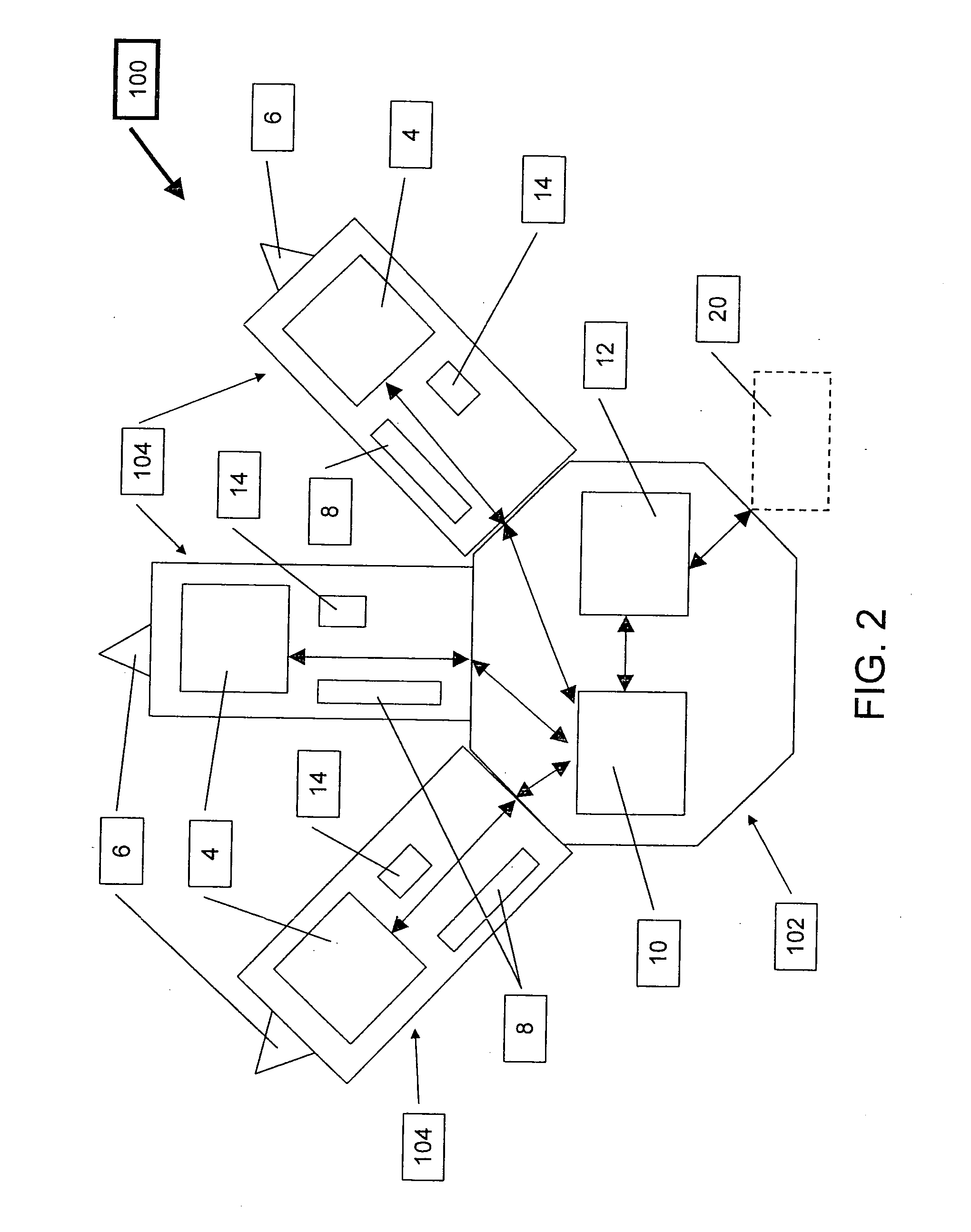
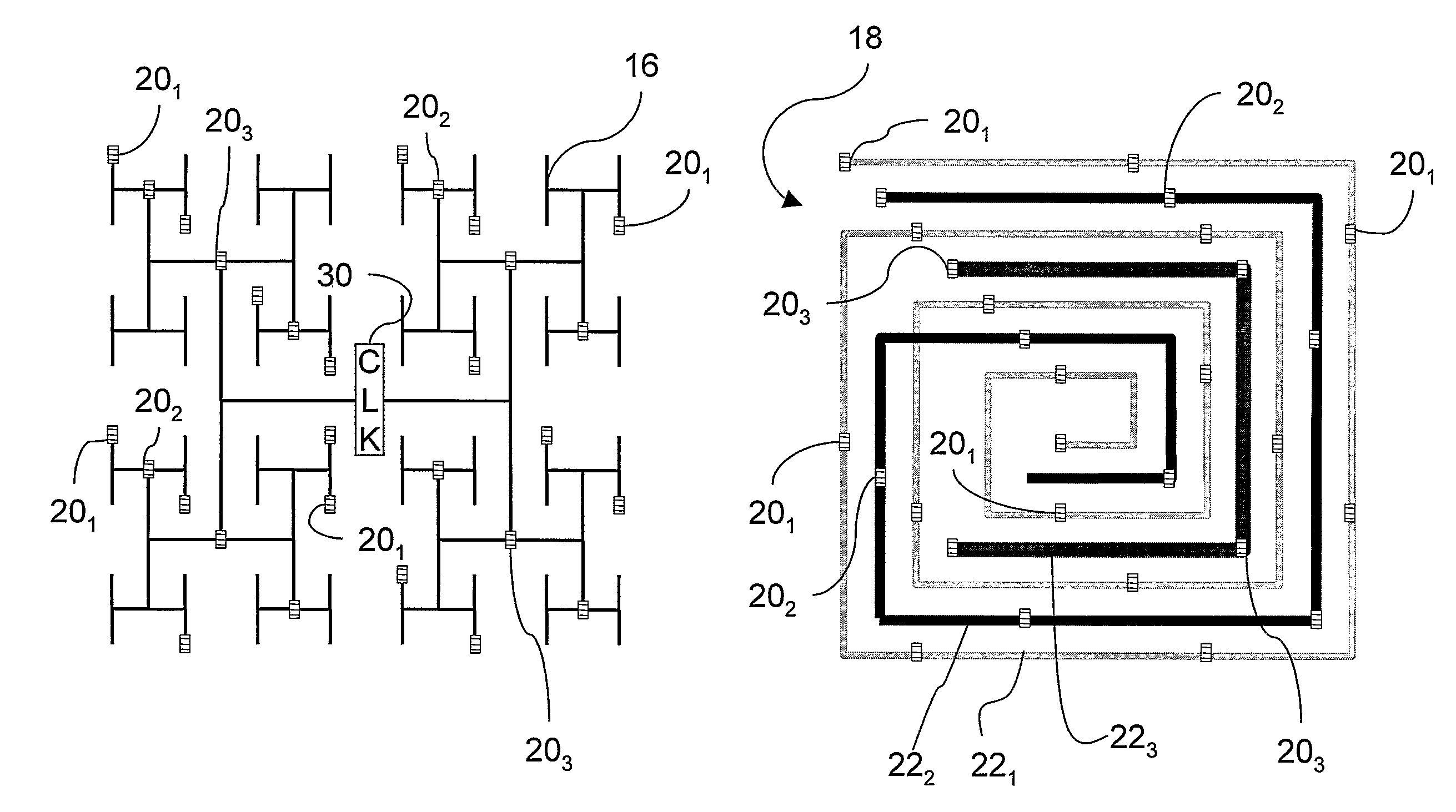
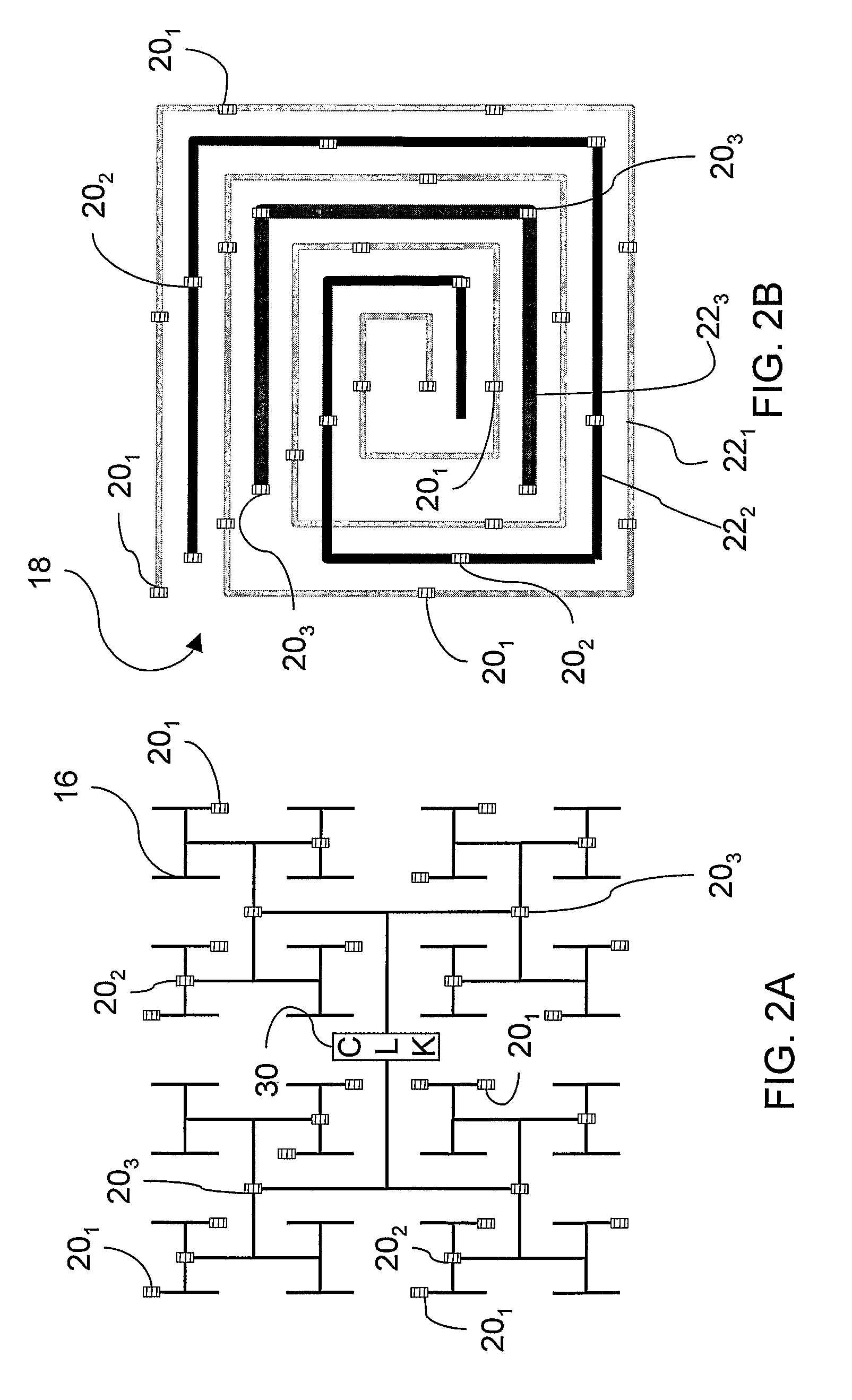
Frequency adjustment techniques in coupled LC tank circuits
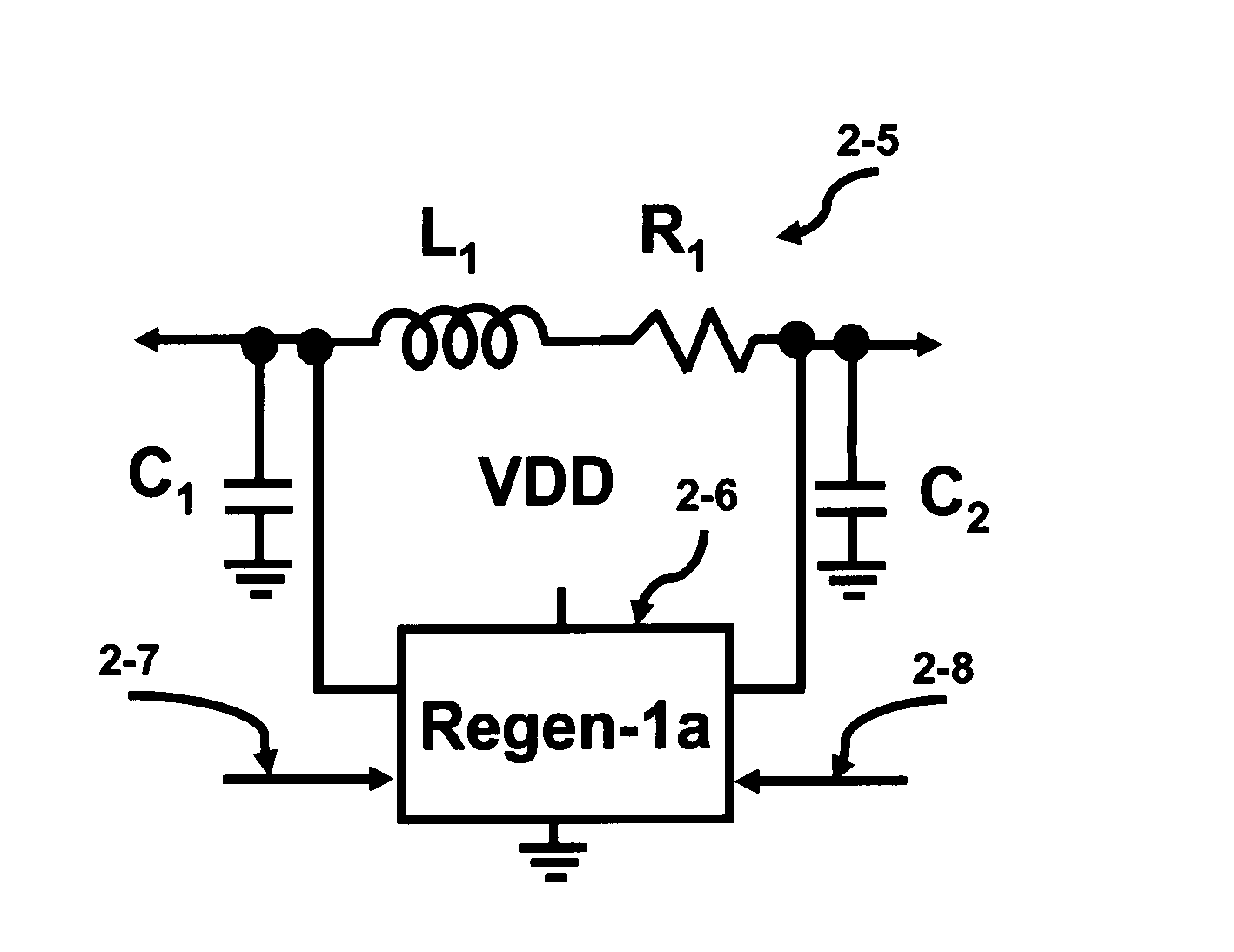
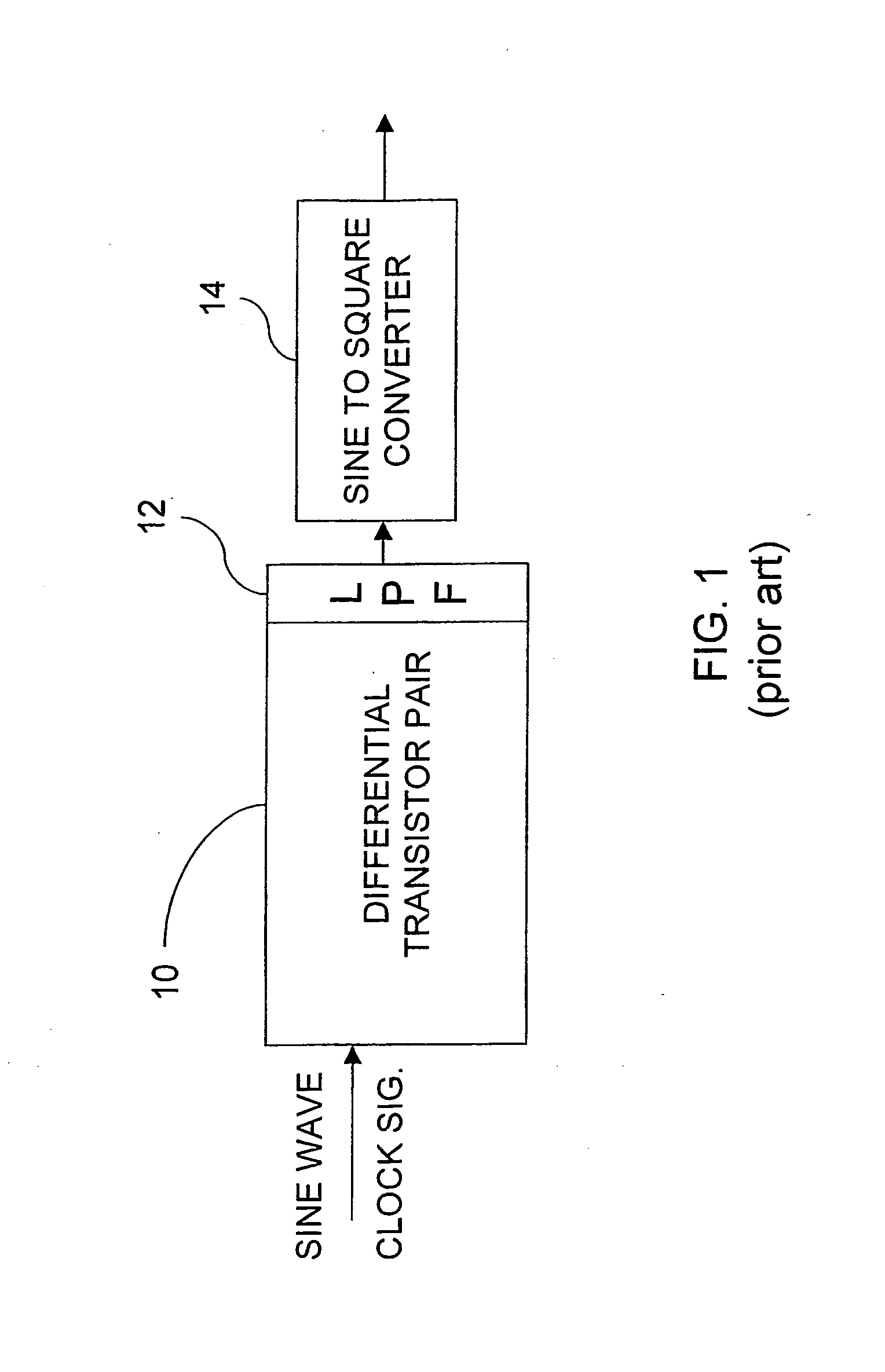
CMOS LC tank circuits and flux linkage between inductors can be used to distribute and propagate clock signals over the surface of a VLSI chip or μprocessor. The tank circuit offers an adiabatic behavior that recycles the energy between the reactive elements and minimizes losses in a conventional sense. Flux linkage can be used to orchestrate a number of seemingly individual and distributed CMOS LC tank circuits to behave as one unit. Several frequency-adjusting techniques are presented which can be used in an distributed clock network environment which includes an array of oscillators. A passive flux linkage, mechanical, and finite state machine technique of frequency adjustment of oscillators are described.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
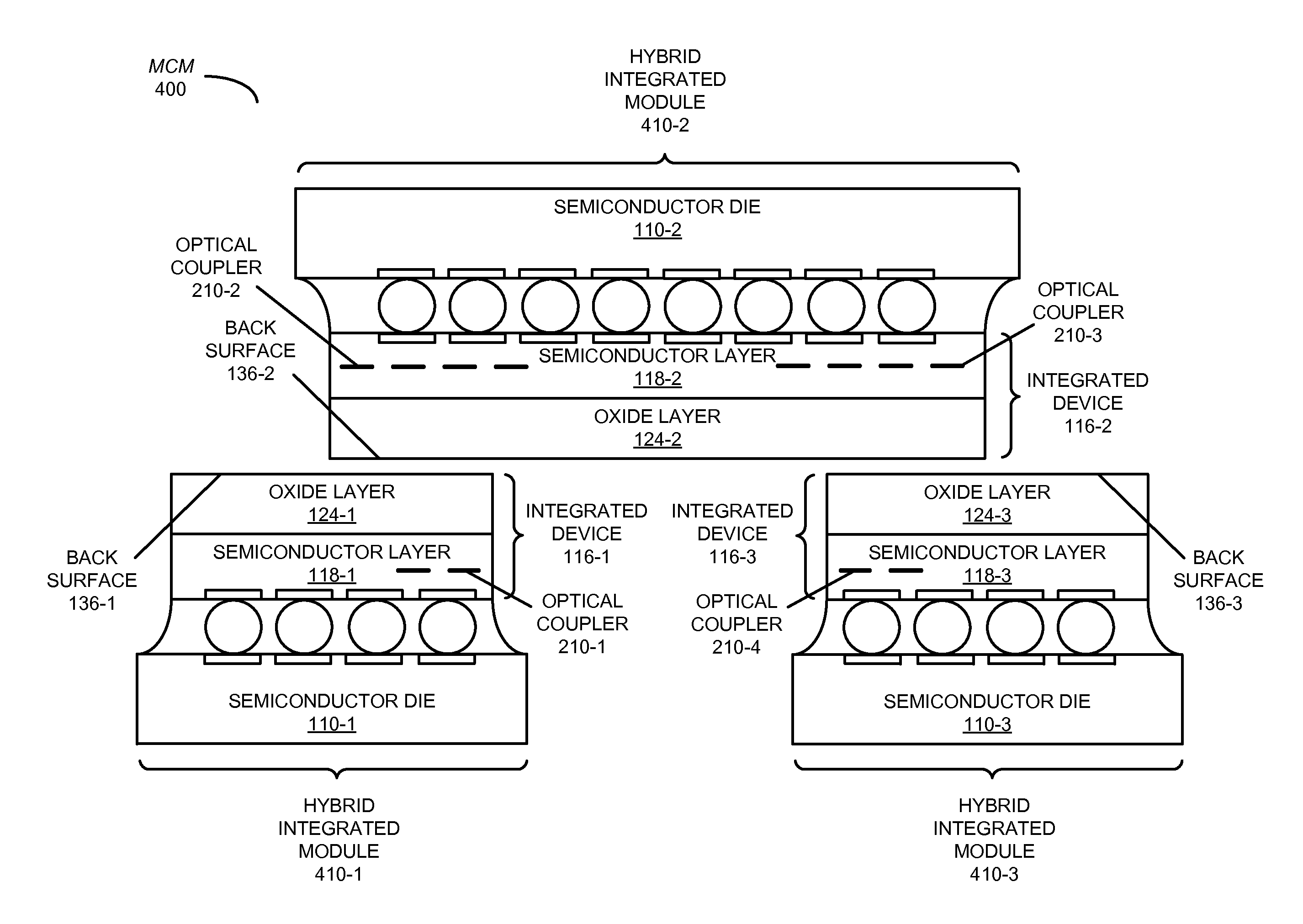
Hybrid substrateless device with enhanced tuning efficiency
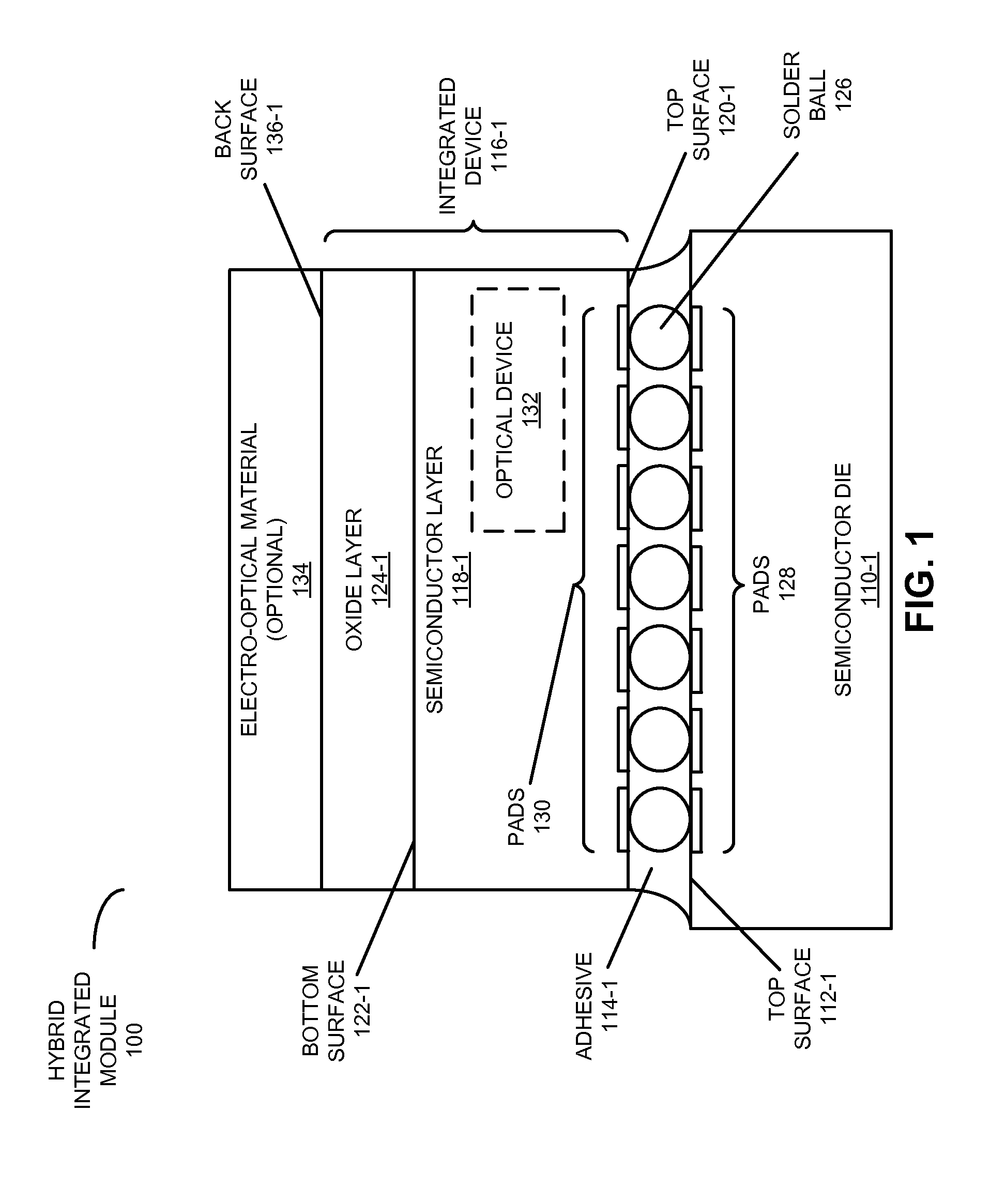
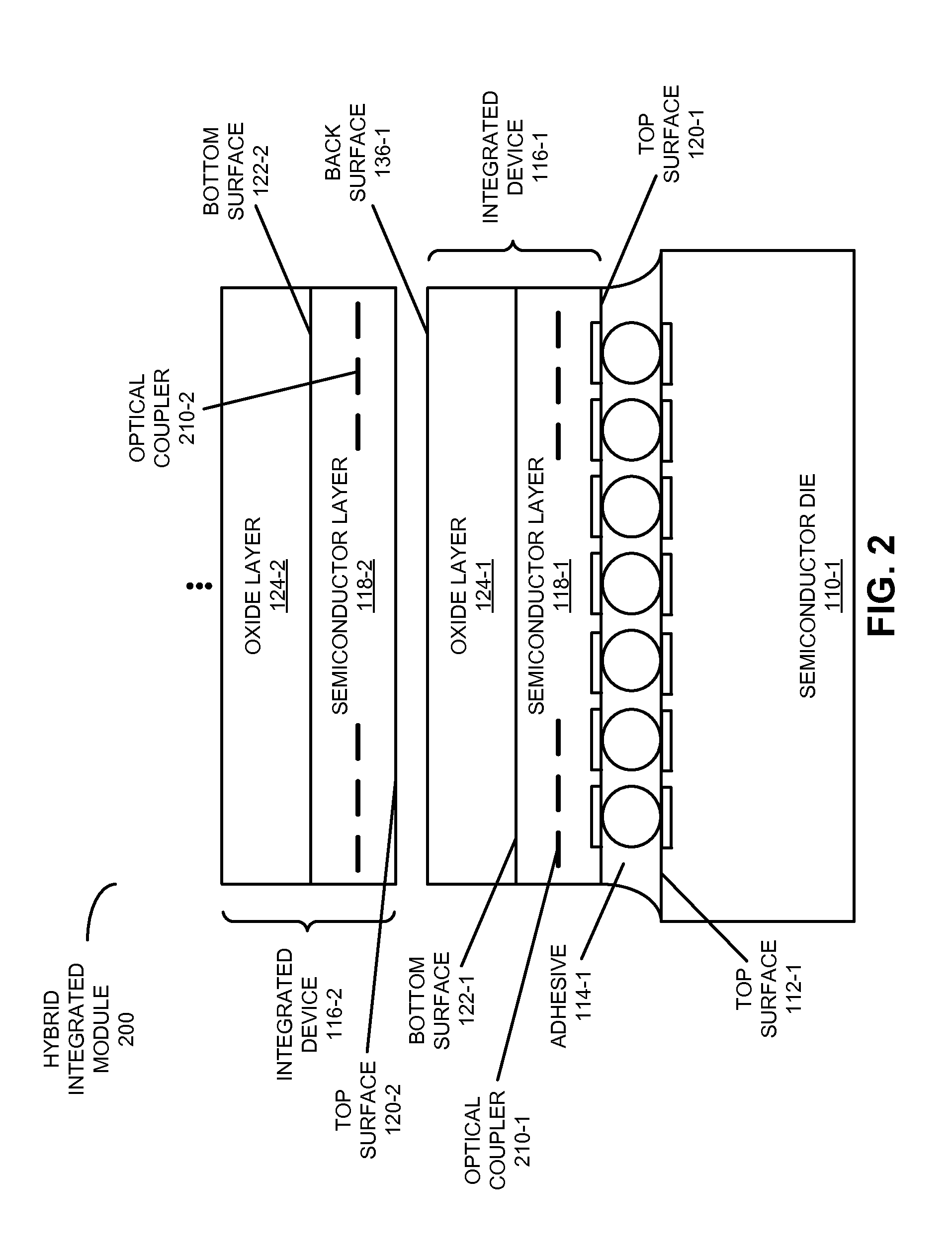
ActiveUS20130037905A1Improve device performanceEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingEngineering
In a hybrid integrated module, a semiconductor die is mechanically coupled face-to-face to an integrated device in which the substrate has been removed. For example, the integrated circuit may include an optical device fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer in which the backside silicon handler has been completely removed, thereby facilitating improved device performance and highly efficient thermal tuning of the operating wavelength of the optical device. Moreover, the semiconductor die may be a VLSI chip that provides power, and serves as a mechanical handler and / or an electrical driver. The thermal tuning efficiency of the substrateless optical device may be enhanced by over 100× relative to an optical device with an intact substrate, and by 5× relative to an optical device in which the substrate has only been removed in proximity to the optical device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
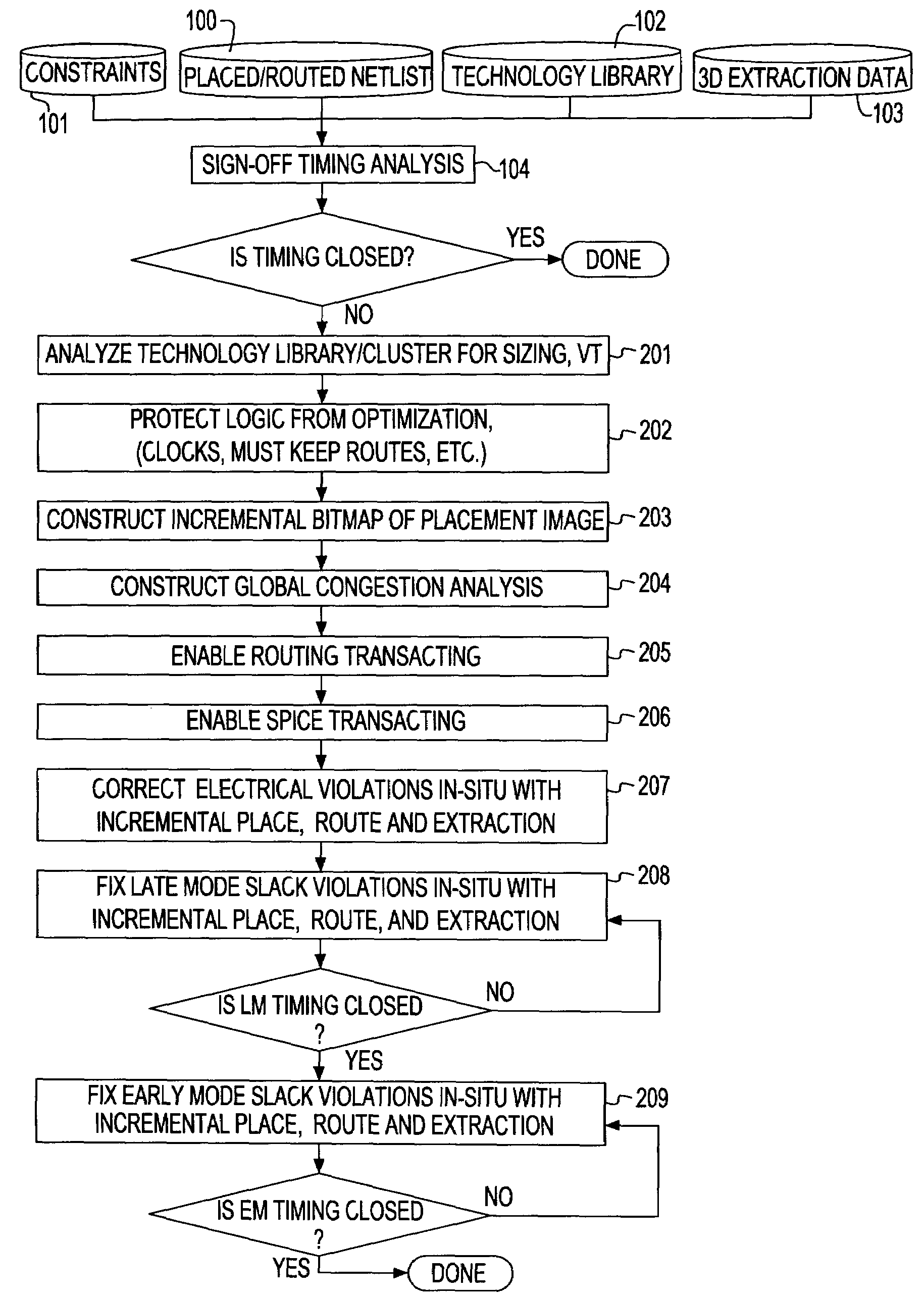
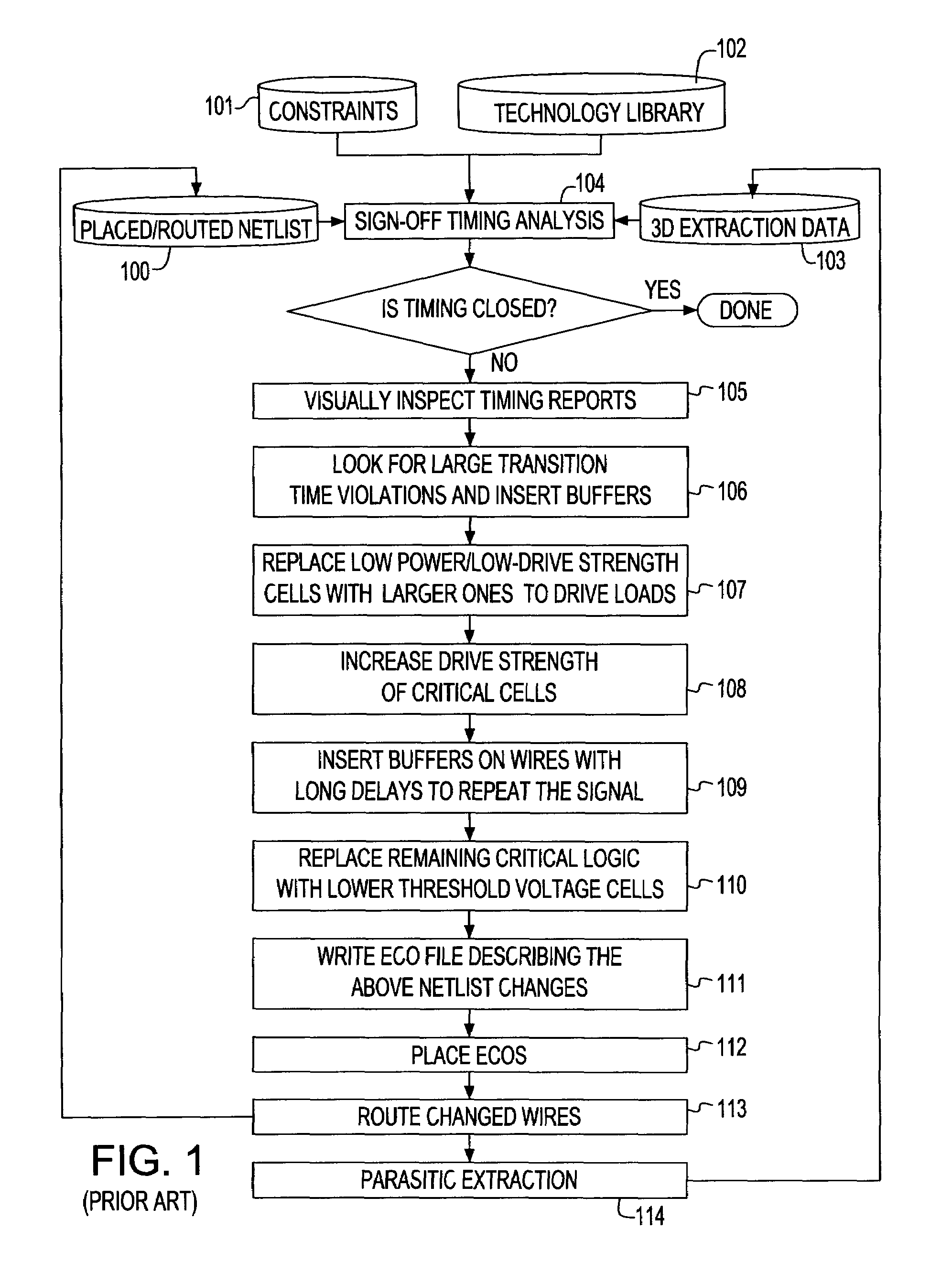
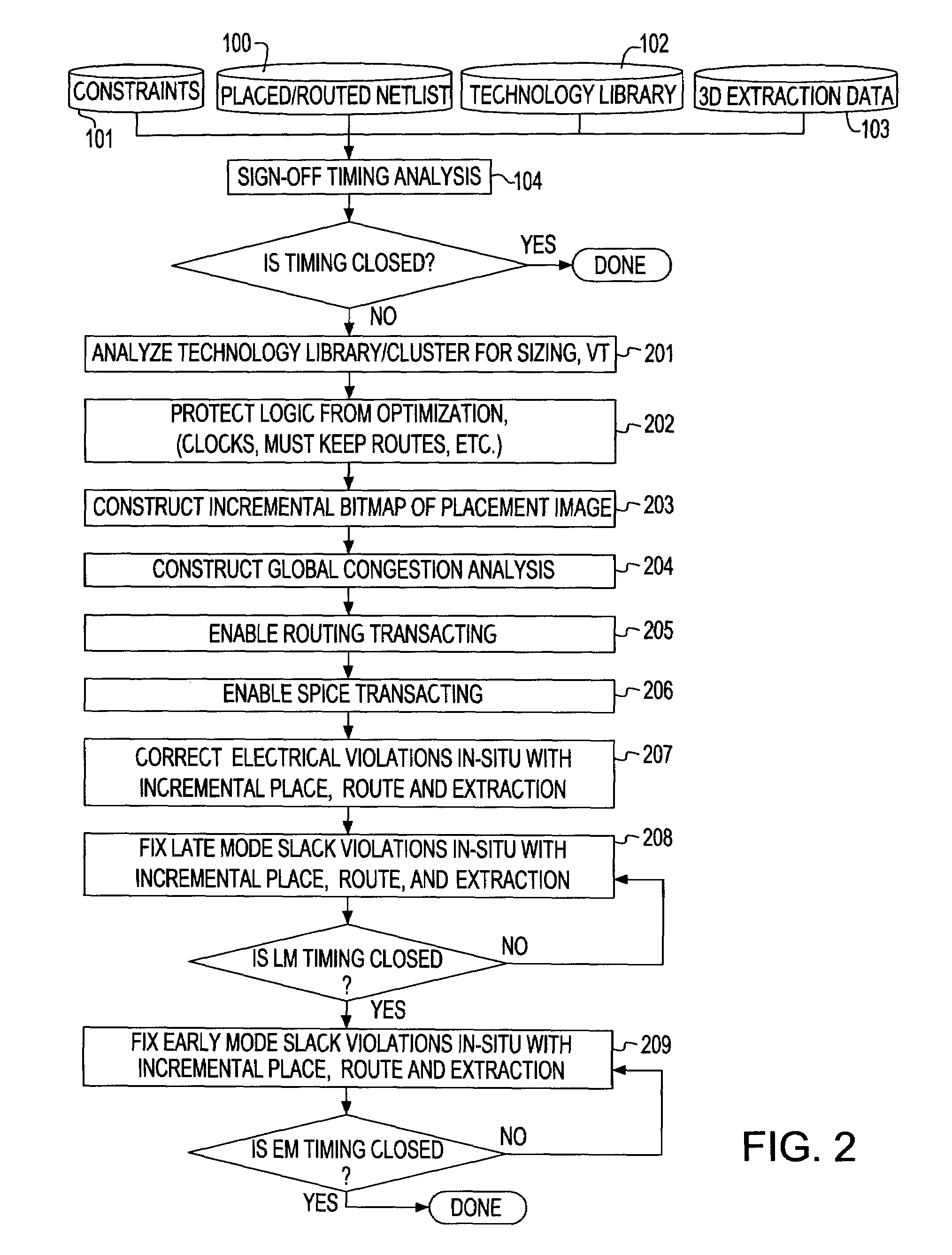
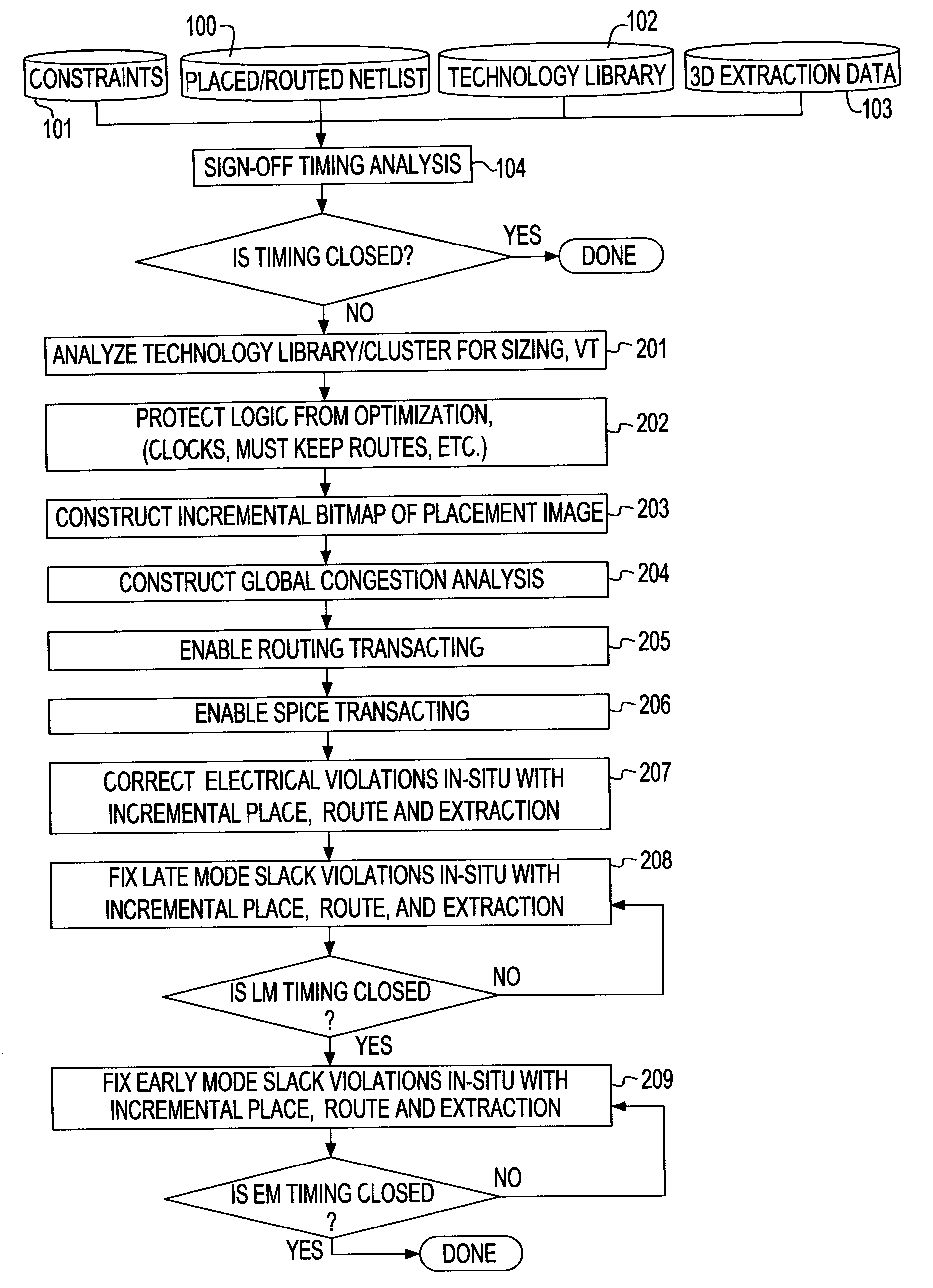
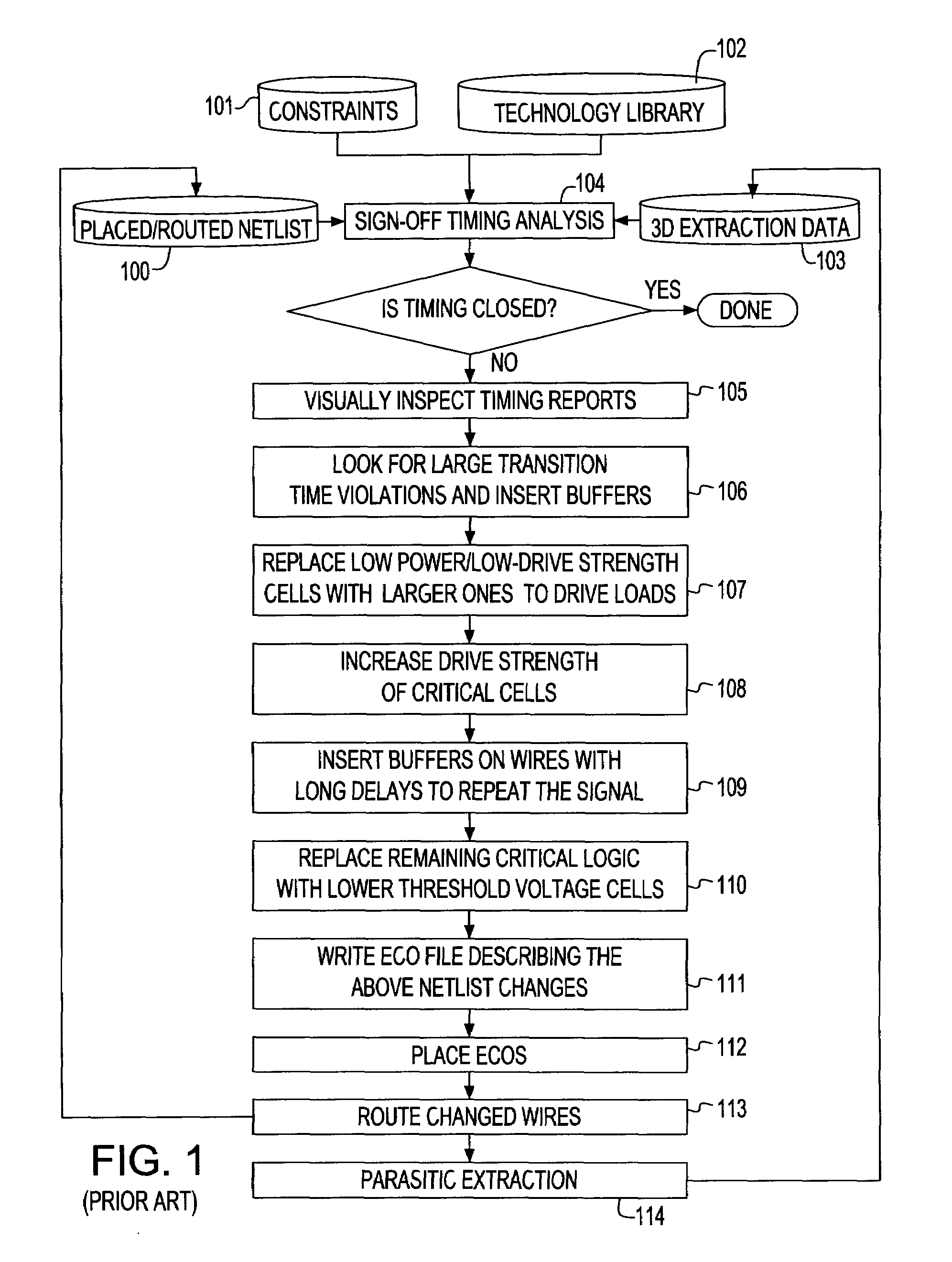
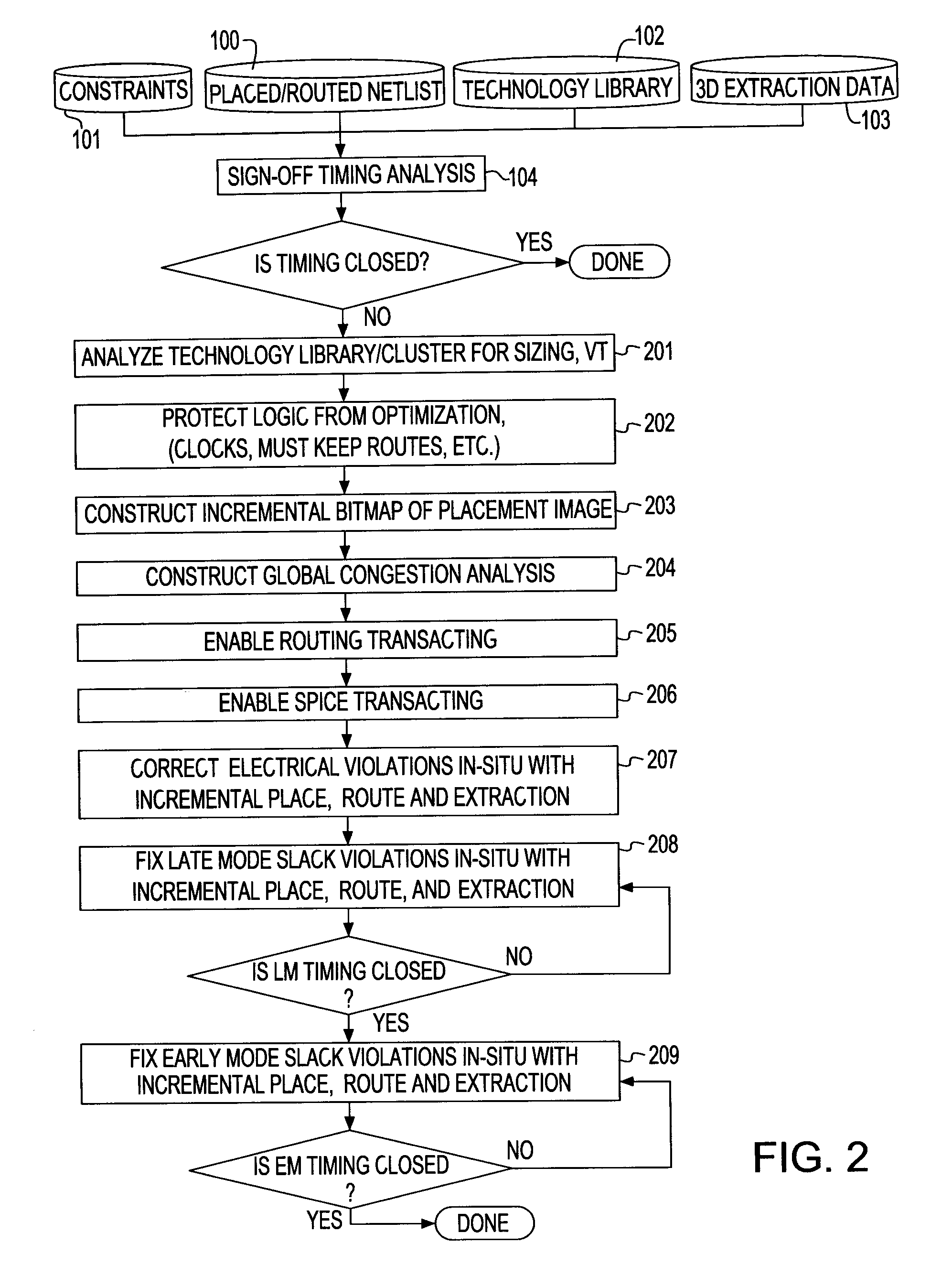
System and method for sign-off timing closure of a VLSI chip
InactiveUS7581201B2Efficiently improve the timing and electrical violationsMinimal placement and routing disruptionCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitancePathPing
A method for performing timing optimization of a detail routed netlist, incorporating statistical variability information, common path pessimism reduction, and capacitative coupling information, in a tightly coupled, incremental manner with minimal perturbations to the placement, routing, and asserted parasitic information. The method corrects violations in a placed and routed design of a VLSI circuit chip, where the design is represented by a netlist describing logical and physical characteristics of the design and by a corresponding timing graph, the method including the steps of: identifying violations in the design; iteratively eliminating the violations by incrementally transforming the logical and the physical characteristics of the design, incorporating in the design only legal placements and routes; and applying incremental timing to evaluate the transformations, and updating the existing timing graphs to reflect changes consisting of the legal placements and routes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer based on M*N ports of silicon substrate liquid crystal
InactiveCN103281153AIngenious structureFunctionalWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesWavelengthVlsi chip
The invention discloses a reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) based on M*N ports of silicon substrate liquid crystal. The ROADM comprises an optical fiber collimator input array with M ports, a spherical reflector, a body optical grating, an LCoS Opto-VLSI chip, a lens and an optical fiber collimator output array with N ports. The ROADM based on M*N ports of LCoS is realized. An optical system inside the equipment is unique in design, exquisite in structure, and good in function, uses the high-density scoring body grating as a dispersion element, adopts a method that phase gratings of different two-dimension orientations are loaded on an LCoS chip, and realizes efficient and flexible assignments of a large scale optical integrated chip on an incident wave length passage through changing the period of the grating and grating orientation modulation light beam phases. The ROADM has a high port number and optimized spectrum flexibility, has the functions of dispersion adjustments, pulse shaping and the like, and can conduct remote control and upgrade conveniently through software.
Owner:MINZU UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
System and method for sign-off timing closure of a VLSI chip
InactiveUS20080209376A1Reduce variability effectAvoid a lot of timeCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitanceCoupling
A method for performing timing optimization of a detail routed netlist, incorporating statistical variability information, common path pessimism reduction, and capacitative coupling information, in a tightly coupled, incremental manner with minimal perturbations to the placement, routing, and asserted parasitic information. The method corrects violations in a placed and routed design of a VLSI circuit chip, where the design is represented by a netlist describing logical and physical characteristics of the design and by a corresponding timing graph, the method including the steps of: identifying violations in the design; iteratively eliminating the violations by incrementally transforming the logical and the physical characteristics of the design, incorporating in the design only legal placements and routes; and applying incremental timing to evaluate the transformations, and updating the existing timing graphs to reflect changes consisting of the legal placements and routes.
Owner:IBM CORP
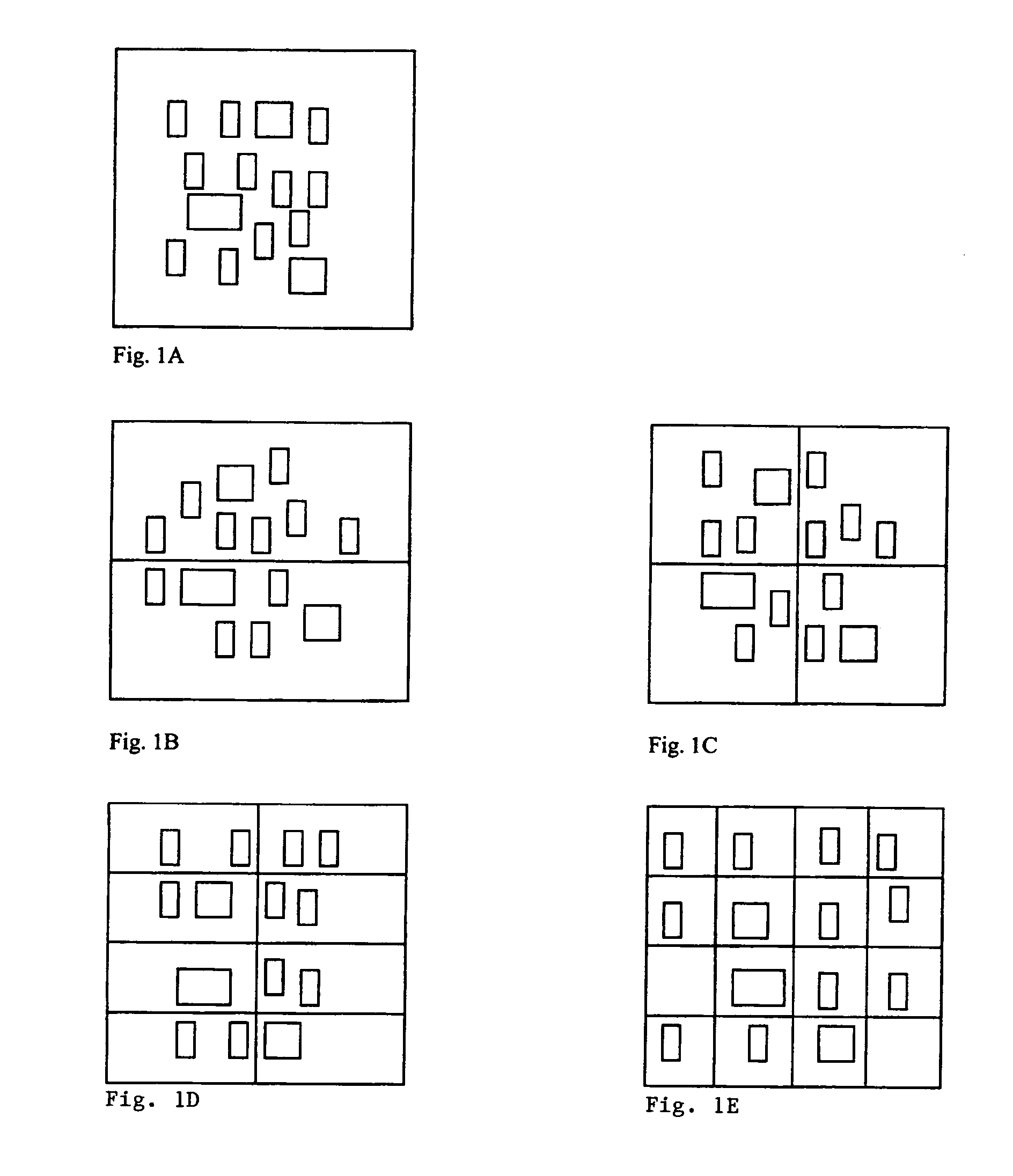
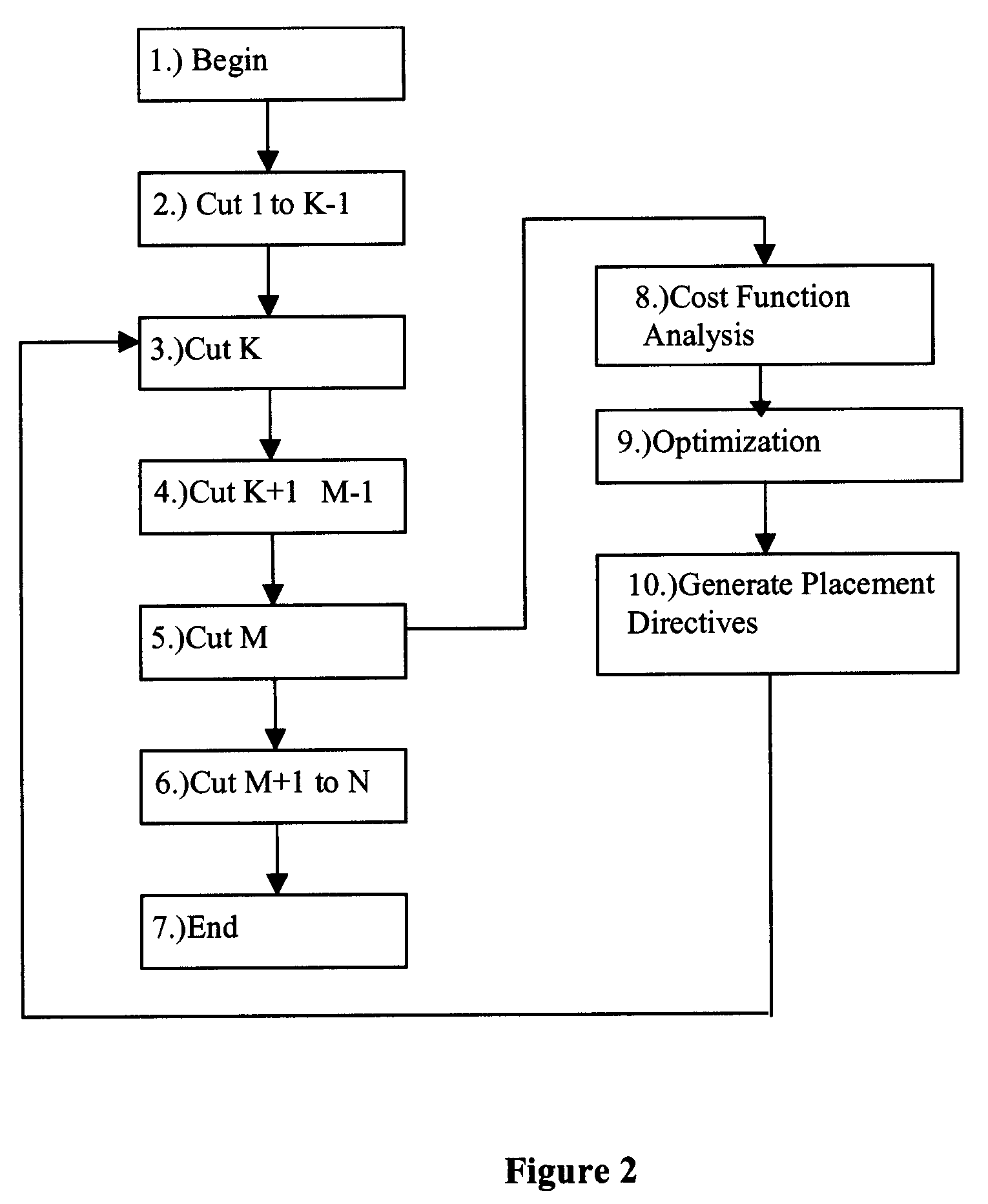
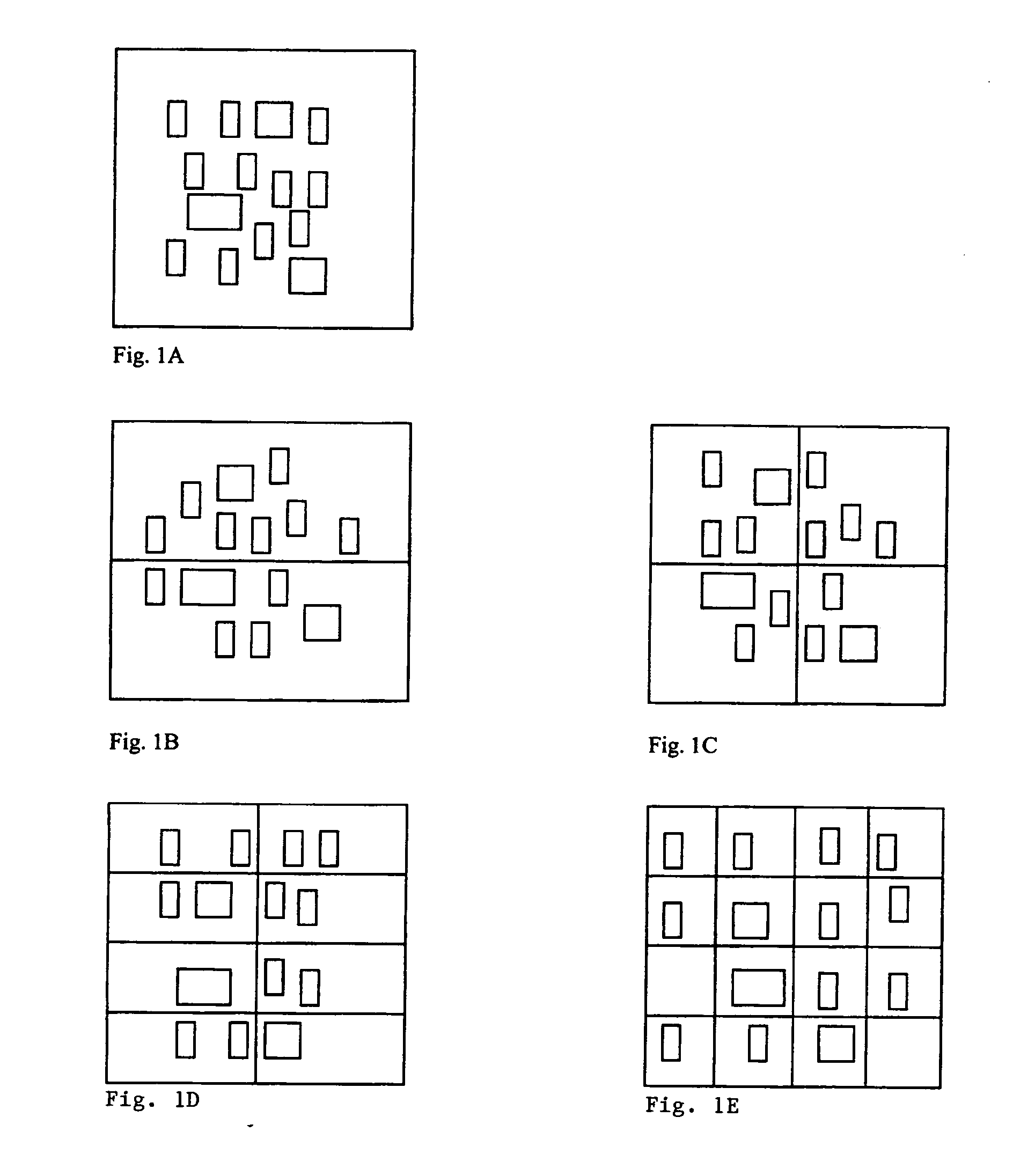
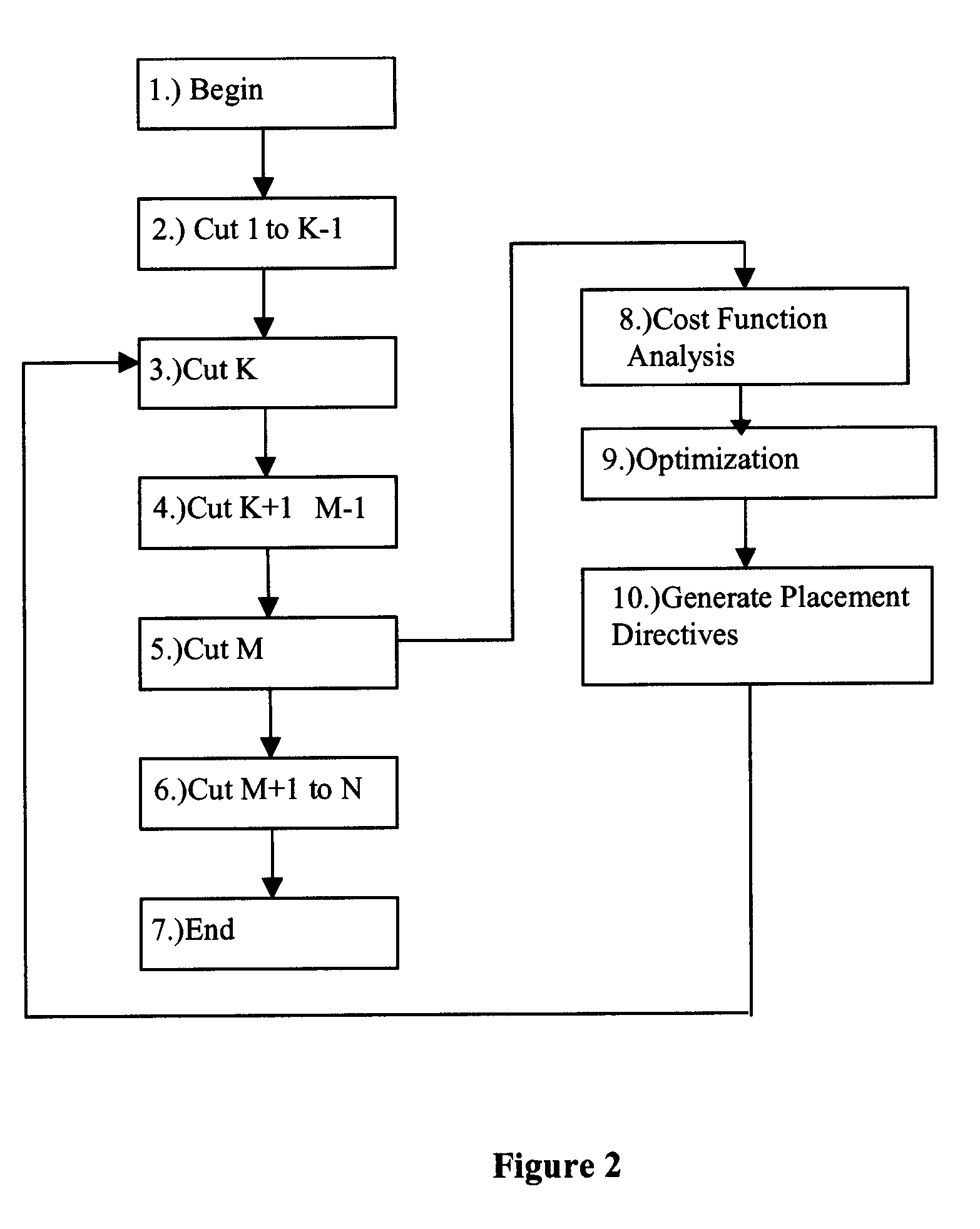
Method for successive placement based refinement of a generalized cost function
InactiveUS7076755B2Quality improvementEasy to placeMulti-objective optimisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCost metricComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Layout methodology and system for automated place and route
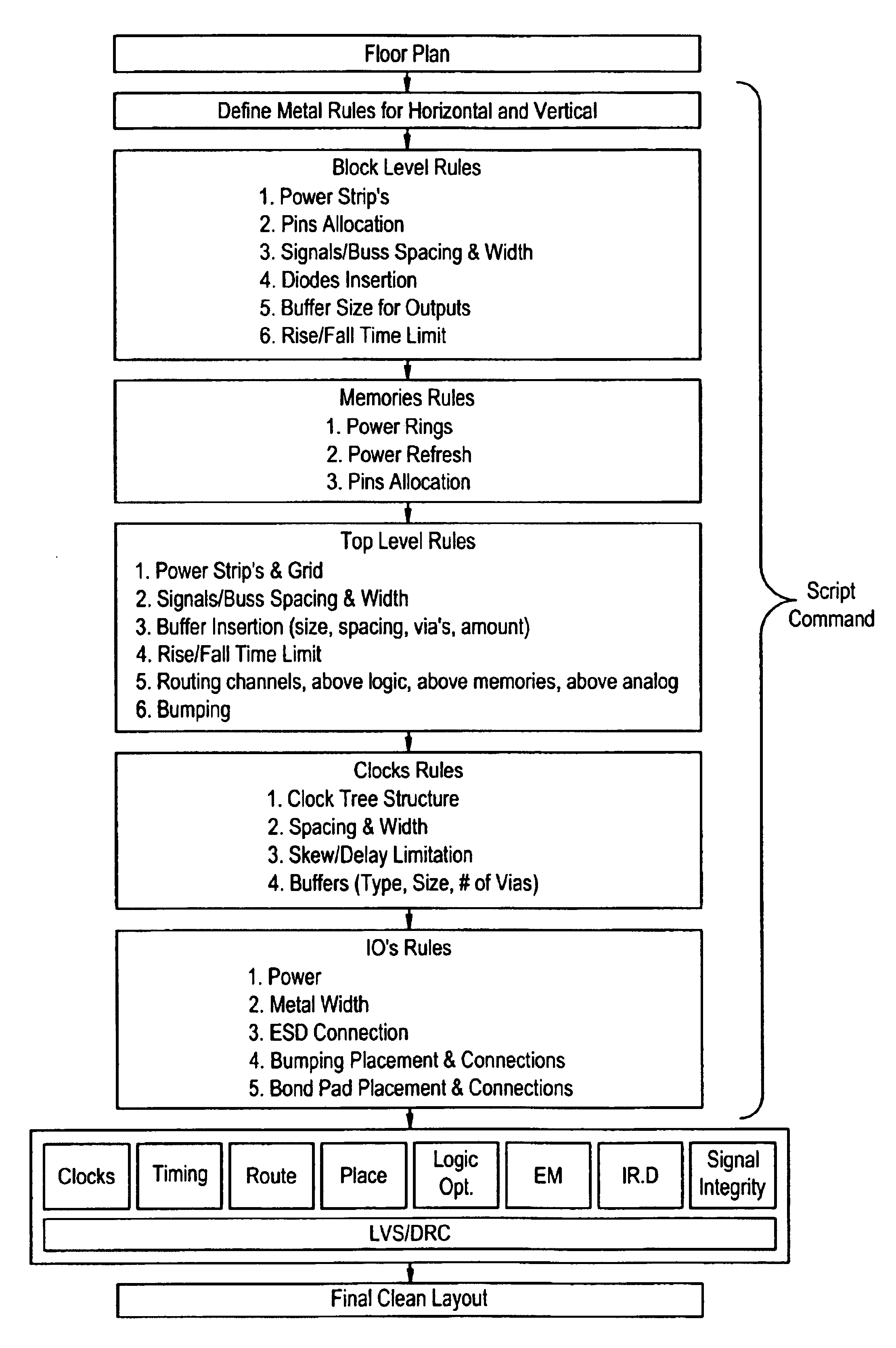
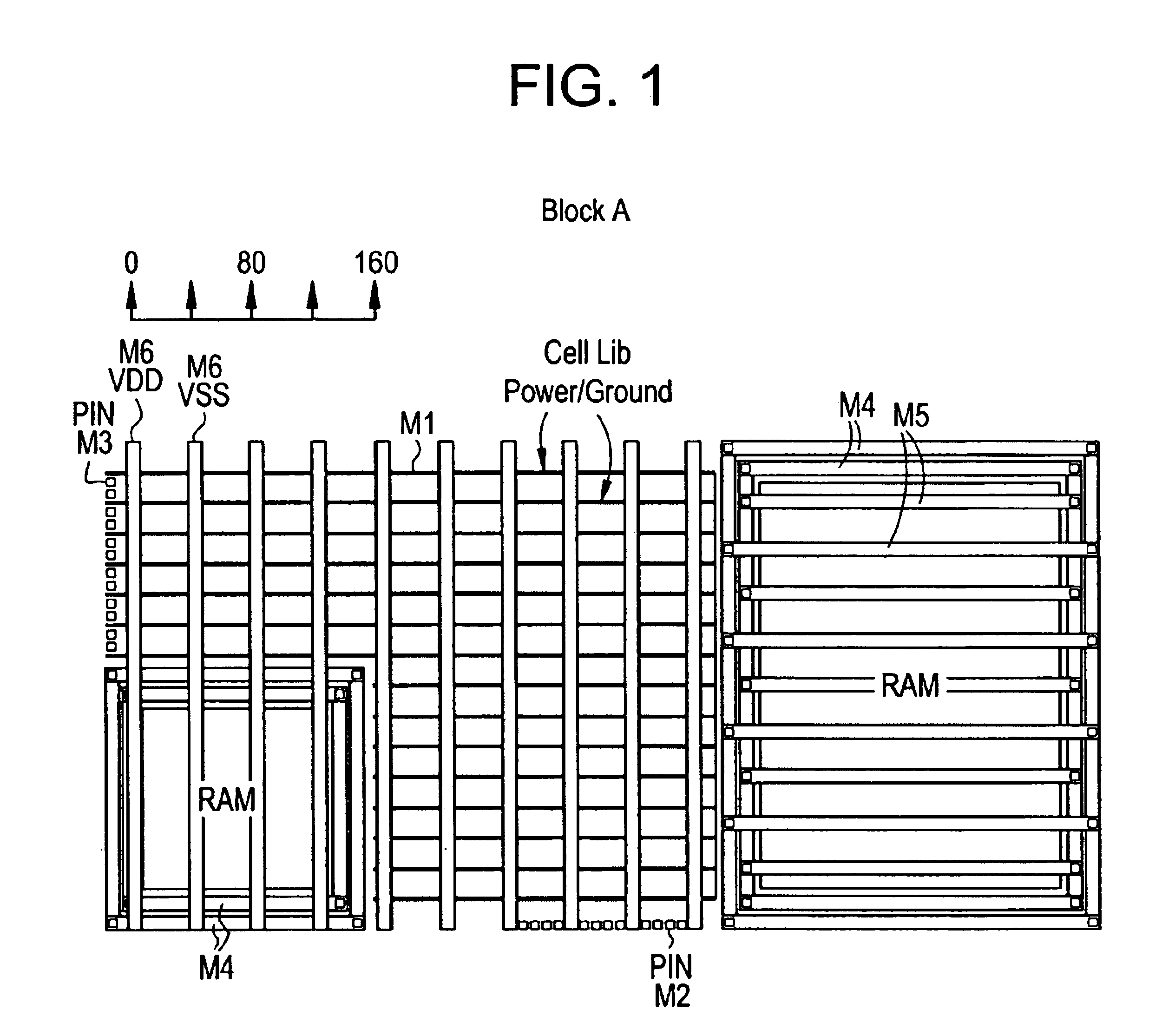
InactiveUS6934924B2Minimized required human resourceSimple and robustCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringVlsi chip
A new simple novel Layout methodology for high integration VLSI chip is proposed, which is reduced dramatically the complexity, the cost and the schedule for implementing a complex chip such as System On a Chip (SOC) that required hierarchical layout implementation. A set of rules is provided for the place and route process.
Owner:TERACHIP
Super CMOS devices on a microelectronics system
ActiveUS8476689B2Significant costSignificant performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSSchottky barrier
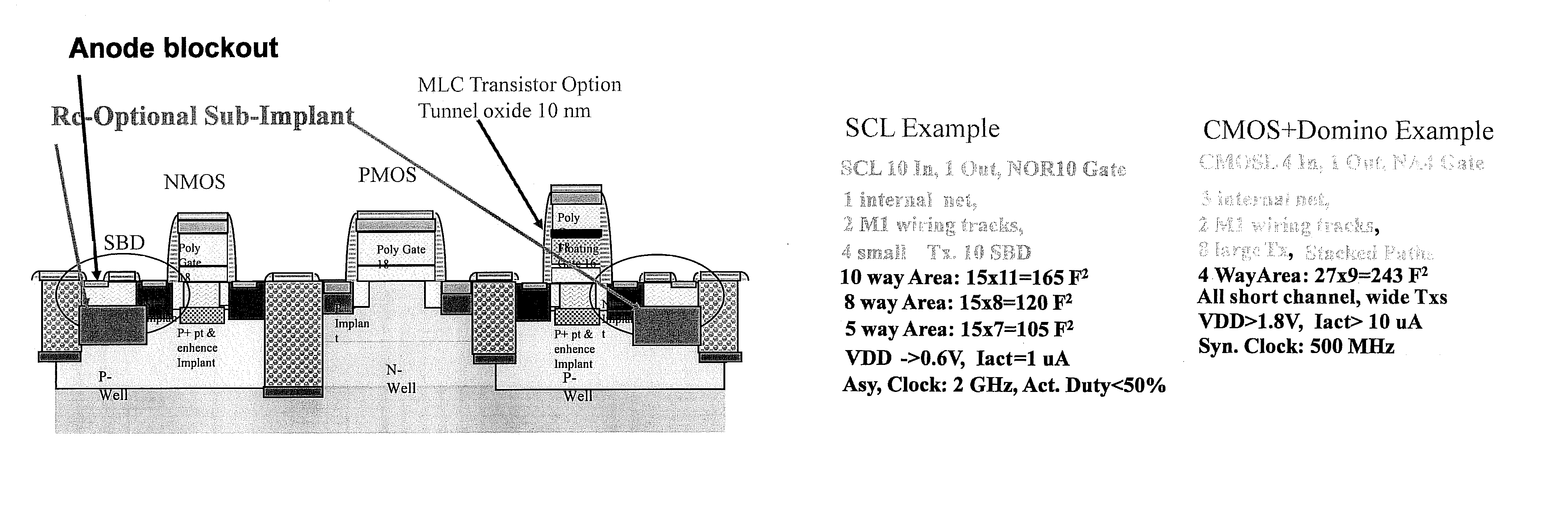
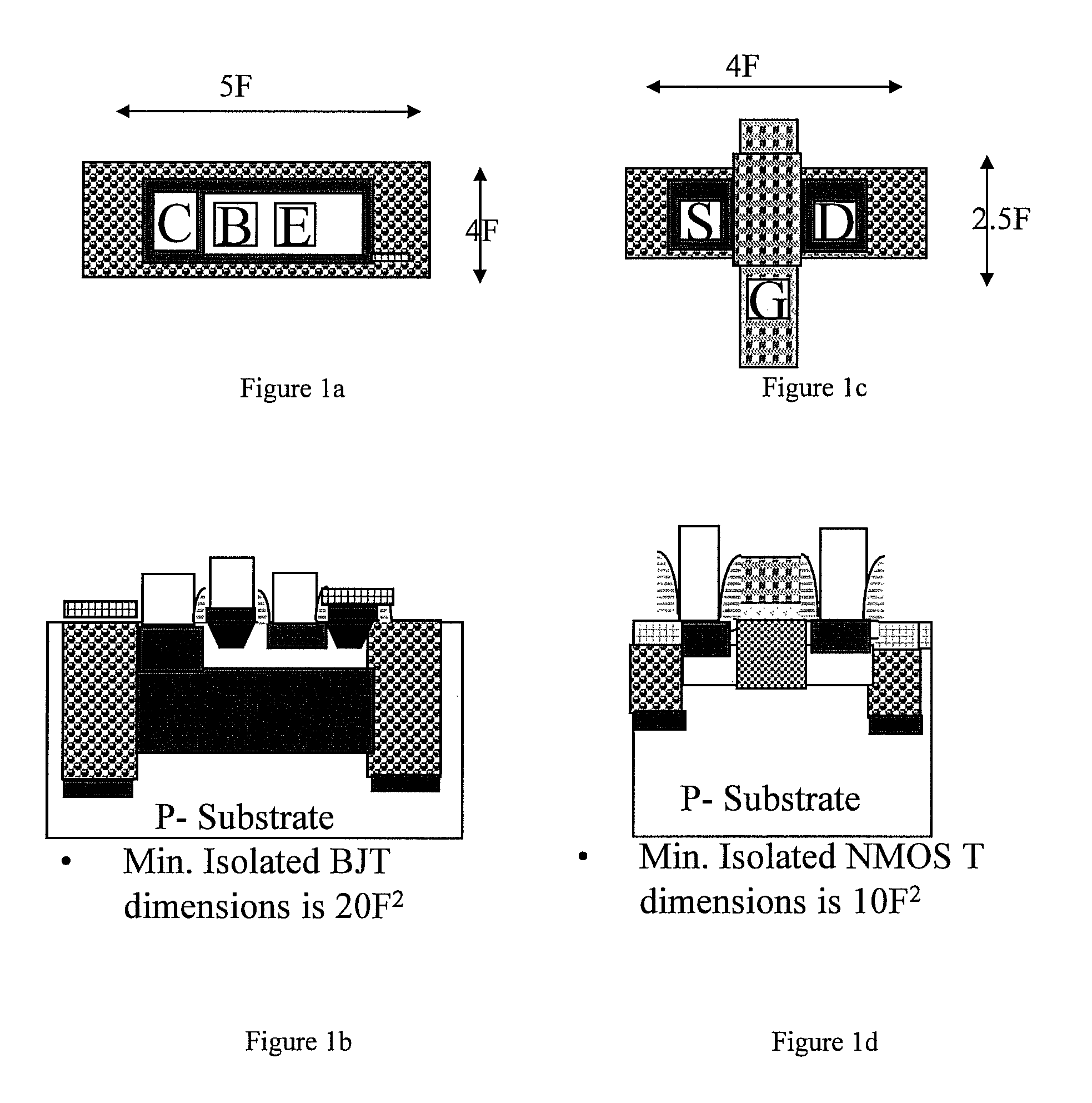
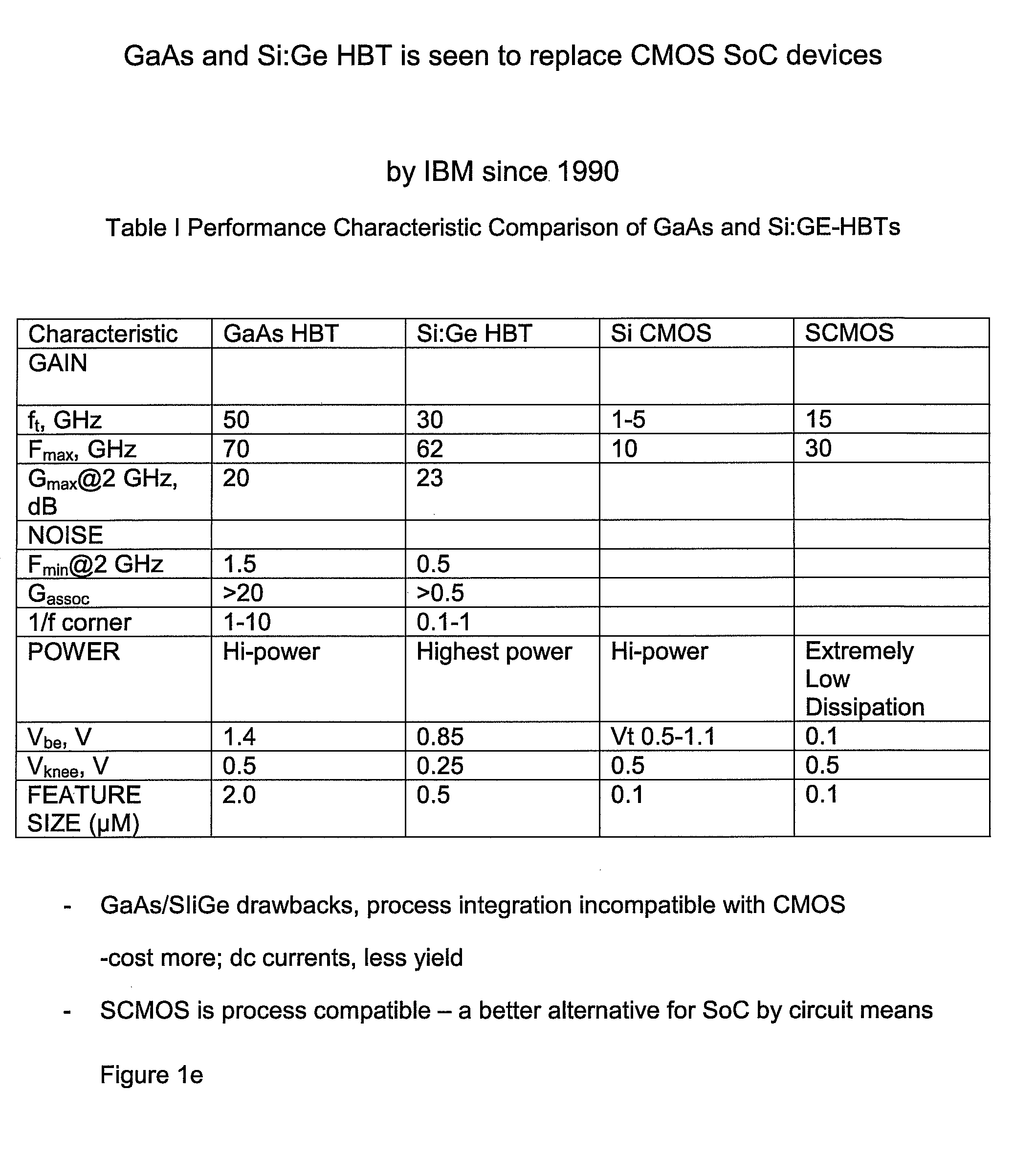
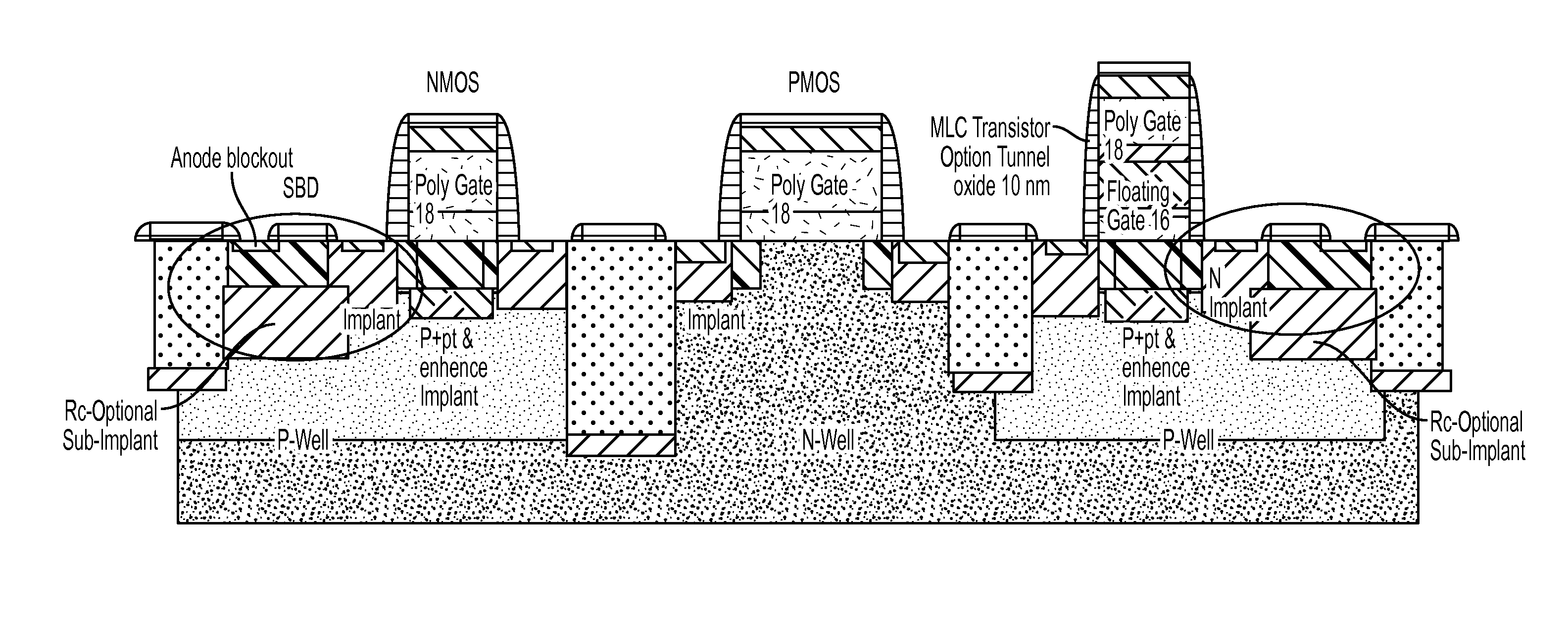
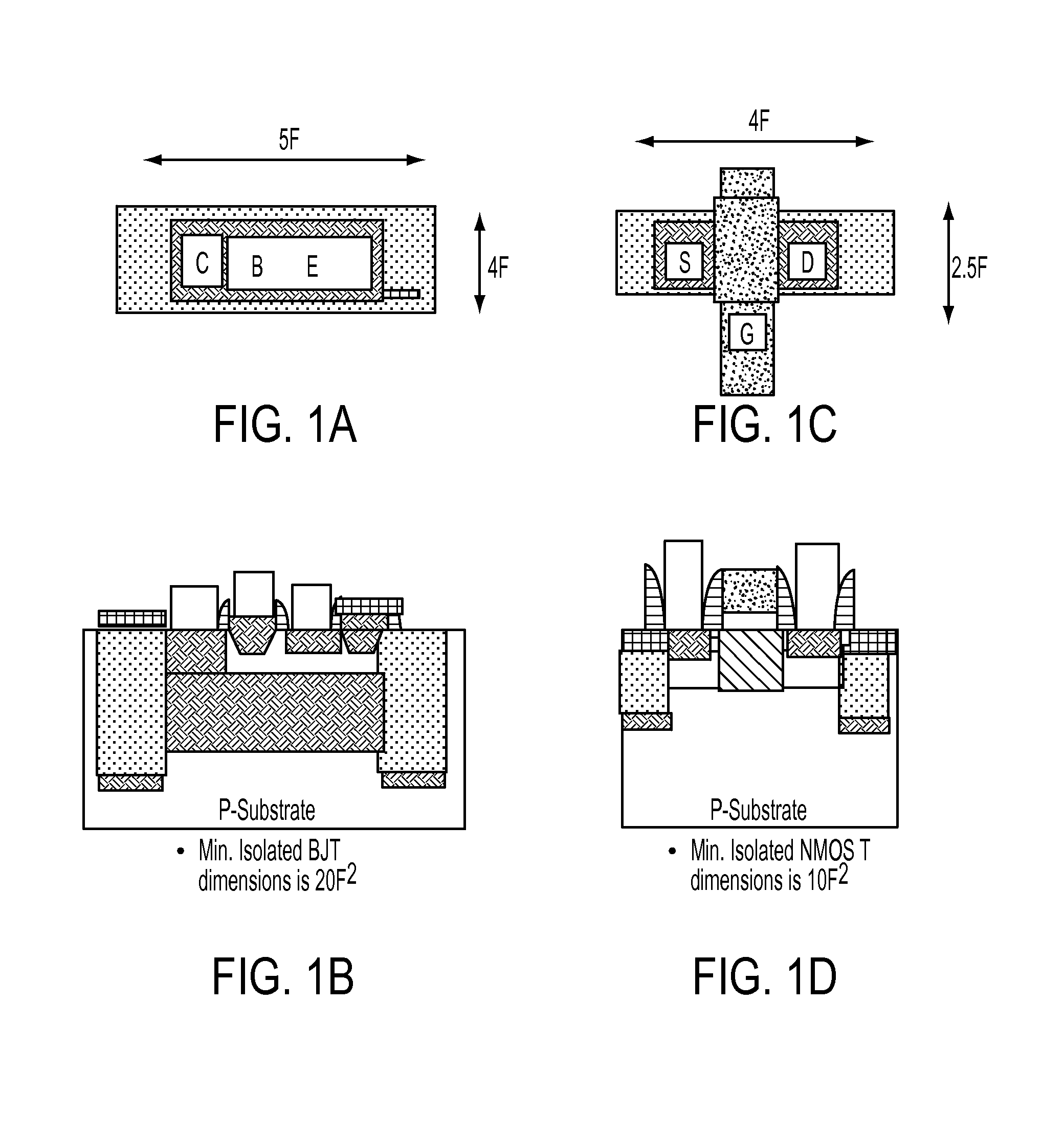
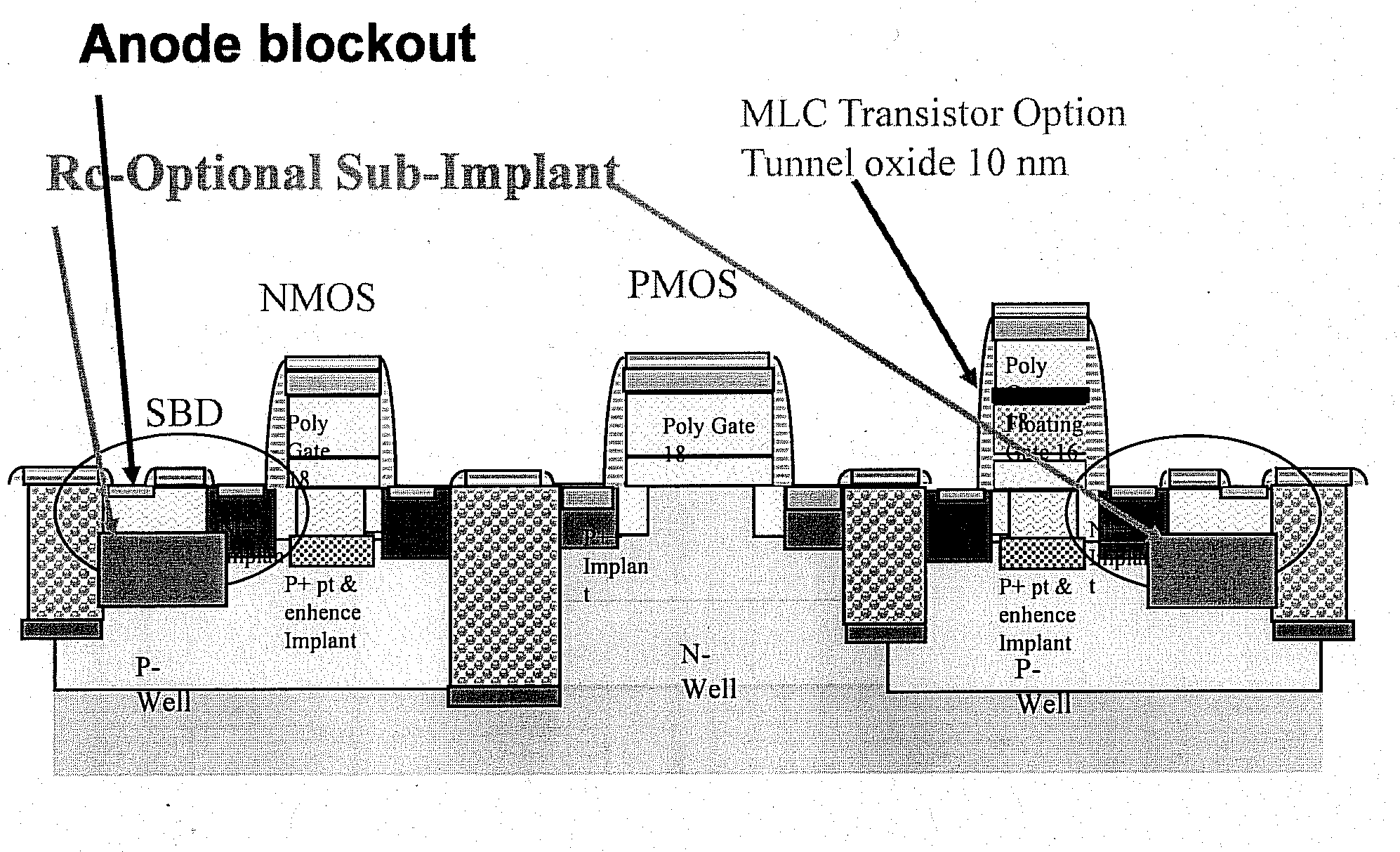
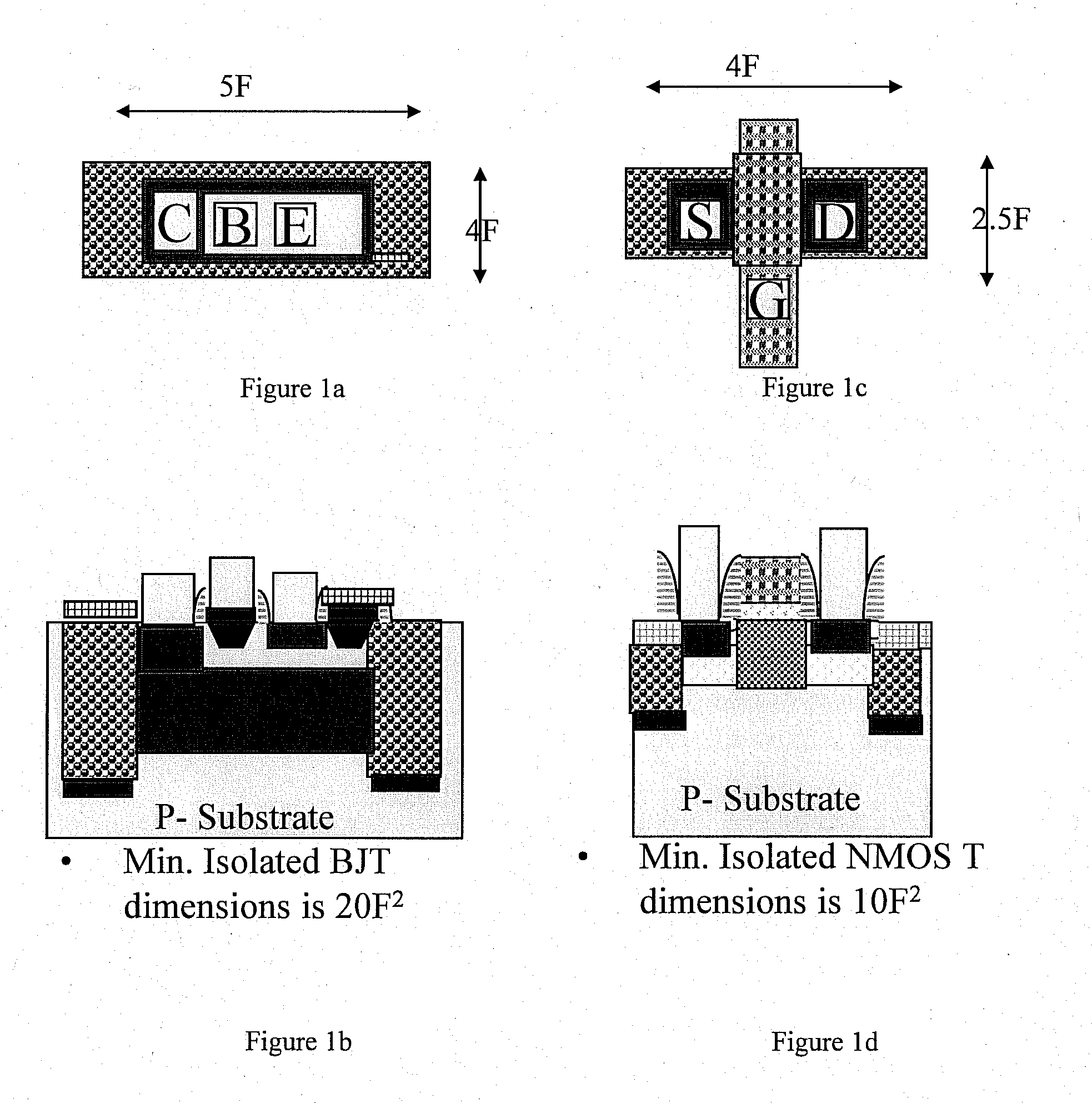
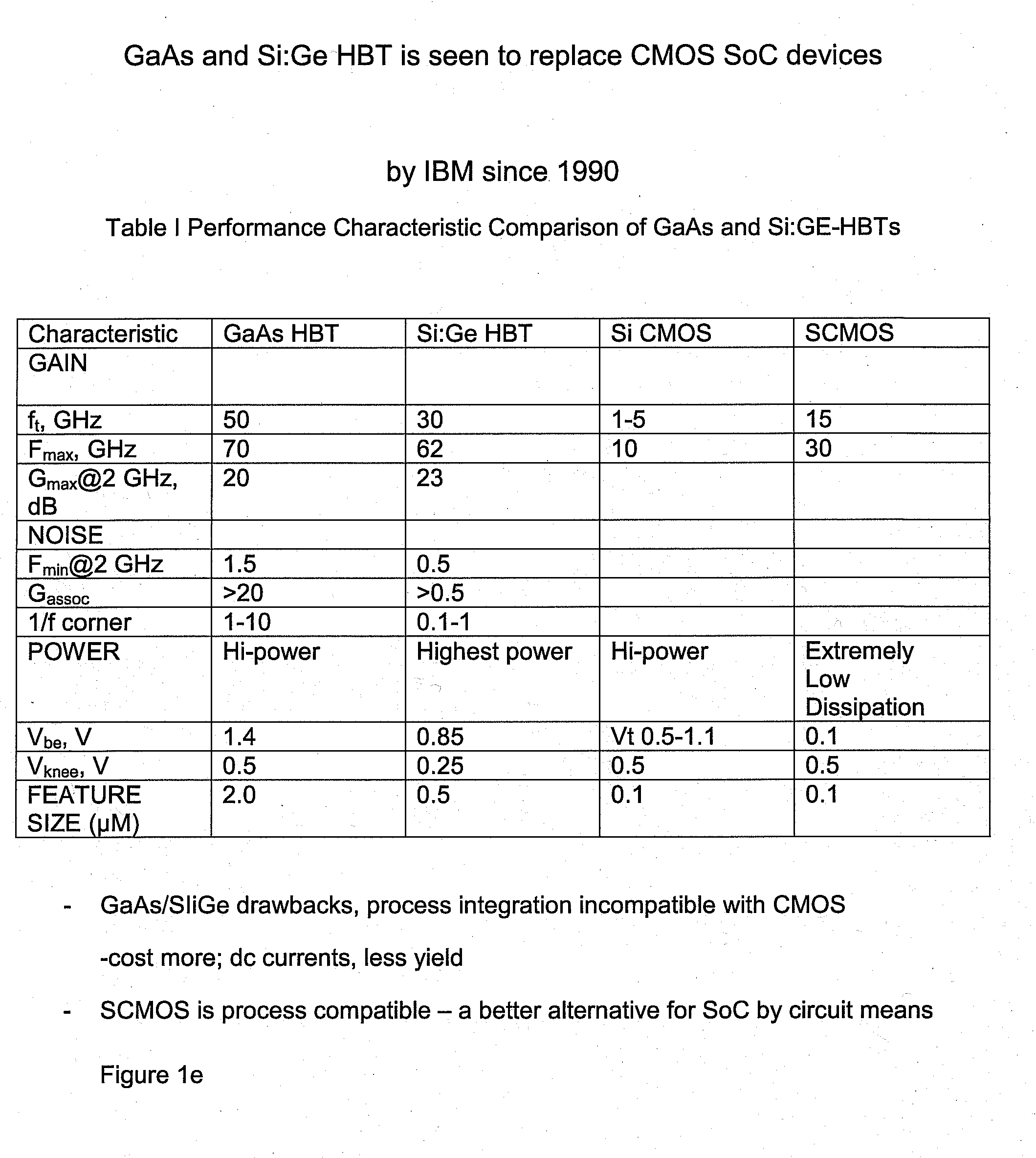
A low cost IC solution is disclosed in accordance with an embodiment to provide Super CMOS microelectronics macros. Hereinafter, the Super CMOS or Schottky CMOS all refer to SCMOS. The SCMOS device solutions with a niche circuit element, the complementary low threshold Schottky barrier diode pairs (SBD) made by selected metal barrier contacts (Co / Ti) to P- and N- Si beds of the CMOS transistors. A DTL like new circuit topology and designed wide contents of broad product libraries, which used the integrated SBD and transistors (BJT, CMOS, and Flash versions) as basic components. The macros are composed of diodes that are selectively attached to the diffusion bed of the transistors, configuring them to form generic logic gates, memory cores, and analog functional blocks from simple to the complicated, from discrete components to all grades of VLSI chips. Solar photon voltaic electricity conversion and bio-lab-on-a-chip are two newly extended fields of the SCMOS IC applications.
Owner:SCHOTTKY LSI
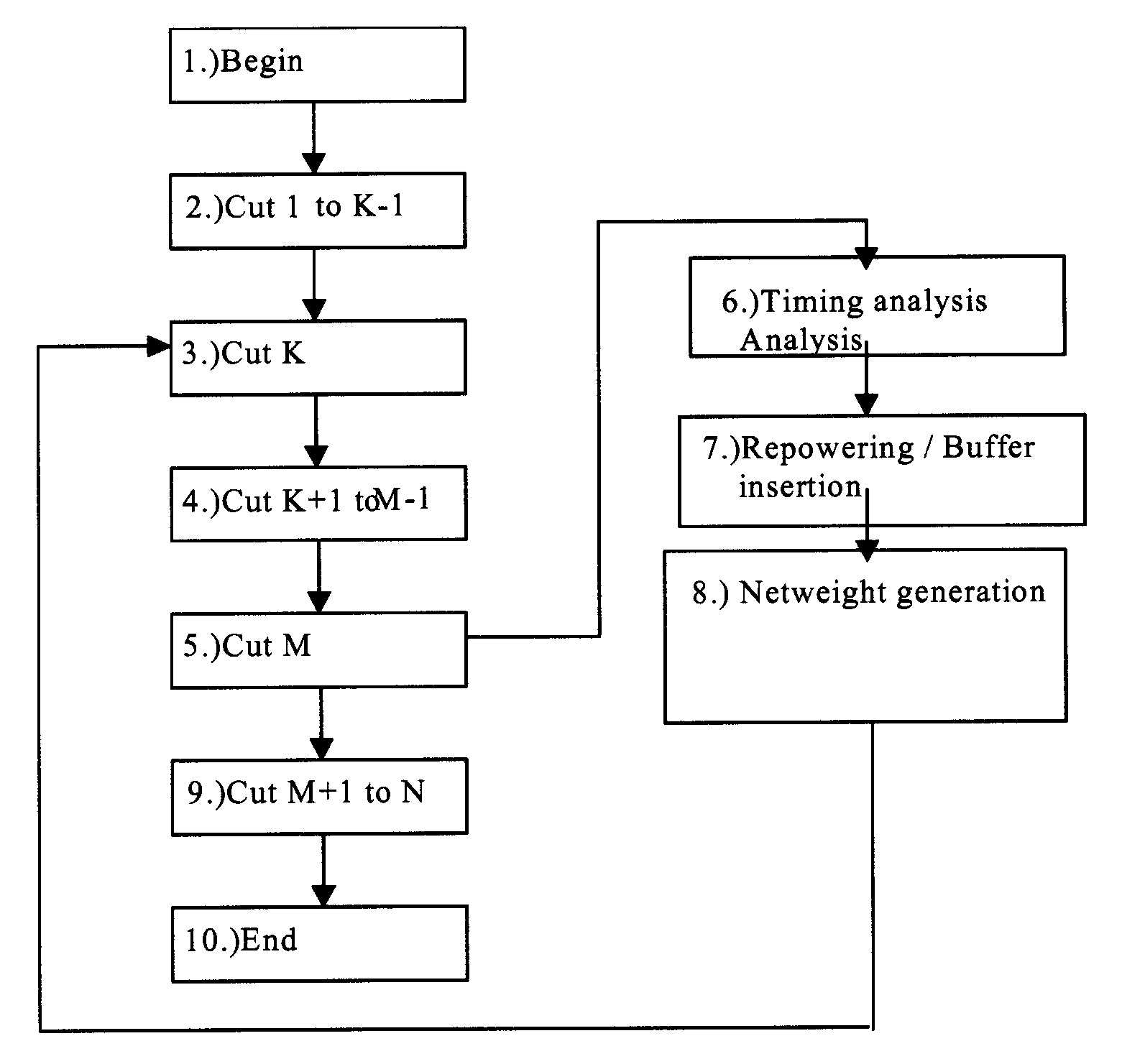
Method for performing timing closure on VLSI chips in a distributed environment
InactiveUS7178120B2Quality improvementComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSingle processPresent method
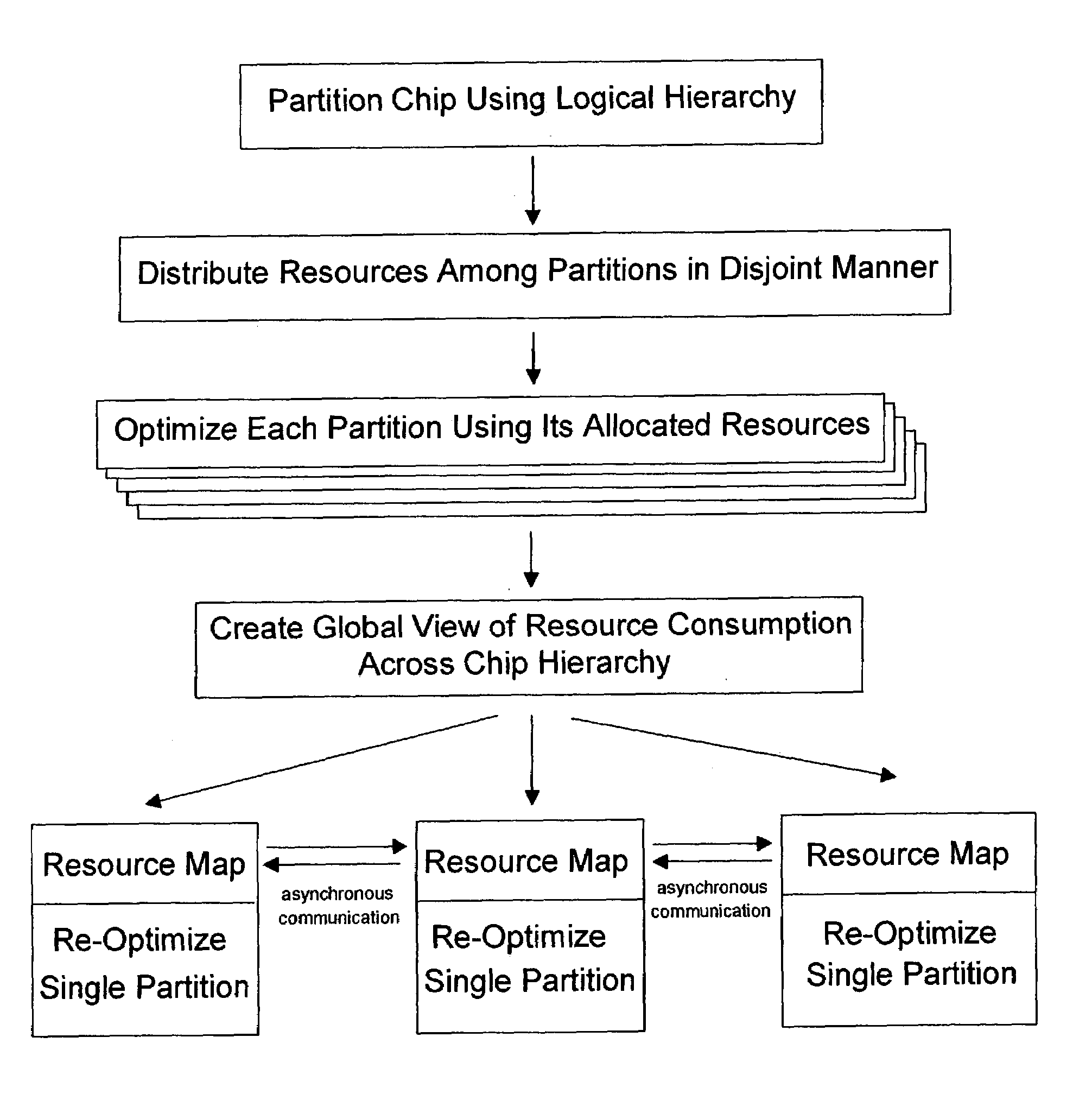
A method for performing timing closure on VLSI chips in a distributed environment is described. Abstracting the physical and timing resources of a chip and providing an asynchronous method of updating that abstraction allows multiple partitions of a chip to be optimized concurrently. A global view of physical and timing resources is supplied to local optimizations which are applied concurrently to achieve timing closure. Portions of the hierarchy are optimized in separate processes. Partitioning of the chip is performed along hierarchical lines, with each process owning a single partition in the hierarchy. The processes may be executed by a single computer, or spread across multiple computers in a local network. While optimizations performed by a single process are only applied to its given portion of the hierarchy, decisions are made in the context of the entire hierarchy. These optimizations include placement, synthesis, and routing. The present method can also be expanded to include other resources, such as routing resource, power supply current, power / thermal budget, substrate noise budget, and the like, all of which being able to be similarly abstracted and shared.
Owner:IBM CORP
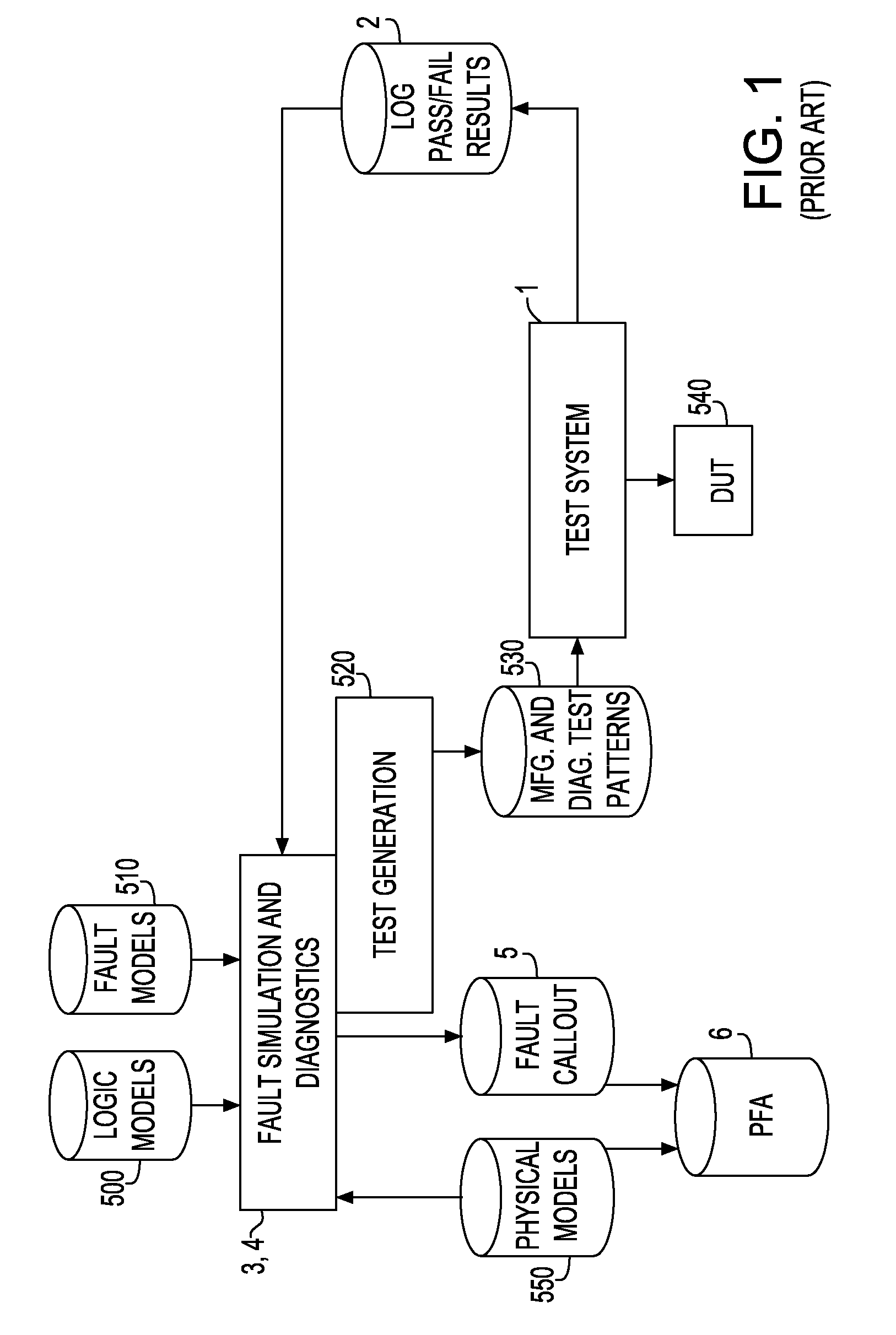
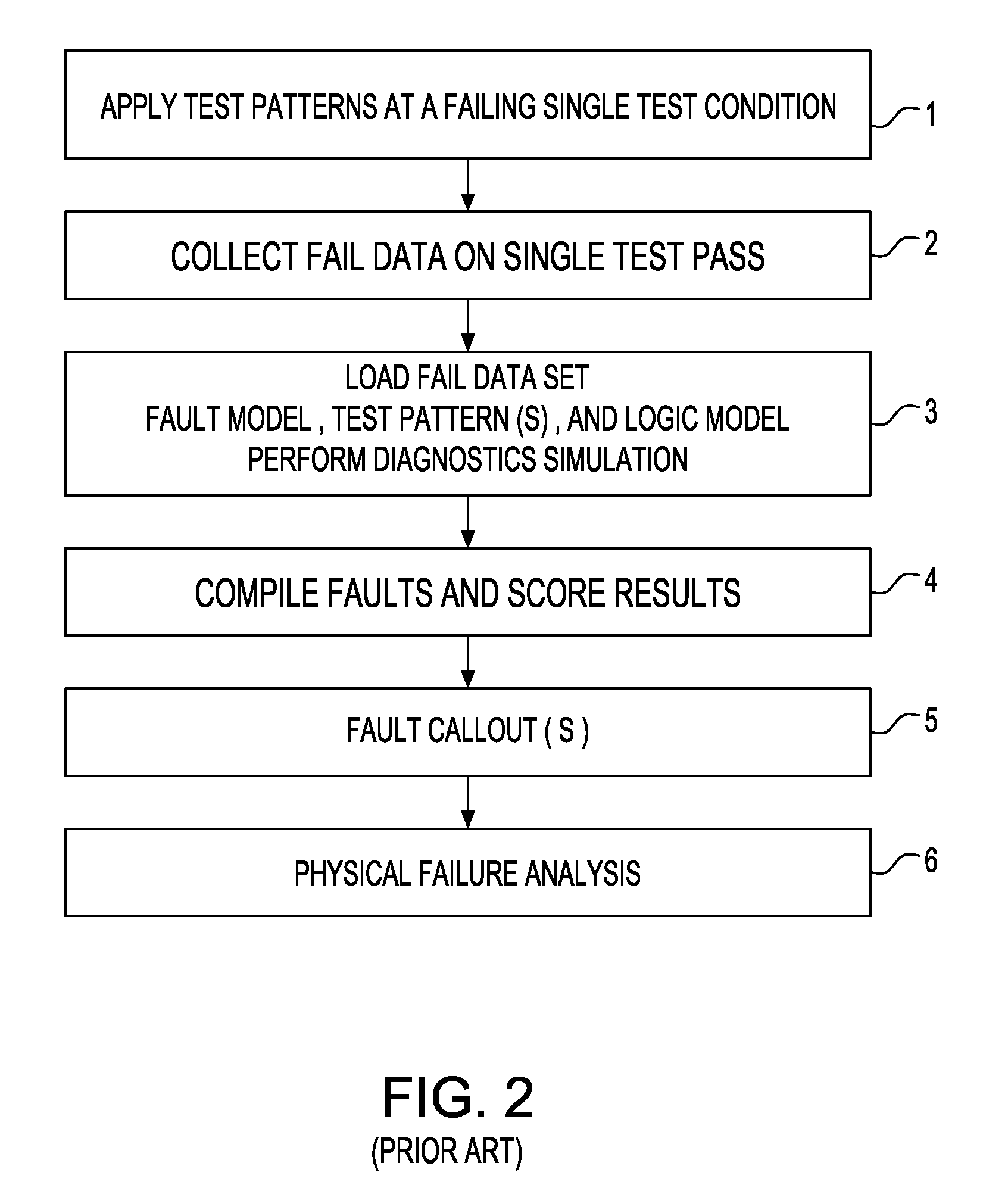
Method for enhancing the diagnostic accuracy of a VLSI chip
InactiveUS20080172576A1Improve diagnostic accuracyHigh simulationFunctional testingImage resolutionPattern generation
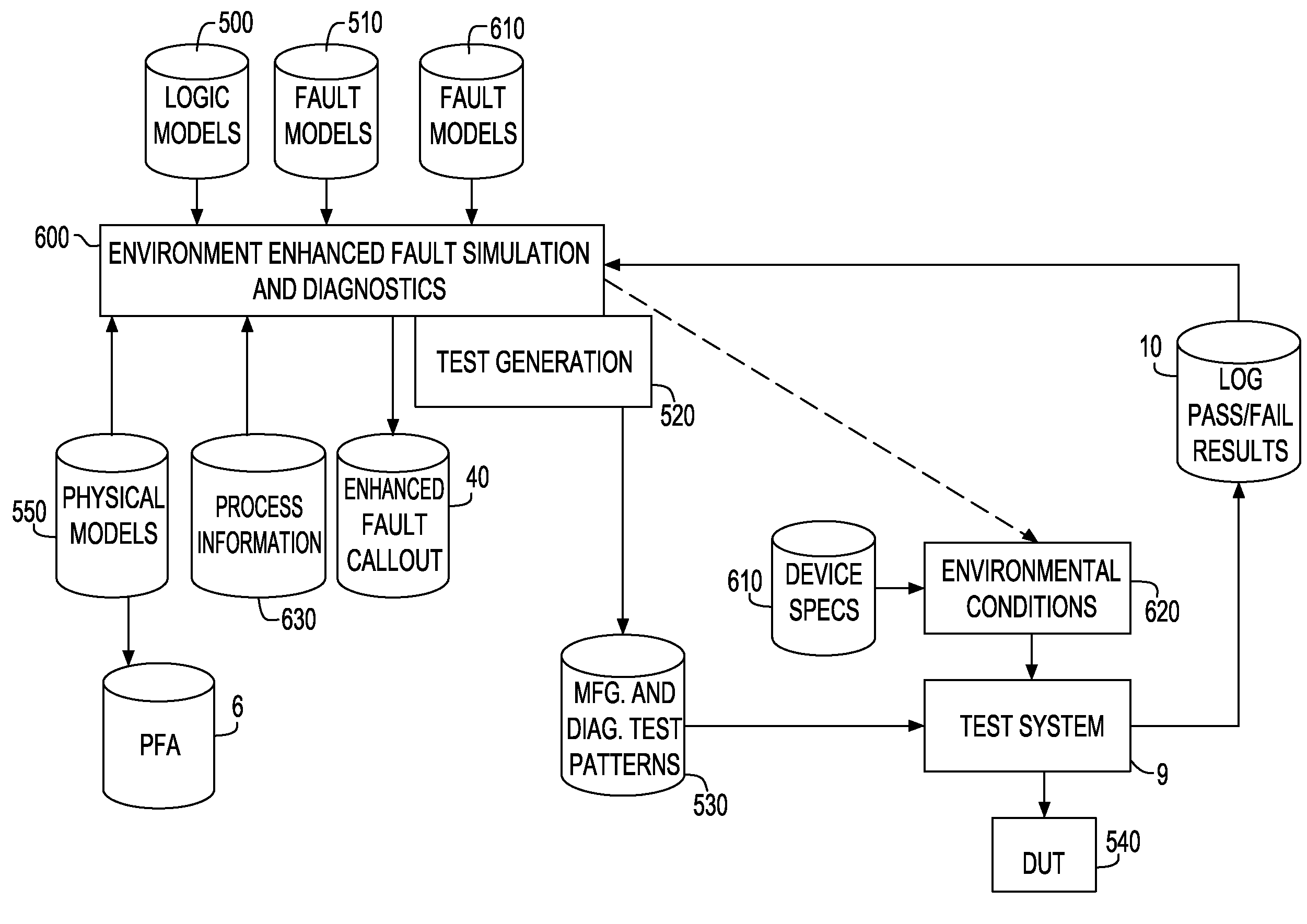
A diagnostic process applicable to VLSI designs to address the accuracy of diagnostic resolution. Environmentally based fail data drives adaptive test methods which hone the test pattern set and fail data collection for successful diagnostic resolution. Environmentally based fail data is used in diagnostic simulation to achieve a more accurate environmentally based fault callout. When needed, additional information is included in the process to further refine and define the simulation or callout result. Similarly, as needed adaptive test pattern generation methods are employed to result in enhanced diagnostic resolution.
Owner:IBM CORP
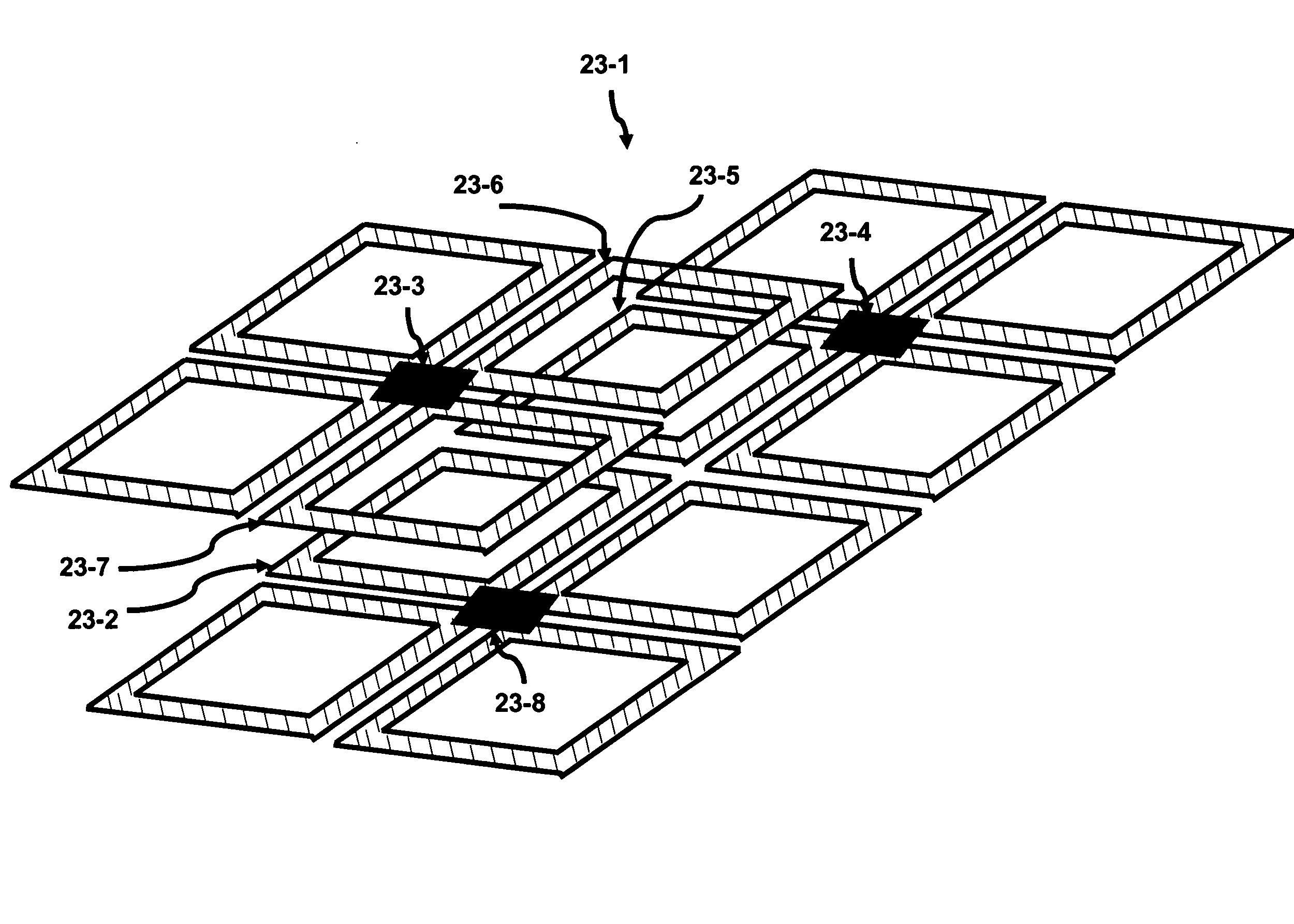
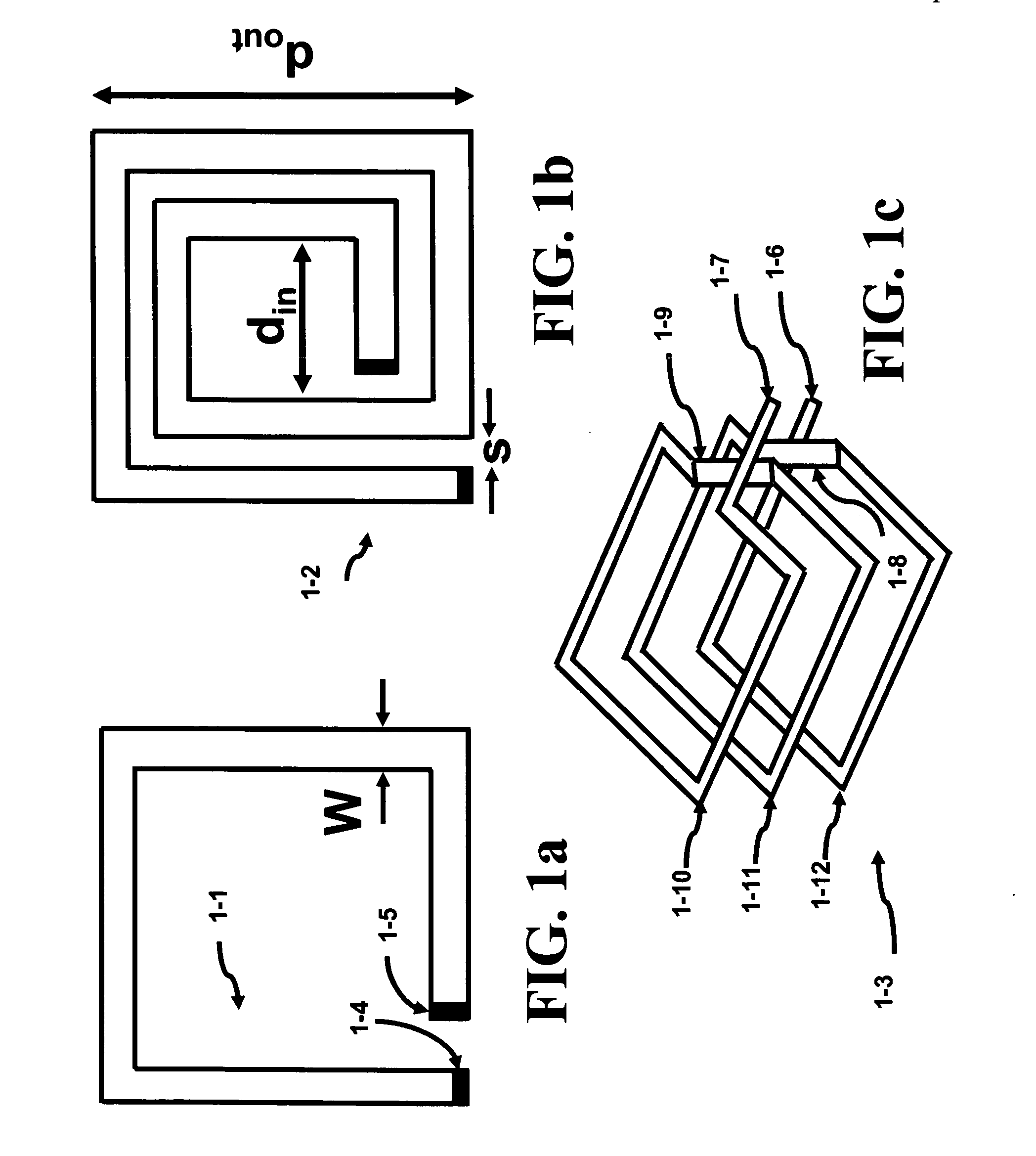
Multi-phase Closed Loop LC Tank Circuits
InactiveUS20080074202A1Solid-state devicesGenerating/distributing signalsInterconnectivityMetal interconnect
LC tank circuits can be coupled together to form closed loop oscillators. The interconnectivity of these LC tank circuits were performed by a physical connection such as a metal interconnect. The LC tank circuits may also comprise a plurality of inductors that are coupled together in parallel. These closed loop oscillators generate oscillations which have multi-phase components. Such circuits are useful for RF designs, clock generation for VLSI chips, adiabatic circuitry, analog circuitry, and high-speed digital circuitry.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 70
Error detection and correction in data transmission packets
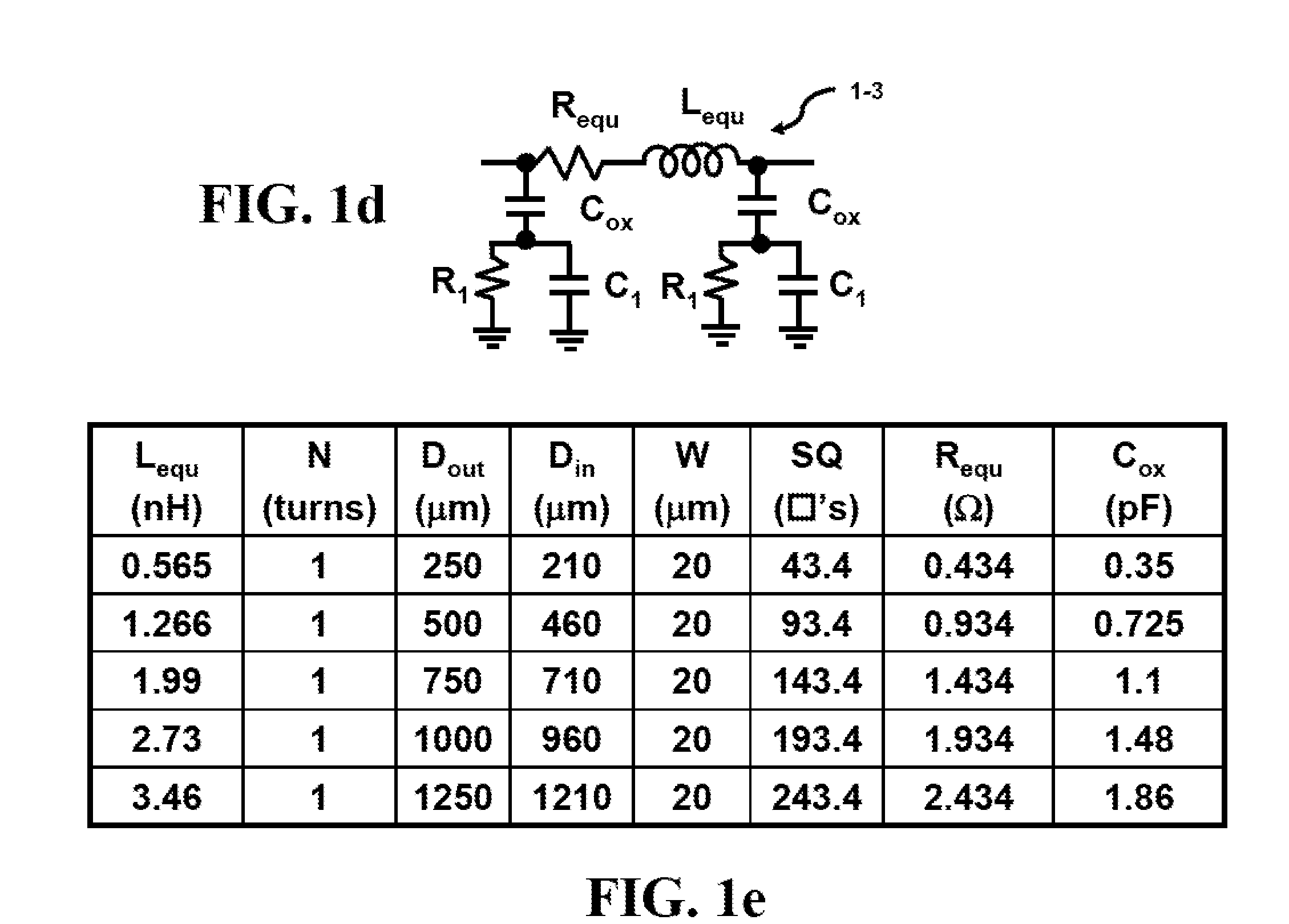
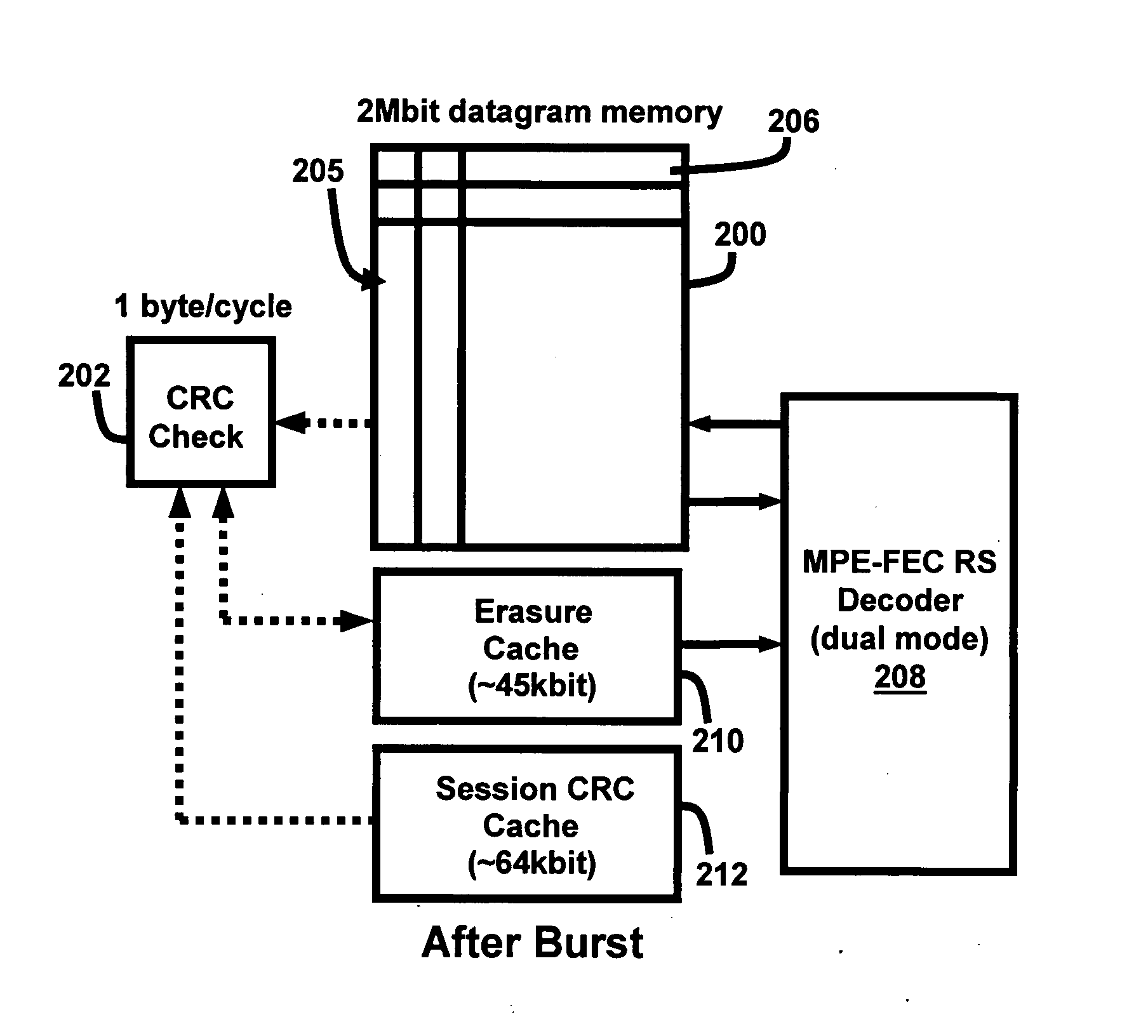
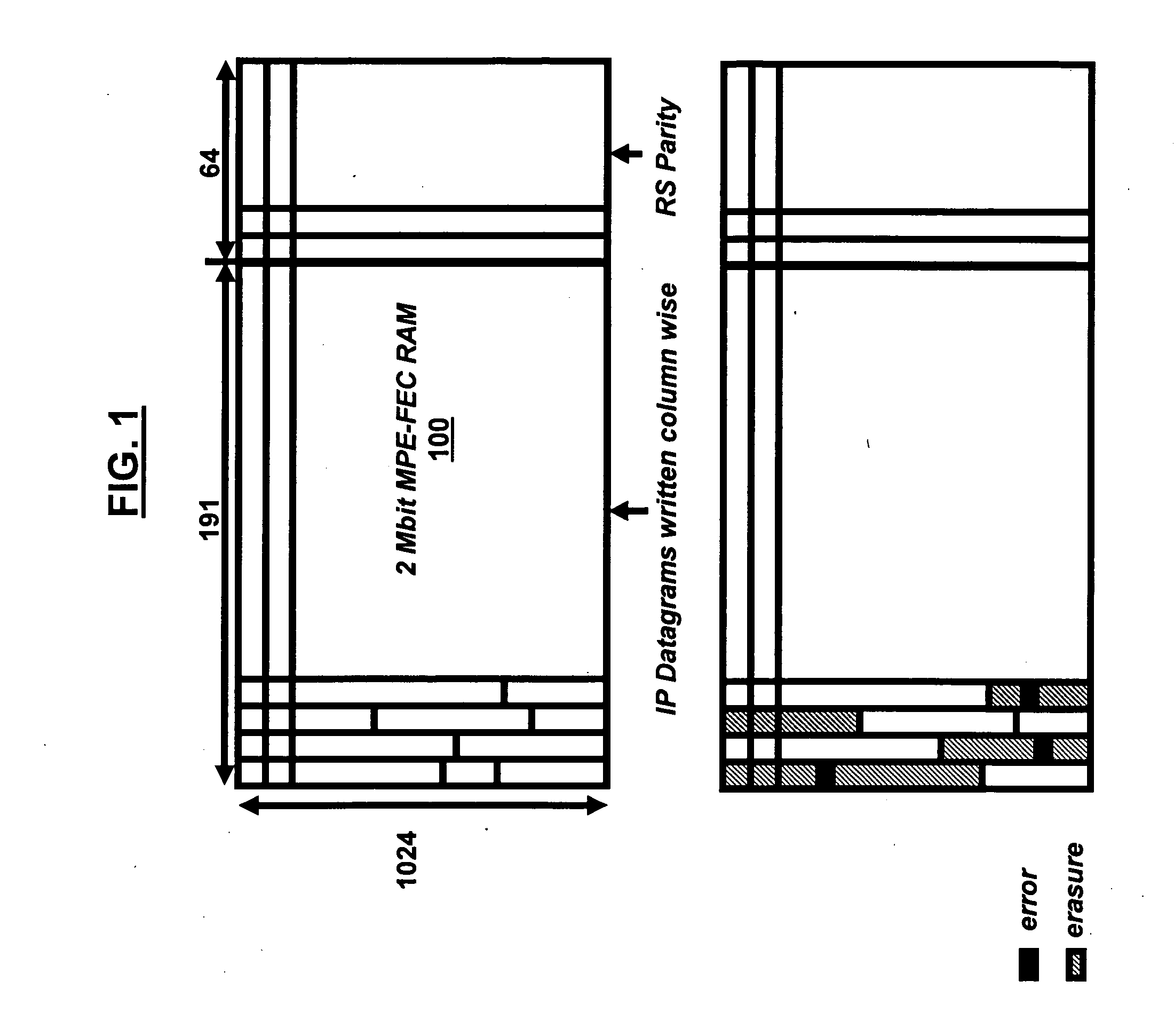
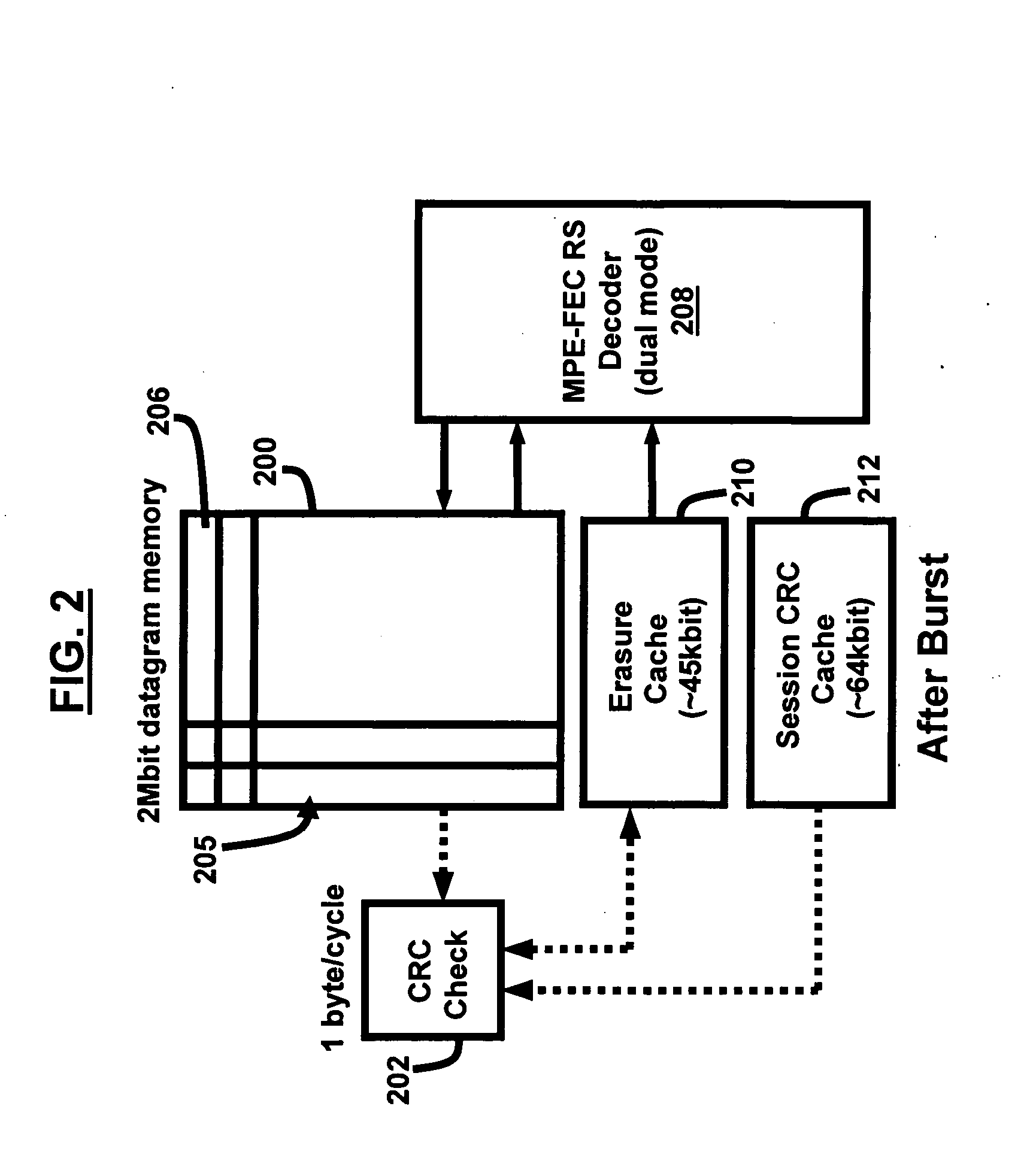
A system and method of using recursive cyclic redundancy check (CRC)+forward error correction (FEC) for enhancing the channel coding gain for a DVB-H receiver, and using a physical (PHY) Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder+FEC to achieve better coding gain. The system and method utilize a dual mode RS decoder (erasure mode and error mode) for FEC decoding. The PHY RS is used to provide smaller granularity for FEC. The system includes a cache memory management scheme for implementing the recursive CRC / RS+FEC in very large scale integrated circuit chip (VLSI) hardware.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
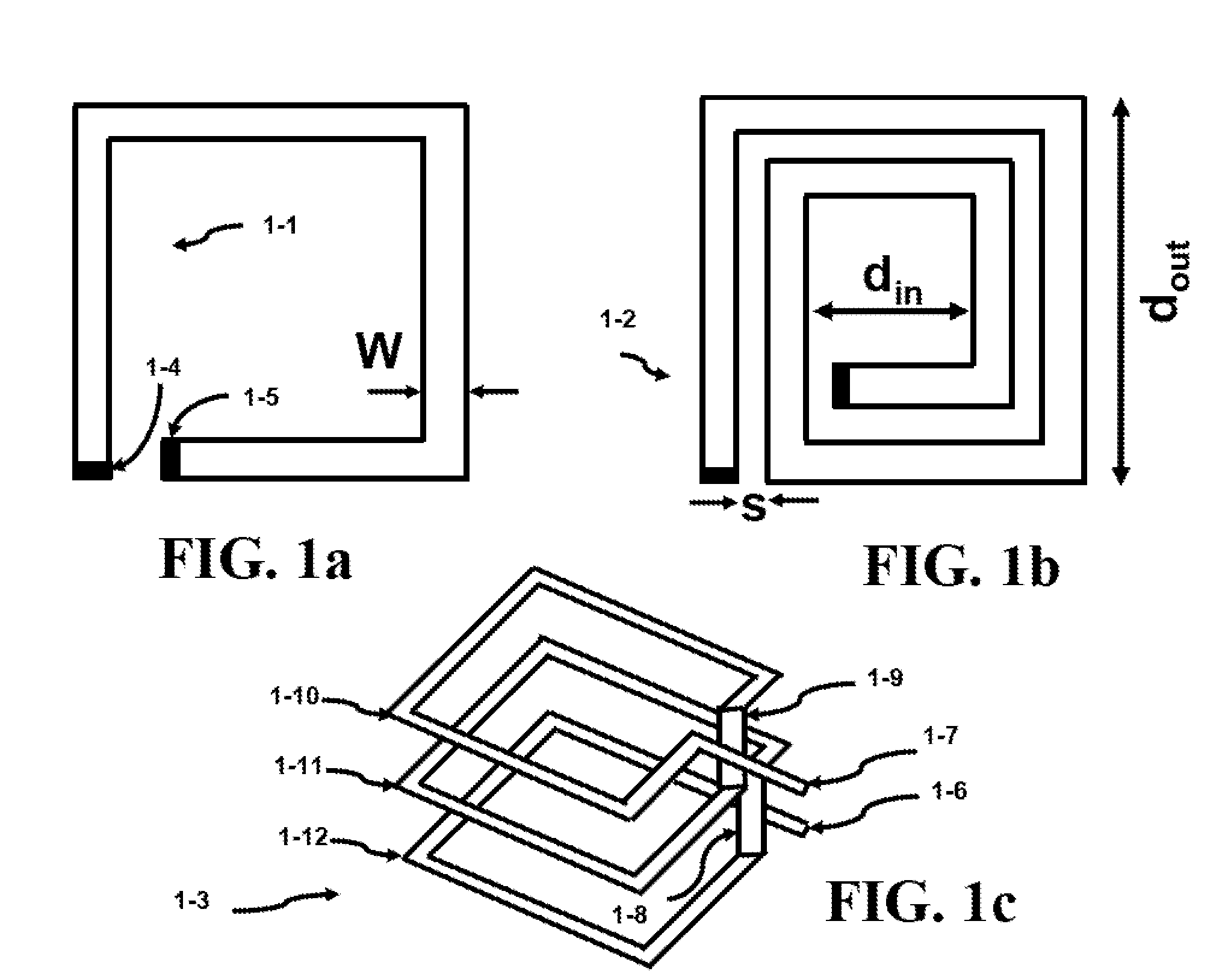
High Speed Clock Distribution Transmission Line Network
ActiveUS20080030252A1Mitigate the clock jitterNetwork can be lowReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDistribution treeElectrical conductor
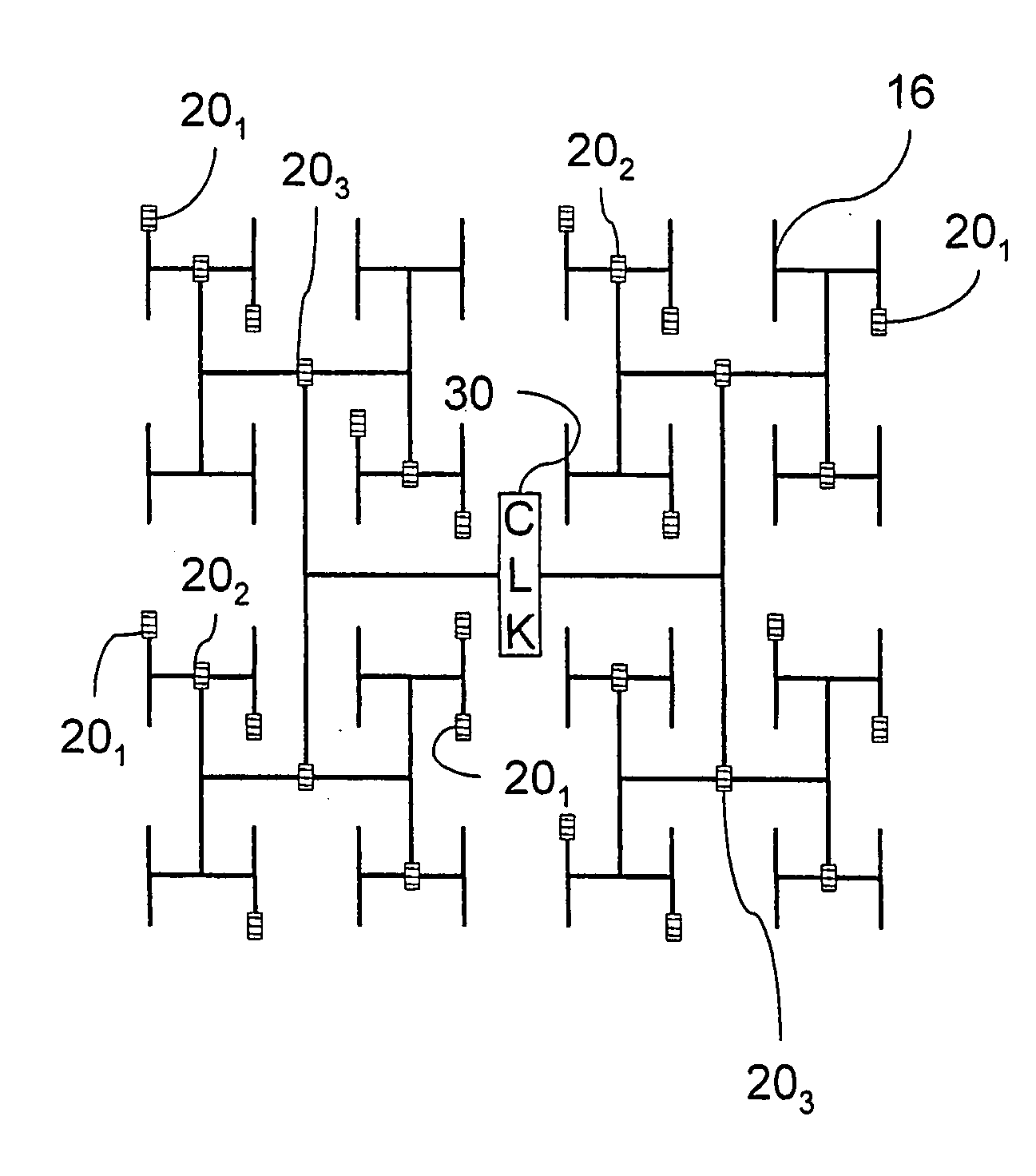
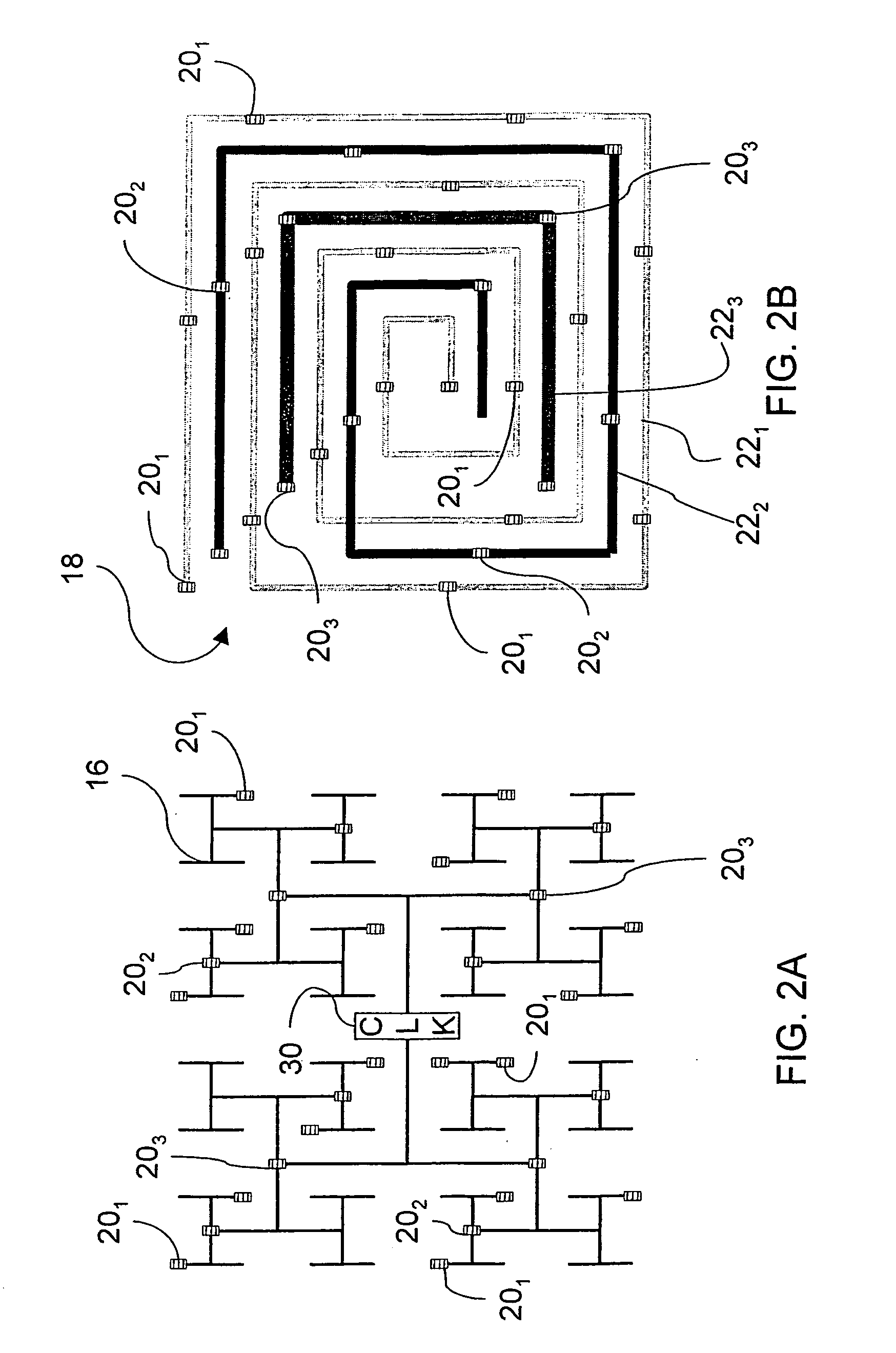
The invention is directed to a method for clock distribution and VLSI circuits include a clock distribution network. In a method of the invention, a transmission lines are patterned as to connect a clock tree and a periodic waveform clock, preferably a sine waveform, is used to control clock skew, even at frequencies extending into the gigahertz range. In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, an overlay includes differential pairs of transmission lines that connect the drivers of a clock distribution tree. In preferred embodiments of the invention, an H-tree clock distribution scheme is overlayed with a spiral of transmission lines, each realized by a differential conductors and driven using a sinusoidal standing wave to distribute global clock signals into local regions of the chip. Each transmission line connects drivers in the H-tree that are at the same level of the H-tree. In a VLSI chip according to an embodiment of the invention, the transmission line overlay delivers sinusoidal clock signals to local areas that are locally converted into digital clock signals. The invention thus presents a passive technique for clock distribution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for optimization of logic circuits for routability
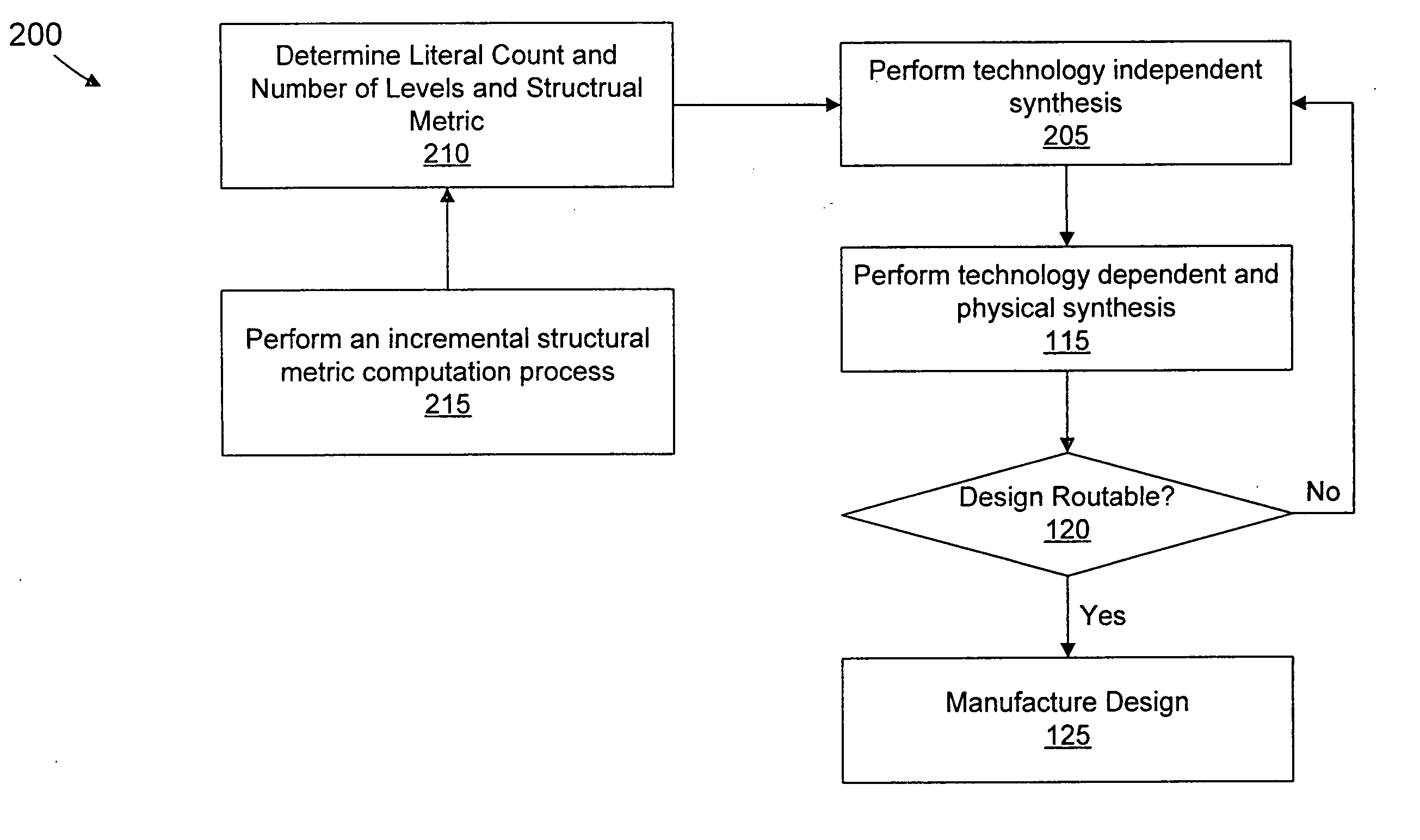
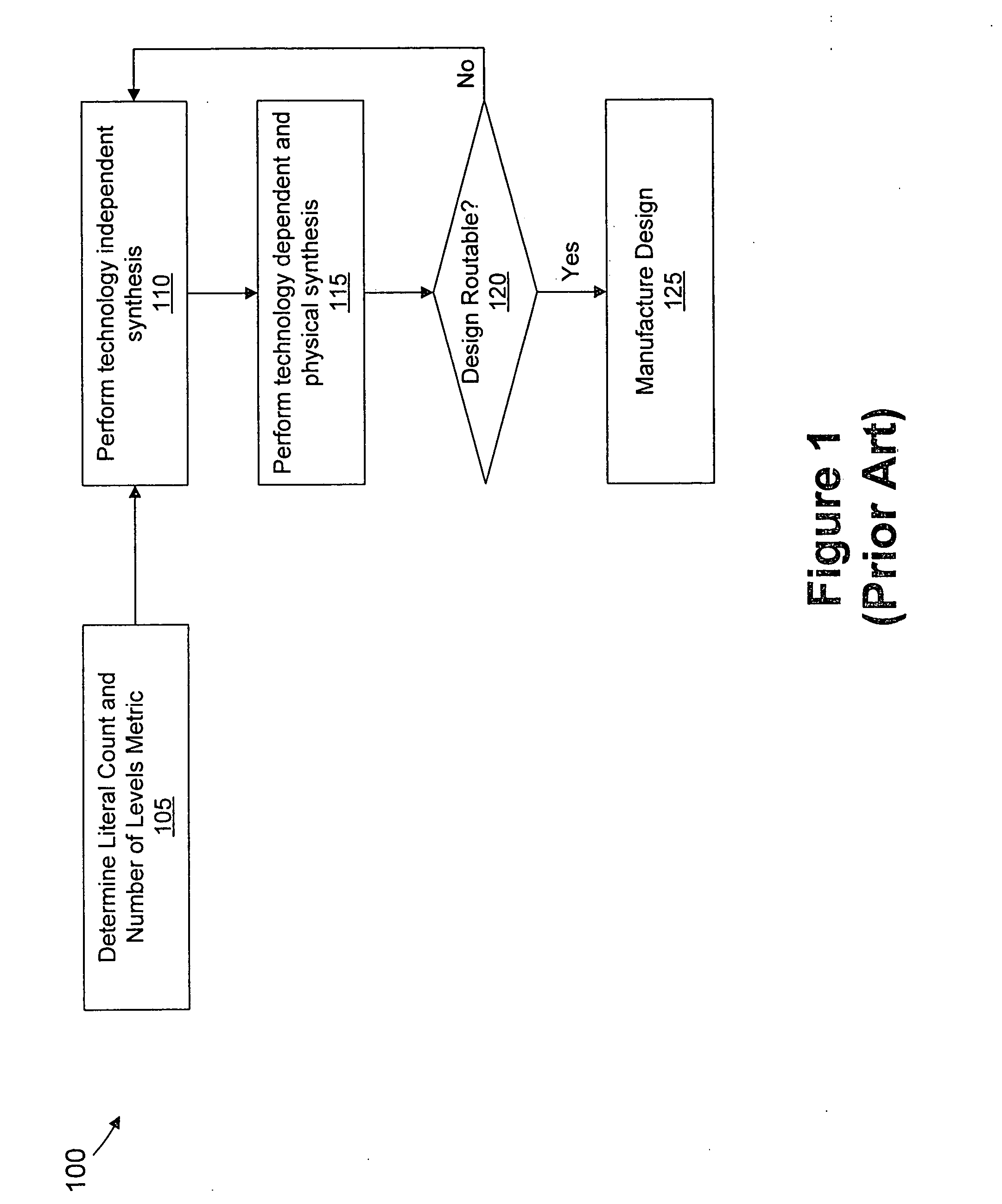
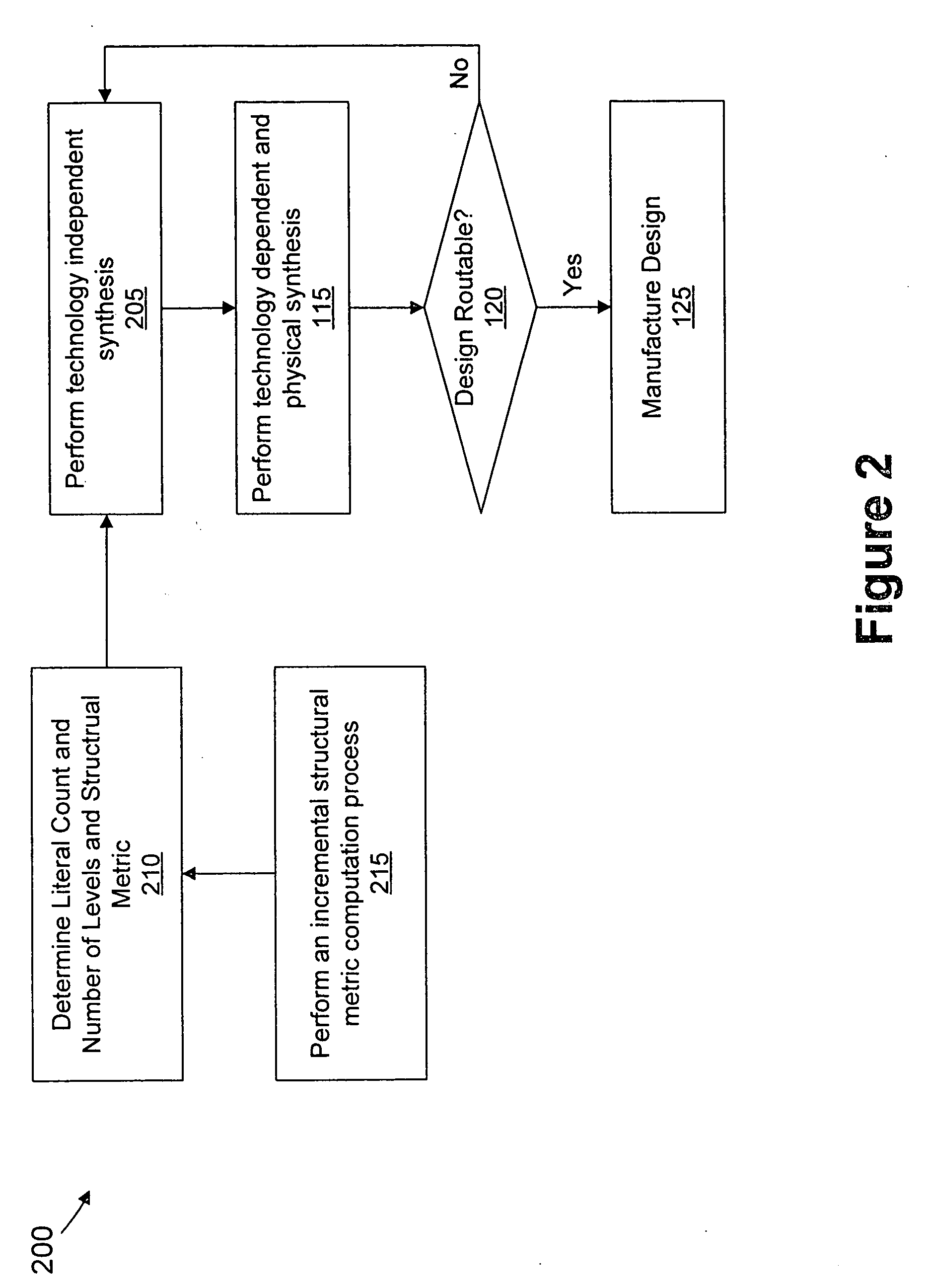
Routability (or wiring congestion) in a VLSI chip is becoming increasingly important as chip complexity increases. Congestion has a significant impact on performance, yield, and chip area. The present invention targets the optimization of congestion early in technology independent synthesis prior to physical design. Instead of attempting to optimize the logic structure as well as the spatial placement of a circuit, we pose a more modest goal limiting such optimization to the scope of logic synthesis. That is, we propose an aggressive optimization approach that is cognizant of circuit structure during technology independent synthesis and produces more predictable implementations which give better routability and yield.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Super CMOS devices on a microelectronics system
ActiveUS20140152343A1Significant costSignificant performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSSchottky barrier
A low cost IC solution is disclosed in accordance with an embodiment to provide Super CMOS microelectronics macros. Hereinafter, the Super CMOS or Schottky CMOS all refer to SCMOS. The SCMOS device solutions with a niche circuit element, the complementary low threshold Schottky barrier diode pairs (SBD) made by selected metal barrier contacts (Co / Ti) to P— and N—Si beds of the CMOS transistors. A DTL like new circuit topology and designed wide contents of broad product libraries, which used the integrated SBD and transistors (BJT, CMOS, and Flash versions) as basic components. The macros are composed of diodes that are selectively attached to the diffusion bed of the transistors, configuring them to form generic logic gates, memory cores, and analog functional blocks from simple to the complicated, from discrete components to all grades of VLSI chips. Solar photon voltaic electricity conversion and bio-lab-on-a-chip are two newly extended fields of the SCMOS IC applications.
Owner:SCHOTTKY LSI
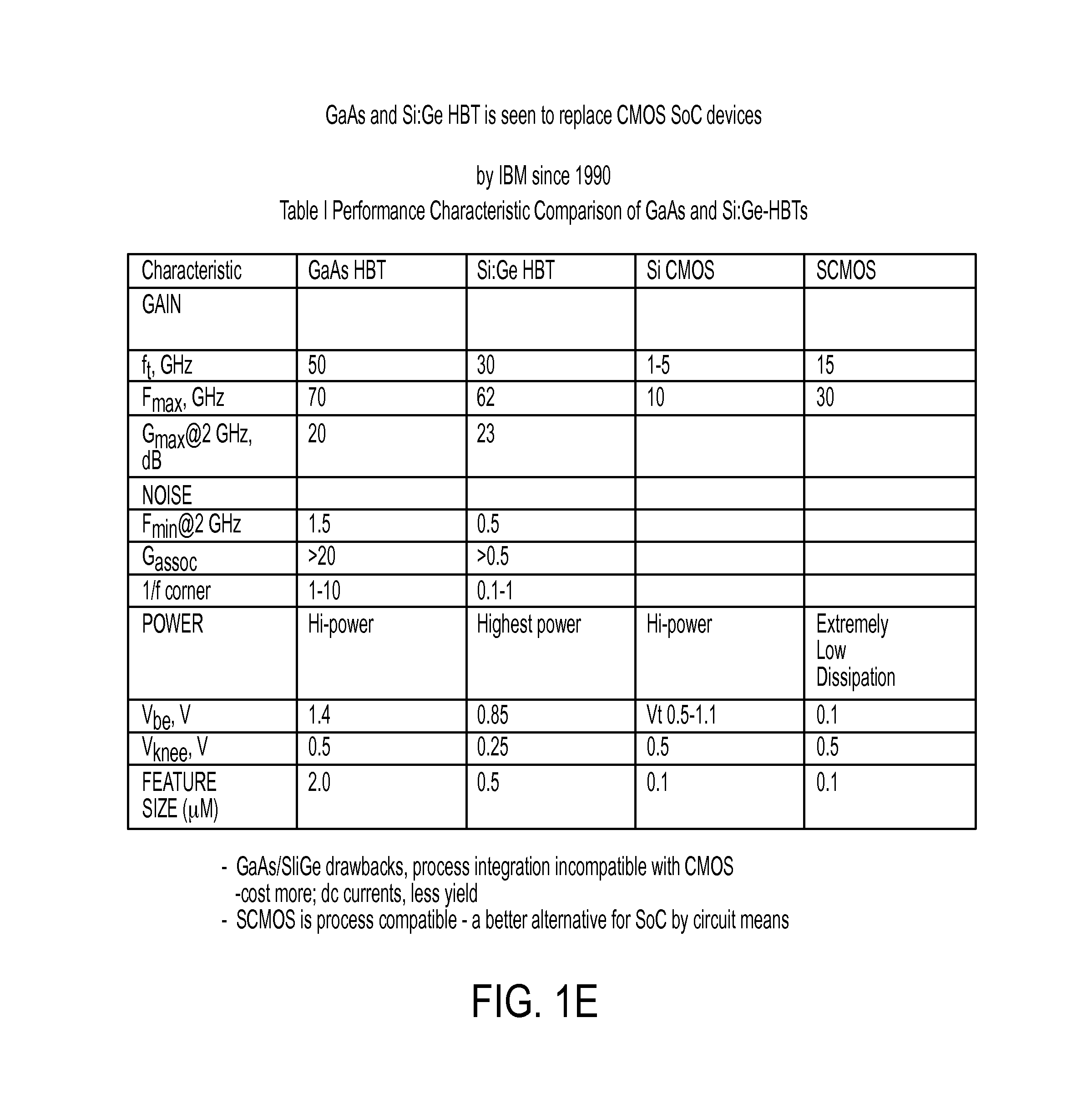
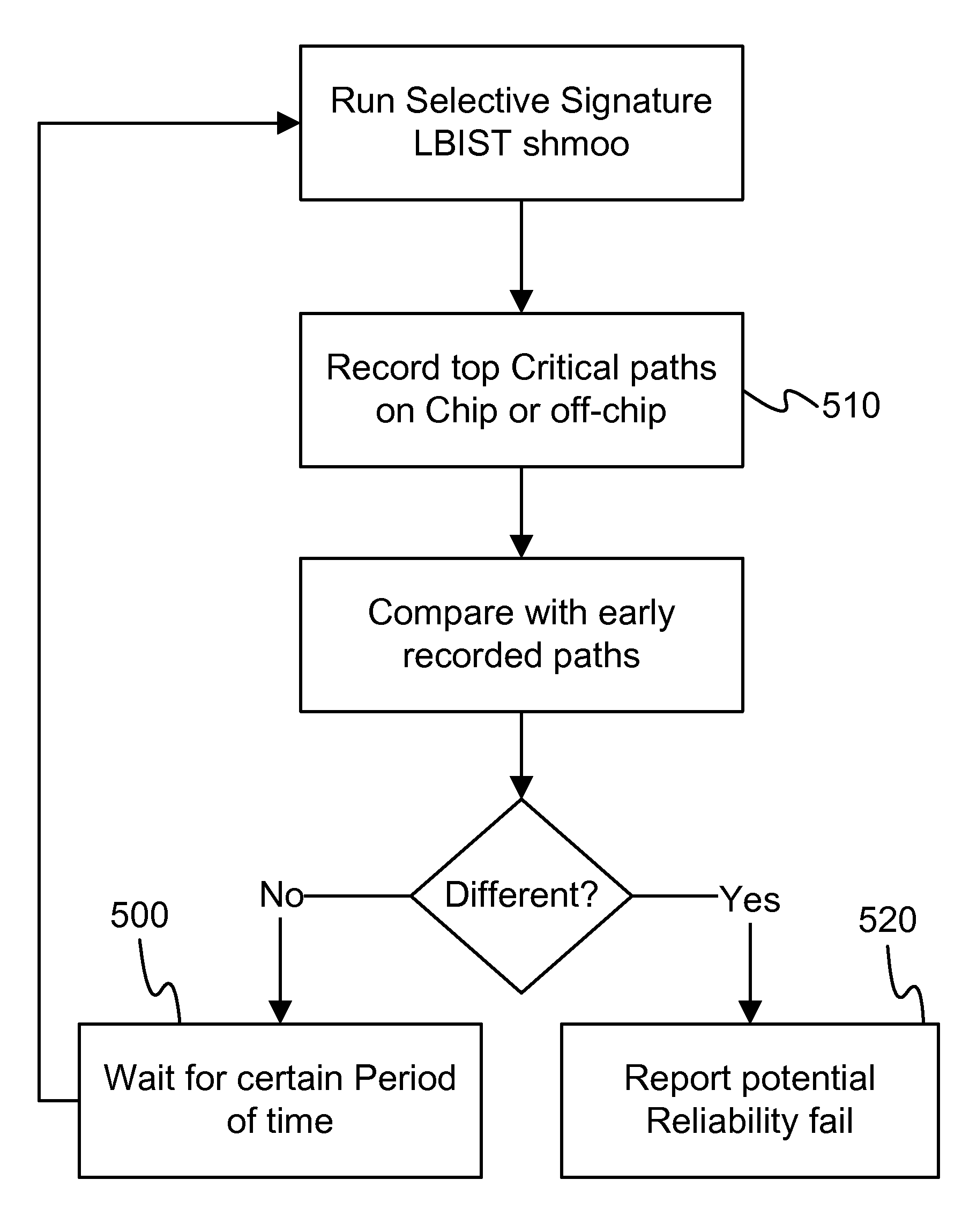
Measuring and predicting VLSI chip reliability and failure
InactiveUS7480882B1Reliability concernElectronic circuit testingVoltage-current phase angleDependabilityCycle time
This embodiment replaces the use of LBIST to get a pass or no-pass result. A selective signature feature is used to collect the top failing paths, by shmooing the chip over a cycle time. These paths can be stored on-chip or off-chip, for later use. Once the chip is running in the field for a certain time, the same procedure is performed to collect the top failing paths, and this is compared with the stored old paths. If the order of the top paths changes, it indicates that (for example) there is a path (not the slowest path before) that slows more than others, which could be potential reliability concern. Therefore, a potential reliability failure is identified in the field.
Owner:IBM CORP
Manufacturing method of carbon nano-tube micro-channel cooler system
InactiveCN102169838AImprove cooling effectNanostructure manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEvaporation (deposition)Ptru catalyst
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a carbon nano-tube micro-channel cooler system for a radiating chip in a very-large scale integrated circuit (VLSI), which comprises the following steps of: firstly, manufacturing a pattern with required fine scale through a photoetching and peeling process; meanwhile, adhering a catalyst film obtained through an evaporation method on a surface ofthe pattern; secondly, placing a silicon wafer with the catalyst film in a heating furnace of a carbon nano-tube growth machine, growing in a high-temperature chemical vapor deposition mode to obtainthe required carbon nano-tube cluster; finally, transferring the carbon nano-tube cluster on a surface of a heating chip by adopting a transferring process through a metal coating sprayed on the surface of the carbon nano-tube, heating a sealing cover, then finishing the manufacturing process of the carbon nano-tube micro-channel cooler; then radiating through the cooling liquid flowing through an entry guide to finish the manufacturing of the carbon nano-tube micro-channel cooler system. The radiating performance is obviously improved and a more efficient radiating method is provided for radiating the chip in the integrated circuit.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for successive placement based refinement of a generalized cost function
InactiveUS20050166164A1Quality improvementMulti-objective optimisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCost metricComputer science
A generalized method for optimizing the global placement of a VLSI chip across multiple cost metrics, such as total wire length, timing, congestion, and signal integrity is described. The method relies upon a “look ahead” technique, combined with any generic cost function that can be used to set placement directives. These placement directives include net weights and cell spreading. The method of performing the placement involves the iterative reuse of the process of successive partitioning. This iterative reuse establishes the capability of looking ahead to determine what is to happen. Based on the look ahead, it is possible to evaluate the qualities of the placement about to be generated. The method proceeds through the placement from while maintaining the current state of the placement along with the look-ahead state of the placement. Directives are generated and modified in order that the next steps applied to the current state of the placement will cause it to change to achieve an ultimate higher quality final output.
Owner:IBM CORP
Indium features on multi-contact chips
InactiveUS20070224722A1Improve leakage currentThicker regionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium metalIndium bump
A device comprising a pixilated semiconductor detector or VLSI chip having plurality of individual indium bumps arrayed on a surface of the detector, wherein the indium bumps are in electrical contact with the surface and are situated in defined locations on the surface is provided. Additionally, a hybrid detector comprising a pixilated detector in electrical contact with a VLSI chip, wherein electrical contacts formed from indium metal are made between the pixels of the semiconductor and regions on the VLSI chip corresponding thereto is provided. In another embodiment, a method of forming electrical contacts on a pixilated detector comprising the steps of constraining a shadow mask having an array of holes in predetermined locations above a surface on the detector, aligning the mask above the detector, and evaporating indium metal under vacuum through holes in the mask onto the surface of the detector to form the contacts is described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
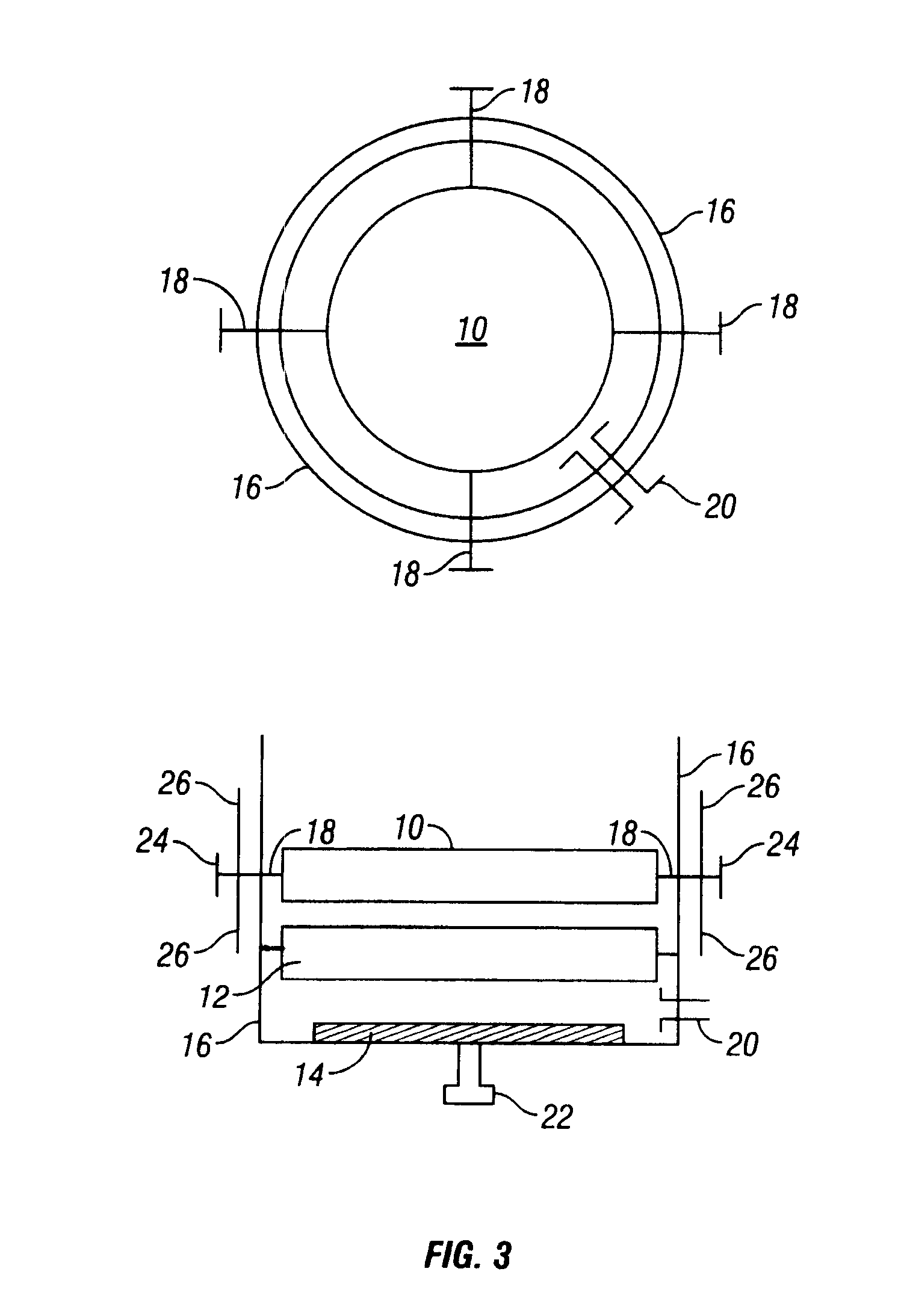
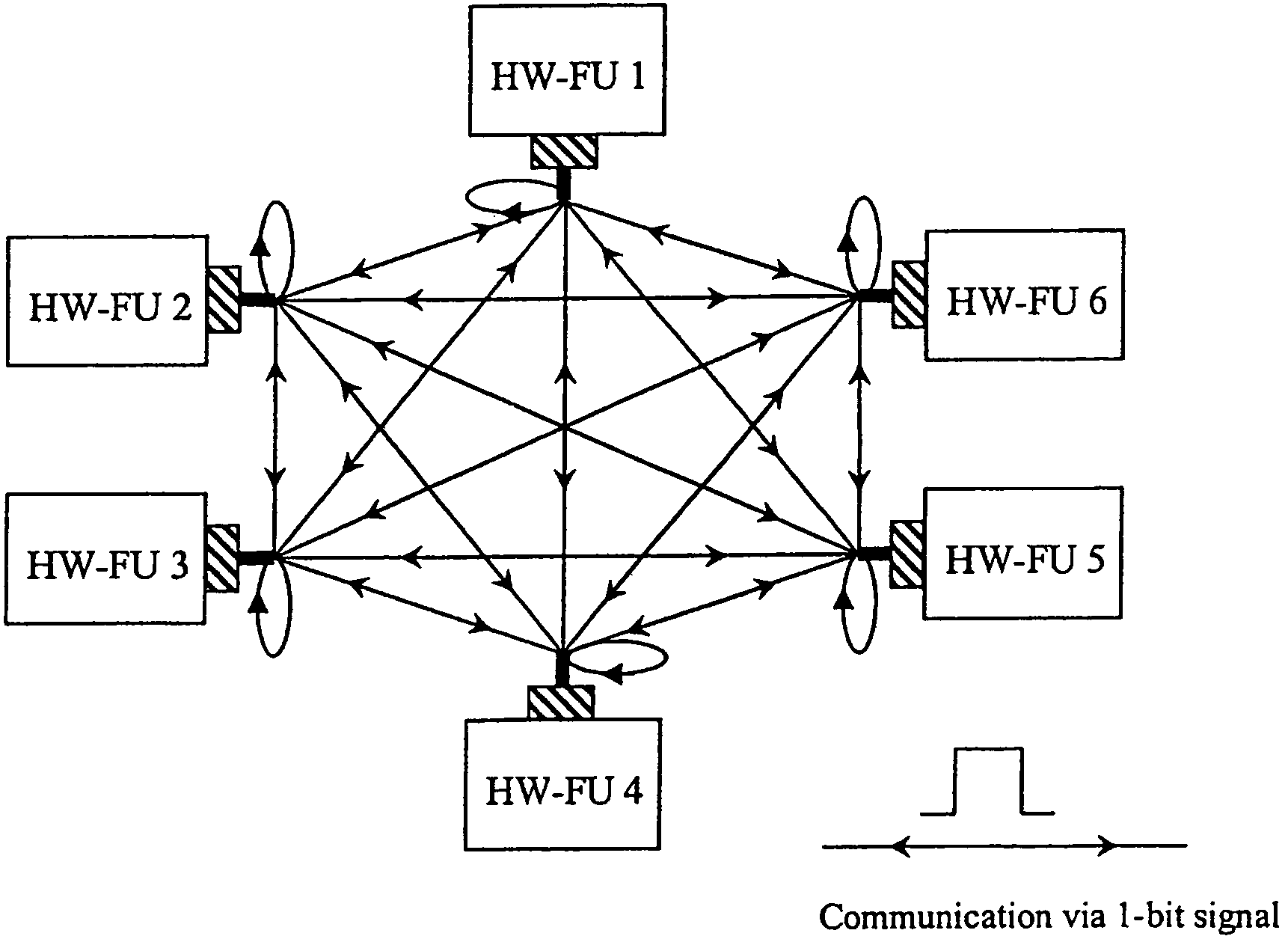
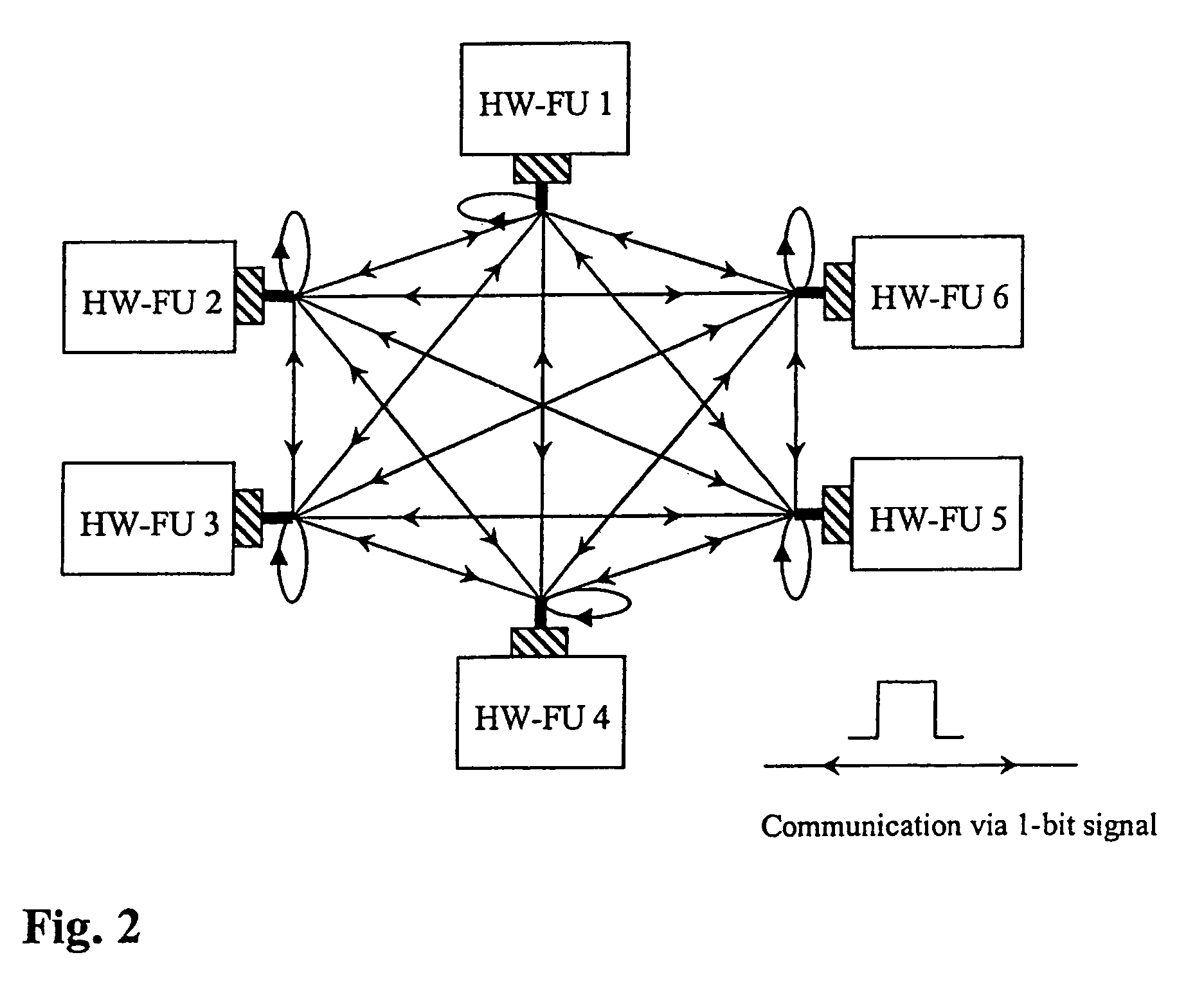
Decentralised fault-tolerant clock pulse generation in VLSI chips
InactiveUS7791394B2Improve stabilityError detection/correctionElectric pulse generatorPulse synchronizationComputer science
The invention relates to a method for distributed, fault-tolerant clock pulse generation in hardware systems, wherein the system clock pulse is generated in distribution by a plurality of intercommunicating fault-tolerant clock pulse synchronization algorithms (TS-Algs), in which an arbitrary number of such TS-Algs exchange information between one another via a user-defined and permanent network (TS-Net) of clock pulse signals, susceptible to transient faults, and each TS-Alg is assigned to one or more functional units (Fu1, Fu2, . . . ), whose local clock pulses are generated by it, and further all local clock pulses are synchronized with respect to frequency in an assured manner, and a specified number of transient and / or permanent faults may occur in the TS-Algs or in the TS-Net, without adversely affecting the clock pulse generation and / or the synchronization accuracy, and the system clock pulse automatically achieves the maximum possible frequency. The invention further relates to such a hardware system.
Owner:VIENNA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Super CMOS devices on a microelectronics system
ActiveUS20100155782A1Significant costSignificant performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSSchottky barrier
A low cost IC solution is disclosed in accordance with an embodiment to provide Super CMOS microelectronics macros. Hereinafter, the Super CMOS or Schottky CMOS all refer to SCMOS. The SCMOS device solutions with a niche circuit element, the complementary low threshold Schottky barrier diode pairs (SBD) made by selected metal barrier contacts (Co / Ti) to P- and N- Si beds of the CMOS transistors. A DTL like new circuit topology and designed wide contents of broad product libraries, which used the integrated SBD and transistors (BJT, CMOS, and Flash versions) as basic components. The macros are composed of diodes that are selectively attached to the diffusion bed of the transistors, configuring them to form generic logic gates, memory cores, and analog functional blocks from simple to the complicated, from discrete components to all grades of VLSI chips. Solar photon voltaic electricity conversion and bio-lab-on-a-chip are two newly extended fields of the SCMOS IC applications.
Owner:SCHOTTKY LSI
Array of very light readers for active RFID and location applications
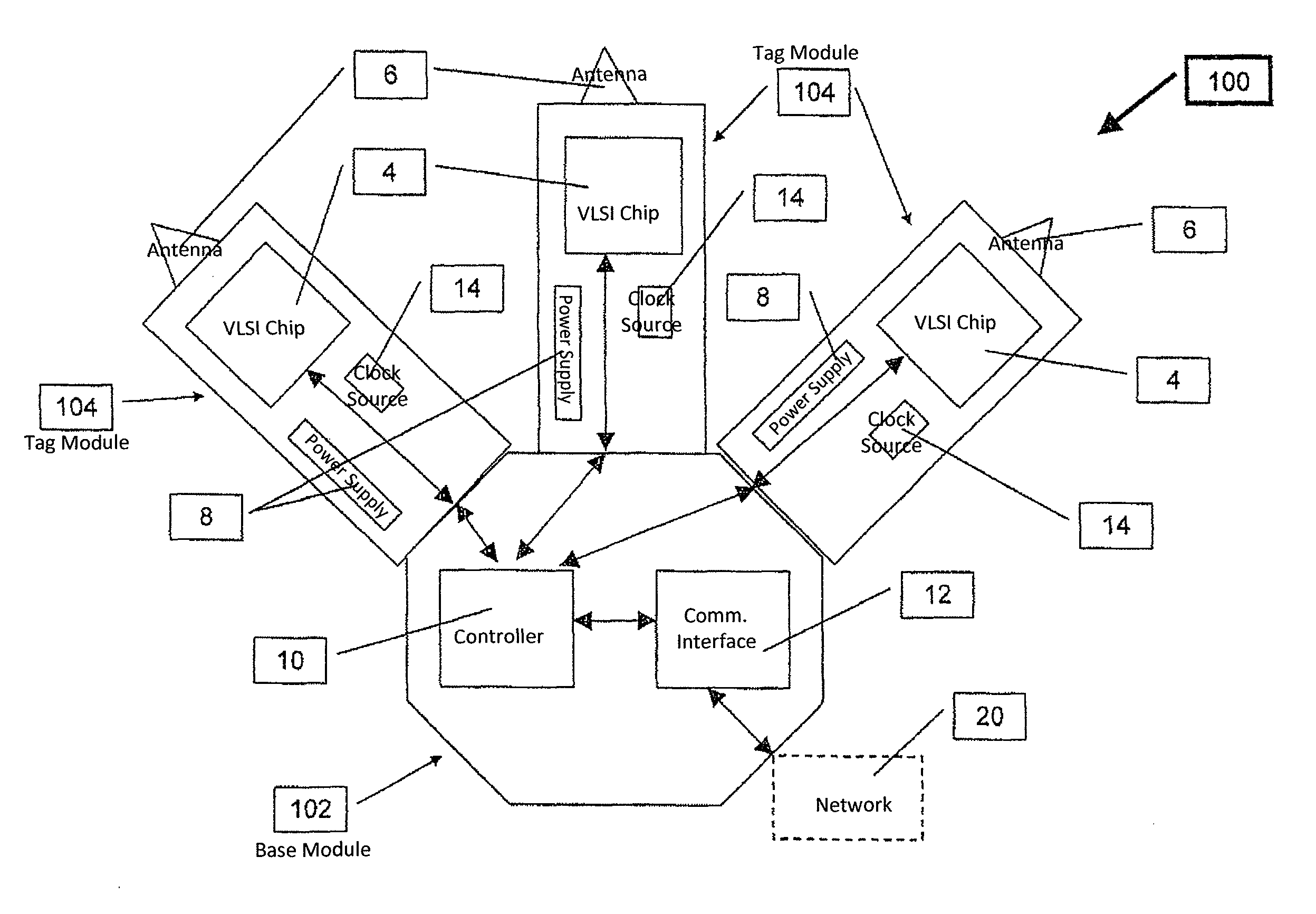
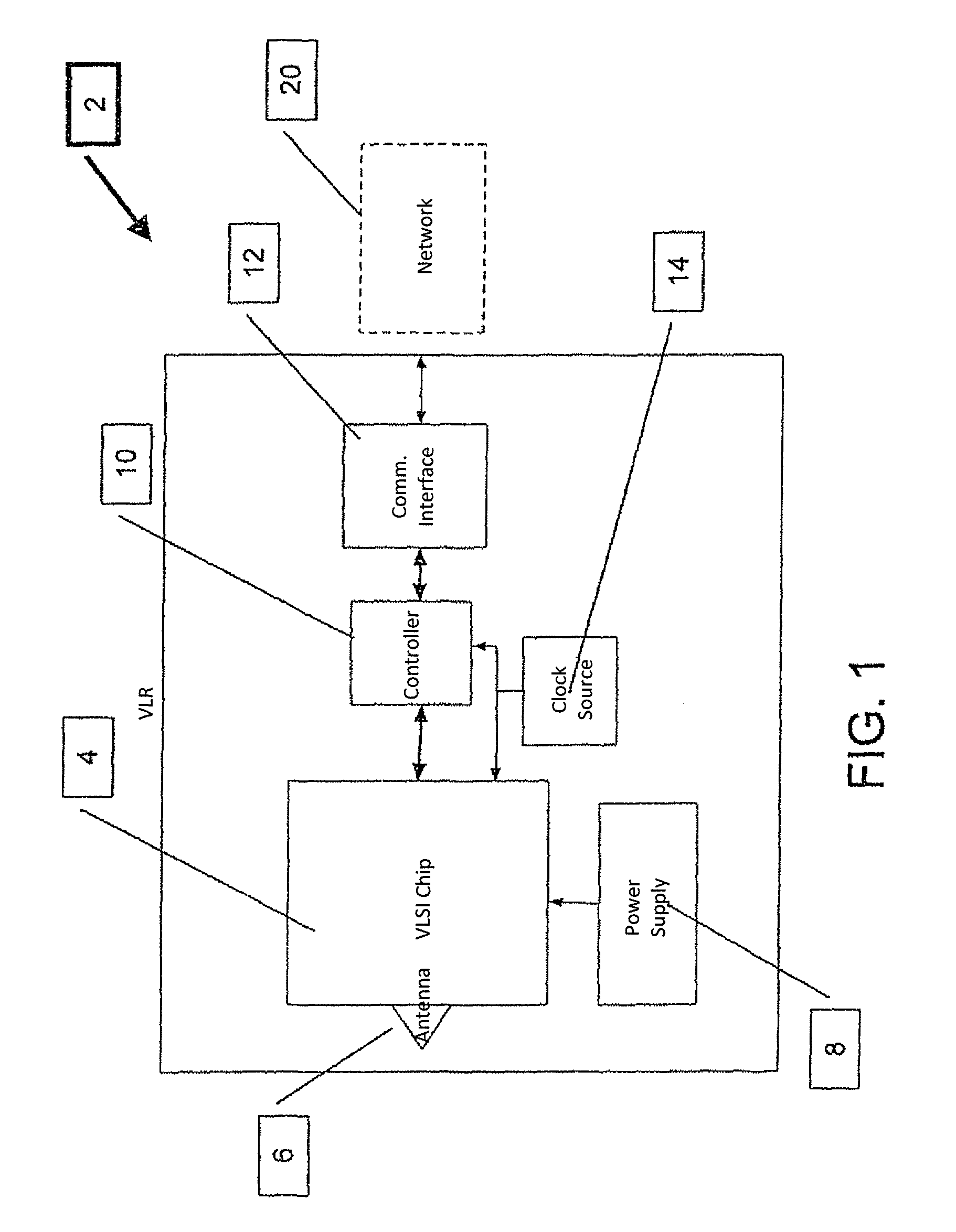
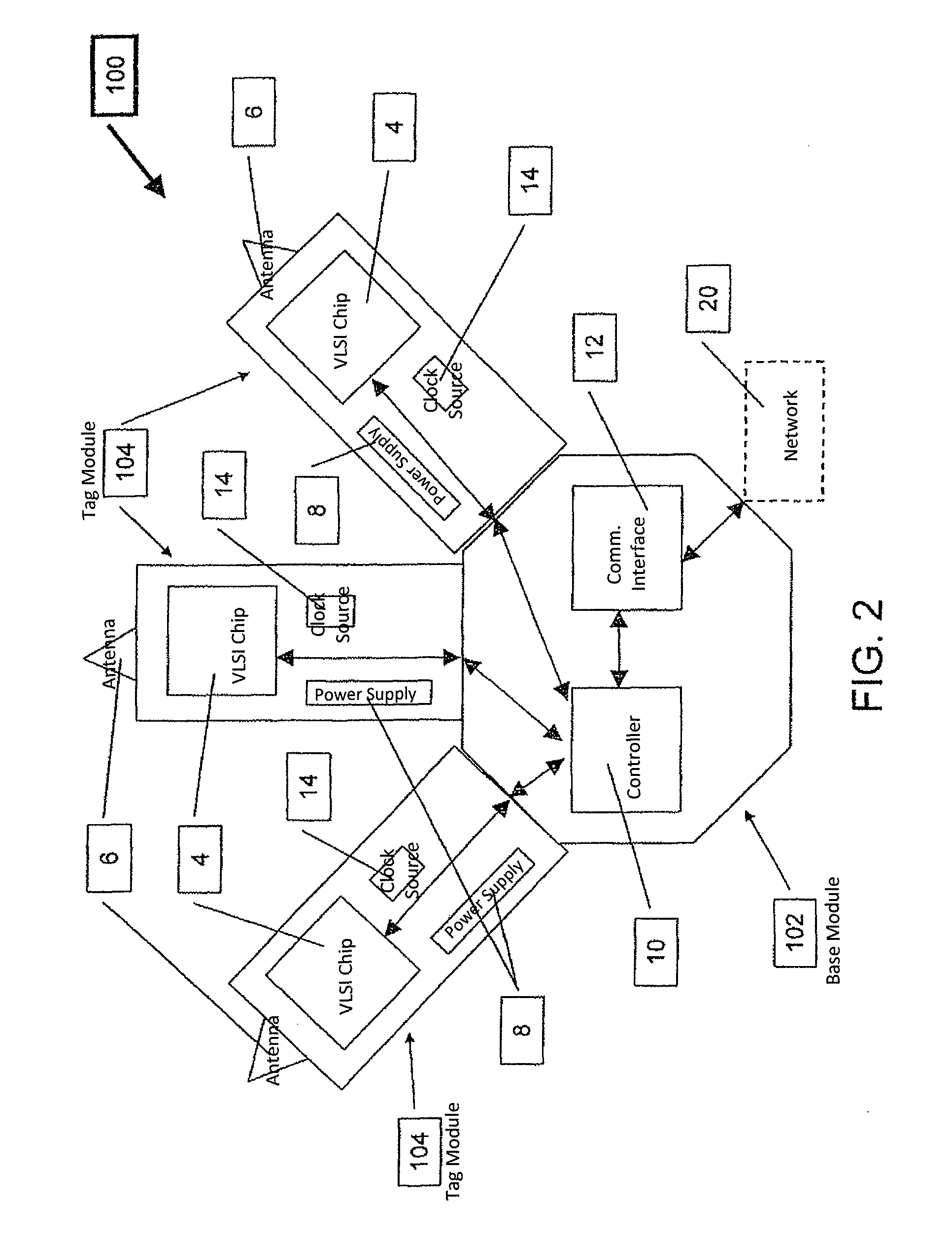
ActiveUS20100164690A1Improve Backhaul reliabilityReduce collisionSensing record carriersSubscribers indirect connectionData packCommunication interface
The Very Light Readers of the present invention are based on an augmented Tag circuit with a preferred embodiment including at least one VLSI chip integrating a UWB front end, digital transceiver, and possibly an internal controller; a UWB Antenna; a power supply; a controller configured to implement the Media Access Control protocol of the system; a Communication Interface subsystem for connection to the system network and a clock source. Also described is a system capable of reducing collision occurrence in a network for communicating between multiple readers and a plurality of RF Tags. Tags are configured to receive interrogation signals and transmit response signals. Readers are configured to transmit interrogation signals, receive response signals, estimate the quantity of responses received to an interrogation, determine the round trip delay time of each response and estimates whether a collision between responses has occurred. If so, the Reader transmits an additional interrogation signal. The Reader also transmits an acknowledgment packet to responding Tags so responding Tag will not answer again to that broadcast session. Other Readers in the network also receive the acknowledge packet and do not try again to reach the responding Tags, thereby lowering congestion directed toward Tags from multiple Reader transmissions.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Flux linked LC tank circuits forming distributed clock networks
ActiveUS20070018740A1High circuit operationHigh-frequency behaviorSolid-state devicesGenerating/distributing signalsFinite-state machineEngineering
CMOS LC tank circuits and flux linkage between inductors can be used to distribute and propagate clock signals over the surface of a VLSI chip or processor. The tank circuit offers an adiabatic behavior that recycles the energy between the reactive elements and minimizes losses in a conventional sense. Flux linkage can be used to orchestrate a number of seemingly individual and distributed CMOS LC tank circuits to behave as one unit. In one example, the distribution of a 45° separated multi-phase balanced oscillations over the surface of die 1.6 cm×1.6 cm at 10 GHz is expected to dissipate under 10 W and offers a potential to significantly reduce the road map predictions of 100 W. Simulations of several CMOS tank circuits indicate that the power dissipation can be reduced an order of magnitude when compared to conventional techniques. A passive flux linkage, mechanical, and finite state machine technique of frequency adjustment of an oscillator are described.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
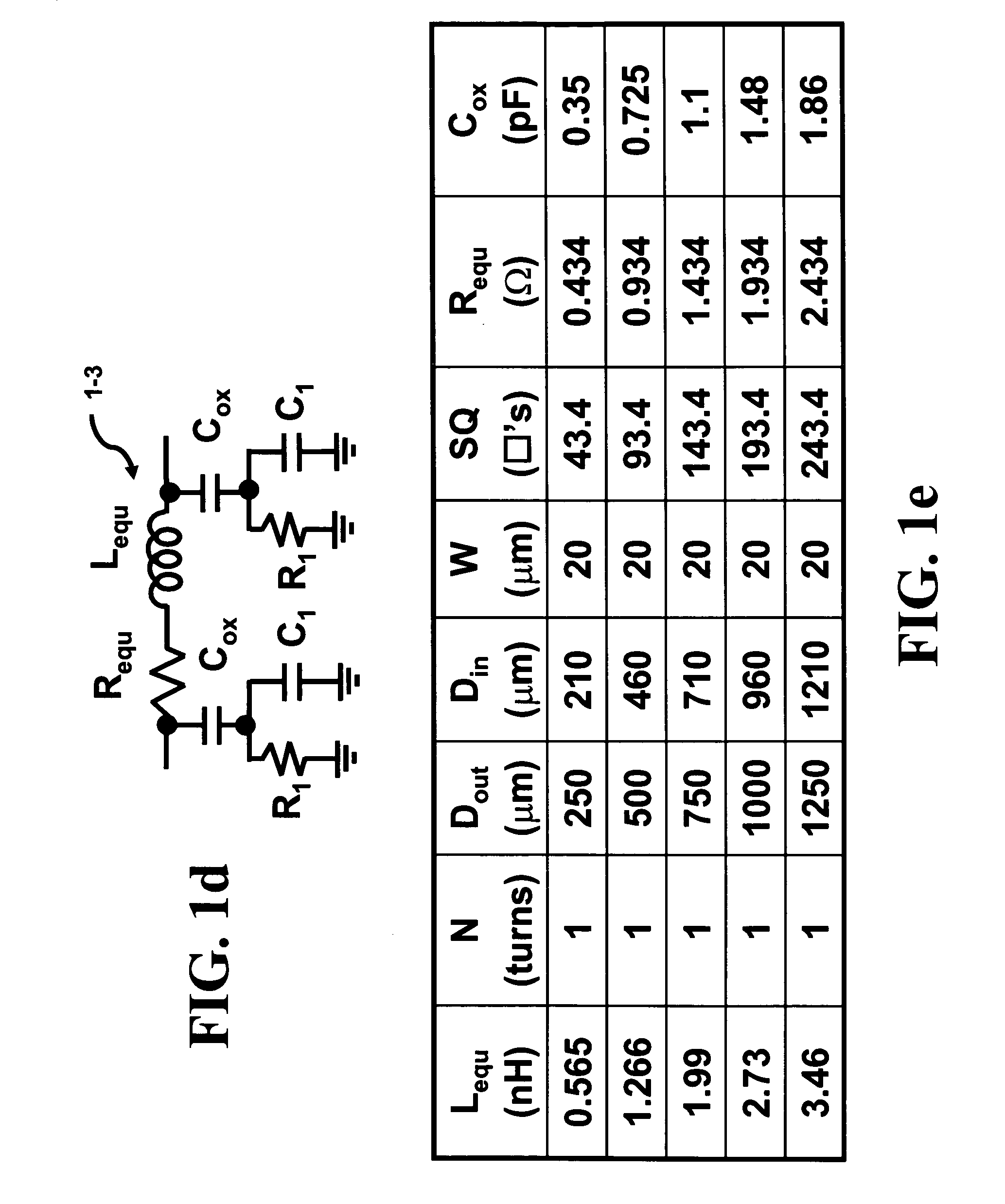
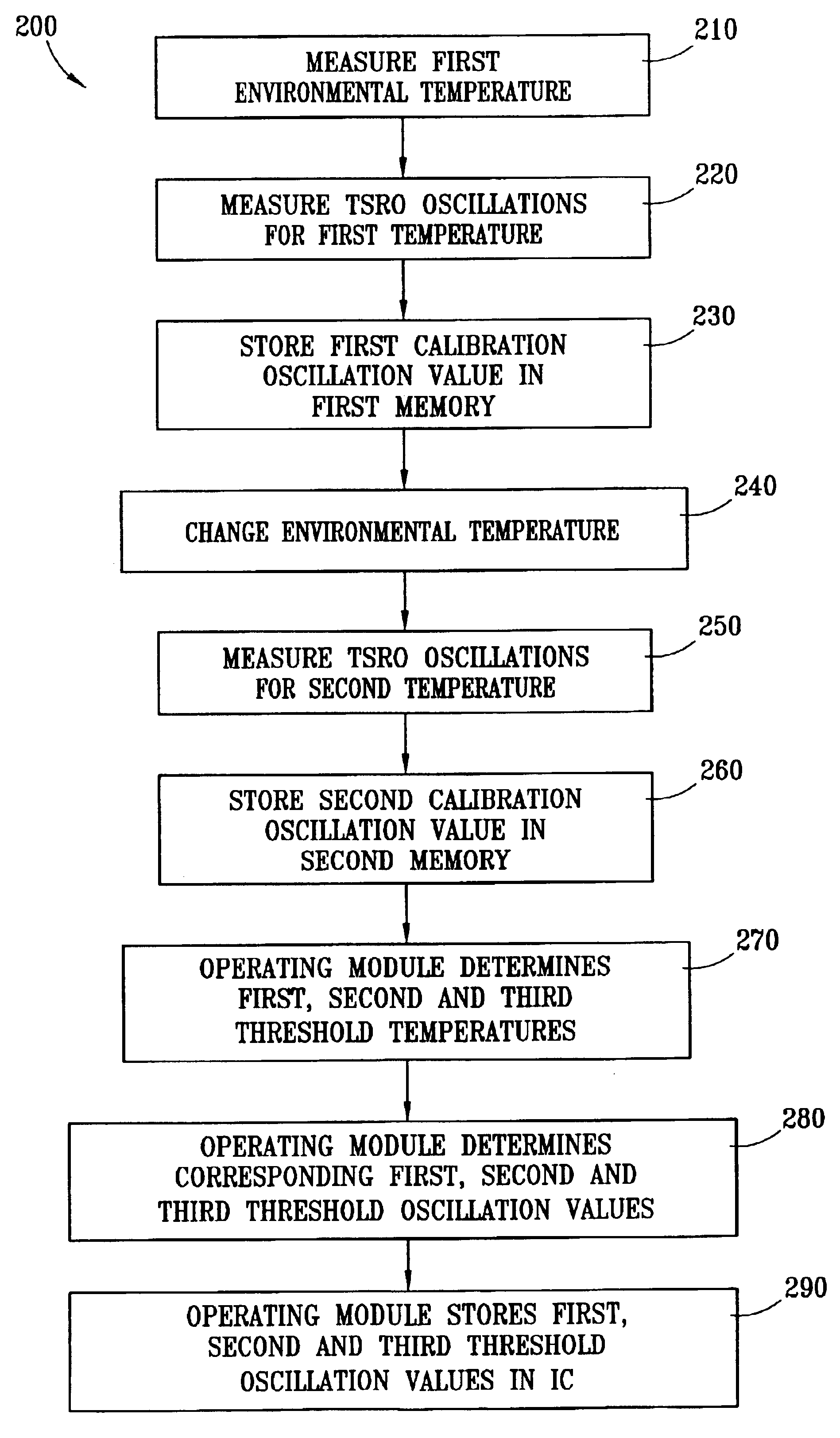
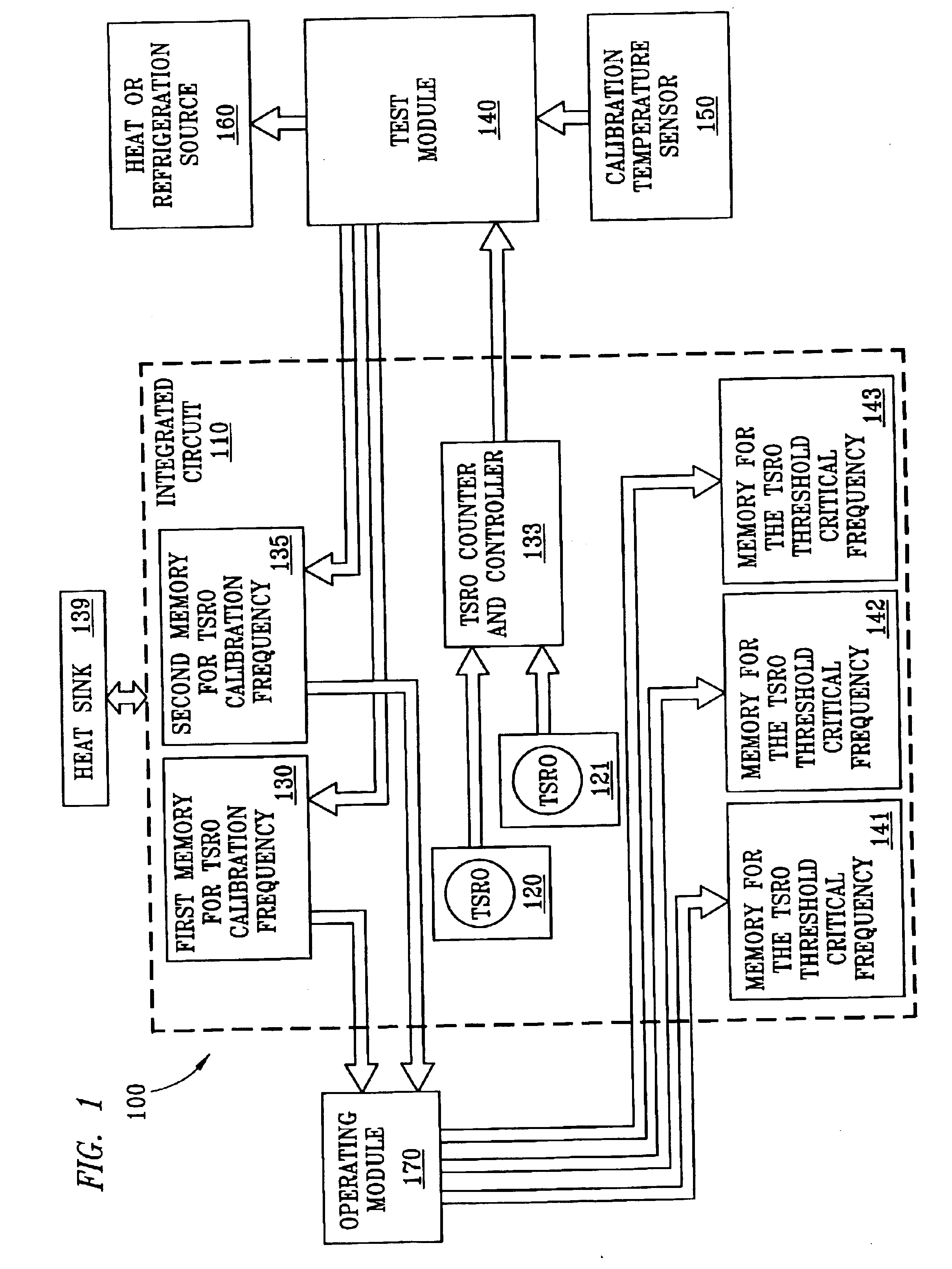
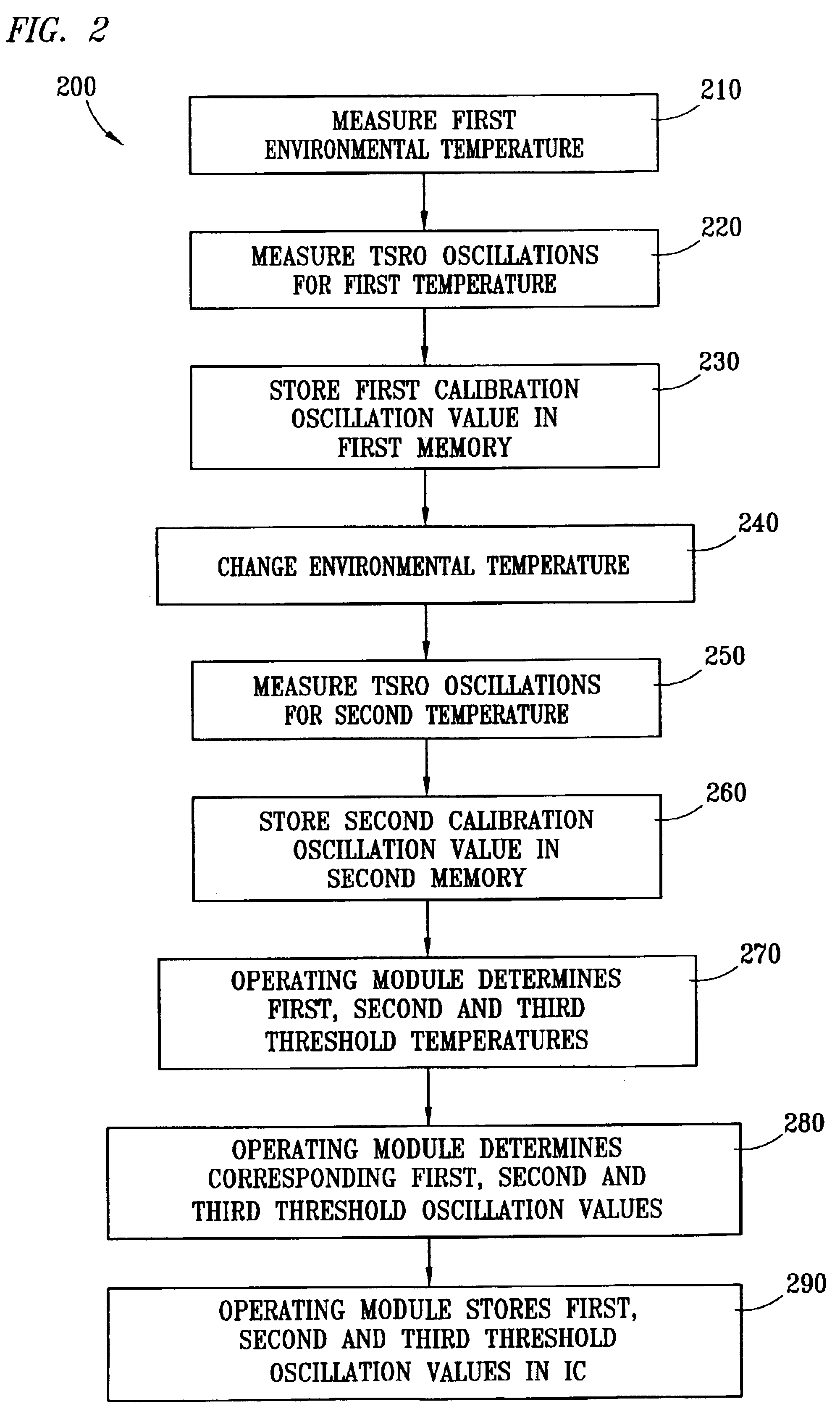
Method and apparatus to dynamically recalibrate VLSI chip thermal sensors through software control
The present invention provides an integrated circuit VLSI temperature system for the calibration of threshold temperatures. A temperature sensitive ring oscillator (TSRO) generates a TSRO calibration parameter. A memory is employable to store the TSRO calibration parameter. A module is employable to determine a threshold TSRO oscillation frequency from the TSRO calibration parameter. A memory is employable for storing at least one threshold TSRO oscillation frequency.
Owner:IBM CORP
High speed clock distribution transmission line network
ActiveUS7679416B2Mitigate the clock jitterNetwork can be lowReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDistribution treeElectrical conductor
The invention is directed to a method for clock distribution and VLSI circuits include a clock distribution network. In a method of the invention, a transmission lines are patterned as to connect a clock tree and a periodic waveform clock, preferably a sine waveform, is used to control clock skew, even at frequencies extending into the gigahertz range. In an exemplary embodiment of the invention, an overlay includes differential pairs of transmission lines that connect the drivers of a clock distribution tree. In preferred embodiments of the invention, an H-tree clock distribution scheme is overlayed with a spiral of transmission lines, each realized by a differential conductors and driven using a sinusoidal standing wave to distribute global clock signals into local regions of the chip. Each transmission line connects drivers in the H-tree that are at the same level of the H-tree. In a VLSI chip according to an embodiment of the invention, the transmission line overlay delivers sinusoidal clock signals to local areas that are locally converted into digital clock signals. The invention thus presents a passive technique for clock distribution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
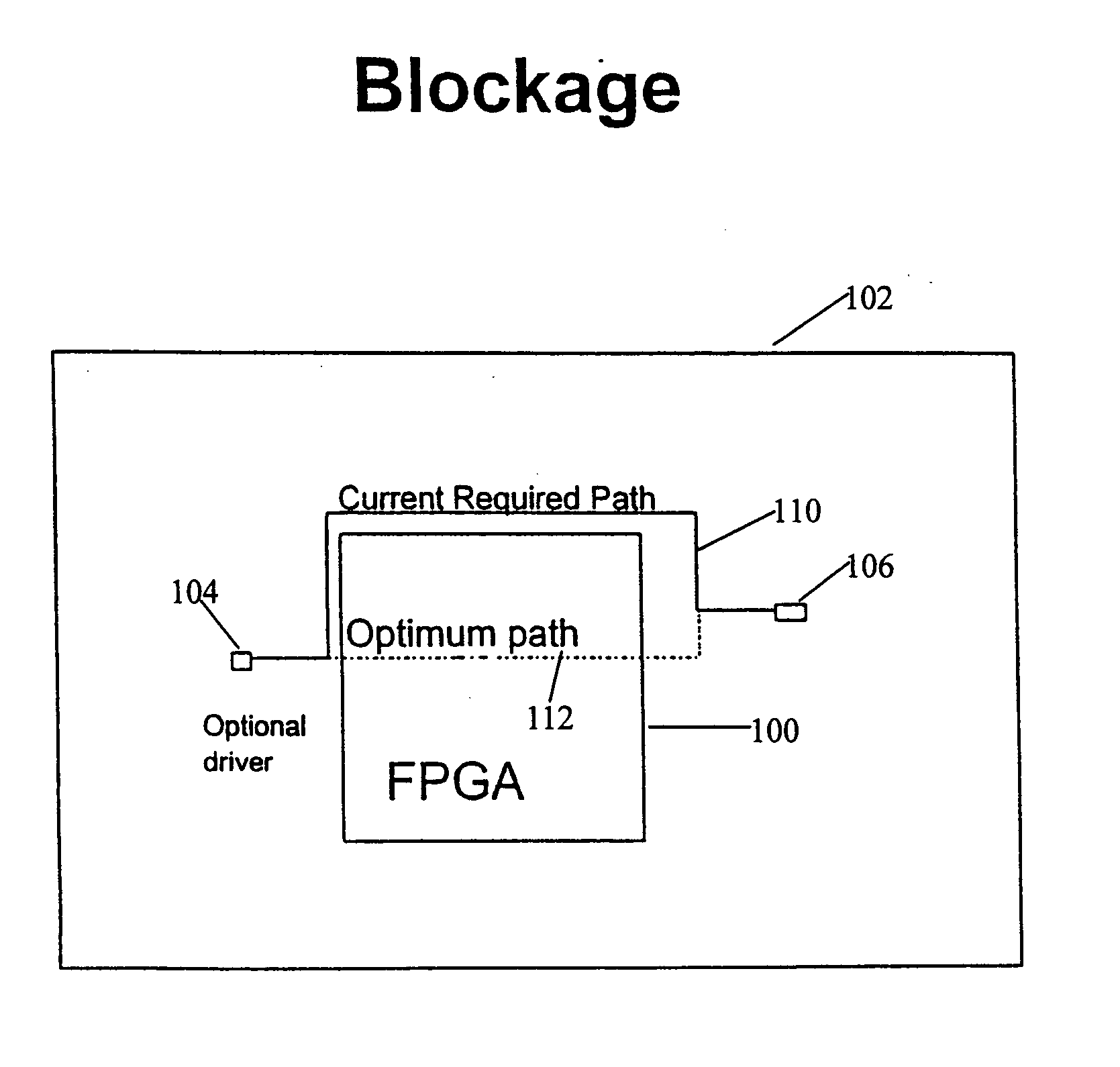
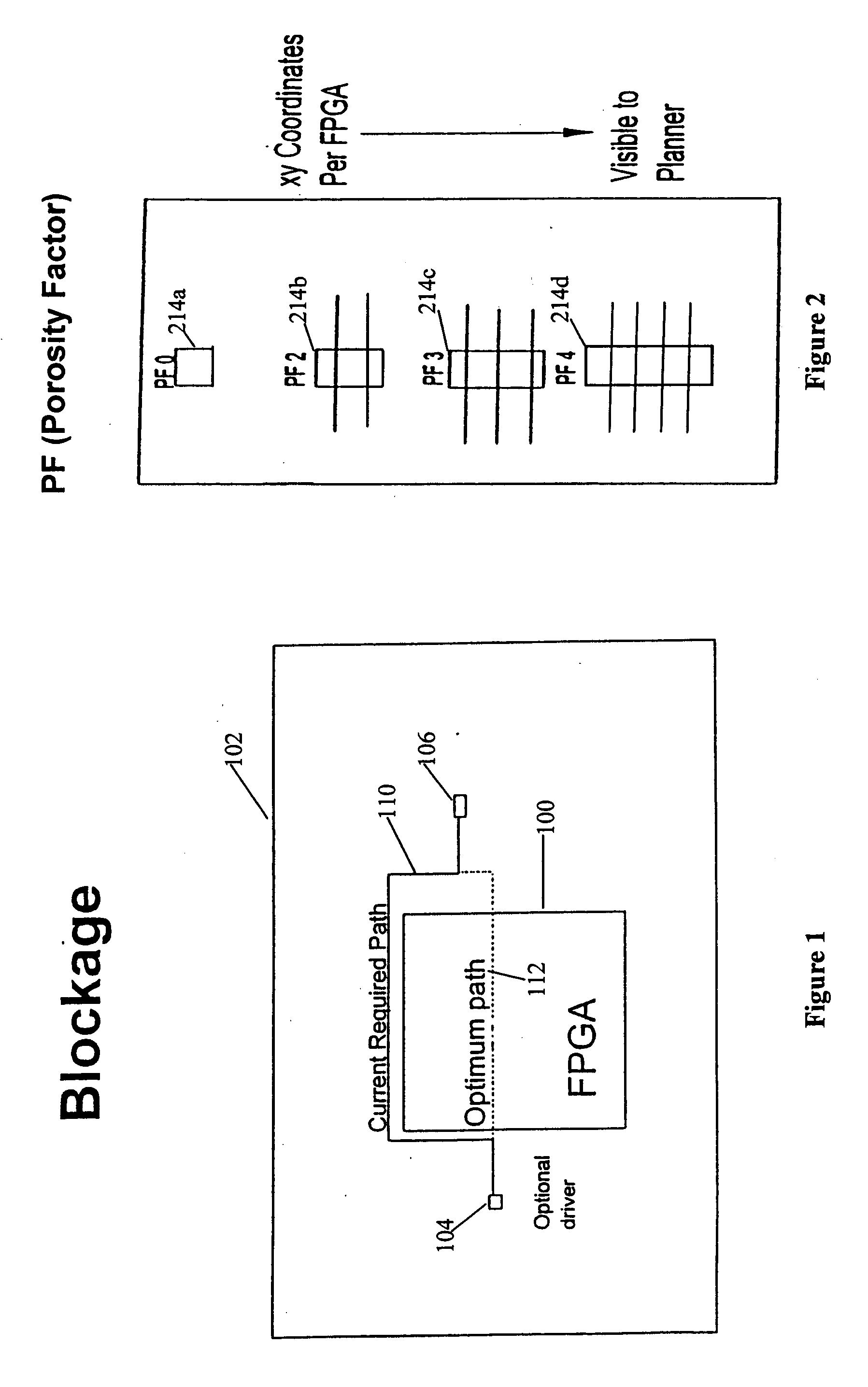
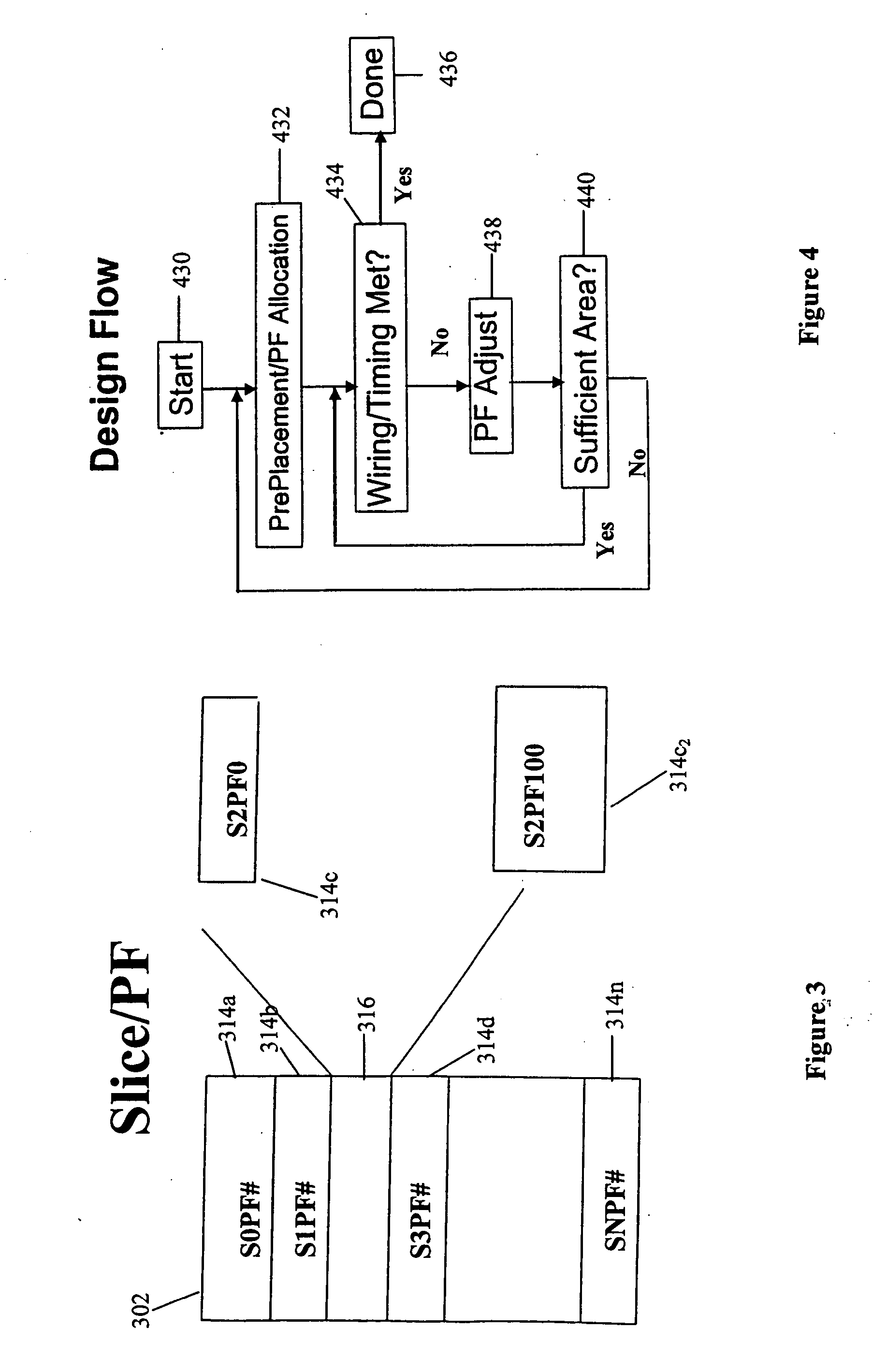
FPGA blocks with adjustable porosity pass thru
InactiveUS20050121698A1Minimizing chip floor planMinimizing timing impactSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPorositySemiconductor chip
A field programmable gate array is described for use in a semiconductor chip such as a VLSI chip. The array is provided with variable wire-through porosity to allow for optimum chip-level routing through the array. This is achieved by dividing the array into blocks which can be individually assessed for required porosity. Then blocks that have been prefabricated with differing porosities are placed in the macro to optimize local chip level routing. The routing of wires is determined by developing a chip floor plan to include early timing allocation and a proposed placement of the array. The floor plan is then overlaid with critical logical wiring nets. From this, an initial selection of blocks is made based on proposed wiring density, and the macro is assembled with the blocks strategically placed therein. The procedure is likewise applicable to other types of densely obstructed cores embedded with a chip.
Owner:IBM CORP
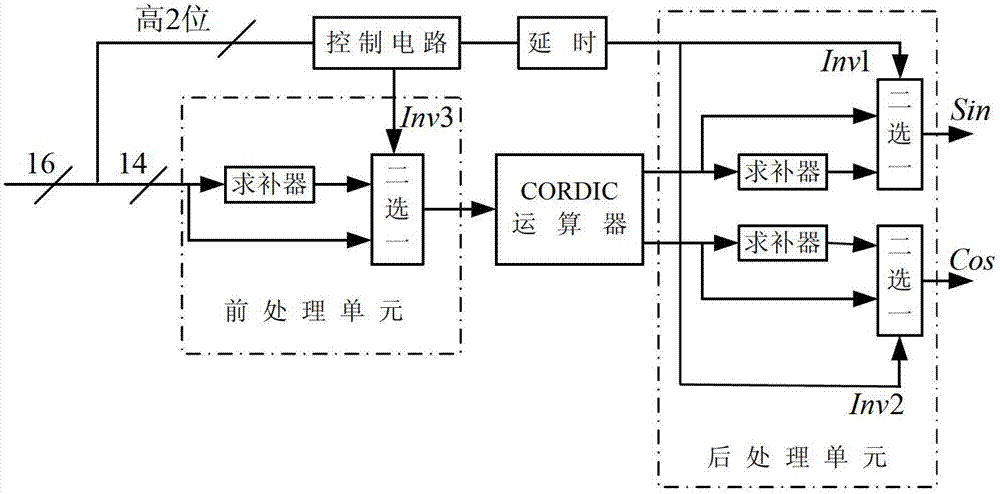
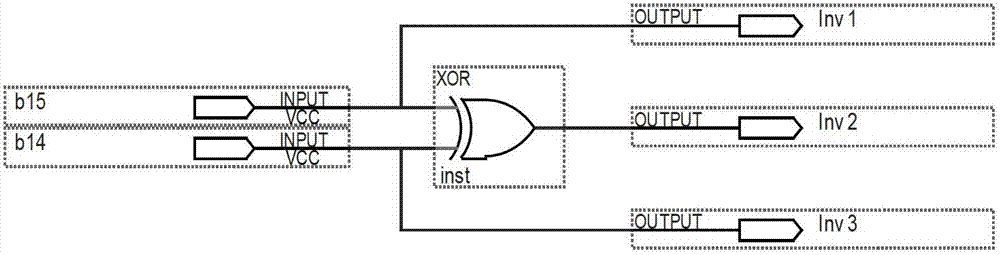
DDS (Direct Digital Synthesizer) signal spurious suppression method and system on basis of CORDIC (Coordinated Rotation Digital Computer) algorithm
InactiveCN102789446AHigh precisionHigh speedComplex mathematical operationsVery large scale integrated circuitsImage resolution
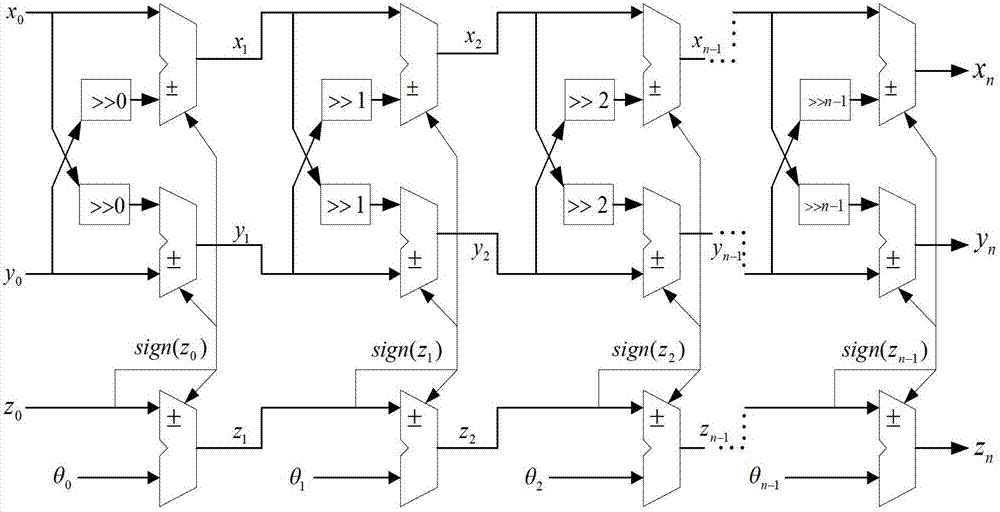
The invention discloses a DDS (Direct Digital Synthesizer) signal spurious suppression method and a DDS signal spurious suppression system on the basis of the CORDIC (Coordinated Rotation Digital Computer) algorithm. In the method, sine and cosine signals of a signal are calculated by the CORDIC algorithm to complete the phase / amplitude conversion in a DDS system; and all angles are transformed into the first quadrant by CORDIC transformation, then according to an output data symbol, a quadrant in which the signal is positioned is judged and the transformation is carried out so as to cover a (minus pi, pi) complete period. The system comprises a control circuit, a preprocessing unit, a CORDIC operational unit and a post-processing unit. According to the method and the system, the sine and the cosine values of the signal are directly calculated by the CORDIC algorithm without consuming more ROM (Read Only Memory) resources; the calculation of the sine and the cosine values of the signal can be completed only by carrying out simple iterative operations such as shift, addition and subtraction and the like; and the method and the system can also be easily implemented on a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integrated Circuits) chip and is very suitable for places with ultrahigh requirements on the resolution ratio and the accuracy of the signal frequency.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
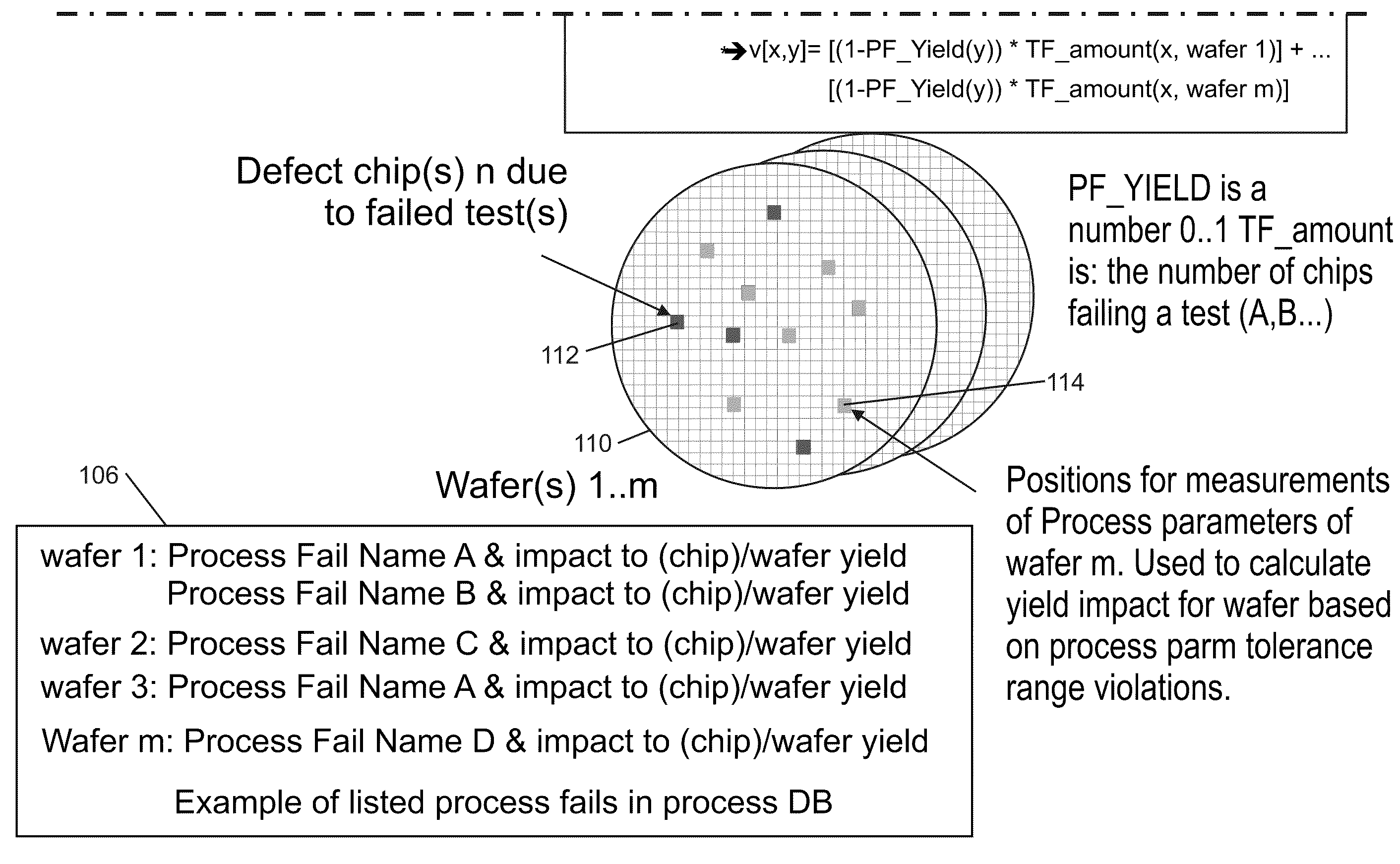
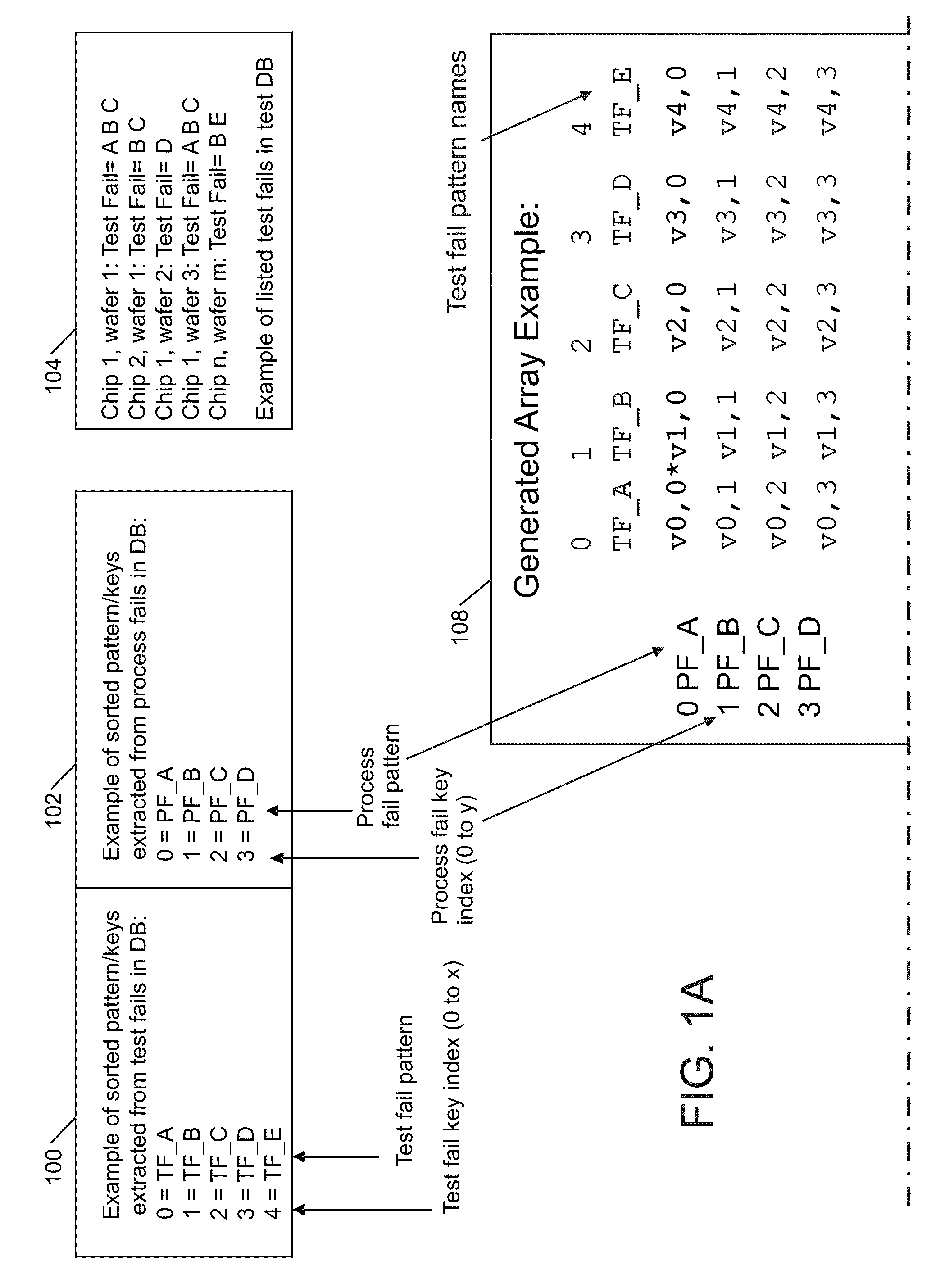
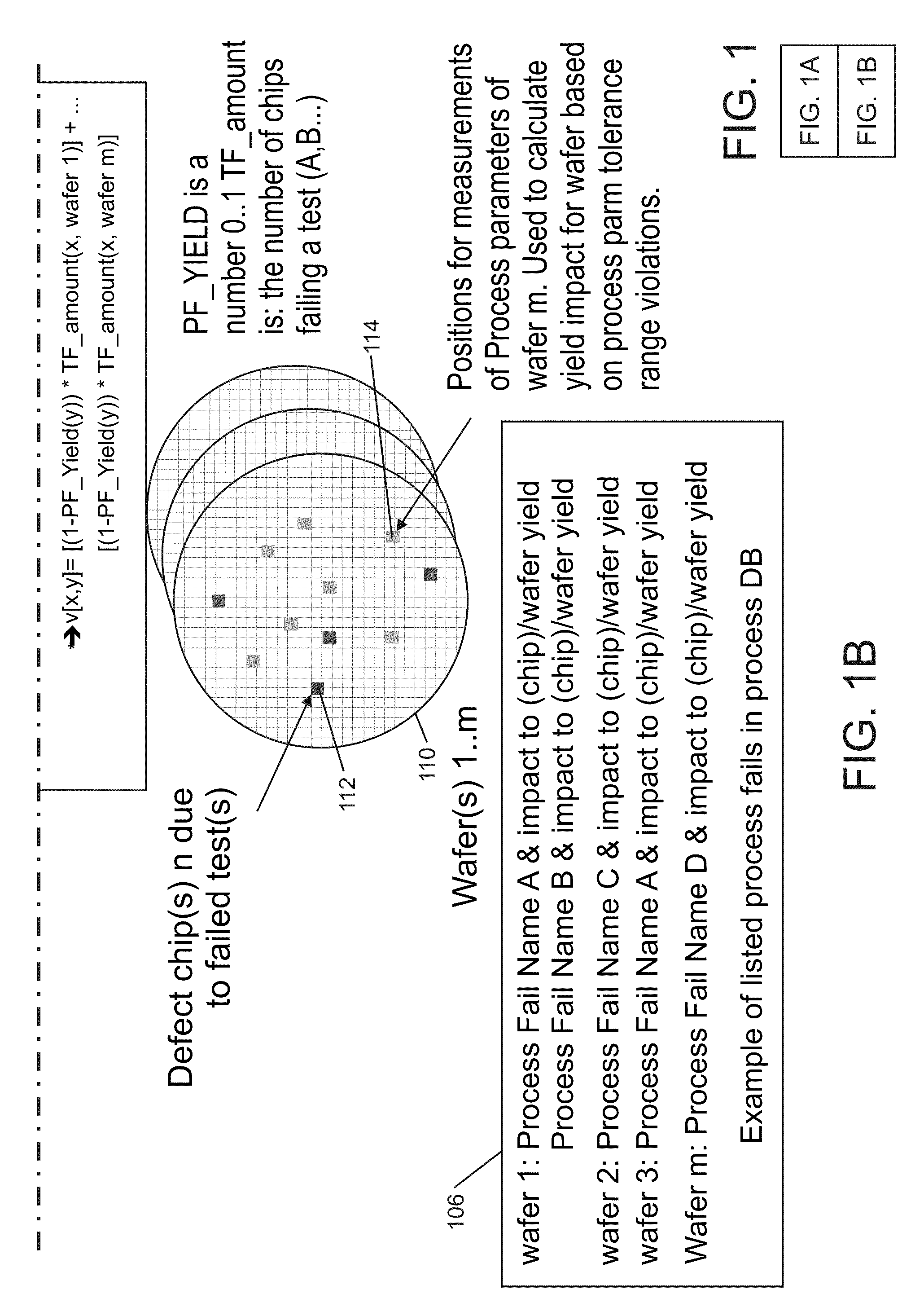
Test fail analysis on VLSI chips
Compact graphical representations of common test fail signatures and process related test fails are provided through methods of selecting, calculating and / or presenting information. The input may be a list of failing tests on a sample of devices under test from chip and / or wafer process fails. The failing tests are identified and then other tests that fail at the same time may be identified. Several graphical outputs are provided, including all possible combinations between test fails and between test fails and process fails. The dependencies are printed as sorted two dimensional bitmaps that are compact representations of the results using color codes. Subtraction of two independent bitmaps is provided, which eliminates common properties and emphasizes differences between multiple bitmaps which allows for quick identification of differences of process fails potentially different between the two different bitmaps indicating potential root causes for the selected one of the test fails.
Owner:IBM CORP
Array of very light readers for active RFID and location applications
ActiveUS9307554B2Low costImprove rendering capabilitiesCo-operative working arrangementsSubscribers indirect connectionCommunication interfaceTransceiver
The Very Light Readers of the present invention are based on an augmented Tag circuit with a preferred embodiment including at least one VLSI chip integrating a UWB front end, digital transceiver, and possibly an internal controller; a UWB Antenna; a power supply; a controller configured to implement the Media Access Control protocol of the system; a Communication Interface subsystem for connection to the system network and a clock source. Also described is a system capable of reducing collision occurrence in a network for communicating between multiple readers and a plurality of RF Tags. Tags are configured to receive interrogation signals and transmit response signals. Readers are configured to transmit interrogation signals, receive response signals, estimate the quantity of responses received to an interrogation, determine the round trip delay time of each response and estimates whether a collision between responses has occurred. If so, the Reader transmits an additional interrogation signal. The Reader also transmits an acknowledgment packet to responding Tags so responding Tag will not answer again to that broadcast session. Other Readers in the network also receive the acknowledge packet and do not try again to reach the responding Tags, thereby lowering congestion directed toward Tags from multiple Reader transmissions.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com