Patents
Literature
67 results about "Indium metal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Indium Metal. Indium Metal is extracted from indium bearing based metal ores and refined to various grades in high volume utilizing state of the art SPC controlled refining technologies. Rigorous quality standards and advanced analytical instrumentation such as ICP and GDMS, insures consistent product quality lot to lot.
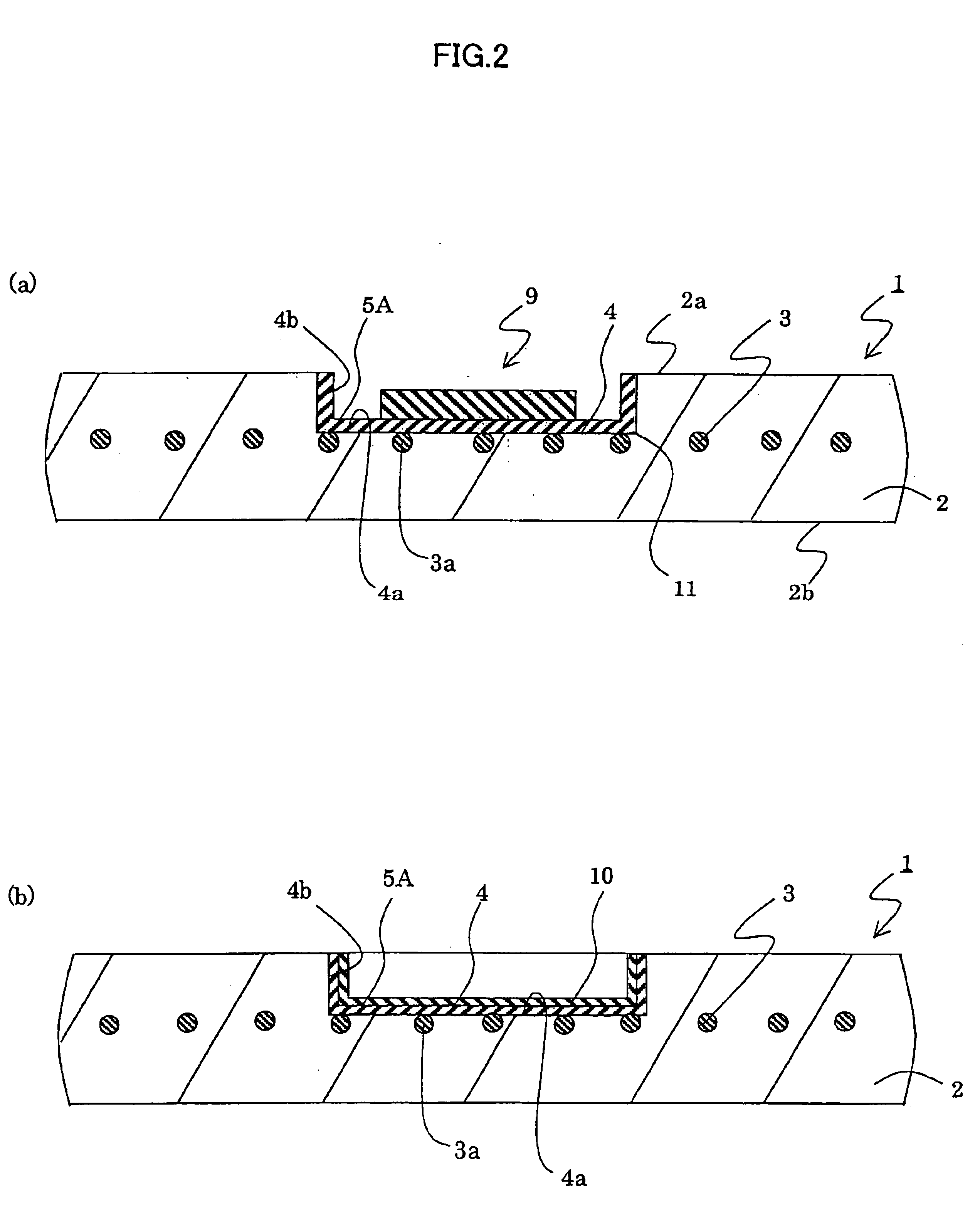
Novel focal plane array electrical interconnection process
InactiveCN102881607AImprove performanceAvoid the problem of increased thermal conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal membranePhotoresist
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectronic imaging and relates to a novel focal plane array electrical interconnection process which solves the problem of increase of thermal conductance caused by deformation of indium columns during cold welding of a focal plane detector. The focal plane array electrical interconnection process includes the steps: firstly, a photoetching process on a read-out circuit of the focal plane detector; secondly, a metal membrane deposition process, namely depositing a nickel or copper metal membrane and then depositing an indium metal membrane, wherein the nickel or copper metal membrane is thicker than the indium metal membrane; thirdly, a photoresist stripping process on the read-out circuit; fourthly, an indium column reflux balling process on the read-out circuit; fifthly, an electrode manufacturing process on a focal plane chip; and sixthly, a cold welding interconnection process of the focal plane chip and the read-out circuit. Since nickel or copper is used as indium column support and electrical communication metal, the problem of increase of thermal conductance caused by deformation of indium columns during cold welding interconnection is avoided, and performances of the focal plane array detector are improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
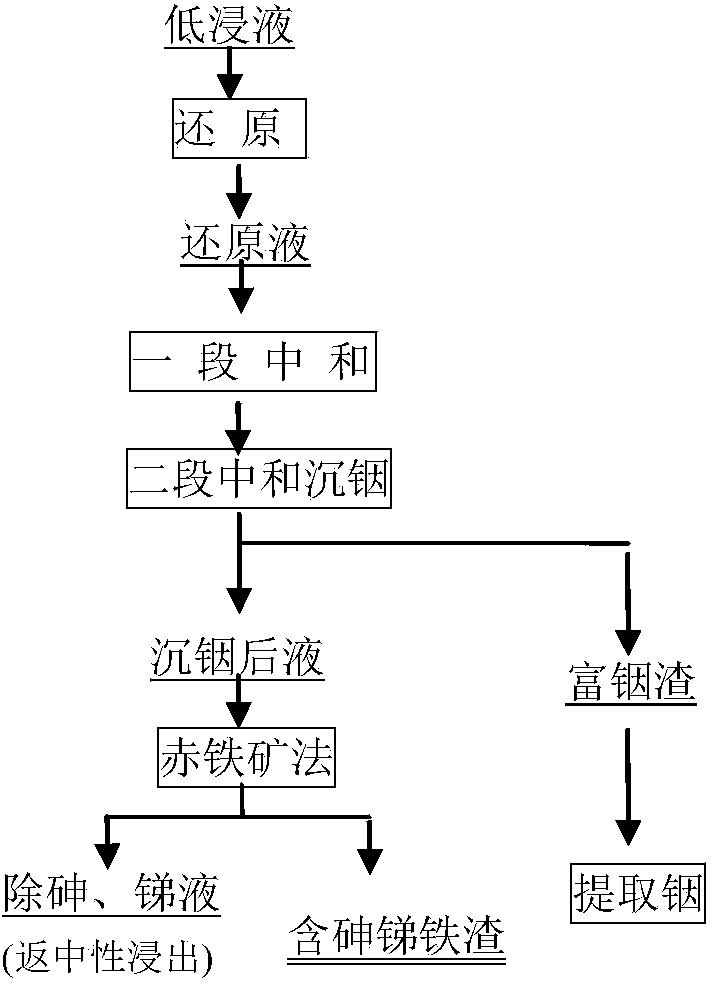
Method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor
InactiveCN103911512AEfficient use ofStable physical and chemical propertiesProcess efficiency improvementIndium metalPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a method for removing arsenic and antimony from zinc smelting leach liquor, and relates to a method for removing arsenic and antimony from a solution produced during zinc smelting by purifying. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: comprehensively recovering valuable components of zinc, indium, iron and the like by purifying in an arsenic and antimony removing process consisting of pre-reduction, neutralization of precipitated indium and a hematite process under the condition that zinc smelting low-acid leach liquor is taken as a raw material; turning high-valence iron into low-valence iron by taking zinc concentrate, zinc sulfite, sulfur dioxide and the like as reducing agents in the low-acid leach liquor, wherein the content of high-valence iron (Fe<3+>) in the reduced liquor is lower than 2g / L; performing two-stage neutralization by using lime, limestone, secondary zinc oxide, calcined sand and zinc oxide to regulate the pH value of reduced liquor to 4.0-5.4 in order to enrich indium precipitate; and removing arsenic and antimony from indium-precipitated liquor to fulfill the aim of efficiently cleaning and purifying the solution. The method has the advantages of high indium metal recovery rate, high arsenic and antimony removing rates, small residue amount, stable performance and environmental friendliness.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
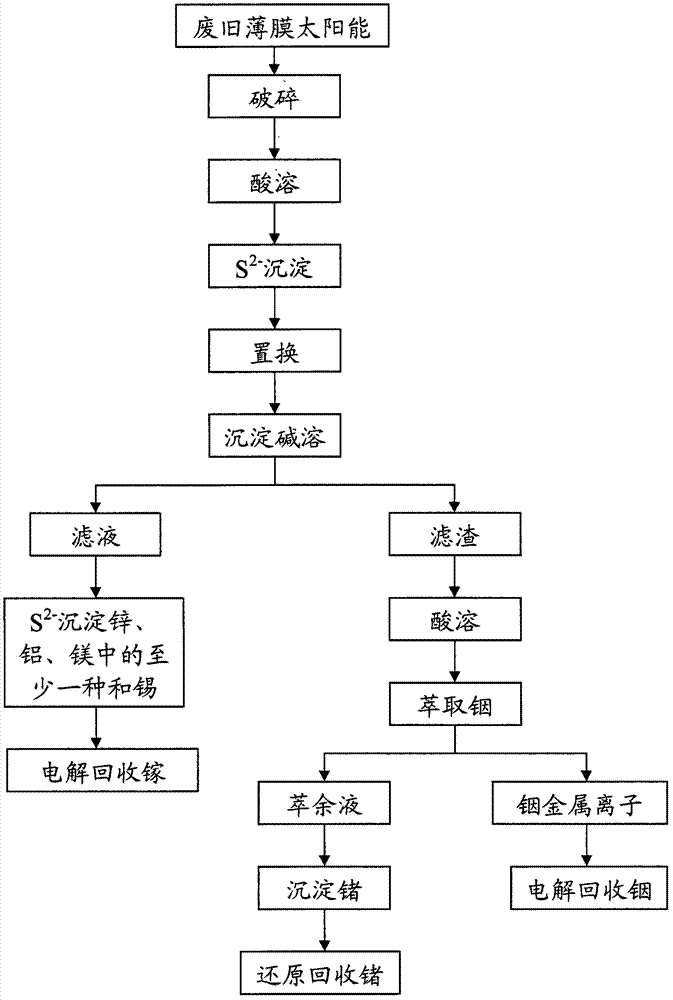
Method for recycling gallium, indium and germanium from wasted thin-film solar cells
ActiveCN103199148AHigh purityReduce recycling costsFinal product manufactureElectronic waste recyclingIndiumCopper
The invention provides a method for recycling gallium, indium and germanium from wasted thin-film solar cells. The method includes the steps: obtaining first separation liquid containing metal ions of the gallium, the indium, the germanium, cadmium, copper, tin and zinc; obtaining second separation liquid; obtaining filter residues containing the gallium, the indium, the germanium and the tin; obtaining fourth separation liquid and an indium and germanium metal solid which is not dissolved in a lye solution; conducting the steps of recycling gallium metal; conducting the steps of recycling indium metal; and conducting the steps of recycling germanium metal. According to the method for recycling the gallium, the indium and the germanium from the wasted thin-film solar cells, various dissipated metal such as the gallium, the indium and the germanium can be respectively recycled step by step, recycling cost can be effectively reduced, the recycling efficiency is improved, and the method is simple in process and is suitable for industrial production. In addition, through the method for recycling the gallium, the indium and the germanium from the wasted thin-film solar cells, the various dissipated metal such as the gallium, the indium and the germanium is high in purity, and the purity can reach up to 99.99%.
Owner:GEM CO LTD
Self-restoring micro-fluid inertia power switch device
The invention discloses a self-restoring micro-fluid inertia power switch device, which comprises a gallium-indium metal liquid drop, a poly(N,N'-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMA) base, a glass cover board, a liquid drop storage pool, a rectangular micro-channel, a U-shaped micro-channel and metal electrodes, wherein the liquid drop storage pool, the U-shaped micro-channel and the rectangular micro-channel are arranged on a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) plate; the metal electrodes are bonded on the glass cover board; the gallium-indium metal liquid drop is initially located in the liquid drop storage pool; and when the inertia force on a switch is greater than the threshold of a passive valve, a metal liquid breaks through the passive valve and enters a micro-channel electrode, and the switch is connected. The liquid flows to a cutoff passive valve in the U-shaped micro-channel at most; when the inertia force disappears, a capillary force difference of the liquid exists between two ends of the micro-channel, so that the liquid automatically flows to the initial position, and the property of the switch is restored. The self-restoring micro-fluid inertia power switch device disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, stable and reliable in contact; and compared with an existing micro-fluid inertia switch, the switch has self-restoring capability, and can be used for a plurality of times.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
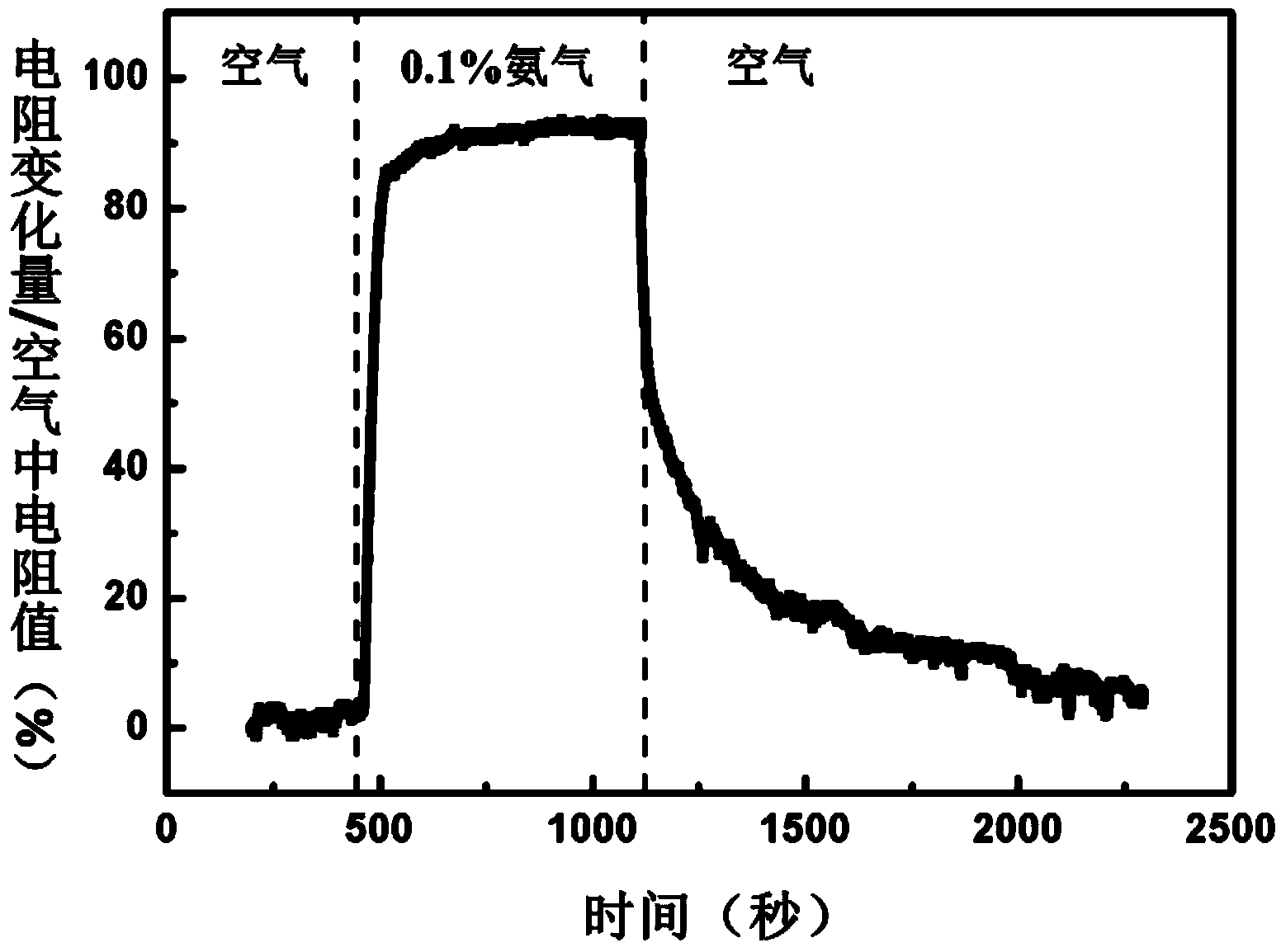
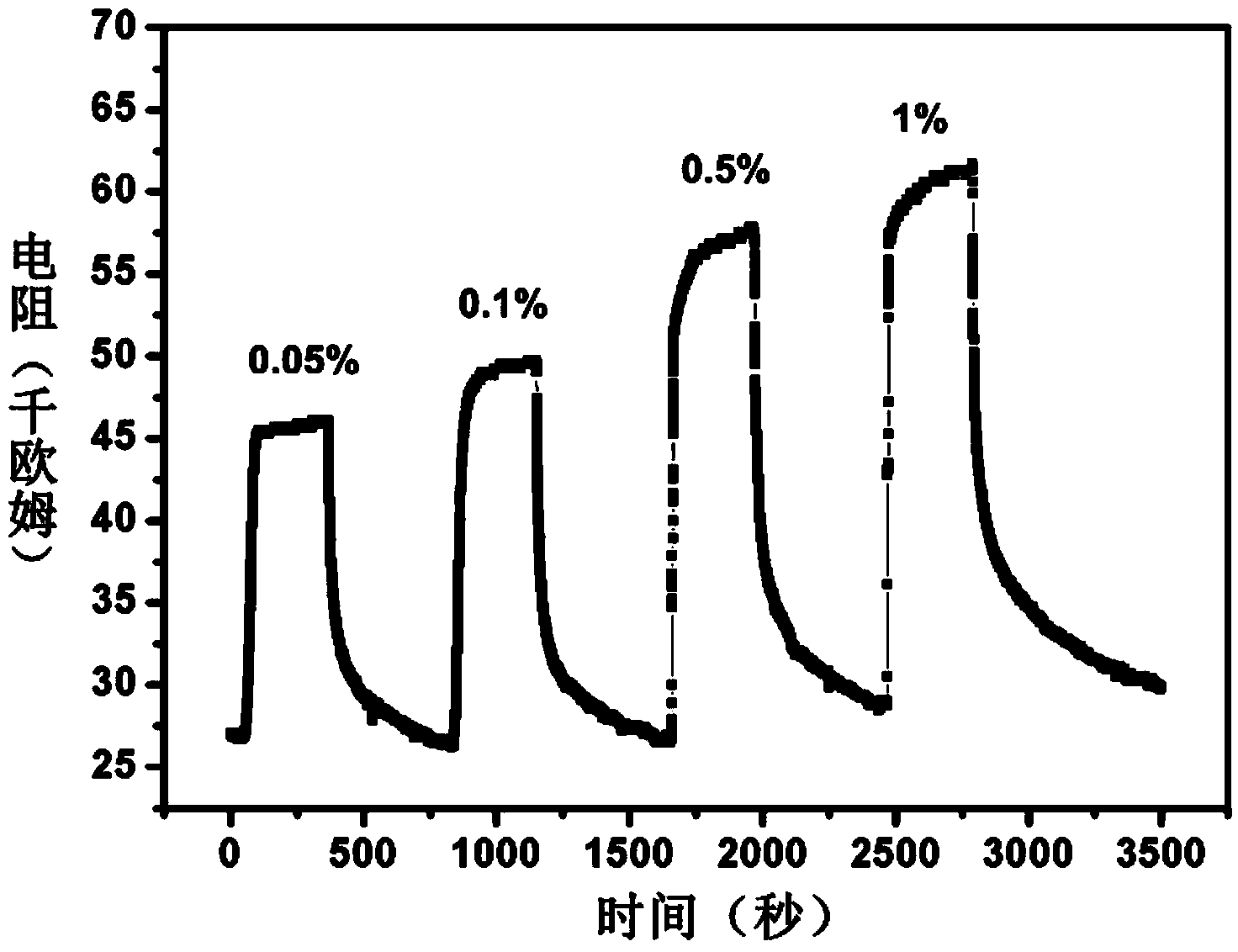
Ammonia gas sensor based on polyaniline/graphene nanoribbons/silicon dioxide/silicon
ActiveCN104297301AReduce energy consumptionSimple processMaterial resistanceFiltrationSilicon dioxide
The invention belongs to the field of ammonia gas sensors, and in particular relates to an ammonia gas sensor based on polyaniline / graphene nanoribbons / silicon dioxide / silicon. A preparation method of the ammonia gas sensor comprises the following steps: transferring a graphene nanoribbon film onto a silicon wafer via a suction filtration method and a transfer printing method, and carrying out low-temperature reduction so as to obtain a graphene nanoribbon / silicon dioxide / silicon heterostructure material; then carrying out polyaniline modification on the surface of the heterostructure material via a chemical method; and finally, smearing silver colloid and an indium metal layer on the upper surface and the lower surface of the heterostructure material to serve as an upper electrode and a lower electrode, thereby preparing the ammonia gas sensor which is based on polyaniline / graphene nanoribbons / silicon dioxide / silicon and is excellent in ammonia gas sensitivity. The ammonia gas sensor does not require a heater and can work at room temperature, and also has the characteristics of low energy consumption, simple process, high sensitivity, short response and recovery time and the like. Thus, the ammonia gas sensor has important application prospect in the field of gas detection.
Owner:薛洁
Preparation method of nanometer grade indium tin oxide composite powder
A process for preparing the indium tin oxide (ITO) nanoparticles includes such steps as respectively dissolving In and Sn in strong acid or the soluble In salt and Sn salt in water, mixing, stirring while adding precipitant to obtain InSn deposit, washing with water and organic solvent, solid-liquid separation, adding organic solvent, azeotropic distilling, drying the filtered cake, breaking and calcining.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
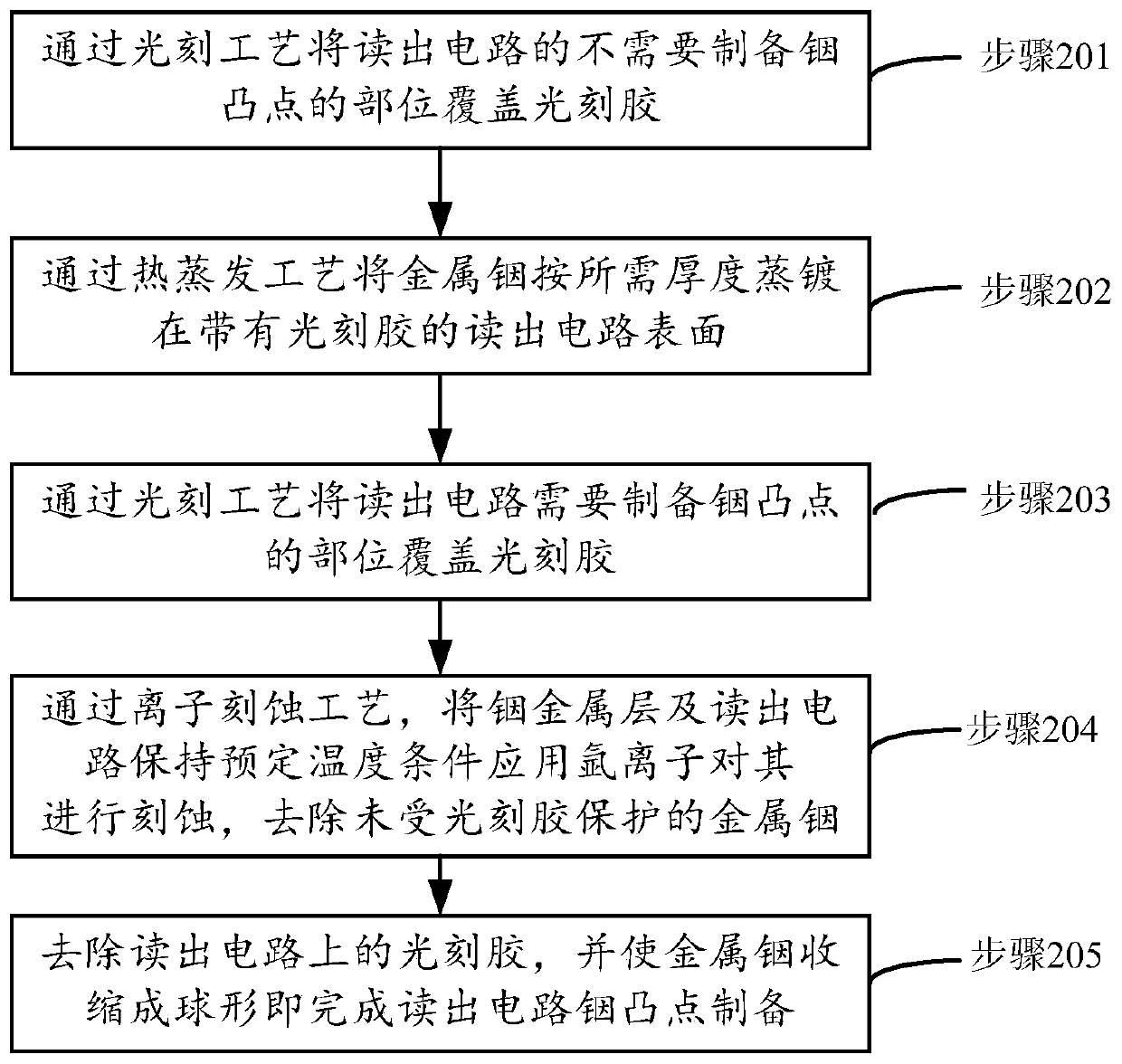
Method for preparing indium bumps of reading circuit of infrared detector
ActiveCN110660690AImprove uniformityReduce manufacturing difficultySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium metalLithography process
The invention discloses a method for preparing indium bumps of a reading circuit of an infrared detector. The method comprises steps of covering photoresist on a part, which does not need to be provided with indium bumps, of the reading circuit through the photoetching process; evaporating metal indium on a surface of the reading circuit with the photoresist according to the required thickness through the thermal evaporation process; covering photoresist on the part of the reading circuit, which needs to be provided with the indium bumps, through the photoetching process; through the ion etching process, etching the indium metal layer and the reading circuit by using argon ions while keeping the preset temperature condition, and removing the metal indium which is not protected by the photoresist; and removing the photoresist on the reading circuit, and shrinking the metal indium into a sphere to finish preparation of the indium bumps of the reading circuit.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
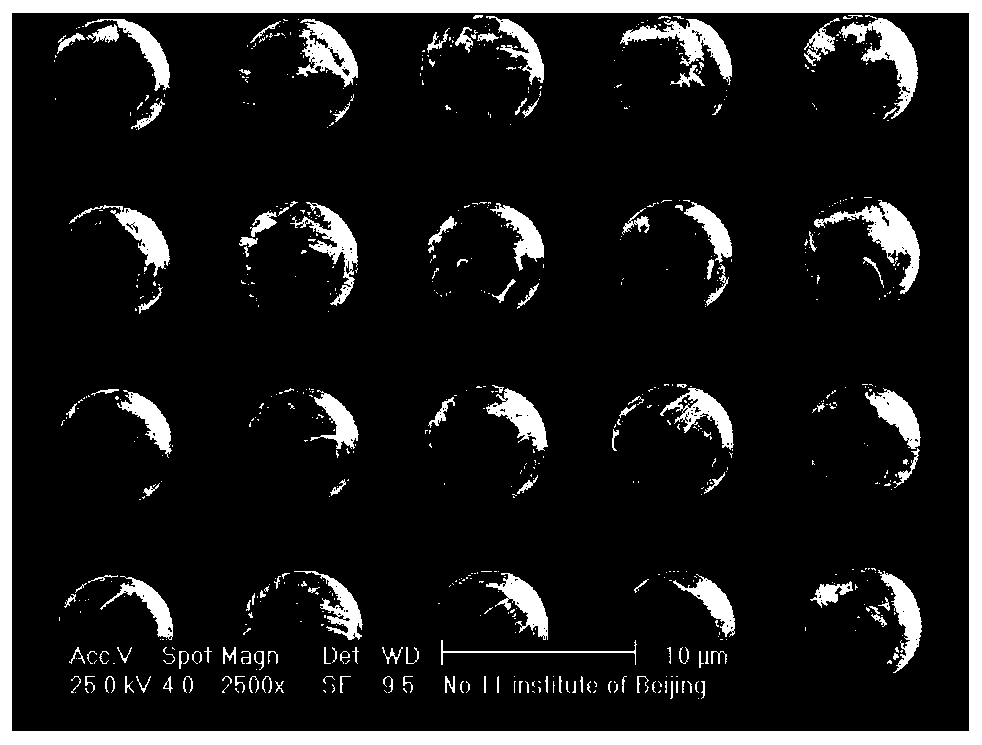
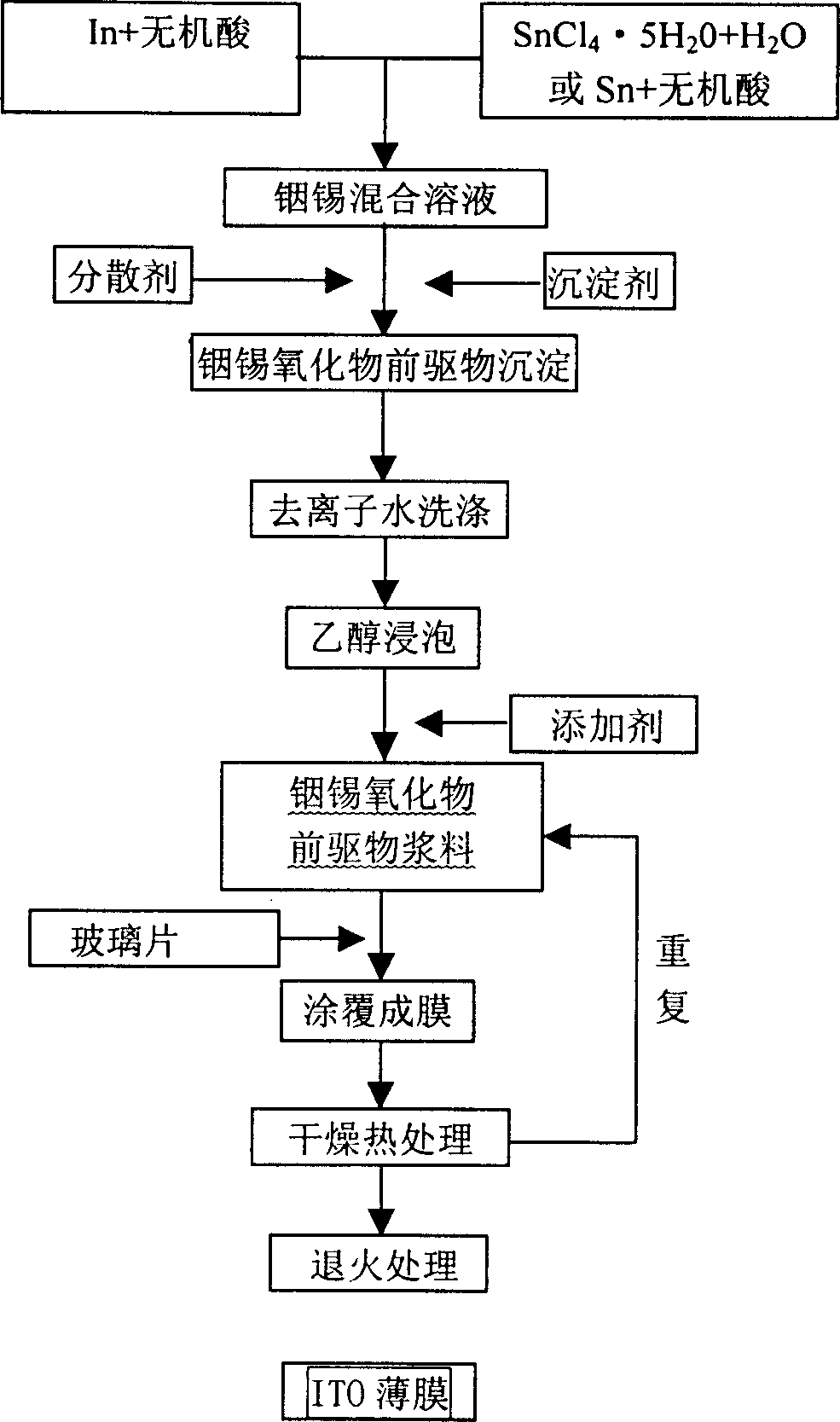
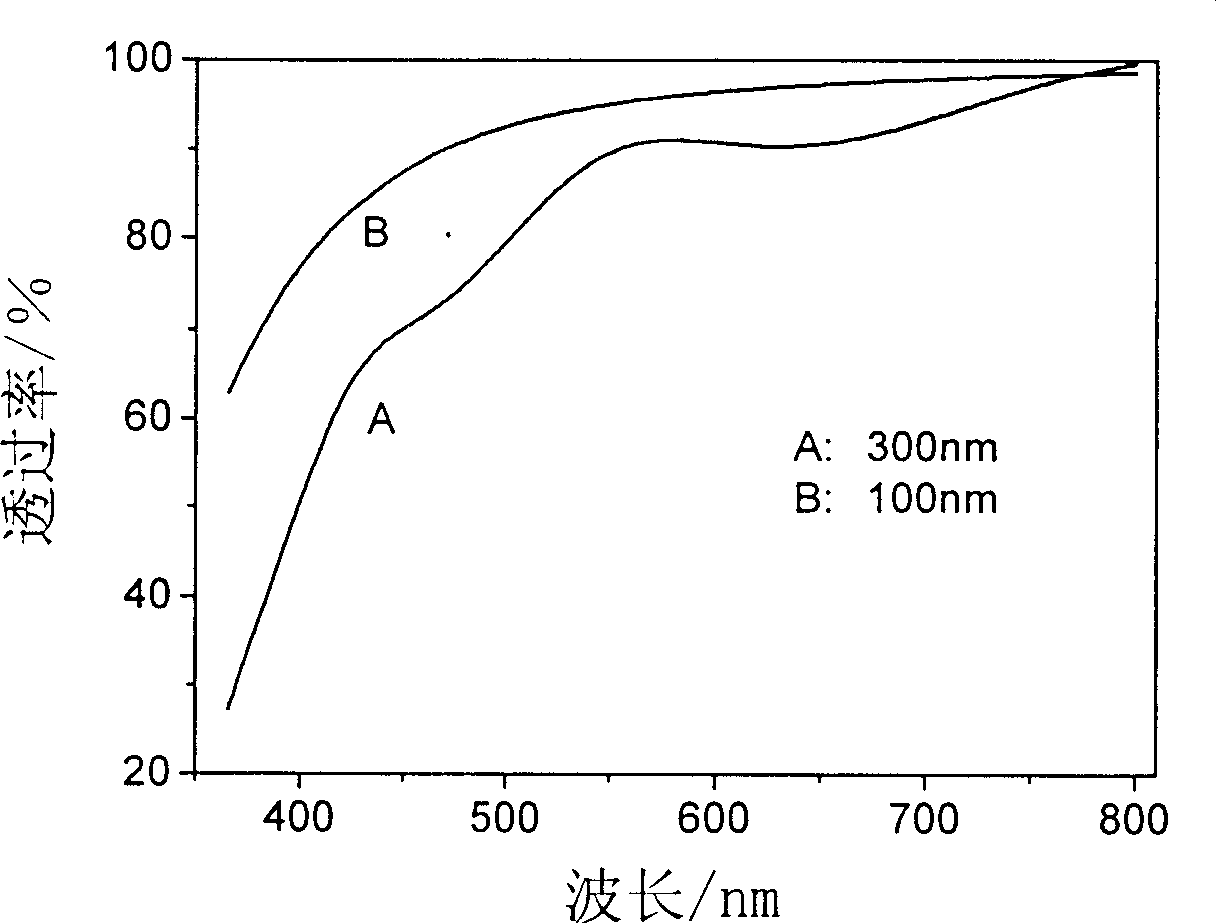
Preparation method of indium tin oxide precusor size and ITO thin film
A process for preparing the precursor slurry of indium tin oxide (ITO) includes such steps as dissolving In and Sn in strong acid respectively or dissolving the soluble In salt and Sn salt in water respectively, mixing, stirring while adding precipitant to obtain InSn deposit, washing with deionized water, adding disperser and precipitant to obtain the colloid deposit of indium tin hydroxide (or carbonate), and adding alcohol and additive to obtain the target slurry. An ITO film is prepared through coating said slurry on the glass plate and calcining.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Indium series metal particle and mfg. method thereof, coating liquid containing same, base material with covering film and dispay device
To provide indium based metal fine particles and a dispersion sol appropriately usable for forming a transparent and conductive film having an excellent antistatic property and electromagnetic shielding property and also having an excellent manufacturing reliability and cost effectiveness. The indium based metal fine particles have a 2-200 nm average particle size. The indium based metal fine particles contain indium metal only or one or more kinds of metal components selected from among Sb, Sn, Ag, Au, Zn, Cu, Bi and Cd together with the indium metal. The indium based metal fine particles dispersion sol is obtained by dispersing the indium based metal fine particles in water and / or an organic solvent. In a method for manufacturing the indium based metal fine particles, a reducing agent is added to a mixed alcohol solution containing an indium compound and an organic stabilizing agent and having a >=40 wt.% alcohol content in the solvent.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Method of preventing silver tarnishing
ActiveUS20130224515A1Avoid tarnishingReduce contact resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingJewelleryIndiumElectroplating
A thin indium metal layer is electroplated onto silver to prevent silver tarnishing. The indium and silver composite has high electrical conductivity.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
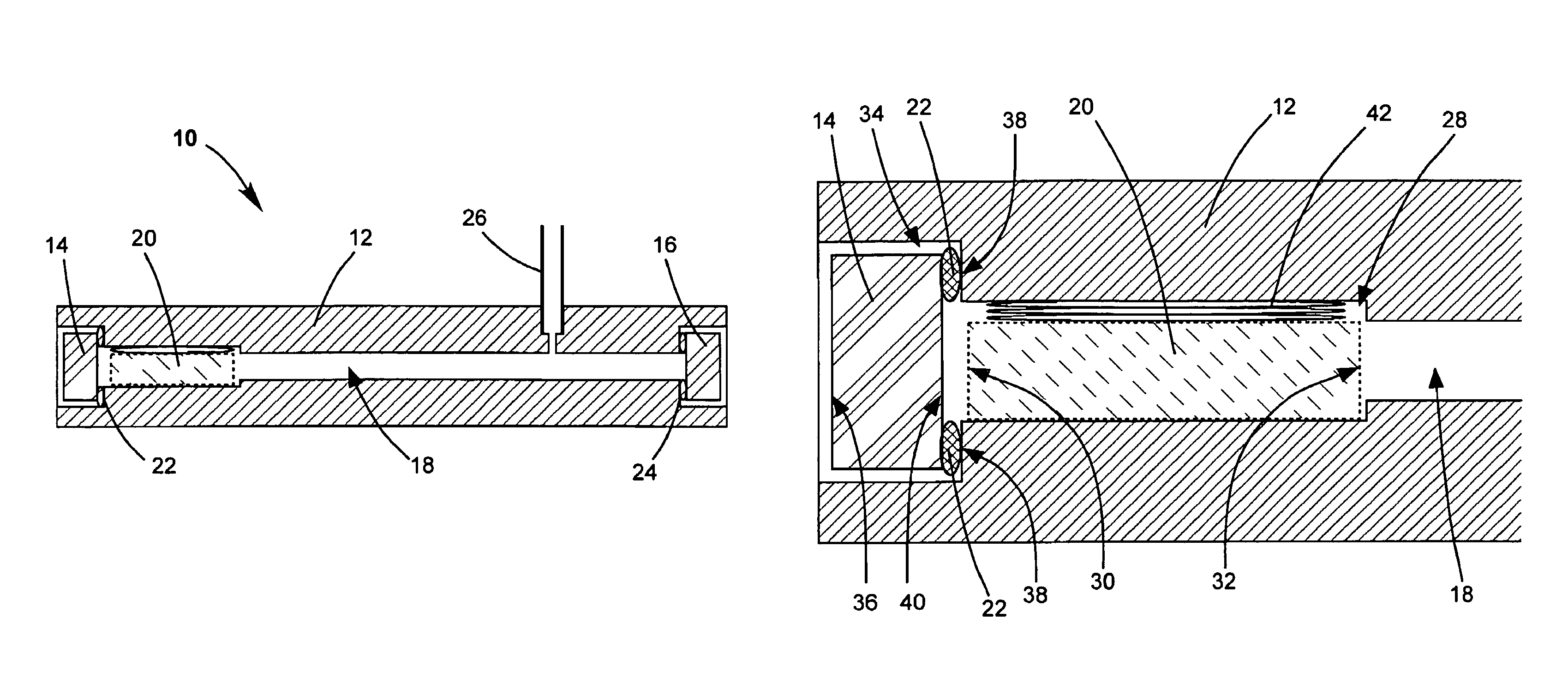
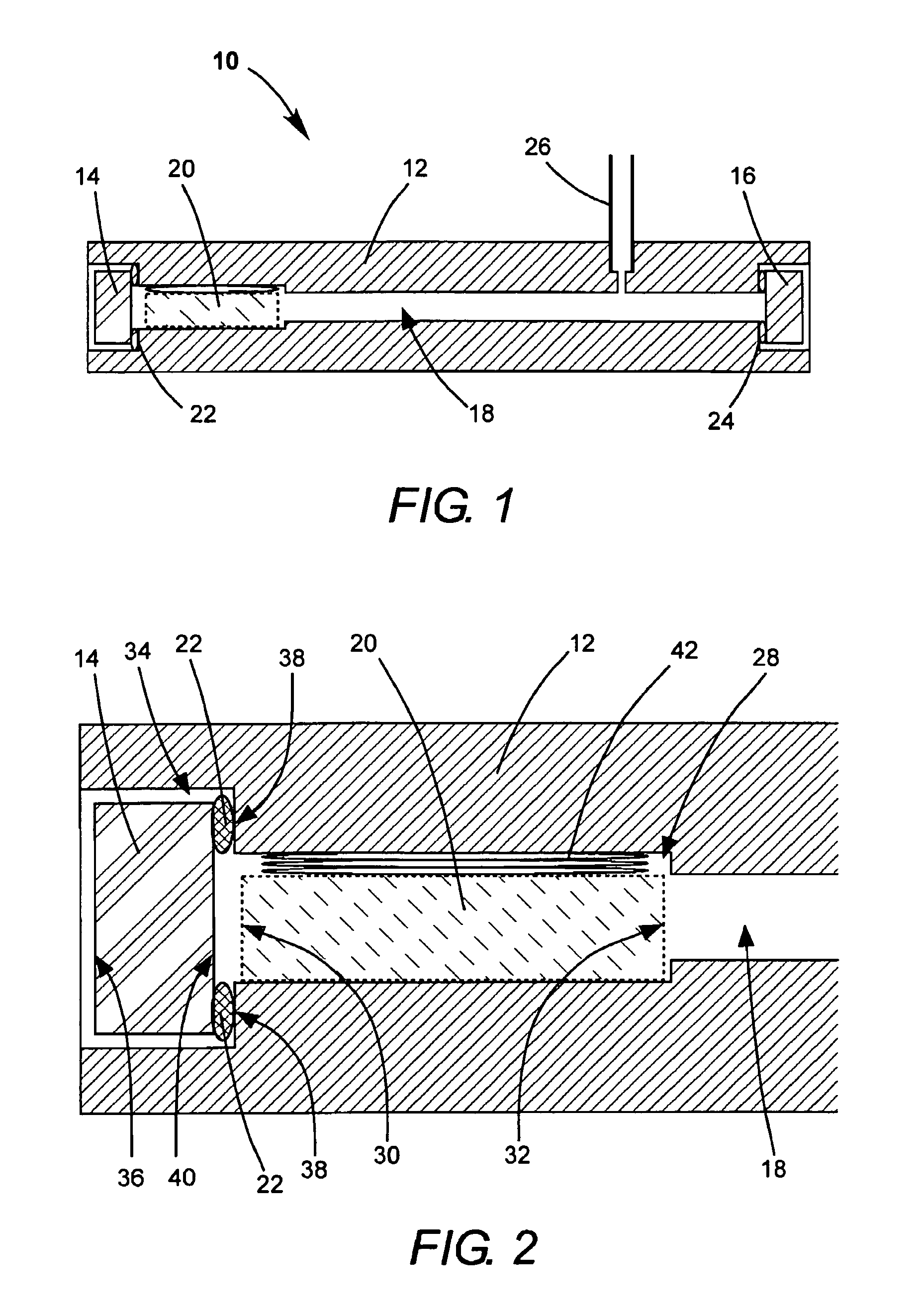
Indium features on multi-contact chips
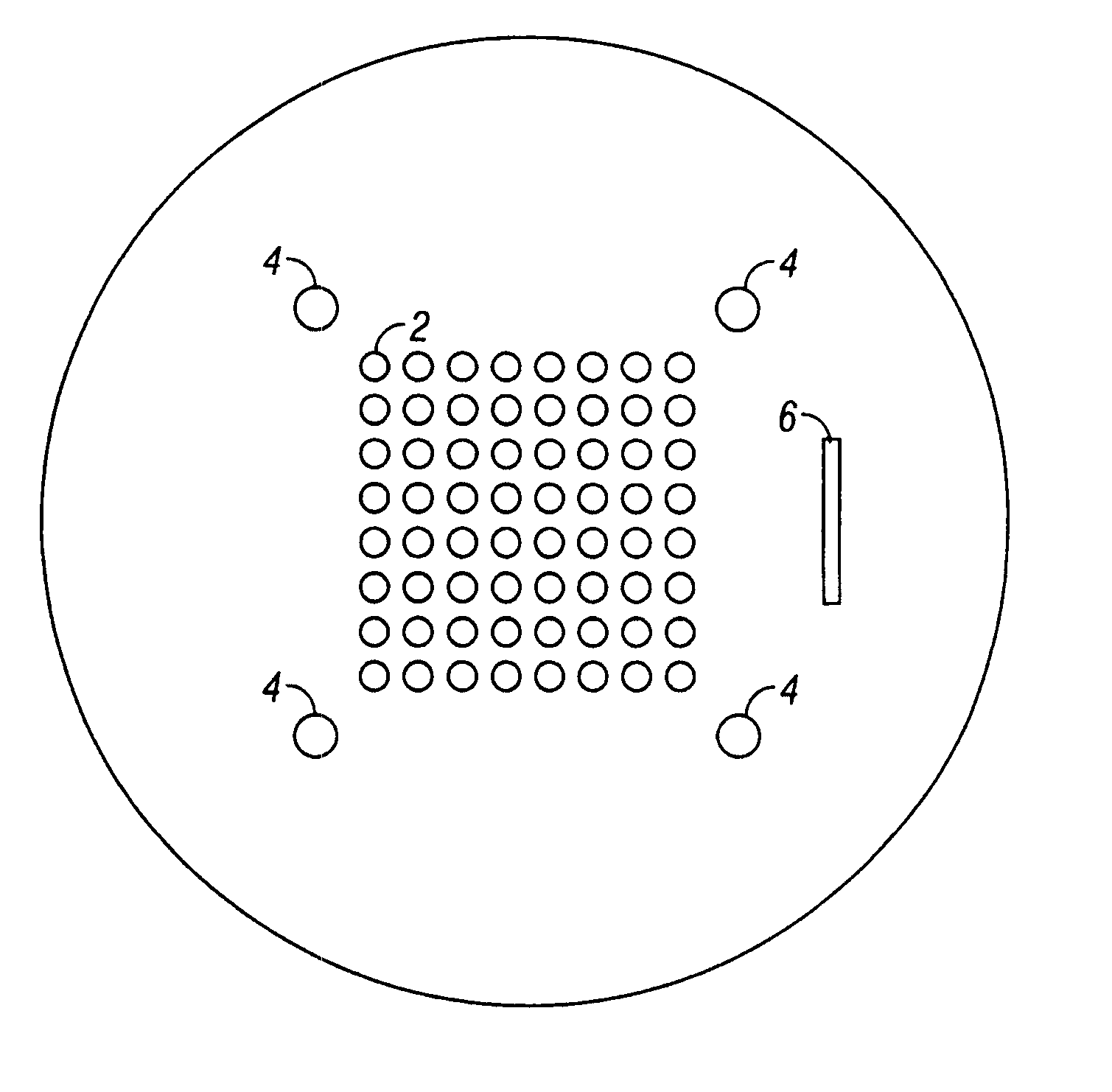
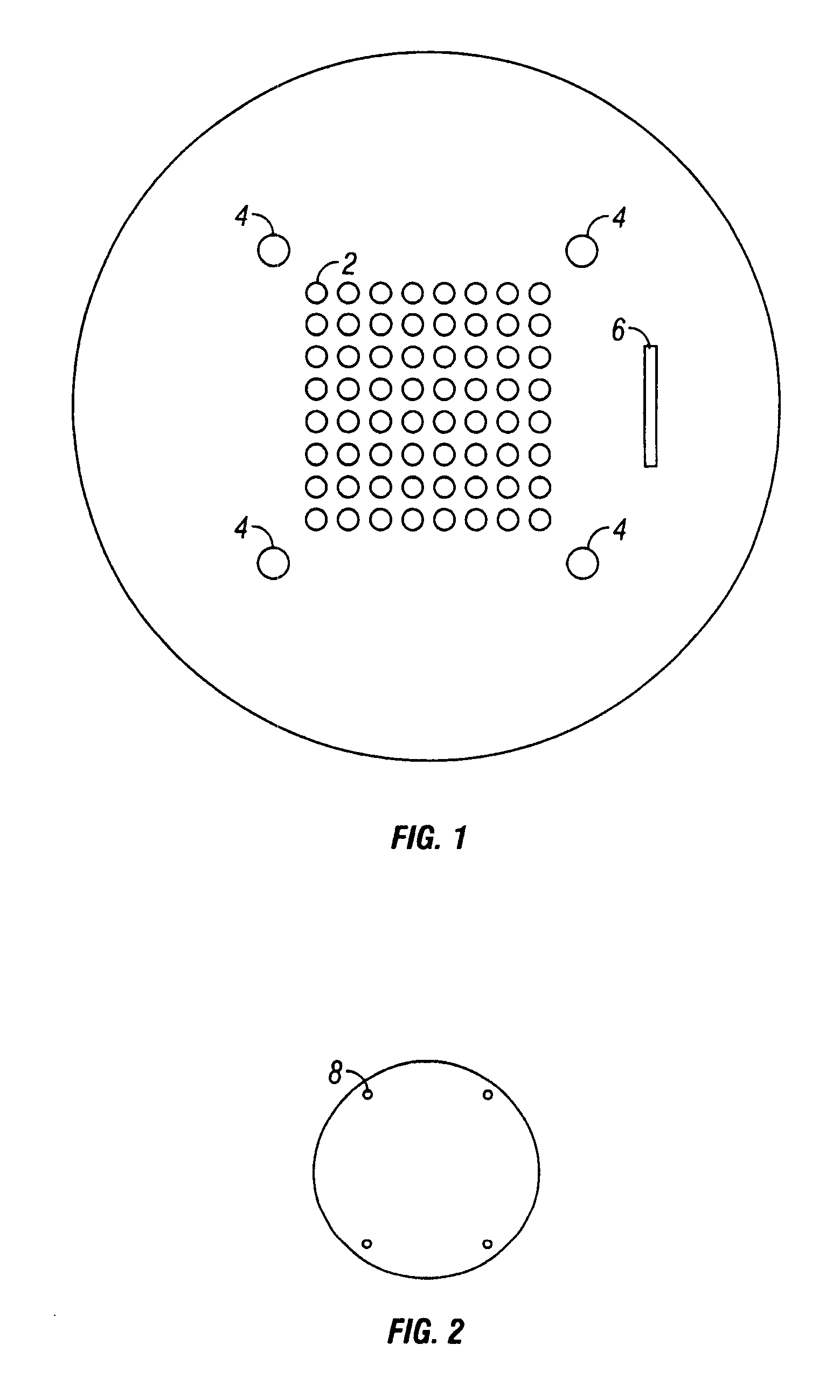
InactiveUS20070224722A1Improve leakage currentThicker regionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium metalIndium bump
A device comprising a pixilated semiconductor detector or VLSI chip having plurality of individual indium bumps arrayed on a surface of the detector, wherein the indium bumps are in electrical contact with the surface and are situated in defined locations on the surface is provided. Additionally, a hybrid detector comprising a pixilated detector in electrical contact with a VLSI chip, wherein electrical contacts formed from indium metal are made between the pixels of the semiconductor and regions on the VLSI chip corresponding thereto is provided. In another embodiment, a method of forming electrical contacts on a pixilated detector comprising the steps of constraining a shadow mask having an array of holes in predetermined locations above a surface on the detector, aligning the mask above the detector, and evaporating indium metal under vacuum through holes in the mask onto the surface of the detector to form the contacts is described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
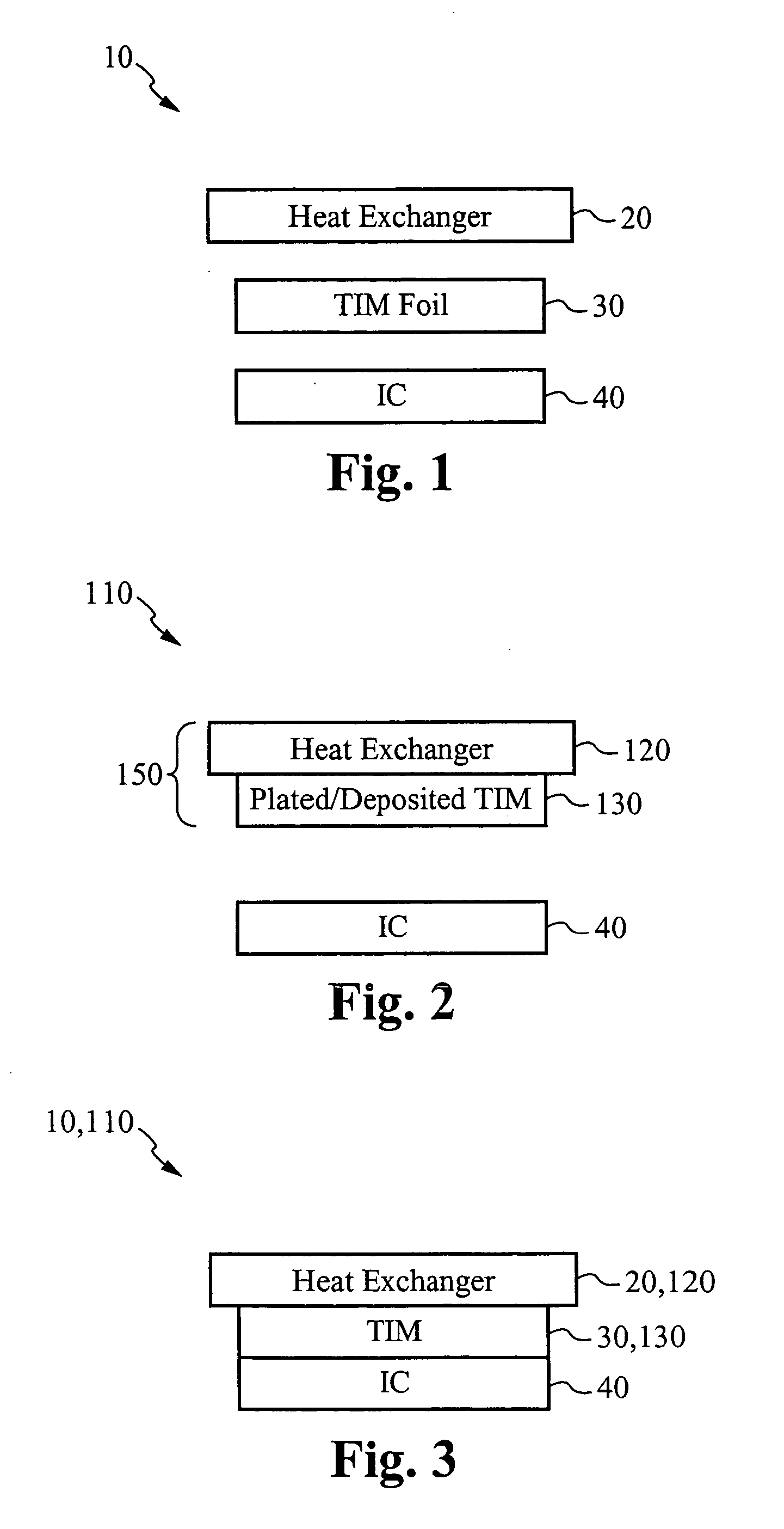
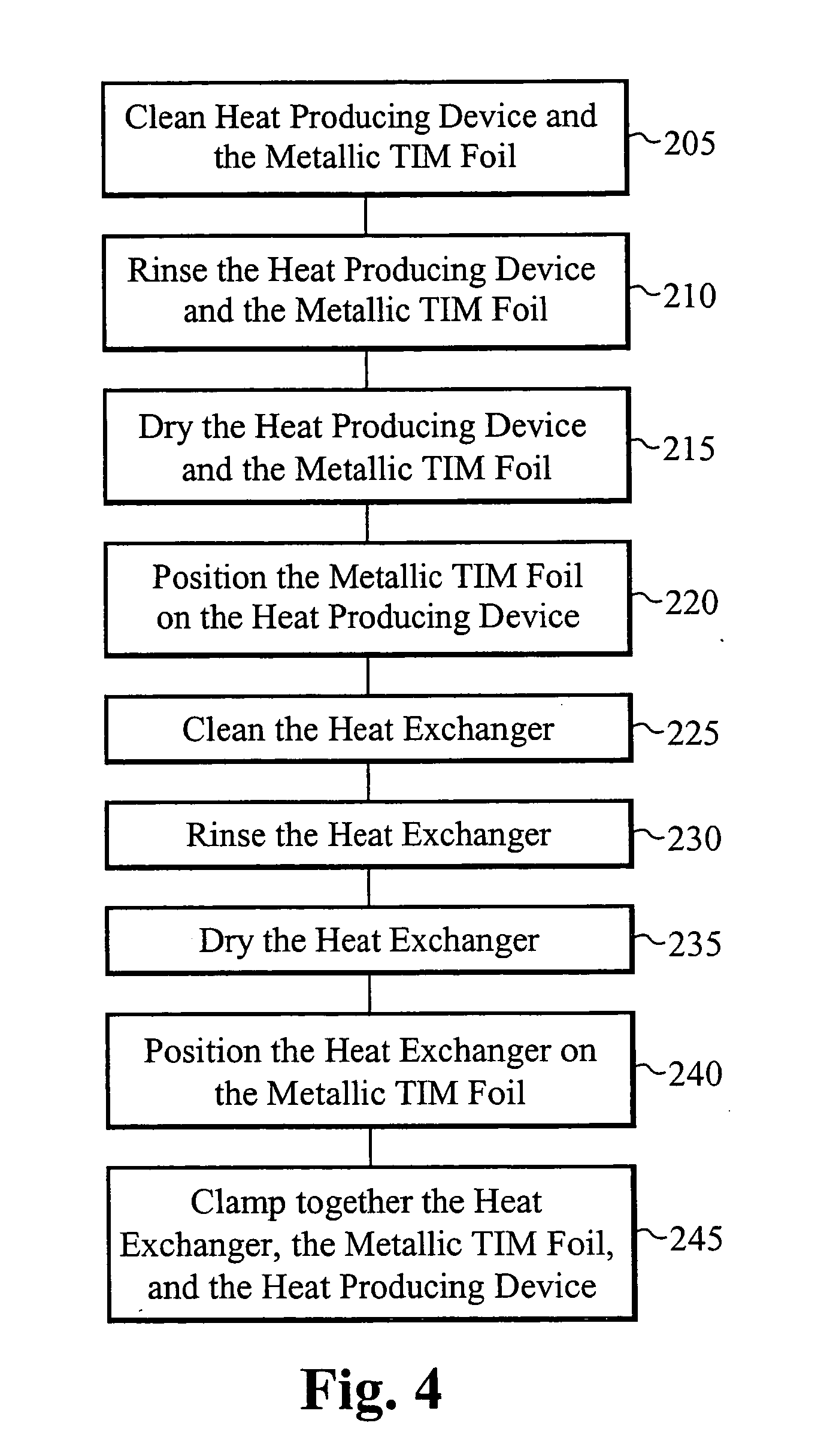
Re-workable metallic TIM for efficient heat exchange
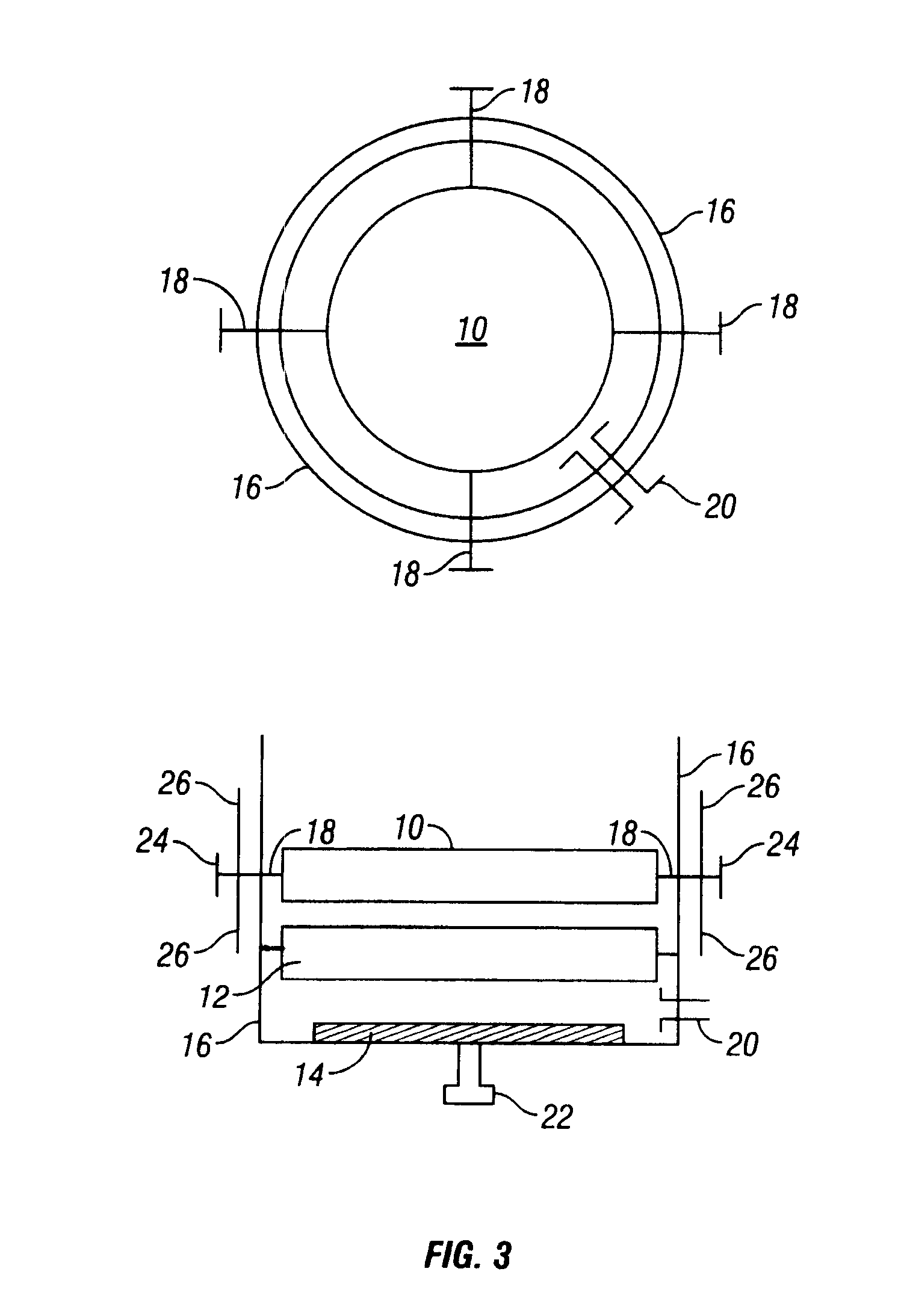
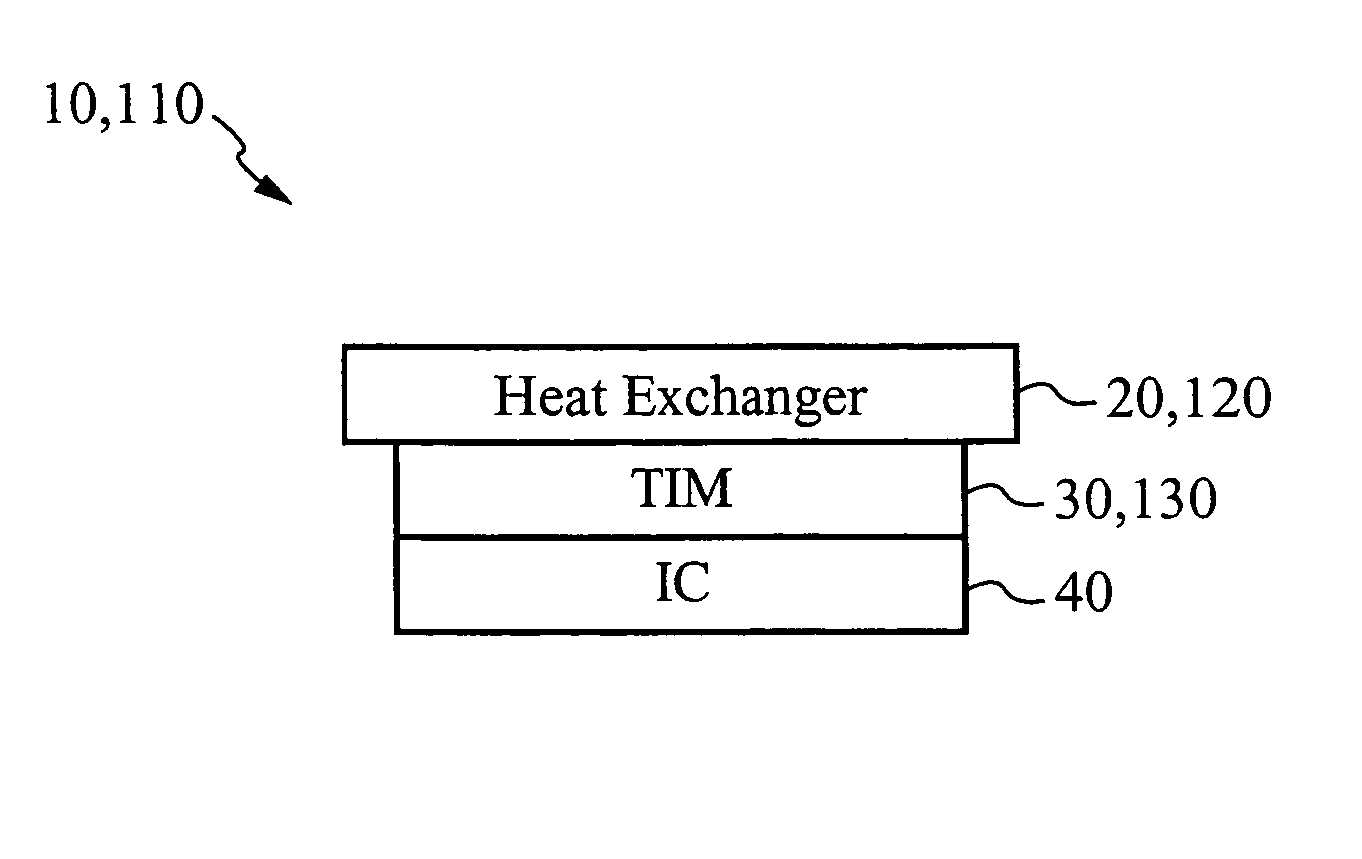
InactiveUS20070175621A1Minimize stress transferredSimplify the assembly processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndiumMetallic materials
A heat exchanging system uses a metallic TIM for efficient heat transfer between a heat source and a heat exchanger. The heat source is preferably an integrated circuit coupled to a circuit board. The metallic TIM preferably comprises indium. The metallic TIM is comprised of either a separate metallic TIM foil or as a deposited layer of metal material. The metallic TIM foil is mechanically joined to a first surface of the heat exchanger and to a first surface of the integrated circuit by applying sufficient pressure during clamping. Disassembly is accomplished by un-clamping the heat exchanger, the metallic TIM foil, and the integrated circuit from each other. Once disassembled, the heat exchanger and the metallic TIM foil are available to be used again. If the metallic TIM is deposited onto the heat exchanger, disassembly yields a heat exchanging sub-assembly that is also reusable.
Owner:COOLIGY INC
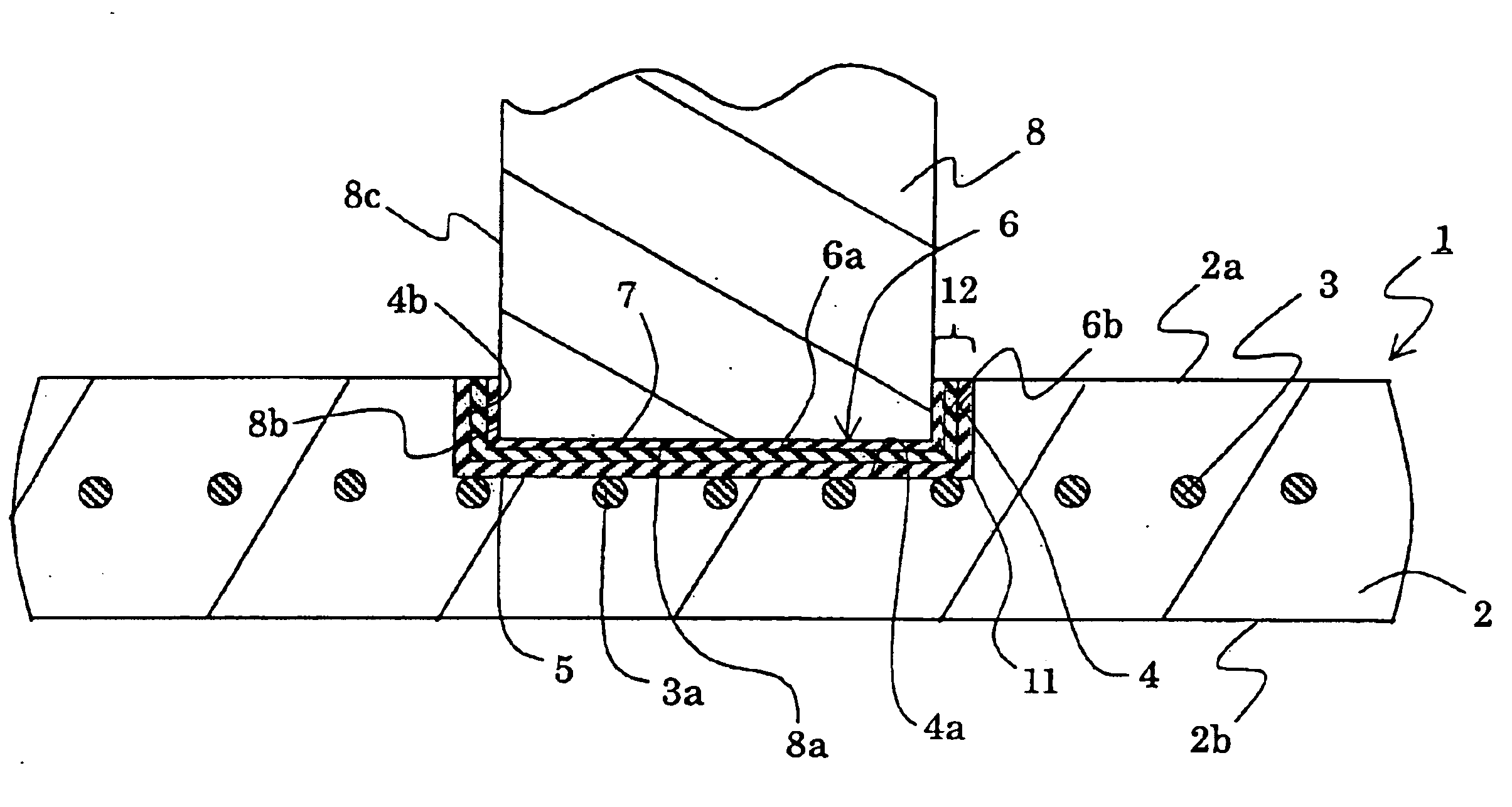
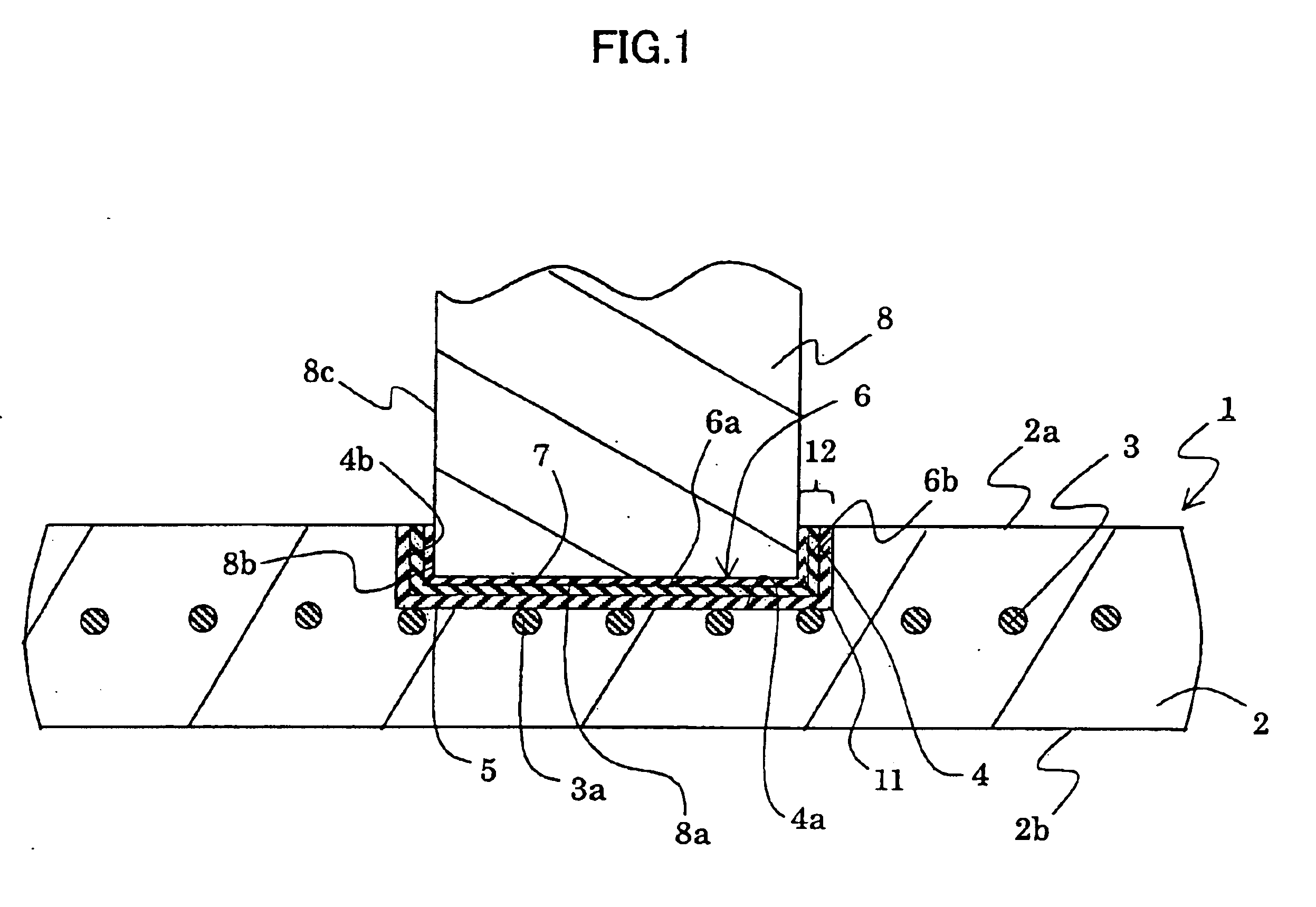
Joined structures of metal terminals and ceramic members, joined structures of metal members and ceramic members, and adhesive materials
InactiveUS6869689B2High bonding strengthInhibition formationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndium metalAdhesive materials
A joined structure of a metal terminal and a ceramic member has a joining layer between the terminal and the ceramic member. The joining layer has a metal adhesive layer containing at least indium metal. The invention further provides a joined structure of a metal member and a ceramic member. The metal member has a tip face and a side face. A hollow is formed in the ceramic member. A joining layer is formed between a bottom surface facing the hollow and the tip face of the member, and further formed between a side wall surface facing the hollow and the side face of the member. The joining layer has a metal adhesive layer containing at least indium metal.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method for using ICP-AES to accurately measure precious metal content in solution
InactiveCN107037037AReduce mistakesDetection speedPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOmegaLinearity
The invention discloses a method for using ICP-AES to accurately measure precious metal content in a solution. The method comprises the first step of preparing a precious metal single element standard stocking solution; the second step of preparing an indium internal standard stocking solution; the third step of preparing a precious metal standard working solution, wherein the precious metal standard can be a precious metal single element standard or a standard of mixing of several kinds of precious metal elements); the fourth step of preparing a precious metal sample testing solution; the fifth step of conducting measuring, wherein a proper inductive coupling plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-AES) is selected to test conditions (including setting of an internal standard mode), and a series of solutions like the precious metal standard working solution are measured to draw a working curve, the linearity of the working curve is made larger than or equal to 0.99995, and a sample testing solution B is measured under an equal condition. An instrument automatically searches for the precious metal content value ws in the given sample testing solution B, and the unit is mg / g. The precious metal content Omega p of a precious metal sample is obtained according to fixed weight dilution folds, wherein the formula of Omega p is (ws*m30*100*m27) * 100 / (m28*m25), the unit is %, and the precious metal is Au, Pt, Pd, Rh, Ir, and Ru.
Owner:SINO PLATINUM METALS CO LTD
Device and method for unbinding flat target material and rotary target material
PendingCN109161862AHigh unbinding efficiencyUnbreakableVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndium metalEngineering
The invention relates to a device and method for unbinding a flat target material and a rotary target material. The device comprises an oil bath, a heating element, a flat target material grid bracket, a rotary target material bracket and an indium collection basket, wherein the bottom surface of the oil bath is arranged obliquely; an indium collection basket placing groove is formed at the lowestposition of the bottom surface of the oil bath; the indium collection basket is placed in the indium collection basket placing groove; the heating element consists of a connecting rod and a pluralityof heating rods uniformly mounted on the connecting rod; the heating element is mounted in the oil bath; the flat target material grid bracket comprises a plurality of partition boards, small holes are formed in each of the partition boards, the partition boards are arrayed obliquely at a certain distance, and the two sides of each of every two adjacent partition boards are connected with each other by an upper rod and a lower rod; the rotary target material bracket is formed by two guide rails and a rotary target material support glidingly mounted on the guide rails. The device and the method are suitable for unbinding a target material bound by an indium metal and can be used for unbinding the flat target material and the rotary target material in batch, the unbinding temperature is uniform, the target materials are in good condition after unbinding, and the unbinding efficiency is high.
Owner:GUANGXI CRYSTAL UNION PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIALS CO LTD
Composition for producing metal film, method for producing metal film, and method for producing metal powder
InactiveCN102197444ACost-effective manufacturingTransportation and packagingConductive materialAlcoholSurface layer
Provided are a composition with which a metal film can be produced directly from a high-atomic-valence metal compound, a method for producing a metal film, and a method for producing a metal powder. The composition for producing a metal film of copper, silver, or indium comprises a high-atomic-valence compound of copper, silver or indium; a linear, branched or cyclic C1-18 alcohol; and a group VIII metal catalyst. The copper, silver, or indium metal film is produced by subjecting a film formed from the same composition to heating and reduction. The copper, silver, or indium metal film can also similarly be produced by substituting the high-atomic-valence compound of copper, silver, or indium with copper, silver, or indium metal particles wherein the surface layer is formed from the high-atomic-valence compound of copper, silver, or indium.
Owner:TOSOH CORP +1
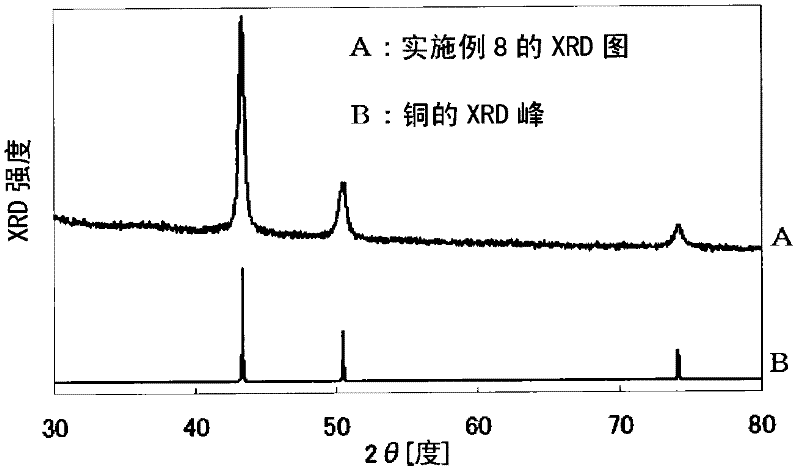
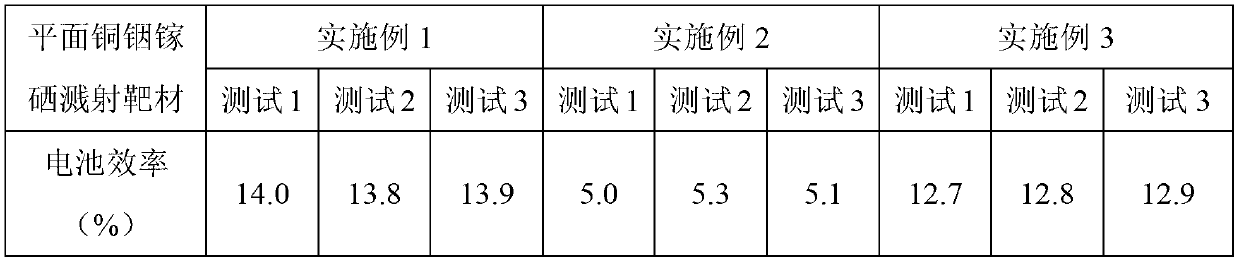
Preparation method of planar copper-indium-gallium-selenium sputtering target material
InactiveCN103215541AImprove conversion efficiencyReduce manufacturing costVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOxygenMaterials science
The invention provides a planar copper-indium-gallium-selenium sputtering target material which is a Cu-In-Ga-Se2 quaternary alloy system composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium with an atomic ratio of (20-25): (10-19): (6-12.5): (50-60). The invention also provides a preparation method of the planar copper-indium-gallium-selenium sputtering target material. The target material is the Cu-In-Ga-Se2 quaternary alloy system composed of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium. With the target material, copper-indium-gallium-selenium film battery production cost can be greatly reduced, and copper-indium-gallium-selenium film battery production can be greatly industrialized. According to the target material preparation method, high-purity metals copper, indium, gallium, and selenium are adopted as raw materials, and processes such as ball milling, sieving, hot pressing, and the like are carried out, such that the planar copper-indium-gallium-selenium sputtering target material is obtained. The process is simple, the cost is low, and the method is suitable for industrialized productions. The prepared target material has a relative density up to 89% or higher, oxygen density up to 150-250ppm, and conductivity up to 50-80 ohmcm. The size of the material can be 40-100 micrometers.
Owner:无锡舒玛天科新能源技术有限公司
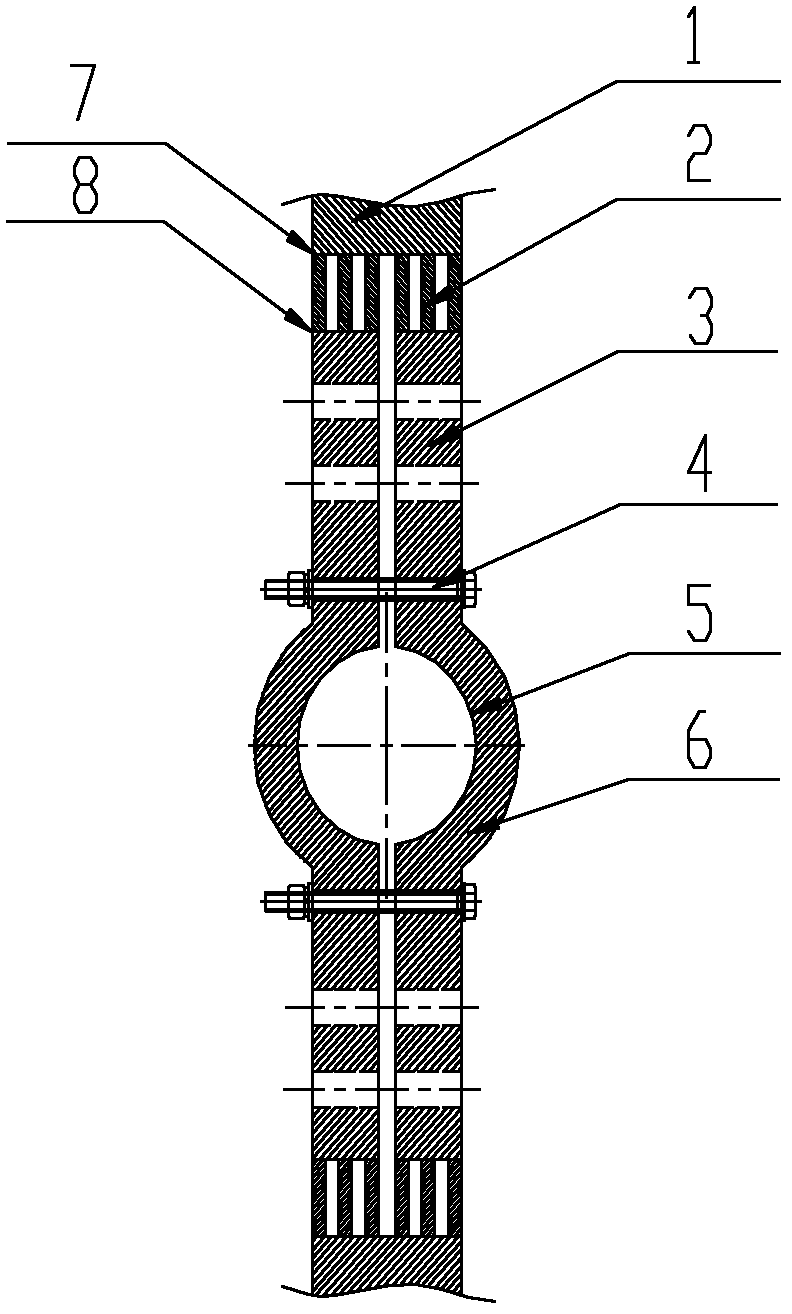
Hough-type transition connection device for large-current high-temperature superconducting cable terminal
InactiveCN102570076ALower body resistanceReduce lossSoldered/welded conductive connectionsClamped/spring connectionsIndium metalElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a Hough-type transition connection device for a large-current high-temperature superconducting cable terminal. A Hough-type current lead terminal of the Hough-type transition connection device is formed by arranging two symmetrical arch current lead terminals oppositely up and down. The middle circular arc parts of the two arch current lead terminals are Hough-type current lead terminal connection sections (6); and two upper straight plate parts and two lower straight plate parts of the two arch current lead terminals are Hough-type current lead terminal welding deformation transition sections (3), and a plurality of through holes (9) are uniformly distributed on the Hough-type current lead terminal welding deformation transition sections (3). Indium metal layers (5) are plated on the inner circular arc surfaces of the Hough-type current lead terminal connection sections. Transition metal plates (2) are connected between the Hough-type current lead terminal welding deformation transition sections (3) and a conventional conductor (1). The transition metal plates (2) are connected with the Hough-type current lead terminal connection sections (6) and the conventional conductor (1) by welding.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of bearing bush with high bearing capacity
InactiveCN102424996AImprove crack resistanceImprove the performance of anti-delaminationIndium metalCrack resistance
The invention relates to a method for preparing a bearing bush with high bearing capacity, which comprises the following steps: (1) plating a lead-tin-copper ternary alloy friction reducing layer on a substrate; (2) electroplating an indium layer on the lead-tin-copper ternary alloy friction reducing layer; (3) after electroplating the indium layer, allowing the substrate to diffuse in an oil or glycerol solution for three hours at a temperature of up to 150 DEG C so as to allowing the indium layer to be uniformly diffused on the lead-tin-copper ternary alloy friction reducing layer. Compared with the prior art, the invention adds indium on the basis of the lead-tin-copper ternary alloy friction reducing layer of the bearing bush; indium is an element with soft texture and good ductility, so the crack resistance and delamination resistance of the bearing bush are greatly improved, and the bearing capacity is greatly increased; in addition, with the preparation method of the present invention, indium is uniformly diffused on the lead-tin-copper ternary alloy friction reducing layer, which improves the fatigue strength to 90-105 MPa; and the invention overcomes the problems that indium metal is active, and the electroplating and diffusion of indium in ternary alloy has certain technical difficulties.
Owner:广东韶配动力机械有限公司
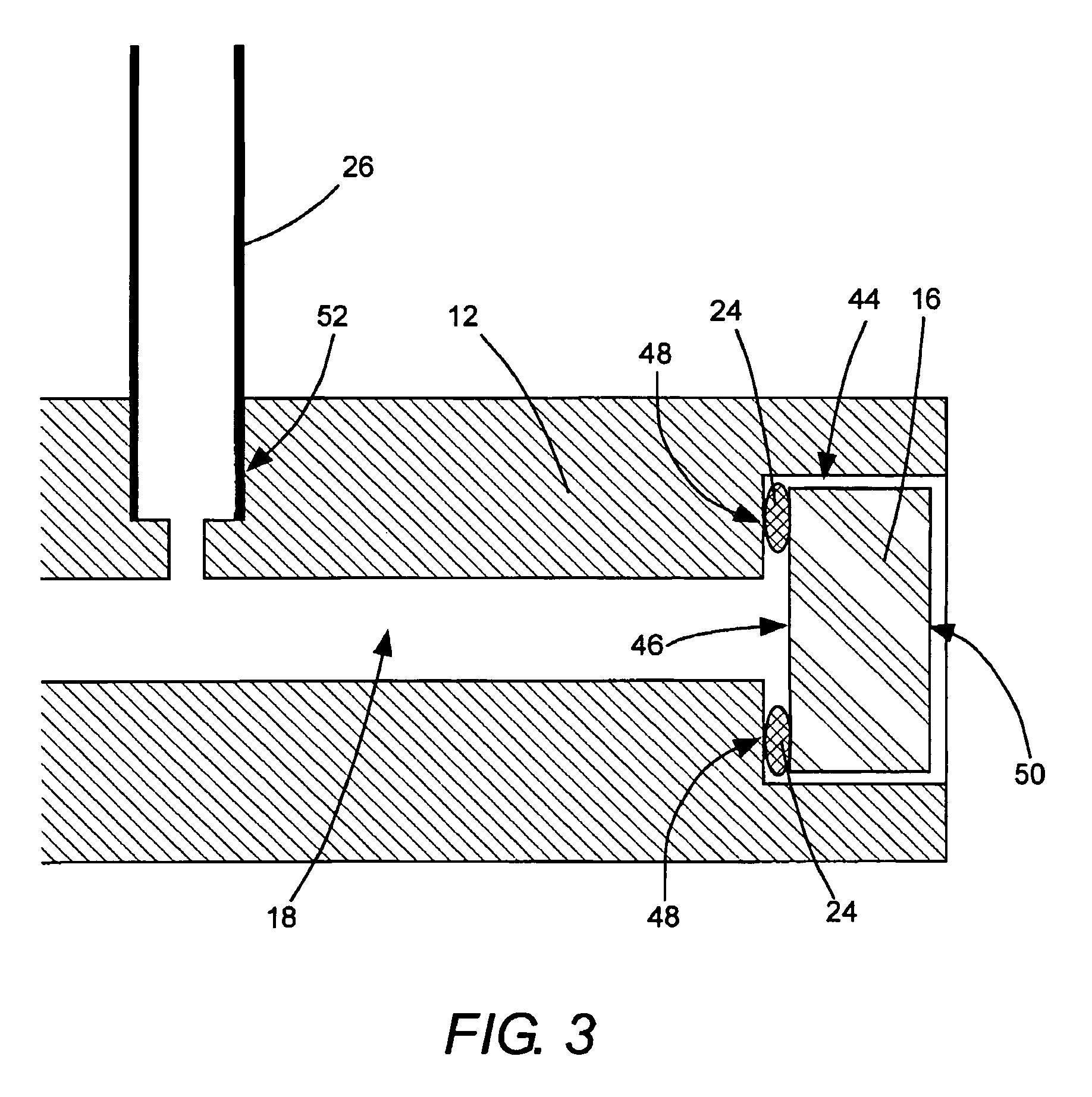
Vacuum cell for optical components
A moisture sensitive optically nonlinear crystal is enclosed in a hermetically sealed elongated vacuum cell. The vacuum cell has an input window at one end and an output window at an opposite end providing optical access to the crystal by a laser beam. The windows are attached to the cell by cold-formed, indium-metal ram-seals. In an example of the cell in which the crystal is arranged to generate UV radiation from the laser beam, the output window is located at a sufficient distance from the crystal that the flux of UV radiation incident on the output window is below the damage threshold of the window for the UV radiation.
Owner:COHERENT INC
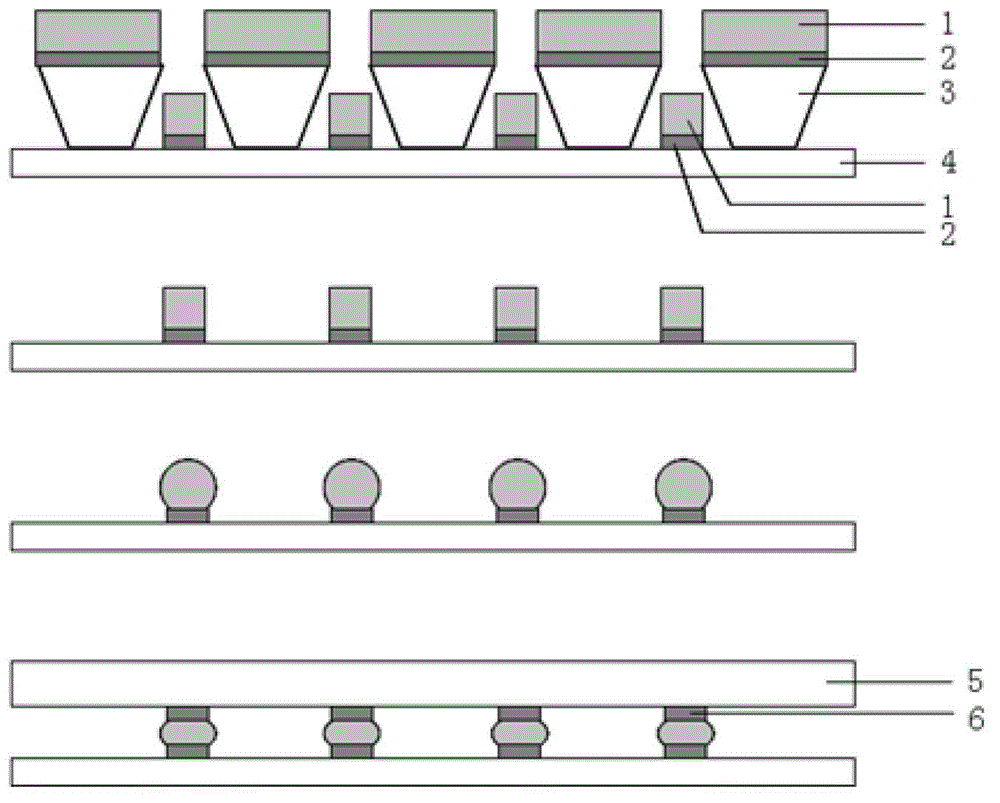
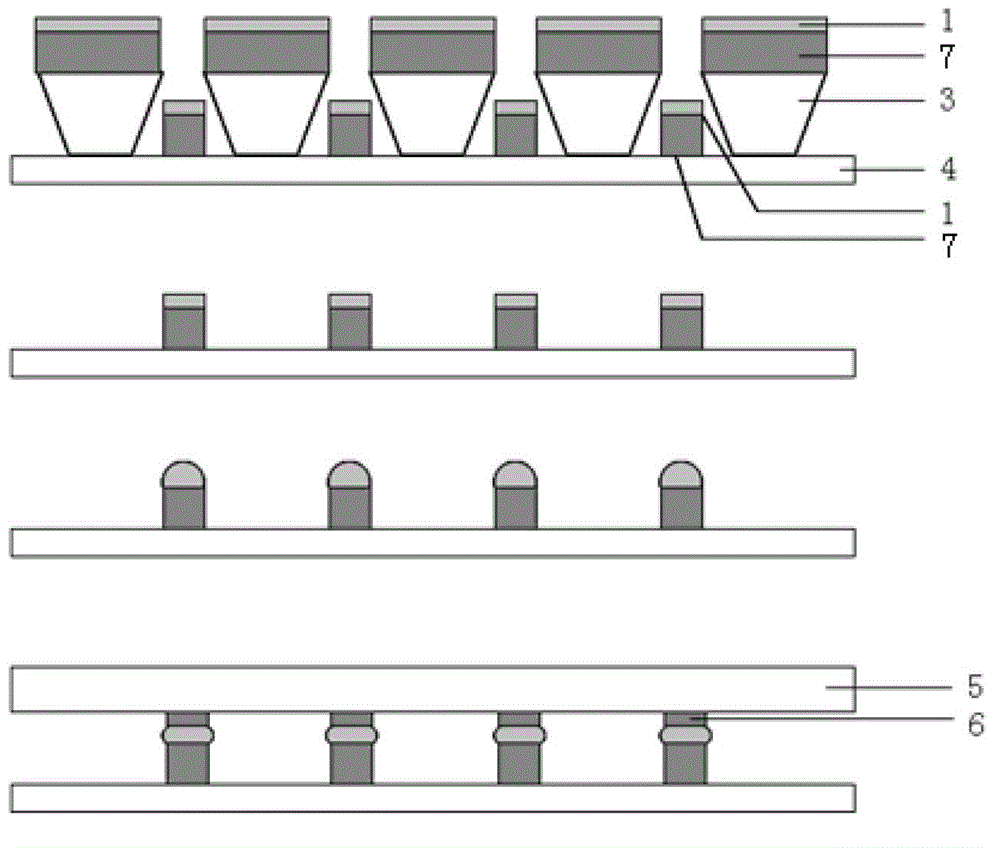
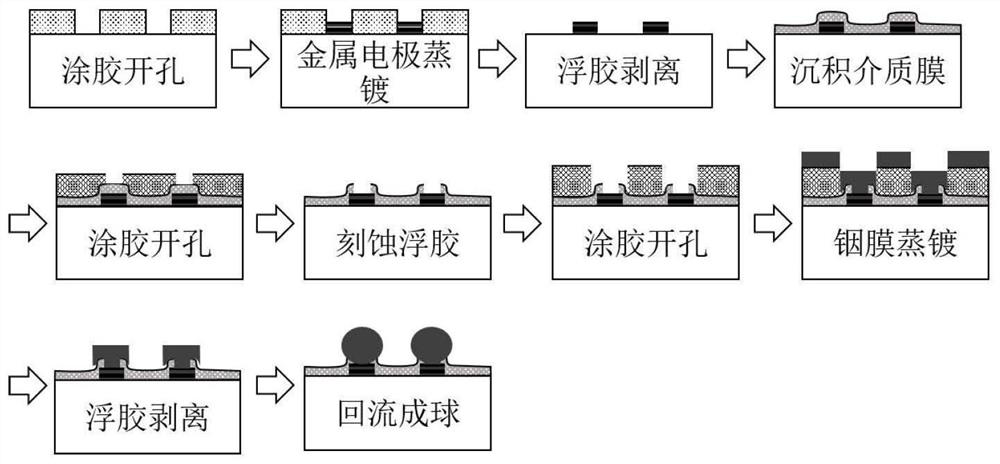
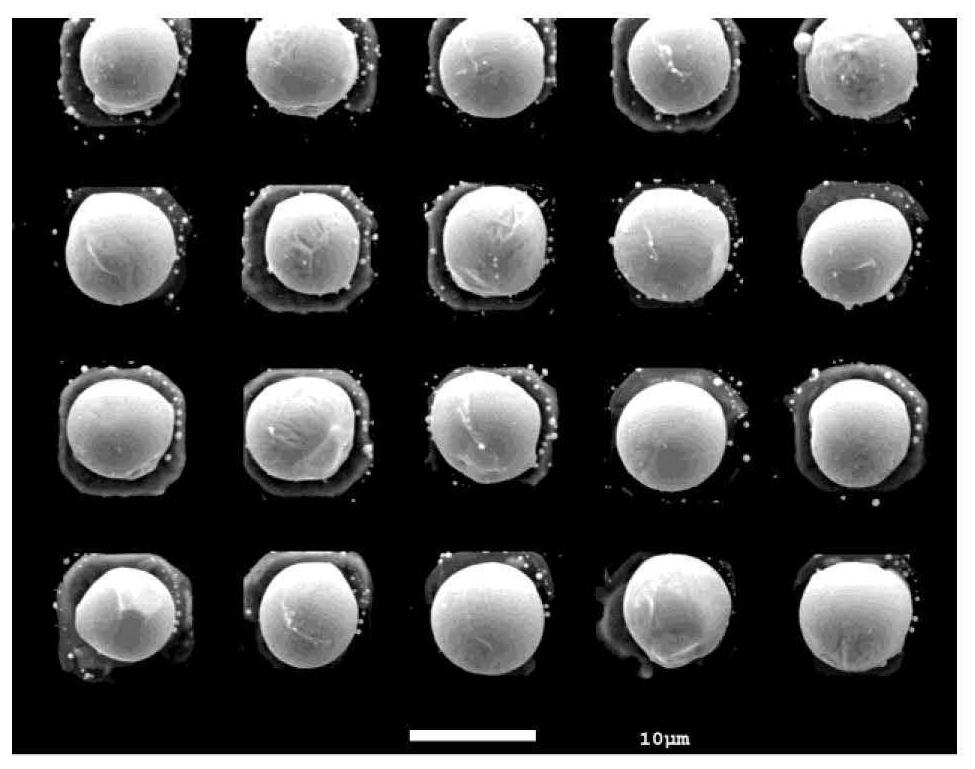
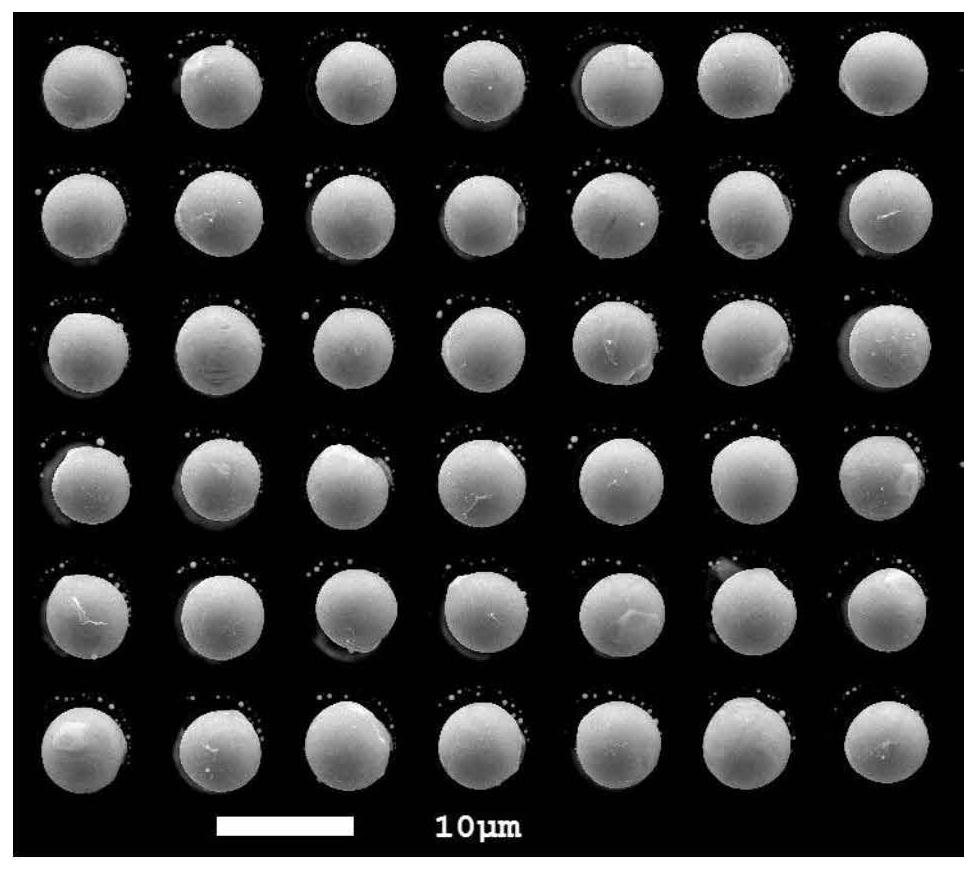
Method for manufacturing indium ball array of small-center-distance focal plane detector
PendingCN111739806AFix interface issuesSolve the problem of poor ball consistencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndium metalFocal plane detector
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing an indium ball array of a small-center-distance focal plane detector, which comprises the following steps of 1) coating photoresist on a chip, and generating an electrode hole pattern on the photoresist, 2) sequentially evaporating chromium, nickel and gold layers, 3) removing the photoresist to generate a metal electrode, 4) depositing a dielectric film layer, 5) coating a photoresist, and generating a contact hole pattern on the photoresist, 6) etching to remove the dielectric film in the hole, and removing the photoresist, 7) coating a photoresist, and generating an indium hole pattern on the photoresist, 8) evaporating indium metal, 9) removing the photoresist to generate an indium column array, and 10) conducting heat reflux treatmentto generate an indium ball array. The method has the advantages that the problem that indium columns manufactured through a traditional gold priming coat process are poor in morphology consistency after balling is solved, the high-uniformity and high-fullness indium ball array with the larger duty ratio can be manufactured, and the communication rate of a focal plane and reading circuit flip-chipbonding interconnection is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
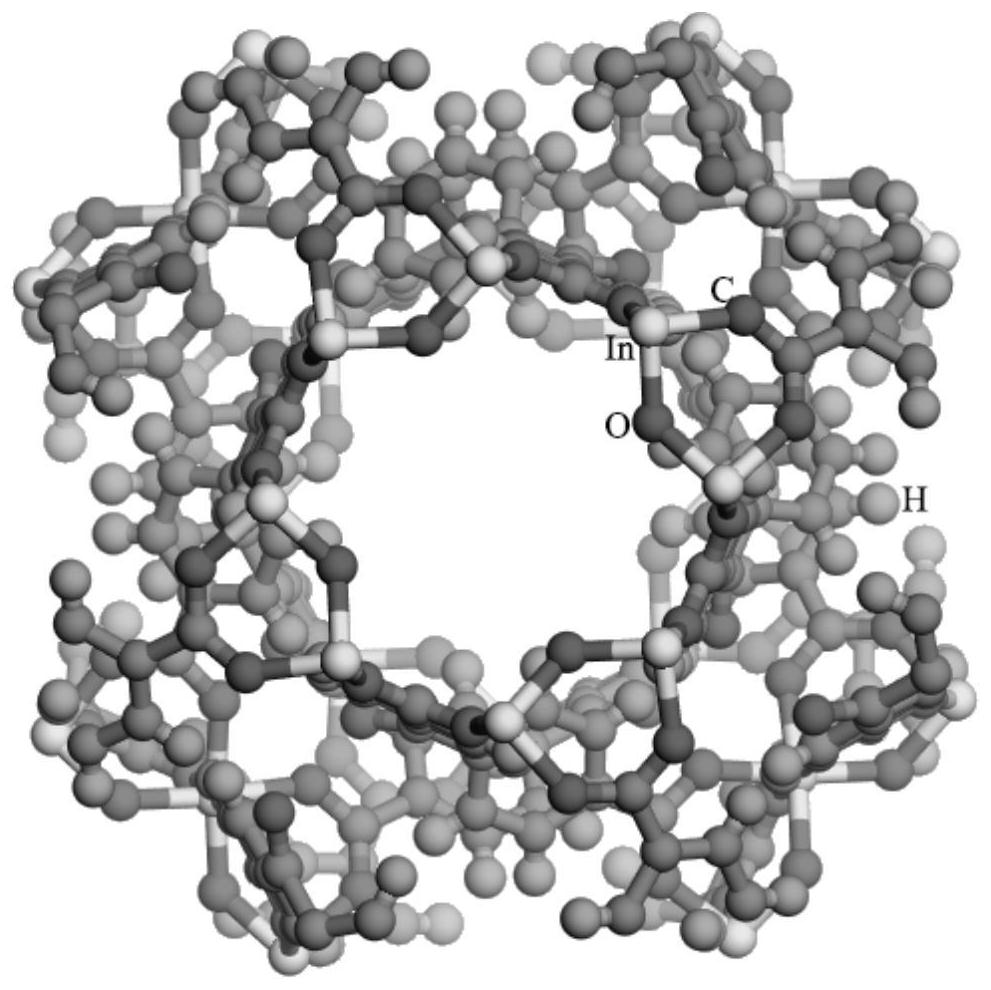
Preparation method and application of indium-based metal organic framework material
ActiveCN112778122AExcellent water vapor stabilityHigh adsorption selectivityNitrogen purification/separationOrganic compound preparationIndium TrichlorideMetal-organic framework
The invention provides a preparation method and application of an indium-based metal organic framework material, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: dropwise adding a sodium formate solution into an indium trichloride solution, heating and stirring to obtain an indium metal cluster; dispersing the indium metal cluster in N, N-dimethylformamide to obtain a first mixed solution; dispersing benzophenone-4, 4' -dicarboxylic acid in N, N-dimethylformamide to obtain a second mixed solution; and dropwise adding the second mixed solution into the first mixed solution, adding formic acid and H2O, transferring into a high-pressure reaction kettle, and performing solvothermal synthesis reaction to obtain the indium-based metal organic framework material. The indium-based metal organic framework material prepared by the method has high adsorption selectivity on adsorption and separation of CH4 and N2, under the same condition, the adsorption selectivity on CH4 and N2 is more than 7.5 times of the selectivity of traditional adsorption materials such as a carbon molecular sieve, and the material has excellent water vapor stability. The indium-based metal organic framework material is applied to separation of CH4 and N2 in coal bed gas and has an excellent separation effect.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
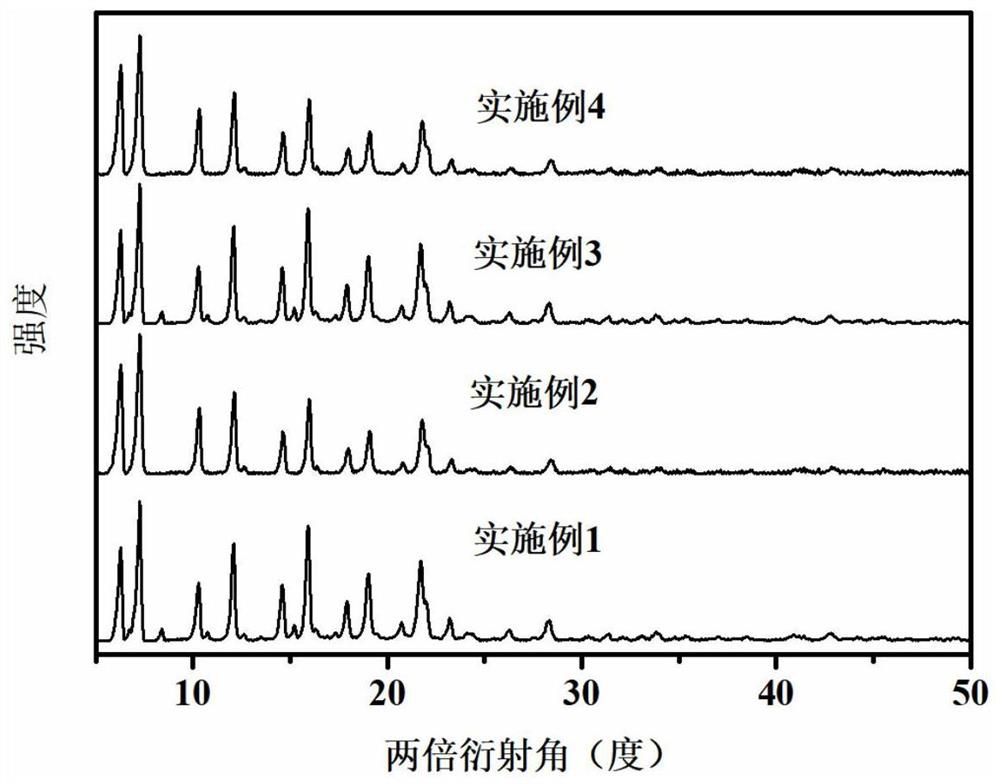
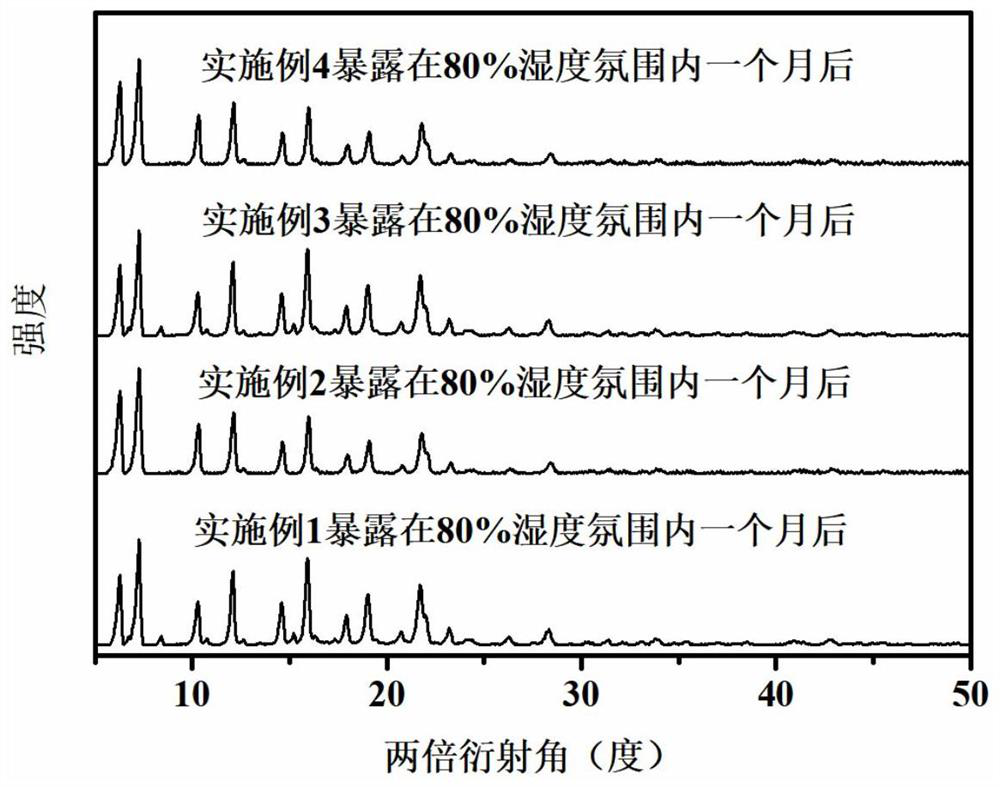
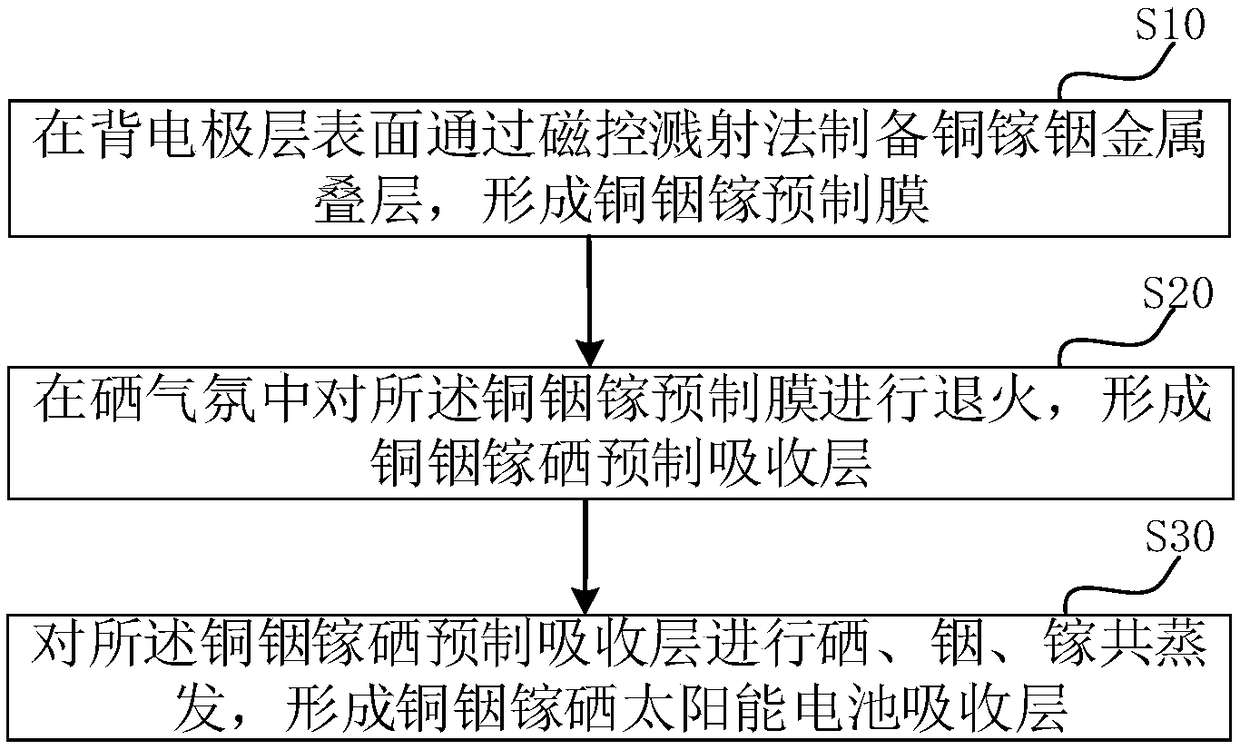
Copper-indium-gallium-selenium solar cell absorption lay, preparation method and solar cell
PendingCN109273542AImprove conversion efficiencyFavorable to obtain buried PN junctionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumEvaporation
The invention relates to a preparation method of an absorption layer of a copper indium gallium selenium solar cell, comprising the steps of preparing a copper gallium indium metal stack on the surface of a back electrode layer by a magnetron sputtering method to form a copper indium gallium preformed film; Annealing the copper indium gallium preform film in a selenium atmosphere to form a copperindium gallium selenium preform absorption layer; Co-evaporation of selenium, indium and gallium is carry out on that copper-indium-gallium-selenium prefabricated absorption lay to form an absorptionlayer of the copper-indium-gallium-selenium solar cell. The copper-indium-gallium-selenium solar cell absorbing layer prepared by the method provided by the present application is combined with the upper buffer layer to facilitate obtaining the buried PN junction, thereby improving the conversion efficiency of the copper-indium-gallium-selenium solar cell.
Owner:上海祖强能源有限公司
Flexible antenna array based on microwave energy transmission
ActiveCN113036457AHigh gainImprove efficiencyRadiating elements structural formsDisturbance protectionPatch arrayDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a flexible antenna array based on microwave energy transmission. The flexible antenna array comprises a dielectric substrate, a patch array and an equivalent grounding plate layer. One surface of the dielectric substrate is fixedly connected with the patch array, and the other surface of the dielectric substrate is fixedly connected with the equivalent grounding plate layer. A liquid metal antenna which works at 2.45 GHZ and is used for microwave energy transmission is printed by applying a liquid metal printing technology and a flexible material. The liquid metal patch antenna gives full play to the advantages of repairability, flexibility, reconfigurability, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance and the like of the liquid gallium indium metal and the flexible dielectric substrate, is applied to integrated small-sized electronic equipment, realizes receiving and transmitting of electromagnetic waves, is applied to long-distance energy wireless transmission, and overcomes the disadvantage of low unit energy collection and conversion efficiency of a traditional antenna.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Indium electroplating compositions and methods for electroplating indium
InactiveUS20180016689A1Reduce harmSmoother surface morphologySemiconductor devicesIndiumElectroplating
Indium electroplating compositions electroplate substantially defect-free uniform layers which have a smooth surface morphology on metal layers. The indium electroplating compositions can be used to electroplate indium metal on metal layers of various substrates such as semiconductor wafers and as thermal interface materials.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
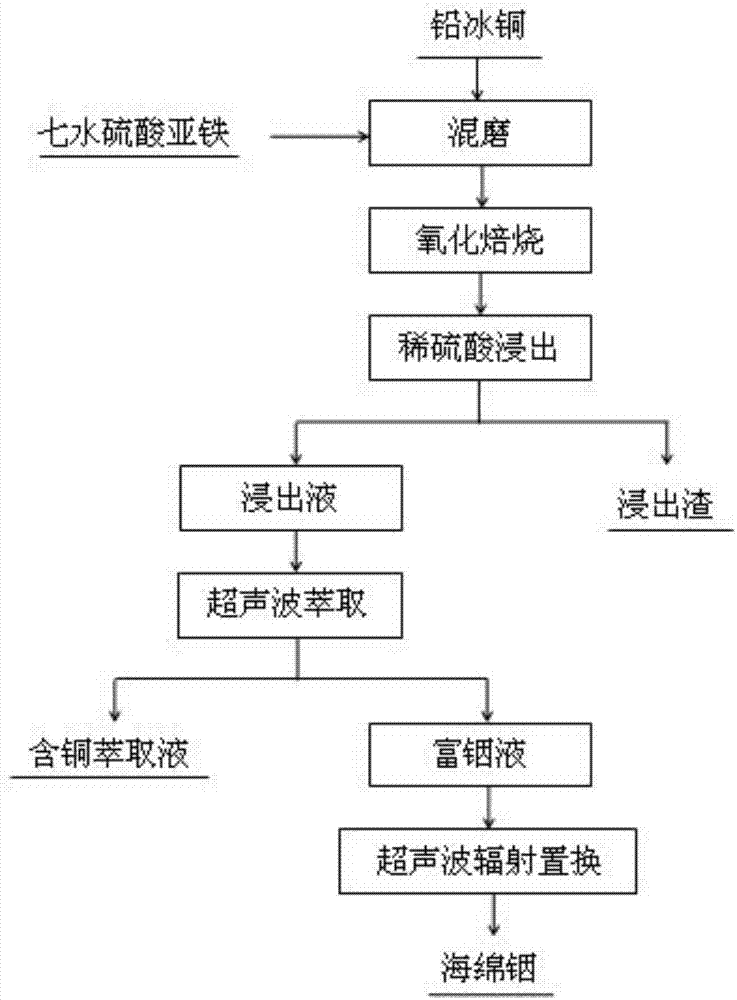
Method for extracting indium from lead copper matte
ActiveCN107034368AHigh recovery rateEliminate emulsificationProcess efficiency improvementIndium metalPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses a method for extracting indium from lead copper matte. The method comprises the following steps that A, the lead copper matte and ferrous sulfate are mixed and ground, and the mass ratio of the lead copper matte to the ferrous sulfate is (0.1-1.5):1 according to the mass ratio; B, the mixed and ground materials are put into a tube furnace to be subjected to oxidizing roasting through oxygen containing gas, and roasting matter is obtained; C, the roasting matter is leached through dilute sulphuric acid, then filtering and washing are carried out, and leaching residues and lixivium are obtained; D, the lixivium is subjected to indium extraction under ultrasonic radiation, and copper containing extraction liquid and indium-enriched liquid are obtained; and E, metal replacement is adopted by the indium-enriched liquid under ultrasonic radiation to obtain sponge indium. According to the method, the leaching rate and the recovery rate of the indium are increased; meanwhile, ultrasonic waves are introduced in the extraction process, and the emulsification problem of the indium in the extraction process is eliminated; the ultrasonic waves are introduced in the indium metal replacement process, the replacement effect is improved, and the replacement time is shortened; and the whole-process technology is simple, industrialization can be achieved easily, and good industrial application prospects are achieved.
Owner:昆明寰世科技开发有限公司
Method for preparing indium target metal film
ActiveCN102925868AChange physical propertiesImprove deposition methodFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndium metalSulfidation
The invention discloses a method for preparing indium target metal film. One or more metal solid solutions or alloys with melting points being higher than that of indium are added into the indium metal, thus the physical property of the indium is changed and the physical vapordeposit method of the indium is improved, the surface roughness of a precursor metal film is greatly reduced, the surface roughness of an absorption layer can be reduced in a selenylation and sulphidation process of the precursor metal film, so that the absorption layer is uniform in components and meets the requirement of production.
Owner:赣州市创发光电科技有限公司
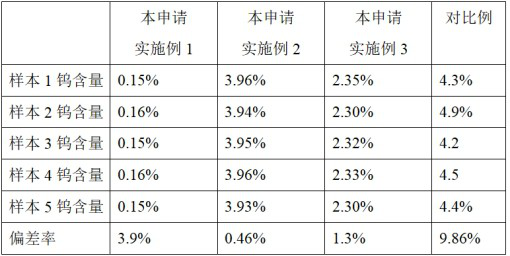
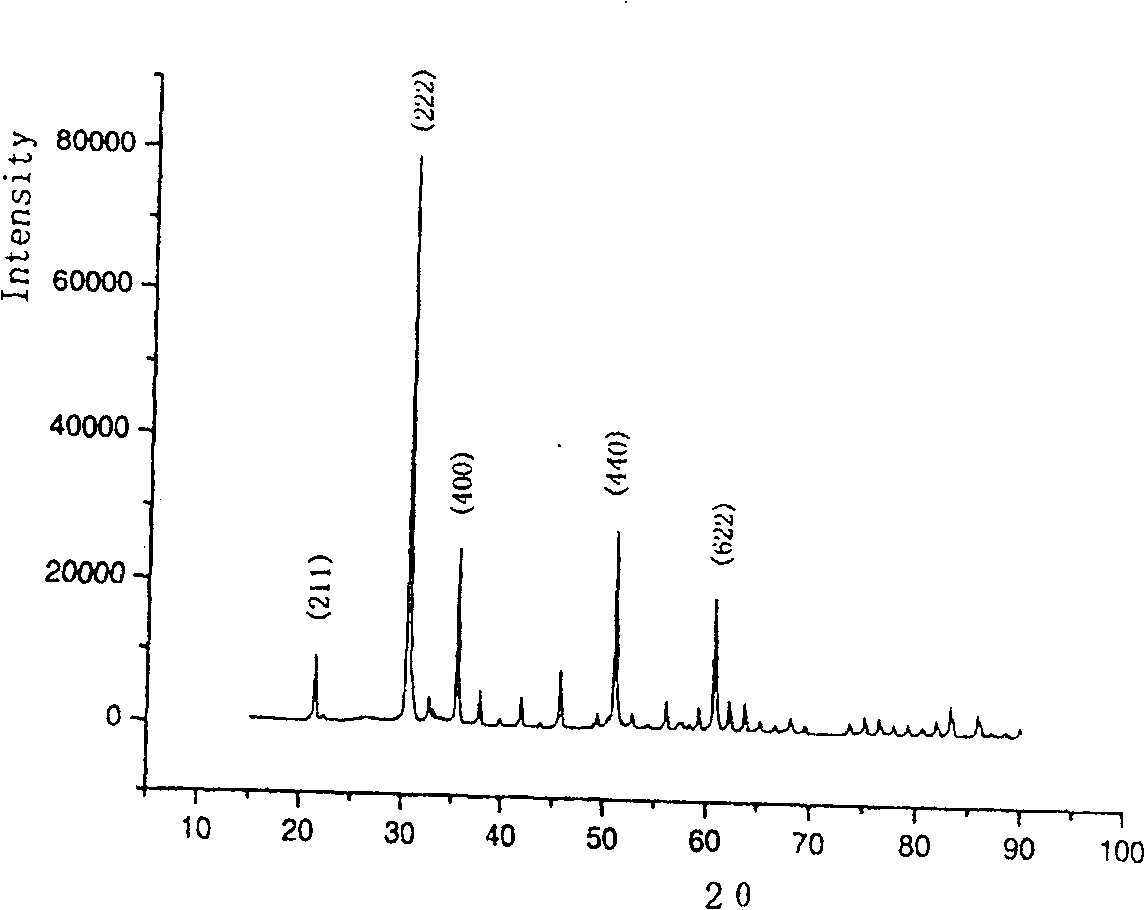
Preparation method of tungsten-doped indium oxide target material
ActiveCN112853285AEvenly dopedWell mixedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAmmonium paratungstateAmmonium metatungstate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a tungsten-doped indium oxide target material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) preparing an indium-containing raw material, specifically, dissolving metal indium in organic acid to obtain an organic acid indium solution for later use, or further adding alcohol into the organic acid indium solution to generate indium hydroxide precipitate for later use; (2) mixing a tungsten-containing raw material, specifically, dissolving ammonium paratungstate or ammonium metatungstate in the organic acid indium solution or a mixture of indium hydroxide and water; (3) carrying out spray drying to obtain powder in which elements indium and tungsten are uniformly mixed, wherein the powder is an IWO precursor; (4) calcining the obtained IWO powder precursor to obtain IWO powder; and (5) carrying out forming and sintering to obtain the IWO target material. According to the method, at least one of the indium-containing raw material and the tungsten-containing raw material exists in the form of a solution, and the indium-containing raw material and the tungsten-containing raw material are mixed, and due to liquid-liquid mixing or liquid-solid mixing, the mixing is more uniform than powder mixing, so that tungsten are doped in the prepared IWO target material more uniformly.
Owner:GUANGXI CRYSTAL UNION PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method of nanometer grade indium tin oxide composite powder
The present invention is a process for preparing nano-scale indium tin oxide composite powder by co-precipitation method, which is characterized in that metal indium, metal tin, or soluble metal indium salt and metal tin salt are respectively dissolved by inorganic single strong acid or mixed strong acid aqueous solution Dissolve in water, mix the prepared two solutions, add a precipitant under the condition of vigorously stirring the mixed solution to produce indium tin coprecipitate, after washing with water, organic solvent washing and solid-liquid separation, add an organic solvent for azeotropic distillation, the filter cake Ultrafine ITO composite powder is obtained by drying, breaking up and calcining. The indium tin oxide powder prepared by the process of the present invention is fired by a simple process, and the relative theoretical density of the ITO target can reach more than 99%.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
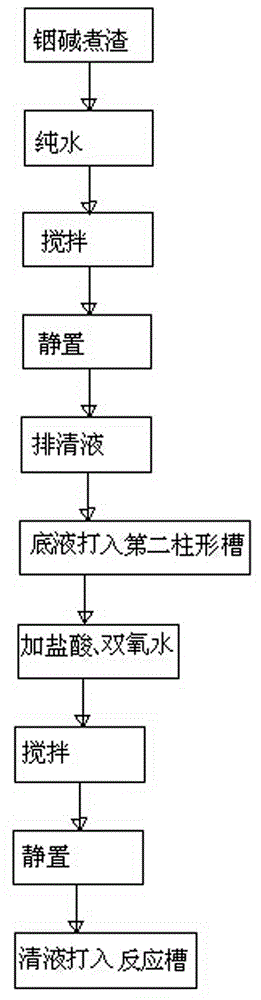
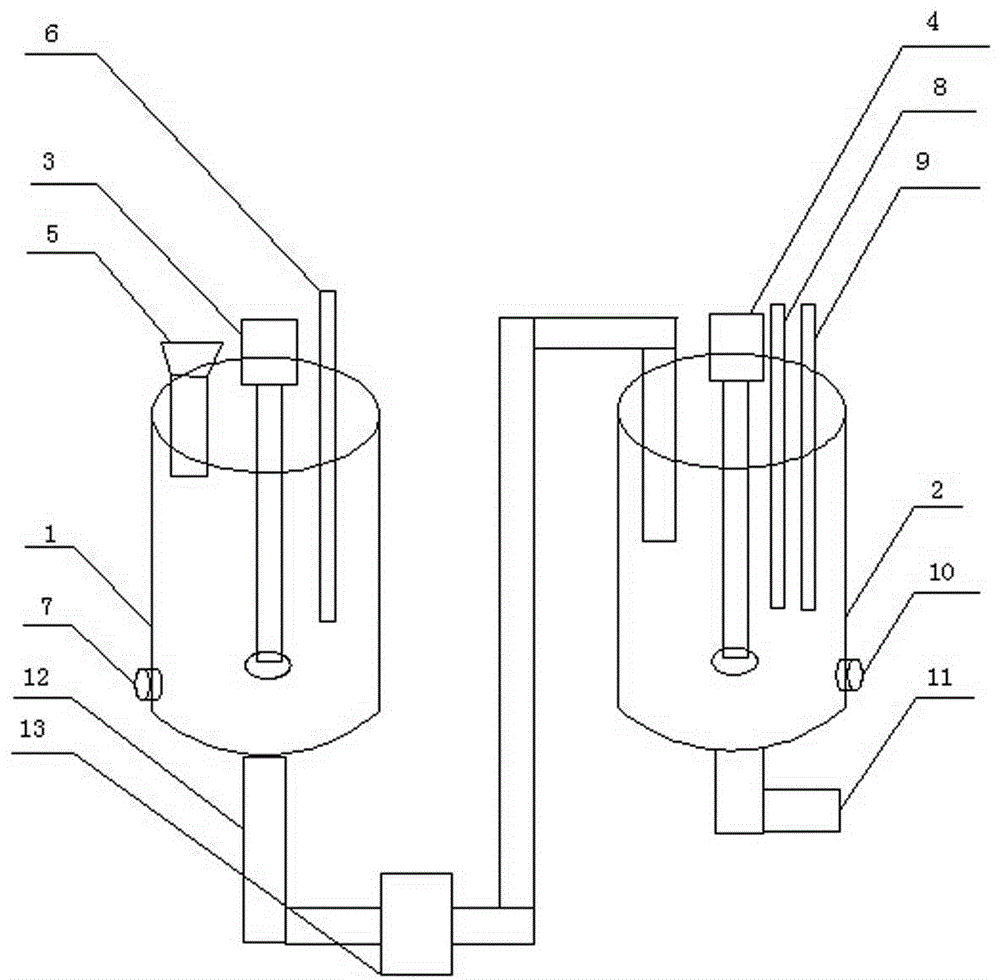
Treatment process and device for indium alkali boiled residue
InactiveCN104561557AReduce acid consumptionOvercoming damage toolsProcess efficiency improvementIndiumMetal
The invention belongs to the technical field of recovery of indium metal, and in particular relates to a treatment process and device for indium alkali boiled residue produced by smelting coarse indium through an indium block. The process comprises the following steps: adding the indium alkali boiled residue to be treated to a reaction tank; adding pure water to dissolve indium alkali boiled residue to obtain upper sodium hydroxide supernate and a lower turbid solution I; discharging and storing sodium hydroxide supernate; pumping the lower turbid solution I into another reaction tank, and synchronously adding acid and hydrogen peroxide; transferring the upper sodium hydroxide supernate into an indium production system reaction tank; discharging and storing the lower turbid solution II. The device comprises a first cylindrical tank equipped with a first agitator and a second cylindrical tank equipped with a second agitating tank, wherein the first cylindrical tank and the second cylindrical tank are communicated through a first lower solution conveying pipe; a conveying pump is arranged in the middle of the first lower solution conveying pipe. According to the technical scheme, the process and device have the advantages that sodium hydroxide in the alkali boiled residue can be utilized again; the dosage of acid can be reduced; the problem that tools and devices are damaged due to excessive heat release can be overcome.
Owner:济源豫金靶材科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com