Patents
Literature
209 results about "Patch array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
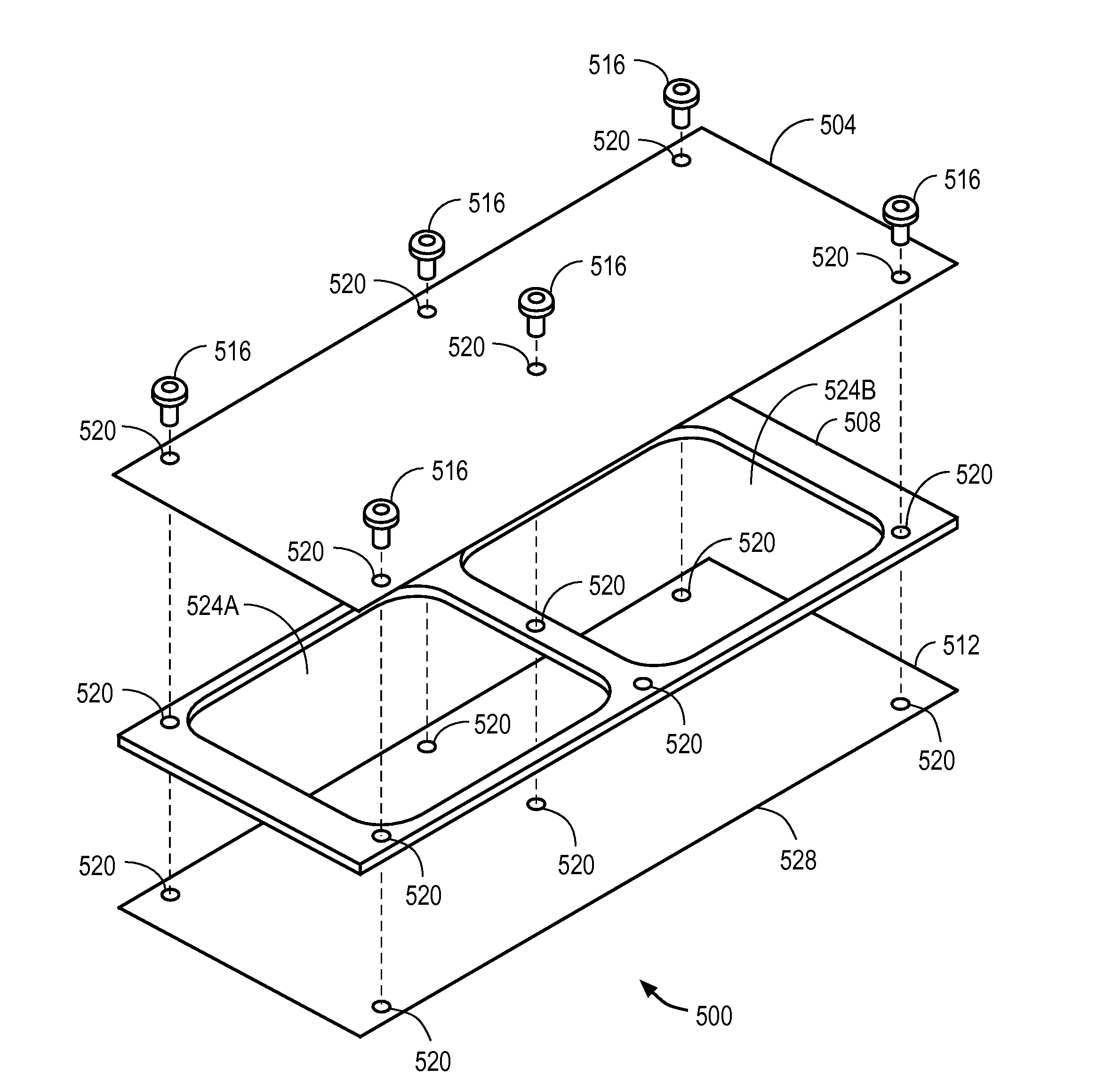
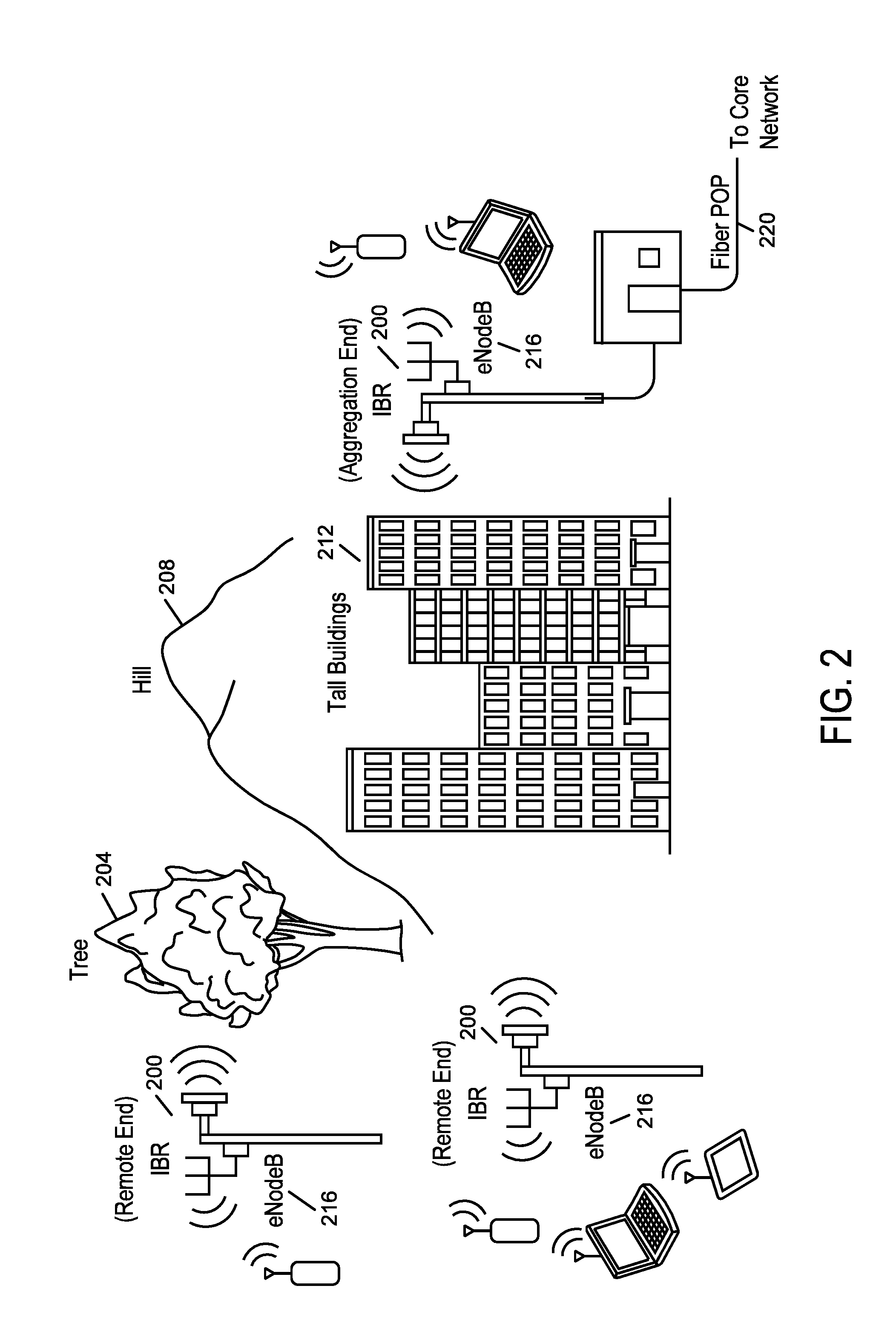
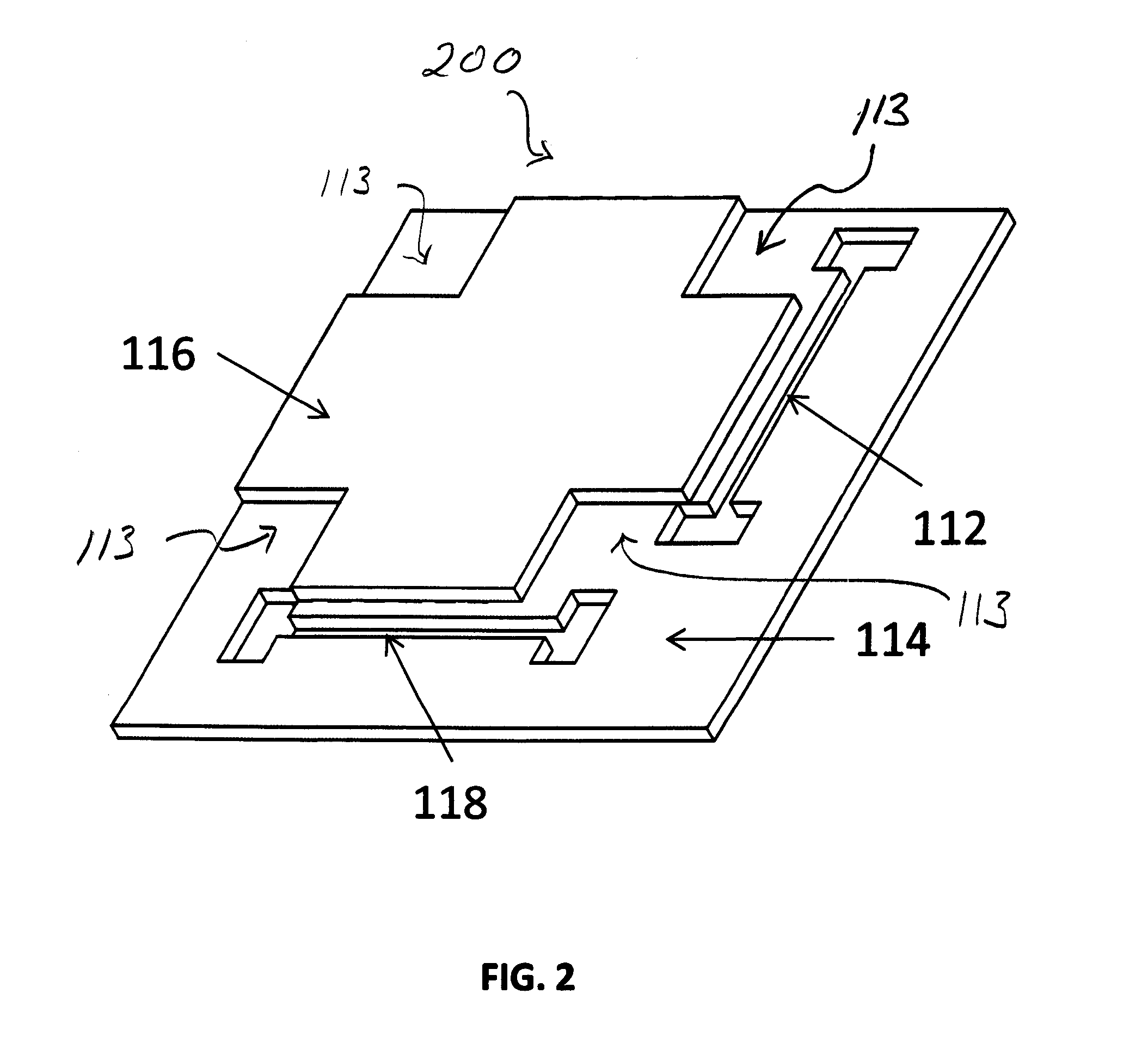
Backhaul radio with an aperture-fed antenna assembly
ActiveUS20140184455A1Connection managementIndividually energised antenna arraysPatch arrayAntenna element
Directive gain antenna elements implemented with an aperture-fed patch array antenna assembly are described. A feed network for the aperture-fed patch array may include offset apertures and may also include meandering feed lines. Scalable aperture shapes and orientations that can be used with antennas operating at any frequency and with dual orthogonal polarizations are also disclosed. Directive gain antenna elements implemented with arrays of orthogonal reflected dipoles are also described with optimal feed networks and parasitic elements to achieve desired directive gain characteristics. Such arrayed dipole antennas feature dual orthogonal polarizations with assembly tabs that lower cost and improve reliability. Backhaul radios that incorporate said antennas are also disclosed.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Wireless point multipoint system
InactiveUS20060170595A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectricPatch array
A patch array antenna includes a planar base on which is defined a ground plane and feed positions that are electrically isolated from the ground plane. A plurality of patch elements are configured to resonate over a predetermined frequency range. Each patch element is isolated from the ground plane and disposed on the base over the ground plane so that an air dielectric is defined between the patch element and the ground plane. Each patch element defines a resonant portion that is electrically connected to a respective feed position. A feed network is defined on the base that electrically connects the feed positions to one or more output points on the base.
Owner:TRANGO NETWORKS LLC
Backhaul radio with a substrate tab-fed antenna assembly
Directive gain antenna elements implemented with an aperture-fed patch array antenna assembly are described. A feed network for the aperture-fed patch array may include offset apertures and may also include meandering feed lines. Scalable aperture shapes and orientations that can be used with antennas operating at any frequency and with dual orthogonal polarizations are also disclosed. Directive gain antenna elements implemented with arrays of orthogonal reflected dipoles are also described with optimal feed networks and parasitic elements to achieve desired directive gain characteristics. Such arrayed dipole antennas feature dual orthogonal polarizations with assembly tabs that lower cost and improve reliability. Backhaul radios that incorporate said antennas are also disclosed.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
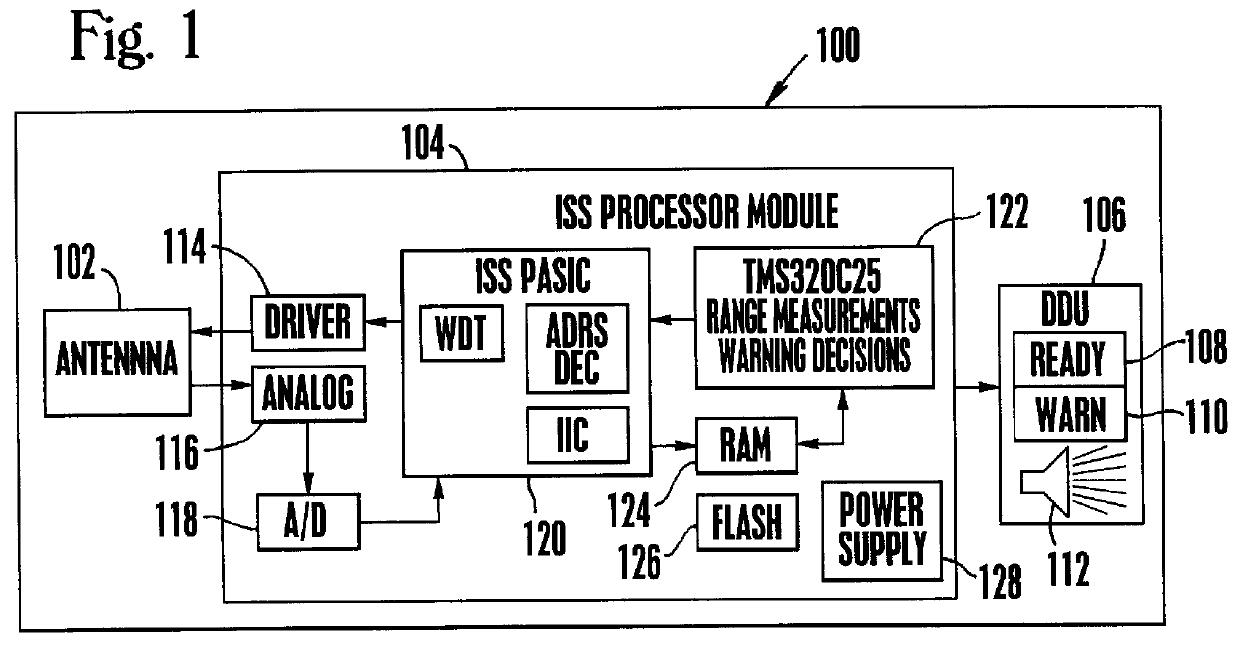
Method and apparatus for rejecting rain clutter in a radar system
InactiveUS6127965ADue to rain clutter are dramatically reducedReduces false alarmsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPatch arrayRadar systems
A method and apparatus for detecting the presence of objects in a vehicle operator's blind spots. The apparatus comprises a side-facing Doppler radar system using continuous wave (CW) transmission with frequency modulation (FM) operation from a frequency modulation switching technique. The radar system determines the presence, range and closing rate of detected targets. The radar system detects targets even when operated in adverse weather conditions and will not generate false warnings due to rain clutter caused by wet roads and other wet surroundings. The radar system uses ranging techniques to reject false targets that are detected outside of a predetermined target detection zone. In accordance with the present invention, the radar system indicates that a target is detected if and only if any part of the target is within the detection zone and it: (1) remains in front of the antenna for at least TH1 seconds; (2) is at a range between Rangemin and Rangemax; and (3) is moving faster than Closing-Speedmin relative to the antenna. By rejecting targets that are closer than Rangemin feet to the antenna, false alarms due to rain clutter are dramatically reduced. Also, by rejecting targets that are further than Rangemax feet from the antenna, the radar system reduces false alarms caused by wet foliage and other wet "non-road" surroundings. In one embodiment, the radar system uses a patch array antenna oriented into a diamond-shape configuration to effectively create a natural linear amplitude taper that aids in rejecting clutter caused by wet road surfaces.
Owner:BENDIX COMML VEHICLE SYST LLC
Micromachined millimeter-wave frequency scanning array
ActiveUS20150263429A1Available bandwidthIncrease rangeRadiating elements structural formsLinear waveguide fed arraysPatch arrayFrequency multiplier
A frequency scanning traveling wave antenna array is presented for Y-band application. This antenna is a fast wave leaky structure based on rectangular waveguides in which slots cut on the broad wall of the waveguide serve as radiating elements. A series of aperture-coupled patch arrays are fed by these slots. This antenna offers 2° and 30° beam widths in azimuth and elevation direction, respectively, and is capable of ±25° beam scanning with frequency around the broadside direction. The waveguide can be fed through a membrane-supported cavity-backed CPW which is the output of a frequency multiplier providing 230˜245 GHz FMCW signal. This structure can be planar and compatible with micromachining application and can be fabricated using DRIE of silicon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
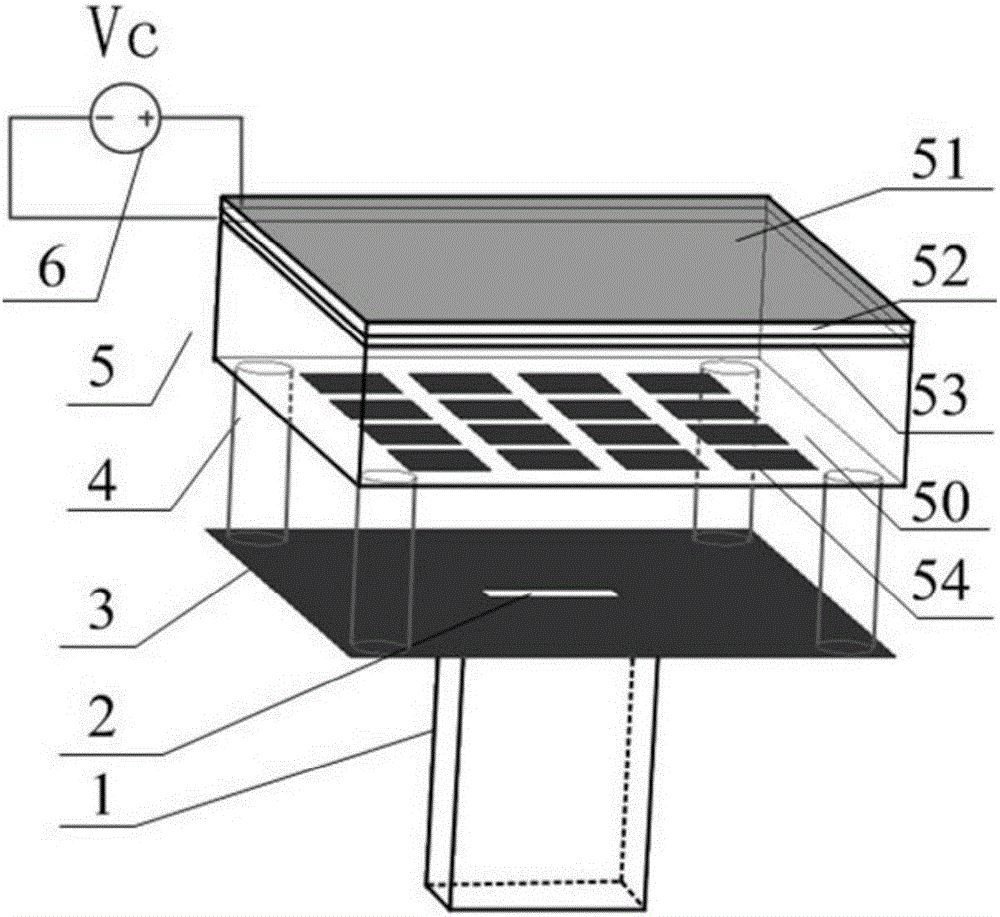
Pattern-reconfigurable antenna based on graphene composite structure frequency selective surface
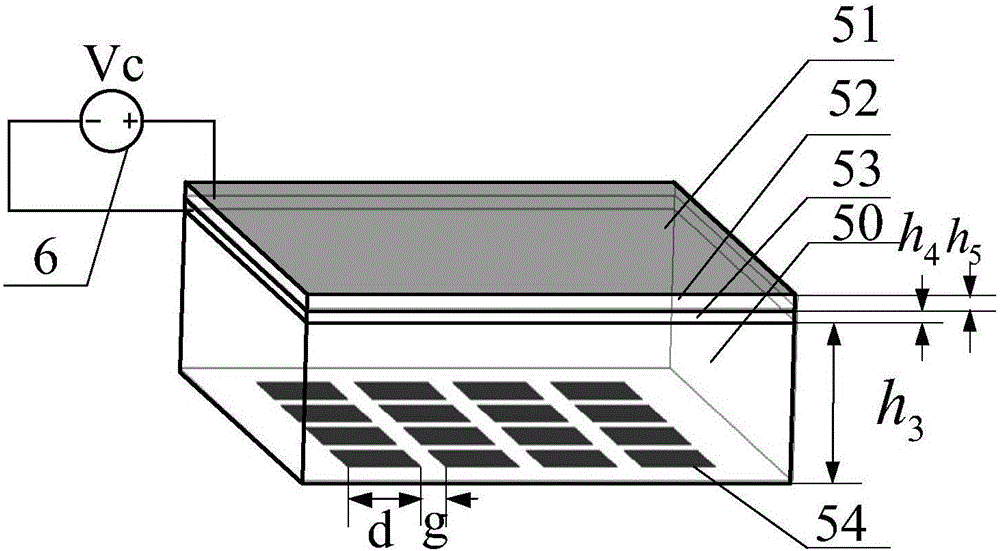
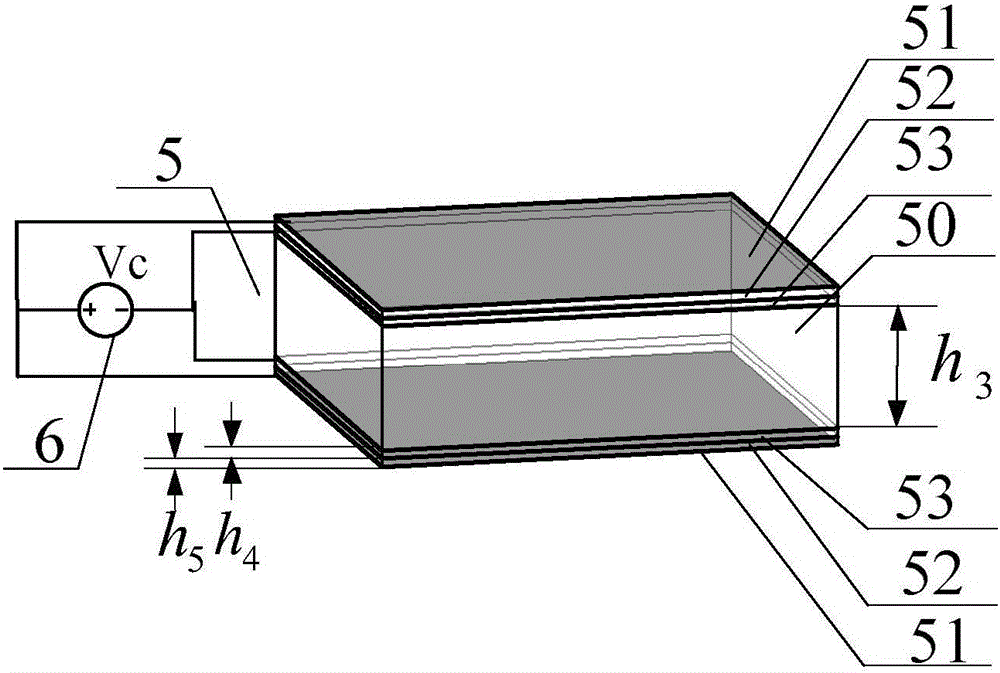
The invention provides a pattern-reconfigurable antenna based on a graphene composite structure frequency selective surface to solve the problem that the gain and beam bandwidth of an antenna cannot be changed flexibly in the prior art. The pattern-reconfigurable antenna comprises a rectangular waveguide feeder, a rectangular radiation element, a baffle board, a frequency selective surface, and a direct-current bias voltage Vc. The frequency selective surface includes a graphene composite structure, a dielectric substrate, and a square patch array or graphene composite structure, which are stacked from top to bottom. The graphene composite structure is composed of a graphene layer, an alumina layer and a polycrystalline silicon layer which are stacked sequentially. The direct-current bias voltage Vc is applied between the graphene layer and the polycrystalline silicon layer. The rectangular radiation element is arranged on the baffle board, the frequency selective surface is fixed above the baffle board through four support columns, and the rectangular waveguide feeder is fixed below the baffle board. The radiation gain and beam bandwidth of the antenna can be changed flexibly, and reconfigurable pattern of a millimeter wave antenna is realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Backhaul radio with a substrate tab-fed antenna assembly
Directive gain antenna elements implemented with an aperture-fed patch array antenna assembly are described. A feed network for the aperture-fed patch array may include offset apertures and may also include meandering feed lines. Scalable aperture shapes and orientations that can be used with antennas operating at any frequency and with dual orthogonal polarizations are also disclosed. Directive gain antenna elements implemented with arrays of orthogonal reflected dipoles are also described with optimal feed networks and parasitic elements to achieve desired directive gain characteristics. Such arrayed dipole antennas feature dual orthogonal polarizations with assembly tabs that lower cost and improve reliability. Backhaul radios that incorporate said antennas are also disclosed.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Ku band transmit-receive co-caliber multi-layer printed antenna
ActiveCN104037497ACompact structureReduce volumeAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsElectricityPatch array
The invention discloses a Ku band transmit-receive co-caliber multi-layer printed antenna which is characterized by including, from top to bottom, a radiation patch array and emission feed network layer provided with a radiation patch array and an emission feed network, a first dielectric layer, a metal formation, a second dielectric layer, a receiving feed network layer provided with a receiving feed network, a third dielectric layer, a meta ground connection support layer, a fourth dielectric layer, and an amplifying circuit layer provided with a receiving amplifying circuit and an emitting amplifying circuit; the emitting amplifying circuit is connected with the emission feed network, and the receiving amplifying circuit is connected with the receiving feed network. The Ku band transmit-receive co-caliber multi-layer printed antenna has the advantages of compact microstrip antenna structure, small volume, light weight, and the like, a low noise amplifier and power amplifier are integrated in the back side of the antenna, feeder loss between the low noise amplifier and power amplifier and the antenna is reduced, and the complete machine quality factor and efficiency can be improved. At the same time, the whole circuit structure adopts a multilayer printing technology, and is simple in process and low in cost.
Owner:HUADONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHN INST OF ANHUI PROVINCE
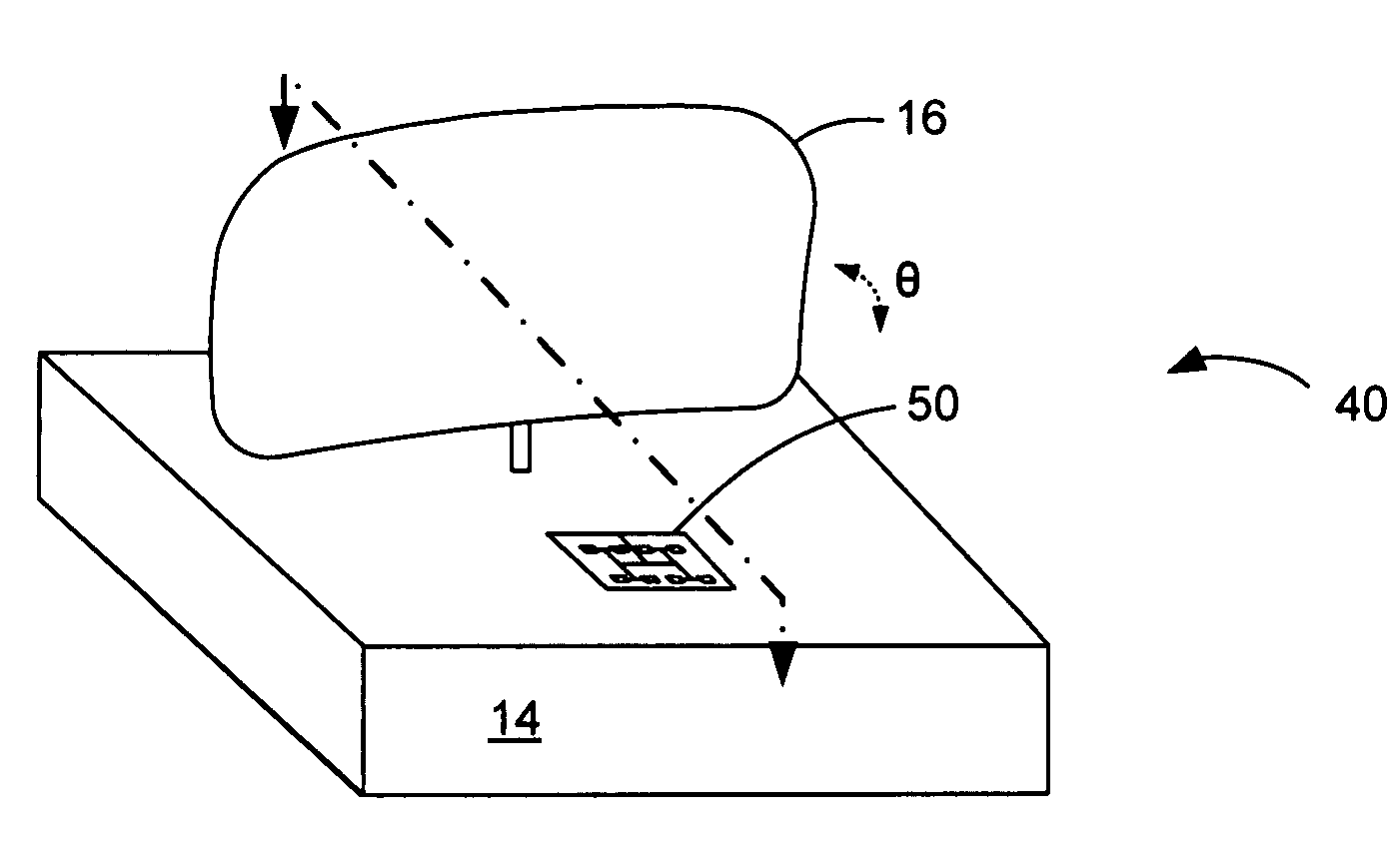
Patch array feed for an automotive radar antenna
ActiveUS7187334B2Reduce lossesSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPatch arrayTransceiver
An improved transceiver assembly for a vehicle for detecting potentially hazardous objects is disclosed. The transceiver assembly preferably comprises a patch array feed antenna having an array of a plurality of patches for generating a beam and for detecting the beam as reflected from the potential hazards. The antenna is formed in or on a housing which also contains a parabolic dish that moves to sweeps the beam of radiation towards the potential hazards outside of the vehicle. In a preferred embodiment, approximately 77 GHz radiation is generated from and detected by the antenna.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
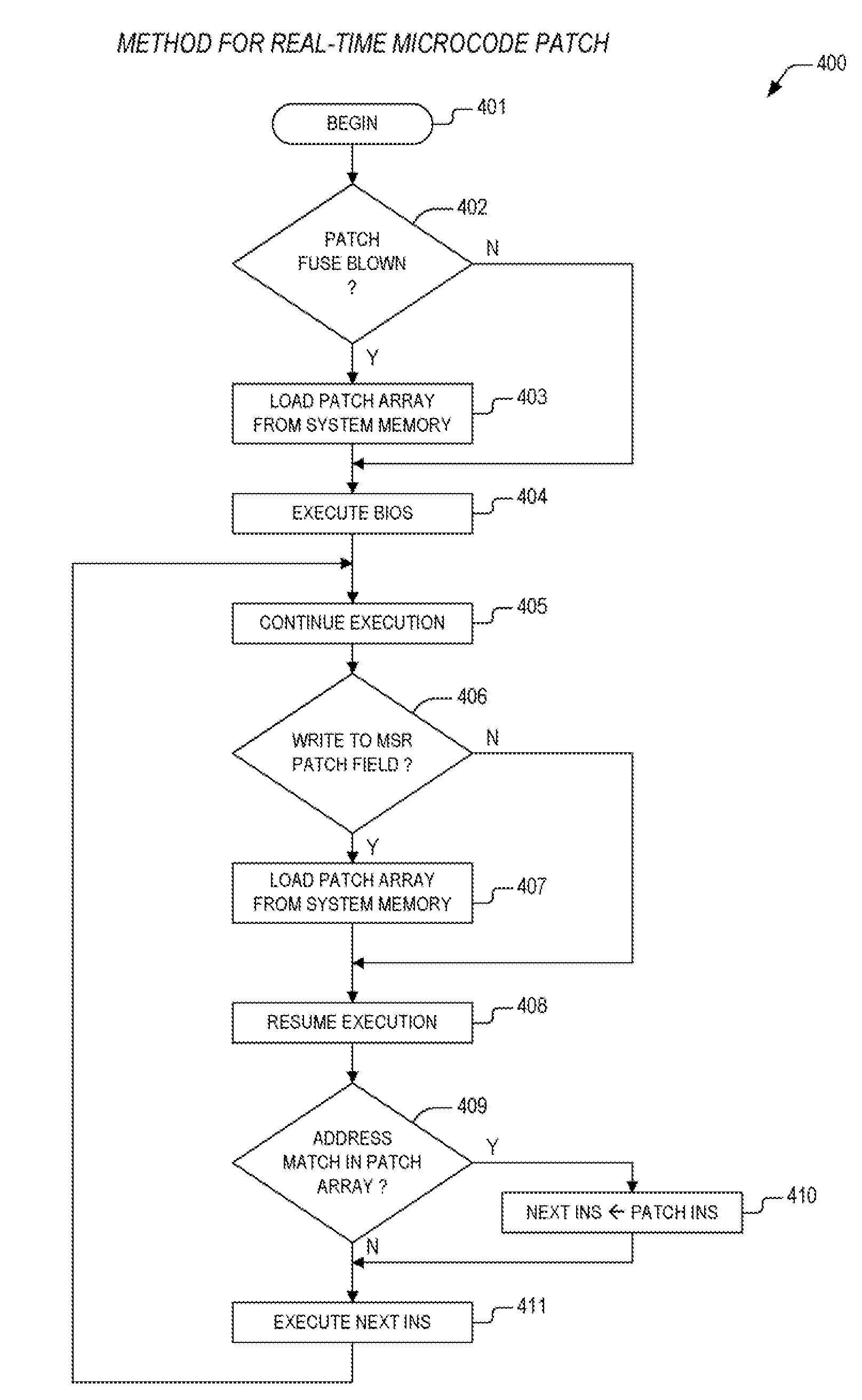
Apparatus and method for real-time microcode patch
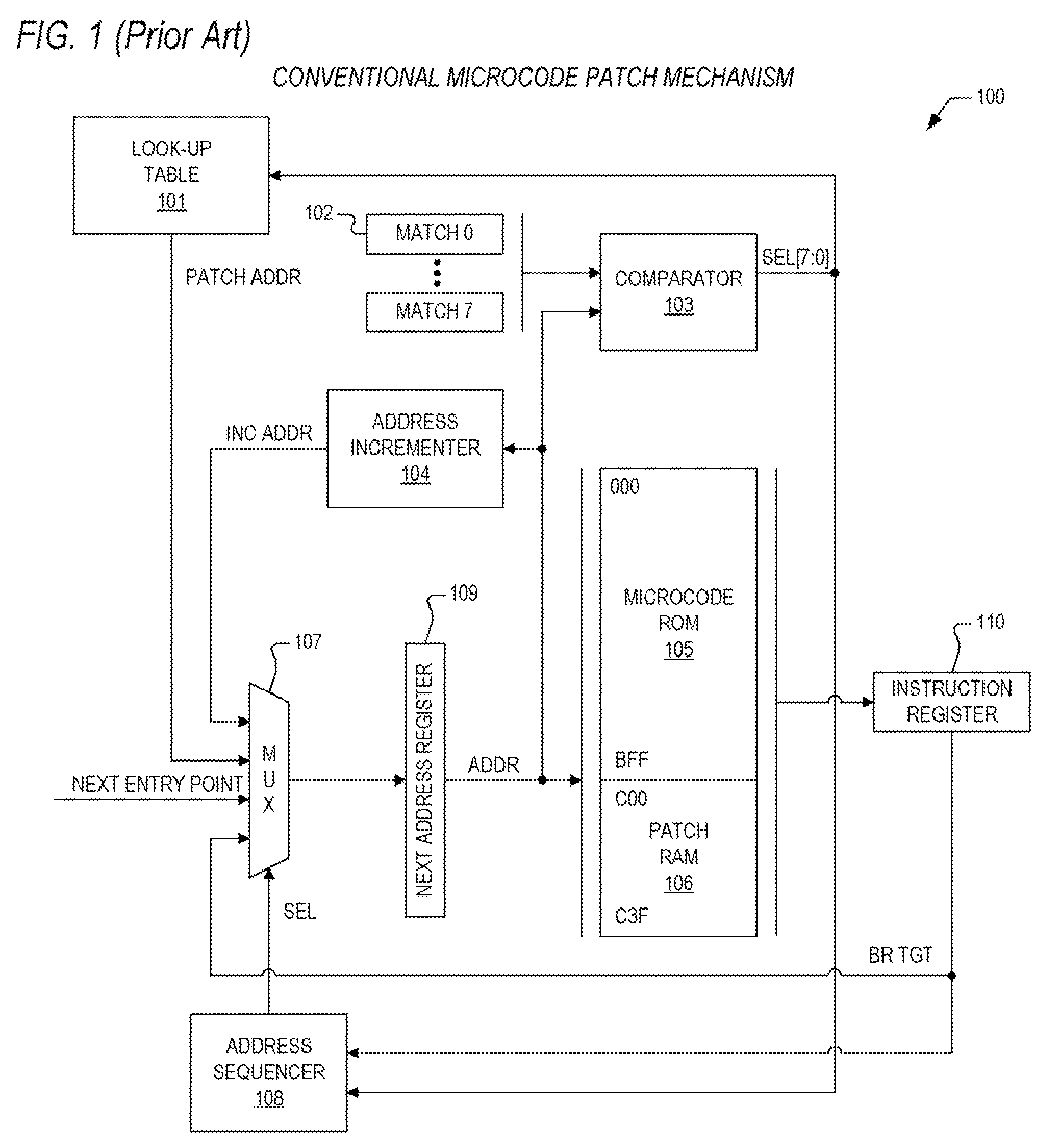
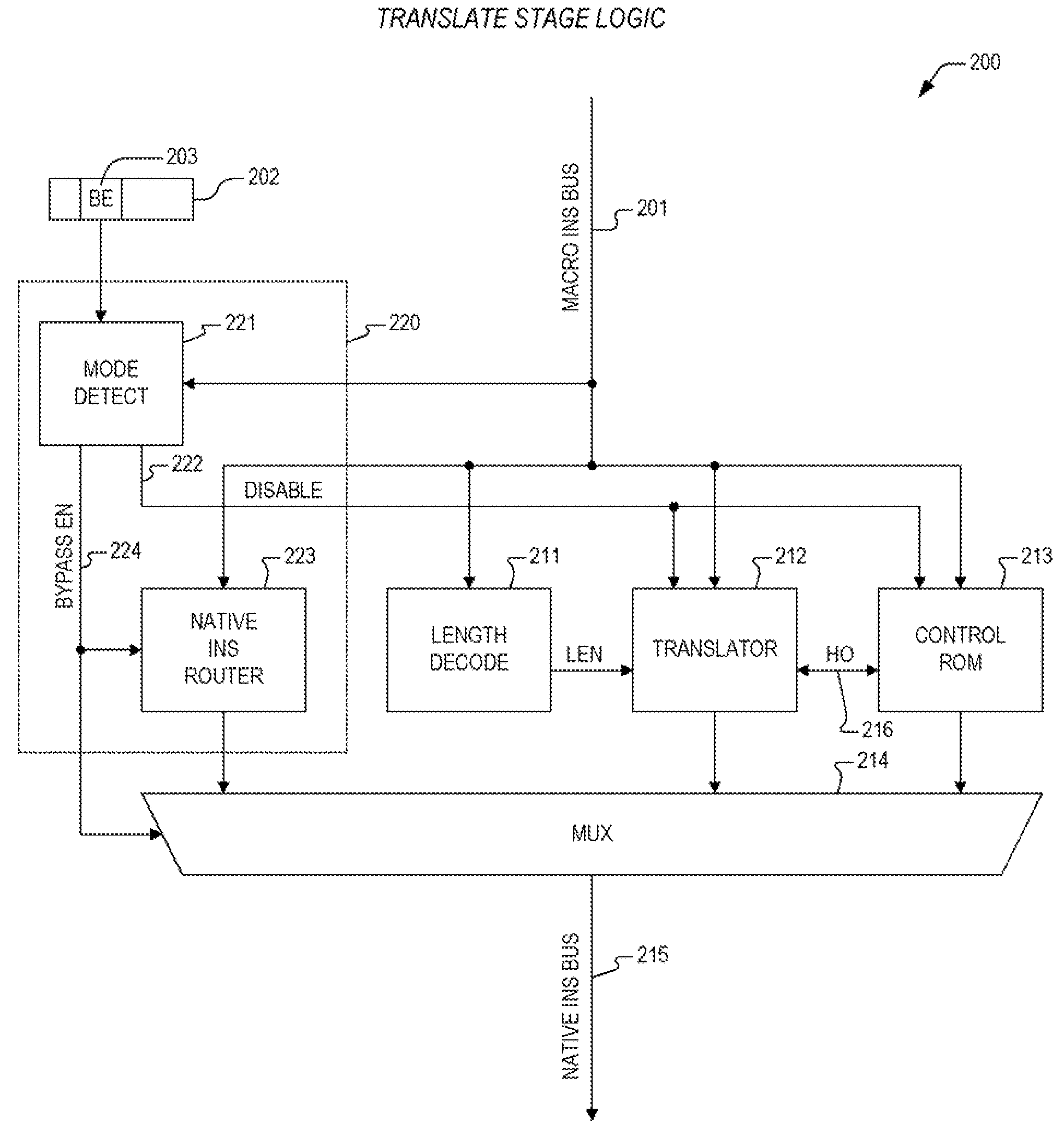
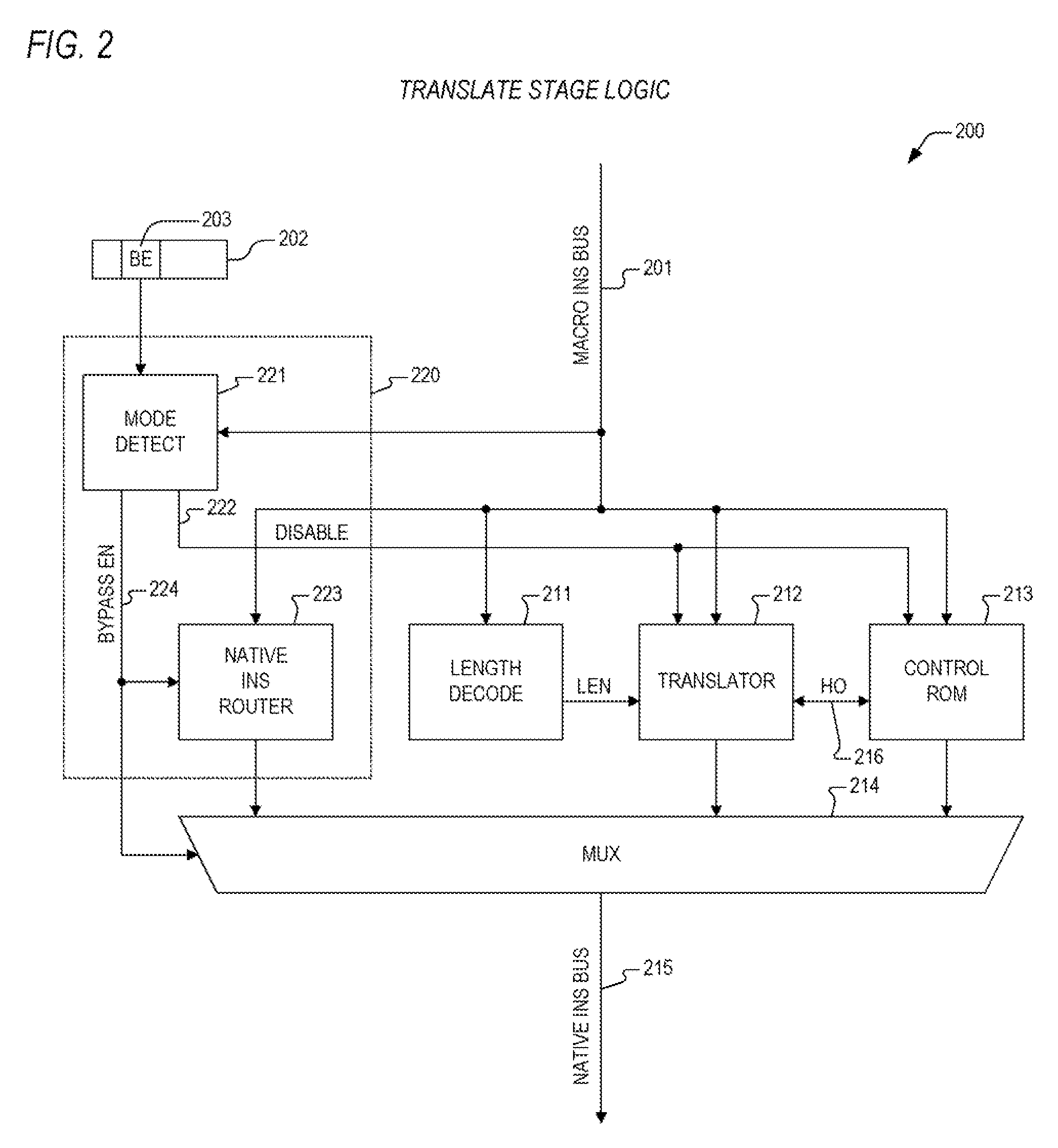
InactiveUS20090031121A1Flexible and fastInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsPatch arrayOperating system
An apparatus for performing microcode patches that is both fast and flexible. In one embodiment, an apparatus for performing a real-time microcode patch is provided. The apparatus includes a patch array and a mux. The patch array receives a microcode ROM address and determines that the microcode ROM address matches one of a plurality of entries within the patch array. When the microcode ROM address matches, the patch array outputs a corresponding patch instruction and to assert a hit signal. The mux receives the patch instruction from the patch array and a micro instruction corresponding to the microcode ROM address from a microcode ROM. The mux provides the micro instruction or the corresponding patch instruction to an instruction register based upon the state of the hit signal.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
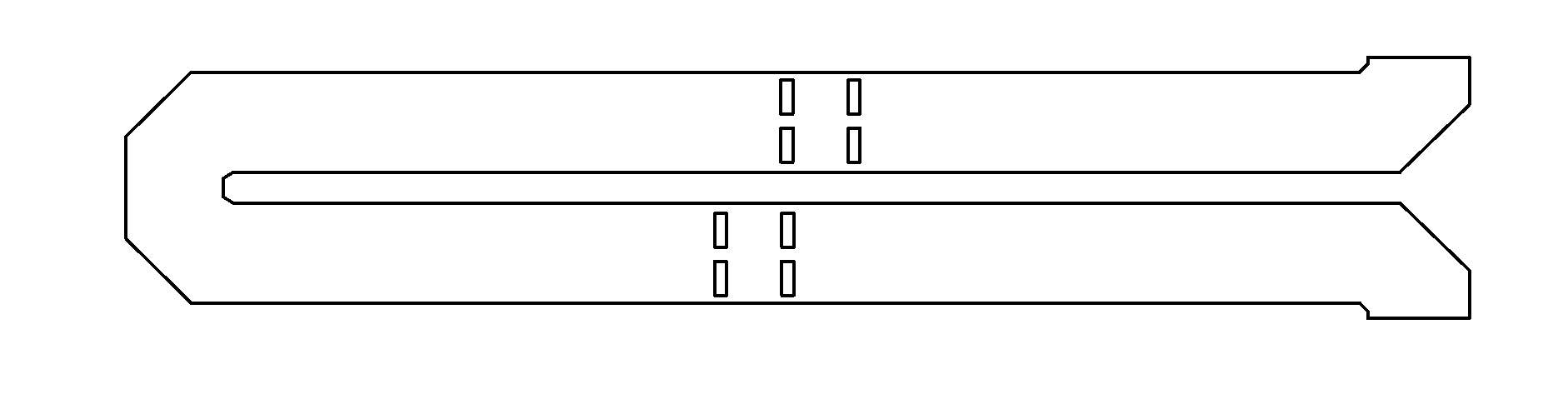
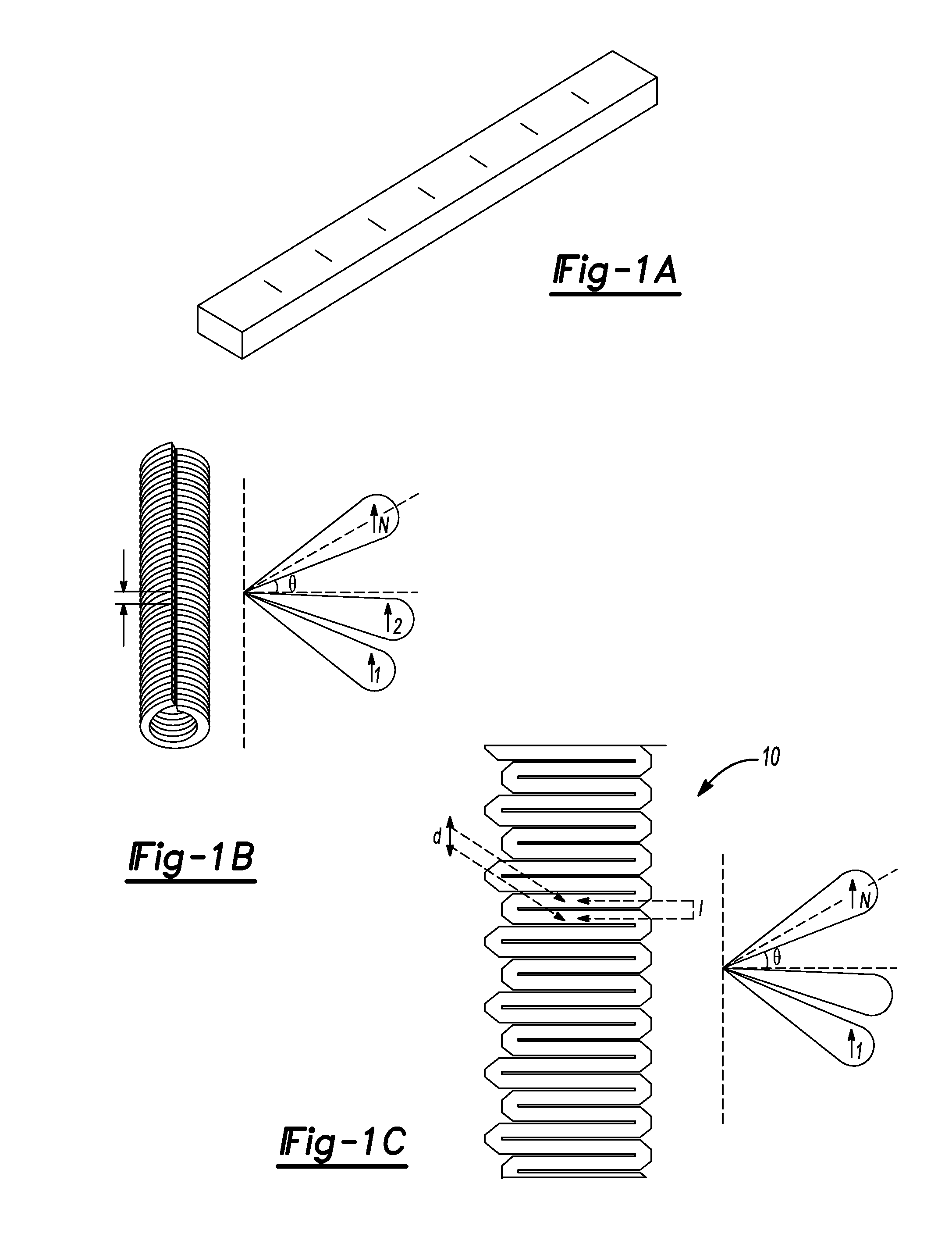
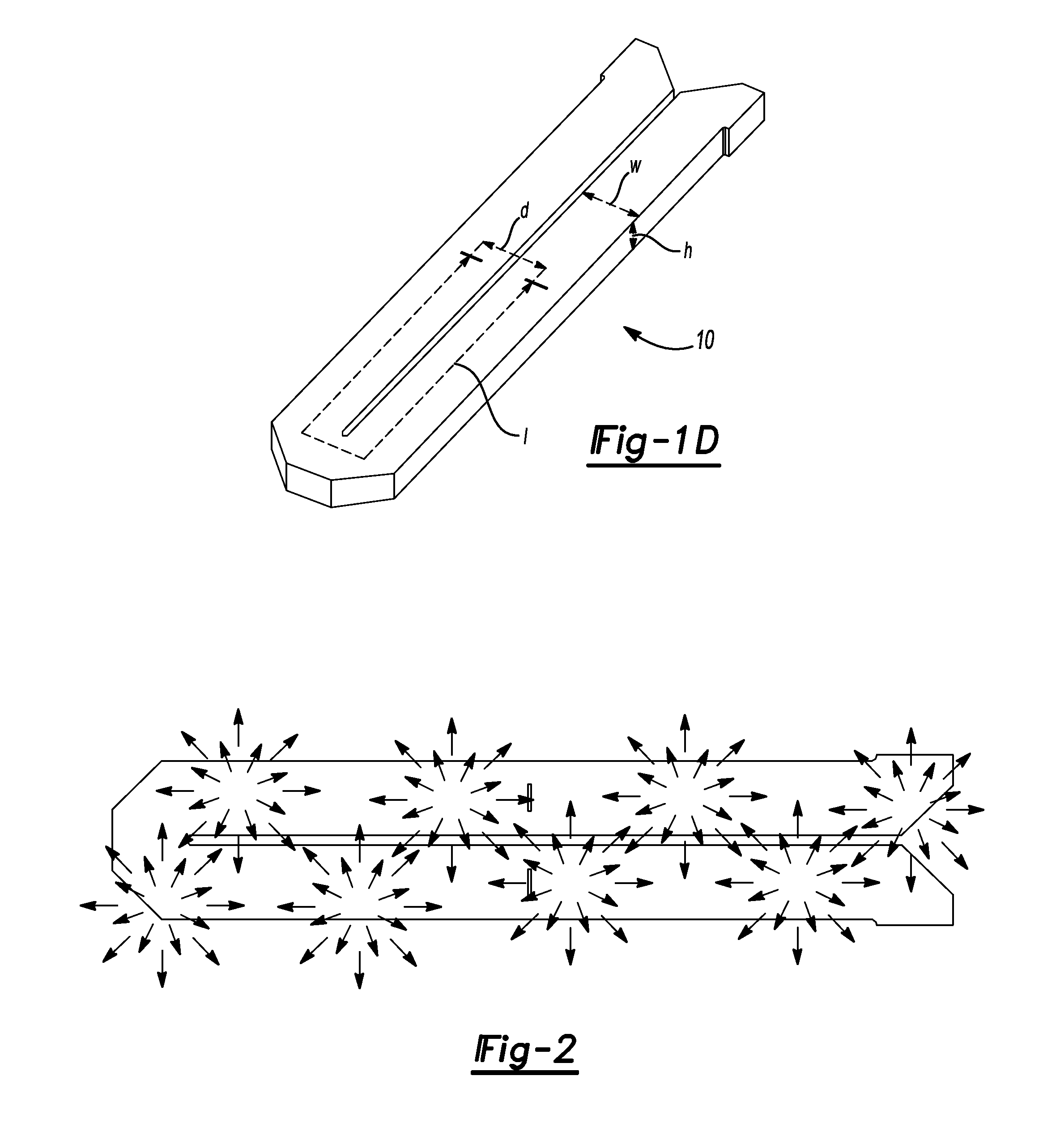
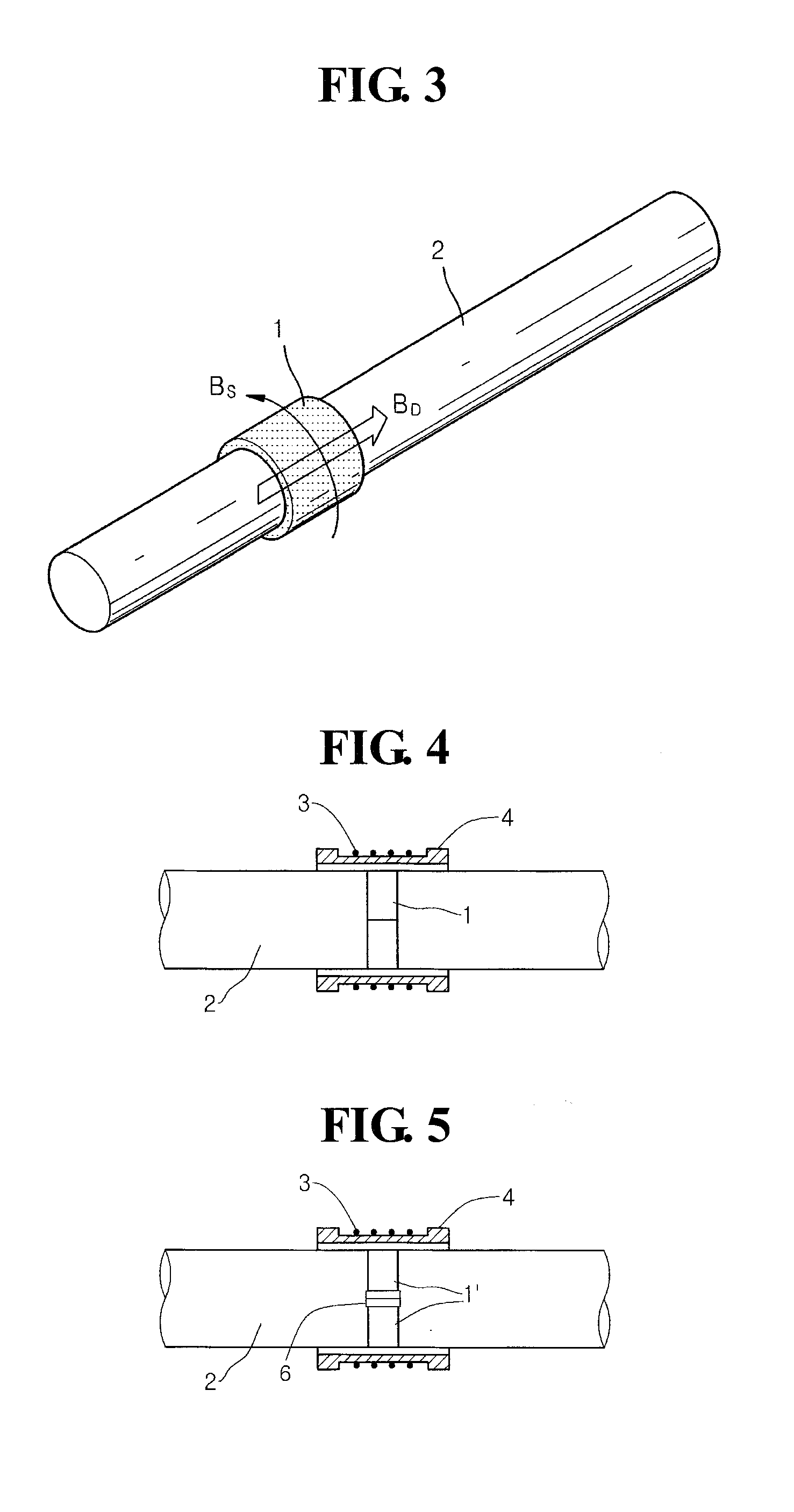
Segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, apparatus for diagnosing structural fault by using the same, and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20100259252A1Accurate detectionDirection is limitedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetsPatch arrayMeander
A segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer capable of generating a high frequency shear wave in a structure such as a rod or a pipe, a structural fault diagnosing apparatus including the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, and a method of operating the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer are shown. The segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer includes a plurality of magnetostrictive patches attached along a circumference of a rod member; a plurality of insulators that are disposed on the magnetostrictive patches; a plurality of meander coils, each of the meander coils comprising a plurality of coil lines extending along the circumference direction of the rod member on each of the insulators, wherein a current flows through adjacent coil lines in opposite directions to one another; and a plurality of magnets that respectively form a magnetic field along the circumferential direction of the rod member on the magnetostrictive patches.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
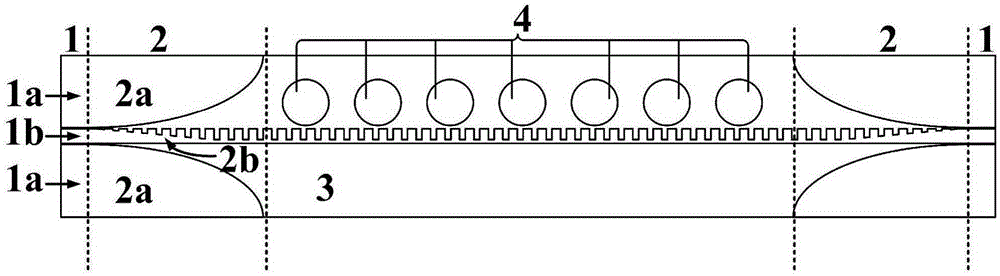
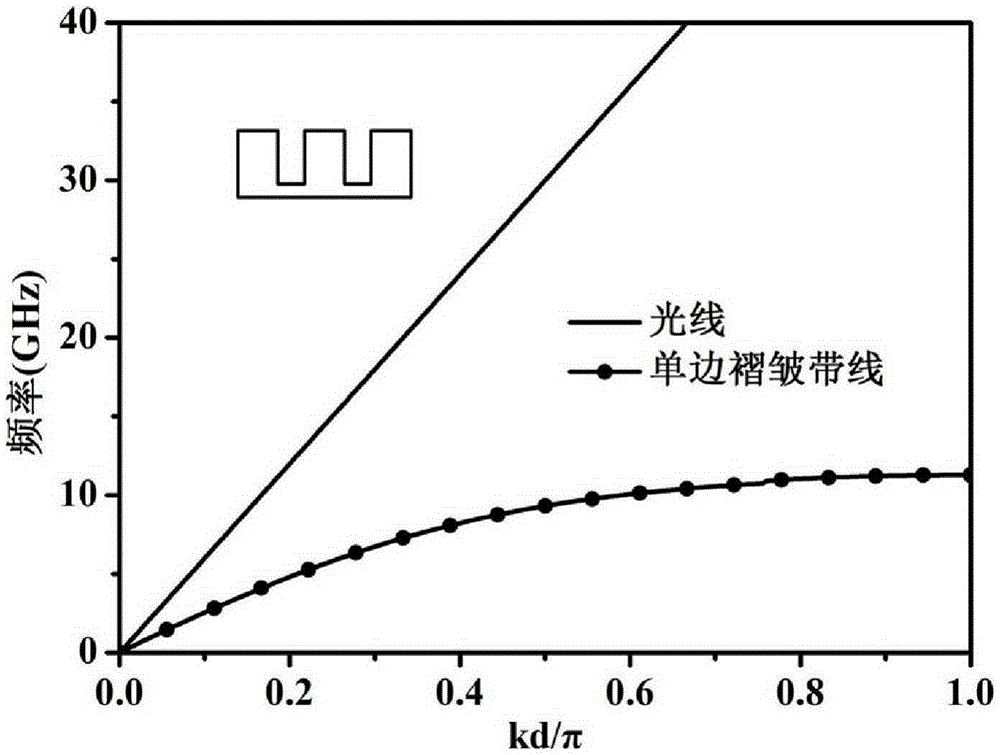
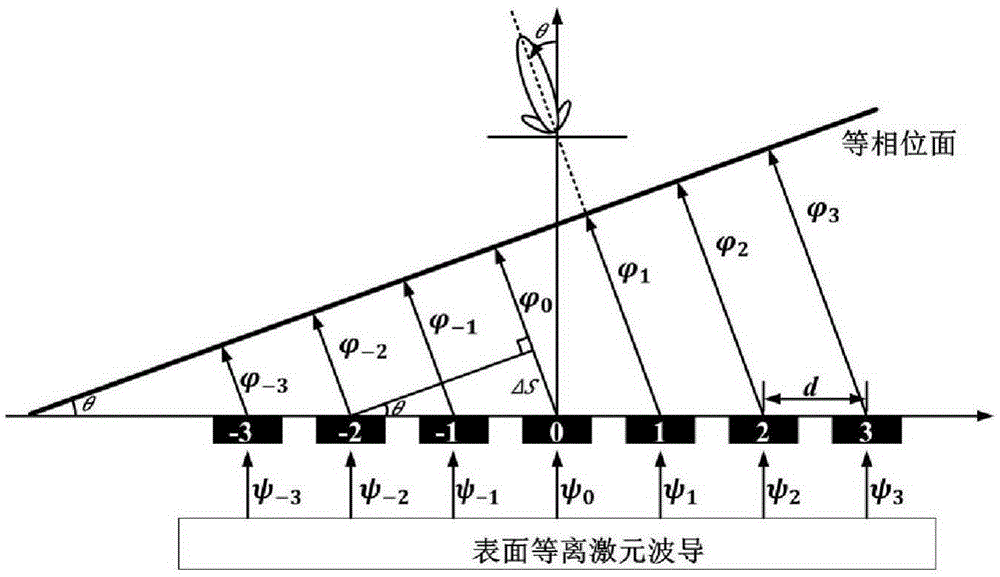
Patch array capable of realizing wide angle frequency scanning by employing planar surface plasmon feed
ActiveCN105305099AFacilitates maximum power transferWide range of radiation frequenciesAntenna arraysSlot antennasPatch arraySurface plasmon
The invention discloses a patch array capable of realizing wide angle frequency scanning by employing planar surface plasmon feed. The metal structure comprises coplanar waveguide transmission line feed parts (1) arranged at the two ends, transition parts (2) from coplanar waveguide transmission lines to surface plasmon waveguides, a surface plasmon waveguide part (3) and a round metal patch array (4), wherein the surface plasmon waveguide part (3) is arranged in the middle, the two transition parts (2) are arranged at the two sides of the surface plasmon waveguide part (3), the two coplanar waveguide transmission line feed parts (1) are arranged at two outer sides of the transition parts (2), and the round metal patch array (4) is arranged on the upper part the surface plasmon waveguide part (3). With the structure disclosed by the invention, wide-angle scanning of a beam from the rear side to the front side in a wideband range can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for fast one-to-many microcode patch
A microcode patch apparatus including a patch array, a mux, and a RAM. The patch array receives a microcode ROM address and determines that the microcode ROM address matches one of a plurality of entries within the patch array. The patch array outputs a corresponding branch instruction and asserts a hit signal. The branch instruction prescribes a microcode branch target address. The mux receives the branch instruction from the patch array and a micro instruction corresponding to the microcode ROM address from a microcode ROM. The mux provides the micro instruction or the corresponding branch instruction to an instruction register based upon the state of the hit signal. The RAM stores a plurality of patch instructions that are to be executed in place of the micro instruction. The first one of the plurality of patch instructions is stored at a location in the RAM corresponding to the microcode branch target address.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Frequency-control wave beam/focal point scanning plane reflective array/reflector
The invention discloses a frequency-control wave beam / focal point scanning plane reflective array / reflector. The basic structure of the plane reflective array and the basic structure of the reflector respectively comprise a printed patch array, a primary feed source and a corresponding supporting structure. The plane reflective array is irradiated by spherical waves, focusing of wave beams is realized in a far field, and the plane reflective array can be used in a modern wireless communication system and a modern radar system. The reflector is irradiated by plane waves or cylindrical waves or spherical waves, can realize wave beam focusing in a near field and can be applied to an imaging system. The plane reflective array and the reflector respectively enable the phase value actually obtained on each frequency point to meet the theoretically required value through selection of the size and freedom degree parameters of each unit, therefore, in-phase superposition, in different directions, of the array at different frequency points is realized, and the function of wave beam or focal point scanning is achieved. The frequency-control wave beam / focal point scanning plane reflective array / reflector has the advantages that electric wave beam / focal point scanning and high gain are realized through the simple array surface structure, and the cost, the loss and the complexity of a current scanning array / imaging system are greatly reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Metal-only dielectric-free broadband aperture-coupled patch array
InactiveUS20150162663A1Wide bandwidthEnhanced radiationIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna earthingsDielectricPatch array
Owner:NUVOTRONICS
Millimeter-wave microstrip array antenna
InactiveCN106505312AHigh gainLow sidelobeParticular array feeding systemsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip array antennaPatch array
The invention relates to the technical field of antennas, in particular to a millimeter-wave microstrip array antenna. The millimeter-wave microstrip array antenna comprises a dielectric plate, patch array antennas and a feed network, wherein the dielectric plate comprises a double-layer plate body, and a metal ground is clamped between the two layers of the double-layer plate body; the feed network is a one-to-n path of T-type power dividing circuit, each branch port of the feed network is provided with a feed point, the patch array antennas are arranged in n columns, and central symmetry points of the patch array antennas are provided with coaxial feed probes which penetrate the dielectric plate vertically so as to connect the feed points with the patch array antenna; and on the same column of the patch array antennas, the coaxial feed probes are directly connected between relatively proximate microstrip patches on a group of patch units, and are interconnected between relatively proximate microstrip patches on another group of patch units by means of 180-degree phase shifters. The millimeter-wave microstrip array antenna has the advantages of high gain, low sidelobe and miniaturization, and can effectively realize the high integration and miniaturization requirements of the whole antenna structure.
Owner:ANHUI SUN CREATE ELECTRONICS
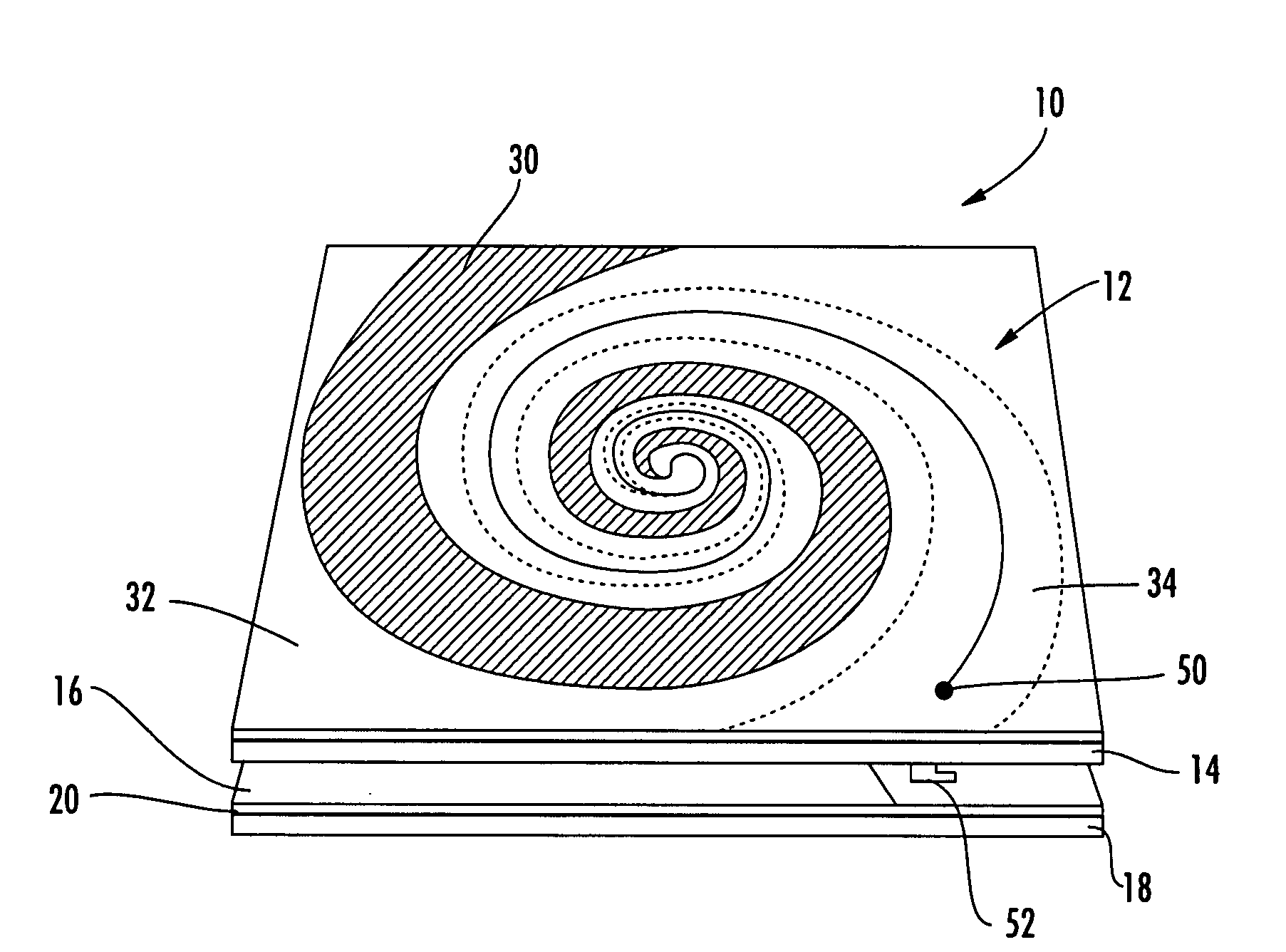
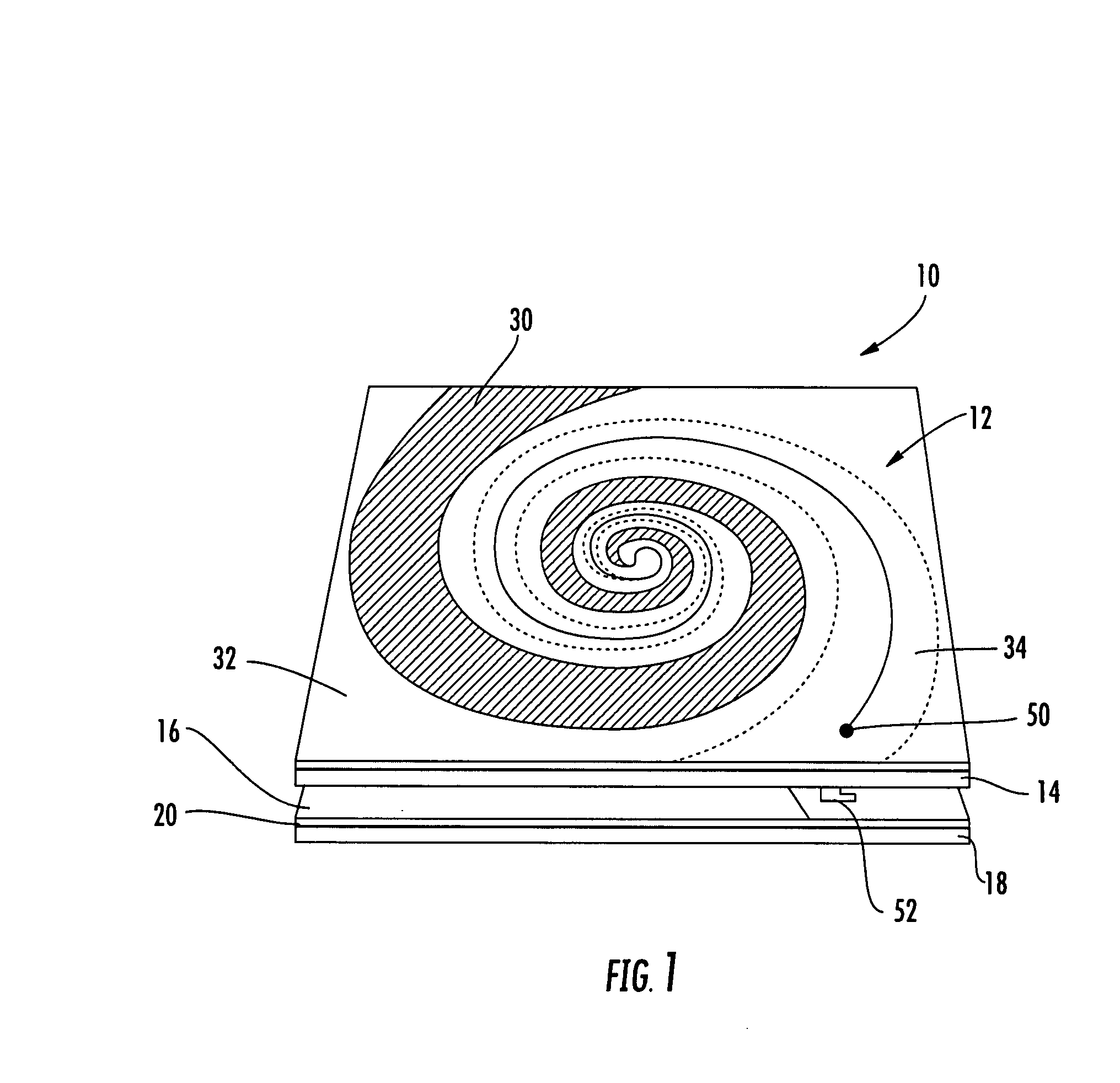
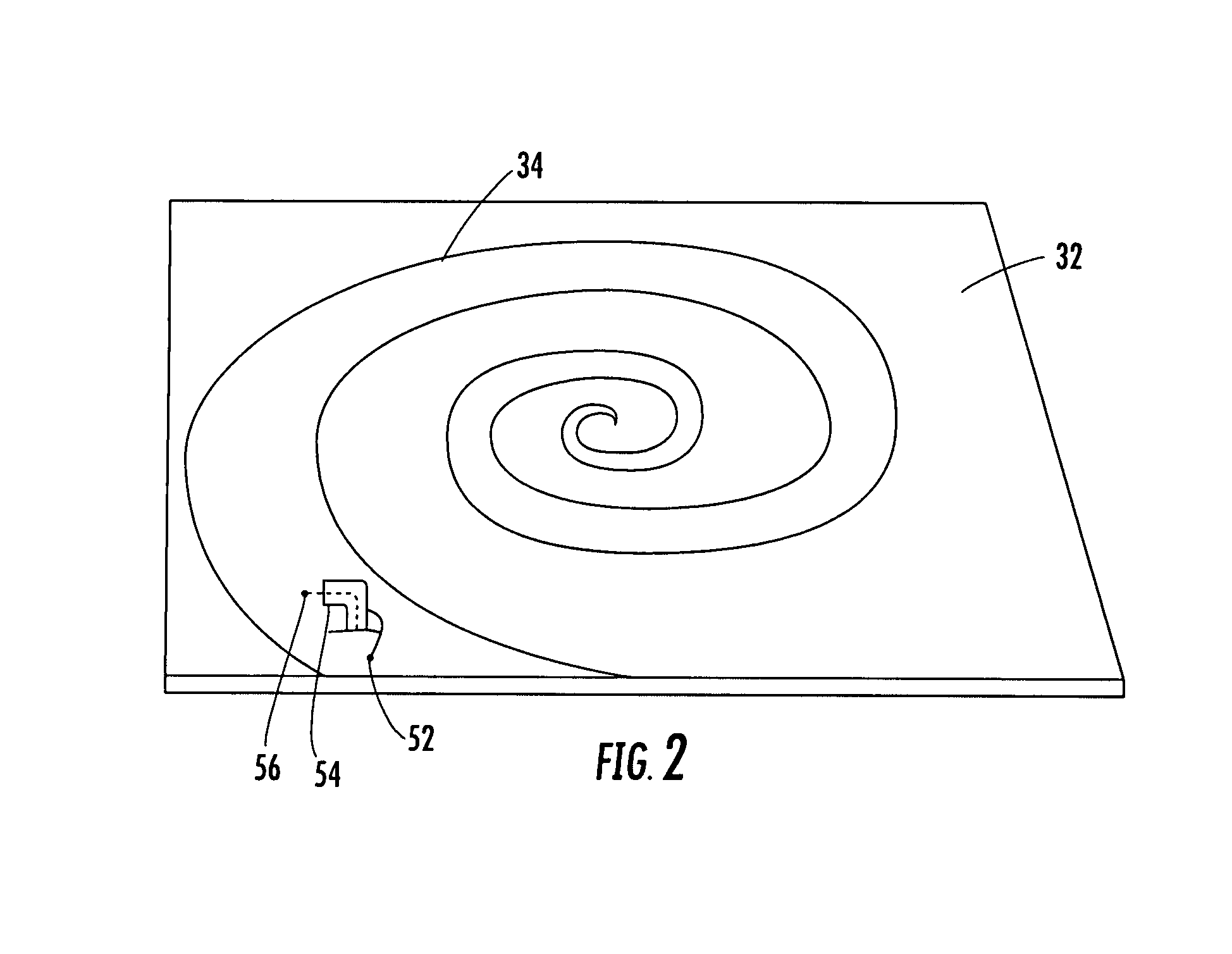
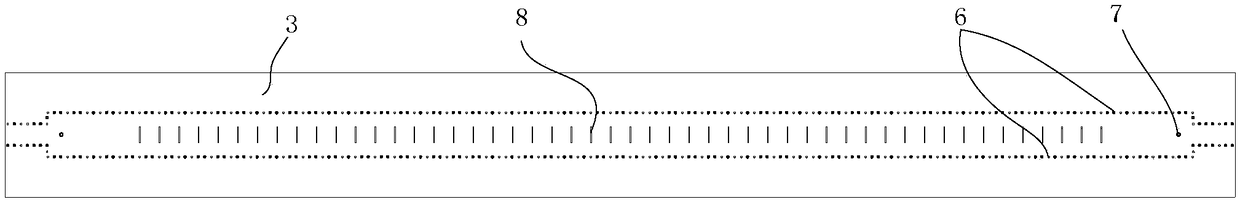
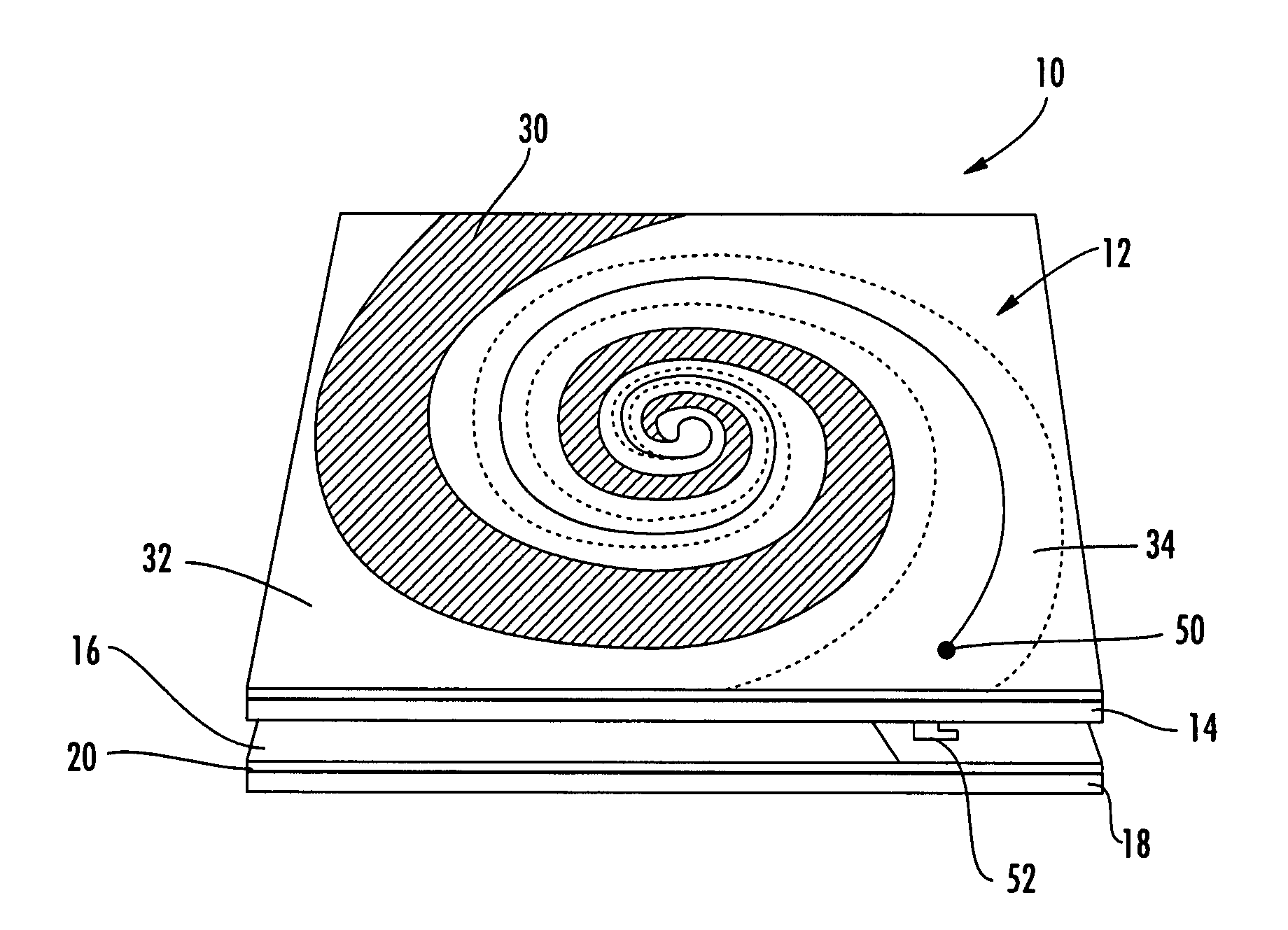
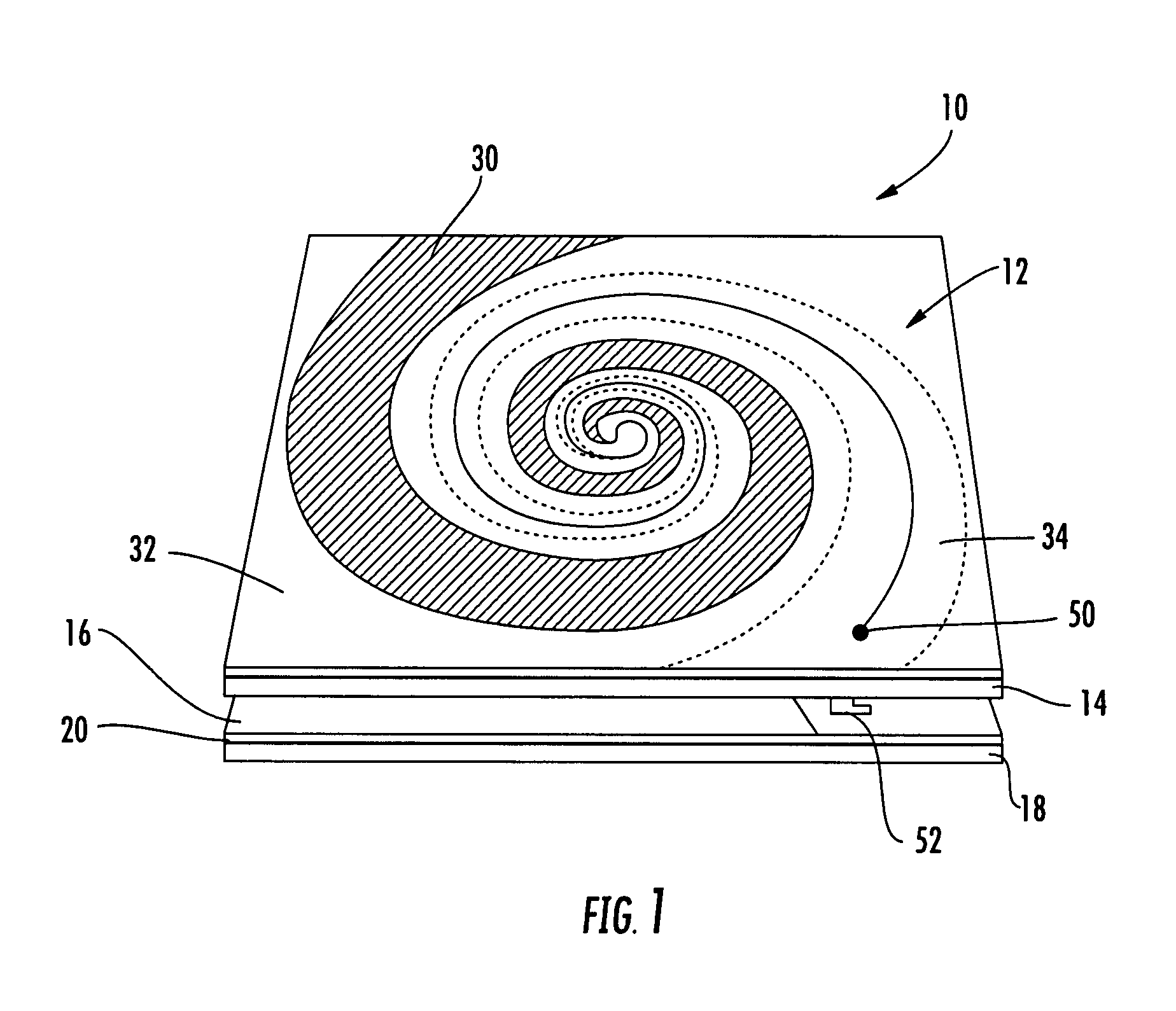
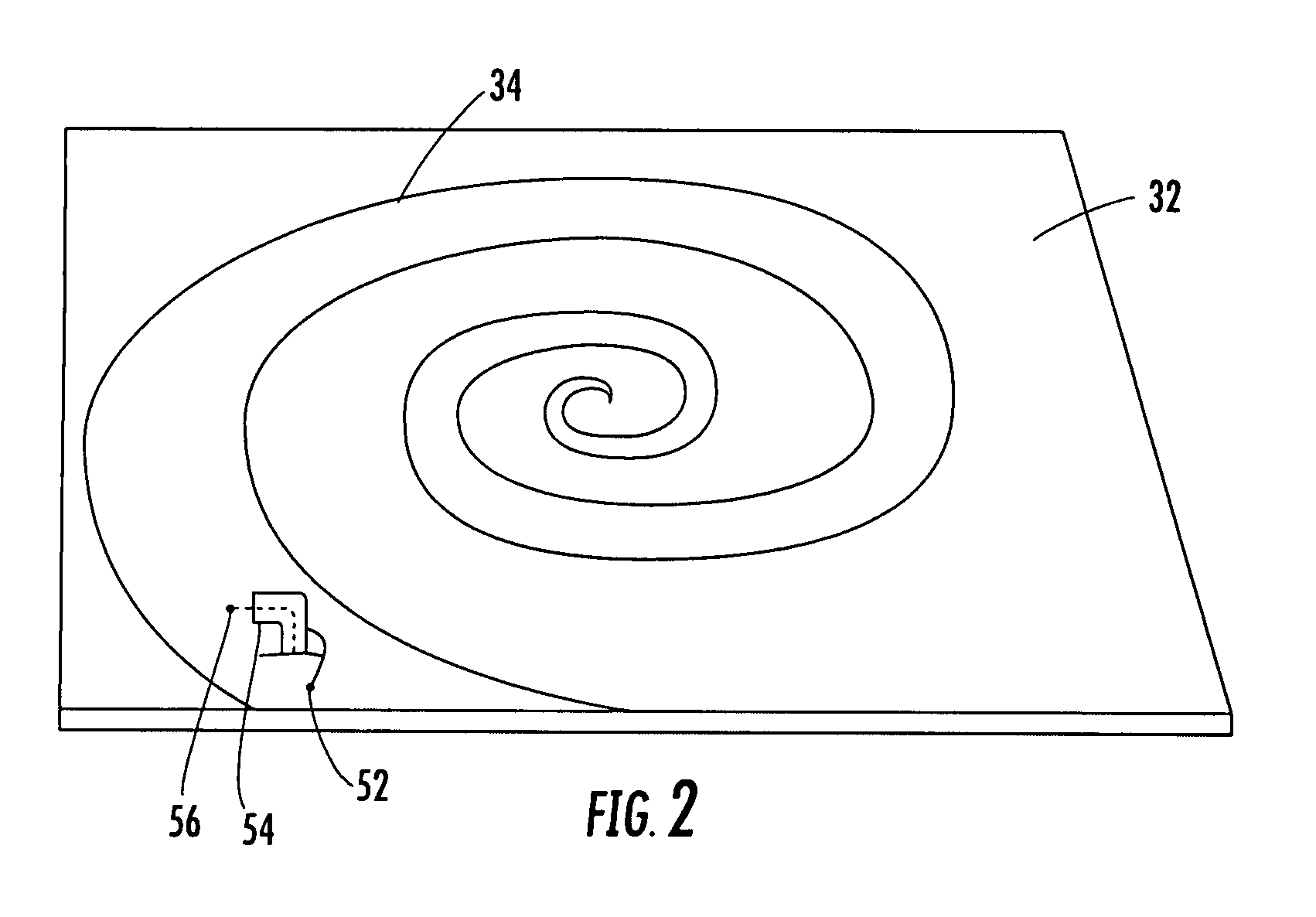
Hybrid antenna including spiral antenna and periodic array, and associated methods
InactiveUS20080284673A1Effective radiationLogperiodic antennasAntenna arraysPatch arrayEnergy coupling
The hybrid antenna includes a spiral antenna, e.g. a log spiral antenna, and a patch array layer adjacent to the spiral antenna and including a passive periodic patch array of conductive patch elements. A conductive ground plane may be adjacent to the patch array layer, and a dielectric layer may be between the conductive ground plane and the patch array. The spiral antenna may include an upper antenna arm, a lower antenna arm and a dielectric sheet therebetween. Each of the upper and lower antenna arms may be a printed planar conductive trace that is wider at a distal end thereof with respect to a center of the log spiral antenna. The patch or periodic array layer operates in conjunction with the ground plane to couple energy into the spiral antenna and thereby improve low frequency antenna efficiency while maintaining electrically small dimensions.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Multilayer micro-strip flat-plate array antenna with symmetric beams
InactiveCN102394359AReduce mutual couplingGood symmetryAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsPatch arrayFeeder line
The invention relates to a multilayer micro-strip flat-plate array antenna with symmetric beams, which consists of a radiation layer, a feeder layer and a reflection plate, wherein radiation patches are symmetrically distributed on an inner surface of the radiation layer, and the radiation patch array is totaled in 18 units of 3*6; the feeder layer is arranged between the radiation layer and the reflection plate, a distance between every two adjacent layers is a quarter wavelength, a grounding surface of the feeder layer is provided with 18 H-shaped coupled gaps in a form of 3*6, a micro-strip feeder line is arranged on the feeder surface of the feeder layer, on a micro-strip feeder-line network, energy is allocated by a first-level power distributor to a second-level power distributor and is opposite to a phase position, finally the energy is allocated to each radiation unit through a serial impedance matching circuit, the reflection plate is a metal plate and forms an inner surface of an antenna shell, the radiation layer also has a function of an antenna cover, and the entire antenna is completely arranged inside a closed shell except a connector.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二〇六研究所
Broadband high-gain double-circle polarized patch antenna
ActiveCN104600425AHigh gainDual Circular Polarization ConvenienceAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsPatch arrayCircularly polarized antenna
The invention discloses a broadband high-gain double-circle polarized patch antenna. The broadband high-gain double-circle polarized patch antenna comprises a floor layer, a feed network, square patch arrays, an upper dielectric substrate, a middle dielectric substrate and a lower dielectric substrate, wherein the upper dielectric substrate, the middle dielectric substrate and the lower dielectric substrate are sequentially arranged from top to bottom and are supported separably through dielectric frames. The square patch arrays are adhered to the lower surfaces of the upper dielectric substrate and the middle dielectric substrate. Each square patch array comprises four square units in two-row two-column arrangement. The floor layer is positioned on the upper surface of the lower dielectric substrate. The feed network is etched on the lower surface of the lower dielectric substrate. Eight radiant gaps are etched on the floor layer. The feed network comprises a directional coupler, six power dividers and an air bridge. The feed network divides an input signal into eight channels of signals, feeds the signals into the radiant gaps and feeds electricity upwardly to the square patch arrays through the radiant gaps, and finally, an antenna radiation effect is achieved through middle and upper radiation. The broadband high-gain double-circle polarized antenna is achieved by the aid of a printed circuit process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Rectenna array for microwave reception
InactiveCN102354805AImprove scalabilityLow profileAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsPatch arrayMicrowave
The invention provides a rectenna array for microwave reception. According to the invention, a linear polarization binary series microstrip rectangular patch array that works at a 2.45 GHz is utilized as a reception rectenna; a microstrip line series feed is employed to enable an antenna and a rectification circuit to be at a same plane; and two short branch knots that are introduced between unit patches can be used for adjusting an orientation of an antenna directional diagram. The above-mentioned structure is very convenient to be expanded and can be applied to a design of a large-scale array. According to the invention, the array has advantages of small profile, small volume and light weight; and the array has a planar structure and is easy for coplane and conformal realization with electric equipment; moreover, the reception rectenna array is wholly manufactured on a same medium substrate and is suitable for mass production with utilization of a printed circuit technology and the costs are low; and the microstrip line feeding mode enables a rectenna array to be easy to carry out array organization; therefore, the array can be applied to a large-power occasion.
Owner:高宝强
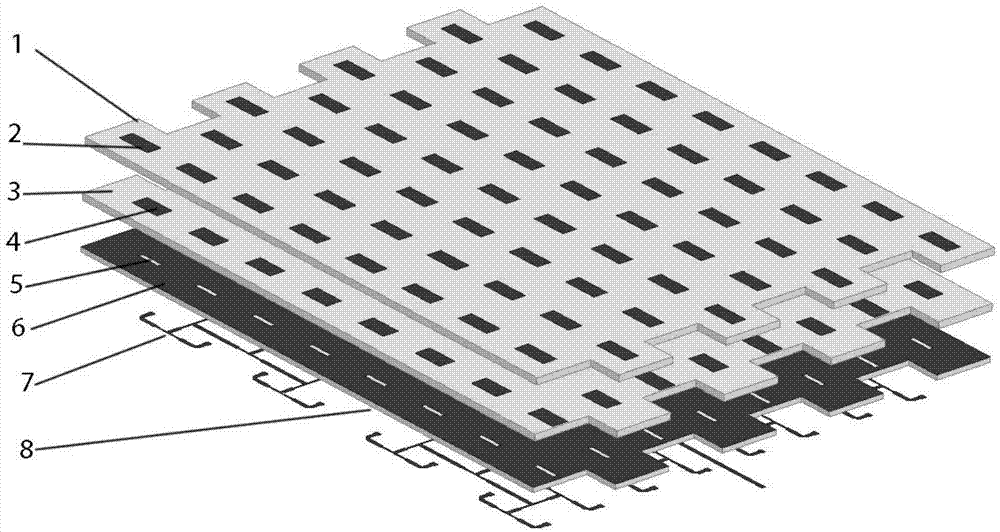
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105185800ADon't enterDon't enter or rarely enterSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiation controlled devicesPatch arrayImaging quality
The invention discloses a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor, comprising an optical filter, a photosensitive operating circuit unit, a silicon substrate, a microlens array, a metal interconnection dielectric layer, a metal interconnection layer, and a silicon substrate epitaxial layer. The corresponding silicon substrate epitaxial layer below each microlens of the microlens array, and the photosensitive operating circuit unit corresponding to a silicon substrate epitaxial layer region are a pixel unit. The sensor also comprises a silicon substrate reflective surface patch array on the bottom surface of the silicon substrate. The curved surface layer of the silicon substrate reflective surface patch array is provided with a reflecting medium layer. An interpixel potential isolating barrier is arranged between two adjacent pixel units. Each interpixel potential isolating barrier extends downwards and passes through the silicon substrate. The sensor can improve photoelectric conversion quantum efficiency, reduces signal crosstalk of carriers, and improves imaging quality of the image sensor under dark field environment.
Owner:QIXINRUIHUA TECH WUHAN CO LTD
Broadband directional microstrip patch antenna
InactiveCN102738572AEasy to processEase of mass productionRadiating elements structural formsPolarised antenna unit combinationsMicrostrip patch antennaPatch array
The invention discloses a broadband directional microstrip patch antenna which is sequentially provided with a first medium layer, a microstrip feeder network arranged on the first medium layer, a second medium layer, a slit grounding surface arranged on the second medium layer, a third medium layer and a radiation patch array arranged on the third medium layer from bottom to top. The broadband directional microstrip patch antenna is simple to process and easy to assemble.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Metasurface based four-beam vortex field Cassegrain lens antenna
The invention provides a metasurface based four-beam vortex field Cassegrain lens antenna, and is used for solving the technical problem of small coverage area of a vortex field in the prior art. Theantenna includes a lens, a feed source, a reflecting surface and a support structure. The lens is of a central hollow structure, and includes K first medium plates which are stacked in order. A firstpatch array consisting of uniformly arranged metal patches is printed on the surfaces, facing the reflecting surface, of the first medium plates of the odd-numbered layers and the surfaces, facing away from the reflecting surface, of the first medium plate of the last even-numbered layer. A second patch array consisting of uniformly arranged regular cross-shaped metal patches is printed on the surfaces, facing the reflecting surface, of the first medium plates of the even-numbered layers. The reflecting surface includes a second medium plate. Uniformly arranged metal ring patches are printed on one side of the reflecting surface, and metal floor is printed on the other side. The reflecting surface is fixed to one side of a lens focus through the support structure. Four vortex fields of different directions are obtained by dividing the first patch array into multiple rectangular regions with an additional phase difference of 180 degrees between adjacent rectangular regions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
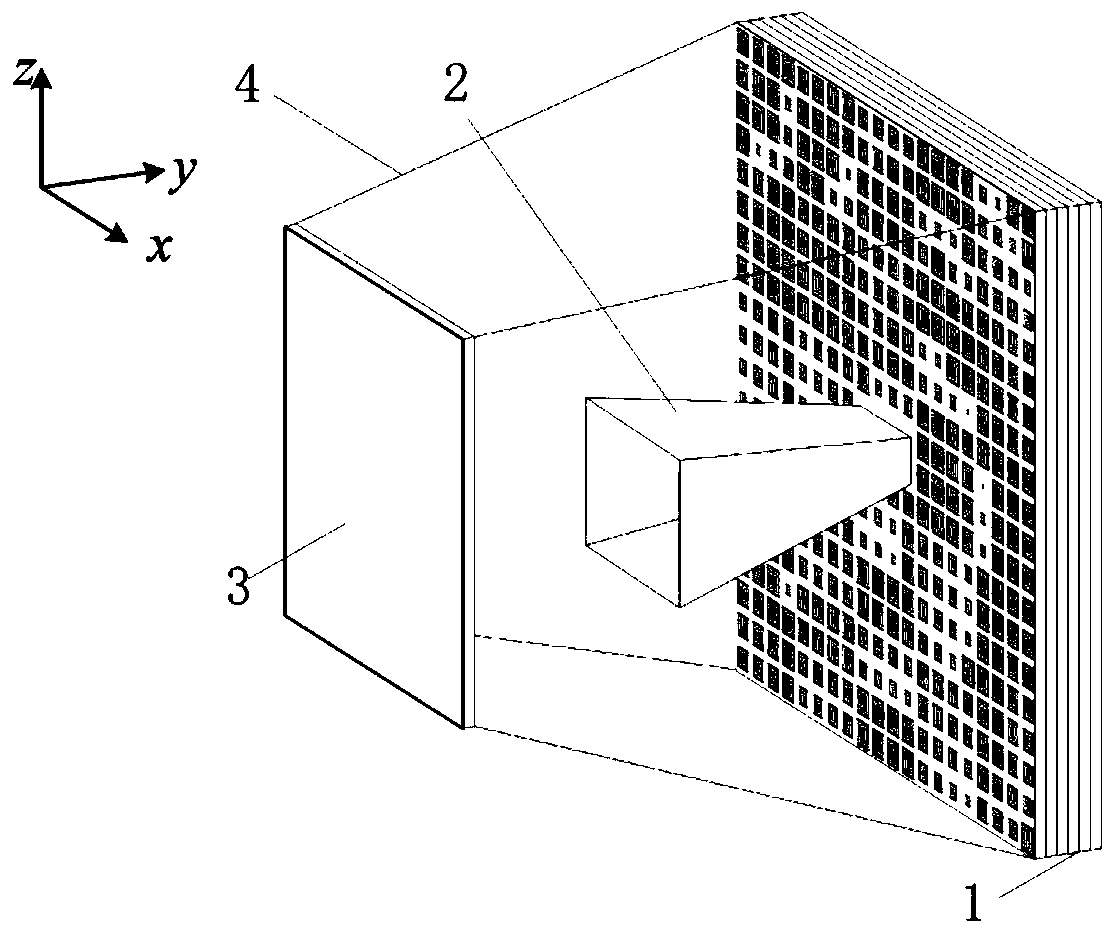
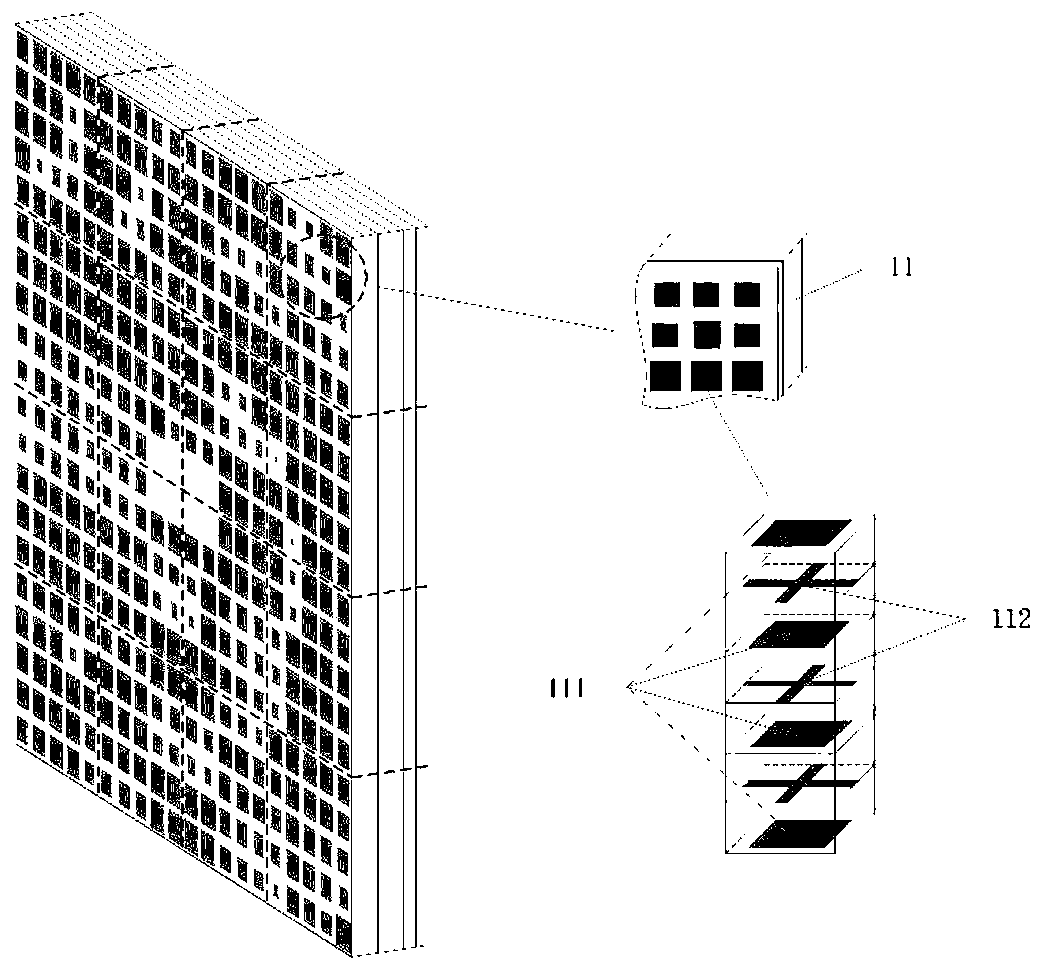
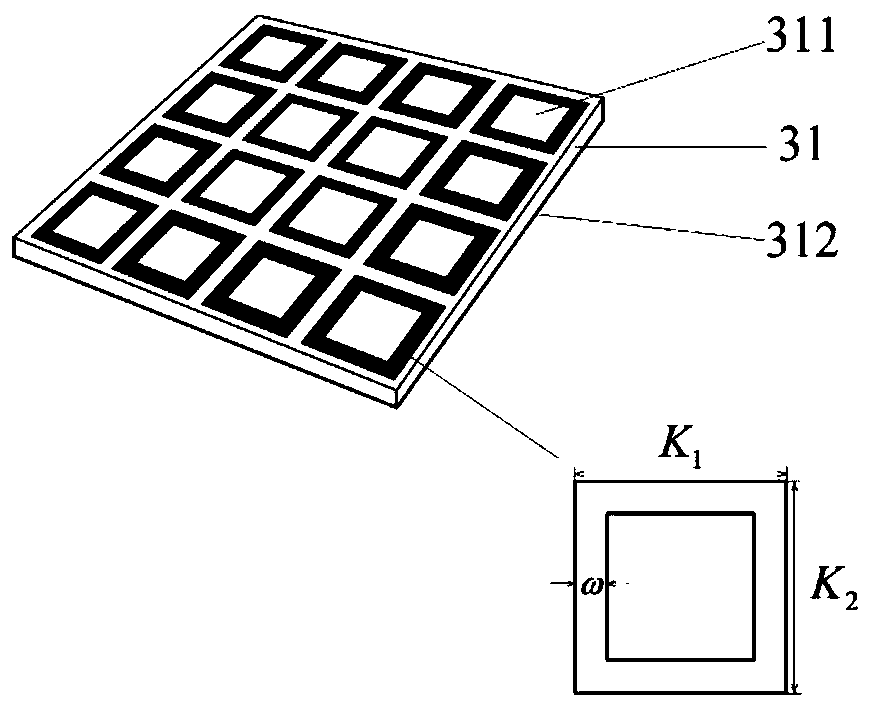
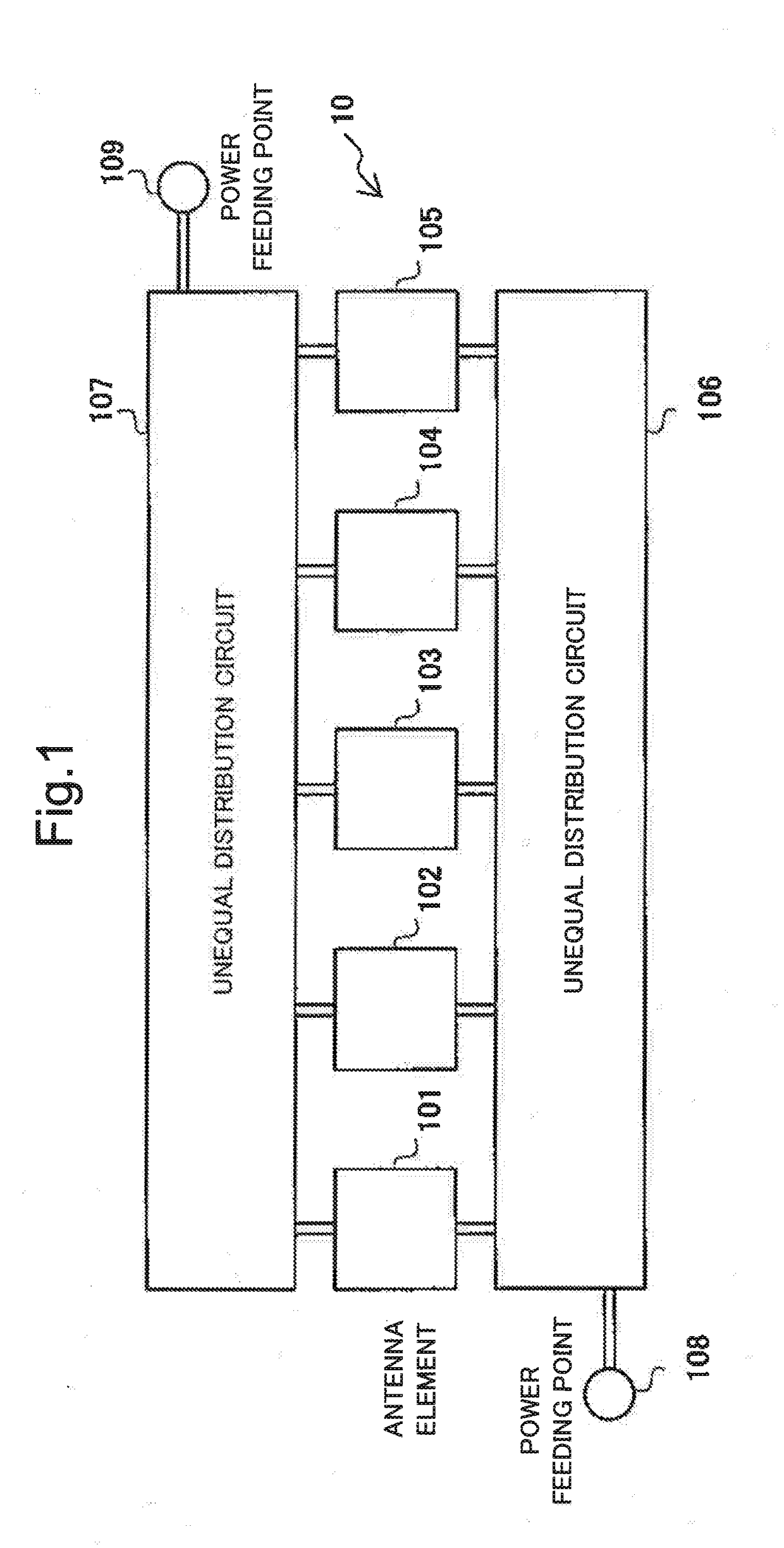
Patch array antenna, directivity control method therefor and wireless device using patch array antenna
ActiveUS20190067813A1Increased durabilityLow costIndividually energised antenna arraysPatch arrayPhase difference
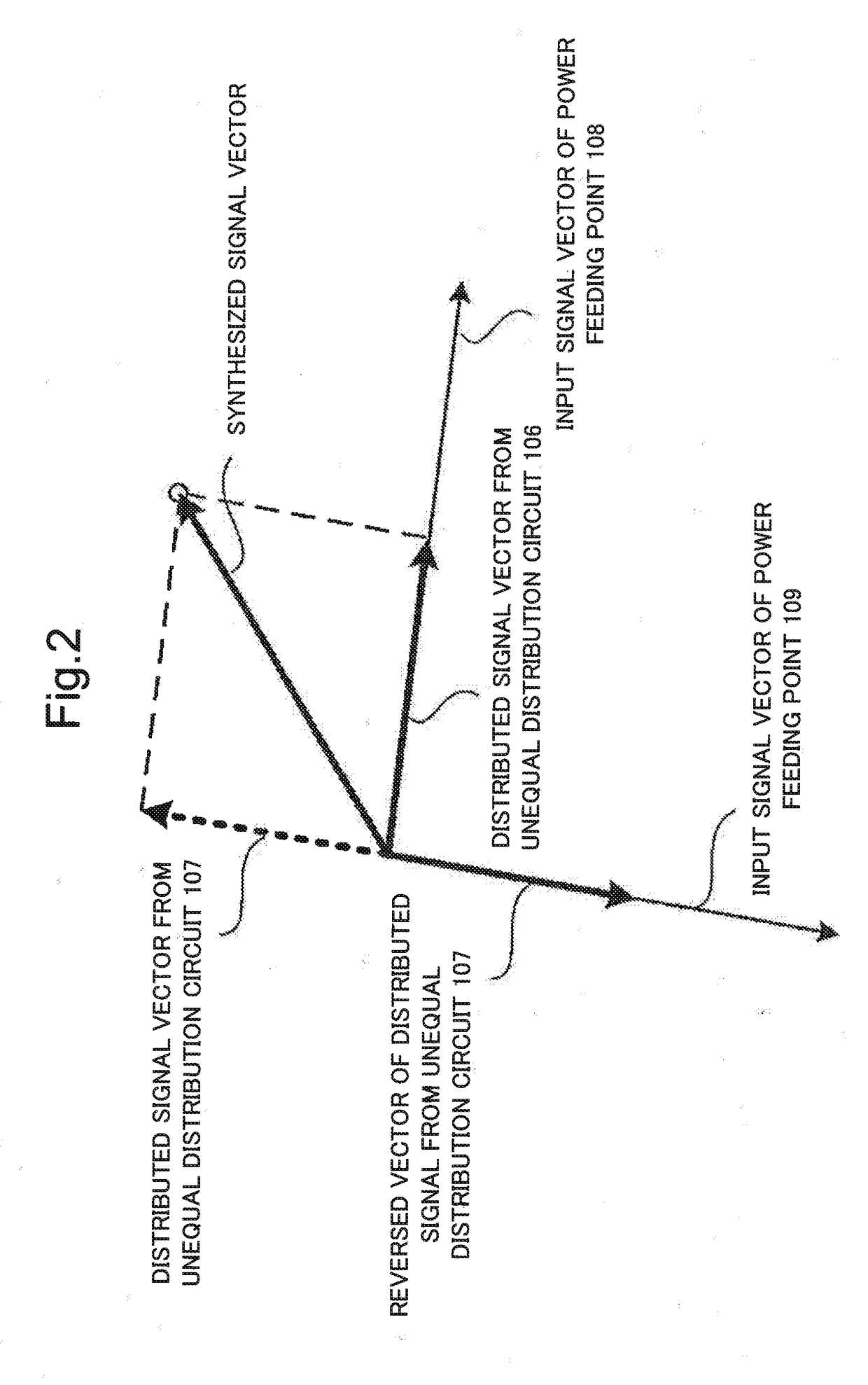
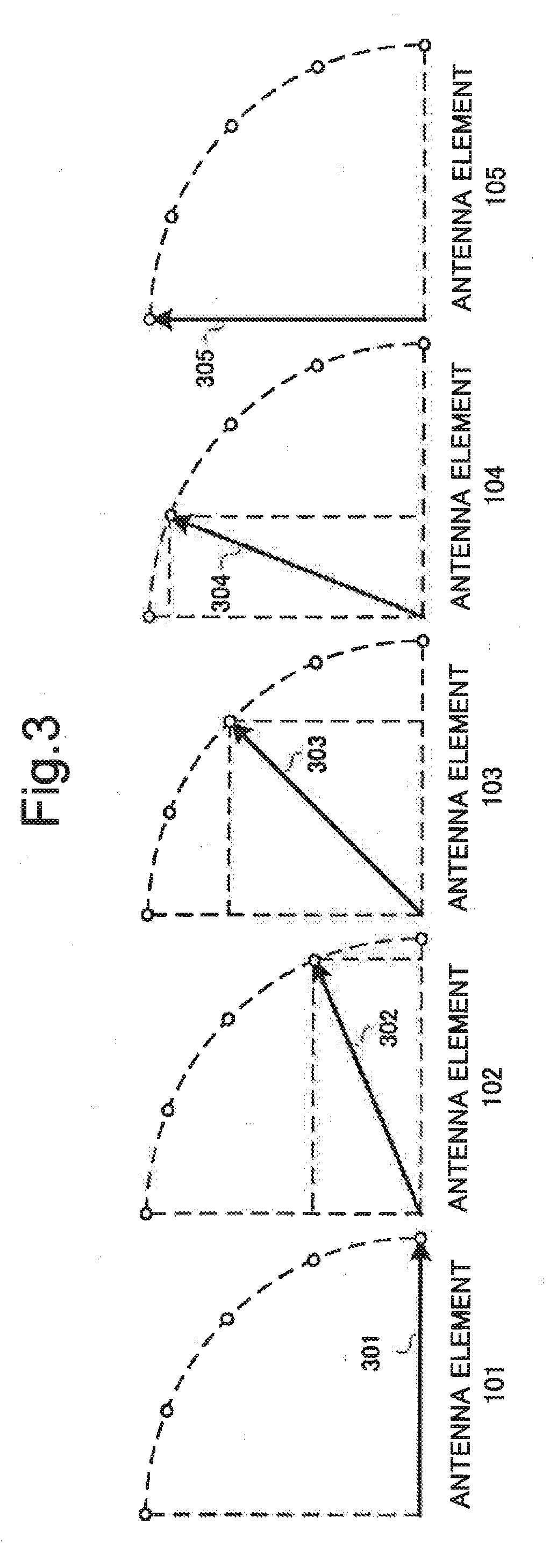
To provide a patch array antenna that allows a limited increase in active component even if the number of antenna elements increases, in a first unequal distribution circuit 106, a first distribution ratio of the power of a first high-frequency signal to be distributed from a first feeding point 108 to first to Nth antenna elements is set to be one of monotone increasing and monotone decreasing with respect to a row of the first to Nth antenna elements. In a second unequal distribution circuit 107, a second distribution ratio of the power of a second high-frequency signal to be distributed from a second feeding point 109 to the first to Nth antenna elements is set to be the other of monotone increasing and monotone decreasing with respect to the row of the first to Nth antenna elements. Directivity is controlled by changing a phase difference between the first and second high-frequency signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Substrate integrated waveguide sinusoidally modulated leaky wave antenna
ActiveCN109004341ACompact structureSimple feedingRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysPatch arrayDielectric plate
The invention discloses a substrate integrated waveguide sinusoidally modulated leaky wave antenna, which aims at providing a simple power feeding, and u -1 order harmonic wave radiation utilizing leaky wave antenna. The invention is realized by the following technical scheme: A metal radiation patch array is arrange at that center of the upper surface of the antenna dielectric plate, a cop clad sheet sandwiched on the interface surface of the waveguide dielectric plate and the antenna dielectric plate is formed with a rectangular slot array corresponding to the metal radiation patch array, and the rectangular slot array couples electromagnetic energy from the waveguide to the metal radiation patch array above the antenna dielectric plate to realize linear polarization radiation; A lineararray metallize shielding via through that waveguide dielectric plate is for on both sides of the rectangular slot array from top to bottom, and a metal coupling probe through the waveguide dielectricplate is arranged on the inn sides of the contracted linear array at both ends of the linear array metallized shielding via; A sinusoidally modulated leaky wave antenna with field intensity on the plane of antenna dielectric plate is realized by exciting the substrate integrated waveguide with metal-coupled probes and U-shaped slots on the copper clad substrate.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
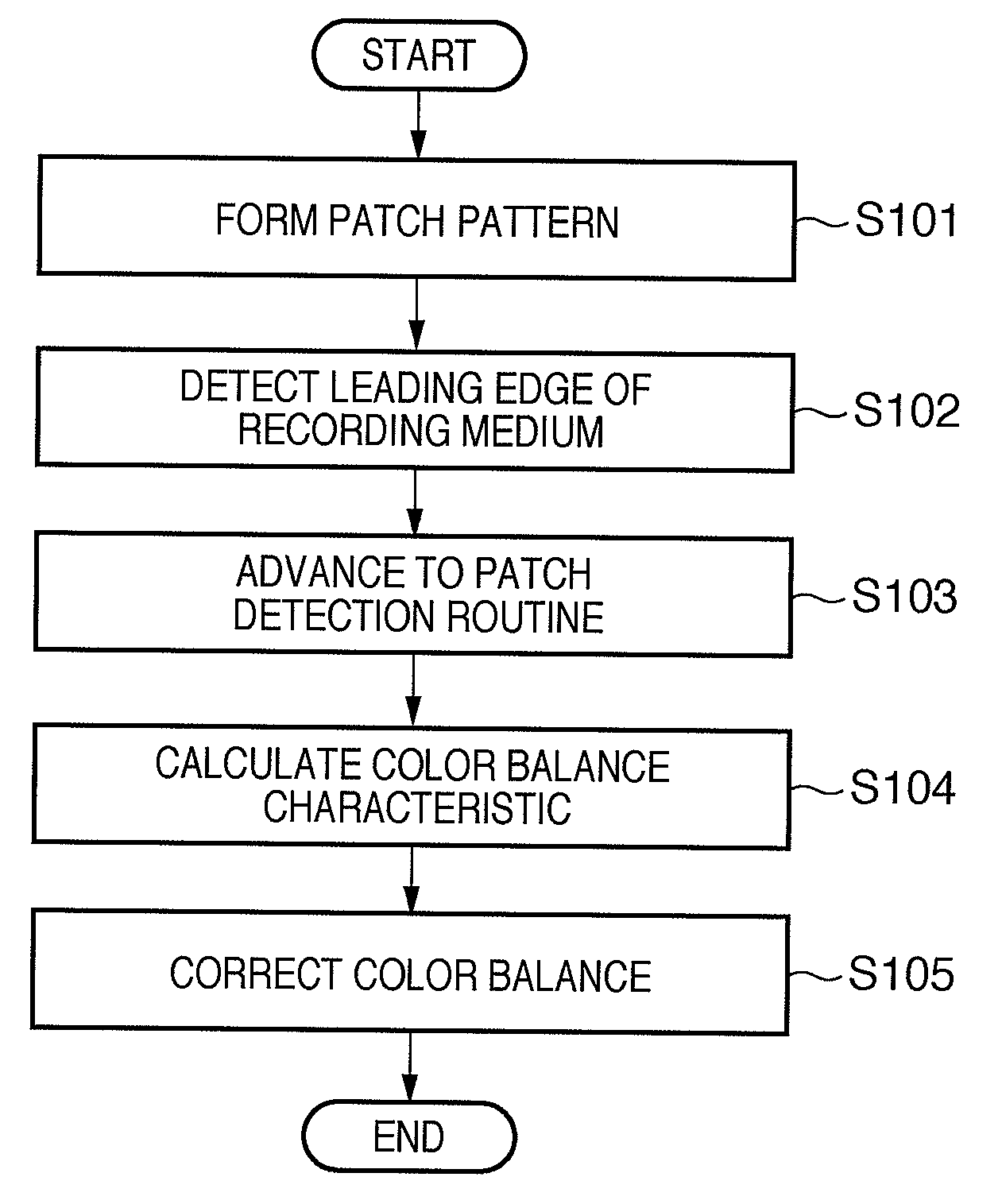
Image forming apparatus and method of controlling the same
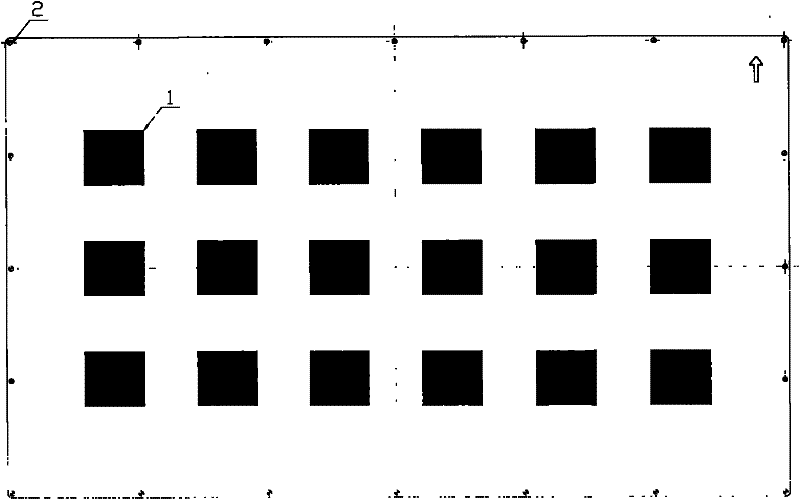
ActiveUS20090154944A1Reliable detectionIncrease consumptionElectrographic process apparatusPatch arrayImage formation
This invention provides an image forming apparatus capable of more reliably detecting patches formed on a recording medium while suppressing an increase in the consumption of printing media and toners. In an image forming apparatus which detects the density or color of each patch of a patch array fixed on a recording medium that is conveyed and corrects an image formation condition based on the detection result, the patches are formed as the patch array so that the conveyance-direction length of each patch gradually increases in an order of detection by the patch detection unit, and the conveyance-direction length of each patch gradually increases according to increasing of a detection position variation amount of a patch in the order of detection by the patch detection unit.
Owner:CANON KK
LTCC aperture coupling array antenna
InactiveCN104733843AClosely arrangedRealize wide-angle scanningAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip array antennaPatch array
The invention provides an LTCC aperture coupling array antenna, belongs to the technical field of antennas and aims at overcoming the defects of an existing micro-strip array antenna in the aspect of giving consideration to miniaturization, broadband and high gain. The LTCC aperture coupling array antenna comprises upper and lower layer radiation metal patch units, upper, middle and lower layer dielectric substrates, a grounded metal layer, resonance apertures and a micro-strip feed network, wherein the upper layer radiation metal patch units are arranged in triangular lattices, and the lower radiation metal patch units are arranged in rectangular lattices. Compared with regular micro-strip patch array antennas based on organic media or ceramic substrates, the LTCC aperture coupling array antenna is capable of obtaining a larger antenna bandwidth under the same size limit and giving better consideration to the performance requirements of miniaturization, broadband and high gain of the patch antenna.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Narrow beam H-shaped slot-coupling microstrip paster array antenna
InactiveCN107834176AAchieving Broadband FeaturesRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationPatch arrayDielectric substrate
The present invention relates to a narrow beam H-shaped slot-coupling microstrip paster array antenna. The antenna comprises a coupled paster layer, an air layer, a radiation paster layer, a strip line feed network layer and a phase shift feed network layer. The strip line feed network layer is a two-layer dielectric substrate, the coupled paster layer, the air layer, the radiation paster layer, the strip line feed network layer and the phase shift feed network layer are overlapped and connected in order, the overlapping total thickness of the coupled paster layer, the air layer, the radiationpaster layer, the strip line feed network layer and the phase shift feed network layer is 6.2mm, and the antenna is fixed by employing four screws at the periphery. The antenna provided by the invention has advantages of a high frequency band, a high gain and circular polarization.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
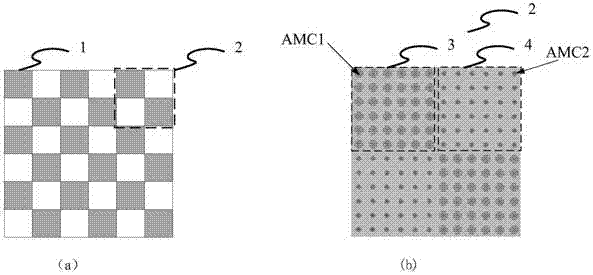
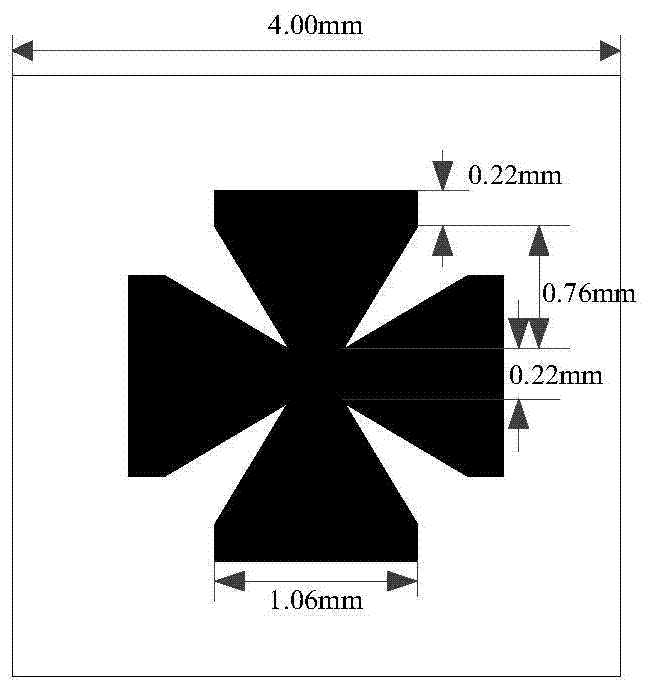
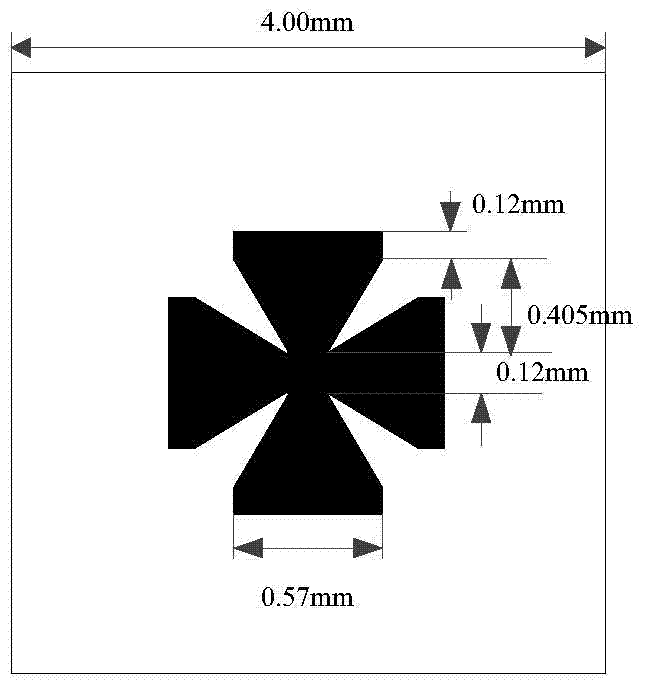
Broadband reduction RCS composite material based on crossed bow-tie-shaped AMC
The invention provides a broadband reduction RCS composite material based on crossed bow-tie-shaped AMC (artificial magnetic conductors). The material is characterized in that the composite material is in a three-layer structure, and comprises an AMC patch array, a medium substrate, and a metal floor in sequence from top to bottom, wherein the AMC patch array is arrays respectively formed by two kinds of crossed bow-tie-shaped AMC patches. The shapes of the two kinds of crossed bow-tie-shaped AMC patches are that the center is square, four edges of the square are respectively connected with four trapezoids, the short bottom edges of the trapezoids are connected with the square, the long bottom edges of the four trapezoids are connected with rectangles in sequence, and each patch is a whole integrated structure. The composite material is good in broadband performance. Compared with a metal sheet in the same size, the composite material has RCS reduction of more than -10 dB in the frequency range of 16.2-27.2 GHz, covering the whole K-band. The composite material is small in thickness, and can be conformal easily. The composite material is suitable to manufacture ultralight and ultrathin wave absorbers or radar absorbing materials. The composite material is simple in structure and materials, and is low in processing and manufacturing difficulty.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com