Patents
Literature
452 results about "Scanning plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and Method for Alignment of Instrumentation in Image-Guided Intervention
InactiveUS20090221908A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorSonification
The invention provides systems and methods for aligning or guiding instruments during image-guided interventions. A volumetric medical scan (image data) of a patient may first be registered to patient space data regarding the patient obtained using a tracking device. An ultrasound simulator fitted with position indicating elements whose location is tracked by the tracking device is introduced to the surface of the anatomy of the patient and used to determine an imaginary ultrasound scan plane for the ultrasound simulator. This scan plane is used to reformat the image data so that the image data can be displayed to a user in a manner analogous to a handheld ultrasound transducer by re-slicing the image data according to the location and orientation of the ultrasound simulator. The location of an instrument fitted with position indicating elements tracked by the tracking device may be projected onto the re-sliced scan data.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
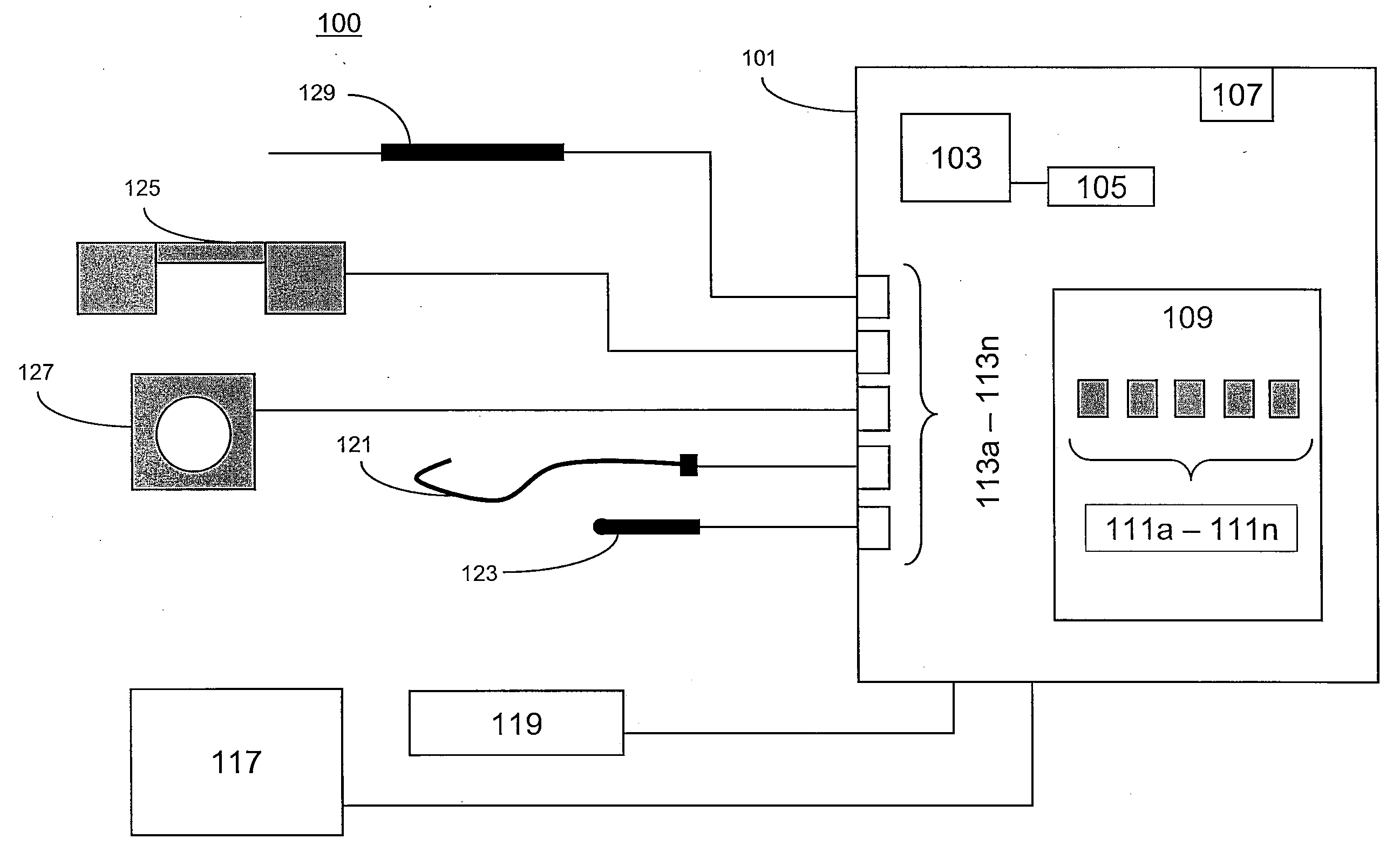
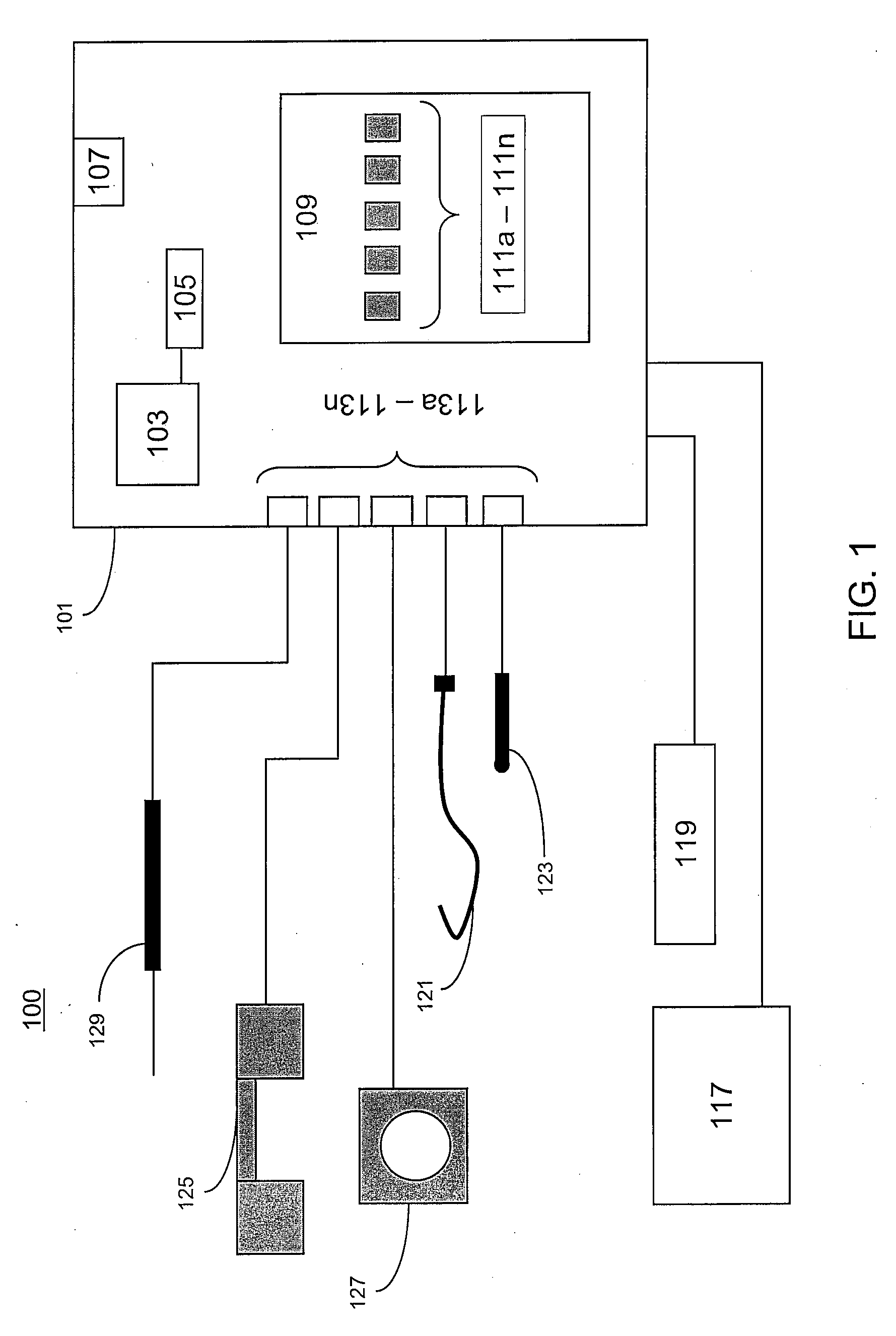
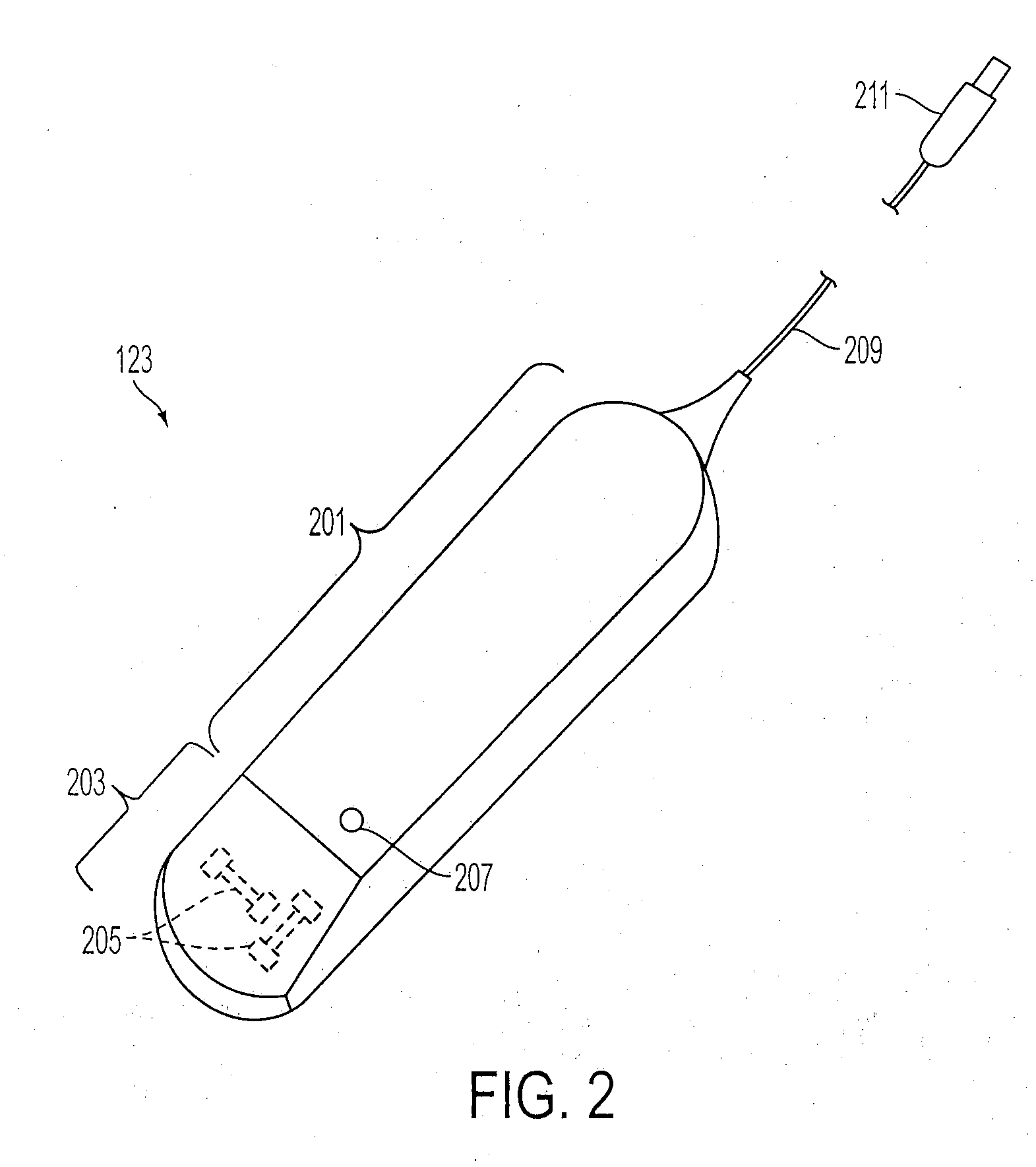
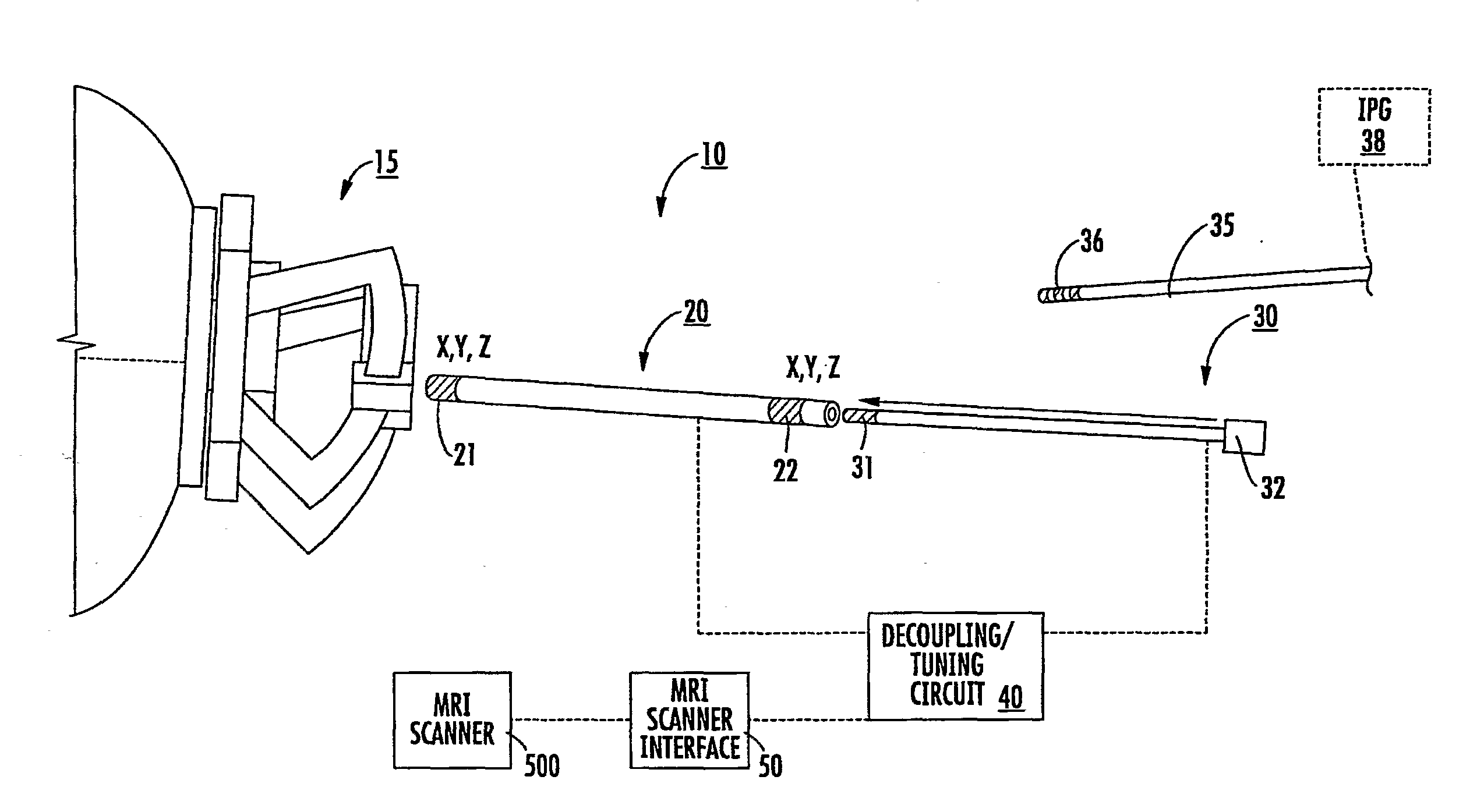
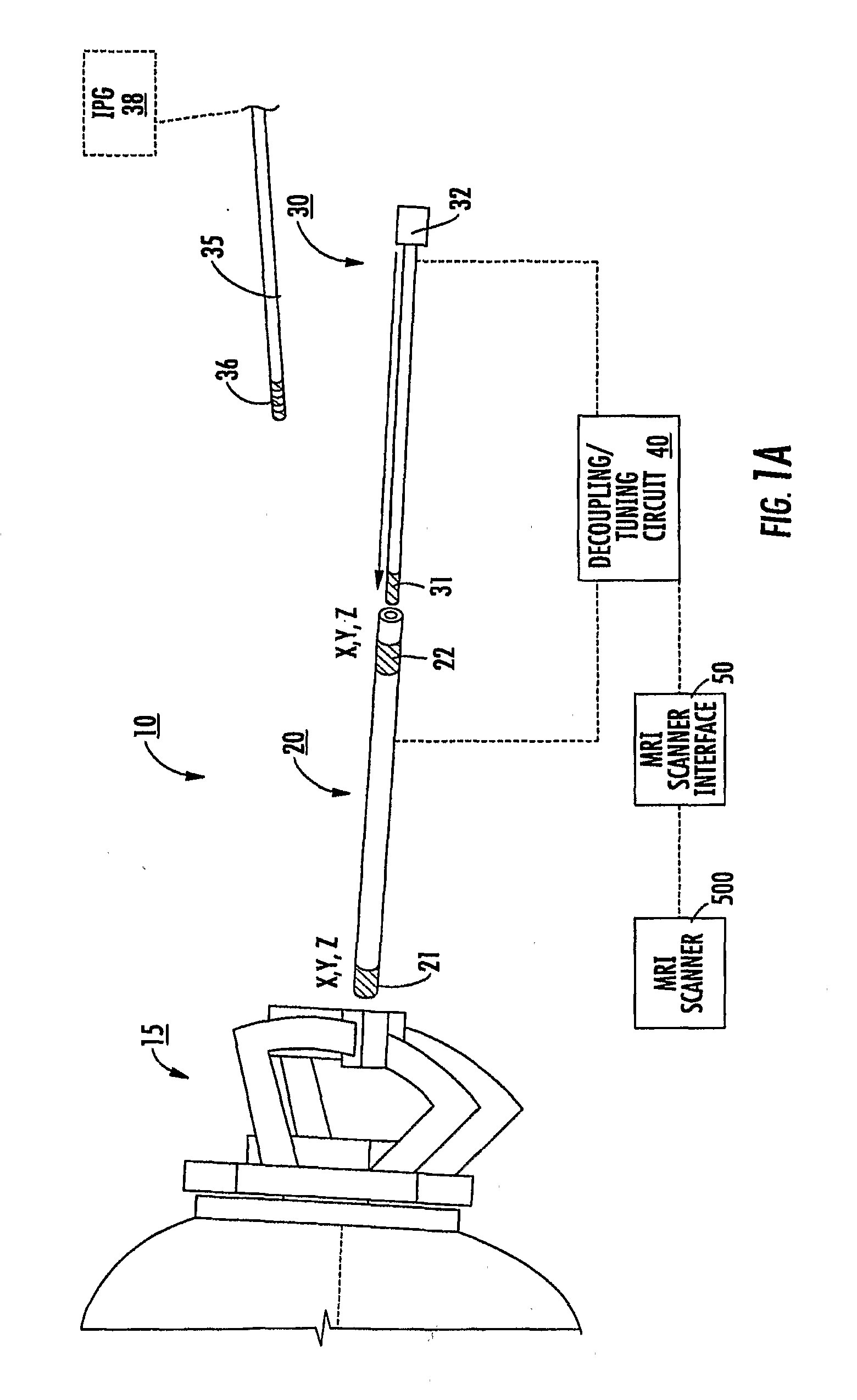
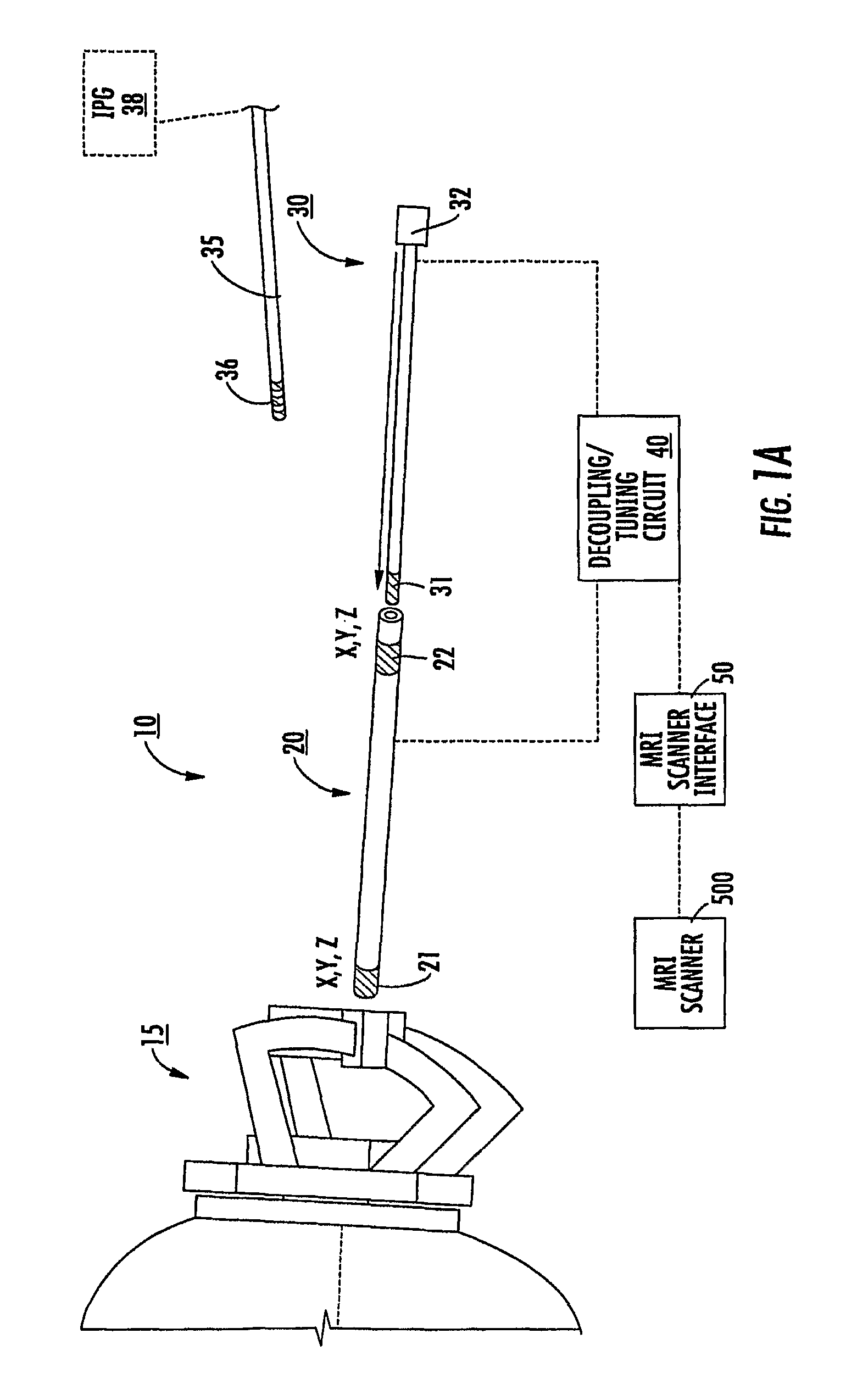
Mri-guided localization and/or lead placement systems, related methods, devices and computer program products
MRI compatible localization and / or guidance systems for facilitating placement of an interventional therapy and / or device in vivo include: (a) a mount adapted for fixation to a patient; (b) a targeting cannula with a lumen configured to attach to the mount so as to be able to controllably translate in at least three dimensions; and (c) an elongate probe configured to snugly slidably advance and retract in the targeting cannula lumen, the elongate probe comprising at least one of a stimulation or recording electrode. In operation, the targeting cannula can be aligned with a first trajectory and positionally adjusted to provide a desired internal access path to a target location with a corresponding trajectory for the elongate probe. Automated systems for determining an MR scan plane associated with a trajectory and for determining mount adjustments are also described.
Owner:CLEARPOINT NEURO INC
Computed tomographic scanner using rastered x-ray tubes
ActiveUS7233644B1Reduce coolingReduced Power RequirementsRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusComputing tomographyComputed tomography scanner
A high speed computed tomography x-ray scanner using a plurality of x-ray generators. Each x-ray generator is scanned along a source path that is a segment of the scanner's source path such that each point in the source path is scanned by at least one tube. X-ray generators and detectors can be arranged in different scan planes depending on the available hardware so that a complete and near planar scan of a moving object can be assembled and reconstructed into an image of the object.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
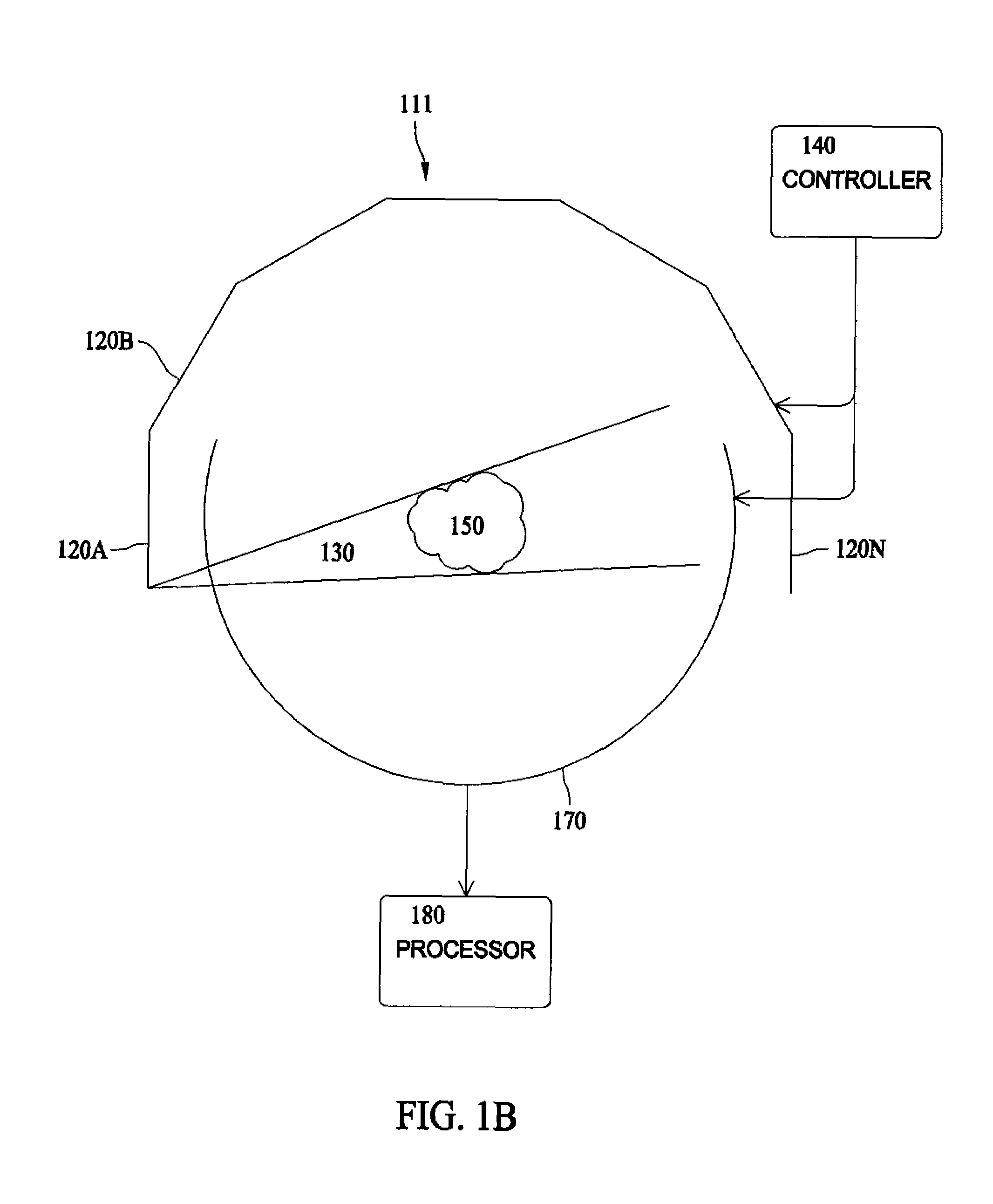
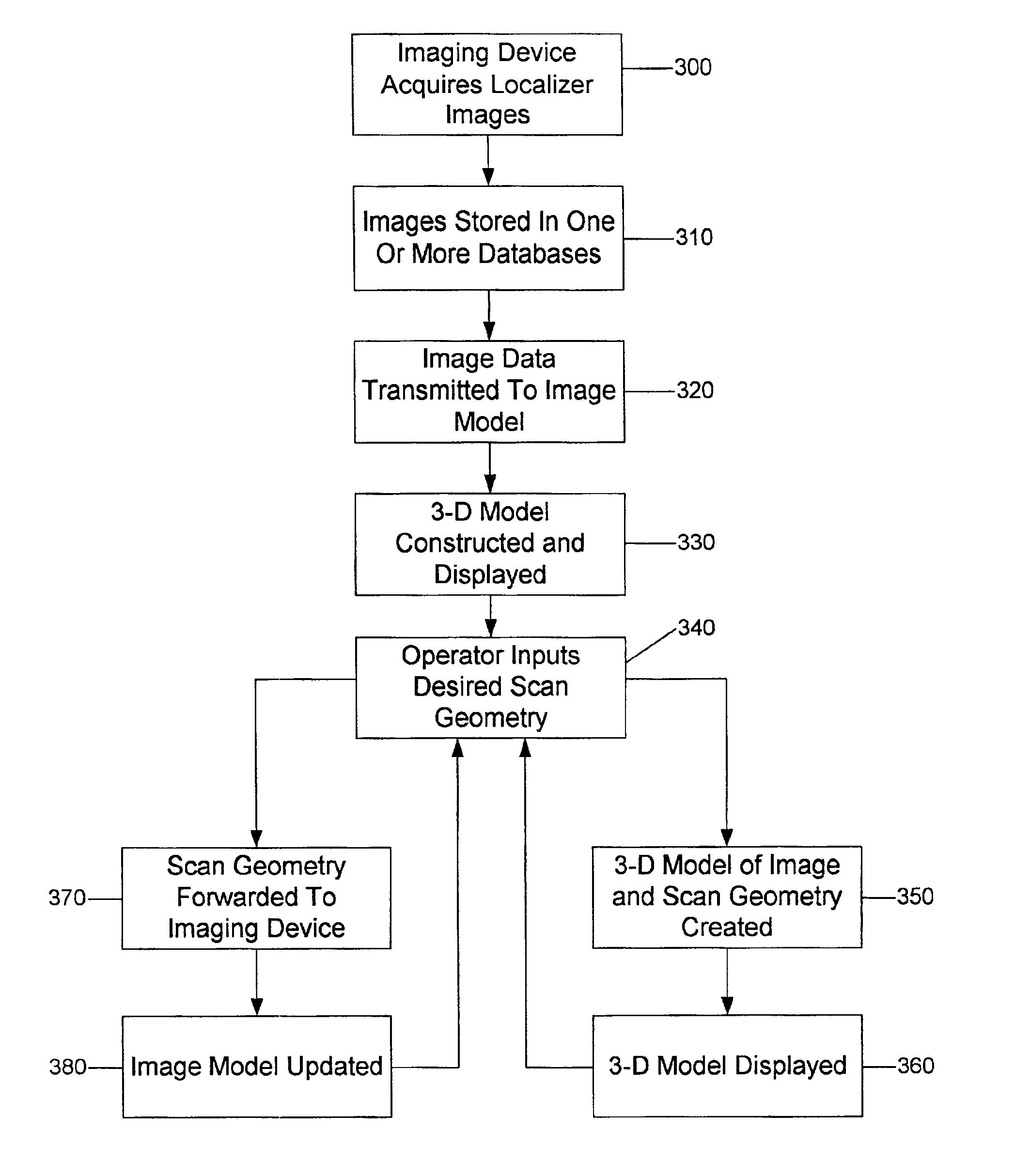
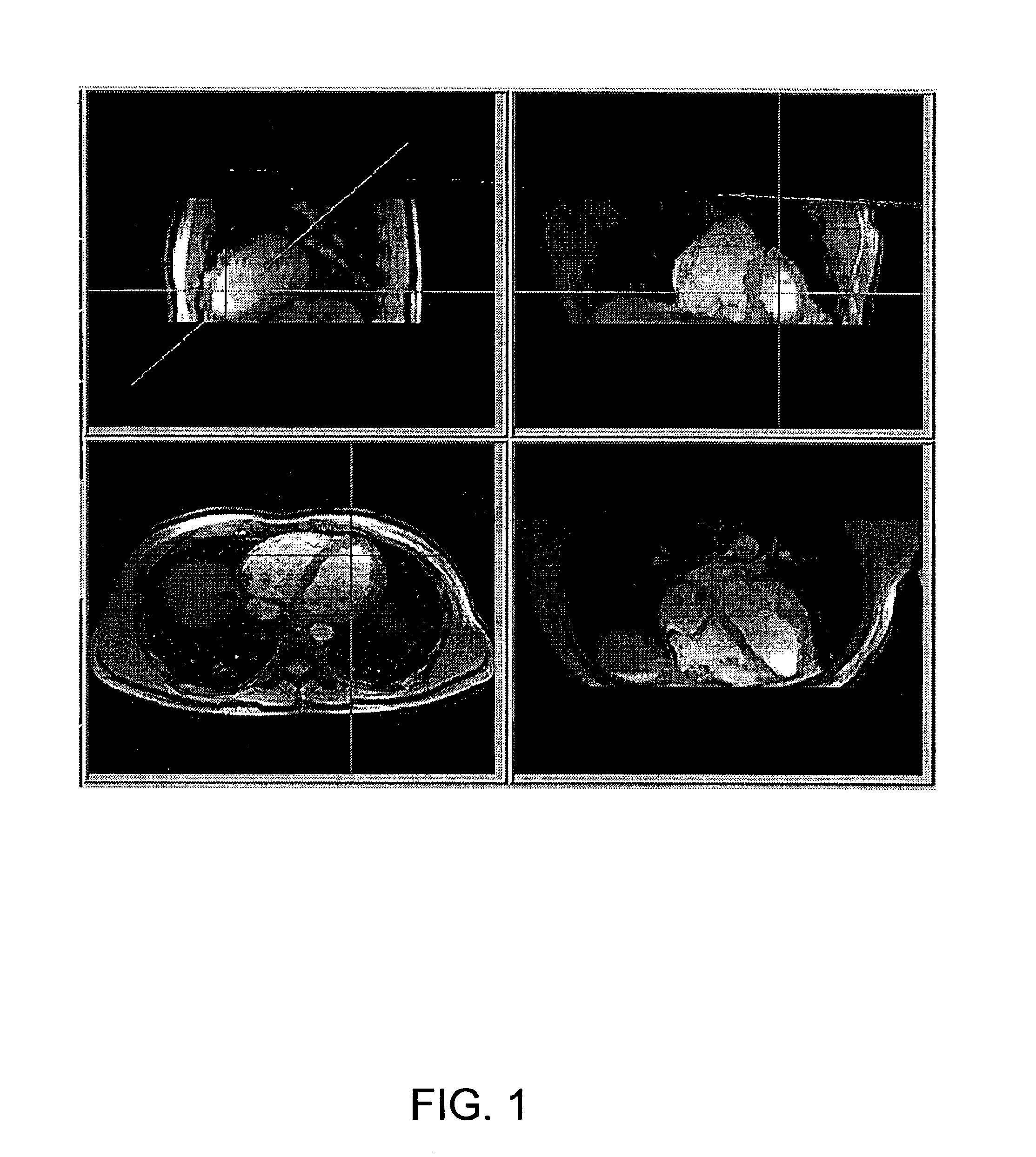
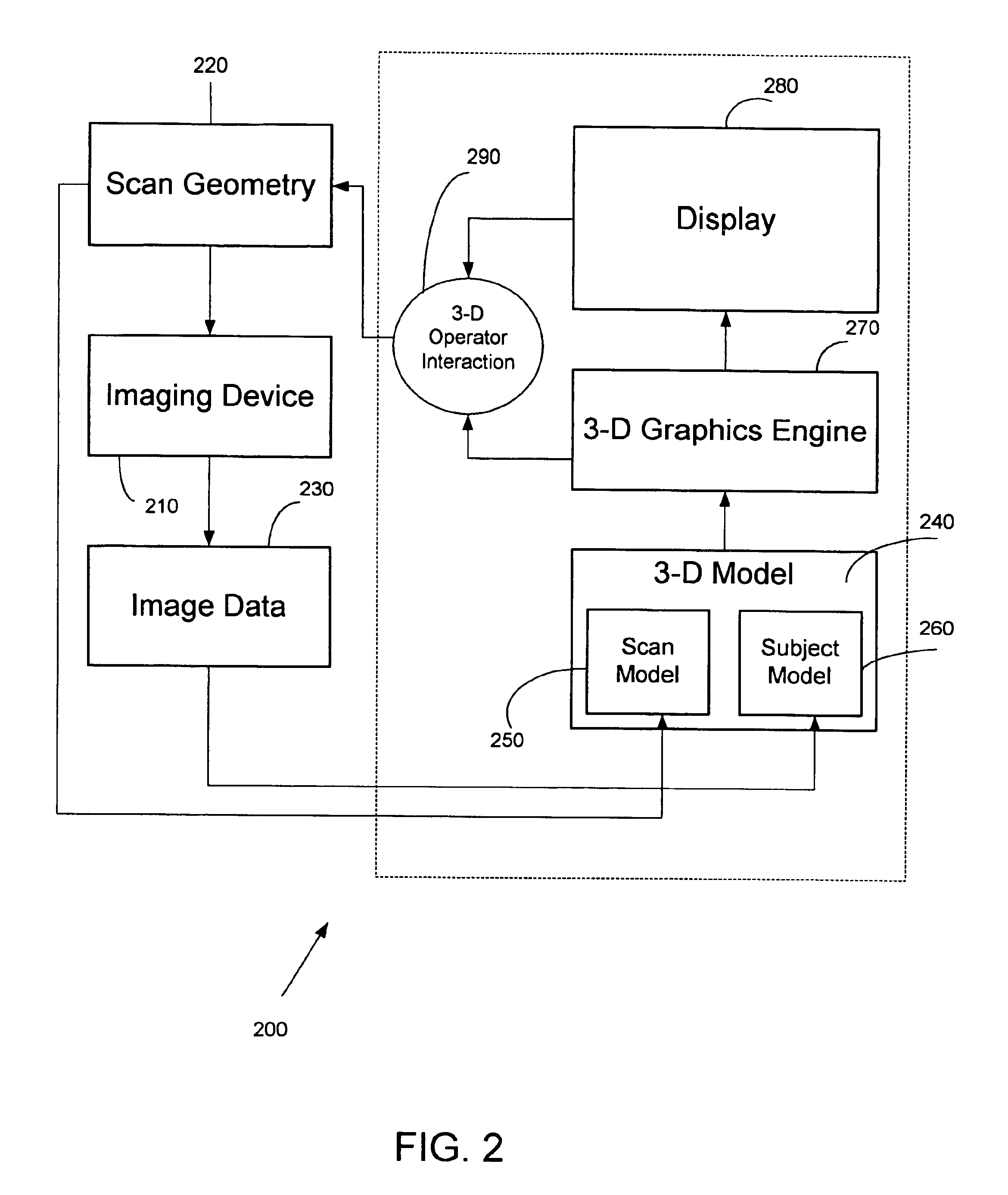
Systems, methods and computer program products for the display and visually driven definition of tomographic image planes in three-dimensional space
InactiveUS6898302B1Easy and more comprehensive understandingEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionImage generationDisplay deviceData acquisition
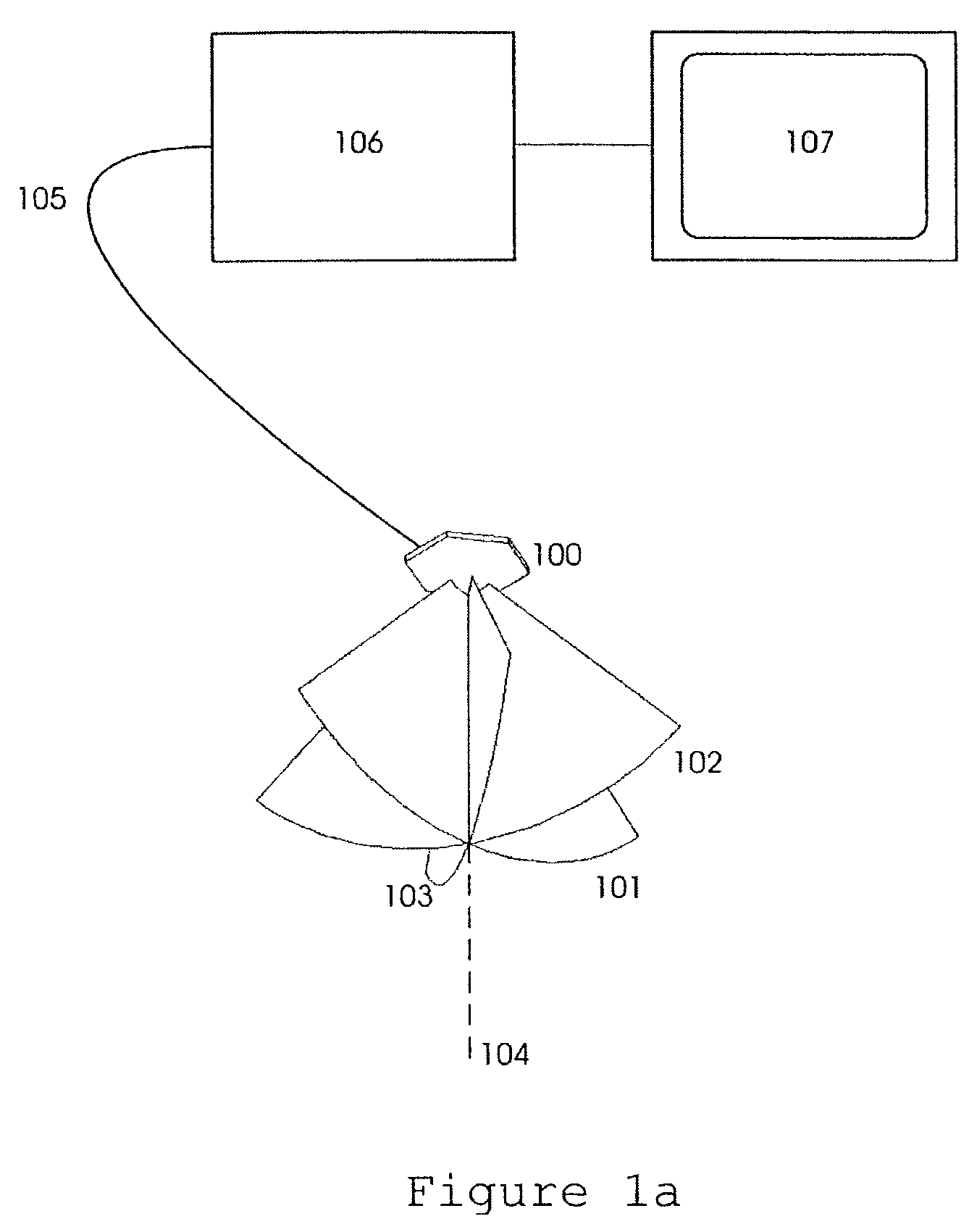
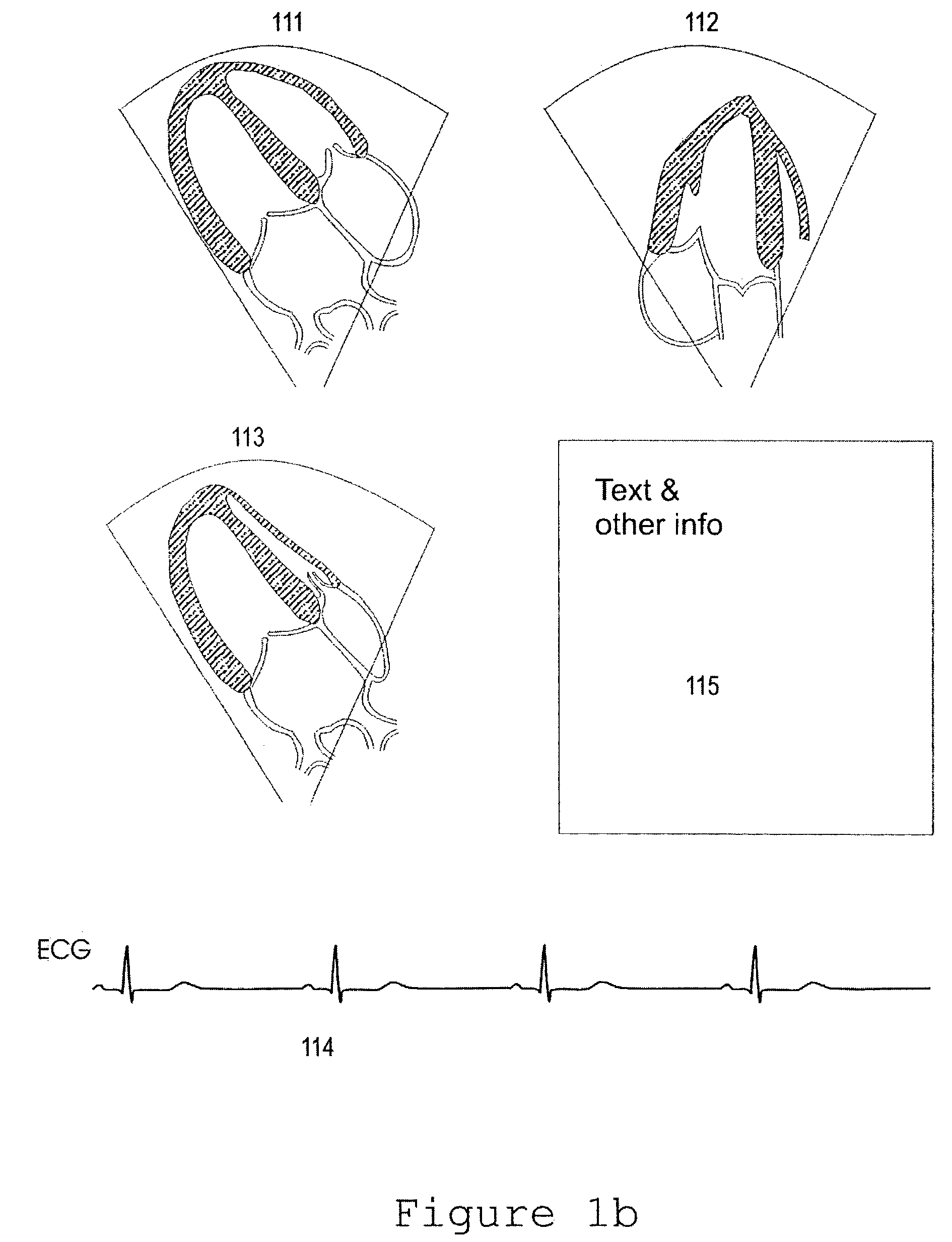
Apparatuses, methods and computer program products for scan plane geometry definition in tomographic data acquisition via an interactive three-dimensional (3-D) graphical operator interface. The apparatuses, methods and computer program products are initially proposed for use in cardiac MRI, but have a much broader area of application. The apparatuses and methods utilize 3-D computer graphics aspect views of slice planes to show a new scan, represented as semi-transparent uniformly-colored planes. Intersections of these planes with opaque texture-mapped gray-level views of previously acquired images enable the orientation of a new scan to be viewed in a much more intuitive fashion. Advantageously, the apparatuses and methods of the present invention provide for more efficient elimination of positional ambiguity that is often associated with conventional 2-D intersection line views. In addition, any misregistration between localizer scans can be detected immediately in the integrated 3-D display by misalignment of anatomy in the previously acquires image planes.
Owner:UNIV EMORY
Lateral-scanning interferometer with tilted optical axis
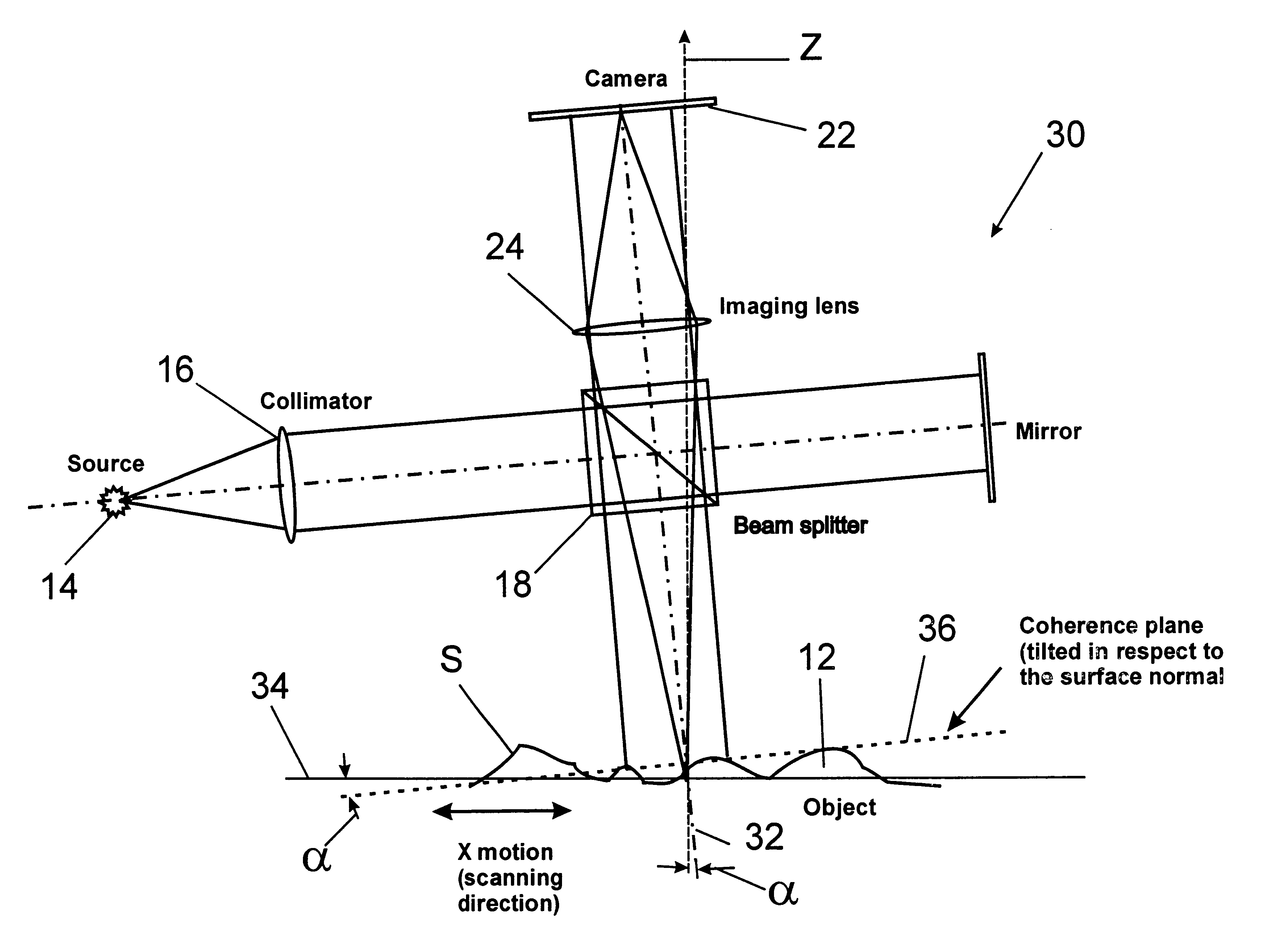
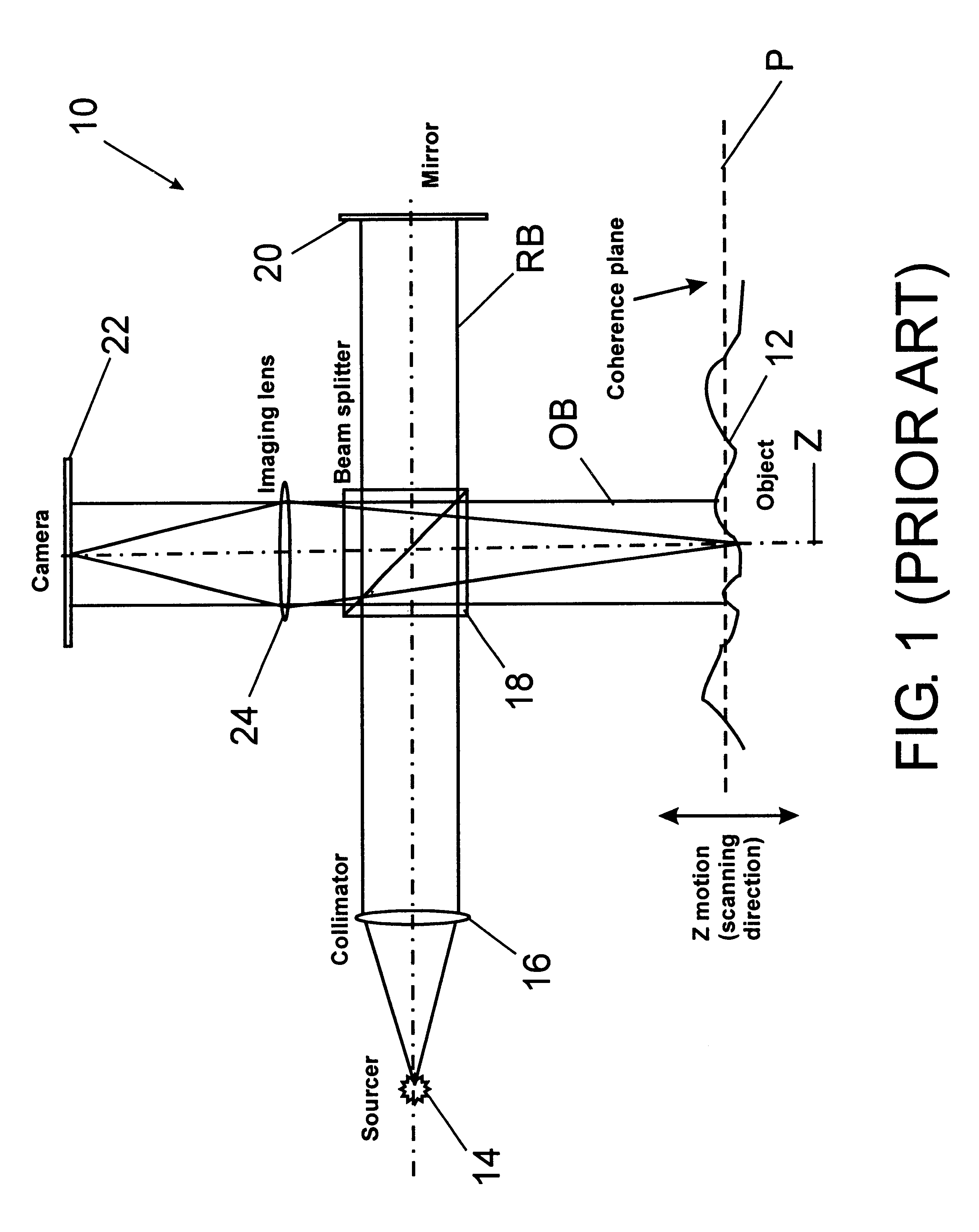
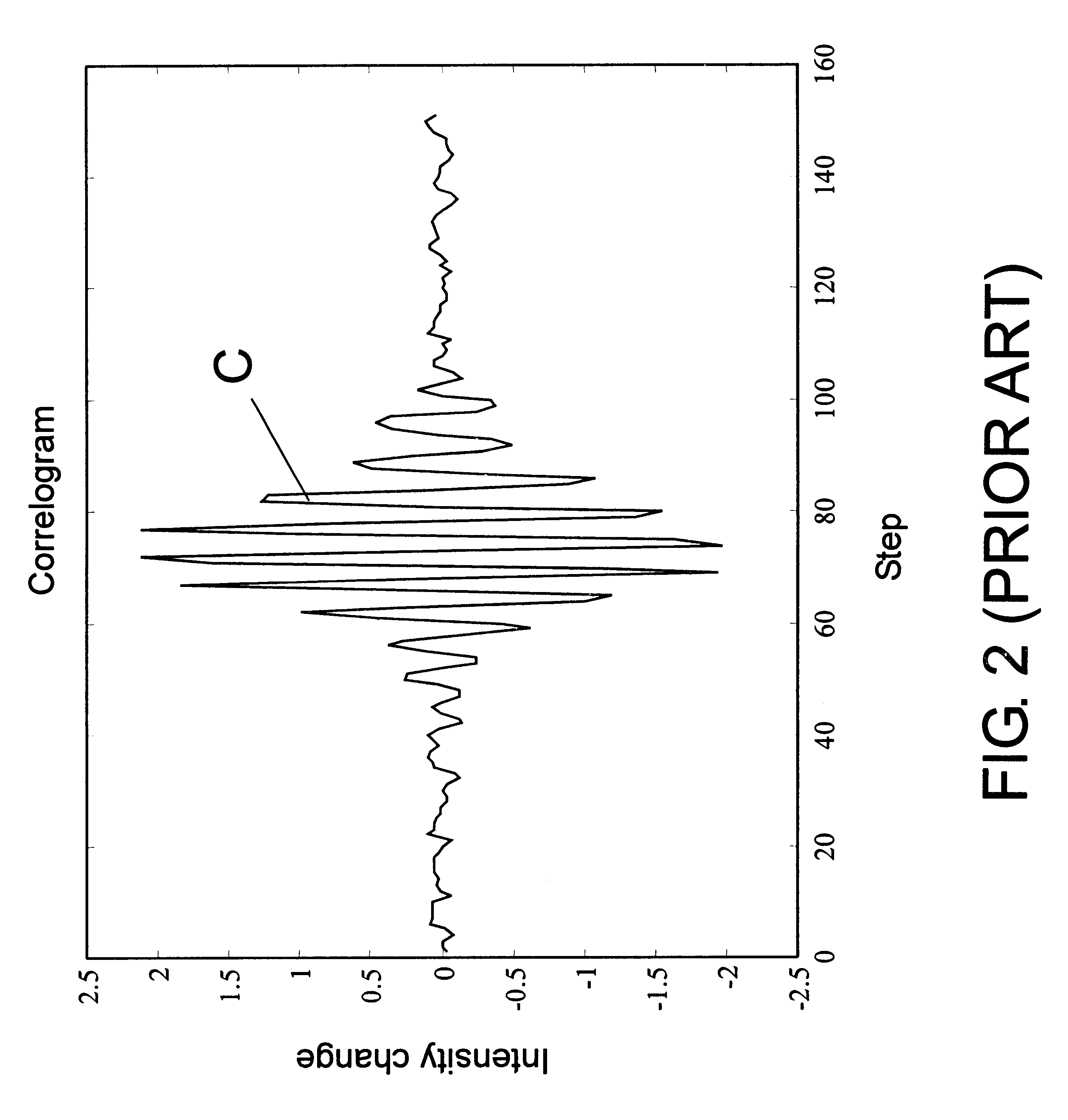
An interferometer scans the sample surface laterally with respect to the optical axis of the interferometric objective. The objective is tilted, so that the sample surface is placed at an angle with respect to the maximum coherence plane of the instrument. By moving the sample stage laterally, at an angle, through a point at a set distance from the objective on the objective's optical axis, rather than vertically along the optical axis, different parts of the object intersect the maximum coherence plane at different times as the surface passes through the coherence plane, the precise time depending on the profile of the surface. When the OPD of a point on the object's surface is greater than the coherence length of the light source, the intensity of light reflected from this point does not produce interference fringes. Therefore, the intensity registered by the detector is approximately constant. However, when the object point enters the zone of coherence, the interference effects modulate the intensity the same way as in a regular VSI procedure. As the object moves along the scanning direction, it also has a relative vertical speed with respect to the objective because of the tilt of the objective's optical axis with respect to the scanning plane; therefore, the lateral scanning motion produces an OPD variation as the vertical scan in a conventional system. As a result, light intensity data are acquired continuously as the test surface is scanned, thus elimination the need for stitching multiple sub-sets of data.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
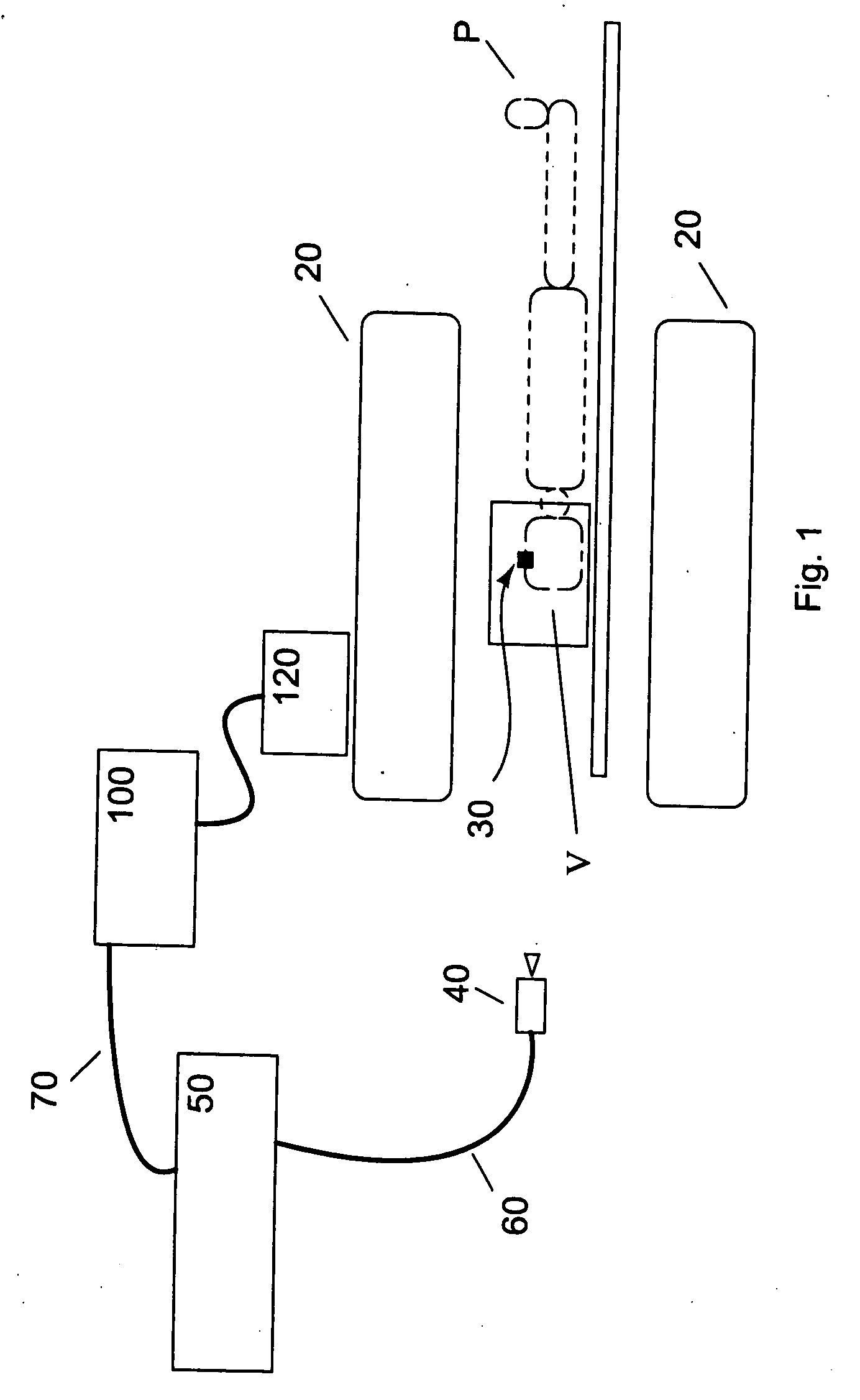
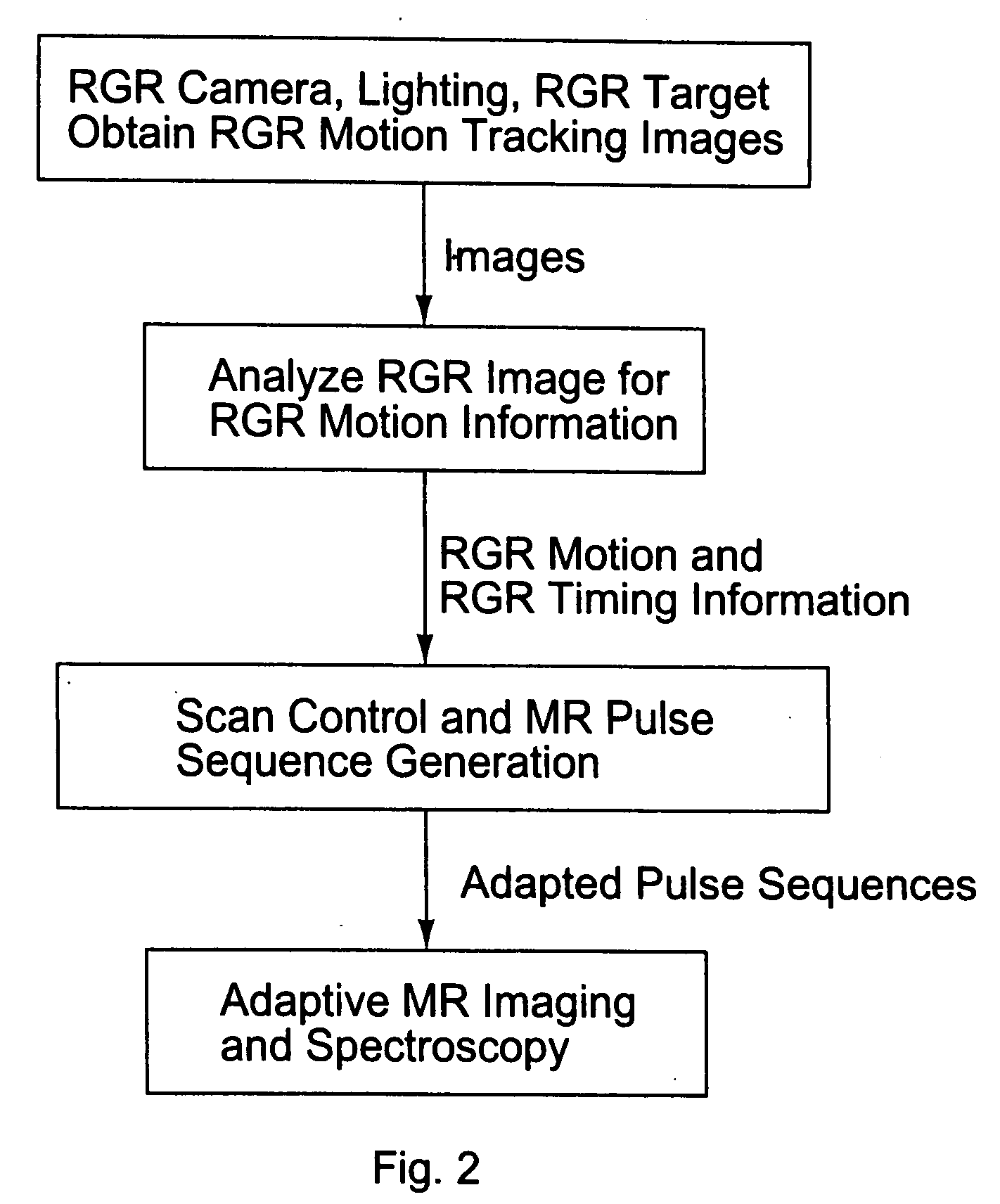
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070280508A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingUsability
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
Voltage contrast test structure
InactiveUS7217579B2Increase speedNo wasteMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectricityVoltage contrast
A method for electrically testing a semiconductor wafer during integrated-circuit fabrication process, the method including: (i) providing a scanning charged-particle microscope (SCPM), having a defined scanning plane and operative, while in any one mechanical state, to scan a surface in the scanning plane within a two-dimensional scanning window, which has a given maximum size; (ii) providing in association with any layer of the wafer, it being a test layer, one or more test structures, each test structure including normally conductive areas within a normally non-conductive background in one or more layers, which include said test layer, the conductive areas formed as one or more patterns; the patterns in said test layer include one or more clusters of mutually isolated pads; each pad is conductively connected with a corresponding distinct point on the patterns and all the pads in any one cluster are sized and arranged so that at least a significant portion of each pad falls within a common window whose size does not exceed said maximum size of said scanning window; (iii) with said test layer forming the top surface of the wafer, placing the wafer on the SCPM and adjusting the mechanical state of the SCPM so that at least a significant portion of each pad in any one of said clusters is within said scanning window; (iv) causing the SCPM, while in said mechanical state, to scan all of the pads of said one cluster and thereby to provide information about the electrical state of the respective test structure.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
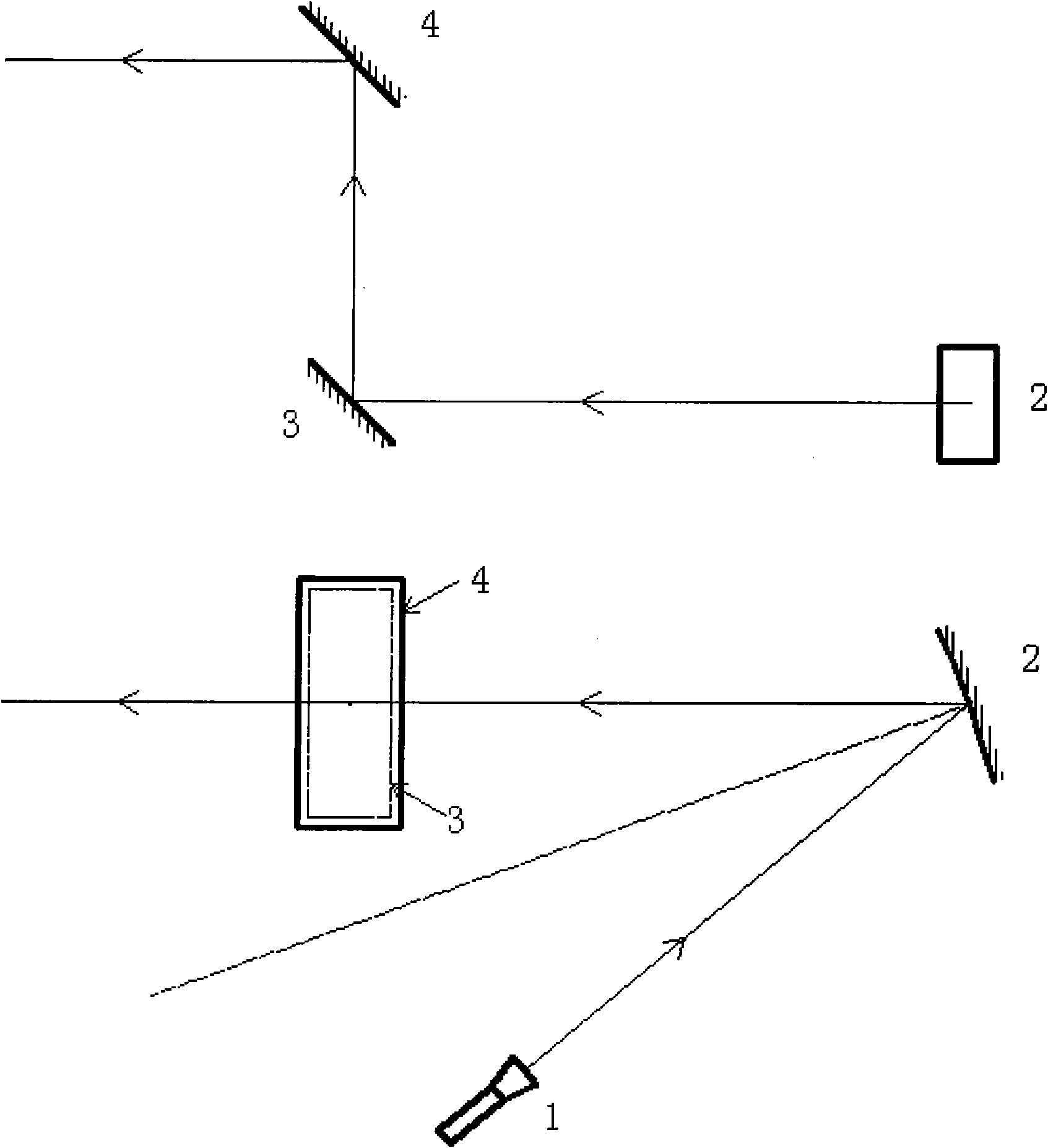
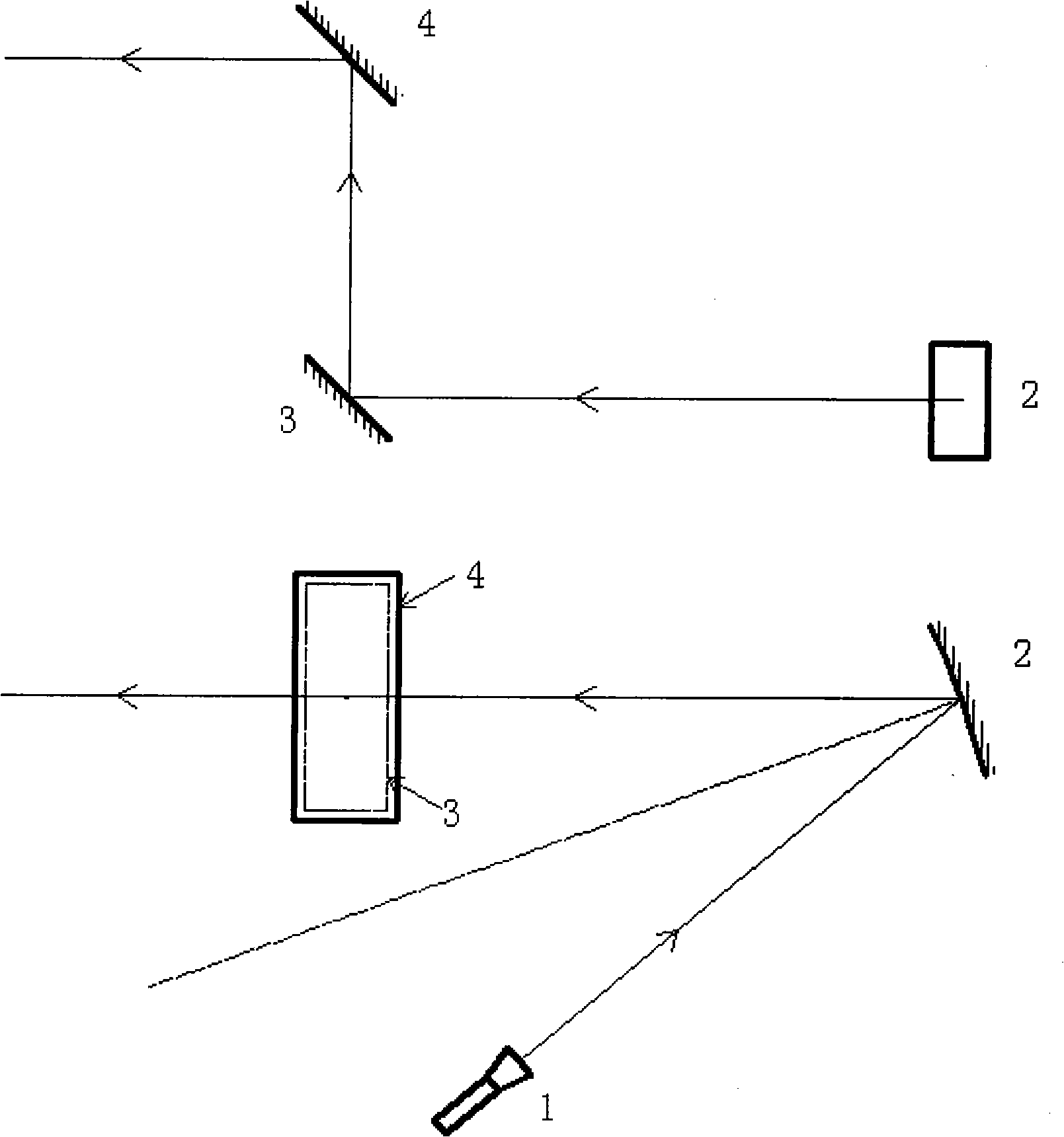
Calibration method of correlation between single line laser radar and CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera
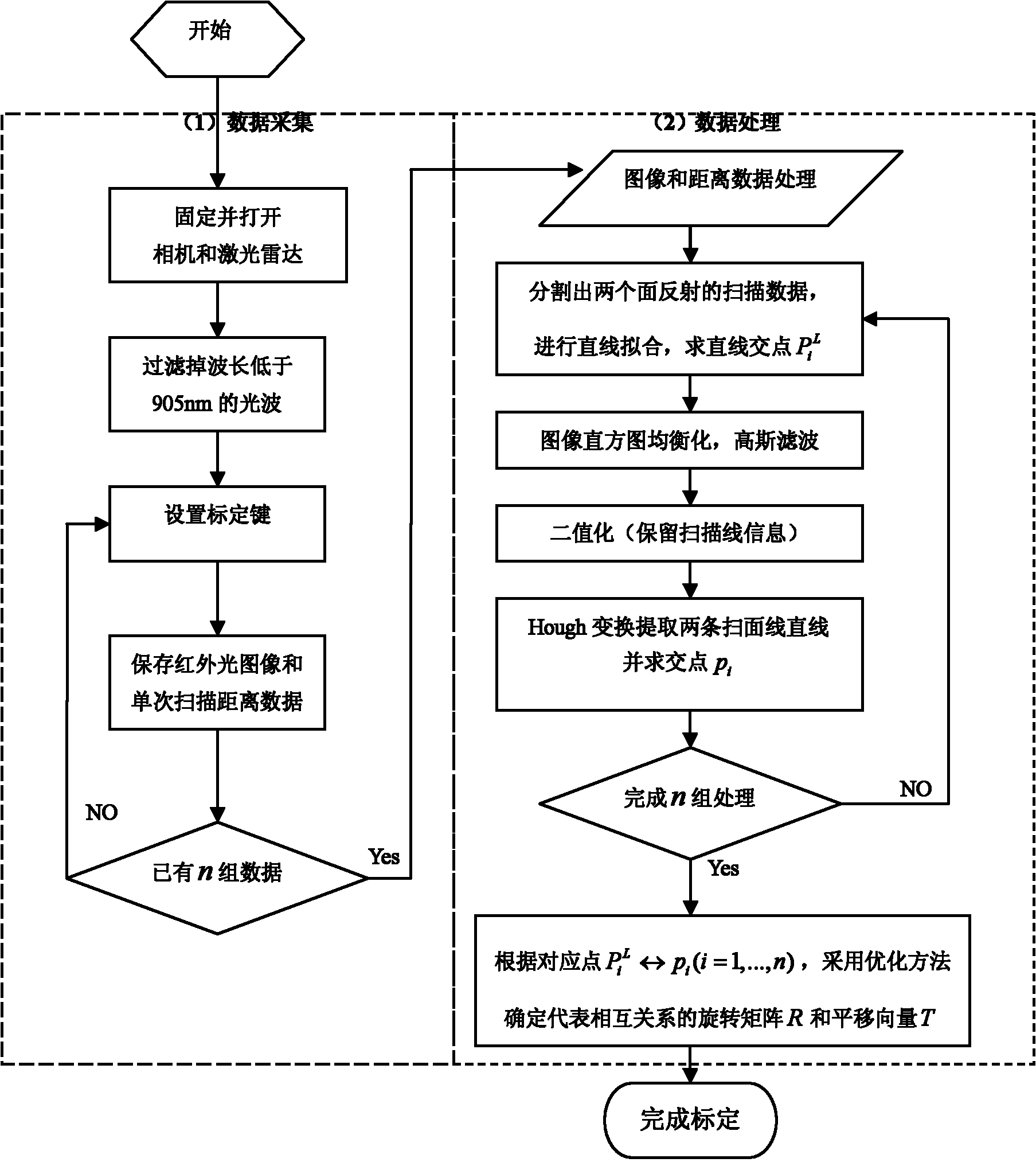
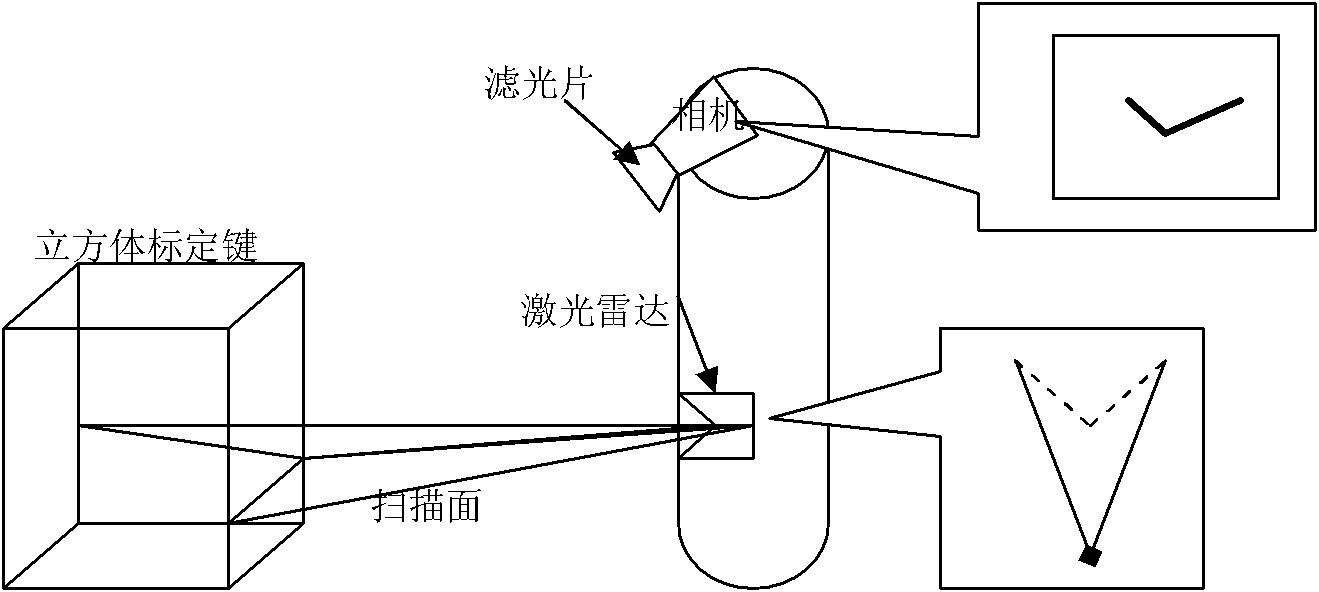
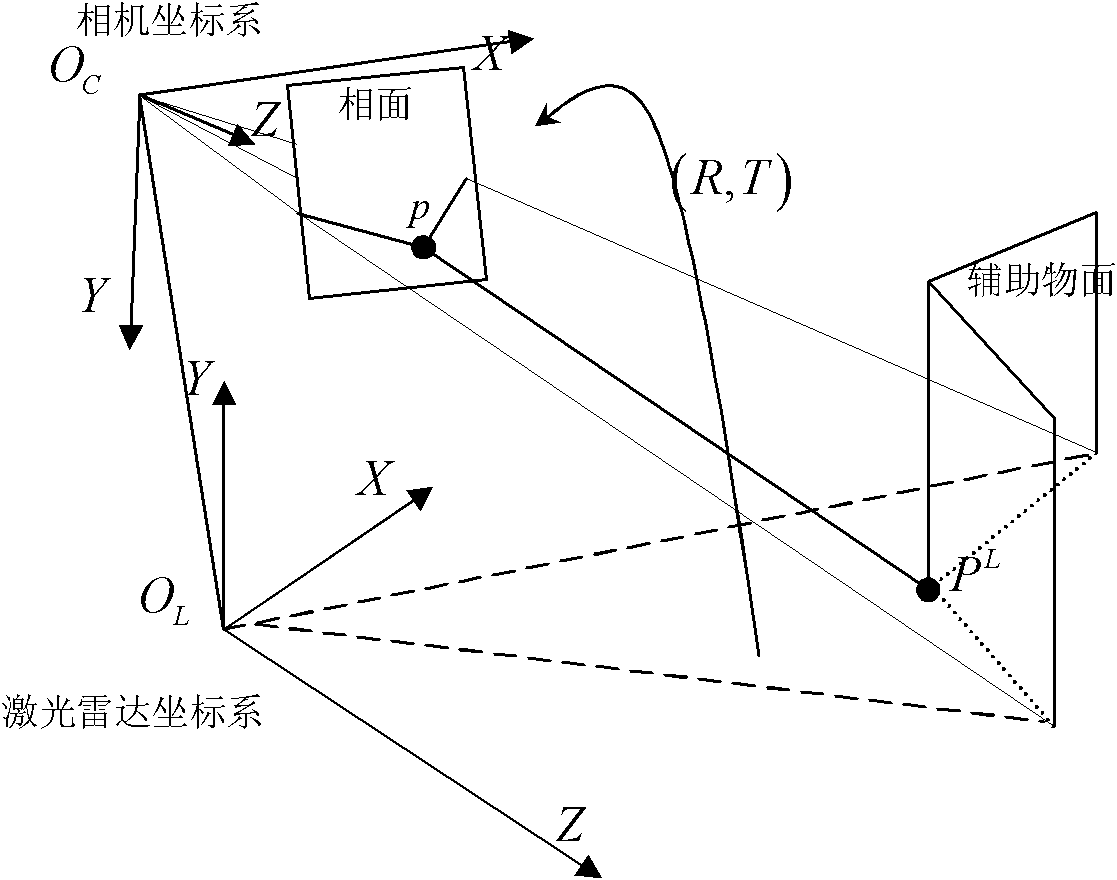
InactiveCN101882313AEasy to makeEasy to buyImage analysisElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser scanningIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a calibration method of correlation between a single line laser radar and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, which is based on the condition that the CCD camera can carry out weak imaging on an infrared light source used by the single line laser radar. The calibration method comprises the steps of: firstly, extracting a virtual control point in a scanning plane under the assistance of a cubic calibration key; and then filtering visible light by using an infrared filter to image infrared light only, carrying out enhancement, binarization treatment and Hough transformation on an infrared image with scanning line information, and extracting two laser scanning lines, wherein the intersection point of the two scanning lines is the image coordinate of the virtual control point in the image. After acquiring multiple groups of corresponding points through the steps, a correlation parameter between the laser radar and the camera can be solved by adopting an optimization method for minimizing a reprojection error. Because the invention acquires the information of the corresponding points directly, the calibration process becomes simpler and the precision is greatly improved with a calibrated angle error smaller than 0.3 degree and a position error smaller than 0.5cm.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
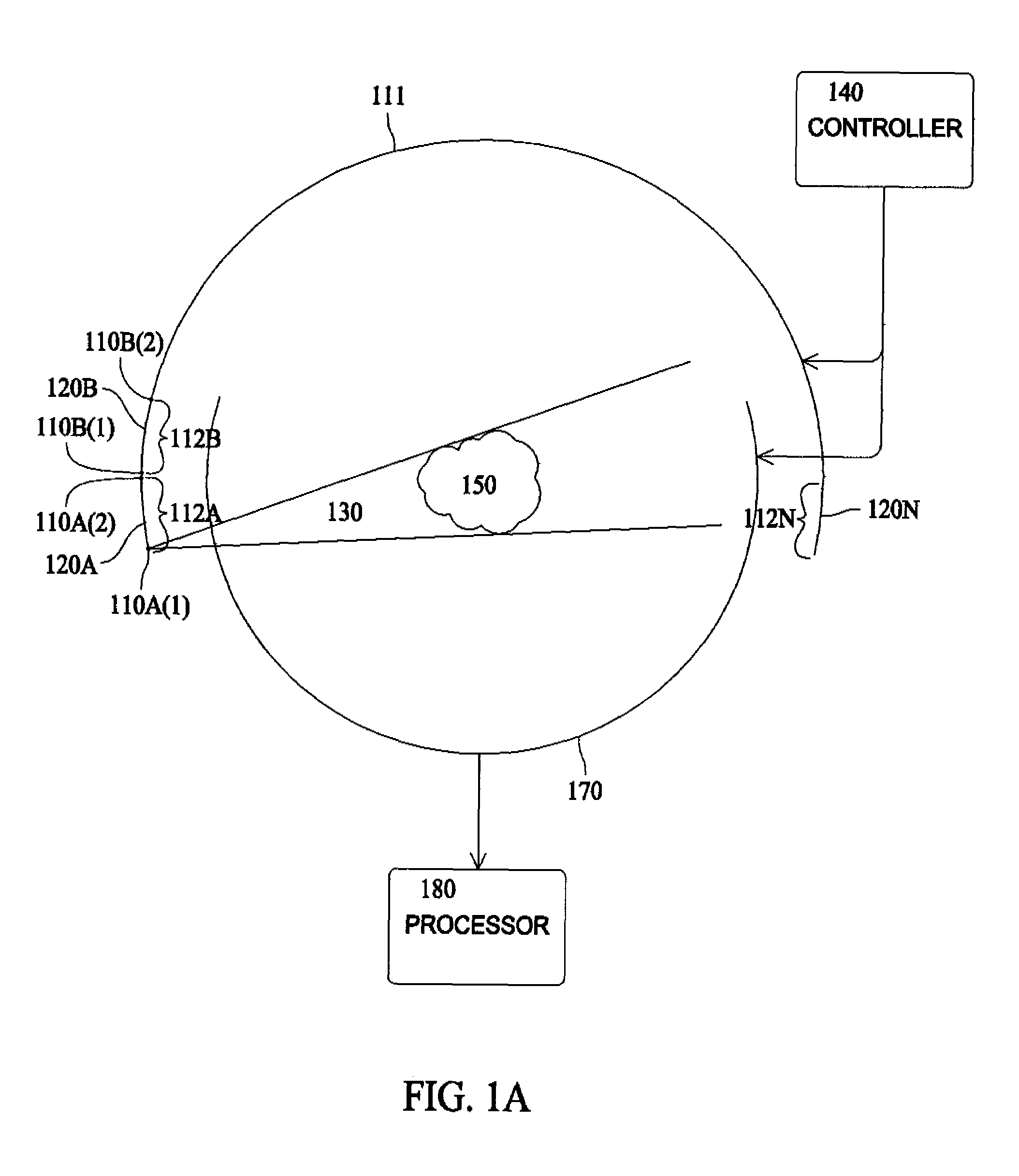
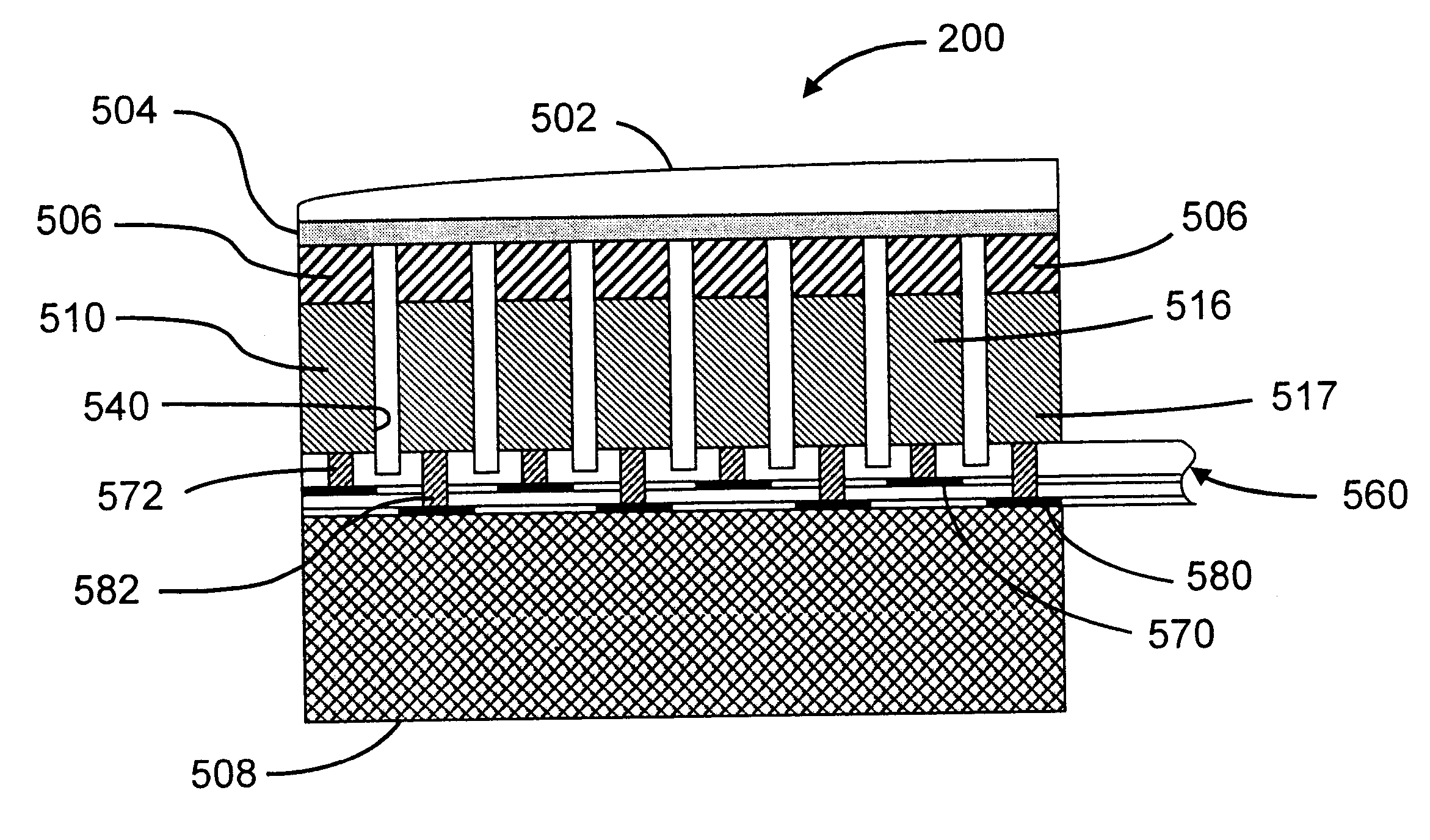
Ultrasound imaging with acquisition of imaging data in perpendicular scan planes
InactiveUS6537220B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasonic imaging array has two independent, interleaved linear subarrays occupying a common array face. The subarrays are independently steerable and focusable in different imaging planes. The subelements making up the elements in of the subarrays is preferably quadrilateral. Adjacent subelements in each element are electrically connected via an interconnect portion such that the interconnect portion connecting each pair of adjacent subelements in each element is substantially linear and is aligned with the diagonals of the adjacent subelements. A preferred acoustic lens is curved in both azimuth and elevation directions, whereby the subarrays are independently focusable. By transmitting in one plane and simultaneously receiving in a different, orthogonal plane, a system including the array can image a 3-D region of interest (ROI). In a volumetric embodiment of the invention two orthogonal B-mode images of a structure within the ROI are displayed simultaneously. The user may then trace the outlines of the images and the system therefrom calculates the volume of the structure.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
MRI-guided localization and/or lead placement systems, related methods, devices and computer program products
MRI compatible localization and / or guidance systems for facilitating placement of an interventional therapy and / or device in vivo include: (a) a mount adapted for fixation to a patient; (b) a targeting cannula with a lumen configured to attach to the mount so as to be able to controllably translate in at least three dimensions; and (c) an elongate probe configured to snugly slidably advance and retract in the targeting cannula lumen, the elongate probe comprising at least one of a stimulation or recording electrode. In operation, the targeting cannula can be aligned with a first trajectory and positionally adjusted to provide a desired internal access path to a target location with a corresponding trajectory for the elongate probe. Automated systems for determining an MR scan plane associated with a trajectory and for determining mount adjustments are also described.
Owner:CLEARPOINT NEURO INC
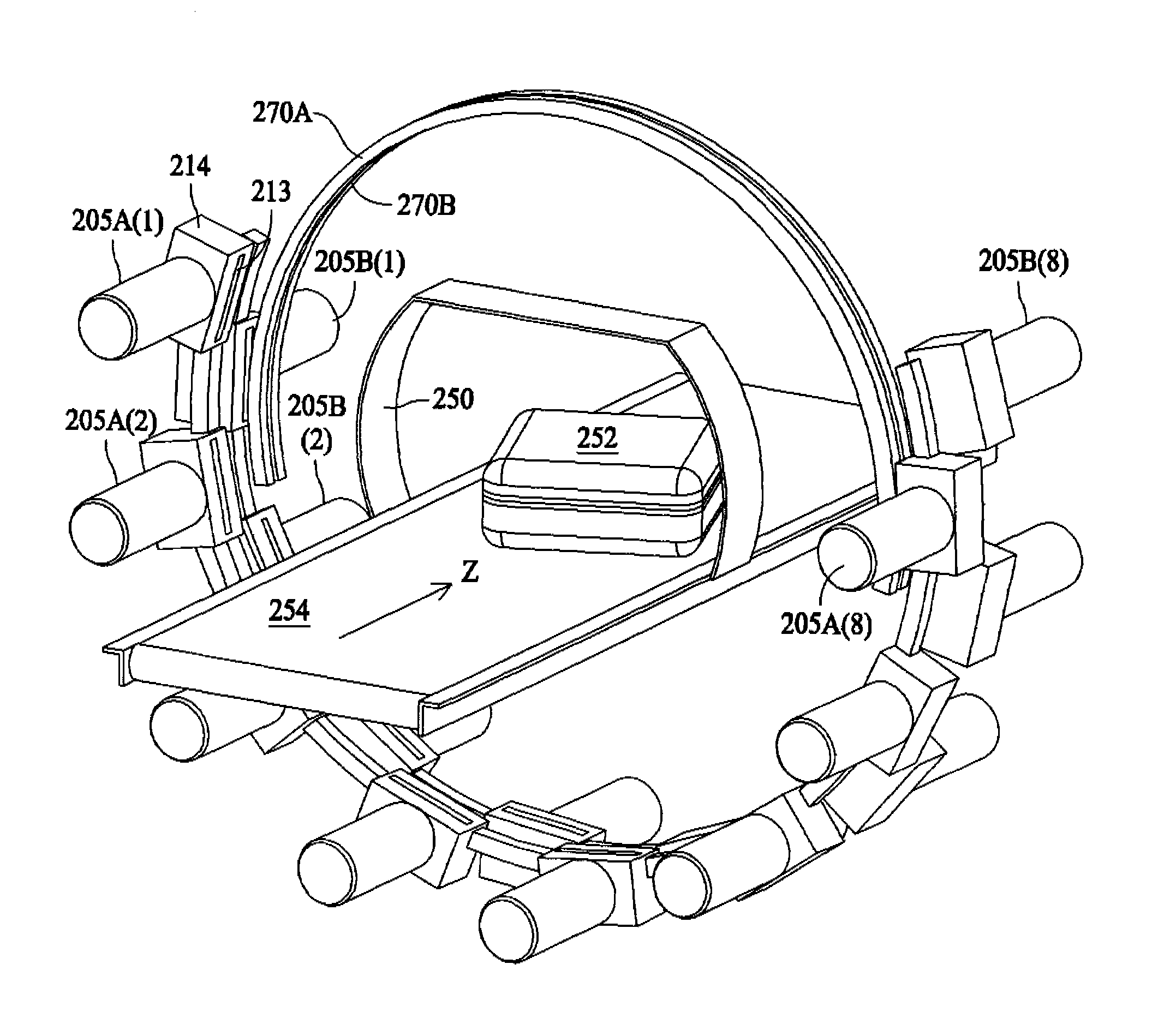
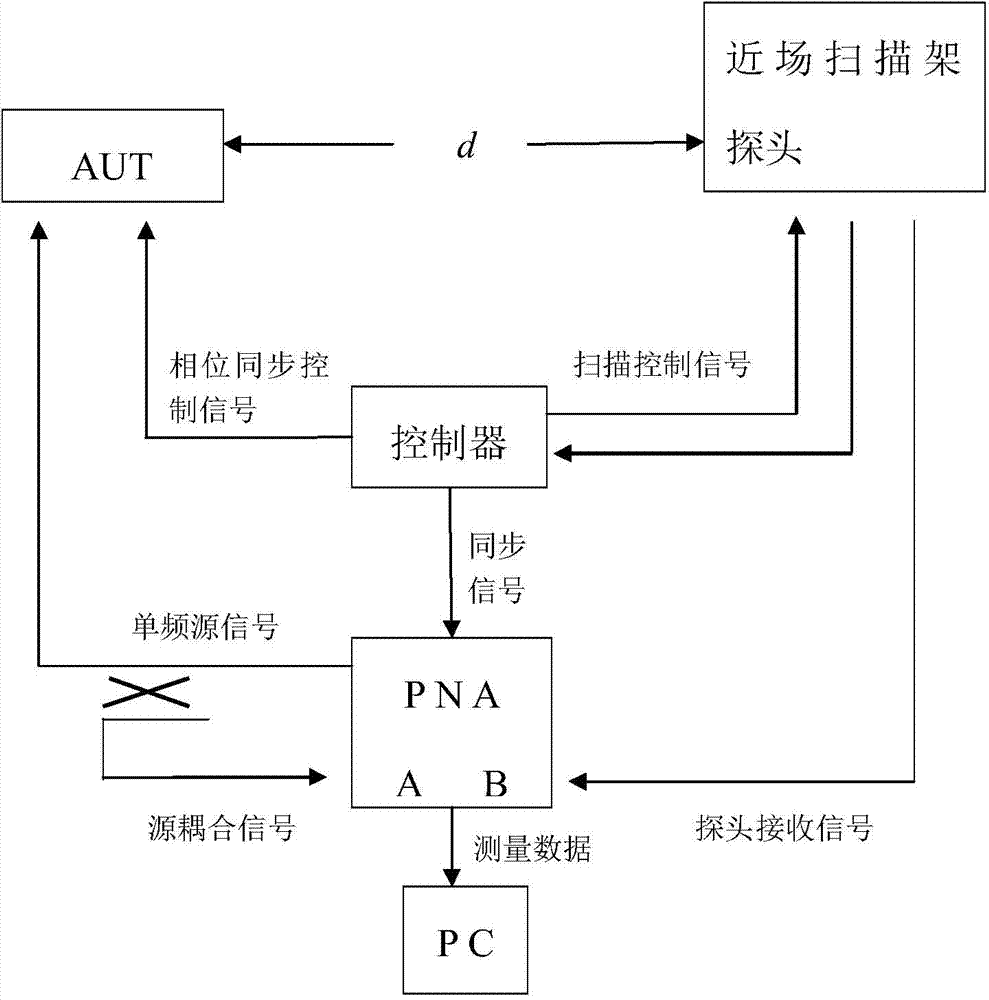
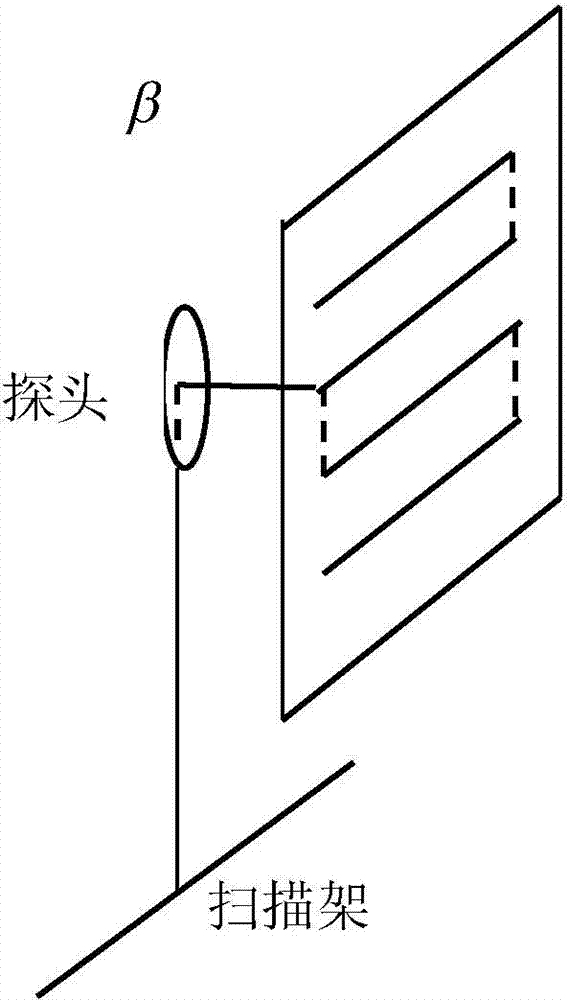
Phased array antenna unit characteristic near-field measurement method
ActiveCN103926474AEliminate coupling interferenceSolve the technical problem of coupling interferenceAntenna radiation diagramsMeasurement pointArray element
The invention provides a phased array antenna unit characteristic near-field measurement method. The near-field measurement method can measure directional diagrams and opening surface near fields of independent units when all the units work at the same time. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps of selecting a measured phased array antenna AUT, and using a vector network analysis meter PNA connected with a PC and a controller and a near-field scanning frame probe respectively connected with the PNA and the controller to form a near-field measuring system for detecting the antenna unit amplitude phase characteristics. The AUT is used as a transmitting antenna, the probe is used as a receiving antenna, and the scanning frame probe is arranged in front of the opening face of a measuring antenna. Devices are connected according to a near-field measuring method, when the magnitude-phase characteristic am of the mth unit of the phased-array antenna is measured, a vector average method is adopted by each measuring point in a near-field scanning plane, a T / R component, an array element and the magnitude-phase characteristic H m<n>=a<m> S m<n>, n=1,...N from the array element to a measuring point space link assembly of the mth unit are measured and calculated, and the magnitude-phase characteristic am of the phased-array measuring unit is calculated.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
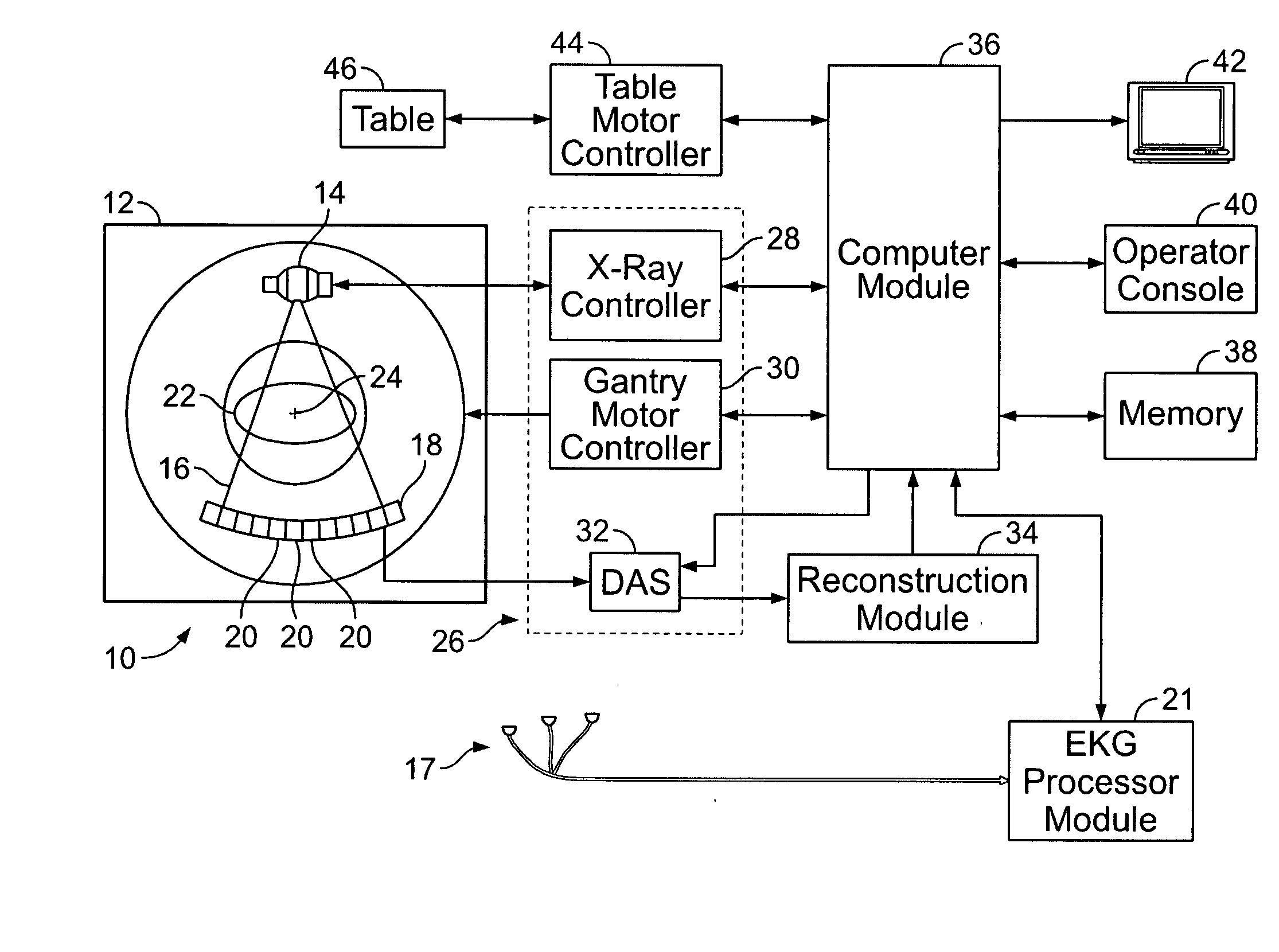
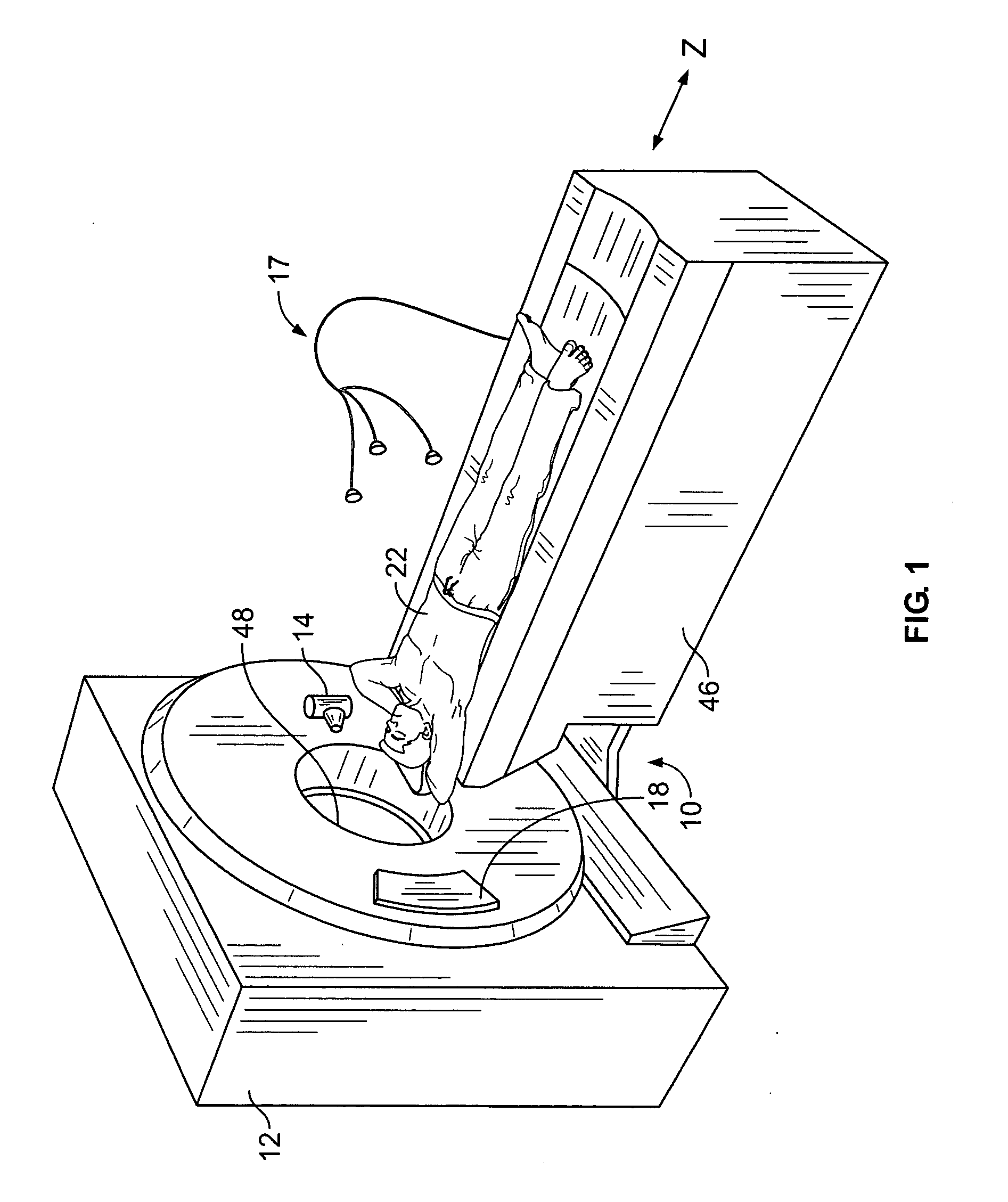
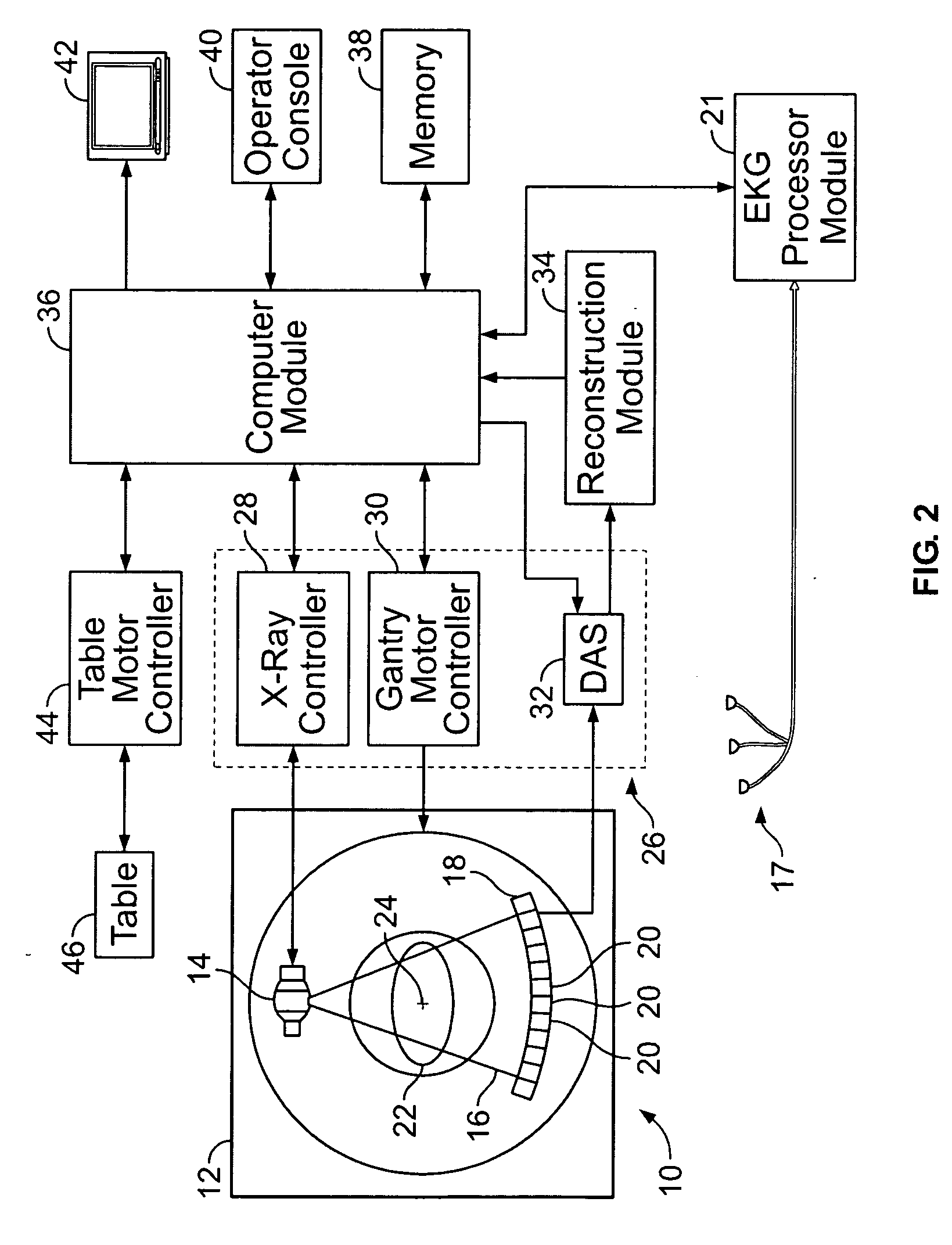
Method and system for performing CT image reconstruction with motion artifact correction
InactiveUS20070116171A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationData set
In one embodiment, a method is provided for performing computed tomography (CT) imaging. The method includes obtaining EKG gating information from an object and obtaining attenuation measurements from the object utilizing a detector that is rotated in a scan plane around the object. The method further includes performing a first reconstruction based on a first portion of the attenuation measurements that are collected by a first region of the detector, where the first reconstruction is performed independent of the EKG gating information to obtain a first reconstruction data set. A second reconstruction is performed based on a second port of the attenuation measurements that are collected by a second region of the detector, where the second reconstruction is performed based on the EKG gating information to obtain a second reconstruction data set.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
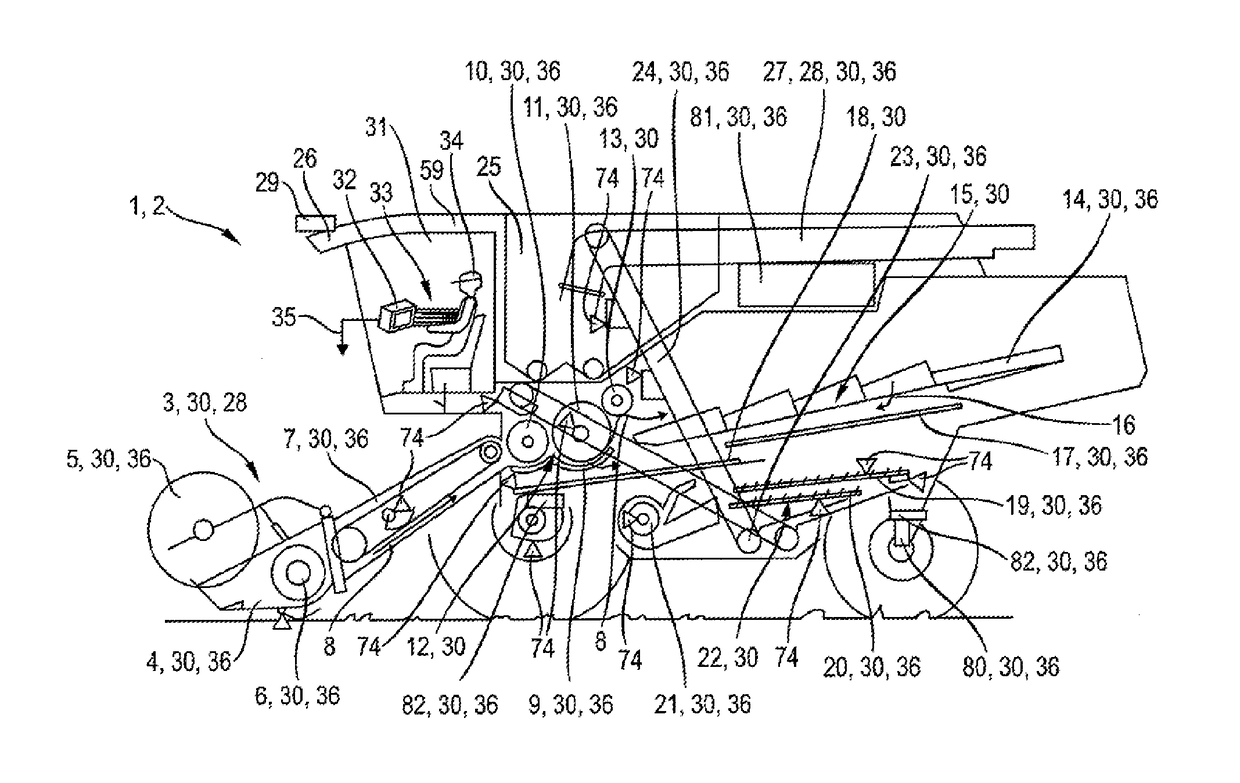
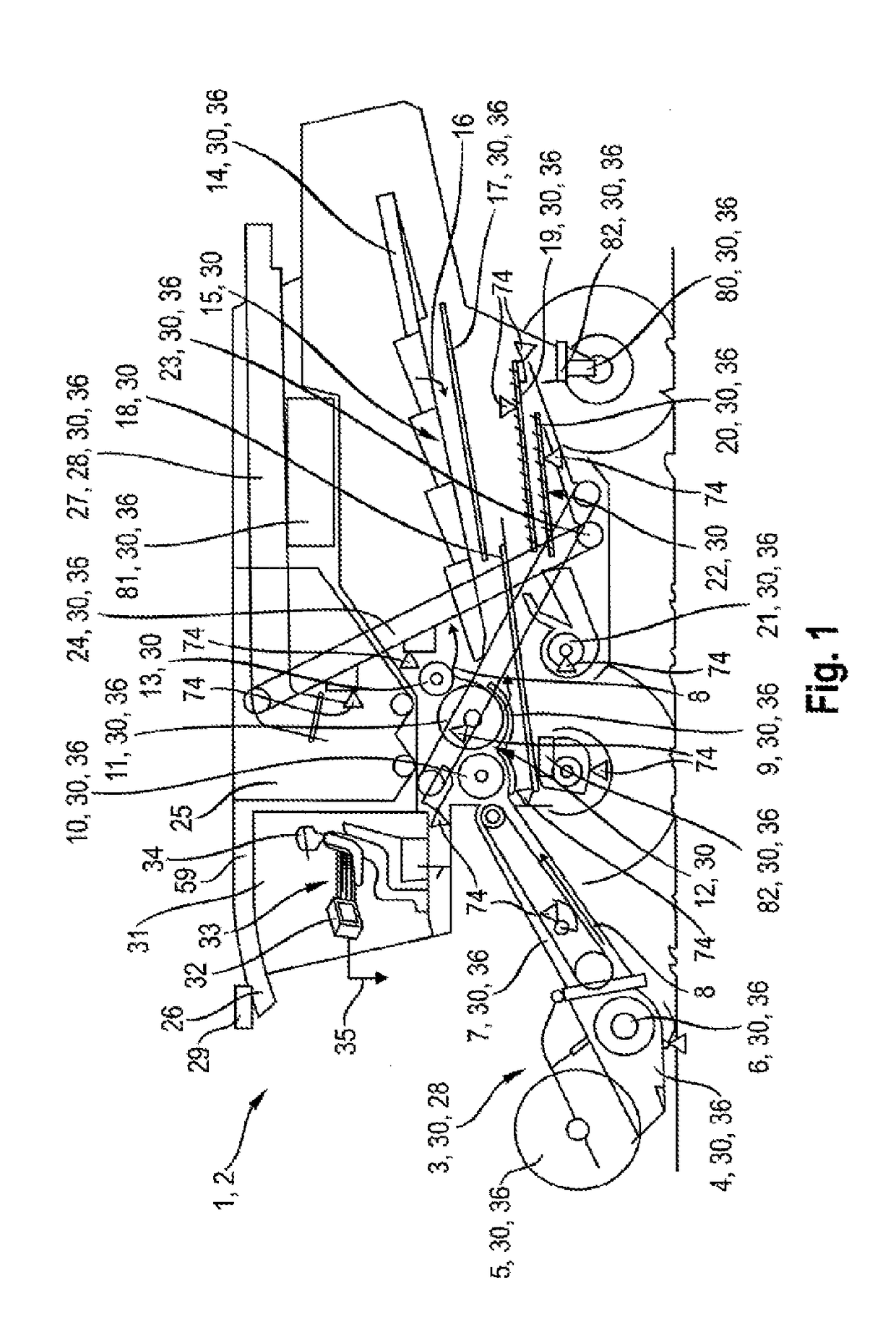
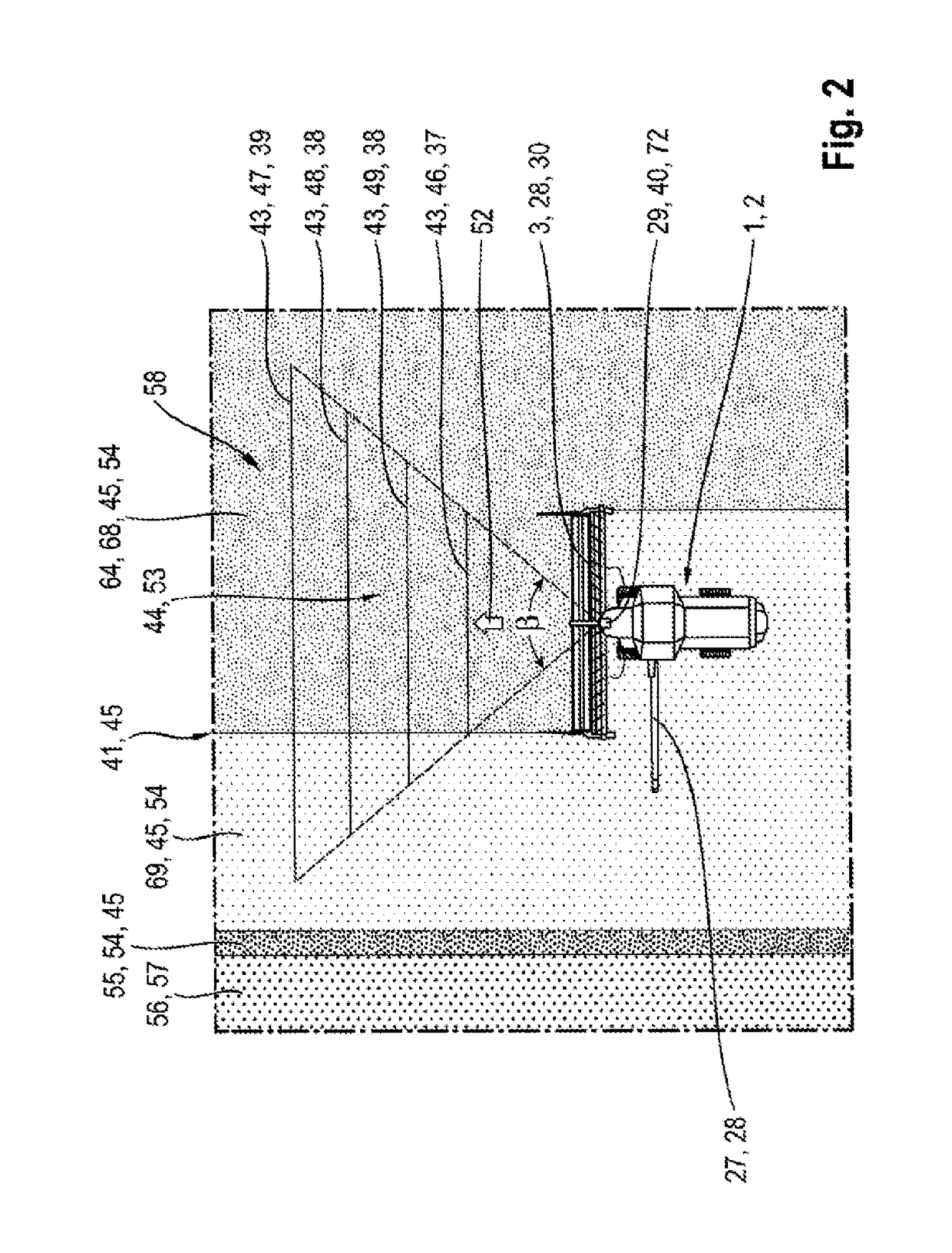
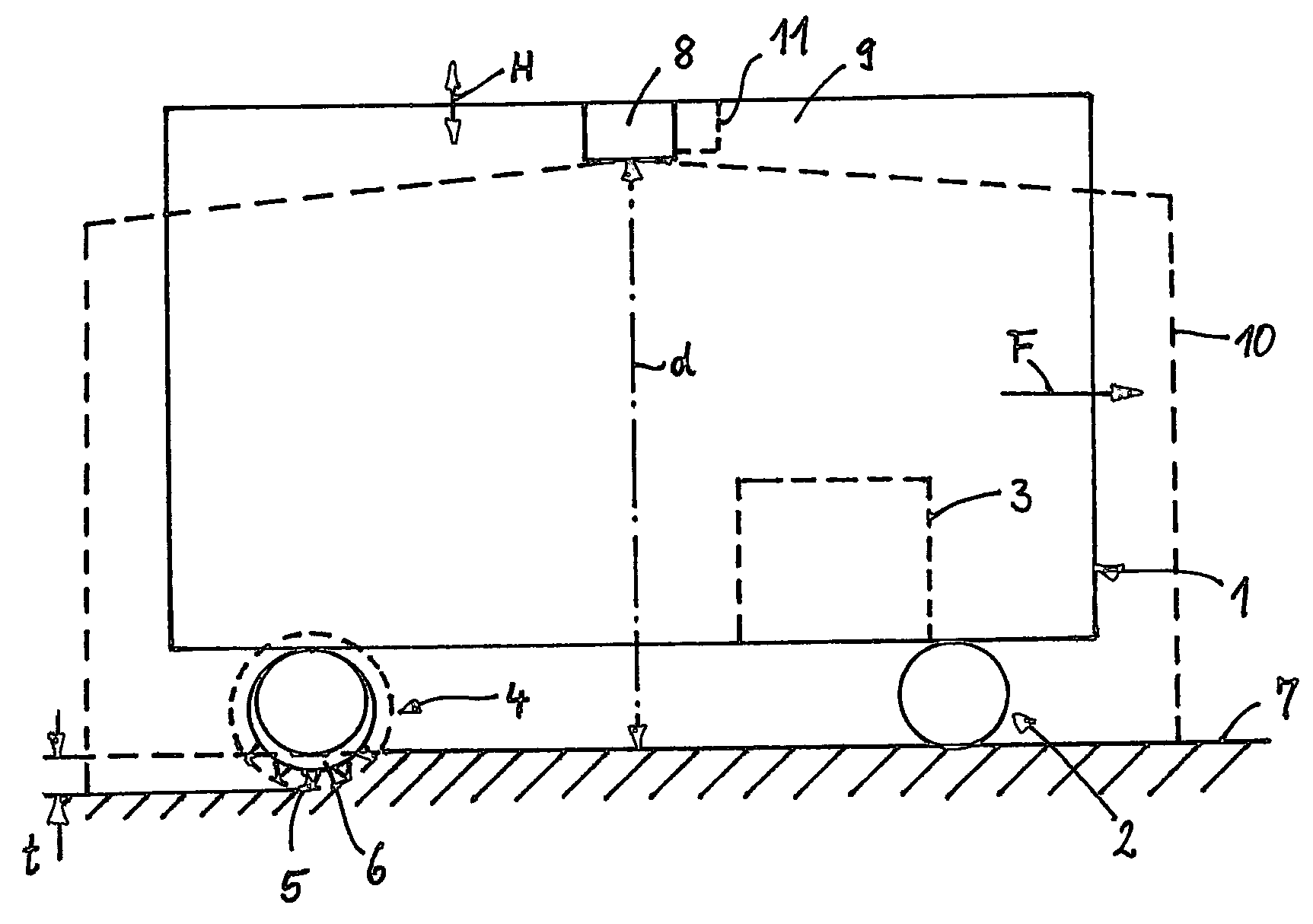
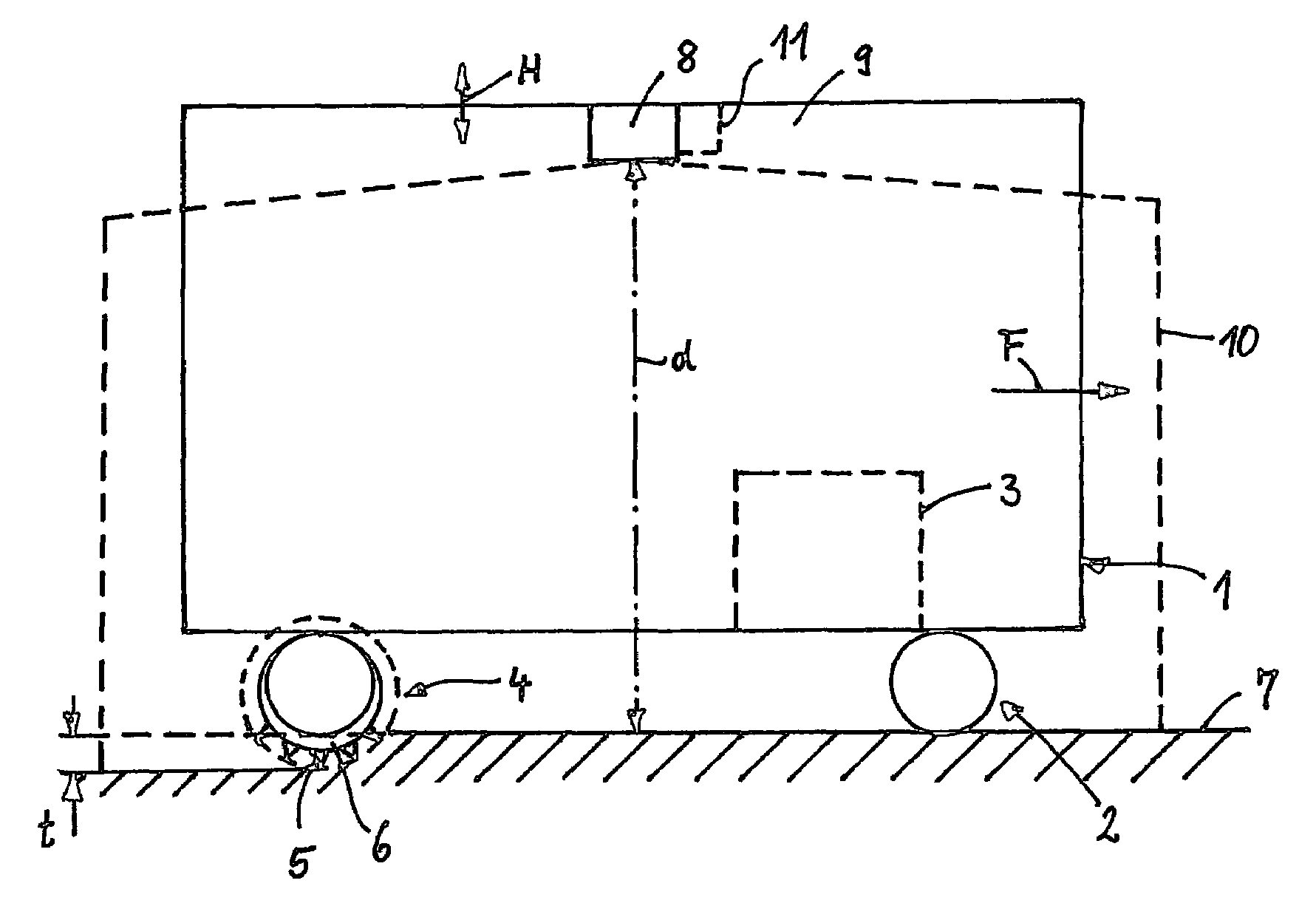
Surroundings detection device for agricultural work machines
ActiveUS20170118915A1Improve efficiencyReduce material impactLawn-mowersGuiding agricultural machinesAgricultural machineryIndustrial engineering
An agricultural work machine is provided comprising a surroundings detection device for detecting a surroundings in sections, and one or more controllable working elements, wherein the surroundings detection device generates surroundings detection signals, which can be processed in a control and regulating device assigned to the agricultural work machine, wherein the surroundings detection device is designed as a scanner, which scans the surroundings in scanning planes, and wherein each scanning plane is assigned to the control of working elements.
Owner:CLAAS SELBSTFAHRENDE ERNTEMASCHINEN GMBH
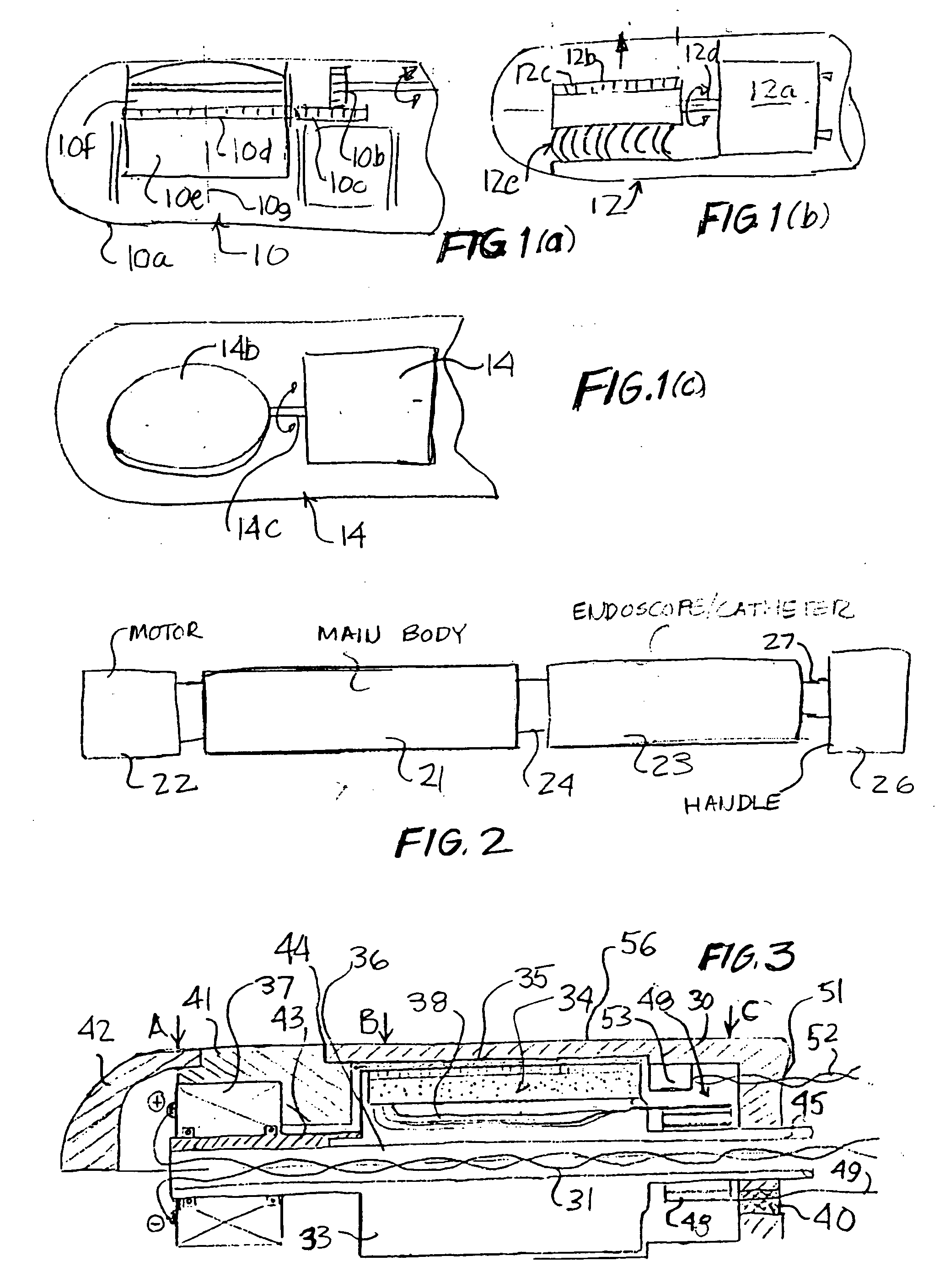
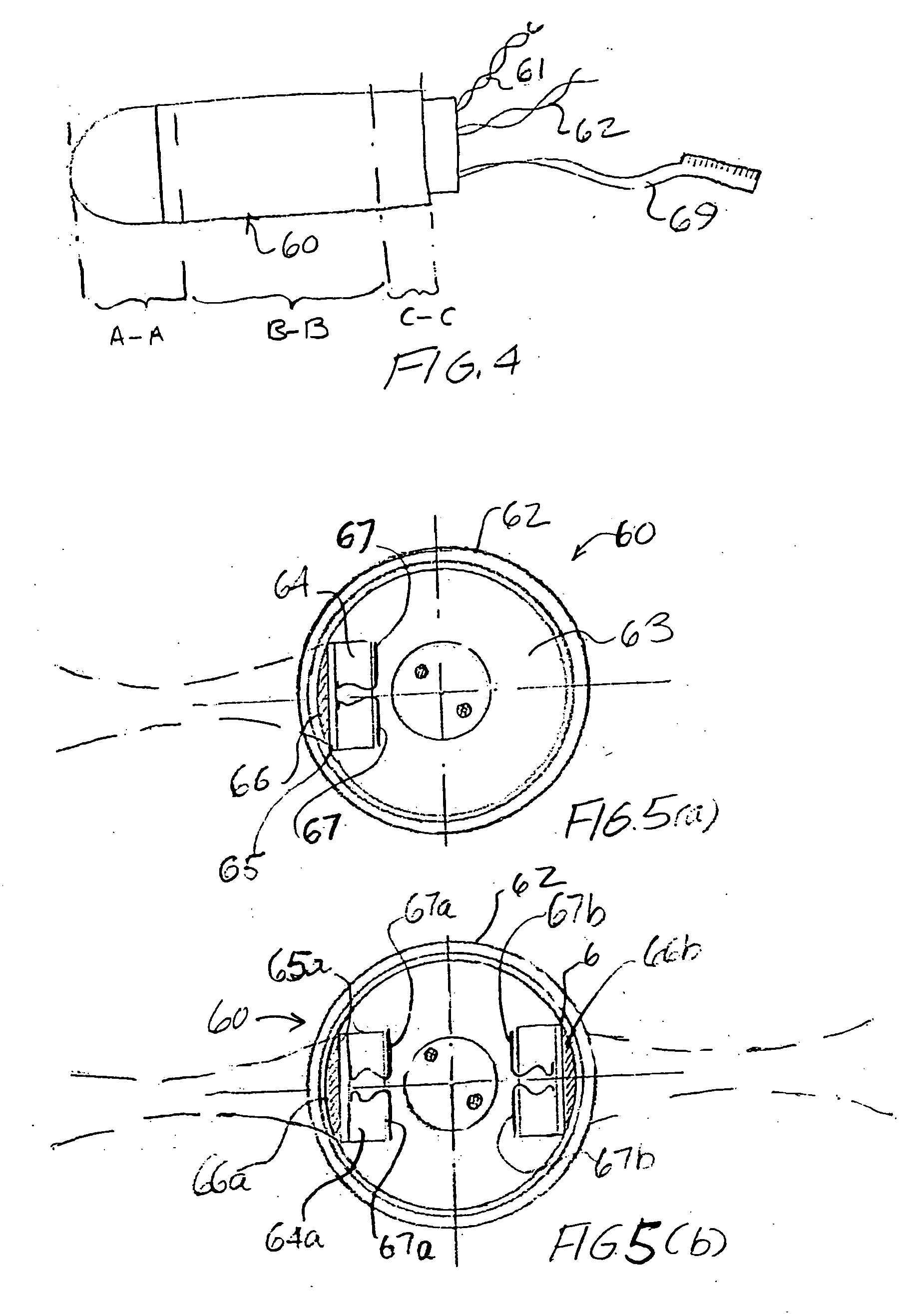
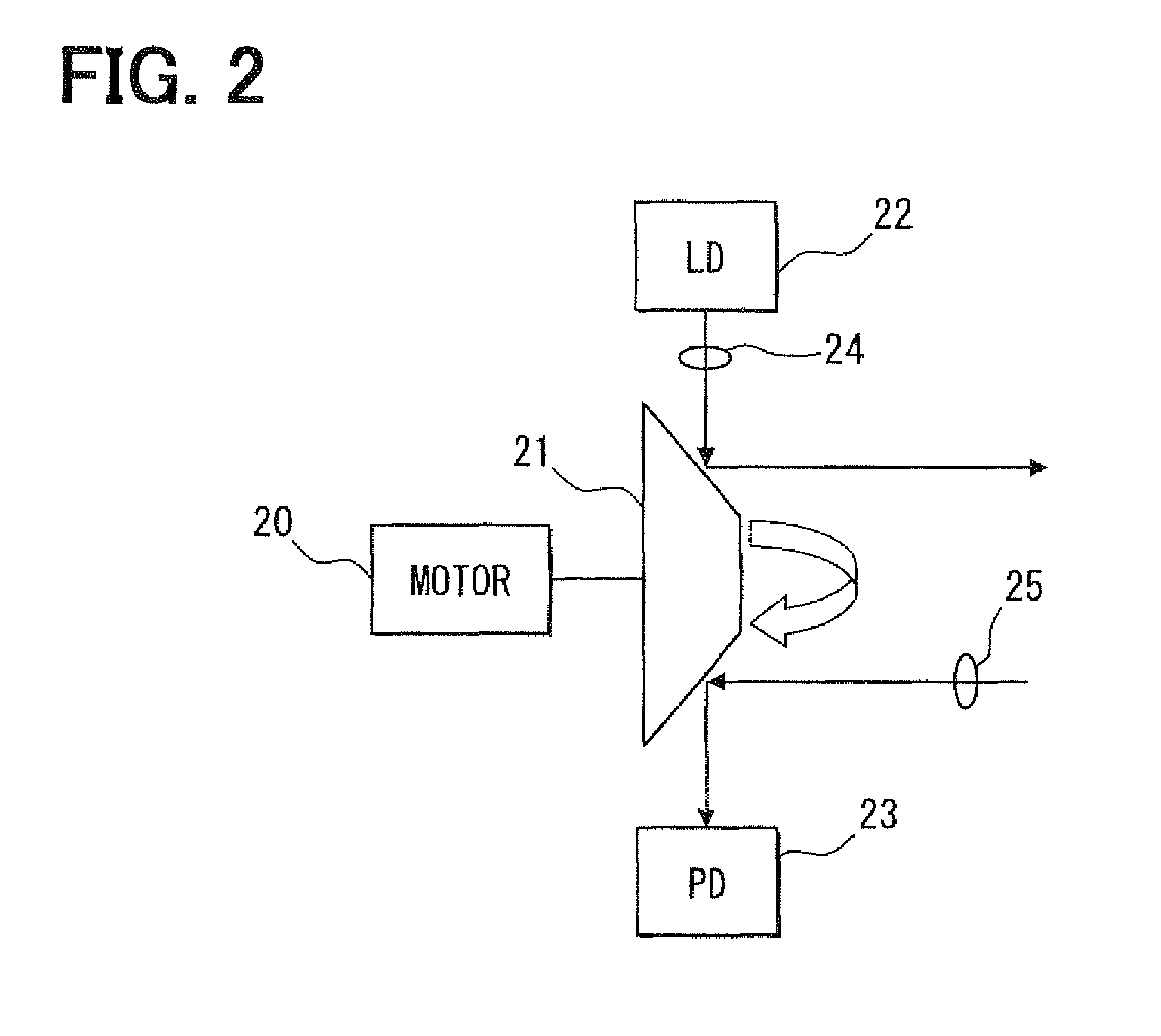
Motorized ultrasonic scanhead
ActiveUS20070038110A1Improved EMI protectionImprove eyesightUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterContinuous scanningLaparoscopes
A motorized scanhead device is capable of rotating an array transducer through 360 degrees of angular rotation in a manner such as to provide acquisition of images in successive scanning planes arranged around the principal axis of the device. The device can be incorporated in endoscopes (e.g., transesophageal endoscopes), laparoscopes, endocavity or intracavity probes so as to provide an expanded angle of vision or to render 3D images, without the need for external movement of the device. The motorized scanhead device includes a motor that is isolated from the transducer signal interconnections in order to minimize electrical discharges associated with motor operation and to provide more room between an associated probe housing and the scanhead device.
Owner:VERMON
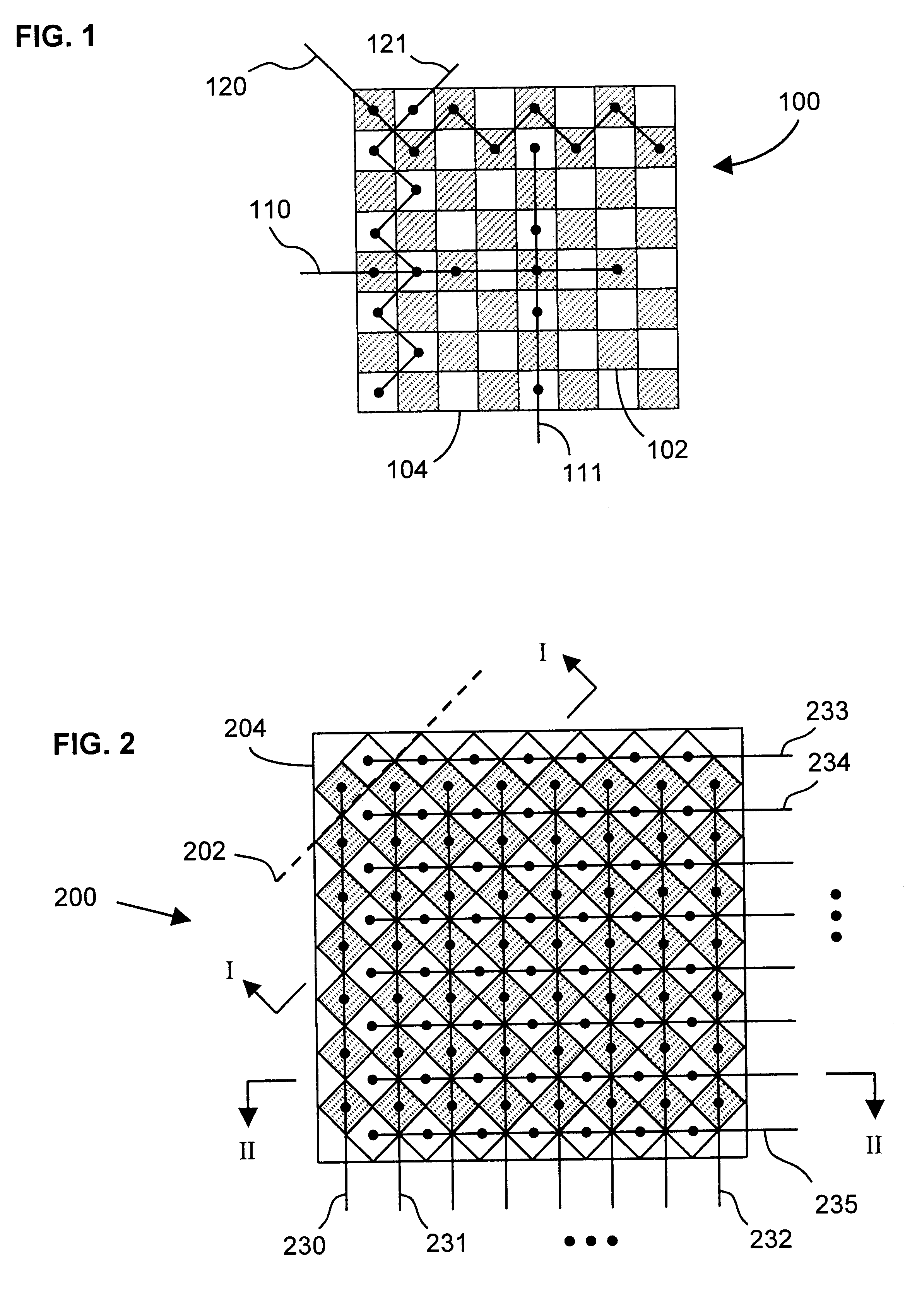
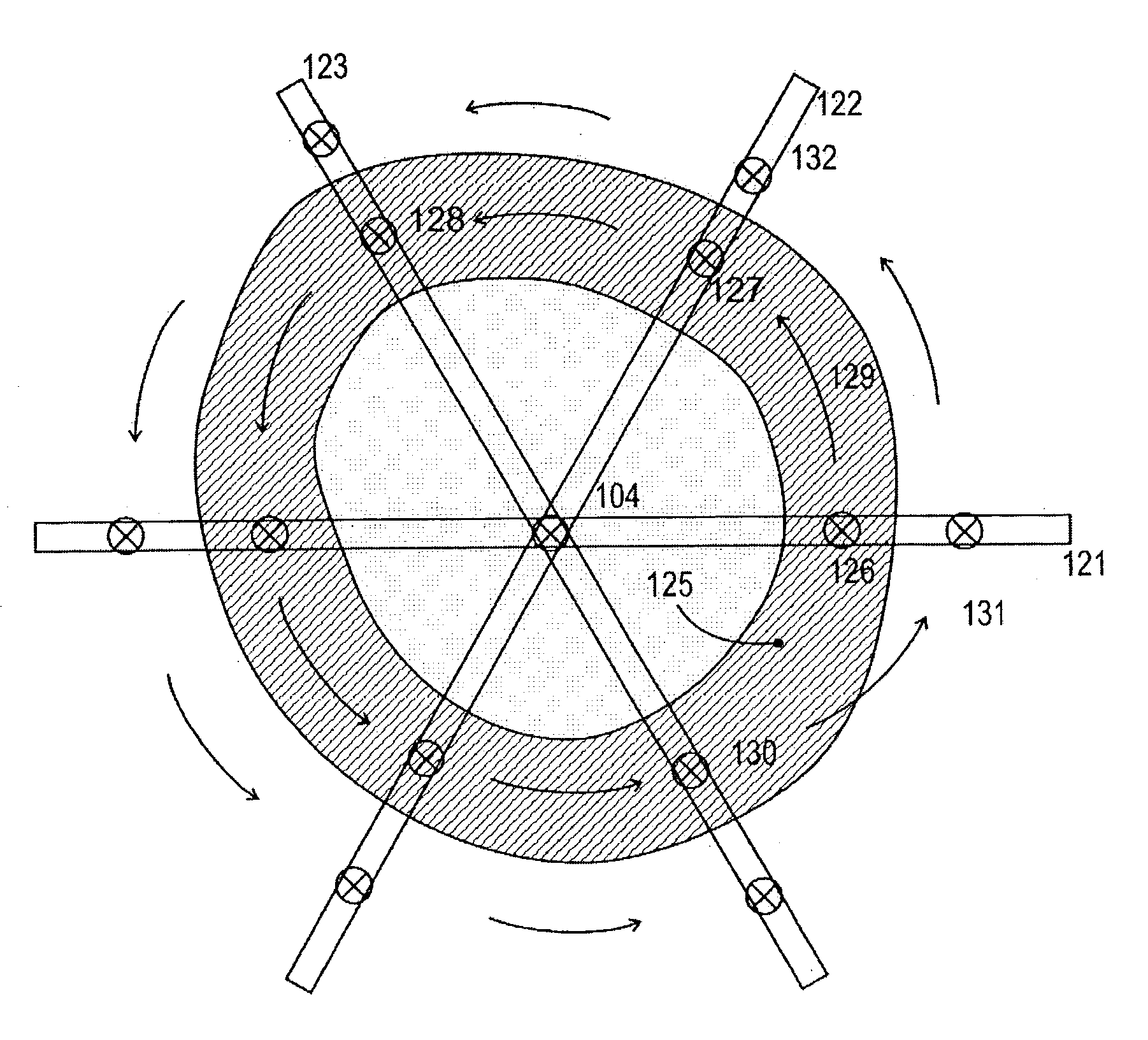
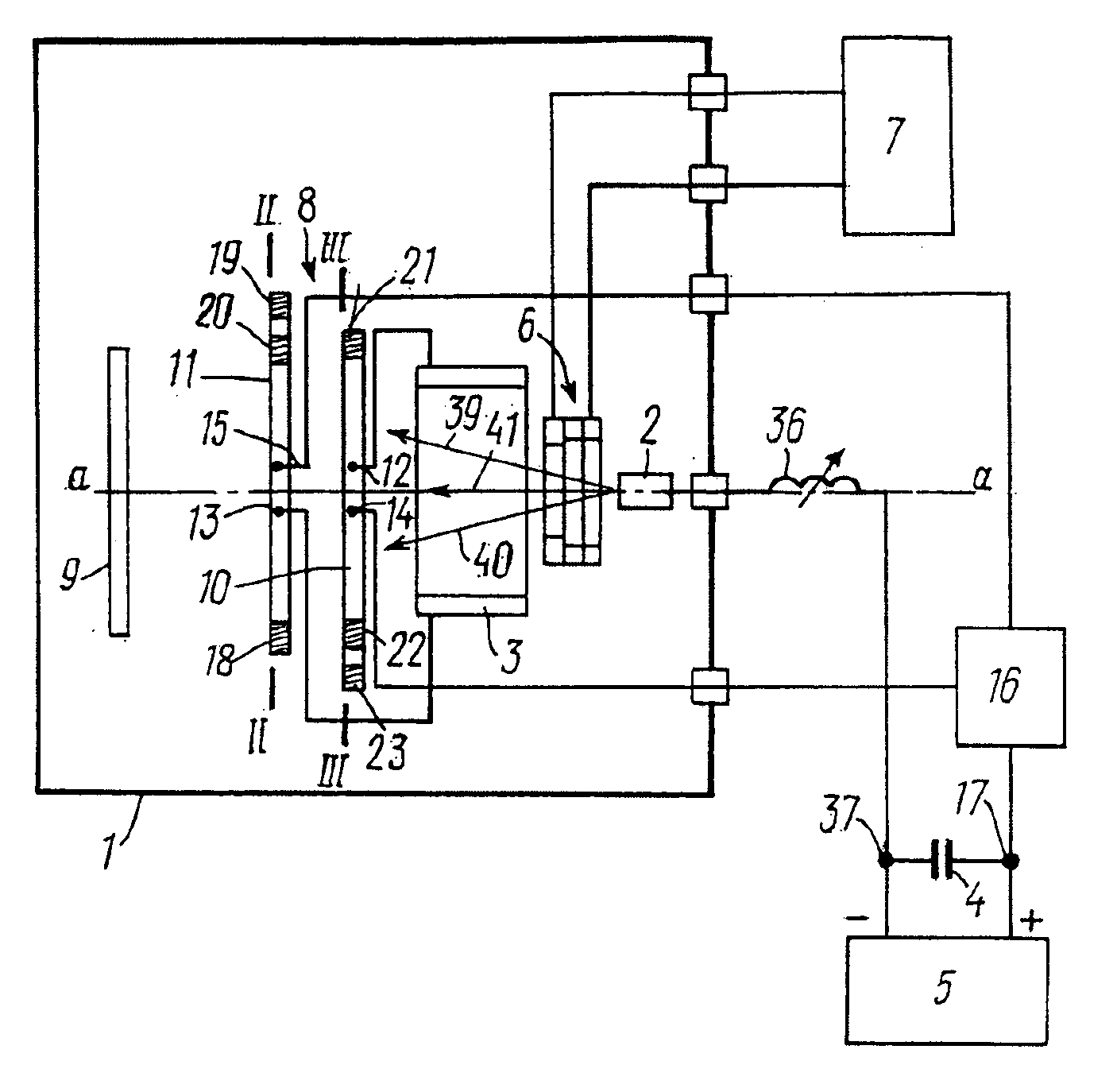
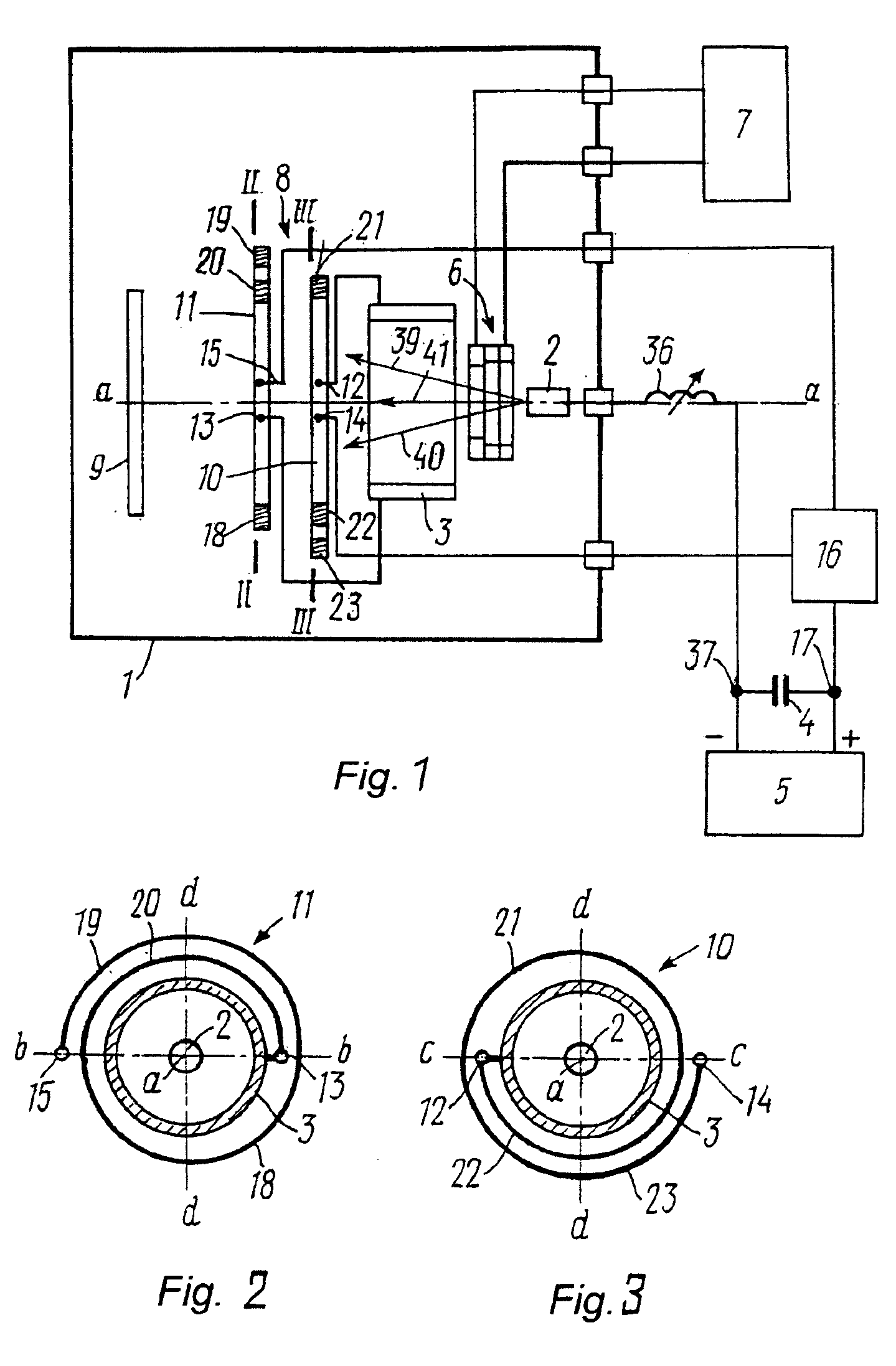
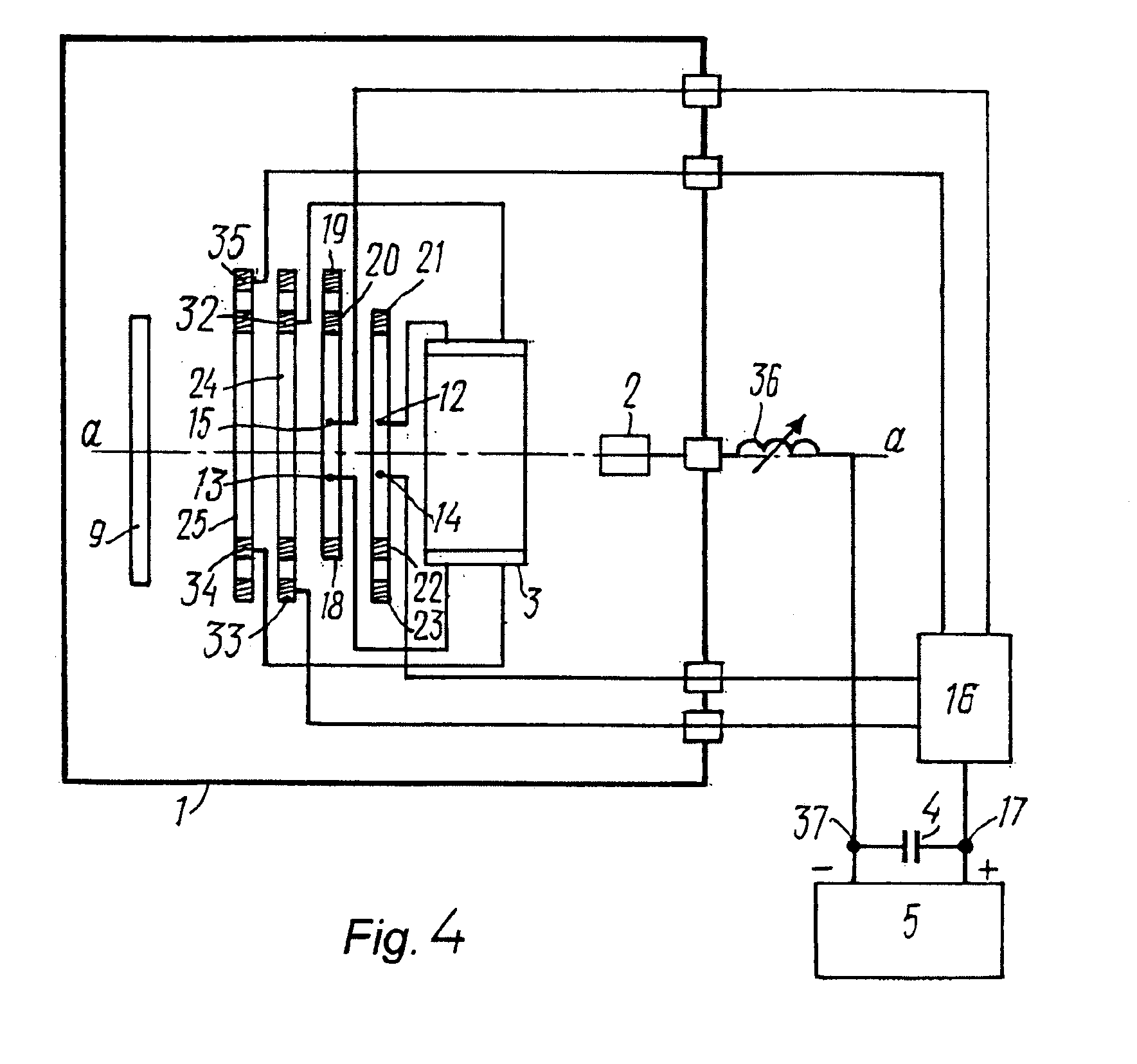
Multiple scan-plane ultrasound imaging of objects
ActiveUS20030216646A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingFiber
A method of real time ultrasound imaging of an object in at least three two-dimensional scan planes that are rotated around a common axis, is given, together with designs of ultrasound transducer arrays that allows for such imaging. The method is also introduced into a monitoring situation of cardiac function where, combined with other measurements as for example the LV pressure, physiological parameters like ejection fraction and muscular fiber stress is calculated.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Methods and apparatus for defining a protocol for ultrasound imaging
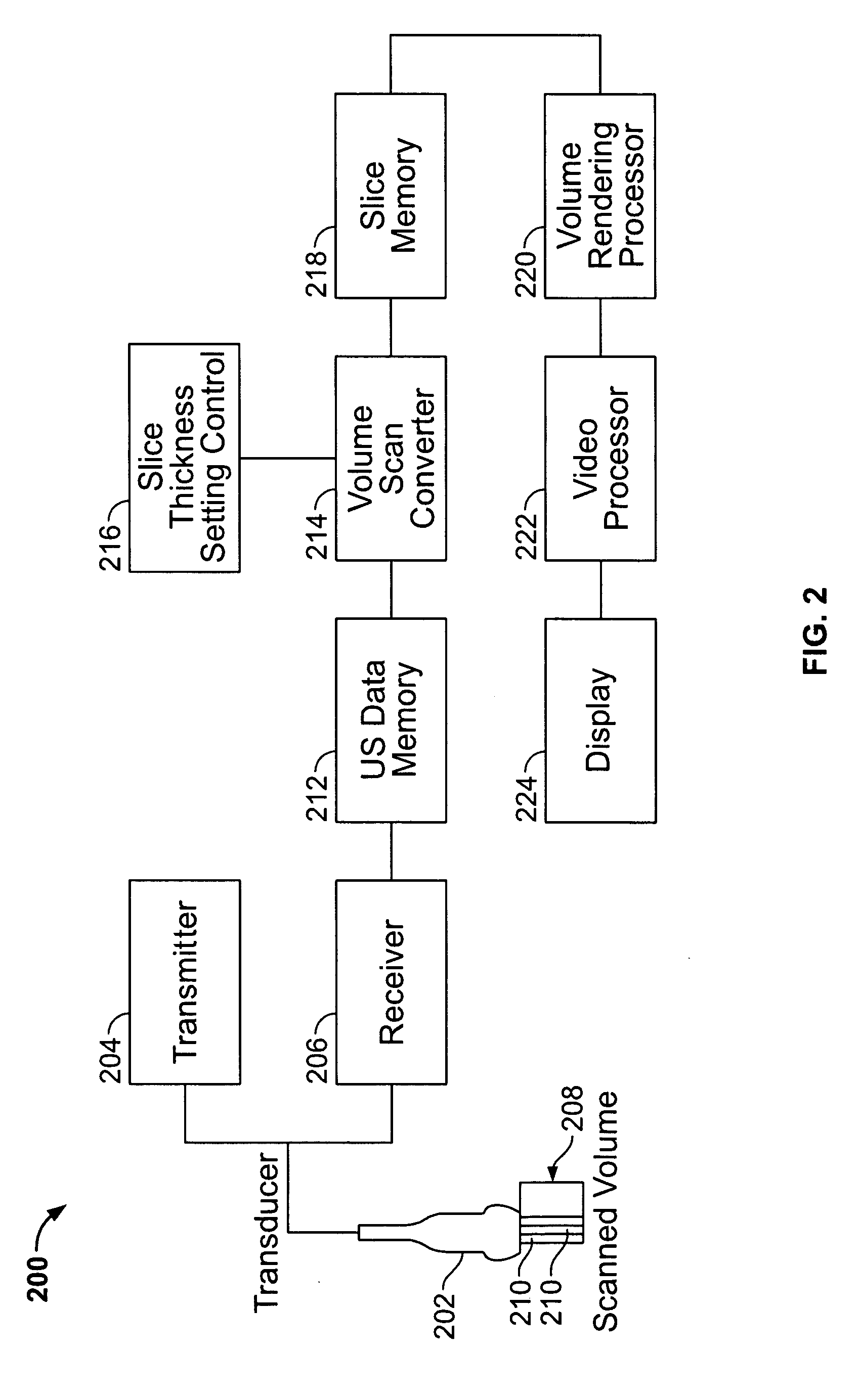
InactiveUS20050281444A1Organ movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasonic imagingCell based
A protocol-based ultrasound method is provided. The ultrasound method provides a template comprised of cells. Each of the cells contain scan parameters defining a scan sequence for acquisition of ultrasound images along one or more scan planes through an object. Prior to scanning the object, parameter values for the scan parameters associated with cells in the template are entered to define the scan sequences along at least two scan planes. The object is scanned with an ultrasound probe to automatically and successively acquire ultrasound images along at least two scan planes based on the parameter values for the scan parameters in the cells. The method displays ultrasound images of an object that is changing states in accordance with a protocol. Each of the ultrasound images is acquired along a corresponding scan plane through the object. A collection of ultrasound images is provided. Each of the ultrasound images is acquired along an associated scan plane while the object is in an associated state. The display is segmented into at least two quadrants. A corresponding ultrasound image is presented in the quadrants, wherein co-displayed ultrasound images correspond to one of a common state of the object and a common scan plane through the object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
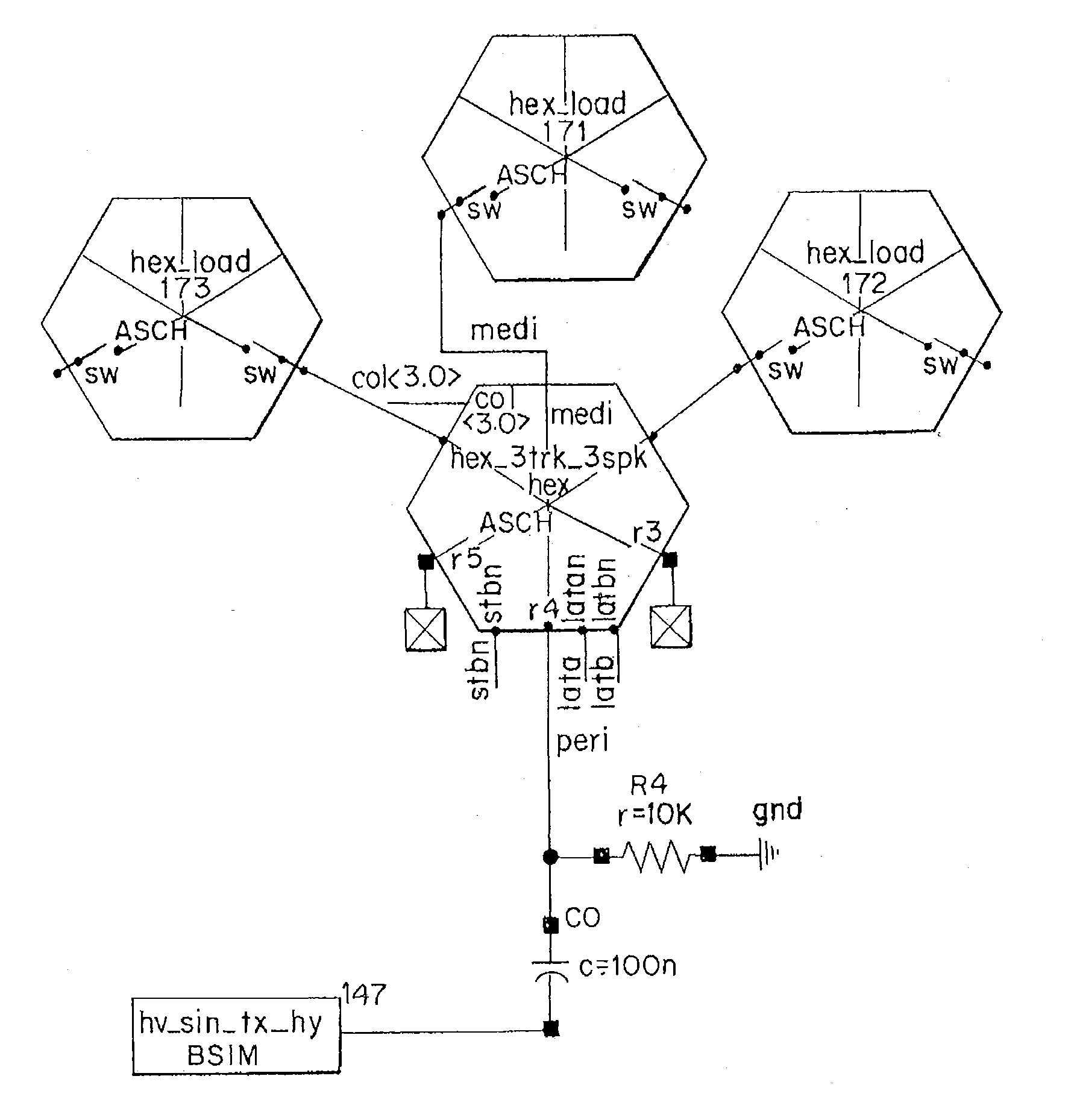
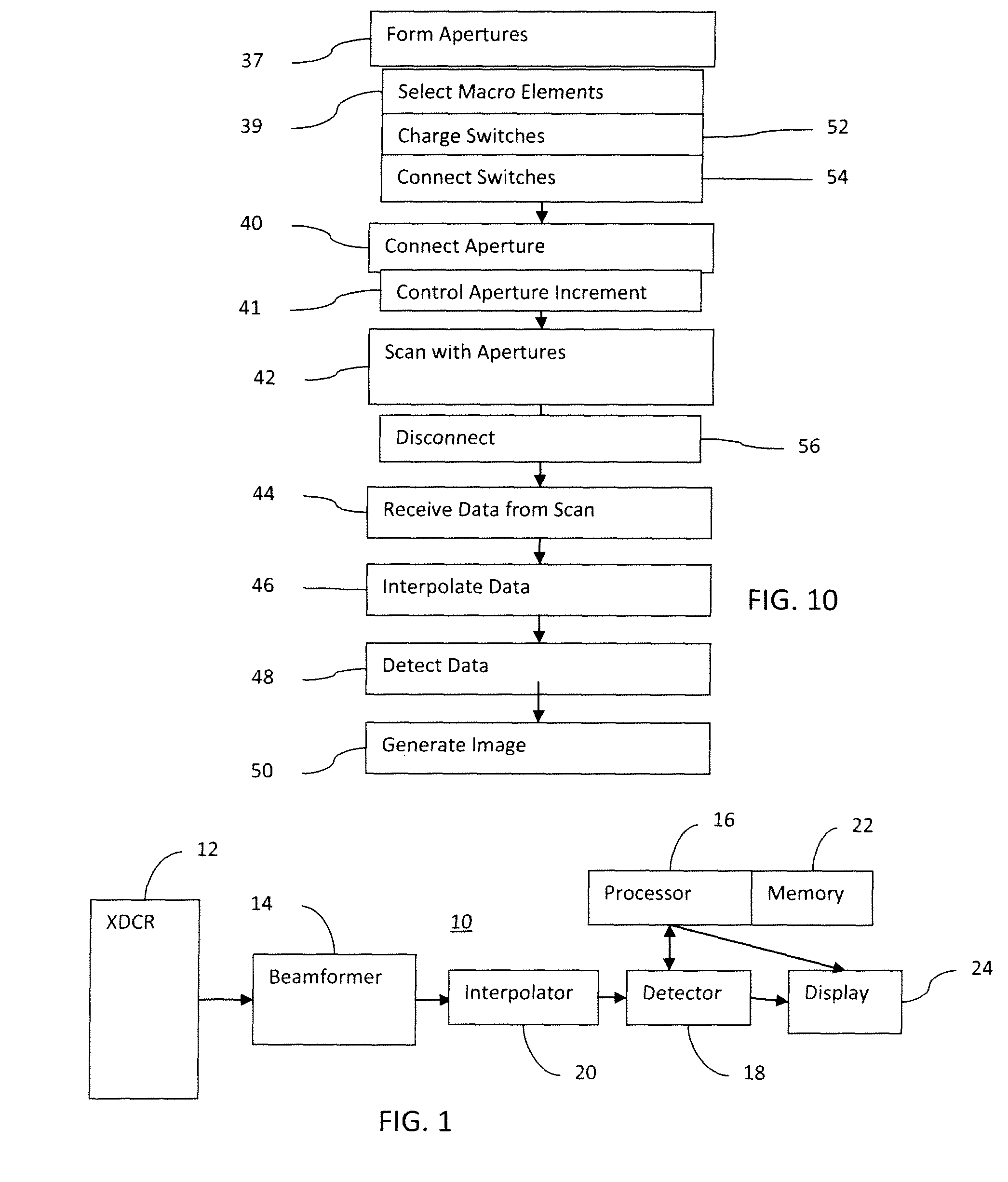
Switch for Aperture Control in Medical Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging
ActiveUS20110021920A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingTransducer
Switching is provided in a transducer array of medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging. The switching controls the formation of macro elements or aperture for scanning a plane or volume. The switches are implemented with one or more transistors. The control causes the gates of the transistor to float during the “on” connection. While on, the switch connects, allowing ultrasound signals to pass through the switch.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
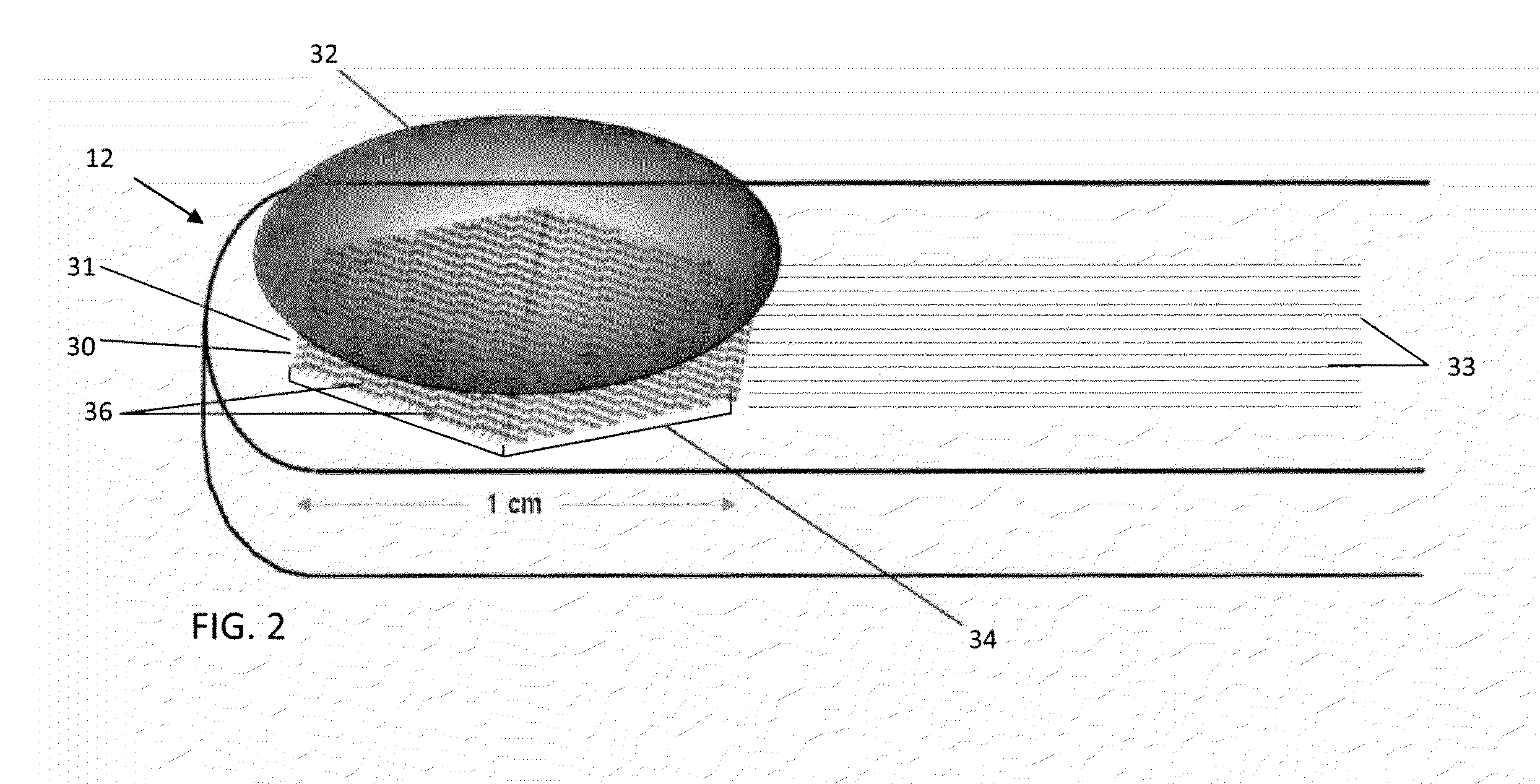
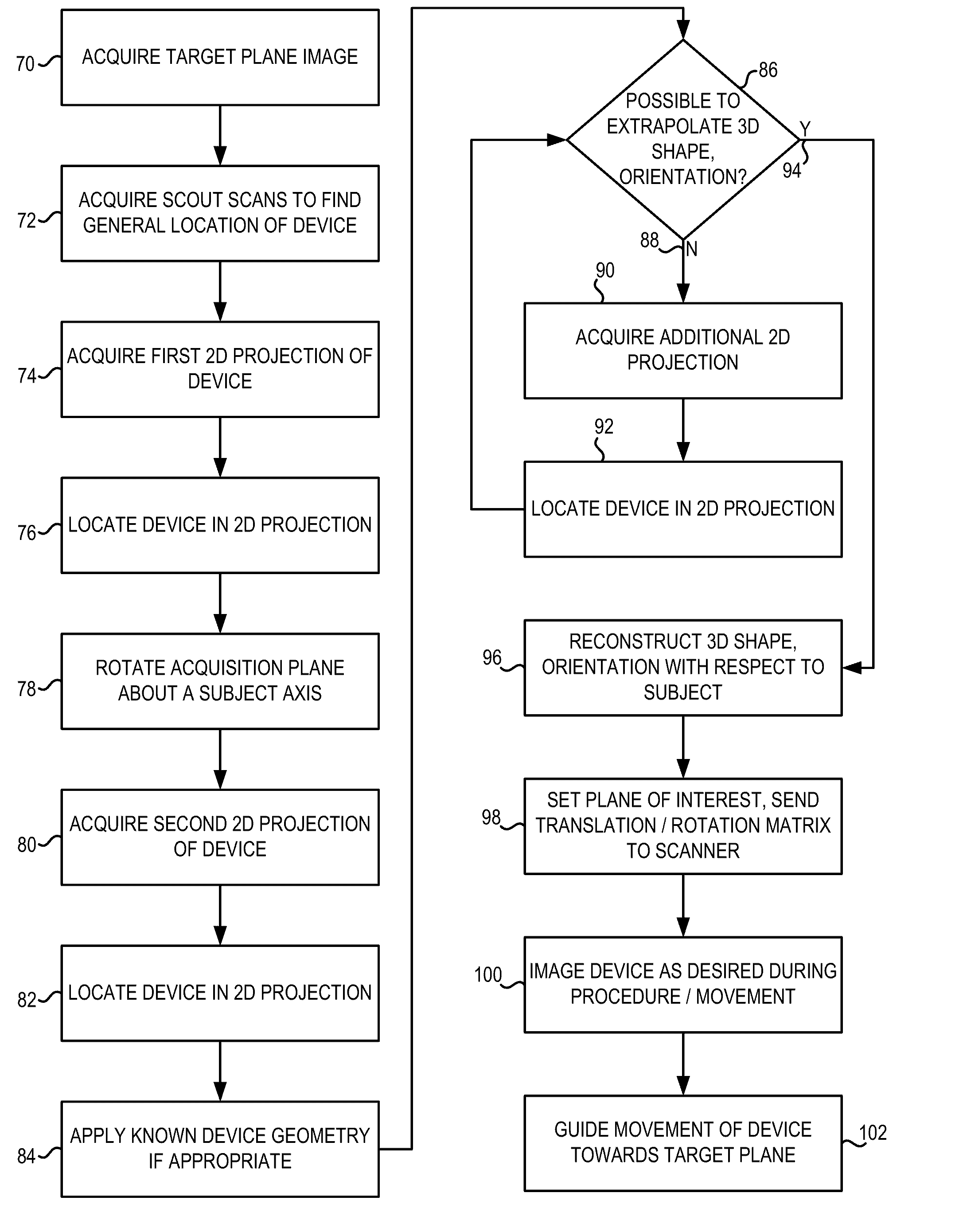
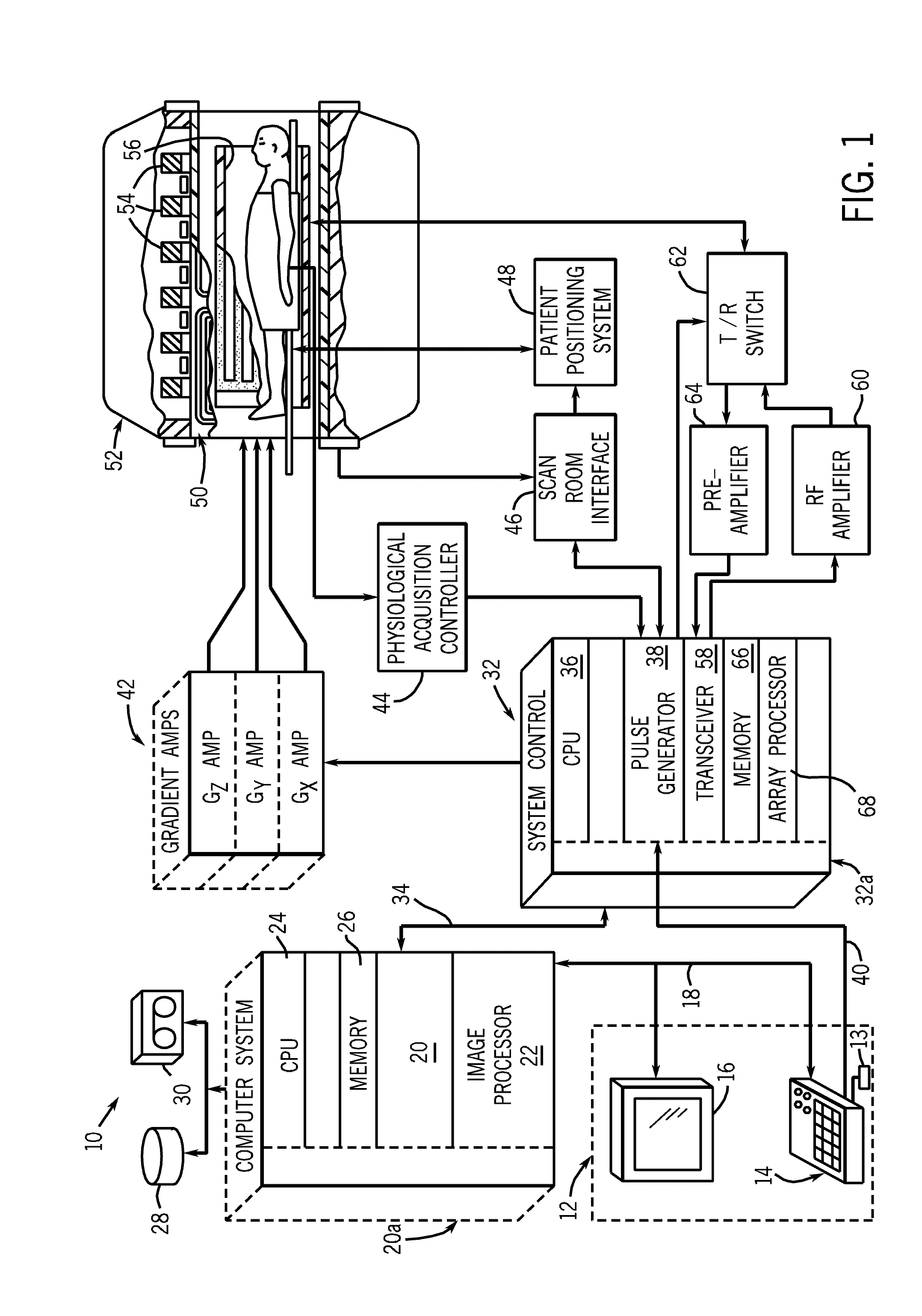
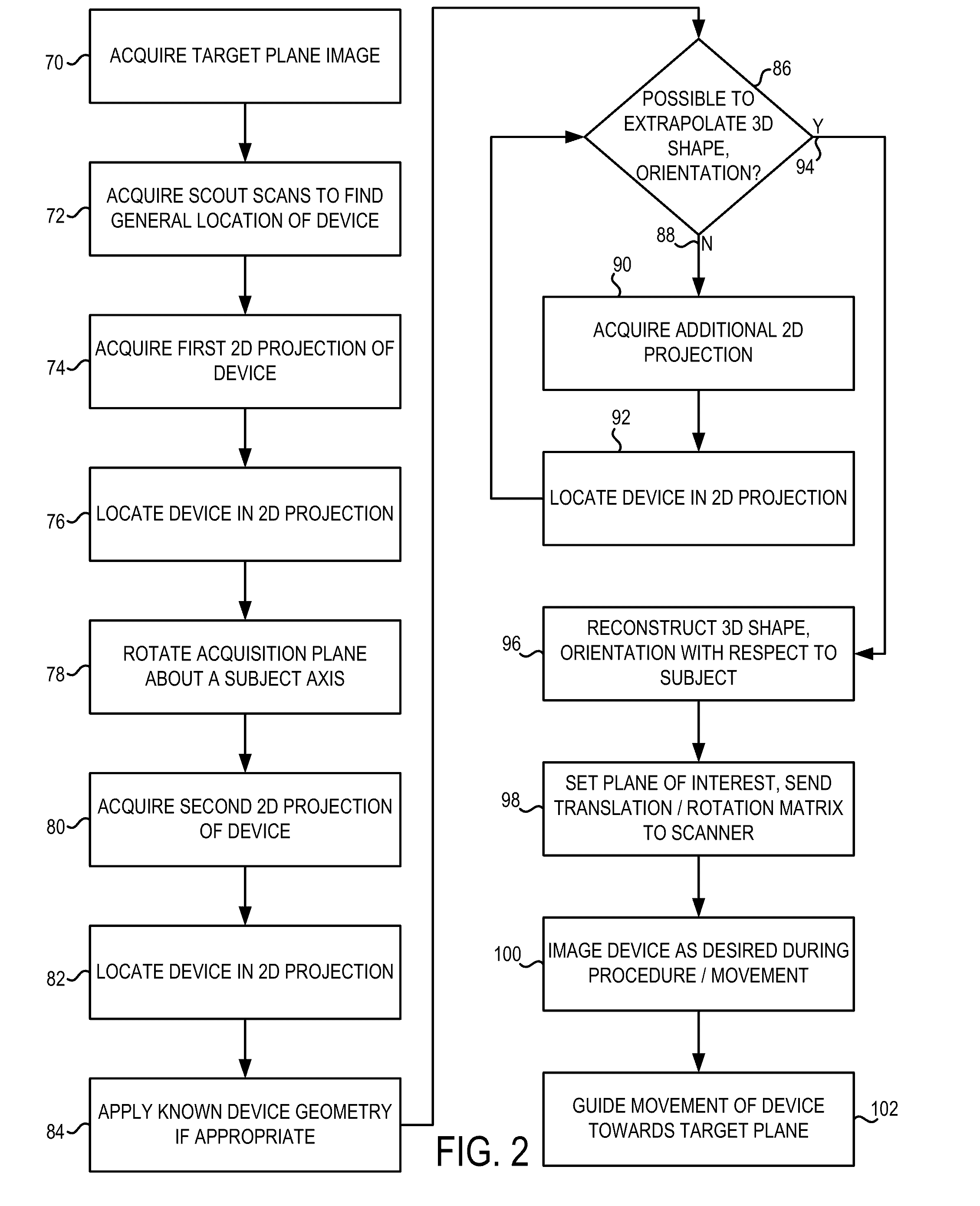
System and method for image-based interventional device tracking and scan plane guidance
An MR system and method for tracking a device of an interventional procedure within a scan subject is disclosed. At least two MR projections of the device are acquired, from which 3D coordinates of the device are determined. Subsequent image acquisition is adjusted with respect to the coordinates of the device to guide movement thereof towards target anatomy. The present system and method provide the ability to locate and visualize continuous portions of an interventional device in 3D, and do not require the use of embedded RF localizing coils.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
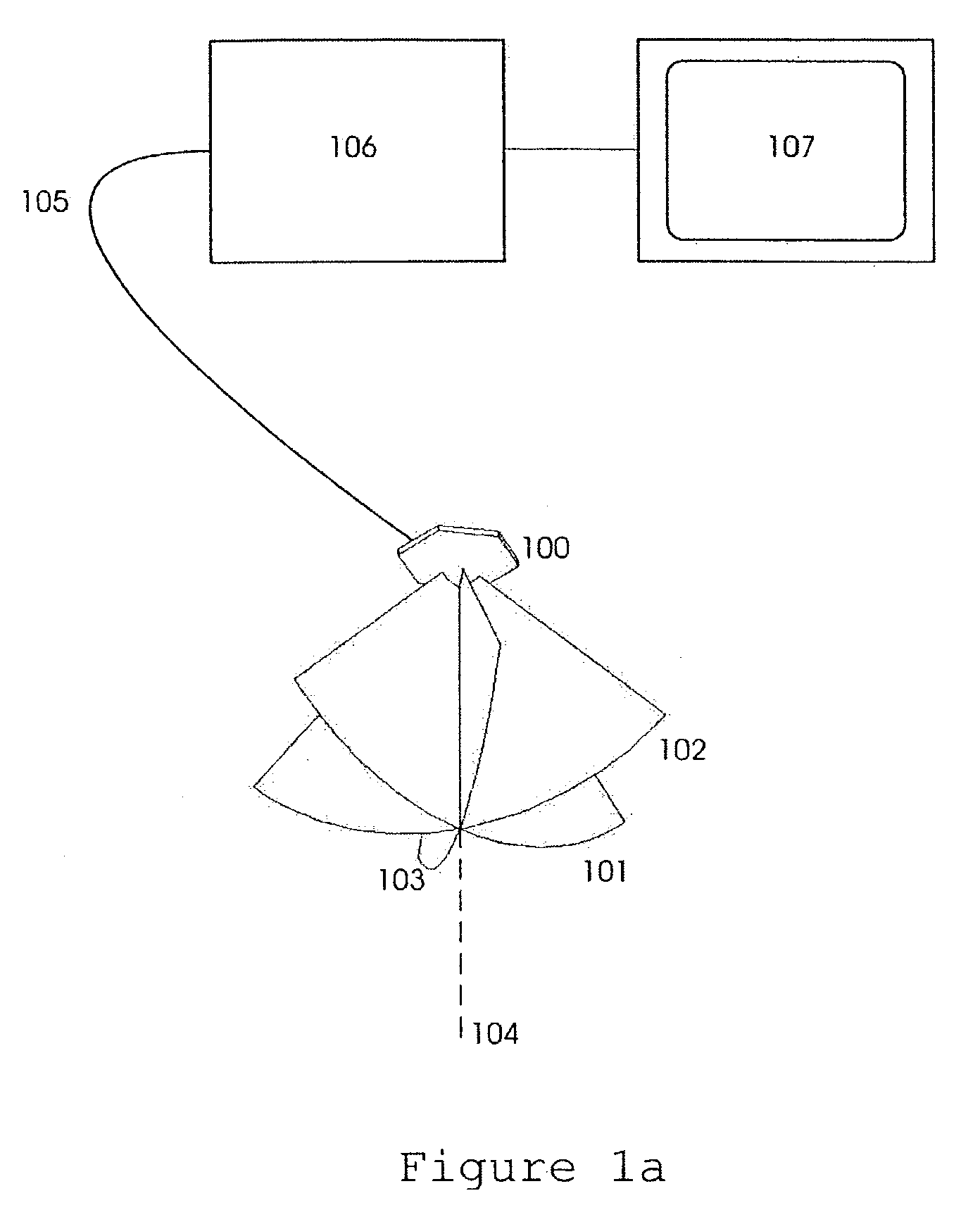
Method and apparatus for real time ultrasound multi-plane imaging
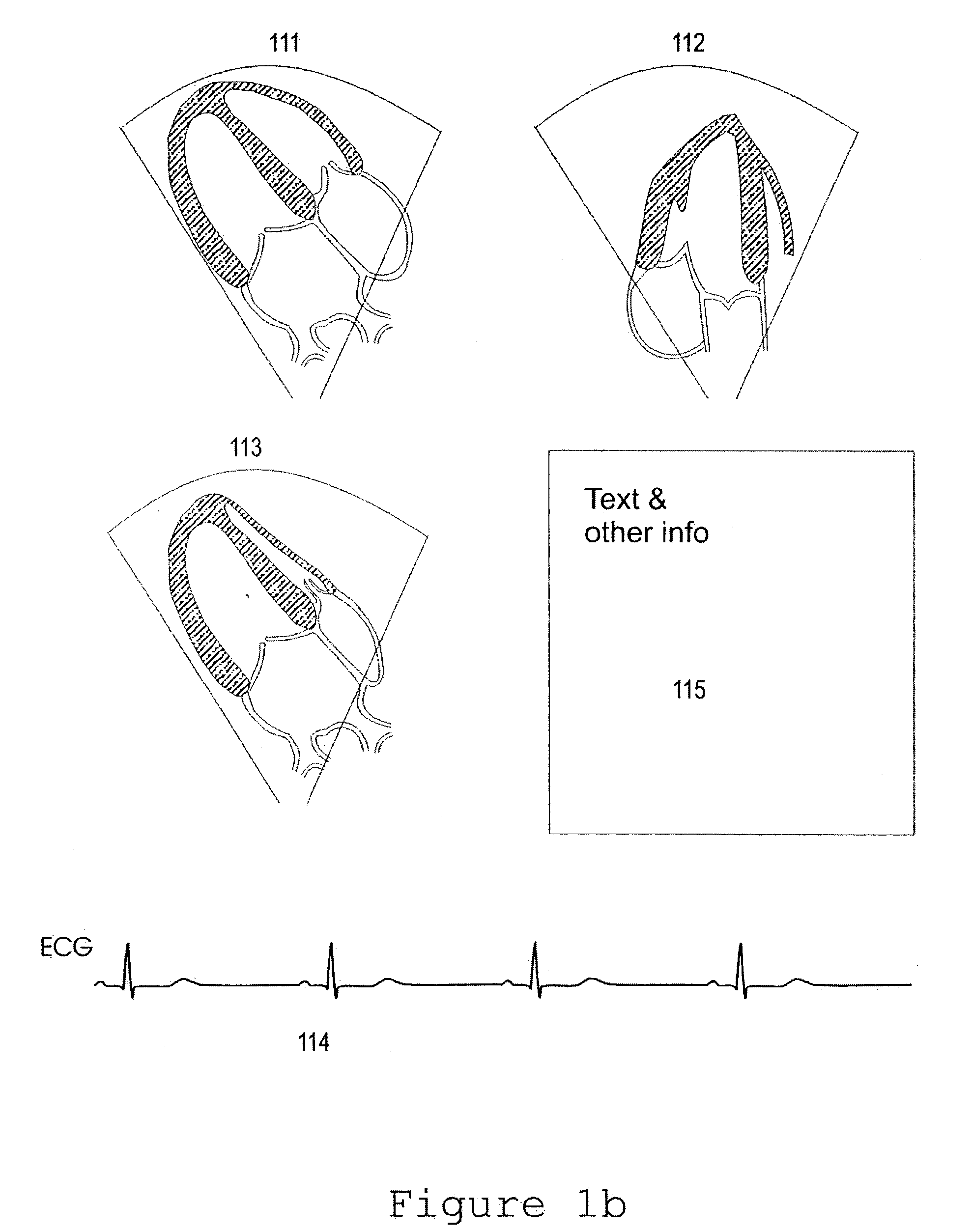
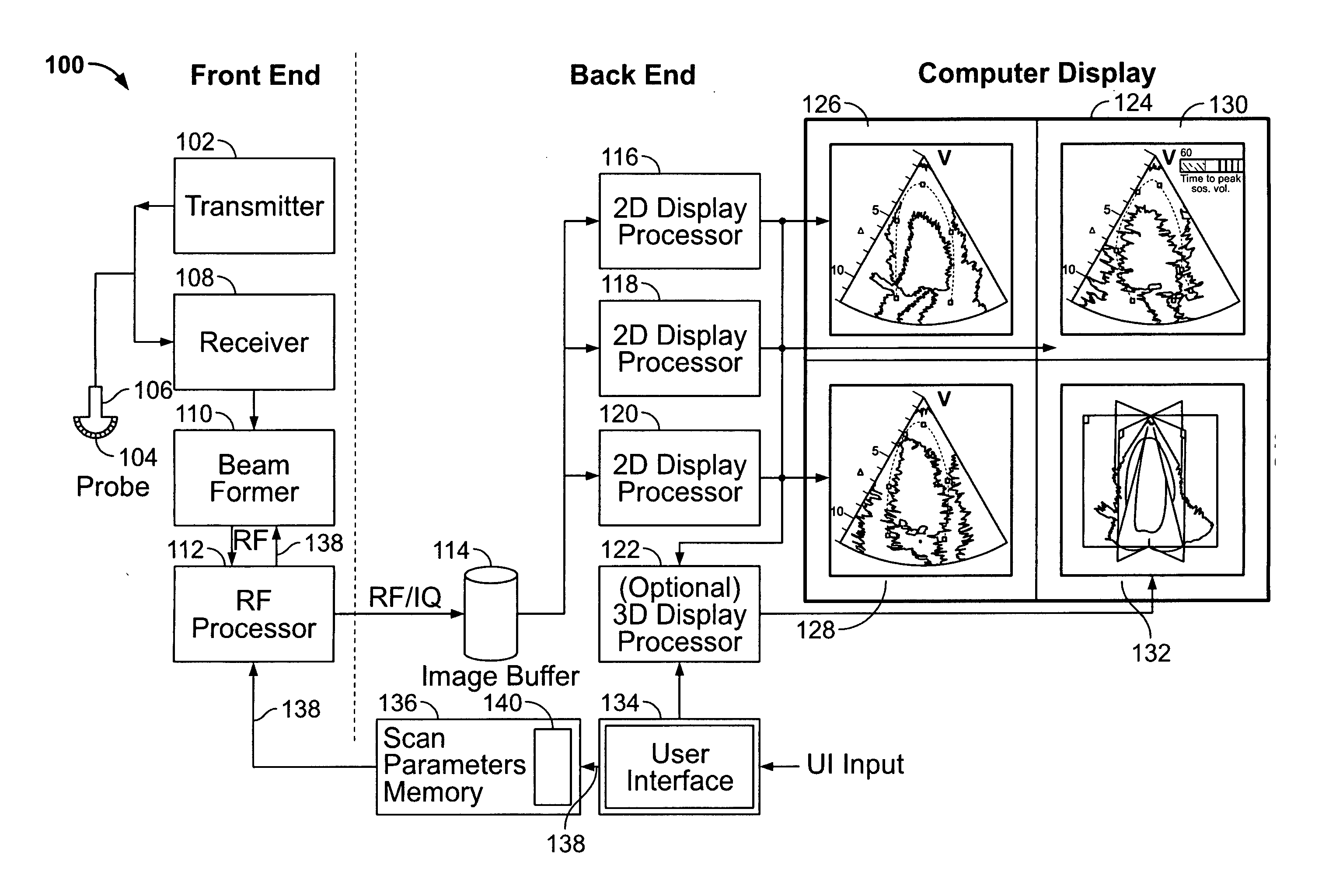
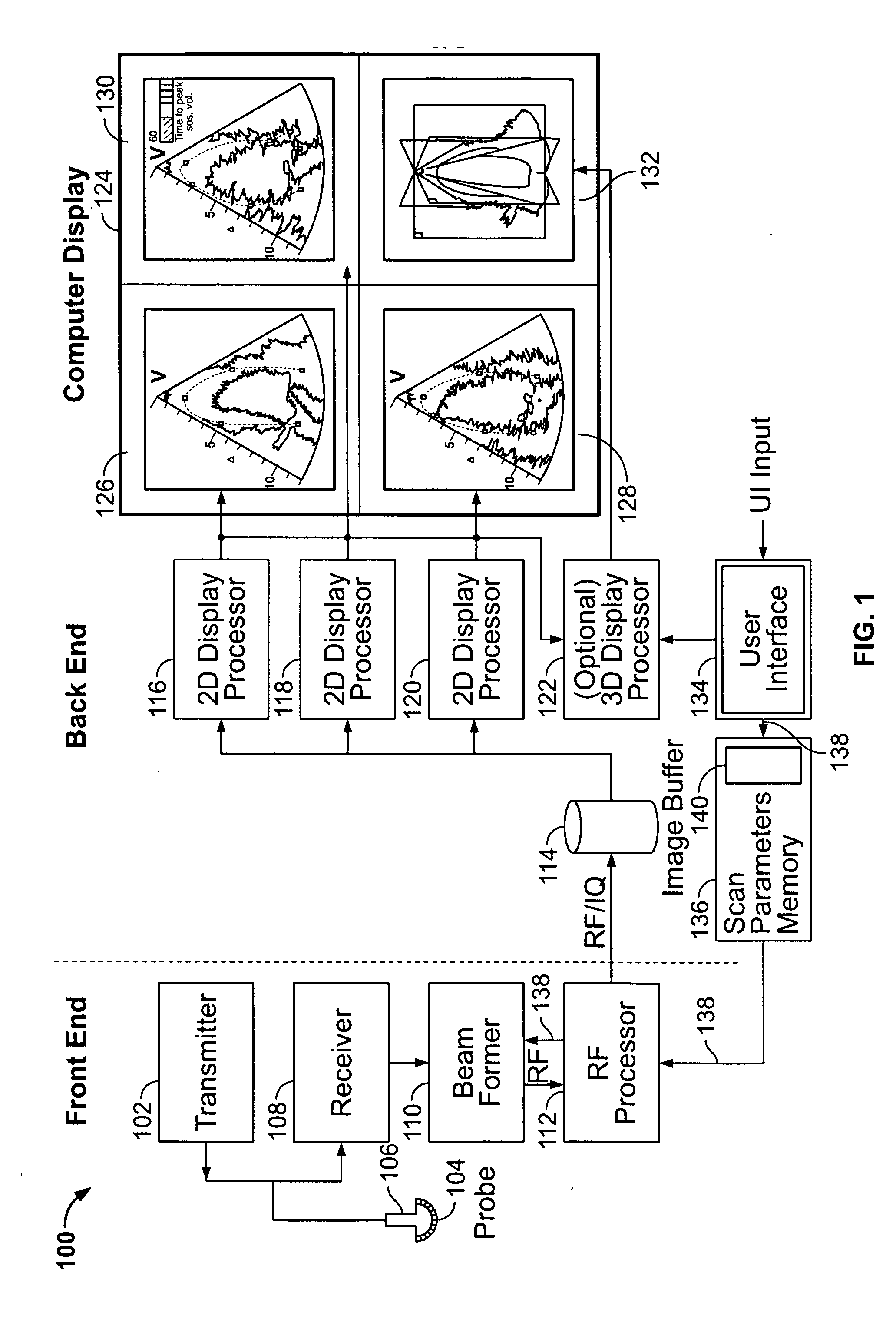
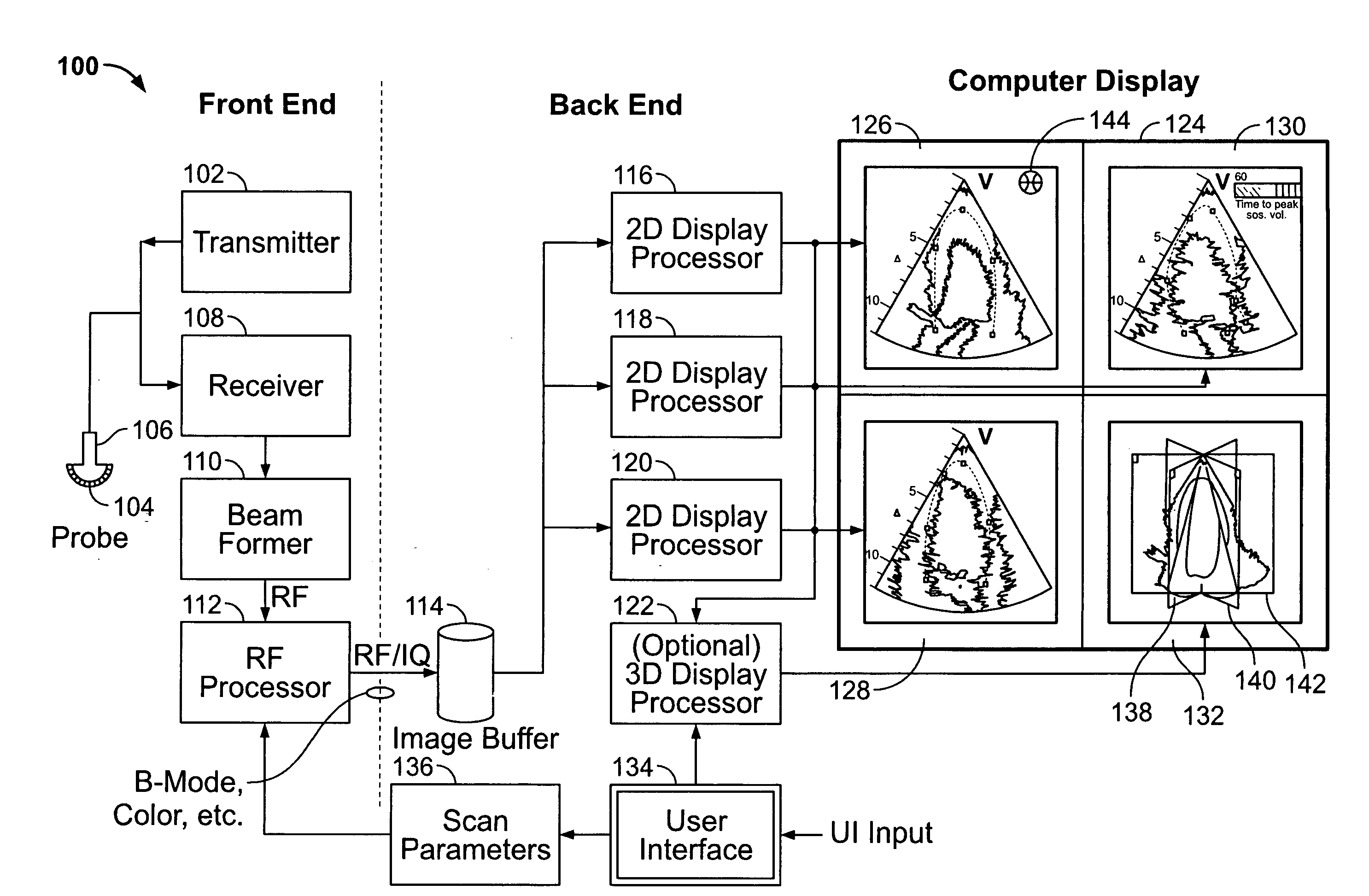
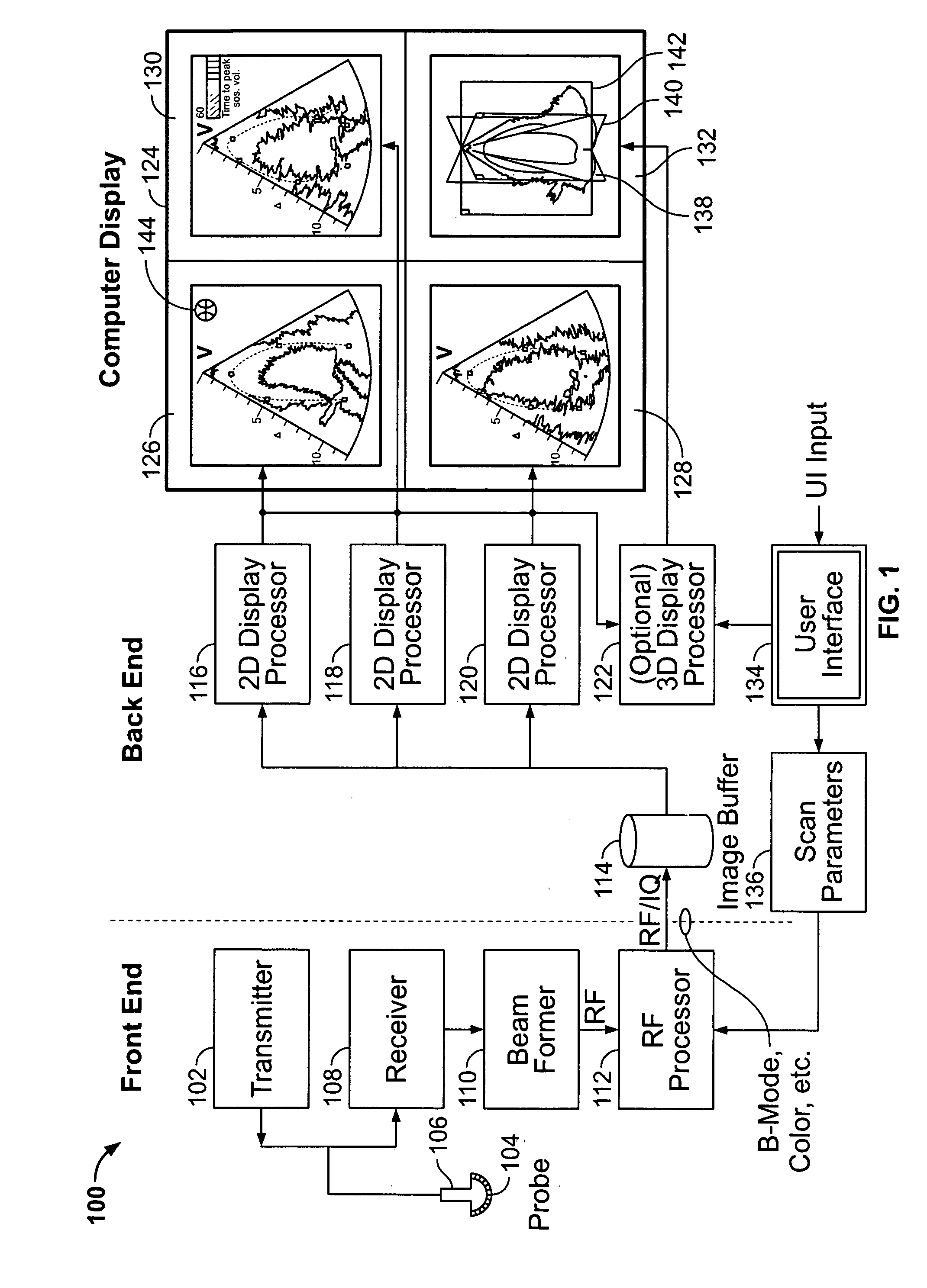
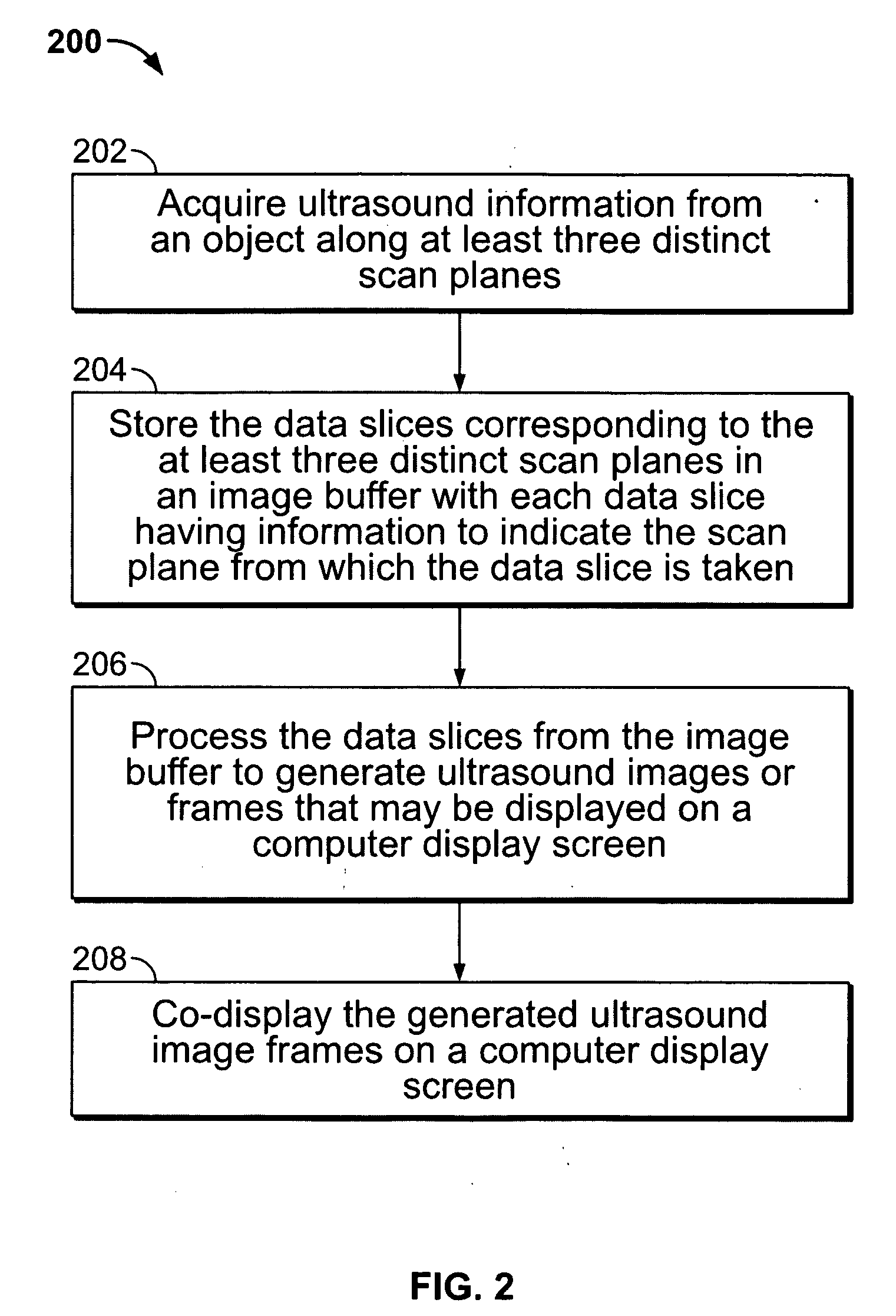
ActiveUS20050283078A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationDisplay device
An ultrasound system is provided that includes a probe for successively acquiring ultrasound information from an object along at least three distinct scan planes. The scan planes intersect one another along an axis extending from the probe through the object. A memory is included for storing data slices corresponding to the at least three distinct scan planes based on the ultrasound information. Also included is a processor that accesses the memory to select and obtain the data slices and generates ultrasound images based on the data slices. A display is included for co-displaying the ultrasound images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pulsed carbon plasma apparatus
InactiveUS6855237B2High degreeImprove life performanceCellsElectric discharge tubesDiamond-like carbonMachine parts
The present invention provides a pulsed carbon plasma apparatus to produce a diamond-like carbon coating over an extended object, the coating having a high degree of thickness uniformity achieved by scanning the plasma flow over the surface of the object. The pulsed carbon plasma apparatus of the invention comprises a carbon plasma flow scanning device having at least one pair of deflecting coils, where the deflecting coils have, in the scanning plane, a different number of turns on opposite sides. The object may be made of metal, ceramic, glass or plastic. The coatings may be used to improve life and operating performance of tools and machine parts, and as decorative coatings.
Owner:INT TECH EXCHANGE
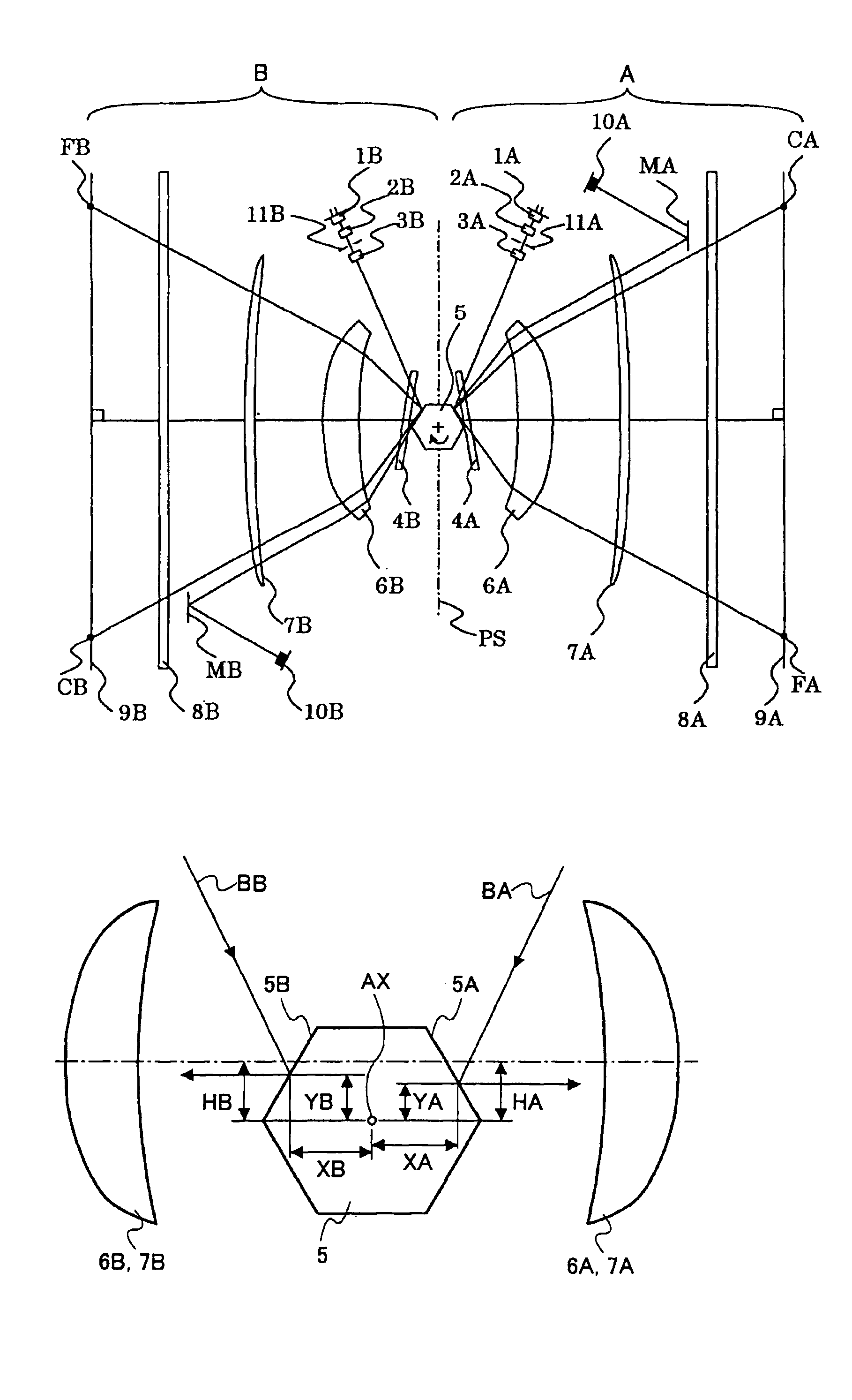
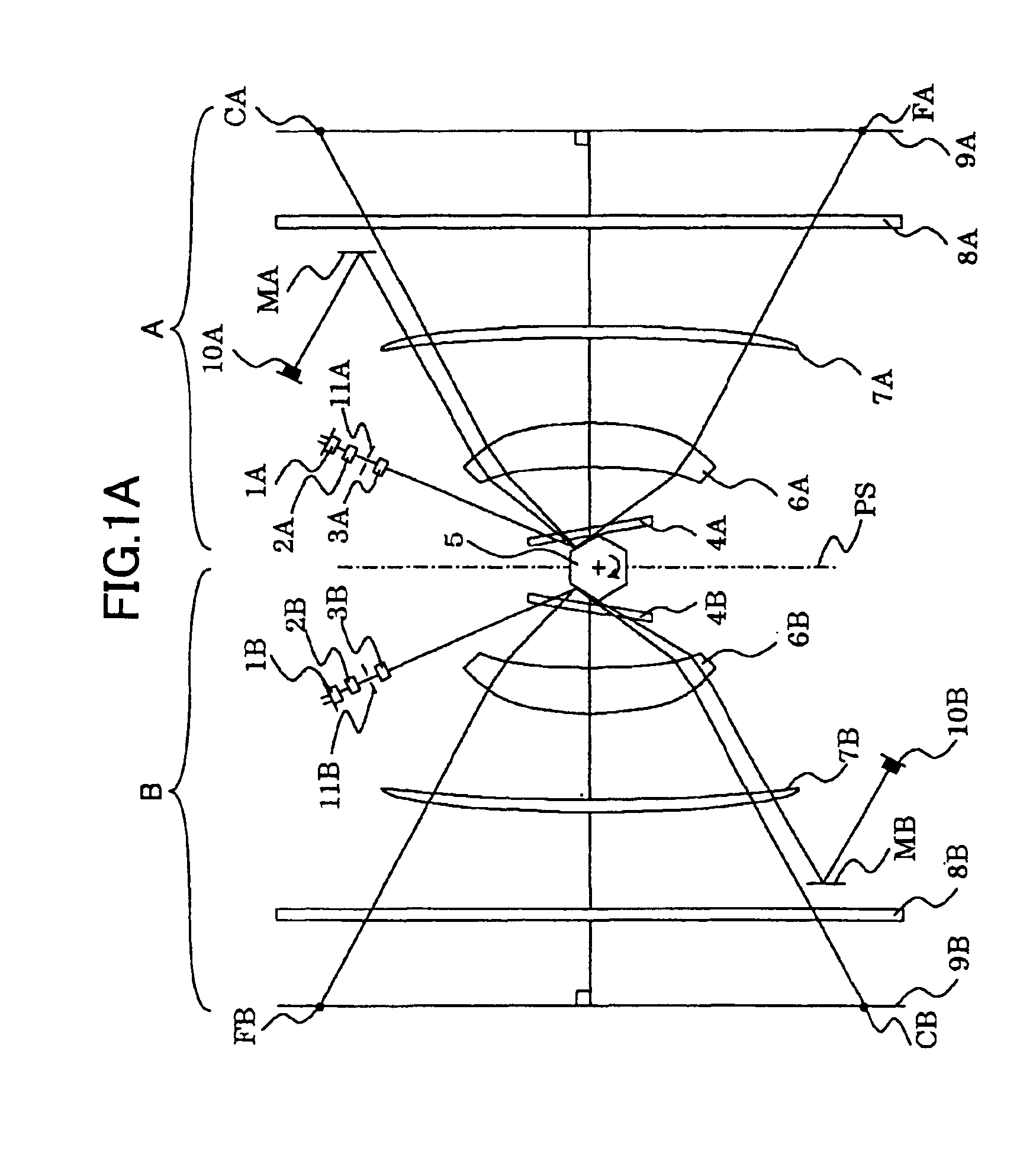
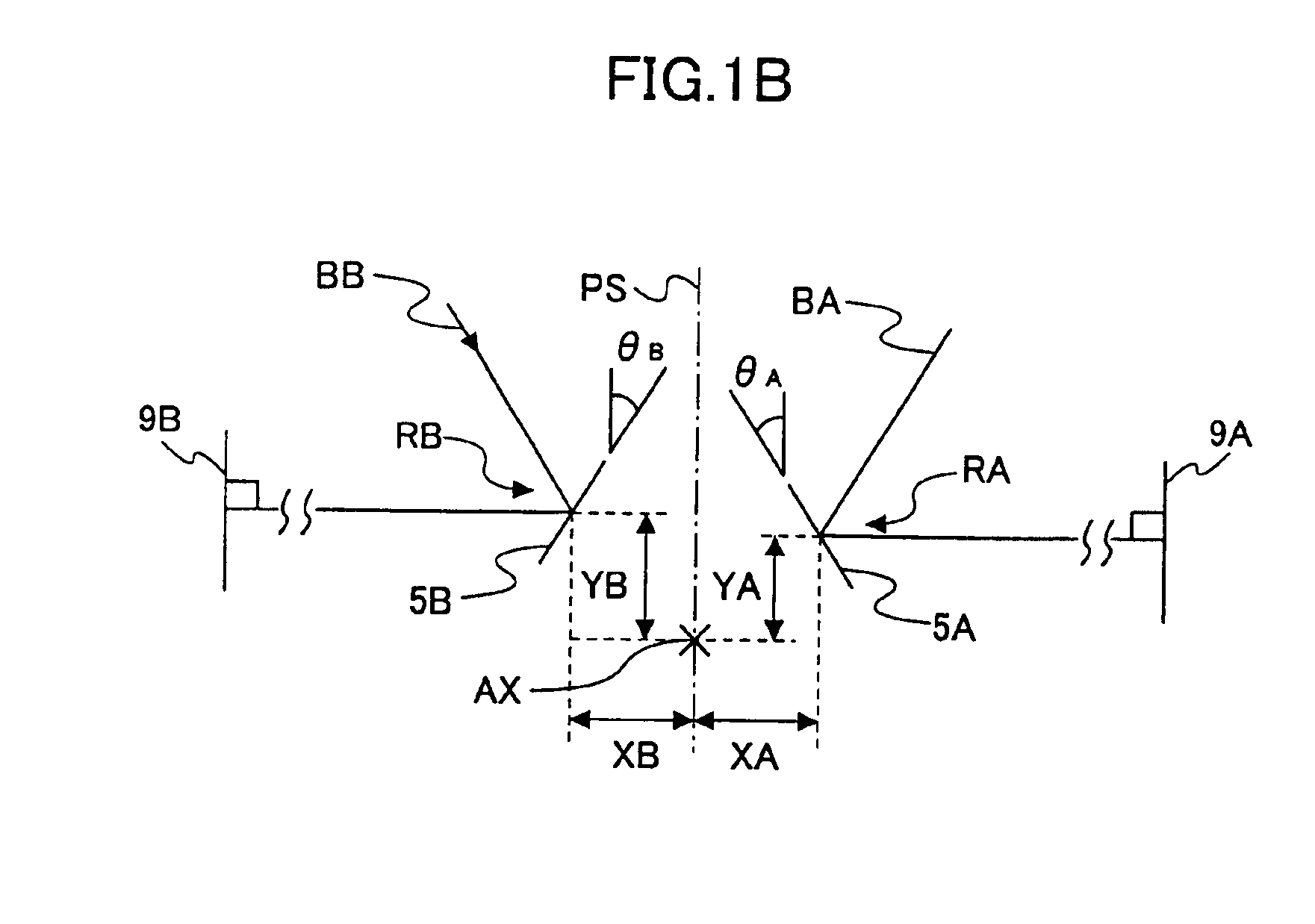
Optical scanner and image reproducing apparatus
ActiveUS6934061B2Reduce the dot offsetEffectiveInking apparatusOther printing apparatusOptical scannersCentre of rotation
An optical scanner includes at least a pair of optical scanning systems and a light deflector used in common between the optical scanning systems, each optical scanning system having a scan lens for guiding the beam deflected from the light deflector onto the associated scanned plane. One of the optical scanning systems has a first reference reflecting position on the light deflector, and the other optical scanning system has a second reference reflecting position on the light deflector. The first and second reference reflecting positions are asymmetric with respect to the reference plane of the optical scanner. The scan lenses of said pair of optical scanning systems are arranged to be symmetric with respect to a line passing through the rotational center of the light deflector and extending in parallel to the scanned planes.
Owner:RICOH KK
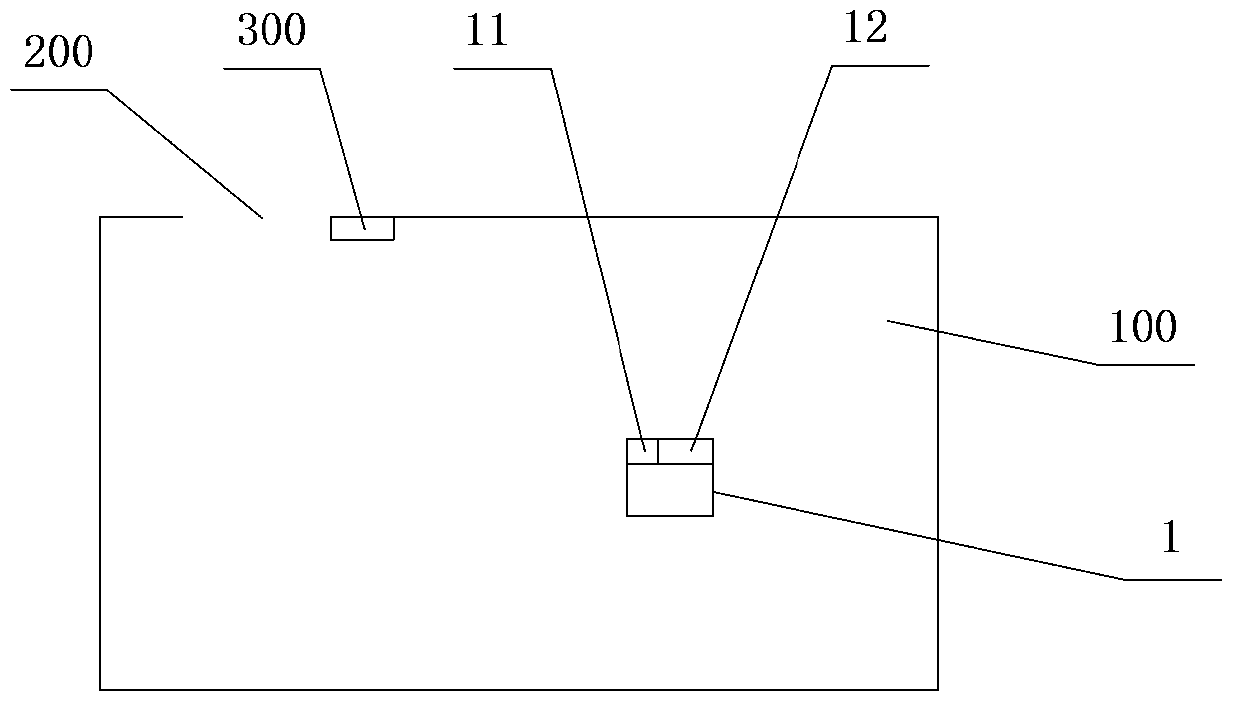
Automatic-mobile robot walking scope restriction system and restriction method thereof
ActiveCN103631262ASave energyImprove effective working timeElectromagnetic wave reradiationPosition/course control in two dimensionsWork periodEngineering
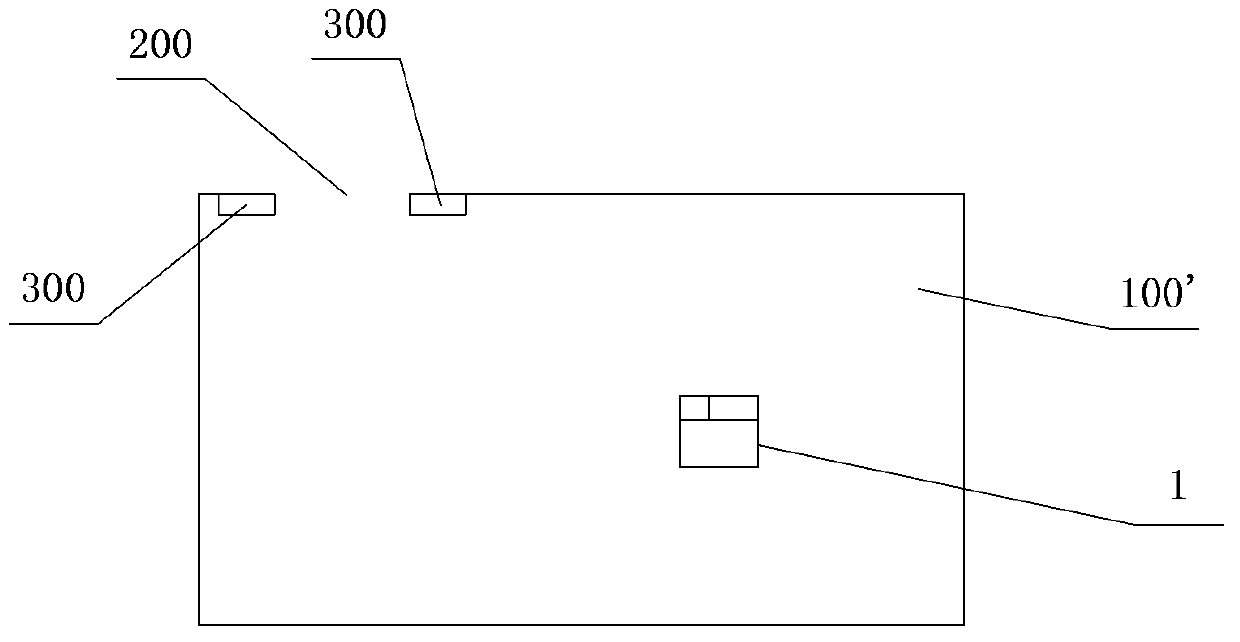
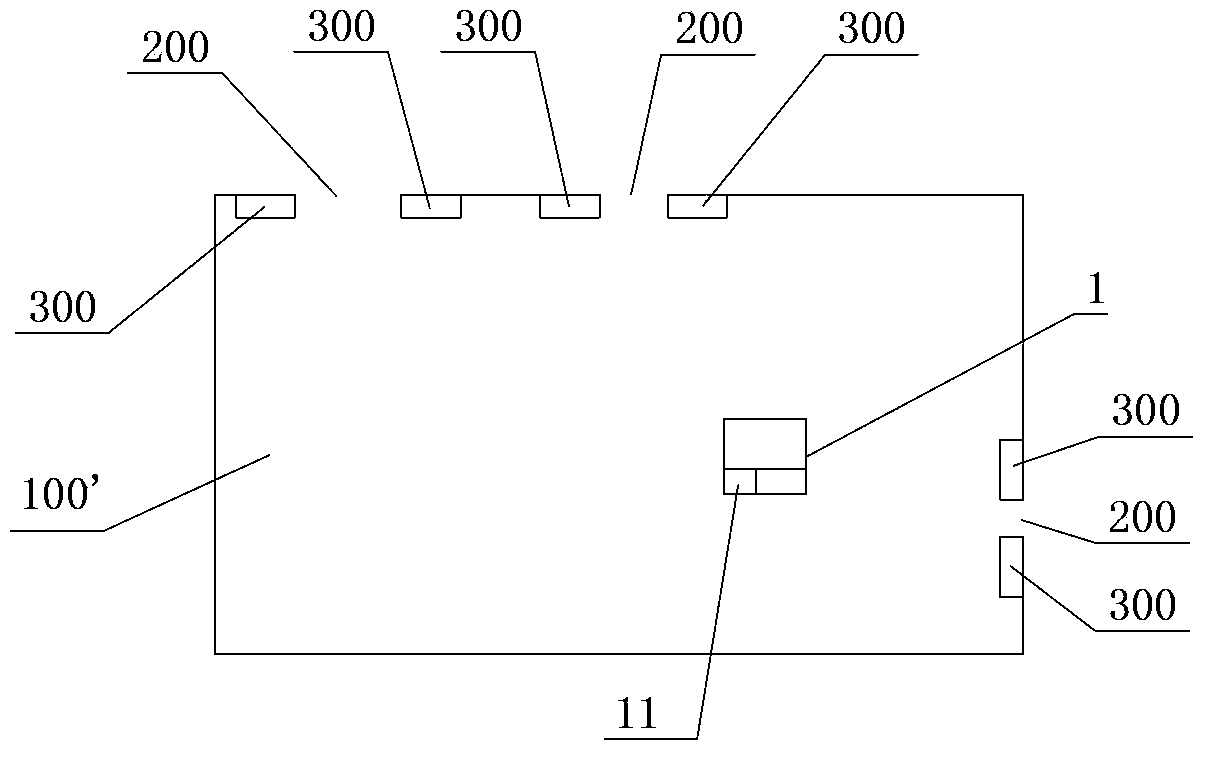
An automatic-mobile robot walking scope restriction system and a restriction method thereof are provided; the restriction system comprises the following structures: a boundary mark (300) used for determining restriction boundary positions of a work space (100), and the boundary mark comprises regression reflection material; an automatic-mobile robot (1) walking and working in the work space, and the robot comprises a scan range finder (12) sending and receiving light signals so as to form a scanning plane, thereby carrying out range finding and scanning process to the work space; the robot also comprises a control device (11) used for receiving scan and range finding signals of the scan range finder and setting up a coordinate chart of the work space. The control device receives the scan and range finding signals reflected from the boundary mark by the scan range finder, so the positions of the boundary mark are determined; the coordinates of the restricted boundary are determined according to the positions of the boundary mark, so the automatic-mobile robot can be controlled to work in an area in the restricted boundary. The automatic-mobile robot walking scope restriction system and the restriction method thereof can save energy, are long in effective work time, high in sensitivity and low in cost.
Owner:ECOVACS ROBOTICS (SUZHOU ) CO LTD
Autonomous moving apparatus having obstacle avoidance function
InactiveUS6515614B2Effective avoidanceReduce power consumptionAnti-collision systemsAutomatic initiationsRadarDetect and avoid
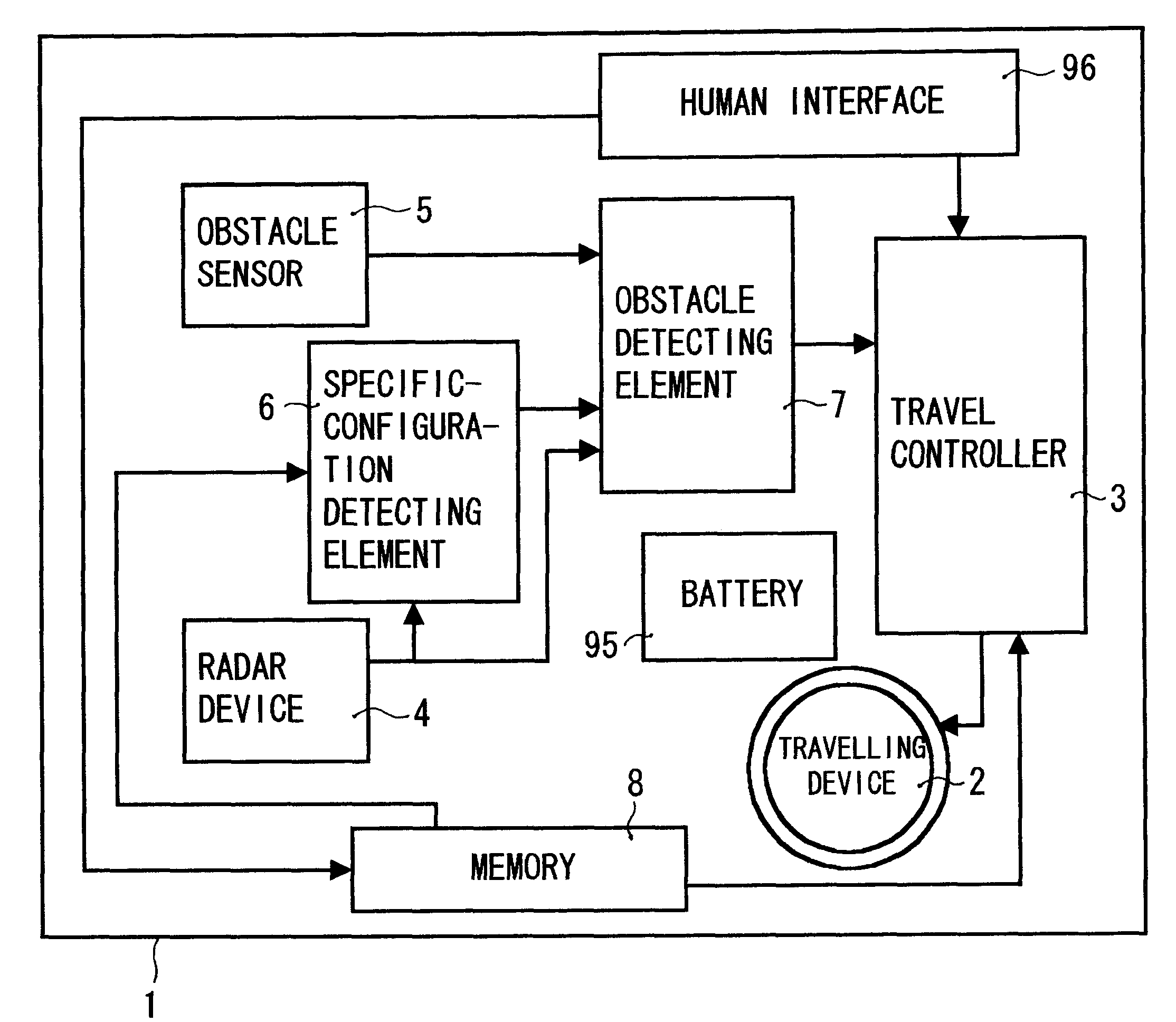
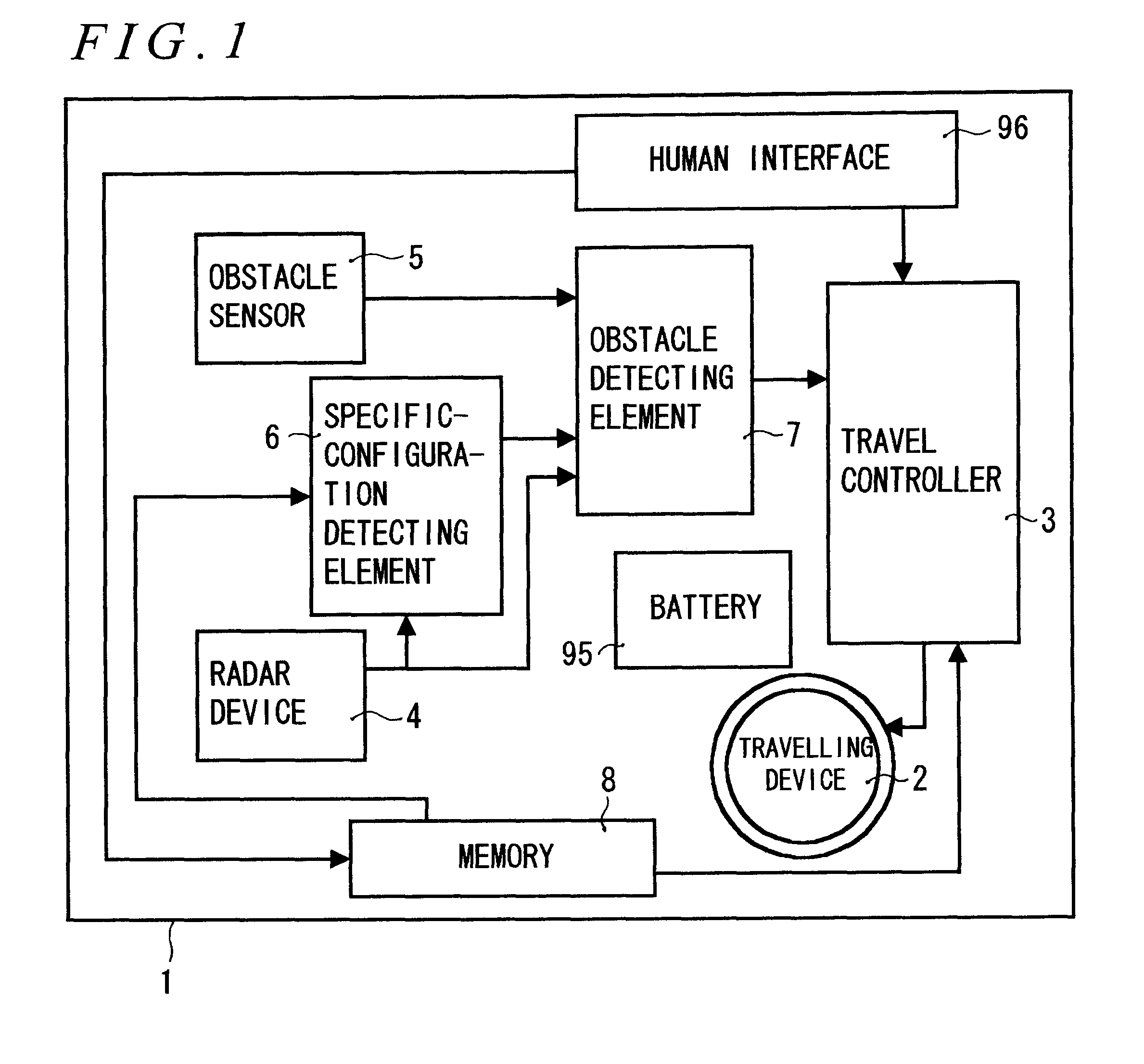
An autonomous moving apparatus moving to a destination while detecting and avoiding an obstacle includes a radar device for scanning a horizontal plane in its travelling direction to thereby detect a position of an obstacle and an obstacle sensor for detecting an obstacle in a space different from the scanning plane of the radar device. The apparatus moves to the destination under such control as to avoid the obstacle based on detection information from the radar device and the obstacle sensor from a detection output provided by a specific-configuration detecting element for detecting a present specific configuration from scanning information by the radar device. By providing such a specific-configuration detecting element that detects a specific configuration based on the scan information by the radar device that can accurately know about position information, it is possible to guess an obstacle having an upper structure, thus providing efficient avoidance.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
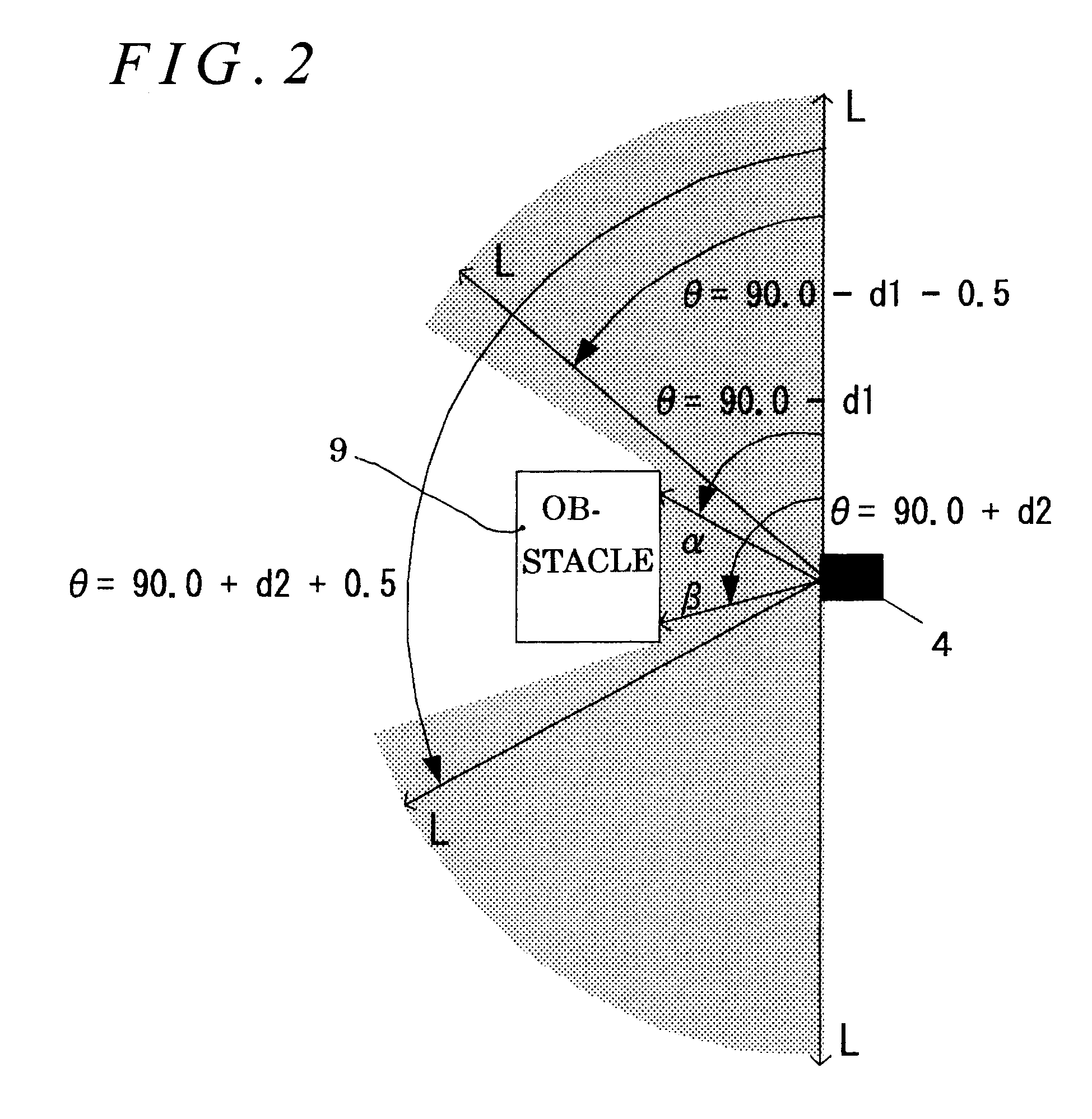
Treatment planning system, device for calculating a scanning path and particle therapy system
ActiveUS20120001085A1Improve uniformityThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTomographyNuclear medicine
In a particle therapy treatment planning system for creating treatment plan data, the movement of a target (patient's affected area) is extracted from plural tomography images of the target, and the direction of scanning is determined by projecting the extracted movement on a scanning plane scanned by scanning magnets. Irradiation positions are arranged on straight lines parallel with the scanning direction making it possible to calculate a scanning path for causing scanning to be made mainly along the direction of movement of the target. The treatment planning system can thereby realize dose distribution with improved uniformity.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for table/gantry alignment in imaging systems
InactiveUS6917666B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingNuclear medicineLaser beams
In an imaging system including a gantry having a patient bore, and a patient table having a cradle, a method of aligning the cradle with a scan plane in the patient bore is disclosed. The method comprises positioning a laser device at least partially within the patient bore, the laser device producing an alignment laser beam projecting along a center axis of the patient bore normal to the scan plane. The method further comprises aligning the cradle of the patient table such that when the cradle is translated into the scan plane in the patient bore, the alignment laser beam intersects a positioning target on the cradle.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiple scan-plane ultrasound imaging of objects
ActiveUS7758509B2Delay is slowImprove acousticsBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionFiberUltrasound imaging
A method of real time ultrasound imaging of an object in at least three two-dimensional scan planes that are rotated around a common axis, is given, together with designs of ultrasound transducer arrays that allows for such imaging. The method is also introduced into a monitoring situation of cardiac function where, combined with other measurements as for example the LV pressure, physiological parameters like ejection fraction and muscular fiber stress is calculated.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Vehicle door control apparatus and method for controlling vehicle door
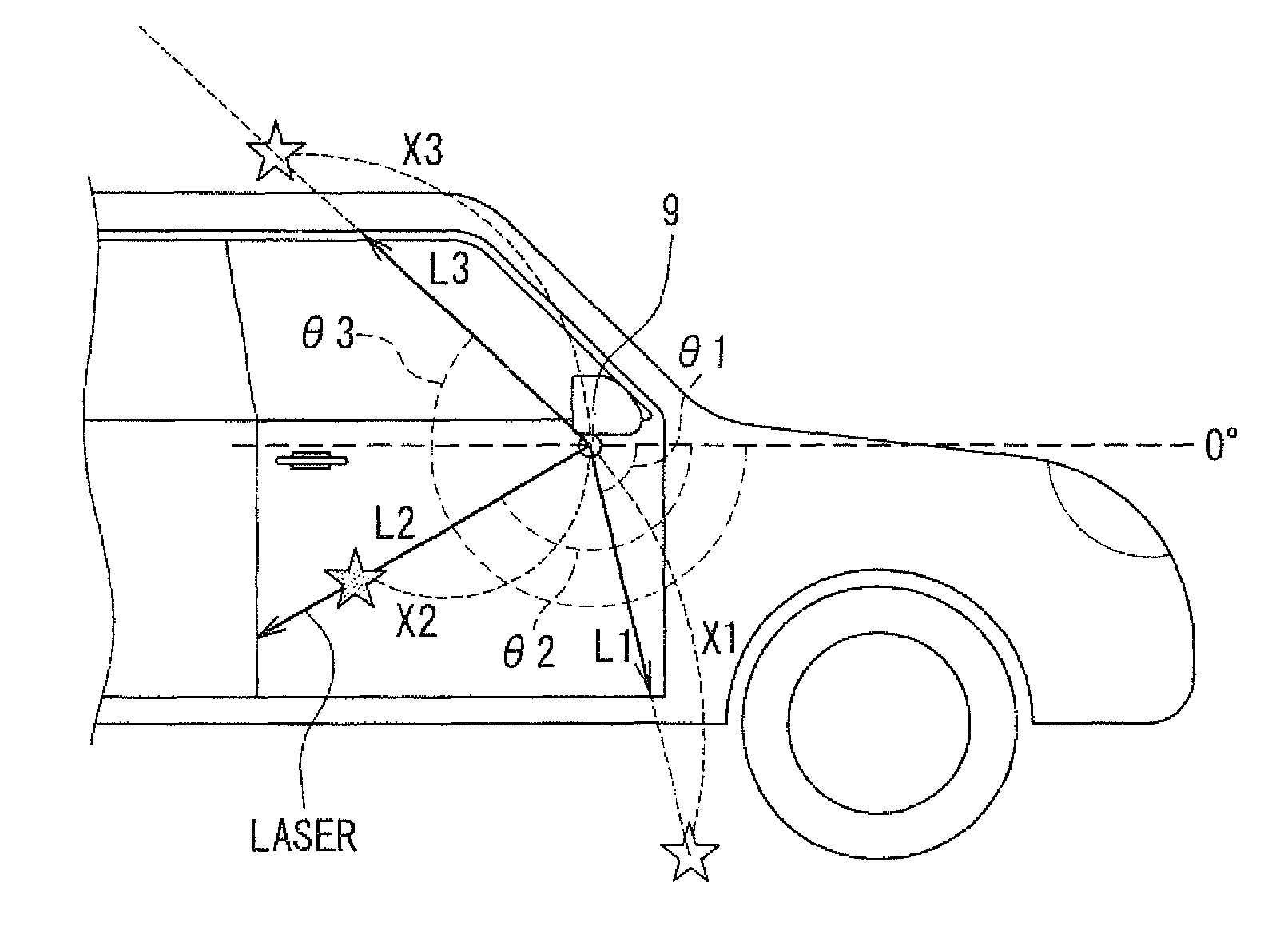
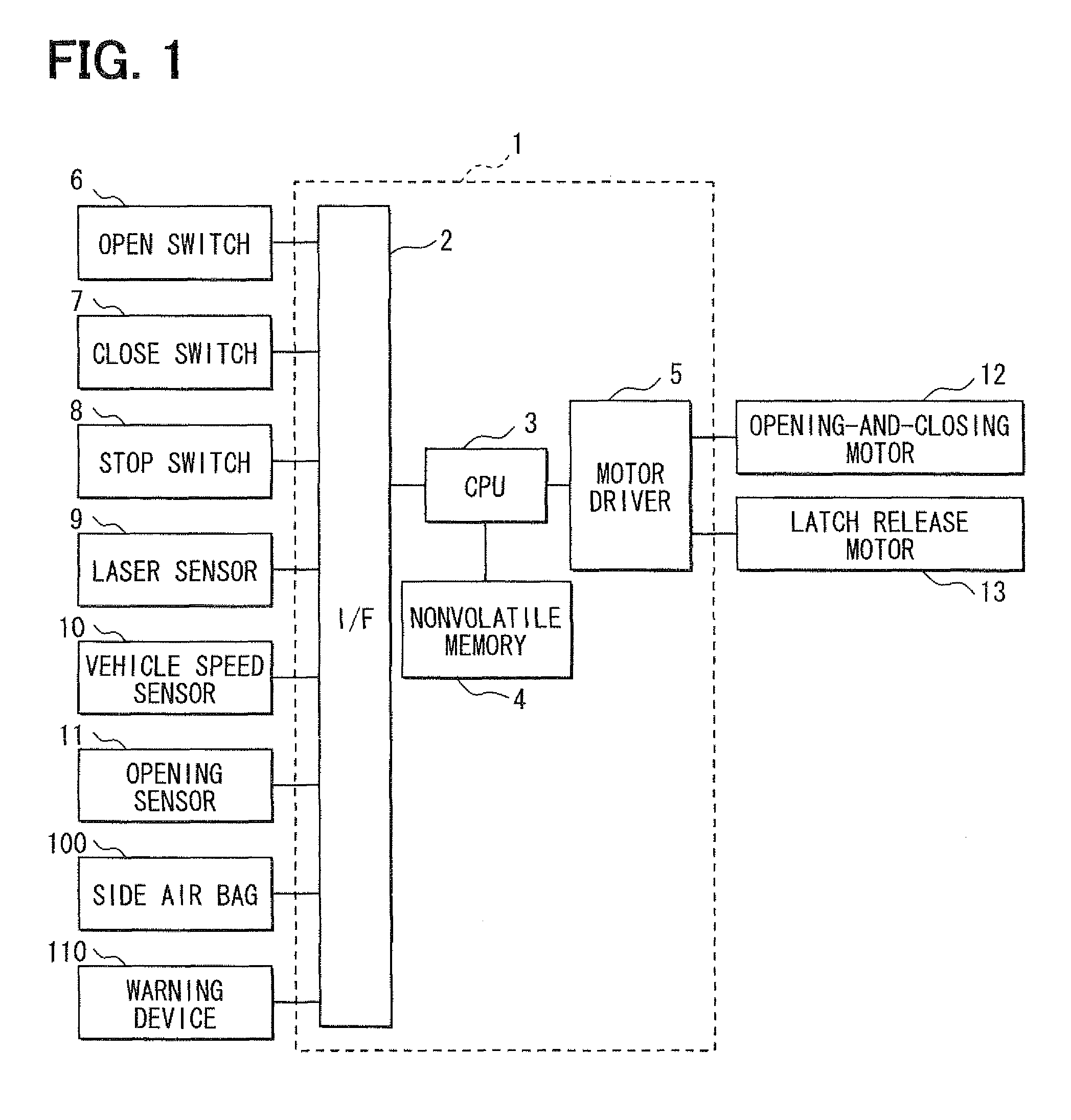
A laser sensor is located close to a rotation axis of a vehicle door and configured to emit a laser beam to a surface of the vehicle door and accept reflected light reflected from an obstacle for scanning a scanning plane shifted in a door-opening direction, in which the vehicle door is openable. A determination section determines whether an obstacle, which is possible to make contact with the vehicle door, exists in the door-opening direction of the vehicle door, based on a result of emission and acceptance of the laser beam of the laser sensor. An opening regulating section regulates an opening of the vehicle door in response to determination of the determination section that the obstacle exists.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
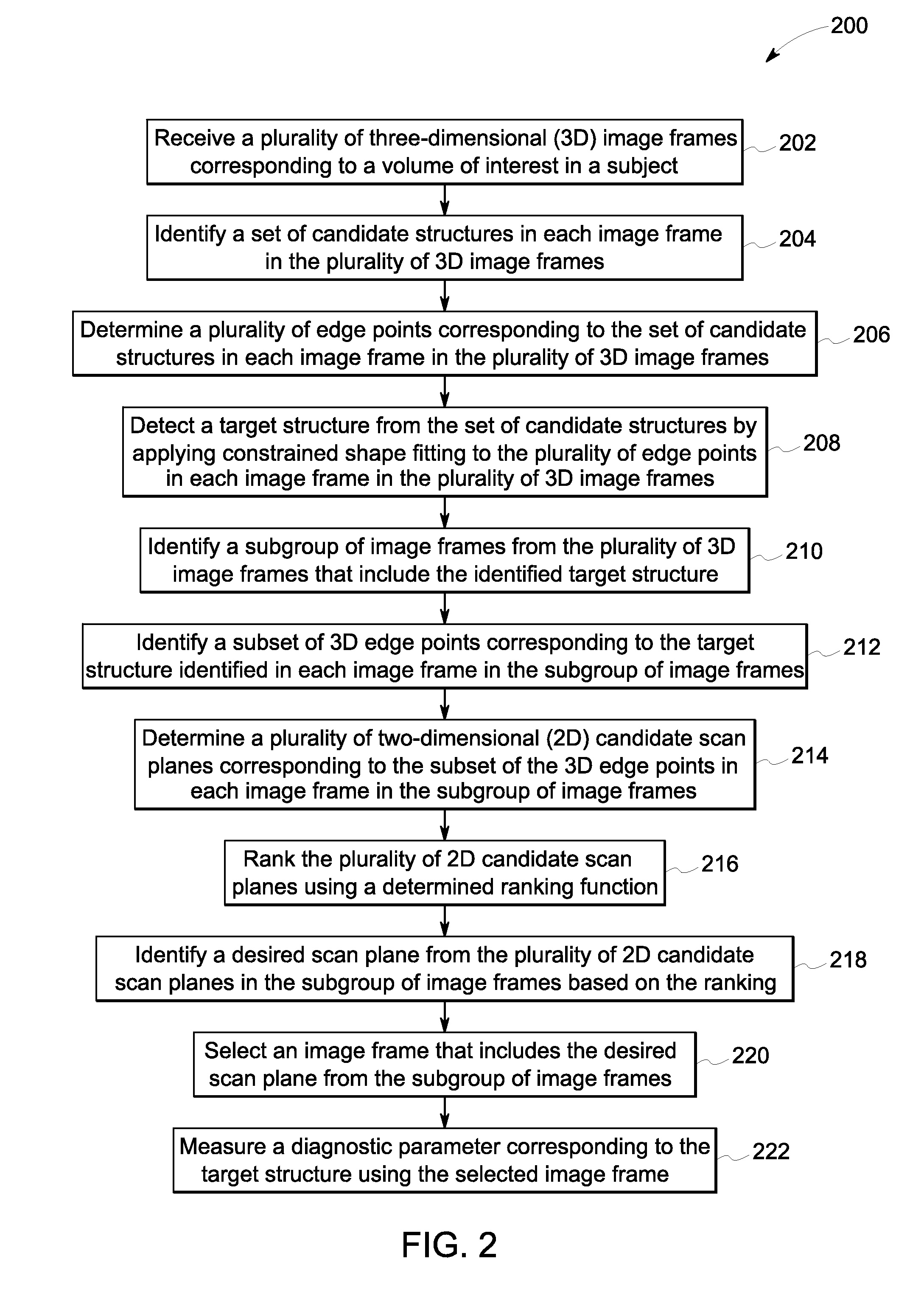
Method and system for automated detection and measurement of a target structure
A system and method for imaging a subject are disclosed. A plurality of edge points corresponding to a set of candidate structures are determined in each image frame in a plurality of 3D image frames corresponding to a volume in the subject. A target structure is detected from the set of candidate structures by applying constrained shape fitting to the edge points in each image frame. A subgroup of image frames including the target structure is identified from the 3D frames. A subset of edge points corresponding to the target structure is determined in each of the subgroup of image frames. A plurality of 2D scan planes corresponding to the subset of edge points is determined, and ranked using a determined ranking function to identify a desired scan plane. A diagnostic parameter corresponding to the target structure is measured using a selected image frame that includes the desired scan plane.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Machine for milling traffic areas
InactiveUS7510347B2Simple waySlitting machinesRoads maintainenceLaser scanningElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention relates to a machine for milling traffic areas. The machine has a vertically adjustable chassis which carries a steerable traveling mechanism and a drive unit for moving the machine and for driving a milling mechanism coupled to the drive unit. A laser scanner is attached to at least on one side of the chassis. With the laser scanner, the height relative to the surface of a traffic area to be milled can be measured and the chassis can be set vertically in accordance with the measured values relative to the surface of the traffic area to be milled. The laser scanner is attached in the center side-wall region of the chassis. The scanning plane of the laser scanner is essentially parallel to the side-wall region of the chassis and at a height which permits monitoring of a hazard region which extends at least over the side length of the machine. The laser scanner produces a trigger signal if a disturbance occurs in the scanning plane.
Owner:ABG ALLG BAUMASCHINEN GMBH
Single wave beam scanning imaging method of passive THz wave imaging system
The invention relates to a fast scanning method based on the passive imaging of a single wave beam THz wave. Aiming at the problems of longer scanning time and overhigh system construction cost in an earlier scanning imaging method of the single beam THz wave, a rocker of a crank and rocker mechanism is adopted to drive a line scanning plane mirror to sway horizontally so as to achieve fast transverse scanning motion, and a field scanning plane mirror swaying vertically in a reciprocating way is utilized to realize longitudinal scanning motion, thereby realizing the two-dimensional scanning imaging over object space. On the premise of construction cost reduction, the invention greatly improves the scanning speed per se and simultaneously amplifies the scanning viewing field. In addition, the invention is not only suitable for the passive type THz wave single wave beam scanning imaging, but also suitable for the active type single wave beam scanning imaging of the THz wave.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com