Patents
Literature
81 results about "Real time ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
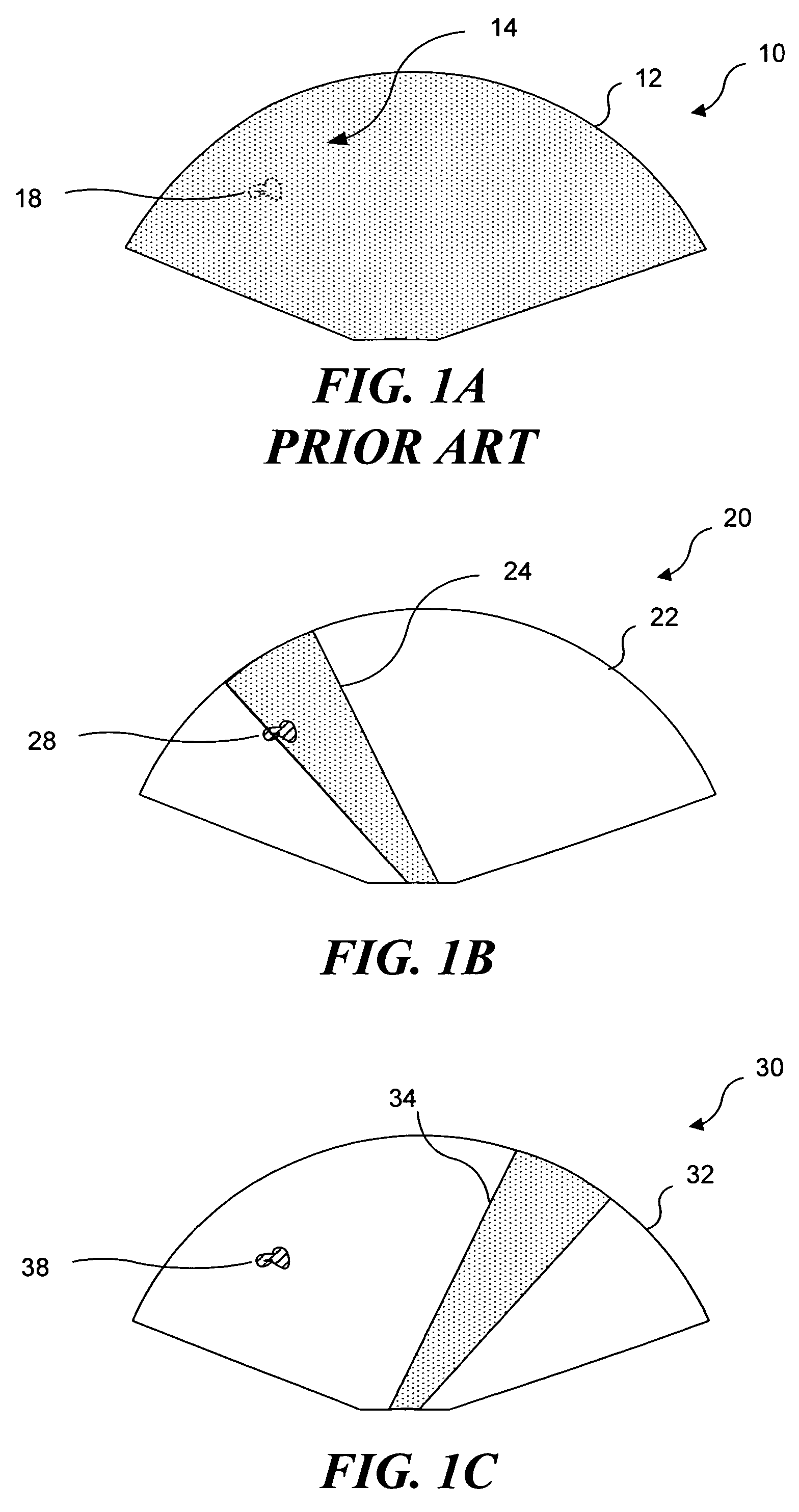
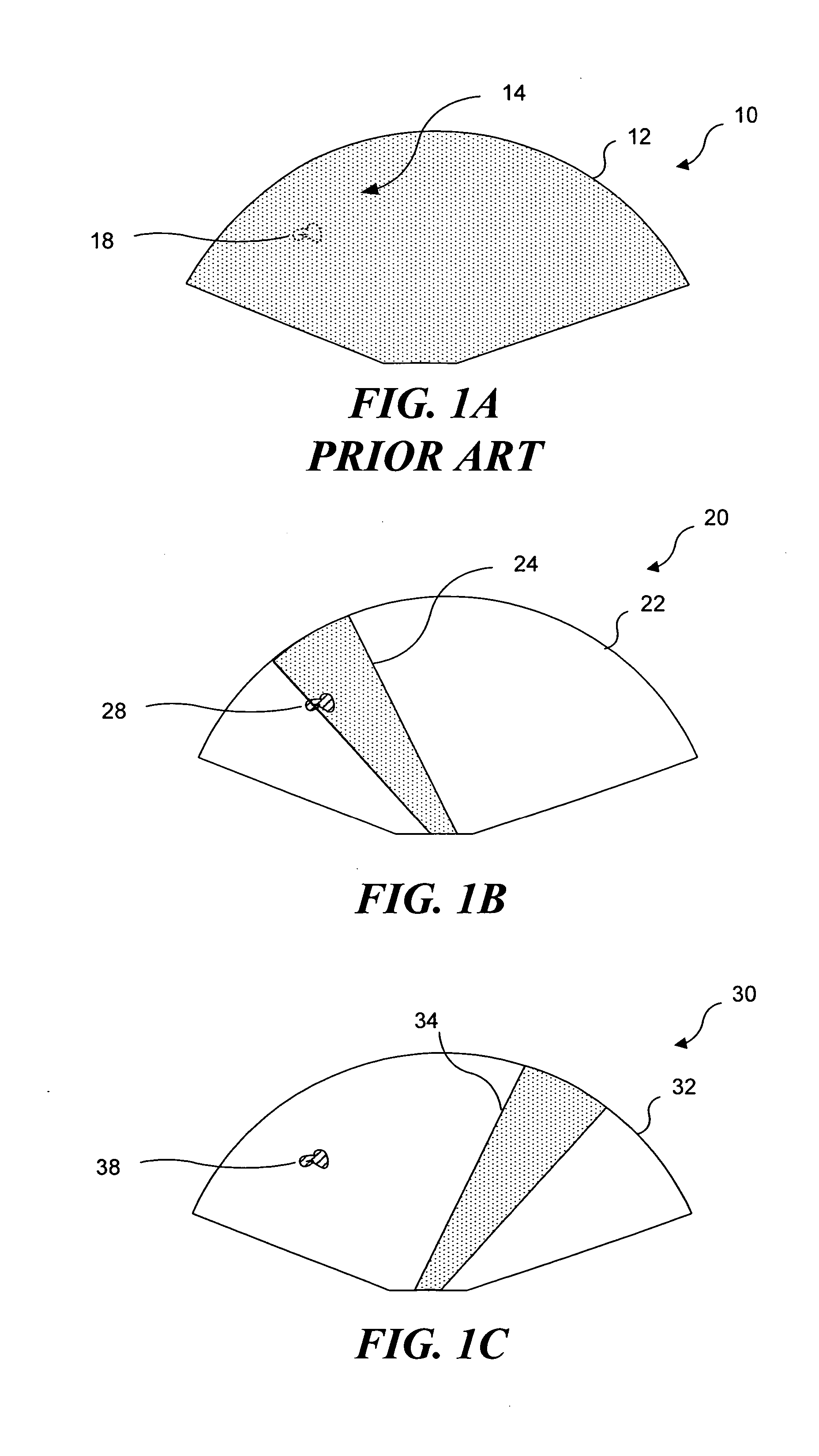
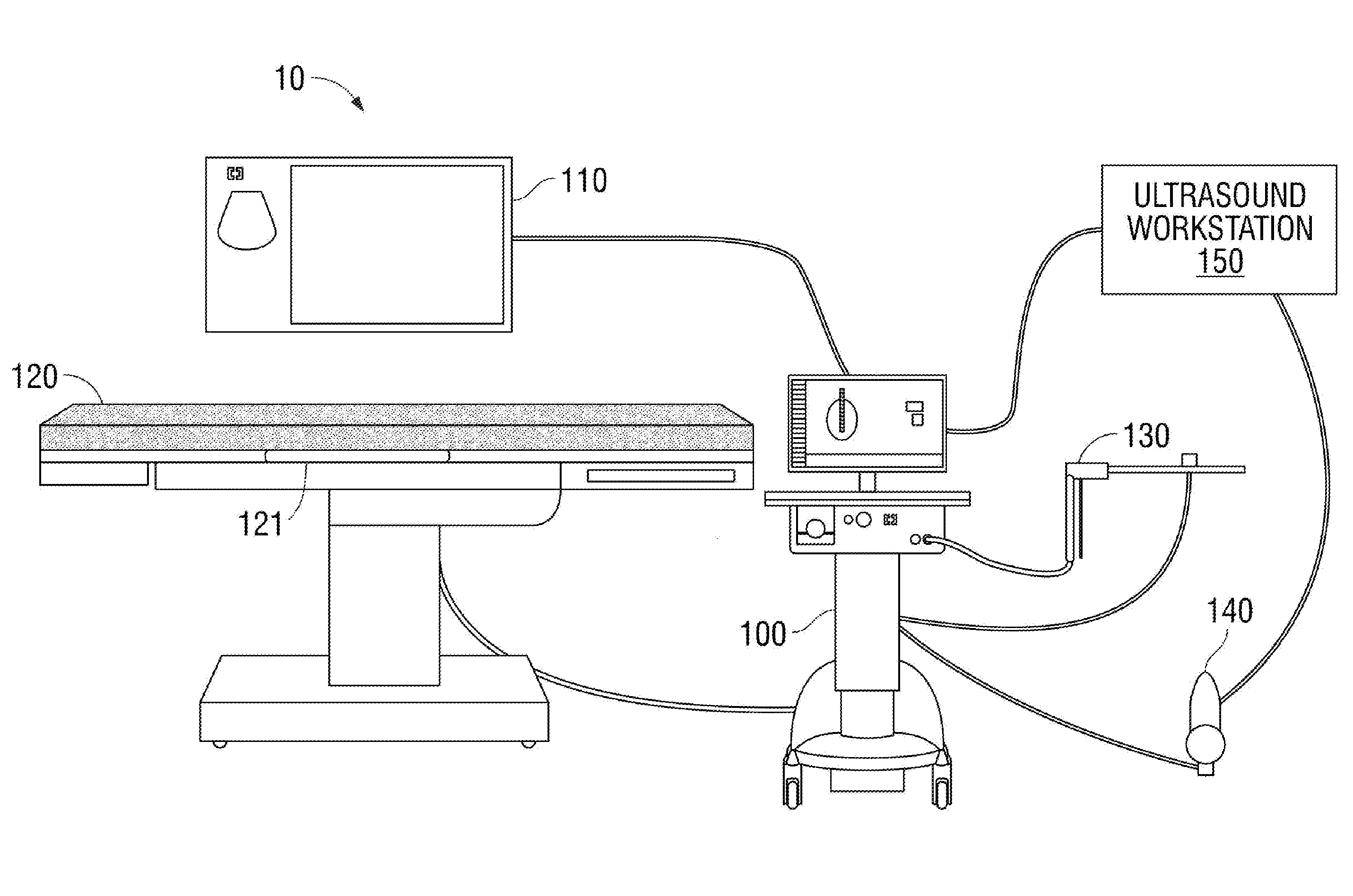
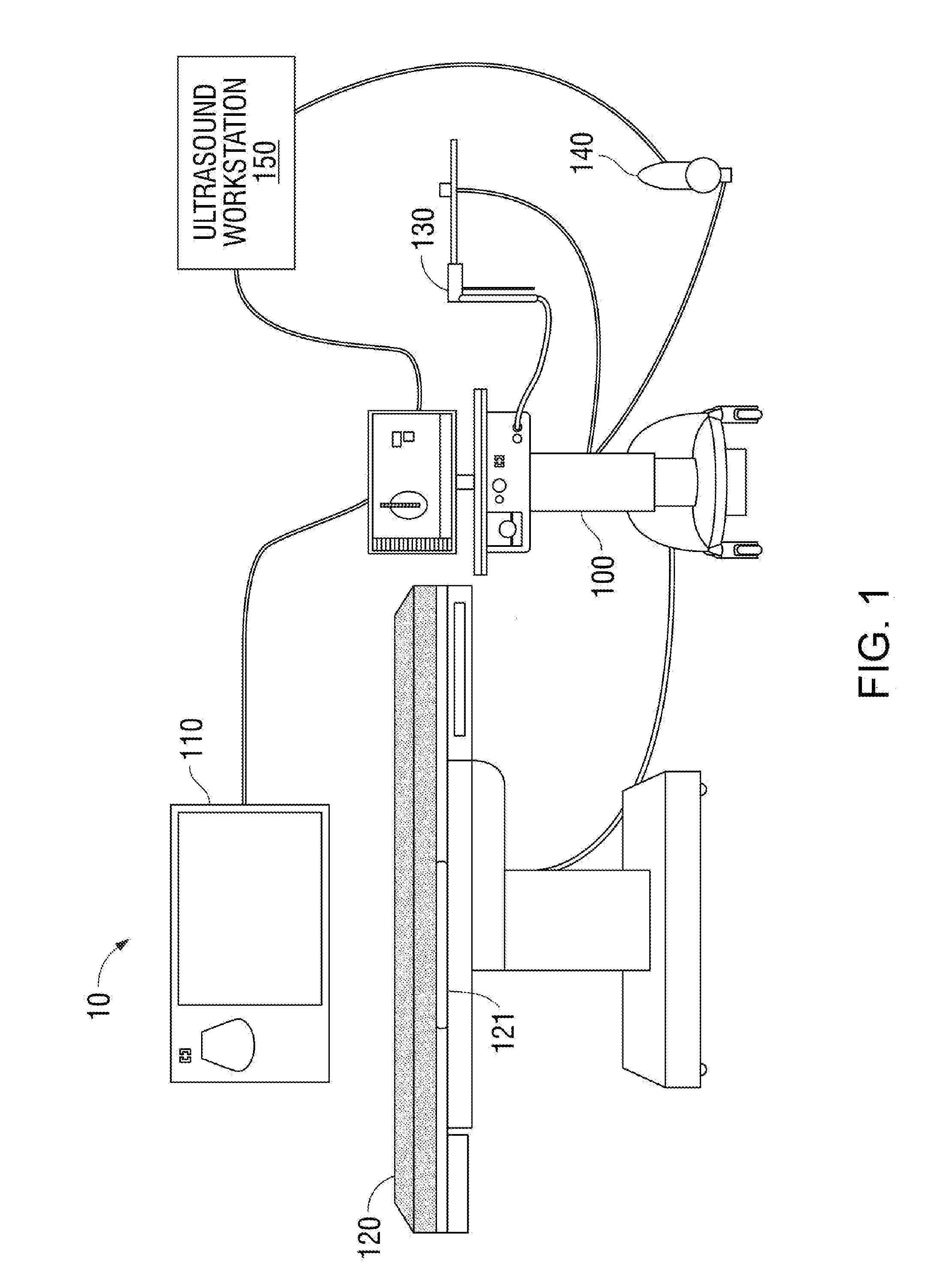
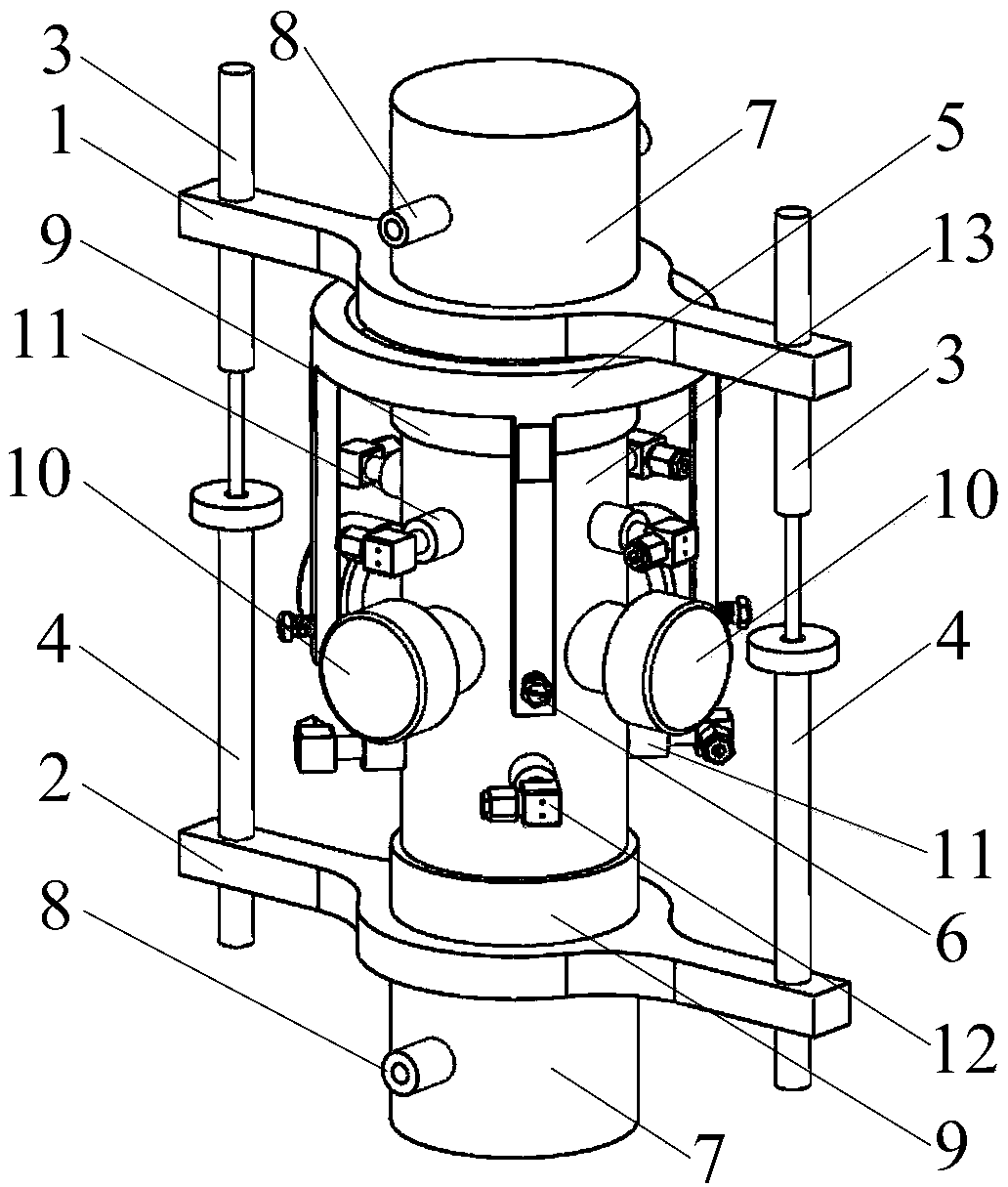
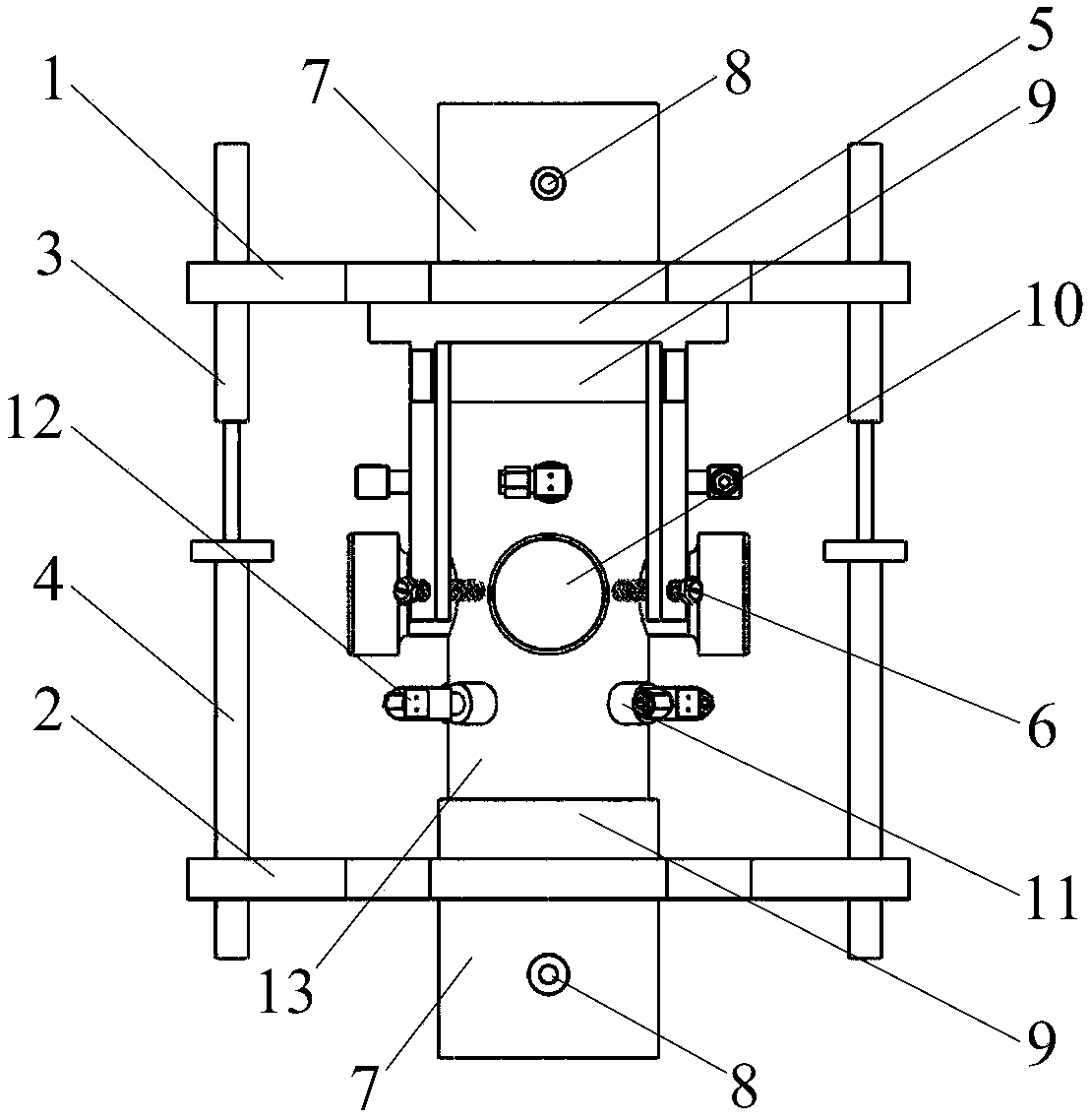
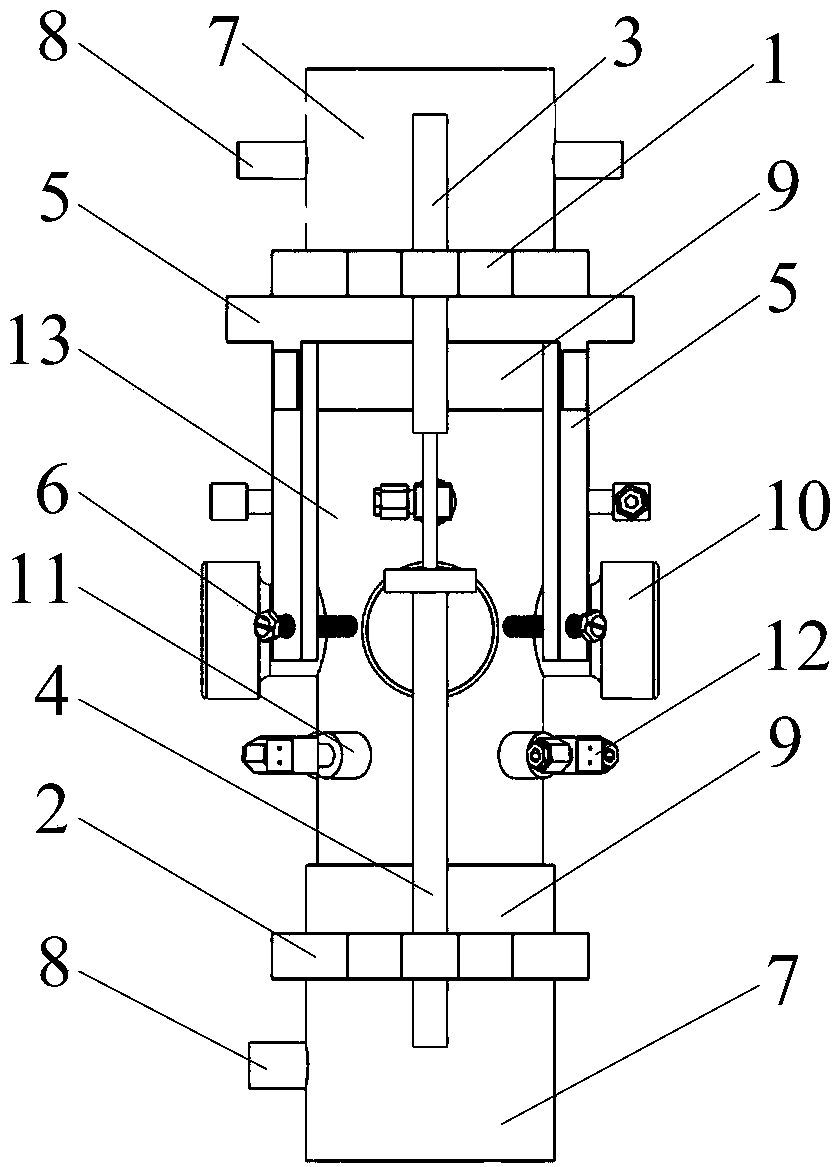
Medical devices with enhanced ultrasonic visibilty
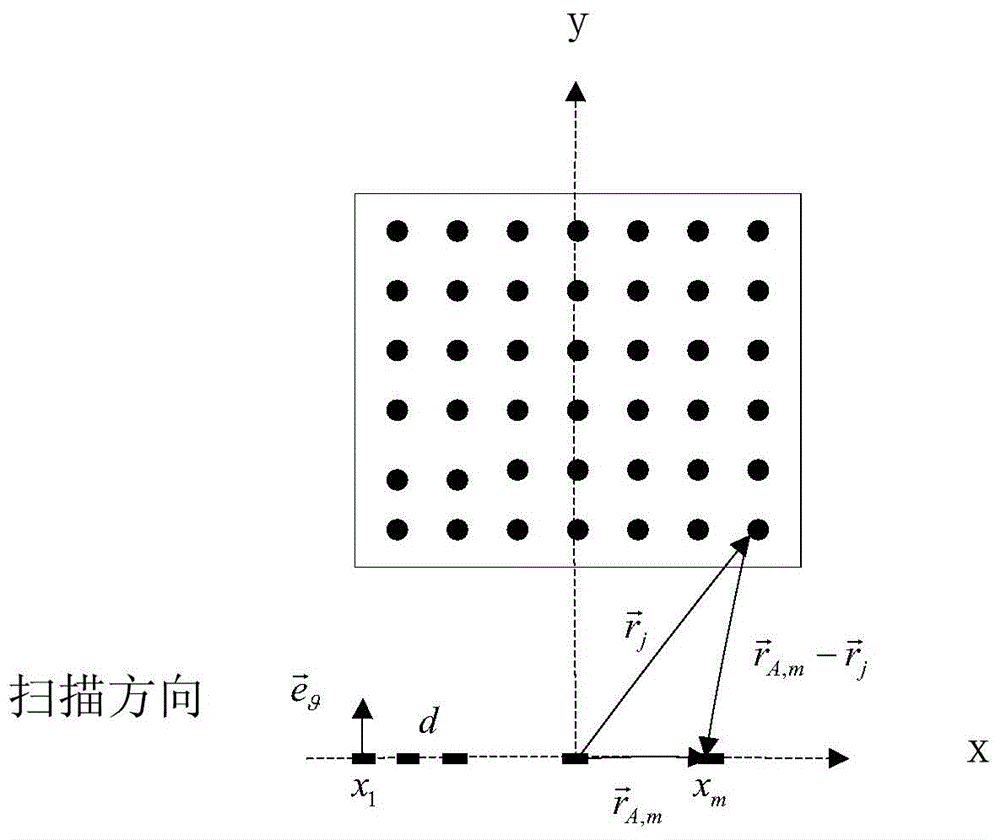
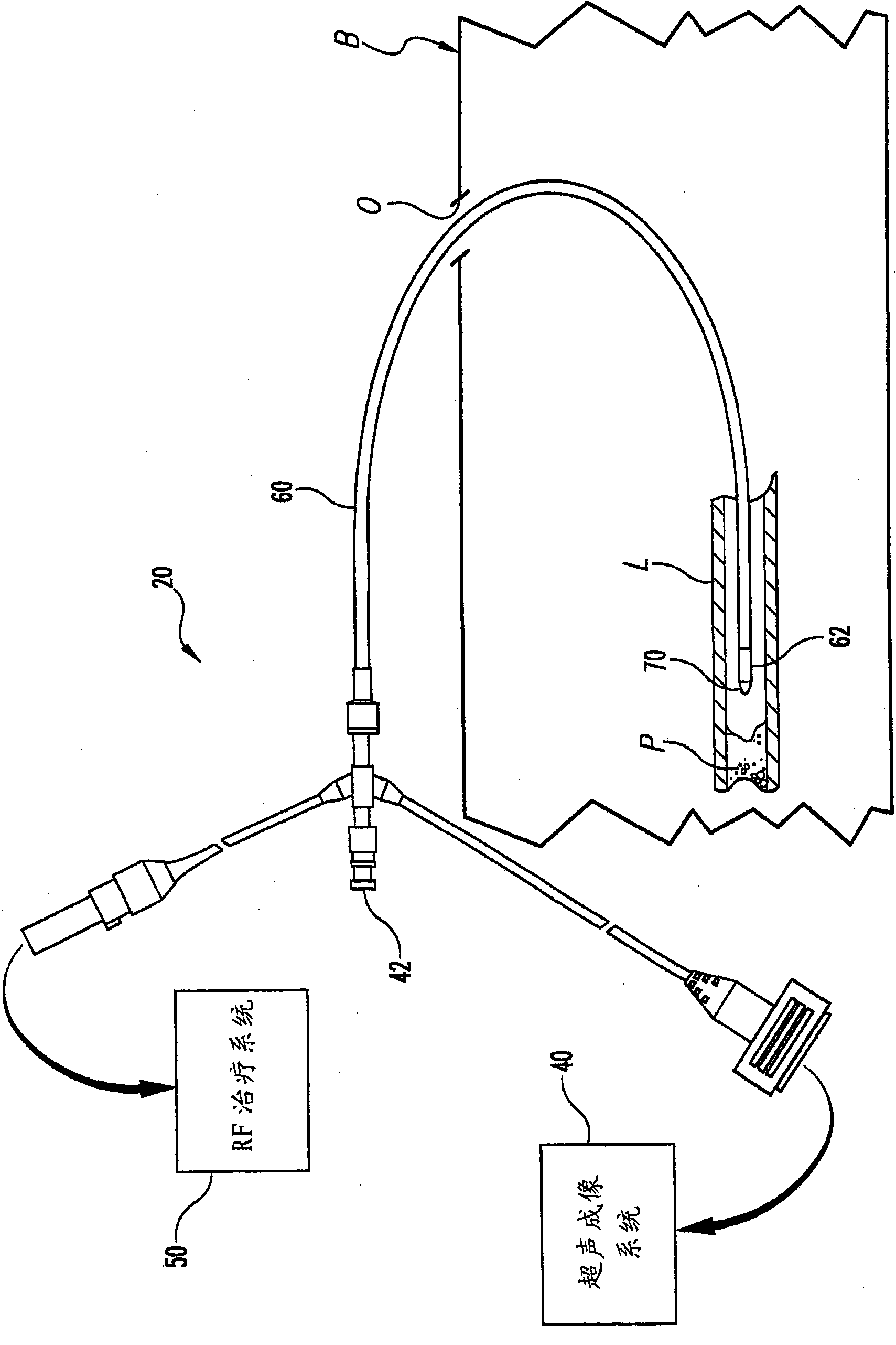
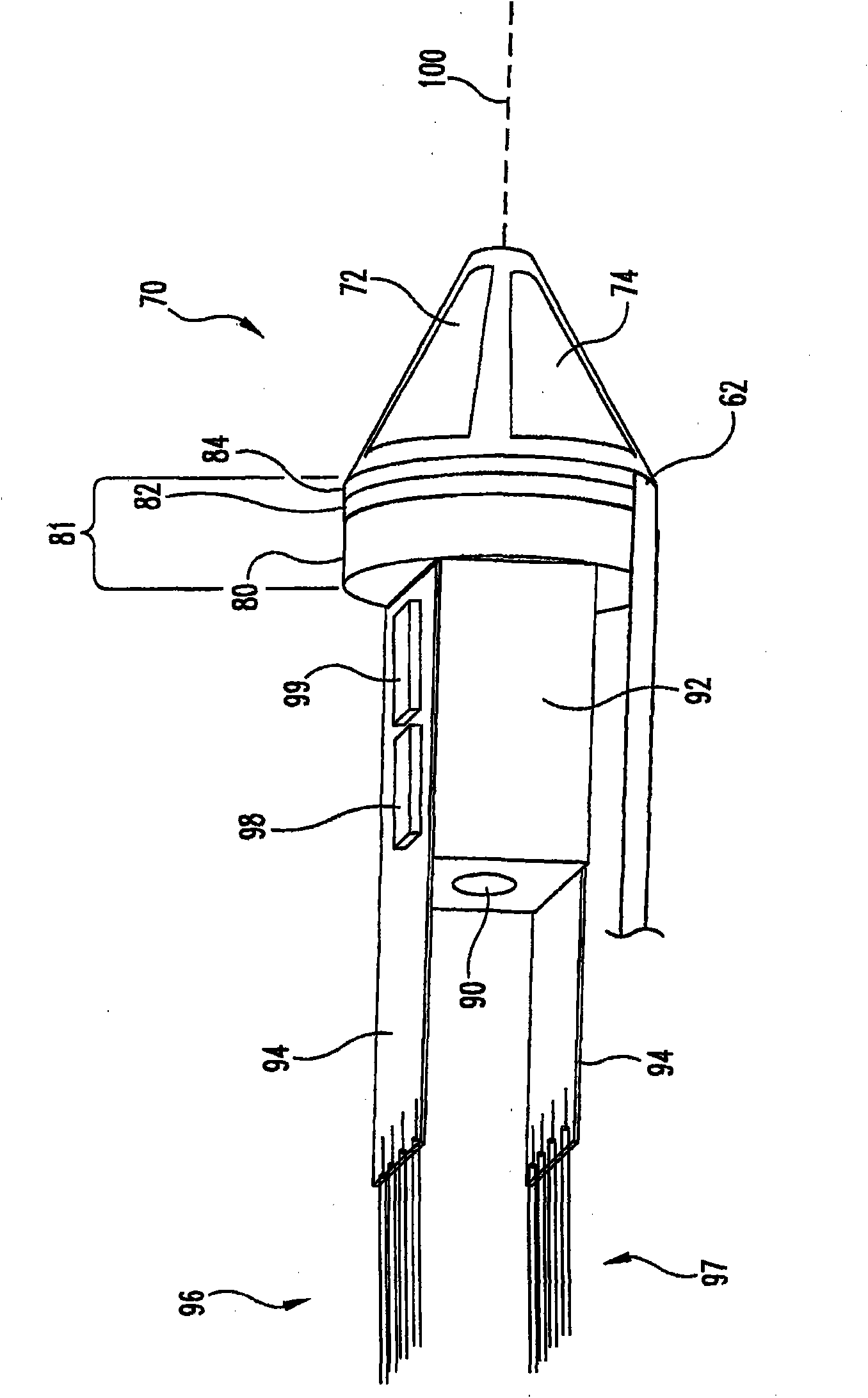
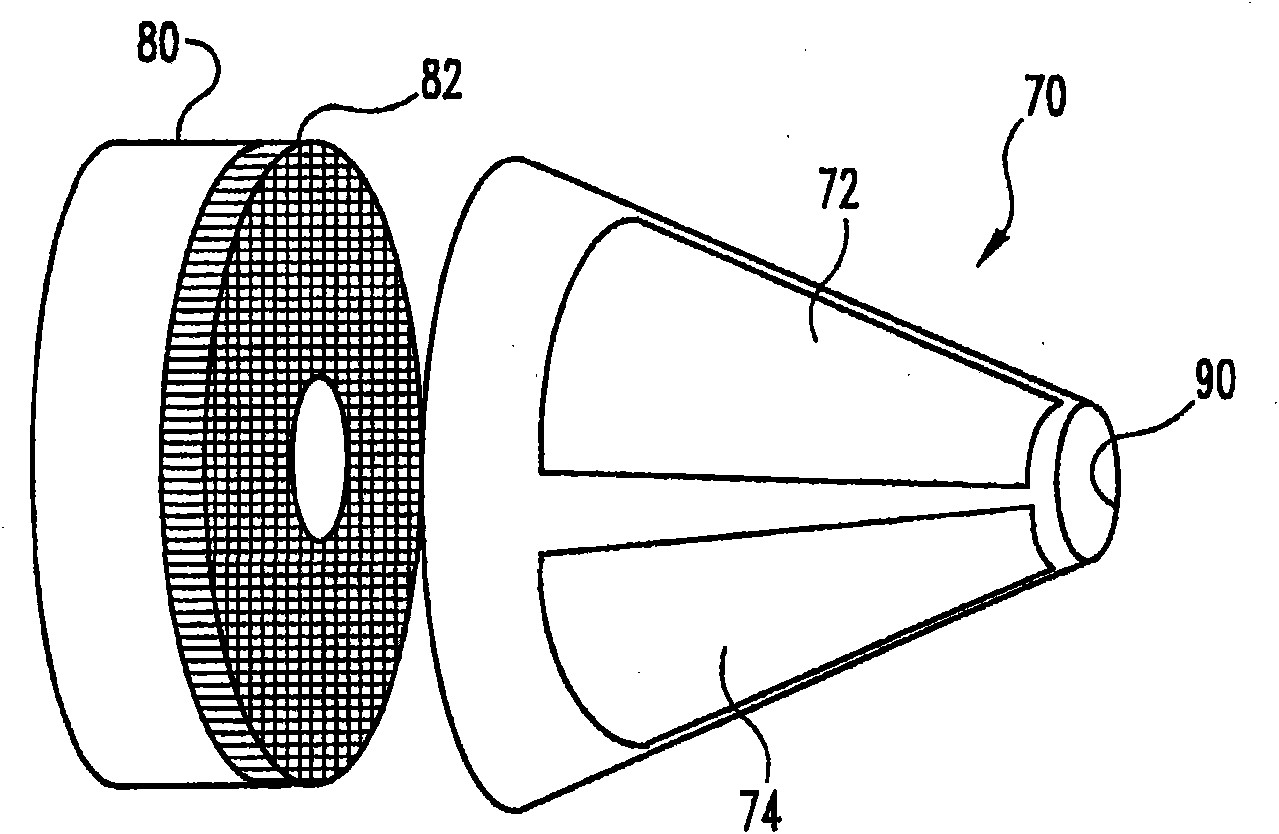
InactiveUS20070197954A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyTip positionSolid tissue
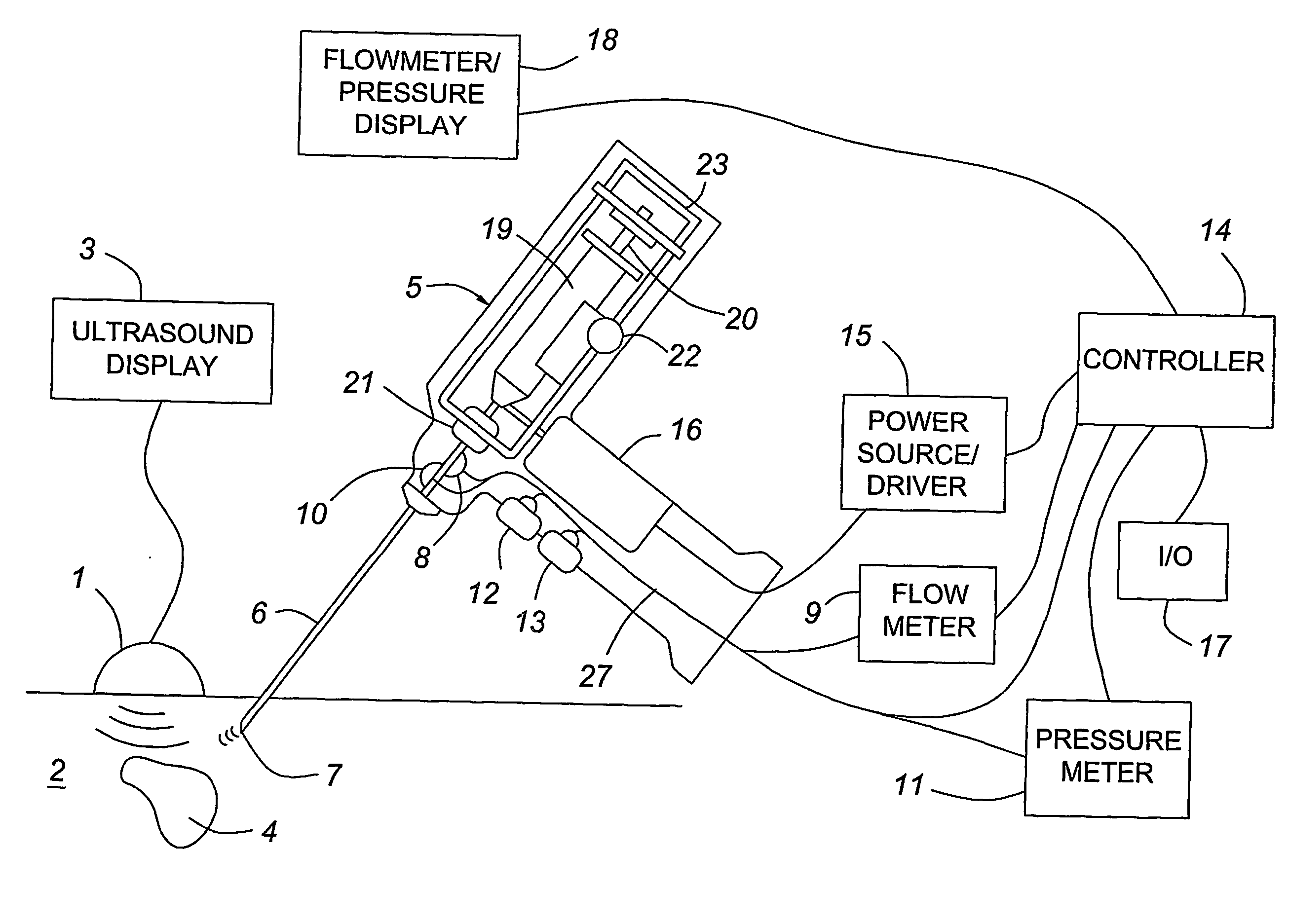
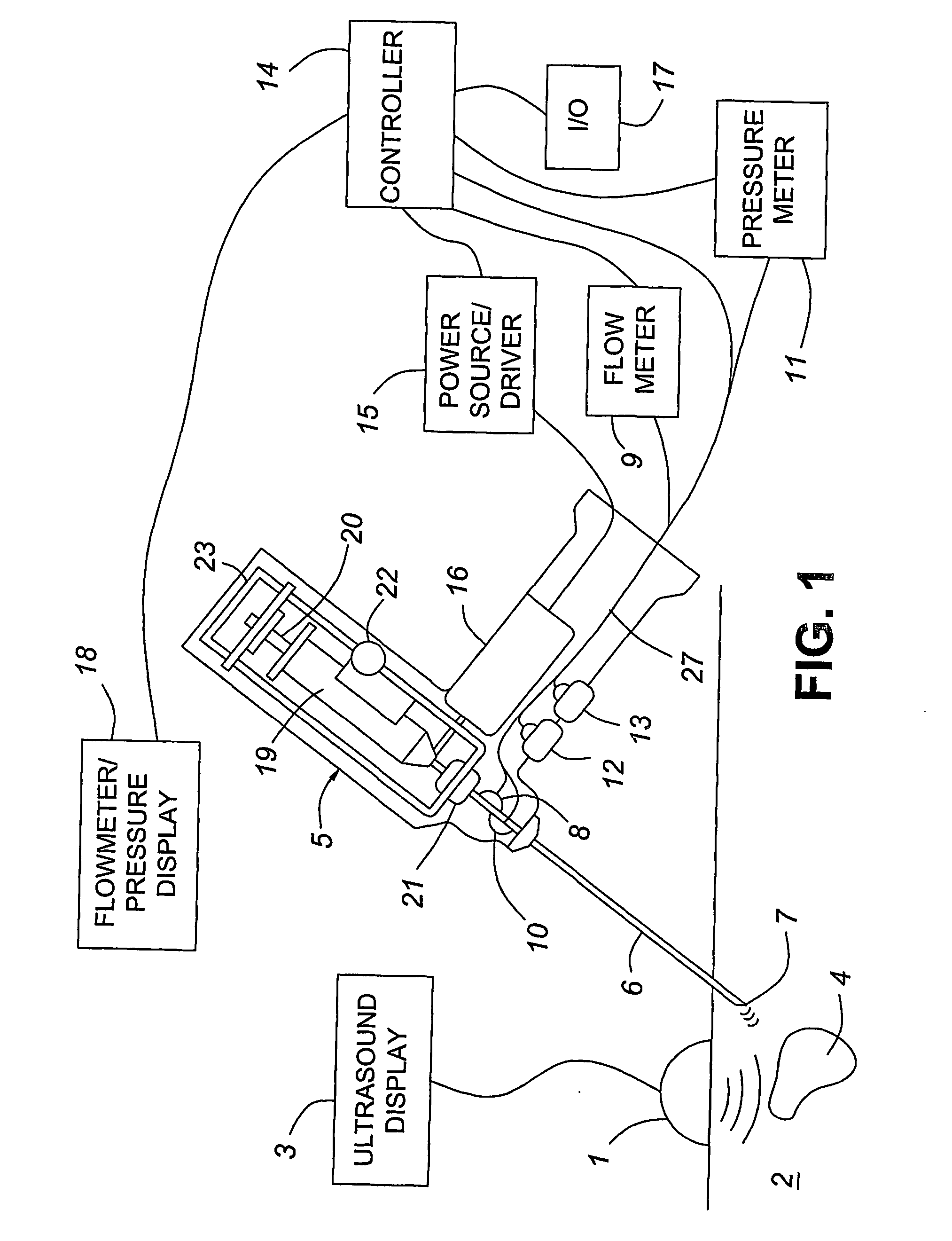
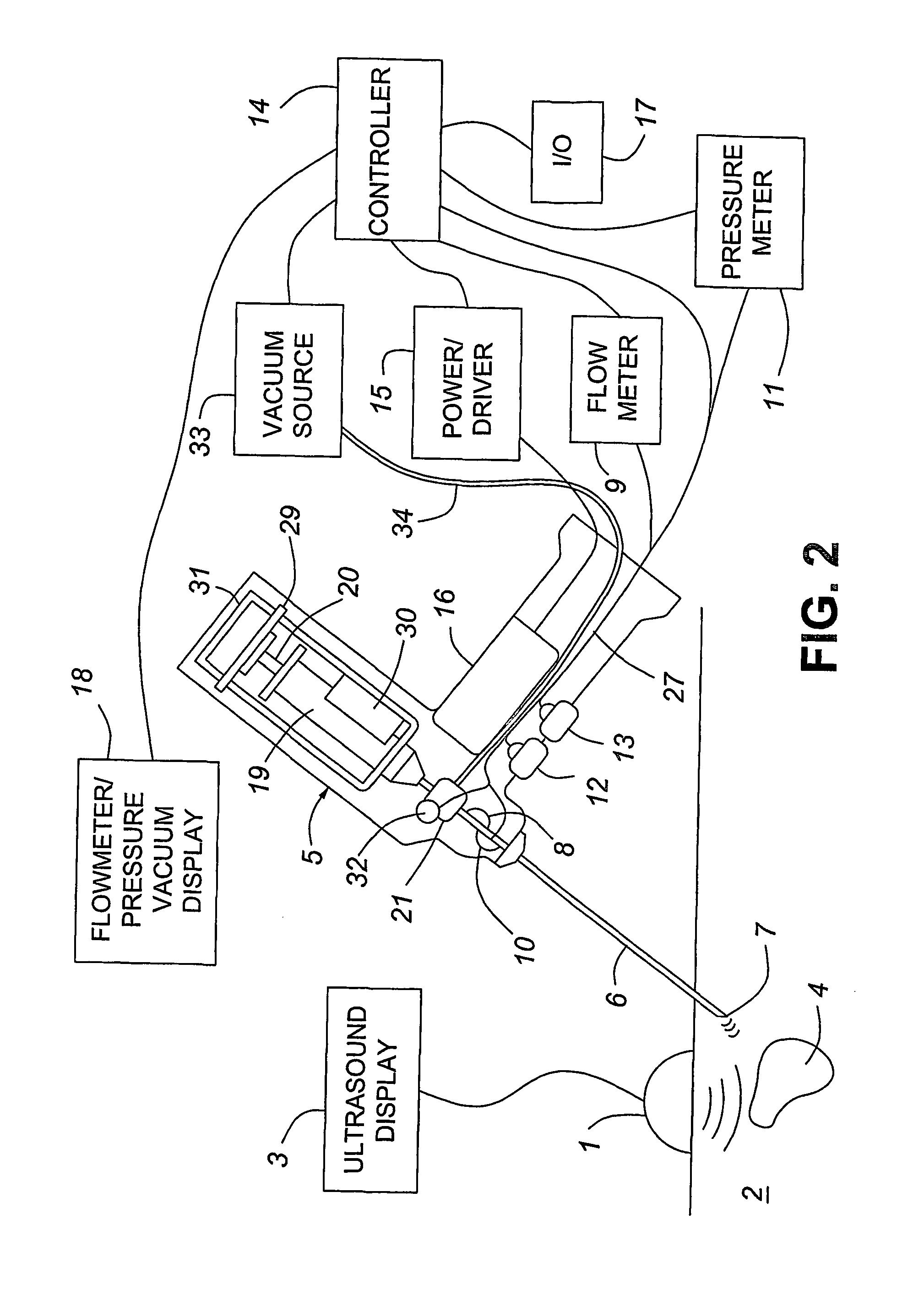
A medical device having enhanced ultrasonic visibility is provided. The device permits localized drug delivery, probe positioning, fluid drainage, biopsy, or ultrasound pulse delivery, through the real-time ultrasound monitoring of the needle tip position within a patient. The device permits controlled dispersion of a drug into solid tissue, the lodging of particles into solid tissue, and drug delivery into specific blood vessels. As a needle is inserted, a fluid that contrasts echogenically with the organ environment is injected into the patient. The fluid travels a brief distance before being slowed and stopped by the patient's tissue and this fluid flow will be detectable by ultrasound. The needle position during insertion will be monitored using ultrasound until it is at the desired point of action. A therapeutic drug is then delivered or a probe inserted
Owner:ARTENGA
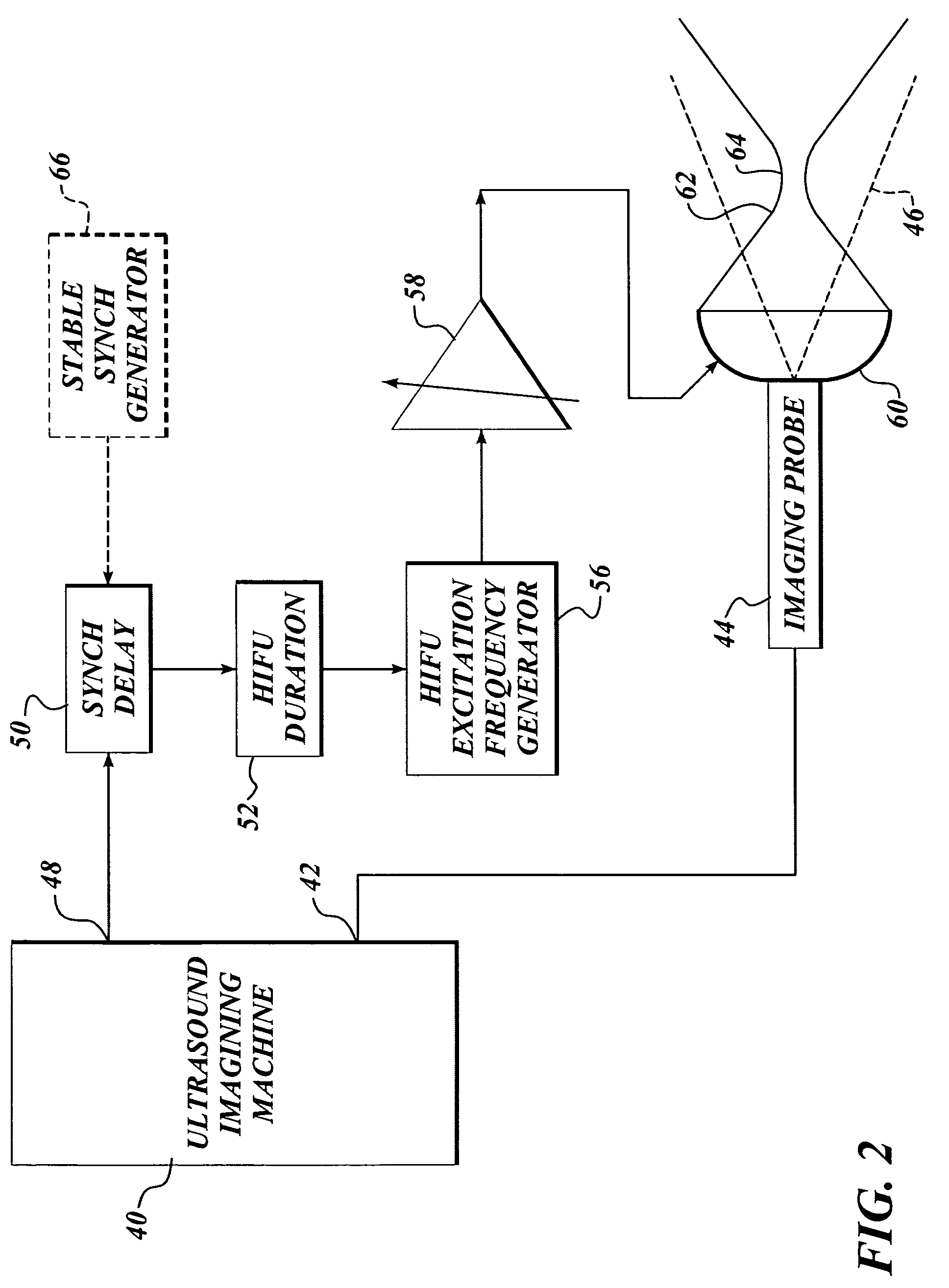
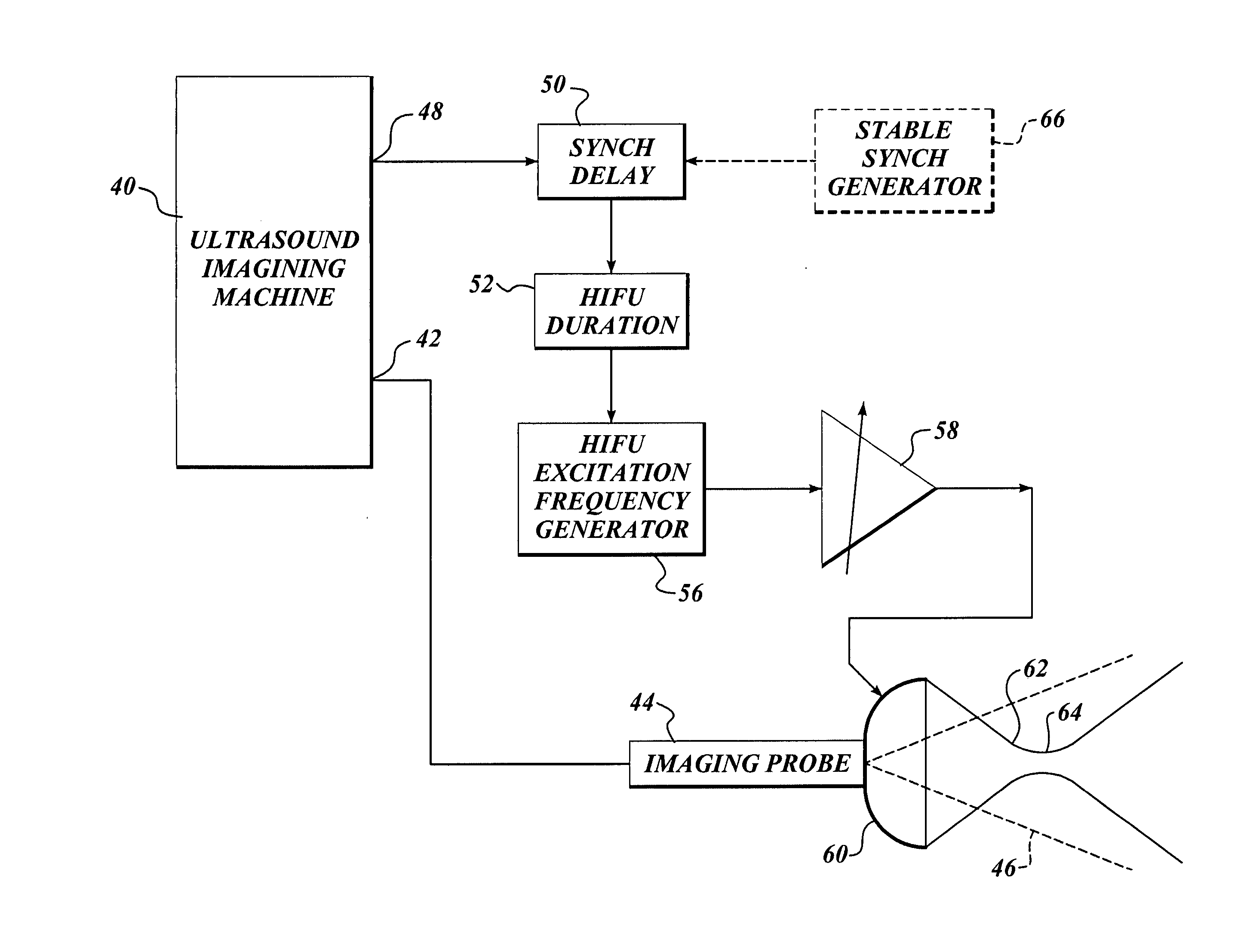
Ultrasound guided high intensity focused ultrasound treatment of nerves
InactiveUS7510536B2Relieve painEasy procedureUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationHigh doses
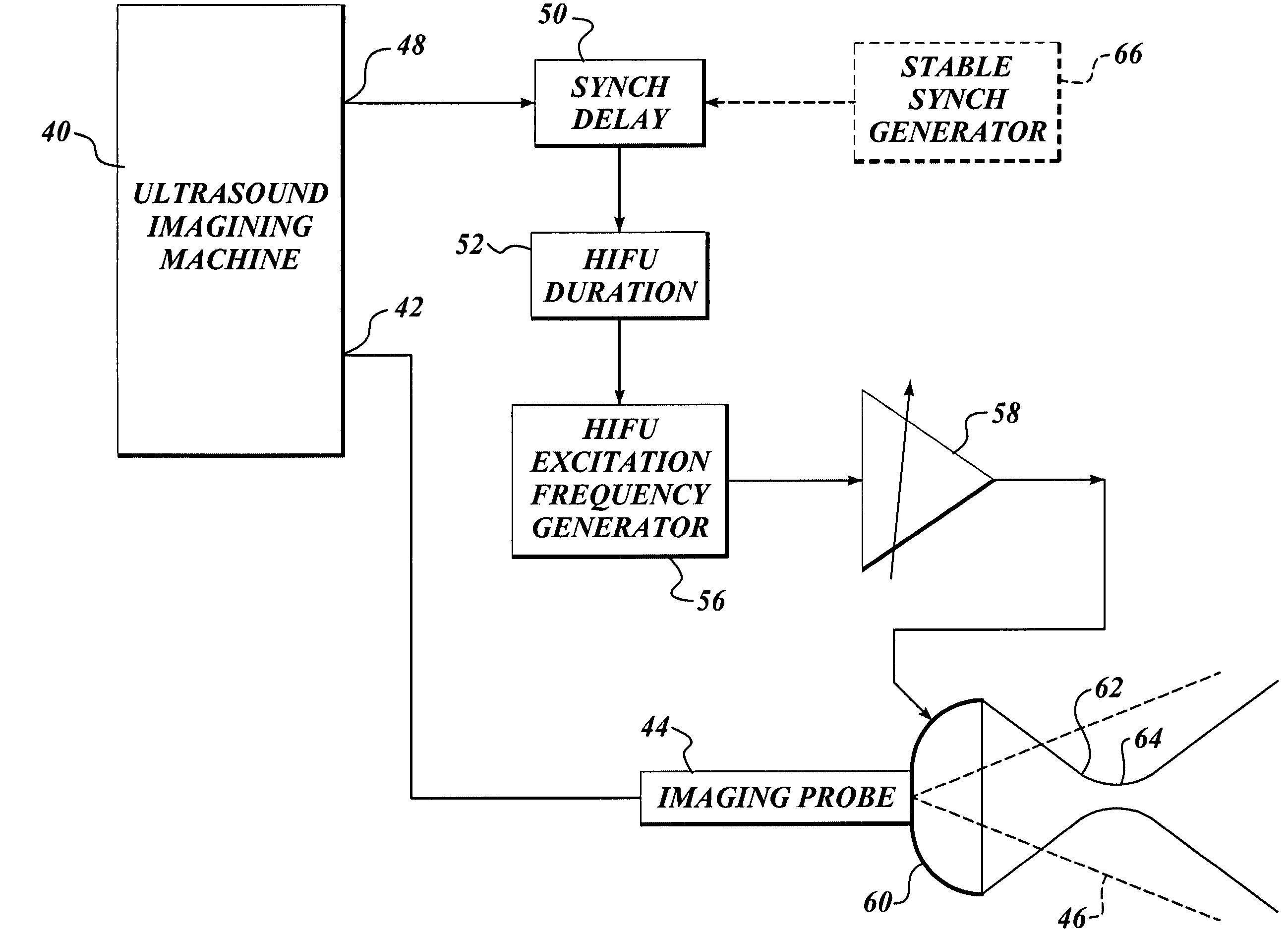
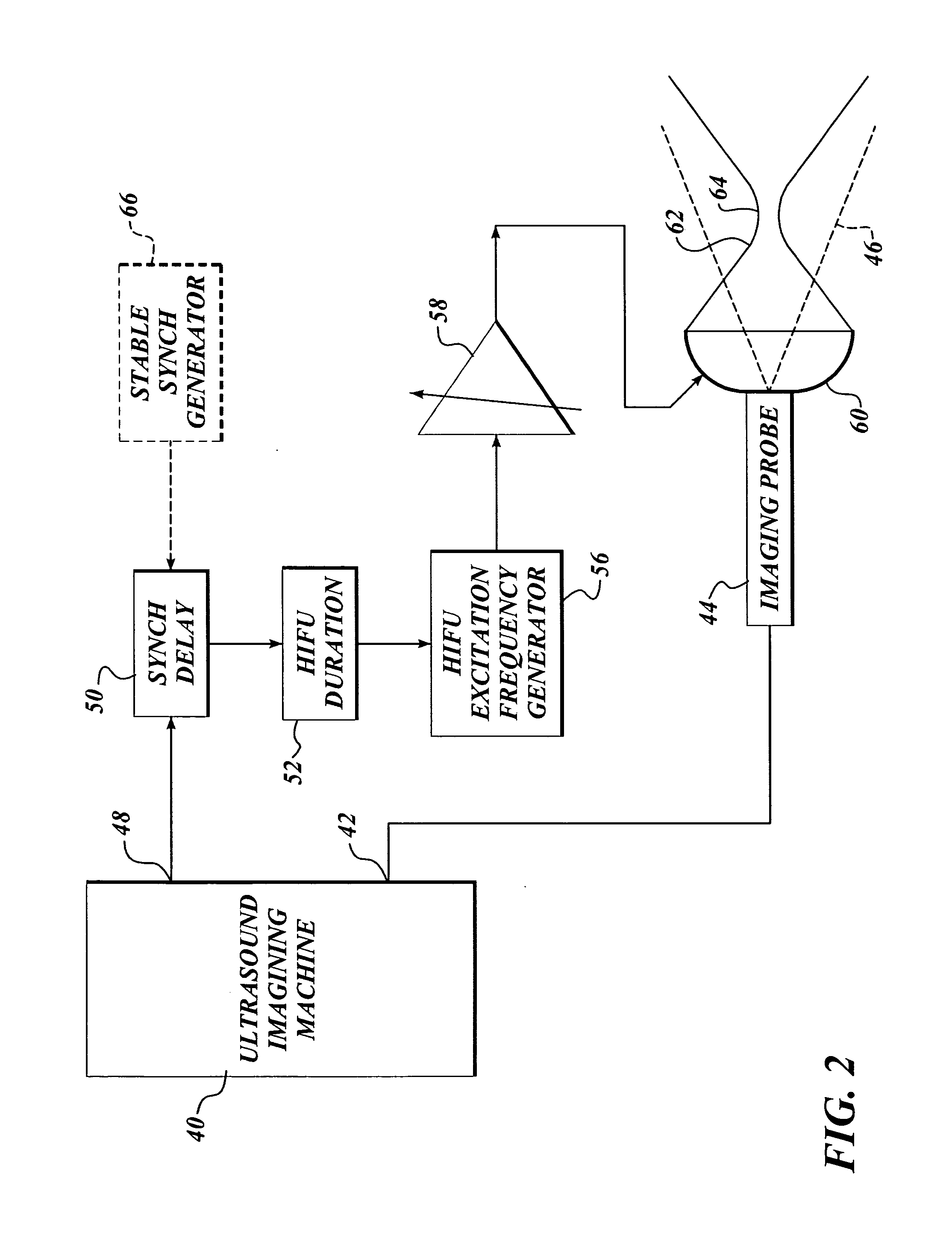
A method for using high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) to treat neurological structures to achieve a desired therapeutic affect. Depending on the dosage of HIFU applied, it can have a reversible or irreversible effect on neural structures. For example, a relatively high dose of HIFU can be used to permanently block nerve function, to provide a non-invasive alternative to severing a nerve to treat severe spasticity. Relatively lower doses of HIFU can be used to reversible a block nerve function, to alleviate pain, to achieve an anesthetic effect, or to achieve a cosmetic effect. Where sensory nerves are not necessary for voluntary function, but are involved in pain associated with tumors or bone cancer, HIFU can be used to non-invasively destroy such sensory nerves to alleviate pain without drugs. Preferably, ultrasound imaging synchronized to the HIFU therapy is used to provide real-time ultrasound image guided HIFU therapy of neural structures.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Ultrasound guided high intensity focused ultrasound treatment of nerves
InactiveUS20050240126A1Relieve painEasy procedureUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesAbnormal tissue growthHigh doses
A method for using high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) to treat neurological structures to achieve a desired therapeutic affect. Depending on the dosage of HIFU applied, it can have a reversible or irreversible effect on neural structures. For example, a relatively high dose of HIFU can be used to permanently block nerve function, to provide a non-invasive alternative to severing a nerve to treat severe spasticity. Relatively lower doses of HIFU can be used to reversible a block nerve function, to alleviate pain, to achieve an anesthetic effect, or to achieve a cosmetic effect. Where sensory nerves are not necessary for voluntary function, but are involved in pain associated with tumors or bone cancer, HIFU can be used to non-invasively destroy such sensory nerves to alleviate pain without drugs. Preferably, ultrasound imaging synchronized to the HIFU therapy is used to provide real-time ultrasound image guided HIFU therapy of neural structures.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
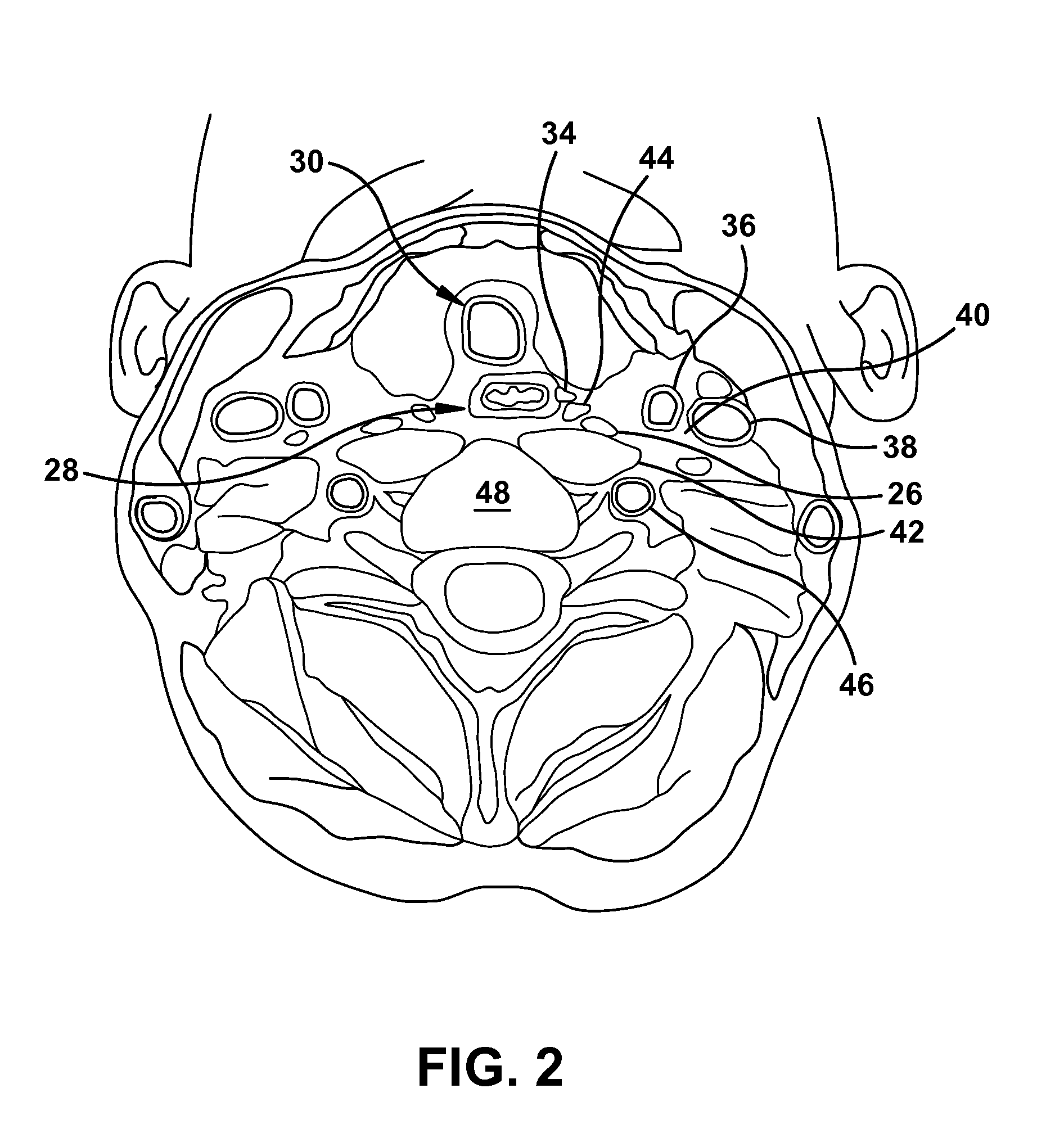
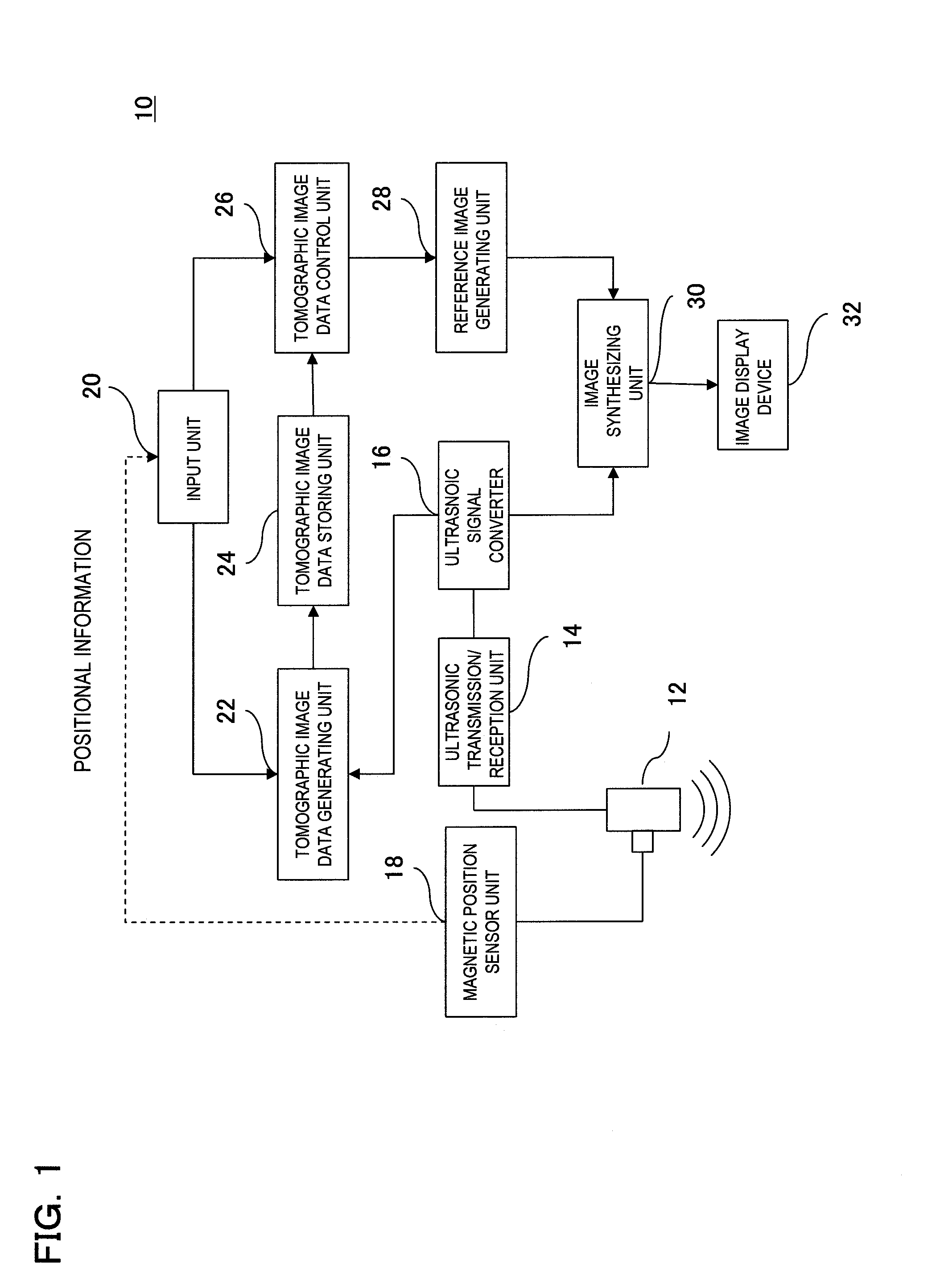
Method of detecting organ matter shift in a patient
InactiveUS6968224B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDisplay deviceNavigation system
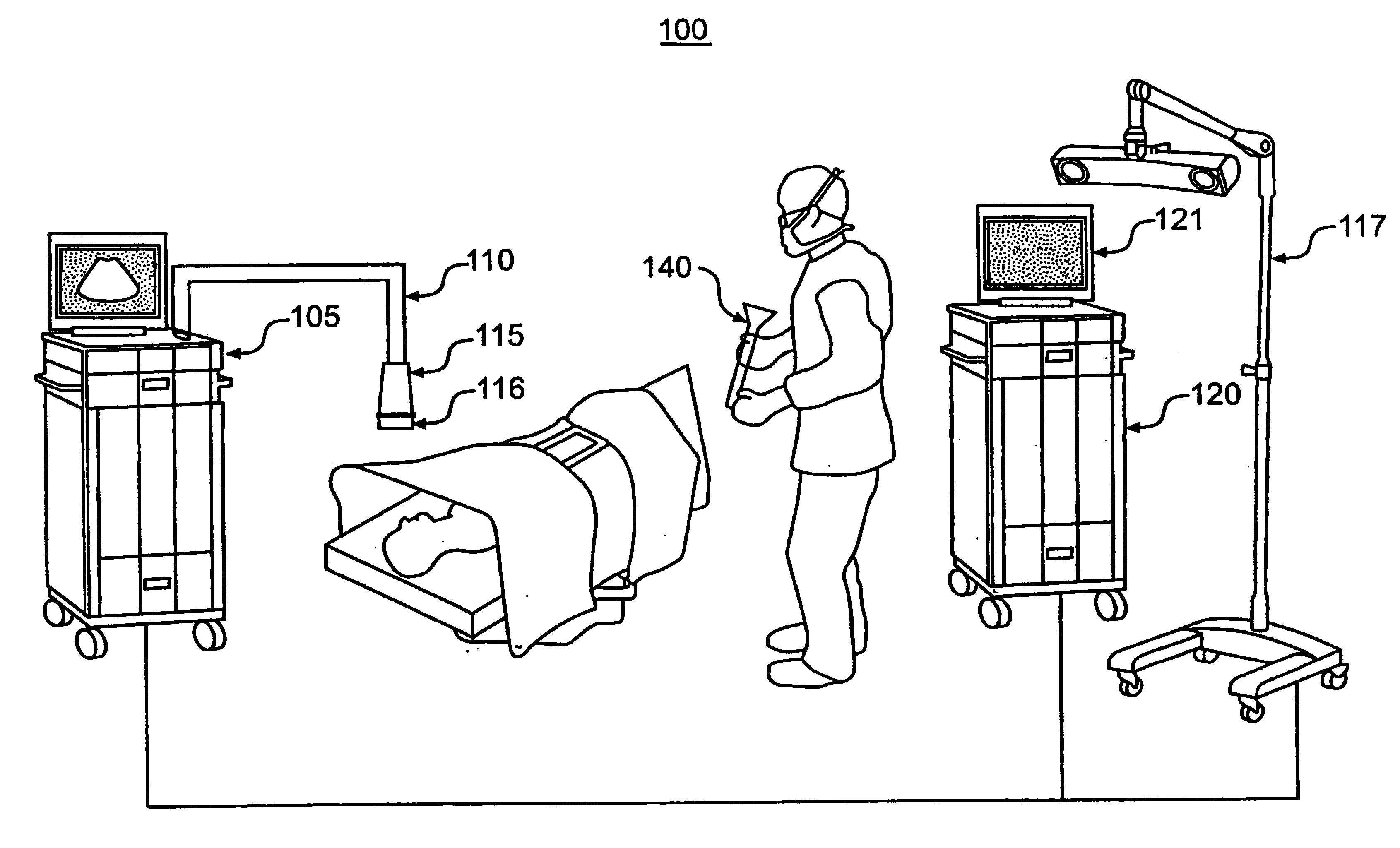
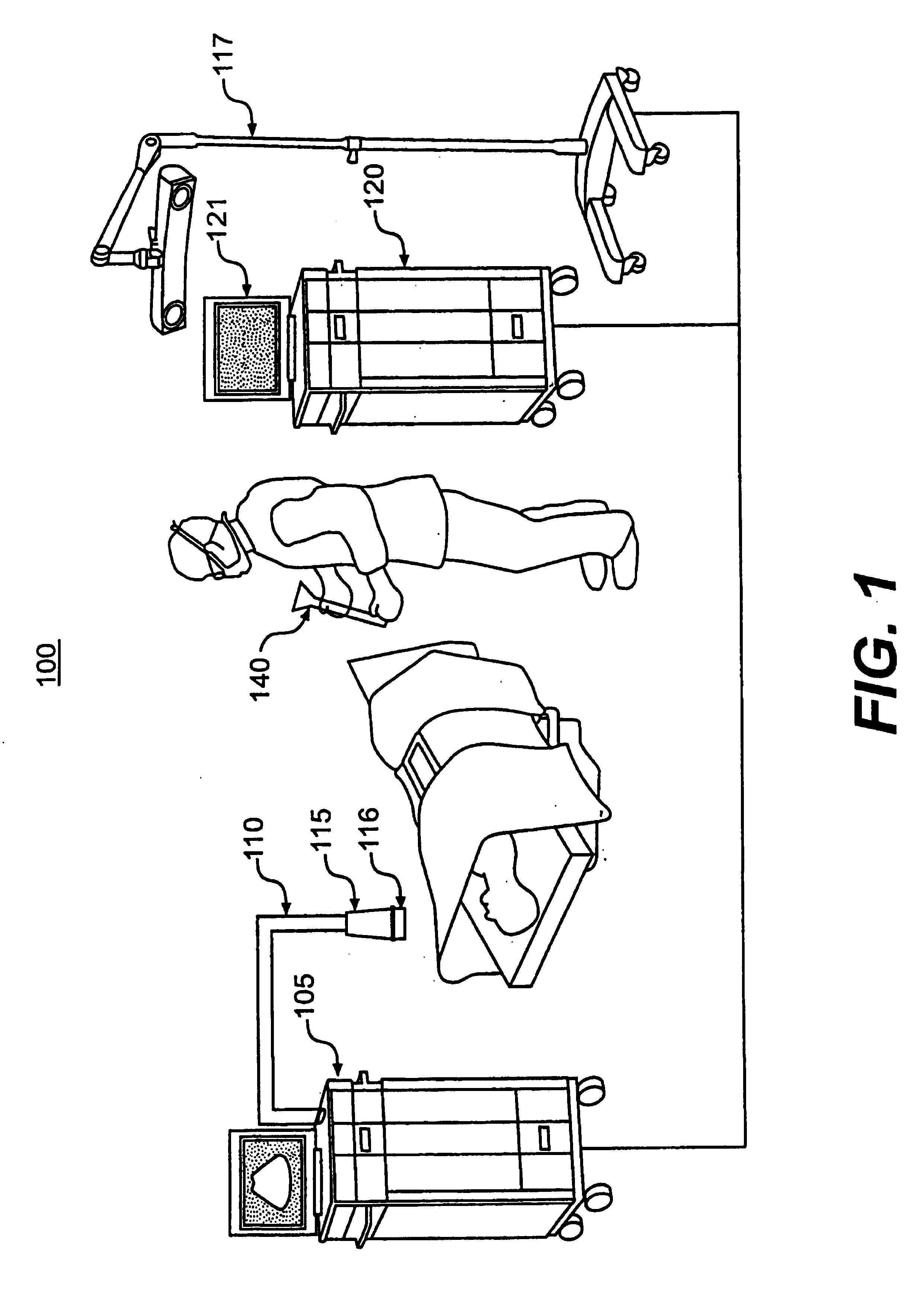
A surgical instrument navigation system comprises an ultrasound machine and a computer coupled to the ultrasound machine. A memory is coupled to the computer and includes computer instructions that when executed by the computer cause the computer to generate an icon representing the surgical instrument with a tip and the surgical instrument's trajectory and to overlay the icon on a real-time ultrasound image having an image plane, such that when the surgical instrument crosses the ultrasound image plane the format of the surgical instrument's trajectory is changed to represent the surgical instrument's crossing of the ultrasound image's plane. The system also comprises a localizer coupled to the ultrasound machine, and a display coupled to the computer for displaying the generated icon superimposed on the real-time image.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
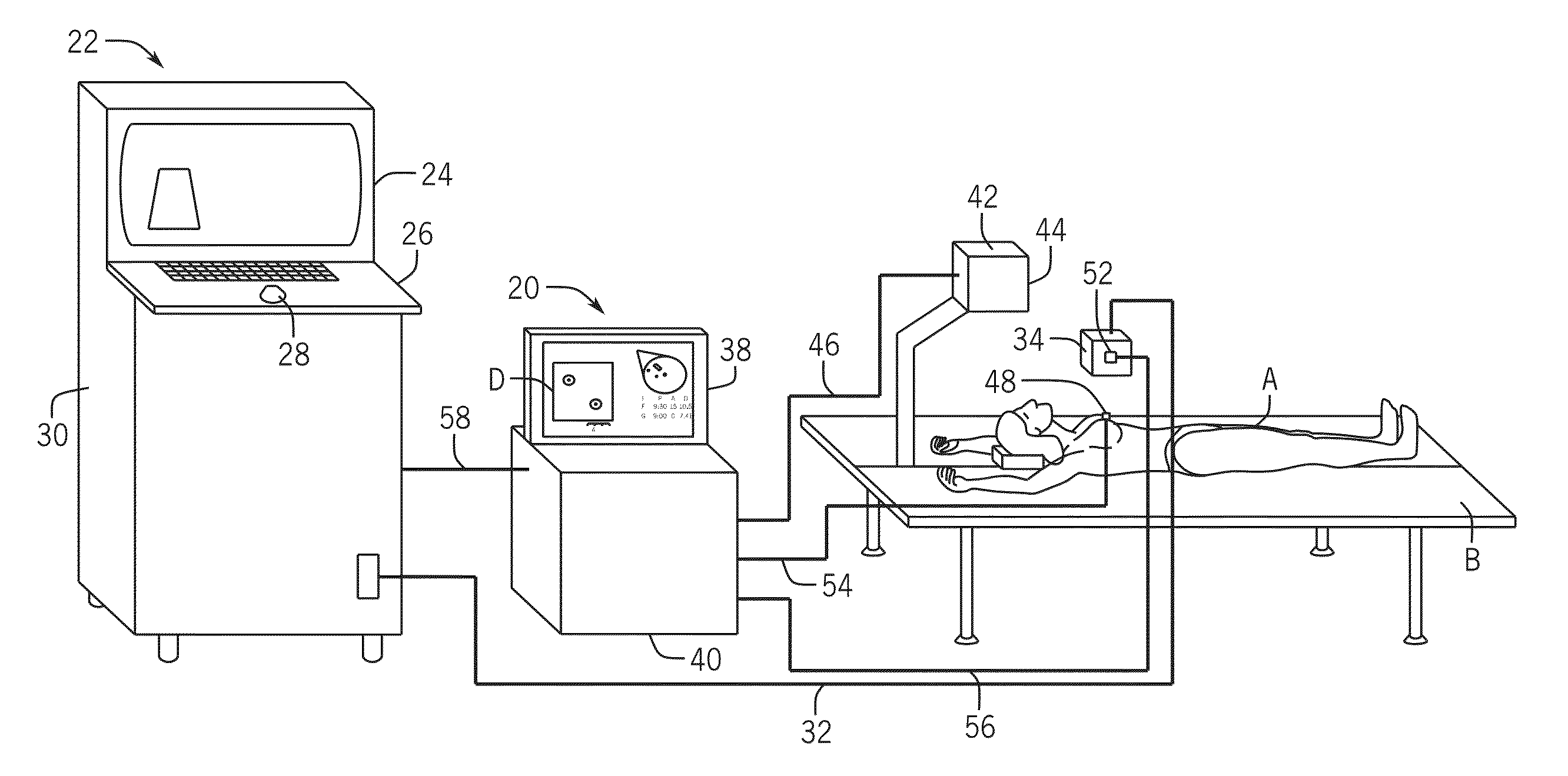
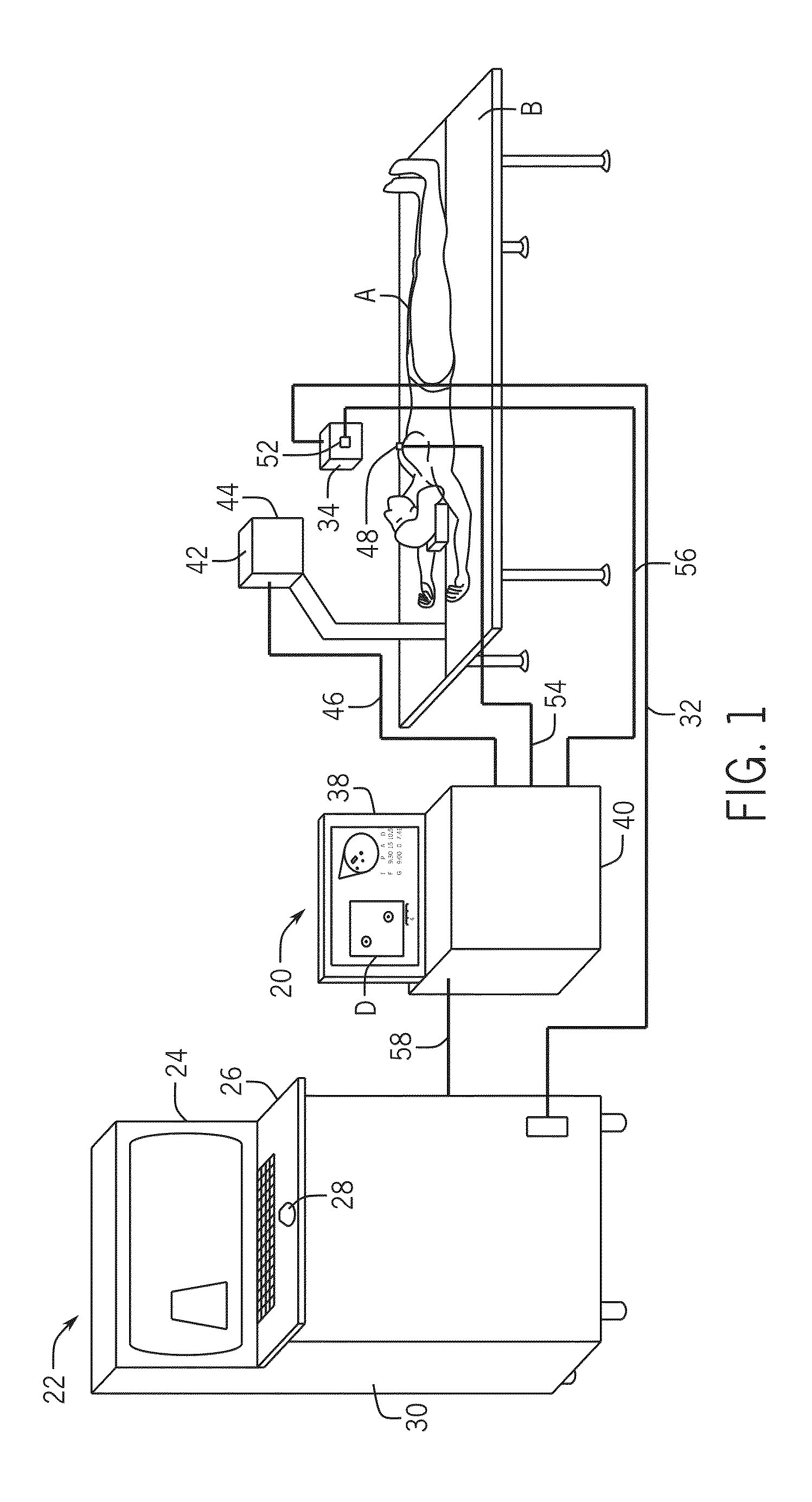
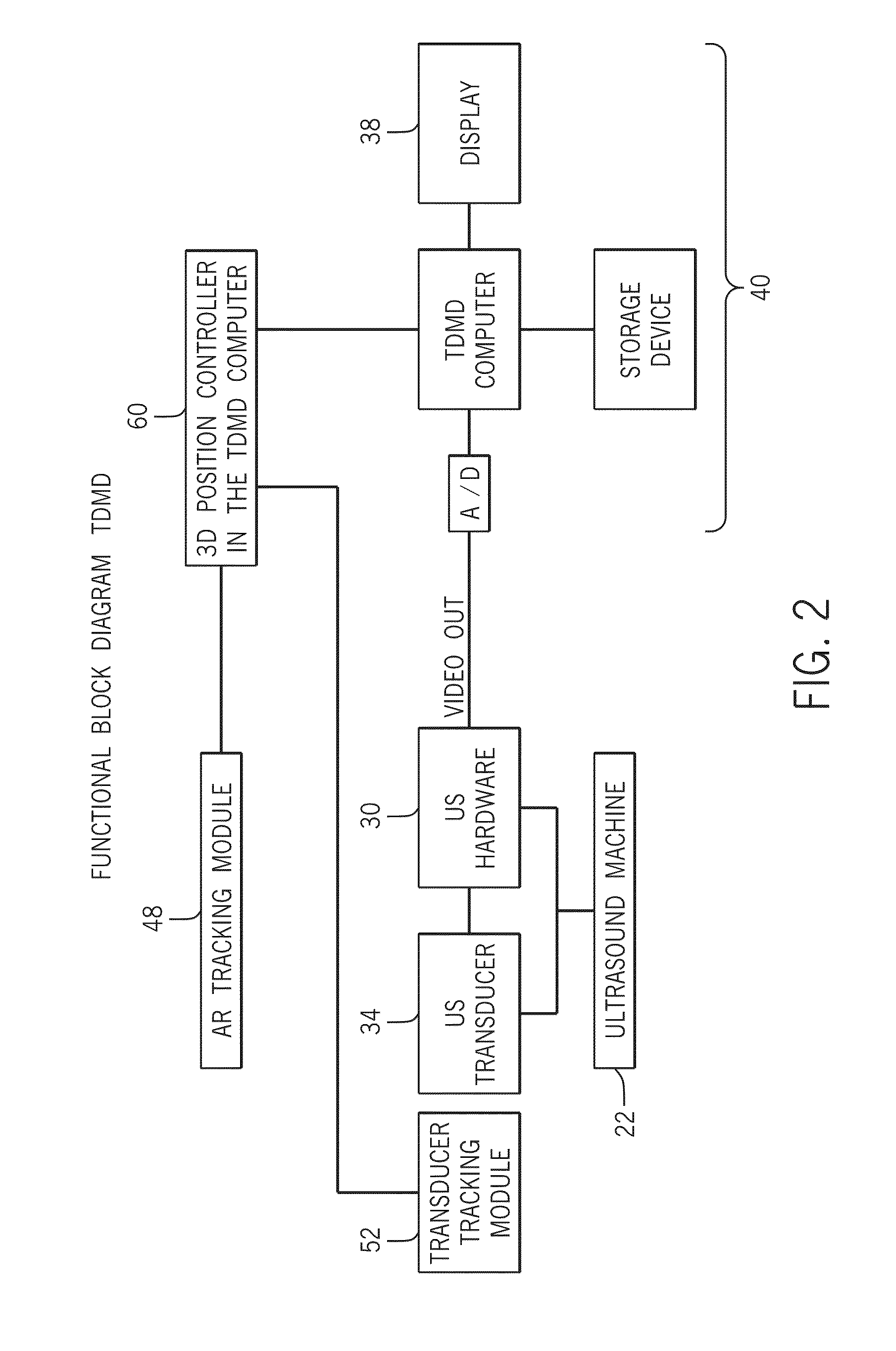
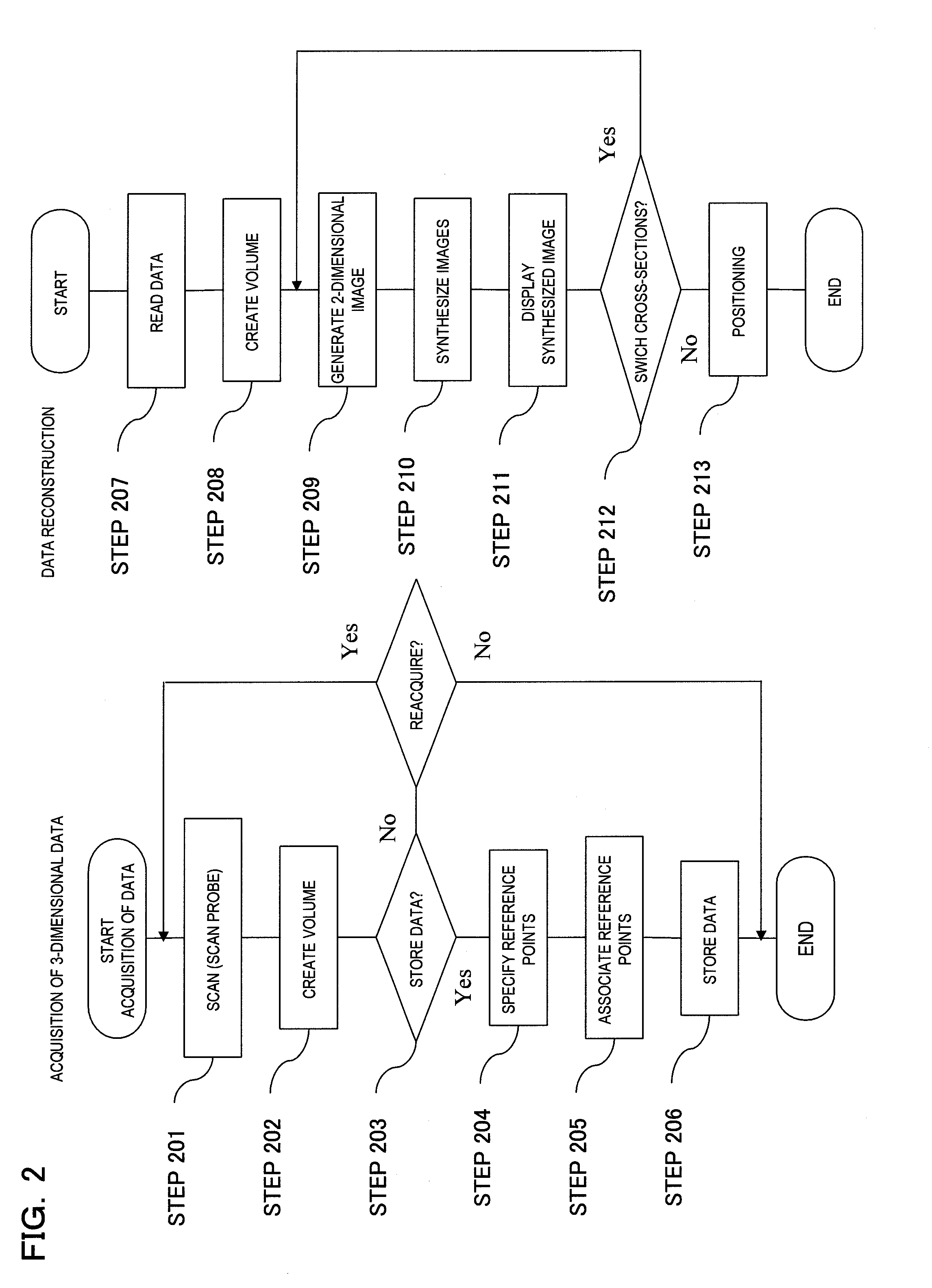
Three Dimensional Mapping Display System for Diagnostic Ultrasound Machines
ActiveUS20150051489A1Shorten the timeTime-consuming to eliminateOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImaging interpretation
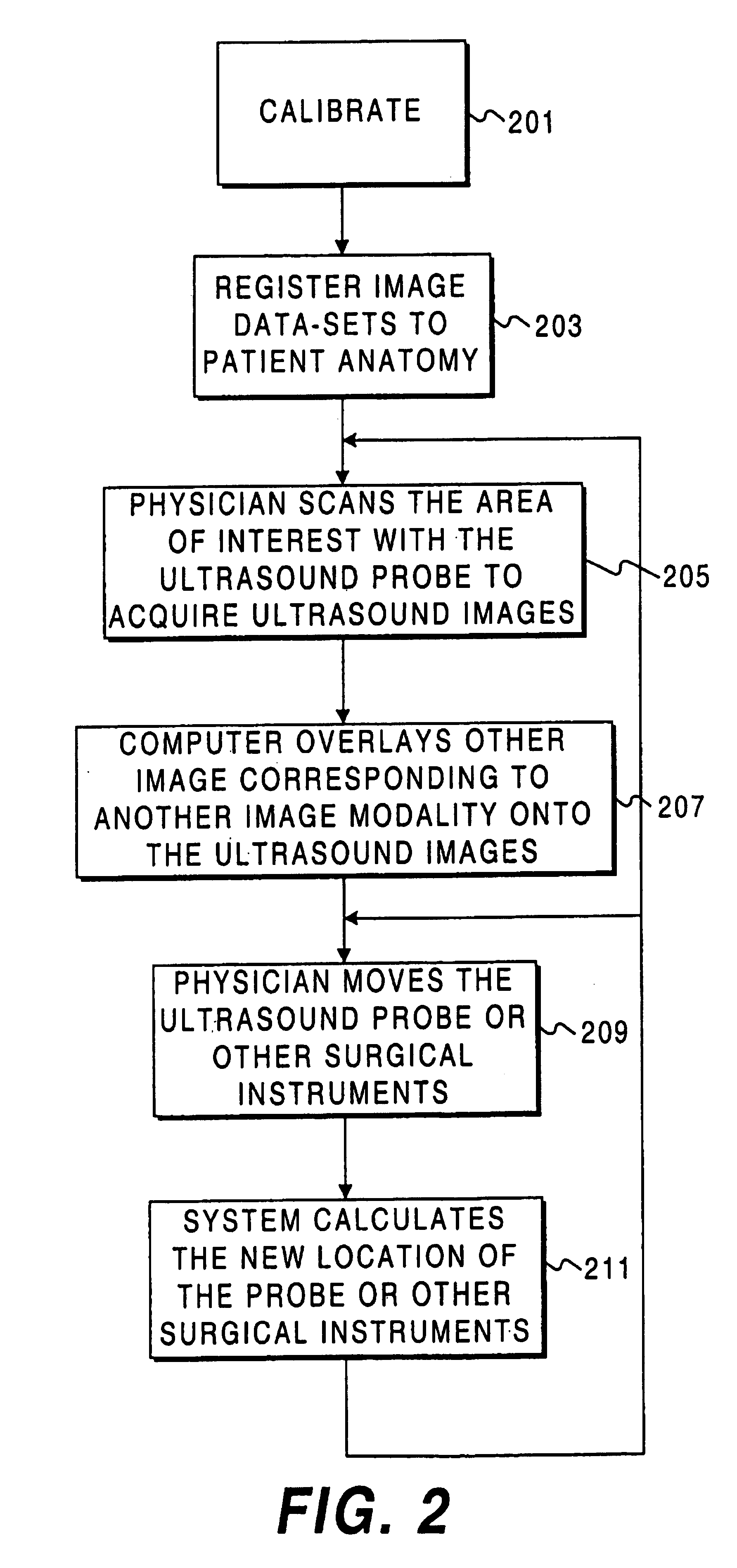
An automated three dimensional mapping and display system for a diagnostic ultrasound system is presented. According to the invention, ultrasound probe position registration is automated, the position of each pixel in the ultrasound image in reference to selected anatomical references is calculated, and specified information is stored on command. The system, during real time ultrasound scanning, enables the ultrasound probe position and orientation to be continuously displayed over a body or body part diagram, thereby facilitating scanning and images interpretation of stored information. The system can then record single or multiple ultrasound free hand two-dimensional (also “2D”) frames in a video sequence (clip) or cine loop wherein multiple 2D frames of one or more video sequences corresponding to a scanned volume can be reconstructed in three-dimensional (also “3D”) volume images corresponding to the scanned region, using known 3D reconstruction algorithms. In later examinations, the exact location and position of the transducer can be recreated along three dimensional or two dimensional axis points enabling known targets to be viewed from an exact, known position.
Owner:METRITRACK
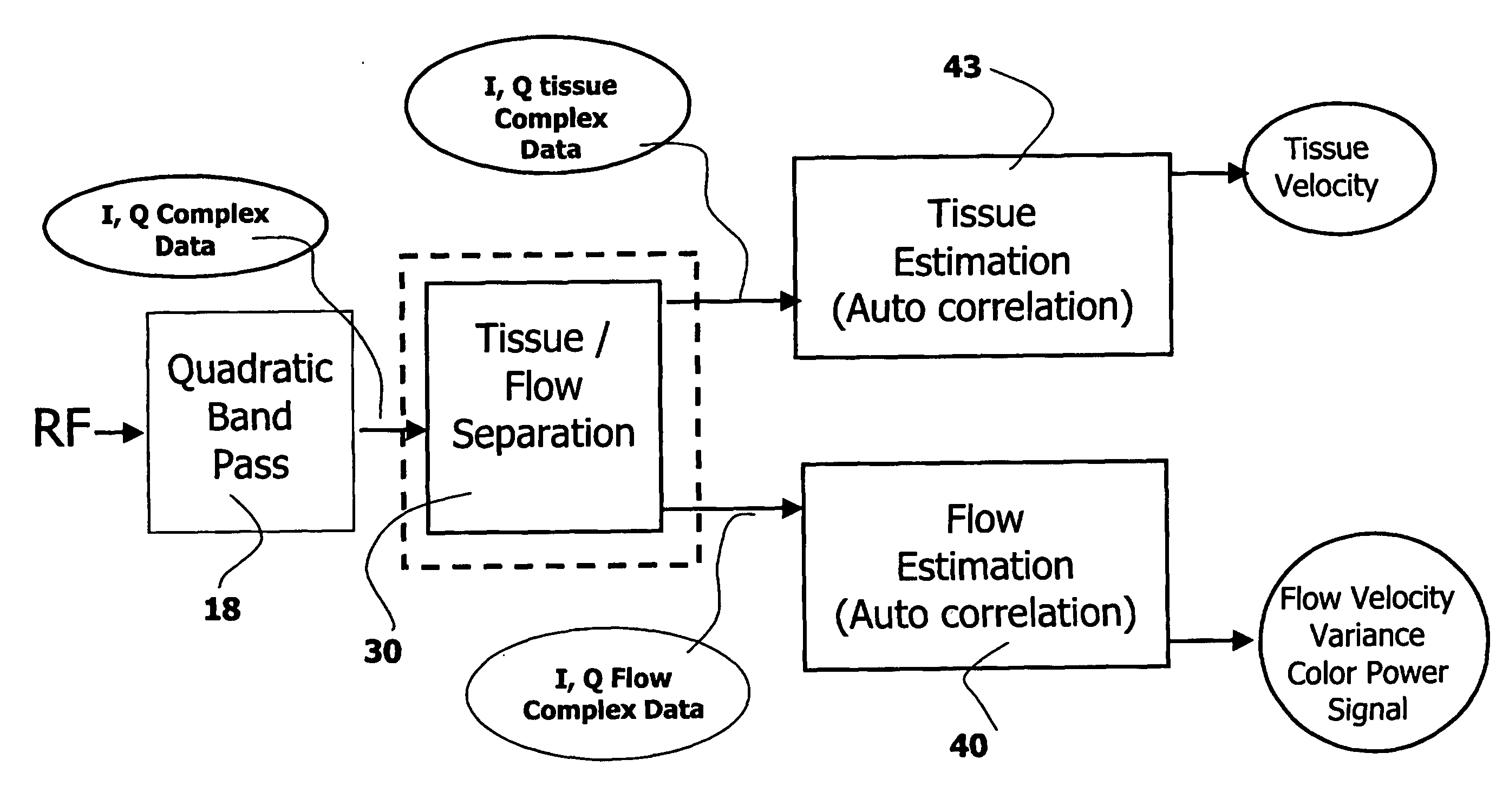
Phased array acoustic system for 3d imaging of moving parts
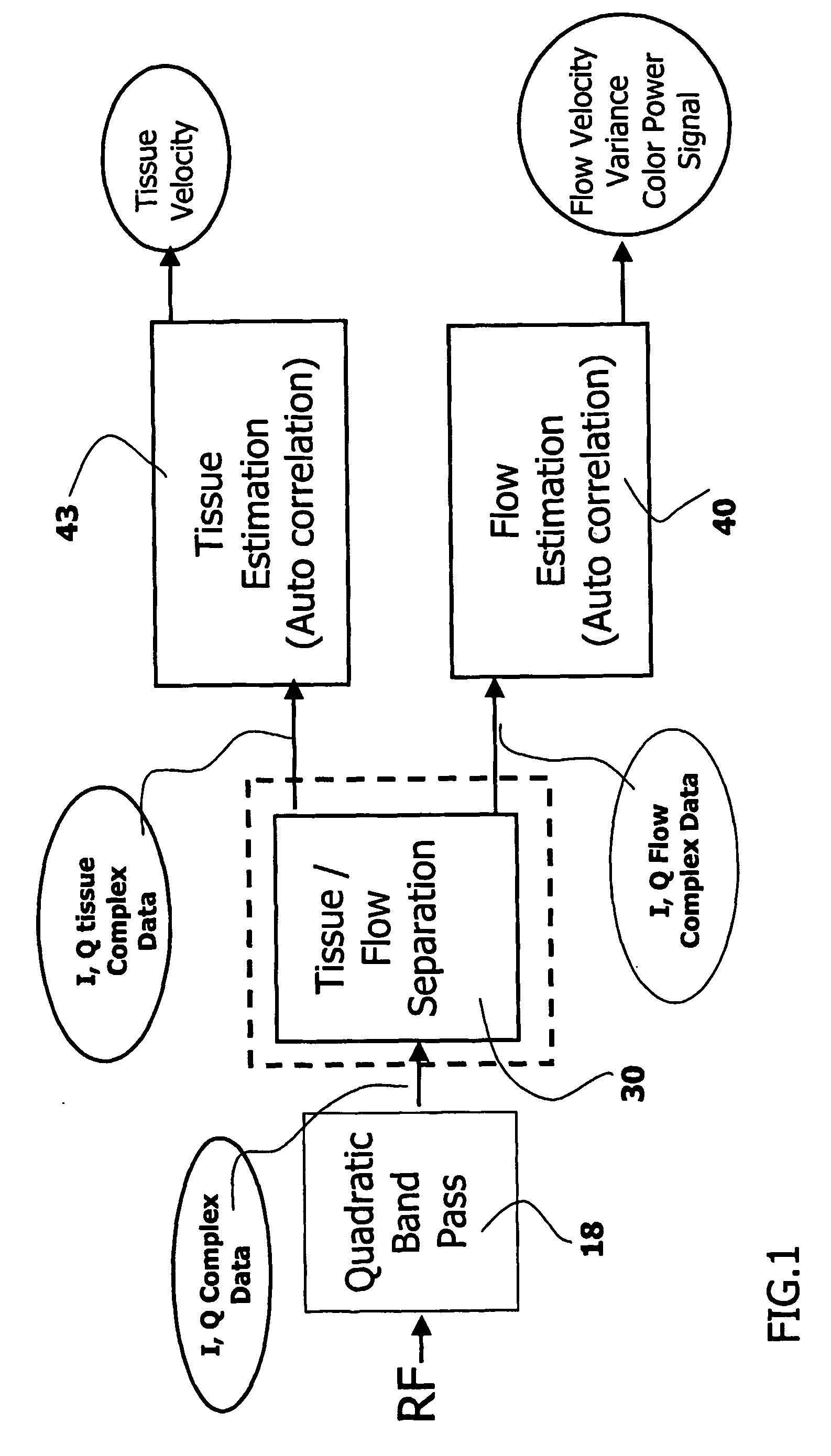
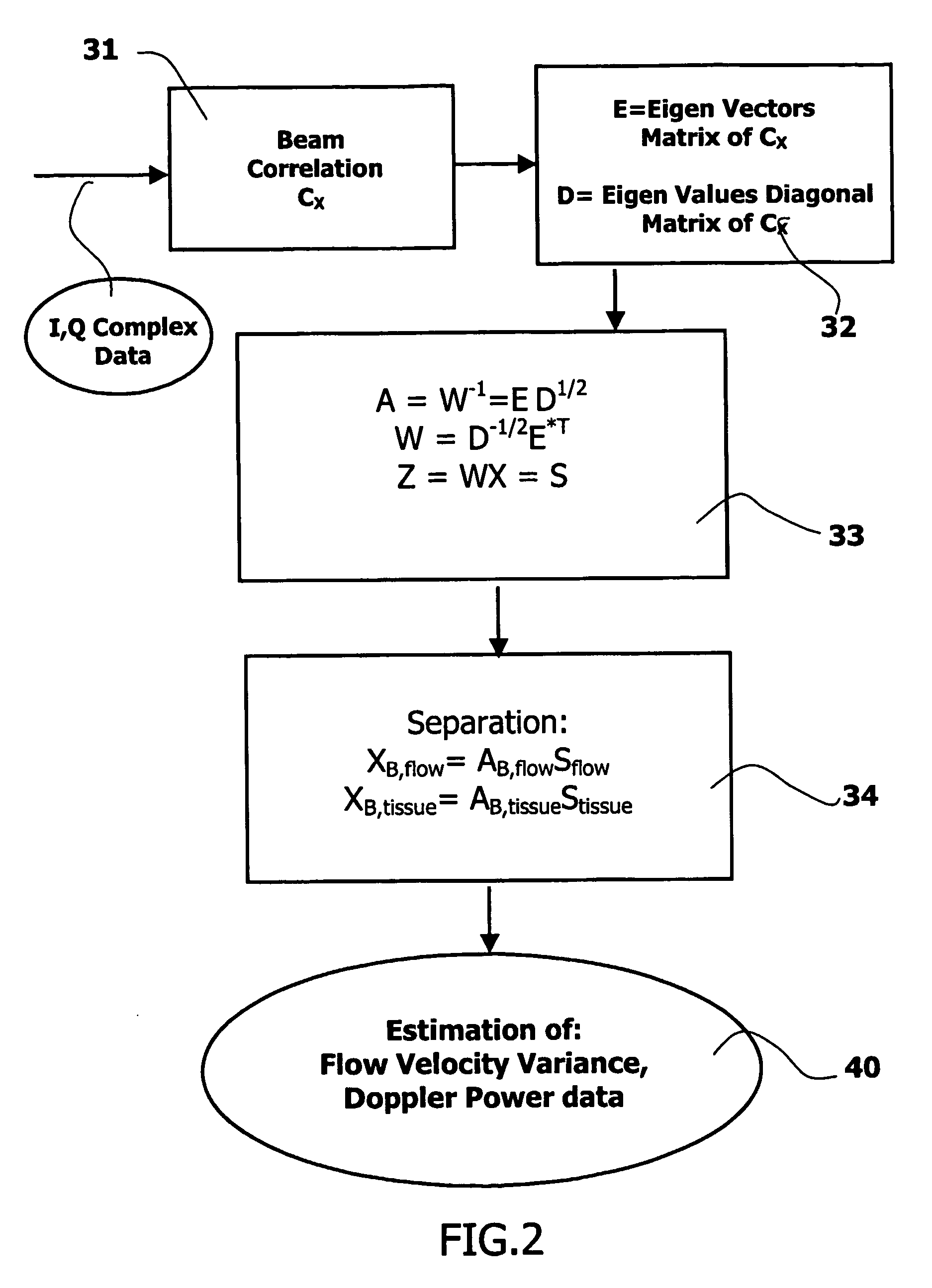
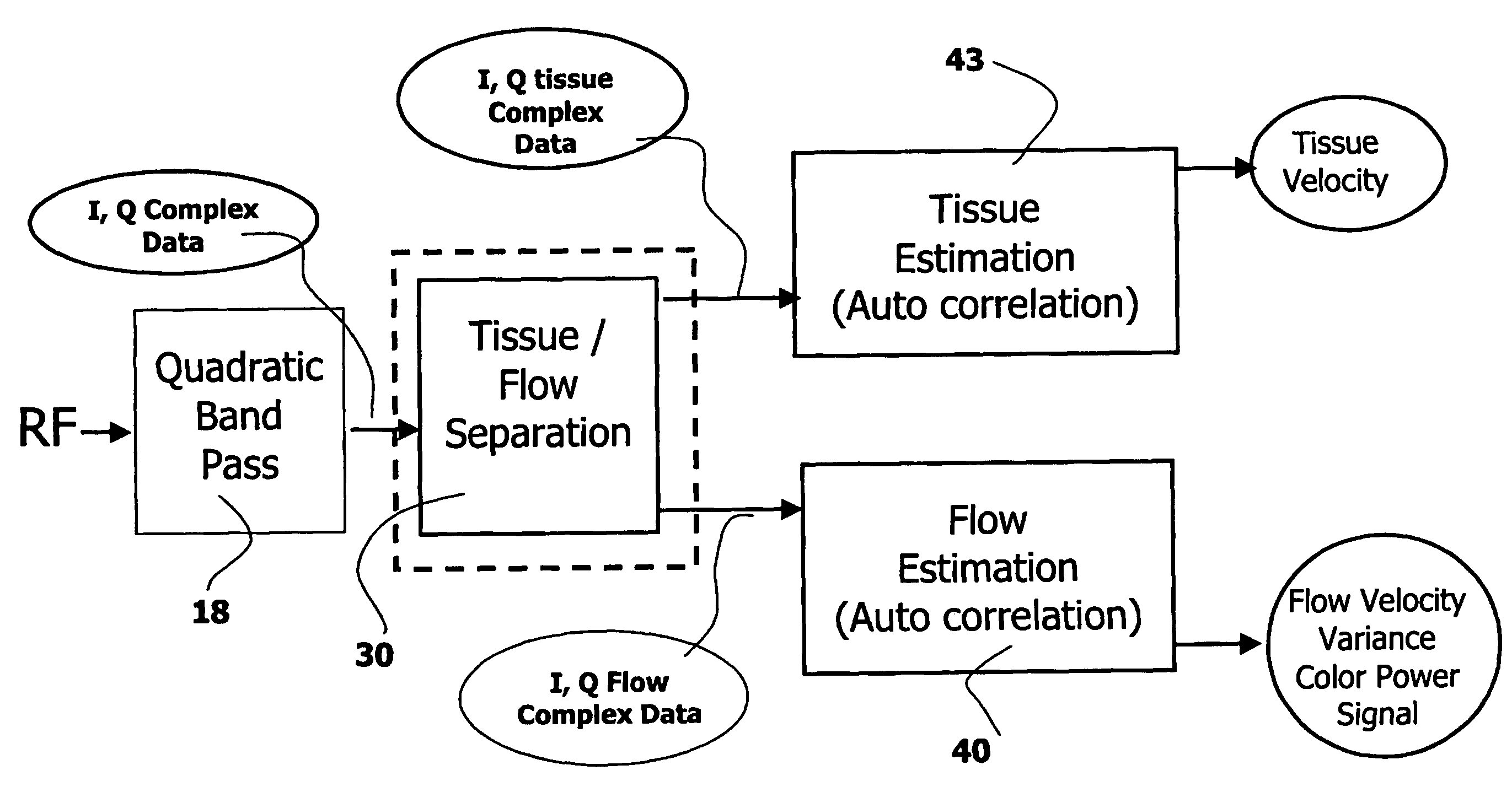
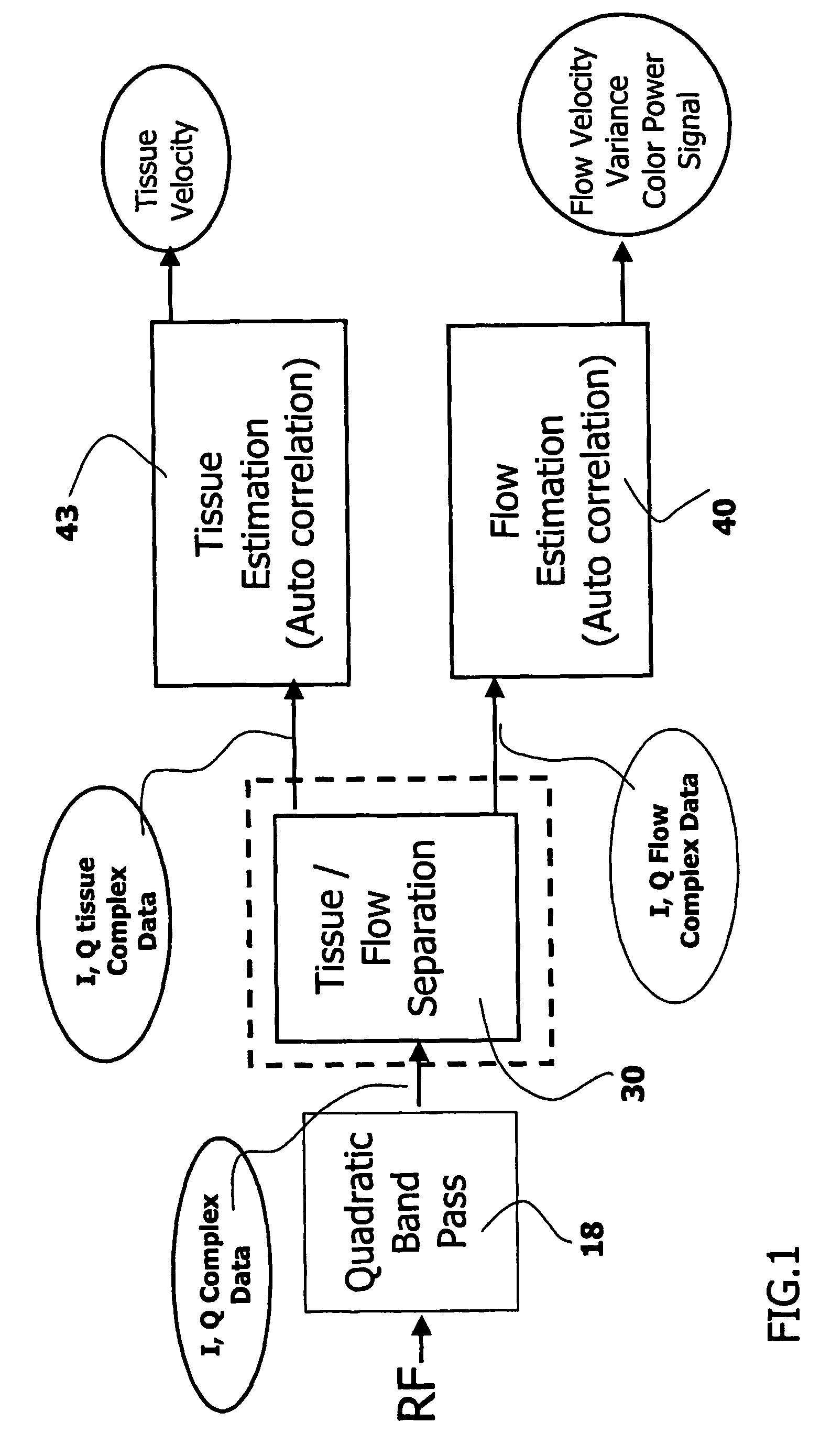
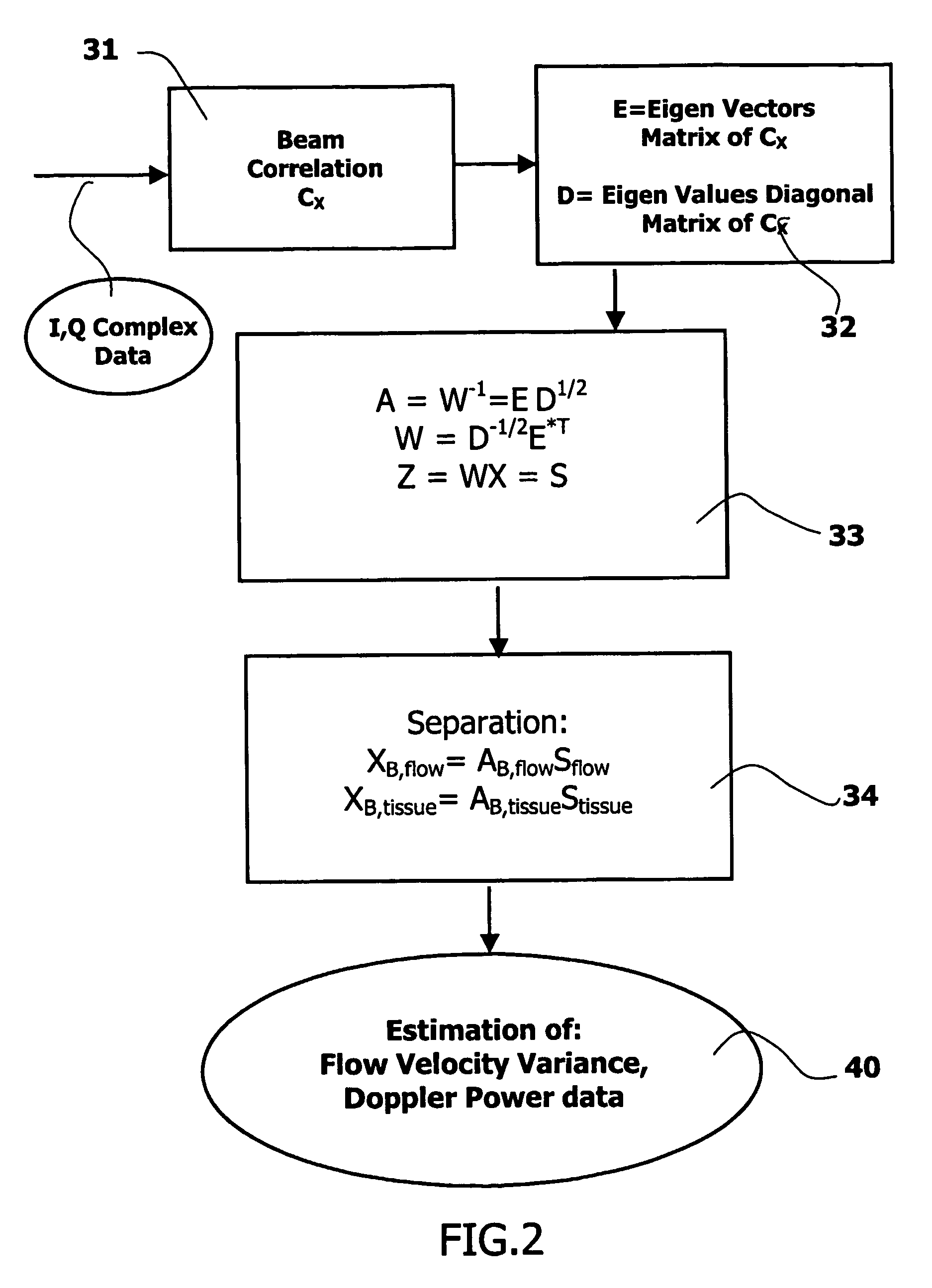
InactiveUS20060074309A1Minimize acquisition time durationReduce acquisition timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationTransducer
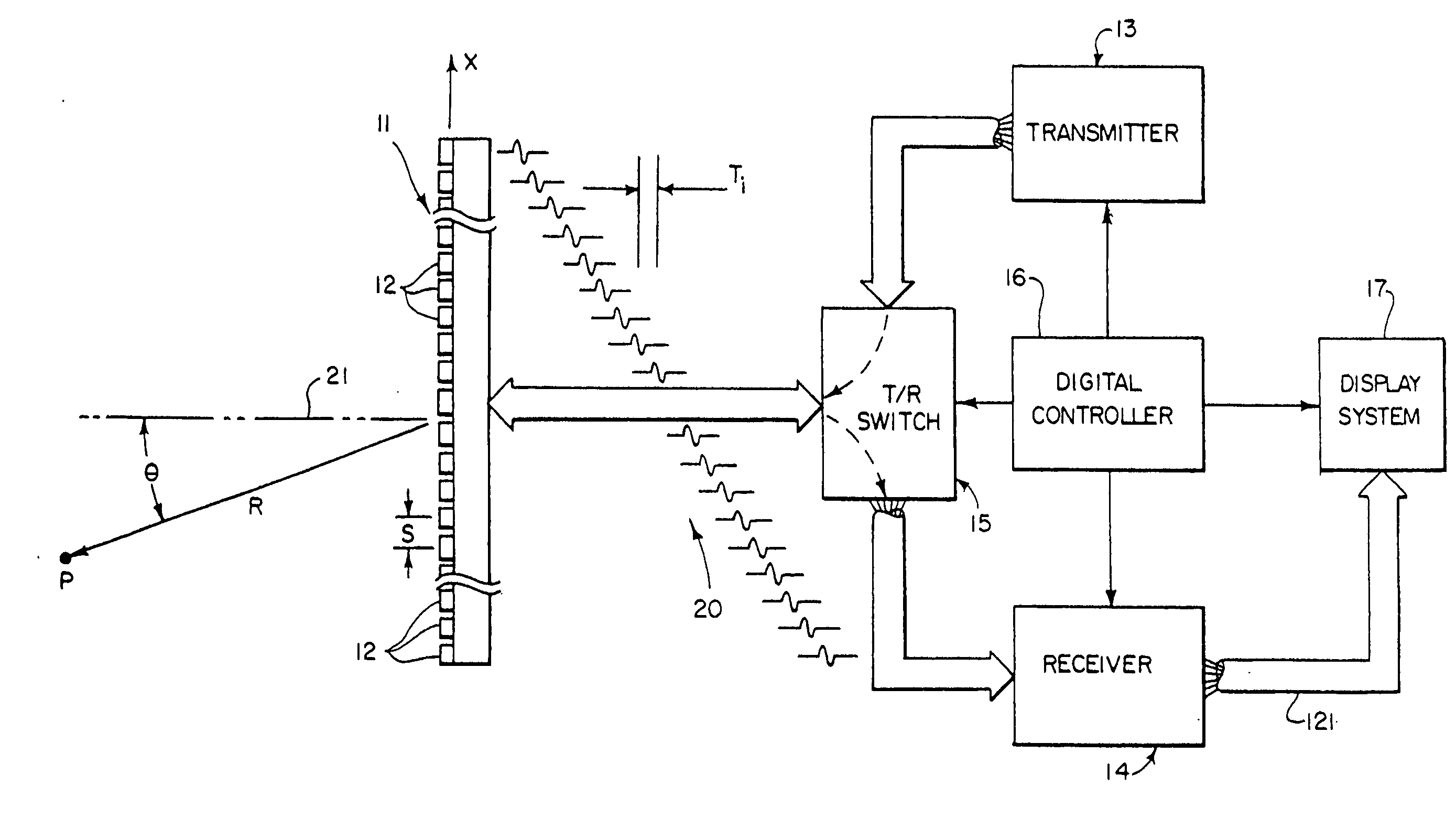
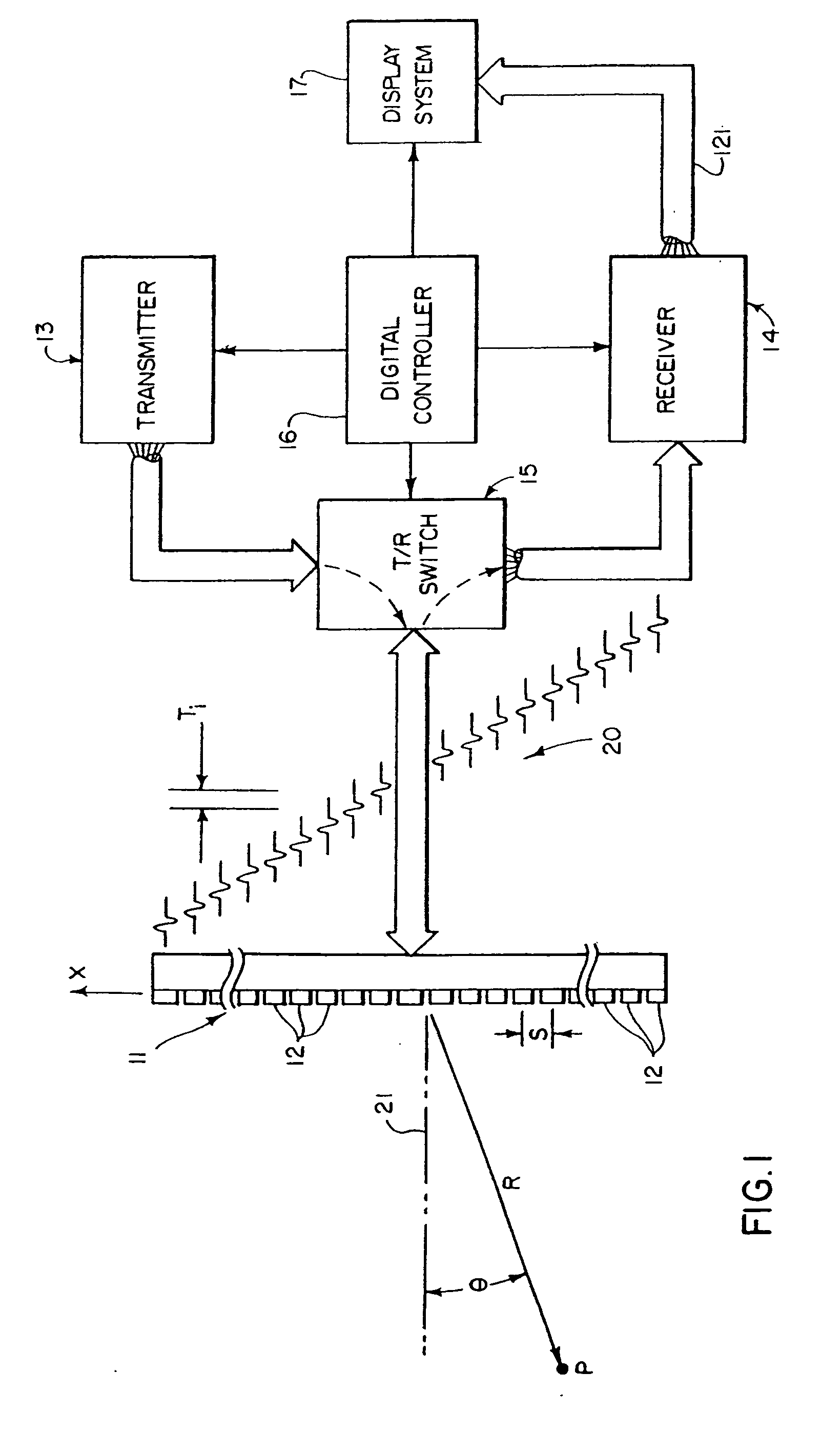
The invention relates to an ultrasound phased array imaging system comprising: probe (10) with a 2-D array of transducer elements (12) for acquiring 3-D ultrasound data of a volume of a body, including moving tissue and fluid flow; a beamforming system (10, 12, 14, 16) for emitting and receiving in real time ultrasound beams in said volume, which provides, in real time and in 3-D, more than one spatial receive beams signals for each transmission beam within an ensemble length of more than two temporal samples, among which the receive flow beam signals and the receive tissue beam signals are substantially temporally uncorrelated but spatially correlated; separation means (30) for processing in real time the receive beams signals, comprising adaptive spatial tissue filtering means using simultaneously more than one spatial receive beam signals acquired in 3-D within the ensemble length of more than two temporal samples, which separation means analyzes temporal variations of the respective successive receive signals and extracts flow receive beam signals from spatial combinations of receive beam signals; processing means (40, 50) and display means (62, 60) for processing flow Doppler signals and for displaying images based on said processed flow Doppler signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
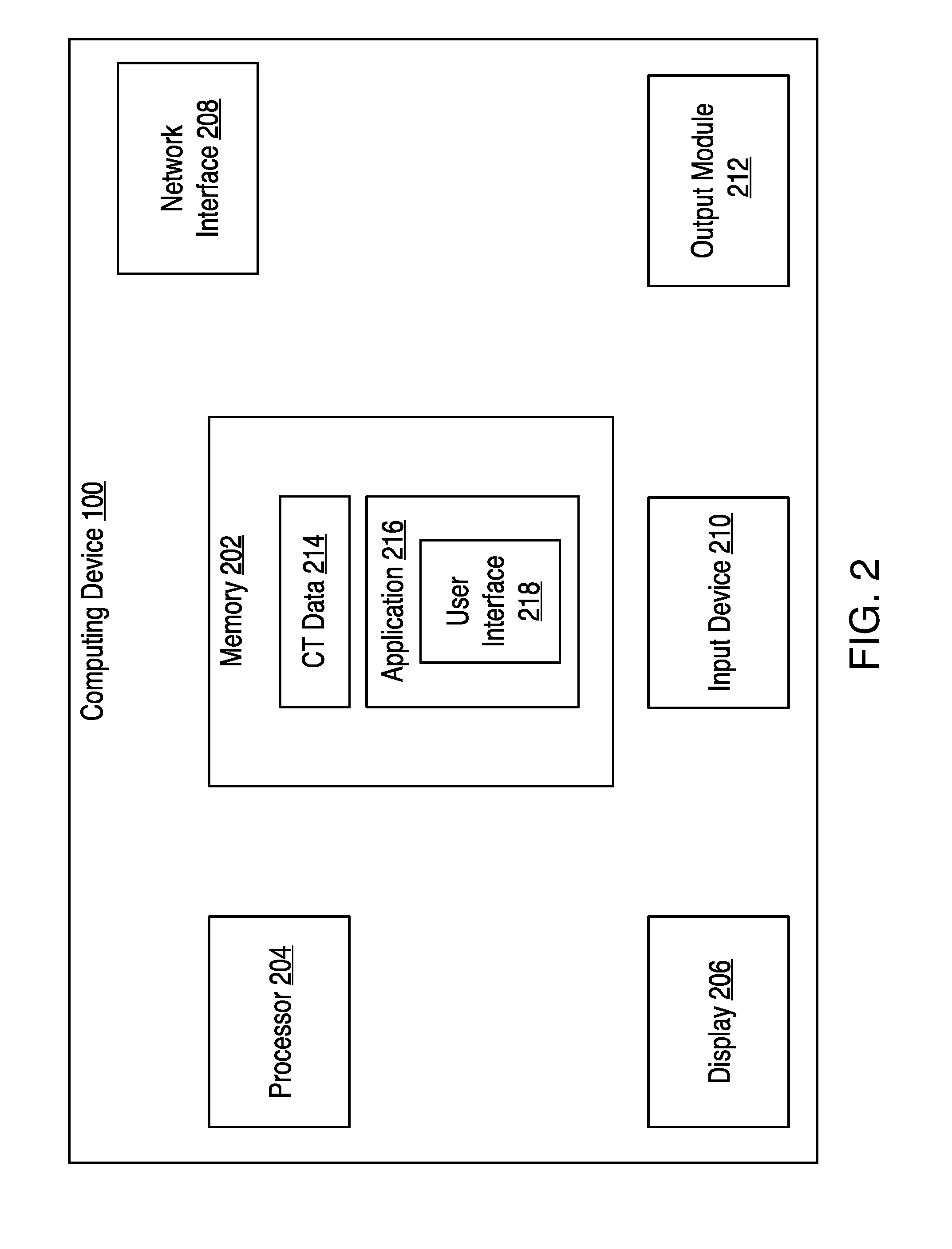
System and Method for Real-Time Ultrasound Guided Prostate Needle Biopsy Based on Biomechanical Model of the Prostate from Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data
A method and system for real-time ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsy based on a biomechanical model of the prostate from 3D planning image data, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, is disclosed. The prostate is segmented in the 3D ultrasound image. A reference patient-specific biomechanical model of the prostate extracted from planning image data is fused to a boundary of the segmented prostate in the 3D ultrasound image, resulting in a fused 3D biomechanical prostate model. In response to movement of an ultrasound probe to a new location, a current 2D ultrasound image is received. The fused 3D biomechanical prostate model is deformed based on the current 2D ultrasound image to match a current deformation of the prostate due to the movement of the ultrasound probe to the new location.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
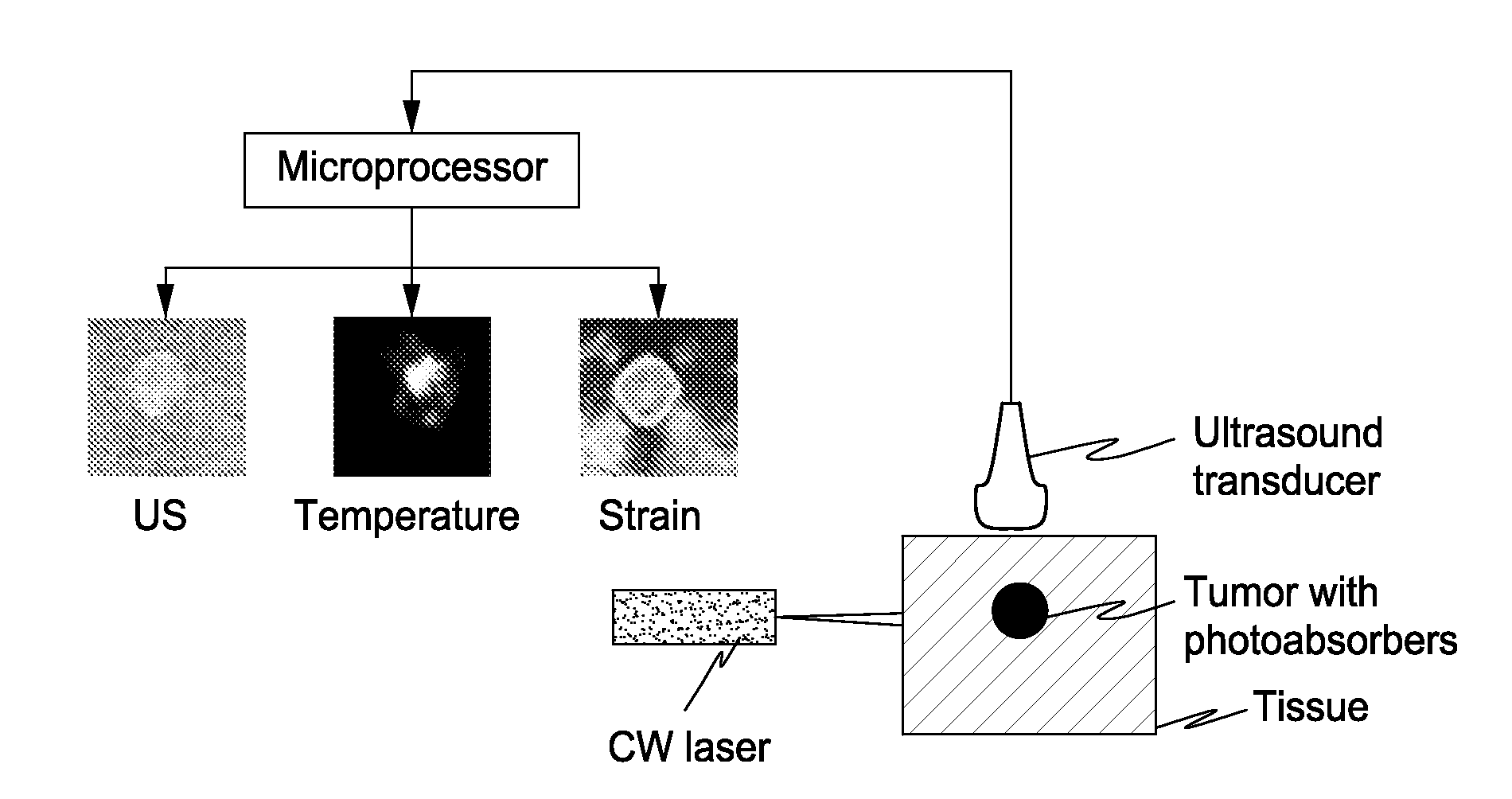
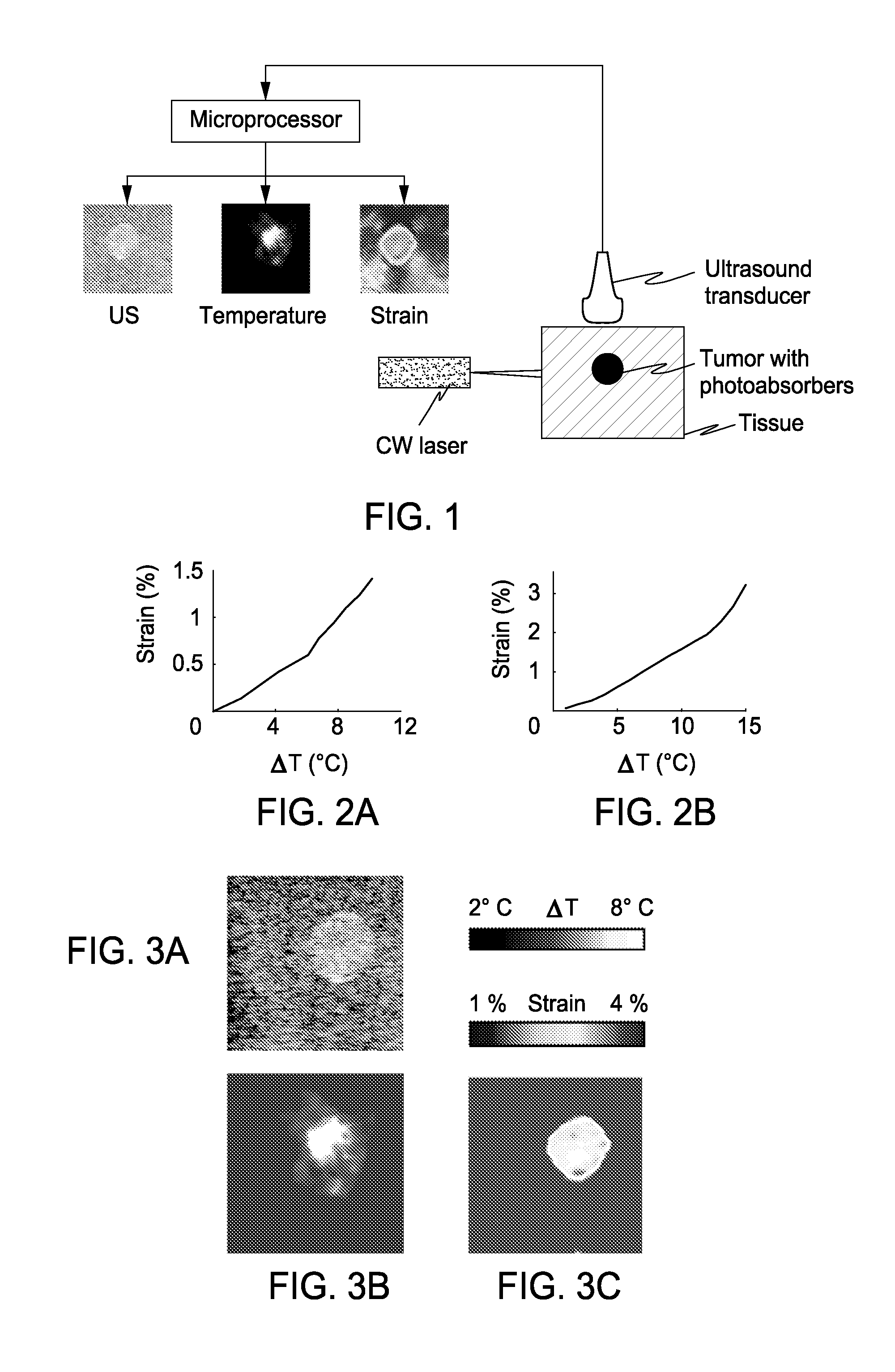
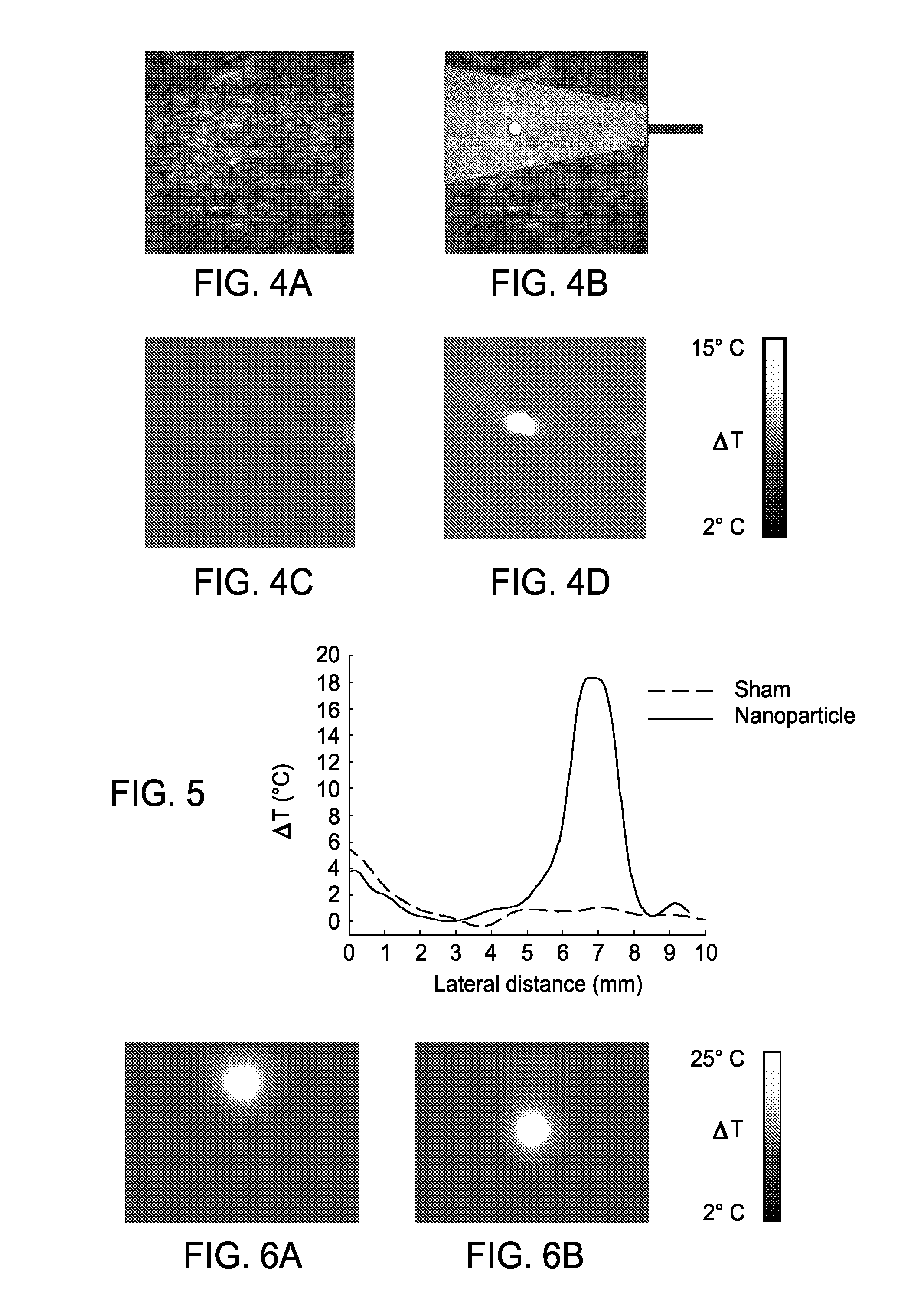
Real-Time Ultrasound Monitoring of Heat-Induced Tissue Interactions
InactiveUS20090105588A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsRadiation therapyReal time ultrasound
The present invention includes an apparatus, method and system for monitoring and controlling radiation therapy, the system including a radiative source that emits energy that enters a tissue and is absorbed at or a near a target site in the tissue to heat the tissue; an ultrasound transmitter directed at the target site, wherein the ultrasound transmitter emits ultrasound signals to the tissue that has been heated by the radiative source; an ultrasound receiver directed at the target site, wherein the ultrasound receiver receives ultrasound signals emitted from the ultrasound transmitter and reflected from the tissue that has been heated by the radiative source; and a signal processor that processes the received ultrasound signal to calculate a tissue composition scan or tissue temperature scan.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
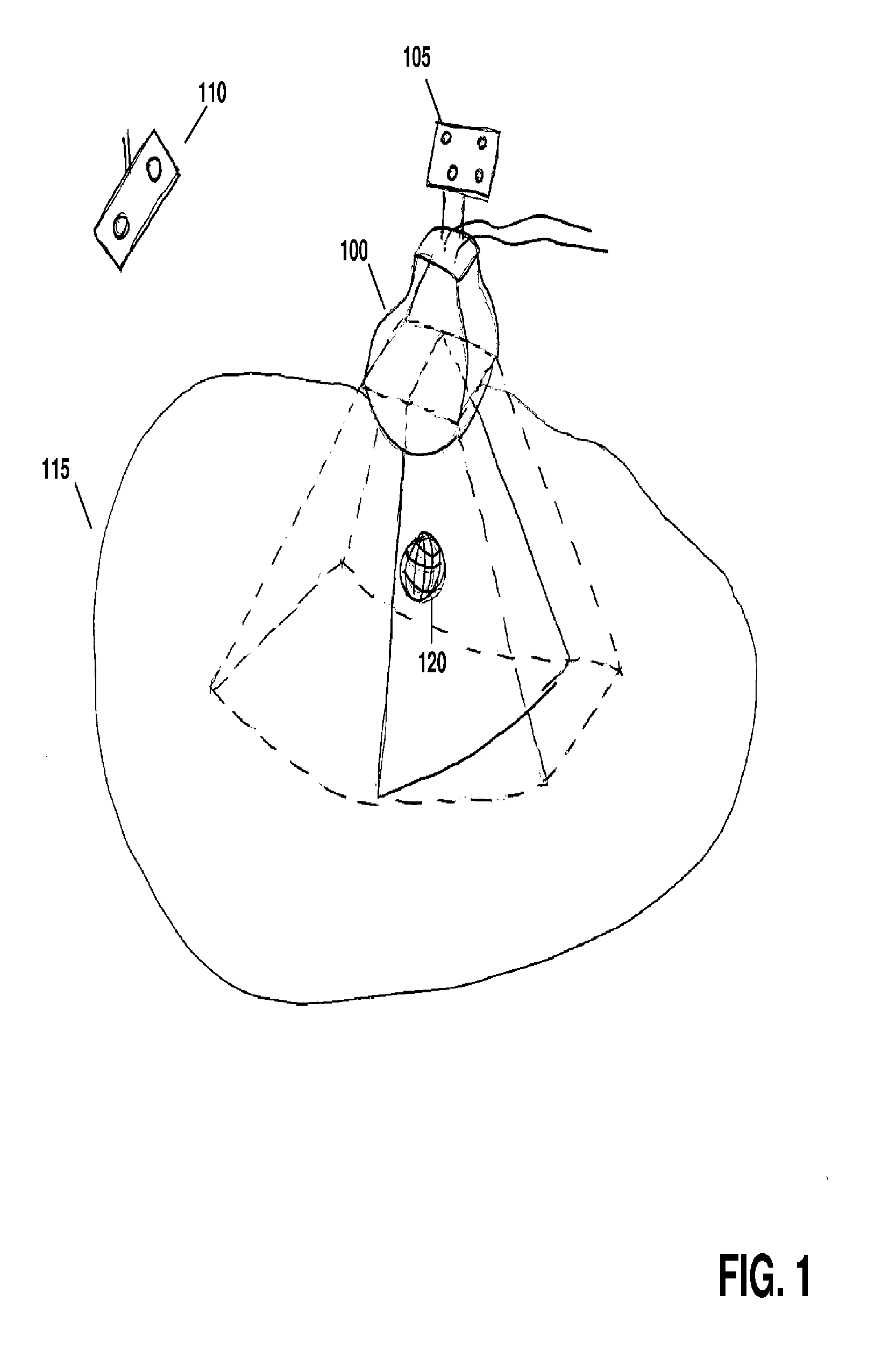
Real time ultrasound monitoring of the motion of internal structures during respiration for control of therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060241443A1Organ movement/changes detectionChiropractic devicesHelical computed tomographyReal time ultrasound
A method of targeting therapy such as radiation treatment to a patient includes: identifying a target lesion inside the patient using an image obtained from an imaging modality selected from the group consisting of computed axial tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, positron emission tomography, and ultrasound; identifying an anatomical feature inside the patient on a static ultrasound image; registering the image of the target lesion with the static ultrasound image; and tracking movement of the anatomical feature during respiration in real time using ultrasound so that therapy delivery to the target lesion is triggered based on (1) movement of the anatomical feature and (2) the registered images.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
Multiple scan-plane ultrasound imaging of objects
ActiveUS20030216646A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingFiber
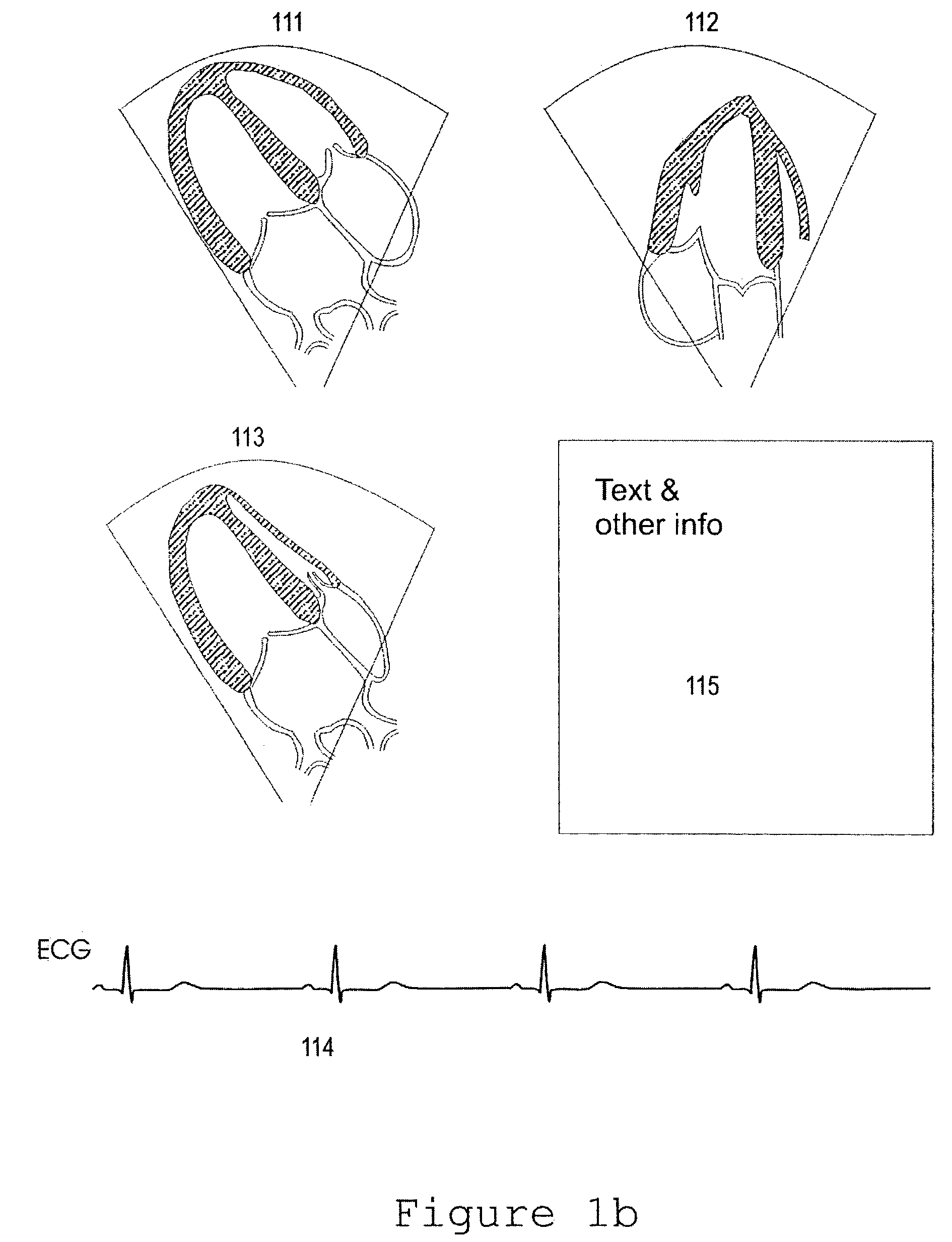
A method of real time ultrasound imaging of an object in at least three two-dimensional scan planes that are rotated around a common axis, is given, together with designs of ultrasound transducer arrays that allows for such imaging. The method is also introduced into a monitoring situation of cardiac function where, combined with other measurements as for example the LV pressure, physiological parameters like ejection fraction and muscular fiber stress is calculated.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
System and method for fusing real-time ultrasound images with pre-acquired medical images
InactiveCN101681504AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationComputer science
A method, apparatus and system for fusing real-time ultrasound images with pre-acquired medical images are described.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
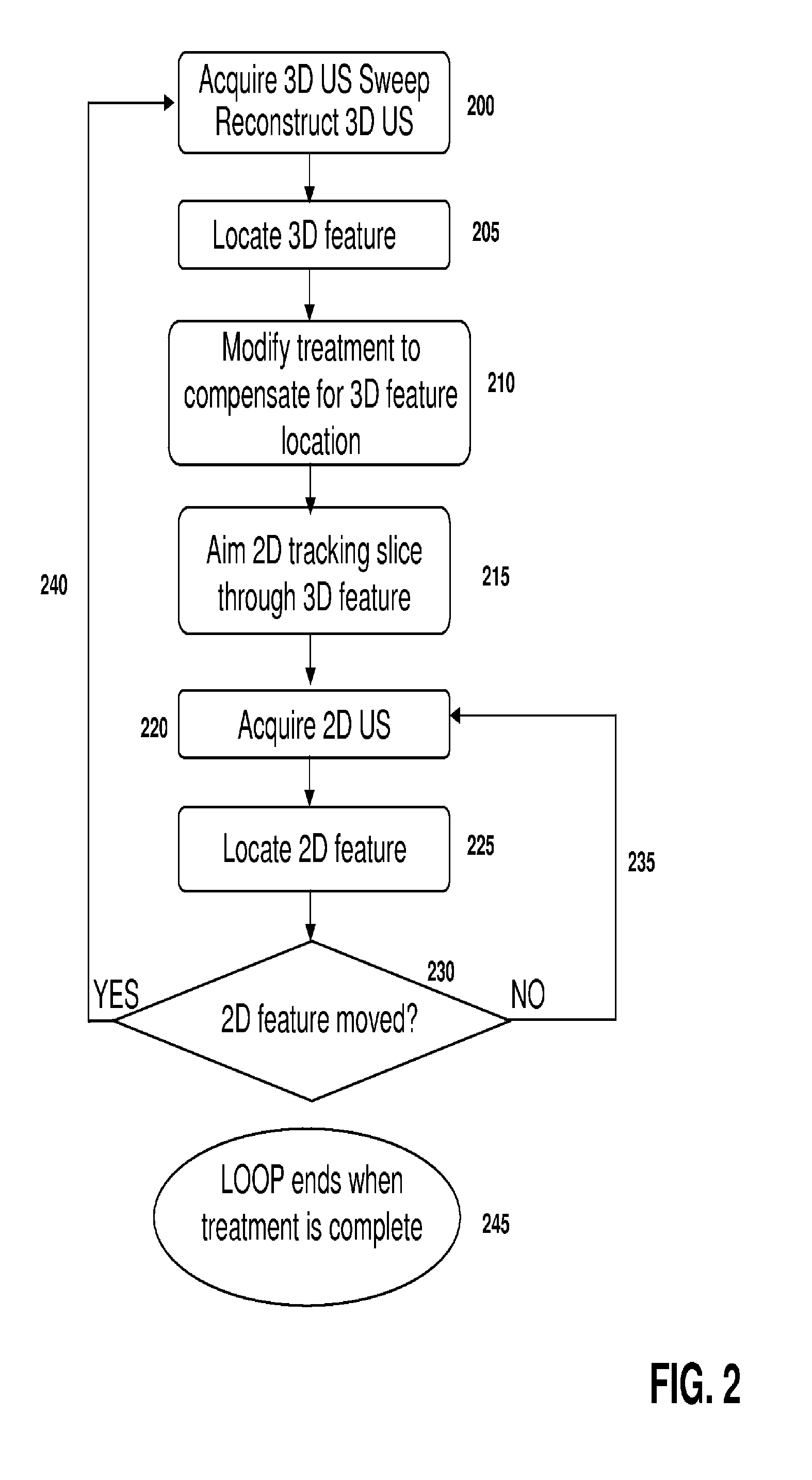
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
ActiveUS20120071758A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
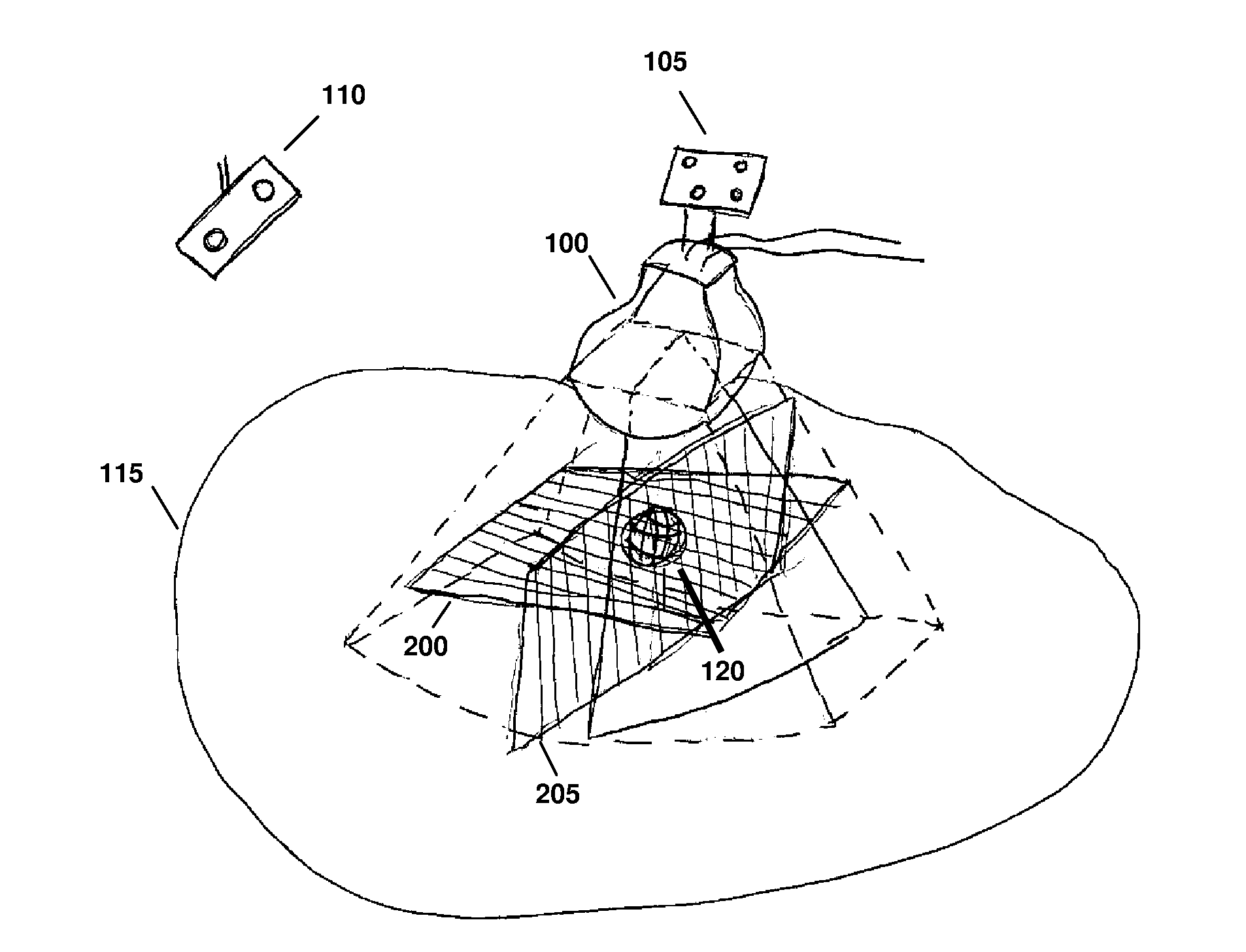
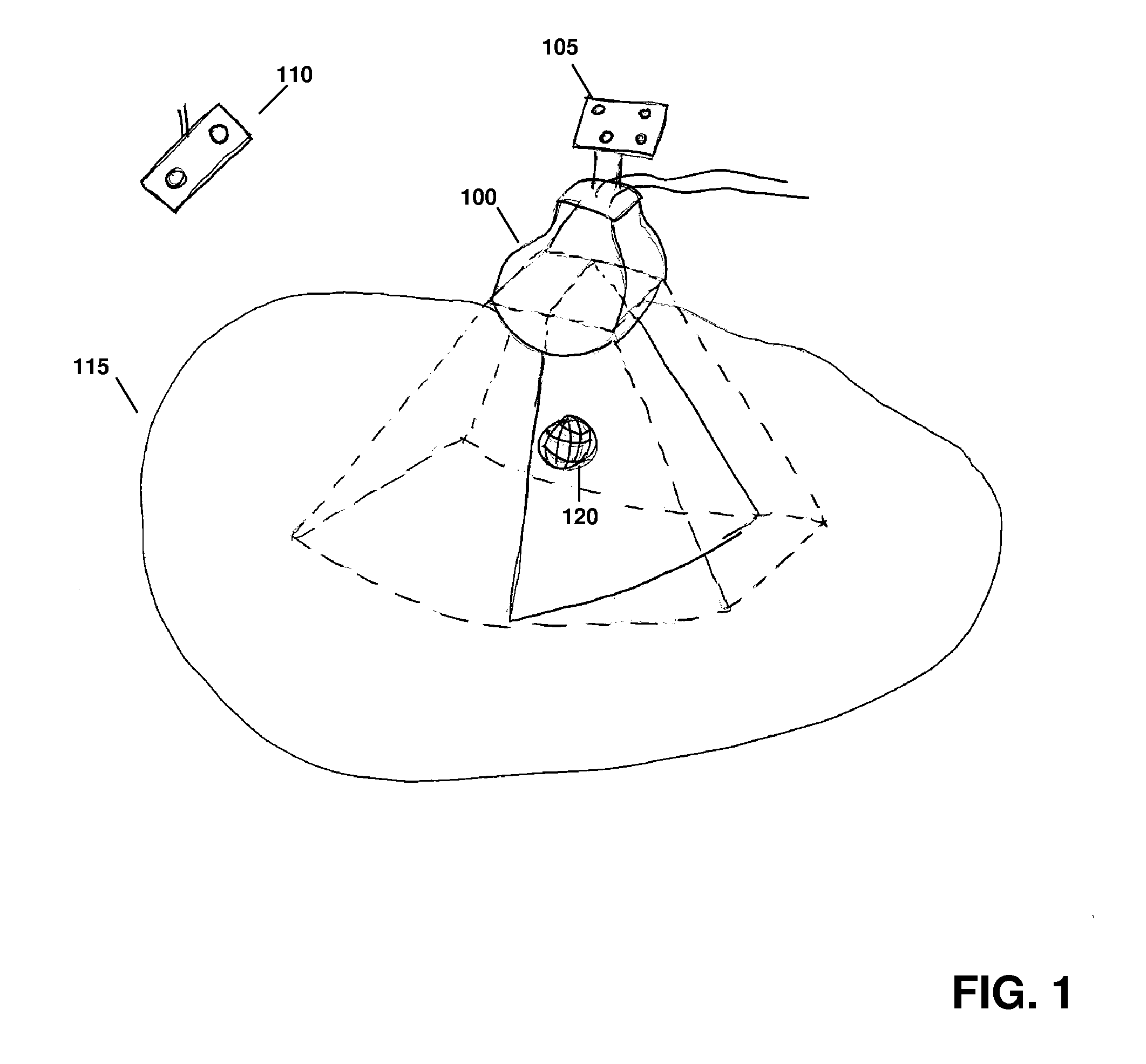
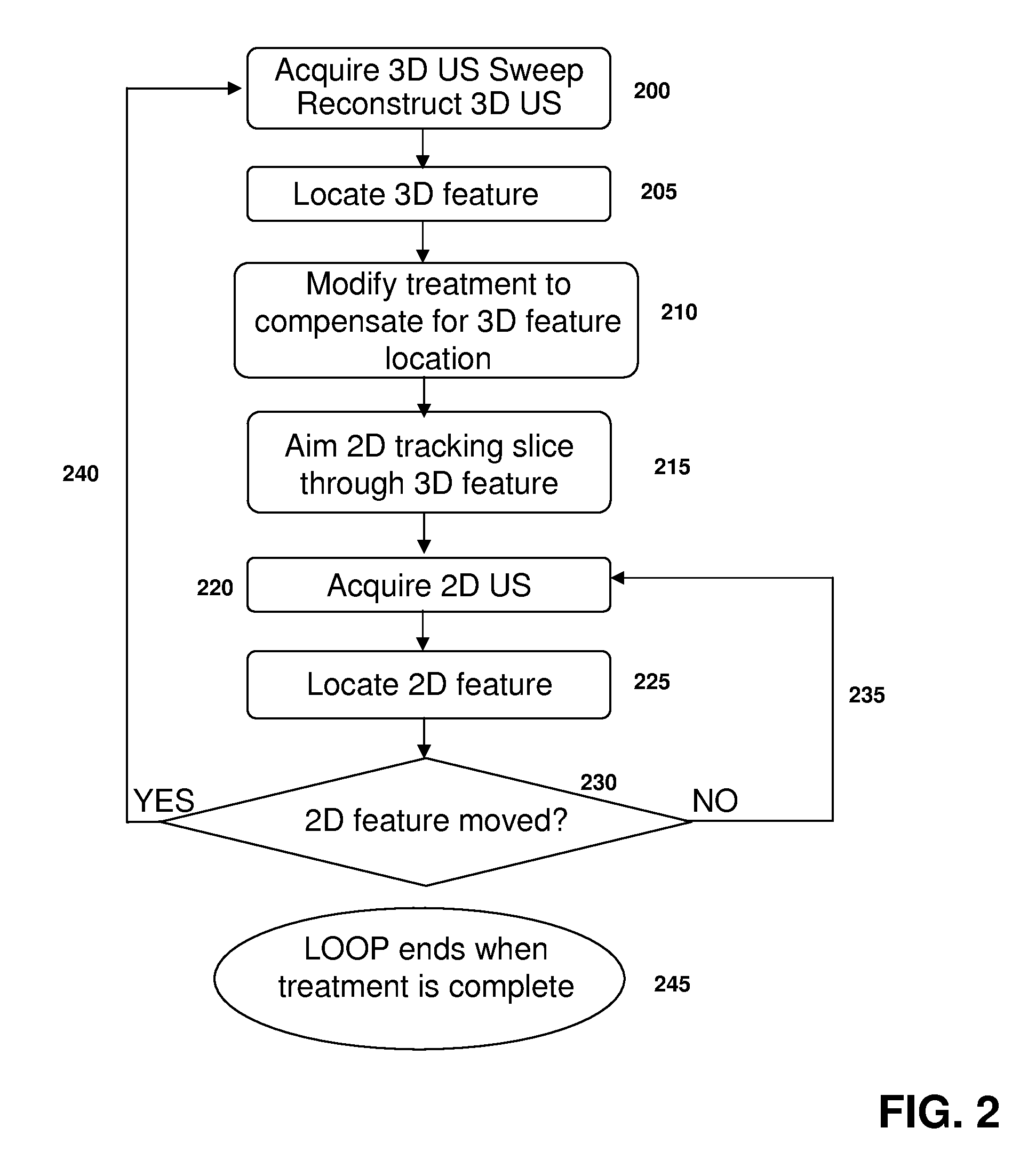
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
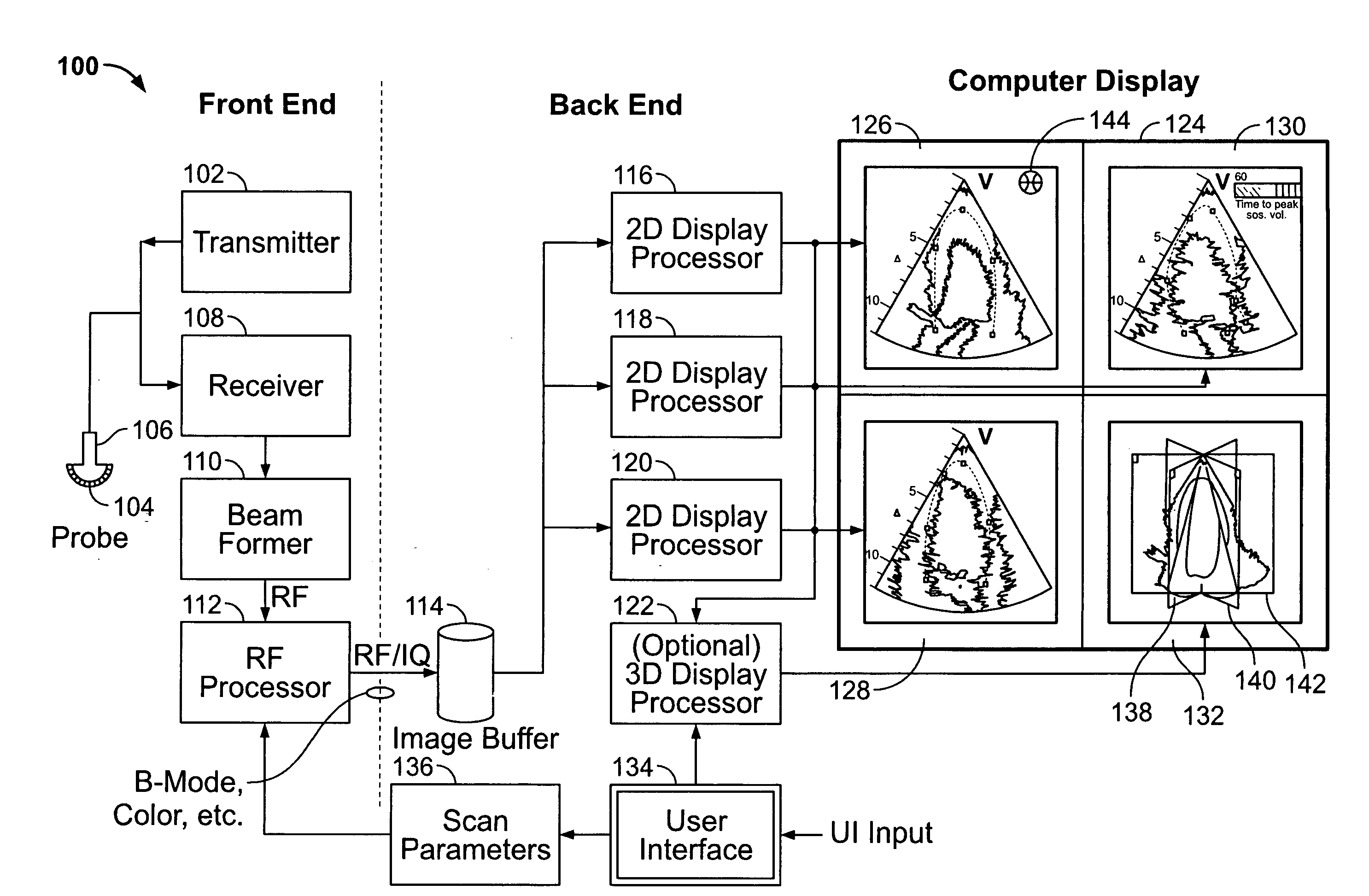
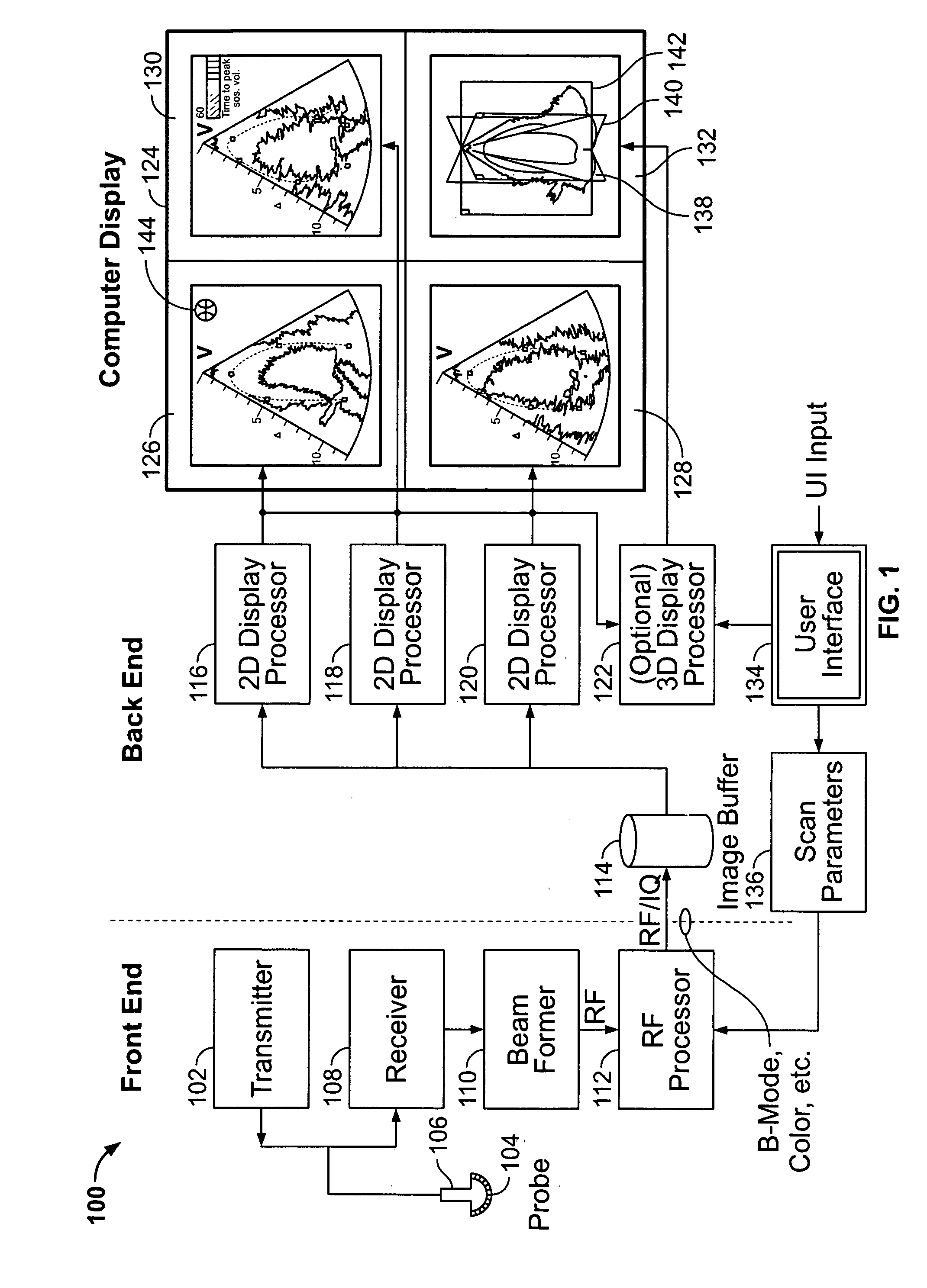
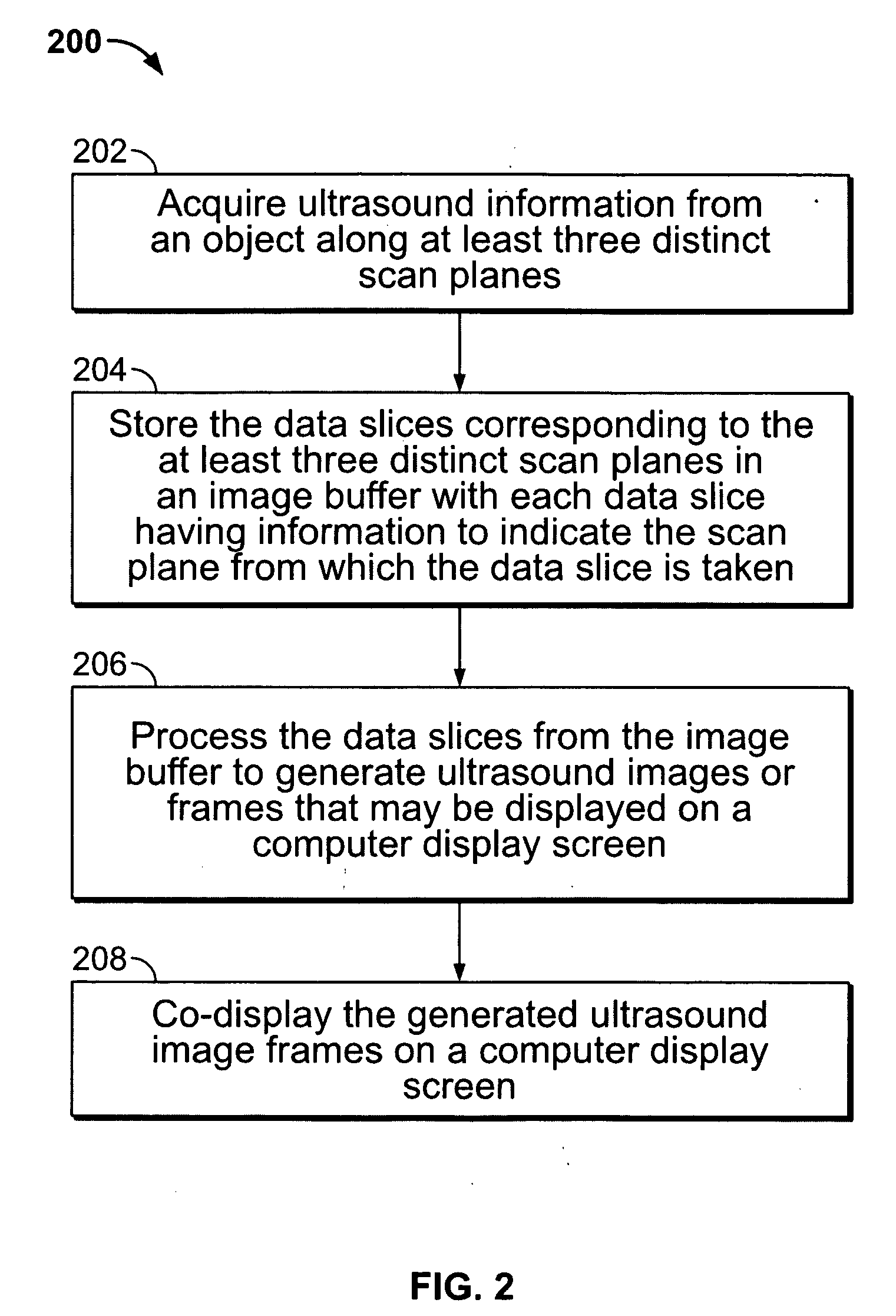
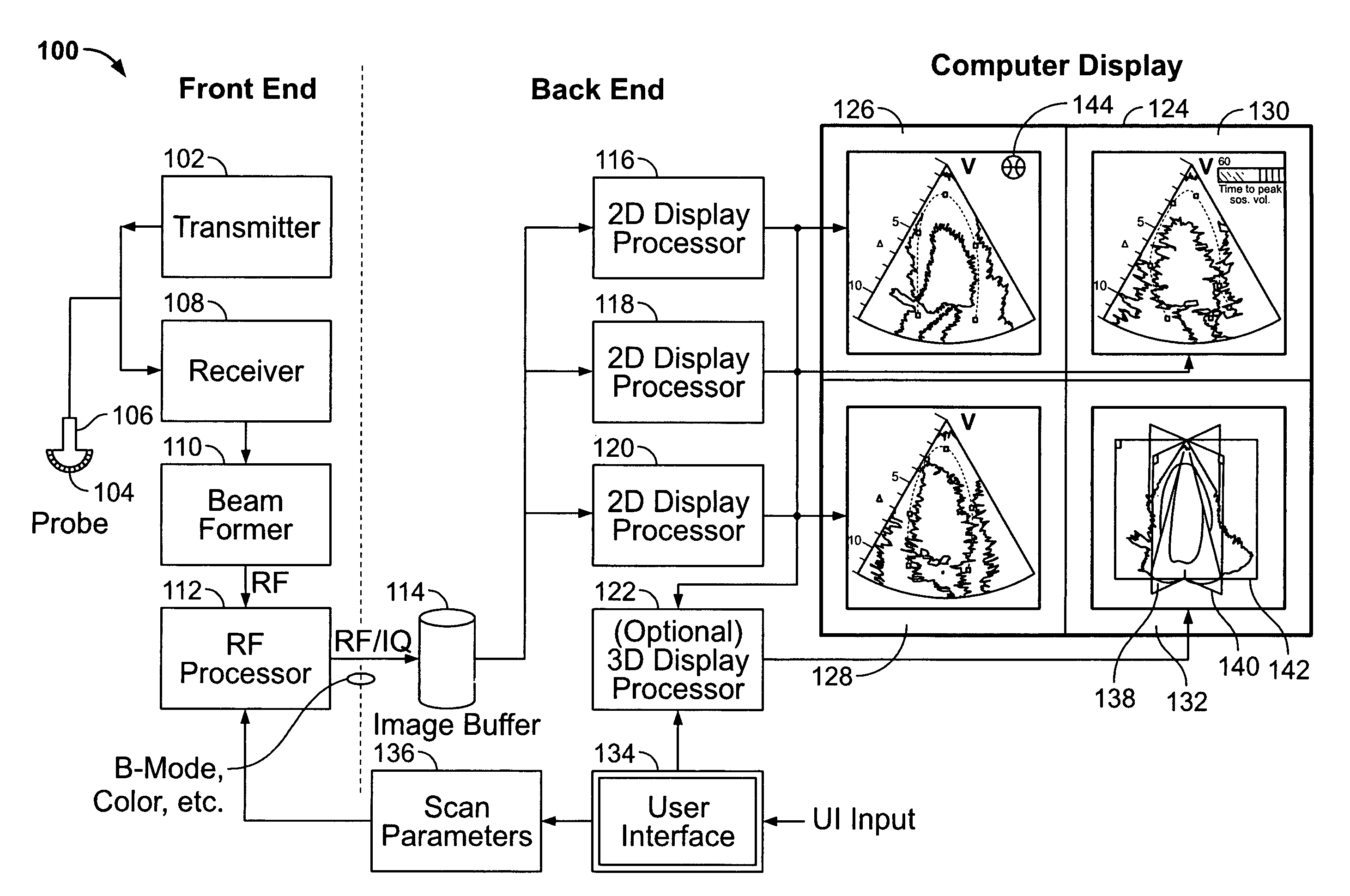
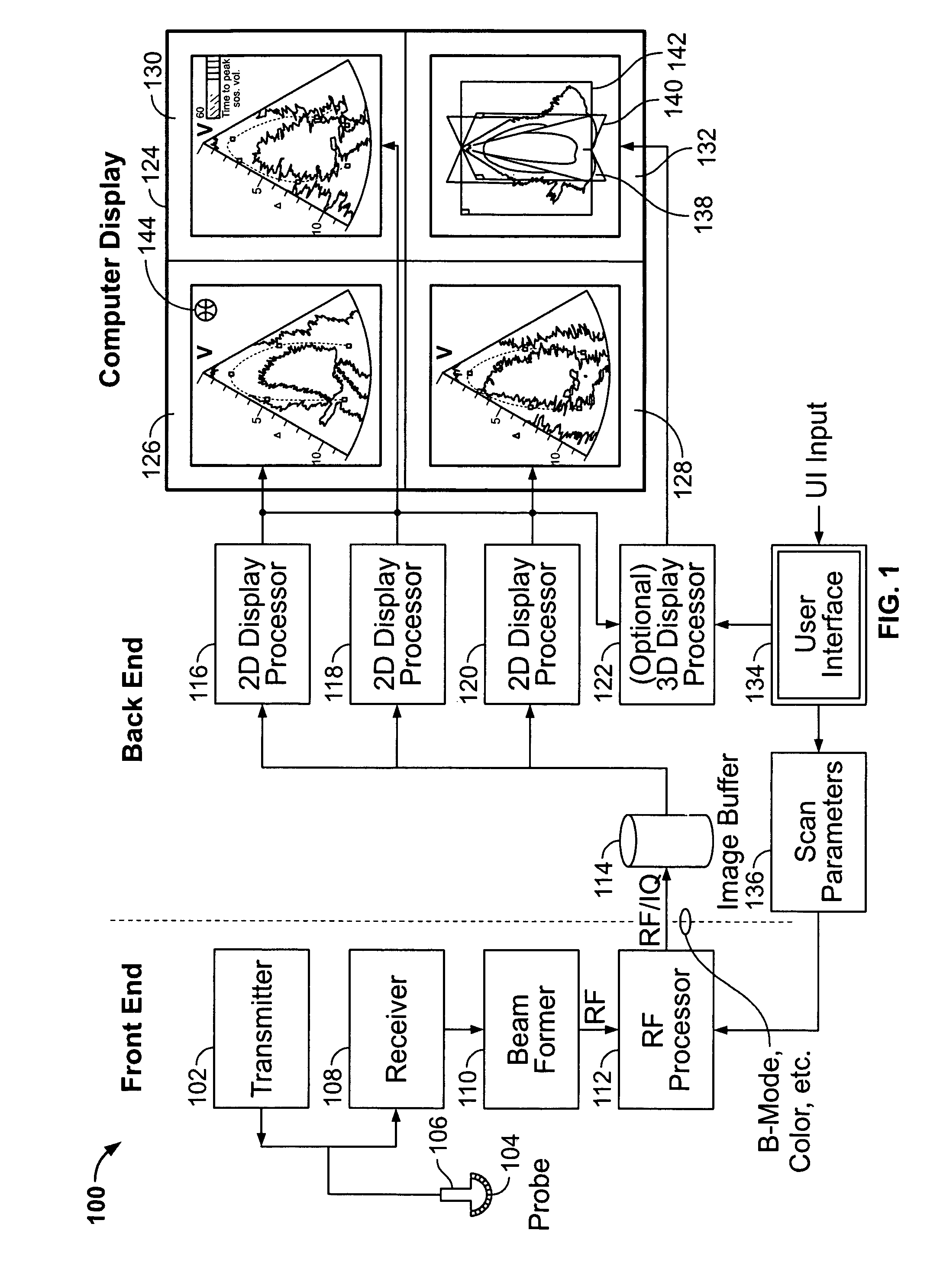
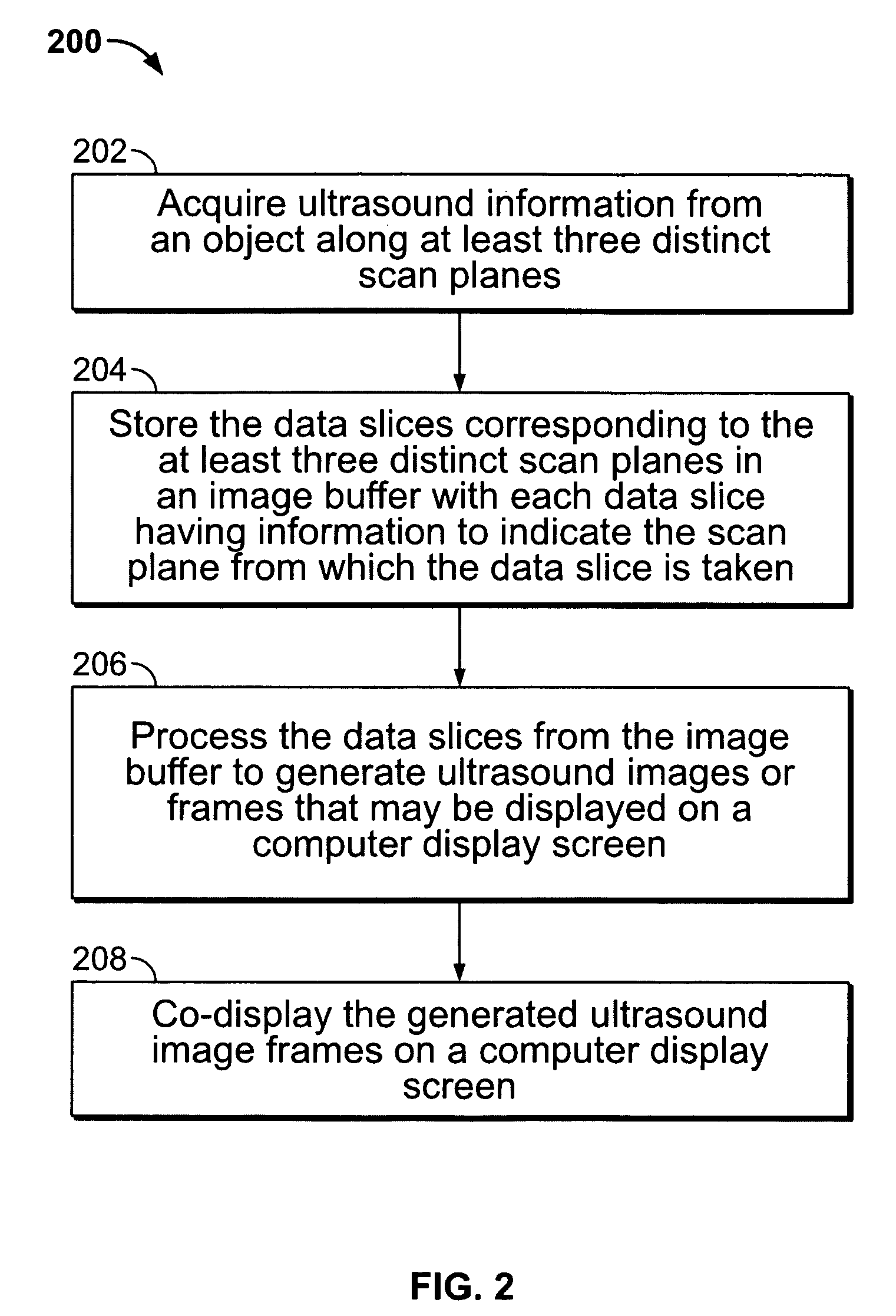
Method and apparatus for real time ultrasound multi-plane imaging
ActiveUS20050283078A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationDisplay device
An ultrasound system is provided that includes a probe for successively acquiring ultrasound information from an object along at least three distinct scan planes. The scan planes intersect one another along an axis extending from the probe through the object. A memory is included for storing data slices corresponding to the at least three distinct scan planes based on the ultrasound information. Also included is a processor that accesses the memory to select and obtain the data slices and generates ultrasound images based on the data slices. A display is included for co-displaying the ultrasound images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Phased array acoustic system for 3D imaging of moving parts
InactiveUS7347820B2Minimize acquisition time durationReduce acquisition timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationTransducer
The invention relates to an ultrasound phased array imaging system comprising: probe (10) with a 2-D array of transducer elements (12) for acquiring 3-D ultrasound data of a volume of a body, including moving tissue and fluid flow; a beamforming system (10, 12, 14, 16) for emitting and receiving in real time ultrasound beams in said volume, which provides, in real time and in 3-D, more than one spatial receive beams signals for each transmission beam within an ensemble length of more than two temporal samples, among which the receive flow beam signals and the receive tissue beam signals are substantially temporally uncorrelated but spatially correlated; separation means (30) for processing in real time the receive beams signals, comprising adaptive spatial tissue filtering means using simultaneously more than one spatial receive beam signals acquired in 3-D within the ensemble length of more than two temporal samples, which separation means analyzes temporal variations of the respective successive receive signals and extracts flow receive beam signals from spatial combinations of receive beam signals; processing means (40, 50) and display means (62, 60) for processing flow Doppler signals and for displaying images based on said processed flow Doppler signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
InactiveUS20110172526A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Microwave ablation planning and procedure systems
Disclosed are systems for performing a microwave ablation procedure comprising an ablation probe, an electromagnetic tracking system configured to track the location of the ablation probe inside a patient's body while the ablation probe is navigated inside the patient's body, an ultrasound imager configured to generate real-time ultrasound images, and a computing device configured to display guidance for navigating the ablation probe to at least one ablation target within the patient's body, display the tracked location of the ablation probe on the real-time ultrasound images based on the tracked location of the ablation probe inside the patient's body, iteratively update the displayed location of the ablation probe as the location of the ablation probe is tracked while the ablation probe is navigated inside the patient's body, and display guidance for ablating the at least one target when the ablation probe is navigated proximate to the at least one target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Multiple scan-plane ultrasound imaging of objects
ActiveUS7758509B2Delay is slowImprove acousticsBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionFiberUltrasound imaging
A method of real time ultrasound imaging of an object in at least three two-dimensional scan planes that are rotated around a common axis, is given, together with designs of ultrasound transducer arrays that allows for such imaging. The method is also introduced into a monitoring situation of cardiac function where, combined with other measurements as for example the LV pressure, physiological parameters like ejection fraction and muscular fiber stress is calculated.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Non-invasive diagnosis of breast cancer using real-time ultrasound strain imaging
InactiveUS20050283076A1Easy diagnosisReduce hardware costsImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationVisual assessment
A series of ultrasound strain images of a breast lesion are acquired along with corresponding B-mode images using a real-time ultrasound strain imaging system and a free-hand technique. A visual assessment of the lesion is made by the sonographer after image acquisition. A conspicuity metric is calculated from the strain images based on the weighted sum of lesion contrast values in each strain image. The weighting of each lesion contrast value is based on observed characteristics of malignant lesions in a series of strain images. Diagnosis is made based on the visual assessment and the conspicuity metric
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Medical devices with enhanced ultrasonic visibility
InactiveCN1791440AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesShortest distanceSolid tissue
The present invention provides medical devices with enhanced ultrasound visibility. The device uses real-time ultrasound monitoring of the position of the needle tip within the patient's body for topical drug delivery, probe positioning, fluid drainage, biopsy, or delivery of ultrasound pulses. The device controls the diffusion of drugs in solid tissues, injects particles into solid tissues, and delivers drugs to specific blood vessels. As the needle is inserted, a fluid with a different ultrasound visibility than the organ environment is injected into the patient. The fluid travels a short distance before being slowed and stopped by the patient's tissues, and the flow can be detected ultrasonically. During needle insertion, the needle position is monitored with ultrasound until the needle is at the ideal point of action. Therapeutic drugs are then delivered through the needle or probes are inserted to perform treatments such as removing tumors with radiofrequency heat. The flow rate can be adjusted during needle insertion to maintain a properly set image of the needle tip. At the point of application, the ultrasound imaging agent can be repeated and pulsed at different flow rates until a satisfactory fluid profile is obtained, after which the drug can be delivered. Ultrasound can also be sent through the needle with a detector mounted in the handheld assembly.
Owner:ARTENGA
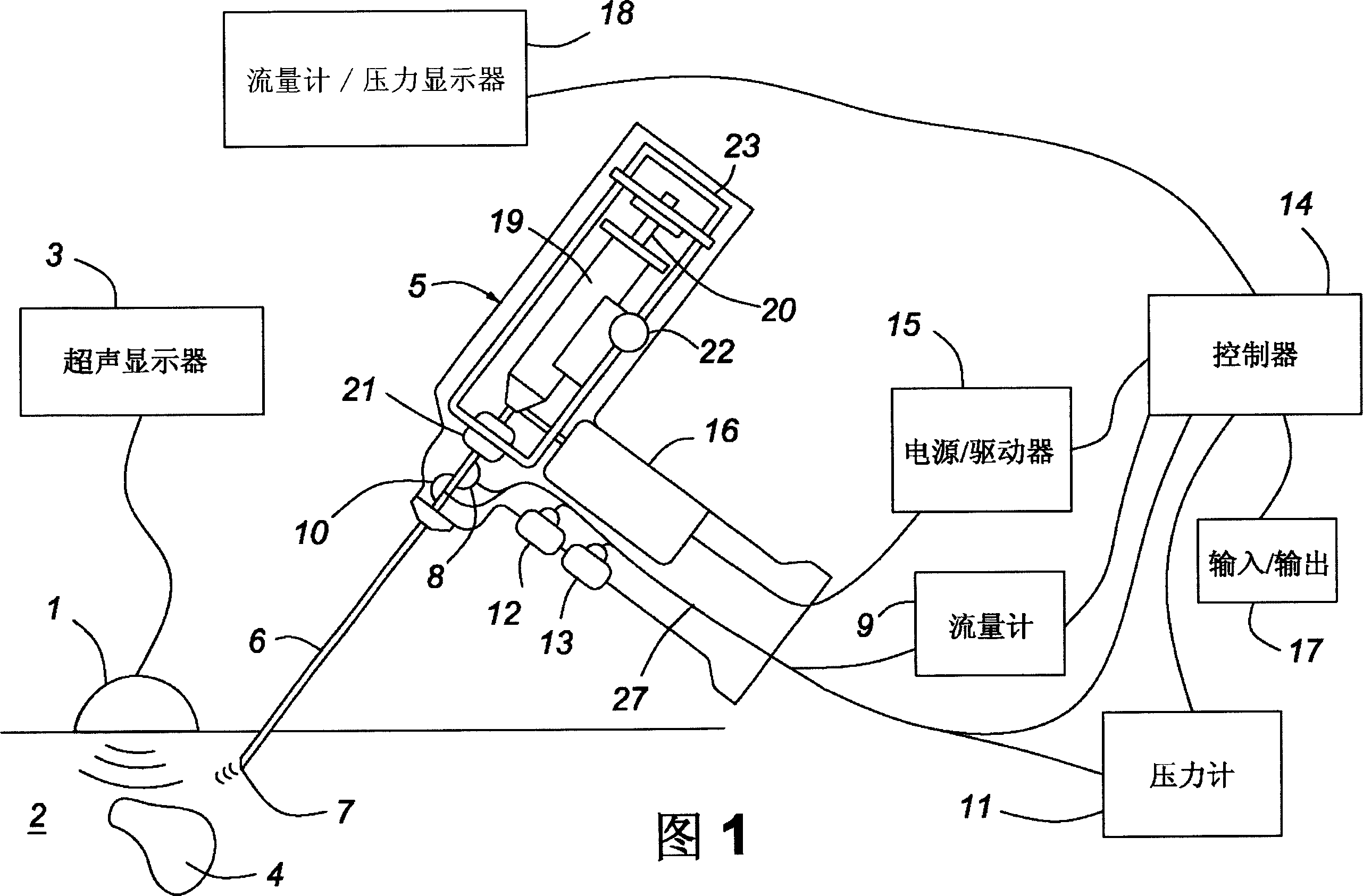
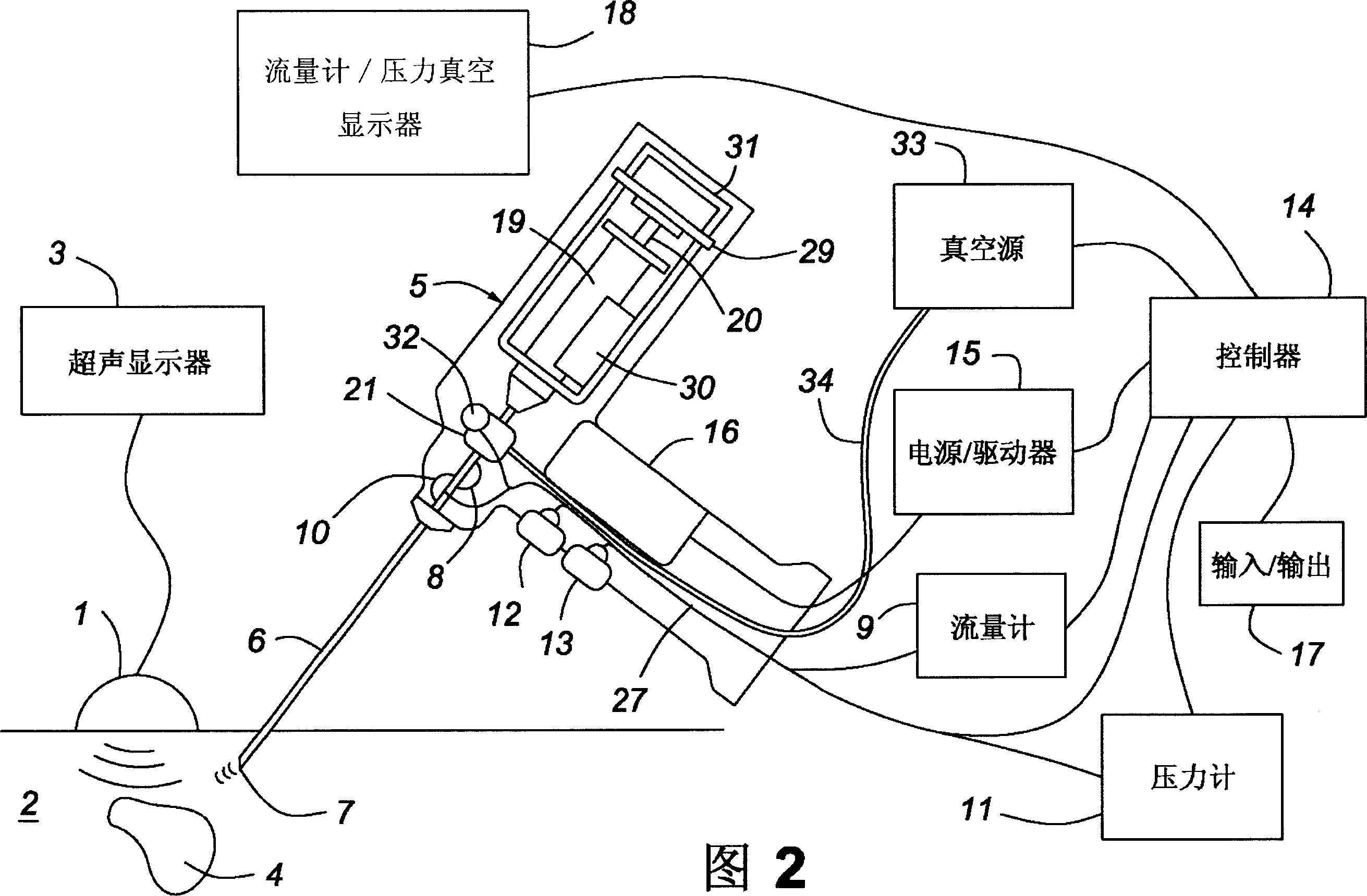
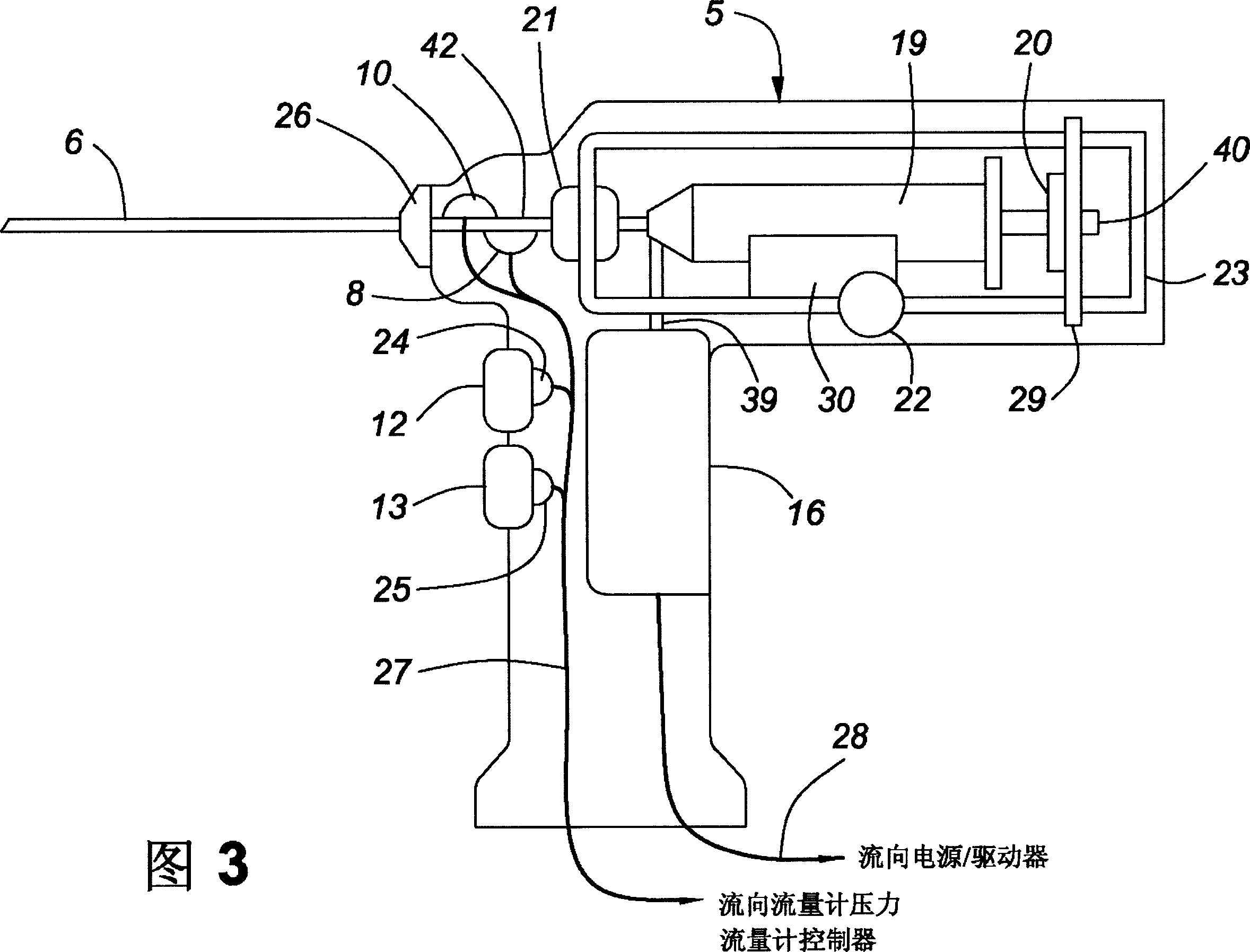
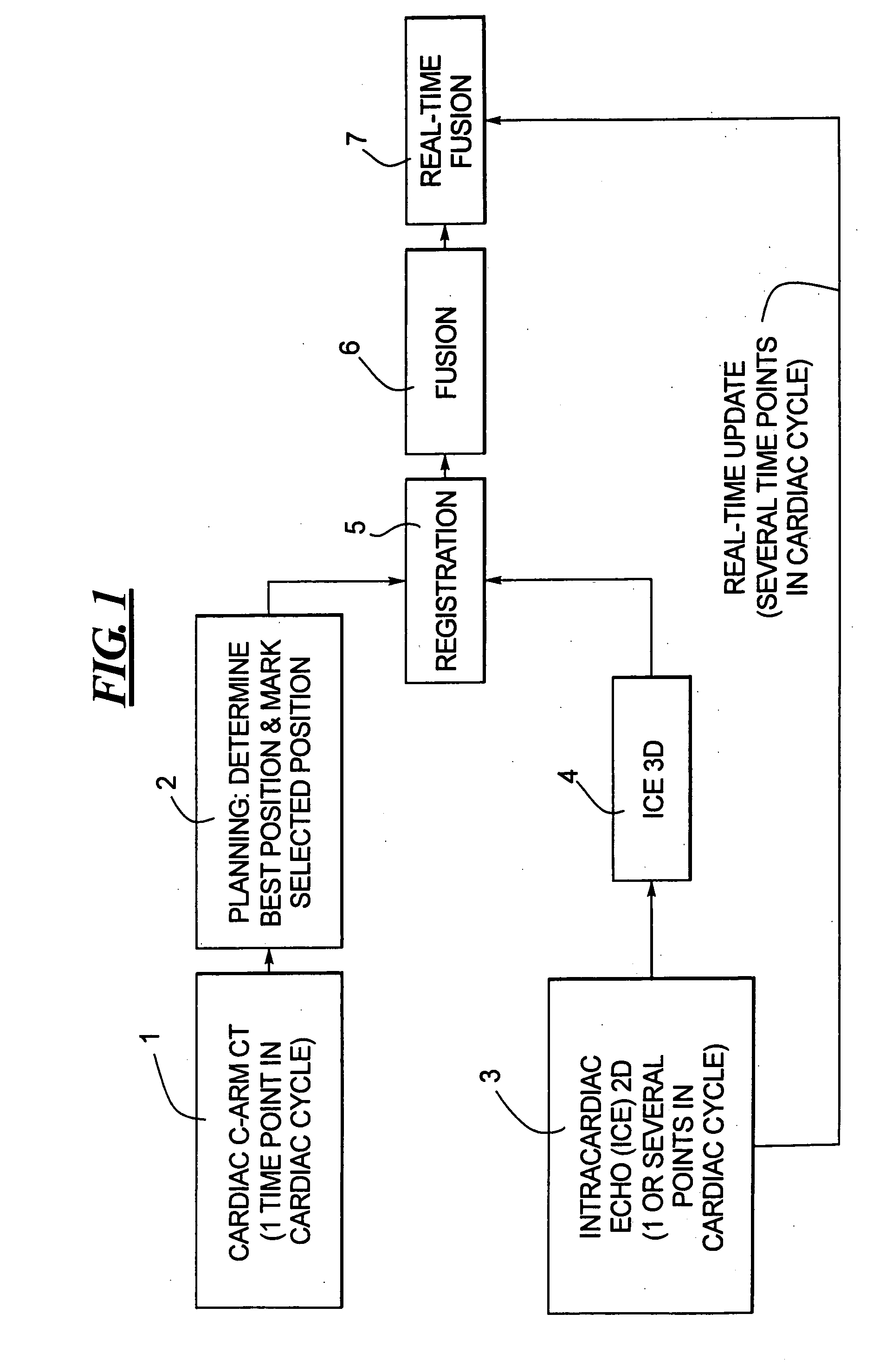
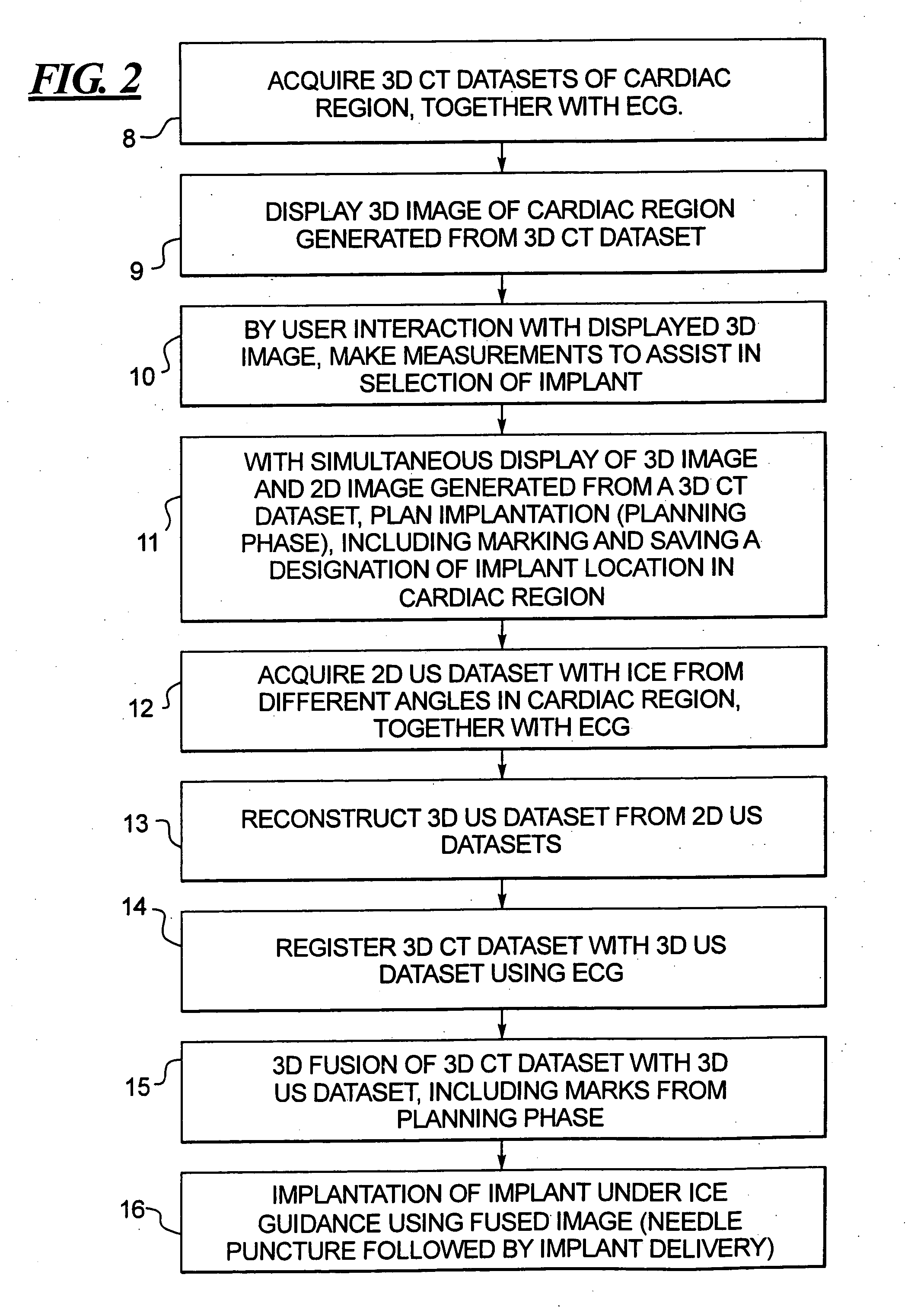
Method for implanting a cardiac implant with real-time ultrasound imaging guidance
InactiveUS20080146919A1Reduce disadvantagesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterUltrasound imaging2d ultrasound
In a method for implanting a cardiac implant, a 3D CT dataset of a cardiac region of interest at which an implant is to be implanted, is displayed and the implantation procedure is planned, which includes the physician electronically marking a best implantation site in the displayed image. This marking is then included in the 3D CT dataset. A 3D ultrasound dataset of the region of interest is acquired, and is brought into registration with the 3D CT dataset that incorporates the marking, and a fused image is produced therefrom. The fused image is displayed during the implantation procedure, and is updated with multiple real-time 2D ultrasound images obtained using the catheter that is employed to deliver the implant to the implantation site.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
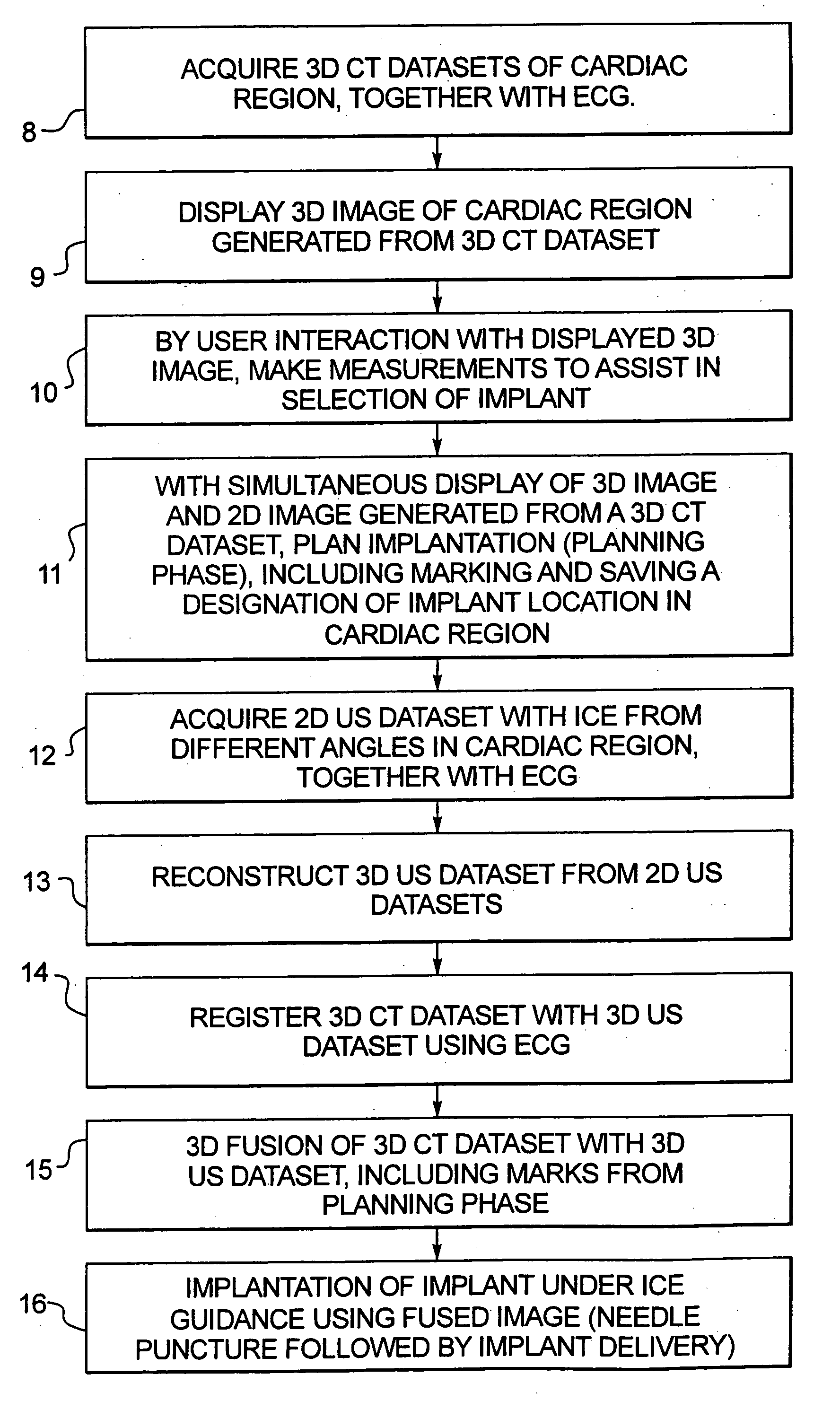
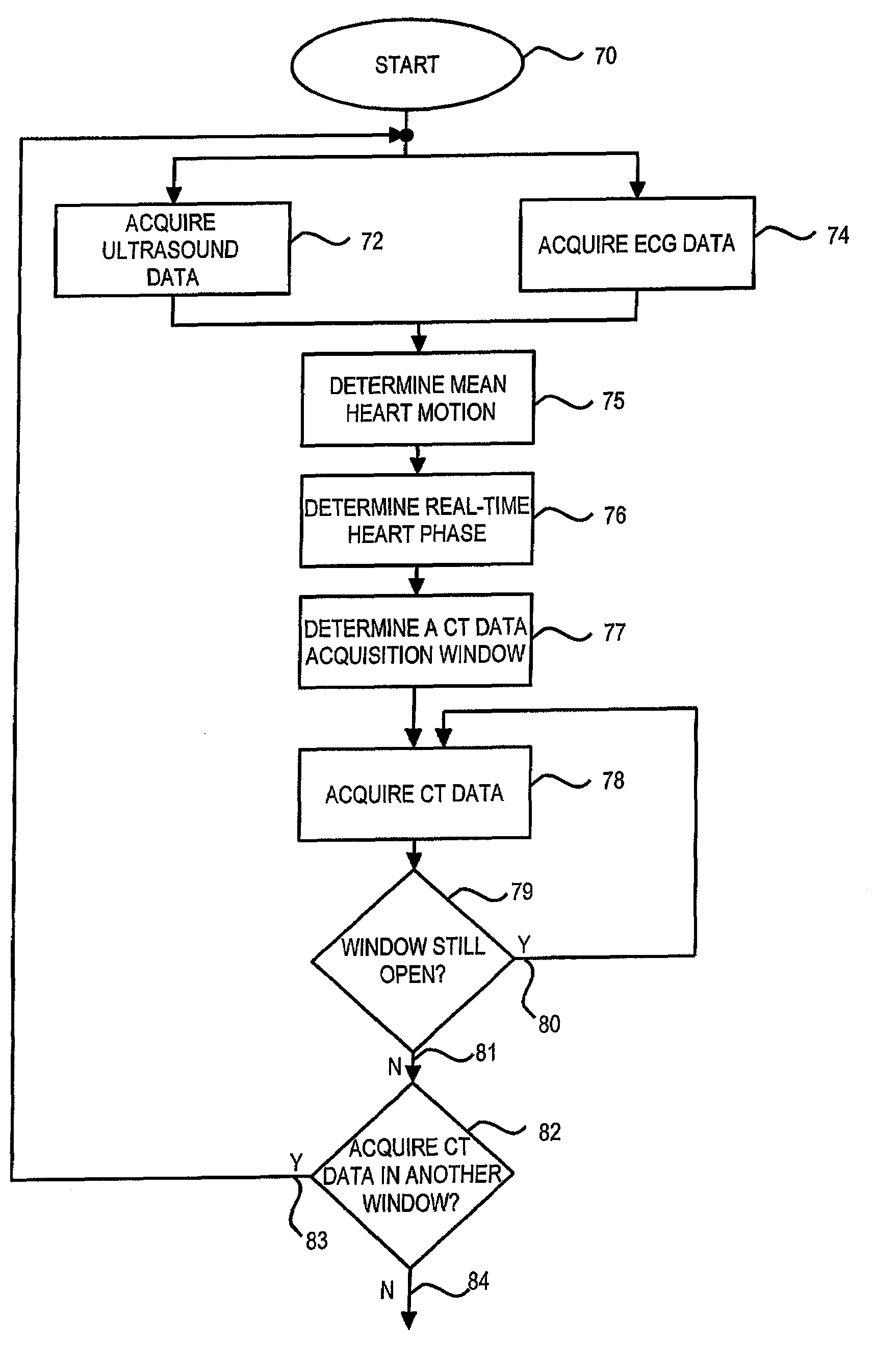
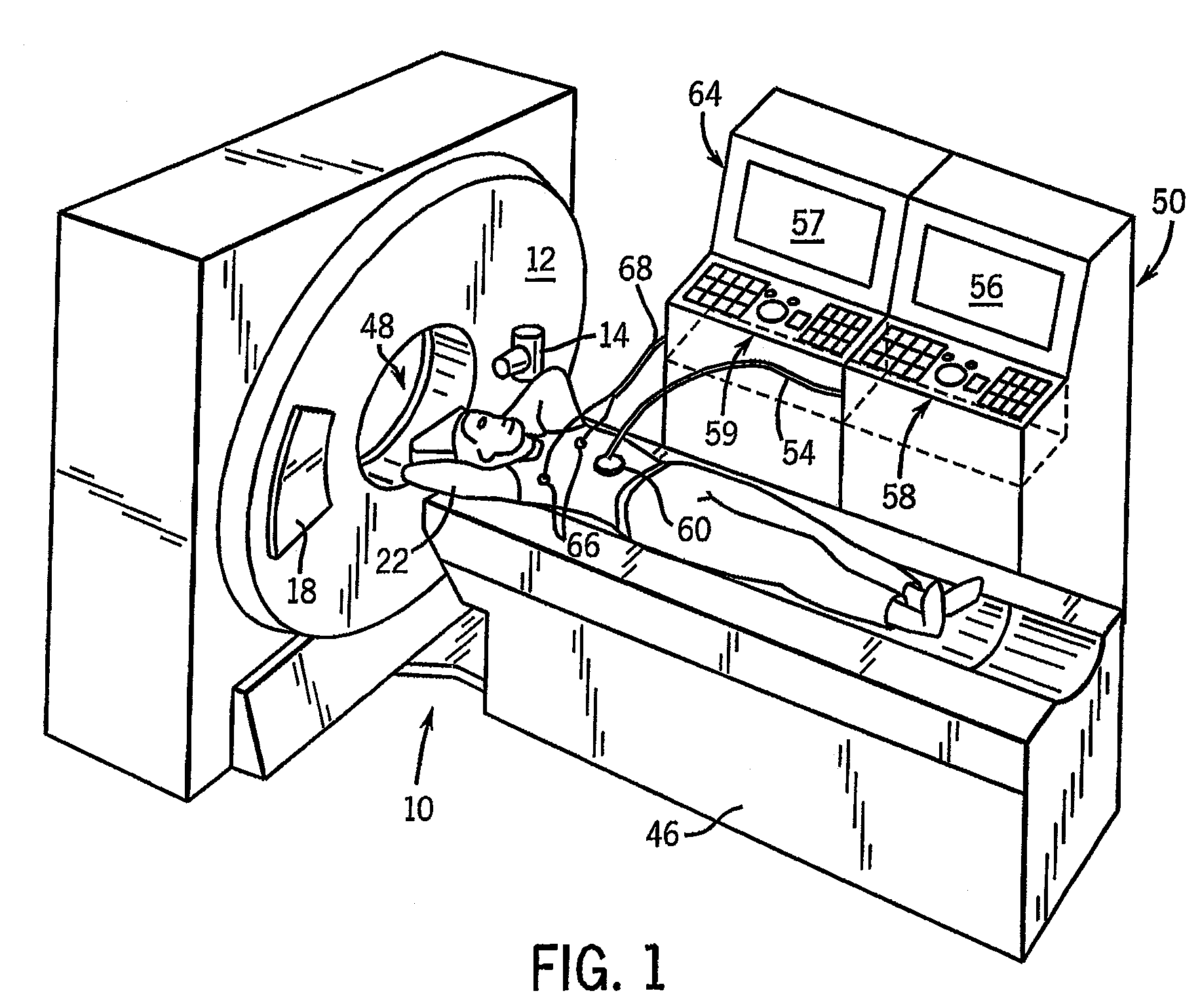
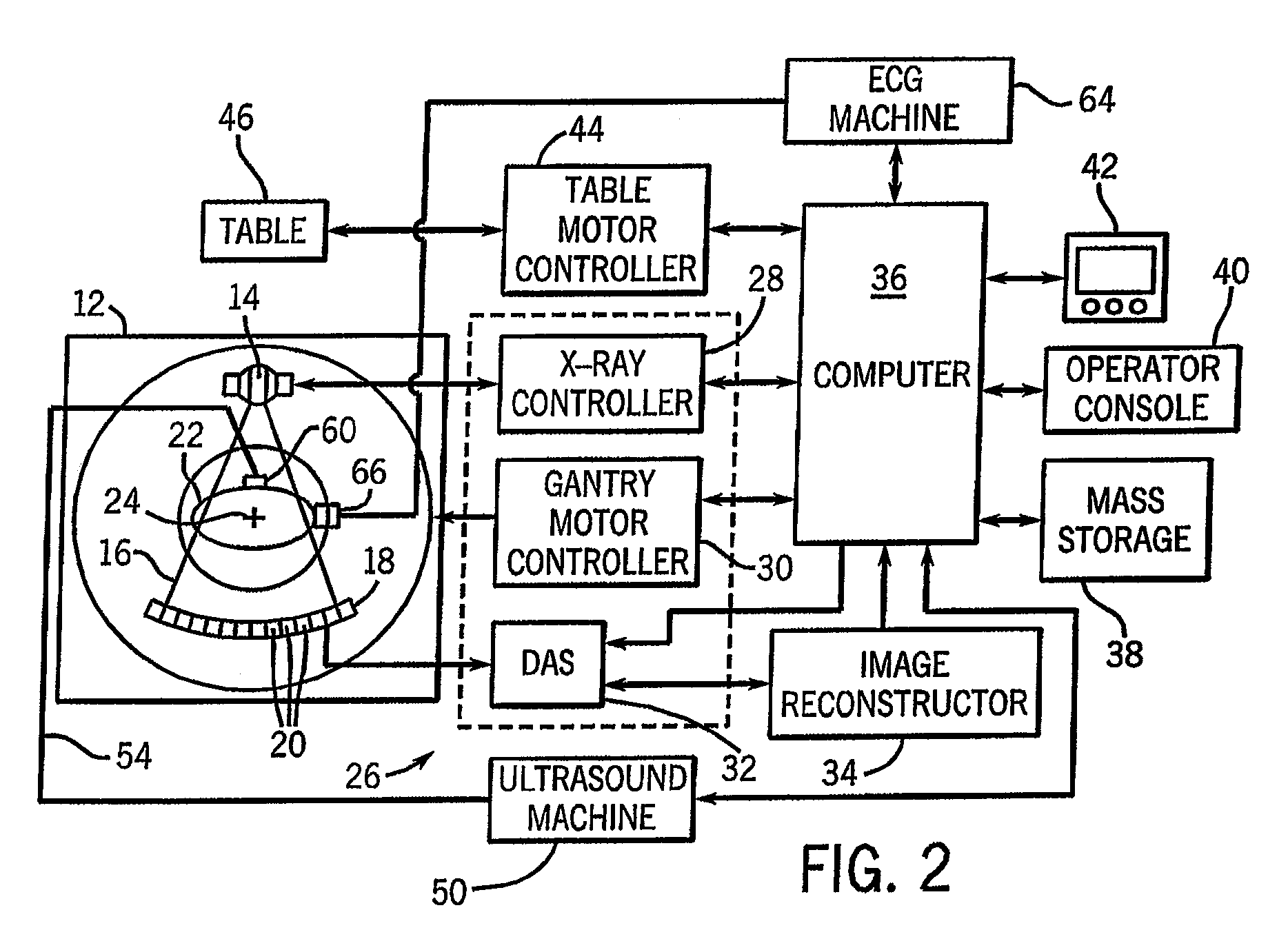
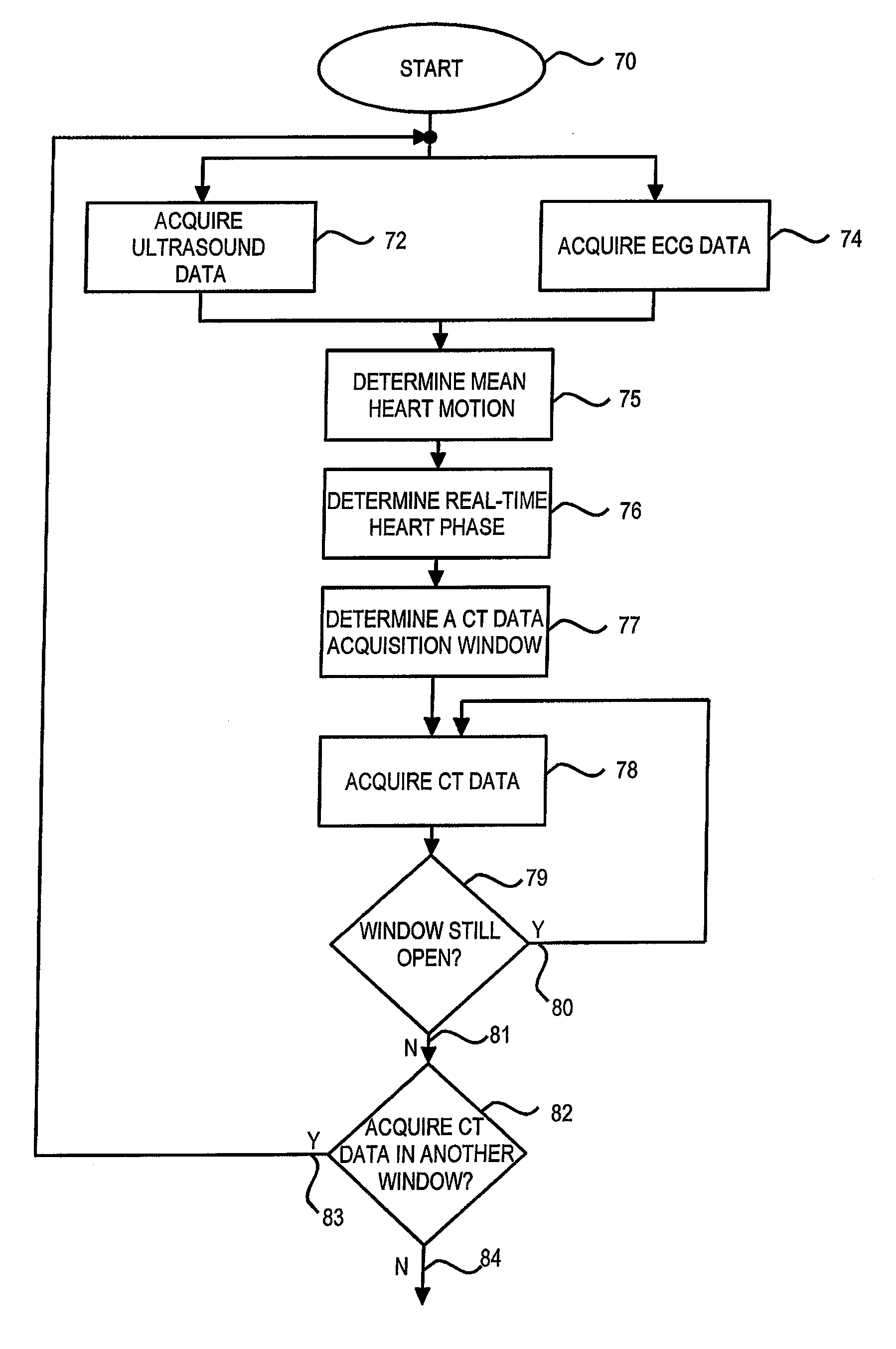
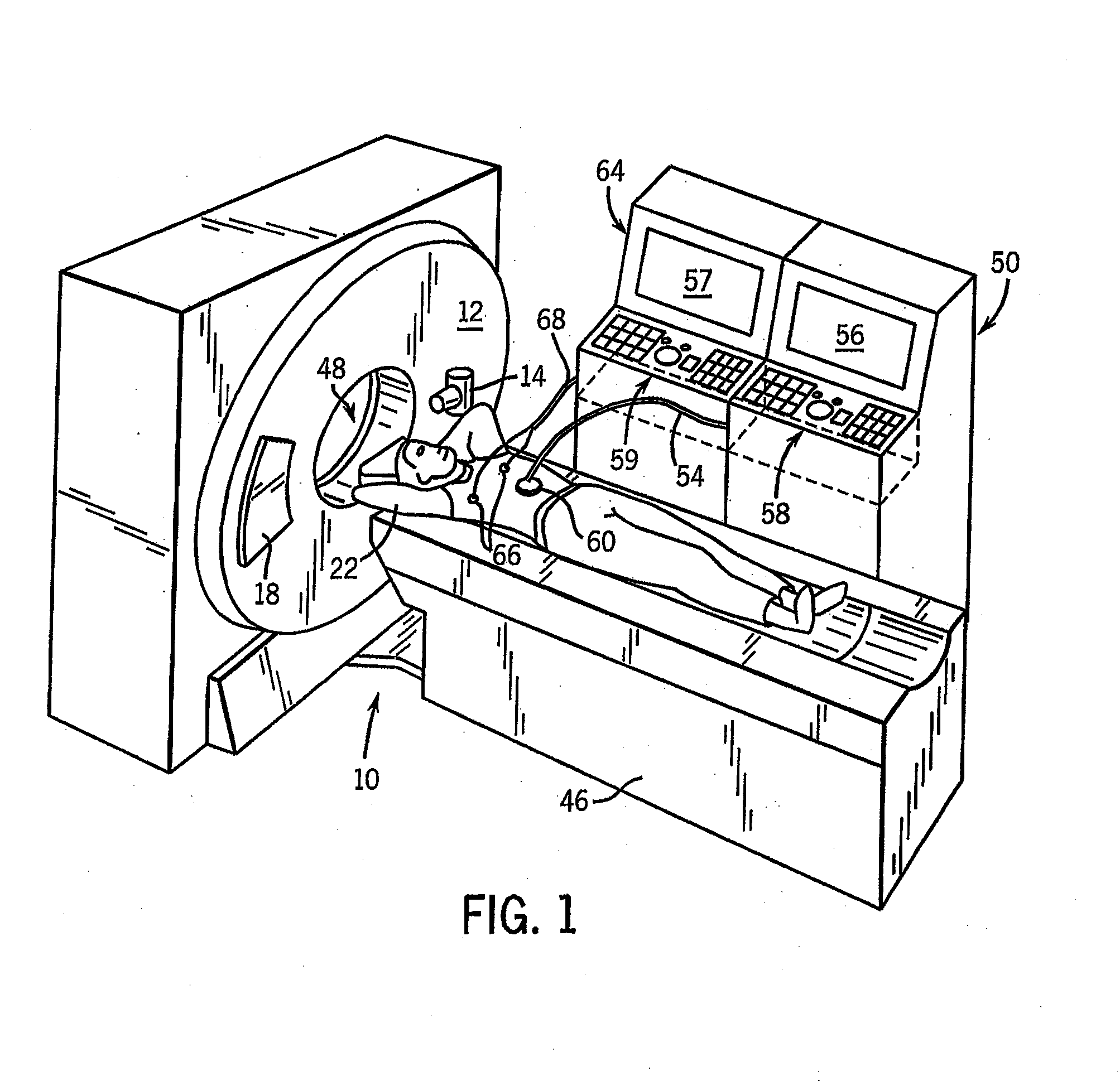
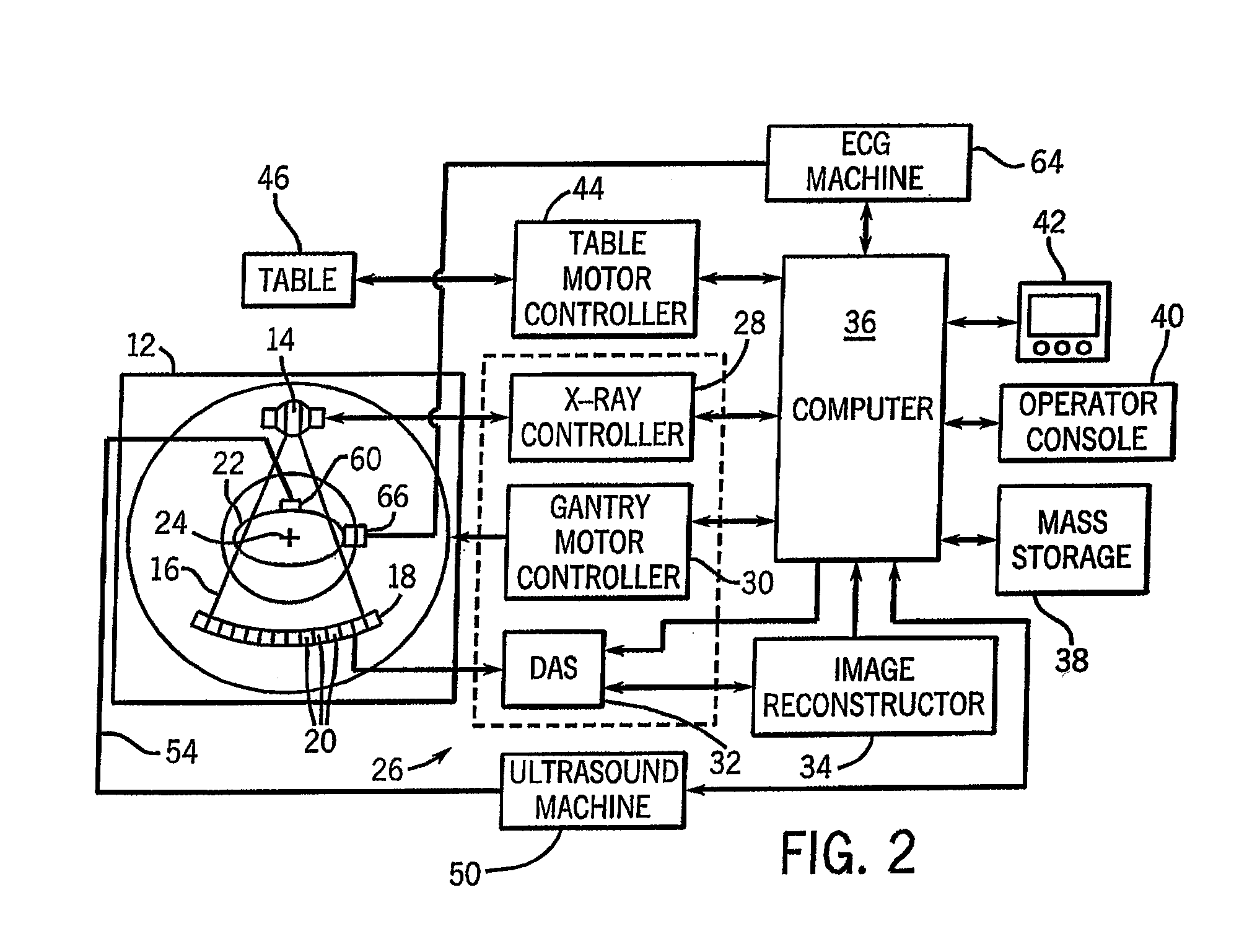
Method and apparatus of CT cardiac diagnostic imaging using motion a priori information from 3D ultrasound and ECG gating
ActiveUS7415093B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingEcg gatingSonification
ECG and ultrasound data of the heart are acquired in real-time during a scan. A data acquisition module is controlled during the scan to prospectively gate acquisition of CT data as a function of the real-time ECG data and the real-time ultrasound data. An image is reconstructed from the acquired CT data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus of ct cardiac diagnostic imaging using motion a priori information from 3D ultrasound and ECG gating
ActiveUS20080101532A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingEcg gatingSonification
ECG and ultrasound data of the heart are acquired in real-time during a scan. A data acquisition module is controlled during the scan to prospectively gate acquisition of CT data as a function of the real-time ECG data and the real-time ultrasound data. An image is reconstructed from the acquired CT data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods for microwave ablation planning and procedure
InactiveUS20160317229A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesRadiologyReal time ultrasound
Disclosed are methods for displaying guidance for navigating an ablation probe to at least one ablation target within a patient's body comprising tracking the location of the ablation probe inside the patient's body while the ablation probe is navigated, displaying the position of the ablation probe on real-time ultrasound images, iteratively updating the displayed position of the ablation probe as the location of the ablation probe is tracked while the ablation probe is navigated inside the patient's body, and displaying guidance for ablating the at least one target when the ablation probe is navigated proximate to the at least one target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
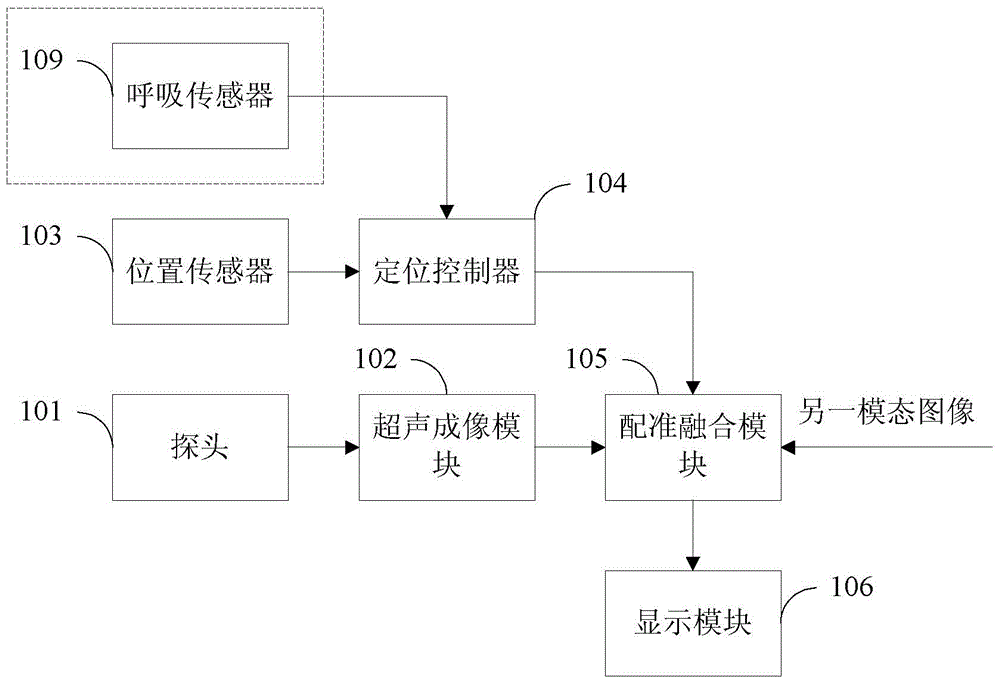
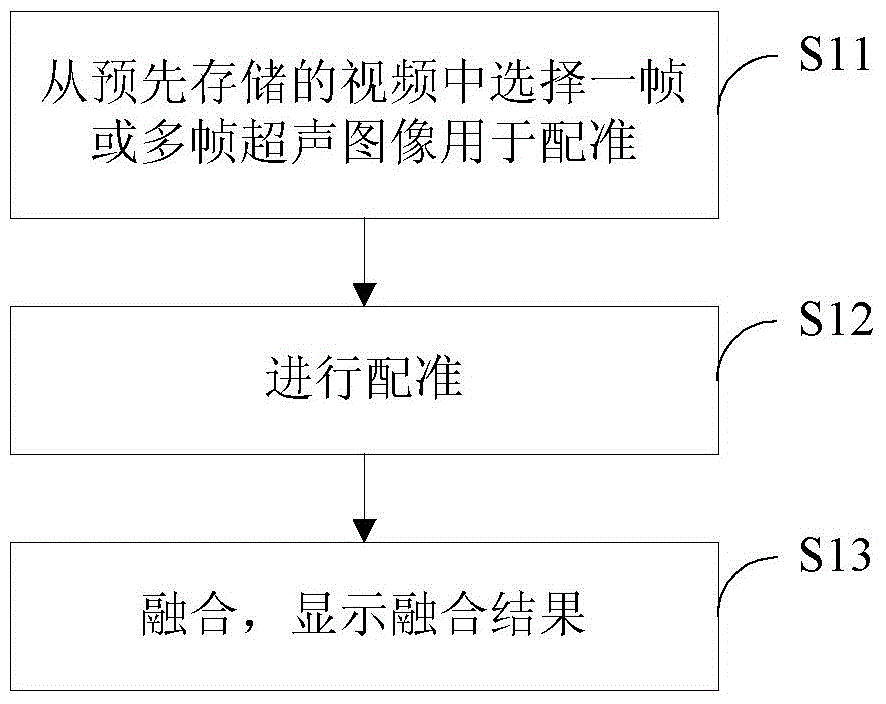
Ultrasonic fusion imaging method and ultrasonic fusion imaging navigation system
ActiveCN104574329AMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
The present application relates to an ultrasound fusion imaging method and an ultrasound fusion imaging navigation system. The ultrasound fusion imaging method comprises: a selection step, comprising selecting at least one ultrasound image from at least one previously stored piece of ultrasound video data according to an input instruction, wherein the ultrasound video data comprises an ultrasound image obtained by acquiring a target object from at least one plane and location-pointing information corresponding to the ultrasound image; a registration step, comprising registering the selected at least one ultrasound image with a modality image, wherein the registration process uses the location-pointing information of the at least one ultrasound image; and a fusion step, comprising image fusion of the registered ultrasound image with the modality image. The present invention differs from the existing registration-fusion methods based on real-time ultrasound in using a recorded registration video by scanning a target object prior to registration, and then selecting one or more ultrasound images to perform registration.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
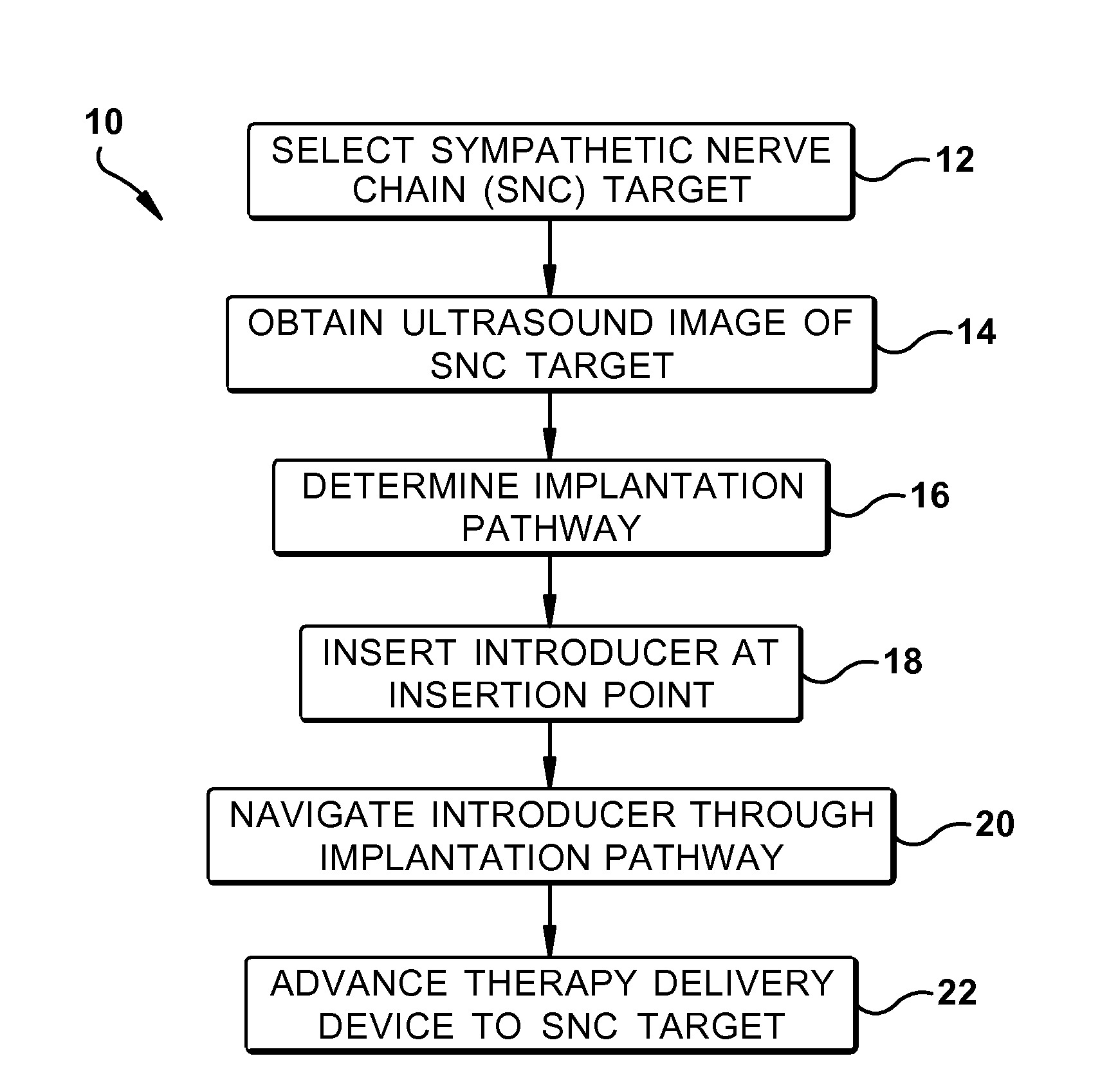
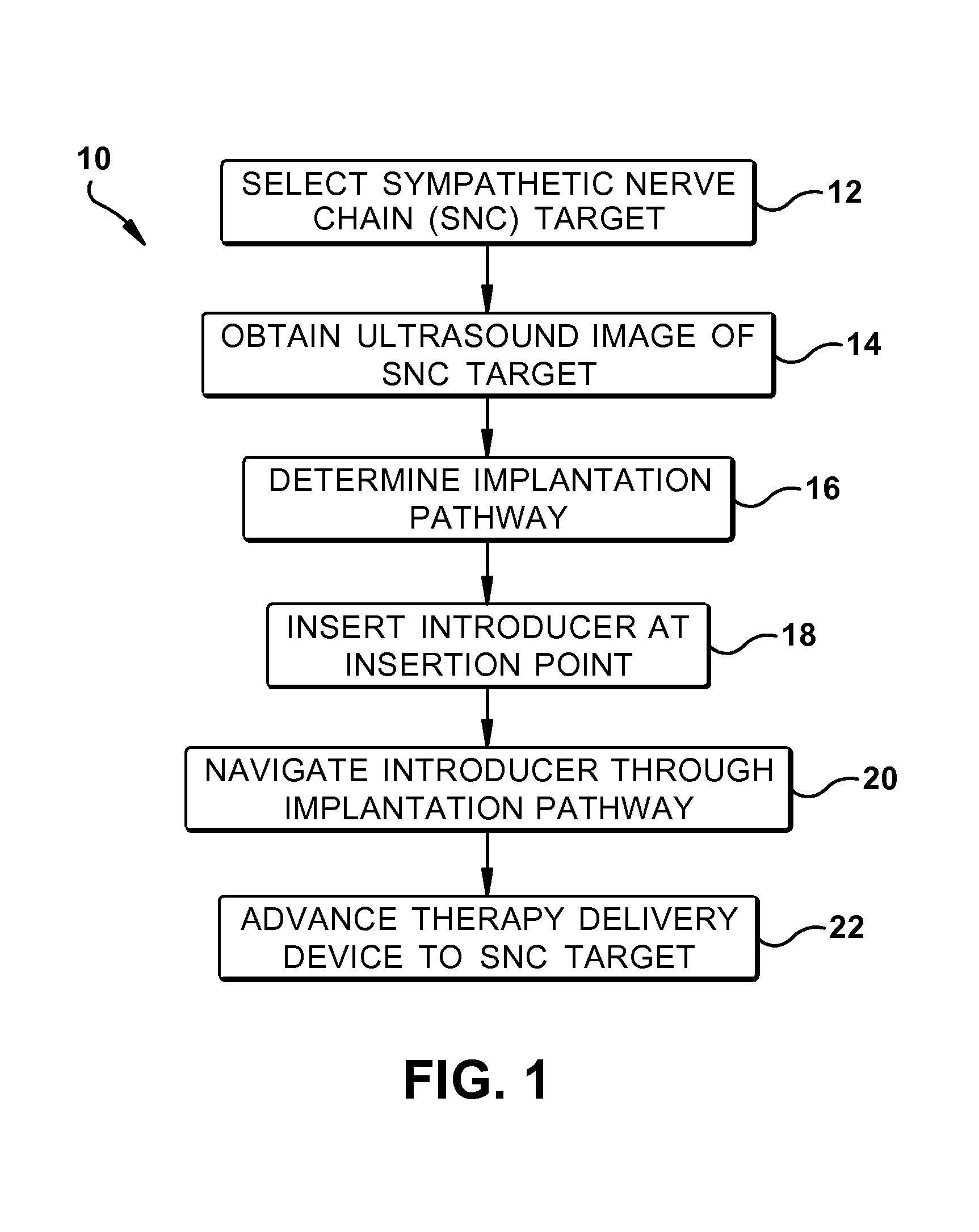
Ultrasound-guided delivery of a therapy delivery device to a nerve target
ActiveUS20100204568A1Spinal electrodesOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical structuresUltrasound imaging
A method for guiding a therapy delivery device to a sympathetic nerve chain target of a subject includes: (a) selecting a sympathetic nerve chain target; (b) using ultrasound imaging to obtain an ultrasound image of anatomical structures relevant to the sympathetic nerve chain target; (c) determining an implantation pathway based on the ultrasound image, the implantation pathway defining a trajectory that avoids the relevant anatomical structures and extends between an insertion point on the skin of the subject and a bony spinous target; (d) inserting an introducer into the insertion point, the introducer including a bevel located at a distal end thereof; (e) navigating the introducer through the implantation pathway until the distal tip is positioned adjacent or proximate to the bony spinous target; and (f) advancing the therapy delivery device through the introducer to the sympathetic nerve chain target. Steps (d)-(f) are performed using real-time ultrasound imaging.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method and apparatus for real time ultrasound multi-plane imaging
ActiveUS8012090B2Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationDisplay device
An ultrasound system is provided that includes a probe for successively acquiring ultrasound information from an object along at least three distinct scan planes. The scan planes intersect one another along an axis extending from the probe through the object. A memory is included for storing data slices corresponding to the at least three distinct scan planes based on the ultrasound information. Also included is a processor that accesses the memory to select and obtain the data slices and generates ultrasound images based on the data slices. A display is included for co-displaying the ultrasound images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sample sealing device and method for testing active and passive real-time acoustic waves in rock breaking process
PendingCN109459318AObtaining damage and degradation location informationOvercoming the disadvantages of testing the speed of sound aloneMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringRock sample
The invention provides a sample sealing device and method for testing active and passive real-time acoustic waves in the rock breaking process, and belongs to the technical field of rock breaking testing. The sample sealing device comprises a load application module, a displacement monitoring module, a load ultrasonic monitoring module and an acoustic emission monitoring and positioning module; the load application module comprises a rigid cushion block and a triaxial electro-hydraulic servo tester; the displacement monitoring module comprises a longitudinal extensometer upper clamp, a longitudinal extensometer lower clamp, extensometer helical wires, extensometer helical wire sleeves, a longitudinal extensometer circular hoop ring and miniature screws; and the load ultrasonic monitoring module comprises ultrasonic probes and U-shaped ultrasonic probes, and the acoustic emission monitoring and positioning module comprises an acoustic emission sensor and an acoustic emission clamping device. According to the sample sealing device, a rock sample is subjected to real-time ultrasonic testing through an acoustic wave instrument and the six ultrasonic probes, rock acoustic emission damage parameters are obtained through an acoustic emission acquisition instrument and eight acoustic emission probes, and the sample sealing device has high laboratory guiding significance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
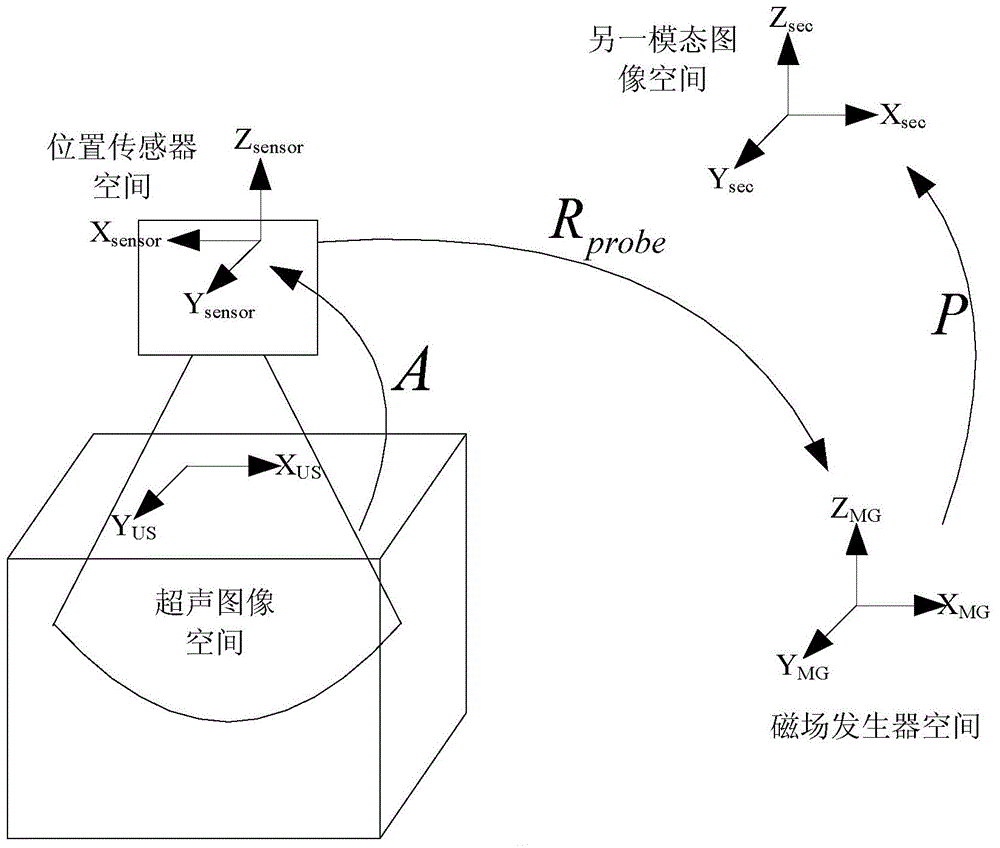
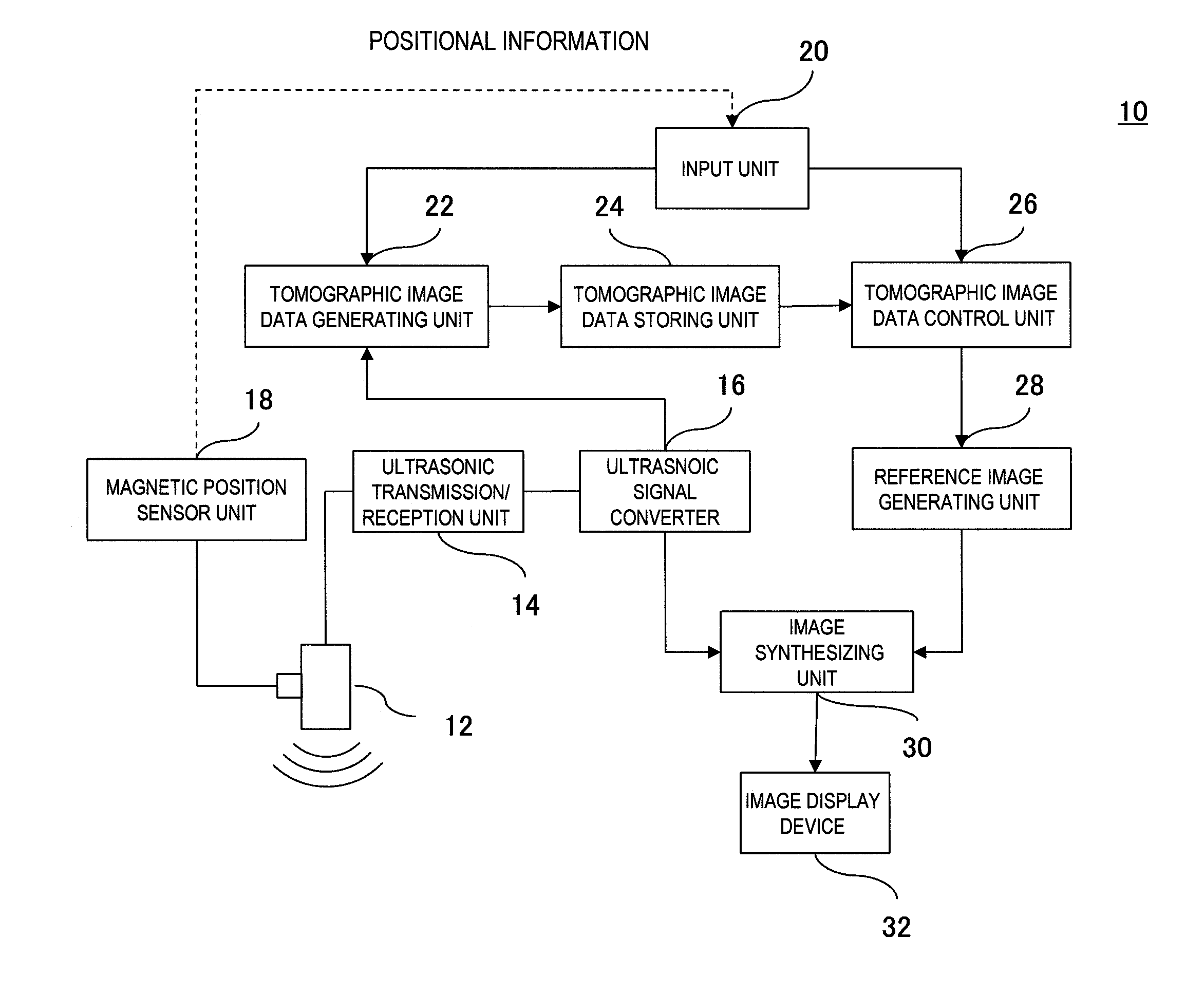
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and method for calculating coordinates of scanned surface thereof
InactiveUS20110144500A1Improve matchUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBody contourTomographic image
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus includes a storage unit configured to store information about the contour of an object to be examined and information about the position of a specified region of the ultrasonic image of the object both corresponded to a body contour model coordinate system and a coordinate calculating unit configured to correspond the object coordinate system to the body contour model coordinate system according to the information about the position of the specified region of the object, associating with each other the object coordinate system and the body contour model coordinate system used when comparing an ultrasonic tomographic image based on ultrasonic tomographic data stored in an image storage unit with a real-time ultrasonic tomographic image scanned by an ultrasonic probe, and thereby calculating the coordinates of the scanned plane of the real-time ultrasonic tomographic image in association with the object coordinate system.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
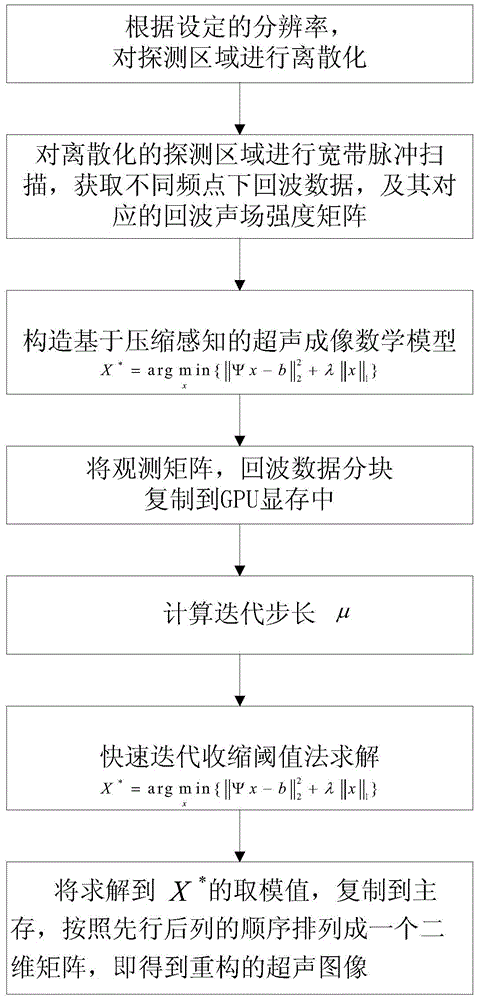
Compressive sense ultrasound imaging method through GPU (graphics processing unit)
InactiveCN104306022AFast imagingReduce rebuild timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsVideo memoryBroadband pulse
The invention discloses a compressive sense ultrasound imaging method through GPU (graphics processing unit) and solves the problem that the imaging reconstruction is performed slowly by the compressive sense theory. The method includes 1, according to a set resolution, discretizing the detection region and performing broadband pulse scanning on the region, acquiring echo vectors and observation matrix, and establishing an ultrasound imaging mathematical model; 2, partitioning and copying the echo vectors and observation matrix to a GPU video memory; 3, calculating an iteration step in the GPU; 4, substituting the iteration step into a fast iterative shrinkage threshold algorithm to figure out a reconstructed observation scene scattering intensity; 5, copying the scattering intensity to a main memory and arraying two-dimensional matrix, and obtaining a reconstructed ultrasound image. Compared with a traditional fast iterative shrinkage threshold algorithm, the method has the advantages that the reconstructing time is reduced by the millisecond level from the minute level, the real-time performance of ultrasound imaging is improved greatly, and the method can be applied to the field of real-time ultrasound processing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image-guided intravascular therapy catheters
InactiveCN101902972AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterUltrasound angiographyReal time ultrasound
An intravascular ultrasound catheter having an imaging array and ablation electrodes is provided. The imaging array and ablation electrodes are forward facing and the catheter can be used to ablate plaque in partially or totally occluded blood vessels under real time ultrasound visualization. The ablation electrodes are integrated into the distal face of the catheter and allow ultrasound to pass through them, which provides the ability to achieve highly accurate real time visualization of the tissue undergoing treatment.
Owner:MERIDIAN CARDIOVASCULAR SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com