Patents
Literature
32 results about "Strain imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Strain imaging evaluates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium) using cardiac ultrasound. This method is used to identify subtle changes in heart function.
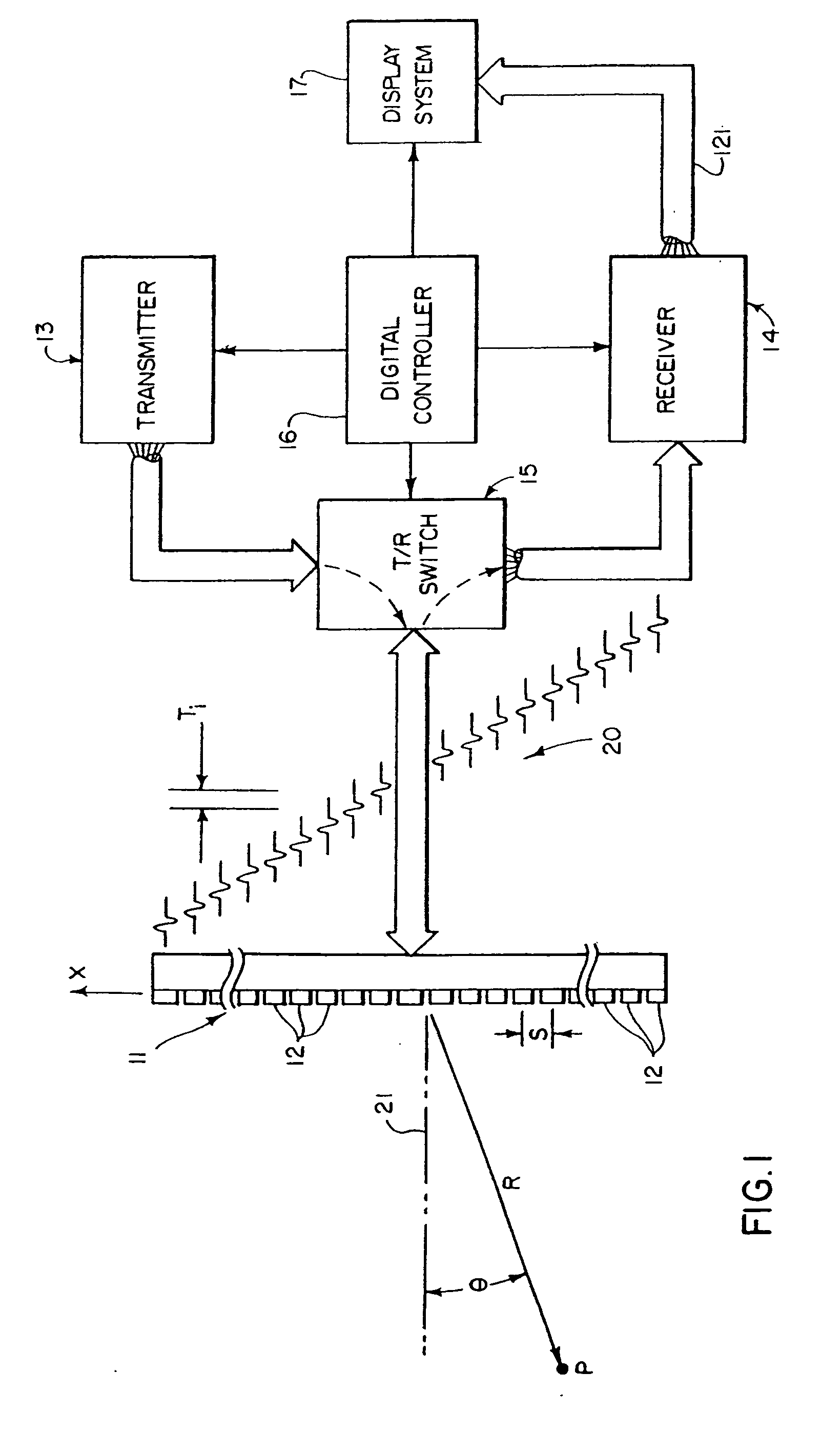
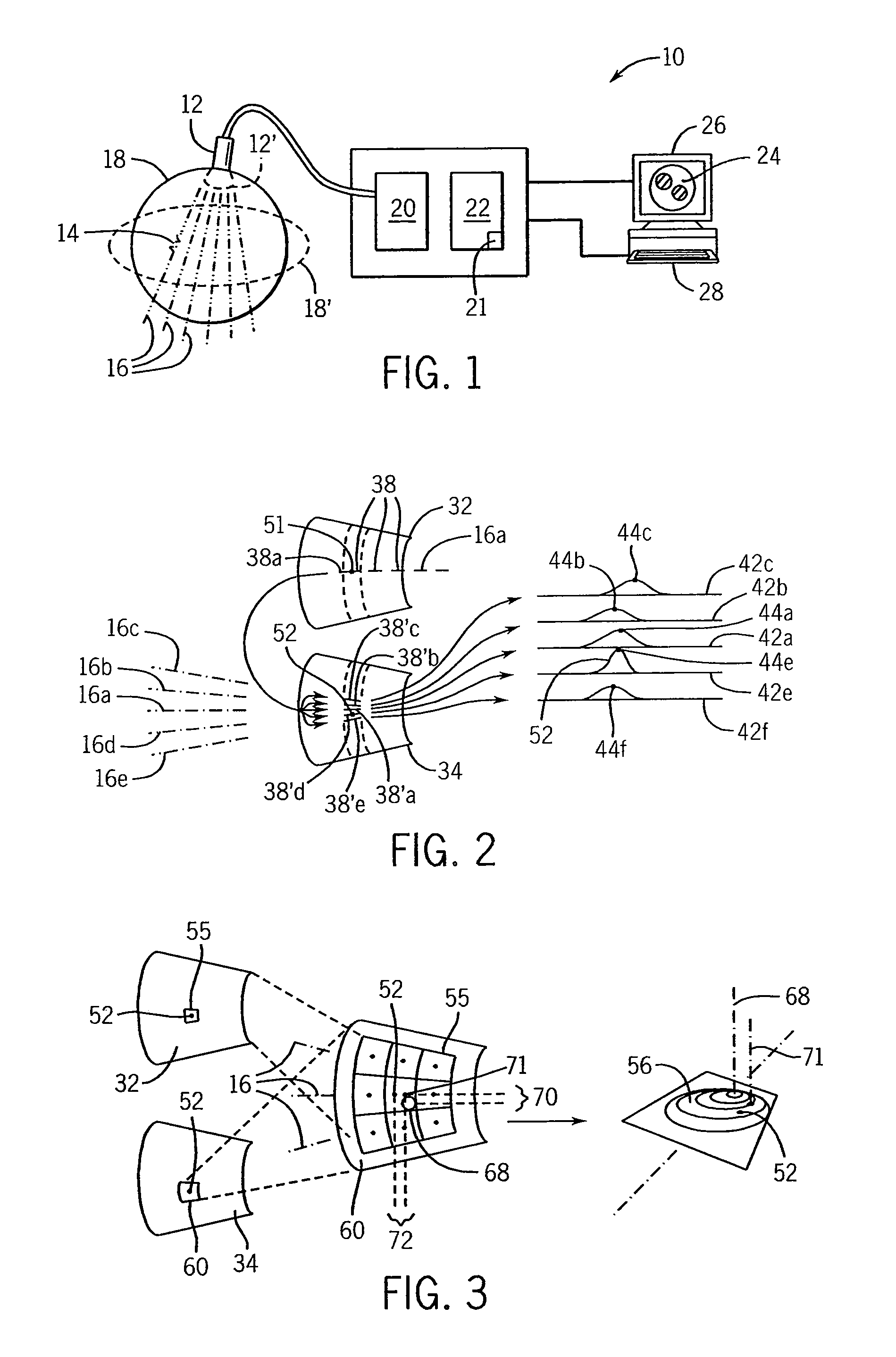
Methods and apparatus for ultrasound strain imaging
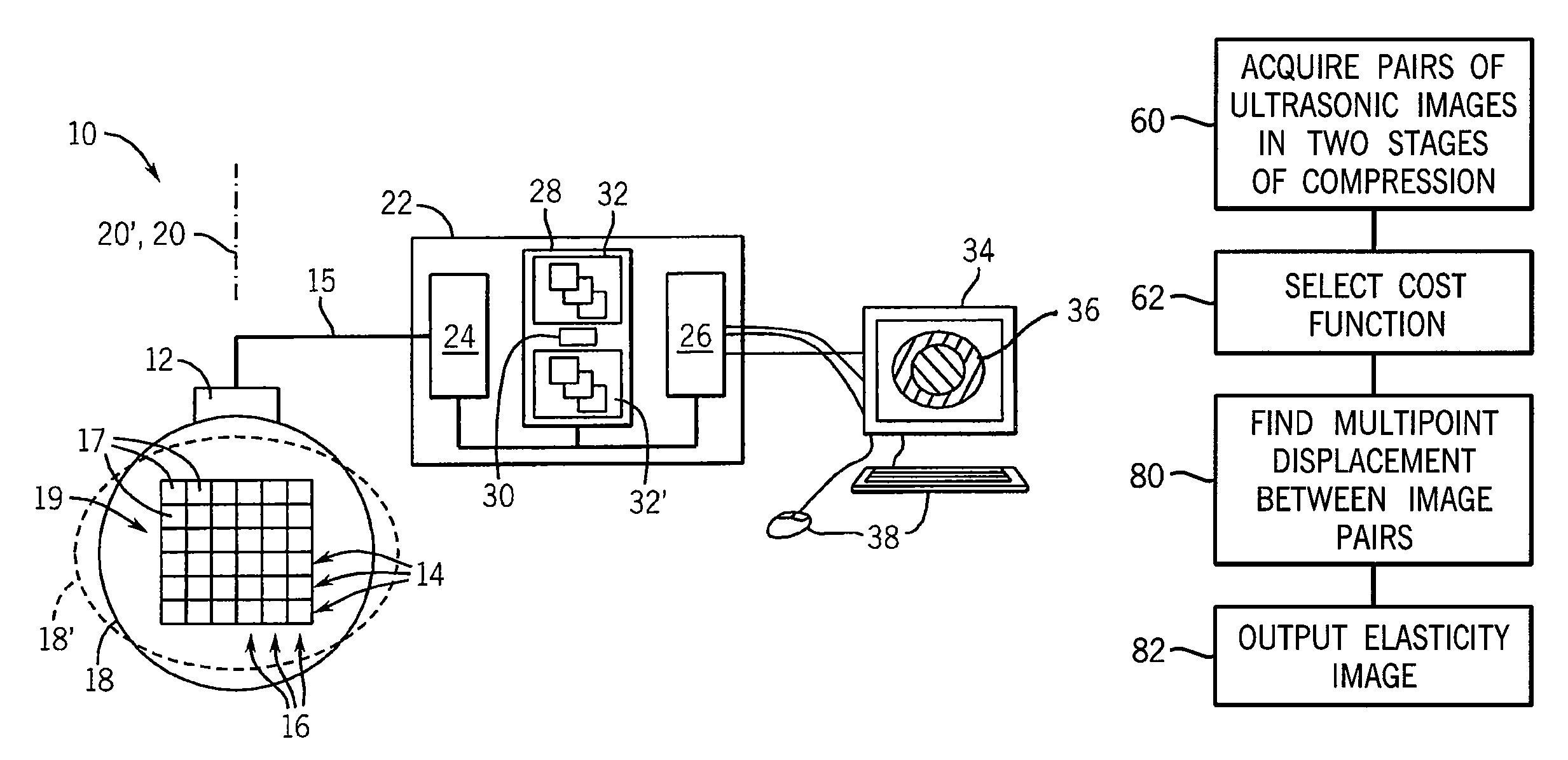
ActiveUS20110237945A1Minimize cost functionMedical automated diagnosisInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingAccelerometer
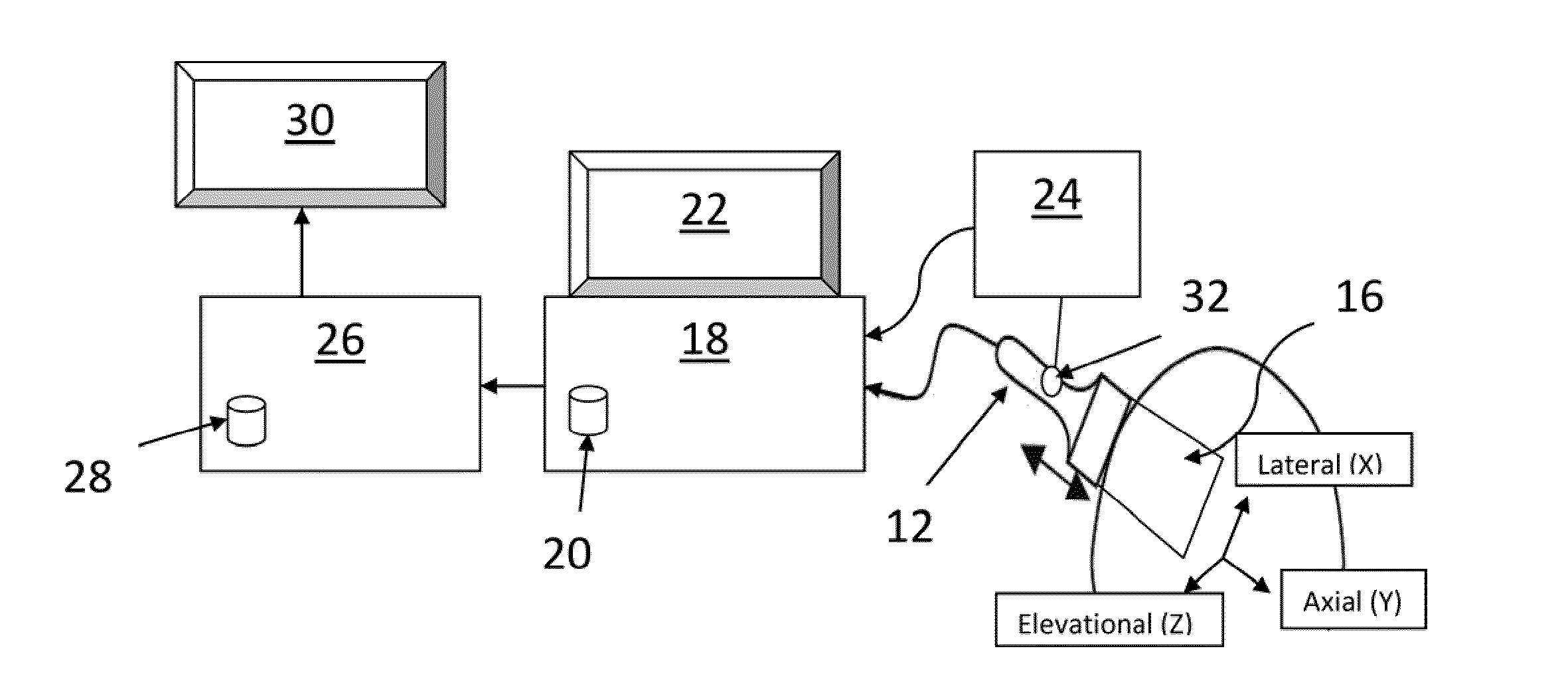
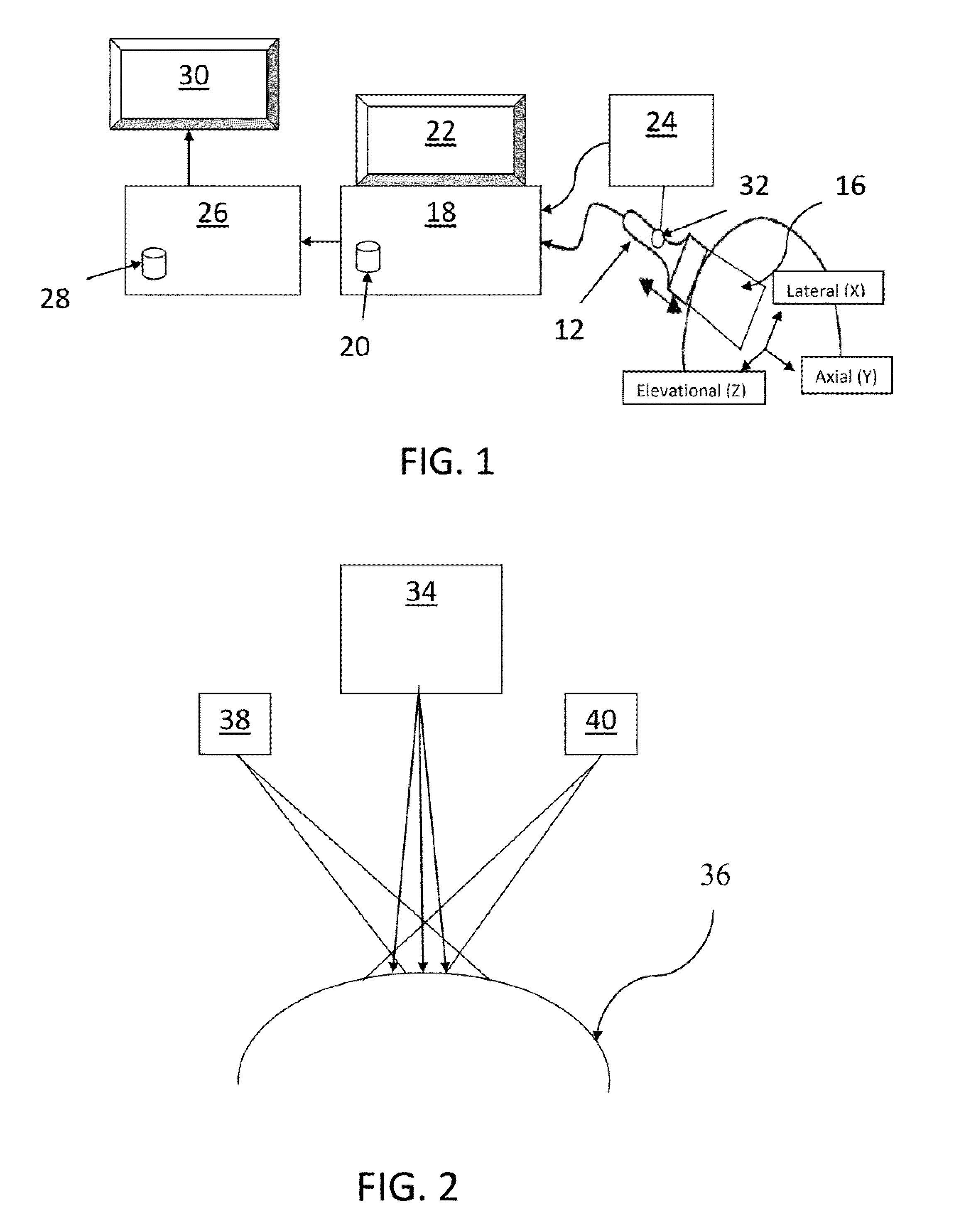
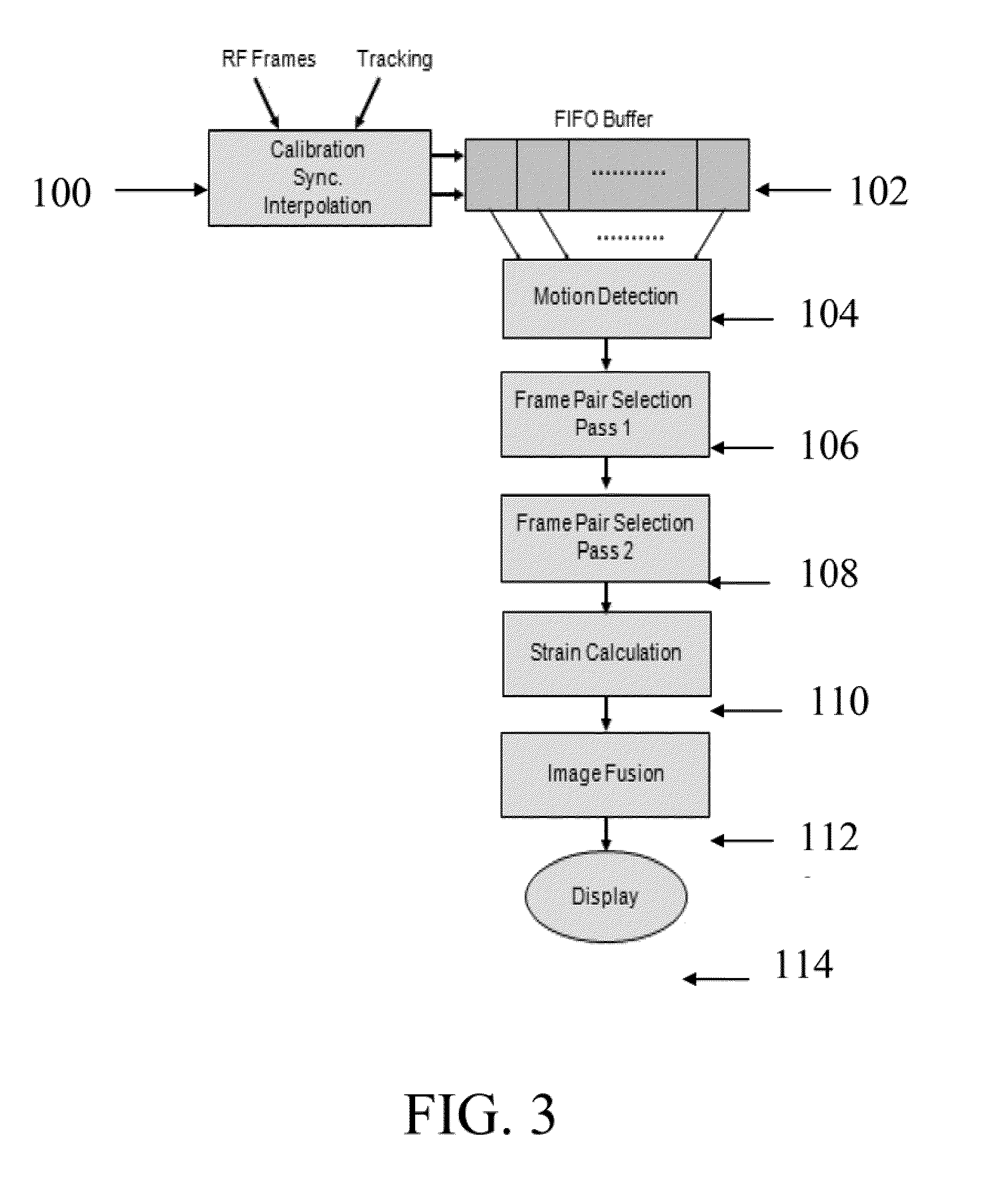
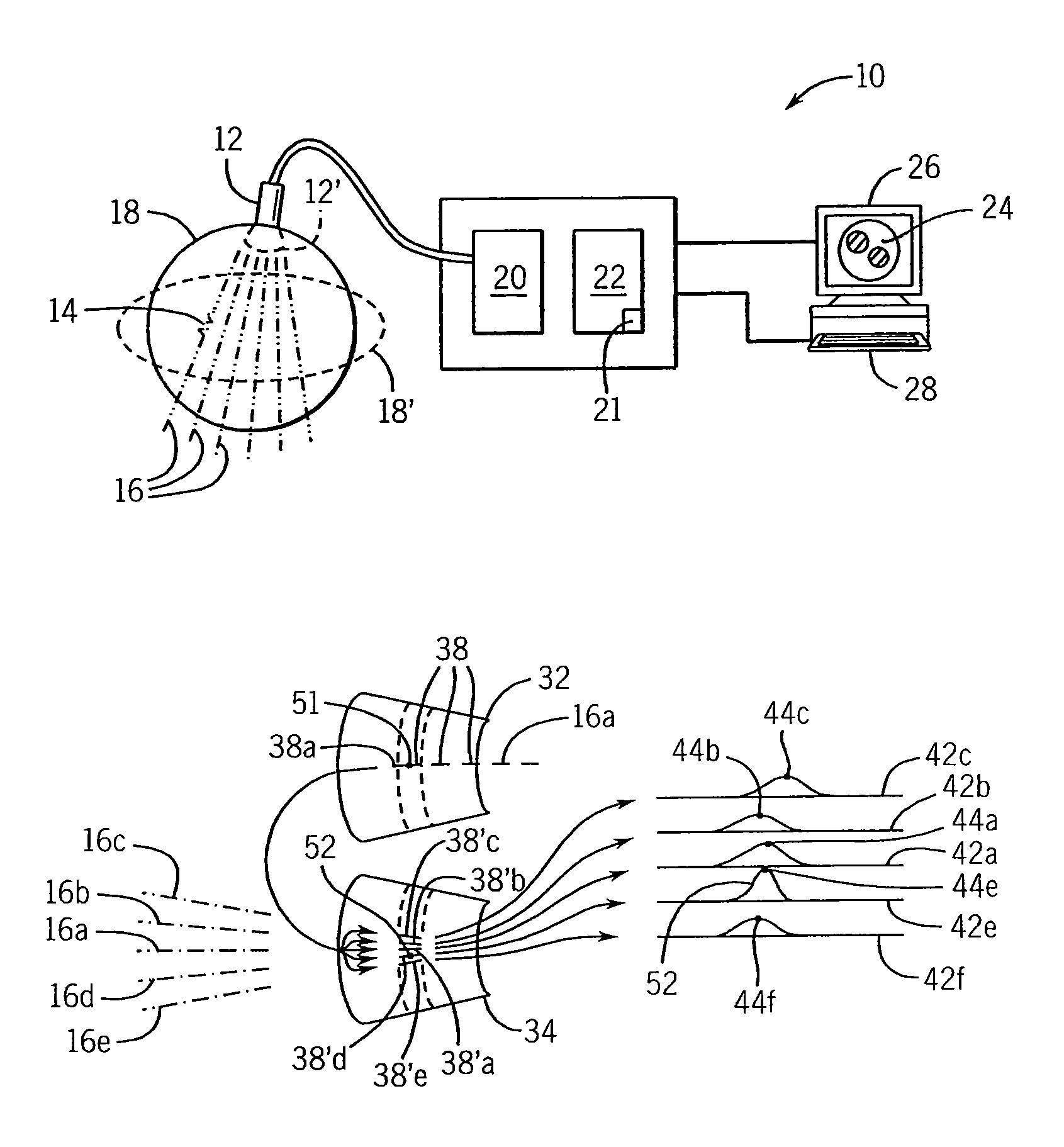
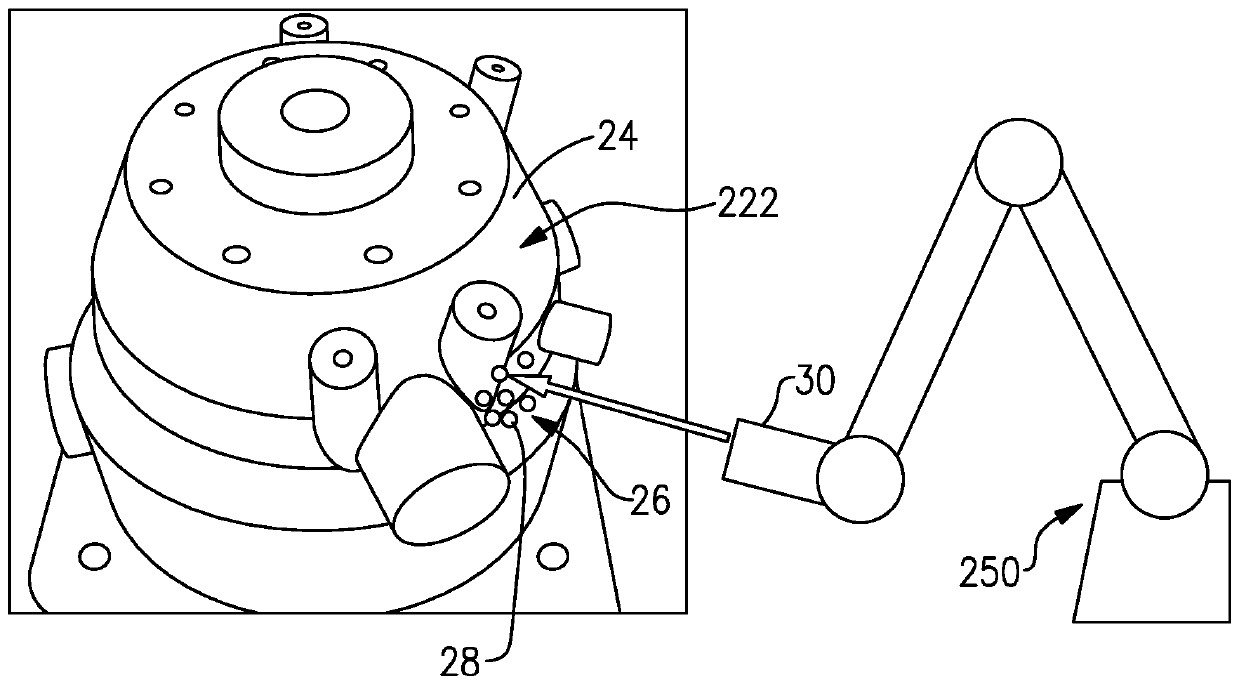
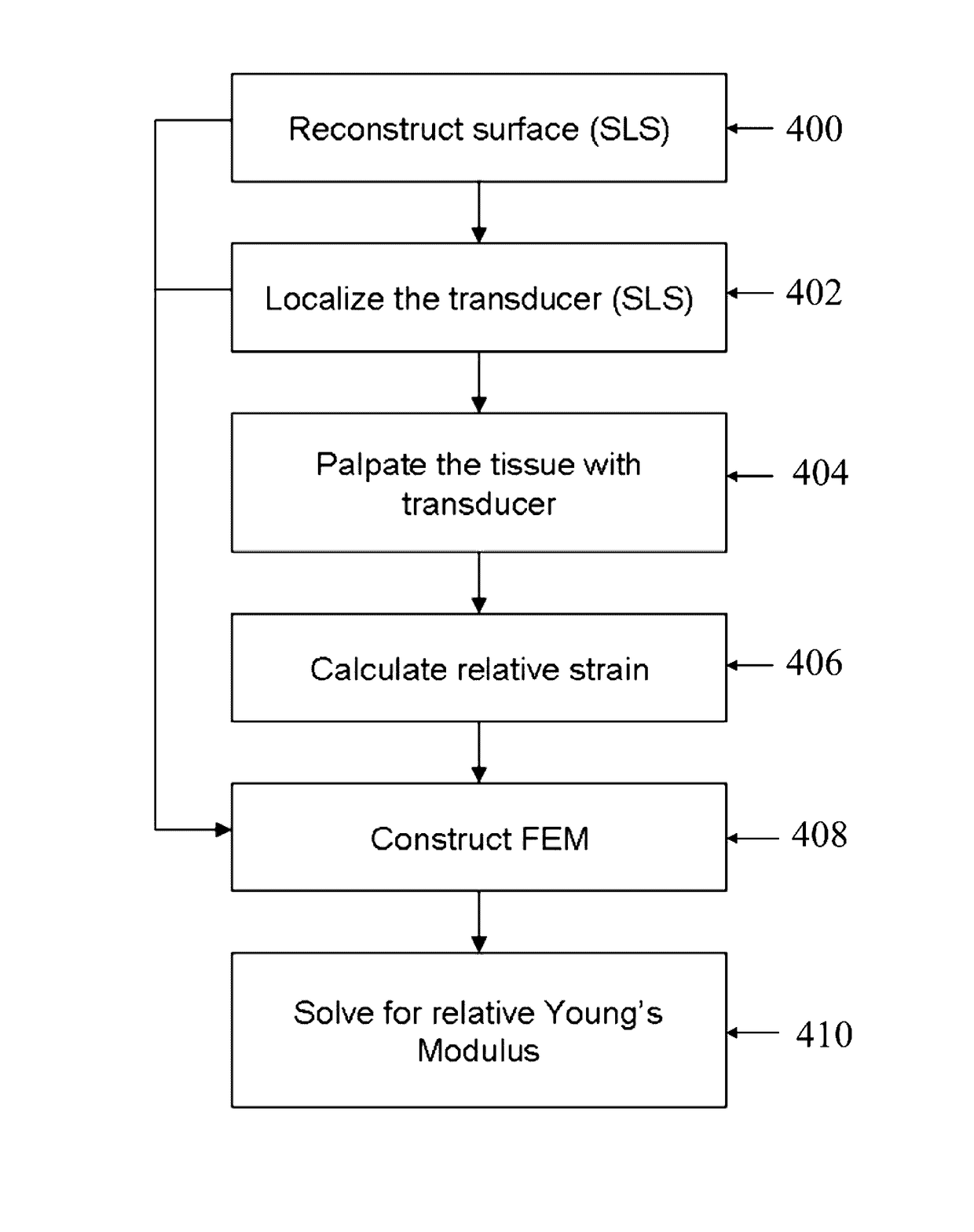
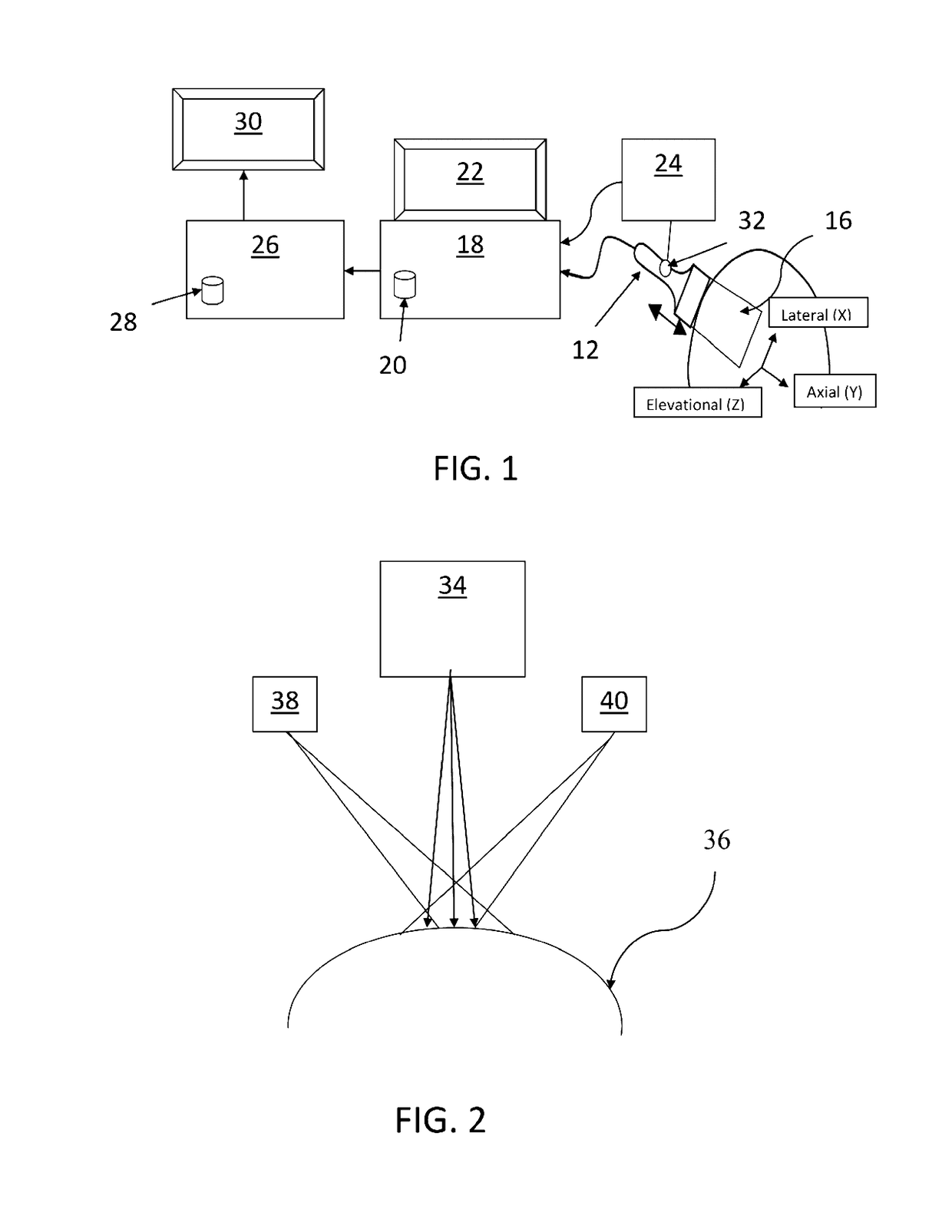
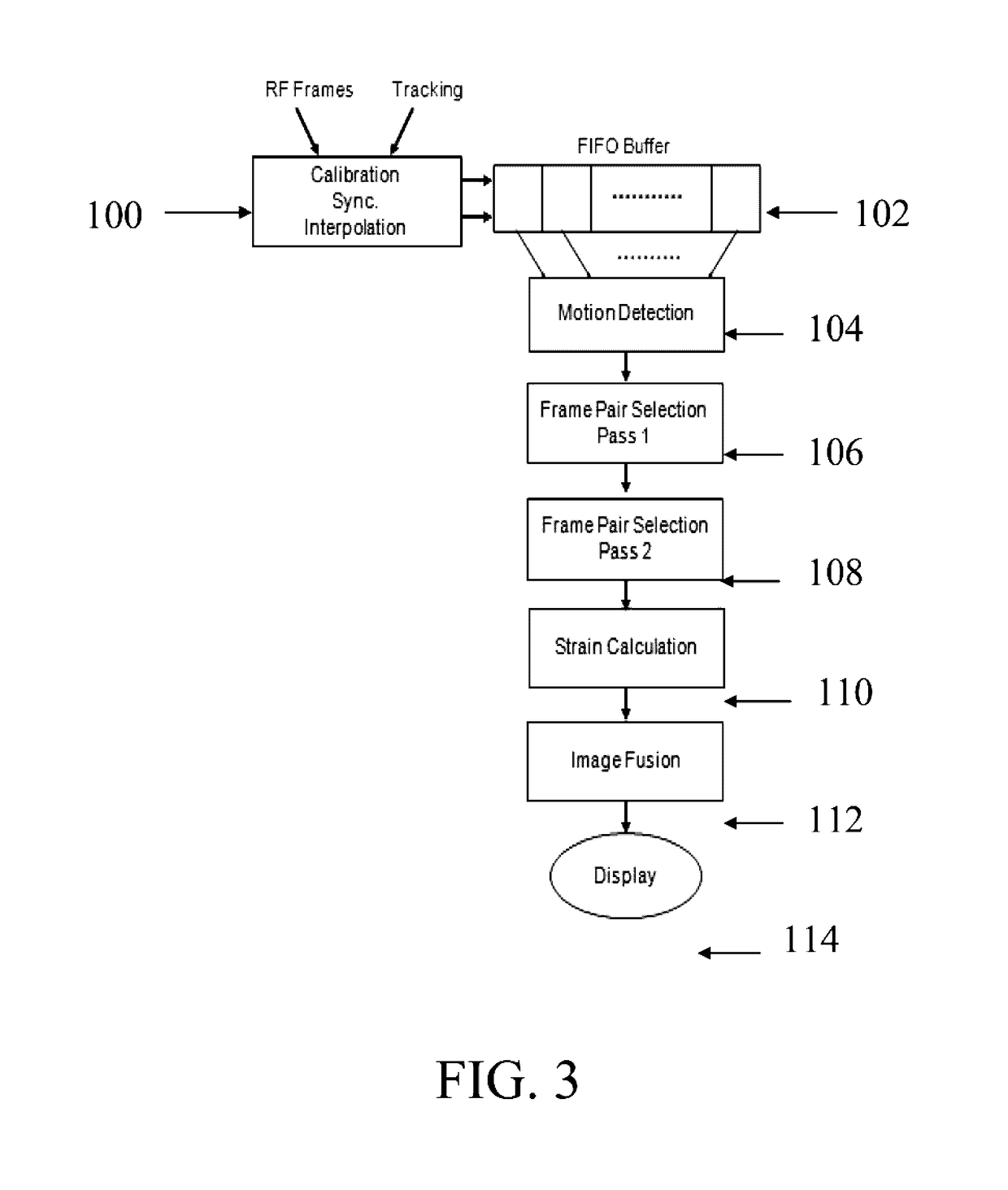
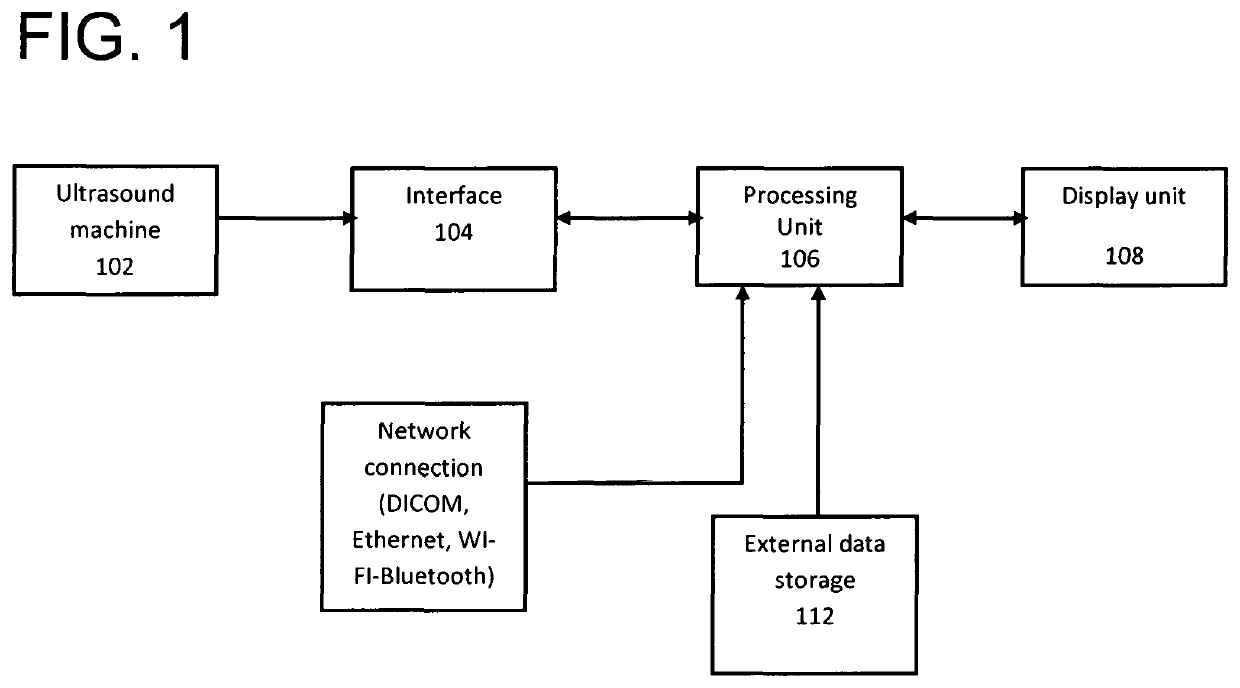
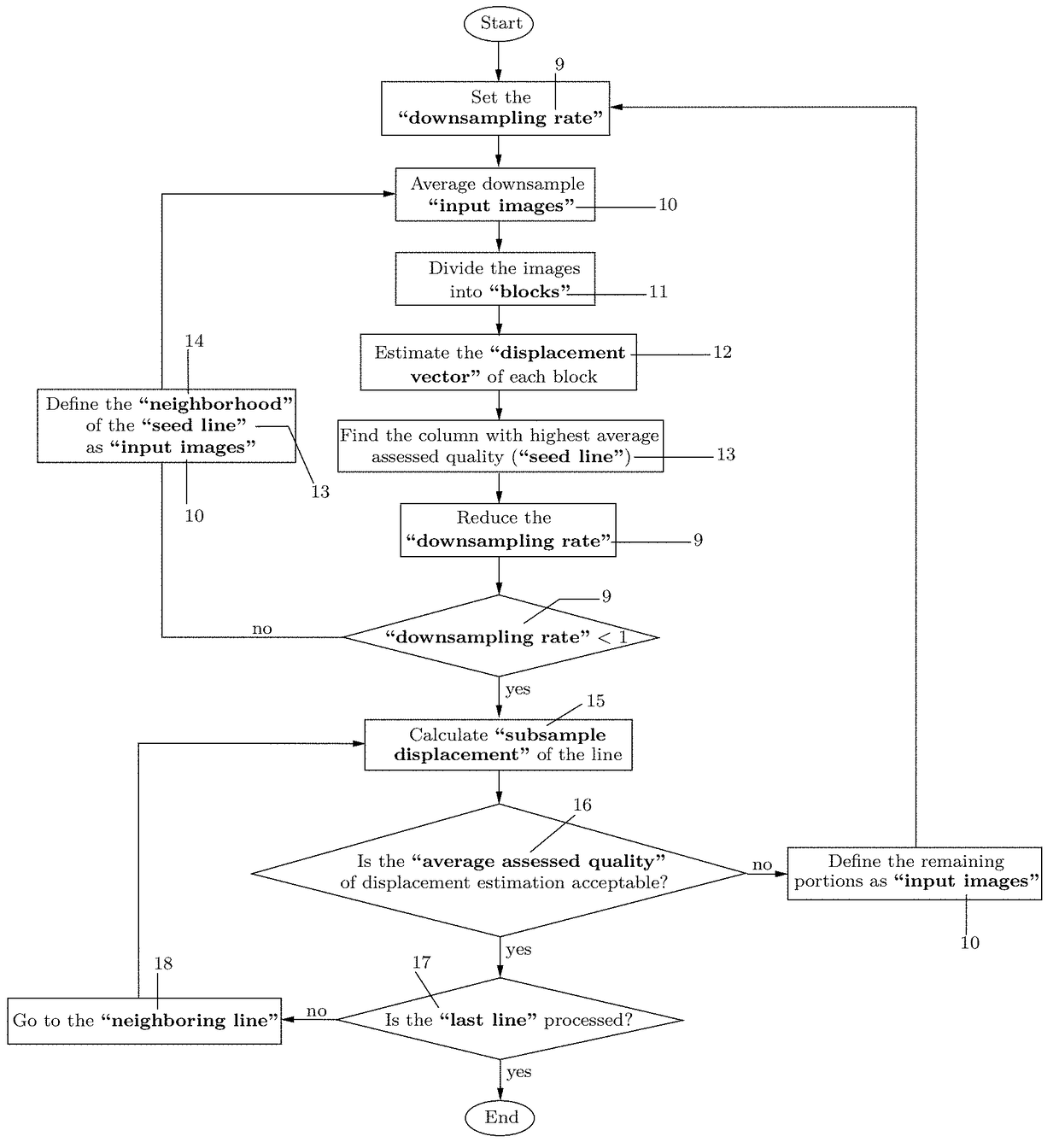
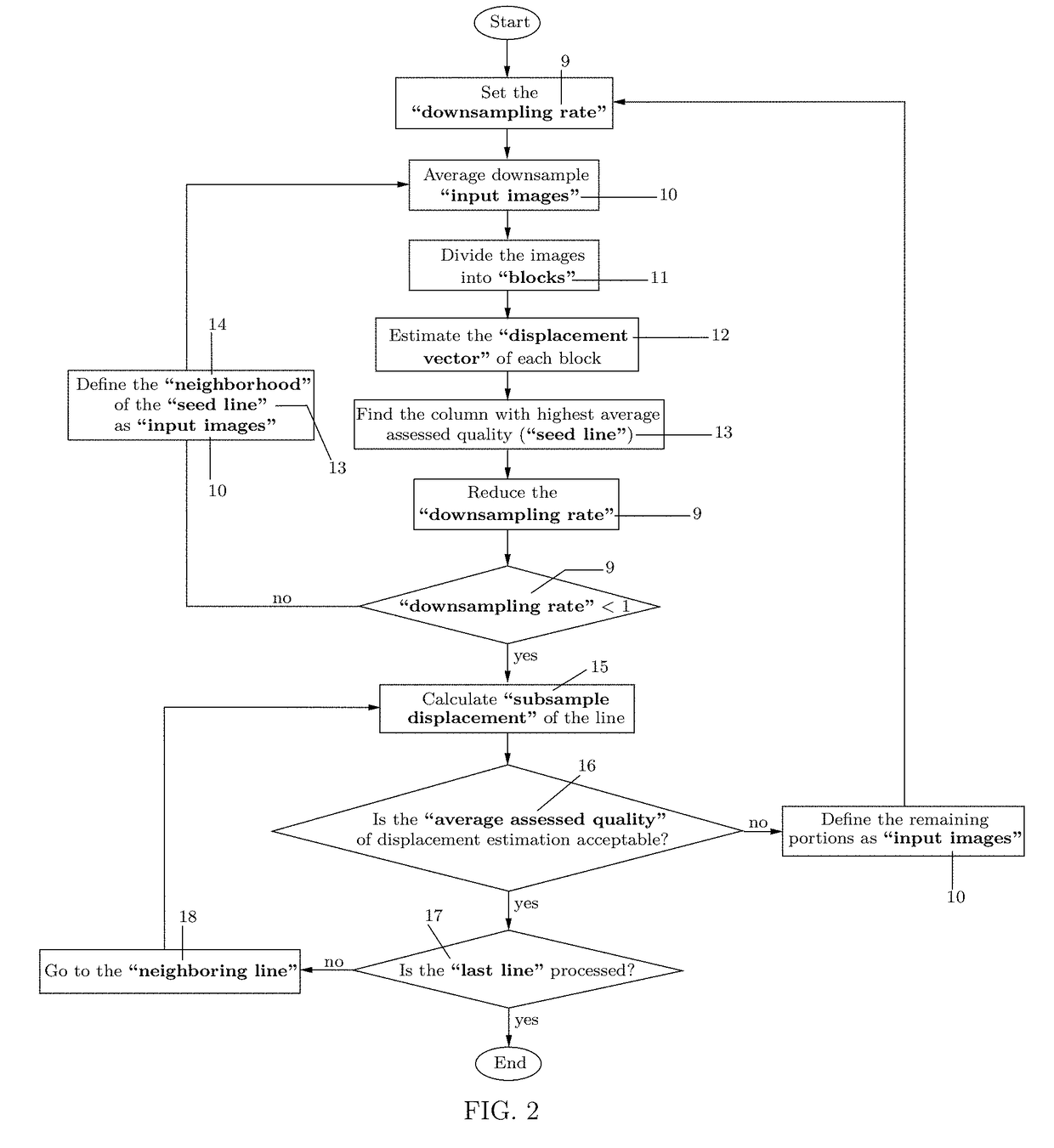
A system and method for improved ultrasound strain imaging includes using data from a tracking system to enhance the quality of ultrasound strain image and to reduce the dependency of image quality of the user's expertise. The tracking information is synchronized with the RF frames and interpolated to find the transformation corresponding to each frame. The RF frames with their transformations are incorporated into calculation of ultrasound strain images. The tracking system may be an optical tracker, electromagnetic tracker, accelerometer, or a structured light system. The structured light system may also be used for probe calibration, by calibrating the surface of the probe pre-operatively. In addition, a relative Young's Modulus may be calculated using tracking information that is independent from the distribution of input force.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Non-invasive diagnosis of breast cancer using real-time ultrasound strain imaging
InactiveUS20050283076A1Easy diagnosisReduce hardware costsImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationVisual assessment
A series of ultrasound strain images of a breast lesion are acquired along with corresponding B-mode images using a real-time ultrasound strain imaging system and a free-hand technique. A visual assessment of the lesion is made by the sonographer after image acquisition. A conspicuity metric is calculated from the strain images based on the weighted sum of lesion contrast values in each strain image. The weighting of each lesion contrast value is based on observed characteristics of malignant lesions in a series of strain images. Diagnosis is made based on the visual assessment and the conspicuity metric
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
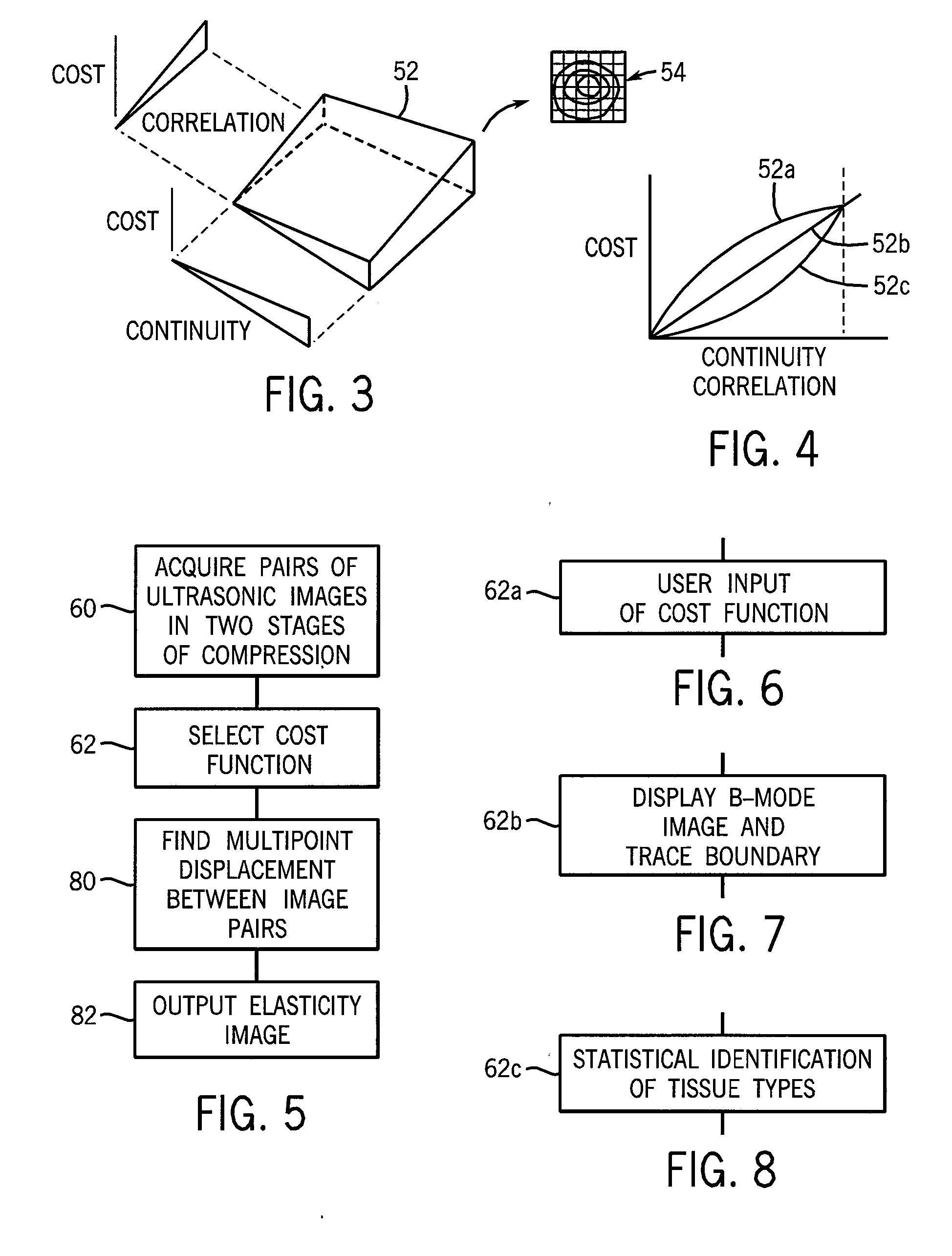
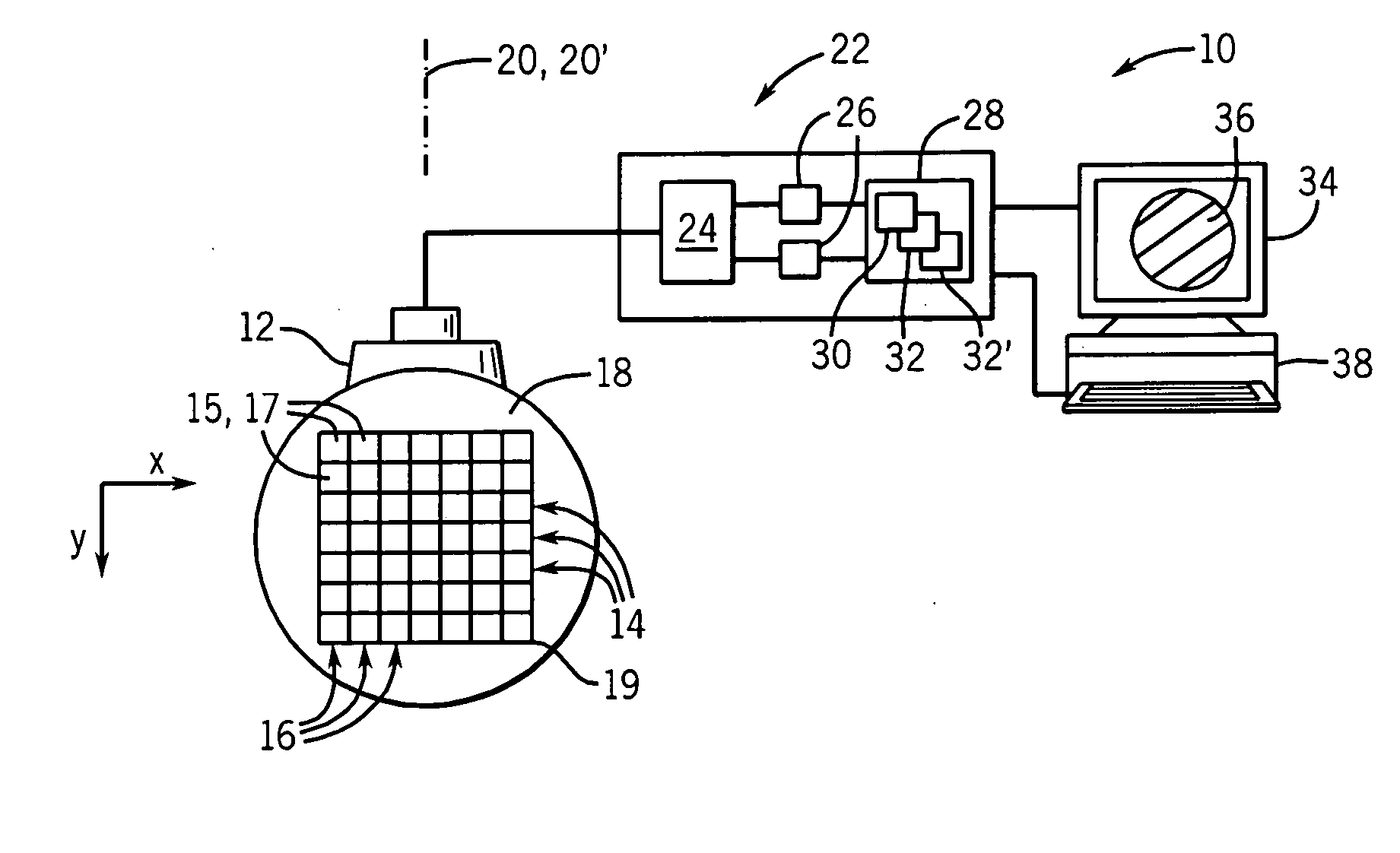
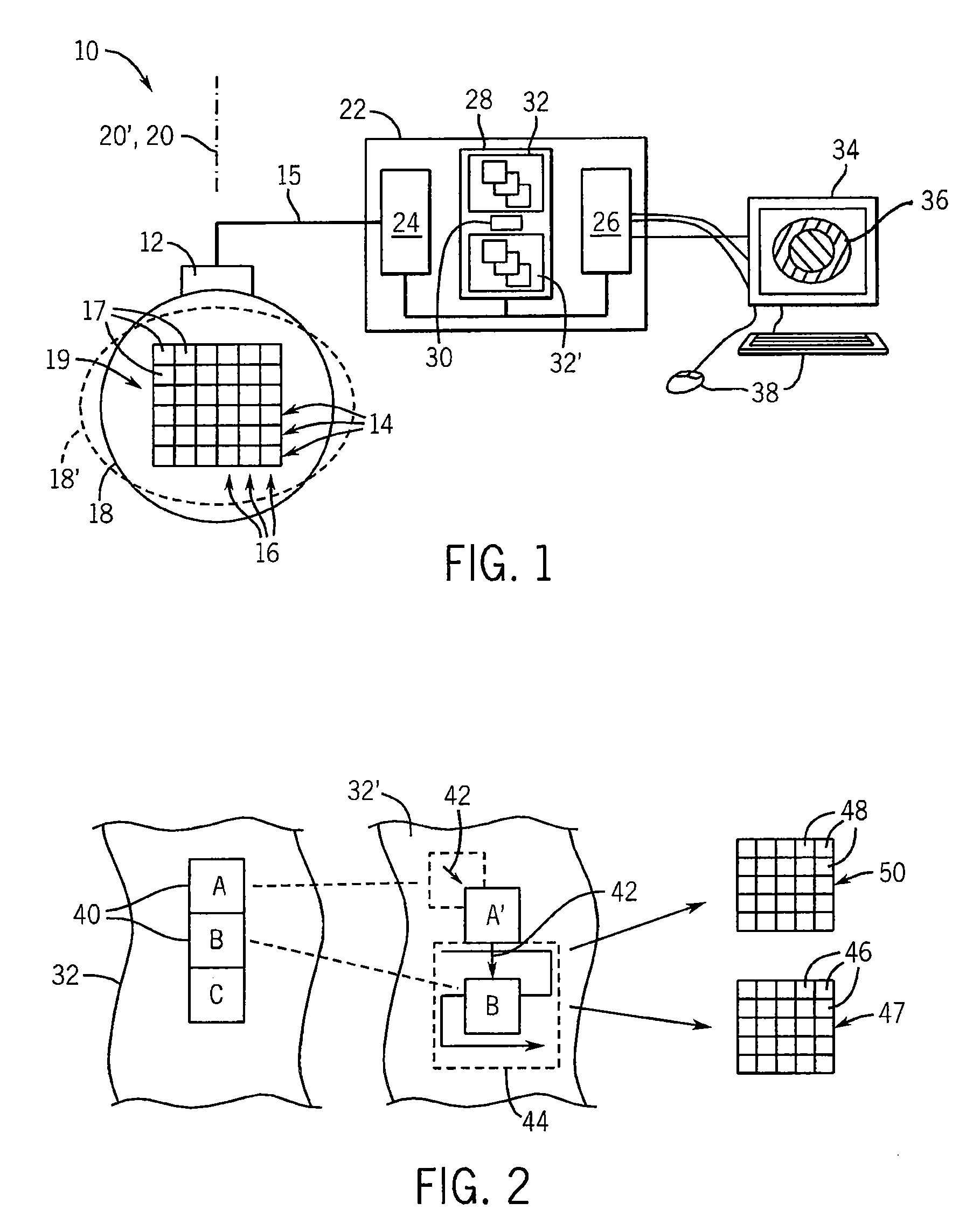
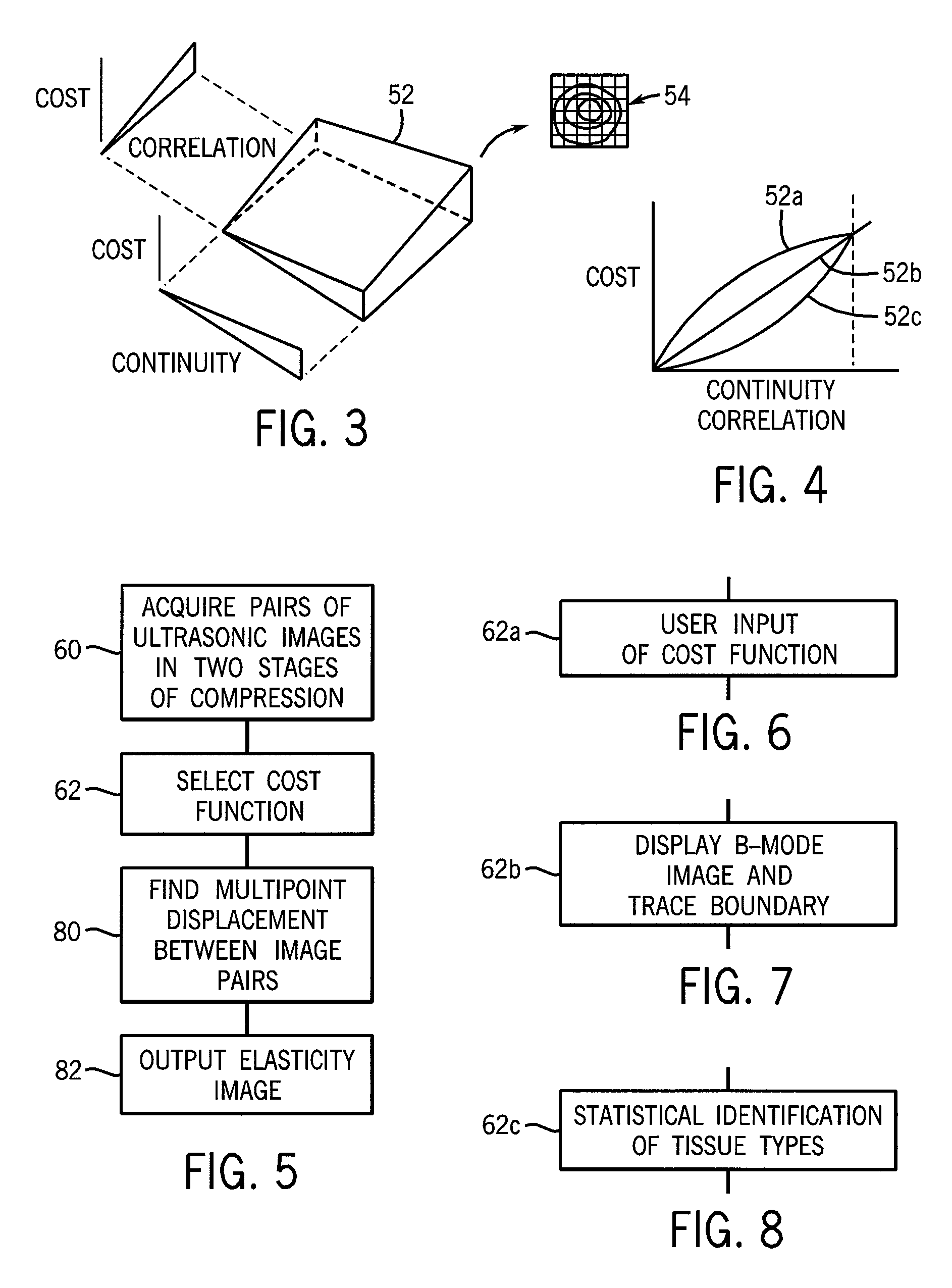
Ultrasonic strain imaging device with selectable cost-function
ActiveUS20100106018A1Enhance the imageInherent tensionOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPre deformationTissues types
An elasticity measuring system determines tissue displacement between a pre-deformation and post-deformation image by a matching process using a cost function accepting as its arguments continuity of the tissue motion and correlation of the tissue in making the block matching. The invention allows the selection among different cost functions for different imaging situations or tissue types, to provide improved displacement calculations using a priori knowledge about the tissue and structure of tissue interfaces or information derived during the scanning process.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
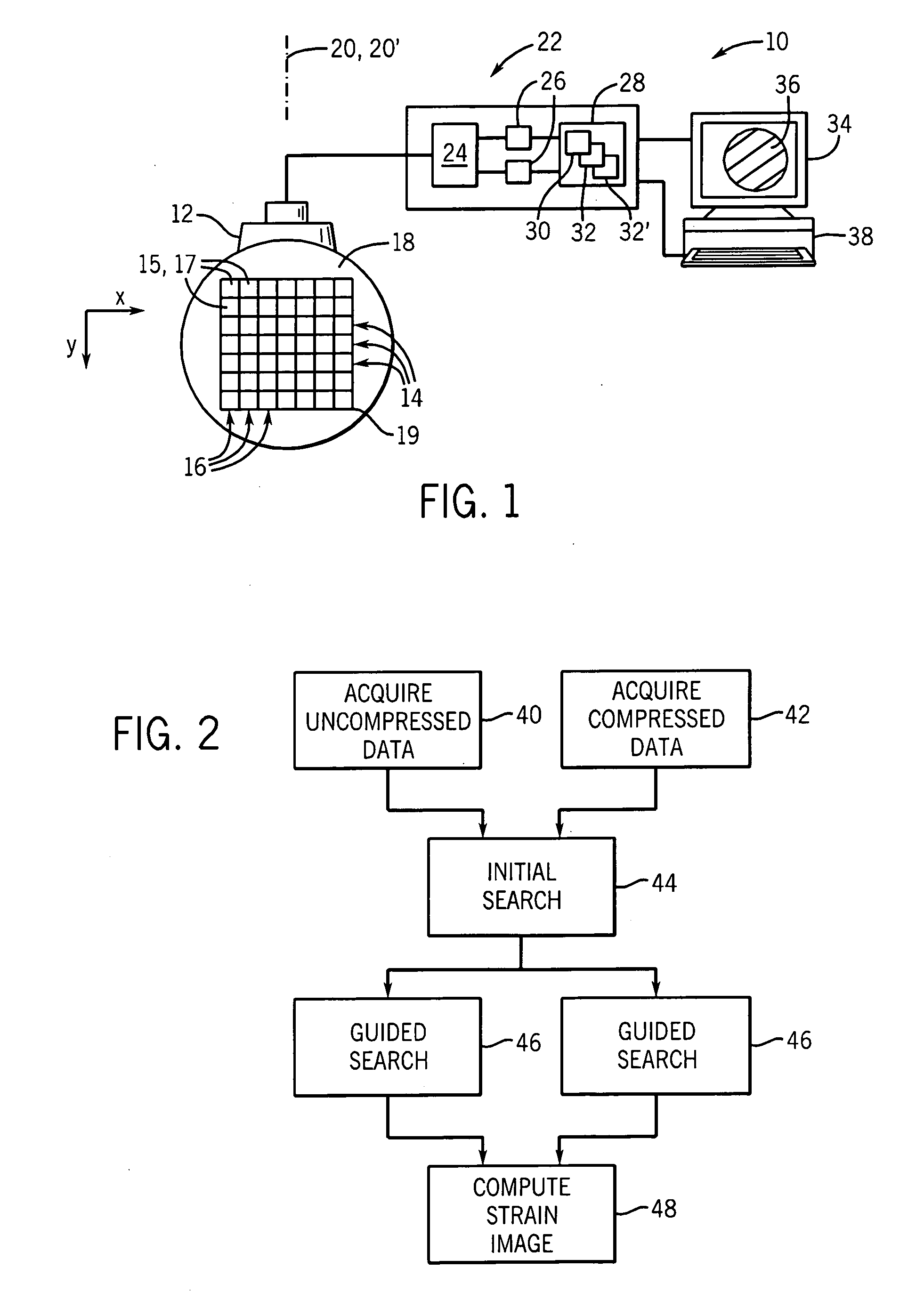
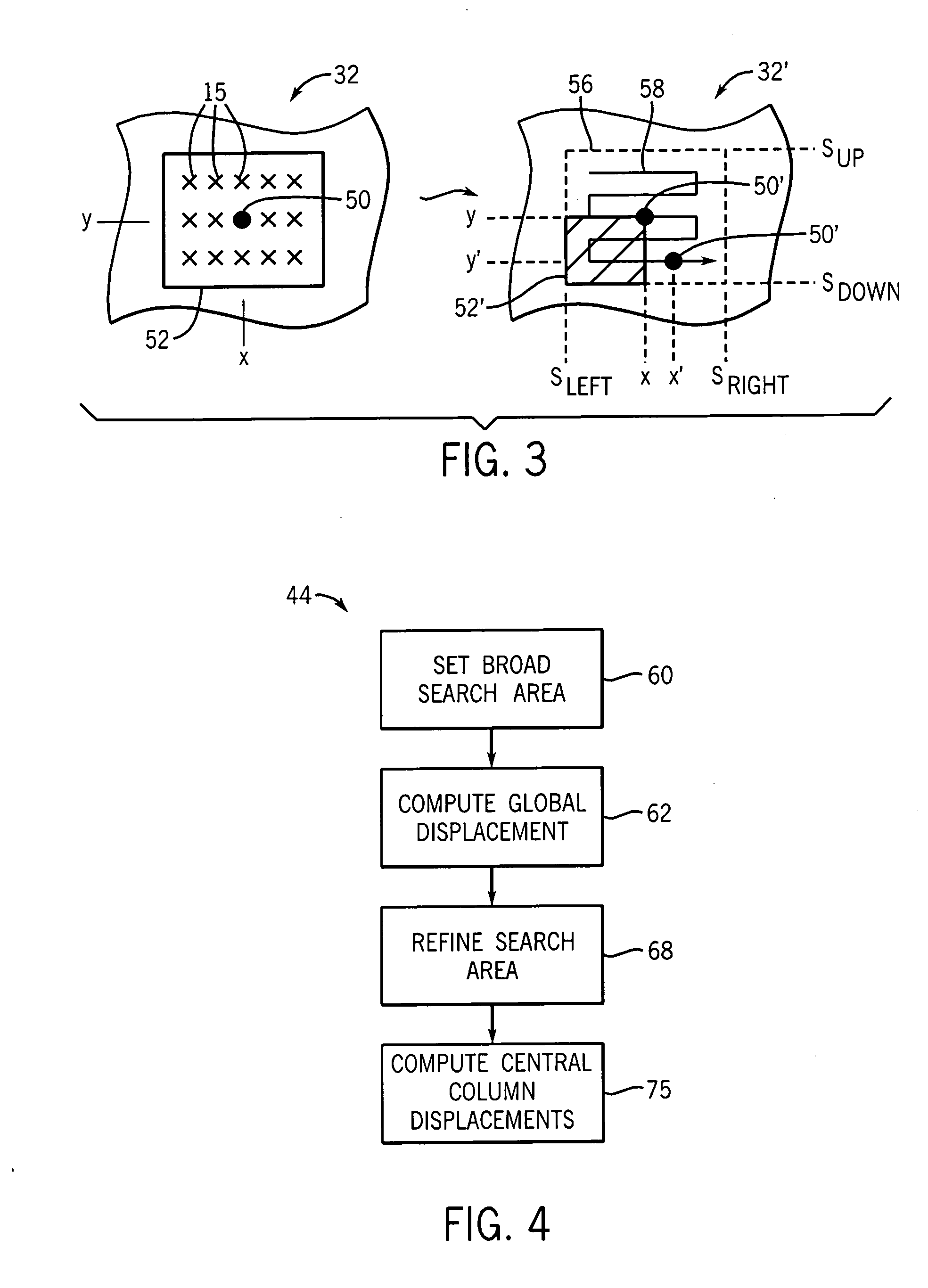
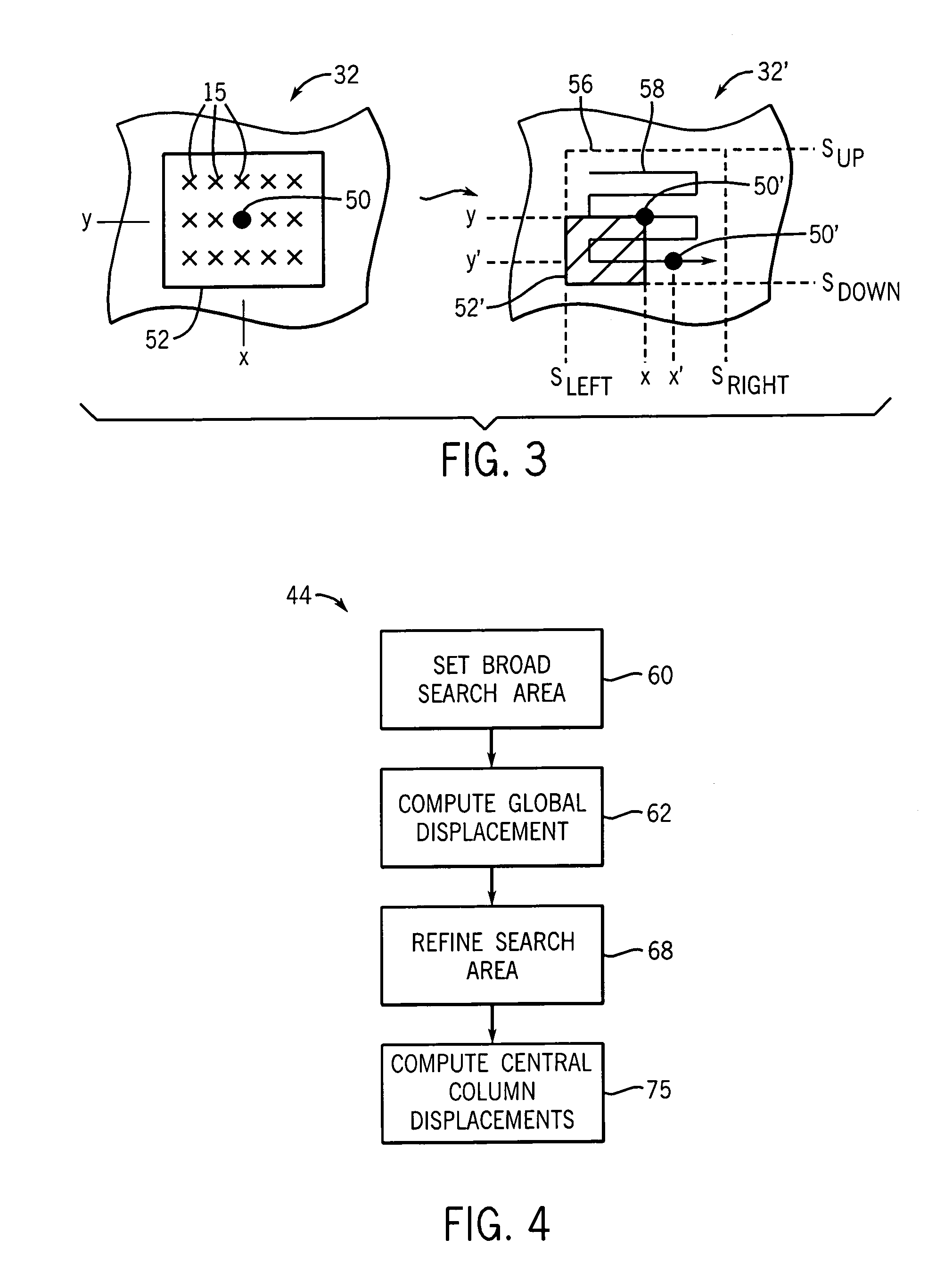
Ultrasonic strain imaging device and method providing parallel displacement processing
ActiveUS20070234806A1Eliminate the problemEliminate CollisionsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesData setPre deformation
A device for ultrasonic strain imaging computes displacement of tissue between a pre-deformation and post-deformation data set along columns to provide for independent calculations that may be parallelized for multiprocessor systems.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
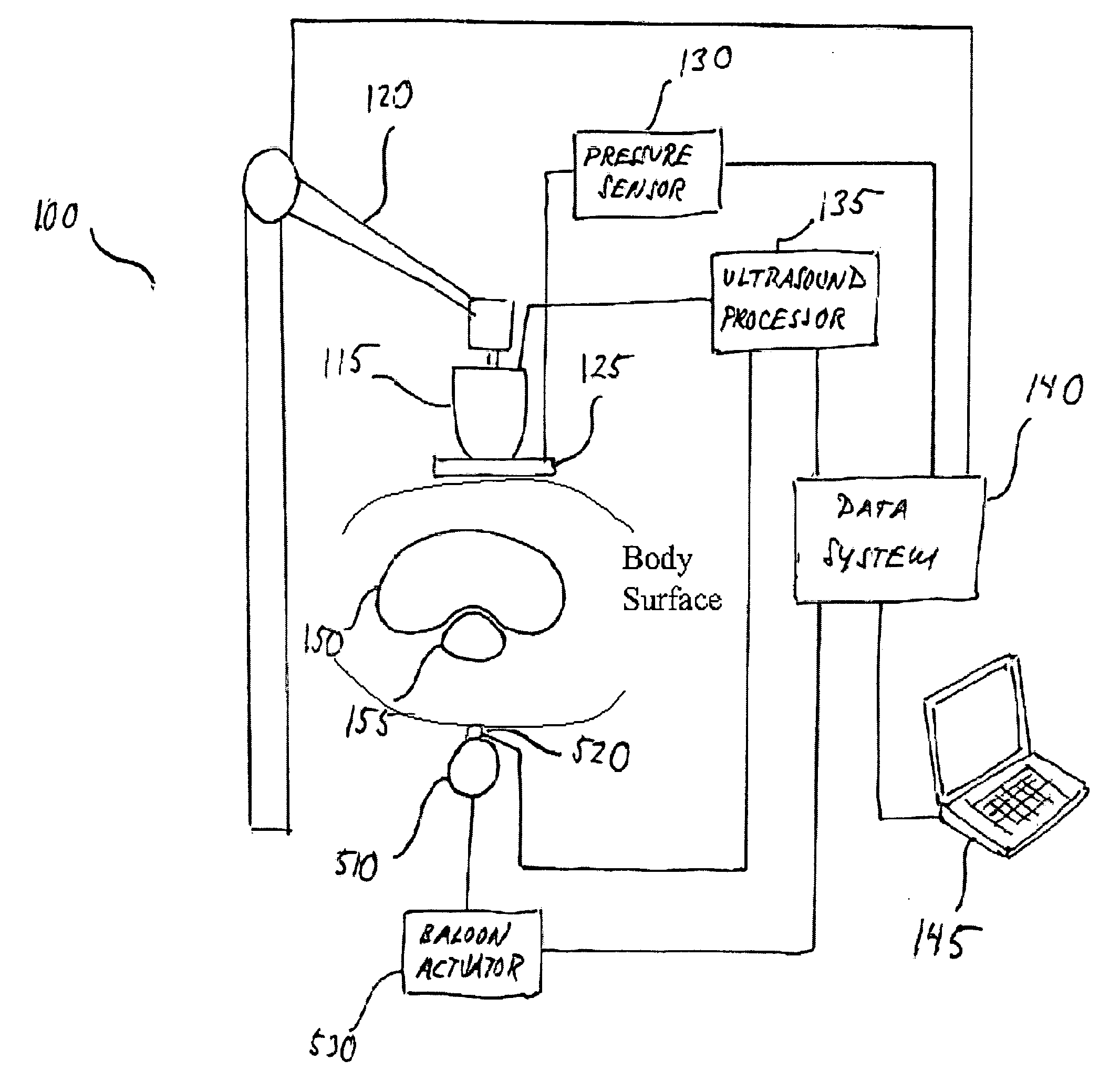
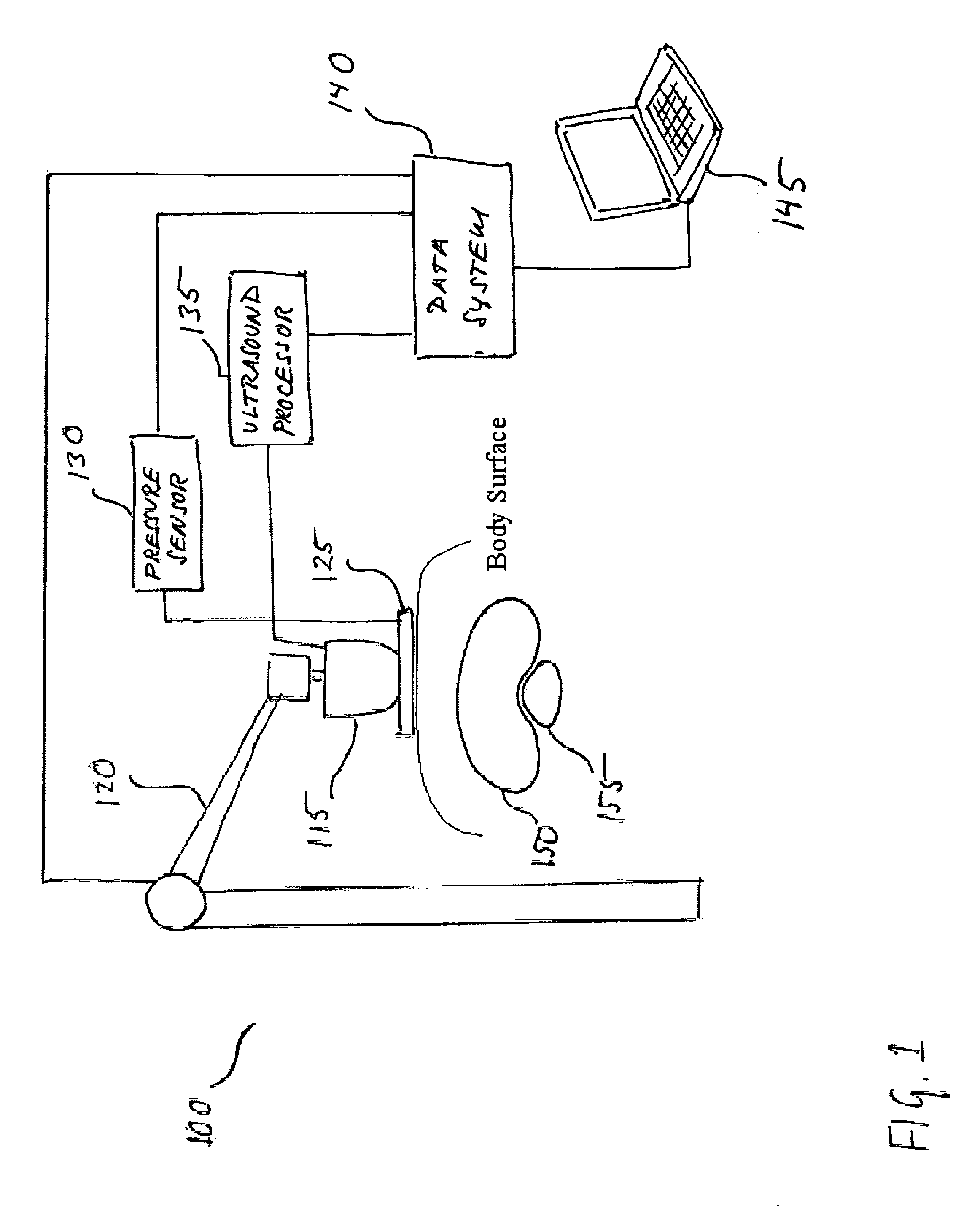
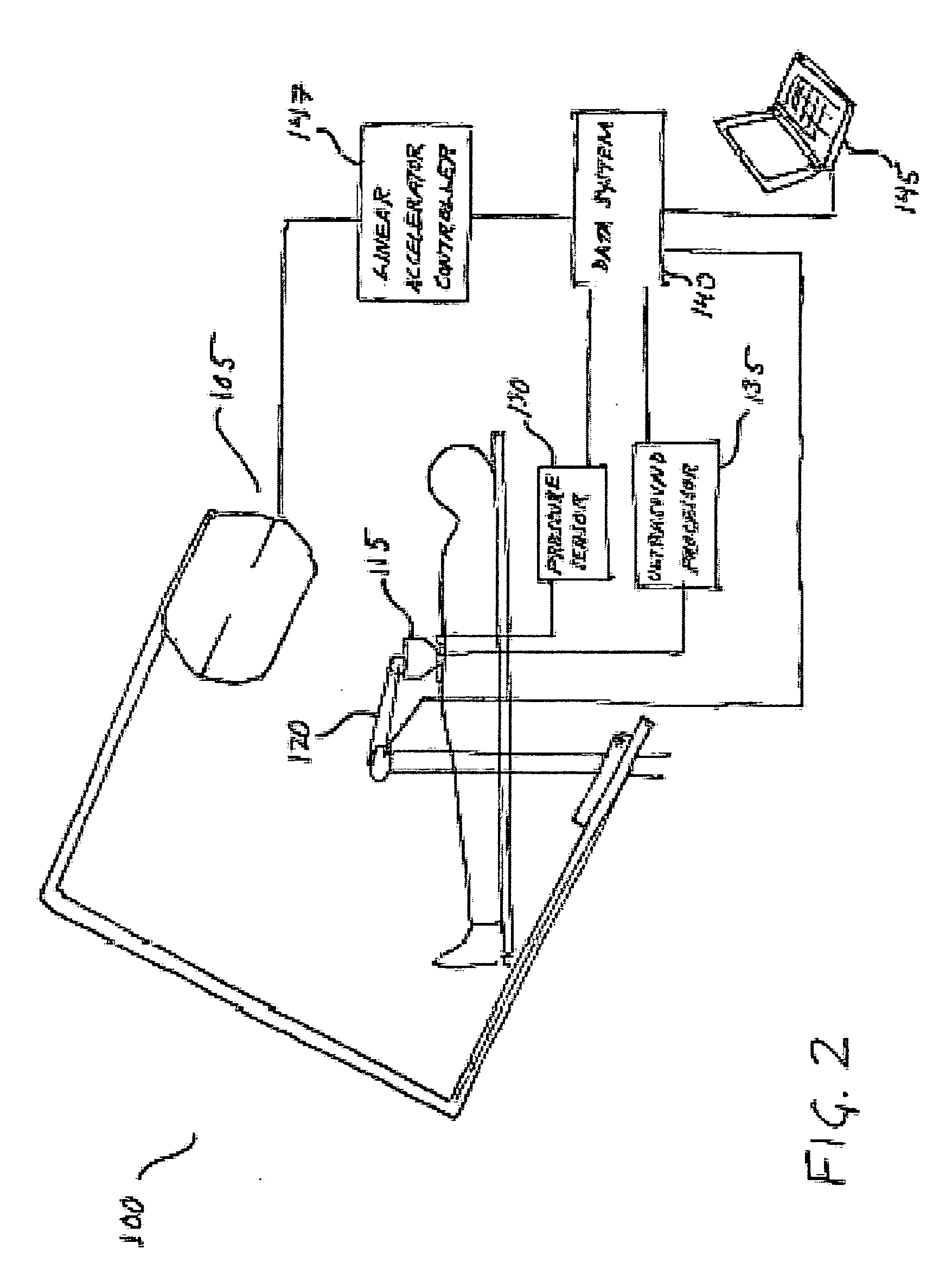
Ultrasound strain imaging in tissue therapies
InactiveUS20050267368A1Reduce exposureMaximizing thatOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical instrument detailsSonificationStrain imaging
Disclosed is a system and method for providing ultrasound strain imaging of a soft tissue, such as a prostate, so that the soft tissue may be more precisely targeted during radiation treatment. The system includes a mechanical arm with a pressure interface for applying incremental pressure to the patient's abdomen, and a data system for correlating the ultrasound signals acquired before and after each application of incremental pressure. By correlating the pre and post-pressure ultrasound signals, acoustic interfaces corresponding to the prostate, which define the contours of the prostate, may be displayed. Further, data corresponding to the contours of the prostate may be provided to a linear accelerator to enable the linear accelerator to more precisely target the prostate.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
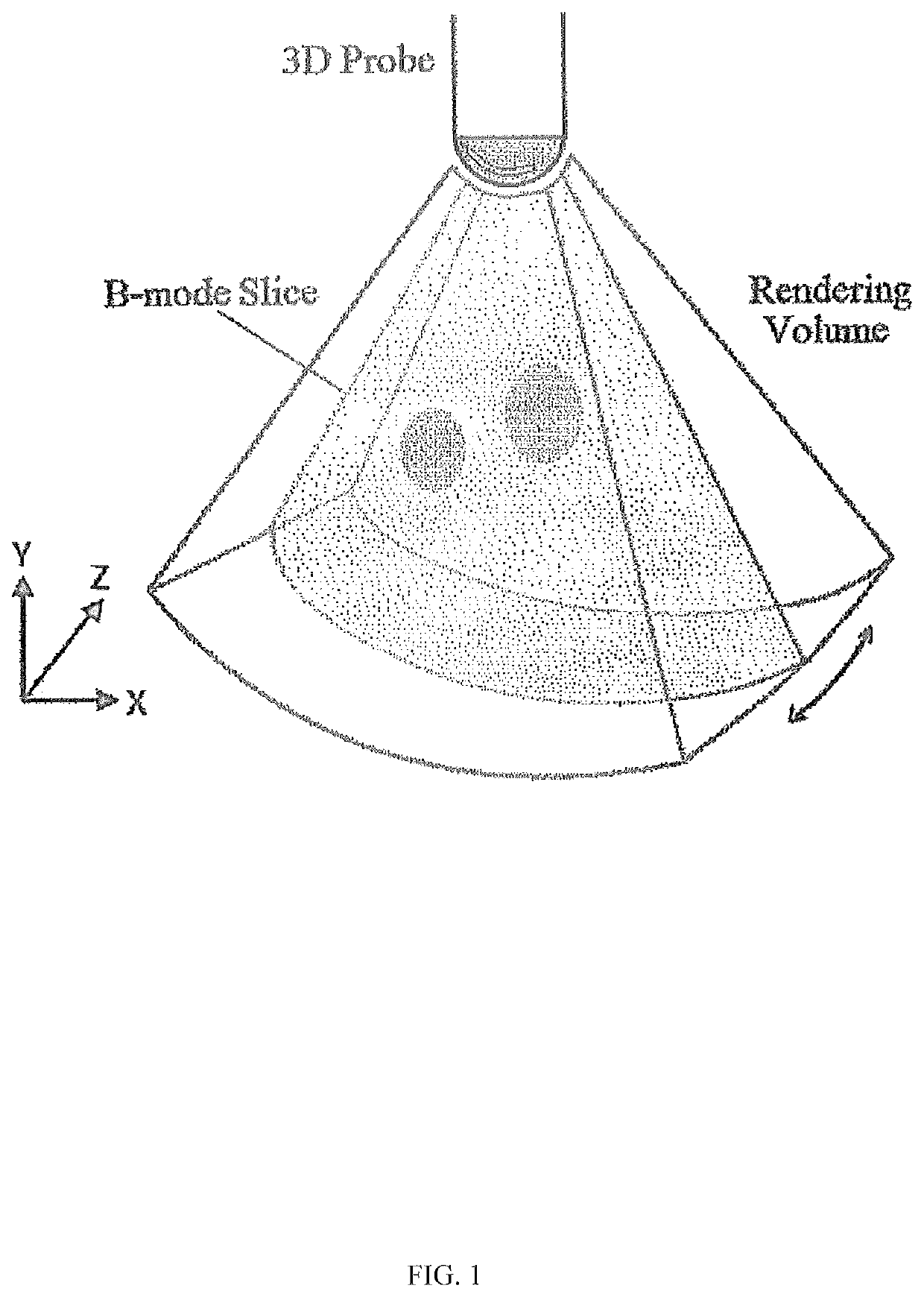
System and Device for Tumor Characterization Using Nonlinear Elastography Imaging
ActiveUS20140288424A1Smoothly measuredHealth-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorHuman tumor
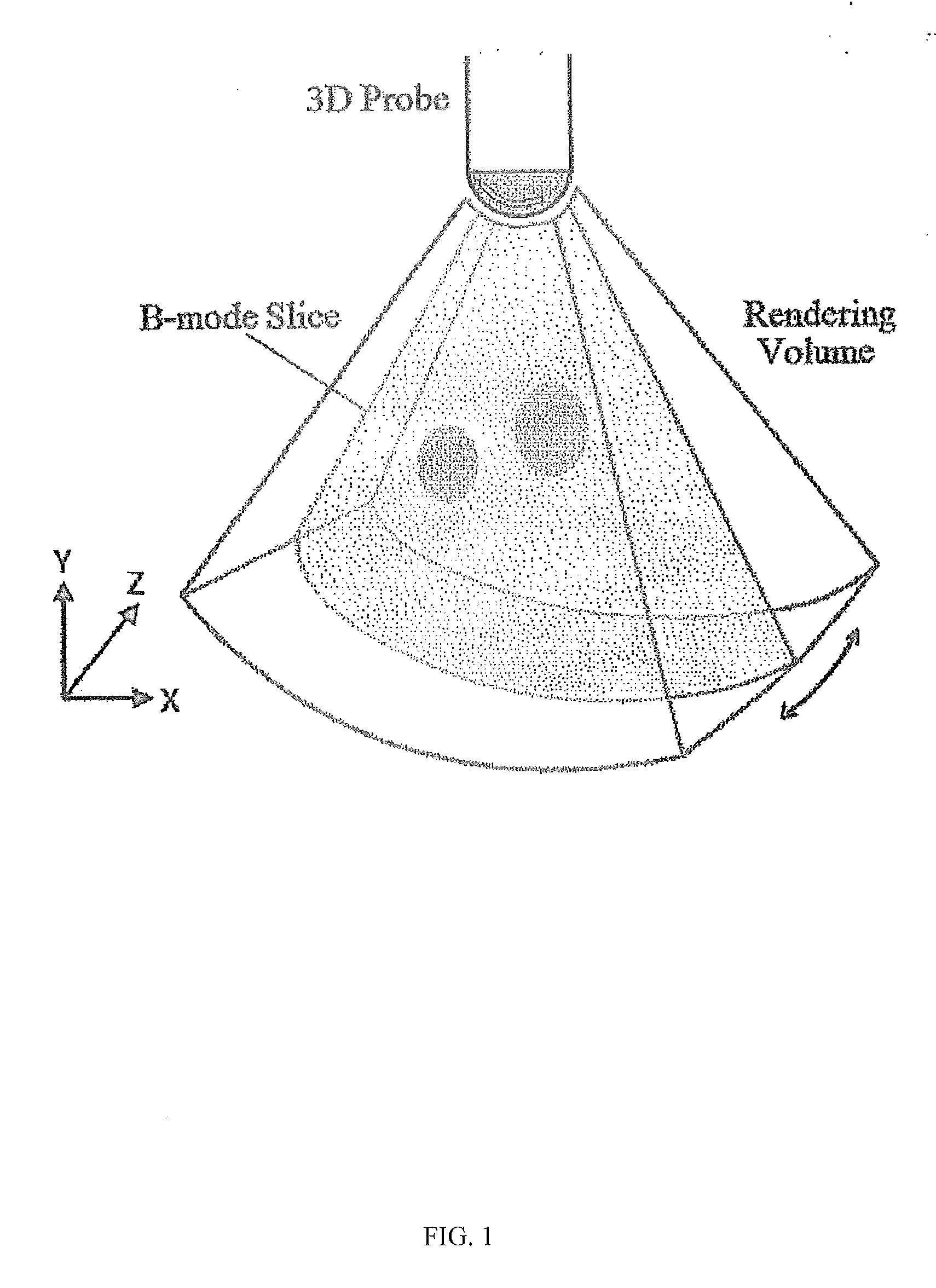
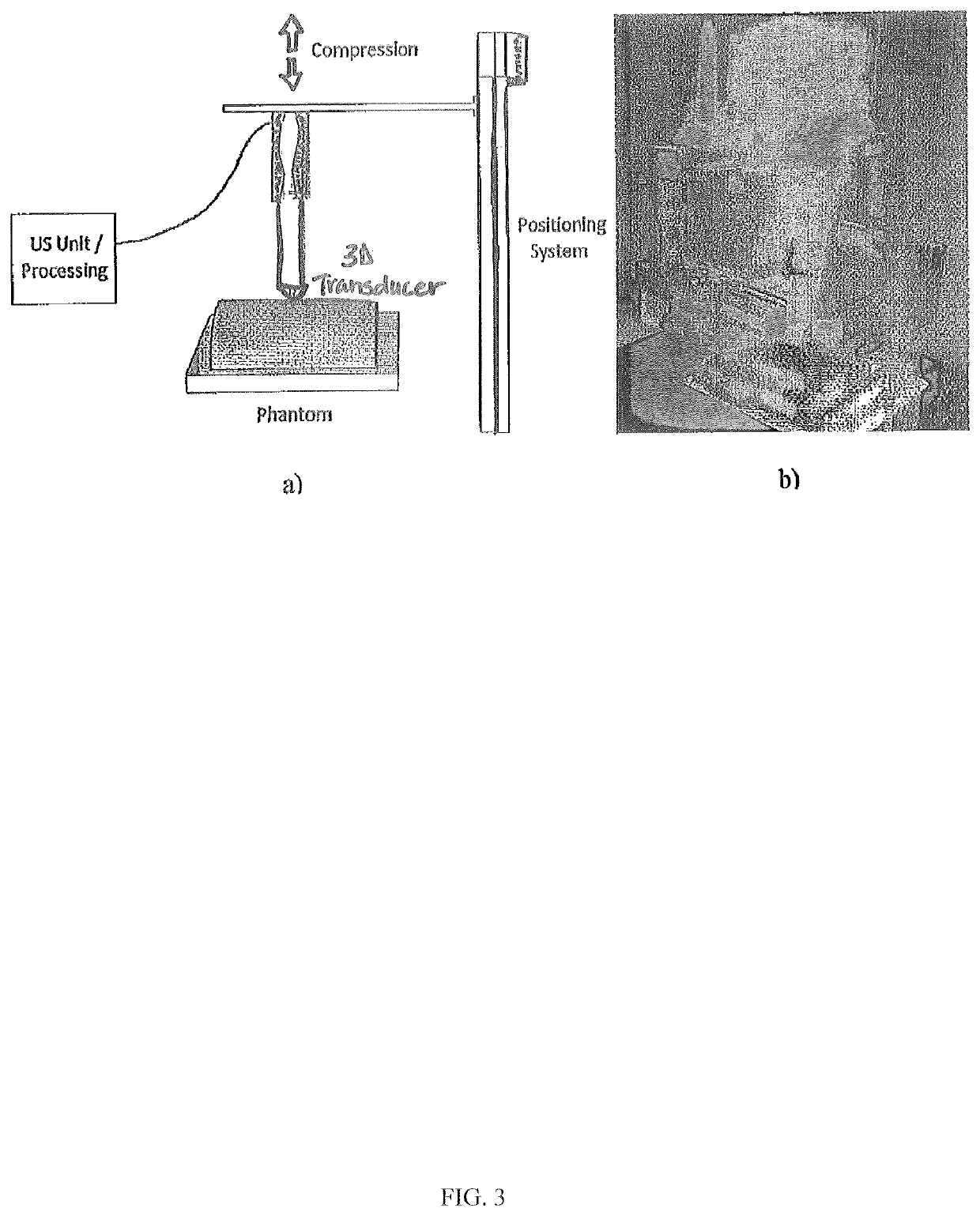
The present invention provides a method and a device to image and characterize human tumors, and to classify the tumors as either malignant or benign. The method includes using a multi-compression technique upon the tissue or organ combined with a 3D ultrasound strain imaging of the compressed tissue or organ for acquiring raw data and analyzing the raw data using a computer processing unit equipped with a nonlinear biomechanical tissue model for tumor classification. A device is provided having a compression stage for delivering multi-compression with continuous force measurements, and a 3D ultrasound transducer strain imaging probe, wherein the imaging probe and the compression stage are in communication with a computer processing unit.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
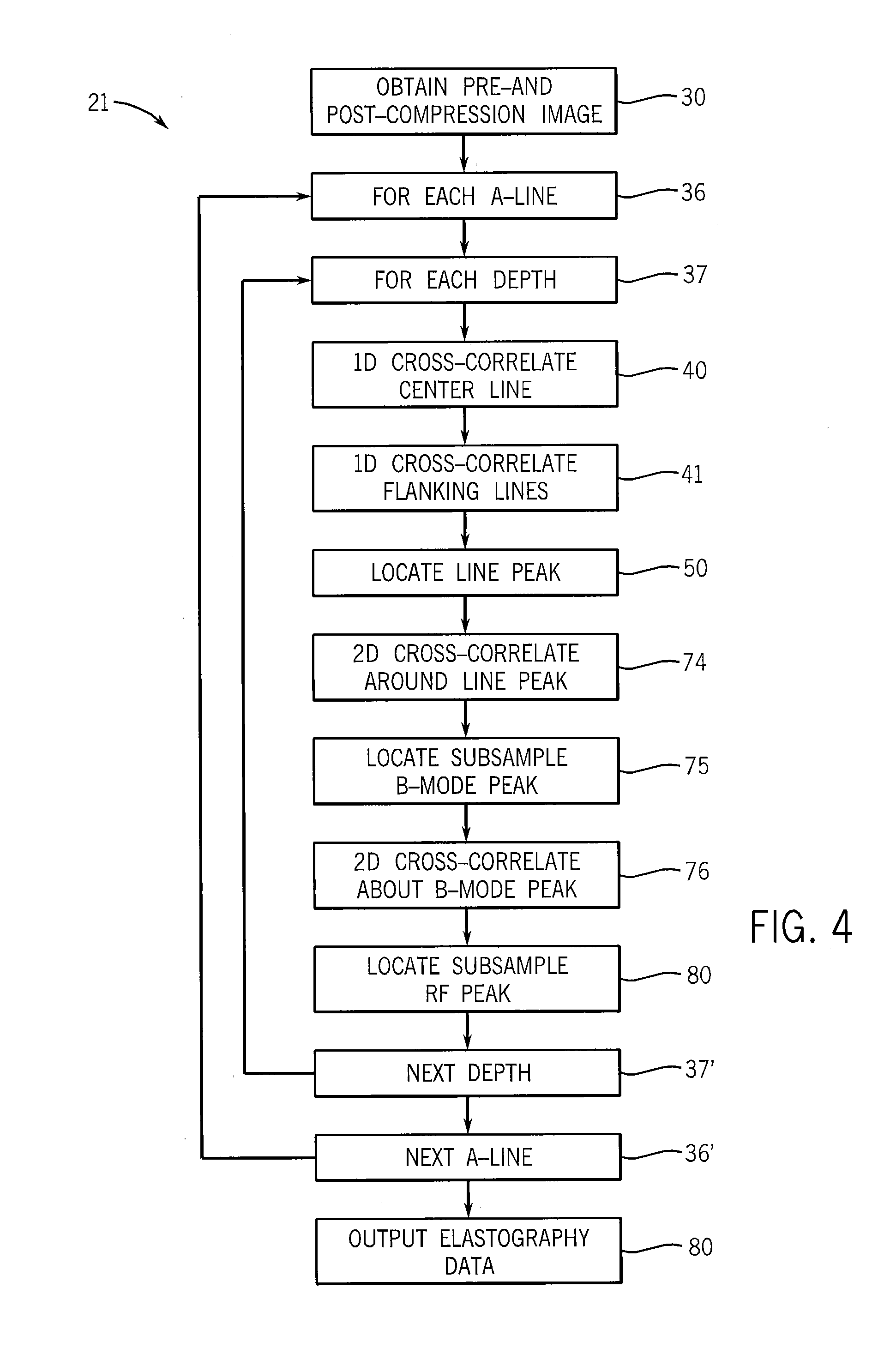
Rapid two/three-dimensional sector strain imaging
ActiveUS20090247871A1Processing speedHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisElastographyImage resolution
An elastographic imaging system providing for axial, lateral and elevational strain measurements employs a series of one-dimensional axial measurements to deduce a coarse axial, lateral and / or elevational displacement that is used to guide one or more two or three-dimensional cross-correlations of smaller kernels providing improved image resolution.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
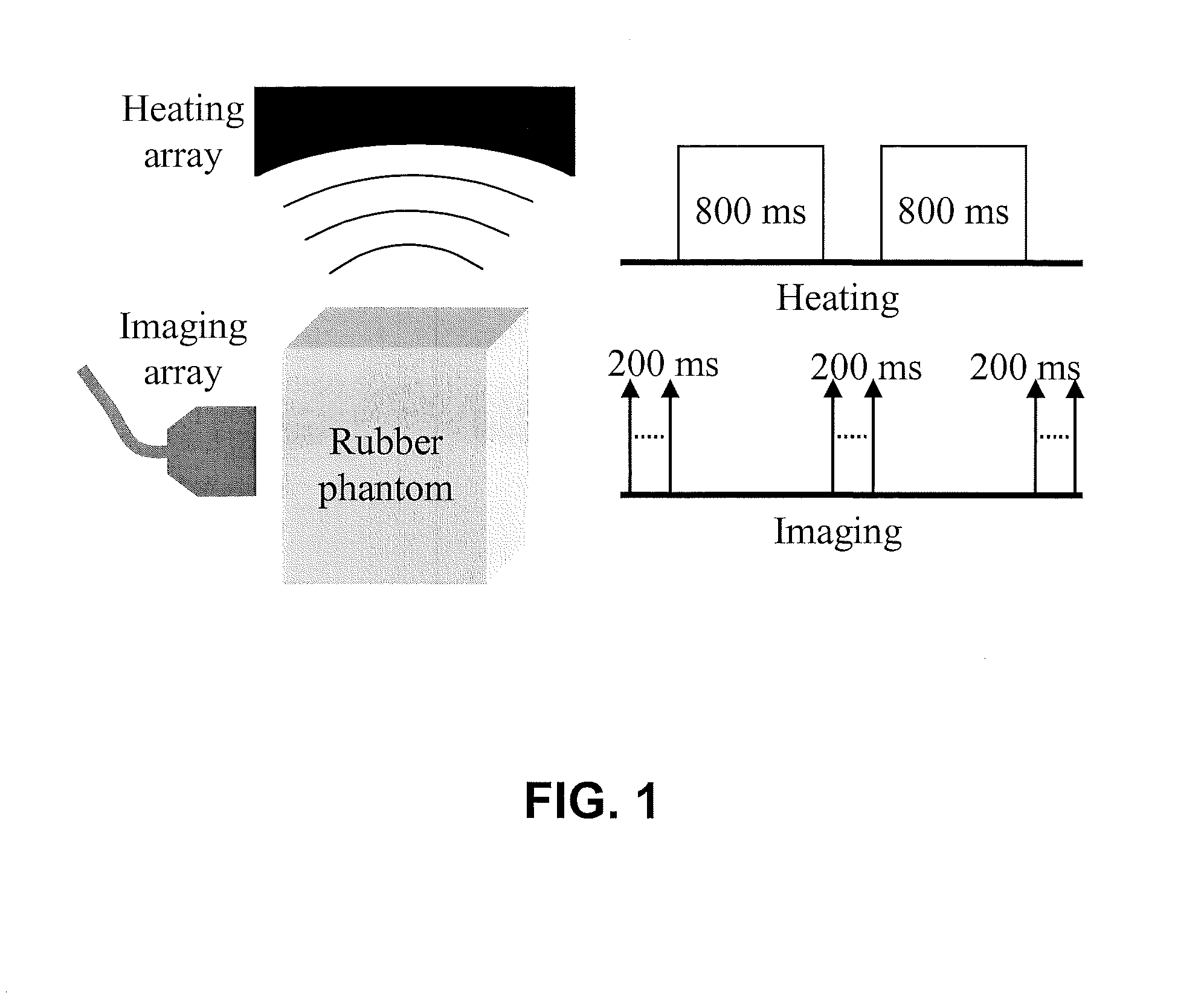
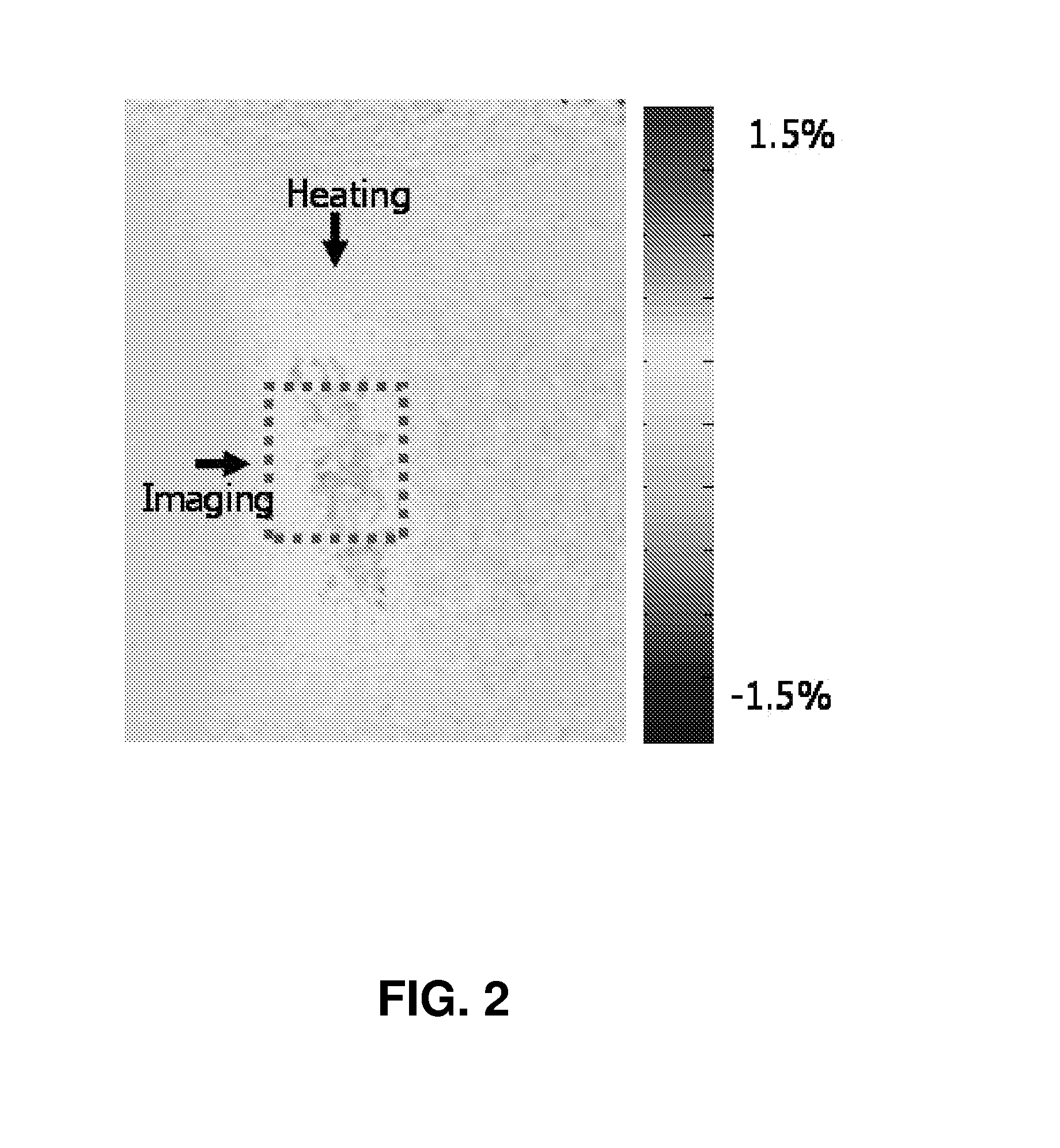
Thermal strain imaging of tissue
InactiveUS20080081995A1Easy to detectEasy diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryWater basedLipid formation
Thermal strain imaging can be used to identify vascular plaques. Methods include heating and imaging with ultrasound to identify vulnerable plaques, which typically consist of a large lipid-rich core, in peripheral arteries of a patient. Lipid-bearing tissue has a negative temperature dependence of sound speed, whereas water-based tissue has a positive one, allowing thermal strain imaging to differentiate the two different types of tissues with high contrast to characterize plaque composition. Apparatus and methods of the present teachings allow noninvasive and reliable plaque identification.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method of noninvasive high-precision vessel wall elastography
InactiveCN104055540AElastic expressionReflect elastic propertiesOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationUltrasonic imaging
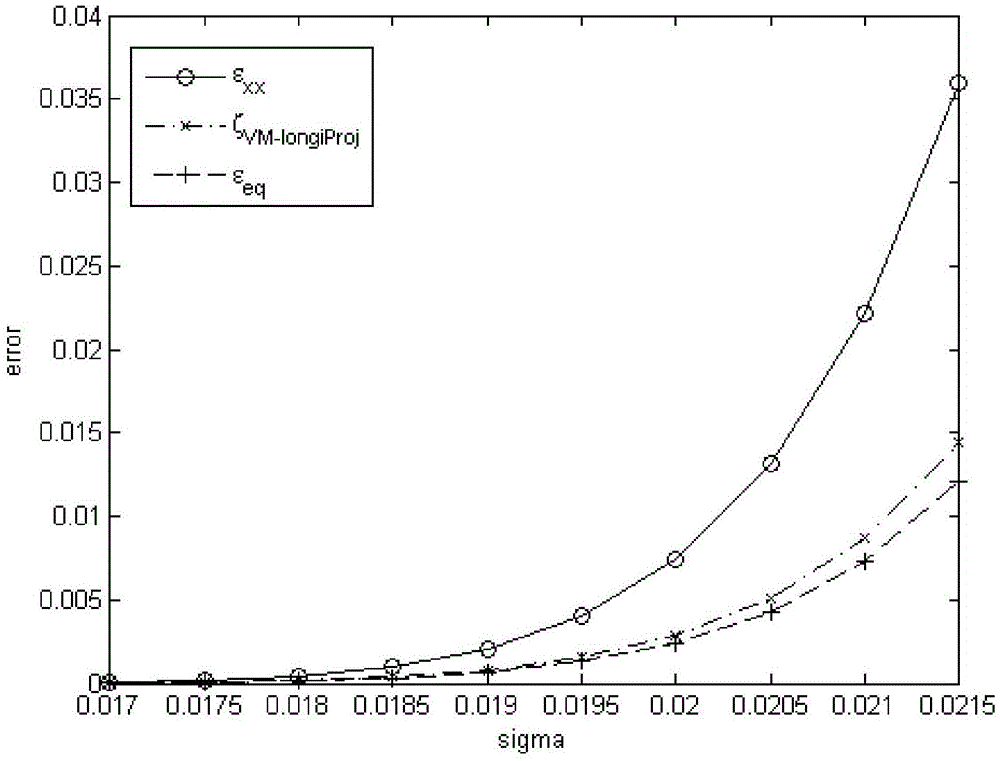
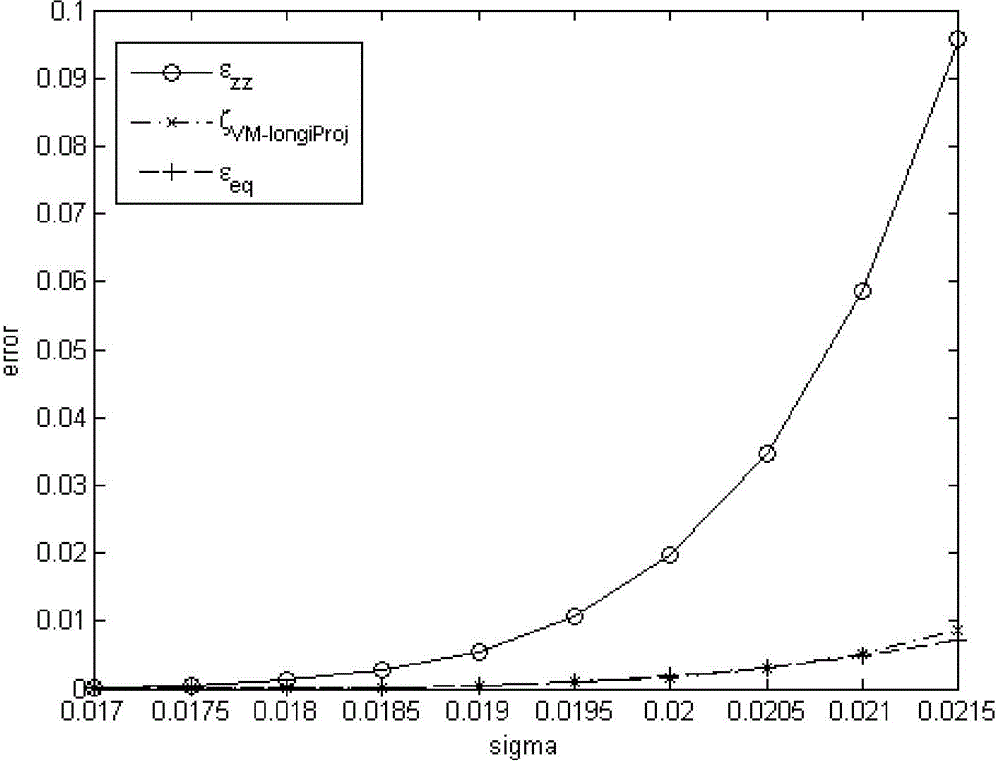
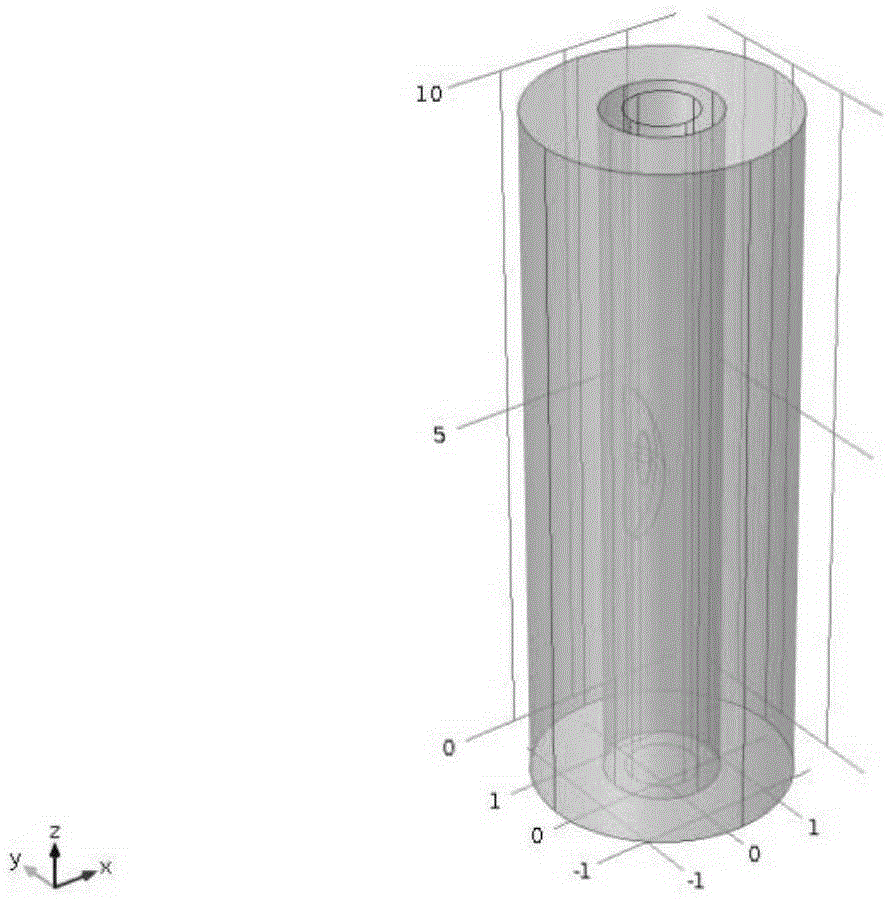
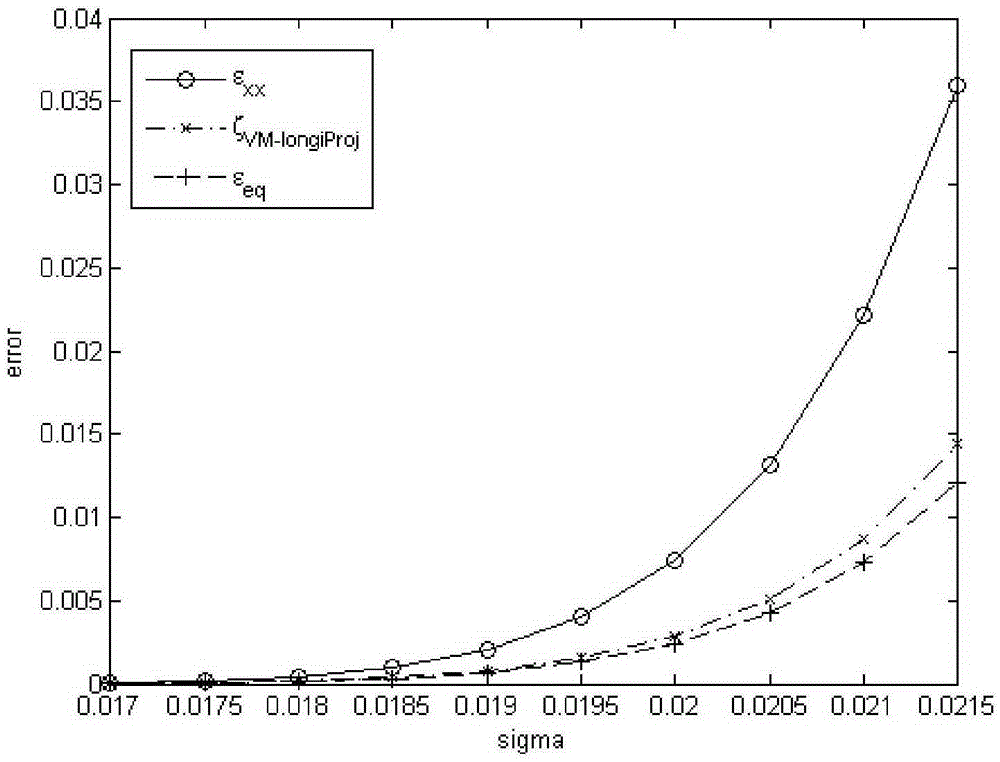
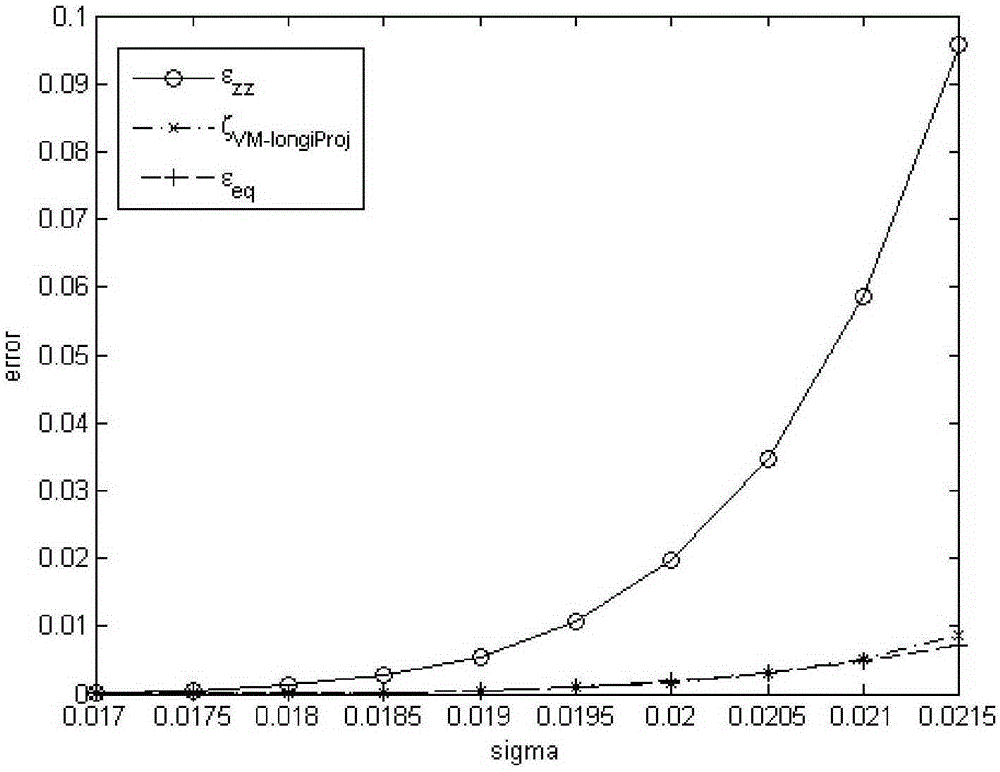
The invention discloses a method of noninvasive high-precision vessel wall elastography. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the radio-frequency data or video data of B-mode ultrasonic imaging of a vessel wall longitudinal section; making an off-line analysis on the acquired radio-frequency data or video data to obtain the displacement field of each frame of radio-frequency data or video data; filtering the displacement fields of the radio-frequency data or video data with an FIR two-dimensional difference filter to obtaining strain components on the longitudinal section, including a strain component Epsilonxx in the axial direction of a ultrasonic emission beam, a lateral strain component Epsilonzz and a shearing strain component Epsilonxz; giving a Von Mises strain projection parameter ZetaVM-longiProj and a calculation formula thereof, and imaging the Von Mises strain projection parameter ZetaVM-longiProj to achieve noninvasive high-precision vessel wall elastography. Precise and quantitative vessel wall elastography can be achieved through the method, and the result is superior to those of the conventional other vessel wall strain imaging methods.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Rapid two/three-dimensional sector strain imaging
ActiveUS8403850B2Quick identificationAccelerated settlementImage enhancementImage analysisElastographyImage resolution
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
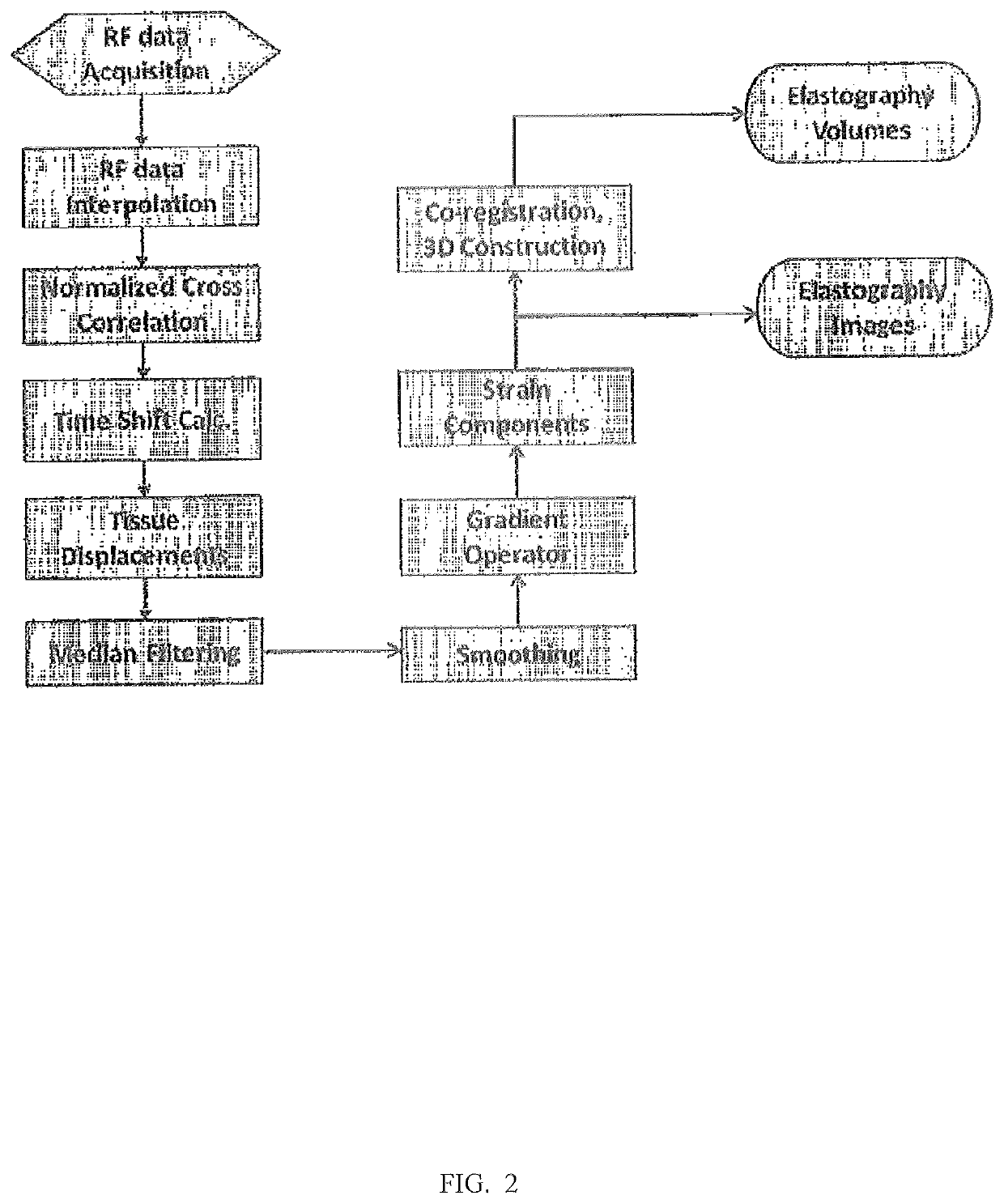
Method and apparatus to measure tissue displacement and strain
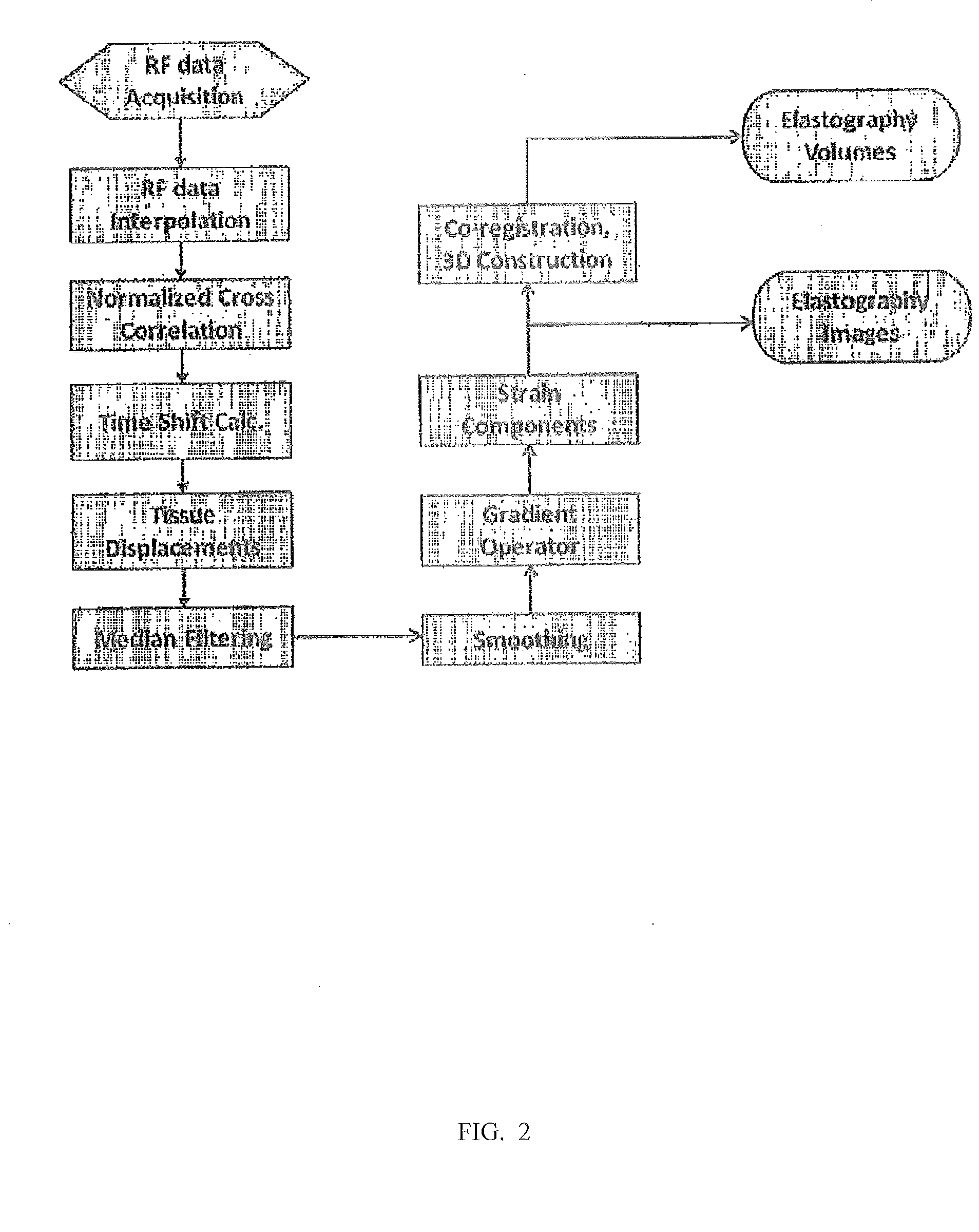
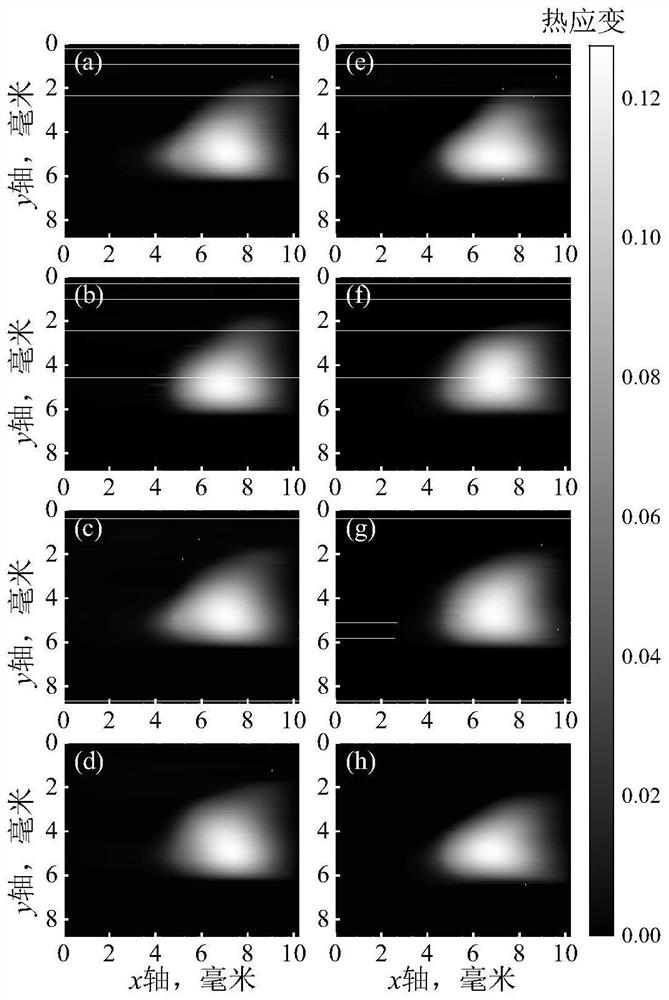
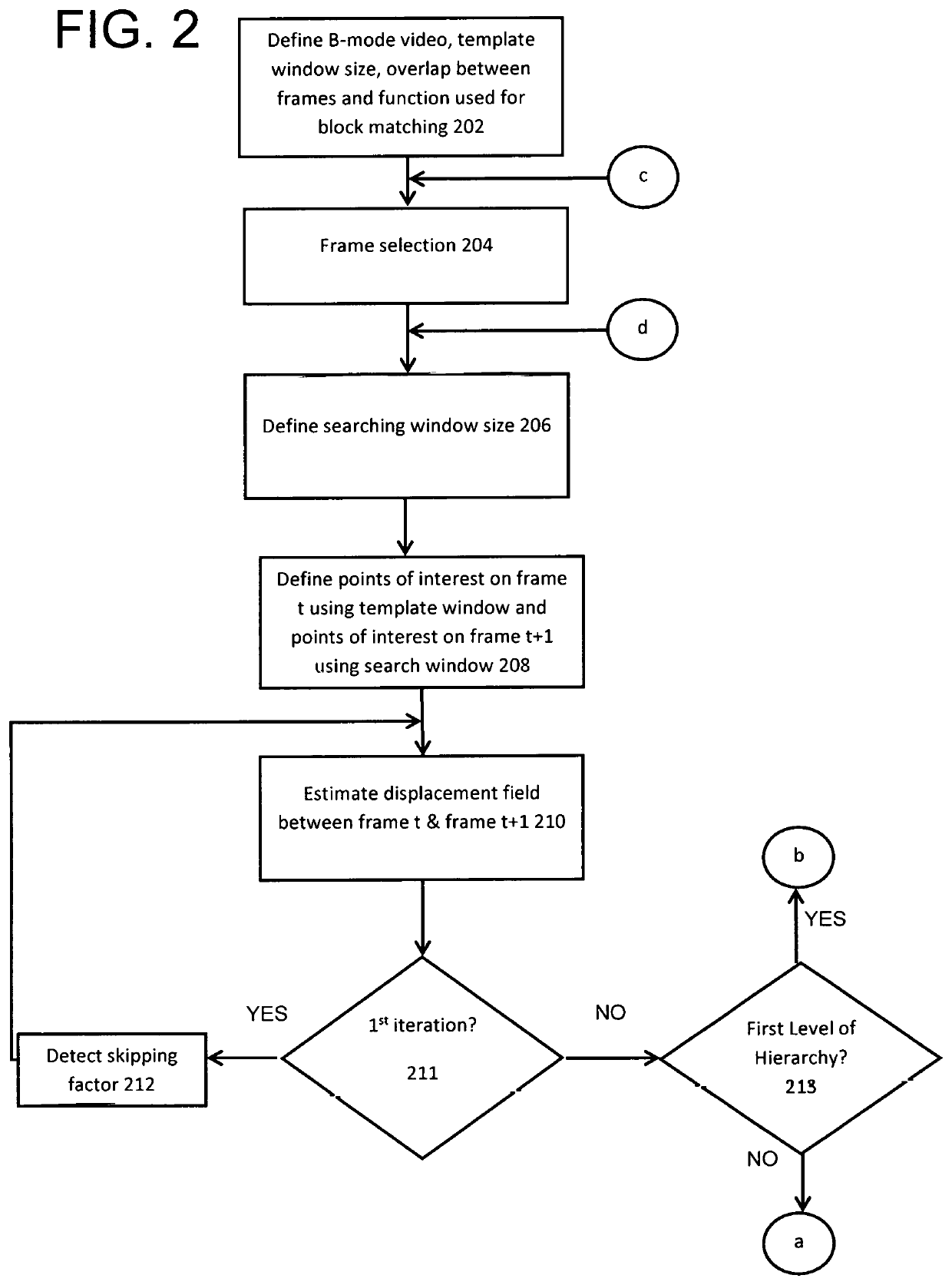
A method for reconstructing displacement and strain maps of human tissue of a subject in vivo or other objects includes applying a mechanical deformation for a target area, imaging tissues while deformation is applied on the target area, measuring the axial and lateral displacements and axial, lateral, and shear strains of tissue in the target area, differentiating between tissues of different stiffness and strain responses, and labeling tissues of different stiffness and strain responses. In some embodiments, displacement and strain imaging are performed using a high-resolution, high-speed, highly-accuracy hierarchy recursive displacement tracking from conventional ultrasound brightness mode images. Particularly, this invention relates to the reconstruction of displacement and strain images from conventional ultrasound B-mode images acquired using any ultrasound machine of different manufacturers without the need to use carrier signals.
Owner:MAHMOUD AHMED M EHAB +1
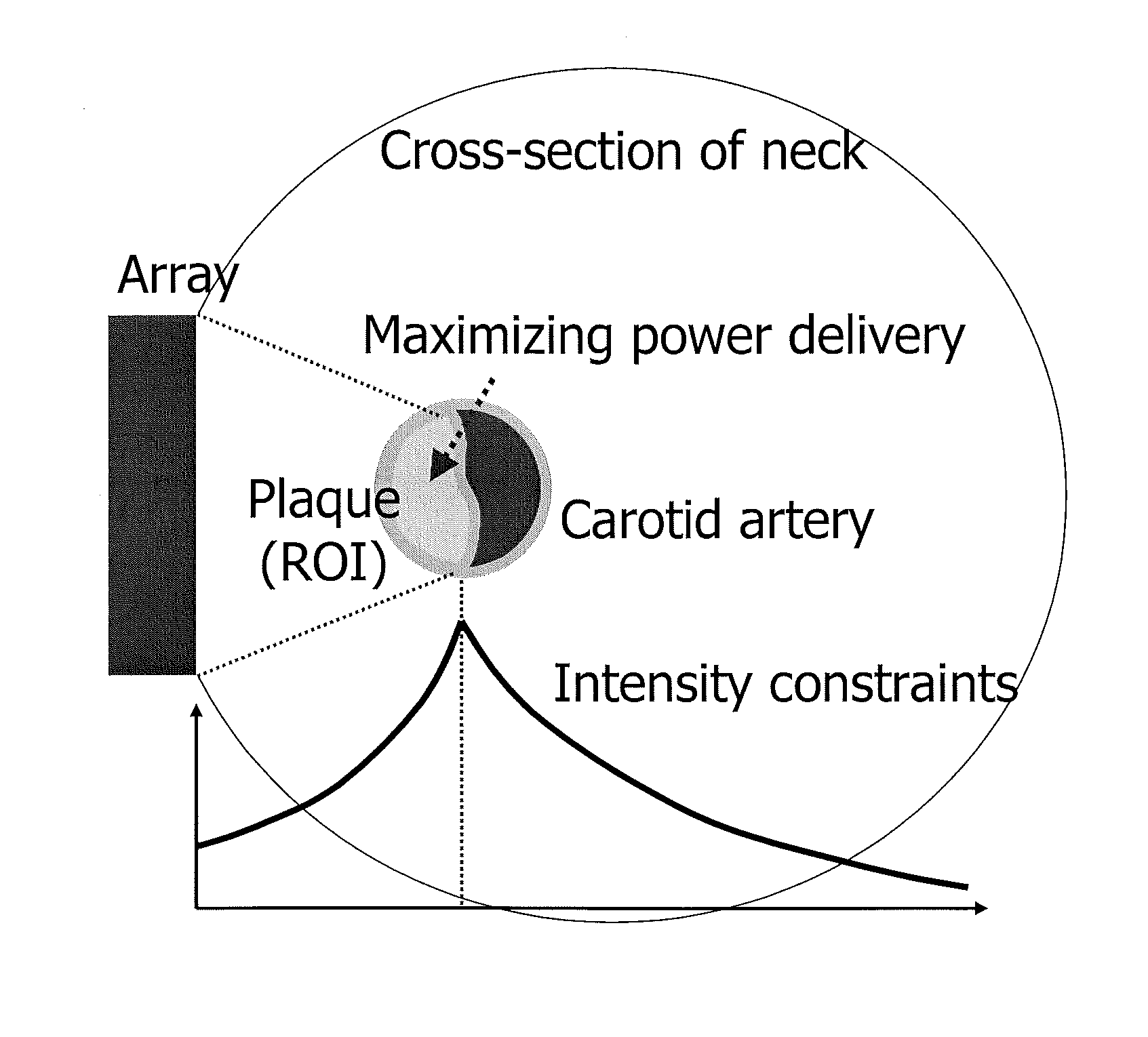
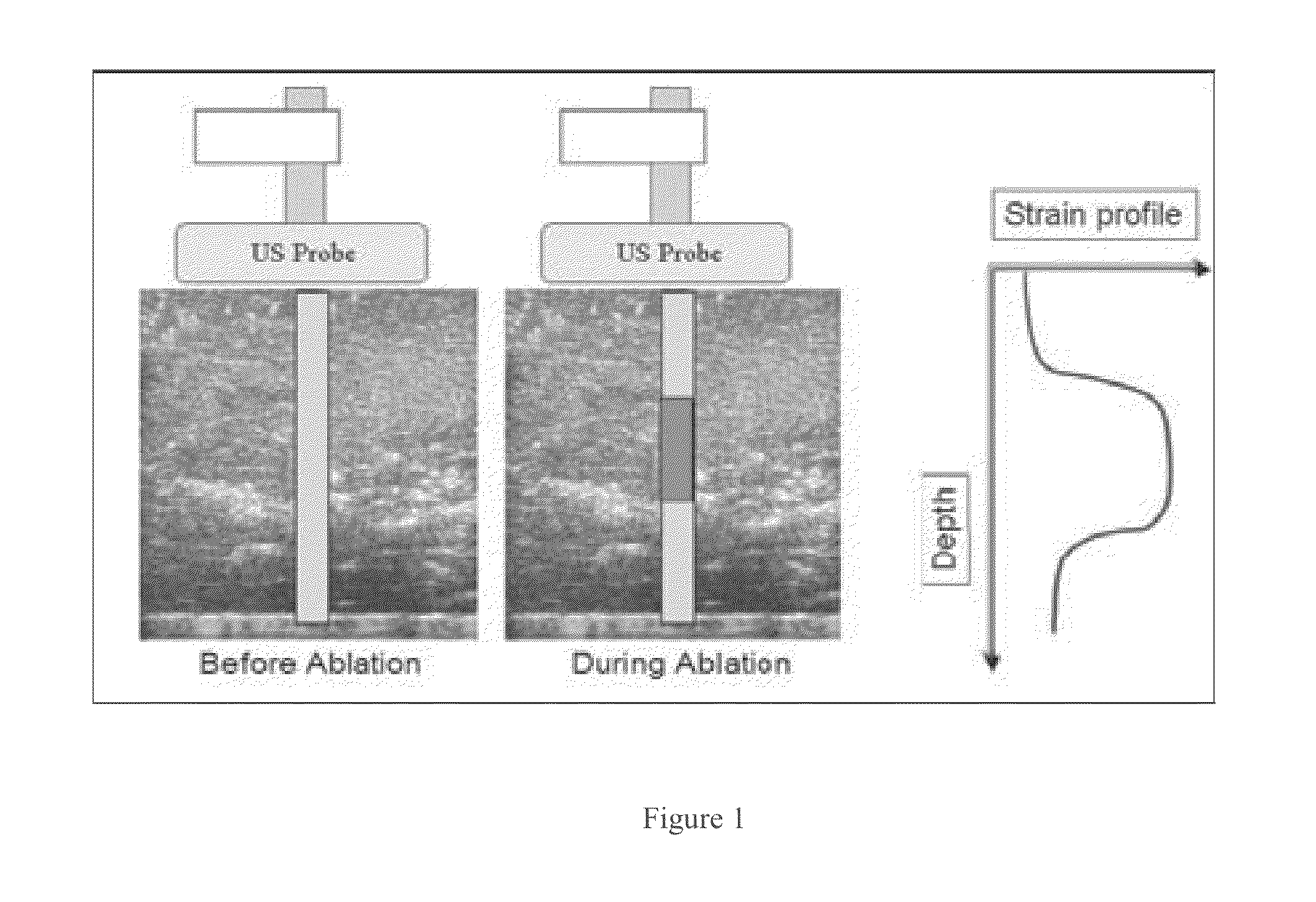
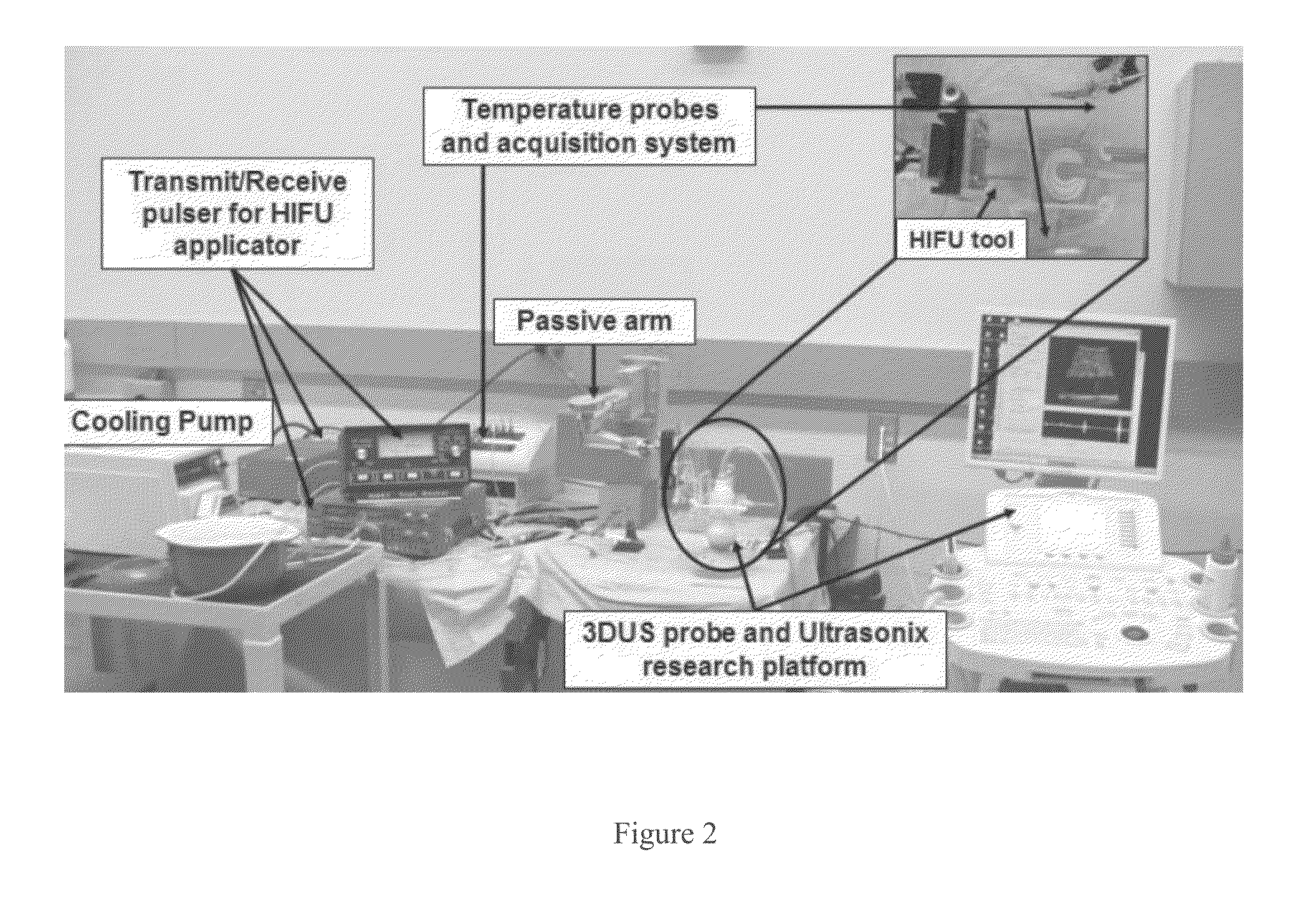
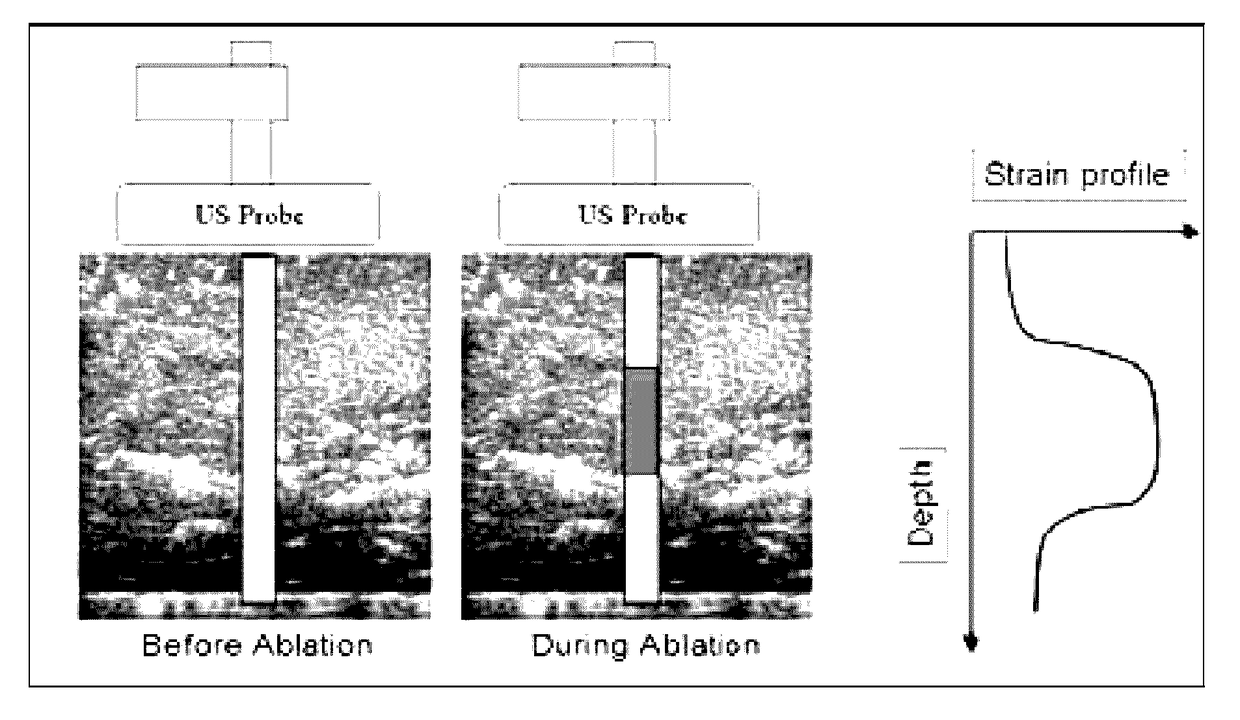
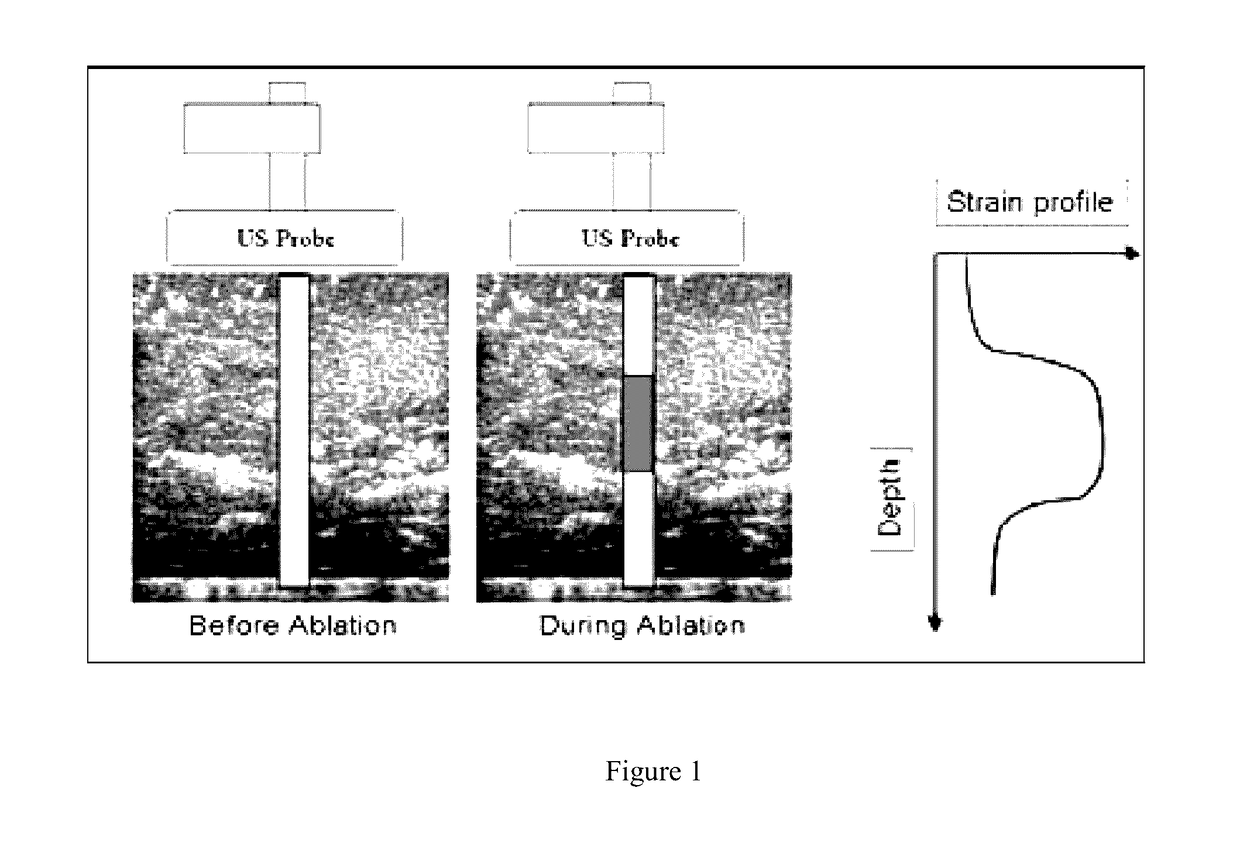
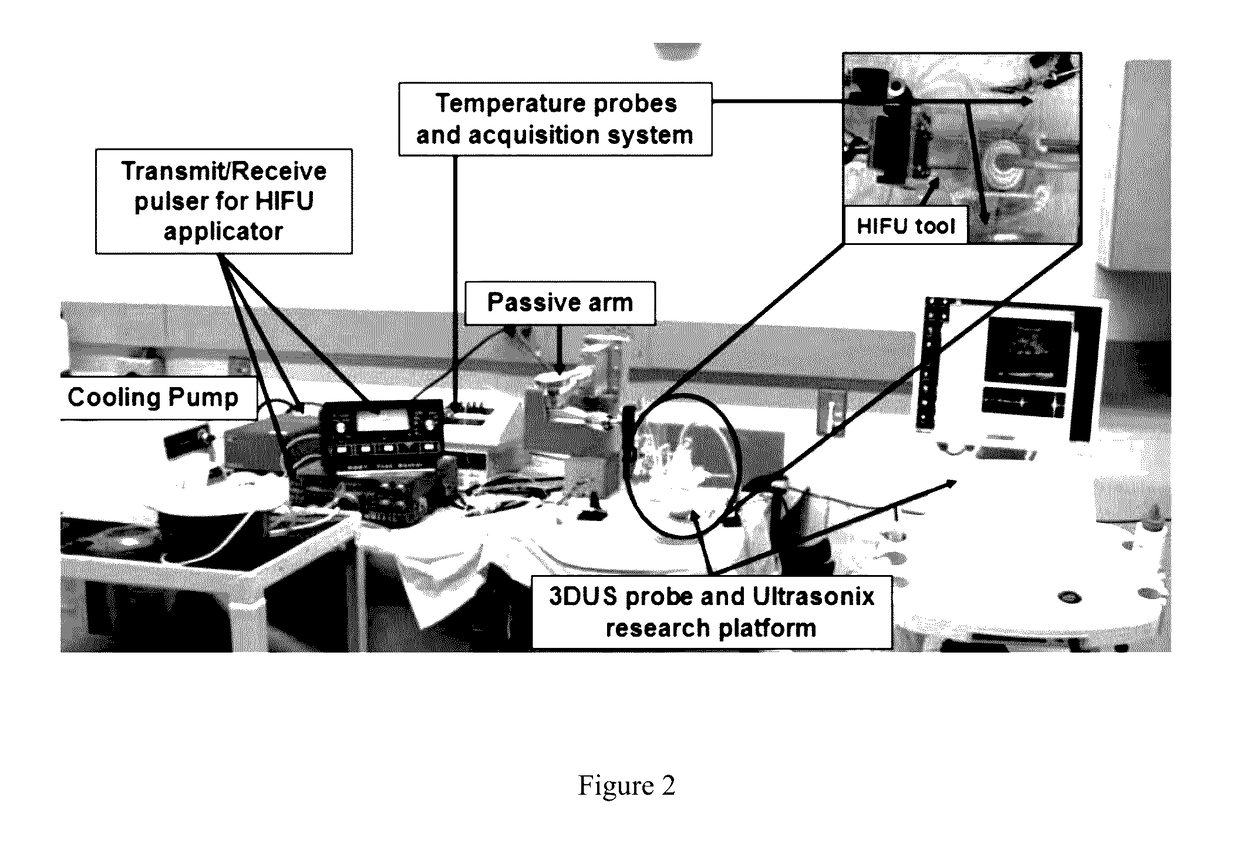
Real time three-dimensional heat-induced echo-strain imaging for monitoring high-intensity acoustic ablation produced by conformal interstitial and external directional ultrasound therapy applicators
ActiveUS20160015417A1Increase powerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationStrain imaging
A system for thermal treatment or ablation of tissue includes an ultrasonic thermal ablation probe, an ultrasonic three-dimensional imaging probe that captures an image from radio frequency image data obtained before the radio frequency image data is processed, a control system for multi-axis control of the imaging probe's position, and an ultrasonic feedback mechanism that measures ultrasound echo strain to estimate heat-induced structural changes of an area surrounding the ultrasonic thermal ablation probe, from the image. The ultrasonic thermal ablation probe is either an interstitial ablator inserted into tissue, a natural cavity or a vessel to emit high intensity ultrasound energy to deposit thermal dose, or an external applicator that emits a directional high intensity ultrasound energy to deposit thermal dose via surface contact with tissue. The control system adjusts power levels of the ultrasonic thermal ablation probe based on the estimated heat-induced structural changes.
Owner:ACOUSTIC MEDSYST +1
Ultrasonic strain imaging device and method providing parallel displacement processing
ActiveUS7632231B2Eliminate the problemEliminate CollisionsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesData setPre deformation
A device for ultrasonic strain imaging computes displacement of tissue between a pre-deformation and post-deformation data set along columns to provide for independent calculations that may be parallelized for multiprocessor systems.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Real time three-dimensional heat-induced echo-strain imaging for monitoring high-intensity acoustic ablation produced by conformal interstitial and external directional ultrasound therapy applicators
ActiveUS9649127B2Increase powerUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationStrain imaging
A system for thermal treatment or ablation of tissue includes an ultrasonic thermal ablation probe, an ultrasonic three-dimensional imaging probe that captures an image from radio frequency image data obtained before the radio frequency image data is processed, a control system for multi-axis control of the imaging probe's position, and an ultrasonic feedback mechanism that measures ultrasound echo strain to estimate heat-induced structural changes of an area surrounding the ultrasonic thermal ablation probe, from the image. The ultrasonic thermal ablation probe is either an interstitial ablator inserted into tissue, a natural cavity or a vessel to emit high intensity ultrasound energy to deposit thermal dose, or an external applicator that emits a directional high intensity ultrasound energy to deposit thermal dose via surface contact with tissue. The control system adjusts power levels of the ultrasonic thermal ablation probe based on the estimated heat-induced structural changes.
Owner:ACOUSTIC MEDSYST +1
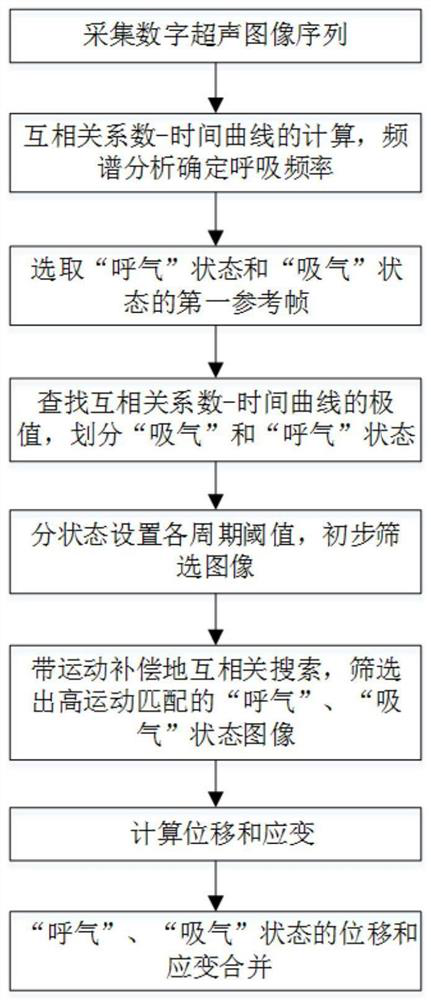
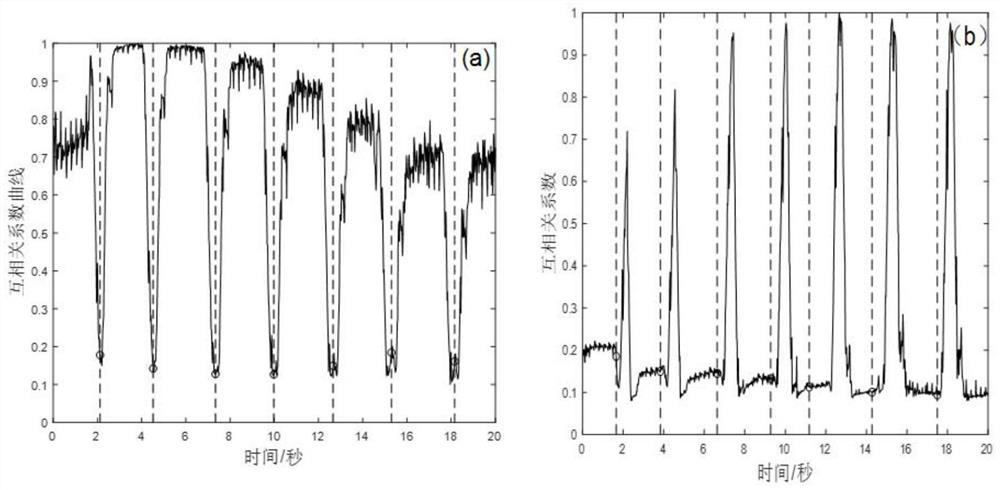
Respiration separation type strain imaging method based on ultrasonic images of living body
ActiveCN111681740AShorten the time intervalImprove real-time performanceImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingRadiology
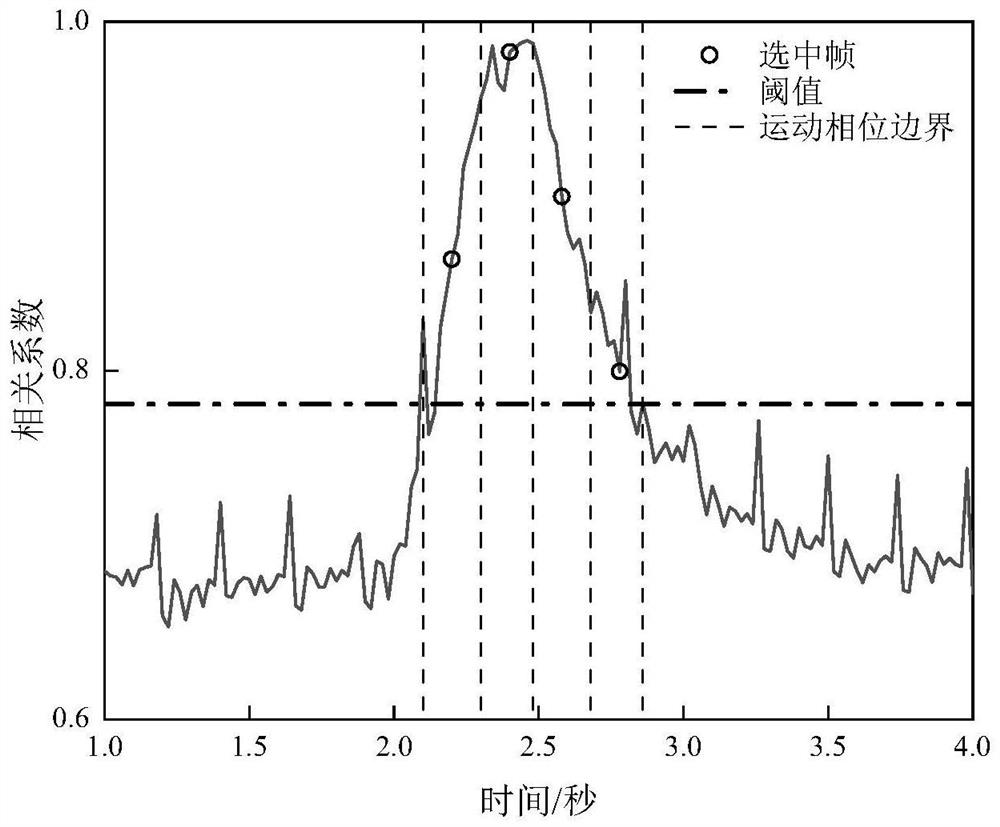
The invention discloses a respiration separation type strain imaging method based on ultrasonic images of a living body, and belongs to the field of medical image processing. The method comprises thesteps of acquiring a digital ultrasonic image sequence, obtaining the respiration and heartbeat frequency of a living body through two-dimensional cross-correlation calculation and spectrum analysis,then performing alternate extremum retrieval in a cross-correlation curve to divide the image sequence into an expiration state and an inspiration state, performing primary image screening, then respectively extracting an image sequence with the most matched motion state and a motion compensation amount corresponding to the image sequence, and calculating a spatial displacement and a spatial strain image sequence of a tissue according to the image sequence; and finally, combining the displacement image sequences and the strain image sequences of the two states respectively. The invention aimsto overcome the defects that physiological motions such as respiration and heartbeat of a living body influence speckle tracking precision to cause large artifacts and errors in a space strain image in the prior art, and the invention can obtain an accurate tissue internal displacement and strain distribution image.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
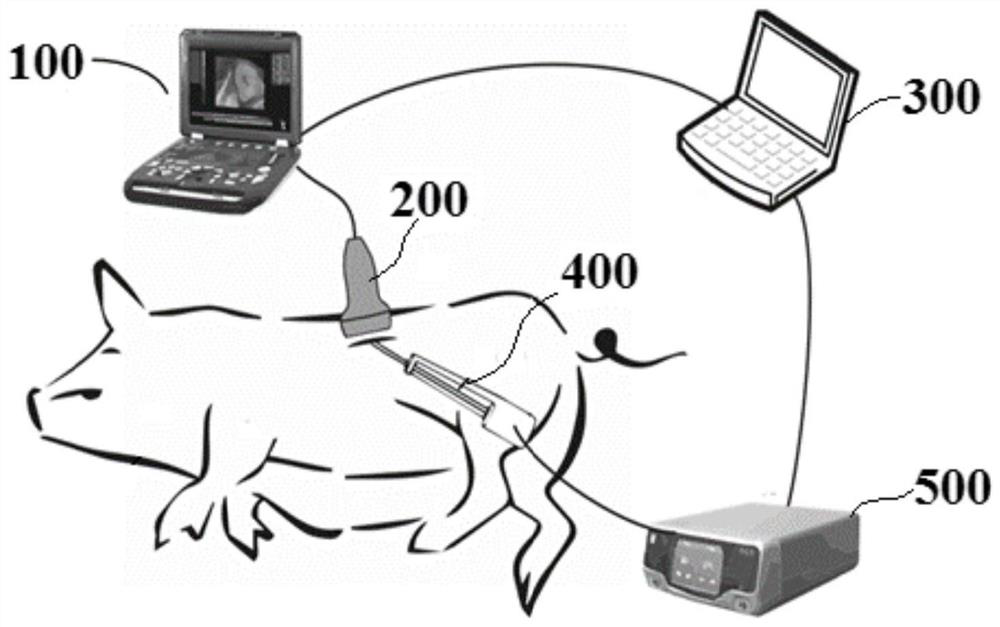
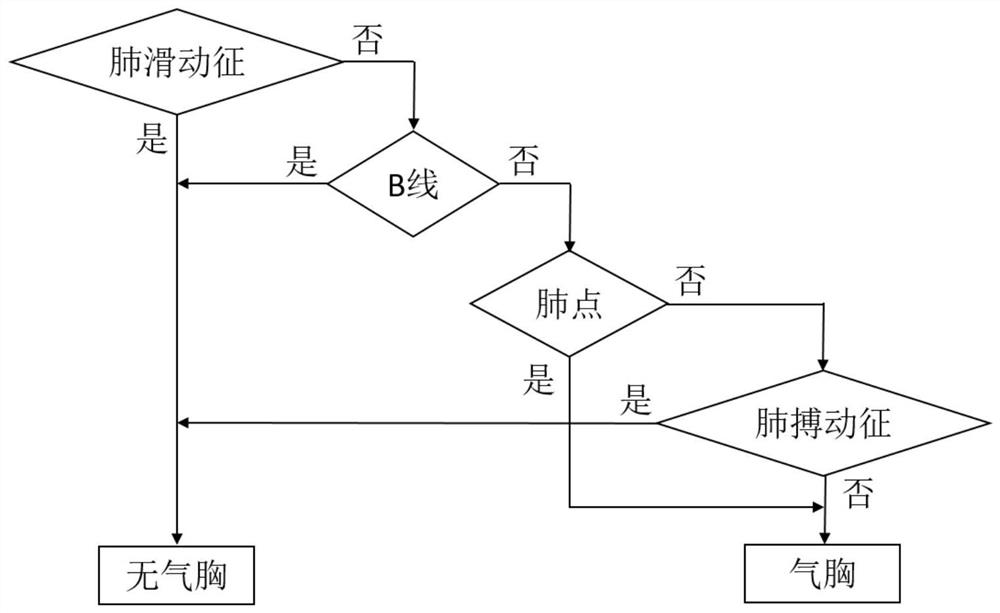
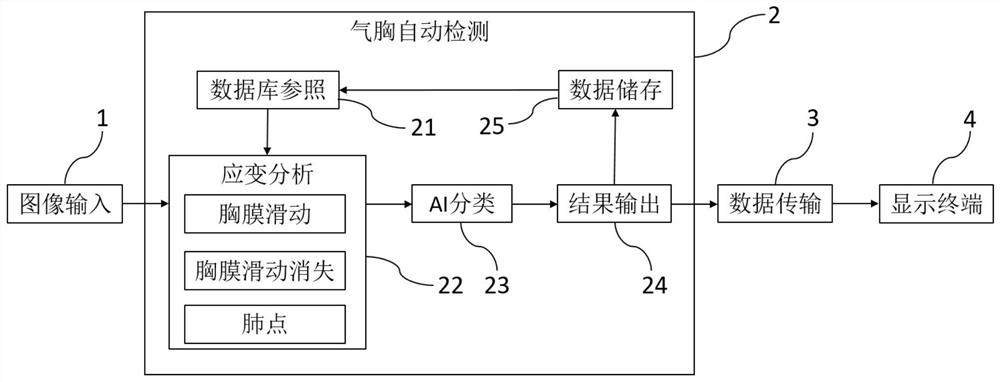
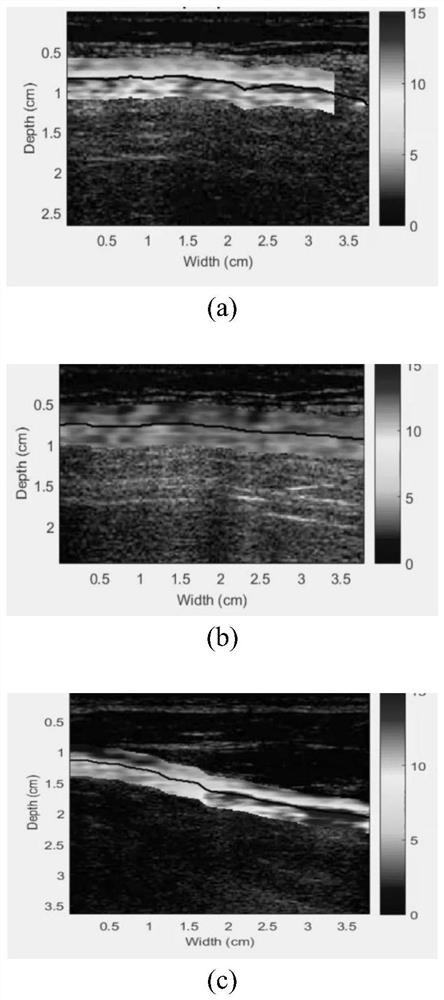
Automatic pneumothorax detection system based on ultrasonic strain imaging
PendingCN112801957ASmall amount of calculationThe result is stableImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareEmergency treatment
The invention provides an automatic pneumothorax detection system based on ultrasonic strain imaging. The automatic pneumothorax detection system comprises an image input module, an automatic pneumothorax detection module, a data transmission module and a display terminal module. The image input module comprises an ultrasonic probe, and the output end of the image input module is in one-way electric connection with the input end of the automatic pneumothorax detection module; the output end of the automatic pneumothorax detection module is in one-way electric connection with the input end of the data transmission module; the output end of the data transmission module is in one-way electric connection with the input end of the display terminal module. The automatic pneumothorax detection system based on ultrasonic strain imaging comprises a rapid pneumothorax ultrasonic detection algorithm based on strain calculation, can be integrated into handheld ultrasonic equipment, greatly enhances portability and flexibility, reduces the requirements of pneumothorax ultrasonic diagnosis on experience and skills of doctors, can be applied to more scenes, such as emergency treatment, ICU, first-aid sites, battlefields and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Process for non-destructive testing using direct strain imaging
A process for non-destructive testing includes applying a photo-curable dye to a surface of an article, selectively curing an array of dots of the photo-curable dye on the surface, removing the photo-curable dye that has not been selectively cured, mechanically testing the article, and direct strain imaging the article during the mechanical testing based on the array of dots.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE INC
Methods and apparatus for ultrasound strain imaging
ActiveUS9610063B2Organ movement/changes detectionMedical automated diagnosisUltrasound imagingAccelerometer
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
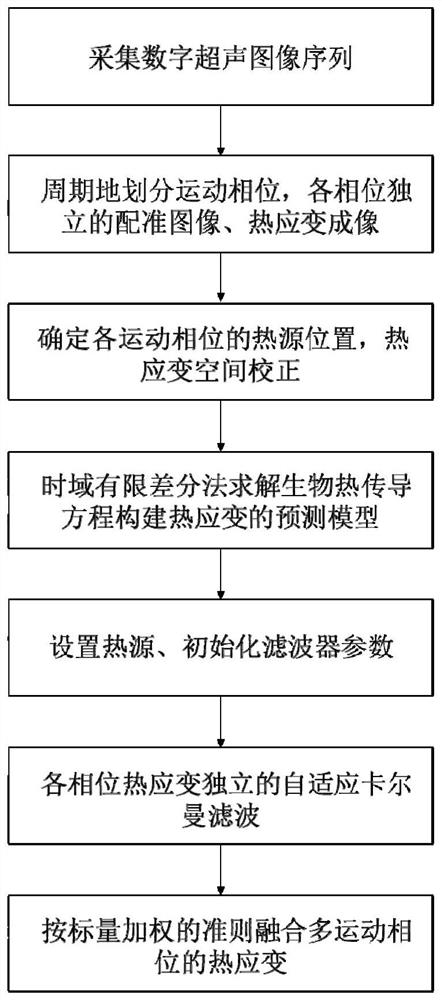
Multi-thread strain imaging method and device based on living body ultrasonic image
PendingCN114240815AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingStrain imaging
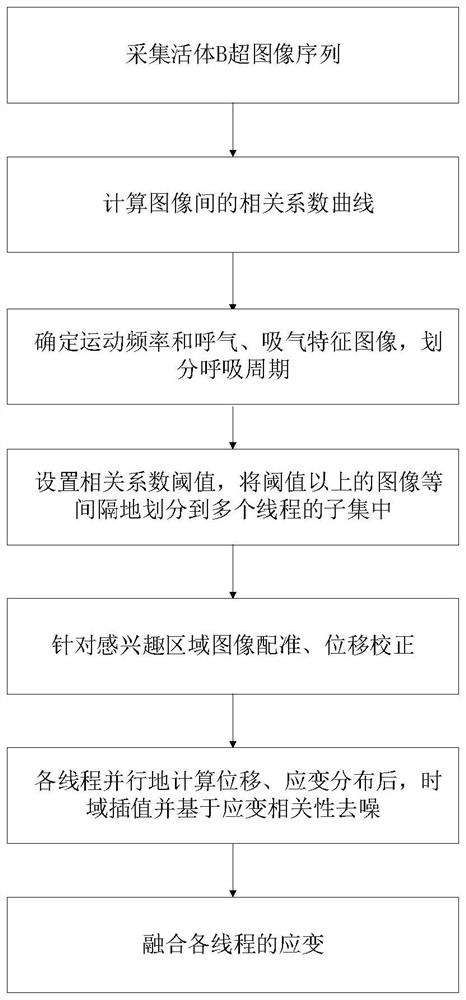
The invention discloses a multi-thread strain imaging method and device based on a living body ultrasonic image, and belongs to the field of medical image processing. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a living body B ultrasonic image sequence, analyzing the correlation characteristics of the image, judging the respiratory rate, and dividing the image into different respiratory cycles and synchronous phase periods during the cycles; a calculation thread is established for each phase period, after displacement correction and image registration, the threads calculate strain in parallel, and noise reduction is carried out according to correlation between the threads; and finally, fusing multi-thread strain results to obtain accurate and high-time-density strain output. According to the method, the problems of artifacts and errors generated by physiological movement in strain imaging in the prior art can be solved, the strain distribution of multiple movement phase periods can be obtained, and the living body strain distribution image which is accurate, high in robustness and high in time density is obtained after denoising and fusion are further combined with the spatial correlation of the strain distribution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
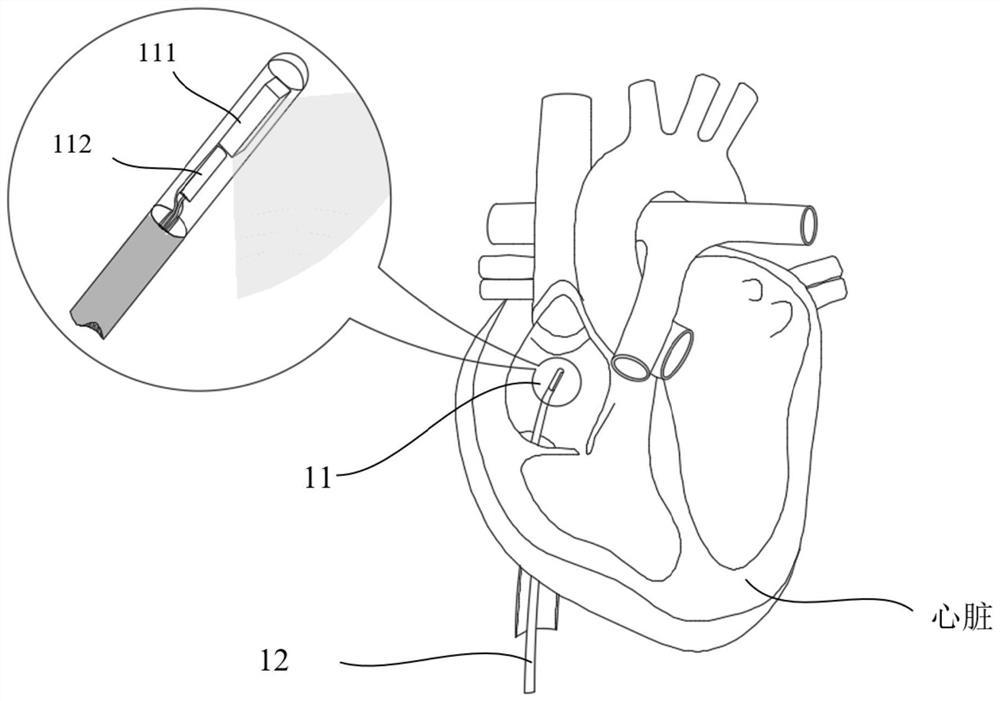
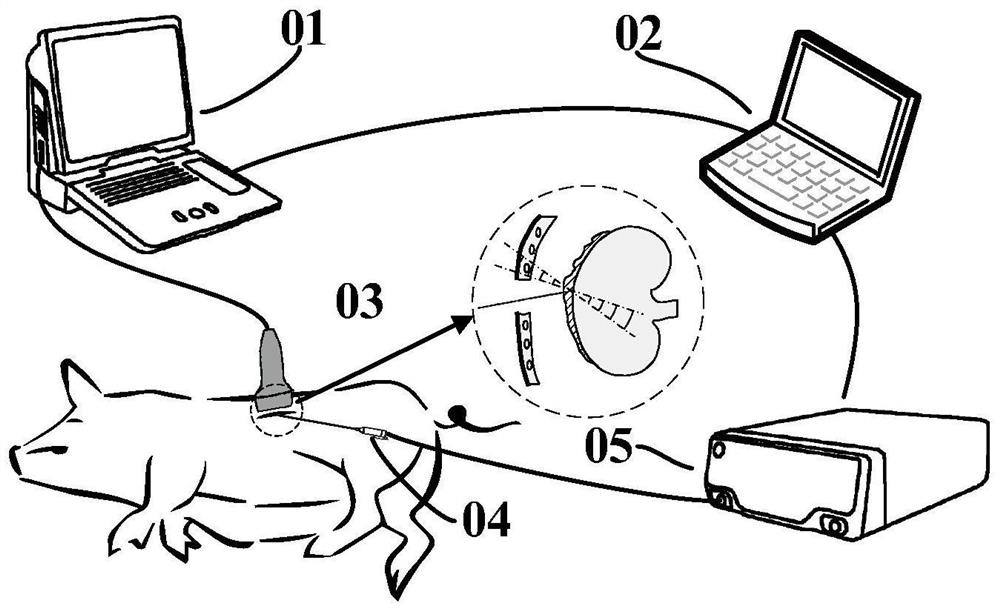
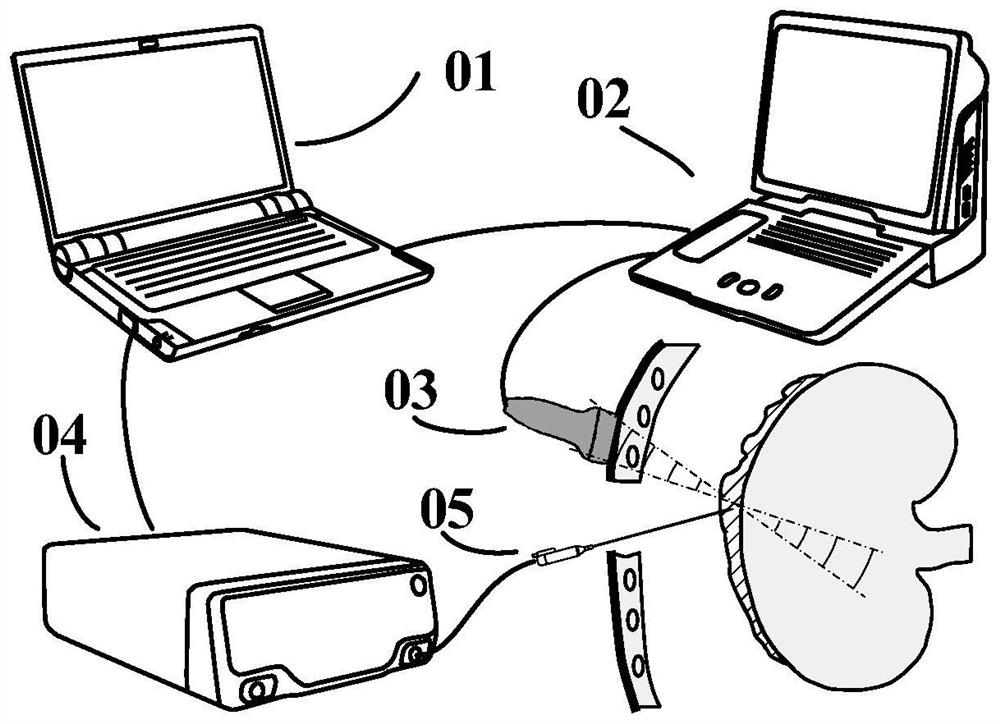
Method and system for measuring mechanical parameters of heart tissue
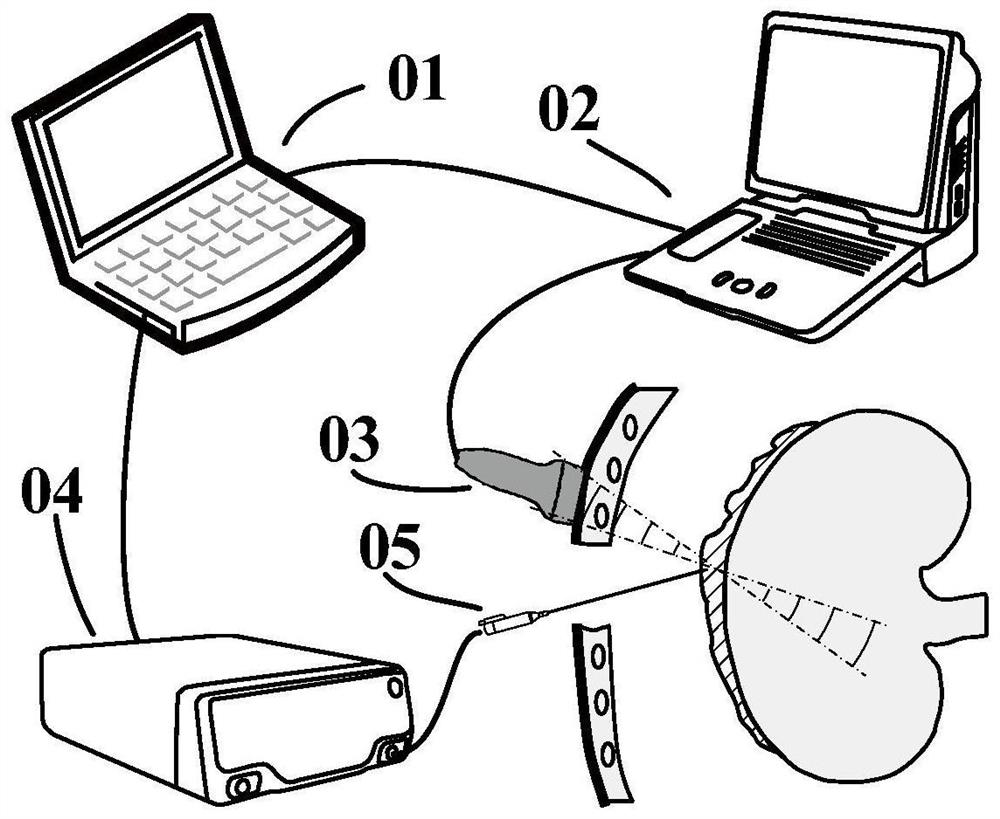
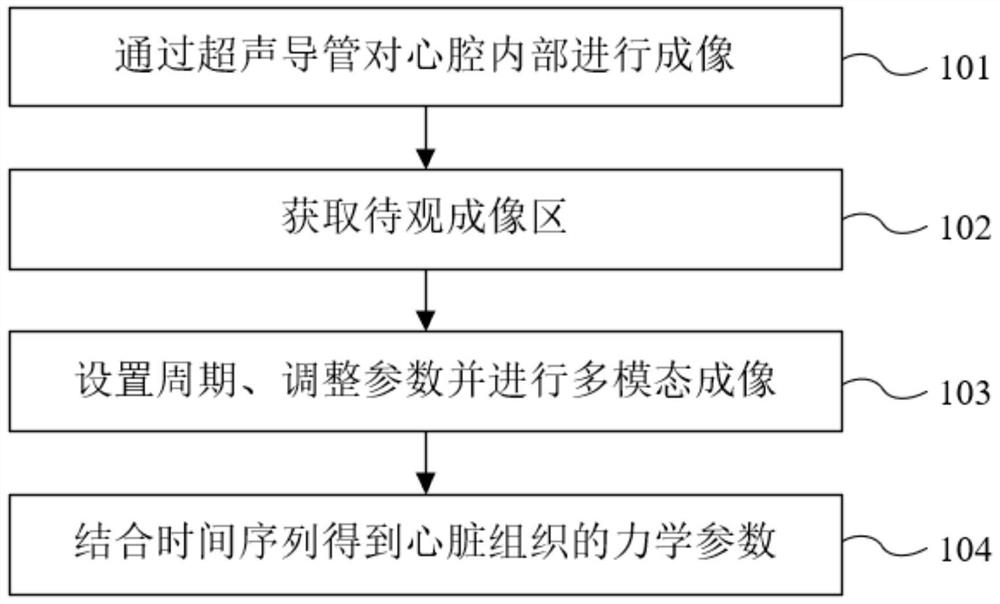
PendingCN114711825ARealize the measurement of mechanical propertiesElastic Full AccessOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryUltrasonic imagingCatheter
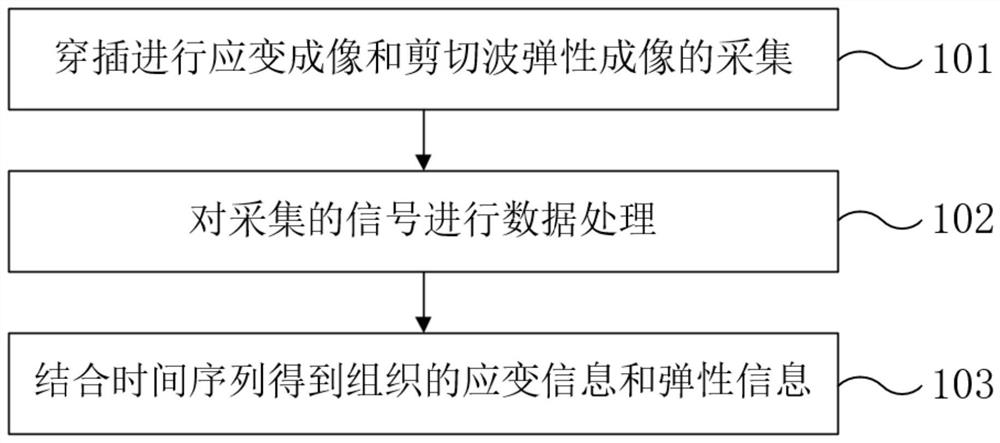
The invention provides a heart tissue mechanical parameter measuring method and system, and the method comprises the steps: inserting an ultrasonic imaging catheter connected with a probe into a heart along a blood vessel, and carrying out the real-time B-mode imaging; the position of the probe is adjusted, and a to-be-imaged area in the heart is obtained; setting an acquisition period and imaging parameters of preset multi-modal imaging acquisition based on the heartbeat period, and performing multi-modal imaging acquisition on the to-be-imaged area; the collected ultrasonic signals are processed, and two-dimensional mechanical parameters related to the heart tissue are obtained; and calculating the mechanical parameters of the heart tissue of the to-be-imaged area in combination with a time sequence acquired by multi-modal imaging. According to the scheme, on the basis of a special ultrasonic imaging sequence, ultrasonic strain imaging and shear wave elasticity imaging can be conducted on the heart tissue, and the mechanical parameters of the heart tissue are obtained according to the collected ultrasonic signals.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSIGHTSONICS CO LTD
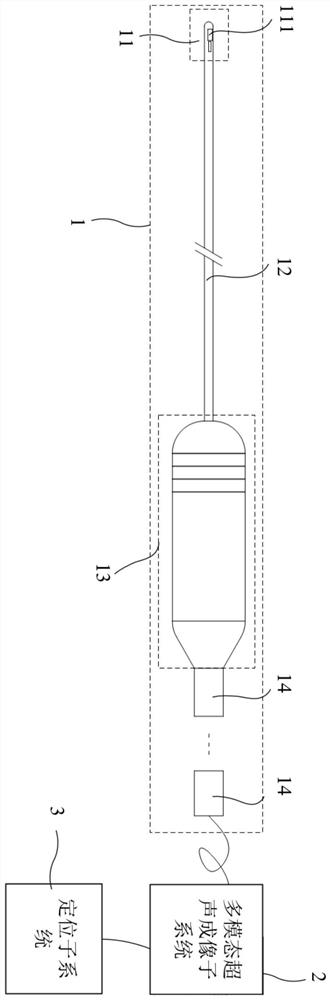
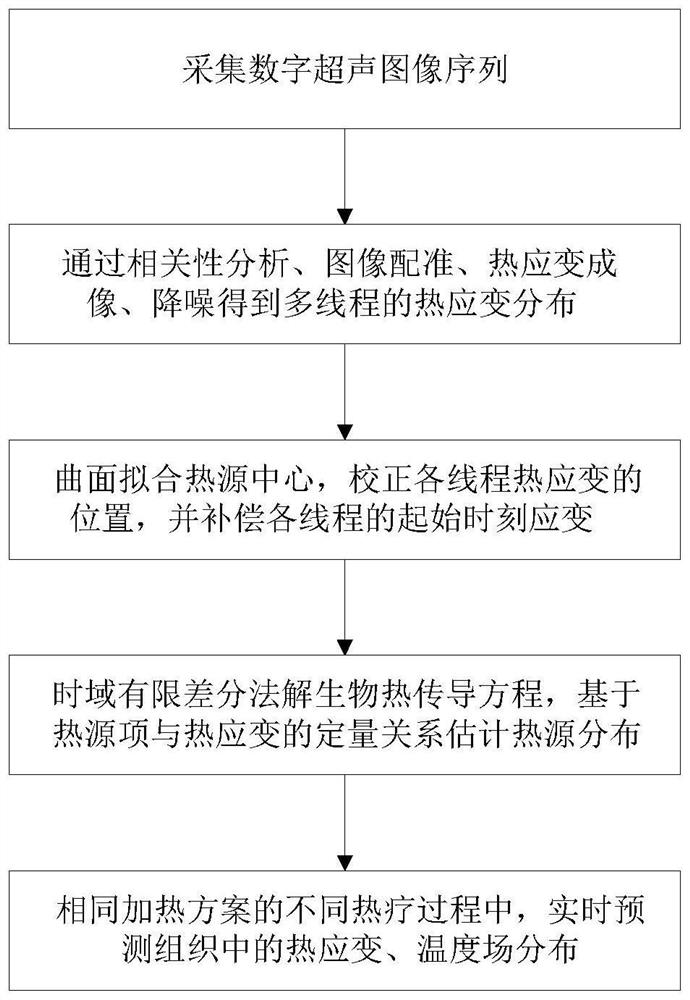
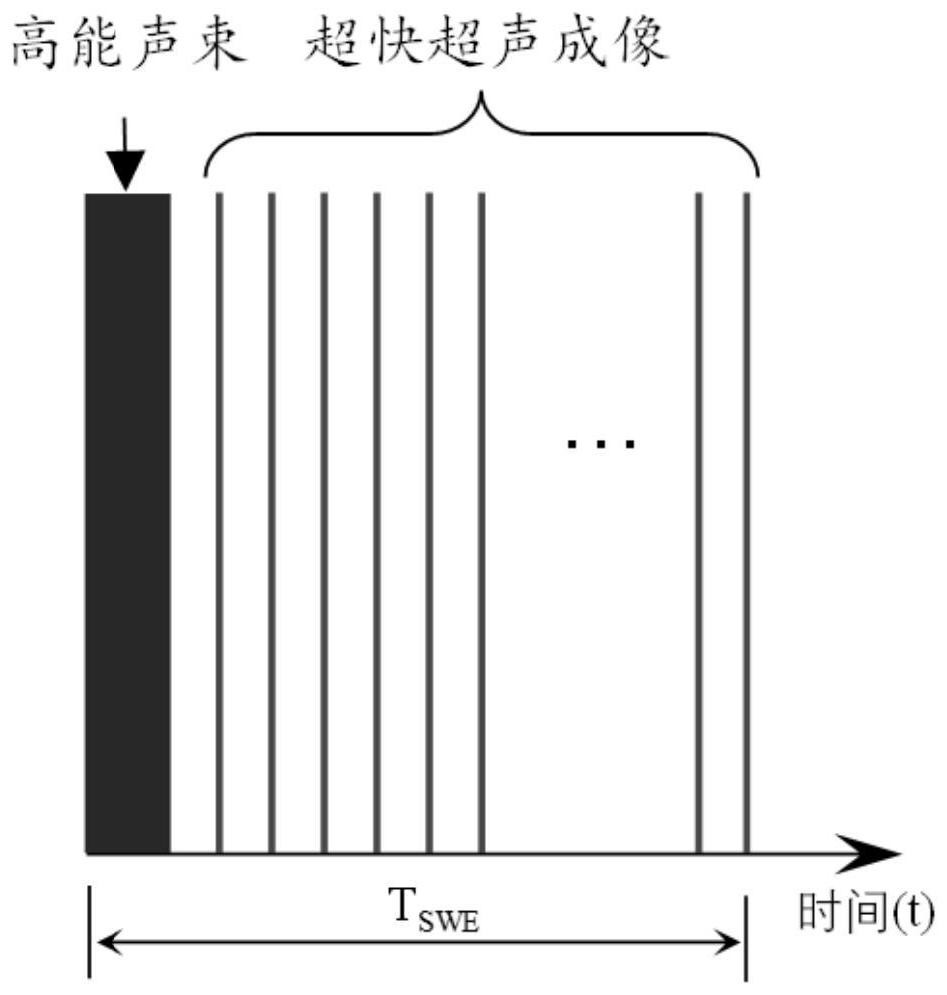
Method and device for estimating in-vivo heat source distribution based on ultrasonic imaging
PendingCN114299125AGood motion inhibitionImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringStrain imaging
The invention discloses a method and device for estimating in-vivo heat source distribution based on ultrasonic imaging, and belongs to the field of medical image processing. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a digital ultrasonic image sequence in a living body, performing multi-thread division, image registration and thermal strain imaging, denoising a thermal strain image based on spatial correlation, fitting a heat source position in the thermal strain image based on a curved surface function, and correcting thermal strain distribution and compensating an initial strain value of each thread according to the heat source position. And then, estimating the heat source distribution by the thermal strain image sequence through a finite difference time domain method. And real-time prediction of thermal strain and temperature field distribution in the tissue is realized for different thermal therapy processes adopting the same heating scheme. According to the method, the spatial distribution of the heat source in the tissue can be effectively estimated without intrusive monitoring equipment, the thermal strain and temperature distribution can be predicted according to the spatial distribution, and an important dose-effect evaluation means can be provided for clinical thermal therapy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method and apparatus to measure tissue displacement and strain
A method for reconstructing displacement and strain maps of human tissue of a subject in vivo or other objects includes applying a mechanical deformation for a target area, imaging tissues while deformation is applied on the target area, measuring the axial and lateral displacements and axial, lateral, and shear strains of tissue in the target area, differentiating between tissues of different stiffness and strain responses, and labeling tissues of different stiffness and strain responses. In some embodiments, displacement and strain imaging are performed using a high-resolution, high-speed, highly-accuracy hierarchy recursive displacement tracking from conventional ultrasound brightness mode images. Particularly, this invention relates to the reconstruction of displacement and strain images from conventional ultrasound B-mode images acquired using any ultrasound machine of different manufacturers without the need to use carrier signals.
Owner:MAHMOUD AHMED M EHAB +1
A non-invasive and high-precision method for elastography of blood vessel walls
InactiveCN104055540BElastic expressionReflect elastic propertiesOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonic imagingStrain imaging
The invention discloses a method of noninvasive high-precision vessel wall elastography. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the radio-frequency data or video data of B-mode ultrasonic imaging of a vessel wall longitudinal section; making an off-line analysis on the acquired radio-frequency data or video data to obtain the displacement field of each frame of radio-frequency data or video data; filtering the displacement fields of the radio-frequency data or video data with an FIR two-dimensional difference filter to obtaining strain components on the longitudinal section, including a strain component Epsilonxx in the axial direction of a ultrasonic emission beam, a lateral strain component Epsilonzz and a shearing strain component Epsilonxz; giving a Von Mises strain projection parameter ZetaVM-longiProj and a calculation formula thereof, and imaging the Von Mises strain projection parameter ZetaVM-longiProj to achieve noninvasive high-precision vessel wall elastography. Precise and quantitative vessel wall elastography can be achieved through the method, and the result is superior to those of the conventional other vessel wall strain imaging methods.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultrasonic strain imaging device with selectable cost-function
ActiveUS9078592B2High correlationEnhance the imageOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPre deformationStrain imaging
An elasticity measuring system determines tissue displacement between a pre-deformation and post-deformation image by a matching process using a cost function accepting as its arguments continuity of the tissue motion and correlation of the tissue in making the block matching. The invention allows the selection among different cost functions for different imaging situations or tissue types, to provide improved displacement calculations using a priori knowledge about the tissue and structure of tissue interfaces or information derived during the scanning process.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System and device for tumor characterization using nonlinear elastography imaging
The present invention provides a method and a device to image and characterize human tumors, and to classify the tumors as either malignant or benign. The method includes using a multi-compression technique upon the tissue or organ combined with a 3D ultrasound strain imaging of the compressed tissue or organ for acquiring raw data and analyzing the raw data using a computer processing unit equipped with a nonlinear biomechanical tissue model for tumor classification. A device is provided having a compression stage for delivering multi-compression with continuous force measurements, and a 3D ultrasound transducer strain imaging probe, wherein the imaging probe and the compression stage are in communication with a computer processing unit.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
Assessment of Myocardial Infarction by Real-Time Ultrasound Strain Imaging
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and apparatus for real-time and robust strain imaging
ActiveUS9687213B2Improve robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityElastography
A robust algorithm is disclosed for real-time strain imaging. The method can be implemented on conventional medical imaging modalities such as ultrasound, MRI, etc. The pre- and post-deformation images, acquired by an imaging system, are used by the algorithm to produce the strain map. Deformation can be performed by any available means, such as an existing part of the imaging device (as in freehand elastography) or a separate compression fixture. Due to the computational efficiency of the algorithm, any conventional processing platform, including personal computers, tablet PCs, and smart phones can be employed for strain imaging, to construct an ultra-portable strain imaging system.
Owner:SHARAFAT AHMAD R +1
Multi-mode ultrasonic elastography method and system
PendingCN114748095ASolving Elasticity ProblemsOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTissue elasticityRadiology
Owner:SHENZHEN INSIGHTSONICS CO LTD
Multi-thread fusion living body ultrasonic thermal strain imaging method and device
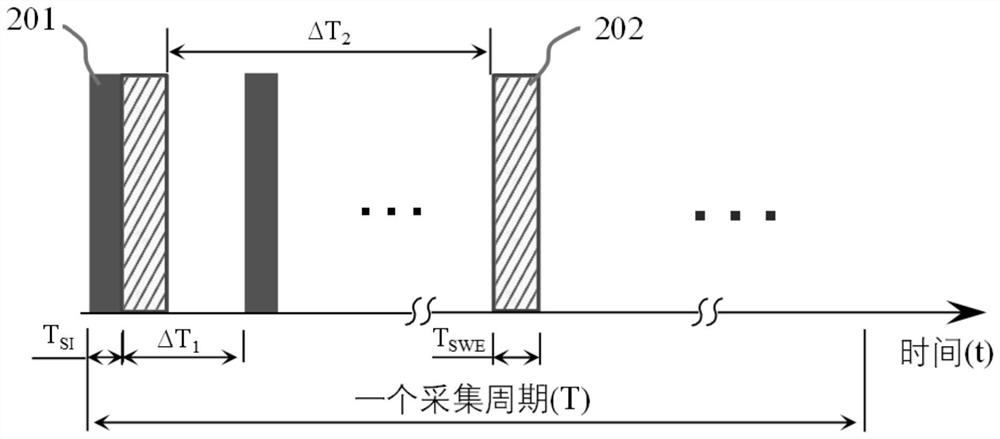
PendingCN114332065ADoes not affect workImprove reliabilityImage analysisImage manipulationStrain imaging
The invention discloses a multi-thread fusion living body ultrasonic thermal strain imaging method and device, and belongs to the field of medical image processing. According to the method, after an ultrasonic image sequence is collected, images are divided into a plurality of threads according to correlation, and image registration and thermal strain imaging are carried out. Furthermore, a biological heat conduction equation solved by a time domain finite difference method is used as a prediction model, and a self-adaptive Kalman filter is used for filtering the thermal strain sequence. And finally, fusing the thermal strain of each thread according to a scalar weighted linear minimum variance information fusion criterion. According to the method, the defects that in existing living body thermal strain imaging, an imaging result depends on a single motion phase, physiological motion is difficult to accurately compensate, so that thermal strain contour distortion and a poor signal-to-noise ratio are caused, and conventional spatial filtering is at the cost of sacrificing spatial resolution are overcome, and a living body thermal strain imaging result which is accurate, high in robustness and high in temporal-spatial resolution can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Non-invasive estimation of the mechanical properties of the heart
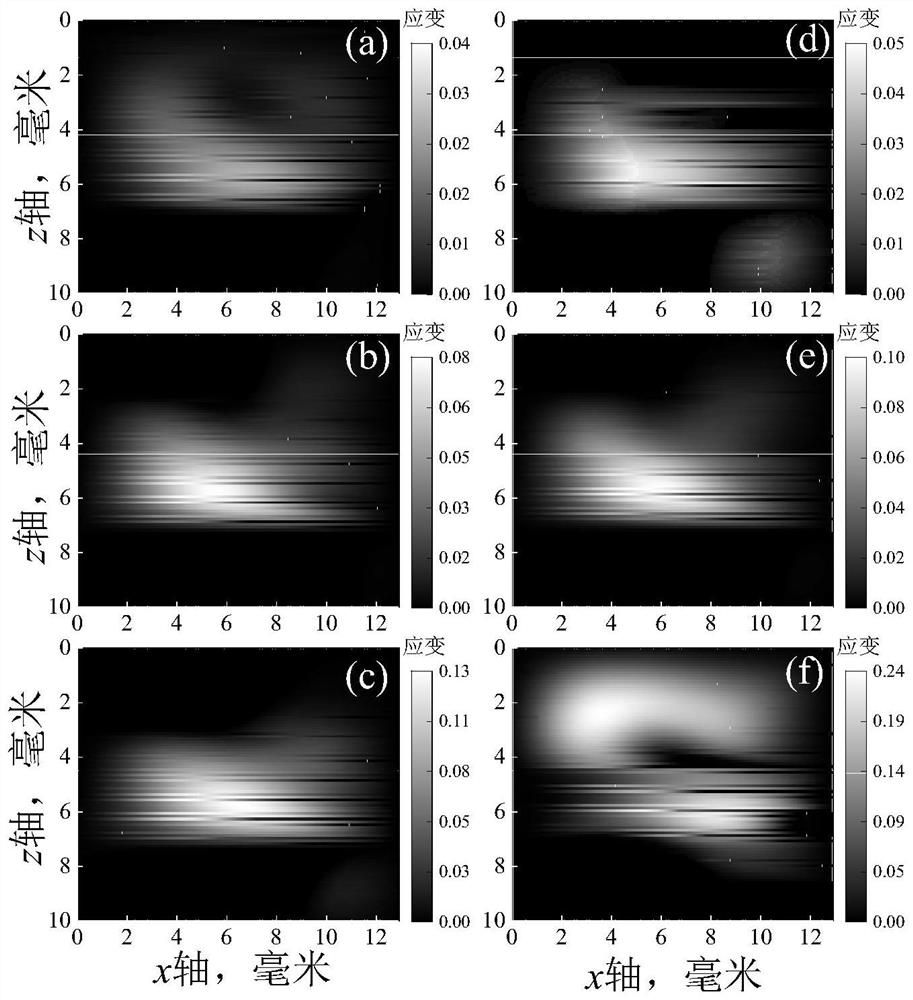
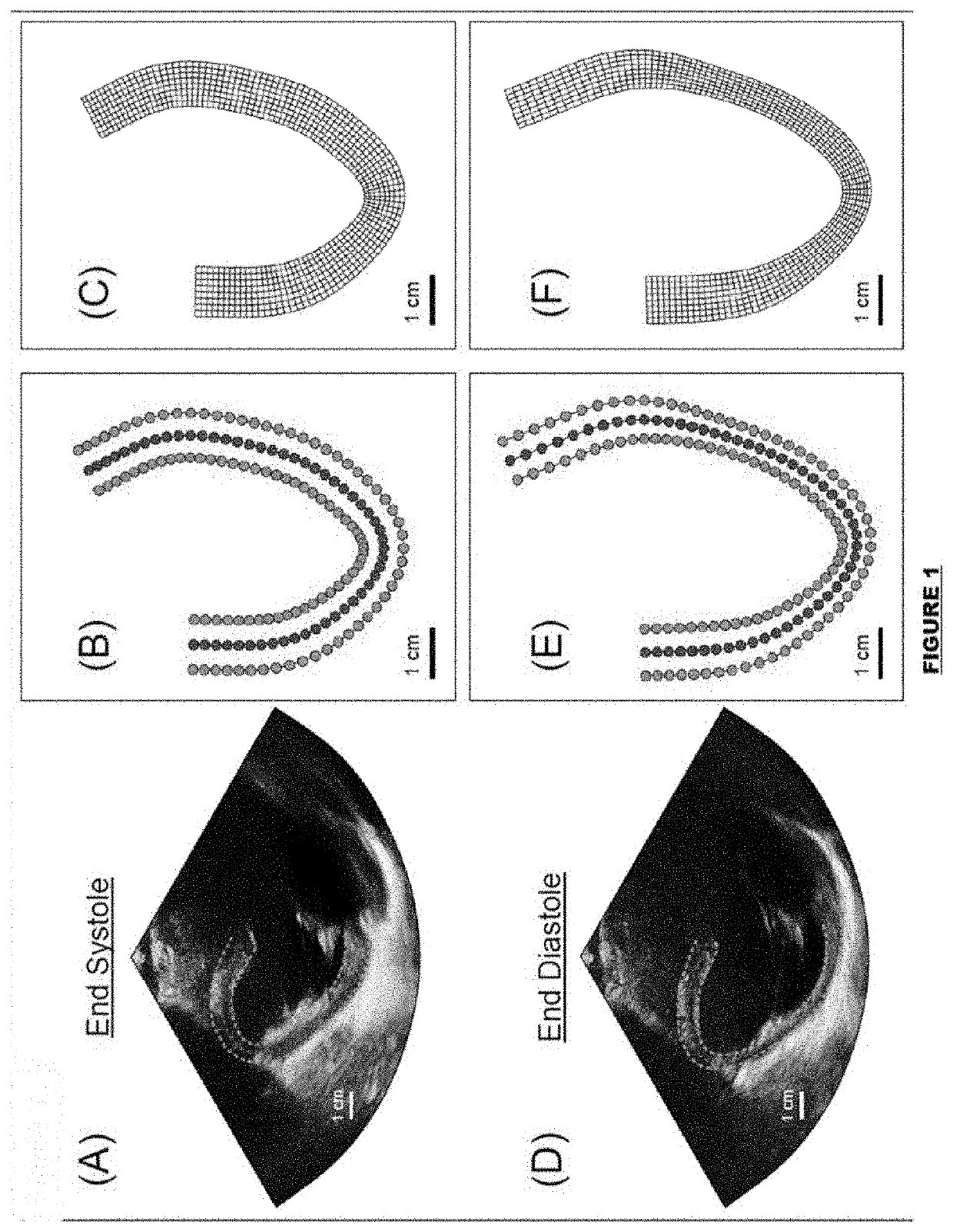
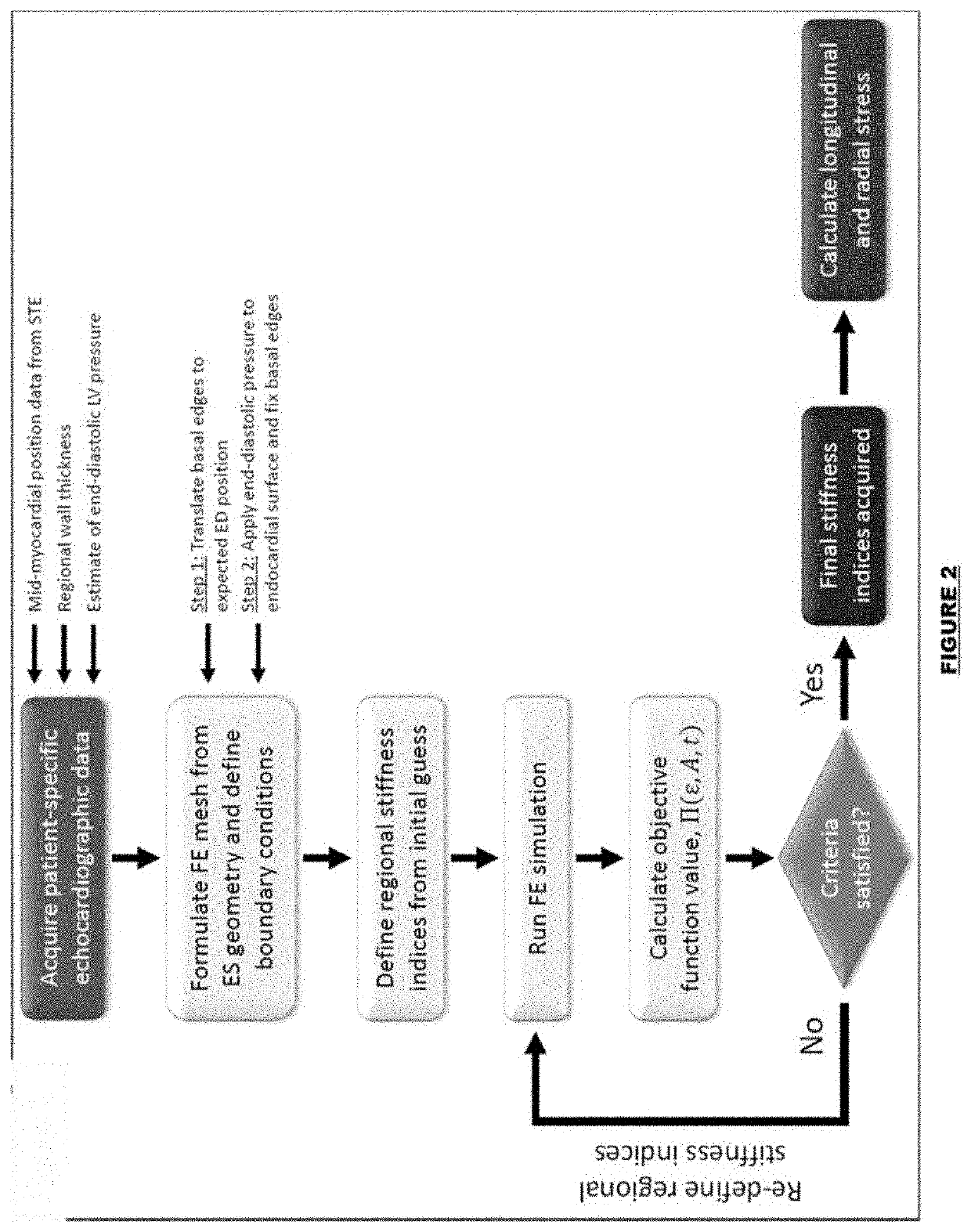
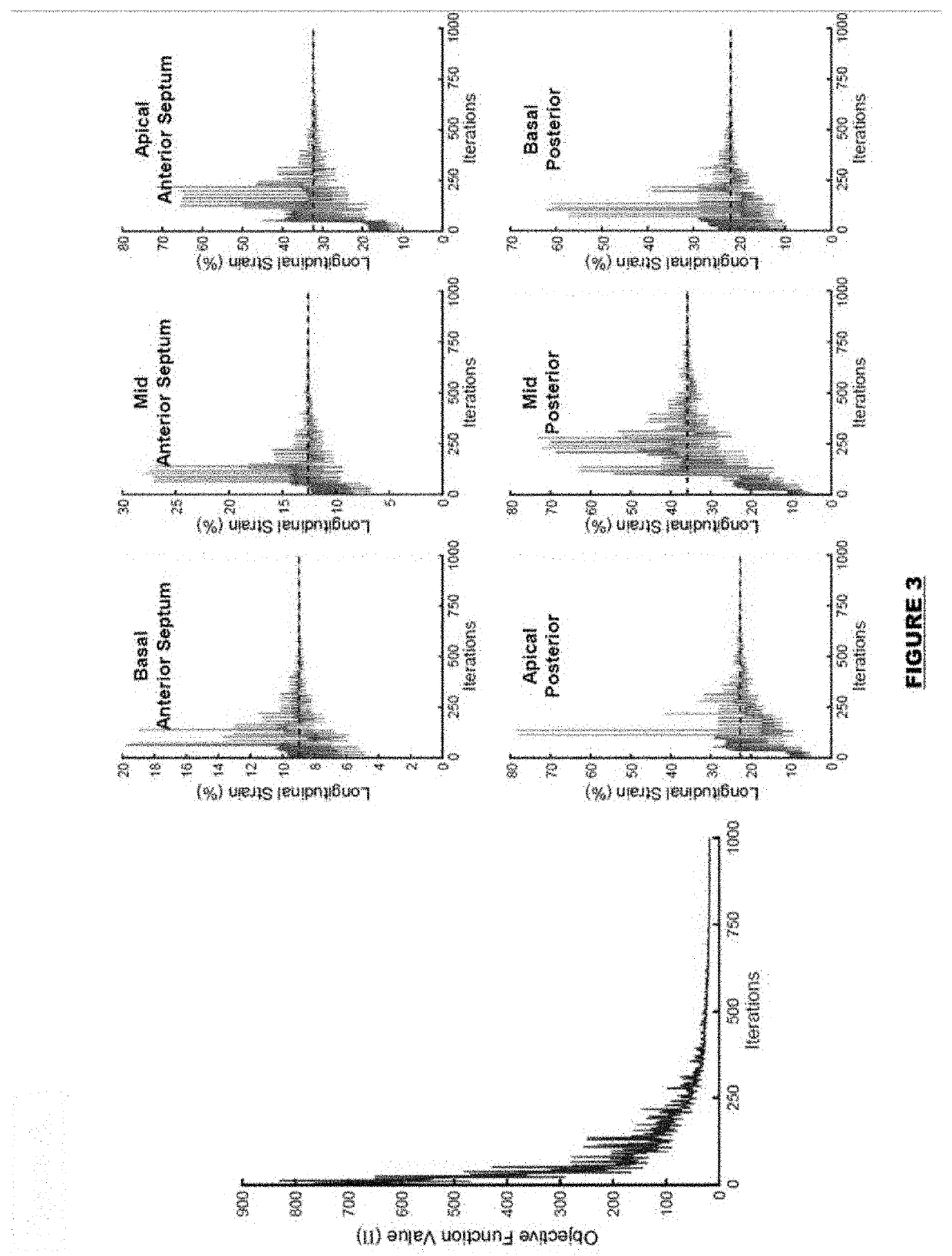
ActiveUS20200100768A1Easy to implementOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsCardiac muscleStrain imaging
Methods and systems for utilizing myocardial strain imaging in an inverse framework to identify mechanical properties of the heart and to determine structural and functional milestones for the development and progression to heart failure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com