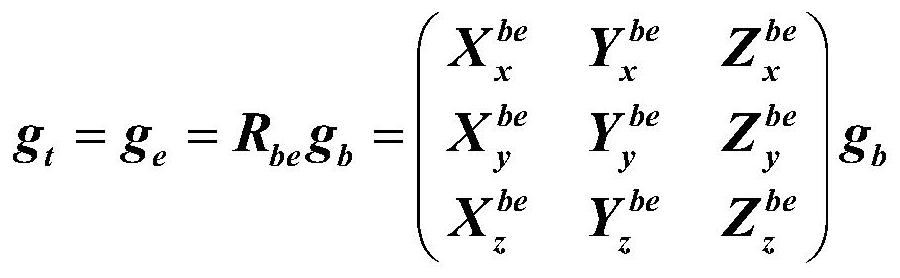Patents
Literature
66 results about "Physiological movement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physiological movements or normal movements are the natural movements that occur in human joints. They are also known as osteokinematic movements. The study of these movements is known as kinesiology.
Movable disc implant
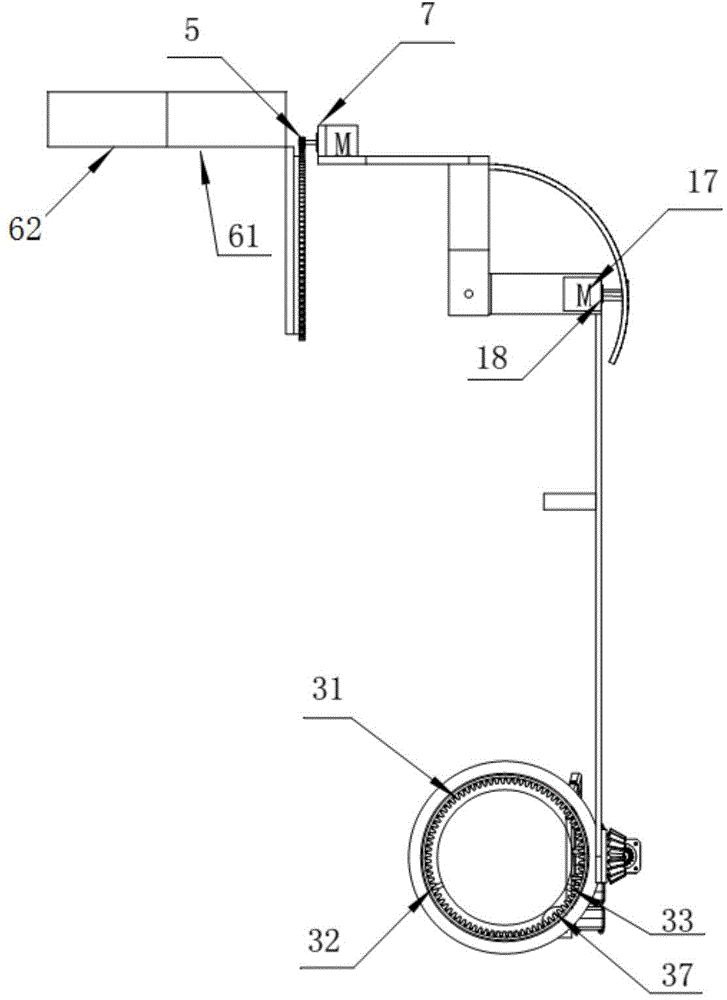
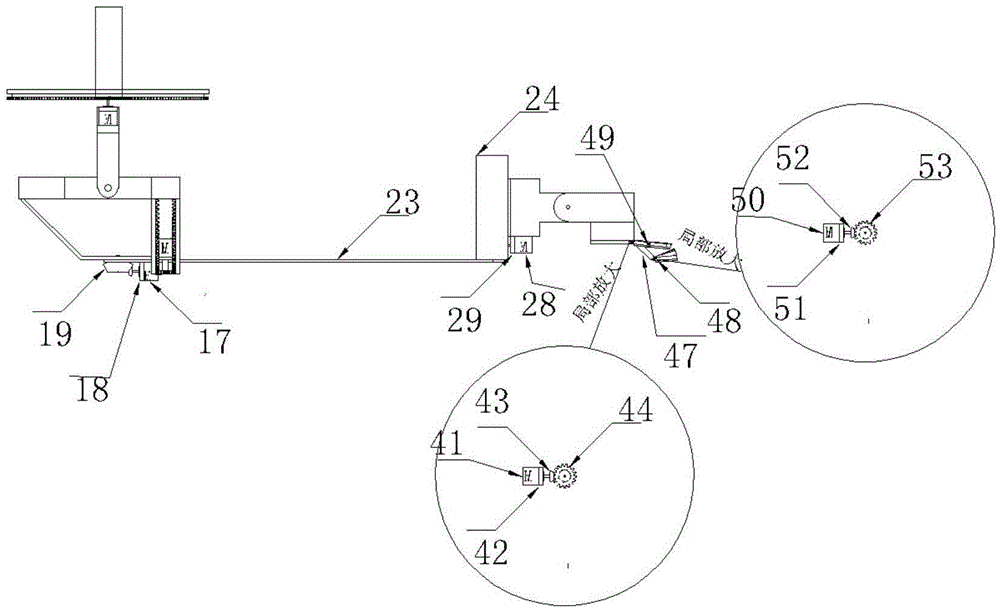
ActiveUS20060116768A1Maintain positionReduce noiseDiagnosticsJoint implantsPhysiological movementBiomedical engineering
A disc implant is provided which maintains intervertebral spacing and stability within the spine. In an embodiment, a disc implant may include three or more components. Components of the implant may imitate certain physiological movements associated with a healthy spine. In certain embodiments, the components of the implant may limit physiological movements to within certain ranges, imitating normal spinal movements.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
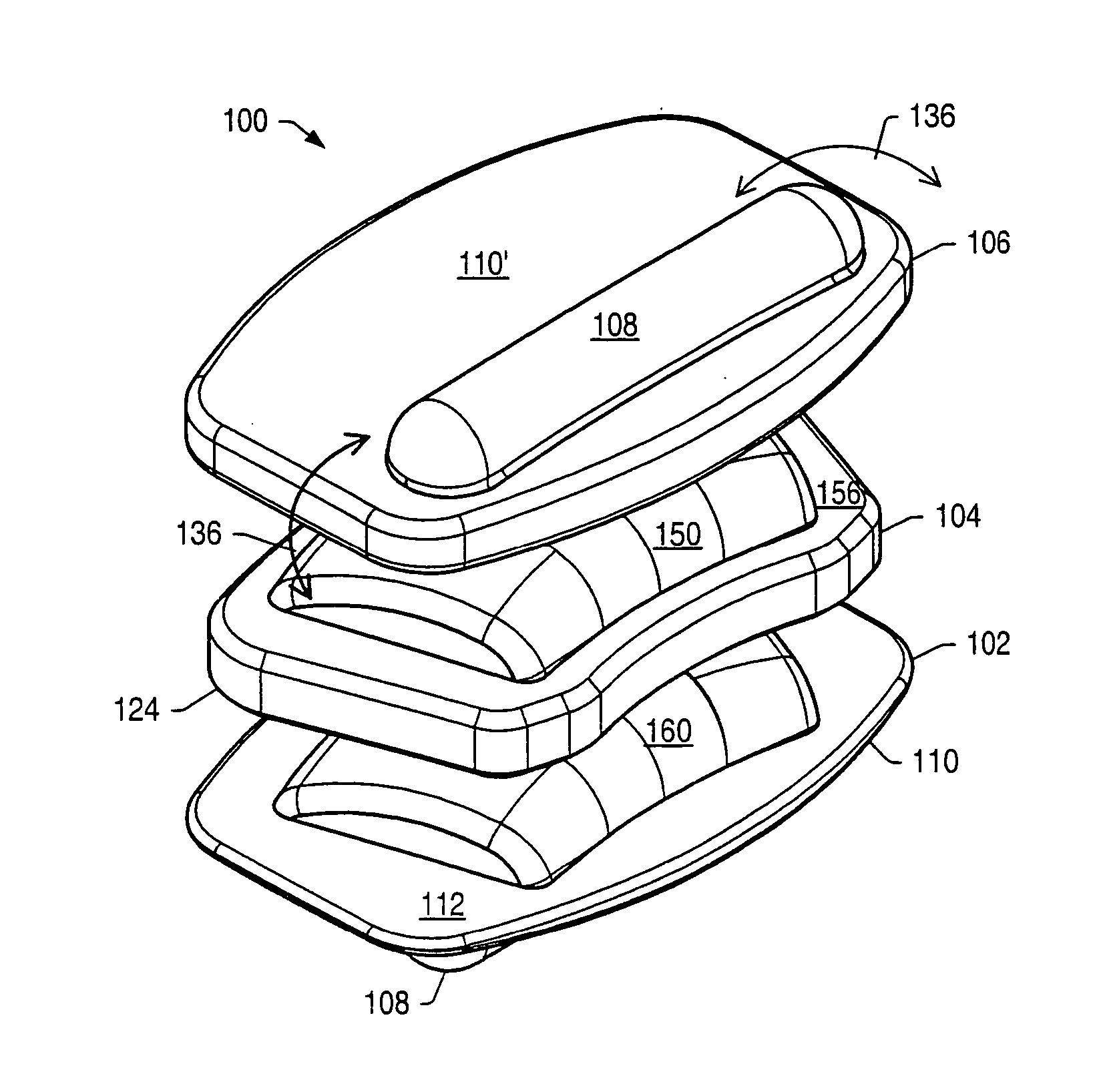
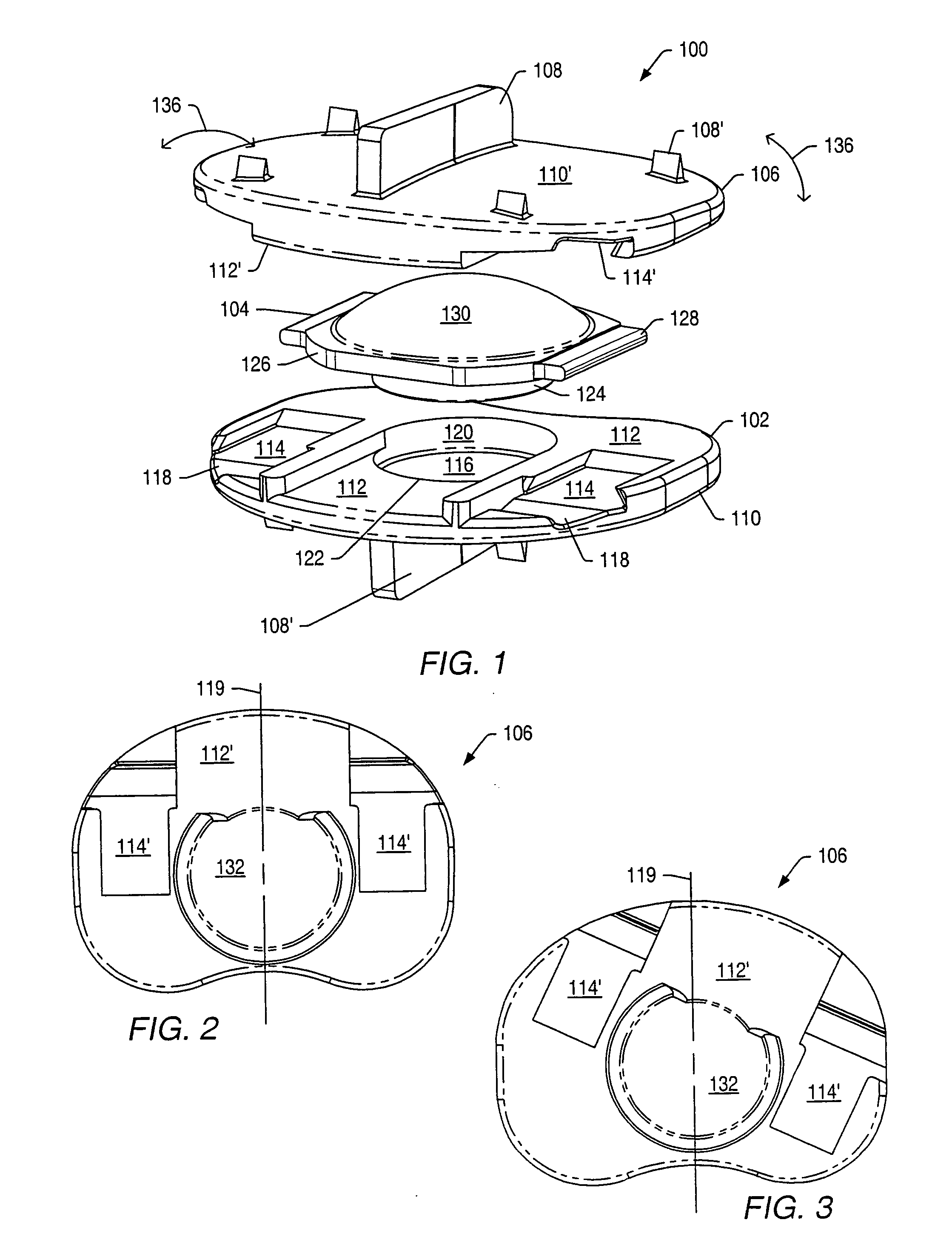
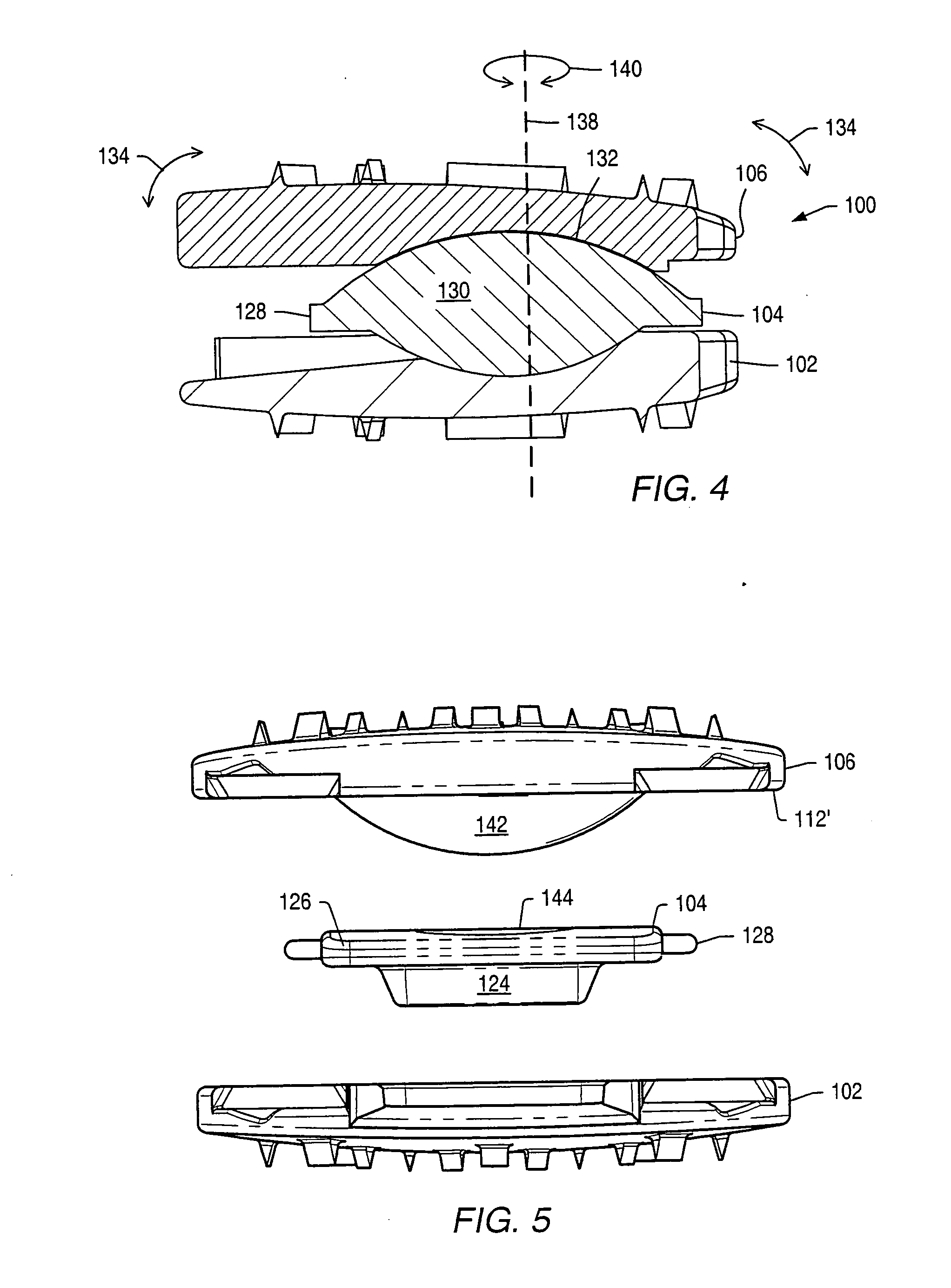
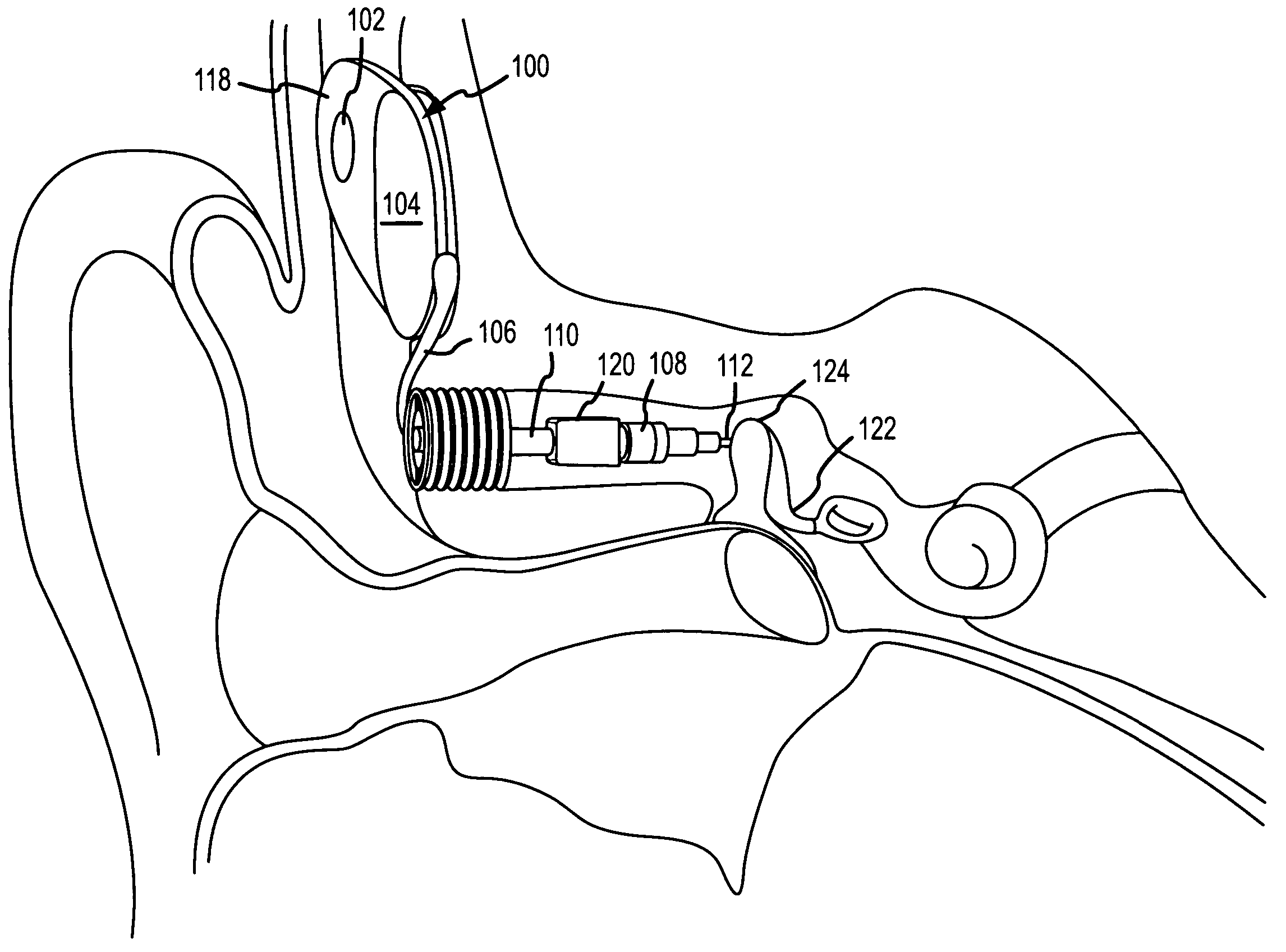
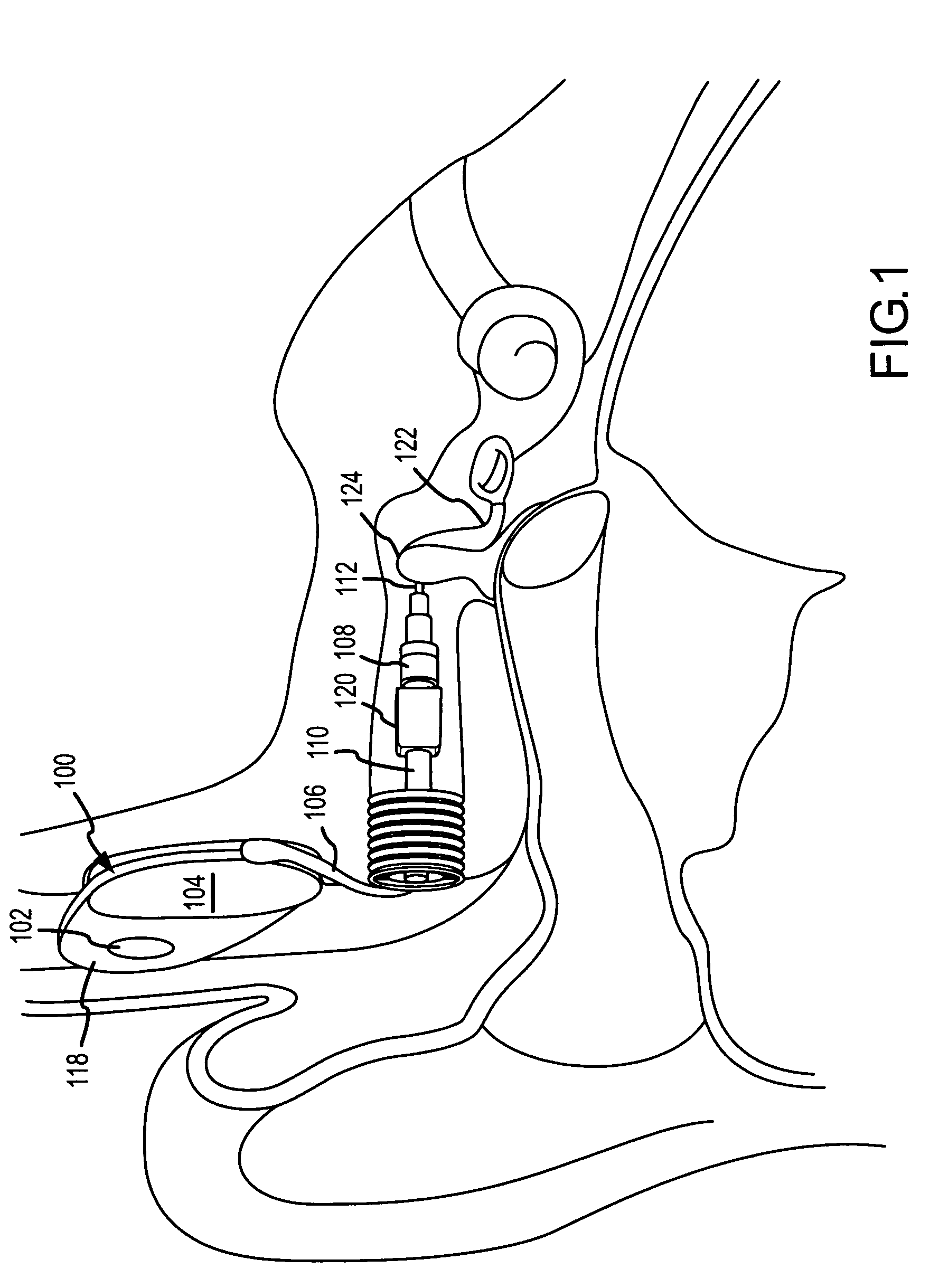
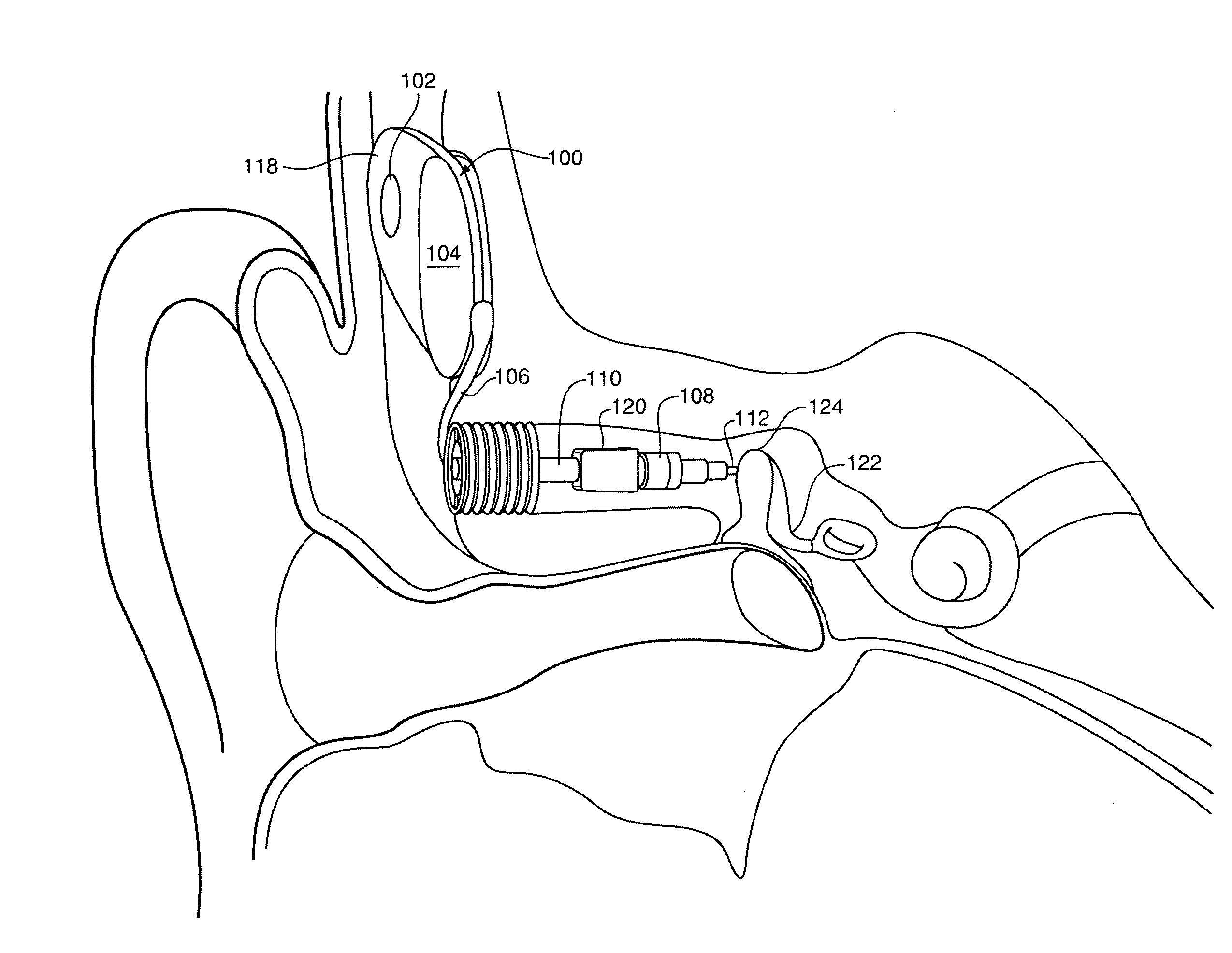
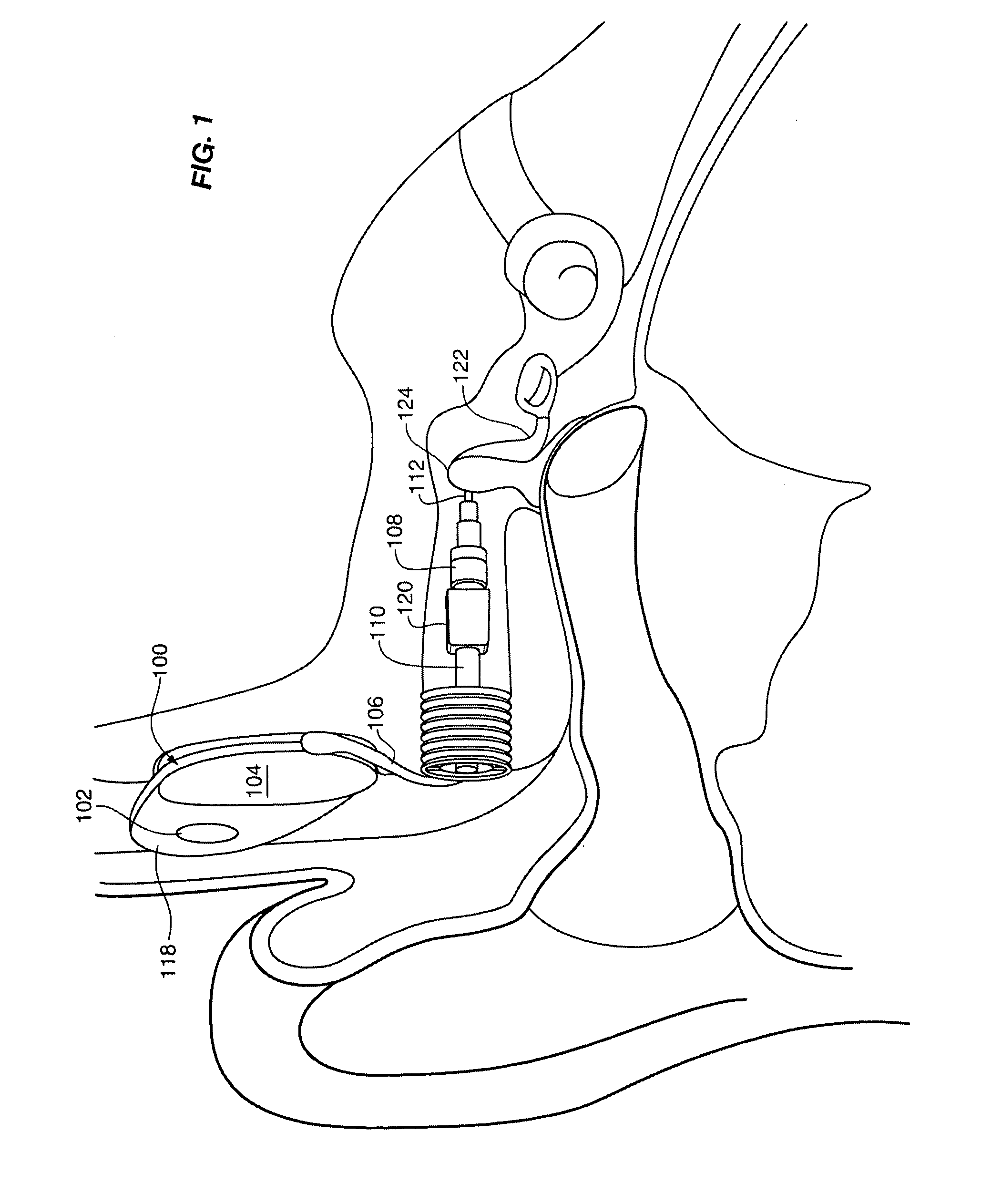
Implantable hearing aid transducer interface
InactiveUS20050101830A1Additional transducerGuaranteed uptimeDeaf-aid setsPhysiological movementTransducer
An implantable hearing aid transducer interface disposable between an implantable transducer and a mounting apparatus and having at least a portion that is displaceable in response to a predeterminable range of transducer movement. According to one aspect of the invention, the predeterminable range of transducer movement includes movement in response to a physiological movement of an auditory component that results in pressure on the implantable transducer. In this case, the compliant interface permits adaptive movement of the implantable transducer in response to the pressure to maintain a desired interface between the implantable transducer and an auditory component. According to another aspect, the predeterminable range of transducer movement may be transducer vibration resulting from an acoustic stimulation of an auditory component by the implantable transducer. In this case, the compliant interface reduces the transmission of transducer vibration over a feedback path to a microphone of a hearing aid.
Owner:OTOLOGICS
Altering the stiffness, size and/or shape of tissues for breathing disorders and other conditions
InactiveUS20050121039A1Inhibiting a sleep-related breathing disorder of a patientMitigates the sleep-related breathing disorderPhysical therapyTeeth fillingDiseasePhysiological movement
Medical devices, systems, and methods mitigate a variety of disorders, including sleep-related breathing disorders. A stiffness, shape, and / or size of a reinforced tissue structure can be altered by applying a magnetic field and / or electrical field. The upper airway can be remodeled at night while maintaining physiological movement (such as swallowing, speaking, singing, and the like) when awake. Biasing of the tissue structures may also be employed.
Owner:PAVAD MEDICAL
Electrically activated alteration of body tissue stiffness for breathing disorders
InactiveUS20050115572A1Mitigates sleep-related breathing disorderMitigate sleep-related breathing disorderPhysical therapyTeeth fillingElectricityDisease
Medical devices, systems, and methods mitigate a variety of disorders, including sleep-related breathing disorders. A stiffness, shape, and / or size of a reinforced tissue structure can be altered by applying a magnetic field and / or electrical field. The upper airway can be remodeled at night while maintaining physiological movement (such as swallowing, speaking, singing, and the like) when awake. Biasing of the tissue structures may also be employed.
Owner:PAVAD MEDICAL
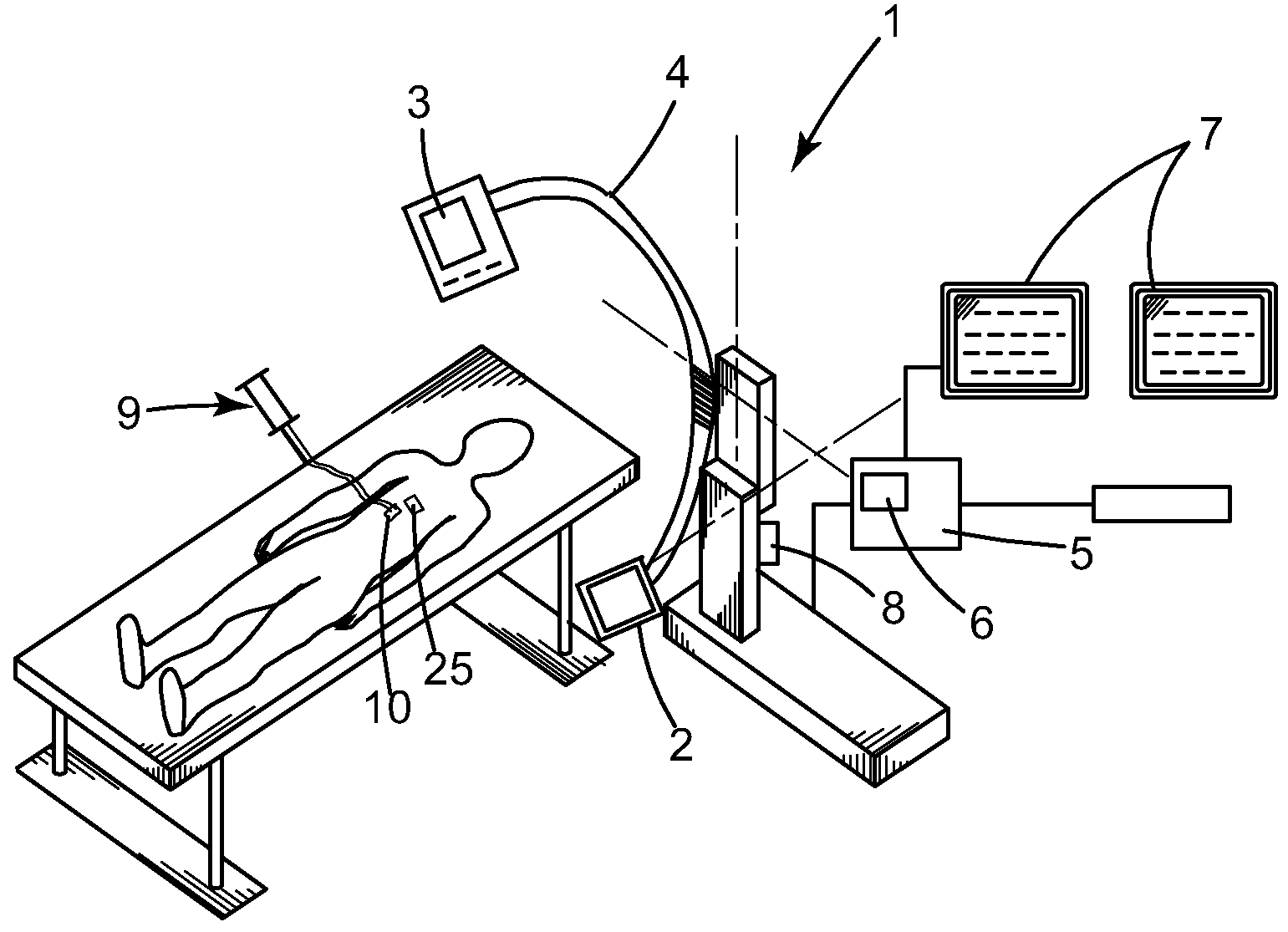
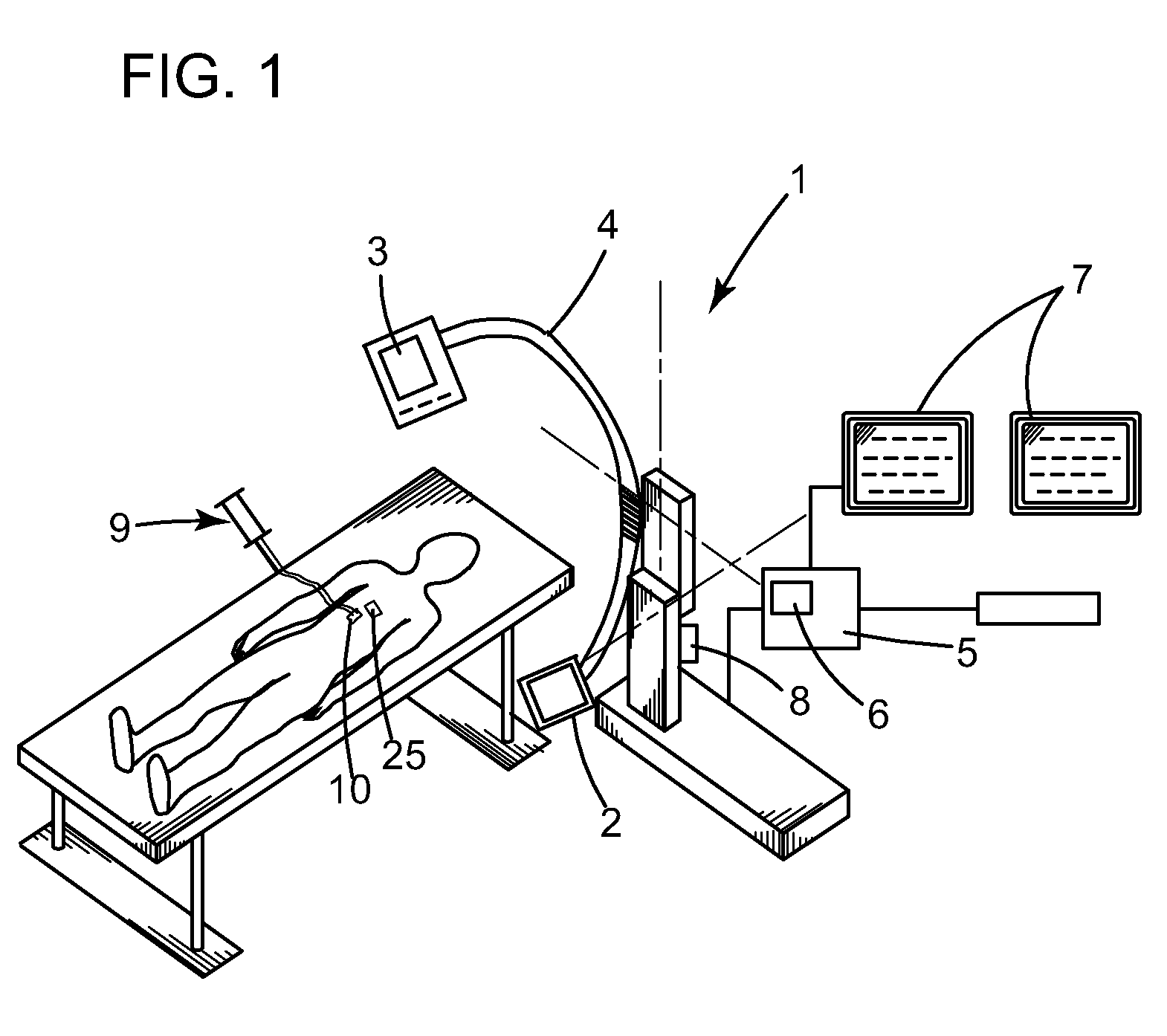
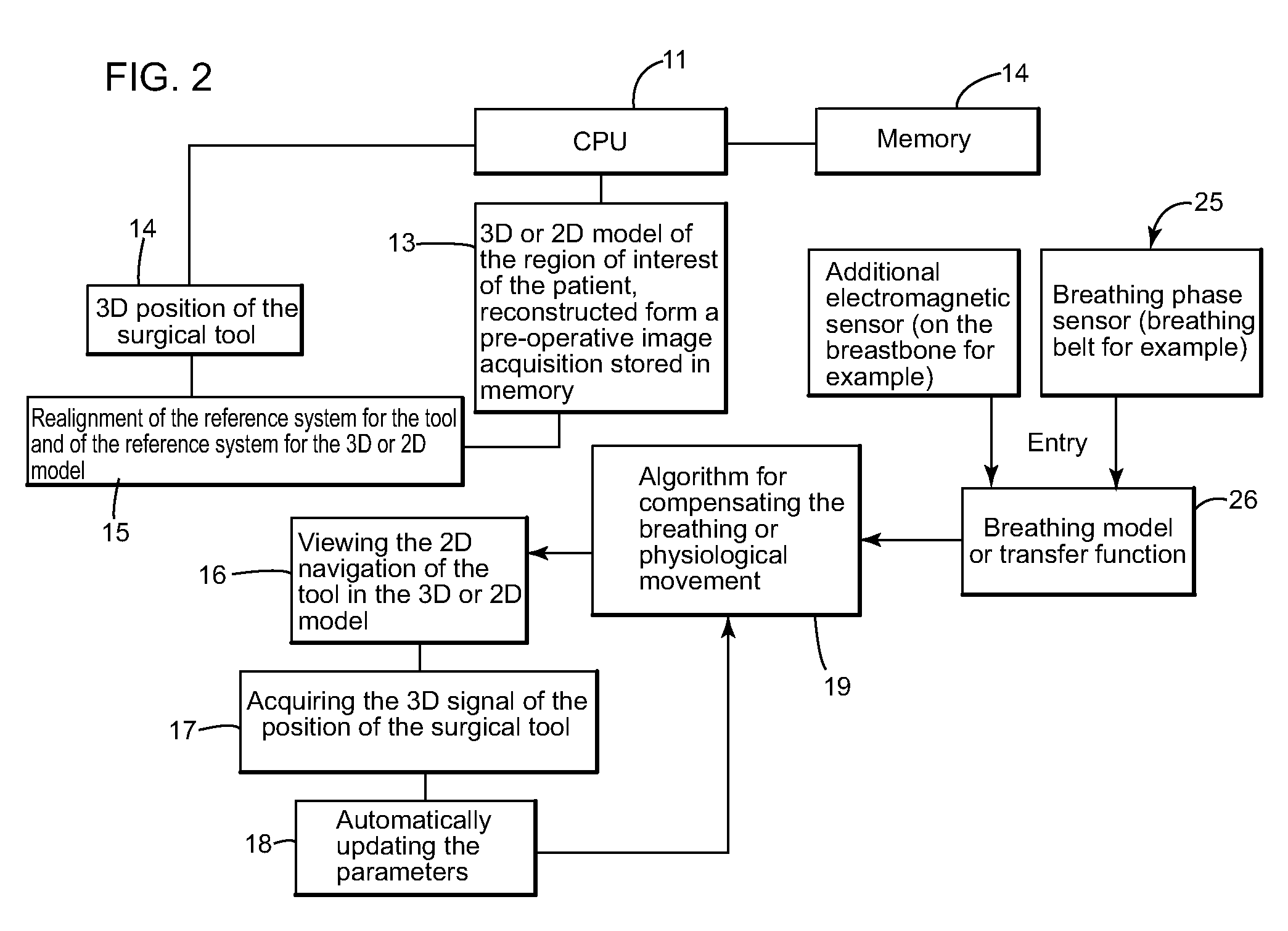
Method and device for guiding a surgical tool in a body, assisted by a medical imaging device
InactiveUS20090216114A1Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringReal time navigationPhysiological movement
A method and device for real time navigation of a surgical tool handled by an operator in a region of interest of a body itself subject to at least one physiological movement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
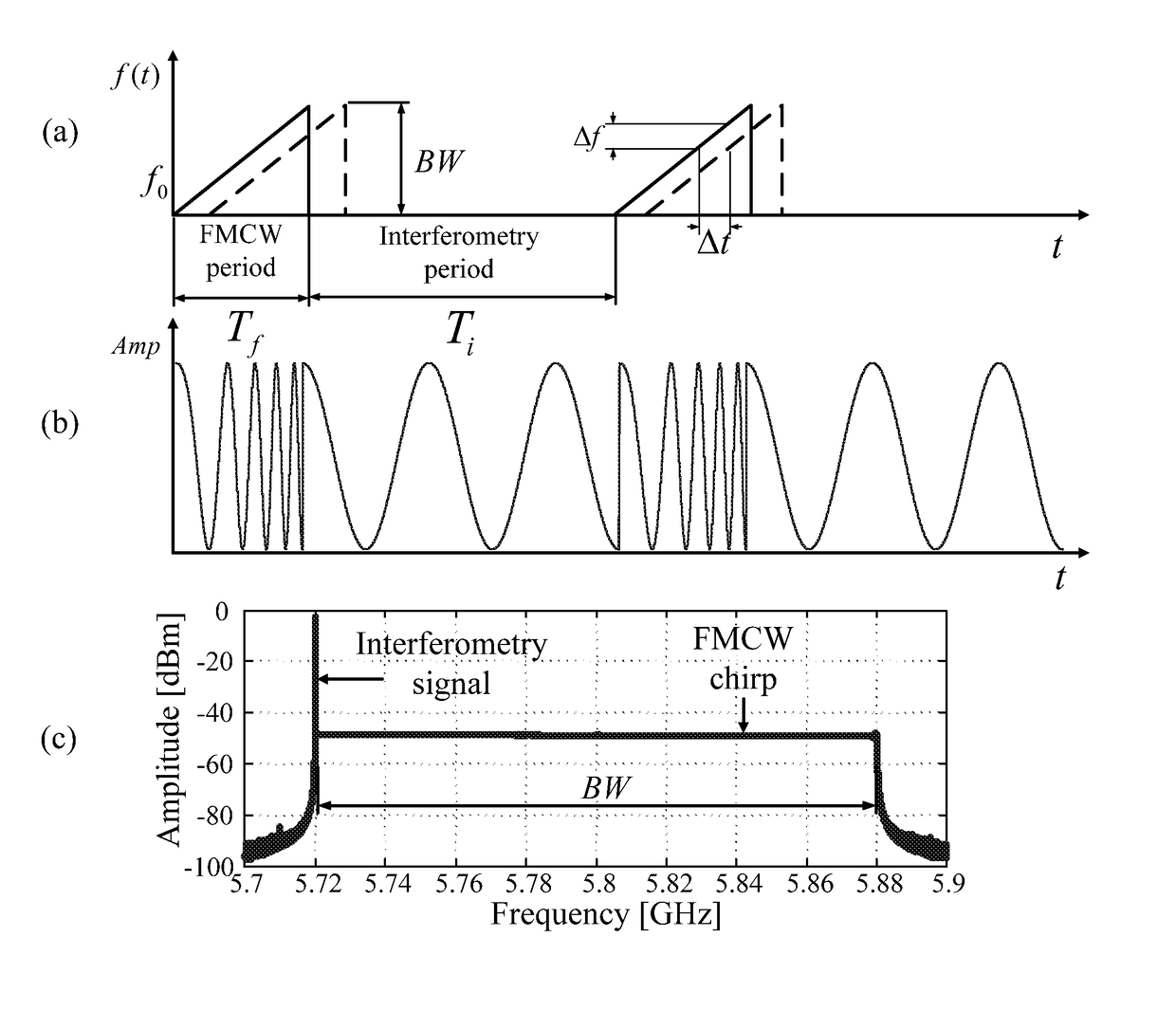
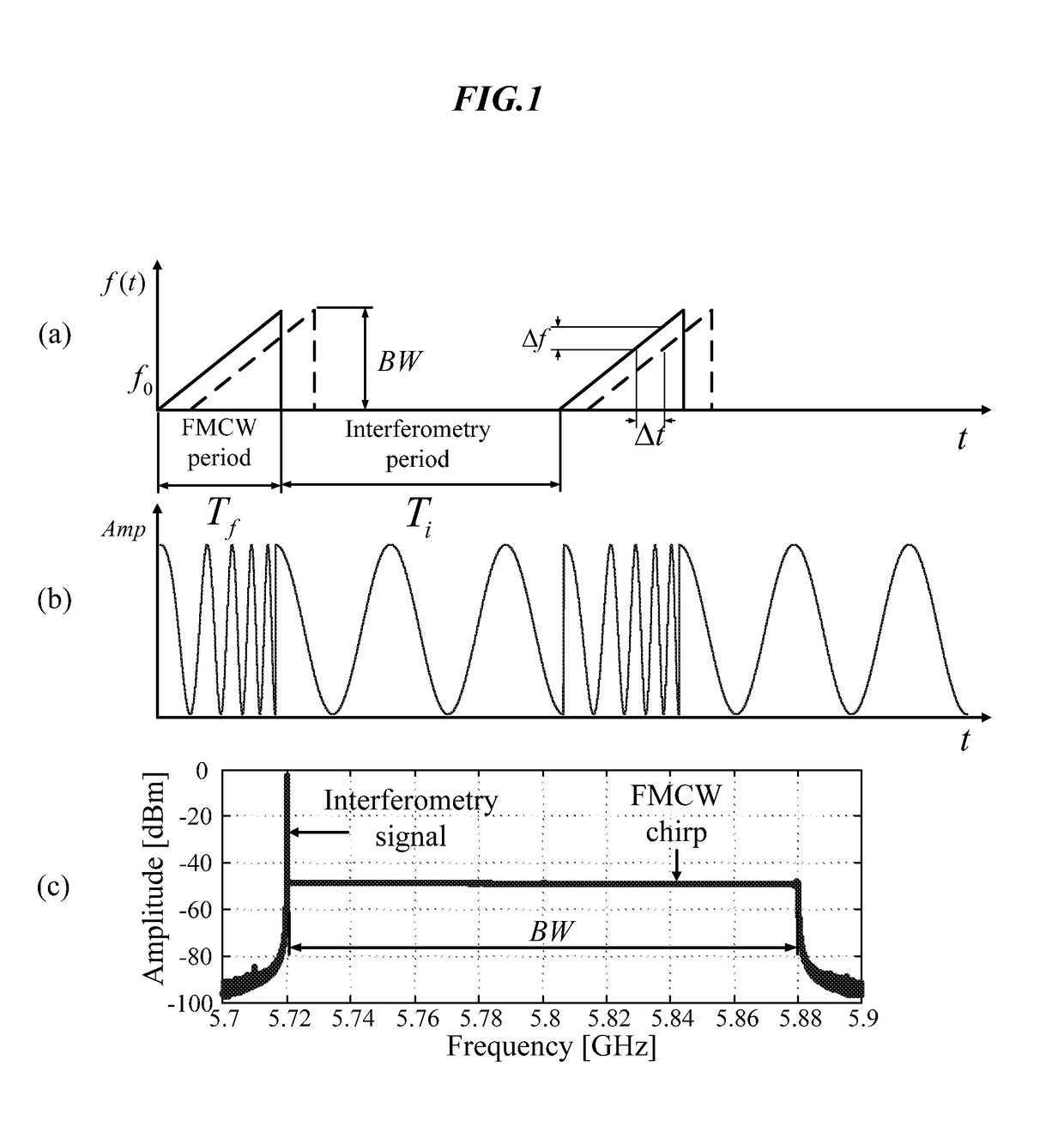
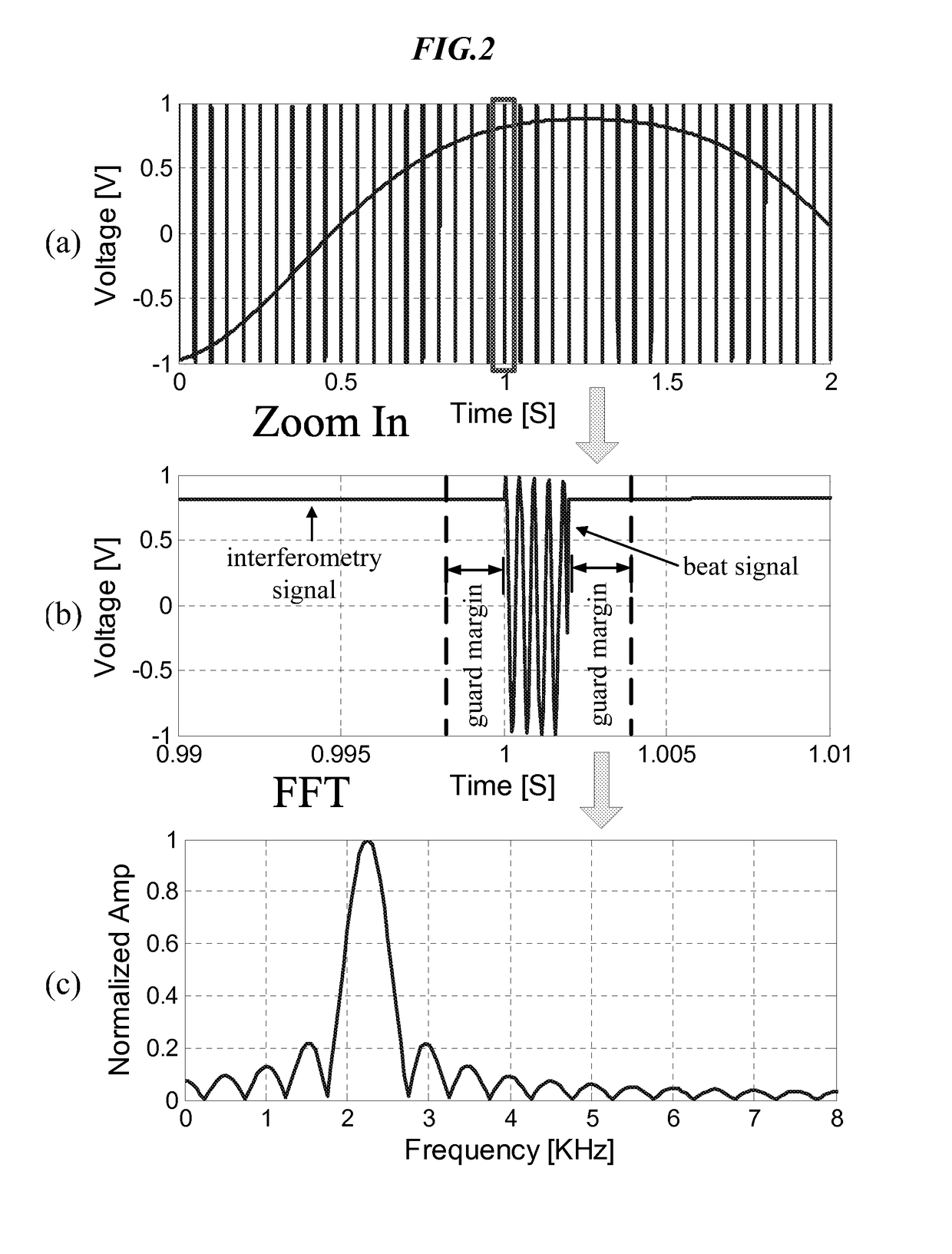
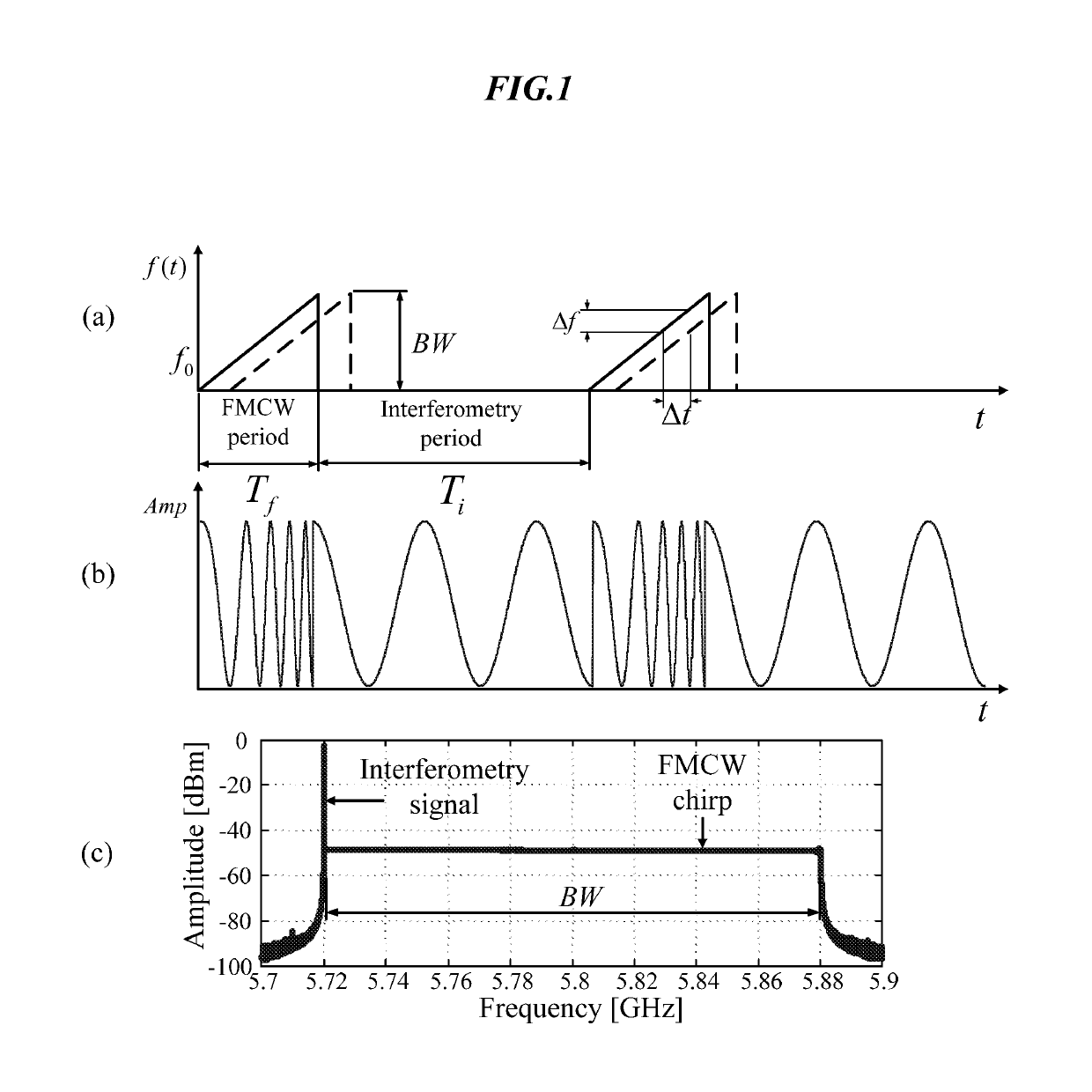
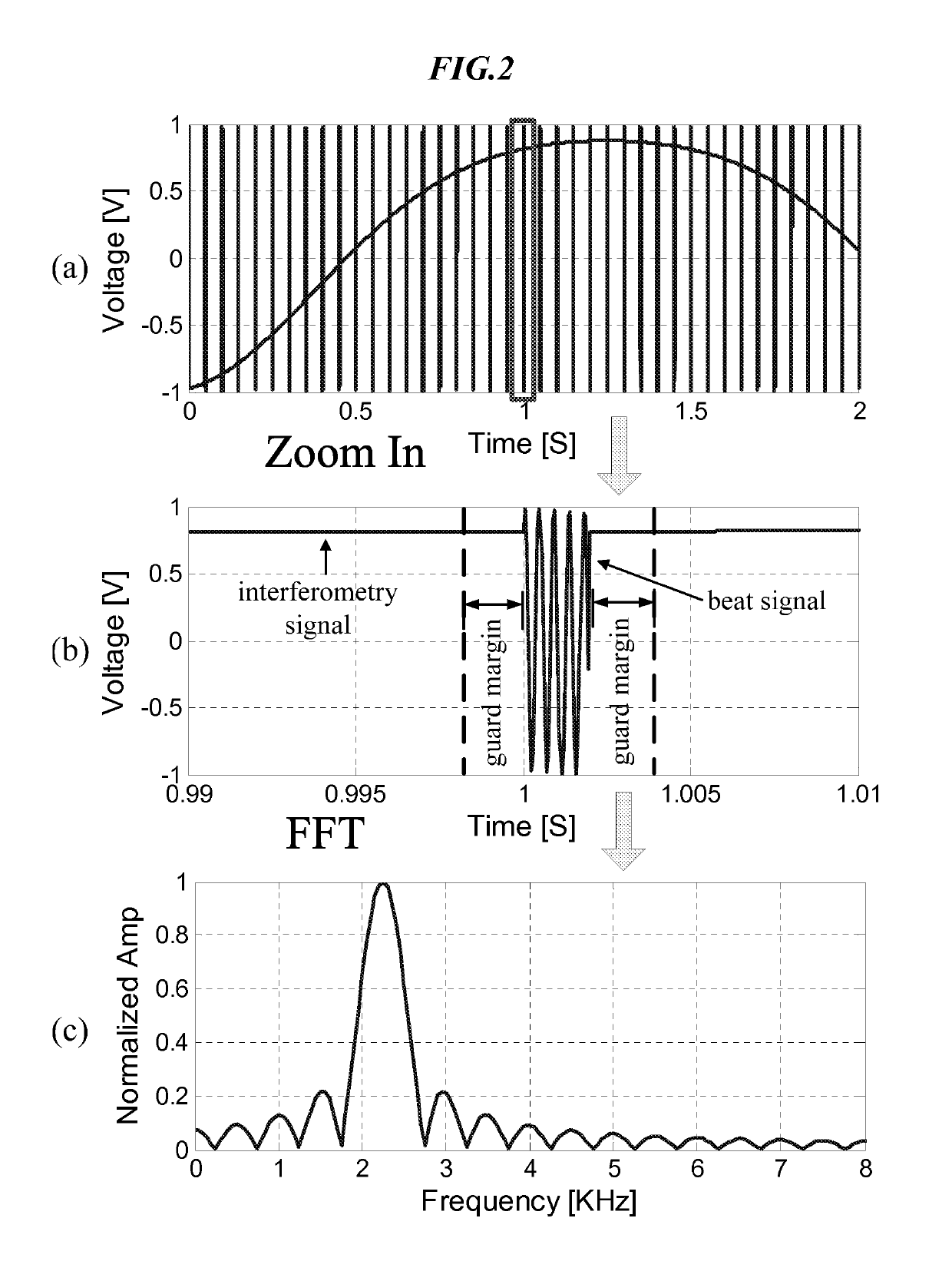
Hybrid fmcw-intererometry radar for positioning and monitoring and methods of using same
ActiveUS20170102457A1Reduce sidelobeImprove isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhysiological movement
Disclosed is a system and method for a hybrid radar system that integrates frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) mode and interferometry mode. The radar works as a time division system that continuously switches between the FMCW mode and interferometry mode. The FMCW mode is responsible for absolute range detection and the interferometry mode takes cares of the weak physiological movement monitoring. The respective accuracies in range detection and displacement measurement complements the advantages of the two radar modes, providing versatile performance. By steering the antenna beam, the proposed radar system becomes an ideal solution for indoor health care, human localization, and human-computer interaction. Objects or human targets with or without stationary clutters can be precisely located. At the same time, the targets' vital signs and gestures can be monitored.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
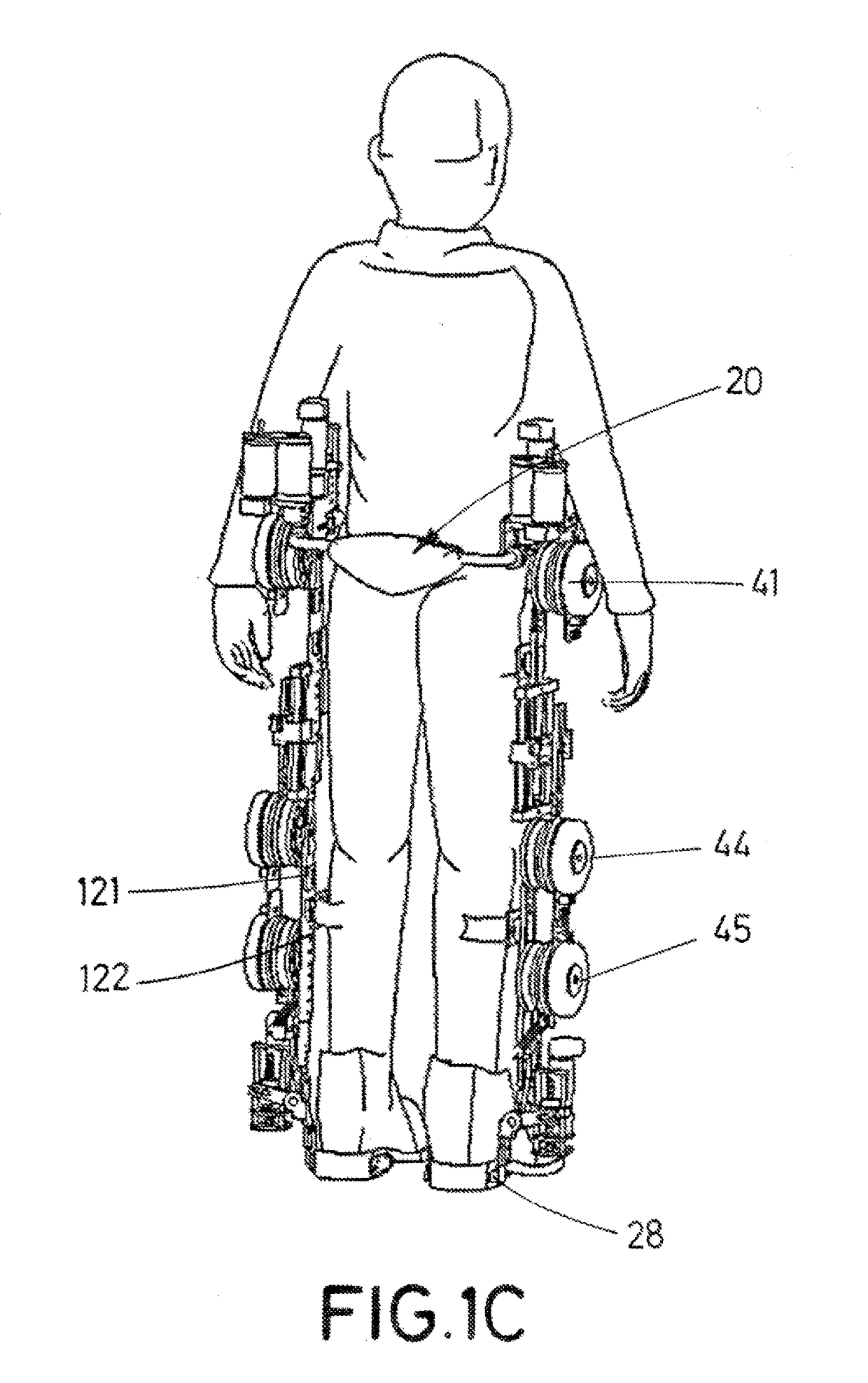
Exoskeleton for assisting human movement
ActiveUS20170340504A1Ensure maintenanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsSagittal planePhysiological movement
The invention relates to an exoskeleton for assisting human movement, which can be fitted to the user in terms of dimensions, tension and ranges of joint motion, either manually or automatically. Said exoskeleton can be fitted to the user in the anteroposterior direction in the sagittal plane, with the user in a horizontal or sitting position, without requiring a functional transfer. The exoskeleton has a modular design which is compatible with human biomechanics and reproduces a natural and physiological movement in the user, with up to 7 actuated and controlled degrees of movement per limb, ensuring that the user maintains equilibrium during locomotion.
Owner:MARSI BIONICS +2
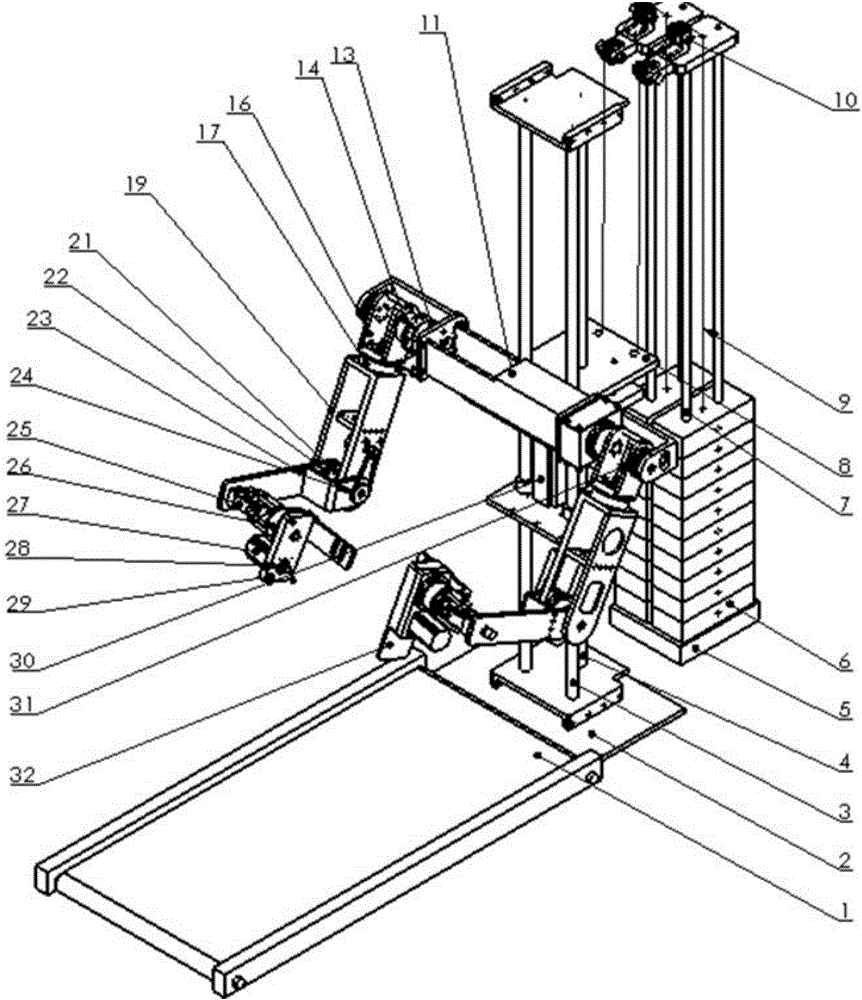
Whole-body-coordinating multifunctional four-arm robot and operating method thereof
ActiveCN105997437AImprove the effect of rehabilitation trainingReduce loadChiropractic devicesWalking aidsPhysiological movementWhole body
Owner:GUANGDONG MINGKAI MEDICAL ROBOTS CO LTD
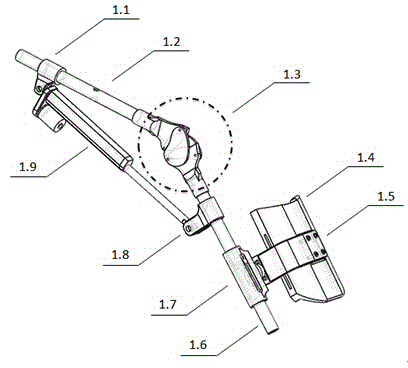
Walking aid lower limb of exoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a walking aid lower limb of an exoskeleton robot. The walking aid lower limb comprises a first actuator fixing part (1.1), a thigh rod (1.2), a bionic knee-joint (1.3), a shank guard board (1.4), a shank guard board fixing part (1.5), a shank rod (1.6), a shank guard board connecting piece (1.7), a second actuator fixing part (1.8), and an actuator (1.9). The invention provides a walking aid lower limb of an exoskeleton robot, combined with a crossed four-bar linkage structure, a bionic mechanism which accords with physiological movement characteristics of human knee joints is designed. The walking aid lower limb can eliminate harmful applied forces generated by man-machine offset, and solves problems of radial deviation and tangential rotation offsets generated by man-machine system microscopic offset along a shank, so as to improve use security and wearing comfortableness of a rehabilitation exoskeleton.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Implantable hearing aid transducer interface
InactiveUS20060281963A1Additional transducerIsolate feedbackDeaf-aid setsPhysiological movementTransducer
An implantable hearing aid transducer interface disposable between an implantable transducer and a mounting apparatus and having at least a portion that is displaceable in response to a predeterminable range of transducer movement. According to one aspect of the invention, the predeterminable range of transducer movement includes movement in response to a physiological movement of an auditory component that results in pressure on the implantable transducer. In this case, the compliant interface permits adaptive movement of the implantable transducer in response to the pressure to maintain a desired interface between the implantable transducer and an auditory component. According to another aspect, the predeterminable range of transducer movement may be transducer vibration resulting from an acoustic stimulation of an auditory component by the implantable transducer. In this case, the compliant interface reduces the transmission of transducer vibration over a feedback path to a microphone of a hearing aid.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Smart contact lens system with cognitive analysis and aid
ActiveUS20190332168A1Input/output for user-computer interactionNon-optical adjunctsCommunication interfacePhysiological movement
A smart lens system may include a hardware processor coupled to a smart contact lens, which may include a microprocessor, an image capturing sensor, and a wireless communication interface. The smart lens system may determine reading factors associated with a user with respect to the user reading content item, based on data related to the user's physiological movements captured by the smart contact lens. The reading factors may include a user's cognitive state determined at least from analyzing data representing the user's physiological movements. Responsive to determining that the user's cognitive state is above a threshold value, the smart lens system may generate an assistive action associated with the content item and transmit a signal to at least one assistive device to perform the assistive action. The assistive device performs the assistive action responsive to receiving the signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
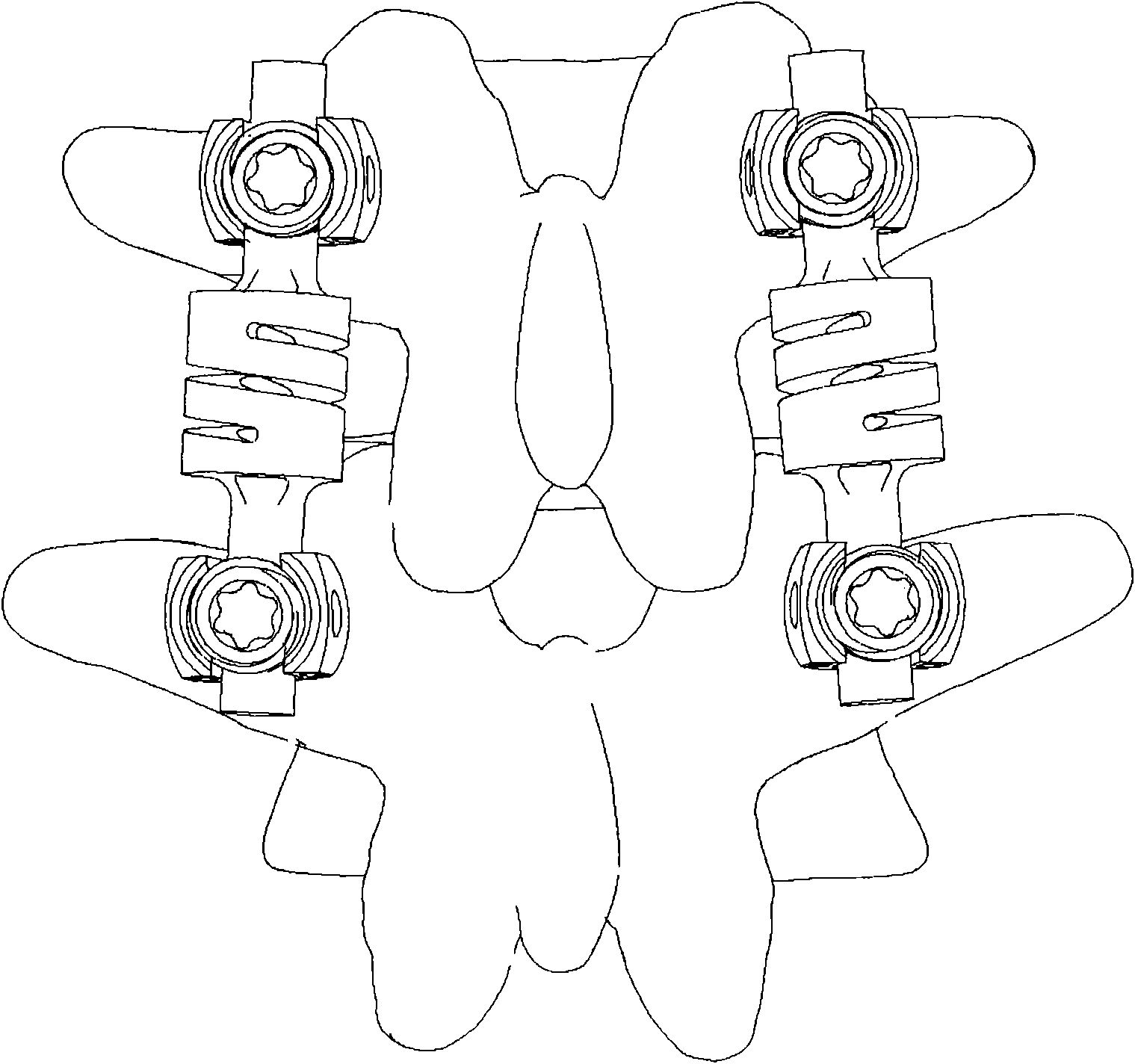
Spinal column dynamic connection rod
InactiveCN102106750AExcellent structureImprove performanceInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnPhysiological movement
The invention provides a spinal column dynamic connection rod, comprising an upper connection part, a lower connection part and an elastic piece, wherein the upper connection part and the lower connection part are connected with each other via the elastic piece. The spinal column dynamic connection rod is characterized in that: the upper connection part, the lower connection part and the elastic piece are integrally formed; the elastic piece is provided with an elastic hole; and an elastic groove is formed on an external periphery of the elastic piece. The spinal column dynamic connection rodprovided by the invention can realize stability of the spinal column and keep the normal physiological movement of the spinal column with a simple structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS
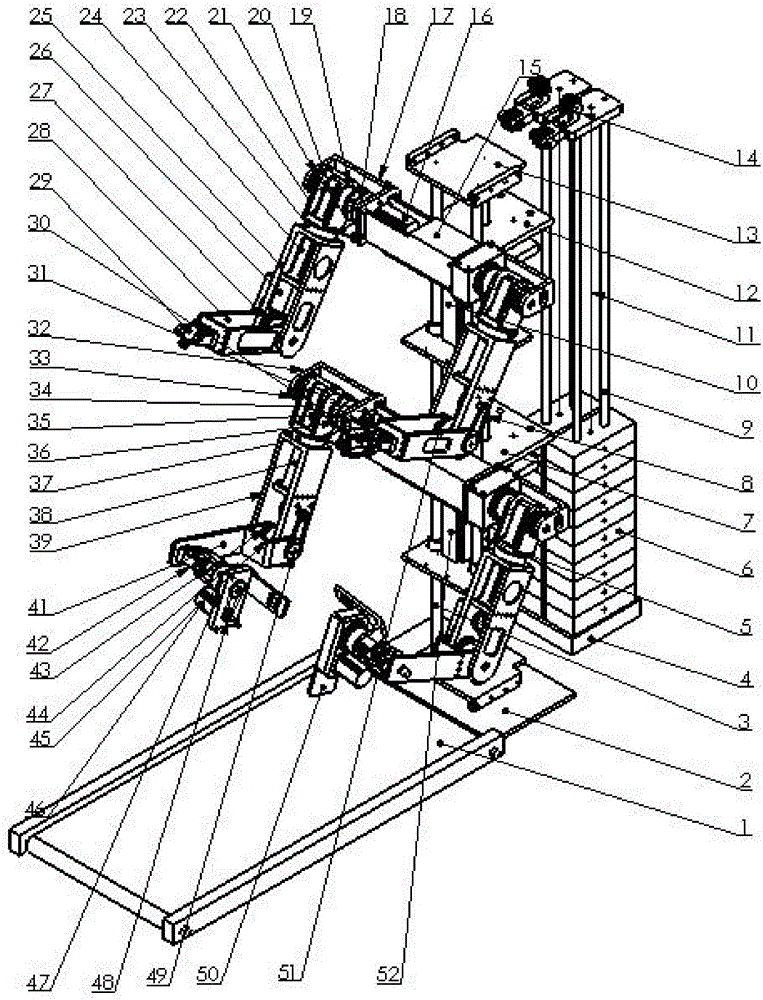
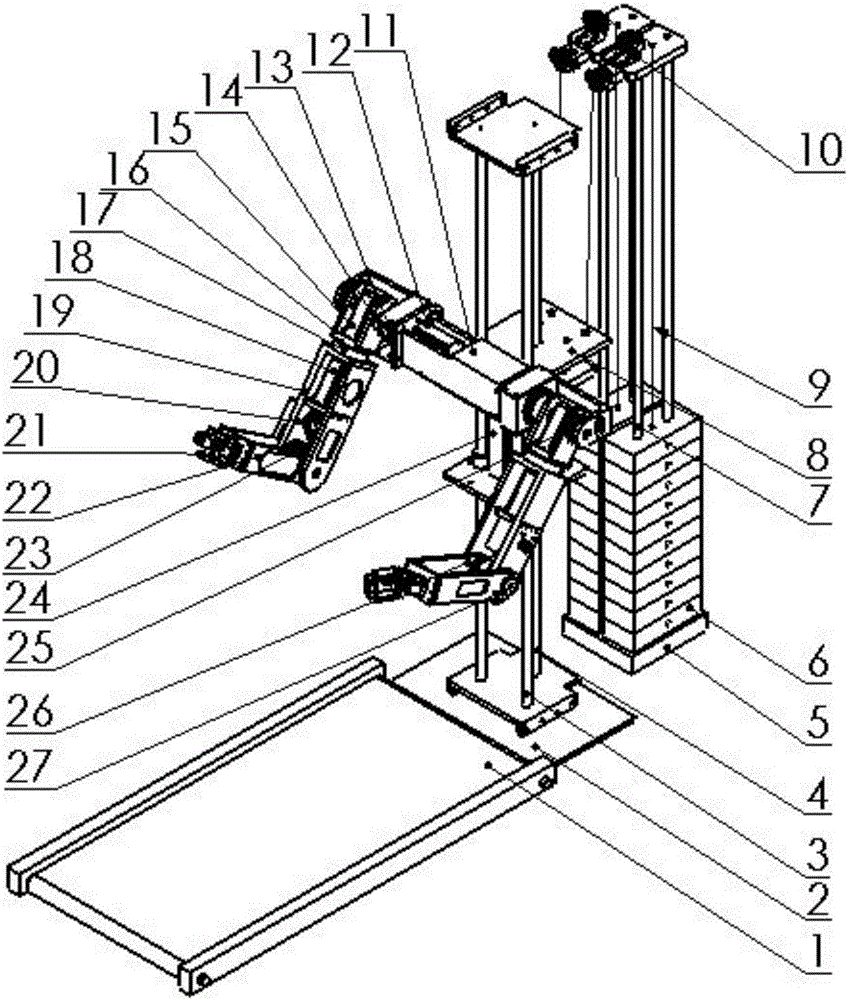
Dual-arm support rehabilitation training robot and operation method thereof
ActiveCN106109183AImprove the effect of rehabilitation trainingChiropractic devicesWalking aidsPhysiological movementEngineering
The invention discloses a dual-arm support rehabilitation training robot and an operation method of the dual-arm support rehabilitation training robot. The dual-arm support rehabilitation training robot comprises a crawler type walking machine, a base, a lifting screw mechanism, a manipulator part and a counterweight mechanism, wherein the manipulator part comprises shoulder joints, rotary joints, elbow joints and wrist joints, wherein each joint comprises a motor, a harmonic reducer and an output end. By adopting the dual-arm support rehabilitation training robot, the rehabilitation training of three-linear degree-of-freedom and two-rotational degree-of-freedom on hips of a human body can be realized in a gait training process; physiological movements of the hips in the gait training process can be highly simulated to effectively enhance the rehabilitation training effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG MINGKAI MEDICAL ROBOTS CO LTD
Hybrid FMCW-interferometry radar for positioning and monitoring and methods of using same
ActiveUS10436888B2Quick fixImprove accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhysiological movement
Disclosed is a system and method for a hybrid radar system that integrates frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) mode and interferometry mode. The radar works as a time division system that continuously switches between the FMCW mode and interferometry mode. The FMCW mode is responsible for absolute range detection and the interferometry mode takes cares of the weak physiological movement monitoring. The respective accuracies in range detection and displacement measurement complements the advantages of the two radar modes, providing versatile performance. By steering the antenna beam, the proposed radar system becomes an ideal solution for indoor health care, human localization, and human-computer interaction. Objects or human targets with or without stationary clutters can be precisely located. At the same time, the targets' vital signs and gestures can be monitored.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
Knee joint function training device
The invention discloses a knee joint function training device. The device comprises a rack, a supporting device, a driving device, a fixing pressing device and a control device; the supporting devicecomprises a supporting frame slidingly connected with a shell and vertically arranged, a foot fixing sleeve rotatably connected with the supporting frame, a calf placement frame rotatably connected with the upper end of the supporting frame and located at the side close to the upper limb of a patient and a thigh placement frame rotatably connected with the end, away from the foot fixing sleeve, ofthe calf placement frame; the other end of the thigh placement frame is rotatably connected with the end, close to the upper limb of the patient, of the shell; the fixing pressing device comprises afirst airbag belt, a second airbag belt and an intermittent inflation pressure pump; since the lower limb of the patient is subjected to isometric contraction and isotonic contraction which are closerto the physiological movement of the human body simultaneously, the venous blood flow stasis is relieved, the venous thrombosis is prevented, and the recovery of the patient is facilitated; due to the addition of the isometric contraction in the whole isotonic contraction process, part of attention of the patient in the pressurization and pressure relief process is distracted, and the pain brought to the patient is reduced.
Owner:南通市中医院
Multifunctional double-supporting rehabilitation exercising robot and operation method thereof
ActiveCN106074090AImprove the effect of rehabilitation trainingOffset its own weightChiropractic devicesPhysiological movementEngineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional double-supporting rehabilitation exercising robot. The multifunctional double-supporting rehabilitation exercising robot comprises a crawler type walking machine, a base, a lifting screw rod mechanism, a manipulator part and a counterweight mechanism, wherein the manipulator part comprises shoulder joints, revolving joints, elbow joints and wrist joints; each joint comprises a motor, a harmonic speed reducer, and an output end. The multifunctional double-supporting rehabilitation exercising robot has the advantages that the rehabilitation exercising on three linear degrees of freedom and two revolving degrees of freedom of the hips of human body is realized in the step training process; the physiological movement of the hips can be highly simulated in the step training process, and the effect of rehabilitation training is effectively improved.
Owner:威海台一盈拓机械科技有限公司
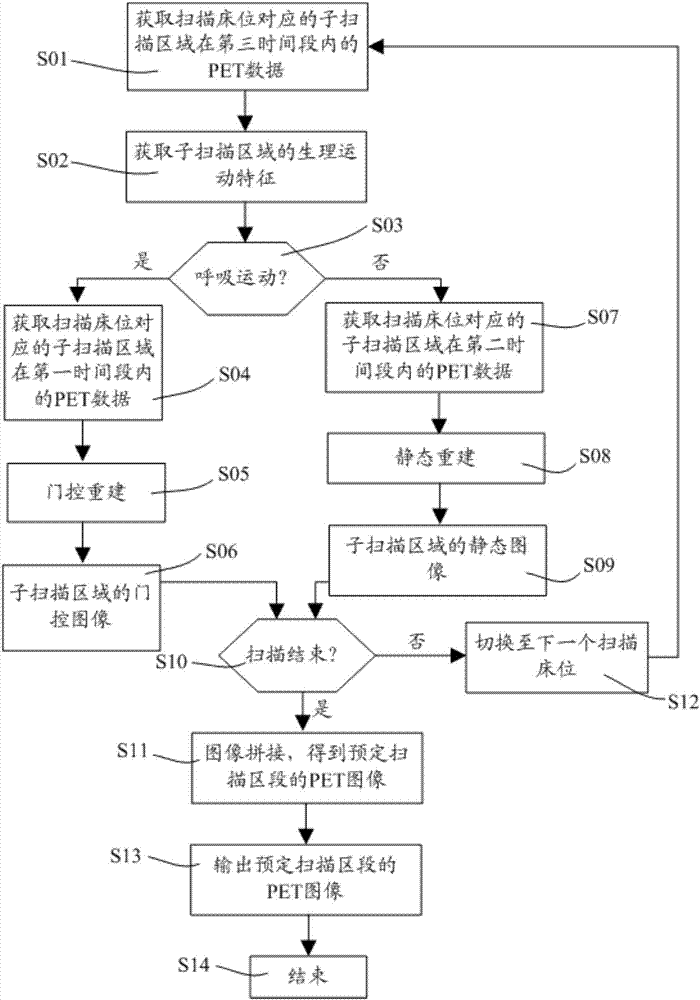
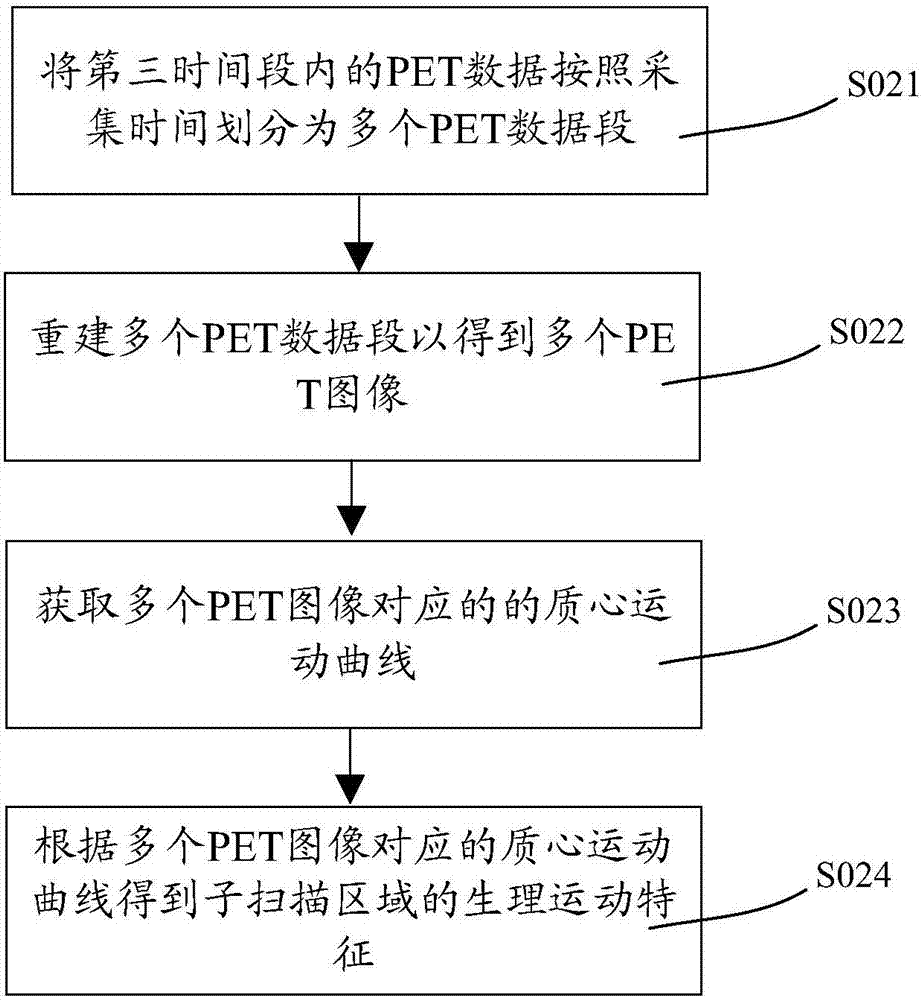
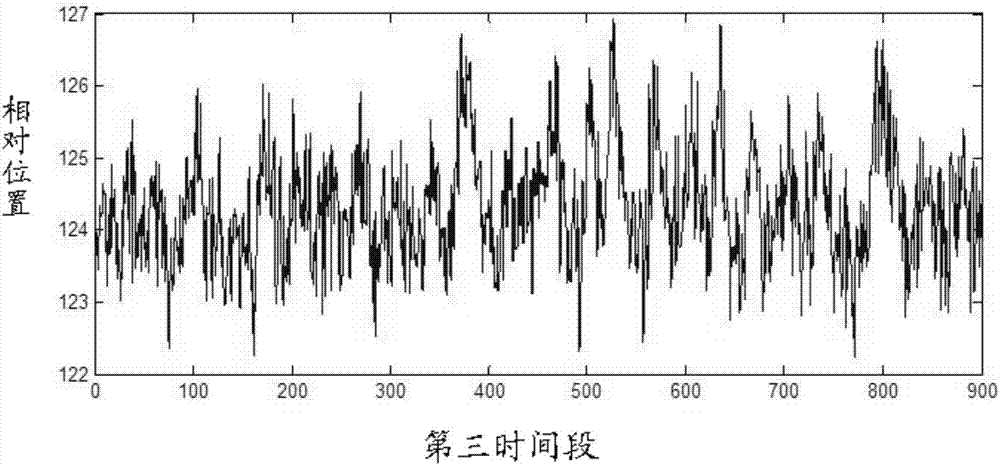
PET imaging system and imaging method thereof
PendingCN106963410AReduce rebuild timeShort scan timeImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPhysiological movementPet imaging
The invention relates to a PET imaging system and an imaging method thereof. The PET imaging method comprises the following steps: dividing a predetermined scanning section into one or more sub-scanning areas, wherein each sub-scanning area corresponds to a scanning bed; prejudging whether or not there is physiological movement in the corresponding sub-scanning area for each scanning bed; if yes, obtaining PET data of the sub-scanning area corresponding to the scanning bed in a first time period through a first data acquisition mode and obtaining the gated image of the sub-scanning area at least based on the PET data in the first time period; if not, obtaining the PET data of the sub-scanning area corresponding to the scanning bed in a second time period through a second data acquisition mode and obtaining the static image of the sub-scanning area according to the PET data in the second time period. The PET imaging system comprises a dividing unit, a judging unit, a scanning unit and a reconstruction unit, and is used for obtaining the static or gated image of the sub-scanning area through the imaging method.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Flow compensation method for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN104459587AWeakening flow phenomenonAttenuated flow phenomenon has artifacts in existing FSE imagesMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoPhysiological movement
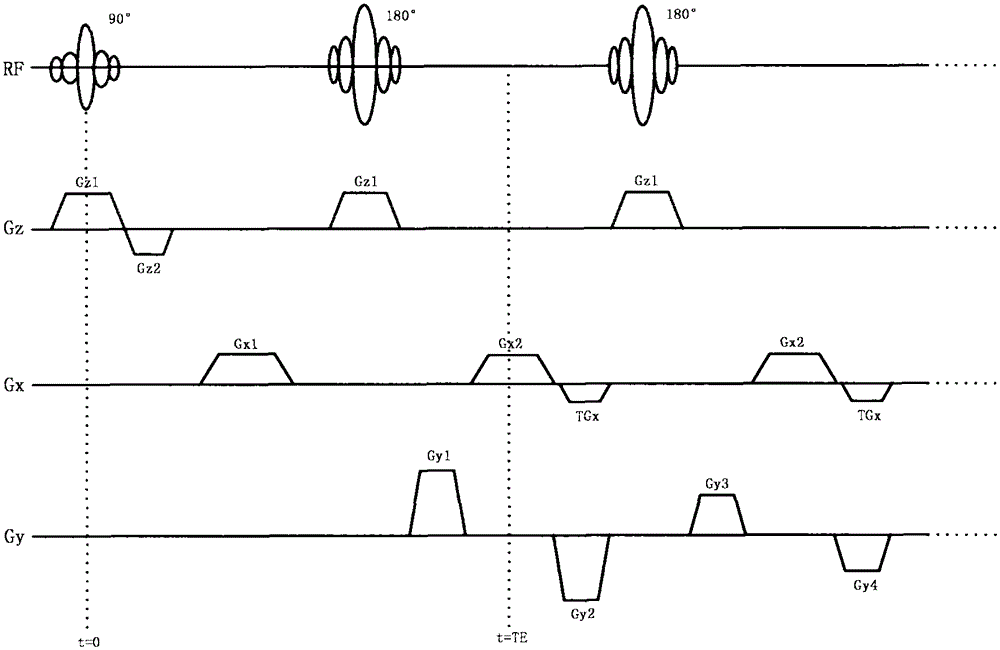
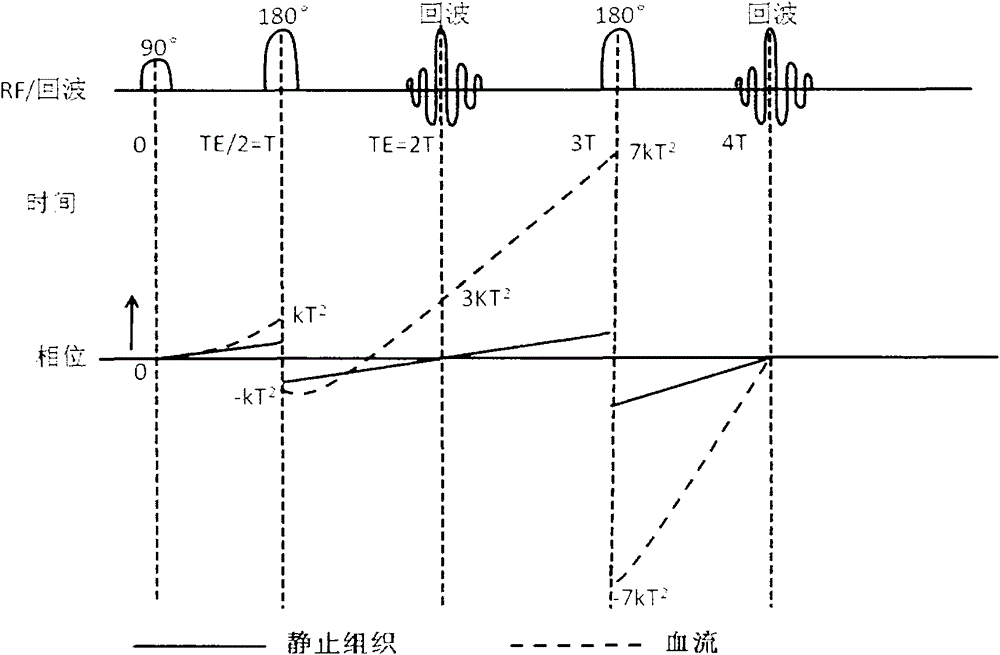
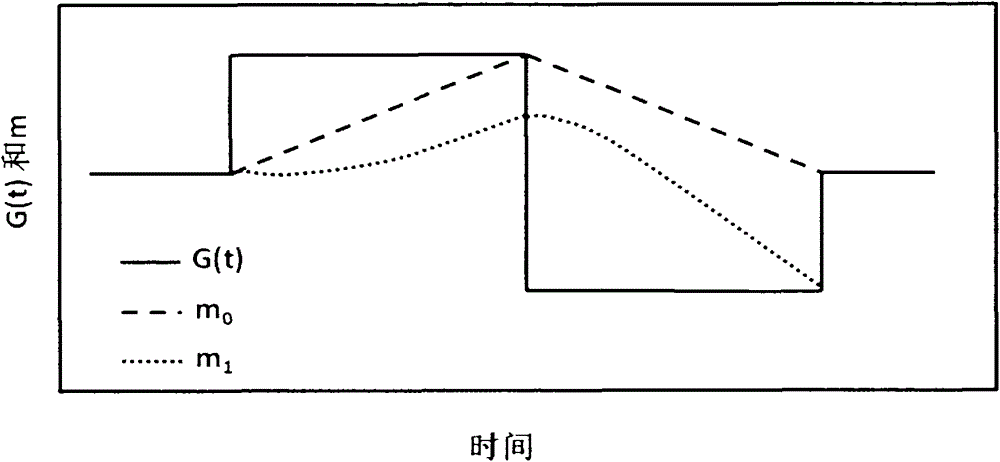
The invention discloses a flow compensation method for a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system. The flow compensation method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: (1) gradient combined pulses which satisfy flow compensation are applied in a frequency encoding direction between a 90-degree radio frequency pulse time series and a 180-degree radio frequency pulse time series of a fast spin echo (FSE) sequence; (2) a scattering gradient is applied before a signal acquisition gradient and before 180-degree radio frequency pulses, and a compensation gradient is applied after the acquisition gradient, and the signal acquisition gradient, the scattering gradient and the compensation gradient jointly form a first-order gradient velocity compensation gradient; (3) phase encoding gradient amplitude is set to be zero, and the time series of the sequence is set, and the amplitudes of the gradients are adjusted, and the amplitude of echo signal peaks of an echo chain is made to reach a maximum value, and the debugging of the sequence is completed; and (4) the sequence is outputted to a spectrometer, so that flow compensation can be realized. With the flow compensation method for the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system of the invention adopted, situations such as cerebrospinal fluid flow and spinal fluid flow artifacts and image blurring can be significantly inhibited, and therefore, the problem of image artifact generation which is caused by physiological movement such as blood flow or periodic movement can be alleviated.
Owner:BEIJING WANDONG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Buffer-type artificial ankle joint
InactiveCN102920536AAnatomically CompliantBiomechanical propertiesAnkle jointsJoint implantsSurgical ManipulationArticular surface
The invention discloses a buffer-type artificial ankle joint which comprises an implant used for being installed in cancellous bones at the lower end of a tibia, a tibia end foundation plate, a tibia end joint surface, a talus end joint surface, a talus end foundation plate and a buffer device. The implant is hollow, and the circumferential wall is provided with holes. One end of the tibia end foundation plate is movably connected with the implant, and the other end of the tibia end foundation plate is connected to the tibia end joint surface in a clamping mode. The talus end joint surface is connected with the talus end foundation plate in a shaft matched mode. The talus end foundation plate is provided with shocking proof holes used for installation of the buffer device. The structural design of the buffer-type artificial ankle joint meets requirements of human body ankle joint anatomy, imitates ankle joint physiological movement, and fits biomechanics characteristics. The buffer device can reduce collision, reliefs stress conduction, effectively reduces movement load, and overcomes overall pressure stress. The buffer-type artificial ankle joint is simple in operation, and is wide in applicable diseases.
Owner:黄国富 +1
Electromagnetic wave physiological movement imaging system
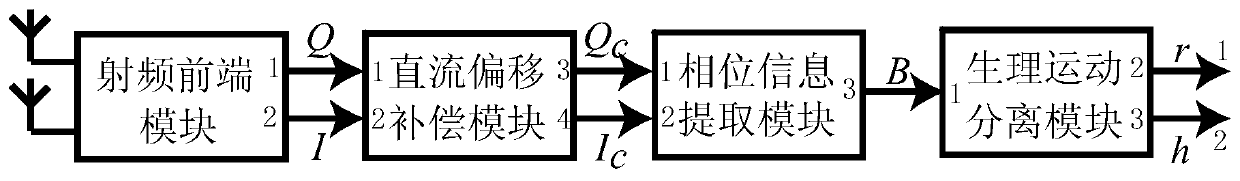
InactiveCN103340619ALow costReduce Radiation HazardsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePhysiological movementComputer module
The invention discloses an electromagnetic wave physiological movement imaging system which comprises a radio-frequency front end module, a direct-current offset compensation module, a phase information extraction module and a physiological movement separation module. The first output end and the second output end of the radio-frequency front end module are connected with the first input end and the second input end of the direct-current offset compensation module respectively, the first output end and the second output end of the direct-current offset compensation module are connected with the first input end and the second input end of the phase information extraction module respectively, the output end of the phase information extraction module is connected with the input end of the physiological movement separation module, and the first output end and the second output end of the physiological movement separation module are connected with the first output end and the second output end of the electromagnetic wave physiological movement imaging system respectively. Compared with the prior art, the electromagnetic wave physiological movement imaging system has the advantages of being low in cost, small in radiological hazard and high in anti-interference performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
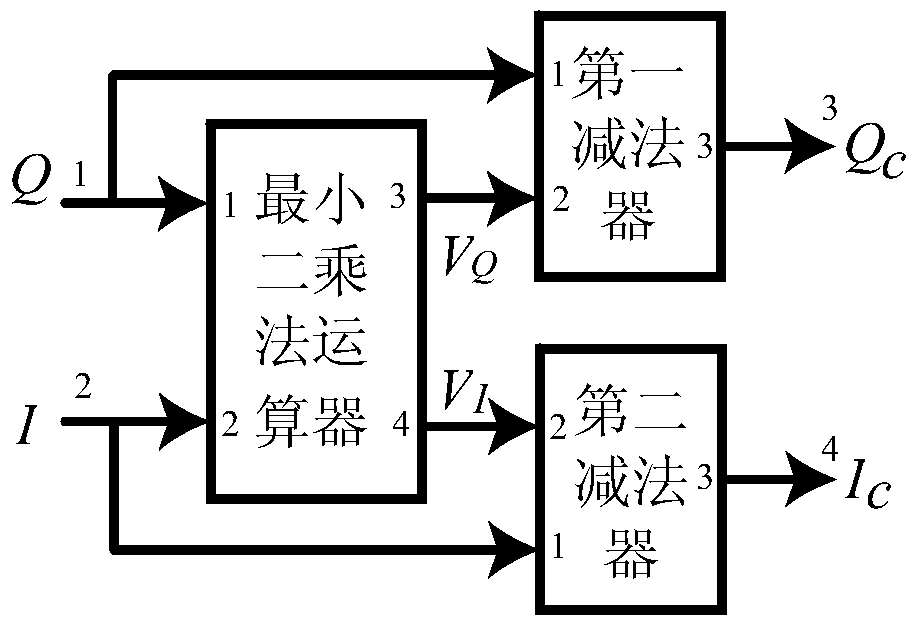
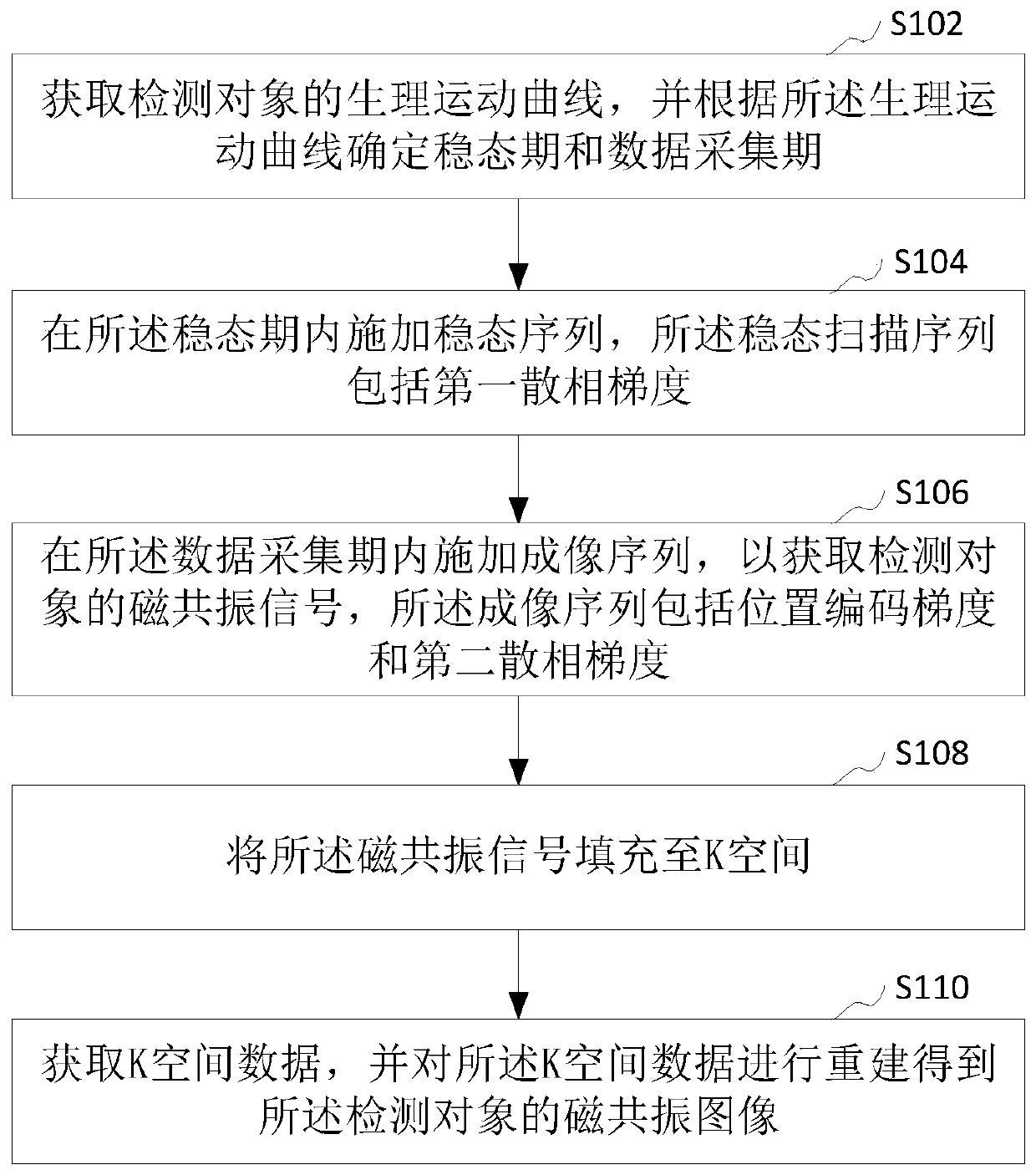
Magnetic resonance imaging scanning method and device, computer device and storage medium
ActiveCN109917315ASteady breathingReduce noiseDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhysiological movementData acquisition
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging scanning method and device, a computer device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a physiological movementcurve of a detection object, and determining a steady state period and a data collection period according to the physiological movement curve; applying a steady state sequence in the steady state period, wherein the steady state sequence comprises a first dispersed phase gradient; applying an imaging sequence in the data collection period to obtain magnetic resonance signals of the detection object, wherein the imaging sequence comprises a position coding gradient and a second dispersed phase gradient; filling the magnetic resonance signals to a K space; and obtaining K space data, and performing reconstruction of the data of the K space to obtain the magnetic resonance images of the detection object. The steady state sequence has no the position coding gradient to reduce the noise in thesteady state period, allow the detection object to stably breathe and reduce the breathing artifacts in the magnetic resonance images.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
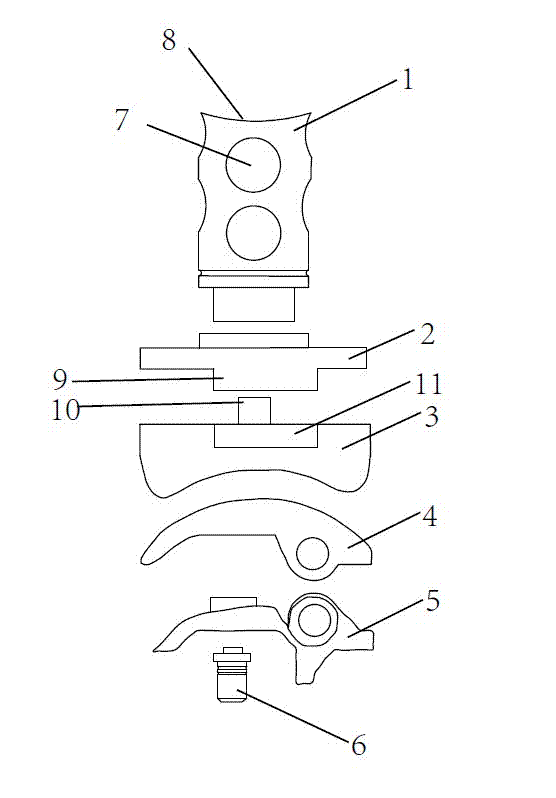
Support orthopaedic device for a knee joint
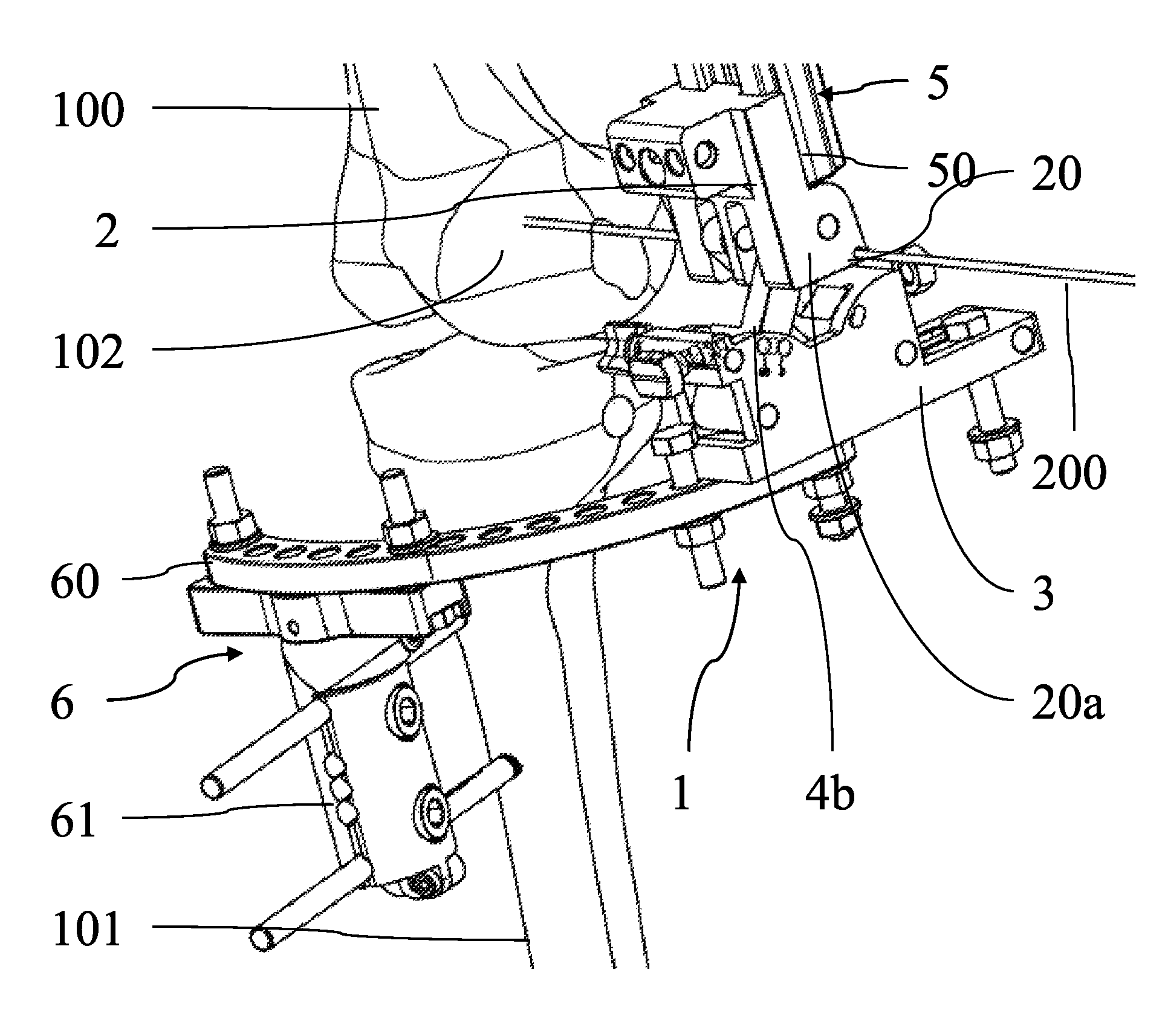
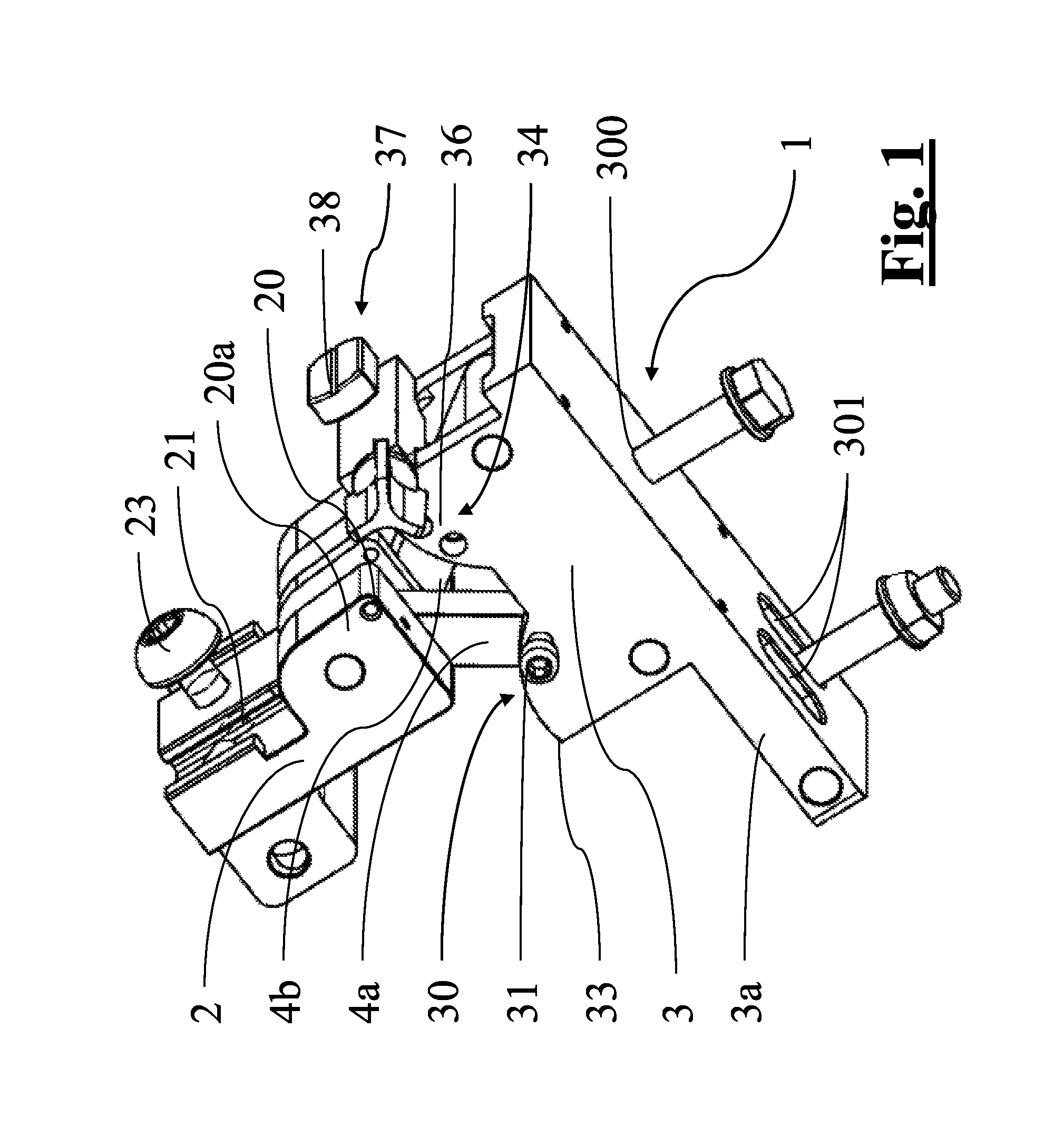
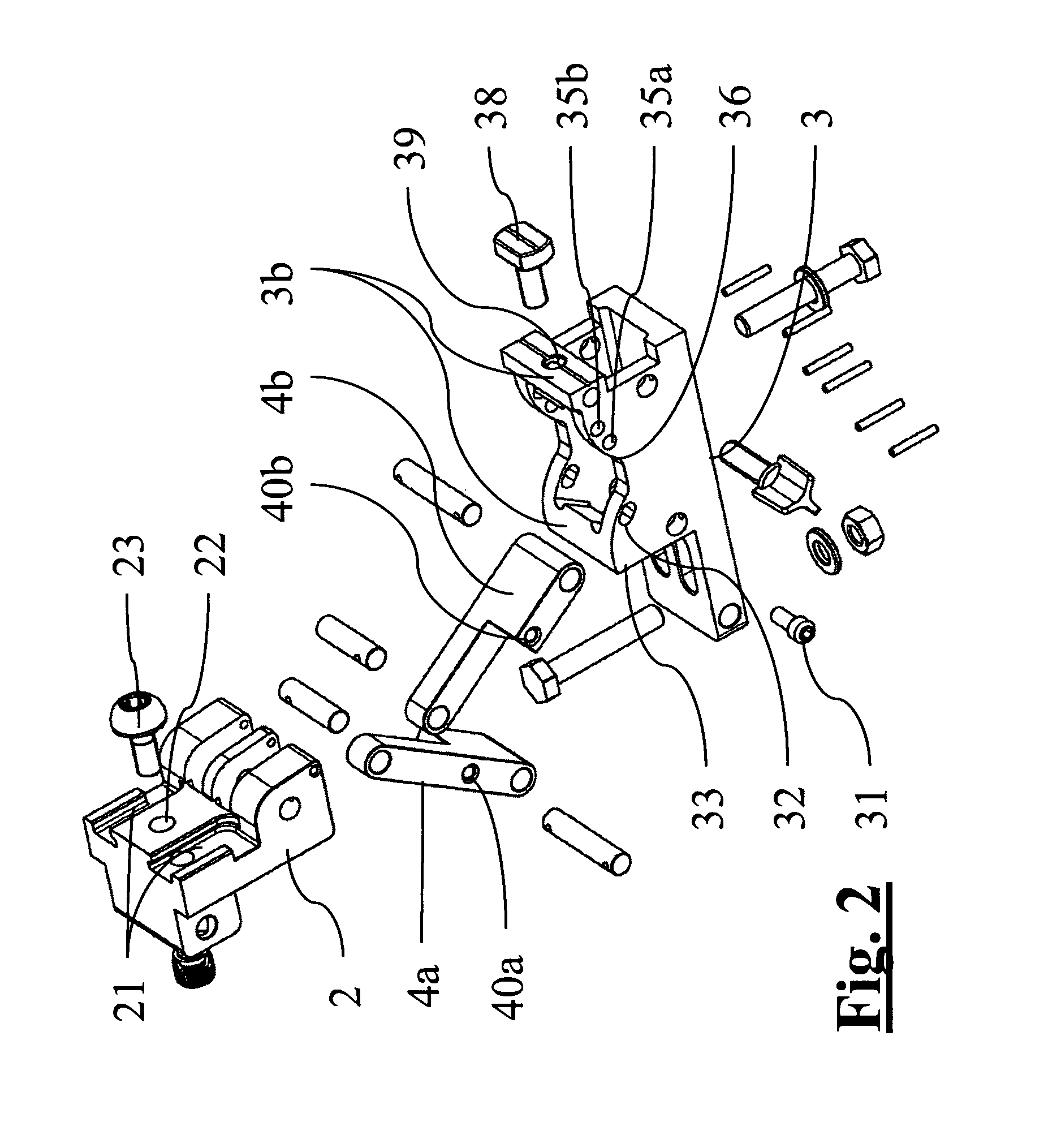
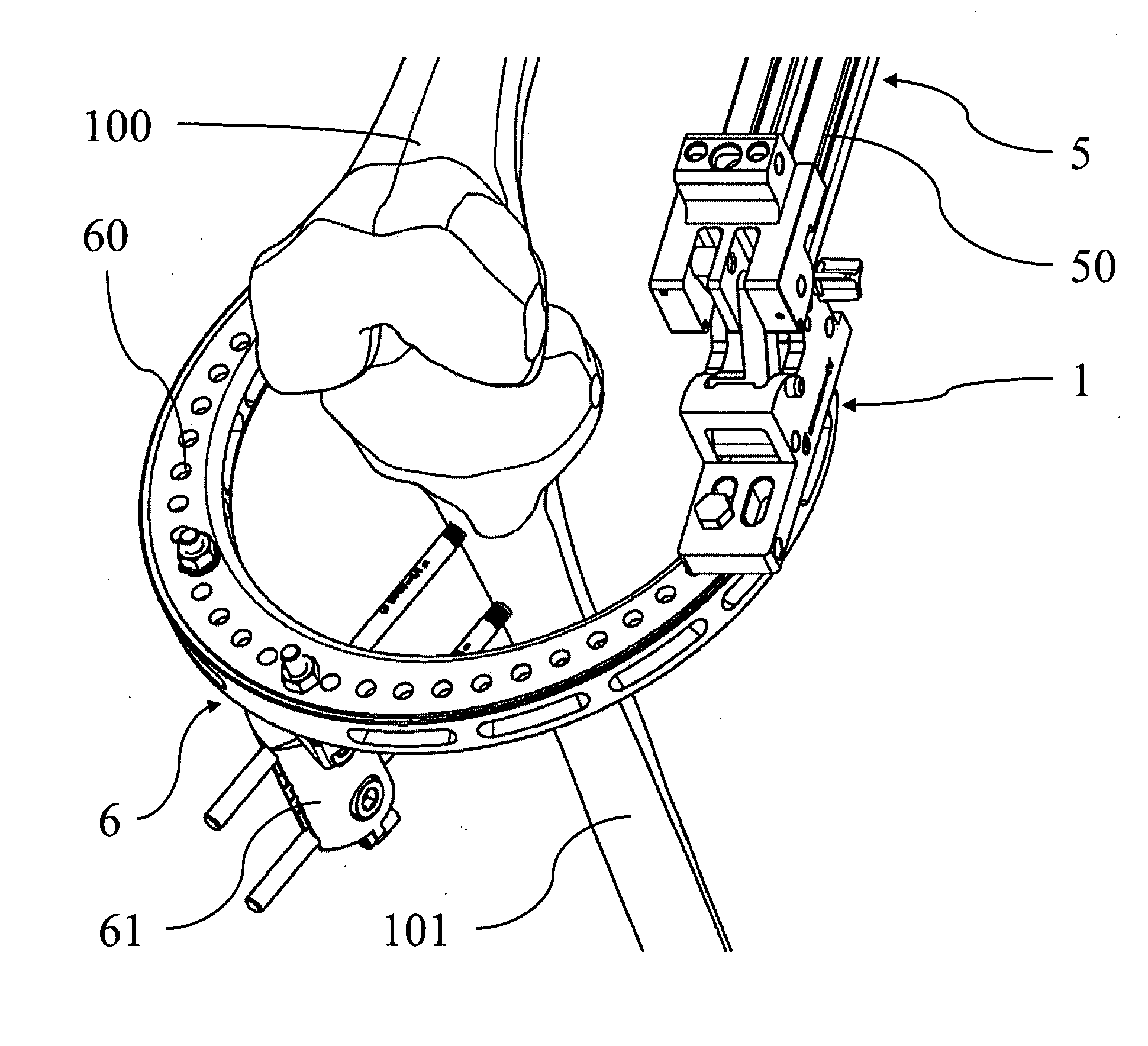
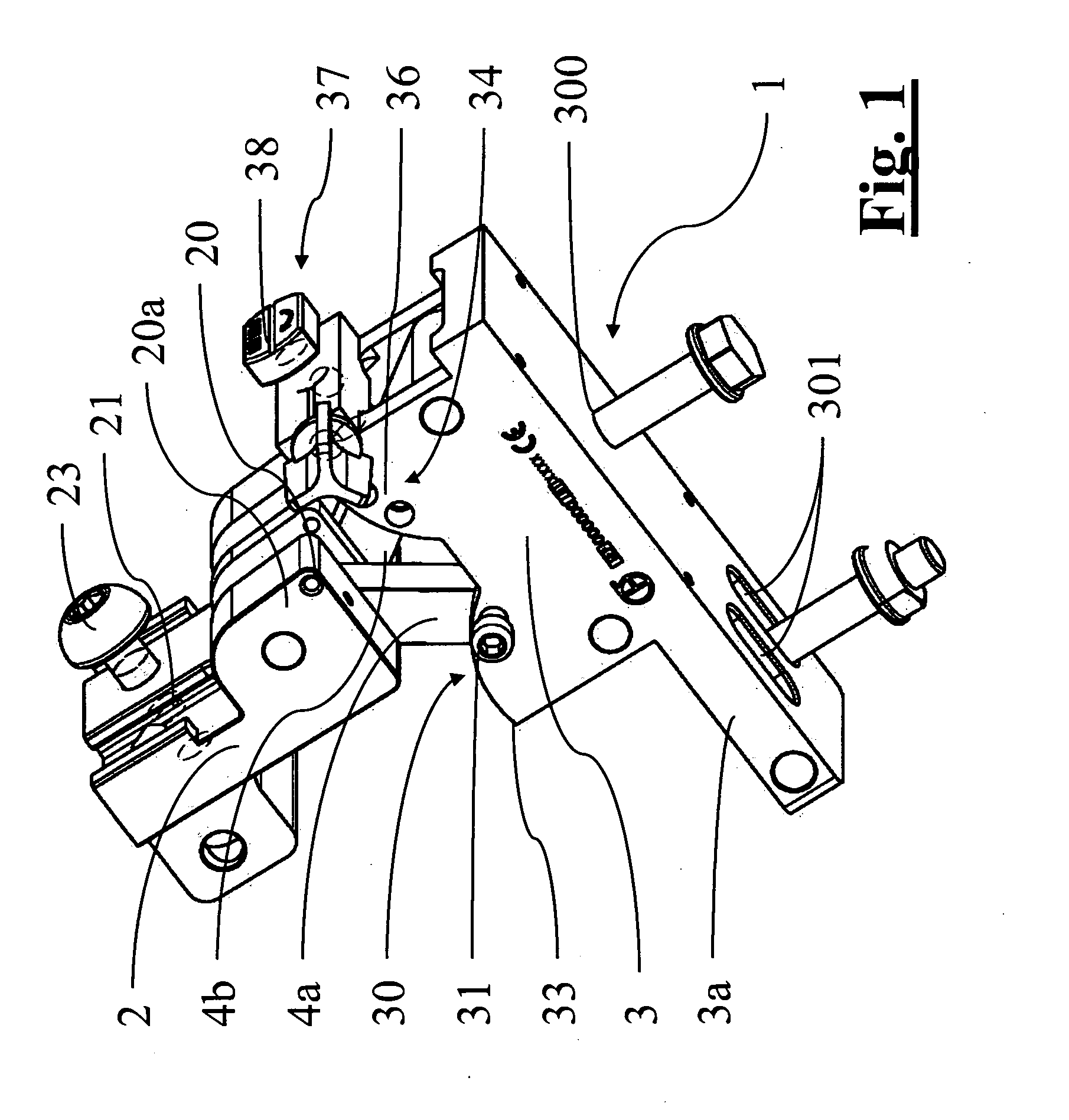
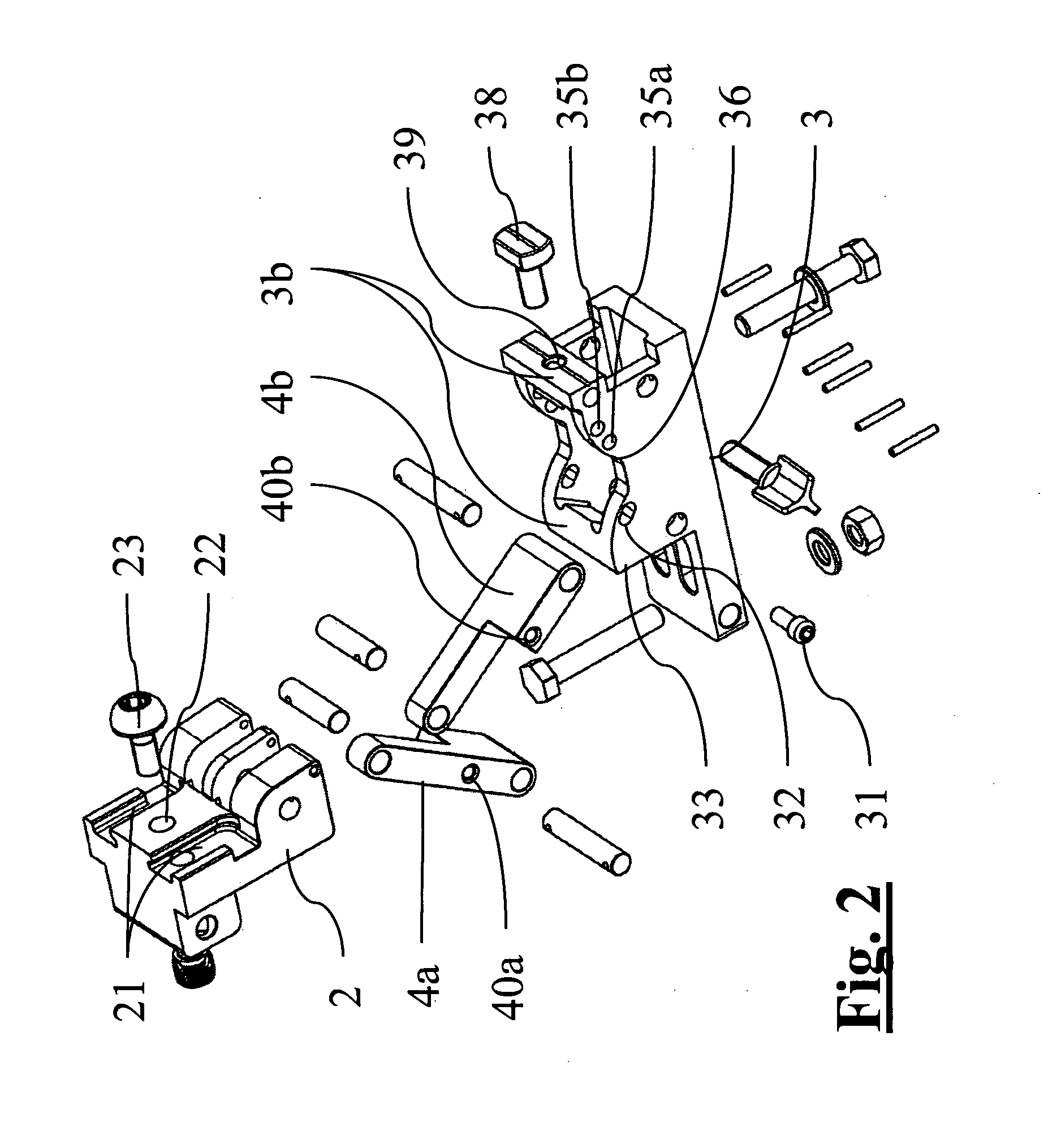
ActiveUS8388625B2Precise positioningFast and precise implantDiagnosticsFractureOrthopaedic devicePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Support orthopaedic device (1) for a knee joint, comprising a proximal connector (2) and a distal connector (3), articulated among themselves and respectively intended to be associated with a proximal bone (100) and a distal bone (101) of a lower limb connected among themselves by a knee joint. The device comprises a first rod (4a) and a second rod (4b), which are hinged, according to hinging axes normal to a median excursion plane of the orthopaedic device (1), to the proximal connector (2) and to the distal connector (3) so as to form with them an articulated quadrilateral. The articulated quadrilateral is planarly mobile according to a plane parallel to the excursion plane between a configuration corresponding to an extended position of the knee joint and configurations corresponding to bendings of different entity of the knee joint; the relative motion imposed to the proximal and distal connectors (2, 3) by the articulated quadrilateral is consistent with the physiological movement of the knee joint.
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
A seven-degree-of-freedom upper limb assisting exoskeleton robot
ActiveCN106031668AFitting Physiological StructureIncrease freedomProsthesisExoskeleton robotRange of motion
The invention provides a seven-degree-of-freedom upper limb assisting exoskeleton robot and belongs to the technical field of rehabilitation robots. The seven-degree-of-freedom upper limb assisting exoskeleton robot comprises a wrist part, a palm part and a finger part. The wrist part is connected with the palm part. The wrist part comprises a wrist ring toothed rail and a wrist slider arranged on the wrist ring toothed rail. The palm part comprises a palm protecting plate and is connected with the finger part which comprises a thumb plate and a four-link finger plate. Compared with the prior art, the seven-degree-of-freedom upper limb assisting exoskeleton robot can simulate the bending / extending and the inward rotation and outward rotation of wrists, the bending / extending of palms and the bending / extending of thumbs of the upper limbs of human bodies, thereby having high degree of freedom; the movement ranges of the degrees of freedom are based on reasonable distribution and restriction, so that the robot can better fit the physiological structure of the hands of human bodies, assist the hands of the human bodies in moving flexibly at multiple angles and better assist wearers in making basic physiological movement.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
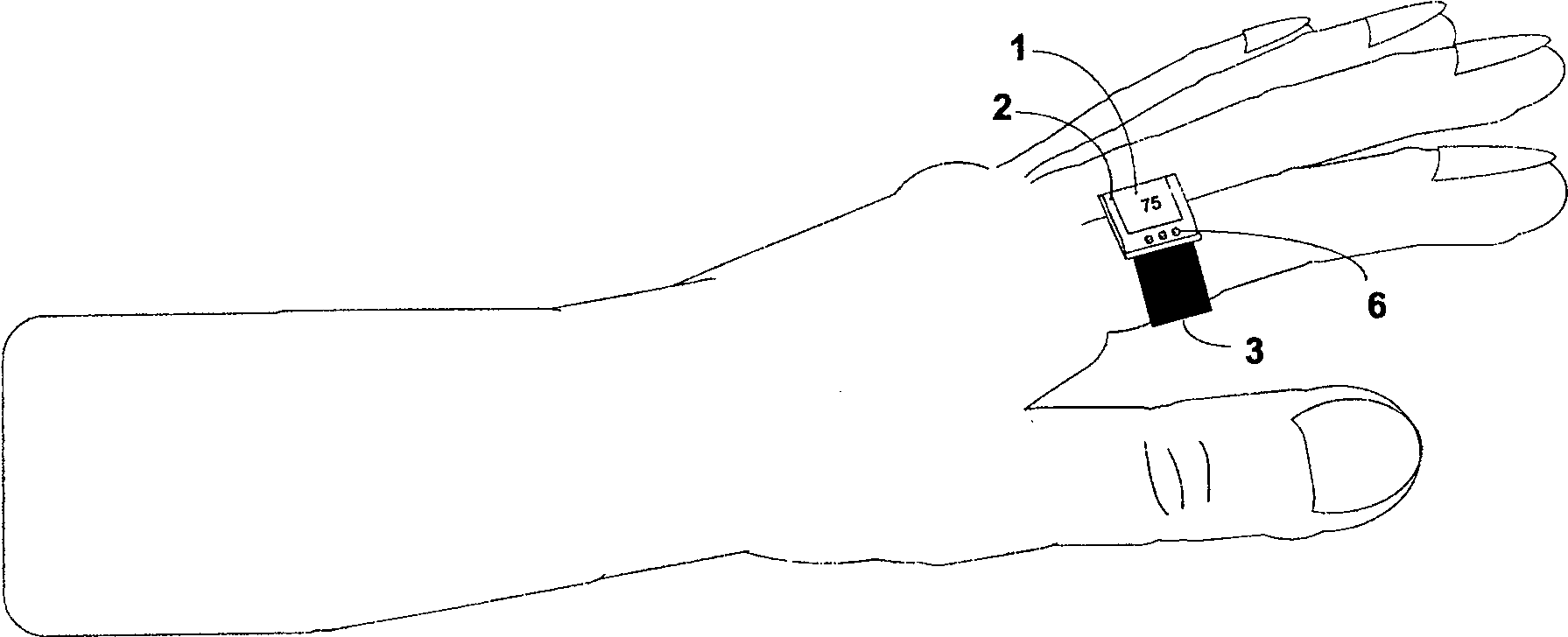
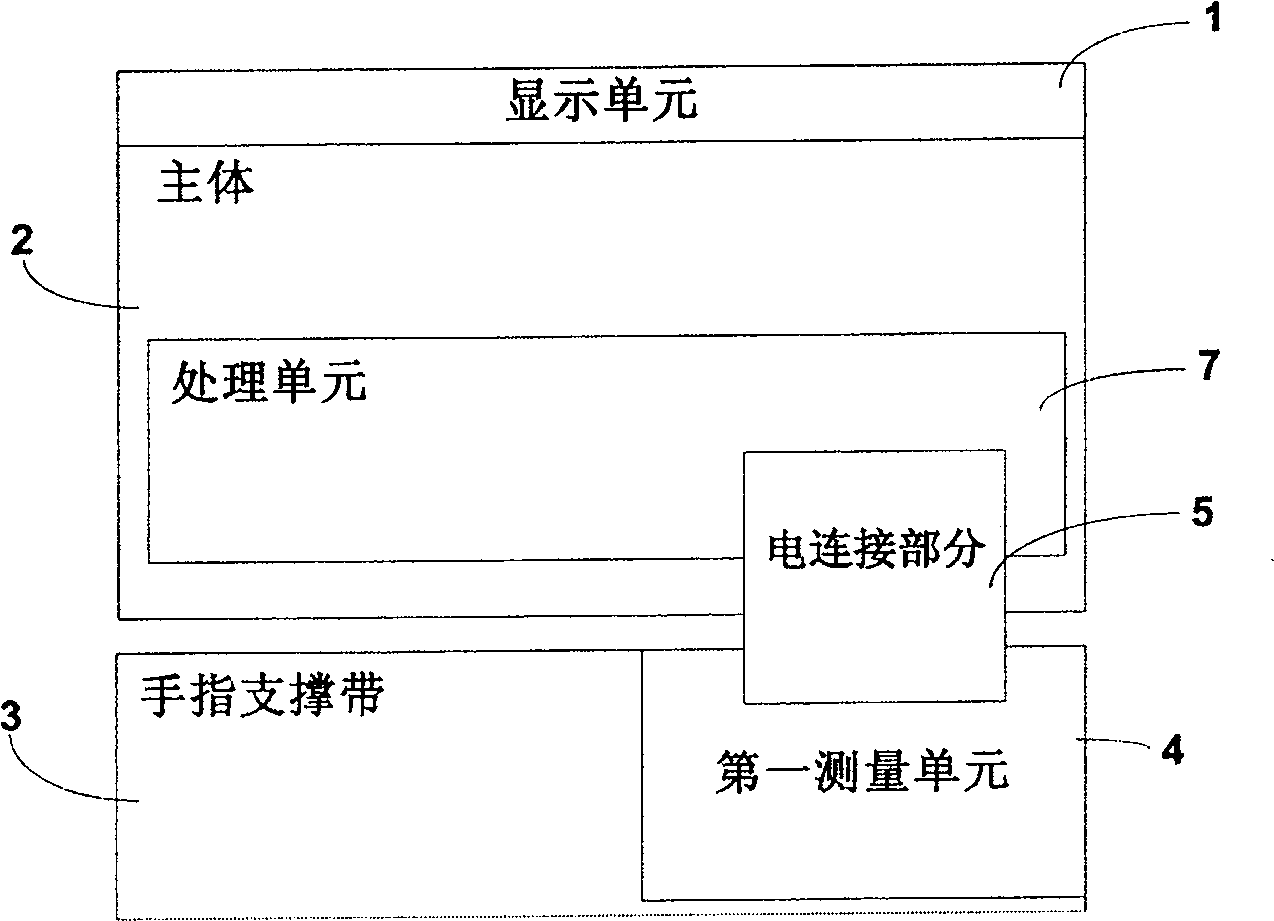
Finger ring type physiological information monitoring device
The present invention provides a ring-type physiological information monitoring device, which can obtain physiological signals from a user's finger, and determine and display physiological information, such as heart rate and blood pressure, according to the physiological signals. The device includes a main body, a finger support belt, a measurement unit, a display unit and a processing unit. The processing unit is located in the main body, is electrically connected with the display unit and the measurement unit, and is used for determining physiological information and controlling the measurement unit and the display unit. The measuring unit is located on the inner surface of the finger support belt and is in contact with the belly of the finger during use. The display unit is located on the upper surface of the main body and displays the obtained physiological information. The present invention may also include finger cots for measuring physiological signals and reducing motion noise therein. The blood pressure measurement of the physiological information monitoring device does not need to use a cuff, can continuously and synchronously measure blood pressure, heart rate and blood flow signals for a long time, the monitoring result is accurate, and it is easy to wear. The determined physiological information can also be displayed on the remote terminal by using the wireless transmission function.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Movable intelligent type regional return air in air conditioner and sterlizing unit
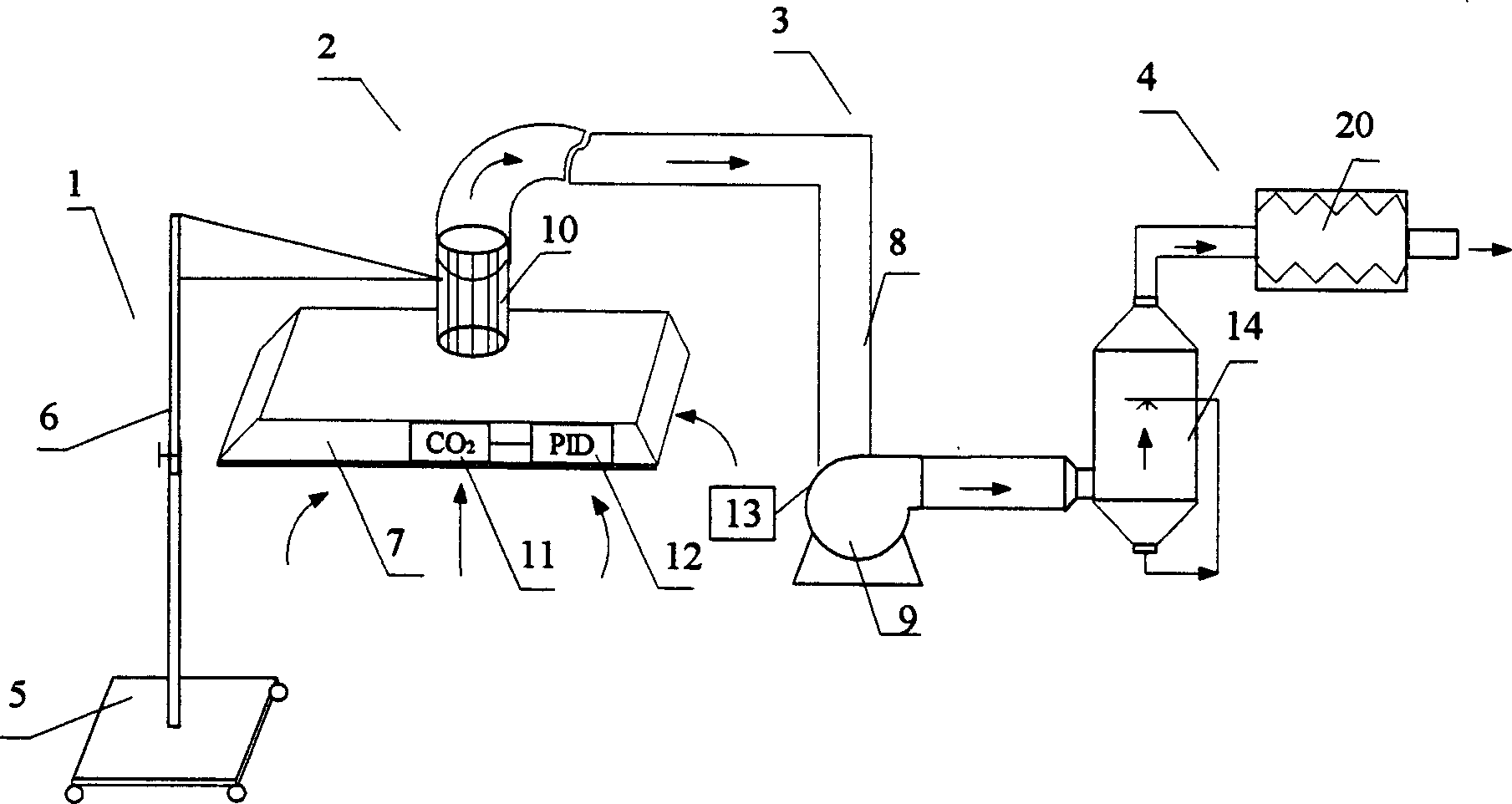
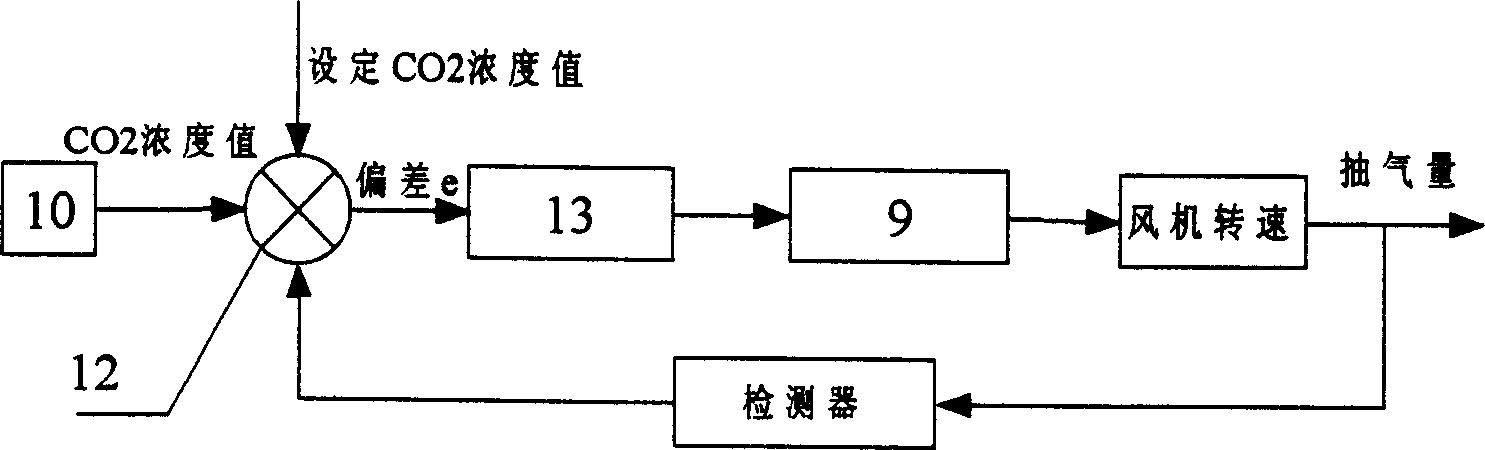
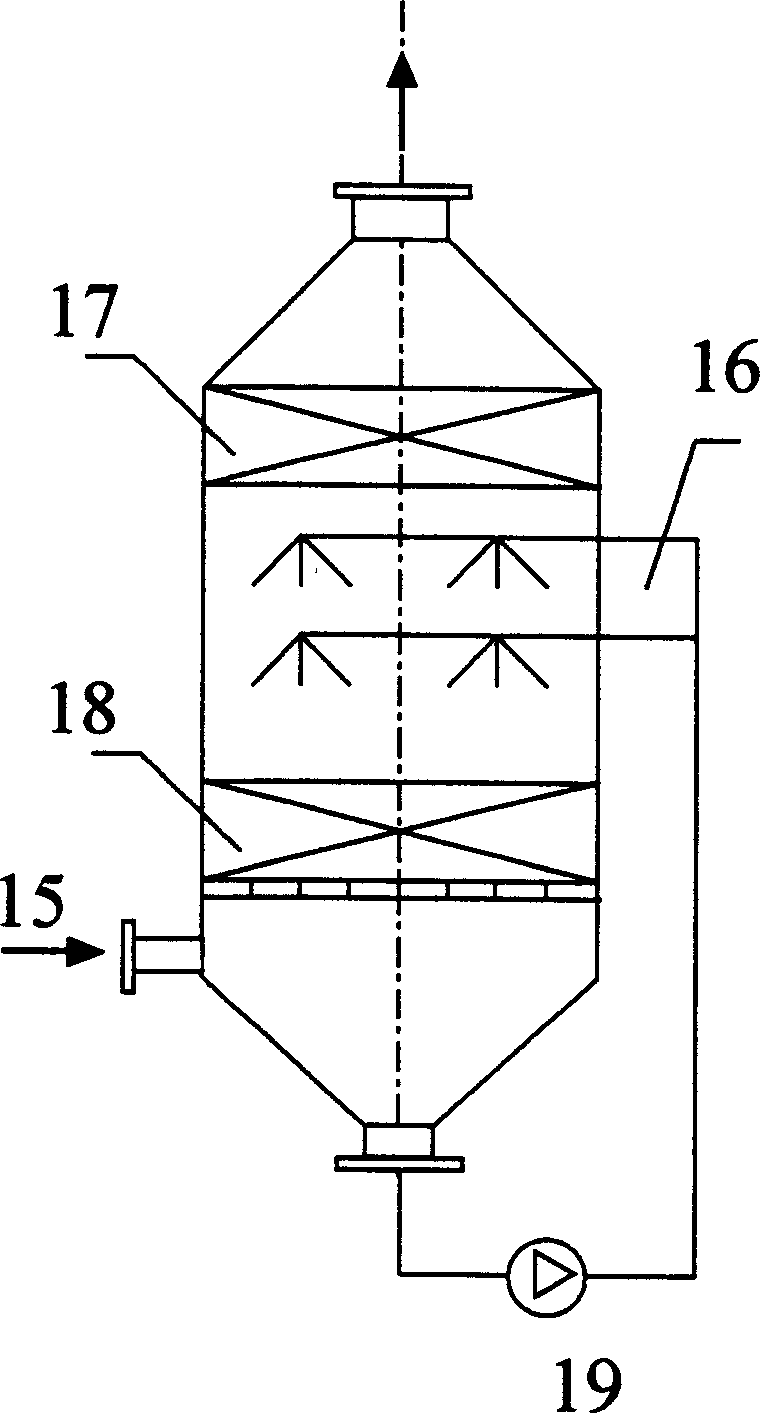
InactiveCN1462852ARealize air purificationEasy to useLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsMedical wardAir volume
A movable intelligent air circulating and disinfecting equipment of air conditioner for local space, especially for infectious sickroom, is composed of supporting frame system, local sucking exhaust system, CO2 concentration monitoring and fan's rotation speed controlling system, and return air disinfecting system. It features that the volume of sucked air is automatically regulated according to the physiological movement of human body and ambient environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
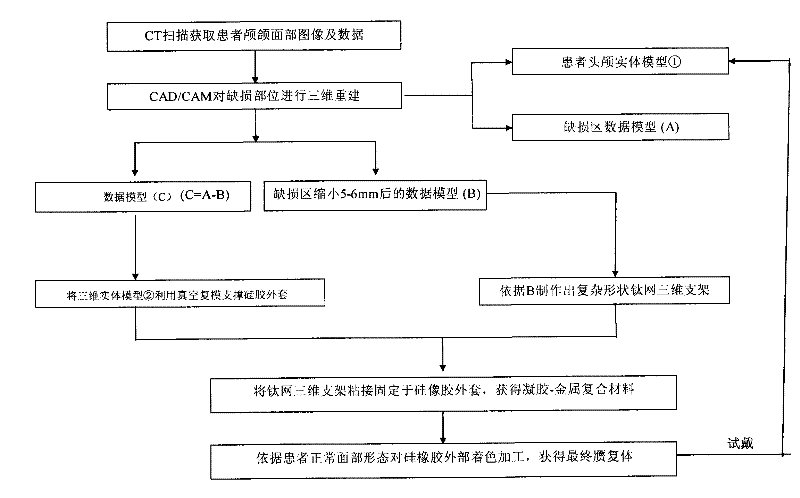
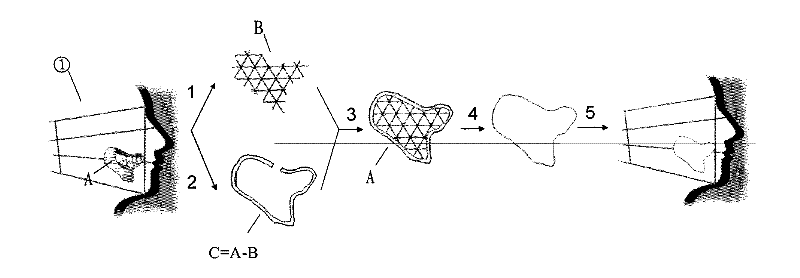
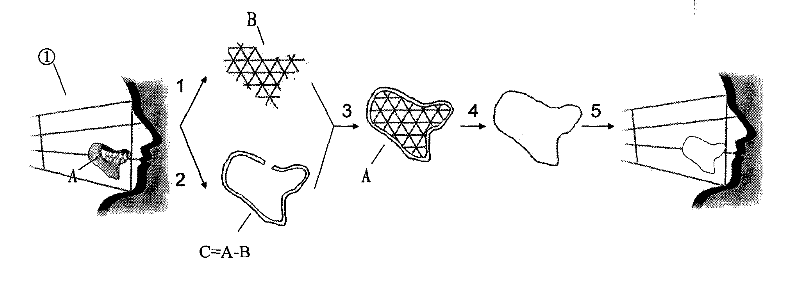
Complex-shaped gel-metal composite prosthesis and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102451048AOvercome problems such as poor retention and local inflammationSolve problems such as poor retention and local inflammationBone implantComposite constructionSide effect
The invention discloses a complex-shaped gel-metal composite prosthesis and a manufacturing method thereof. The prosthesis consists of a silicon rubber jacket and a three-dimensional bracket inside the silicon rubber jacket, wherein the silicon rubber jacket and a titanium mesh three-dimensional structure are simulated and manufactured through the assistance of a computer. The prosthesis can be completely attached to soft and hard tissue defects, has a good edge sealing and fixing effect, has certain supporting strength on the basis of recovering the attractive appearance of a patient, can resist physiological movement of an oral cavity jaw face, is difficult to deform, and provides a new direction for solving the problems of heavy weight, low elasticity, high hardness, a large number of side effects and the like of the conventional prosthesis.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
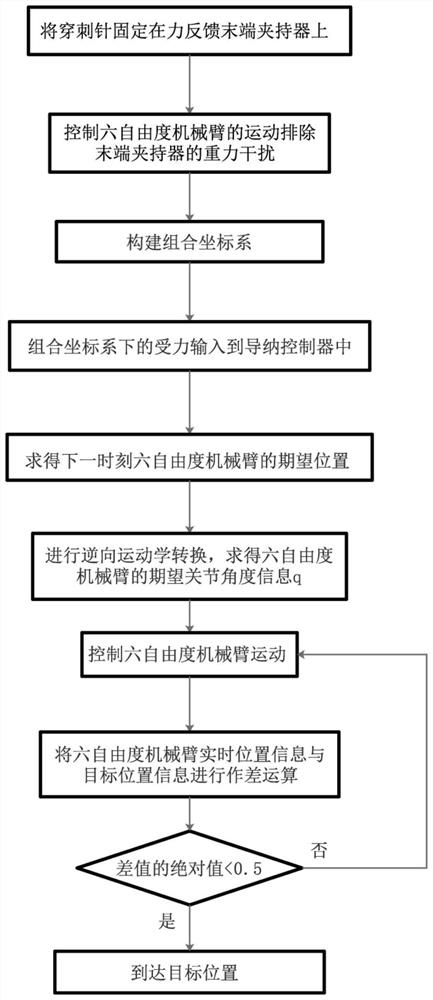
Force feedback end holder admittance control method
ActiveCN113977602AImprove accuracyFilter out noiseJointsArmsPhysiological movementClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a force feedback end holder admittance control method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, solving the equivalent mass of an end holder by controlling the movement of a six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm so as to eliminate the self-weight interference of the end holder, then collecting a puncture needle end force signal as an input signal of an admittance controller through the end holder, solving the zero-force compensation position variable quantity through the Runge-Kutta method, calculating the corresponding joint angle posture through inverse kinematics, driving the mechanical arm by the position controller to move to the corresponding position, and achieving zero-force following. By means of the method, zero-force following control over the puncture needle at the tail end of a puncture operation robot can be achieved, interference caused by physiological movement of tissue to the puncture operation is reduced, and the accuracy and safety of the operation are improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for determination of physiological activity signals
ActiveUS20170150906A1Clearly markedComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysiological movementEngineering
In a method and apparatus for determining a physiological activity signal in a subject using various movement sensors that each transmit a temporal movement signal, a physiological reference signal is determined from the various movement signals that best depicts a physiological movement of the subject, the movement sensor that generates the physiological reference signal is identified as a physiological reference sensor, at least one physiological addition signal is determined from the temporal movement signals that is similar to the physiological reference signal up to a limit, and the physiological reference signal and the at least one addition signal are added to form the physiological activity signal.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Support orthopaedic device for a knee joint
ActiveUS20110034963A1Precise positioningFast and precise implantDiagnosticsJoint implantsOrthopaedic devicePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Support orthopaedic device (1) for a knee joint, comprising a proximal connector (2) and a distal connector (3), articulated among themselves and respectively intended to be associated with a proximal bone (100) and a distal bone (101) of a lower limb connected among themselves by a knee joint. The device comprises a first rod (4a) and a second rod (4b), which are hinged, according to hinging axes normal to a median excursion plane of the orthopaedic device (1), to the proximal connector (2) and to the distal connector (3) so as to form with them an articulated quadrilateral. The articulated quadrilateral is planarly mobile according to a plane parallel to the excursion plane between a configuration corresponding to an extended position of the knee joint and configurations corresponding to bendings of different entity of the knee joint; the relative motion imposed to the proximal and distal connectors (2, 3) by the articulated quadrilateral is consistent with the physiological movement of the knee joint.
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
Artificial cervical intervertebral disc
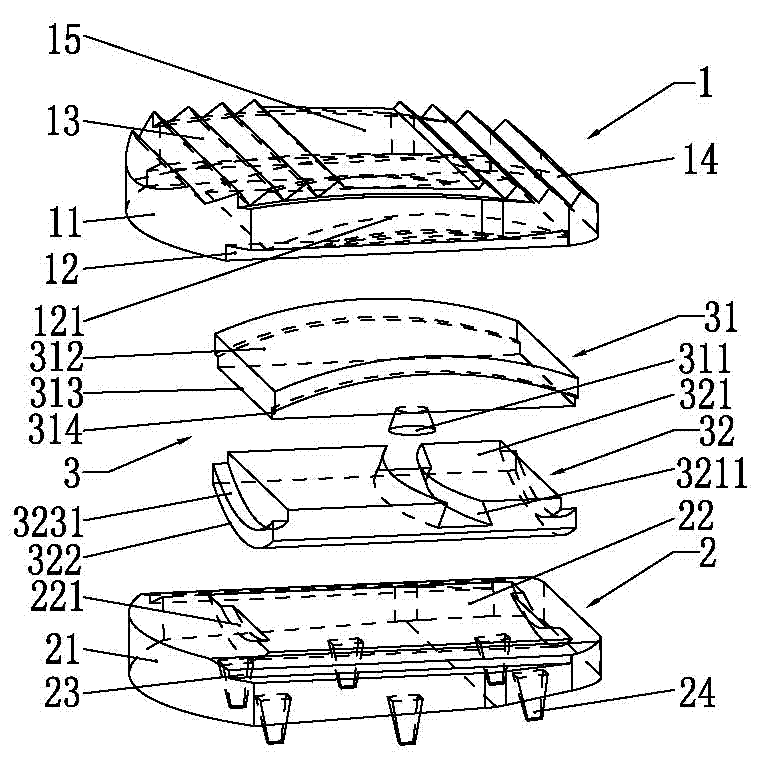
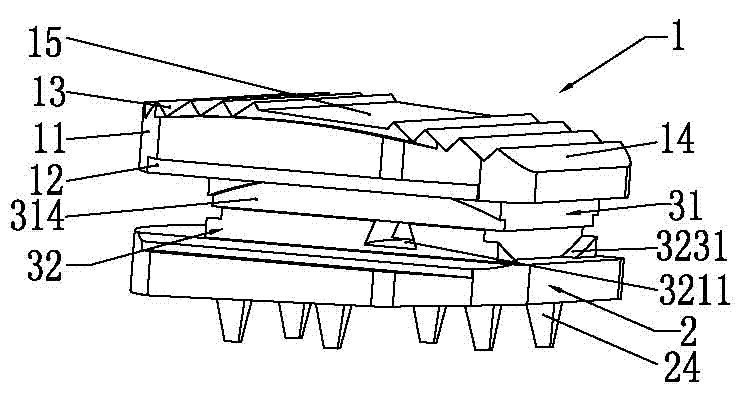
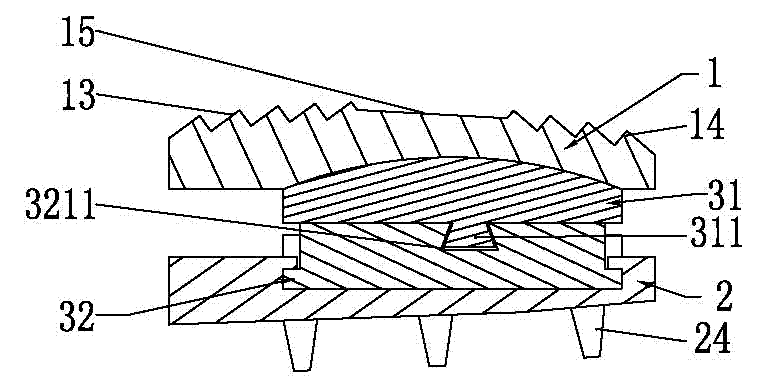
InactiveCN102727329AAvoid damagePrevent long-term sinkingSpinal implantsPhysiological movementProsthesis
The invention relates to an artificial cervical intervertebral disc, which comprises an upper bottom plate, a lower bottom plate and a nucleus pulposus arranged between the upper bottom plate and the lower bottom plate, wherein the nucleus pulposus consists of an upper nucleus pulposus and a lower nucleus pulposus; the upper nucleus pulposus is provided with a convex cylinder; the lower nucleus pulposus is used for allowing an arc-shaped dovetail groove to be nested with the convex cylinder; the upper nucleus pulposus and the lower nucleus pulposus are mutually buckled; the upper bottom plate and the upper nucleus pulposus are cooperated and rotate around a coronal axis so as to simulate the fore flexion and back extension function of the cervical intervertebral disc; the upper bottom plate and the upper nucleus pulposus are permitted to generate front and back relative micro translation; the upper nucleus pulposus and the lower nucleus pulposus are cooperated, can rotate around the rotation axis of the self convex cylinder of the upper nucleus pulposus and also can perform revolution around the rotary track of the arc-shaped dovetail groove of the lower nucleus pulposus; the lower nucleus pulposus and the lower bottom plate are cooperated, and rotate around a sagittal axis to bear motor functions of left and right lateral curvature; and the lower bottom plate and the lower nucleus pulposus are permitted to generate left and right relative micro translation. According to the cervical intervertebral disc prosthesis disclosed by the invention, different construction members of the cervical intervertebral disc prosthesis are permitted to mutually move, and a rotation center in the moving process is coincident with the rotation center of cervical spine segmental physiological movement, so that the natural physiological state of the cervical vertebra can be furthest restored.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com