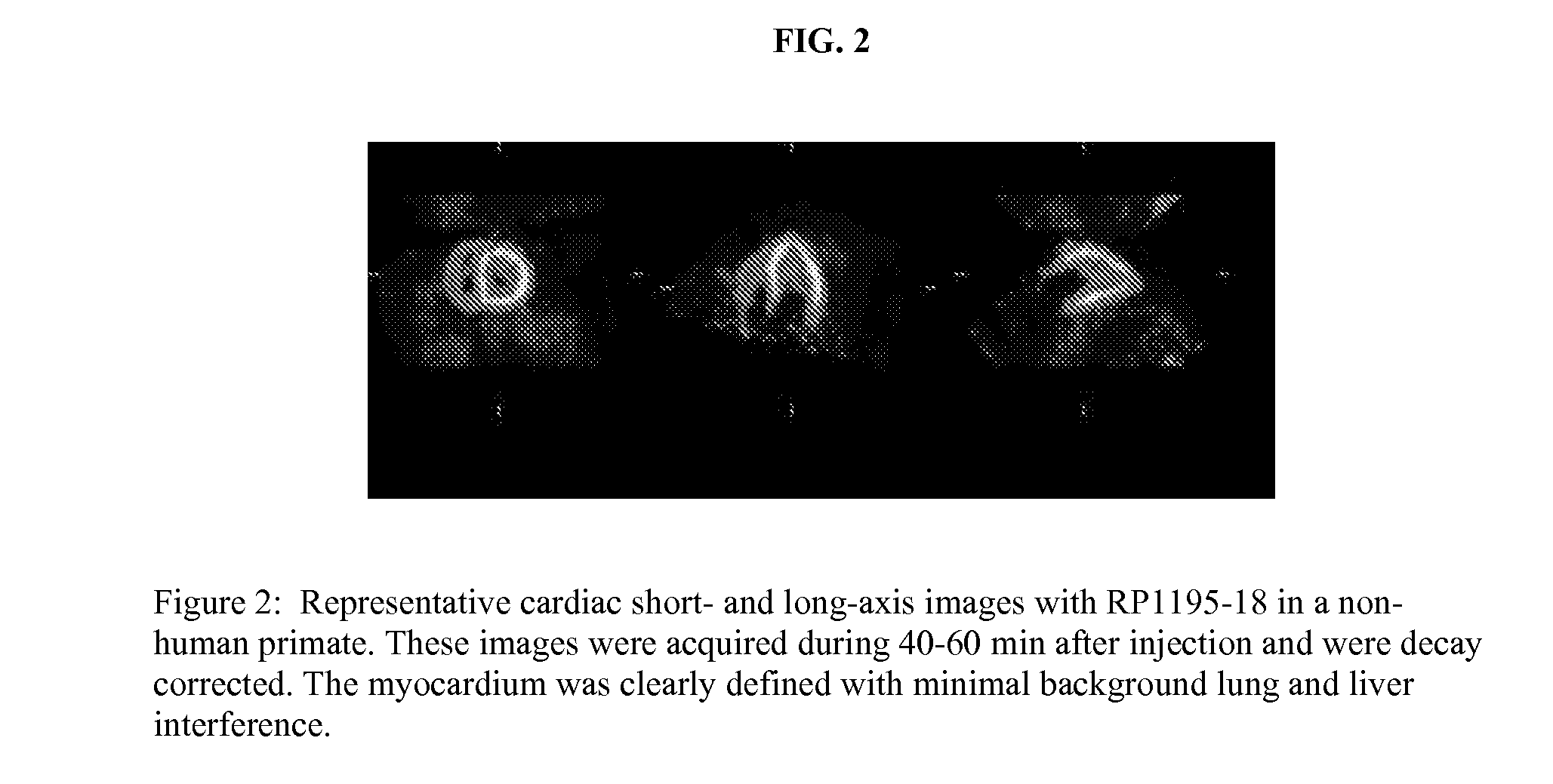
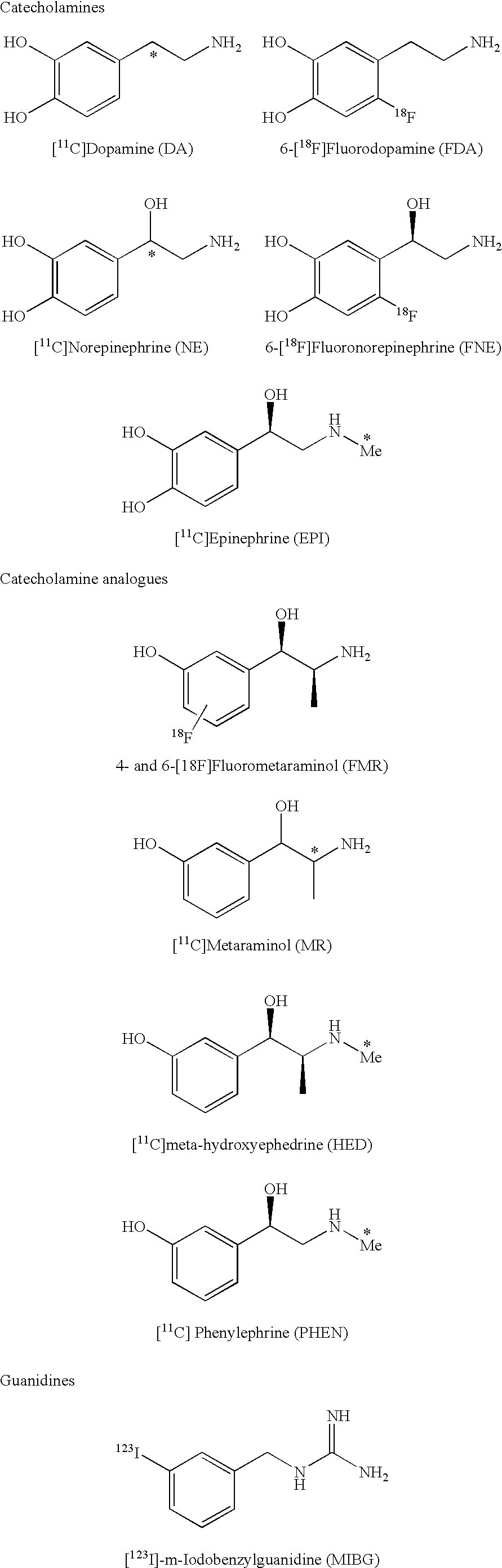
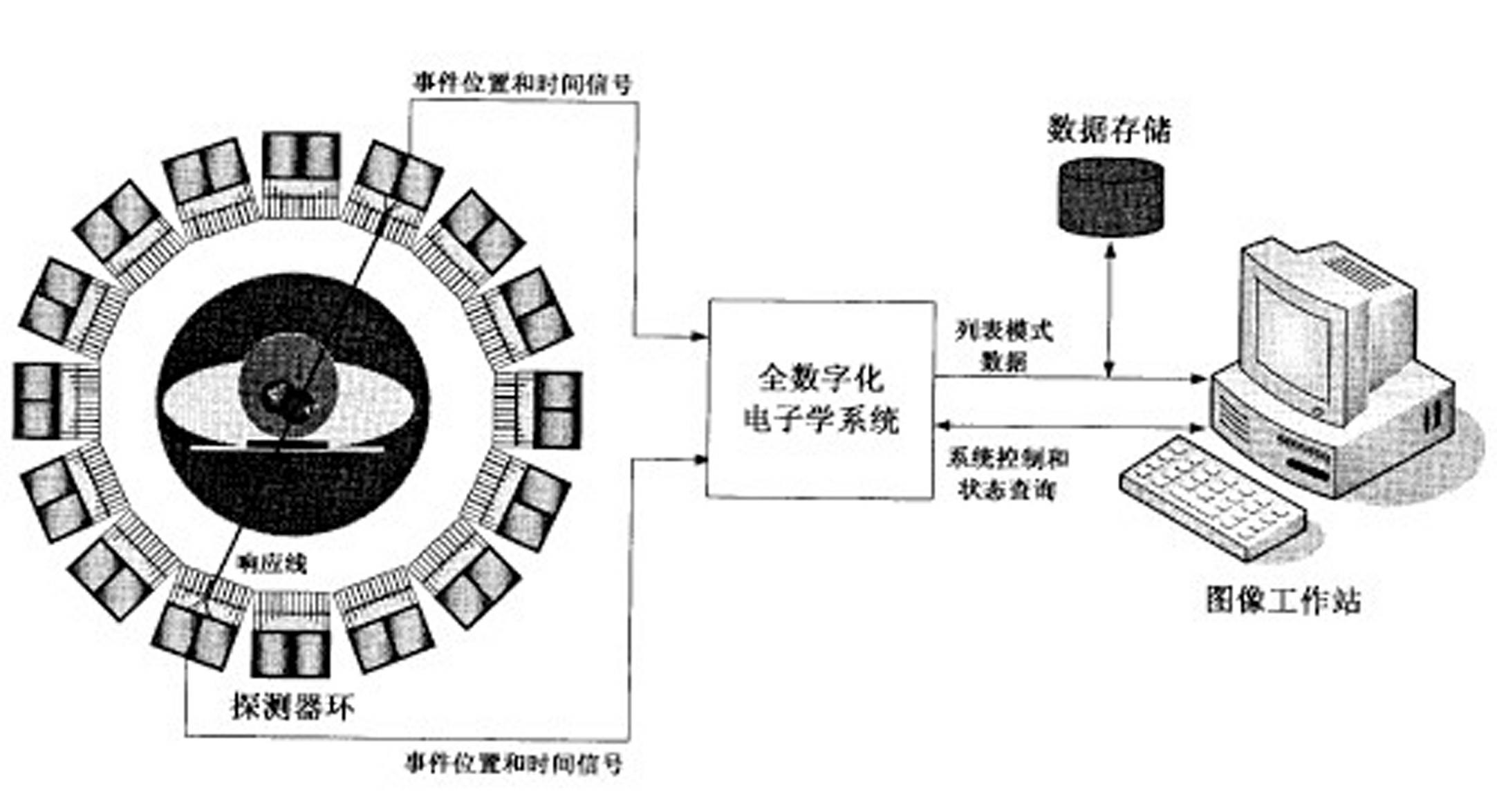
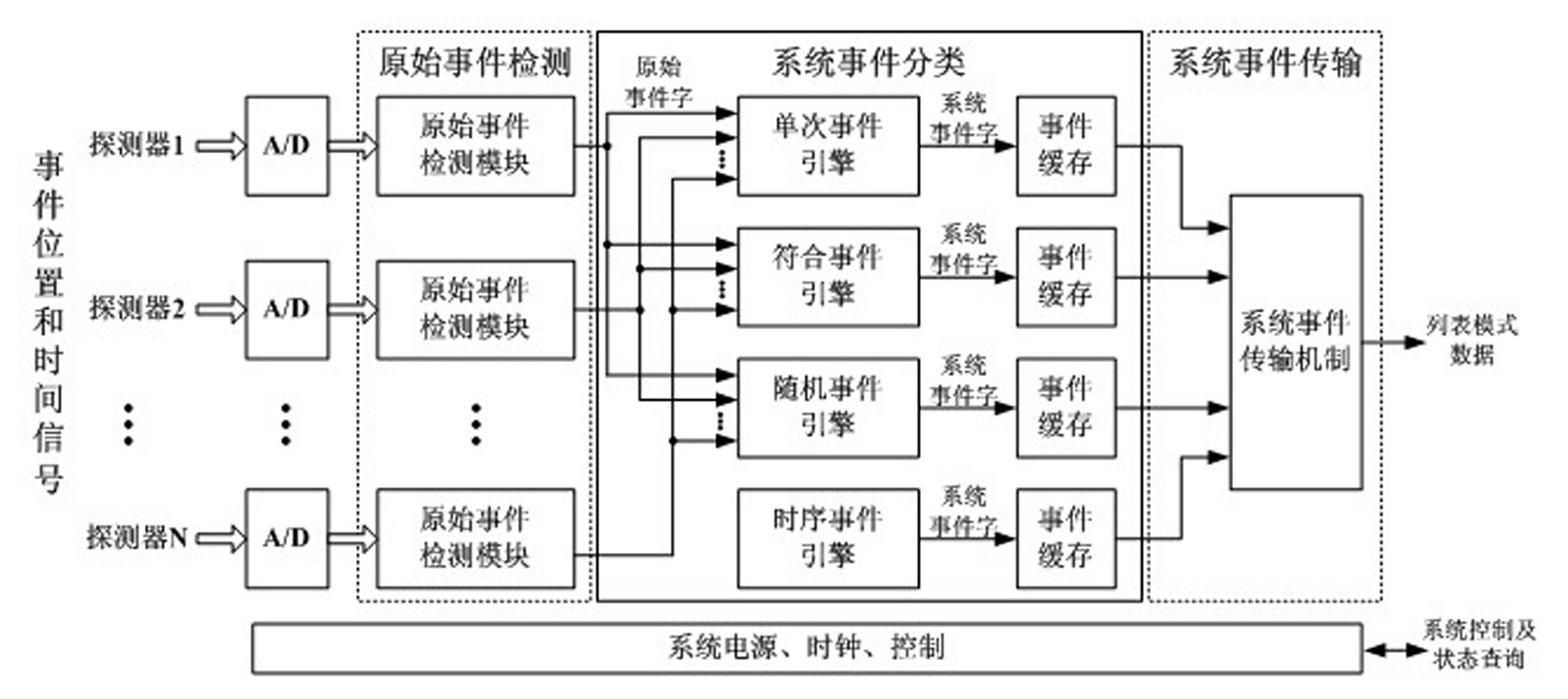
Patents
Literature
488 results about "Pet imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
PET Imaging. Positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear imaging technology (also referred to as molecular imaging) that enables visualization of metabolic processes in the body. The basics of PET imaging is that the technique detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide (also called radiopharmaceuticals,...
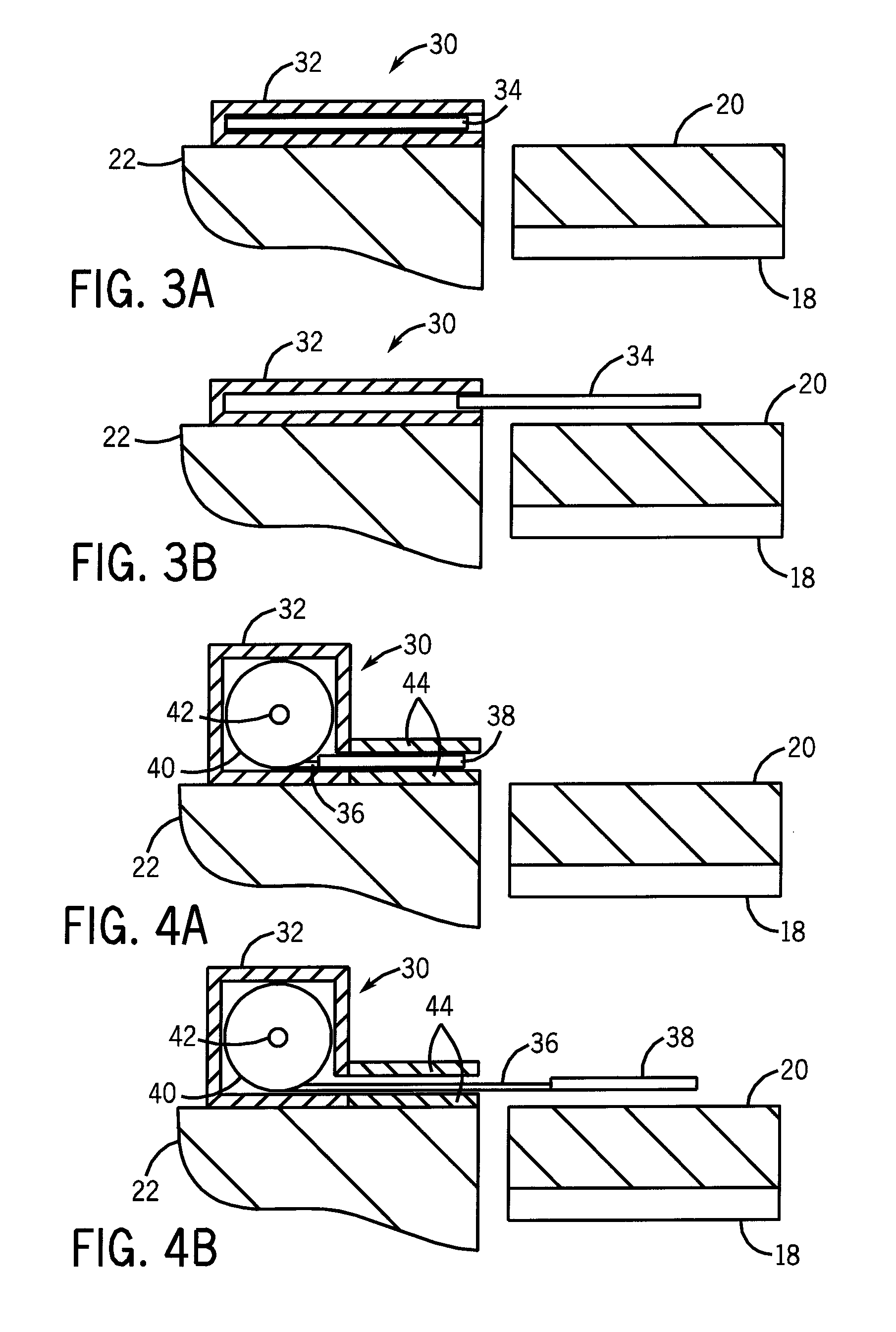
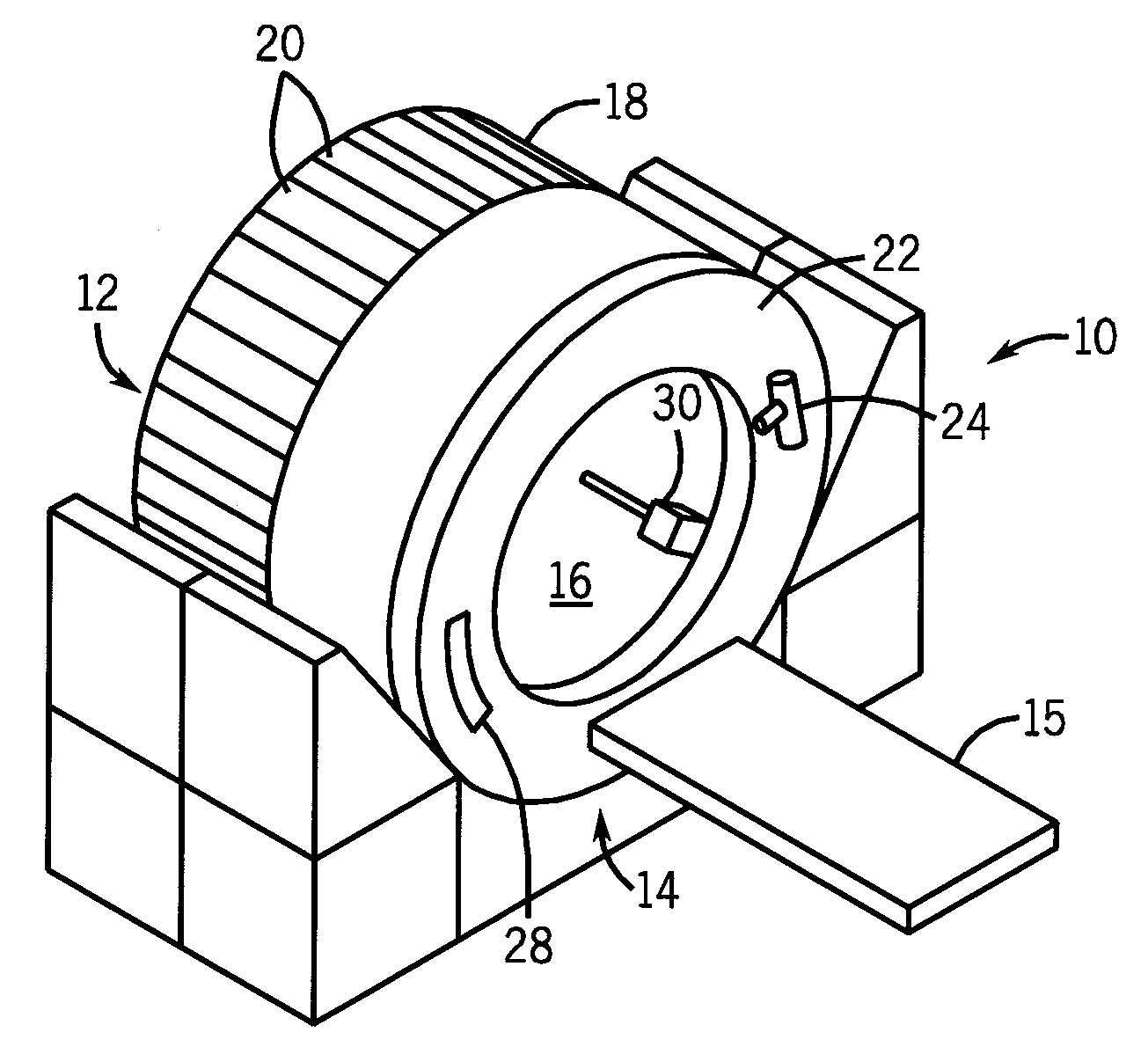
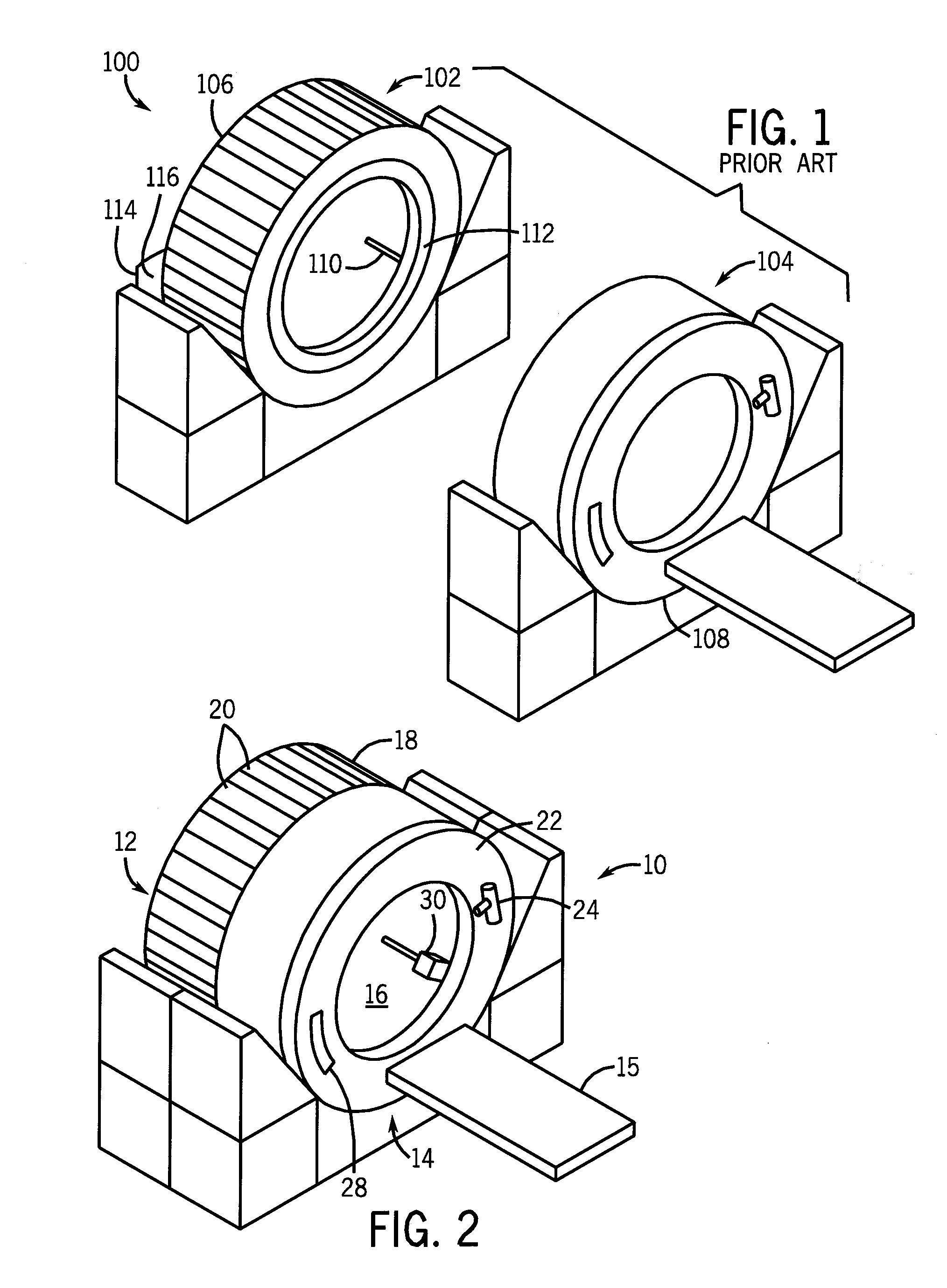
Adjusting acquisition protocols for dynamic medical imaging using dynamic models
ActiveUS20100183206A1More standardizedBetter quantifiableImage enhancementImage analysisDynamic modelsHemodynamics
The invention relates to automatically adjusting an acquisition protocol for dynamic medical imaging, such as dynamic CT, MRI or PET imaging. The protocols are adjusted based on anatomic and dynamic models (10, 12, 14) which are individualized or fitted to each patient based on a scout scan (6, 8). The adjustment can compensate for changes in the patient due to patient motion (e.g. breathing or heartbeat) or flow of contrast or tracing agent during the sequence. This ensures that changes in the reconstructed images are indicative of pathological changes in the patient and not caused by patient motion or changes in scanning parameters or timing. The dynamic model can be a motion model (12) used to predict the motion of anatomic / physiologic features, typically organs, during scanning, or a haemodynamic model (14) used to predict flow of the contrast agent allowing for precise timing of the scanning sequence.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
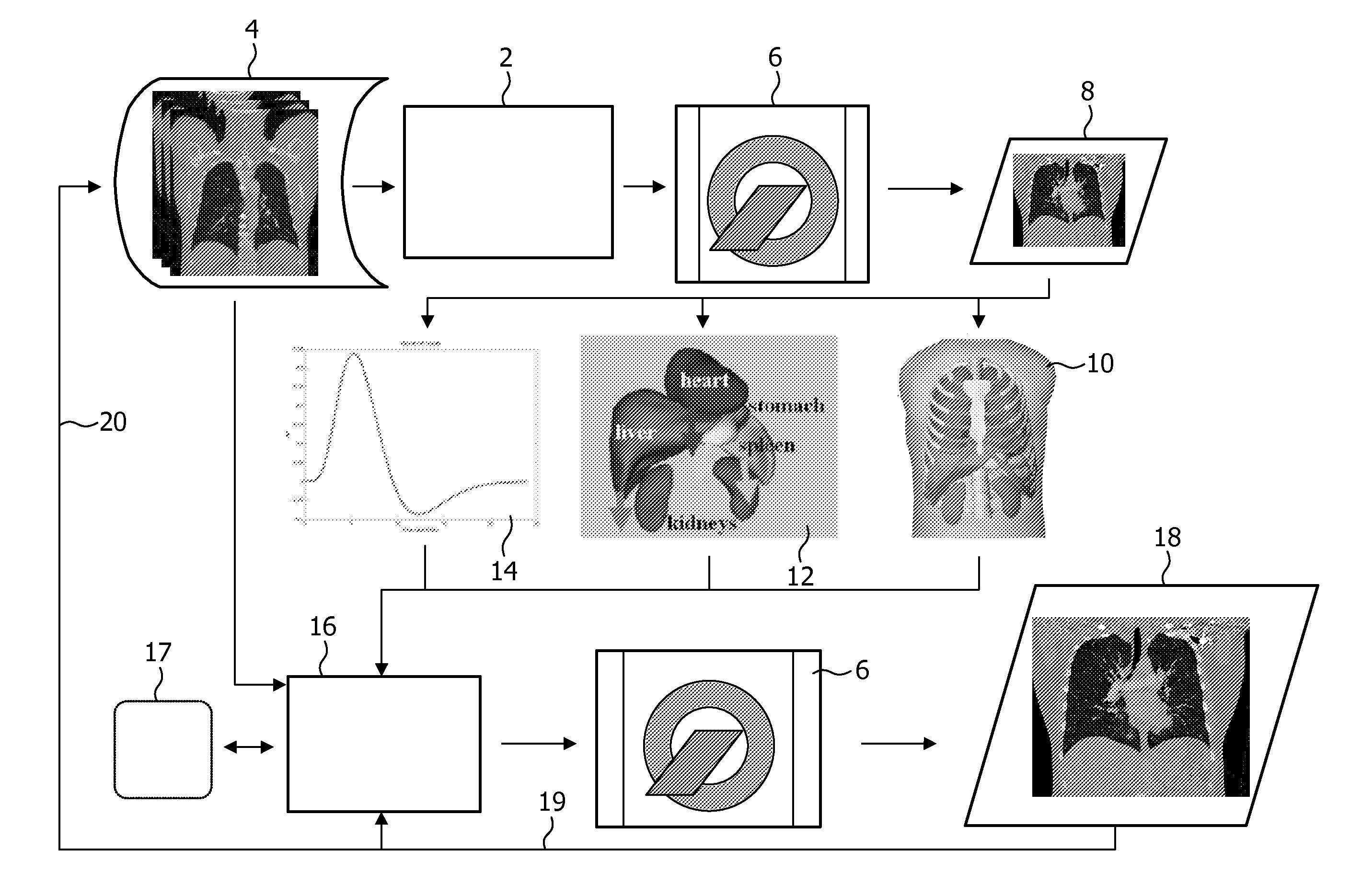
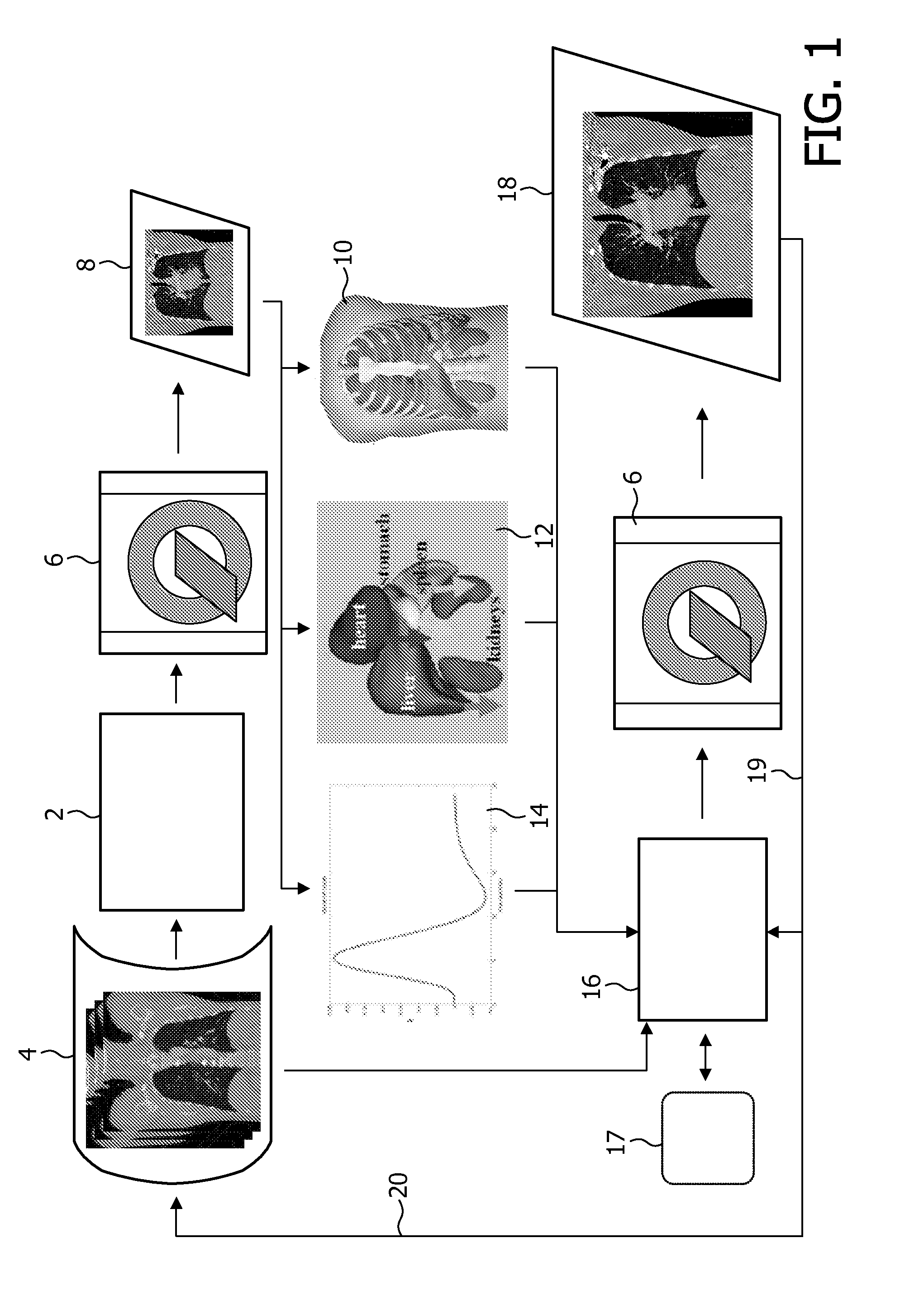
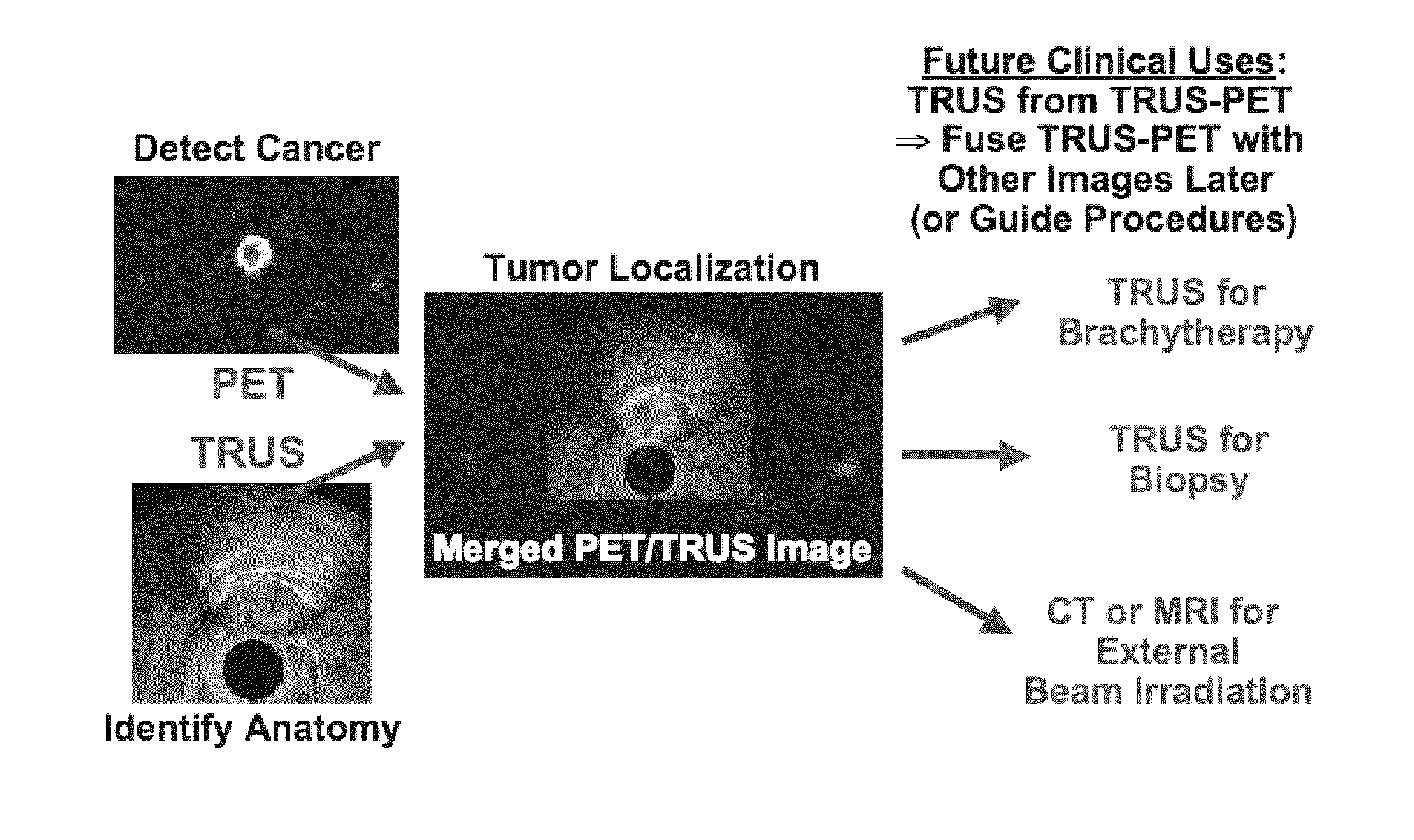
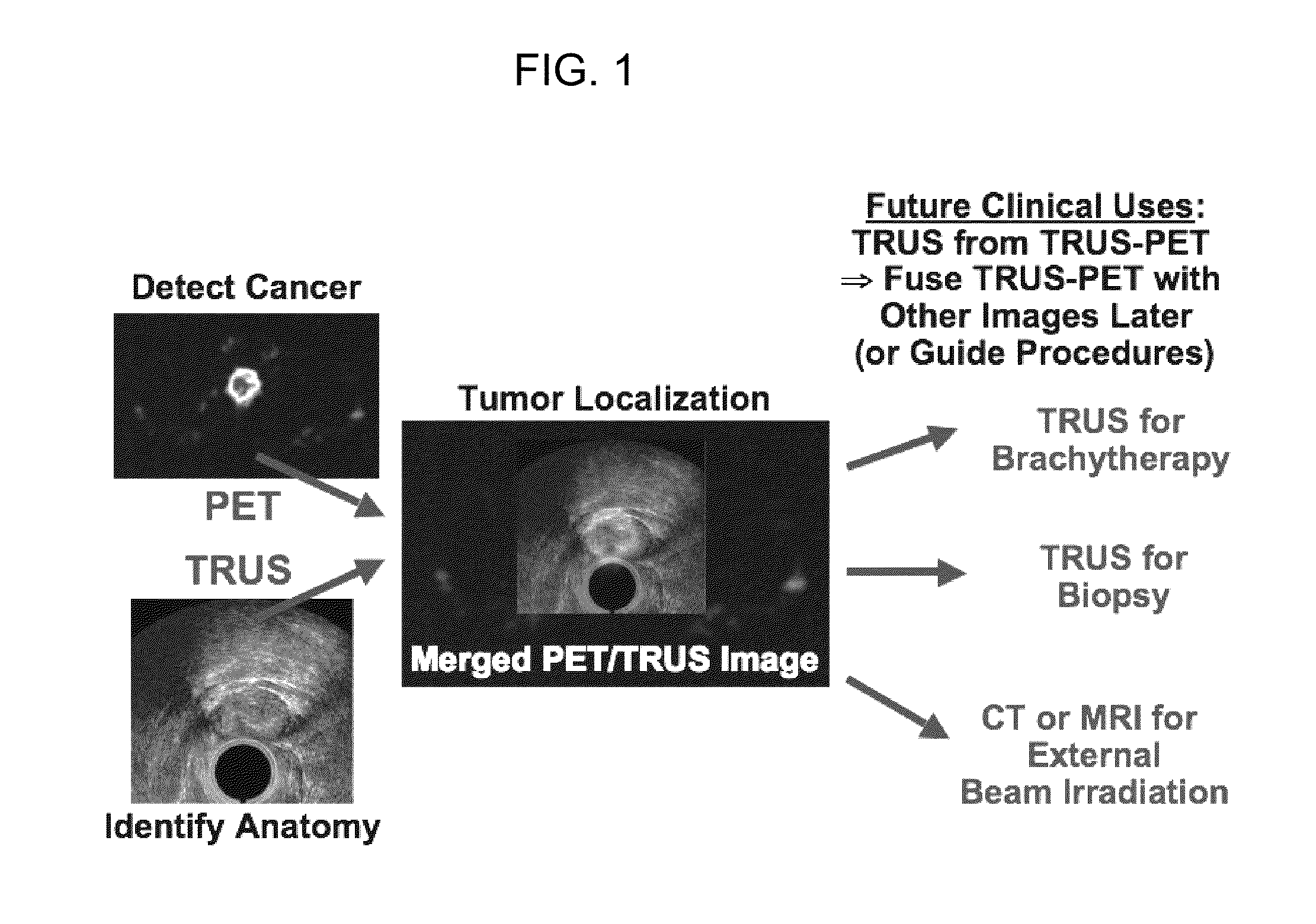
Multi-Modality Phantoms and Methods for Co-registration of Dual PET-Transrectal Ultrasound Prostate Imaging
InactiveUS20100198063A1Precise registrationPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansUltrasound imagingSonification
Herein are described methods and tools for acquiring accurately co-registered PET and TRUS images, as well as the construction and use of PET-TRUS prostate phantoms. Ultrasound imaging with a transrectal probe provides anatomical detail in the prostate region that can be accurately co-registered with the sensitive functional information from the PET imaging. Imaging the prostate with both PET and transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) will help determine the location of any cancer within the prostate region. This dual-modality imaging should help provide better detection and treatment of prostate cancer. Multi-modality phantoms are also described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
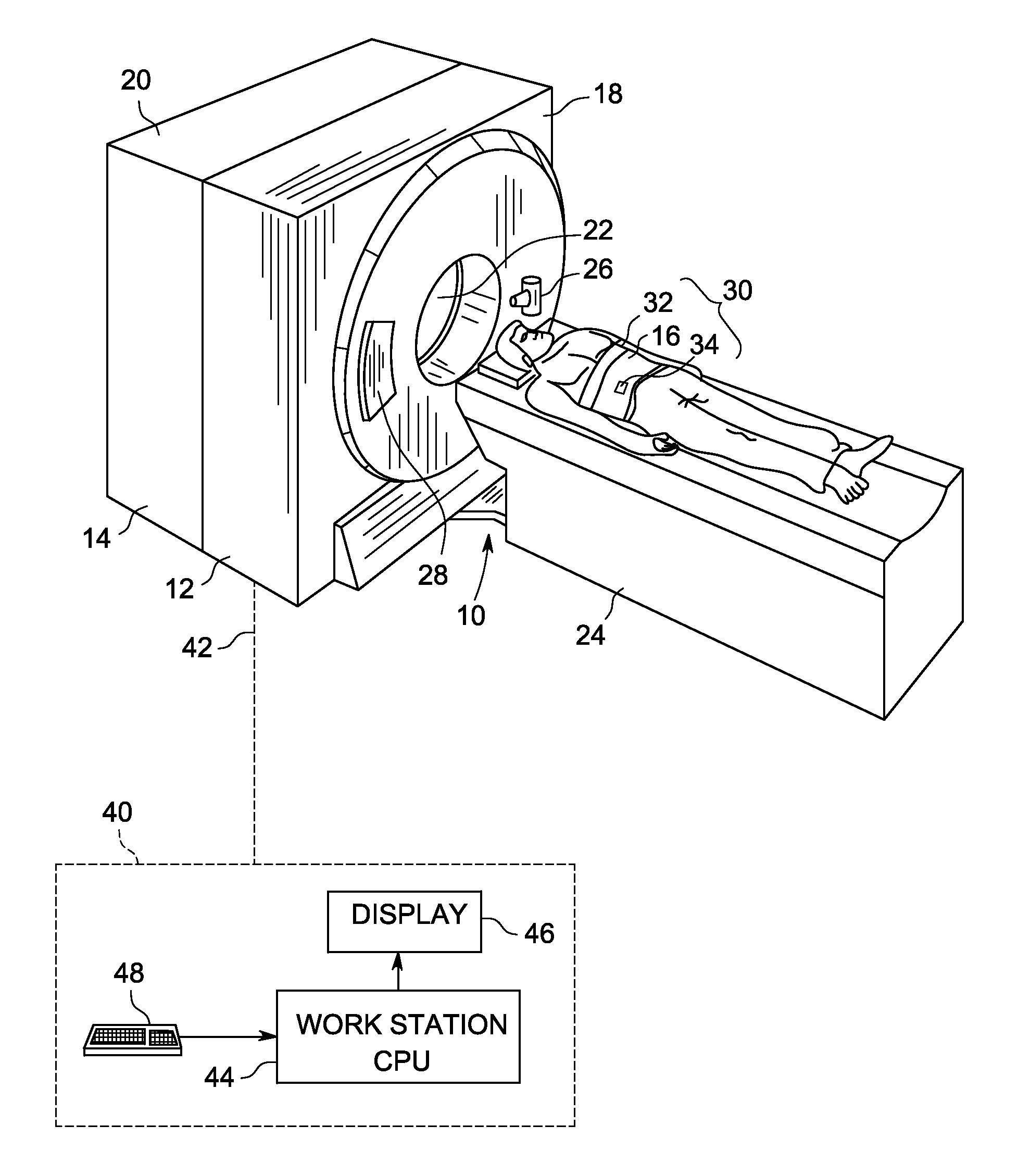
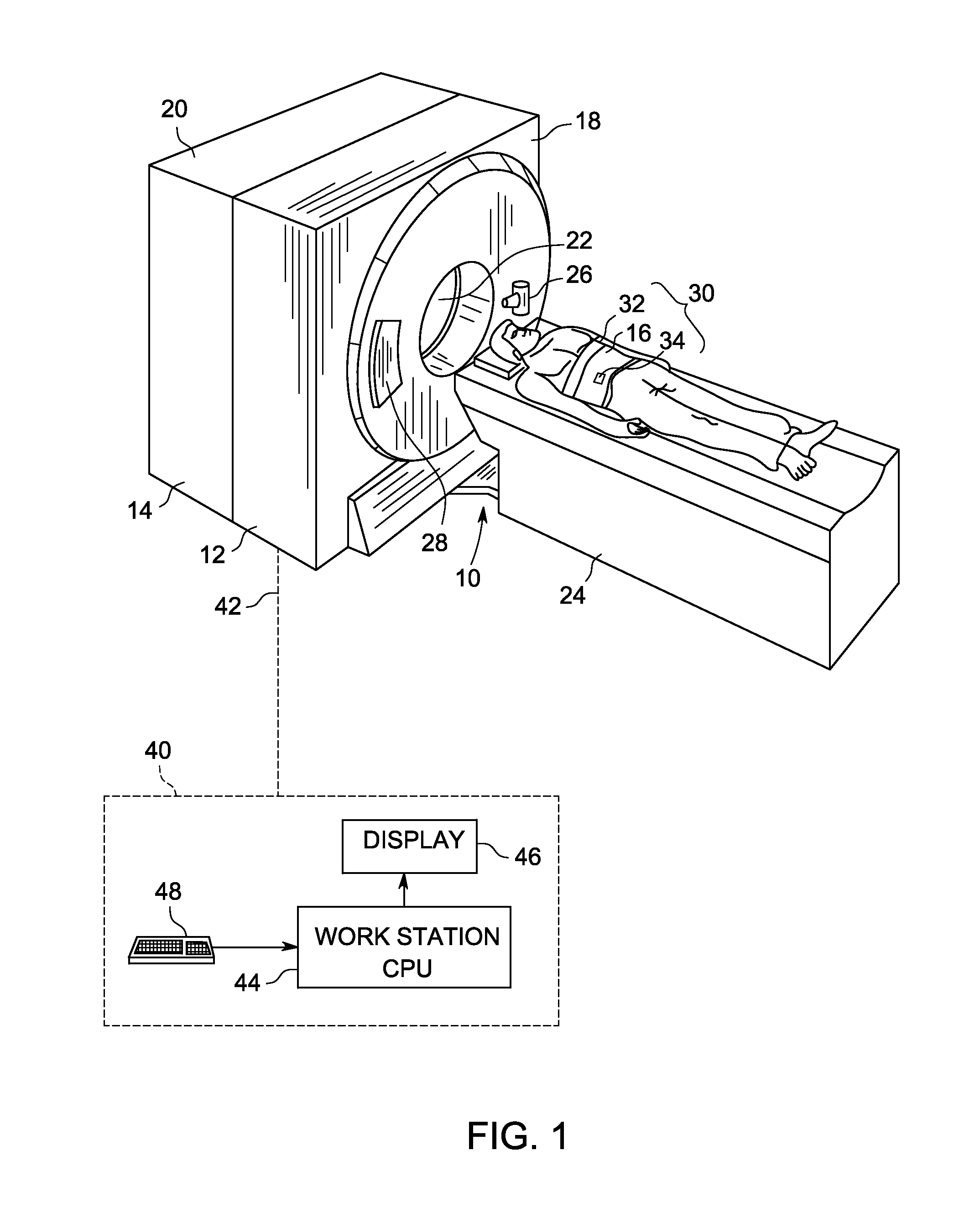
Large bore pet and hybrid pet/ct scanners and radiation therapy planning using same
ActiveUS20100040197A1Quick responseReduced radially inward extentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsLines of responseRadiation planning
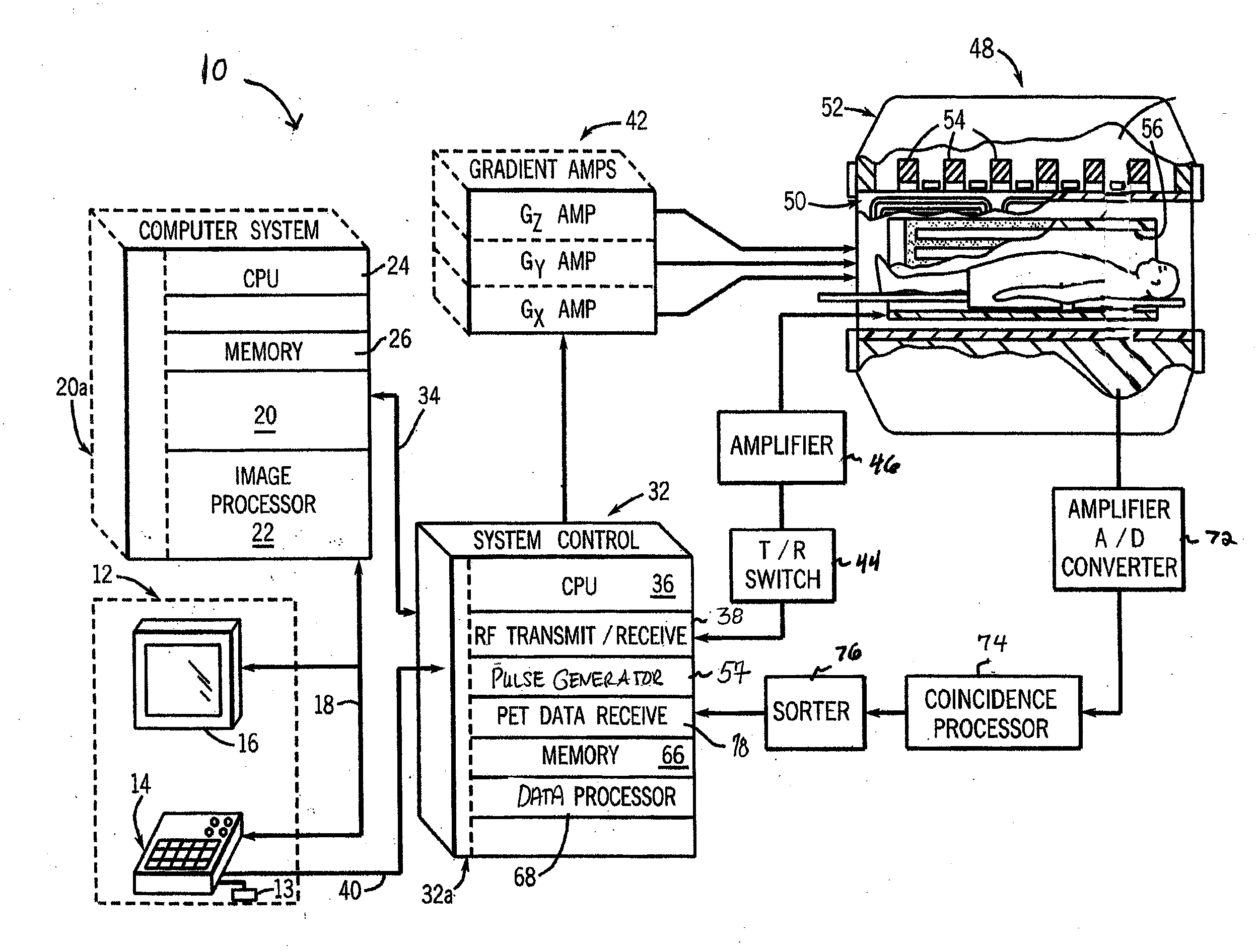
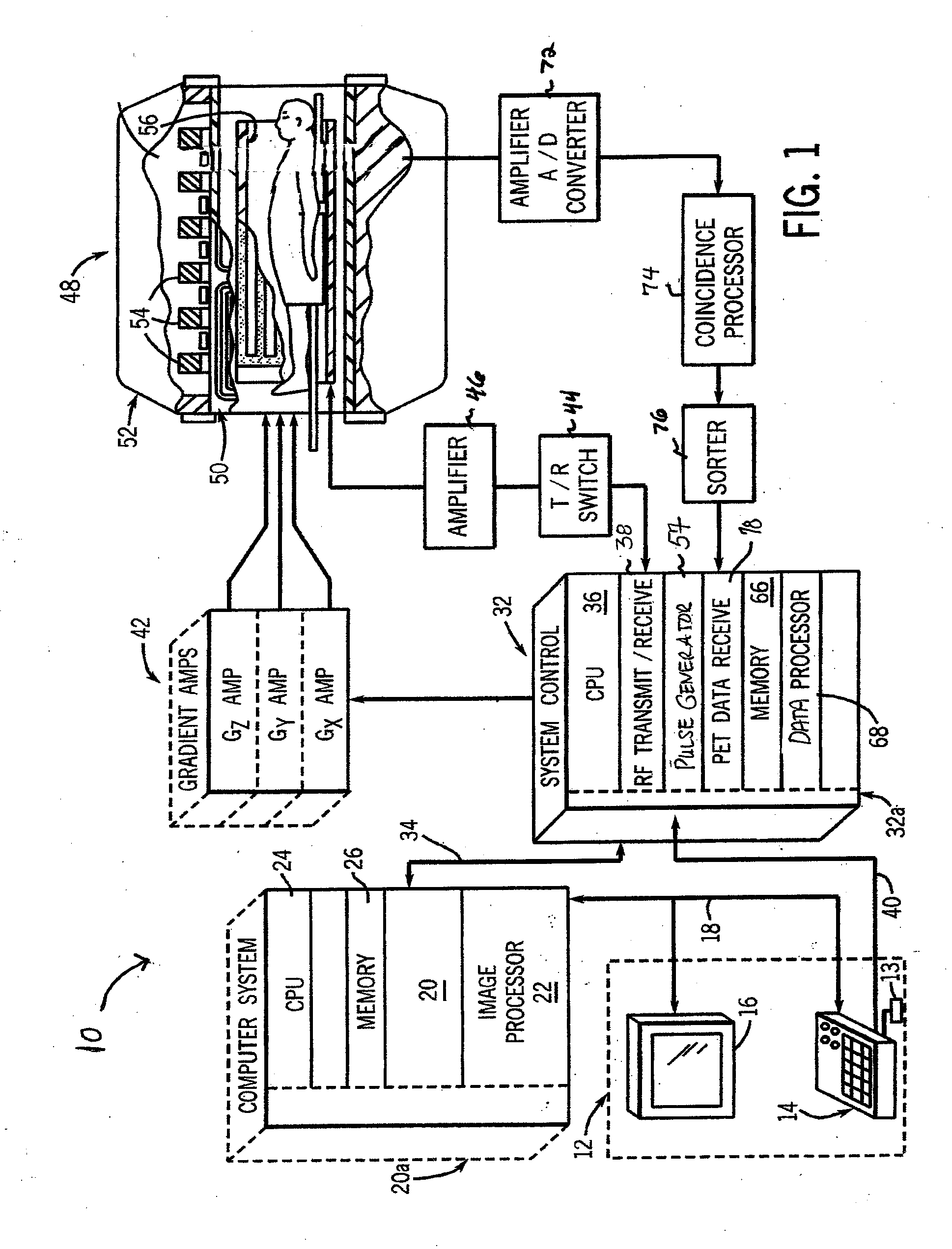
An imaging system comprises: a ring of positron emission tomography (PET) detectors; a PET housing at least partially surrounding the ring of PET detectors and defining a patient aperture of at least 80 cm; a coincidence detection processor or circuitry configured to identify substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events corresponding to electron-positron annihilation events; and a PET reconstruction processor configured to reconstruct into a PET image the identified substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events based on lines of response defined by the substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events. Radiation planning utilizing such an imaging system comprises: acquiring PET imaging data for a human subject arranged in a radiation therapy position requiring a patient aperture of at least about 80 cm; reconstructing said imaging data into a PET image encompassing an anatomical region to undergo radiation therapy; and generating a radiation therapy plan based on at least the PET image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Compton camera detector systems for novel integrated compton-Pet and CT-compton-Pet radiation imaging
The invention provides novel Compton camera detector designs and systems for enhanced radiographic imaging with integrated detector systems which incorporate Compton and nuclear medicine imaging, PET imaging and x-ray CT imaging capabilities. Compton camera detector designs employ one or more layers of detector modules comprised of edge-on or face-on detectors or a combination of edge-on and face-on detectors which may employ gas, scintillator, semiconductor, low temperature (such as Ge and superconductor) and structured detectors. Detectors may implement tracking capabilities and may operate in a non-coincidence or coincidence detection mode.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a pet/mri scanner
ActiveUS20080265887A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nuclear medicine tomography systems, detectors and methods
ActiveUS20150119704A1Reduce spatial resolutionAvoid interferenceRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImage resolution
An N-M tomography system comprising: a carrier for the subject of an examination procedure; a plurality of detector heads; a carrier for the detector heads; and a detector positioning arrangement operable to position the detector heads during performance of a scan without interference or collision between adjacent detector heads to establish a variable bore size and configuration for the examination. Additionally, collimated detectors providing variable spatial resolution for SPECT imaging and which can also be used for PET imaging, whereby one set of detectors can be selectably used for either modality, or for both simultaneously.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
System and apparatus for detecting gamma rays in a PET/MRI scanner
ActiveUS7667457B2X/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentElectric/magnetic detectionPhotodetectorRadio frequency
A gamma ray detector ring for a combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system is integrated into a radio frequency (RF) coil assembly such that the detector ring is integrated with a RF shield. Each gamma ray detector in the detector ring includes a scintillator component that emits light when a gamma ray is detected and a photodetector component designed to be sensitive to the frequency of light produced by the scintillator. A RF shield may be integrated into a detector ring such that the RF shield is positioned between the scintillator and photodetector components of each detector, thereby saving valuable radial space within the imaging system. Multiple such detector rings may be located adjacent to one another to increase axial coverage and enable three-dimensional PET imaging techniques.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and compounds for targeting tissues
The present invention relates to peptides which home to cells, e.g. heart cells, with high selectivity and which can be useful in the form of compositions. Such compositions can be used, e.g., for selectively targeting a systemically administered therapeutic agent or imaging agent to a cell or tissue in a subject. The present invention further relates to methods of using the compositions for imaging, e.g. PET imaging, and targeting cells, e.g. for delivering a therapeutic agent to one or more target cells in a subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
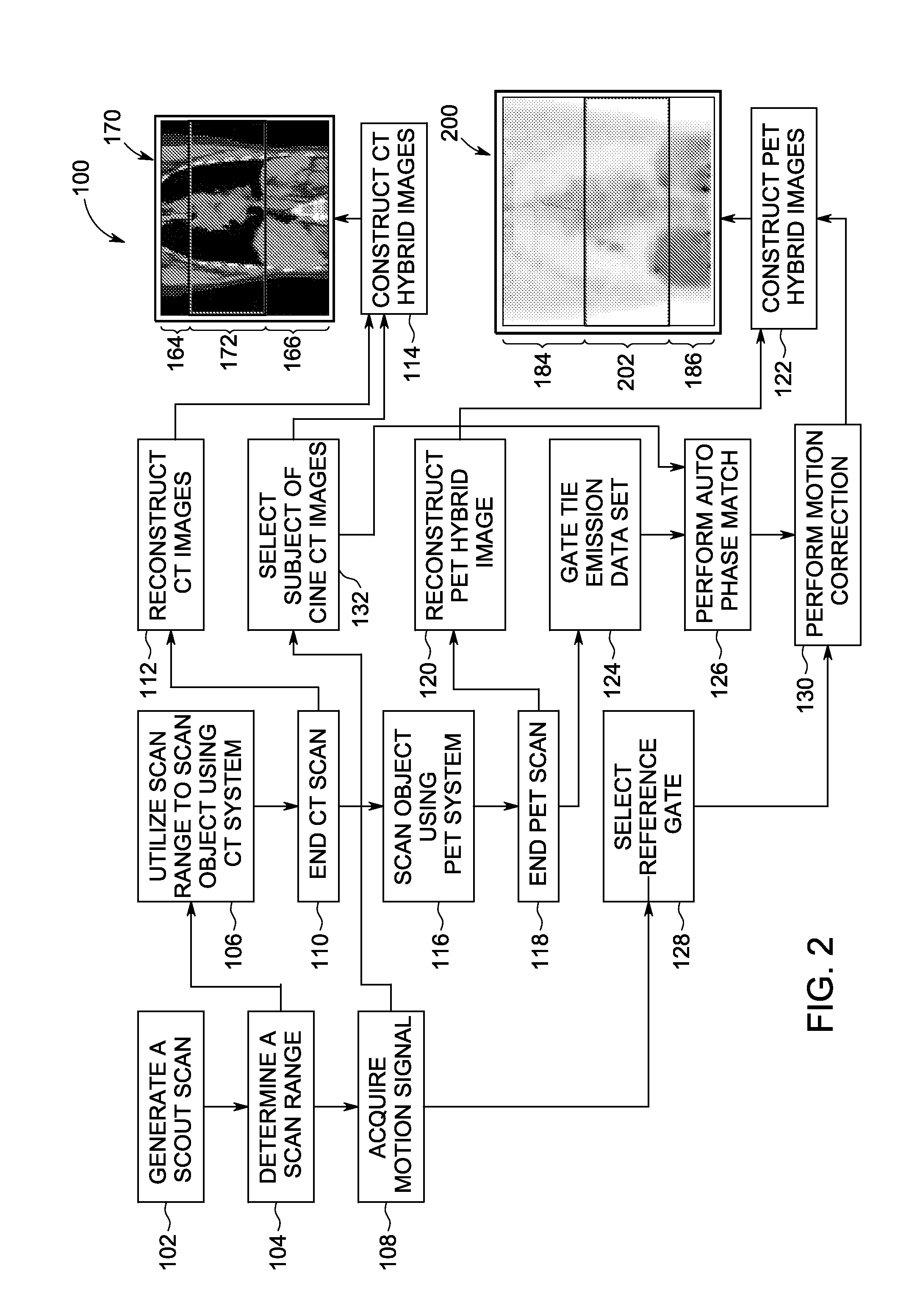
Method and apparatus for generating medical images
InactiveUS20120078089A1Improve medical qualityMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringData setPet imaging
A method for generating a hybrid imaging volume includes acquiring a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging dataset of an object using a PET imaging system, the PET imaging dataset including at least one motion affected portion and at least one non-motion affected portion, identifying a motion affected portion of the PET imaging dataset, motion correcting the identified portion of the PET imaging dataset to generate a hybrid portion, and constructing a hybrid PET image volume using the hybrid portion and the at least one non-motion affected portion. A system for implementing the method is also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Large bore PET and hybrid PET/CT scanners and radiation therapy planning using same
ActiveUS8063376B2Quick responseReduced radially inward extentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsLines of responseRadiation planning
An imaging system comprises: a ring of positron emission tomography (PET) detectors; a PET housing at least partially surrounding the ring of PET detectors and defining a patient aperture of at least 80 cm; a coincidence detection processor or circuitry configured to identify substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events corresponding to electron-positron annihilation events; and a PET reconstruction processor configured to reconstruct into a PET image the identified substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events based on lines of response defined by the substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events. Radiation planning utilizing such an imaging system comprises: acquiring PET imaging data for a human subject arranged in a radiation therapy position requiring a patient aperture of at least about 80 cm; reconstructing said imaging data into a PET image encompassing an anatomical region to undergo radiation therapy; and generating a radiation therapy plan based on at least the PET image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
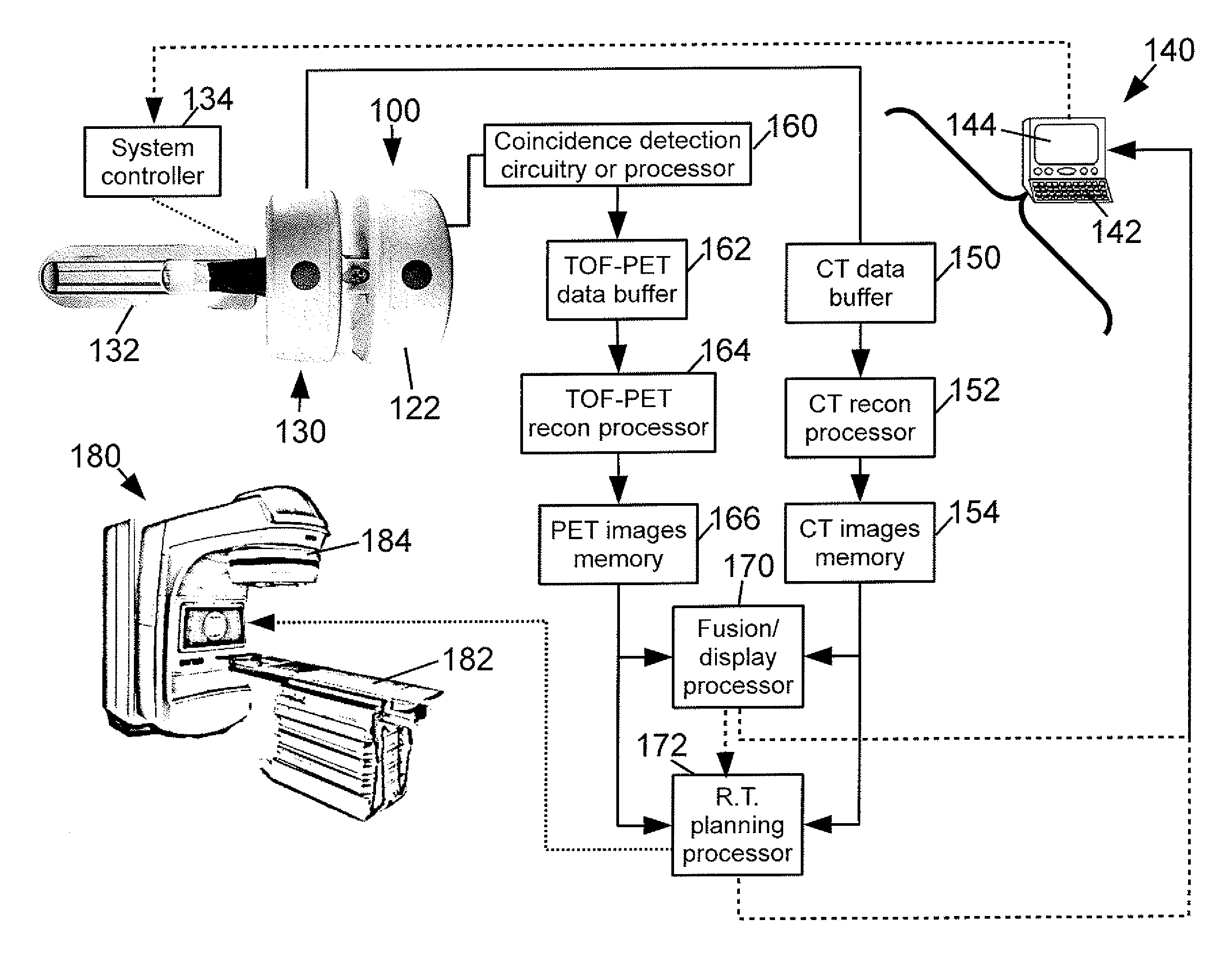
CT gantry mounted radioactive source loader for PET calibration
InactiveUS7755057B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPet imagingMedical imaging
A medical imaging system is provided including a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging apparatus and a computed tomography (CT) imaging apparatus. The CT imaging apparatus includes a rotatable gantry. A radioactive source loader is attached to the rotatable gantry to rotate therewith. The radioactive source loader further includes a radioactive source to calibrate the PET imaging apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combined pet/mrt unit and method for simultaneously recording pet images and mr images
A combined PET / MRT unit is disclosed that includes a PET detector which is reduced by comparison with the prior art, and that consists, for example, of a PET detector with a polygonal arrangement of the detector elements or with a PET detector ring. The PET detector is reduced in an axial direction by comparison with the detectors of the prior art, as a result of which the costs for producing the expensive PET detectors are lowered. The reduction of the PET detector is possible because the MR measurement usually lasts longer than the PET measurement, and so a reduced PET detector can be used for the temporally sequential recording of a number of PET tomograms by mechanical displacement of the PET detector. Since the MR measurement lasts substantially longer, this mechanical displacement does not lead to a lengthening of the measuring time. The invention also relates to methods for simultaneously recording MR and PET tomograms in which the PET / MRT units according to the invention are used.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
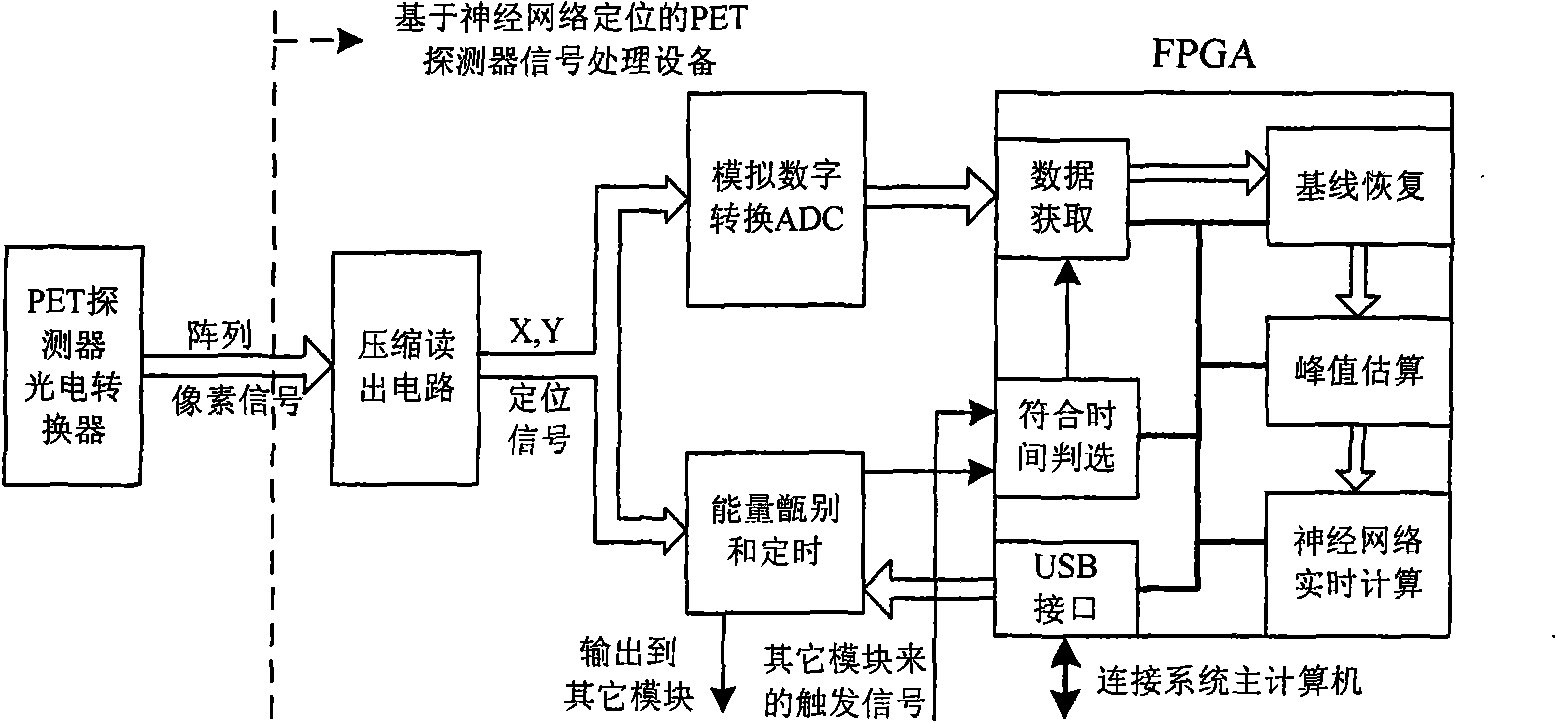
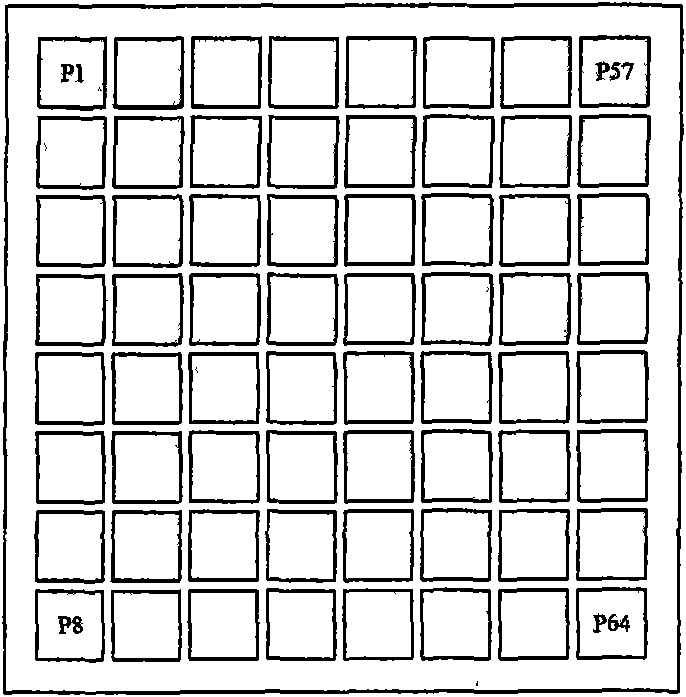
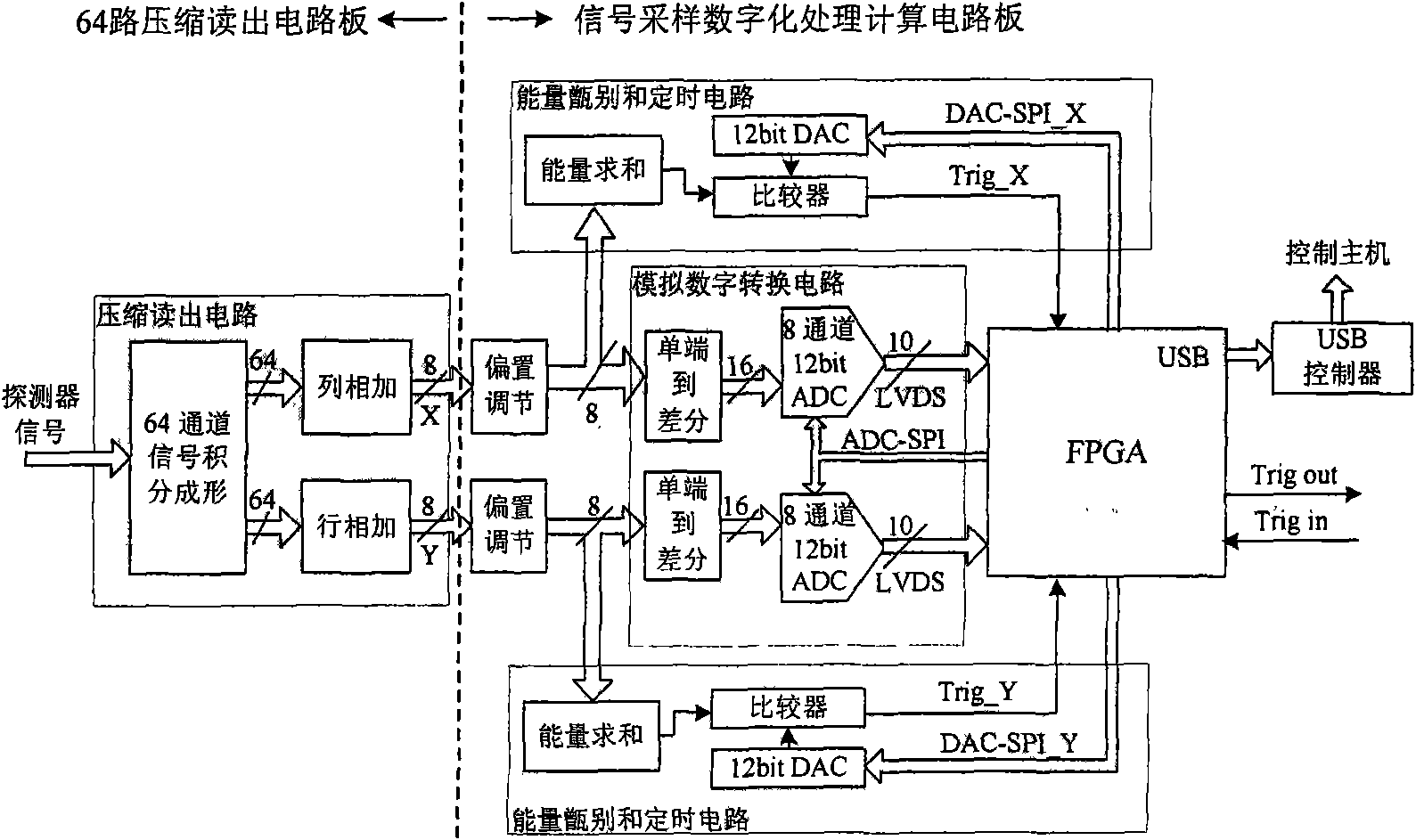
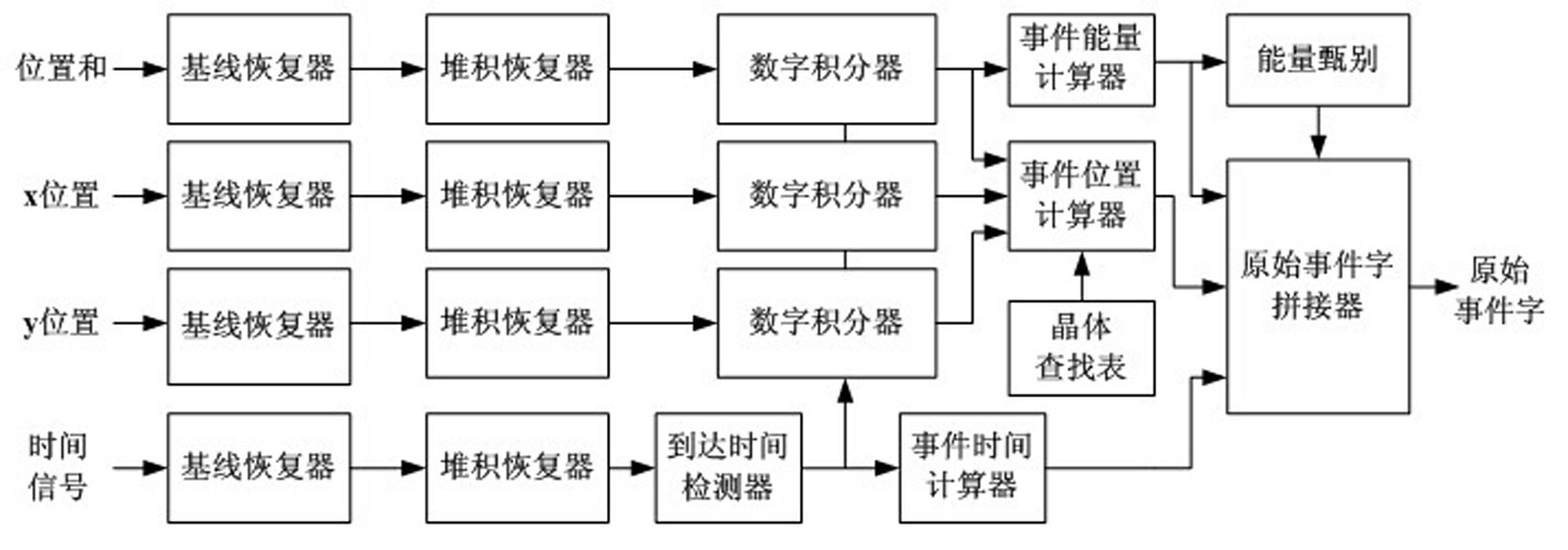
Signal processing equipment of PET detector based on neural network localizer
InactiveCN101606846AImproved real-time performance of signal processingHighly integratedComputerised tomographsTomographyPeak valueProper time
The invention provides signal processing equipment of a PET detector based on a neural network localizer. The equipment integrates and realizes procedures for processing a series of signals from a photoelectric switching signal outputted by a detector to the action position coordinate of the gamma ray counted by a neural network in real time. The equipment comprises a compression read processing circuit to an array pixel signal outputted by a photoelectric switching device, an analog-digital switching circuit, an energy identifying and timing circuit, a proper time judging circuit, a base line recovery circuit, a signal peak value estimating circuit, a neural network real-time computing circuit, a USB interface circuit, etc. Due to the realization of the technology for processing various digital nuclear signals based on FPCA and especially the real-time computing of the neural network, the instantaneity and the integration level of the system are greatly improved. The invention has compact structure, complete performance, strong on-line data processing performance, and can be conveniently assembled into an integral detector module with the PET detector, wherein the detector module is important intermediate equipment for researching and developing novel PET imaging equipment based on neural network positioning.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Kalman filtering image reconstruction method in PET imaging
ActiveCN101499173AQuality improvementRaise the bias2D-image generationComputerised tomographsFractographyImaging quality
The invention provides a method for rebuilding Kallman filtering image in PET imaging. The method includes steps as follows: obtaining a sinusoidal chart of an original projective line through PET positron emission faultage scanner, establishing a state space system, getting radioactivity activity distribution through the Kallman filtering method based on the state space and rebuilding image. The method rebuild PET image by using the Kallman filtering method based on the state space system which can increase the rebuild image quality efficiently; compared with the prior rebuild method, declination and dispersion of the rebuild result are increased greatly.
Owner:刘华锋
Ct gantry mounted radioactive source loader for pet calibration
InactiveUS20080217541A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPet imagingMedical imaging
A medical imaging system is provided including a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging apparatus and a computed tomography (CT) imaging apparatus. The CT imaging apparatus includes a rotatable gantry. A radioactive source loader is attached to the rotatable gantry to rotate therewith. The radioactive source loader further includes a radioactive source to calibrate the PET imaging apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ligands for imaging cardiac innervation
ActiveUS20100221182A1Improve stabilityDecreased NE releaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsArylRadioactive tracer
Novel compounds that find use as imaging agents within nuclear medicine applications (PET imaging) for imaging of cardiac innervation are disclosed. These PET based radiotracers may exhibit increased stability, decreased NE release (thereby reducing side effects), improved quantitative data, and / or high affinity for VMAT over prior radiotracers. Methods of using the compounds to image cardiac innervation are also provided. In some instances the compounds are developed by derivatizing certain compounds with 18F in a variety of positions: aryl, alkyl, a keto, benzylic, beta-alkylethers, gamma-propylalkylethers and beta-proplylalkylethers. Alternatively or additionally, a methyl group a is added to the amine, and / or the catechol functionality is either eliminated or masked as a way of making these compounds more stable.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
Fully digital processing device for positron emission tomography electronics system
The invention relates to a fully-digitalized processing device of a positron emission tomography imaging electronic system, relating to the technical field of medical imaging, in particular to the field of positron emission tomography imaging, more particularly relating to electronics, signal processing and data processing methods and equipment in the positron emission tomography imaging system. The technical scheme of the invention is that the positron emission tomography imaging electronics system comprises detectors, a fully-digitalized electronics system and an image working station, wherein the detectors are annularly arranged in an arrayed way. According to the invention, the structure and the system are greatly simplified; and because the PET (Positron Emission Tomography) signal detection and processing, data acquisition, and the like are realized in a fully-digitalized way, the system integration level is high, the functions are powerful, the processing real-time property is good, the performance is stable and reliably, and the system function adjusting and upgrading are convenient. In the assembly process, the system can be conveniently adjusted and corrected, and the production cost and the production cycle of PET imaging equipment are effectively reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU SINOWAYS (ZHONGHUI) MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Maximum posteriori reconstruction method of PET (positron emission tomography) image based on generalized entropy and MR (magnetic resonance) prior
The invention discloses a maximum posteriori reconstruction method of a PET (positron emission tomography) image based on generalized entropy and MR (magnetic resonance) prior. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring detection data before PET imaging by PET imaging equipment, meanwhile, obtaining various data correction parameter values in the imaging equipment and a system matrixof the imaging equipment; (2) constructing a mathematic statistical model for reconstructing the PET image; (3) obtaining a PET initial value image by a maximum likelihood method on the basis of mathematic statistical model solution; (4) registering the previously obtained MR image and the PET initial value image; (5) introducing anatomical prior by virtue of the generalized entropy and the registered MR image, carrying out reconstruction model transformation on the mathematic statistical model of the PET image by adopting a maximum posteriori method so as to obtain an optimization equation with a constraint objective function; and (6) carrying out iterative computation by a one-step-behind algorithm so as to finally obtain the final reconstructed medical image. By adopting the method, the visual effect and the quantitative index of the PET reconstructed image can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Low impedance interface circuit to maximize bandwidth and provide bias control
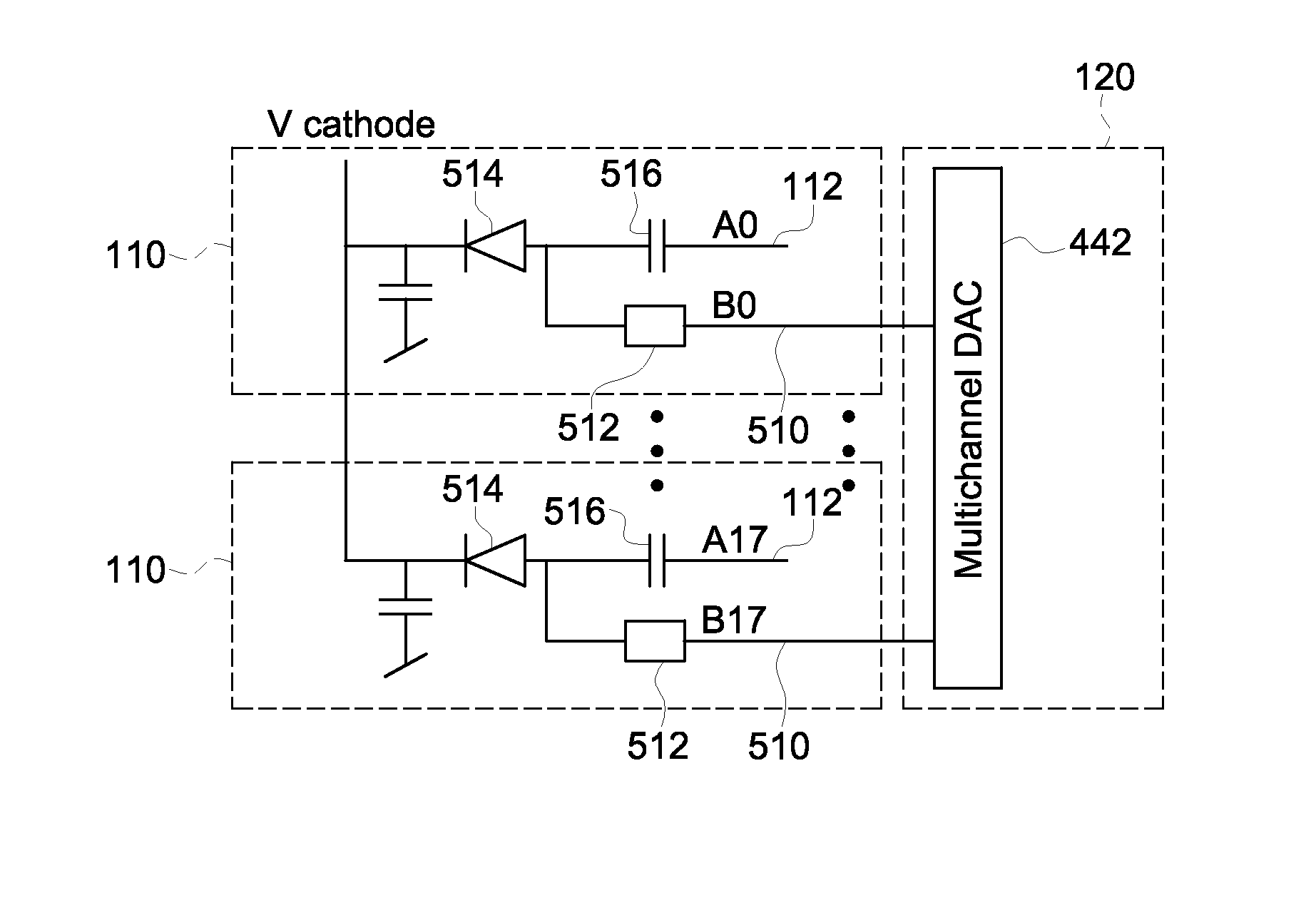
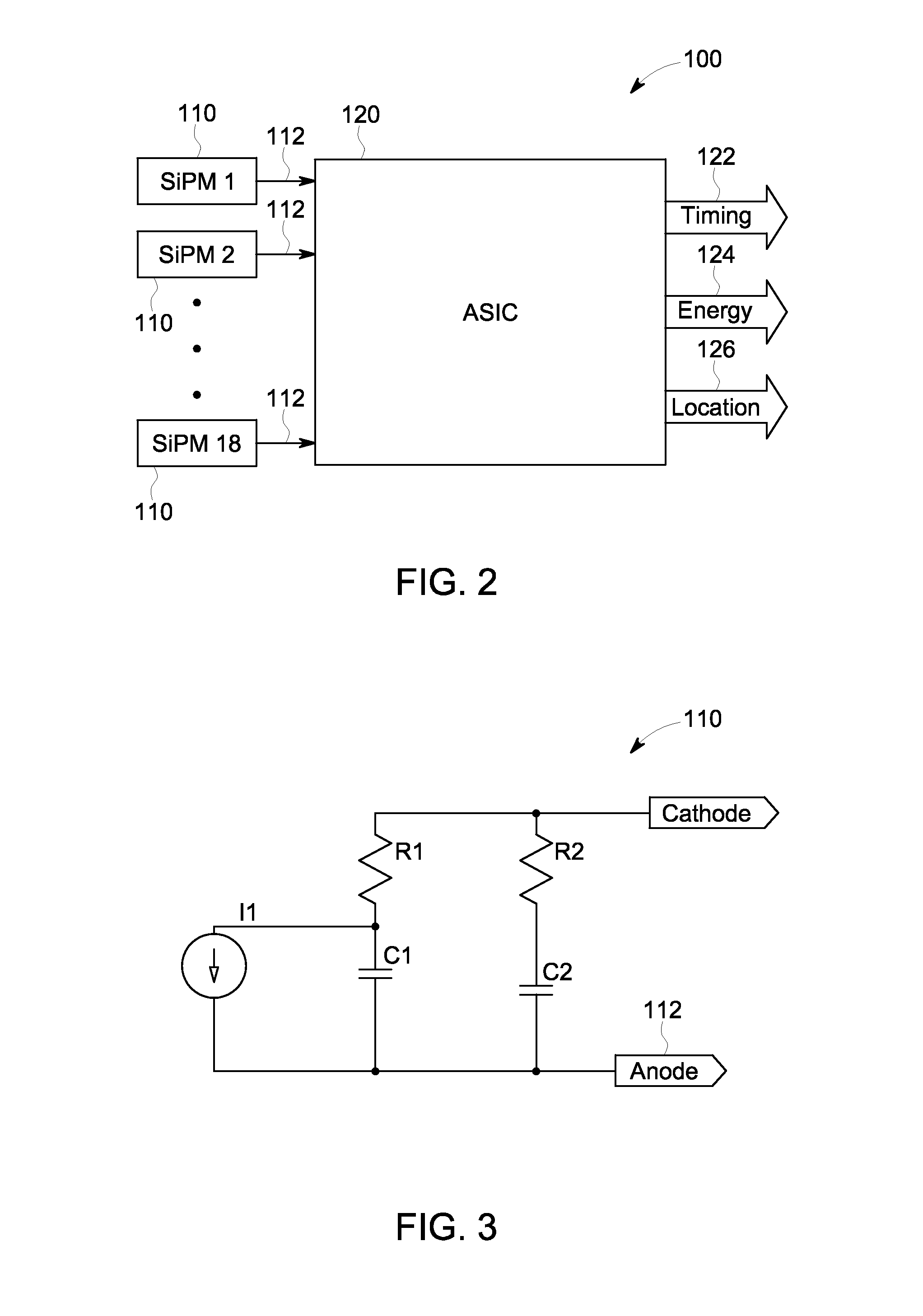
A multichannel application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) for interfacing with an array of photodetectors in a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging system includes a front end circuit configured to be coupled to the photodetectors and to receive discrete analog signals therefrom. The ASIC further includes a time discriminating circuit operably coupled to the front end circuit and configured to generate a hit signal based on a combination of the discrete analog signals, and an energy discriminating circuit operably coupled to the front end circuit and configured to generate a summed energy output signal based on each of the discrete analog signals and summed row and column output signals based on each of the discrete analog signals. The summed energy output signal represents an energy level of the detected radiation in the array of photodetectors, and the summed row and column output signals represent a location of the detected radiation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compositions and methods for detecting and treating cancer
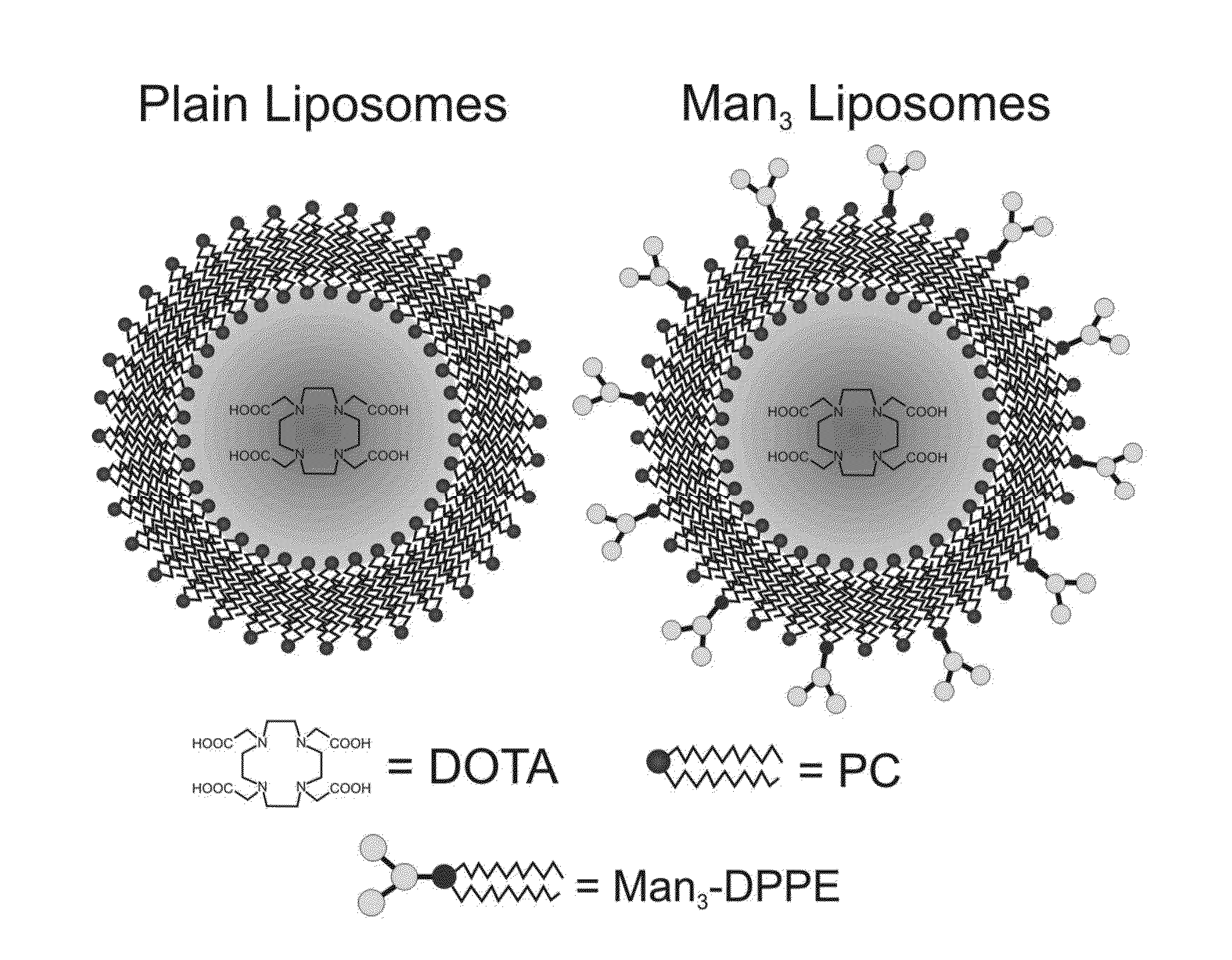
InactiveUS20130330274A1Increase contrastEnhance the imagePreparing sample for investigationBiological testingCancer cellFluorescence
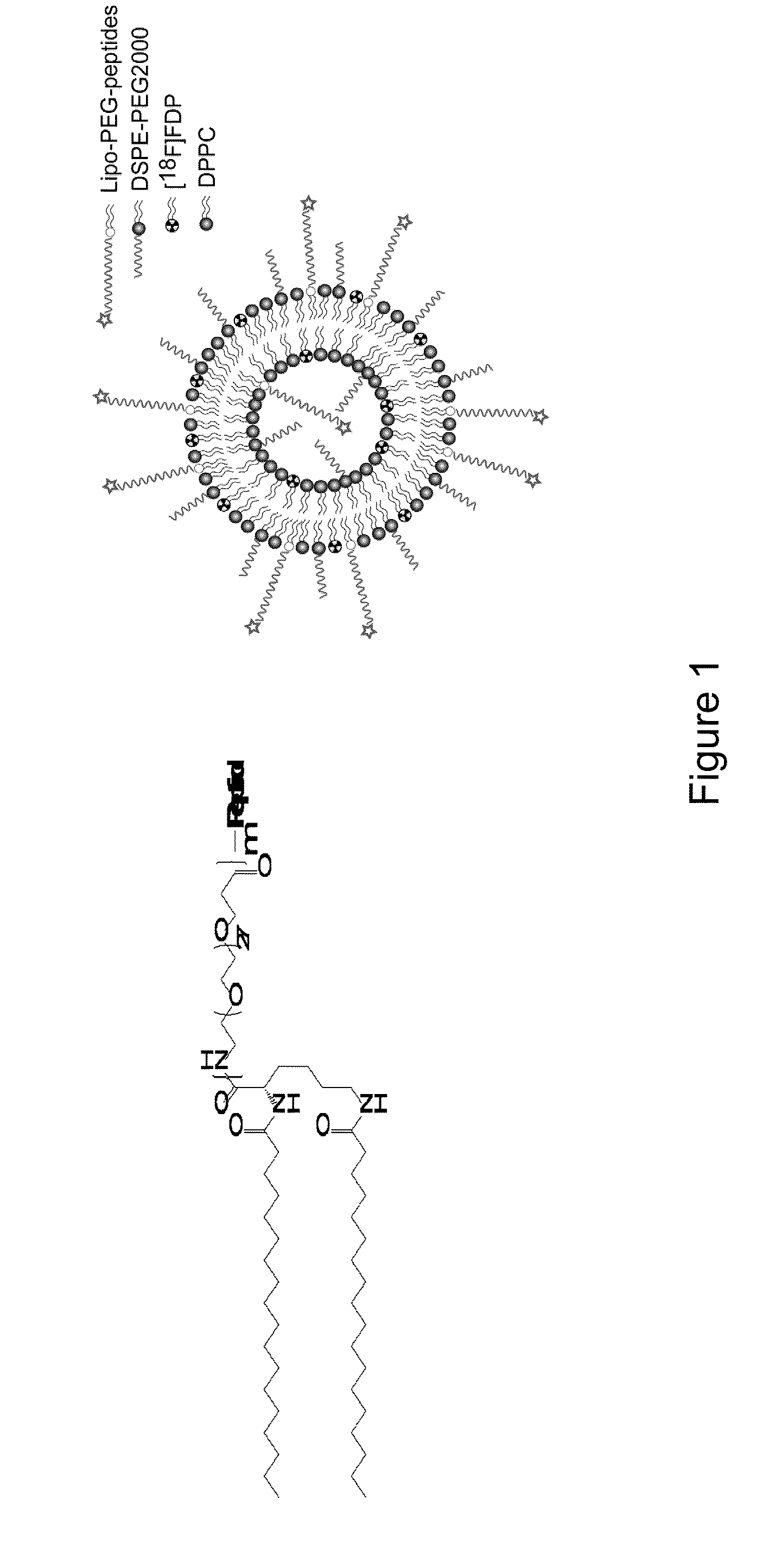
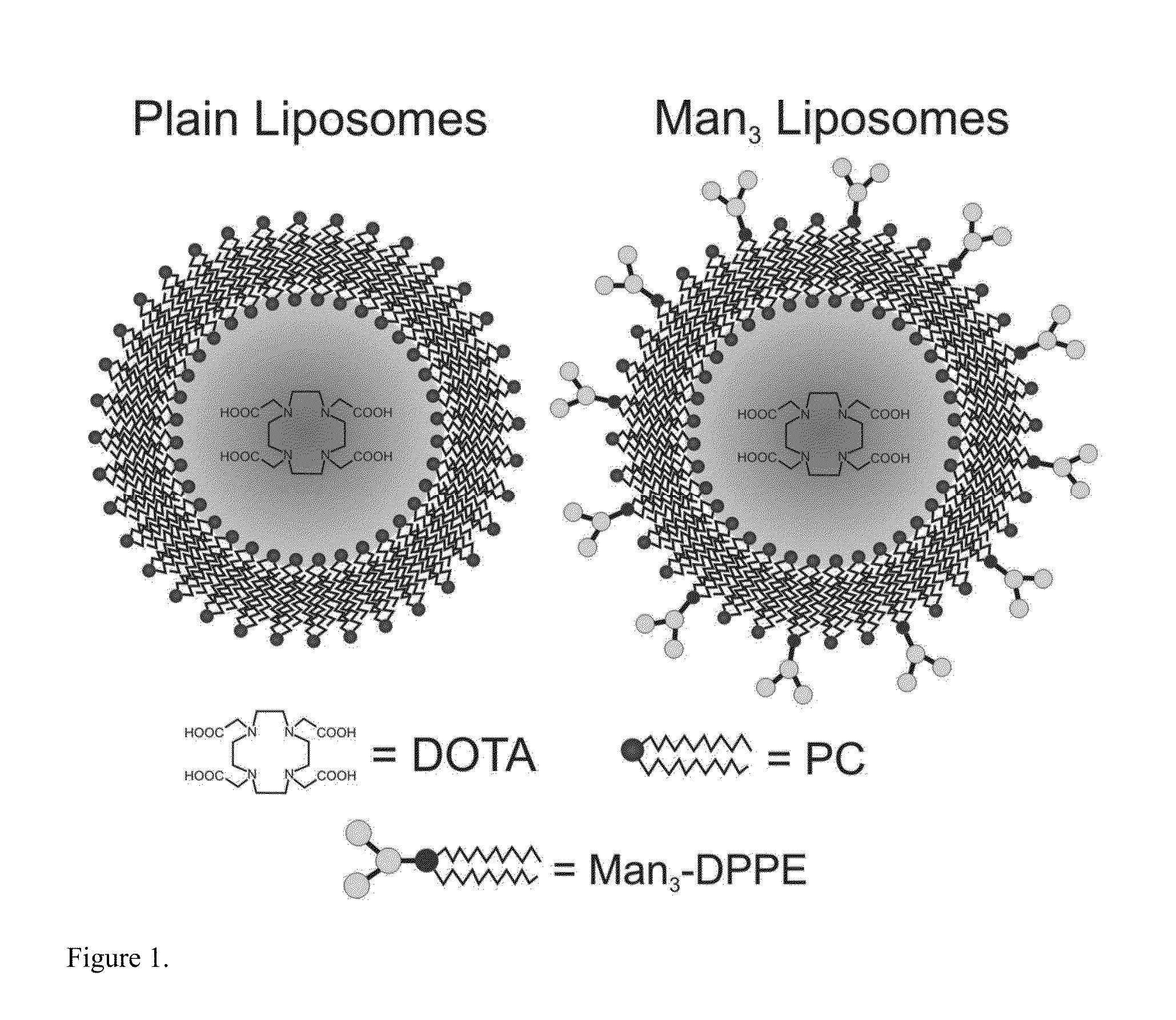
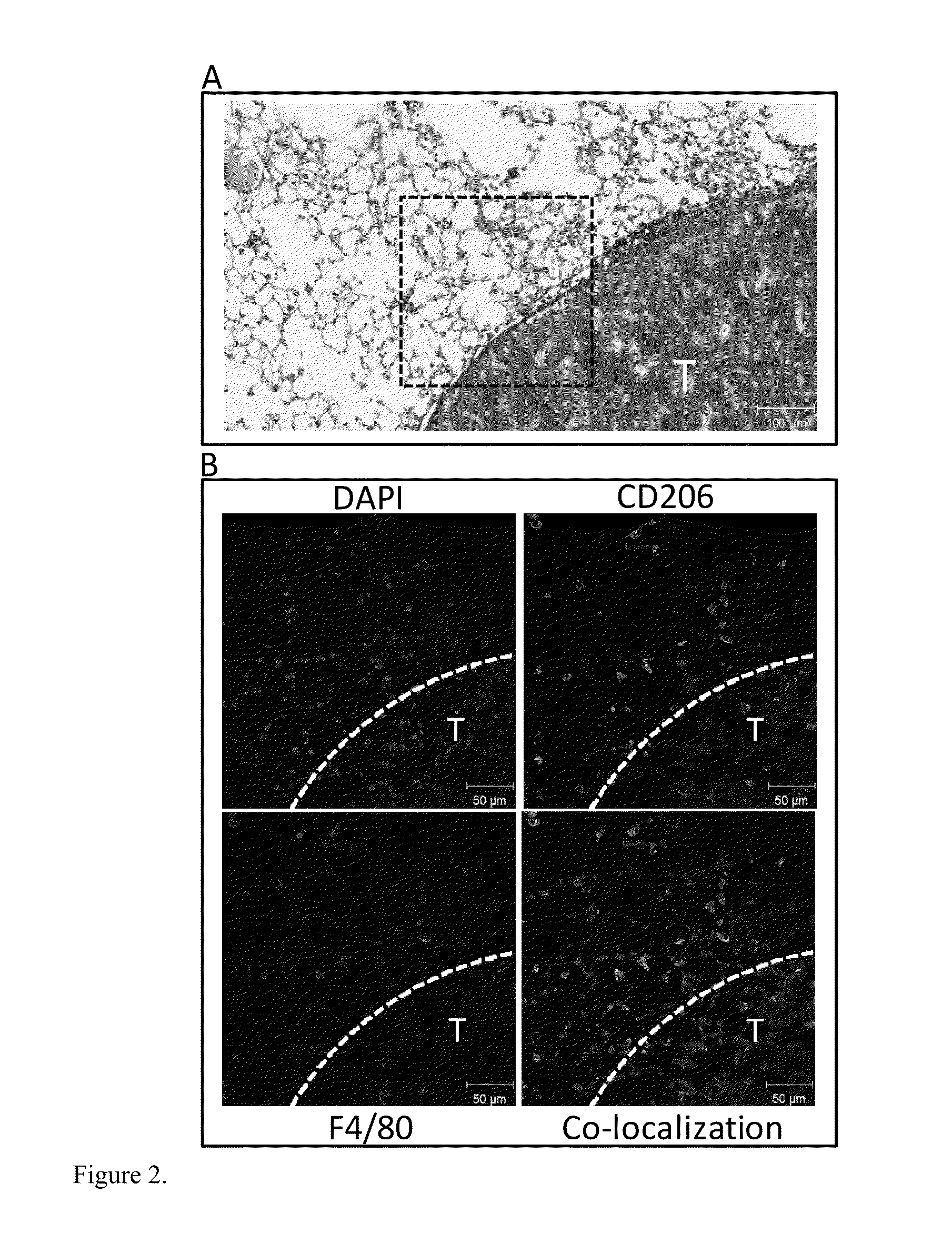
Macrophages within the tumor microenvironment, also called tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) have been shown to play a major role in the growth and spread of many types of cancer. Cancer cells produce cytokines that cause the macrophages to differentiate into an M2 subtype. We have designed a mannosylated liposome (MAN-LIPs) and successfully showed it to accumulate in TAMs in a mouse model of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. These liposomes are loaded with 64Cu to allow tracking by PET imaging, and contain a fluorescent dye in the lipid bilayer permitting subsequent fluorescence microscopy. MAN-LIPs are a promising new vehicle for the delivery of imaging agents to lung TAMs. In addition to imaging, they hold the potential for delivery of therapeutic agents to the tumor microenvironment.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
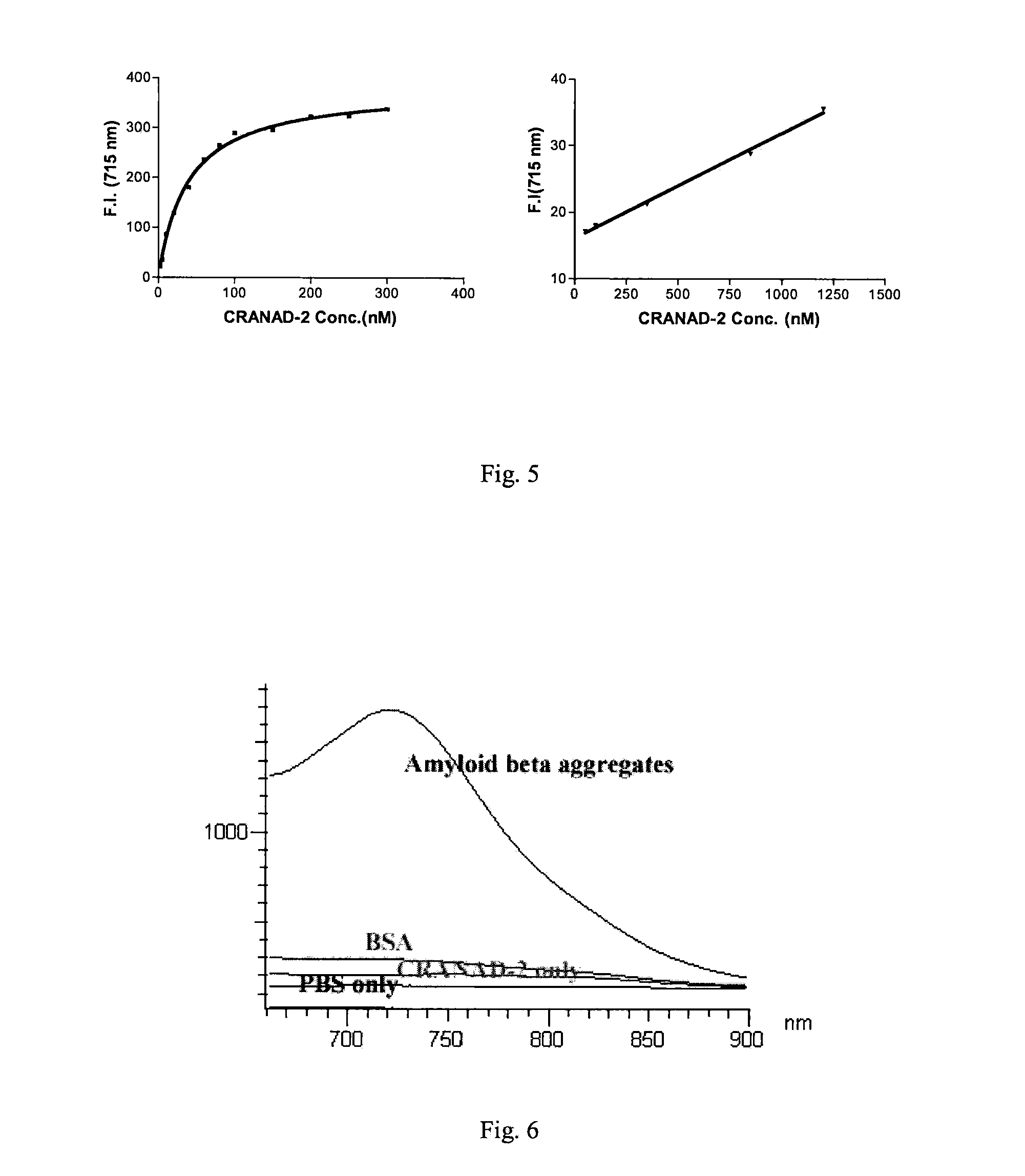
Curcumin Derivatives for Amyloid-Beta Plaque Imaging
InactiveUS20110208064A1Significant fluorescence property changeImprove lipophilicityNervous disorderMagnetic measurementsInfraredAmyloid beta
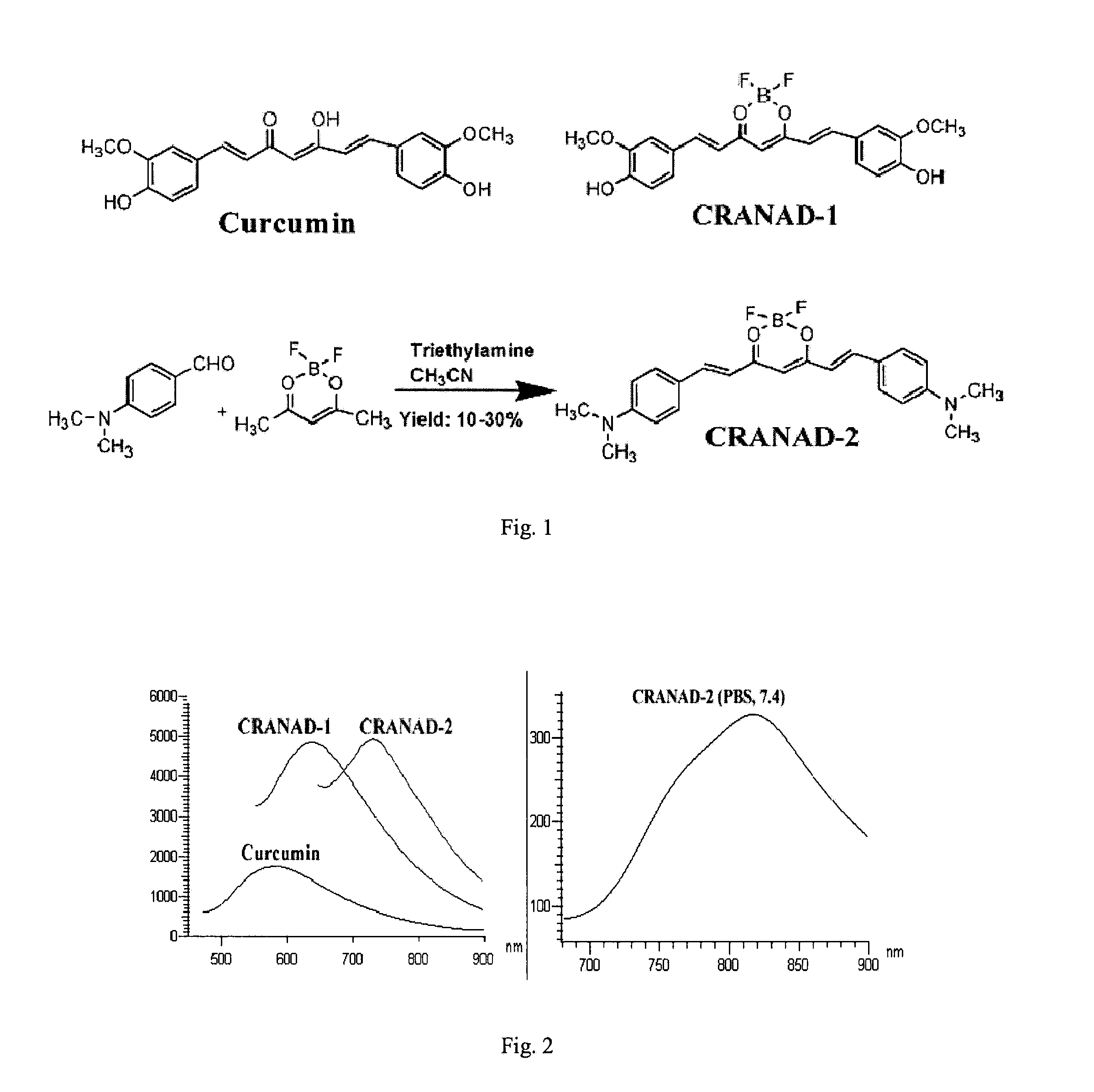
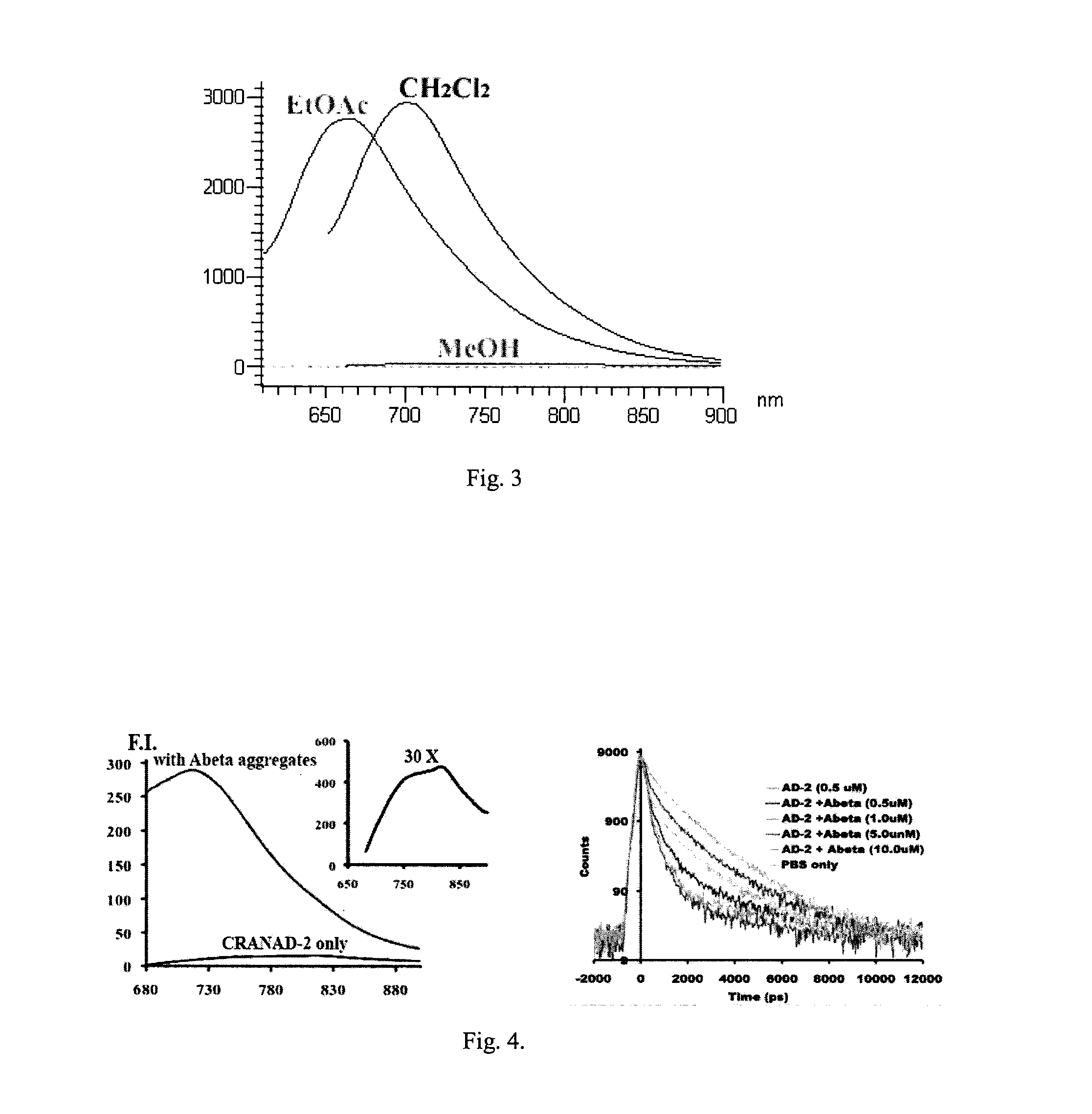
The present invention provides curcumin-derived near infrared (NIR) imaging probes. Upon interacting with amyloid β aggregates, these probes undergo a range of changes, qualifying them as “smart” probes. The inventors have demonstrated that probes of the invention have the capacity to monitor the progression of Alzheimer's disease in an in vivo animal model. In addition, the present invention encompasses probes useful as PET imaging agents, MRI imaging agents and multimodal imaging agents, as well as related methods of detecting and imaging amyloid β aggregates and plaques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Semiconductor scintillation detector
The present invention relates to a radiation detection device for detecting gamma or x-ray radiation quanta with improved timing accuracy and improved energy resolution. The radiation detection device finds application in the detection of gamma and x-ray radiation and may be used in the field of PET imaging, and in spectral CT. The radiation detection device includes a semiconductor scintillator element and a photodetector. The photodetector is in optical communication with the scintillator element. The scintillator element has two mutually opposing faces; a cathode is in electrical communication with one of the two faces and an anode is in electrical communication with the other of the two faces.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dynamic PET image denoising method based on combined image guiding
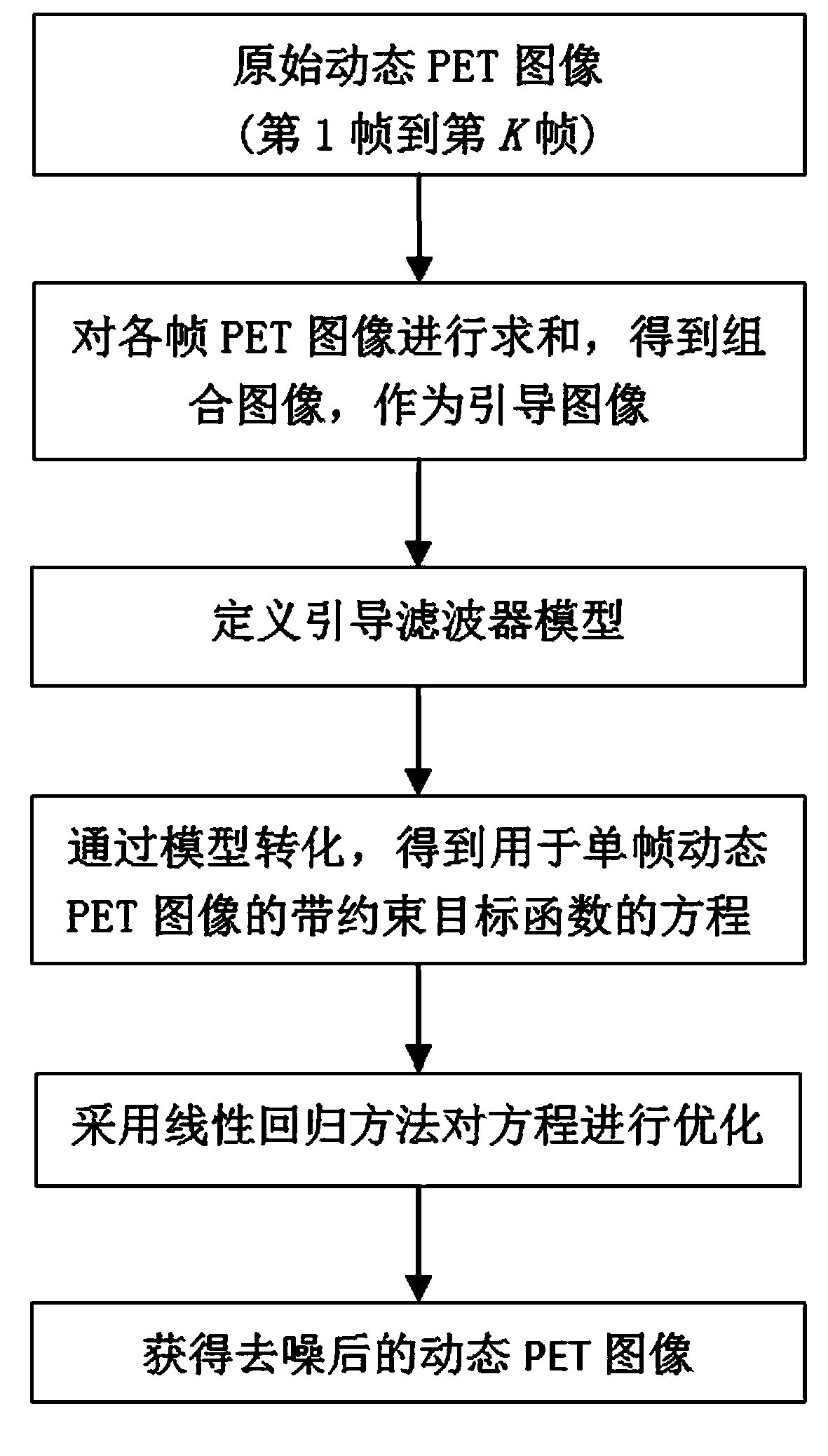
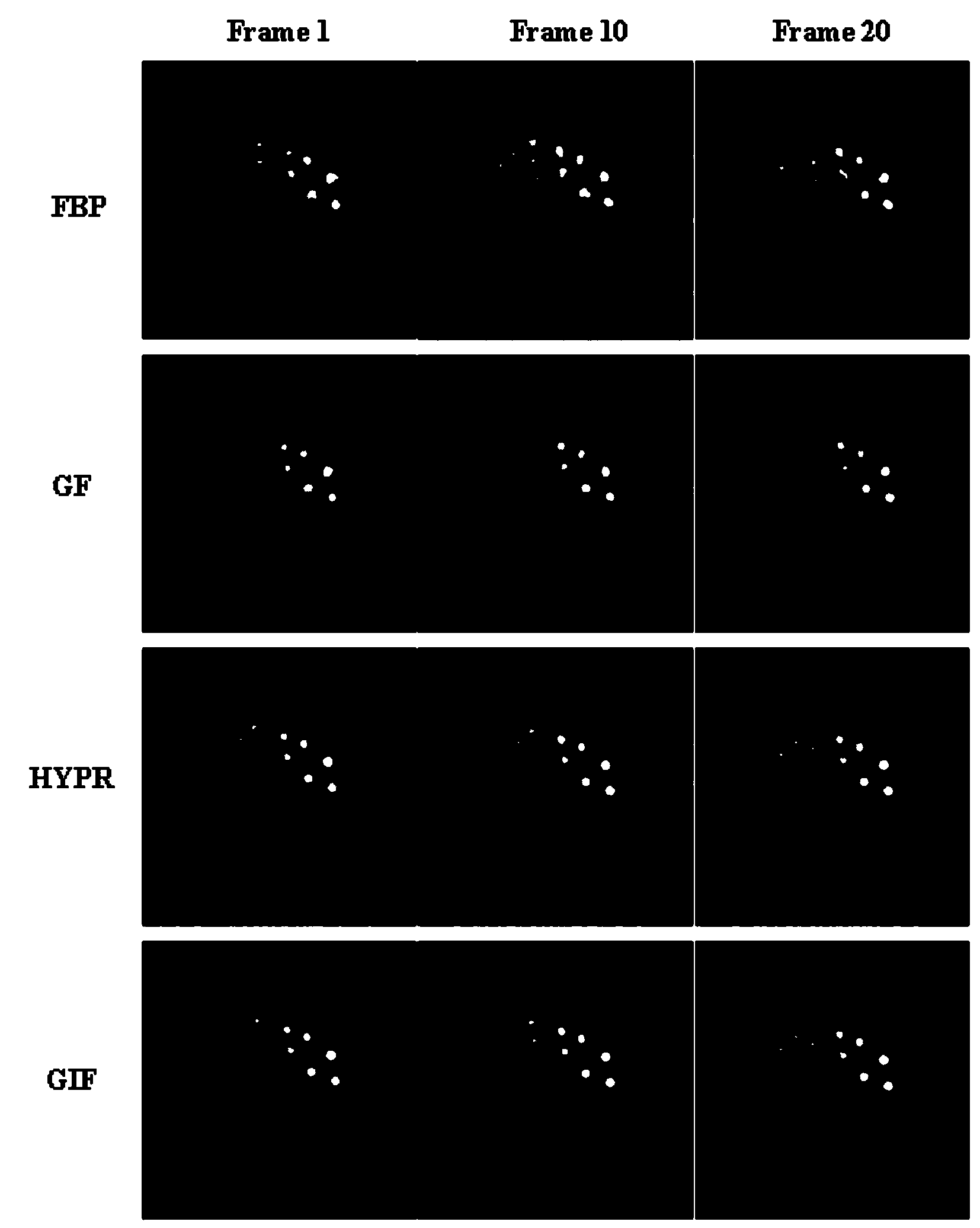
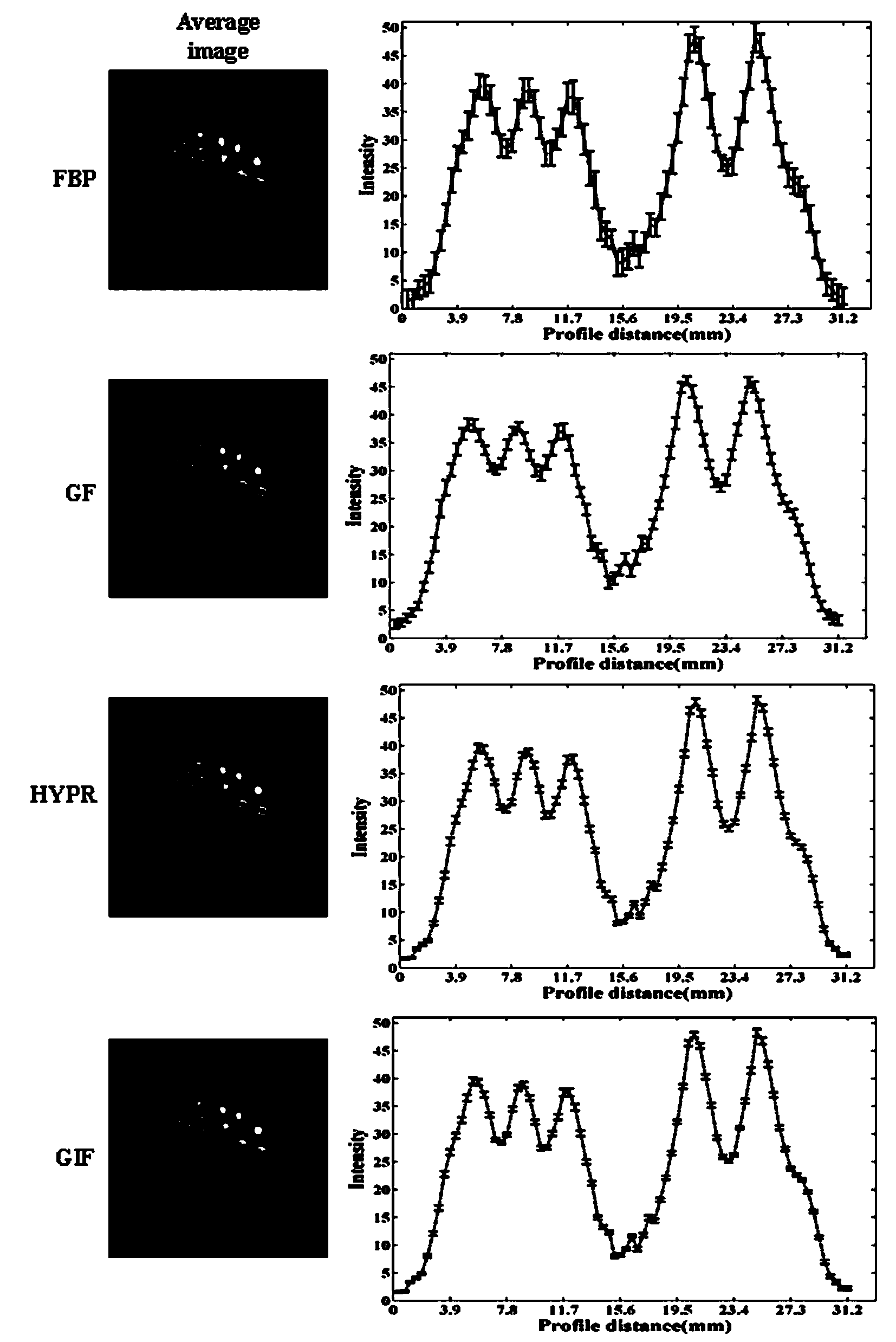
InactiveCN103955899AQuality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementComputerised tomographsPattern recognitionImage denoising
The invention discloses a dynamic PET image denoising method based on combined image guiding. The method comprises the first step of utilizing a PET imaging device to carry out dynamic scanning and reestablishing a dynamic PET image, the second step of calculating and obtaining a combined image according to the reestablished PET image obtained in the first step, the third step of defining a guiding filter model and a kernel function of the guiding filter model, the fourth step of regarding the combined image obtained in the second step as a guiding image, and converting the model obtained in the third step to obtain an equation with a constraint target function for the single-frame dynamic PET image, and the fifth step of carrying out calculation to obtain the denoised dynamic PET image based on the linear regression method and overall parameter selection on the equation according to the result obtained in the fourth step. According to the method, the combined image serves as the guiding image, the noise of the single-frame dynamic PET image can be effectively reduced, and the quality of the dynamic PET image can be greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Dedicated mobile high resolution prostate PET imager with an insertable transrectal probe
ActiveUS20100187424A1Fast dataLarge active fieldRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsMaterial analysis by optical means3d imageImage resolution
A dedicated mobile PET imaging system to image the prostate and surrounding organs. The imaging system includes an outside high resolution PET imager placed close to the patient's torso and an insertable and compact transrectal probe that is placed in close proximity to the prostate and operates in conjunction with the outside imager. The two detector systems are spatially co-registered to each other. The outside imager is mounted on an open rotating gantry to provide torso-wide 3D images of the prostate and surrounding tissue and organs. The insertable probe provides closer imaging, high sensitivity, and very high resolution predominately 2D view of the prostate and immediate surroundings. The probe is operated in conjunction with the outside imager and a fast data acquisition system to provide very high resolution reconstruction of the prostate and surrounding tissue and organs.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Imaging positioning system having robotically positioned D-arm
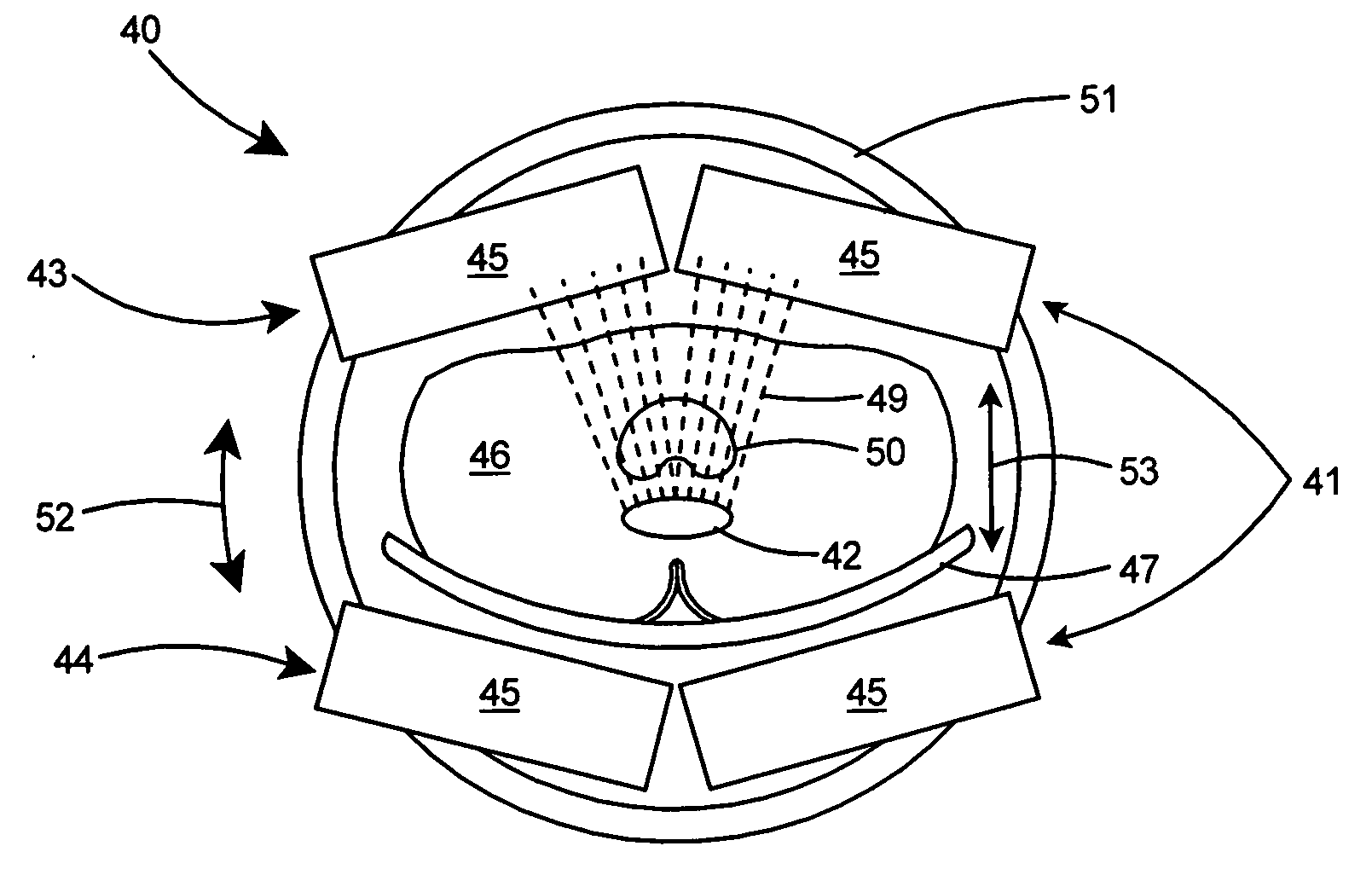
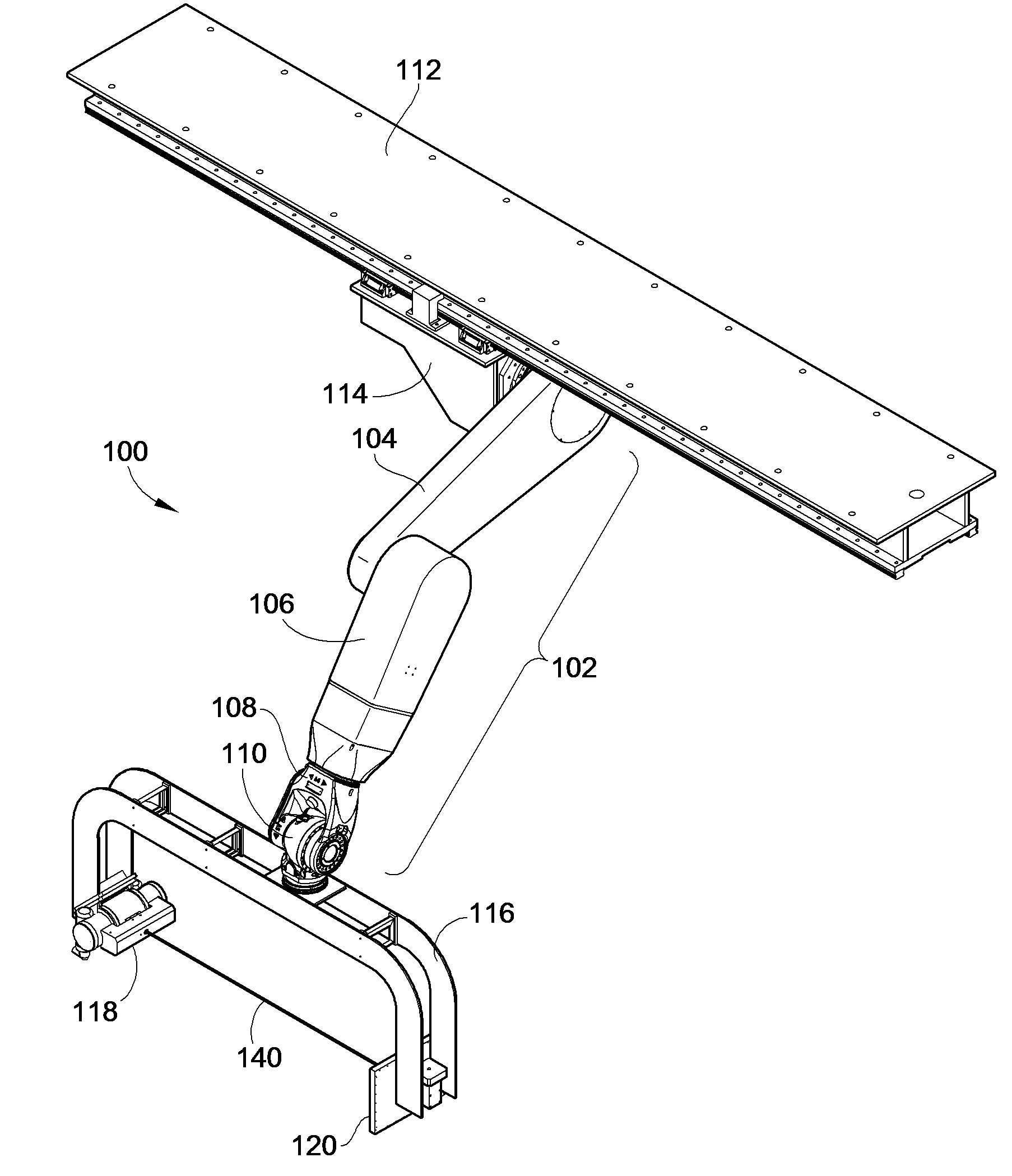
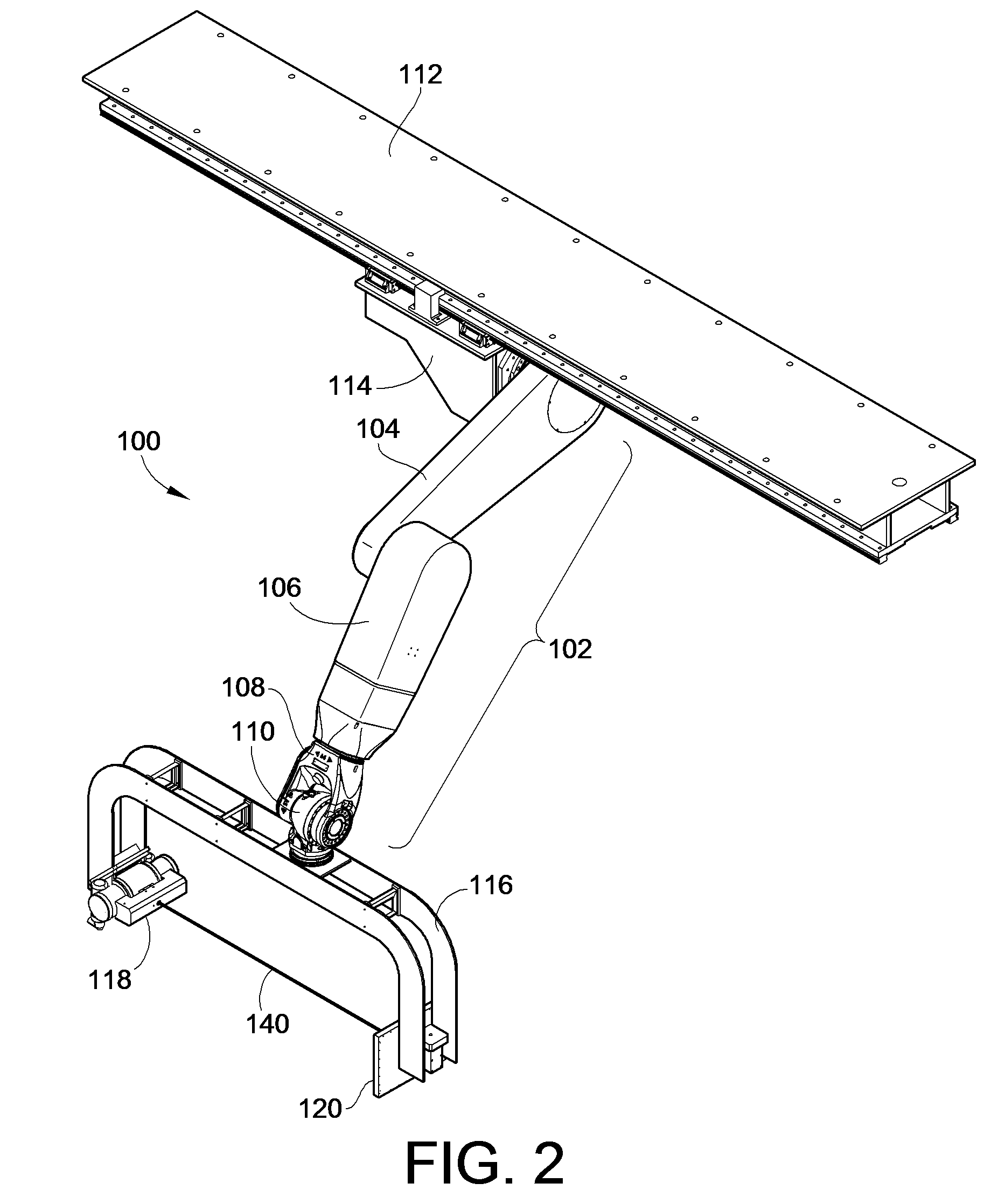
InactiveUS7695192B2Maximize available spacePrecise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDynamic fieldRobotic arm
An imaging positioning system having a robotically positioned support structure is provided. By utilizing a robotic arm, imaging along multiple planes within a patient treatment room without having to move the patient is provided. Such a configuration allows multiple axis x-ray imaging, cone beam CT acquisitions having a dynamic field of view, and PET imaging within the treatment room. Rotation of the imaging panel on the support structure allows the imaging system to simulate a gantry rotation when a fixed beam is used for treatment. Beam line x-ray imaging is also provided by tilting the imaging panel or by moving the support structure on which the x-ray source is positioned. Laser distance scanning for collision avoidance and force torque sensing movement enhance the safety thereof. The support structure may be in the form of a ring along which the imaging components may move.
Owner:FIRST MIDWEST BANK +1
Scintillation detector for positron emission tomography
InactiveUS20090224164A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementGamma photonPhotodetector
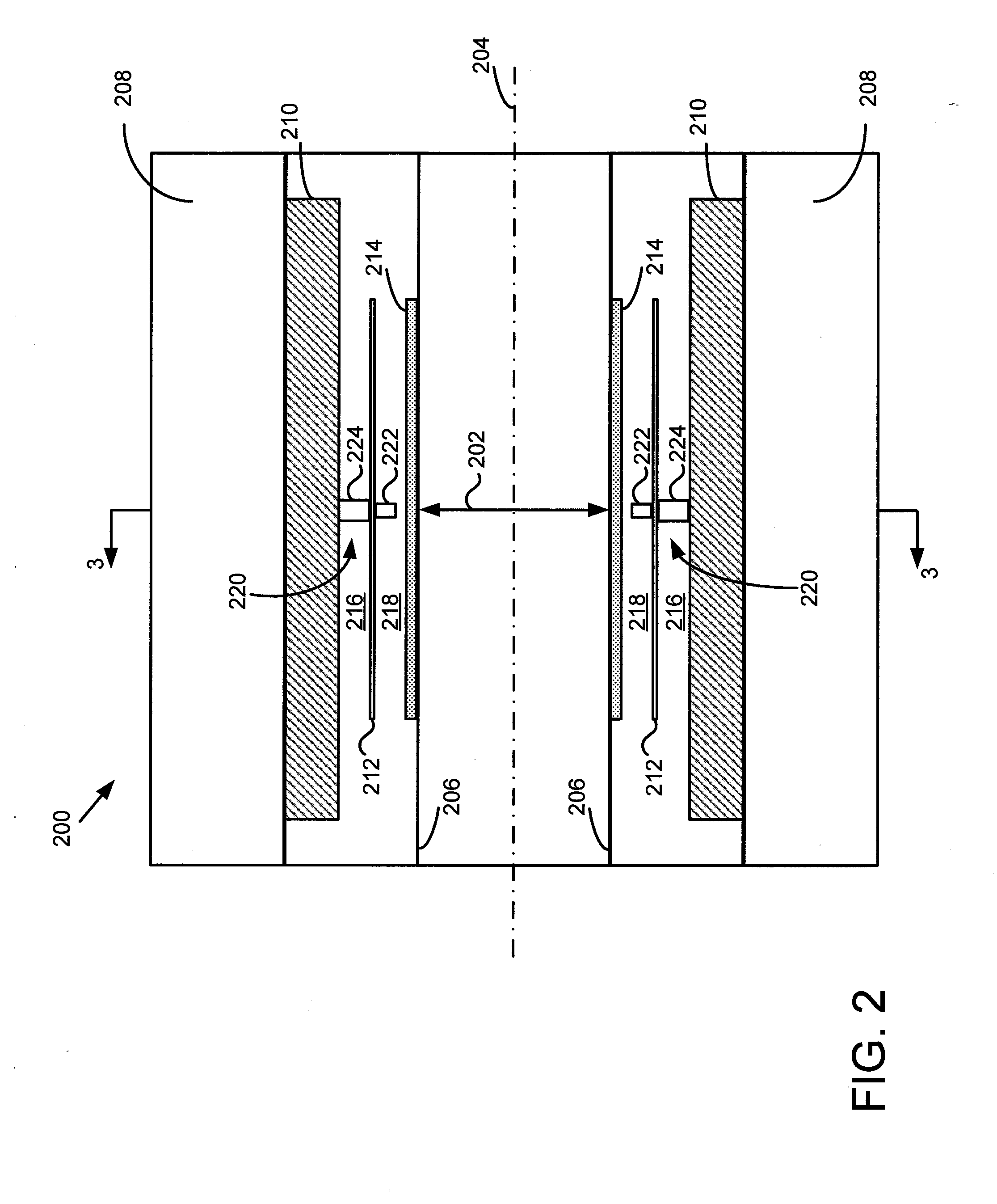
The invention disclosed herein is directed to scintillation detectors capable of detecting the position or depth of gamma photon interactions occurring within a scintillator, thereby improving the resolution of ring based positron emission tomography (PET) imaging systems. In one embodiment, the invention is directed to a scintillation detector that comprises at least one pair of side-by-side conjunct scintillation crystal bars having a shared interface between, and a solid-state semiconductor photodetector optically coupled to each output window of each individual scintillation crystal bar. The solid-state semiconductor photodetector includes an array of discrete sensitive areas disposed across a top surface of a common substrate, wherein each sensitive area contains an array of discrete micro-pixelated avalanche photodiodes, and wherein the output window of each scintillation crystal bar is optically coupled to each respective sensitive area in a one-on-one relationship.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Maximum posteriori optimizing image rebuilding method in PET imaging
InactiveCN101156780AImage data processing detailsRadiation diagnosticsMathematical modelSystem matrix
The invention discloses a maximal posteriori optimized image reconstruction method for leading in a general Gibbs experiment in the PET imaging. The method comprises the following procedures: (1) PET imaging equipment is utilized to collect detector data before imaging, and the corrective parameter value and the system matrix of various data in the imaging equipment are obtained simultaneously; (2) a mathematical statistic statistical model used for reconstructing an image is reconstructed according to a statistical feature that is met by the corrective data acquainted by the procedure (1) before imaging; (3) the general Gibbs experiment is led in aiming at the compute of a mathematical model in the procedure (2) , a maximal posteriori estimate method is adopted to perform the conversion of a reconstruction model, to obtain an optimized equation with a constrained objective function used for obtaining a PET reconstruction image; (4) a parabola is adopted to replace a coordinate descent algorithm, to perform the iterative computation treatment and to reconstruct the image based on the selection of a global parameter in the optimized equation through a result obtained by the procedure (3). The invention can greatly improve the quality of the PET reconstruction image.
Owner:陈武凡
Method and apparatus for motion correcting medical images
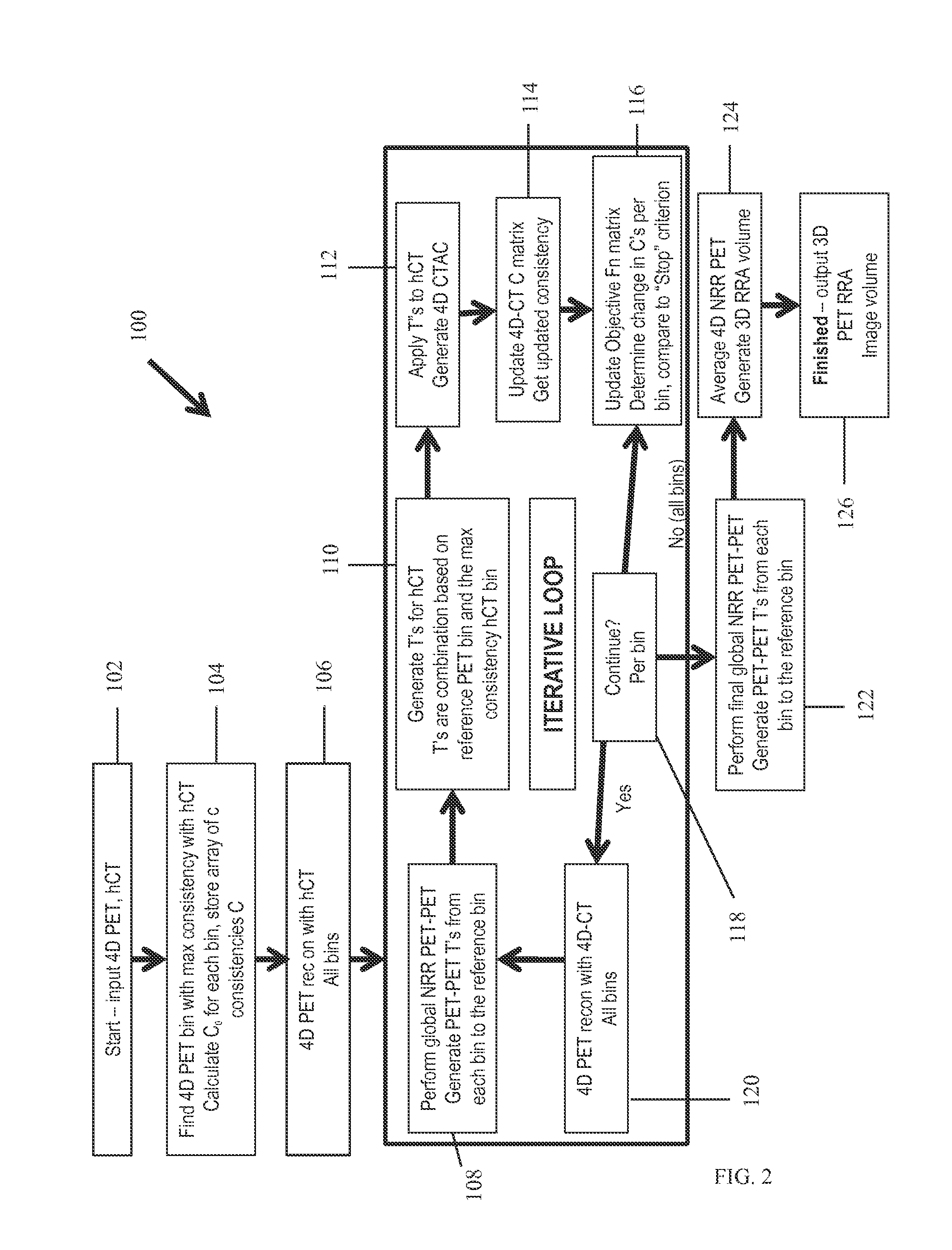
A method for reducing, in an image, motion related imaging artifacts. The method includes obtaining a single image of a subject using a computed tomography (CT) imaging system, obtaining a plurality of images of the subject using a positron emission tomography (PET) imaging system, generating a plurality of consistency values, and utilizing the plurality of consistency values to register the CT image and the plurality of PET images.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Methods of perispinal extrathecal administration of large molecules for diagnostic use in mammals
InactiveUS20090130019A1Improving Imaging EfficiencyImprove efficiencyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsDrug compositionsMammalImaging agent
This application concerns novel methods which enable or improve the ability of molecules, particularly large molecules, to cross the blood-brain barrier, the blood-eye barrier, and / or the blood-nerve barrier and therefore be of improved diagnostic and / or therapeutic use in humans and other mammals. These methods involve perispinal administration of imaging agents without direct intrathecal injection. Perispinal administration is defined as administration of the molecule into the anatomic area within 10 cm of the spine. Perispinal administration results in absorption of the imaging agent into the vertebral venous system. The vertebral venous system is capable of transporting molecules into the brain, the eye, the retina, the auditory apparatus, the cranial nerves, the head, the spine, the spinal cord, the vertebral bodies, the dorsal root ganglia, and the nerve roots via retrograde venous flow, thereby bypassing the blood-brain barrier and similar barriers and delivering the molecules to the brain, the eye, the retina, the auditory apparatus, the cranial nerves, the head, the spine (including the vertebral bodies), the spinal cord, the dorsal root ganglia, or the nerve roots. This method may be utilized for a wide variety of diagnostic agents, including, but not limited to biologics, monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, monoclonal antibody fragments, antibodies to tumor antigens, hormones, cytokines, anti-cytokines, interleukins, anti-interleukins, interferons, colony-stimulating factors, cancer chemotherapeutic agents, growth factors, anti-virals and antibiotics, including those which are radiolabeled, iodinated, or otherwise altered to facilitate diagnostic imaging. Included in these novel methods are perispinal delivery of amyloid imaging agents, and other ligands radiolabeled with [11C] or [18F] to faciliate PET imaging of the brain.
Owner:TACT IP
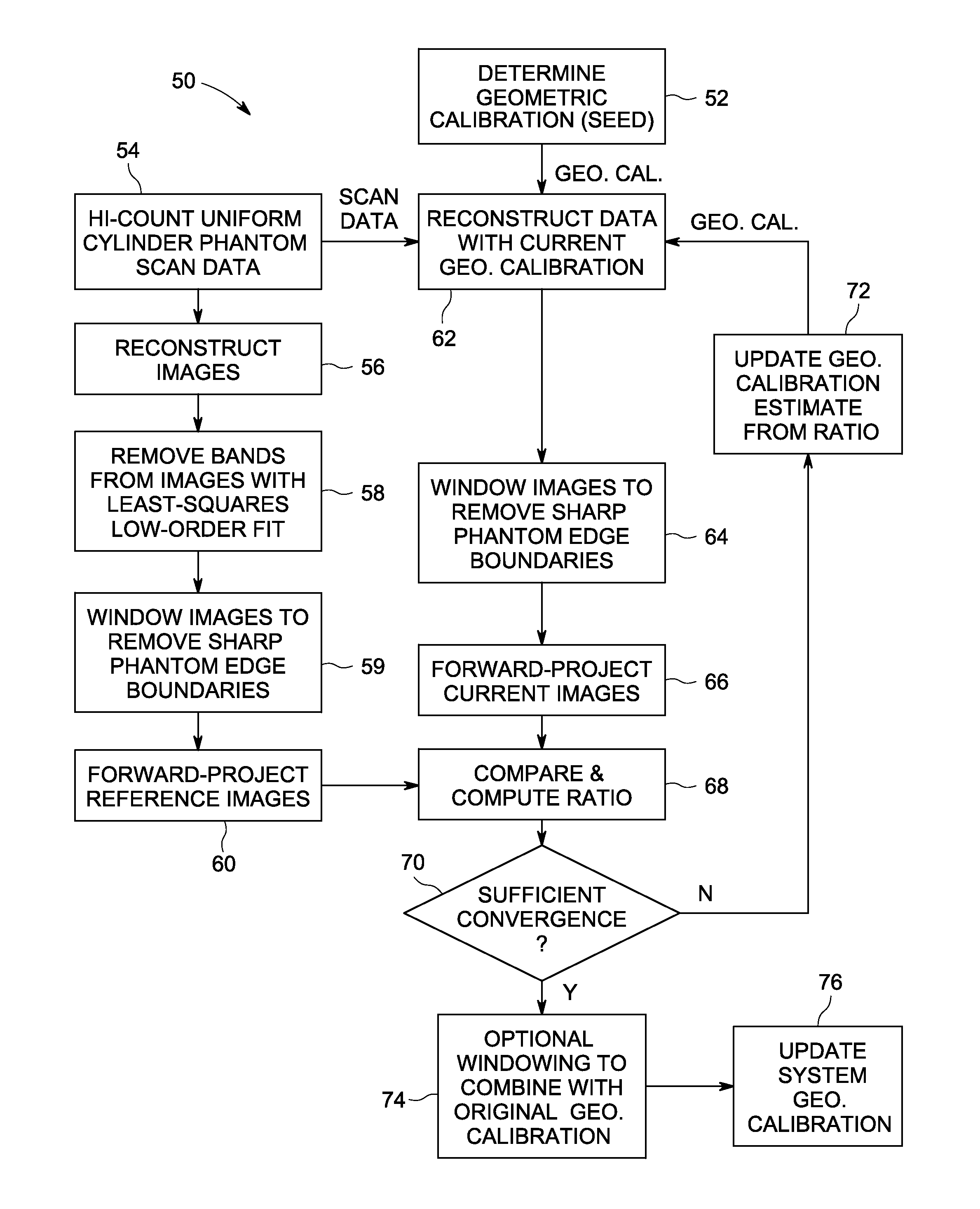
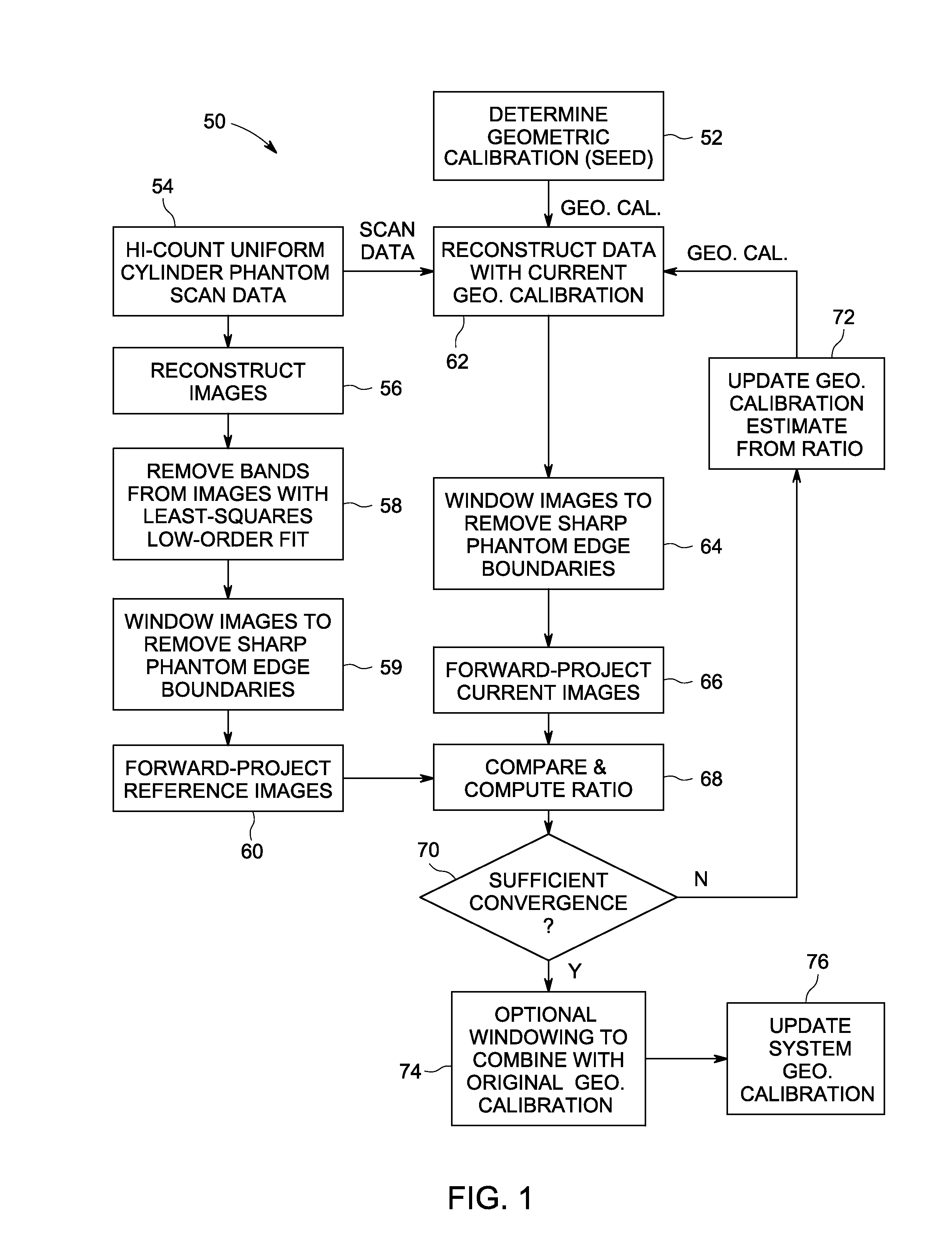
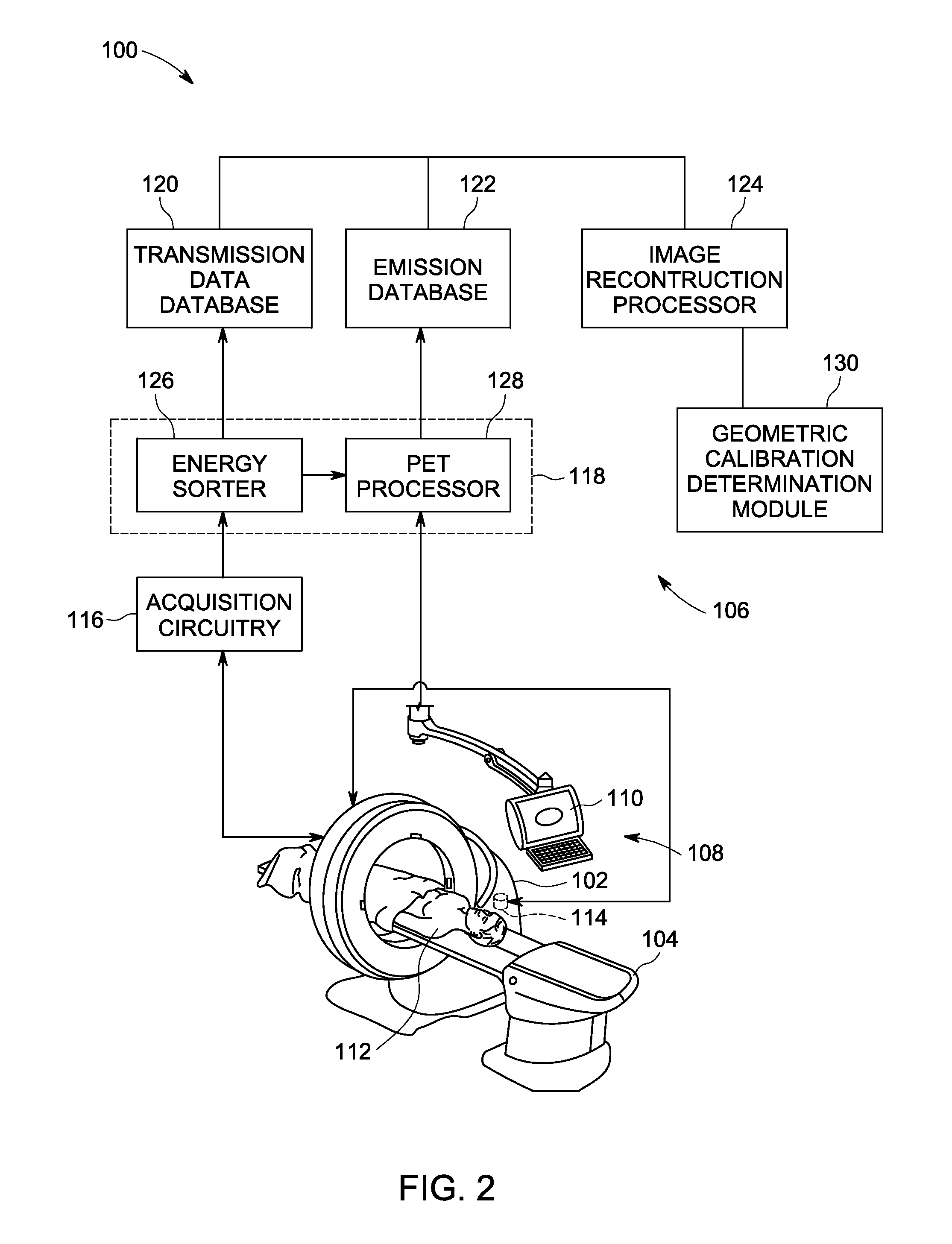
Apparatus and methods for geometric calibration of positron emission tomography systems
ActiveUS20110135179A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionReference imagePet imaging
Apparatus and methods for geometric calibration of positron emission tomography (PET) systems are provided. One method includes obtaining scan data for a uniform phantom and generating reference images based on the scan data for the uniform phantom. The method further includes reconstructing images of the uniform phantom using a PET imaging system and determining a geometric calibration for the PET imaging system based on a comparison of the reconstructed images and the reference images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com