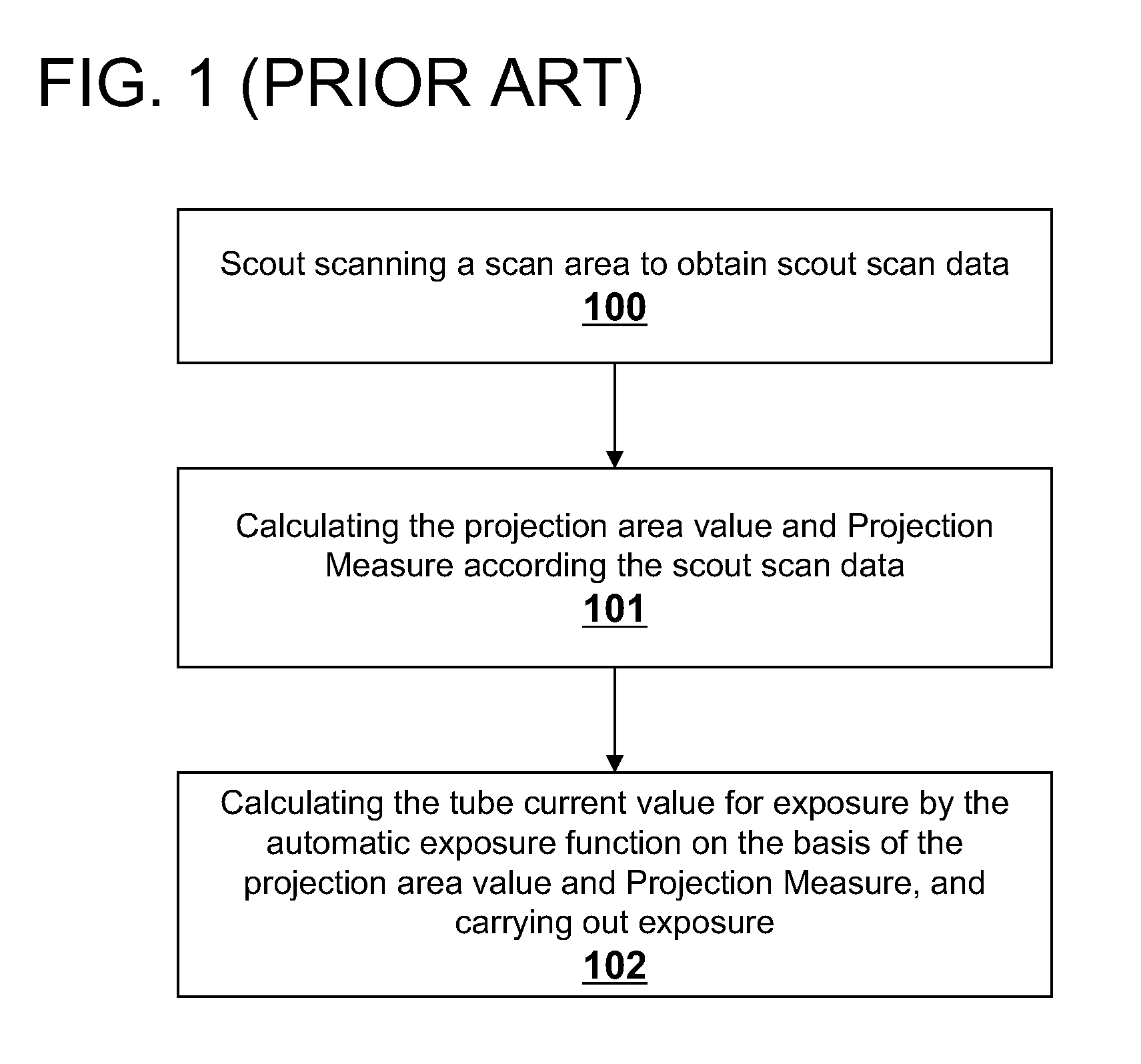
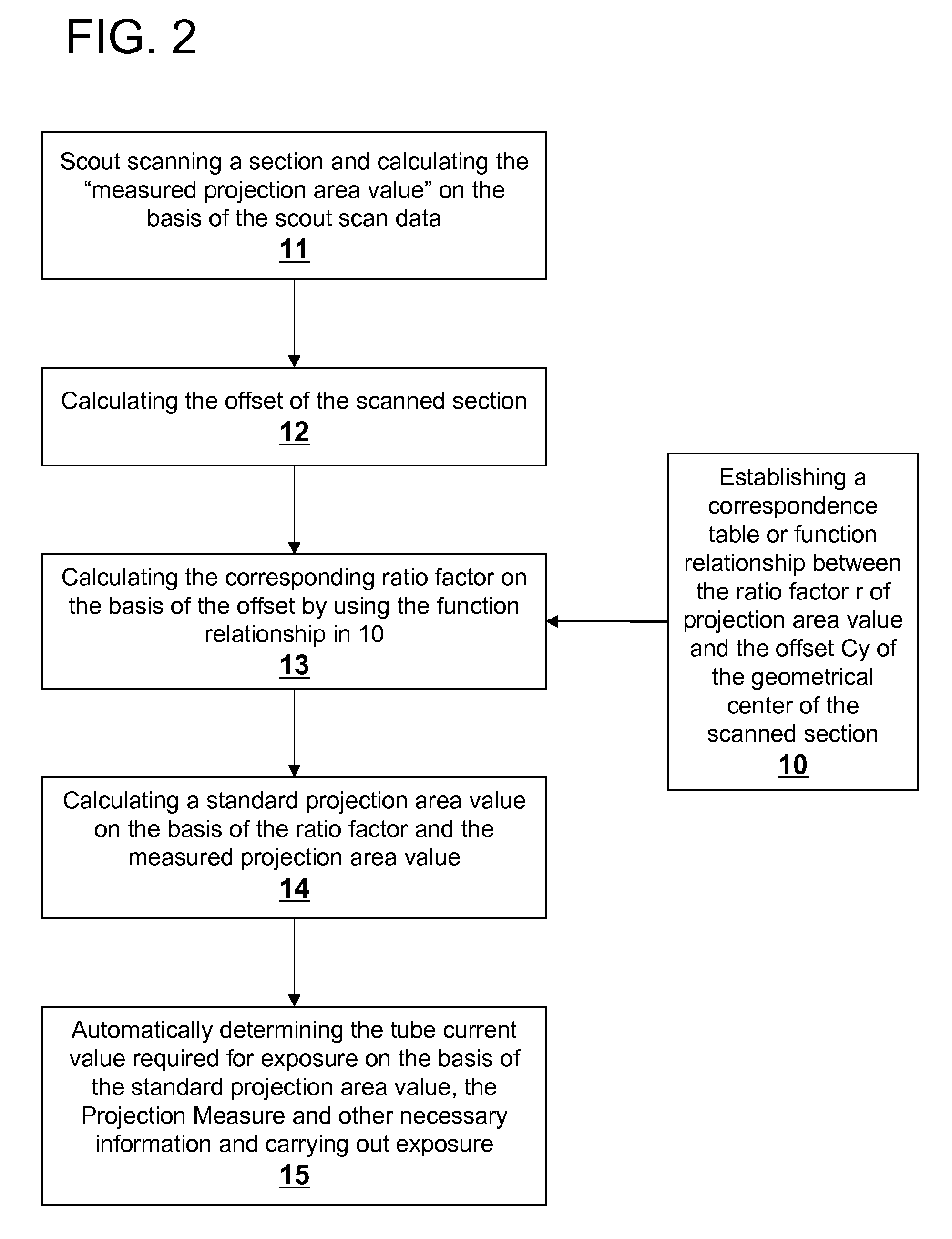
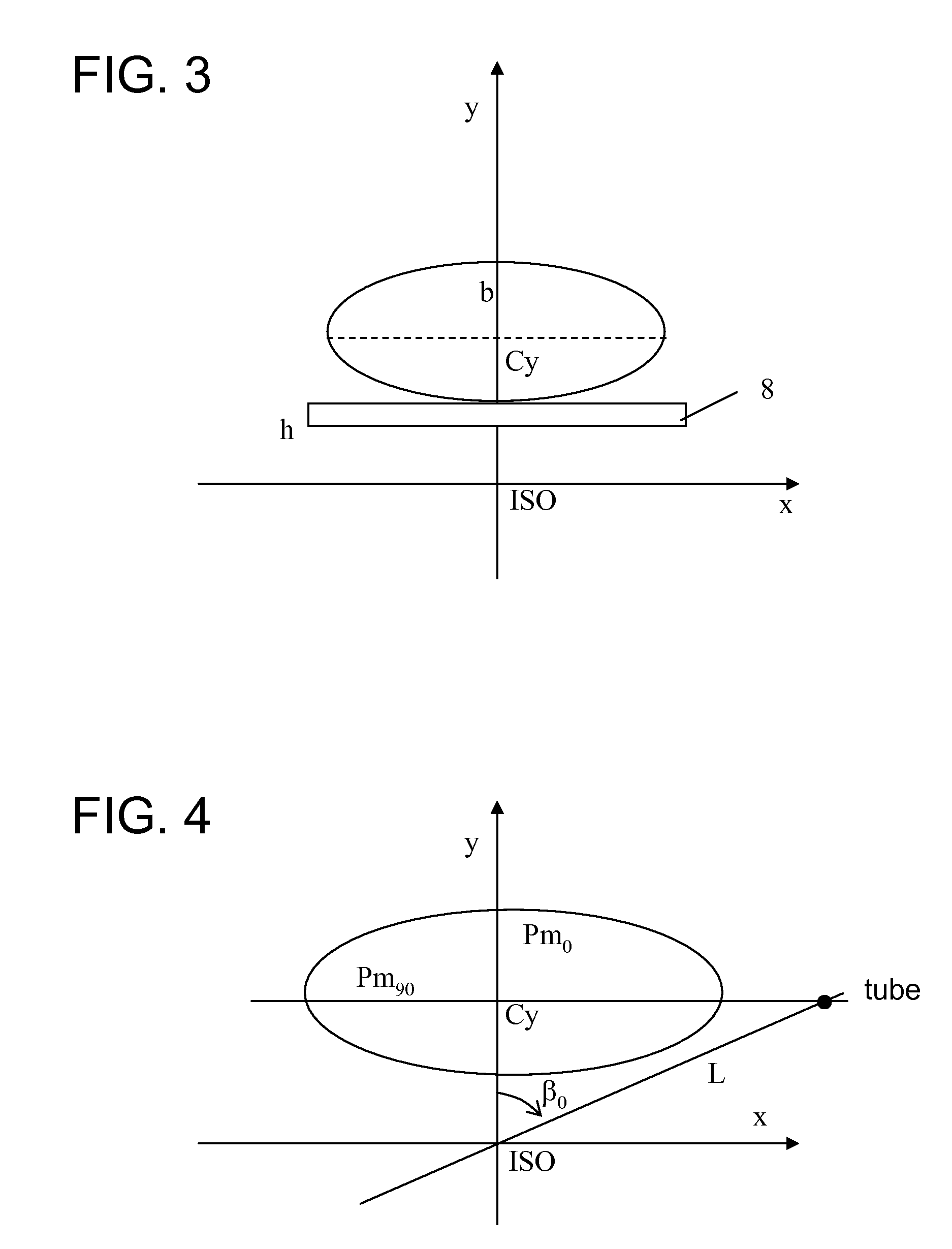
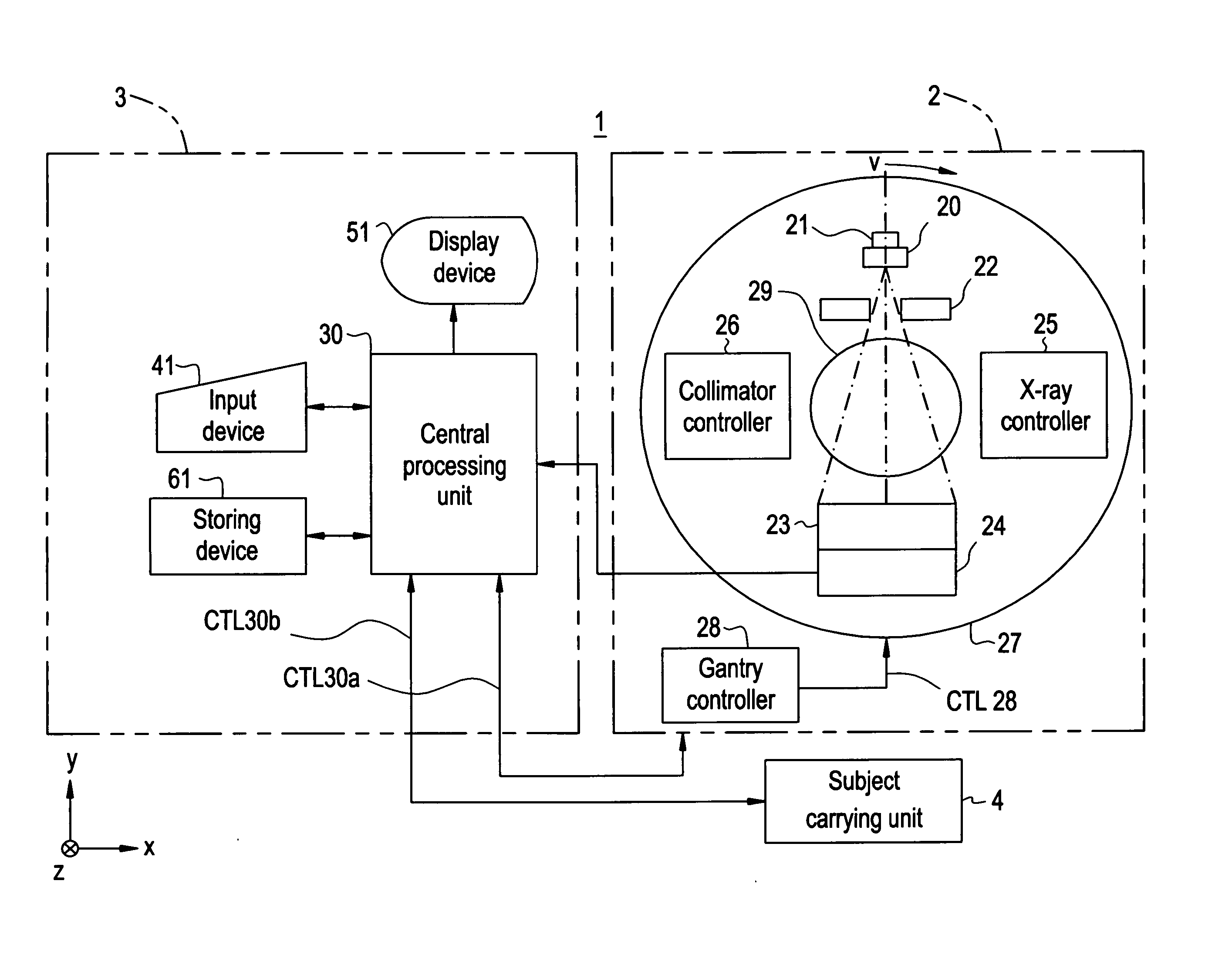
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Scout Scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
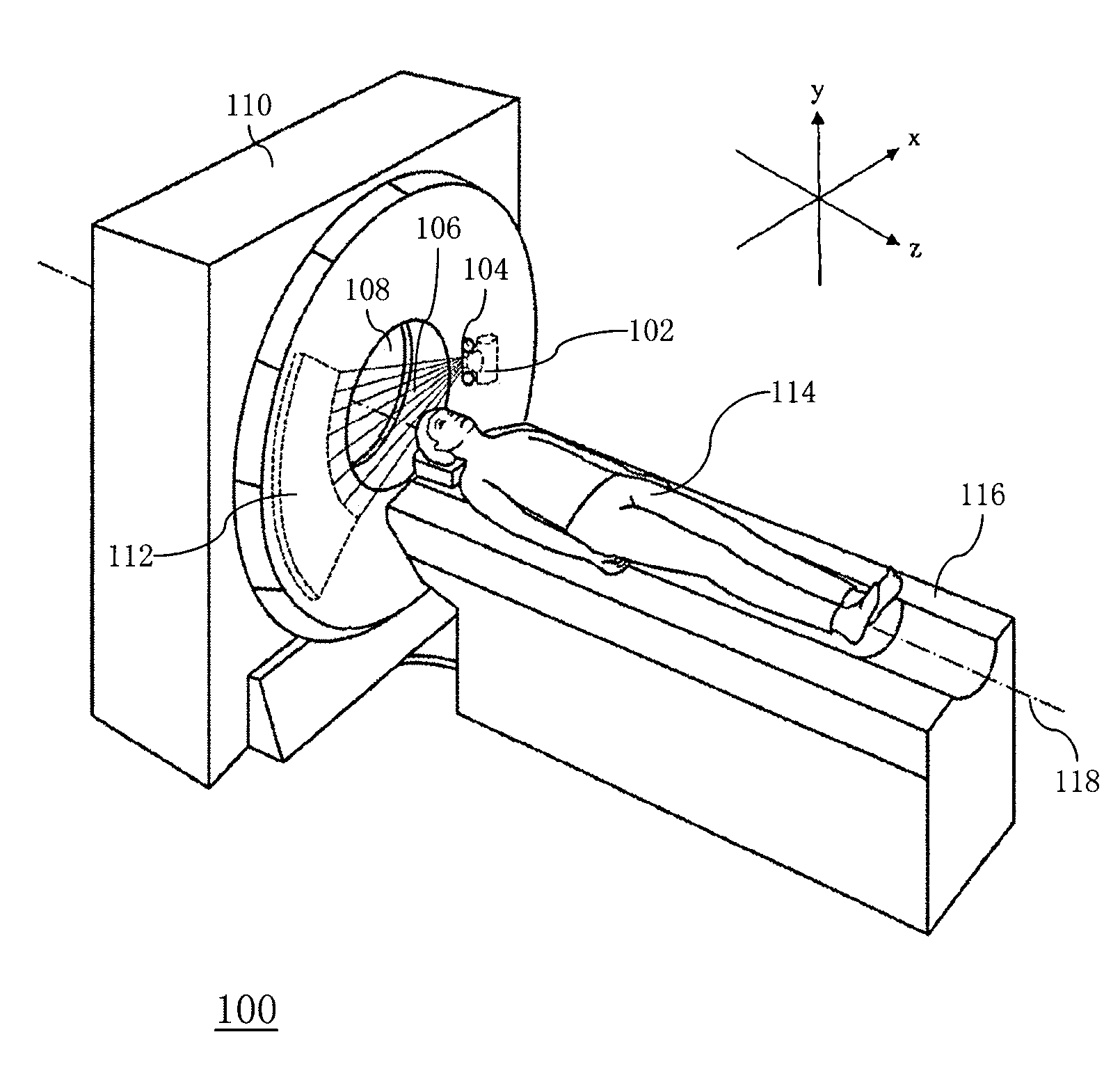
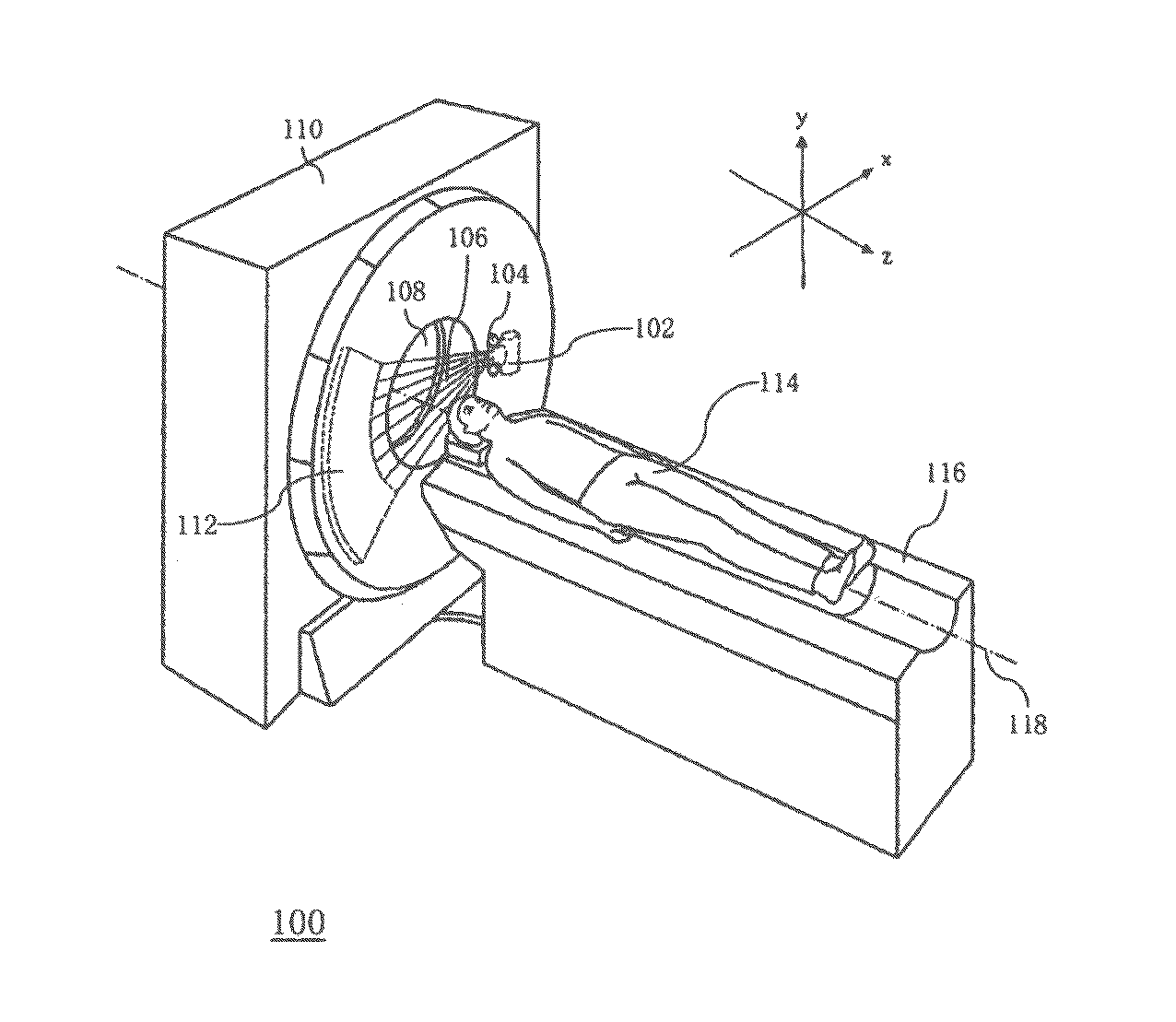
An initial scan with only the minimal detail needed to select the desired range of bed positions to be used in subsequent scans.
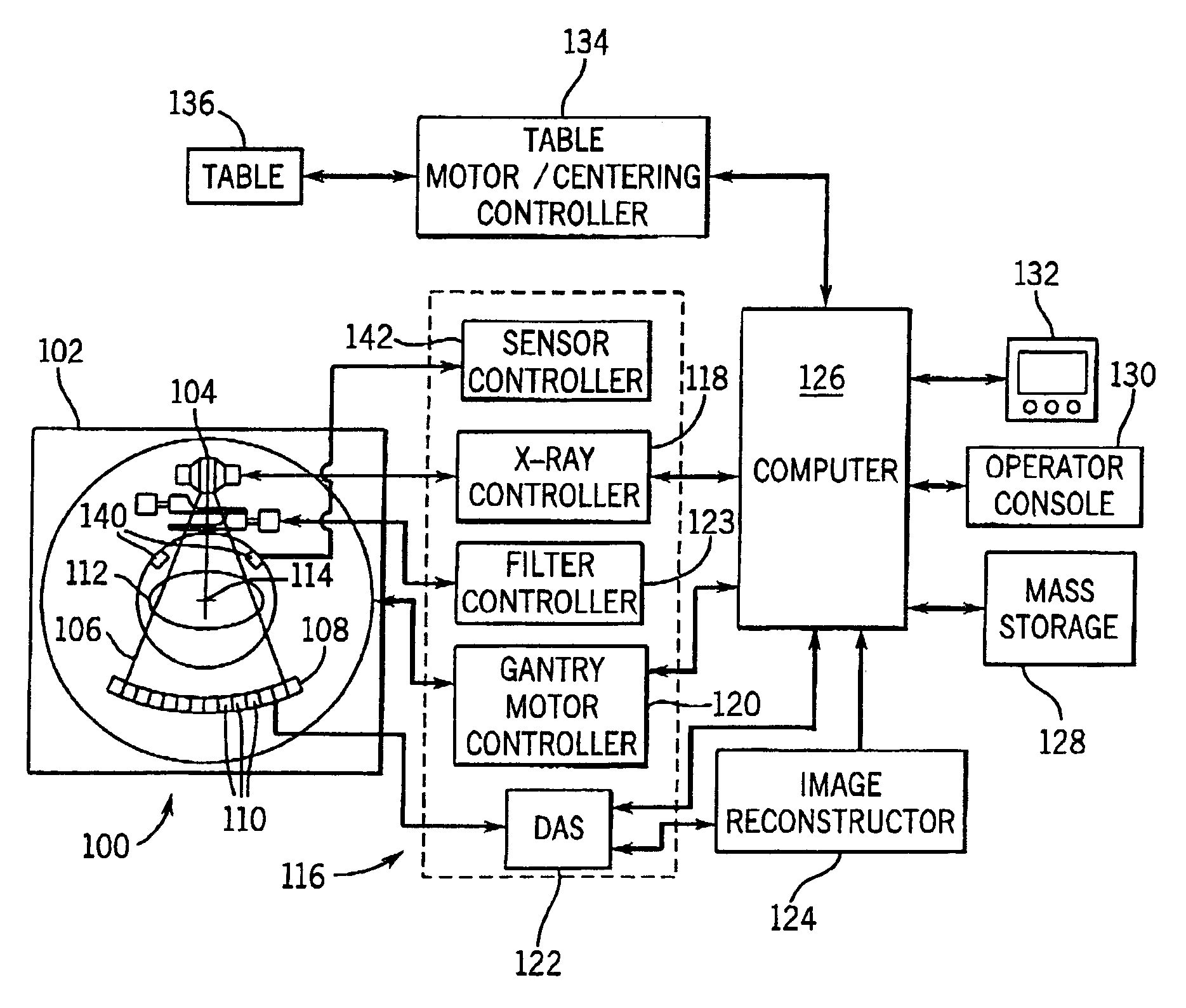
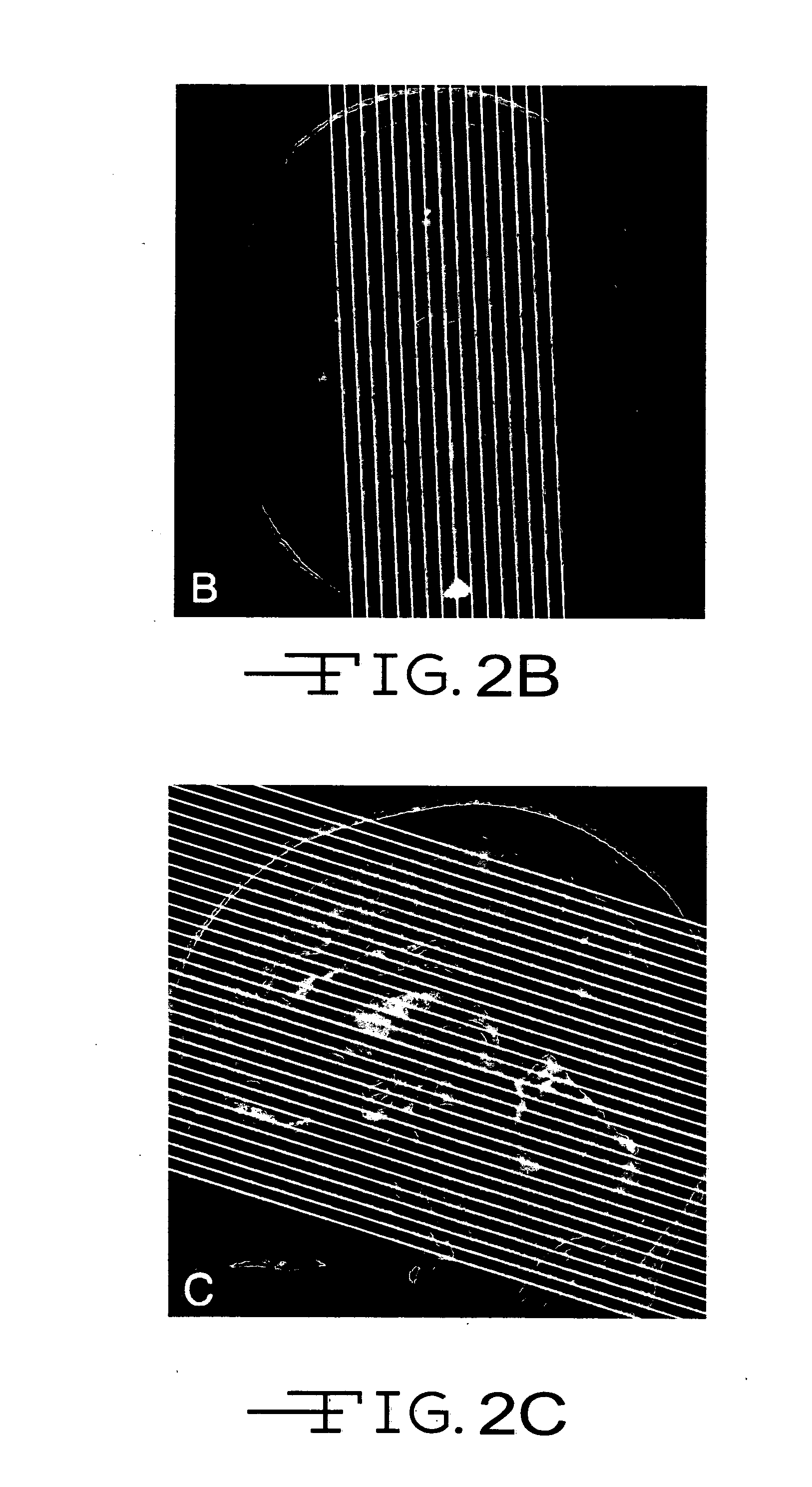
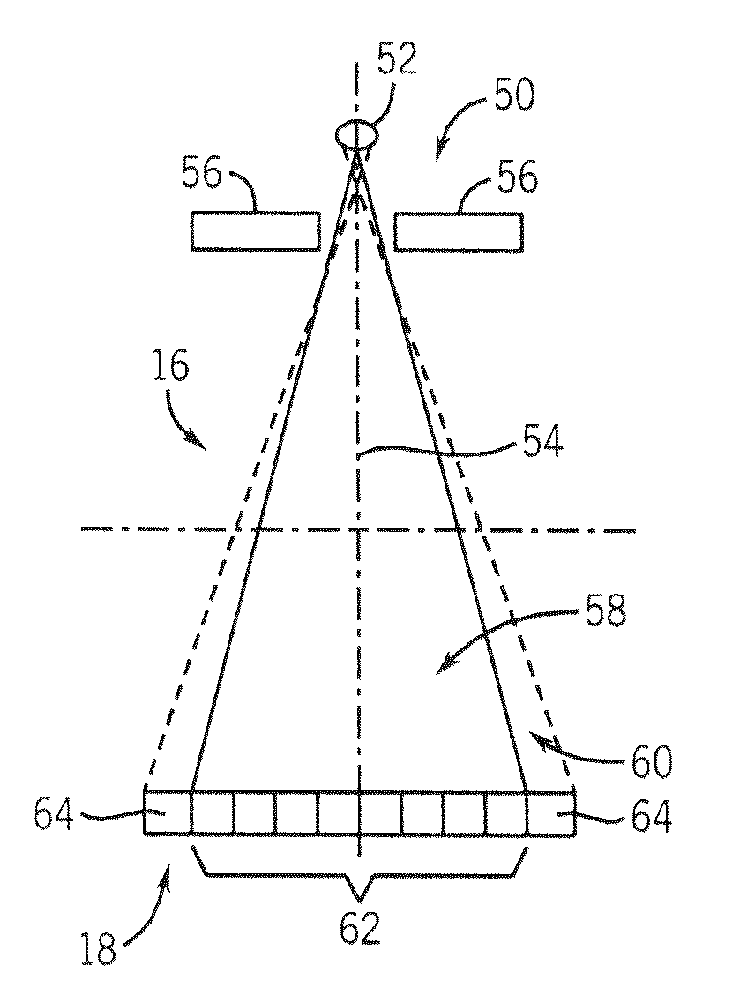
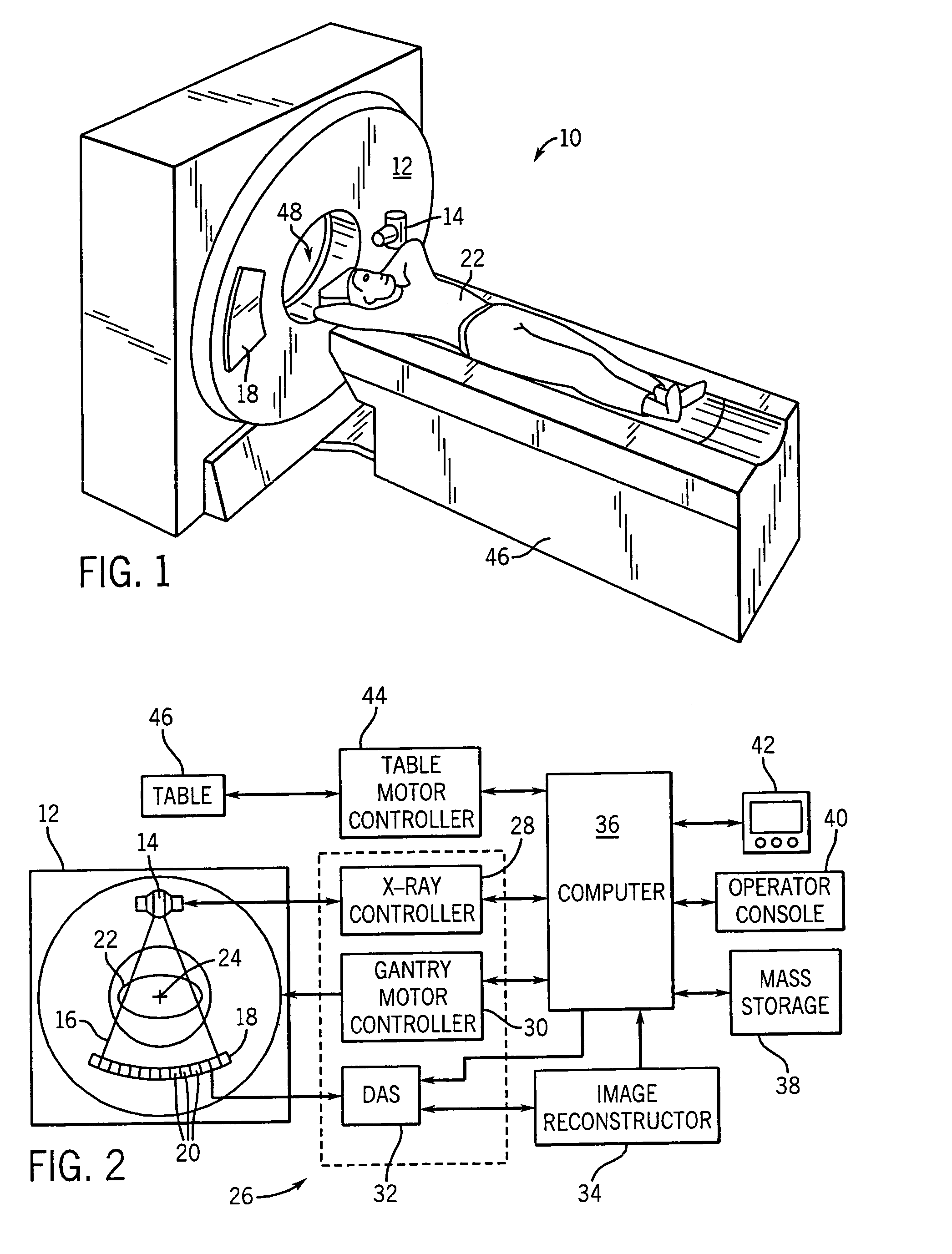
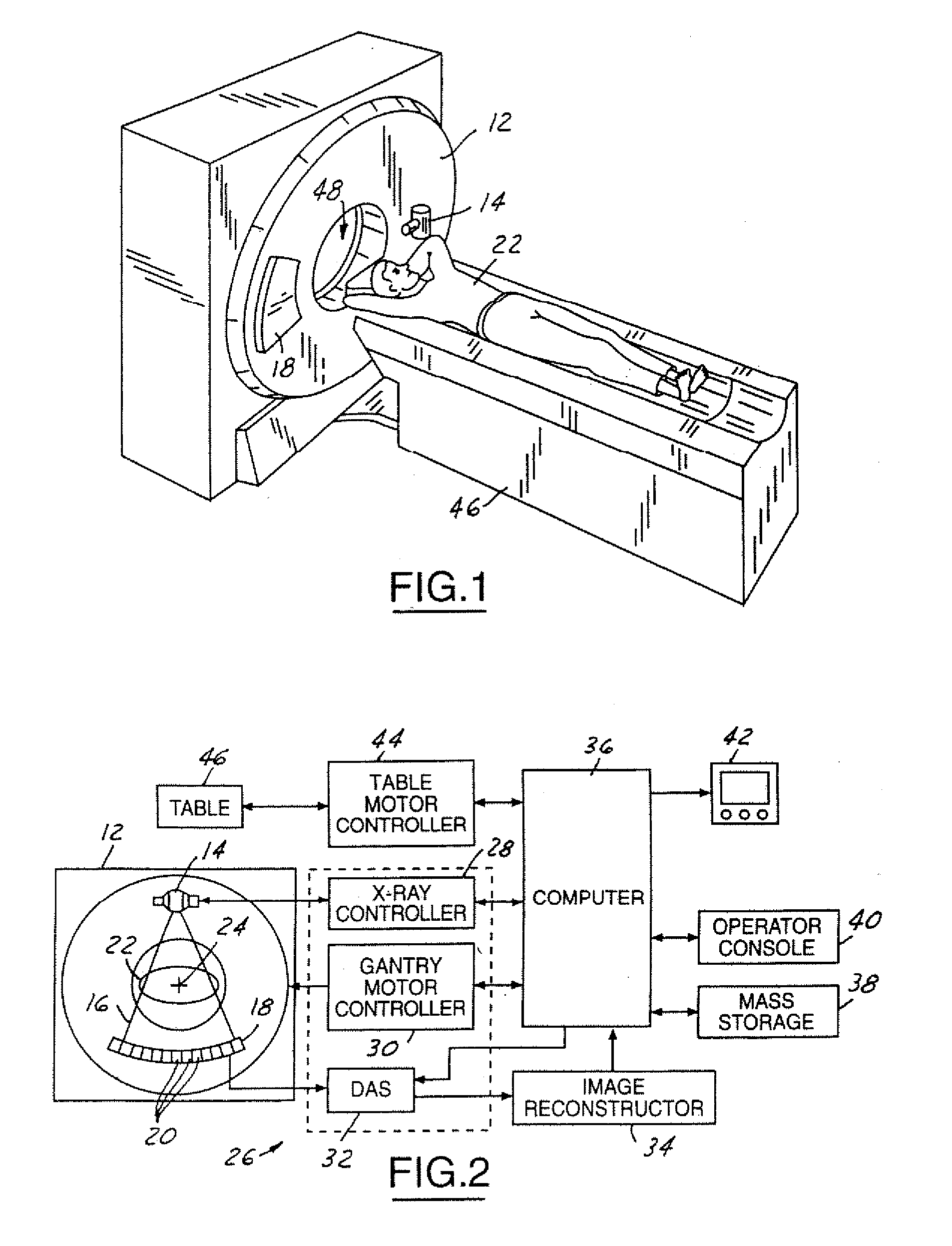
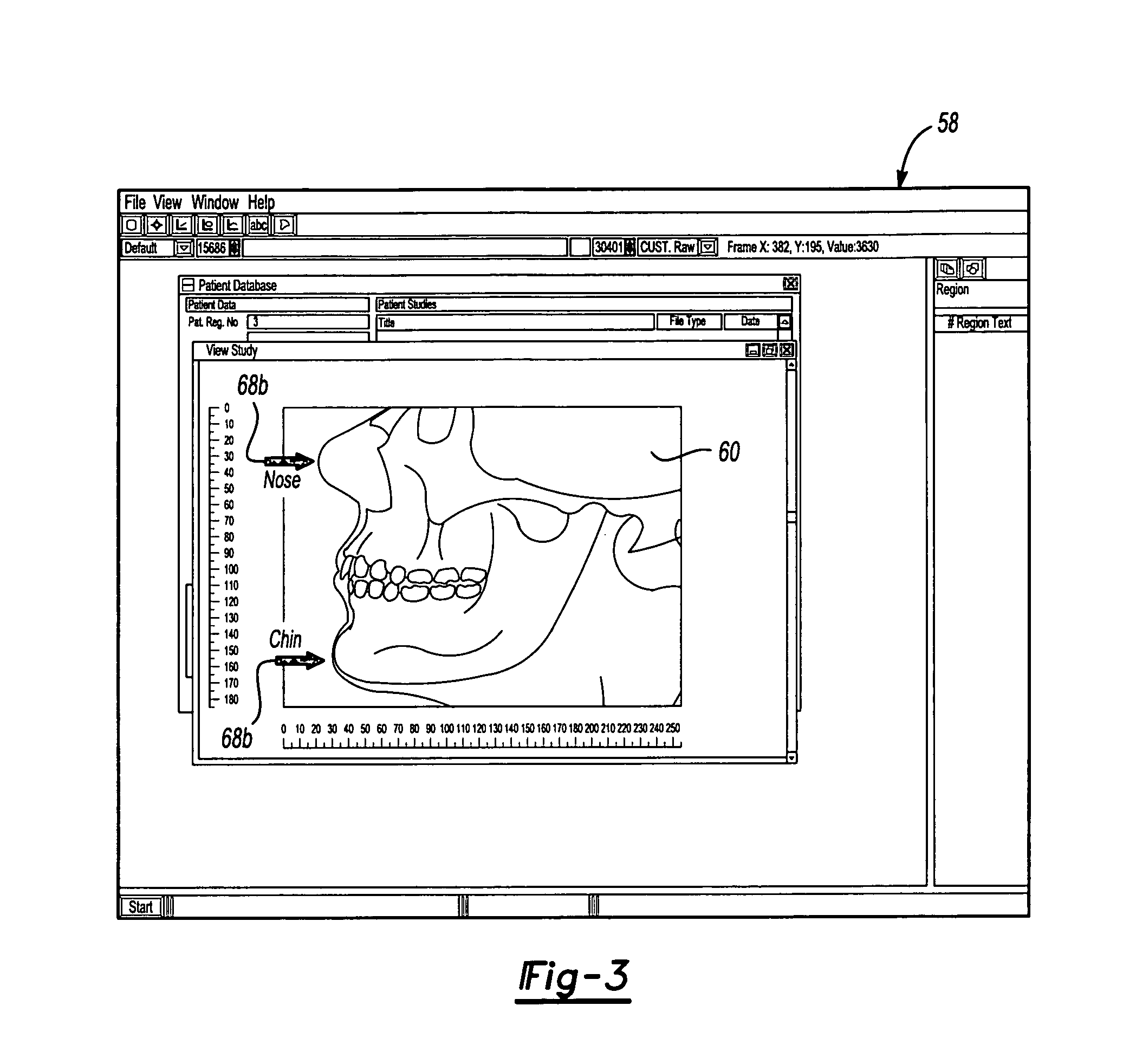
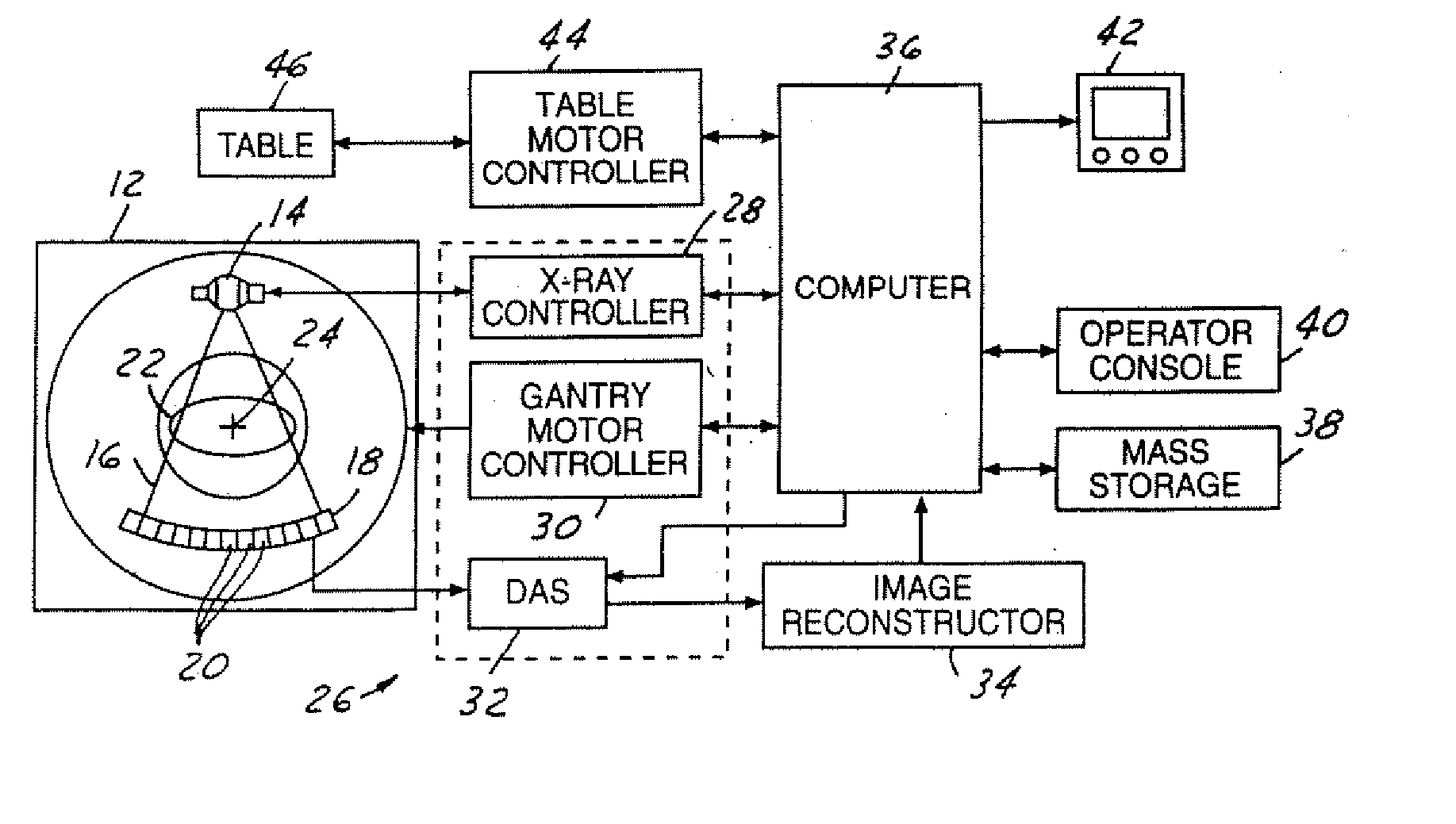
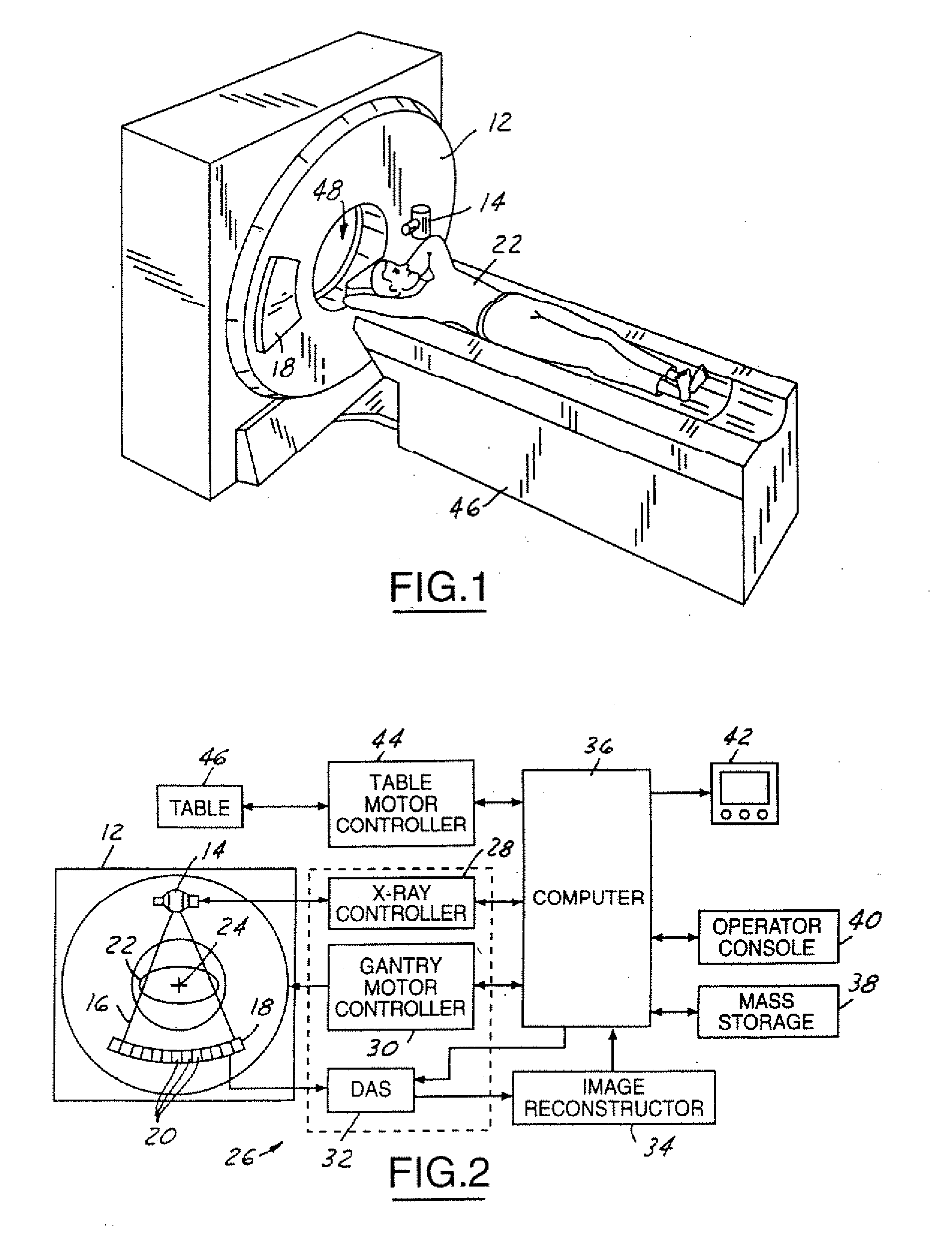
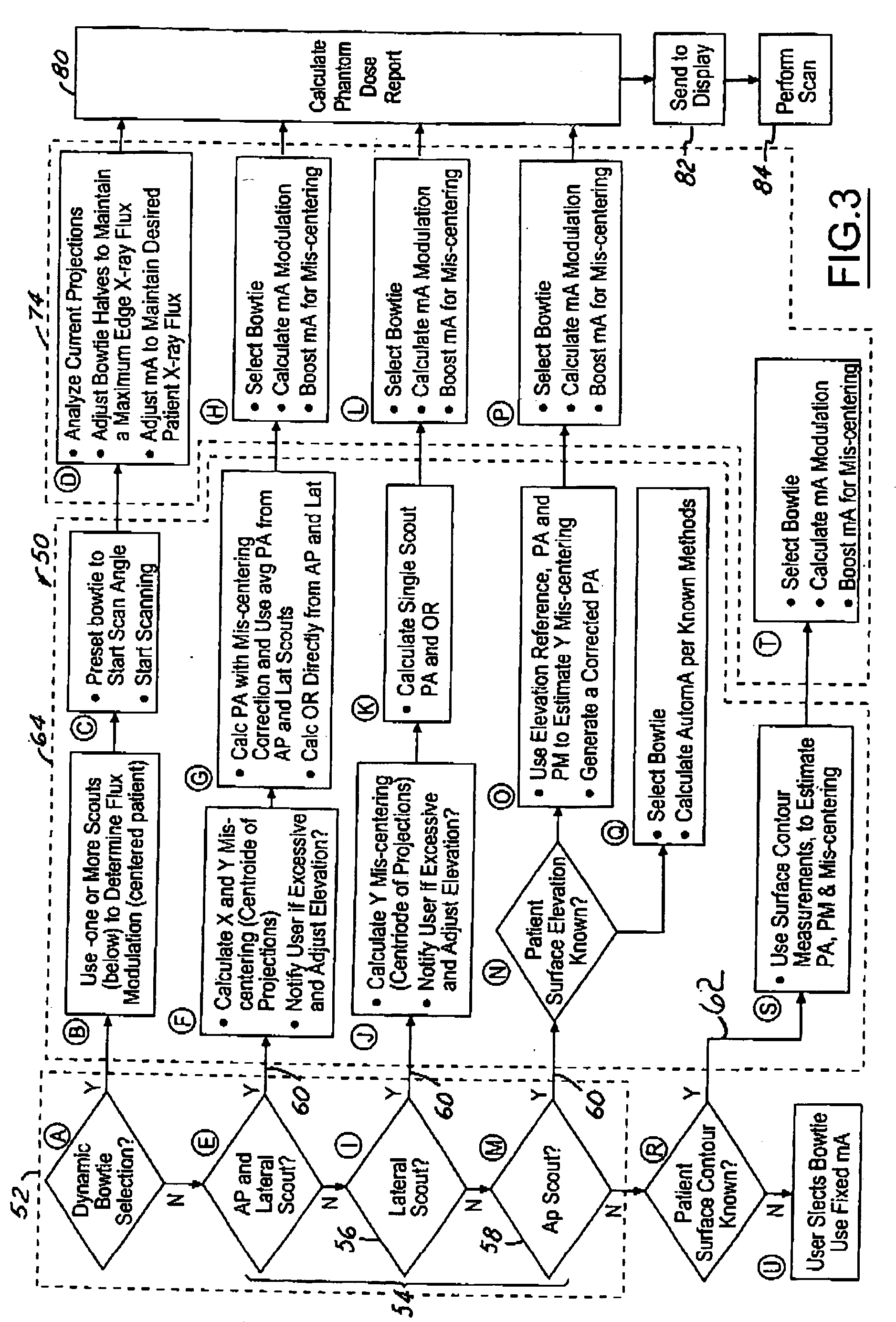
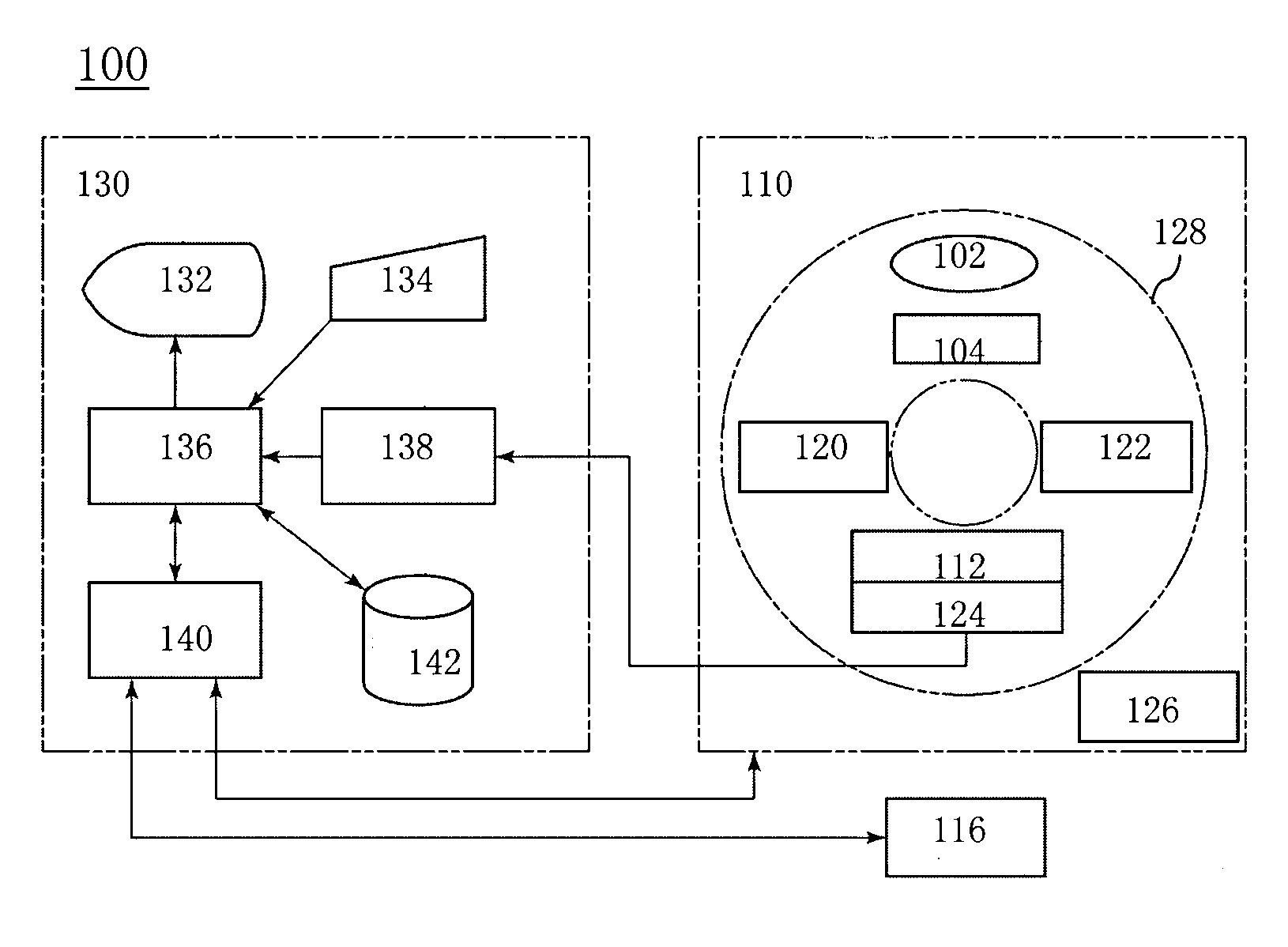
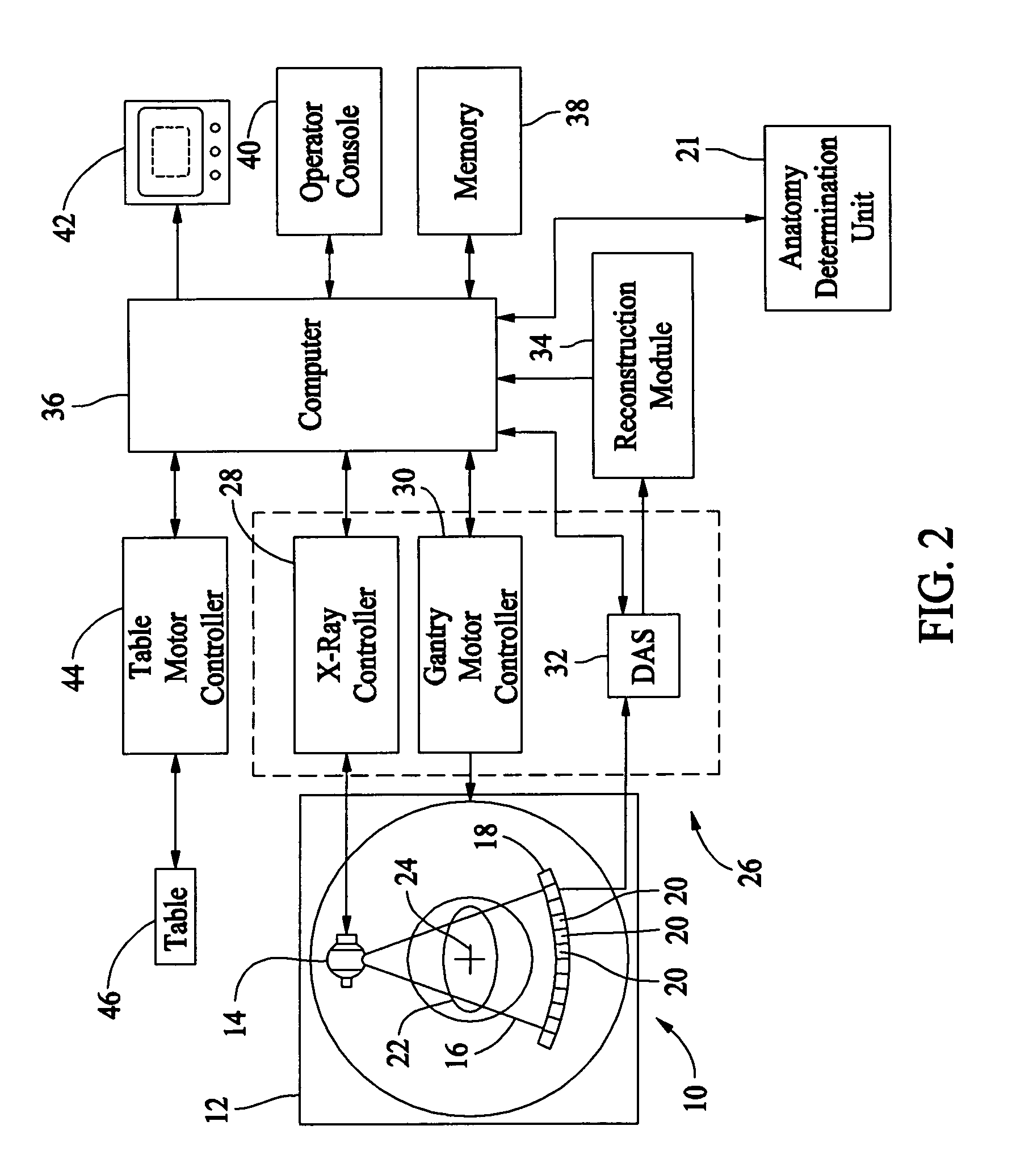
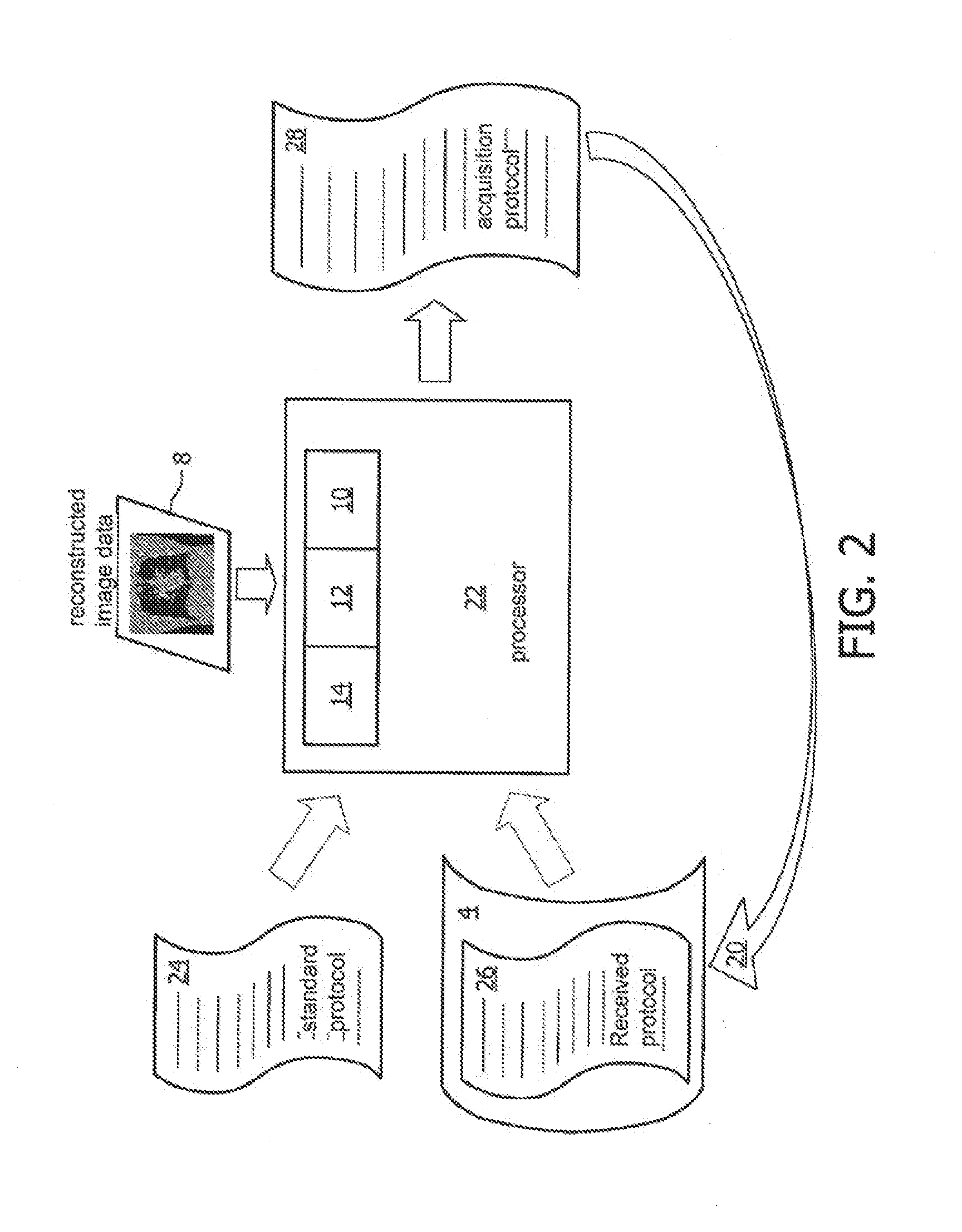
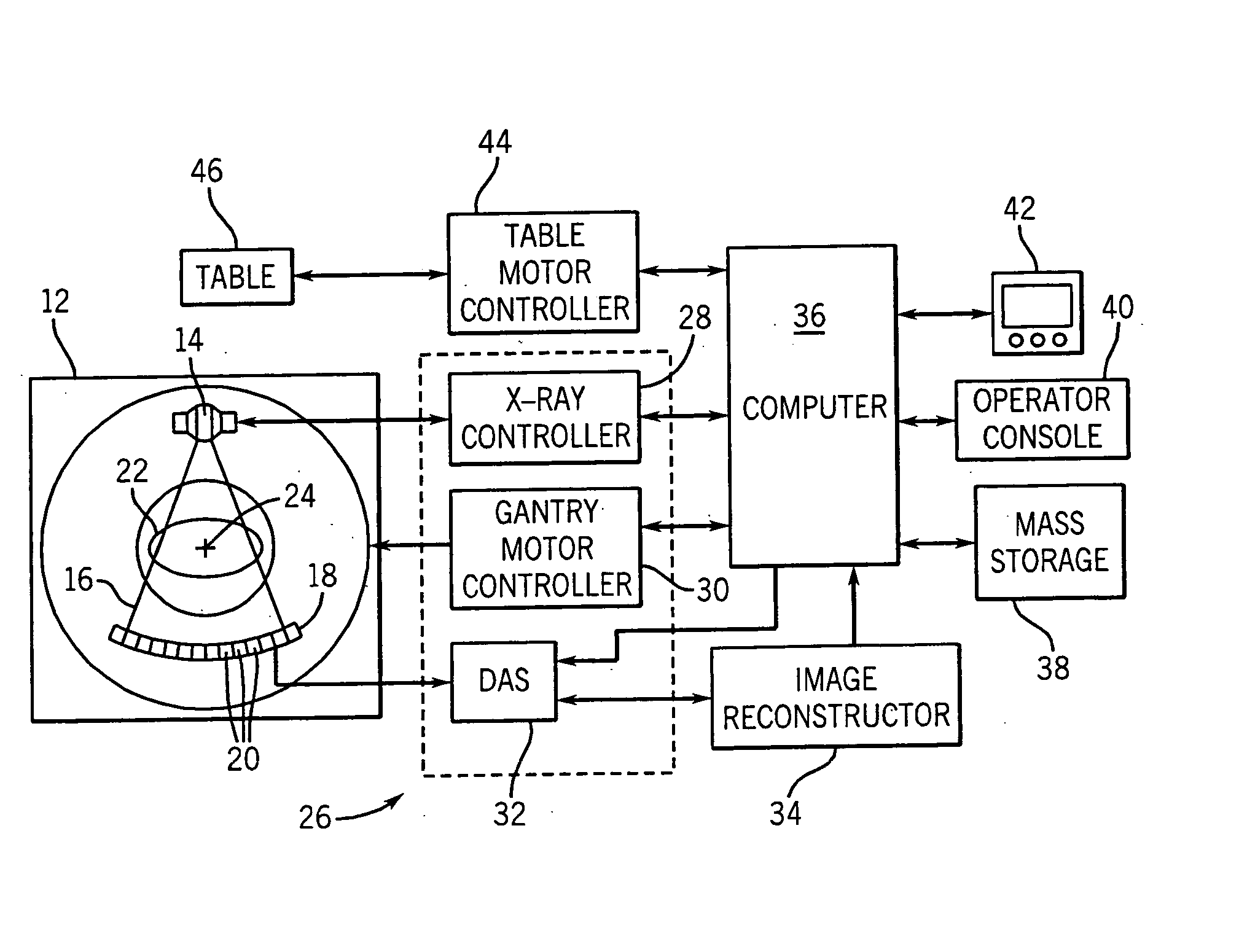
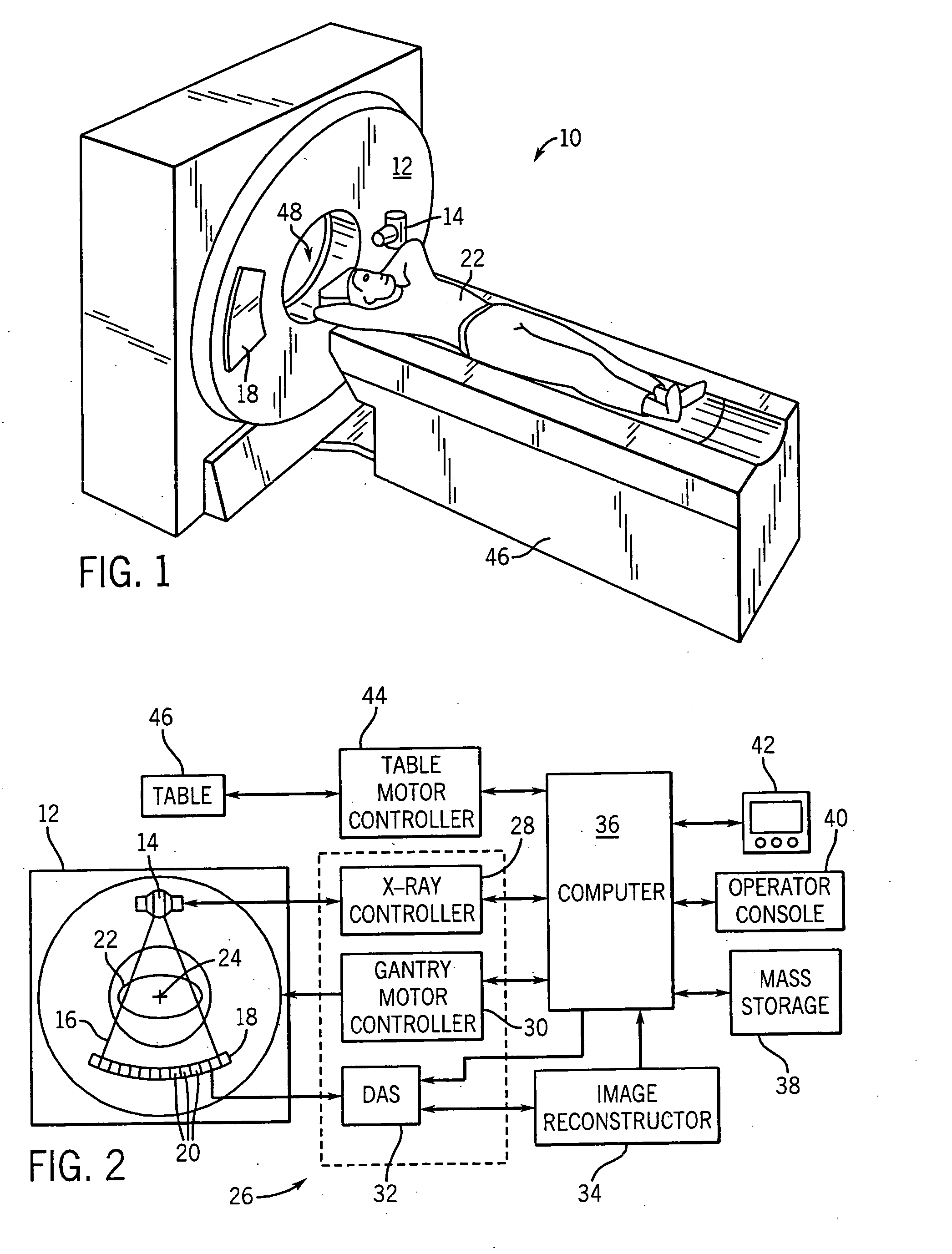
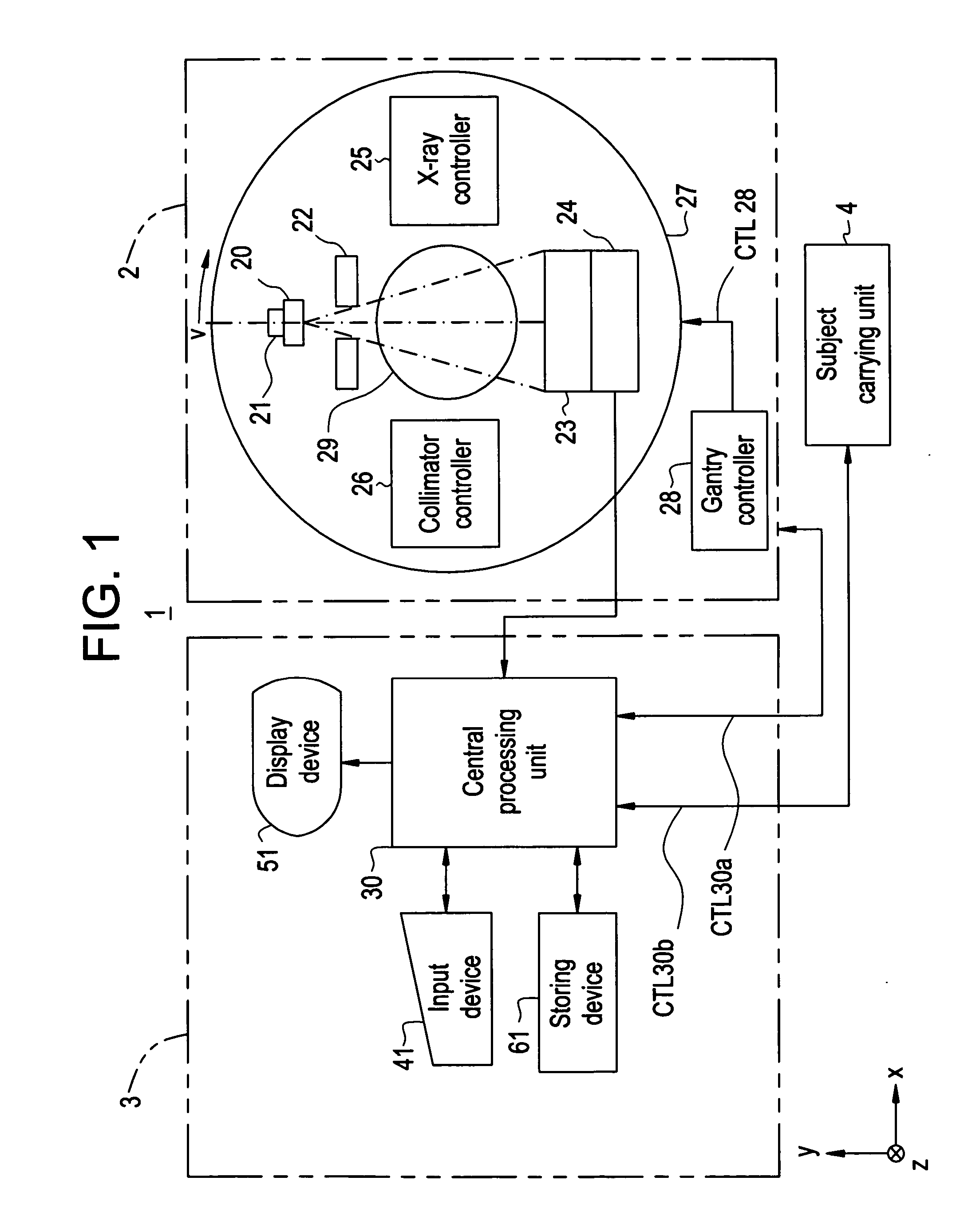
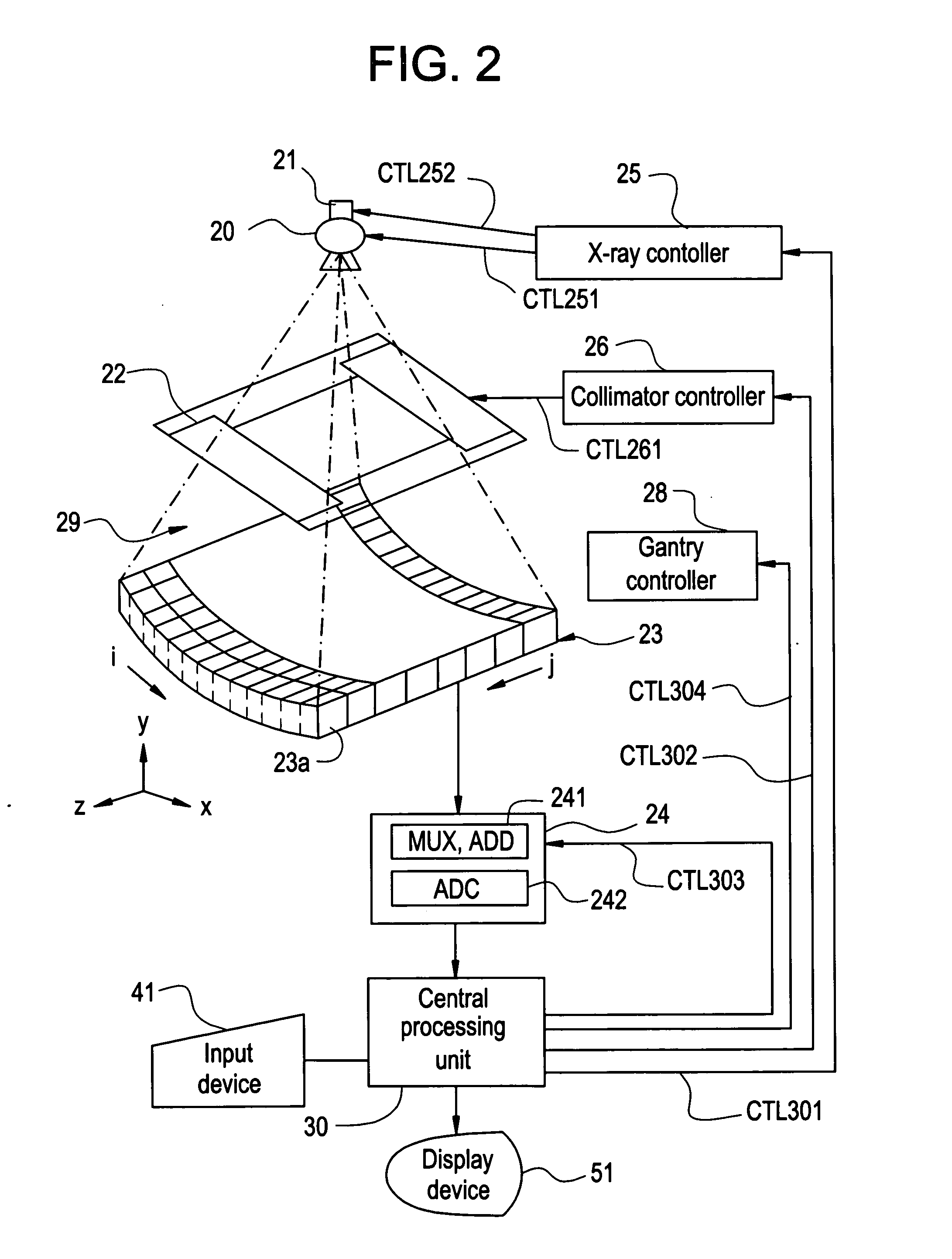
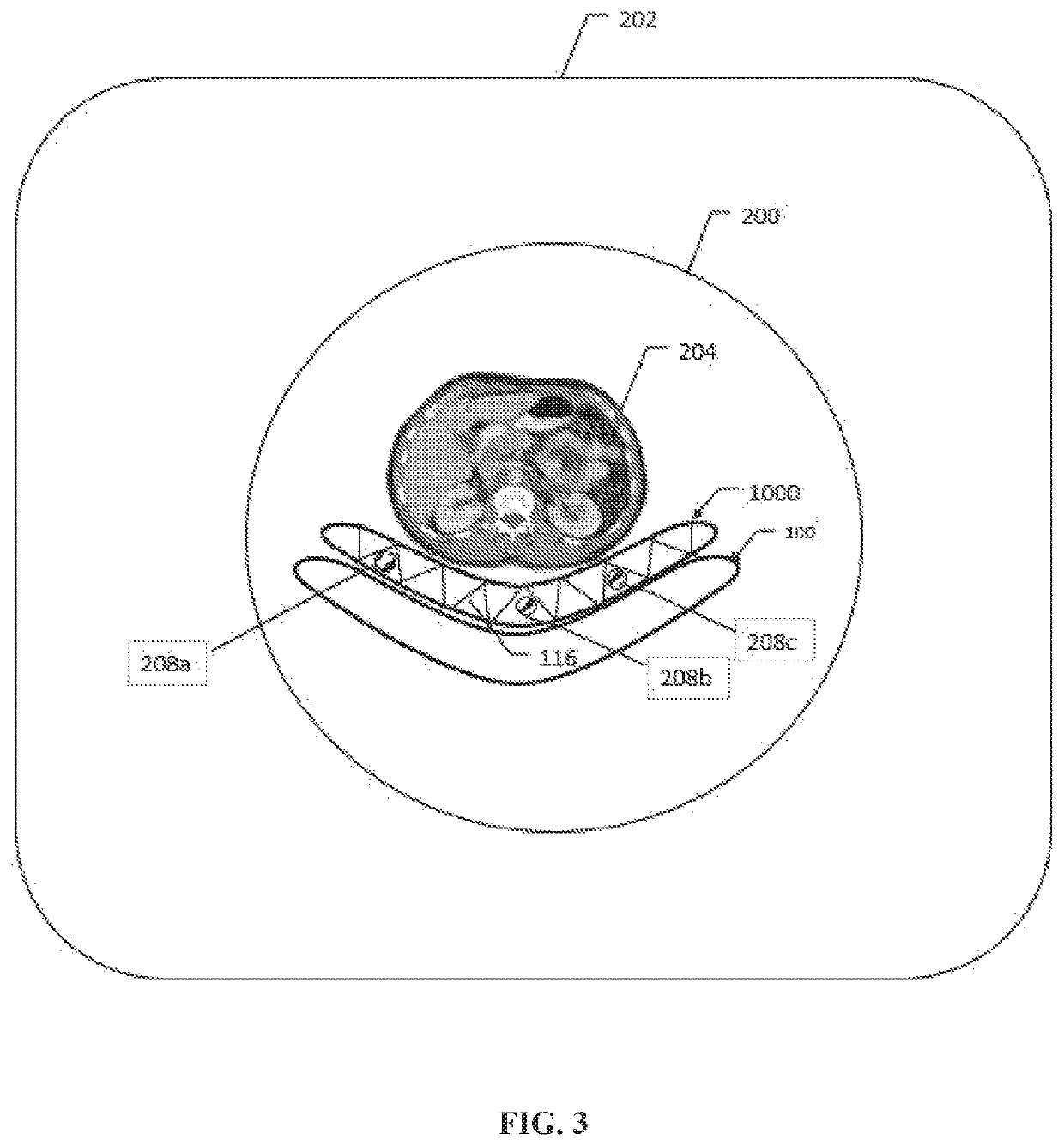
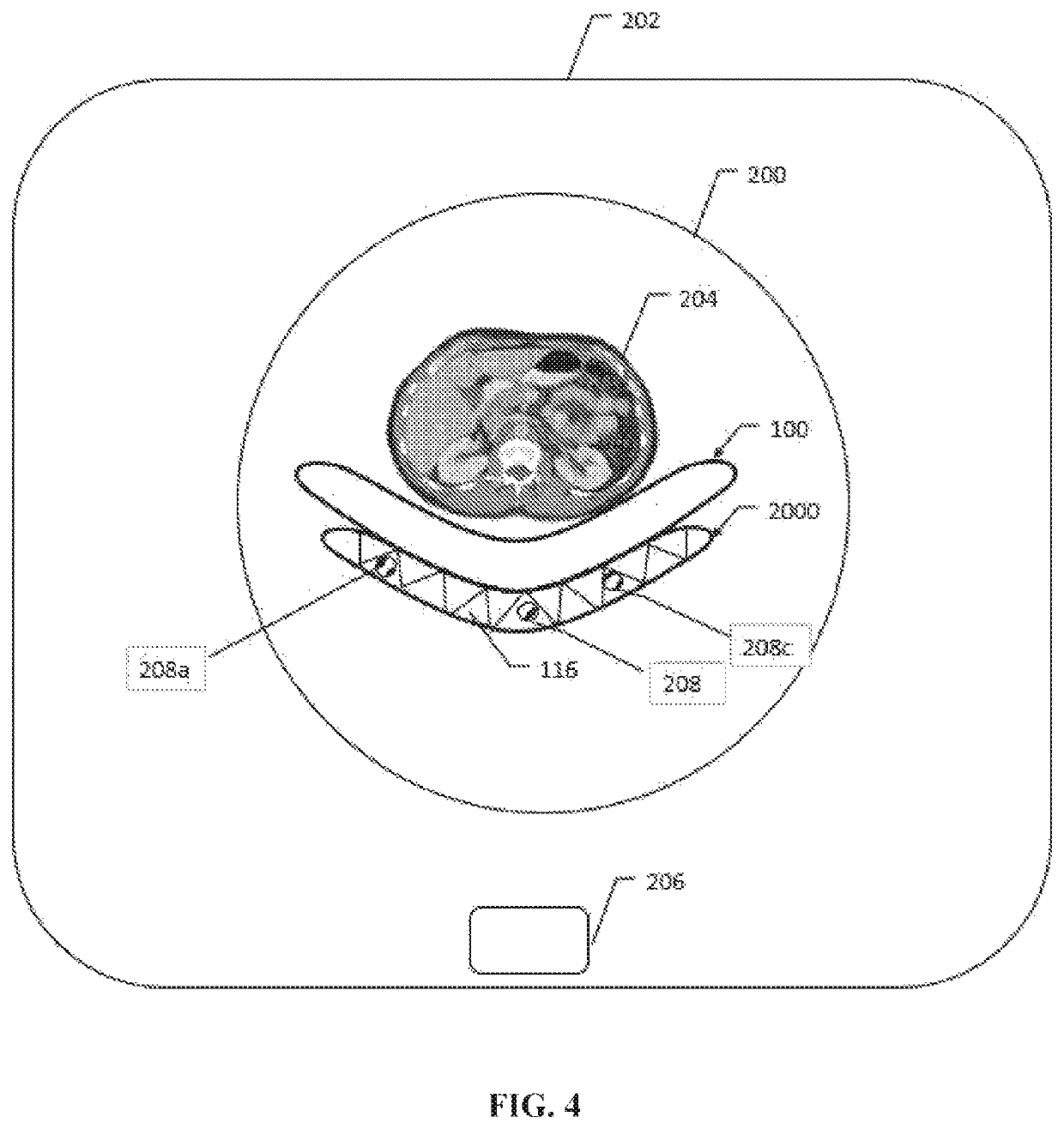
System and method of determining a user-defined region-of-interest of an imaging subject for x-ray flux management control
ActiveUS6990171B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationX-ray
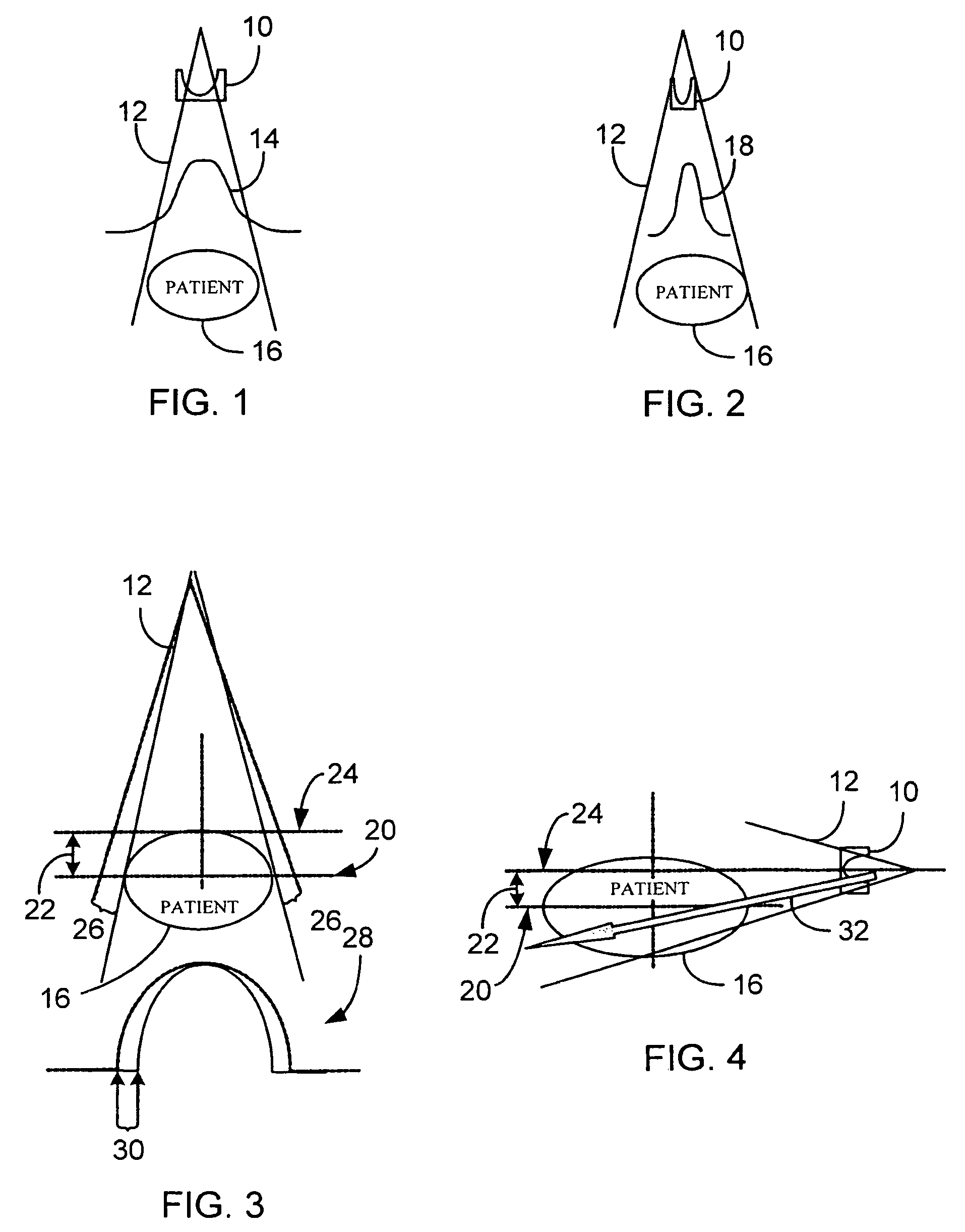
A system and method of diagnostic imaging is provided that includes positioning a subject in an imaging device, performing at least one scout scan, and marking a user-defined region-of-interest. An attenuation characteristic of an attenuation filter is then automatically adjusted based on the user-defined region-of-interest. The present invention automatically selects a proper attenuation filter configuration, corrects patient centering, and corrects noise prediction errors, thereby increasing dose efficiency and tube output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Adjusting acquisition protocols for dynamic medical imaging using dynamic models
ActiveUS20100183206A1More standardizedBetter quantifiableImage enhancementImage analysisDynamic modelsHemodynamics
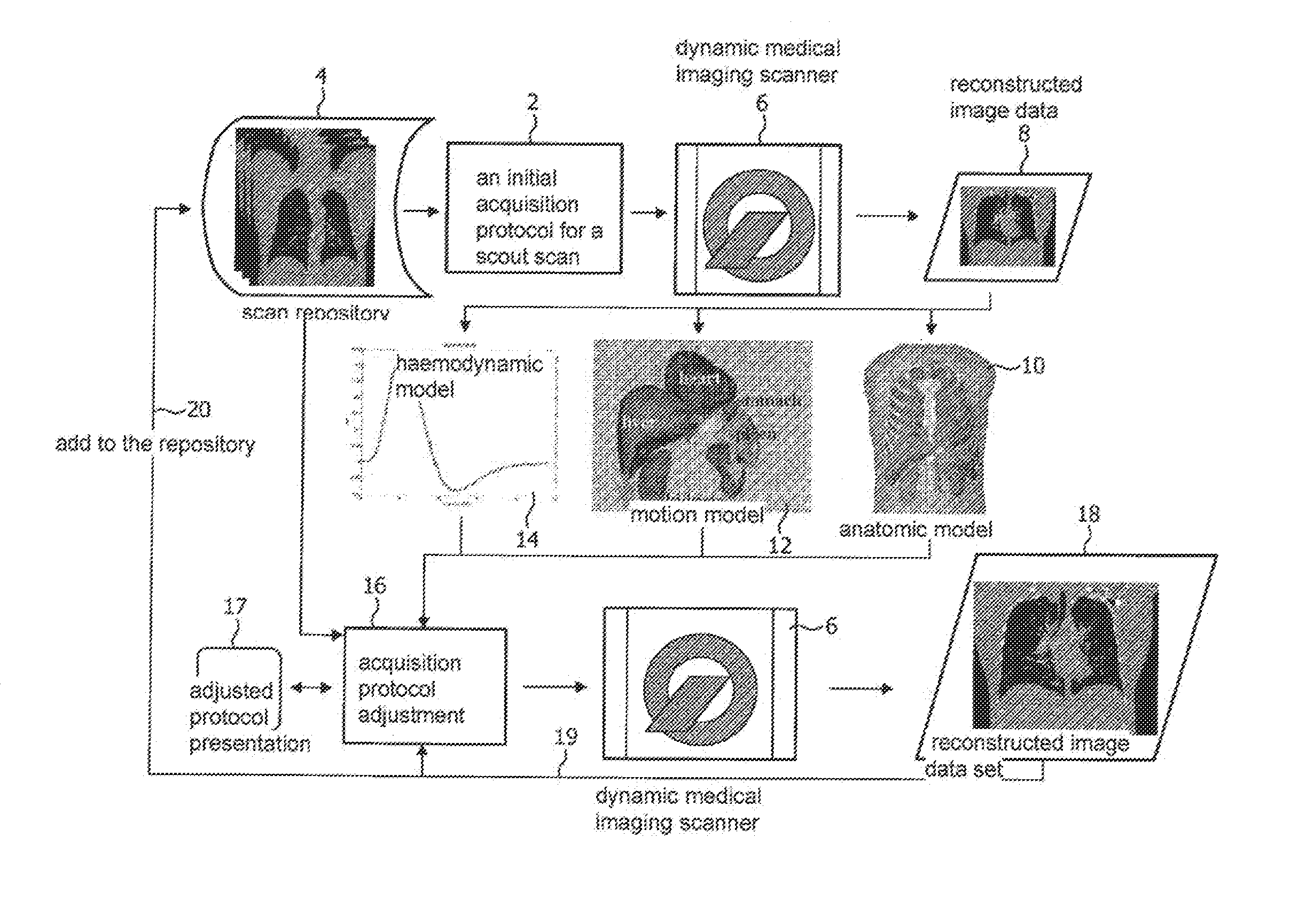
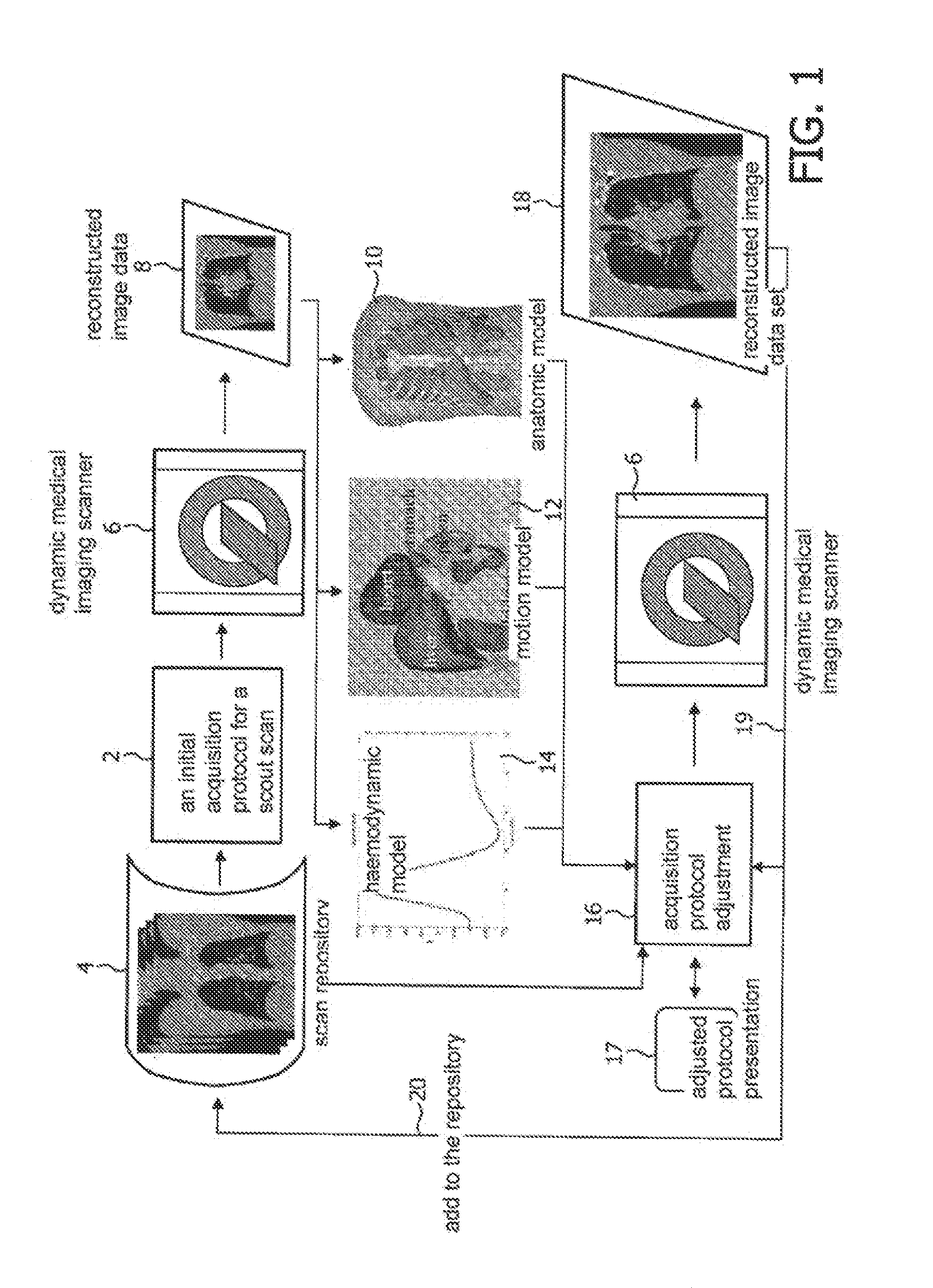
The invention relates to automatically adjusting an acquisition protocol for dynamic medical imaging, such as dynamic CT, MRI or PET imaging. The protocols are adjusted based on anatomic and dynamic models (10, 12, 14) which are individualized or fitted to each patient based on a scout scan (6, 8). The adjustment can compensate for changes in the patient due to patient motion (e.g. breathing or heartbeat) or flow of contrast or tracing agent during the sequence. This ensures that changes in the reconstructed images are indicative of pathological changes in the patient and not caused by patient motion or changes in scanning parameters or timing. The dynamic model can be a motion model (12) used to predict the motion of anatomic / physiologic features, typically organs, during scanning, or a haemodynamic model (14) used to predict flow of the contrast agent allowing for precise timing of the scanning sequence.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
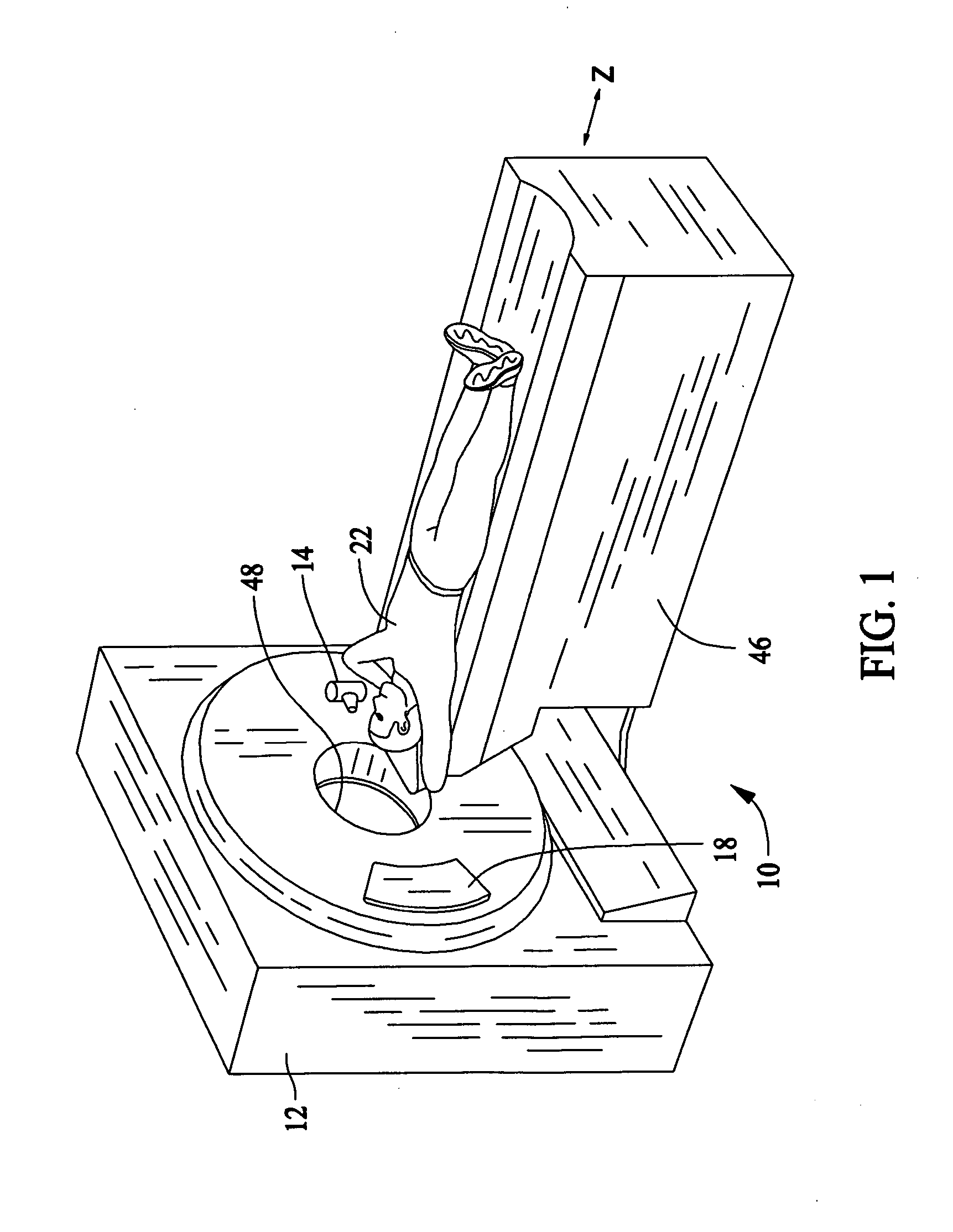
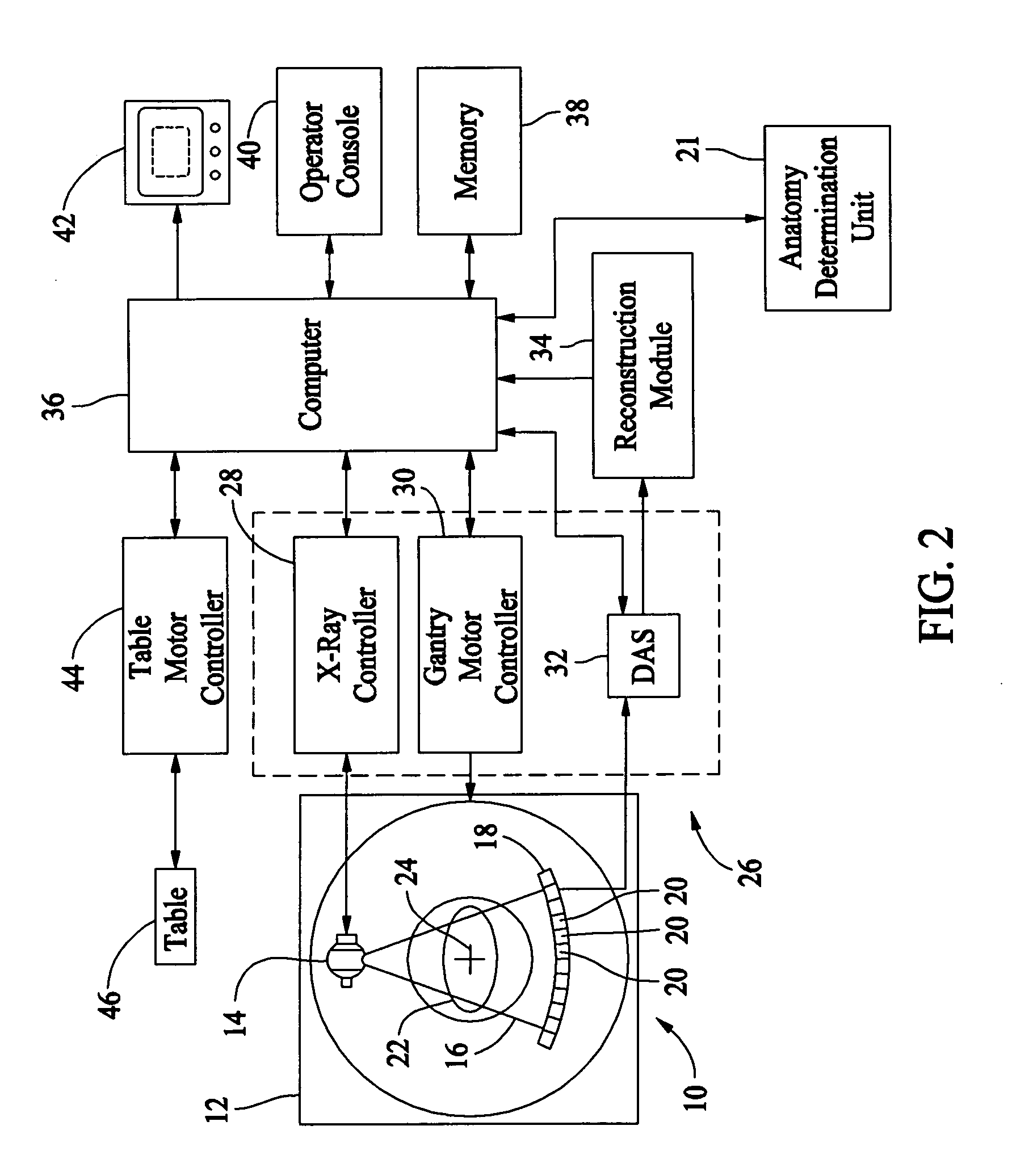
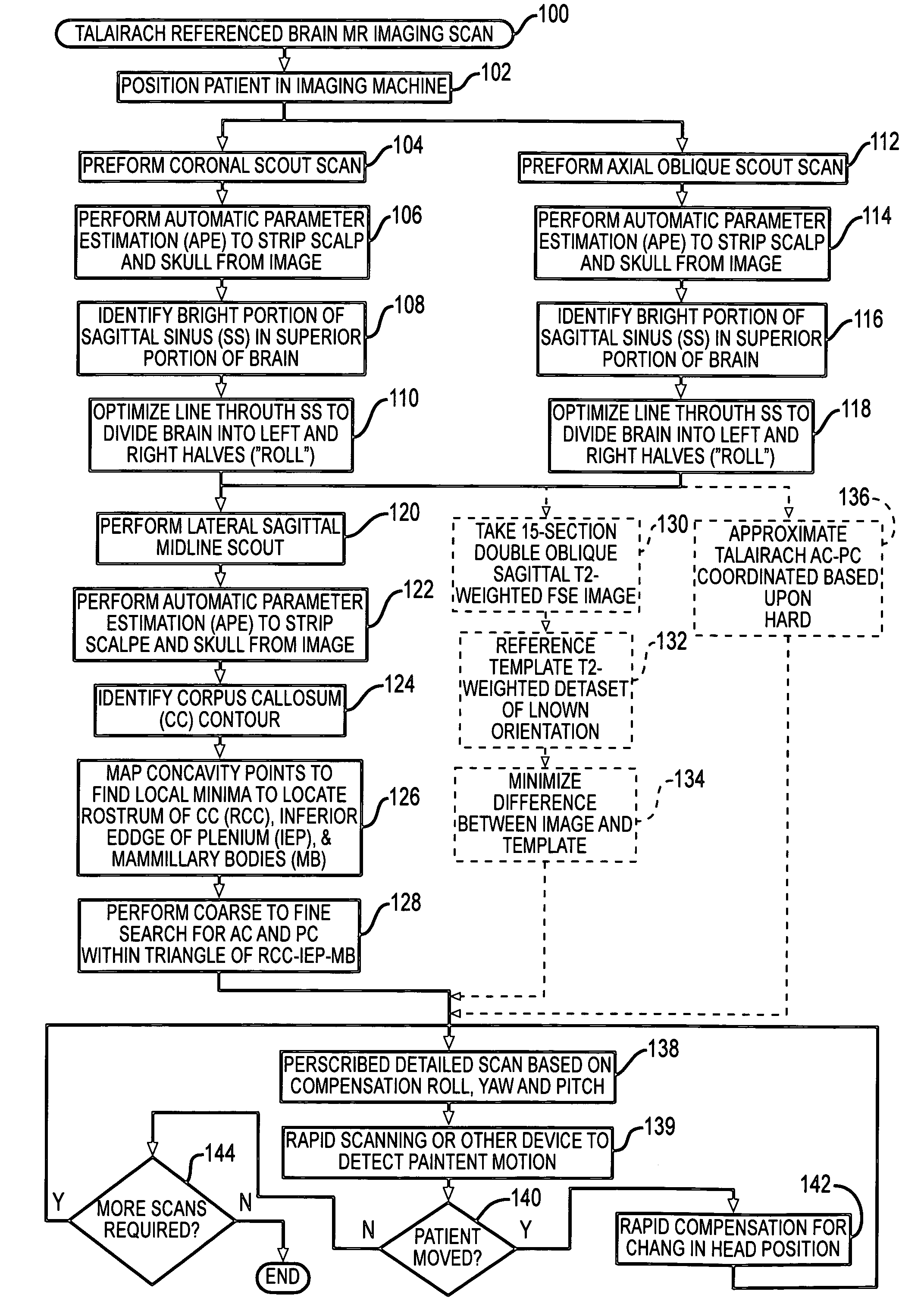
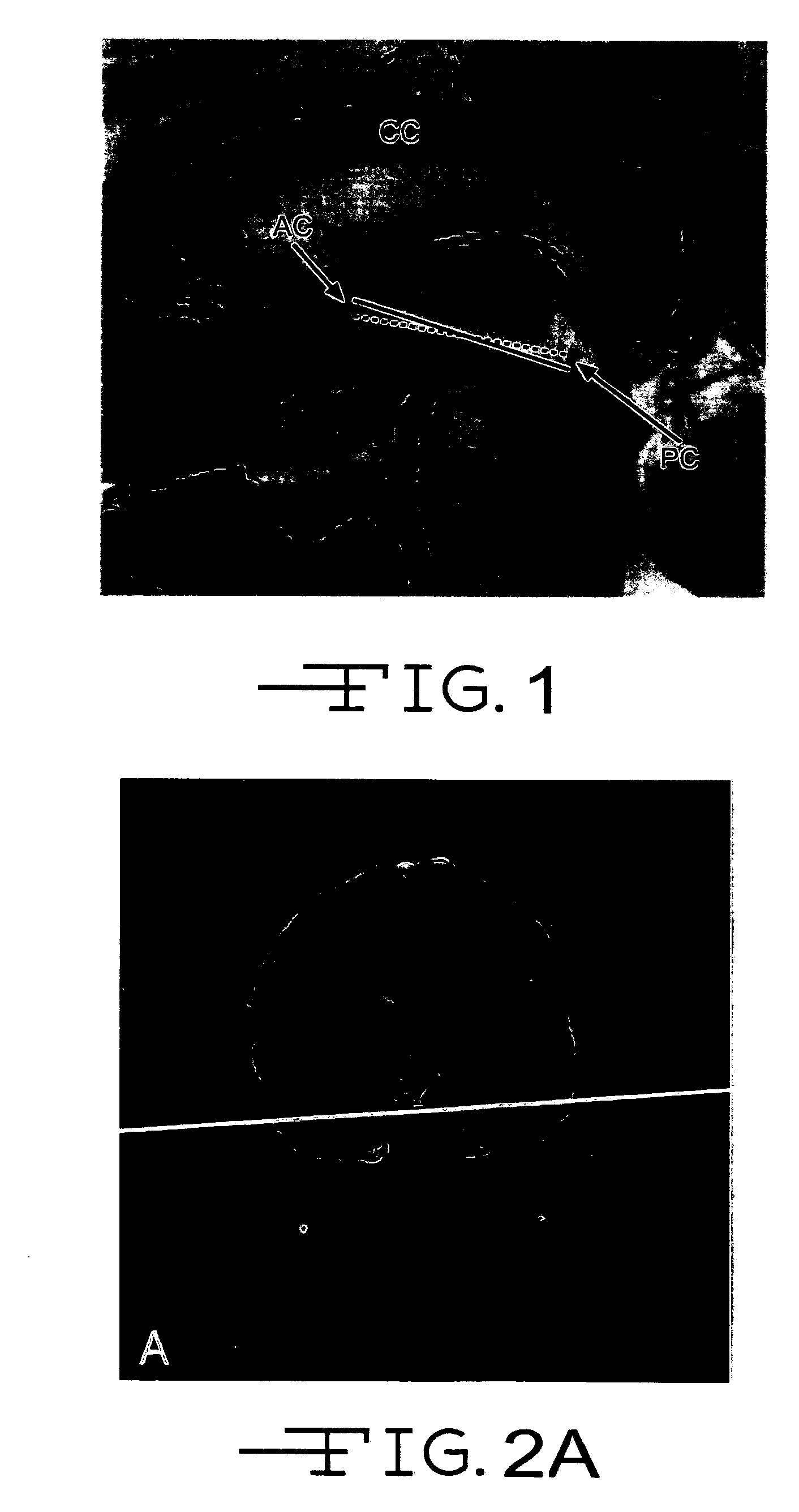
Automated brain MRI and CT prescriptions in Talairach space
InactiveUS20050165294A1Minimizes variabilitySurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic modalitiesAnterior commissure
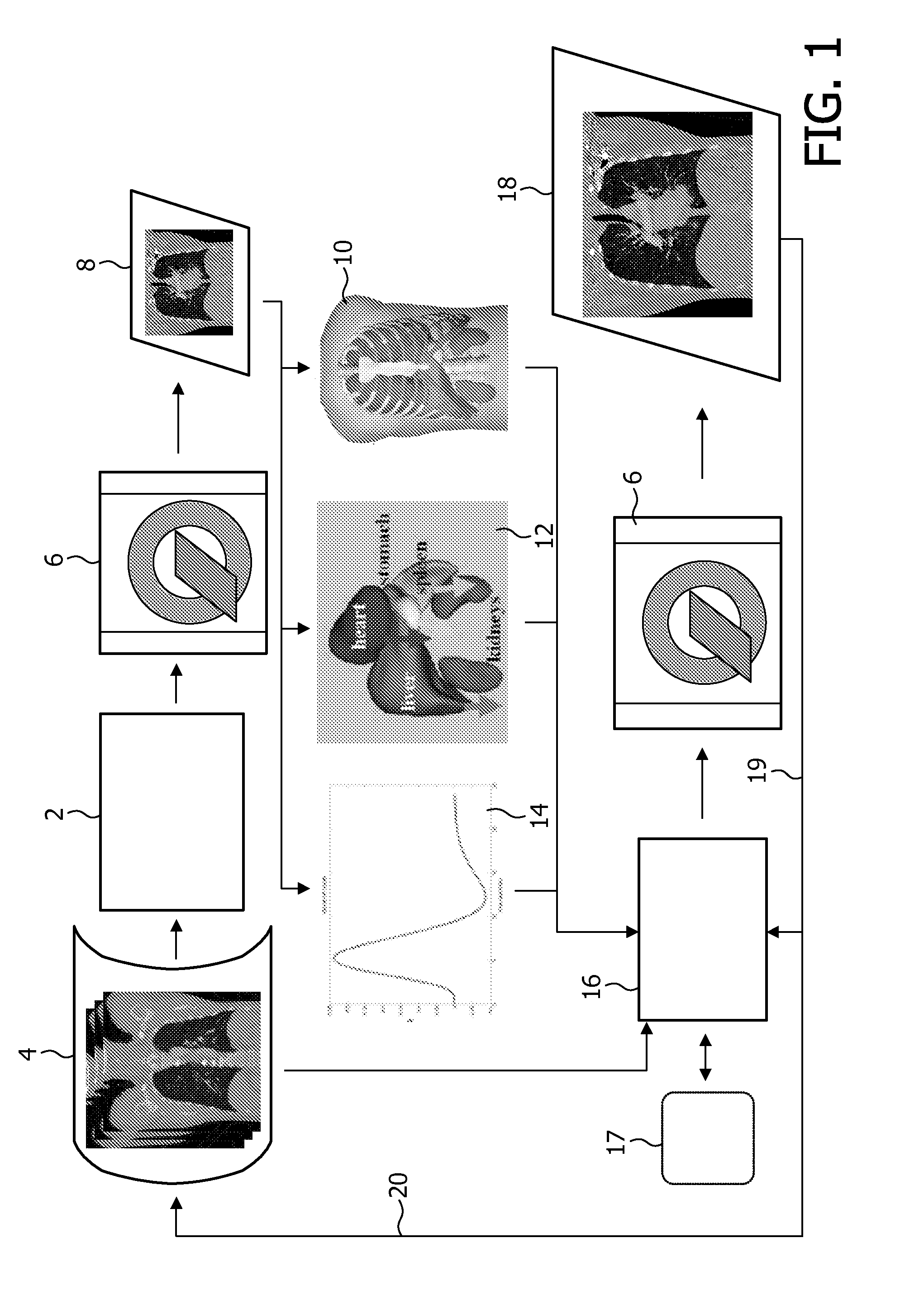
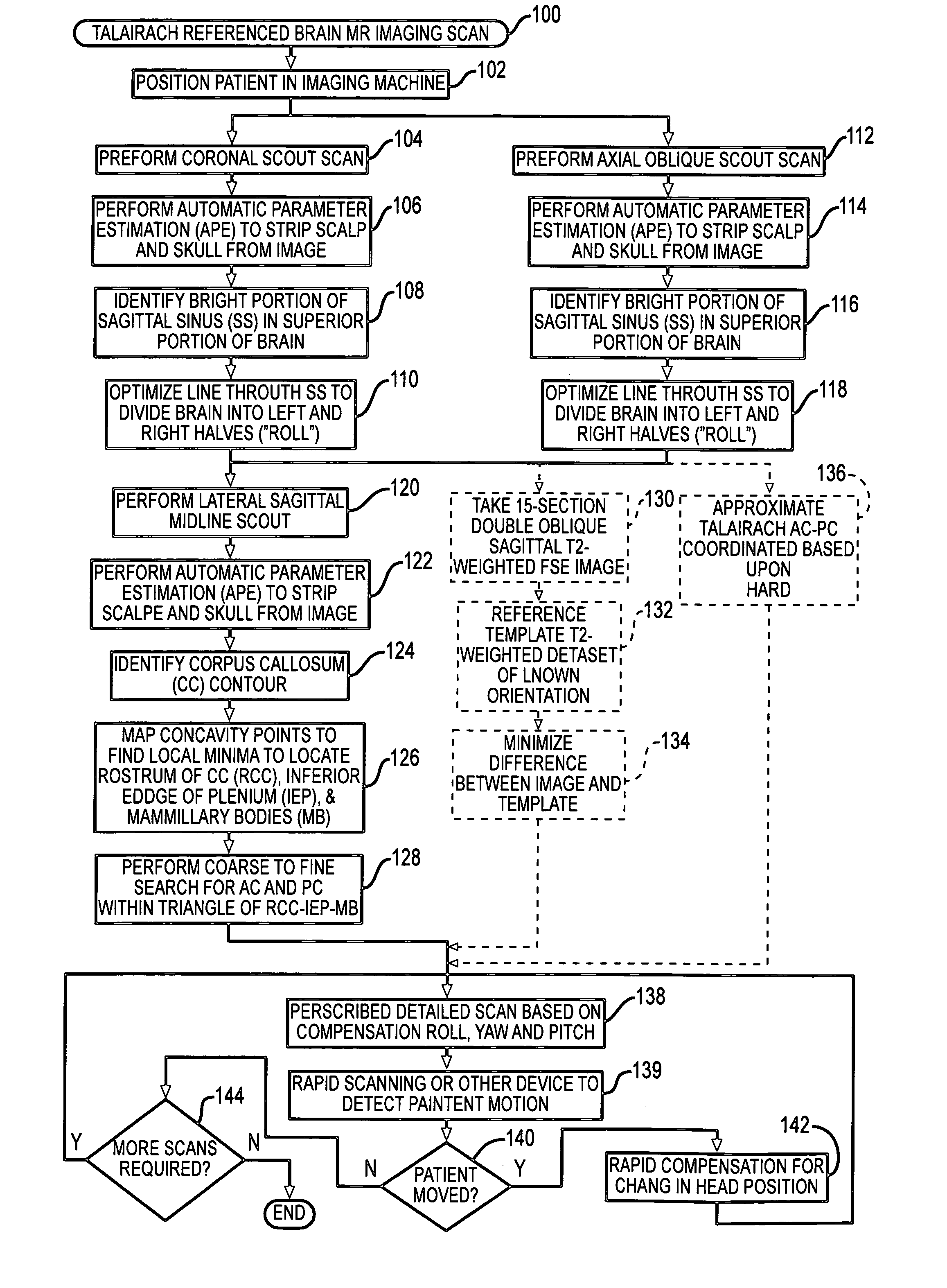
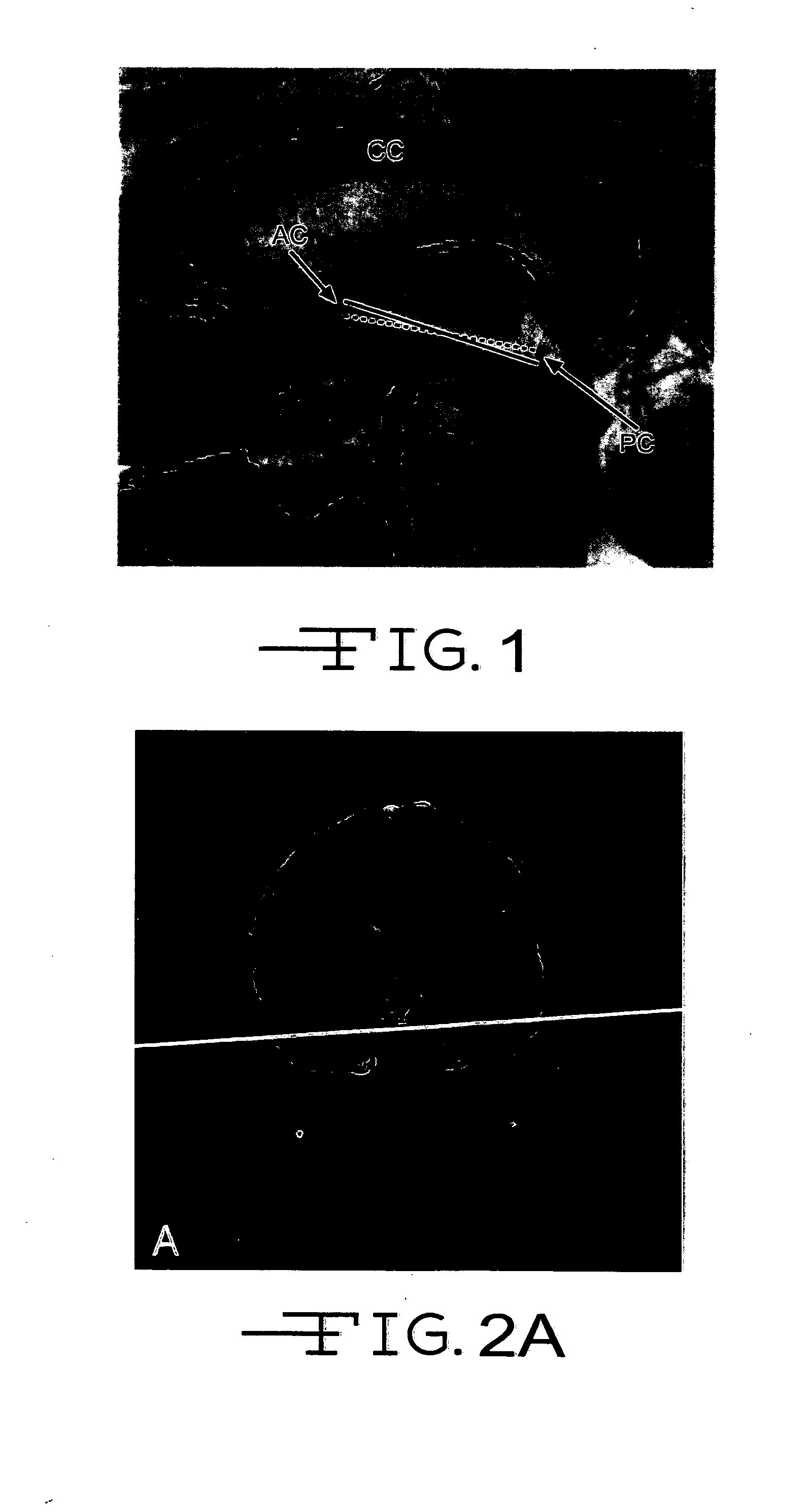
Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computerized Tomotography (CT), or other diagnostic modalities may employ a three-step procedure during initial (“scout”) cranial pre-scans that corrects for patient positioning (i.e., roll, yaw and pitch) to reduce inter- and intra-patient variation, thereby enhancing the diagnostic and comparative value of subsequent detail scans even across different diagnostic platforms. In MRI, for instance, locating the saggital sinus (SS) and optimizing a line to bisect the brain through this SS may be automated to correct for roll and yaw. By then identifying the contour of the corpus callosum in a lateral saggital scout scan, the Talairach anterior commissure (AC)—posterior commissure (PC) reference line may be found for correcting pitch. Prescription of detailed scans are improved, especially when the three-step correction is repeated periodically identifying the need to repeat a detailed scan or to adjust the coordinates of a subsequent scan.
Owner:ABSIST +1
Apparatus for acquisition of CT data with penumbra attenuation calibration
InactiveUS7260171B1Detection sacrificedQuality sacrificedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersUltrasound attenuationScout Scan
The present invention is a directed method and apparatus for collimating a radiation beam such that the full intensity of the radiation beam does not impinge detectors of a radiation detector assembly that are particularly susceptible to saturation or over-ranging. This collimation can be dynamically adjusted on a per view basis using empirical or scout scan data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus to determine tube current modulation profile for radiographic imaging
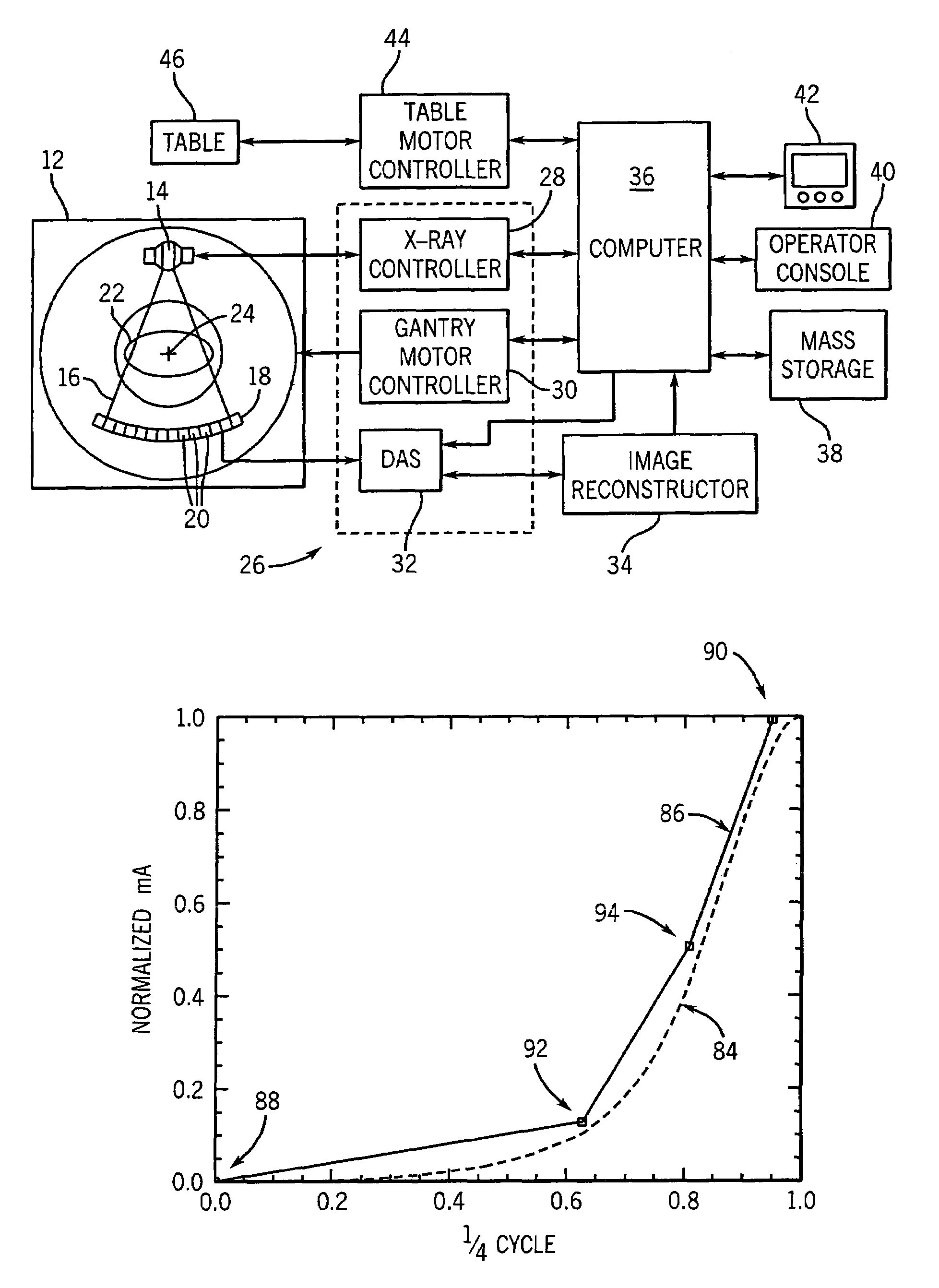
A method and apparatus is disclosed to acquire scout scan data of a subject and analyzed to determine a peak-to-peak modulation amplitude of a normalized waveform indicative of subject size and shape. The scout scan data provides a representation of patient size and shape that is associated with an ideal tube current modulation waveform or profile. The ideal tube current modulation profile may then be sampled or approximated at various points to determine a tube current modulation profile for implementation to acquire CT data with reduced dose but without sacrificing image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
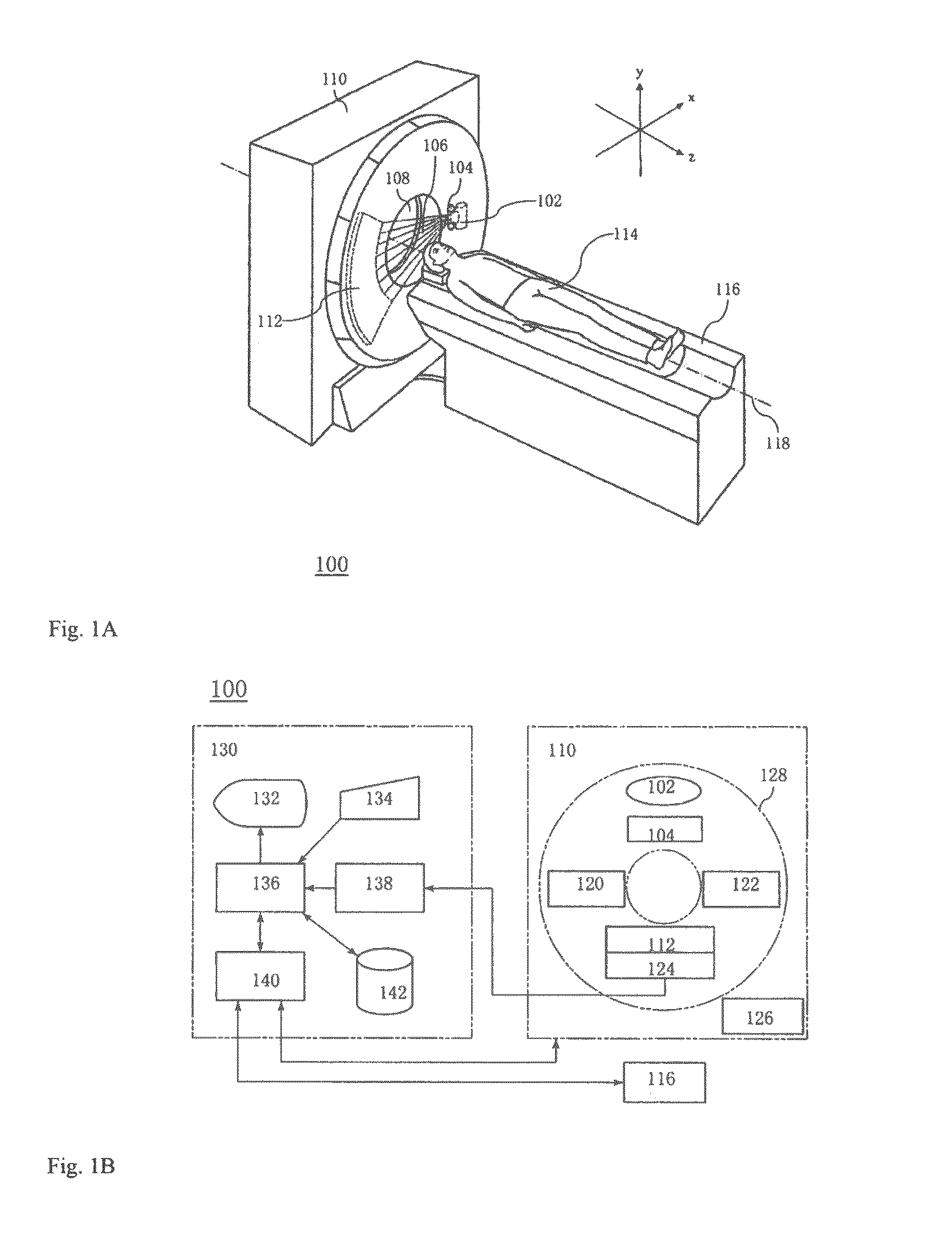
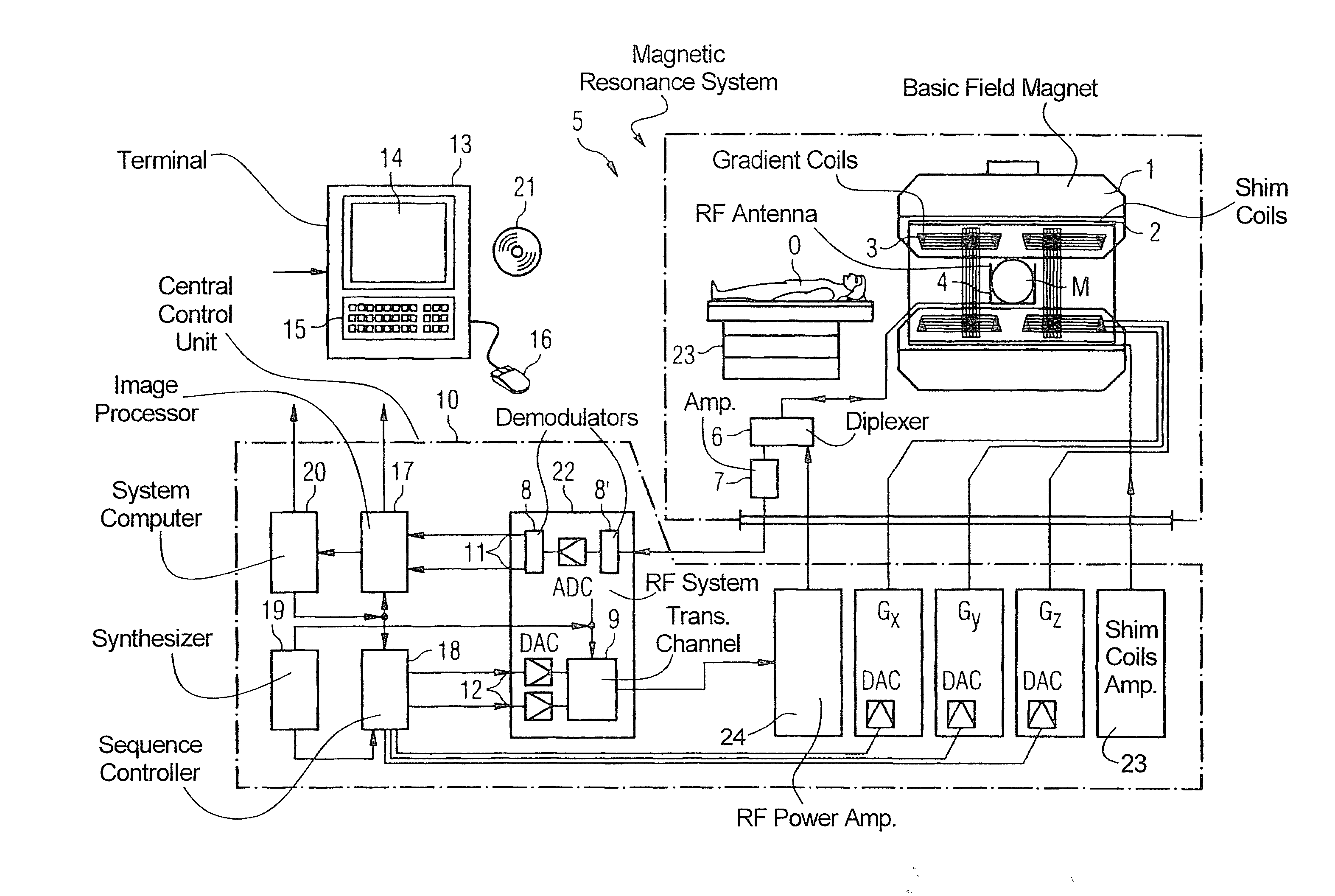
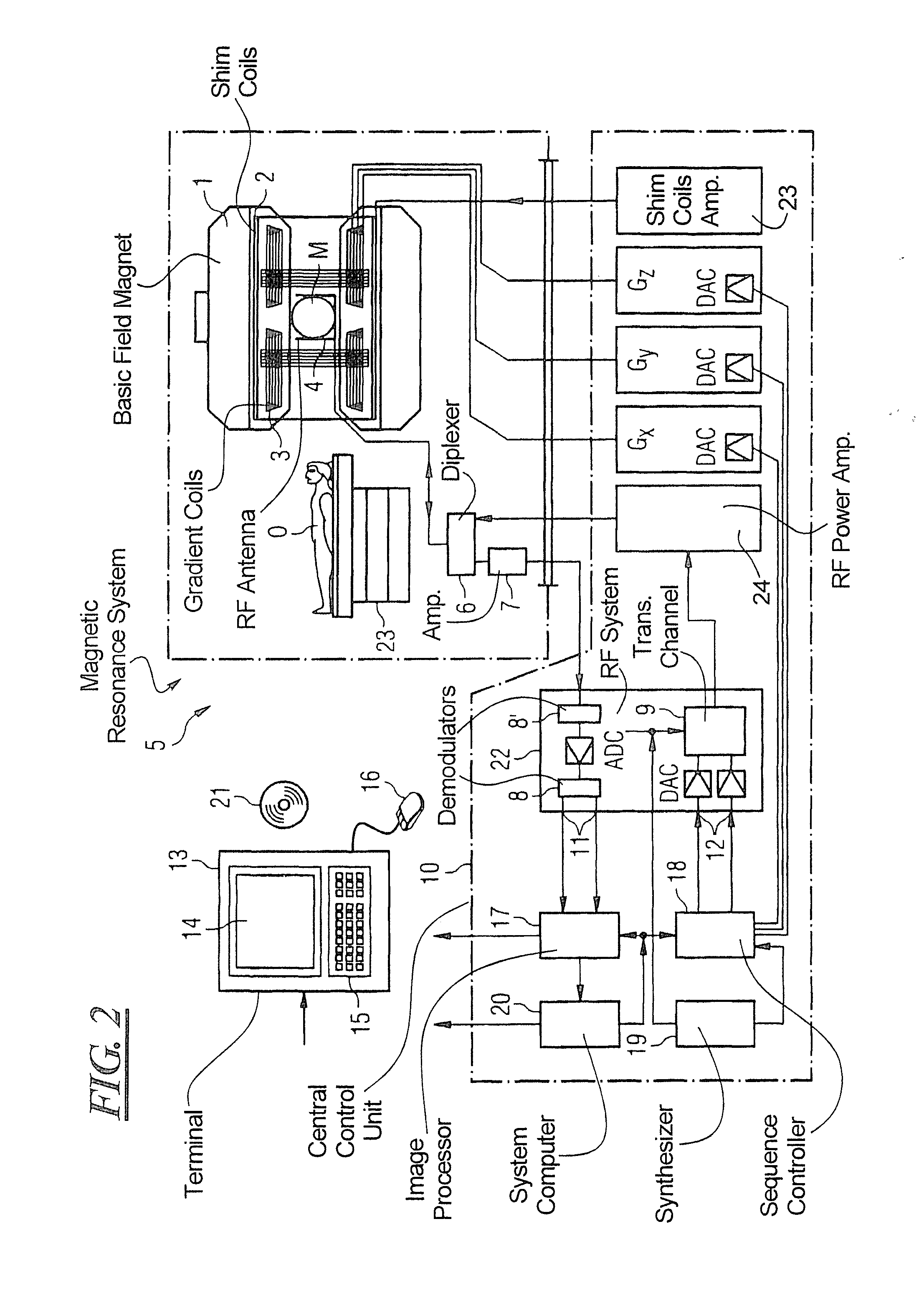
Medical imaging apparatus
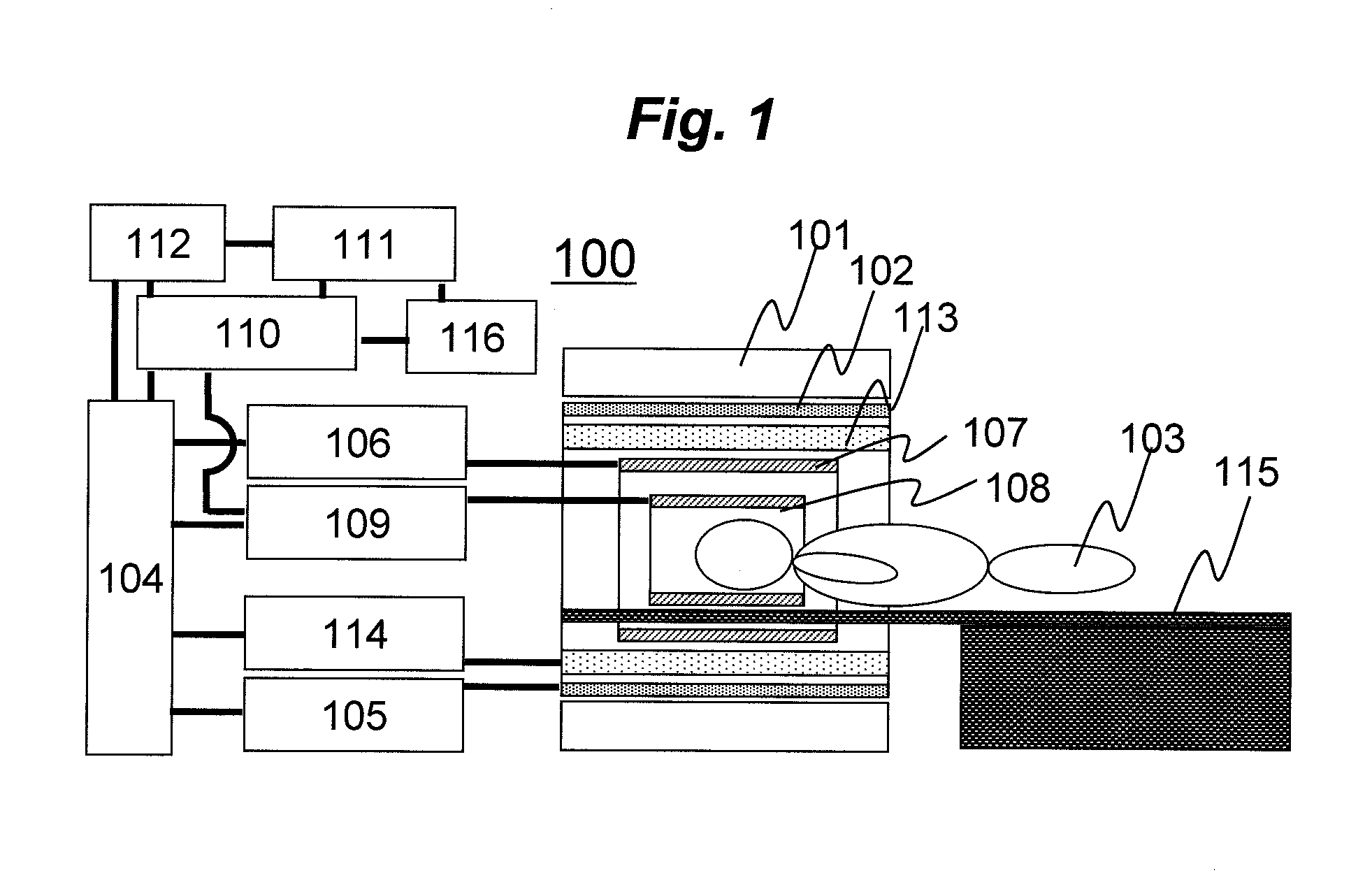
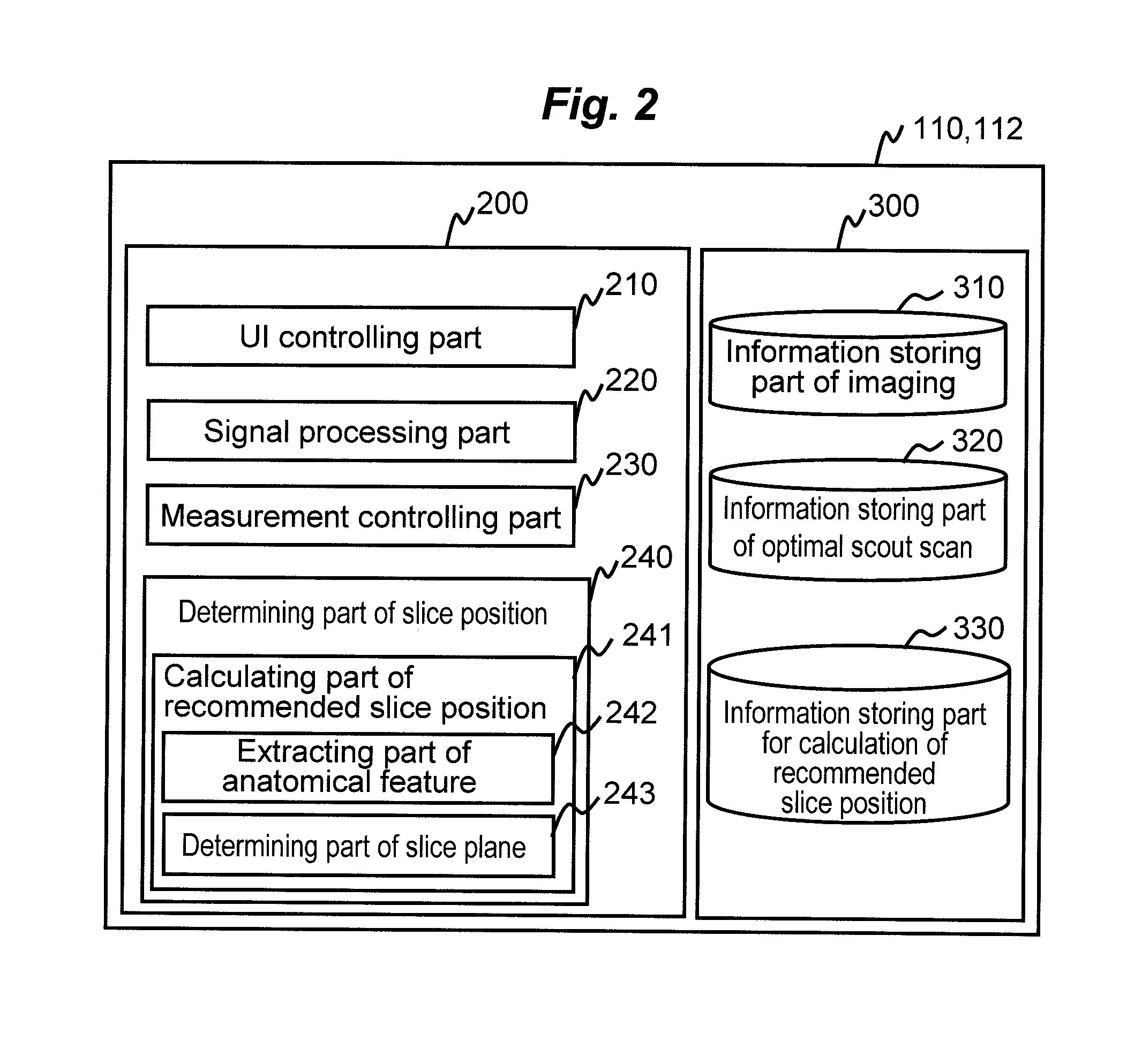
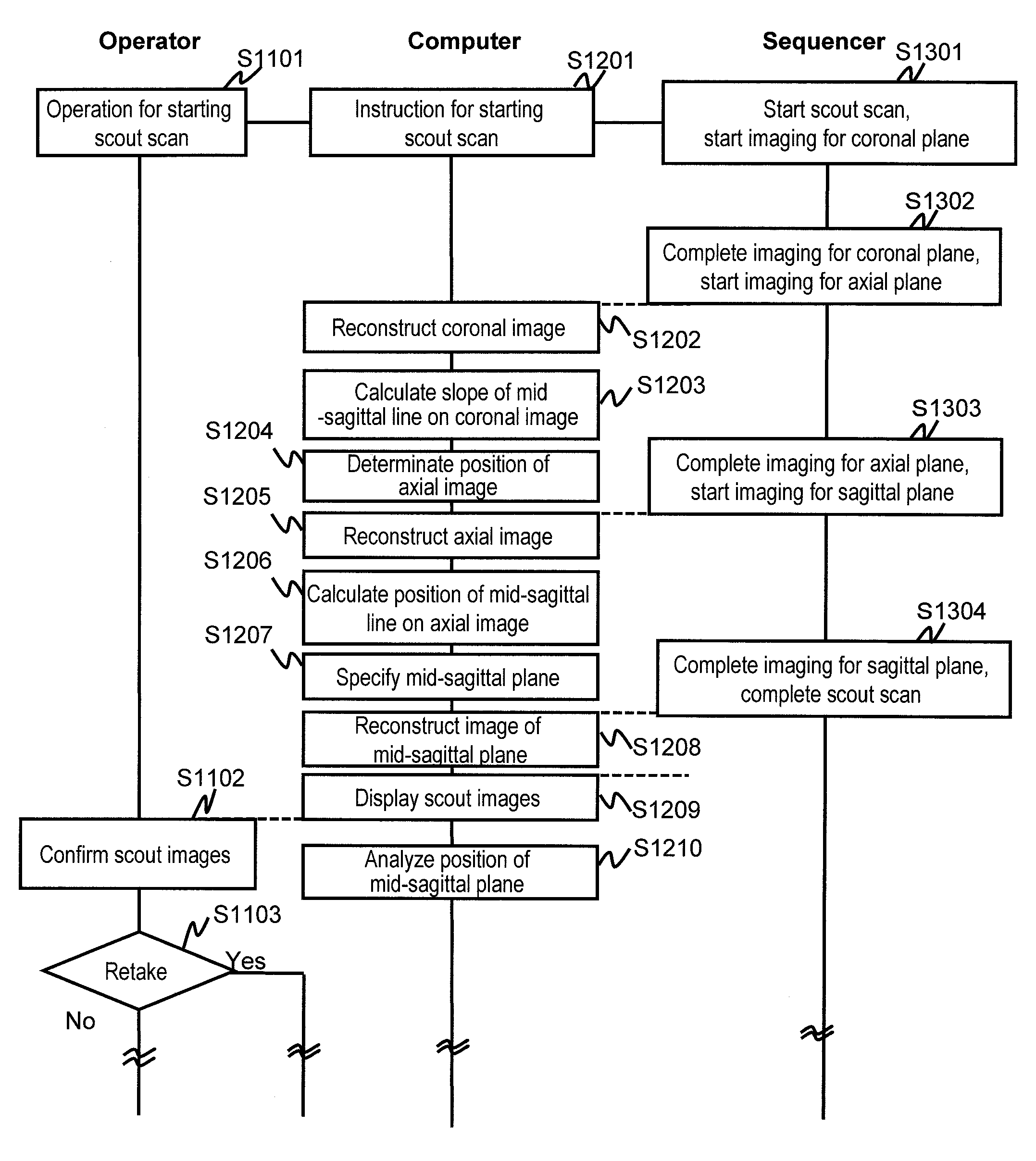
ActiveUS20120093385A1Without prolonging examination timeExtension of timeMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsImaging processingThree-dimensional space
There is provided a technique for, in a medical imaging apparatus enabling imaging of an arbitrary plane in a three-dimensional space, enabling automatic calculation of a slice position and automatic calculation of an extracting slice in MPR, without prolonging examination time. Two-dimensional scout scan similar to that used for manual setting of a slice position is performed, and the obtained scout images are processed to calculate a recommended slice position. Algorithms for the processing and various image processing procedures used for the processing are stored beforehand for every type of imaging region and every type of examination.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
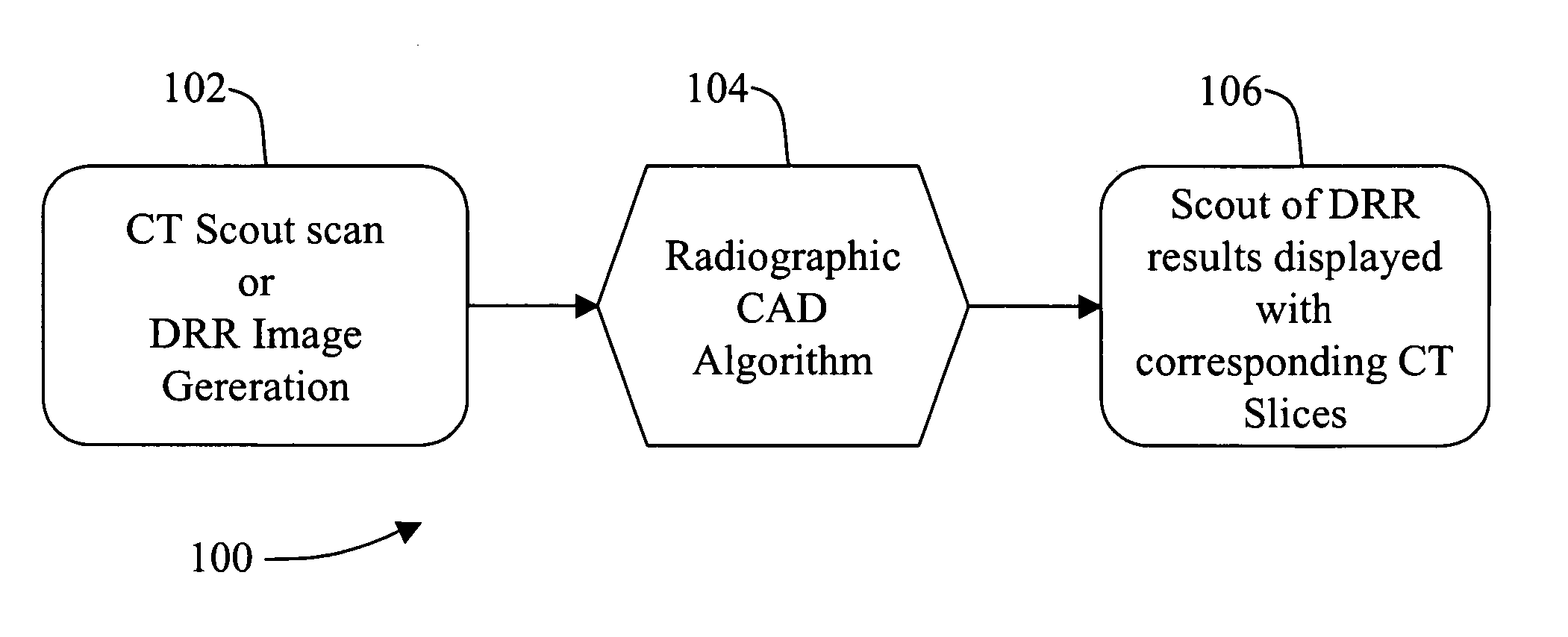
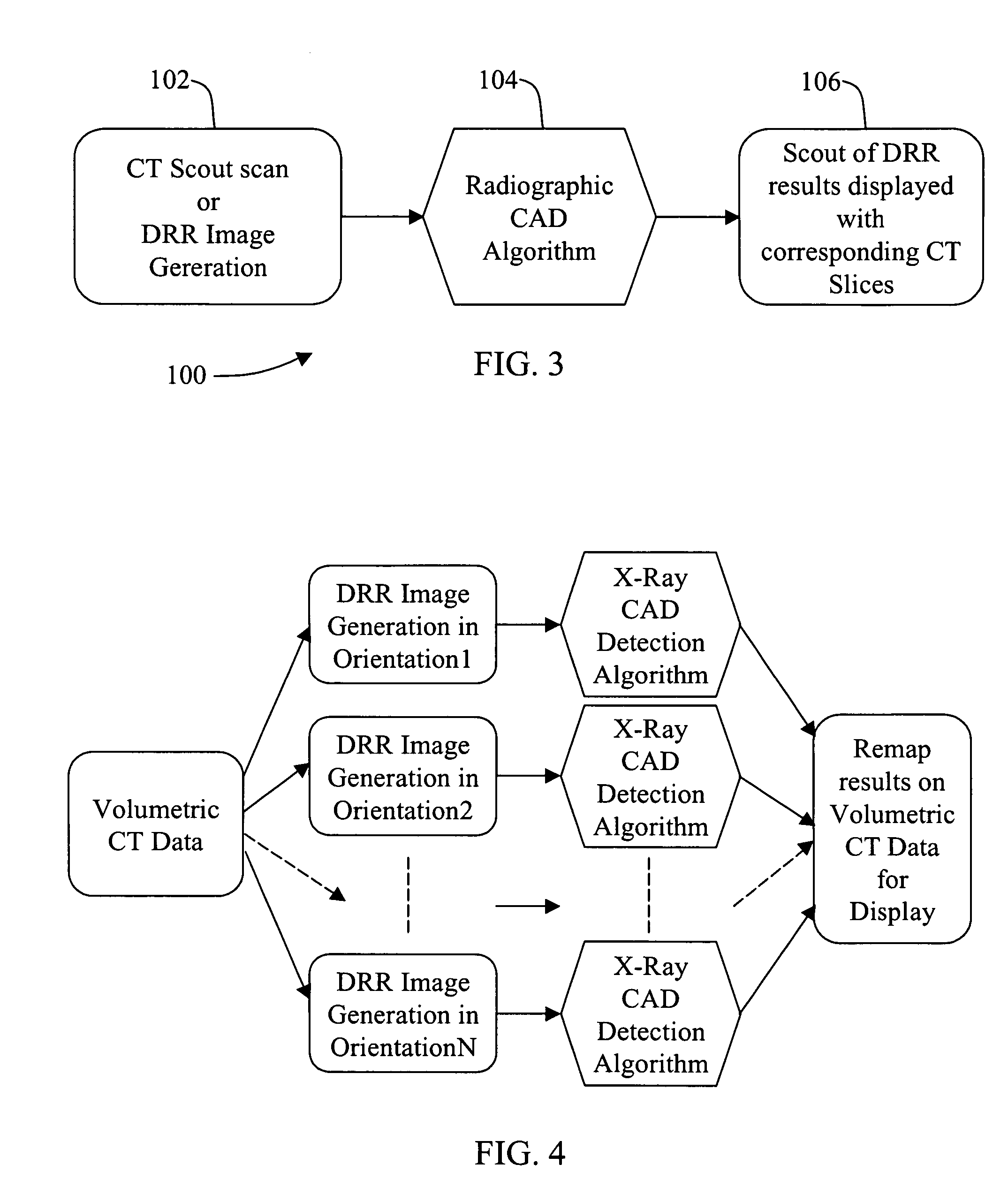
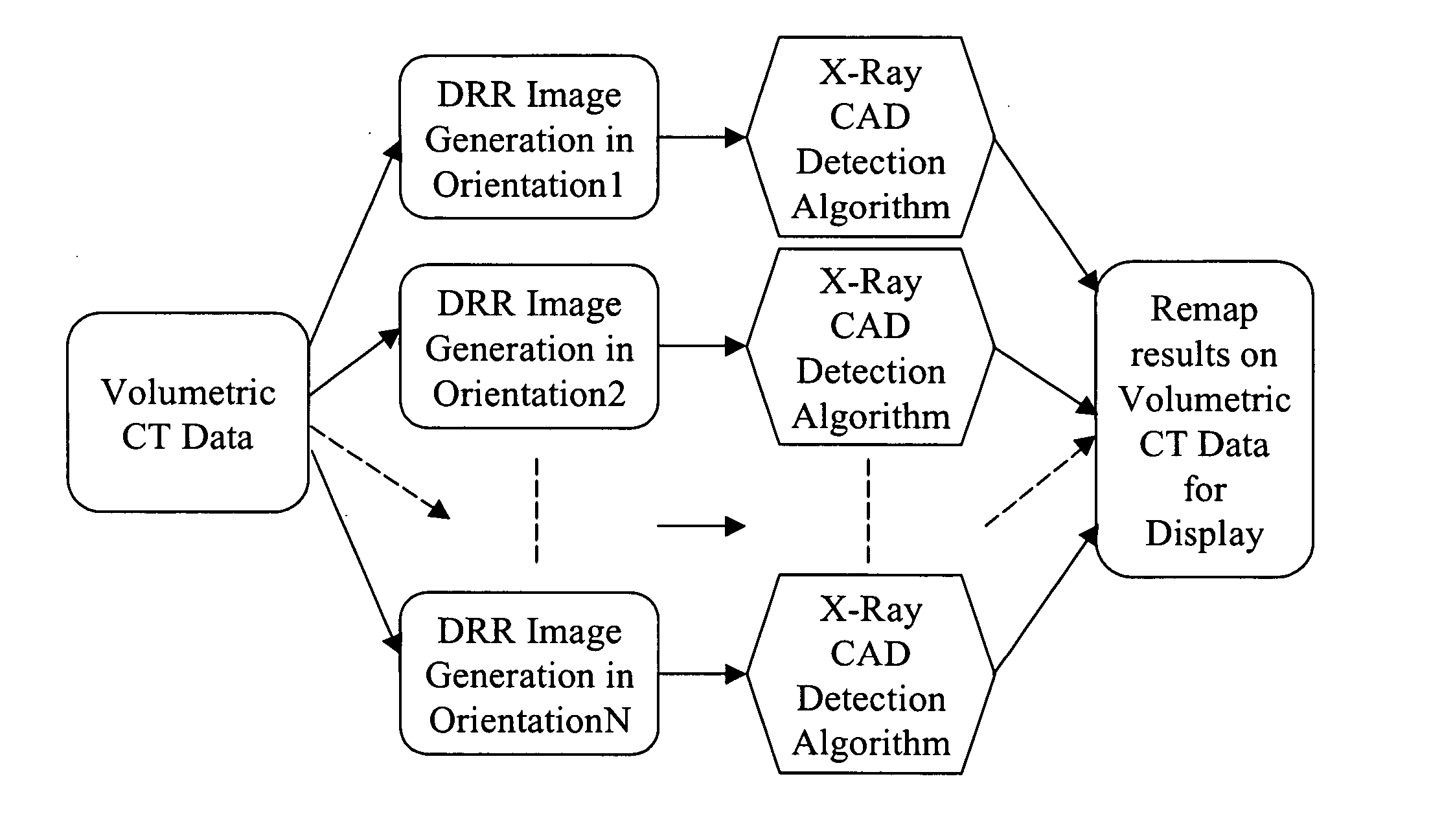
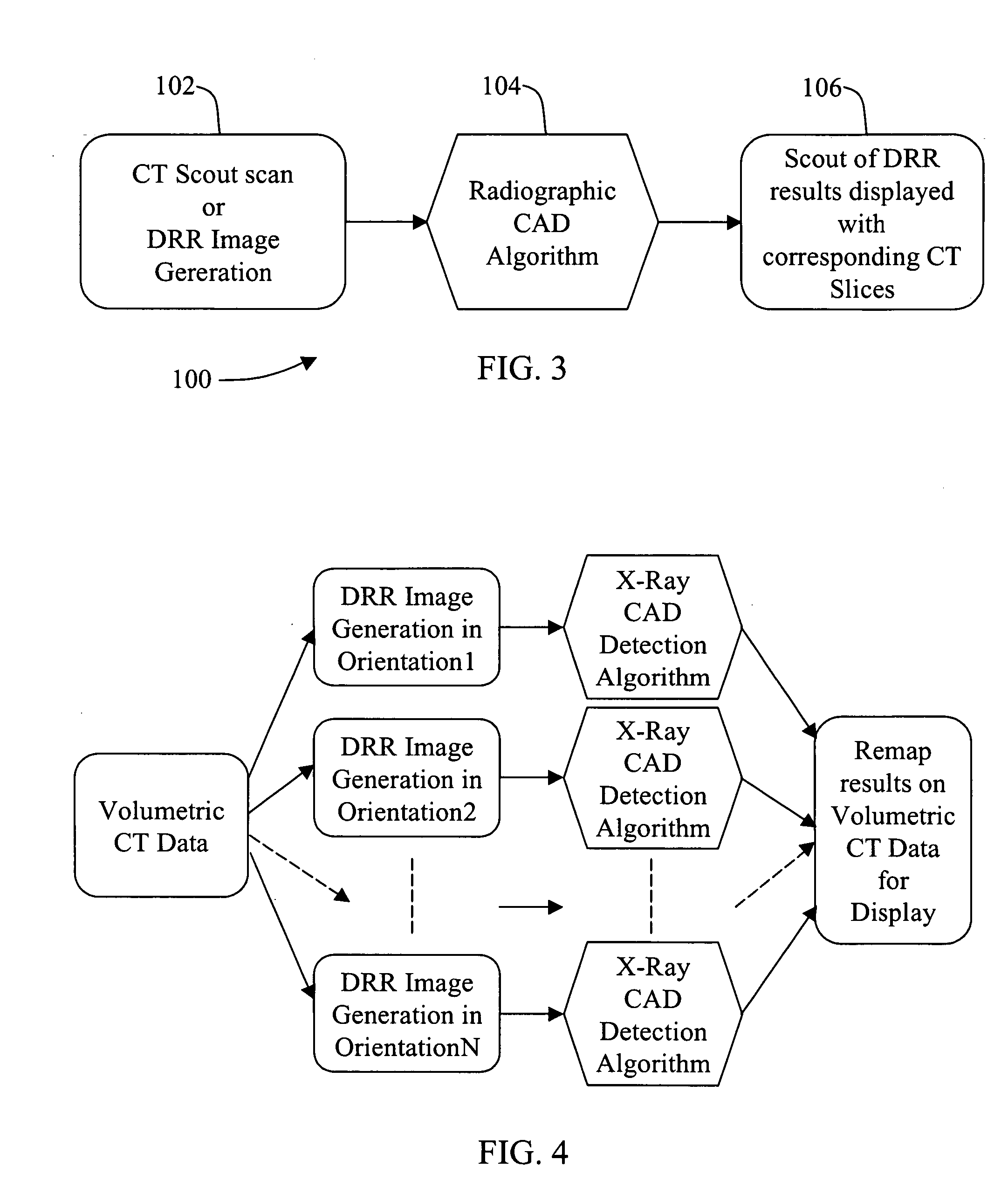
Methods and apparatus for anomaly detection
ActiveUS7072435B2Radiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsAnomaly detectionComputing tomography
A method for detecting an anomaly includes performing a computed tomography (CT) scout scan to obtain data, and supplying the obtained data to a radiographic computer aided detection (CAD) algorithm.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System and method of determining a user-defined region-of-interest of an imaging subject for x-ray flux management control
ActiveUS20050089136A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingUltrasound attenuationX-ray
A system and method of diagnostic imaging is provided that includes positioning a subject in an imaging device, performing at least one scout scan, and marking a user-defined region-of-interest. An attenuation characteristic of an attenuation filter is then automatically adjusted based on the user-defined region-of-interest. The present invention automatically selects a proper attenuation filter configuration, corrects patient centering, and corrects noise prediction errors, thereby increasing dose efficiency and tube output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for anomaly detection
A method for detecting an anomaly includes performing a computed tomography (CT) scout scan to obtain data, and supplying the obtained data to a radiographic computer aided detection (CAD) algorithm.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
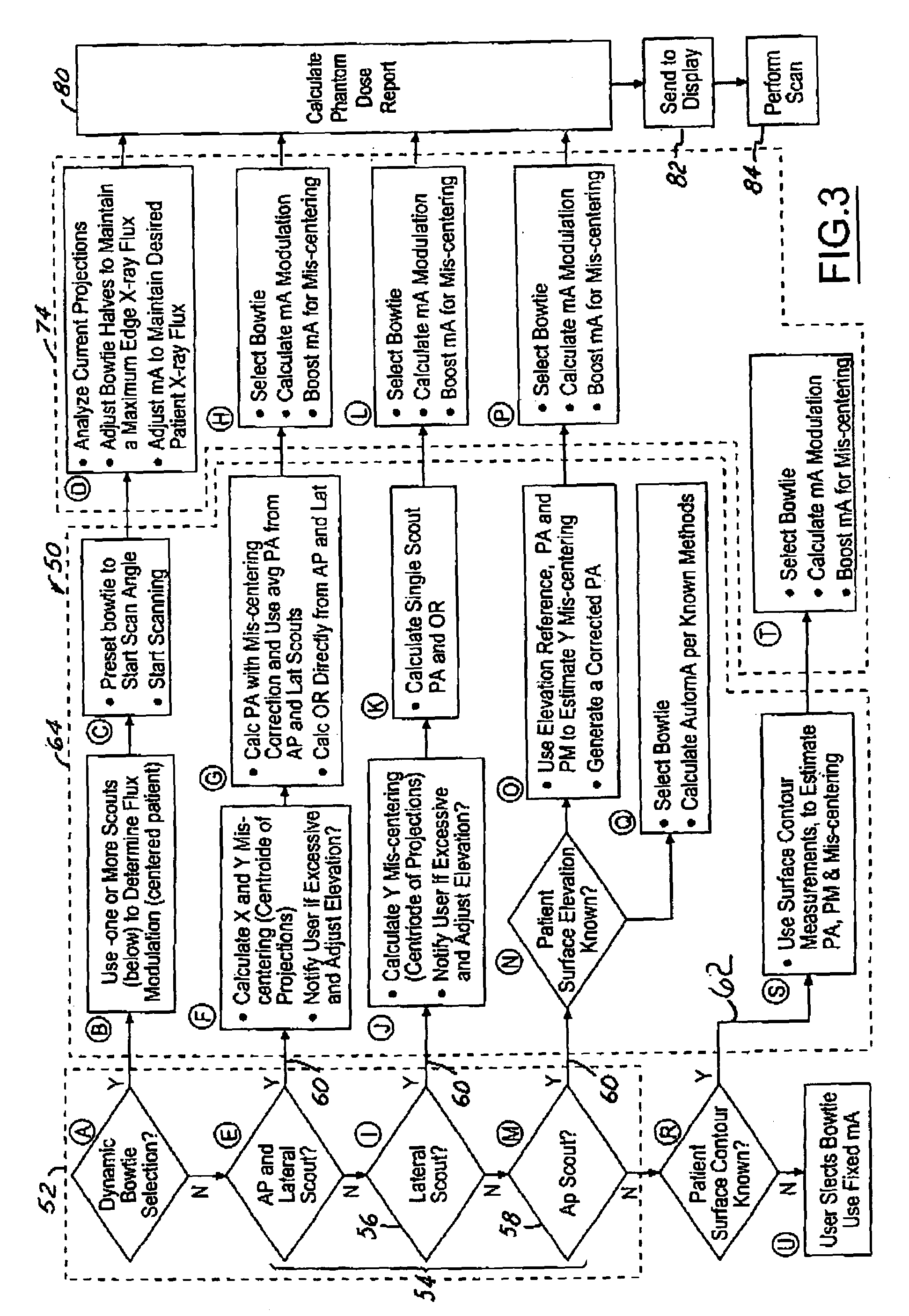
Computed tomography dose indexing phantom selection for dose reporting
ActiveUS7082183B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient modelSoft x ray
A computed tomography assembly is providing including an x-ray gantry assembly, an x-ray source projecting a beam of x-rays, a detector assembly positioned opposite the x-ray source and receiving the beam of x-rays, and a control mechanism in communication with the x-ray source and the detector assembly. The control mechanism includes logic adapted to: execute at least one scout scan of the object to produce a first scout scan image; generate an elliptical patient model based on the first scout scan image; match the elliptical patient model to a phantom diameter approximation; generate a dose report based on the phantom diameter approximation; and display said dose report on a display in communication with the control mechanism.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
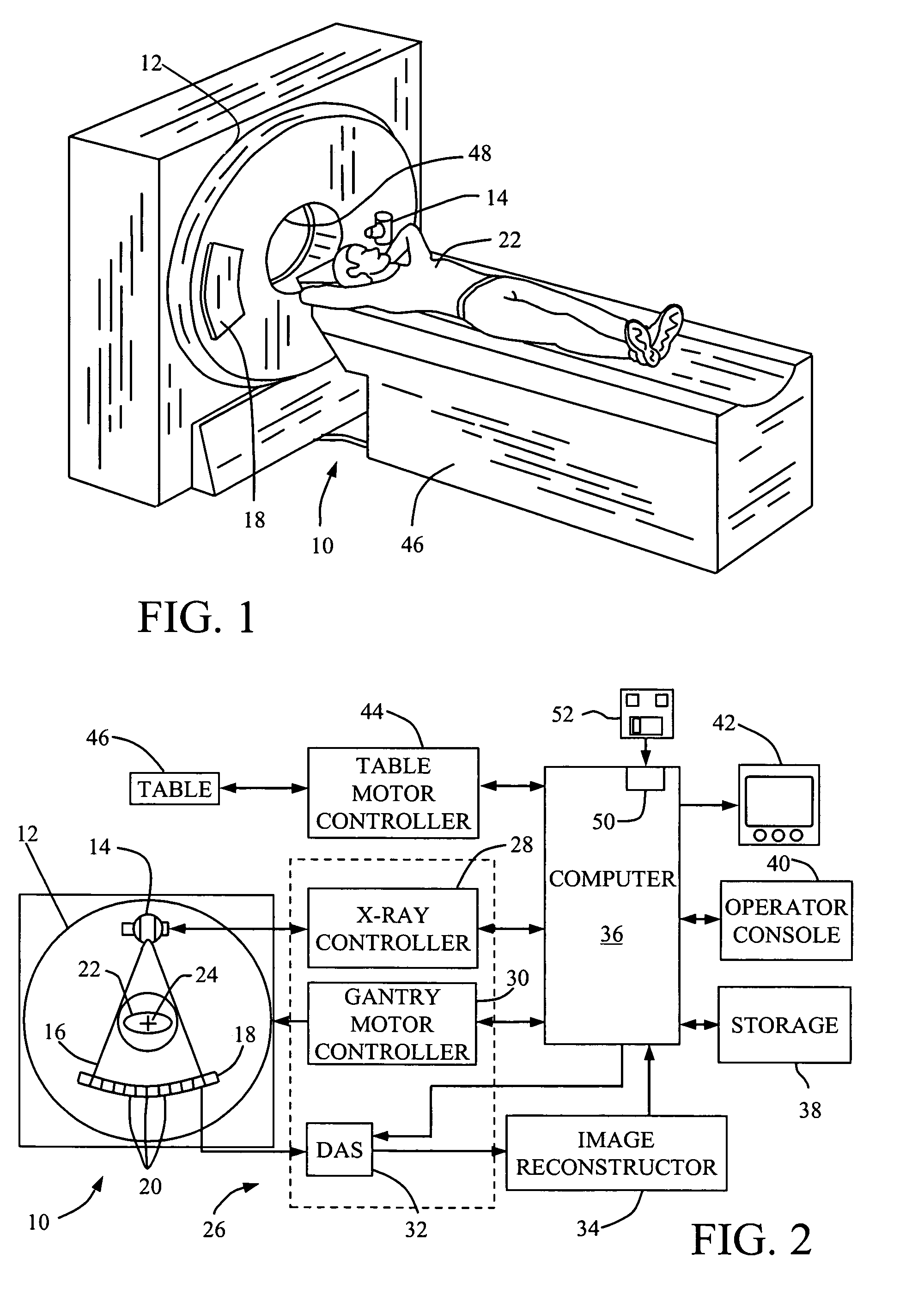
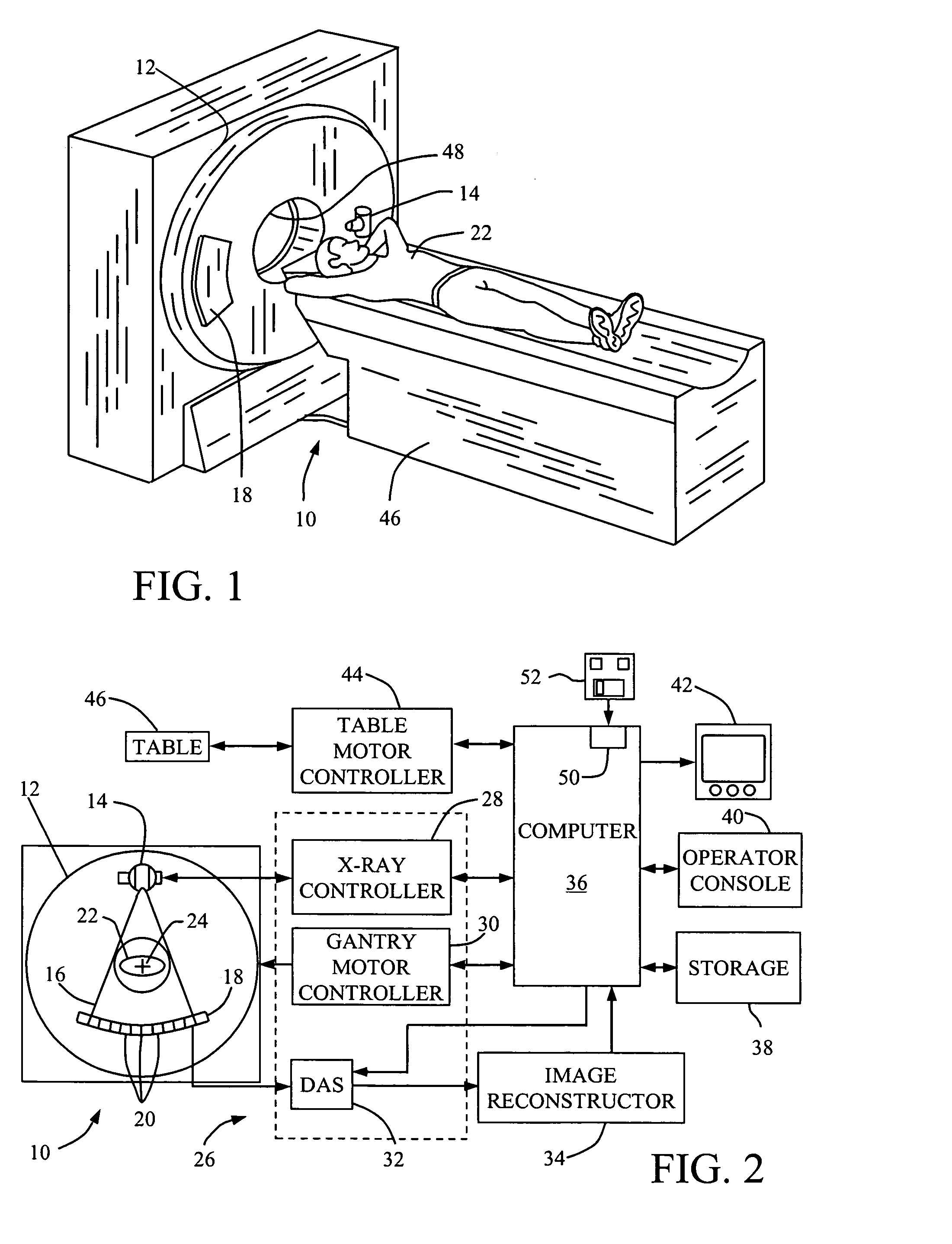
CT scanner system and method for improved positioning
ActiveUS7170968B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersBall screw
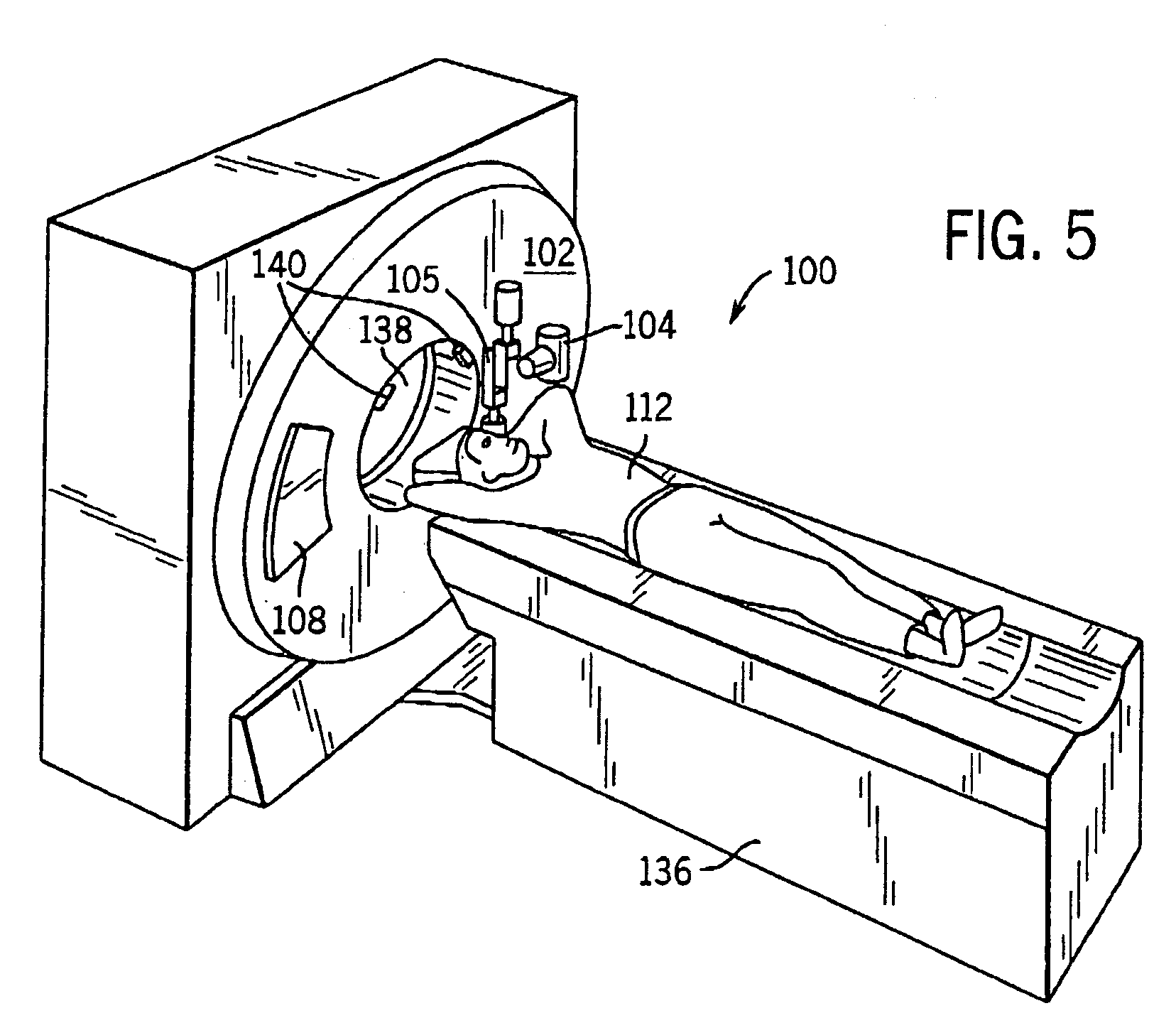
The CT scanning system of the present invention includes a source and detector mounted to a c-arm. The c-arm is positioned on a mounting plate and ball screw to rotate about an axis centered within the c-arm and to also translates along the axis of rotation. A computer controls the rotation of the CT scanner, the x-ray source, and collects the data from the detector to create an image. The CT scanner first takes a scout scan prior to the full acquisition of the data. The scout scan is a single two-dimension image. The CPU draws locating marks on the scout scan image to indicate the desired location. When proper alignment is verified, the processor then controls the motor to perform one complete revolution of the c-arm, during which time the computer collects multiple images from the detector.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Computed tomography dose indexing phantom selection for dose reporting
ActiveUS20060018435A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient modelX-ray
A computed tomography assembly is providing including an x-ray gantry assembly, an x-ray source projecting a beam of x-rays, a detector assembly positioned opposite the x-ray source and receiving the beam of x-rays, and a control mechanism in communication with the x-ray source and the detector assembly. The control mechanism includes logic adapted to: execute at least one scout scan of the object to produce a first scout scan image; generate an elliptical patient model based on the first scout scan image; match the elliptical patient model to a phantom diameter approximation; generate a dose report based on the phantom diameter approximation; and display said dose report on a display in communication with the control mechanism.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
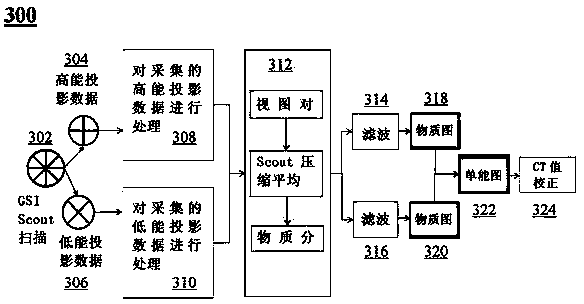
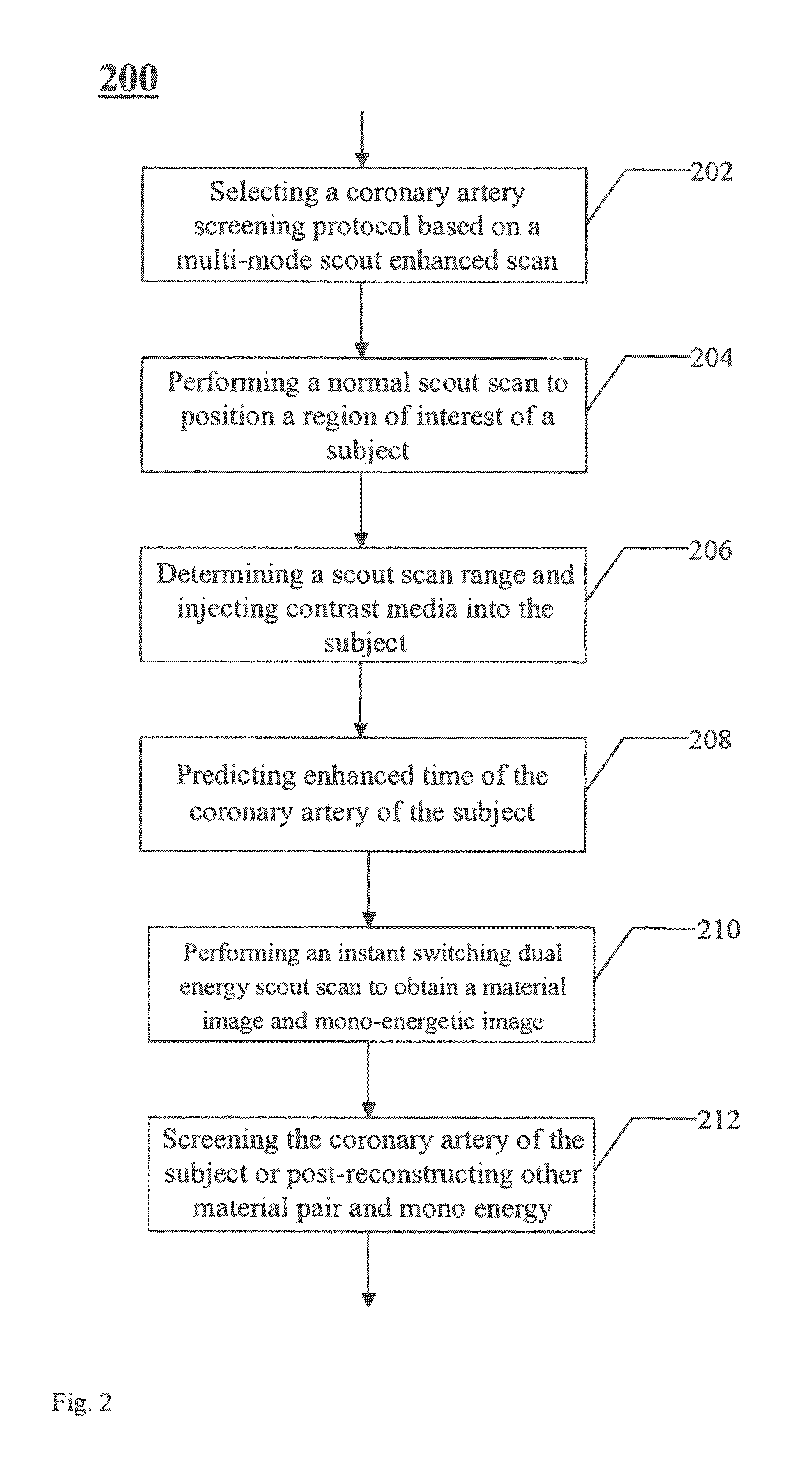
CT (computed tomography) imaging method and CT imaging system based on multi-mode Scout scanning
InactiveCN103892859AReduce X-ray doseReduced imaging timeComputerised tomographsTomographyLow voltageDual energy
A CT imaging method and a CT system based on a multi-mode scout scan. The CT imaging method based on a multi-mode scout scan comprises: performing an instant switching dual energy scout radiation scan on a region of interest of a subject by way of instant switching between high voltage and low voltage to collect dual energy protection data of the region of interest; and reconstructing a material decomposition image and a mono-energetic image based on the collected dual energy projection data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
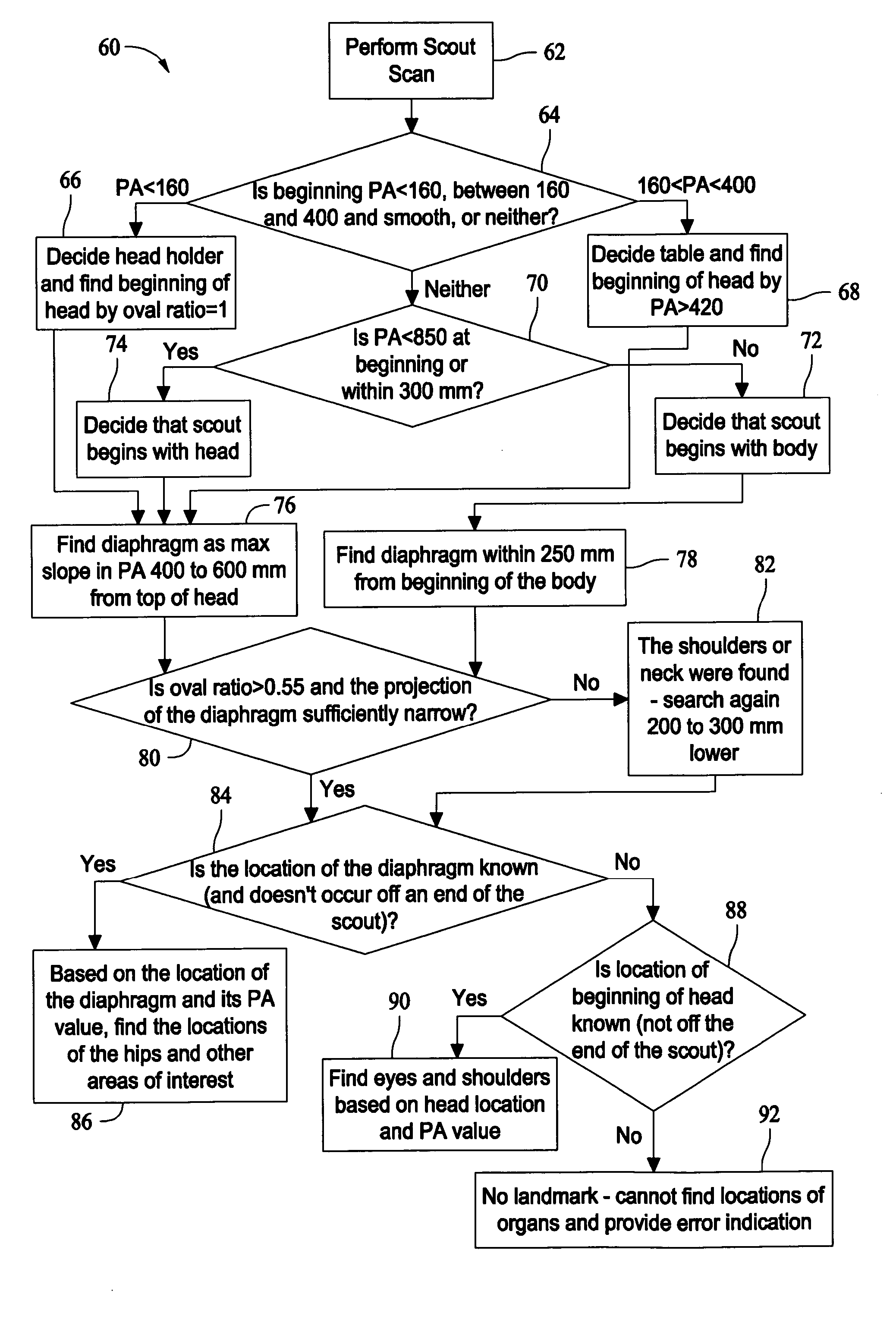
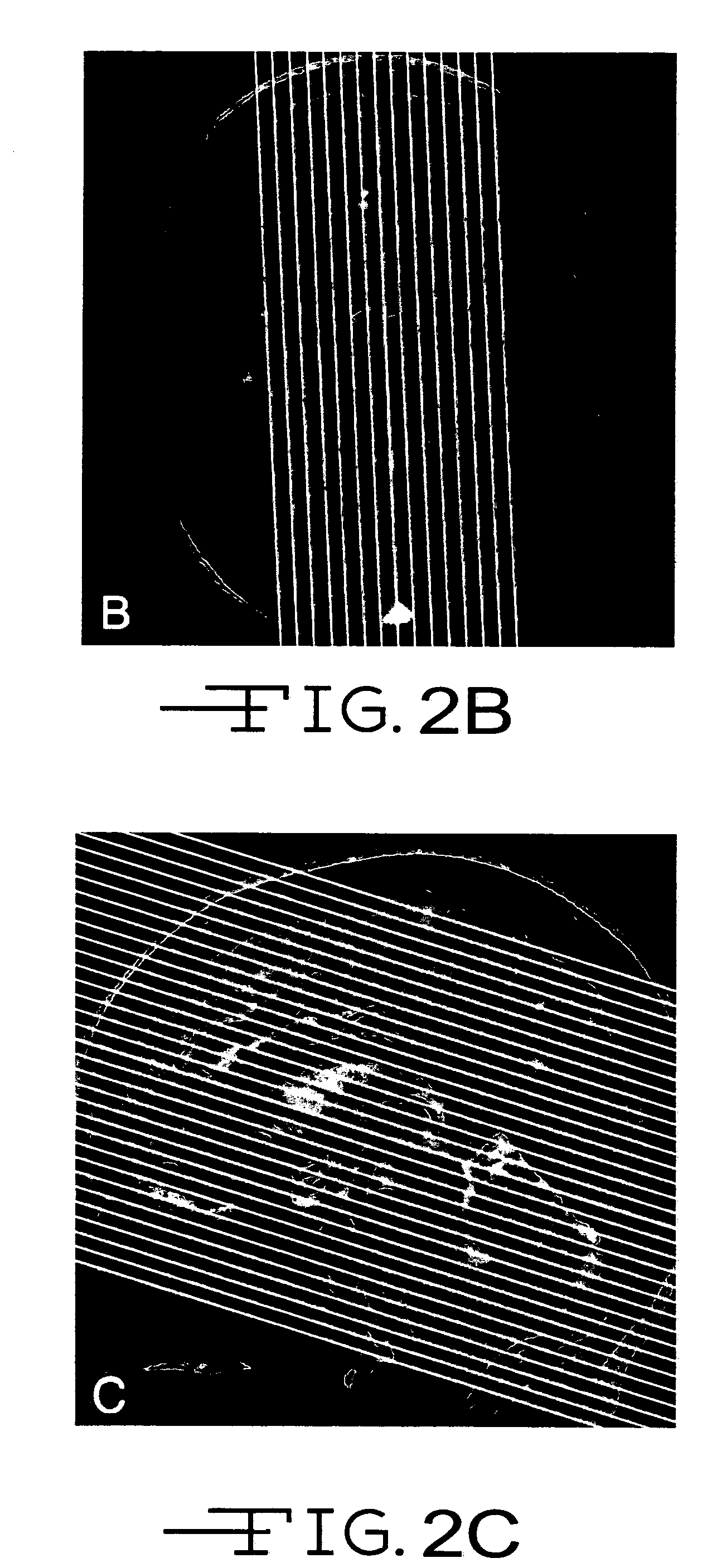
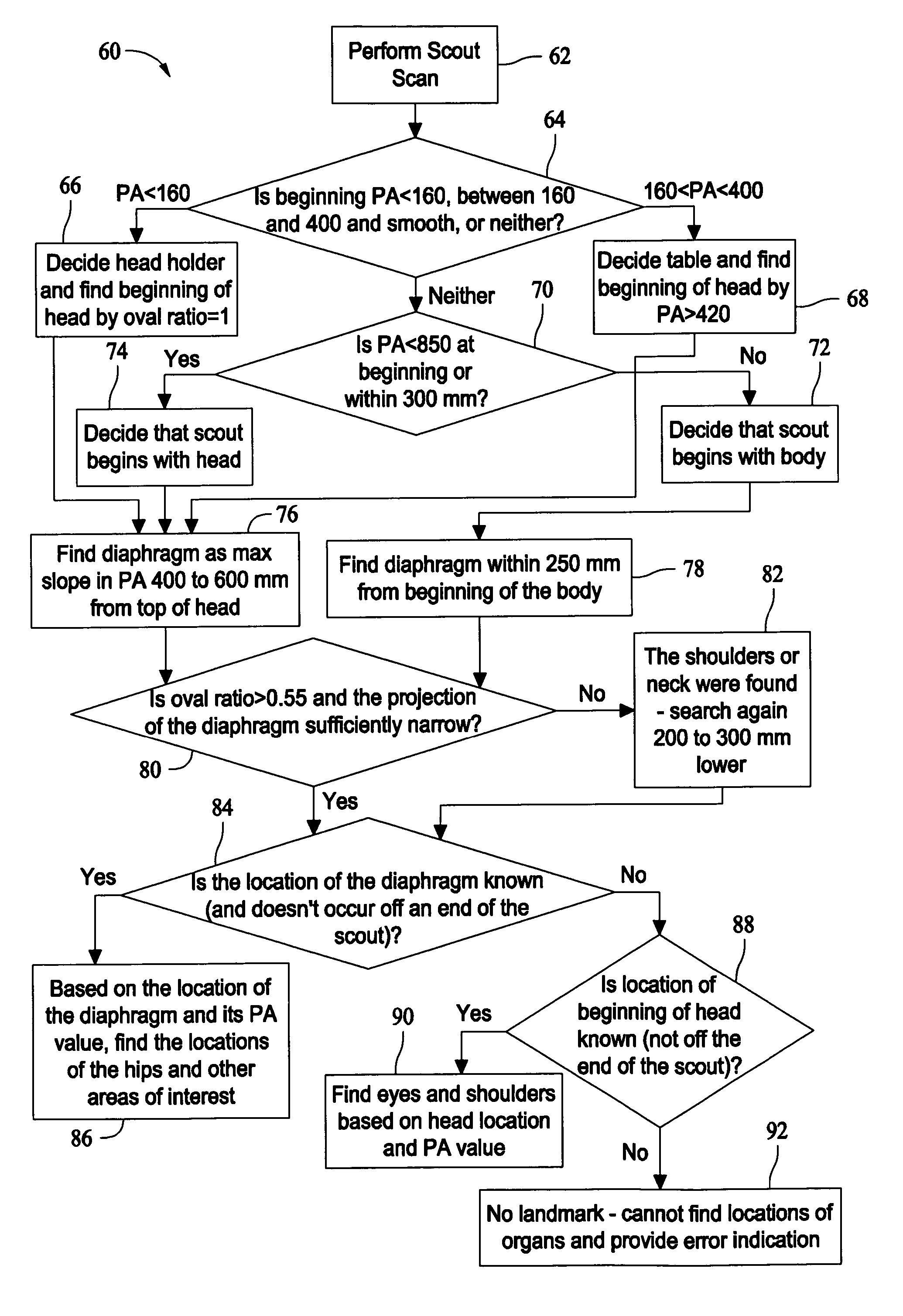
Method and system for automatically determining regions in a scanned object
ActiveUS20070116337A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionUltrasound attenuationScout Scan
A method and system for automatically determining regions in scanned object are provided. The method includes performing a scout scan of an object and automatically determining regions within the object based on attenuation information from the scout scan.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Automated brain MRI and CT prescriptions in Talairach space
InactiveUS7450983B2Minimizes variabilitySurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic modalitiesAnterior commissure
Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computerized Tomotography (CT), or other diagnostic modalities may employ a three-step procedure during initial (“scout”) cranial pre-scans that corrects for patient positioning (i.e., roll, yaw and pitch) to reduce inter- and intra-patient variation, thereby enhancing the diagnostic and comparative value of subsequent detail scans even across different diagnostic platforms. In MRI, for instance, locating the saggital sinus (SS) and optimizing a line to bisect the brain through this SS may be automated to correct for roll and yaw. By then identifying the contour of the corpus callosum in a lateral saggital scout scan, the Talairach anterior commissure (AC)—posterior commissure (PC) reference line may be found for correcting pitch. Prescription of detailed scans are improved, especially when the three-step correction is repeated periodically identifying the need to repeat a detailed scan or to adjust the coordinates of a subsequent scan.
Owner:ABSIST +1
Method and system for automatically determining regions in a scanned object
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
CT imaging method and CT system based on multi-mode scout scan
InactiveUS20140187932A1Reduce X-ray doseReduced imaging timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDual energyRegion of interest
A CT imaging method and a CT system based on a multi-mode scout scan. The CT imaging method based on a multi-mode scout scan comprises: performing an instant switching dual energy scout radiation scan on a region of interest of a subject by way of instant switching between high voltage and low voltage to collect dual energy protection data of the region of interest; and reconstructing a material decomposition image and a mono-energetic image based on the collected dual energy projection data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
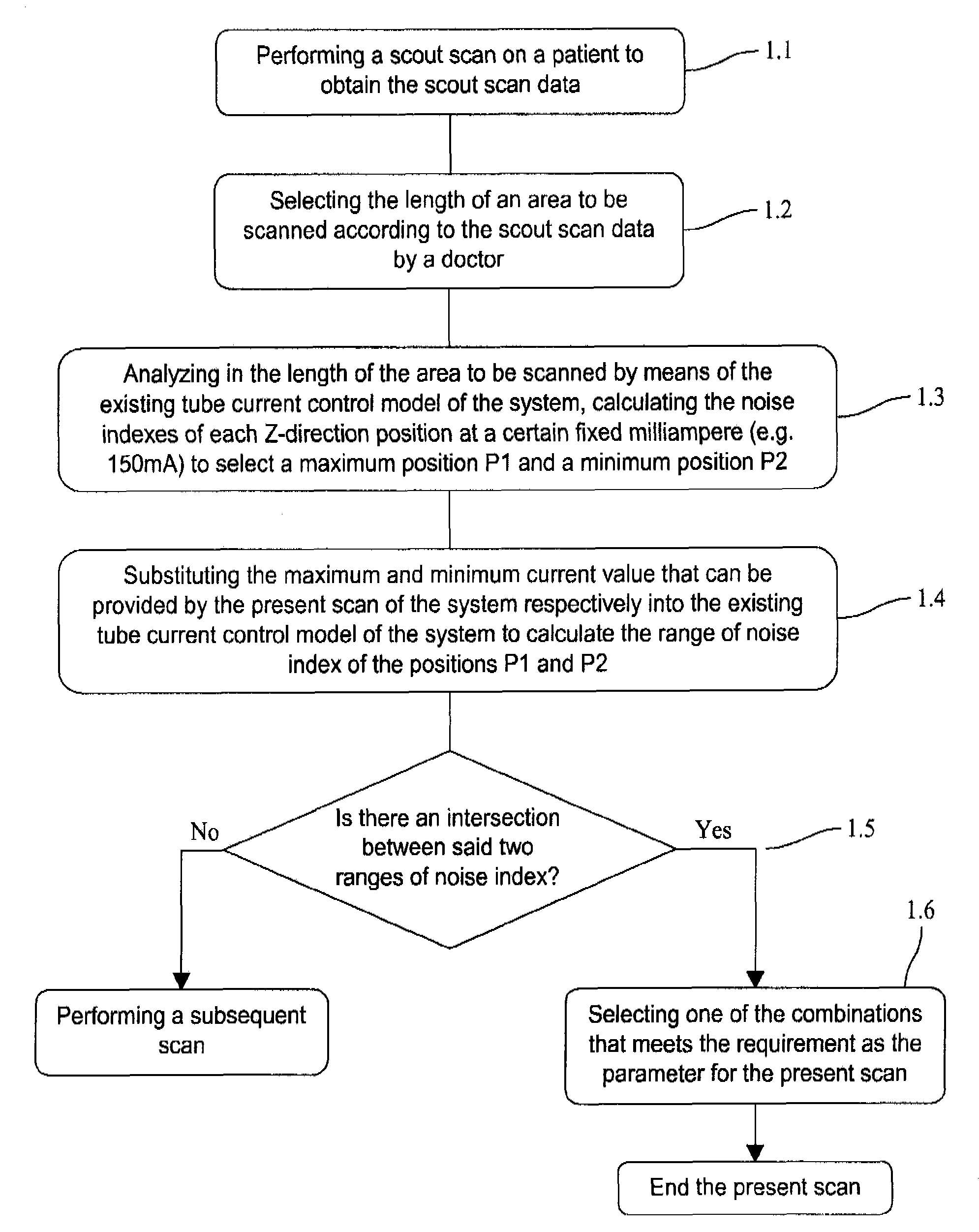
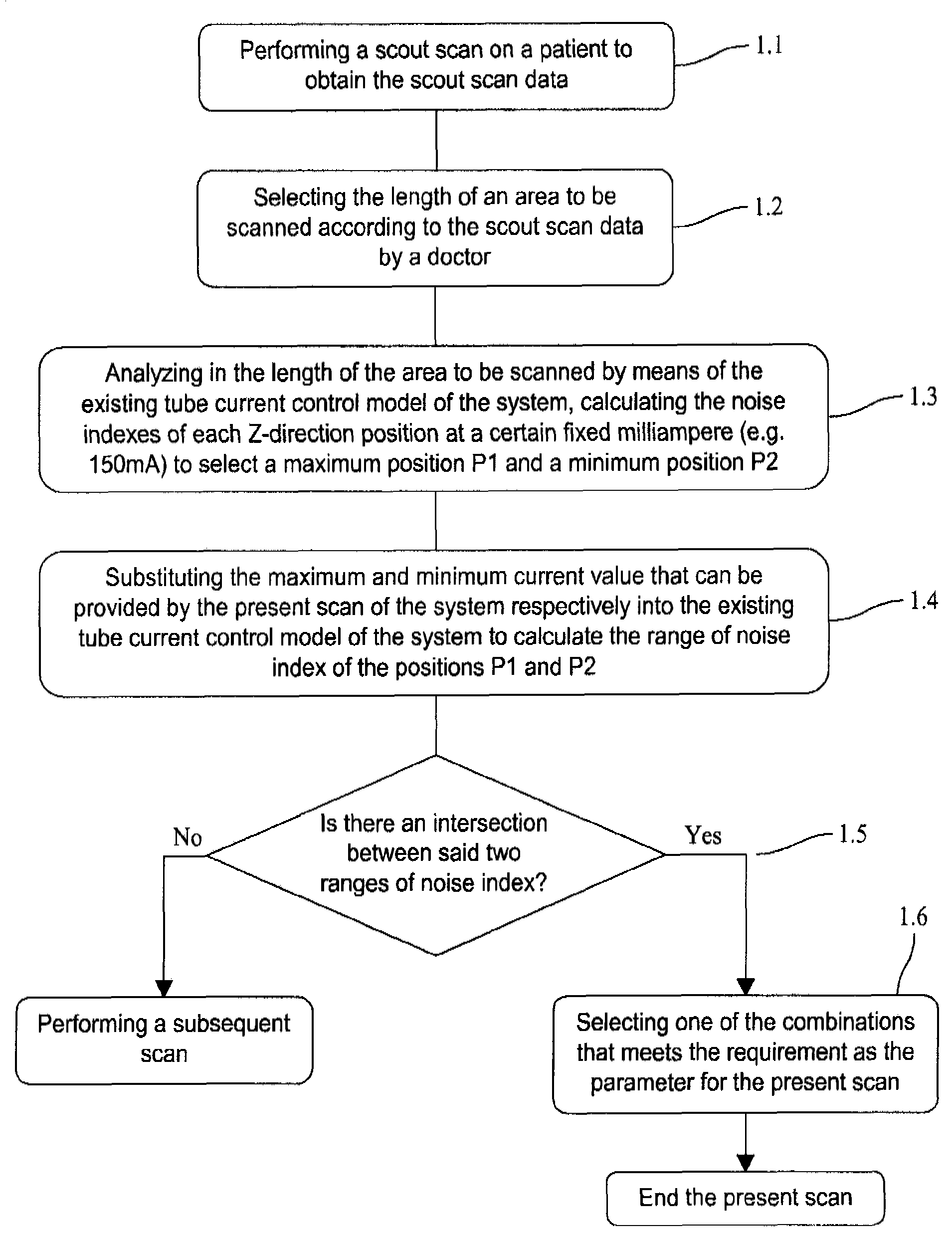
Scanning detection device of an x-ray ct apparatus, an x-ray ct system and method of operation of the same
ActiveUS20090016484A1Reduce radiationEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayControl system
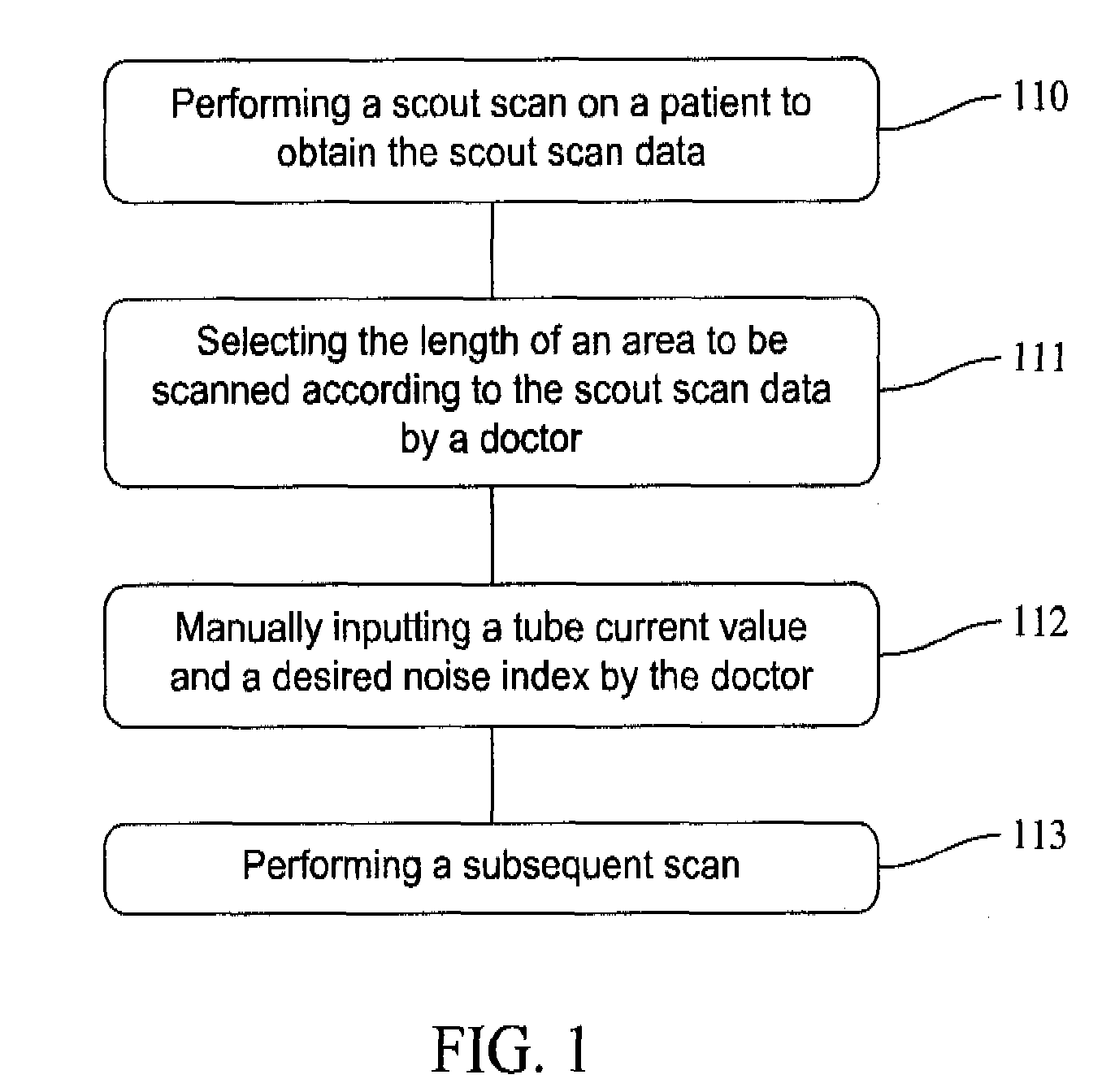
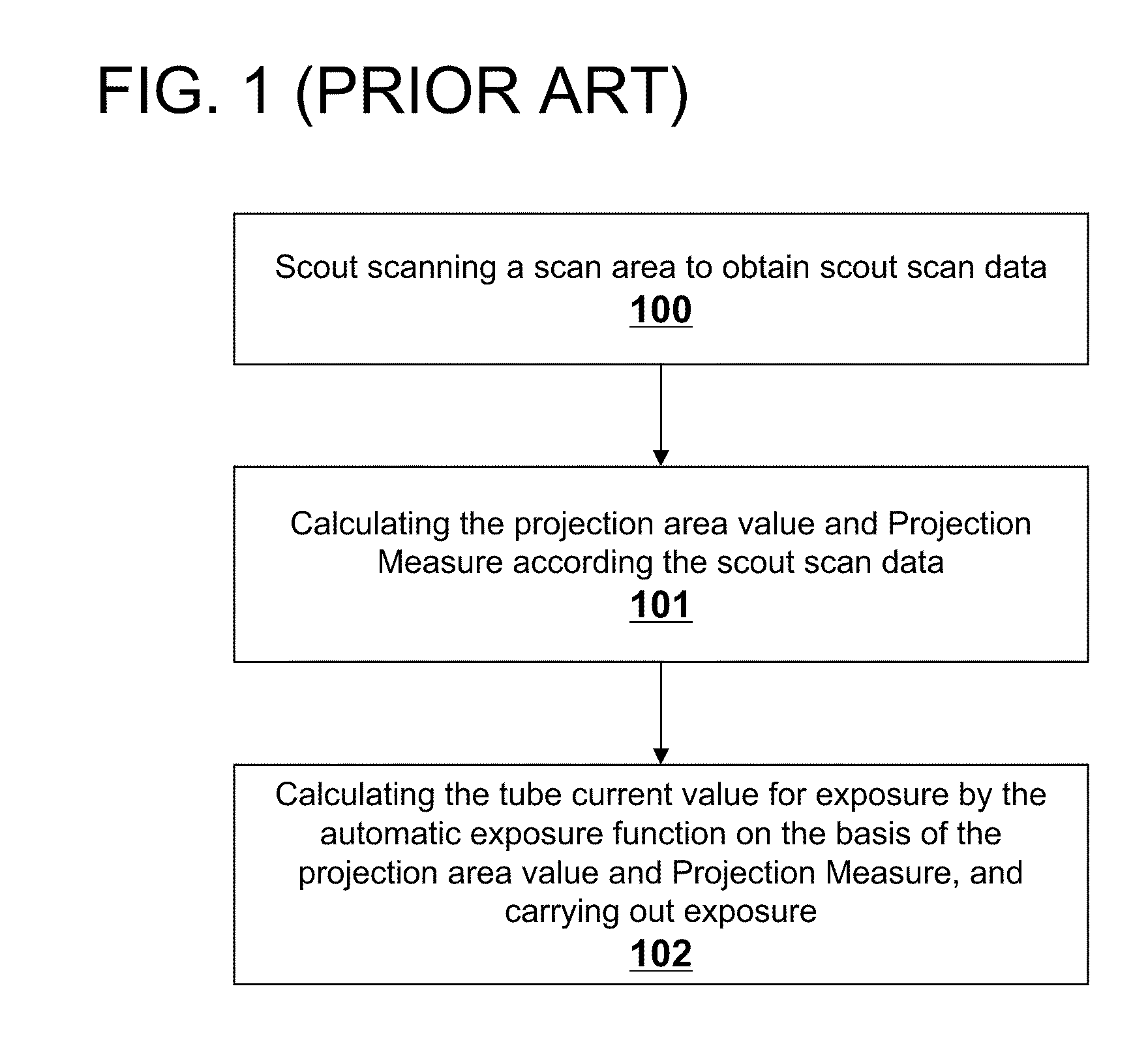
Method of operating an X-ray CT apparatus and the corresponding apparatus and system thereof. A method includes analyzing scout scan data to obtain a position with a minimum noise index and a position with a maximum noise index, calculating noise indexes at the two positions in a range of a maximum and a minimum tube current that can be provided by the system by means of a tube current control model so as to obtain two ranges of noise index, and determining whether there is an intersection between the two ranges of noise index. If such an intersection exists, a combination of the range of tube current value and the range of noise index that meets the requirement is selected within the intersection to control the system to proceed with a subsequent scan. If no such intersection exists, the system ends the present scan.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Adjusting acquisition protocols for dynamic medical imaging using dynamic models
ActiveUS8705819B2Efficient and/or reliable way of adjusting an acquisition protocolImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisDynamic modelsHemodynamics
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus to determine tube current modulation profile for radiographic imaging
A method and apparatus is disclosed to acquire scout scan data of a subject and analyzed to determine a peak-to-peak modulation amplitude of a normalized waveform indicative of subject size and shape. The scout scan data provides a representation of patient size and shape that is associated with an ideal tube current modulation waveform or profile. The ideal tube current modulation profile may then be sampled or approximated at various points to determine a tube current modulation profile for implementation to acquire CT data with reduced dose but without sacrificing image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
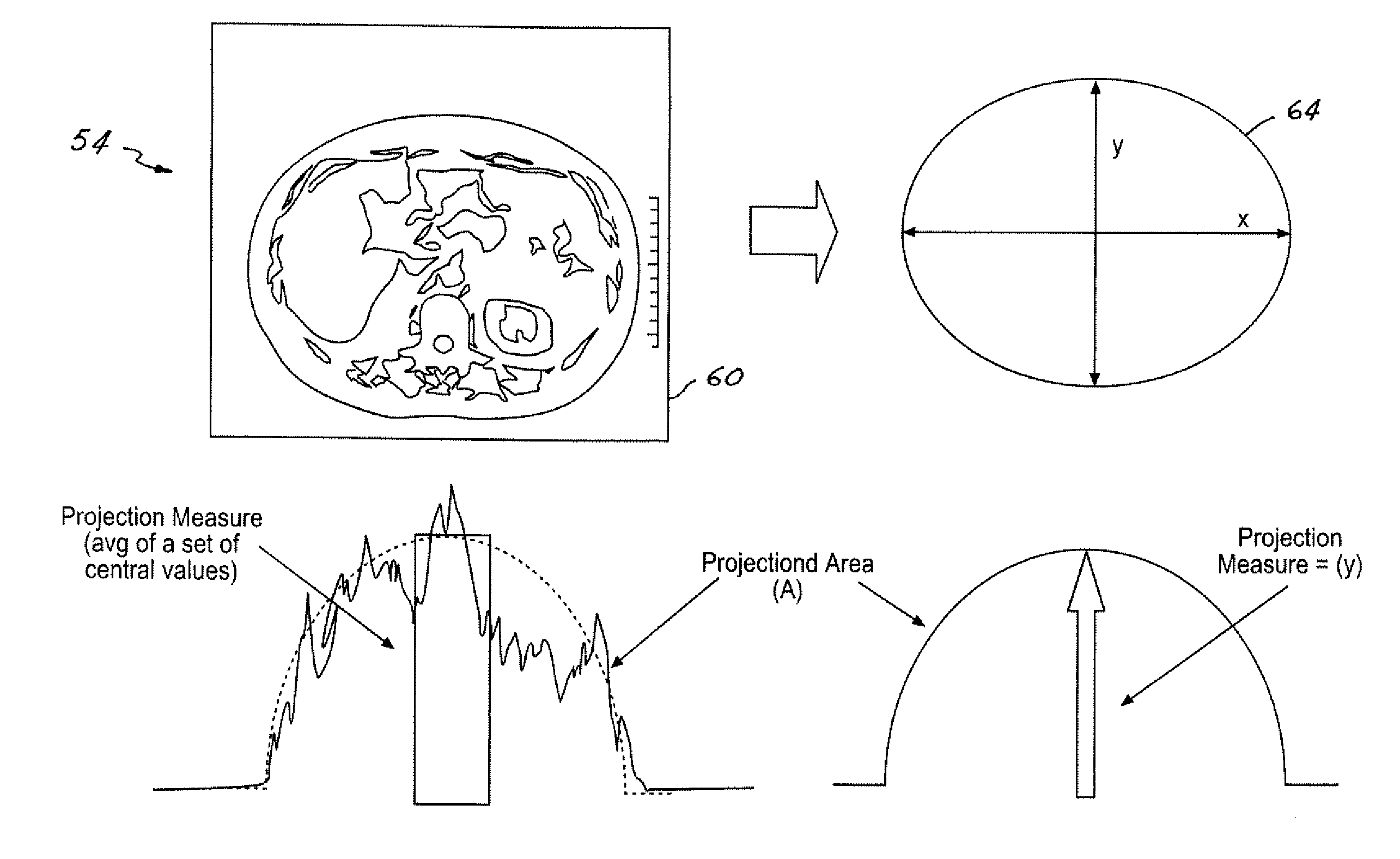
Method for controlling x-ray exposure in x-ray ct system
InactiveUS20090168951A1Improve stabilityImprove robustnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
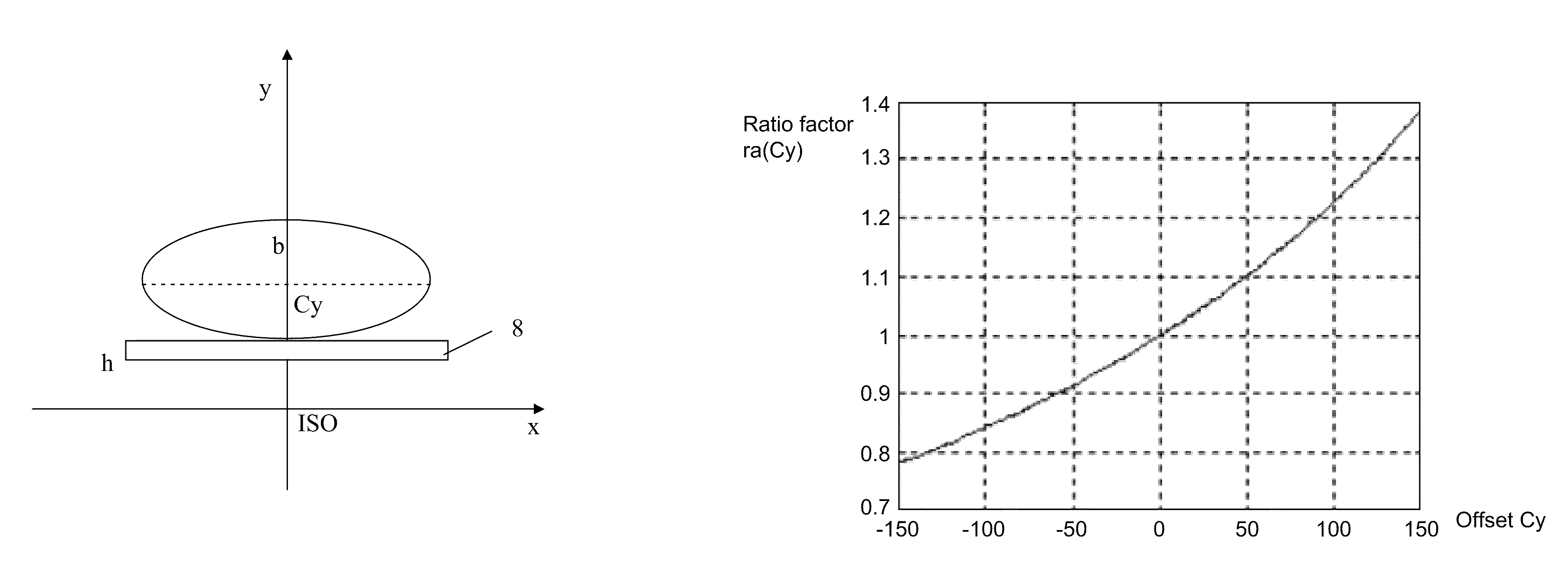
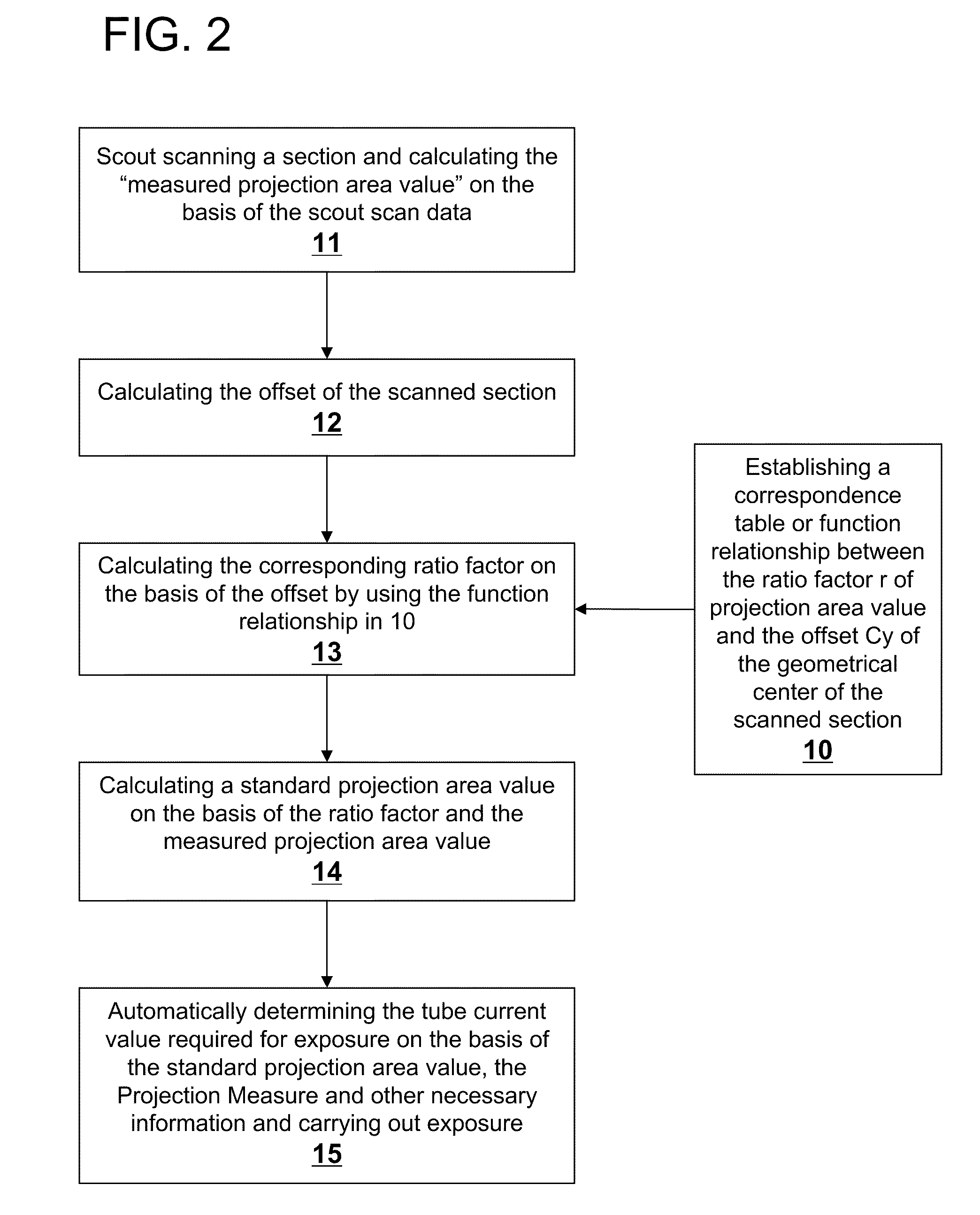
A method for controlling automatic X-ray exposure in an X-ray CT system includes establishing a correspondence table or function relationship between a ratio factor and an offset of a geometrical center of a scanned section, wherein the ratio factor represents a ratio of the projection area value when the geometrical center of the scanned section of a subject deviates from a rotation center to the standard projection area value when the geometrical center of the scanned section of the subject locates at the rotation center, scout scanning the subject, and calculating a “measured projection area value” and Projection Measure based on the scout scan data, calculating the offset of the geometrical center of the scanned section from the rotation center, substituting the offset into the correspondence table or function relationship to obtain a corresponding ratio factor, calculating the standard projection area value based on the ratio factor and the measured projection area value, and automatically determining by an automatic exposure function a tube current value required for exposure based on the calculated standard projection area value, the Projection Measure.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Radiographic apparatus
InactiveUS20060291614A1Easy to getEfficient use ofMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation raysRadiographic equipment
To enable radiation rays to be efficiently used. A scout scan parameter setting unit sets a rotation movement position to which an X-ray tube and an X-ray detector are moved so as to rotate around a subject on the basis of subject information of a subject on which a scout scan is performed at the time of performing a scout scan. At the time of starting execution of the scout scan, a rotating unit moves the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector so as to rotate around the subject to the rotation movement position which is set by the scout scan parameter setting unit. After that, a scout scan is performed in the rotation movement position.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Quantification Phantom for Use with Multiple Imaging Modalities
ActiveUS20180242944A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
Described is an in-scan phantom for use during an imaging procedure. The phantom can include at least one measuring insert and / or at least one measured insert. The measuring insert may have radiation detecting capabilities while the measured insert may include a radioactive material. Also described is an imaging modality system that includes an imaging modality and an in-scan phantom as well as methods of using the in-scan phantom for imaging a patient or performing a scout scan.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
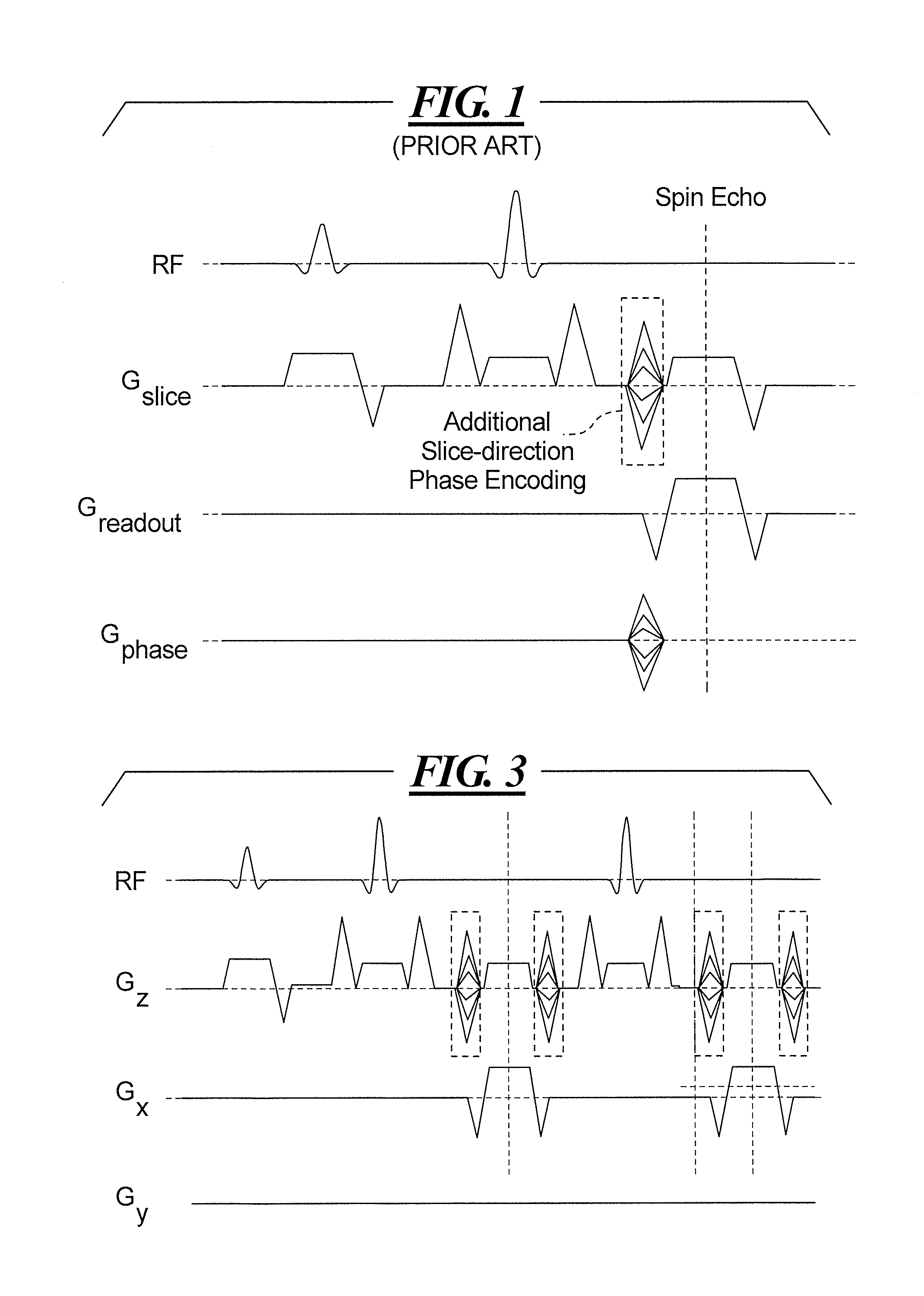
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for obtaining a scout scan of a patient containing a metallic implant
InactiveUS20150177354A1Reduced measurement timeReduce in quantityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMetal ArtifactResonance
In a magnetic resonance method and apparatus, the magnetic resonance apparatus is operated according to a SEMAC (Slice Encoding for Metal Artifact Correction) sequence, and, before executing the SEMAC sequence, a scout sequence is implemented, which is a SEMAC sequence but without phase encoding in the direction perpendicular to the slice selection direction. The number of SEMAC coding steps can then be determined before executing the SEMAC sequence, so that an unnecessarily high number of SEMAC coding steps is avoided.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
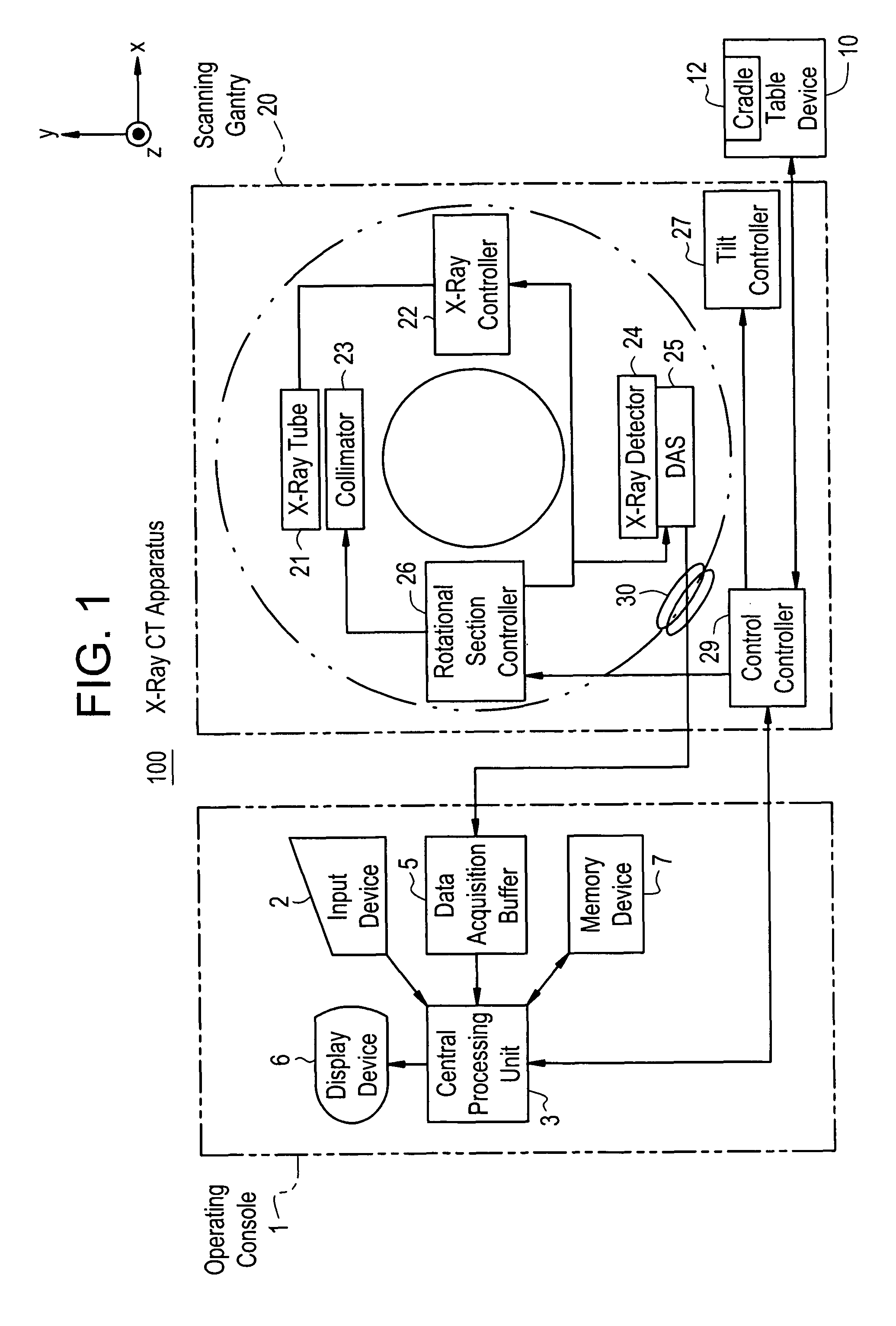
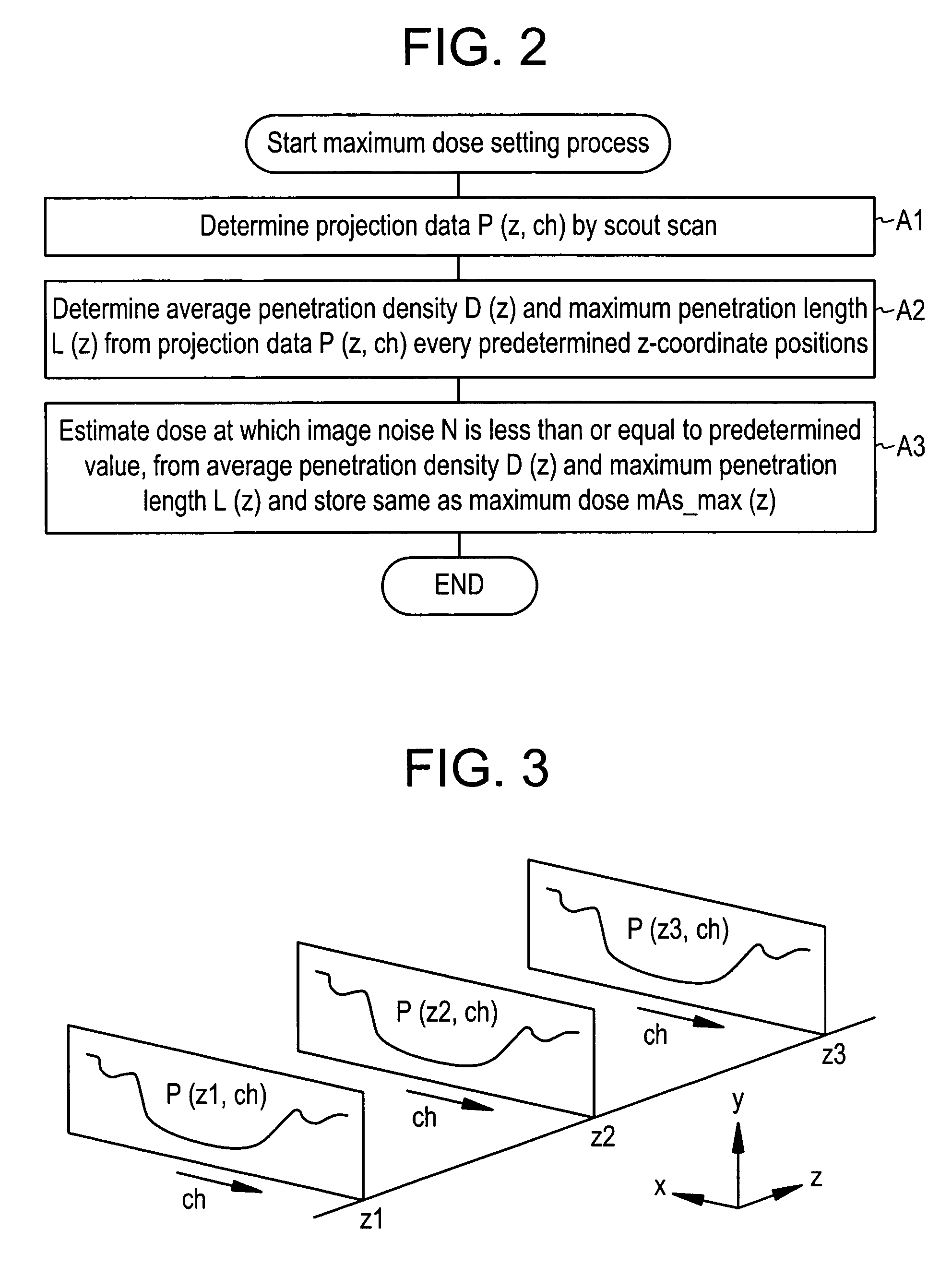
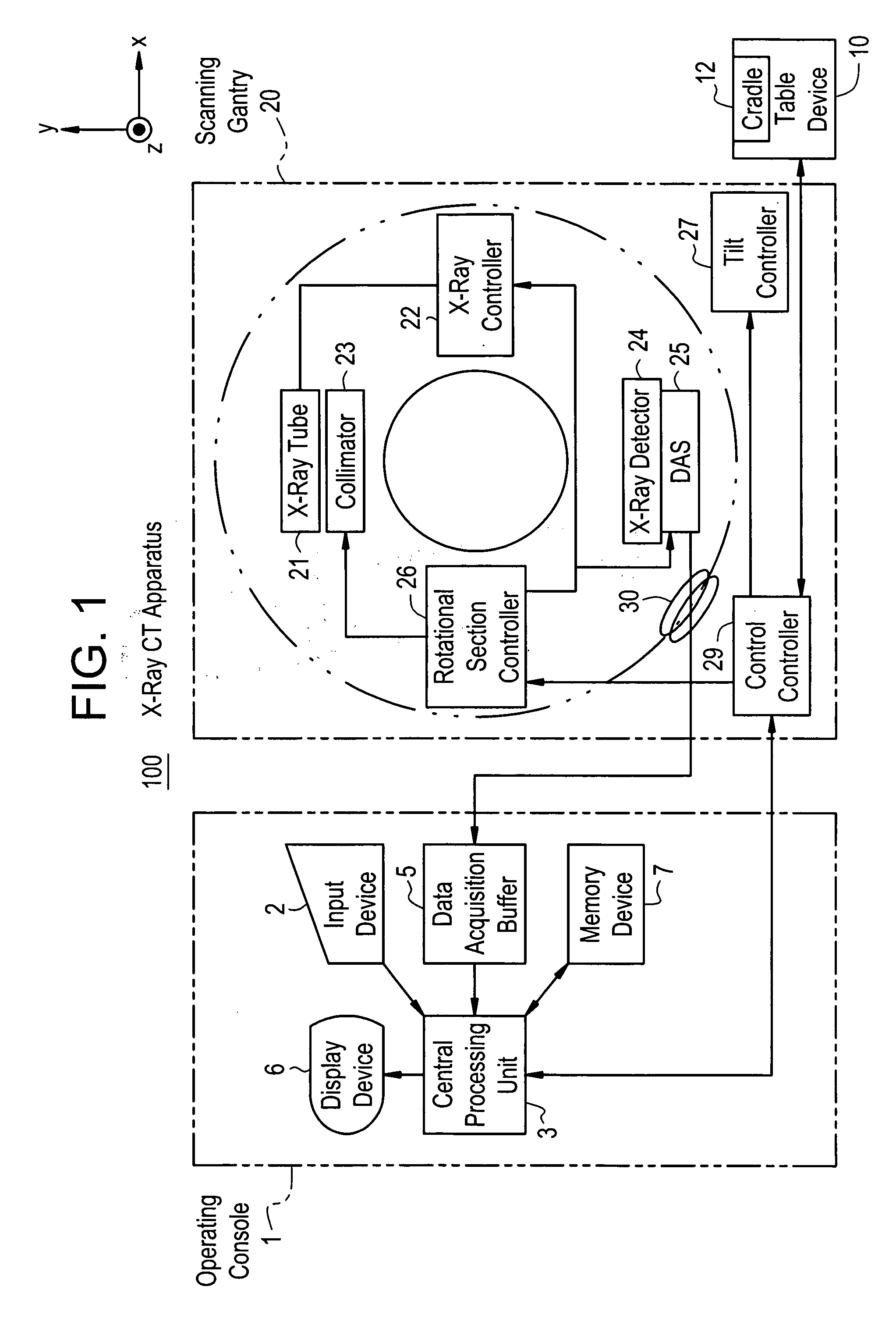
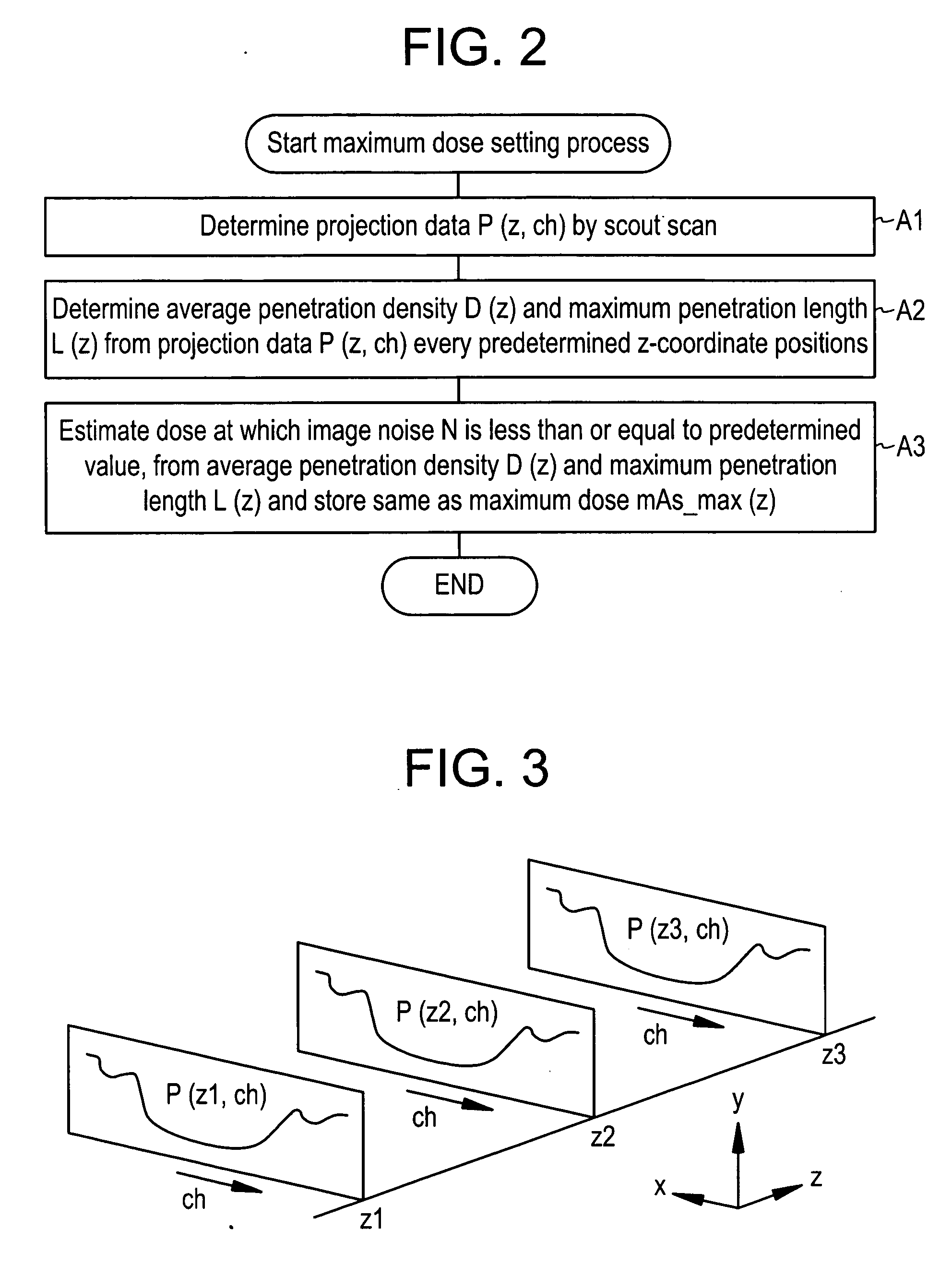
Dose evaluating method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS7756243B2Preventing doseDose can be prevented from becoming excessiveMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayMaximum dose
With the objective of evaluating whether a dose is excessive for a subject, such a dose that image noise reaches less than or equal to a predetermined value is estimated upon an axial scan on the basis of projection data acquired by a scout scan. The dose is set as a maximum dose. An area other than air, of an image obtained by the axial scan is partitioned into a plurality of small areas i. Image noises N(i) at the respective small areas i are calculated. A warning image G1 in which all of pixel values of pixels in small areas in which the image noises N(i) are less than or equal to a predetermined value, are substituted with pixel values expressed in black level, is created and displayed.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Dose evaluating method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060115039A1Prevent dosePreventing doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayMaximum dose
With the objective of evaluating whether a dose is excessive for a subject, such a dose that image noise reaches less than or equal to a predetermined value is estimated upon an axial scan on the basis of projection data acquired by a scout scan. The dose is set as a maximum dose. An area other than air, of an image obtained by the axial scan is partitioned into a plurality of small areas i. Image noises N(i) at the respective small areas i are calculated. A warning image G1 in which all of pixel values of pixels in small areas in which the image noises N(i) are less than or equal to a predetermined value, are substituted with pixel values expressed in black level, is created and displayed.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Scanning detection device of an X-ray CT apparatus, an X-ray CT system, and method of operation of the same
ActiveUS7558365B2Easy to judgeImprove image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingControl systemX-ray
Method of operating an X-ray CT apparatus and the corresponding apparatus and system thereof. A method includes analyzing scout scan data to obtain a position with a minimum noise index and a position with a maximum noise index, calculating noise indexes at the two positions in a range of a maximum and a minimum tube current that can be provided by the system by means of a tube current control model so as to obtain two ranges of noise index, and determining whether there is an intersection between the two ranges of noise index. If such an intersection exists, a combination of the range of tube current value and the range of noise index that meets the requirement is selected within the intersection to control the system to proceed with a subsequent scan. If no such intersection exists, the system ends the present scan.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Medical imaging apparatus
ActiveUS8693760B2Extension of timeMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsThree-dimensional spaceMedical imaging
There is provided a technique for, in a medical imaging apparatus enabling imaging of an arbitrary plane in a three-dimensional space, enabling automatic calculation of a slice position and automatic calculation of an extracting slice in MPR, without prolonging examination time. Two-dimensional scout scan similar to that used for manual setting of a slice position is performed, and the obtained scout images are processed to calculate a recommended slice position. Algorithms for the processing and various image processing procedures used for the processing are stored beforehand for every type of imaging region and every type of examination.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Quantification phantom for use with multiple imaging modalities
ActiveUS10507003B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
Described is an in-scan phantom for use during an imaging procedure. The phantom can include at least one measuring insert and / or at least one measured insert. The measuring insert may have radiation detecting capabilities while the measured insert may include a radioactive material. Also described is an imaging modality system that includes an imaging modality and an in-scan phantom as well as methods of using the in-scan phantom for imaging a patient or performing a scout scan.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method for controlling X-ray exposure in X-ray CT system
InactiveUS7995703B2Improving stability and robustnessImprove effectivenessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayCentre of rotation
A method for controlling automatic X-ray exposure in an X-ray CT system includes establishing a correspondence table or function relationship between a ratio factor and an offset of a geometrical center of a scanned section, wherein the ratio factor represents a ratio of the projection area value when the geometrical center of the scanned section of a subject deviates from a rotation center to the standard projection area value when the geometrical center of the scanned section of the subject locates at the rotation center, scout scanning the subject, and calculating a “measured projection area value” and Projection Measure based on the scout scan data, calculating the offset of the geometrical center of the scanned section from the rotation center, substituting the offset into the correspondence table or function relationship to obtain a corresponding ratio factor, calculating the standard projection area value based on the ratio factor and the measured projection area value, and automatically determining by an automatic exposure function a tube current value required for exposure based on the calculated standard projection area value, the Projection Measure.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com