Patents
Literature
78 results about "Brain magnetic resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
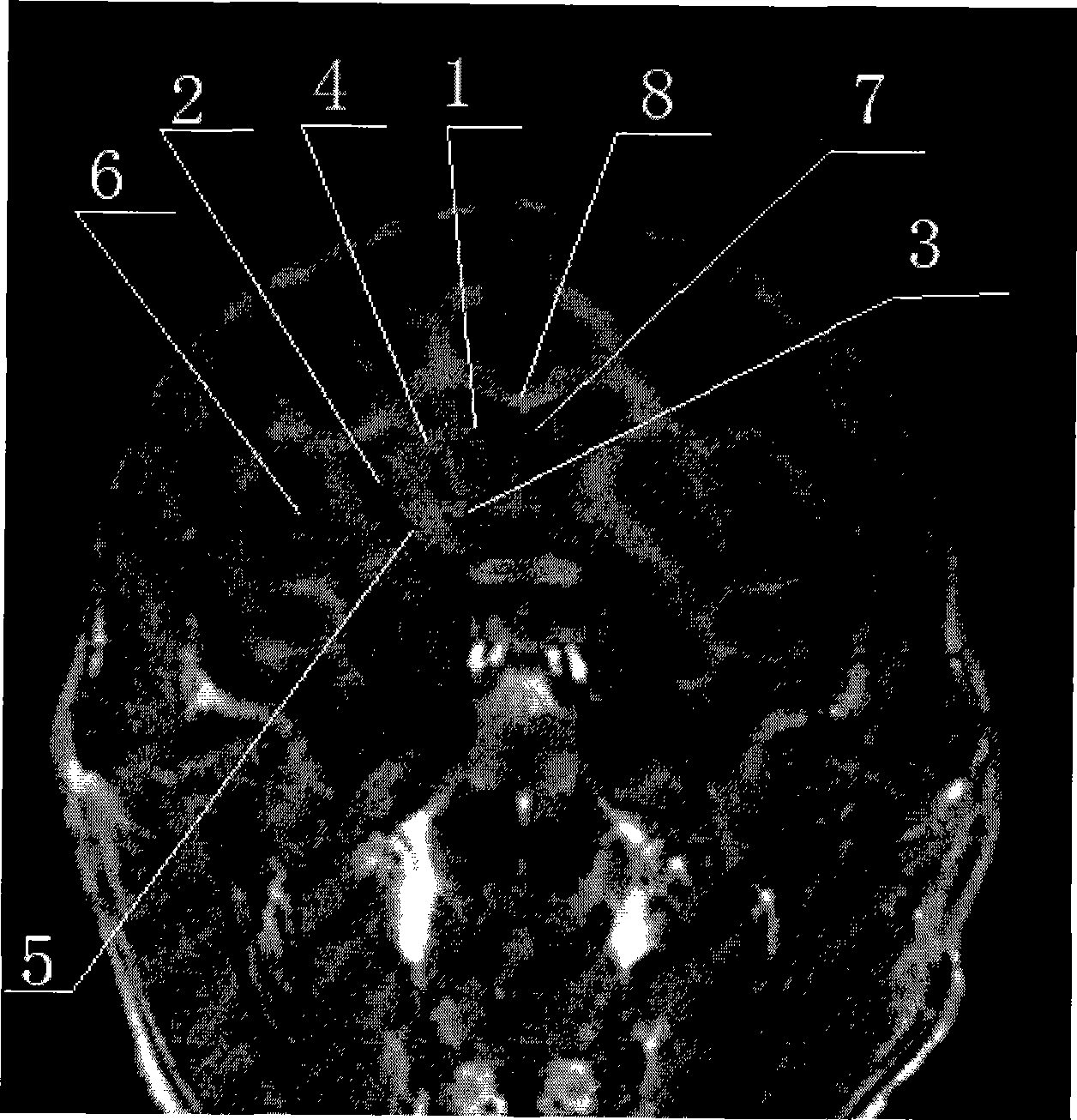
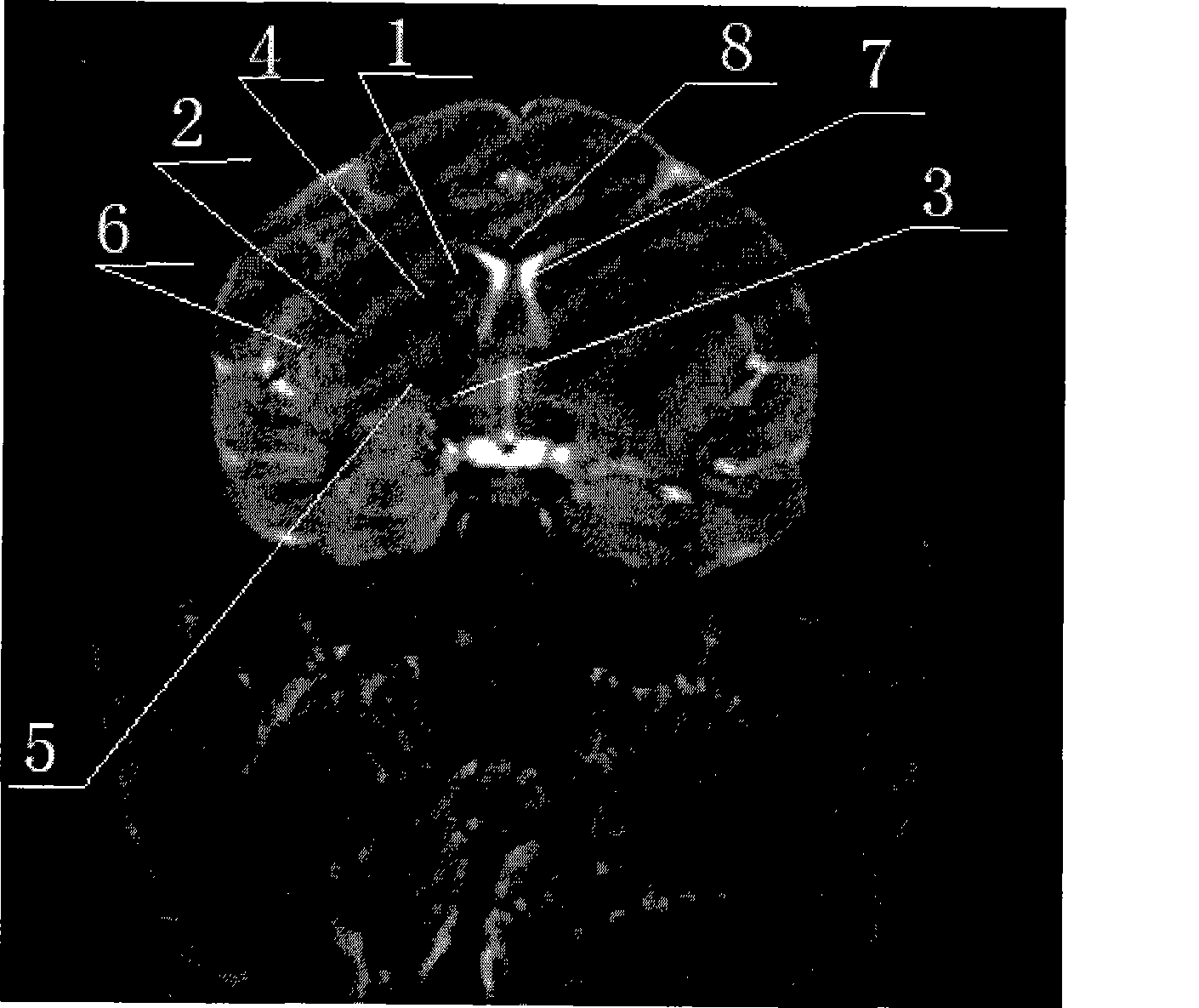
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is a safe and painless test that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the brain and the brain stem.
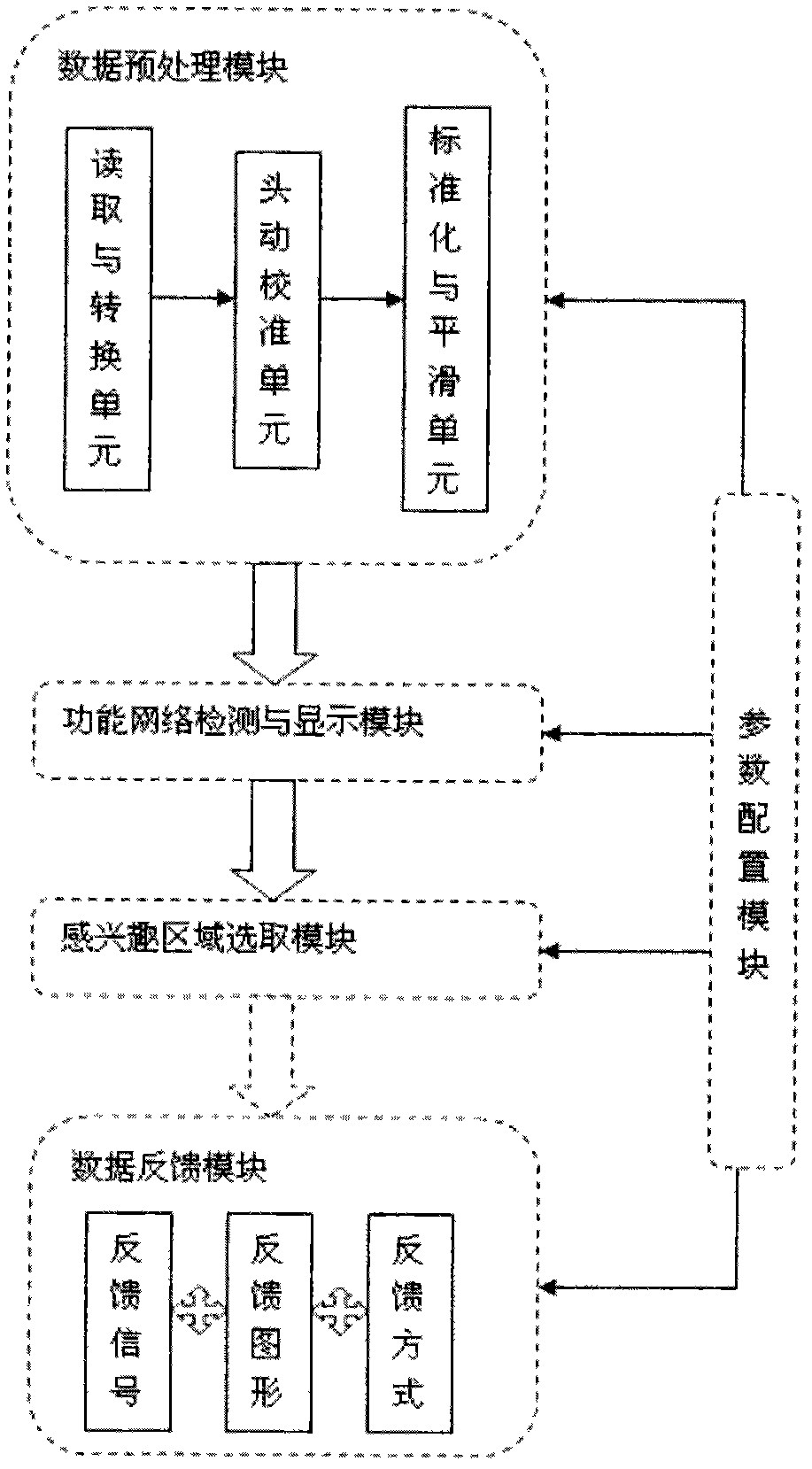
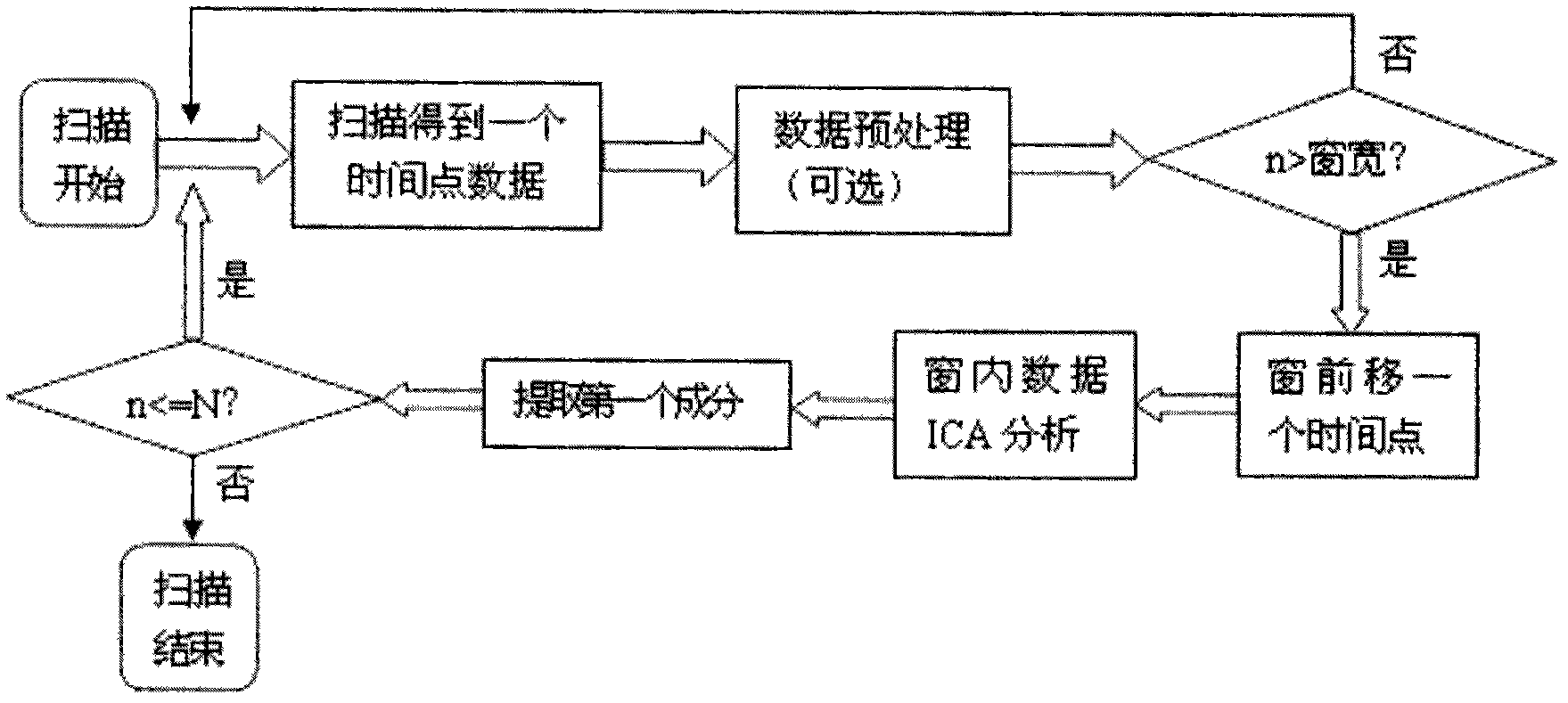
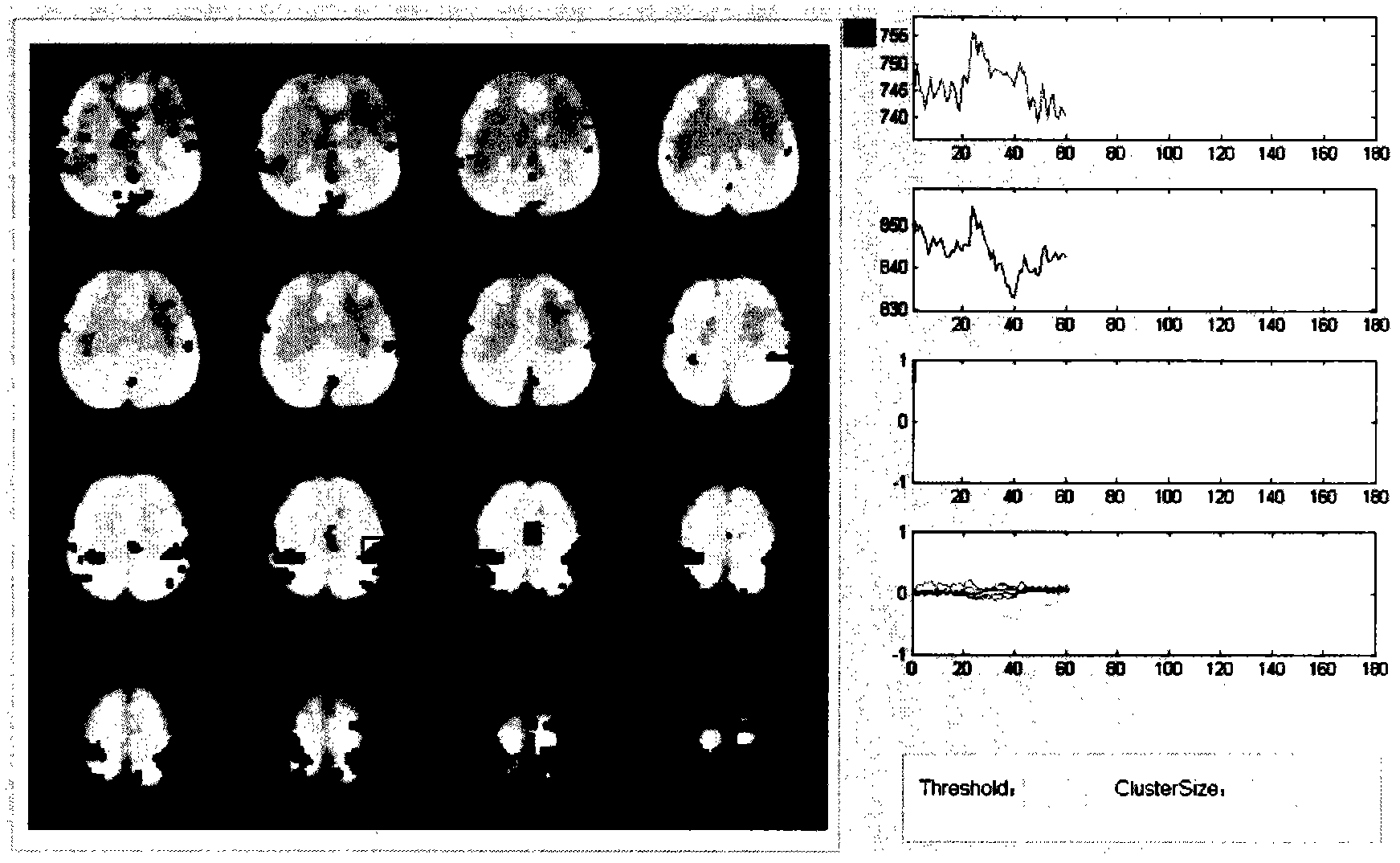
Real-time functional magnetic resonance data processing system based on brain functional network component detection
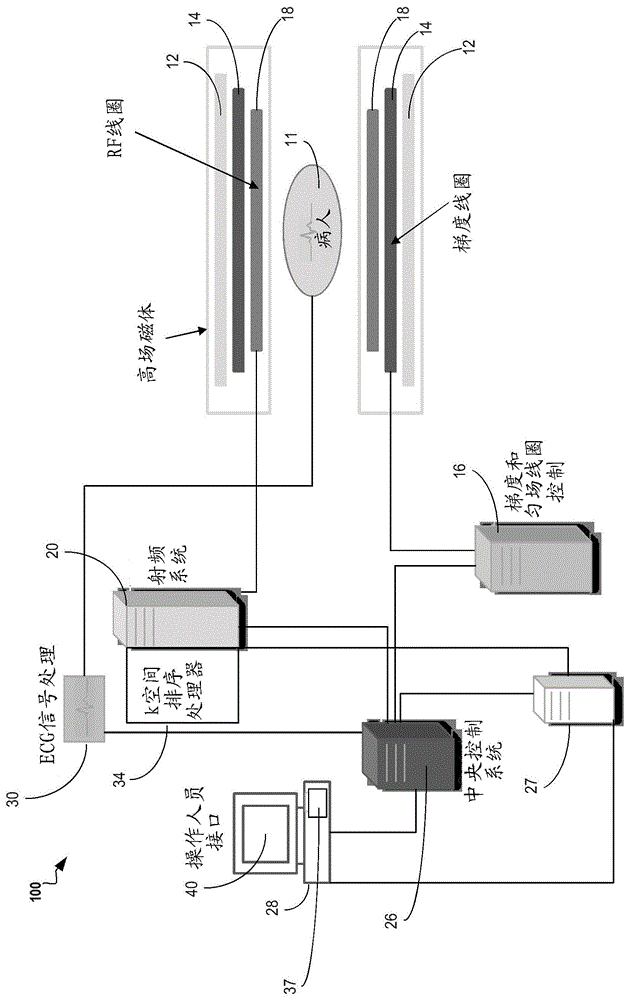
The invention provides a real-time functional magnetic resonance data processing system based on brain functional network component detection, which realizes real-time network analysis of brain functional magnetic resonance images obtained on line. The system comprises a data preprocessing module, a functional network detection and display module, a region-of-interest selection module, a data feedback module and a parameter configuration module, wherein the data preprocessing module is used for improving the signal to noise ratio of the data by image denoising, artifacts removing, etc after carrying out online reading and format conversion on the brain functional magnetic resonance images and for reducing the interference of noises and other factors in the magnetic resonance images; then the functional network detection and display module is used for carrying out real-time network analysis and extracting the functional network components of brain activity in specific state; the region-of-interest selection module is used for recording and saving the activity conditions of one or more node regions of interest in the network; the data feedback module is used for feeding the result data of the regions of interest back to the persons to be tested in real time according to different application requirements or by various ways or judging the result data by categories; and the parameter configuration module is used for providing parameter setting, reading and saving functions for each module and each unit contained by the invention. The system has important application values in multiple fields such as online estimation of quality of data, mind reading, brain function adjustment, clinical treatment, etc.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
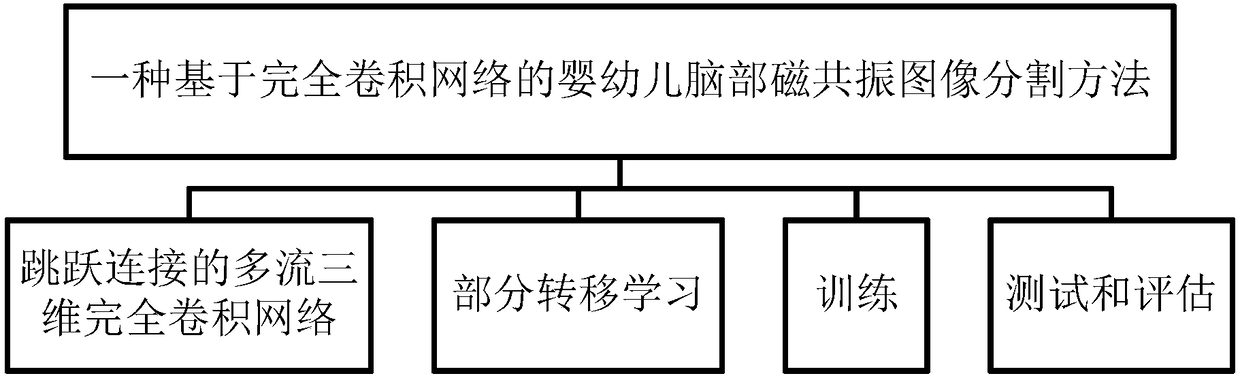
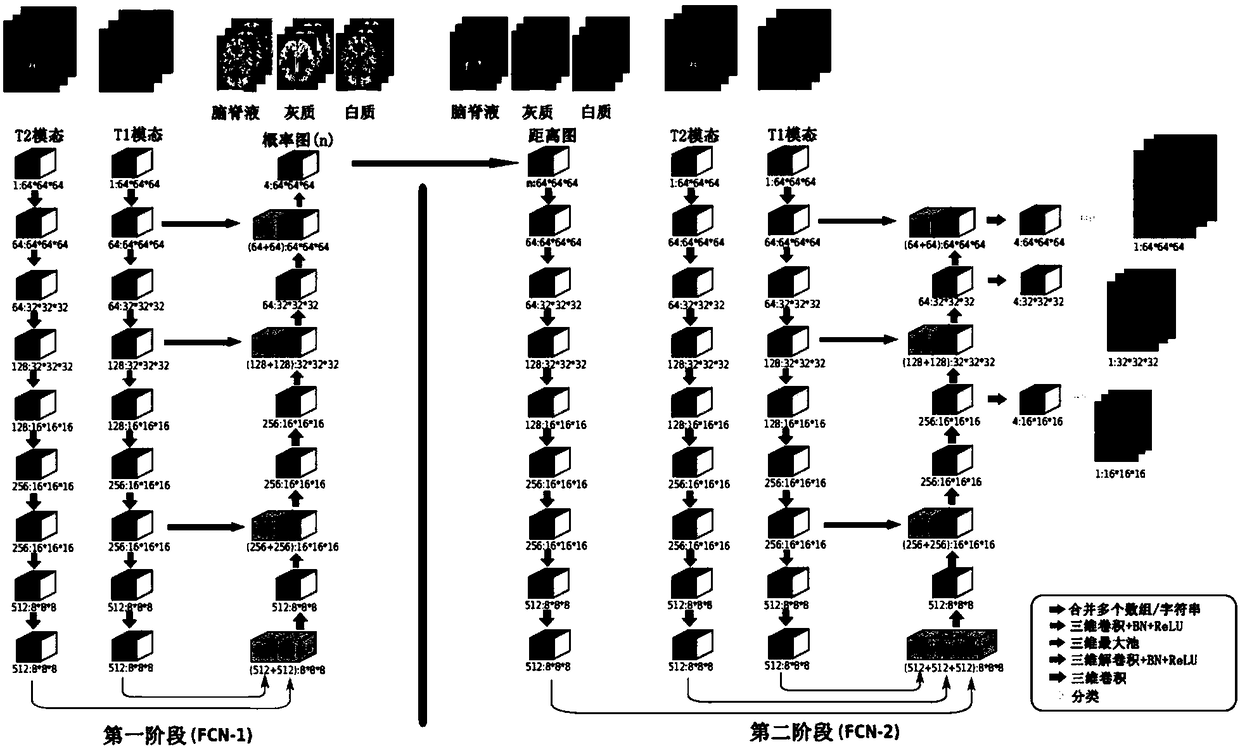
Infant brain magnetic resonance image partitioning method based on fully convolutional network
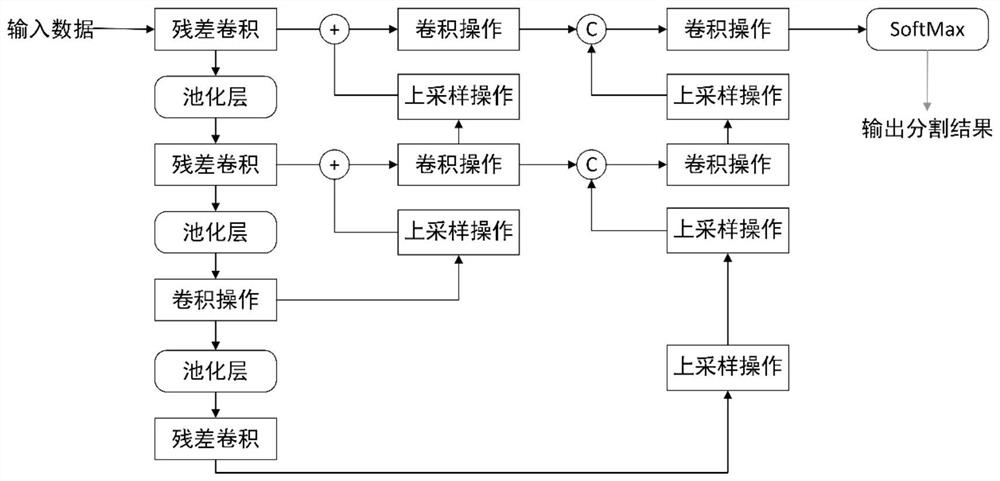
The invention provides an infant brain magnetic resonance image partitioning method based on a fully convolutional network. The main content of the method comprises the multi-stream three-dimensionalfully convolutional network (FCN) with jump connection, partial transfer learning, training and testing and evaluation. According to the process of the method, first, a probability graph of each pieceof brain tissue is learned from a multi-modal magnetic resonance image; second, initial partitions of different brain tissue are obtained from the probability graphs and used for calculating a distance graph of each piece of brain tissue; third, spatial context information is simulated according to the distance graphs; and last, final partitioning is realized by use of spatial correlation information and the multi-modal magnetic resonance image, wherein the training process mainly comprises training data increasing, training patch preparation and iterative training, and various detection values are used for evaluation after testing is performed. Through the partitioning method, a white matter area, a grey matter area and a cerebrospinal fluid area are successfully divided, the potential gradient vanishing problem of multi-level deep supervision is relieved, training efficiency is improved, and partitioning performance is greatly enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
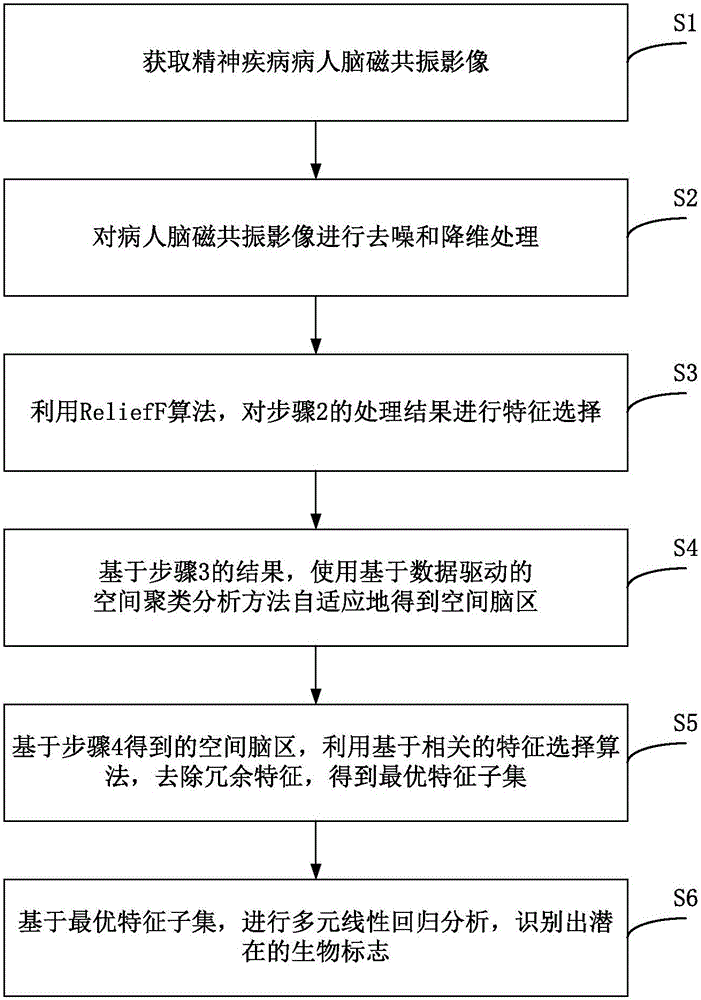
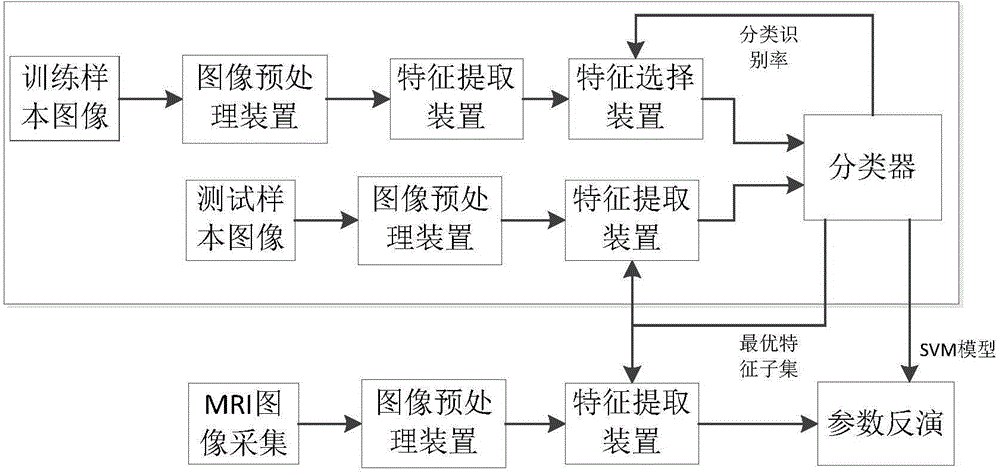
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain disease individual prediction method and system
InactiveCN106156484AImprove generalizationRapid Quantification and Precise PredictionMedical data miningSpecial data processing applicationsReduction treatmentPredictive methods
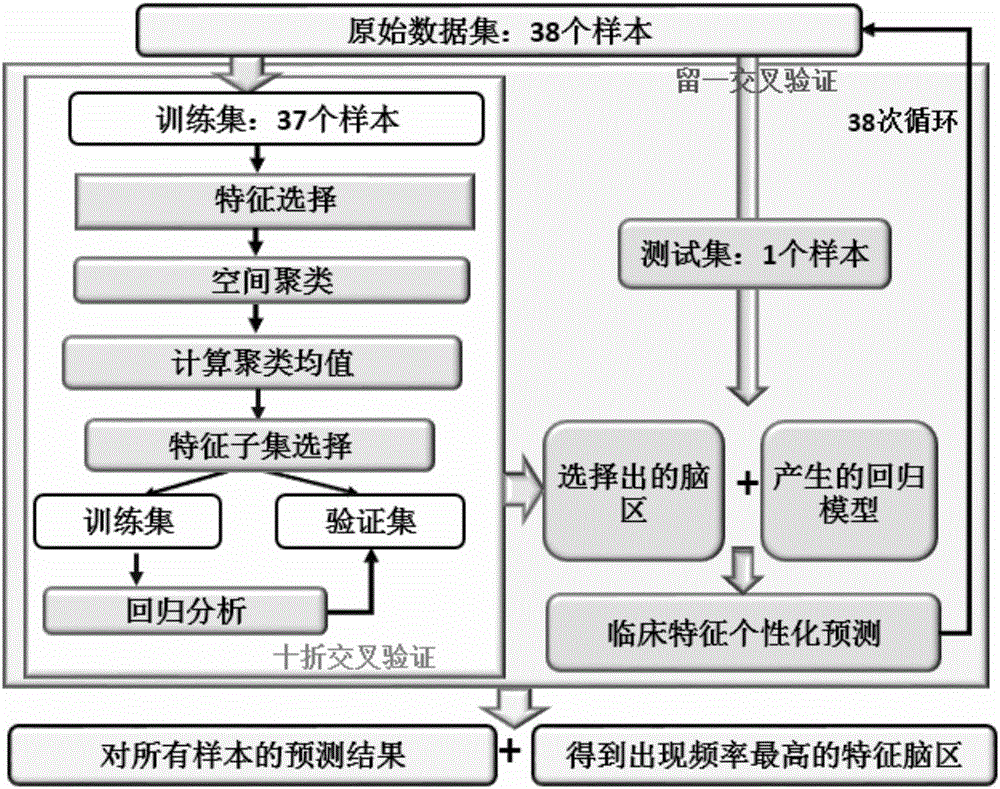
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain disease individual prediction method and a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain disease individual prediction system. The method comprises the following steps: 1: obtaining the MRI of the brain of a patient with mental diseases; 2: carrying out denoising and dimension reduction treatment on the MRI of the brain of the patient; 3: carrying out feature selection by utilizing a ReliefF algorithm; 4: adaptively obtaining a spatial brain area by using a spatial cluster analysis method; 5: removing redundant features by utilizing a correlation-based feature selection algorithm, thus obtaining an optimal feature subset; 6: carrying out multiple linear regression analysis based on the optimal feature subset to recognize potential biomarkers. The method has the beneficial effects that the embodiment of the invention integrates various machine learning methods and can rapidly and conveniently achieve quantitative and individual accurate prediction of the interest features of mental diseases, such as clinical indexes, based on various image data in different mode types, thus being beneficial to understanding the brain structures, function abnormity and potential pathogenesis of the diseases.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-rigid brain image registration method
ActiveCN103700101ASolve matching problemsTroubleshoot registration issuesImage analysisPattern recognitionReference image
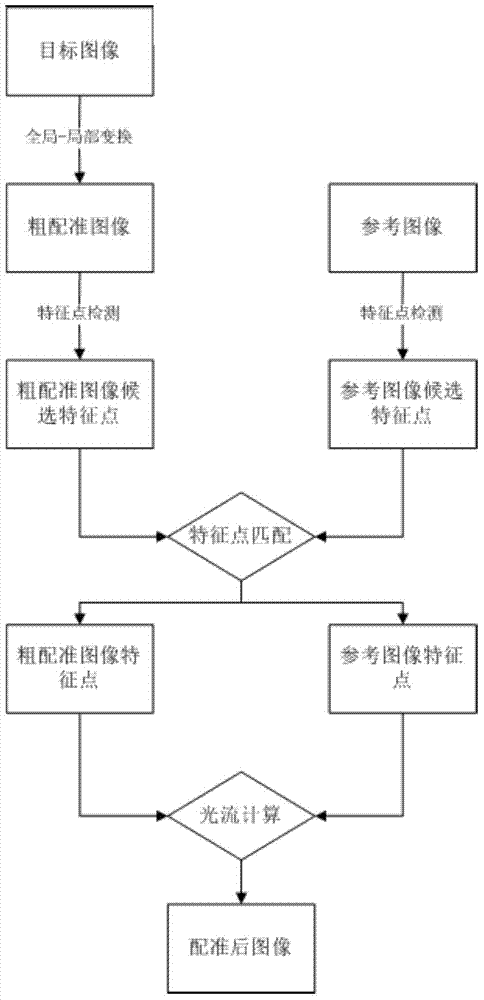
The invention discloses a non-rigid brain image registration method, which comprises the steps of 1, preprocessing a target image according to a reference image to obtain a rough registration image; 2, respectively calculating the candidate characteristic points of the reference image and the rough registration image; 3, constructing characteristic descriptors of the candidate characteristic points, and obtaining matched characteristic points according to the characteristic descriptors; 4, calculating a light stream model of the rough registration image according to the characteristic points to obtain a registration result. Through adopting a descriptor vector based on a Zernike matrix to depict the geometrical characteristics under different scales for describing the regional characteristics of the characteristic points, the characteristic point matching problem during non-rigid registration is solved, and in addition, through fusing characteristic point constraints into the Brox light stream model, the problem of registration of brain magnetic resonance images is solved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
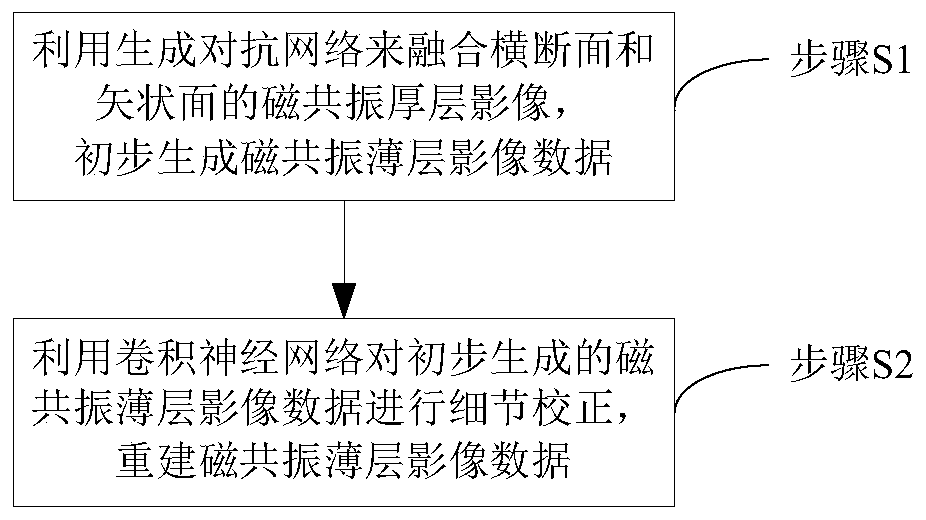
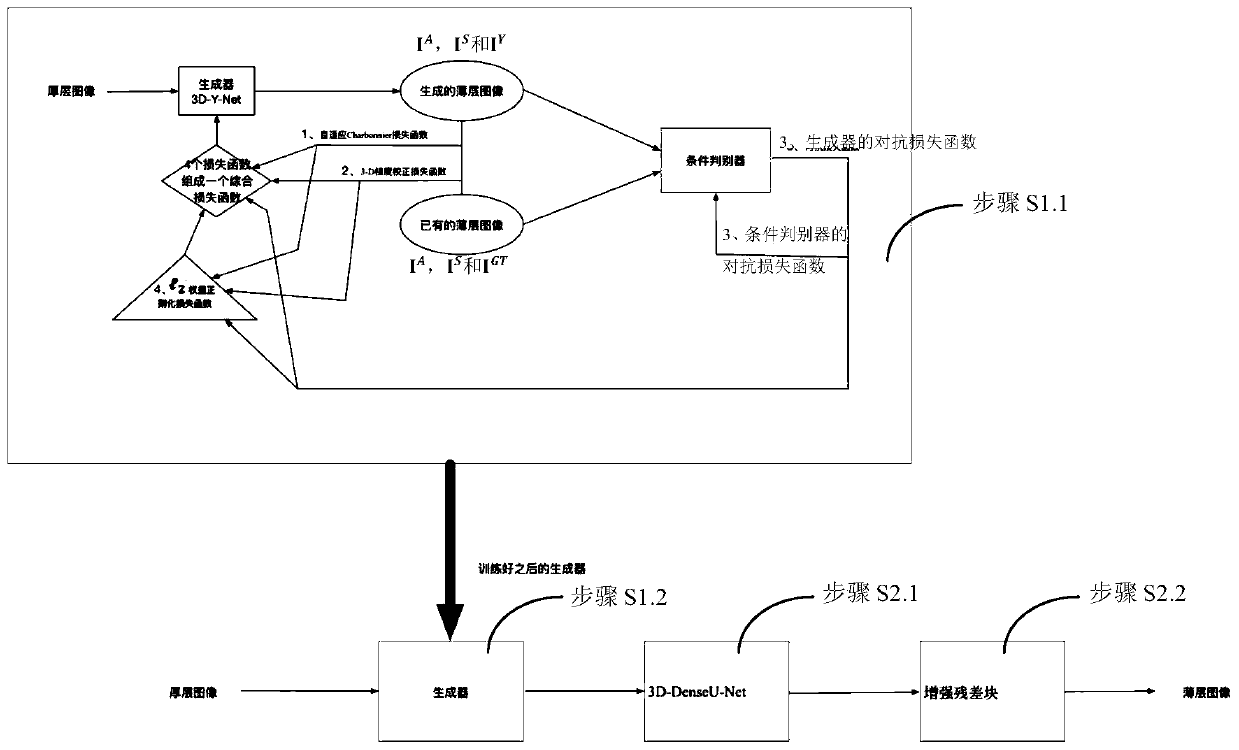
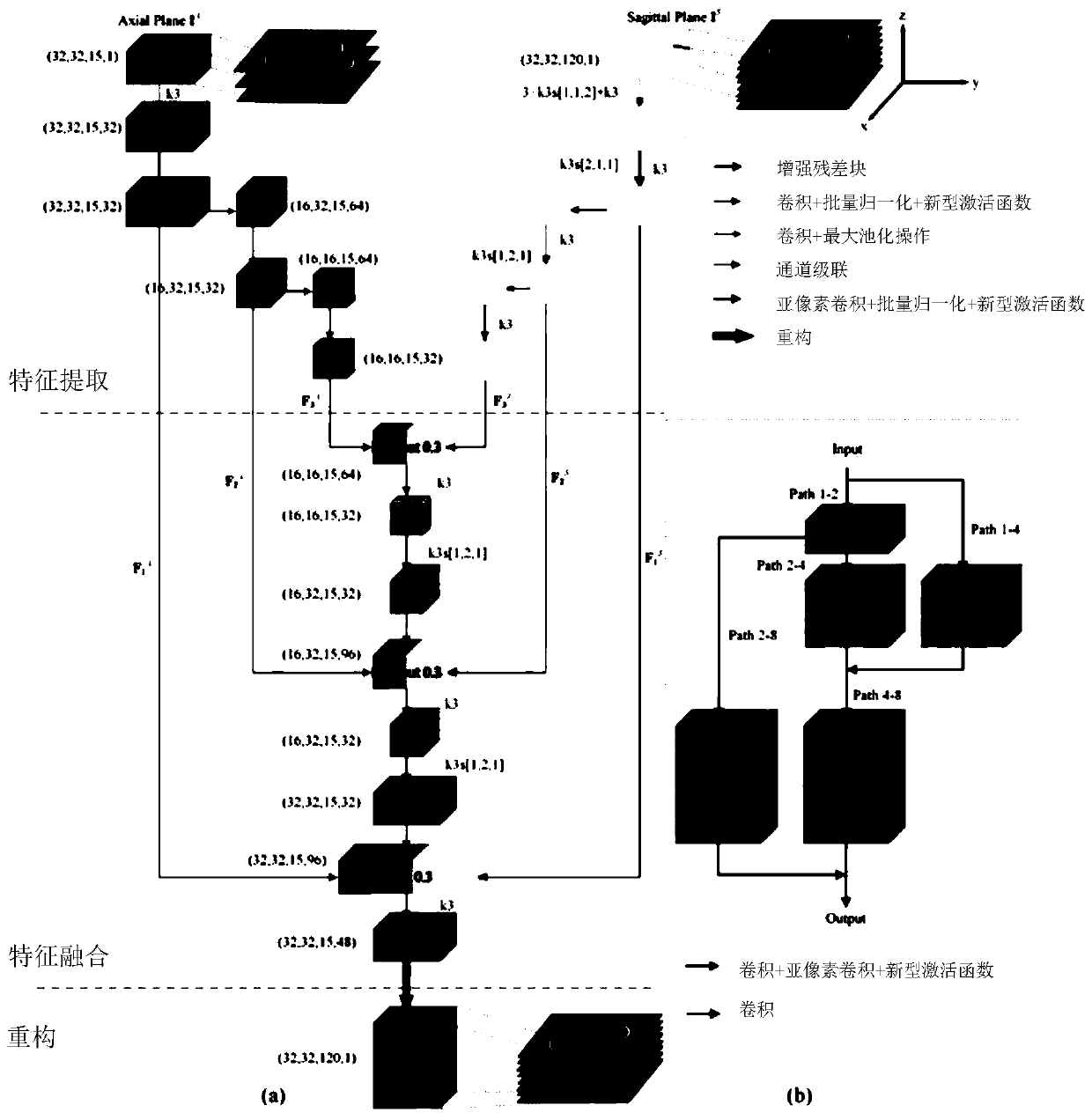
Magnetic resonance thin-layer image reconstruction method
InactiveCN110047138ALarge data capacityImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioNeural architectures3D modellingData capacitySagittal plane
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance thin-layer image reconstruction method, which comprises the following steps of: fusing a magnetic resonance thick-layer image with a cross section and a sagittal plane by utilizing a generative adversarial network, initially generating corresponding magnetic resonance thin-layer image data, and performing detail correction on the initially generated magnetic resonance thin-layer image data by utilizing a convolutional neural network to reconstruct the magnetic resonance thin-layer image data. According to the method, a more real magnetic resonancethin-layer image can be obtained, the peak signal-to-noise ratio, the structural similarity and the regularization mutual information are greatly improved, the child thin-layer brain magnetic resonance image data capacity can be effectively increased, and a foundation is laid for later research.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
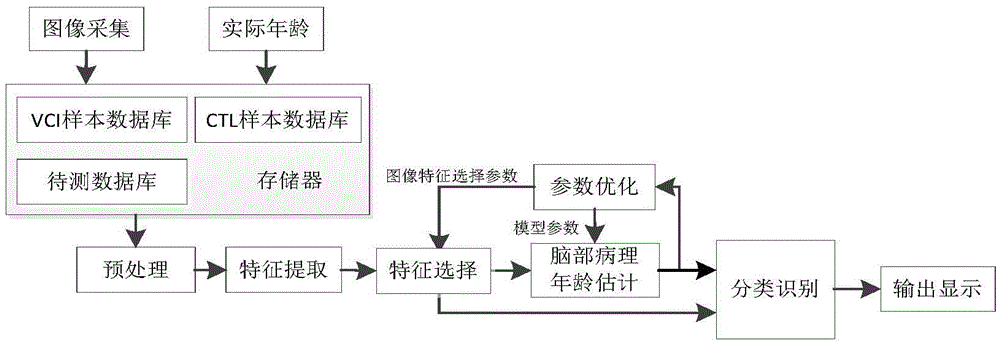
Brain disease detection system based on brain pathological age estimation
ActiveCN105512493AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementMedical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseSimulation training
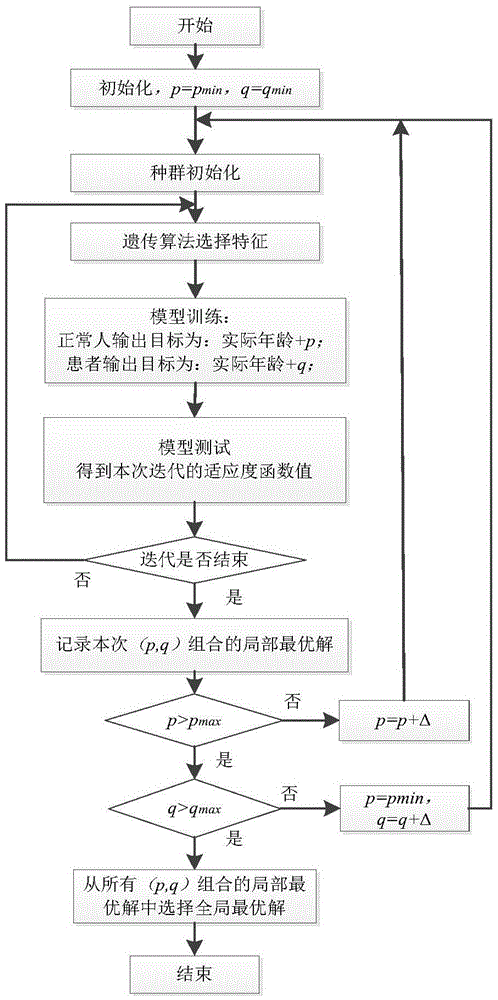
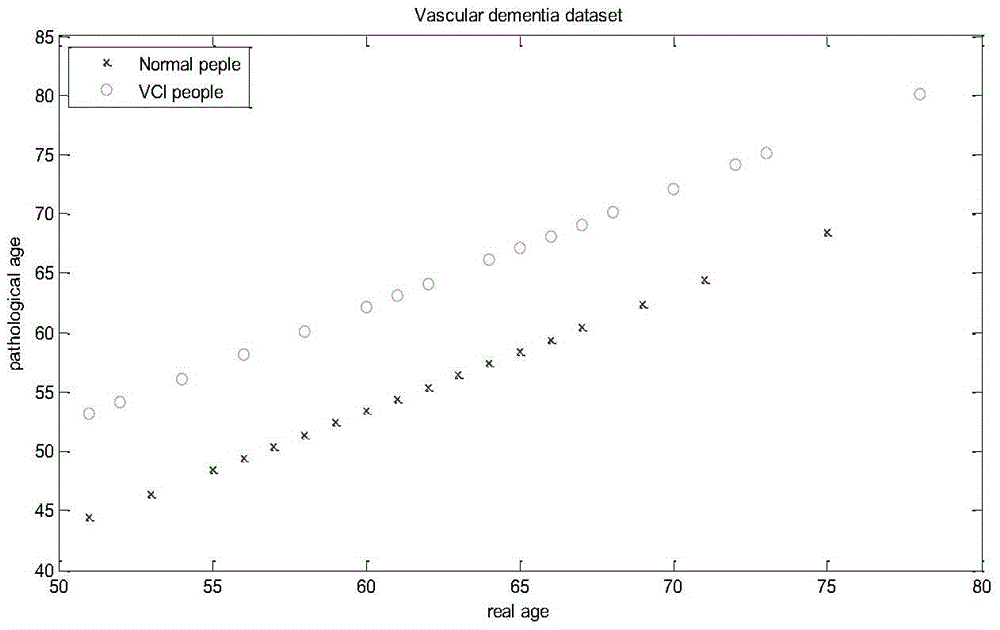
The invention provides a brain disease detection system based on brain pathological age estimation. The brain disease detection system comprises image acquisition equipment, actual age input equipment, a storer, a preprocessing module, a feature extraction module, a feature selection module, a brain pathological age estimation module, a parameter optimization module, a classified recognition module and a result output module; the storer is provided with a VCI sample database, a CTL sample database and a database to be measured. The brain disease detection system has the advantages that the system fully utilizes brain magnetic resonance image characteristics, in combination with the actual age information of samples, simulation training is conducted through a great number of samples, and the obtained brain pathological age estimation module can effectively estimate the brain pathological age of a measured object; meanwhile, deviation between the brain pathological age estimation value and the actual age serves as supplementary information, whether a patient suffers from brain disease or not is effectively diagnosed through infusion with brain image information, the whole system is definite in principle, convenient to implement, more scientific basis is achieved for brain disease detection, reliability is high, and feasibility is high.
Owner:一九一数字科技(深圳)有限公司
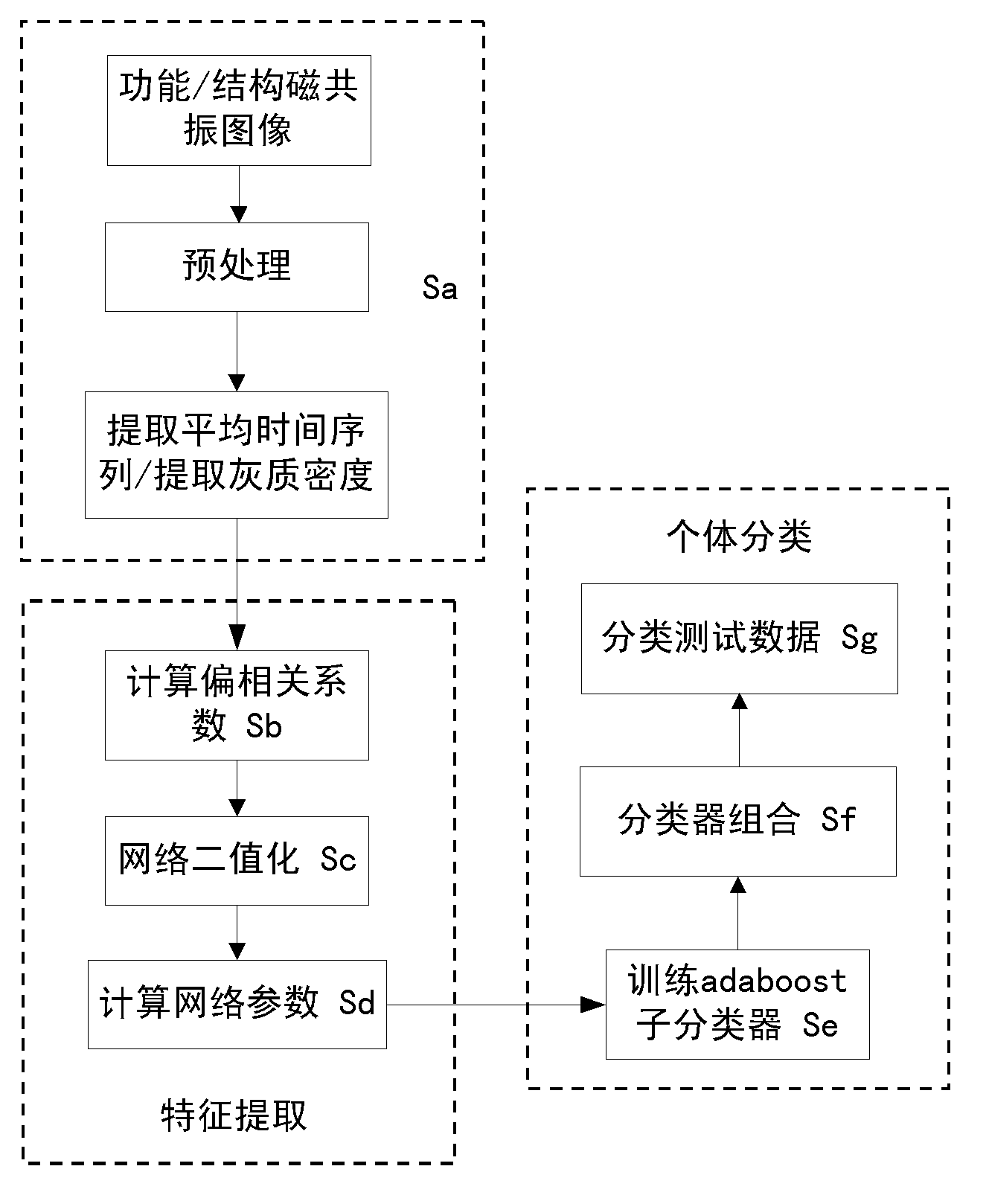
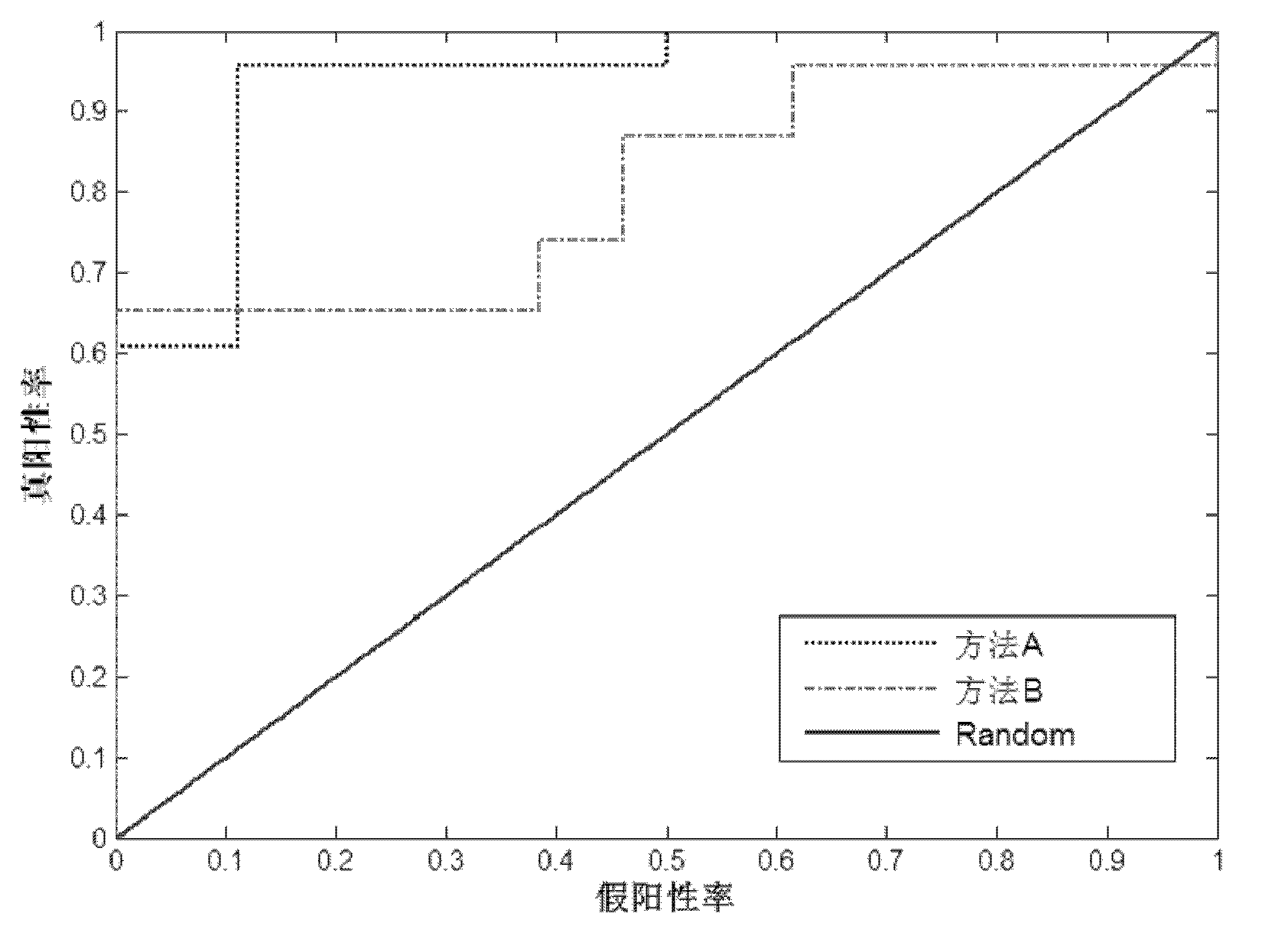
Structure and function magnetic resonance image united classification method based on network analysis
ActiveCN103020653AAccurate classificationMake up for the inability to reflect the inherent properties of brain activityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionBrain magnetic resonance
The invention provides a structure and function magnetic resonance image united classification method based on network analysis. The method includes firstly, establishing a structure and function brain network model, calculating characteristic path length, an agglomeration degree and a network centrality of a brain network to represent different image models, and then training a self-adaption improving classifier by using network parameters. The structure and function magnetic resonance image united classification method can use as many messages as possible in a magnetic resonance image, the brain network parameters can reflect brain activities in nature, and simultaneously, a technology of multiple classifiers is used, so that the defect that inherent attributes of the brain activities can not be reflected by traditional classification methods is made up, and the brain magnetic resonance image can be accurately classified.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
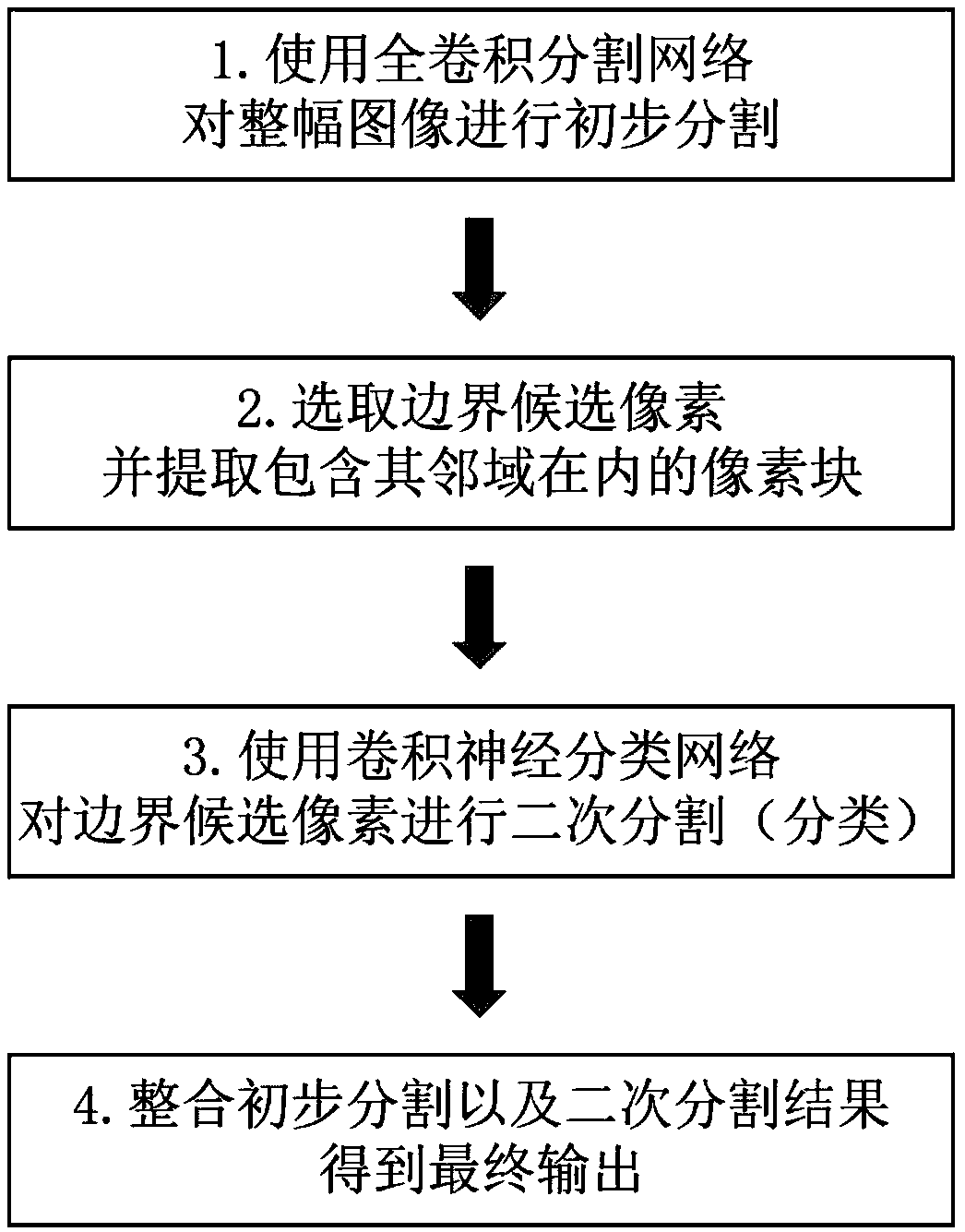
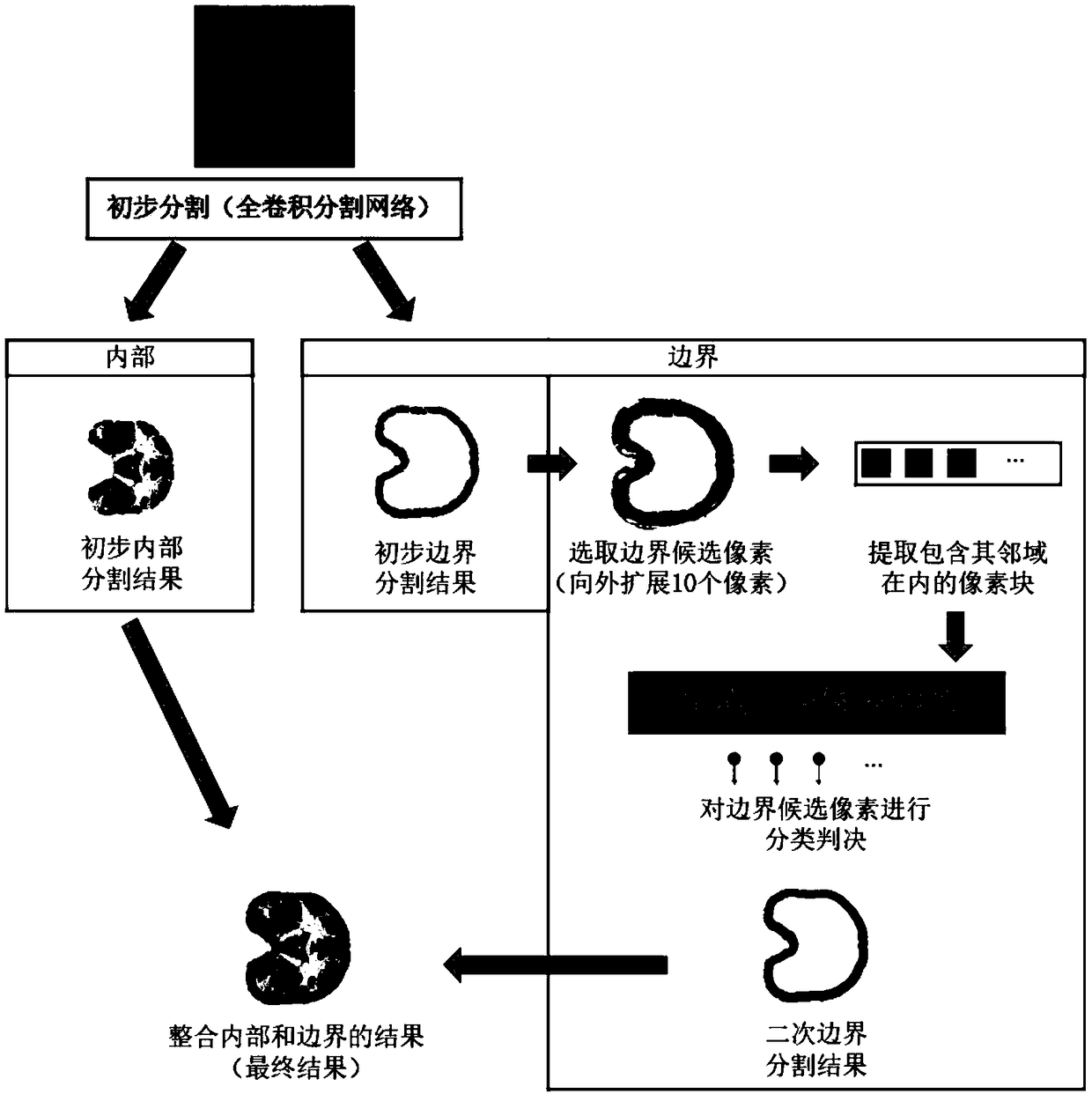
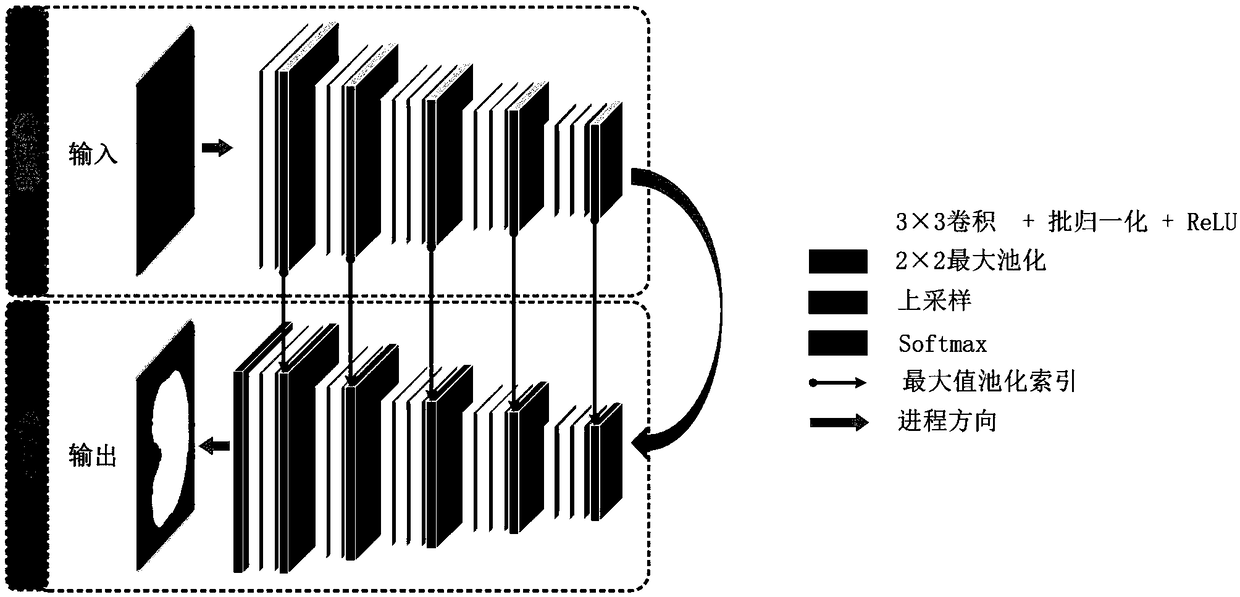
A brain tissue extraction method based on total convolution neural network
ActiveCN109389585AHigh precisionAccurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceBrain magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a brain tissue extraction method based on a full convolution neural network, which comprises the following steps: firstly, a full convolution integral cutting network is used for preliminary segmentation of a two-dimensional original nuclear magnetic resonance image to obtain a preliminary segmentation result; secondly, a full convolution integral cutting network is used for preliminary segmentation of the two-dimensional original nuclear magnetic resonance image. Secondly, according to the preliminary segmentation results, the internal and boundary information of braintissue is separated. Thirdly, these pixels which can not be determined as brain tissue are selected as boundary candidate pixels, and these candidate pixels and their neighborhoods are sent to convolution neural network for secondary segmentation to realize classification and judgment. Finally, we integrate the internal segmentation results and the boundary segmentation results obtained from thesecondary segmentation, and obtain the final brain tissue extraction segmentation results. The invention carries out thick and thin twice segmentation, ensures the calculation efficiency of the method, realizes the fine segmentation goal, can be better applied to the brain magnetic resonance image, and realizes more accurate separation of brain tissue from non-brain tissues such as skull, eyeball,skin, fat and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A brain anatomy teaching system based on magnetic resonance imaging
PendingCN109308680ARealize one-click interactionImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresAutomatic segmentation
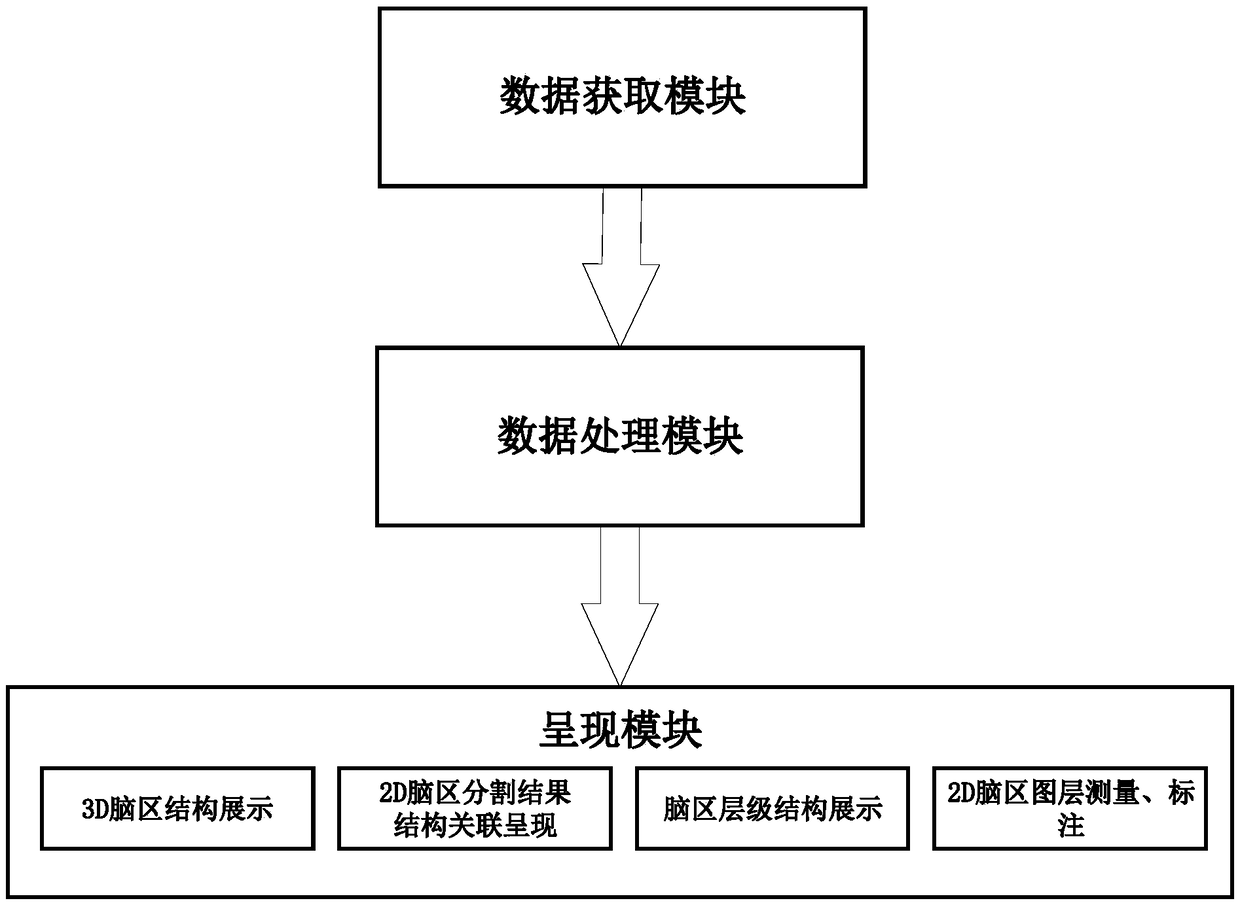
The invention provides a brain anatomy teaching system based on magnetic resonance image, By importing the MRI data of real cases which had been segmented and reconstructed automatically in advance, In order to realize one-key interaction between two-dimensional images and three-dimensional brain anatomy, two-dimensional segmentation structure display and digital three-dimensional model demonstration of any single brain region and multi-brain regions are provided, which provides a scheme for the teaching of brain anatomy based on real cases.
Owner:迈格生命科技(深圳)有限公司
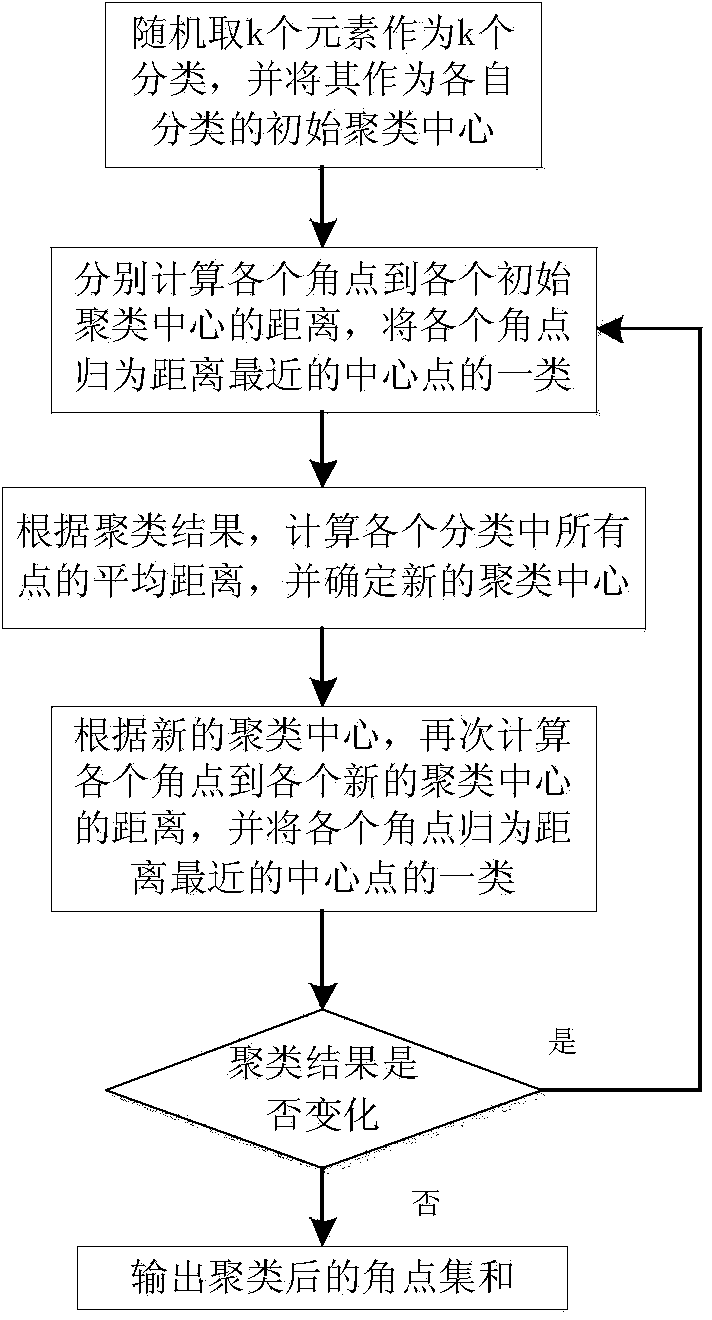
Brain magnetic resonance image registration method based on K-means clustering method
InactiveCN103839272AReduce running timeImprove registration accuracyImage analysisAngular pointBrain magnetic resonance
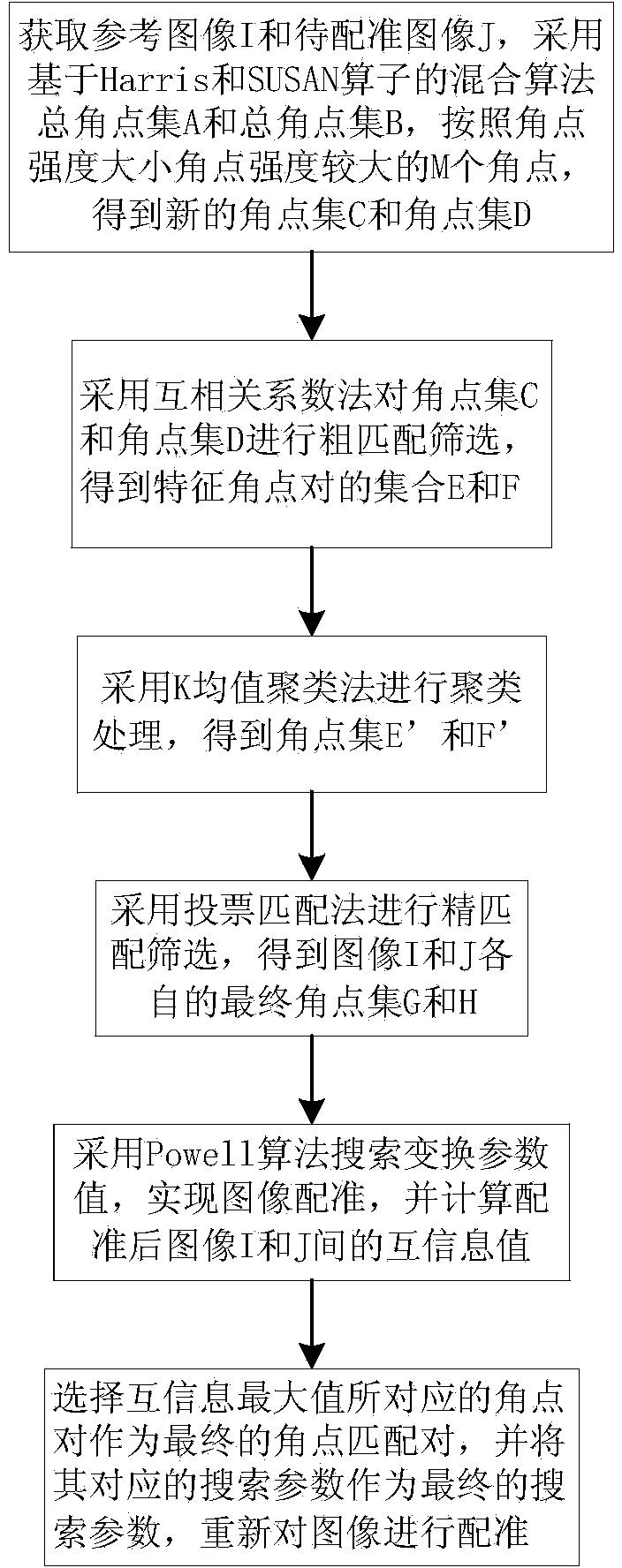
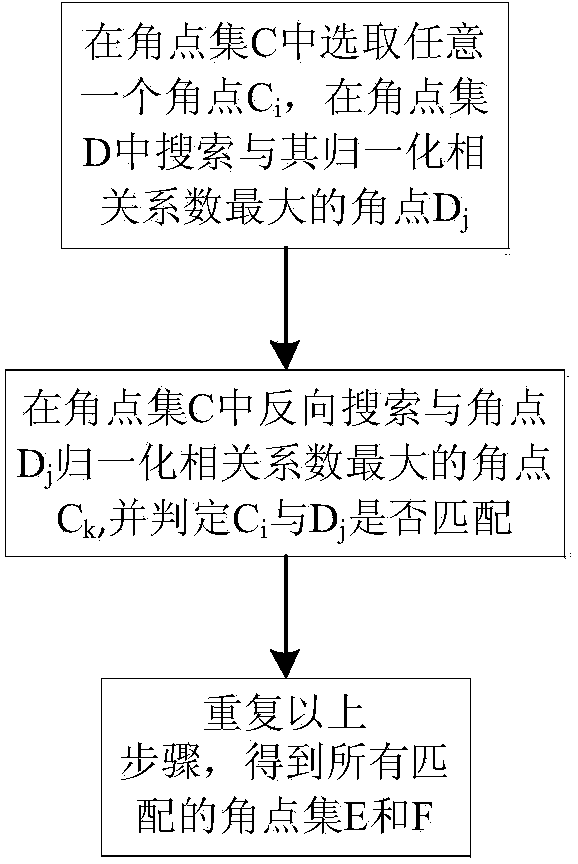
The invention discloses a brain magnetic resonance image registration method based on a K-means clustering method. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an accumulated angle point set is acquired through mixed angle point detection of a Harris operator and a SUSAN operator, a new angle point set is screened out through angle point strength, rough matching screening is carried out through a cross correlation coefficient method, then angle points are clustered by introducing the K-means clustering method, precise angle point pairs are screened out by combining a normalized correlation method and a voting matching method, finally, the angle point set is optimized through a Powell algorithm, a rebuilt parameter value is obtained, and final registration is carried out on images. The brain magnetic resonance image registration method has the advantages that good stability is achieved, feature point information can be described completely and accurately, the running time of a program in subsequent operation is reduced, registration accuracy is improved, an image registration algorithm is improved more precisely and efficiently, and a transformation image fluctuant within a large range can be compatible better.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Detection system based on phosphorylated tau protein content information in brain magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN104867153ARadiation-freeHigh degree of automationImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionBrain magnetic resonance
Owner:芽米科技(广州)有限公司
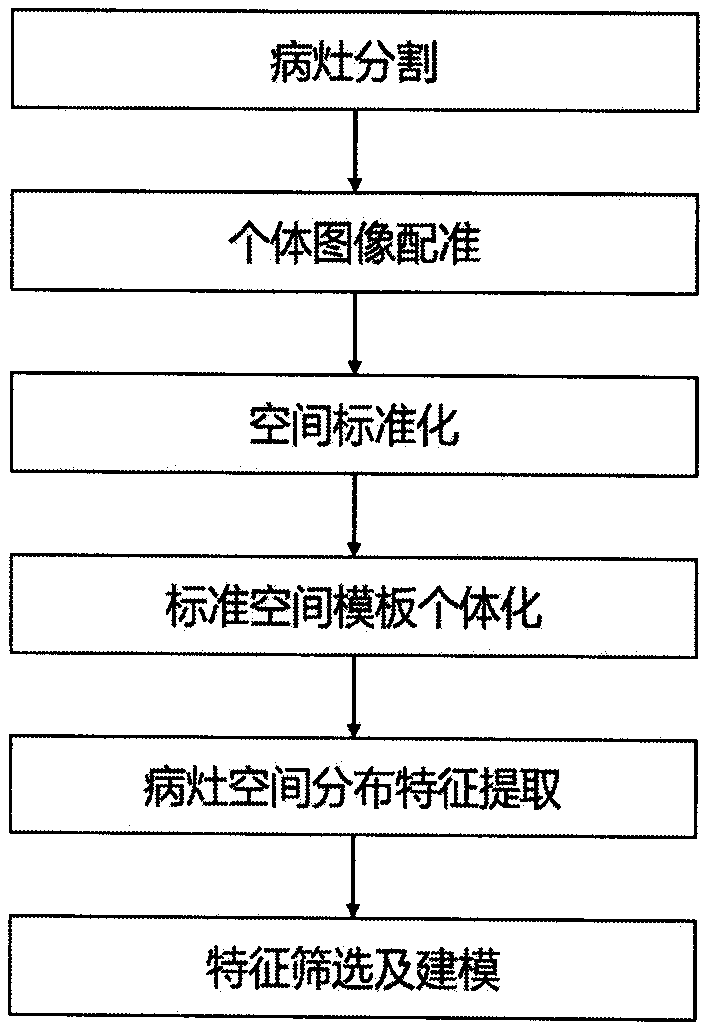
Brain lesion image spatial distribution characteristic classification and identification method based on magnetic resonance imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and application, and particularly relates to a brain lesion image spatial distribution feature classification and identification methodbased on magnetic resonance imaging. The method mainly comprises the steps of focus segmentation, individual image registration, space standardization, standard space template individualization, focus space distribution feature extraction, feature screening, modeling and the like. The core is in that an analysis method of a brain lesion image spatial distribution feature set is constructed by analyzing various features of lesions in an individual space and a standard space, and feature screening and modeling are carried out by using machine learning on the basis of the analysis method. The method can be used for classifying and identifying brain lesion images of different brain diseases or brain states caused by different antibodies, different genes and the like by using brain magnetic resonance images, and effective guidance is provided for clinic and scientific research.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
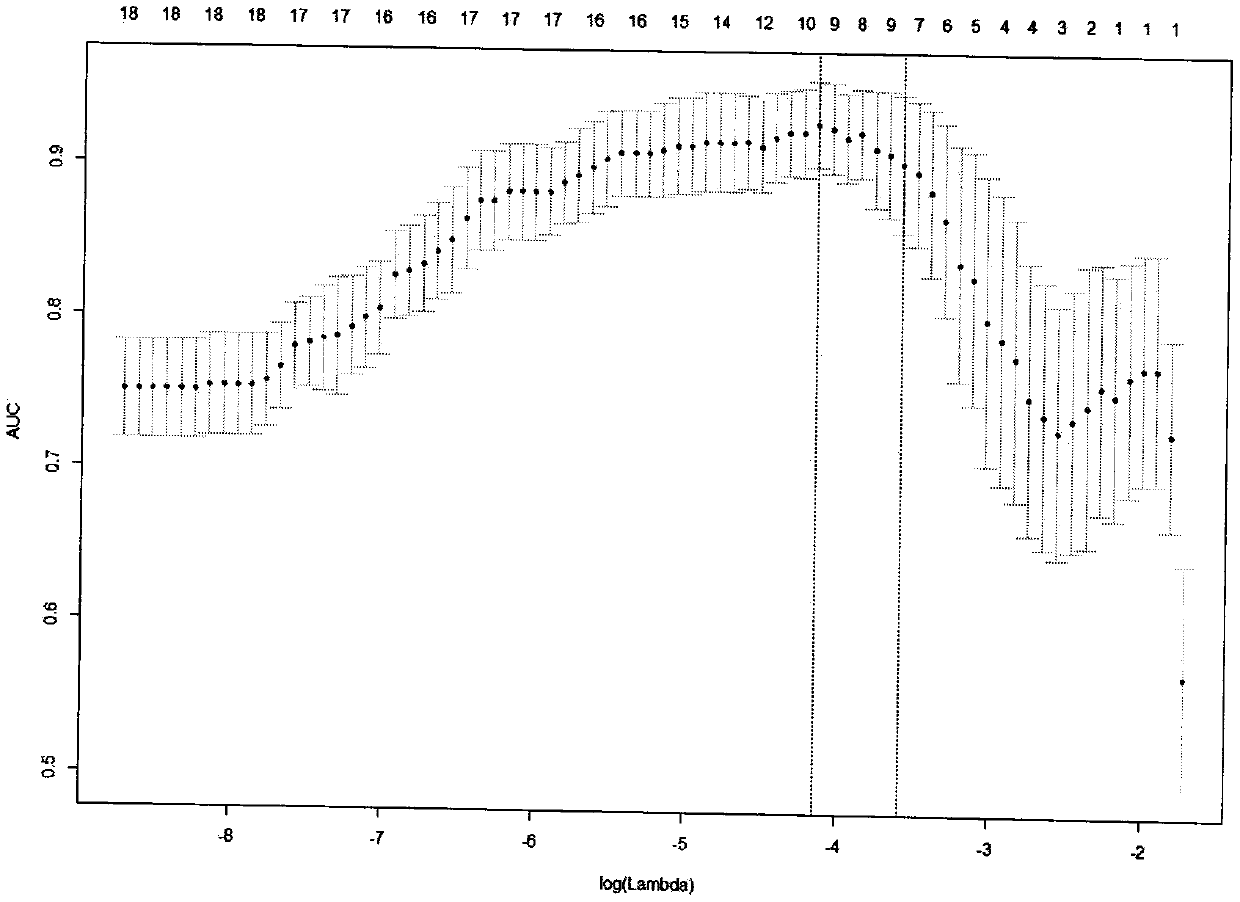
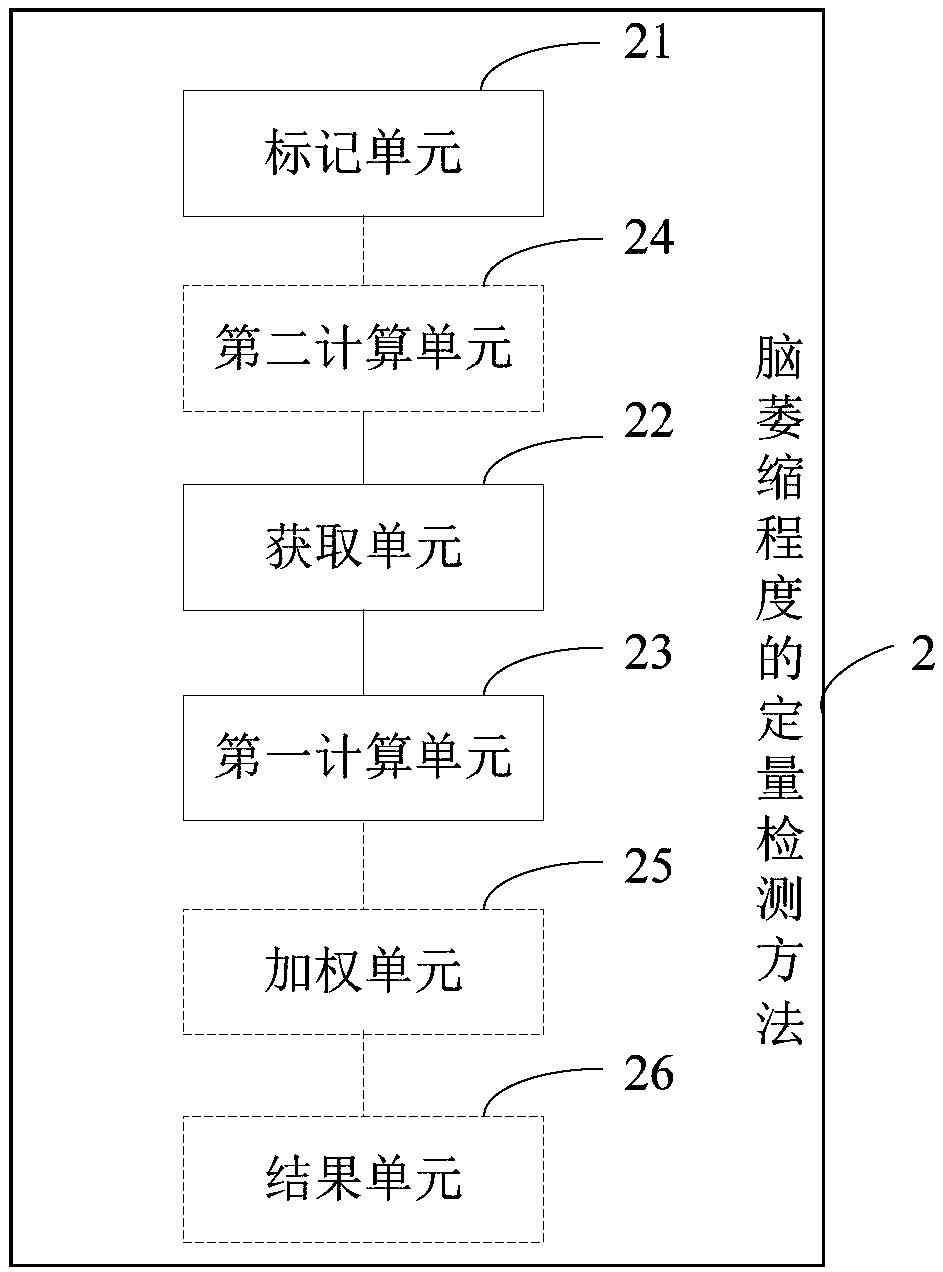
Quantitative detection method and detection device for encephalatrophy degree, and terminal device
The invention being applicable to the field of image processing technology, provides a quantitative detection method and detection device for the encephalatrophy degree, and a terminal device. THe method comprises: a first preset number of first template images and target quantity values of the first template images are obtained, wherein the target quantity values of the first template images aremarked as first target quantity values and the first template images are brain magnetic resonance images of brain healthy individuals at a preset age; a brain magnetic resonance of a to-be-tested individual is obtained, a to-be-tested image is obtained, a target quantity value of the to-be-tested image is calculated, and a second target quantity value is obtained; and according to the first targetquantity values, a percentile of the second target quantity value is calculated and an encephalatrophy degree of the o-be-tested individual is obtained. Therefore, the encephalatrophy degree is quantified and thus the encephalatrophy degree is evaluated effectively.
Owner:SHENZHEN BRAINNOW MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
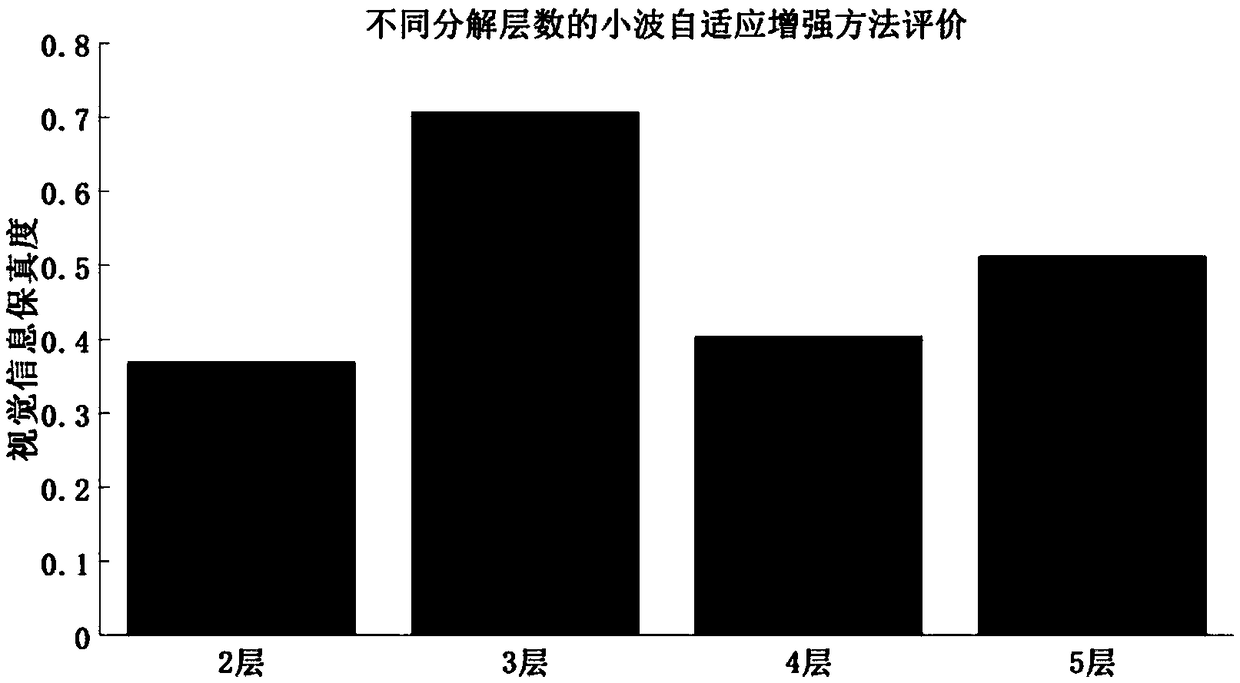
An adaptive enhancement method of brain magnetic resonance volumetric data based on transformed domain HMT model
The invention relates to an adaptive enhancement method of brain magnetic resonance volumetric data based on transformed domain HMT model , belonging to the field of medical image processing. The method organically combines wavelet transform and hidden Markov chain. According to the characteristics of non-Gaussian distribution with long tail and high peak value of the probability density functionof single wavelet coefficients, a Gaussian mixture model is established for the randomness of single wavelet coefficients. At the same time, the persistence of wavelet coefficients is described by Hidden Markov Tree (HMT). The wavelet domain Hidden Markov Tree model is established and the EM algorithm is used to solve the model. Using the solution of HMT model, the expectation of wavelet coefficients is estimated in the absence of noise. The inverse wavelet transform of the noise suppressed wavelet coefficients is used to obtain the enhanced MRI volume data. Through subjective and objective evaluation, the wavelet adaptive enhancement method has better visual information fidelity than wavelet threshold enhancement method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
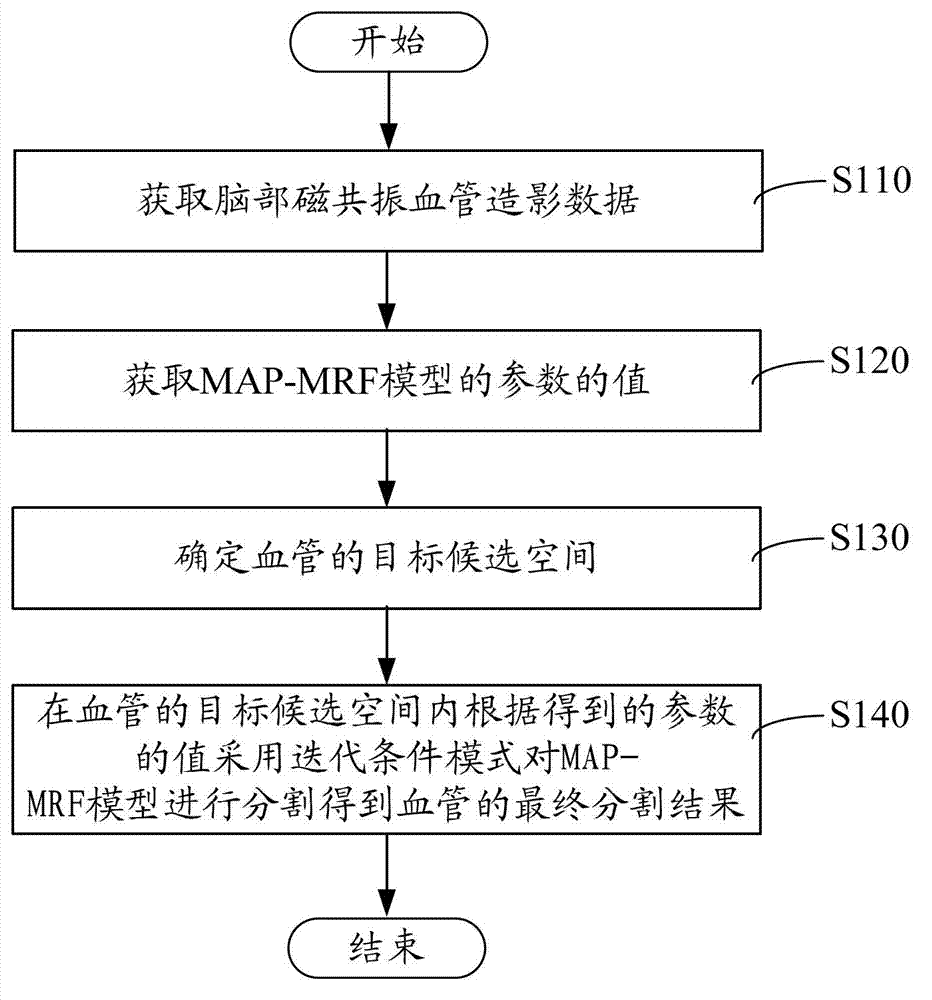
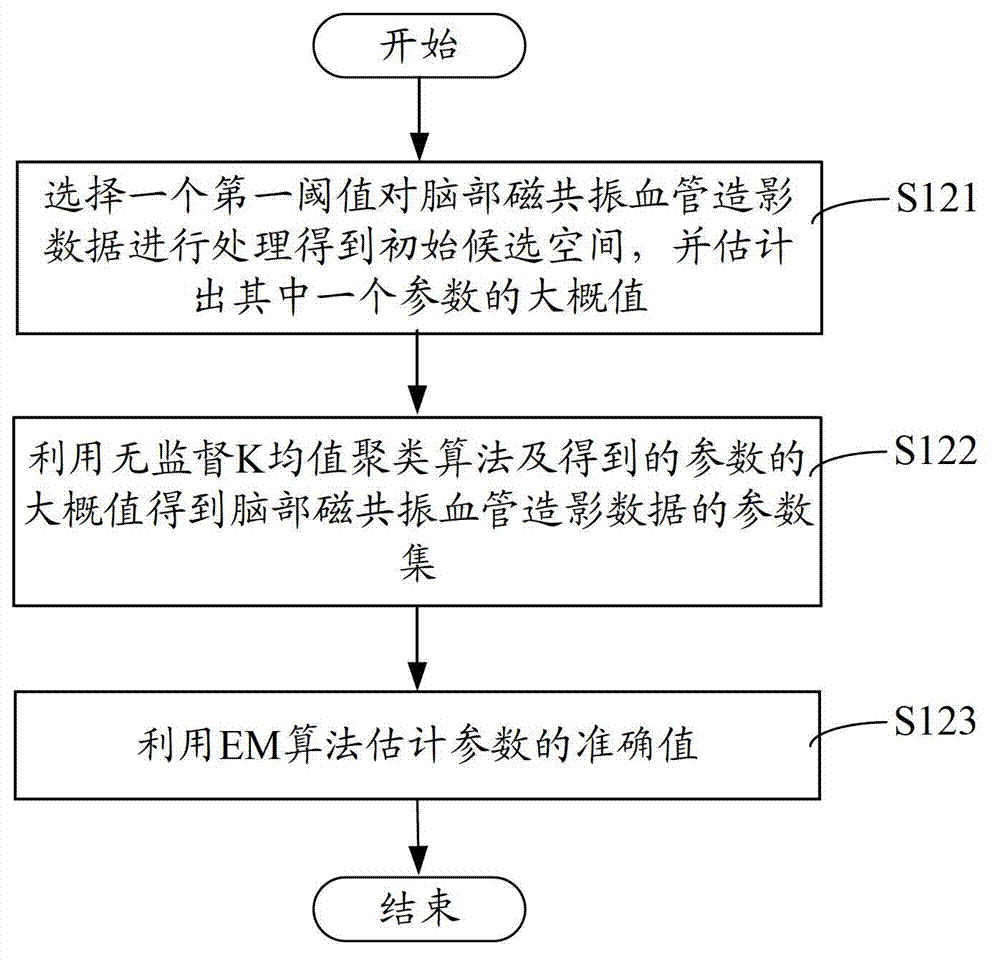
Method and device for dividing brain magnetic resonance angiography data
ActiveCN103049913AReduce computing timeQuick splitImage analysisIterated conditional modesBrain magnetic resonance
The invention provides a method and a device for dividing brain magnetic resonance angiography data. The method for dividing the brain magnetic resonance angiography data comprises the following steps of obtaining the brain magnetic resonance angiography data; obtaining values of parameters of an MAP-MRF (Maximum A Posteriori-Markov Random Field) model; determining target candidate space of a blood vessel; and dividing the MAF-MRF model in the target candidate space of the blood vessel according to the obtained values of the parameters by adopting an iterated conditional mode, and obtaining a final dividing result of the blood vessel. According to the method for dividing the brain magnetic resonance angiography data, disclosed by the invention, the dividing of the blood vessel is completed in the target candidate space, thus the calculating time is greatly reduced, and the brain blood vessel can be quickly divided.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
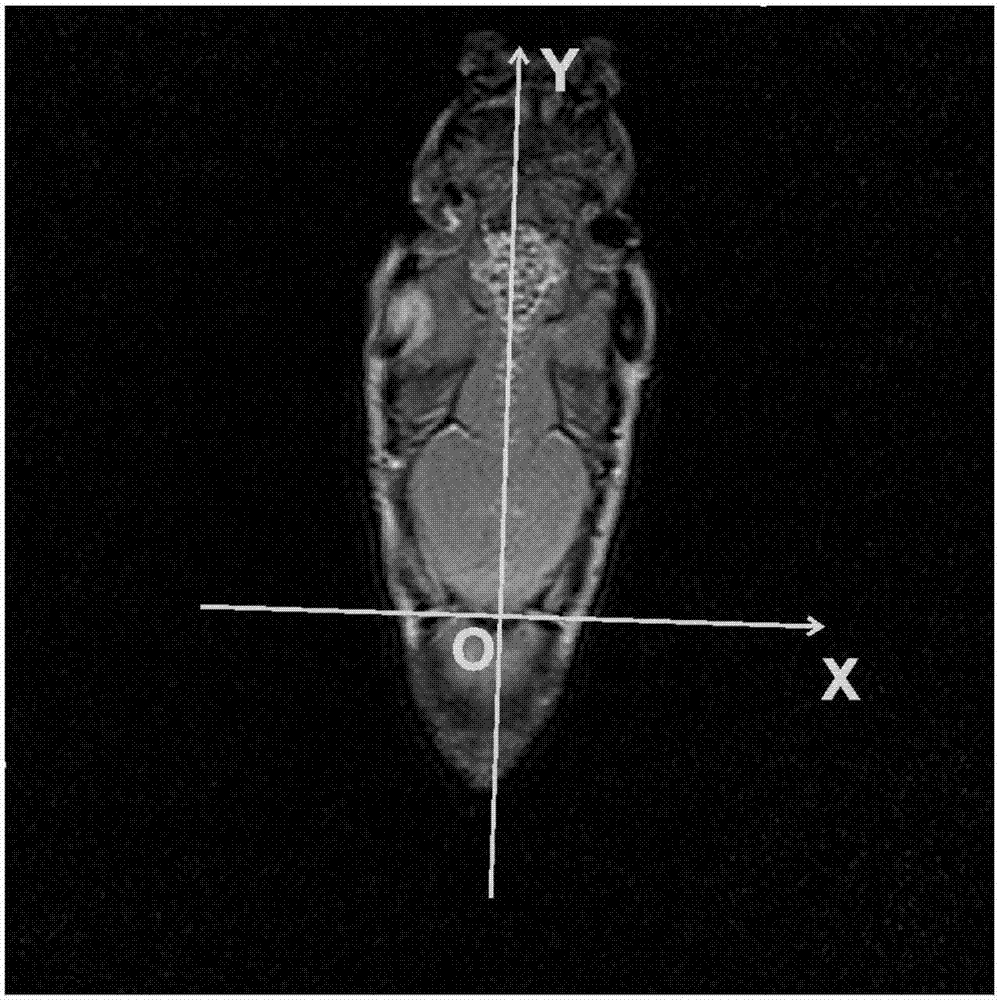
Carp brain electrode implantation method through magnetic-resonance positioning and navigation
InactiveCN106974653AAccurately obtain scale parametersReduce positioning errorsHead electrodesSensorsFast spin echoImplantable Stimulation Electrodes
The invention discloses a carp brain electrode implantation method by means of magnetic resonance positioning and navigation. Taking the first fish scale (the junction of the head and the trunk) as the origin, reference scratches are made on the surface of the skull based on the characteristics of the carp skull to establish Space coordinate system; with the help of the T2WI fast spin echo scanning sequence of the magnetic resonance equipment, the brain is scanned and imaged, the two-dimensional coordinates of the electrode stimulation site are converted into three-dimensional space coordinates, and the spatial coordinates of the brain stimulation electrode implantation site are determined The coordinate value of the system; according to the coordinate value, the brain stimulation electrode is implanted for positioning and navigation. The invention can not only locate and navigate for the implantation of the carp aquatic animal robot brain stimulation electrodes, but also provide new positioning and navigation means for the implantation of various animal robot brain stimulation electrodes.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
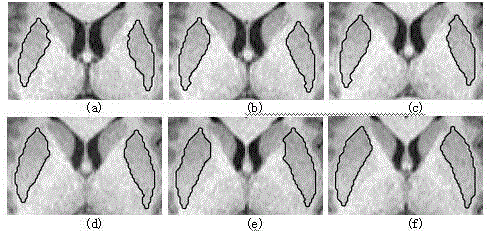
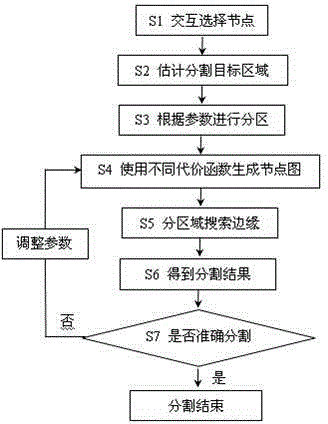
Interactive segmentation method applied to magnetic resonance image putamen
InactiveCN104103071AAccurate segmentationHigh precisionImage analysisImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides an interactive segmentation method applied to magnetic resonance image putamen, and belongs to the field of image processing. According to the method, interactive operation is guided for setting a source node and a target node, further, a target region to be segmented is speculated, and a method of reducing the node number is used for generating a node map for a target region of an image to be segmented; cost functions corresponding to different regions and directions are used on the node map, and a weighted directed map is generated for the target region; and a shortest path optimizing method is used for finding two shortest paths from the source node to the target node in the weighted directed map, and a closed profile is formed for completing the segmentation. The interactive segmentation method has the advantages that various strategies are adopted for designing the cost functions; the shortest path searching range is restrained; and the segmentation of the brain magnetic resonance image putamen region can be accurate, fast and stable through reducing the node number and guiding the interactive operation.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
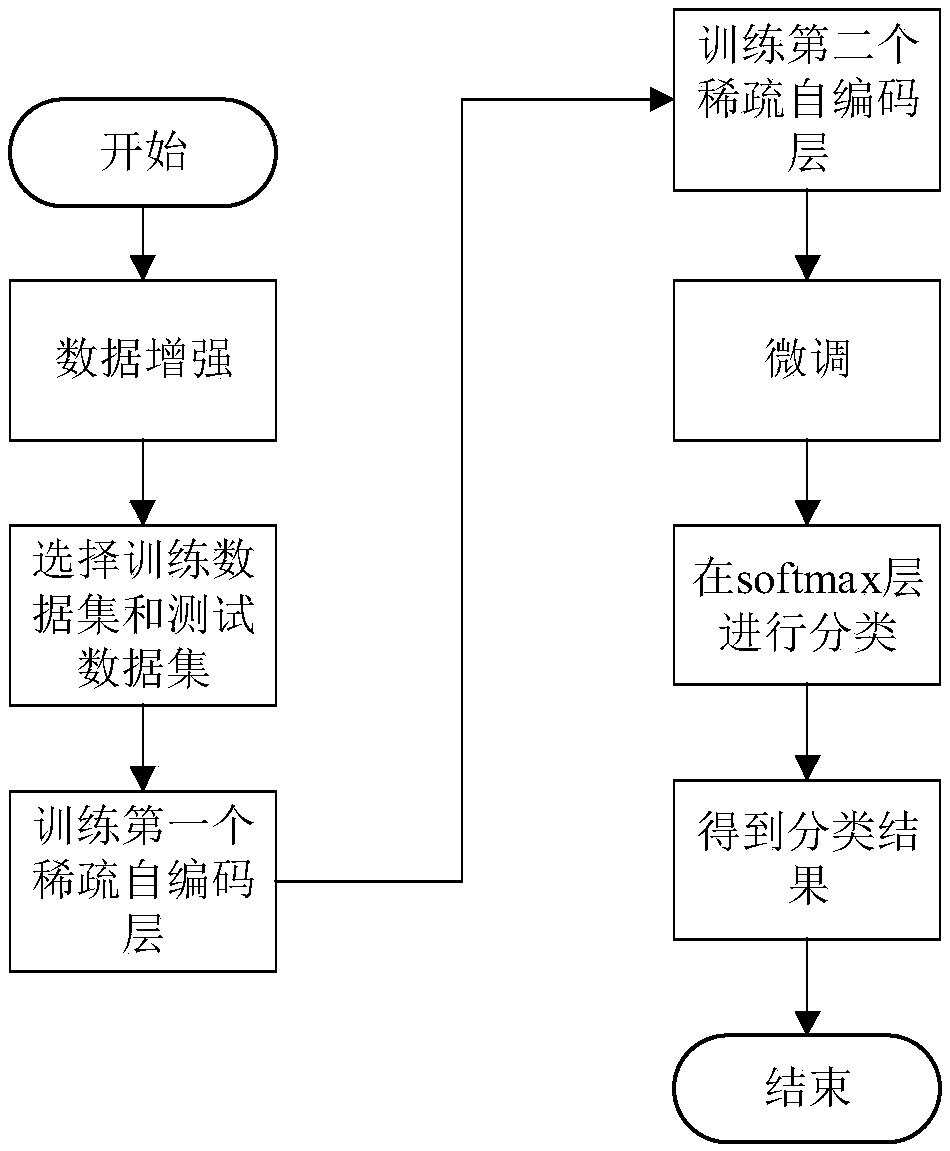
Pathological brain image classification method based on deep stacked sparse autoencoder
InactiveCN108537233AAccurate classificationHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDiseaseBrain magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a pathological brain image classification method based on a deep stacked sparse autoencoder, comprising the following steps of: 1. downloading different types of pathological brain magnetic resonance images, including normal brain images and pathological brain images, from the website of Harvard medical college; 2, using a data enhancement method to increase the number of images in order to balance the data distribution; 3, using the method of deep stacked sparse autoencoder to automatically extract the characteristics of the input image, accurately classifying the image by a Softmax classifier to otbain different disease types 4, training the entire network by a batch conjugate gradient method, and in a fine-adjusting stage, using a scaled conjugate gradient methodto fine adjust the network. The method avoids the loss of some characteristic information. Compared with the traditional method just capable of achieving two classifications of the diseased brain images, the method can accurately obtain the effective classifications of different types of diseases, significantly reduces the doctors' workload, and has a practical application value.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional brain magnetic resonance image brain cortex surface maximum principal direction field diffusion method
InactiveCN101866485AGeometrically preciseExact topologyImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringDifferential coefficientDiffusion methods
The invention relates to a three-dimensional brain magnetic resonance image brain cortex surface maximum principal direction field diffusion method, which has the technical scheme that the method comprises the following steps: carrying out pretreatment and brain cortex surface reconstruction on three-dimensional brain magnetic resonance images; calculating the principal curvature, the principal direction and the differential coefficient of the principal curvature of a peak on the brain cortex surface; using an alpha-expanon graph cut method for minimizing an energy function to carry out diffusion on the maximum principal direction field; and projecting the diffused maximum principal direction field into a tangent plane. The invention has the advantages that: 1. the method sets the weights of smooth items and data items in different regions on the brain cortex surface into different values, so the inherent geometrical structure and discontinuity in the maximum principal direction field can be perfectly maintained; and 2. the principal direction field diffusion is regarded as an energy minimization problem which is converted into a diffusion marking problem, and the alpha-expanon graph cut method can be used for effectively working out the strong local optimum solution of the energy function.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUANGNENG SOLAR ENERGY +1
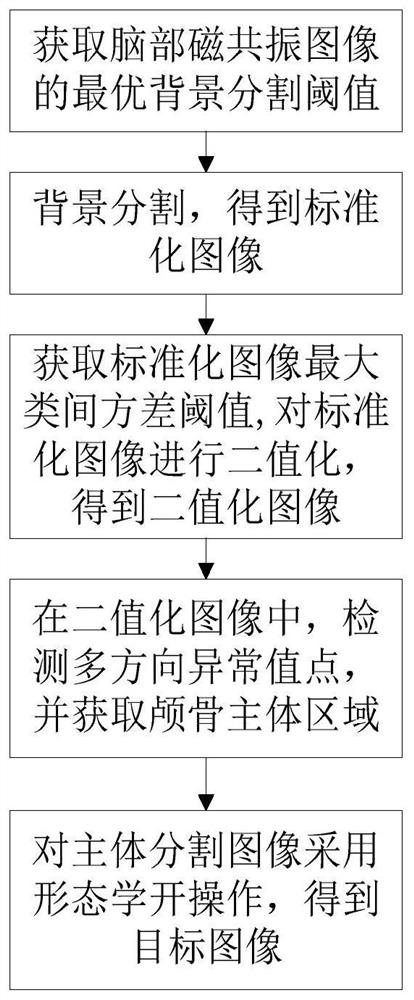
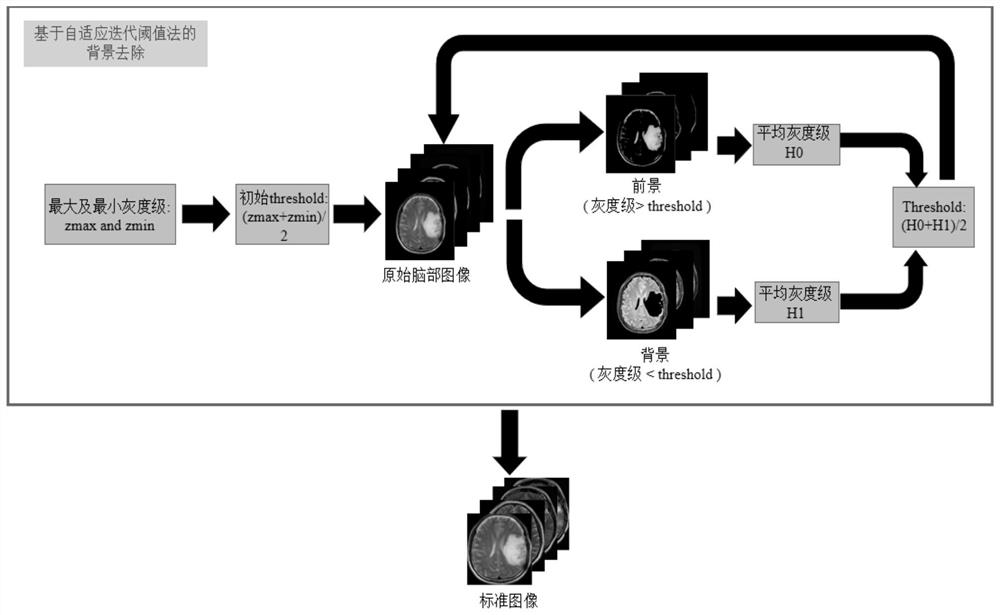
Automatic skull removal method for brain magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN111612793AReduce time complexityCalculation speedImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyBrain magnetic resonance
The invention relates to an automatic skull removal method for a brain magnetic resonance image. The method comprises: obtaining an optimal background segmentation threshold of the brain magnetic resonance image through an adaptive iterative threshold method; performing background segmentation on the brain magnetic resonance image according to the optimal background segmentation threshold to obtain a standardized image; obtaining a maximum inter-class variance threshold of the standardized image through an OSTU threshold method, and binarizing the standardized image according to the maximum inter-class variance threshold to obtain a binarized image; in the binarized image, detecting multi-directional abnormal value points, and obtaining a skull main body area; in the standardized image, assigning 0 to the pixels of the skull main body area to obtain a main body segmentation image; and performing morphological opening operation on the main body segmentation image to obtain a target image. According to the invention, the efficiency of a traditional semi-automatic method is effectively improved, and convenience is provided for operations such as automatic identification and image fusion of brain magnetic resonance images.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cynomolgus monkey magnetic resonance scanning method
InactiveCN101361659AClear MRI imagesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnatomical structuresVisual field loss
The invention aims at improving cynomolgus magnetic resonance scanning methods and consequently providing legible brain magnetic resonance images. The invention provides a cynomolgus magnetic resonance scanning method that utilizes a Philips Intera A chiva 3.0T magnetic resonance machine for scanning, a T1 scanning sequence is IR with the visual field of 120mm, the TR / TE of 2153ms / 13ms, the seam thickness / interval of 3mm / 0.3mm and the matrix of 256 multiplied by 256, while a T2 weighted image scanning sequence is SE with the visual field of 12cm multiplied by 12cm, the TR / TE of 3200ms / 102ms, the seam thickness / interval of 3mm / 0.3mm and the matrix of 256 multiplied by 256. The cynomolgus magnetic resonance scanning method can provide legible brain magnetic resonance images, and has greater significance in the displaying of cynomolgus craniocerebral anatomical structure and cytological marking and magnetic resonance tracing after brain transplantation.
Owner:王任直 +3
Transcranial magnetic stimulation target positioning method
ActiveCN107812313ALower requirementThe method is simple and fastElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSkin surfaceResonance
The invention relates to the field of medical detection, and specifically relates to a transcranial magnetic stimulation target positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: (1), obtaining a craniocerebral magnetic resonance scanning image of a patient; (2), finding a nearest projection pint of an intracerebral to-be-stimulated region on head skin from the image through calculationbased on the magnetic resonance image, wherein the nearest projection pint is called as a head skin target; (3), calculating the nearest distances between at least three mark points on the face of the patient and the head skin target on the head skin surface in the image based on the magnetic resonance image; (4), enabling a flexible rule to take each mark point as the circle center and take thedistance between each mark point and the head skin target as the radius for drawing a circle on the head skin, wherein the intersection point of the circles is the head skin target. The method mainlydepends on the calculation of the cambered surface distance of each mark point on the transcranial magnetic resonance image, so the method is simple and convenient, does not need large-scale equipment, and exerts low requirements for a treatment place. Moreover, compared with a navigation system, the method greatly reduces the cost.
Owner:安徽安壹心理咨询有限公司
Skull image segmentation method based on deep iterative fusion deep learning model
PendingCN112288749AImprove accuracyImprove generalization abilityImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationTest set
The invention discloses a skull image segmentation method based on a deep iterative fusion deep learning model. The method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting a brain magnetic resonance image to be segmented and preprocessing the brain magnetic resonance image; 2, randomly selecting a training set and a test set for the preprocessed brain magnetic resonance image; 3, constructing a deepiterative fusion learning model, wherein the model comprises a convolution module, a residual module and an up-sampling module; 4, performing internal data enhancement on the training set, wherein theinternal data enhancement comprises random scaling and random clipping; and 5, training a model by using the data after data enhancement, and finally testing the test set by using the trained model,so that skull segmentation can be performed on the brain magnetic resonance image. According to the characteristics of strong automatic learning and feature extraction capabilities of the convolutional neural network, a deep iterative fusion model is designed, so that the model has relatively high generalization capability and relatively high segmentation precision on a plurality of data, and a very good effect is achieved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
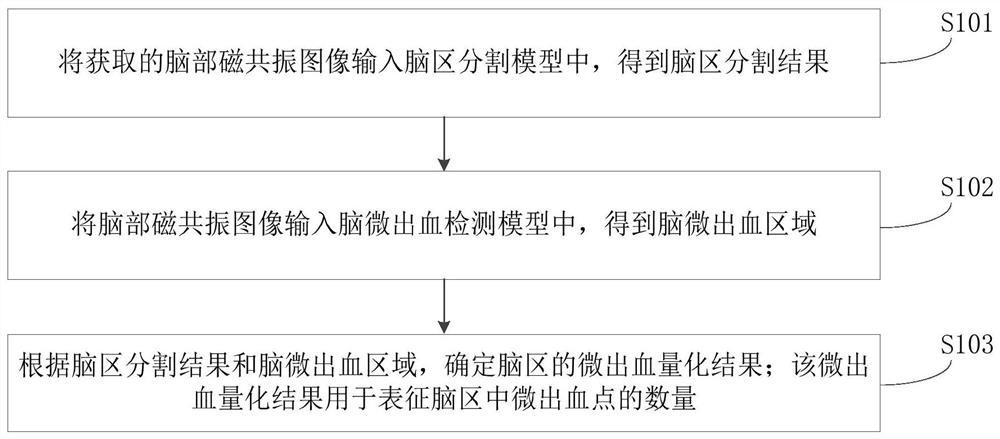
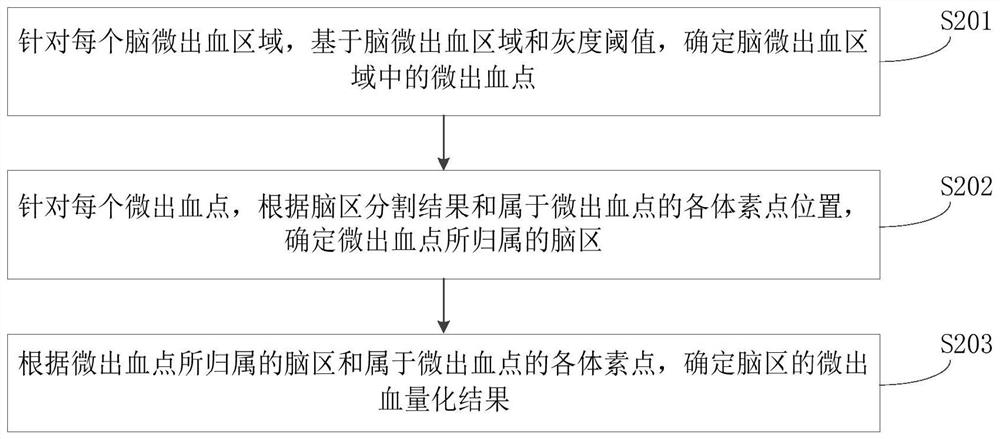
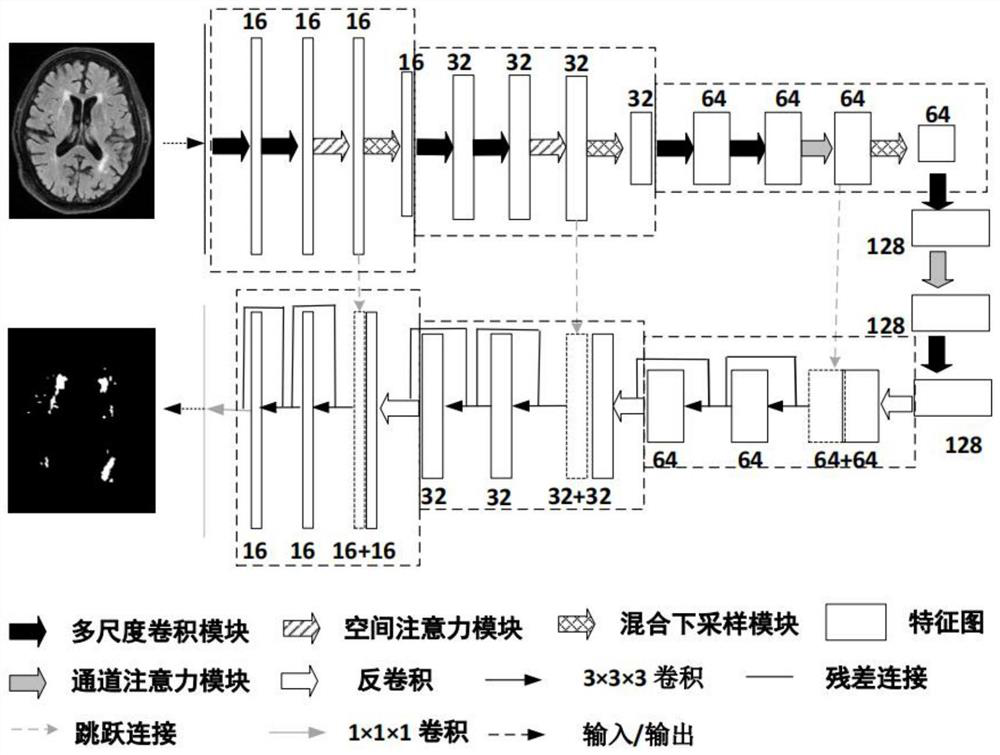
Cerebral microhemorrhage quantification method and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN111640095AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyBrain magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a cerebral microhemorrhage quantification method and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: inputting an acquired brain magnetic resonance image into a brain region segmentation model to obtain a brain region segmentation result; inputting the brain magnetic resonance image into a cerebral microhemorrhage detection model to obtain a cerebral microhemorrhage area; determining a micro-hemorrhage quantification result of the brain area according to the brain area segmentation result and the brain micro-hemorrhage area; wherein the microhemorrhage quantification result is used for representing the number of microhemorrhage points in the brain area. According to the method, the microhemorrhage quantification result of the brain area is obtained through automatic processing of computer equipment, human participation is not needed, and the efficiency of the cerebral microhemorrhage quantification process is greatly improved; moreover, the neural network model is adopted to segment and detect the brain magnetic resonance image so as to obtain the micro-bleeding quantification result of the brain area, and the accuracy of the quantification result is further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for estimating white matter fiber direction through diffusion magnetic resonance images
InactiveCN103413315AImprove angular resolutionImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberDiffusion
The invention discloses a method for estimating the white matter fiber direction through diffusion magnetic resonance images. The method comprises the following steps of S1, reading a plurality of brain diffusion magnetic resonance images, S2, carrying out calculation of the radial direction part and the angle part of OPDF on the brain magnetic resonance images through an OPDT model, S3, building an iOPDT model according to the OPDF of the OPDT model, wherein the radial direction part of the iOPDT model is an average value of the integral of the radial direction part of the OPDT model on a sphere, and the angle part of the iOPDT model is the angle part of the OPDT model, and S4, substituting diffusion fading signals of the read diffusion magnetic resonance images to the iOPDT model to obtain values of the OPDF in any direction of the sphere. According to the method, through the improved OPDT model, the angular resolution of white matter fiber direction estimation is improved, and therefore the ability of distinguishing white matter fiber crossing is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
White matter high-signal segmentation method based on multi-scale fusion and attention splitting
PendingCN114119637AImprove Segmentation AccuracyEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
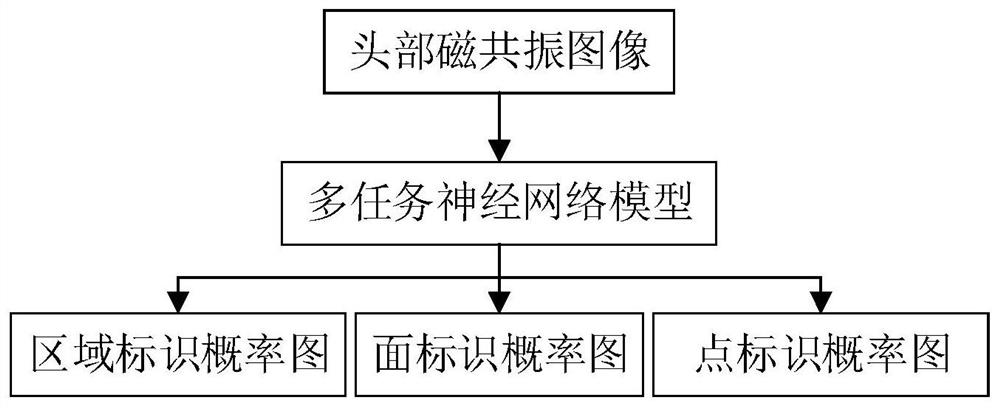
Brain identification extraction method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112950600AEasy extractionSimplify InteractionImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionAlgorithm
The invention relates to a brain identification extraction method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: inputting a brain magnetic resonance image of a target subject into a preset neural network model, obtaining a point identification probability graph, a surface identification probability graph and a region identification probability graph of the brain magnetic resonance image, and according to the point identification probability graph, determining a point identifier of the brain of the target subject; determining a face identifier of the brain of the target subject according to the face identifier probability graph; determining a region identifier of the brain of the target subject according to the region identifier probability graph; and constructing a brain coordinate system according to the point identifier and the surface identifier, and then determining other identifiers of the brain of the target subject according to one or more information in the point identifier, the surface identifier, the region identifier and the brain coordinate system. The brain feature extraction process is greatly simplified, and the brain identification structure is efficiently and accurately extracted.
Owner:WUHAN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE SURGICAL TECH CO LTD
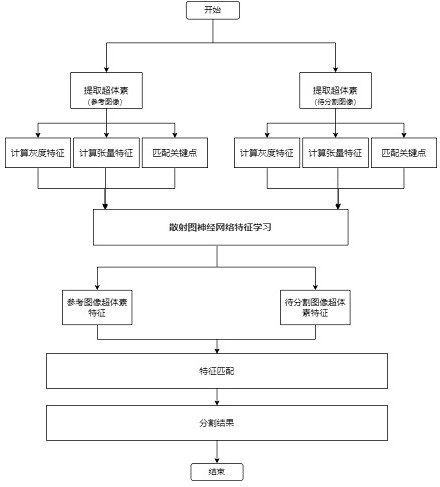
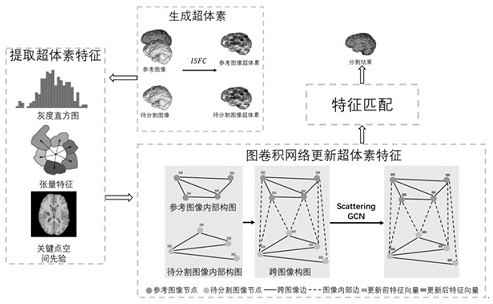
Brain magnetic resonance image segmentation method based on scattering graph neural network
PendingCN114581451AReduce labeling costsImprove segmentation efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelComputation complexity
The invention discloses a brain magnetic resonance image segmentation method based on a scattering graph neural network, and the method comprises the steps: employing super voxels as basic units, and generating the same number of super voxels for a reference image and a to-be-segmented image, so as to reduce the calculation complexity of a model; meanwhile, considering self information, surrounding neighbor information and spatial position information of the super voxels, and pre-extracting gray features, tensor features and key point spatial prior features of the super voxels; thirdly, due to the fact that certain topological structure information is implied among the super voxels of the brain, the super voxels serve as nodes to construct a topological graph, a scattering graph neural network is adopted to learn global topological information, and node features are updated; finally, feature matching is directly conducted on the super voxels of the image to be segmented and the super voxels of the marked reference image, a semantic segmentation result is obtained, the method can be well applied to the brain magnetic resonance image, and the tissue structure of the brain magnetic resonance image is effectively segmented.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
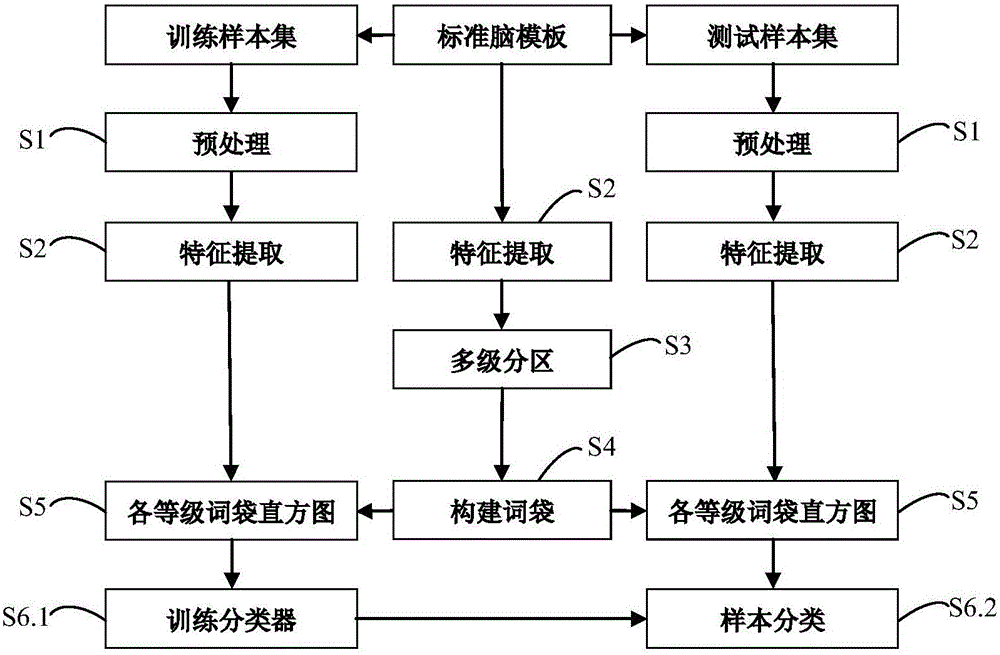
Brain disease identification method based on multistage partition bag-of-words model
ActiveCN105787494ARealize identificationRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsTest sampleResonance
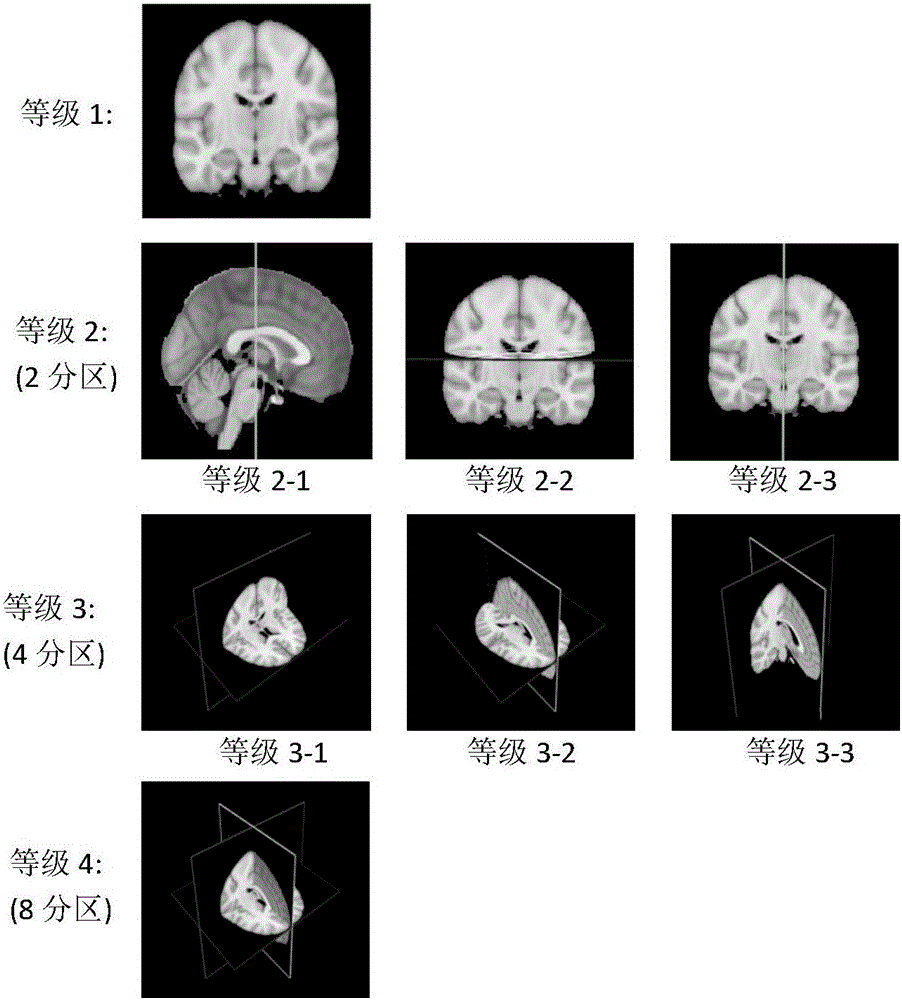
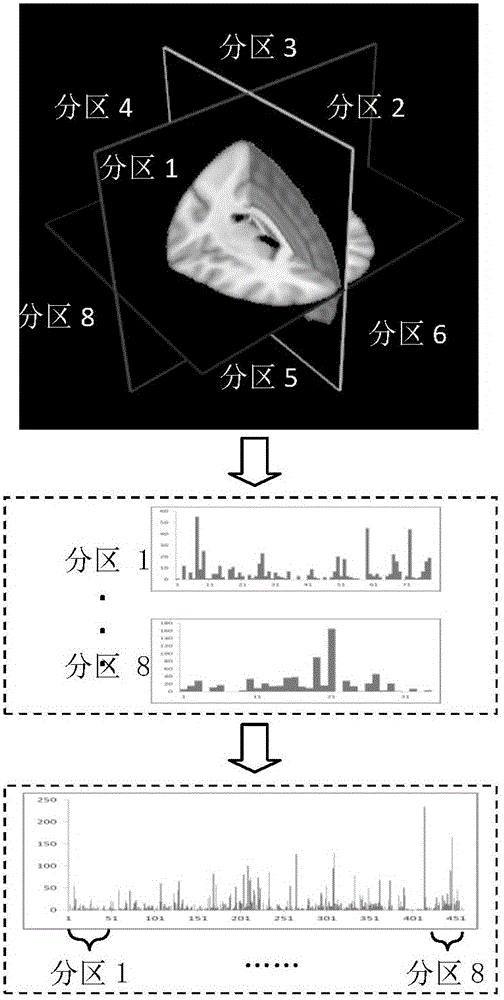
The invention discloses a brain disease identification method based on a multistage partition bag-of-words model. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing brain magnetic resonance structure images of each sample in a training sample set and a test sample set; next, based on a standard brain template, two-dimensional magnetic resonance structure images of each sample of the training sample set and each sample of the test sample set, respectively extracting structural features; then, performing multistage brain partition on the standard brain template; for the structural features of the standard template, respectively constructing a partition bag of words in each partition by use of a supervision-free clustering method; then, by use of the partition bags of words of each grade, constructing a bag-of-words histogram of each grade of each sample; and finally, by use of the bag-of-words histograms of each grade, establishing a multistage classifier for classifying the test samples so as to realize brain disease identification. The brain magnetic resonance structure image classification method based on the multistage partition bag-of-words model, provided by the embodiment of the invention, carries out disease identification and individual attribute determining and provides assistance for brain disease clinic analysis diagnosis.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
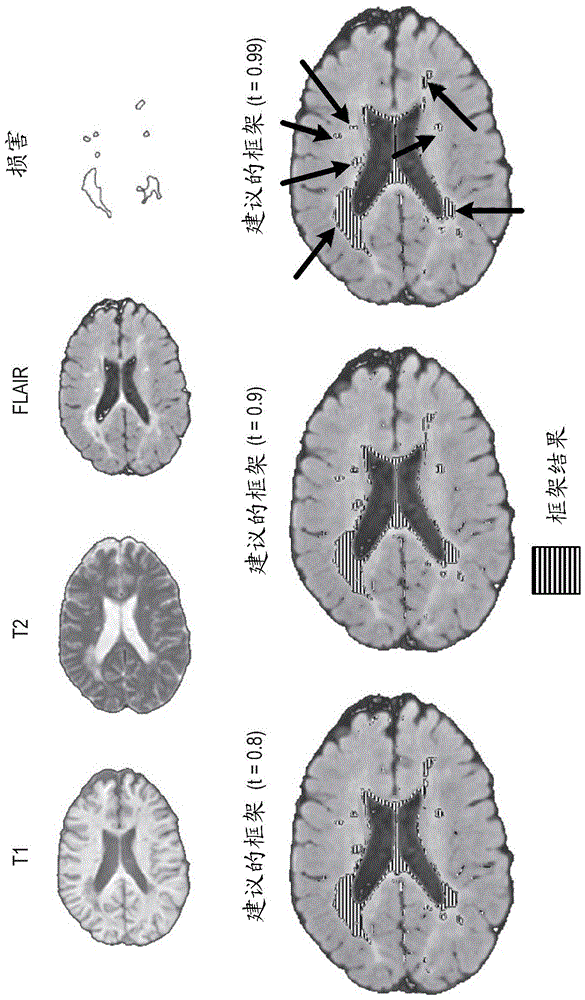
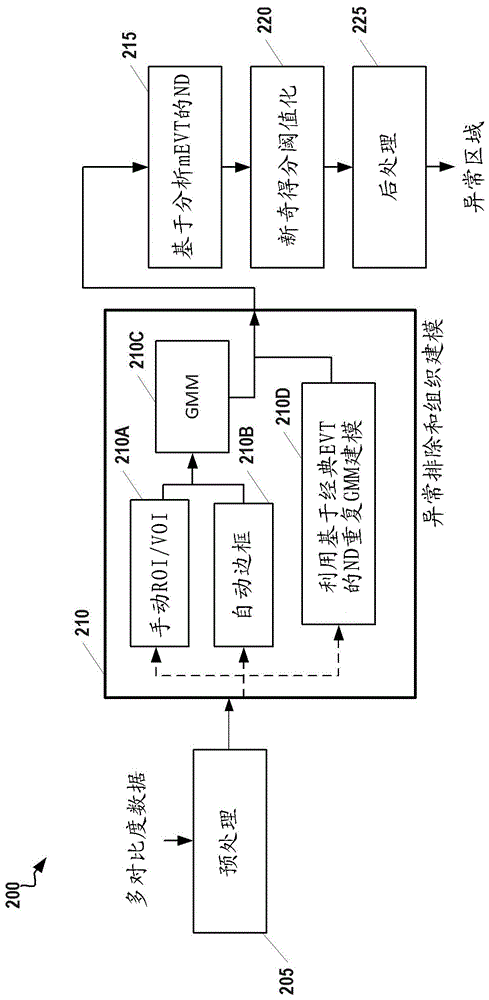
Framework for Abnormality Detection in Multi-Contrast Brain Magnetic Resonance Data
A computer-implemented method for identifying abnormalities in Magnetic Resonance (MR) brain image data includes a computer receiving multi-contrast MR image data of a subject's brain and identifying, within the multi-contrast MR image data, (i) an abnormality region comprising one or more suspected abnormalities and (ii) a healthy region comprising healthy tissue. The computer creates a model of the healthy region, computes a novelty score for each voxel in the multi-contrast MR image data based on the abnormality region and the model, and creates an abnormality map of the subject's brain based on the novelty score computed for each voxel in the multi-contrast MR image data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com