Patents
Literature
76 results about "Potential biomarkers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cumulating data suggest that small noncoding-RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) can be utilized as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of a variety of diseases such as cancer, neurological disorders, cardiovascular disease and Type-II diabetes, etc.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain disease individual prediction method and system
InactiveCN106156484AImprove generalizationRapid Quantification and Precise PredictionMedical data miningSpecial data processing applicationsReduction treatmentPredictive methods
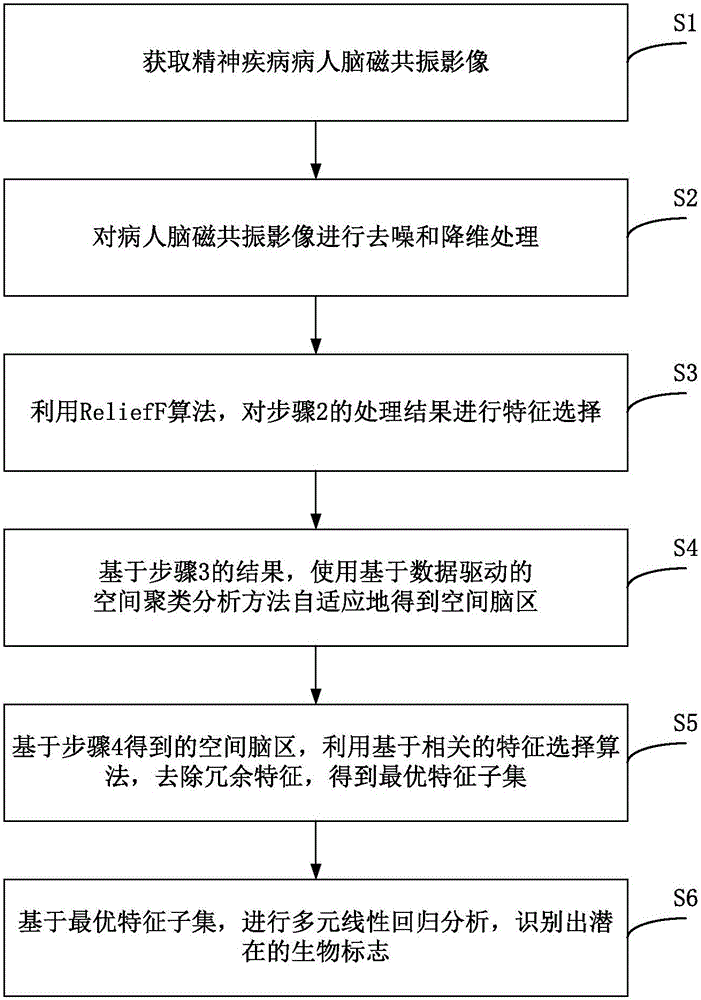
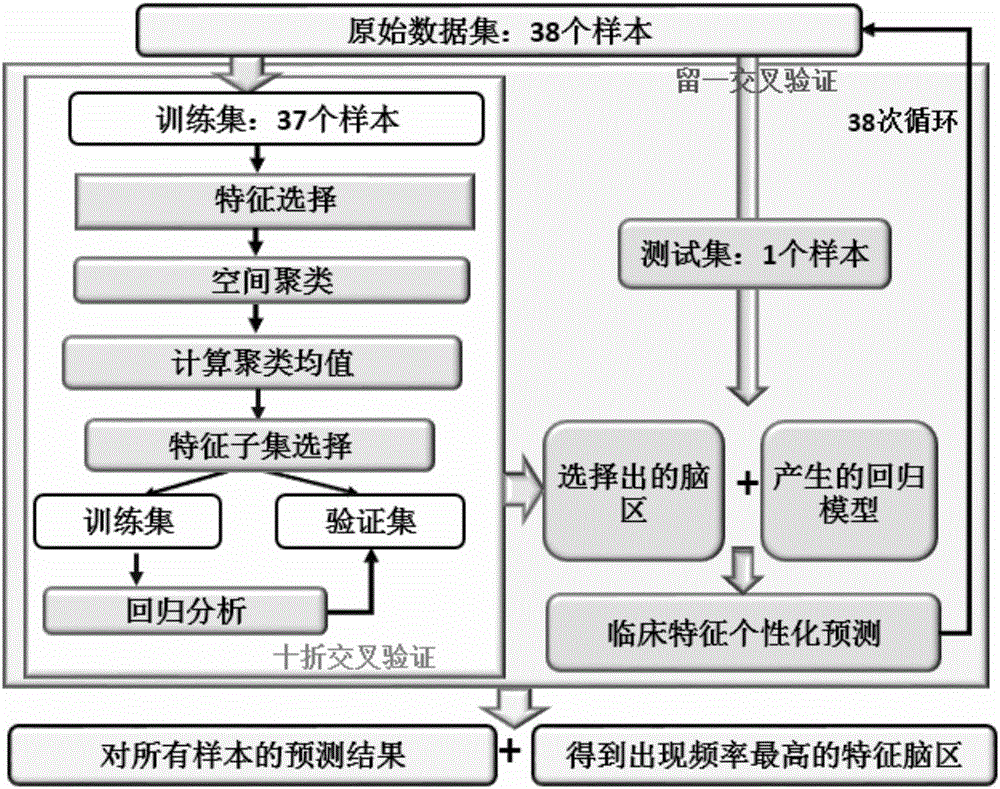
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain disease individual prediction method and a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based brain disease individual prediction system. The method comprises the following steps: 1: obtaining the MRI of the brain of a patient with mental diseases; 2: carrying out denoising and dimension reduction treatment on the MRI of the brain of the patient; 3: carrying out feature selection by utilizing a ReliefF algorithm; 4: adaptively obtaining a spatial brain area by using a spatial cluster analysis method; 5: removing redundant features by utilizing a correlation-based feature selection algorithm, thus obtaining an optimal feature subset; 6: carrying out multiple linear regression analysis based on the optimal feature subset to recognize potential biomarkers. The method has the beneficial effects that the embodiment of the invention integrates various machine learning methods and can rapidly and conveniently achieve quantitative and individual accurate prediction of the interest features of mental diseases, such as clinical indexes, based on various image data in different mode types, thus being beneficial to understanding the brain structures, function abnormity and potential pathogenesis of the diseases.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
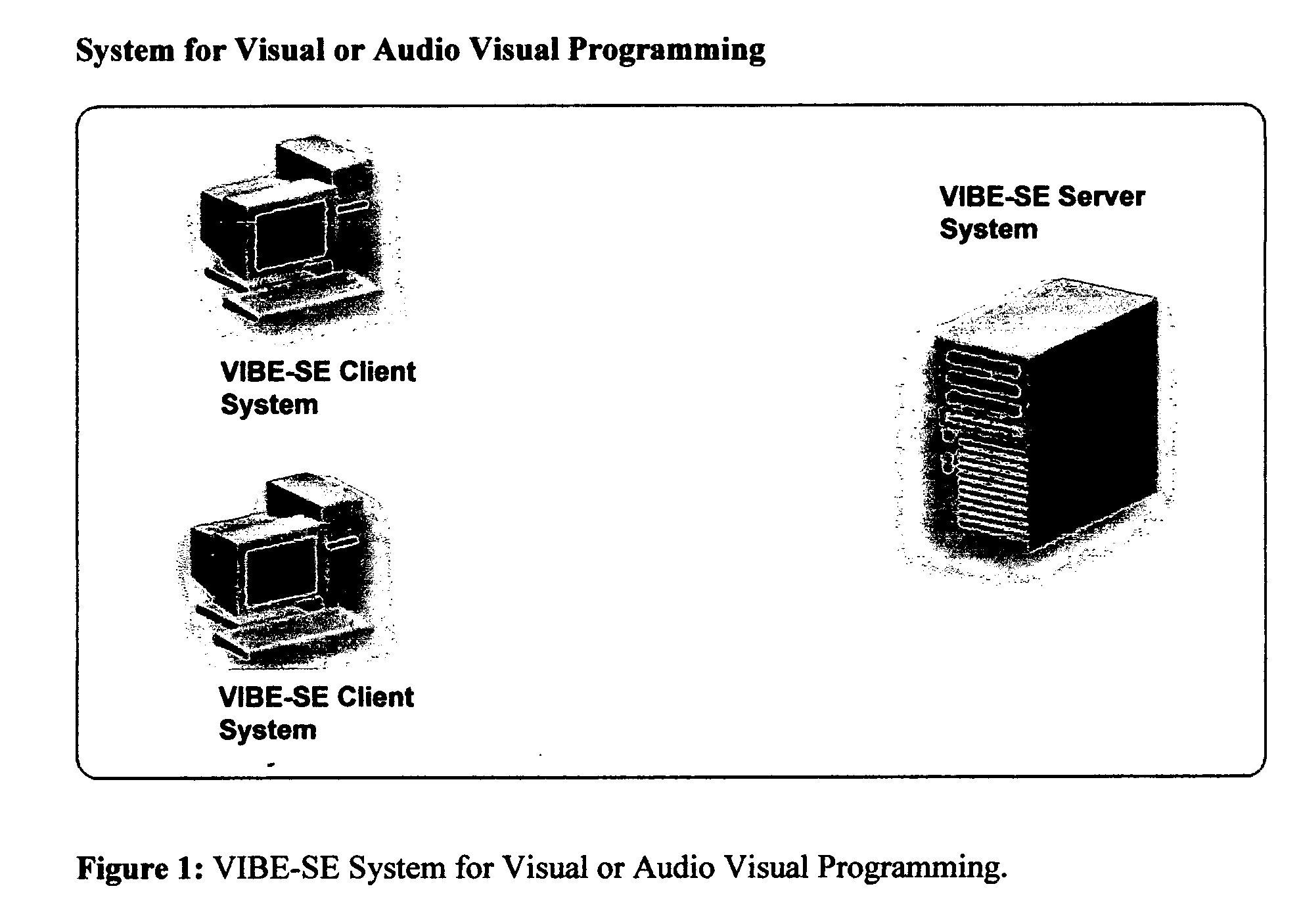
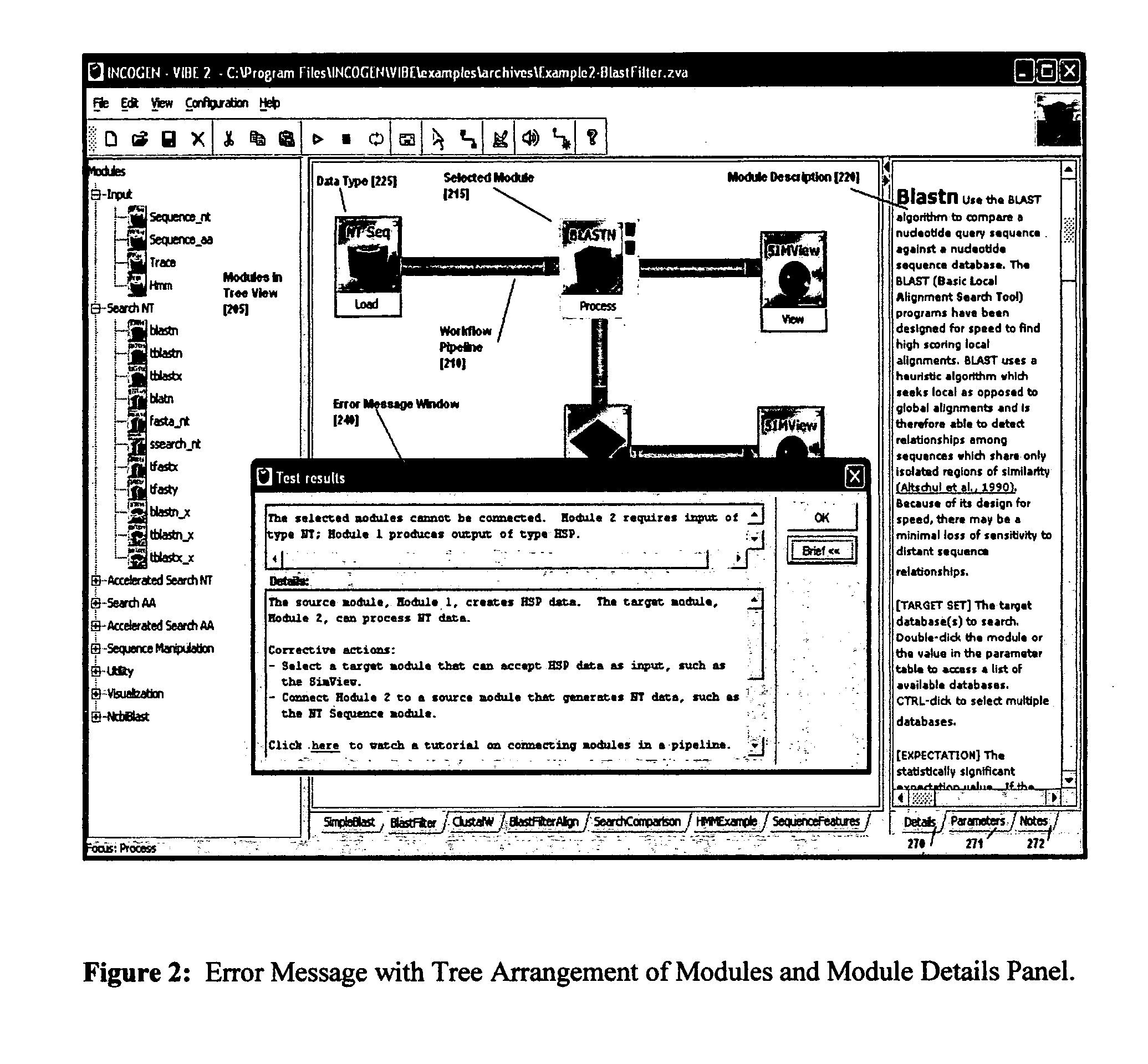
System and method using a visual or audio-visual programming environment to enable and optimize systems-level research in life sciences
InactiveUS20060190184A1Enabling and optimizing systems-level researchEnhances with user-level extensibilityData visualisationBiological testingAnalysis dataProteomic Profile
The current invention provides a visual or audio-visual programming environment for life science and bioinformatics. It is based on the VIBE platform, which is a flexible, extensible, and integrated workflow construction and management platform. The current invention enables researchers to consolidate molecular profiling data from complementary experimental techniques, intelligently reduce the volume of the data, construct disease-specific molecular fingerprints, construct relationship networks among functionally significant genomic, transcriptomic, metabonomic, and proteomic data, integrate information from existing biological databases into those networks, optimize the process through iterative feedback loops, and to generate and validate hypotheses based on the above process. The uses of this integrative, systems-based approach include, but are not limited to, the identification of potential biomarkers, characterization and classification of diseases and pathogens, and discovery of drug targets.
Owner:INCOGEN
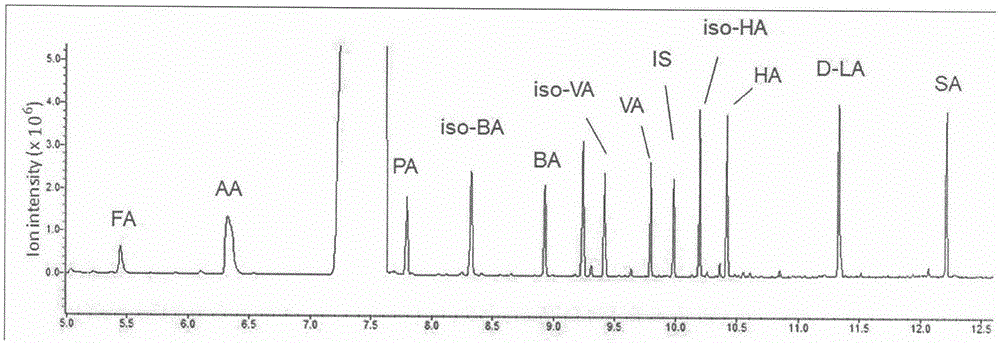
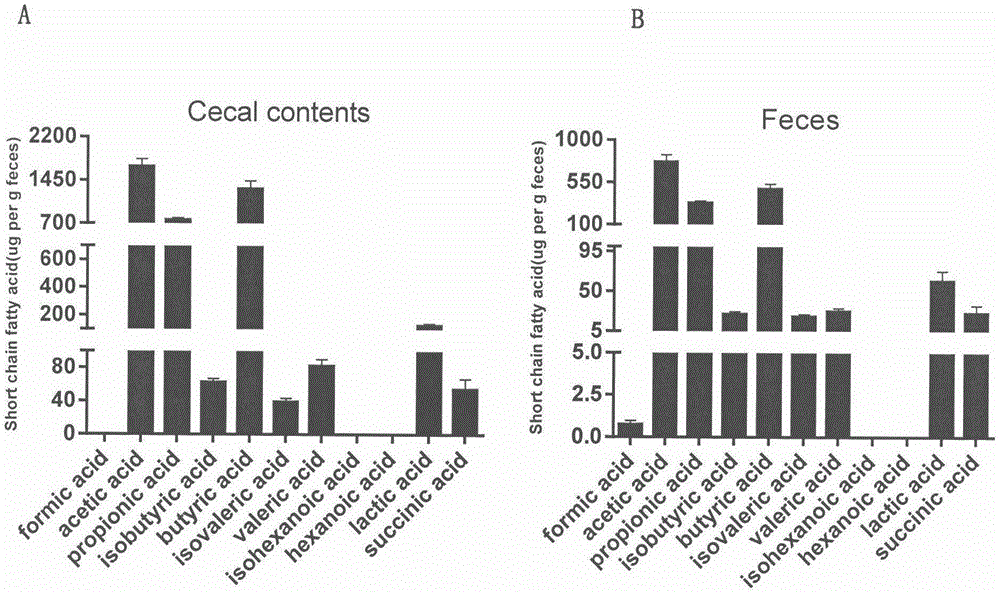
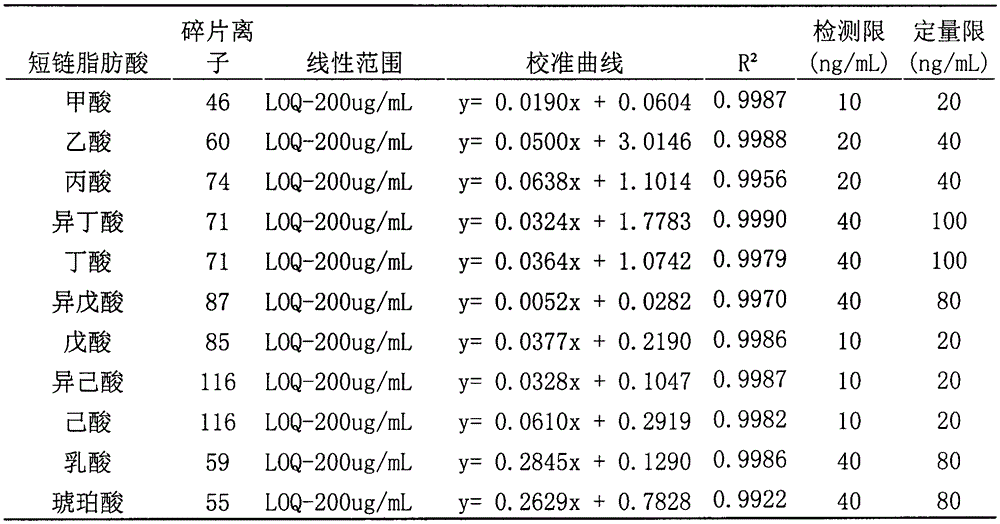
GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometer)-based method for quantifying eleven types of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal contents and fecal samples
InactiveCN105651908AHigh extraction recoveryImprove securityComponent separationGas phasePotential biomarkers
The invention belongs to the technical field of endogenous substance detection and discloses a GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometer)-based method for quantifying eleven types of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal contents and fecal samples. By adoption of a hydrochloric acid solution prepared from saturated salt water for acidification, high-stability ethyl acetate for extraction and N-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-N-methyl trifluoroacetamide MTBSTFA for derivatization, the eleven short-chain fatty acids in mouse intestinal contents and fecal samples are quantified by a gas chromatography-mass spectrometer. The method is high in accuracy and precision and low in detection limit, can be used for quantitative detection of eleven types of short-chain fatty acids and can meet detection requirements on determination of major short-chain fatty acids in the mouse intestinal contents and the fecal samples. Moreover, the method is conducive to analysis and comparison of metabolic disposition laws of the short-chain fatty acids under normal and enteritis conditions and observation whether changes of the short-chain fatty acids can represent dynamic conditions of enteritis or not, thereby providing significant bases for potential biomarkers under the enteritis condition.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
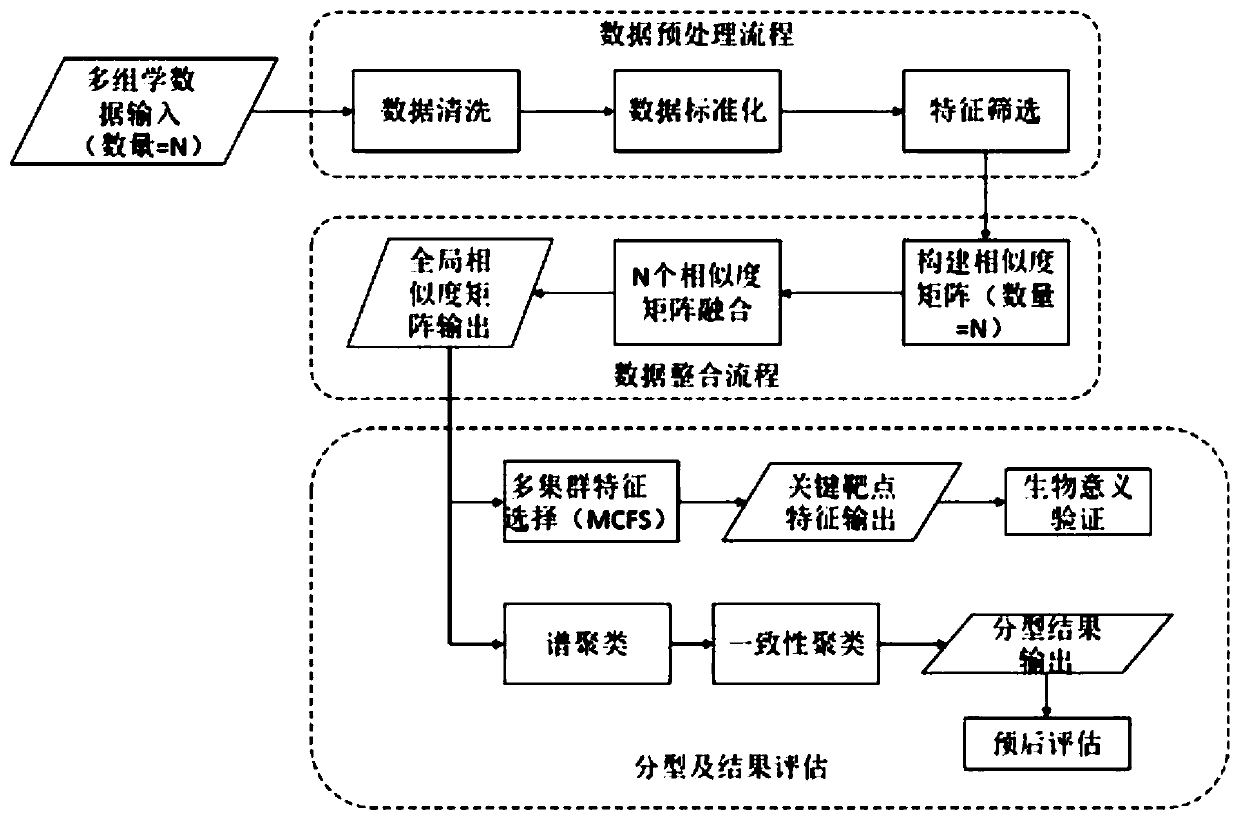
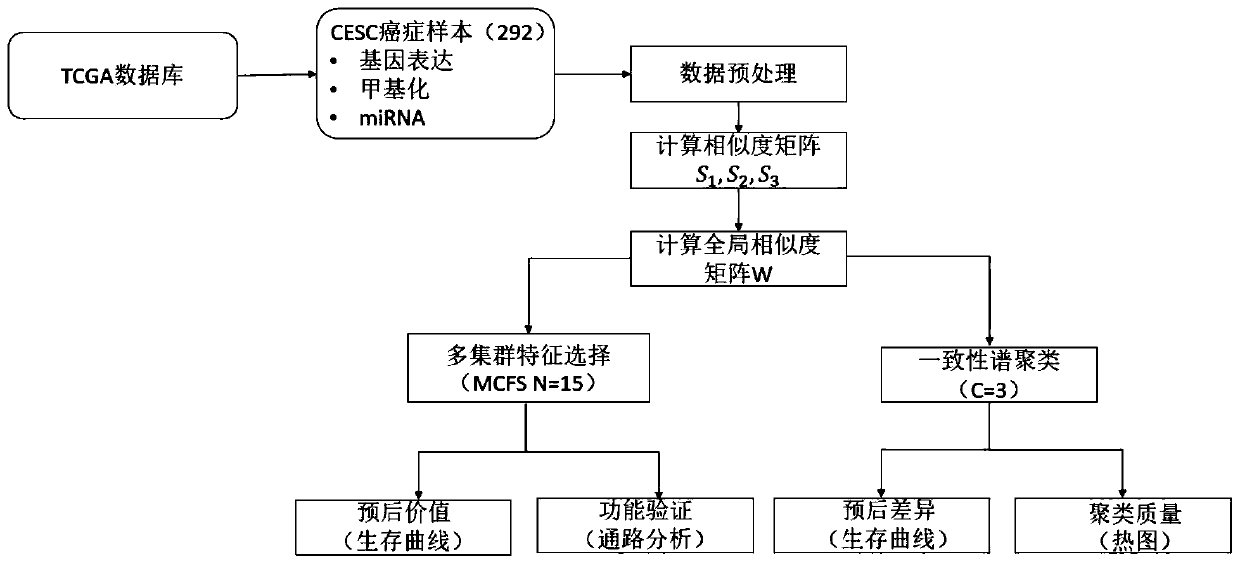
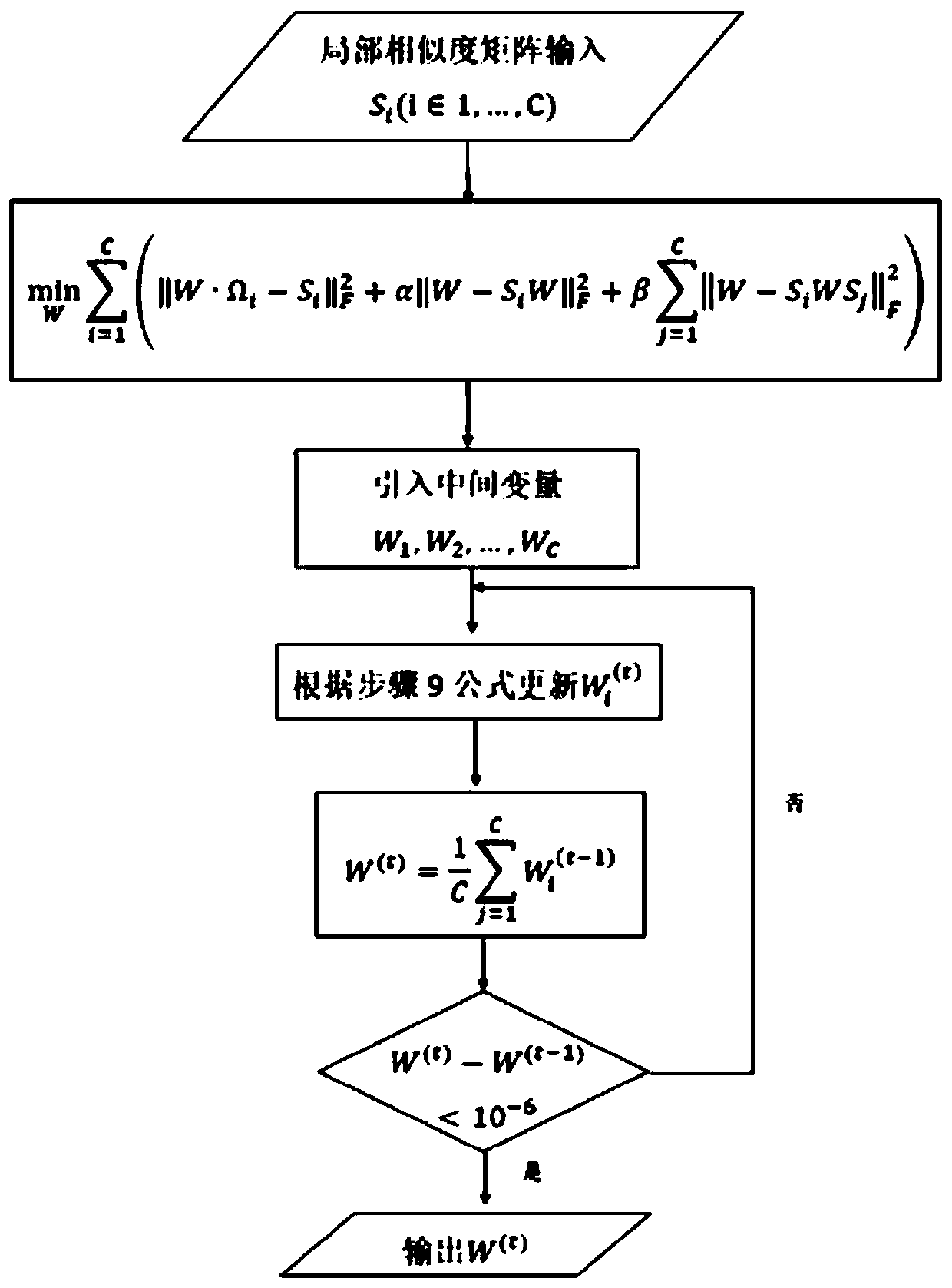
Multi-omics cancer data integrating and analyzing method based on similarity fusion
ActiveCN109994200AHigh precisionImprove stabilityMedical automated diagnosisProteomicsPattern recognitionMulti omics
The invention discloses a multi-omics cancer data integrating and analyzing method based on similarity fusion. The method comprises the steps of calculating a local similarity network, fusing multiplelocal similarity networks, typing according to a global similarity network, and backtracking the characteristic in an original data source according to the global similarity network. Compared with the prior art, the method is advantageous in that through modeling a similarity network connecting path which gradually advances, a fusion algorithm of multiple similarity networks is realized; a more complicated network structure can be described; and higher accuracy and higher stability are realized. Through a consistent alternating multiplier method, quick solving of a network fusion model is realized. The multi-omics cancer data integrating and analyzing method has advantages of utilizing the integrated global similarity network to typing of a cancer patient, obtaining types of the patientswith substantial prognosis difference, and combining with a multi-group characteristic selecting method for screening the key target characteristic. The selected characteristic has a potential of becoming a latent biological marker.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
An integrated method and system for identifying functional patient-specific somatic aberations using multi-omic cancer profiles
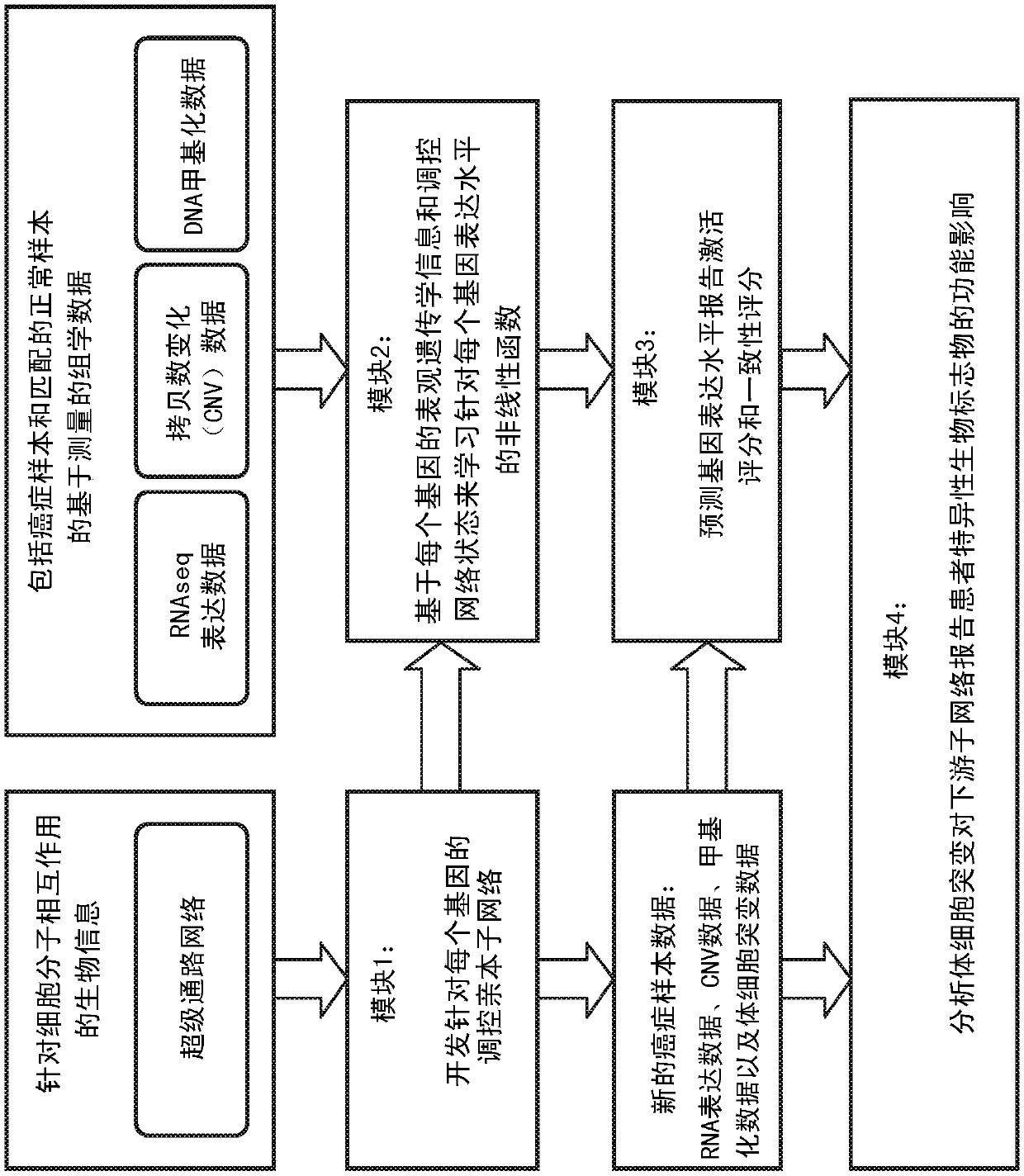
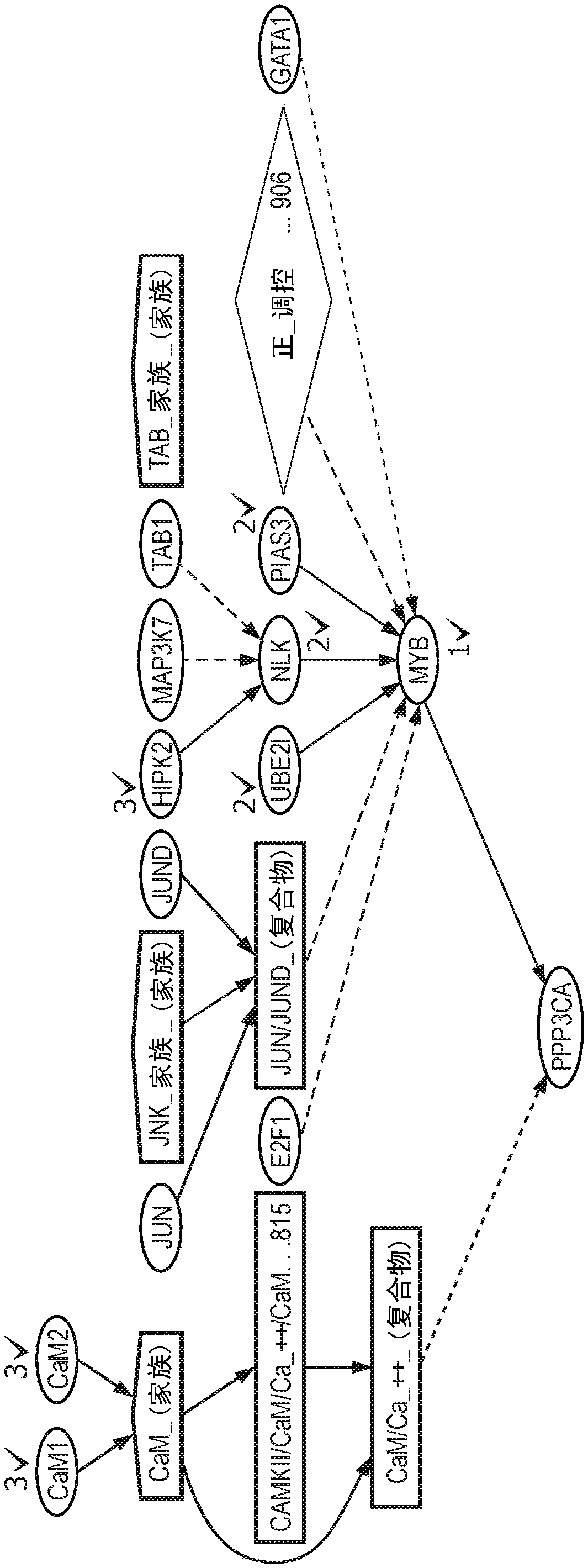
A system and method for determining the functional impact of somatic mutations and genomic aberrations on downstream cellular processes by integrating multi-omics measurements in cancer samples with community-curated biological pathways are disclosed. The method comprises the steps of extracting biological pathway information from well-curated biological pathway sources, using the pathway information to generate an upstream regulatory parent sub-network tree for each gene of interest, integrating measurement-based omic data for both cancer and normal samples to determine a nonlinear function for each gene expression level based on the gene's epigenetic information and regulatory network status, using the nonlinear function to predict gene expression levels and compare activation and consistency scores with inputted patient- specific gene expression data, and using the patient-specific gene expression predictions to identify significant deviations and inconsistencies in gene expressionlevels from expected levels in individual patient samples to identify potential biomarkers in providing predictive information in relation to cancer and cancer treatment.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
Proteomic Methods For The Identification And Use Of Putative Biomarkers Associated With The Dysplastic State In Cervical Cells Or Other Cell Types
InactiveUS20090221430A1Quality improvementHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProteomics methodsCervical cells
The invention relates to methods for detecting and identifying potential biomarkers of high-grade cervical dysplasia in an individual human subject. The invention also relates to newly discovered biomarkers, as set forth in Tables 1-4 herein, which are associated with the dysplastic state of cervical cells. It has been discovered that a differential level of expression of any of these markers or combination of these markers correlates with a dysplastic condition in a human subject, e.g., a patient.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
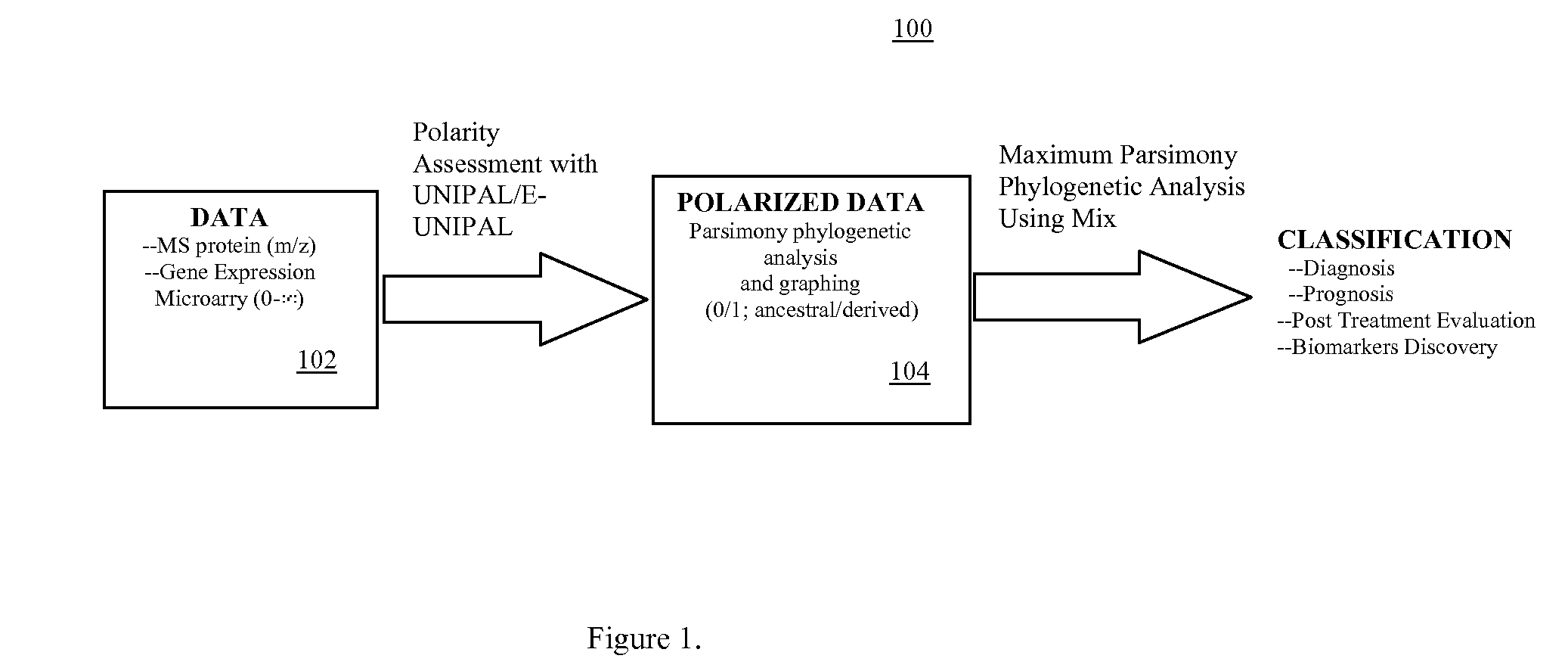
Phylogenetic Analysis of Mass Spectrometry or Gene Array Data for the Diagnosis of Physiological Conditions
ActiveUS20070259363A1Facilitates interplatform comparabilityMedical simulationMedical data miningDiseasePotential biomarkers
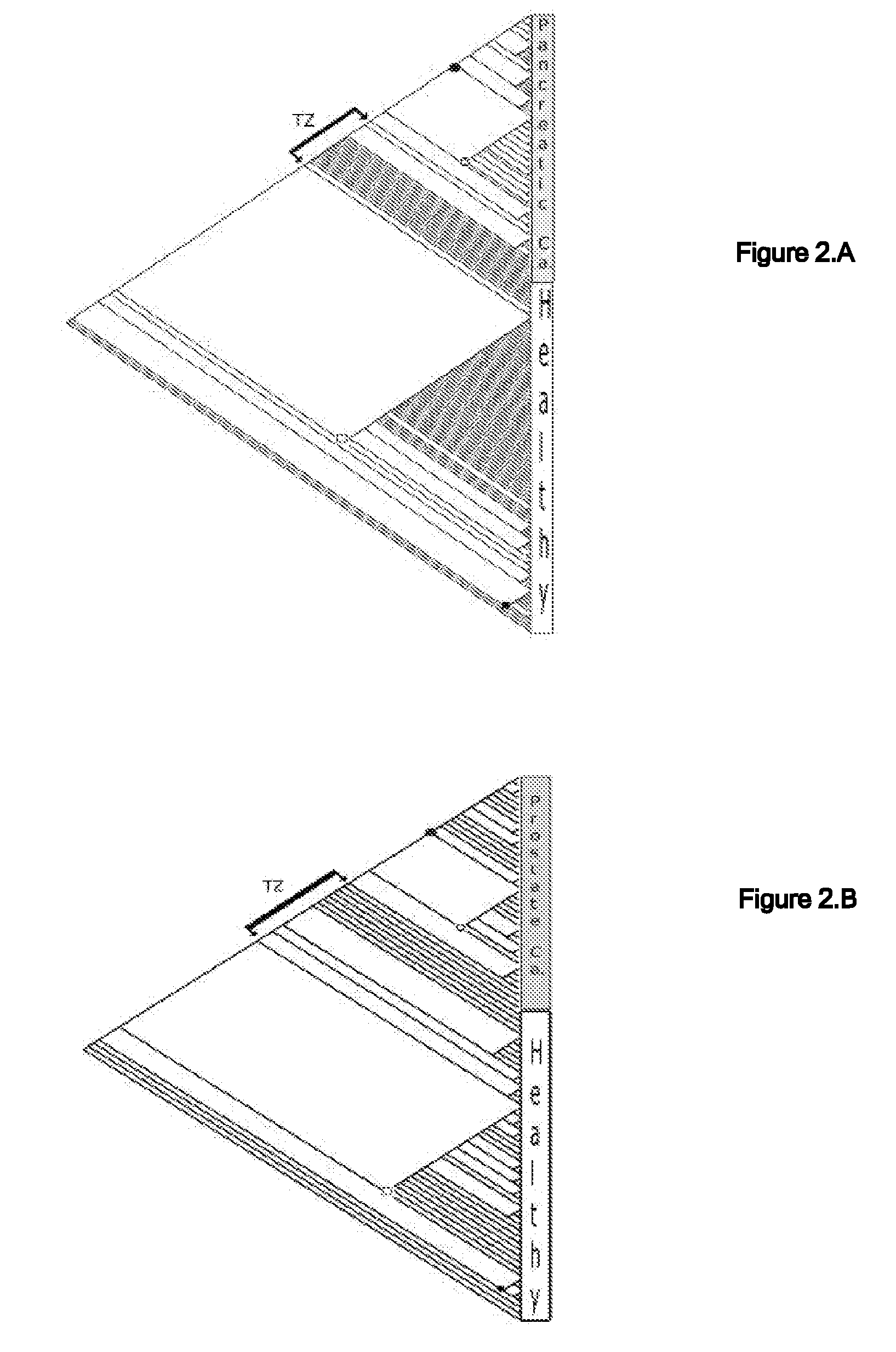
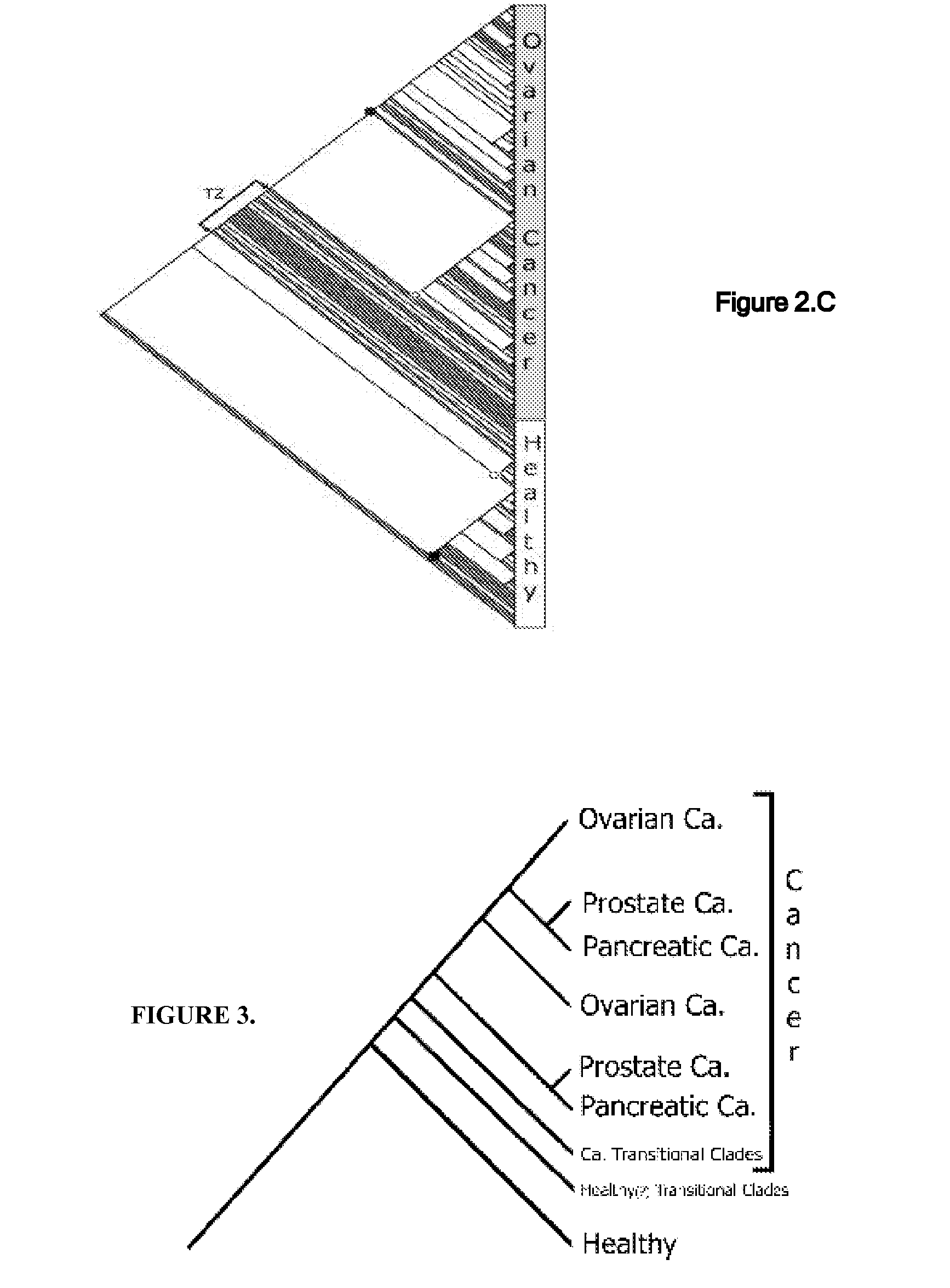
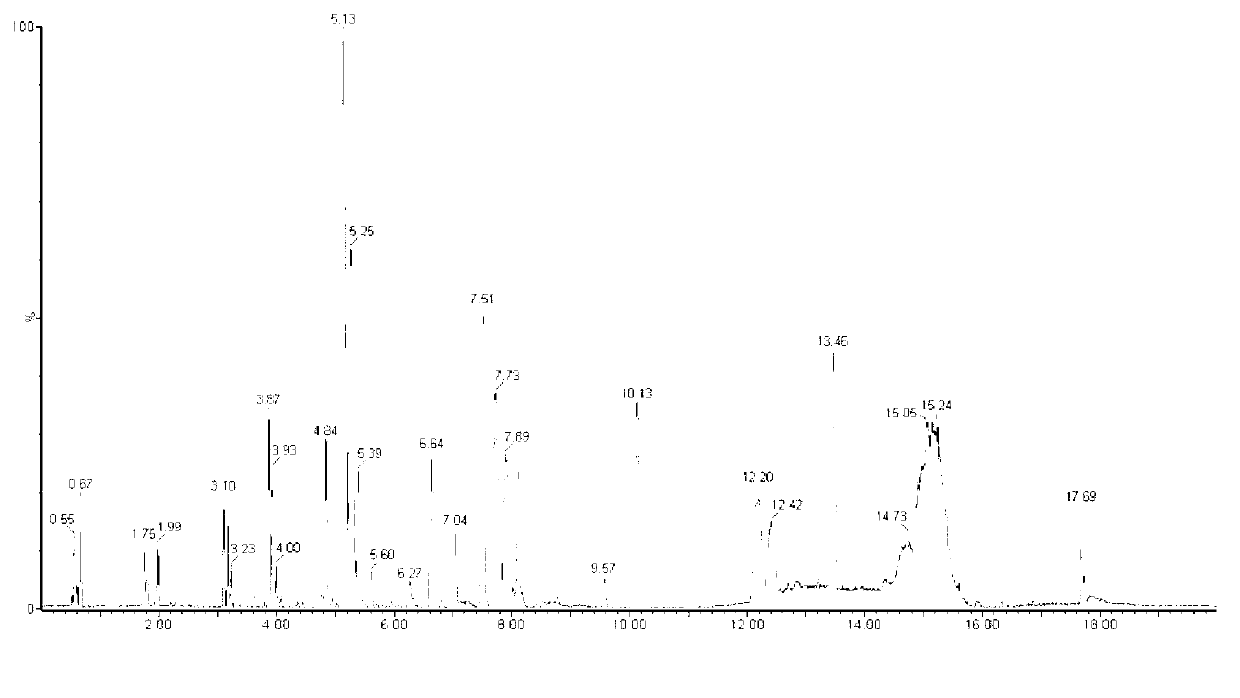
A universal data-mining platform capable of analyzing mass spectrometry (MS) serum proteomic profiles and / or gene array data to produce biologically meaningful classification; i.e., group together biologically related specimens into clades. This platform utilizes the principles of phylogenetics, such as parsimony, to reveal susceptibility to cancer development (or other physiological or pathophysiological conditions), diagnosis and typing of cancer, identifying stages of cancer, as well as post-treatment evaluation. To place specimens into their corresponding clade(s), the invention utilizes two algorithms: a new data-mining parsing algorithm, and a publicly available phylogenetic algorithm (MIX). By outgroup comparison (i.e., using a normal set as the standard reference), the parsing algorithm identifies under and / or overexpressed gene values or in the case of sera, (i) novel or (ii) vanished MS peaks, and peaks signifying (iii) up or (iv) down regulated proteins, and scores the variations as either derived (do not exit in the outgroup set) or ancestral (exist in the outgroup set); the derived is given a score of “1”, and the ancestral a score of “0”—these are called the polarized values. Furthermore, the shared derived characters that it identifies are potential biomarkers for cancers and other conditions and their subclasses.
Owner:AMRI HAKIMA +2
Serum metabonomic method for screening biomarkers of transgenic animal
InactiveCN103278576AThe pre-processing process is simpleReduce mistakesComponent separationMetaboliteMultivariate statistical
The invention relates to a serum metabonomic method for screening biomarkers of a transgenic animal. The serum metabonomic method comprises the following steps of: analyzing serums of a normal animal and the transgenic animal to obtain a metabolic fingerprint spectrum by adopting an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technology; analyzing and comparing the difference between metabolic fingerprint spectrums of the normal animal and the transgenic animal by adopting a multivariate statistical analysis method; and screening potential biomarkers of the transgenic animal. According to the serum metabonomic method, the variation condition of metabolite of the transgenic animal are more comprehensively and synthetically embodied; and the serum metabonomic method is suitable for screening of biomarkers of transgenic animals.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
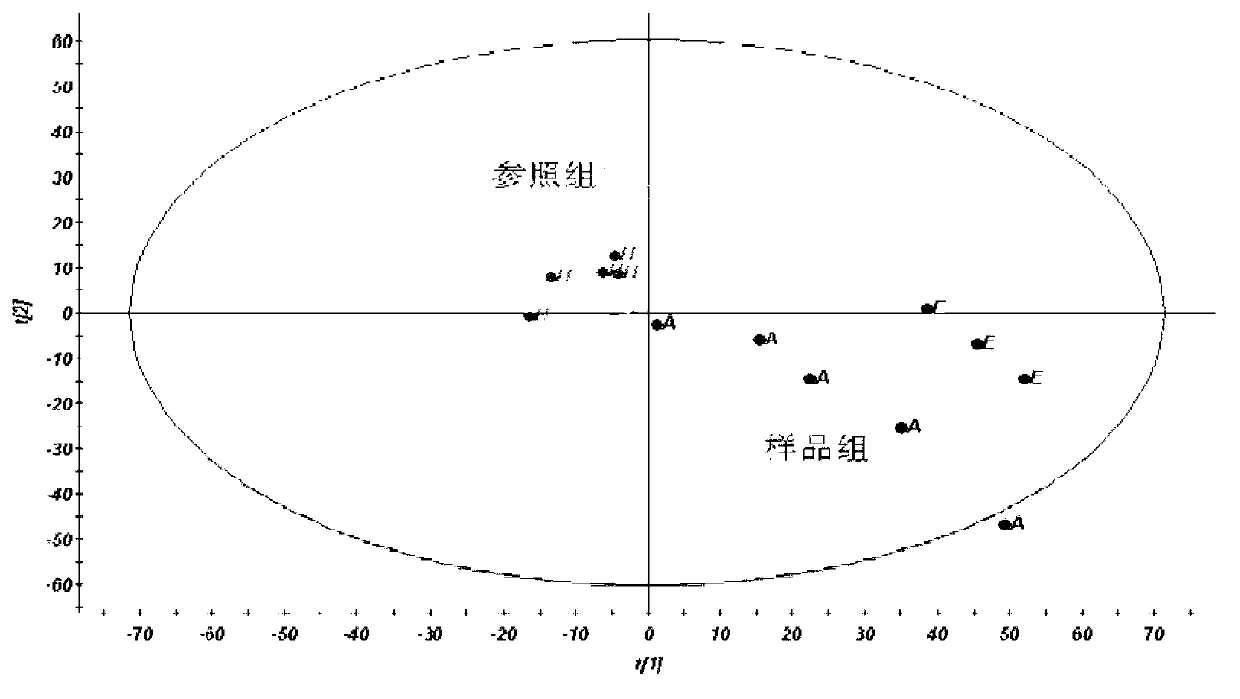
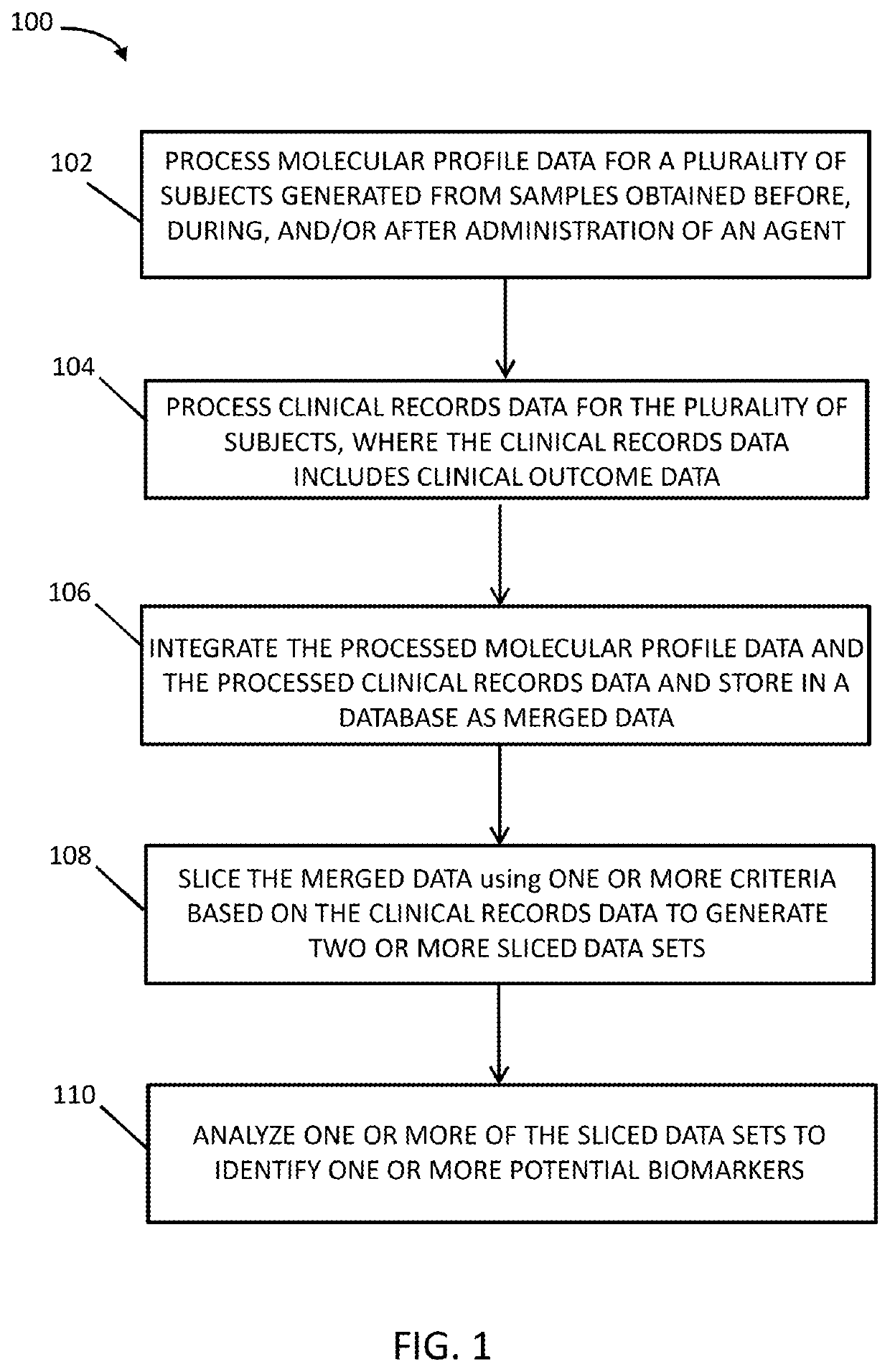
Systems and methods for patient stratification and identification of potential biomarkers
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for identifying one or more potential biomarkers for a clinical outcome related to administration of an agent. The method includes processing molecular profile data for a plurality of subjects where the molecular profile data includes data obtained before, during and / or after administration of an agent to the plurality of subjects. The method also includes processing clinical records data for the subjects, where the clinical records data includes clinical outcome data, integrating the processed molecular profile data and the processed clinical records data for the subjects and storing in a database as merged data, selecting two or more subsets of the merged data using one or more criteria based on the clinical records data to generate two or more selected data sets, and analyzing one or more of the selected data sets to identify one or more potential biomarkers for a clinical outcome related to administration of the agent.
Owner:BERG
Hypermethylation biomarkers for detection of cervical cancer
ActiveUS8859468B2Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPotential biomarkersOncology
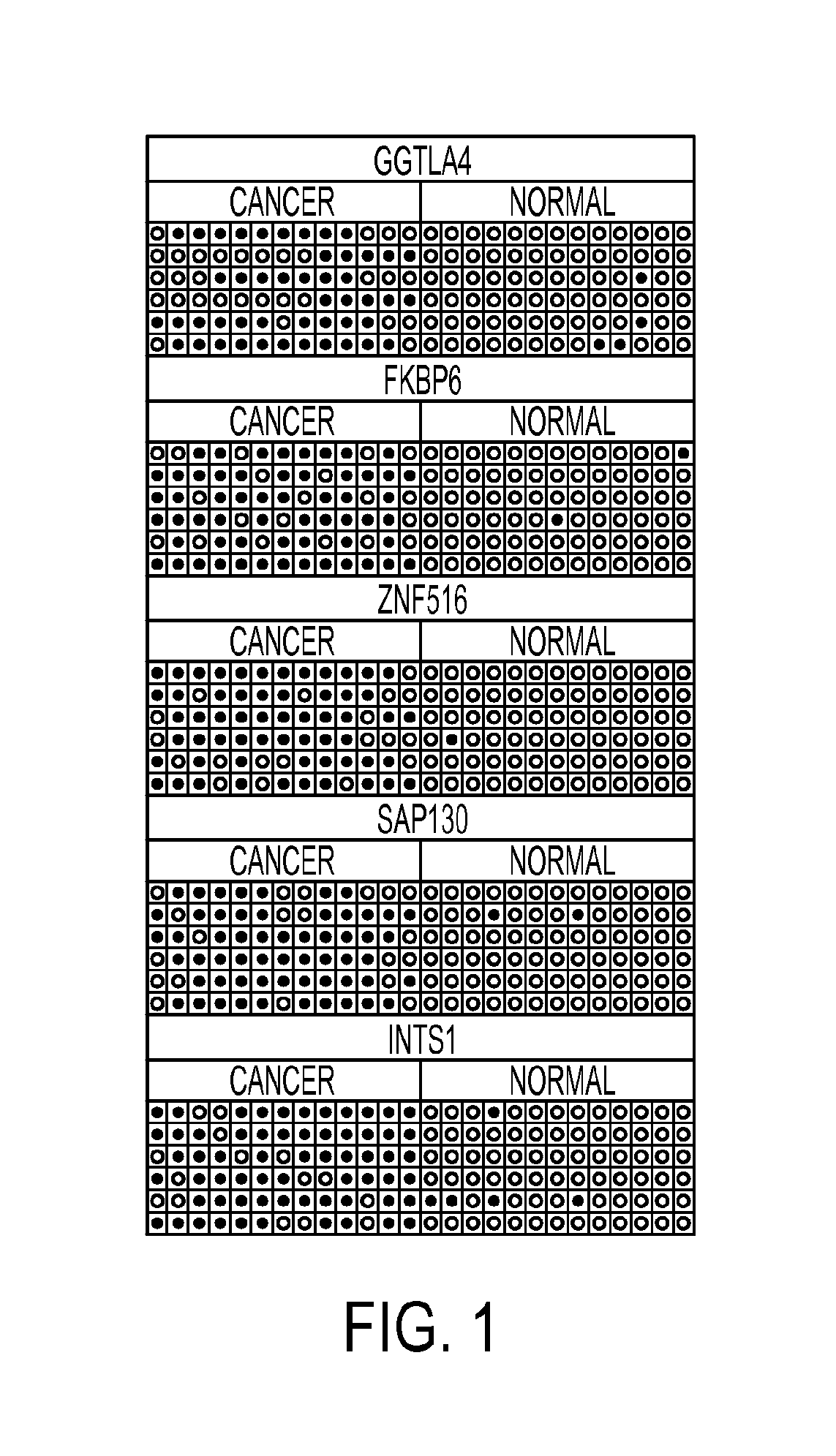
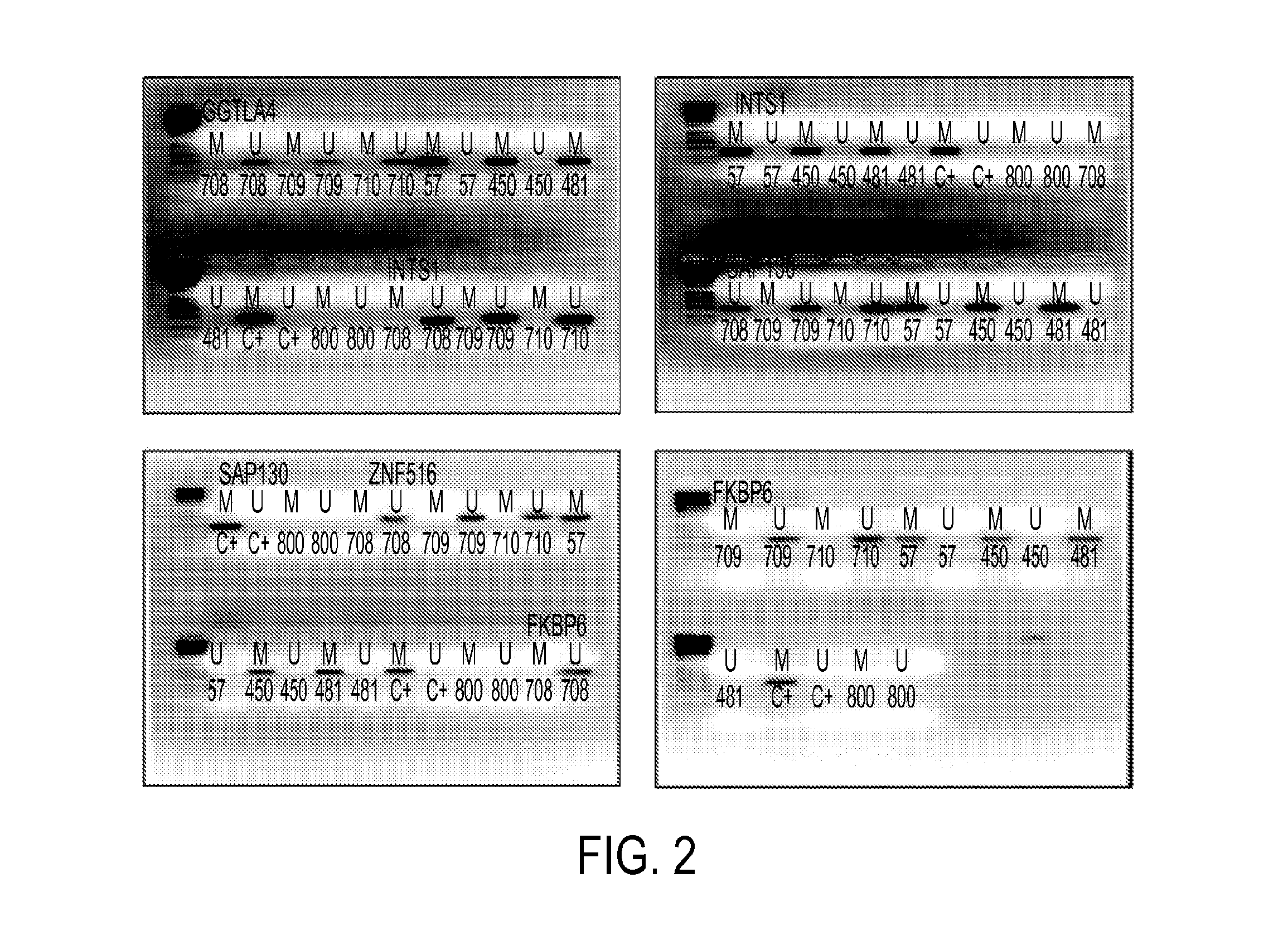
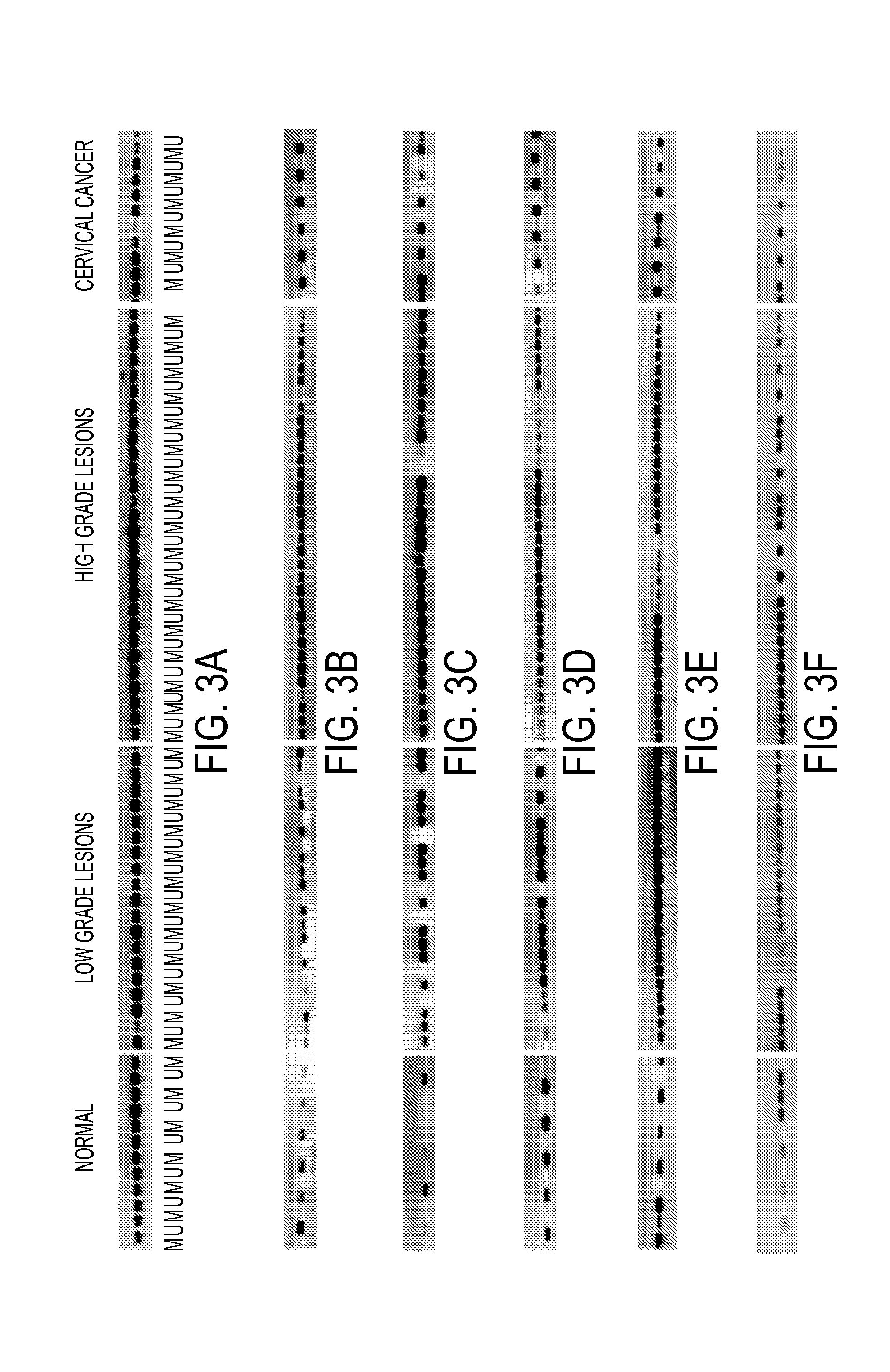
Pap smears and HPV infection tests do not distinguish between lesions that will progress to an invasive carcinoma and those that will not. We aimed to identify epigenetic biomarkers for diagnosis and progression monitoring of premalignant lesions in cervical cancer. Hypermethylated genes were identified as potential biomarkers after validation by MSP, including GGTLA4 and ZNF516. The methylation frequency for these two genes was higher in tumor: GGTLA4 (100%) and ZNF516 (96%); than in normal samples: GGTLA4 (12%) and ZNF516 (16%). The methylation status of GGTLA4 showed a progression in methylation frequency from normal samples to invasive carcinoma. The immunohistochemical expression was lower in tumor for both: GGTLA4 (50.8%) and ZNF516 (66.2%); than in normal samples: GGTLA4 (71.2%) and ZNF516 (88.1%) (p<0.05). In conclusion, we identified methylation biomarkers for the molecular screening and characterization of cervical cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Plasma autoantibody biomarkers for basal like breast cancer
InactiveUS20170363631A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAutoantibody
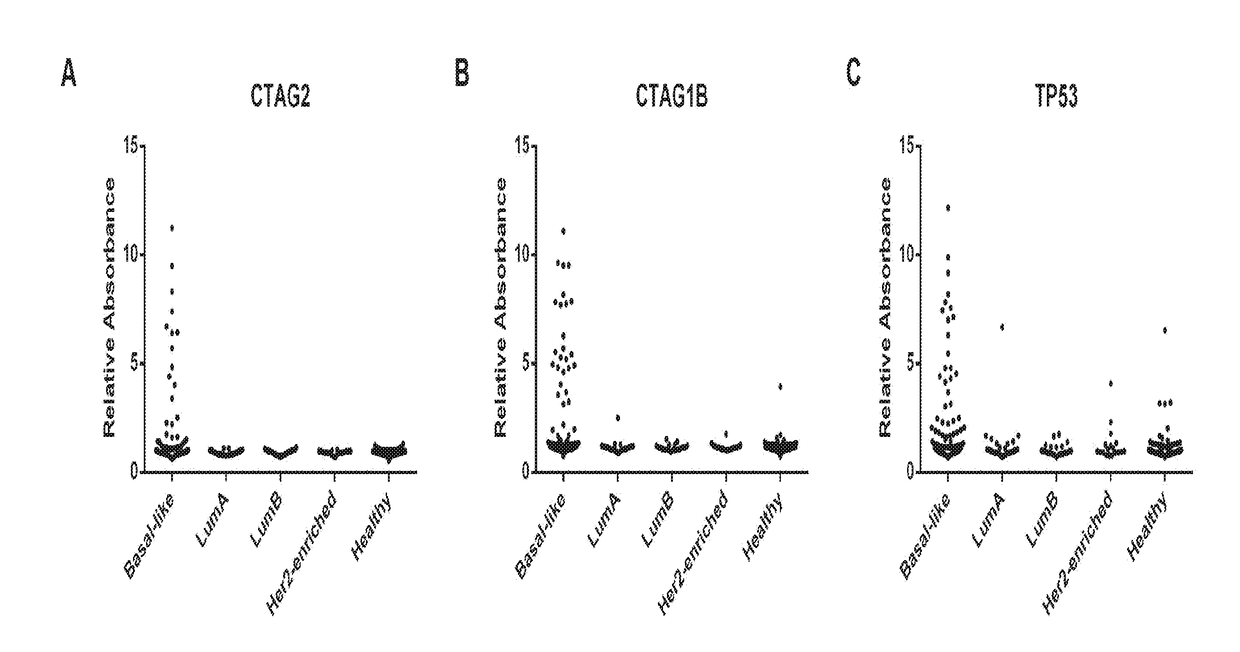
Cancer patients make antibodies to tumor-derived proteins that are potential biomarkers for early detection. Twenty-eight antigens have been identified as potential biomarkers for the early detection of basal-like breast cancer (Tables 1, 2). Also, a 13-AAb classifier has been developed that differentiate patients with BLBC from healthy controls with 33% sensitivity at 98% specificity (Table 3).
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
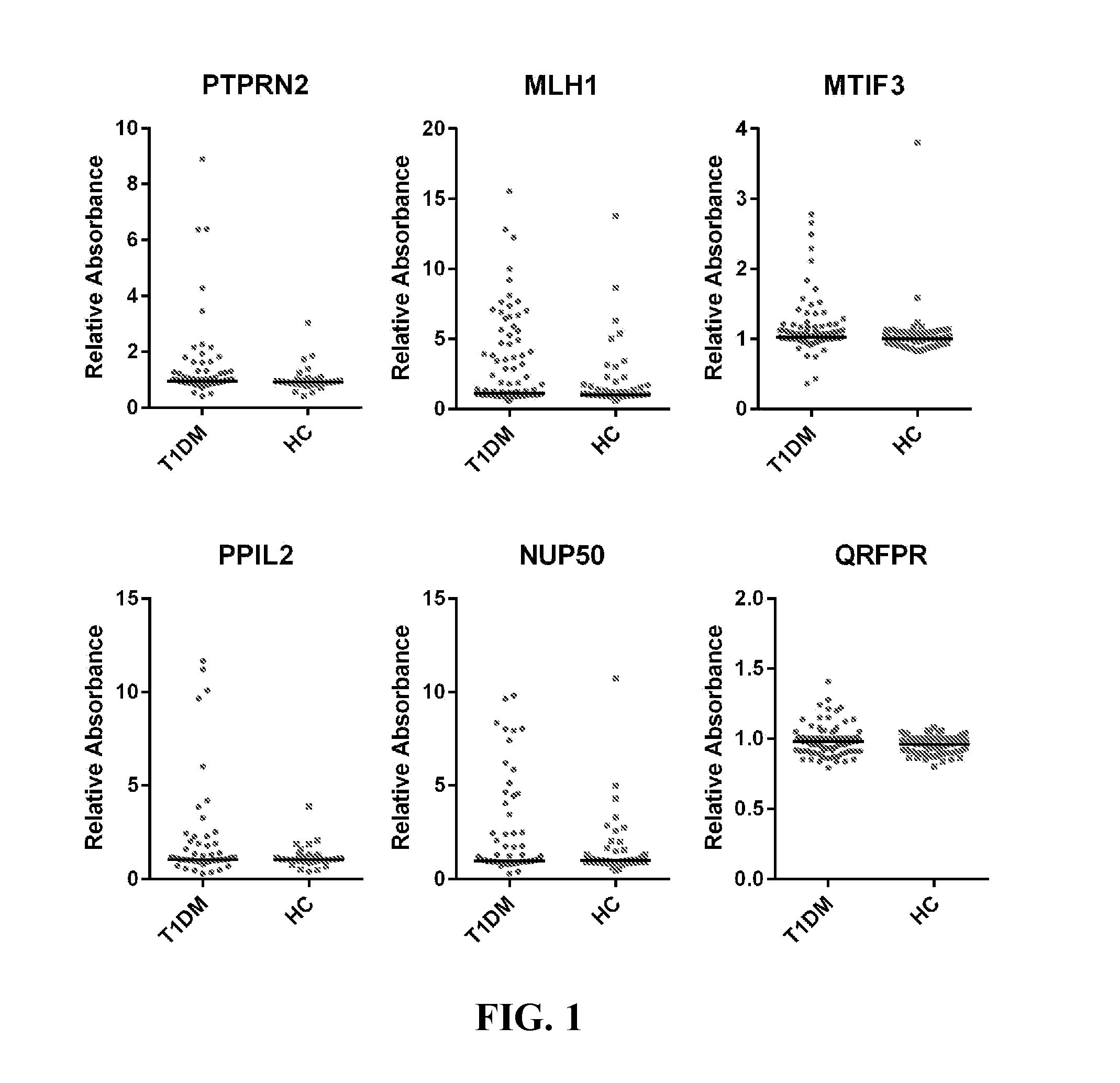
Type 1 Diabetes Biomarkers
InactiveUS20160195546A1Improve risk prediction modelHigh detection sensitivityLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisAntigenPotential biomarkers
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients make antibodies to self-proteins that are potential biomarkers for early detection and risk prediction. We have identified seventeen antigens as biomarkers for early diagnosis and risk prediction of T1D, including the antigens MLH1, MTIF3, PPIL2, NUP50, TOX4, FIGN, C9orf142, ZNF280D, HES1, QRFPR, CTRC, SNX6, SYTL4, ELA2A, IGRP, PAX6, and HMGN3.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
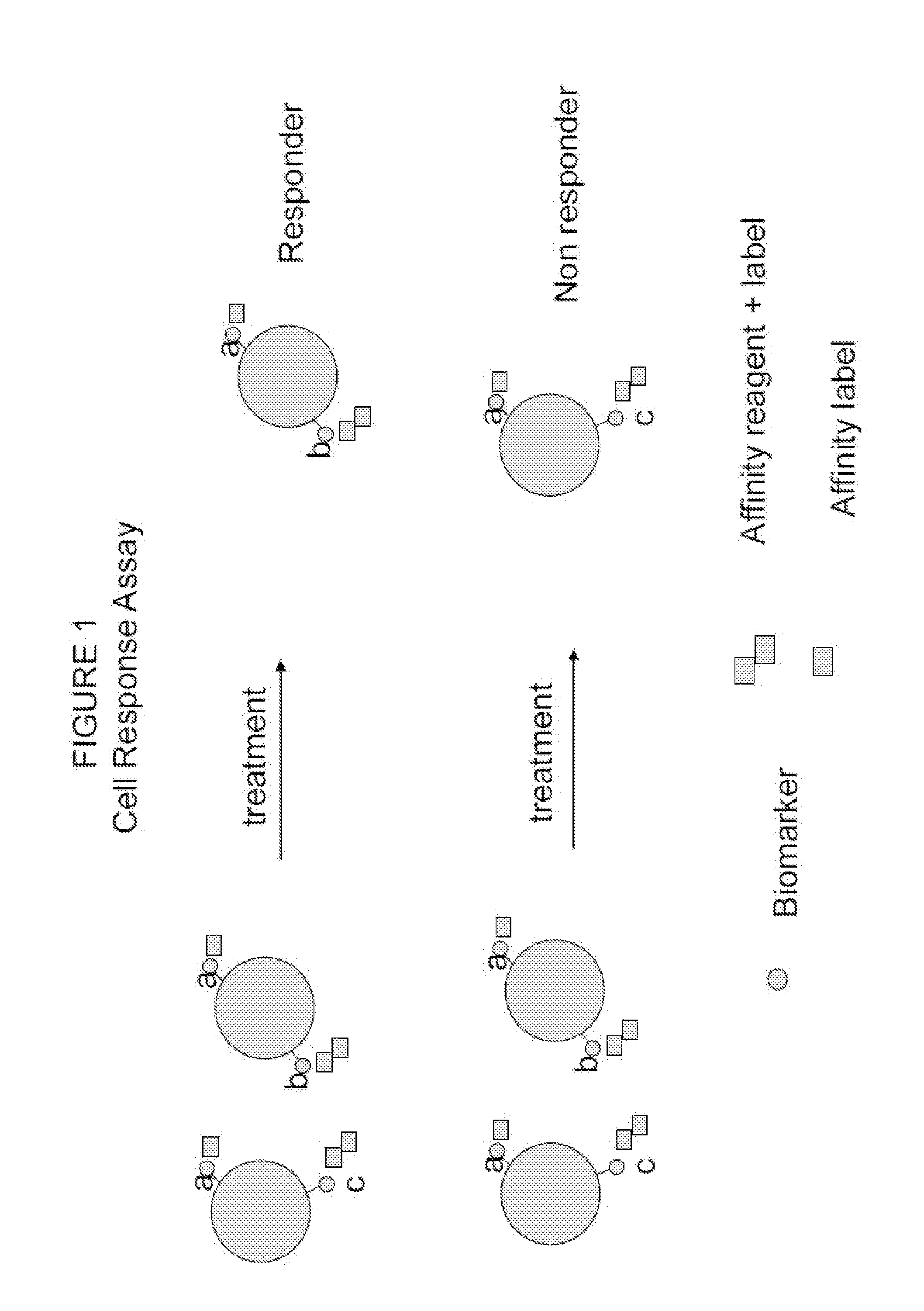
Cell response assay for cancer and methods of producing and using same
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
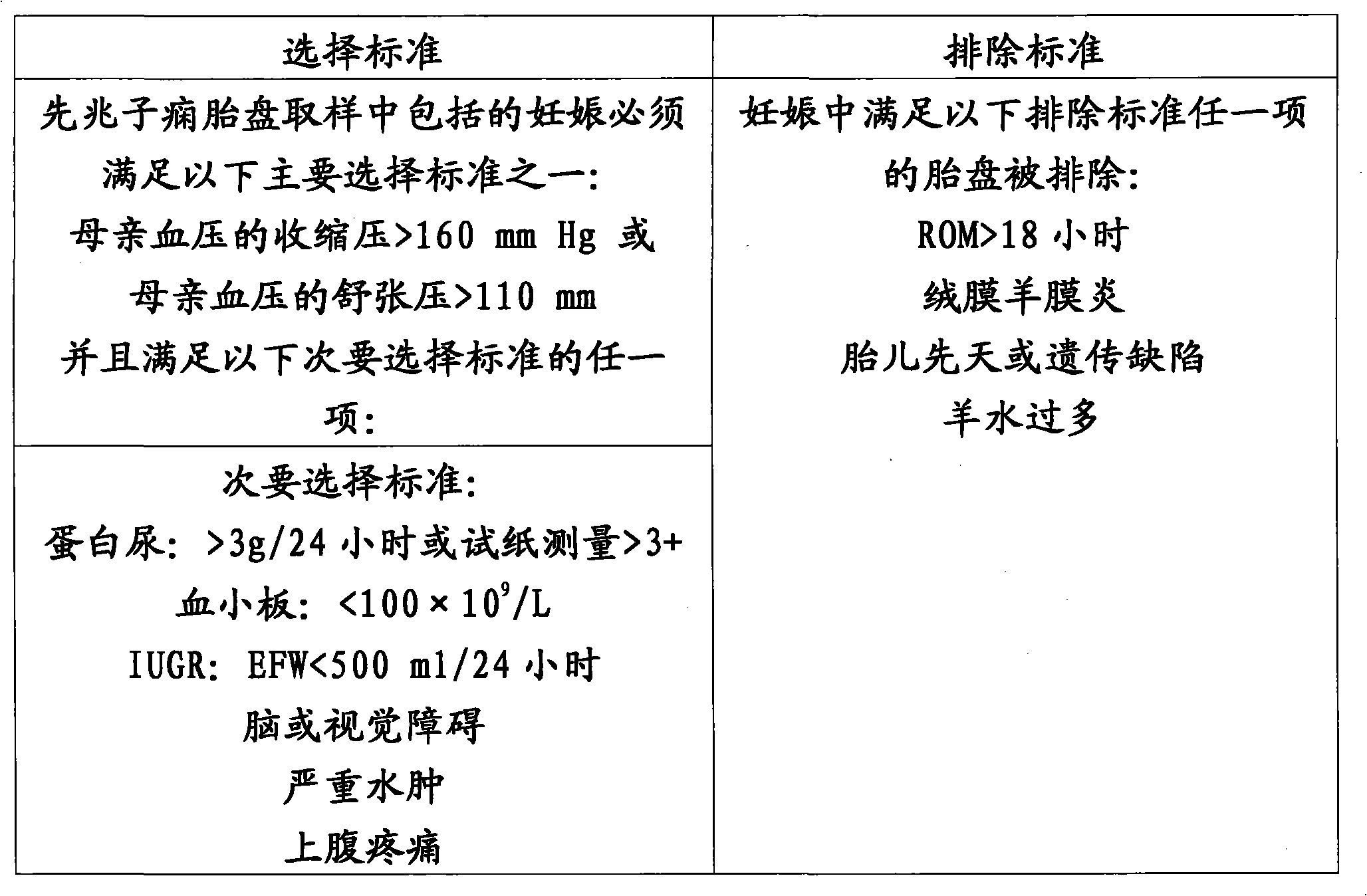
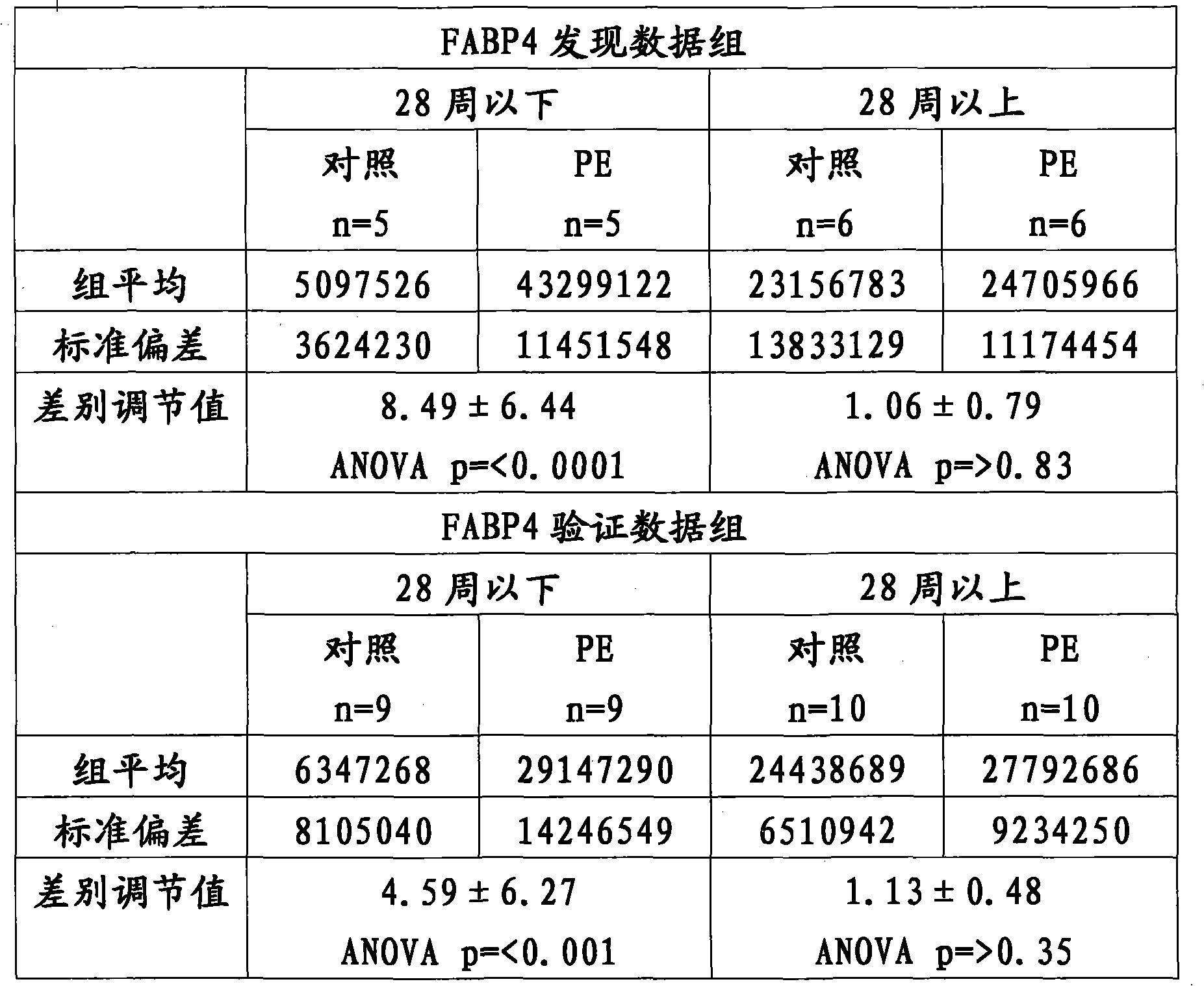
Methods for the detection of preeclampsia
Biomarkers associated with preeclampsia were identified. Nine proteins were identified as being differentially regulated between the control and the under 28-weeks preeclamptic samples. Similarly three proteins were identified as being differentially regulated between the control and the over 28-weeks preeclamptic samples. These 12 proteins can be used as potential biomarkers in the diagnosing andprognosing of preeclampsia.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
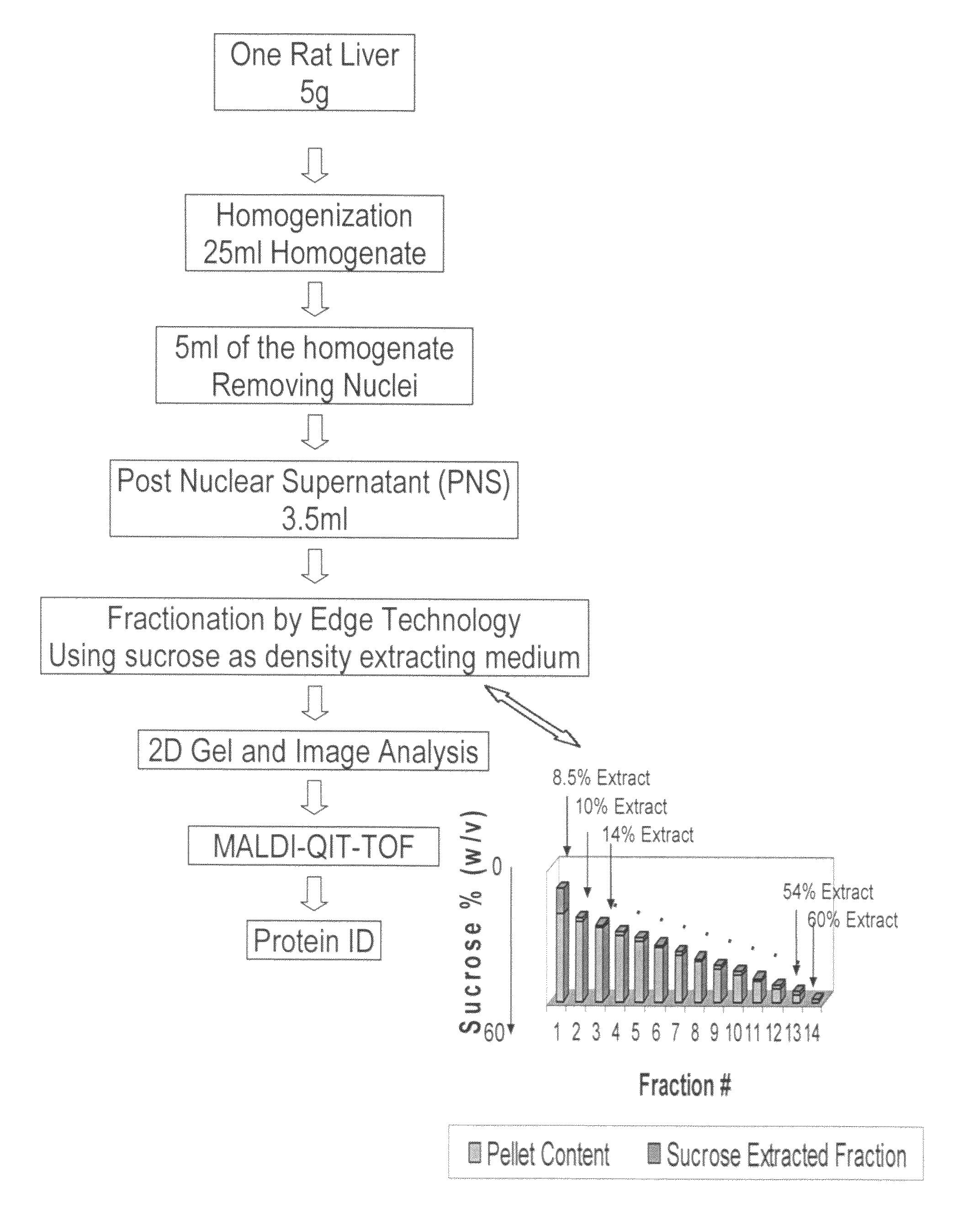
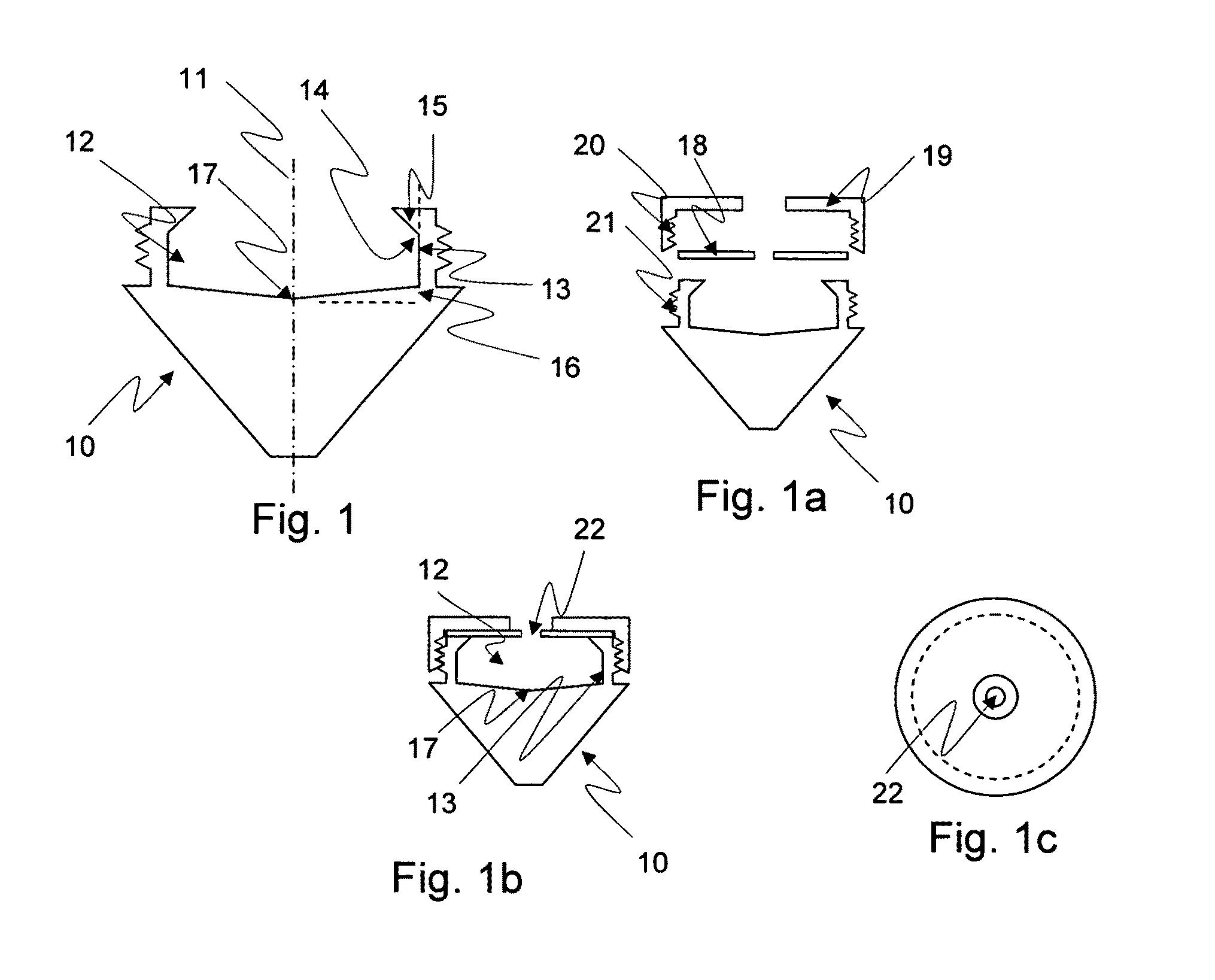
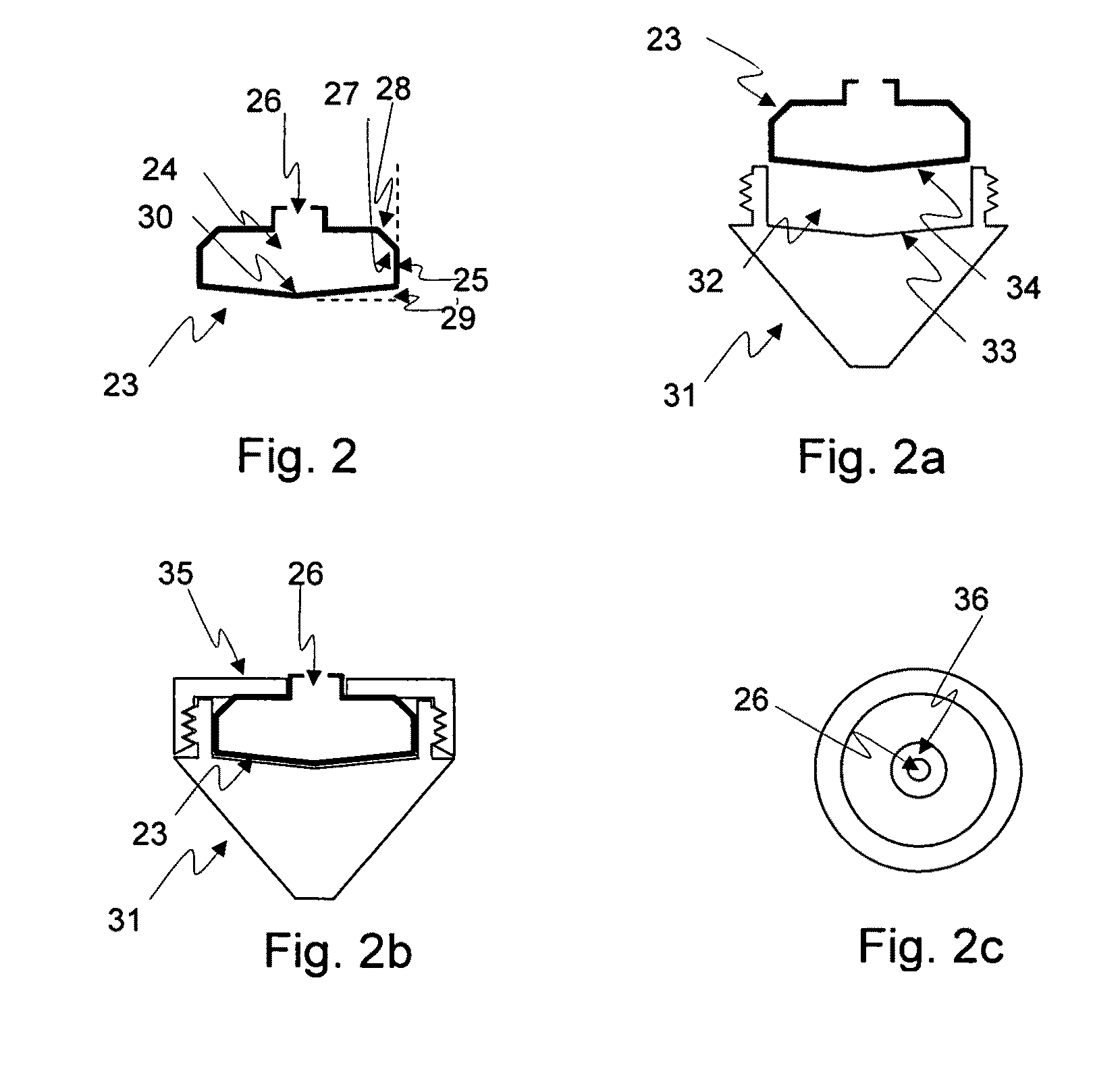
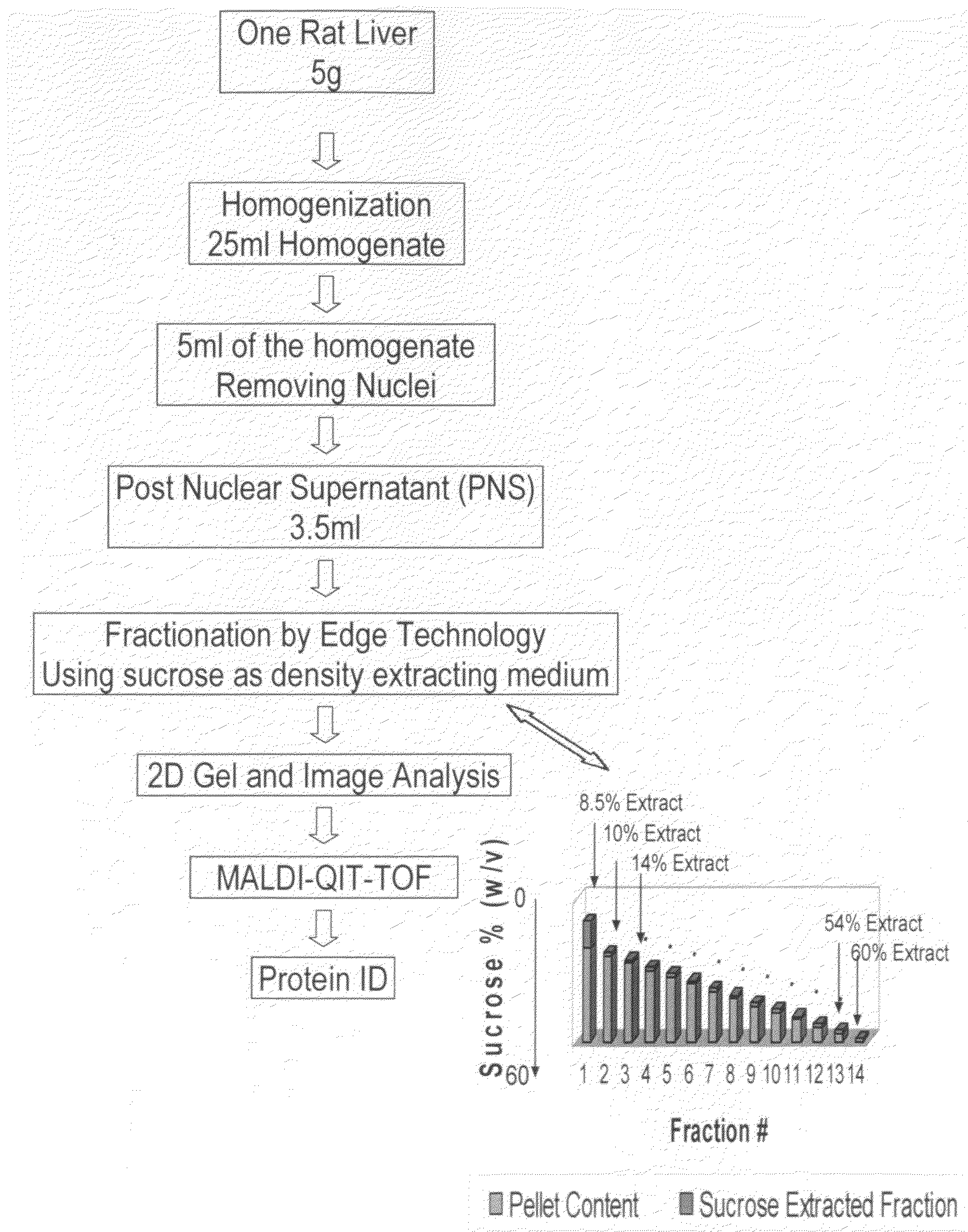
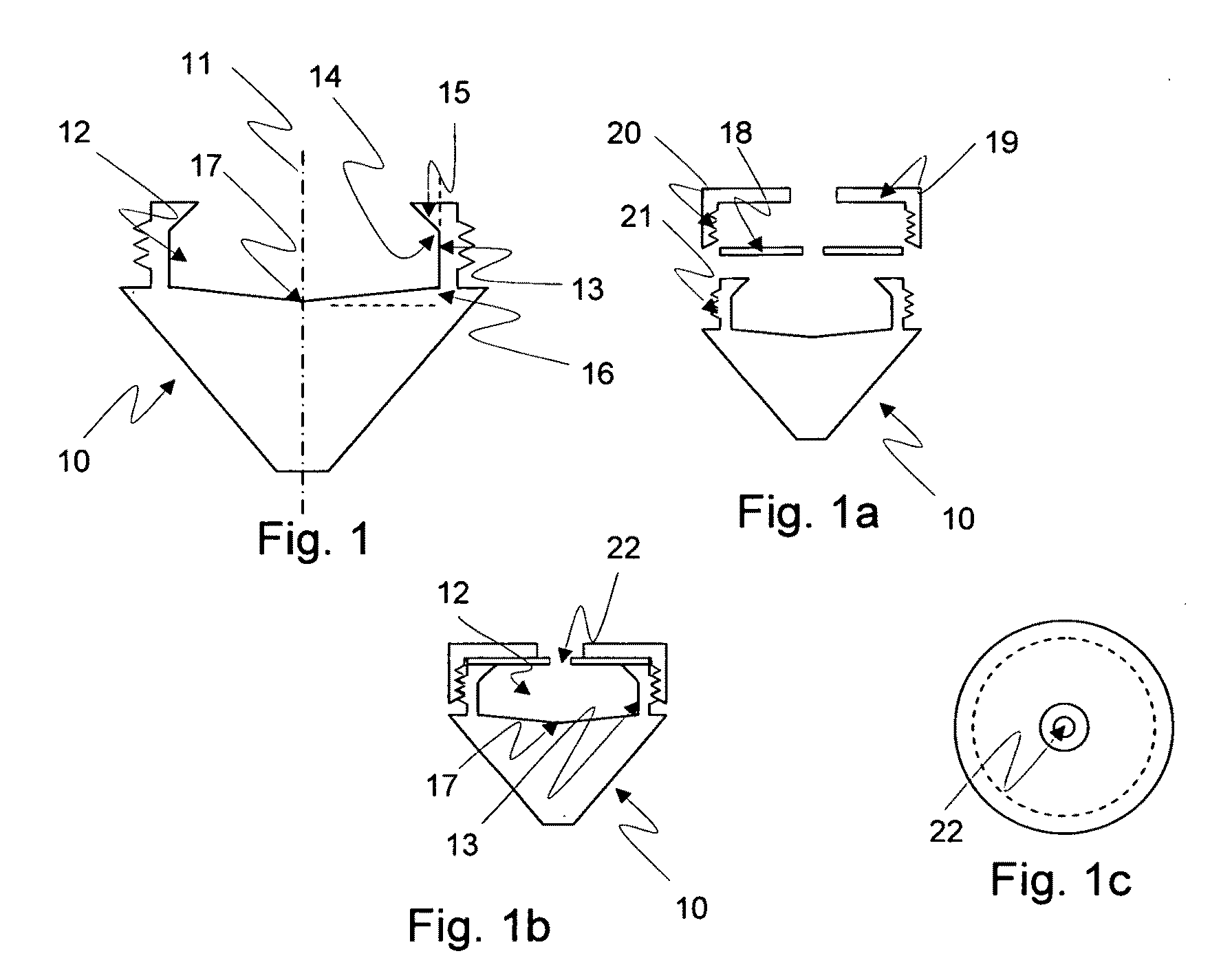
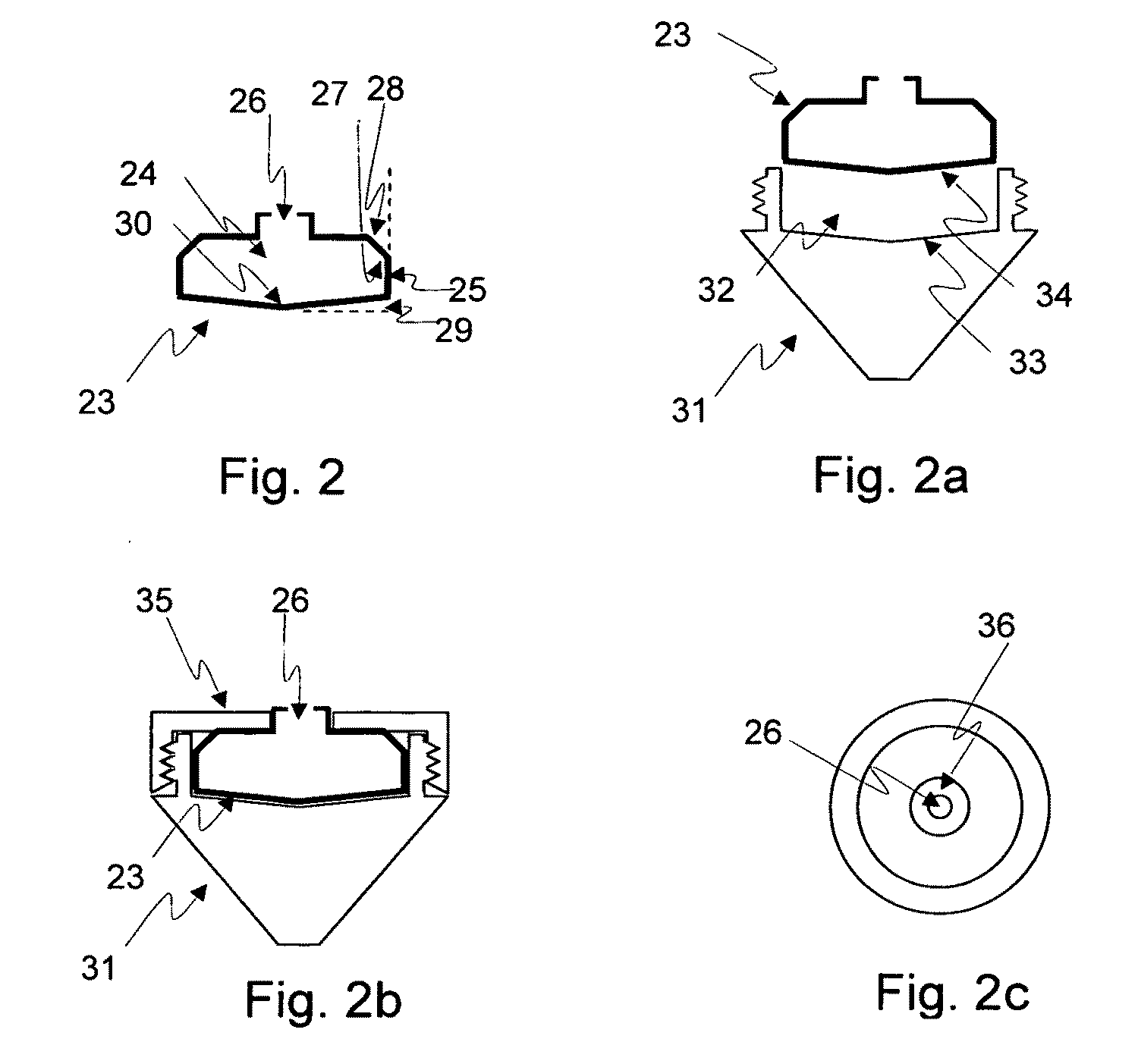
Method for the fractionation and separation of particles by step-wise gradient density extraction
InactiveUS8278118B2Efficient fractionationEfficient processingRotary centrifugesAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionFractionationVolumetric Mass Density
A method for the separation of particles of different densities using a step-wise gradient density extraction method as described herein where a sample is suspended in a liquid volume of an extracting medium of specific density and the particles that have a density less than or equal to that of the extracting medium of specific density can be recovered from a horizonatally rotatable hollow disk or a removable receptacle within a horizontally rotatable hollow disk designed for such purposes while the particles that have a density greater than the extracting medium of specific density form a deposit which can be cycled through the extraction process in an iterative fashion by varying the density of the extracting medium allowing the recovery of discrete particles of differing densities from a test sample. Also disclosed herein is the use of the above method as part of a separate method or system to identify a ratio of biomarkers from different fractions of a sample homogenate or lysate which is useful in the evaluation of potential biomarkers, and for the intraoperative pathological diagnosis of positive margins of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:PROSPECT BIOSYST
Method for the fractionation and separation of particles by step-wise gradient density extraction
InactiveUS20090265184A1Efficient processingReduce needRotary centrifugesAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionFractionationVolumetric Mass Density
A method for the separation of particles of different densities using a step-wise gradient density extraction method as described herein where a sample is suspended in a liquid volume of an extracting medium of specific density and the particles that have a density less than or equal to that of the extracting medium of specific density can be recovered from a horizonatally rotatable hollow disk or a removable receptacle within a horizontally rotatable hollow disk designed for such purposes while the particles that have a density greater than the extracting medium of specific density form a deposit which can be cycled through the extraction process in an iterative fashion by varying the density of the extracting medium allowing the recovery of discrete particles of differing densities from a test sample. Also disclosed herein is the use of the above method as part of a separate method or system to identify a ratio of biomarkers from different fractions of a sample homogenate or lysate which is useful in the evaluation of potential biomarkers, and for the intraoperative pathological diagnosis of positive margins of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:PROSPECT BIOSYST
In vitro method for early detection of severity of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and prognosis
ActiveCN109868315AConvenient diagnosis and treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPotential biomarkersTherapeutic effect
The embodiment of the invention discloses an in vitro method for early detection of the severity of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and prognosis, and the method is carried out by measuring the expression level of microRNAs of plasma exosomes. The embodiment of the invention also provides a product for early detection of the severity of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and prognosis, and the product determines the severity and prognosis of the aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage by measuring the expression level of the microRNAs of the plasma exosomes. The embodiment of the invention utilizes exosome microRNANA sequencing and real-time PCR method and technology for the first time, screens out potential biomarkers closely related to the occurrence and development of aSAH from blood exosomes, determines that the increased expression of microRNA-193b-3p and microRNA-486-3p is related to poor prognosis and the decreased expression of microRNA-369-3p and microRNA-410-3p is related topoor prognosis, provides a new method for monitoring aSAH and evaluating prognosis, and provides theoretical basis and experimental basis for improving the diagnosis and treatment effect of the disease.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WANNAN MEDICAL COLLEGE YIJISHAN HOSPITAL OF WANNAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
Identification of MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in Fecal Samples as Biomarkers for Gastroenterological Cancers
ActiveUS20110086353A1Excellent biomarkersReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationStool specimenPotential biomarkers
A simple, rapid, inexpensive, and promising commercial biomarker assay method for multiple diseases is described herein. The present invention detects miRNA-based biomarkers in human stool specimens. The method of the present invention amplifies miRNA directly from stool specimens without any prior miRNA extraction. Differential expression of specific microRNAs in stool of colorectal cancer CRC and adenoma patients suggest fecal microRNAs as a novel potential biomarker for colorectal neoplasia detection. The method of the present invention has diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic relevance for gastroenterological cancers / colorectal cancer and as well as further acquired or hereditary GI diseases.
Owner:BAYLOR RES INST
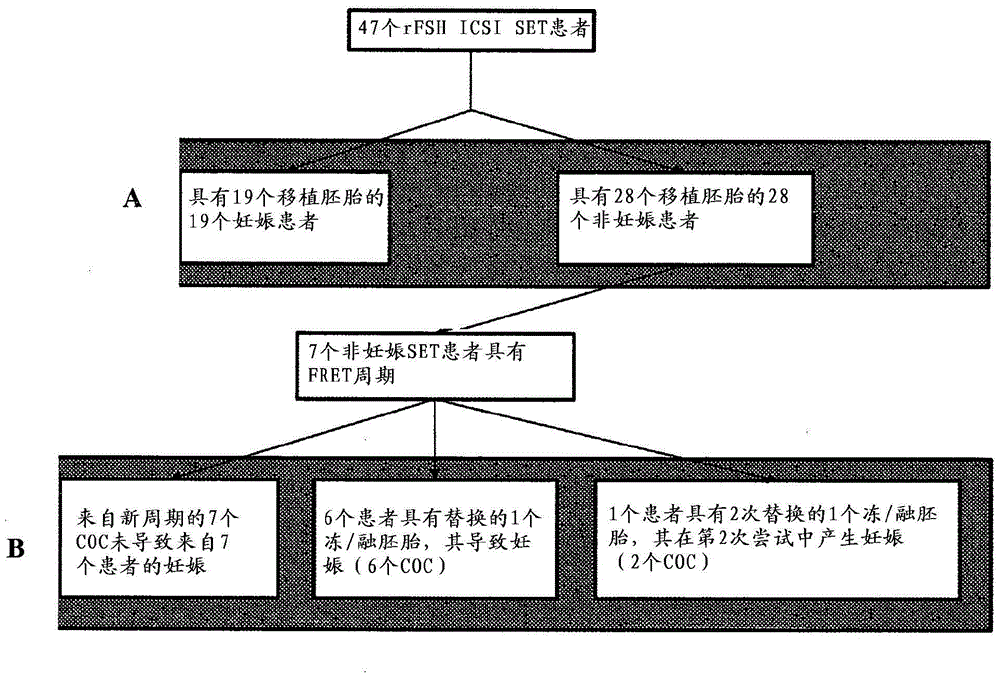
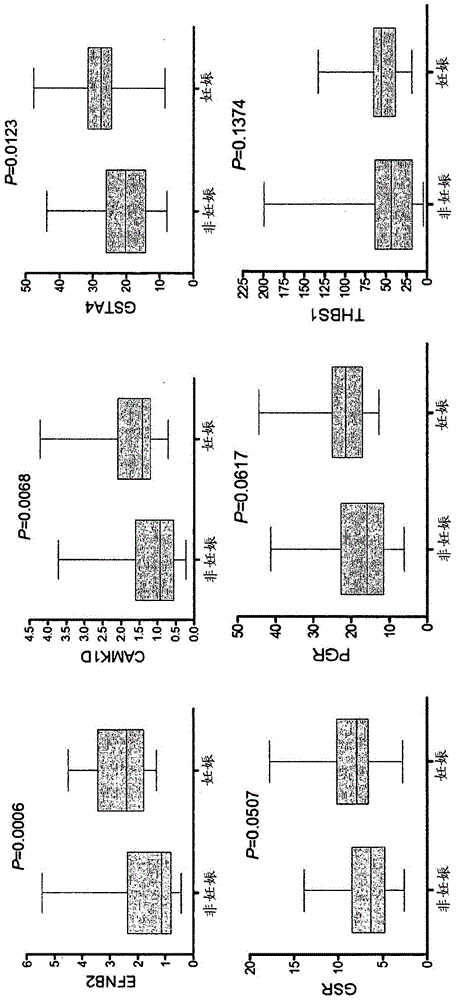
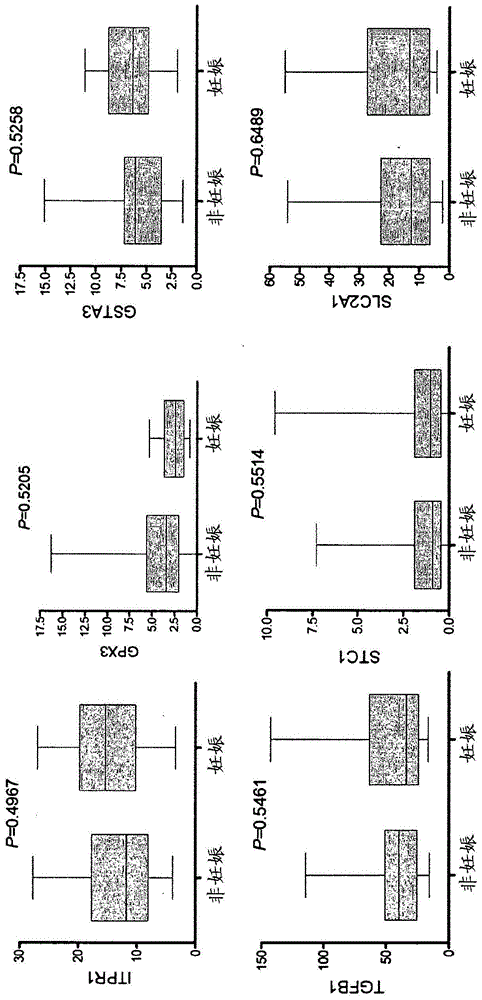
Marker genes for oocyte competence
Cumulus cell (CC) gene expression is explored as an additional method to morphological scoring to choose the embryo with the highest chance to pregnancy. The present invention relates to a novel method of identifying biomarker genes for evaluating the competence of a mammalian oocyte in giving rise to a viable pregnancy after fertilization, based on the use of live birth and embryonic development as endpoint criteria for the oocytes to be used in an exon level analysis of potential biomarker genes. The invention further provides CC-expressed biomarker genes thus identified, as well as prognostic models based on the biomarker genes identified using the methods of the present invention.
Owner:VRIJE UNIV BRUSSEL
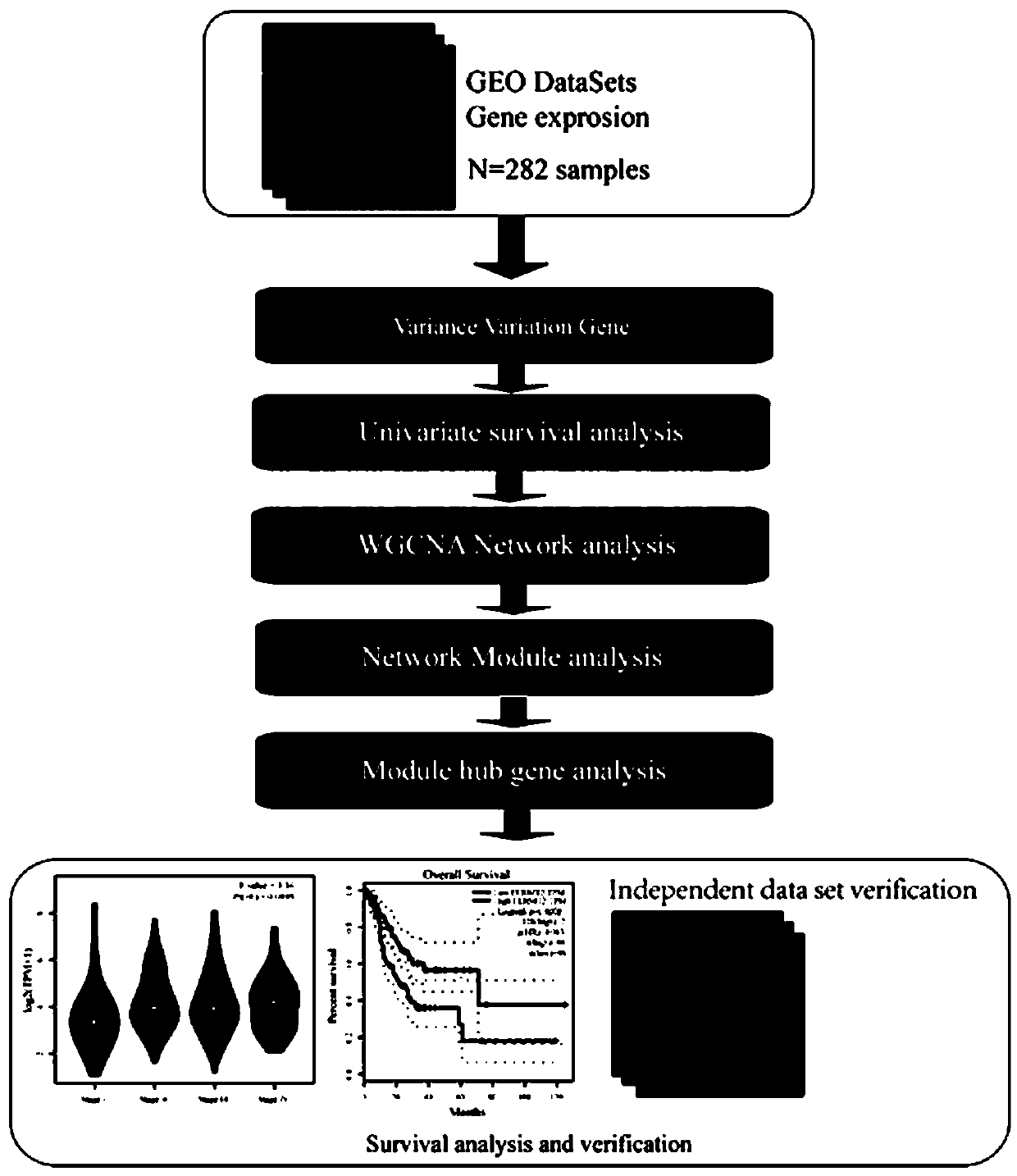
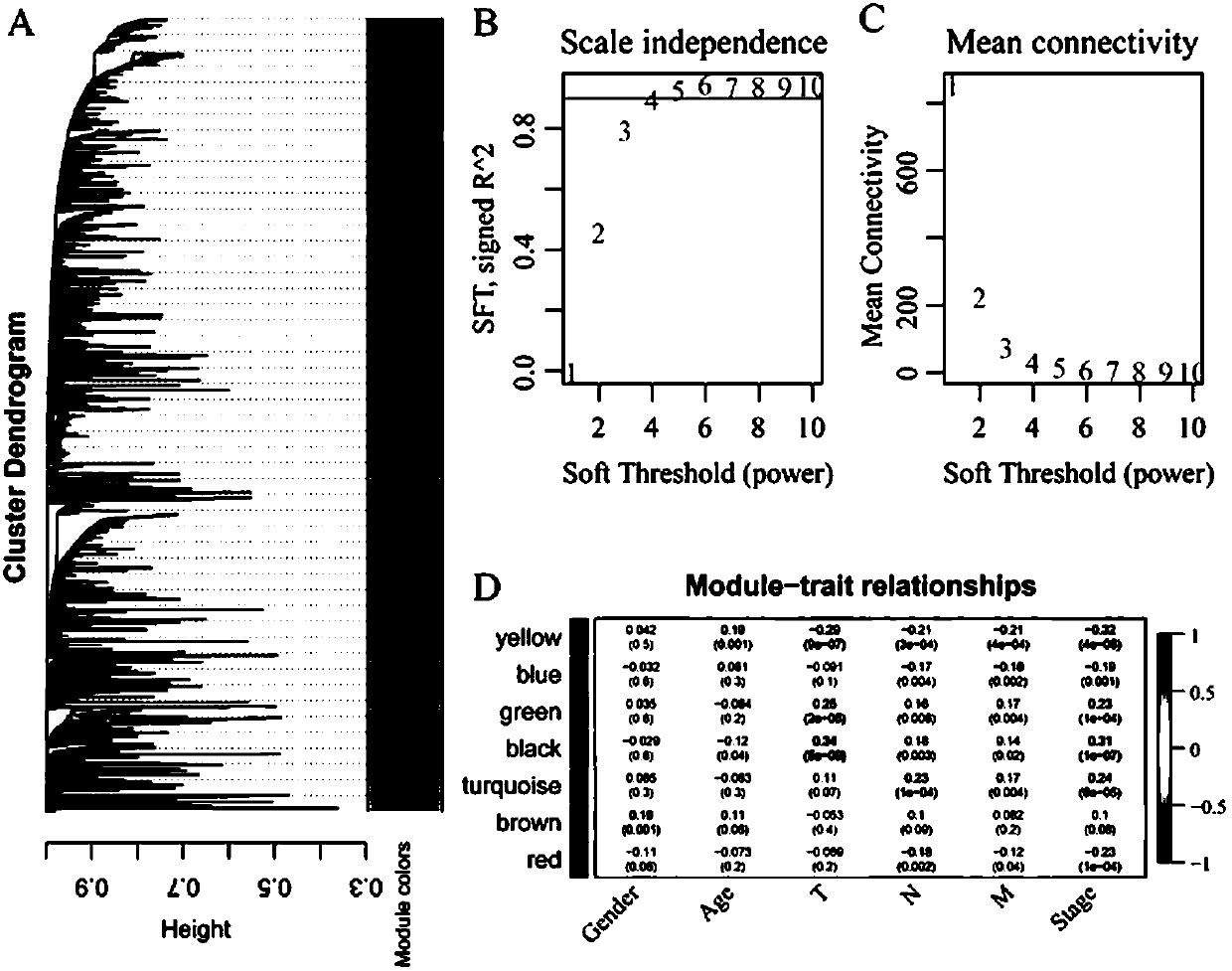
Method for screening potential biomarkers of gastric cancer based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis, and application thereof
ActiveCN109872776AShorten the timeImprove accuracyHealth-index calculationHybridisationIndividualized treatmentScreening method
The invention relates to the biomedicine field, and specifically relates to a method for screening potential biomarkers of gastric cancer based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis, and application thereof. The method for screening potential biomarkers of gastric cancer adopts weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and KEGG pathway and GO enrichment analysis, and other analysis methods. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) is an efficient and comprehensive method for high-dimensional data analysis, and the accuracy and validity in analyzing gene chip data of the WGCNA has been confirmed. The potential biomarker screened by the method of the invention is FERMT2. The method for screening potential biomarkers of gastric cancer based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis provides a new direction for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of gastric cancer, and promotes the development of individualized treatment.
Owner:辽宁省肿瘤医院
Identification of microRNAs (miRNAs) in fecal samples as biomarkers for gastroenterological cancers
ActiveUS8956817B2Excellent biomarkersReduce mortalitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStool specimenPotential biomarkers
A simple, rapid, inexpensive, and promising commercial biomarker assay method for multiple diseases is described herein. The present invention detects miRNA-based biomarkers in human stool specimens. The method of the present invention amplifies miRNA directly from stool specimens without any prior miRNA extraction. Differential expression of specific microRNAs in stool of colorectal cancer CRC and adenoma patients suggest fecal microRNAs as a novel potential biomarker for colorectal neoplasia detection. The method of the present invention has diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic relevance for gastroenterological cancers / colorectal cancer and as well as further acquired or hereditary GI diseases.
Owner:BAYLOR RES INST
Cancer associated gene ly6k
InactiveUS20100291091A1High sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
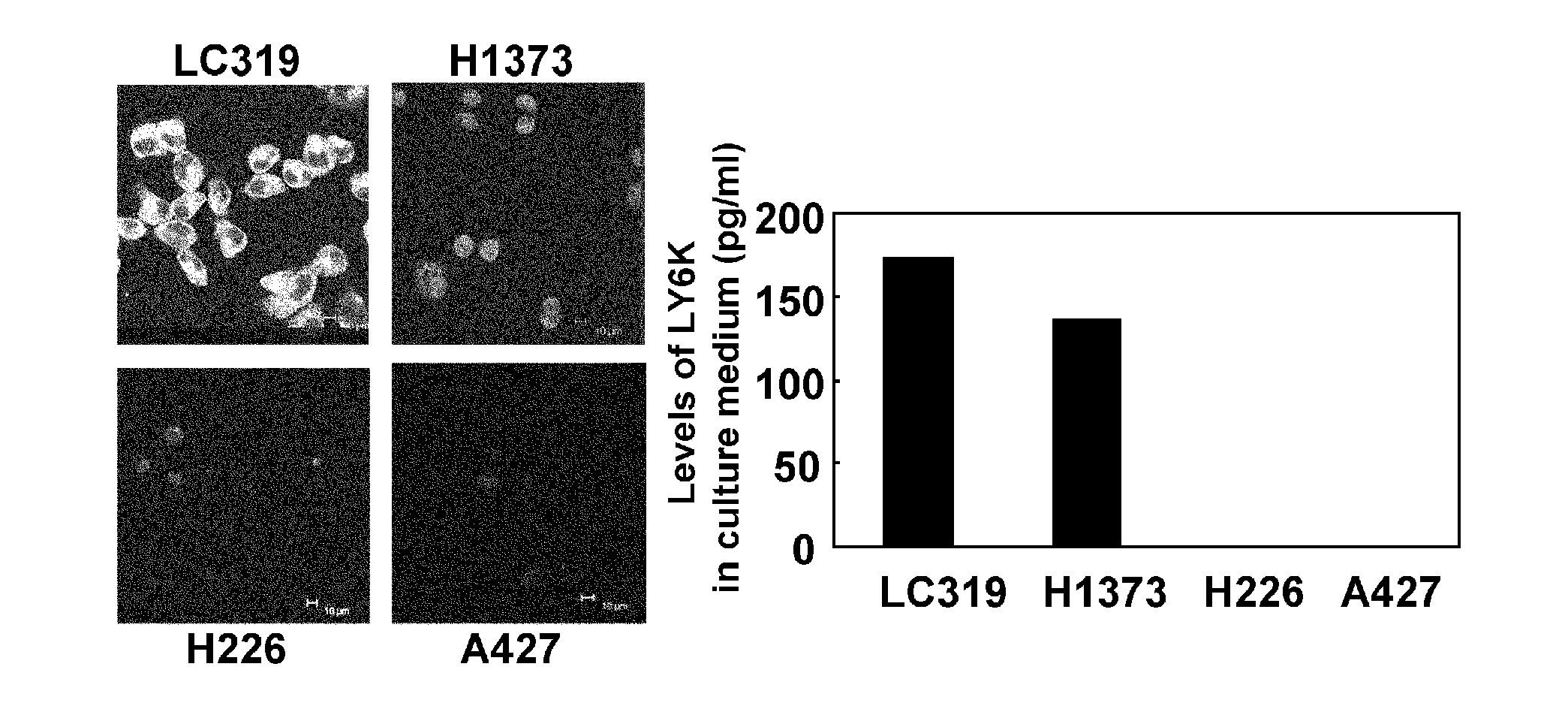
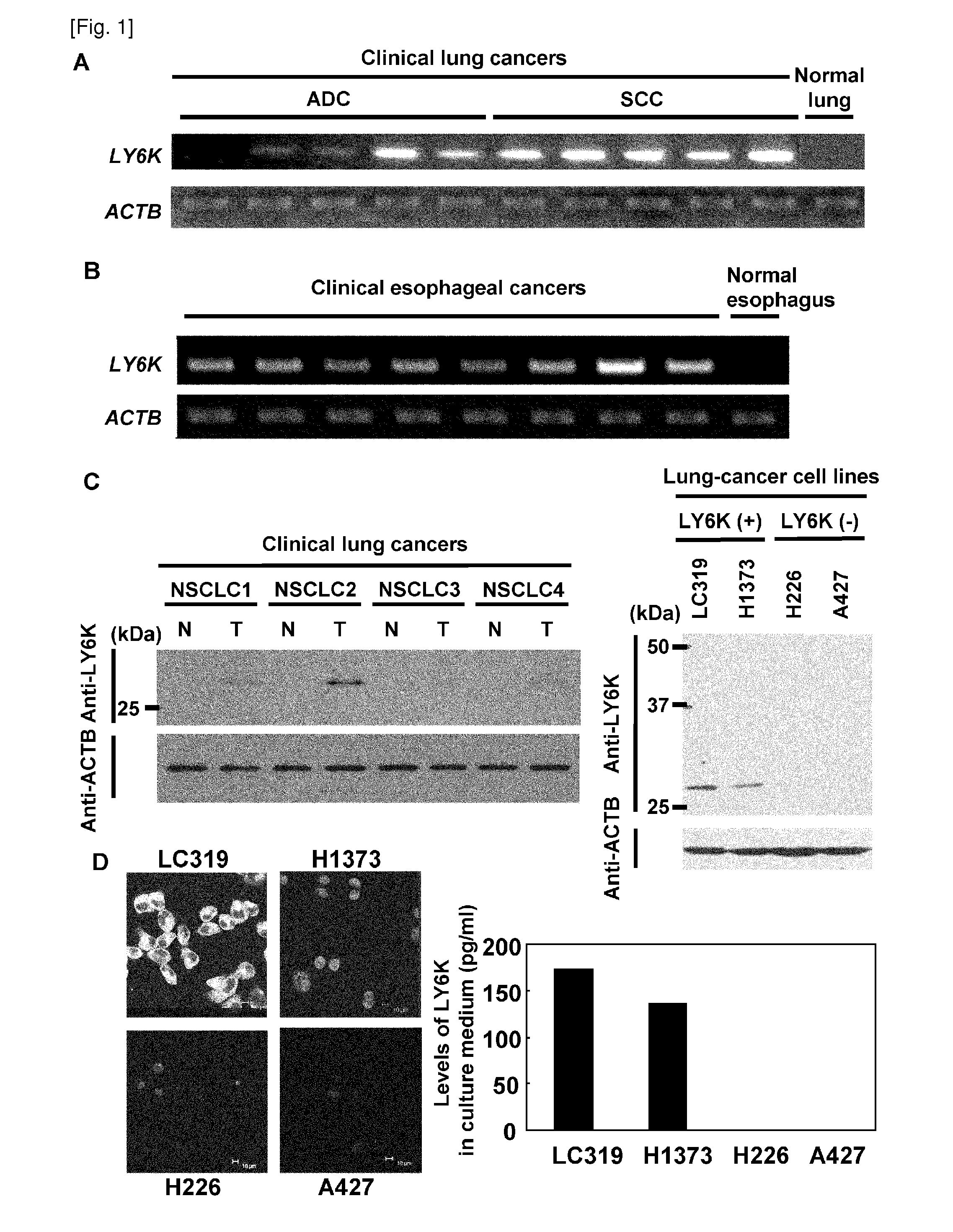
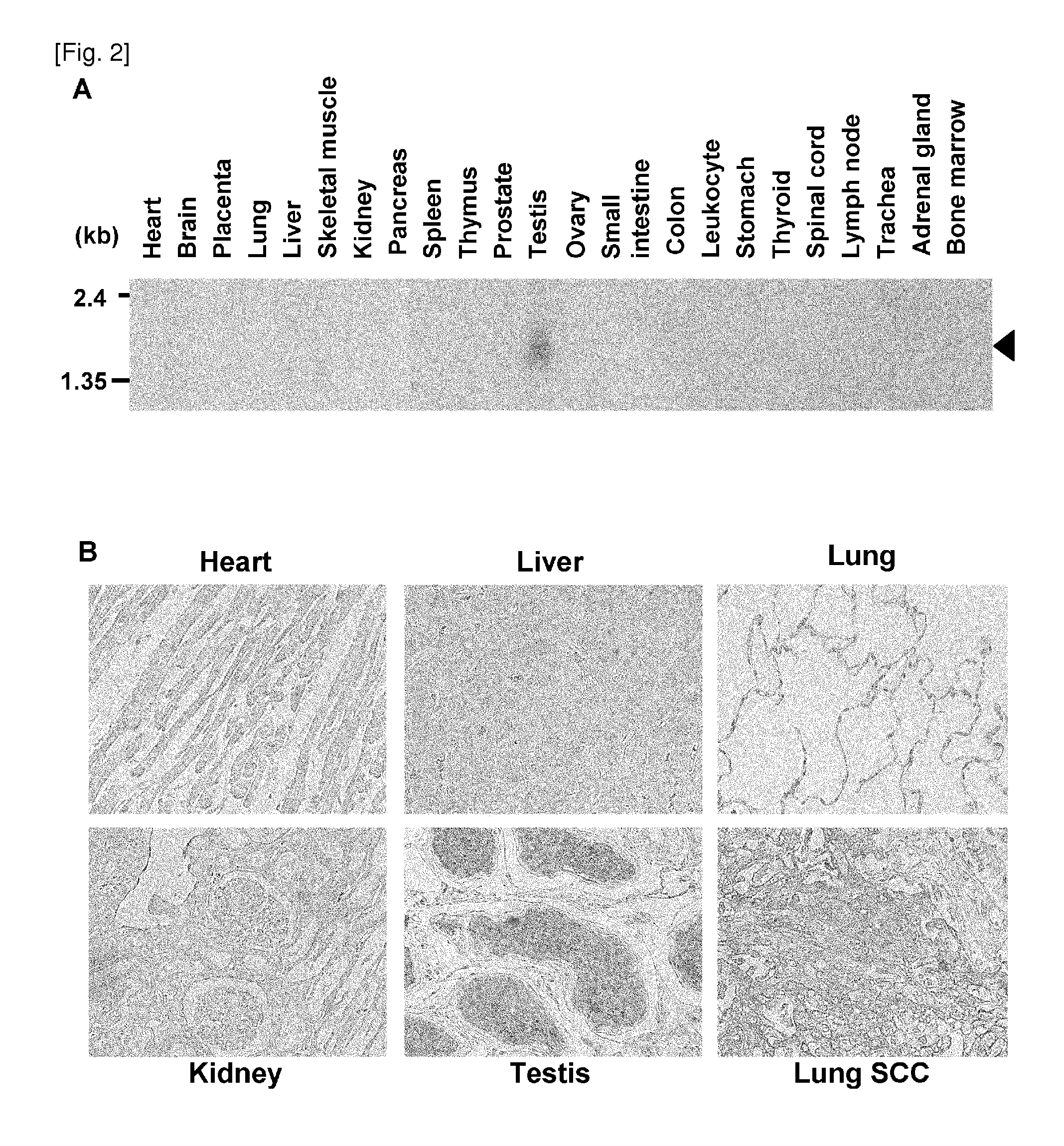
LY6K is identified herein as a potential biomarker useful for the diagnosis of cancer, such as lung and esophageal cancers, as well as for the prognosis of patients with these diseases. As discussed in detail herein, LY6K is specifically over-expressed in most lung and esophageal cancer tissues examined, and is elevated in the sera of a large proportion of patients with these tumors. Accordingly, LY6K may be used in combination with other tumor markers to significantly improve the sensitivity of cancer diagnosis. LY6K may be used in the treatment of ESCC cells, as demonstrated by the fact that small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) of LY6K suppressed growth of the cancer cells. Moreover, the LY6K molecule is also a likely candidate for development of novel therapeutic approaches, such as antibody therapy.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Application of circular RNA as diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for gastric cancer and colorectal cancer
ActiveCN109609643APrevent proliferationWell Diagnosed Stomach CancerMicrobiological testing/measurementPotential biomarkersBlood plasma
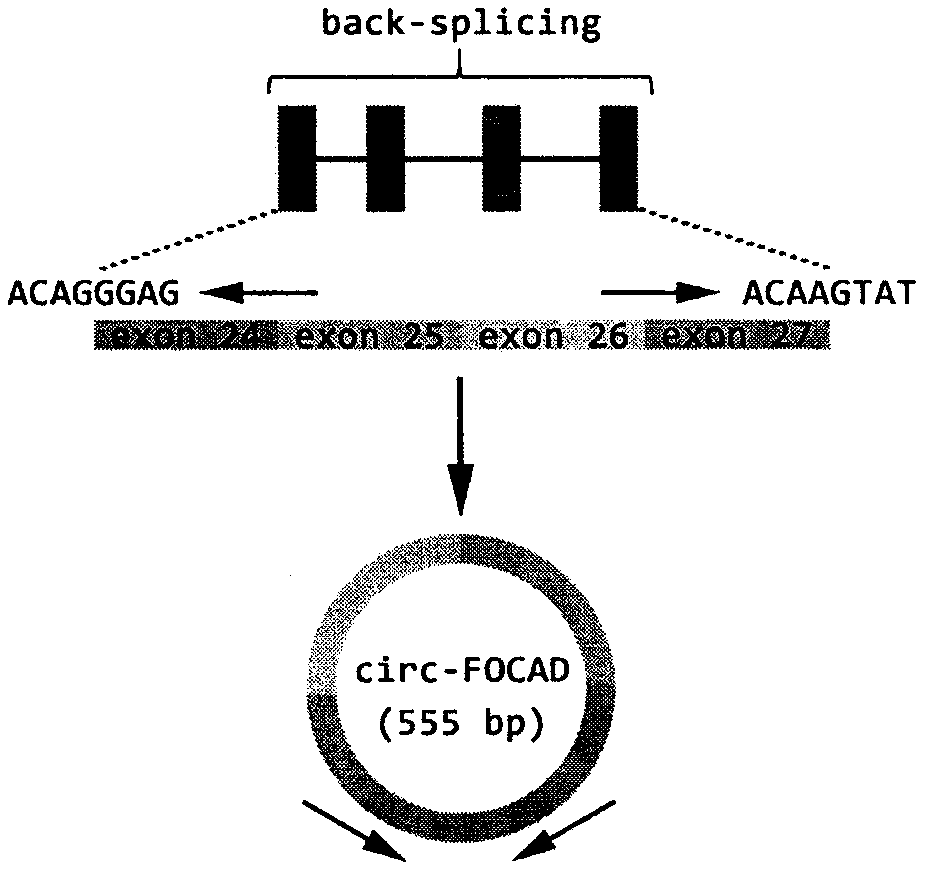
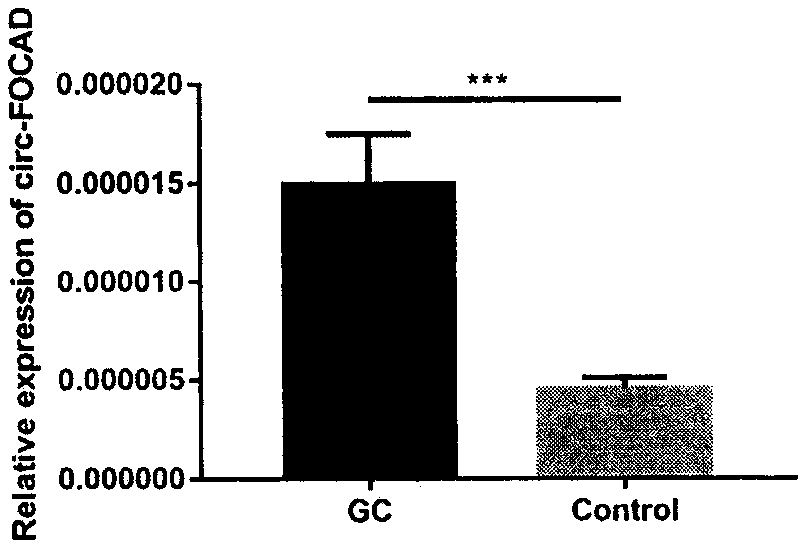
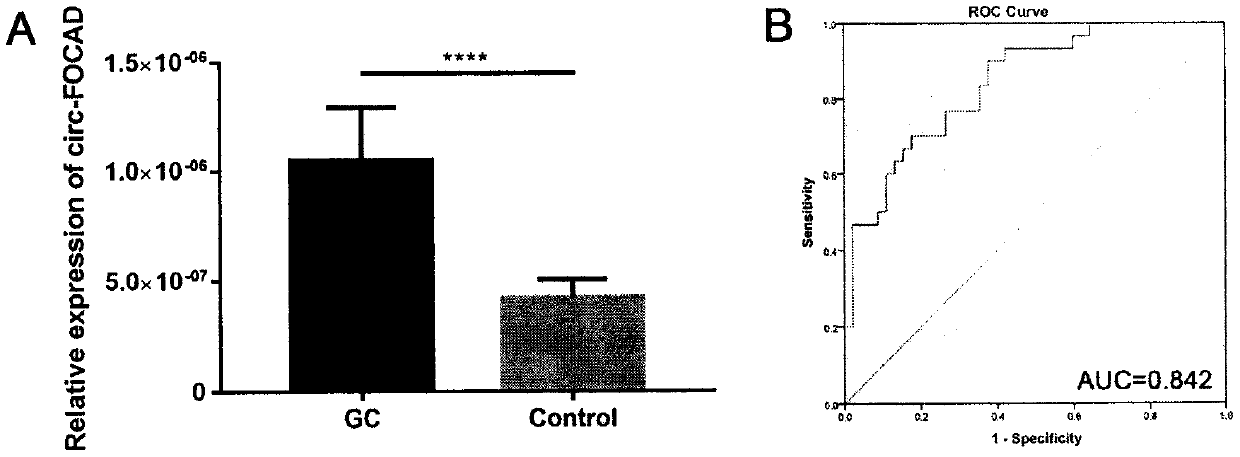
The present invention discloses application of circular RNA FOCAD (circ-FOCAD) as a new potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. The Circ-FOCAD (hsa_circ_0008678|chr9:20923658-20933102+|FOCAD) is formed by reverse splicing of No.24-27 exons of a FOCAD gene with 555 bases. The invention prepares qRT-PCR primers of the circ-FOCAD and a small interfering RNA (siRNA) which interferes with the circ-FOCAD in vitro. Compared with normal controls, the circ-FOCAD is significantly up-regulated in both tumor and plasma samples from patients with gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. In vitro experiments show that the circ-FOCAD plays a role in cancer-promoting genes in gastric cancer and colorectal cancer cells. The results of the present study indicate that the circ-FOCAD is a novel potential biomarker and therapeutic target for gastric cancer and colorectal cancer.
Owner:BEIJING CHAOYANG HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Specific autoantigen of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and application thereof
InactiveCN104292322AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresDisease diagnosisBiological testingDiseasePrimary biliary cirrhosis
The invention discloses a specific autoantigen EIF2C1 of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). According to the specific autoantigen of PBC and the application thereof, six novel autoantigens of PBC are obtained through screening; during the detection on the blood serum of a PBC patient, the positive rate of each autoantigen reaches over 15%, so that the new-found autoantigens are potential biomarkers which are used for accurately diagnosing PBC through distinguishing other autoimmune diseases.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Application of miRNA as biomarker to prediction of IVF-ET outcome
PendingCN112501272AIncrease success rateGood choiceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPotential biomarkersBiomedicine
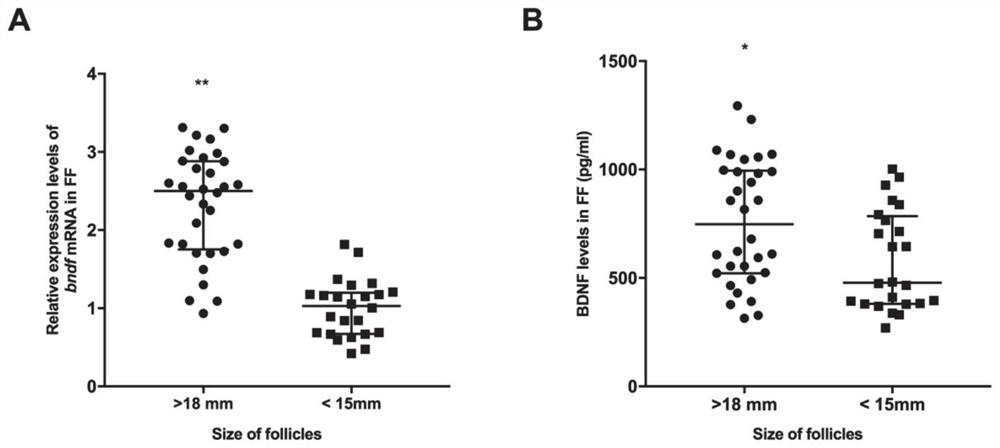
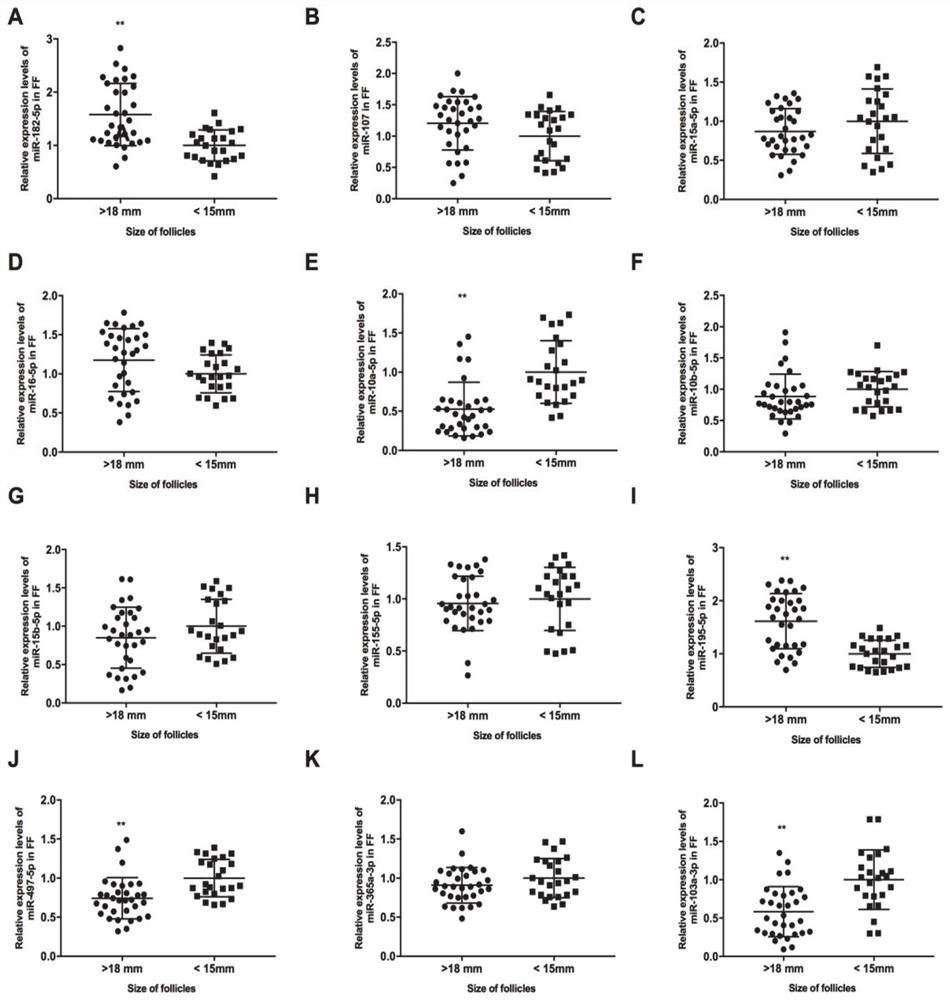
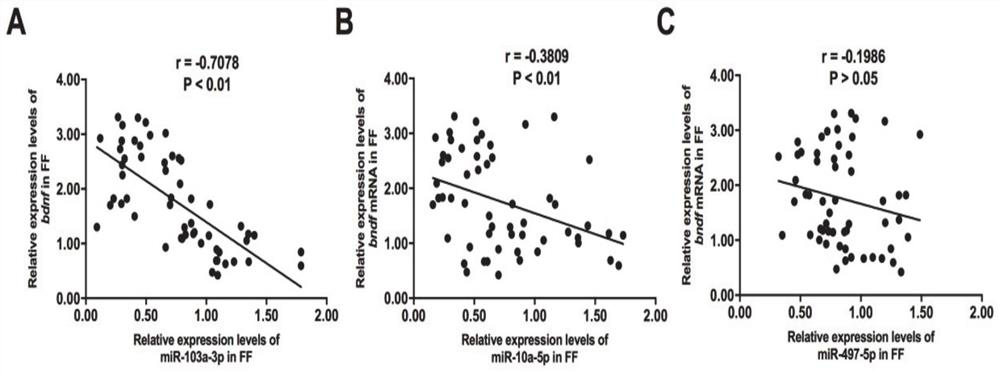
The invention provides an application of miRNA as a biomarker to prediction of IVF-ET outcome, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicines. According to the invention, a series of bioinformatics analysis tools are utilized to predict some candidate miRNAs which are used for targeted regulation of BDNF and are related to follicular development. FFs from mature follicles ( greater than 18 mm)or immature follicles smaller than 15 mm) are then collected, and whether the expression of the miRNAs is negatively correlated to the expression of the BDNF is evaluated. Finally, whether the miRNAscan become potential biomarkers for predicting the IVF-ET outcome or not is further researched. Therefore, two miRNAs, namely miR-103a-3p and miR-10a-5p, are finally screened out, the expression level of the miRNAs in the FF around specific oocyte can predict the outcome of the subsequent IVF treatment of the oocyte, and good practical application value is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
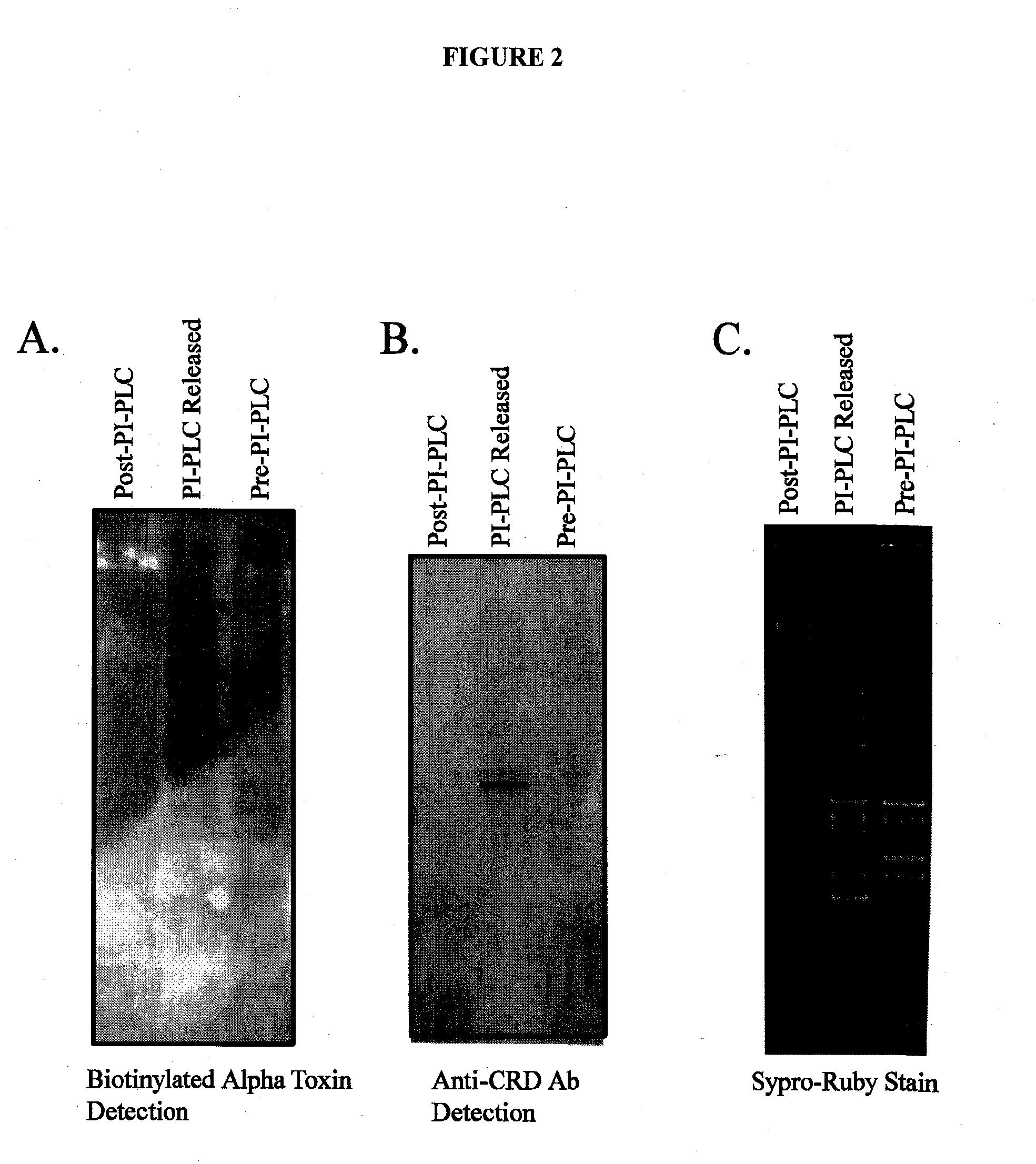
Alpha toxin detection of gpi anchored proteins
InactiveUS20140315212A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseProstate cancer
The present invention relates to a method for the purification, concentration and identification of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchored proteins (GPI-APs) from a biological sample (cells, tissues and / or blood / serum) in a patient or subject, including a human patient or subject. A new method to separate GPI-anchored glycoproteins, a class of glycoproteins found in all animal cells and fluids including serum, from other glycoproteins and proteins for the purpose of identifying potential biomarkers for various diseases, including cancer, especially breast cancer, vaginal cancer, endometrial cancer, uterine cancer, cervical cancer, pancreatic cancer and prostate cancer. The method uses the alpha-toxin from Clostridium septicum to separate GPI-anchored glycoproteins for identification and optionally quantification. The GPI-APs so obtained may be used to raise antibodies for inclusion in an immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis or the monitoring of therapy of cancer in a patient.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Method for screening biomarker related to degree of fatigue in human body fluid by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveCN109425669AWide applicabilityAvoid missing detectionComponent separationHuman bodyScreening method
The invention relates to a method for screening a biomarker related to the degree of fatigue in human body fluid by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting human body fluid samples in different groups; step 2, pretreating the samples collected in step 1; step 3, detecting the samples pretreated in step 2 by the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; step 4, processing data obtained by detection in step 3 and setting threshold values, and screening out potential biomarkers related to the degree of fatigue; step 5, carrying out metabolic pathway retrieval on the potential biomarkers related to the degree of fatigue screened in step 4 and confirming the structure of the potential biomarker; and step 6, comparing structure-confirmed compounds in different groups in step 5, and confirming the biomarkers related to the degree of fatigue. The screening method is good in universality and high in accuracy and confidence level.
Owner:中国民用航空局民用航空医学中心
Model for predicting curative effect of hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy and construction method thereof
ActiveCN112614546AEffectively predict the effect of immunotherapyMedical data miningHealth-index calculationHepatocellular carcinomaPotential biomarkers
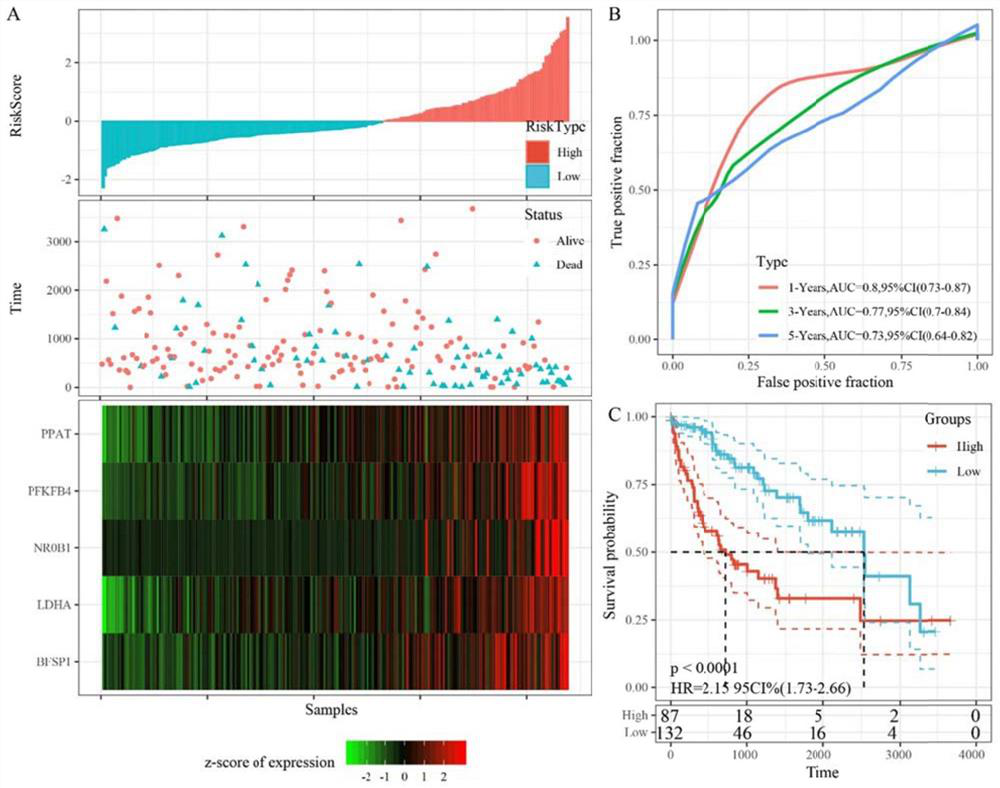
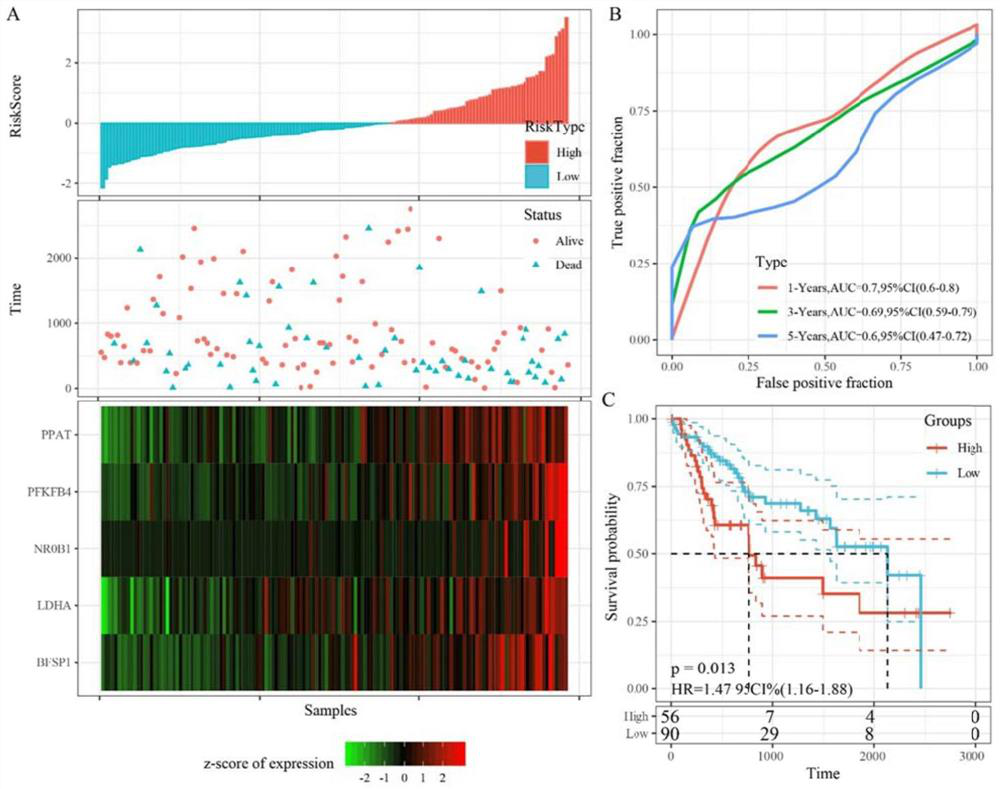
The invention belongs to the field of clinical medicine, and relates to a model for predicting the curative effect of hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy based on 5 genes and a construction method thereof. The model for predicting the immunotherapy effect of hepatocellular carcinoma comprises five genes, namely lactic dehydrogenase A (LDHA), phosphatide phosphoramidate heterogeneous enzyme (PPAT), a bead fiber structural protein 1 (BFSP1), a nuclear receptor sub-fiber 0 group B member 1 (NR0B1) and 6-phosphatide-2-kinase / fructolase-2,6-diphosphatase 4 (PFPFB4). The invention also provides a construction method of the model for predicting the curative effect of hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy based on the 5 genes. Herein, the new immune microenvironment model based on 5 genes is established, so that the effect of a patient on HCC immunotherapy can be effectively predicted, and the 5 genes can be used as potential biomarkers to be clinically applied.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cell response assay for cancer and methods of producing and using same
InactiveUS20170153241A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellAssay
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
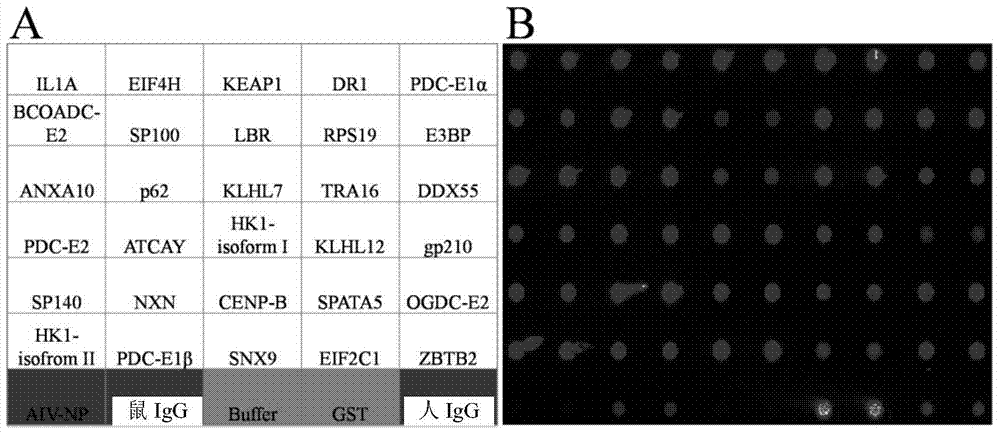
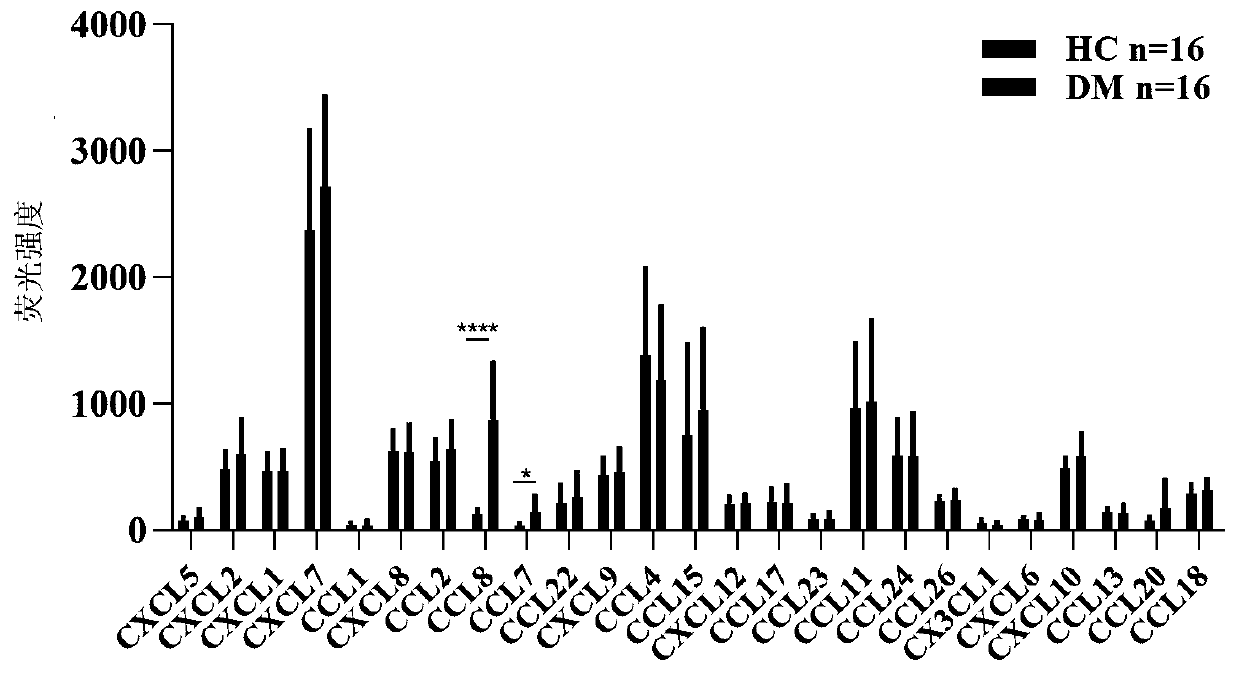
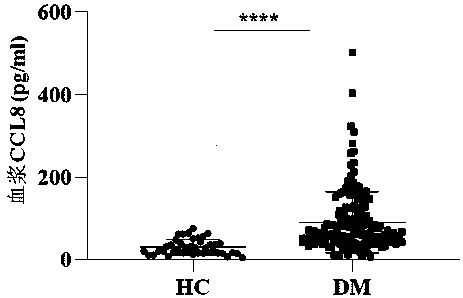
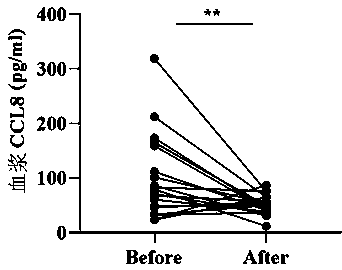
Application of chemotactic factor CCL8 in preparation of dermatomyositis condition and prognosis evaluation reagent
ActiveCN110554202AImproved prognosisDisease diagnosisBiological testingResearch ObjectClinical manifestation
The invention belongs to the field of biological diagnosis and medicine, and particularly relates to an application of a chemotactic factor CCL8 in preparation of a dermatomyositis condition and prognosis evaluation reagent. According to the invention, a patient plasma specimen for definite diagnosis of dermatomyositis is used as a research object; protein chip detection is carried out; a sample is expanded; a protein chip result is verified by an ELISA method; by combining biochemical indexes and clinical manifestation judgment correlation of patients, it is proved that the blood plasma CCL8level of dermatomyositis patients is remarkably higher than that of healthy people, the expression level of the blood plasma CCL8 is related to the illness state and prognosis of the patients, the blood plasma CCL8 level of dermatomyositis patients effective in treatment is remarkably reduced, and CCL8 can aggravate pulmonary lesions of interstitial pneumonia mice. Therefore, the CCL8 can be usedas a potential biomarker to be applied to a reagent for evaluating the illness state and prognosis of dermatomyositis patients, experimental data and theoretical basis are provided for the applicationof the CCL8 to the illness state and prognosis evaluation of the dermatomyositis patients, and the invention further provides a corresponding kit for evaluating the illness state and prognosis of thedermatomyositis patients.
Owner:NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com