In vitro method for early detection of severity of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and prognosis
A technology for subarachnoid space and cerebral aneurysm, which is applied in the field of medical detection and can solve the problems of inaccurate prediction and inability to predict in advance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1 Experimental Design and Specimen Collection
[0031] 1. Experimental design
[0032] All the subjects signed the informed consent form by themselves or their family members, and all the samples used in the research process were approved by the ethics committee. The embodiment of the present invention is divided into three stages: the discovery stage, the coaching group, and the verification stage. Next-generation sequencing was performed on plasma exosomes from brain aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) and the control group, and differential microRNANAs were found. Then, through 10 small samples of plasma, the coaching group's research was carried out to determine the candidate microRNANAs that entered the verification stage. A large sample of candidate microRNANAs was subsequently validated. Neurological prognosis was evaluated by modified Rankin score. Among them, 0-2 is divided into good prognosis, 3-6 is divided into poor prognosis.
[0033] 2...
Embodiment 2
[0035]Example 2 Extraction, electron microscope observation and WB verification of exosomes
[0036] 1. Exosome isolation
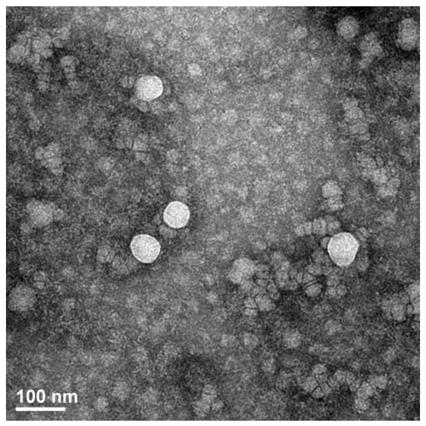
[0037] Exosomes were isolated by exoEasy Maxi Kit (from plasma; Qiagen, Valencia, CA). First filter the specimen through a 0.8 μm filter tube. The sample and buffer XBP were mixed in equal volumes 1:1 and incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. Transfer to a centrifuge tube with a filter membrane, and centrifuge at 500g for 1 minute to remove the centrifugate. The isolated exosomes should be washed with Buffer XWP and centrifuged at 5000g for 5 minutes to remove impurities. Finally, the collected exosomes were lysed with buffer XE. The amount of concentrated exosomes was measured using the BCA method. For transmission electron microscopy, exosomes were absorbed by carbon-coated nickel grids for 1 hour, washed three times with PBS for 5 minutes each time, and fixed with 2% formaldehyde for 10 minutes. Use uranyl acetate and lead citrate for nega...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 NGS sequencing, data collection and differential microRNAs analysis
[0041] 1. NGS sequencing
[0042] Small RNA library construction: Trizol was used to extract total RNA. Use Bioanalyzer 2100 to quantify and test the purity of total RNA, and the purity is qualified if the RIN is greater than 7.0. About 1ug of total RNA can be used to build a library, and IlluminaHiseq2500 is used for sequencing.
[0043] 2. Data collection
[0044] Raw data were collected by ACGT101-microRNA, and dimers, rRNA, tRNA, snRNA, snoRNA and repetitive sequences were removed. The unique sequences of 18-26 nucleotides were then searched by microRNABase 21.0 to identify known microRNANAs and novel 3p- or 5p-microRNANAs.
[0045] 3. Differential microRNANAs analysis
[0046] Applying Fisher's exact test, X 2 2*2 inspection, X 2 The n*n test, t test or ANOVA based on the experimental design were used to test the difference of the sequencing results. The significance thresholds...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com