Patents
Literature
892 results about "Oocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An oocyte (UK: /ˈoʊəsaɪt/, US: /ˈoʊoʊ-/), oöcyte, ovocyte, or rarely ocyte, is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources has been put into action as a means of conserving traditional livestock.
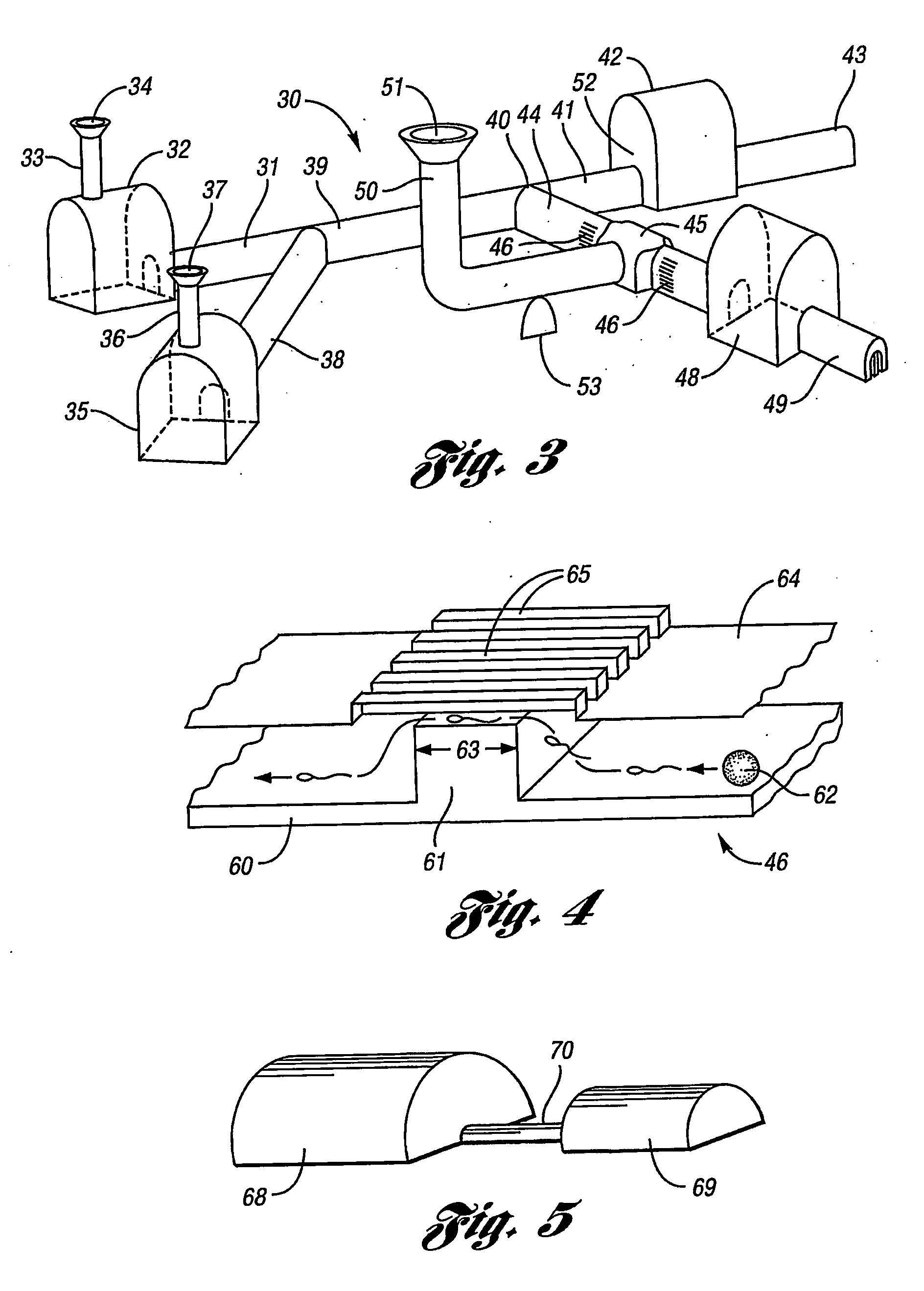
CICM cells and non-human mammalian embryos prepared by nuclear transfer of a proliferating differentiated cell or its nucleus
InactiveUS6235970B1Simple procedureSimplifying and facilitating procedureNervous disorderMuscular disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
Full Karyotype Single Cell Chromosome Analysis
InactiveUS20090098534A1Improve accessibilityReduce nonspecific bindingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell stainingTumor cells
A full set of 24 chromosome-specific probes to analyze single cells or cell organelles to test for abnormalities is described. When used in an assay based on sequential hybridization, the full set is comprised of three subsets of chromosome-specific probes with each set comprised of 8 different probes. Also described are assays using a set of probes to analyze single cells and cellular organelles to accurately determine the number and type of targeted human chromosomes in various types of cells and cell organelles, such as tumor cells, interphase cells and first polar bodies biopsied from non-inseminated oocytes. Methods of selection or generation of suitable probes and hybridization protocols are described, as are preferred probes for frill set of 24 chromosome-specific probes to target all 24 human chromosomes are described in the Tables.
Owner:REPROGENETICS +1
Cloning pigs using donor nuclei from non-quiescent differentiated cells
InactiveUS6235969B1Superior genotypes of pigsSpeed up genetic progressNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPresent method
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated pig cell nuclei into enucleated pig oocytes is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic pig embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Container assembly for intravaginal fertilization and culture and embryo transfer and method of intravaginal fertilization and culture employing such a container
InactiveUS6050935AConvenient inspectionPrecise positioningAnimal reproductionOrganic chemistryLoop of HenleMicroscopic exam
An intravaginal fertilization and culture container includes a main chamber and a microchamber. A culture medium, one or more oocytes and sperm are introduced through an access opening having an associated resealable closure device. The container is enveloped in a capsule of soft elastic material prior to lodgment in the posterior fornix. A loop on one capsule part adapts the length to anatomic variations. The microchamber has a channel which receives the catheter tip to facilitate embryo retrieval while eliminating risk of injury thereto. The microchamber permits embryos to be microscopically inspected in situ before transfer to the uterine cavity.
Owner:LOUISVILLE LAB +2
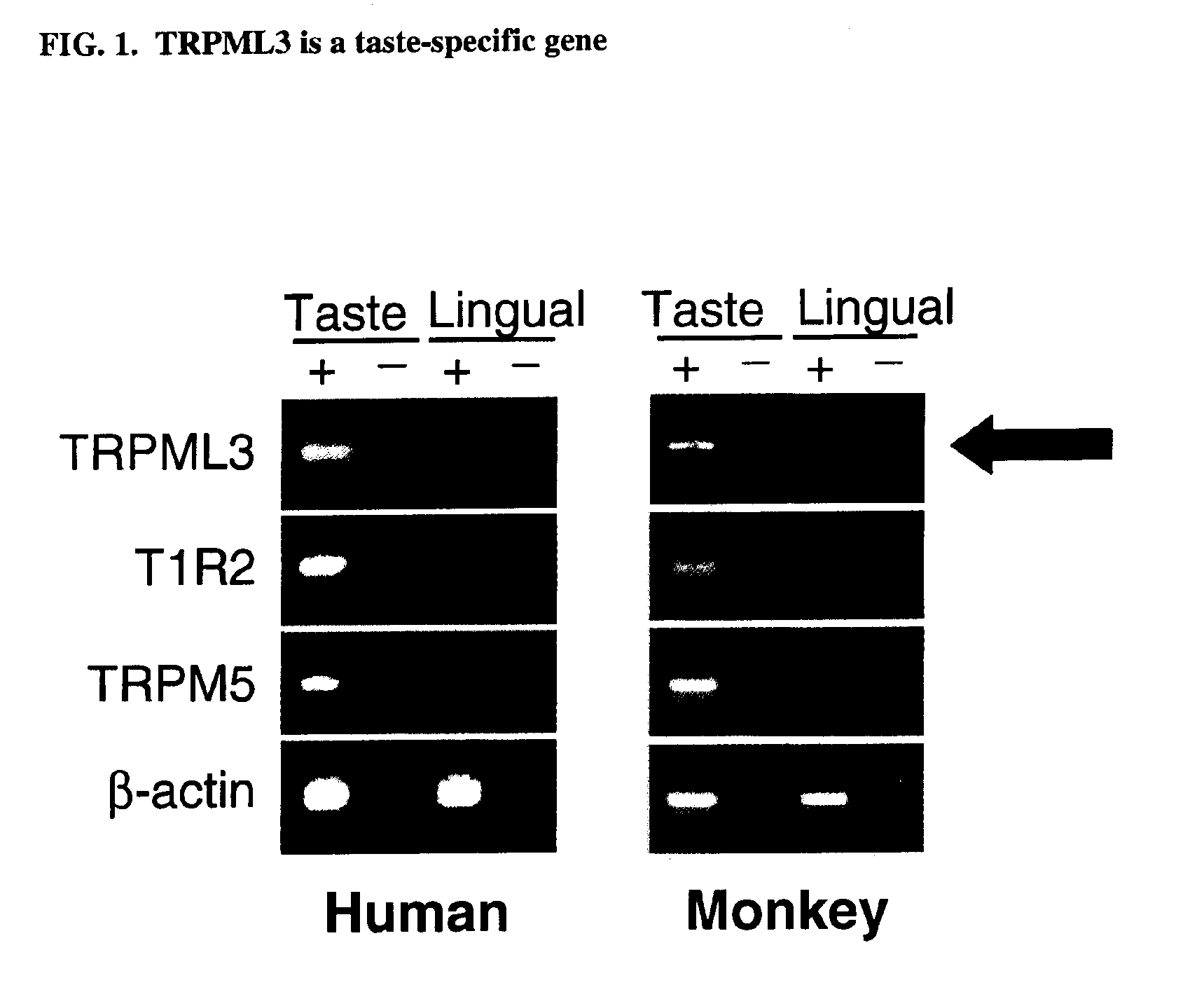
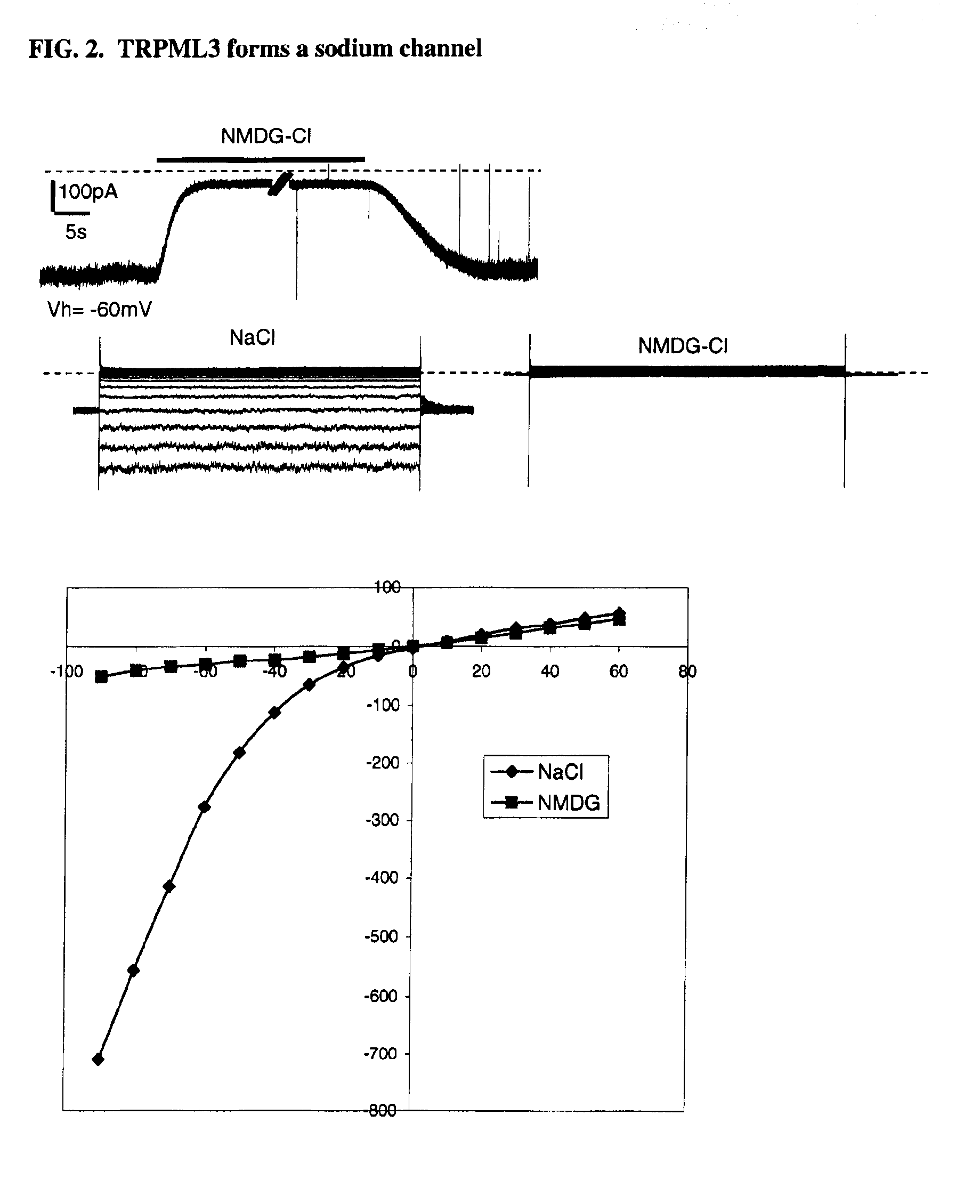
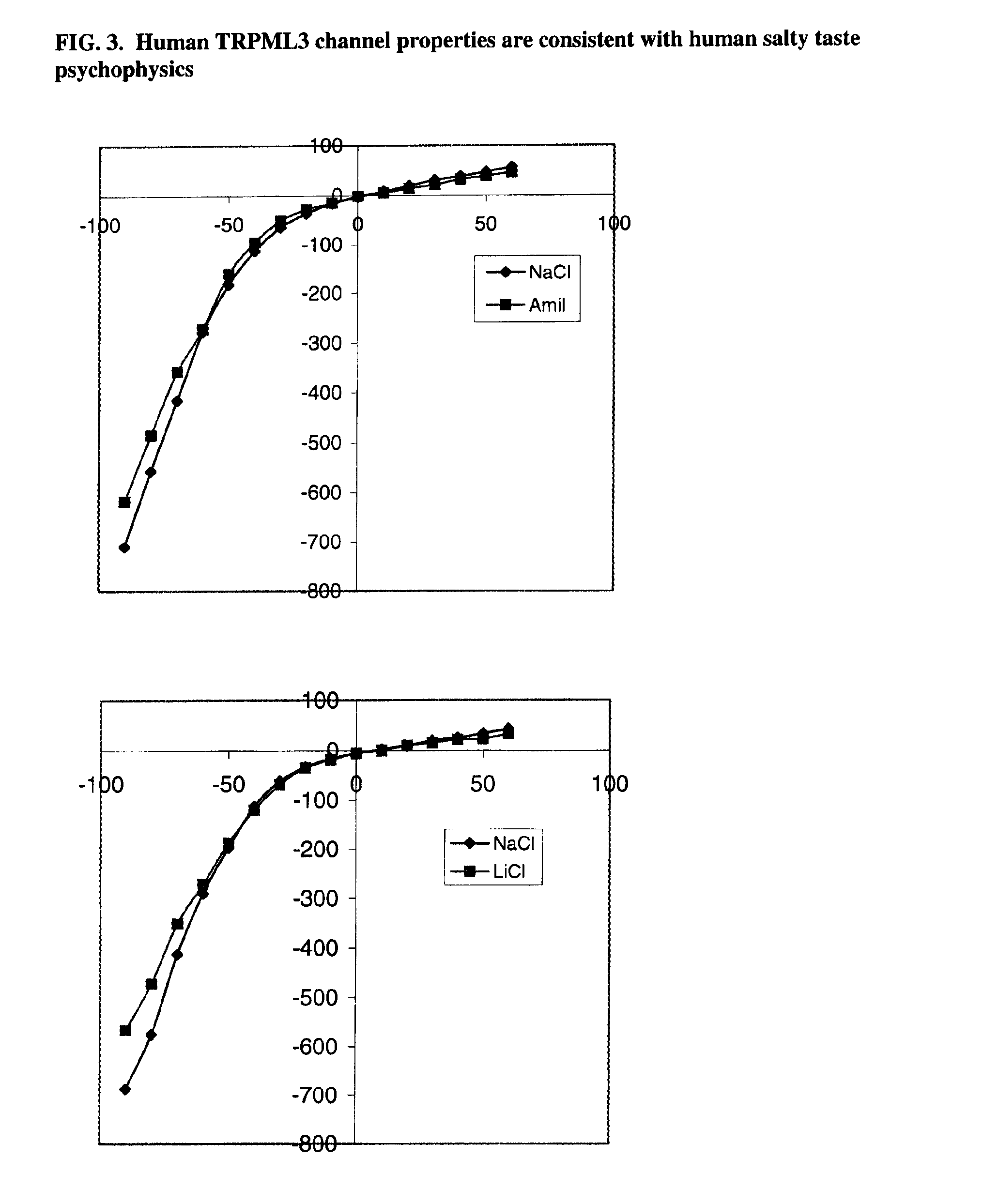
Identification of TRPML3 (MCOLN3) as a salty taste receptor and use in assays for identifying taste (salty) modulators and/or therapeutics that modulate sodium transport, absorption or excretion and/or aldosterone, and/or vasopressin production or release
InactiveUS20090210953A1Reduce volumeIncrease pressureCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSalty taste perceptionReceptor
The present invention relates to the elucidation that TRPML3 is involved in salty taste perception in primates including humans and likely other mammals and based thereon high-throughput mammalian and medium-throughput oocyte-based electrophysiological assays for identifying human TRPML3 modulators, preferably TRPML3 enhancers. Compounds that modulate TRPML3 function in the assay are expected to affect salty taste in humans. The inventive electrophysiological assays, such as the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique, facilitate the identification of compounds which specifically modulate human TRPML3. The assays of the invention provide a robust screen useful to detect compounds that facilitate (enhance) or inhibit TRPML3 function. Compounds that enhance or block TRPML3 channel activity should thereby modulate salty taste. In addition, these compounds may be used to regulate sodium excretion, urinary output and other biological functions relating to sodium levels and TRPML3 related functions.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
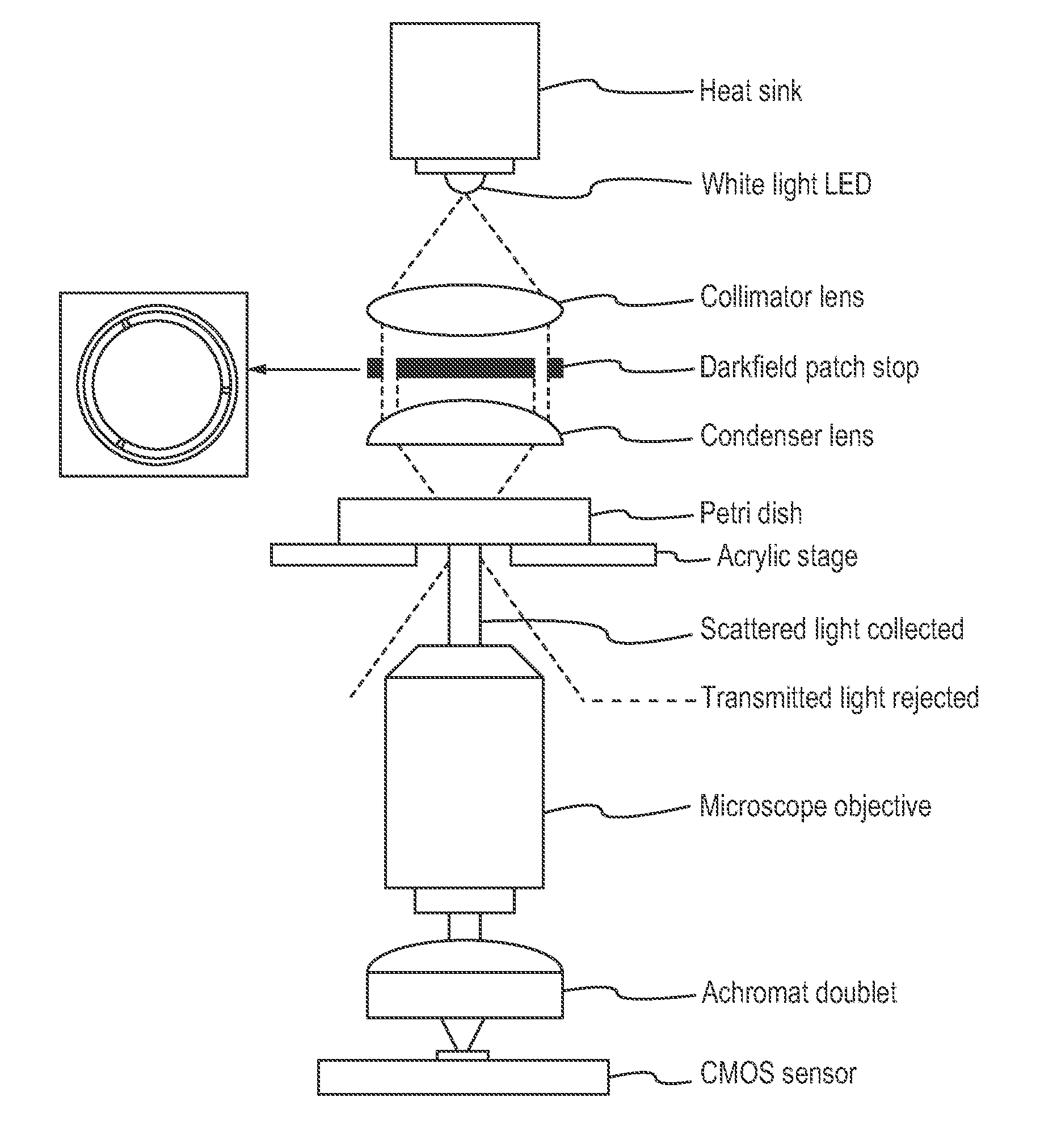
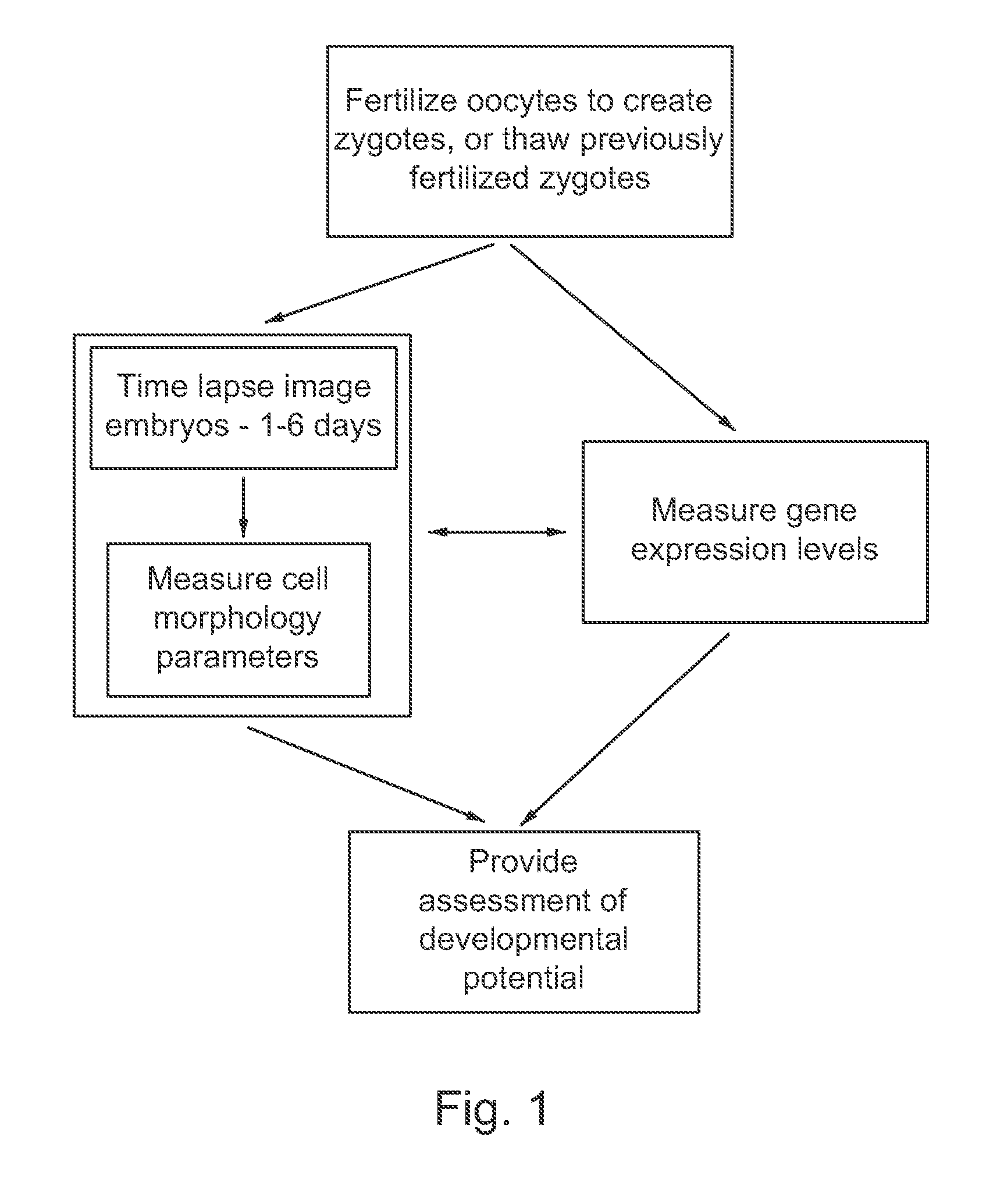
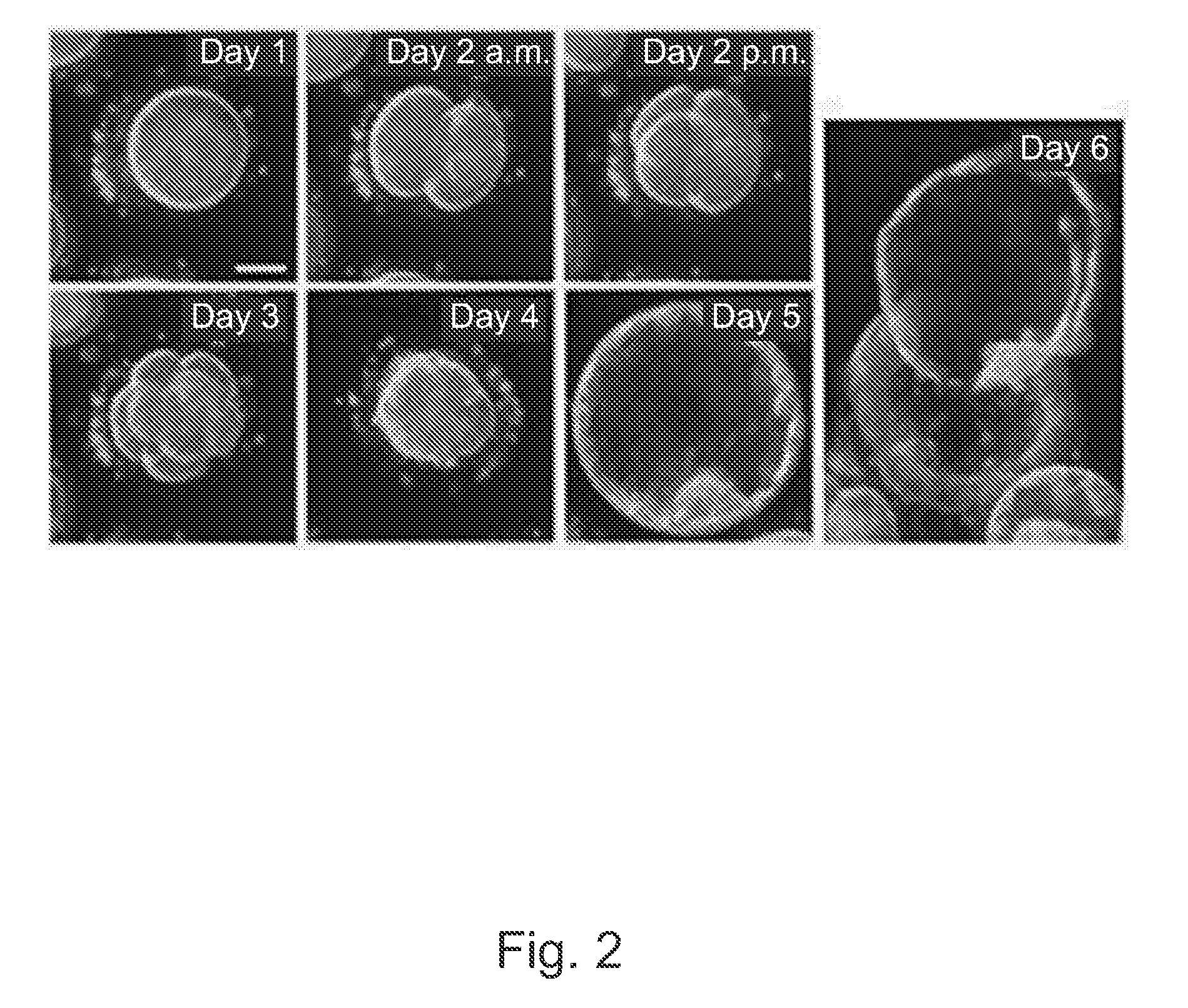
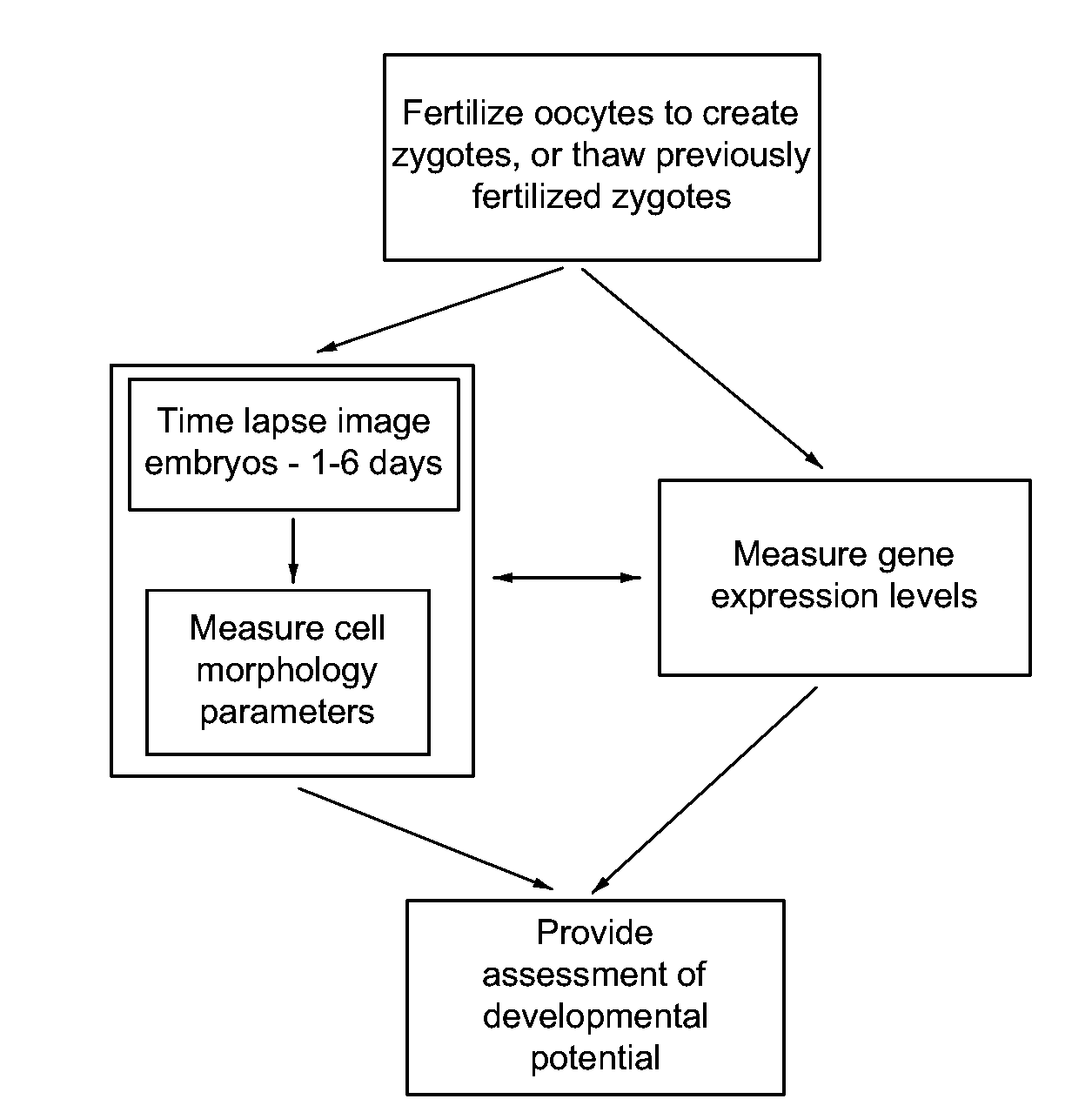
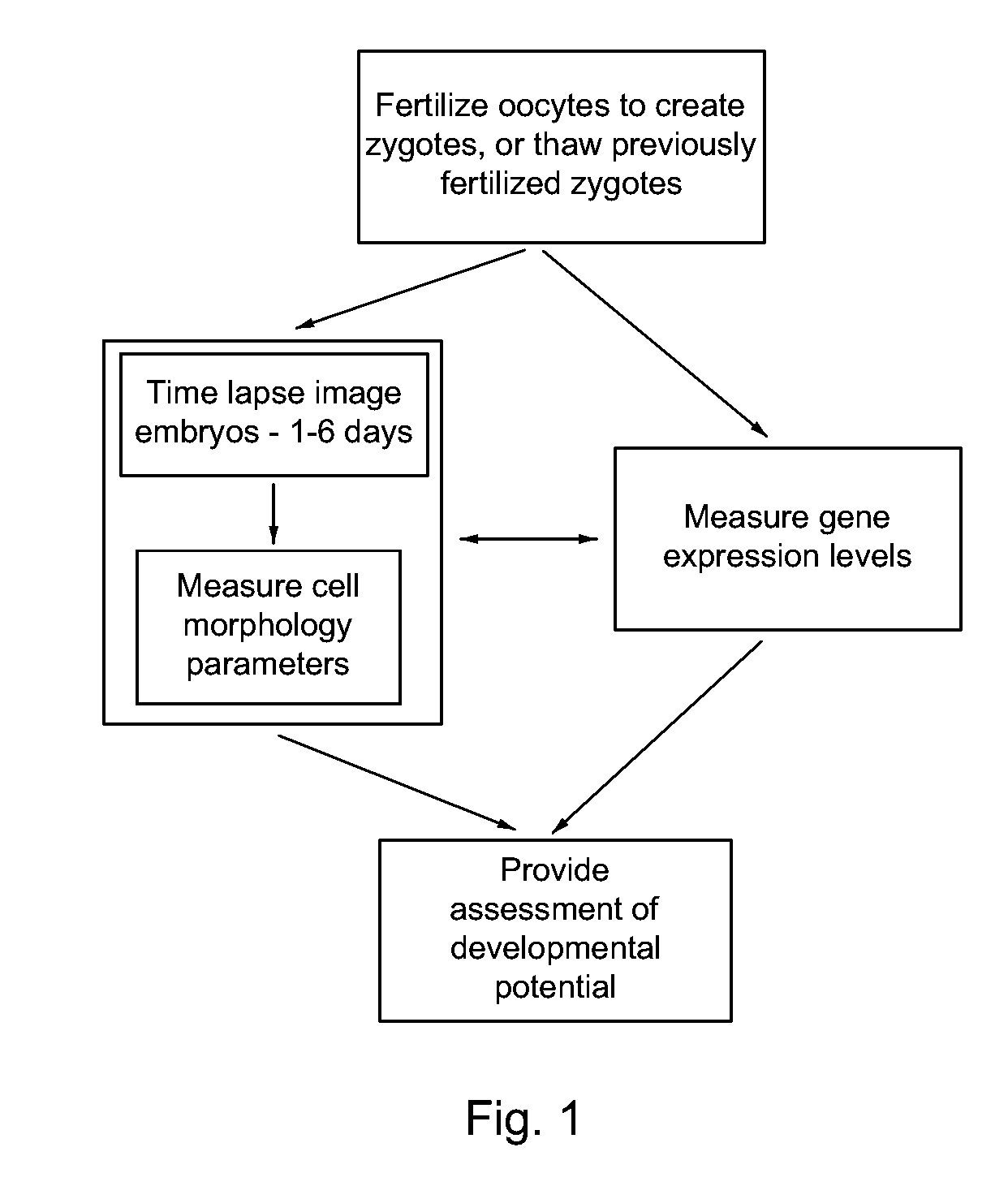
Imaging and evaluating embryos, oocytes, and stem cells
Methods, compositions and kits for determining the developmental potential of one or more embryos or pluripotent cells and / or the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in one or more embryos or pluripotent cells are provided. These methods, compositions and kits find use in identifying embryos and oocytes in vitro that are most useful in treating infertility in humans.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method of cloning reproductive and respiratory syndrome resisting pig
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Hormone normalization therapy and uses therefor
InactiveUS20090137478A1Reduce morbidityAvoid infertilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisMiscarriageAromatase inhibitor
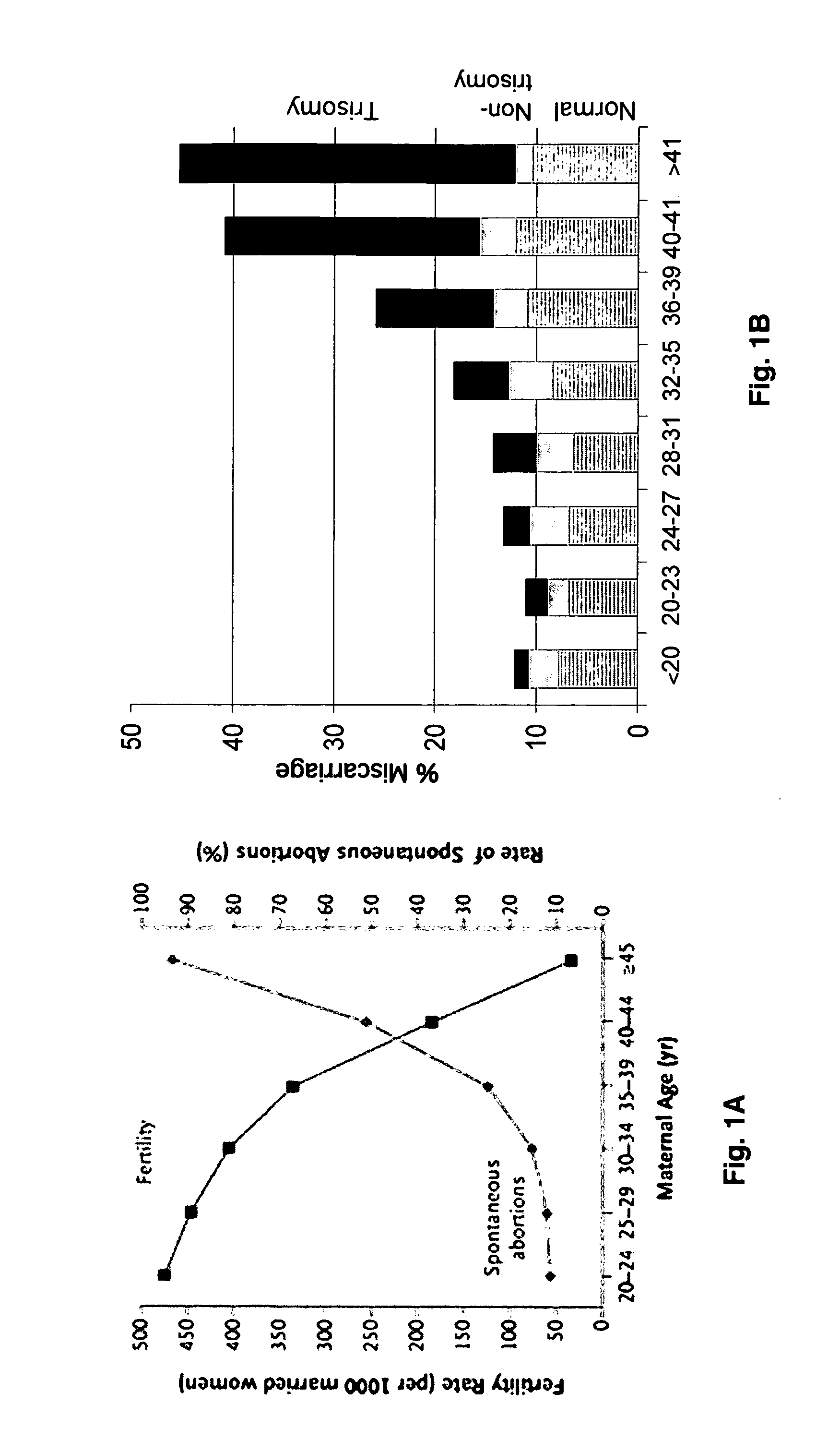
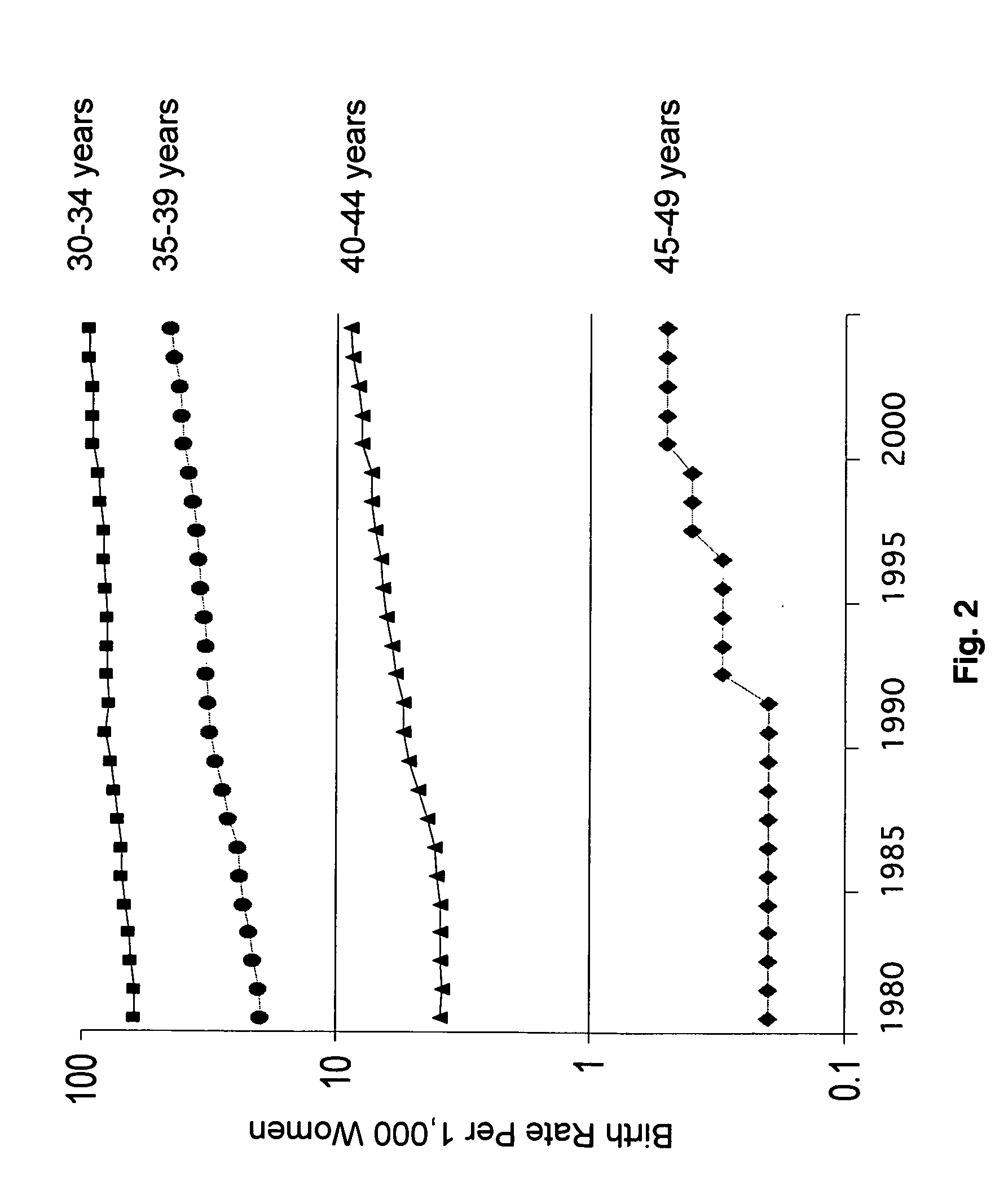
The present invention discloses a novel method of prevention of birth defects, miscarriages and infertility in women. The two therapies, disclosed herein, the hormone normalization therapy and the aromatase inhibitor-hormone normalization therapy, focus on restoring young hormonal levels in women in order to prevent female infertility and miscarriages, guide follicular and oocyte maturation, and promote correct chromosomal segregation in oocytes and early embryos.
Owner:BERNSTEIN LORI R
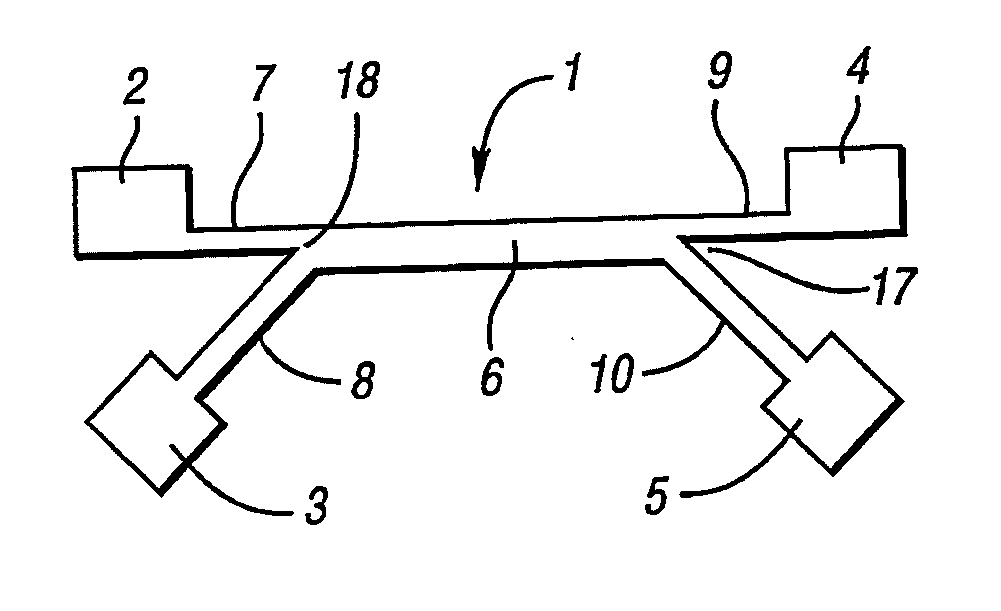
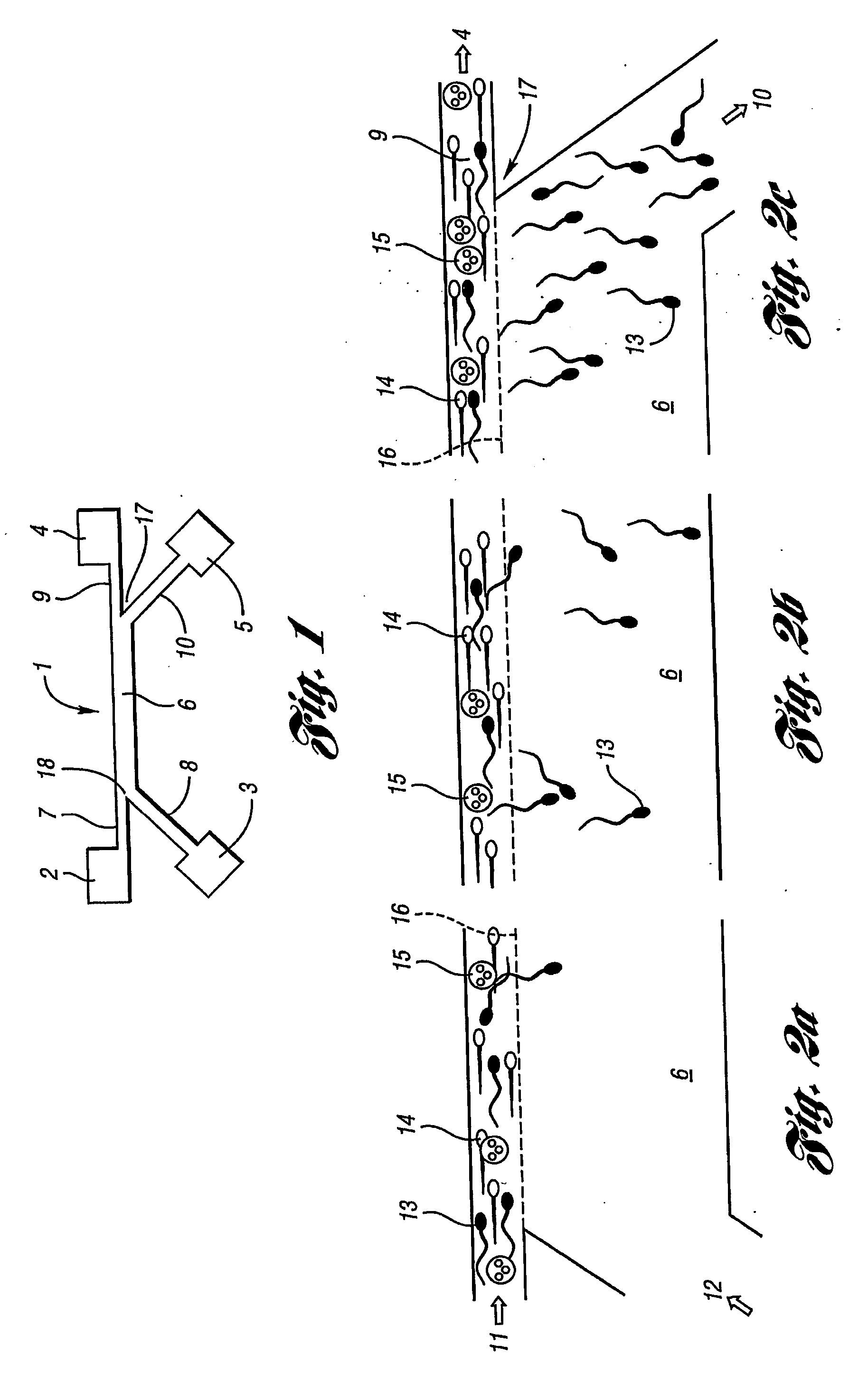
Integrated microfluidic device for single oocyte trapping
ActiveUS20130204076A1Improve developmentEfficient use ofLaboratory glasswaresBiomass after-treatmentEngineeringEmbryo
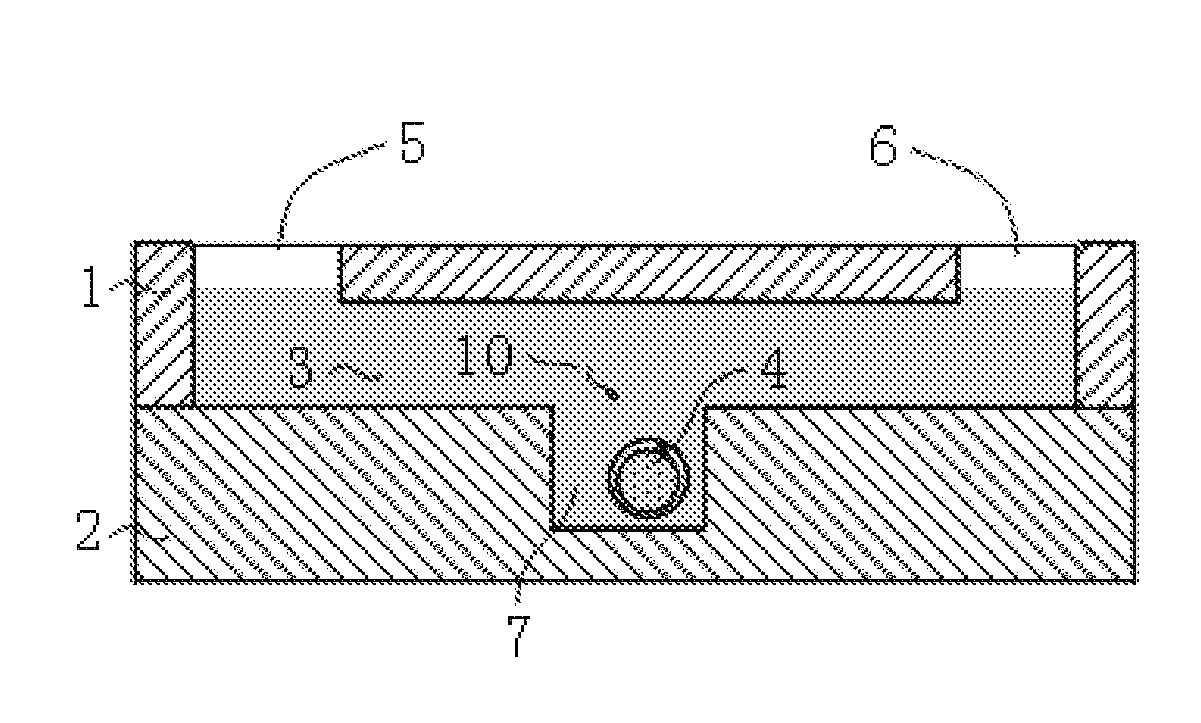
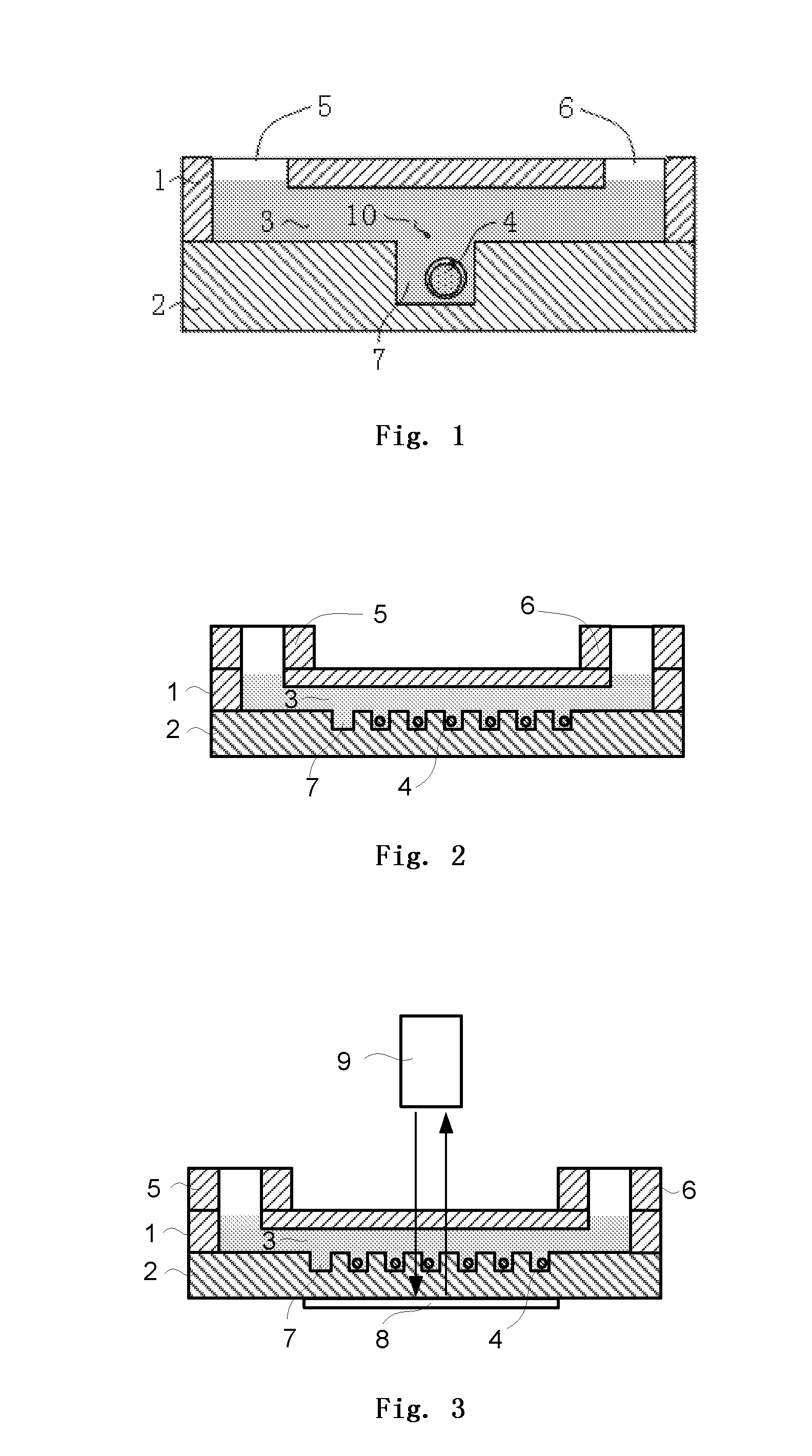
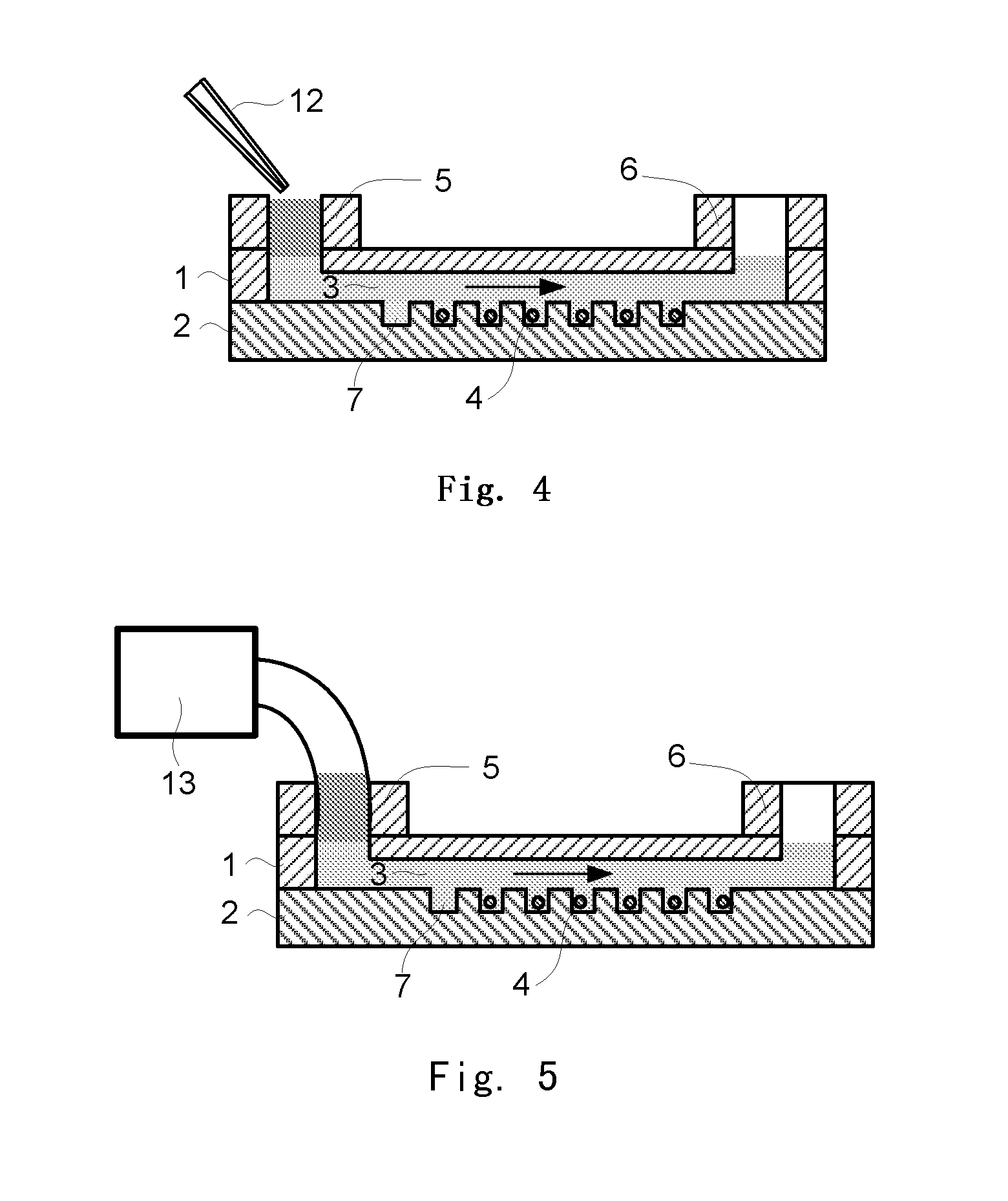
An integrated microfluidic device and its usage are provided. The microfluidic device comprises an upper layer (1) and a lower layer (2), wherein the lower layer (2) is bound to the upper layer (1). The upper layer (1) comprises a micro-channel (3) and the lower layer (2) comprises a micro-well (7) array. The micro-channel (3) is in fluidic connection with the micro-well (7) array, and the height of the micro-channel (3) is greater than the diameter of the oocyte (4) flowing through the micro-channel (3). The integrated microfluidic device has many advantages including low cost, high integration, and convenient operation, and has application prospects in reproductive medicine and the research of fertilization and embryo early development.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Treatment of Infertility
InactiveUS6281013B1Degree of side effect can be improvedDegree of improvementBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhysiologyMeiosis
In an in vitro fertilization method, a woman is treated with a hypothalamic hormone and / or a pituitary hormone or an agonist or antagonist thereof or an active derivative thereof for a short period of time and, thereafter, using in vitro oocyte maturation egg or eggs are retrieved from the woman and are maturated using a meiosis activating compound.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
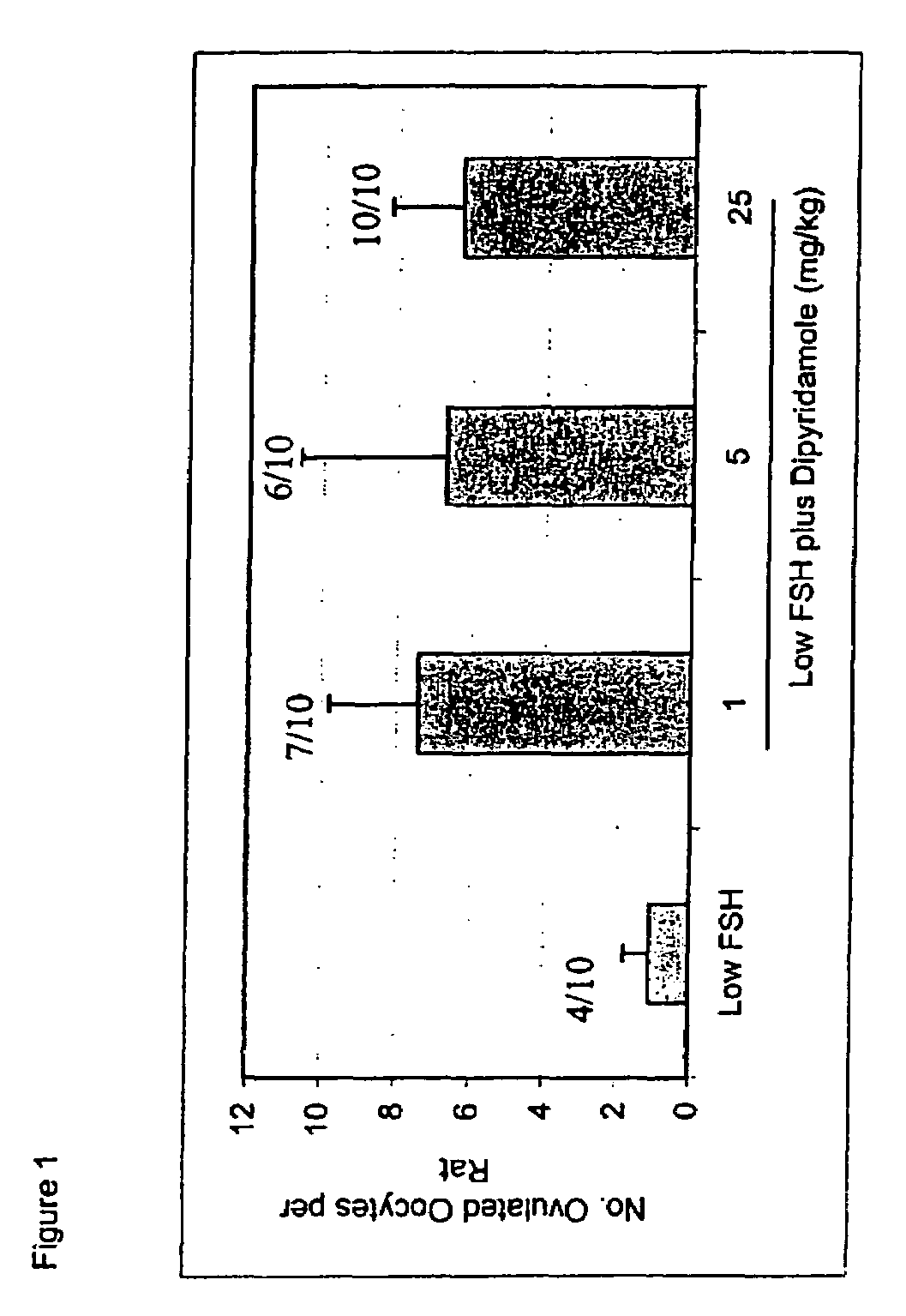
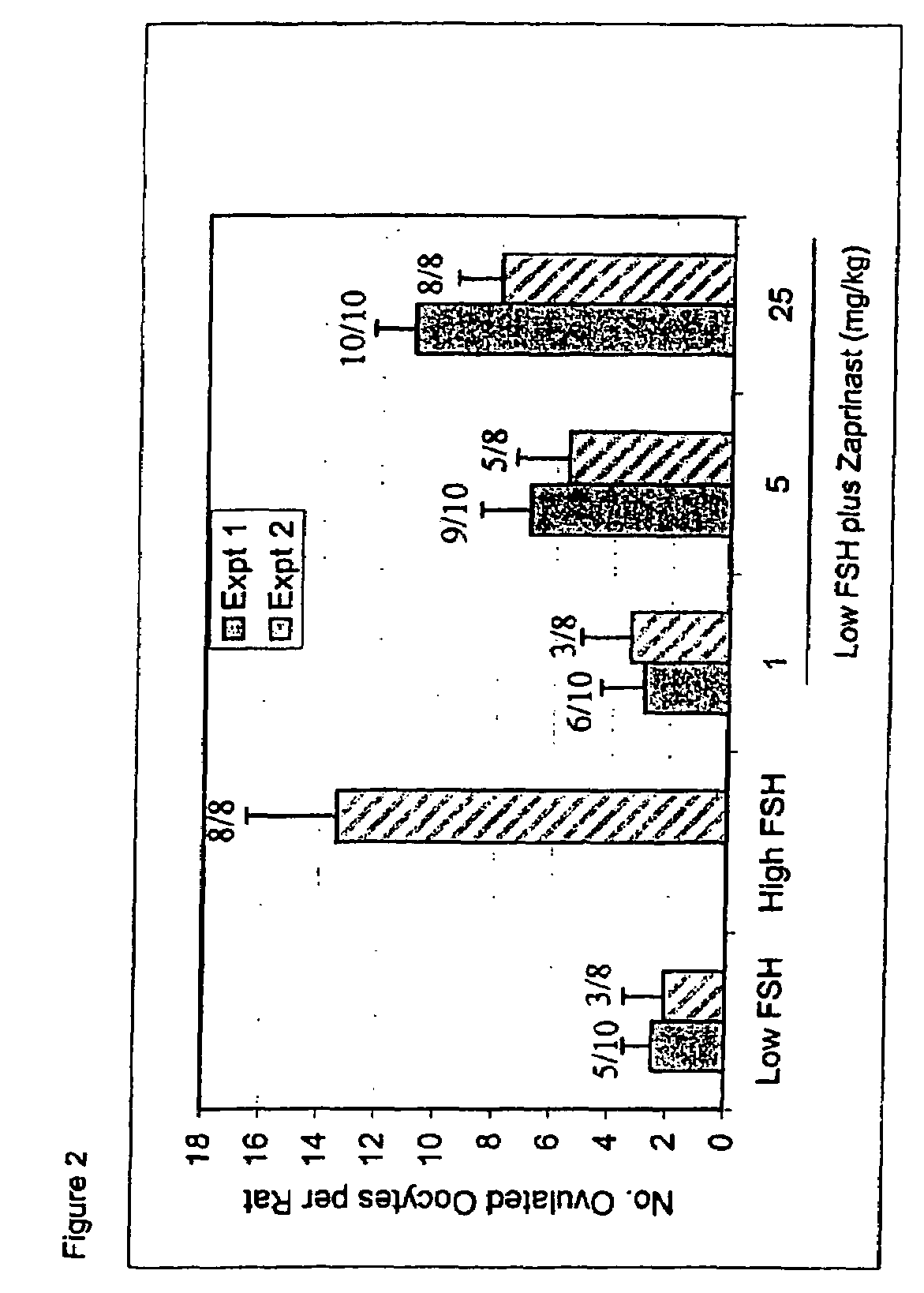
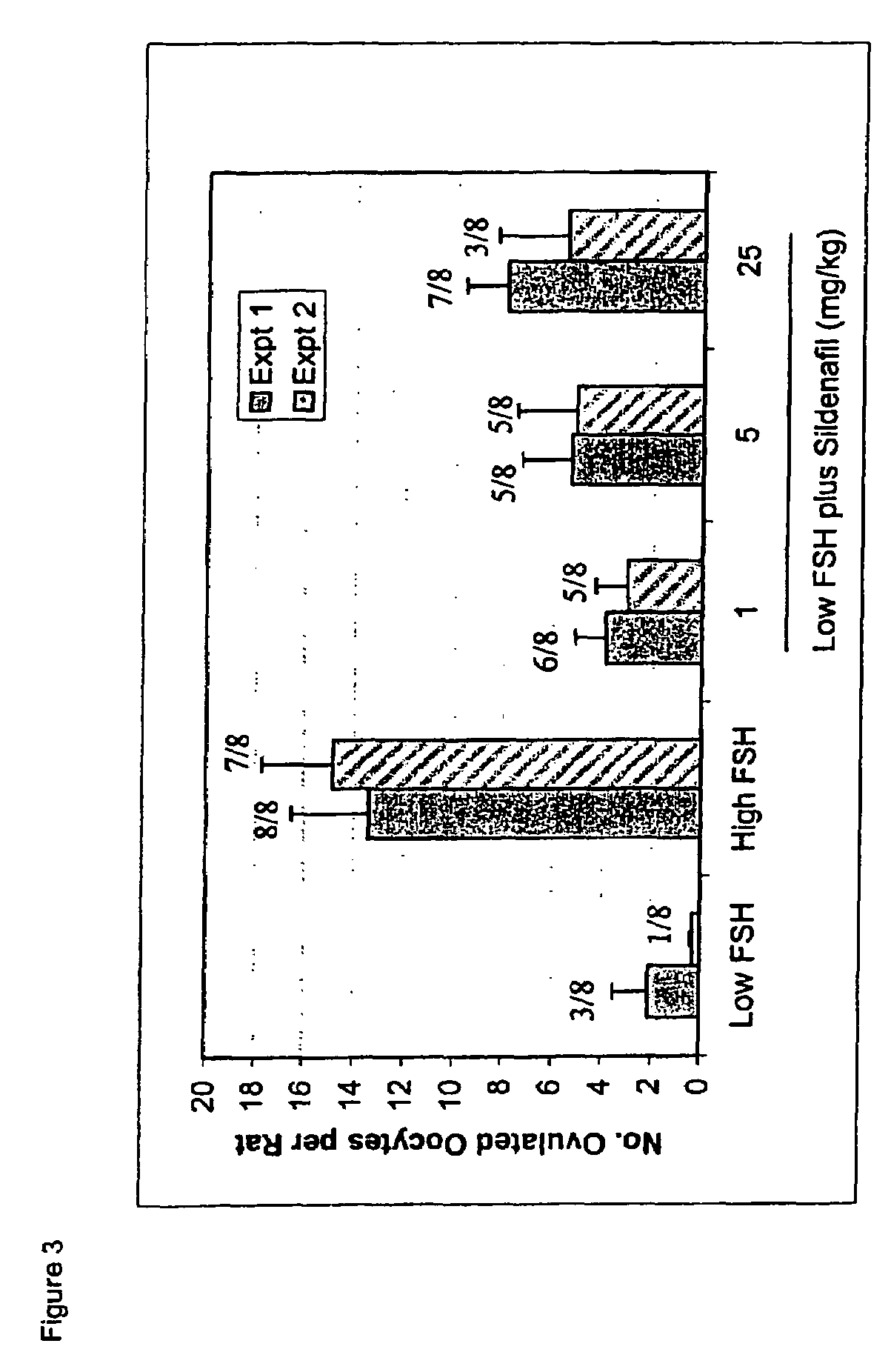
Inhibitors of phosphodiesterases in infertility
The present invention is directed to methods of increasing oocyte production in a mammal. More specifically, the specification describes methods and compositions for inducing follicular maturation using a PDE inhibitor. The inhibitor may be used alone at high doses. Alternatively, the follicular maturation is achieved by combining a low dose of FSH with the PDE inhibitor treatment.
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105087620AHigh copy numberLower activation thresholdVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryInteinEmbryo
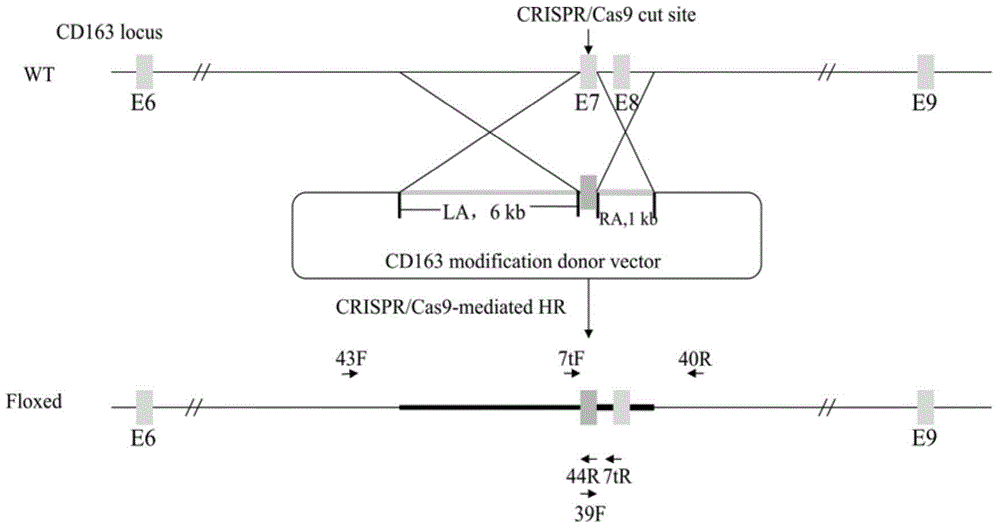
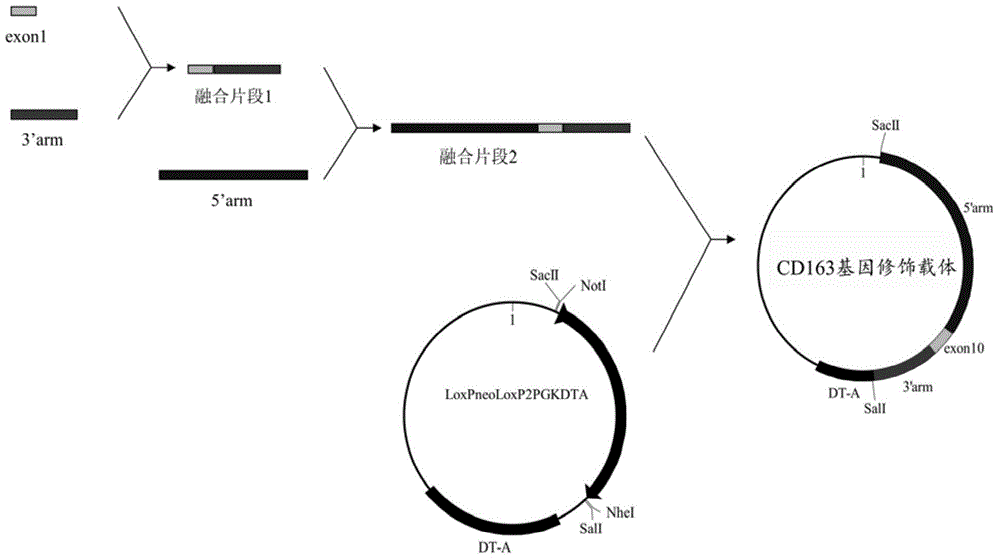
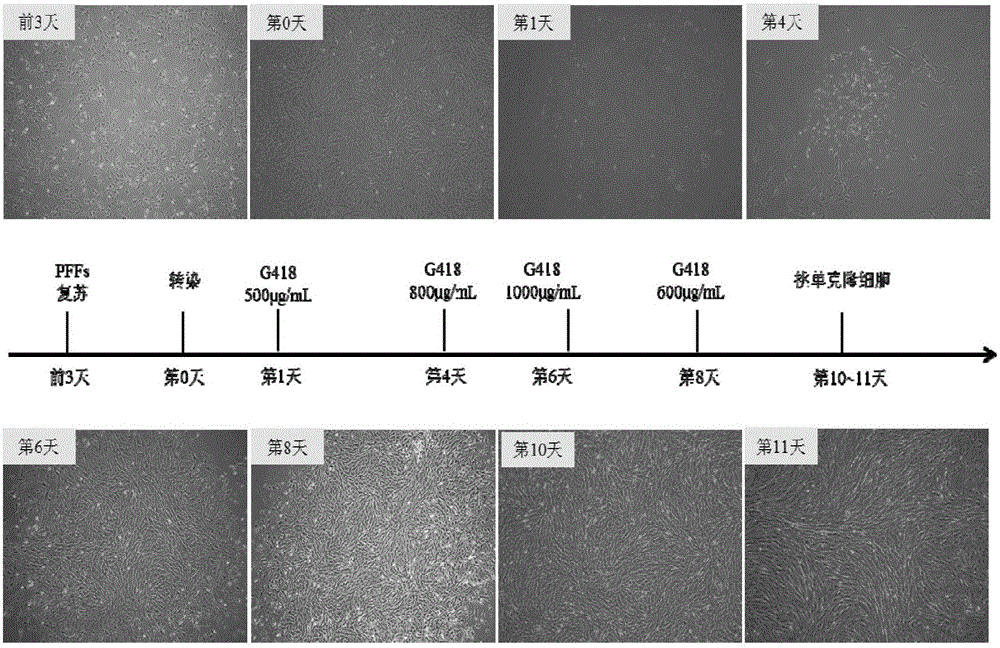
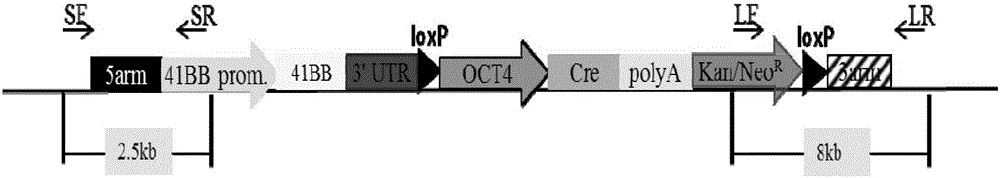
The invention provides an overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on a left homologous arm and a right homologous arm of an intron 1 of a rosa26 gene, a 4-1BB regulatory sequence and an OCT4 specific promoter; the left homologous arm, a 4-1BB expression cassette, LoxP locus-contained Cre and Neo expression cassettes, the right homologous arm and negative selection DTA diphtheria toxin are connected in sequence to obtain a 4-1BB homologous recombinant vector p4BOCNDR; the vector and a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated) targeting vector of sgRNA (small guide ribonucleic acid) containing the intron 1 of the specific targeting porcine rosa26 gene are transferred together into a porcine fetus fibroblast; by taking a positive cell as a donor cell and an oocyte as a recipient cell, a cloned embryo is obtained through a somatic cell nuclear transfer technique; the cloned embryo is transplanted into a porcine uterus for fetation to obtain a transgenic pig integrating a 4-1BB gene at the fixed point of a first intron of the rosa26 gene and automatically deleting a marker gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Integrated microfluidic sperm isolation and insemination device
InactiveUS20060270021A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOocyteBiology
An integrated microfluidic sperm isolation and oocyte insemination device provides the opportunity to perform in vitro insemination with motilityenhanced sperm samples and with minimal manipulation of fragile oocytes. Sperm sorting is performed in a common sort channel wherein more mobile sperm swim across the interface between co-laminar flows of semen and media fluid.
Owner:THE RGT OF THE UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method for preparing high muscle content and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy model cloned pig
InactiveCN105463027AImprove convenienceShorten the timeNucleic acid vectorFermentationHypertrophic cardiomyopathyNuclear transfer
The invention provides application of a Trim63 gene in preparation of a high muscle content and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy model cloned pig. Somatic cells of the Trim63 gene of a modified pig are utilized as nuclear transfer donor cells, oocytes are utilized as nuclear transfer recipient cells, and a cloned embryo is obtained through the somatic cell nuclear transfer technology. The cloned embryo is transferred into a pig uterus to gestate to obtain the Trim63 gene modified high muscle content and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy model cloned pig, artificial intervention methods, such as operation and so on for the cloned pig are not needed any more, and the efficiency of establishment of a disease model is improved. According to the high muscle content and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy model cloned pig, paired Cas9n targeting vectors are utilized for the first time to perform gene editing for large animals. The method is low in cost, sharply shortens the time for obtaining a homozygote pig and lays a foundation for gene function research and the disease model establishment for the large animals by utilizing the CRISPR / Cas9 technology.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
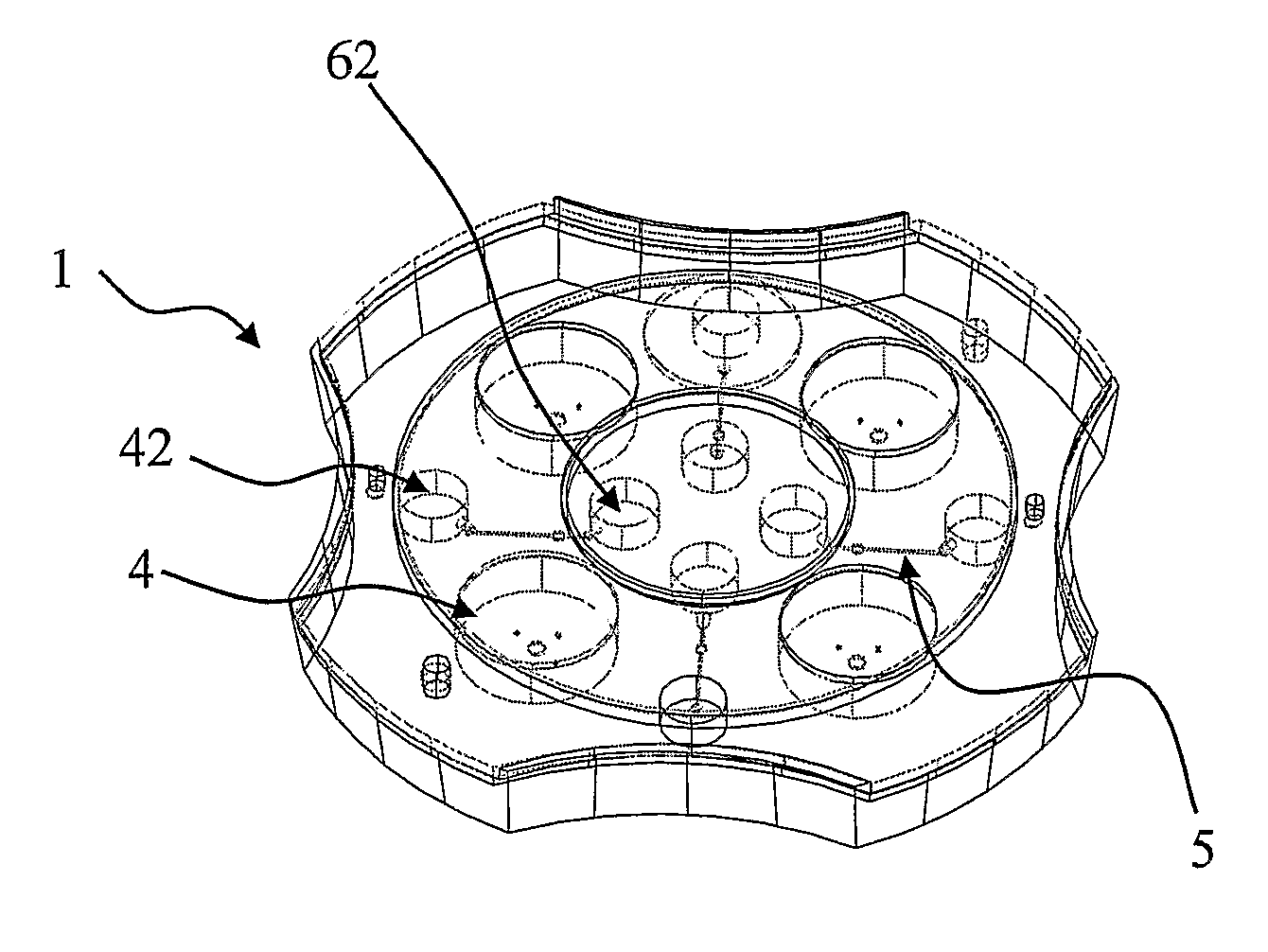
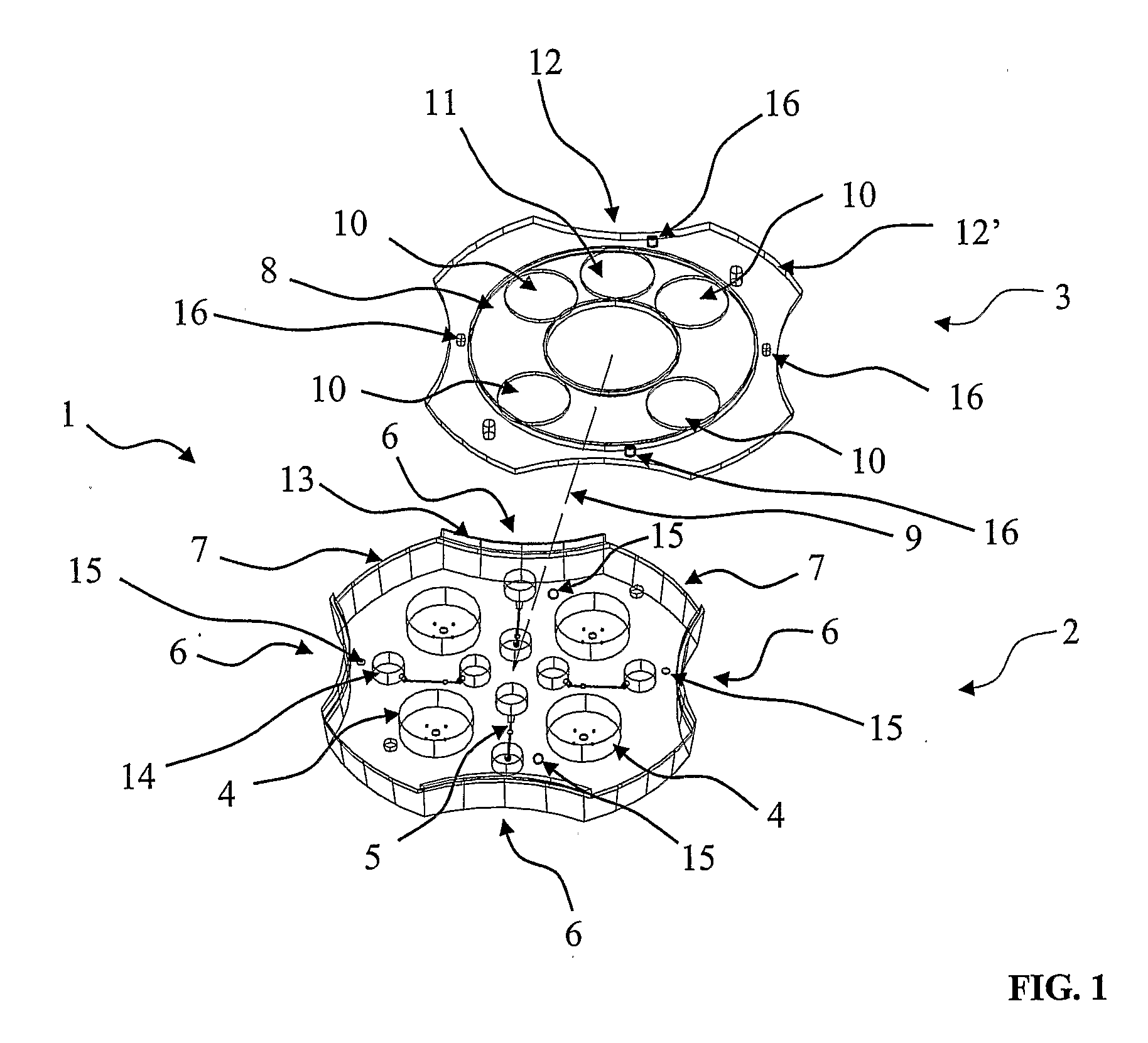
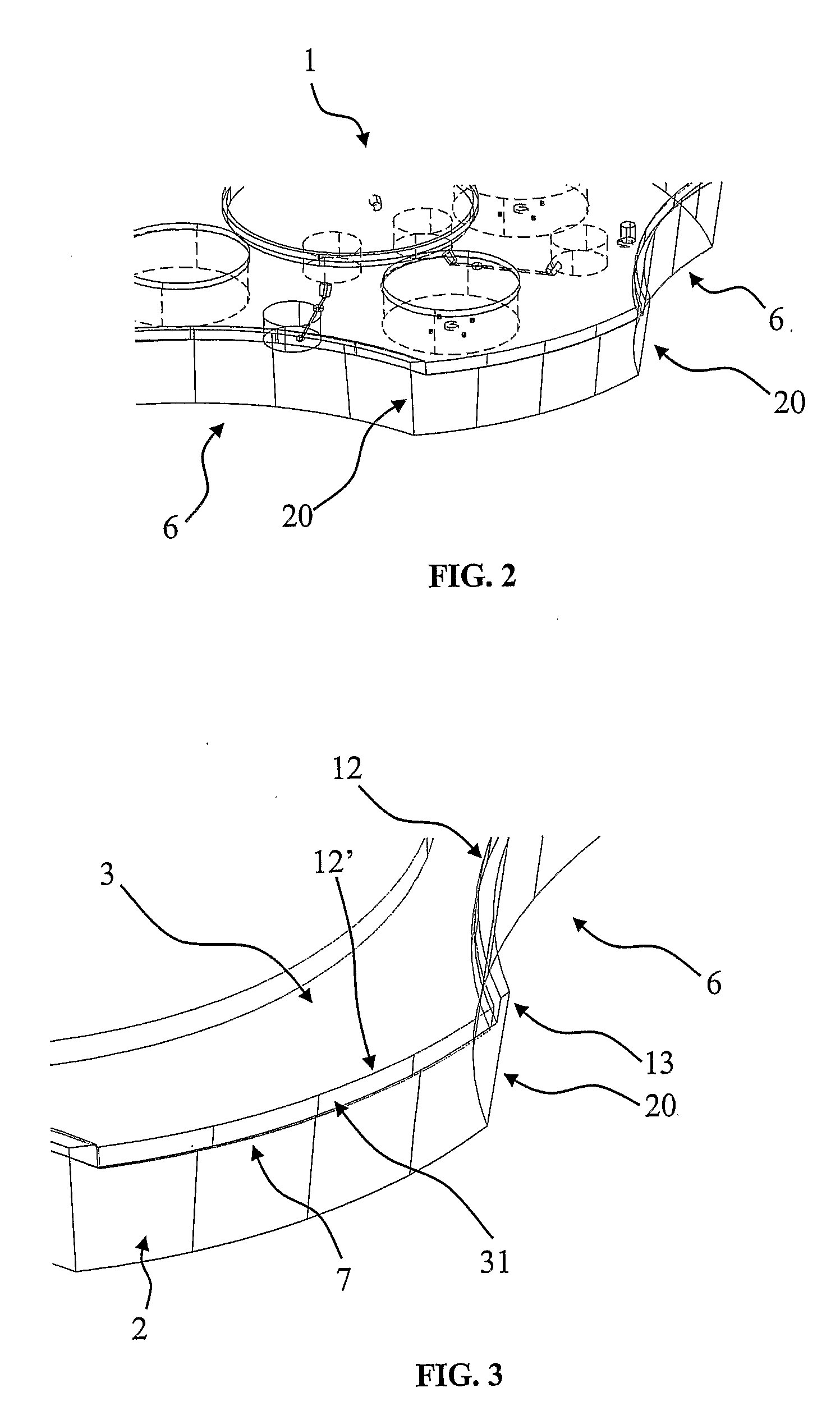
Culture Dish For Culturing Biological Cells
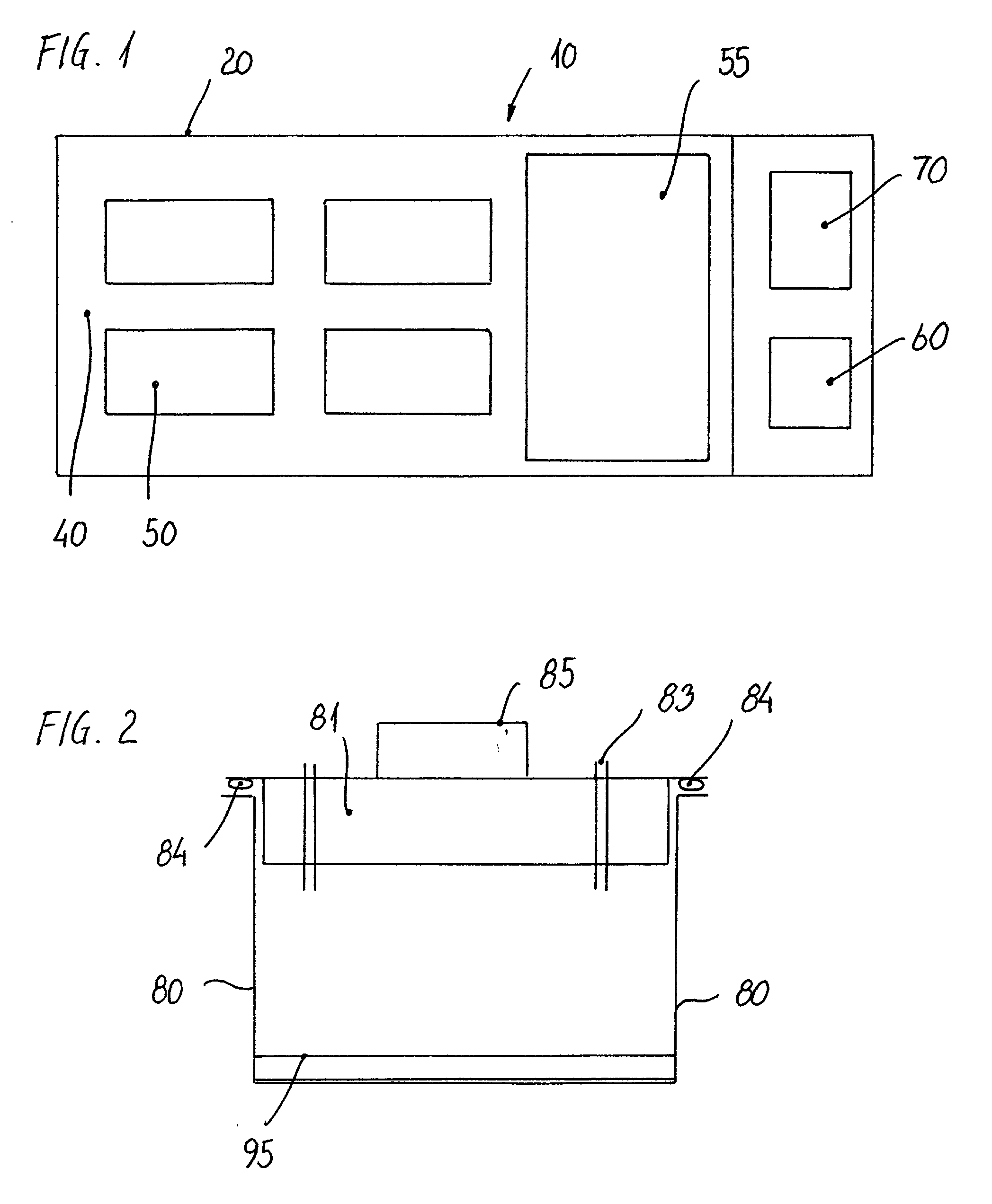
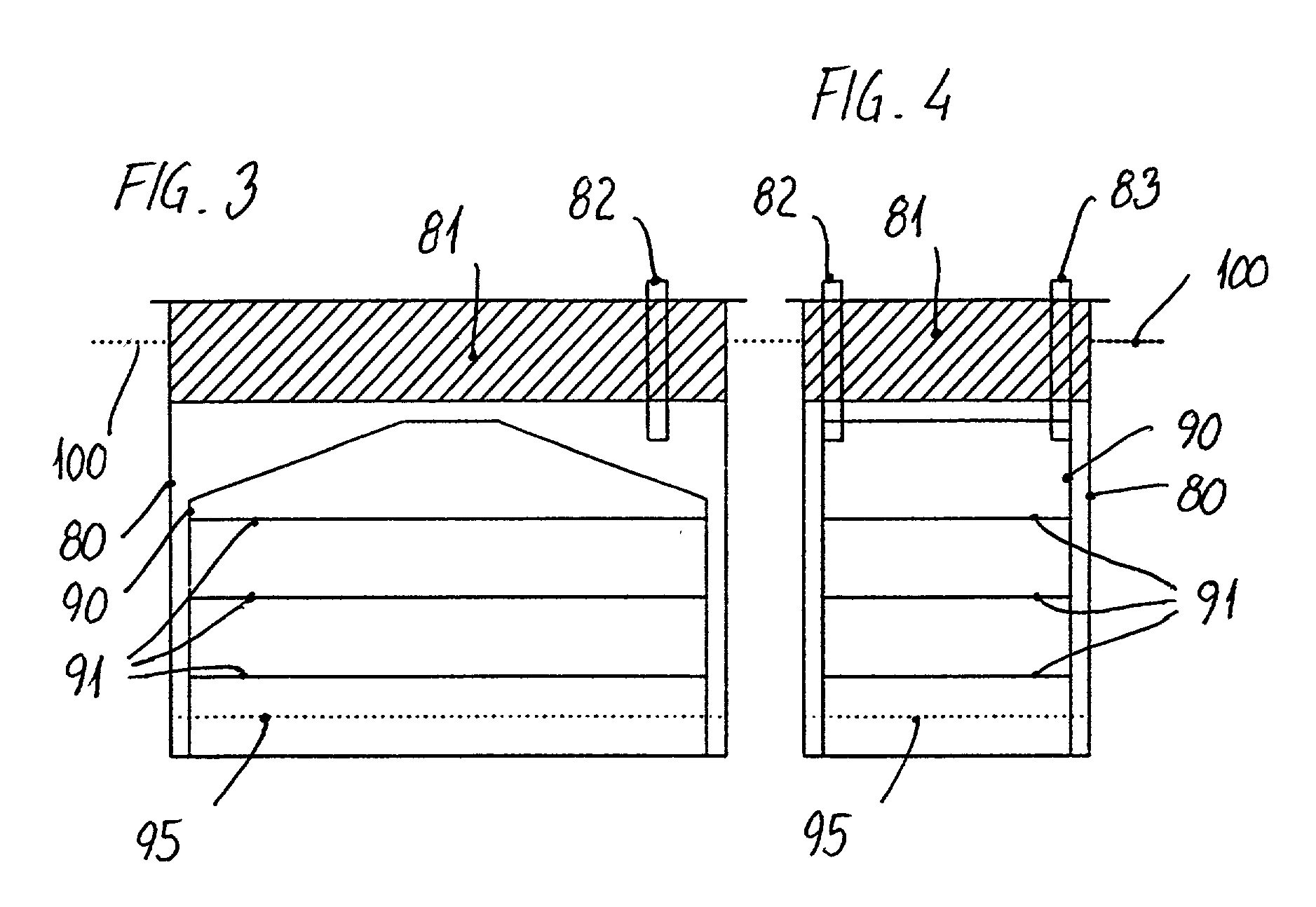
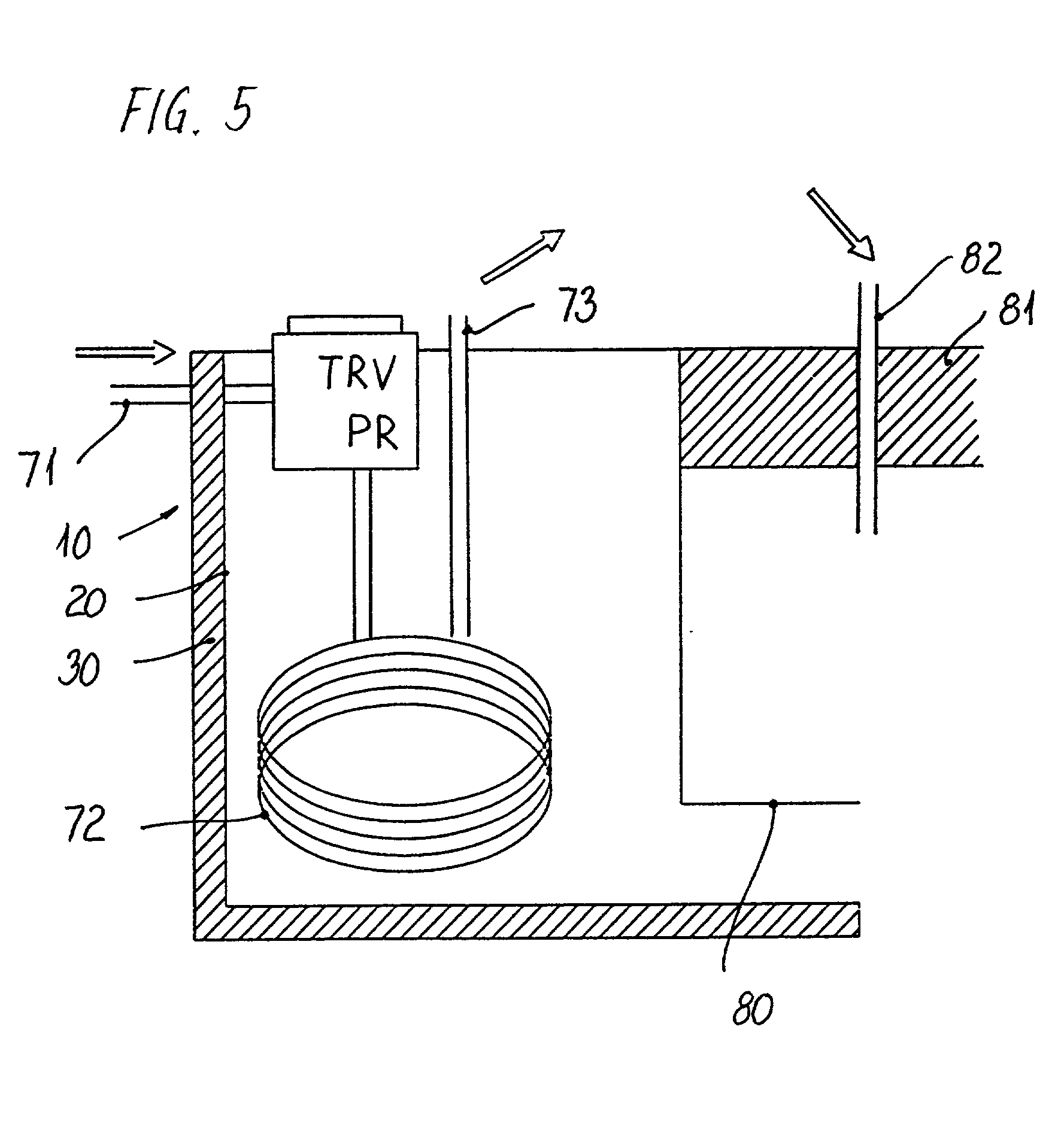
InactiveUS20080090287A1Easy to handleReduce heat lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPetri dishAnatomy
A culture dish (1) comprising a basic structure (2) with a number of macro wells (4) for culturing oocytes and embryos, the culture dish further comprising a lid (3) with a movable part (8), the movable part (8) having an opening (11) adapted to the size of the macro wells (4), the movable part (8) being movable between a first position where all macro wells are closed by the lid (3) and further positions where for each further position (11) the opening (11) is aligned with one of the macro wells (4) to allow access to this macro well (4) through the opening (11) in the lid (3).
Owner:BIOVIR V JACOB MOLLENBACH
Gaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS20020143151A1Improved functional couplingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Methods for cloning mammals using reprogrammed donor chromatin or donor cells
InactiveUS20060212952A1Improve completenessImprove survivabilityNew breed animal cellsRecombinant DNA-technologyReprogrammingMammal
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
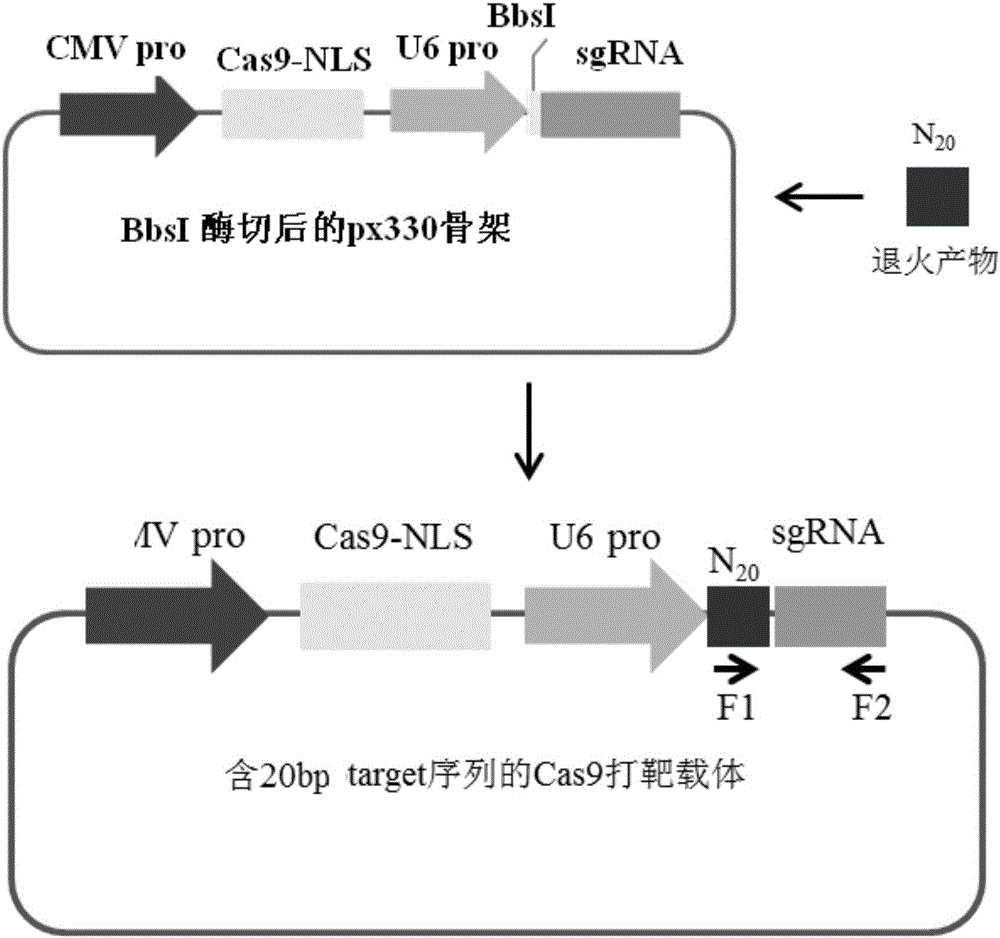
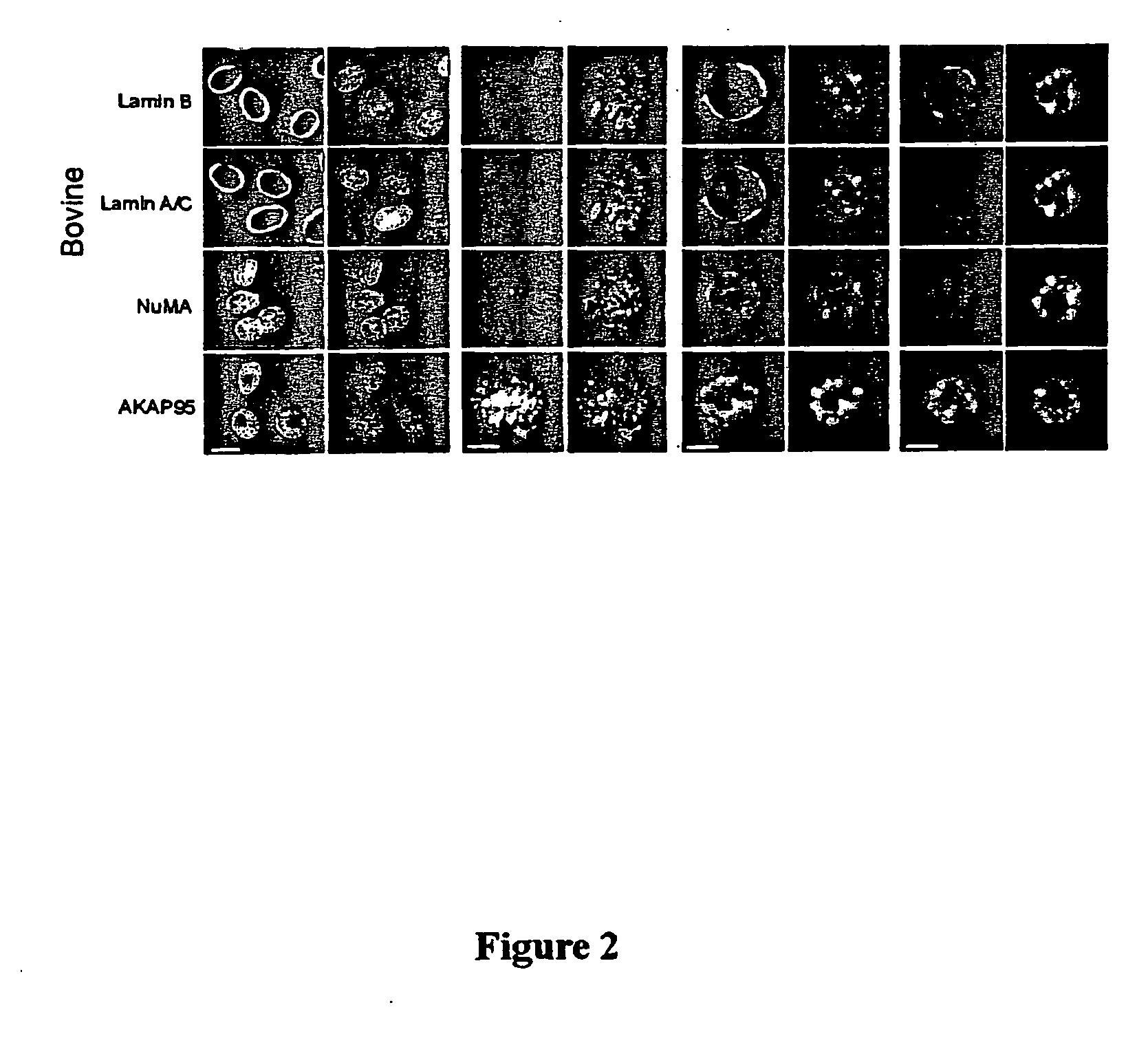
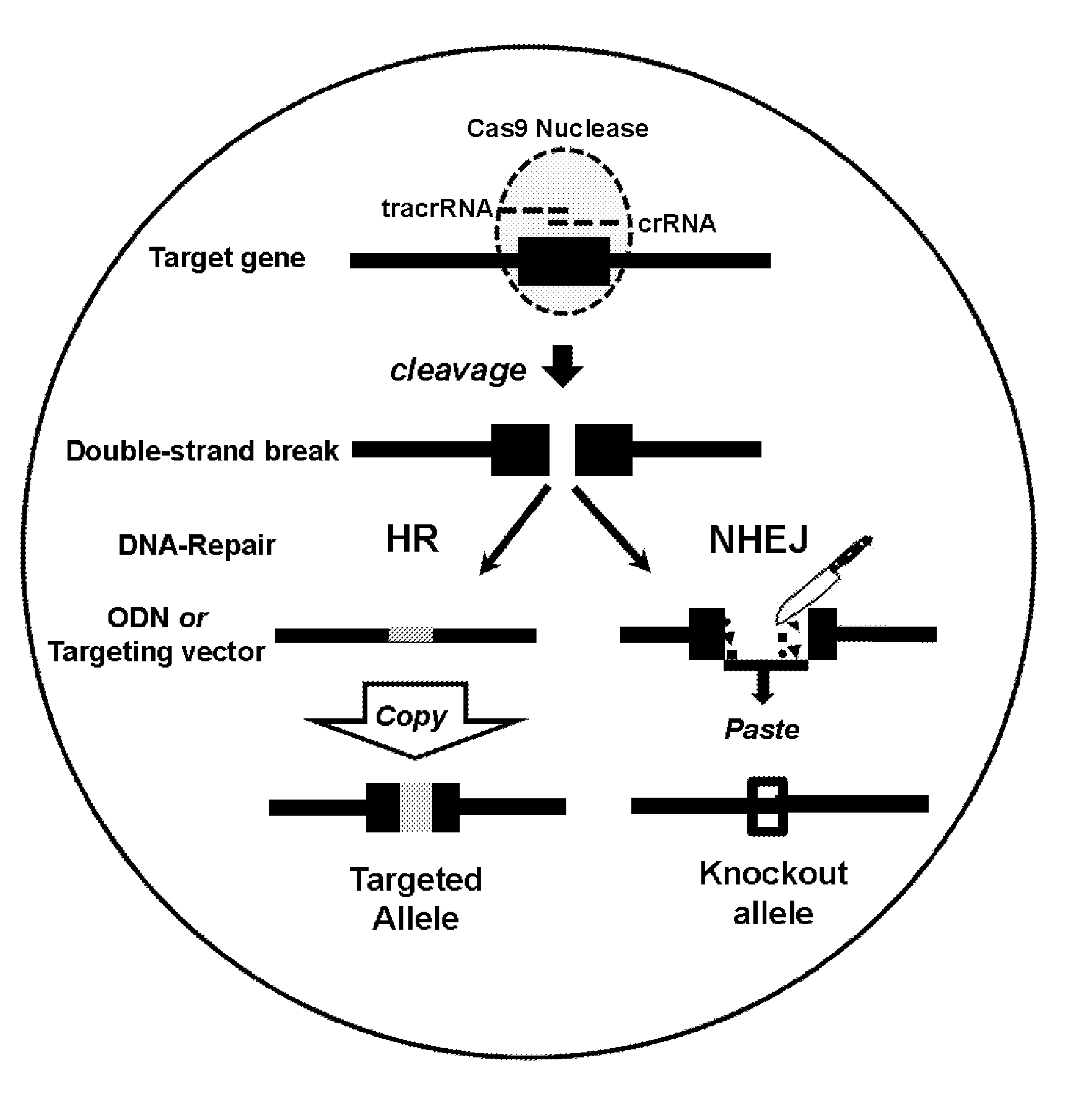
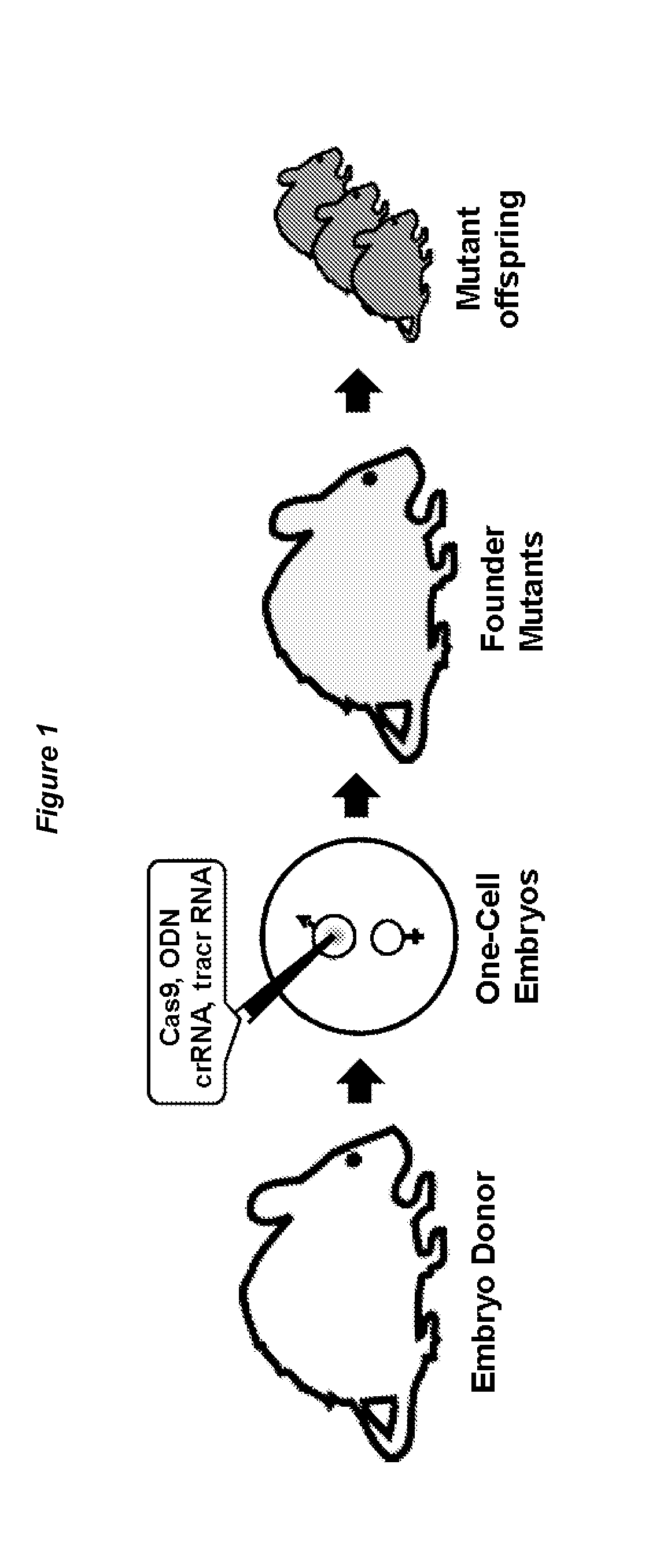
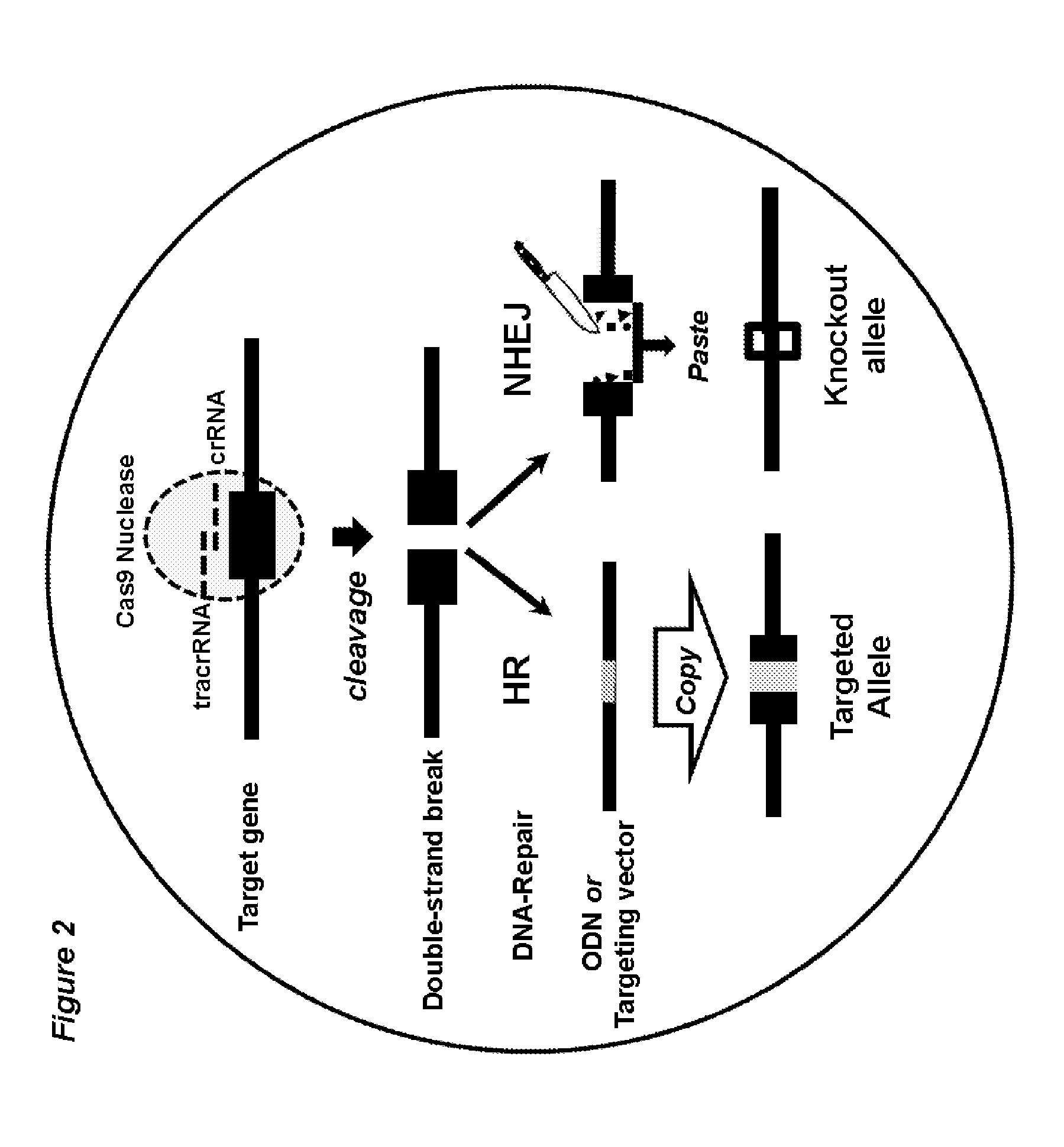
Gene editing in the oocyte by cas9 nucleases
ActiveUS20150376652A1High frequencyStrong specificityAnimal reproductionHydrolasesNucleic acid sequencingRNA Sequence
The present invention relates to a method of producing a non-human, mammalian oocyte carrying a modified target sequence in its genome, the method comprising the steps of introducing into a non-human, mammalian oocyte: (a) a clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated protein 9 (Cas9 protein) or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said Cas9 protein; and (b-i) a target sequence specific CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and a trans-activating crRNA (tracr RNA) or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said RNAs; or (b-ii) a chimaeric RNA sequence comprising a target sequence specific crRNA and tracrRNA or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said RNA; wherein the Cas9 protein introduced in (a) and the RNA sequence(s) introduced in (b-i) or (b-ii) form a protein / RNA complex that specifically binds to the target sequence and introduces a single or double strand break within the target sequence. The present invention further relates to the method of the invention, wherein the target sequence is modified by homologous recombination with a donor nucleic acid sequence further comprising the step: (c) introducing a nucleic acid molecule into the cell, wherein the nucleic acid molecule comprises the donor nucleic acid sequence and regions homologous to the target sequence. The present invention also relates to a method of producing a non-human mammal carrying a modified target sequence in its genome.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT MUNCHEN DEUTES FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR GESUNDHEIT & UMWELT
Imaging and evaluating embryos, oocytes, and stem cells
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
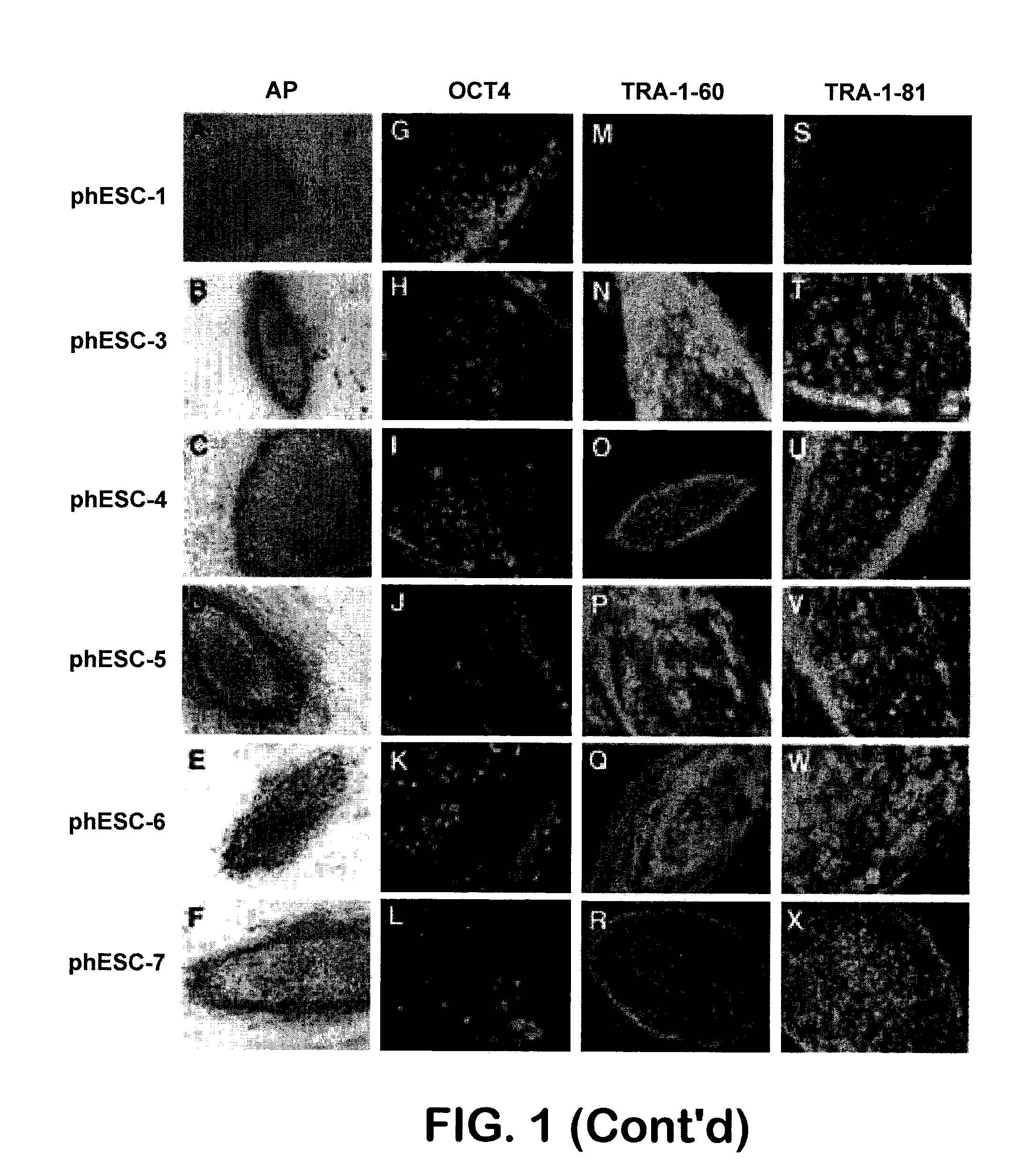
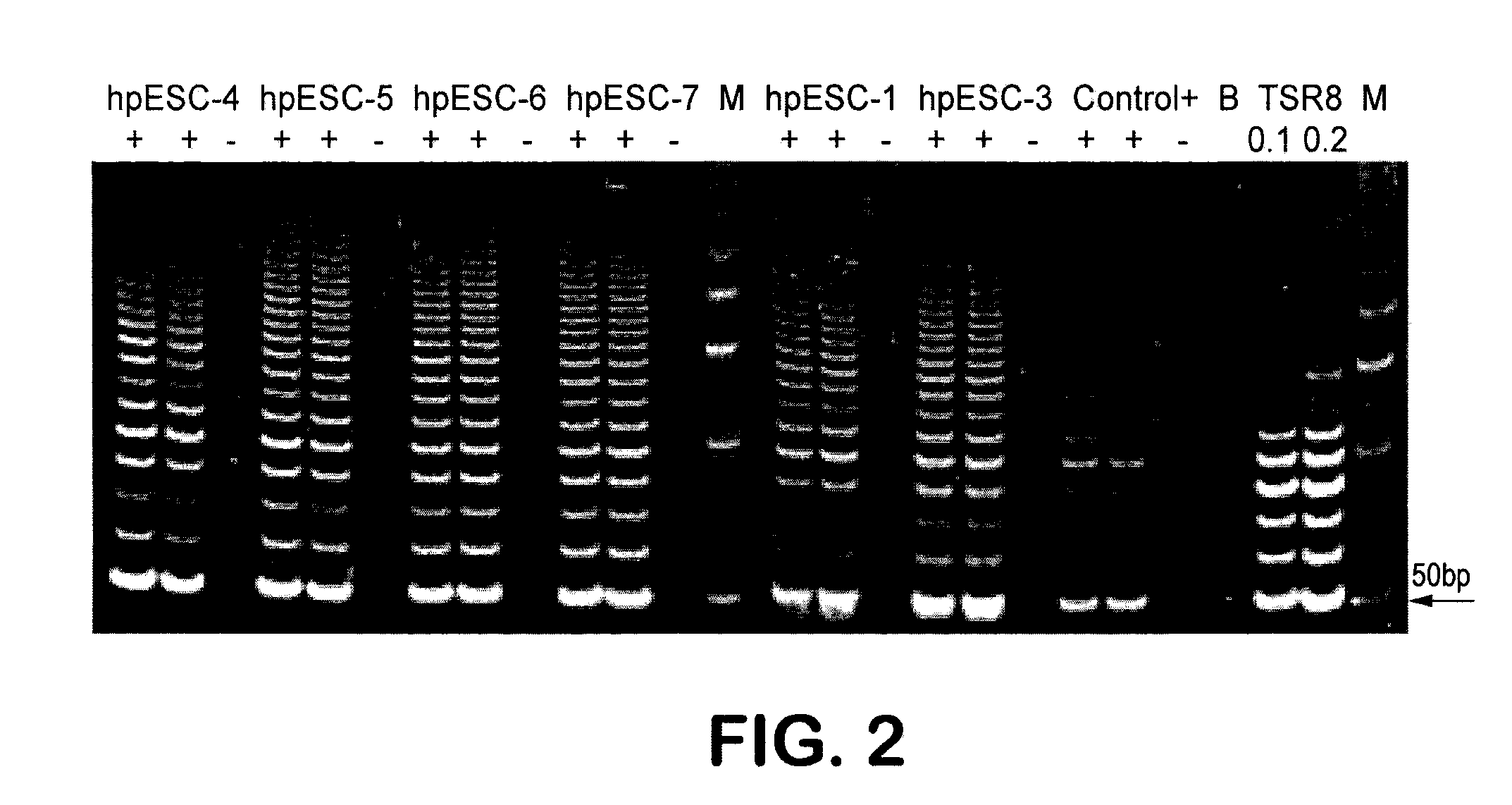
Patient-specific stem cell lines derived from human parthenogenetic blastocysts
InactiveUS20080299091A1Increase alkaline phosphatase activityHigh levelBiocideSenses disorderTelomeraseOocyte donor
Methods are disclosed for generating HLA homozygous parthenogenetic human stem cell (hpSC-Hhom) lines from both HLA homozygous and HLA heterozygous donors. These hpSC-Hhom lines demonstrate typical human embryonic stem cell morphology, expressing appropriate stem cell markers and possessing high levels of alkaline phosphatase and telomerase activity. Additionally, injection of these cell lines into immunodeficient animals leads to teratoma formation. Furthermore, in the case of HLA heterozygous donors, the hpSC-Hhom lines inherit the haplotype from only one of the donor's parents. SNP data analysis suggests that hpSC-Hhom lines derived from HLA heterozygous oocyte donors are homozygous throughout the genome as assessed by single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis. The protocol as disclosed minimizes the use of animal-derived components, which makes the stem cells more practical for clinical application.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
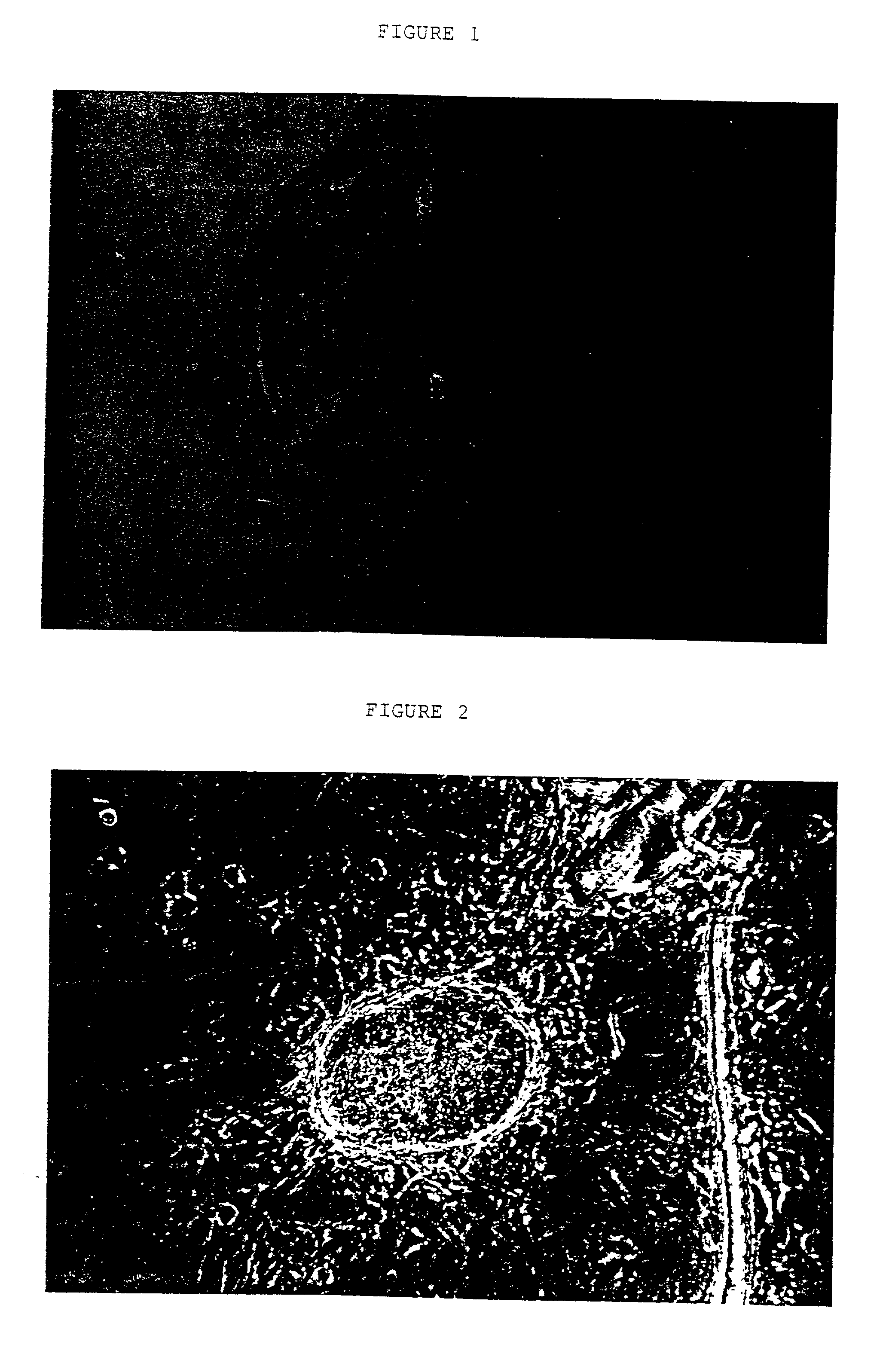
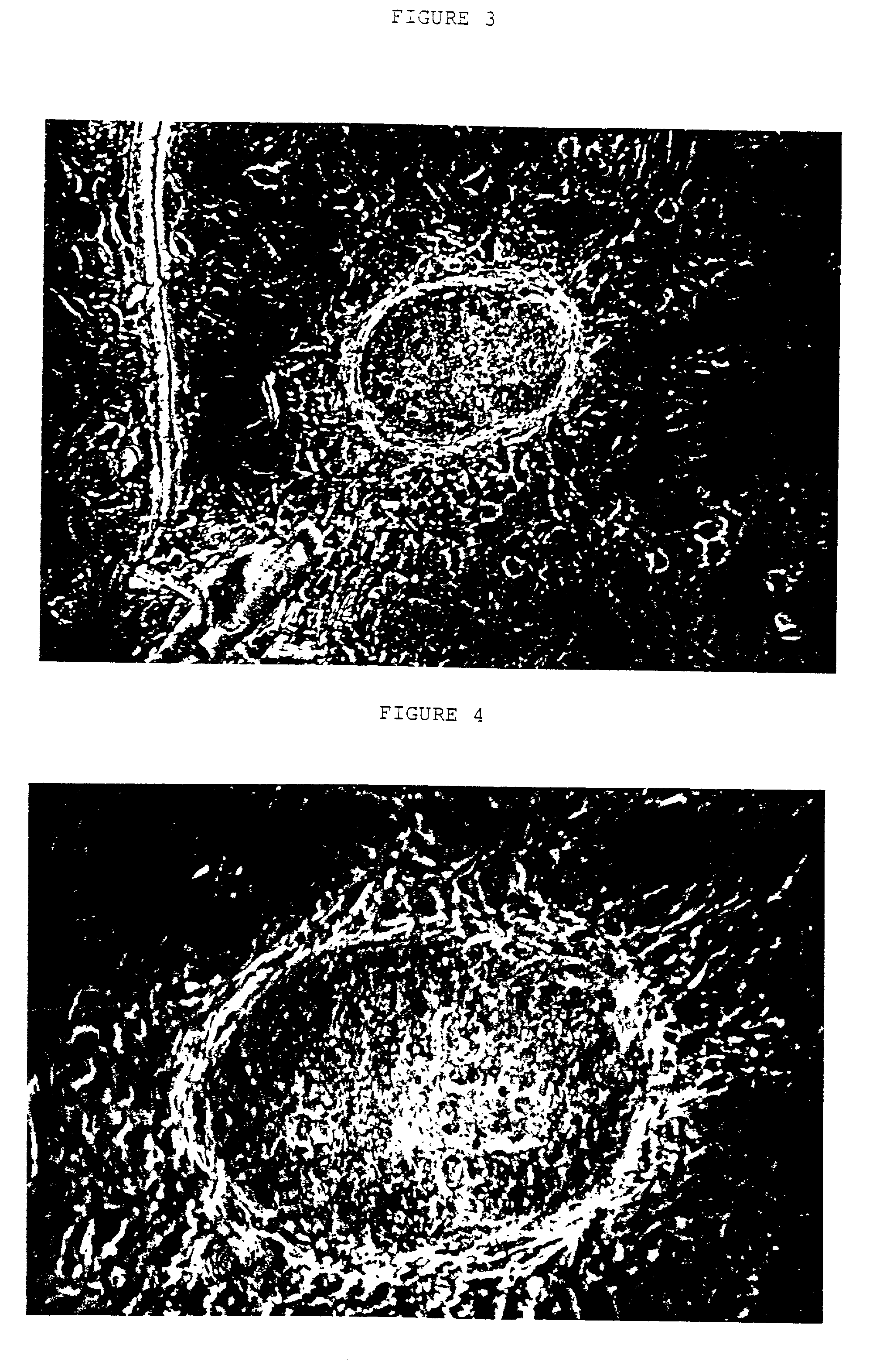
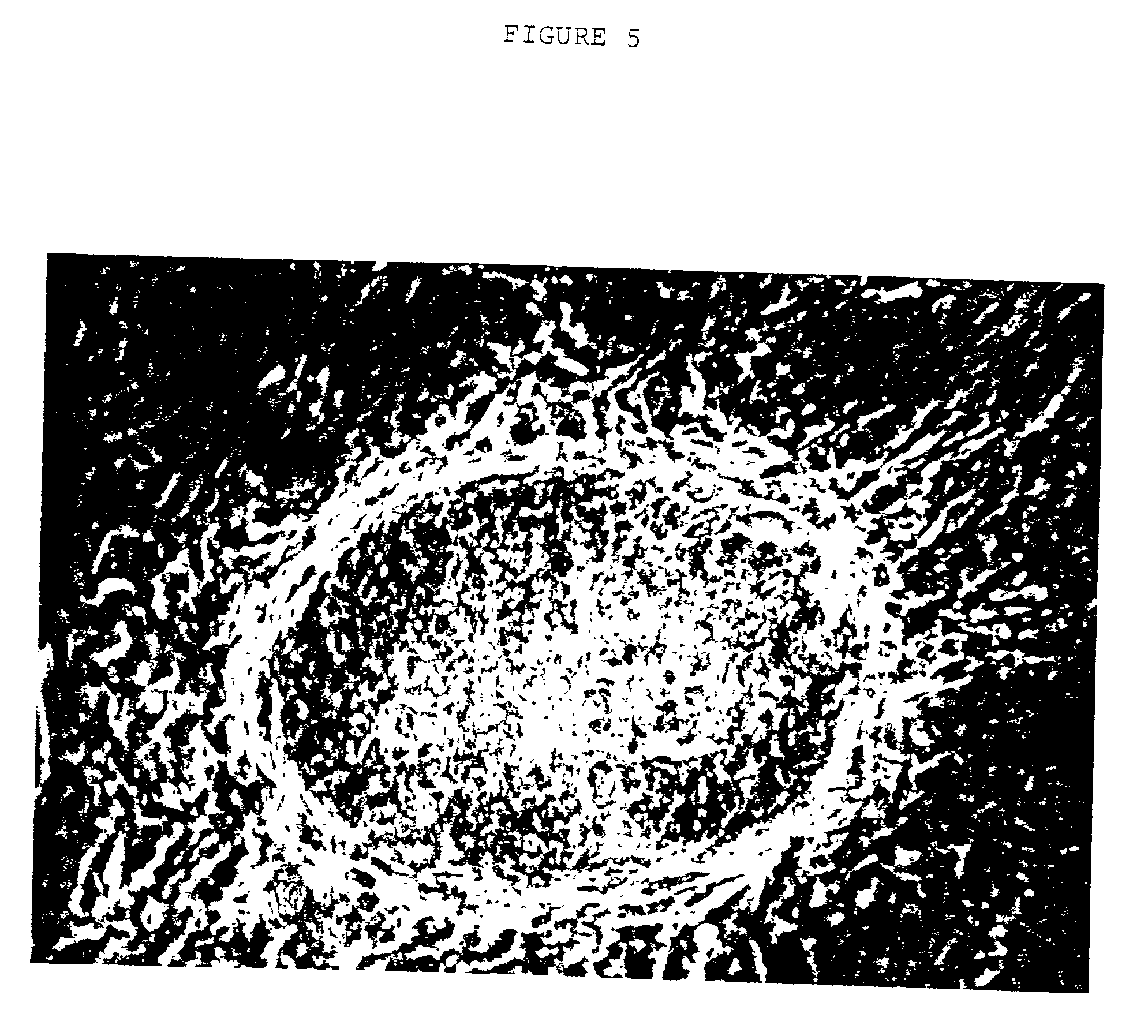
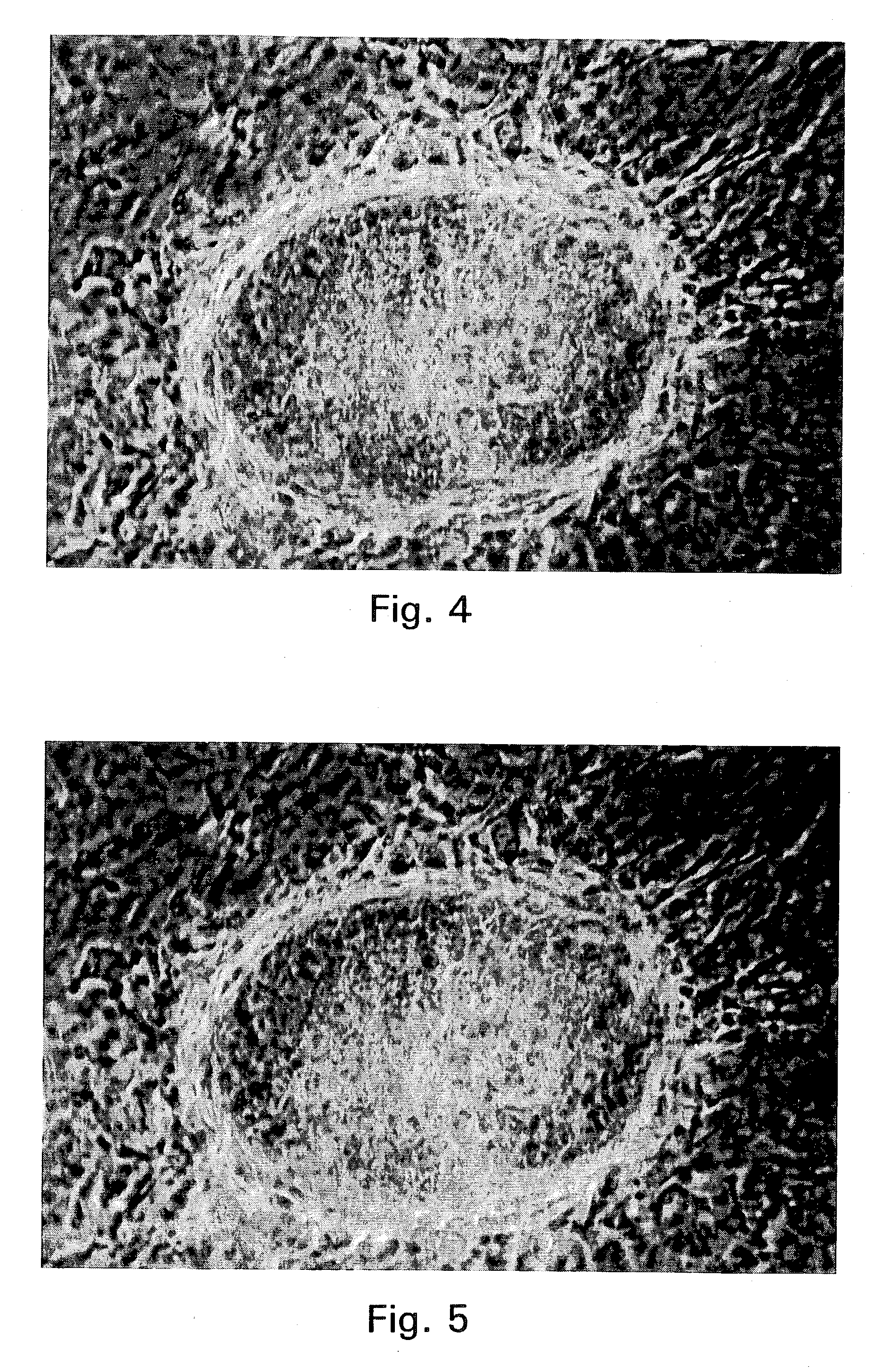
Paraffin wax slicing method of ocean shellfish oocyte
ActiveCN101650273ASolve the inconvenience of operationEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansParaffin waxEgg cell
The invention relates to a paraffin wax slicing method of ocean shellfish oocytes, comprising the steps of fixing, dehydration, clarity, waxdip, imbedment, slicing, dyeing, mounting, and the like. Theparaffin wax slicing method is characterized by solving the problem of the difficult waxdip and imbedment of the ocean shellfish oocytes due to small volume, improving a hematoxylin-eosin dyeing method and obtaining favorable slicing and dyeing effect. The paraffin wax slicing method is simple and easy to operate without adding instruments or equipment, can carry out paraffin wax slicing on mostof the ocean shellfish oocytes with the diameters more than or equal to 40 micrometers, transition steps are carried out among the dehydration, the clarity and the waxdip of the steps and mostly in two-step processing so that a reagent gradually and completely enters a tissue and is preserved in the original structure of the tissue in an intact way so as to provide an effective researching means for shellfish fertilization and early embryonic development research.
Owner:浙江万里学院宁海海洋生物种业研究院
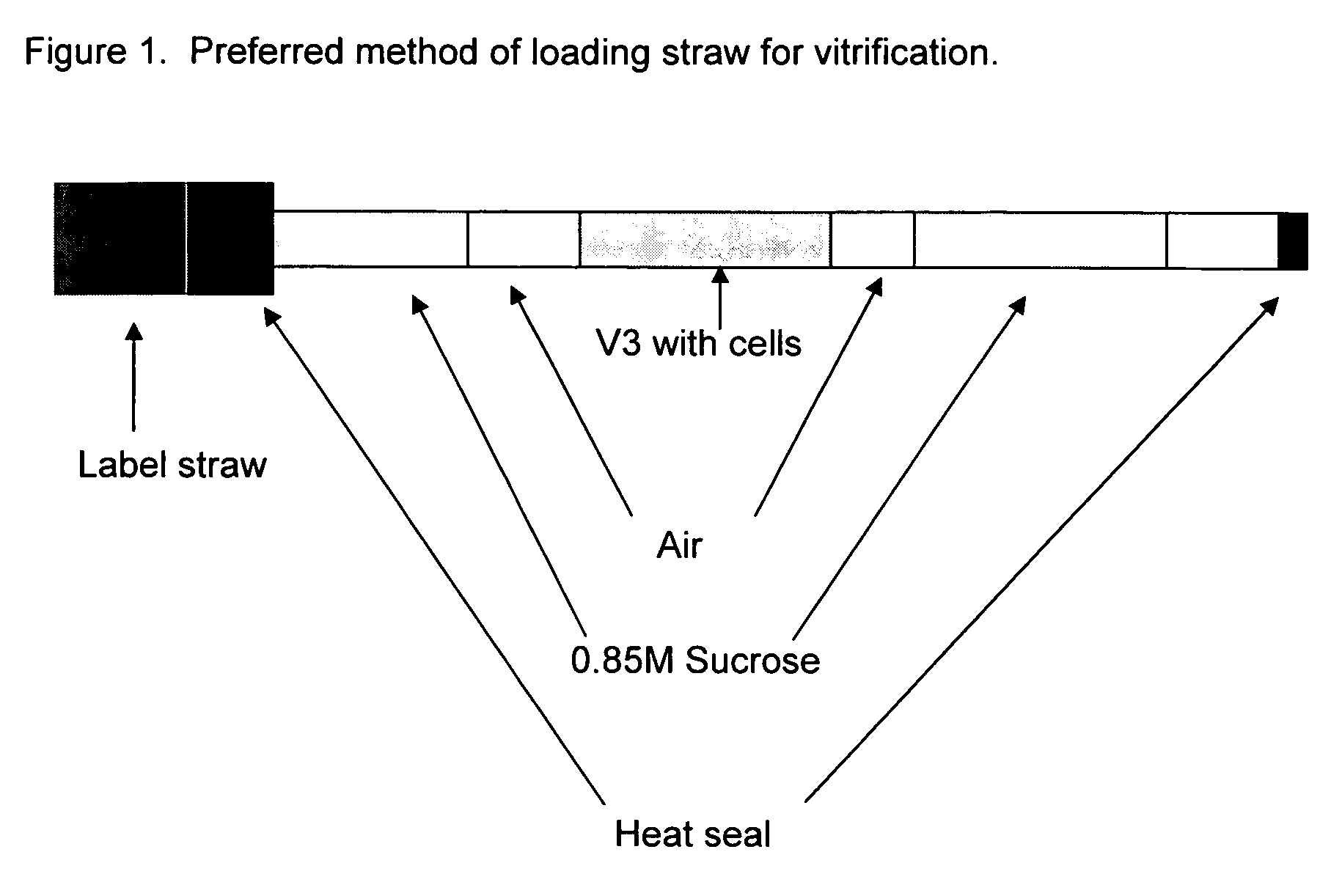
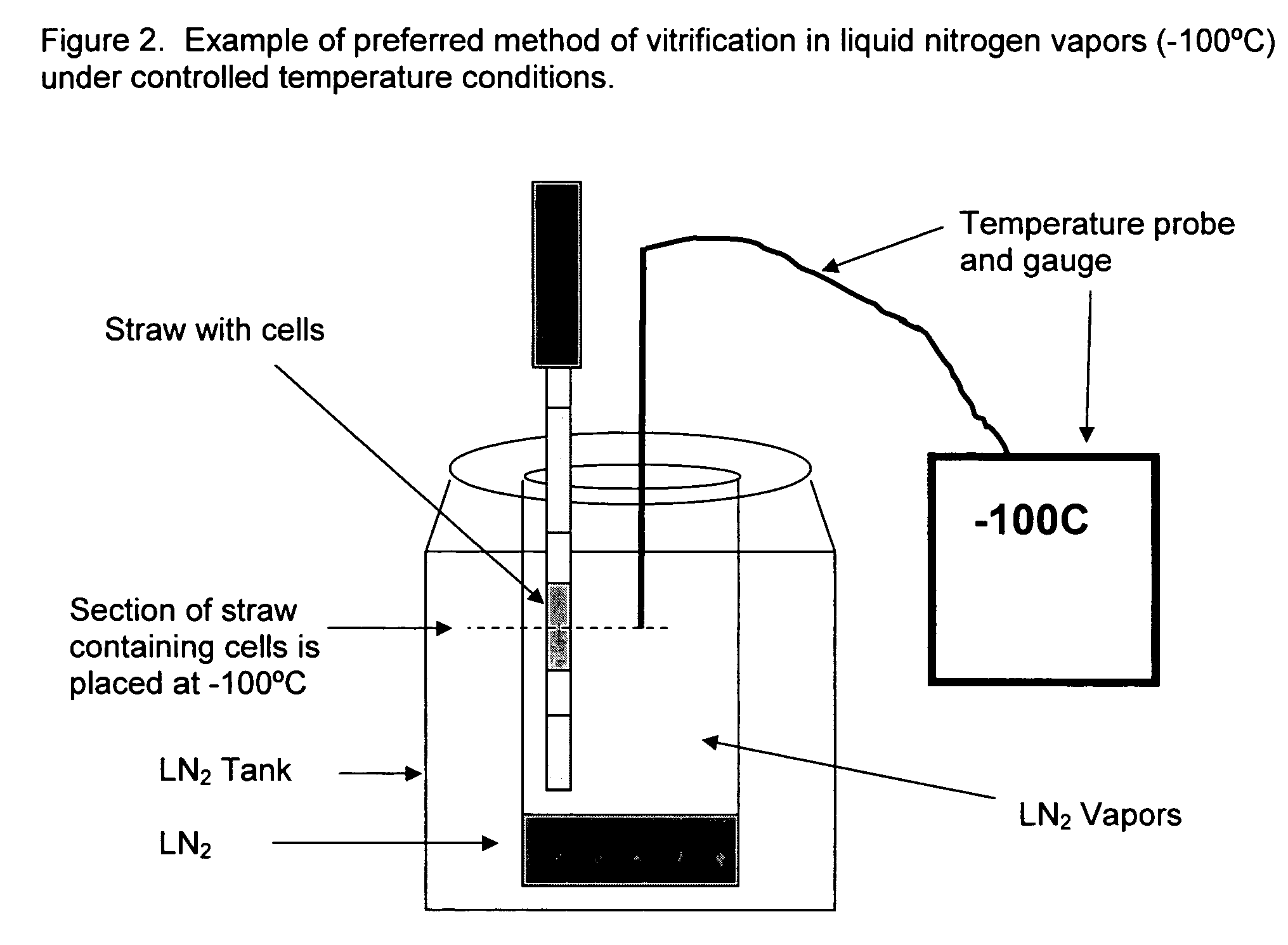
Method for vitrification of mammalian cells
InactiveUS20060046243A1Enough timeAffects successDead animal preservationVitrificationBiological cell
A method of vitrifying mammalian cells. According to the method of the present invention, biological cells of mammalian origin are frozen quickly by a vitrification method. Upon exposure to a coolant, the biological cells undergo vitrification. The biological cells which have undergone vitrification may be stored for a period of time and then devitrified at a later date. The devitrified biological cells remain viable. Preferred biological cells according to the present invention are developmental cells including blastocysts, embryos, and oocytes.
Owner:TYHO GALILEO RES LAB
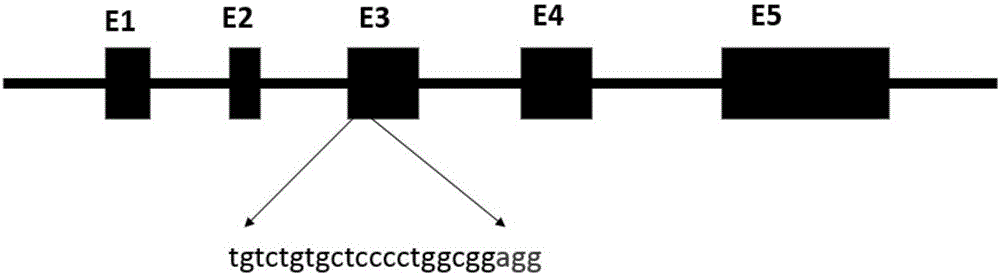
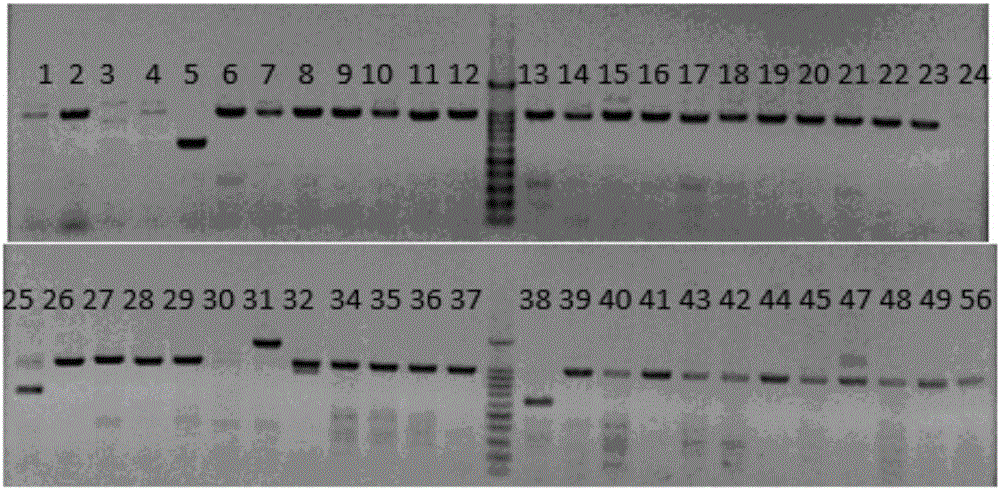
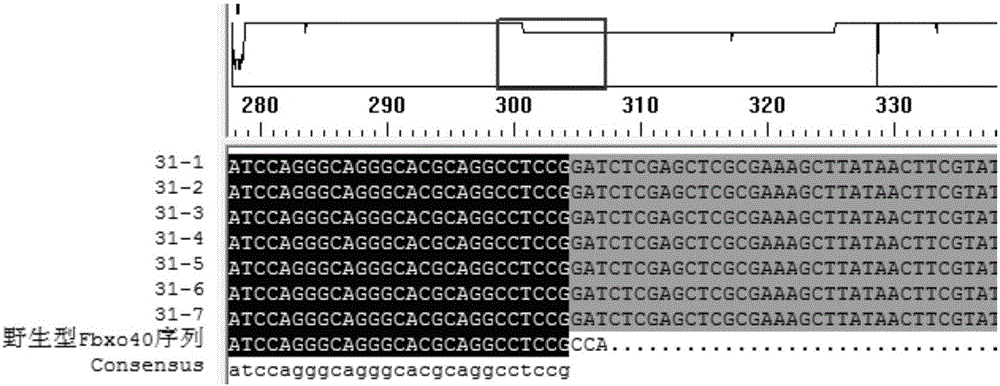
Production method for Fbxo40 gene knockout pigs
InactiveCN105821049AConvenient researchLow costNucleic acid vectorFermentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention provides a production method for Fbxo40 gene knockout pigs. The production method comprises the steps that a CRISPR-Cas9 targeting vector and a PGK-Neo resistant gene are jointly transfected into a porcine embryonic fibroblast to obtain a G418-resistant positive monoclonal cell, an Fbxo40 gene in the positive monoclonal cell generates insertion or deletion mutation, a reading frame generates frame shift and stops in advance, then the obtained cell is cloned to serve as a donor cell for nuclear transfer, and an oocyte serves as a receptor oocyte for nuclear transfer; cloned embryos are obtained through a somatic cell nuclear transfer technique, the high-quality cloned embryos are transferred into the fallopian tube of an oestrous sow, and the Fbxo40 gene knockout pigs are obtained through whole-period development. According to the production method, the Fbxo40 knockout pigs are efficiently obtained through a CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technique at the low cost, and animal models are supplied to research of muscle development and diseases related to the muscles.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
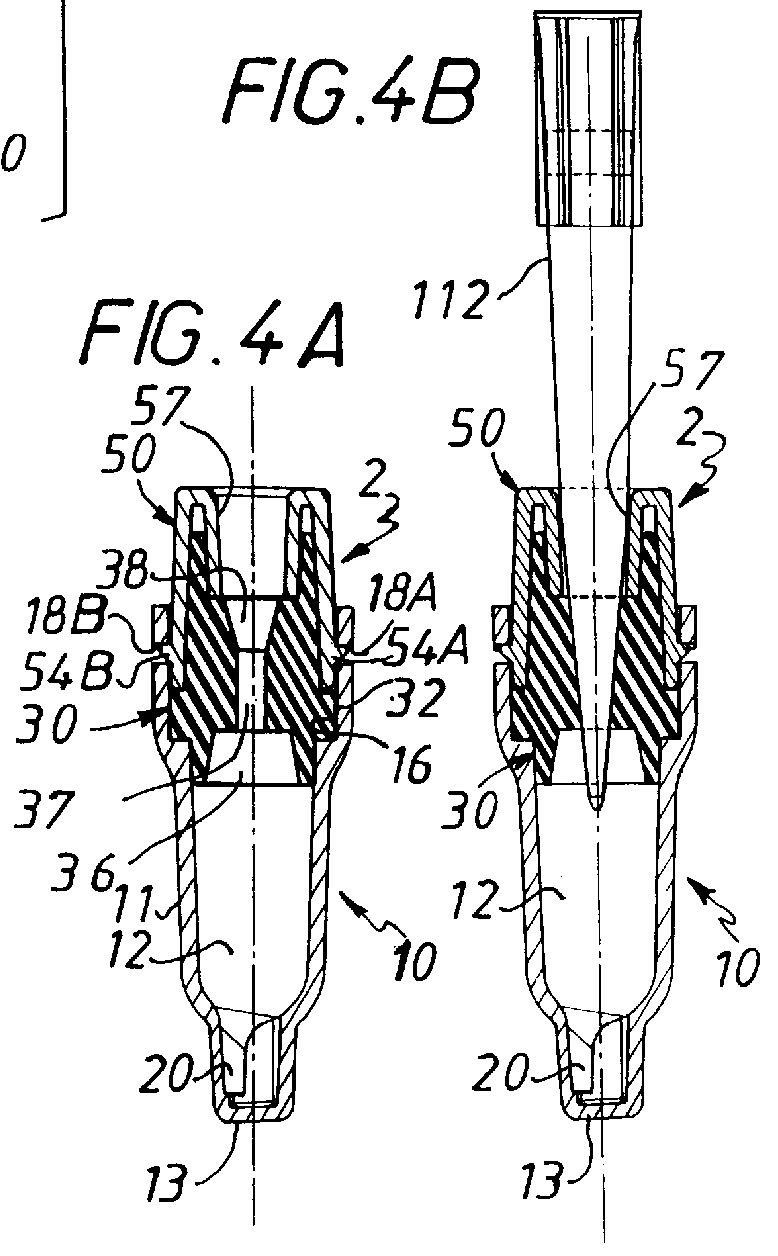
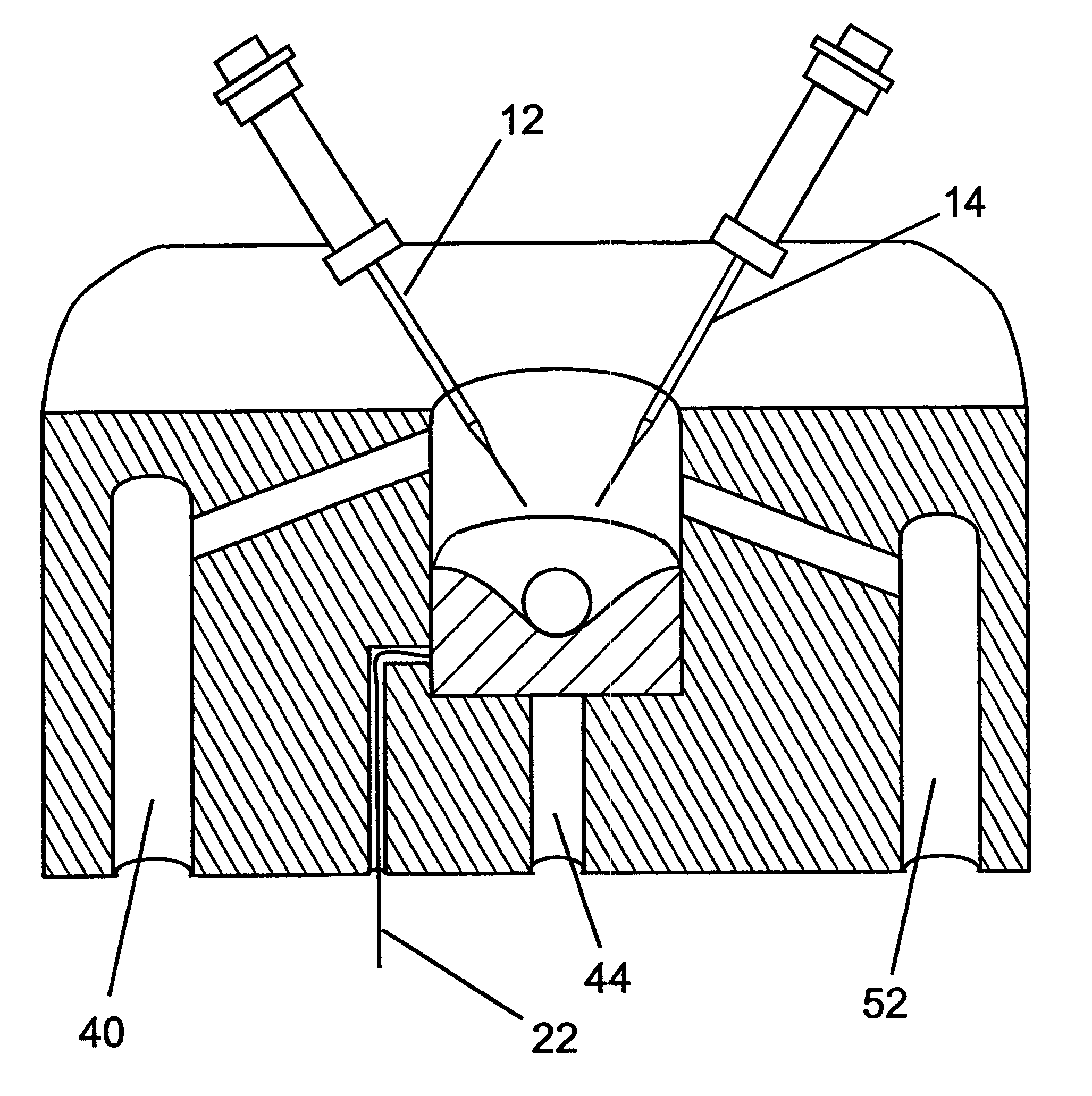
Perfusion chamber for electrophysiological testing of oocytes
InactiveUS6541243B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorosityEngineering
A perfusion chamber includes a porous oocyte support structure. A continuously sloped top surface and a receiving well in the support structure entrap the underside of the oocyte, thereby localizing the cell in a predetermined fixed position within the reach of dedicated voltage-clamp microelectrodes. A test solution is delivered continuously at the top of the chamber, above the oocyte, and withdrawn from the bottom of the chamber, below the oocyte. The porosity of the support material enables the continuous perfusion of test solution around the membrane of the oocyte, including its bottom portion that is held firmly in contact with the holding well. The geometry of the holding well is selected such as to ensure the automatic and precise placement of the oocyte by gravity and to optimize the pressure distribution over its membrane, thereby minimizing the probability of rupture or other damage to the cell. The entire top surface of the support structure is sloped inward toward the substantially central well, and the bottom of the well is contoured to conform to the shape of an oocyte of average size.
Owner:MDS ANALYTICAL TECH US
Methods for enhancing embryo viability
InactiveUS20070006332A1Enough timeImprove pregnancy rateOrganic active ingredientsP53 proteinEmbryoBiology
Owner:BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation and methods for enhancing embryonic development by genetic alteration of donor cells or by tissue culture conditions
InactiveUS20030229908A1Good curative effectIncrease productionNew breed animal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousEmbryo
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of differentiated donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation. Also, methods for improving nuclear transfer efficiency by genetically altering donor cells to inhibit apoptosis, select for a specific cell cycle and / or enhance embryonic growth and development are provided.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Probiotics as alternative medicines against infectious diseases
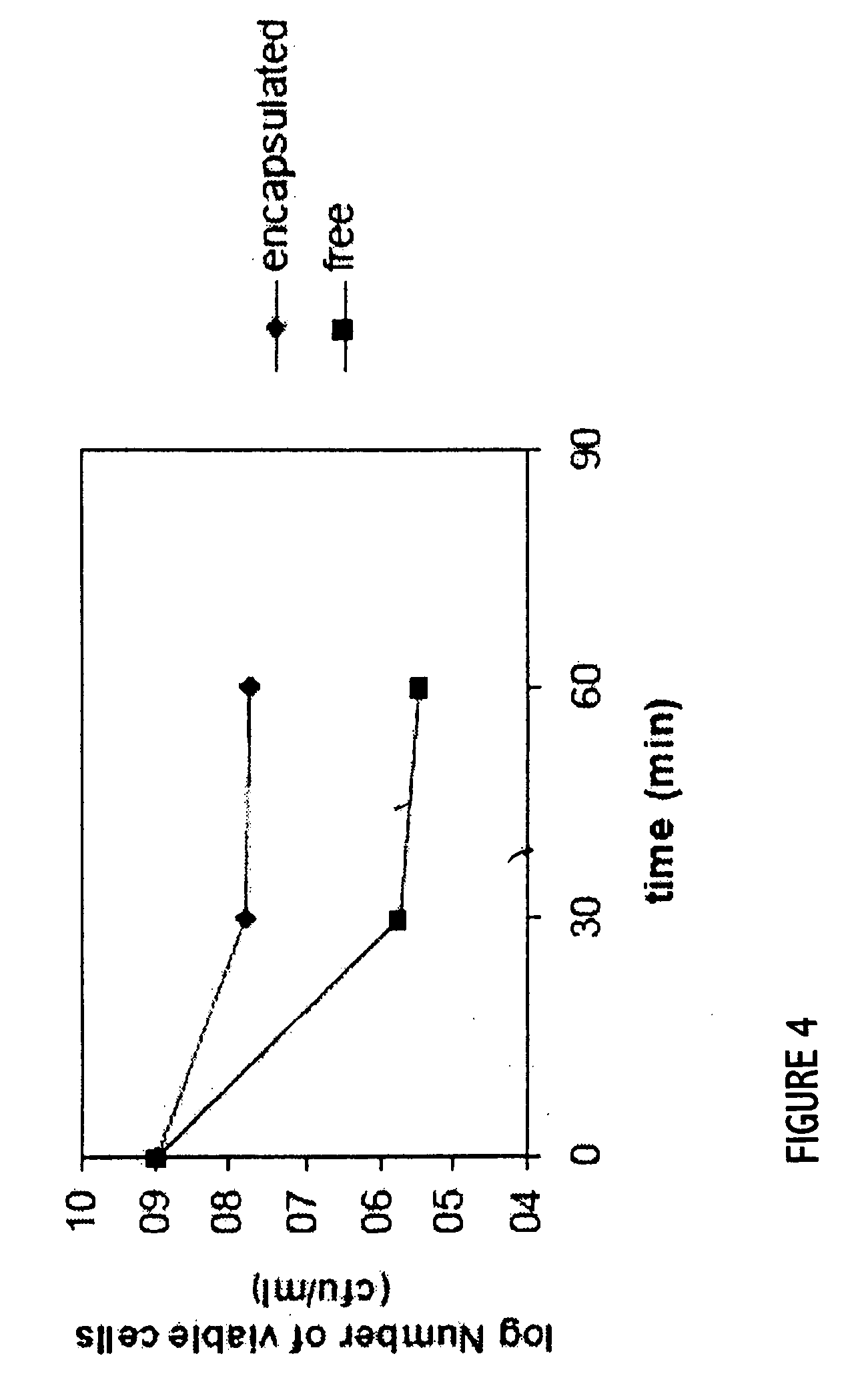
An exemplary embodiment providing one or more improvements includes feeding animals with probiotic microbes encapsulated in a mixture of xanthan gum and chitosan, or in gelatin, specifically Pediococcus acidilactici and Saccharomyces boulardii. Such encapsulation protects the viability of the probiotic microbes against unfavorable temperatures. An exemplary embodiment providing one or more improvements includes methods of using viable probiotics in therapy of birds and mammals infected with infectious diseases. Probiotics acted as adjuvants in stimulating antibody reaction and stimulated a cellular immunity response. In particular, probiotics were shown to reduce the number of viable oocytes from fecal samples, stimulate antibody production, and stimulate of proliferation of splenocytes in chickens infected with Elimeria. In addition, probiotics were shown to relieve symptoms of parvovirus infection in dogs.
Owner:IMAGILIN TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for culturing cells and tissues
InactiveUS20020009803A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOocyteCarbon dioxide
Cells and tissues, in particular sensitive cells and tissues, such as oocytes, fertilized oocytes and preimplantation embryos, which require highly stable physical and chemical environment for in vitro development, are cultured in closed containers submerged or immersed in thermostatically controlled liquid baths, the containers being provided with an appropriate inner atmosphere containing, e.g. carbondioxide, oxygen and humidity in appropriate levels. The incubator containers may e.g. be gas and liquid impervious, flexible, sealable, preferably transparent bags which after sealing are submerged or immersed directly in the thermostatically controlled liquid bath. The liquid in the bath is preferably water. An incubator for submerse or immerse culture of cells and tissues in the above manner is also described. Also a transportable liquid incubator for culturing cells and tissues in the field is described.
Owner:DEMTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com