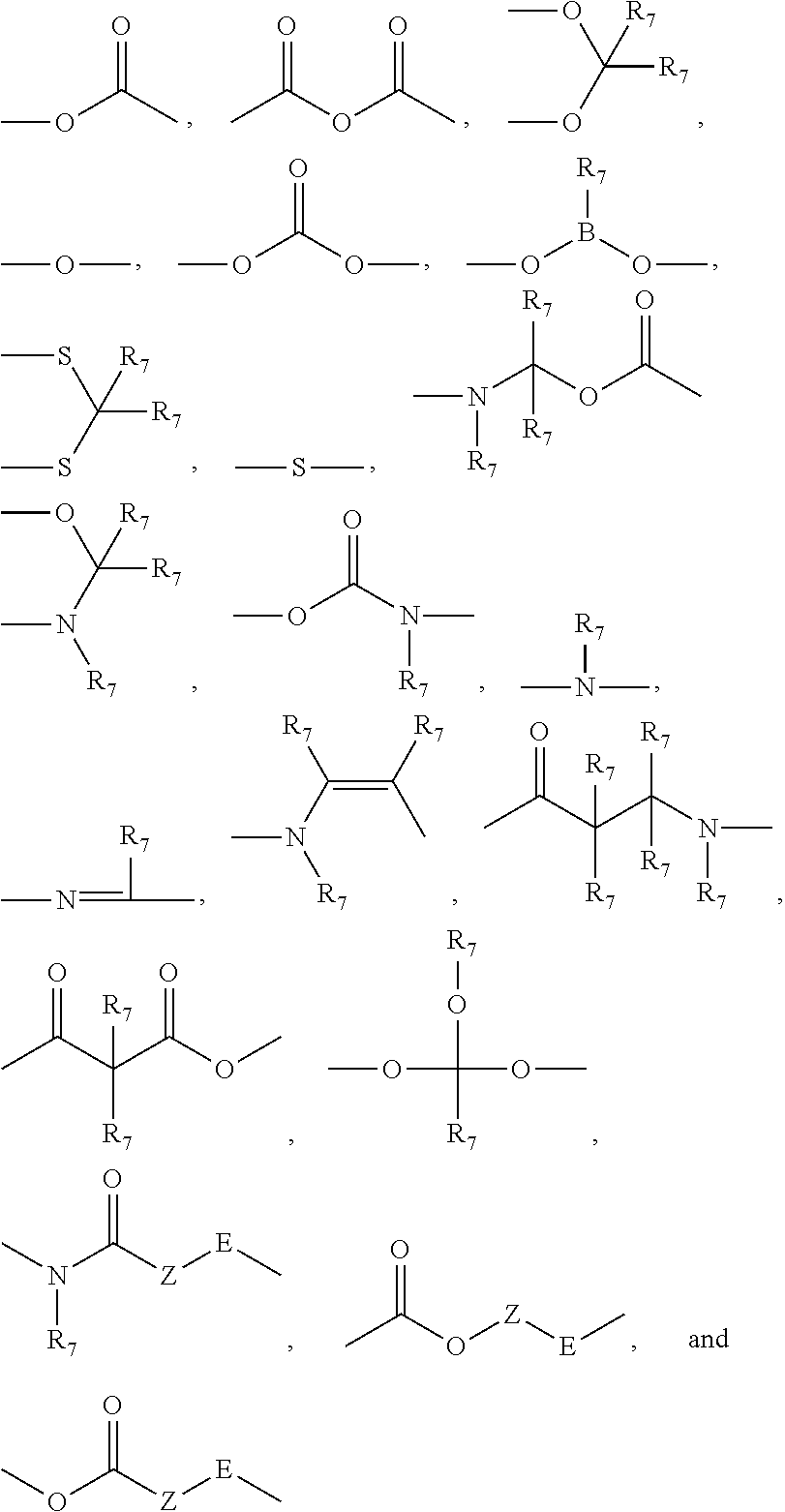
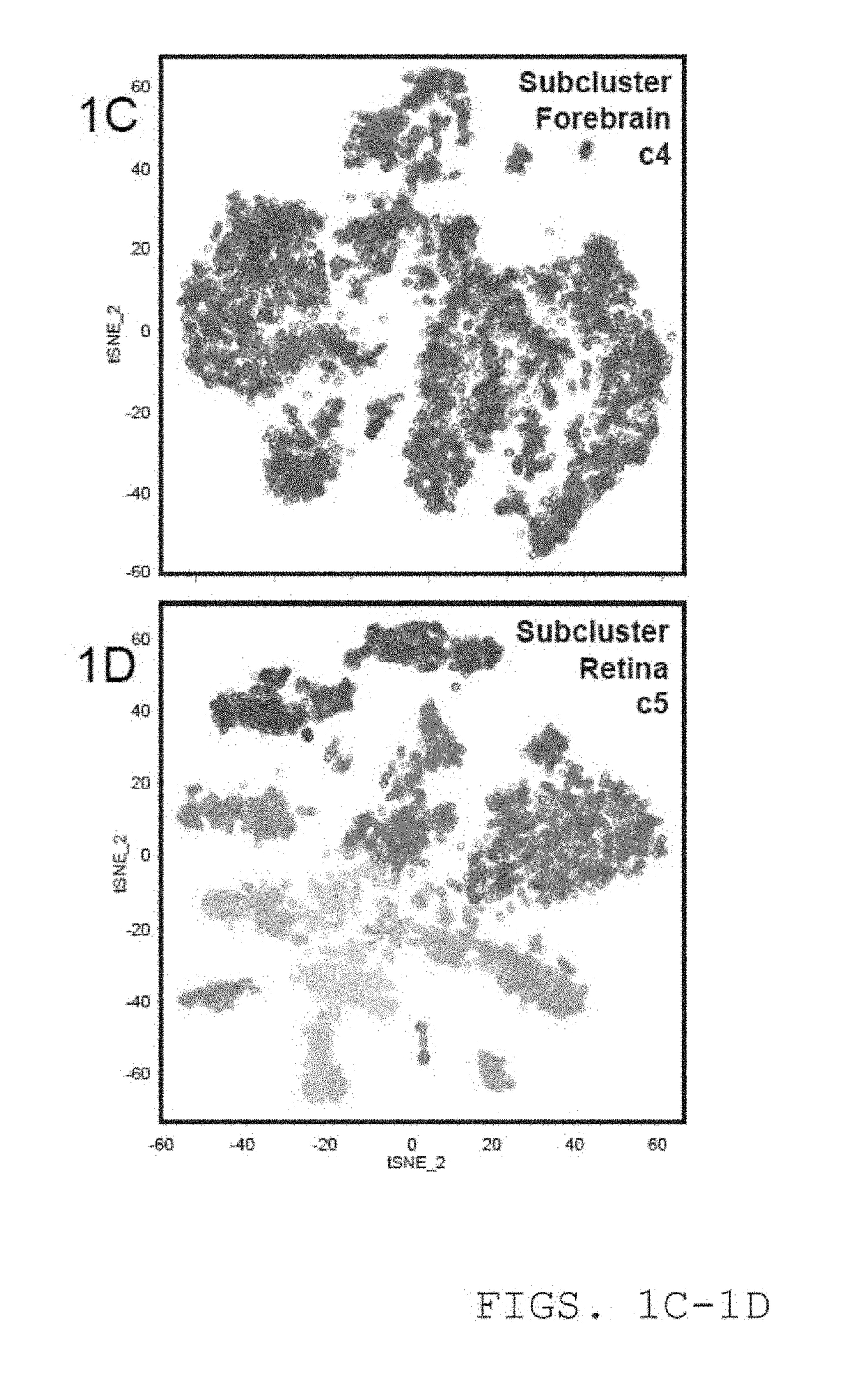
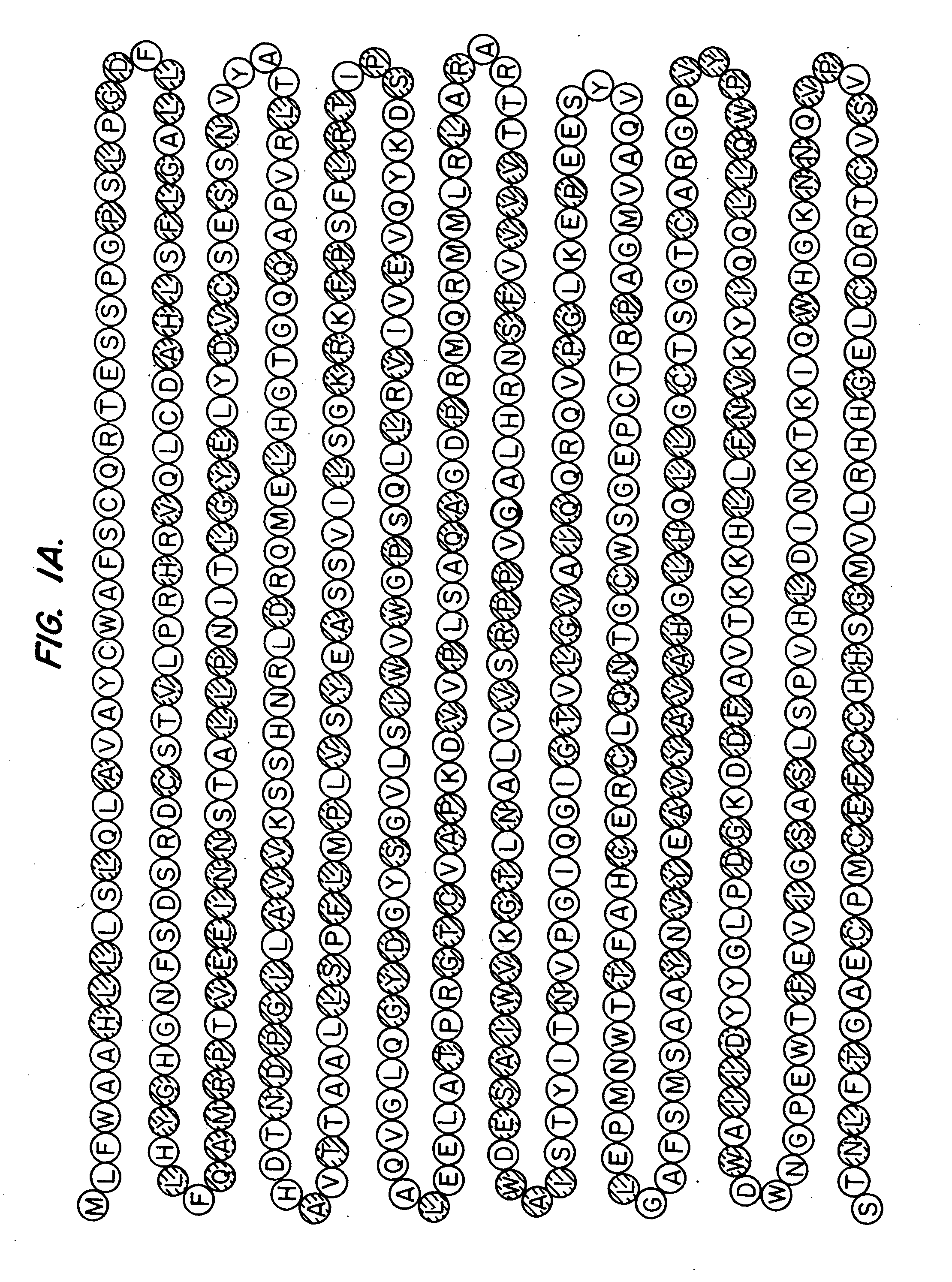
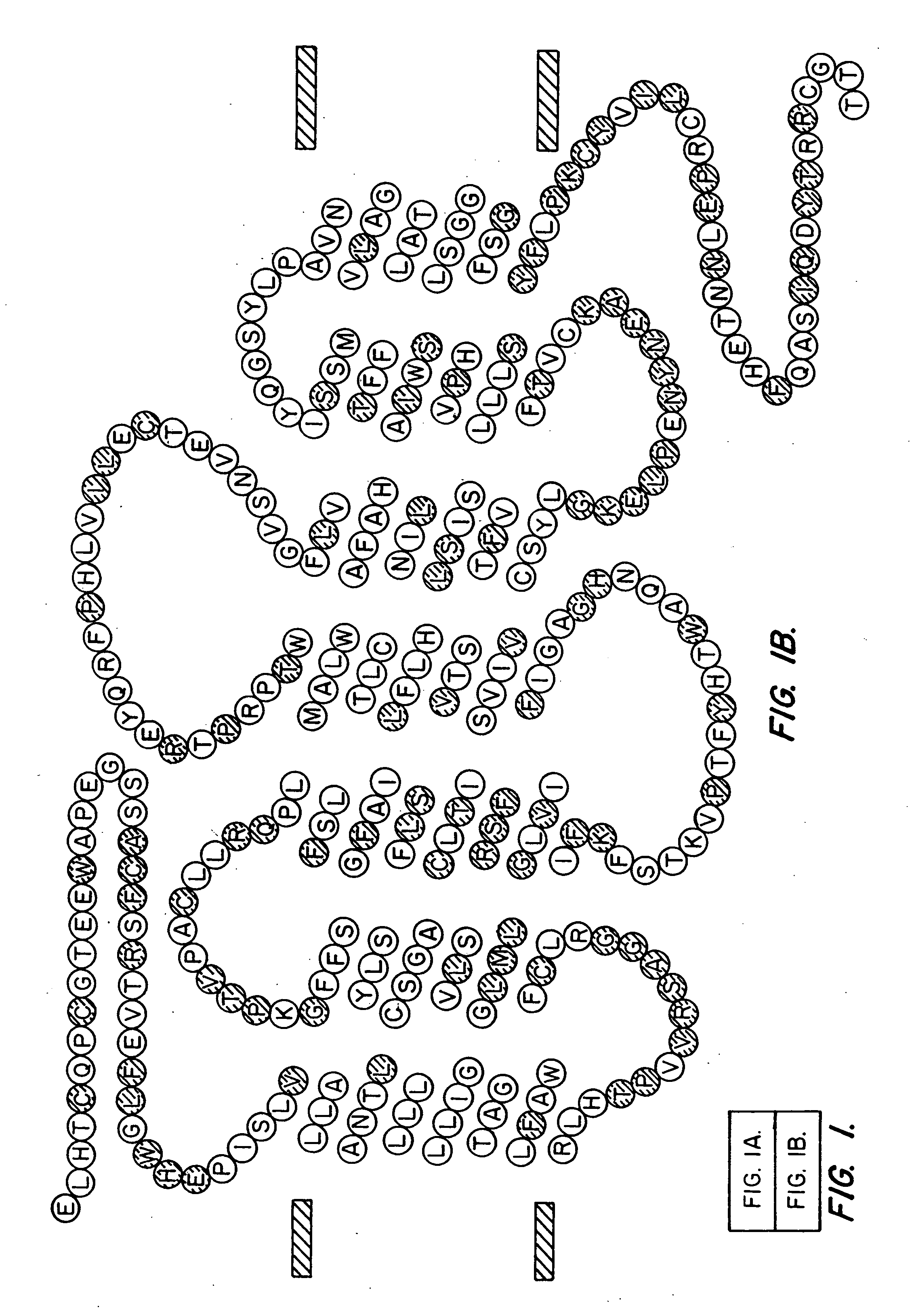
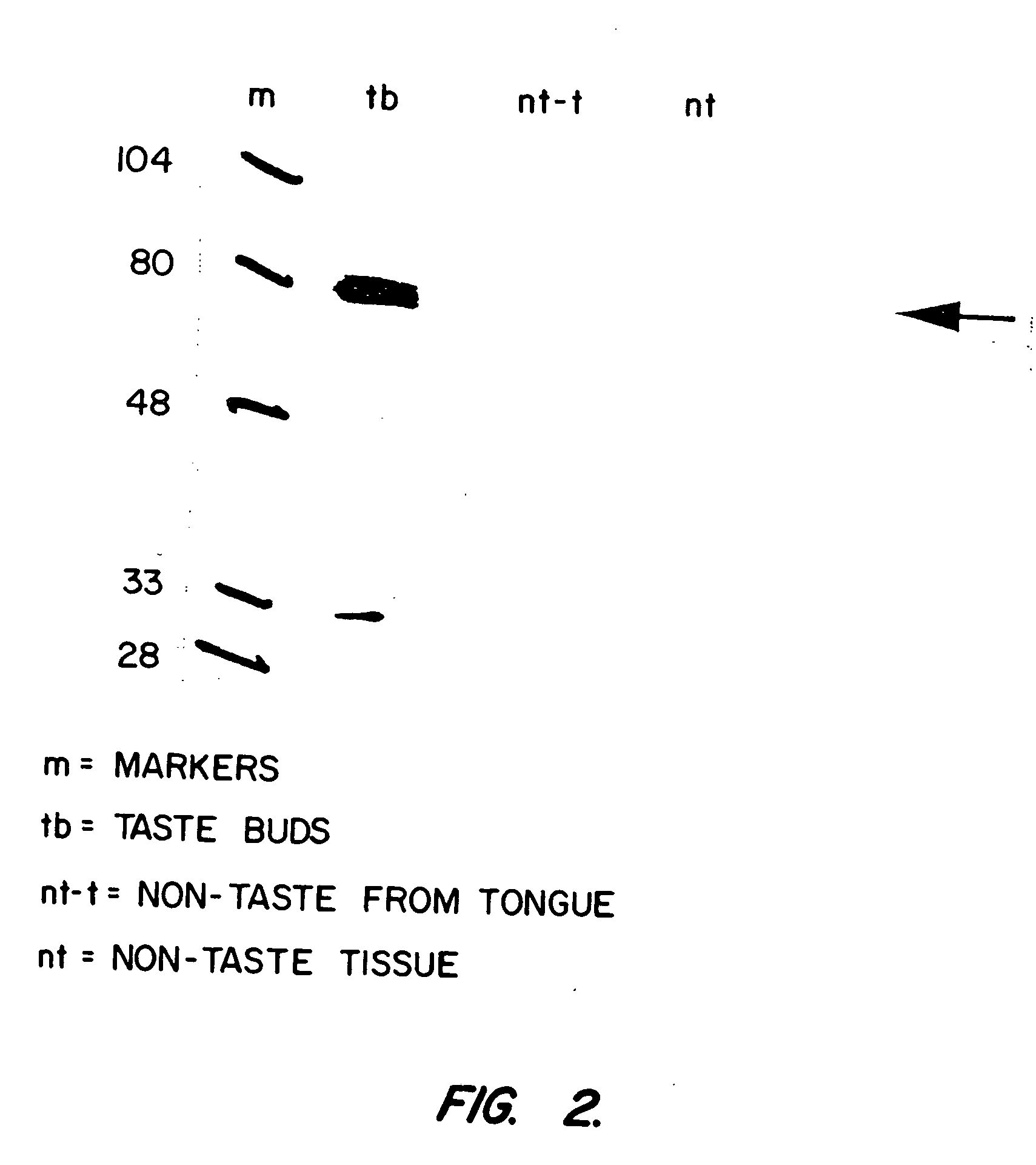
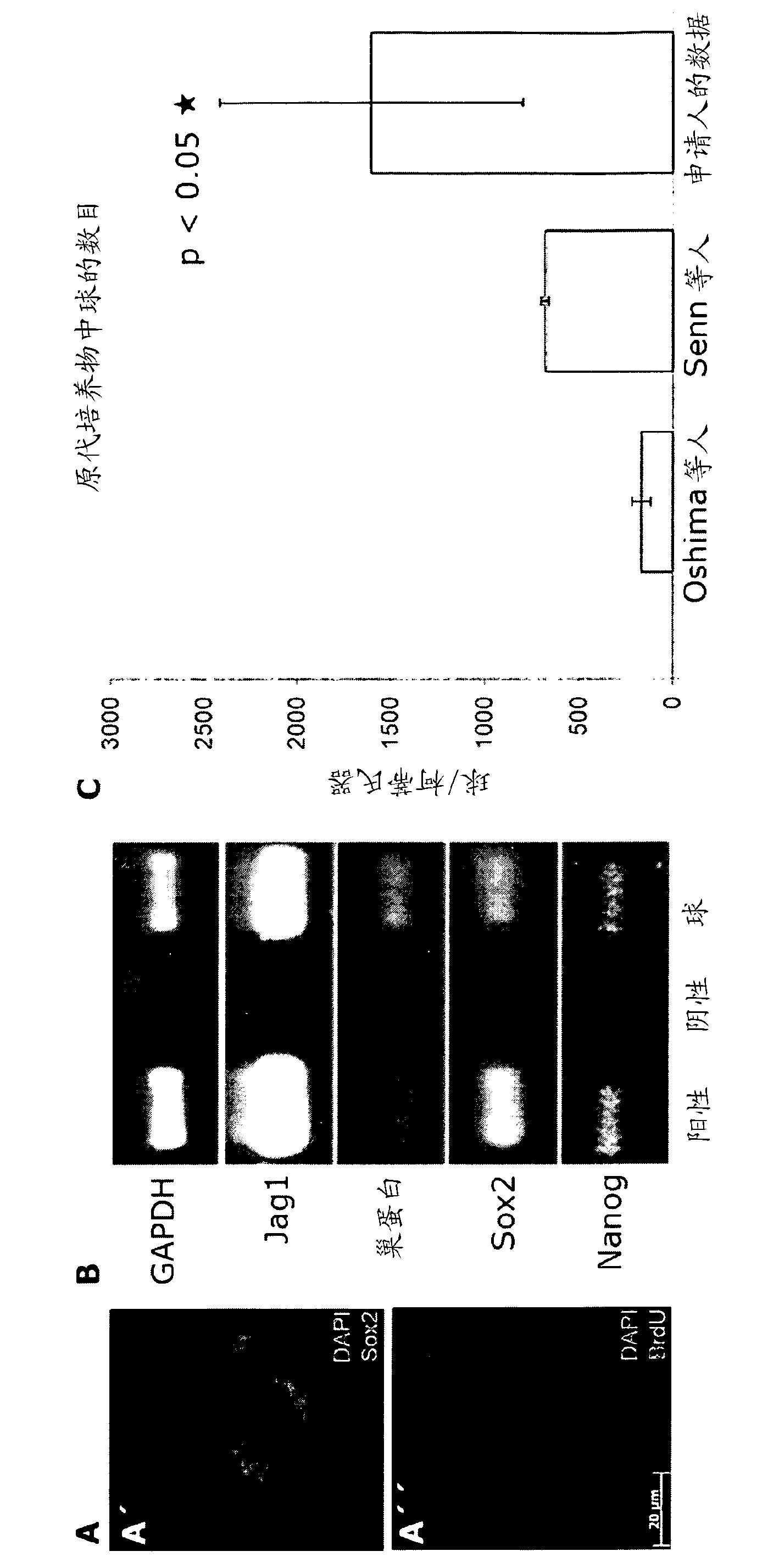
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Sensory cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for neuro-stimulation
InactiveUS20080077192A1Function increaseImprove abilitiesSpinal electrodesFiring/trigger mechanismsSensory cellElectricity
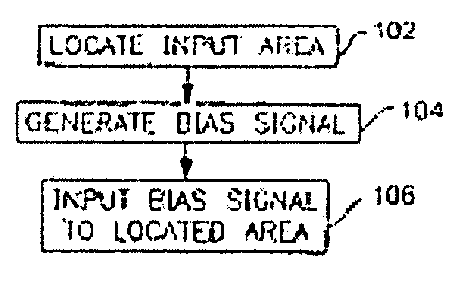
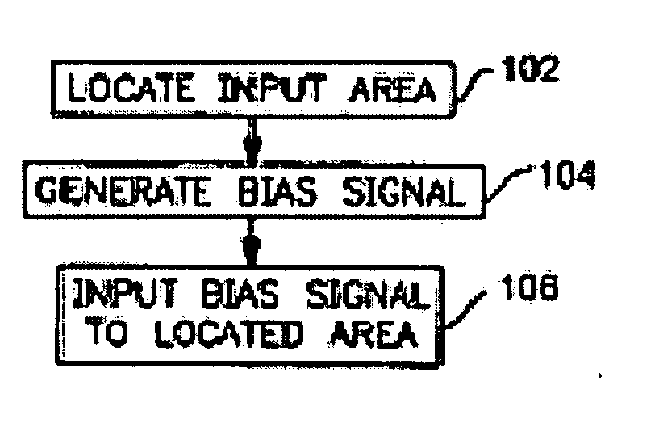
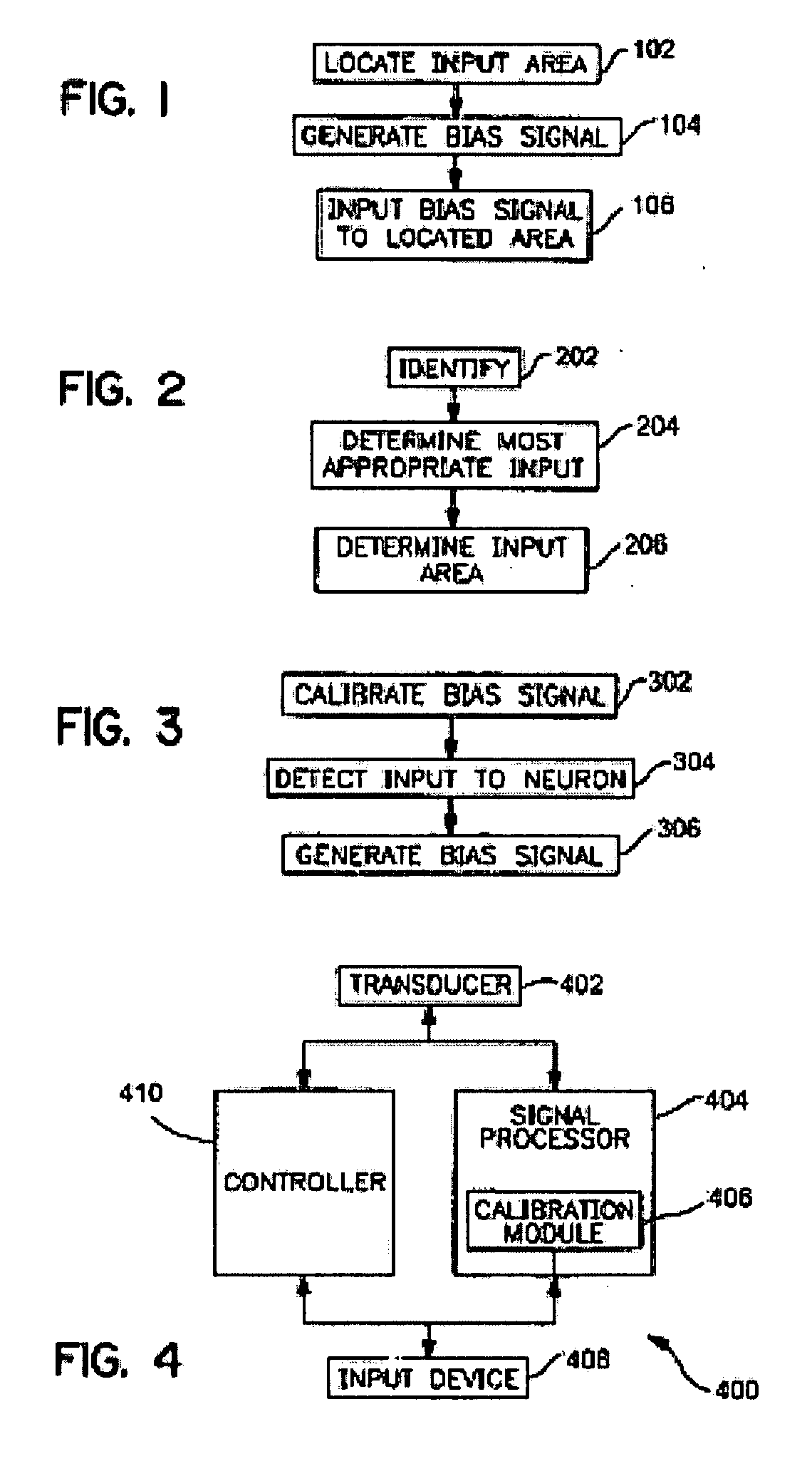
A neuro-stimulation system employs a includes a stimulator which may include electrode devices and / or vibration elements. A controller may be employed to drive the stimulating elements with an electrical signal. In response to the electrical signal, the stimulating elements deliver electrical and / or mechanical stimulation to the body part. The stimulation may be an aperiodic stimulation and / or may be a subthreshold stimulation. In one embodiment, the stimulator is disposable and the processor determines usage of the stimulator and ensures that the stimulator is limited to a certain amount of use. Neuro-stimulation systems may be applied to sensory cells of body parts during movement of the body parts to induce neuroplastic changes. Such movement may involve a variety of therapeutic applications, e.g. in stroke patient therapy.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
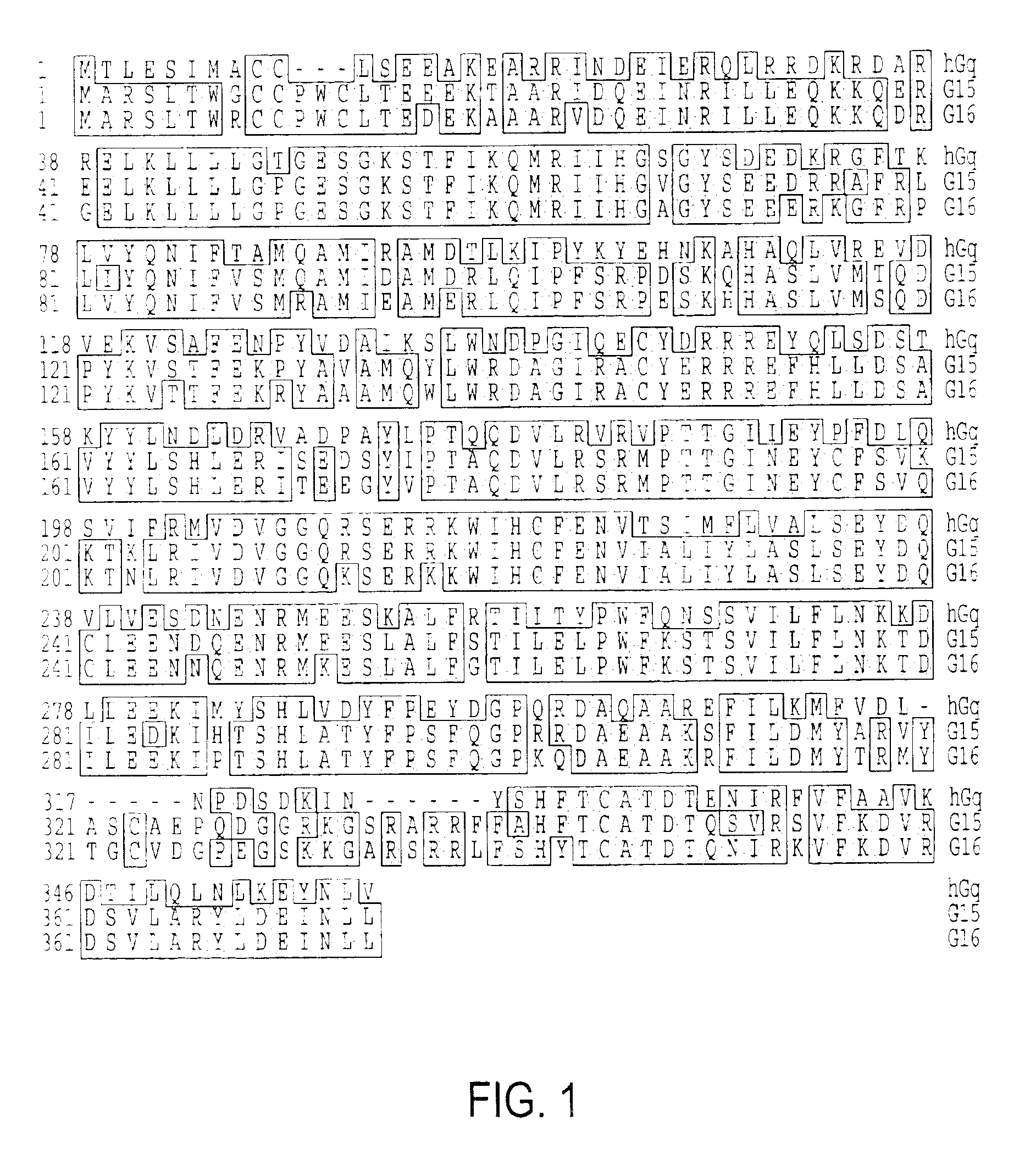
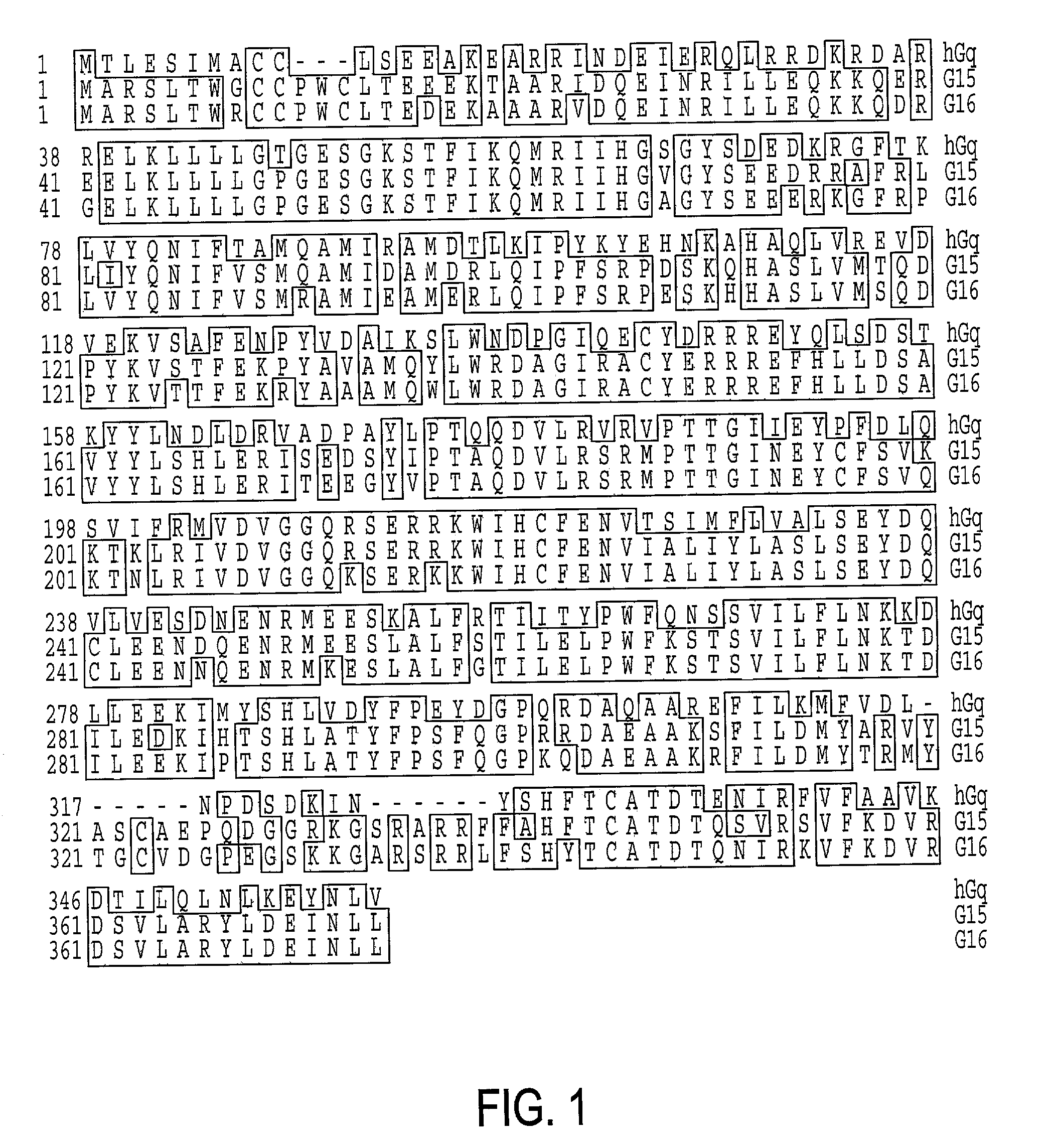
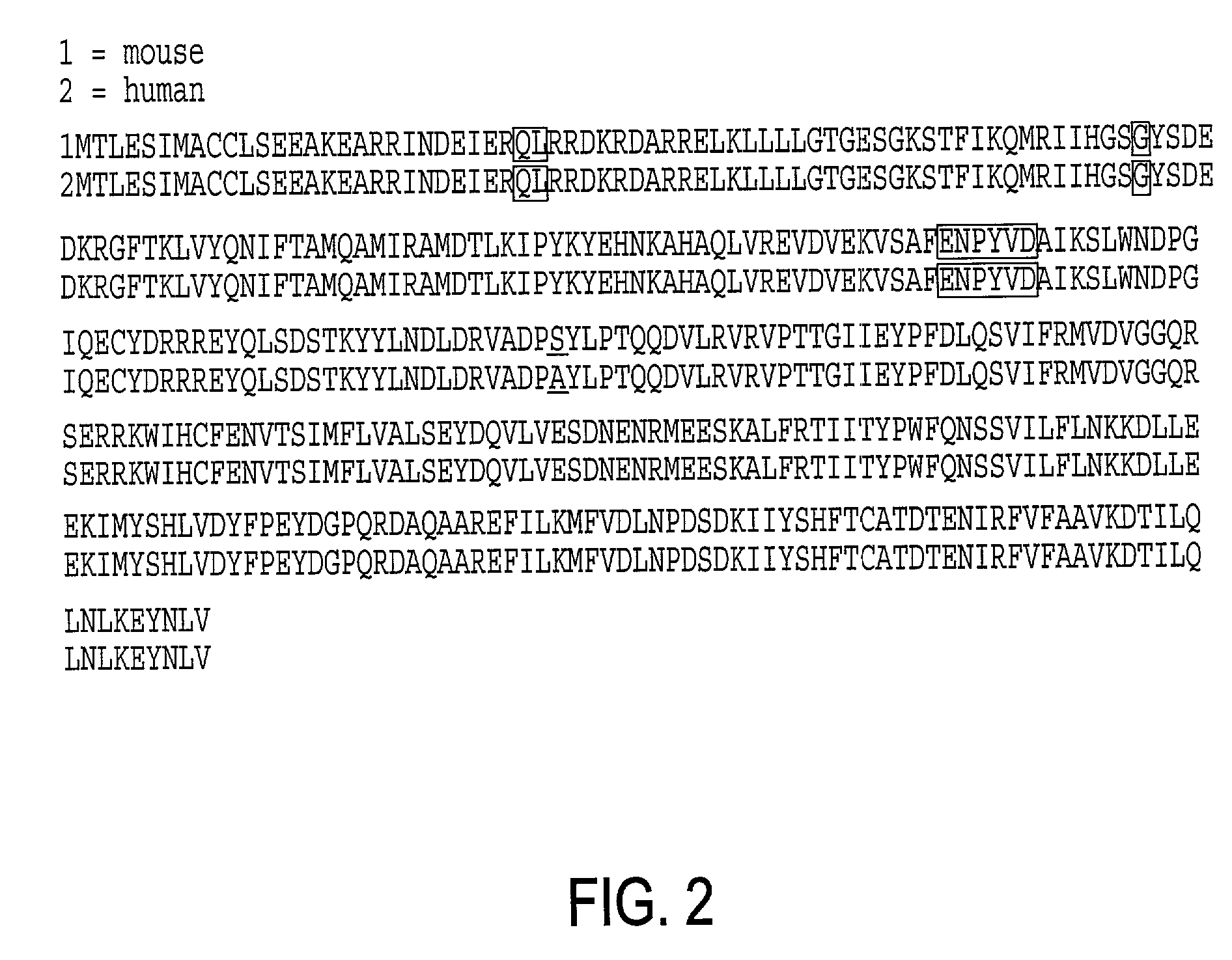
Gaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS20020143151A1Improved functional couplingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
System and method for neuro-stimulation
InactiveUS20140364678A1Function increaseImprove abilitiesSpinal electrodesVibration massageSensory cellElectricity
A neuro-stimulation system employs a includes a stimulator which may include electrode devices and / or vibration elements. A controller may be employed to drive the stimulating elements with an electrical signal. In response to the electrical signal, the stimulating elements deliver electrical and / or mechanical stimulation to the body part. The stimulation may be an aperiodic stimulation and / or may be a subthreshold stimulation. In one embodiment, the stimulator is disposable and the processor determines usage of the stimulator and ensures that the stimulator is limited to a certain amount of use. Neuro-stimulation systems may be applied to sensory cells of body parts during movement of the body parts to induce neuroplastic changes. Such movement may involve a variety of therapeutic applications, e.g. in stroke patient therapy.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
Owner:SENOMYX INC
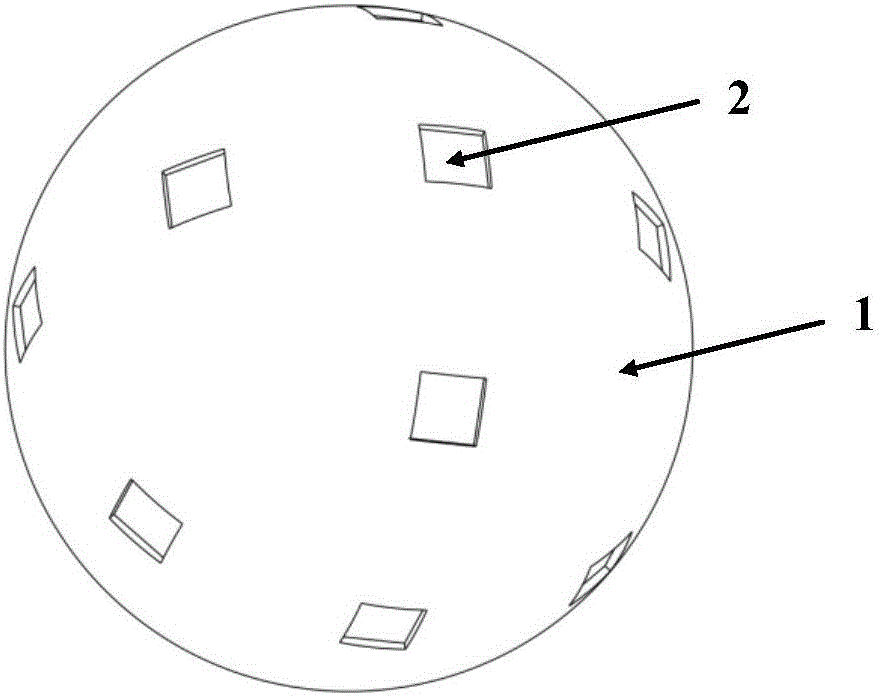
Novel micro ball sensor for sensing space environment changes and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN106885919AEffective calculationEfficient capturePosition fixationFluid speed measurementSensory cellPhase difference
The invention discloses a novel micro ball sensor for sensing space environment changes and a manufacture method thereof. The sensor simulates a biological behavior that lateral lines of a fish identify and locate prey underwater, that is, the exposed lateral line canals in the neuromasts in the lateral lines can mechanically sense the vibration generated during the swim of underwater animals. Positioning is performed according to the time and phase difference that a vibration wave reaches different neuromasts underwater, and a motion signal is converted into a physiological electric signal to be transmitted to sensory cells to sense stimulation such as external water flow changes, low-frequency vibration, and temperature changes. By using a polyvinylidene fluoride direct piezoelectric effect, a spatial airflow change is imitated and sensed and a spatial vibration source is positioned. A single ball sensing unit senses the vibration by using the polyvinylidene fluoride and directly converts the vibration into electric signals so as to calculate a spatial airflow magnitude and angle. A plurality of ball sensing units are arranged in an array, calculate the airflow magnitude and orientation according to the time and phase difference that the vibration wave reaches different sensing units, and improve the spatial airflow magnitude and orientation calculation accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
ActiveUS7041457B2Increase promiscuityHigh activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTissue cultureSensory cellFluorescence
The invention provides a series of Galphaq protein variants that functionally couple to sensory cell receptors such as taste GPCRs (TRs) and olfactory GPCRs (ORs) in an overly promiscuous manner. According to the invention, the functional coupling can be determined, for example, by measuring changes in intracellular IP3, or calcium. In a particular embodiment, the Galphaq protein variants can be expressed in mammalian cell lines or Xenopus oocytes, and then evaluated using calcium fluorescence imaging and electrophysiological recording.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Compound for inhibiting trpv3 function and use thereof
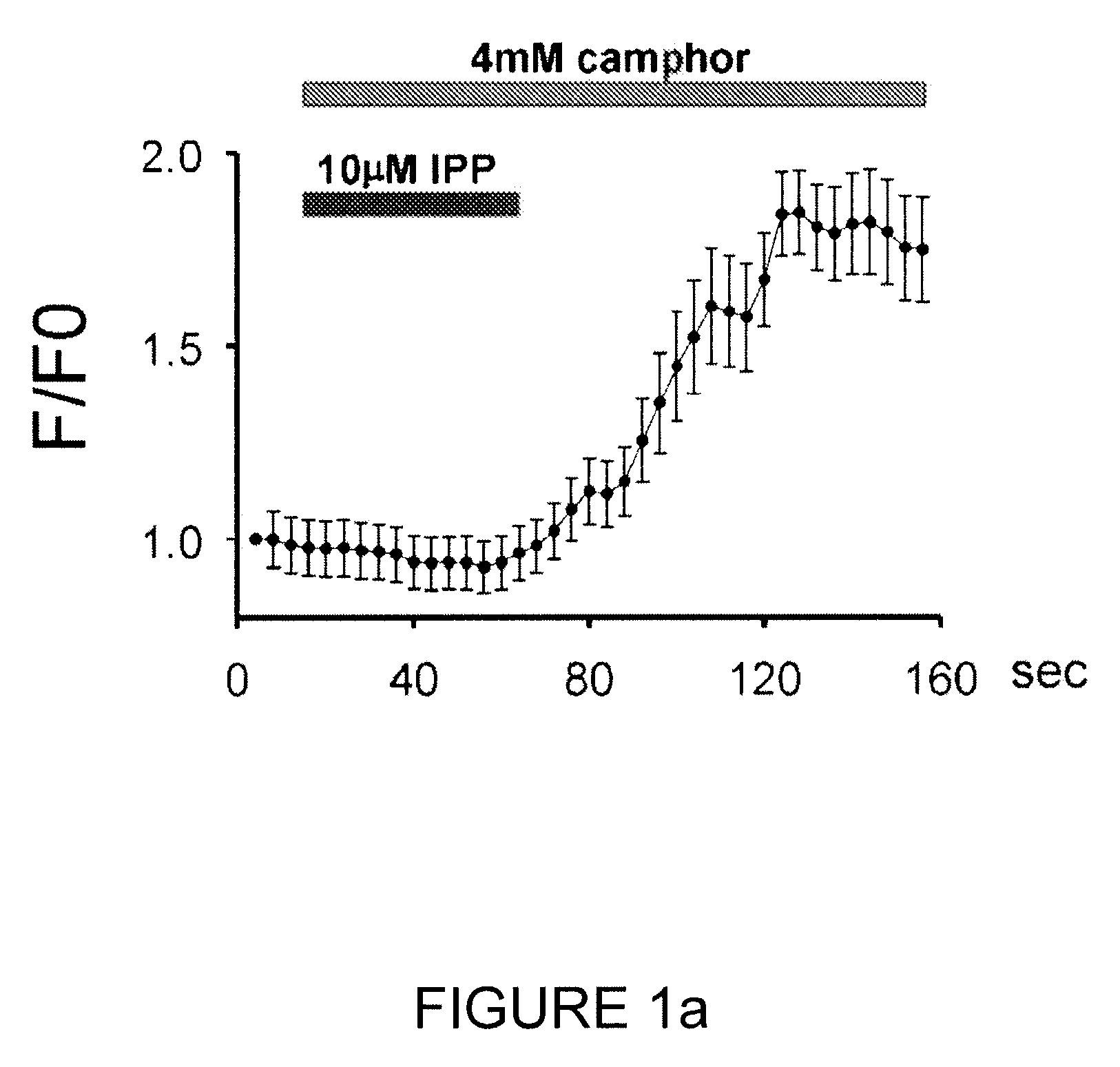
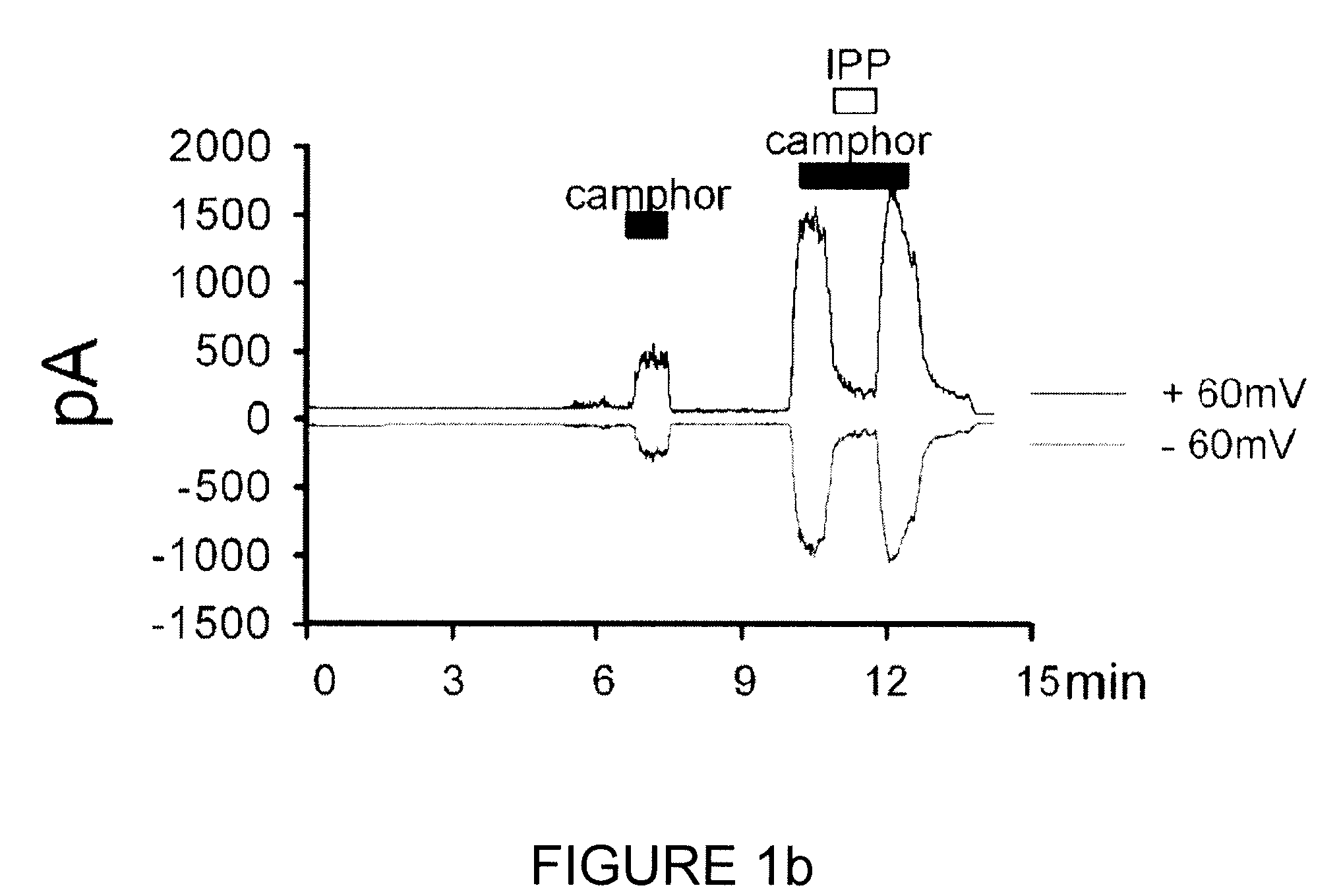
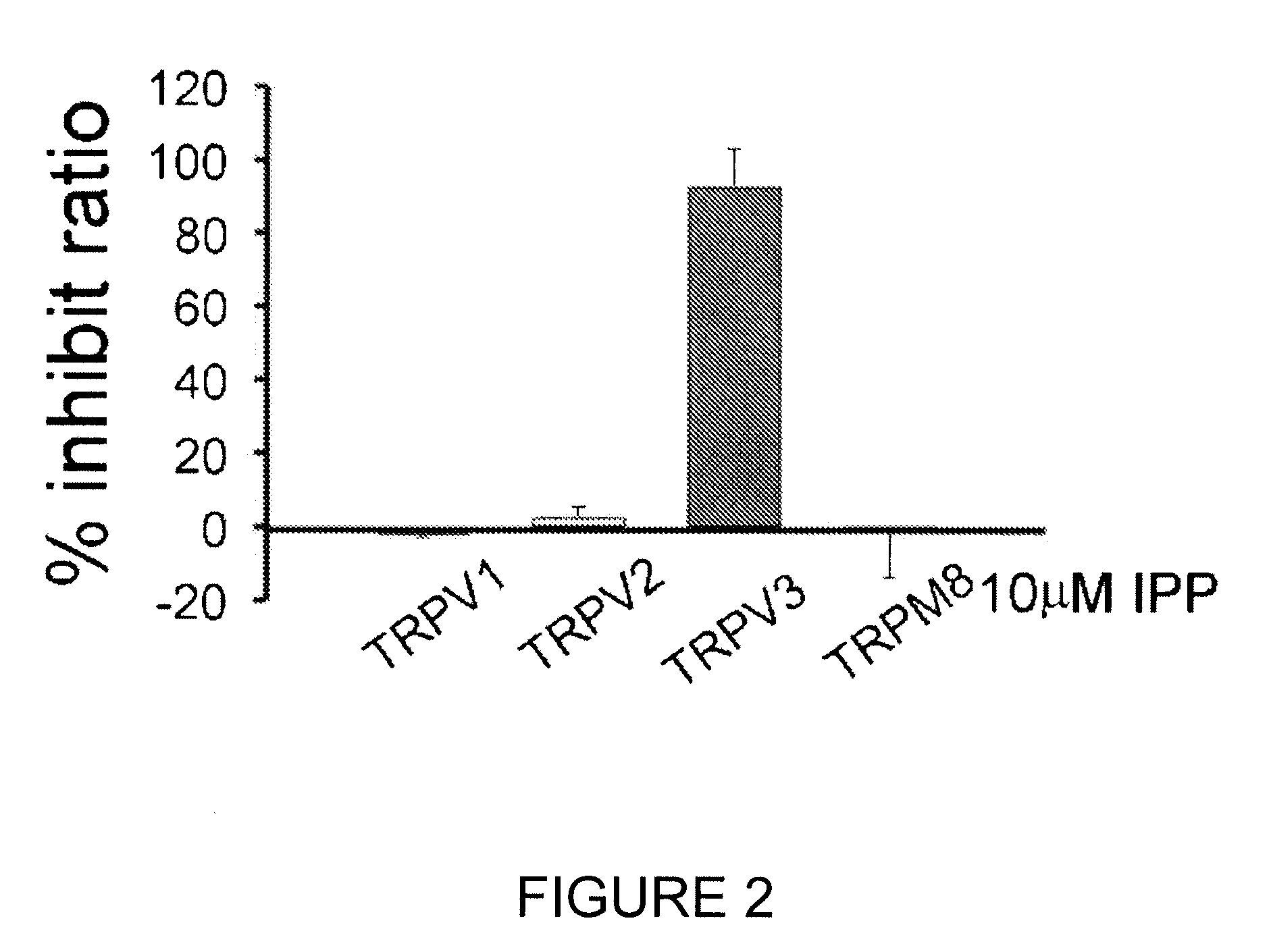
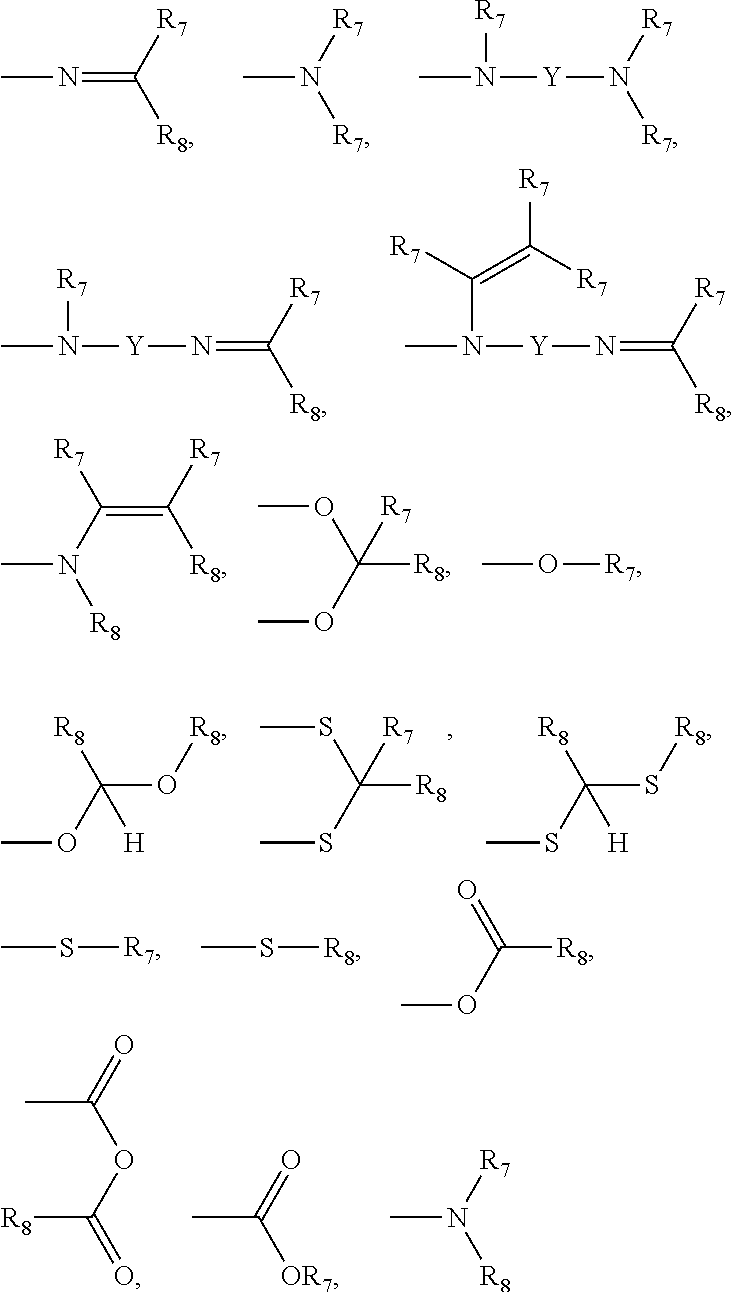
InactiveUS20100137260A1Improve developmentImprove responseBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsSensory cellIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
The present invention relates to a TRPV3 (transient receptor potential vanilloid 3) activity inhibitor, more precisely to a method for inhibiting TRPV3 activity including the step of treating isopentenyl pyrophosphate and a method for treating skin disease containing the step of administering isopentenyl pyrophosphate to a subject with skin disease or applying the same on the skin of the subject. Isopentenyl pyrophosphate of the present invention controls increase of sensory cell reactivity to current or migration and proliferation of skin cells induced by TRPV3, so that it can be effectively used for the development of a pain reliever or a therapeutic agent for skin disease.
Owner:KOREA UNIV IND & ACADEMIC CALLABORATION FOUND
Galphaq protein variants and their use in the analysis and discovery of agonists and antagonists of chemosensory receptors
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Silicone compounds
InactiveUS20190010293A1Cosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsSensory cellHydrophile
The present application relates to silicone compounds, compositions, packaged products and displays comprising such silicone compounds, and processes for making and using such compositions, packaged products and displays comprising such compositions. Such compositions have improved deposition and retention properties that may impart improved benefit characteristics to a composition and / or situs yet which changes its hydrophilicity / charge when desired. Such silicone compounds solve the further problem of malodor reduction as, in addition to maldor masking, such compounds block a malodor's access to a sensory cell, yet leave such sensor cell open to other molecules, for example scent molecules. Thus, the malodor control technologies disclosed herein do not unduly interfere with the scent of the perfumed or unperfumed situs that is treated with the malodor control technology.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
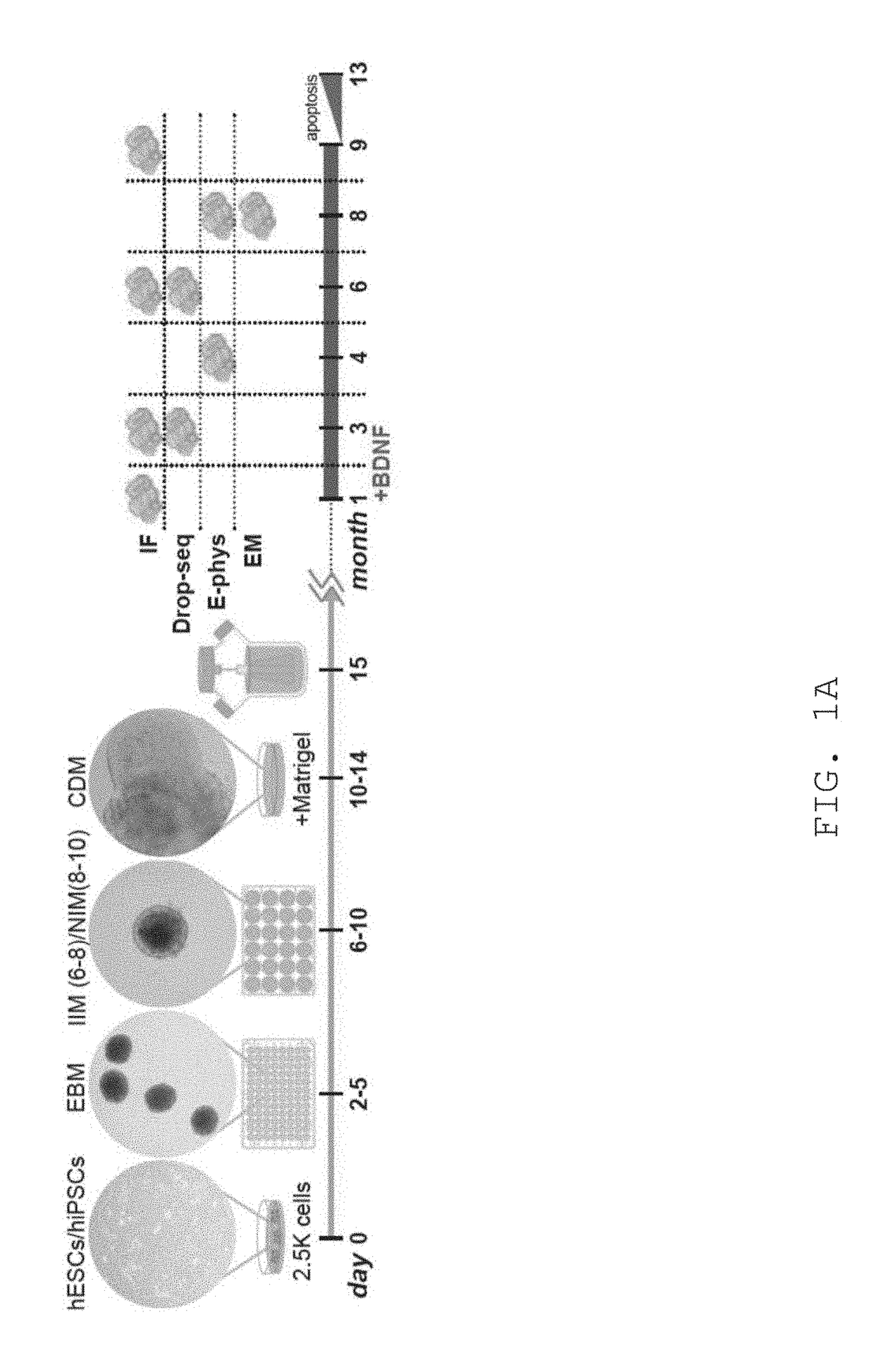
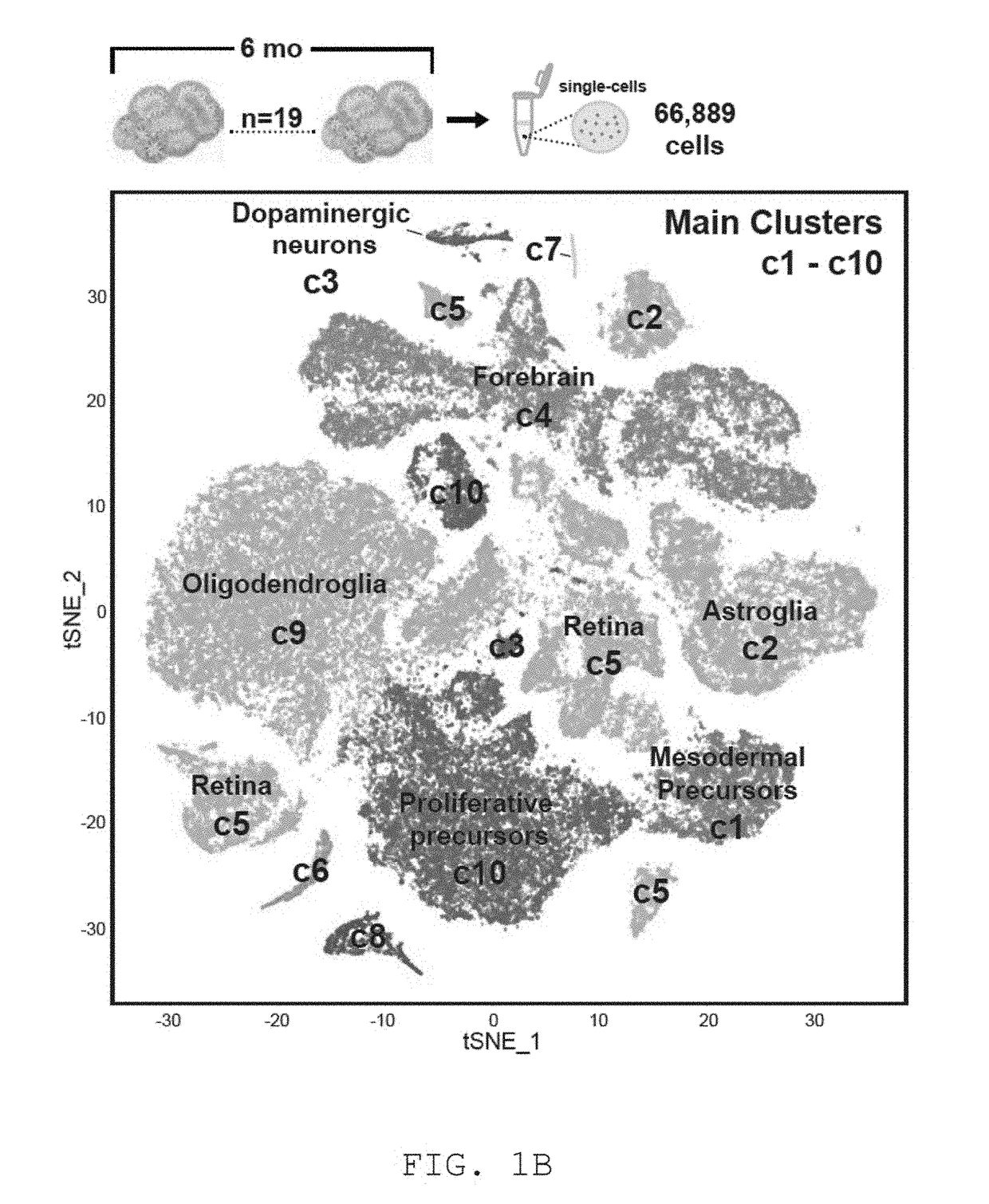
Methods for generating neural tissue and uses thereof
Disclosed herein are 3-D neural tissue structures or “brain organoids” created from human pluripotent cells (e.g., stem cells) differentiated into neuronal cell types that include cortical and subcortical neuronal subtypes along with sensory cells. Also disclosed herein are methods for the in vitro generation of 3-D neural tissue structures capable of sensory perception, methods for generating a “brain organoid-machine interface” (BOMI), and methods for screening of molecular, cellular and network-level defects associated with complex mental diseases through use of patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nucleic acids encoding a G-protein coupled receptor involved in sensory transduction
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Nucleic acids encoding a G-protein coupled receptor involved in sensory transduction
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electromagnetic personnel interdiction control method and system
A non-lethal and non-destructive electromagnetic personnel interdiction control stun type weapon system and method utilizes beamed radio frequency energy in a frequency range and modulated to impose a Lorentz force on the vestibular system or sensory cells of a remote human subject sufficient to disrupt the mechanical transduction process and / or the chemical engine by which sound, position and other sensory input are converted to messages by nerve cells and processed by the brain to produce complete disorientation, confusion, and incapacitation sufficient to temporarily render the subject powerless to resist arrest or subjugation. Removal of the electromagnetic energy leaves the nerve cells and surrounding tissues with no damage and second order effects of severe motion sickness and psychological effects of helplessness remains until the subject's body chemistry returns to normal.
Owner:INVOCON
Nucleic acids encoding proteins involved in sensory transduction
The present invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell-specific polypeptides, antibodies to these polypeptides, methods for detecting these nucleic acids and polypeptides, and methods for screening for modulators of sensory cell-specific polypeptides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel aminoalkyl-oxazole and aminoalkyl-thiazole carboxylic acid amides as regeneration-promoting substances for sensory organs and post-mitotic tissue
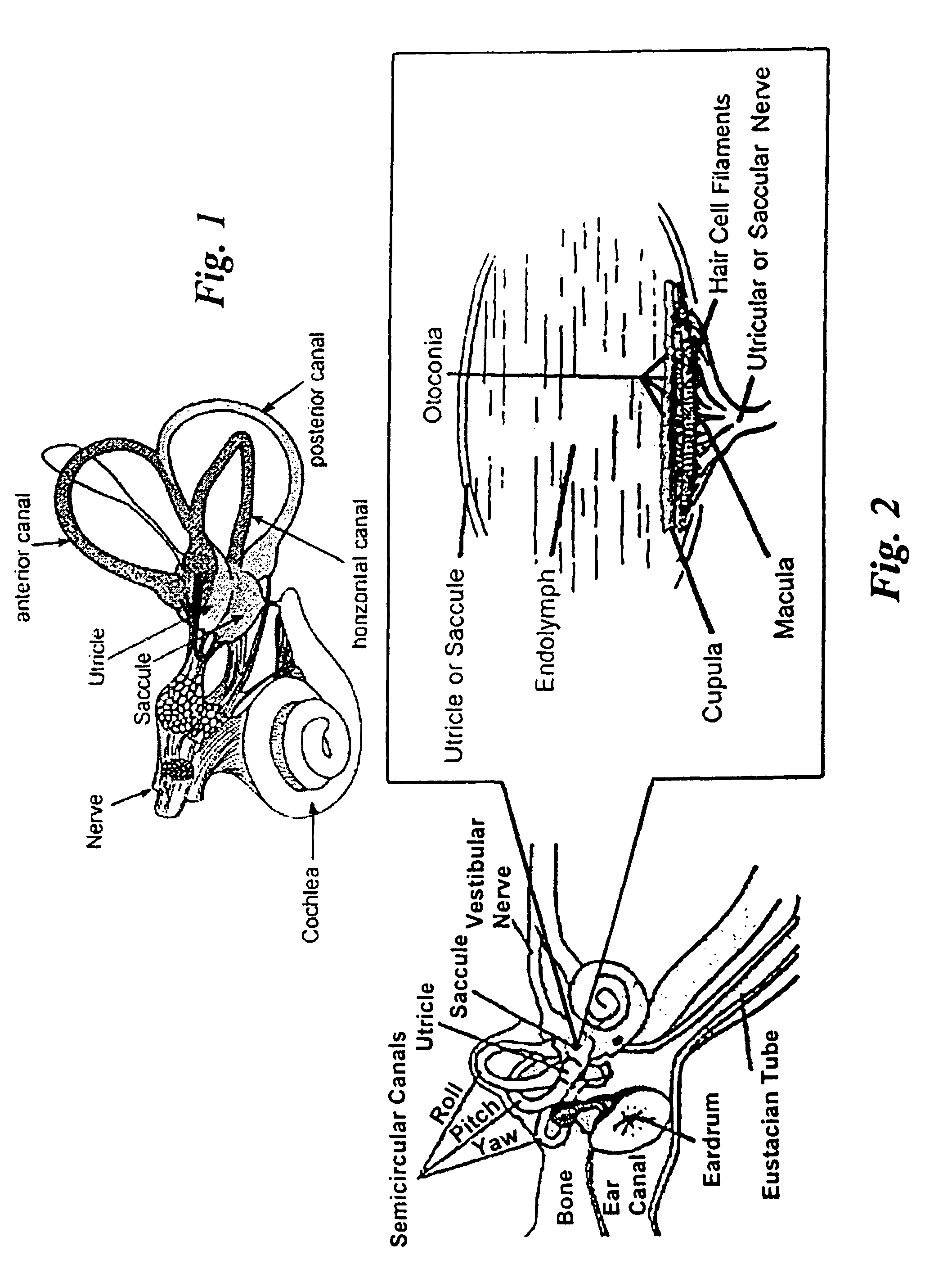
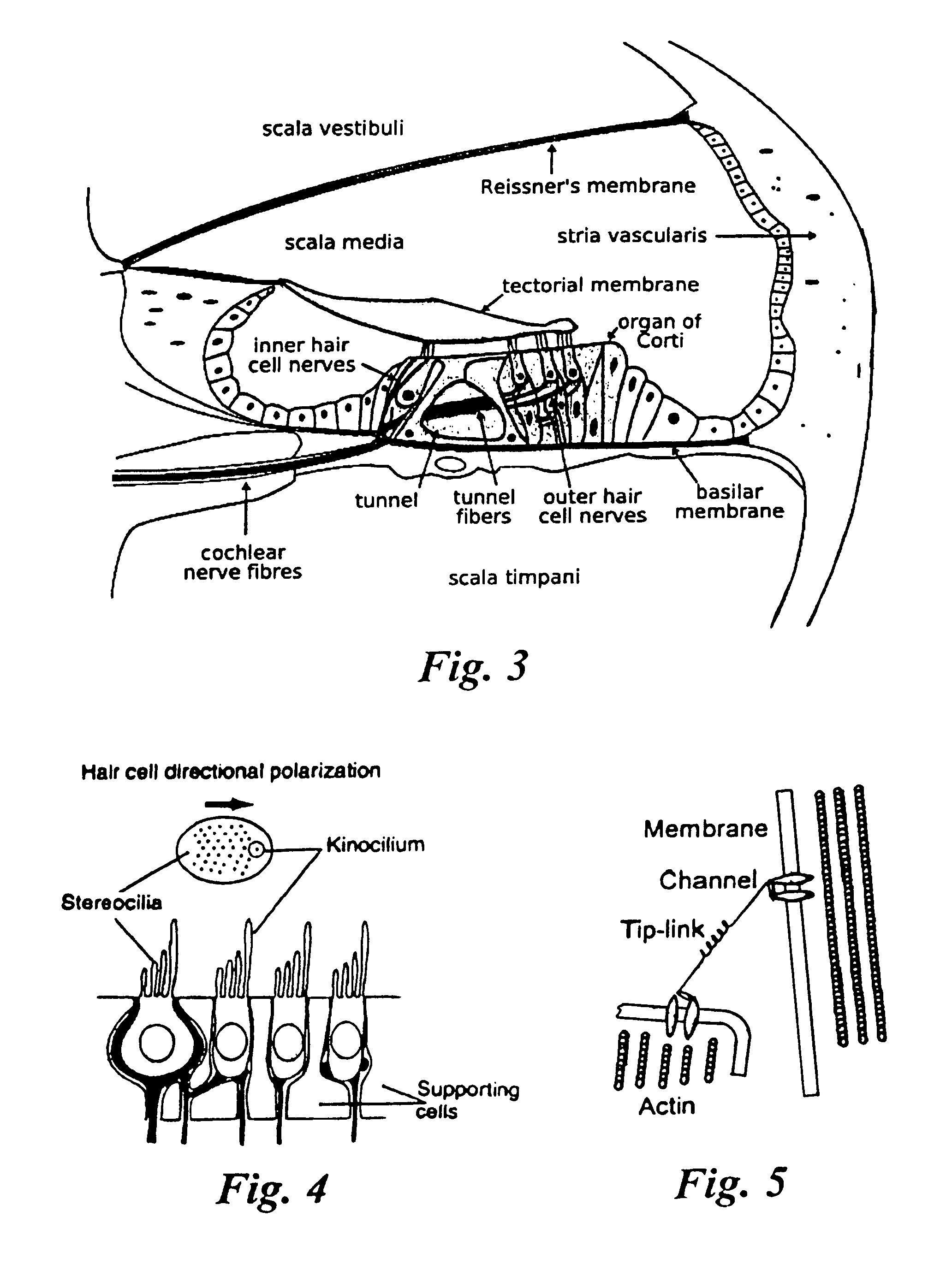
The present invention relates to novel aminoalkyl-oxazole and aminoalkyl-thiazole carboxylic acid amides that stimulate the endogenous regeneration of terminally differentiated cells in highly specialized organs, tissues and sensory epithelia in mammals in situ. The claimed low-molecular-weight compounds are able to induce corresponding cell biological changes such as dedifferentiation, proliferation and the subsequent terminal redifferentiation of cells of the normally post-mitotic tissue. The invention in particular relates to compounds with which a de novo formation of hair sensory cells in the organ of Corti can be obtained by inducing cell separation of supporting cells of the inner ear and hearing can be restored after hair cell loss. The compounds according to the invention for the first time enable a causal treatment of inner ear hardness of hearing caused, for example, by noise, ototoxic substances, symptoms of old age or genetic causes on the basis of regenerative biology. The invention further relates to methods for producing the compounds according to the invention, to the formulation (1) (2) thereof as pharmaceutical preparations and to the use thereof for producing pharmaceuticals for regenerative medicine.
Owner:EMC MICROCOLLECTIONS
Nucleic acids encoding a G-protein coupled receptor involved in sensory transduction
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
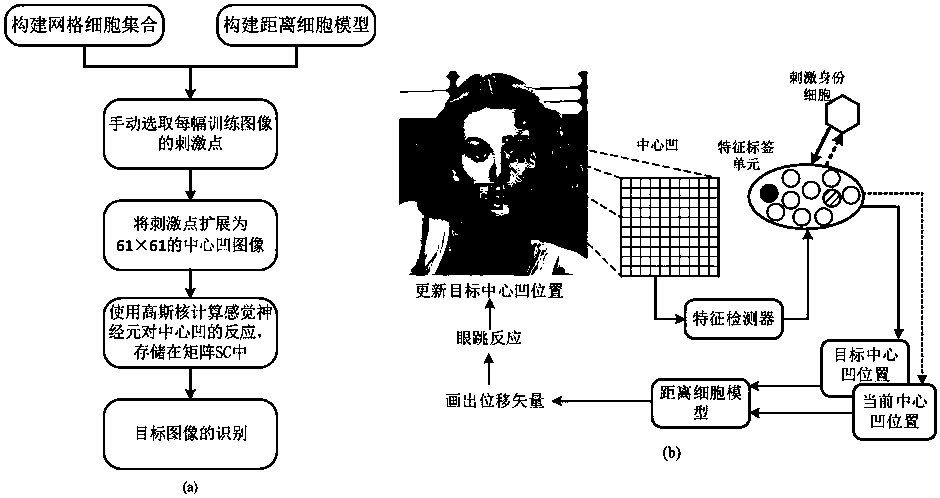
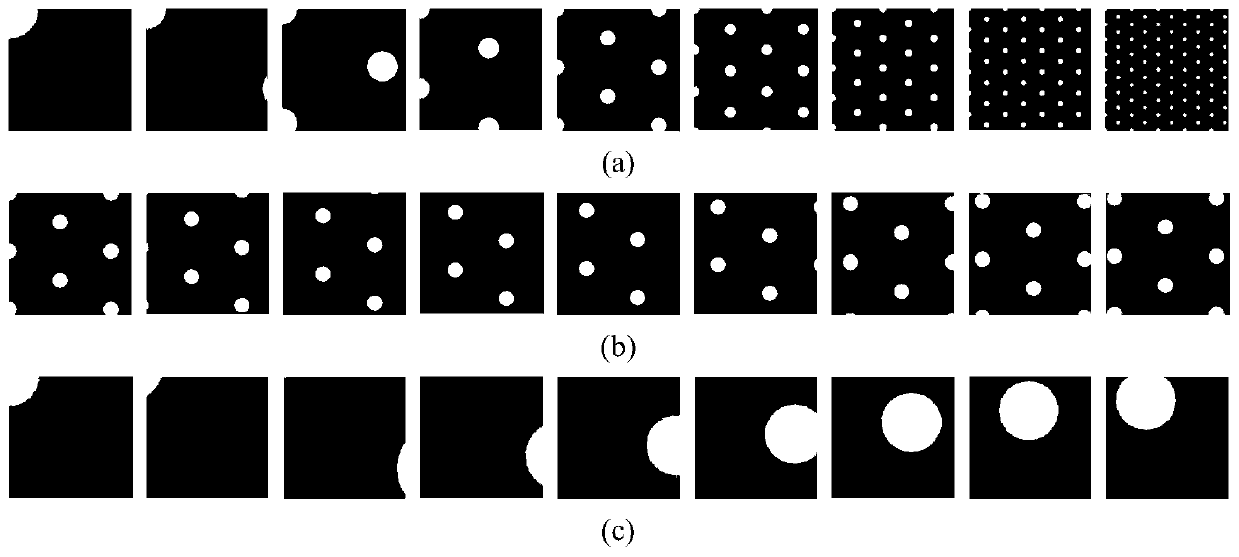
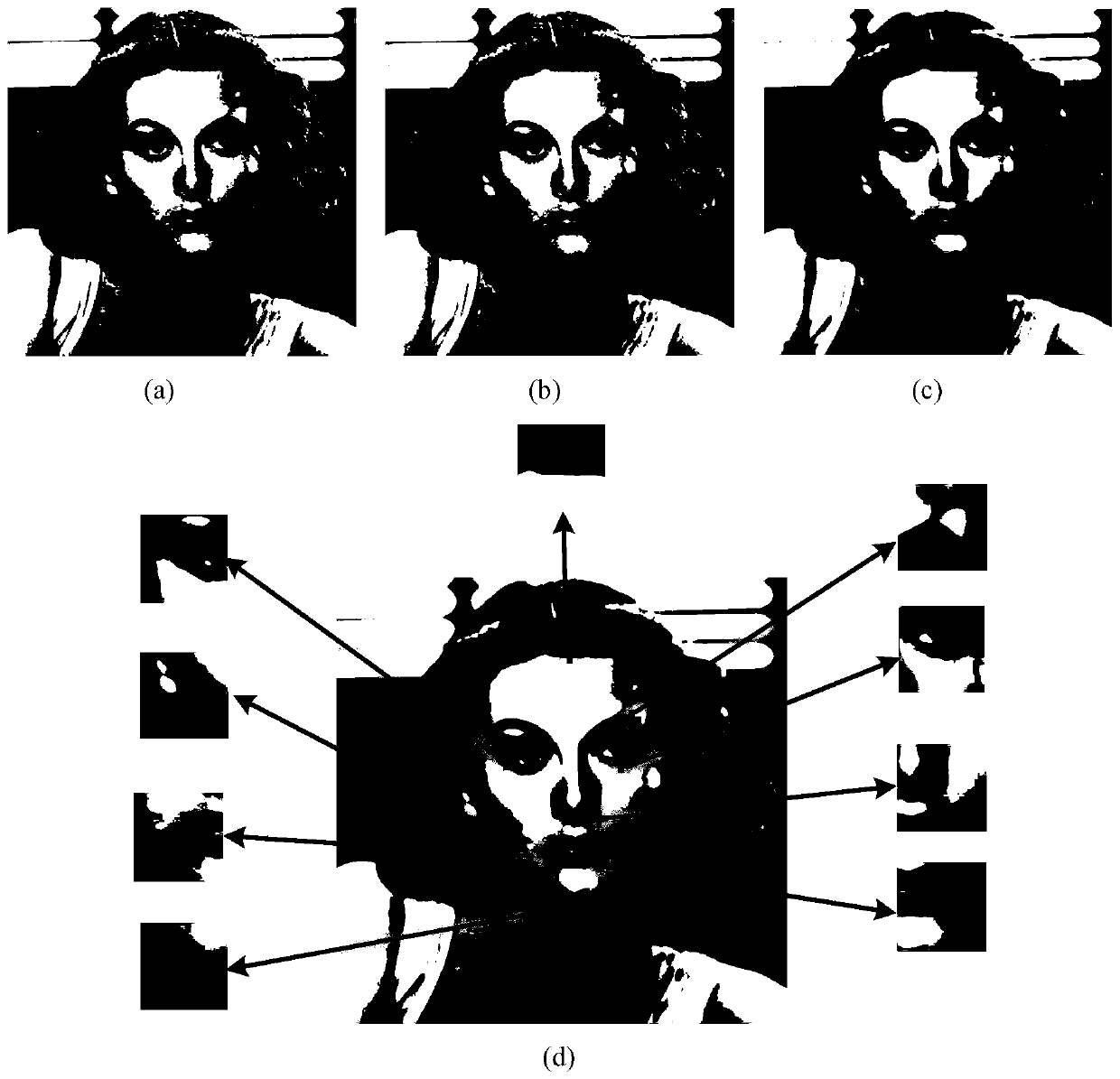
Bionic visual image target recognition method fusing dot-line memory information
ActiveCN110598534APrecise and detailed visual contentImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionSensory cellViewpoints
The invention discloses a bionic visual image target recognition method fusing dot-line memory information, and the method comprises the steps of constructing a grid cell set based on visual drive, constructing a distance cell model, and calculating a displacement vector between the positions coded by a grid cell group vector; calculating the response of all sensory neurons to each central concavepixel k through a Gaussian kernel, wherein the response is used for target recognition; calculating the fovea centralis of the current target image by using Gaussian nuclear sensory cells, taking thefeature tag unit with the strongest response as the next jump point, and accumulating the corresponding stimulated identity cells; selecting a next-hop viewpoint, and updating a foveal displacement vector through a distance cell model; and circularly repeating the calculation of the current position during the target identification process, selecting the next-hop viewpoint, and carrying out the vector calculation until the accumulation of a certain stimulated identity cell reaches a threshold value 0.9, and considering the stimulated identity as the finally identified target. The method provided by the invention has a relatively higher recognition rate for the position change, zooming and shielded images.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
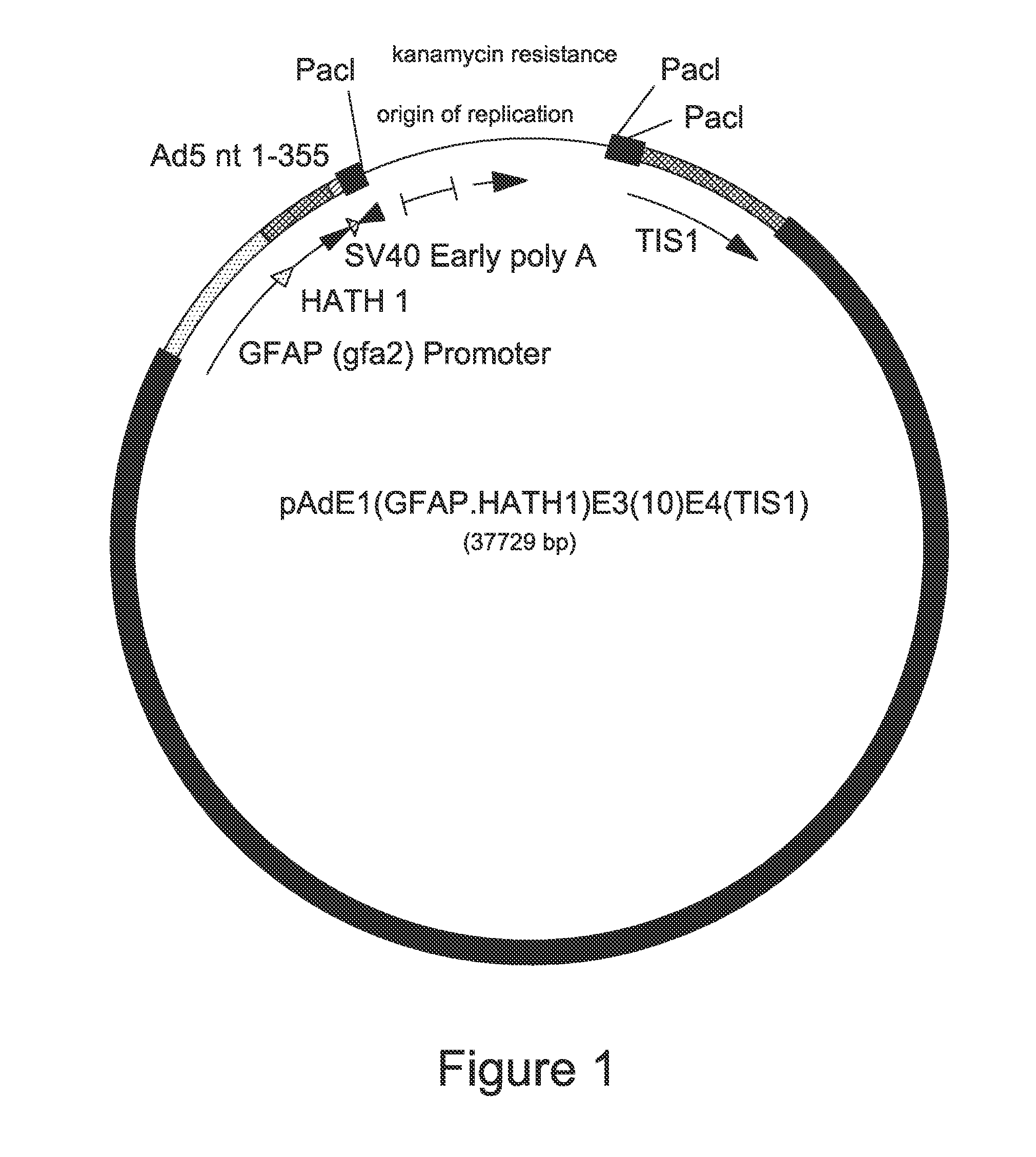
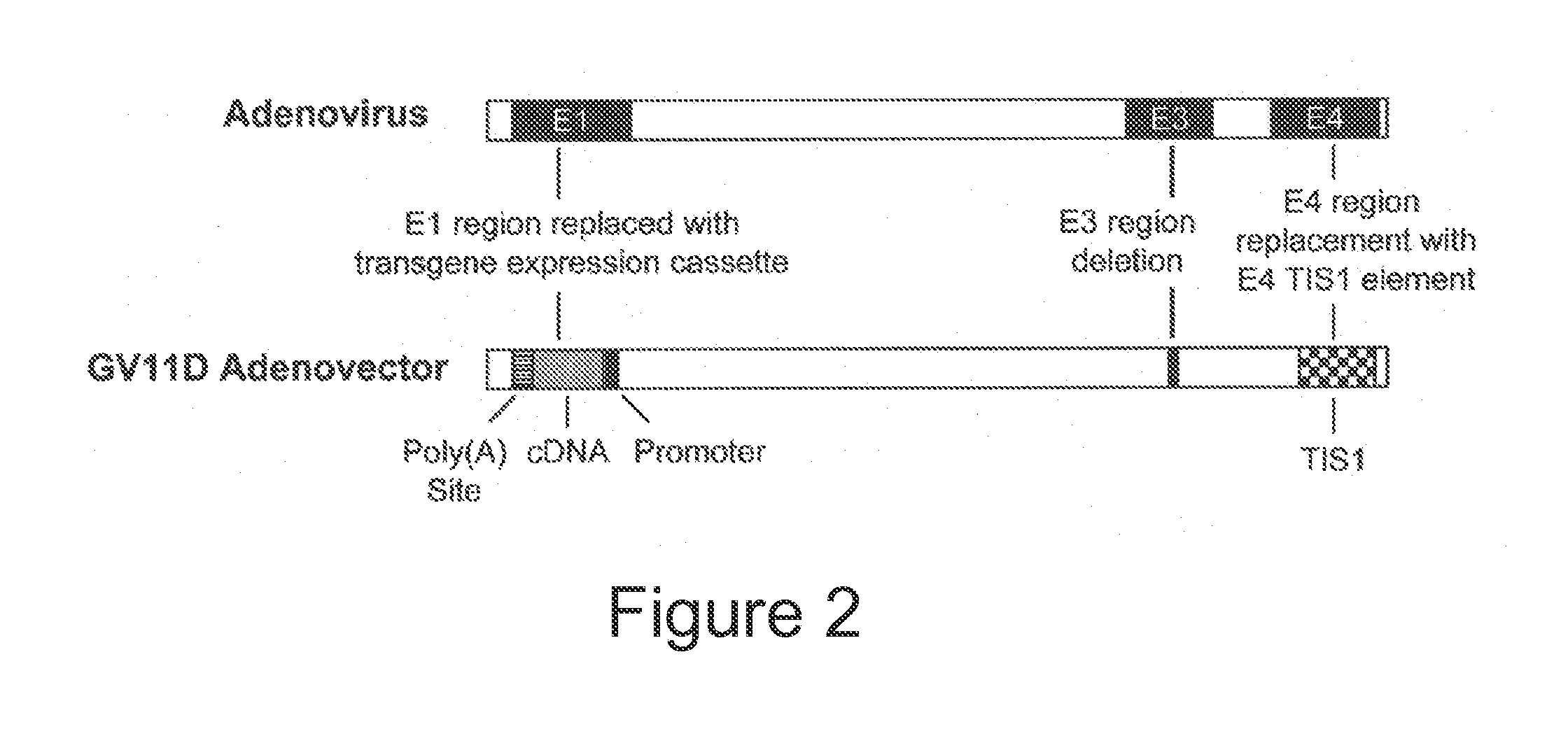
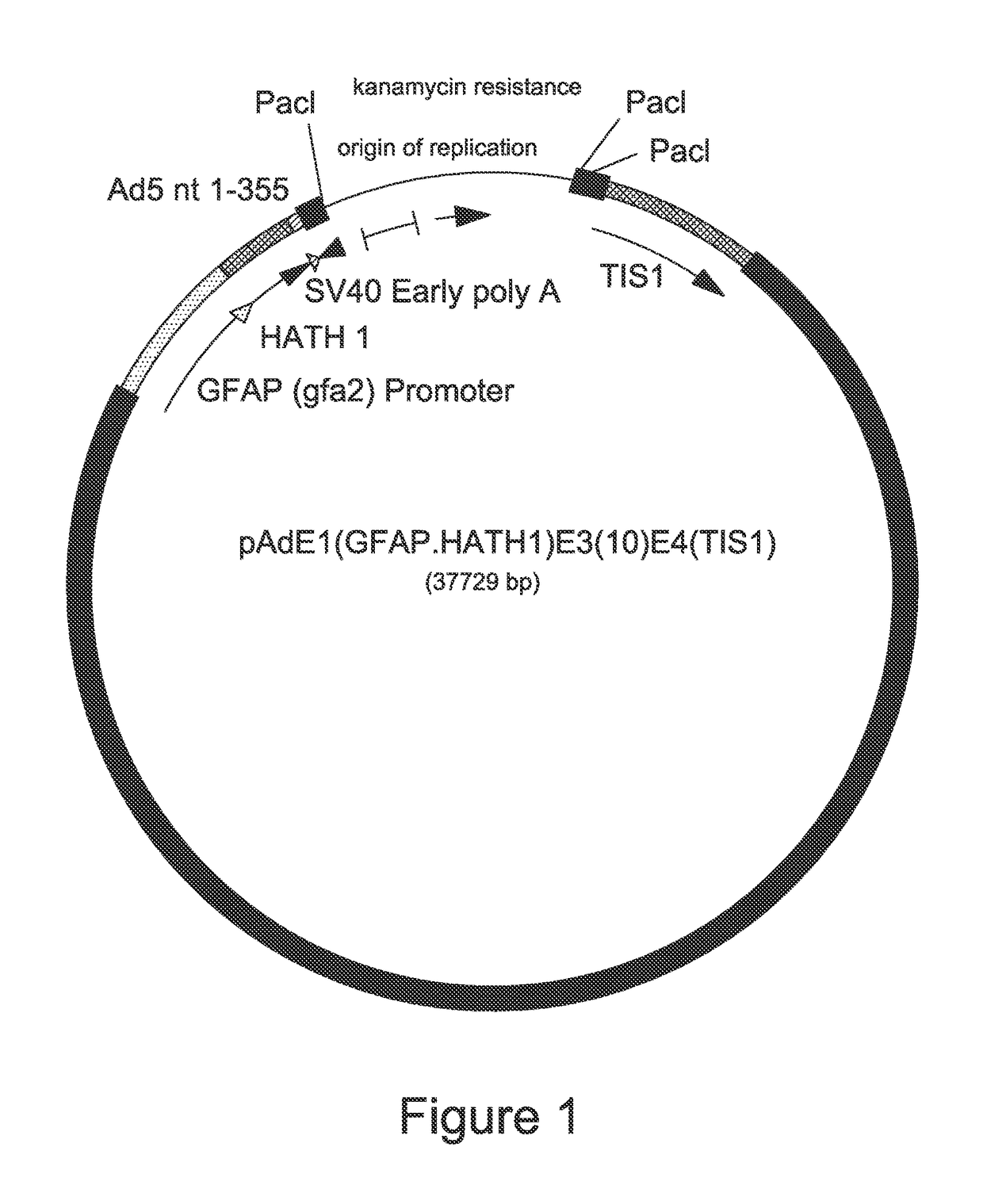
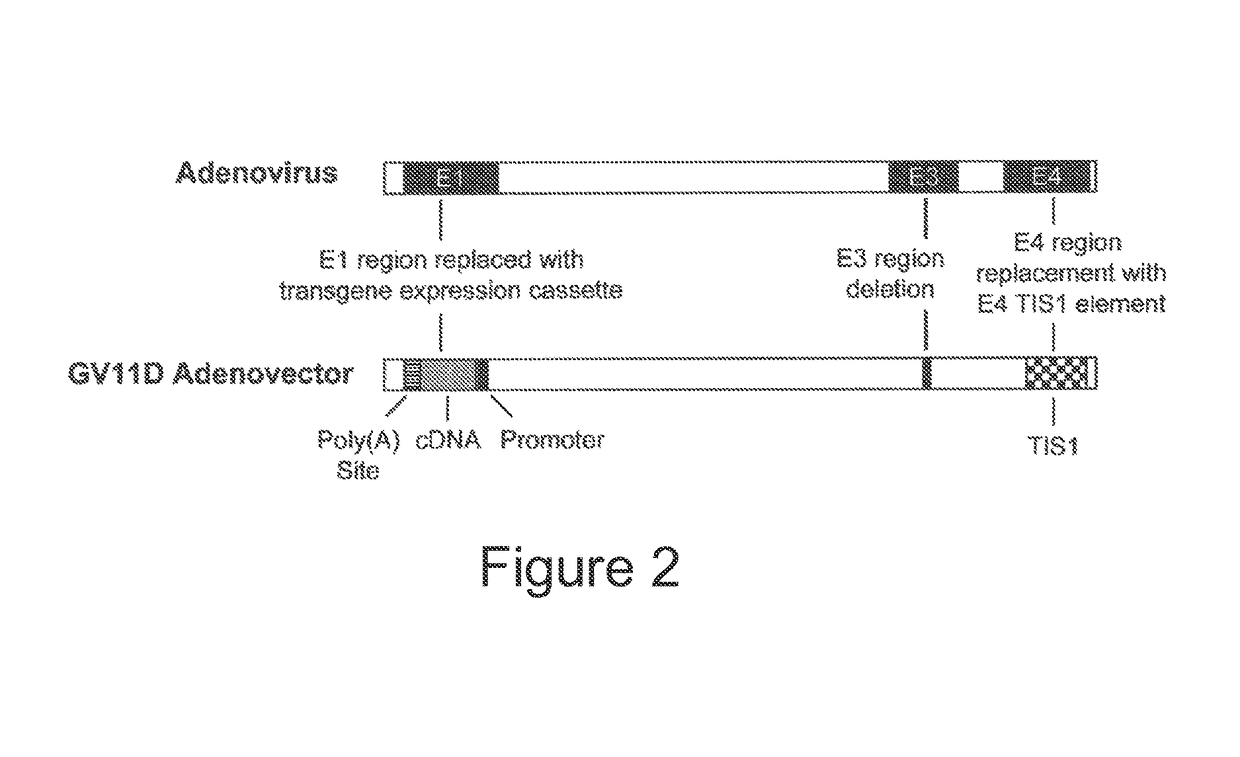
Adenoviral vector encoding human atonal homolog-1 (HATH1)
The invention is directed to a replication-deficient adenoviral vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a human atonal homolog-1 (Hath1) protein operably linked to a human glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoter. The invention also is directed to a composition and method utilizing the adenoviral vector to generate sensory cells in the inner ear of a human.
Owner:GEN VEC INC
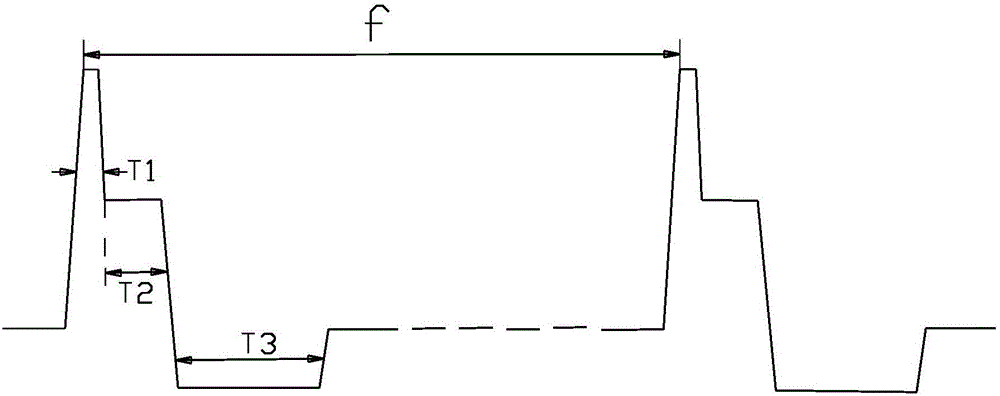
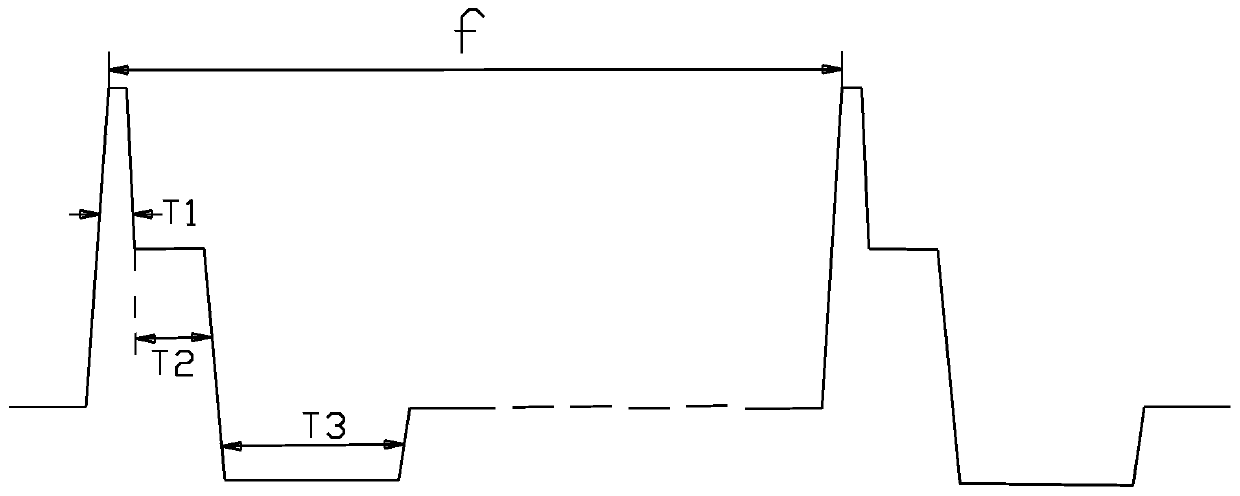
Waveform generation device and method of constant current transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation instrument
ActiveCN106693179ALower impedanceImprove the efficiency of stimulating the subcutaneous nerveExternal electrodesArtificial respirationSensory cellVoltage drop
The invention comprises a waveform generation device and method of a constant current transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation instrument. The waveform generation device includes a constant current control circuit and a waveform control circuit. The control output pulses of the constant current control circuit are in a constant current mode. The control output pulses of the waveform control circuit are characterized in that the control output pulses comprise a starting spike pulse T1; the pulse width of the starting spike pulse is smaller than the minimum time threshold value of nerve sensory cells, so that pain caused by the nerve sensory cells can be avoided; 2-5 mA current intensity causes at least 50V voltage drop under skin impedance which is about 20 to 30 k ohm, and the voltage drop can quickly reduce the skin impedance, and the starting spike pulse is a high-frequency signal with steep edges; and the high-frequency signal with steep edges can penetrate skin and enter a subcutaneous tissue. The starting spike pulse is provided, so that body impedance can be decreased fast without causing any pain, and the efficiency of stimulating subcutaneous nerves can be improved.
Owner:北京心滋乐医疗科技有限公司
Adenoviral vector encoding human atonal homolog-1 (HATH1)
The invention is directed to a replication-deficient adenoviral vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a human atonal homolog-1 (Hath1) protein operably linked to a human glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoter. The invention also is directed to a composition and method utilizing the adenoviral vector to generate sensory cells in the inner ear of a human.
Owner:GENVEC INC
Nucleic acids encoding proteins involved in sensory transduction
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell specific polypeptides, antibodies to such polypeptides, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and polypeptides, and methods of screening for modulators of sensory cell specific polypeptides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Waveform generating device and method for a constant-current transcutaneous ear vagus nerve stimulator
ActiveCN106693179BLower impedanceImprove the efficiency of stimulating the subcutaneous nerveExternal electrodesArtificial respirationSensory cellEngineering
Owner:北京心滋乐医疗科技有限公司
Nucleic Acids Encoding Proteins Involved in Sensory Transduction
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell specific polypeptides, antibodies to such polypeptides, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and polypeptides, and methods of screening for modulators of sensory cell specific polypeptides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
In vitro method for identifying a compound using an eukaryotic mechanosensory transduction channel
The present invention provides, for the first time, nucleic acids encoding a eukaryotic mechanosensory transduction channel (MSC) protein. The proteins encoded by these nucleic acids form channels that can directly detect mechanical stimuli and convert them into electrical signals. These nucleic acids and the proteins they encode can be used as probes for sensory cells in animals, and can be used to diagnose and treat any of a number of human conditions involving inherited, casual, or environmentally-induced loss of mechanosensory transduction activity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
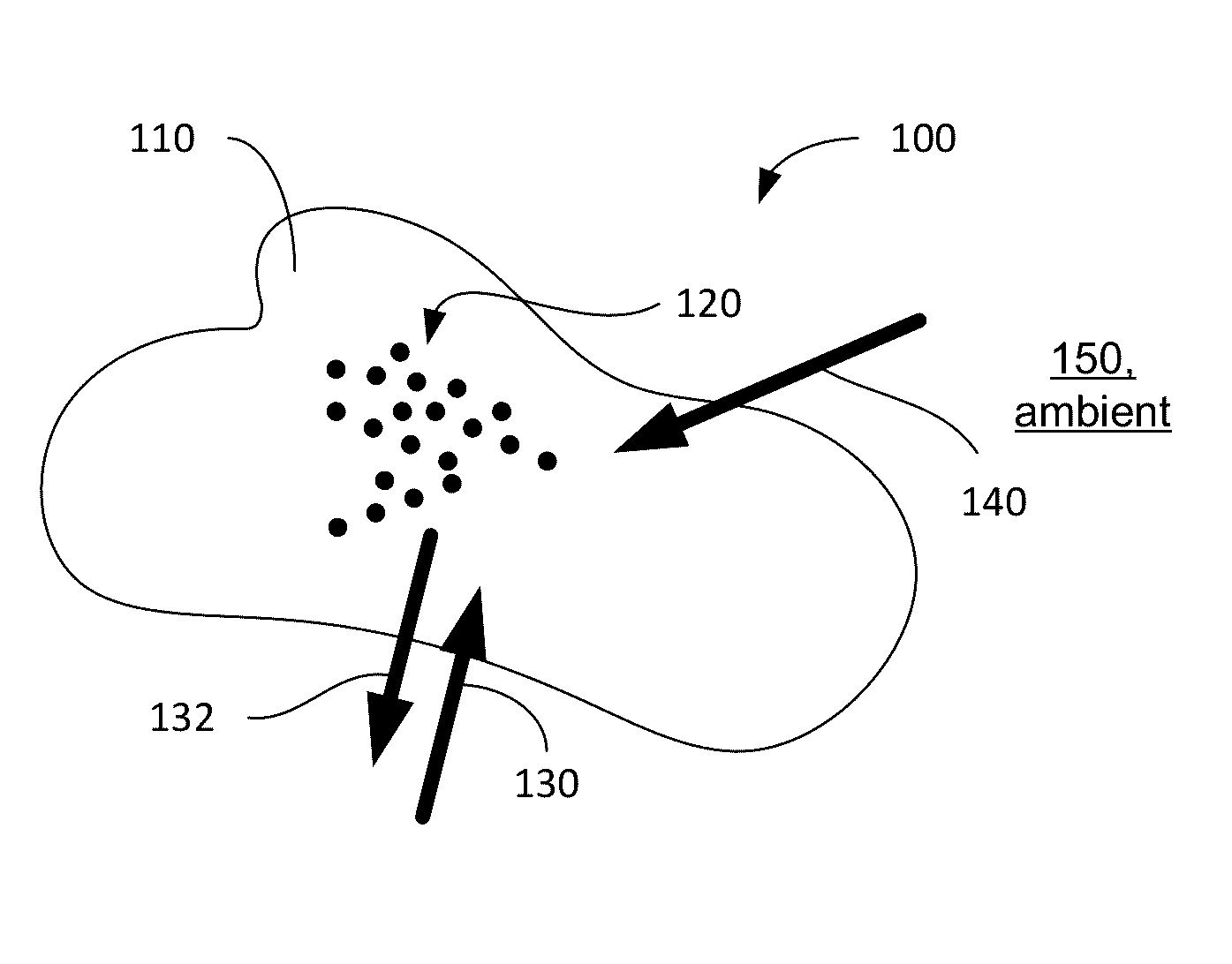
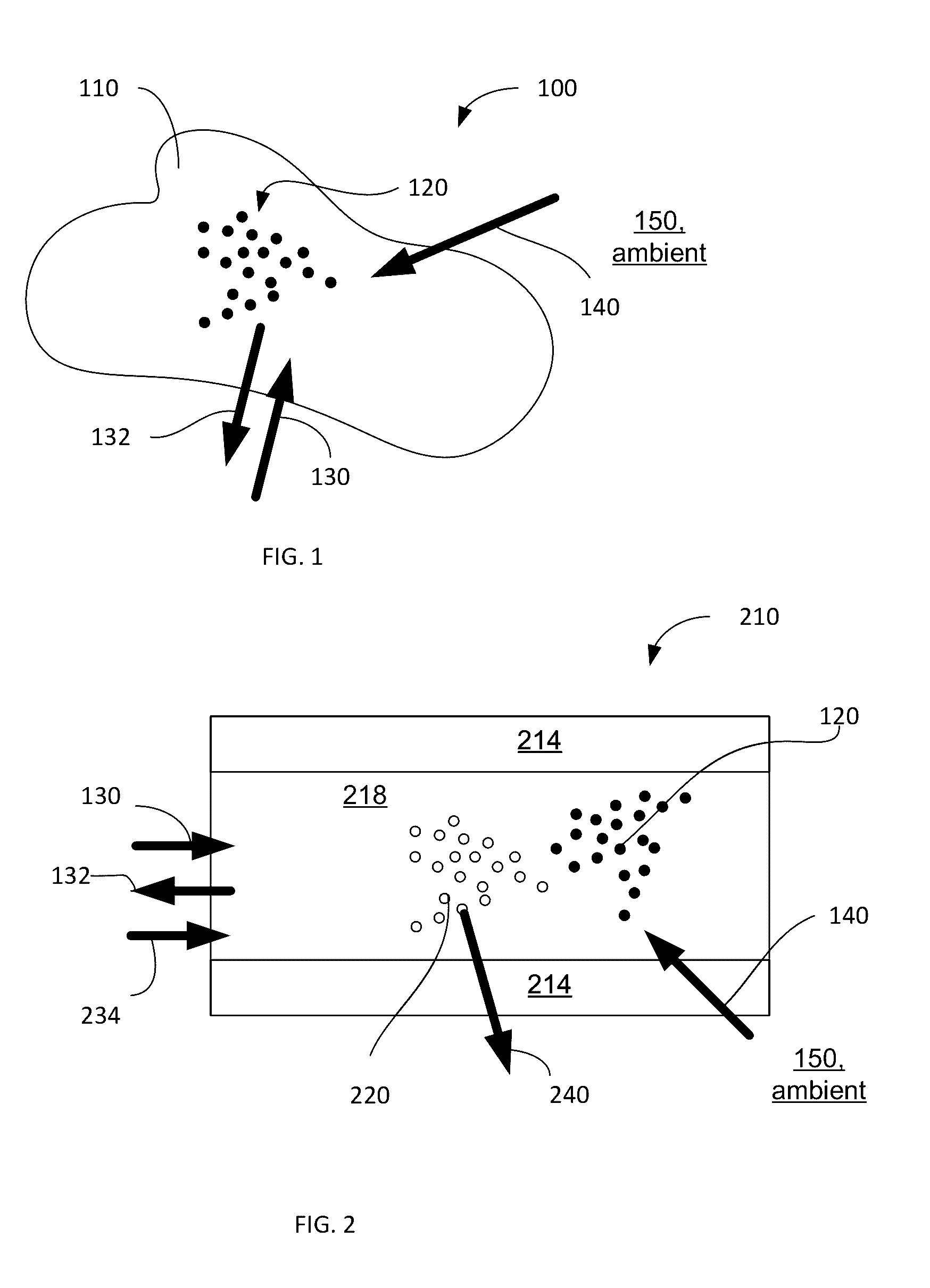
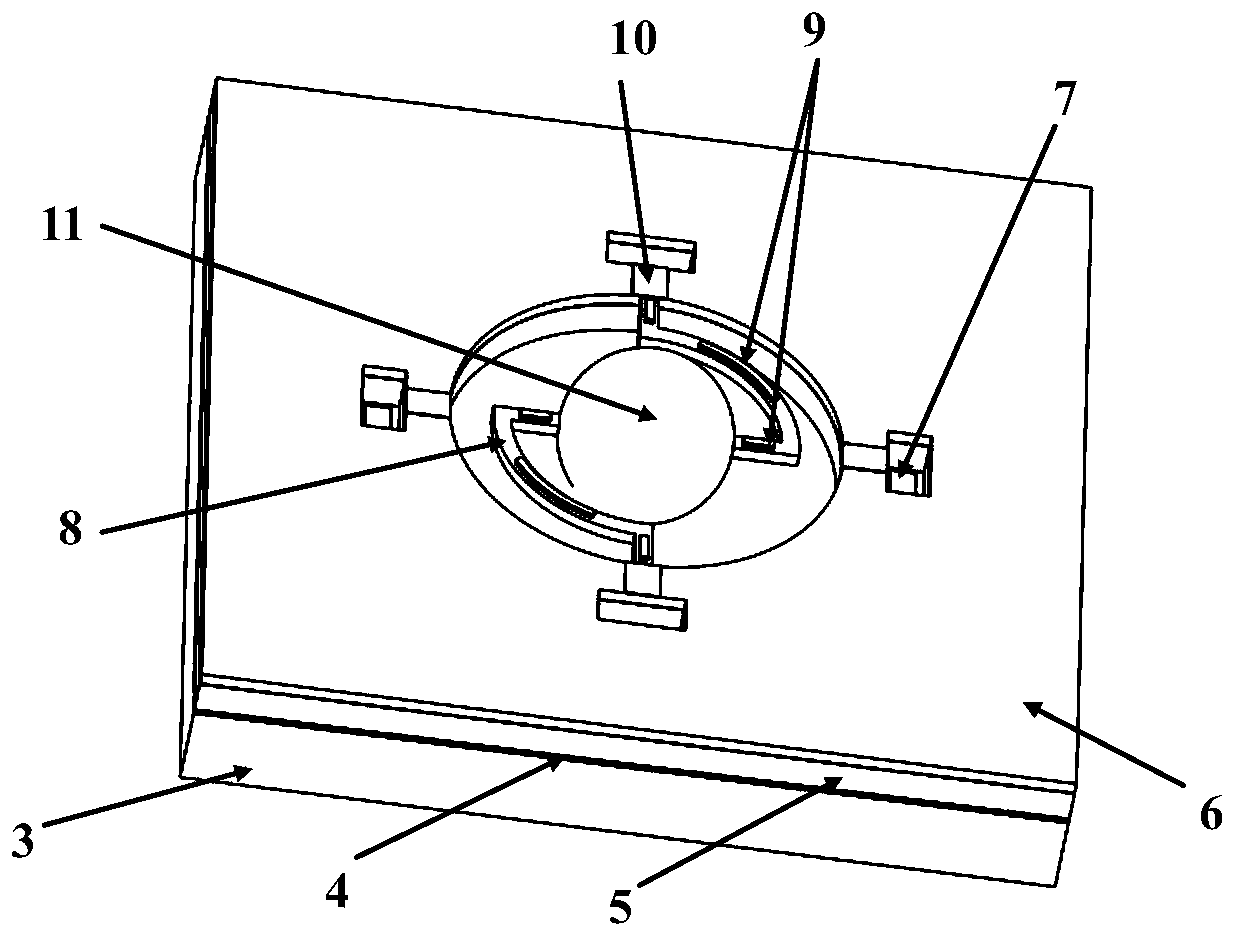
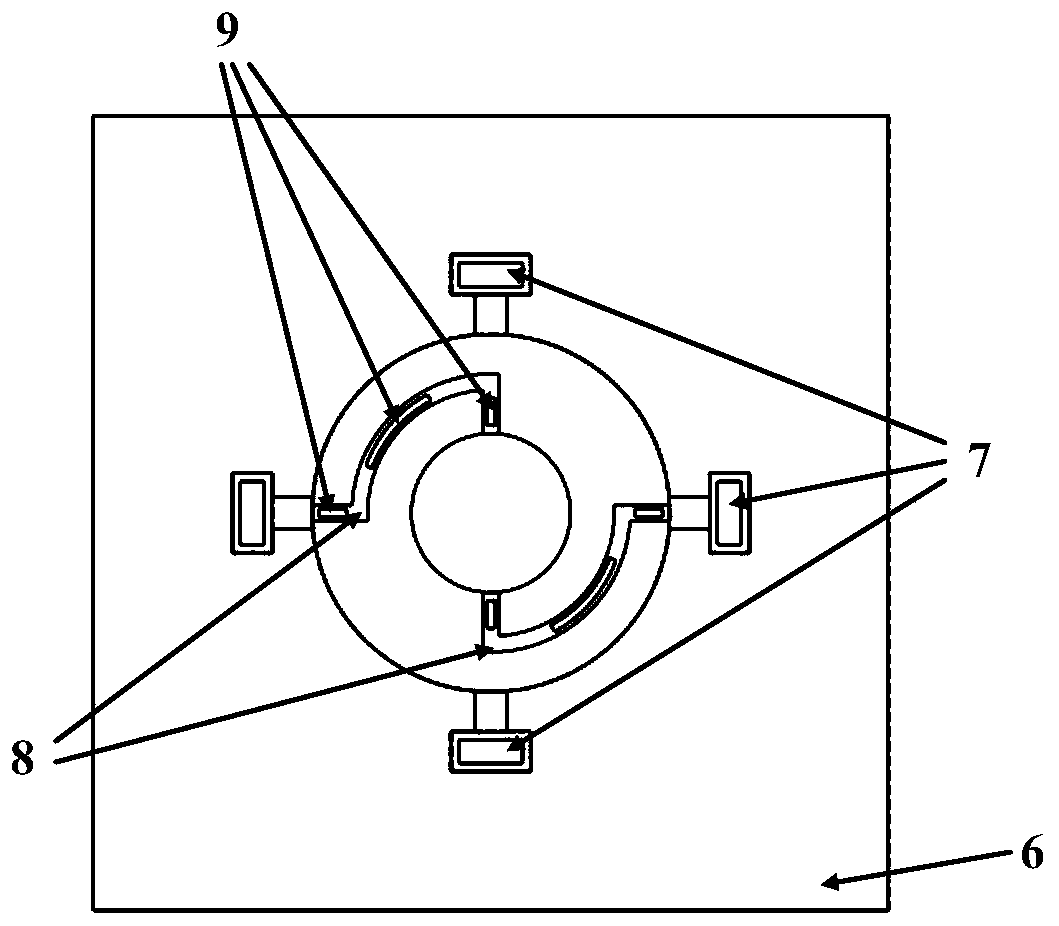
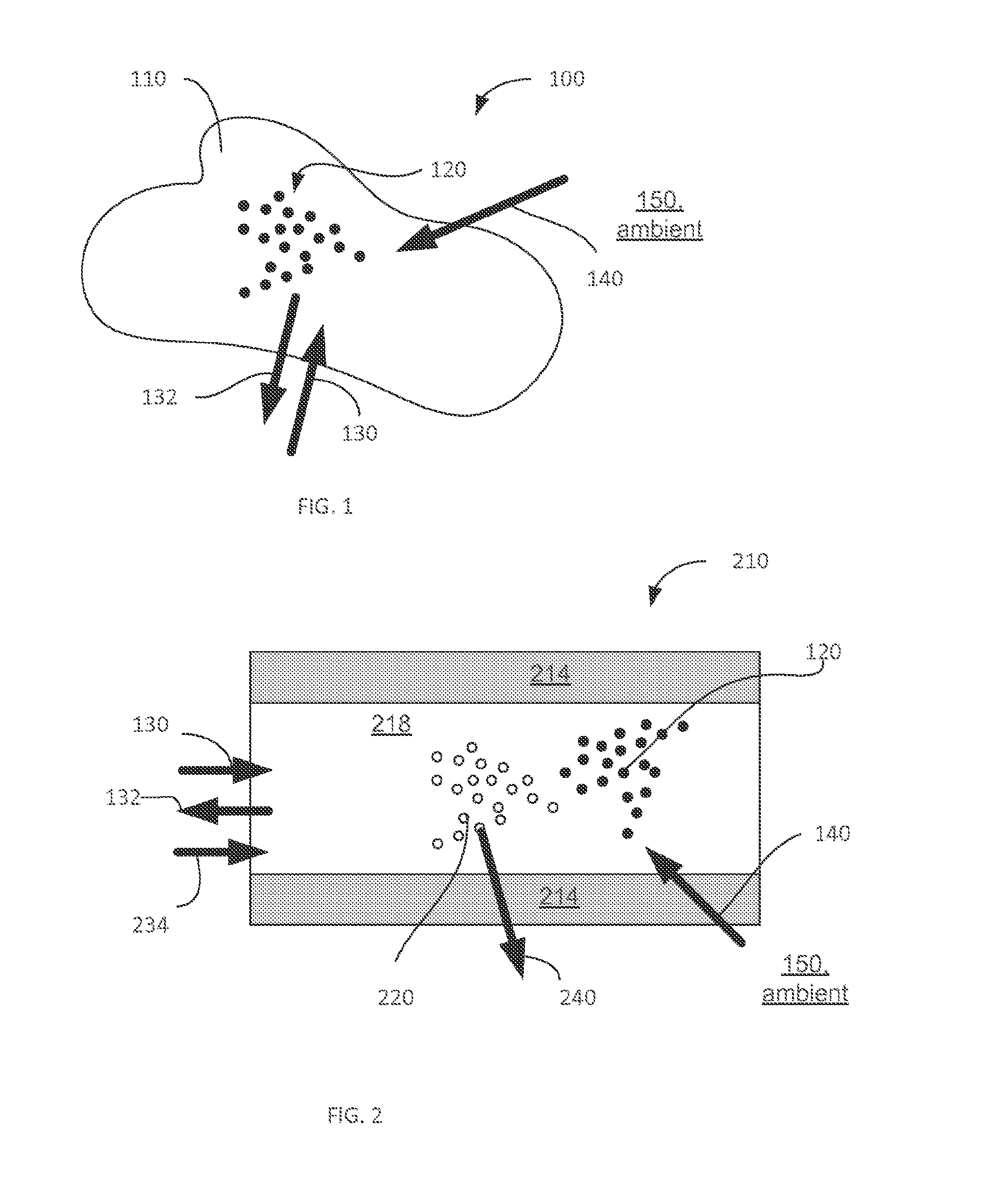
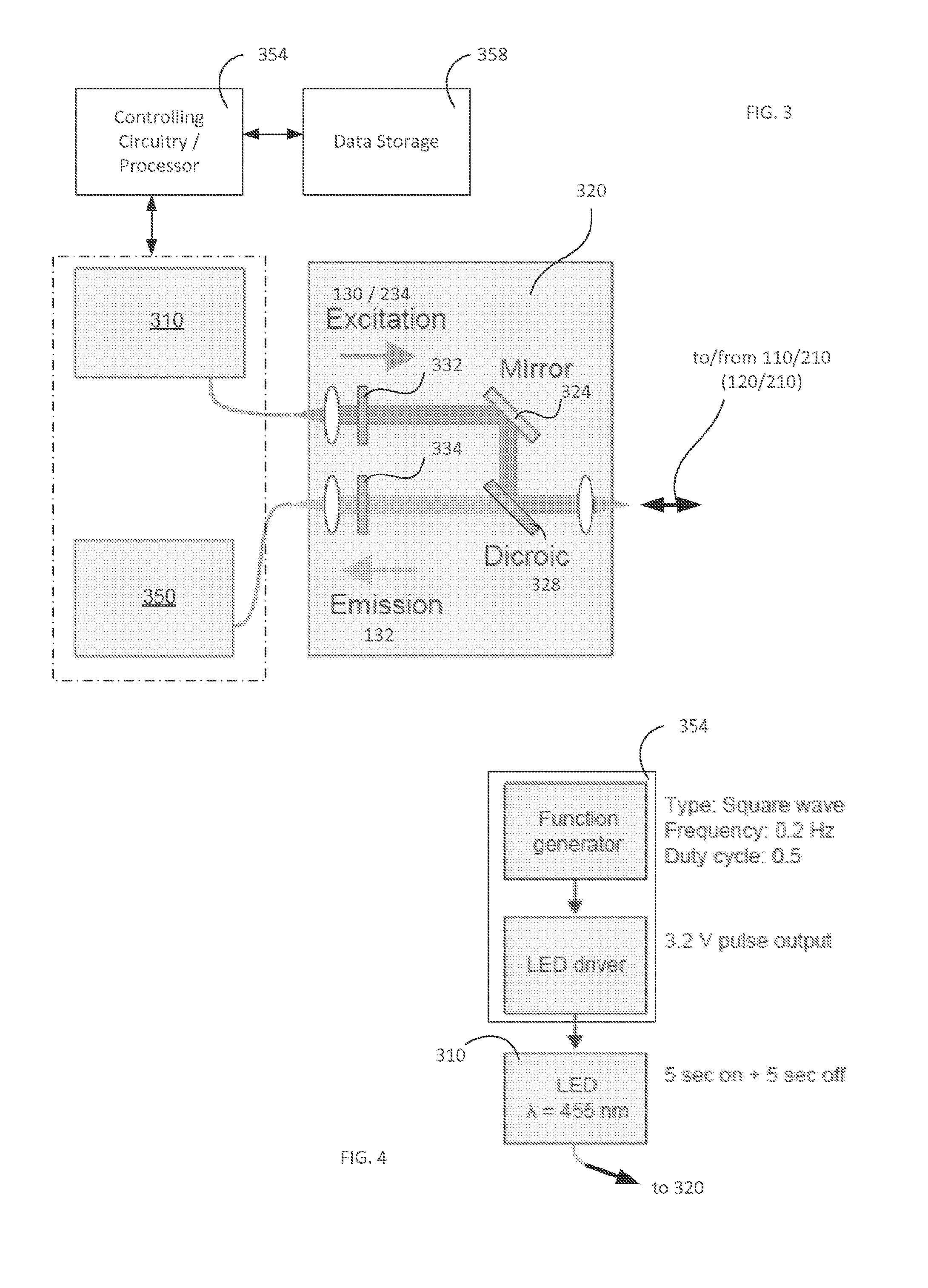
Light-guiding hydrogel devices for cell-based sensing and therapy
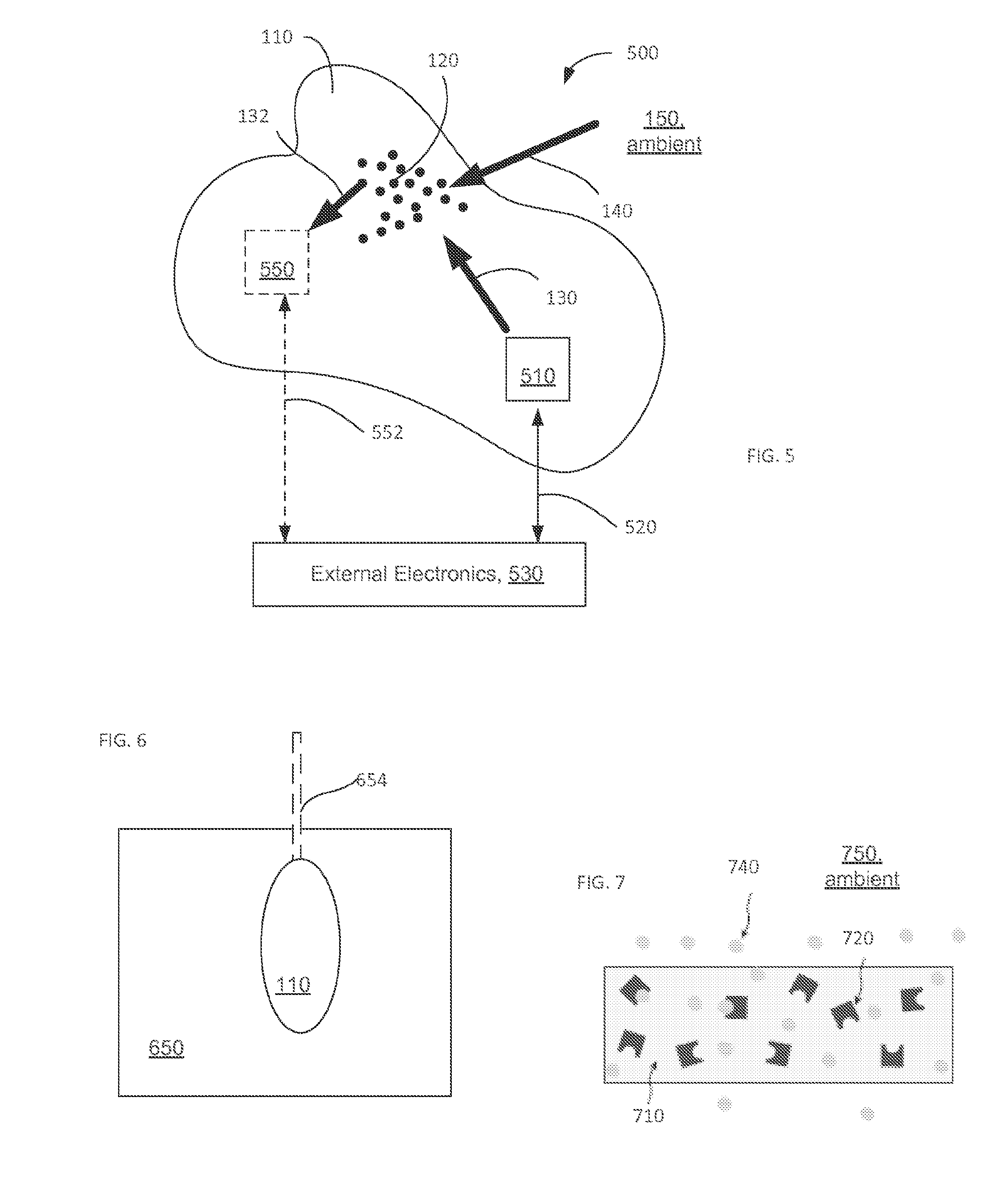
A hydrogel-lightguide based sensory system susceptible to a stimulus signal produced by ambient and stimulating sensory cells embedded in a hydrogel body of the system. Sensory cells generate an optical signal (in response to a user-defined triggering with excitation light or, alternatively, due to bioluminescence) the properties of which, determined based on detection of such signal with an optical detector device, provide characterization of the stimulus and information required for user-defined activation of emitter cells encapsulated in the hydrogel. When activated, emitter cells generate matter and / or light directed to interact with the ambient.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Nucleic acids encoding G protein gamma subunit involved in sensory transduction
InactiveCN1321164ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesSensory cellΓ subunit
The present invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell-specific G protein gamma subunits, antibodies to these subunits, methods for detecting these nucleic acids and subunits, and screening for modulators of sensory cell-specific G protein gamma subunits Methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nucleic acids encoding a g-protein coupled receptor involved in taste transduction
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of sensory cell specific G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:ZUKER CHARLES S +4
A new type of micro-spherical sensor for sensing changes in the space environment and its preparation method
ActiveCN106885919BEfficient captureIncrease the moment of inertiaPosition fixationFluid speed measurementSensory cellPhase difference
The invention discloses a novel micro ball sensor for sensing space environment changes and a manufacture method thereof. The sensor simulates a biological behavior that lateral lines of a fish identify and locate prey underwater, that is, the exposed lateral line canals in the neuromasts in the lateral lines can mechanically sense the vibration generated during the swim of underwater animals. Positioning is performed according to the time and phase difference that a vibration wave reaches different neuromasts underwater, and a motion signal is converted into a physiological electric signal to be transmitted to sensory cells to sense stimulation such as external water flow changes, low-frequency vibration, and temperature changes. By using a polyvinylidene fluoride direct piezoelectric effect, a spatial airflow change is imitated and sensed and a spatial vibration source is positioned. A single ball sensing unit senses the vibration by using the polyvinylidene fluoride and directly converts the vibration into electric signals so as to calculate a spatial airflow magnitude and angle. A plurality of ball sensing units are arranged in an array, calculate the airflow magnitude and orientation according to the time and phase difference that the vibration wave reaches different sensing units, and improve the spatial airflow magnitude and orientation calculation accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Light-guiding hydrogel devices for cell-based sensing of an interactoin with ambient
InactiveUS20160256549A1High molecular weightMechanical flexibilityDrug photocleavagePhotodynamic therapySensory cellLight guide
A hydrogel-lightguide based sensory system susceptible to a stimulus signal produced by ambient and stimulating sensory cells embedded in a hydrogel body of the system. Sensory cells generate an optical signal (in response to a user-defined triggering with excitation light or, alternatively, due to bioluminescence) the properties of which, determined based on detection of such signal with an optical detector device, provide characterization of the stimulus and information required for user-defined activation of emitter cells encapsulated in the hydrogel. When activated, emitter cells generate matter and / or light directed to interact with the ambient.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
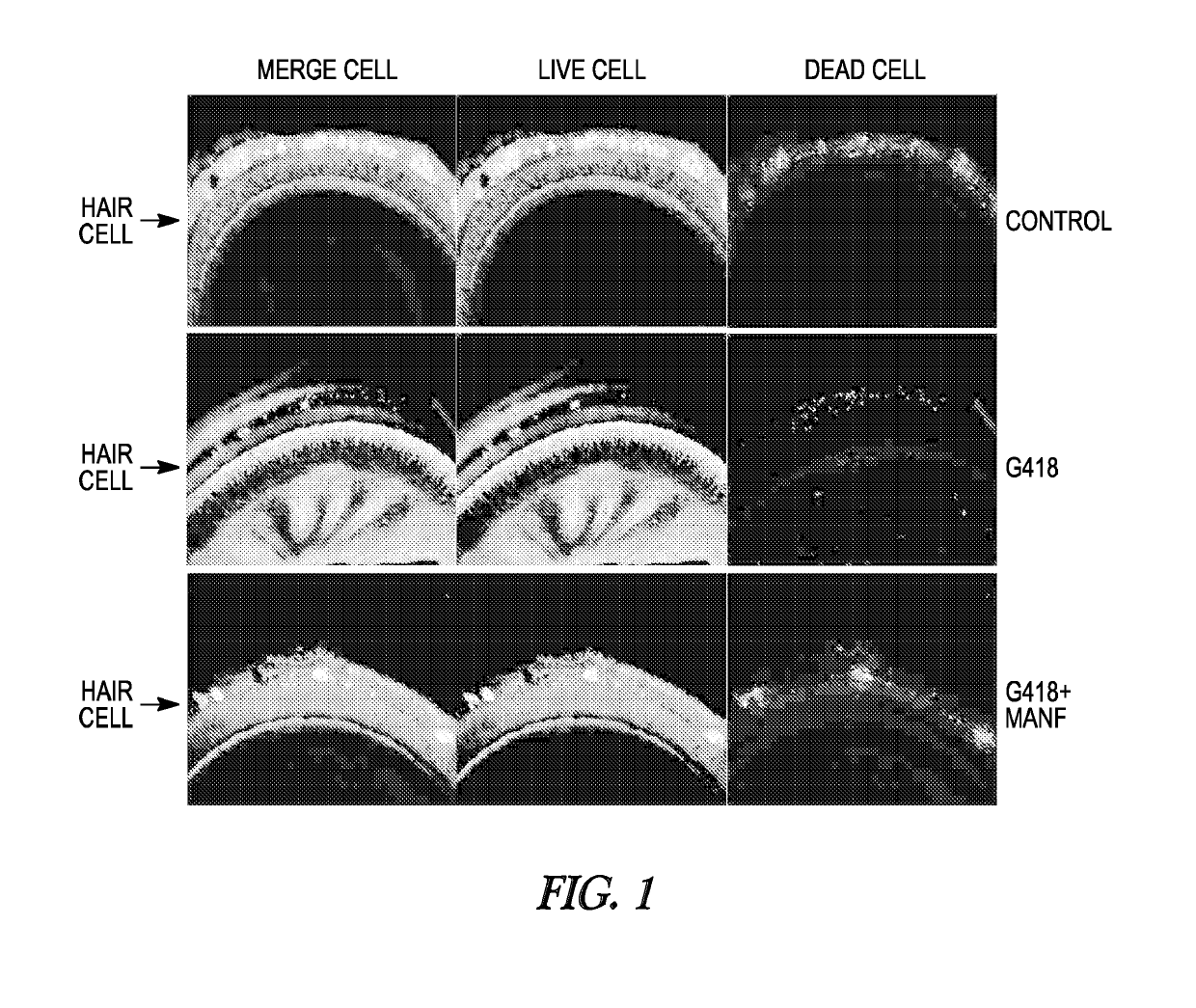
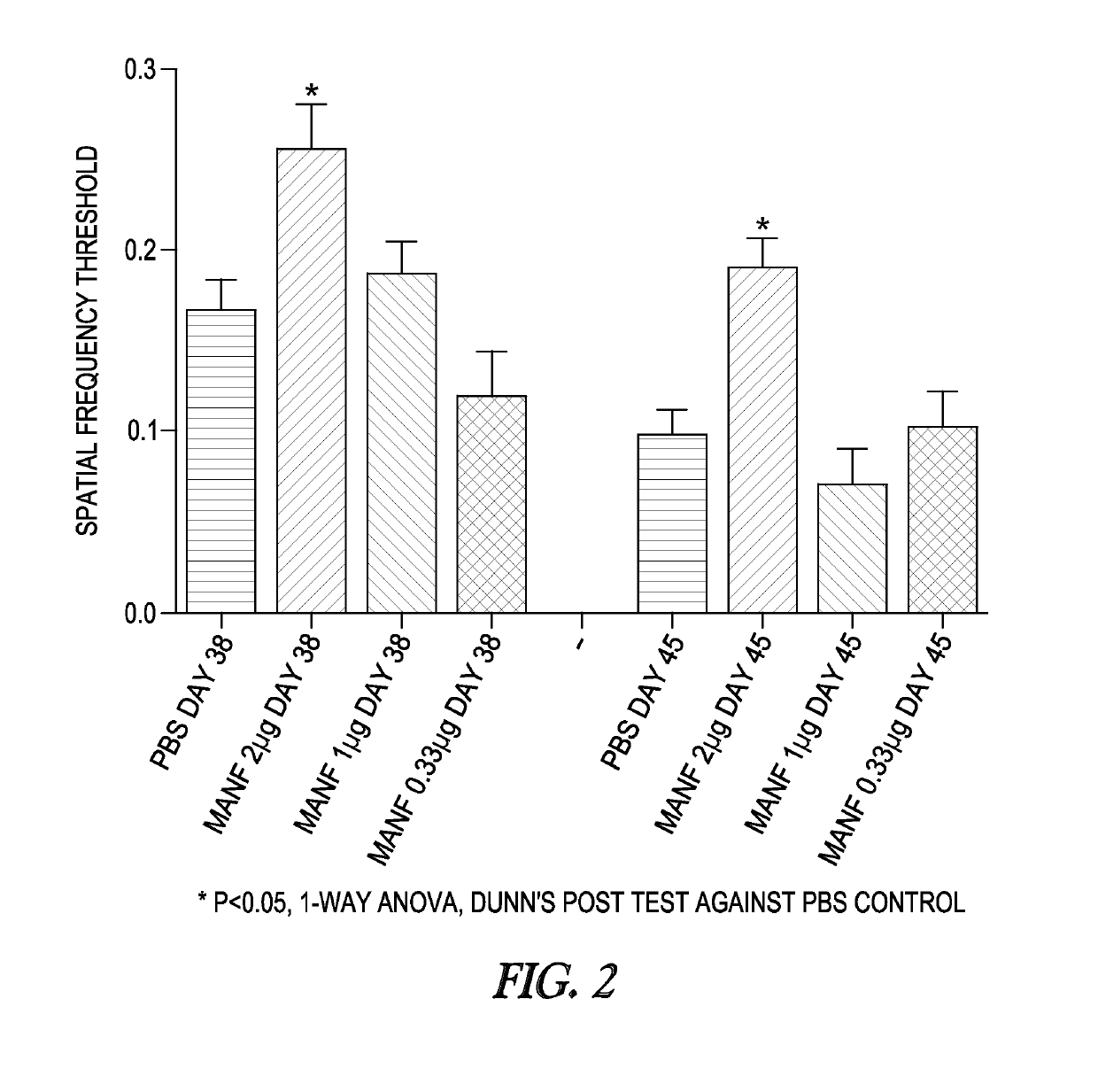
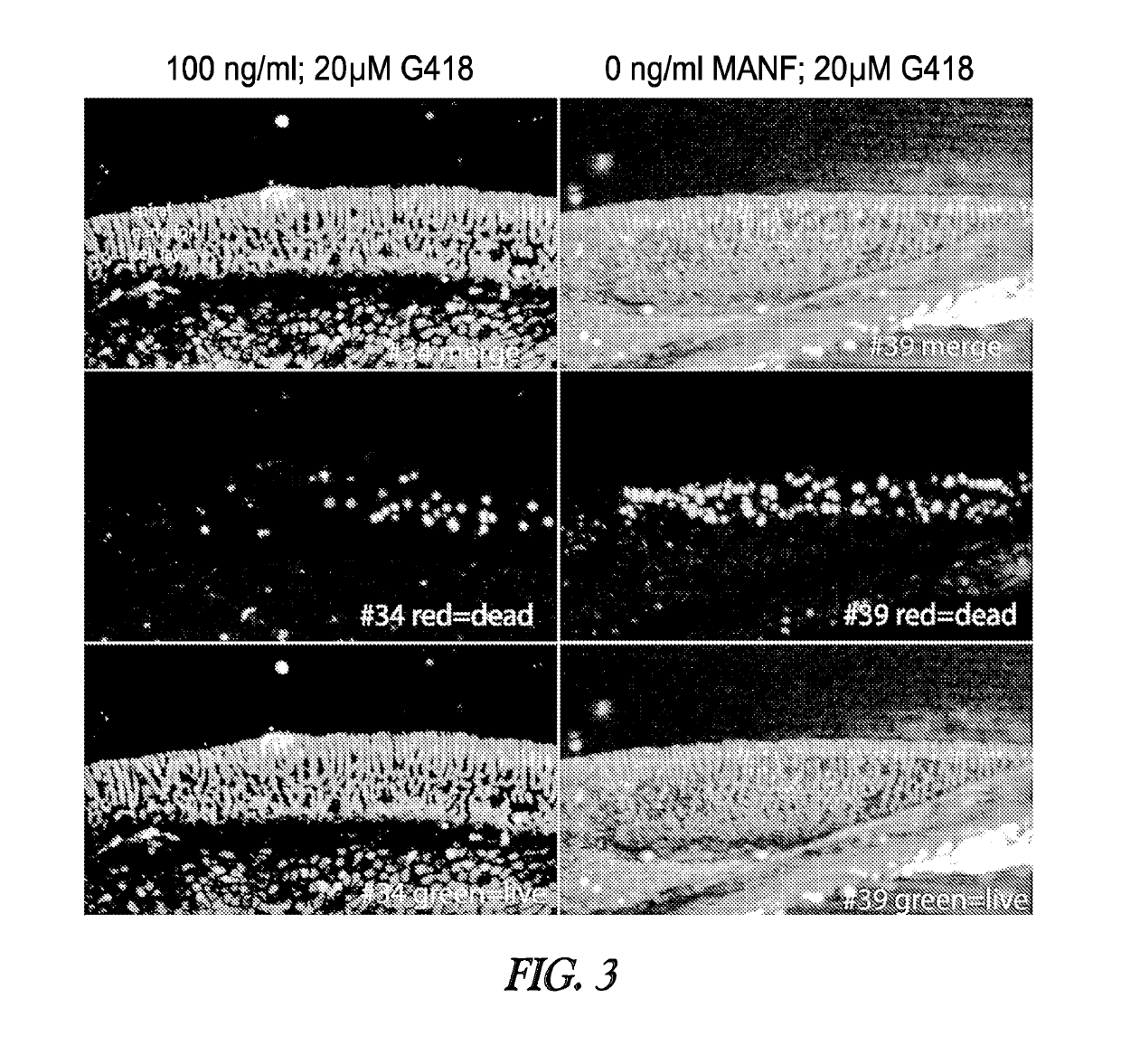
Method of administering MANF for the protection of sensory cells
Disclosed herein are methods of treating or preventing cell death-related sensory cell loss in a subject in need thereof, the method comprising administering an effective amount of one or more neuroprotective peptides to the subject. Also disclosed are methods of treating or preventing drug-induced ototoxicity in a subject in need thereof, the method comprising administering an effective amount of one or more neuroprotective peptides to the subject.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com