Patents
Literature
1471 results about "Grid cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
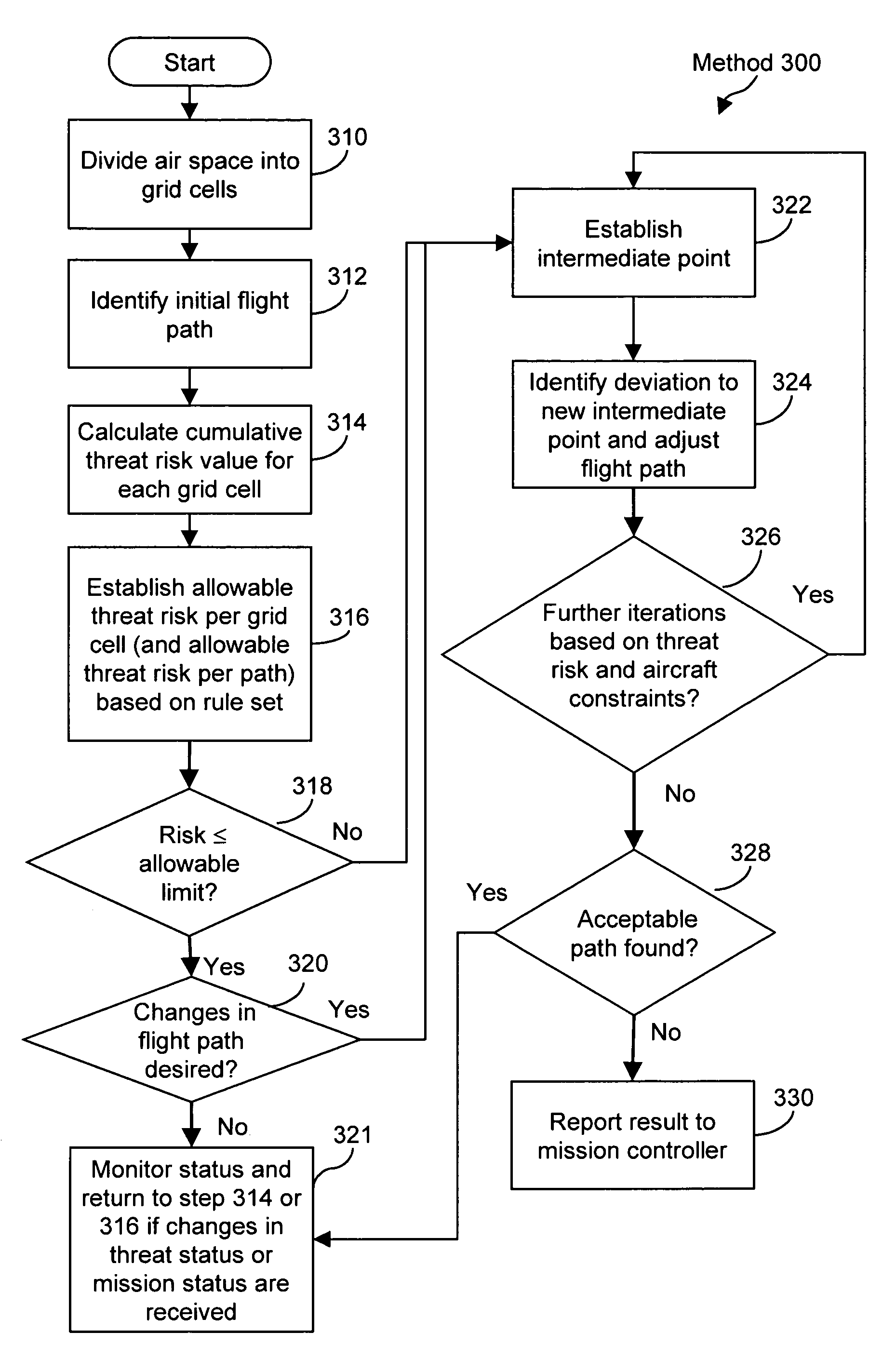
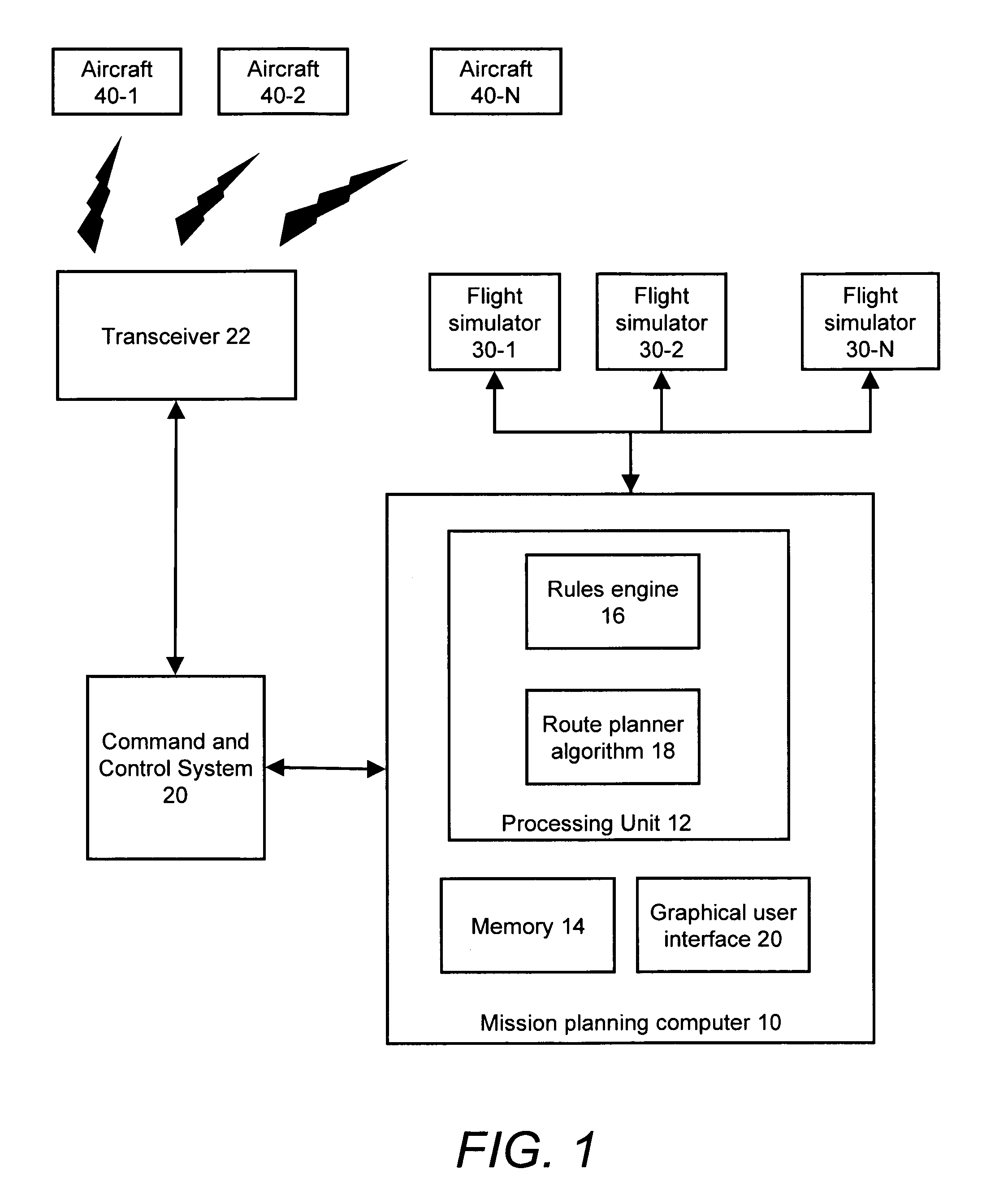
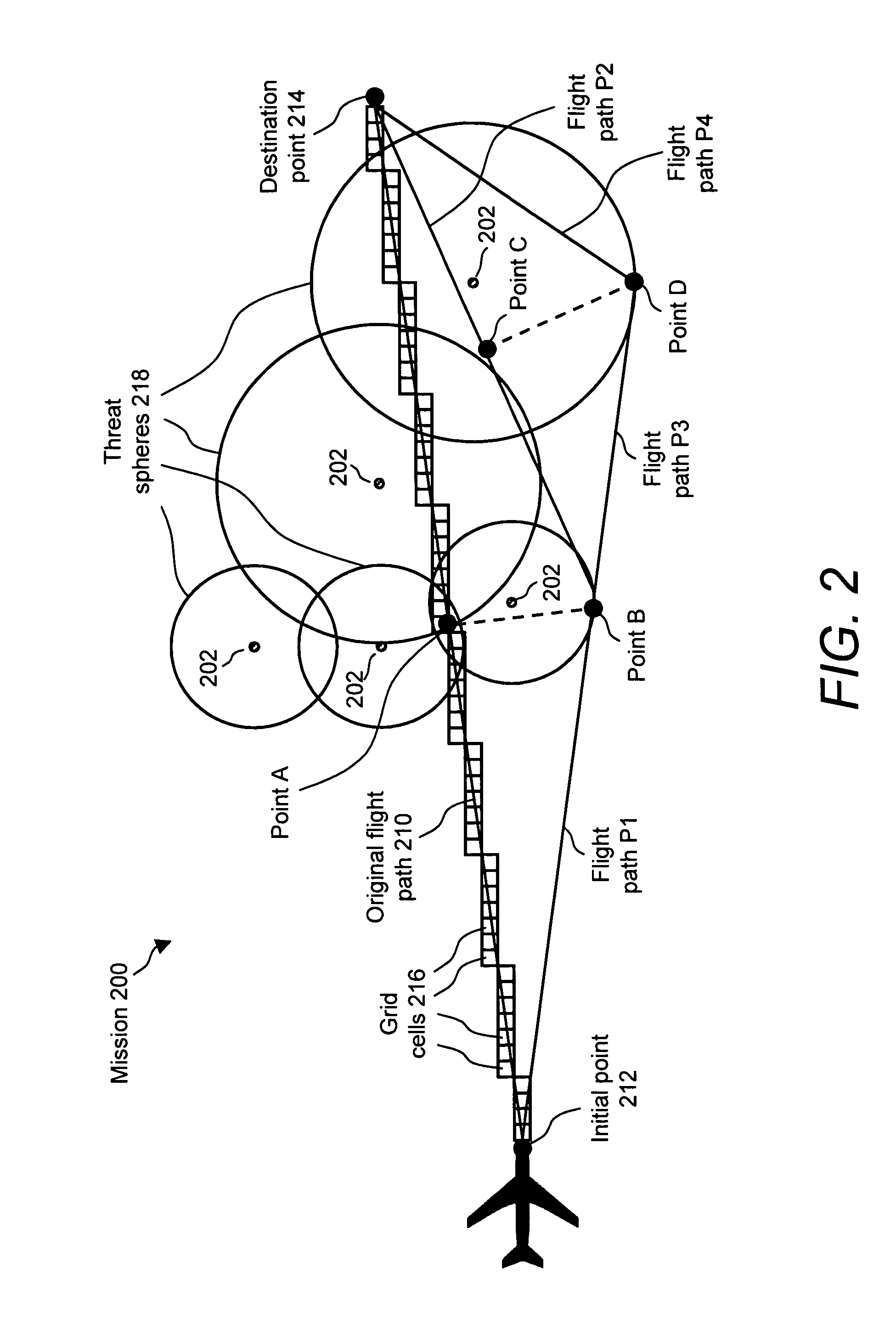
Method and system for route planning of aircraft using rule-based expert system and threat assessment
ActiveUS7194353B1Reduce errorsReduce manpowerInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsRule based expert systemGrid cell
A method and system or determining a flight path for an aircraft between an initial point and a destination point are described. An airspace is divide into a set of grid cells, and a flight path is established between the initial point and the destination point. A cumulative threat risk value for each of the grid cells is calculated, and an allowable threat risk per grid cell is established based on a rule set. An intermediate point from which to deviate the flight path is identified based upon an analysis of the cumulative threat risk values of the grid cells, if the threat risk value of any of the grid cells intersecting the flight path exceeds the allowable threat risk. A deviation from the intermediate point to a new intermediate point is determined such that the new intermediate point has a cumulative threat risk value lower than or equal to the allowable threat risk per grid cell. The flight path is adjusted between the initial point and the destination point to pass through the new intermediate point, thereby providing a modified flight path.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
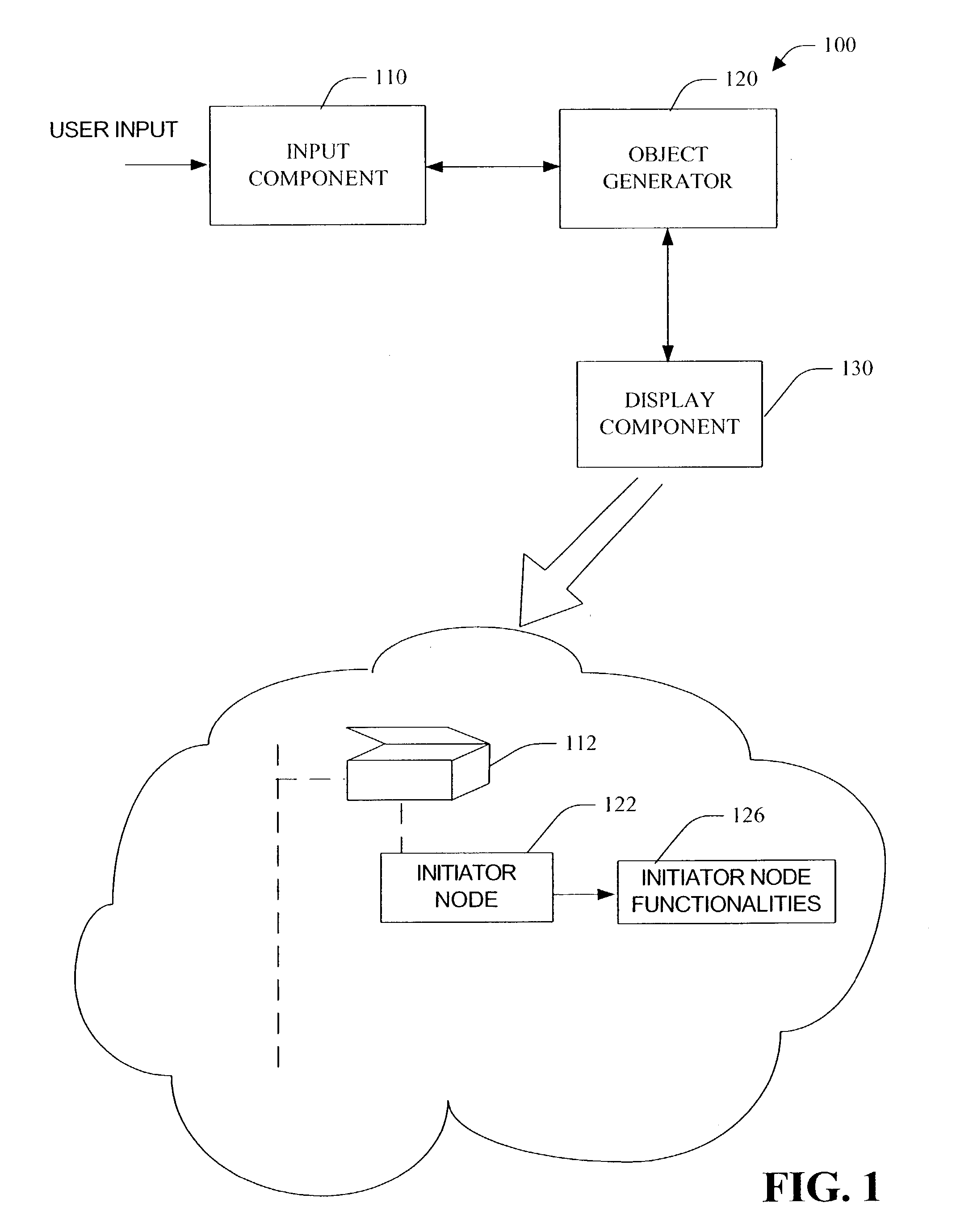
Creation of an object within an object hierarchy structure
ActiveUS7272818B2Avoid less flexibilityMore functionalityMechanical machines/dredgersNon-rotary toothed toolsUser inputGrid cell
An object generator provides for creation of object(s) in an object hierarchy structure. In response to a command to expand a node / object, the object generator provides an initiator node that facilitates generation of a new object within the object hierarchy upon expansion of the node. A display component concurrently displays the initiator node with the expanded node. The initiator node used for creating objects placed (e.g., in-line) within an object hierarchy structure. To create a new object, an instruction (e.g., user input) to expand a node having a initiator node is received. By selecting the initiator node and entering a name, an object of type defined by the initiator node is created. For example, once the object is created the user can enter information defining parameter(s) of the object. Information can be entered through a user interface box (e.g., text box) that is displayed upon the creation of the object. Also, a grid can overlay the object hierarchy structure allowing information to be entered directly into grid cell(s). The grid can further be employed to display defined parameter(s).
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
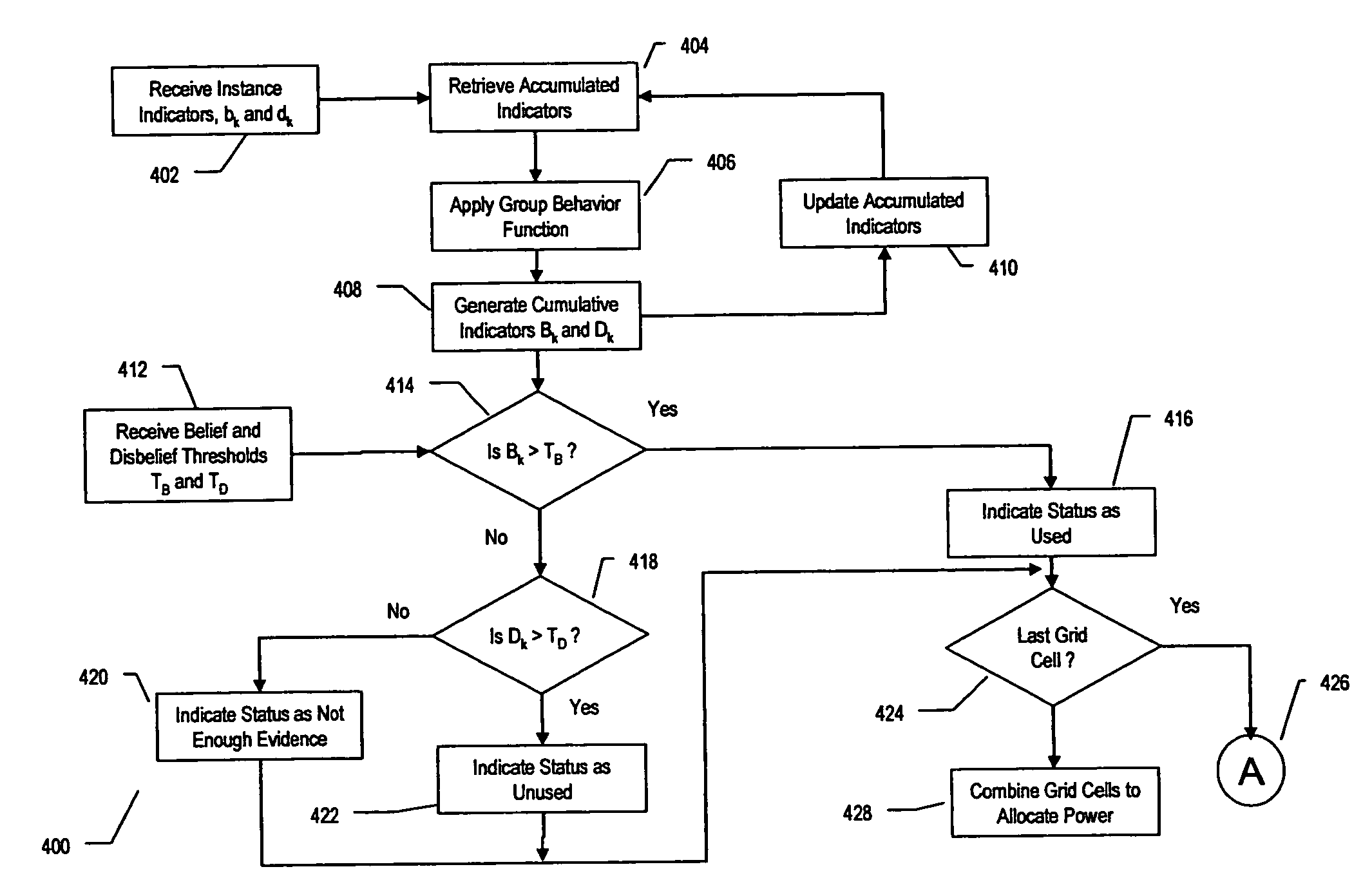
Method and system for determining spectrum availability within a network
InactiveUS7564816B2Shorten the overall cycleHigh transmission powerTransmission monitoringWireless commuication servicesSpectrum availabilityFrequency spectrum
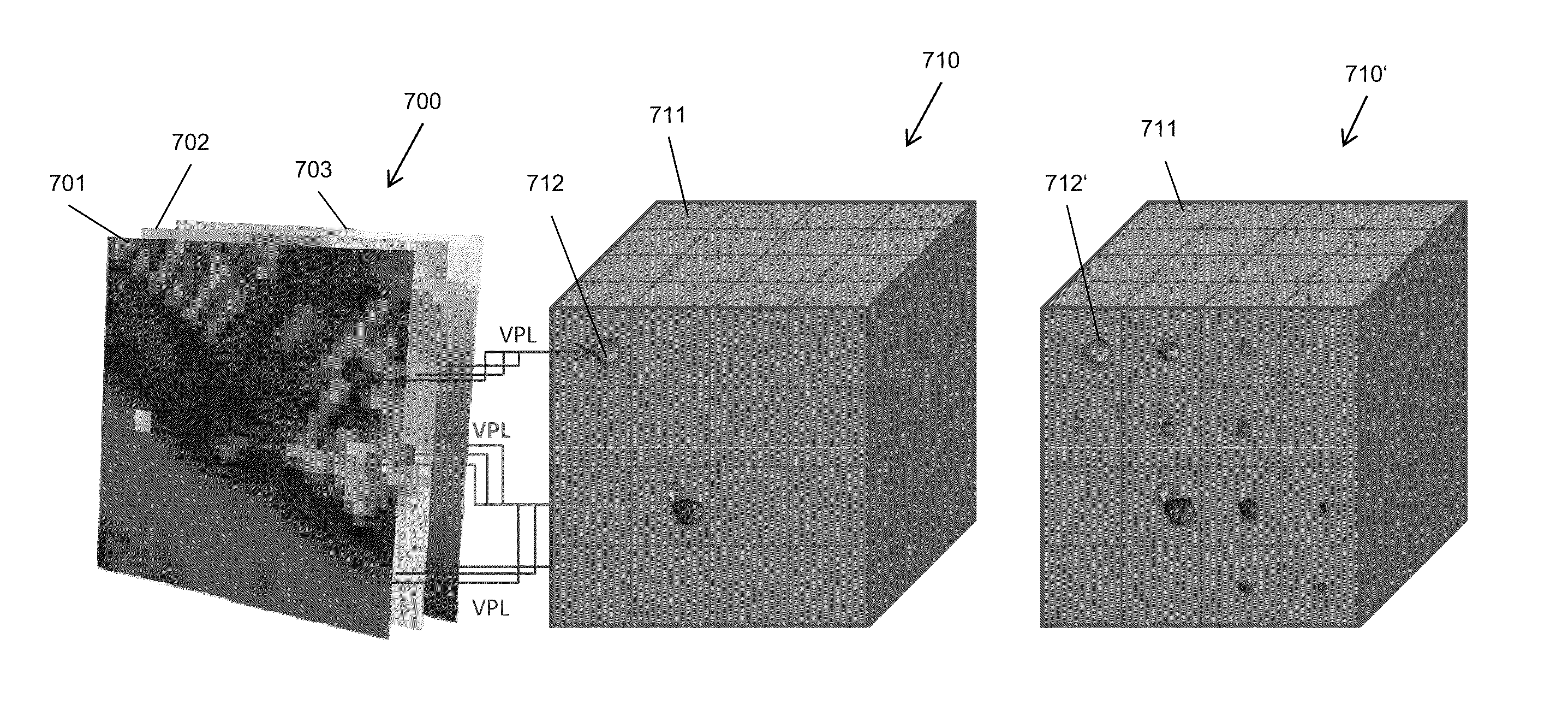
A method and transceiver for determining spectrum availability within a give area is disclosed. The given area includes cells in a grid. A belief evaluator receives a measurement from a signal and assigns an instantaneous belief indicator, an instantaneous disbelief indicator and an instantaneous ignorance indicator based on a detection threshold and the power level of the measurement. The indicators quantify the probability of a presence of a transmitter within the grid cell. A belief accumulator uses the instantaneous indicators along with accumulated belief, disbelief and ignorance indicators from previous measurements to determine cumulative belief, disbelief and ignorance indicators. The accumulated belief, disbelief and ignorance indicators are the results of previous measurements and belief / disbelief / ignorance determinations for the grid cell. An allocator indicates the status of the grid cell and whether a spectrum is available. If a spectrum is available, then the grid cell is added to other available cells within the area to generate the spectrum hole.
Owner:SHARED SPECTRUM
Method, computer graphics image rendering system and computer-readable data storage medium for computing of indirect illumination in a computer graphics image of a scene
ActiveUS20110012901A1High repetition rateQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsGrid cell
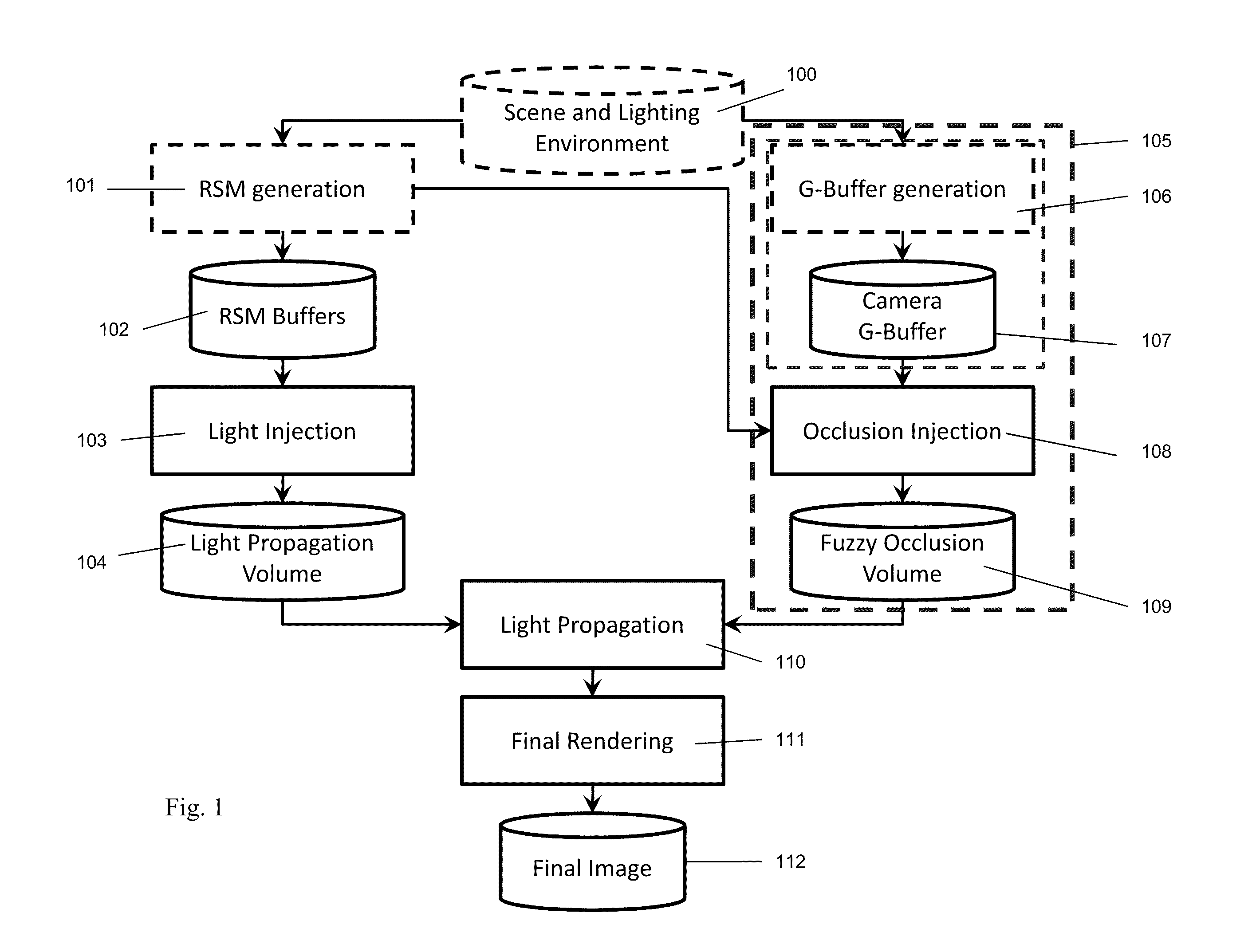
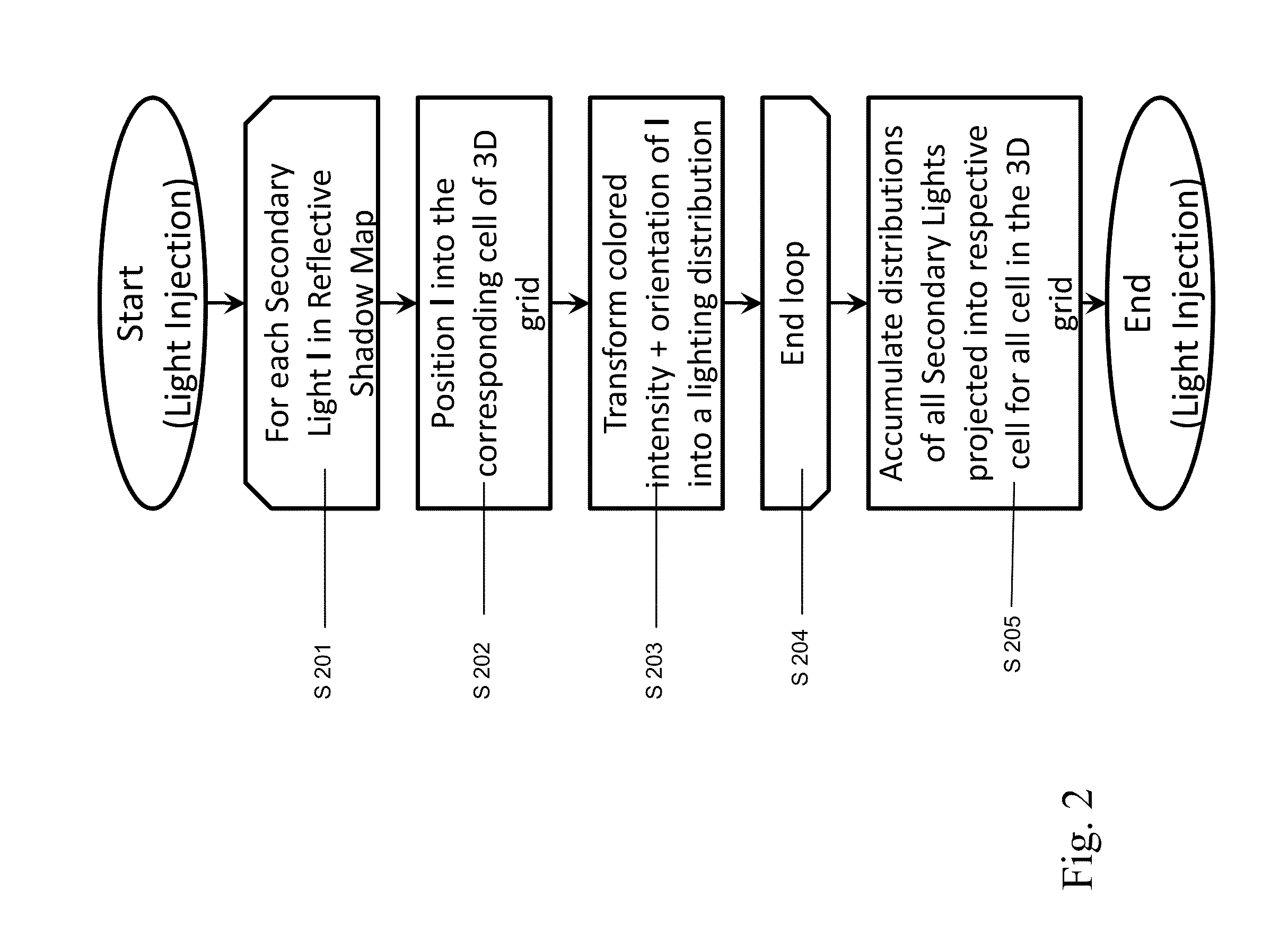
Method for real-time computing of indirect illumination in a computer graphics image of a scene, comprising: defining a light propagation volume as a three-dimensional grid consisting of a plurality of grid cells; allocating a plurality of secondary light sources to grid cells of said light propagation volume; accumulating directional, colored irradiance contributions of all secondary light sources in a respective grid cell and repeating this step of accumulating for all grid cells of the light propagation volume to thereby obtain an initial indirect light intensity distribution. The propagation of light in said light propagation volume is then iteratively computed starting with the initial indirect light intensity to obtain a final indirect light intensity distribution, which is used for rendering the scene illuminated by the final indirect light intensity distribution during a usual scene rendering process from a camera's point of view.
Owner:CRYTEK IP HLDG
Near wellbore modeling method and apparatus
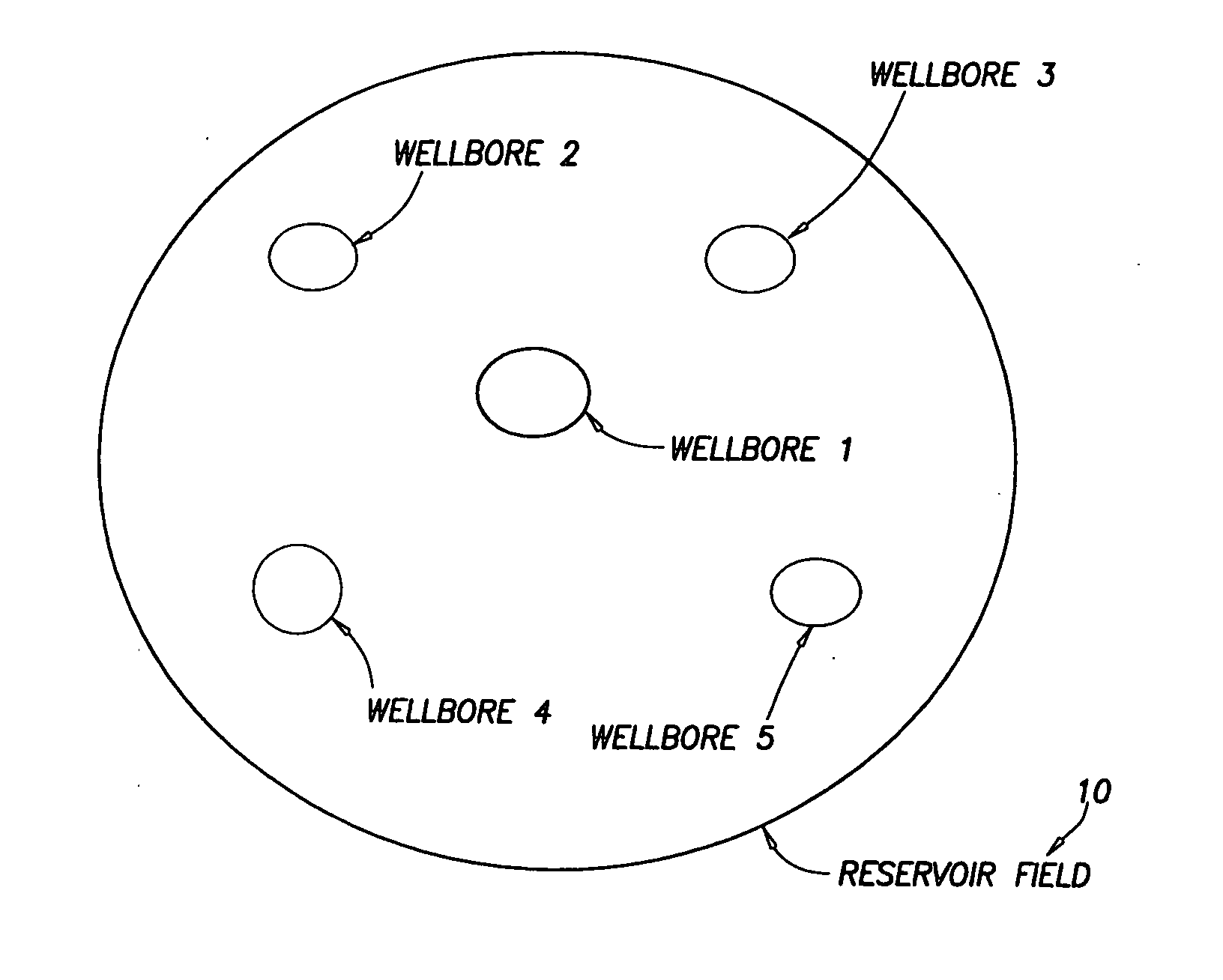
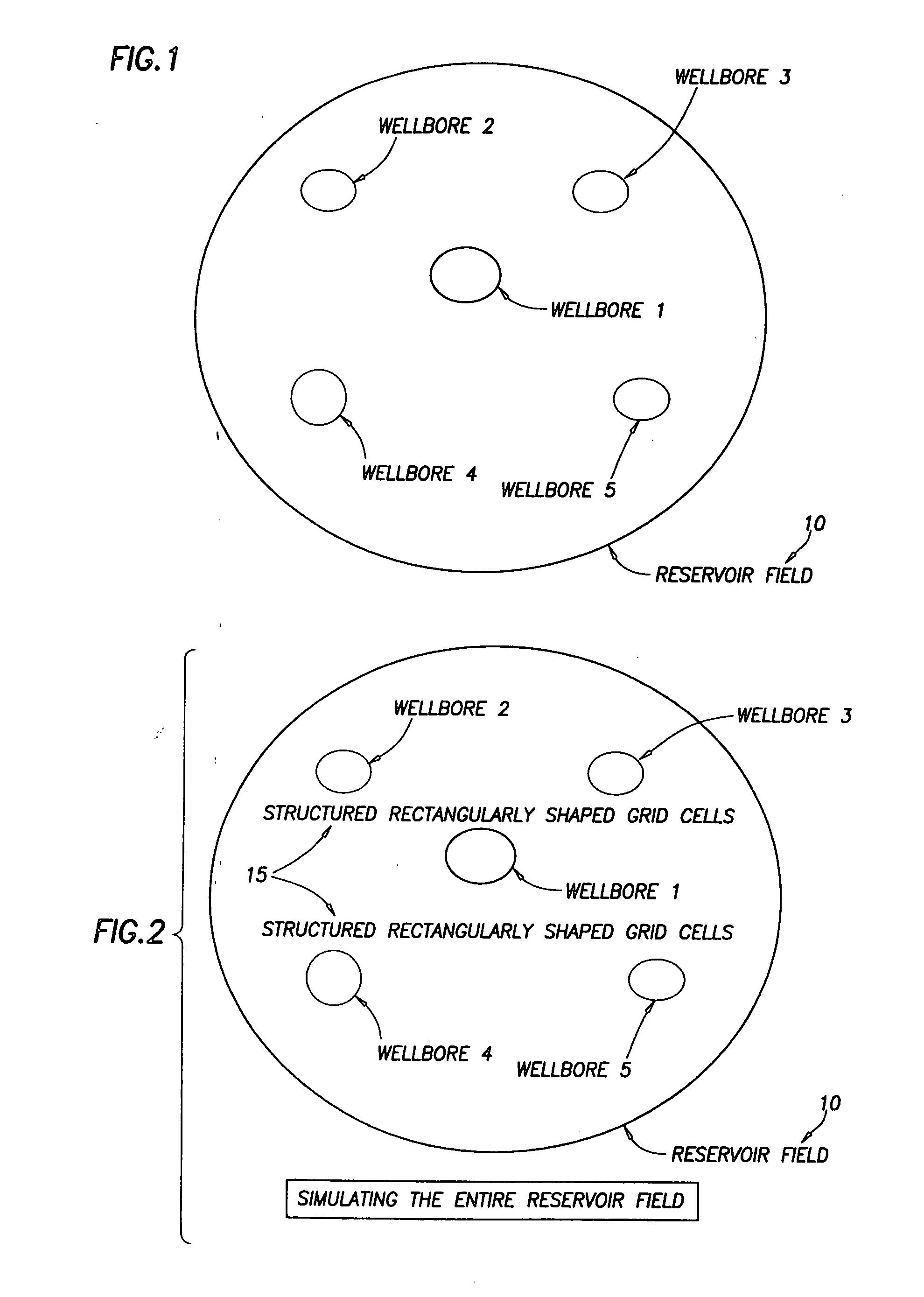
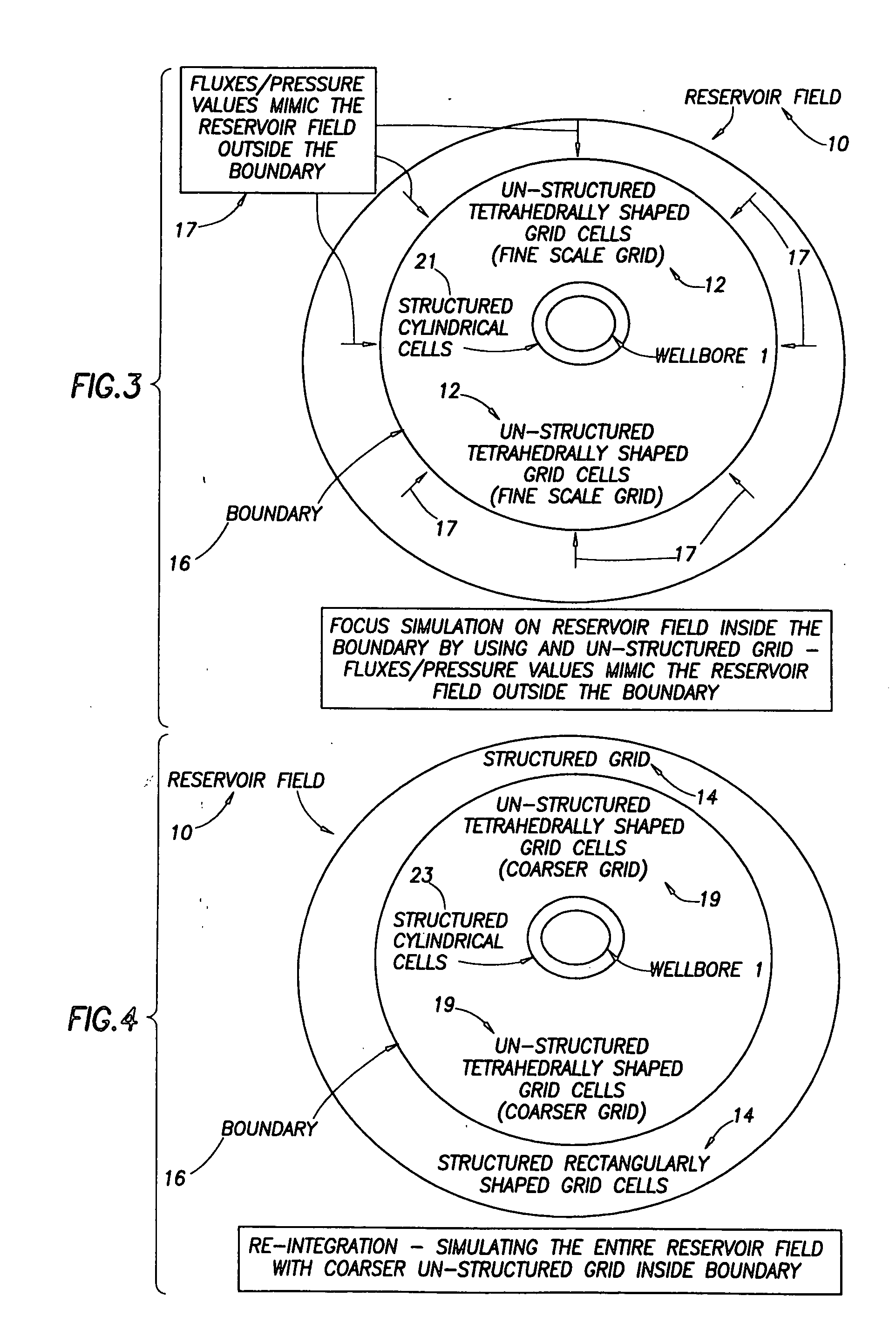
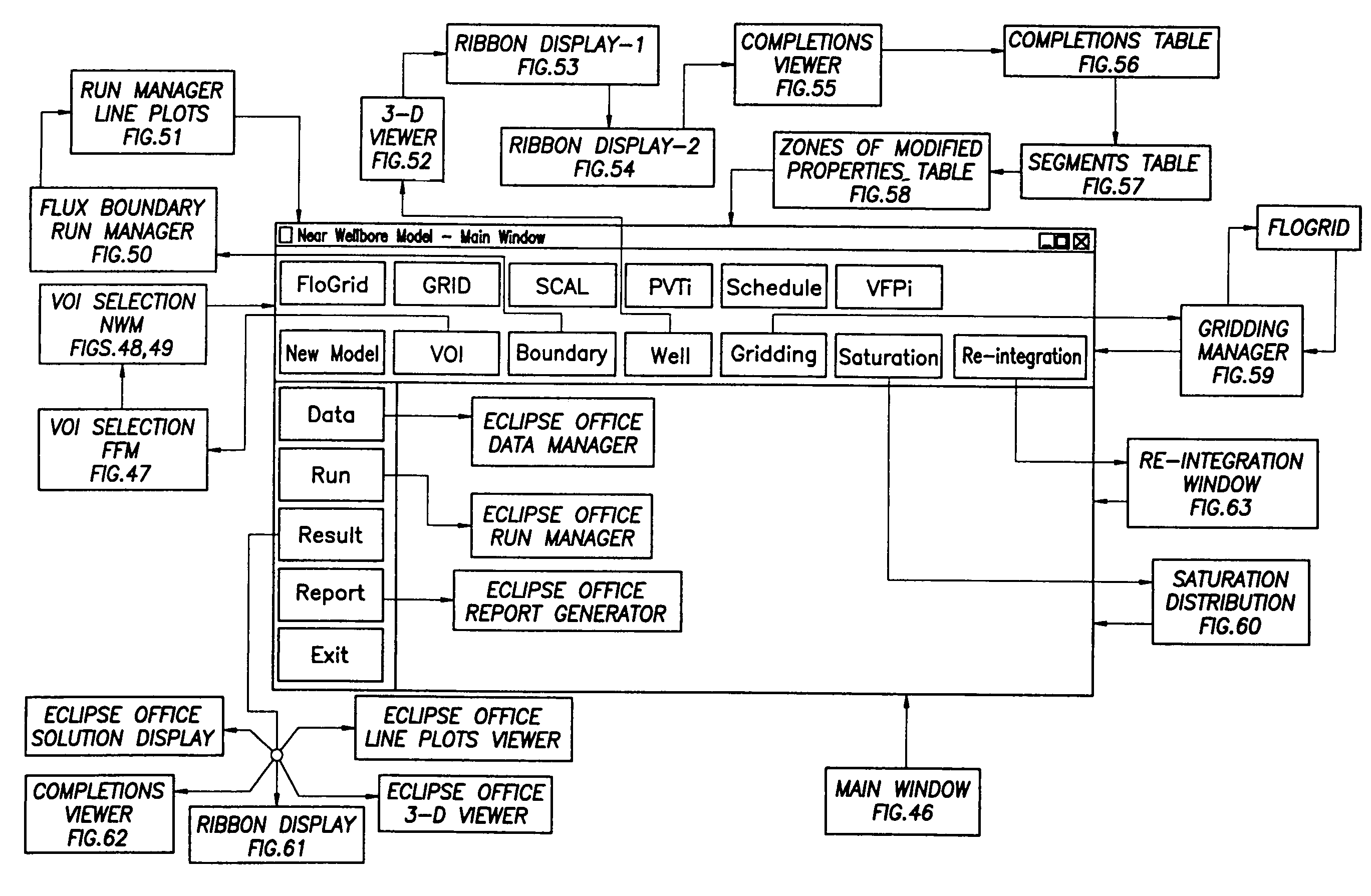
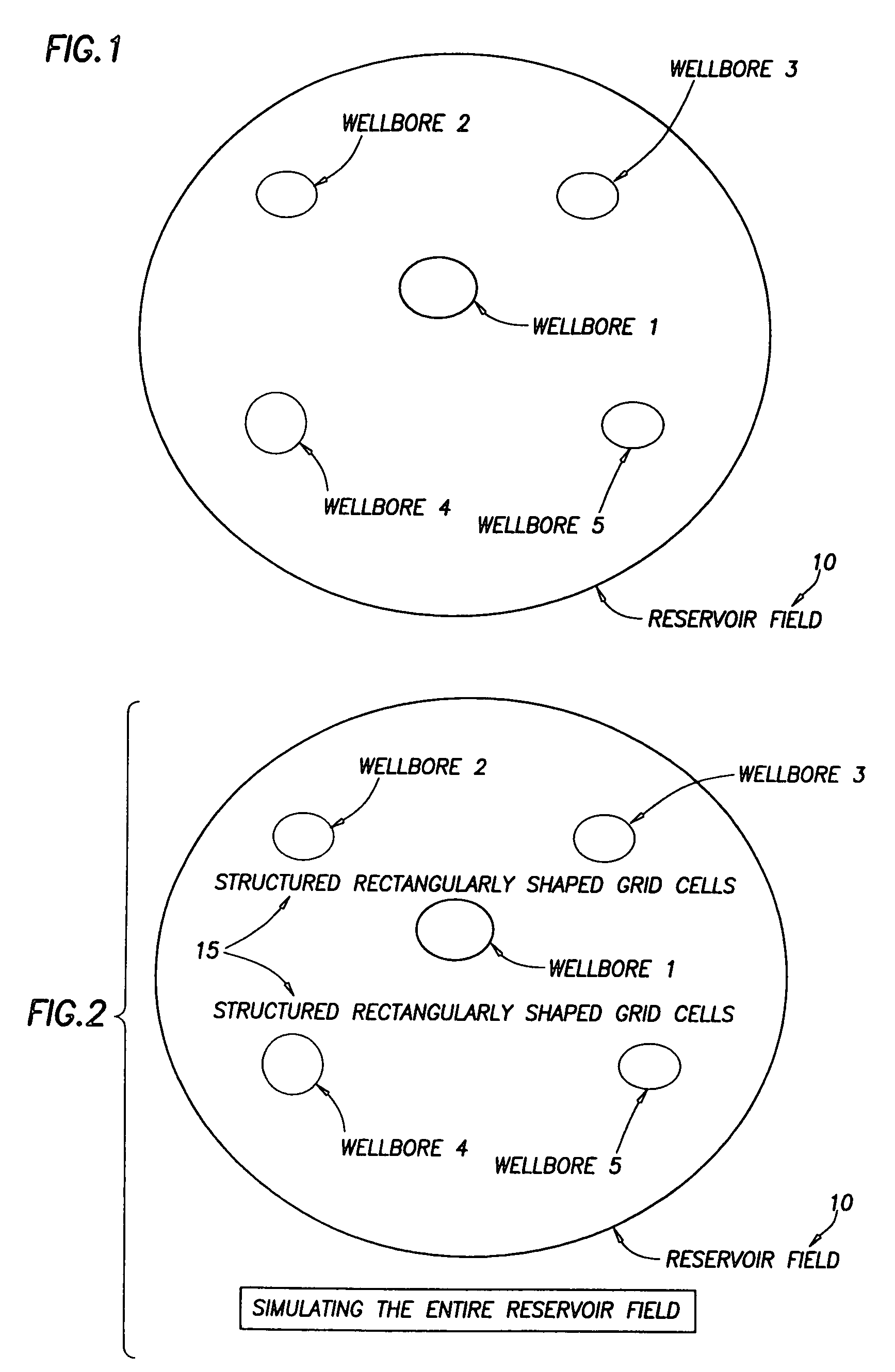
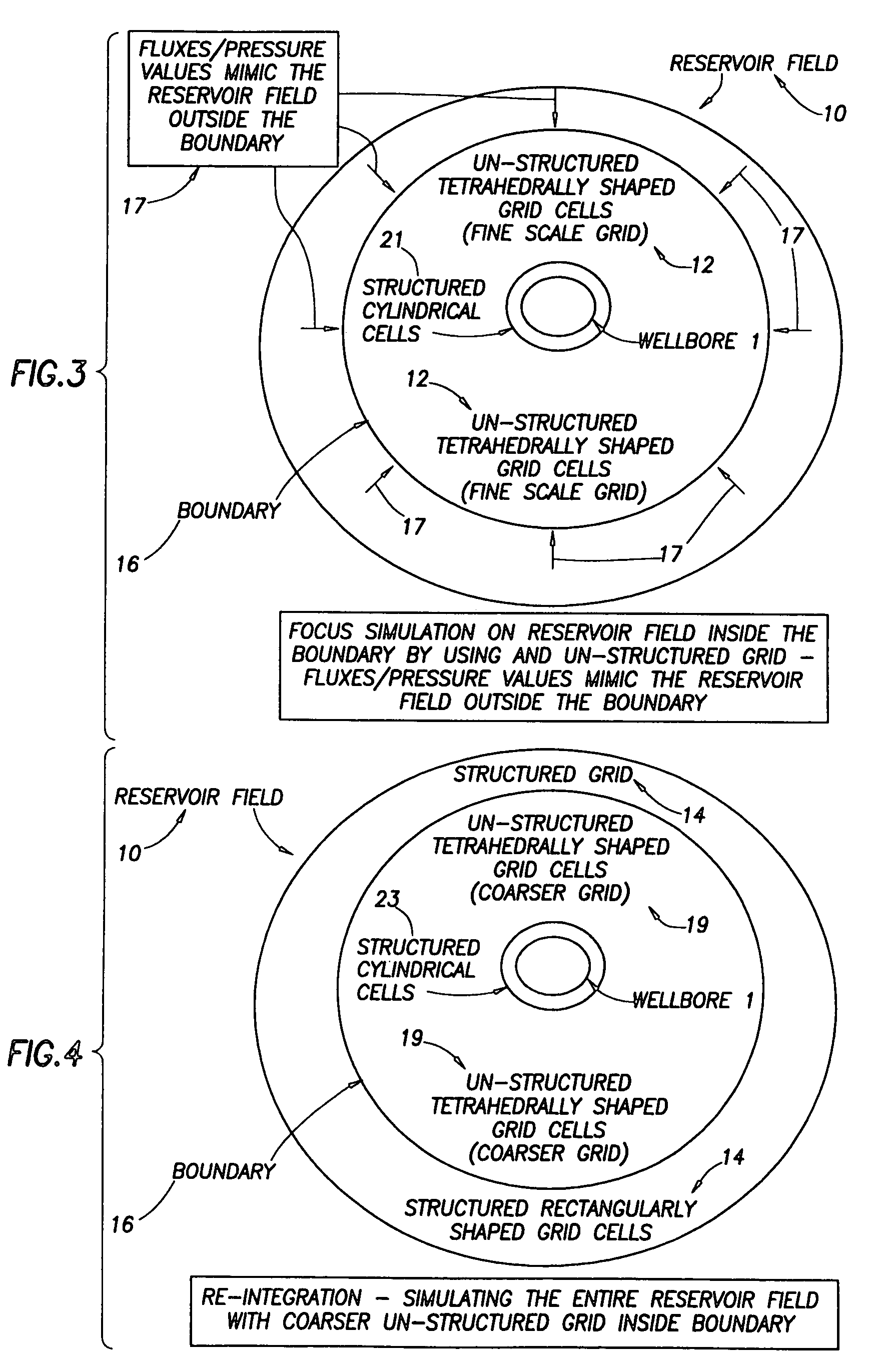
ActiveUS20050015231A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationModel methodScale structure
A “near wellbore modeling” software will, when executed by a processor of a computer, model a localized area of a reservoir field which surrounds and is located near a specific wellbore in the reservoir field by performing the following functions: (1) receive input data representative of a reservoir field containing a plurality of wellbores, (2) establish a boundary around one specific wellbore in the reservoir field which will be individually modeled and simulated, (3) impose an “fine scale” unstructured grid inside the boundary consisting of a plurality of tetrahedrally shaped grid cells and further impose a fine scale structured grid about the perforated sections of the specific wellbore, (4) determine a plurality of fluxes / pressure values at the boundary, the fluxes / pressure values representing characteristics of the reservoir field located outside the boundary, (5) establish one or more properties for each tetrahedral cell of the unstructured grid and each cylindrical grid cell of the structured grid, (6) run a simulation, using the fluxes / pressure values at the boundary to mimic the reservoir field outside the boundary and using the fine scale grid inside the boundary, to thereby determine a plurality of simulation results corresponding, respectively, to the plurality of grid cells located inside the boundary, the plurality of simulation results being representative of a set of characteristics of the reservoir field located inside the boundary, (7) display the plurality of simulation results which characterize the reservoir field located inside the boundary, and (8) reintegrate by coarsening the grid inside the boundary, imposing a structured grid outside the boundary, and re-running a simulation of the entire reservoir field.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Near wellbore modeling method and apparatus
ActiveUS7451066B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal receiversModel methodScale structure
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Density detection using real time discrete photon counting for fast moving targets
A system for detecting and graphically displaying a contents of a fast-moving target object comprises: a radiation source, having a position such that at least a portion of radiation emitted from the radiation source passes through the fast-moving target object, the fast-moving target object having a variable velocity and acceleration while maintaining a substantially constant distance from the radiation source and being selected from the group consisting of: a vehicle, a cargo container and a railroad car; a velocity measuring device configured to measure the variable velocity of the fast-moving target object; a detector array comprising a plurality of photon detectors, having a position such that at least some of the at least a portion of the radiation passing through the target object is received thereby, the detector array having a variable count time according to the variable velocity and a grid unit size; a counter circuit coupled to the detector array for discretely counting a number of photons entering individual photon detectors, the counter circuit measuring a count rate according to a contents within the fast-moving target object; a high baud-rate interface coupled to the counter circuit for sending count information from the counter circuit at a rate fast enough to support real-time data transfer therethrough; and a processor coupled to the velocity measuring device and to the high-baud-rate interface, receiving count information from the high baud-rate interface and generating distortion-free image data in real time as a function of the count information and the variable velocity. A method for using the system is also disclosed.
Owner:LEIDOS
Fracture network characterization method
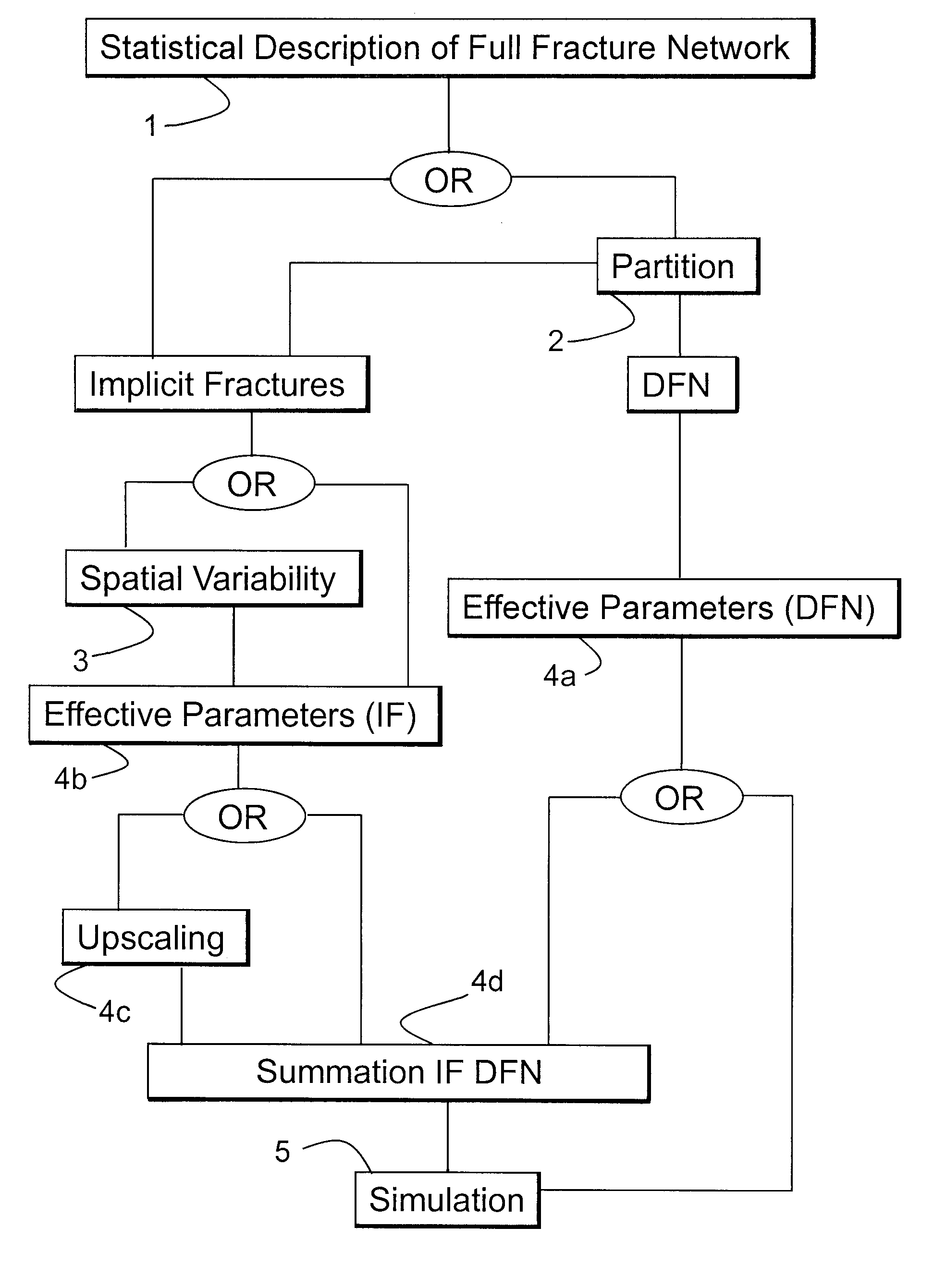
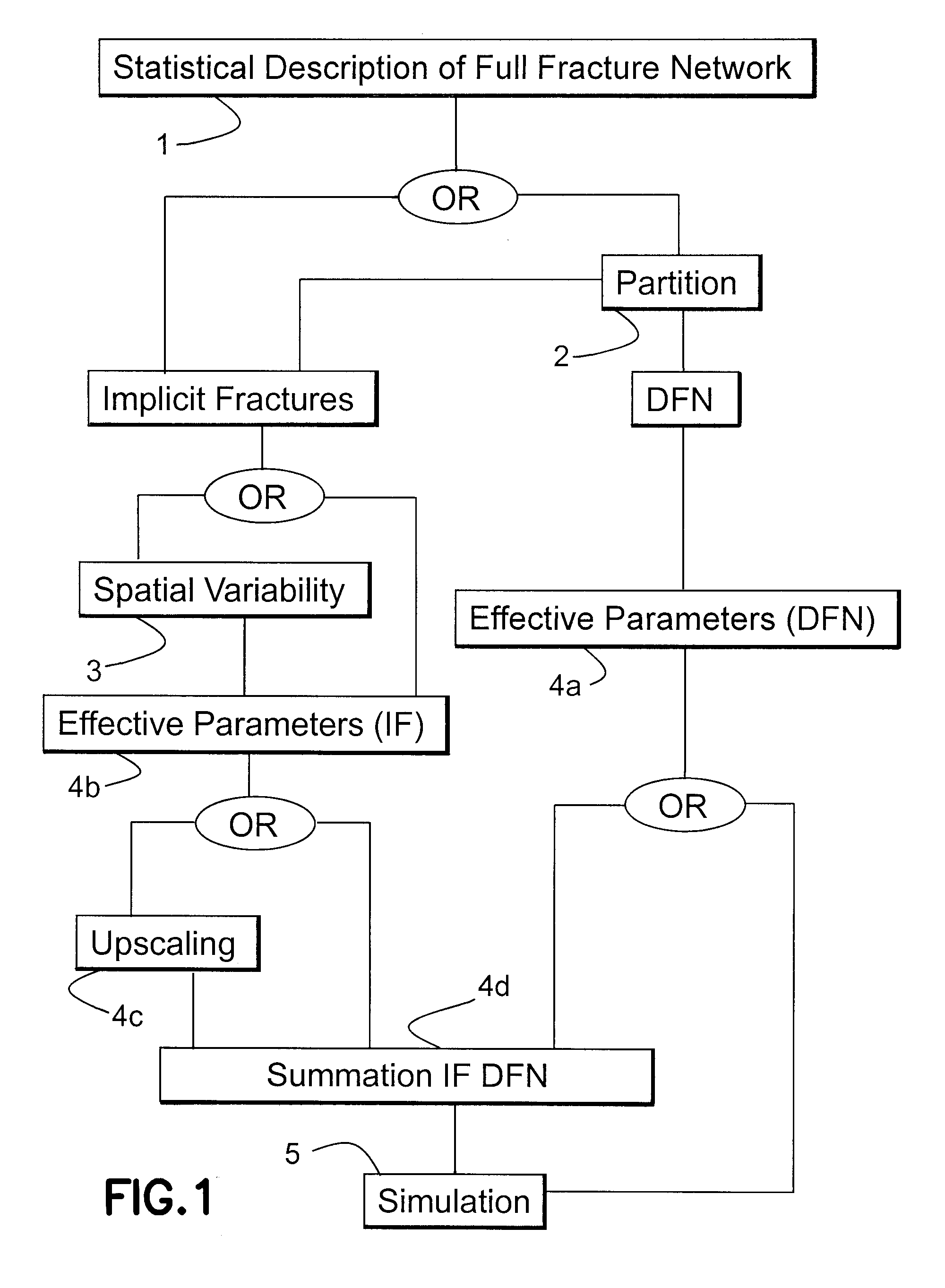
ActiveUS20100312529A1Improve representationReduce storage spaceFluid removalSeismologyArbitrary distributionNetwork characterization
A method of representing and using fractures in a model of a subterranean reservoir is described including the partitioning the fracture network into a discretely modeled part and a remaining statistically described part from a statistical description of all fractures, the determination of the correlation effects caused by fractures with dimensions exceeding dimension of the local grid cells and the determination of petrophysical properties while allowing for arbitrary distribution of fracture orientations, with all three aspects being combinable to improve the modeling of fractures and the simulation of fractured reservoirs.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
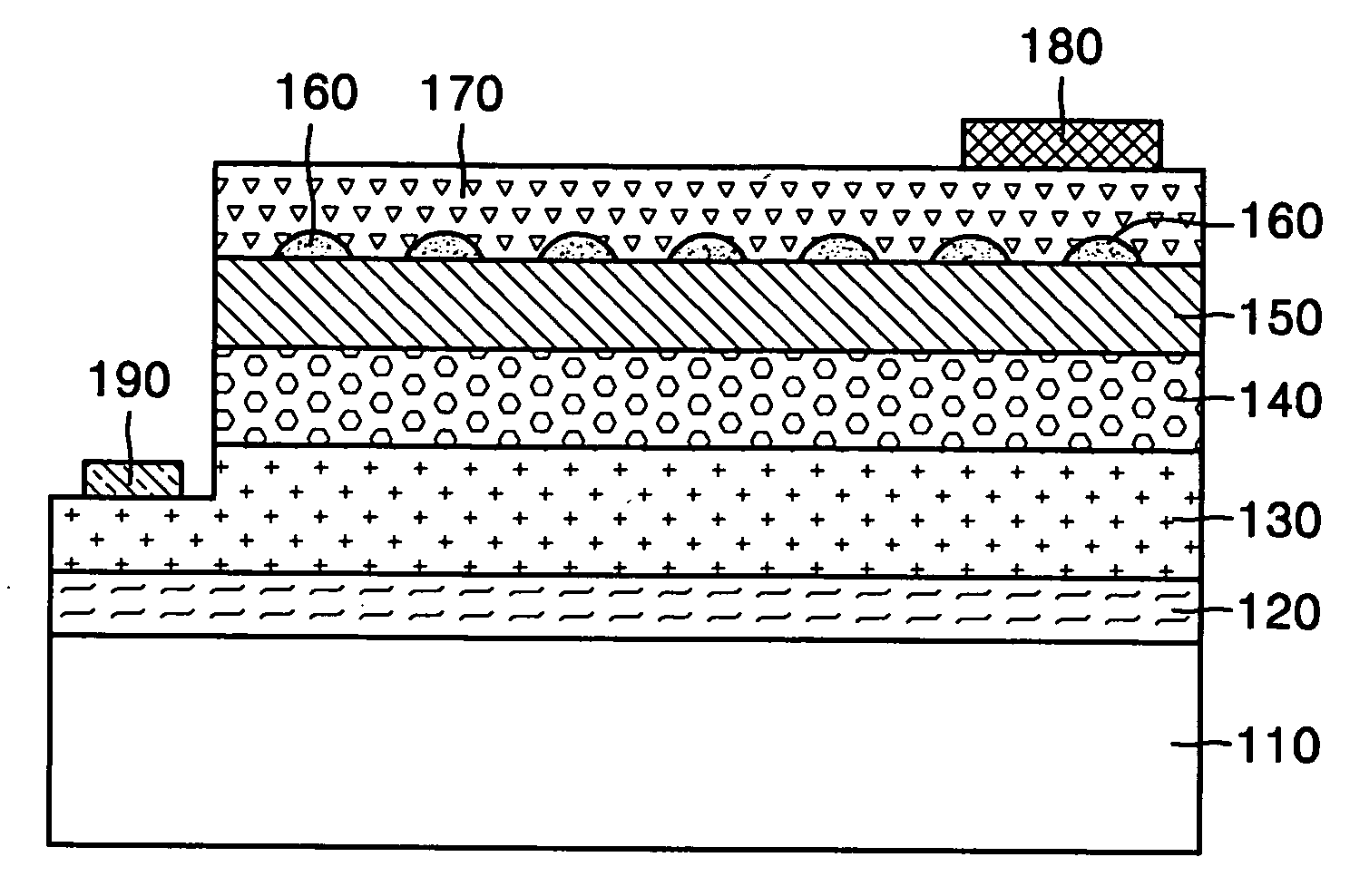
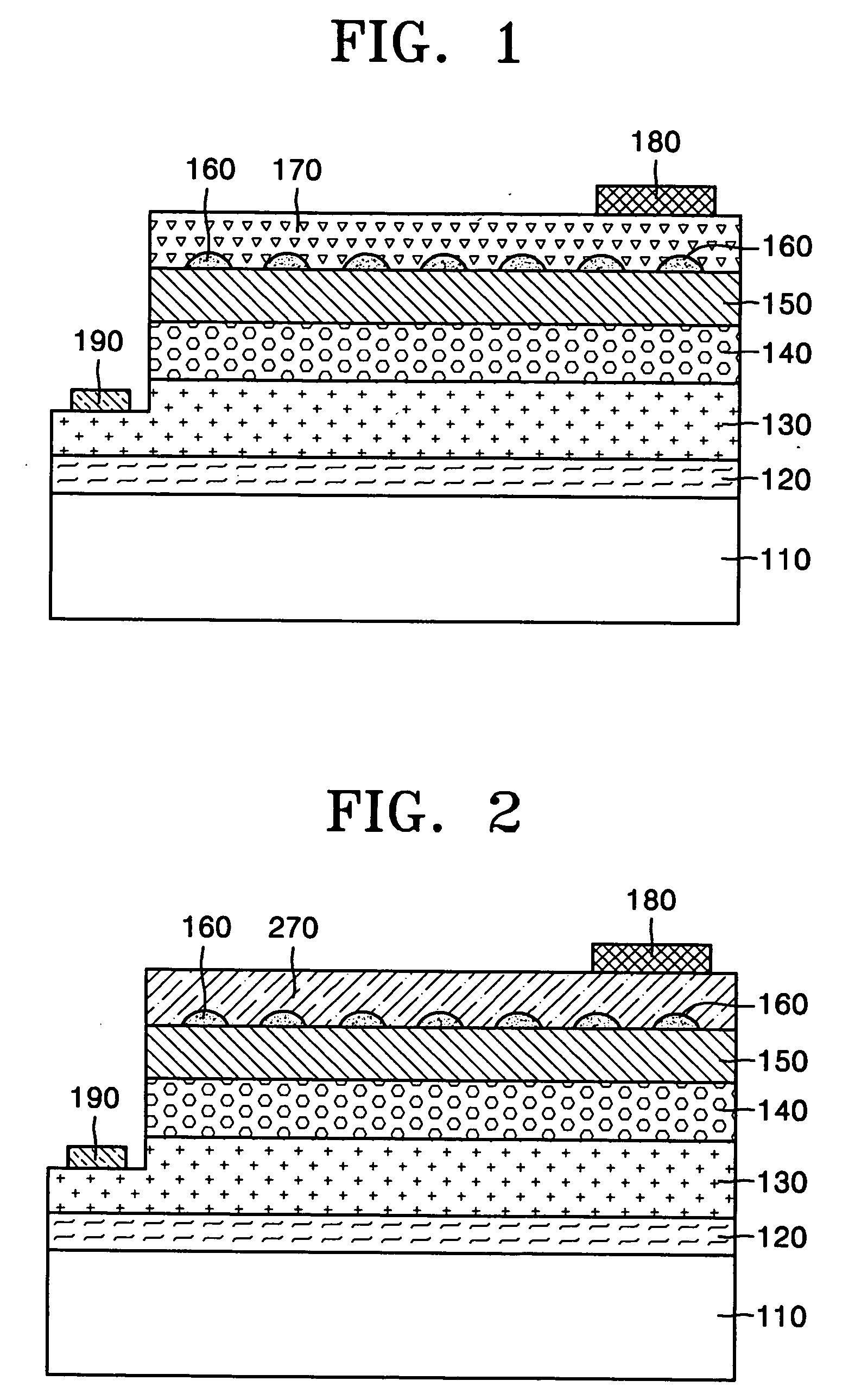
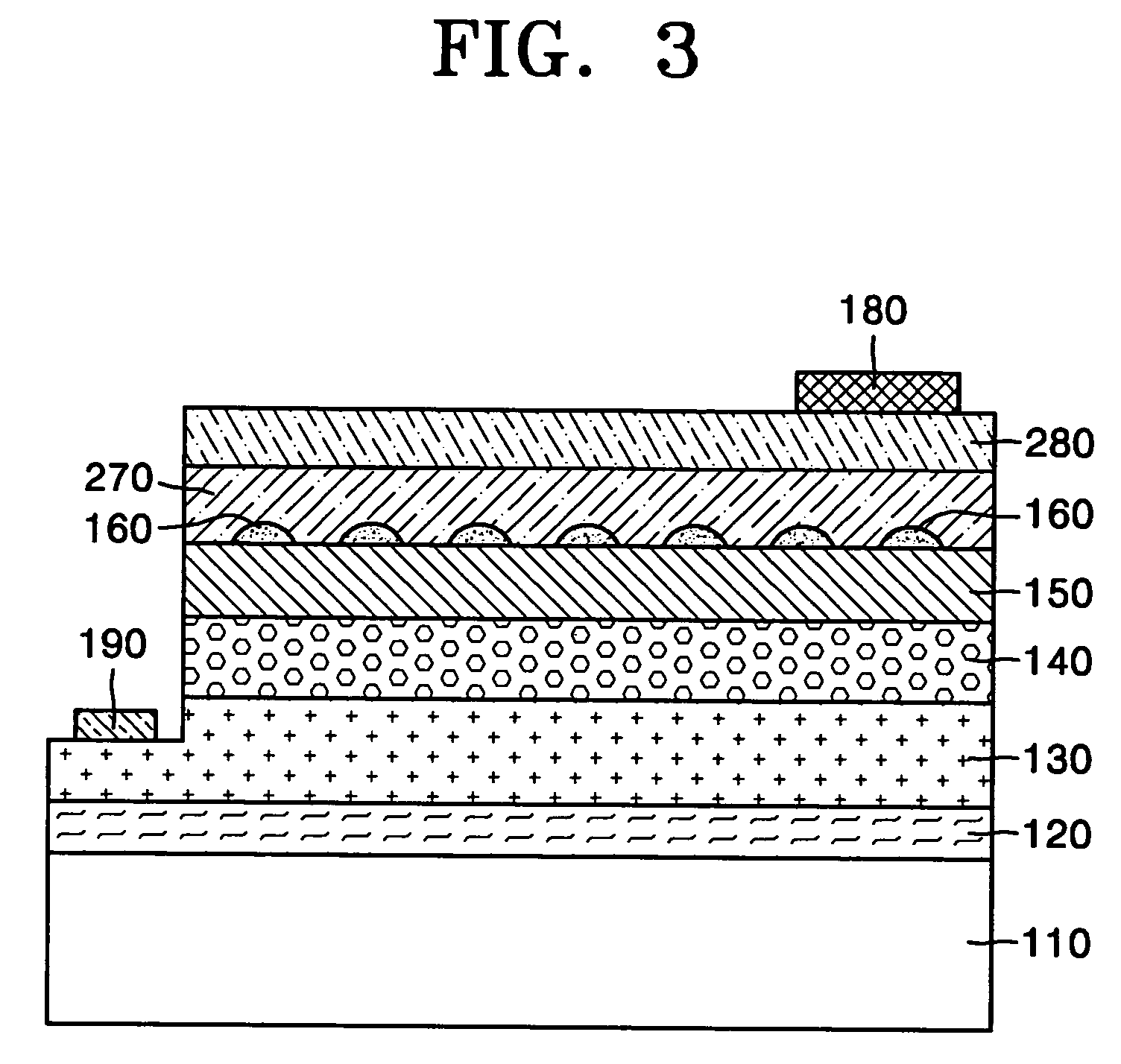
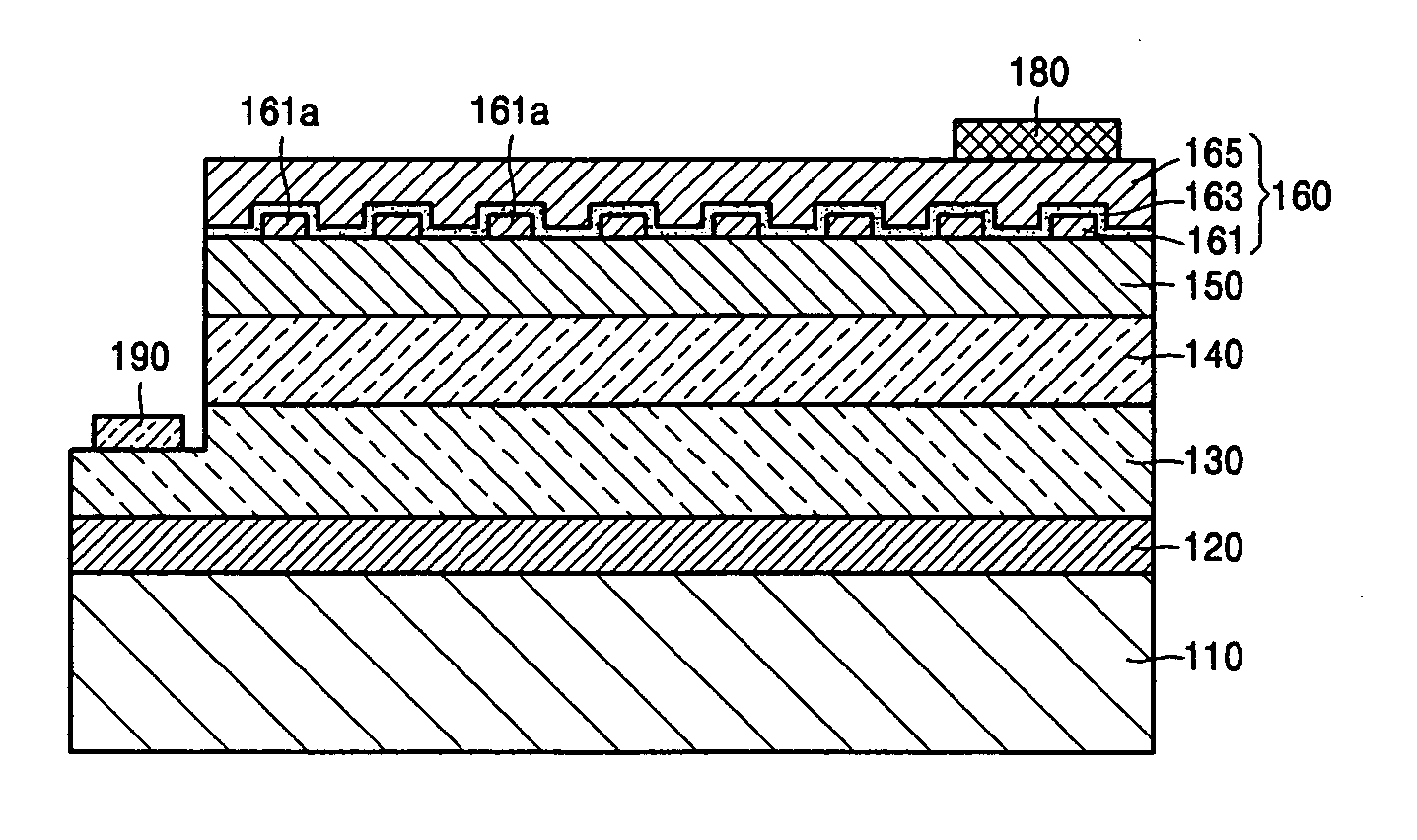
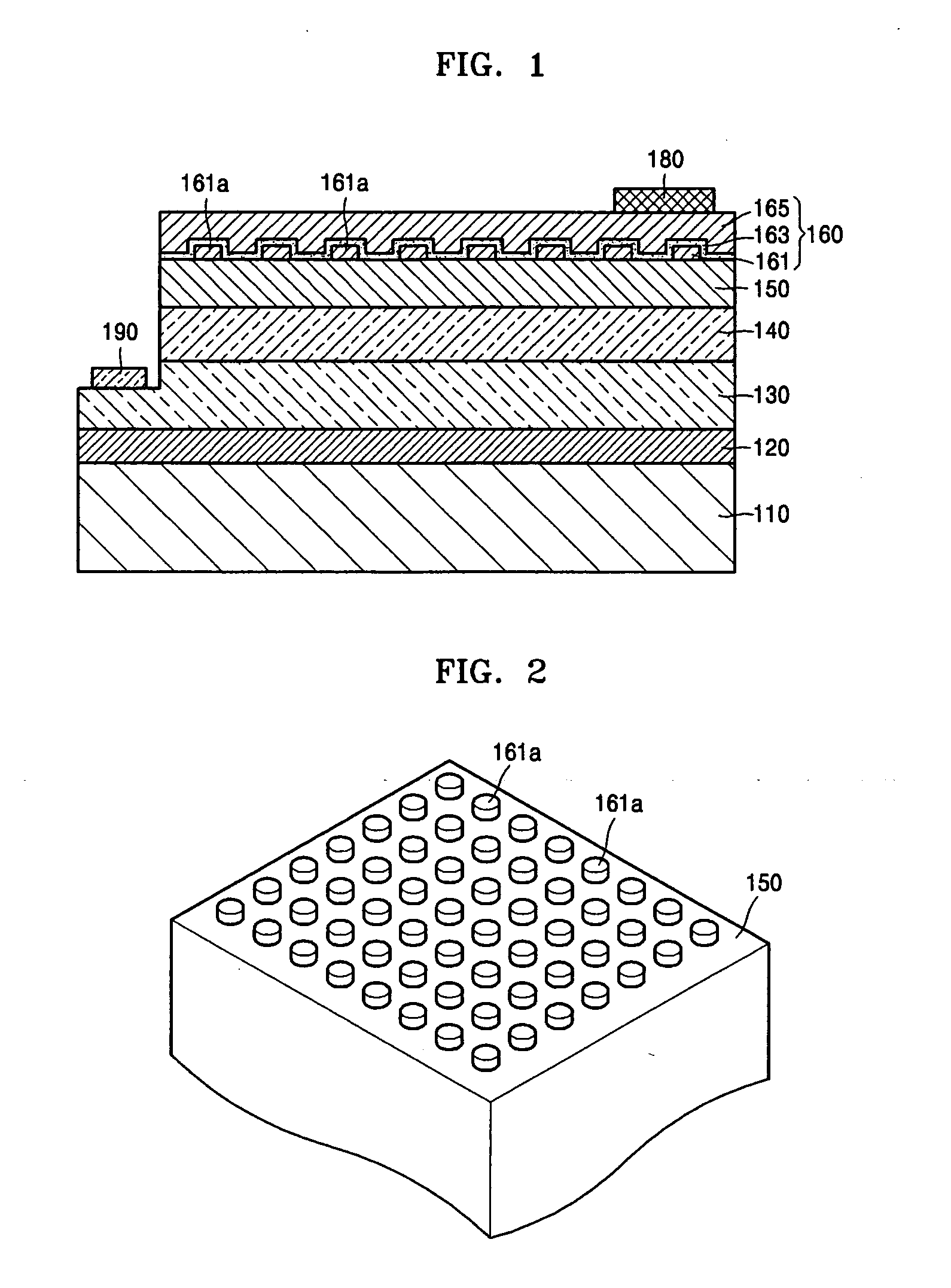
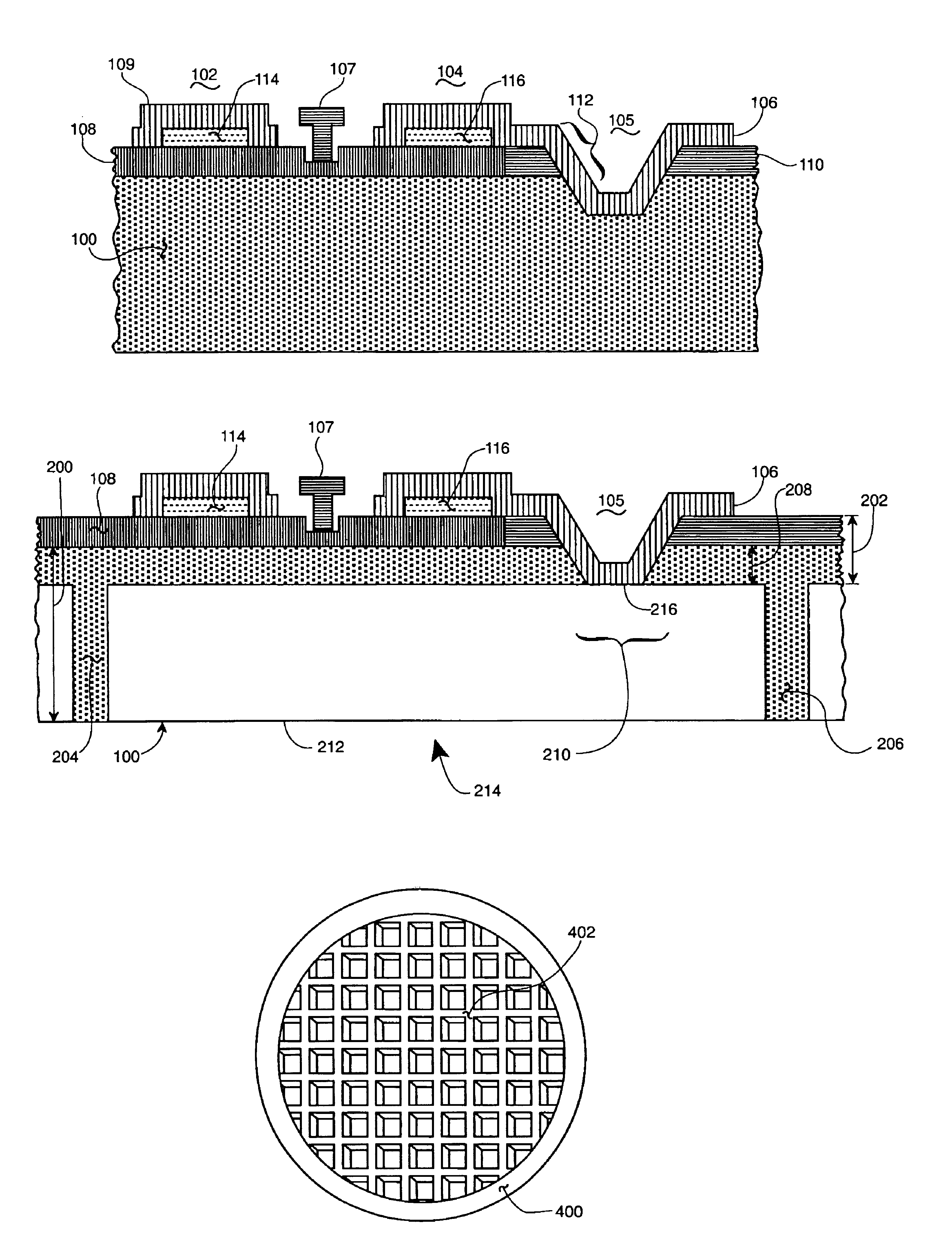
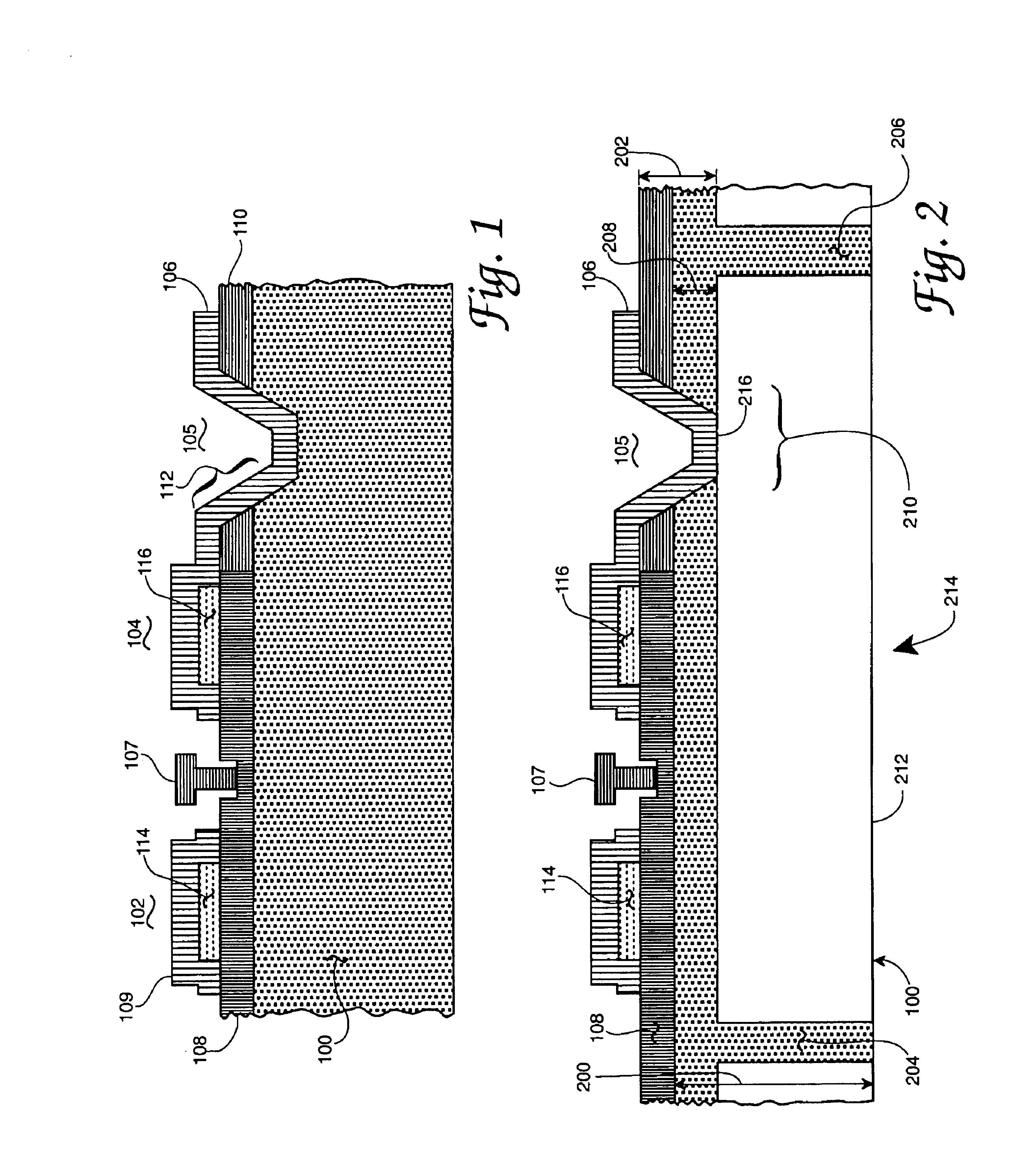
Nitride-based light-emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
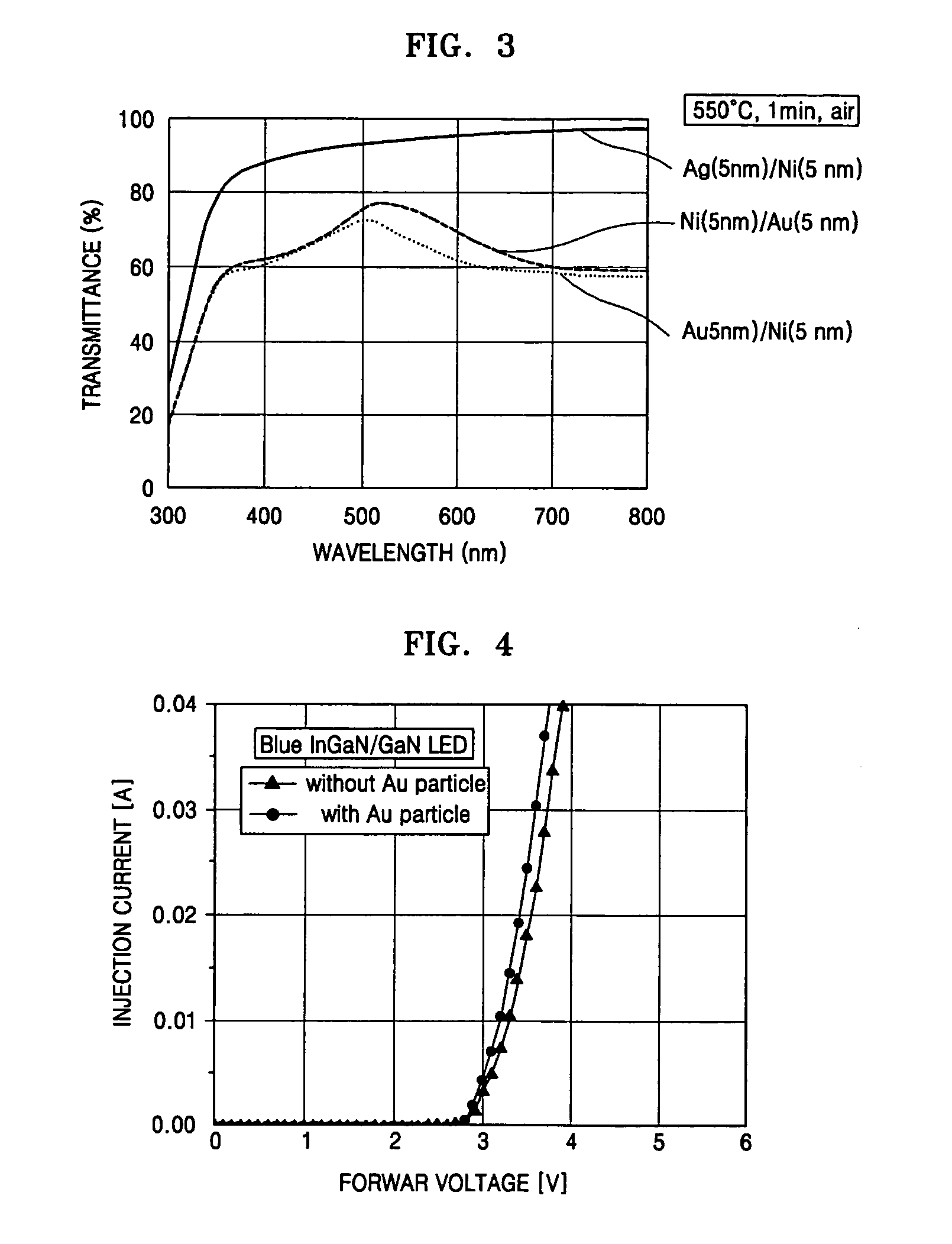
ActiveUS20050199895A1Reduce contact resistivityAvoid performance degradationLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMicrometerOhmic contact
A nitride-based light-emitting device and a method of manufacturing the same. The light-emitting device includes a substrate, and an n-cladding layer, an active layer, a p-cladding layer, a grid cell layer and an ohmic contact layer sequentially formed on the substrate. The grid cell layer has separated, conducting particle type cells with a size of less than 30 micrometers buried in the ohmic contact layer. The nitride-based light-emitting device and the method of manufacturing the same improve the characteristics of ohmic contact on the p-cladding layer, thereby increasing luminous efficiency and life span of the device while simplifying a manufacturing process by omitting an activation process after wafer growth.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
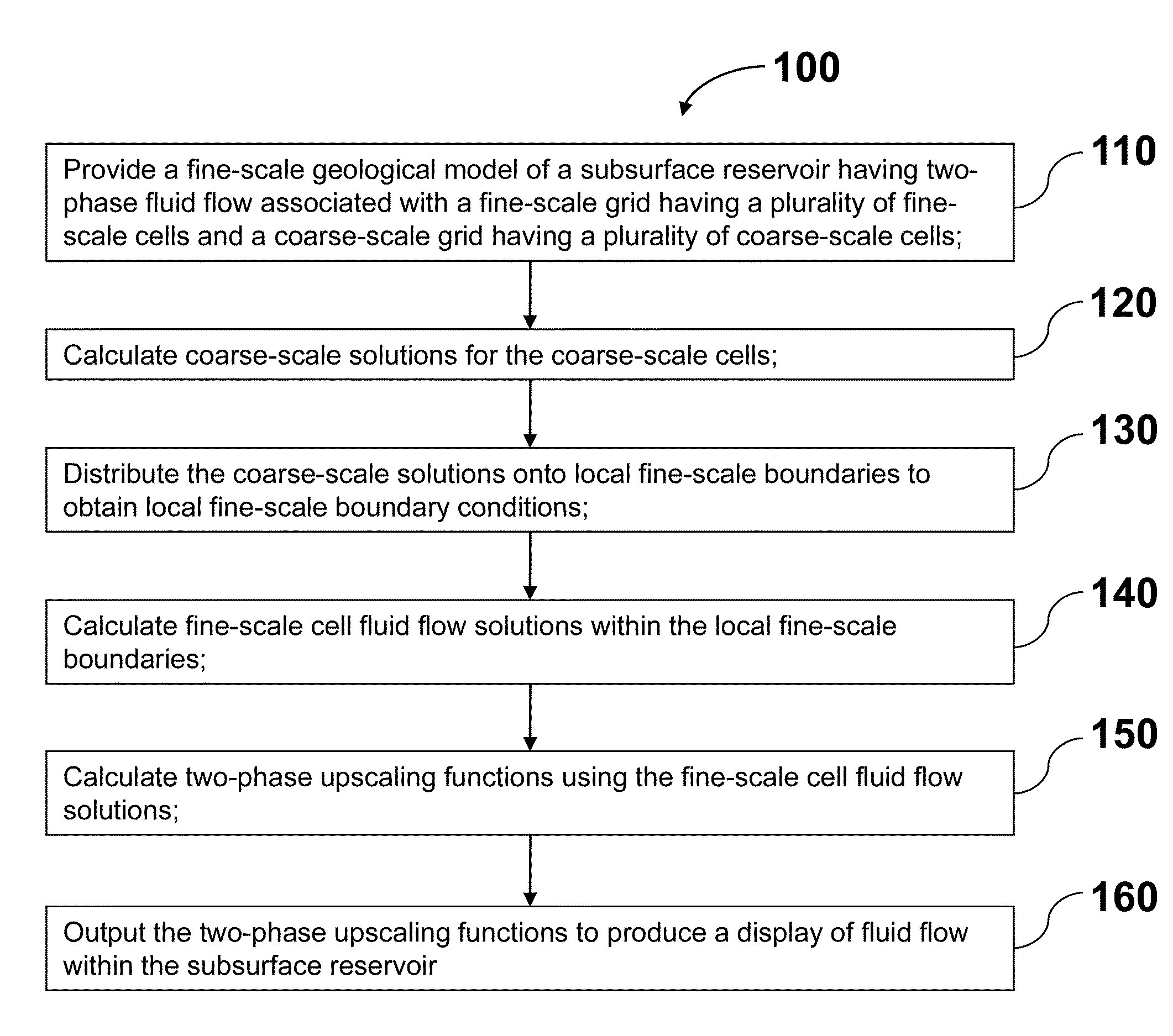
Upscaling of flow and transport parameters for simulation of fluid flow in subsurface reservoirs
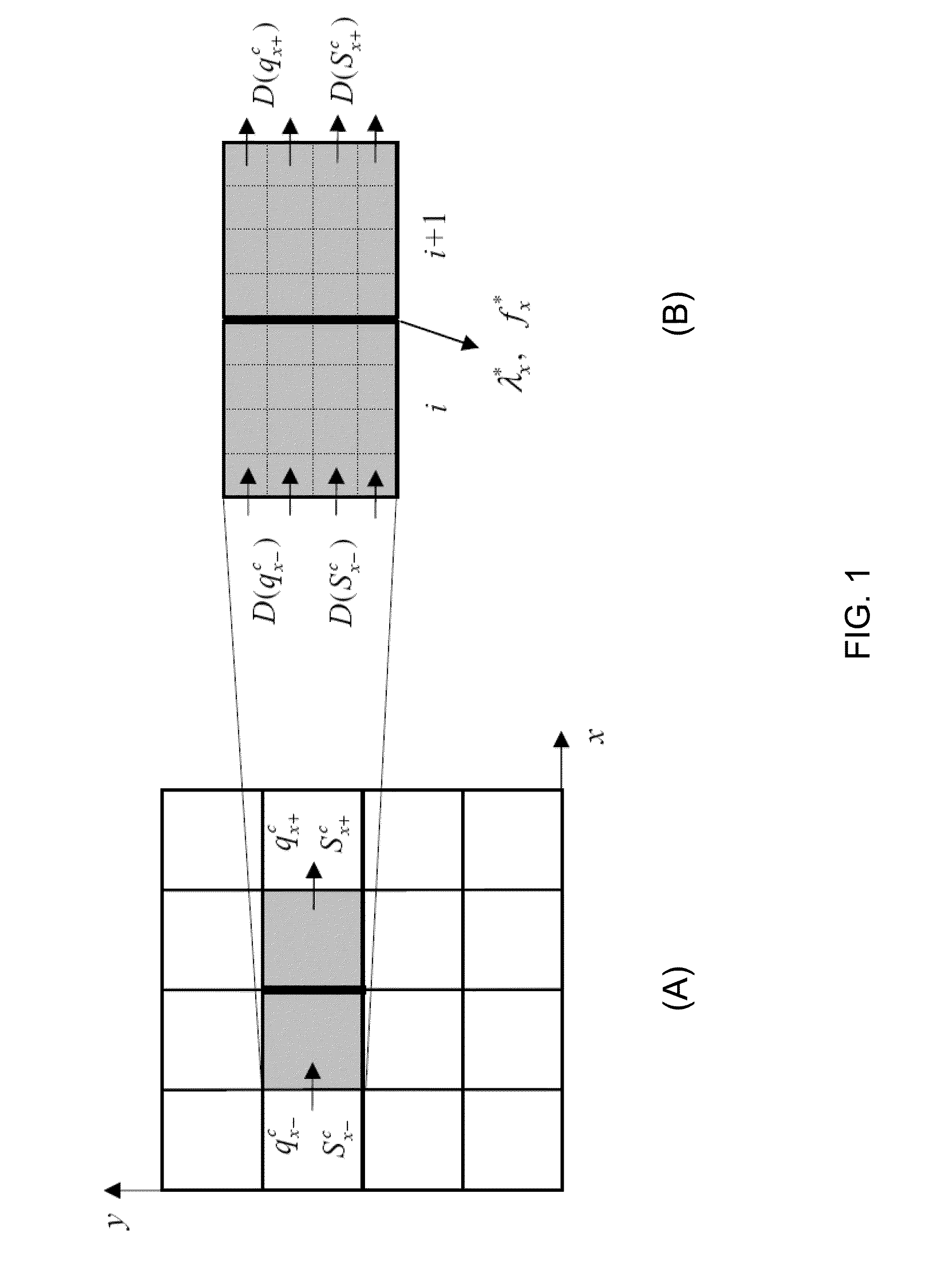
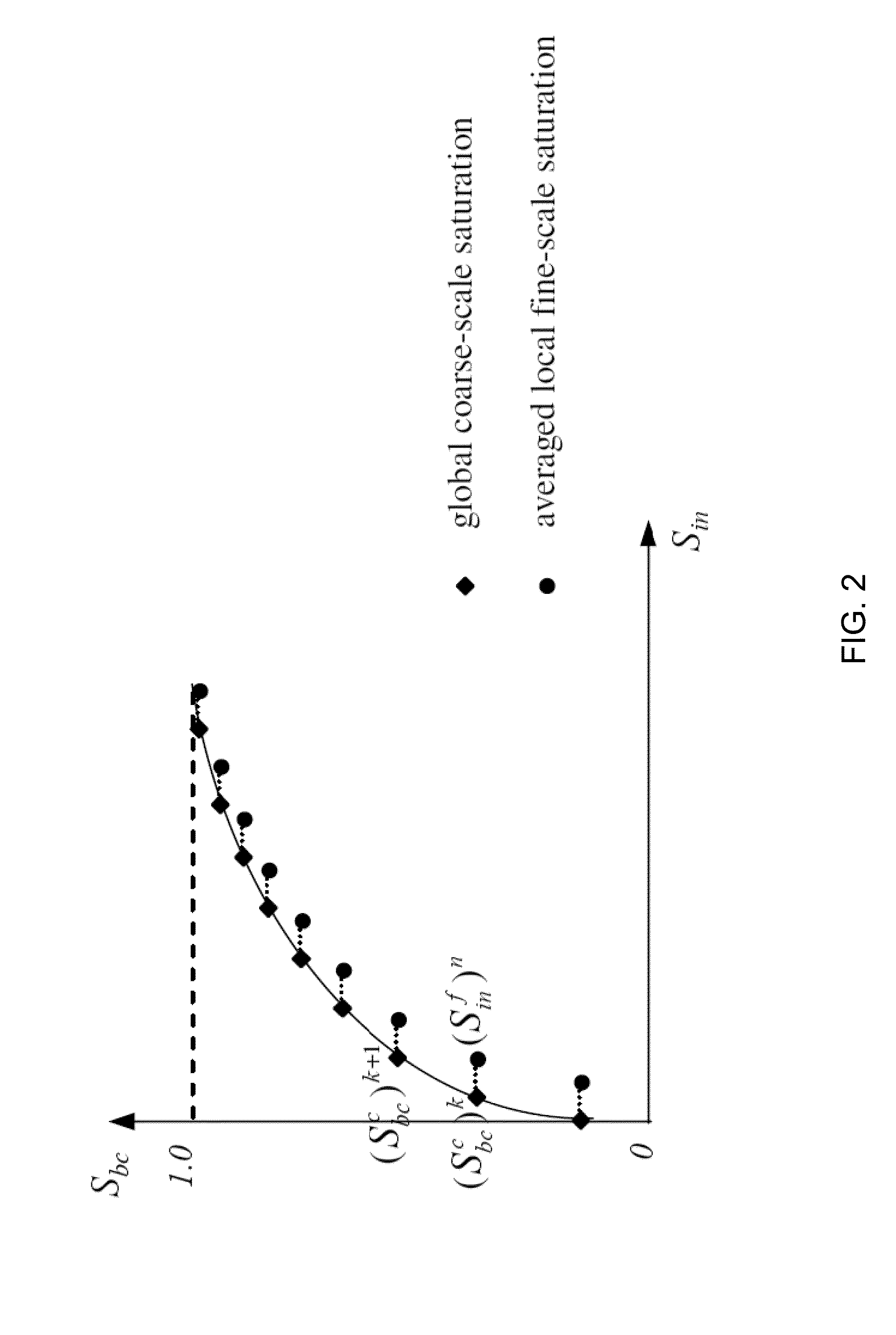
An upscaling method for efficiently simulating a geological model of subsurface reservoir is disclosed. The method includes providing a fine-scale geological model of a subsurface reservoir associated with a fine-scale grid and a coarse-scale grid. Time-dependent fluid flow solutions, such as fluxes and saturations, are computed for the coarse-scale grid cells. The coarse-scale fluid flow solutions are distributed onto local fine-scale boundaries to obtain local fine-scale boundary conditions. Fine-scale cell fluid flow solutions are computed within the local fine-scale boundaries using the local fine-scale boundary conditions. Two-phase upscaling functions are computed with the fine-scale cell fluid flow solutions and are output to produce a display of fluid flow within the subsurface reservoir.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for simulating fluid flows within a medium discretized by a hybrid grid
InactiveUS20070073527A1Analogue processes for specific applications3D modellingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesQuality control
A method for evaluating fluid flows within a heterogeneous formation, crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities, comprising generating a hybrid grid from a CPG type grid and from structured grids having application, for example, in simulation of hydrocarbon reservoirs. The first stage locally deforms a CPG type grid into a non-uniform Cartesian grid. These local grid cell deformations correspond to the change from a so-called “CPG” frame of reference to a so-called “Cartesian” frame of reference defined by the deformation. These deformations are then quantified and applied to the structured grids so as to shift to the “Cartesian” frame. A hybrid g rid is then generated in the “Cartesian” frame from the two thus deformed grids. Finally, the hybrid grid is deformed to return to the “CPG” frame, prior to improving the grid quality, by optimization under quality control in the numerical scheme sense.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
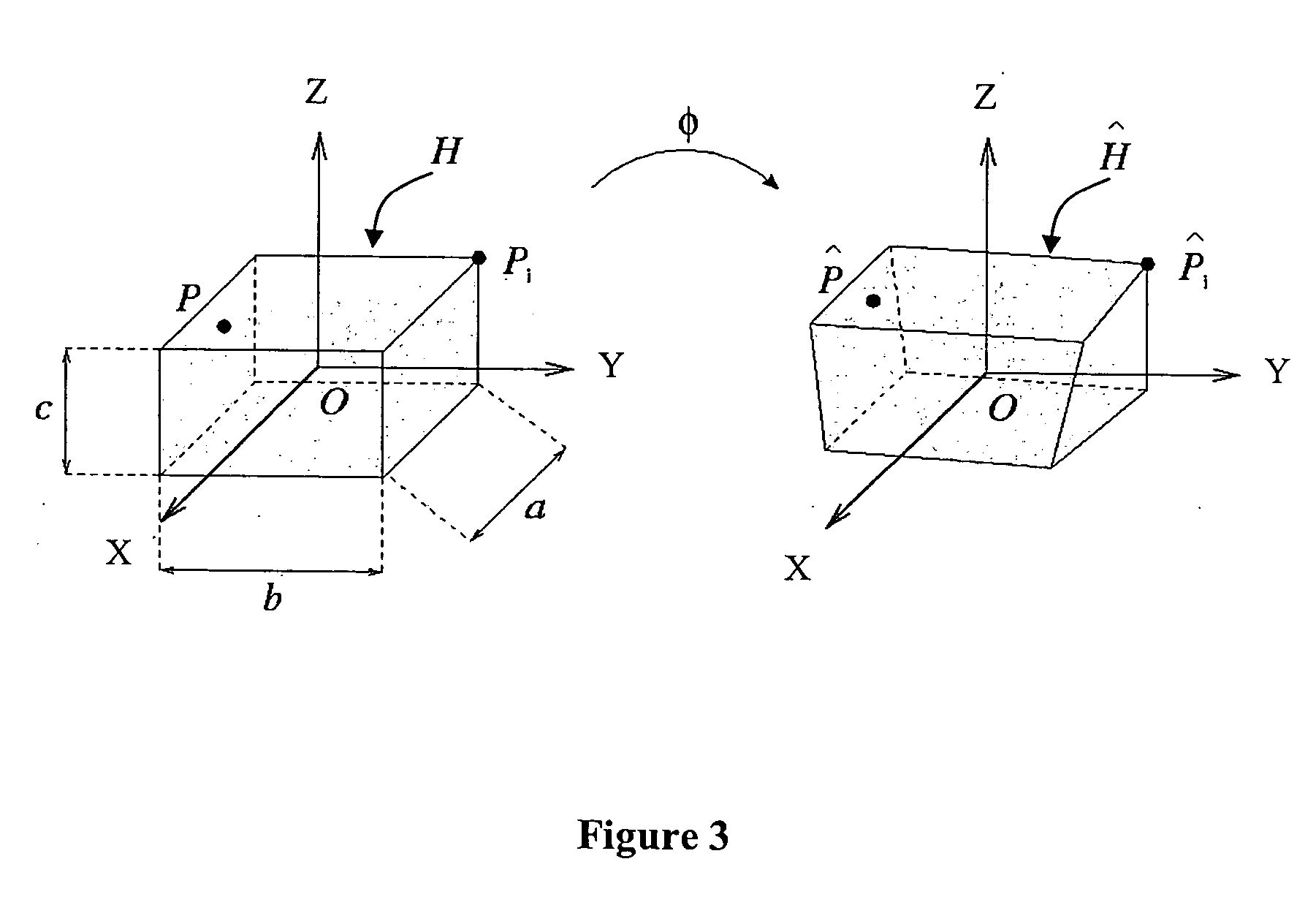
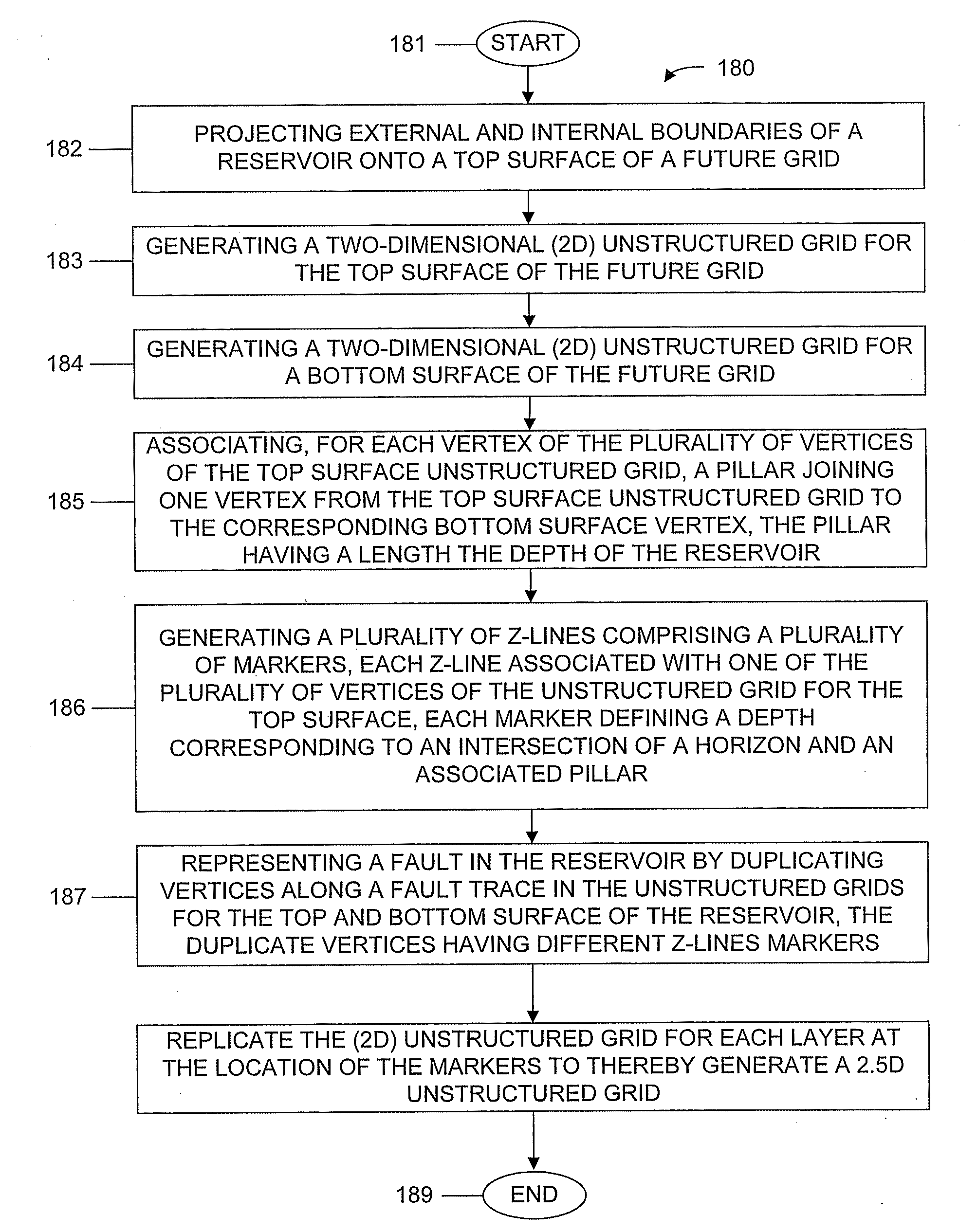
Machine, Program Product, and Computer-Implemented Method to Simulate Reservoirs as 2.5D Unstructured Grids
ActiveUS20110313745A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPrinted circuit aspectsComputational scienceData set
Example embodiments utilize machines to model reservoir geometry having geological layers as 2.5D unstructured grids. Example embodiments include program products to simulate a reservoir by generating a reservoir data system, performing a numerical fluid flow simulation, and visualizing the simulation. Data system embodiments include data structures to model a reservoir geometry as laterally unstructured two-dimensional (2D) grids and associated layer depths defining z-lines to thereby define a 2.5D unstructured grid, including datasets for: vertices of the grid cells for the future grid top and bottom surfaces, a number and listing of vertices for each grid cell, cell center coordinates, and vertex adjacency information using a compressed sparse row format. Computer-implemented methods include projecting external and internal boundaries onto a future grid surface; generating 2D unstructured, e.g., Voronoi, grids, for the top and bottom surfaces; and generating z-lines of depths corresponding to reservoir layers to thereby generate 2.5D unstructured grids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Automated generation of local grid refinement at hydraulic fractures for simulation of tight gas reservoirs
ActiveUS20130073268A1Reasonable computational complexityLow costComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationHorizontal wellsHydraulic fracturing
A computer system and method of automatically generating a Local Grid Refinement (LGR) gridded model of a gas reservoir. A geologic file includes information identifying the locations of one or more wells according to root grid cells within a volume of the earth to be modeled. User inputs specify the number of hydraulic fractures from each well, and such parameters as the fracture length, etc. User inputs also specify the number of “splits” of the root grid cells containing hydraulic fractures; those root grid cells are then split into finer resolution grid cells of increasing width within the root grid cells containing the fractures. For horizontal wells, user inputs indicate the number of splits of root grid cells containing the lateral portions of the wellbore. Non-orthogonal and complex fractures are processed by a“nested” LGR approach. Geologic properties are assigned to each grid cell, with a tensorial adjustment included for non-orthogonal fractures, and the resulting model is available for simulation.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
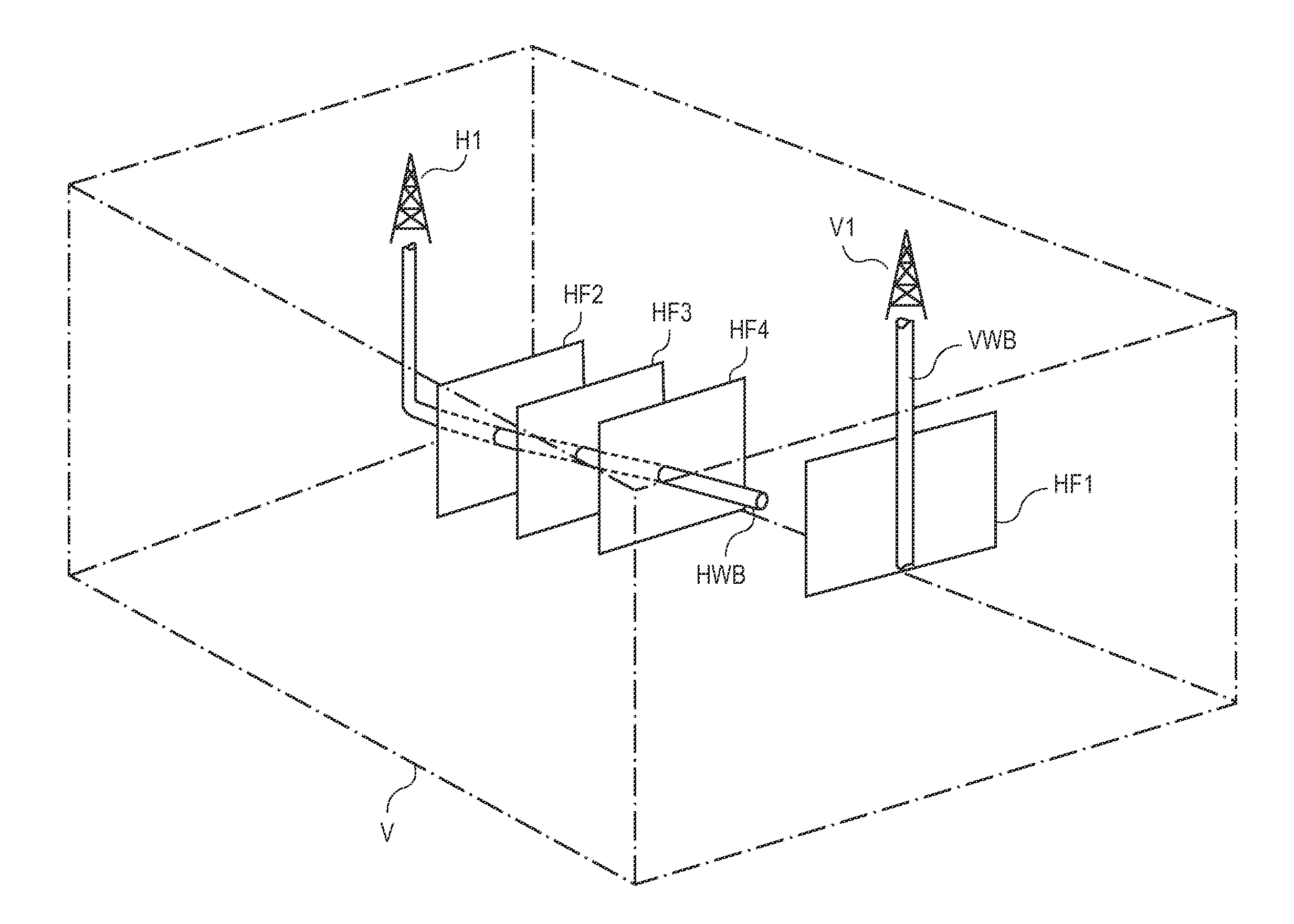
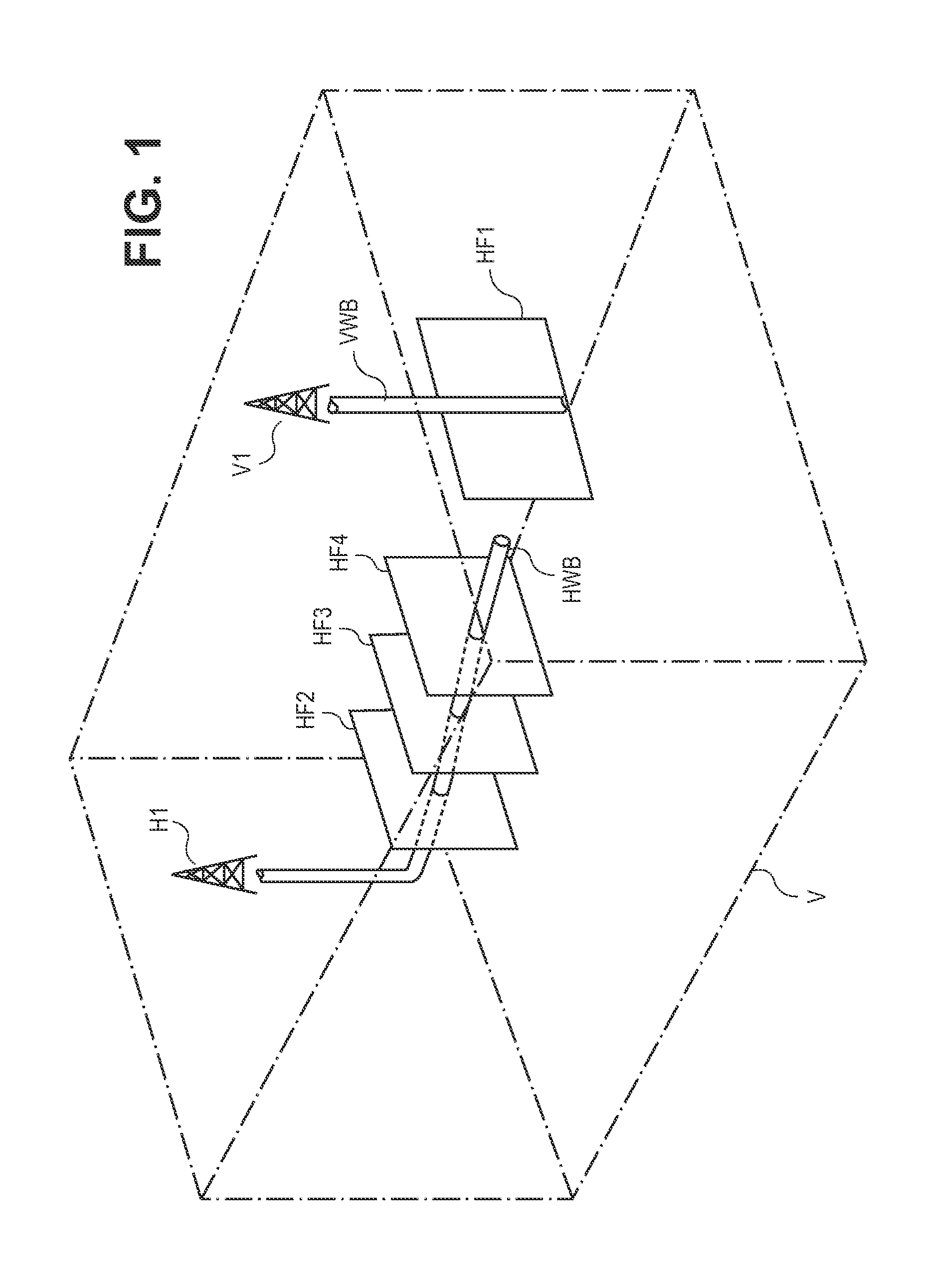
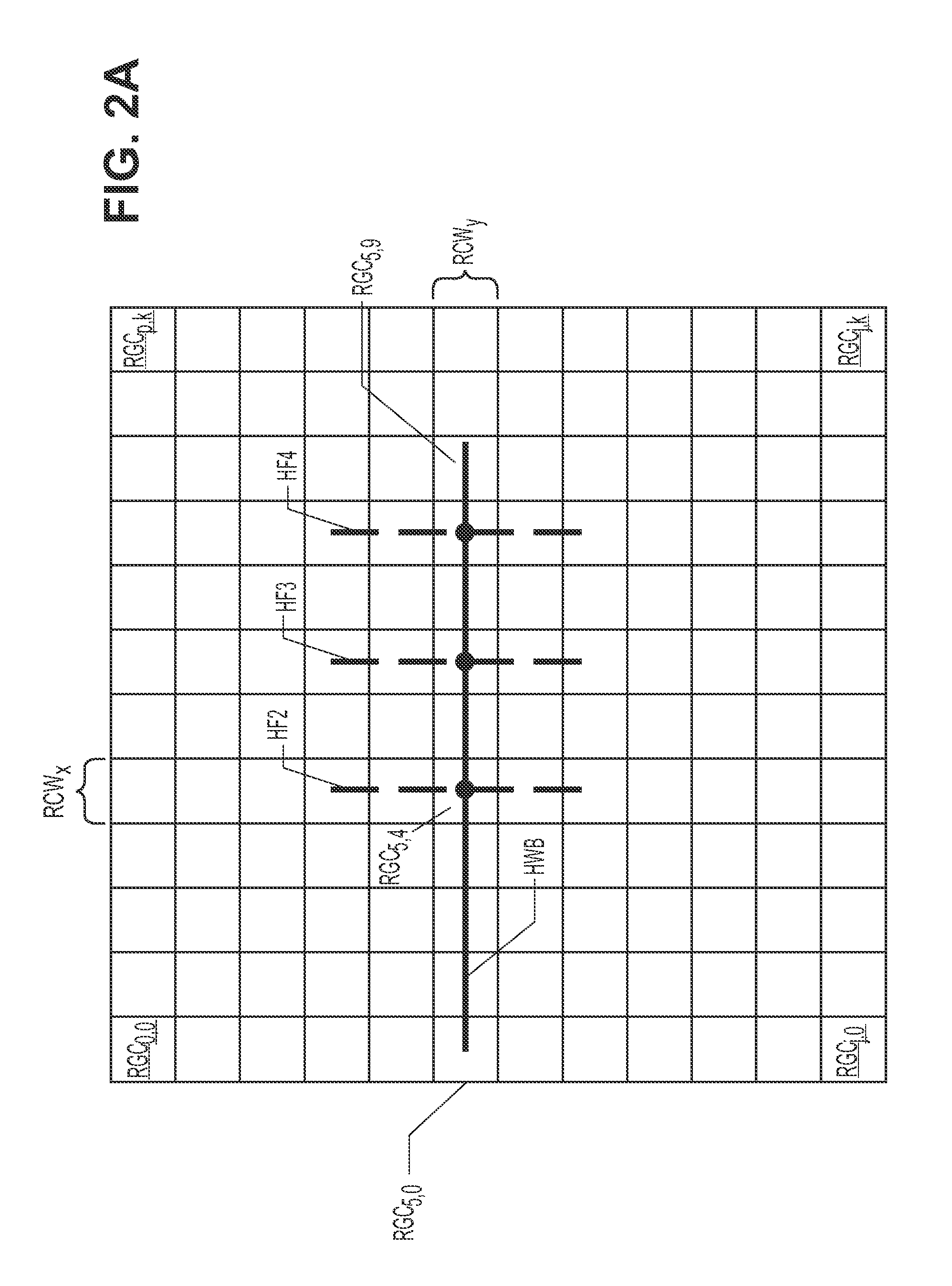
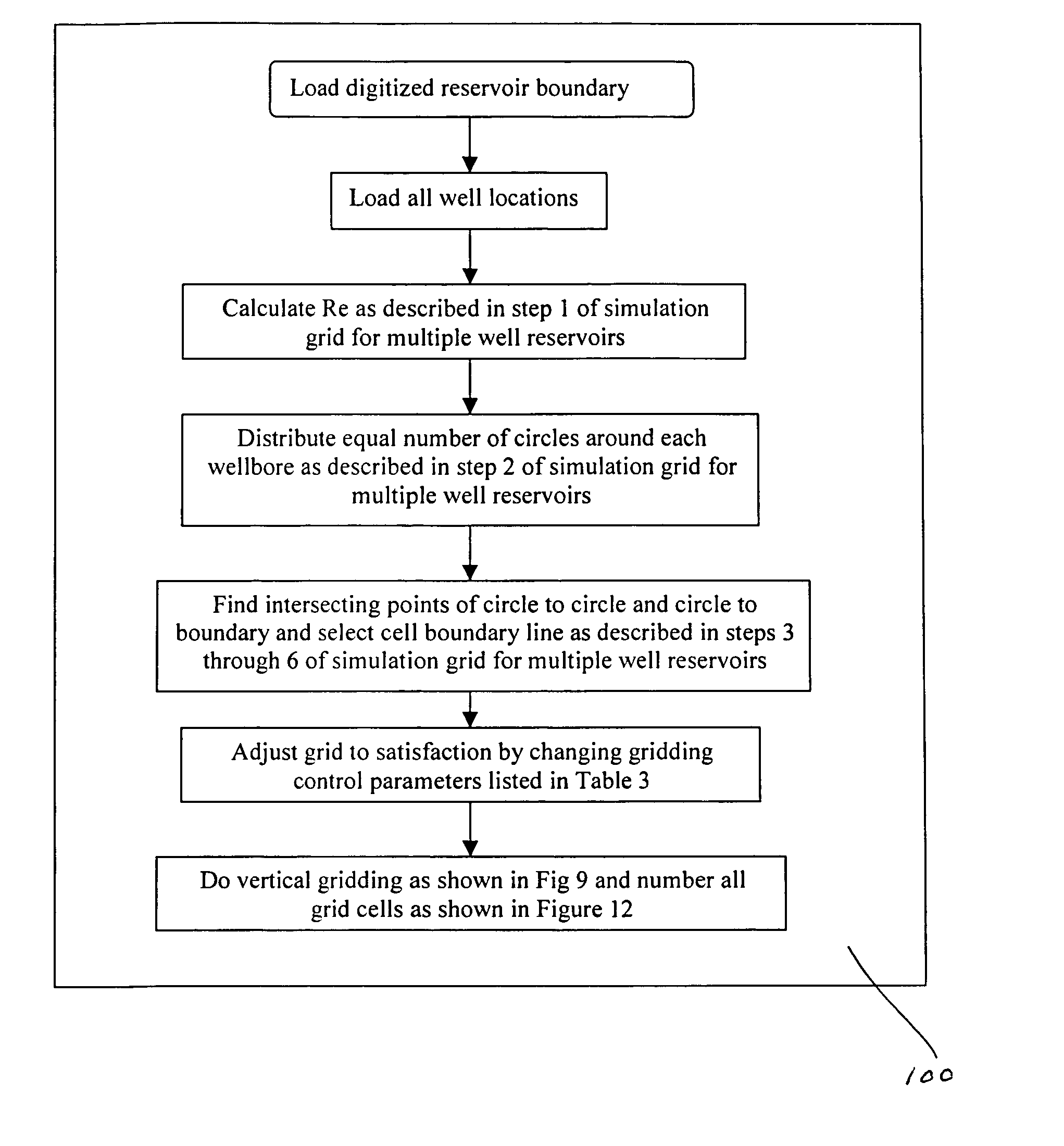
Method for producing full field radial grid for hydrocarbon reservoir simulation
InactiveUS7096122B2Speed up the flowLittle involvementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingClassical mechanicsEngineering
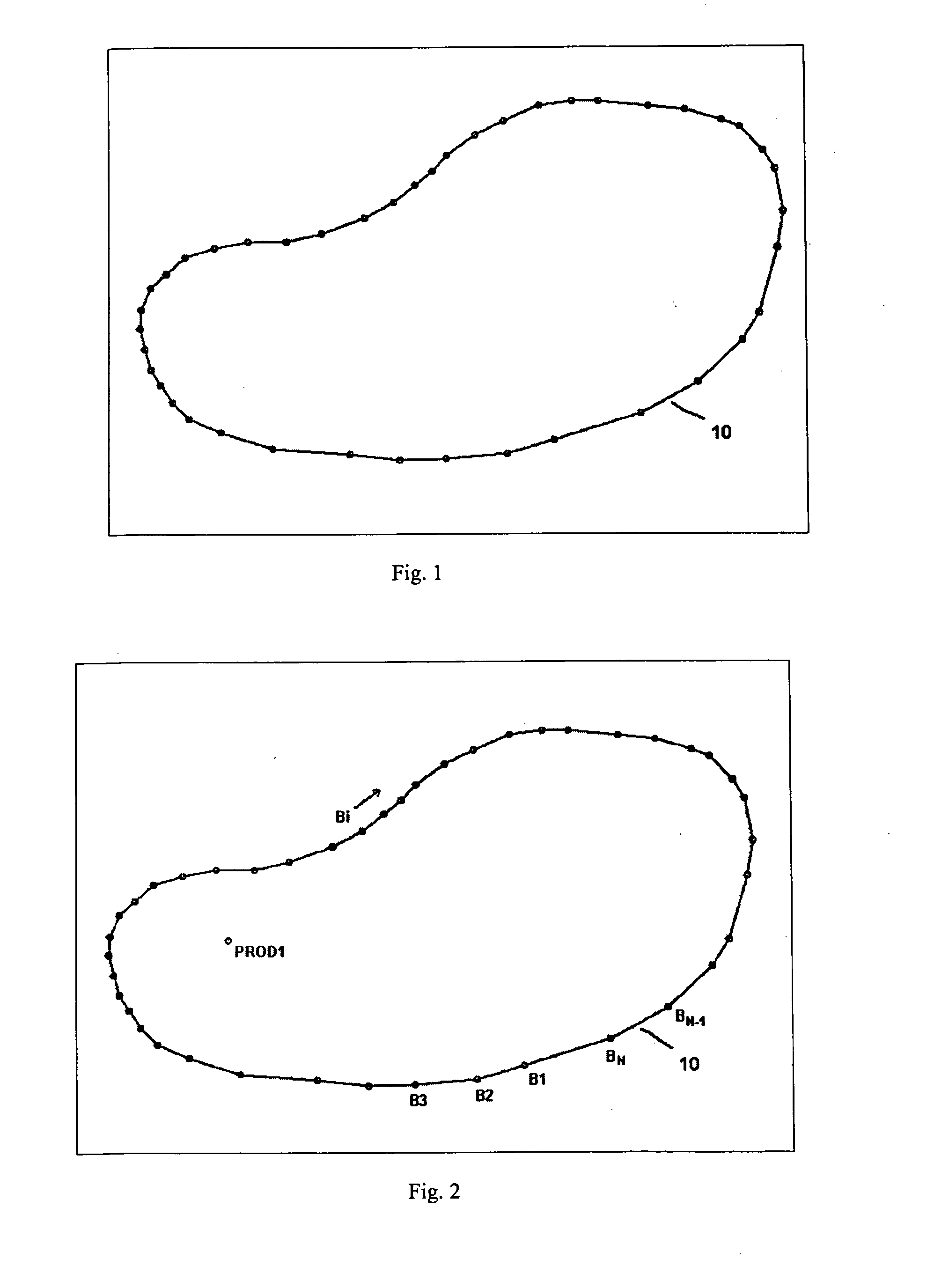
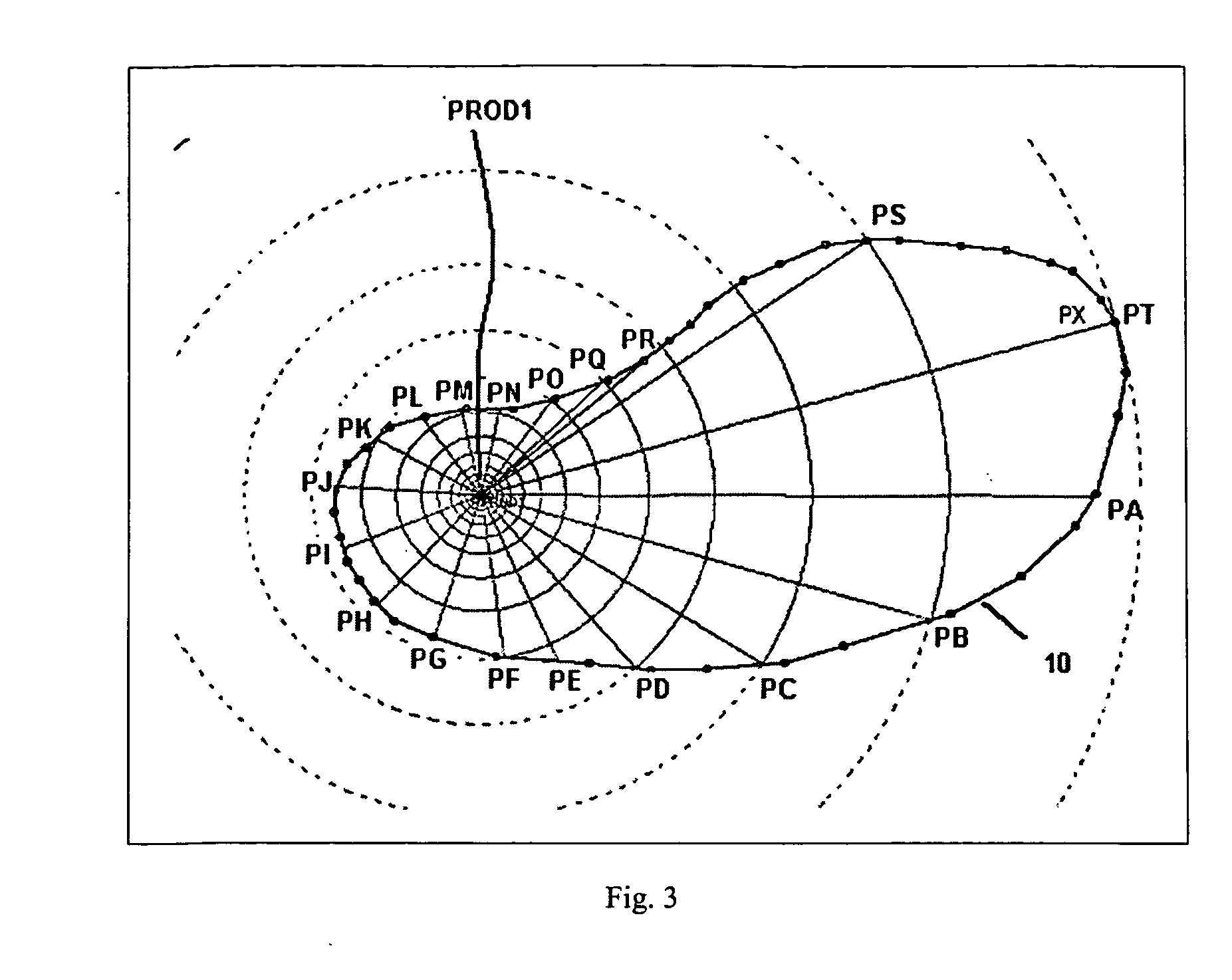
A method producing full field radial grid includes both aerial and vertical gridding to divide a reservoir structure into simulation grid cells. The aerial gridding is performed by 1) specifying a reservoir boundary (including faults) and well locations; 2) distributing a set of concentric circles around each well location; 3) determining the circle-circle and circle-boundary intersection locations of these circles; 4) forming the aerial grid by selecting circles, arc segments of intersecting circles and radial lines which connect the ends of these arc segments to the corresponding well center; 5) and forming additional grid lines by selecting the connecting lines of two wells if their circles intersect, adding additional radial lines to certain wells, and connecting end points of certain selected arc segments. The vertical gridding is performed by casting the aerial grid vertically downwardly through all the layers defined in the reservoir structure.
Owner:HAN DIANLI
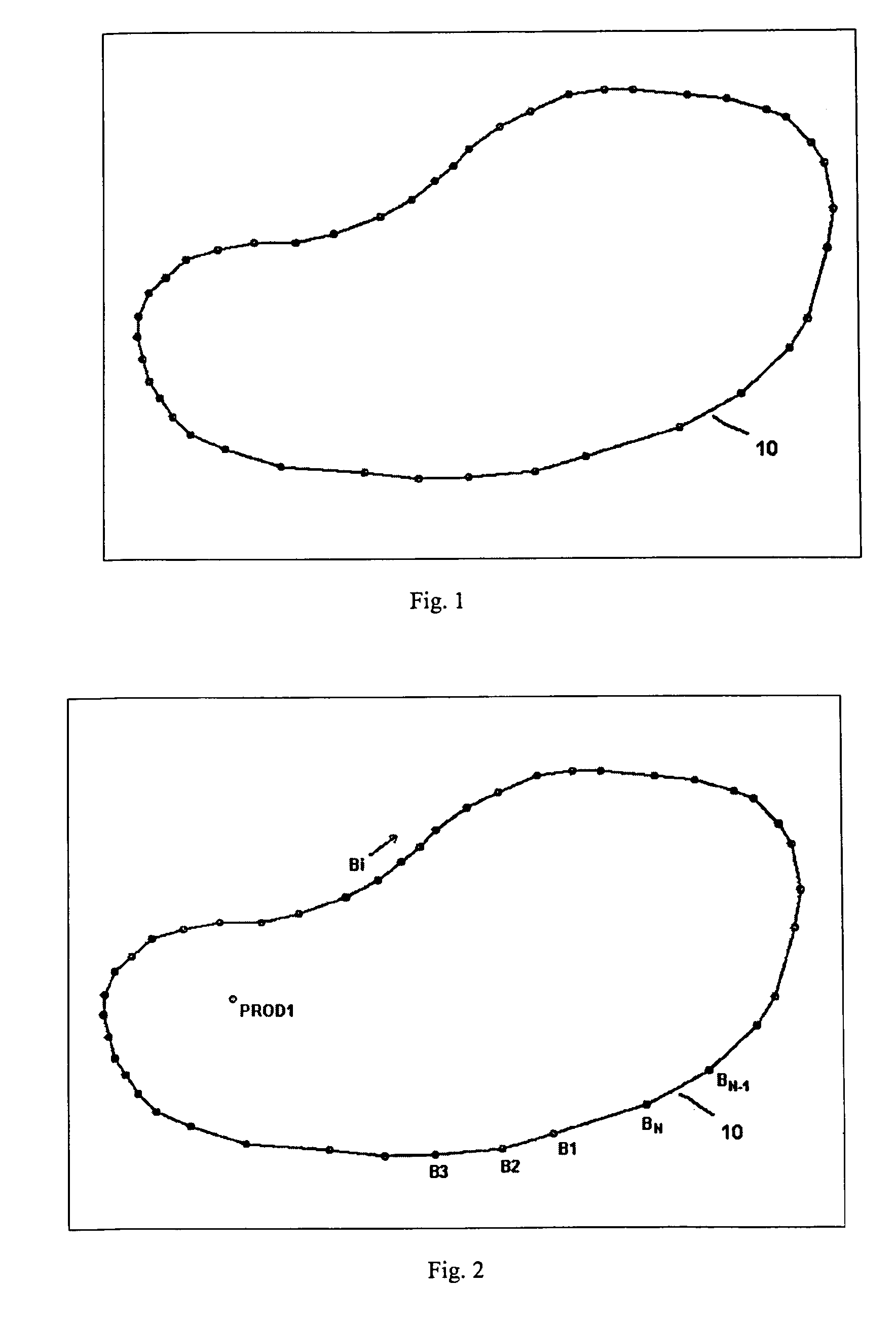
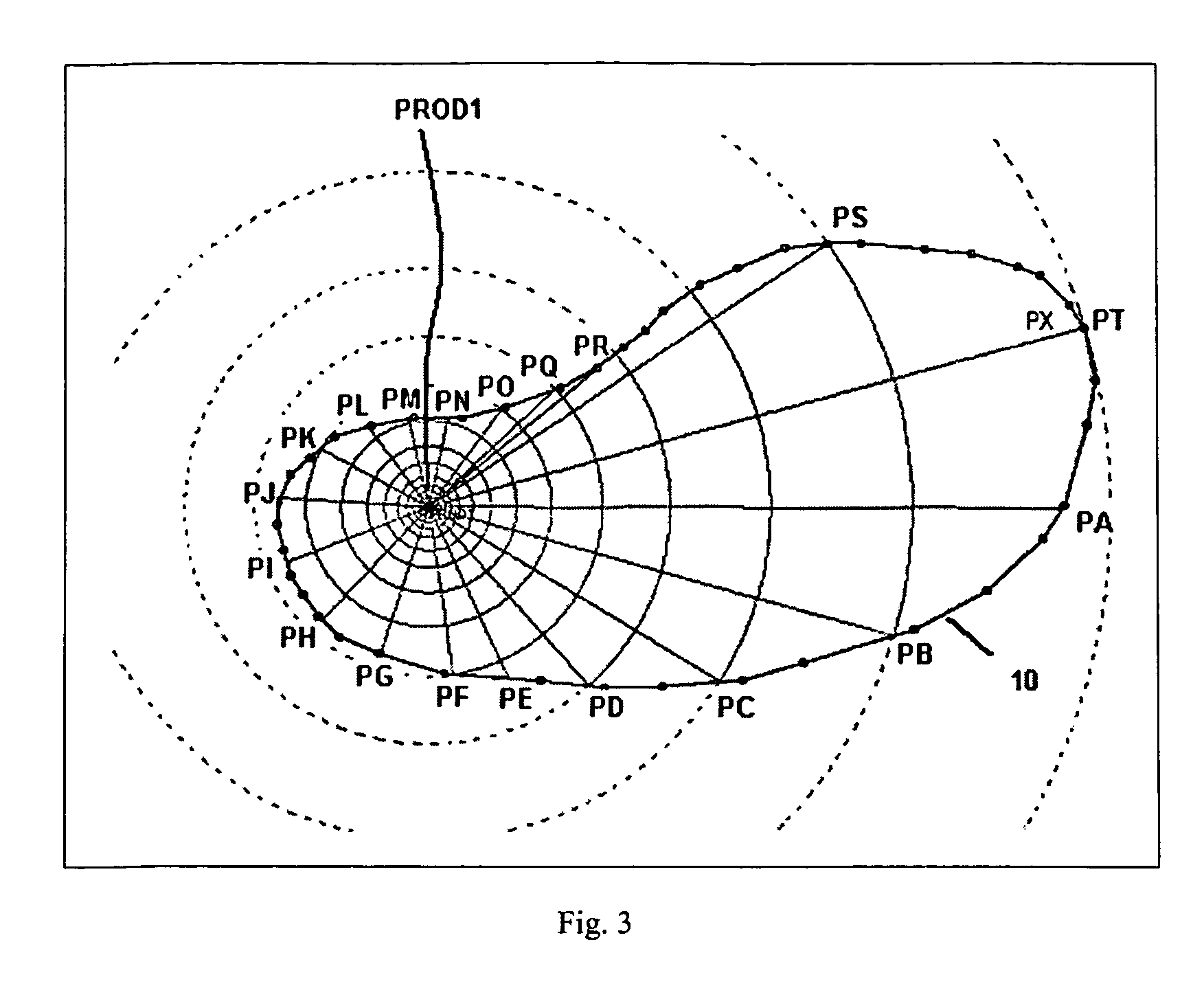
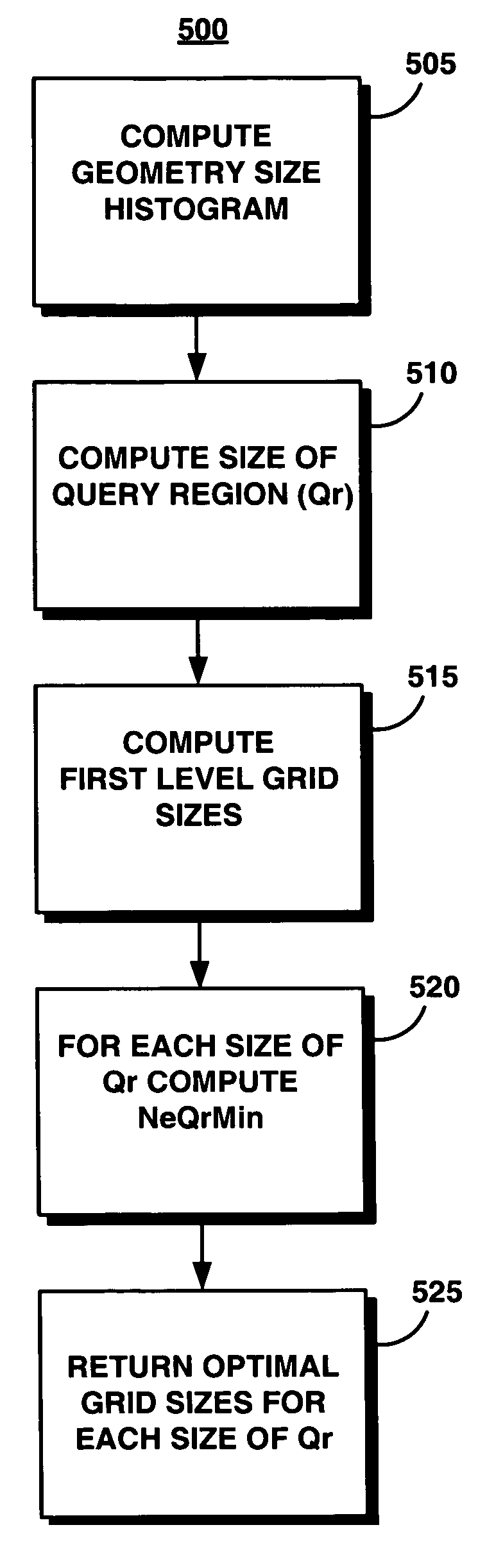
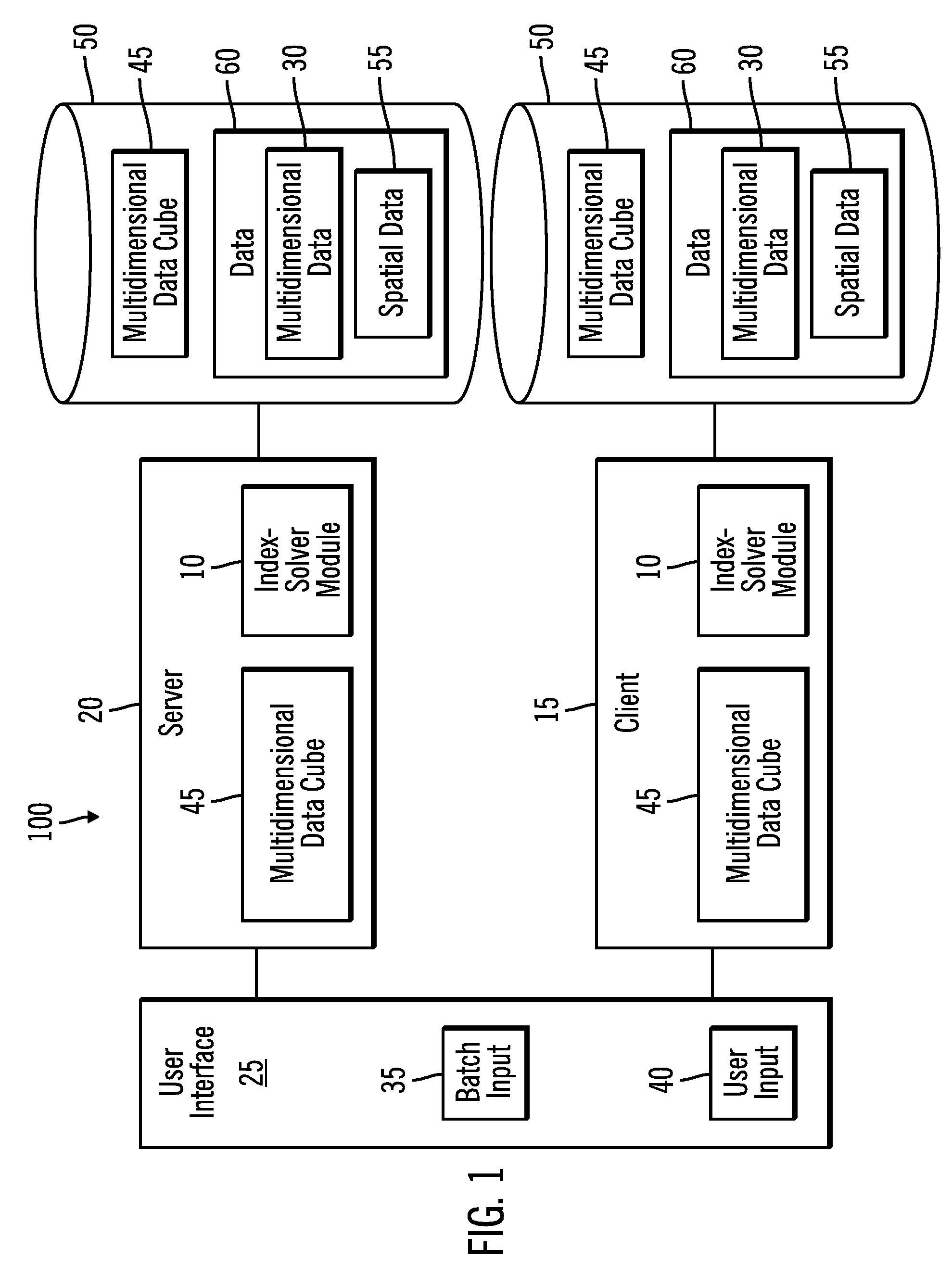
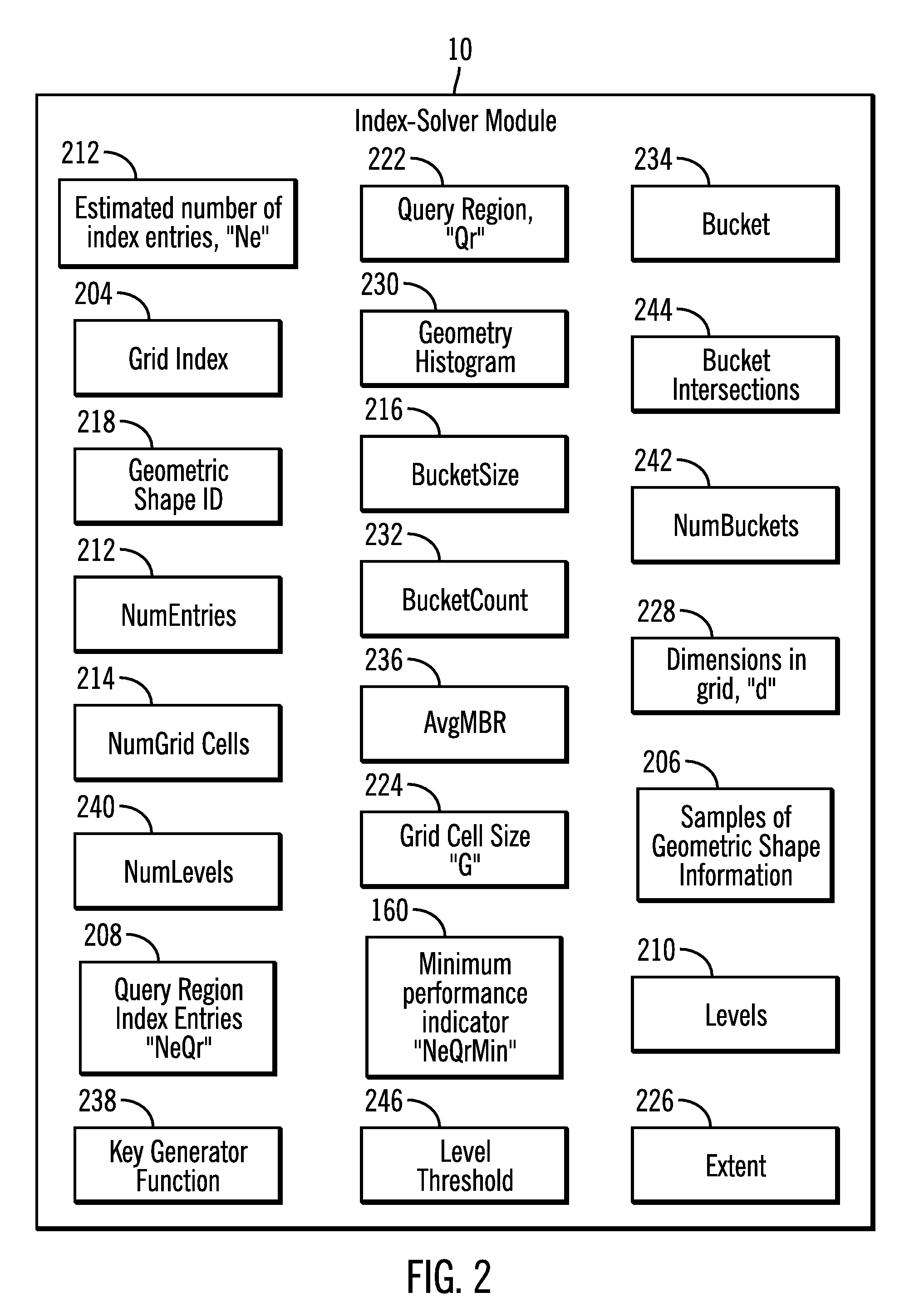
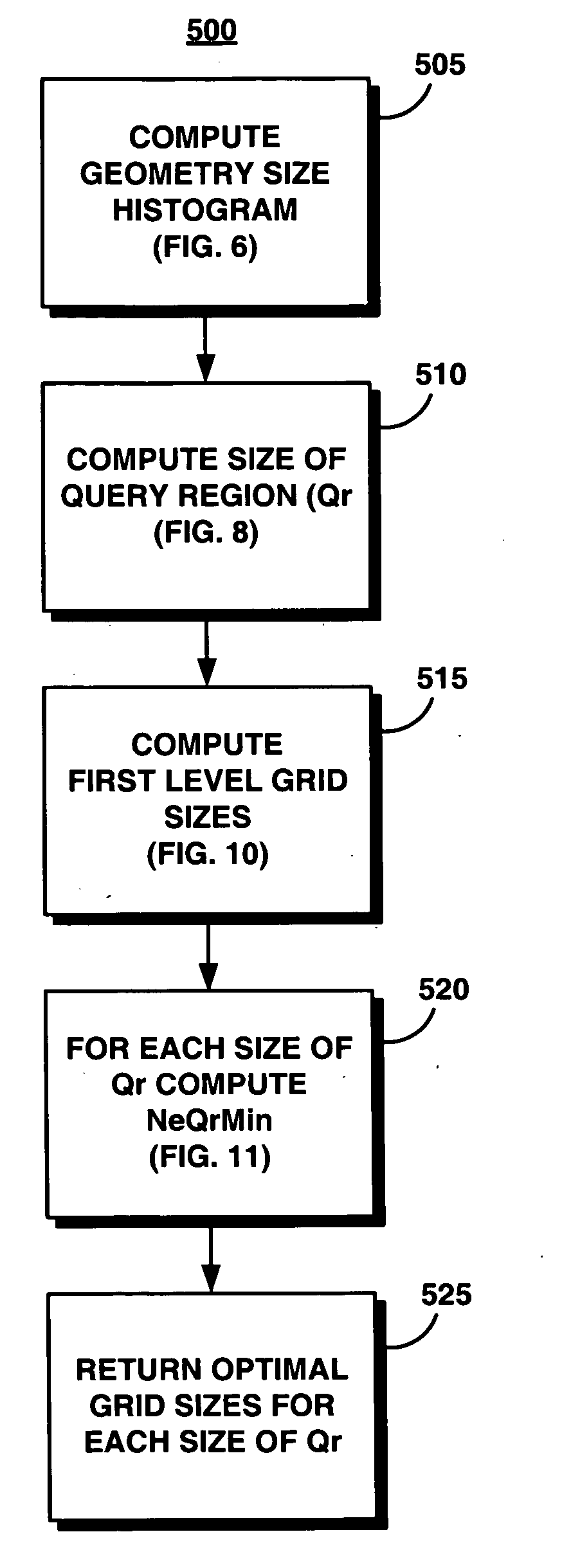
Method for determining an optimal grid index specification for multidimensional data
InactiveUS7389283B2Simple technologyProcess can be minimizedData processing applicationsRoad vehicles traffic controlData setNumber times
A system, method, and associated computer product improve the search of multidimensional databases. The present system determines a near-optimal grid index that is used to locate a geometric shape in a spatial database. More particularly, the present system improves the technique of sampling data for defining the grid cell size in a grid for a given data set, minimizing the number times the data set needs to be sampled, thereby reducing the time to compute the cost of alternative grid index parameters.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
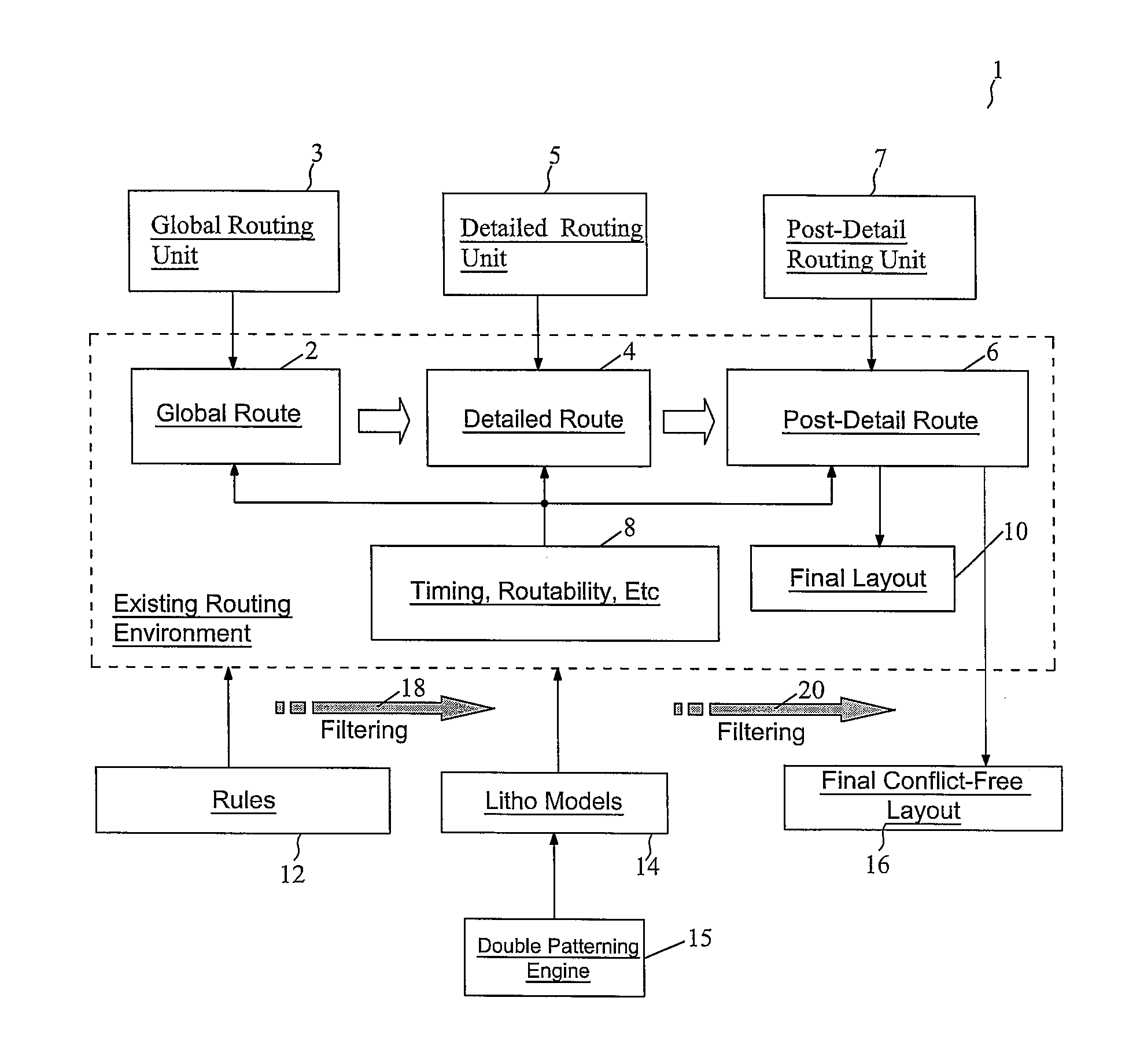
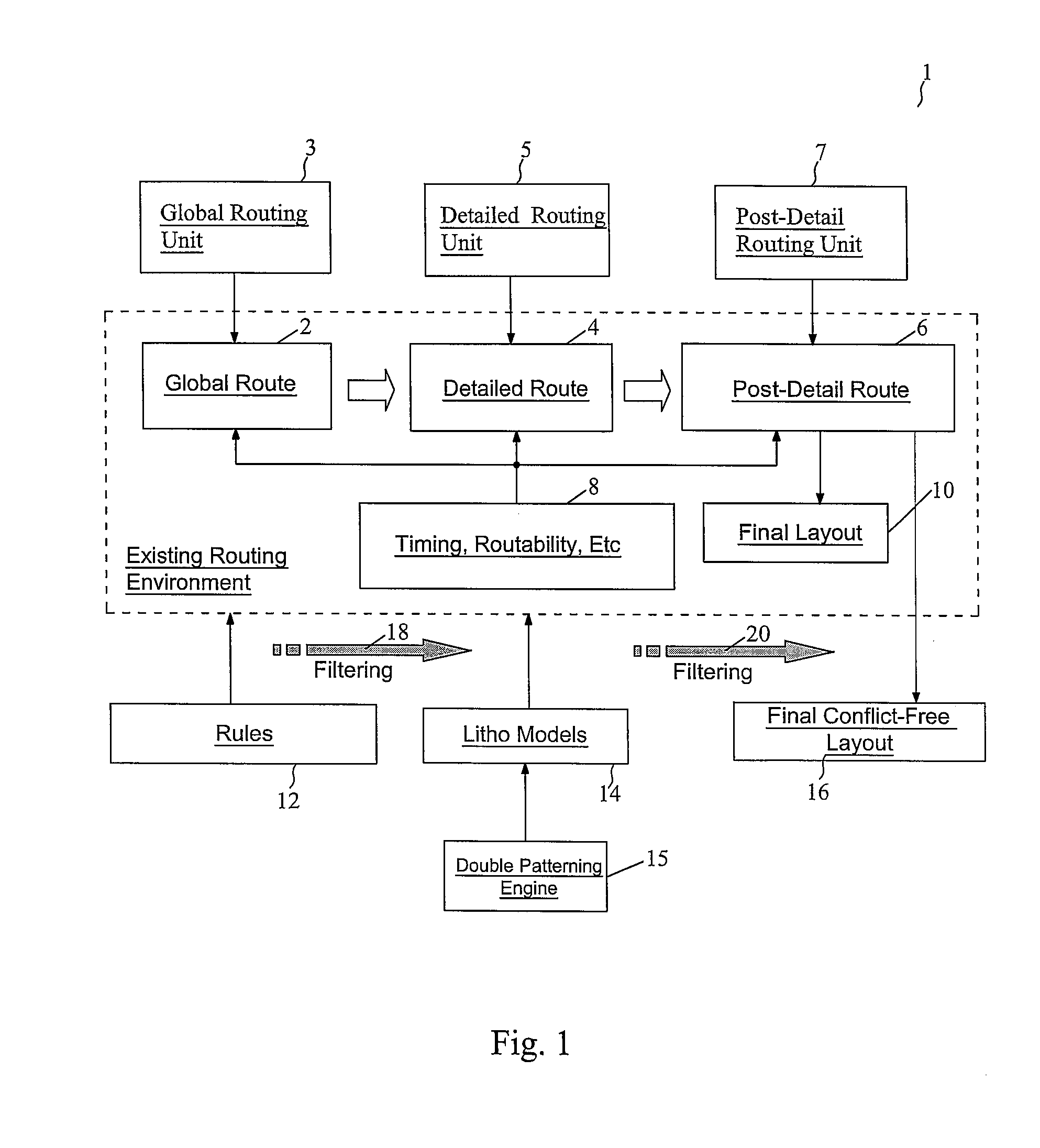
Routing Method for Double Patterning Design
ActiveUS20100199253A1Less Design WorkReduce chip areaPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentEngineeringGrid cell
A method of designing a double patterning mask set includes dividing a chip into a grid comprising grid cells; and laying out a metal layer of the chip. In substantially each of the grid cells, all left-boundary patterns of the metal layer are assigned with a first one of a first indicator and a second indicator, and all right-boundary patterns of the metal layer are assigned with a second one of the first indicator and the second indicator. Starting from one of the grid cells in a row, indicator changes are propagated throughout the row. All patterns in the grid cells are transferred to the double patterning mask set, with all patterns assigned with the first indicator transferred to a first mask of the double patterning mask set, and all patterns assigned with the second indicator transferred to a second mask of the double patterning mask set.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
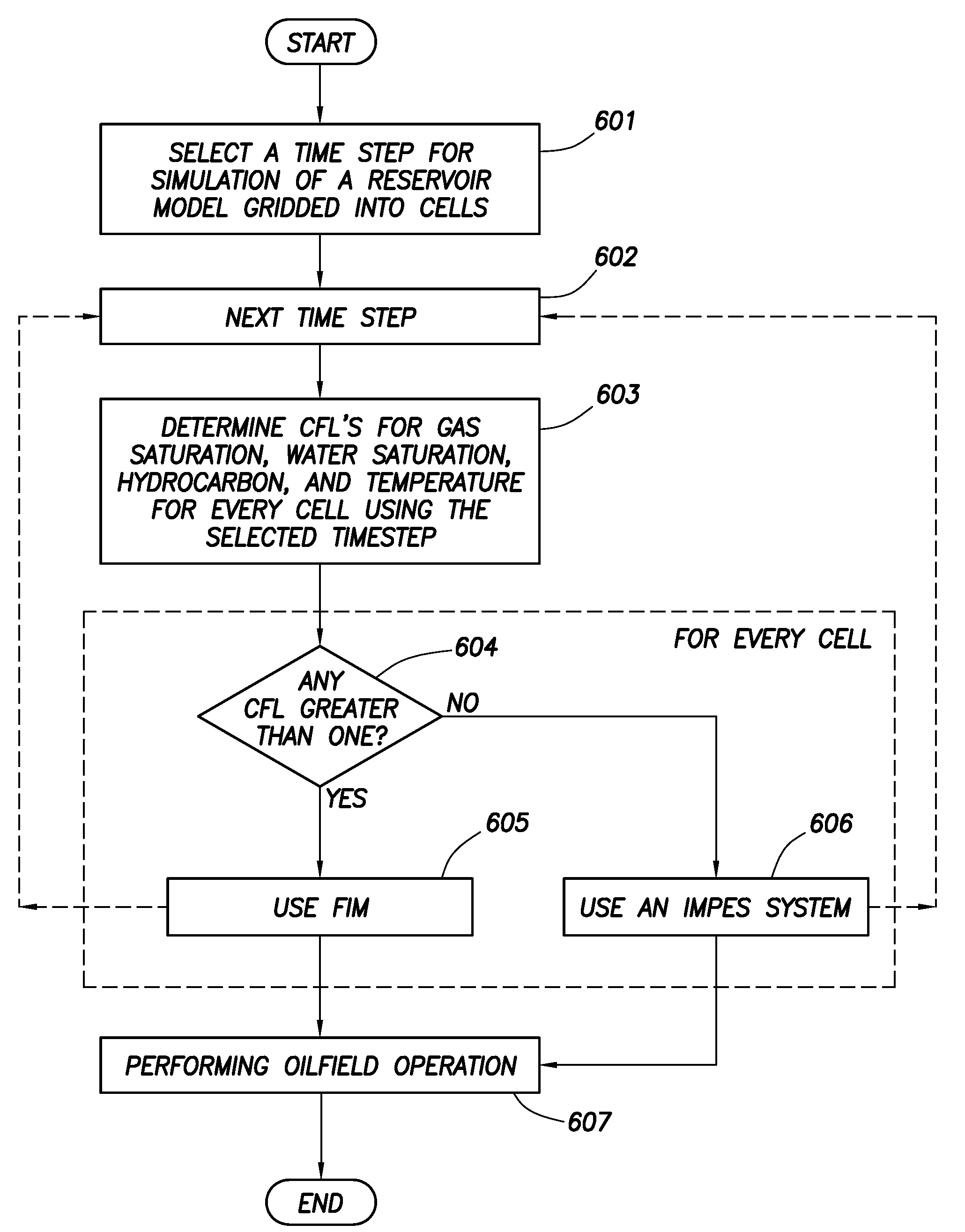
System and method for performing oilfield simulation operations
ActiveUS20090055141A1Easy to use computerReducing time-stepElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalPartial differential equationOil field
The invention relates to a method of performing an oilfield operation of an oilfield having at least one wellsite, each wellsite having a wellbore penetrating a subterranean formation for extracting fluid from an underground reservoir therein. The method includes determining a time-step for simulating the reservoir using a reservoir model, the reservoir being represented as a plurality of gridded cells and being modeled as a multi-phase system using a plurality of partial differential equations, calculating a plurality of Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy (CFL) conditions of the reservoir model corresponding to the time-step, the plurality of CFL conditions being calculated for each of the plurality of gridded cells and comprising a temperature CFL condition, a composition CFL condition, and a saturation CFL condition calculated concurrently, simulating a first cell of the plurality of gridded cells using the reservoir model with an Implicit Pressure, Explicit Saturations (IMPES) system to obtain a first simulation result, the first cell having no CFL condition of the plurality of CFL conditions with a value greater than one, and simulating a second cell of the plurality of gridded cells using the reservoir model with a Fully Implicit Method (FIM) system to obtain a second simulation result, the second cell having at least one CFL condition of the plurality of CFL conditions with a value greater than one, and performing the oilfield operation based on the first and second simulation results.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP +2
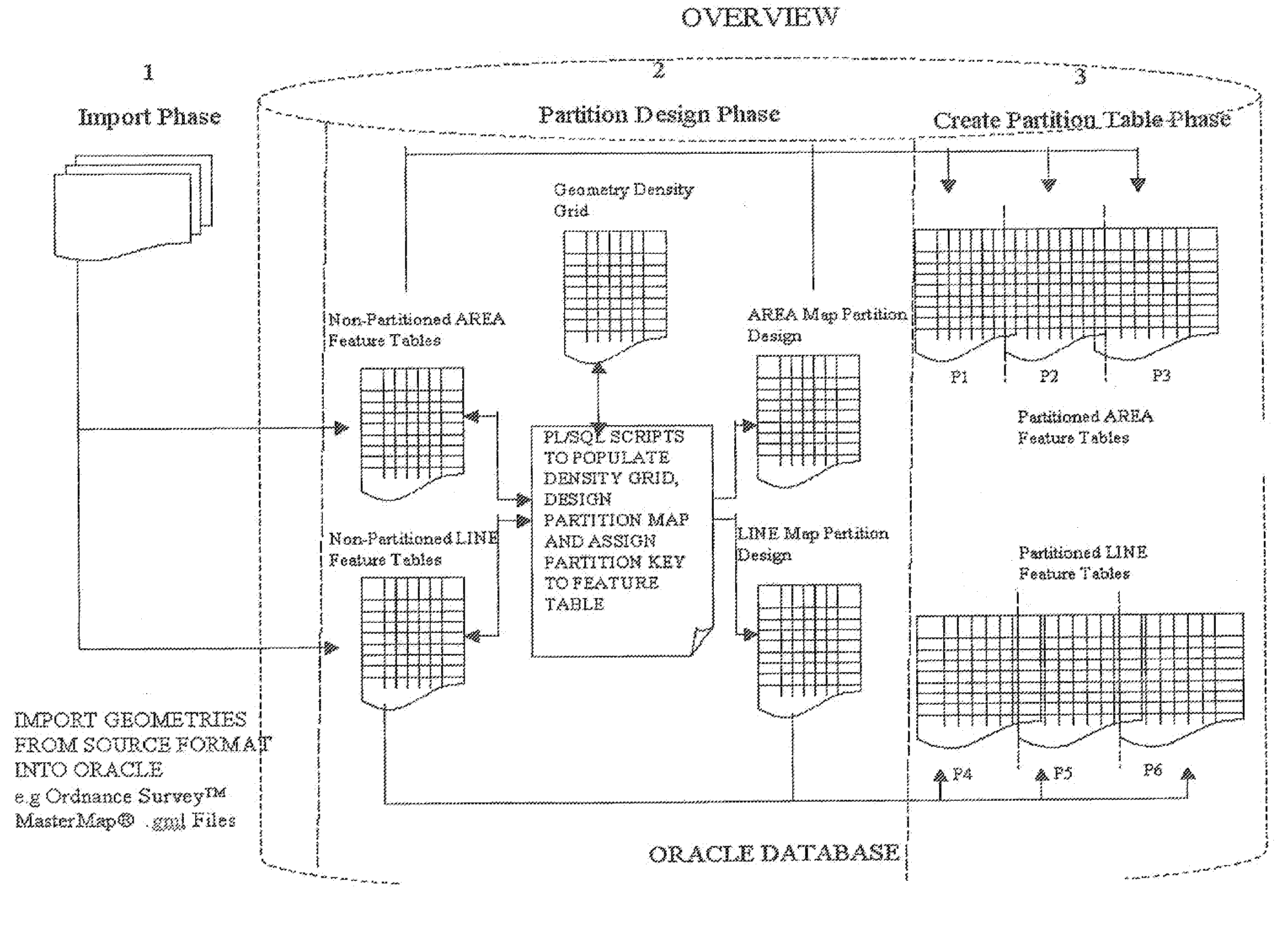
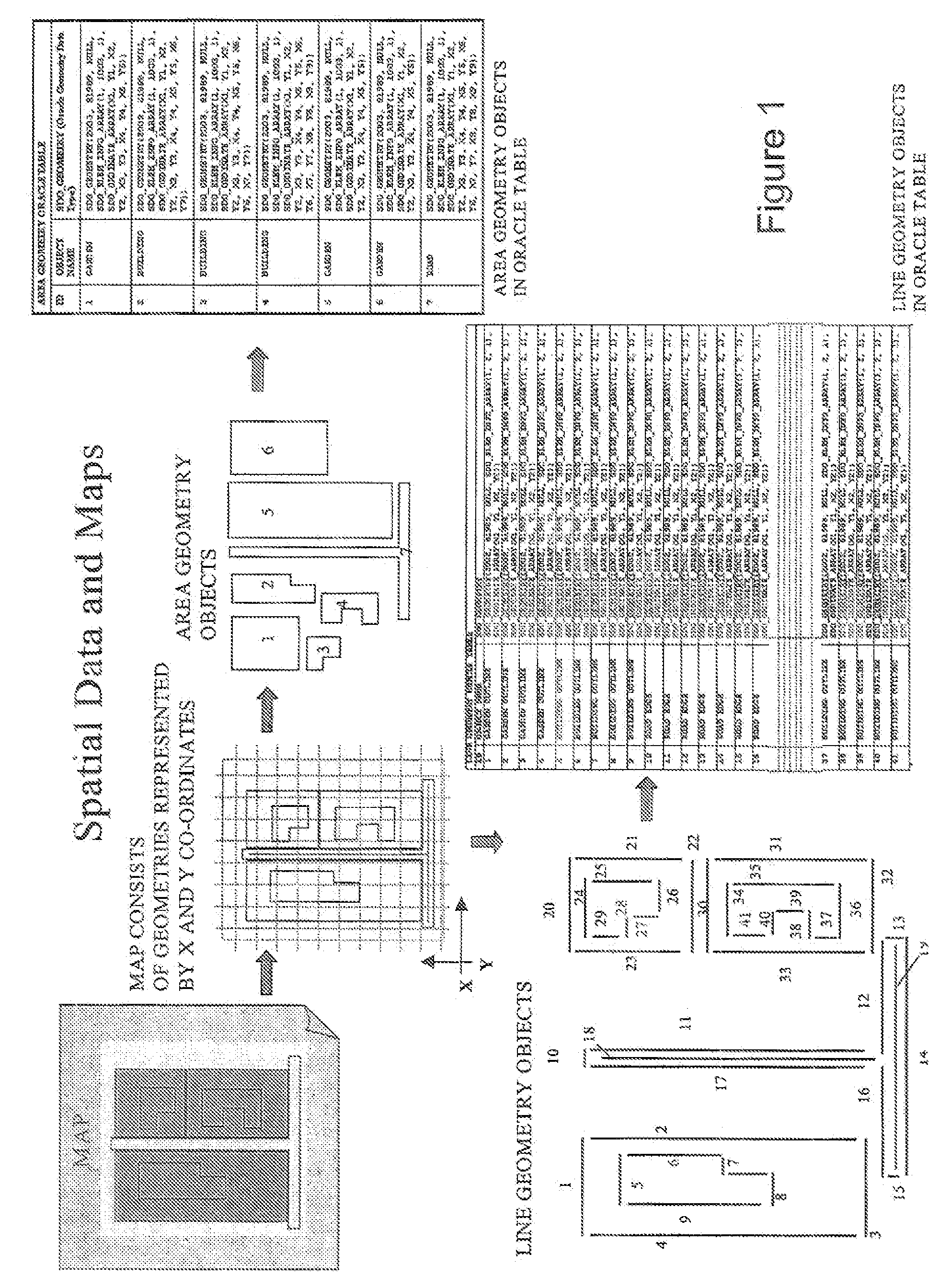
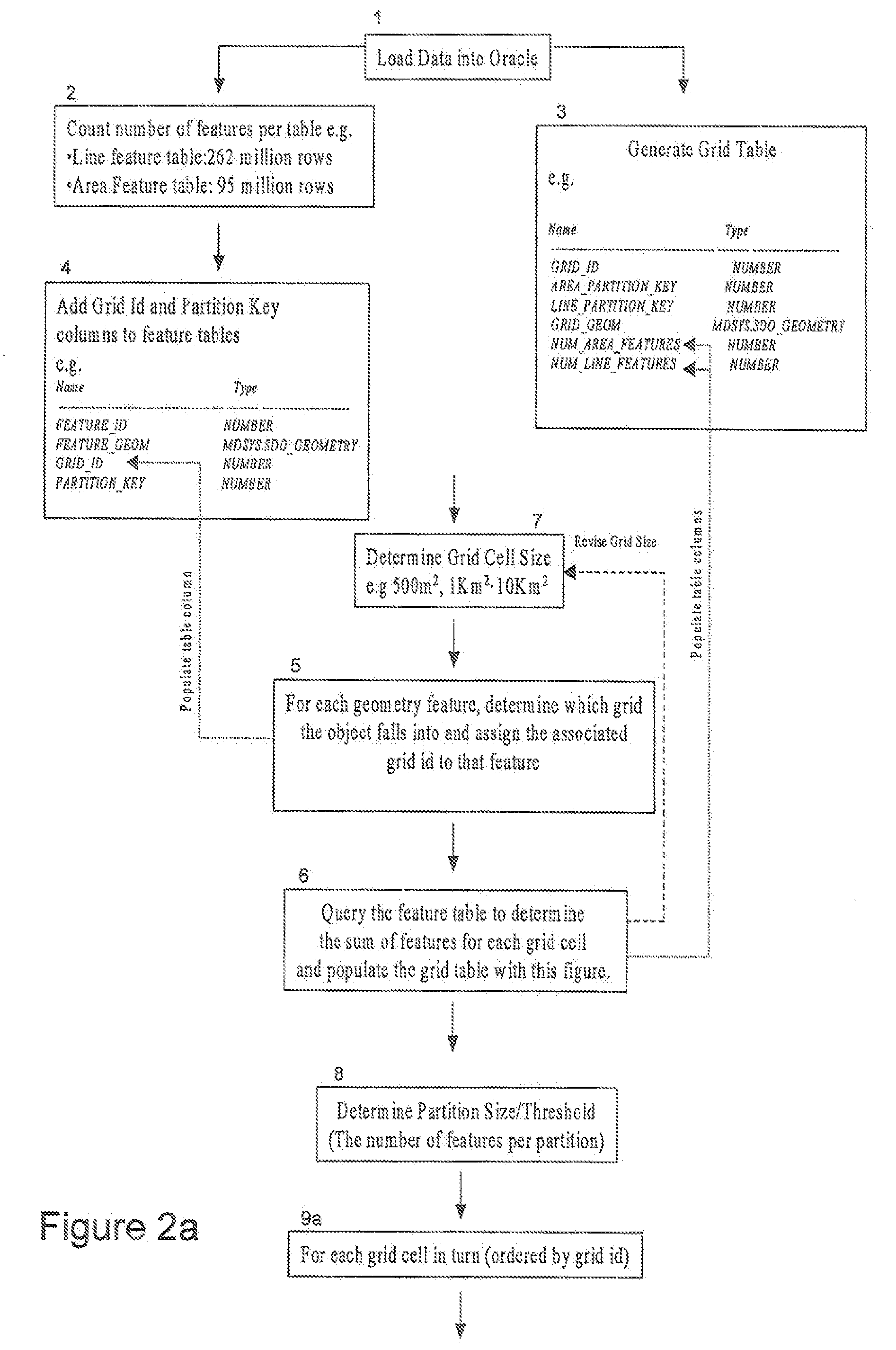
Data Partitioning Systems
InactiveUS20080228783A1Optimize allocationEasy to determineGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial partitionData mining
This invention generally relates to methods, systems, data structures and computer program code for managing spatial data, in particular very large volumes of data such as map data for a region or country. Thus we describe a method of partitioning a database of spatial data, the database including a plurality of spatial feature objections, the method comprising: reading data from said database grid cell-by-grid cell, a said grid cell comprising a cell of a grid spatially subdividing a region of spatial coverage of said database, each said grid cell including spatial feature objects; and determining a set of spatial partitions for said database, each grid cell being allocated to a said partition, responsive to a number of said spatial feature objects in each said grid cell.
Owner:1 SPATIAL GRP
Top-emitting nitride-based light-emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050199888A1High light transmittanceReduce sheet resistanceElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesMicrometerOhmic contact
A top-emitting nitride-based light-emitting device and a method of manufacturing the same. The top-emitting nitride-based light-emitting device having a substrate, an n-cladding layer, an active layer, and a p-cladding layer sequentially formed includes: a grid cell layer formed on the p-cladding layer by a grid array of separated cells formed from a conducting material with a width of less than 30 micrometers to improve electrical and optical characteristics; a surface protective layer that is formed on the p-cladding layer and covers at least regions between the cells to protect a surface of the p-cladding layer; and a transparent conducting layer formed on the surface protective layer and the grid cell layer using a transparent conducting material. The light-emitting device and the method of manufacturing the same provide an improved ohmic contact to the p-cladding layer, excellent I-V characteristics, and high light transmittance, thus increasing luminous efficiency of the device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Road network grid matching, road status messages and introduction route information acquisition method
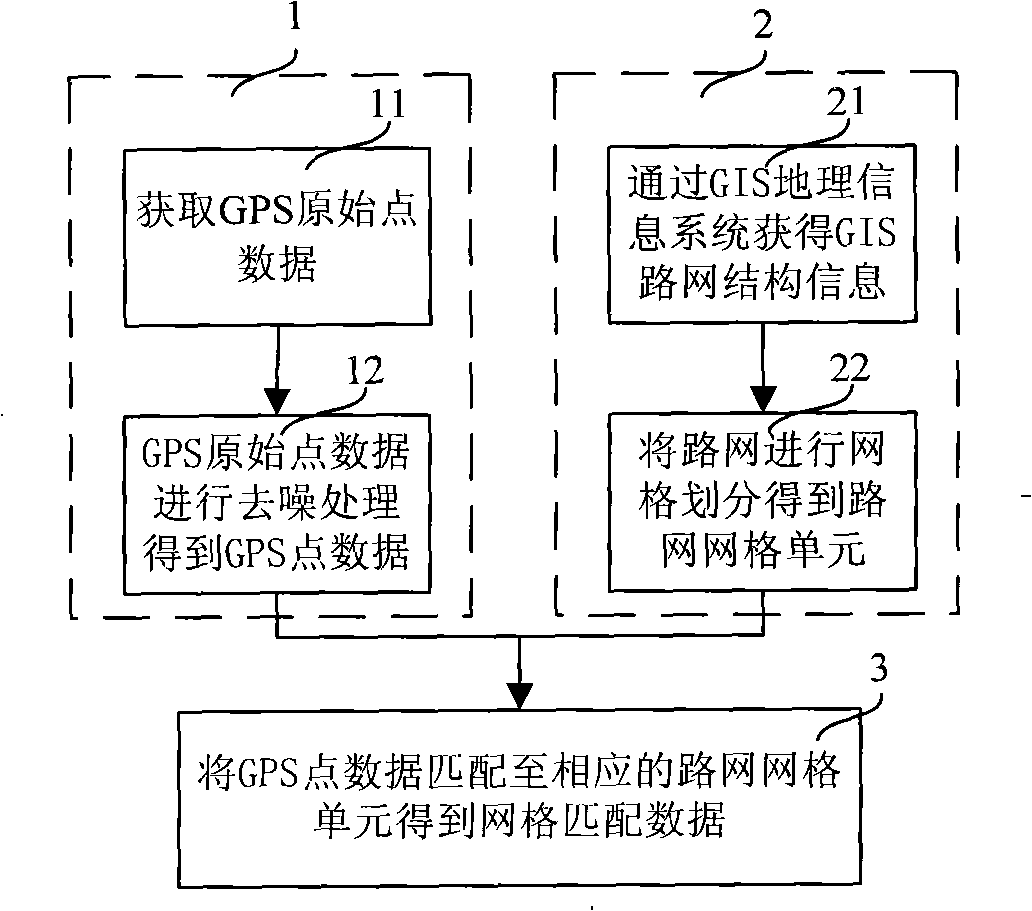
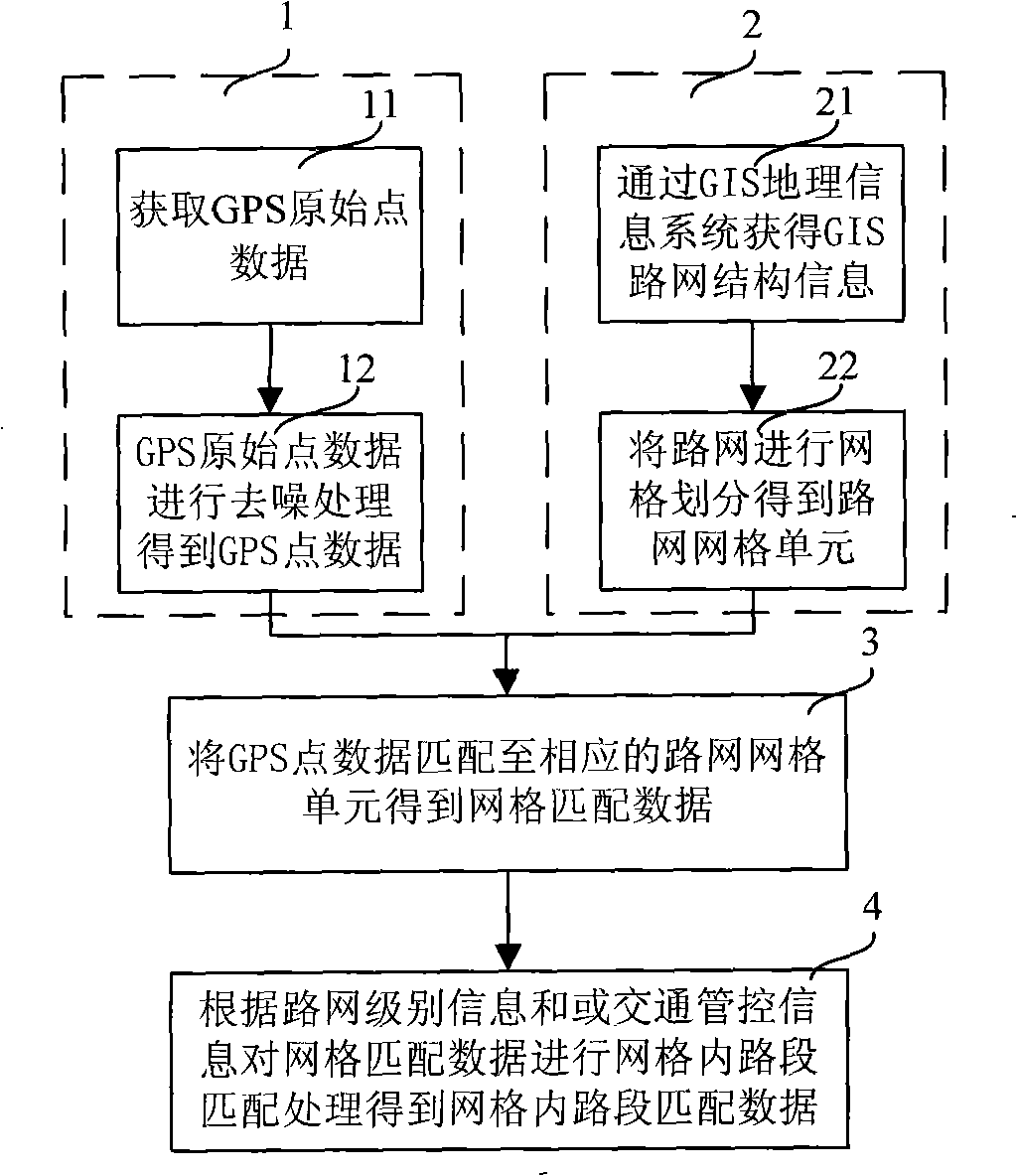
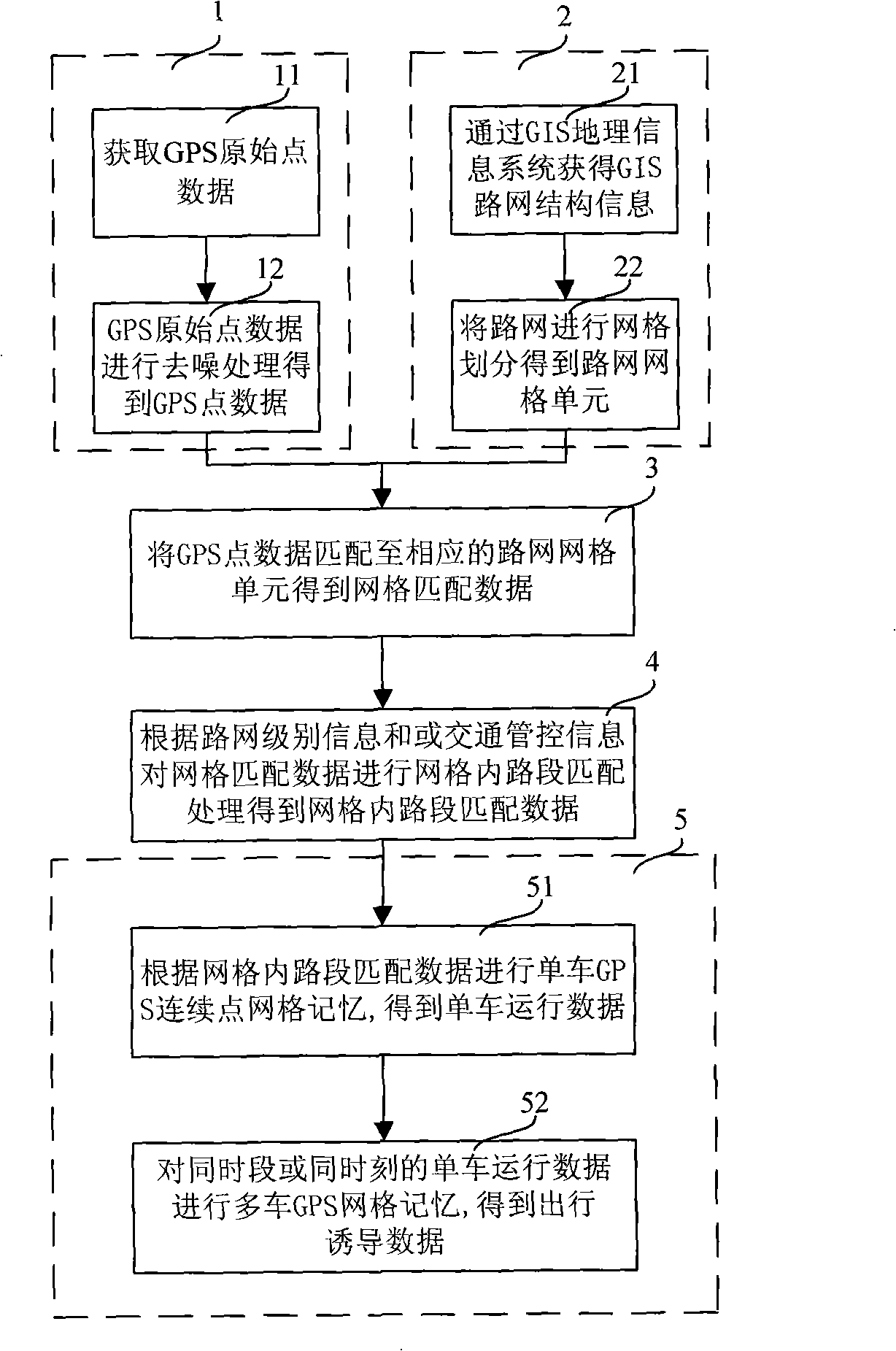
InactiveCN101308029AReal-time processingEfficient acquisitionInstruments for road network navigationSpecial data processing applicationsData matchingRoad networks
The invention relates to a road network grid matching method, which comprises: obtaining GPS original point data and de-noising the GPS original point data to gain GPS point data; partitioning the road network into grids according to the GIS road network structure information to get road network grid units; and matching the GPS point data to the corresponding road network grid units to obtain grid matching data. The invention also relates to an information acquisition method for real-time road conditions, which comprises: matching road network grids to get grid matching data; integrating the grid matching data with GPS traffic flow data; and filtering the integrated data according to types of driving routes to obtain the information of real-time road conditions. The invention provides theroad network grid matching method based on the GPS road network grid partitioning technique aiming at large concurrent GPS data for achieving real-time treatment of the large concurrent GPS data; andacquires information of real-time road conditions and real-time guiding routes by using the road network grid matching method.
Owner:科进英华(北京)智能交通技术有限公司
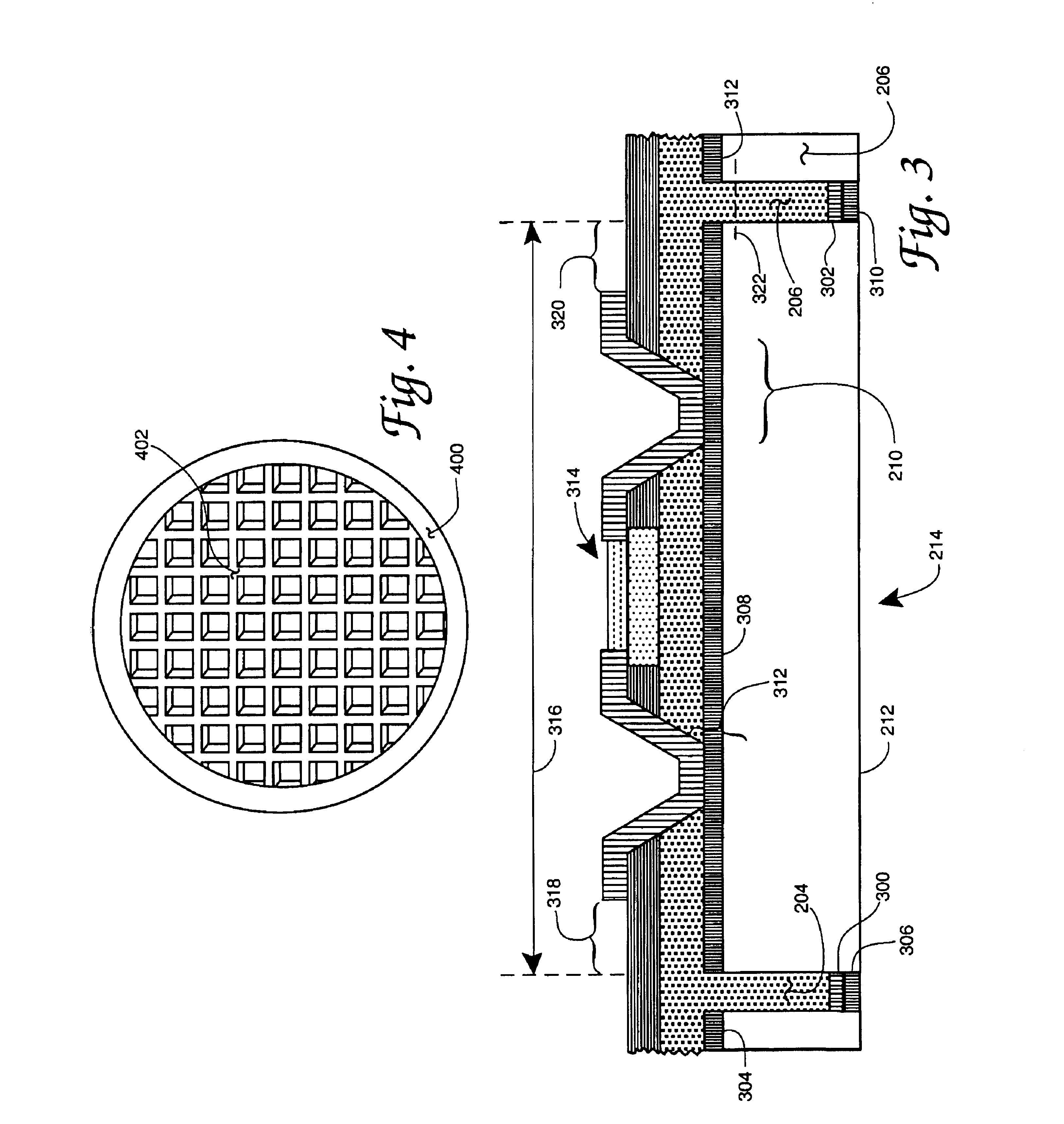
Stiffened backside fabrication for microwave radio frequency wafers
InactiveUS6884717B1Less fragileNot easy to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingSemiconductor materials
An etching based semiconductor wafer thinning arrangement usable as an improved alternative to the usual grinding and polishing wafer thinning. The thinned wafer includes a structurally enhancing wafer backside grid array of original wafer thickness semiconductor material with grid cells surrounding individual thinned wafer areas and serving to improve the strength and physical rigidity characteristics of the thinned wafer. Preferably this grid array is supplemented with an additional, wafer periphery-located, backside ring of semiconductor material also of original wafer thickness. Ability to avoid a wafer front side mounting during thinning accomplishment, fast etching, reduced wafer breakage, enhanced wafer strength and improved wafer handling achieved with the disclosed thinning arrangement all contribute to achieved advantages over conventional wafer thinning. Gallium arsenide or other semiconductor materials are contemplated along with use in radio frequency or other integrated circuit devices of either the single transistor or complete integrated circuit components types.
Owner:SANDVIK AB +1
Method for characterizing the fracture network of a fractured reservoir and method for developing it
ActiveUS20120116740A1Minimize the differenceFluid removalAnalogue computers for fluid flowGeomorphologyEllipse
The invention is a method for constructing a representation of a fluid reservoir traversed by a fracture network and by at least one well. The reservoir is discretized into a set of grid cells and the fractures are characterized by statistical parameters from observations of the reservoir. An equivalent permeability tensor and an average fracture opening is constructed from an image representative of the fracture network delimiting porous blocks and fractures is then deduced from the statistical parameters. A first elliptical boundary zone centered on the well and at least a second elliptical boundary zone centered on the well which form an elliptical ring with the elliptical boundary of the first zone are defined around the well. The image representative of the fracture network is simplified in a different manner for each of the zones which is used to construct the representation of the fluid reservoir.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Ray shooting method utilizing geometrical stencils
ActiveUS20140375641A1Effective trackingCut down high traversalDetails involving 3D image dataProgram controlVisibilityViewpoints
Aspects comprise a ray shooting method based on the data structure of a uniform grid of cells, and on local stencils in cells. The high traversal and construction costs of accelerating structures are cut down. The object's visibility from the viewpoint and from light sources, as well as the primary workload and its distribution among cells, are gained in the preprocessing stage and cached in stencils for runtime use. In runtime, the use of stencils allows a complete locality at each cell, for load balanced parallel processing.
Owner:SNAP INC
System and method for determining an optimal grid index specification for multidimensional data
InactiveUS20060129529A1Simple technologyProcess can be minimizedRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsData setNumber times
A system, method, and associated computer product improve the search of multidimensional databases. The present system determines a near-optimal grid index that is used to locate a geometric shape in a spatial database. More particularly, the present system improves the technique of sampling data for defining the grid cell size in a grid for a given data set, minimizing the number times the data set needs to be sampled, thereby reducing the time to compute the cost of alternative grid index parameters.
Owner:IBM CORP
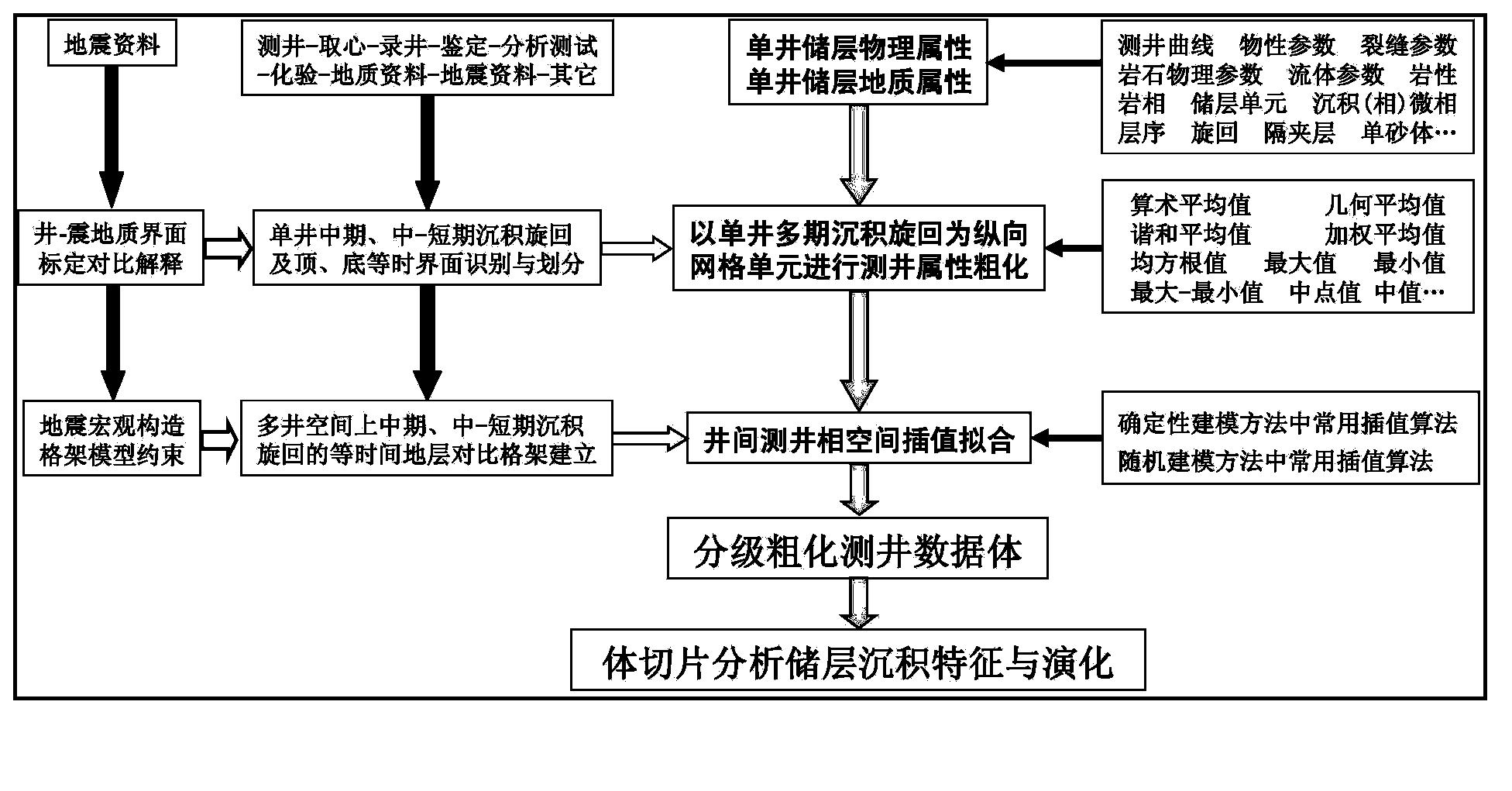
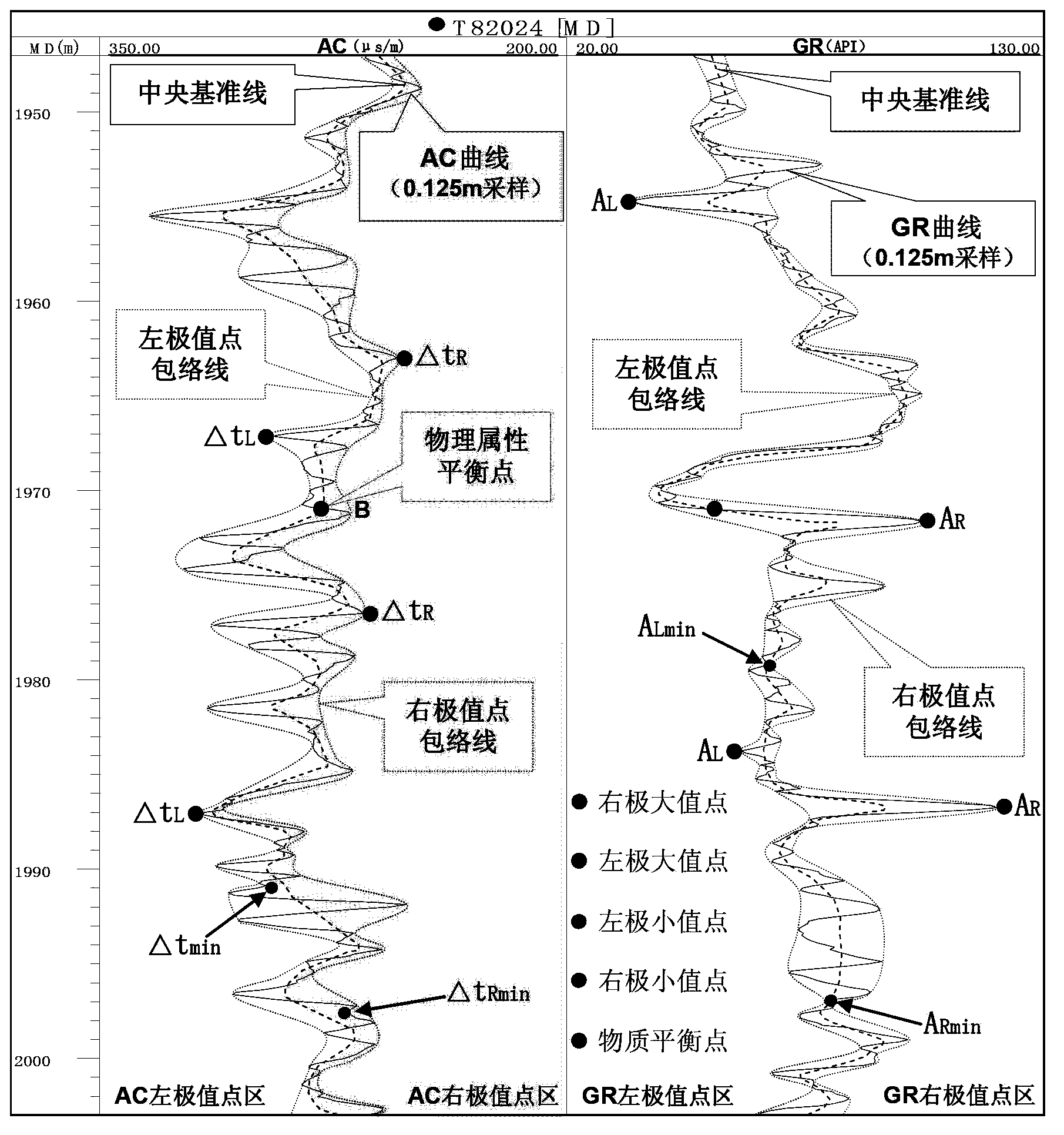
Method for determining deposition characteristics and distribution of reservoirs by combining logging and seismic information
The invention is a method for determining deposition characteristics and distribution of reservoirs by combining logging and seismic information. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of single-well middle-term and middle-short-term deposition cycle division, inter-well fitting is carried out on a deposition cycle interface, correction is carried out with the use of a seismic structural surface, and the trend surfaces of top-bottom interfaces of corresponding grid cells are obtained; and logging attribute parameters in grid cells in the vertical direction are roughly calculated to obtain a unique logging data thinning value, the minimum well spacing of a work area is selected as the step length of the lateral extrapolation distance, and inter-well interpolation and fitting are carried out to obtain a three-dimensional hierarchical coarsening logging data volume reflecting well logging facies or deposition characteristics of reservoirs. According to the method of the invention, single-well reservoir vertical grid dissection in three-dimensional reservoir geological modeling and multi-phase inferior time deposition cycle structure and frame in geo-science, an inside-grid logging attribute sampling point coarsening technology and a geological method, and the single-well-point vertical grid thinning logging attribute value and a multi-well spatial interpolation algorithm are closely combined so as to obtain a three-dimensional hierarchical coarsening analysis data volume capable of reflecting well logging facies or deposition characteristics and change of reservoirs, thus realizing matching and comparative interpretation on the basis of closely combining logging and seismic data.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
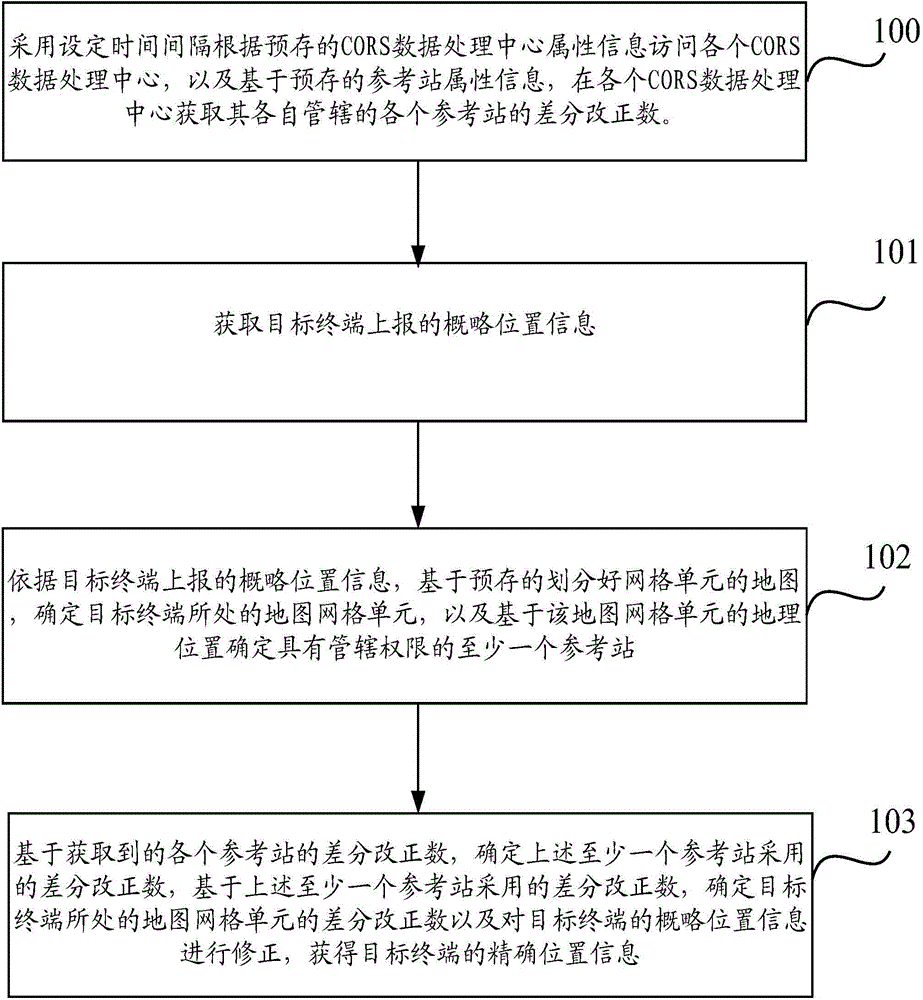
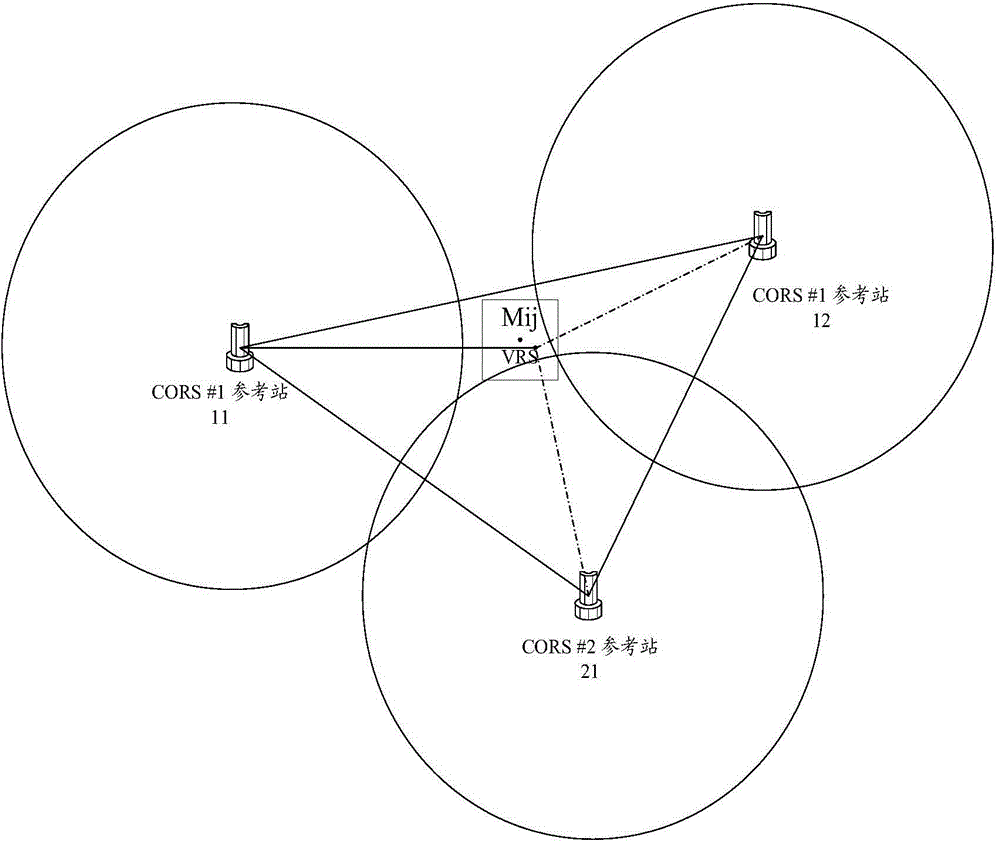
Method and system used for providing position information
The invention discloses a method and a system used for providing position information, which can be used to solve the problem of the prior art of the inability of realizing the large-scale high-precision real-time positioning. The method is characterized in that the access to various CORS data processing centers can be realized by adopting a set time interval according to pre-stored CORS data processing center attribute information, and the differential correction values of various reference stations belonging to the CORS data processing centers can be acquired; approximate position information reported by a target terminal can be acquired; the map grid cell of the target terminal can be determined based on the pre-stored map having the divided grid cells according to the approximate position information reported by the target terminal; according to the acquired differential correction values of various reference stations, the differential correction value of the map grid cell of the target terminal can be determined, and the approximate position information of the target terminal can be corrected, and then the accurate position information of the target terminal can be acquired, and therefore the high-precision real-time positioning of the terminal can be realized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Method for producing full field radial grid for hydrocarbon reservoir simulation
InactiveUS20050021234A1Work flow easyLittle involvementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingFull fieldWork flow
A method producing full field radial grid (called here Radial-X Grid) for more accurate and efficient reservoir simulation and improving simulation work flow. The Radial-X Grid method produces both aerial and vertical gridding to divide a reservoir structure into simulation grid cells. The aerial gridding is performed by 1) specifying a reservoir boundary (including faults) and well locations; 2) distributing a set of concentric circles around each well location; 3) determining the circle-circle and circle-boundary intersection locations of these circles; 4) forming the aerial grid by selecting circles, arc segments of intersecting circles and radial lines which connect the ends of these arc segments to the corresponding well center; 5) and forming additional grid lines by selecting the connecting lines of two wells if their circles intersect, adding additional radial lines to certain wells, and connecting end points of certain selected arc segments. Thus, the aerial boundary of each individual grid cell is formed from elements selected from the group of arc segment, well radial line, reservoir boundary, connection line of well to well, arc segment end to arc segment end. The vertical gridding is performed by casting the aerial grid vertically downwardly through all the layers defined in the reservoir structure. The Radial-X Grid method is advantageous for petroleum reservoir simulation applications because it is easy to use, runs fast, produces no grid orientation effect, provides efficient use of grid cells, provides precision modeling and provides better reservoir boundary and fault conformance.
Owner:HAN DIANLI
Machine, program product, and computer-implemented method to simulate reservoirs as 2.5D unstructured grids
ActiveUS8463586B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPrinted circuit aspectsComputational scienceData set
Example embodiments utilize machines to model reservoir geometry having geological layers as 2.5D unstructured grids. Example embodiments include program products to simulate a reservoir by generating a reservoir data system, performing a numerical fluid flow simulation, and visualizing the simulation. Data system embodiments include data structures to model a reservoir geometry as laterally unstructured two-dimensional (2D) grids and associated layer depths defining z-lines to thereby define a 2.5D unstructured grid, including datasets for: vertices of the grid cells for the future grid top and bottom surfaces, a number and listing of vertices for each grid cell, cell center coordinates, and vertex adjacency information using a compressed sparse row format. Computer-implemented methods include projecting external and internal boundaries onto a future grid surface; generating 2D unstructured, e.g., Voronoi, grids, for the top and bottom surfaces; and generating z-lines of depths corresponding to reservoir layers to thereby generate 2.5D unstructured grids.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
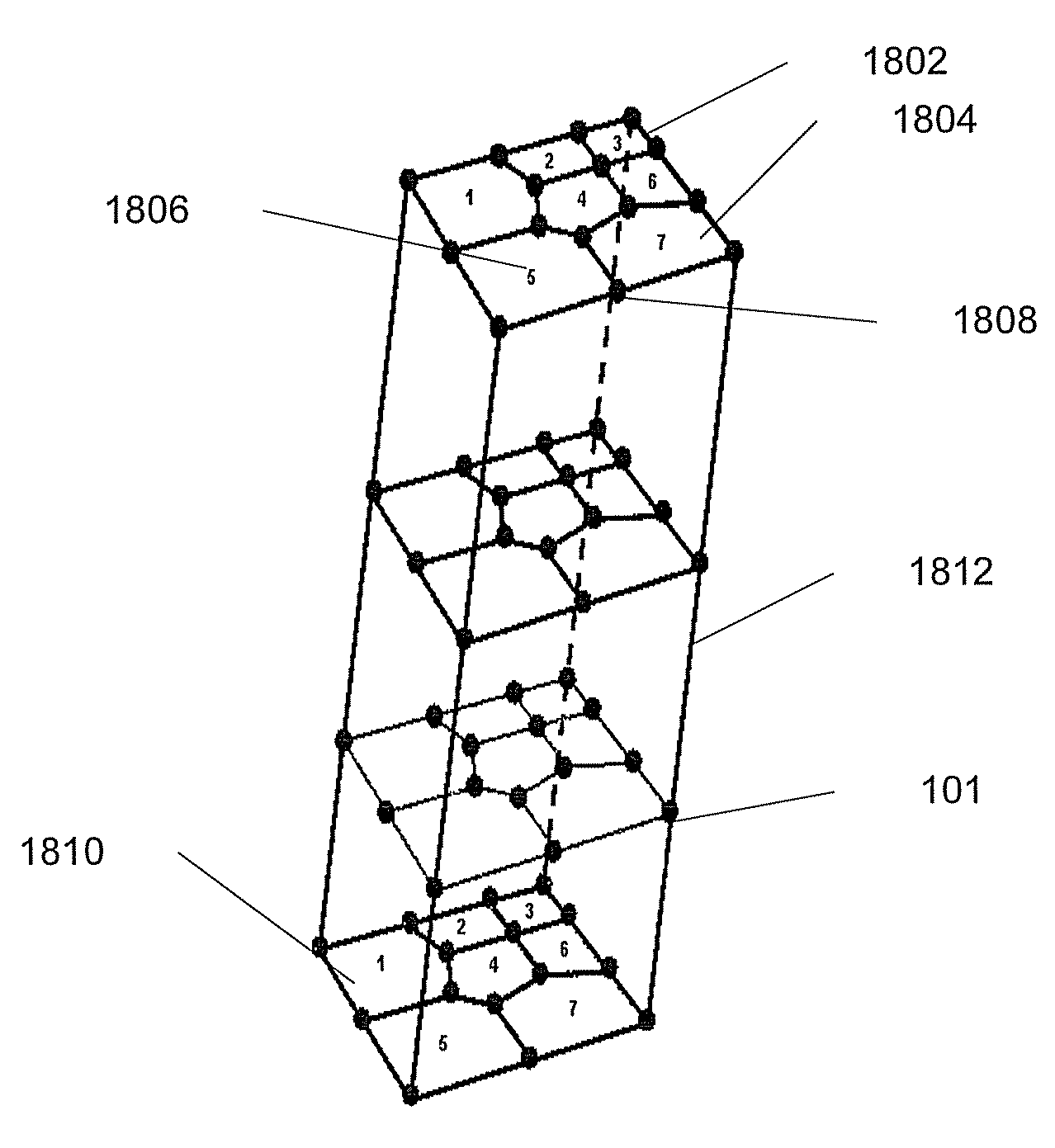
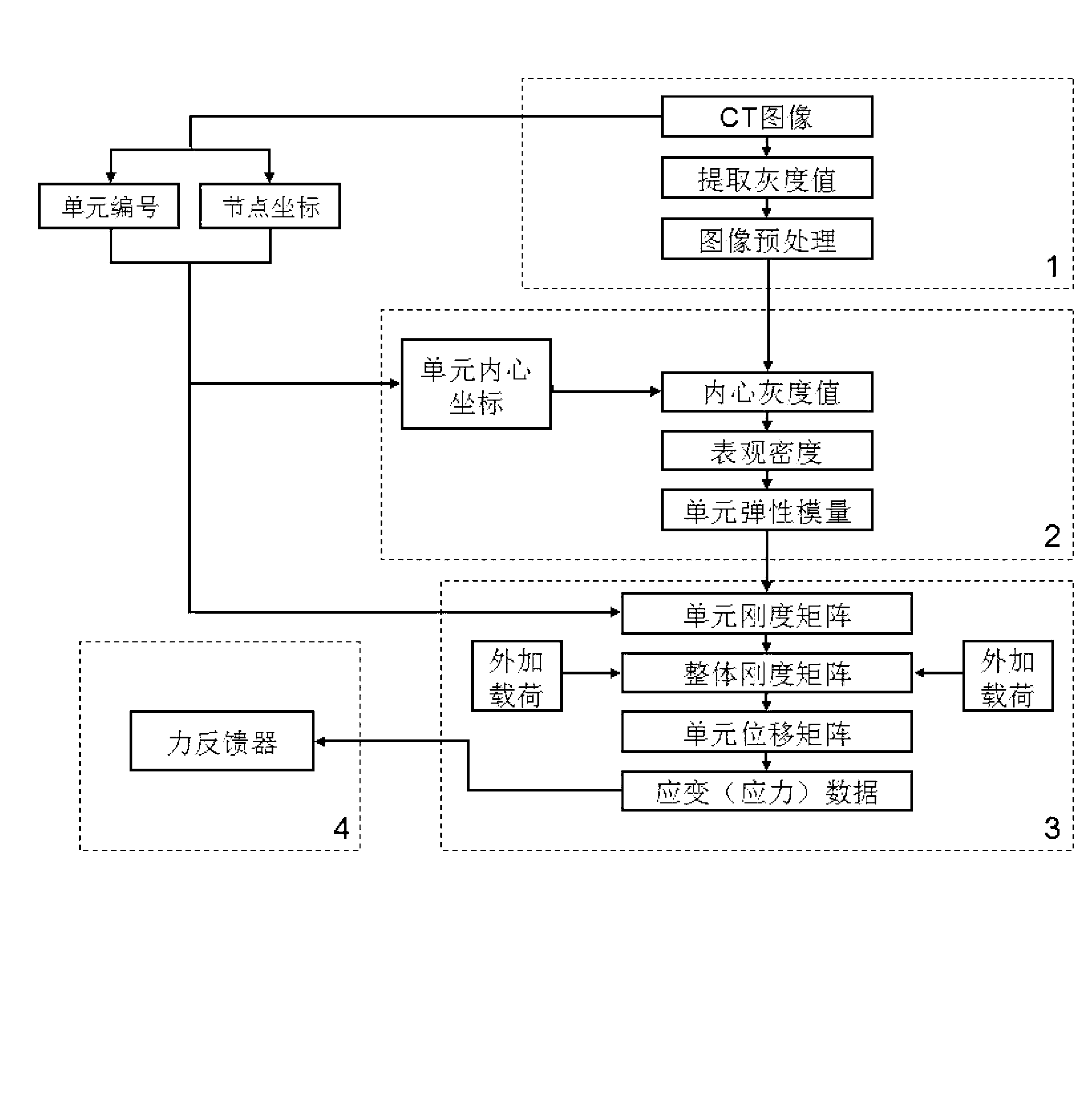
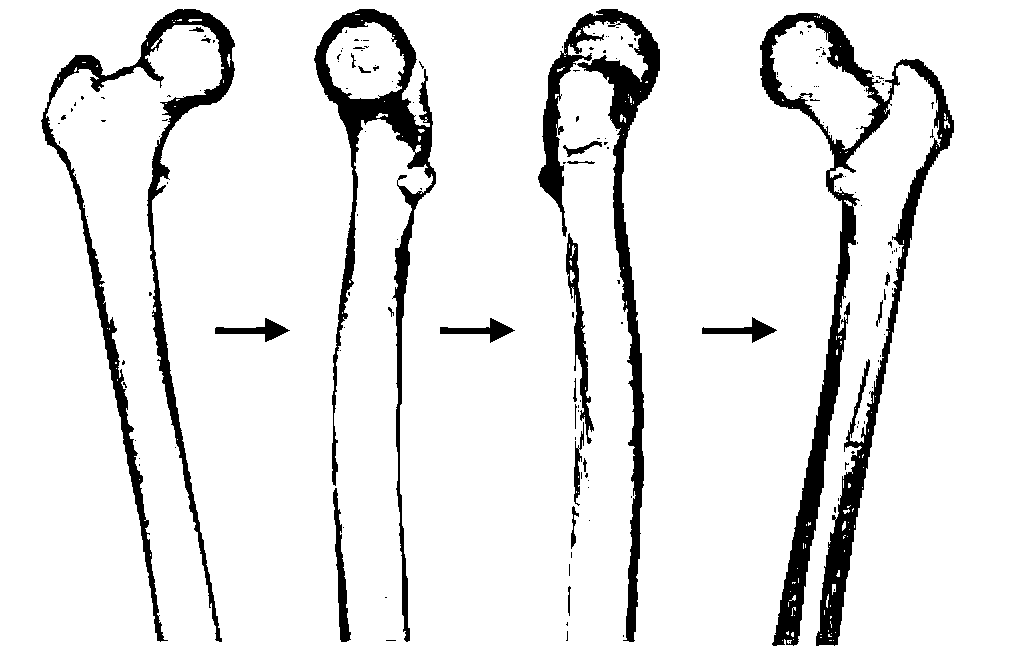
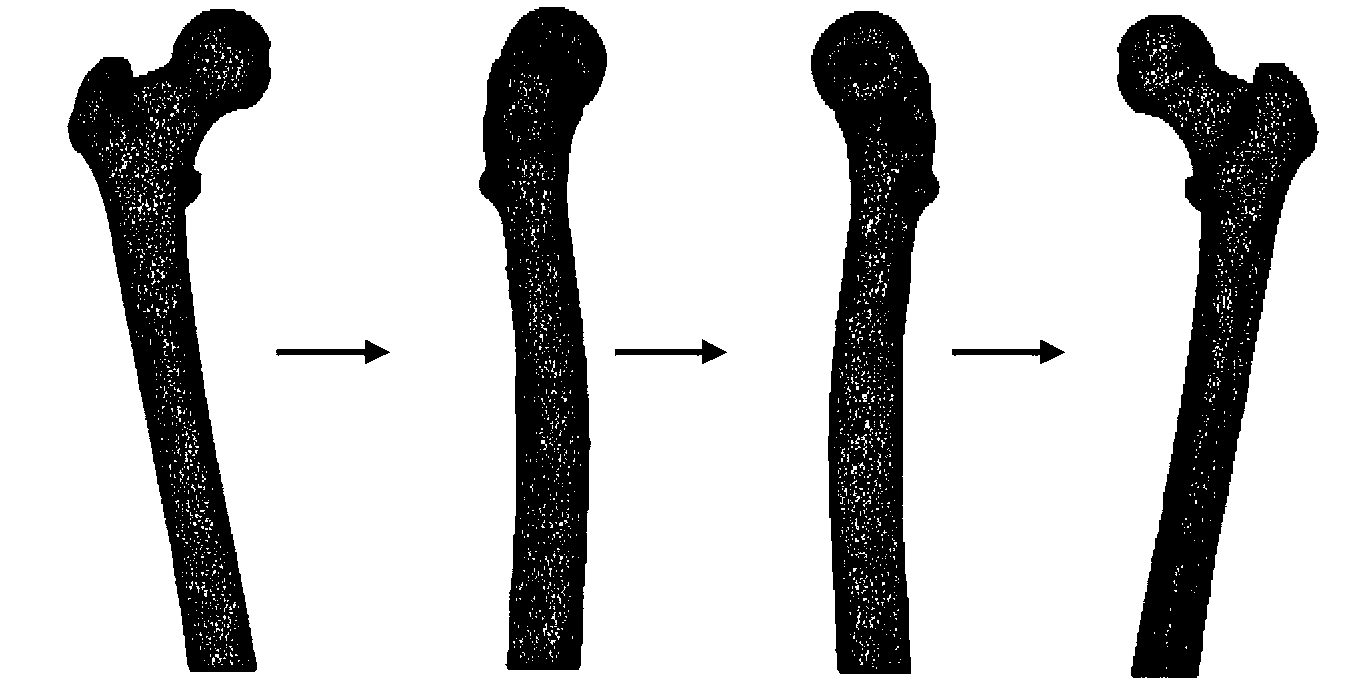
Thighbone biomechanics finite element analysis system based on force feedback
InactiveCN103310072AIncrease success rateLow number of solutionsSpecial data processing applicationsData simulationElement analysis
The invention relates to the field of thighbone modeling software development, discloses a thighbone biomechanics finite element analysis system based on force feedback, and aims to solve the problems that the conventional thighbone modeling analysis software is very complicated to operate, and has lower success rate to guide an external operation. A thighbone CT image gray value extraction module is used for leading various-format CT images; a thighbone elasticity modulus assignment module is used for acquiring inner coordinates of corpus femoris grid cells; a thighbone biomechanics finite element analysis module is used for calculating the stiffness matrix of each corpus femoris grid cell through the elasticity modulus of each corpus femoris grid cell; a force feedback module is used for simulating the mechanical properties, including size and direction, of test points according to the strain data and stress data and also for transmitting the size and direction of a force to a control handle of an external force sensing device; a force feedback device after data conversion can output the force generated when the thighbone actually deforms, and truly percept the biomechanical characteristic of a thighbone model.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Eccentric support grid for nuclear fuel assembly
InactiveUS20060222140A1Reduce stressReduce stepsNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNuclear reactorEngineering
In a nuclear reactor fuel assembly structured to support at least one non-linear fuel rod, the nuclear reactor fuel assembly includes at least two support grids, a first support grid and a second support grid structured to support at least one fuel rod in a non-linear shape. Each support grid has a plurality of generally square cells and wherein the cells on the first support grid and the second support grid are generally vertically aligned. Each cell has a first side, a second side, a third side, and a fourth side. Each cell further has protrusions extending from each the cell sides, wherein the protrusions are selected from the group including a spring, a dimple or an extended dimple. A spring is always disposed opposite of a dimple or an extended dimple. The first support grid includes at least one cell having an extended dimple extending from at least one cell side. The second support grid includes at least one cell aligned with the first support grid at least one cell having an extended dimple, wherein the second support grid cell has an extended dimple extending from a cell side other than cell side having an extended dimple on the first support grid. Thus, the extended dimples cause the fuel rod to be deformed.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com