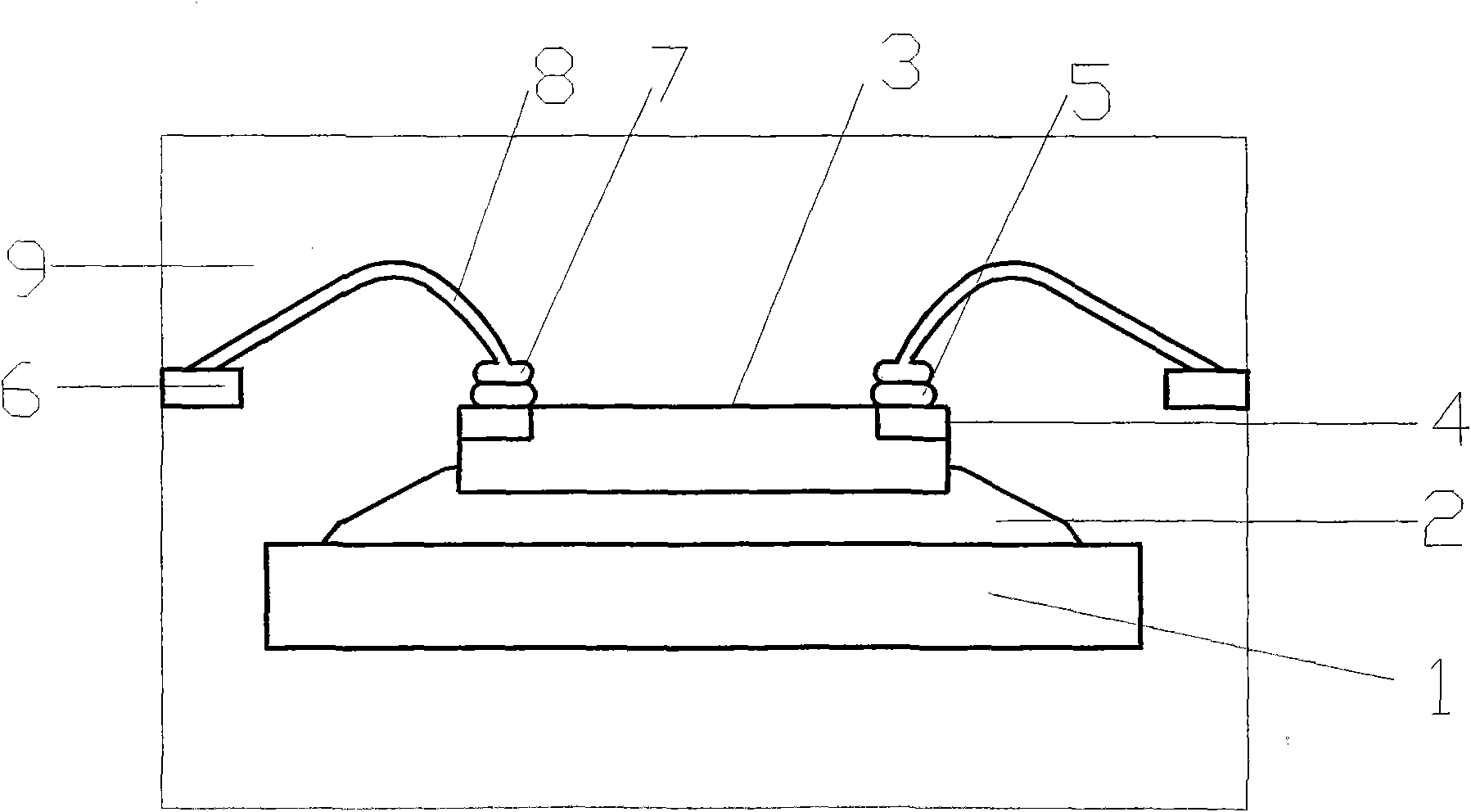
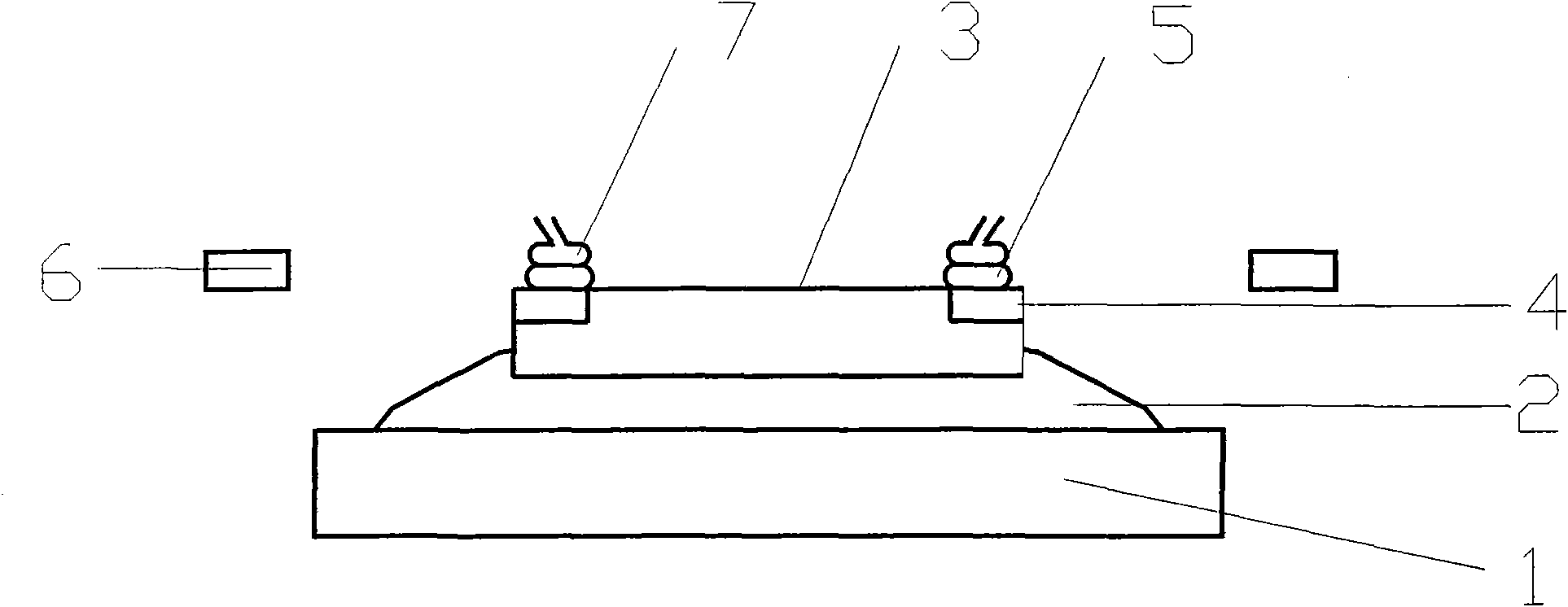
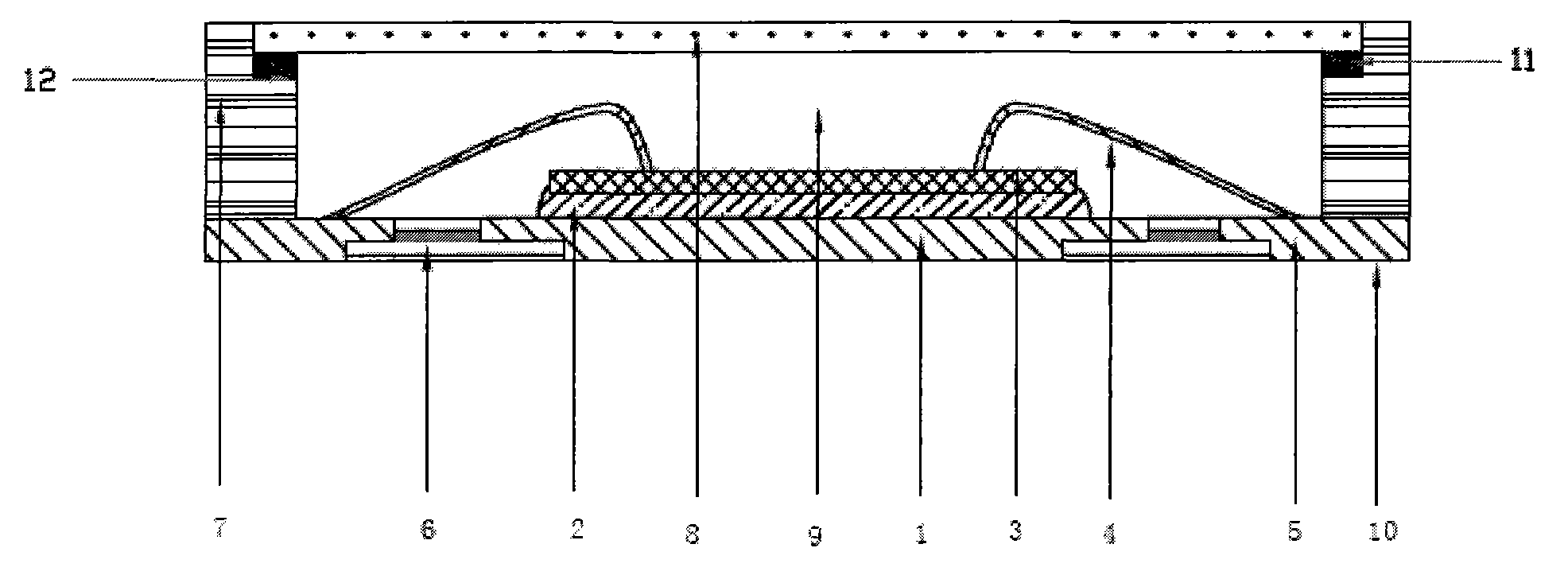
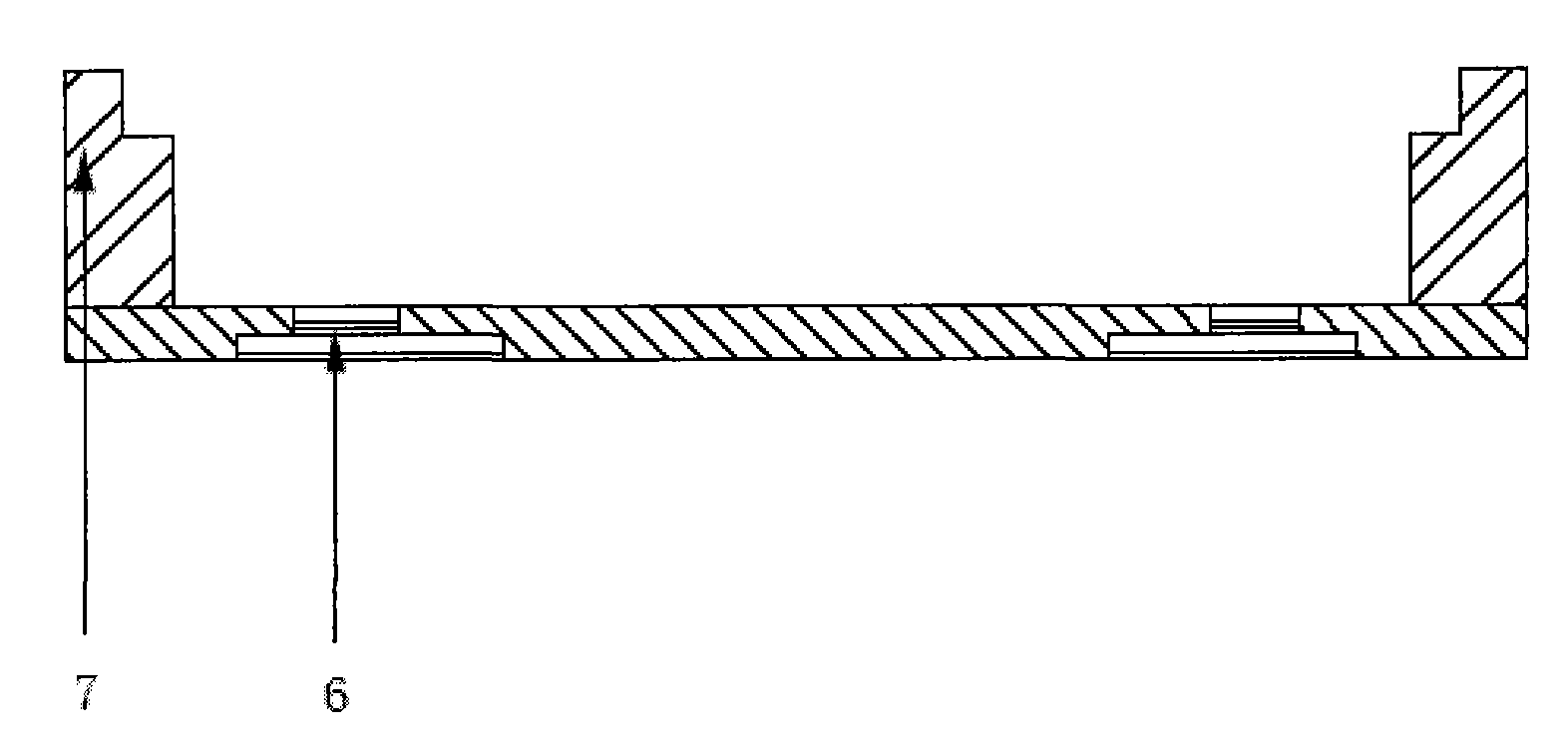
Patents
Literature
346 results about "Wafer thinning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
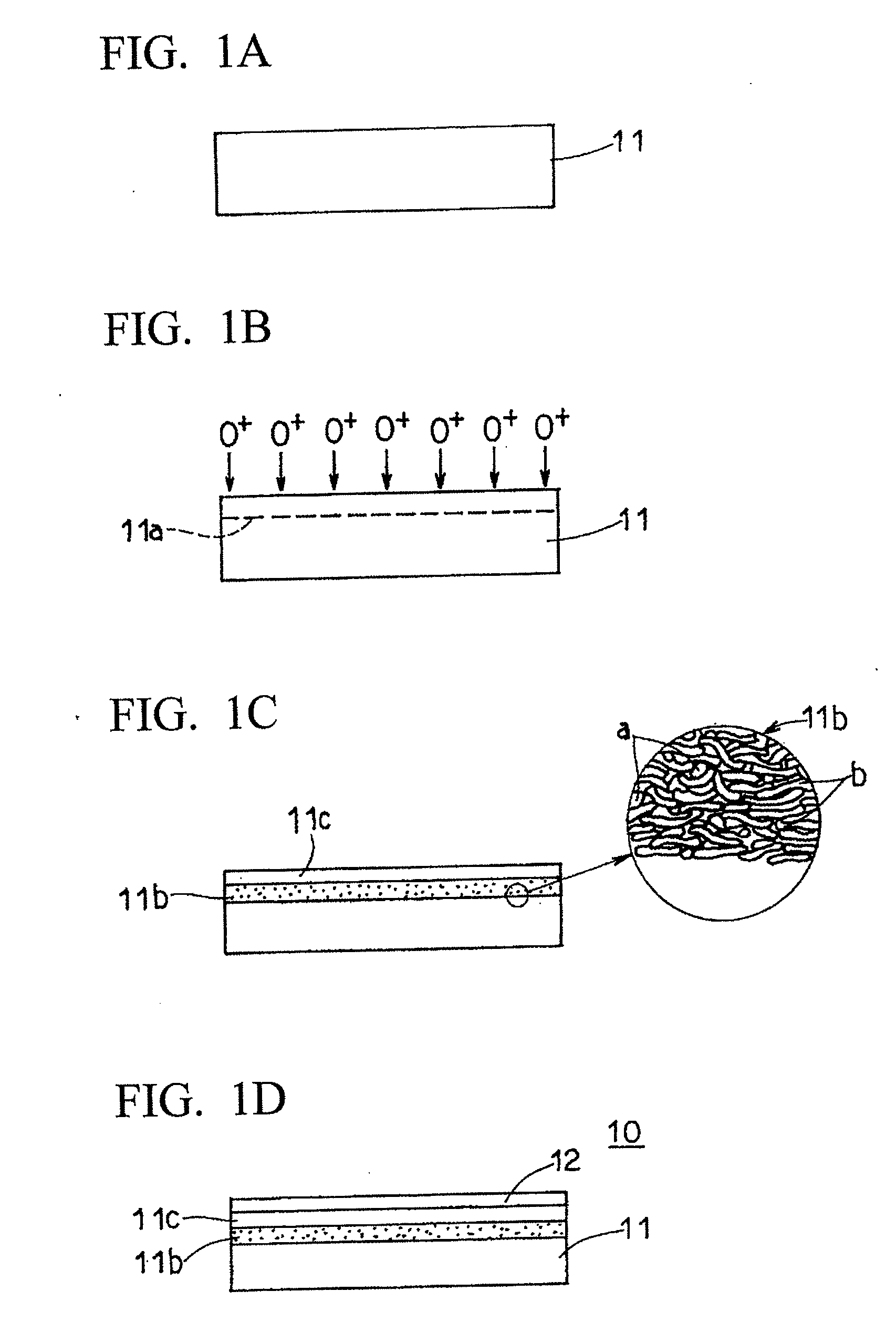
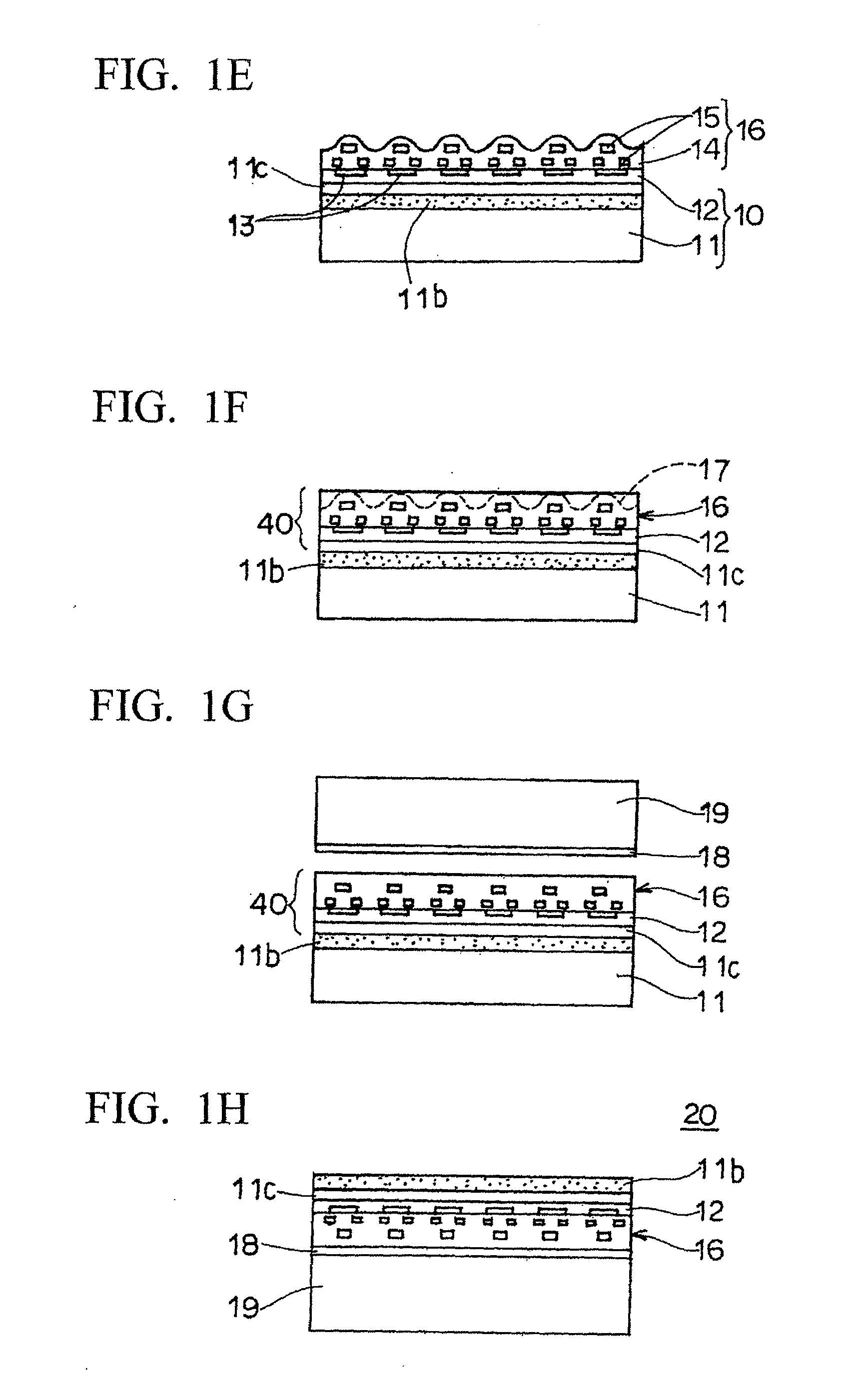
Semiconductor wafer thinning
InactiveUS20070218649A1Easy to implementAvoid contaminationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingWafer thinning
A method for processing a first semiconductor wafer having a first surface and a second surface, by placing, on the second surface of the first wafer, a second wafer with an interposed resist layer, and thinning down the first surface of the first semiconductor wafer.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Spin-on adhesive for temporary wafer coating and mounting to support wafer thinning and backside processing
InactiveUS6869894B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveFluorescence
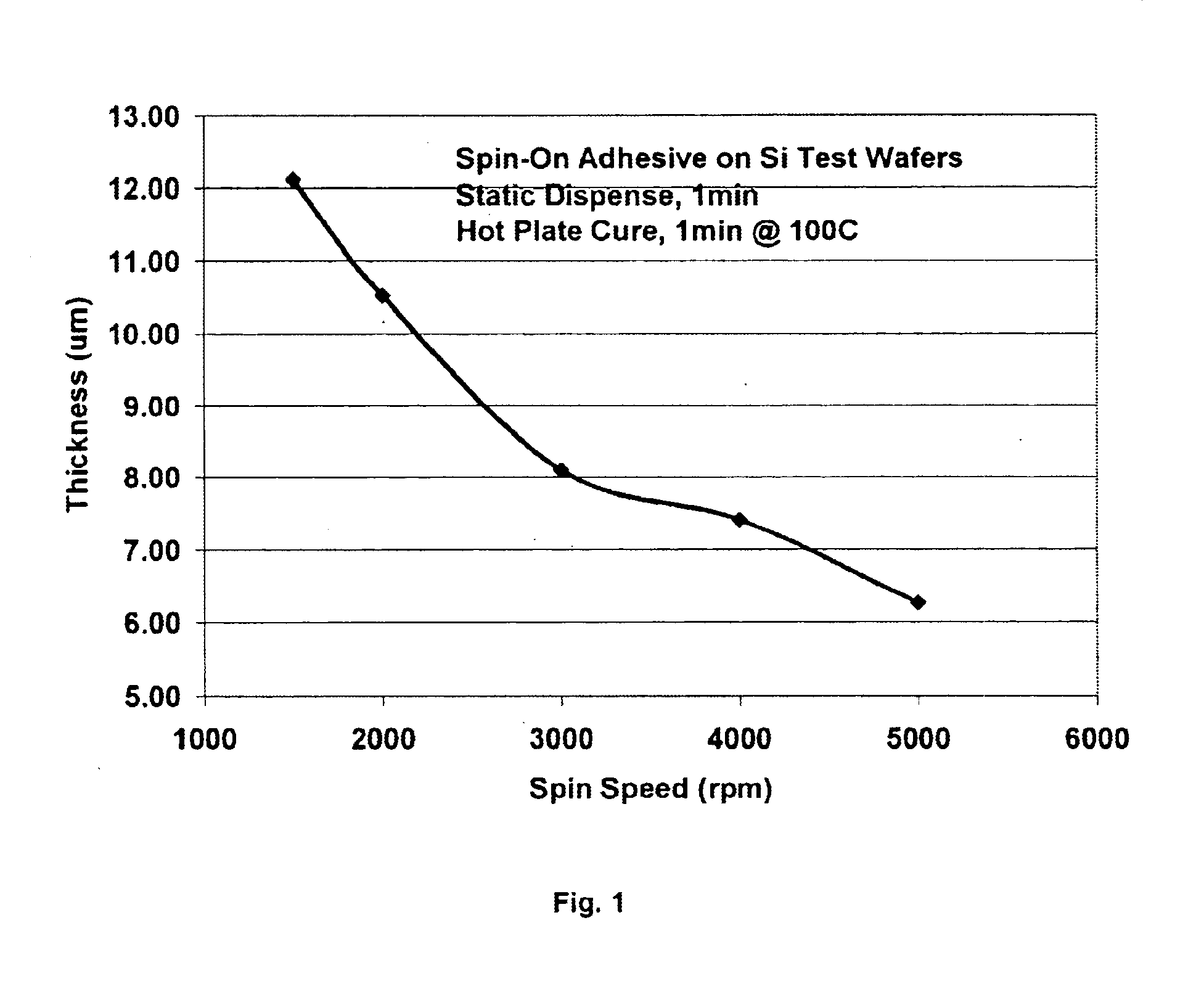
A liquid form adhesive system is provided for spin-coating on wafers and mounting to rigid carrier substrates to support thinning and backside processing. The liquid adhesive comprises about 30-35% of a rosin, between 5-10% of a thermoplastic urethane, a nonionic surfactant present between 1-3%, and a trace of an ultraviolet fluorescing dye. The entire system is dissolved in 50-65%, by weight, of a dual solvent mixture composed of dimethylacetamide and propylene glycol monomethyl ether. When the mixture is made to a specific viscosity, filtered, applied by a spin-coating method to the wafer frontside surface, and cured, the result is a uniform and smooth surface of defined thickness. When the coated wafer is mounted to a rigid substrate, it may be mechanically thinned to thicknesses down to and beyond 25 um, depending upon the wafer composition, diameter, and process. Once thinned, the adhesive is safe for backside processing and is dissolved away at completion to provide a thinned wafer that is clean and ready for final dicing or chipping operations.
Owner:GENERAL CHEM CORP +1
Stiffened backside fabrication for microwave radio frequency wafers
InactiveUS6884717B1Less fragileNot easy to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingSemiconductor materials
An etching based semiconductor wafer thinning arrangement usable as an improved alternative to the usual grinding and polishing wafer thinning. The thinned wafer includes a structurally enhancing wafer backside grid array of original wafer thickness semiconductor material with grid cells surrounding individual thinned wafer areas and serving to improve the strength and physical rigidity characteristics of the thinned wafer. Preferably this grid array is supplemented with an additional, wafer periphery-located, backside ring of semiconductor material also of original wafer thickness. Ability to avoid a wafer front side mounting during thinning accomplishment, fast etching, reduced wafer breakage, enhanced wafer strength and improved wafer handling achieved with the disclosed thinning arrangement all contribute to achieved advantages over conventional wafer thinning. Gallium arsenide or other semiconductor materials are contemplated along with use in radio frequency or other integrated circuit devices of either the single transistor or complete integrated circuit components types.
Owner:SANDVIK AB +1
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110089524A1Reduce thickness variationImprove accuracySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerOxygen ions
A semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same capable of reducing variations in the thickness of a semiconductor device are provided. The amount of oxygen implanted ions is less than the amount of implanted oxygen ions in the conventional epitaxial SIMOX wafers. Oxygen is ion-implanted into the surface layer of a silicon wafer from the surface of the wafer. Then, by heat treating the wafer, a thinning stop layer, which is an imperfect buried oxide film, is formed along the entire plane of the wafer. As a result, variation of the thickness of the semiconductor device formed in an active layer can be reduced, since the, the reliability of the accuracy of the end point of silicon wafer thinning is higher than that of a thinning using the conventional deep trench structure as an end point detector.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Method for chemical-mechanical jet etching of semiconductor structures
InactiveUS7037854B2Quickly and accurately removing large amounts of materialRapidly producing large-scale featuresDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureCompound (substance)
A chemical-mechanical jet etching method rapidly removes large amounts of material in wafer thinning, or produces large-scale features on a silicon wafer, gallium arsenide substrate, or similar flat semiconductor workpiece, at etch rates in the range of 10–100 microns of workpiece thickness per minute. A nozzle or array of nozzles, optionally including a dual-orifice nozzle, delivers a high-pressure jet of machining etchant fluid to the surface of the workpiece. The machining etchant comprises a liquid or gas, carrying particulate material. The liquid may be a chemical etchant, or a solvent for a chemical etchant, if desired. The areas which are not to be etched may be shielded from the jet by a patterned mask, or the jet may be directed at areas from which material is to be removed, as in wafer thinning or direct writing, depending on the size of the desired feature or etched area.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
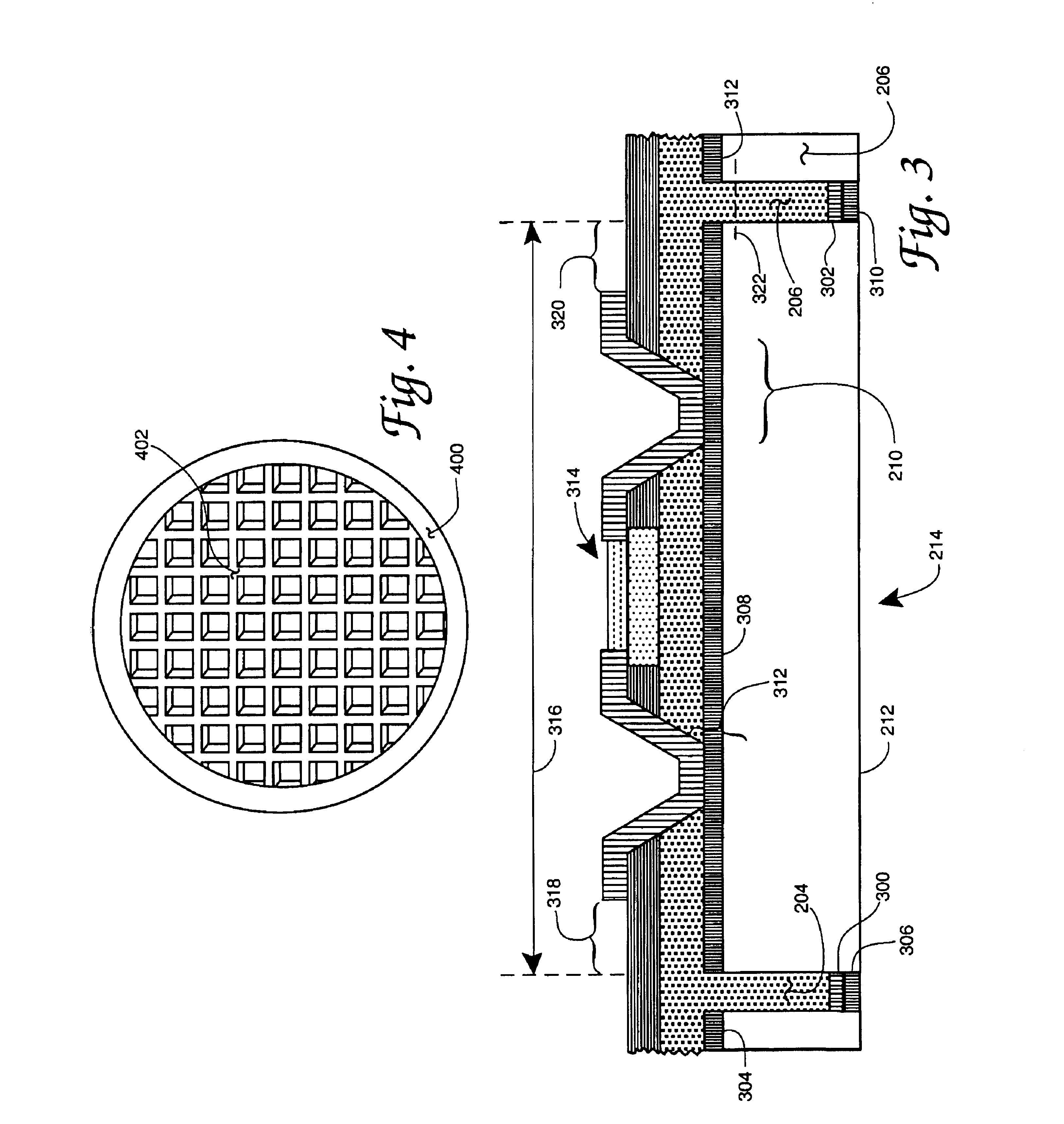
Edge Protection of Bonded Wafers During Wafer Thinning
InactiveUS20130328174A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorWafer stacking
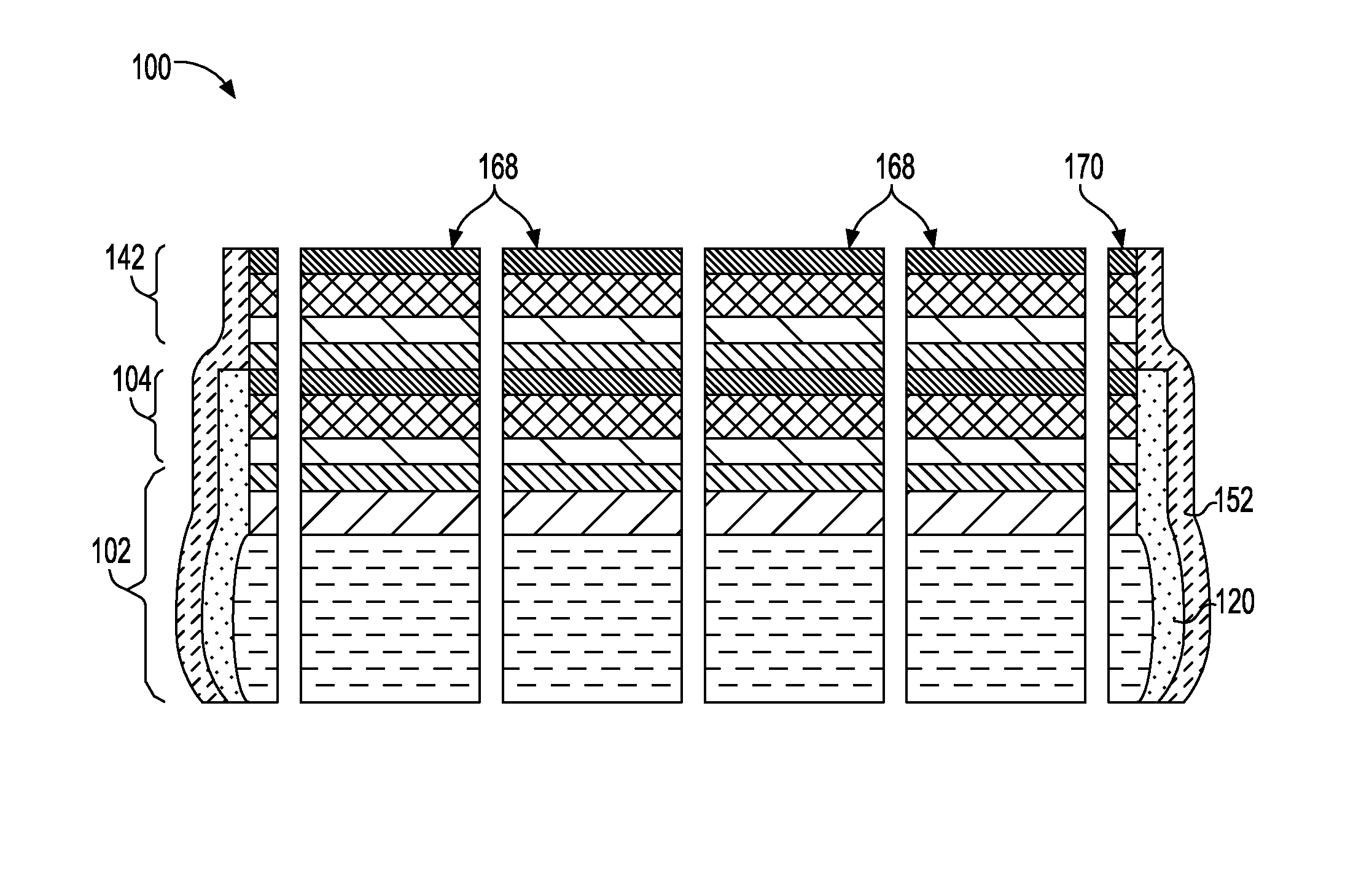
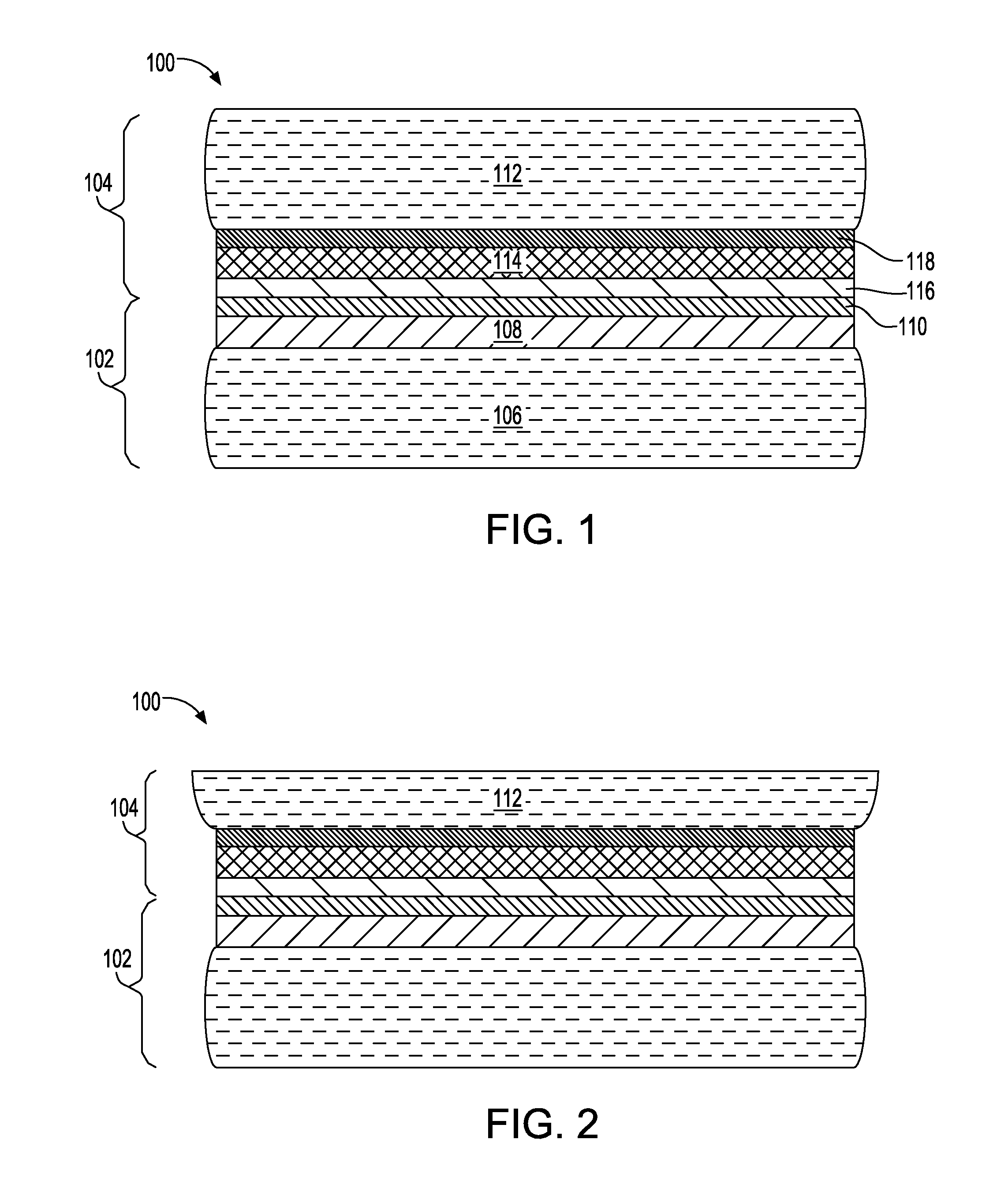
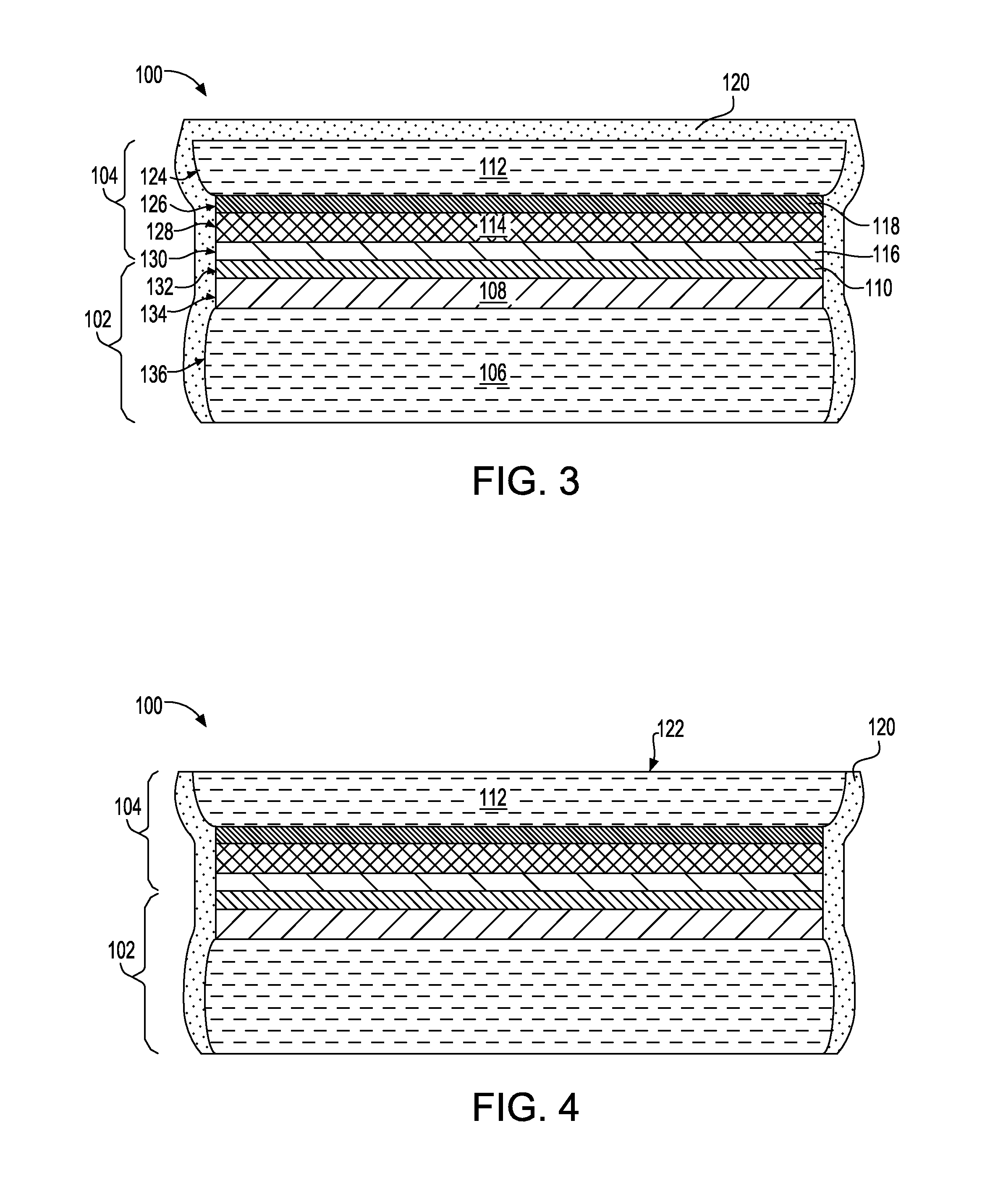
A method of edge protecting bonded semiconductor wafers. A second semiconductor wafer and a first semiconductor wafer are attached by a bonding layer / interface and the second semiconductor wafer undergoes a thinning process. As a part of the thinning process, a first protective layer is applied to the edges of the second and first semiconductor wafers. A third semiconductor wafer is attached to the second semiconductor wafer by a bonding layer / interface and the third semiconductor wafer undergoes a thinning process. As a part of the thinning process, a second protective layer is applied to the edges of the third semiconductor wafer and over the first protective layer. The first, second and third semiconductor wafers form a wafer stack. The wafer stack is diced into a plurality of 3D chips while maintaining the first and second protective layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor wafer thinning method, and thin semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS6930023B2Low costLow cost productionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingWafer thinning
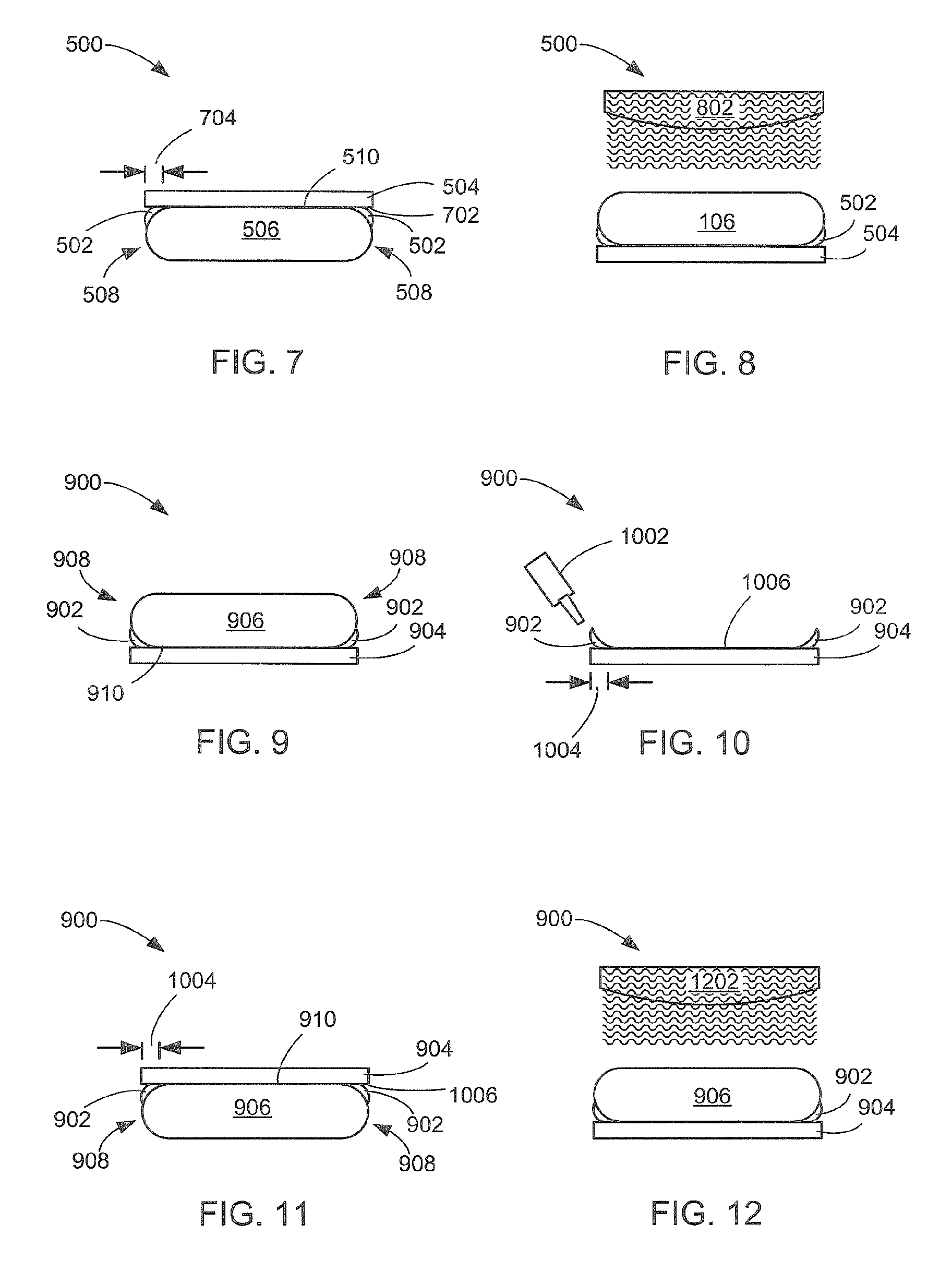
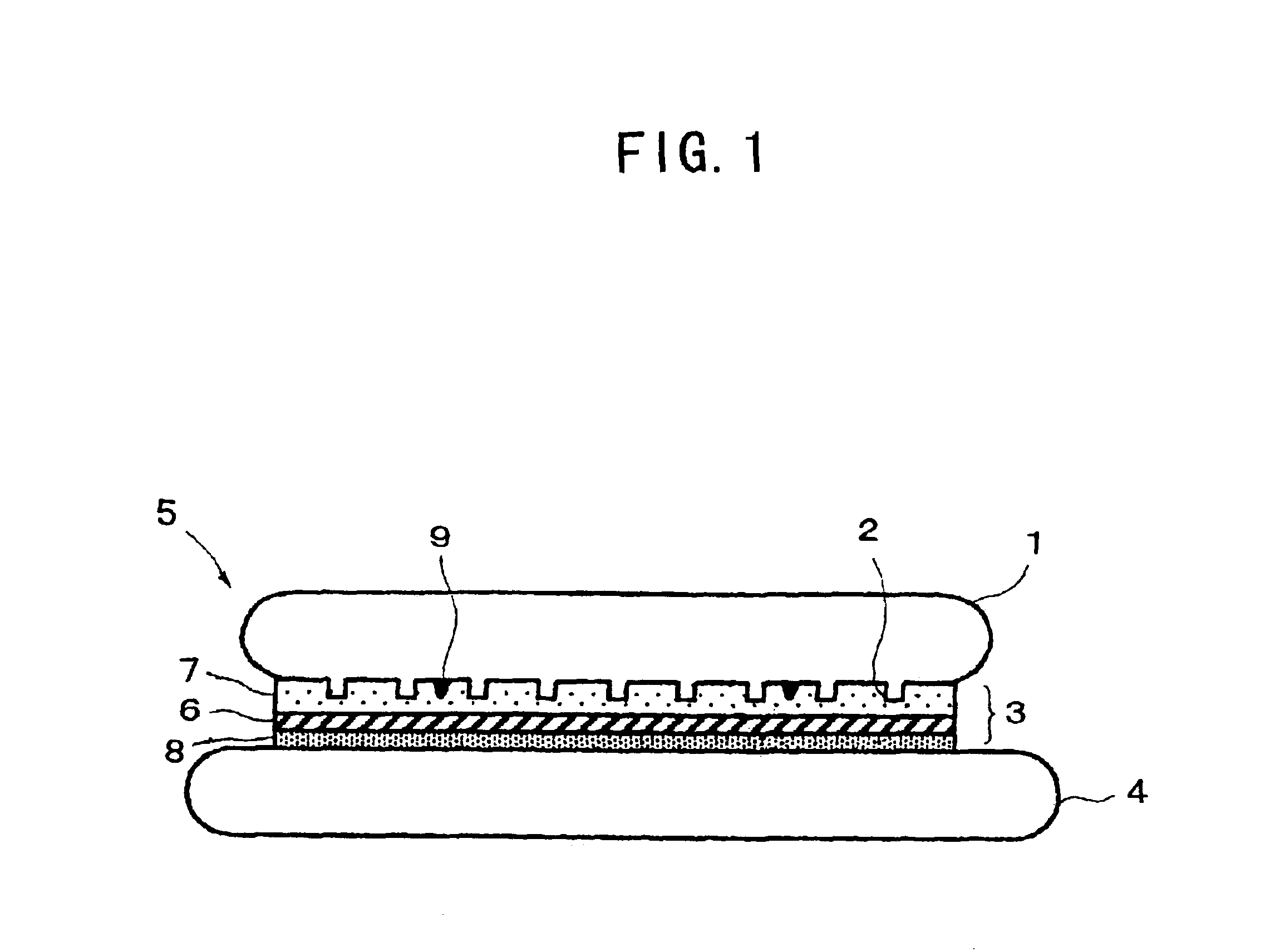
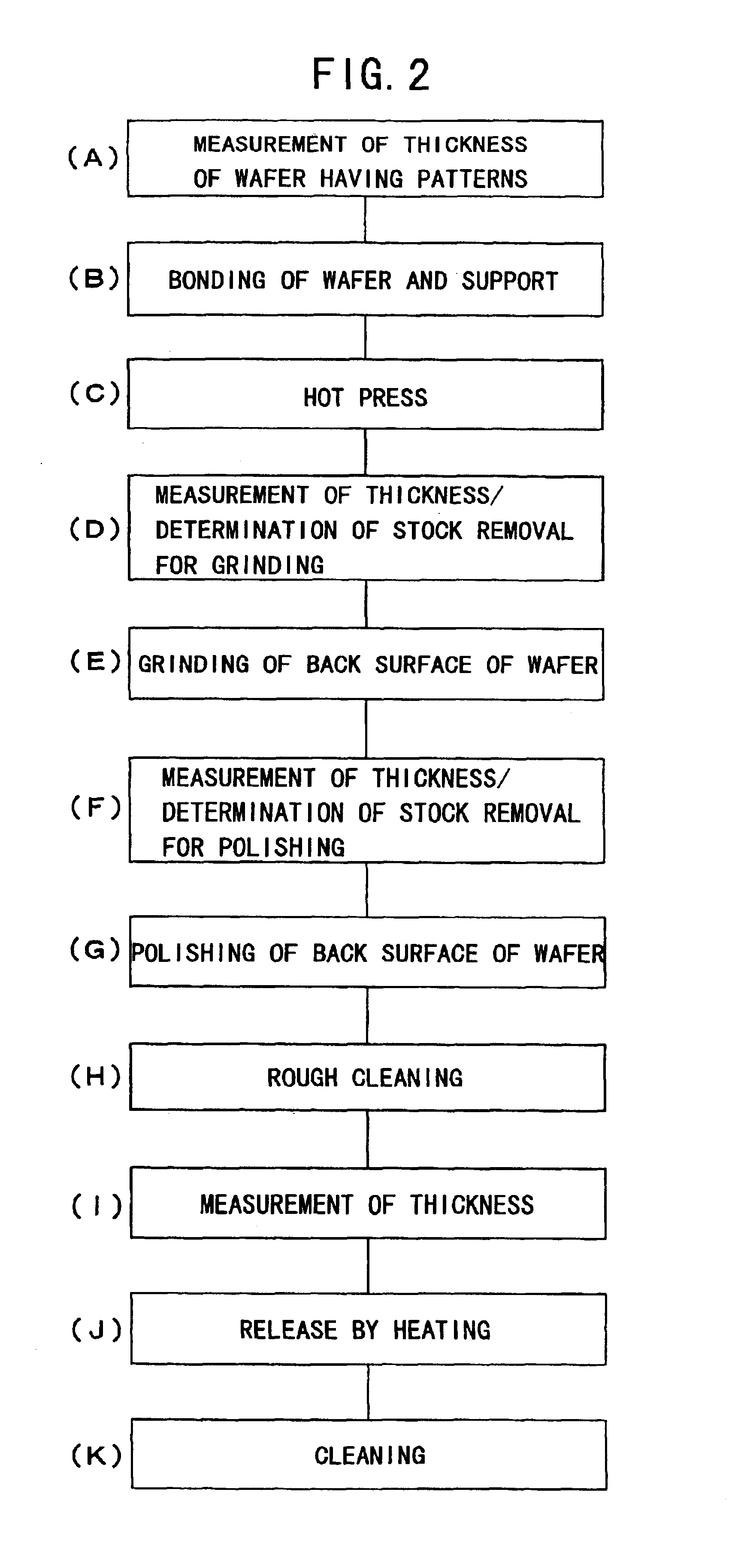
In a method for thinning a semiconductor wafer by grinding a back surface of the semiconductor wafer in which semiconductor devices 2 are formed on its surface, the surface of the semiconductor wafer 1 is adhered to a support 4 via an adhesive layer 3, the back surface of the semiconductor wafer is ground while holding the support, and then the thinned semiconductor wafer is released from the support. Preferably, a semiconductor wafer is used as the support, a thermal release double-sided adhesive sheet is used as the adhesive layer, and they are separated by heating after grinding. Thus, there are provided a method for thinning a semiconductor wafer, which enables production of semiconductor wafers having a thickness of about 120 μm or less without generating breakage such as cracking or chipping during the processing step and so forth as much as possible at a low cost, and a semiconductor wafer thinned further compared with conventional products in spite of a large diameter of 6 inches (150 mm) or more.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Thinning method for backing side of wafer
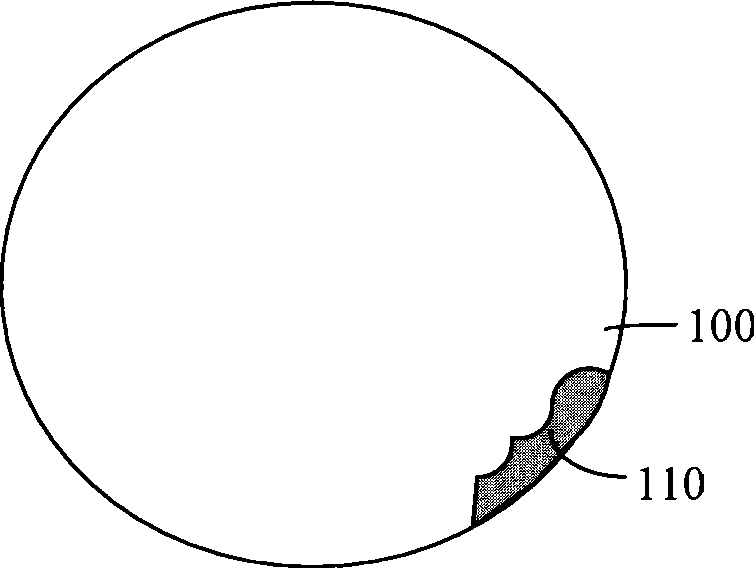
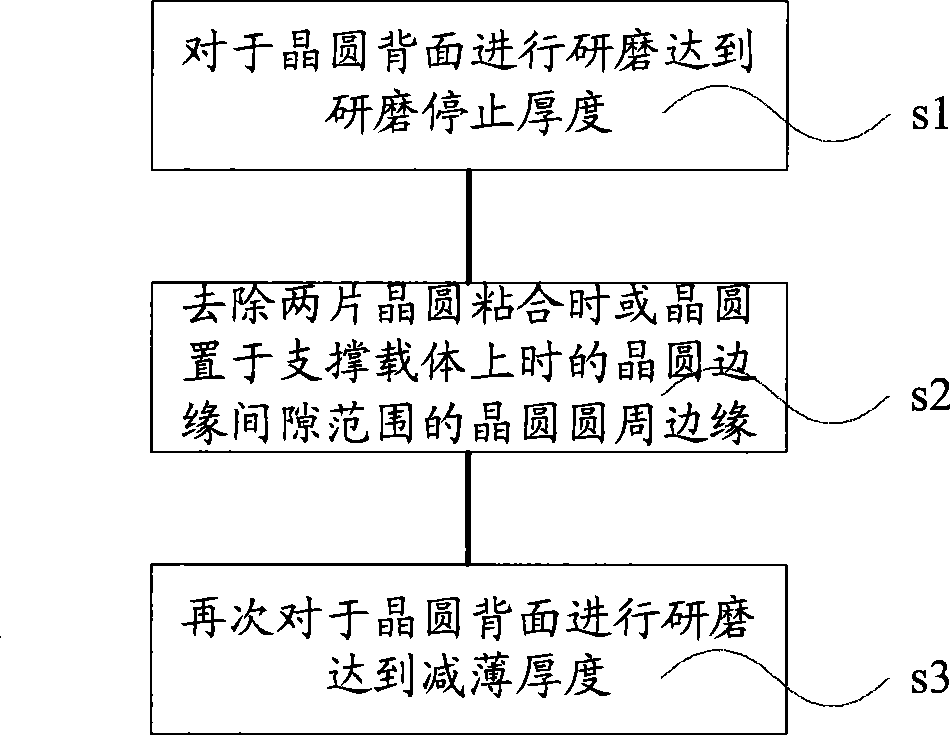
InactiveCN101399195AQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWafer thinningEngineering
The invention relates to a method for thinning the back of a wafer, and the method comprises the following steps: the back of the wafer is grinded until the grinding stop thickness is achieved; the wafer periphery edge within the wafer edge clearance range when two wafers are bonded or the wafer is placed on a supporting carrier is removed; the back of the wafer is grinded until the thinning thickness is achieved. The method for thinning the back of the wafer solves the problem of easy bend or even fracture of the wafer edge when the back of the wafer is thinned, thus improving the quality of wafer thinning.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Copper-free flat packaging piece of AAQFN frame product and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveCN103474406AImprove package reliabilityLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsWafer thinning
Owner:HUATIAN TECH XIAN
Wafer thinning method
ActiveUS20170025275A1Wafer thickness reductionWear amount of abrasive can be suppressedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringWafer thinning
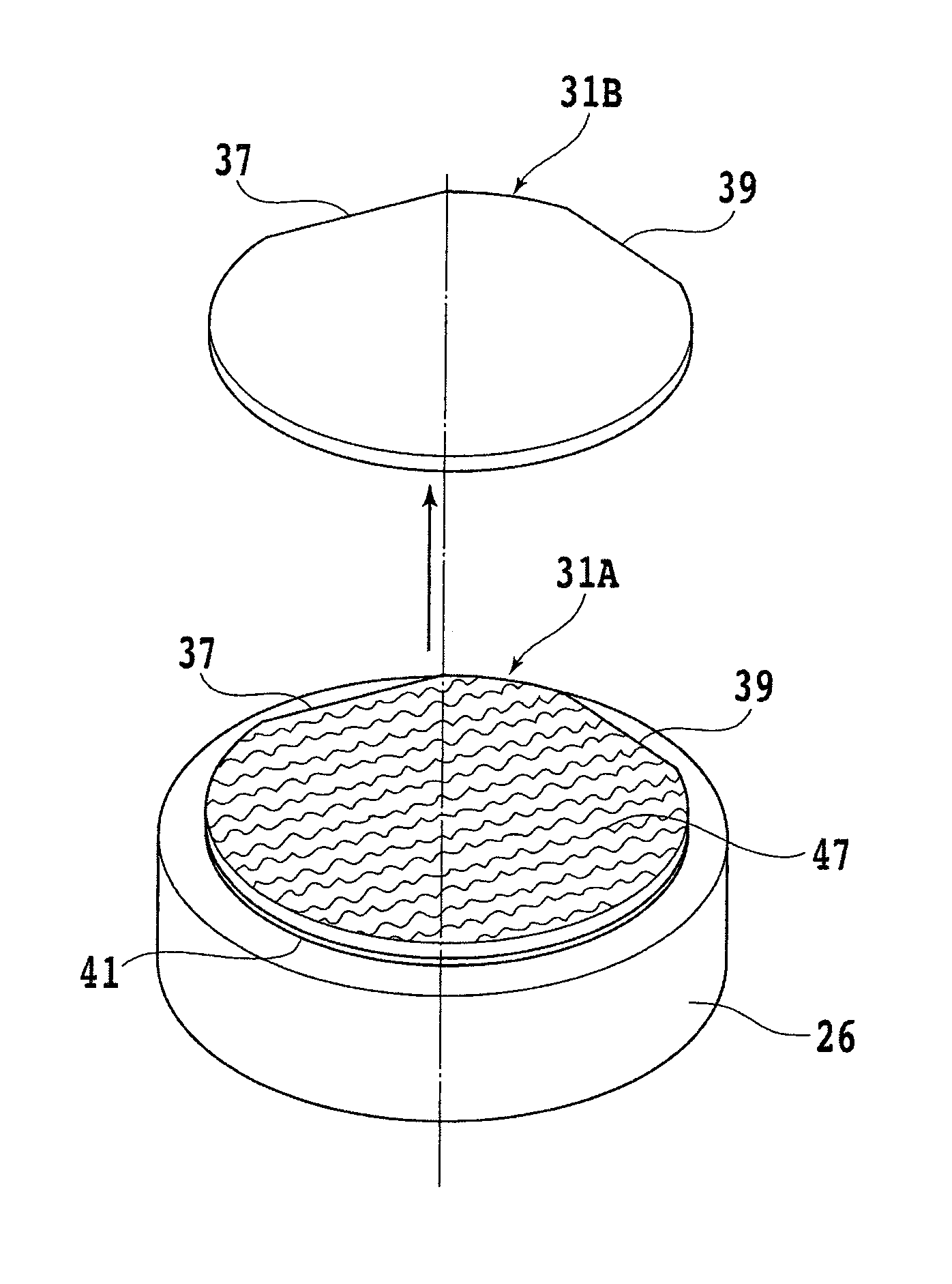
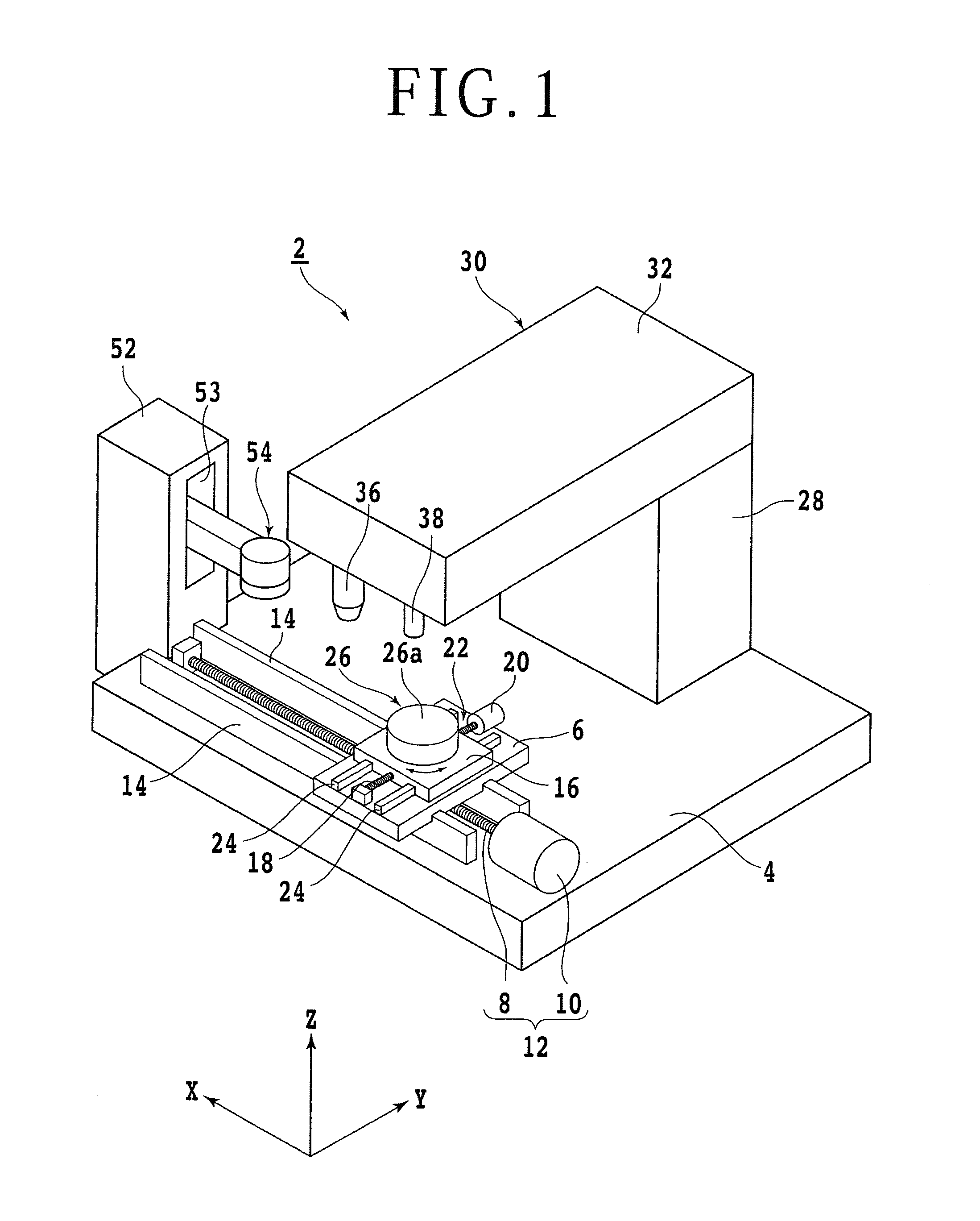
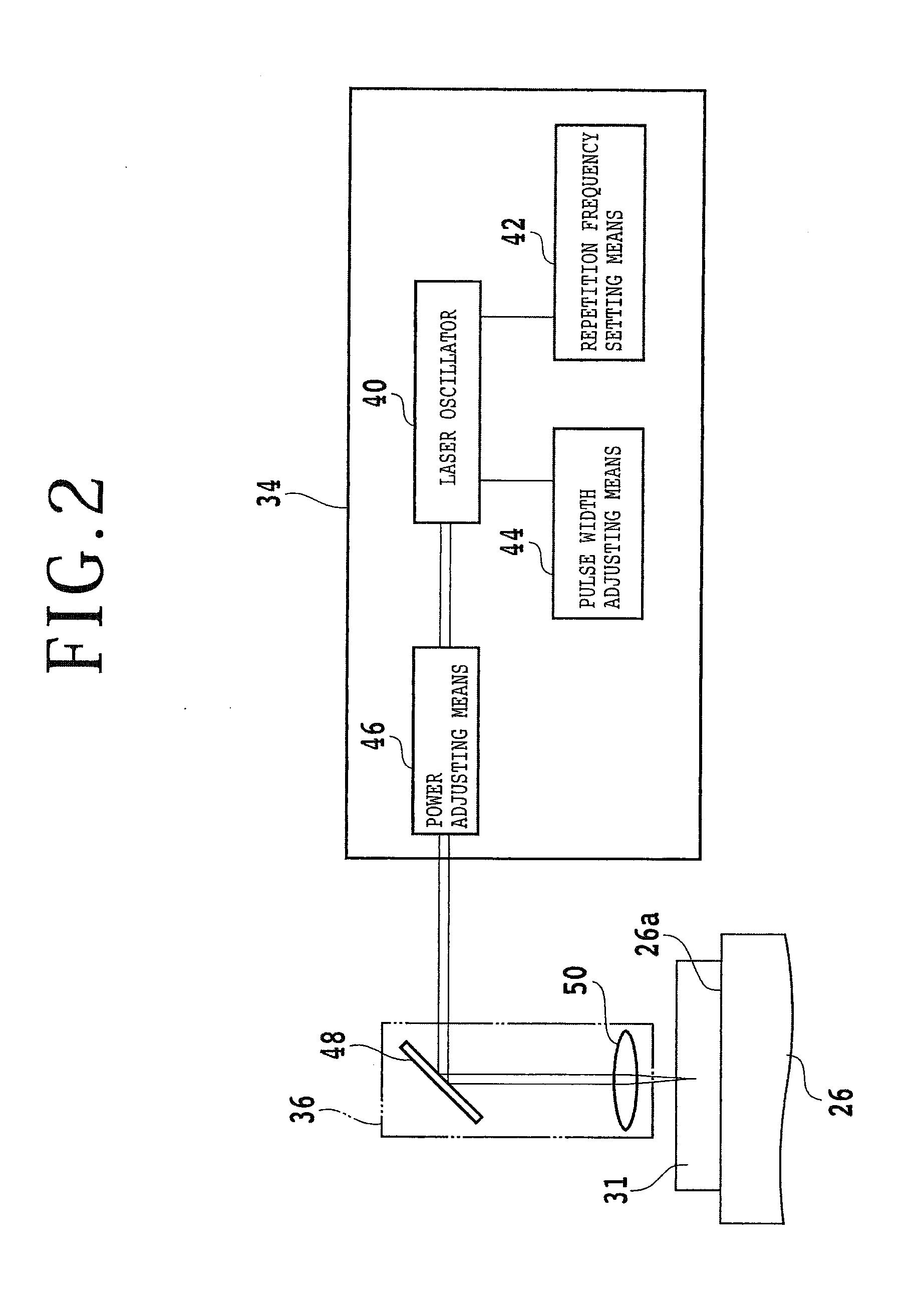
Disclosed herein is a wafer thinning method for thinning a wafer formed from an SiC substrate having a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface. The wafer thinning method includes an annular groove forming step of forming an annular groove on the second surface of the SiC substrate in an annular area corresponding to the boundary between a device area and a peripheral marginal area in the condition where a thickness corresponding to the finished thickness of the wafer after thinning is left, and a separation start point forming step of applying the laser beam to the second surface as relatively moving a focal point and the SiC substrate to thereby form a modified layer and cracks inside the SiC substrate at the predetermined depth.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Cantilever type IC (Integrated Circuit) chip stack package of BT (Bismaleimide Triazine) substrate and production method of cantilever type IC chip stack package
ActiveCN102629604AAvoid short circuitReduce short circuitSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPlastic packagingSolder ball
The invention discloses a cantilever type IC (Integrated Circuit) chip stack package of a BT (Bismaleimide Triazine) substrate and a production method of the cantilever type IC chip stack package. The package comprises a substrate carrier to which the BT substrate is adhered, wherein at least three layers of IC chips with the same appearance and size are stacked and adhered on the substrate; the back face of the substrate carrier is provided with a substrate back face bonding pad; the substrate back face bonding pad is connected with a substrate front face bonding pad; the surface of the substrate back face bonding pad is provided with bumps, solder and solder balls in sequence; two adjacent IC chips are arranged in a staggered way in the horizontal direction, the staggering distance is the same, and the IC chips are connected through a bonding wire; and a layer of IC chip on the substrate is connected with the substrate front face bonding pad through the bonding wire. The stack package is manufactured through the following steps of: thinning a wafer; scribing; loading the chip and roasting; performing plasma cleaning; performing pressure welding and plastic packaging; post-curing; mounting balls; performing reflux welding; and the like. According to the package, the height of each layer of bonding wire is reduced to the greatest extent, short circuiting between different annular layers of bonding wires is avoided, and the problems of stack package and unilateral bonding wire of the chips of the same size are solved.
Owner:TIANSHUI HUATIAN TECH +1
Method for judging wafer thinning, device structure and device and its manufacture method
ActiveCN101339893ANot physically limitedEnhance the outstanding effectPolishing machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWafer thinningEngineering
The invention relates to a method for judging wafer thinning, device structure, mechanism and its manufacture method. Basis material is ground and removed from semiconductor device; current change in grinding device is detected and responds to multiple first group of device structure exposing with basis material; the grinding and removing step responds to detected current change and stops; polishing step is performed to repairing surface, and extra basis material is continuously removed; other one or multiple groups of device structures with exposing material is monitored to judge extra amount of basis material to be removed; the other one or multiple groups of device structures is positioned inside semiconductor device at known depth other than the position depth of the first group structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Wafer thinning method
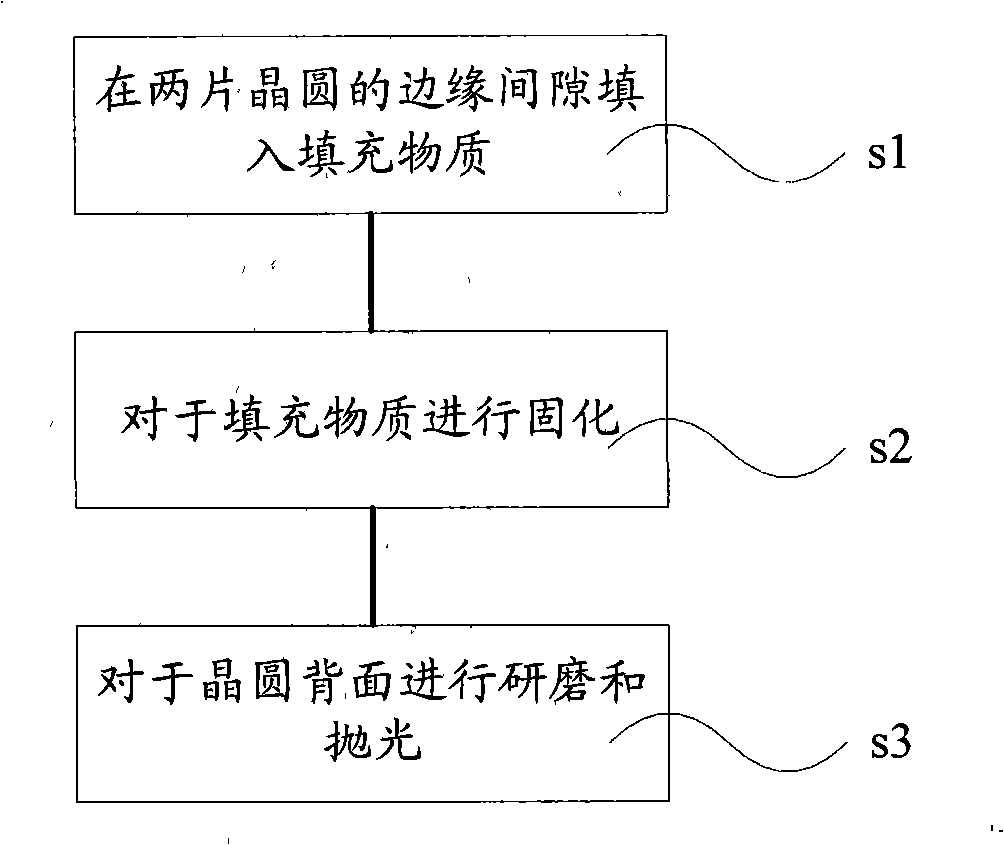
ActiveCN103413772AImprove area utilizationAvoid scratchesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBonding processWafer thinning
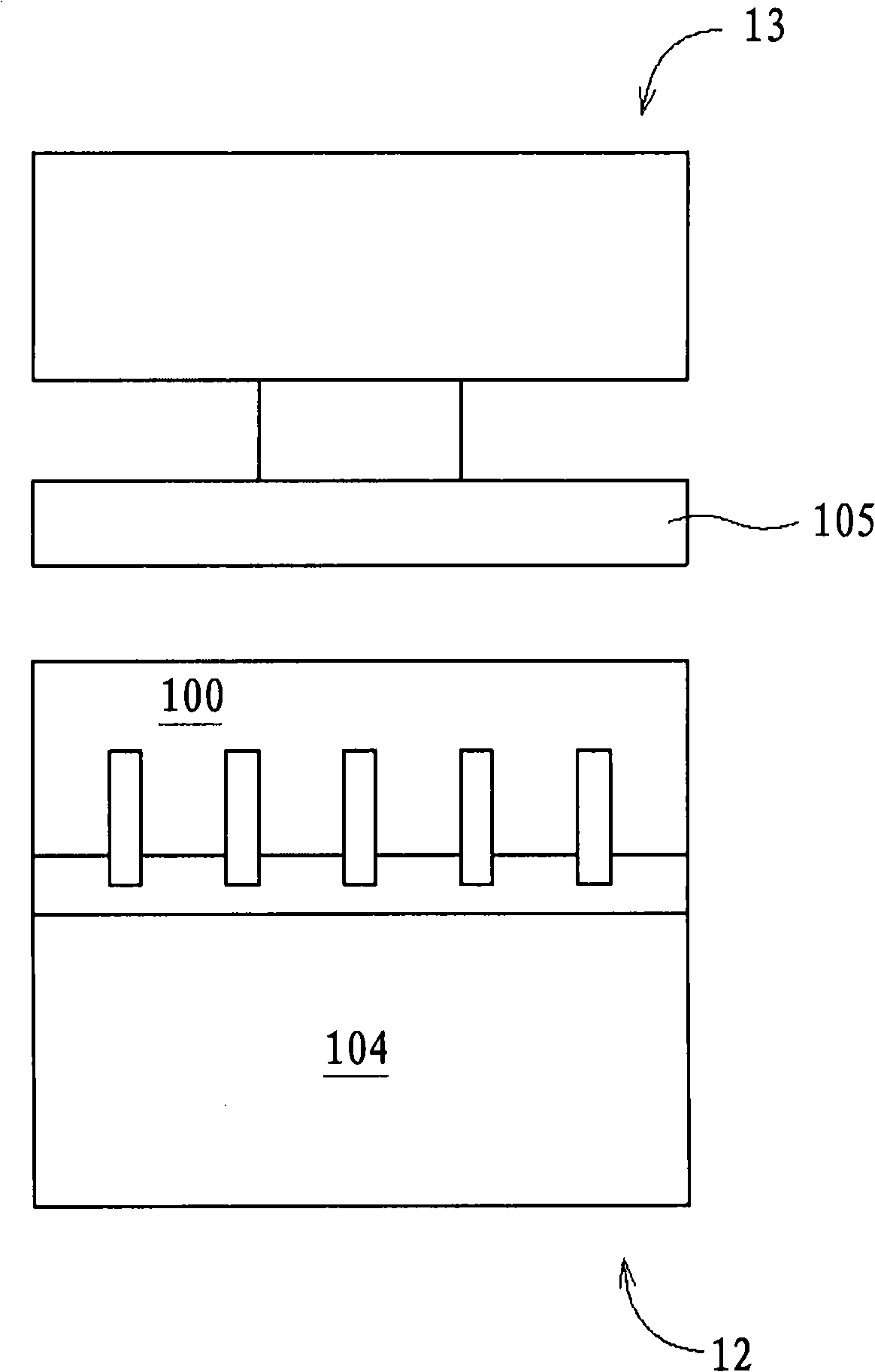
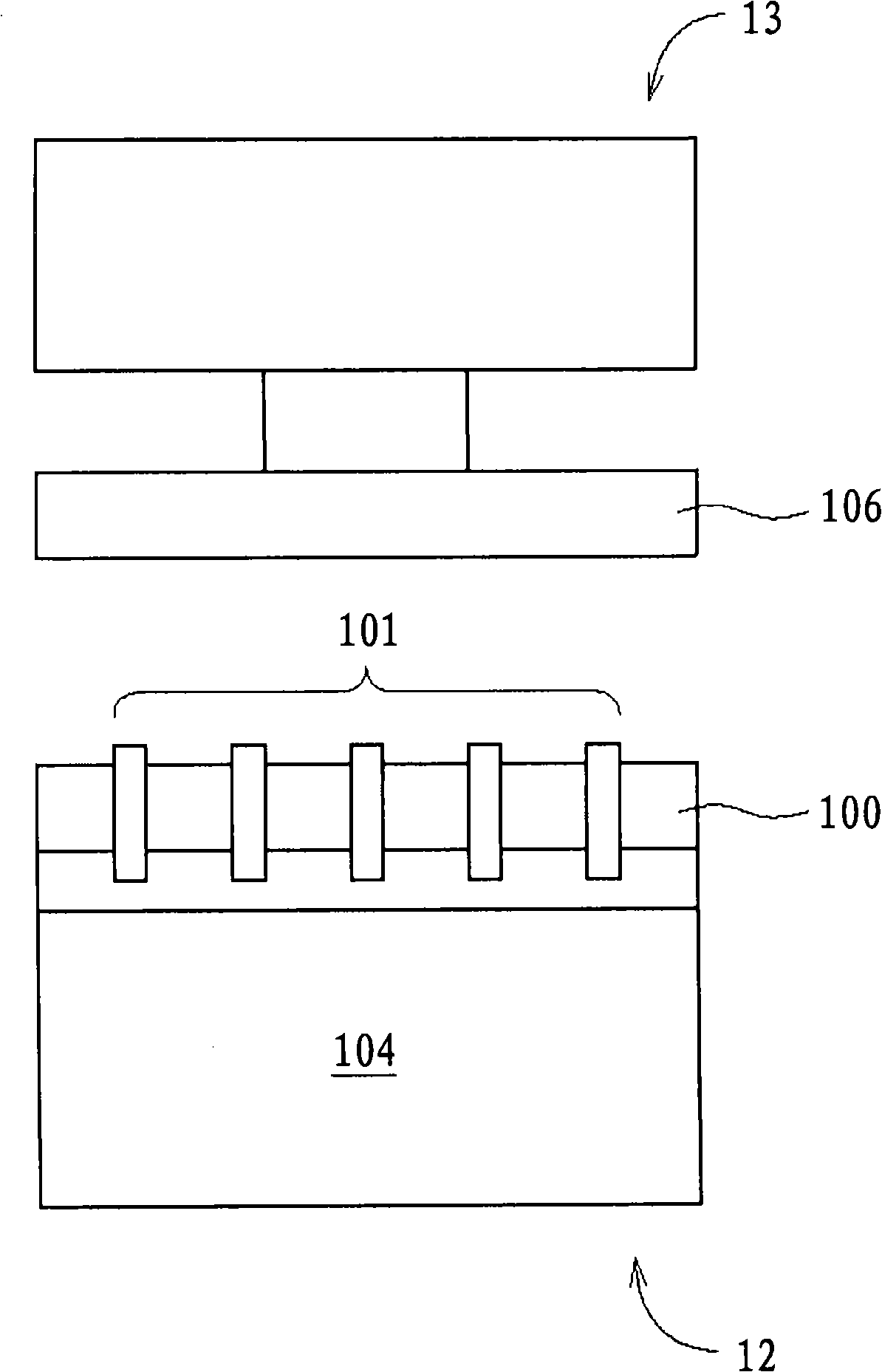
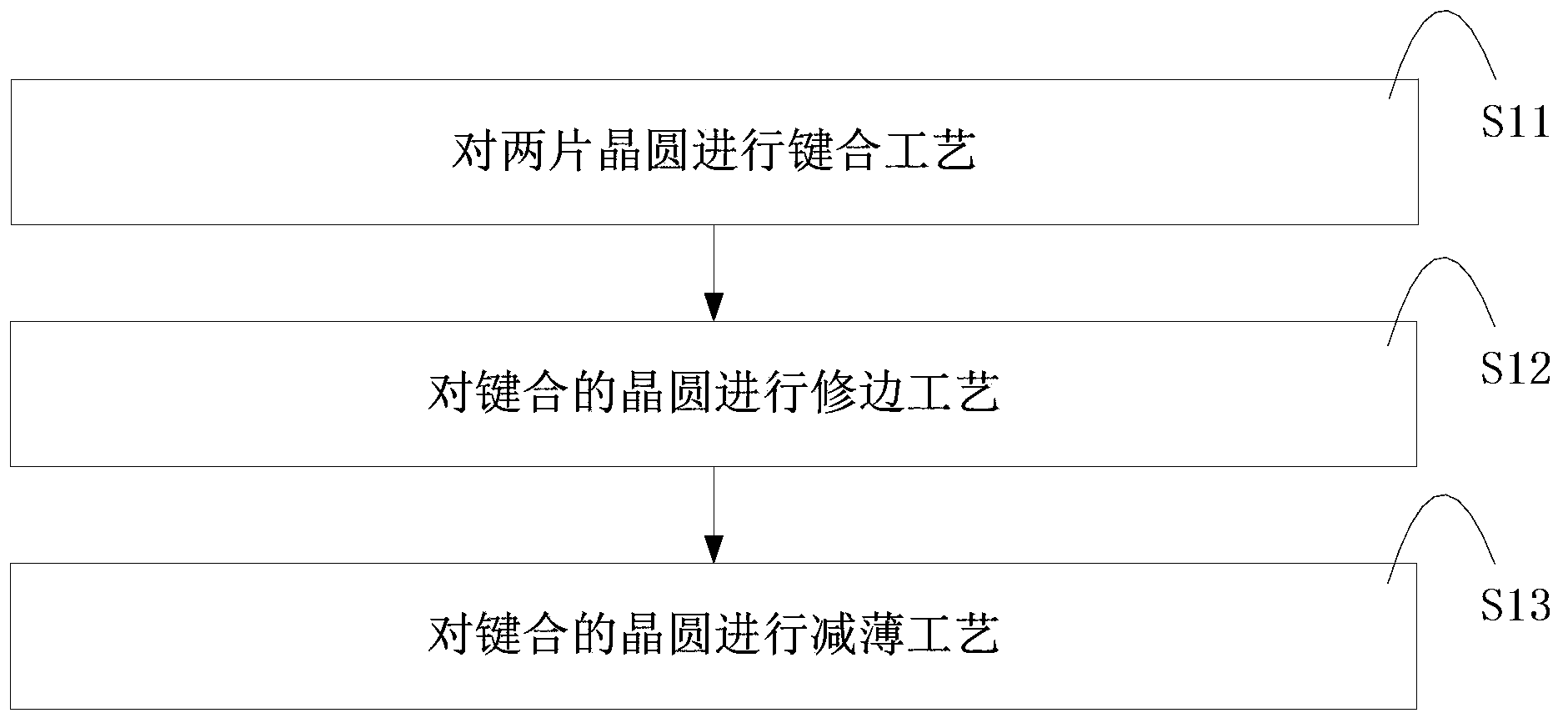
The invention discloses a wafer thinning method, which comprising the steps of: carrying out bonding process on multiple layers of wafers; adding filler in edge gaps of the boned wafers; performing solidification process on the filler; carrying out thinning process on the bonded upmost layer wafer and / or downmost layer wafer; and removing the filler. According to the method provided by the invention, the edges of the wafers cannot be fractured due to stress when thinning the wafers, thereby avoiding scratches and residuals formed on the surfaces of the wafers caused by chippings produced in fracture; and since the trimming process is not needed, the technical process is simplified, the cost is reduced, and the wafer area utilization ratio is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Technique for thinning back side of silicon wafer
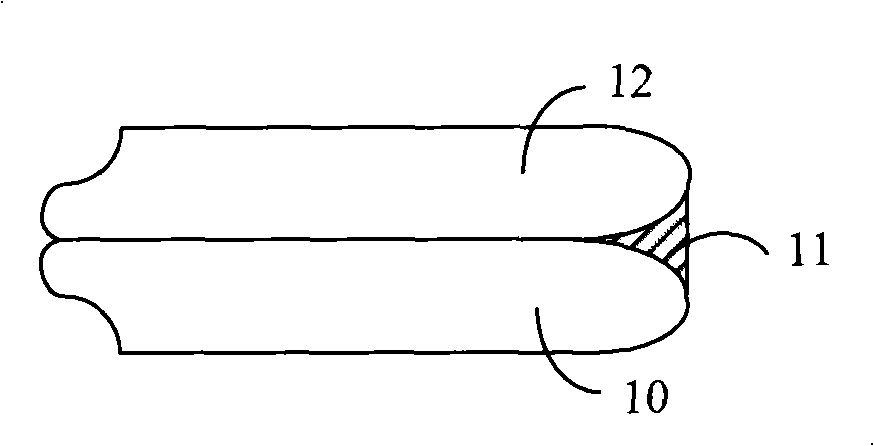
ActiveCN101327572AQuality improvementAvoid enteringPolishing machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringWafer thinning
The present invention discloses a wafer back-thinning technique. A filling substance is filled in the gap between the edges of two wafers or the gap between the edges of a wafer and a supporting carrier; then the back of the wafer is ground, so that the thickness of the wafer can be reduced; finally, after grinding, the back of the wafer is polished. The wafer back-thinning technique of the present invention ensures that the edge of the wafer cannot be curved or broken, thus increasing the wafer-thinning quality.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
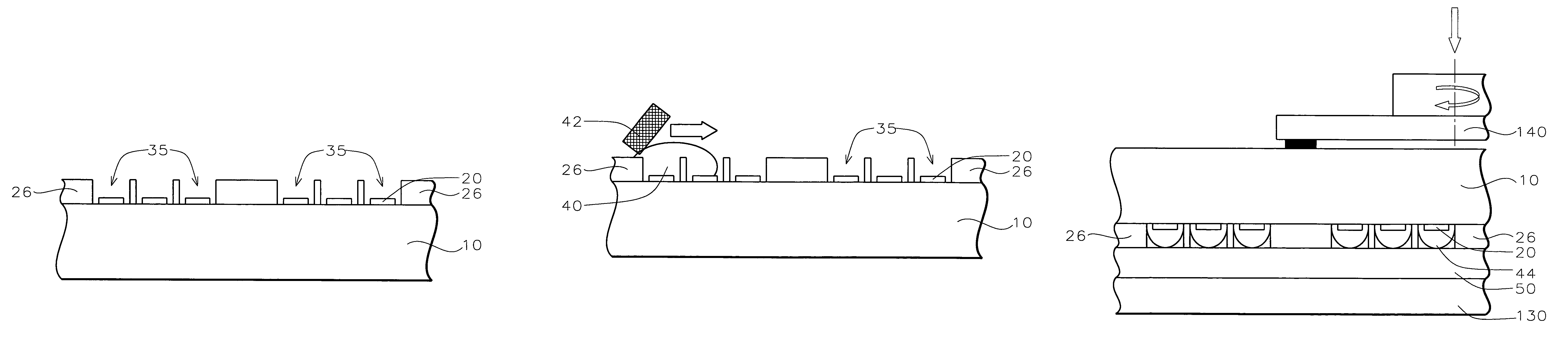
Method for ultra thinning bumped wafers for flip chip
InactiveUS7141487B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingContact pad
In an improved method for bumped wafer thinning, a wafer is provided having a front side and a back side wherein contact pads are formed on the top surface. A dry film is formed on the front side of the wafer and openings are provided in the dry film to the contact pads. Interconnections, such as solder bumps, are formed within the openings on the contact pads. A back grind tape or carrier is attached to the dry film and overlying the interconnections. Thereafter, the wafer is thinned from the back side of the wafer.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
High rate etching using high pressure F2 plasma with argon dilution
The present invention provides for the use of F2 in the process of deposition chamber cleaning which is especially effective if operated under high pressure conditions. In addition, the present invention provides for the use of F2 under high pressure to perform substrate etching or wafer thinning procedures at a high etch rate.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Wafer thinning method
ActiveUS20170025276A1Wafer thickness reductionWear amount of abrasive can be suppressedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsWafer thinning
Disclosed herein is a wafer thinning method for thinning a wafer formed from an SiC substrate having a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface. The wafer thinning method includes a separation start point forming step of applying the laser beam to the second surface as relatively moving the focal point and the SiC substrate to thereby form a modified layer parallel to the first surface and cracks inside the SiC substrate at the predetermined depth, thus forming a separation start point, and a wafer thinning step of applying an external force to the wafer, thereby separating the wafer into a first wafer having the first surface of the SiC substrate and a second wafer having the second surface of the SiC substrate at the separation start point.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Production method of encapsulated component of copper wire bonding IC chip
InactiveCN101626008ASolving the crater puzzleSaving wire costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGold ballPlastic packaging
The invention relates to a production method of an encapsulated component of a copper wire bonding IC chip. A welding plate of the IC chip is provided with a golden ball on which copper bonding balls are stacked, an arch wire is provided with a copper welding point on an inner pin of a lead frame, and a welding plate of the IC chip is connected with the pin of the lead frame. A plastic packaging body is covered on the IC chip, the copper balls stacked on the packed golden ball, the copper welding point of the arch wire on the inner pin of the lead frame and partial inner pins of the lead frame to form a whole circuit. The production method comprises wafer grinding, wafer scribing, core installing, press welding, plastic package, post curing, printing, punching separation, inspection, packaging and warehousing. The invention has simple and reasonable structure, easy use and high qualified rate in encapsulation and testing as well as high reliability, avoids craters, the intensity of the welding point is improved, the pull force of copper welding wires and the shearing strength of the welding point through the production method are greater than that in a copper (golden) bonding production method through direct wire threading, and unsoldering can not happen to the inner welding point.
Owner:TIANSHUI HUATIAN TECH
Photoelectric packaging part with cavity and production method thereof
ActiveCN101562191AImprove packaging yieldImprove the qualified rate of installationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPlastic packagingInterference resistance
The invention provides a photoelectric packaging part with a cavity. An annular outer cavity with inner steps is arranged on a lead frame outer pin by a plastic packaging die, and a plastic packaging outer cavity covers the lead frame outer pin; and gap between an inner pin and a lead frame carrier is connected by a plastic packaging body to form the whole circuit. The production method comprises the following steps: making the plastic packaging outer cavity; thinning down and scribing silicon wafer; molding core; bonding; cementing a glass cover plate; curing; electroplating; printing; and cutting, separating and feeding. The photoelectric packaging part is characterized by simple structure, no exposed outer pin, no coplanarity defect, high chip packaging yield and high installation qualification rate of finished devices. The adopted production method has the advantages of no dambar and forming process, high utilization rate of materials, the adopted glass cover plate made from low-temperature glass and other materials, and higher production efficiency, which is beneficial to product installation. The photoelectric packaging part has the advantages of low cost, small size, high sensitivity, low power consumption, strong anti-interference capacity and good reliability.
Owner:TIANSHUI HUATIAN TECH
Methods and materials useful for chip stacking, chip and wafer bonding
ActiveUS7932161B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWafer dicingWafer thinning
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Method for precisely controlling thinning of wafer
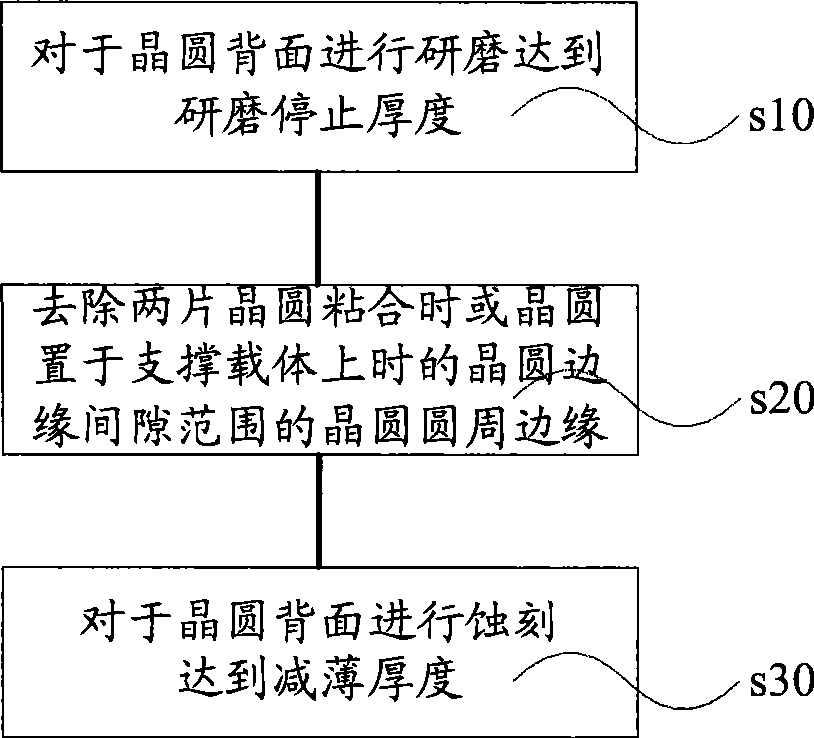
ActiveCN103035489AControl thicknessReduce thickness differenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingEngineering
The invention discloses a method for precisely controlling thinning of a wafer. The method for precisely controlling thinning of the wafer includes that a step of etching of a silicon wafer groove is added in a chip machining process, fillers are arranged in the groove, after the machining process of a front-side chip of a wafer is completed, the back side of the silicon wafer is thinned to the bottom of the groove, and precision control of wafer thinning is achieved. The method for precisely controlling thinning of the wafer can precisely control the thinning of the wafer, differences of thickness among wafers are reduced, and influence of the thickness of a blue film on thinning precision is prevented.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Substrate chip carrier CSP package and production method thereof
InactiveCN104124216ALarge carrier areaAccommodate moreSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringWafer thinning
The invention provides a substrate chip carrier CSP package and a production method thereof. The package comprises a substrate having a middle supporting layer, opposite side walls of the middle supporting layer are provided with a plurality of connecting holes, a first metal layer is formed in each connecting hole, two end faces of the middle supporting layer are provided with first bonding pads and second bonding pads having the same quantity with the connecting holes, two ends of each first metal layer are respectively connected to the corresponding first bonding pad and the corresponding second pad, the pipe core adhering area of the middle supporting layer is provided with a plurality of ventilation holes in which cylindrical second metal layers are formed, the bonding pads of an IC chip are connected to the second bonding pads, a package body is fixedly packaged on the substrate. The substrate chip carrier CSP package is produced through the steps of thinning and scribing a wafer, connecting pipe cores by adhesive, bonding by a wire, packaging, marking, cutting and separating, testing and visually inspecting. The package body is compact in size, applied to IC components with fewer leading-out terminals, and replaces TSSOP and other conventional packaging; for an IC chip which is 0.350mm thick, the packaging thickness can be lower than 1mm.
Owner:TIANSHUI HUATIAN TECH
Method and structure for three-dimensional packaging based on TSV
ActiveCN103346097AReduce forceReduce warpageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPlastic packagingPlastic materials
The invention provides a method and structure for three-dimensional packaging based on TSV. The technology that plastic packaging is conducted on a wafer and a chip for at least twice is adopted by the method and structure for three-dimensional packaging based on the TSV. A first plastic packaging layer and a following plastic packaging layer are sequentially covered. The coefficients of thermal expansion of every two adjacent layers of plastic packaging materials are different, so that the stress generated by one of every two layers of the plastic packaging materials in the plastic packaging process is different from that generated by the adjacent layer of the plastic material in direction, the stress is counteracted between every two adjacent layers, the action force of the plastic materials to the washer is reduced, the effect that the warping degree of the washer is reduced is achieved, and therefore the smooth implementation of the non-substrate washer thinning technology is guaranteed.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
Method and apparatus for measuring thickness of a material
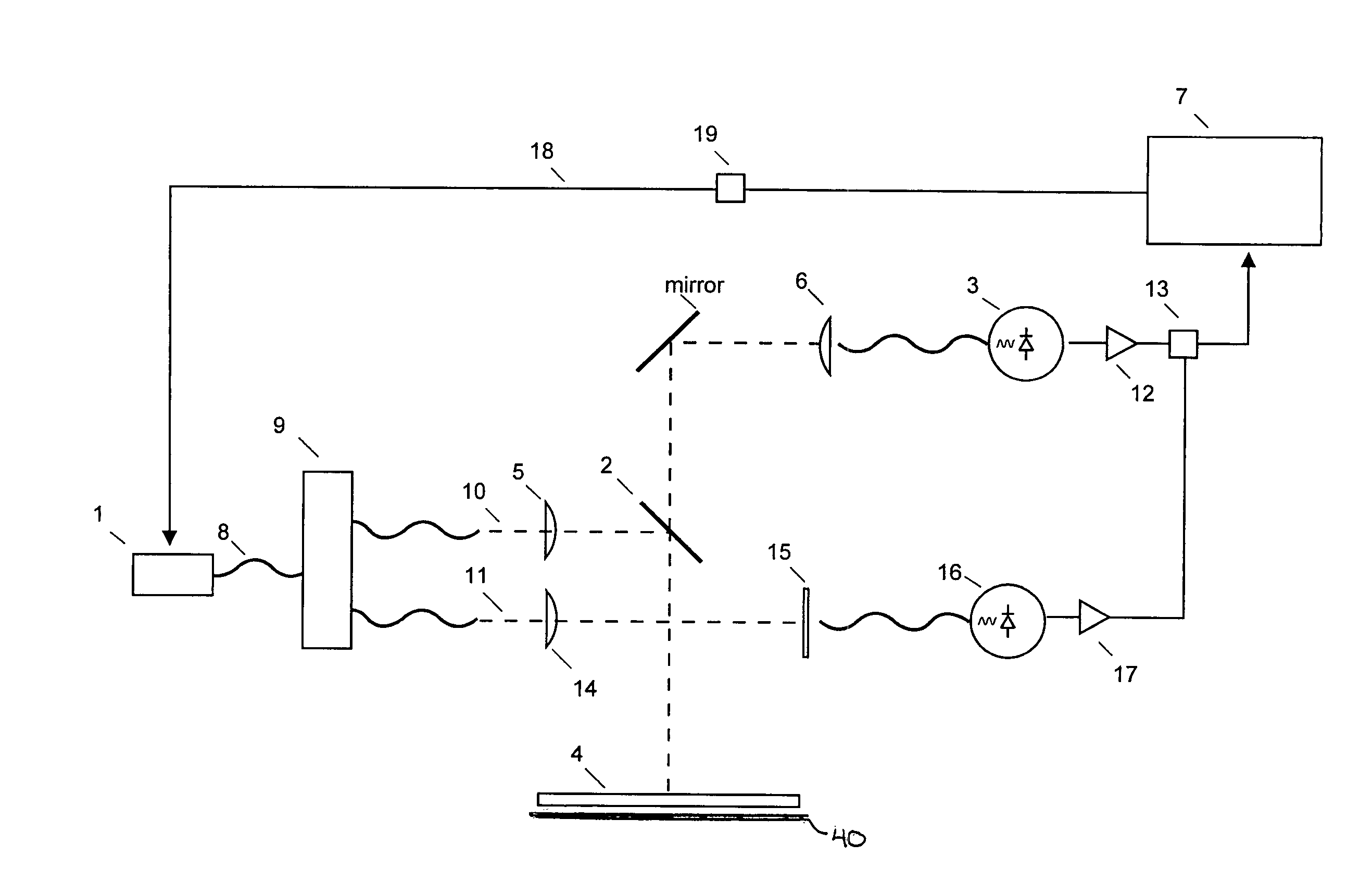
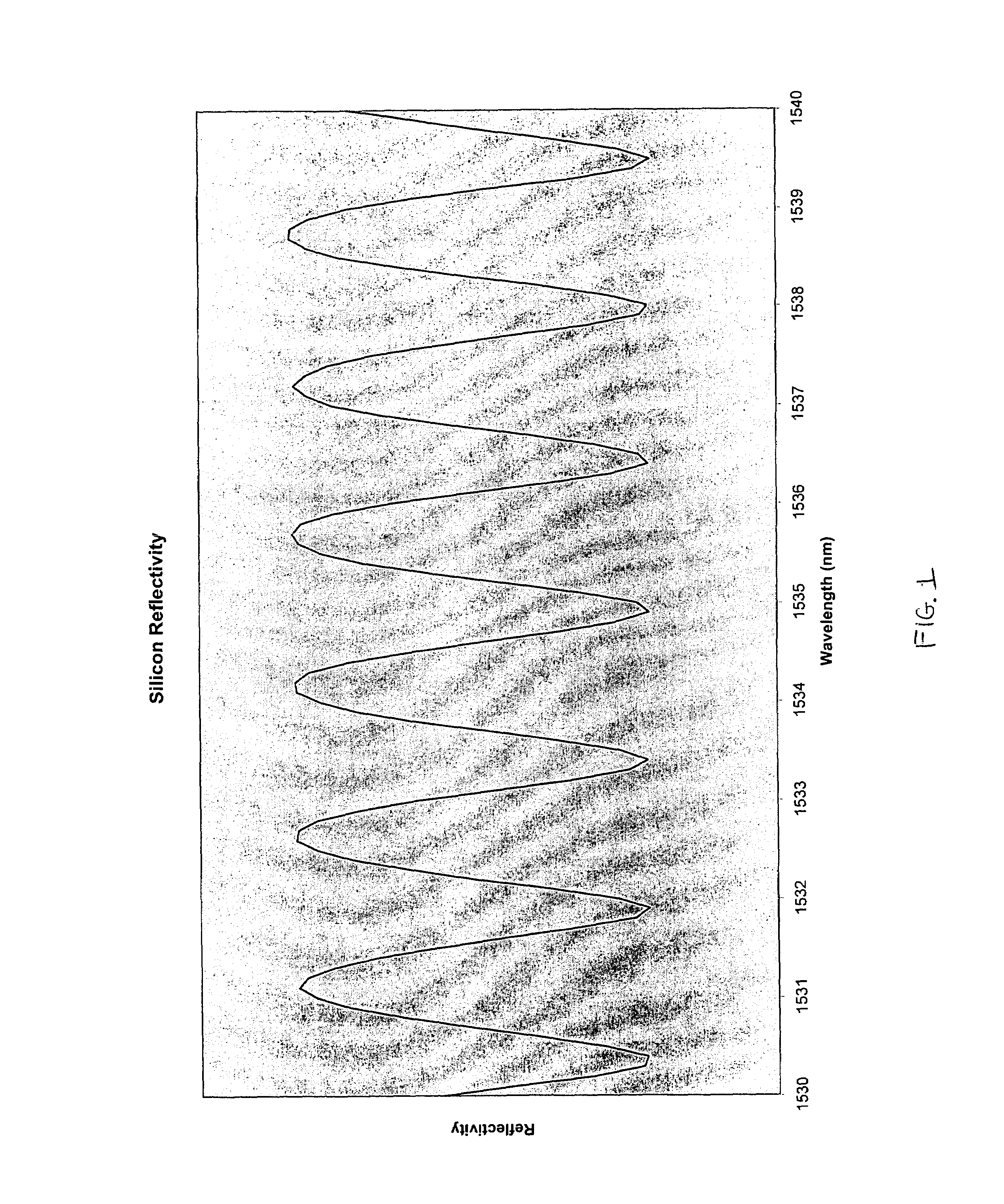
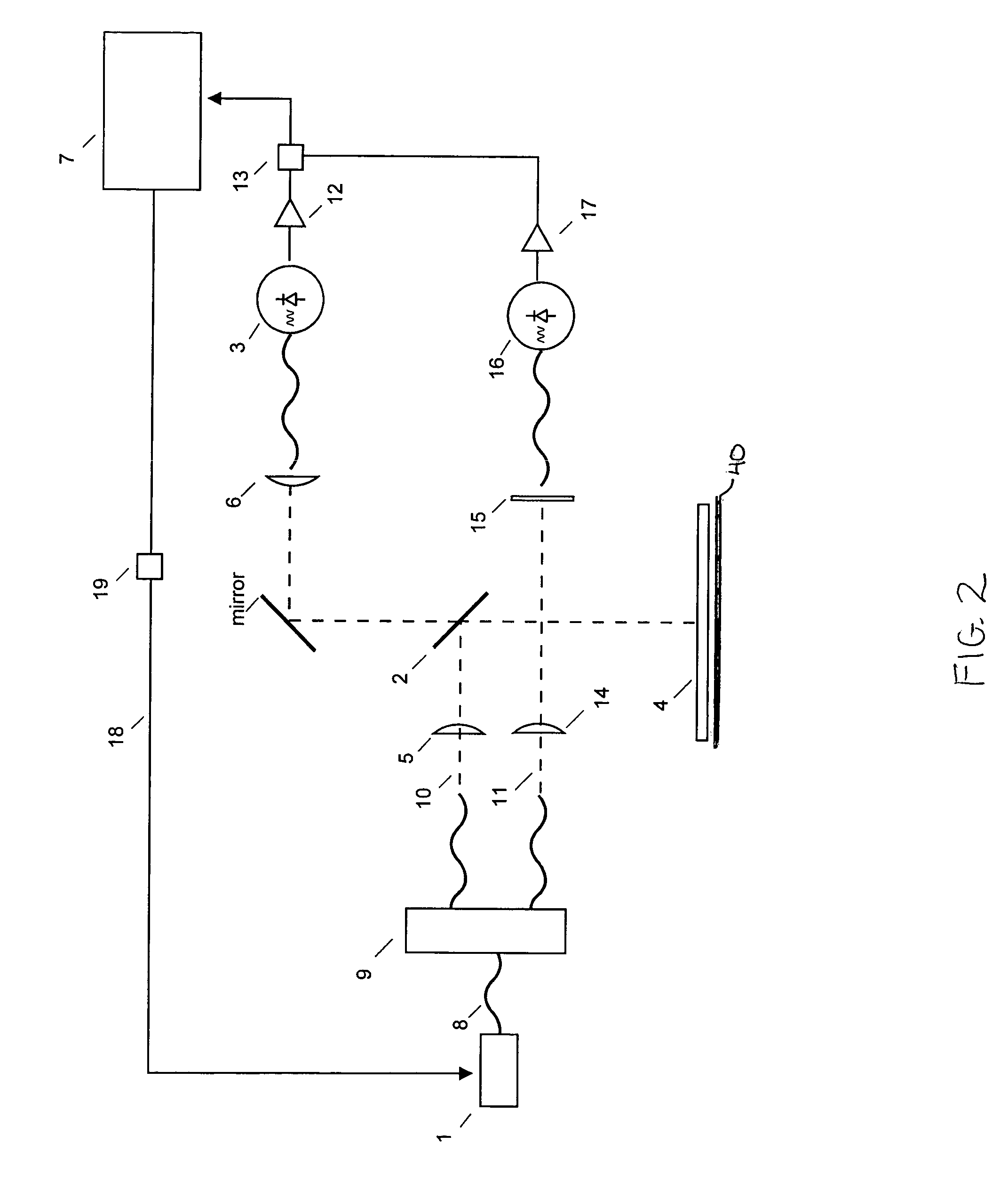
A method and apparatus for measuring wafers, thin films, or other planar layers are disclosed. This invention utilizes a tunable, monochromatic light source reflected from or transmitted through the layer to be measured. The wavelengths of light are selected such that the light is partially transmitted through the material to be measured so as optical interference is seen among the interfaces of the layer(s). The wavelengths are also controlled to sufficiently small increments to resolve these interference features. This apparatus relates to the need to monitor wafer thinning, film deposition, and other semiconductor device related processes.
Owner:FILMETRICS
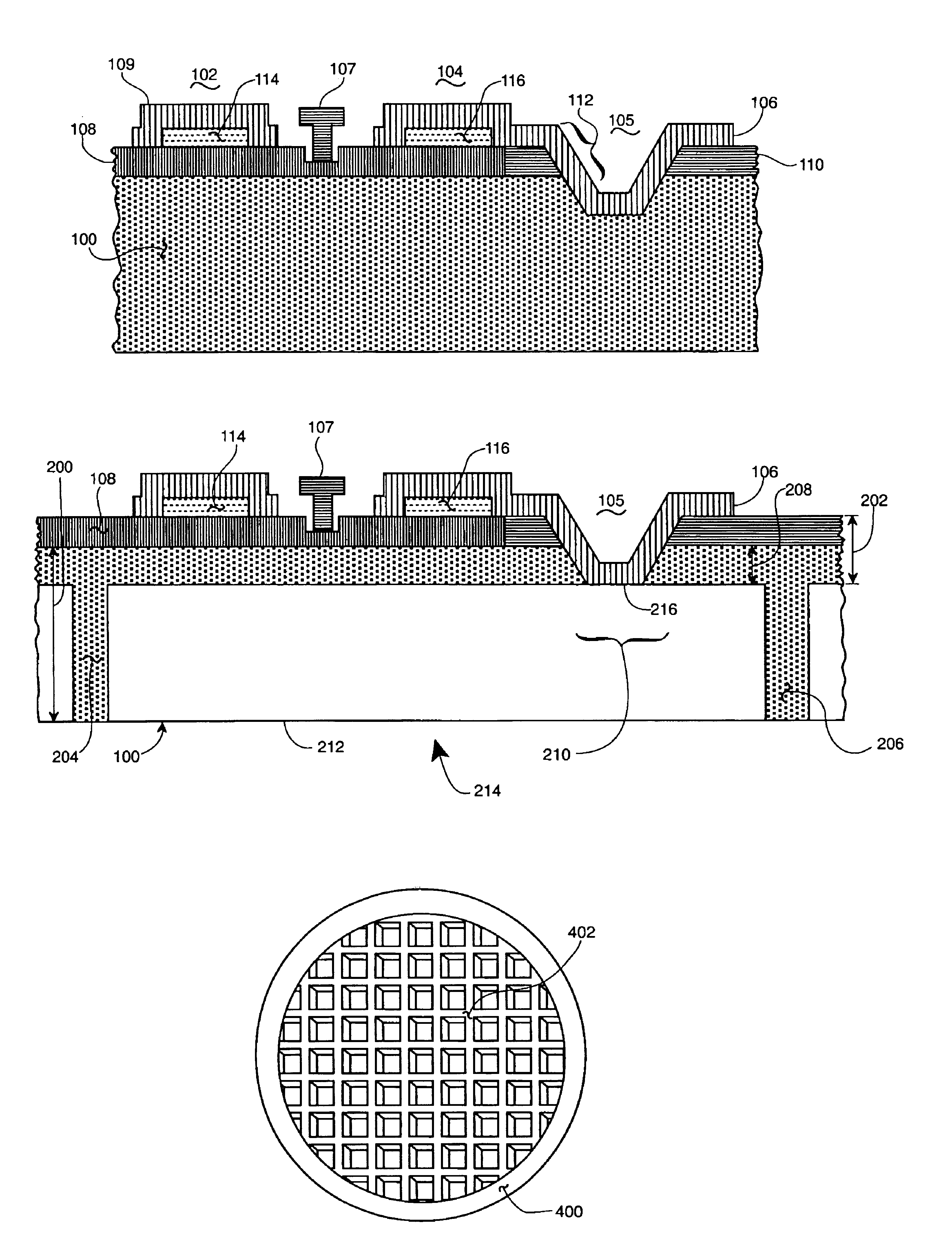
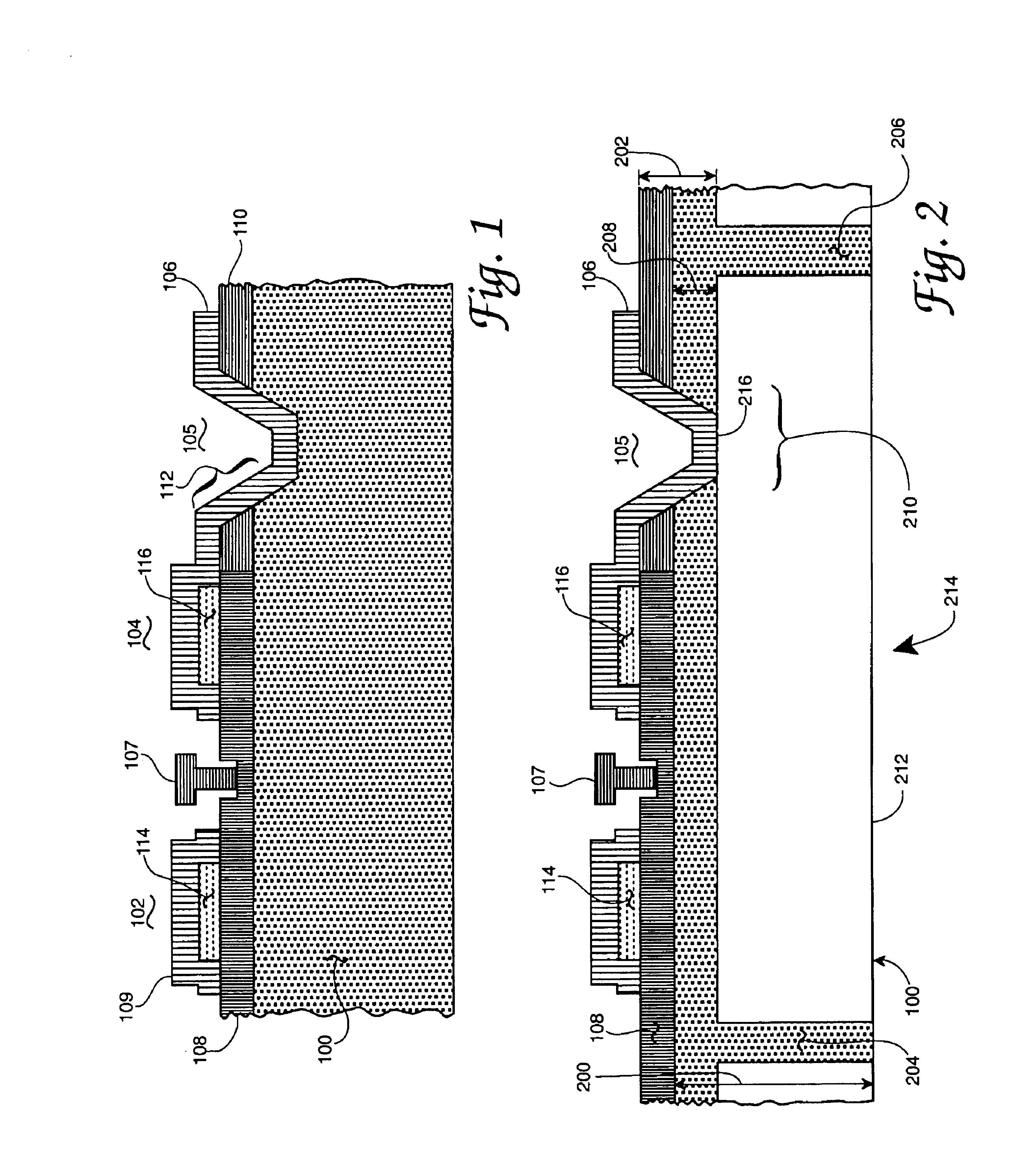
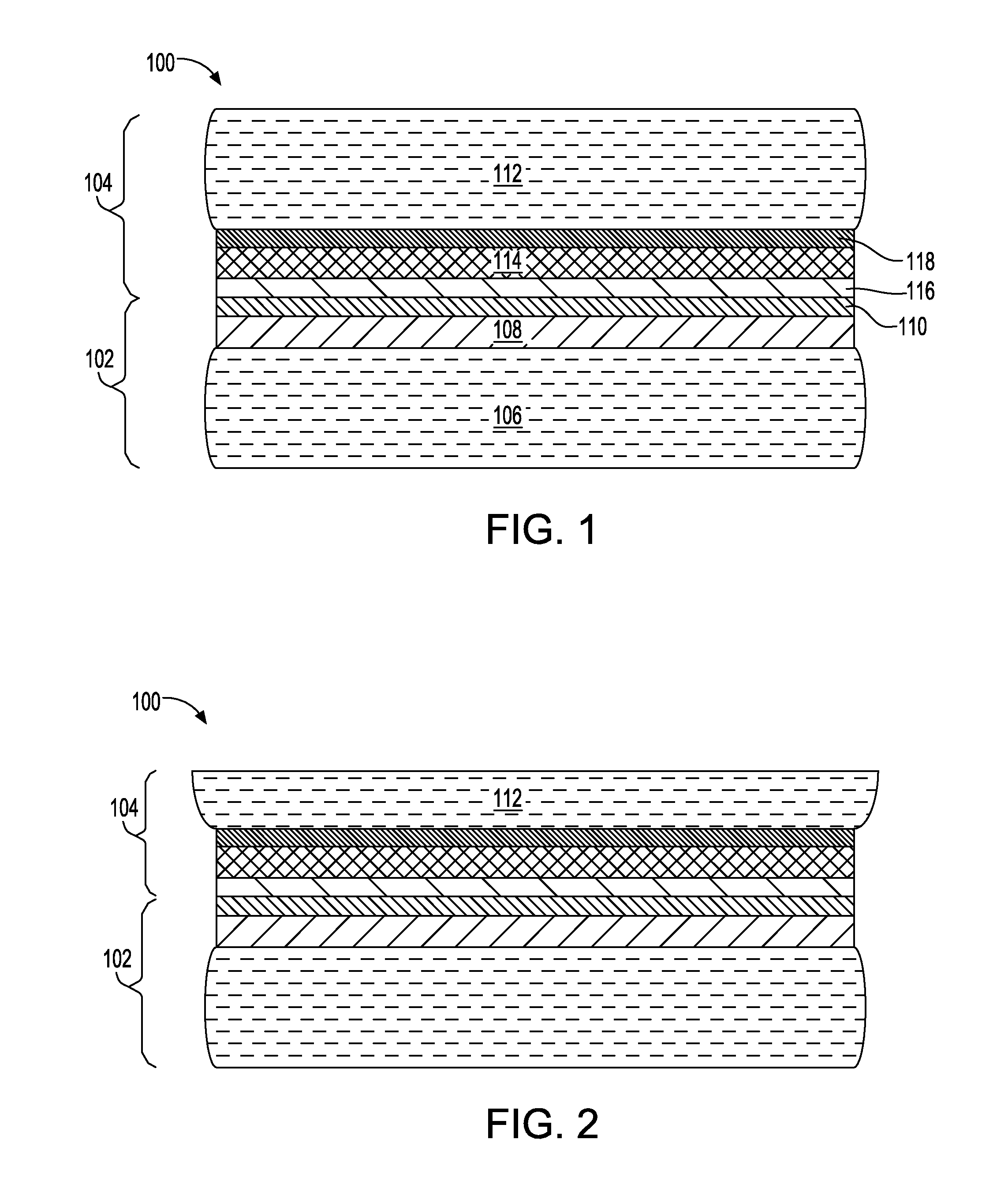
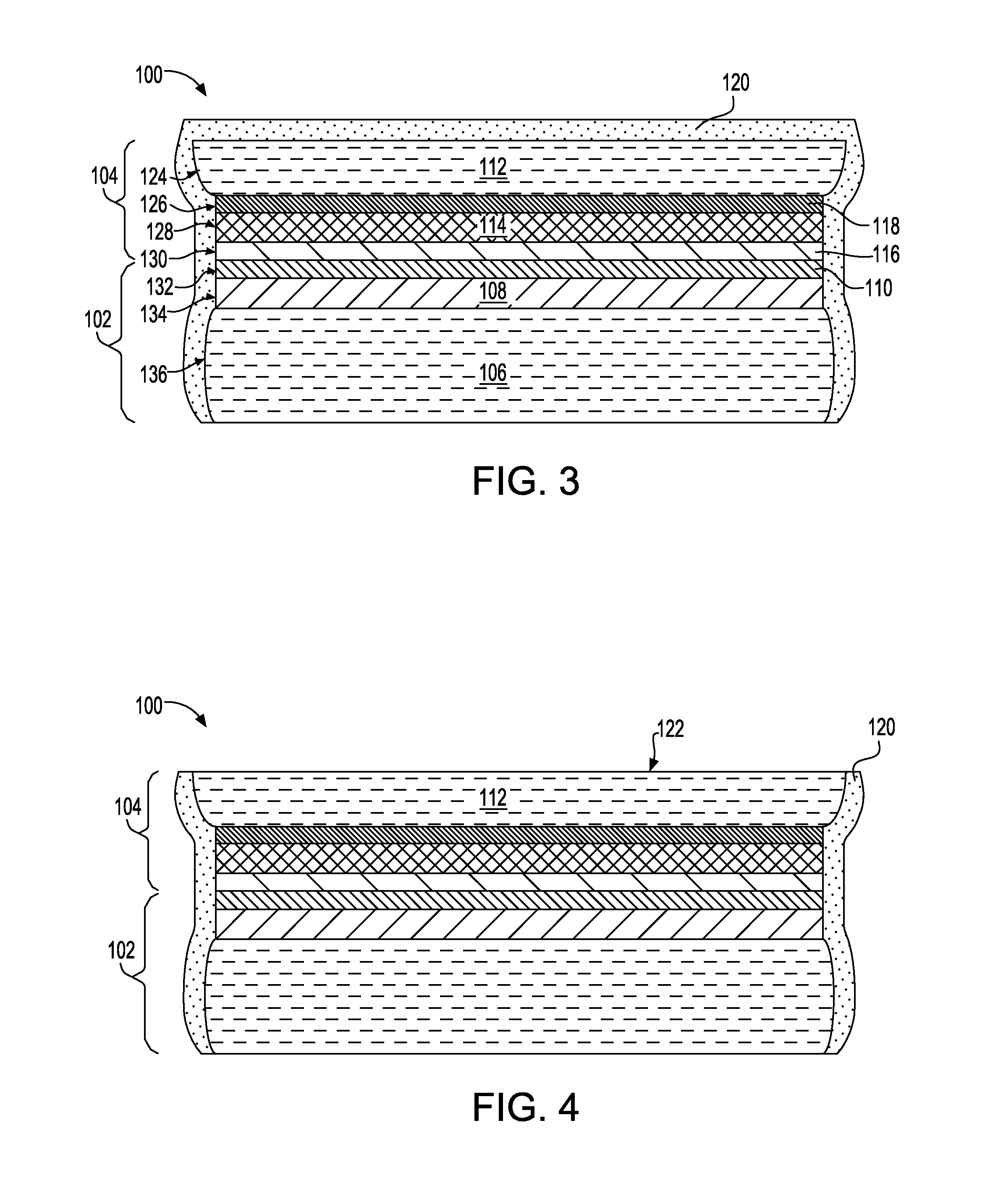
Edge protection of bonded wafers during wafer thinning
InactiveUS8765578B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingElectrical conductor
A method of edge protecting bonded semiconductor wafers. A second semiconductor wafer and a first semiconductor wafer are attached by a bonding layer / interface and the second semiconductor wafer undergoes a thinning process. As a part of the thinning process, a first protective layer is applied to the edges of the second and first semiconductor wafers. A third semiconductor wafer is attached to the second semiconductor wafer by a bonding layer / interface and the third semiconductor wafer undergoes a thinning process. As a part of the thinning process, a second protective layer is applied to the edges of the third semiconductor wafer and over the first protective layer. The first, second and third semiconductor wafers form a wafer stack. The wafer stack is diced into a plurality of 3D chips while maintaining the first and second protective layers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
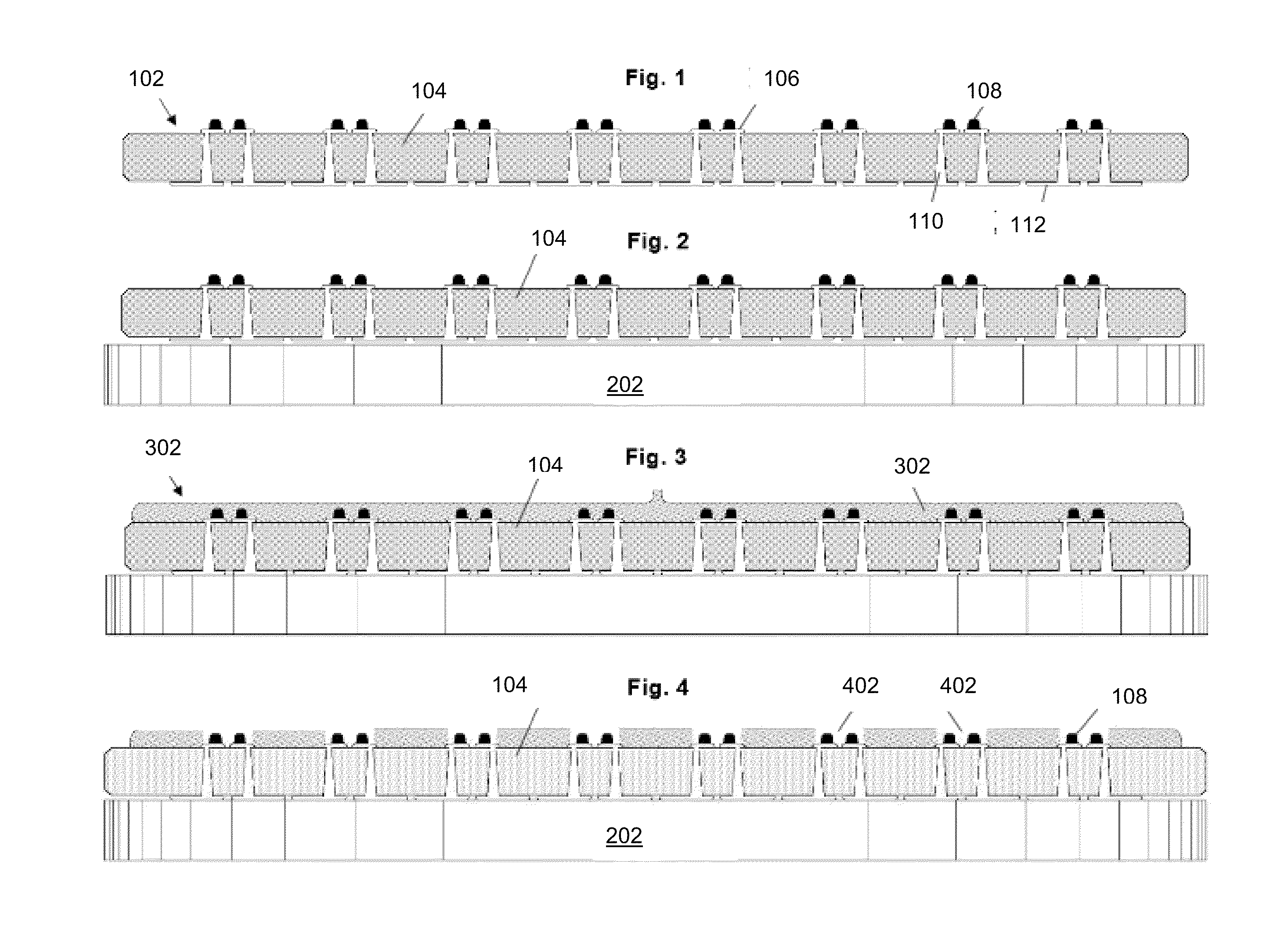
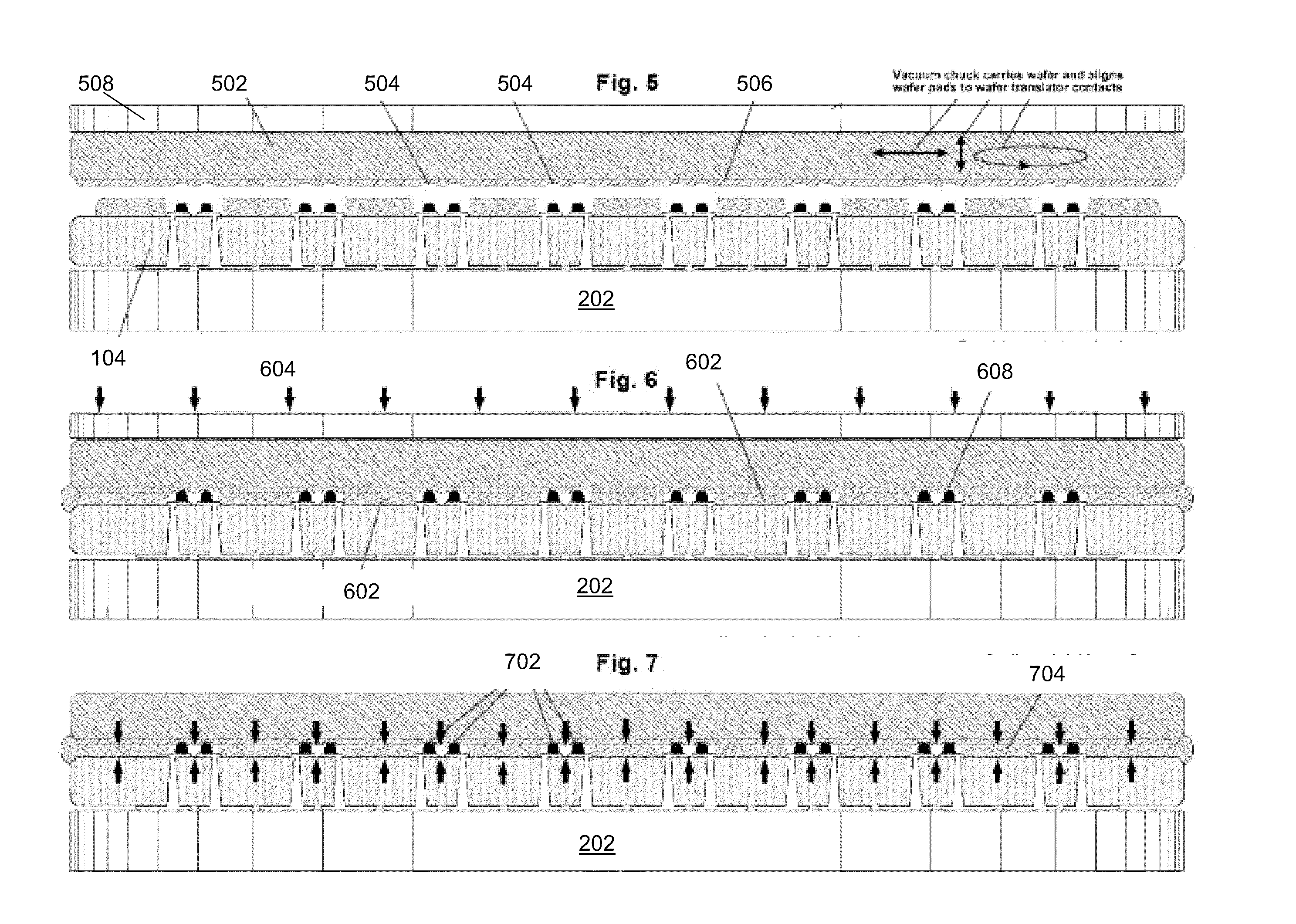
Methods and Apparatus For Thinning, Testing And Singulating A Semiconductor Wafer
ActiveUS20100144069A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsWaferingWafer dicing
A wafer translator is provided with a patterned layer of wafer bonding thermoset plastic and is removably attached with a wafer so as to form a wafer / wafer translator pair. The wafer translator acts as a mechanical support during a thinning process as well as during a wafer dicing operation. The singulated integrated circuits are then removed from the wafer translator. In some embodiments, wafer level testing of the integrated circuits on the wafer is performed subsequent to the wafer thinning process but before the wafer and wafer translator are separated. In other embodiments, wafer level testing of the integrated circuits on the wafer is performed subsequent to the wafer dicing operation but before the diced wafer and wafer translator are separated.
Owner:TRANSLARITY INC
Method of thinning a wafer
InactiveUS20070259509A1Avoid crackingIncrease minimum thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringWafer thinning
A method of thinning a wafer. A wafer is provided, and the front surface of the wafer is bonded to a carrier wafer with a bonding layer. The bonding layer is a thermal release tape or a UV tape. Subsequently, a wafer thinning process is performed to thin the wafer from the back surface.
Owner:TOUCH MICRO SYST TECH
Method for ultra thinning bumped wafers for flip chip
InactiveUS20060003550A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact padInterconnection
In an improved method for bumped wafer thinning, a wafer is provided having a front side and a back side wherein contact pads are formed on the top surface. A dry film is formed on the front side of the wafer and openings are provided in the dry film to the contact pads. Interconnections, such as solder bumps, are formed within the openings on the contact pads. A back grind tape or carrier is attached to the dry film and overlying the interconnections. Thereafter, the wafer is thinned from the back side of the wafer.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
High temperature and chemical resistant process for wafer thinning and backside processing
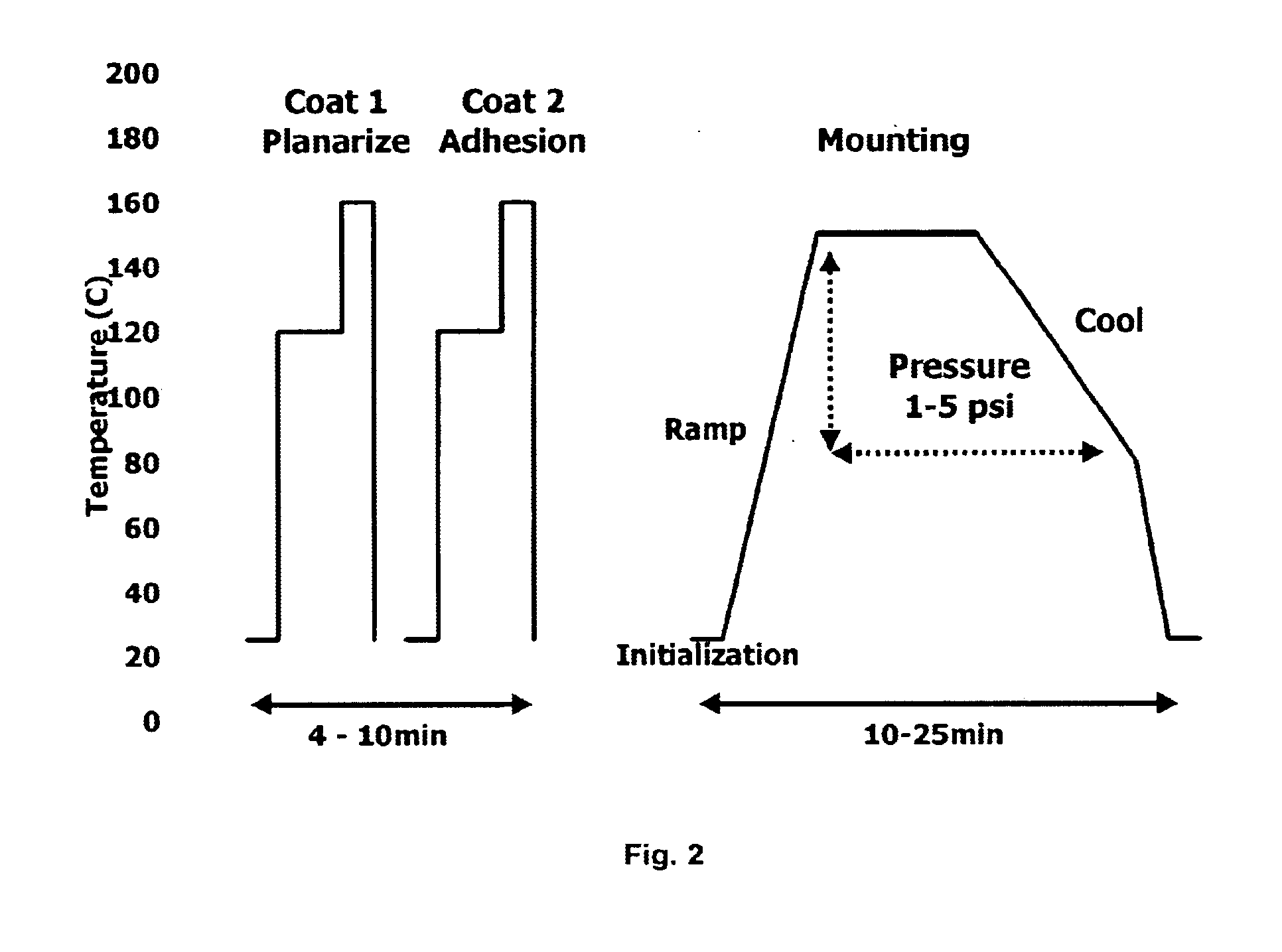
InactiveUS7232770B2Easy to installSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMonomerThermal oxide
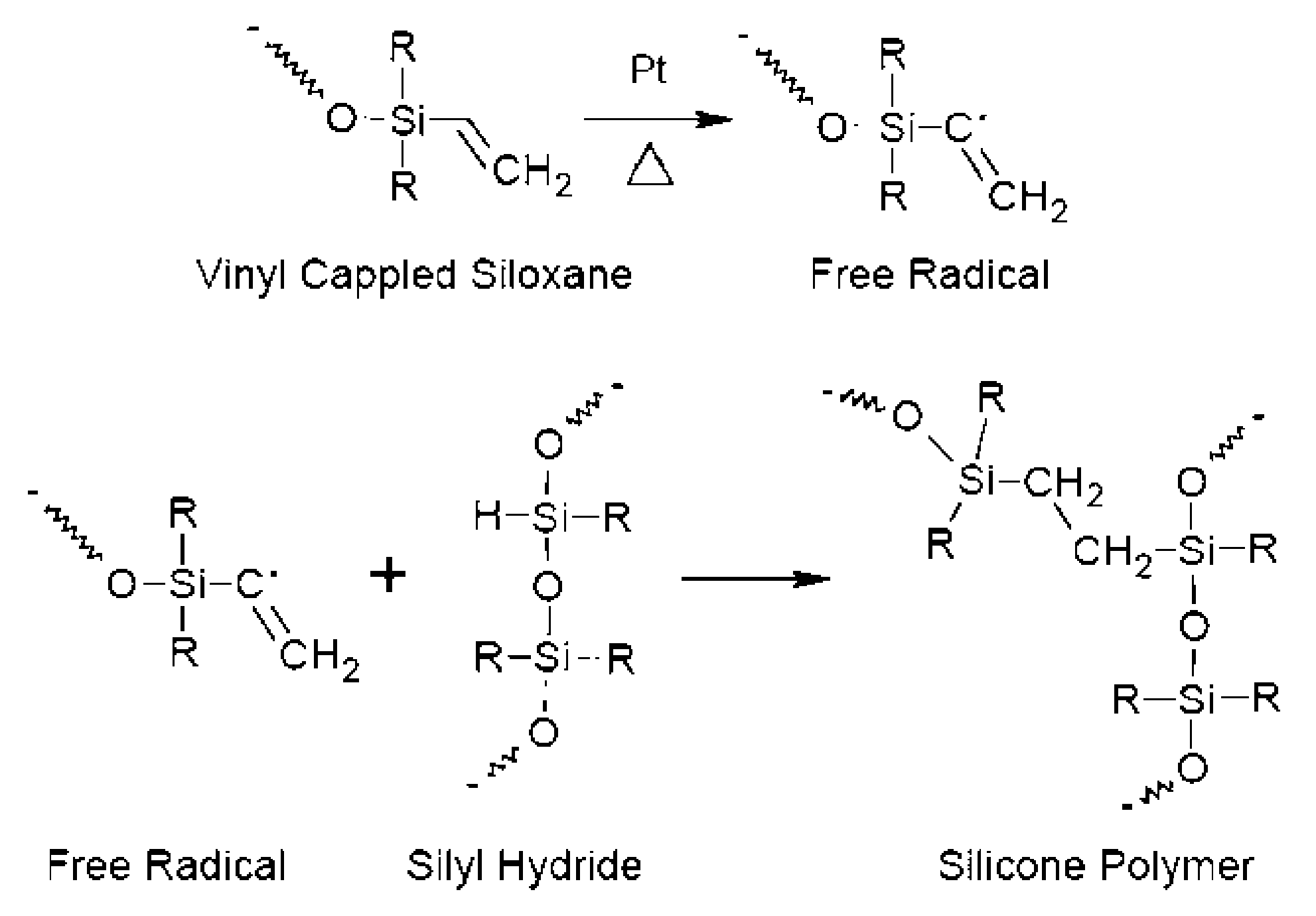
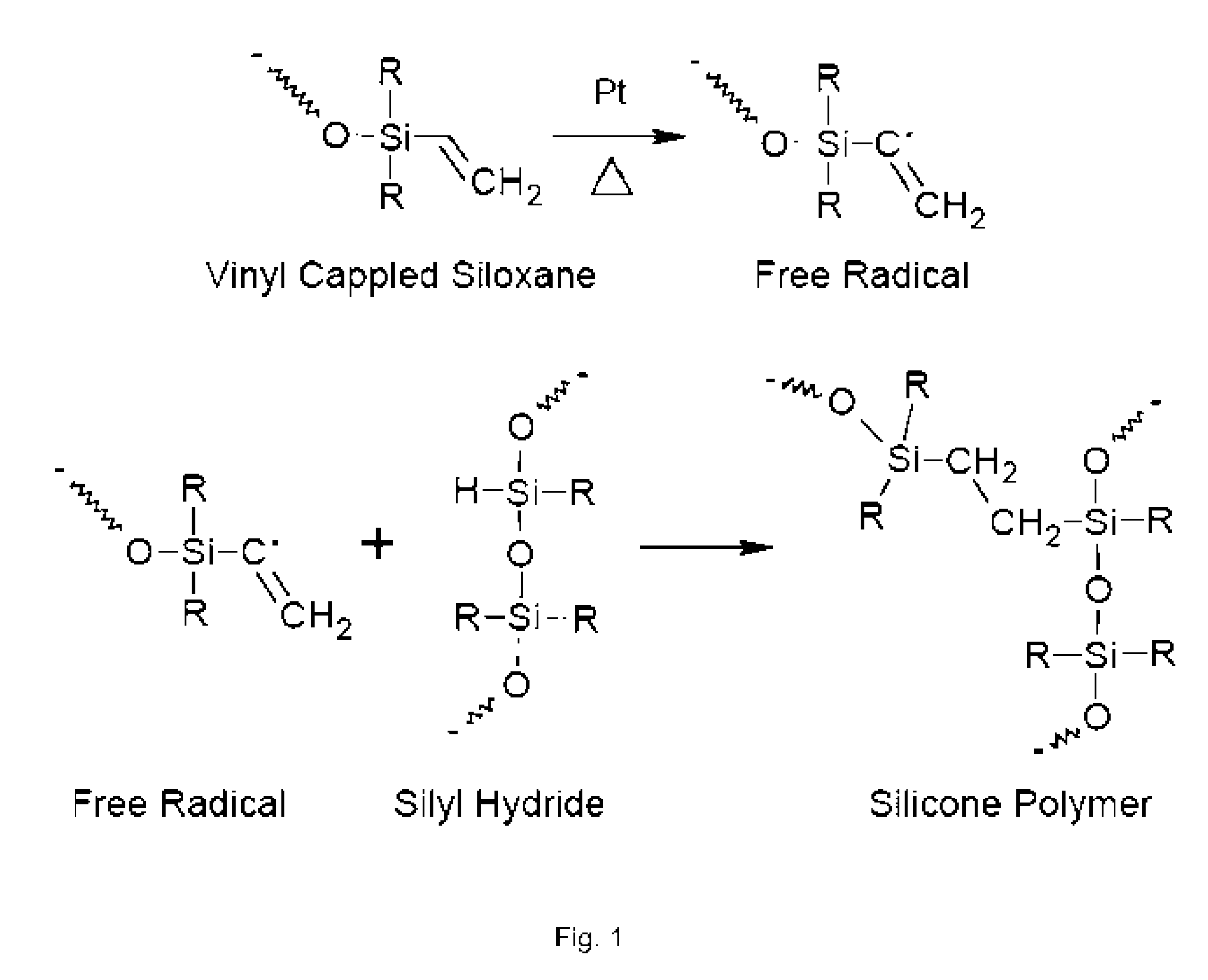
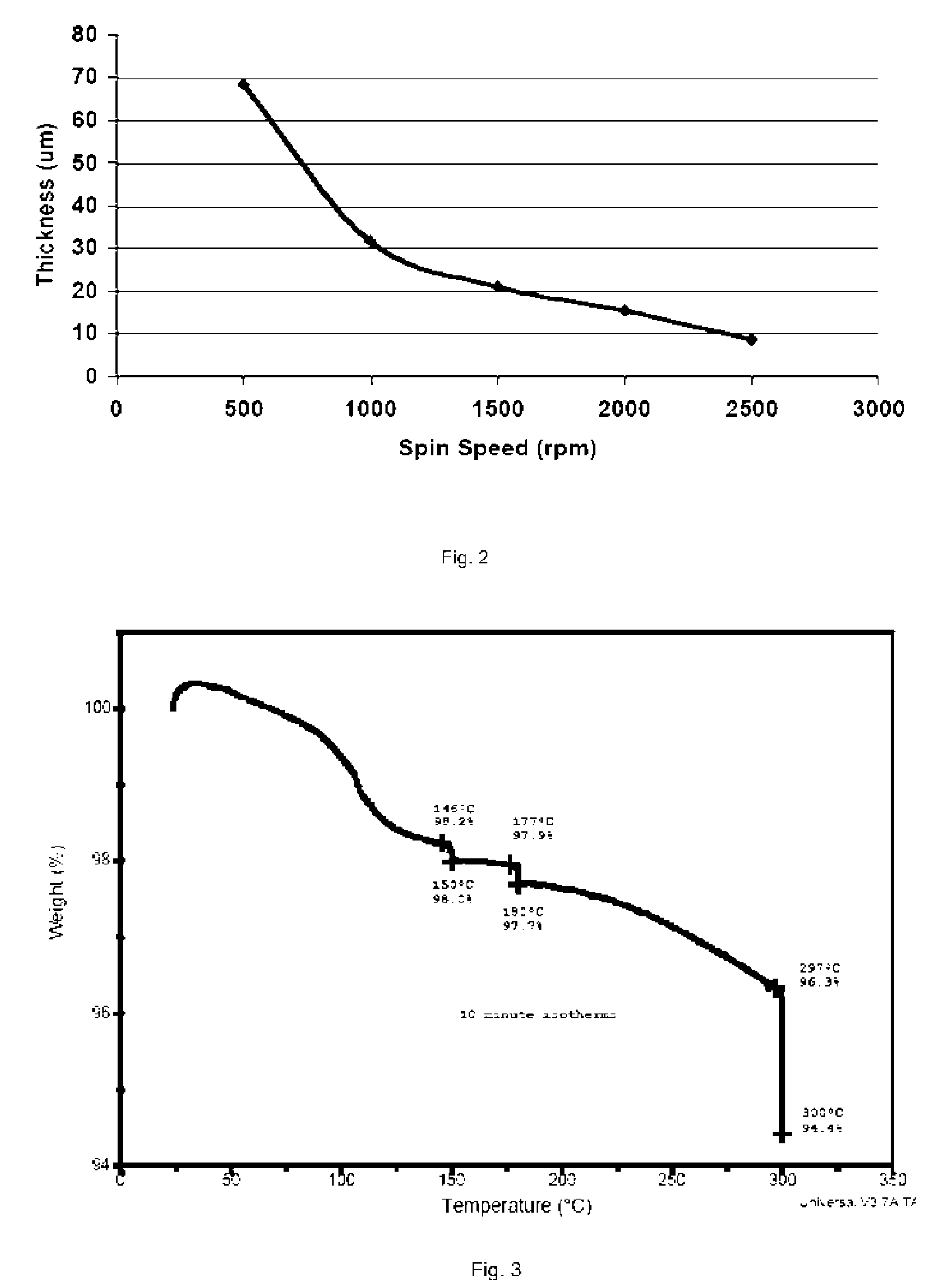
A process which uses a silicone resin to form a wafer-to-carrier bonded package that enables wafer thinning and backside processing while the cured resin exhibits high chemical and thermal resistance. The process is versatile in that the constructed wafer package allows for a wide range of chemical exposures to include dilute acid and base etchants, resist and residue strippers, electroplating chemistries, and also providing use in a range of deposition and etch processes that may exceed 300° C. The process utilizes a mixture of silicone monomers that when applied to semiconductor wafers by a spin-coat application, the result is a planarization of the front side device area, and when a subsequent thin coat is applied will facilitate bonding of the wafer-to-carrier package when heat and pressure are applied. The cured silicone bonded wafer-to-carrier package allows for wafer thinning consistent to industry objectives. Backside processing may include thermal oxide deposition, installed vias, and subsequent metallization in plating baths. Upon completion of a thinned and processed wafer, detachment occurs as described in prior art. Specialty chemical systems which completely dissolves the cured silicone and allows the wafer substrate to be easily rinsed and dried and become available for subsequent processing or final dicing and packaging.
Owner:KMG ELECTRONICS CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com