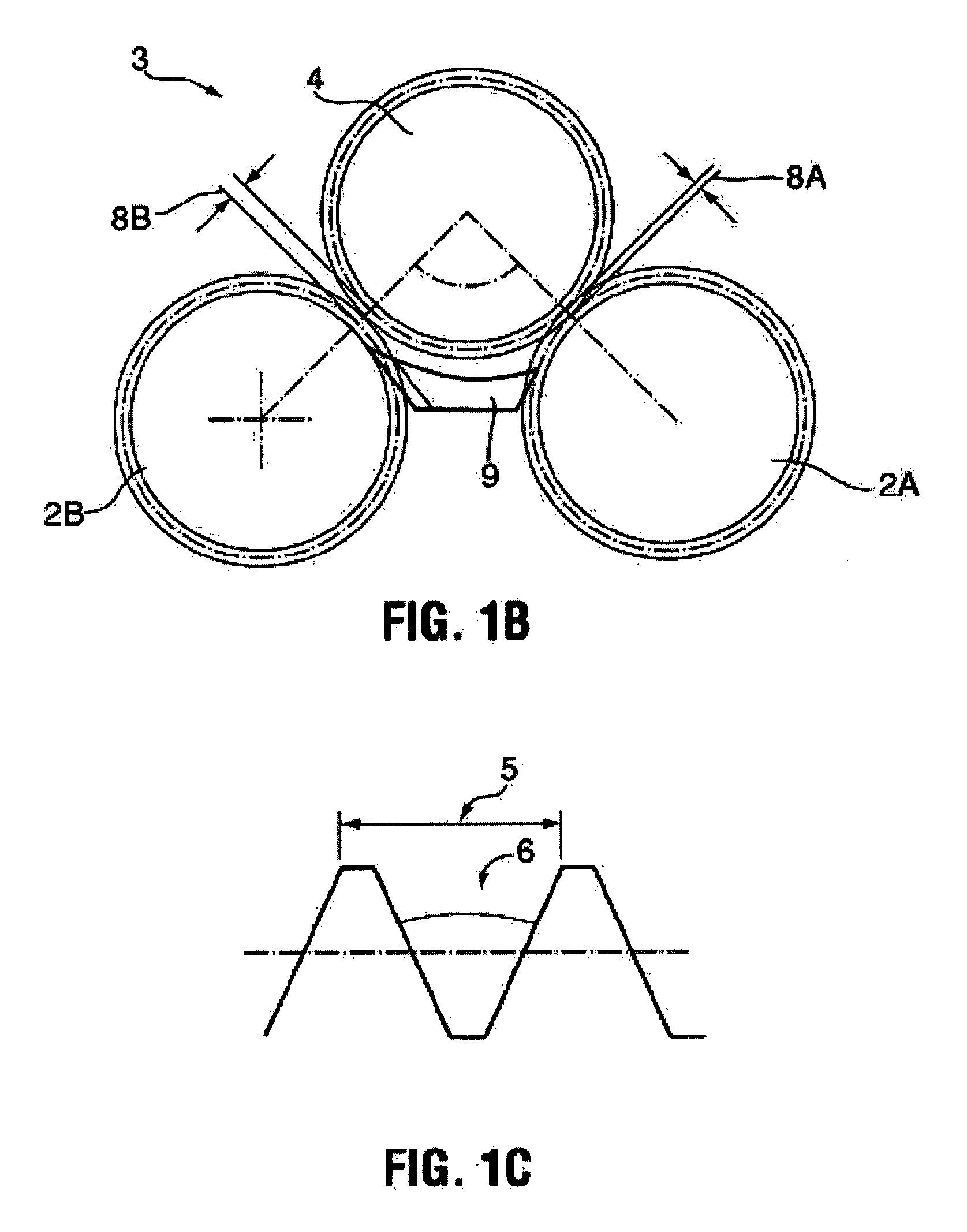
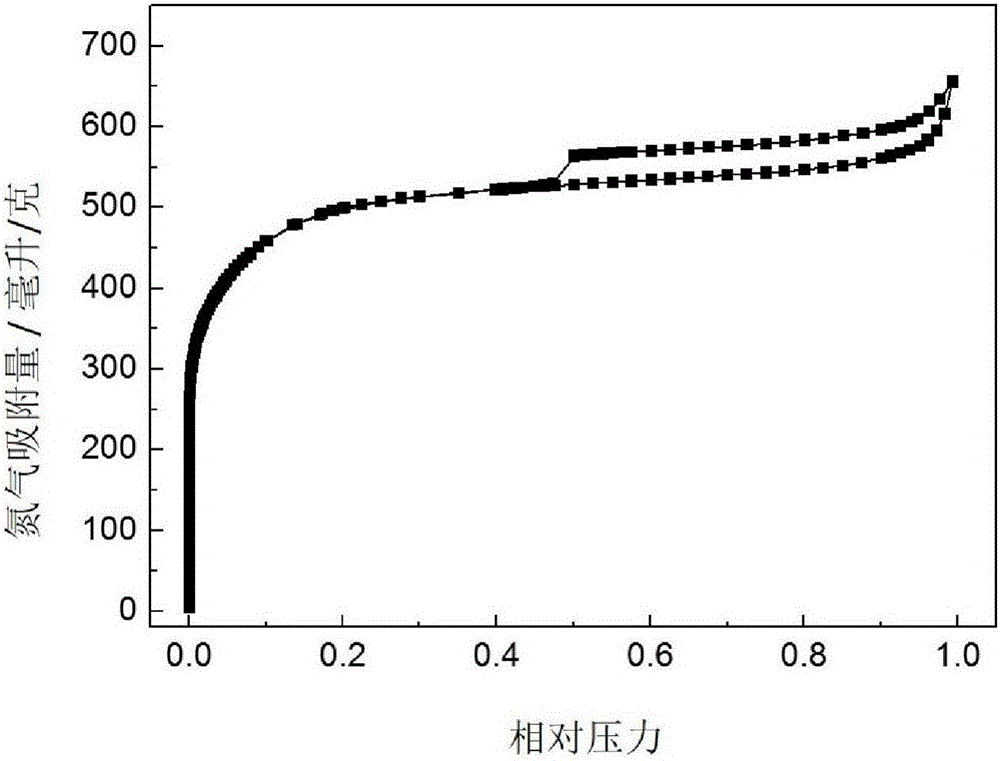
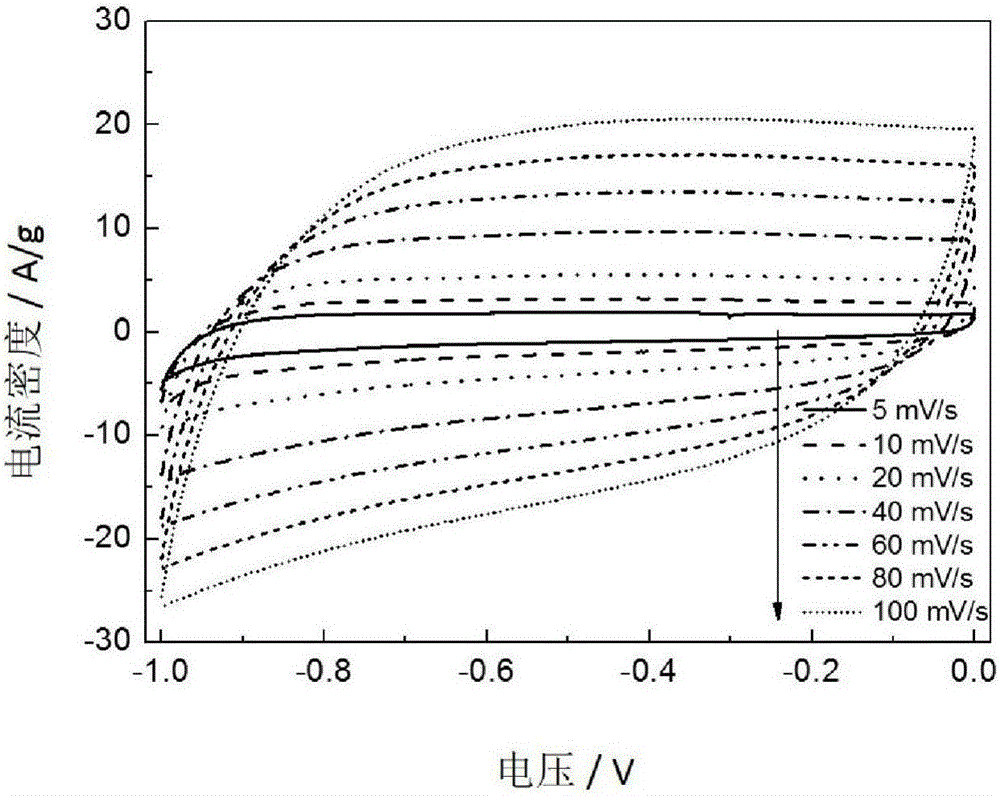
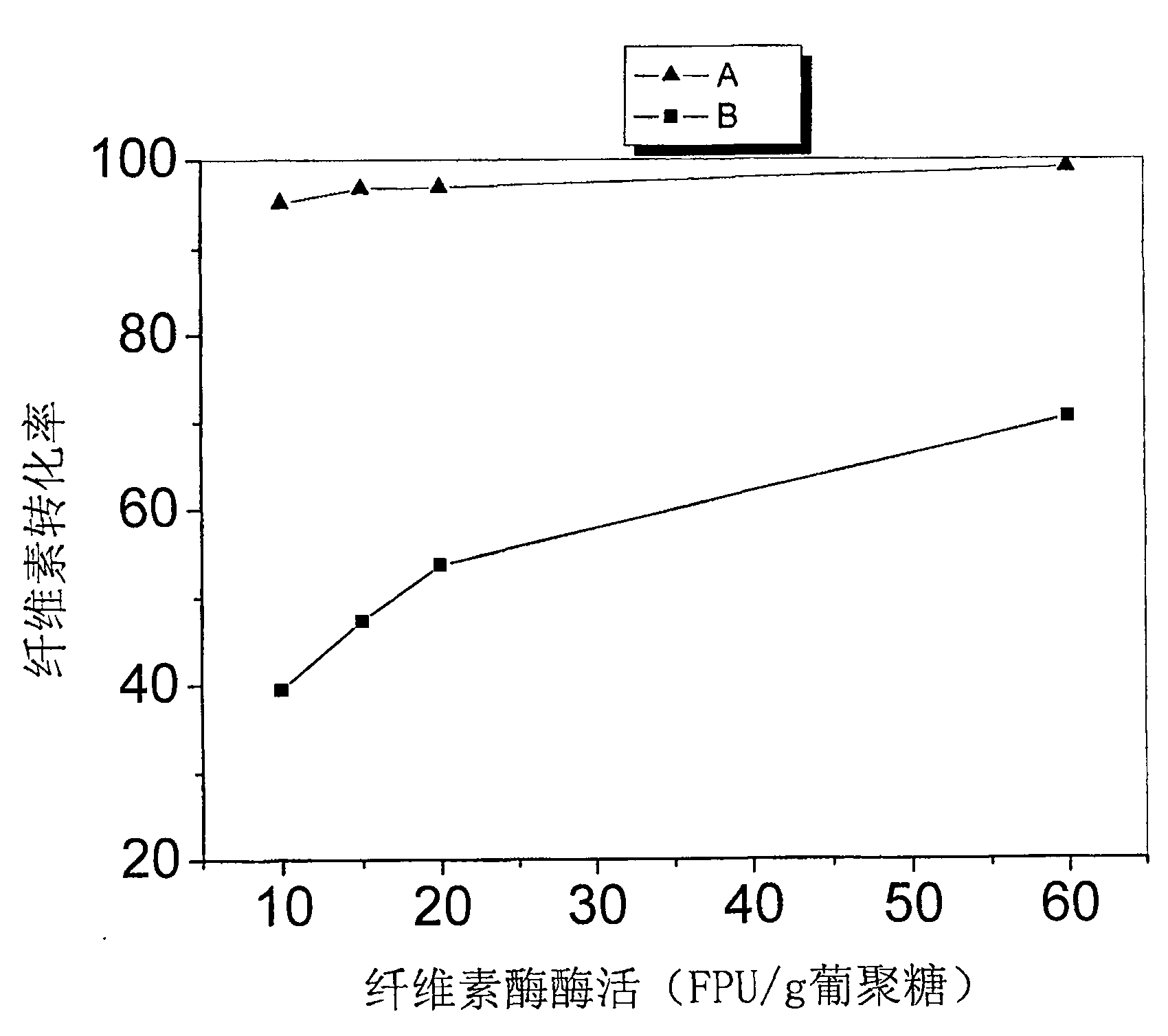
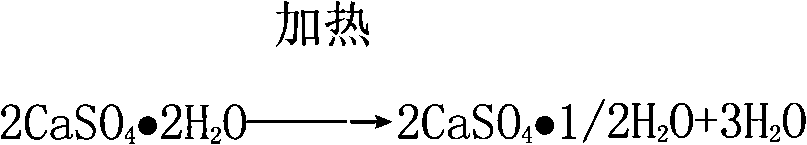Patents
Literature
1669 results about "Dilute acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dilute acid is simply an acid dissolved in a solvent at low concentration. The term “dilute” is relative and not quantitatively defined so it is not possible to give a specific answer to this question.
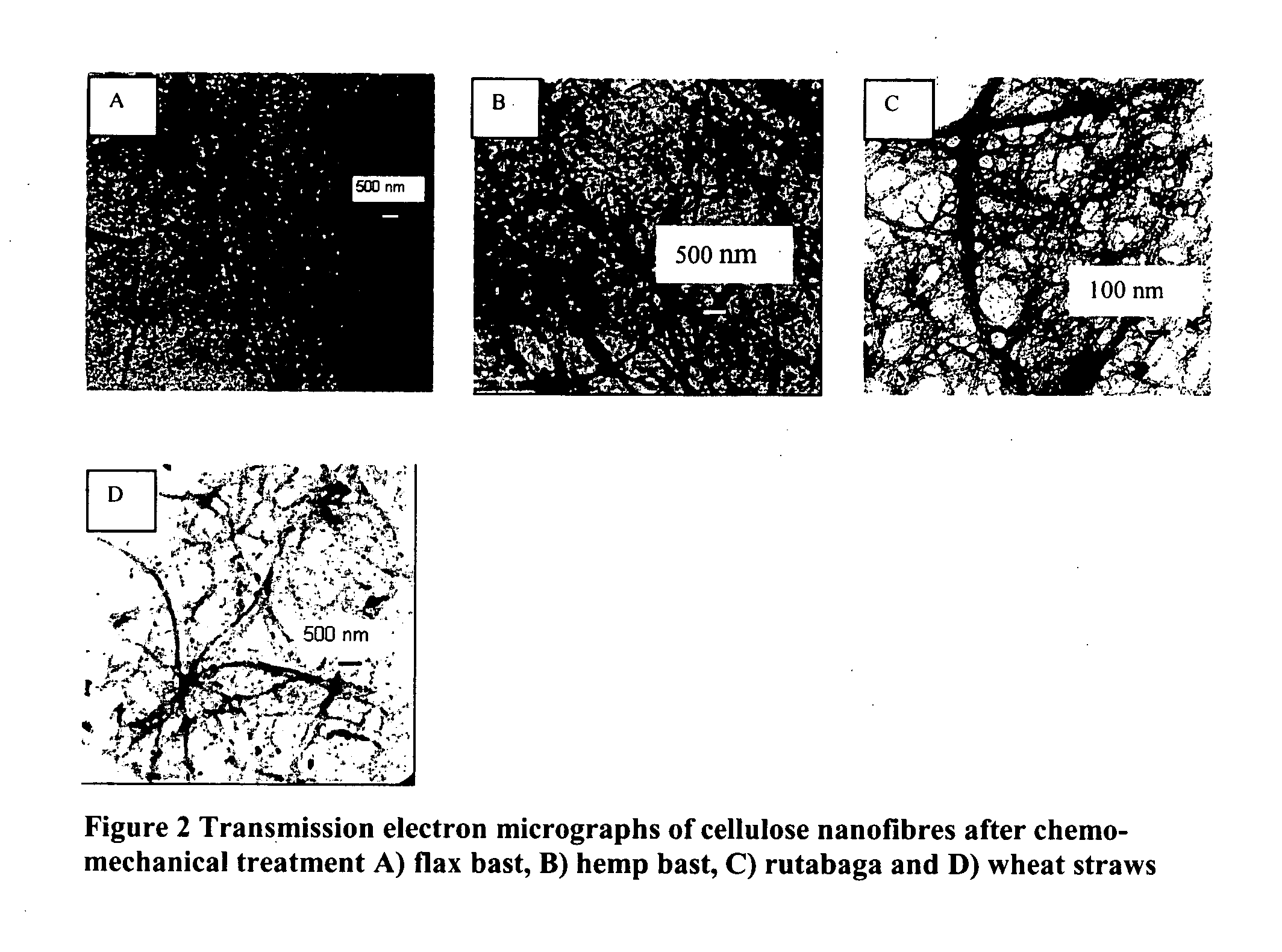
Manufacturing process of cellulose nanofibers from renewable feed stocks
InactiveUS20080146701A1High aspect ratioRaise the potentialMaterial nanotechnologyFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpCelluloseNatural fiber
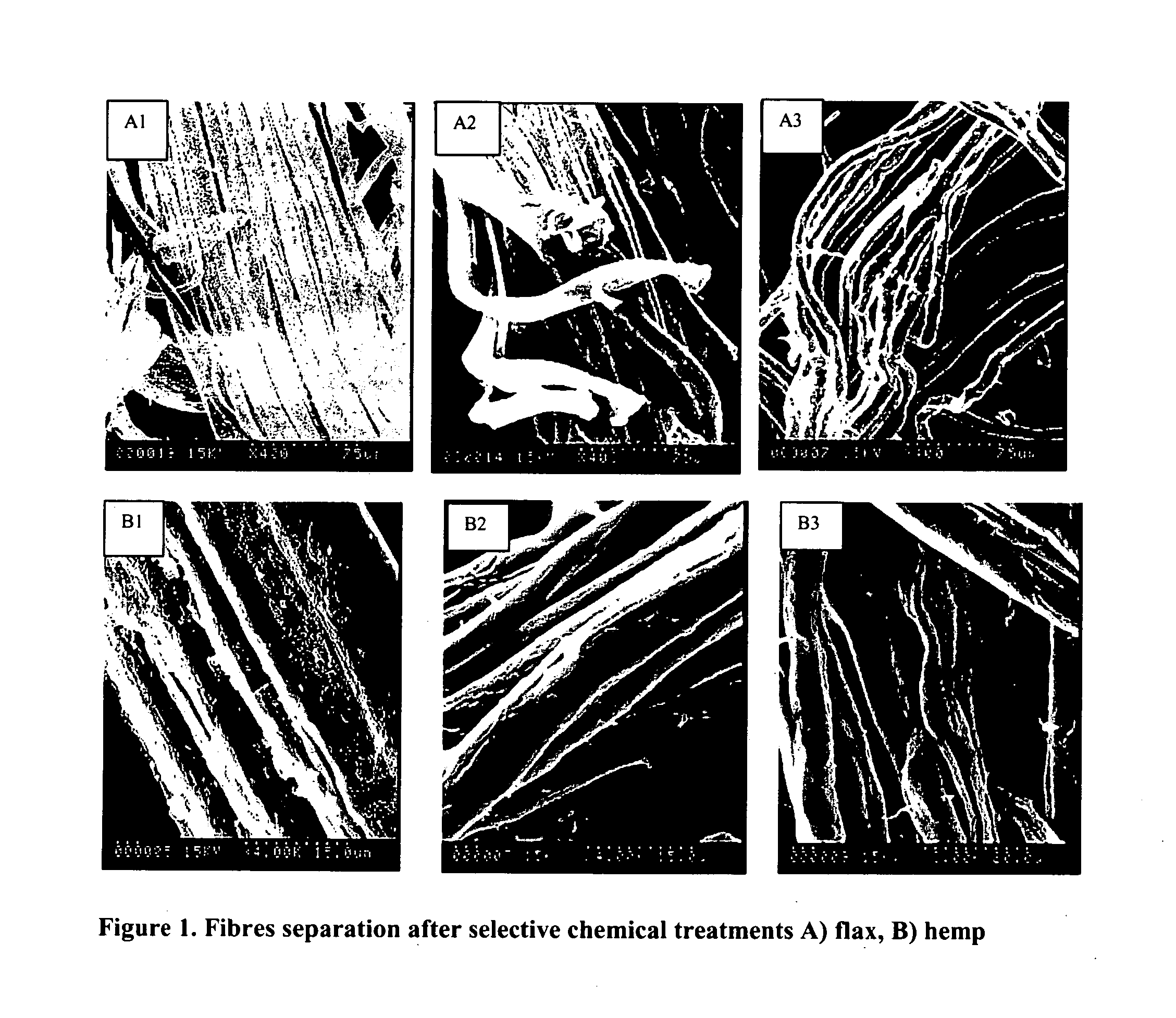
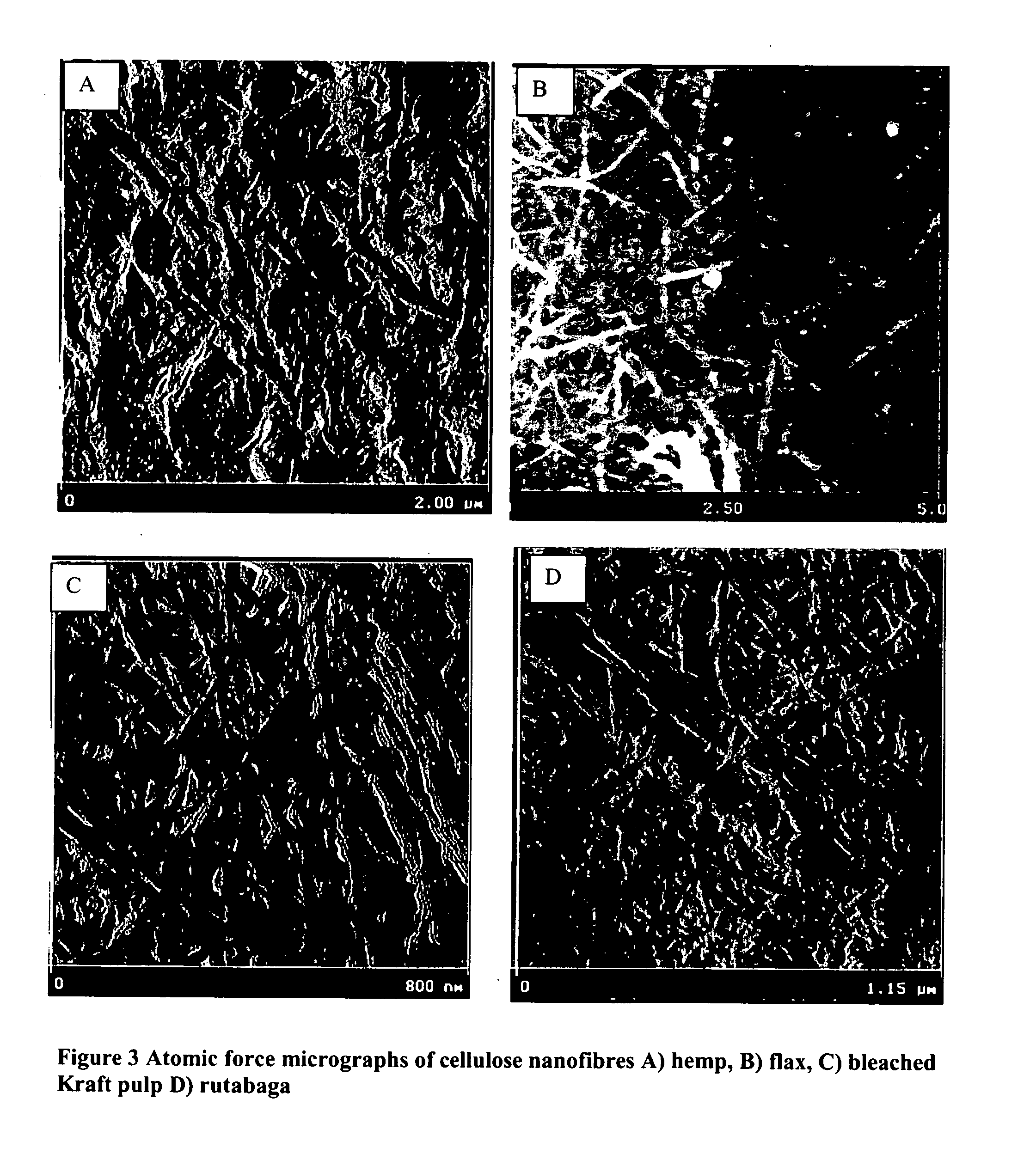
Cellulose nanofibers have been processed from renewable feedstock in particularly from natural fibers, root crops and agro fibers, wherein the pulp was hydrolysed at a moderate temperature of 50 to 90 degree C., one extraction was performed using dilute acid and one extraction using alkali of concentration less than 10%; and residue was cryocrushed using liquid nitrogen, followed by individualization of the cellulose nanofibers using mechanical shear force. The nanofibers manufactured with this technique have diameters in the range of 20-60 nm and much higher aspect ratios than long fibers. Due to its lightweight and high strength its potential applications will be in aerospace industry and due to their biodegradable potential with tremendous stiffness and strength, they find application in the medical field such as blood bags, cardiac devices, valves as a reinforcing biomaterial.
Owner:SAIN MOHINI M +1
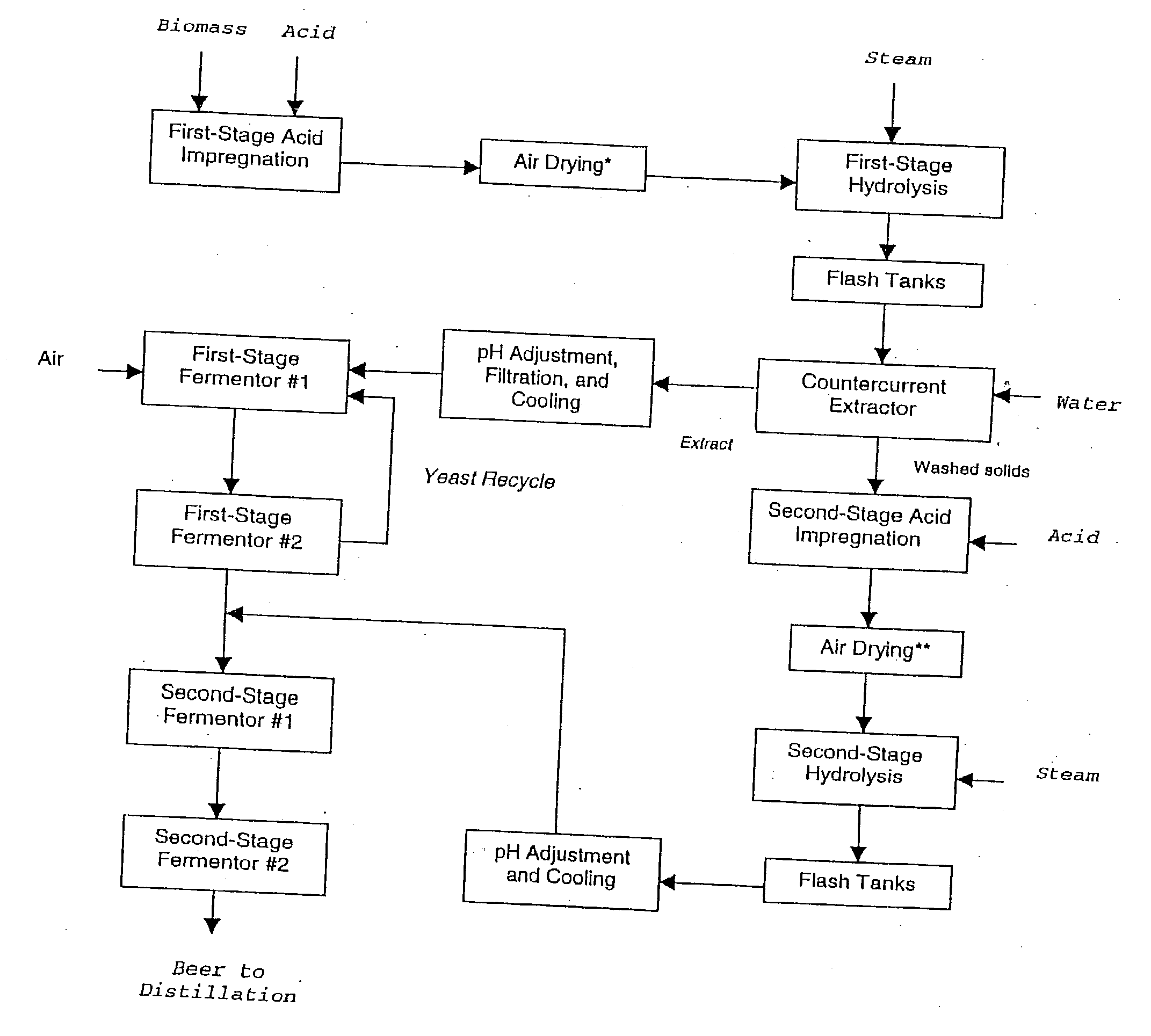
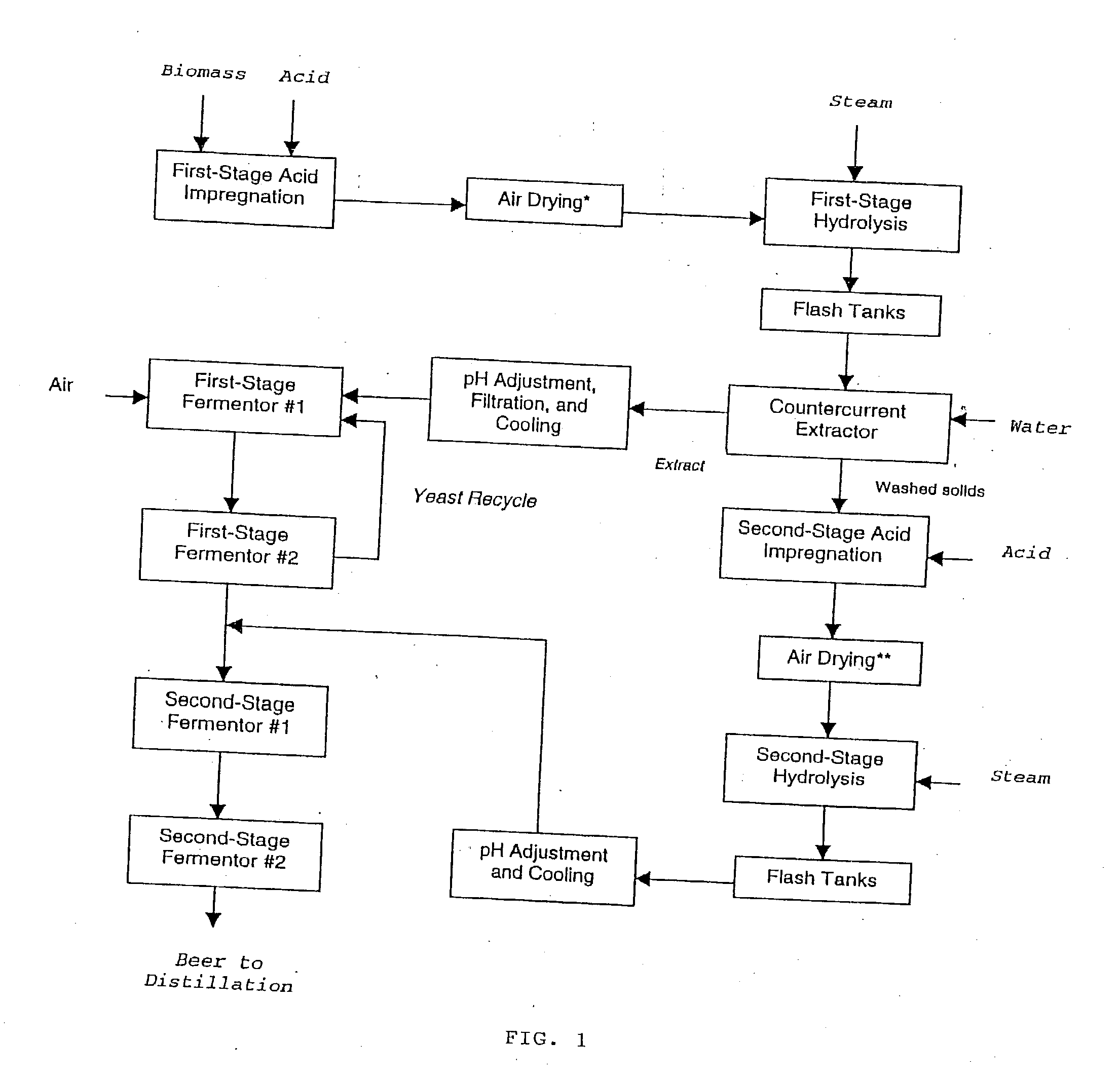
Ethanol production with dilute acid hydrolysis using partially dried lignocellulosics
InactiveUS20030199049A1Increase sugar yieldImprove digestibilityBiofuelsWaste based fuelCelluloseGrowth phase
In a process for converting lingnocellulosic biomass to ethanol, the improvement of obtaining higher fermentable soluble sugar yields by drying acid impregnated biomass particles, comprising: a) feeding moist lignocellulosic biomass into an acid impregnator to render it acid-soaked and draining the acid-soaked biomass to about 30% to 35% by weight solids; b) dewatering the acid-soaked biomass by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of the biomass and arrive at about 40% to 60% by weight solids; c) subjecting the acid-impregnated biomass to a first-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature of from 130° C. to 220° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars, and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank-the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for a counter-current extractor; d) washing the hydrolysate, adjusting the pH of the sugar extract to about 5, and recovering more than 95% of the soluble sugars in the first-stage hydrolysate slurry by a counter-current extractor; e) subjecting remaining washed-first stage solids of pretreated biomass to a second-stage acid and metal salt impregnator and dewatering by drying or centrifugation to prevent compaction of biomass to arrive at 40% to 60% by weight solids; f) subjecting the acid and metal salt-impregnated biomass to a second-stage hydrolysis reactor at a temperature from 190° C. to 240° C. and discharging formed hydrolysate into a flash tank, at about 120° C. to 140° C. to hydrolyze most of the remaining soluble oligosaccharides to monomeric sugars and flashing remaining hydrolysate to a second flash tank at a lower temperature than the first flash tank, the second flash tank serving as a feed surge tank for second-stage fementors; g) cooling pH-adjusted extract from the counter-current extractor, feeding the extract to a first-stage fermentor and air sparging the first-stage fermentor at a rate sufficient to promote enough yeast growth to compensate for loss through second-stage fermentors; h) pH adjusting second-stage hydrolysate slurry to 4.5, cooling the slurry and adding it into the top of the first fermentor of a two-fermentor train in the second stage fermentors, pumping broth from the bottom of the first stage fermentors to the second stage fermentors while the yeast is in the growth phase for a period sufficient to consume over 95% of fermentable sugars; and i) recovering ethanol.
Owner:MIDWEST RES INST
Pretreatment method of wood fiber raw materials
InactiveCN101864683ARealize comprehensive utilizationRealize full-price developmentPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsCelluloseFiber
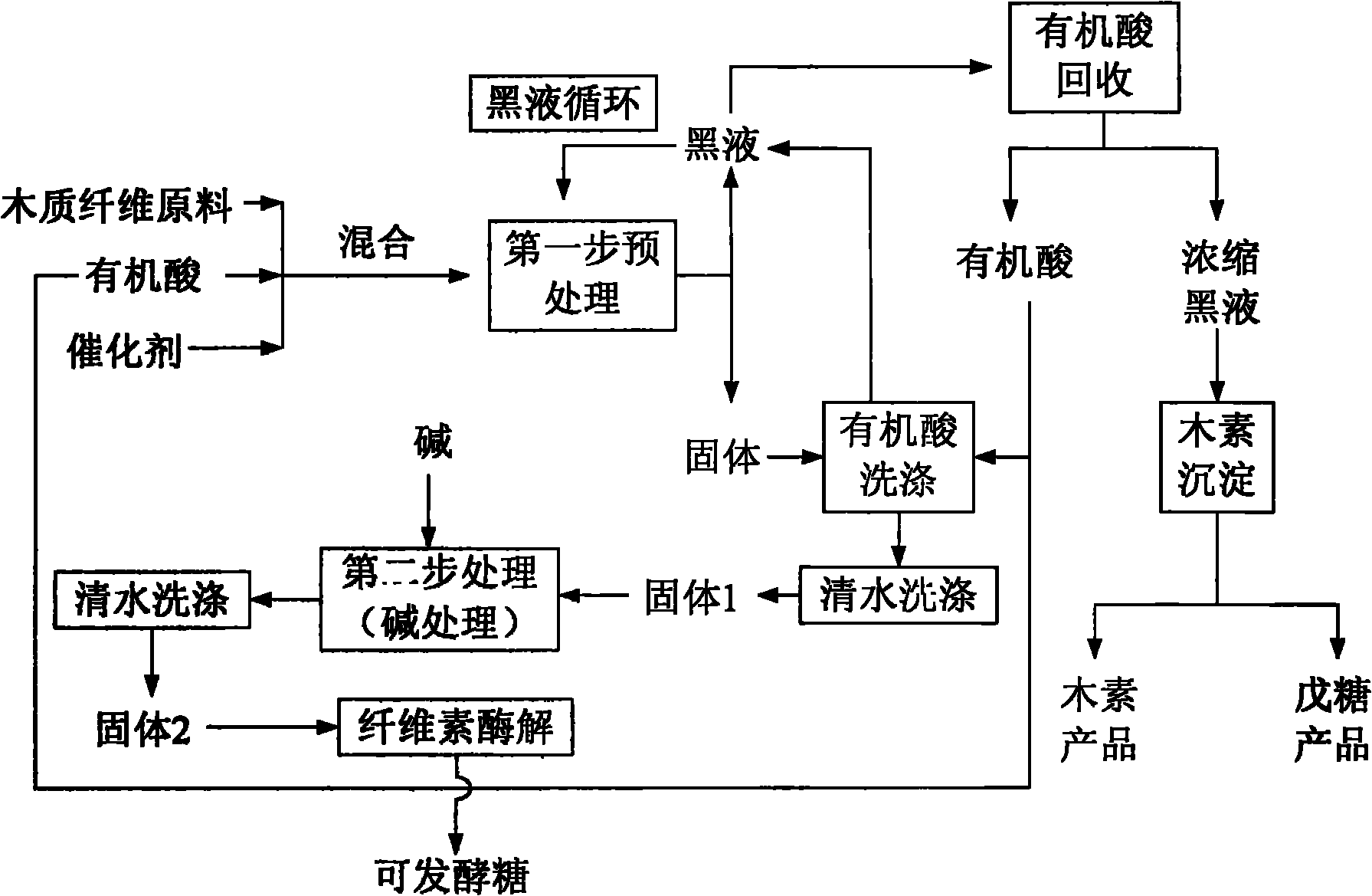
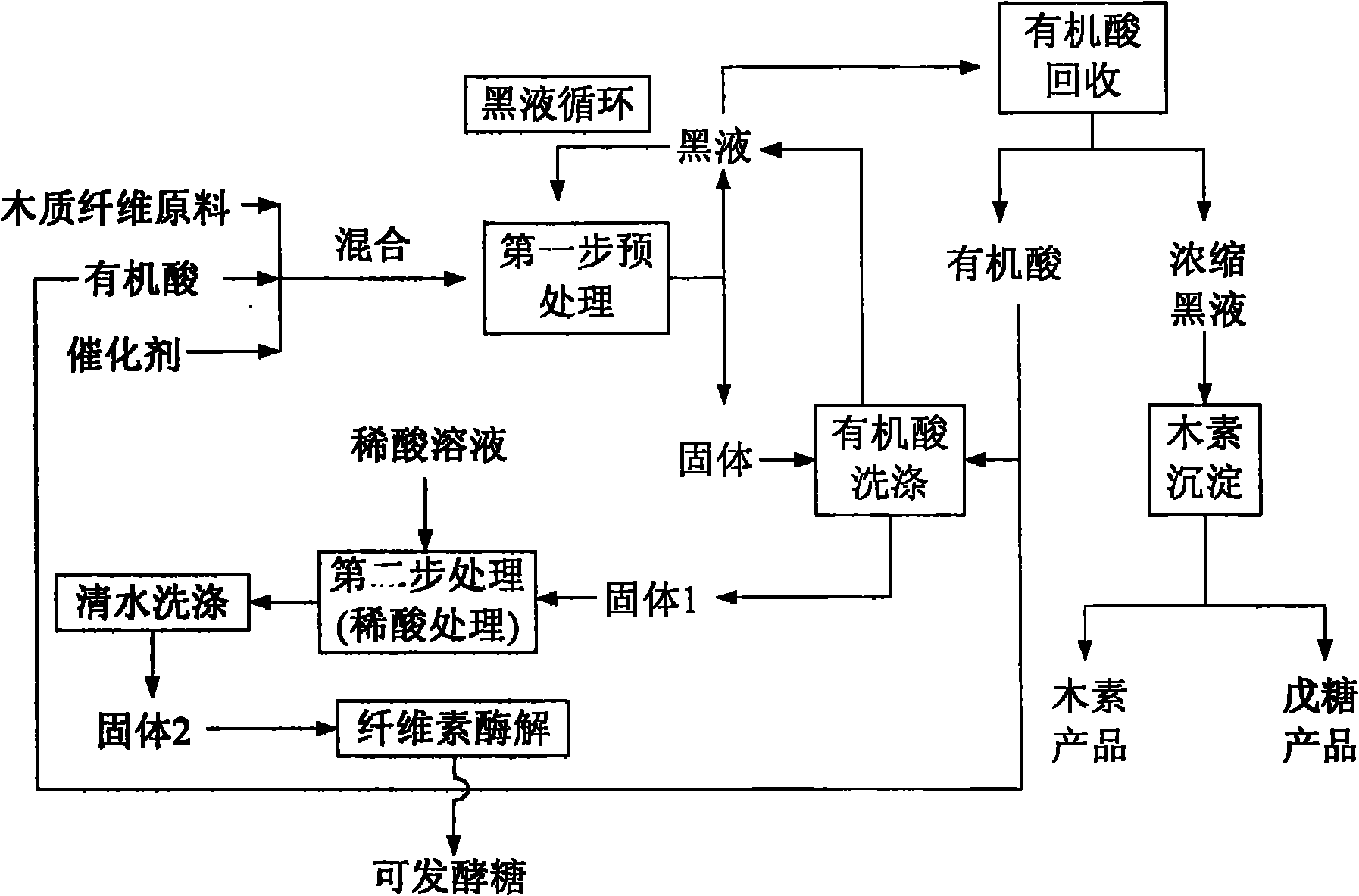
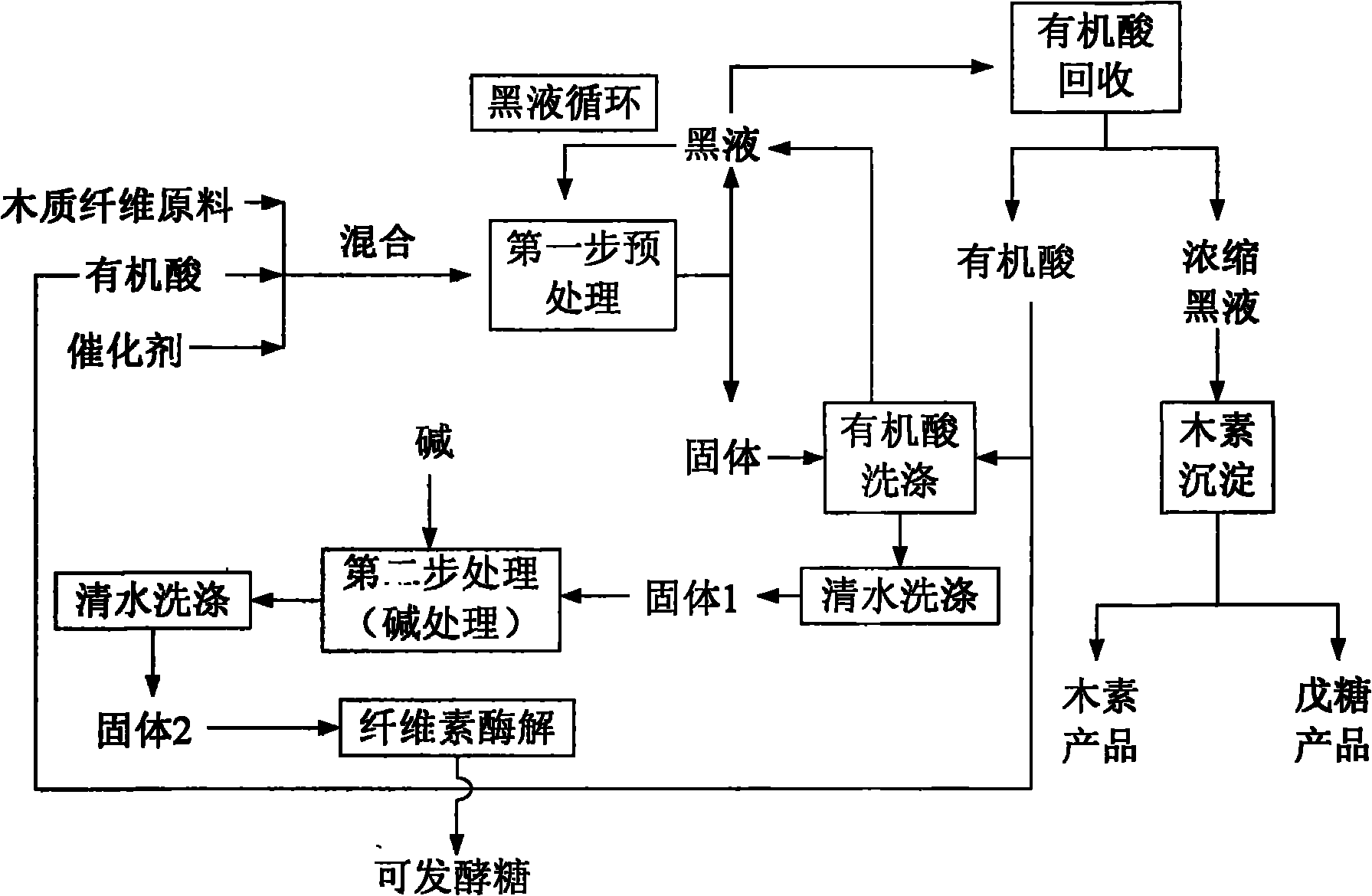
The invention relates to a pretreatment method of wood fiber raw materials, which belongs to the technical field of biomass chemical engineering. The process comprises the following steps: carrying out the first-step treatment after the wood fiber raw materials are mixed with mixed liquid of an organic acid solution and catalysts to obtain a liquid-solid mixture; separating the obtained liquid-solid mixture to obtain pretreatment black liquid and cellulose solids; washing the obtained cellulose solids by the organic acid solution to obtain washing black liquid and cellulose solids; adopting diluted acid or alkali for carrying out the second-step treatment on the obtained cellulose solids; mixing the obtained pretreatment black liquid and the obtained black liquid to obtain mixed black liquid; circularly using the mixed black liquid in the first-step treatment process; and recovering organic acids, lignin products and syrup solutions from the black liquid in the cyclic use for at least three times. The invention has the advantages that the full-rate development of raw materials can be realized, in addition, the environment-friendly effect can be realized, and the invention conforms to the requirement of modern biorefinery development.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing liquid seaweed fertilizer
InactiveCN104447008AReduce moistureEasy to breakOrganic fertilisersLiquid fertilisersBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTHigh activity
The invention discloses a method for preparing a liquid seaweed fertilizer. The seaweeds serve as raw materials, and the method sequentially comprises the following steps: pulping and crushing fresh seaweeds or soaking and swelling dried seaweeds for pulping and crushing, performing ultrasonic extraction, performing solid-liquid separation, performing alkaline extraction on solid seaweeds, compounding the seaweed extraction solution and common fertilizers, thereby obtaining the liquid seaweed fertilizer. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the extraction efficiency of active ingredients in the seaweeds can be obviously improved, and compared with a traditional chemical extraction method, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that because a mild method is adopted, for example, ultrasonic extraction and relatively low temperature and dilute acid / dilute alkali assisted ultrasonic extraction are adopted, and the alkali extraction time is obviously shortened. According to the process technology, the activity of the active ingredient can be obviously preserved in the extraction process, so that high-activity seaweed extract and products thereof are obtained.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
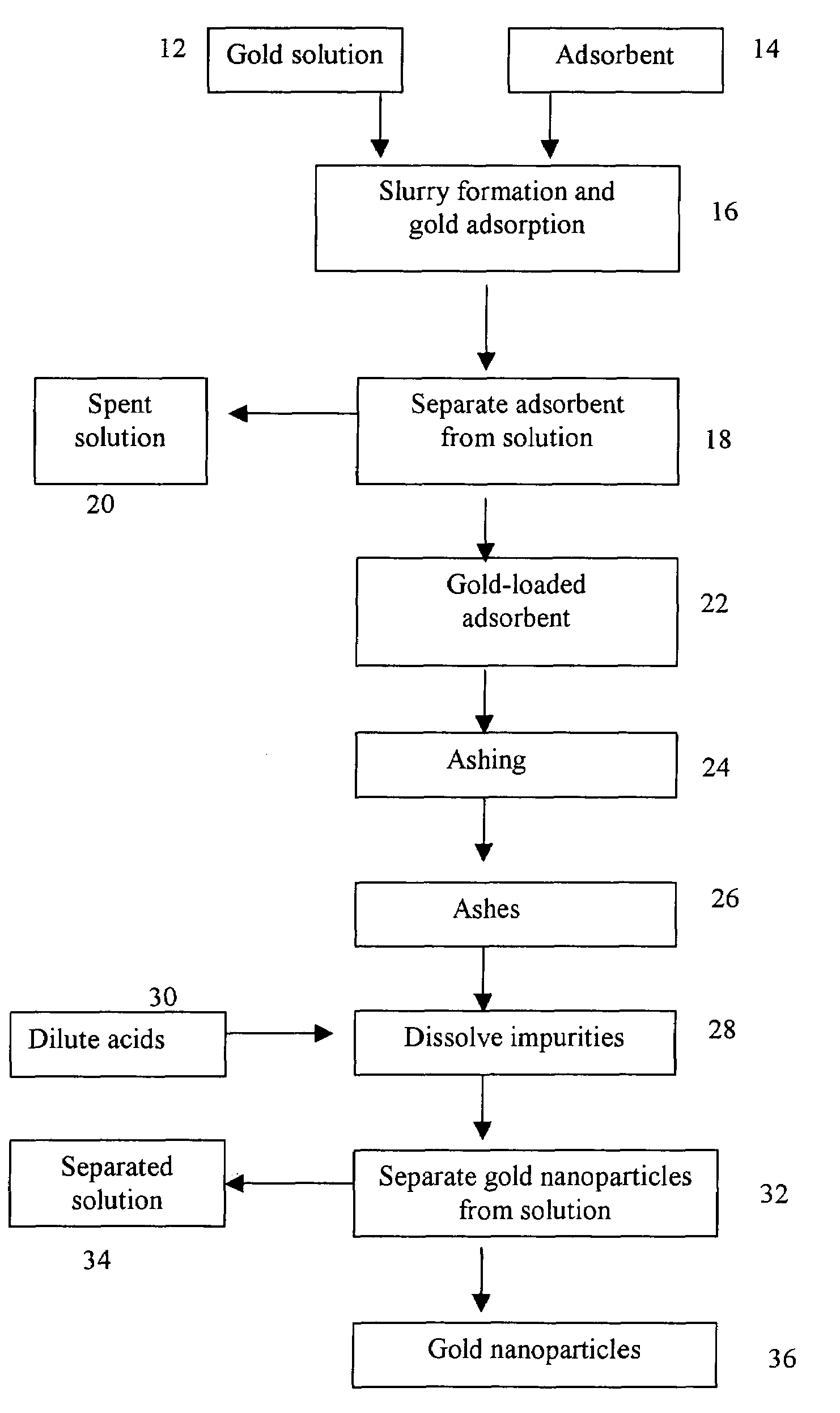
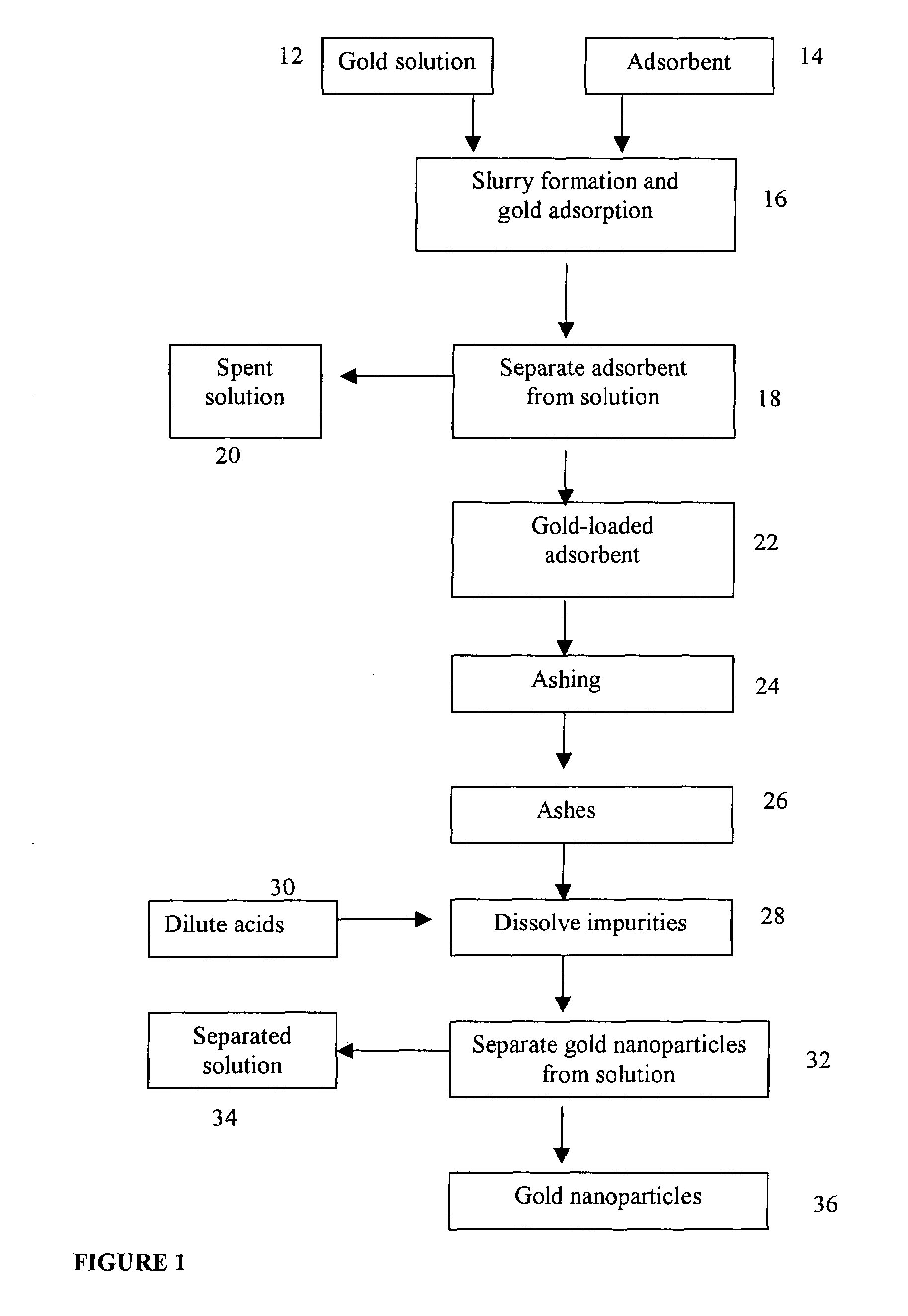
Method of producing gold nanoparticle
A method for producing gold nanoparticles is disclosed. When gold salt solution is mixed with an adsorbent, gold in the form of complexes is adsorbed onto the surface of the adsorbent. The gold-loaded adsorbent, after being separated from the solution by screening, filtration, settling or other methods, is ashed to form ashes. The ashes contain gold nanoparticles and impurities such as oxides of sodium, potassium and calcium. The impurities can be removed by dissolution using dilute acids. The relatively pure gold nanoparticles are obtained after the impurities are removed. Activated carbon or gold-adsorbing resin can be used as the adsorbent. Silver or platinum group metal nanoparticles can also be produced by this method.
Owner:LIN HSING KUANG +1
Method for recovering valuable metals from electroplating sludge
The invention relates the recovering metal method from electroplating sludge, comprising the following step: 1 using diluted acid to extract metal from electroplating sludge, filtering and separating, getting pickle liquor; 2 setting the copper from pickle liquor with sulphide at 85-100Deg.C, filtering and separating, getting cupric sulfide and deposition mother liquid; 3 adding 5-20% queous alkali into deposition mother liquid, and controlling the PH between 5.0 and 6.0, setting chromium and aluminium, filtering and getting the chromium-aluminium slag and the mother liquid containing iron, zinc and nickel. The method has the advantages of good technology versatility, easy controlling, simple equipment and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Lithium hydrate and carbamide composition solvent for dissolving cellulous fiber and its use
InactiveCN1546556AHigh strengthWide range of usesMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentSpinning solutions preparationAcid waterLithium hydroxide
The invention relates to a dissolvent for cellulose dissolution through freezing-unfreezing method or direct dissolution method, and process for preparing the regenerated cellulose fibers and films by utilizing the dissolvent, wherein the dissolvent is the water solution of lithium hydroxide and urea whose compositions are 3.0-7.0wt% of lithium hydroxide, 4.0-30.0.0wt% of urea, the rest is water. The water solution of lithium hydroxide and urea can directly dissolve cellulose through freezing-unfreezing method or by pre-cooling the dissolvent in advance to -10 deg. C - -4 deg. C. It can be used to obtain high dissolvability transparent concentrated cellulose solution. By using the concentrated cellulose solution and through 3-5wt% diluted acid water solution coagulation, regeneration, regenerated cellulose films and fibers can be prepared.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Clarithromycin water soluber preparation for injection use
InactiveCN101045063AImprove solubilityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryChemistryWater soluble
A water-soluble clarithromycin for injection is prepared from clarithromycin or its analog, and beta-cyclodextrin or its pharmacologically acceptable water-soluble derivative through proportional mixing, adding diluted acid, stirring for dissolving, and regulating pH=4.5-6.5 to obtain a stable inclusion compound.
Owner:REGENEX PHARMA LTD
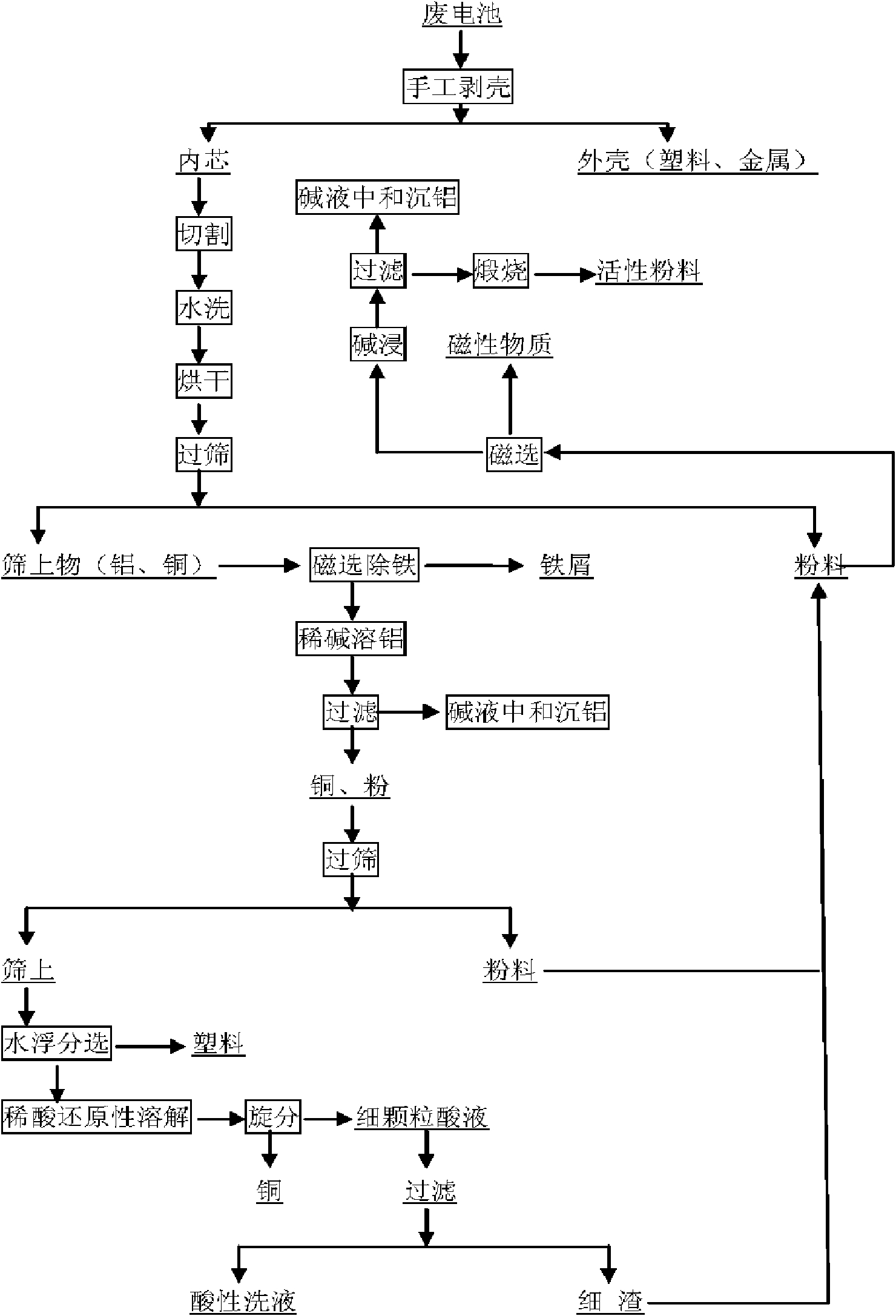
Method for efficiently recovering active materials of positive poles in waste lithium batteries
InactiveCN101599563AWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementCycloneElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for efficiently recovering active materials of positive poles in waste lithium batteries, which is mainly characterized by adding crushed electrical core fragments into hot water, stirring the mixture, and performing first vibration screening after the filtration and drying to separate most of an active material; dissolving aluminum foil through alkaline leaching after an oversize part is magnetically separated, adjusting the pH value of an alkaline leaching filtrate by dilute acid and ammonium bicarbonate solution, and recovering aluminum; performing second vibration screening after the filtration and drying to separate a residual powder material; and placing the oversize part into water for water cyclone separation, dumping to remove an upper-layer plastic diaphragm, then using dilute sulfuric acid and sodium thiosulfate solution to wash a copper sheet to ensure that carbon powder and active powder which are adhered to the copper sheet are loosened and fall off, making the powder float on an upper layer through cyclone separation after the washing, mixing the powder and the active powders obtained by two screenings, using NaOH solution to soak the mixture after the magnetic separation, calcining the alkali-leached active powder material after the filtration and drying, and taking the active powder material as active powder for subsequent treatment. The use of the method can ensure that the recovery rates of copper and aluminum in waste lithium ion batteries reach 98.5 percent and 97 percent respectively, and the recovery rate of the active materials is about 99 percent.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of nitrogen-rich multimode beehive carbon-sulfur composite anode material
ActiveCN103746098ALarge specific surface areaHigh nitrogen contentPositive electrodesLi-accumulatorsArgon atmosphereOxide composite
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lithium sulphur battery composite anode material. The preparation method is as follows: preparing a mixed solution of carbon tetrachloride, a nitrogen source and carbonate, heating and flowing back to obtain a nitrogen-rich polymerization / carbonic acid salt compound; high temperature pyrolyzing in a nitrogen or argon atmosphere after drying the compound, so as to form the nitrogen-rich carbon / oxide compound; adding dilute acid to remove vestigial oxide, so as to form the nitrogen-rich multimode beehive carbon material of a multilevel porthole structure; uniformly mixing the nitrogen-rich multimode beehive carbon and sublimed sulfur, heat preserving under vacuum condition, injecting sulfur gas to the nitrogen-rich multimode beehive carbon material, so that the lithium sulphur battery composite positive material can be obtained. The composite anode material provided by the invention is alveolate, and has the advantages that portholes are abundant, sulfur content is high, sulfur particle can be distributed uniformly in the nitrogen-rich multimode beehive carbon material of the multilevel porthole structure, and the carbon sulfur particles can be combined more tightly, the material mechanical stability is high, discharge specific capacity is high, cycle performance is excellent, and technological process is simple, pollution is avoided, cost is low, and the method is liable to large scale production and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Chemical method for silver coating on copper powder surface
The invention relates to a method for copper powder surface chemical plating silver, belonging to field of chemical silver plating. Said method comprises following steps: putting copper powder into diluted acid of 5-10% to remove oxide on surface of copper powder; adding disperser of 1-30% of copper powder by weight, stabilizer of 10-60% of copper powder by weight into deionized water to form reducing liquid, adding copper powder and stirring; adding silver nitrate into deionized water, adding ammonia, stirring and adding sodium-hydroxide and getting silver amine solvent; adding silver amine solvent into reducing liquid under stirring, finishing chemical silver plating of copper surface 10-50 minutes later; filtering, separating and washing, vacuum drying and getting silver-coated copper powder. The process is characterized by simple preparation and raw material, reduced silver-plated layer on container wall by adding silver amine solvent into reducing liquid, high silver converting rate. The electrical resistance of got copper powder is smaller than 2*10-4 omegacm.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Process for Producing a Pretreated Feedstock
ActiveUS20080045762A1Improve efficiencyReduce riskBiocideSolid waste disposalFood scienceDilute acid
A process for producing a pretreated feedstock is provided. The feedstock is selected from grasses, cereal straws, stover, and combinations thereof, and least about 80% of the feedstock has a particle length of between about 2 cm and about 40 cm. This process comprises wetting the feedstock in liquid, pressing the wet feedstock through one roll press or a series of roll presses to remove at least a portion of water and soluble substances from the wetted feedstock and to shear the feedstock to produce feedstock particles of a size suitable for pumping at a solids concentration of about 8% to about 20% when slurried. At least one roll press, or at least one roll press in the series of roll presses comprises rolls with circumferential v-shaped grooves. The pressed feedstock particles are slurried to produce a slurried feedstock having a consistency of between about 8% and about 20%, and the slurried feedstock pumped into a pretreatment reactor. Dilute acid pretreatment of the slurried feedstock is carried out at a temperature of 160° C. to 280° C.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Preparation method of biomass-based nitrogenous porous carbon, porous carbon prepared by method and use thereof
ActiveCN106601490AWidely distributedAbundant resourcesHybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon preparation/purificationPorous carbonNitrogen doped
The invention discloses a preparation method of biomass-based nitrogenous porous carbon, the porous carbon prepared by the method and the use of the prepared nitrogenous porous carbon in a super capacitor. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) drying a biomass material, and grinding the biomass material into fine powders, (2) evenly mixing the biomass material powders and water or a dilute acid solution, (3) placing the above mixture into a reactor for hydrothermal reaction, and (4) drying and grinding an obtained hydrothermal reaction product, and calcining the hydrothermal reaction product in a tube furnace to obtain a nitrogen-doped porous carbon material with a large surface area. According to the method of the invention, cheap and renewable plant is used as carbon and nitrogen precursors, and the porous nitrogen-doped carbon material is prepared through a hydrothermal method. The method has the advantages of simple preparation process, no need of an activator or template agent, low cost, environmental protection, and convenient operation, problems of strong corrosion, a high price of transition metal and environmental pollution caused by heavy metal are avoided, and the method is suitable for mass production.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method for preparing collagen peptide by using cod skin
InactiveCN101407834AIncrease contentNo pollution in the processPeptide preparation methodsFermentationCollagen VIPollution
The invention relates to a method for preparing a collagen peptide by taking a cod skin as a material; in the method, the cod skin is selected as the material and is washed clearly by fresh water; 0.2 percent-0.5 percent mixed liquid of calcium hyduloxide and sodium hydroxide is added for dipping; then the cod skin is washed by fresh water until the pH value is neutral; after the water liquid of 0.3 percent to 0.6 percent diluted acid is added for dipping, the cod skin is washed by fresh water again until the pH value is neutral; the cod skin is cracked and is stirred and extracted in hot water for extracting a collagen; then undissolved substances are removed through filtering; the pH value of the extraction liquid of the collagen is adjusted to be neutral; under the stirring conditions, enzymes are added for carrying out zymohydrolysis and obtaining a zymohydrolysis liquid; and after the enzymes are eliminated and filtering is carried out, the powder of the collagen peptide is obtained through vacuum condensing and sponging drying. The method has the advantages of simple technique, less device investment, no environment pollution and being suitable for industrialization production. The collagen content of the powder of the prepared collagen peptide is higher; and the color, smell and biological properties are excellent. The powder of the collagen peptide can be broadly applied to the industries of health-care foods, medicines, and the like.
Owner:TAIXIANG GRP TECH DEV
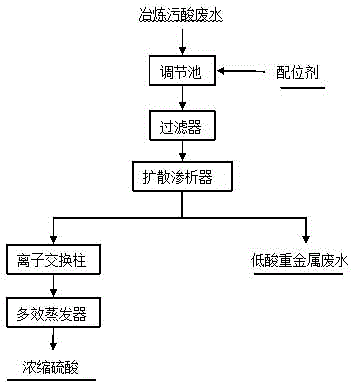
Method for purifying smelting waste acid
ActiveCN104445095AEfficient removalAchieve separationSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidSmall footprintIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a method for purifying smelting waste acid. The method comprises the following steps: adding a coordination agent into a centralized inflow adjusting pool of waste acid discharged from a sulfuric acid smelting system, stirring uniformly, and filtering the mixture in a filter to further remove insoluble granular impurities; separating dilute acid nearly containing no metal ion and low-acid wastewater through a diffusion dialyzer; adsorbing such residual anion impurities as fluorine and chlorine in the dilute acid through ion exchange resin, concentrating the dilute acid in a multi-effect evaporator and recycling the dilute acid in the sulfuric acid system; further treating the low-acid wastewater to reach the national sewage drainage standard. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly and efficiently separating acid from heavy metal ions in the smelting waste acid, the separated dilute acid can be recycled in a sulfuric acid production procedure after being concentrated, and the method has the advantages of low energy consumption and few residues, and can be used for effectively and comprehensively recycling resources in the waste acid. The wastewater treatment cost is low, and the economic benefit is good. The process is simple, the occupation area of equipment is small and industrialized application is easy to achieve.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method for high-concentration graphene-polyaniline nanofiber composite dispersion liquid and high-concentration graphene-polyaniline nanofiber composite film
The invention relates to a preparation method for a high-concentration graphene-polyaniline nanofiber composite dispersion liquid and a high-concentration graphene-polyaniline nanofiber composite film. The method comprises: respectively adding graphite oxide and polyaniline nanofiber to two parts of distilled water to carry out ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a graphene oxide dispersion liquid and a polyaniline nanofiber dispersion liquid; adding the polyaniline nanofiber dispersion liquid to the graphene oxide dispersion liquid in a dropwise manner, then carrying out ultrasonic dispersion toform a composite dispersion liquid; mixing the composite dispersion liquid and a reducing agent, then carrying out the reaction under conditions of a constant temperature and ultrasonic wave to obtain the graphene-polyaniline nanofiber composite dispersion liquid; carrying out vacuum filtration for the graphene-polyaniline nanofiber composite dispersion liquid to prepare the composite film; adopting dilute acid leaching to prepare the self-supporting composite film with high conductivity. According to the method, the polyaniline nanofiber is adopted as the dispersion stabilizer for the graphene to prepare the high-concentration composite dispersion liquid, such that the problem of difficult removal of the traditional dispersing agent is solved, the synergistic effect of the composite material is easily provided. In addition, the prepared self-supporting composite film has good flexibility and high conductivity.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
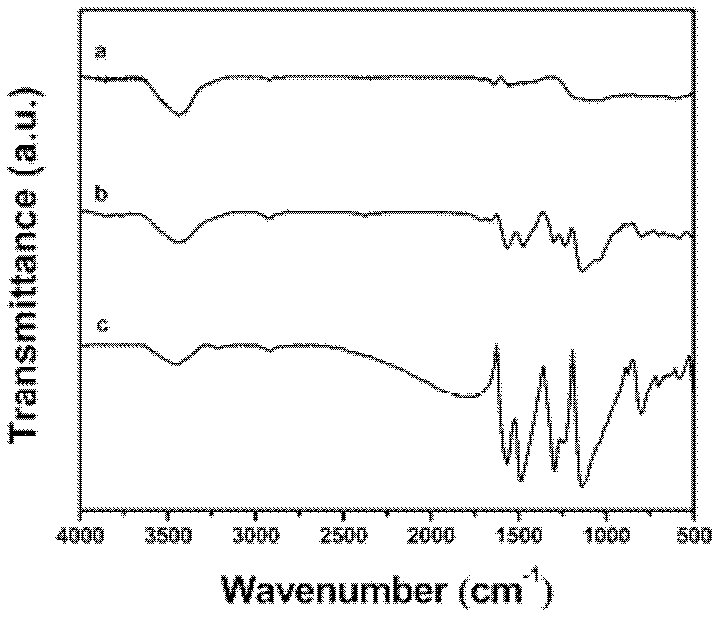
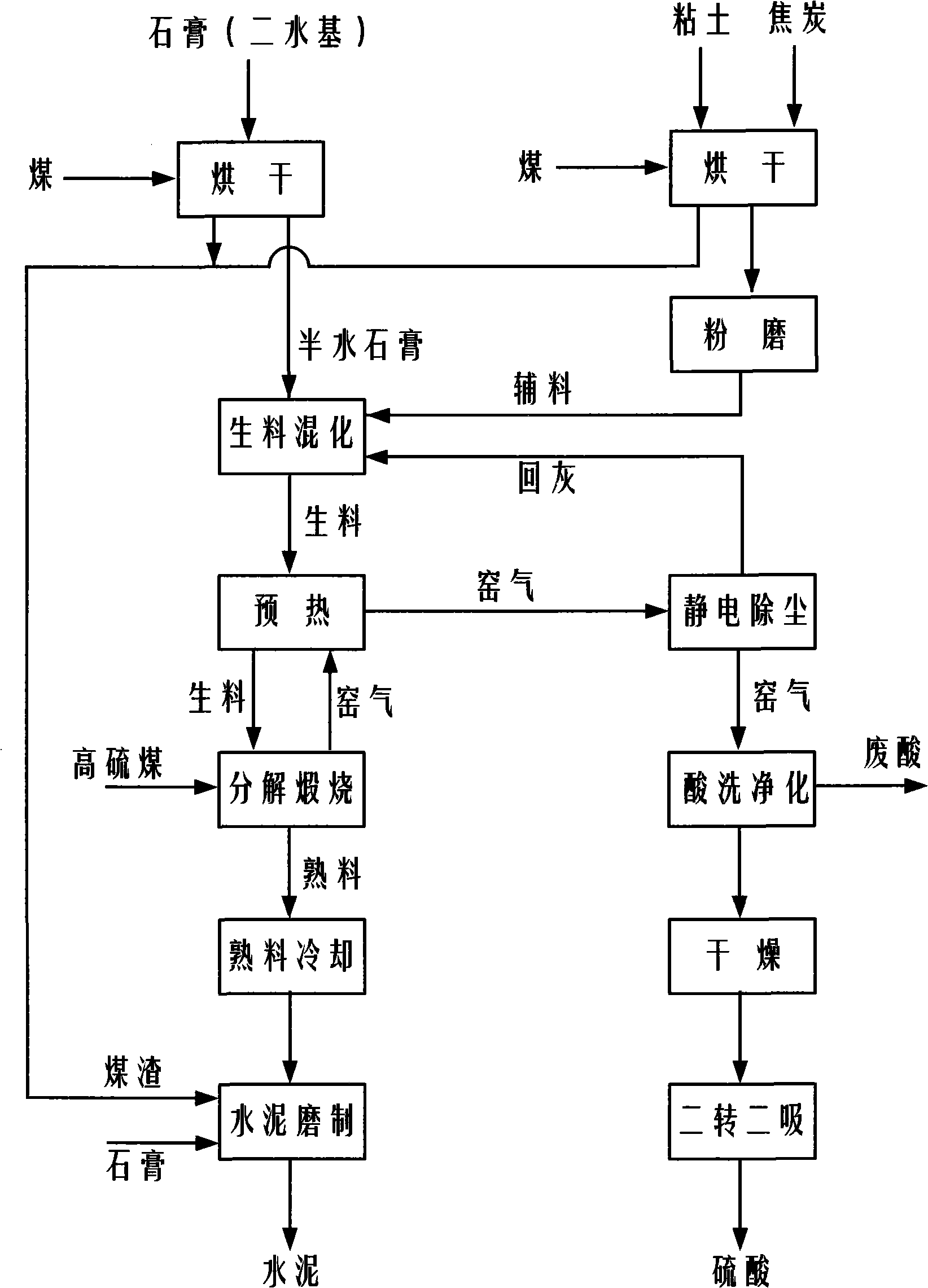
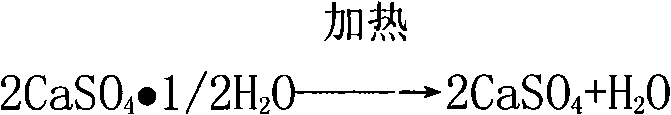
Improved preparation technique for preparing sulphuric acid and cement with gypsum
ActiveCN101343047AEliminate pollutionAlleviate supply shortagesCement productionSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidSource materialAcid washing
The invention provides an improved production process of utilizing gypsum to produce sulfuric acid and cement, which relates to the sulfuric acid and cement industry production technology, and the resource comprehensive utilization and environmental protection governing field of the industrial byproduct gypsum. The improved production process is characterized in that natural gypsum with the CaSO4*2H2O as the main composition or the industrial byproduct gypsum is adopted as the main source material; clay, coke and fly ash clinker are used as supplementary materials; the half-water drying gypsum flow, the single stage powder grinding, raw material mixing melting, suspension preheater kiln decomposing calcination, closing diluted acid washing and purification, two-turning and two-suction processes are adopted; the sulfuric acid and cement products are prepared through six steps of source material homogenizing, drying and dehydration, raw material preparation, clinker burning, kiln gas acid production and cement grinding; the improved production process has the advantages of wide range source material, solving the land occupation and environmental pollution problems of the gypsum waste residue, realizing the circulation utilization of sulfur resource, adopting a plurality of new processes and devices, realizing the large scale production easily, advanced technology, mature process, easy operation in production control, low energy consumption, high benefit, no waste water and waste residues exhaust.
Owner:SHANDONG LUBEI ENTERPRISE GROUP
Method for preparing porous graphene material
InactiveCN102107868ALow oxygenImprove the degree of graphitizationNanotechnologyPorous grapheneSolvent
The invention provides a method for preparing a porous graphene material. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dispersing nano granules of a metal oxide into a solvent; (2) adding a soluble salt of a graphitization catalyst and a polymer into the product obtained in the step (1), and performing uniform mixing; (3) heating and vacuumizing the product obtained in the step (2) to remove the solvent; (4) thermally treating the product obtained in the step (3) for 0.5 to 400 minutes in inert atmosphere at the temperature of between 500 and 1,000 DEG C, and collecting a solid product after cooling; and (5) treating the solid product by using dilute acid to dissolve and remove the catalyst and the nano granules of the metal oxide so as to obtain the porous graphene material. The porous graphene material prepared by using the method has low oxygen content and high graphitization degree, and holes with diameter of more than 2 nanometers are distributed on the graphene sheet layer. The preparation method is simple, the raw materials are easily obtained, and the preparation method can be used for batch preparation and is easy to realize industrialized production.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
A nitric oxides (NOX) waste pollution control in industrial process and resource reclaiming method
InactiveCN1864812AGood governanceSimple processDispersed particle separationHydrogen NitrateHigh concentration
The invention relates to a method for treating and reusing waste gas containing nitrogen oxide generated in industrial process. It comprises following steps: mixing waste gas containing nitrogen oxide with air according to a certain proportion, plural serial adsorbing it in tower by introducing it from bottom of head tower, discharging it from top of tail tower, discharging generated hydrogene nitrate of low concentration from bottom of head tower, proceeding decompressing and thickening process in thickening tower, which includes bleaching and dewatering; hydrogen nitrate of low concentration is introduced from top of thickening tower, hydrogen nitrate of high concentration being 45-65% is discharged from bottom; supercharging nitrogen oxide extracted from thickening tower top with vacuum system, then introducing it into adsorbing process again; the water or diluted acid from thickening tower is used as adsorbent and is added from top of tail tower in adsorbing process and counter current contacts with gas in tower for mass transferring. The waste gas treatment effect is good, and the discharging concentration of nitrogen oxide in exhaust gas is less than 50 ppm; all the nitrogen oxide in exhaust gas is recycled to generate aqua fortis with mass concentration being more than 55%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
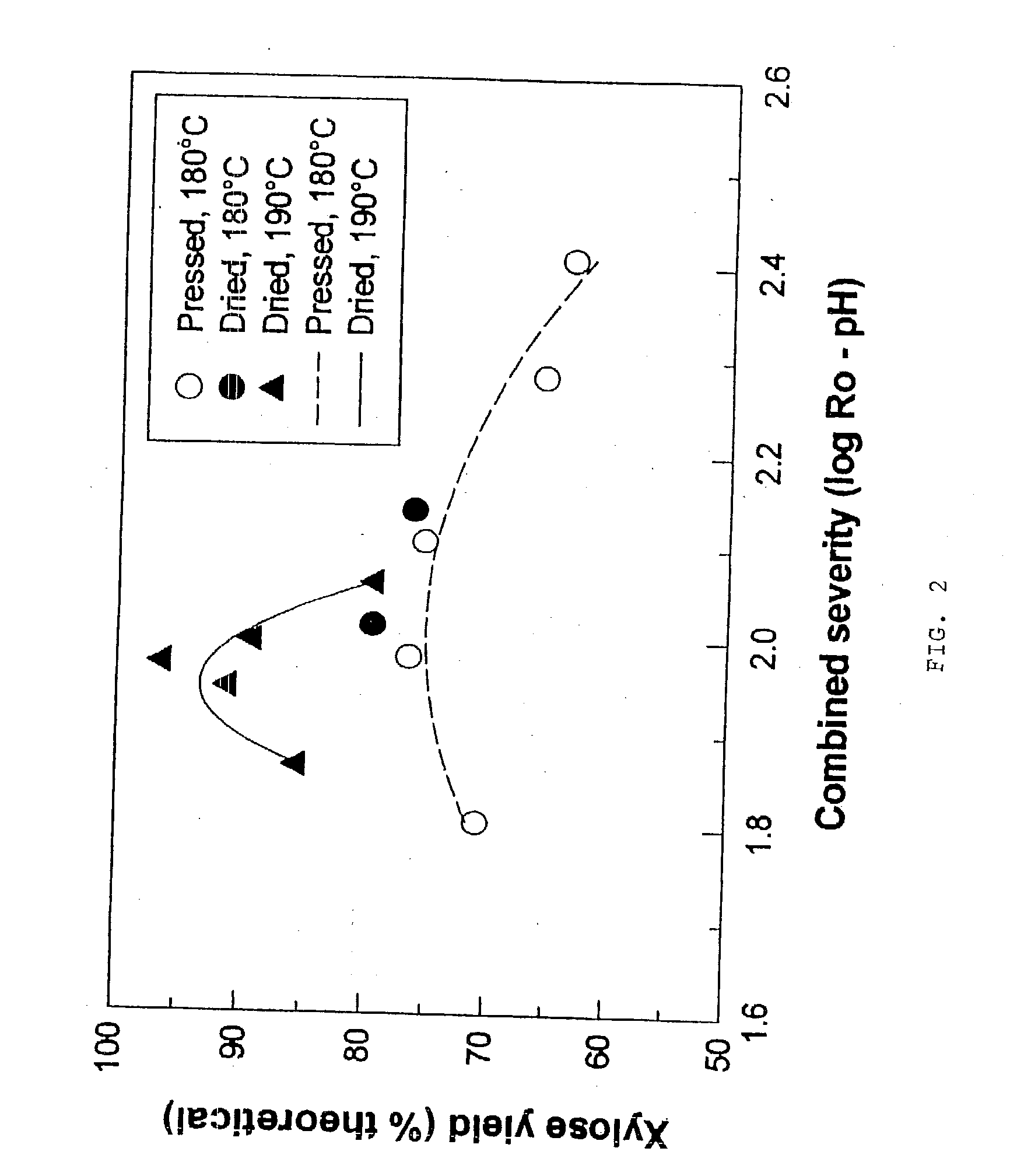
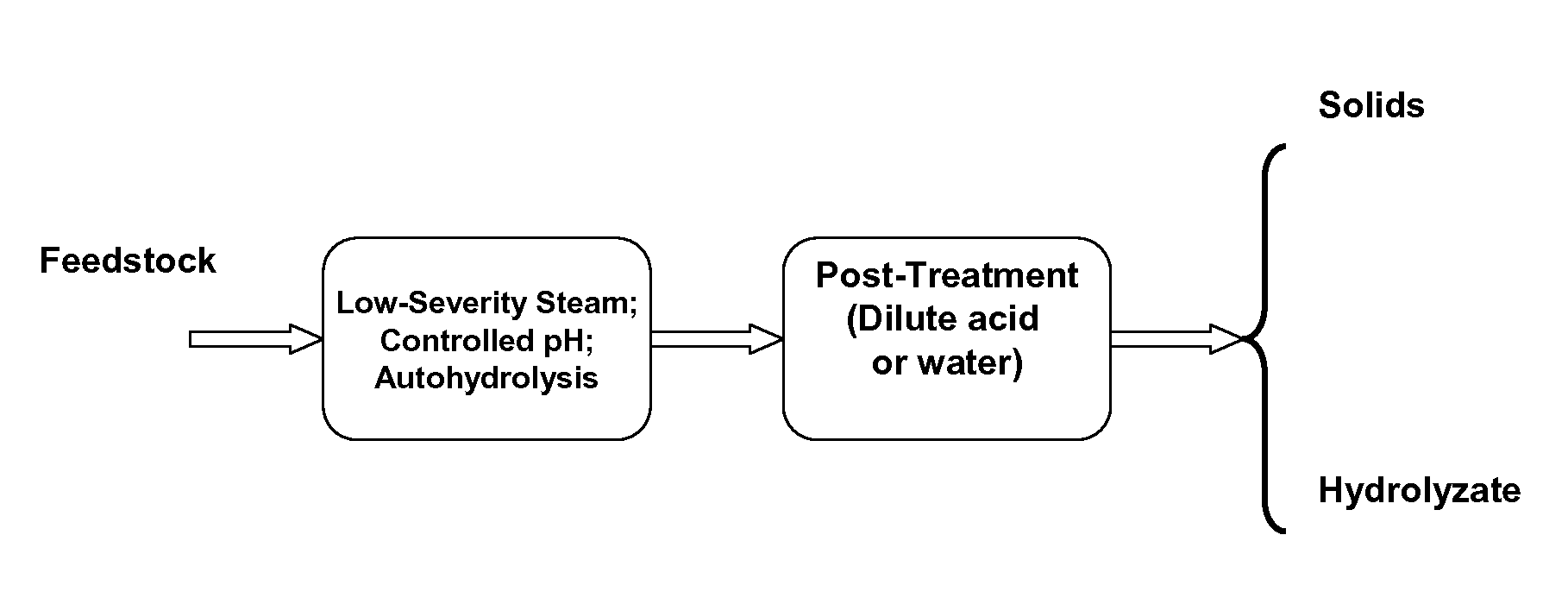
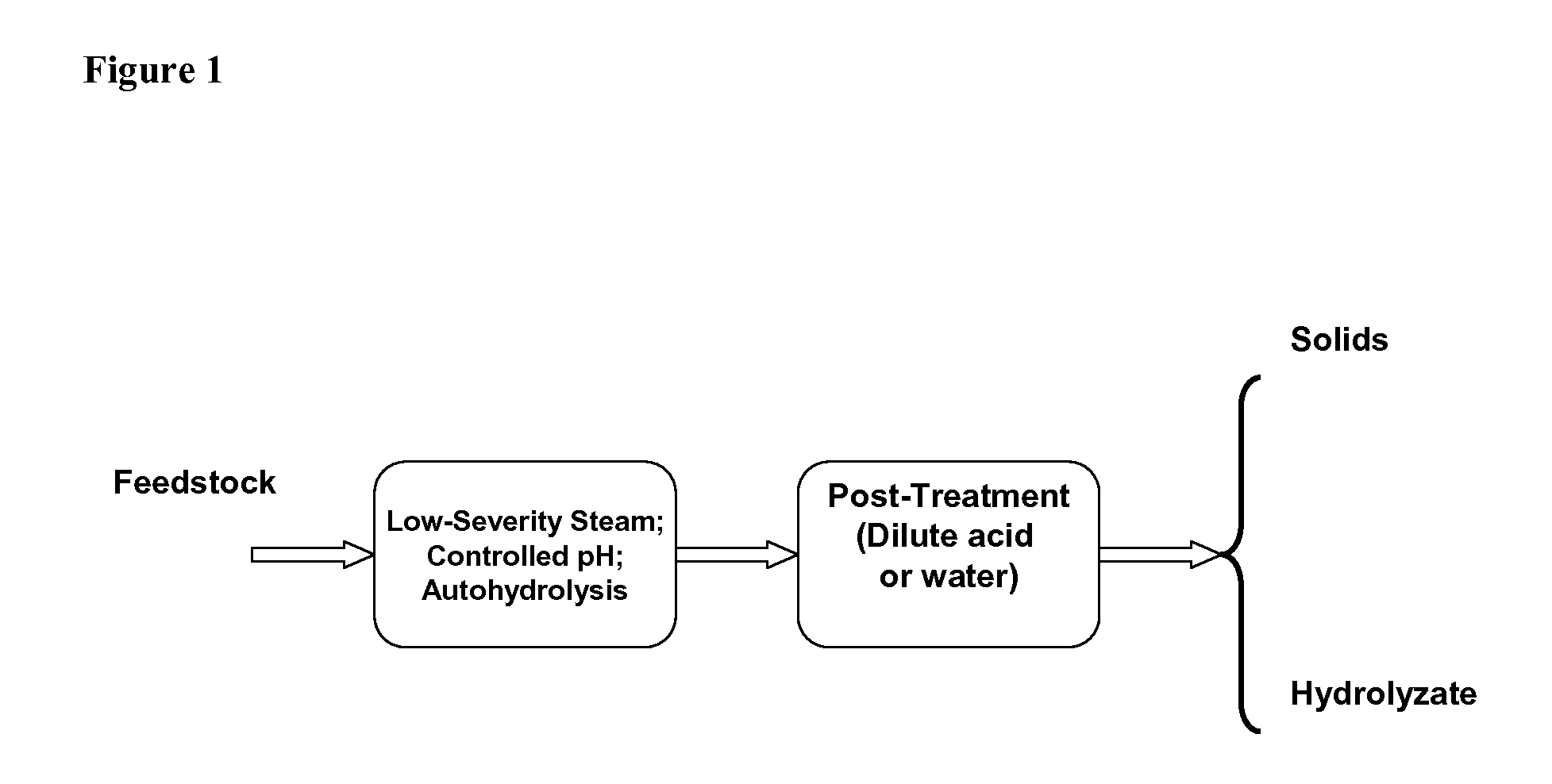
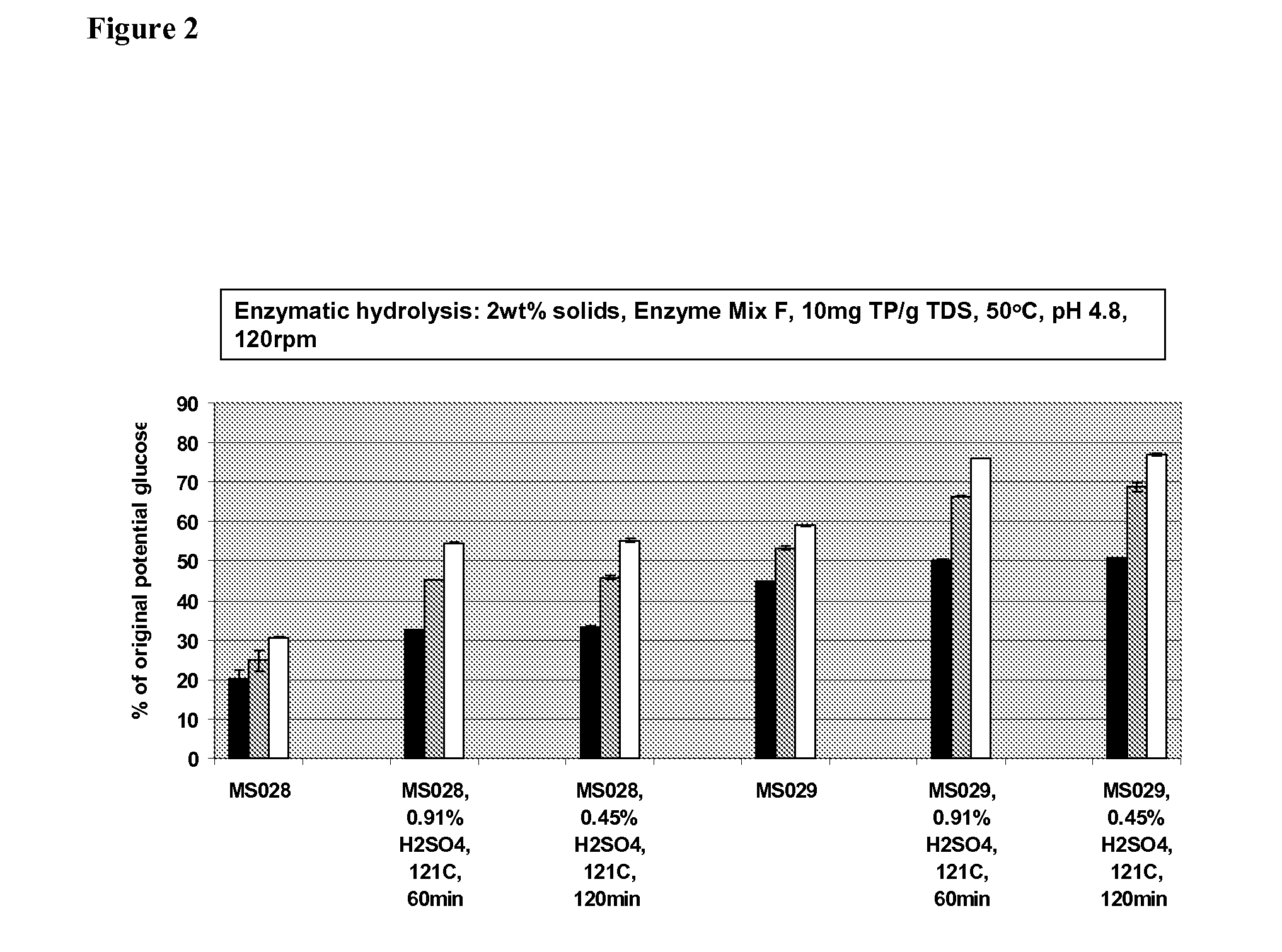
Two-Stage Process for Biomass Pretreatment
InactiveUS20110300586A1Increase rangeImprove digestibilityBiofuelsPulping with acid salts/anhydridesAcid hydrolysisLignocellulosic biomass
Described herein are improved methods of pretreating lignocellulosic biomass. One aspect of the invention relates to a two-stage pretreatment process comprising a relatively low severity steam treatment, a controlled pH pretreatment, or autohydrolysis, followed by hydrolysis with dilute acid or hot water at a relatively low temperature. In certain embodiments, the methods increase hemicellulose sugar yields, substrate digestibility, and suitability for fermentation as compared to steam explosion or acid hydrolysis alone. The two-stage pretreatment processes also employ few chemicals, minimizing the costs associated with pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Moreover, the two-stage pretreatment process may expand the range of suitable feedstocks for bioethanol production.
Owner:MASCOMA CORPORATION
Chitose aquagel evoked original position synthesis of super-paramagnetism nano ferriferrous oxide particles
InactiveCN101113022AGood biocompatibilityUniform particle size distributionFerroso-ferric oxidesIron nanoparticleParamagnetism
The invention provides superparamagnetic nano Fe3O4 particles synthesized through in-situ induction of chitosan hydrogels, relating to a method for synthesizing the superparamagnetic nano Fe3O4 particles. The invention solves the problems of serious aggregation of the nano Fe3O4 particles and the complicated method for inducing the chitosan into the surface of the Fe3O4 in the current nano Fe3O4 particles. The method of the invention is that: 1. the chitosan powder is added into dilute acid solution; 2. cross-linking agent is added to make the chitosan hydrogels; 3. the chitosan hydrogels are sequentially dipped in Fe3+ aqueous solution, water, Fe2+ aqueous solution and water, and a plurality of times of circular leaching are made so as to form the chitosan hydrogels that contains iron ions; 4. then basification treatment is carried out; 5. the hydrogels is dissolved or degraded again, and finally the black superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nano particles are obtained upon centrifugalization. The method of the invention requires simple technique and mild conditions and the equipment used in the method is simple and can be obtained easily, thereby mass production can be achieved. The average diameter of the particles is 15 to 25nm, and the particles distribute evenly with superparamagnetism.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
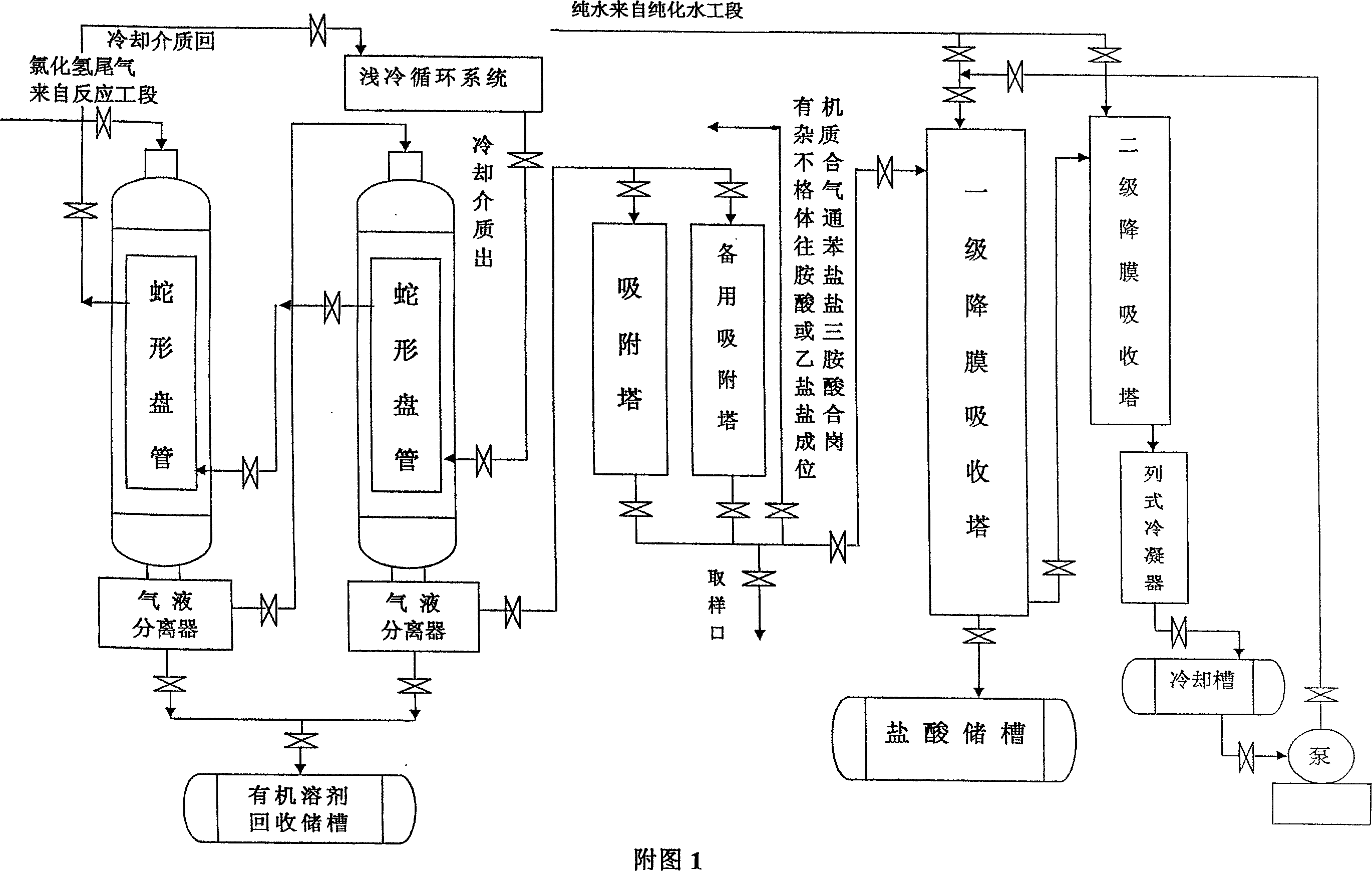
Process for preparing high purity hydrochloric acid by circularly absorbing hydrogen chloride by-product
InactiveCN1951801ASatisfied with the resultExpand the range of industrial applicationsChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationActive particlesPolypropylene
The invention discloses a preparing method of high-purity alcaine technology through circulating and adsorbing by-product of hydrogen chloride, which comprises the following steps: aerating hydrogen chloride gas with organic impurity in the condenser at -10- -40 deg.c and gas-liquid separator; adsorbing gas with little impurity through active particle charcoal; aerating adsorbed gas into one-grade and two-grade graphite falling-film; adsorbing through pure water to obtain the high-purity alcaine; adsorbing non-adsorbed hydrogen chloride through cold water; putting hydrogen chloride and diluted acid in the graphite polypropylene falling-film adsorbing tower into cooling groove; utilizing circulating pump to transmit the inlet of one-grade falling-film adsorbing tower; circulating the adsorption.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Transfer method of graphite film
InactiveCN103224231AReduce pollutionQuality improvementGrapheneElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
The invention discloses a transfer method of graphite film, which belongs to the field of material processing. The method aims at graphite prepared on nickel and other metal films by chemical vapor deposition method (CVD), and employs hydrogen bubble generated by reaction of a dilute acid solution and a metal substrate to separate the graphite layer and the metal substrate. PMMA and other polymers are not needed to cover the upper layer of the graphite for transferring carrier according to the invention, so no pollutants are introduced, and damage of graphite surface is greatly reduced; the peeling process is carried out by a direct chemical reaction between the acidic solution and the metal, thereby realizing separation of graphite on the upper and lower surface of the metal film and the metal film simultaneously with high efficiency and without external power source and electrochemical reaction. The invention has a simple operation technology and does not relate to harmful chemical substances. The metal substrate can be used for multitime with repetition, and the cost is greatly reduced. The invention has a large application value in the industrial field for large scale preparation of graphite.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for recovering valuable metals from waste lithium iron phosphate battery cathode material
ActiveCN108110357AReduce usageRealize high-grade optimal recoveryWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementAfter treatmentLithium iron phosphate
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable metals from a waste lithium iron phosphate battery cathode material. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) fully roastingand oxidizing the disassembled, broken and ground lithium iron phosphate battery cathode material, so that Fe and Li metal elements in the battery cathode material are generated into Fe2O3, FePO4 andLi3PO4 through being roasted and oxidized; (2) placing a roasted material that is fully-roasted and oxidized in the step (1) in a dilute acid solution for soaking, so that Li3PO4 in the roasted material is fully dissolved and filtered to realize the separation of the Li3PO4 in the roasted material from the Fe2O3 and the FePO4; (3) taking a filtrate after treatment in the step (3) and regulating the filtrate to be alkaline, so that Li3PO4 in the filtrate is directly separated out into a precipitate. Therefore, the recovery of the solid Li3PO4 is realized. The method disclosed by the invention is short in technical process, simple to operate, low in cost and environmentally-friendly and can preferentially select and recycle the high-grade lithium metals in the lithium iron phosphate batterycathode material, thereby having a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:MEISHAN SHUNYING POWER BATTERY MATERIALS CO LTD
Novel method for saccharification of ligno-cellulose
InactiveCN101434976AAvoid high temperature and pressureSave operating timeBiofuelsFermentationCellulaseXylanase
The invention relates to a new method for processing lignocellulose by saccharification, comprising dilute acid pretreatment, milling and crushing, cellulase compounding and enzymolysis saccharification process. The detail method thereof comprises the following steps: the crushed lignocellulose raw materials are pretreated with dilute acid with the H <+> concentration of 0.01mol / L-0.1mol / L and later milled and crushed, and then acidolysis sugar solution is obtained; at least two types of cellulase are mixed with xylanase for obtaining compound cellulase, and then further enzymolysis saccharification treatment is carried out to the rest solid after enzymolysis and milling for obtaining enzymolysis sugar solution. By using the process that the milling of dilute acid is combined with the one-step enzymolysis of compound enzyme, the hydrolysis sugar yield of the lignocellulose raw materials can be up to more than 90 percent. The method has the advantages of mild reaction condition, simple operation, and high enzymolysis efficiency; moreover, the obtained sugar solution after being processed produces no inhibition to the follow-up fermentation, can be comprehensively utilized, and causes no environmental pollution, etc.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method for preparing hollow high voltage nickel manganese acid lithium anode material
ActiveCN103474650ACalcination temperature is highIncrease shell thicknessCell electrodesParticulatesManganese
The invention discloses a method for preparing hollow high voltage nickel manganese acid lithium anode material, and belongs to the technical field of material synthesis. The method includes the steps that firstly, manganese carbonate is prepared and then calcined under a certain temperature to make the outer shell of the manganese carbonate become manganese dioxide, then, the inner core of the manganese carbonate is dissolved away with dilute acid, the manganese dioxide outer shell is left and mixed with a lithium source and a nickel source, and the hollow nickel manganese acid lithium material is obtained in a calcined mode. The nickel manganese acid lithium material prepared with the method is of a uniform micrometer / nanometer structure and is 1-5um secondary particulates formed by 30-400nm particulates, and primary particulates in small sizes shorten the transmission distance of lithium ions, increase the area of contact between electrodes and electrolytes, and improve the rate capacity. The nickel manganese acid lithium material particulates prepared with the method are of a hollow structure, gaps can buffer structural stress and size changes caused by ithiation, and circulating performance is improved.
Owner:南京时拓能源科技有限公司
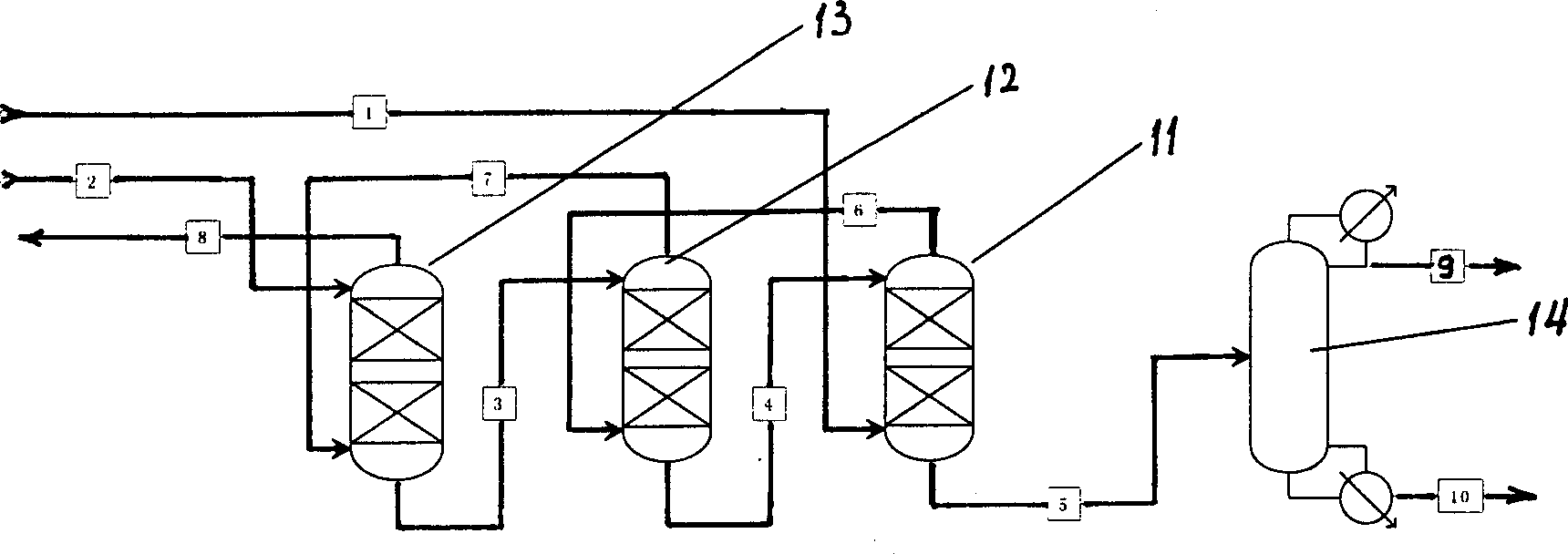
Combined pretreatment method of wood cellulose and system thereof
InactiveCN100564667CImprove conversion rateHigh removal ratePaper material treatmentPretreatment methodEnzymatic hydrolysis
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Struvite circulating crystallization method for treating synthetic ammonia wastewater
InactiveCN102336504AReduce processing costsGuaranteed removal rateBio-organic fraction processingMultistage water/sewage treatmentMagnesium saltRaw material
The invention relates to a struvite circulating crystallization method for treating synthetic ammonia wastewater. The method comprises the following steps of: A, adding soluble phosphate and magnesium salt into the synthetic ammonia wastewater at the ammonium nitrogen concentration of 1,000-2,065mg / L; B, adding alkali into the acquired struvite solid, and performing pyrolysis at the temperature of between 80 and 100DEG C for 1 to 3 hours; C, treating the synthetic ammonia wastewater by using a pyrolysis solid product, and adding a small amount of magnesium salt, wherein ammonia generated in the pyrolysis process is absorbed by a dilute acid solution, and the obtained ammonium salt is used as a raw material for producing a fertilizer; and D, using struvite which cannot be recycled as a sustained-release fertilizer. For the synthetic ammonia wastewater at the ammonium nitrogen concentration of 1,000-2,065mg / L, the struvite can be recycled for 3 to 6 times, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate is higher than 87 percent, the ammonium nitrogen concentration of effluent is lower than 200mg / L, agents are saved through recycle, and nitrogen resources are recycled. The pretreated wastewater meets the requirement of an A / O biochemical treatment process on nitrogen and phosphorus, and can be subjected to biochemical treatment further.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparation of unidimensional monocrystal titanium dioxide nano material
InactiveCN1699636ALow priceEasy to getPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPotassium hydroxideSingle crystal
The present invention belongs to the field of nanometer material technology. The procedure is: 1) adding 1-30 parts of TiCl4 or TiO2 powder to 70-99 parts of organic solvent, obtaining evenly distributed mixture, 2) dissolving 10-60 parts of potassium hydroxide in 40-90 parts of deionization water, obtaining NaOH solution, 3) adding 20-80 parts NaOH solution of step 2)to 10-50 parts solution of step 1), stirring and moving to an autoclave, thermostatically heating at 50-300 degree C, 4) cooling down and pouring out the supernatant liquid, washing the bottom precipitation with deionization water and diluted acid solution, followed by centrifugal separating and drying at 10-200 degree C. The product obtained is one dimension single crystal nanometer material (nano-wire, nano-rod, and nano-tube) of TiO2 with diameter of 10-100 nm and length of micrometer order of magnitude. The product of the present invention is of high purity and high yield rate, and the form and pattern can be adjusted through selecting different solvents.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of thermoregulation cellulose fiber with intelligent thermoregulation function
InactiveCN1995497APrevent leakageHigher than the surfaceHeat-exchange elementsArtifical filament manufactureHeat stabilityCellulose fiber
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for tempering cellulose fiber with intelligent tempering performance, characterized in that microcapsule grout of phase change energy storage materials with the weight of 10-230% of the fiber is put into the fiber stock solution of cellulose so as to form spinning dope by even mixture, which enters into the dilute caustic soda solution and dilute sulfate in turn to form the fiber; tempering cellulose fiber is formed by dilute acid decoppering, washing and drying. It is provided with simple process, low manufacturing cost and wide applicable range. The tempering cellulose fiber has the base material of cellulose fiber and the functional additive material of microcapsule of phase changer energy storage materials. The phase change energy storage materials are not easy to leak and is provided with good heat stability and tempering effect. When it is applied in down-proof fabric and duvay the phase change energy storage materials can strengthen the tempering performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com