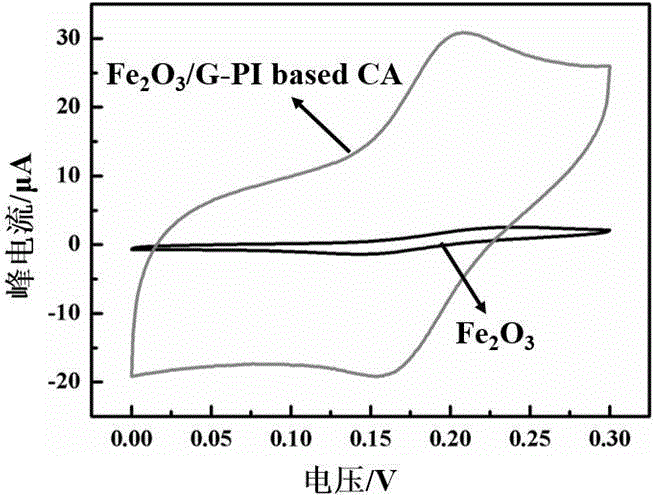
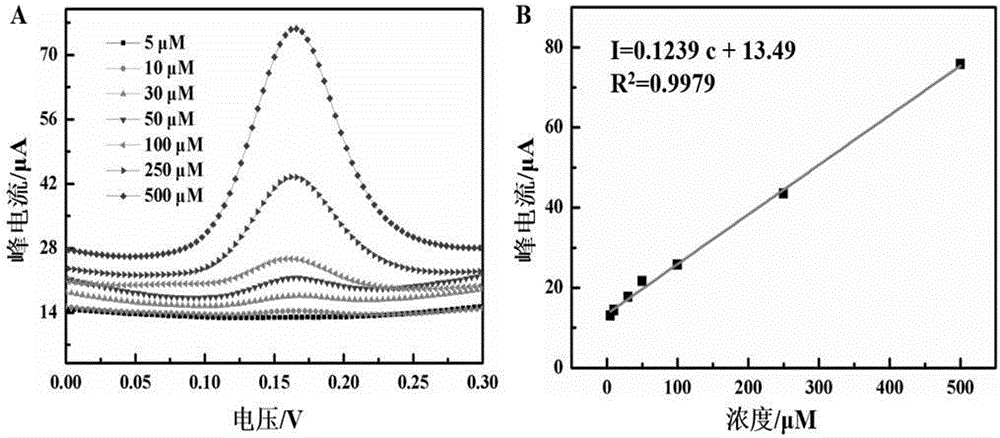
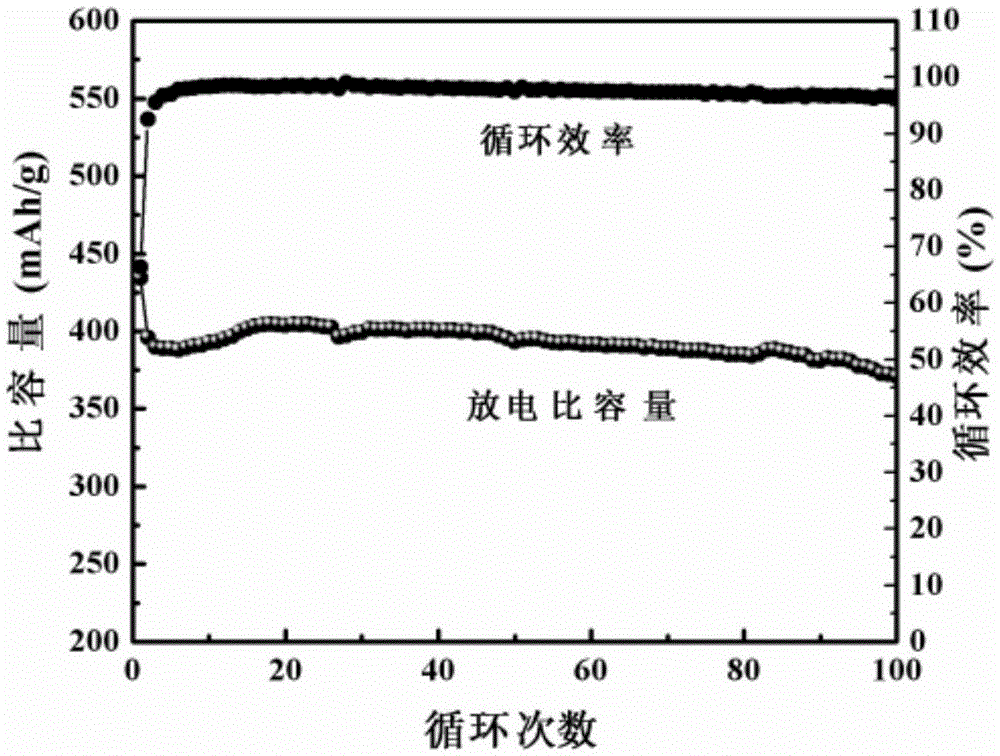
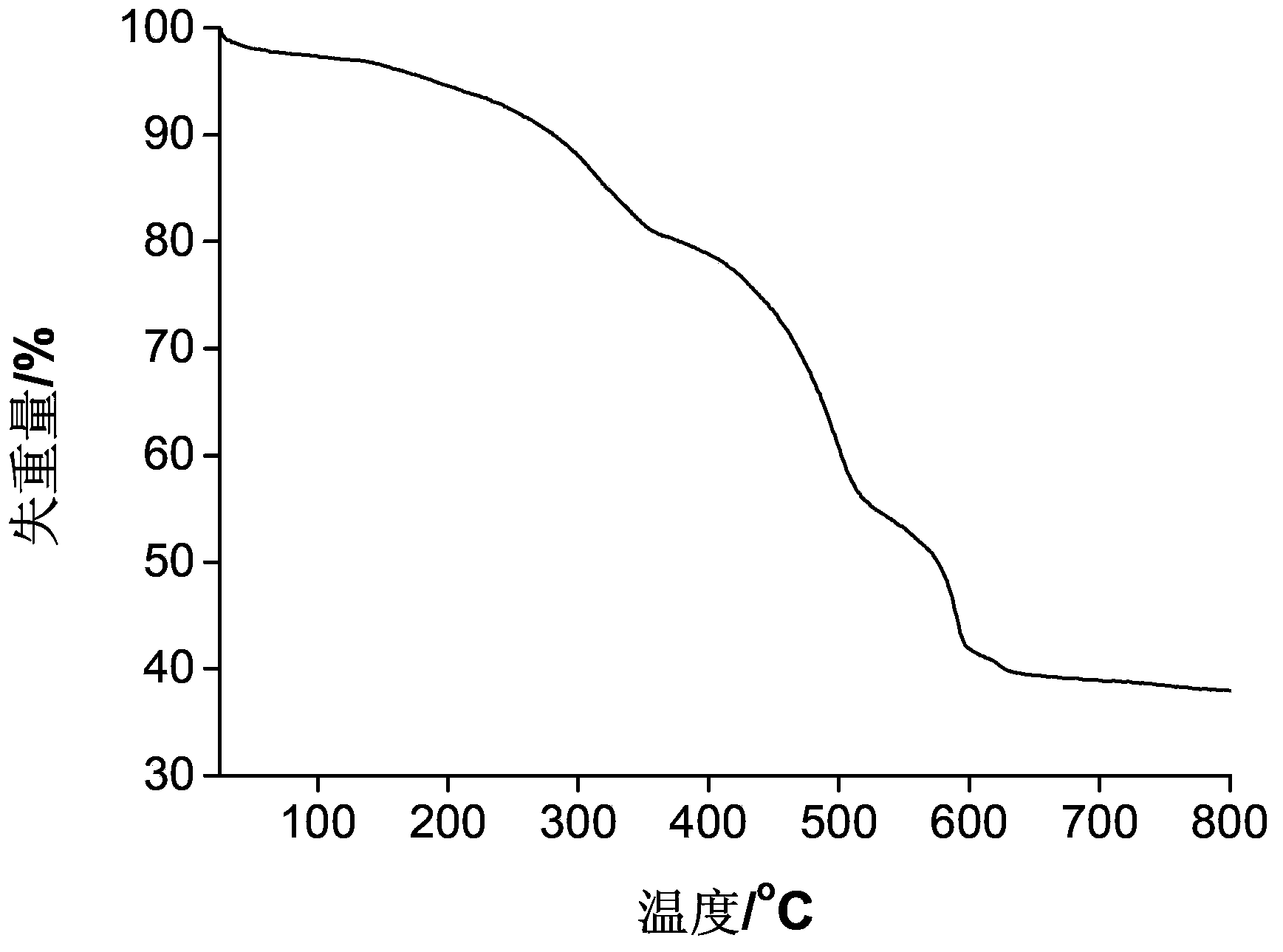
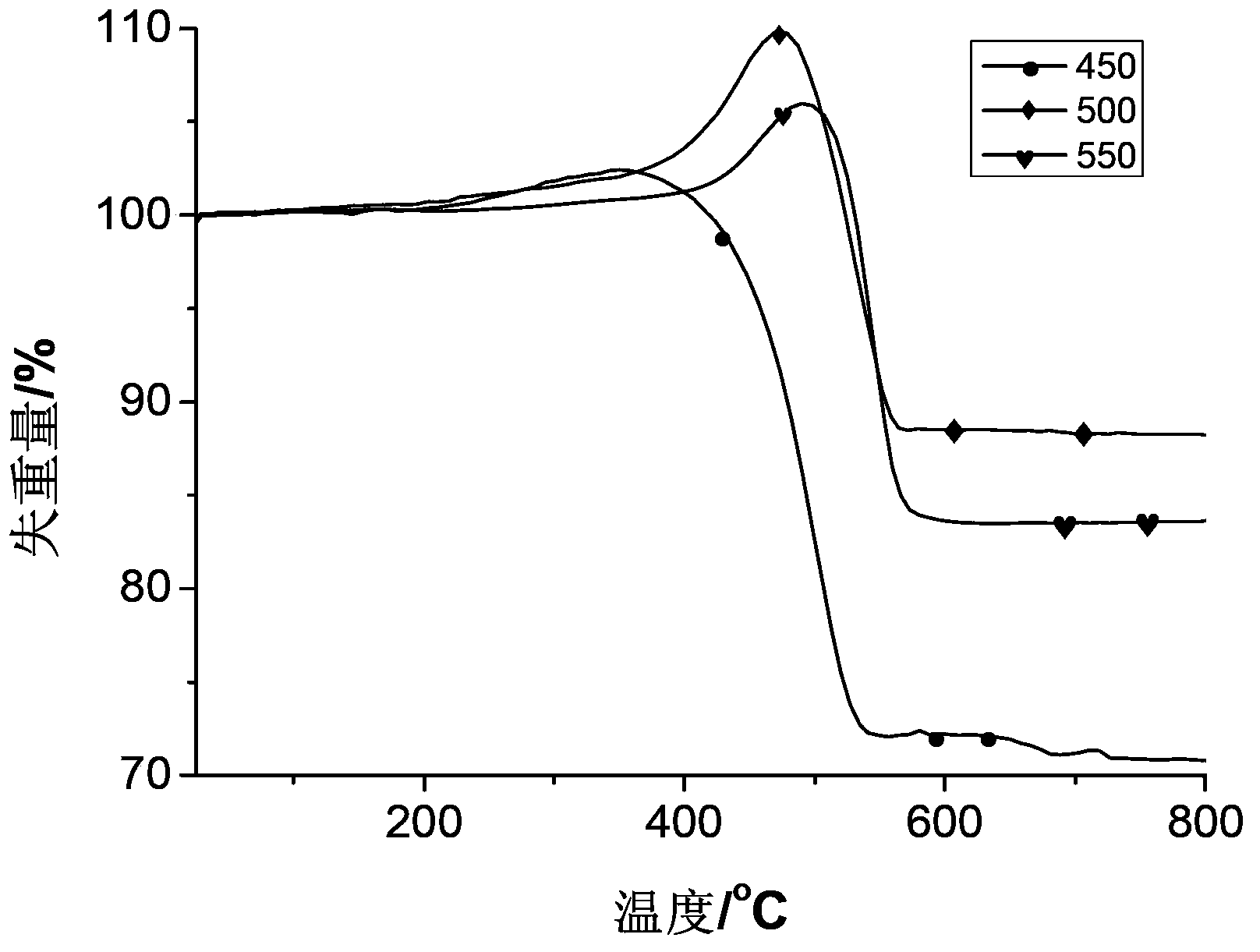
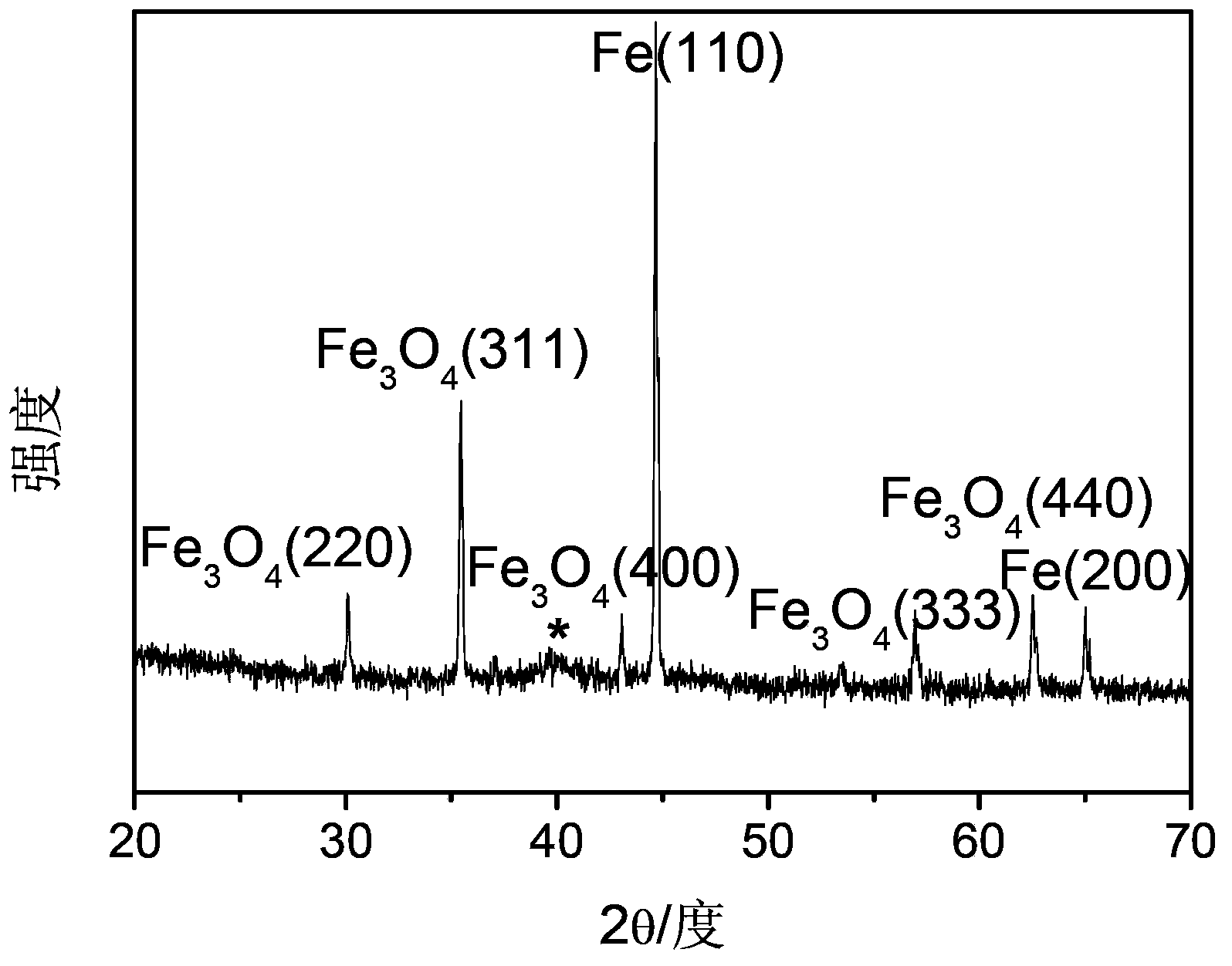
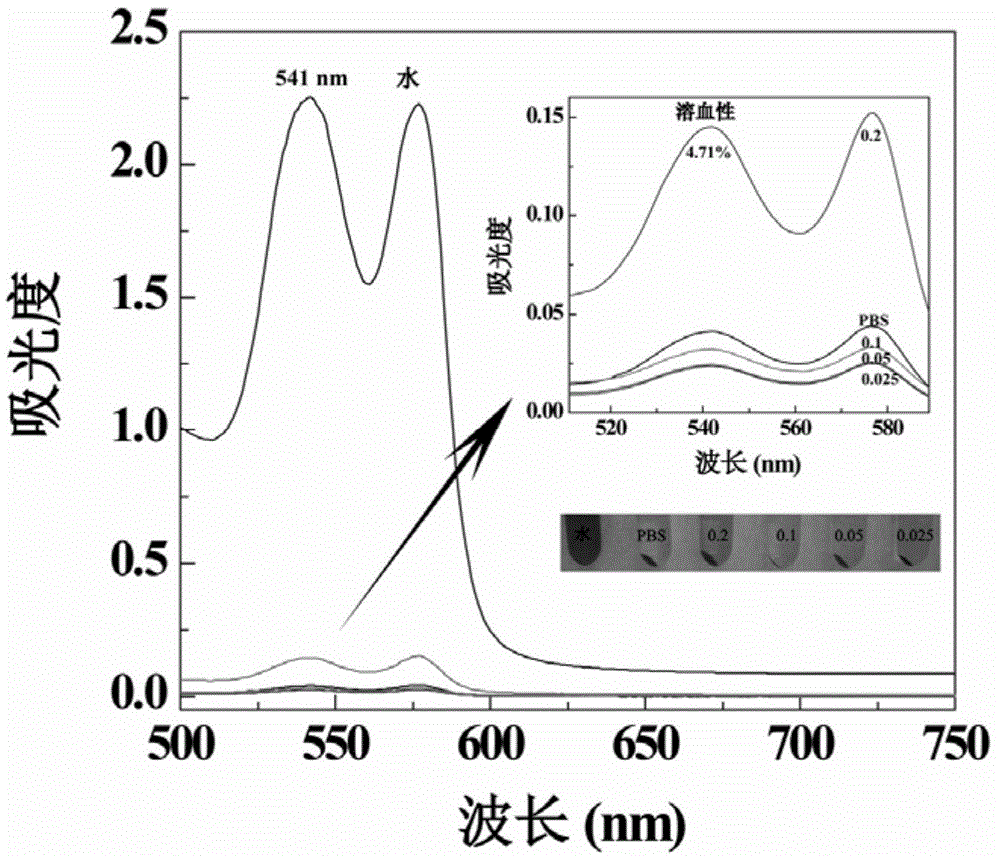
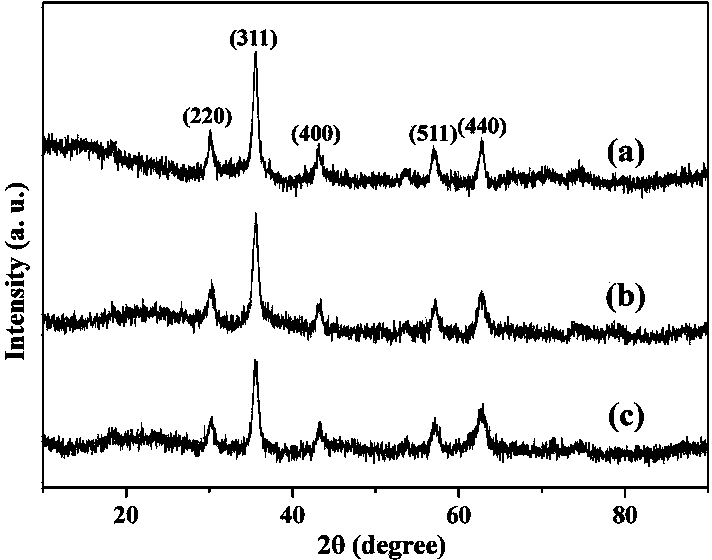
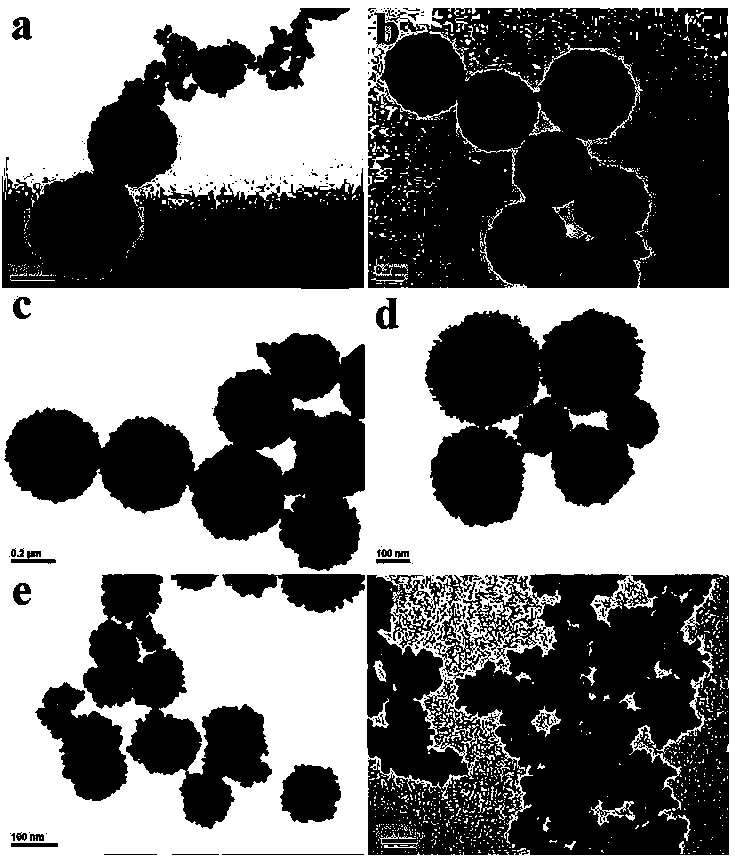
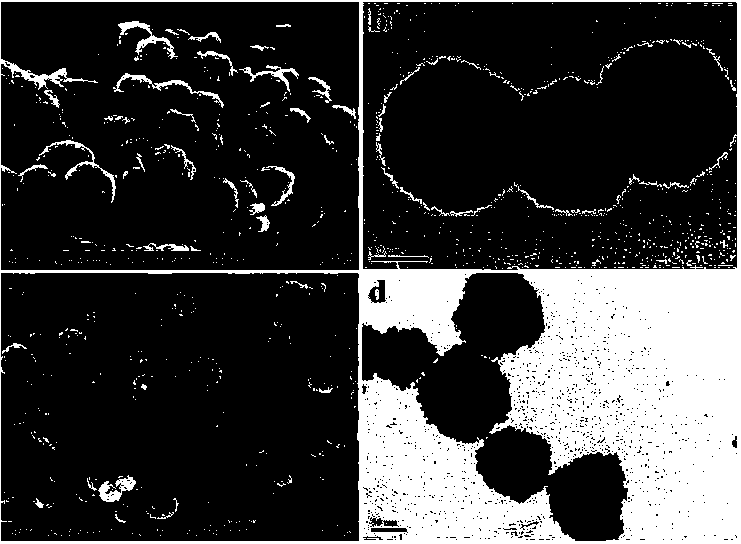
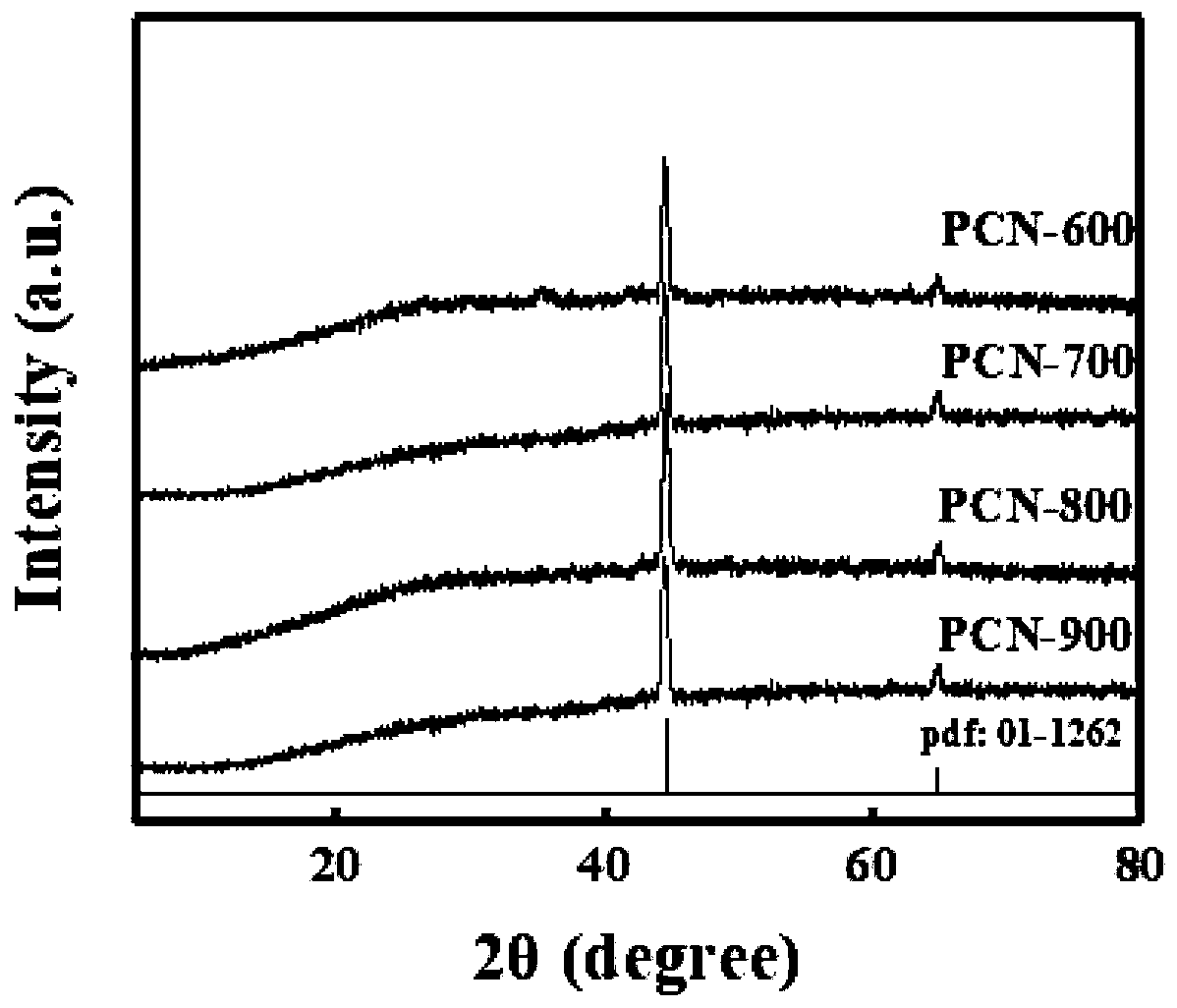
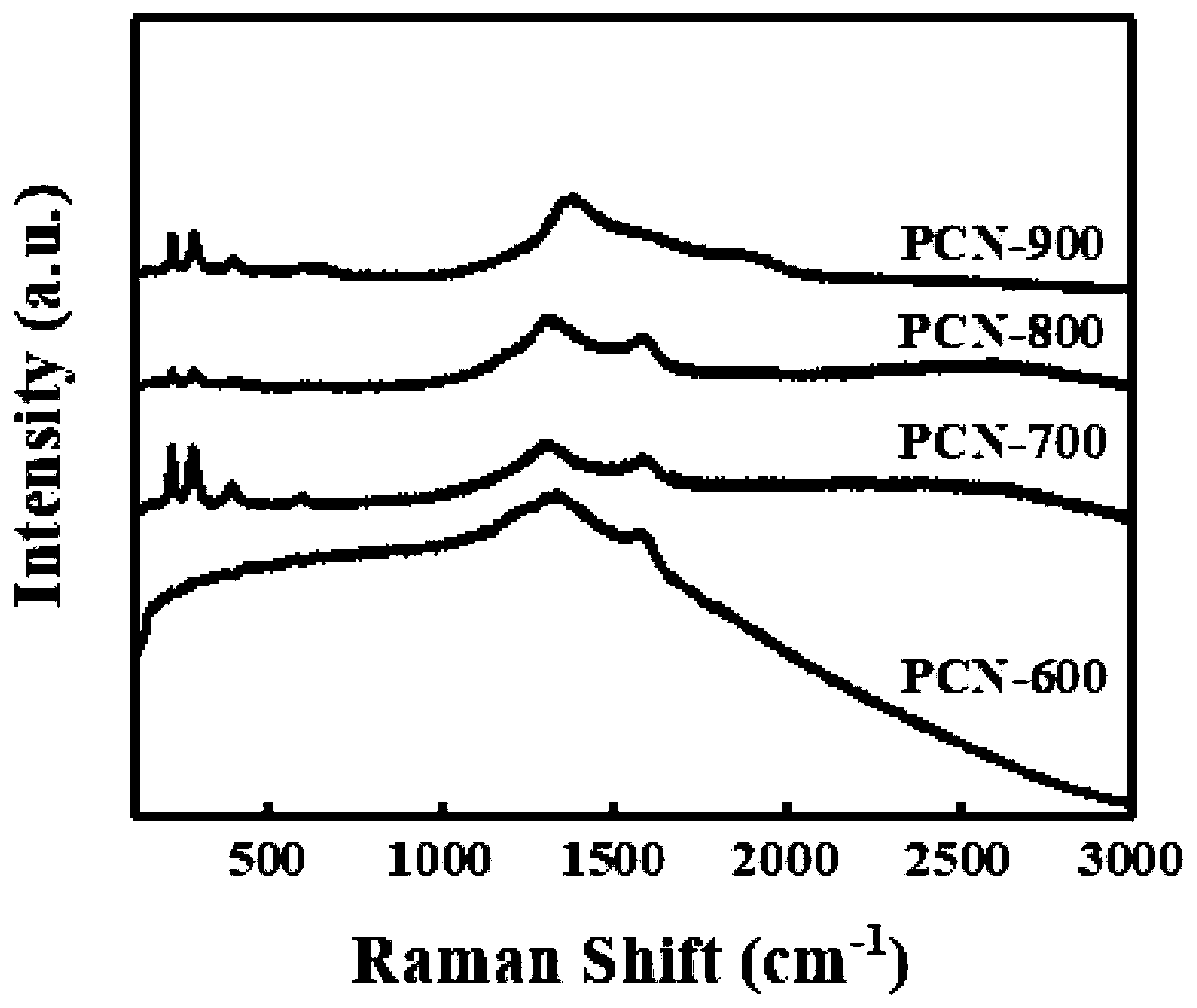
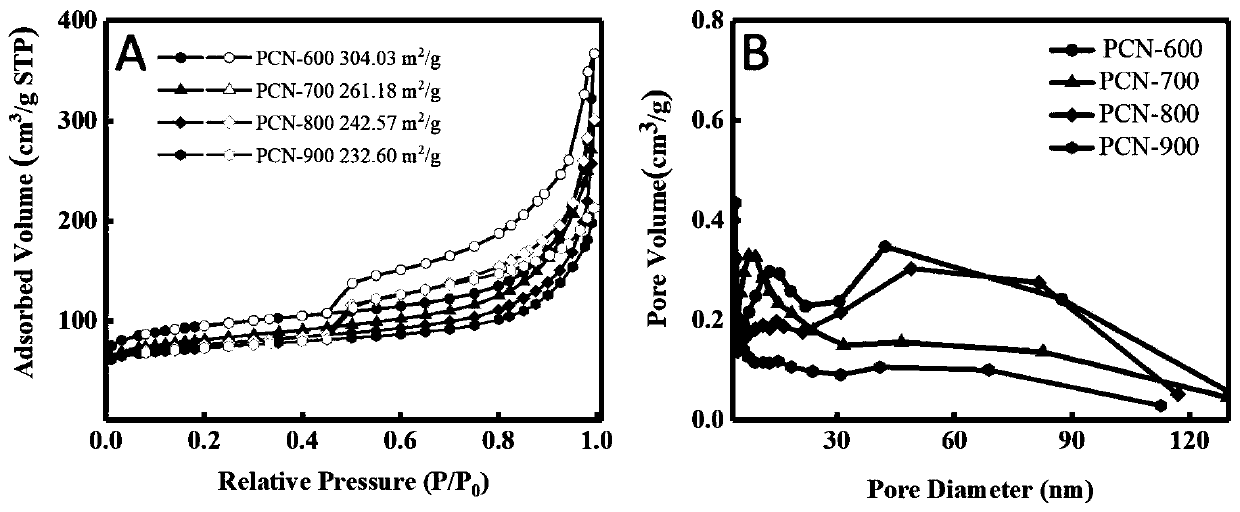
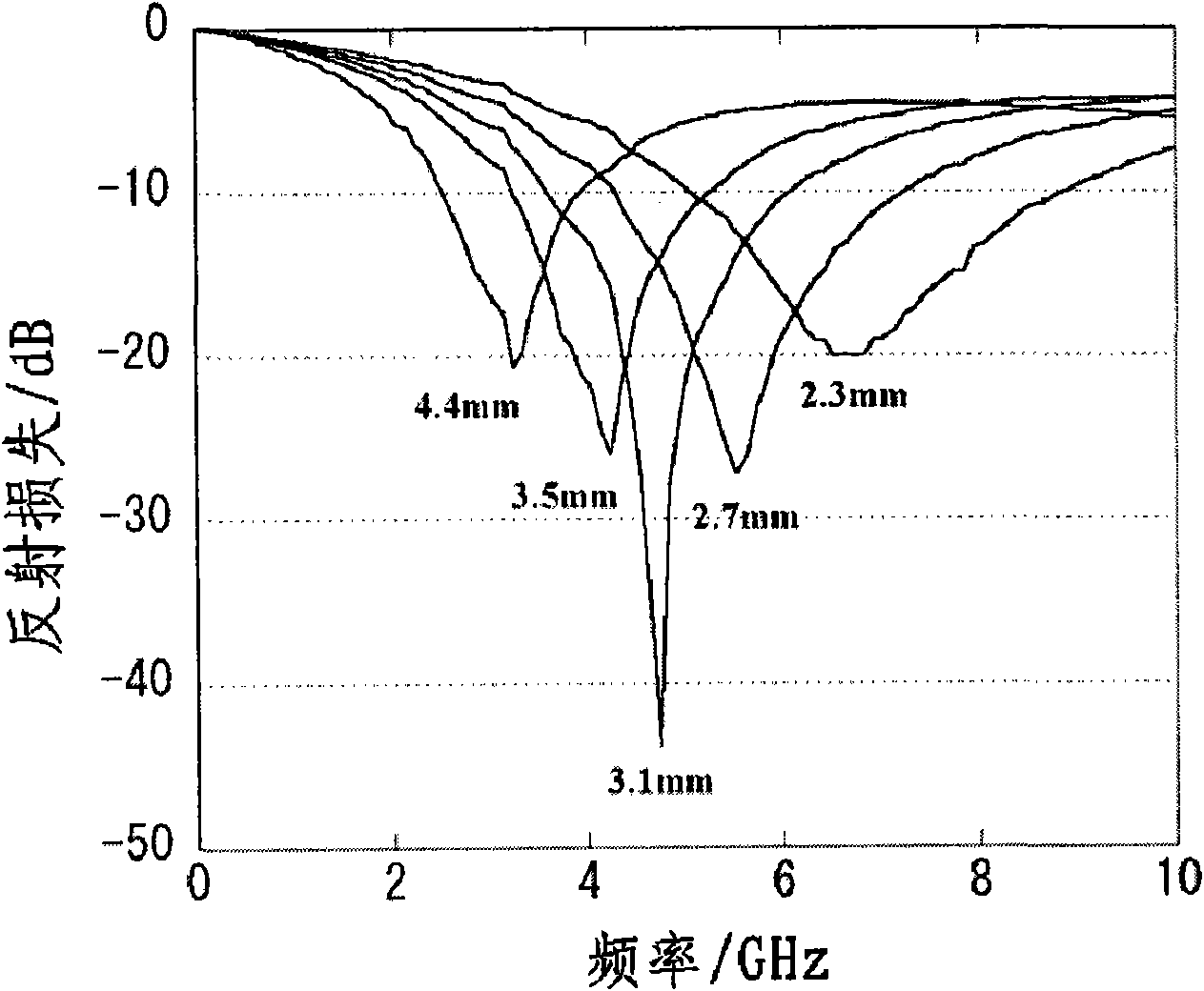
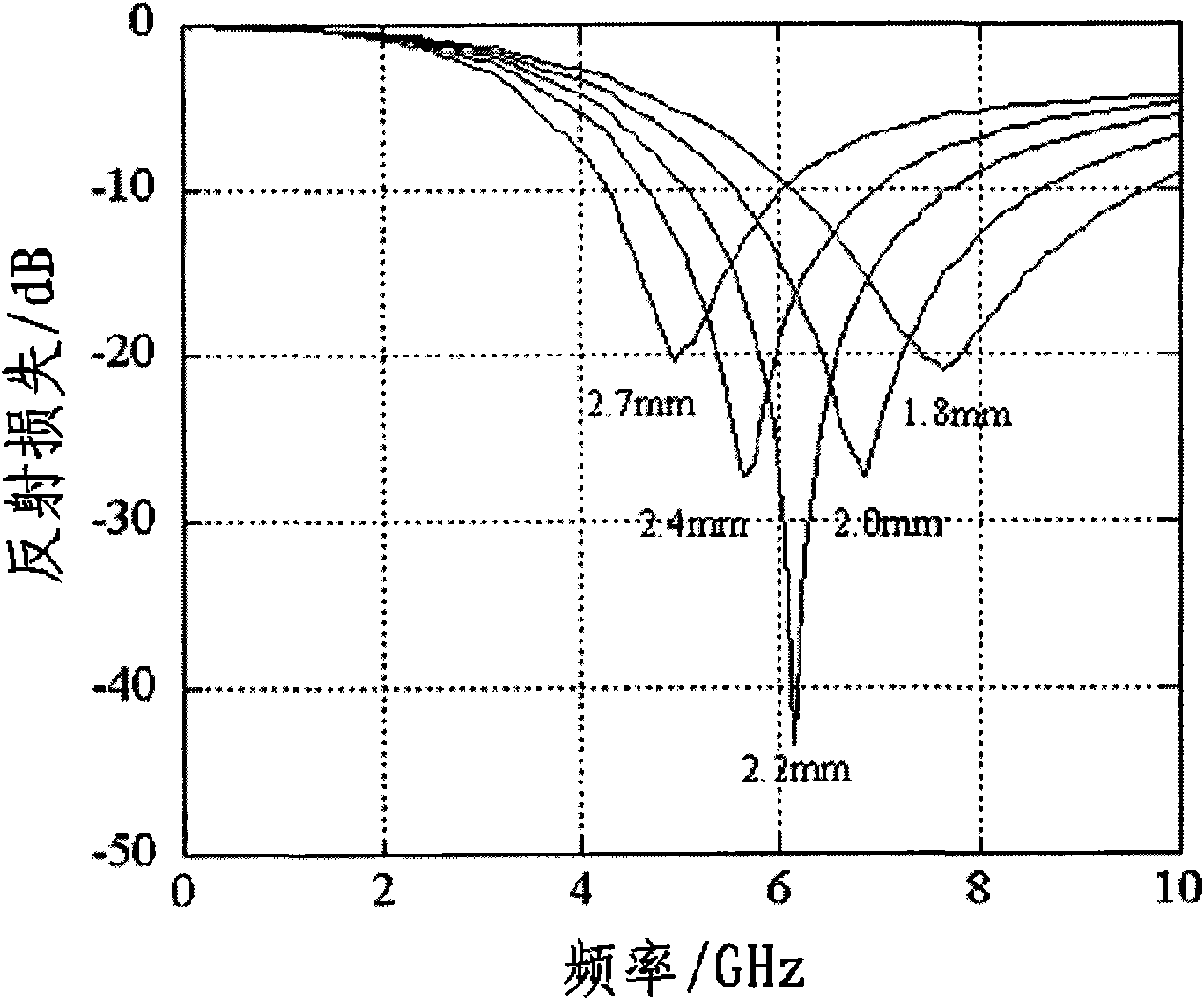
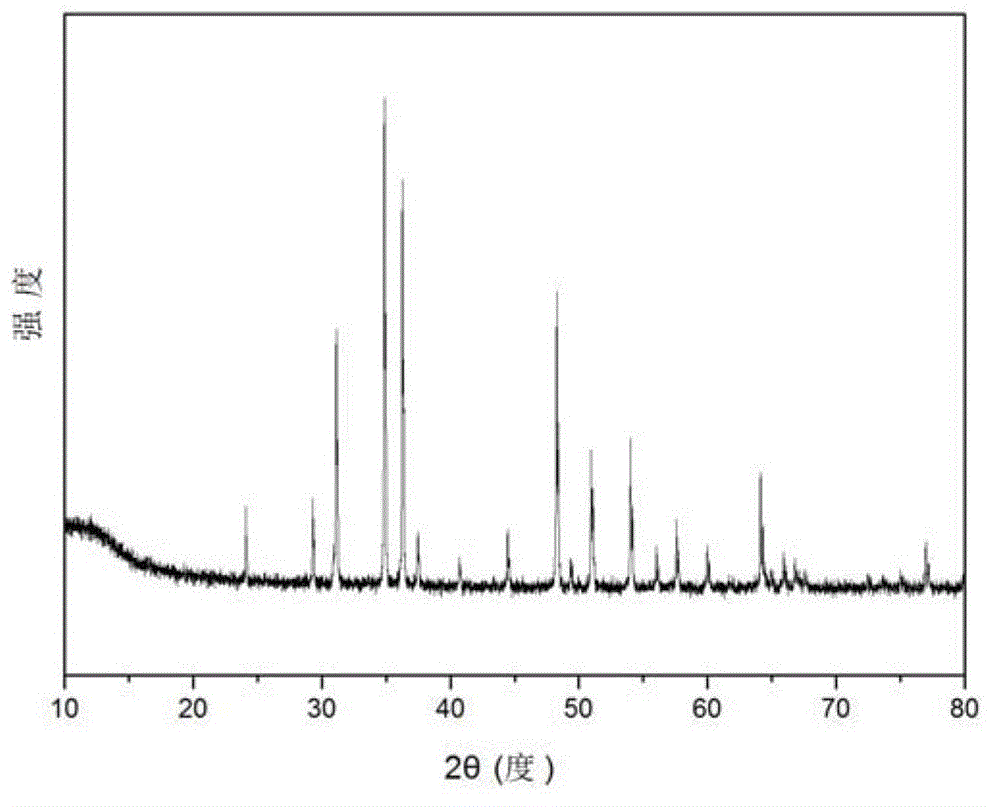
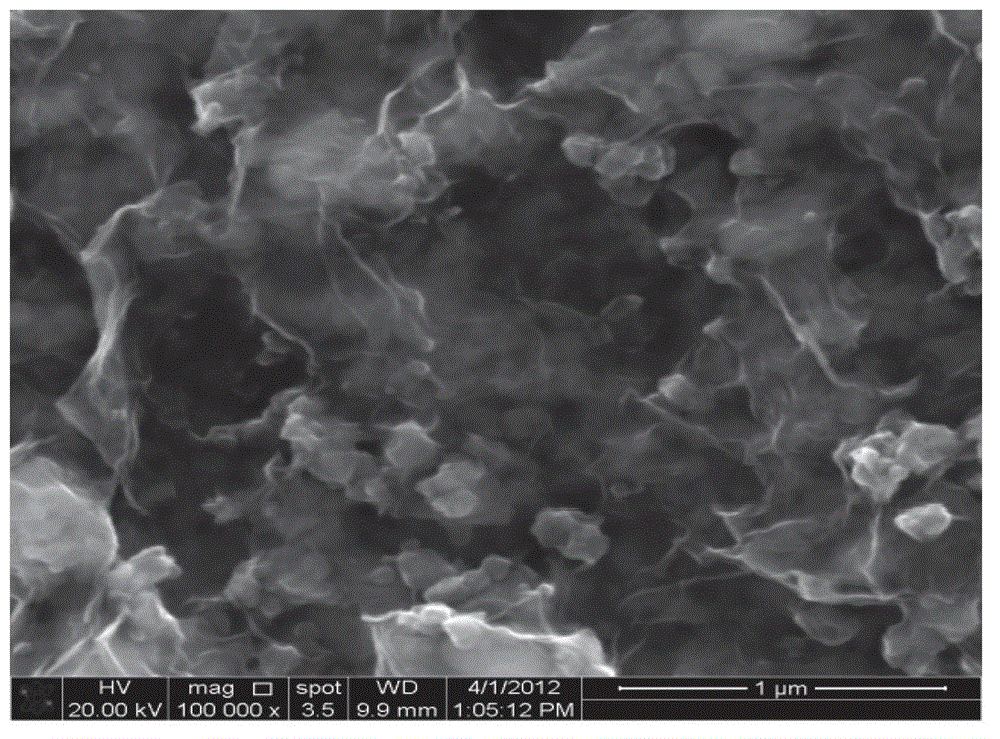
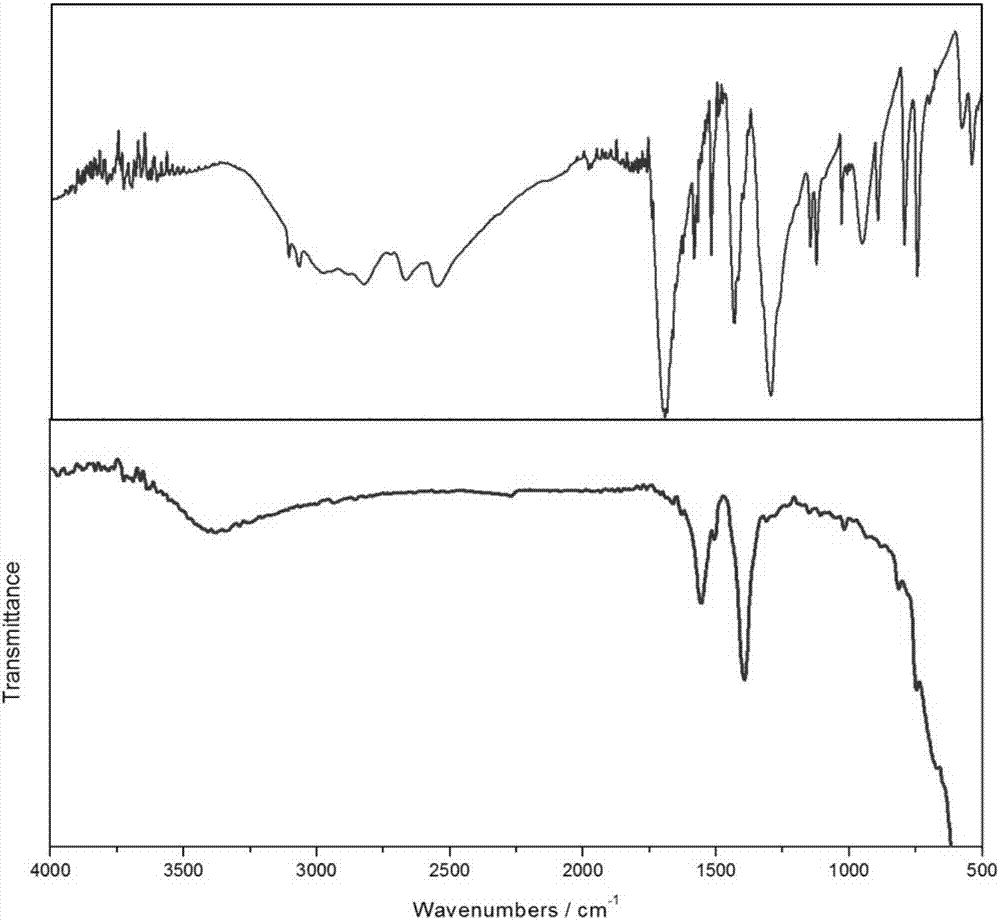
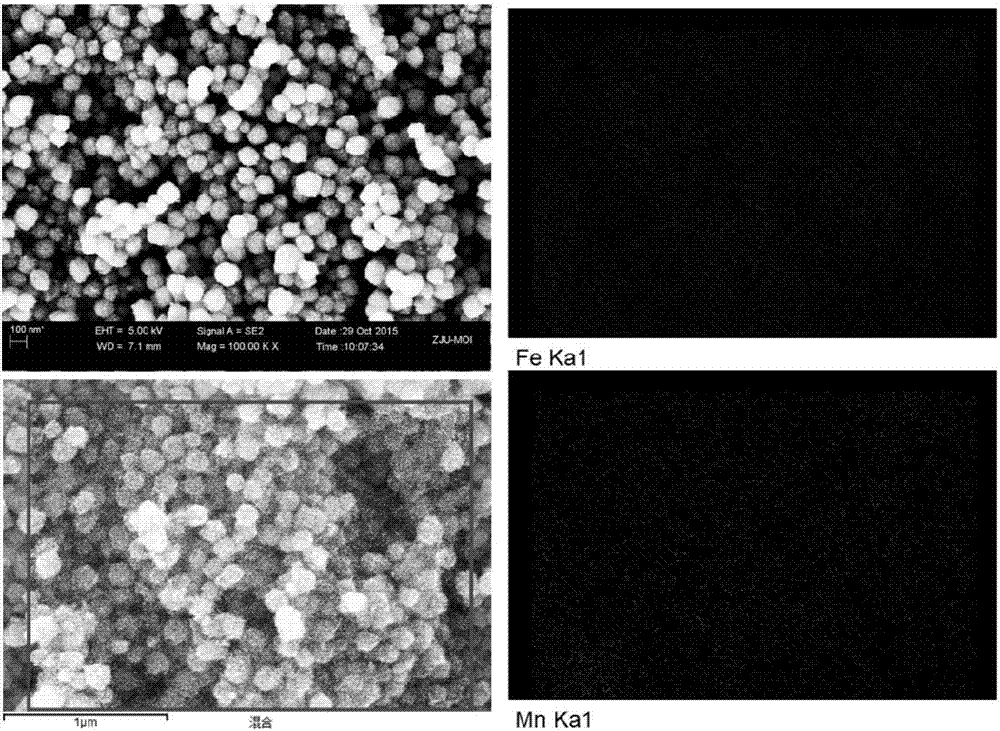
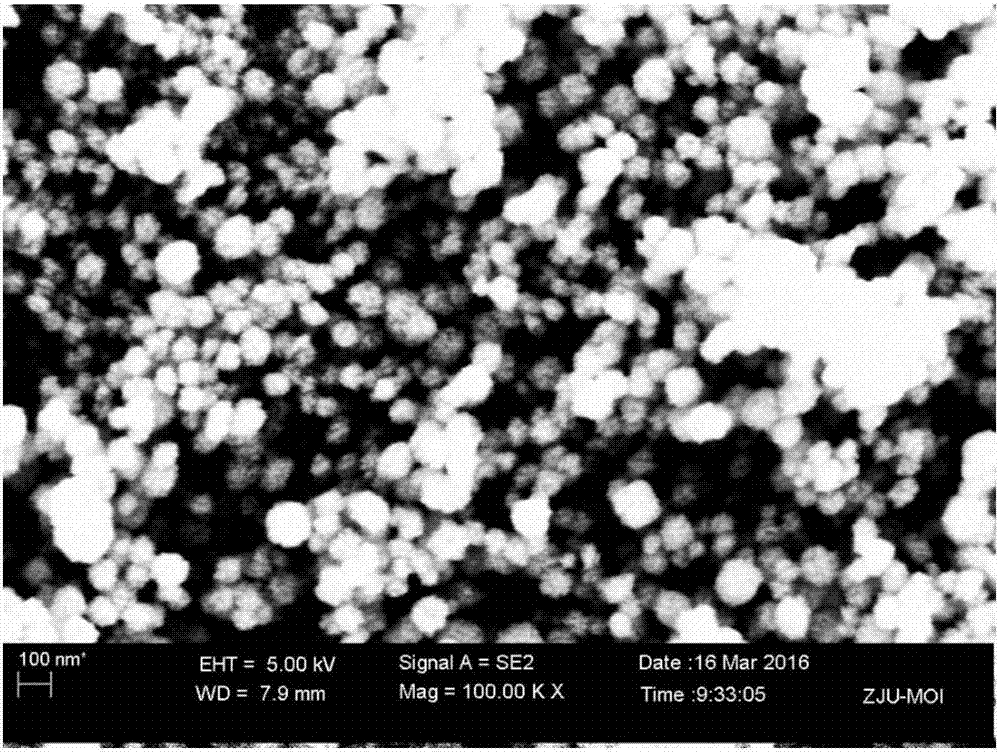
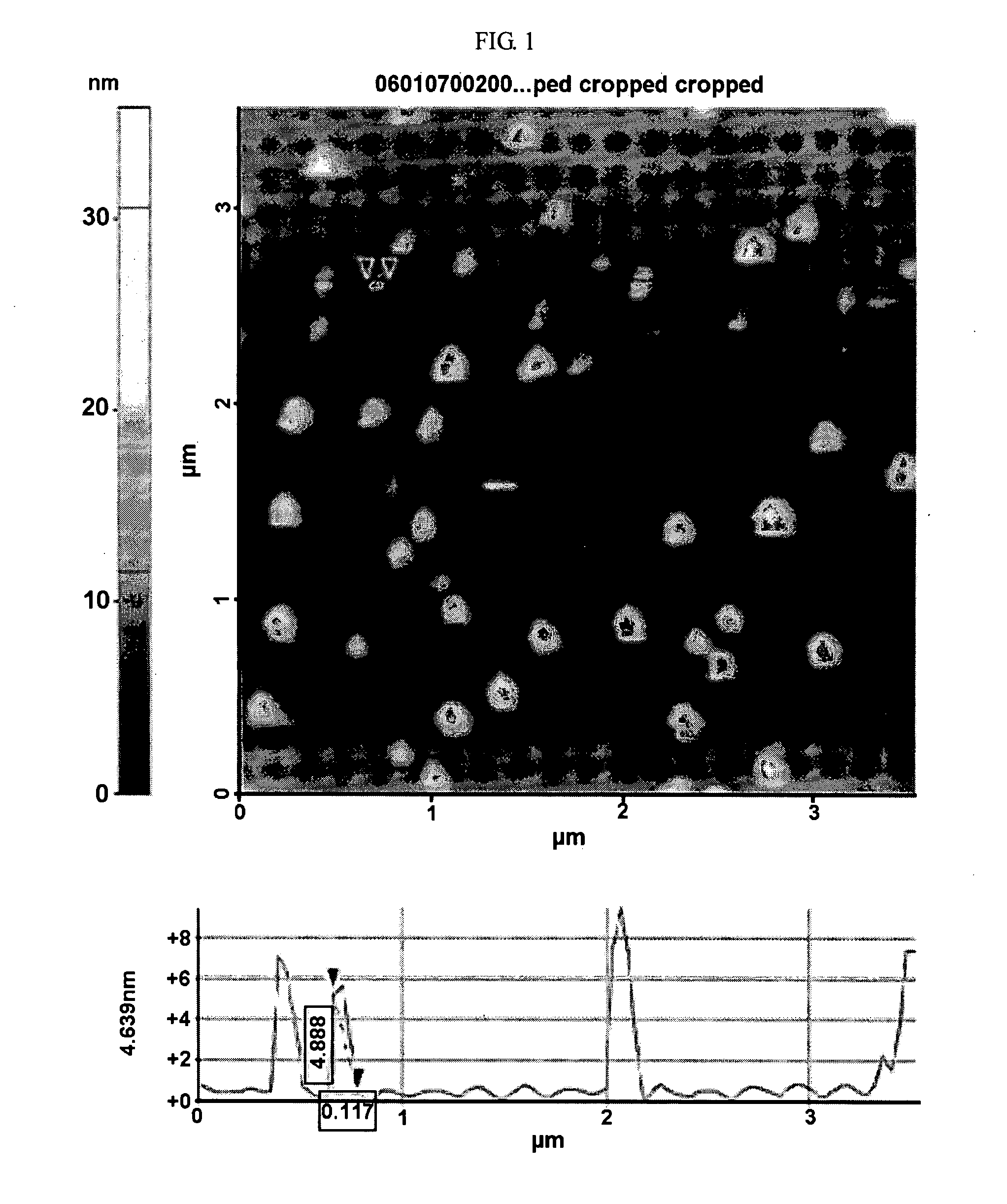
Patents
Literature
456 results about "Iron nanoparticle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
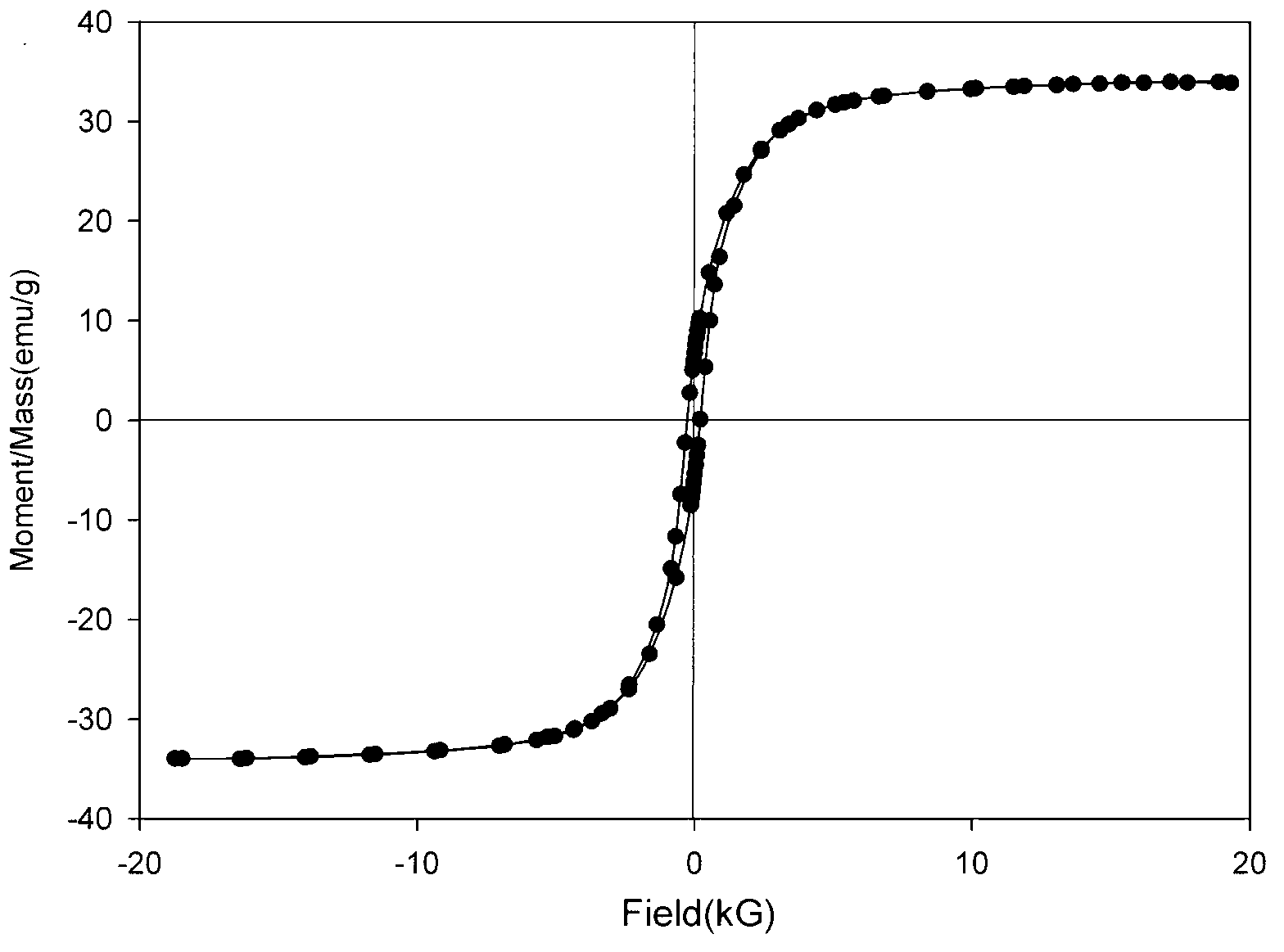
Synthesis. Iron nanoparticles can be synthesized by the reduction of Fe(II) or Fe(III) salt with sodium borohydride in an aqueous medium.. Reactivity. When exposed to oxygen and water, iron oxidizes.
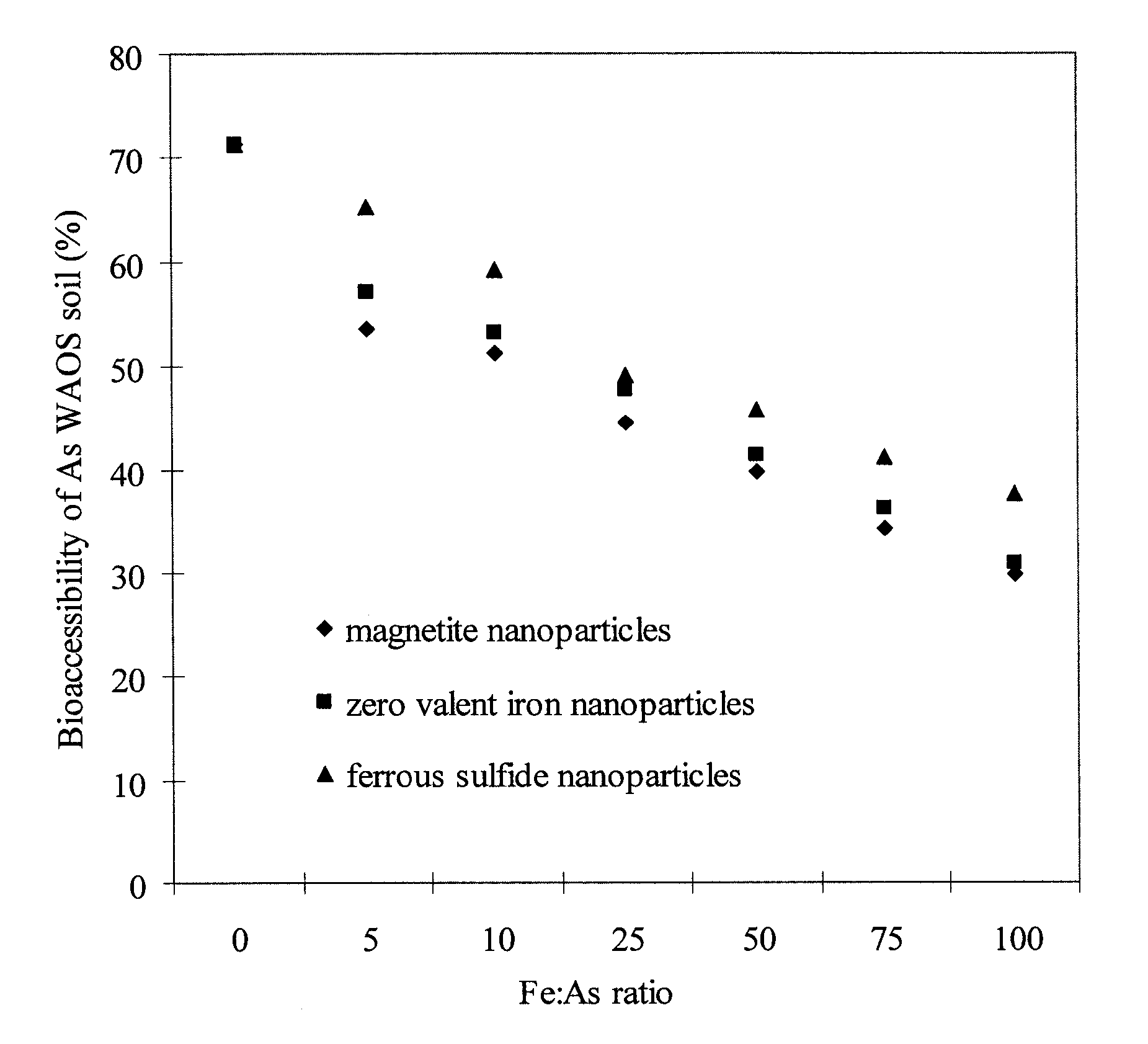
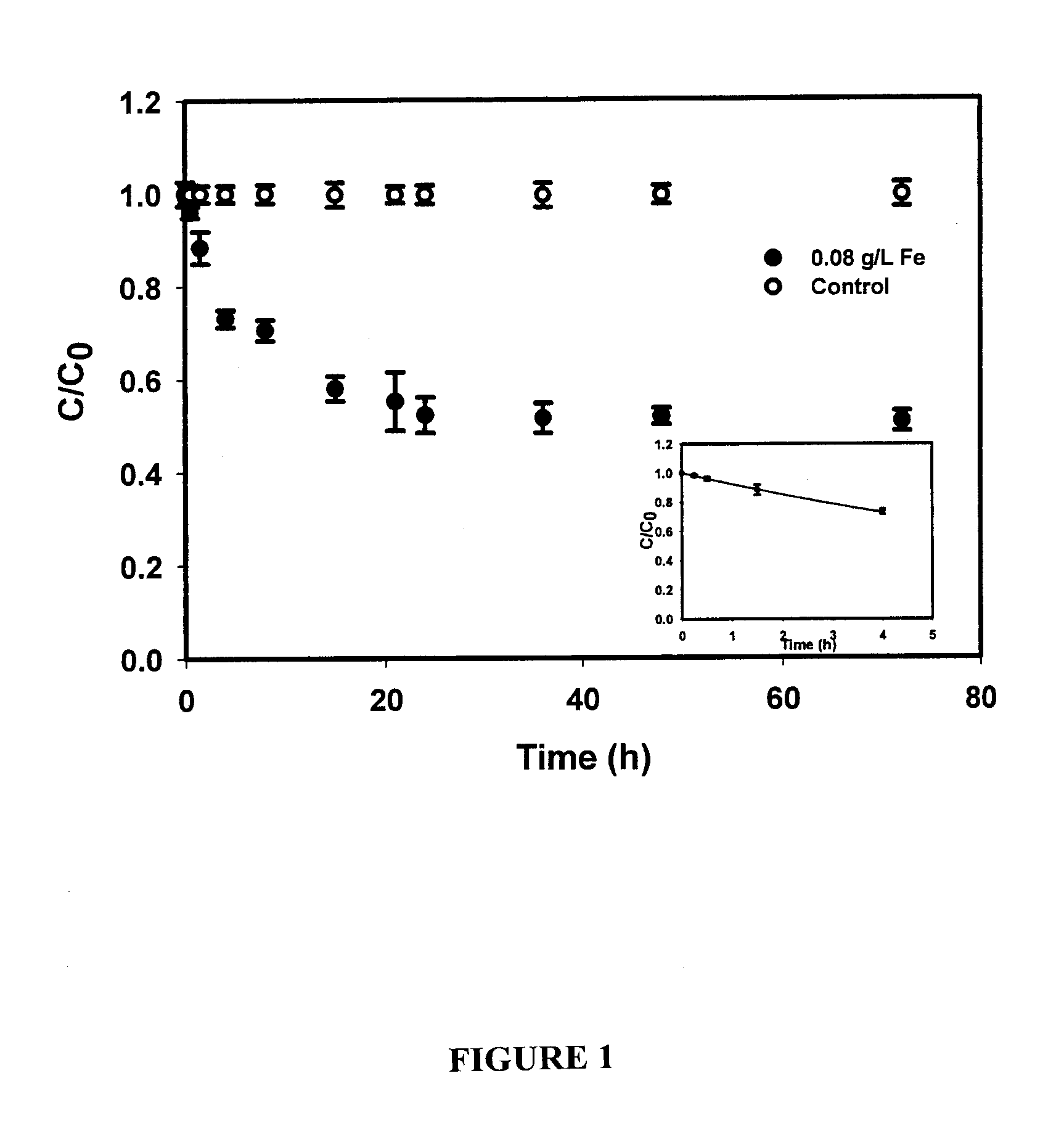
In Situ Remediation of Inorganic Contaminants Using Stabilized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070256985A1Low costProcess environmental protectionMaterial nanotechnologyWater treatment compoundsCelluloseMaterials science
A method for preparing highly stabilized and dispersible zero valent iron nanoparticles and using the nanoparticles as a remediation technology against inorganic chemical toxins in contaminated sites. The method employs a composition containing select polysaccharides (starch or cellulose) as a stabilizer for the iron nanoparticles in a liquid carrier, and results in suspensions of iron nanoparticles of desired size and mobility in water, brine, soils or sediments. The stabilizer facilitates controlling the dispersibility of the iron nanoparticles in the liquid carrier. An effective amount of the composition is delivered to a contaminated site so that the zero valent iron nanoparticles can remediate one or more toxins such as an arsenate, a nitrate, a chromate, or a perchlorate in the contaminated site.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Synthesis and conjugation of iron oxide nanoparticles to antibodies for targeting specific cells using fluorescence and mr imaging techniques
InactiveUS20100209352A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDispersion deliveryFluorescenceAntibody conjugate
The invention provides for methods for producing water-soluble iron oxide nanoparticles comprising encapsulating the nanoparticles in phospholipids micelles. Also provided are methods for conjugating the inventive nanoparticles via functionalized phospholipids to a target molecule, such as an antibody. The invention further provides methods for using the nanoparticle-antibody conjugate of the invention as a contrast agent to image specific cells or proteins in a subject using fluorescent and magnetic imaging techniques.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Drug Release from Thermosensitive Liposomes by Applying an Alternative Magnetic Field
Thermosensitive liposomes encapsulating paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are used as a drug controlled release system. Paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are used to generate heat by applying alternative magnetic field to cause leakage of drugs in the liposomes.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Chitose aquagel evoked original position synthesis of super-paramagnetism nano ferriferrous oxide particles
InactiveCN101113022AGood biocompatibilityUniform particle size distributionFerroso-ferric oxidesIron nanoparticleParamagnetism
The invention provides superparamagnetic nano Fe3O4 particles synthesized through in-situ induction of chitosan hydrogels, relating to a method for synthesizing the superparamagnetic nano Fe3O4 particles. The invention solves the problems of serious aggregation of the nano Fe3O4 particles and the complicated method for inducing the chitosan into the surface of the Fe3O4 in the current nano Fe3O4 particles. The method of the invention is that: 1. the chitosan powder is added into dilute acid solution; 2. cross-linking agent is added to make the chitosan hydrogels; 3. the chitosan hydrogels are sequentially dipped in Fe3+ aqueous solution, water, Fe2+ aqueous solution and water, and a plurality of times of circular leaching are made so as to form the chitosan hydrogels that contains iron ions; 4. then basification treatment is carried out; 5. the hydrogels is dissolved or degraded again, and finally the black superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nano particles are obtained upon centrifugalization. The method of the invention requires simple technique and mild conditions and the equipment used in the method is simple and can be obtained easily, thereby mass production can be achieved. The average diameter of the particles is 15 to 25nm, and the particles distribute evenly with superparamagnetism.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation method and application of nanometer zero-valent ion composite material
ActiveCN106745645AHigh Efficiency RecyclingSolve reunionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by reductionNitrogen gasOrganic glass
The invention relates to a nanometer zero-valent ion composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that corn straw biochar is prepared, modified by being soaked with nitric acid, washed to be neutral and then dried for use; FeSO4.7H2O is reduced into zero-valent iron in a nitrogen environment through a liquid phase reduction method, and the zero-valent iron is loaded on the biochar; solid-liquid separation is conducted on the solution obtained after reacting, and the biochar-loaded nanometer zero-valent ion composite material is obtained. The material is used for removing lead in underground water, the agglomeration and activity reduction problems of iron nanoparticles in the using process are solved, secondary contamination cannot be generated in repair practice, a removal experiment of the lead in the underground water is simulated in a constructed organic glass simulation reaction column, and the removal rate can reach 90% or above.
Owner:山西省环境科学研究院
In situ remediation of inorganic contaminants using stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles
InactiveUS7635236B2Good dispersionEasy to remedyMaterial nanotechnologyWater treatment compoundsMaterials scienceChromic Ion
A method for preparing highly stabilized and dispersible zero valent iron nanoparticles and using the nanoparticles as a remediation technology against inorganic chemical toxins in contaminated sites. The method employs a composition containing select polysaccharides (starch or cellulose) as a stabilizer for the iron nanoparticles in a liquid carrier, and results in suspensions of iron nanoparticles of desired size and mobility in water, brine, soils or sediments. The stabilizer facilitates controlling the dispersibility of the iron nanoparticles in the liquid carrier. An effective amount of the composition is delivered to a contaminated site so that the zero valent iron nanoparticles can remediate one or more toxins such as an arsenate, a nitrate, a chromate, or a perchlorate in the contaminated site.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
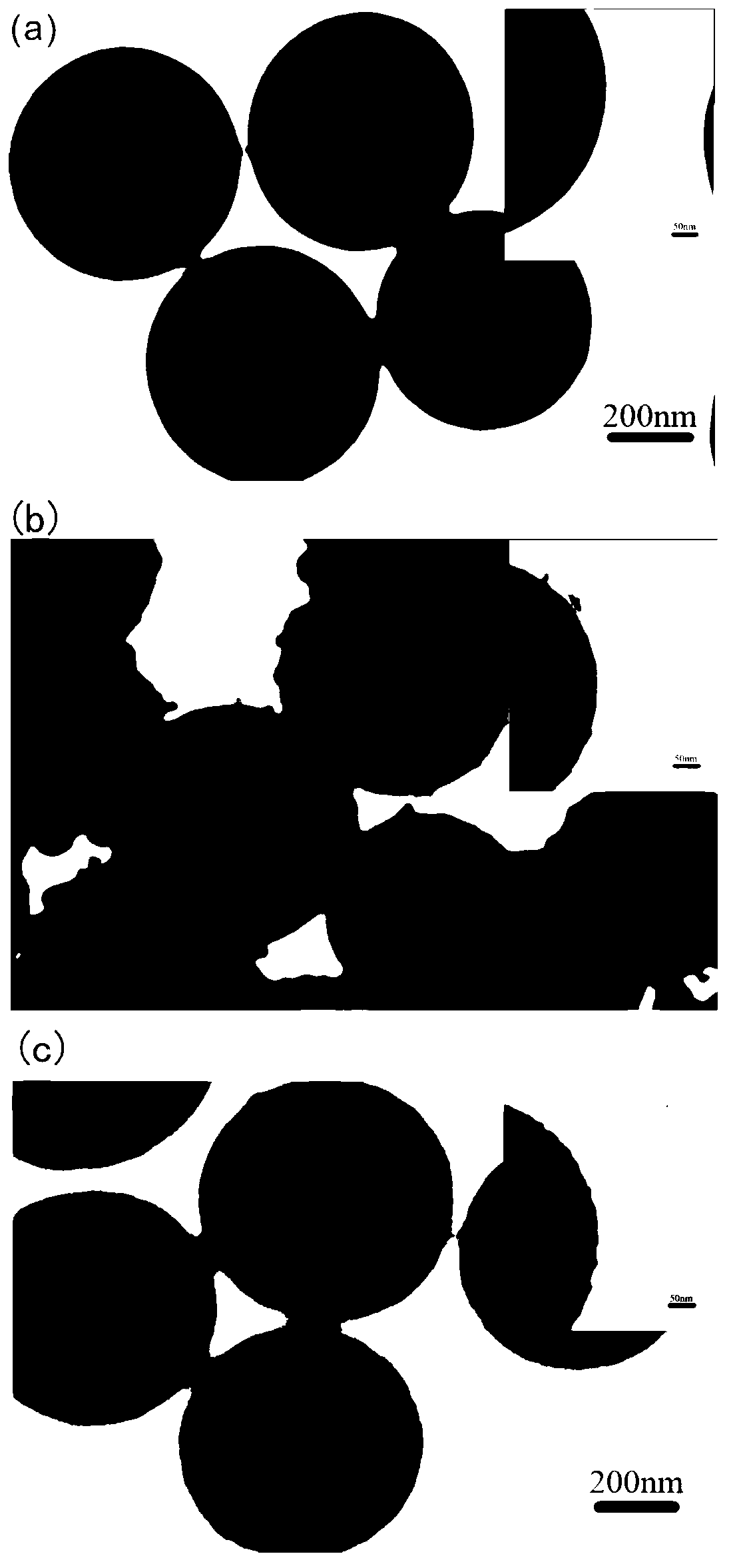
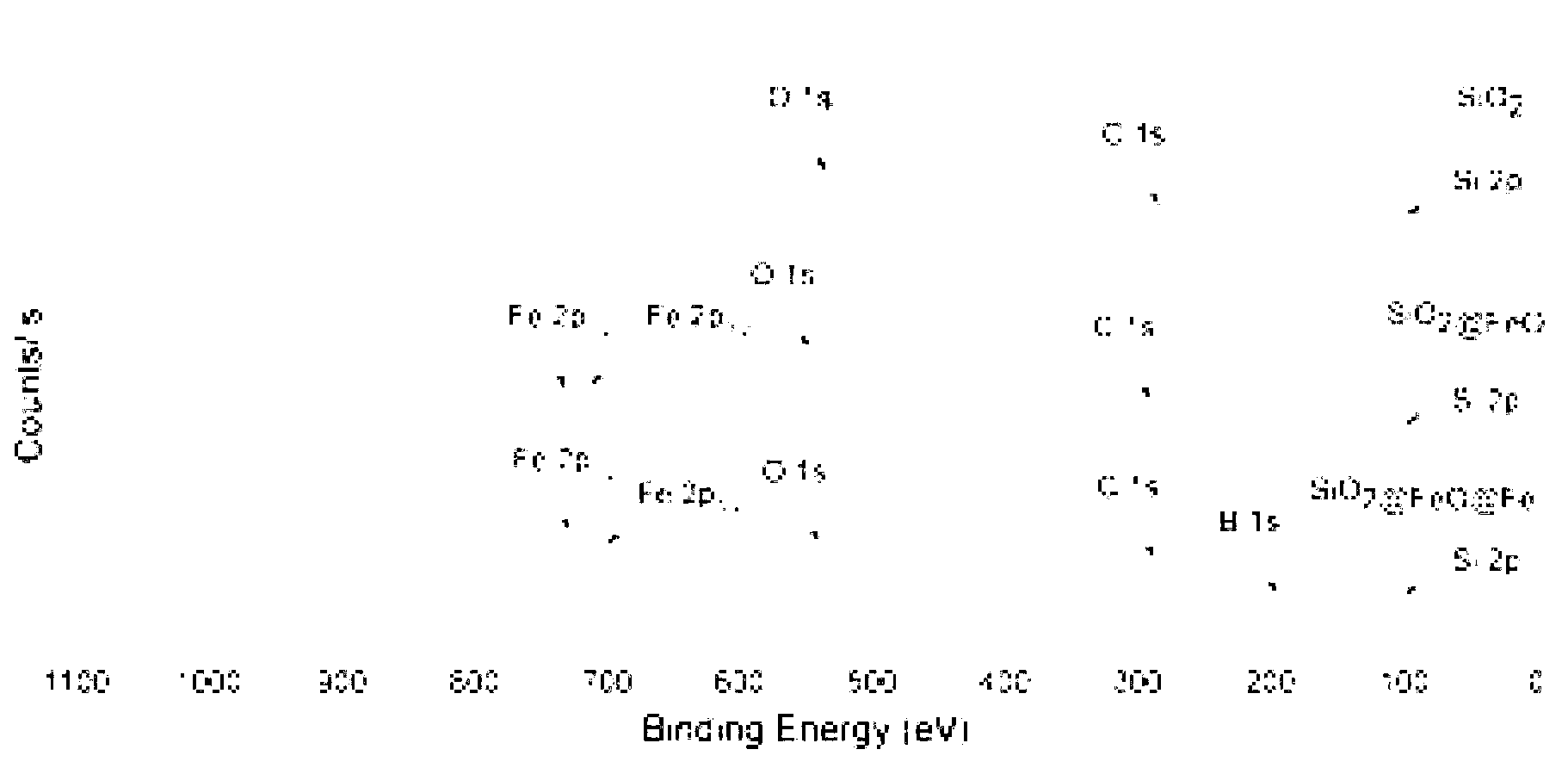
Mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticle (SiO2@ FeOOH@ Fe) and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102701297AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationMicrosphereIron nanoparticle
The invention discloses a mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof. The mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticle has a structure as follows: the center is mesoporous SiO2, the middle layer is FeOOH, the surface of the outermost layer is coated with FeO, and ultimately a SiO2@ FeOOH@Fe structure, namely a spherical particle, is formed. The preparation method is easy to operate and mild in reaction conditions, can be carried out at room temperature and normal pressure, and is short in time consumption and low in energy consumption; the prepared mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticles have the particle size of 400-500nm and are spherical particles; the specific surface areas of the prepared mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticles are detected to be 383.477m2 / g by a BET-N2 specific surface area analysis method; and the prepared mesoporous silicon dioxide microsphere-loaded zero-valent iron nanoparticles are good in lattice morphology, good in fluidity and good in dispersion and can be used for decomposing organic pollutants in the environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
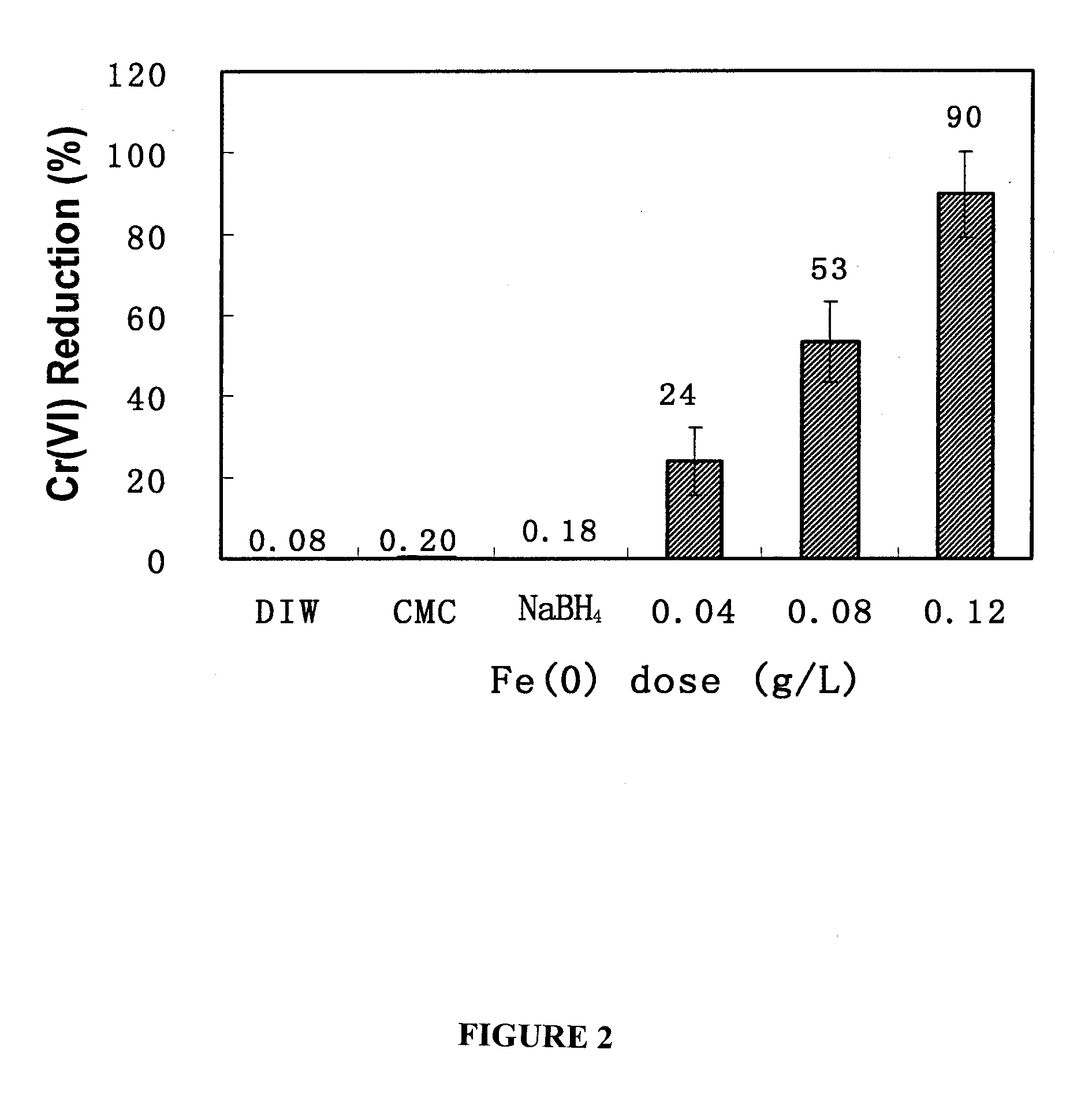
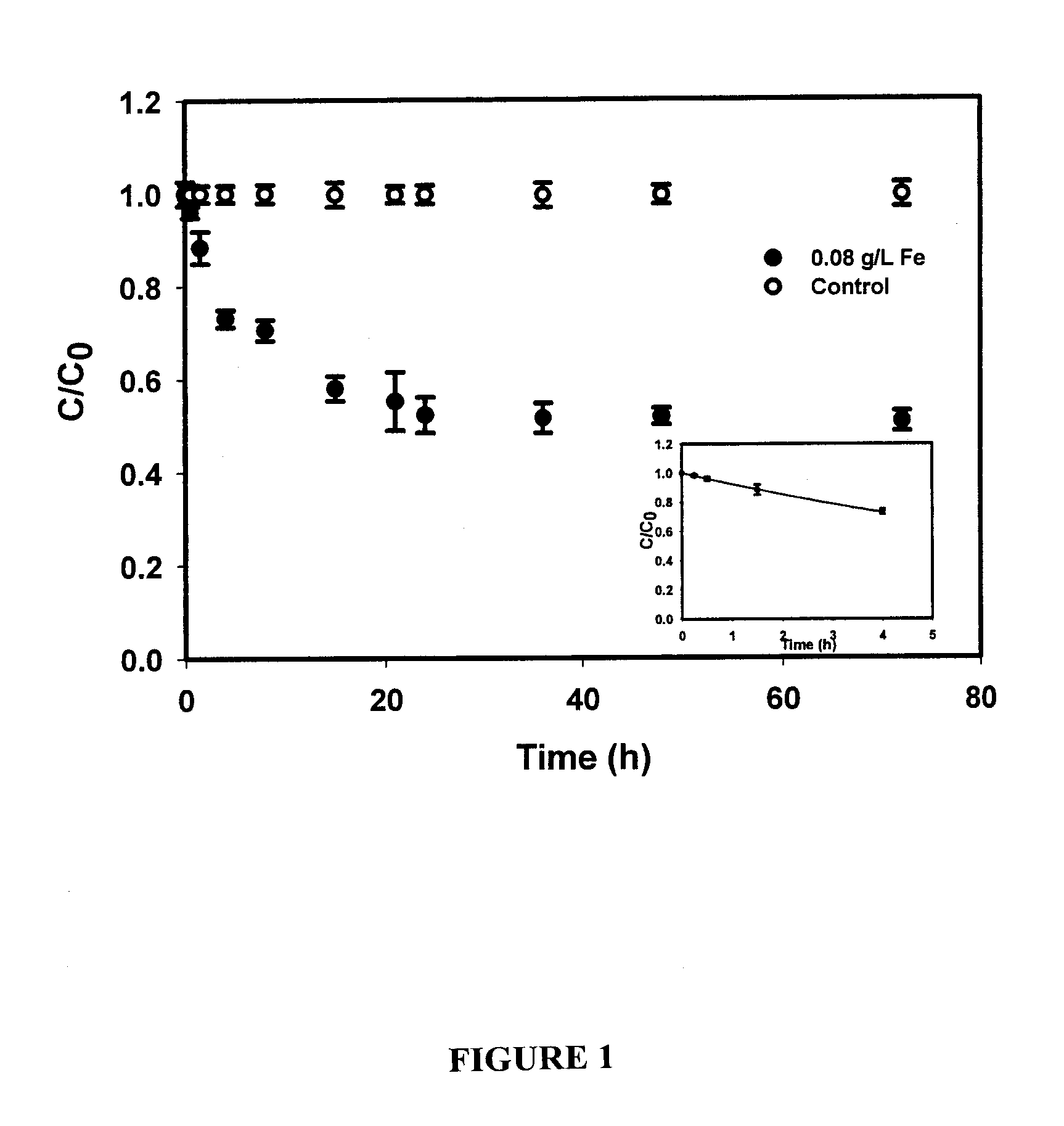
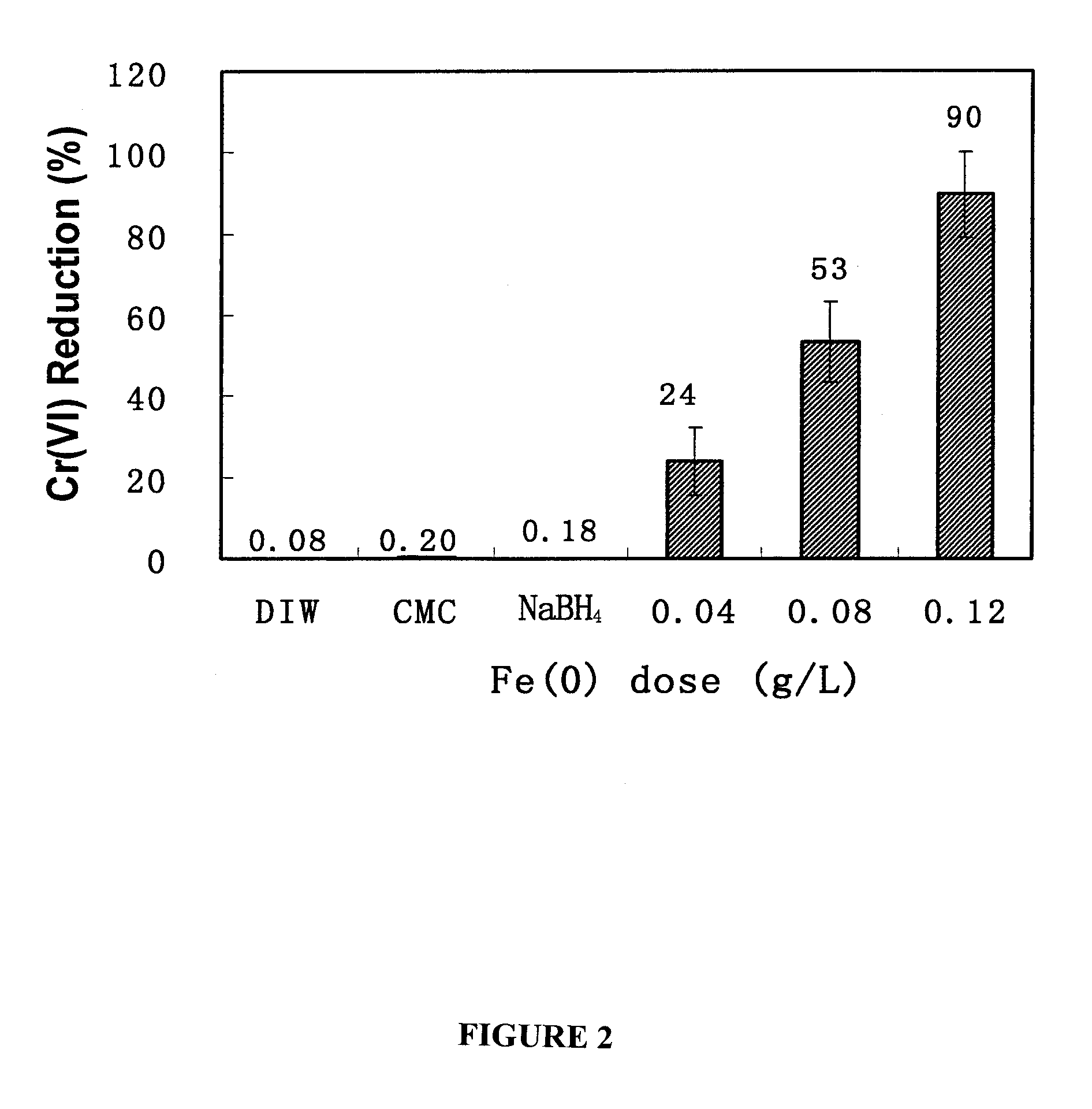
Method for restoring hexavalent-chromium-polluted underground water by virtue of stable zero-valent iron nanoparticles
InactiveCN103949469AEasy to moveLarge specific surface areaContaminated soil reclamationWater/sewage treatment by reductionIn situ remediationIron nanoparticle
The invention relates to a method for restoring hexavalent-chromium-polluted underground water by virtue of stable zero-valent iron nanoparticles. According to the method, for preventing the agglomeration of the nanoparticles and prolonging the reaction activities of the nanoparticles, water-soluble polysaccharide (CMC) is utilized as a stabilizer and a dispersing agent to synthesize stable iron-based nanoparticles, so that high dispersity and long reaction activities can be realized, the nanoparticles are effectively transferred to a target pollution source of a heavy metal pollution field by virtue of an injection method, and toxic heavy metal Cr (VI) contained in the nanoparticles is reduced, adsorbed and fixed, so that the transfer capabilities of the nanoparticles in soil and underground water are reduced, and finally an in-situ restoring purpose of the pollution field is realized; the method can be applied to the industries such as electroplating, printing and dyeing, electronic device machining, heavy metal machining and the like, and zero-valent iron and nanometer iron oxide have excellent application prospects in restoring processes of environmental pollutants due to special superiorities and wide decontamination and water purification capacities.
Owner:山西敏达科技有限公司
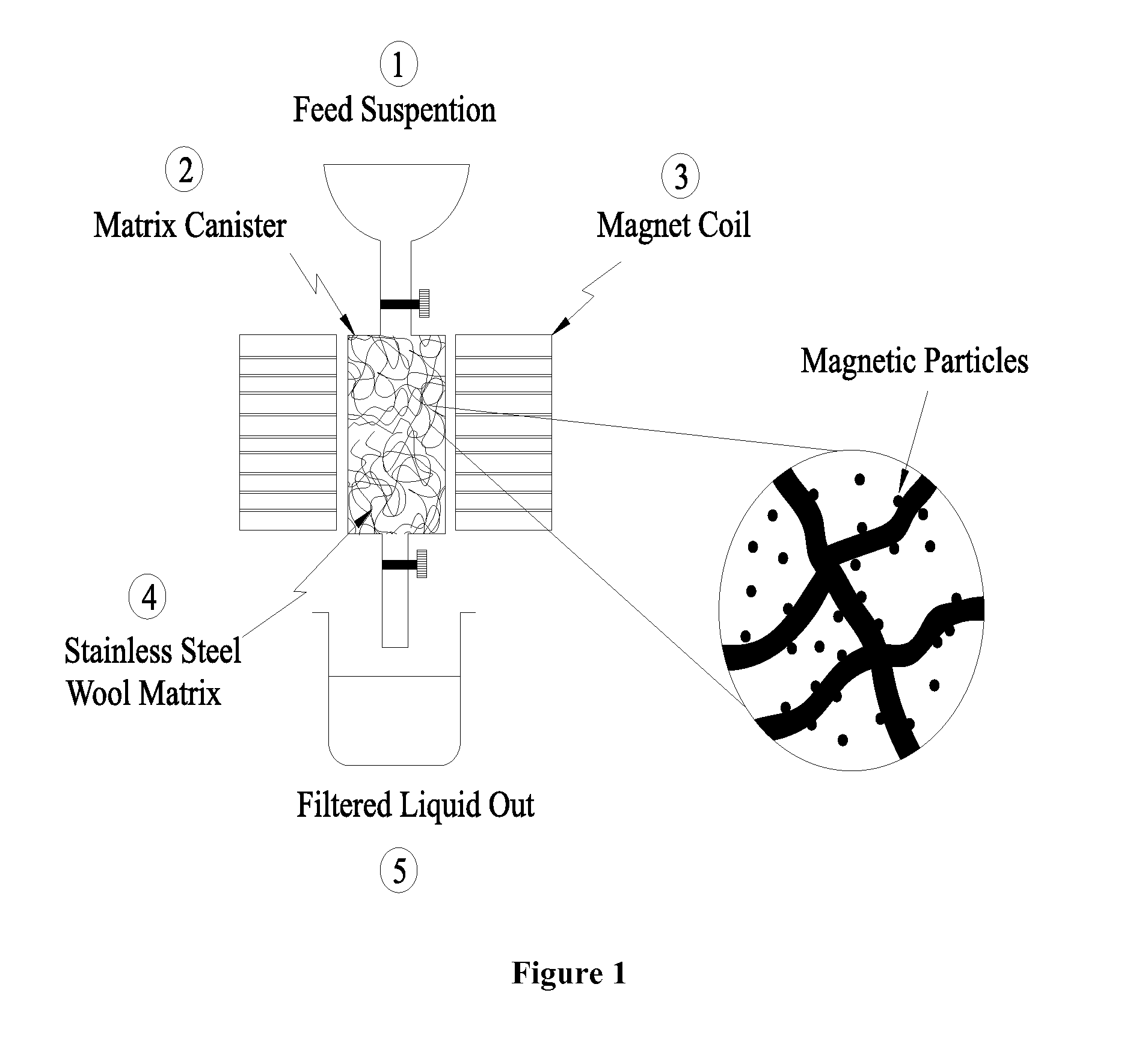
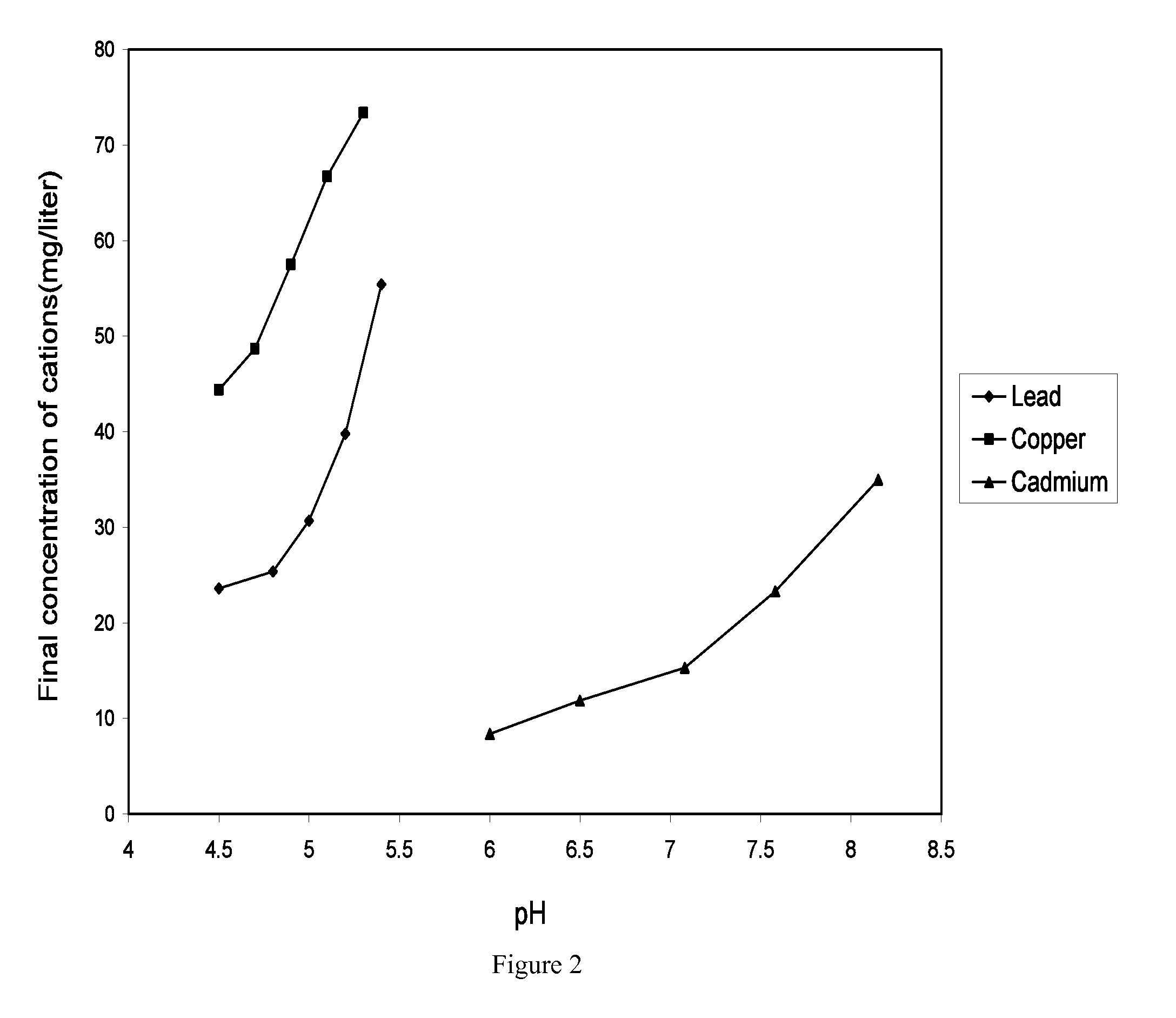
Heavy metal cations elimination from aqueous media by nanotechnology
InactiveUS20100051557A1Easily substitutedReduced pHWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsIron oxide nanoparticlesIron nanoparticle
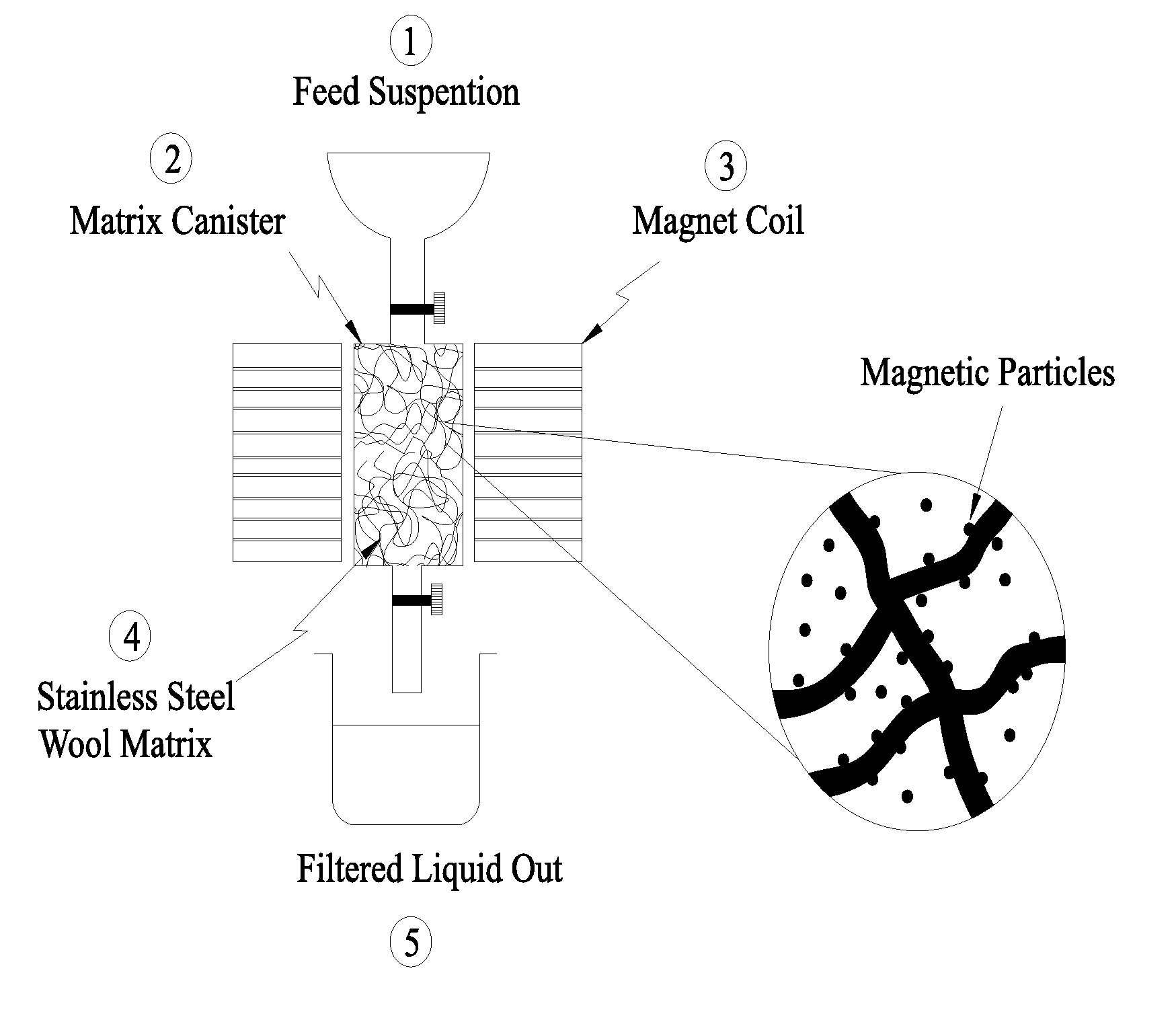
Disclosed is a process, which is used to eliminate heavy metal cations from the aqueous media, and provides a better solution for the existing problems of the separation systems like low efficiency and high costs. The heavy metal cations selected for this purpose are cadmium, lead and copper. The separation system consists of a two stage process: In the first stage, the iron oxide nanoparticles are suspended in an aqueous medium contaminated with the heavy metal cations. In the second stage, the solution is brought into contact with a ferromagnetic matrix (or a paramagnetic matrix) magnetized by the application of an outside magnetic field. The heavy metal cations are deposited on the matrix under the imposed magnetic field. This two-stage process makes it possible to separate the heavy metal cations from the aqueous medium. The wire matrices are upon the completion of separation washed away by water or air current.
Owner:ISFAHAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Graphene-iron oxide complex and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20120168383A1Efficient and selective separationImprove adsorption capacityMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteIron nanoparticleCvd graphene
A graphene-iron oxide complex consists of graphene and needle-like iron oxide nanoparticles grown on a surface of the graphene, and a fabricating method thereof includes (A) preparing a reduced graphene dispersed solution, (B) mixing the dispersed solution with a solution containing iron oxide precursors to prepare a mixture, (C) stirring the mixture to prepare a graphene-iron oxide dispersed solution containing the graphene-iron oxide complex that needle-like iron oxide nanoparticles are grown on the surface of the graphene, and (D) separating the graphene-iron oxide complex from the graphene-iron oxide complex dispersed solution.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Nano-iron powder prepn. method
InactiveCN1751829AImprove reducibilityImprove magnetic propertiesCoatingsIron saltsHydrazine compound
A process for preparing iron nanoparticles includes such steps as proportionally dissolving iron salt in alcohol, water, or their mixture, proportionally adding NaOH solution and hydrazine hydrate solution, stirring, and heating at 80-120 deg.C while refluxing until the mother liquid becomes colorless and transparent. Its advantages are high purity, adjustable granularity and high output rate (more than 99%).
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
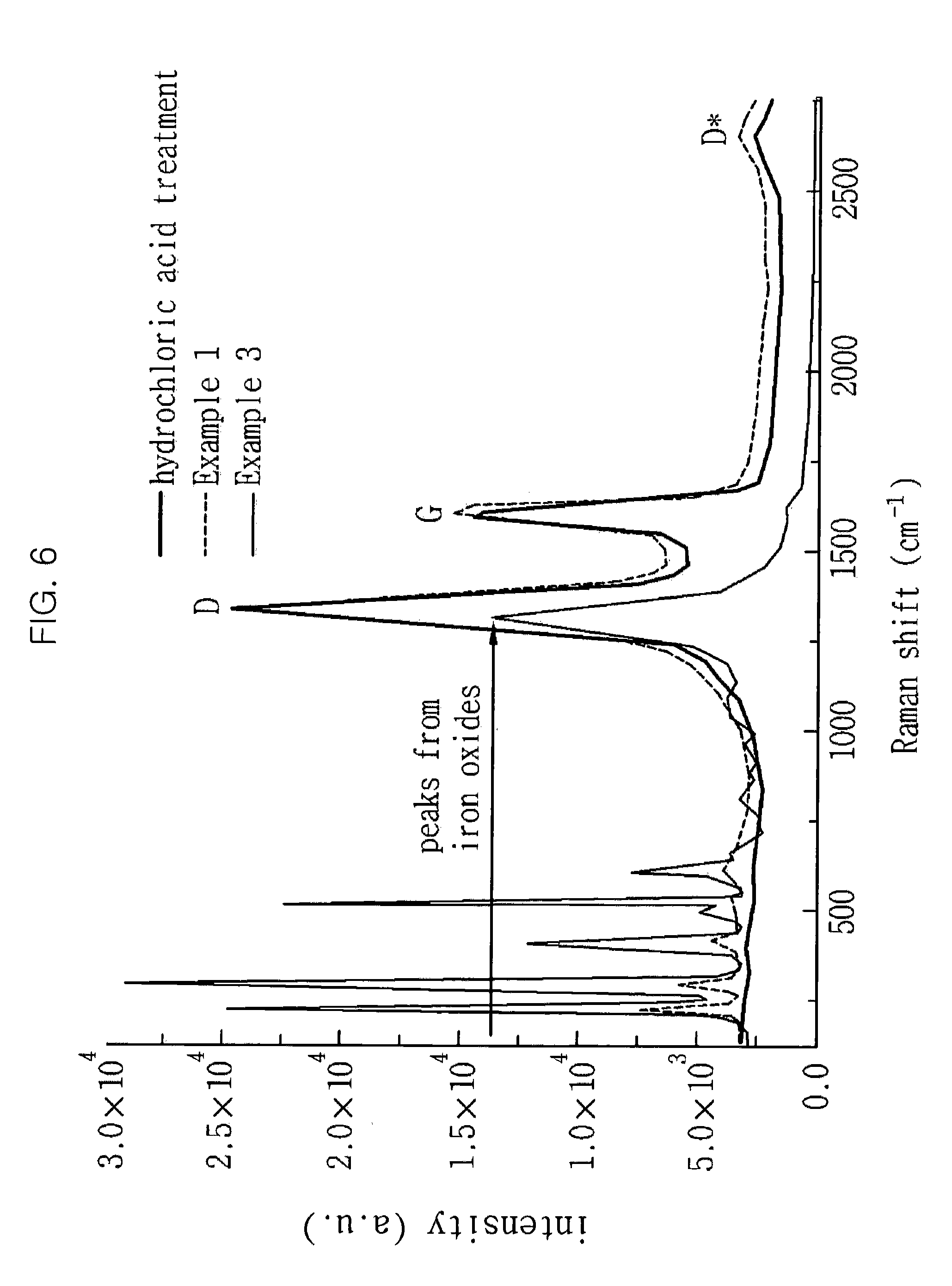
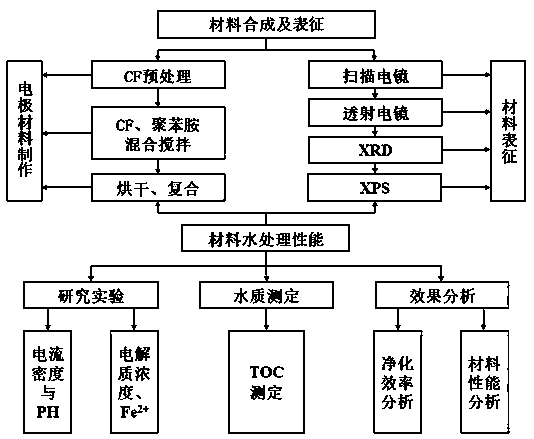
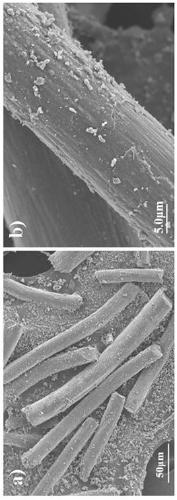
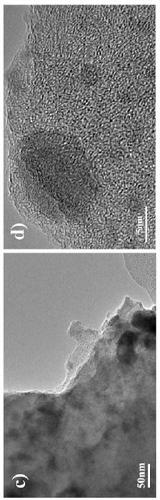
Preparation method of electro-Fenton cathode material based on carbon felt-supported iron nanoparticles and application of electro-Fenton cathode material in degradation of organic pollutants in water
ActiveCN109896598ALarge specific surface areaImprove processing efficiencyWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a preparation method of an electro-Fenton cathode material based on carbon felt-supported iron nanoparticles and application of the electro-Fenton cathode material in the degradation of organic pollutants in water, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of electro-Fenton cathode materials and electro-Fenton water treatment. The preparation method and the electro-Fenton cathode material are characterized in that polyaniline is supported on a pure carbon felt through electrochemical deposition, iron particles are supported to obtain an iron carbon-doped porouscomposite carbon fiber material; a carbon felt acting as a cathode material can be applied to an electro-Fenton water treatment apparatus, air is charged in, and therefore, hydroxyl radicals are generated by catalysis at a cathode, and organic pollutants in water can be degraded. With the characteristic fully utilized that a carbon fiber has large specific surface area, the preparation method herein has the advantages of high treatment efficiency and greenness and the like, and has economic and social benefits for the field of treatment of industrial printing and dyeing waster and groundwater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of dispersed iron nanoparticles
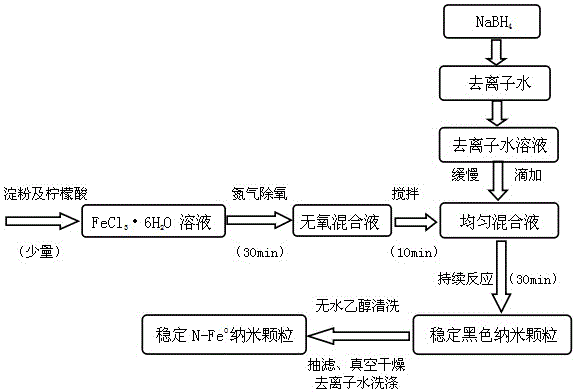
The invention discloses a preparation method of dispersed iron nanoparticles and relates to a preparation method of a metal nanomaterial. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a solution by using a soluble divalent ferric salt or tervalent ferric salt serving as a raw material and distilled water or a mixed solution of distilled water and ethanol; adding a surfactant and a complexing agent; adding a dispersant; dropwise adding a prepared hydroboron aqueous solution in a stirring state; dropwise adding the prepared hydroboron aqueous solution at room temperature till fully reacting; performing suction filtration on the obtained reaction product; and washing with distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, and drying to obtain black dispersed iron nanoparticles. The produced iron nanoparticles have the advantages of small particle diameter, uniformity in dispersion, narrow particle diameter range, simple process, low cost and contribution to further expansion of the production scale.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Iron oxide nano-particle/graphene-polyimide-based carbon aerogel composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105244484AAvoid reunionImproving dopamine detection performanceHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesPotassium hydroxideBio sensor
The invention belongs to the technical field of transition metal oxide-carbon aerogel, and particularly discloses an iron oxide nano-particle / graphene-polyimide-based carbon aerogel composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is formed by evenly loading iron oxide nano-particles on graphene-polyimide-based carbon aerogel. The method comprises the following preparation step: carrying out in-situ growth of the iron oxide nano-particles on the graphene-polyimide-based carbon aerogel activated by potassium hydroxide through a one-step solvothermal method. The method disclosed by the invention is free of use of a toxic reagent, namely formaldehyde; and the prepared iron oxide nano-particle / graphene-polyimide-based carbon aerogel composite material has the advantages of small iron oxide nano-particles, uniform distribution, high porosity, high specific surface area, high conductivity, stable physical and chemical properties and the like, and can be used for preparing a high-sensitivity biosensor, a high-performance adsorption material and ideal electrode materials for new energy devices of a super capacitor, a lithium-ion battery and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
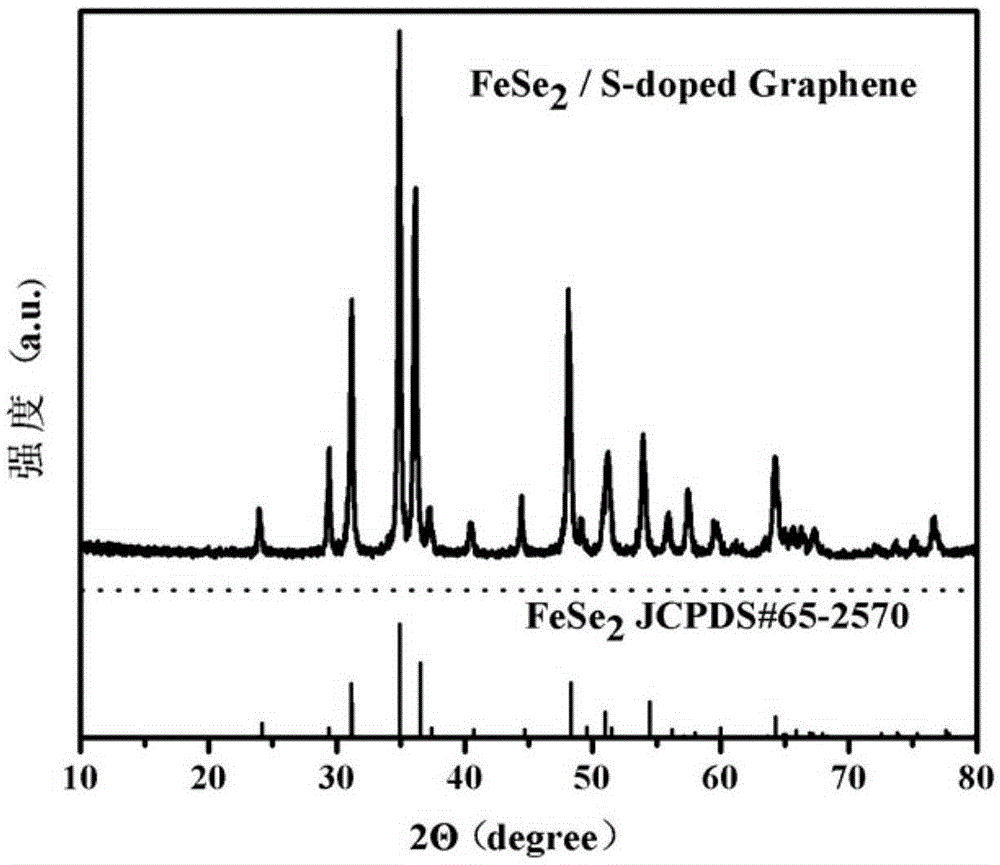
Iron diselenide/sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material for sodium-ion battery and preparation method of iron diselenide/sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material
ActiveCN105390674AAvoid irregular topographyAvoid reunionCell electrodesSecondary cellsSe elementMaterials science
The invention discloses an iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material for a sodium-ion battery and a preparation method of the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a sulfur source, a selenium-containing inorganic matter, an iron-containing inorganic salt and citric acid or sodium citrate into a graphene oxide solution; dropwise adding hydrazine hydrate to form a light black solution, adding the light black solution to a hydrothermal reaction kettle for reaction, and naturally cooling the product after the reaction is ended; and carrying out repeated washing, suction filtration and drying on a reaction sediment with distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, so as to obtain the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene composite material. According to the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene composite material prepared by the method, iron diselenide nano-particles are evenly distributed on the surface of the sulfur-doped graphene and the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene composite material has excellent electrochemical properties as a sodium-ion battery anode material. The iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material is prepared by a simple hydrothermal process; synchronous sulfur doping, graphene oxide reduction and graphene oxide and iron diselenide recombination can be achieved; and the iron diselenide / sulfur-doped graphene anode composite material is simple in preparation technology and low in cost, and has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Magnetic iron-carbon composite material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103623824AEasy to separateGood orientationOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCarbon compositesIron nanoparticle
A disclosed magnetic iron-carbon composite material comprises carbon-coated metallic iron nanoparticles and nanometeriron oxide particles, wherein the iron content is 45%-90% by weight and the specific surface area is 100-500 m<2> / g, and further the composite material comprises a compound composed of the carbon-coated metallic iron nanoparticles and the nanometeriron oxide particles. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the magnetic iron-carbon composite material. The magnetic iron-carbon composite material provided by the invention is relatively high in iron content, resistant to 400 DEG C high-temperature oxidation, excellent in magnetic property, easy for magnetic separation and guiding role and high in specific surface area; employed precursors are nontoxic and the preparation conditions are mild; and the material loaded with precious metals has extremely good activity on catalytic hydrogenation reactions, and the composite material is applicable to different catalytic reactions as an excellent catalyst carrier.
Owner:西安荣轩分析测试技术服务有限公司
Polymer ferric oxide microsphere preparation method
InactiveCN103012828AUniform particle sizeThe size is easy to controlOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismCoatingsMicrosphereOxide composite
The invention discloses a polymer ferric oxide microsphere preparation method. The method includes the steps: (1) preparing porous polymer microspheres; (2) using the coprecipitation method for synthesizing ferric oxide nano particles in the polymer microspheres obtained at the step (1) to obtain polymer / ferric oxide composite microspheres; and (3) coating silicon dioxide on the surfaces of the composite ferric oxide microspheres obtained at the step (2) to obtain magnetic microspheres. The particle size of the magnetic microspheres made by the method is controllable in the range of 300 nanometers to 100 micrometers, and the microspheres are uniform in particle size, controllable in size and stable in chemical property and have potential application value in nucleic acid separation, protein separation, immobilized enzyme, cell separation and antibody purification.
Owner:SUZHOU KNOWLEDGE & BENEFIT TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of graphene-supported iron oxide nanoparticle composite wave-absorbing agent
InactiveCN107779172AEvenly distributedImprove absorbing performanceMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesMaterials scienceAnhydrous Dextrose
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene-supported iron oxide nanoparticle composite wave-absorbing agent, comprising: (1) preparing composite precursor powder by a spray process, to be specific, using iron nitrate nonahydrate as an iron source, anhydrous glucose as a carbon source and sodium chloride as a template with a molar ratio of Fe, C and NaCl being (0.75-2):30:100, dissolving the iron source, the carbon source and the sodium chloride in deionized water, magnetically stirring to obtain aa homogenous mixed solution, and subjecting the solution mixed well to spray drying to obtain precursor powder; reducing the composite precursor powder by calcining; oxidizing the composite precursor powder by calcining; removing the NaCl template. The graphene-supported iron oxide nanoparticle composite prepared by using the preparation method is applied to electromagnetic wave absorption.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
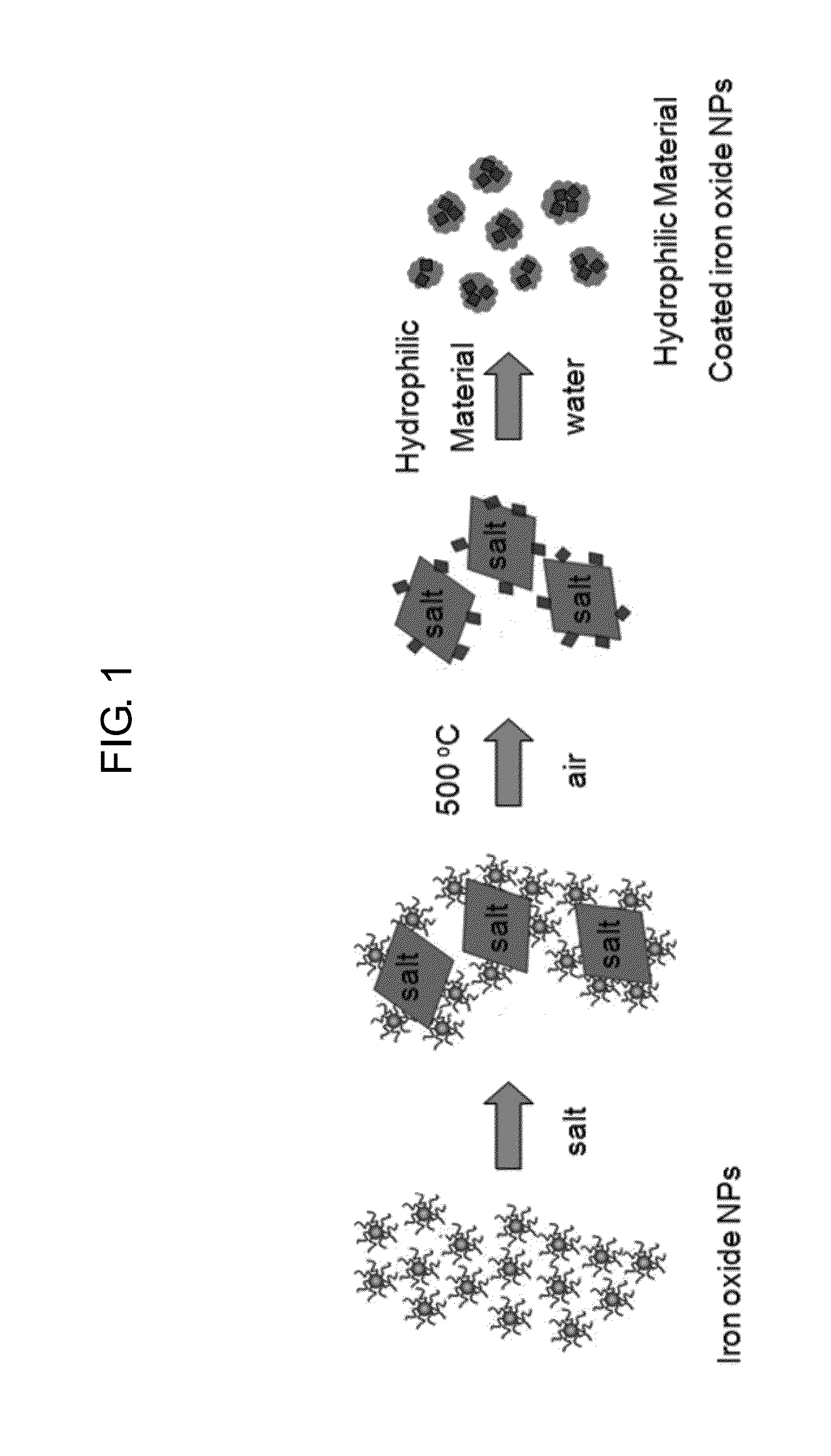
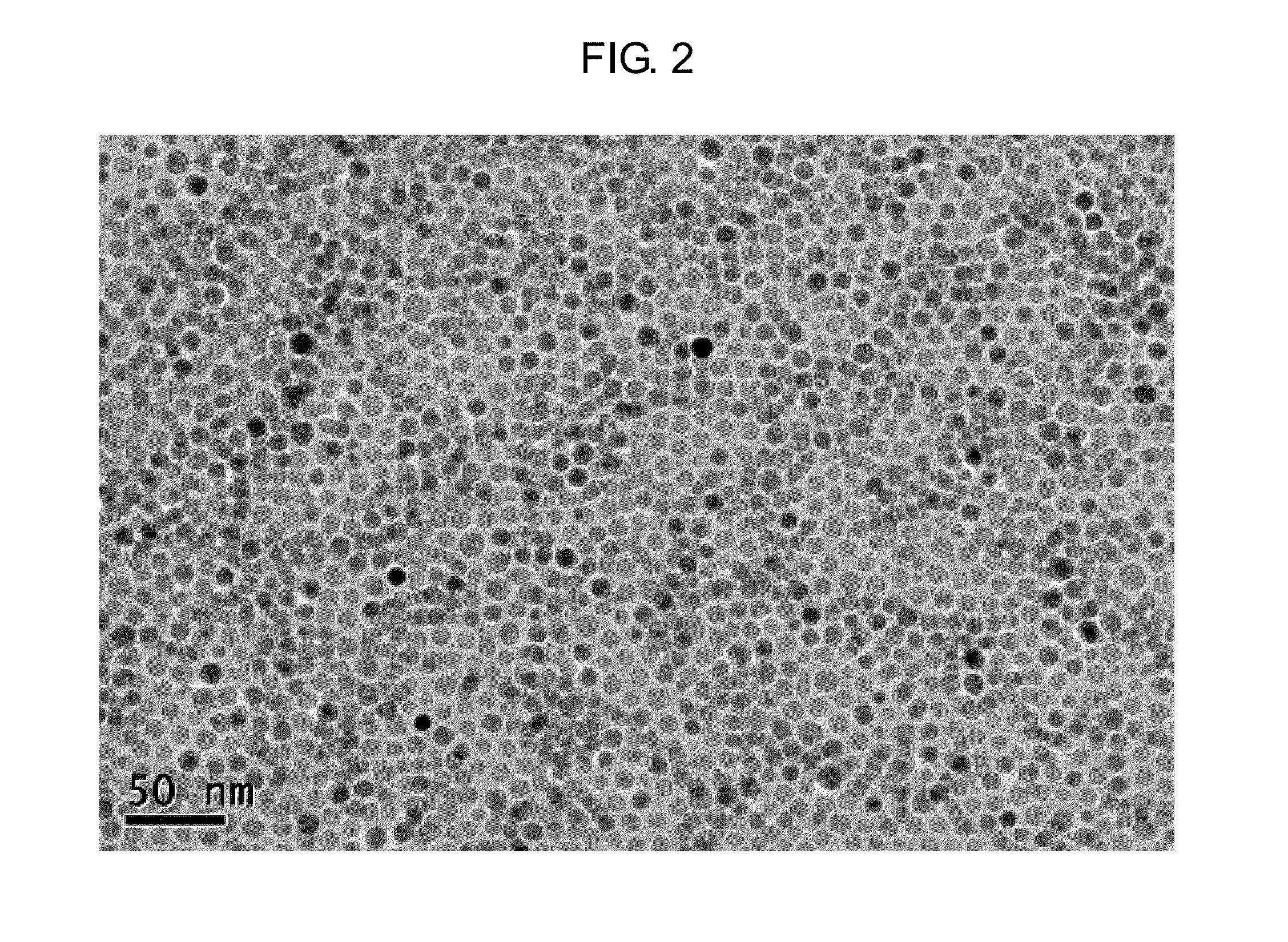
Method of preparing iron oxide nanoparticles coated with hydrophilic material, and magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent using the same
ActiveUS20130323182A1High crystallinityImprove magnetic propertiesBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyMagnetic resonance imaging contrast mediumIron oxide nanoparticles
The present invention relates to a method of preparing biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles by coating iron oxide nanoparticles having improved magnetism via annealing treatment using salt particles with a hydrophilic material and to a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent including the iron oxide nanoparticles prepared thereby. Among hydrophilic materials, carboxymethyl dextran (CM-dextran) is the most efficient in terms of stabilizing the annealed iron oxide nanoparticles and exhibiting contrast effects.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
Preparation method of ferric oxide nanoparticle supported sodium alginate nanogel
InactiveCN104606687ASimple processEasy to operate and separateEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of ferric oxide nanoparticle supported sodium alginate nanogel. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: (1), PEI (polyethylenimine) coated Fe3O4 nano-particles (Fe3O4-PEI) are synthesized with a hydrothermal method; (2), an aqueous solution of sodium alginate is firstly activated by EDC (carbodiimide) and has a double emulsion reaction to form a W / O / W polymer emulsion; (3), Fe3O4-PEI in the step (1) is taken as a crosslinking agent and added into the polymer emulsion in the step (2) to have a crosslinking reaction, and the ferric oxide nanoparticle supported sodium alginate nanogel is obtained after an organic solvent and a surface active agent are removed. The method is very simple, and operation and separation are easy; meanwhile, sources of raw materials are extensive; the prepared sodium alginate nanogel has a smaller grain diameter, is uniformly distributed, high in relaxation rate and low in cost, has a remarkable radiography effect, simultaneously has excellent water solubility, gel stability, biocompatibility and blood compatibility, doesn't have a harmful effect on a living body, and has potential application value in the magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis field.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method and purpose thereof of spherical ferriferrous oxide nano particles with controllable size
InactiveCN104167536AUniform shapeThe particle size can be adjustedCell electrodesSecondary cellsActive agentEngineering
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method and application of carbon-iron composite material with porous structure
InactiveCN111359580AImprove adsorption capacityEfficient regenerationOther chemical processesWater treatment compoundsPtru catalystPorous carbon
The invention provides a preparation method and an application of a carbon-iron composite material with a porous structure. The material can be used as an adsorbent of various antibiotics and a Fentonreaction catalyst under a wide pH condition. According to the material, a metal organic framework is used as a raw material, a one-step pyrolysis method is adopted, annealing conditions are controlled for synthesis, and iron nanoparticles in the obtained material are uniformly loaded on the surface of an ultrathin carbon nanosheet with a porous structure. The porous structure can effectively enhance the transmission and capture capacity of substances, and meanwhile, THE iron nanoparticles loaded on the porous carbon nanosheet can be complexed with antibiotic molecules through sites on the surface of transition metal, so that the adsorption efficiency is further improved, and the material has better adsorption performance than common activated carbon. In addition, the iron nanoparticles are also active sites of the Fenton reaction and can adsorb pollutants in a circulating mode. Meanwhile, the material has magnetism and can be quickly and conveniently recycled from a water phase. Therefore, the material is a green, efficient and recyclable adsorbent.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Iron-carbon nano composite electromagnetic wave absorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101853727AHigh saturation susceptibilityHigh resistivityInorganic material magnetismGas phaseCarbon nanocomposite
The invention relates to an iron-carbon nano composite electromagnetic wave absorption material and a preparation method thereof. Carbonyl iron, methane and acetylene serving as main raw materials are directly synthesized into the iron-carbon nano composite material in a gas-phase reaction device at the temperature of between 300 and 1,000 DEG C. The nano composite material has good stability and uniformity. The iron-carbon nano composite material is wrapped outside iron nano granules by nano-scale C to form a C film; and the iron-carbon nano composite material has the characteristics of good electromagnetic wave absorption performance, wide absorption coverage frequency range, strong corrosion and oxidation resistance and low cost, and is applicable to electromagnetic shielding in a radio communication system, electromagnetic radiation and leakage of equipment of high frequency prevention, microwave heating and the like, construction of microwave darkrooms and hiding technology.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Graphene and ferrum diselenide composite material and method for preparing same
InactiveCN102942165ARich sourcesSimple preparation processMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsHydrazine compoundReaction temperature
The invention discloses a graphene and ferrum diselenide composite material and a method for preparing the same. The method for preparing comprises the following steps: selenium-containing inorganic salt and ferrum-containing inorganic salt are put into a stainless steel reactor; hydrazine hydrate and source graphene solution are mixed together and stirred uniformly to form an ink black solution to be added into the reactor, and the reactor is closed so as to carry out reaction; and after the reaction is completed, natural cooling is carried out, reaction precipitate is subjected to repeated washing and suction filtering through distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, and after the drying, the product is collected and stored in a drying device. According to the prepared graphene and ferrum diselenide composite material, a graphene sheet wraps ferrum diselenide nanoparticles, the ferrum diselenide is tightly combined with the graphene sheet, so that high specific surface area and excellent magnetic performance are obtained. The method adopts a simple hydrothermal method, the graphene reduction oxide and the composite preparation of the praphene and the ferrum diselenide can be synchronously carried out, and the method has the advantages of simplicity in technology, low reaction temperature, low cost, green, controllability and applicability for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Environmental-function nano material Cu-Fe/TiO2 nanotube array, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102071449AIncrease the areaAperture adjustableWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingTio2 nanotubePhotocatalytic reaction
The invention discloses an environmental-function nano material Cu-Fe / TiO2 nanotube array, and preparation and application thereof. The preparation method of the Cu-Fe / TiO2 nanotube array comprises the following steps: preparing a TiO2 nanotube array by using an anodic oxidation process; depositing copper on the inside and surface of the TiO2 nanotube by using a pulse electrodeposition process, so that the Cu-TiO2 composite nanotube array has stronger adsorption capability and electronic conduction capability; and depositing iron nanoparticles on the inside of the Cu-TiO2 composite nanotube by using a pulse electrodeposition process, thereby increasing the concentration of hydroxyl free radicals in the photocatalytic reaction process. The electrodeposition of multiple metals by multiple steps is favorable for obtaining the uniformly-distributed granular photocatalytic nano material. The TiO2 nanotube array modified by iron and copper effectively widens the absorption range of TiO2 in visible light regions, reduces the photo-corrosion, enhances the photoelectric conversion efficiency, and shows excellent photocatalytic efficiency in the research on photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic pollutants and photo-reduction of heavy metal ions.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Process for producing nano-Ni/Fe bimetallic material
InactiveCN101428221AFast dechlorinationEasy to storeWater/sewage treatmentMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMetallic materialsNitrogen gas
The invention provides a method for preparing nano-sized Ni / Fe duplex metal, which comprises the following steps: firstly, preparation of iron nanoparticles: adding an ethanol aqueous solution of water-soluble Fe salts in a container, adding an aqueous solution of NaBH4 into the container under stirring in the presence of nitrogen gas to obtain black iron nanoparticles, and washing with diluted HCl and deoxygenated and deionized water for 3 to 5 times in the presence of nitrogen gas; then, soaking the iron nanoparticles in an ethanol aqueous solution of water-soluble Ni salts, and washing the resulting particles with anhydrous alcohol for 3 to 5 times; and finally, filtering and oven-drying to obtain the final product of nano-sized Ni / Fe duplex metal.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Recovery method of nanometer iron powder from cold rolling emulsion liquid
InactiveCN1559715AConcentrated particle size distributionImprove washing effectWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsRecovery methodIron powder
A method for recovering the iron nanoparticles from the emulsion used by cold rolling includes such steps as centrifugal separation to remove the most of dirt oil, and washing with detergent which is prepared from Na2CO3, Na2SiO3, detergent TX-10, n-butanol and water through proportional mixing.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
MnO doped ferroferric oxide/C graded nanosphere structure composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107032408ANovel microscopic appearanceNovel preparation methodCell electrodesFerroso-ferric oxidesCarbon layerMn doped
The invention discloses a MnO doped Fe3O4@C graded nanosphere structure composite material and a preparation method thereof. The material is provided with a nanosphere structure formed by self-assembling MnO uniformly-doped ferroferric oxide nanoparticles with surfaces uniformly coated with carbon layers. The preparation method includes the preparation steps: firstly, preparing Mn doped MOFs material nanospheres; secondly, performing one-step heat treatment by taking the Mn doped MOFs material nanospheres as precursors to obtain the MnO doped Fe3O4@C graded nanosphere structure composite material. The method is novel in idea, simple and convenient in operation, short in synthesis period and low in cost, and the prepared MnO doped Fe3O4@C graded nanosphere structure composite material has a great application potential in the field of energy storage of lithium batteries, sodium batteries and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of active carbon nanotube/ferric oxide lithium ion battery electrode material
InactiveCN103022422ARealize the activation processIncreased insertion/extractionMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPotassium hydroxideLithium-ion battery
The invention belongs to the technical field of energy nano new function materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of an active carbon nanotube / the ferric oxide lithium ion battery electrode material. The method specifically comprises the following steps: mixing the unpurified original samples of the carbon nanotube with the powder of potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide, and grinding uniformly; placing the materials in a reaction container, and introducing inert gases to carry out a reaction, then heating to a certain temperature, and adjusting the carrier gas; and carrying out the reaction continuously for hours, then filtering, rinsing and vacuum-drying the reaction products to obtain the active carbon nanotube / the ferric oxide hybridization material. In the invention, solid-phase oxidizing agent is adopted to modify the surface structure of the original carbon nanotube, the specific surface area of the carbon nanotube is improved obviously, simultaneously, ferric nanoparticles are directly oxidized into ferric oxide, the active carbon nanotube / the ferric oxide lithium ion battery electrode material is directly prepared through the one-step method. In addition, according to the invention, the raw materials are simple and easily obtainable, preparation technology is simple, the conditions are easy to control, the cost is low, and is suitable for continuous, large-scale and batch production.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
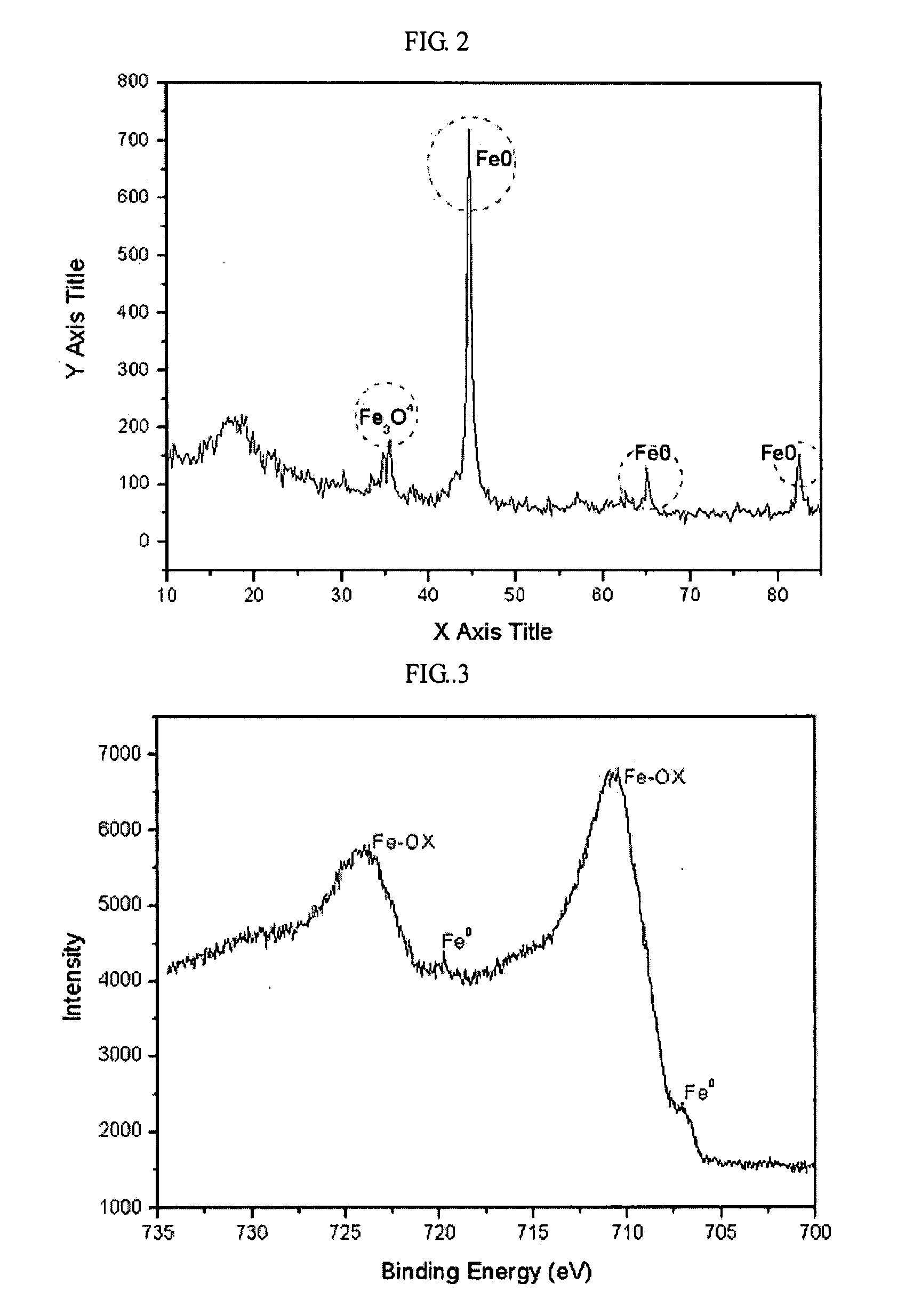
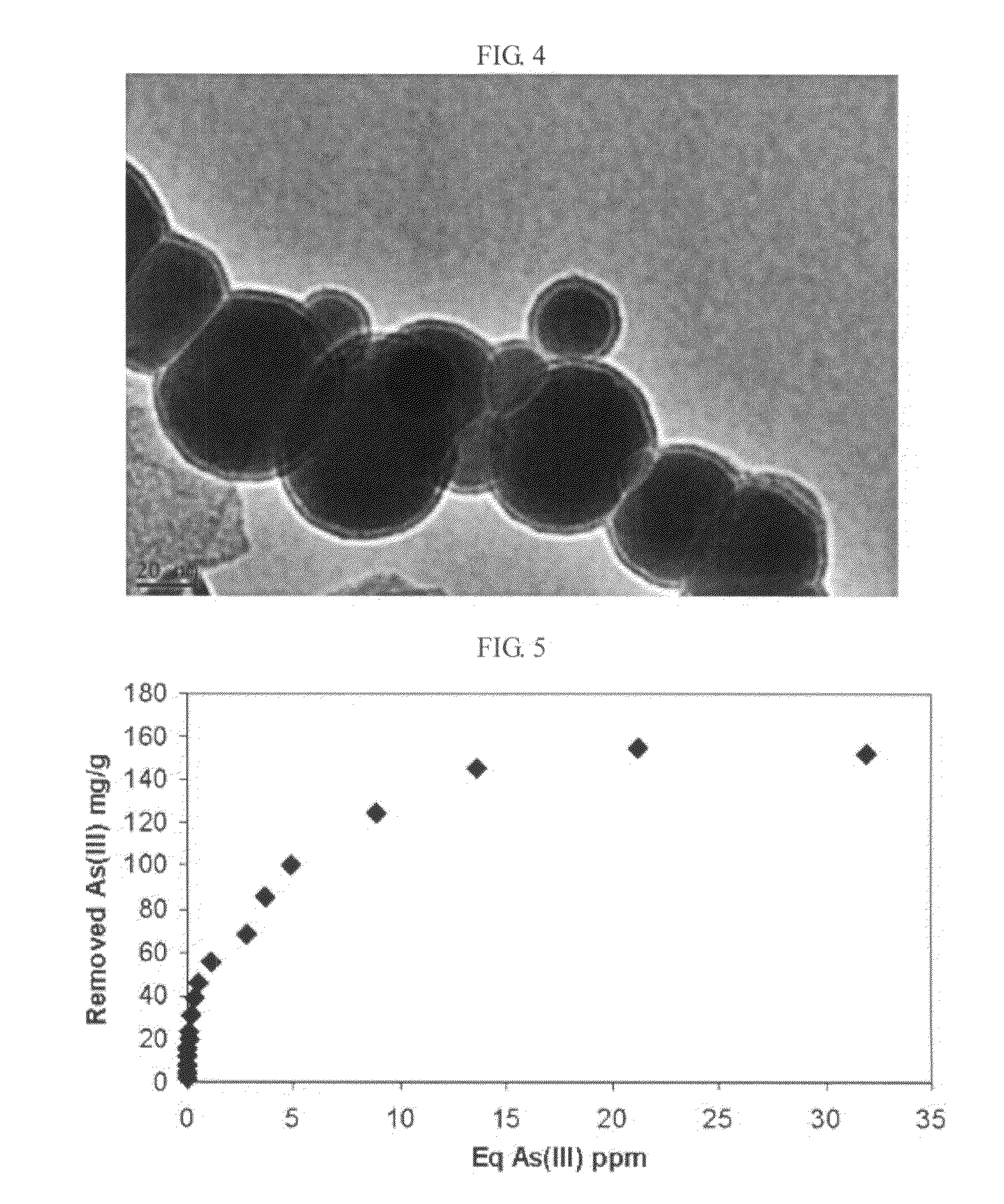
Method of synthesizing air-stable zero-valent iron nanoparticles at room temperature and applications
InactiveUS20080091054A1Improve responseInhibit aggregationMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureRoom temperatureIron nanoparticle
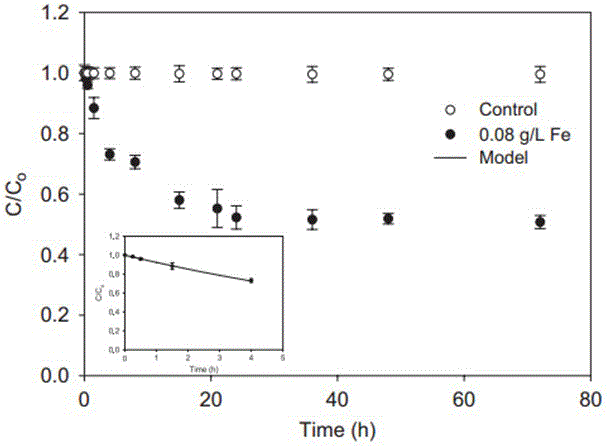
A method of synthesizing air-stable nano-scale zero-valent iron (NZVI) particles at room temperature is provided. Also, a method of treating environmental pollutants using nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized by the above method is provided.According to the method, air-dried NZVI is very effective in removing pollutants such as arsenic, and the method is simple, cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and can stabilize the NZVI in air for more than 10 months.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com