Patents
Literature
186 results about "Nitrite concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
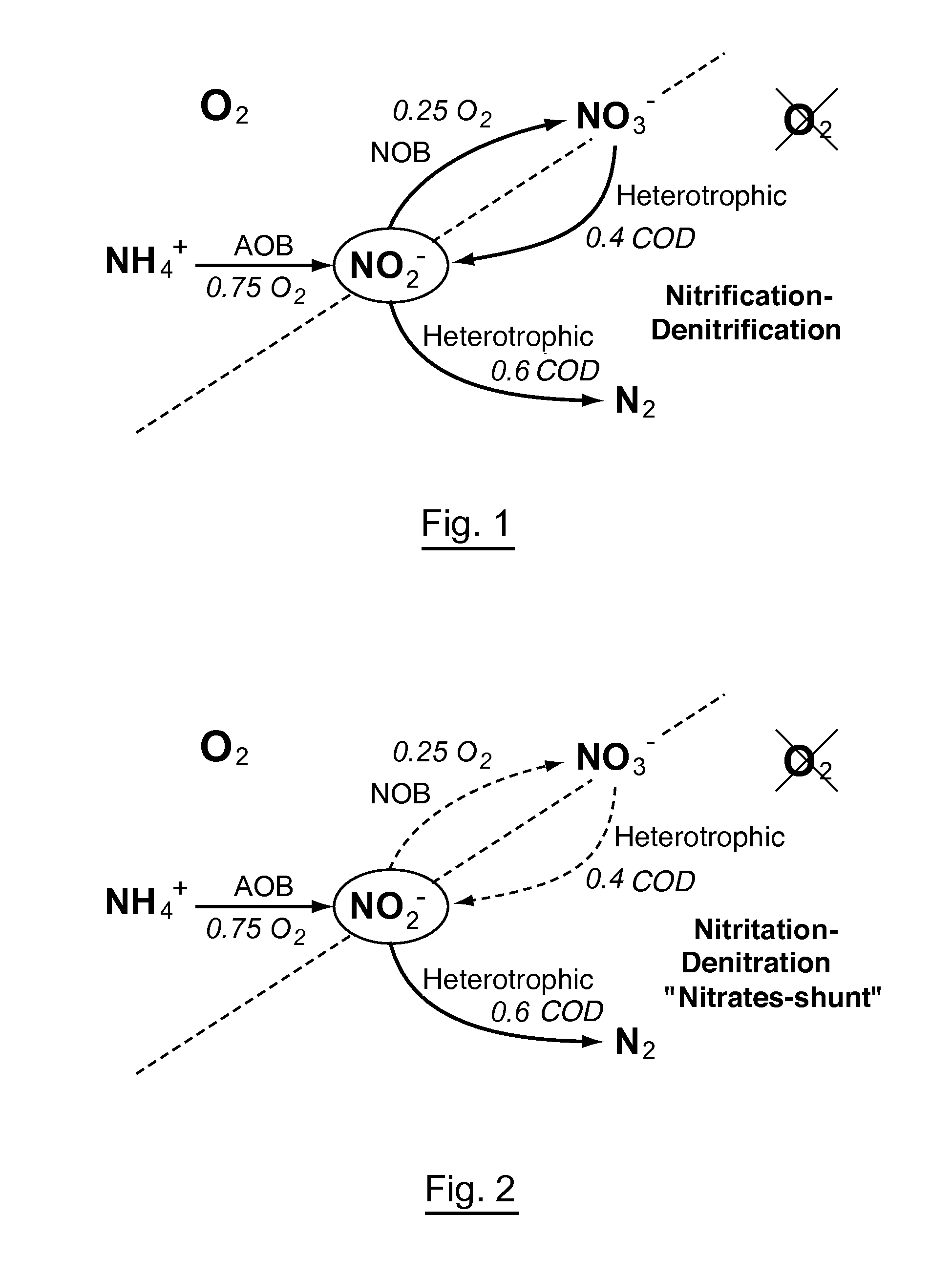
Dietary nitrate may be found in cured meats, various leafy vegetables, and drinking water; nitrite consumption is primarily determined by the amount of processed meats eaten, and the concentration of nitrates in these meats. Nitrite and water are converted in the body to nitric oxide, which could reduce hypertension.
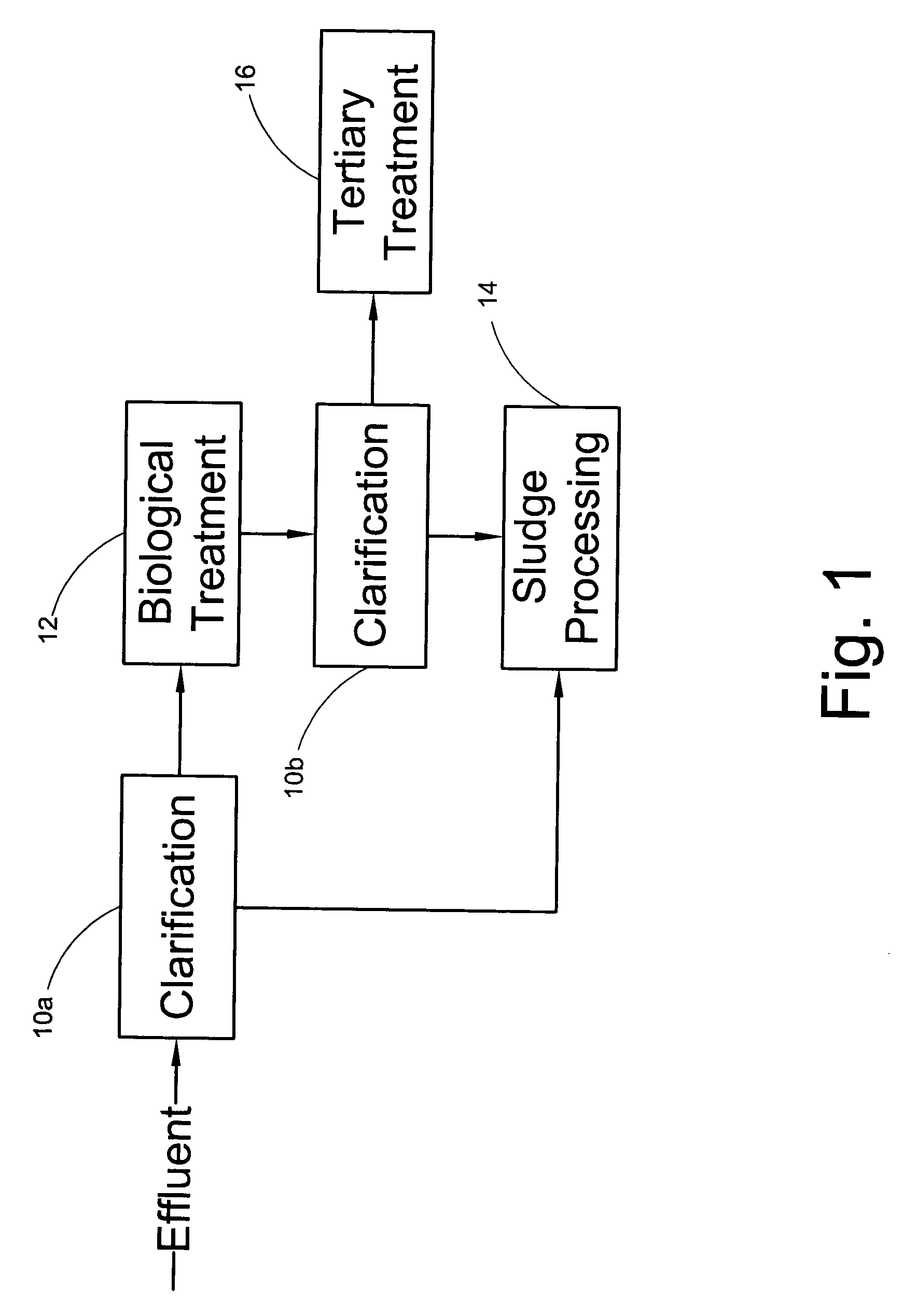
Treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen
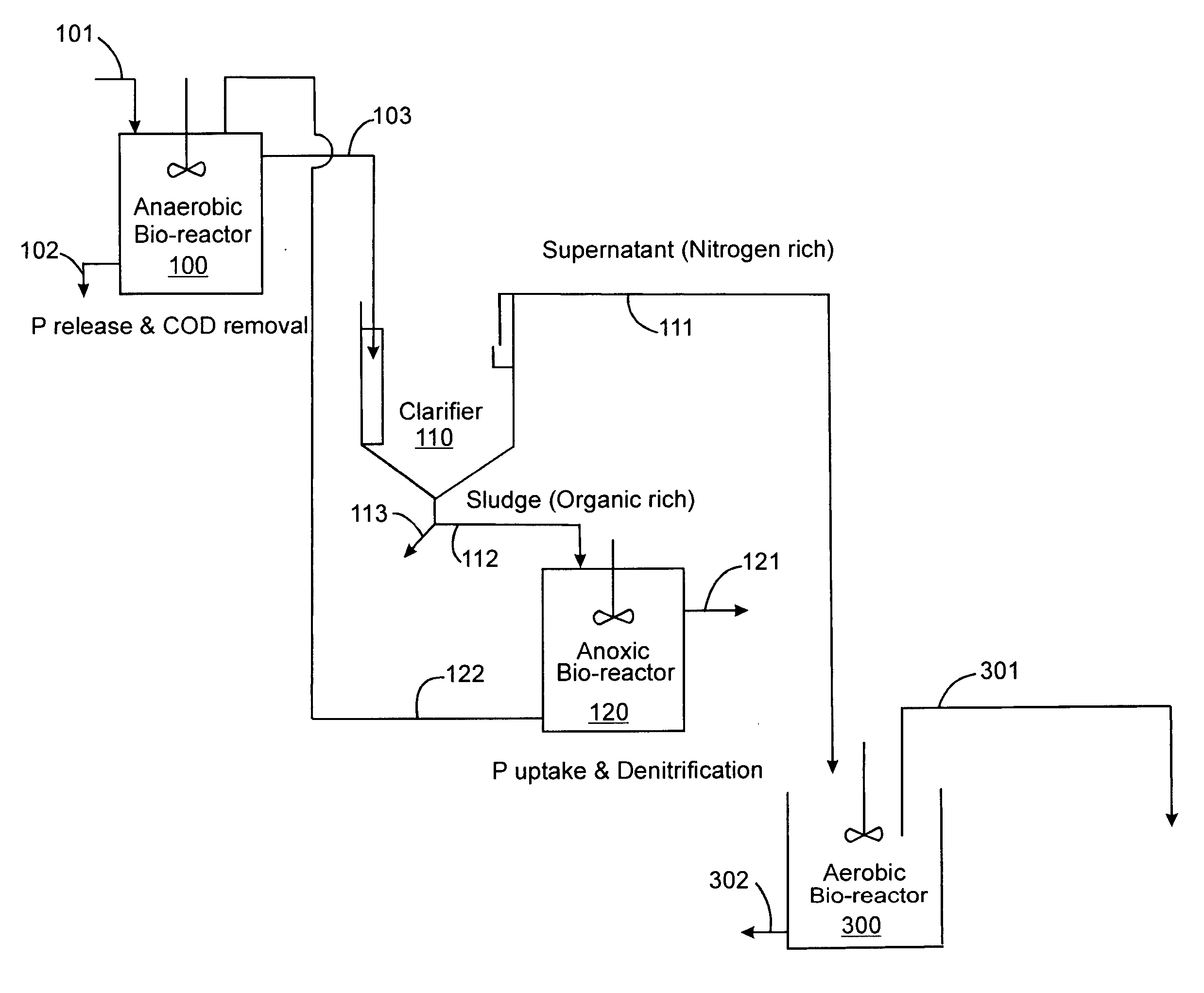
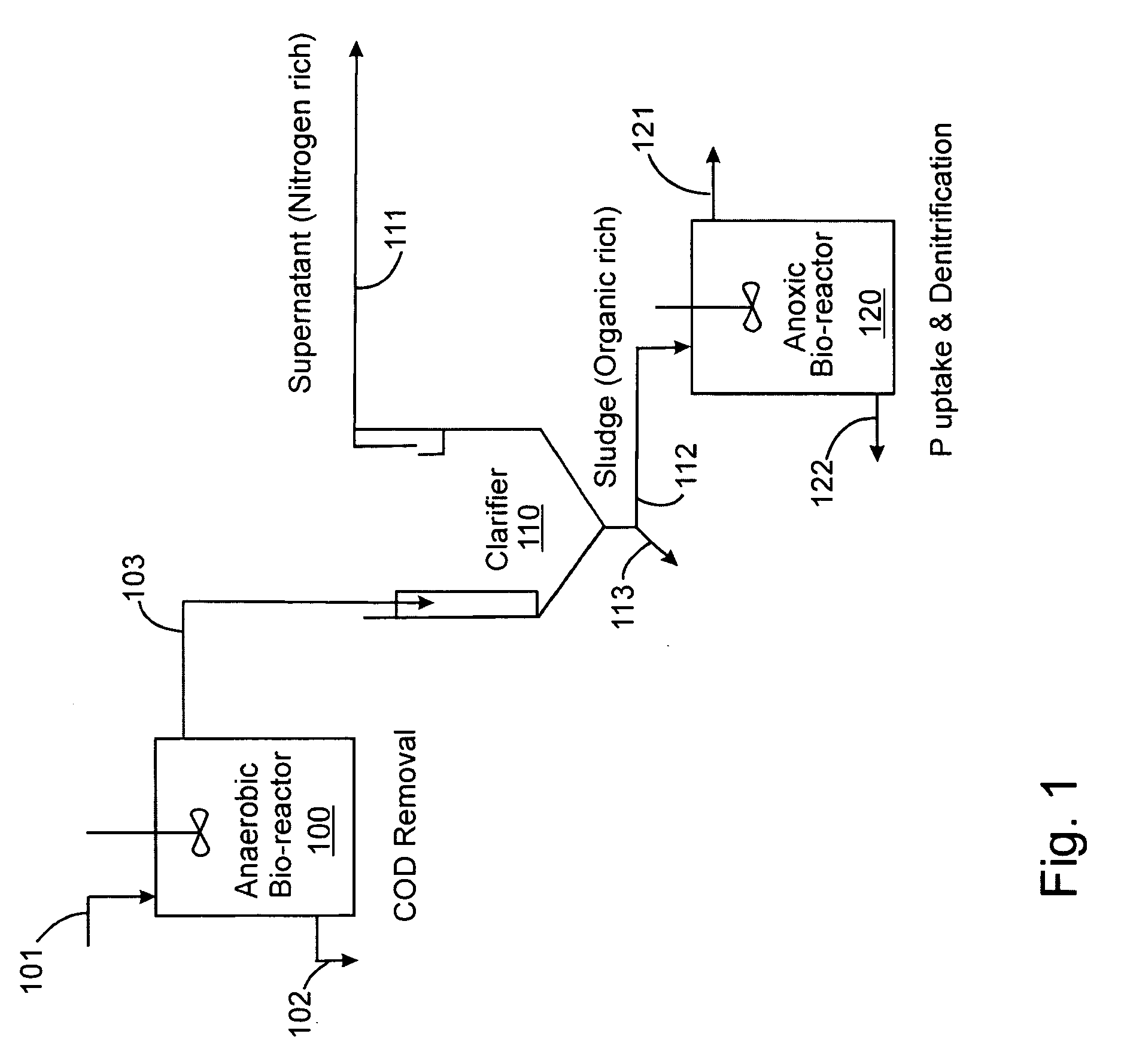
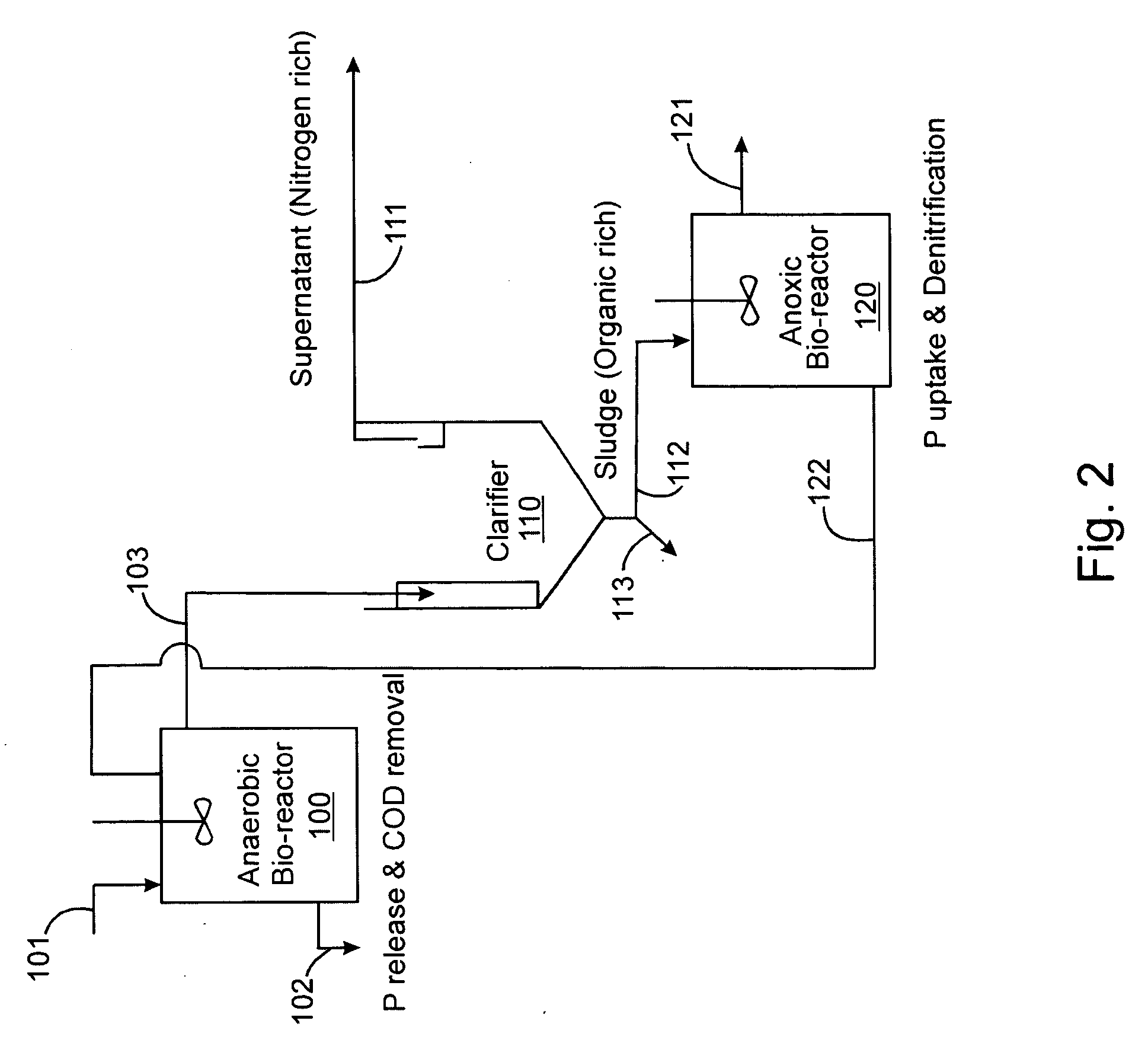
InactiveUS20060249449A1Great extent of P releaseHigh P uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesOxygenClarifier
A method and process for the treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen. The wastewater is first anaerobically treated to produce an anaerobic effluent from which insoluble organic carbon is separated to form a sludge rich in organic carbon that is used as a substrate during anoxic treatment of the wastewater by de-nitrifying phosphorous accumulating organisms (DPAO's) and ordinary de-nitrifying organisms. The separation of insoluble organic carbon is normally conducted using a clarifier located intermediate the anaerobic and anoxic bio-reactors. In one embodiment, the ammonia rich clarifier supernatant is directed to an aerobic reactor for nitrification and the nitrate produced is recycled to the anoxic bio-reactor. The final effluent may be membrane filtered to retain nitrifying biomass within the aerobic bio-reactor. The invention reduces overall hydraulic residence time and sludge volume, which results in a smaller, less expensive wastewater treatment system.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Catalyst and method for reduction of nitrogen oxides
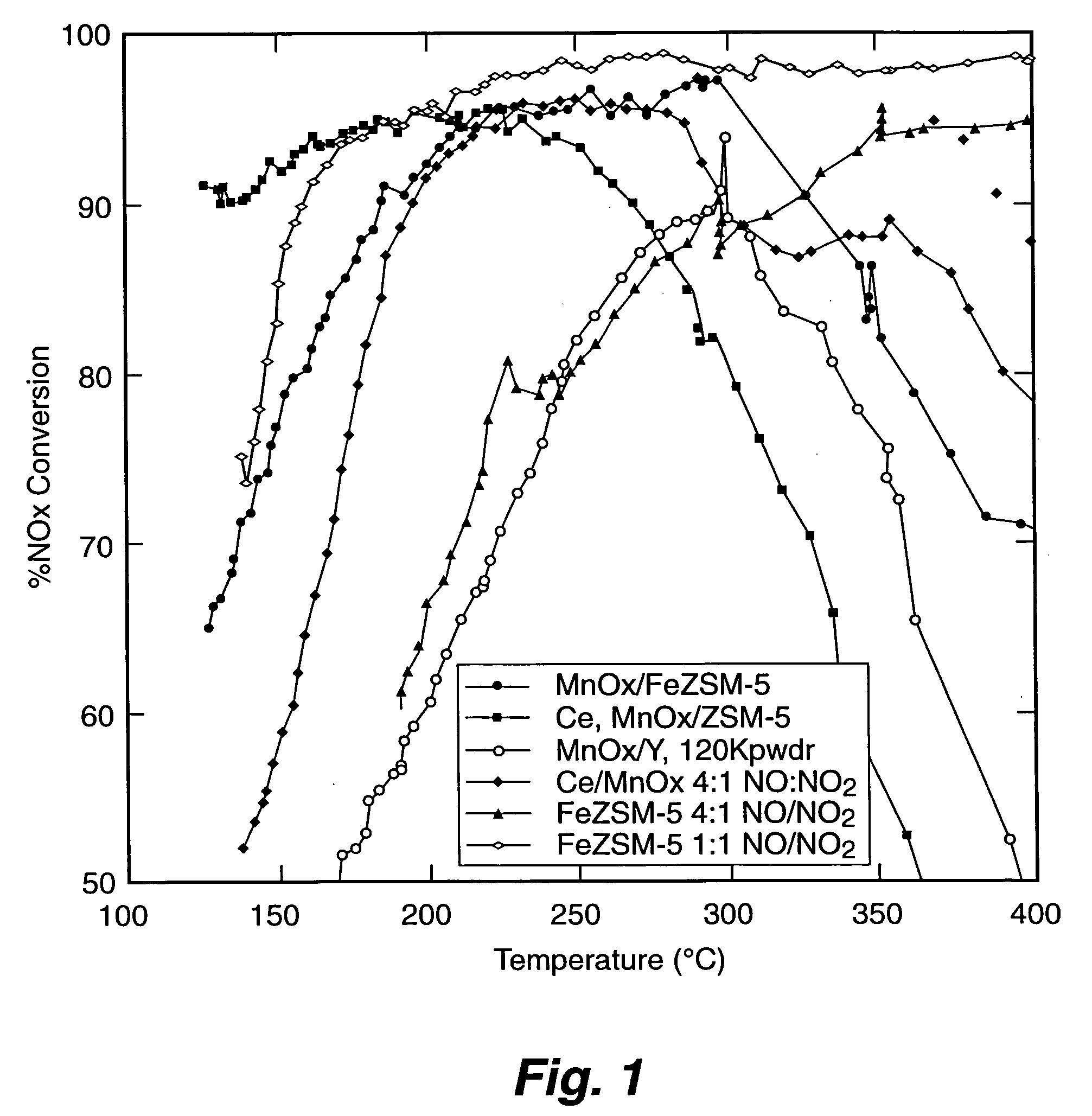
InactiveUS20060029535A1Efficient workSelective catalytic reductionNitrous oxide captureNitrogen compoundsCerium nitrateIron salts
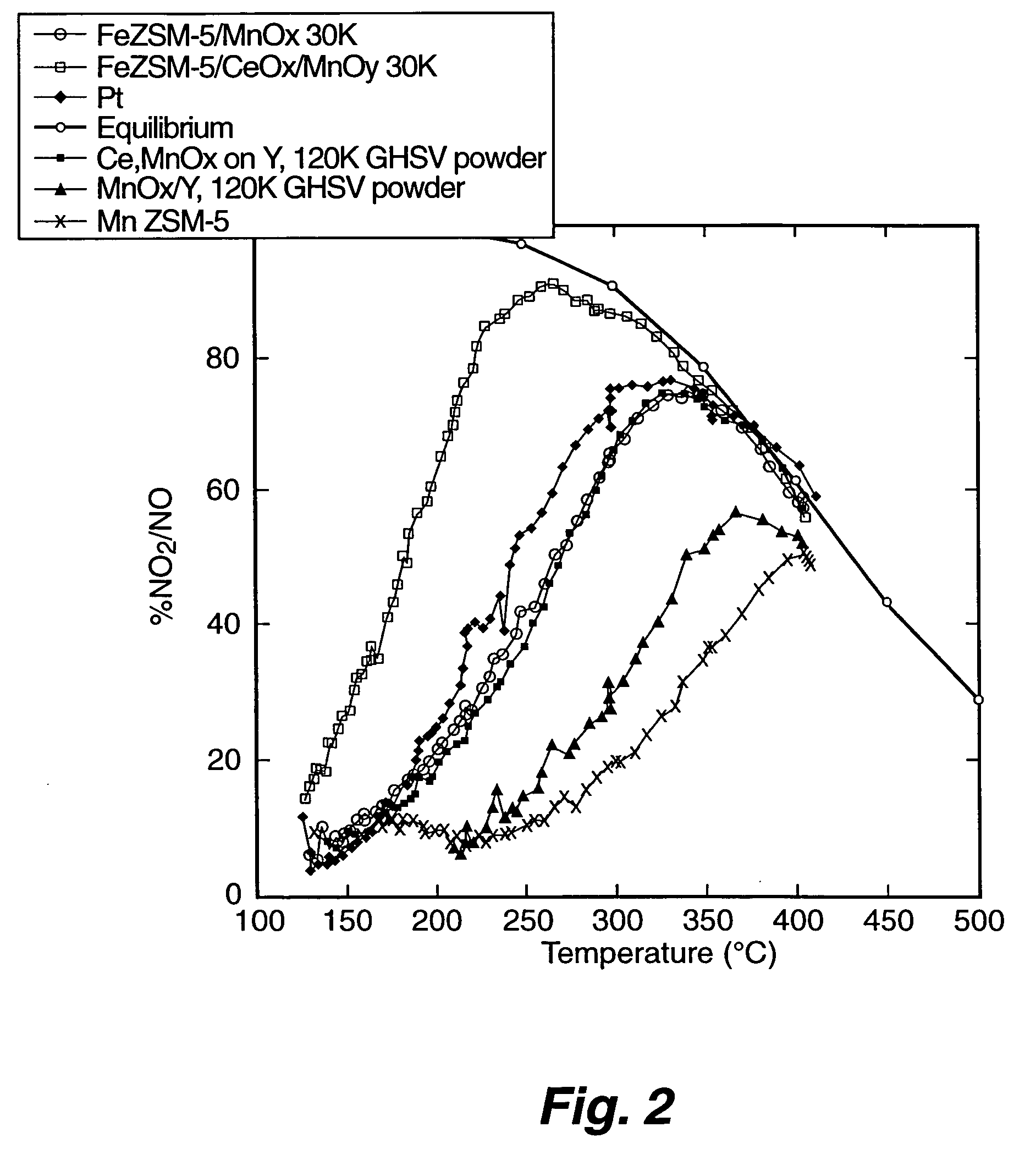
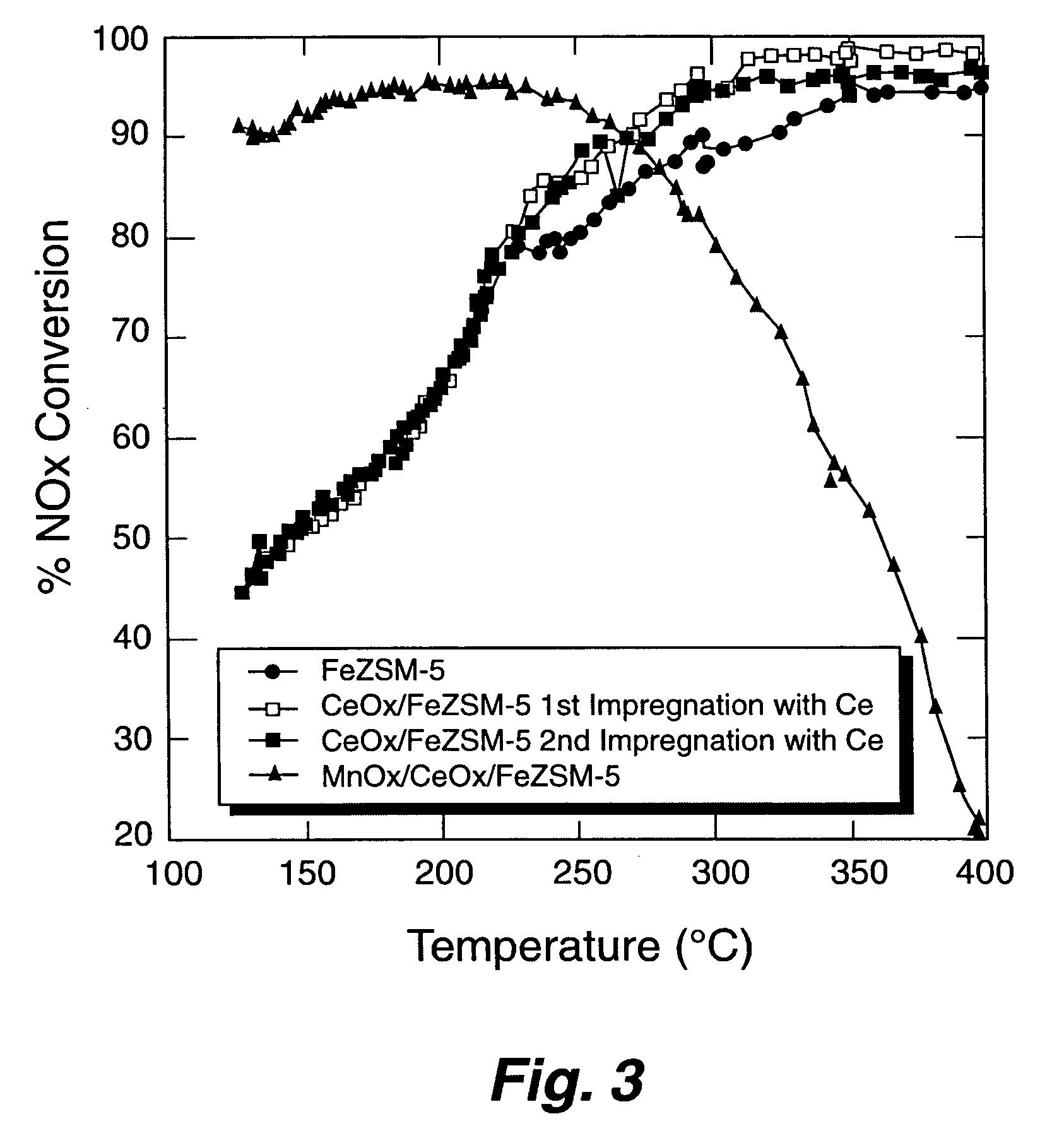
A Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) catalyst was prepared by slurry coating ZSM-5 zeolite onto a cordierite monolith, then subliming an iron salt onto the zeolite, calcining the monolith, and then dipping the monolith either into an aqueous solution of manganese nitrate and cerium nitrate and then calcining, or by similar treatment with separate solutions of manganese nitrate and cerium nitrate. The supported catalyst containing iron, manganese, and cerium showed 80 percent conversion at 113 degrees Celsius of a feed gas containing nitrogen oxides having 4 parts NO to one part NO2, about one equivalent ammonia, and excess oxygen; conversion improved to 94 percent at 147 degrees Celsius. N2O was not detected (detection limit: 0.6 percent N2O).
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Coating compositions containing single wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20060188723A1Sufficient loadImprove the level ofPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyNitratePhosphate
The present invention relates to a coating composition comprising an aqueous dispersion of single wall carbon nanotubes with covalently attached hydrophilic species selected from the group consisting of carboxylic acid, nitrates, hydroxyls, sulfur containing groups, carboxylic acid salts, and phosphates, in an amount of at least 0.5 atomic % of said carbon nanotubes, wherein said carbon nanotubes are present in an amount of at least 0.05 wt. % of said dispersion.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Water-quality assessment system
InactiveUS20050207939A1More transmissionExisting designTesting waterBiological testingTotal dissolved solidsPhosphate
A simple, effective and inexpensive water-quality measurement system comprises a housing suitable for travel on or in a body of water; one or more sensors for measuring water properties as the housing travels; a memory for storing information relating to the measured water properties; and software for processing measured properties. This invention combines into a single, inexpensive, and comprehensive system the sensors, computer hardware, signal-processing, Geographic Information System data, and Decision Support Software. This integration yields a system of novel and unparalleled utility. The water properties measured by the system may include: water temperature, water conductivity, pH level, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, water depth, salinity, total dissolved solids (TDS), ORP, chlorides, nitrates, and phosphates. A geographic information system (GIS) based on a global positioning satellite (GPS) technology is operative to determine geographic location and other factors, and an internal or external processor is operative to generate a map coordinating one or more of the listed characteristics to one or more of the water properties. A barometric pressure sensor may also be provided. In the preferred embodiment, the housing is a floating buoy.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
In Situ Remediation of Inorganic Contaminants Using Stabilized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070256985A1Low costProcess environmental protectionMaterial nanotechnologyWater treatment compoundsCelluloseMaterials science
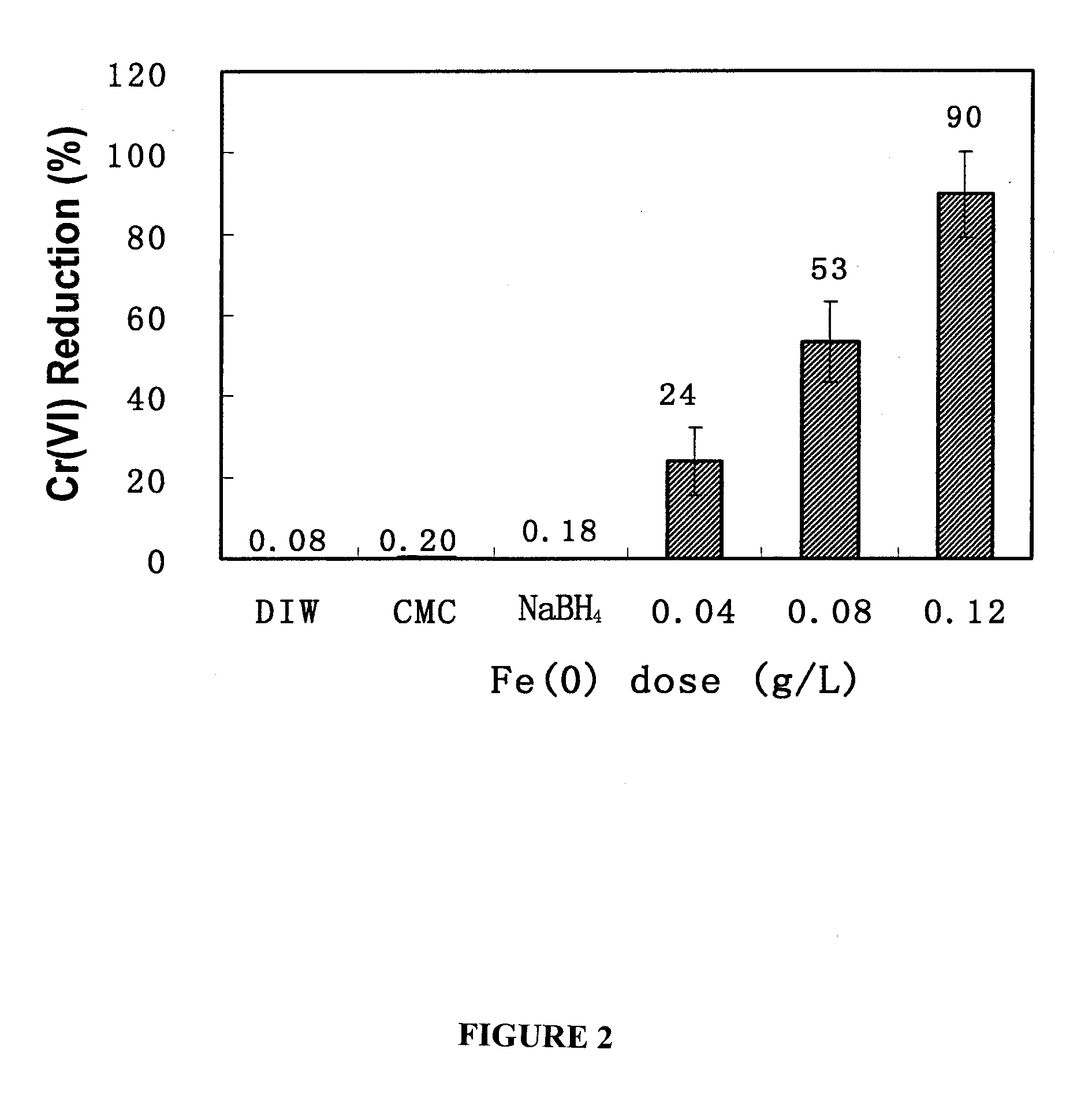
A method for preparing highly stabilized and dispersible zero valent iron nanoparticles and using the nanoparticles as a remediation technology against inorganic chemical toxins in contaminated sites. The method employs a composition containing select polysaccharides (starch or cellulose) as a stabilizer for the iron nanoparticles in a liquid carrier, and results in suspensions of iron nanoparticles of desired size and mobility in water, brine, soils or sediments. The stabilizer facilitates controlling the dispersibility of the iron nanoparticles in the liquid carrier. An effective amount of the composition is delivered to a contaminated site so that the zero valent iron nanoparticles can remediate one or more toxins such as an arsenate, a nitrate, a chromate, or a perchlorate in the contaminated site.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Man-rated fire suppression system
InactiveUS20050115721A1Reducing particulateReduce smokeFire rescueFire extinguisherParticulatesHeat management
A fire suppression system for producing an inert gas mixture having a minimal amount of carbon monoxide, particulates, or smoke. The inert gas mixture may be generated by combusting a gas generant. The gas generant may be a composition that includes hexa(ammine)-cobalt(III)-nitrate. The fire suppression system also includes a heat management system to reduce a temperature of the inert gas mixture. A method of extinguishing fires is also disclosed.
Owner:ORBITAL ATK INC
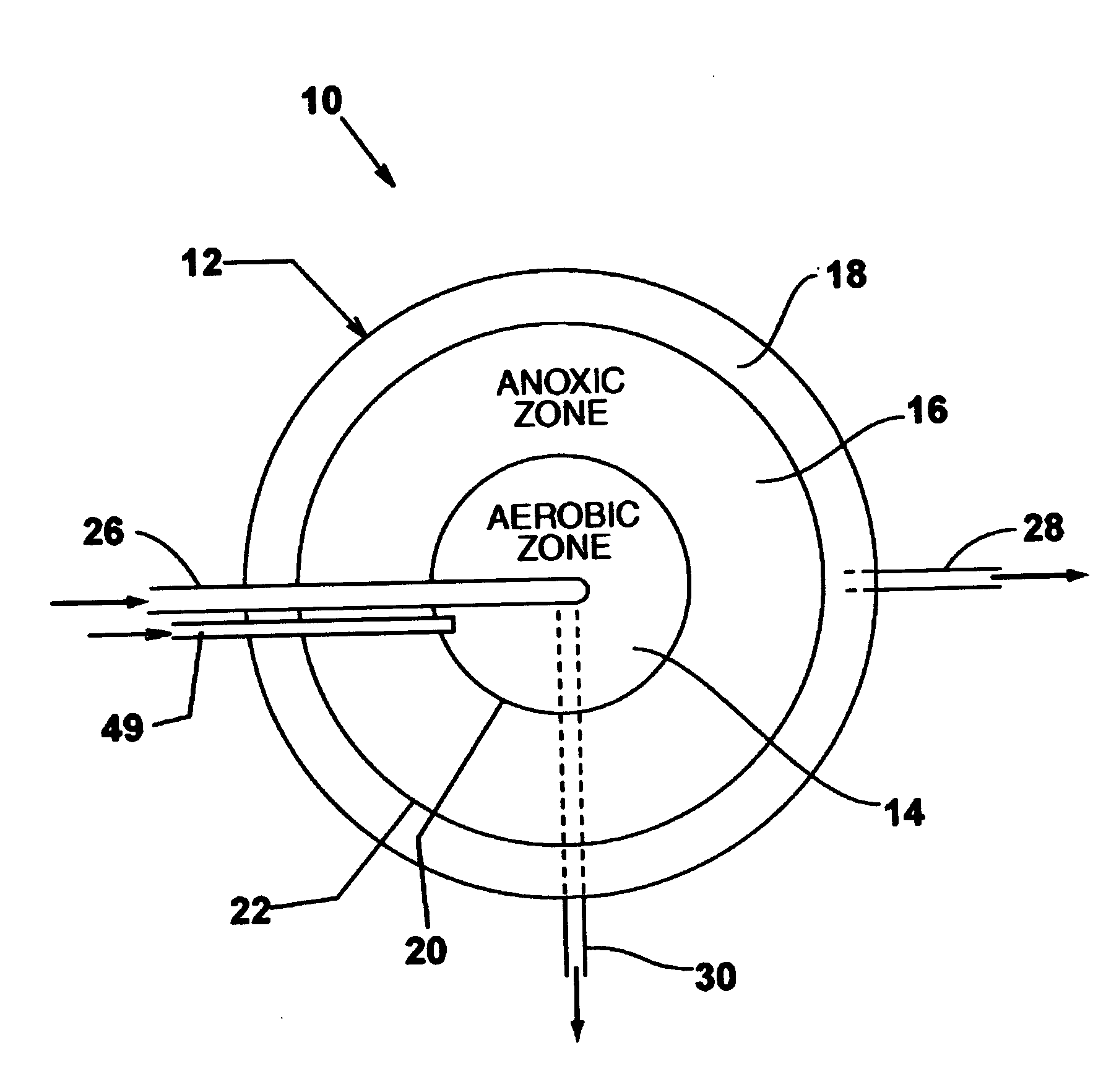
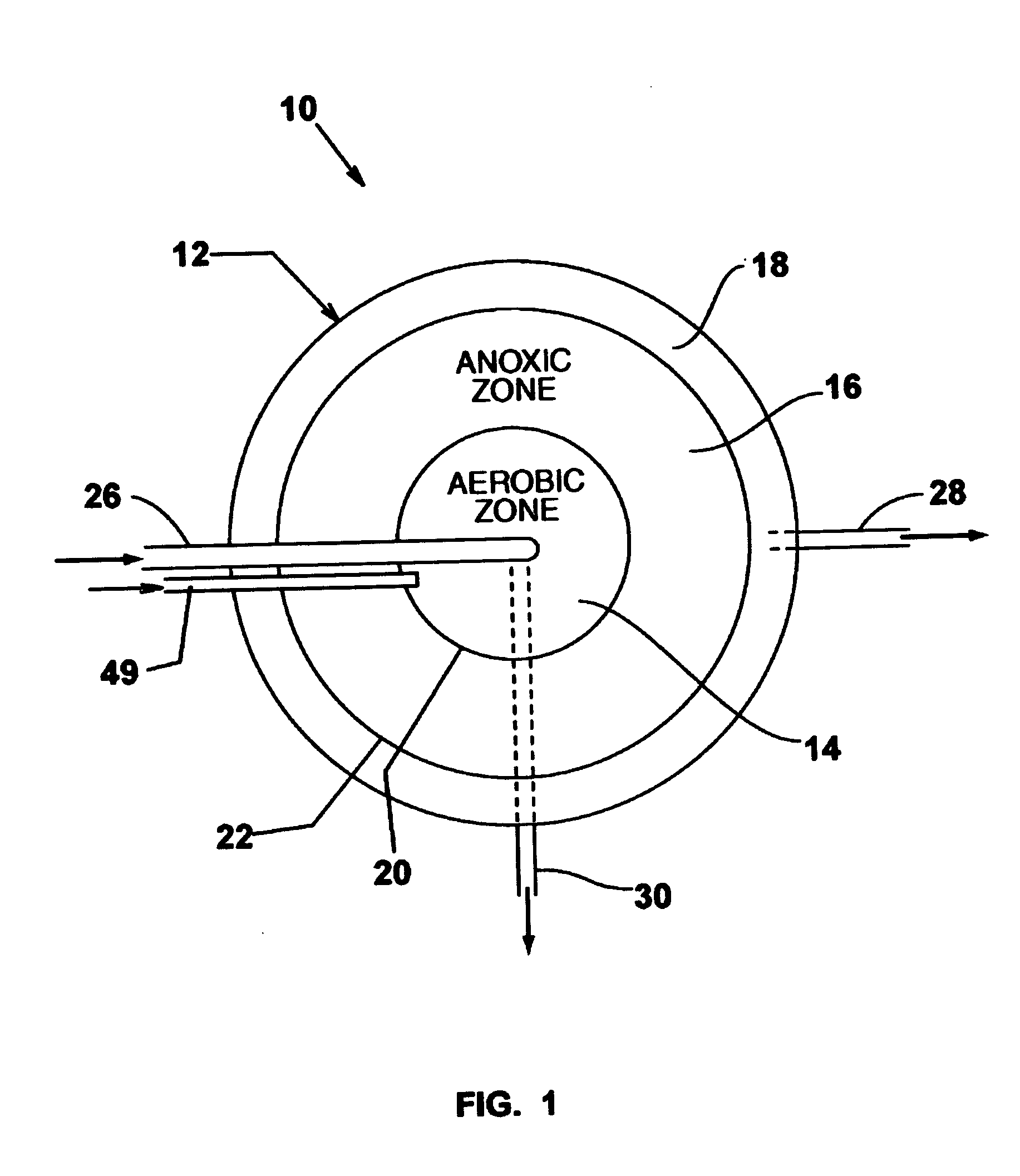
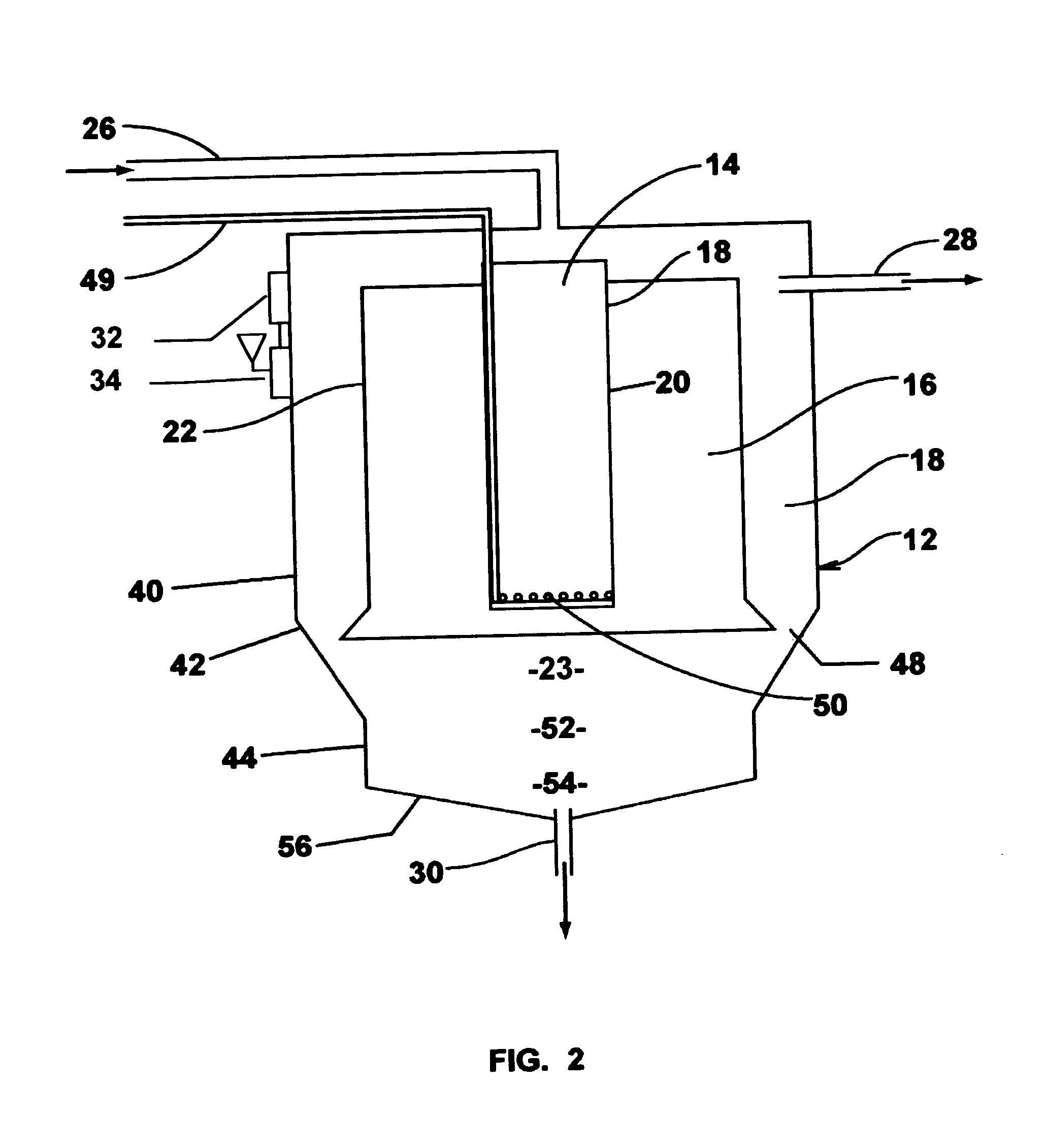
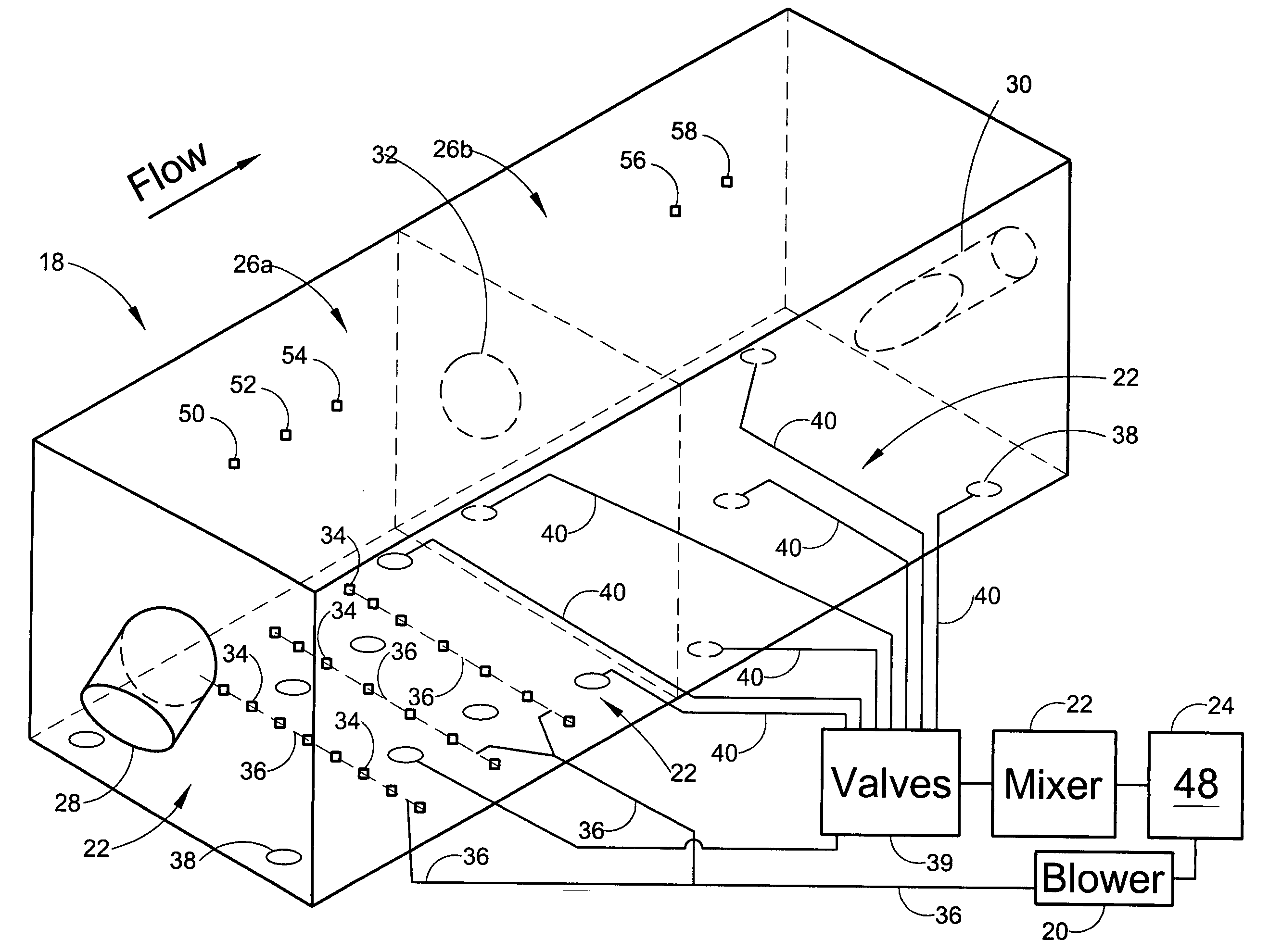
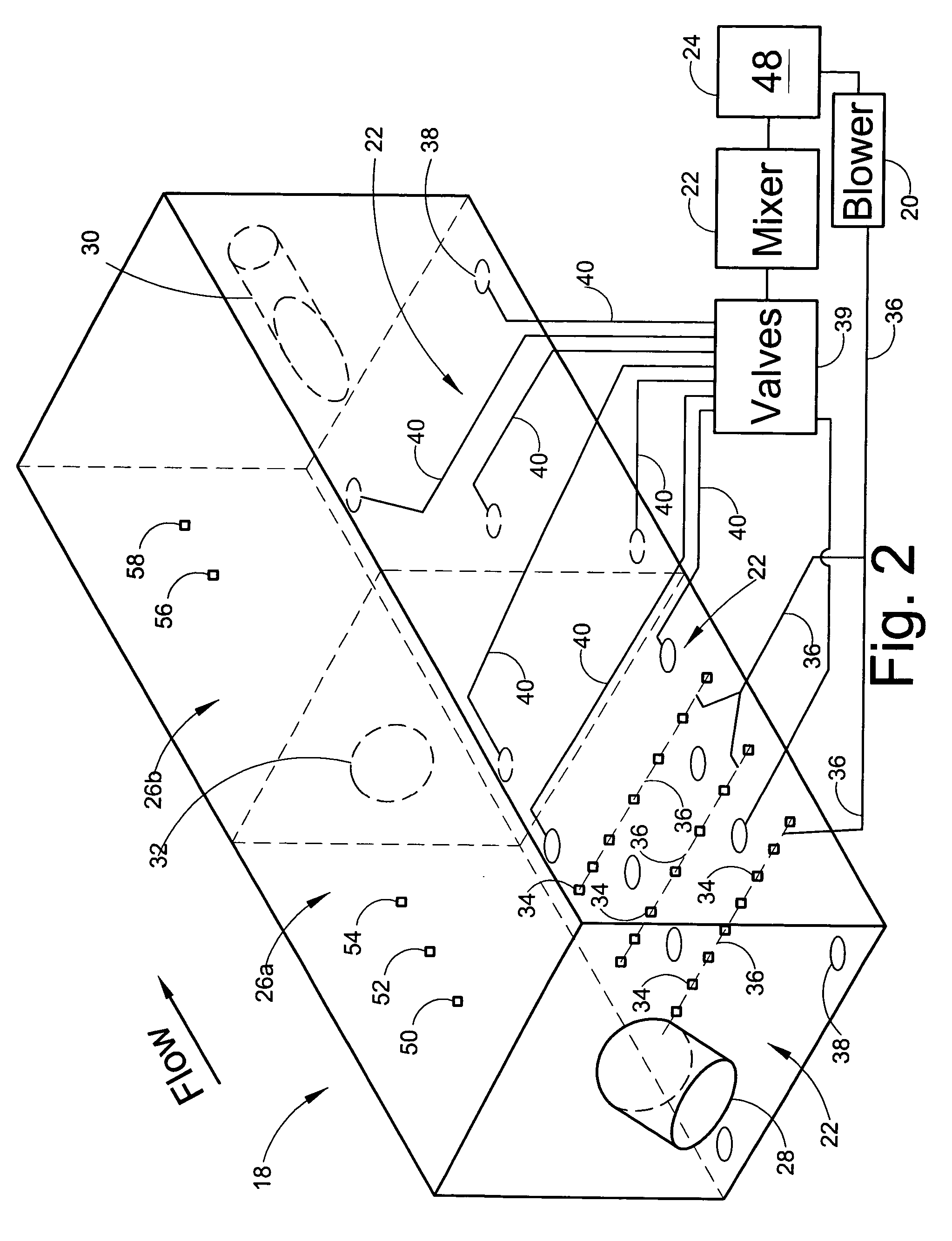
Single vessel multi-zone wastewater bio-treatment system
ActiveUS20050040107A1Suitable for processingSemi-permeable membranesTreatment using aerobic processesSingle vesselNitrate
A process for treating wastewater and a system for practicing the process includes: providing a plurality of zones within a single vessel wastewater treatment system; feeding wastewater into the system; maintaining an aerobic zone in the upper central portion of the vessel; feeding air into the aerobic zone for oxygenation and creating an upflow; maintaining an annularly disposed anoxic zone about said aerobic zone; causing the upflow from the aerobic zone to produce a downflow in the anoxic zone; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the aerobic zone; maintaining an annularly disposed clarification zone about said anoxic zone for clarified liquid, including an upflow; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the clarification zone; maintaining a facultative transition zone below the upper aerobic, anoxic and clarification zones; maintaining an anaerobic zone below the facultative zone for absorbing solids settled by gravity and synthesizing volatile fatty acids; withdrawing substantially clarified liquid from the upflow of the clarified liquid zone; withdrawing substantially solids from about the bottom of the anaerobic zone; employing the aerobic zone for breaking down carbon chains and oxidizing volatile fatty acids dispersed from the anaerobic zone; interacting the aerobic and anoxic zones for the removal of nitrates; and interacting the aerobic, anaerobic ananoxic zones for the removal of phosphorus.
Owner:KASPARIAN ANN
Polishing composition for noble metals
ActiveUS20060024967A1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhosphateOxidation state
The invention provides a polishing composition and a method of chemically-mechanically polishing a substrate comprising a noble metal, the polishing composition comprising (a) an oxidizing agent that oxidizes a noble metal, (b) an anion selected from the group consisting of sulfate, borate, nitrate, and phosphate, and (c) a liquid carrier. The invention further provides a polishing composition and a method of chemically-mechanically polishing a substrate comprising ruthenium, the polishing composition comprising (a) an oxidizing agent that oxidizes ruthenium above the +4 oxidation state, (b) a polishing additive selected from the group consisting of metal sequestering polymers, metal chelators, organic thiols, compounds that reduce ruthenium tetraoxide, lactones, and α-hydroxycarbonyl compounds.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Nanoparticles of rare earth oxides
ActiveUS20070104629A1Increase volumeLow cost productionMaterial nanotechnologyLanthanum oxide/hydroxidesCeriumScandium
Rare earth compositions comprising nanoparticles, methods of making nanoparticles, and methods of using nanoparticles are described. The compositions of the nanomaterials discussed may include scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lanthanum(La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium(Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and lutetium (Lu). The nanoparticles can be used to make organometallics, nitrates, and hydroxides. The nanoparticles can be used in a variety of applications, such as pigments, catalysts, polishing agents, coatings, electroceramics, catalysts, optics, phosphors, and detectors.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Mixer and process controller for use in wastewater treatment processes
ActiveUS20060254979A1Less energyReduce stepsWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesNitrateNitrite concentration
A system and method of wastewater treatment in a tank provides large mixing bubbles generated in the lower portion of the tank. In embodiments providing aerobic wastewater treatment, the system further provides oxygen to the wastewater by way of tiny aerating bubbles provided by diffusers. At least one sensor in the tank provides measurements of at least one wastewater treatment parameter such as total suspended solids, dissolved oxygen, ammonium or nitrate. An automatic controller in the system, responsive to measurements provided by the sensor, adjusts the rate of mixing provided by the large mixing bubbles. In some aerobic embodiments, the controller, responsive to measurements from the sensor, further adjusts the rate of oxygenation supplied to the wastewater by the tiny aerating bubbles.
Owner:KOOPMANS RICHARD J +1
Method of preparation for carbon nanotube material
InactiveUS20060062714A1Overcomes drawbackSolve UtilizationMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a carbon nanotube material, comprising the steps of: (a) preparing a modified montmorillonite by an ion exchange reaction comprising the substeps of: i) acidifying an alkylamine with equal mole of a concentrated HCl; ii) mixing the resulting acidified alkylamine with a montmorillonite dispersion in 1:1˜2 volume ratio of the acidified alkylamine to the montmorillonite dispersion; and iii) precipitating, filtering and pulverizing to obtain a modified montmorillonite; (b) preparing a catalyst by a hydrogenation reduction method, comprising the substeps of: i) mixing an aqueous solution of nickel nitrate and an alumina-silica hybrid in a weight ratio of 35-45 parts of nickel to 55-65 parts of alumina-silica hydrid, wherein the alumina-silica hydrid contains 10 wt % of alumina and has a particle size of 10-30 μm; ii) drying and calcining the resulting product; and iii) reducing the product with a reducing gas containing hydrogen to produce a nickel-supported catalyst; (c) preparing a polyolefin mixture of a polyolefin, the modified montmorillonite prepared in step a) and the catalyst prepared in step b) in a mixer in the weight ratio of 75˜97.5:0˜20:0˜5 provided that the amounts of the modified montmorillonite and the catalyst are not both 0; and (d) preparing and purifying a nanotube, comprising the substeps of: i) placing the polyolefin mixture obtained in step (c) in a crucible and heating the temperature inside crucible up to 550° C.˜650° C., wherein the heating time begins from the burning of the polymer and ends when no flame can be observed and cooling the polyolefin mixture to obtain a mixture of carbon nanotube, nickel catalyst and montmorillonite; ii) adding a hydrofluoric acid with a concentration of 20-50% to the mixture, mixing, and separating to obtain a carbon powder; and iii) adding a mixture of a concentrated sulfuric acid and a concentrated nitric acid, refluxing, and separating to obtain a purified carbon nanotube. The carbon source material used in the present invention was polyolefin or recovered polyolefin whose price was low and whose source was abundant. The manufacturing facilities involved for preparing supported catalyst and modified montmorillonite were simple. The mixer used was that of the conventional fabricating equipment for polymeric materials while the facilities used for synthesizing carbon nanotube material were porcelain crucible and common flame. The method could simultaneously solve the problem of recovery and utilization of waste plastics.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Substrates with small particle size metal oxide and noble metal catalyst coatings and thermal spraying methods for producing the same
A substrate having a catalytic surface thereon characterized as a coating of metal oxide and noble metal particles in the nominal diameter size distribution range of <3 microns, and more particularly <1 micron, is produced by thermal spraying a mixture of large size particles (e.g., in a nominal size distribution range of >10 micrometers) of hydroxides, carbonates or nitrates of the metals: cerium, aluminum, tin, manganese, copper, cobalt, nickel, praseodymium or terbium particles; and hydroxides, carbonates or nitrates of the noble metals: ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, iridium, platinum and gold onto the substrate. The coating adheres to the surface and provides desirable catalyst properties.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Phosphorus and potassium fertilizer for all forms of perennial trees, vines and annual crops
InactiveUS20050119124A1Desirable resultEfficient evaporationBiocideAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserMonopotassium phosphateChemistry
Energizing formulations of phosphorous and potassium fertilizer are disclosed that comprise maximally efficient phosphorous pentoxide and di-potassium monoxide combinations. Methods of manufacture and use for these compounds and formulations are also disclosed. The fertilizer formulations comprise both solid and liquid formulations having variable or fixed pH ranges that are acceptable for aerial, foliar, and soil applications, and suitable for all forms of perennial trees, vines and annual crops. The formulations further possess the ability to control pathogenic soil microorganisms through the use of, for example, formulations comprising combinations of monopotassium phosphite, monopotassium phosphate. monopotassium nitrite, monopotassium nitrate, monopotassium sulfite and monopotassium sulfate.
Owner:ALYESHMERNI ALFRED
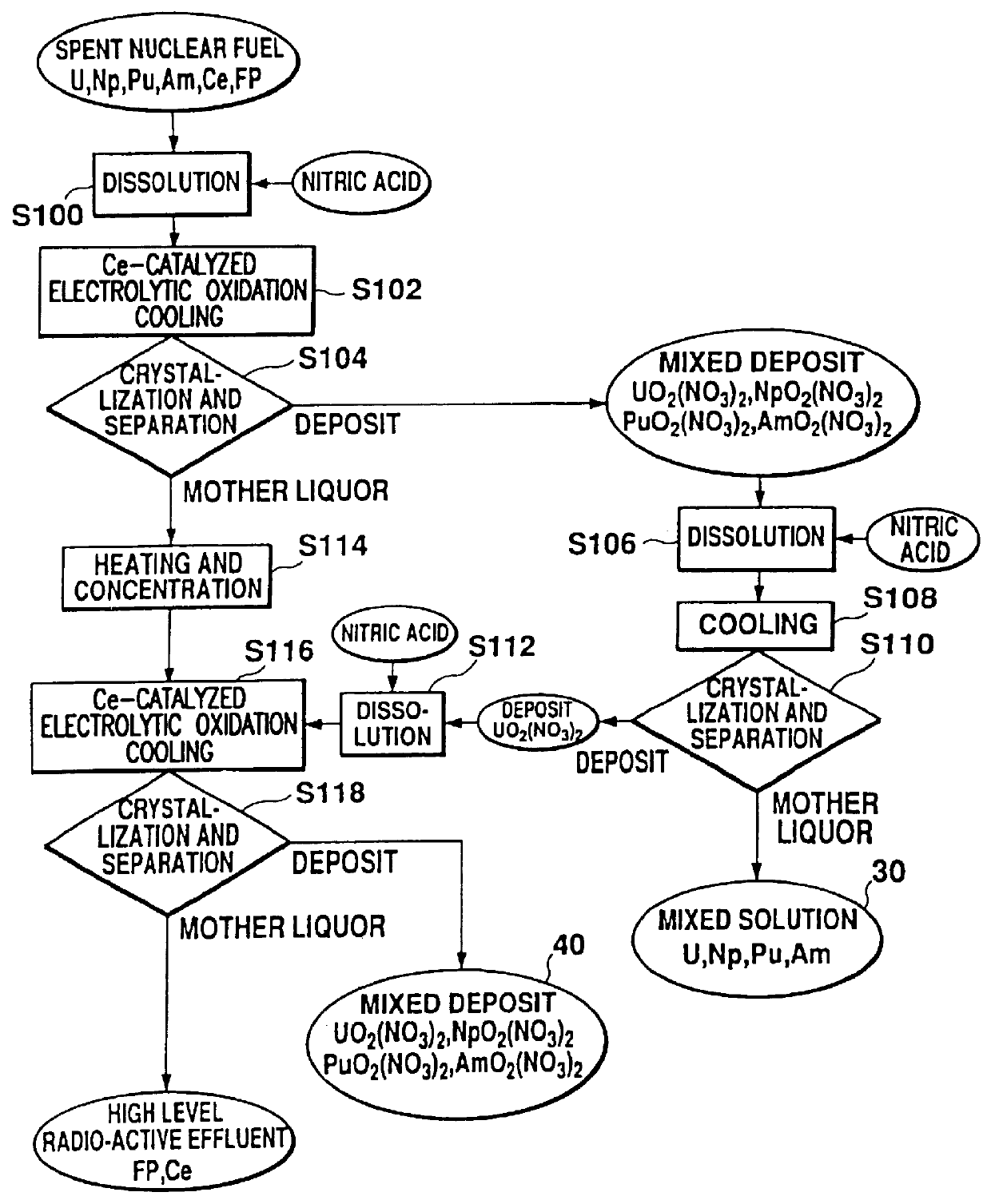
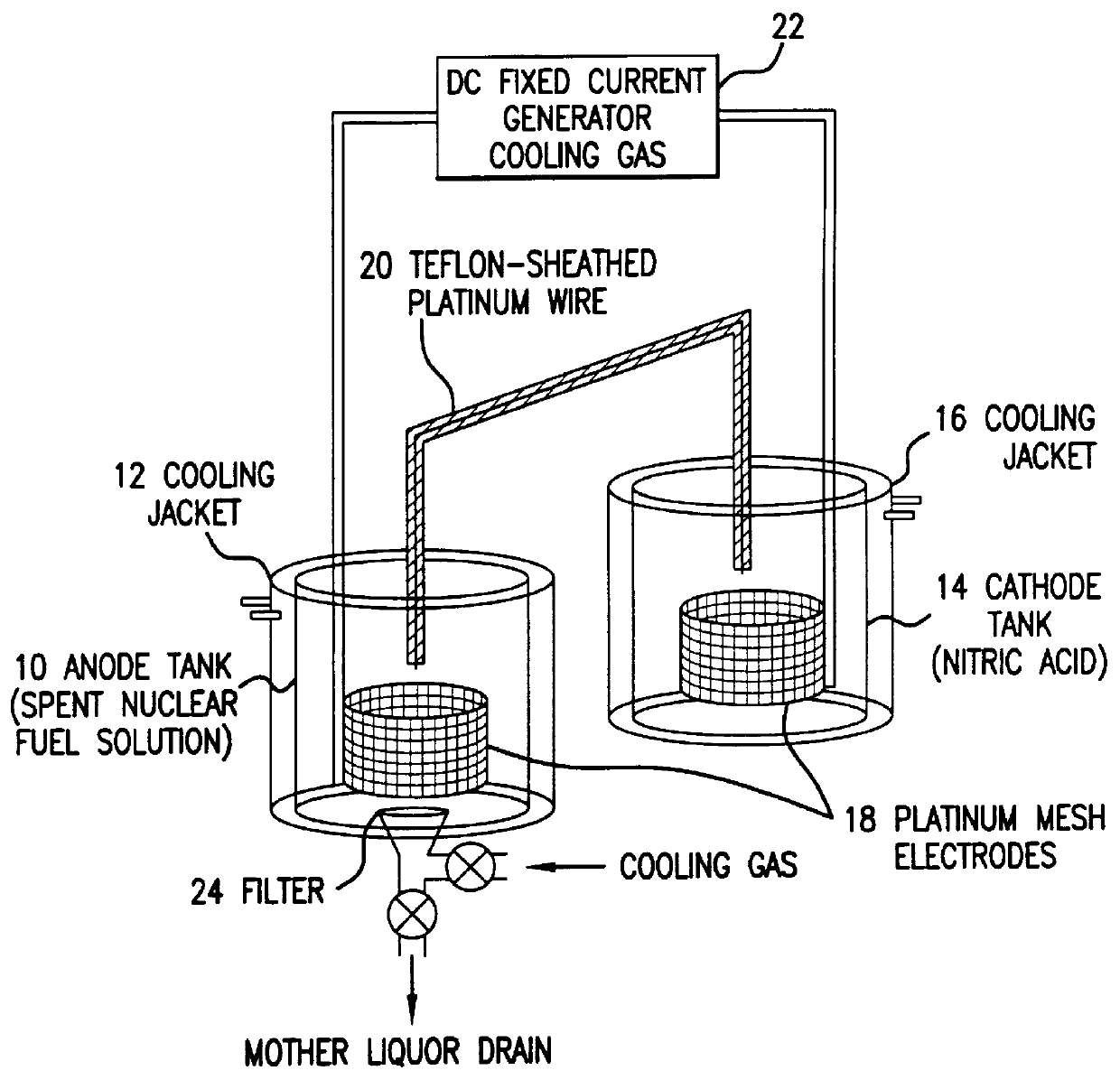
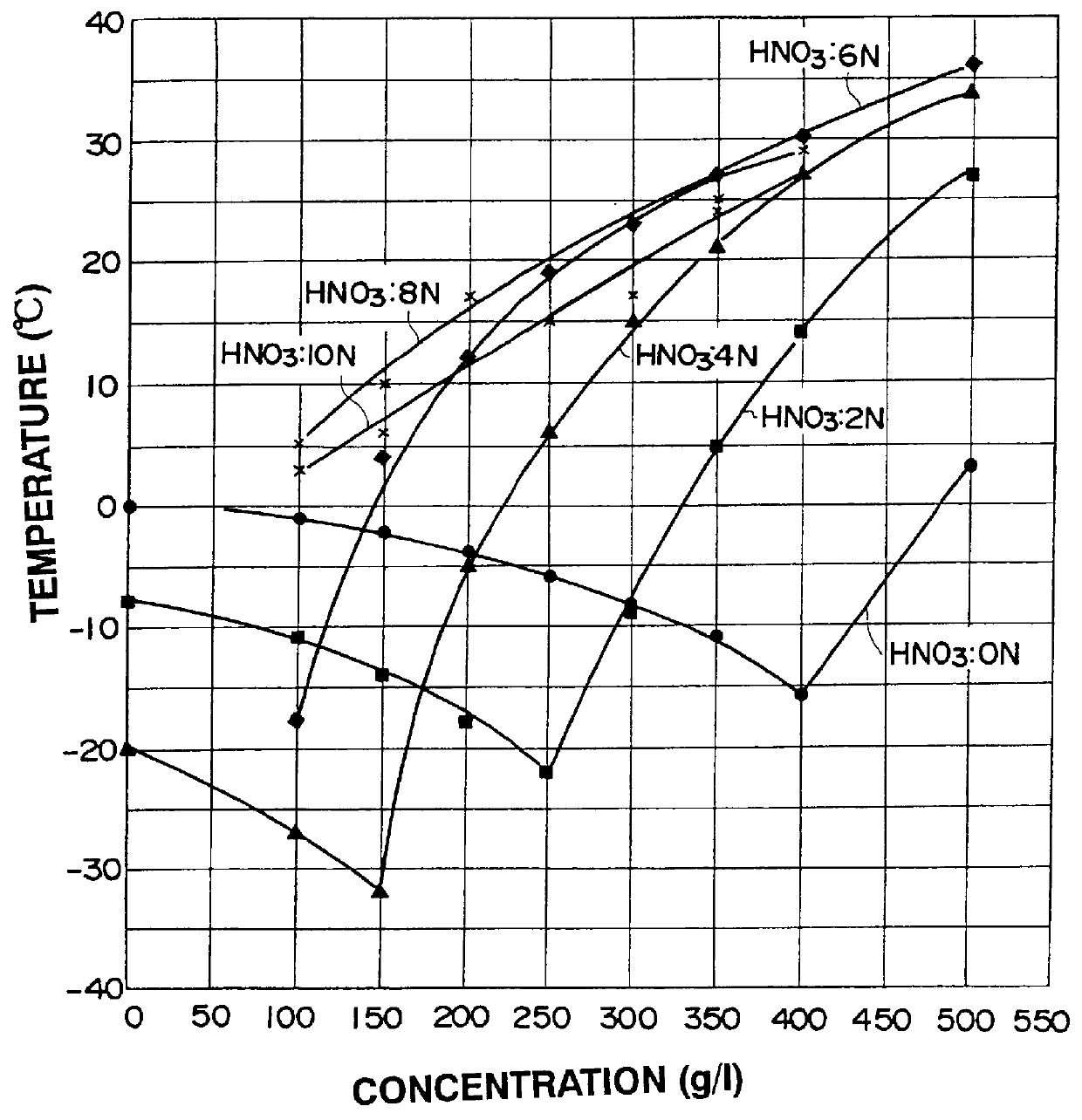
Method of recovering uranium and transuranic elements from spent nuclear fuel
InactiveUS6033636AReduce solubilityPromote recoveryElectrolysis componentsSolvent extractionSolventWaste material
The steps for recovering uranium and transuranic elements are simplified, and the generation of waste solvent and waste materials is suppressed. Spent nuclear fuel is dissolved in nitric acid (S100) and the resulting solution is subjected to electrolytic oxidation so that U, Np, Pu, Am is oxidized to VI using Ce as oxidation catalyst. The solution is cooled, and nitrates of valence VI thereby deposit as crystals and are separated from the mother liquor (S104). The mother liquor is heated and concentrated (S114). The mixed crystalline deposit is dissolved in nitric acid (S106), uranyl nitrate is deposited alone by cooling (S108), and the crystals are separated from the U, Np, Pu, Am mixed solution (S110). The uranyl nitrate is dissolved in nitric acid (S112), and the heated and concentrated mother liquor is added to it to prepare another mixed solution. This mixed solution is then subjected to electrolytic oxidation to oxidize the remaining U, Np, Pu, Am to valence VI, and the solution is cooled so that U, Np, Pu, Am are coprecipitated with uranyl nitrate as crystals, and can be separated from high level radioactive effluent (S118).
Owner:DORYOKURO KAKUNENRYO KAIHATSU JIGYODAN
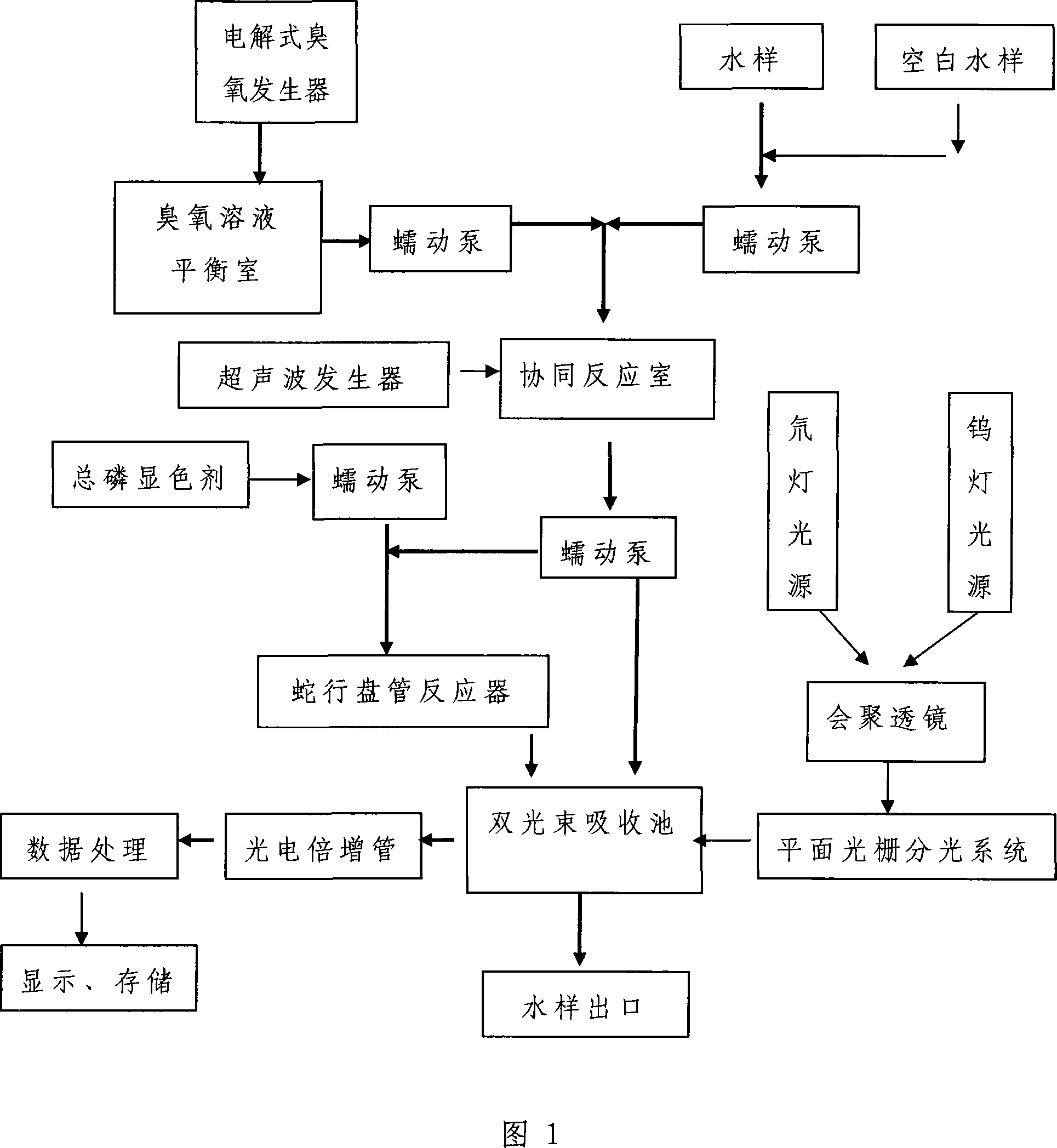
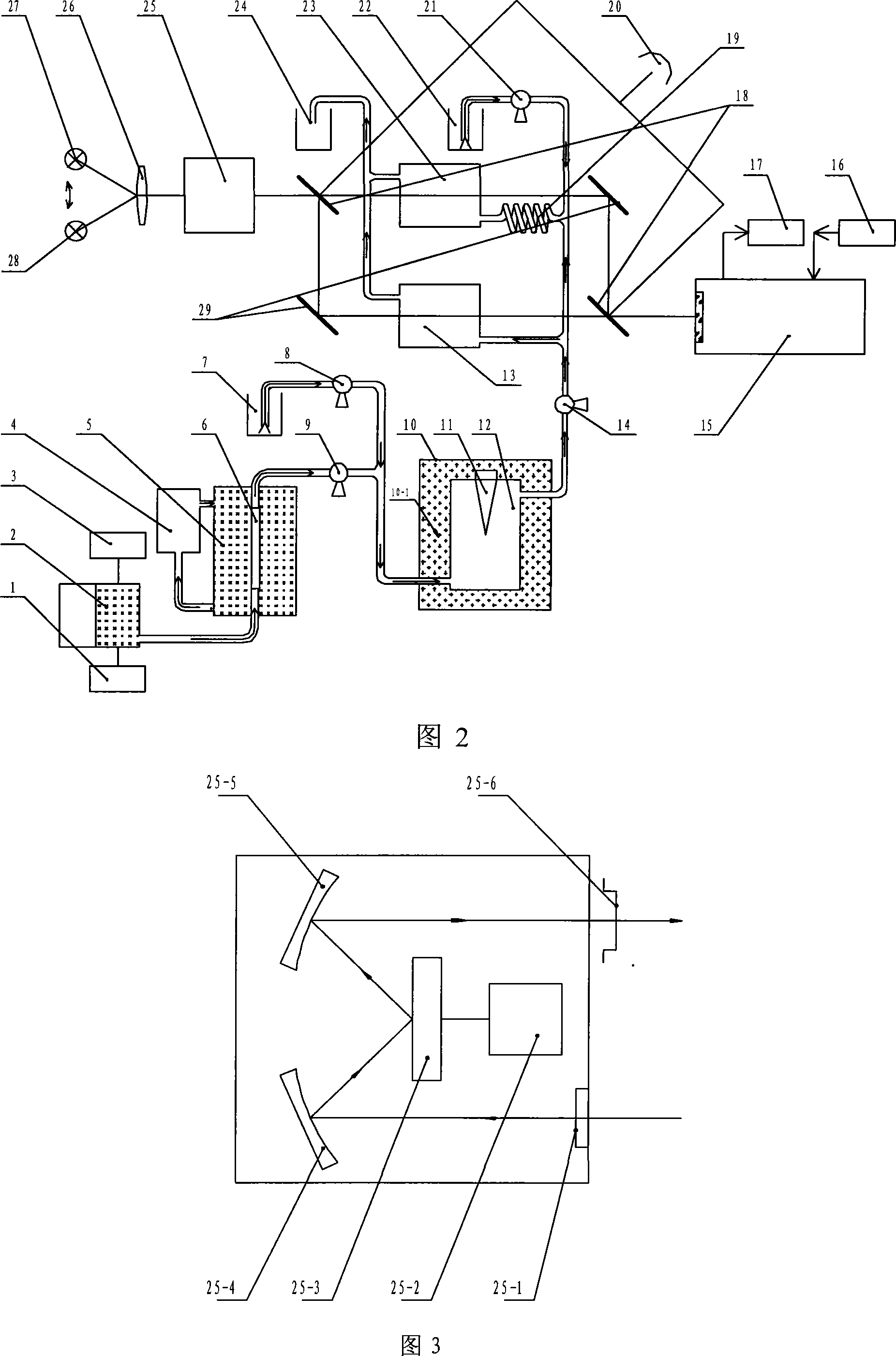
Method for measuring water body total nitrogen and total phosphorous by digestion spectrophotometry of supersonic wave cooperating with ozone
InactiveCN101105439AEasy to operateEasy to installMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationCavitationPhosphate
The invention provides an ultrasonic wave and ozone coordinated luminosity counteraction method for measuring the total nitrogen and total phosphorus of water. The invention can solve the problem of the prior method that the real-time measuring can not be taken, the analyzing time is long, the analysis process is numerous and diverse, the measuring condition is harsh and the energy consumption is big, in particular that secondary pollution can be produced. Cavitations effect and ozone oxidation coordinated water sample counteraction method is adopted in the invention, the organic nitrogenous and inorganic nitrogen in the water sample are transformed into nitrate under the normal temperature and pressure, the phosphates of the water sample are transformed into normal phosphates; and lastly, the phosphates and the normal phosphates are measured by an ultraviolet visible light measuring system and the index of the total nitrogen and total phosphorus of water can be obtained.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Man-rated fire suppression system and related methods
ActiveUS20060278409A1Reducing particulateReduce smokeFire rescueBoring toolsParticulatesThermal management system
A fire suppression system for producing an inert gas mixture having a minimal amount of carbon monoxide, particulates, or smoke. The inert gas mixture may be generated by combusting a gas generant. The gas generant may be a composition that includes hexa(ammine)-cobalt(III)-nitrate. The fire suppression system also includes a heat management system to reduce a temperature of the inert gas mixture. In one embodiment, the system includes multiple gas generators and is configured to ignite the respective gas generant of each gas generator in a predetermined, time based sequential order. For example, the gas generant of each gas generator may be ignited in a sequential order at specified time intervals. Methods of extinguishing fires are also disclosed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
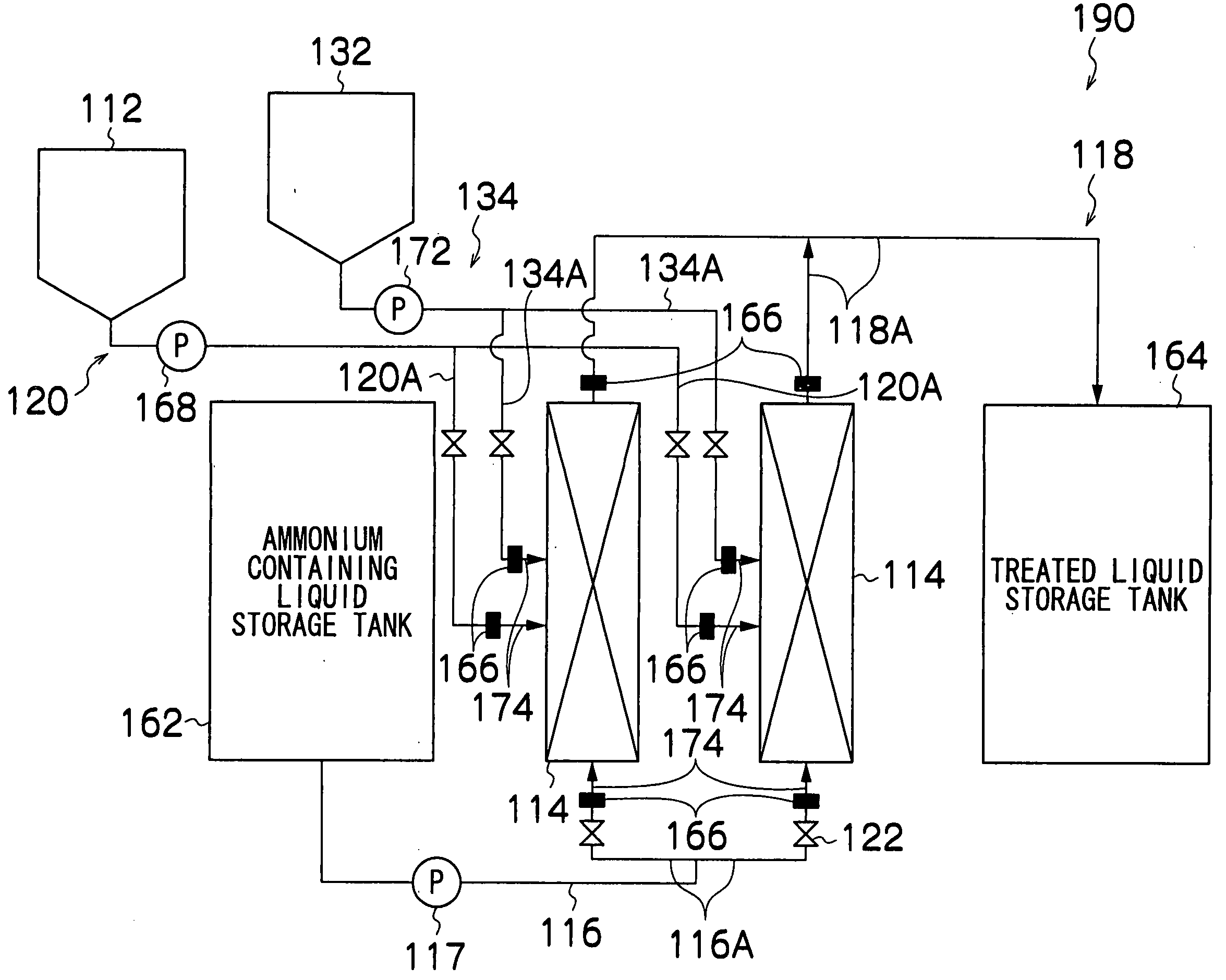
Process and equipment for treating ammonium containing liquid
ActiveUS20060191846A1Low costConstantly stableOther chemical processesWater contaminantsReduction treatmentNitrite concentration
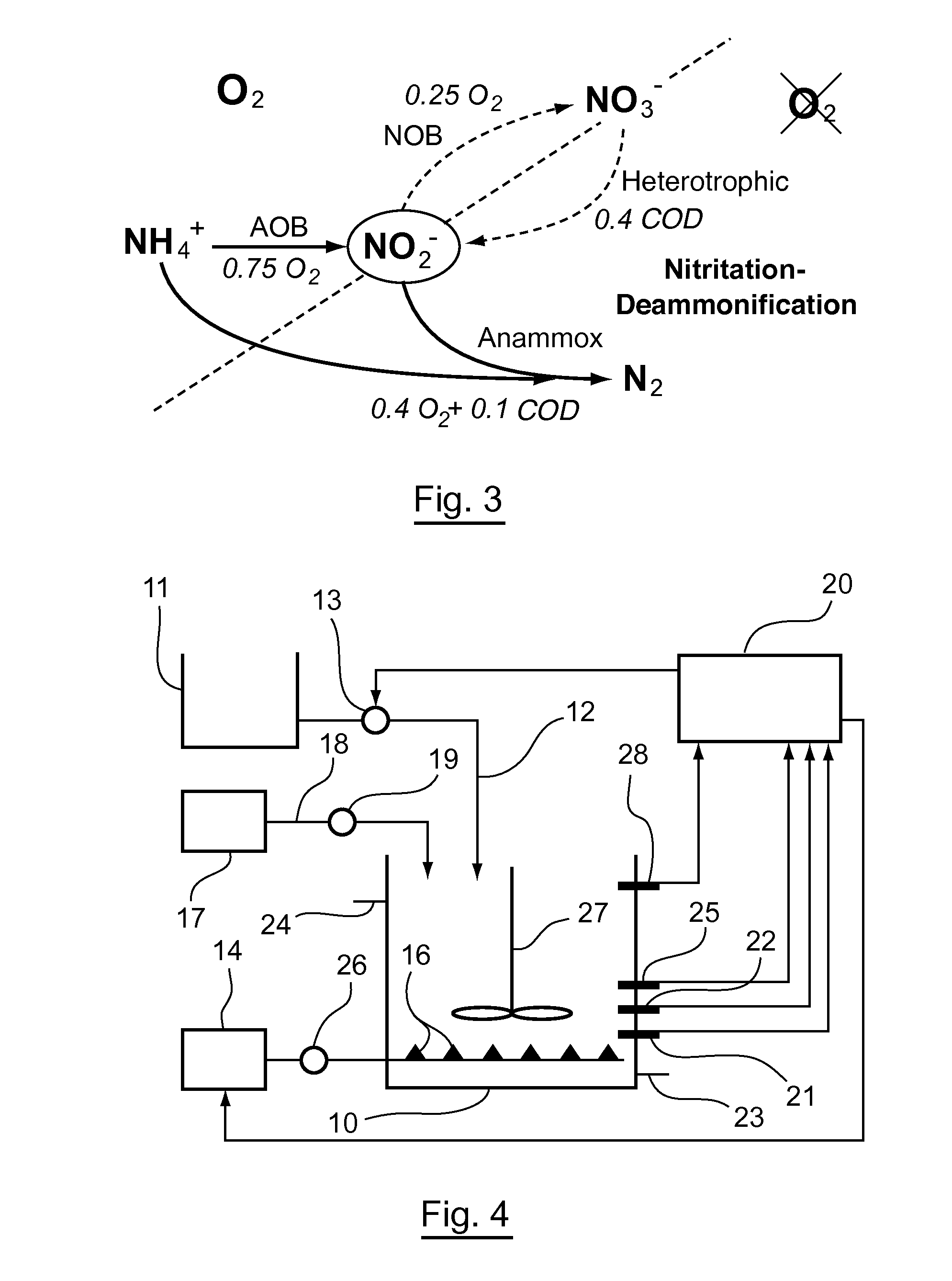
The process for treating an ammonium containing liquid by denitrification treatment of an ammonium containing liquid containing at least ammonium comprises carrying out nitrate reduction treatment of reducing nitrate contained in or added to the ammonium containing liquid to nitrite, and carrying out anaerobic ammonium oxidation treatment of simultaneously anaerobically denitrifying nitrite produced in the nitrate reduction treatment and ammonium contained in the ammonium containing liquid by anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
A Rigid Composite Structure with a Superhard Interior Surface
InactiveUS20070256345A1Easy to keepHigh strengthCylinder headsCylindersSuperhard materialPolycrystalline diamond
A rigid composite structure has a first bore formed in a metallic material and a second bore formed by a super hard interior segment or segments disposed within the first bore. Each segment may be lined adjacent to one another and held under compression within the first bore. The segments may be made of super hard materials such as natural diamond, synthetic diamond, polycrystalline diamond, single crystalline diamond, cubic boron nitrate or other superhard composite materials which exhibit low thermal expansion rates and are generally chemically inert. The resultant rigid composite structure may possess higher tolerances to high pressures and high temperatures within the second bore.
Owner:NOVATEK IP +1
Selenium-based biocidal formulations and methods of use thereof
Biocidal formulations that include a selenium compound selected from the group consisting of RSeH, RSeR, RSeR′, RSeSeR, RseSeR′, and RseX, wherein each of R and R′ is an aliphatic or phenolic residue, and wherein X is a protecting group selected from the group consisting of a halogen, an imide, a cyamide, an azide, a phosphate, a sulfate, a nitrate, a carbonate, selenium dioxide, and combinations thereof, are provided. The selenium compounds may be disposed in a mixture or solution or deposited on a surface and non-covalently attached thereto, or the selenium compounds may be present in a suspension and maintained therein through non-covalent interactions. Methods for preventing growth of a species of interest on an object or in a composition are also provided.
Owner:SELENIUM
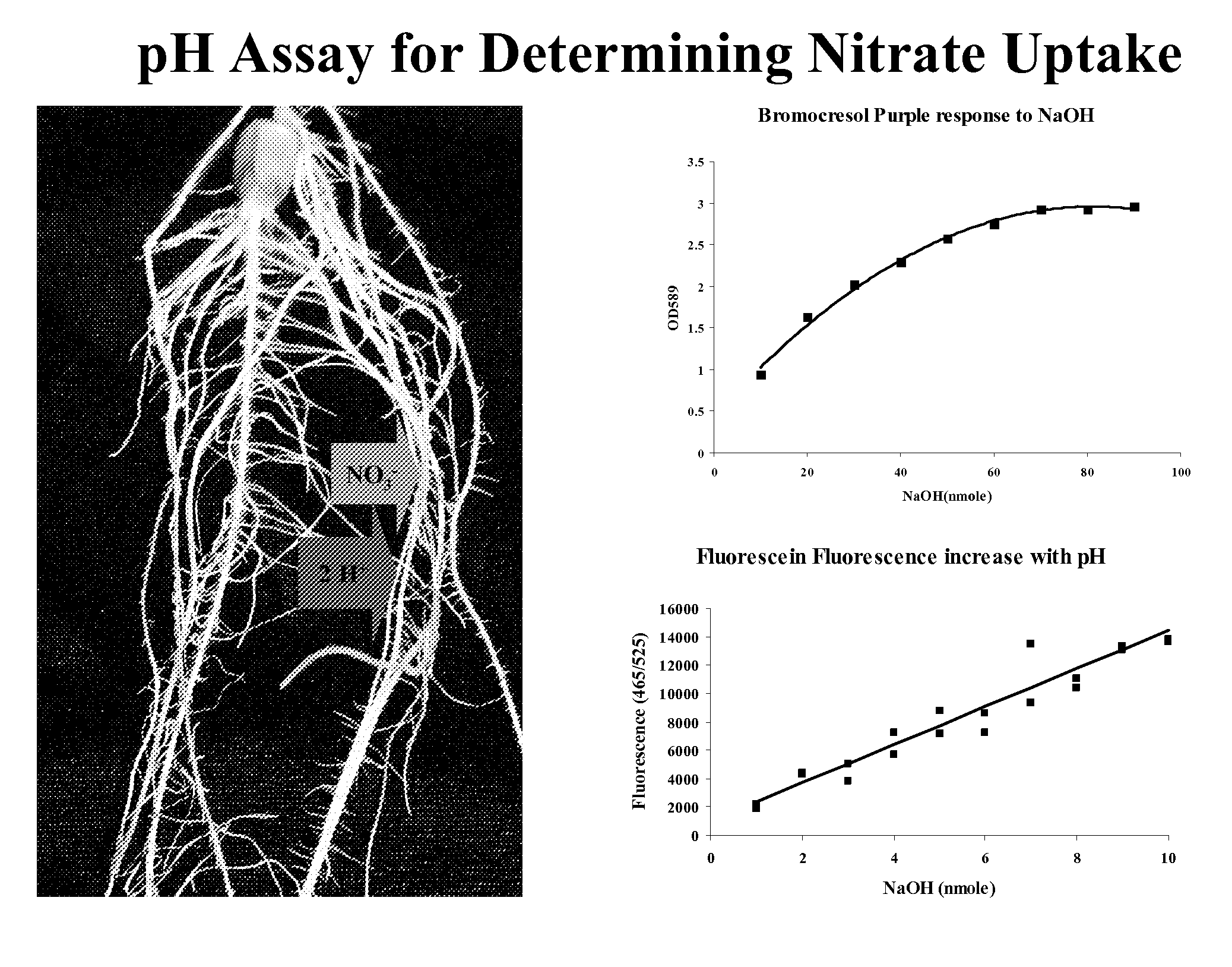
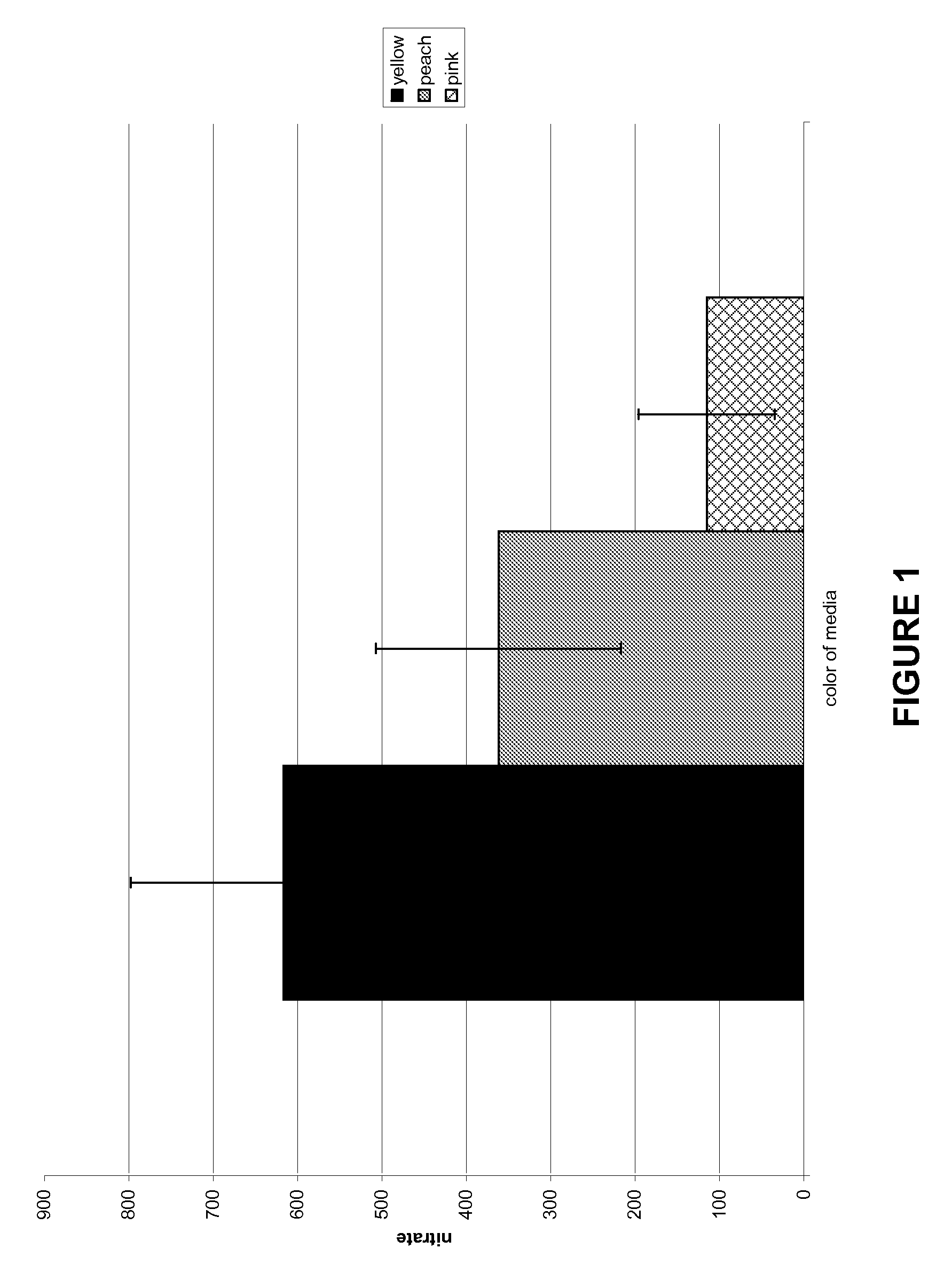
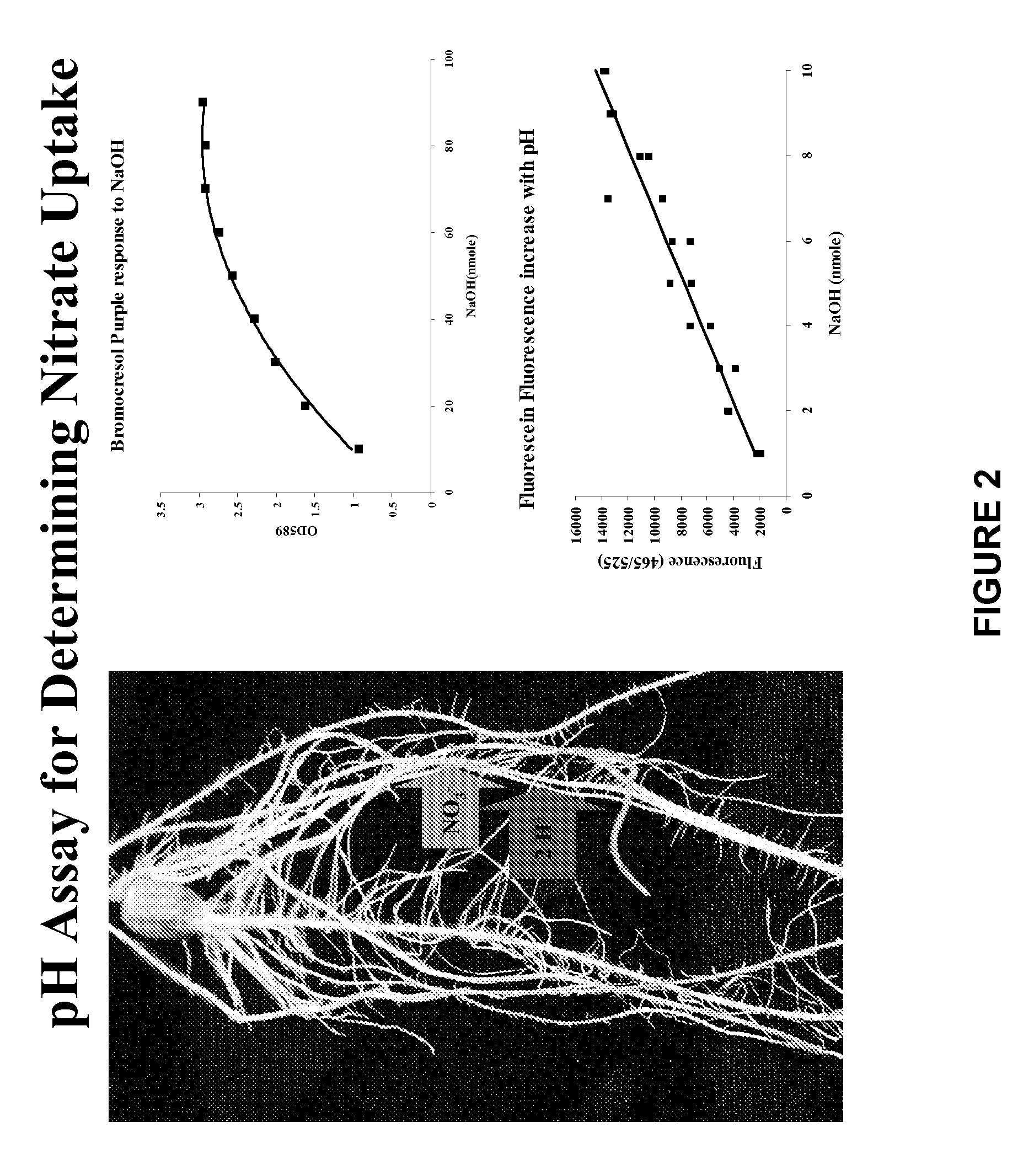
Methods and Assays for the Detection of Nitrogen Uptake by a Plant and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090011516A1Rapid and efficient methodRapid and efficient and assayBiological testingTesting plants/treesNitrogen sourceNitrite concentration
The invention provides a rapid and efficient method and assay for monitoring nitrogen uptake by a plant using a pH indicator. The plant is exposed to medium comprising one or more sources of nitrogen, such as nitrate or ammonia, and a pH indicator. The plant is exposed to the source of nitrogen for a time sufficient for it to be taken up by the plant. As nitrate is taken up from the medium, the medium becomes more basic, that is the pH increases. Conversely, as ammonia is taken up from the medium, the medium becomes more acidic and the pH decreases. The change in the pH of the medium may be optically detected and correlated to the amount of nitrate or ammonia remaining in the medium. Accordingly, the amount of nitrate or ammonia taken up by the plant or remaining in the medium may be determined.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
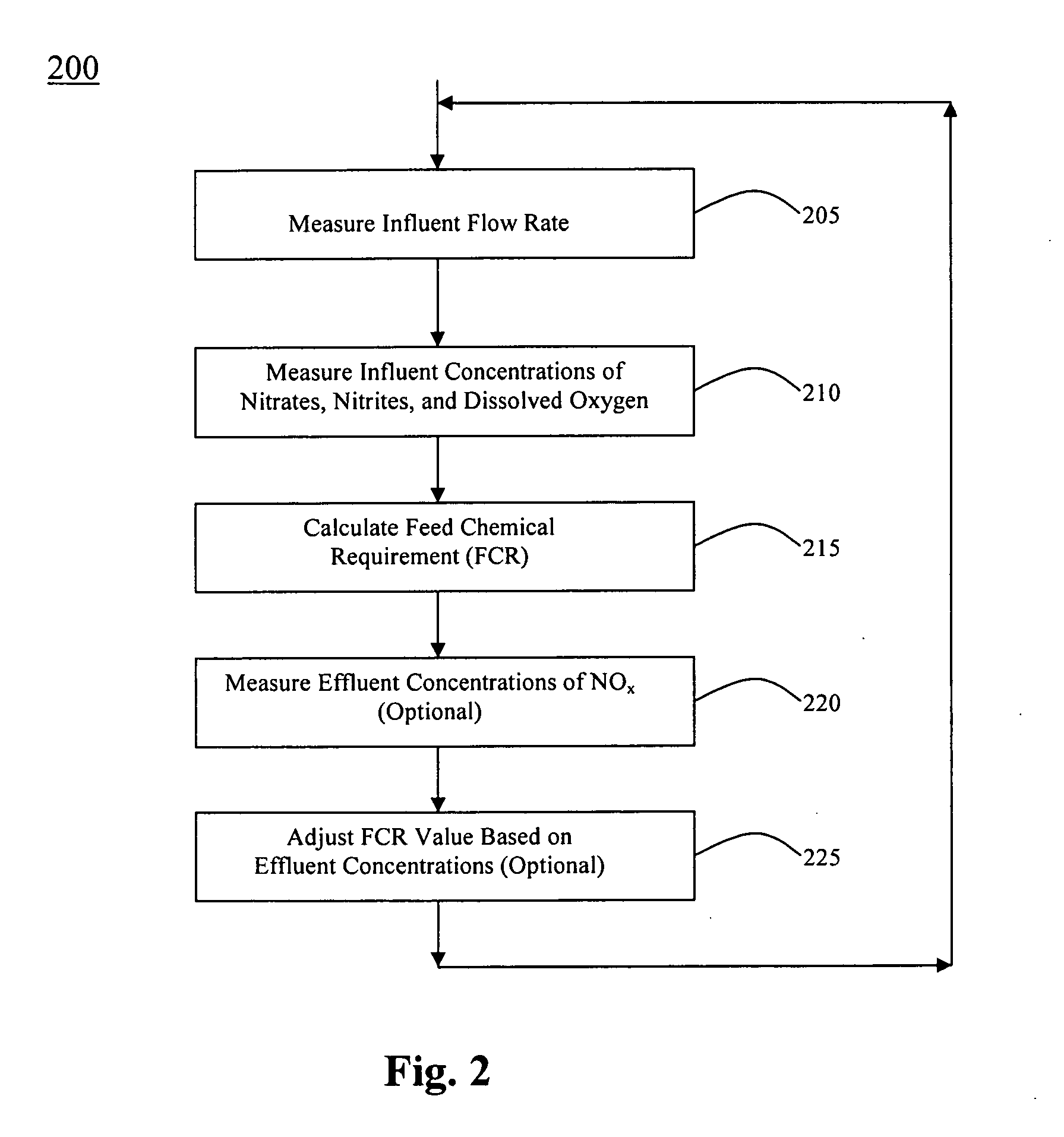
Denitrification process and system
ActiveUS20070144966A1Water treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesWastewaterNitrite concentration
A process and system for denitrification of wastewater. The process includes the steps of measuring an influent flow rate, measuring influent concentrations of nitrates, nitrites, and dissolved oxygen in the wastewater, and using the influent concentrations to determine a nominal amount of methanol to be provided for denitrification. The invention also contemplates the measurement of effluent concentrations of nitrates and nitrites (i.e., NOx), and optionally using the effluent concentrations to adjust the nominal amount of methanol being provided.
Owner:PARKSON
Method for etching non-conductive substrate surfaces
ActiveUS20070099425A1High bonding strengthSufficient surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolyetherimideNitrate
An etching composition for non-conductive substrates such as polyester, polyether, polyimide, polyurethane, epoxy resin, polysulfone, polyethersulfone, polyetherimide, and polyamide, comprising a halogenide and / or nitrate of a metal selected from the group consisting of Na, Mg, Al, Si, Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ca, Zn, and combinations thereof such as FeCl3, FeCl2, TiCl3, CaCl2, CuCl2, CrCl3, ZnCl2, MgCl2, MnCl2, and Cr(NO3)3; and a related method for etching.
Owner:MACDERMID ENTHONE INC
Method for Treating Water Within a Sequential Biological Reactor Including an In-Line Measurement of the Nitrite Concentration Inside Said Reactor
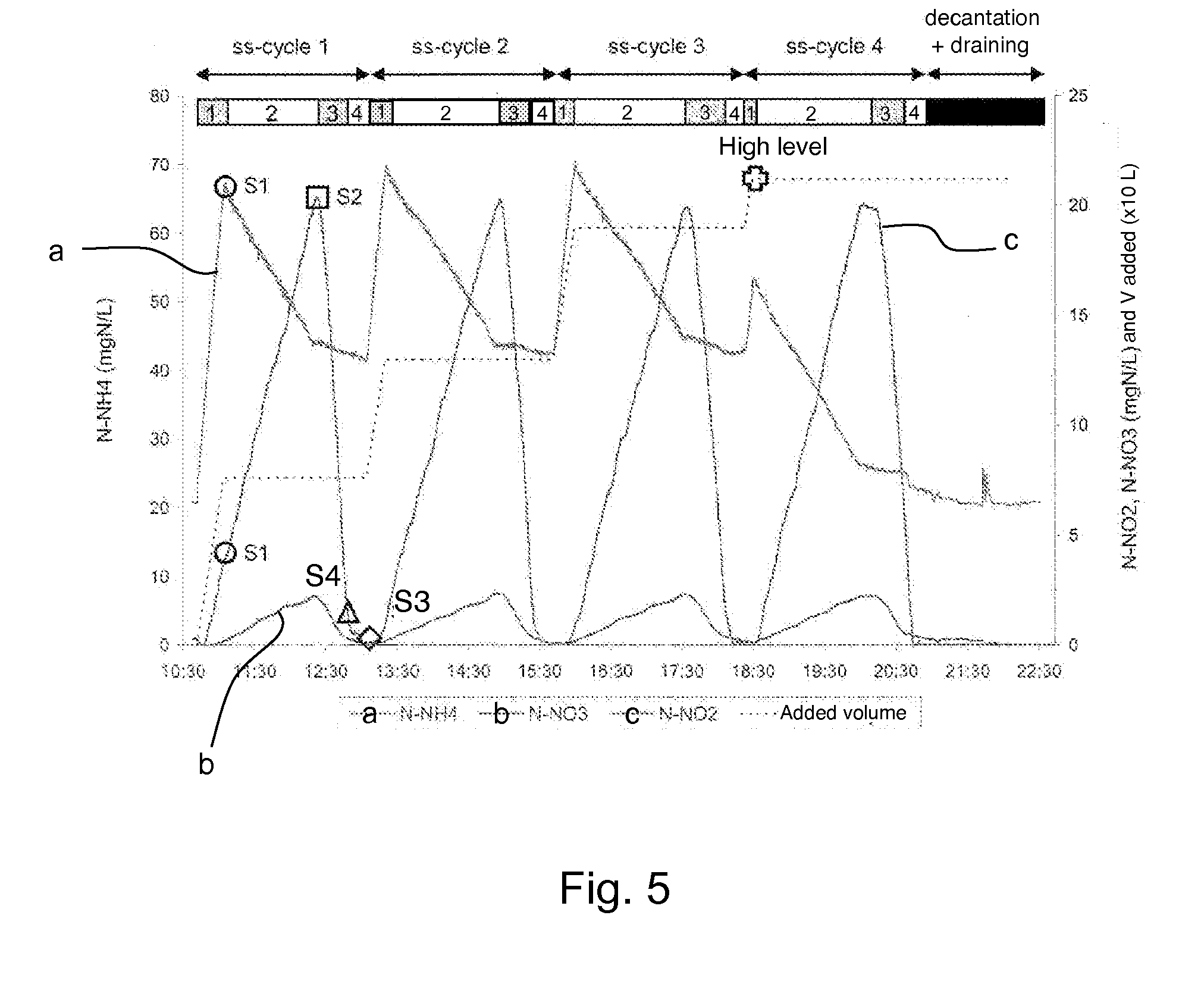
InactiveUS20120261335A1Implement economyOptimize total duration of cycleWater treatment parameter controlIon-exchanger regenerationNitrationNitrogen
The invention relates to a method for treating water laden with nitrogen in the form of ammonium by means of nitritation-denitritation, wherein said method includes at least: a first step (i) of supplying at least one sequential biological reactor (10) with said water; an aerated nitration step (ii); an anoxia denitritation step (iii); and a step (iv) of extracting treated water from said reactor. According to the invention, the method also includes the in-line measurement of the nitrite concentration of said water in said reactor, and at least one monitoring step of at least one step of the method, said monitoring step taking into account the results from said in-line measurement of the nitrite concentration.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Method for Forming Zno Nano-Array and Zno Nanowall for Uv Laser On Silicon Substrate
InactiveUS20070220713A1Excellent laser characteristicSuperior laser characteristicMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthHexamethylenetetramineZno nanoparticles
Provided are low-temperature formation methods of a perfectly oriented ZnO nanorod array and a new-type ZnO nanowall array having a new crystal growth rate, morphology, and orientation, from ZnO nanoparticles coated on a substrate. The method of forming the ZnO nanorod array includes synthesizing ZnO nanoparticles, coating on a substrate the ZnO nanoparticles serving both as a buffer layer and a seed layer, and growing the ZnO nanoparticles into crystals in a nutrient solution containing Zn nitrate, Zn acetate, or a derivative thereof, and hexamethylenetetramine. The method of forming the ZnO nanowall array includes synthesizing ZnO nanoparticles, coating on a substrate the ZnO nanoparticles serving both as a buffer layer and a seed layer, and growing the ZnO nanoparticles into crystals in a nutrient solution containing Zn acetate or its derivative and sodium citrate.
Owner:NANOHYBRID CO LTD
System and process for quantifying potentially mineralizable nitrogen for agricultural crop production
ActiveUS20140273253A1Material analysis by optical meansEarth material testingFluorescenceProcess Measures
The invention is generally directed to a system and process for fluorometrically quantifying potentially mineralizable nitrogen for agricultural crop production. The soil analysis process measures potentially mineralizable nitrogen and calibrates the application of soil-based nitrogen for site or field specific management of nitrogen fertilizers for crops grown on a wide variety of soil textures including sandy loam, silt loam and clay soils. The spectrofluorometric system and process may be utilized for routine soil testing with a lower sample to sample variability, and the automation of the spectrofluorometric system and process allows for simultaneous determination of potentially mineralizable soil organic nitrogen, ammonium and nitrate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Method for determining content of oxynitride in air
InactiveCN104458619ADamage minimizationSolve secondary pollutionColor/spectral properties measurementsNitrogen oxideNitrite concentration
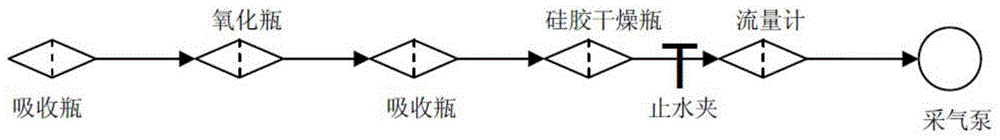
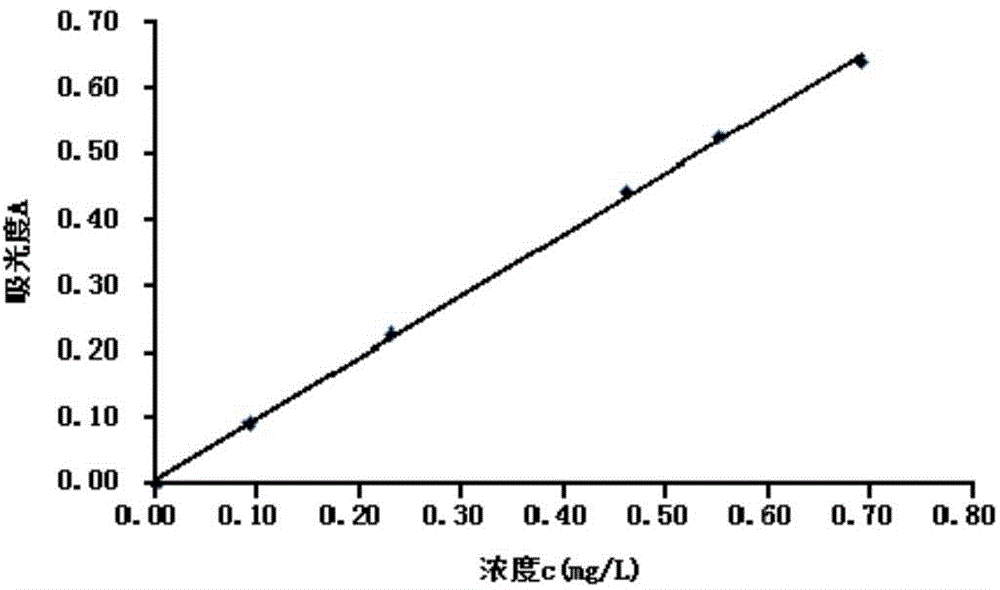
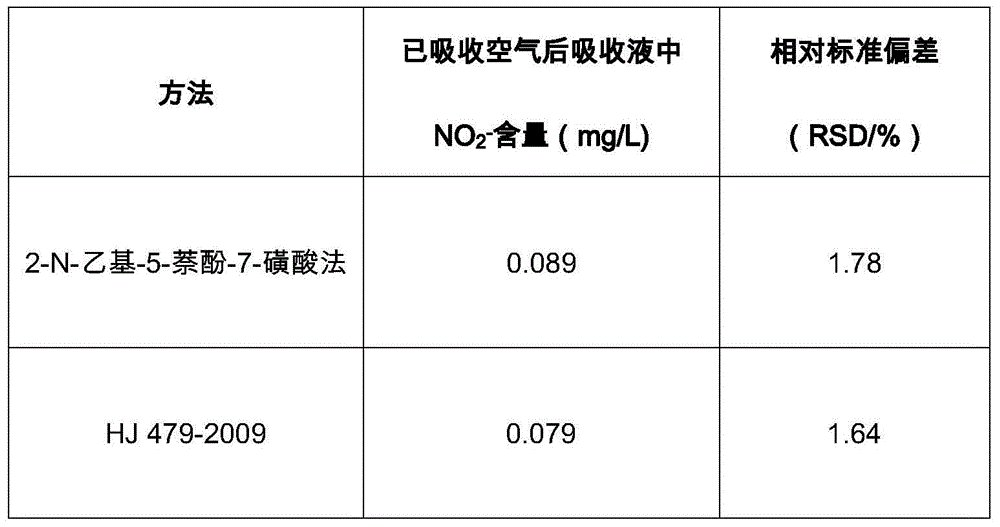
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of oxynitride in air. The method comprises the following steps: continuously enabling air collected in atmosphere with a predetermined flow and at a preset time to pass through a first absorption tube, an oxidization bottle and a second adsorption tube which are connected in series to absorb oxynitride in reaction air; putting an absorption liquid which is reacted with air in absorption reaction in the first and second adsorption tubes into a reaction bottle filled with a diazo reaction liquid for diazo reaction; putting a diazo reaction liquid which is reacted in diazo reaction in the reaction bottle filled with the diazo reaction liquid into a reaction bottle of a coupled reaction liquid for azo reaction; and by taking a blank liquid of a reagent as a reference liquid, determining the absorbancy of the diazo reaction liquid after azo reaction and calculating concentration of oxynitride in air based on a standard work curve, wherein the vertical coordinate and horizontal ordinate of the standard work curve are respectively absorbancy and nitrite concentration. The determining method is convenient and efficient to operate, relatively high in sensitivity, accurate in result and suitable for popularization.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
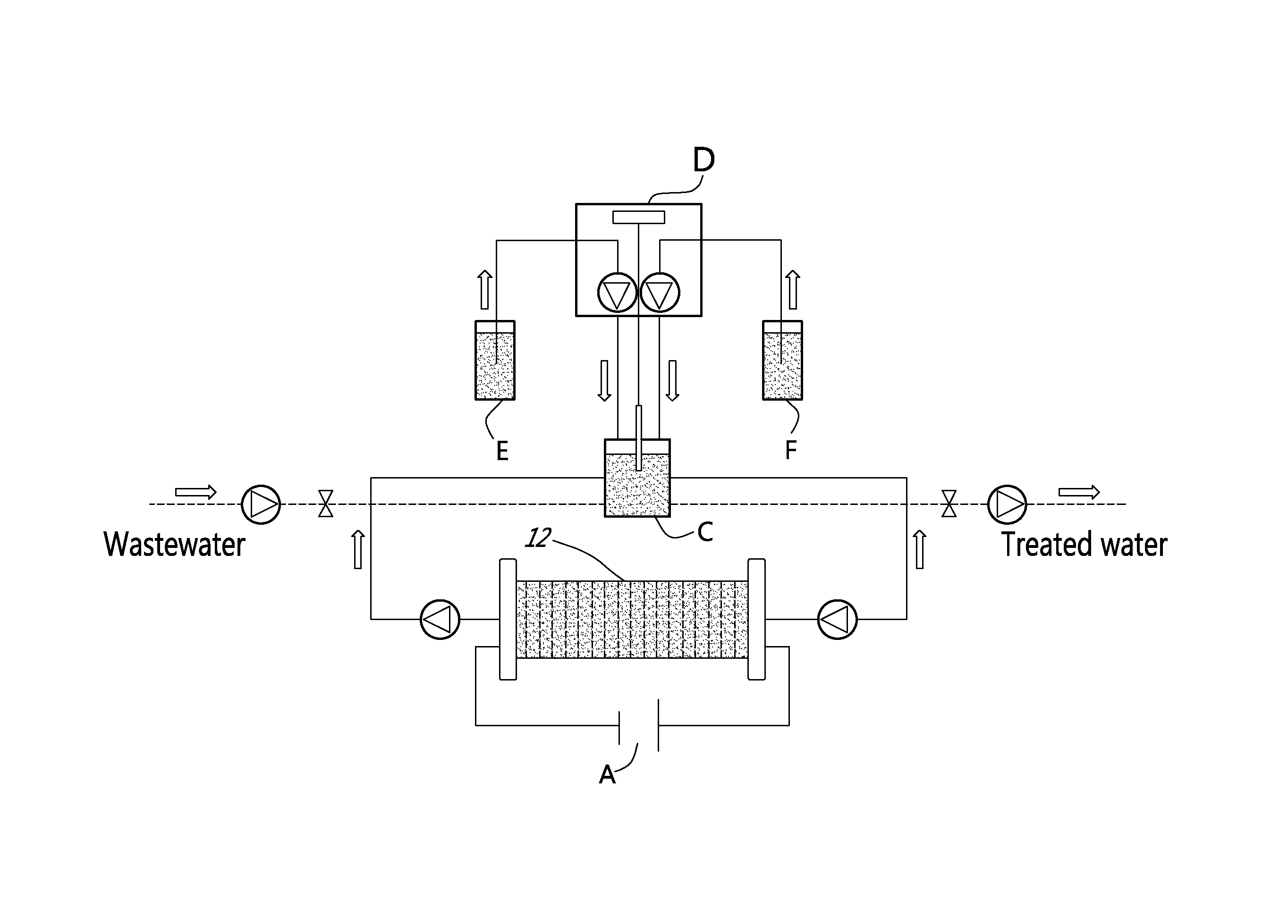
Method and system for electrochemical removal of nitrate and ammonia
InactiveUS20130168262A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove electrical activityCellsMachining electric circuitsAlloyElectrochemistry
An electrochemical method and system for removing nitrate and ammonia in effluents, using an undivided flow-through electrolyzer, said electrolyzer comprising at least one cell, each cell comprising at least one anode and one cathode, the cathode being in a copper / nickel based alloy of a high corrosion resistance and a high electroactivity for nitrate reduction to ammonia and the anode being a DSA electrode of a high corrosion resistance and a high electroactivity for ammonia oxidation to nitrogen in presence of chloride.
Owner:TRANSFERT PLUS S E C +1
Method and device for culturing oxidizing bacteria capable of quickly enriching nitrite
ActiveCN102583705AGrowth inhibitionEasy to handleTreatment using aerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentActivated sludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention provides a method and a device for culturing oxidizing bacteria capable of quickly enriching nitrite. According to the invention, a sequencing batch activated sludge process is mainly adopted, and the enrichment is realized by gradually increasing the nitrite concentration in nutrient solution and controlling a dissolved oxygen process, wherein the main ingredient of the adopted enrichment nutrient solution is inorganic salt and the enrichment nutrient solution comprises trace element nutrient solution, buffer solution and sodium nitrite; and by adopting the device, the concentration of the dissolved oxygen is kept to be above 5mg / L, pH is kept at 7.2-7.9, and temperature is kept at 22-25 DEG C. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the growth of heterotrophic bacteria and ammonia oxidizing bacteria in sludge can be obviously inhibited, and finally, the nitrite-enriching oxidizing bacteria account for 85-90% of the total amount of the microorganism bacteria in the activated sludge and can bear higher and higher nitrite concentration; and finally, the oxidizing bacteria can treat nitrite waste water of which the concentration is up to 1000mg / L is obtained,and reduce the high-concentration nitrite in the waste water to be below 0.2mg / L.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nitrifying method and treating method of water containing ammonium-nitrogen
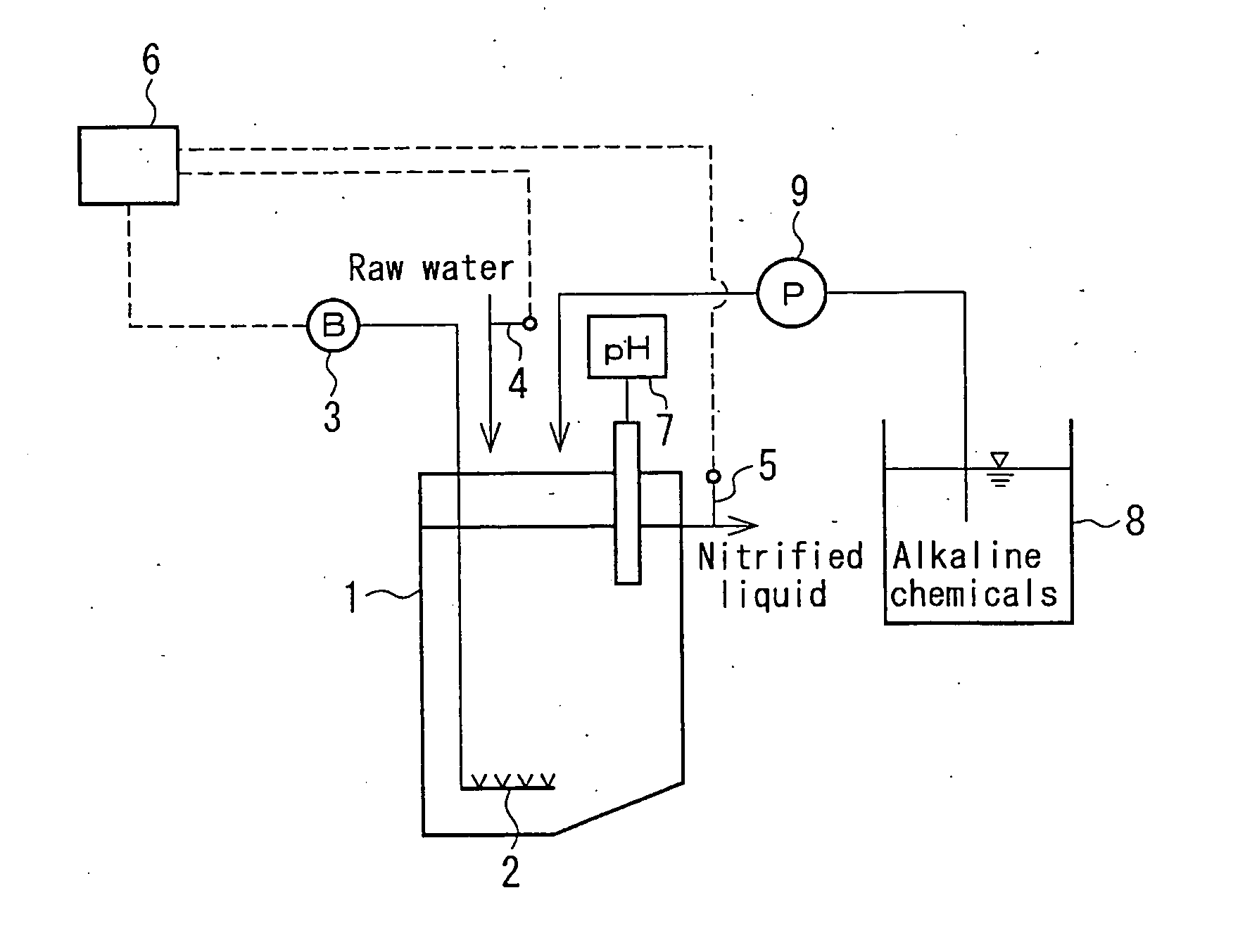
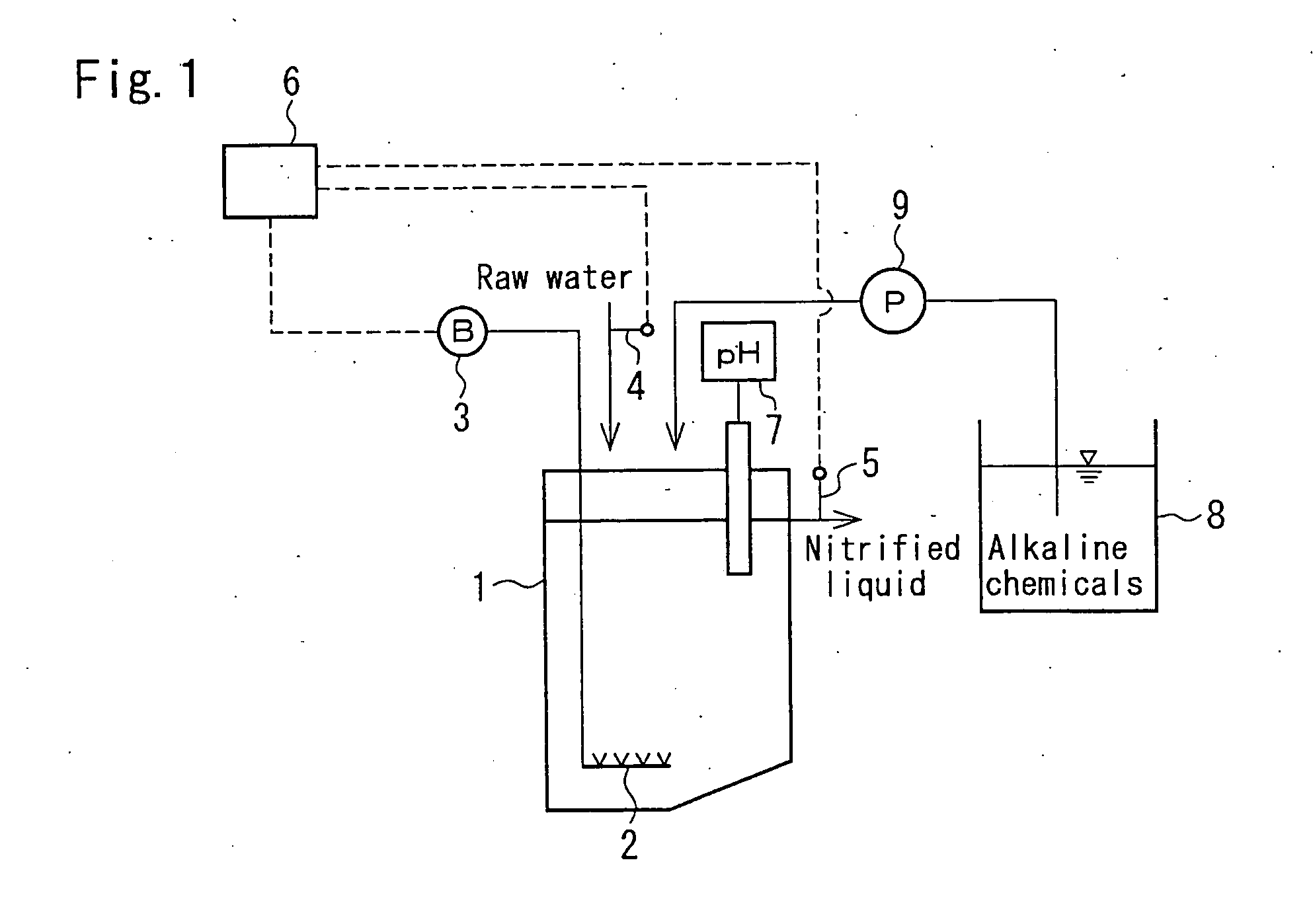
ActiveUS20060283796A1Improve efficiencyWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesDenitrifying bacteriaNitrifying bacteria
In treating water containing ammonium-nitrogen by a combination of a nitrification process and autotrophic denitrification bacteria, high efficiency denitrification treatment is achieved by providing adequate ratio between nitrite and ammonia in effluent of the nitrification process. Ammonium-nitrogen concentration of the raw water introduced to a nitrification reactor 1 and the ammonium-nitrogen concentration of the nitrified liquid from the nitrification reactor 1 is measured by NH4—N concentration measuring apparatuses 4, 5 and, on the basis of the measurement results, the flow volume for aeration by a blower 3 would be controlled by a blower controller 6. From the difference in NH4—N concentration between the influent and the effluent of the nitrification reactor 1, the nitrite concentration A in the nitrified liquid is calculated, and the ratio A / B of the nitrite concentration A with the ammonia concentration B in the nitrified liquid is calculated in the controller 6. The flow volume for aeration by the blower 3 to the nitrification reactor 1 is controlled such that the value of the A / B becomes 1.1 or more, preferably from 1.1 to 2.0, more preferably from 1.2 to 1.5, especially preferably from 1.3 to 1.4.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Centrifugal micro-fluidic chip for detecting nitrate and nitrite and preparation method of centrifugal micro-fluidic chip
InactiveCN102784672AQuick checkReal-time detectionLaboratory glasswaresColor/spectral properties measurementsNitrite concentrationCentrifugal force
The invention relates to a centrifugal micro-fluidic chip for detecting nitrate and nitrite and a preparation method of the centrifugal micro-fluidic chip. The centrifugal micro-fluidic chip is a disk type centrifugal micro-fluidic chip with a microstructure and a microchannel; the mixing, reacting and separating process of a sample and a reagent is finished under the drive of a centrifugal force generated by rotating a centrifugal machine; and the contents of nitrate and nitrite in the sample are quantitatively or qualitatively detected by an ultraviolet visible light spectrophotometer. According to the centrifugal micro-fluidic chip, the required reagents and samples are fewer; the pretreatment is avoided; and a plurality of samples can be simultaneously treated and detected, and thus the integration, the micromation and the automation of the detection are realized; and the centrifugal micro-fluidic chip has the characteristics of economy, quickness, portability and high efficiency and provides a brand-new analysis technology for quickly and quantitatively detecting the nitrate and the nitrite in water bodies, soil and foods.
Owner:SUZHOU WENHAO MICROFLUIDIC TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com