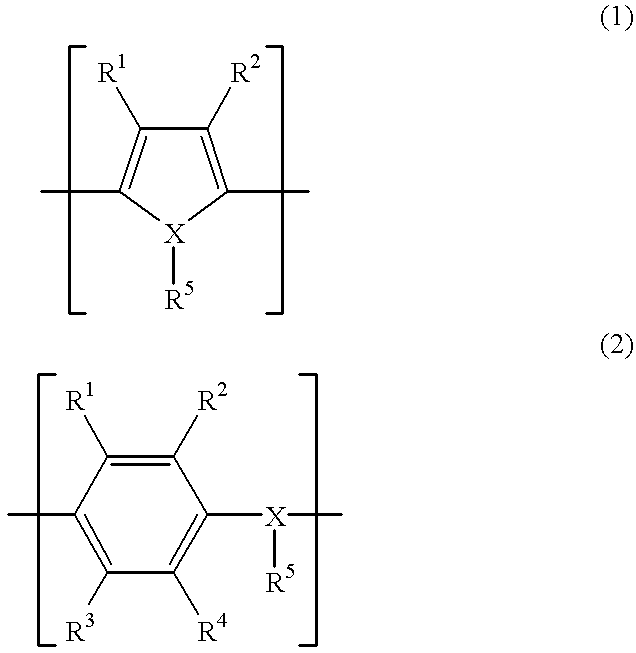
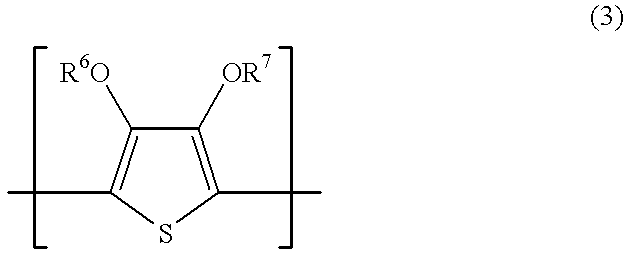
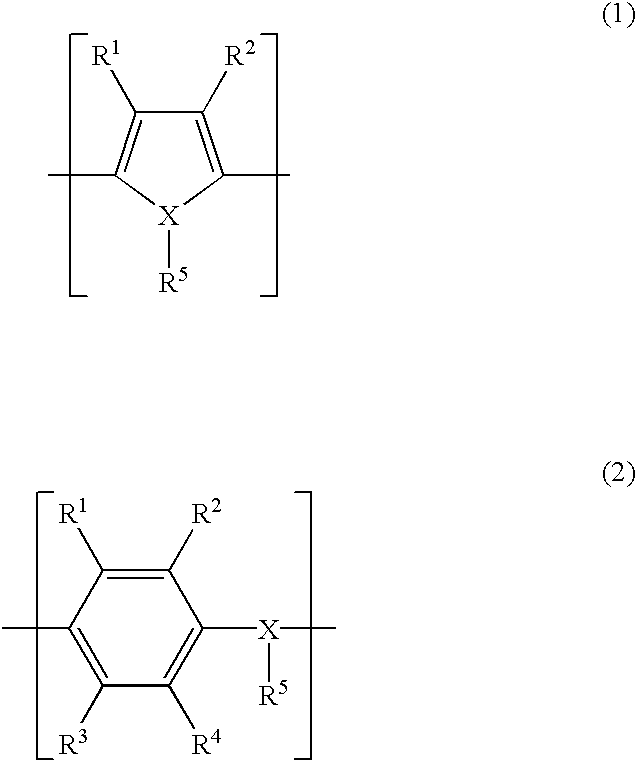
Patents
Literature
853 results about "Thulium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thulium is a chemical element with the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth and third-last element in the lanthanide series. Like the other lanthanides, the most common oxidation state is +3, seen in its oxide, halides and other compounds; because it occurs so late in the series, however, the +2 oxidation state is also stabilized by the nearly full 4f shell that results. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble thulium compounds form coordination complexes with nine water molecules.
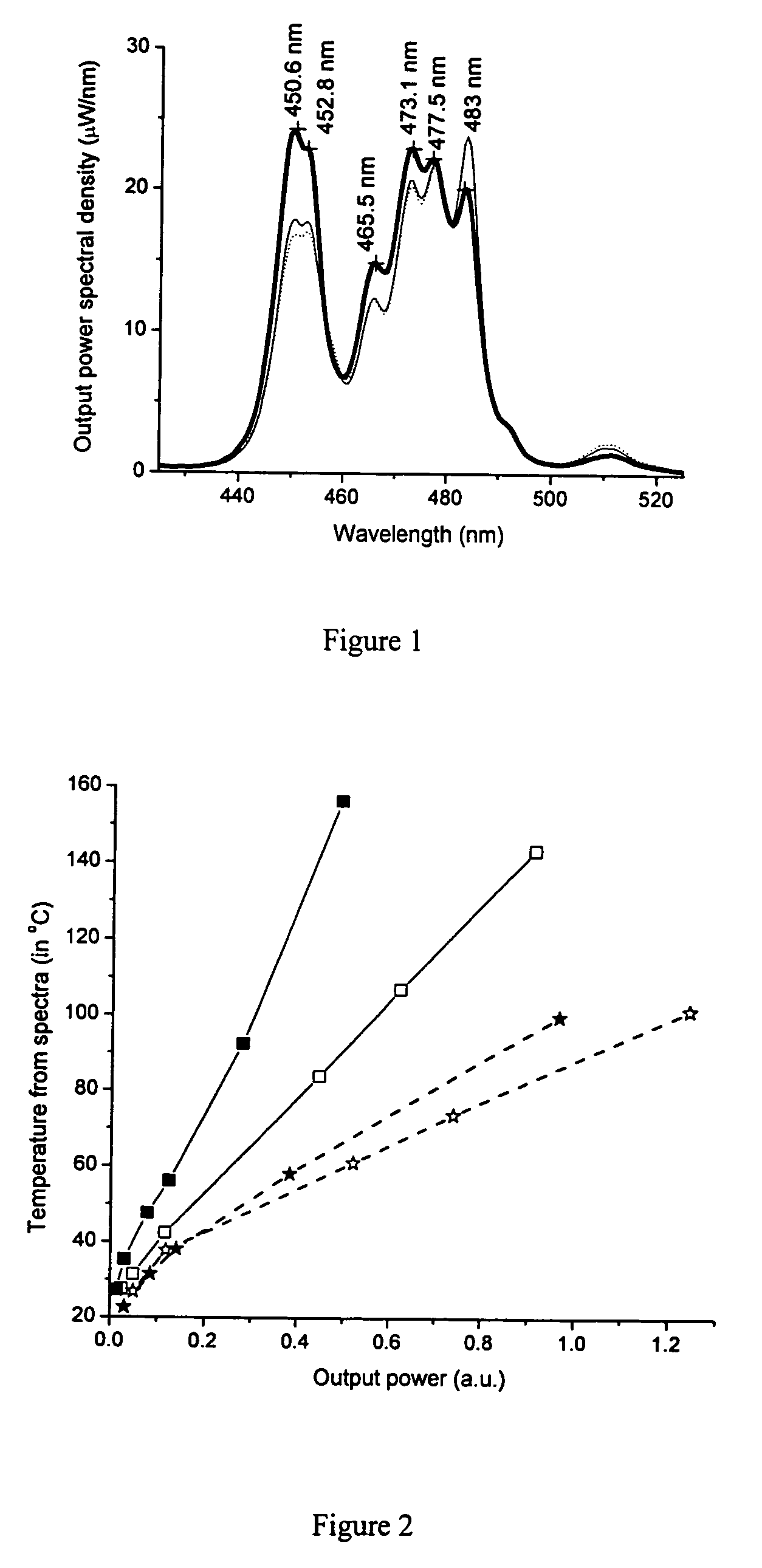
Single phosphor for creating white light with high luminosity and high CRI in a UV LED device
InactiveUS6853131B2Avoids and reduces problemGas-filled discharge tubesDischarge tube luminescnet screensX-rayUltraviolet
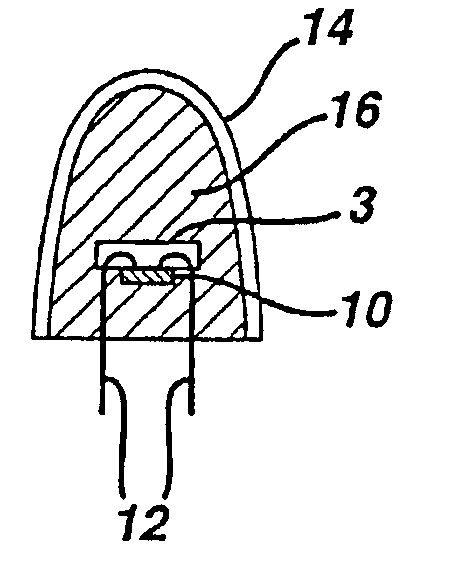
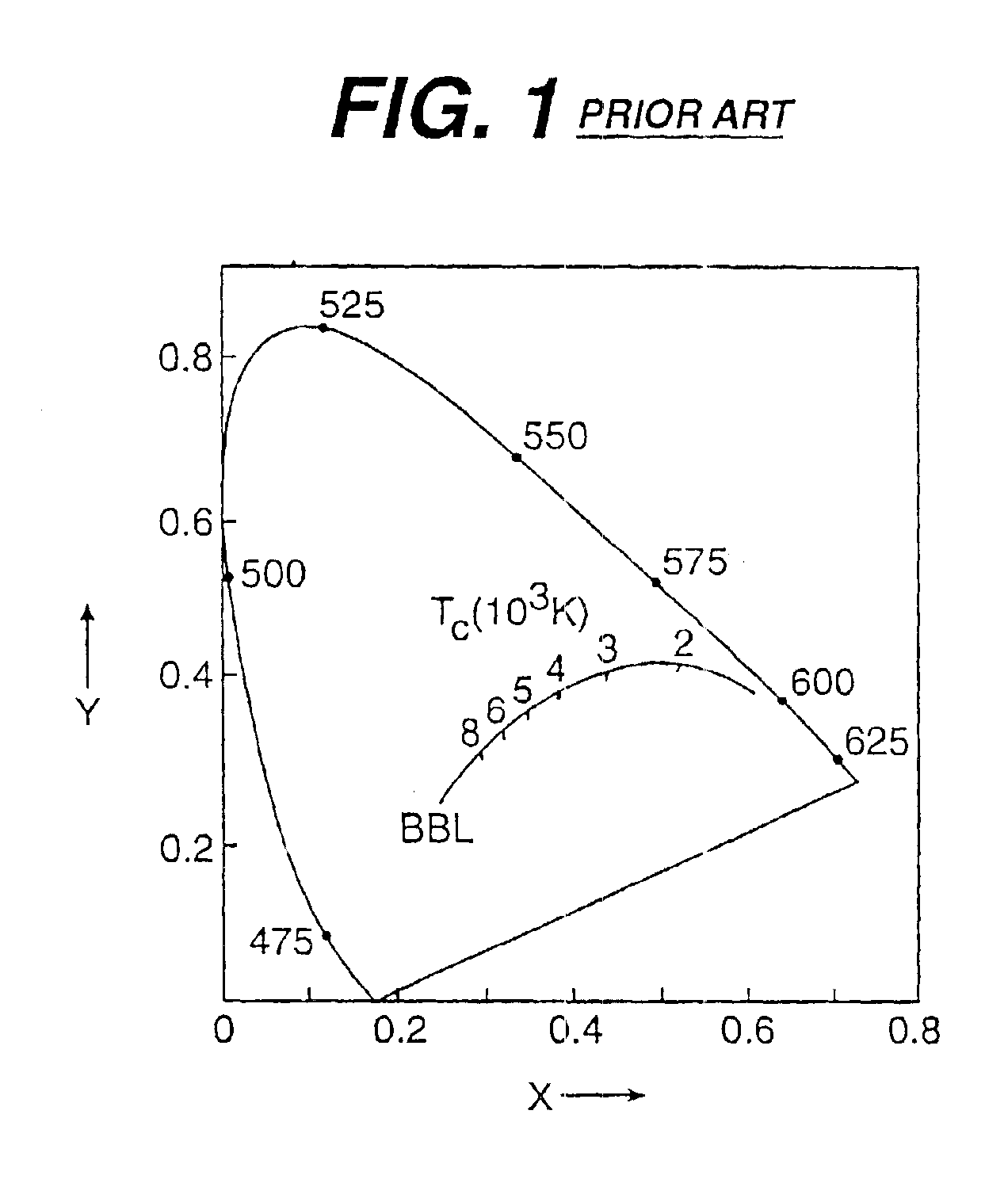
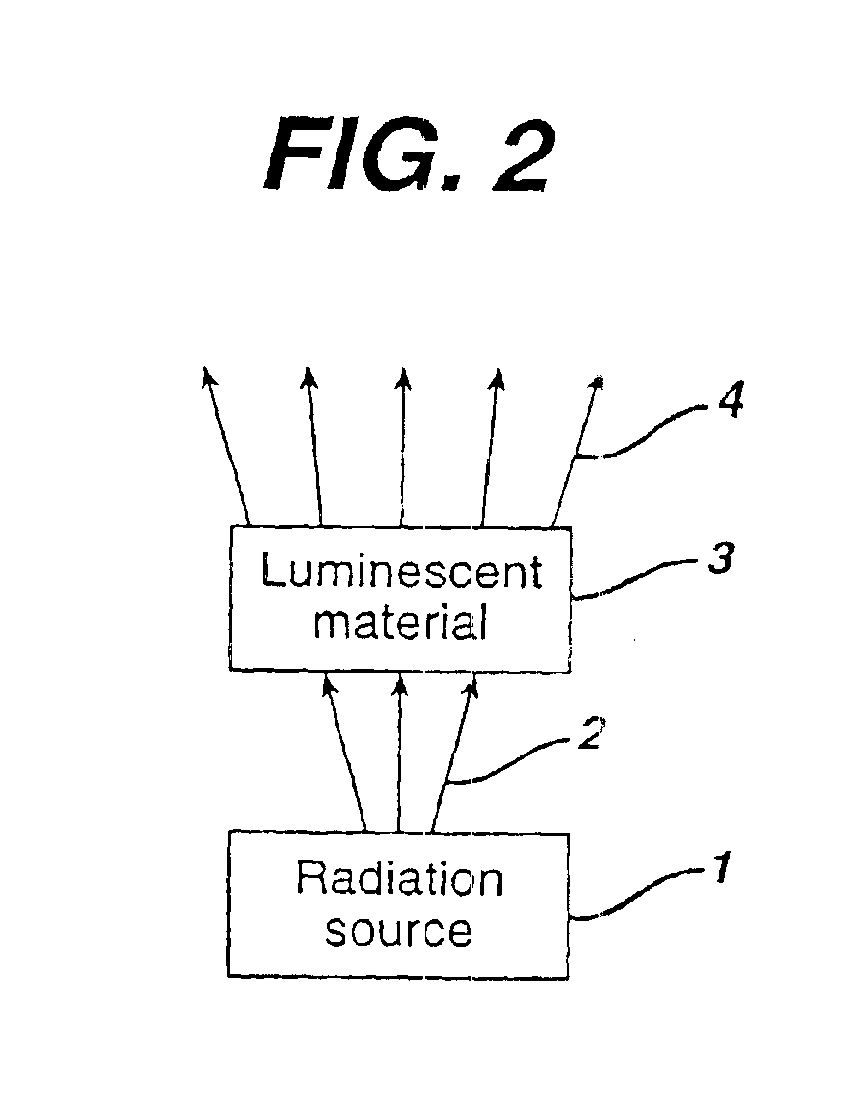
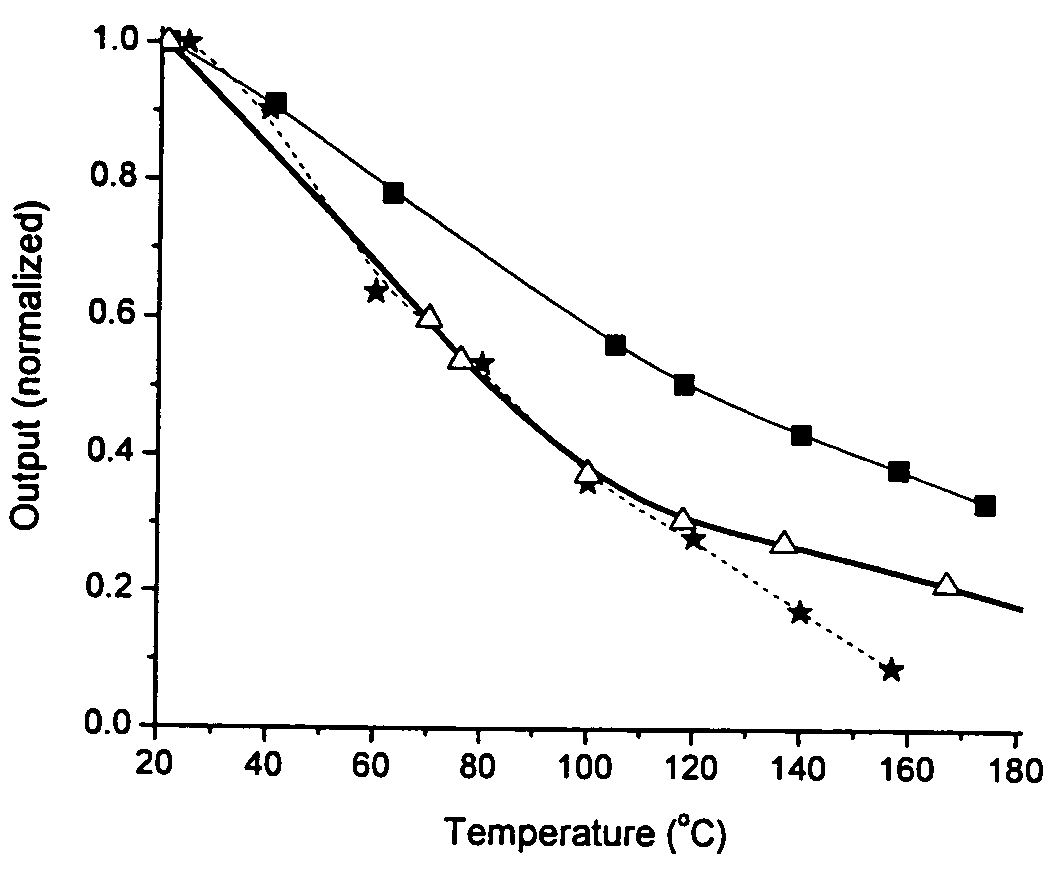
There is provided a white light illumination system. The illumination system includes a radiation source which emits either ultra-violet (UV) or x-ray radiation. The illumination system also includes a luminescent material which absorbs the UV or x-ray radiation and emits the white light. The luminescent material has composition A2−2xNa1+xExD2V3O12. A may be calcium, barium, strontium, or combinations of these three elements. E may be europium, dysprosium, samarium, thulium, or erbium, or combinations thereof. D may be magnesium or zinc, or combinations thereof. The value of x ranges from 0.01 to 0.3, inclusive.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
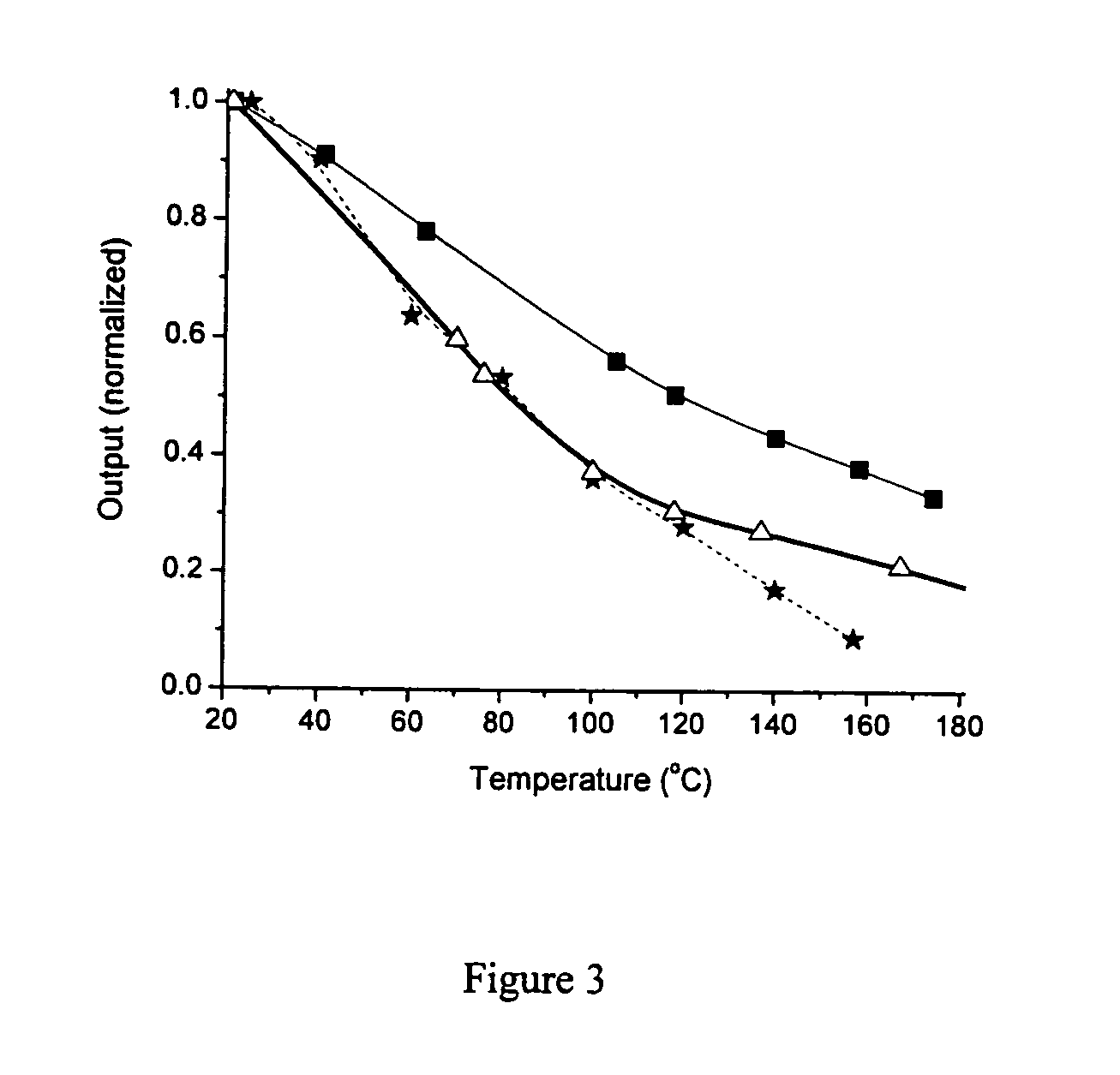
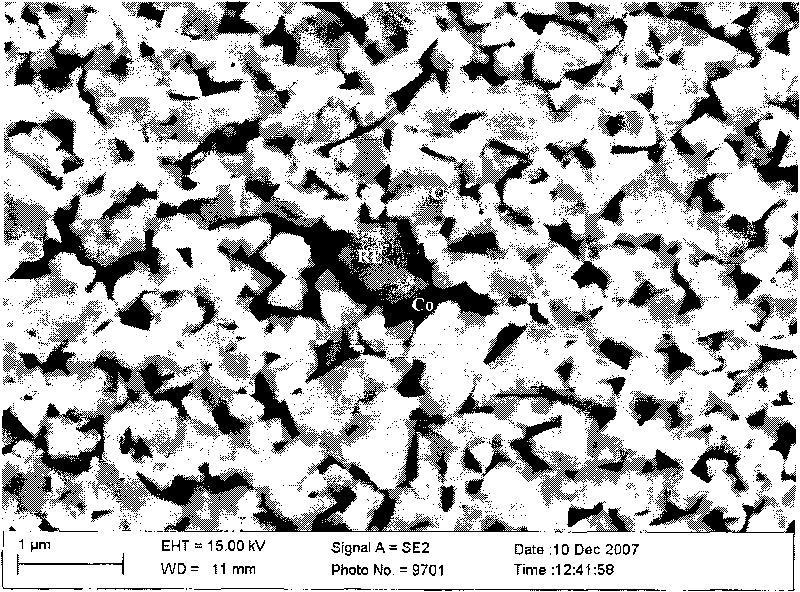
Substrate design for optimized performance of up-conversion phosphors utilizing proper thermal management
InactiveUS7075707B1Improve luminous efficiencyDigital storageLight demodulationDisplay deviceUp conversion
Methods and compositions for using an up-conversion phosphor as an emitting material in a reflective displays and Polymer compositions for display mediums, and blue green red (BRG) display mediums. Roles of the pumping duration and character on the temperature and the efficiency of the up-conversion process in (Ytterbium, Erbium or Thulium) co-doped fluoride crystals are set forth. Methods, compositions and display mediums for using up-conversion phosphors in both reflective and transmissive displays in which the substrate and pixel shapes are designed to maximally remove heat deposited in the emitting material and thereby improve the efficiency of up conversion.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
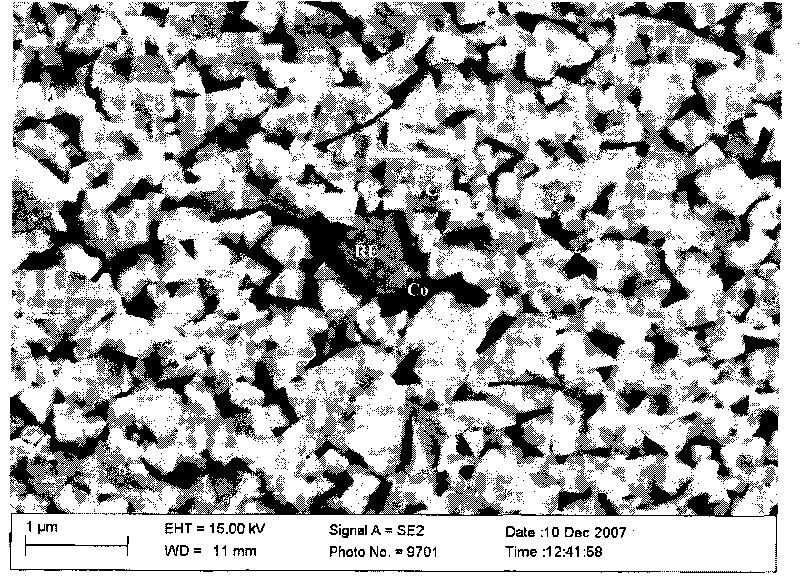
Superfine WC-Co cemented carbide containing rare-earth elements and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101760685AChange processSteady improvement in overall performanceRare-earth elementChemical reaction
The invention discloses a superfine WC-Co cemented carbide containing rare-earth elements and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of cemented carbide. In the cemented carbide, the weight of WC rigid phase accounts for 85-94% of that of the cemented carbide, the weight of Co binder phase accounts for 5-14% of that of the cemented carbide, the weight of grain growth inhibitor accounts for 0.3-2.0% of that of the cemented carbide, and the weight of the thulium in the rare earth addition accounts for 0.2-1.2% of that of the Co binder phase. The method comprises the following steps: weighing various powder stocks, ball-milling, drying and pelletizing to form a compound; and suppressing and shaping the compound, sintering and cooling to obtain the cemented carbide. The adding mode of nano rare earth oxide or Co-RE composite powder can be implemented easily and conveniently, and the rare earth is diffusely and evenly distributed, thereby facilitating to perform physo-chemical reactions; and the cemented carbide has the advantages of low production cost, stable and enhanced performance and easy implementation, production and application.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Layered thermal barrier coatings containing lanthanide series oxides for improved resistance to CMAS degradation
InactiveUS20070160859A1Avoid damageElimination of expensiveBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesReaction layerCerium
A coating applied as a two layer system. The outer layer is an oxide of a group IV metal selected from the group consisting of zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and combinations thereof, which are doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide. These metal oxides doped with a lanthanum series addition comprises a high weight percentage of the outer coating. As used herein, lanthanum series means an element selected from the group consisting of lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), lutetium (Lu) and combinations thereof, and lanthanum series oxides are oxides of these elements. When the zirconium oxide is doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide, a dense reaction layer is formed at the interface of the outer layer of TBC and the CMAS. This dense reaction layer prevents CMAS infiltration below it. The second layer, or inner layer underlying the outer layer, comprises a layer of partially stabilized zirconium oxide.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High performance lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high performance lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate and a preparation method of the material. The lithium manganate is a doped lithium manganate LiMn2-yXy04 which is doped with one kind or a plurality of other metal elements X, wherein X element is at least one kind selected form the group of aluminium, lithium, fluorine, silver, copper, chromium, zinc, titanium, bismuth, germanium, gallium, zirconium, stannum, silicon, cobalt, nickel, vanadium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and rare earth elements lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium, and y is larger than 0 but less than or equal to 0.11. The lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate provided in the invention has extraordinary charge and discharge cycle performance both in the environments of normal temperature and high temperature. According to the invention, the preparation method of the material is a solid phase method, the operation is simple and controllable and the cost is low so that it is easy to realize large-scale productions.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
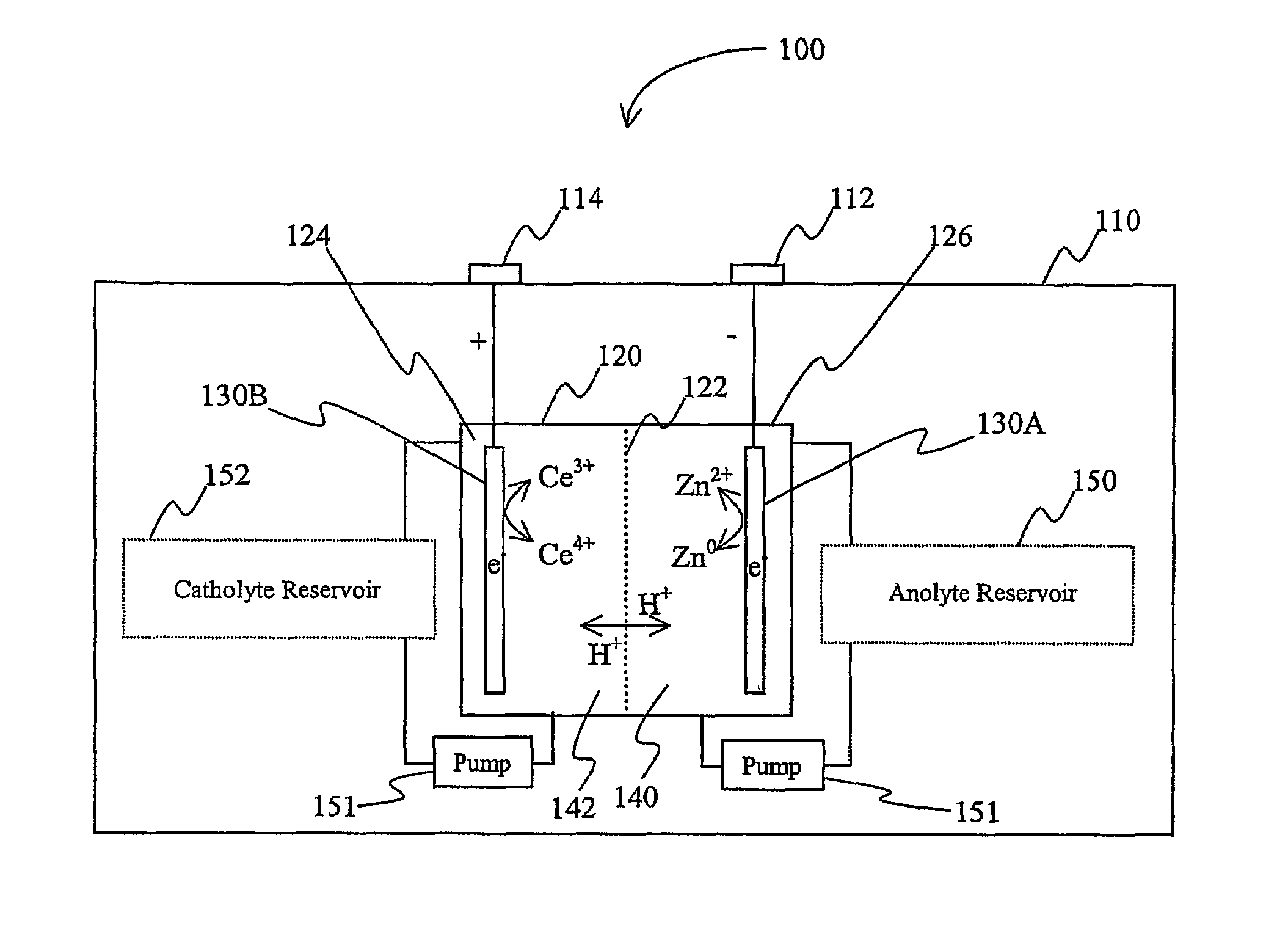
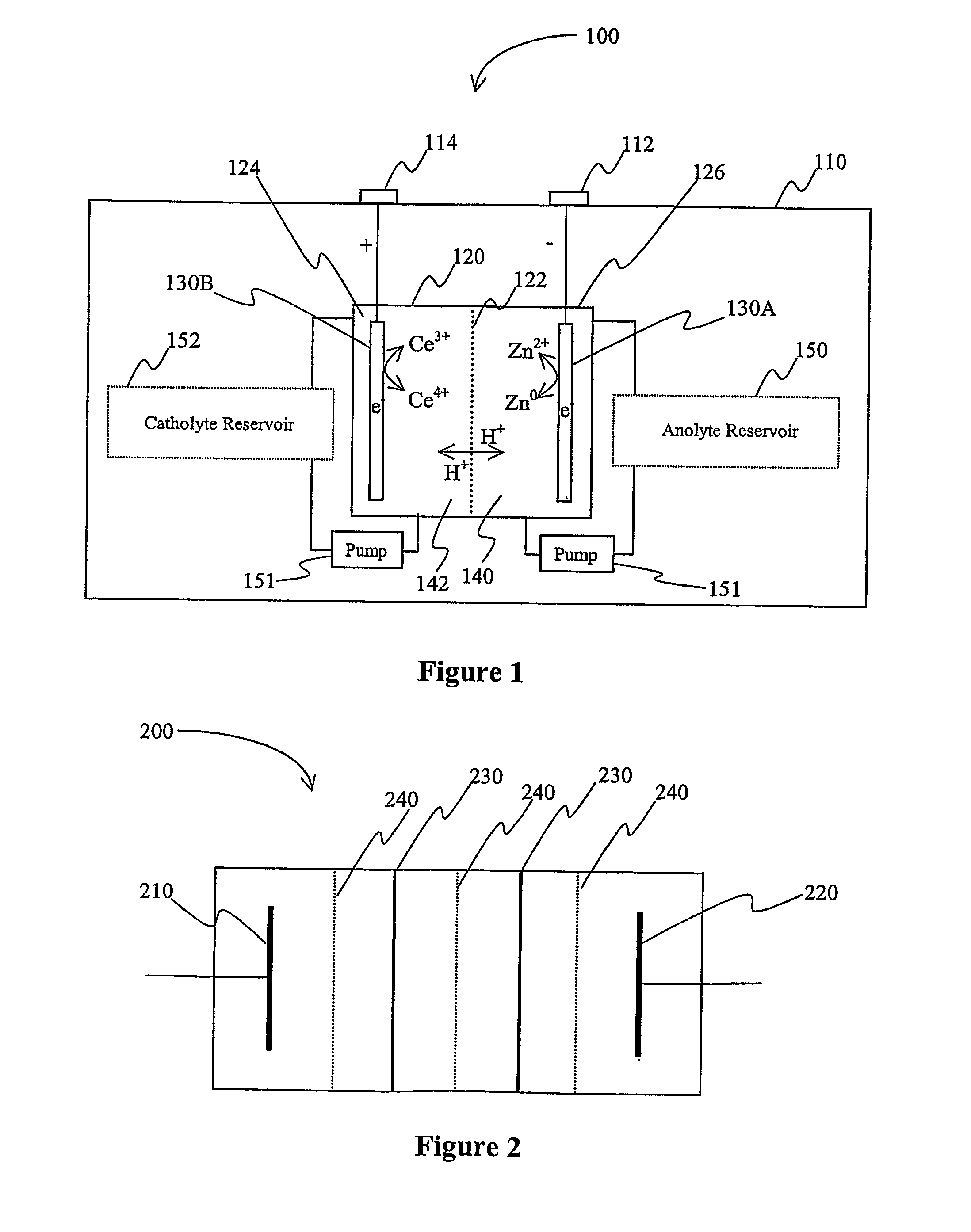
Lanthanide batteries
InactiveUS7252905B2Wide capacity rangeLarge capacityAlkaline accumulatorsSolid electrolyte cellsLanthanideCerium
A battery (100) comprises an electrolyte in which a lanthanide and zinc form a redox pair. Preferred electrolytes are acid electrolytes, and most preferably comprise methane sulfonic acid, and it is further contemplated that suitable electrolytes may include at least two lanthanides. Contemplated lanthanides include cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, terbium, and dysprosium, and further contemplate lanthanides are samarium, europium, thulium and ytterbium.
Owner:PLURION LTD
Ceramic bonding composition, method of making, and article of manufacture incorporating the same
A ceramic bonding composition comprises a first oxide and at least a second oxide having a formula of Me2O3; wherein the first oxide is selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, scandium oxide, and combinations thereof; Me is selected from the group consisting of yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and combinations thereof. The ceramic bonding composition can further comprise silica. An article of manufacture comprising at least two members attached together with the ceramic bonding composition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rare earth aluminum alloy, and method and device for preparing same
The invention discloses a rare earth aluminum alloy, and a method and a device for preparing the same. The alloy contains at least one rare earth metal of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, lutetium, scandium and yttrium, the content of raw earth is 5 to 98 weight percent, and the balance is aluminum and inevitable impurities. The device for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy is characterized in that: a) graphite serves as an electrolysis bath, a graphite plate is an anode, a tungsten bar is a cathode and a molybdenum crucible serves as a rare earth aluminum alloy receiver; b) the diameter of the tungsten bar is 30 to 55 mm; and c) the anode of the graphite consists of a plurality of graphite plates. The rare earth aluminum alloy, and the method and the device for preparing the same have the advantages that: the alloy has uniform components, little segregation and low impurity content; technology for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy through fusion electrolysis can maximally replace a process for preparing single medium-heavy metal through metallothermic reduction, greatly reduce energy consumption and the emission of fluorine-containing tail gas and solid waste residue, improve current efficiency and metal yield and reduce the consumption of auxiliary materials and the energy consumption; and the rare earth aluminum alloys with different rare earth contents can be obtained by controlling different electrolytic temperatures and different cathode current densities.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
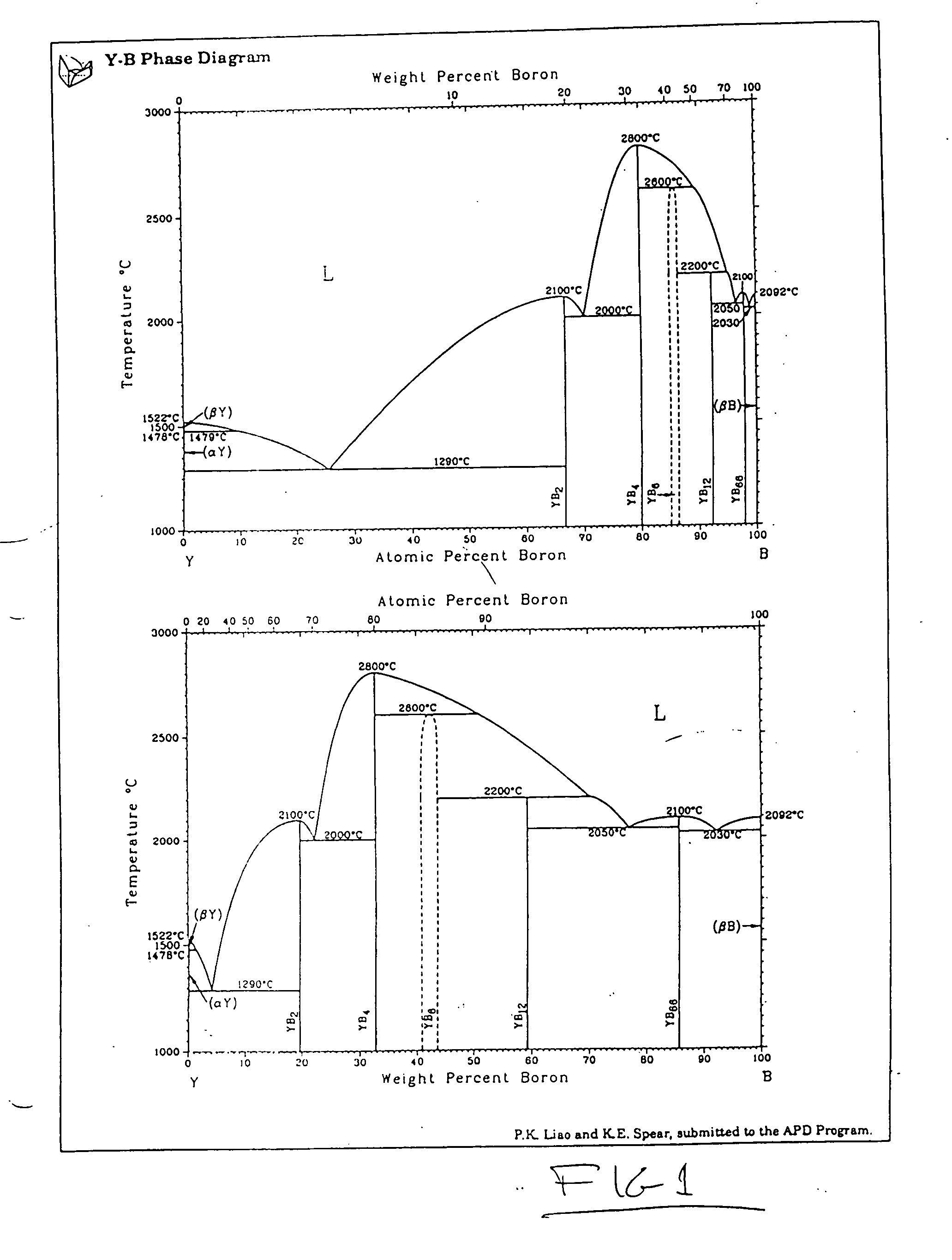
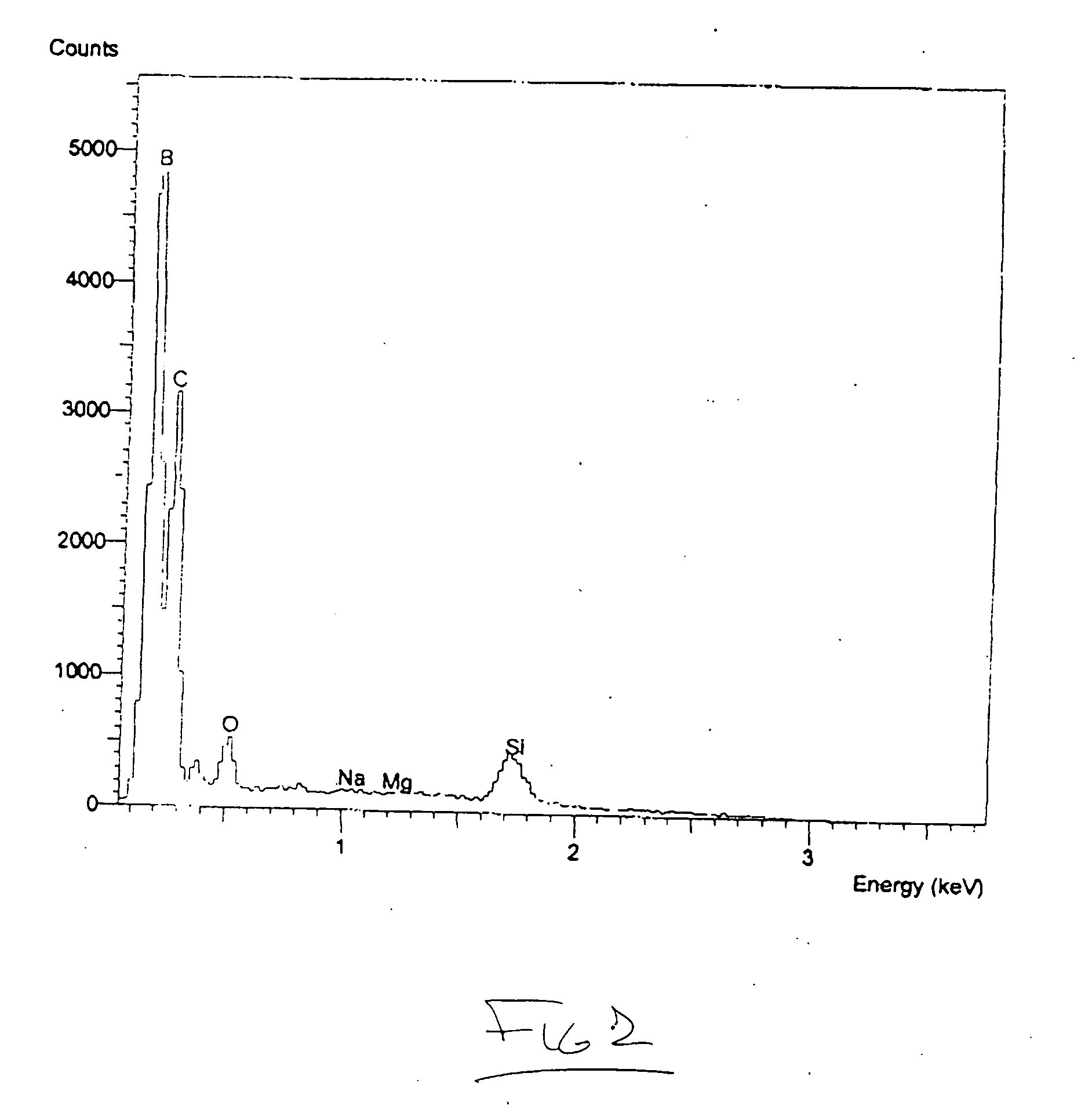
Method for depositing boron-rich coatings
InactiveUS20050208218A1Not readyReduce usageSpark gapsLiquid surface applicatorsLutetiumControl manner
A method is disclosed for coating substantially pure boron or highly boron-rich borides in a controlled manner. Such a method of coating of boron has a variety of applications, including surface chemical and wear protection, neutron absorption, prevention of impurity emission from heated filaments and ion beams, elimination of metal dust from vacuum systems, boridizing, boron cluster emission, and reactive chemistry. Borides with a boron-to-metal ratio of 20 or more are known to exist and may be used as a feedstock for substantially pure boron coatings for deposition processes requiring feedstock electrical conductivity, and / or enhanced reactivity. While most metal borides coincidentally produce significant metal vapor as a by-product, certain borides of yttrium, holmium, erbium, thulium, terbium, gadolinium, and lutetium have been identified as capable of producing substantially pure boron vapor.
Owner:IBADEX
CMAS resistant thermal barrier coating
ActiveUS20070172703A1Reduce componentsReduces sand related distressMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesIndiumCerium
A turbine engine component is provided which has a substrate and a thermal barrier coating applied over the substrate. The thermal barrier coating comprises alternating layers of yttria-stabilized zirconia and a molten silicate resistant material. The molten silicate resistant outer layer may be formed from at least one oxide of a material selected from the group consisting of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, scandium, indium, zirconium, hafnium, and titanium or may be formed from a gadolinia-stabilized zirconia. If desired, a metallic bond coat may be present between the substrate and the thermal barrier coating system. A method for forming the thermal barrier coating system of the present invention is described.
Owner:RTX CORP
Catalysts for solid base for producing biodiesel
InactiveCN101041130AImprove performanceNothing producedCatalyst carriersPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionAlkaline earth metalTransesterification
The invention discloses a solid base catalyst for preparing bio-diesel, characterized in that porous material with the same cubage is dipped in alkali metal or alkaline earth metal soluble salt solution and transition metal element or thulium soluble salt solution, whose weight proportion is that porous material: alkali metal or alkaline earth metal soluble salt: transition metal element of thulium soluble salt is 1: 0.02-1: 0.001-0.2; it is dried, baked, rubbed and screened to be obtained. The invention is provided with good catalytic performance, easy treatment after transesterification, no waste liquid generated and easy separation. It can be used repeatedly and it is easy to be used in industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUNRISE POLYMER MATERIAL CO LTD
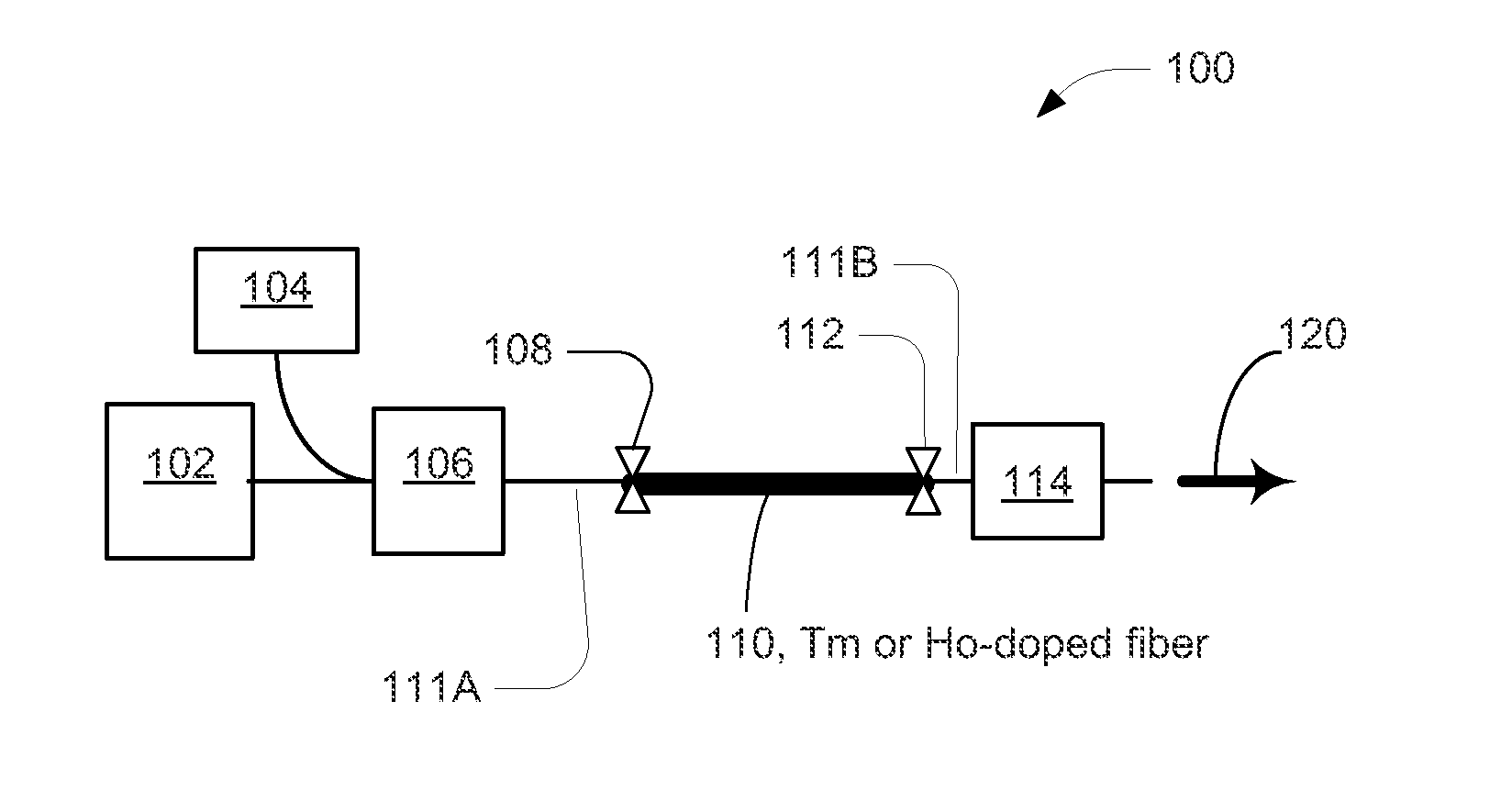
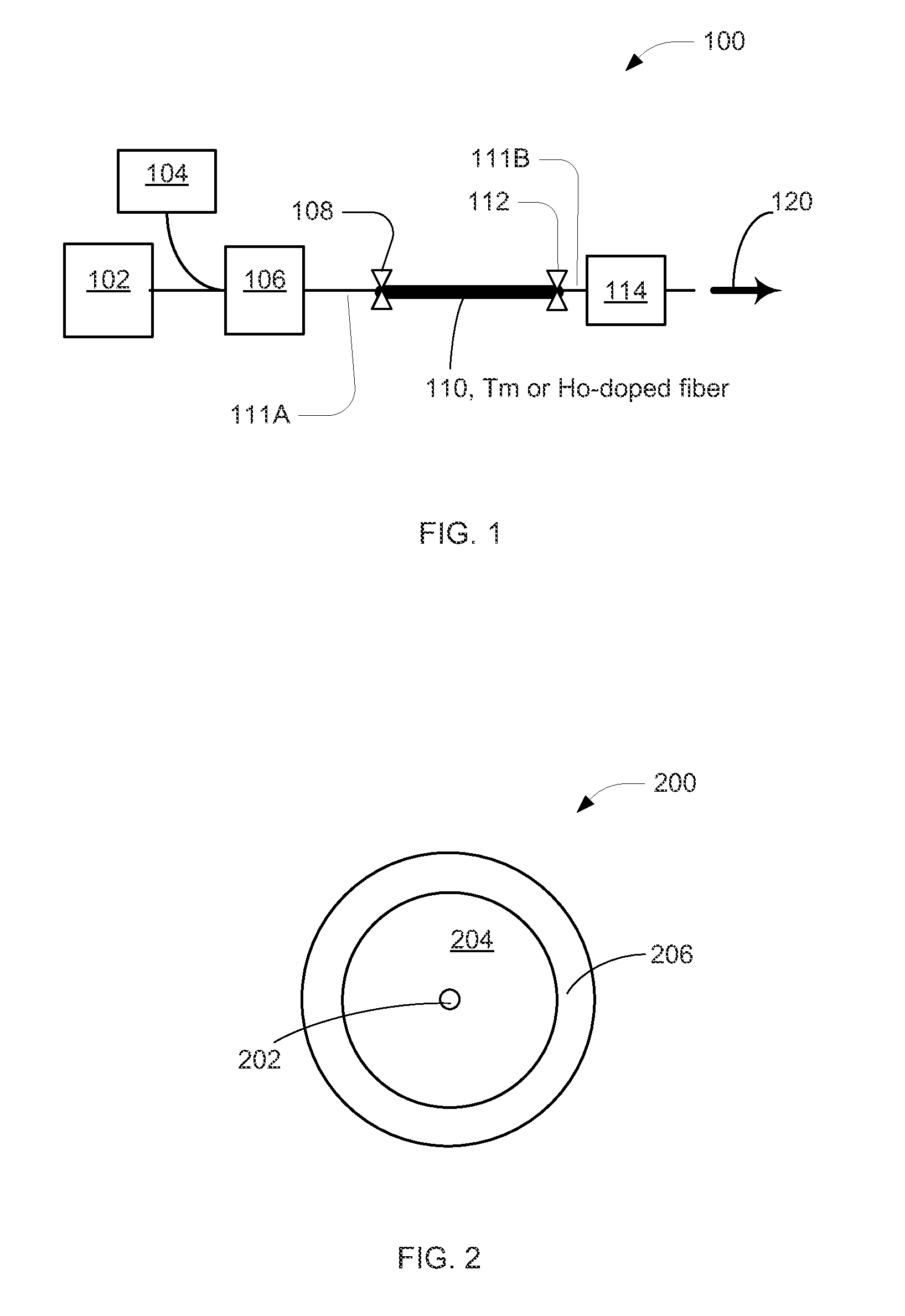
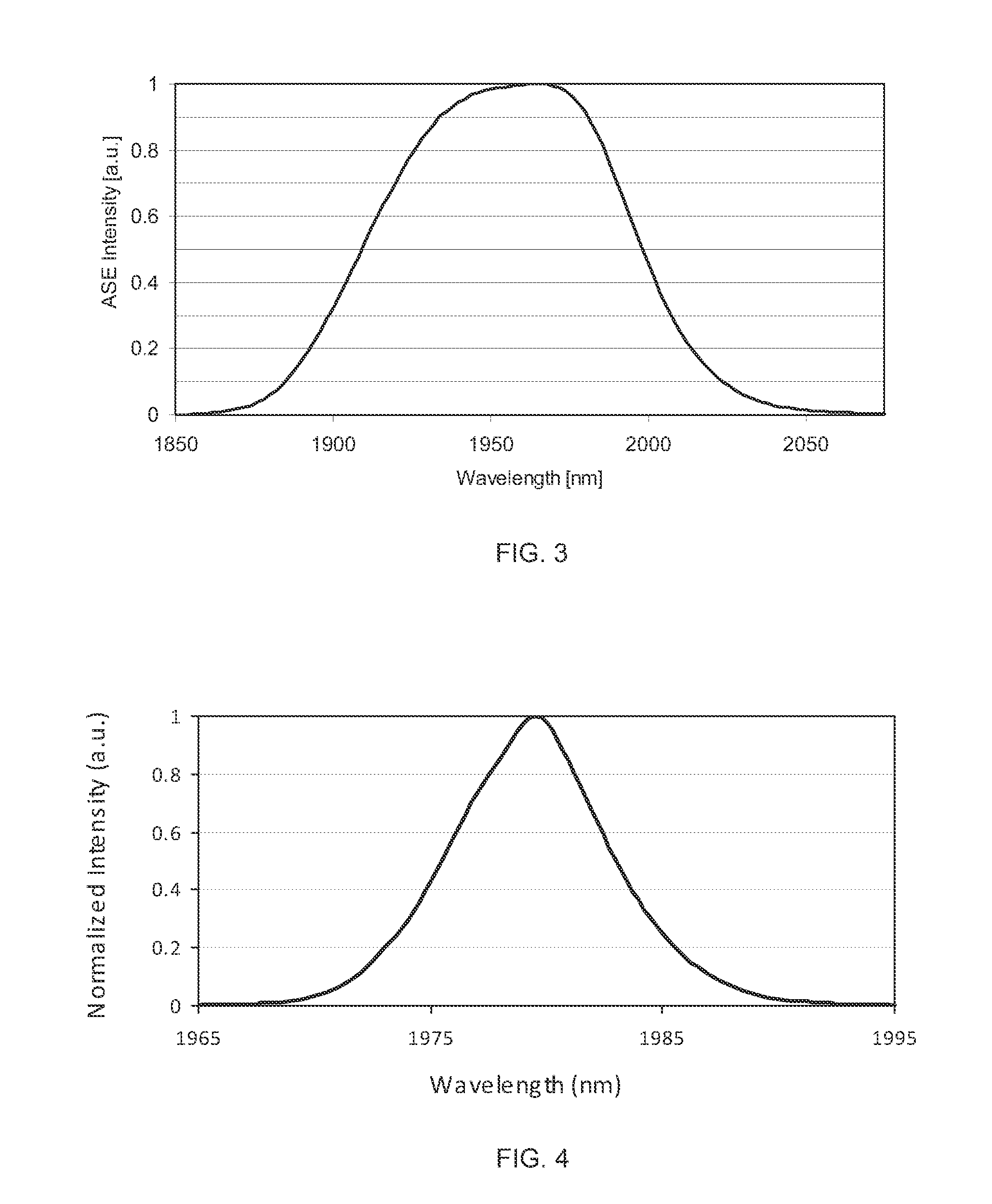
Mode-Locked Two-Micron Fiber Lasers
A mode-locked fiber laser comprising a multicomponent glass fiber doped with a trivalent rare-earth ion of thulium and / or holmium and including a fiber-optic based passive saturable absorber that contains an adhesive material mixed with a saturable absorbing components and is disposed along the length of an optical fiber such as to assure that a mode propagating within the fiber spatially overlaps with the volume occupied by the saturable absorbing components.
Owner:ADVALUE PHOTONICS
Nanoparticles of rare earth oxides
ActiveUS20070104629A1Increase volumeLow cost productionMaterial nanotechnologyLanthanum oxide/hydroxidesCeriumScandium
Rare earth compositions comprising nanoparticles, methods of making nanoparticles, and methods of using nanoparticles are described. The compositions of the nanomaterials discussed may include scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lanthanum(La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium(Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and lutetium (Lu). The nanoparticles can be used to make organometallics, nitrates, and hydroxides. The nanoparticles can be used in a variety of applications, such as pigments, catalysts, polishing agents, coatings, electroceramics, catalysts, optics, phosphors, and detectors.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
High-density scintillators for imaging system and method of making same
InactiveUS20060219927A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAlkaline earth metalCerium
A scintillator composition comprising a garnet represented by (M1-x-yNxAy)3(Al5-a-bCaDb)O12, where M comprises yttrium, or terbium, or gadolinium, or holmium, or erbium, or thulium, or ytterbium, or lutetium, or combinations thereof, where N comprises additives including a lanthanide, or an alkali metal, or an alkaline earth metal, or combinations thereof, where A comprises a suitable activator ion including cerium, or europium, or praseodymium, or terbium, or ytterbium, or combinations thereof, where C or D comprises lithium, or magnesium, or gallium, or an element from group IIIa, or IVa, or Va, or IIId transition metal, or IVd transition metal, or combinations thereof, where x ranges from about 0 to about 0.90, y ranges from about 0.0005 to about 0.30, and a sum of a and b ranges from about 0 to 2.0.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Catalyst carrier, catalyst and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20100331172A1Improve heat resistanceHigh catalytic ability without increasing the specific surface areaCatalyst carriersCell electrodesIndiumCerium
The present invention provides a catalyst carrier having excellent durability and capable of attaining high catalytic ability without increasing the specific surface area thereof, and a catalyst obtainable by using the catalyst carrier. The catalyst carrier of the present invention comprises a metal oxycarbonitride, preferably the metal contained in the metal oxycarbonitride comprises at least one selected from the group consisting of niobium, tin, indium, platinum, tantalum, zirconium, copper, iron, tungsten, chromium, molybdenum, hafnium, titanium, vanadium, cobalt, manganese, cerium, mercury, plutonium, gold, silver, iridium, palladium, yttrium, ruthenium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and nickel. Moreover, the catalyst of the present invention comprises the catalyst carrier and a catalyst metal supported on the catalyst carrier.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Single-frequency narrow linewidth 2 μm fiber laser
InactiveUS7106762B1Facilitating splicingGuaranteed uptimeLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionLow noiseGrating
Owner:NP PHOTONICS A CORP OF DELAWARE
Passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with waveband of 2.0 microns
InactiveCN102368584AGood environmental stabilityEasy to realize industrial applicationActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionGratingNonlinear optics
The invention relates to a passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with a waveband of 2.0 microns and belongs to the field of a laser technology and nonlinear optics. The passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with the waveband of 2.0 microns mainly comprises a laser pumping source, a pumping combiner, thulium-doped or thulium-holmium-codoped rear earth doped fibers, a circulator, a saturable absorber, a laser beam splitter, an isolator, a fiber bragg grating, a polarization controller and the like. The thulium-doped or thulium-holmium-codoped rear earth doped fibers are used as a gain medium; the saturable absorber is used as a passive mode-locking device; and the output of an ultrashort laser pulse which is in the waveband of 2.0 microns and has high pulse energy is realized. Due to the adoption of the all-fiber structure design, the passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with the waveband of 2.0 microns has the advantages of simple structure, high environment stability and the like, and the industrialization application is easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Niobium powder, sintered body thereof, and capacitor using the same
InactiveUS20020064476A1Improve heat resistanceLarge capacitance per unit weightTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusIndiumCerium
A niobium powder comprising at least one element selected from the group consisting of chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, boron, aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium, cerium, neodymium, titanium, rhenium, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, zinc, silicon, germanium, tin, phosphorus, arsenic, bismuth, rubidium, cesium, magnesium, strontium, barium, scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, praseodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, hafnium, vanadium, osmium, iridium, platinum, gold, cadmium, mercury, lead, selenium and tellurium; a sintered body of the niobium powder; and a capacitor comprising a sintered body as one electrode, a dielectric material formed on the surface of the sintered body, and counter electrode provided on the dielectric material.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
High-strength high-modulus magnesium alloy and preparation method
A high-strength high-modulus magnesium alloy comprises 3-20% of alloying element and the balance of magnesium substrate, wherein the alloying element comprises heavy rare earth, silicon and / or germanium, and tin and / or antimony and / or zinc; Si and Ge as well as Sn, Sb and Zn can be simultaneously added and can also be added individually; and the heavy rare earth is selected from at least one of gadolinium, dysprosium, terbium, holmium erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium. The preparation method comprises the steps of: heating and melting pure magnesium in protective atmosphere, adding pure silicon to the pure magnesium melt, stirring, dissolving, heating-up to 20-30 DEG C, sequentially adding an interalloy of the other components, stirring, controlling the interalloy to be completely molten until the casting time is less than or equal to 4min, and casting to obtain a cast ingot. The high-strength high-modulus magnesium alloy is reasonable in component proportioning, and easy to process and manufacture; and the prepared high-strength high-modulus magnesium alloy has high room-temperature strength and elasticity modulus and better plasticity, and comprehensive performances apparently higher than those of the existing magnesium-rare earth, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Illumination System Comprising a Red-Emitting Ceramic Luminescence Converter
InactiveUS20080191609A1Suitable light extraction efficiencySuitable transparencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsScandiumAntimony
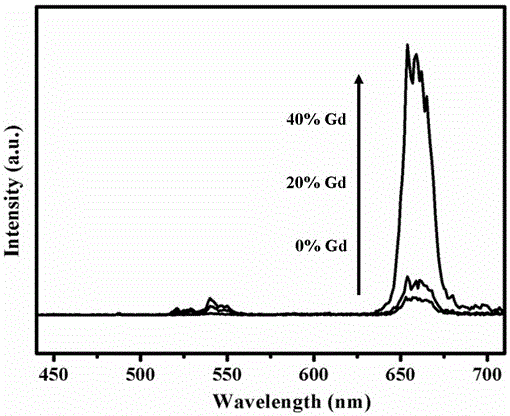
An illumination system, comprising a radiation source and a monolithic ceramic luminescence converter comprising at least one phosphor capable of absorbing a part of light emitted by the radiation source and emitting light of wavelength different from that of the absorbed light; wherein said at least one phosphor is an europium(III)-activated rare earth metal sesquioxide of general formula (YY-x-XEx)2-z(EU1-a-3Aa)z, wherein RE is selected from the group of gadolinium, scandium, and lutetium, A is selected from the group of bismuth, antimony, dysprosium, samarium, thulium, and erbium, 0≦x<1, 0.001≦z≦0.2; and 0≦a<1 can provide light sources having high luminosity and color-rendering index, especially in conjunction with a light emitting diode as a radiation source. The invention is also concerned with an amber to red-emitting a monolithic ceramic luminescence converter comprising an europium(III)-activated rare earth metal sesquioxide of general formula (Y1-x-REx)2-zO3:(Eu1-aAa)Z, wherein RE is selected from the group of gadolinium, scandium, and lutetium, A is selected from the group of dysprosium, samarium, thulium, and erbium, 0≦x<1, 0.001≦z≦; and 0≦a<1.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Up converting fluorescent material with nanometer level molybdate substrate and its prepn
The present invention belongs to the field of nano fluorescent material. Lanthanum oxide (or yttrium or gadolinium oxide), ytterbium oxide and erbiom oxide (or thulium or holmium oxide) are first dissolved in acid to prepare solution; complexone and sodium or potassium molybdenate are added into the solution to produce precipitate, which is centrifugally separated and water washed to prepare aqueous gel, aqueous gel or further prepared alcoholic gel is finally cinerated in a high temperature furnace or heated in a hydrothermal reactor to obtain the nano level up converting fluorescent material. The said material has lanthanum molybdenate as matrix and ytterbium molybdenate and erbium molybdenate as dopant. The material thus prepared has small and homogeneous size, average size 50-60 nm and high light glowing strength and may meet the requirement as biological molecular fluorescent mark material.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Upconversion fluorescent ink for inkjet printer and preparation method of upconversion fluorescent ink
The invention discloses an upconversion fluorescent ink for an inkjet printer. The upconversion fluorescent ink comprises, by weight, 1-10 parts of rare-earth doped upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles, 1600-2000 parts of ink solvent and 300-800 parts of thickener, the rare-earth doped upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles are sodium yttrium fluoride nanoparticles co-doped by rare-earth activator and rare-earth sensitizer, the rare-earth activator is erbium, thulium or holmium, and the rare-earth sensitizer is ytterbium or erbium. The upconversion fluorescent ink for the inkjet printer has the advantages of good anti-counterfeiting effect and long fixation time and storage life and can realize individualized instant anti-counterfeiting printing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation of upper conversion fluorescent nano particle
InactiveCN101497792ASmall and uniform particle sizeGood dispersionLuminescent compositionsRare earthSurface-active agents
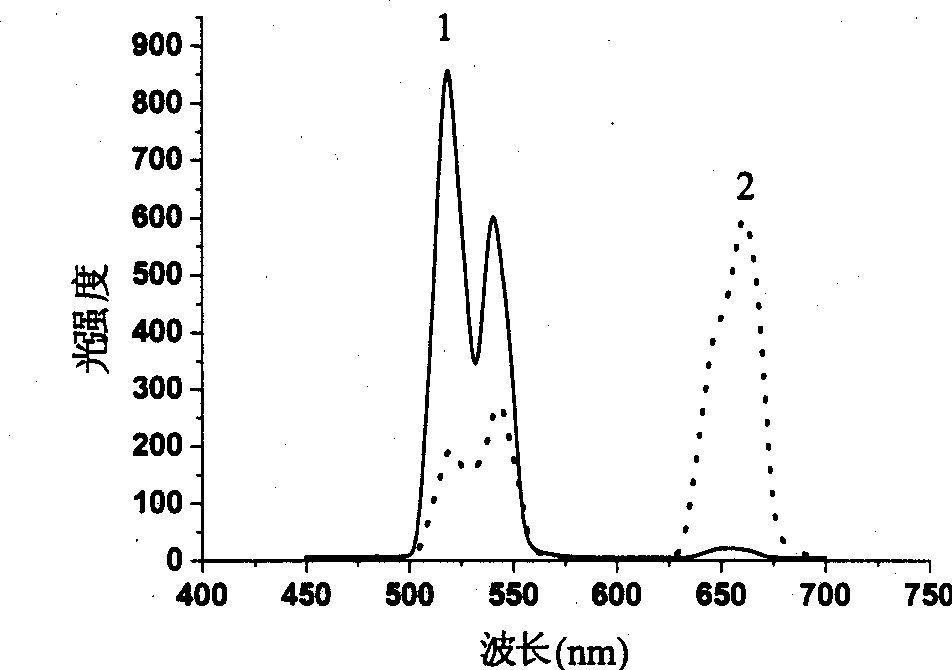
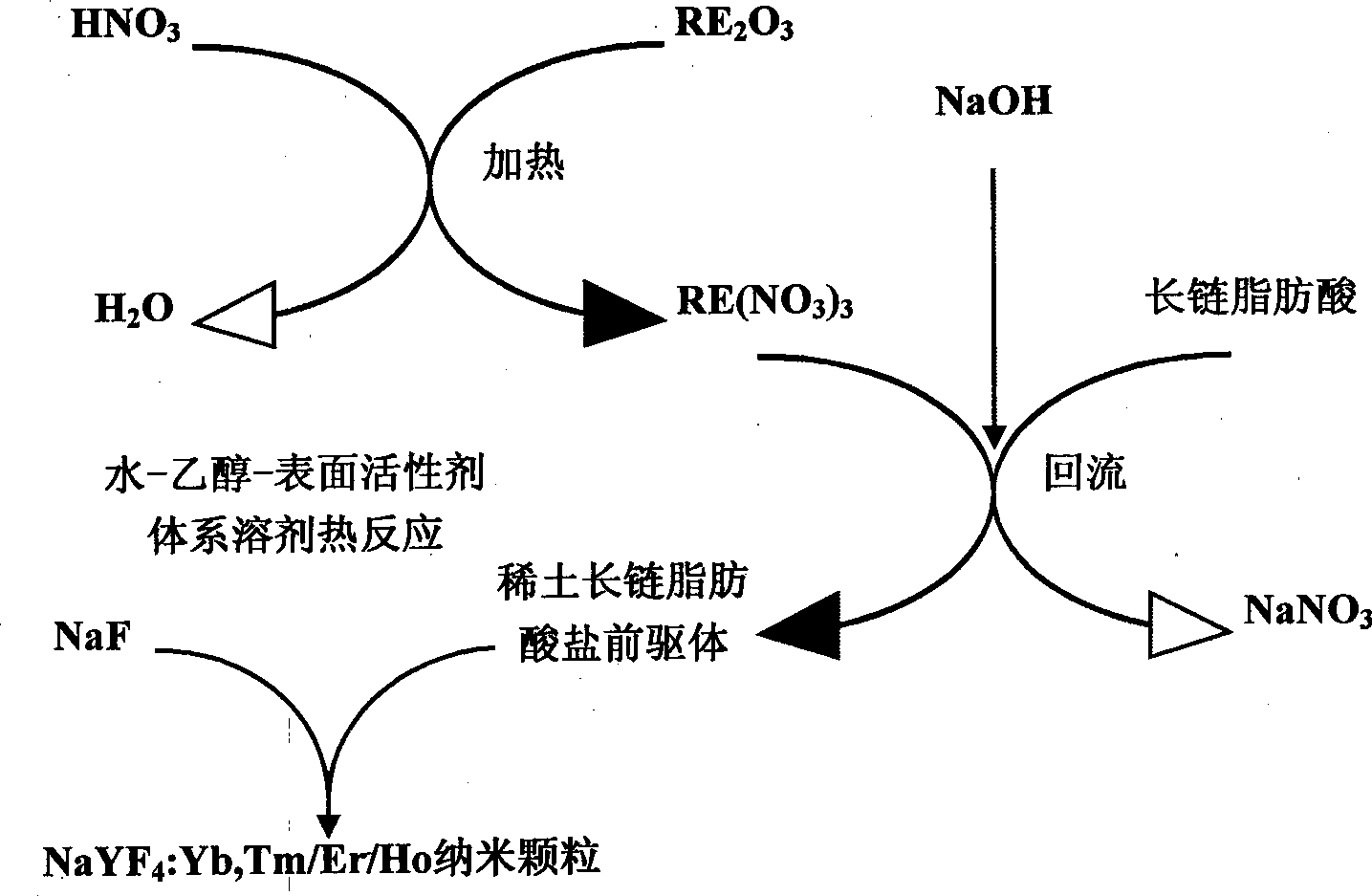
A preparation method of up-conversion phosphor nanometer particles belongs to the technical field of materials and comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving rare-earth inorganic acid salt powder by ethanol to obtain rare-earth inorganic acid salt ethanol solution; (2) adding long-chain fatty acid, performing the reflux reaction under the mixing condition, and preparing a long-chain fatty acid precursor of rare-earth; (3) adding one of an erbium precursor, a thulium precursor and a holmium precursor as well as a yttrium precursor and a ytterbium precursor into a water-ethanol mixing system, adding and uniformly mixing sodium fluoride and surface active agent, and heating and reacting for 2-24h under the obturating condition; (4) adding organic solvent after lowering the temperature, centrifugalizing, and drying or naturally withering after washing white precipitate. The preparation method has simpler process, easy synthesis condition, good repetitiveness, low cost and higher productive rate.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
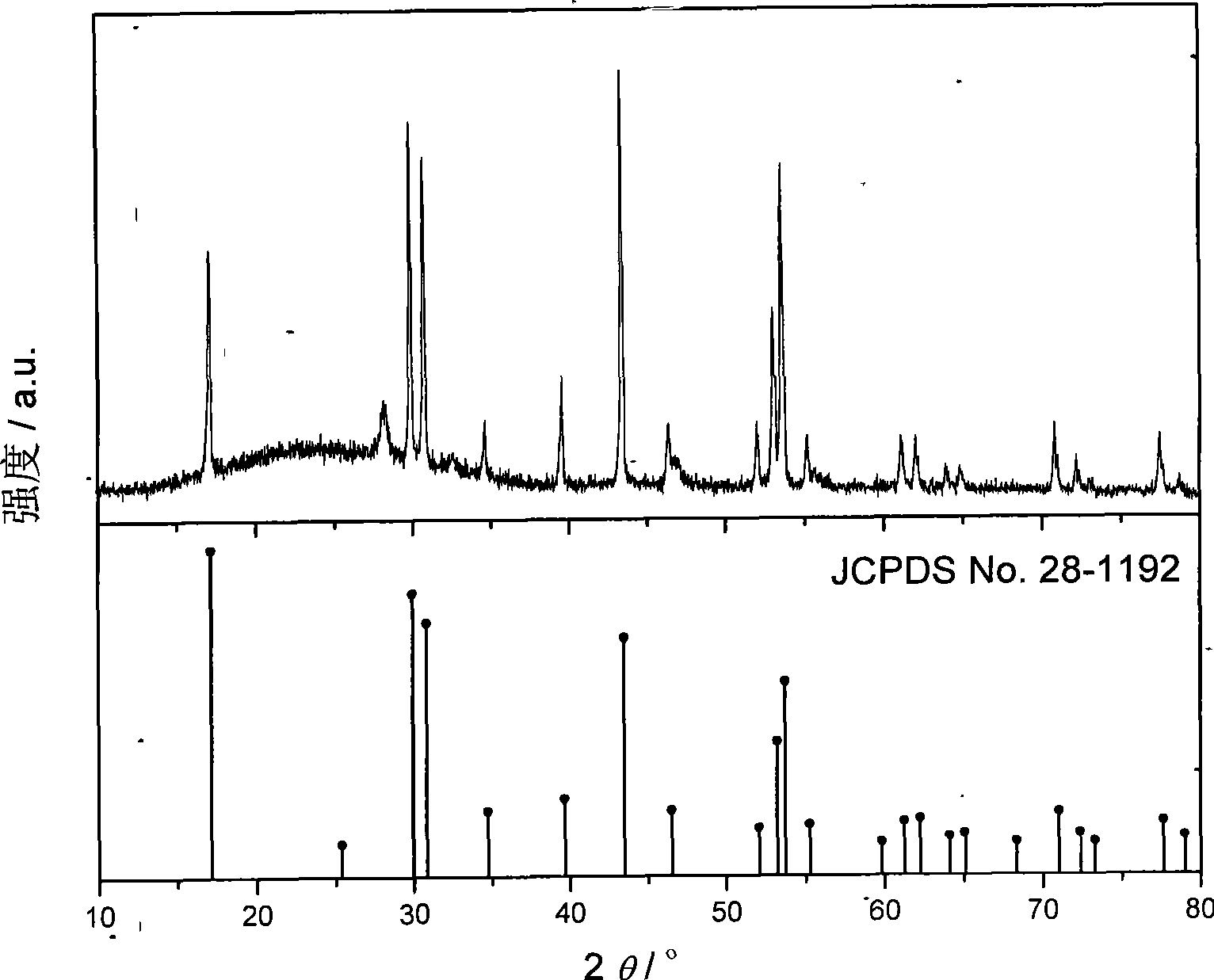
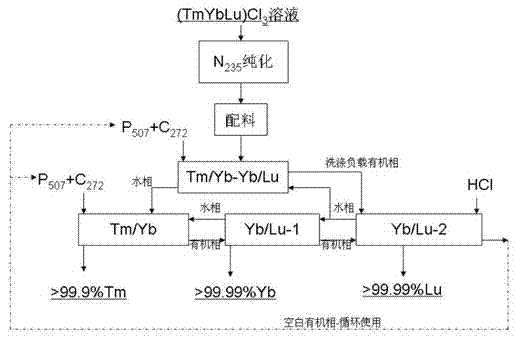
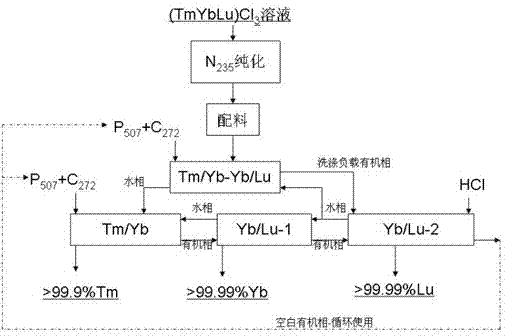
Preparation method for separating and purifying single heavy rare earth by using full-extraction process
InactiveCN102230093AStrong adaptability to distribution changesReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementLutetiumRare earth
The invention relates to a preparation method for purifying heavy rare earth, in particular to a preparation method for separating and purifying the heavy rare earth by using a full-extraction process. The technical scheme adopted by the invention comprises the steps of adopting thulium, ytterbium and lutetium concentrate as a raw material, and carrying out non-rare earth impurity purification by using N235 and then carrying out full-extraction separation and purification by using a double extracting agent system of P507 and C272 so as to respectively obtain high-purity single rare earth products of Tm2O3, Yb2O3 and Lu2O3. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method for separating and purifying the heavy rare earth by using the full-extraction process, provided by the invention, has the following advantages of: strong adaptability to raw material distribution variation of the input and output process parameters specified by the full-extraction separating and purifying process compared with the input and output process parameters in the production of a traditional ion exchanging method, an extraction chromatographic method or a single P507 extraction method have the advantages of, low balancing acid value, less acid and alkali raw material consumption, continuous production, large capacity, low comprehensive production cost, high product purity, stable quality and the like.
Owner:GANZHOU ZHANHAI IND & TRADING
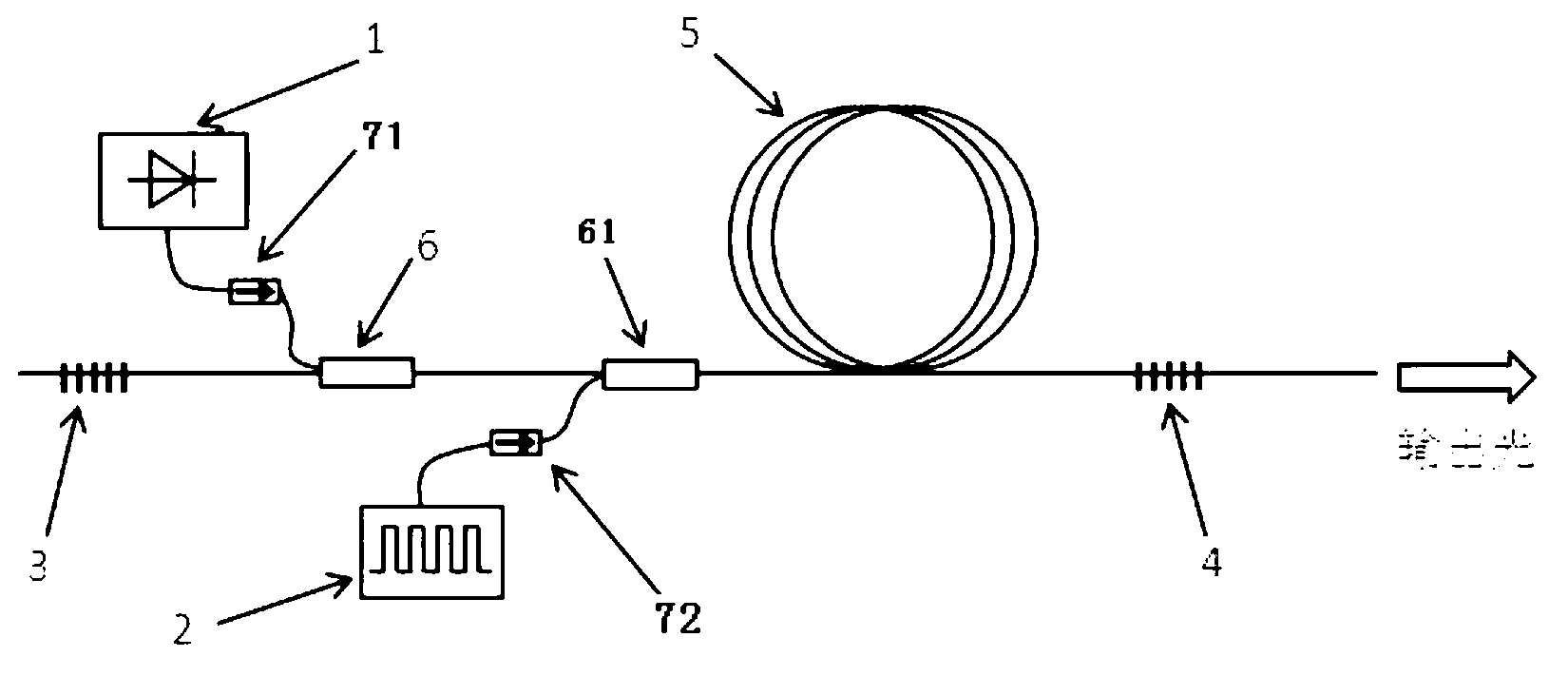
2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser of hybrid pump
InactiveCN103078243ALower threshold energyHigh energyActive medium shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
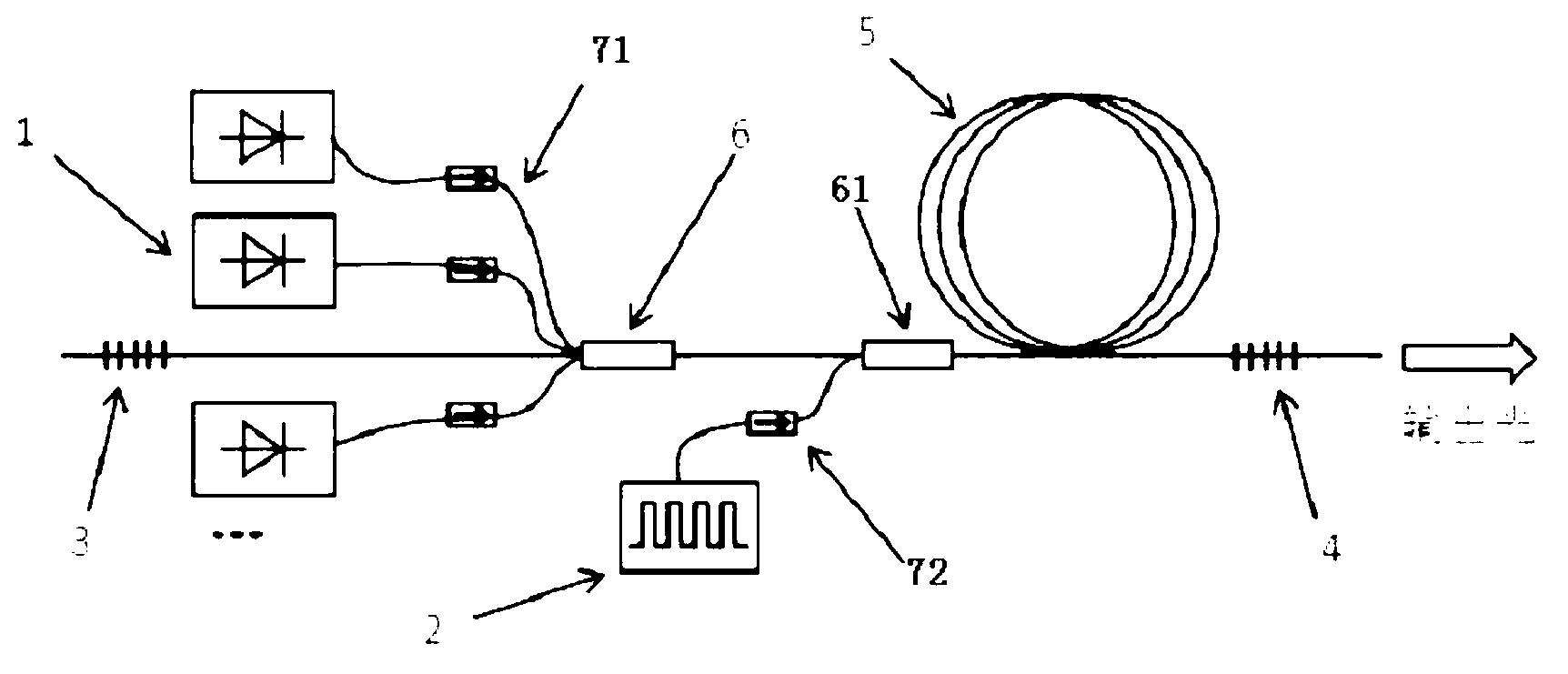
The invention discloses a 2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser of a hybrid pump. The 2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser comprises a first fiber grating, a first fiber beam combiner, a second fiber beam combiner, a gain fiber and a second fiber grating, which are connected in sequence, wherein a first pumping source is connected with a second input end of the first fiber beam combiner through a first optical isolator, a second pumping source is connected with a second input end of the second fiber beam combiner through a second optical isolator, the first fiber gating and the second fiber gating form a laser resonance cavity, the first pumping source is a continuous laser diode, the second pumping source is a pulsed laser, and the gain fiber is a thulium-doped fiber. The 2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser is reduced in the threshold valve energy of a pumping pulsed light in a gain switch technology, is capable of obtaining pulse with higher energy compared with other laser pulse producing technologies such as regulating Q and mode locking, has the characteristics of full-fiber connection, simple structure and the like, and brings convenience for application and popularization.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
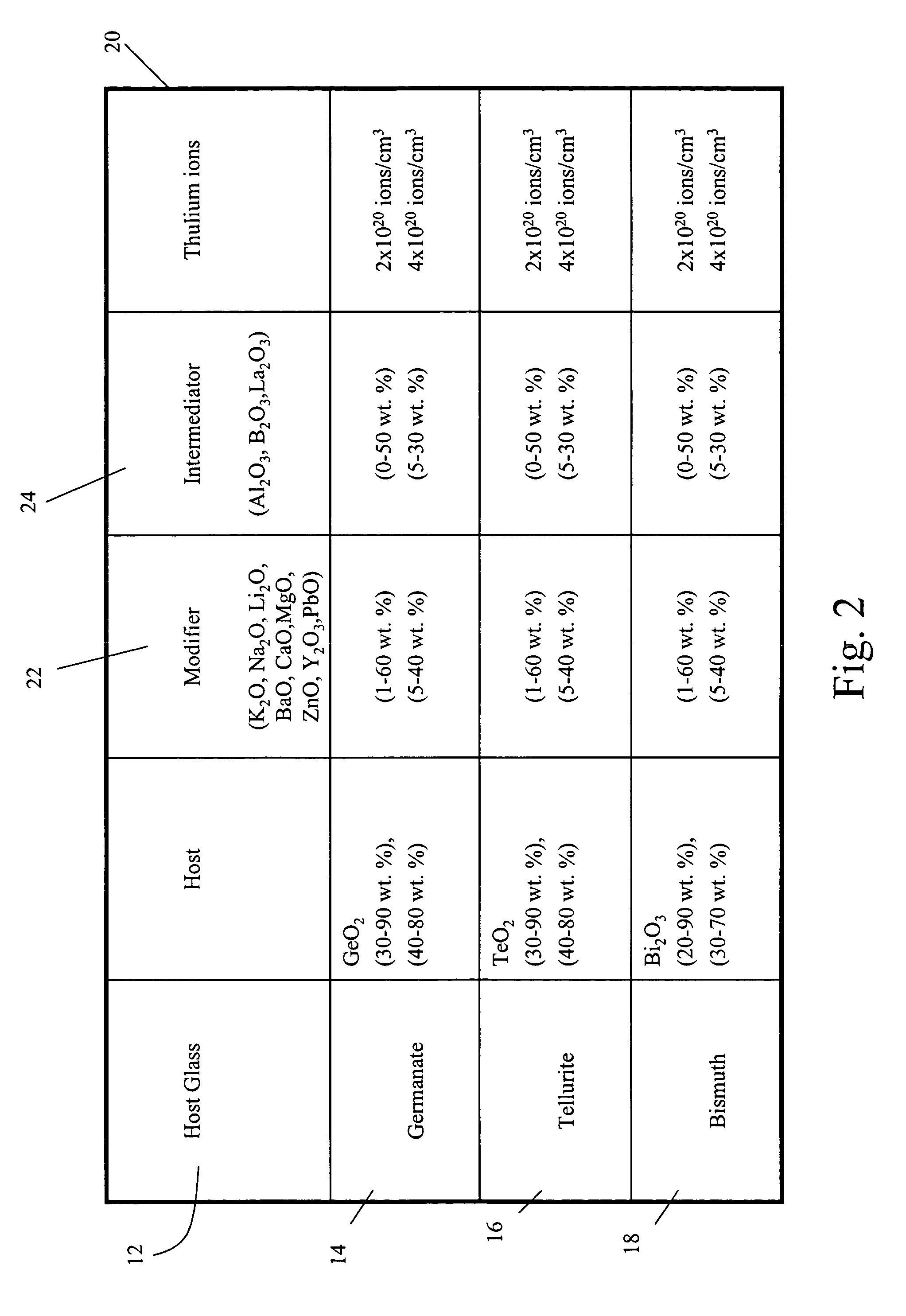
Thulium-doped heavy metal oxide glasses for 2UM lasers
ActiveUS7298768B1Improve quantum efficiencyEnhance laser emissionLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialEnergy transferCross relaxation
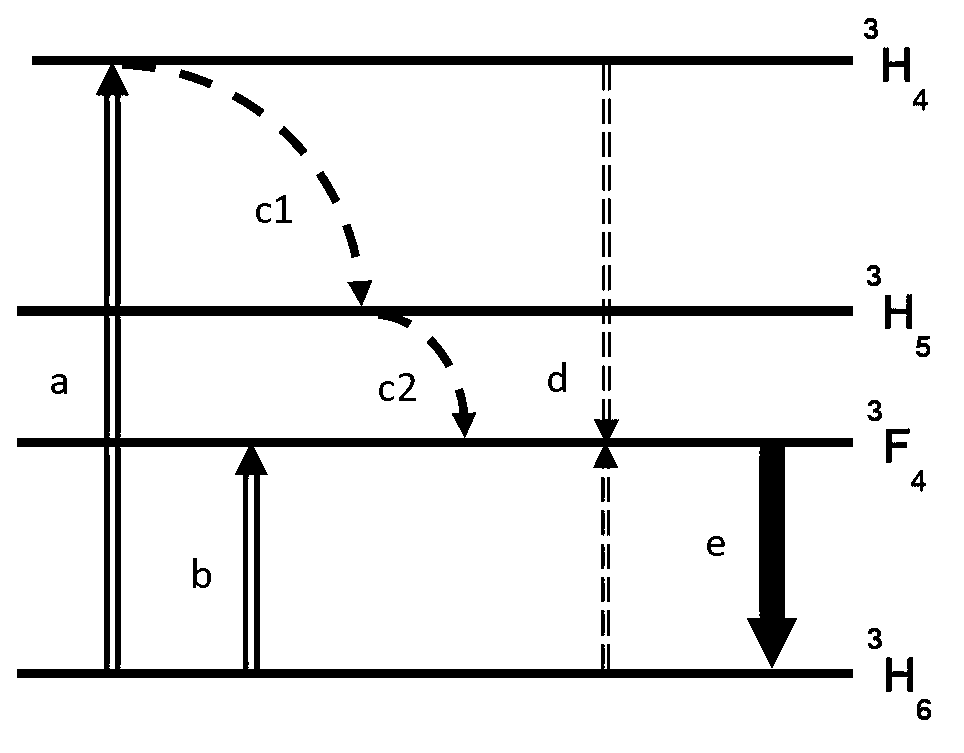
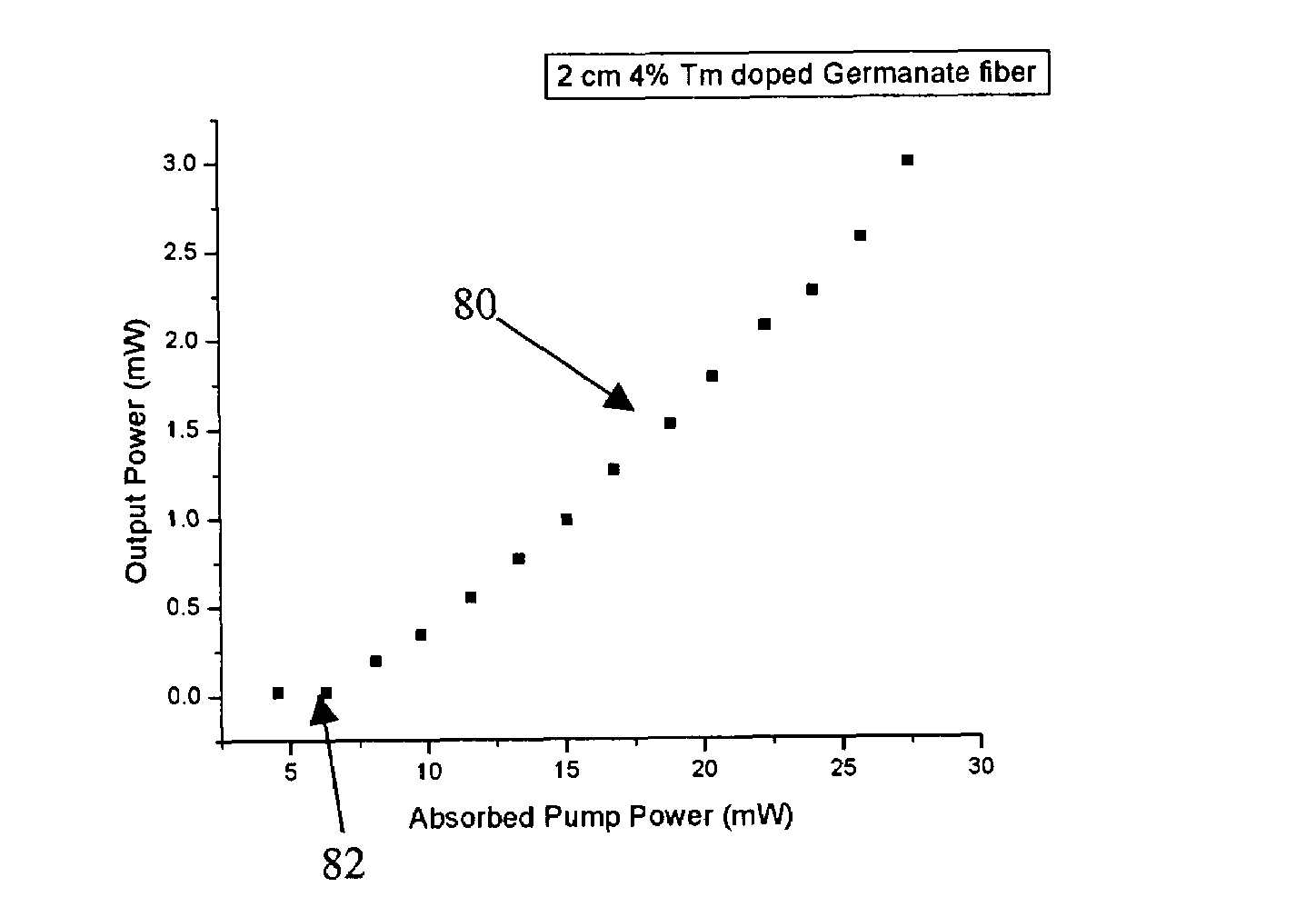
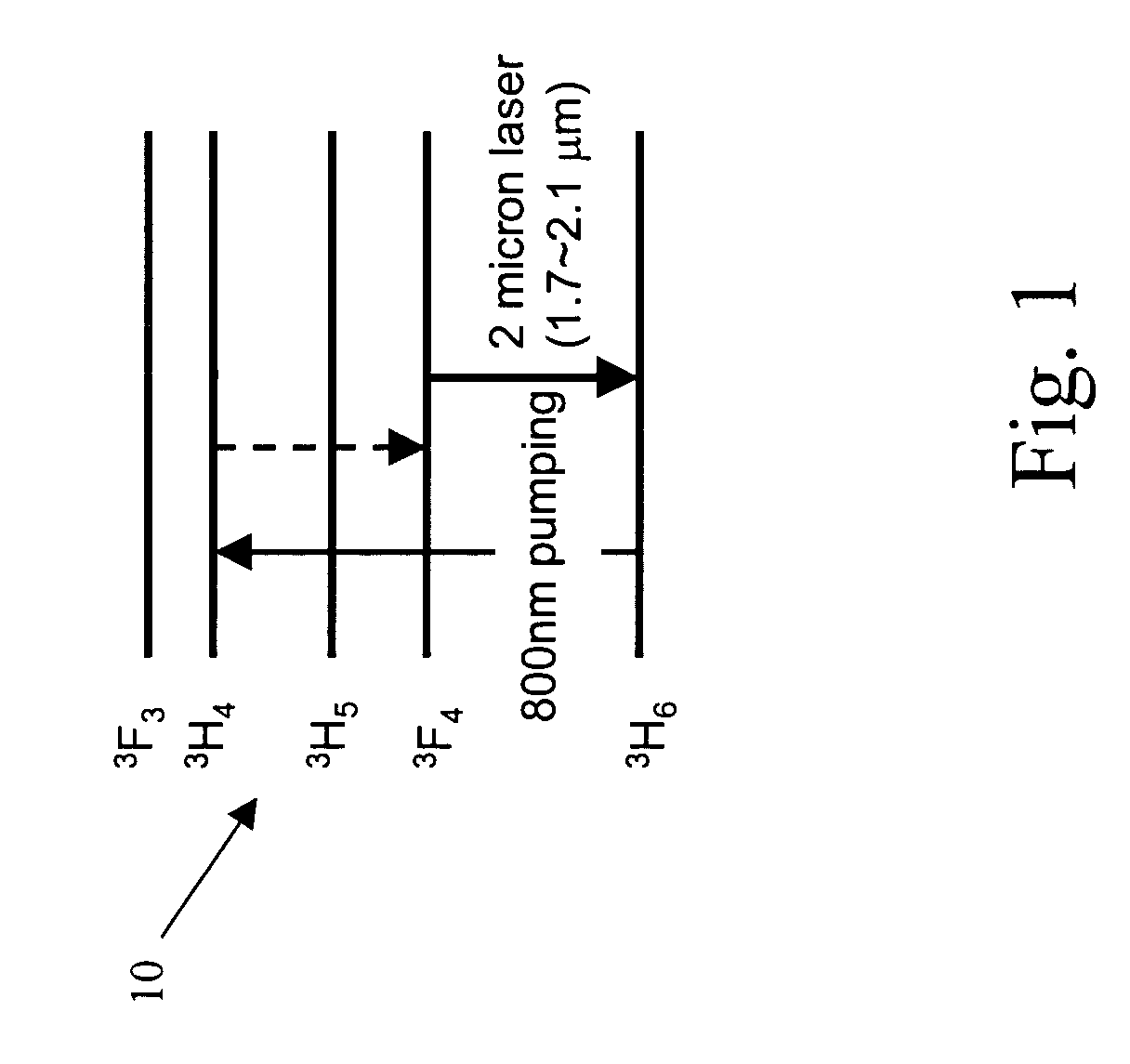
A heavy metal oxide glass selected from germanate, tellurite and bismuth oxide glasses provides a host for highly efficient Thulium doped 2 μm oxide glass and fiber lasers. The concentration of Thulium ions is high enough that energy transferred by the phenomenon of cross-relaxation will enhance laser emission at 2 μm and suppress emission at 1.5 μm so that 2 μm emission is dominant.
Owner:NP PHOTONICS A CORP OF DELAWARE
Ion thermal growth method of near infrared light upper conversion fluoride nano crystal
InactiveCN101476151ALow melting pointNon-volatilePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSolubilityLuminous intensity
The invention relates to an ion thermal growth method for converting fluoride nano crystal near infrared light which includes steps as follows: weighing some solid yttrium nitrate (lanthanum nitrate), ytterbium nitrate, erbium nitrate (thulium nitrate or holmium nitrate) pro rata. Mol ratio of the rare earth ion is that yttrium ion (lanthanum ion) : ytterbium ion : erbium ion (thulium ion, holmium ion) equal to 70-90 : 0 : 0.001-15; adding tetrafluoroborate type ion liquor into the mixing solid, selective adding some NaCl solid according with various basic, then placing the mixing solution into a high pressure reaction kettle with polyfluortetraethylene lining, placing into an oven for heating reacting, finally, washing, centrifugating, drying and obtaining the product. The prepared nano upper converting fluorescence material has small and uniform granule, strong lighting strength, better water-solubility and can satisfy need of biomolecule fluorescence mark material.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing gadolinium ion doped lutetium sodium fluoride upconversion nano/micro crystal
InactiveCN105062485AObvious red light enhancement effectIncrease the intensity of red lightLuminescent compositionsDispersityLutetium
The invention discloses a method for preparing a gadolinium ion doped lutetium sodium fluoride upconversion nano / micro crystal with a red light enhancement effect. The method comprises the steps that a citric acid solution and deionized water are mixed and magnetically stirred, then lutetium nitrate, ytterbium nitrate, erbium nitrate, thulium nitrate and gadolinium nitrate solutions are sequentially added, a sodium fluoride solution is added after even stirring, corresponding deionized water is added, and a white turbid solution is formed after full stirring; the turbid solution is transferred to a stainless steel reaction still with a bush to be subjected to a hydrothermal reaction; the reacted turbid solution is centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain the final product. The gadolinium ion doped lutetium sodium fluoride upconversion nano / micro crystal with the red light enhancement effect is prepared. The obtained material is good in dispersity, the upconversion red light intensity is greatly increased, and wide application prospects are achieved in the fields of biology, photovoltaics, display, infrared detection and the like. Equipment required by the preparation method is simple, operation and popularization are easy, and the method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Nanoparticles of rare earth oxides
ActiveUS7229600B2Increase volumeLow cost productionMaterial nanotechnologyLanthanum oxide/hydroxidesCeriumScandium
Rare earth compositions comprising nanoparticles, methods of making nanoparticles, and methods of using nanoparticles are described. The compositions of the nanomaterials discussed may include scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and lutetium (Lu). The nanoparticles can be used to make organometallics, nitrates, and hydroxides. The nanoparticles can be used in a variety of applications, such as pigments, catalysts, polishing agents, coatings, electroceramics, catalysts, optics, phosphors, and detectors.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Aluminum superalloys for use in high temperature applications
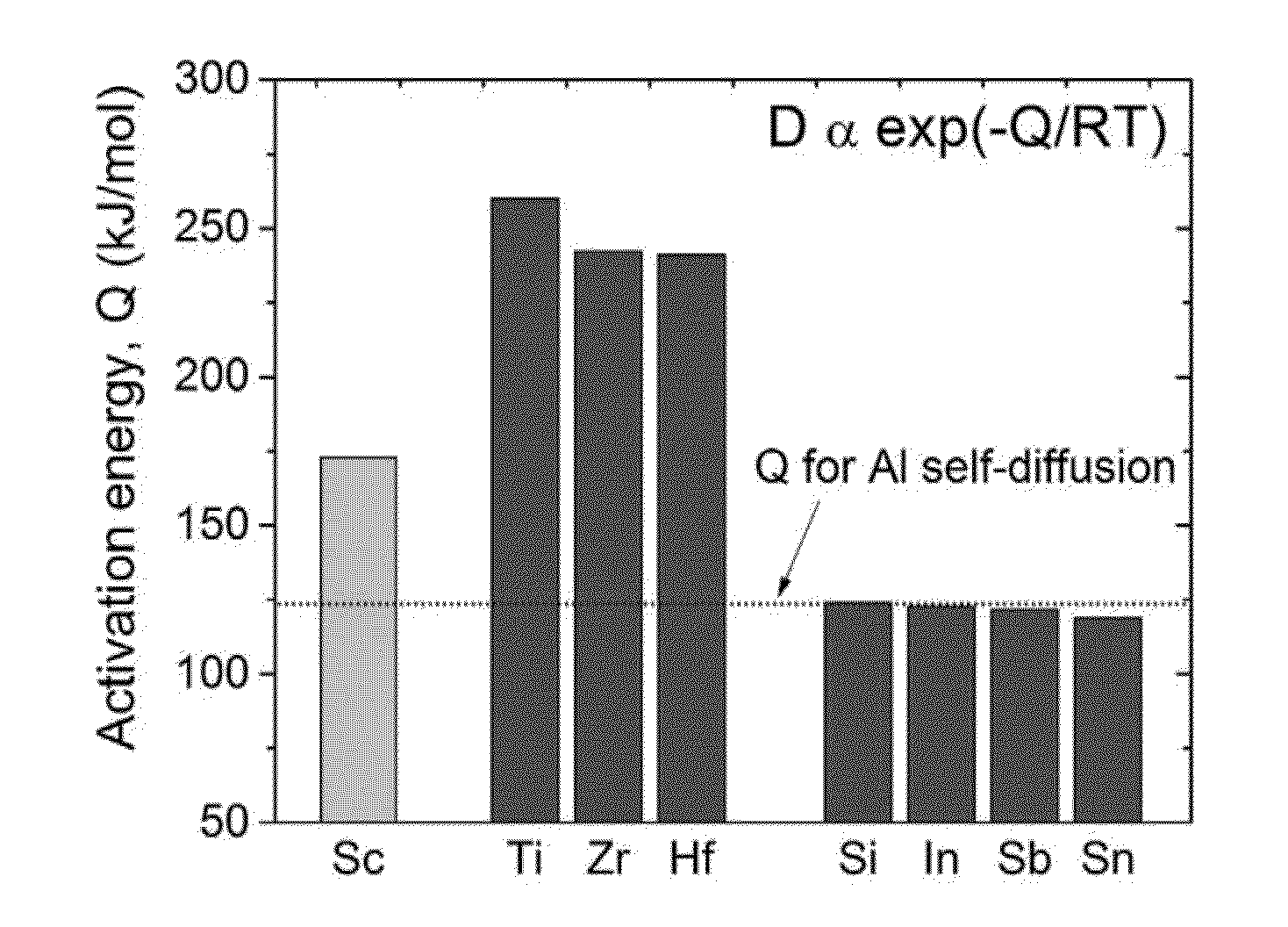
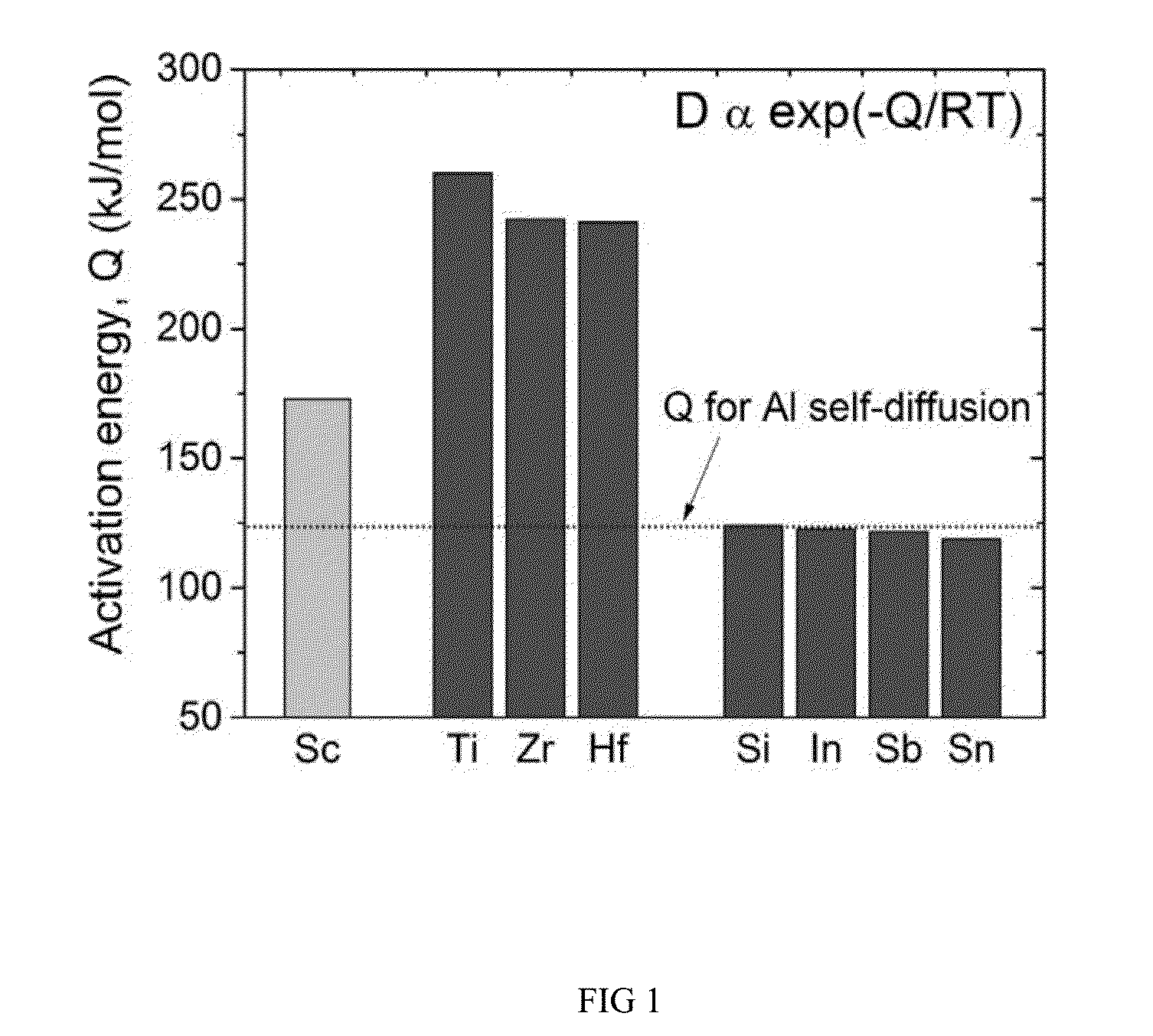
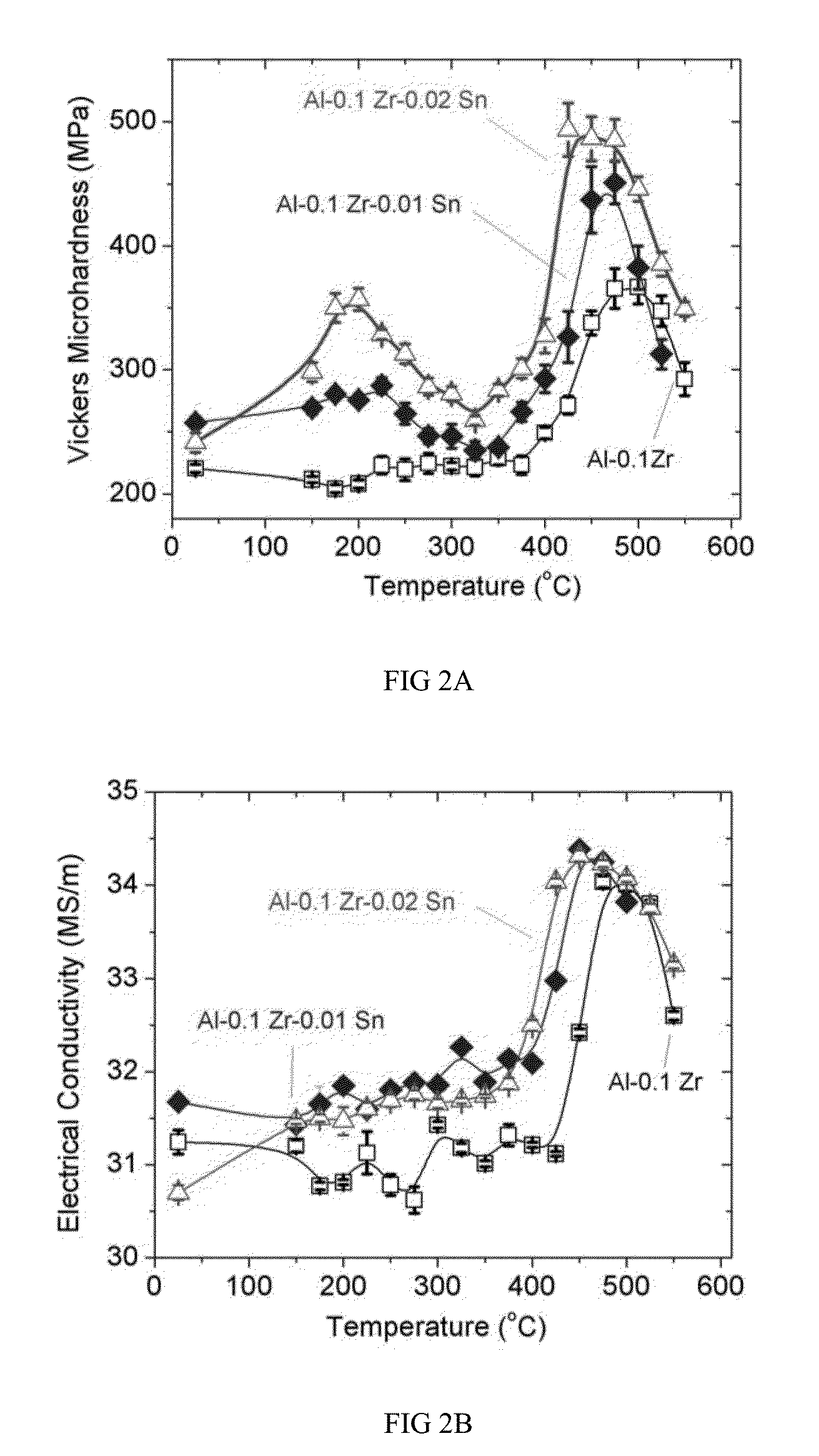
Aluminum-zirconium and aluminum-zirconium-lanthanide superalloys are described that can be used in high temperature, high stress and a variety of other applications. The lanthanide is preferably holmium, erbium, thulium or ytterbium, most preferably erbium. Also, methods of making the aforementioned alloys are disclosed. The superalloys, which have commercially-suitable hardness at temperatures above about 220° C., include nanoscale Al3Zr precipitates and optionally nanoscale Al3Er precipitates and nanoscale Al3(Zr,Er) precipitates that create a high-strength alloy capable of withstanding intense heat conditions. These nanoscale precipitates have a L12-structure in α-Al(f.c.c.) matrix, an average diameter of less than about 20 nanometers (“nm”), preferably less than about 10 nm, and more preferably about 4-6 nm and a high number density, which for example, is larger than about 1021 m−3, of the nanoscale precipitates. The formation of the high number density of nanoscale precipitates is thought to be due to the addition of inoculant, such as a Group 3A, 4A, and 5A metal or metalloid. Additionally, methods for increasing the diffusivity of Zr in Al are disclosed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com