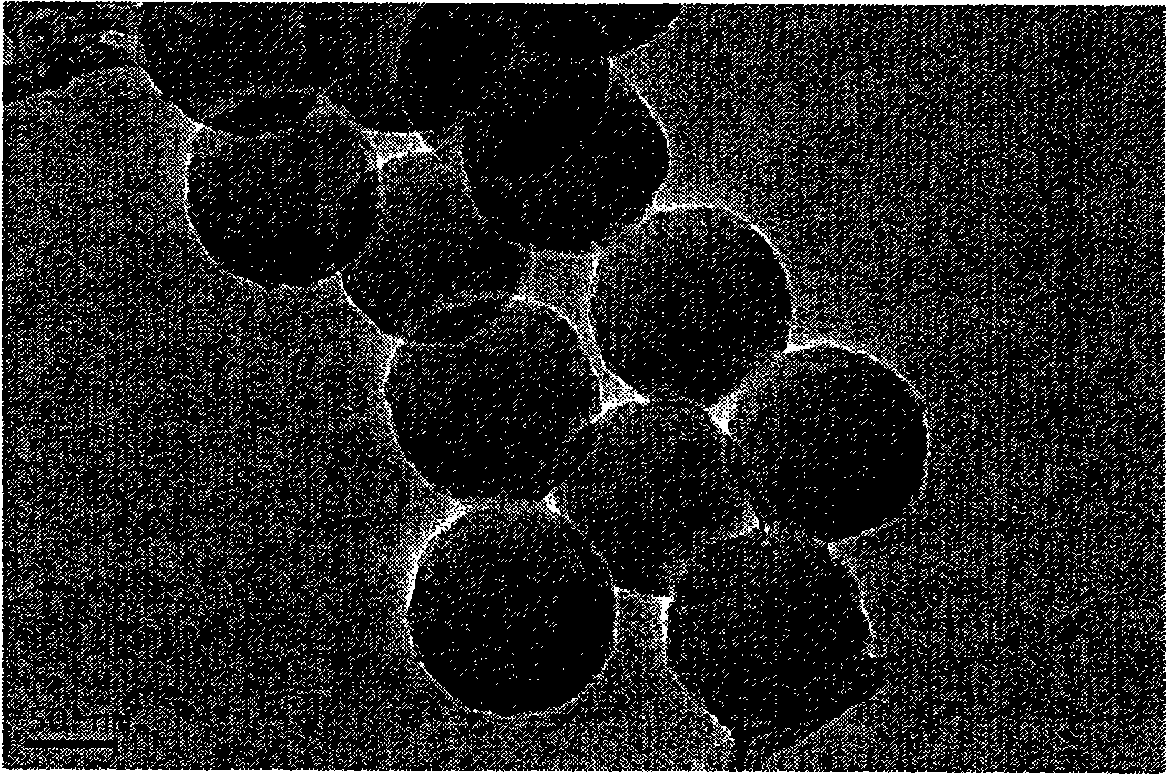
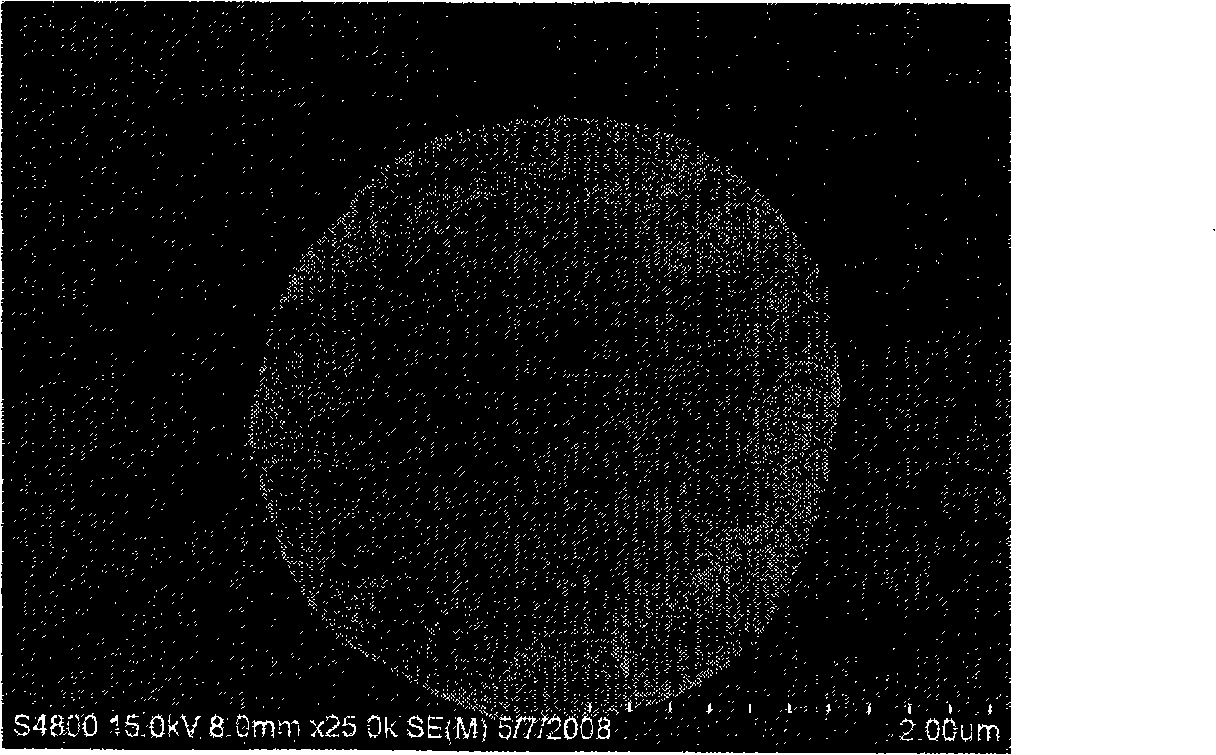
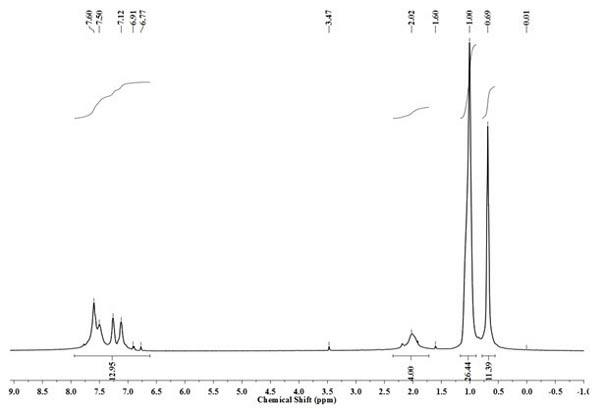
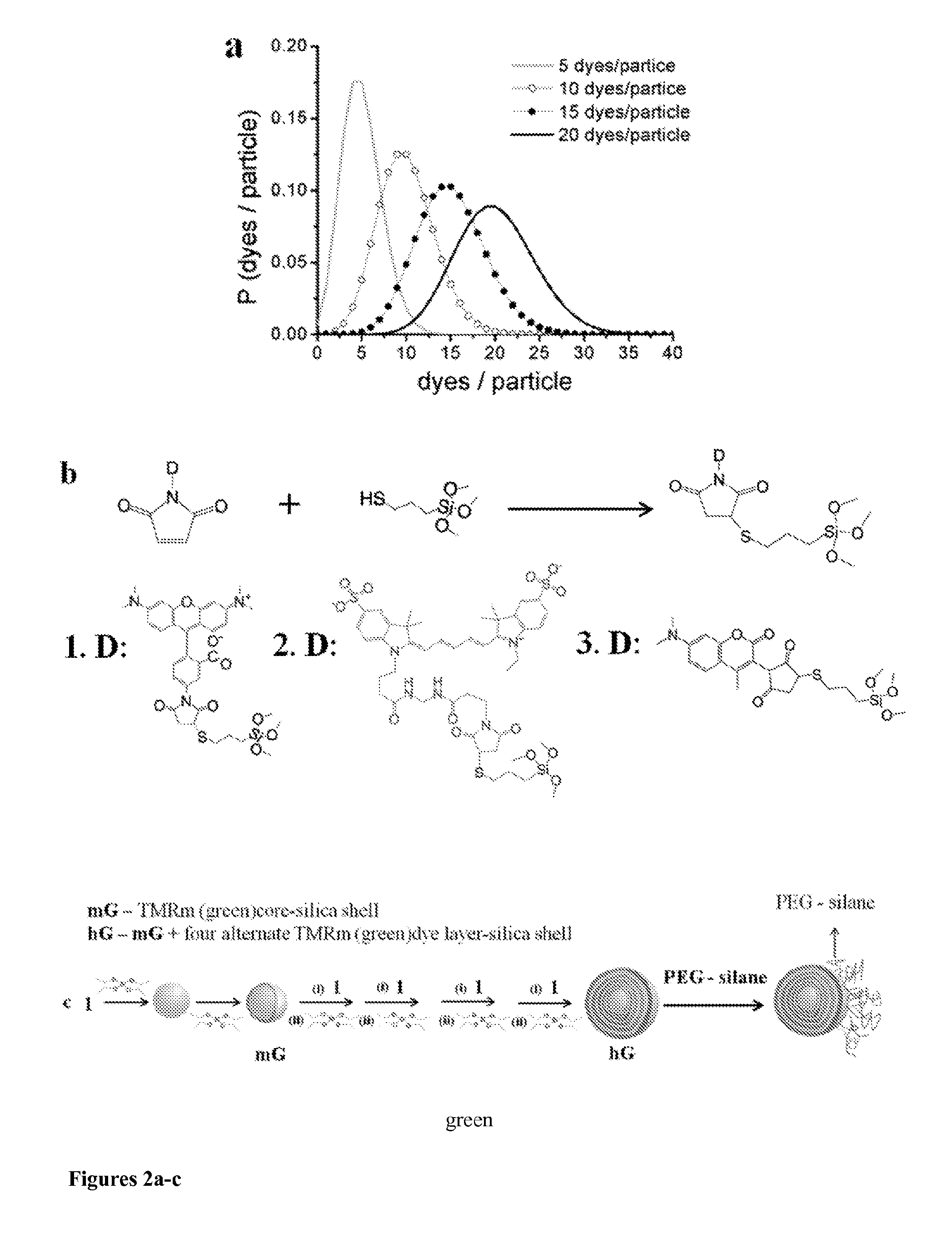
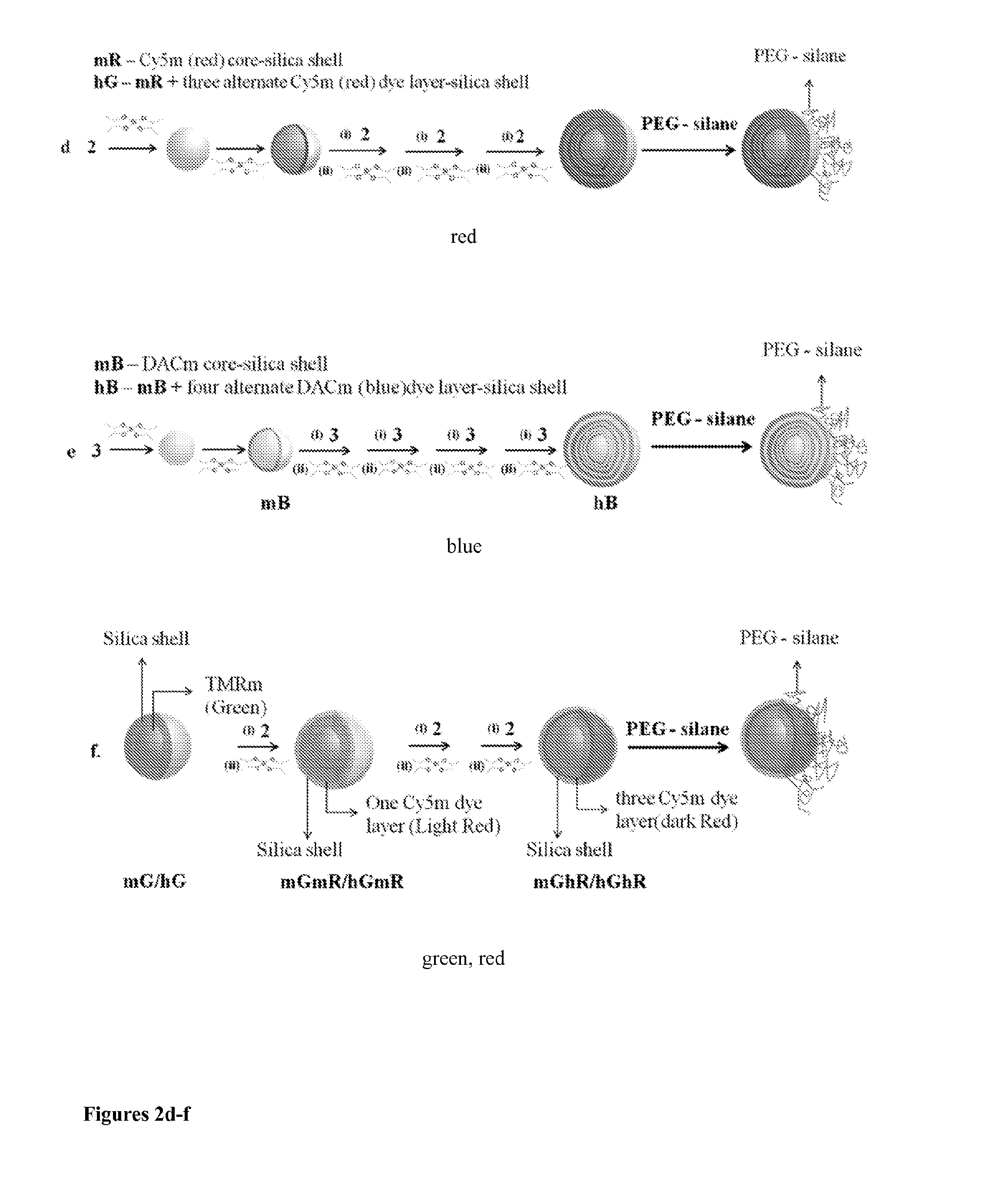
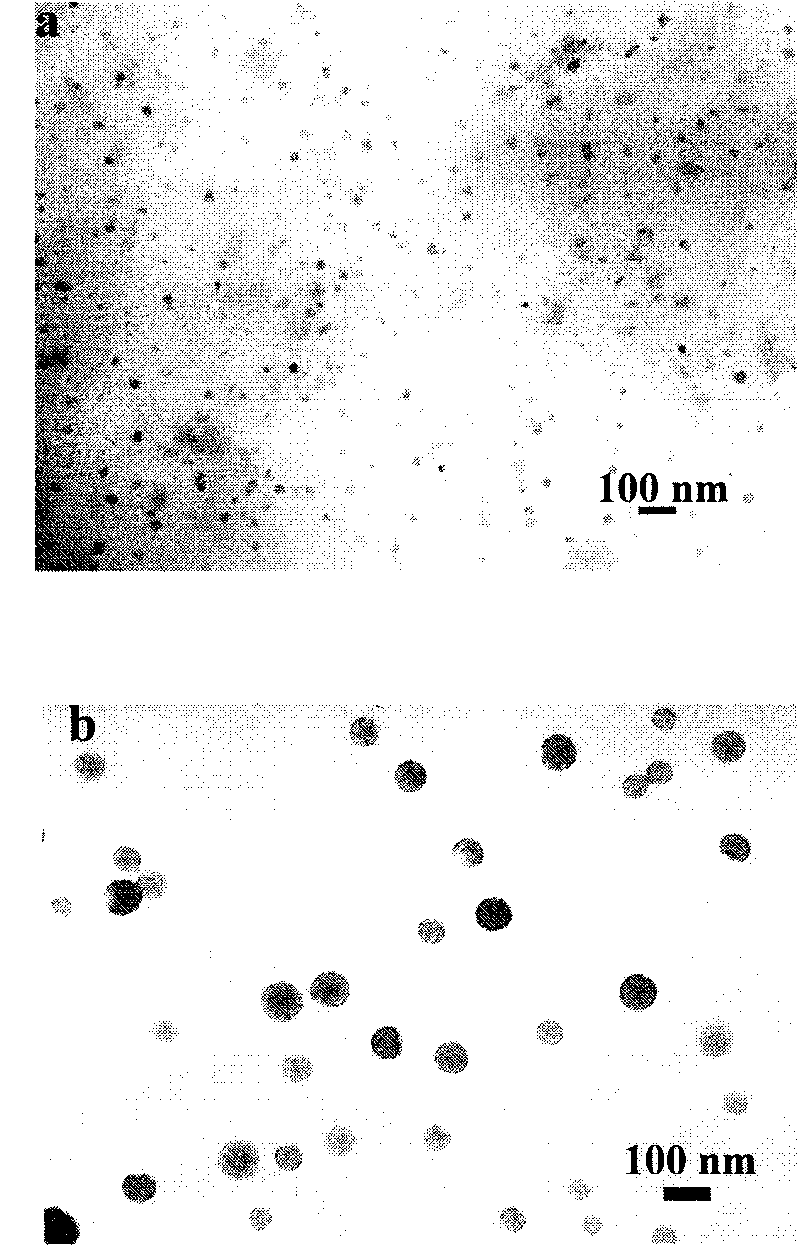
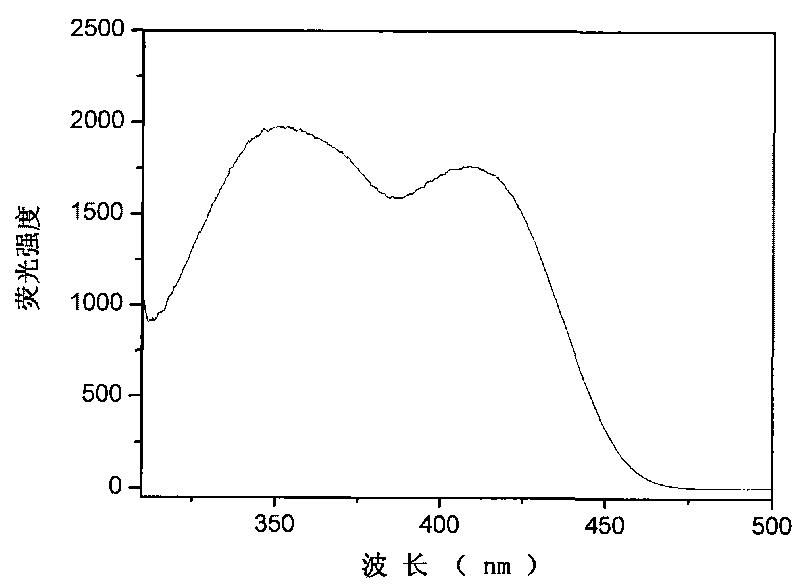
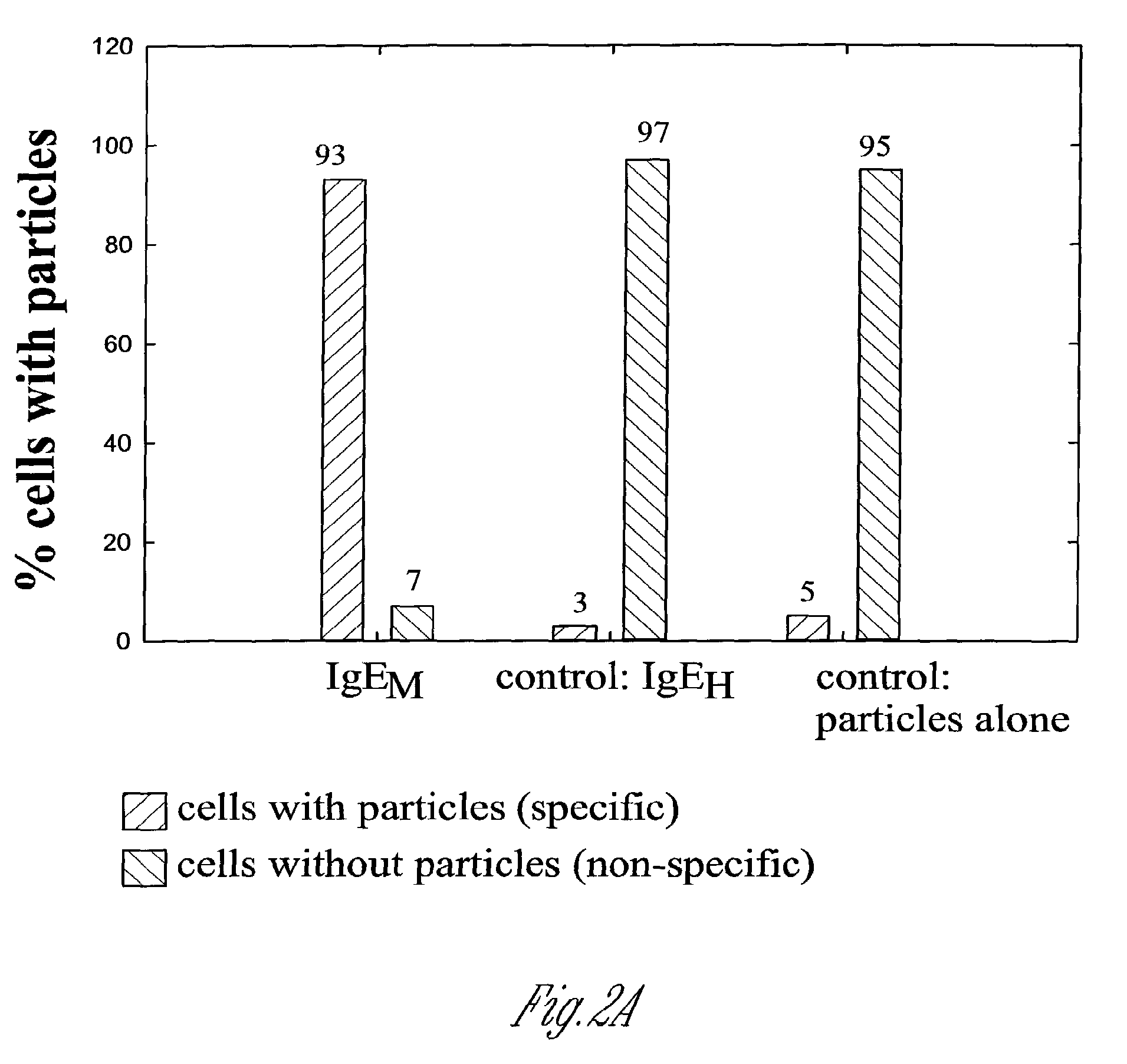
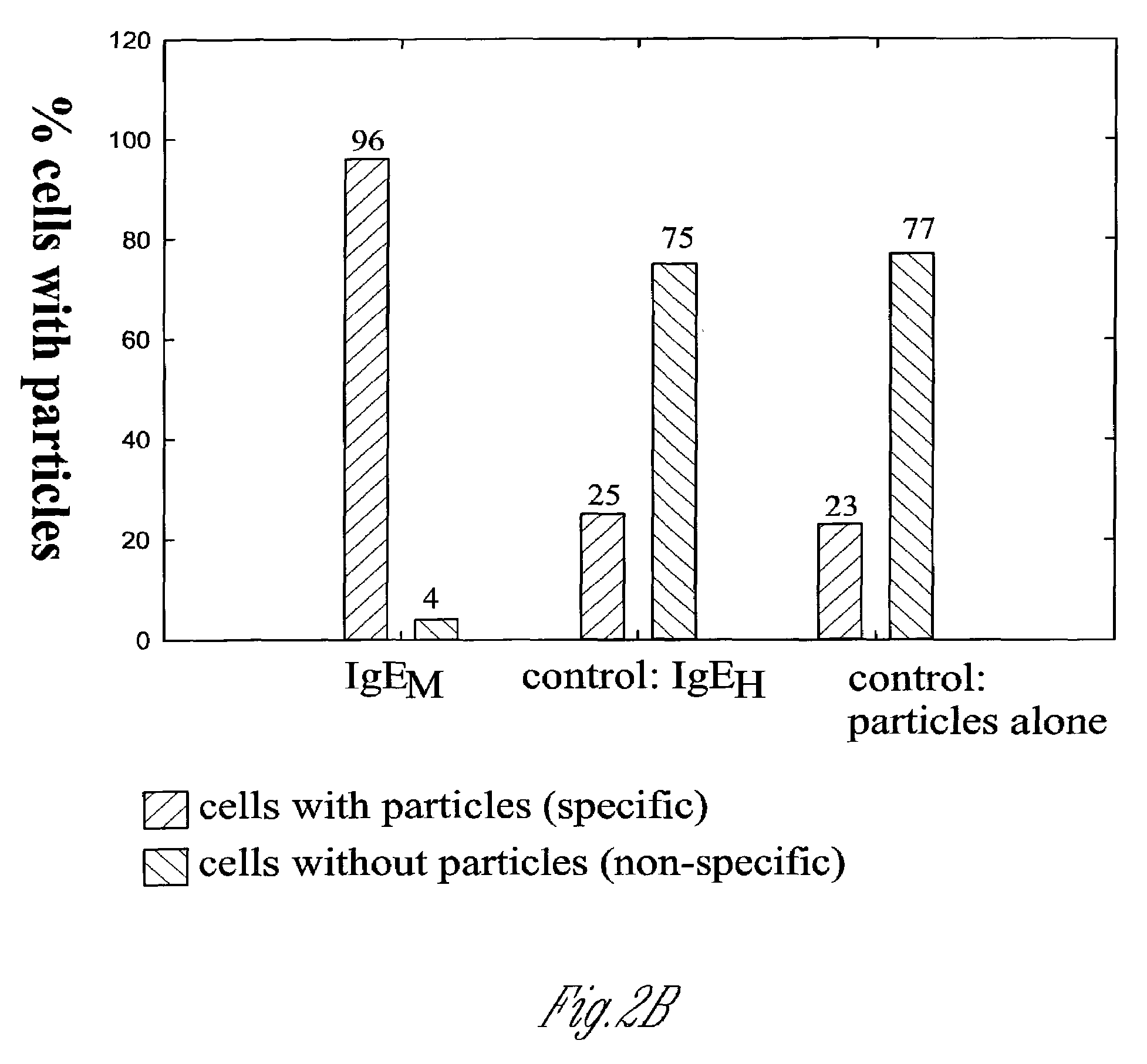
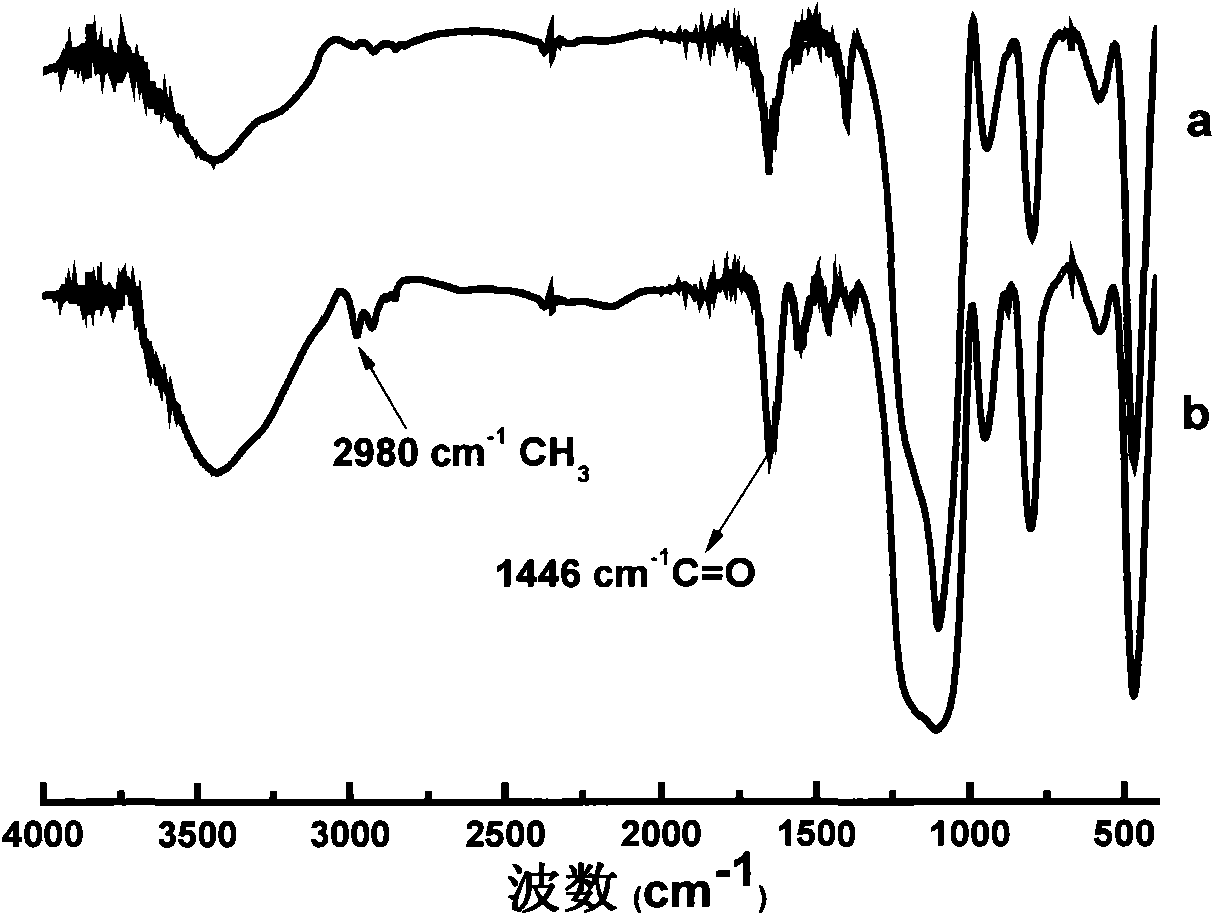
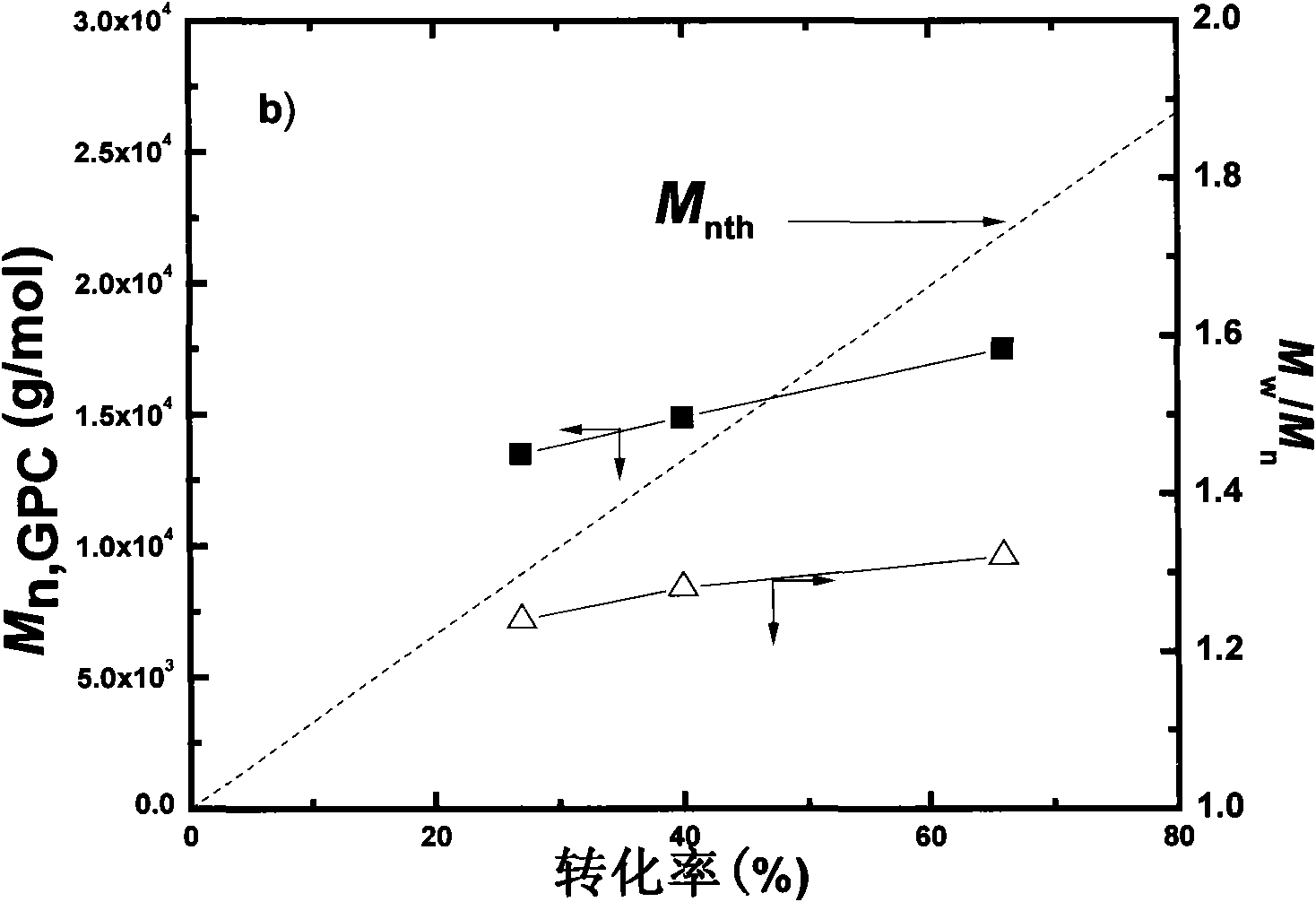
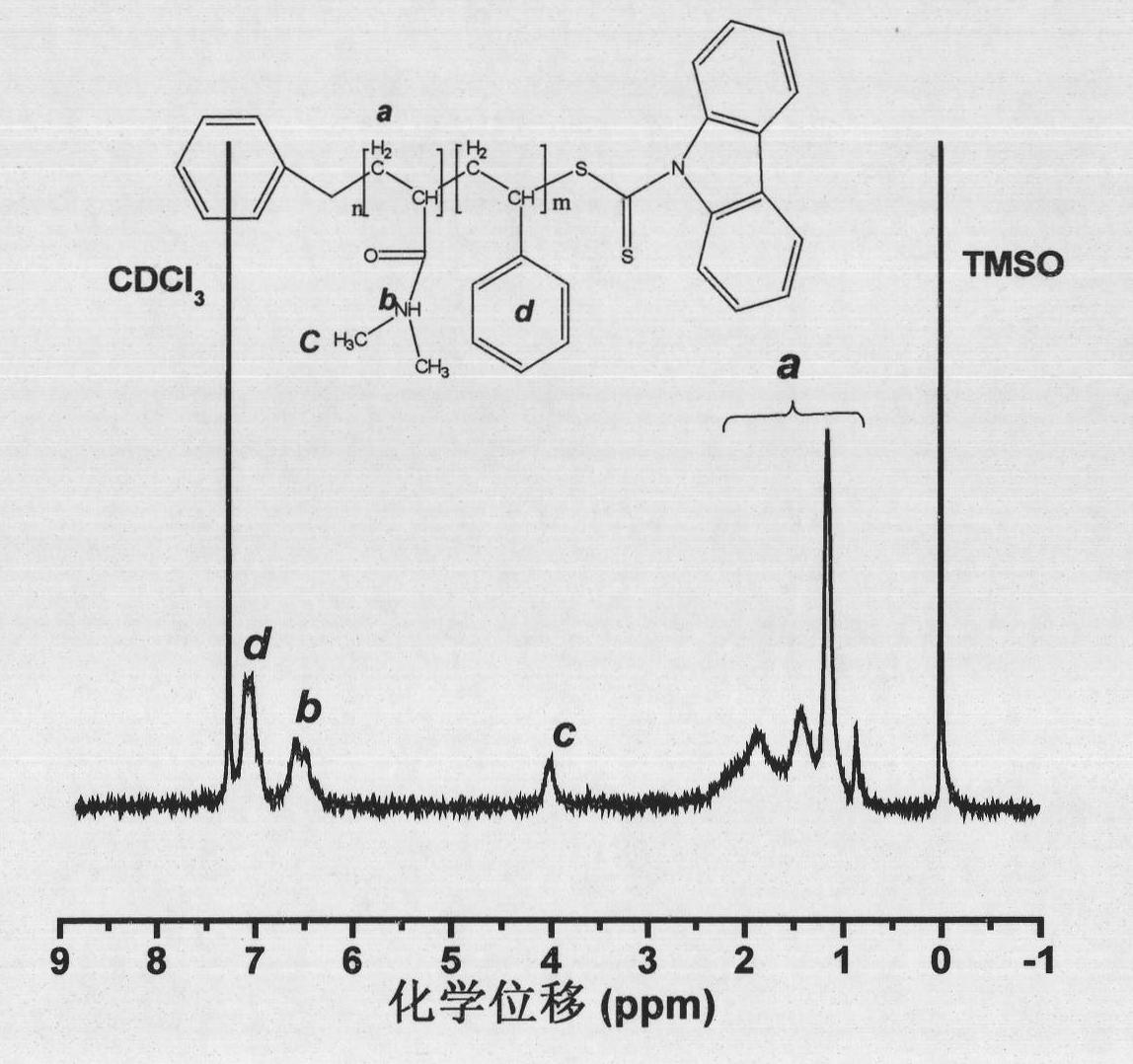
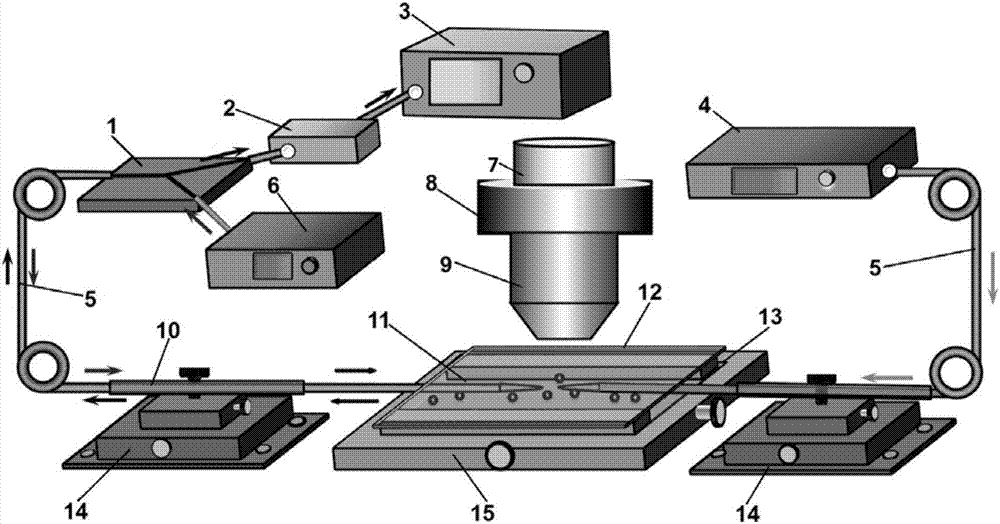
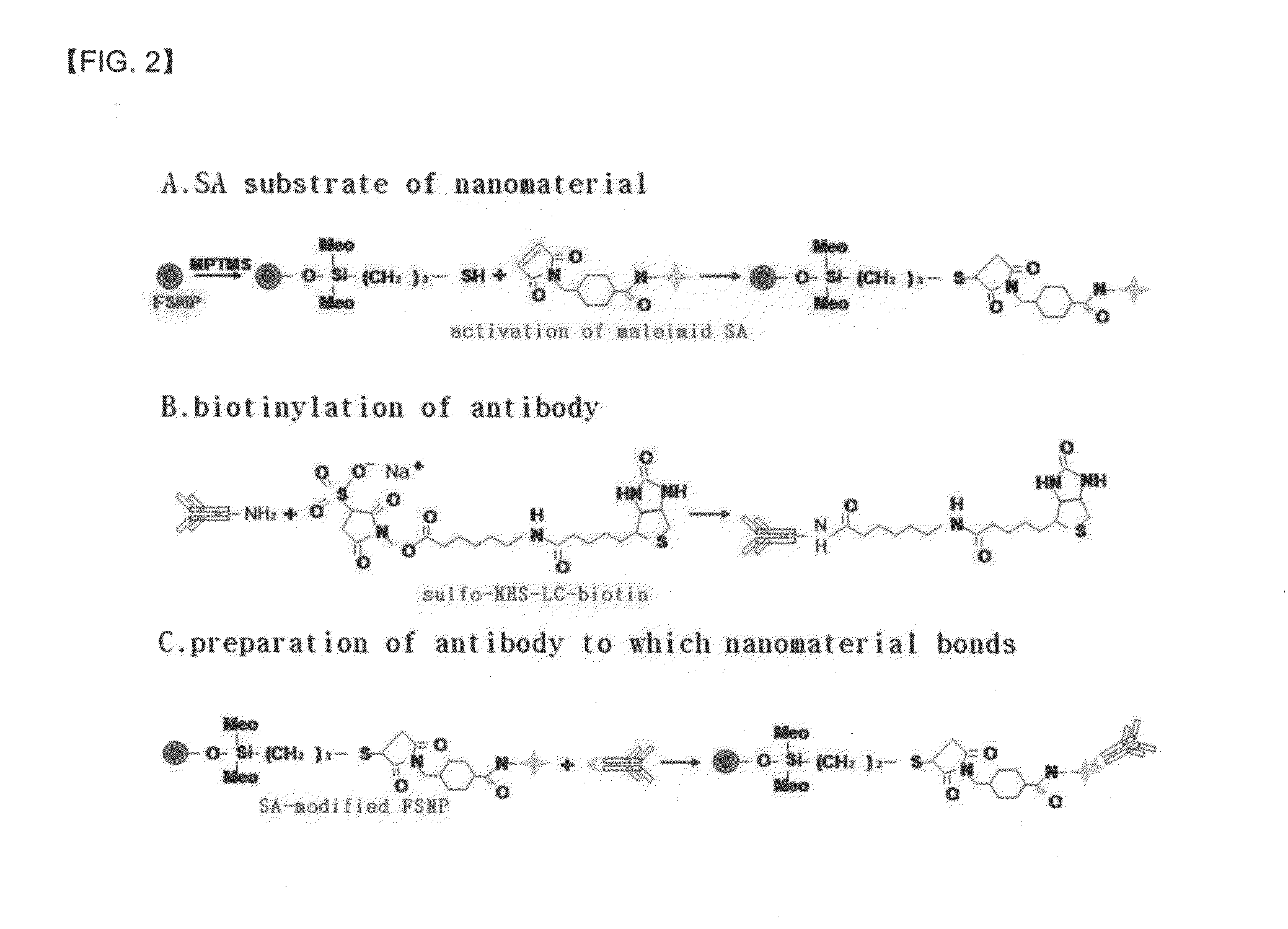Patents
Literature
325 results about "Fluorescent nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20060246524A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryIn situ hybridisationOrganic chemistry
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Nanoparticle treated medical devices
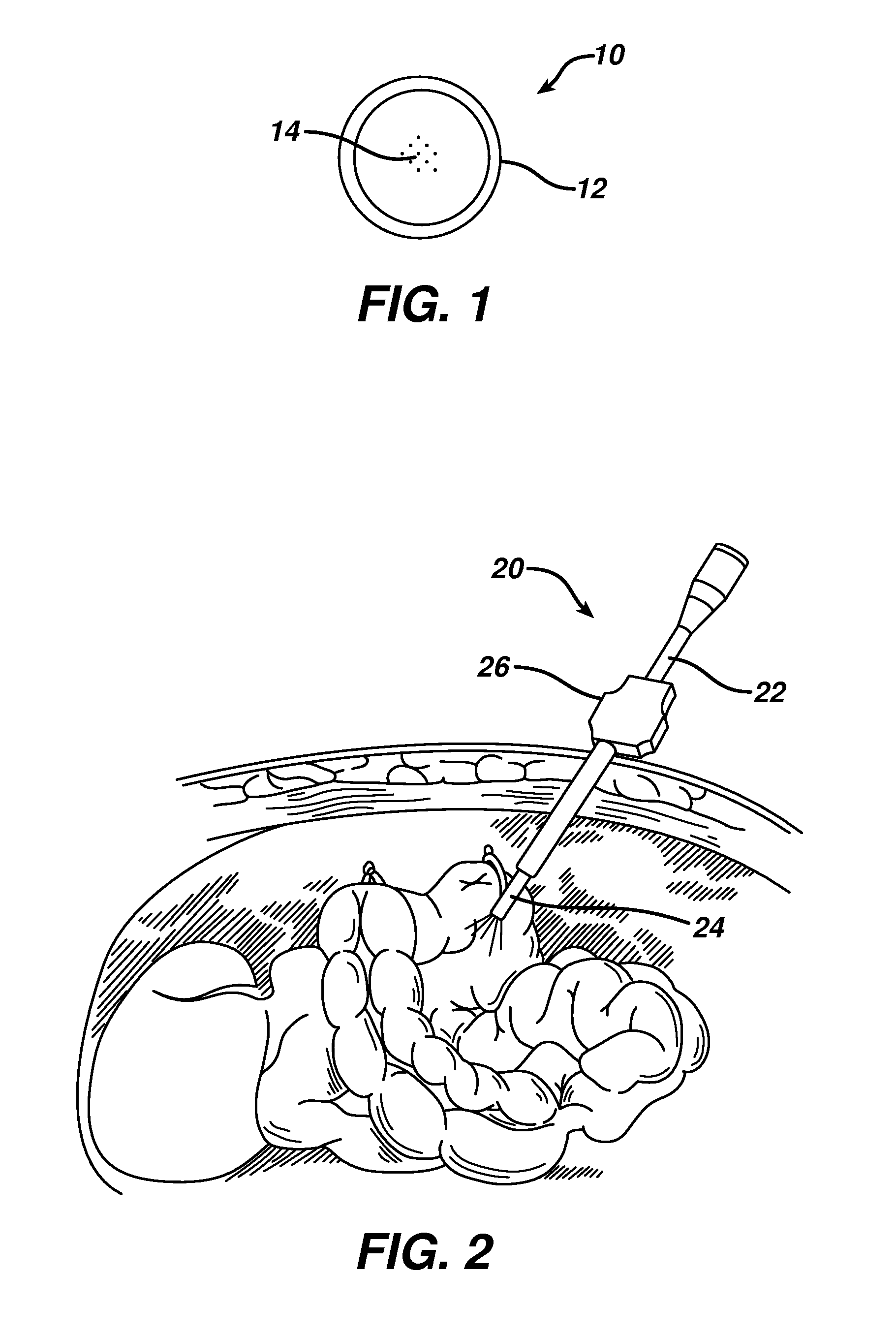
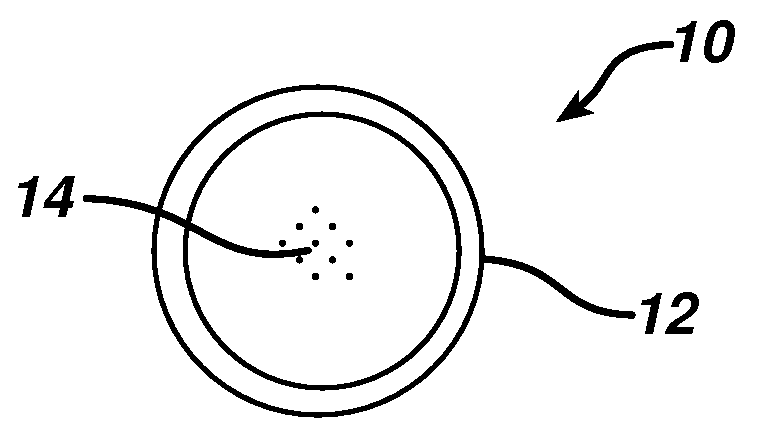
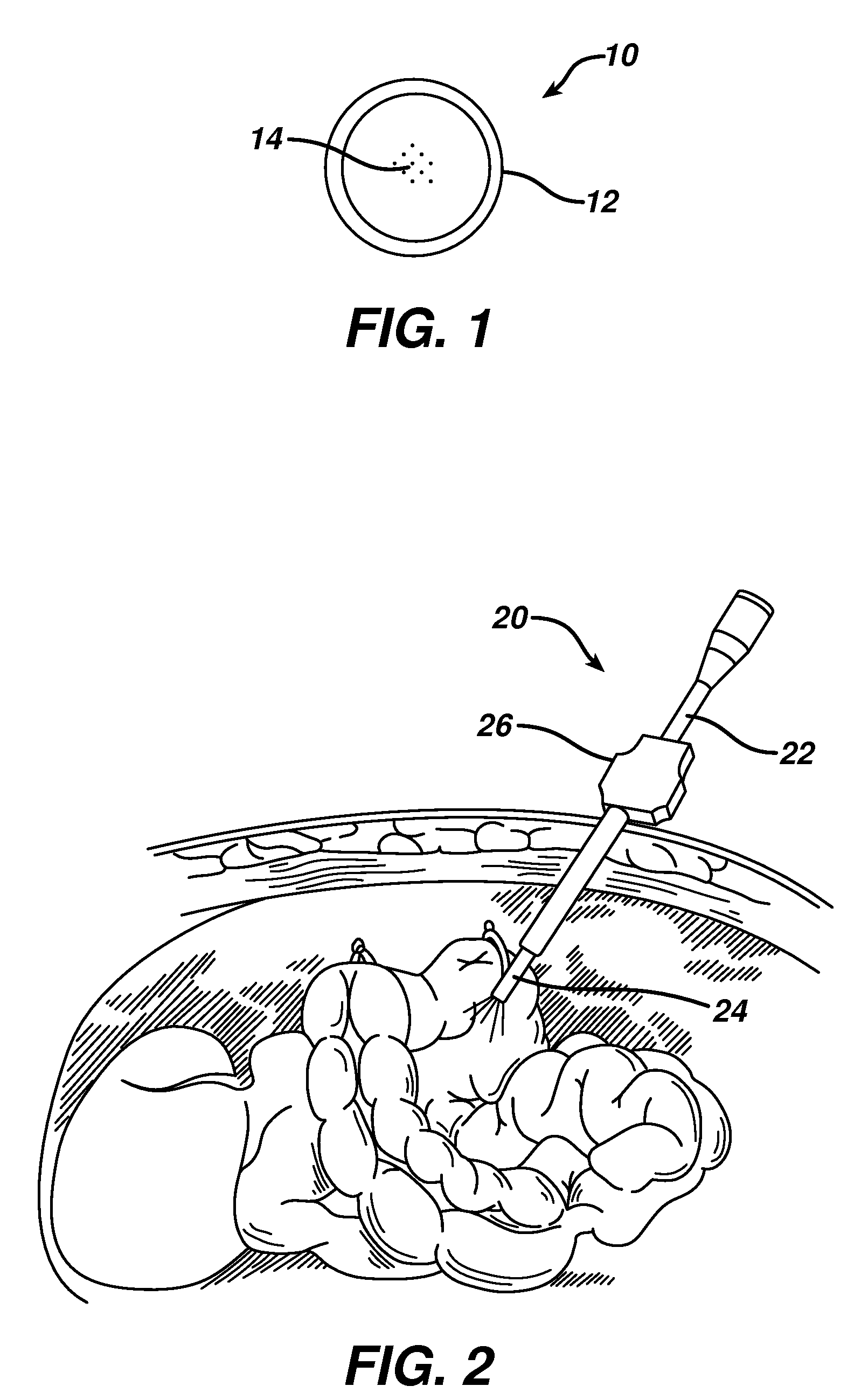
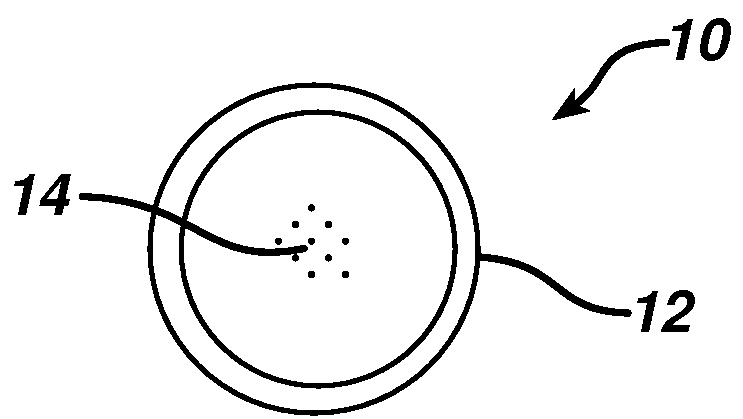
Various compositions, methods, and devices are provided that use fluorescent nanoparticles, which can function as markers, indicators, and light sources. The fluorescent nanoparticles can be formed from a fluorophore core surrounded by a biocompatible shell, such as a silica shell. In one embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be delivered to tissue to mark the tissue, enable identification and location of the tissue, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the tissue. In another embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be used on a device or implant to locate the device or implant in the body, indicate an orientation of the device or implant, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the device or implant. The fluorescent nanoparticles can also be used to provide a therapeutic effect.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Biocompatible nanoparticle compositions and methods
ActiveUS20080255537A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryTherapeutic effectBiocompatible nanoparticles
Various compositions, methods, and devices are provided that use fluorescent nanoparticles, which can function as markers, indicators, and light sources. The fluorescent nanoparticles can be formed from a fluorophore core surrounded by a biocompatible shell, such as a silica shell. In one embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be delivered to tissue to mark the tissue, enable identification and location of the tissue, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the tissue. In another embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be used on a device or implant to locate the device or implant in the body, indicate an orientation of the device or implant, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the device or implant. The fluorescent nanoparticles can also be used to provide a therapeutic effect.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Microparticles with multiple fluorescent signals and methods of using same
This invention provides a novel fluorescent particle including a core or carrier particle having on its surface a plurality of smaller polymeric particles or nanoparticles, which are stained with different fluorescent dyes. When excited by a light source they are capable of giving off multiple fluorescent emissions simultaneously, which is useful for multiplexed analysis of a plurality of analytes in a sample. The coupled complex particles carrying on their surface fluorescent nanoparticles, methods of preparing such polymer particles, and various applications and methods of using such particles are claimed.
Owner:LUMINEX
Magnetic nanoparticle therapies
Various compositions, methods, and devices are provided that use fluorescent nanoparticles, which can function as markers, indicators, and light sources. The fluorescent nanoparticles can be formed from a fluorophore core surrounded by a biocompatible shell, such as a silica shell. In one embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be delivered to tissue to mark the tissue, enable identification and location of the tissue, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the tissue. In another embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be used on a device or implant to locate the device or implant in the body, indicate an orientation of the device or implant, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the device or implant. The fluorescent nanoparticles can also be used to provide a therapeutic effect.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
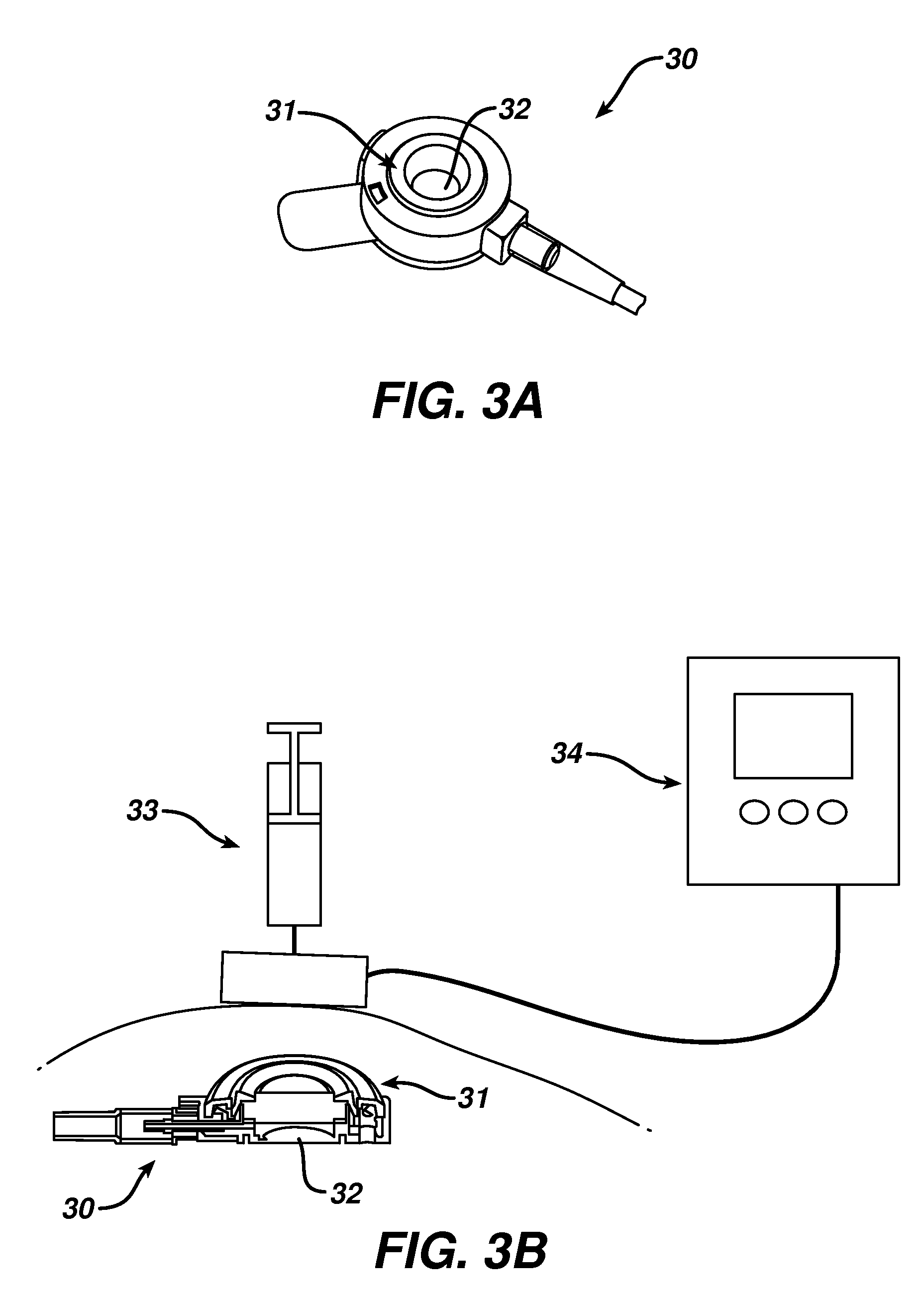
Fluorescent nanoparticle scope
Various compositions, methods, and devices are provided that use fluorescent nanoparticles to function as markers, indicators, and light sources. In one embodiment, an endoscopic adaptor is provided for viewing fluorescent nanoparticles. The adaptor can be configured to removably mate to a portion of an endoscope, such as an eyepiece, and it can be adapted to contain a filter for filtering light received through the viewing lumen of the eyepiece. In an exemplary embodiment, the filter is configured to transmit fluorescent light while blocking visible light, to thereby enable a structure containing one or more fluorescent nanoparticles to be viewed through the endoscope.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Sentinel node identification using fluorescent nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080255459A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliverySentinel nodeTreatment effect
Various compositions, methods, and devices are provided that use fluorescent nanoparticles, which can function as markers, indicators, and light sources. The fluorescent nanoparticles can be formed from a fluorophore core surrounded by a biocompatible shell, such as a silica shell. In one embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be delivered to tissue to mark the tissue, enable identification and location of the tissue, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the tissue. In another embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be used on a device or implant to locate the device or implant in the body, indicate an orientation of the device or implant, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the device or implant. The fluorescent nanoparticles can also be used to provide a therapeutic effect.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Biocompatible Fluorescent Silicon Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080102036A1Efficiently labeledUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoNanometre
The invention features biocompatible fluorescent nanoparticle and their use in in vivo imaging methods.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Preparation method and application of magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with shell-core structure
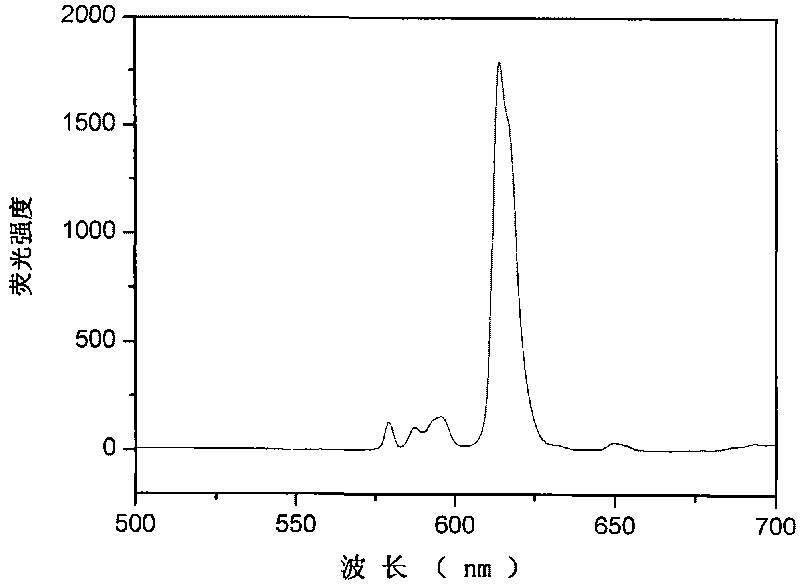
ActiveCN102500291AHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyExcitation spectral bandwidthMagnetic materialsMicroballoon preparationMicrospherePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with a shell-core structure. Firstly, a silica magnetic microsphere with a shell-core structure is prepared by using one or more than one of nanoparticles of Fe3O4, gamma-Fe2O3, MeFe2O4 (Me=Co, Mn, Ni), metal Ni, Co, Fe, and alloy Fe-Co, Ni-Fe as the inner core, and coating a silica shell, and then a fluorescent material (a chelate of Eu3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Tb3+ and the like) is absorbed on the silica shell. Then, a layer of silica is coated on the surface to improve the stability of the fluorescent magnetic microsphere, and to prevent agglomeration and fluorescent material leakage. A lot of rare earth fluorescent materials are wrapped in the shell layer, so the fluorescence intensity signal of a prepared sample is greatly increased. The nanoparticle has dual functions of enrichment and marking, and has wider application prospects in the biomedical field.
Owner:SHENZHEN BIOEASY BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Fluorescent ink
A water-based ink for use in an ink jet printer for printing machine-readable indicia on a substrate is disclosed. The ink jet ink comprises fluorescent nanoparticles having a diameter between about 30 nm and about 100 nm; and an aqueous liquid vehicle. The aqueous liquid vehicle comprises water and a water soluble vehicle in sufficient amounts to achieve an ink viscosity and surface tension effective for application of the ink jet ink to the substrate in a predetermined pattern by ink jet printing.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
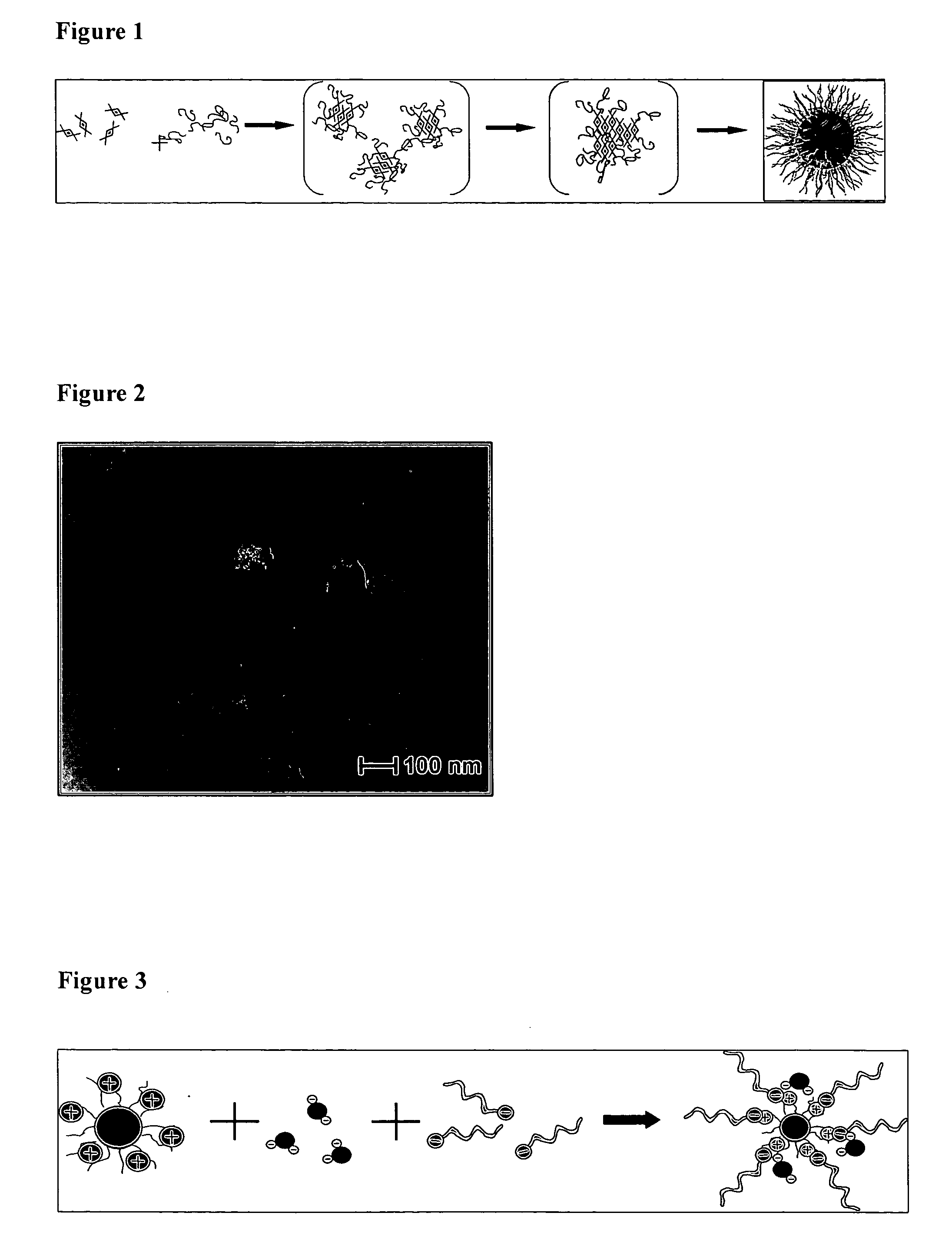
Optically fluorescent nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070104649A1Simple processHigh dye concentrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryPolyelectrolyteActive agent
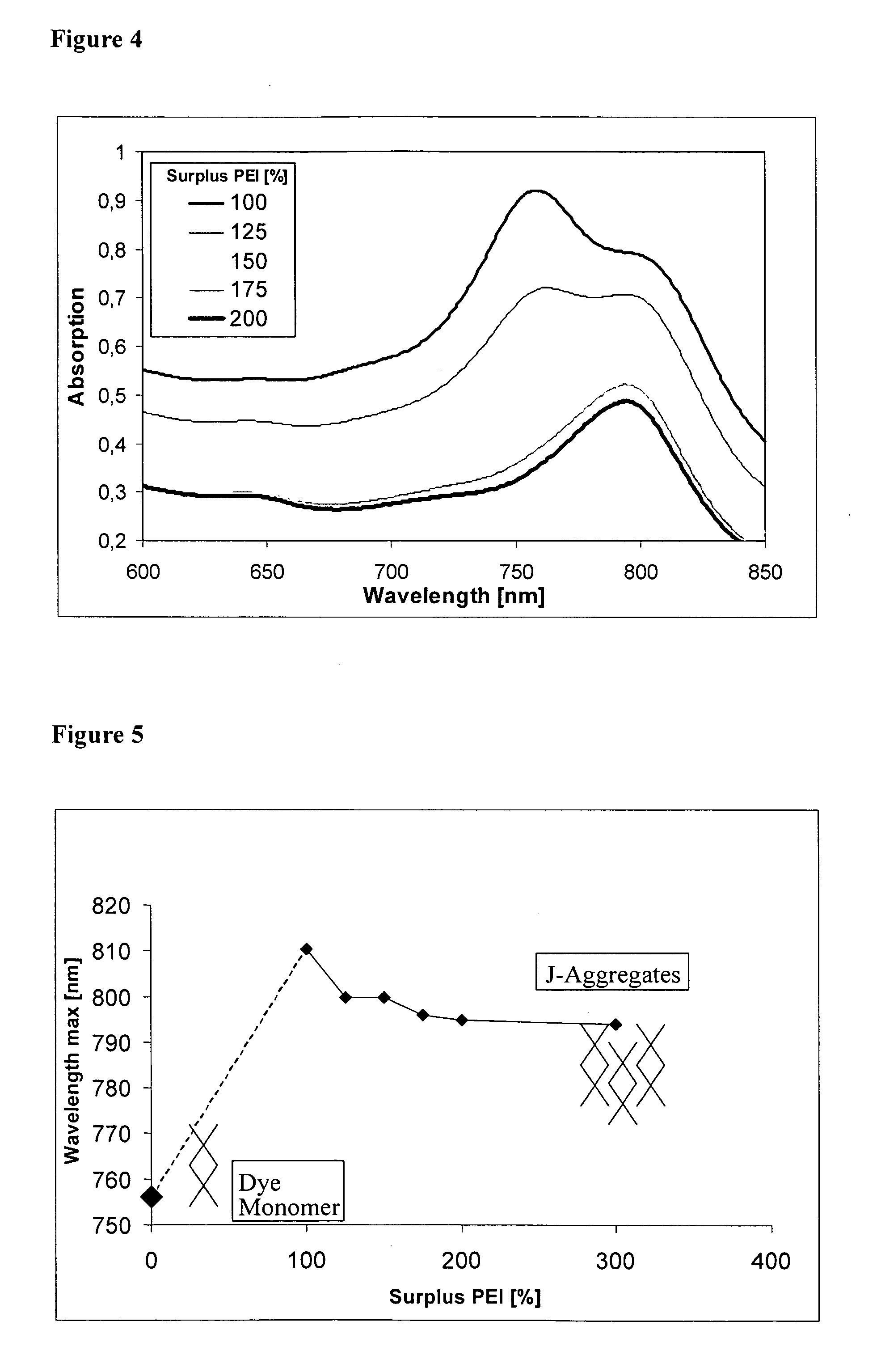
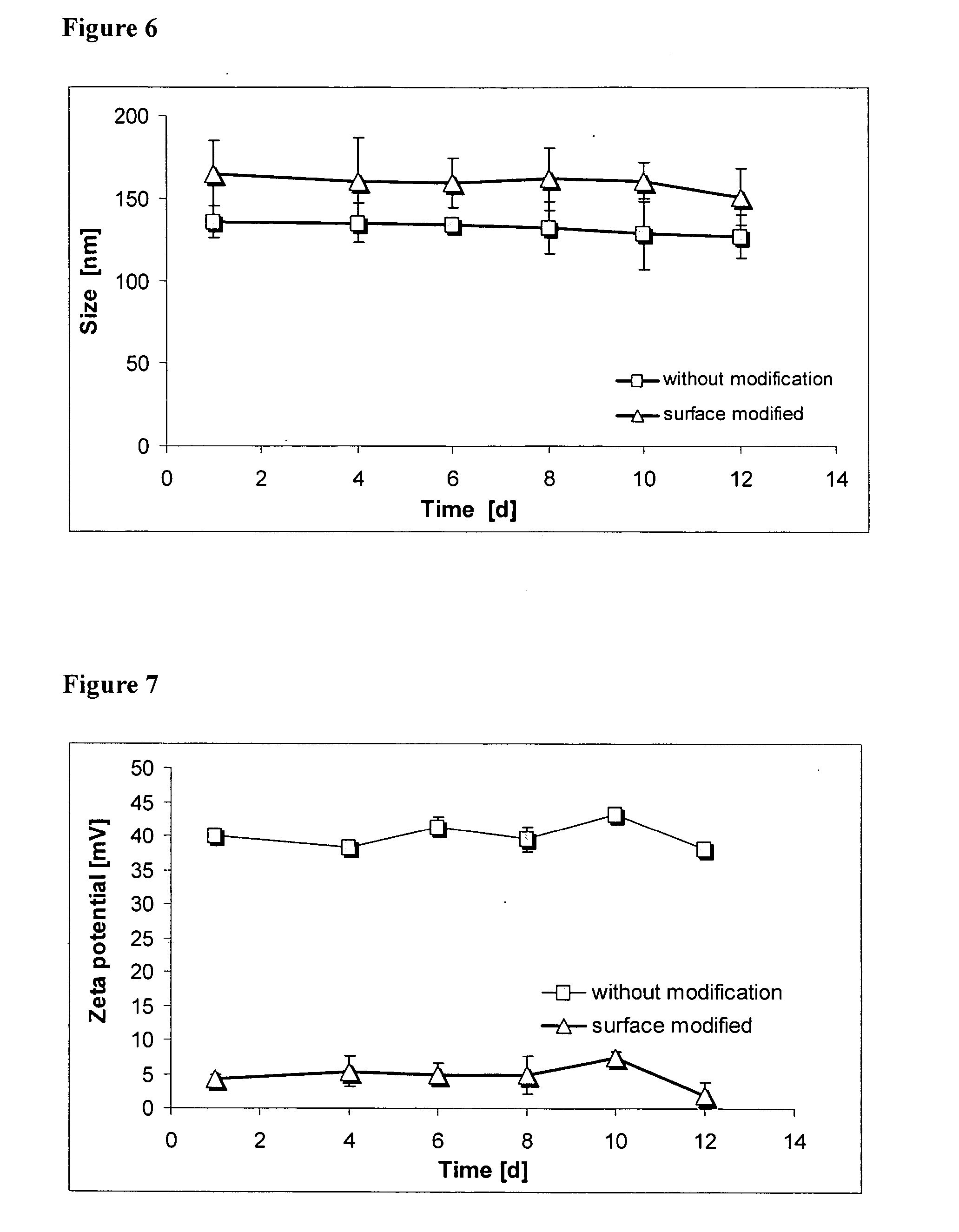
The present invention refers to nanoparticles having optically fluorescent activity. In more detail, the invention refers to a nanoparticle matrix comprising a co-aggregate of at least one charged polyelectrolyte and at least one oppositely charged active agent, wherein the active agent is a hydrophilic optically fluorescent agent, and the invention further refers to a nanoparticle comprising said nanoparticle matrix. Optionally, the nanoparticle is surface modified. The invention also refers to a method for preparing said nanoparticle, and to a method of surface modification. Furthermore, the invention refers to uses of said nanoparticle in vitro and in vivo, and to methods for in vitro and in vivo diagnosis.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Preparation method of chiral fluorescent nanoparticle based on hyperbranched conjugated polymer
InactiveCN102627776AOvercome high pricesOvercoming complexityLuminescent compositionsSolubilityLimonene
The invention discloses a preparation method of a chiral fluorescent nanoparticle based on a hyperbranched conjugated polymer. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a hyperbranched polymer containing 9,9-dioctylfluorene and a bithiophene unit into a trichloromethane solution of which the solubility is 1*10<-3> to 1*10<-1> mg / mL; and adding one of (R)-limonene or (S)-limonene into the trichloromethane solution of the copolymer together with methanol, and mixing uniformly to obtain a stable turbid solution, wherein the volume ratio of the (R)-limonene or (S)-limonene to the methanol to the copolymer is (1-8):(8-1):1. In the method, a solvent chiral transfer technology is applied to the preparation of a hyperbranched polymer chiral fluorescent nanoparticle with a hyperbranched polymer, so that the problems of high price of a chiral reagent, complex synthesis steps and the like existing in the conventional method for synthesizing the hyperbranched polymer chiral fluorescent nanoparticle are solved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
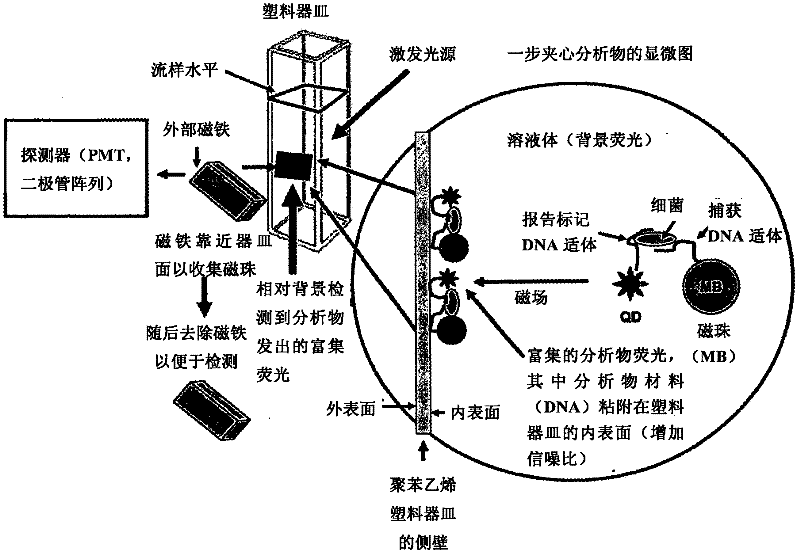
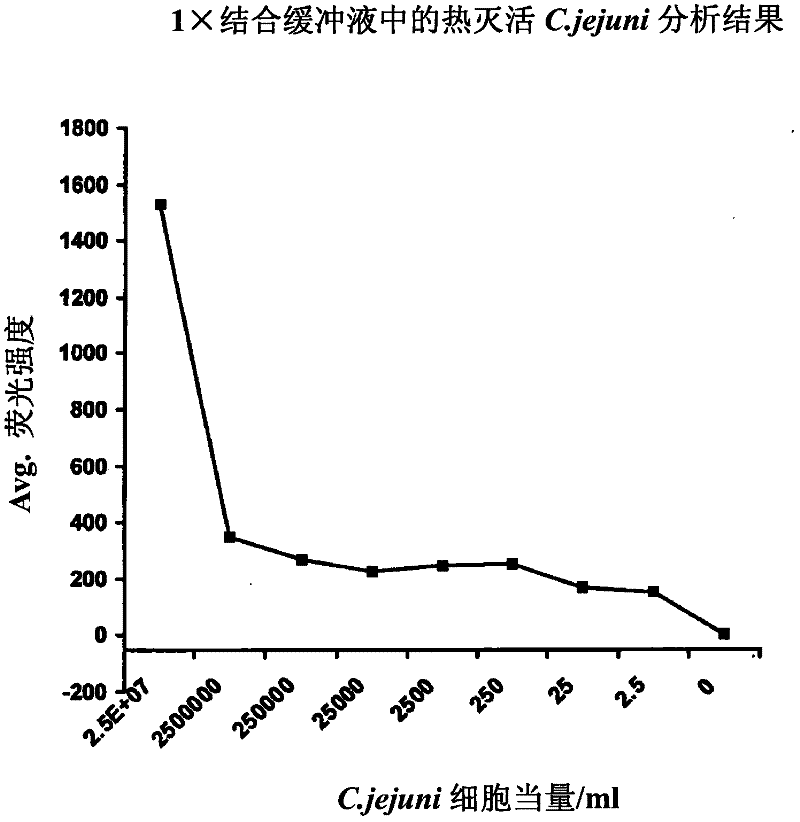
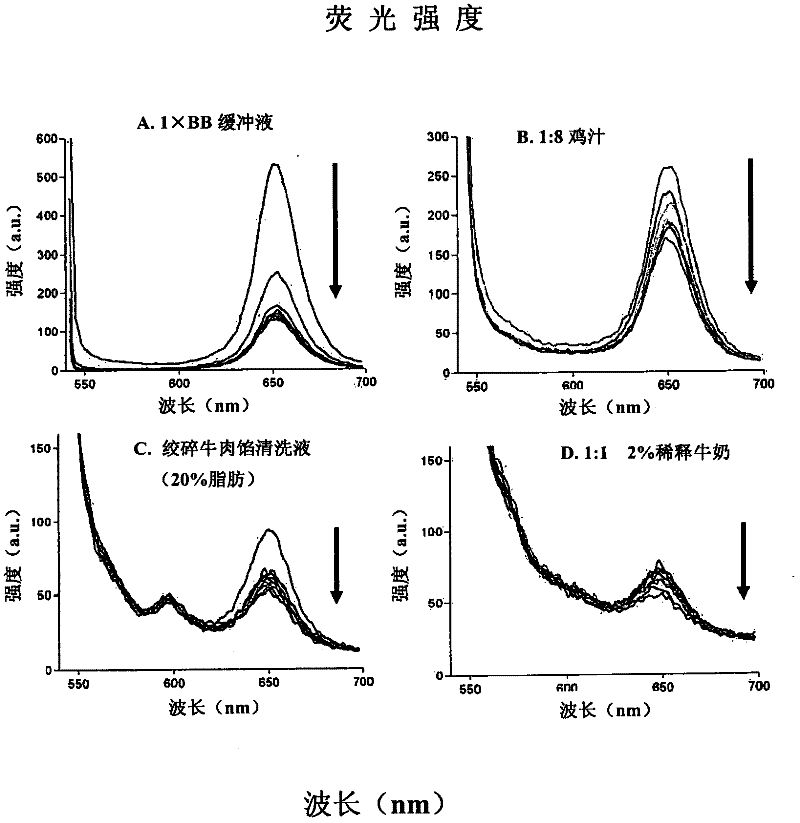
Methods of producing homogeneous plastic-adherent aptamer-magnetic bead-fluorophore and other sandwich assays
Methods are described for assembly of DNA aptamer-magnetic bead ('MB') conjugate plus aptamer-quantum dot ('QD') aptamer-fluorescent nanoparticle or other aptamer-fluorophore, aptamer-chemiluminescent reporter, aptamer-radioisotope or other aptamer-reporter conjugate sandwich assays that enable adherence to glass, polystyrene and other plastics. Adherence to glass or plastics enables detection of surface-concentrated partitioning of fluorescence versus background (bulk solution) fluorescence in one step (without a wash step) even when the external magnetic field for concentrating the assay is removed. This assay format enables rapid, one-step (homogeneous) assays for a variety of analytes without wash steps that do not sacrifice sensitivity.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
Radiation curable ink containing fluorescent nanoparticles
ActiveUS8222313B2Suitable thermal degradation propertySolesBenzoxanthene dyesEmulsion polymerizationParticle growth
Radiation curable compositions, such as UV curable ink compositions, contain a polymeric dispersant, a curable material, that includes a carrier and at least one nanoscale fluorescent pigment particle and an optional non-fluorescent colorant. The fluorescent organic nanoparticle composition includes one or more fluorescent dyes dispersed in a polymeric matrix obtained by modified EA latex process or by emulsion polymerization. In a different embodiment, the nanoscale fluorescent pigment particle composition includes pigment molecules with at least one functional moiety, and a sterically bulky stabilizer compound including at least one functional group, the functional moiety of the pigment associates non-covalently with the functional group of the stabilizer, and the presence of the associated stabilizer limits the extent of particle growth and aggregation, to afford nanoscale-sized pigment particles.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Multilayer fluorescent nanoparticles and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20160018404A1Minimize energy transferNot decrease relative fluorescence emissionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryMaterials scienceFluorescent nanoparticles
A multilayer, fluorescently responsive material (FRM)-containing nanoparticle and compositions comprising such nano-particles. The nanoparticles can be made using a layer-by-layer deposition method. The nanoparticles can be used in imaging methods such as, for example, cellular imaging methods.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
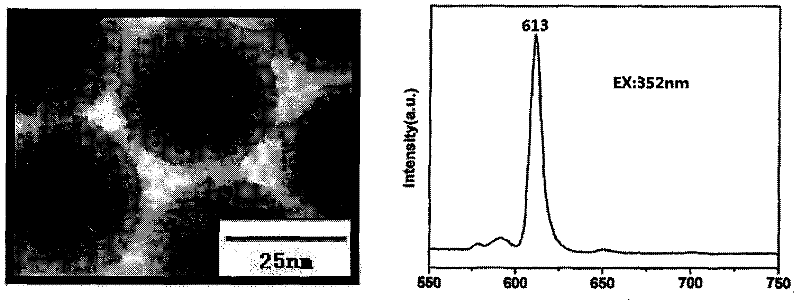
Fluorescent nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101701151ANarrow emission peakHigh strengthLuminescent compositionsMaterial analysisPhotoluminescenceHydrophobic polymer
The invention discloses a class of fluorescent nanoparticles and a preparation method and an application thereof. The fluorescent nanoparticle comprises matrix material and fluorescent dye dispersed in the matrix material, wherein the matrix material is the compound composed of hydrophobic polymer main chain of which is hydrocarbon chain, organo-siloxane and organosilicon-polymer, and the fluorescent dye is rare earth complex with photoluminescence performance. The preparation method of the fluorescent nanoparticle comprises the following steps: dissolving rare earth complex, hydrophobic polymer and compound RSi (OR') 3 into organic solvent miscible with water; adding the mixture into aqueous solution containing surfactant; using precipitation and hydrolytic condensation reaction to form nanoparticles. The nanoparticle of the invention has favourable luminous performance and favourable stability, can have a silicon oxide shell and a surface functional group and can be used for bondingbiomolecules; biological probes based on the fluorescent nanoparticle have wide application prospects on the aspects of high-sensitivity fluorescence immunoassay, imaging and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Upconversion fluorescent ink for inkjet printer and preparation method of upconversion fluorescent ink
The invention discloses an upconversion fluorescent ink for an inkjet printer. The upconversion fluorescent ink comprises, by weight, 1-10 parts of rare-earth doped upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles, 1600-2000 parts of ink solvent and 300-800 parts of thickener, the rare-earth doped upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles are sodium yttrium fluoride nanoparticles co-doped by rare-earth activator and rare-earth sensitizer, the rare-earth activator is erbium, thulium or holmium, and the rare-earth sensitizer is ytterbium or erbium. The upconversion fluorescent ink for the inkjet printer has the advantages of good anti-counterfeiting effect and long fixation time and storage life and can realize individualized instant anti-counterfeiting printing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
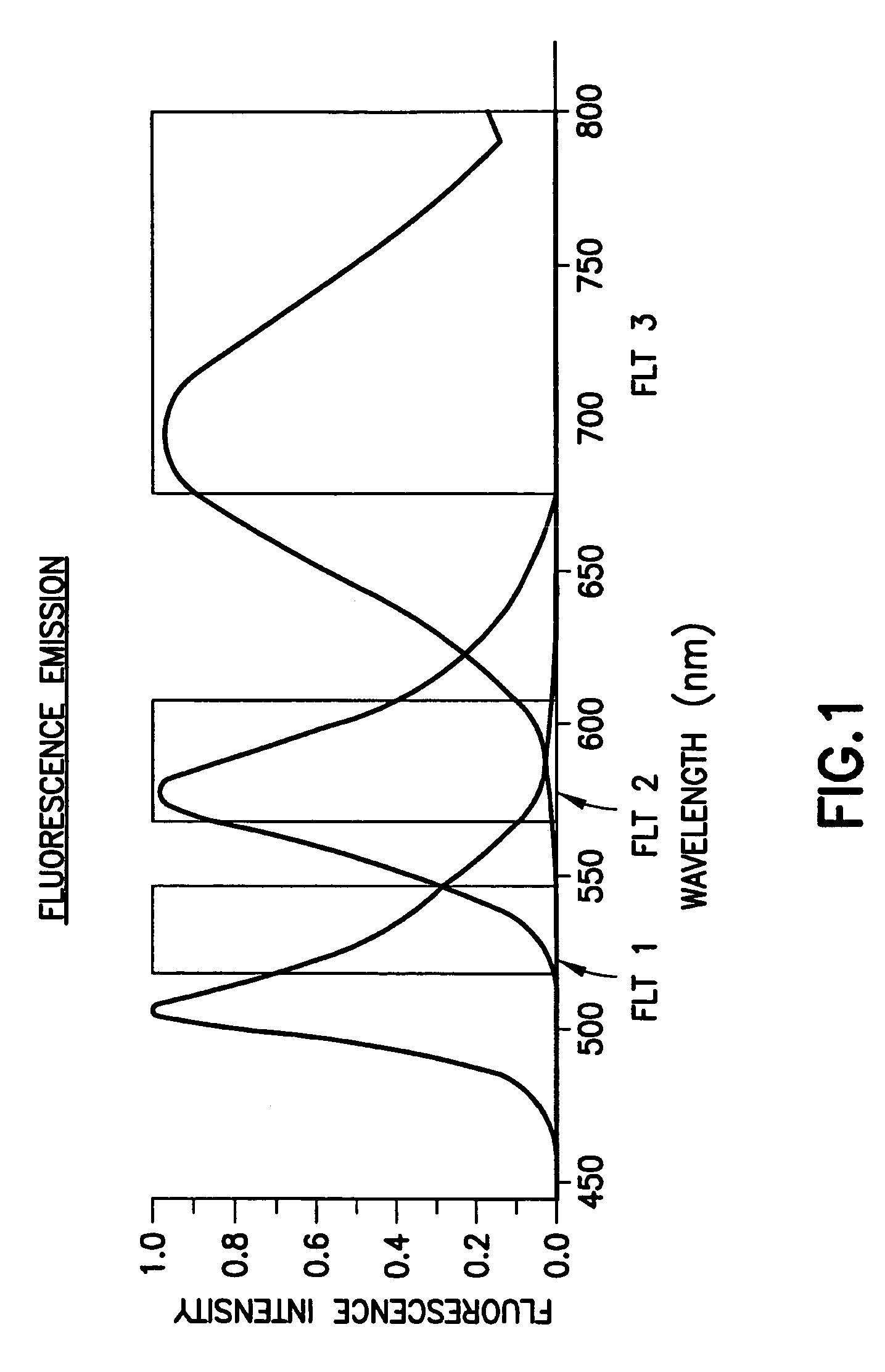
Use of fluorescent nanoparticles to measure individual layer thicknesses or composition in multi-layer films and to calibrate secondary measurement devices
ActiveUS7858953B2Quantity minimizationEffective controlLuminescent dosimetersFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeasurement deviceQuantum dot
Fluorescent nanoparticles such as quantum dots are incorporated into plastic, paper and other web layered products to achieve cross-direction and machine direction on-line analysis of the individual layers therein. Fluorescent nanoparticles markers are added in known proportions into product formulations. By detecting the fluorescence from the nanoparticles, the thickness and other physical characteristics of the web can be traced at various stages of production. In addition, by using different populations of fluorescent nanoparticles that emit radiation at different wavelengths, data from individual layers in a composite structure can be ascertained simultaneously with a single sensor. The technique is particularly suited for monitoring difficult-to-measure polymers in complex multilayer structures.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
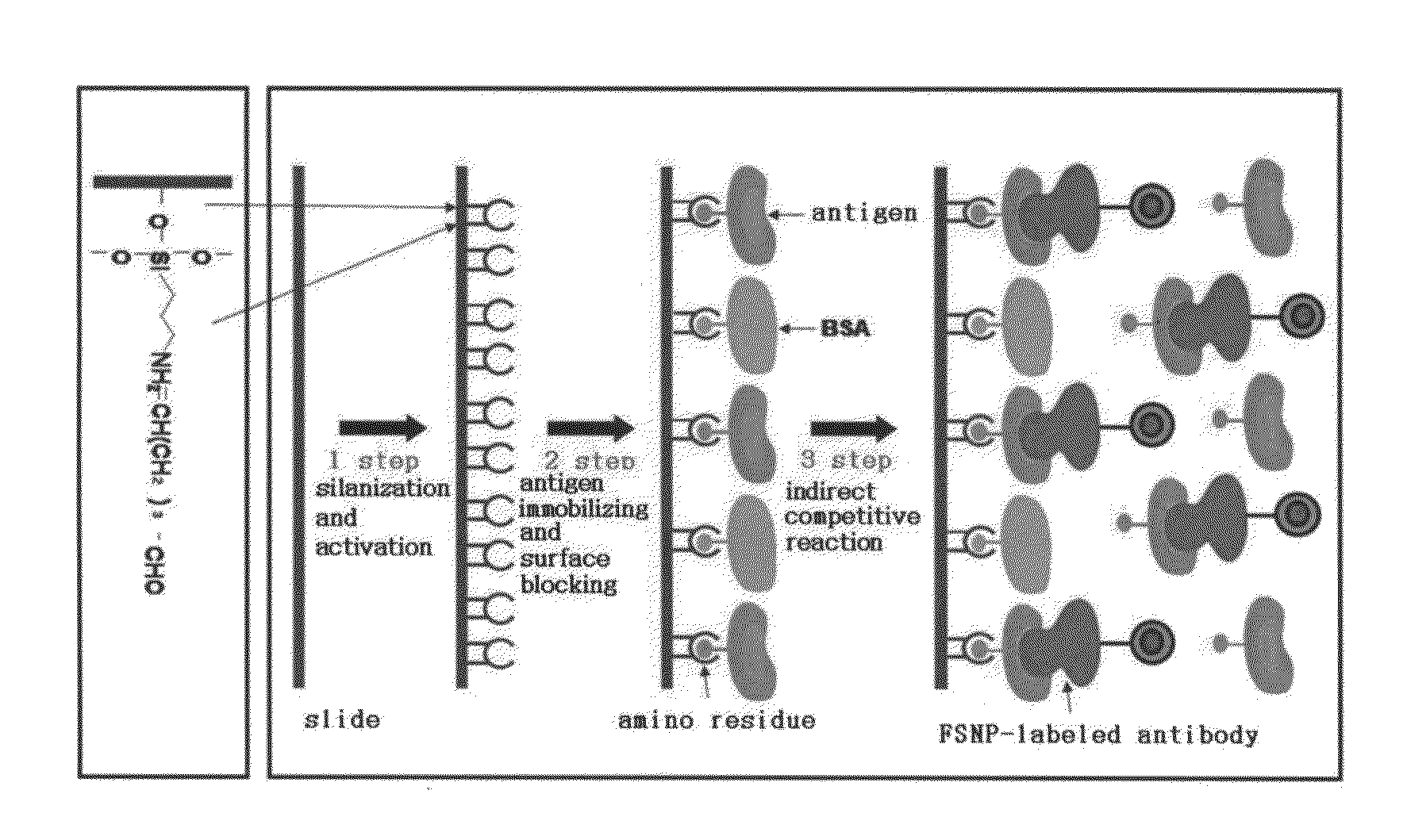
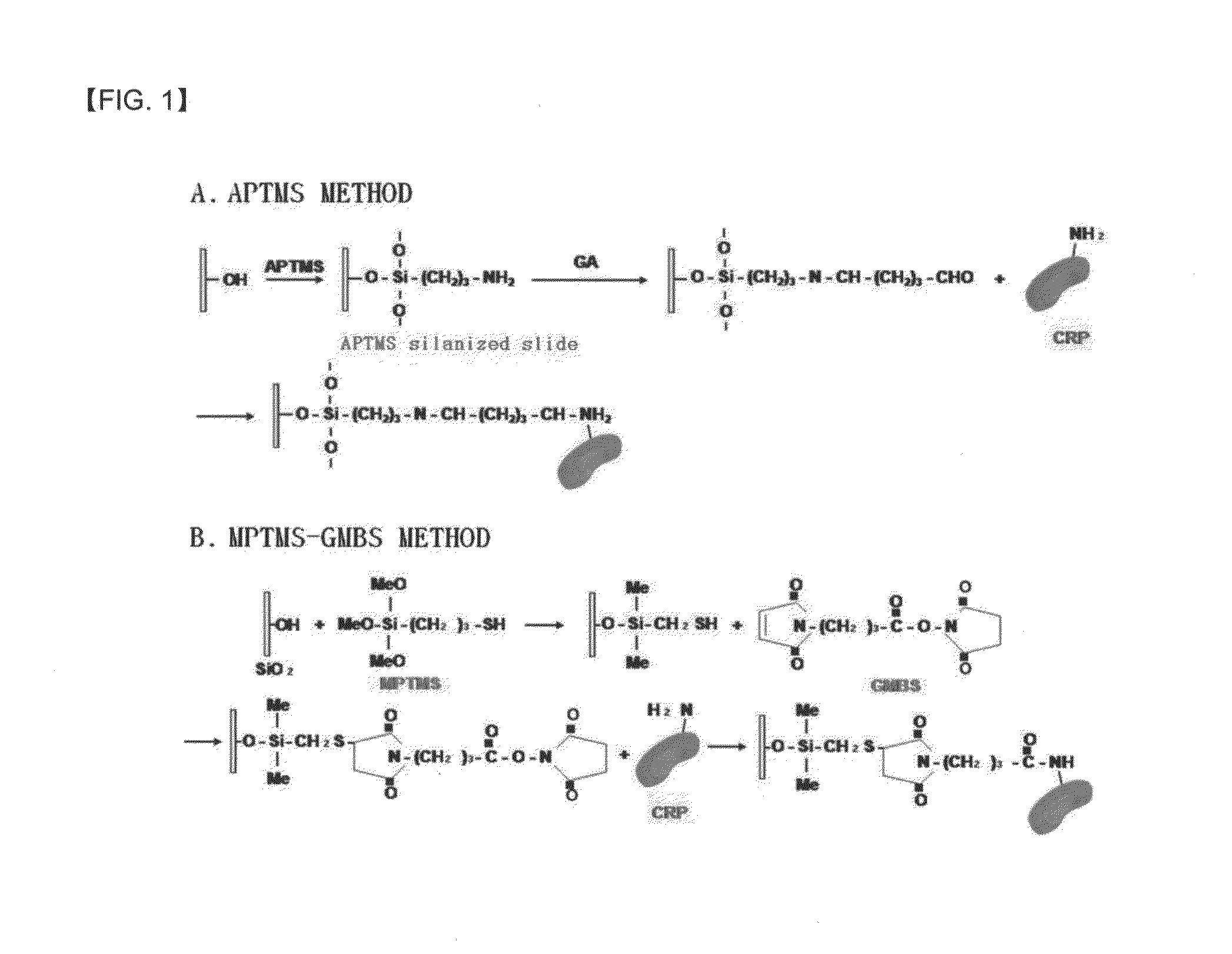
Preparation method of antigen-immobilized immuno- fluorescence slide and immuno-fluoroscence slide prepared thereby
InactiveUS20130029428A1Easily and highly-sensitively measuringBiological material analysisMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenBiotin-streptavidin complex
A method of preparing an antigen-immobilized immuno-fluorescence slide, the method comprising: immobilizing a C-reactive protein on a slide to prepare a protein chip; mixing an antibody that specifically binds to a target protein, with streptavidin to label the antibody with a fluorescent nanoparticle; immuno-reacting the antibody by competitive mixing, assaying with a fluorescence camera, wherein the immobilizing of the C-reactive protein on the slide comprises: modifying the slide with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane to prepare a modified slide; hydrating the slide modified with 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane; activating the modified slide by using a glutaraldehyde solution; dissolving a C-reactive protein at a concentration of 0.01-0.5 mg / ml in a 30-70 mM phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.5-7.8) to prepare an antigen solution for immobilization; placing a petri dish comprising the slide on a spotting guide and spotting 1-100 μl of the antigen solution on spotting points; and performing a reaction on the slide prepared as described above for 1-6 hours to immobilize the antigen, and an immune-fluorescence slide prepared by using the method.
Owner:KOREA FOOD RES INST
Fluorescent silica-based nanoparticles
The present invention provides nanoparticle compositions comprising, for example, a core comprising a fluorescent silane compound; and a silica shell on the core. Also provided are methods for the preparation of nanoparticle compositions including fluorescent nanoparticles, ligated-fluorescent nanoparticles, ligated-fluorescent nanoparticles having therapeutic agents, and ligated-fluorescent nanoparticles coupled or associated with an analyte. Also provided are methods: for the detection of the ligated-fluorescent nanoparticles; for associating the linked-fluorescent nanoparticles with a cellular component of interest and recording or monitoring the movement of the cellular component; for improving the therapeutic properties of the therapeutic agent by combining the therapeutic agent with linked-fluorescent nanoparticles and contacting or administering the combination to a cell or organism; for making and using the fluorescent nanoparticles in, for example, diagnostic agents for the detection of various analytes, and like applications.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Nanoparticle Plasmon Scattering Layer for Photovoltaic Cells
InactiveUS20120031486A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanotechnologyColloidLength wave
The present invention relates to nanoparticle compositions for use in photovoltaic cells. Nanoparticles are utilized to provide increased scattering and also wavelength shifting to increase the efficiency of the photovoltaic cells. Exemplary nanoparticles include colloidal metal and fluorescent nanoparticles.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Fluorescent Silica-Based Nanoparticles
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Preparation method of magnetic fluorescence dual functional thermo-sensitive nano particle
InactiveCN101775112AAvoid reunionReduce quenchingLuminescent compositionsPotassium hydroxideBenzyl chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic fluorescence dual functional thermo-sensitive nano particle. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a nano particle core by a routine method, then packing the magnetic nano particle with a layer of silicon dioxide, performing cholromethylation on the silicon dioxide by utilizing a chloromethyl silane coupling agent, and leading benzyl chloride wrapped on the surface of the nano particle to react with carbon disulfide in the dimethylsulfoxide solution of potassium hydroxide so as to obtain a magnetic fluorescence nano particle the surface of which is modified with an RAFT reagent; and (2) utilizing the magnetic fluorescence nano particle obtained in step (1), a thermo-sensitive monomer, a sacrificed RAFT reagent and an initiating agent to form a polymerizing system and dissolving in solvent, carrying out reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) living radical polymerization, and then performing separating to obtain the magnetic fluorescence dual functional thermo-sensitive nano particle with a nuclear shell structure. RAFT polymerization is directly carried out on the surface of the magnetic silicon oxide nano particle, thus facilitating the magnetic fluorescence dual functional nuclear shell structure to keep the stability of the structure and performance in the actual application process.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Nanometer optical tweezers device and method for accurately controlling nanoparticles and biomolecules
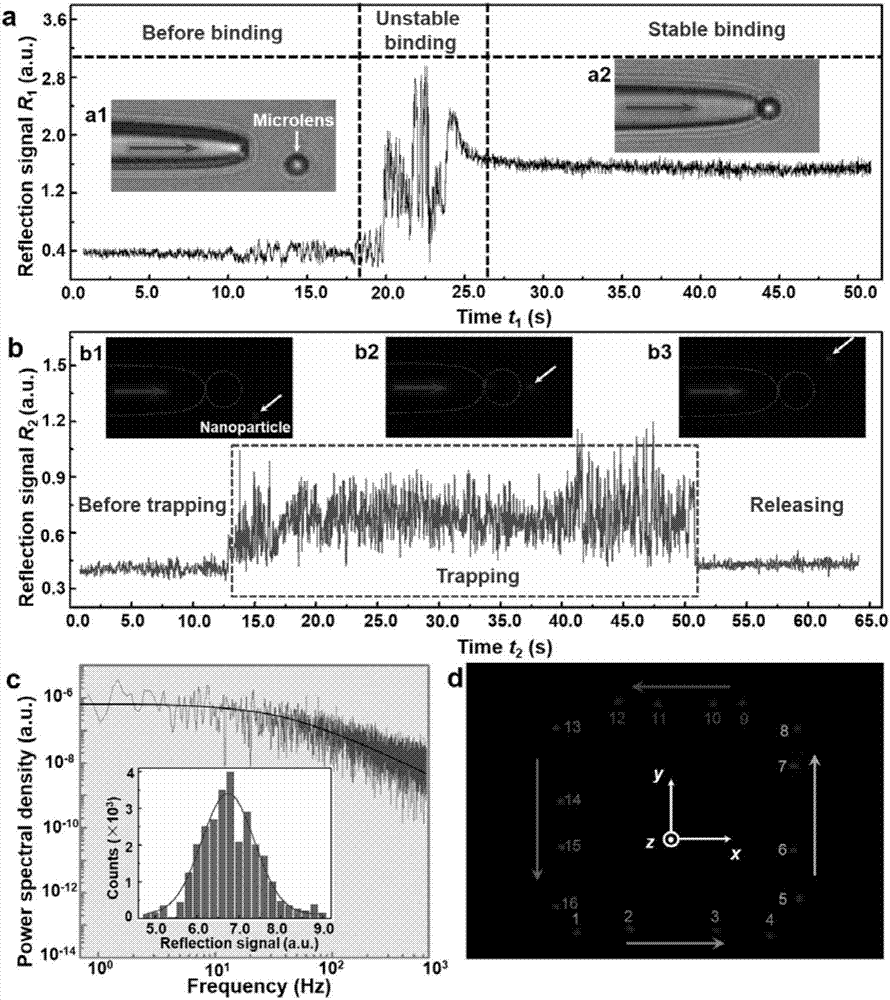
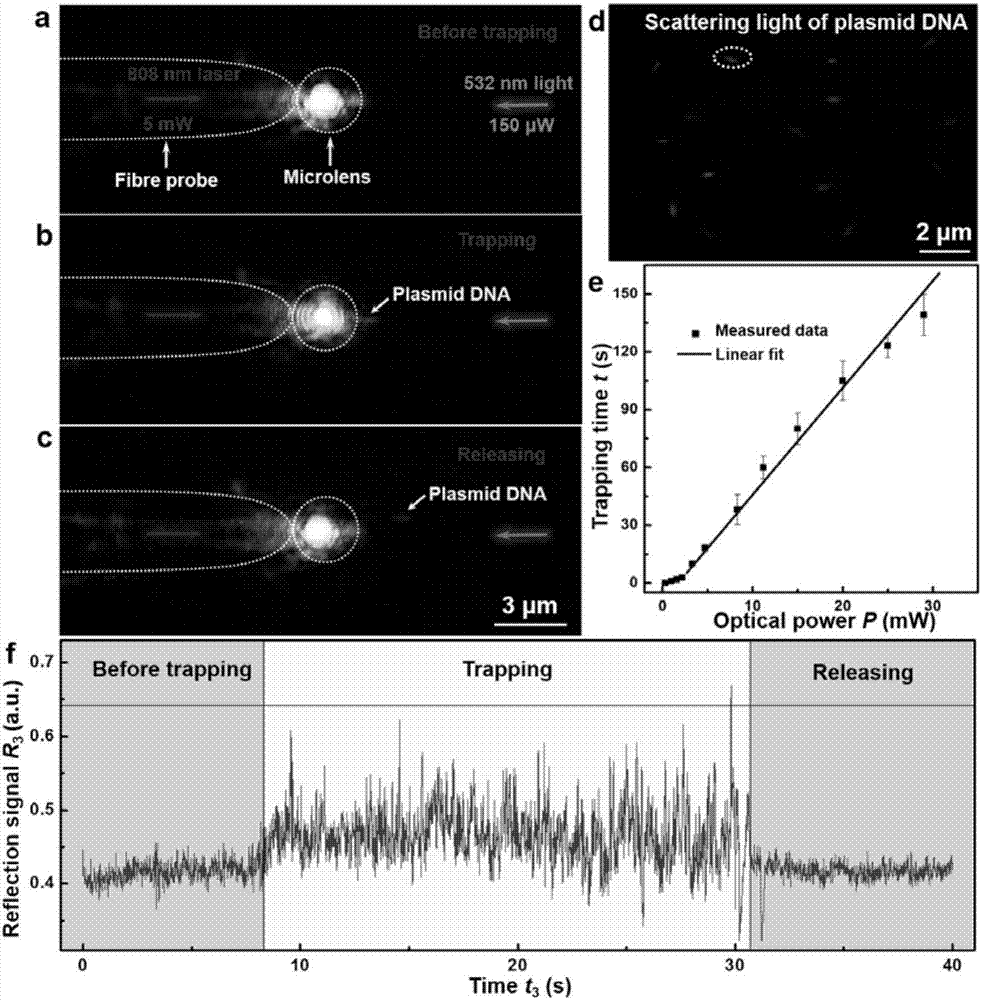
InactiveCN106898407ABreaking through the diffraction limitEasy to controlMicroscopesCoupling light guidesBand-pass filterOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a nanometer optical tweezers device and method for accurately controlling nanoparticles and biomolecules. The device includes a microscope, a microflow channel is arranged on an objective table of the microscope, the microflow channel comprises cover glass and a glass slide, two optical fibers are arranged in the microflow channel and are sleeved by glass capillaries, the glass capillaries are fixed on adjustable optical fiber adjusting frames, the other end of one of the optical fibers is connected with a Y type optical fiber coupler, two other arms of the Y type optical fiber coupler are connected with a band-pass filter and a fiber laser, the other end of the band-pass filter is connected with a photoelectric detector, and the other end of the other optical fiber is connected with a laser. The method includes the following specific steps: 1. preparing a parabola-shaped optical fiber tip used for accurate control; 2. fixing a micro lens on the optical fiber tip; 3. using the micro lens assembled in the Step 2 to capture and control fluorescent nanoparticles; and 4. capturing and controlling DNA molecules.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by oil-soluble initiator
InactiveCN104628923ASimple processEasy to scale up productionLuminescent compositionsIce waterOil phase
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by an oil-soluble initiator. The method comprises the steps of dissolving an aggregation-induced emission type fluorescent monomer, a co-stabilizer and an oil-soluble initiator into a monomeric compound to obtain an oil-phase solution; dissolving a water-soluble emulsifying agent into water to obtain a water solution of the emulsifying agent; and adding the oil-phase solution into the water solution of the emulsifying agent, stirring and pre-emulsifying to obtain a rough emulsion, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion on the rough emulsion in a 0-DEG C ice water bath to prepare a monomeric mini-emulsion, then, introducing nitrogen, removing oxygen, and reacting at the temperature of 40-90 DEG C for 0.5 hour to 2 days under the protection of nitrogen gas to prepare an emulsion of the aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the nanoparticle size, size distribution and fluorescent brightness are conveniently regulated, the stability of a system is good, the preparation process is simple, the process flow is short, and no organic solvents are consumed in preparation and after-treatment processes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Preparation method for one-size nano-particle fluorescence microsphere
InactiveCN101342472AAvoid adsorptionImprove uniformityMicroballoon preparationLuminescent compositionsSolubilityOil phase
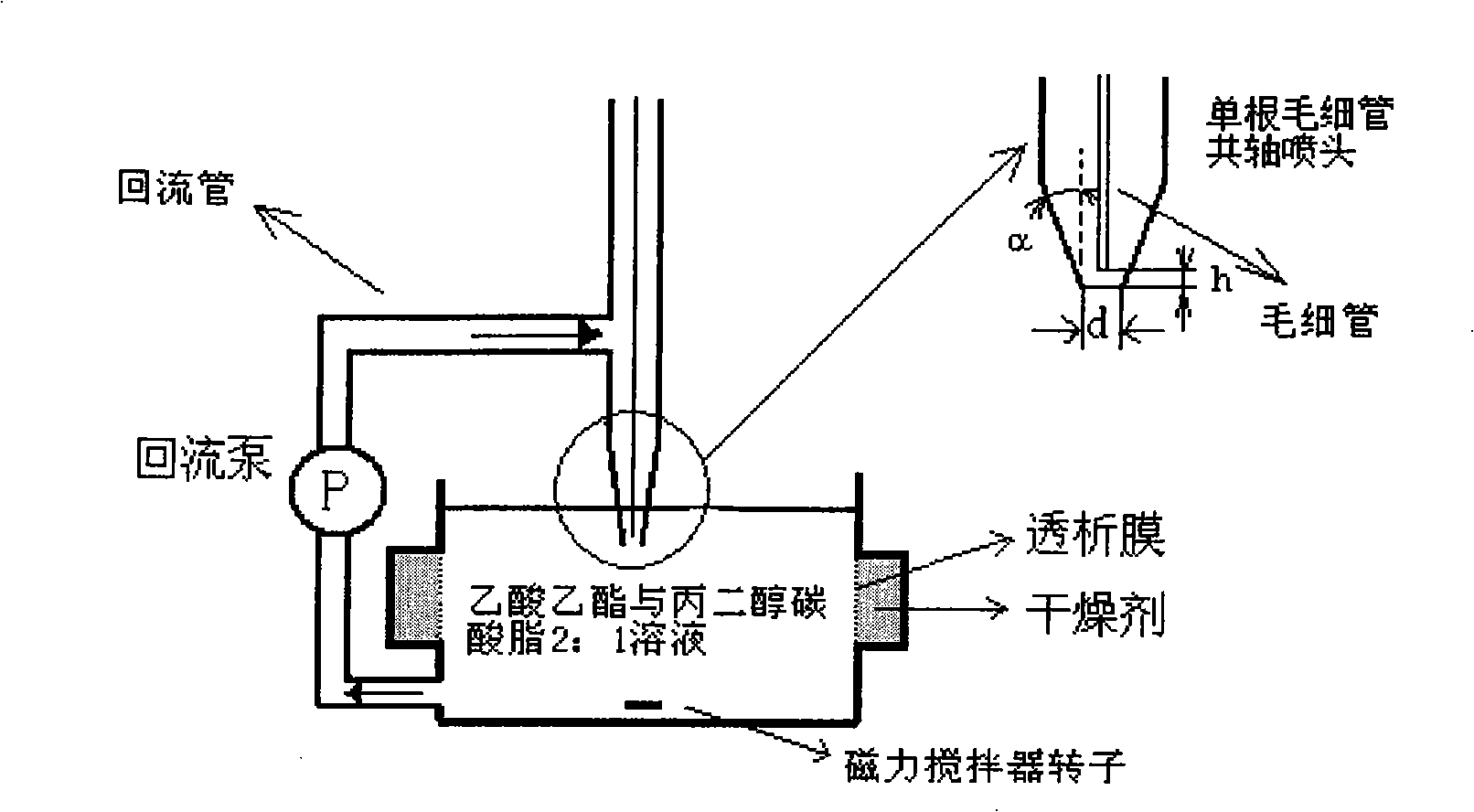
The present invention provides a preparation method of an uniform-size nanoparticle fluorescent microsphere. The density of fluorescent nanoparticle colloidal aqueous solution of the microsphere is adjusted to the micro-mol level so as to obtain the colloidal solution evenly scattered in the aqueous solution; the evenly scattered colloidal solution in the aqueous solution is injected into oil-phase solvent through capillary at the speed of 0.5 to 1.25 percent Vs / min so as to form droplets and Vs is the volume of the oil-phase solvent; the oil-phase solvent adopts bi- or multi-mixture with the solubility between 2 to 10 percent and the density equal to the density of water; containers and reflux pipes adopt the hydrophobic material; the water in droplets is absorbed by the oil phase and the nanoparticles form a dense sphere; an absorbent continuously absorbs the water dissolved in the oil phase, so that the water content in the oil phase is far lower than the saturation; the nanoparticle polymer with the size from dozens of nano to hundreds of nano, the spherical height higher than 5 percent and the size error less than 10 percent is obtained through regulating the density of the quantum pot colloidal solution and the velocity of the reflux pipe.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method and time-resolved biological imaging application of thermally activated delayed long-life fluorescent organic material-based nanoparticles
ActiveCN105400507AStrong fluorescence emissionStable signalOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceStainingPolyethylene glycol
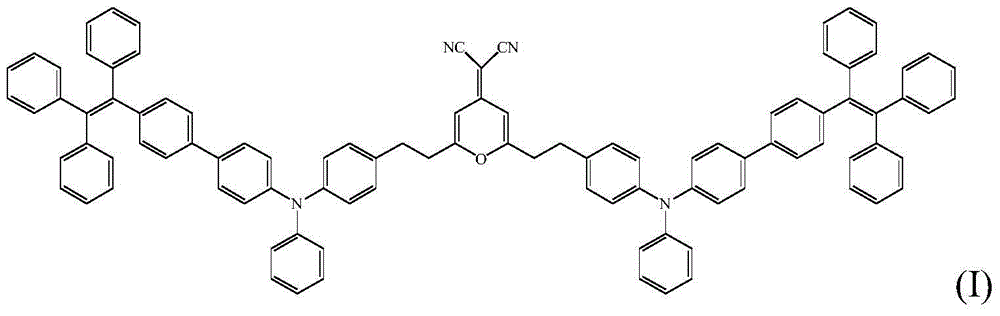
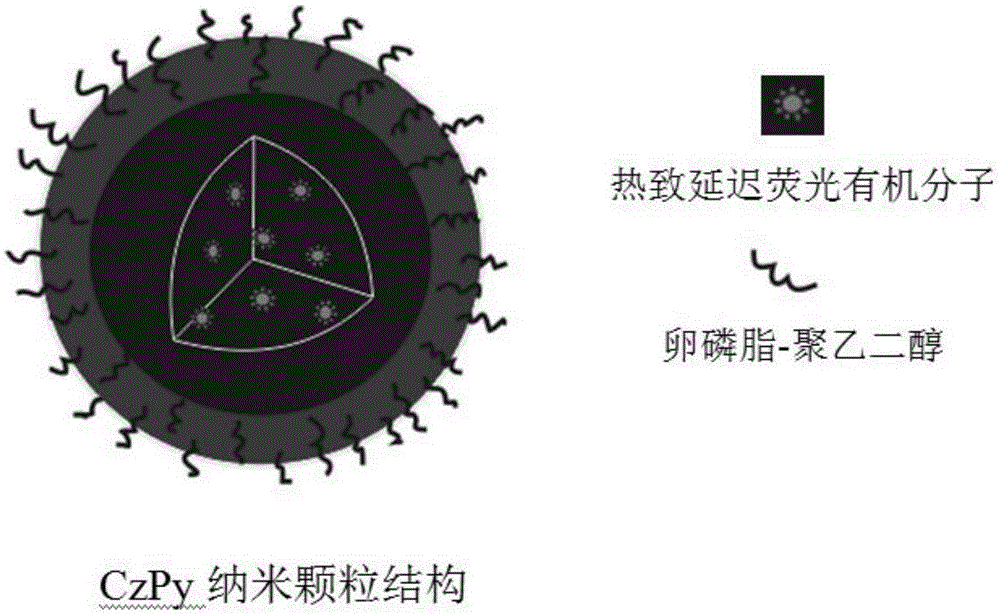
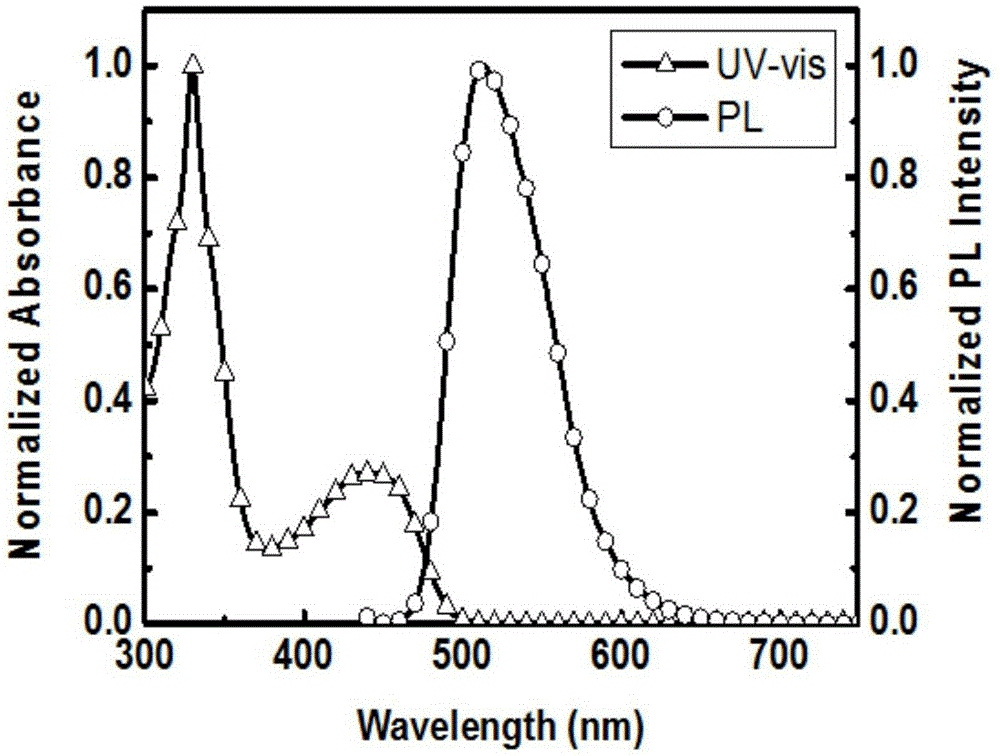
The invention discloses a preparation method and a time-resolved biological imaging application of thermally activated delayed fluorescent (TADF) organic material-based water-soluble long-life fluorescent nanoparticles. The nanostructure of the nanoparticles is represented by figure 1, a thermally activated delayed fluorescent molecule represented by CzPy is represented by a general formula (I). The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing the pure organic TADF micro-molecular material CzPy through adopting a one-step process, and rapidly injecting a CzPy / lecithin-polyethylene glycol mixed solution to deionized water to obtain the CzPy nanoparticles with good water solubility, high luminescence intensity and long fluorescence life. HELA cell dyeing marking and zebra blood vessel imaging results show that the nanoparticles have the advantages of long fluorescence life, low cytotoxicity and biotoxicity, stable spectrum signal, realization of time-resolved fluorescence imaging in cell or in vivo imaging, and good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Quantitative molecular probes
InactiveUS20090104614A1Improved spatial quantificationEasy to quantifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantum dotFluorophore
In accordance with this invention, a molecular probe for detection of a nucleic acid target containing a preselected target sequence is constructed and has at least two sources of a signal: a conventional reporter source and a reference source in a form of a luminescent material, e.g., a fluorophore, quantum dot, fluorescent nanoparticle, or other fluorescent reference dye / nanoparticle / microparticle conjugated to the molecular probe.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
FITC-doped silica fluorescent nanoparticle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101805603APrevent leakageGood chemical stabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluorescein isothiocyanateSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a silica fluorescent nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof, in particular to an FITC-doped silica fluorescent nanoparticle and the preparation method thereof. The method particularly comprises the preparation of a precursor solution and other steps. The FITC is reacted with 3-aminopropyl trimethoxysilane to prepare a precursor, and then the novel FITC-doped silica fluorescent nanoparticle is prepared by a water-in-oil microemulsion method. The prepared nanoparticle is uniformly spherical, has good monodispersity and light stability, difficultly generates dye leakage, has good response to the pH value and can be applied to the real-time monitoring of the pH value of cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for detecting the colon bacillus by combining magnetic nanoparticle enrichment with bi-color flow cytometry
InactiveCN101907556ASensitive detectionQuick checkIndividual particle analysisLuminescent compositionsMagnetite NanoparticlesColor flow
The invention relates to a detection method of colon bacillus, particularly discloses a method for detecting the colon bacillus by combining magnetic nanoparticle enrichment with bi-color flow cytometry. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly co-culturing nanoparticles and samples to be measured and enriching composites formed by the magnetic nanoparticles and the samples to be measured under the action of an externally applied magnetic field; then carrying out immune co-culture and secondary enrichment on colon bacillus antibodies labelled by fluorescent nanoparticles and the enriched samples to be measured; then dyeing the secondarily-enriched samples to be measured by using nucleic acid dyes; finally detecting and viewing the dyed samples to be measured by adopting the multi-parameter flow cytometry and a laser confocal microscope, and analyzing and judging detection results of the colon bacillus contained in the samples to be measured according to the number of detected objects with fluorescent double-positive signals. The detection method has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy, sensitivity, low false positive rate, and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com