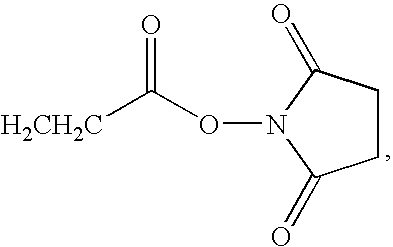
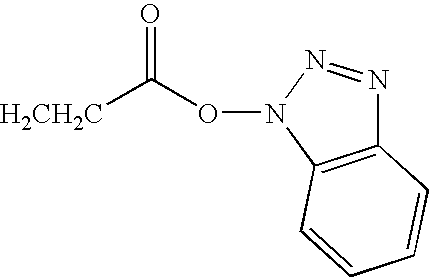
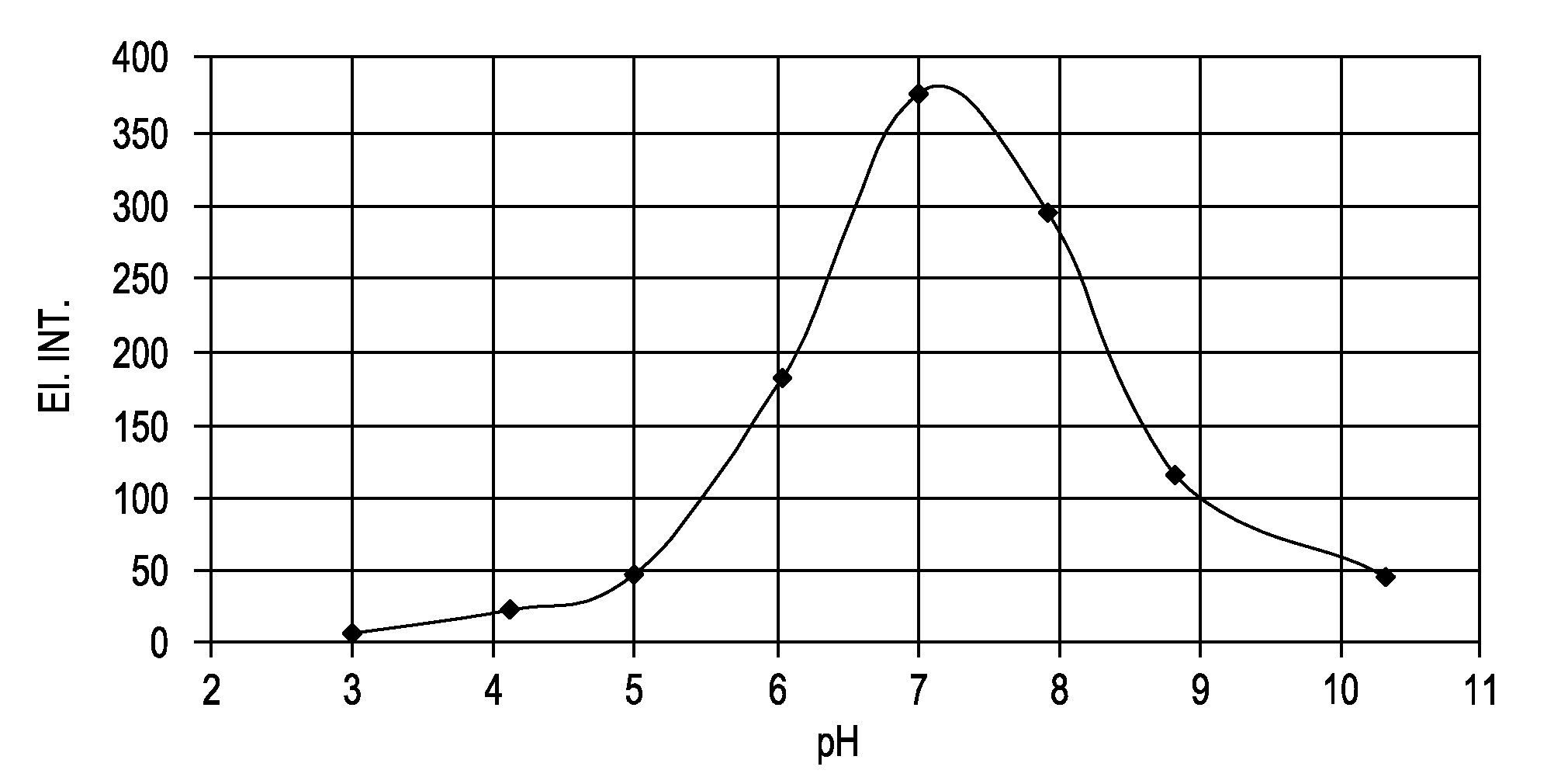
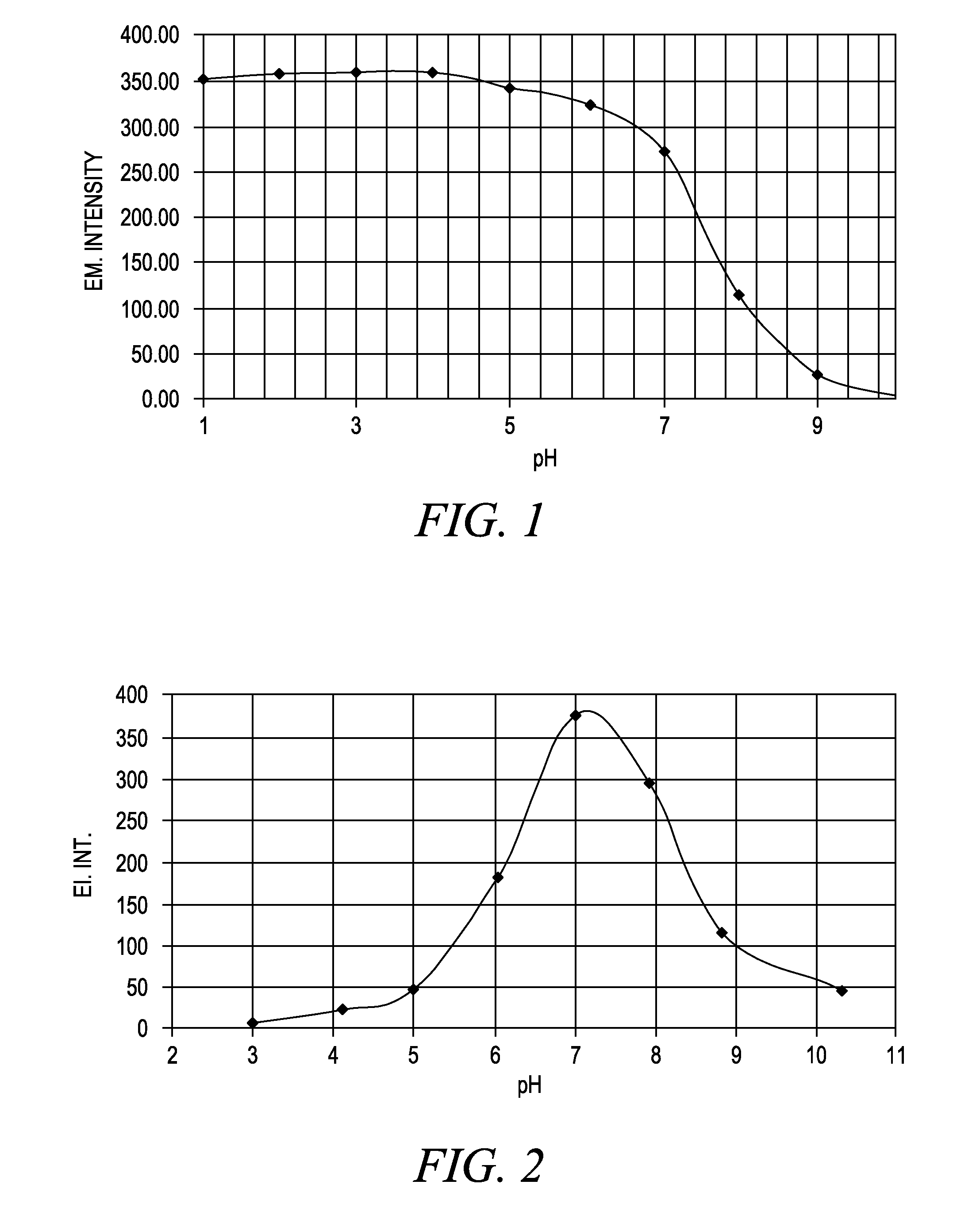
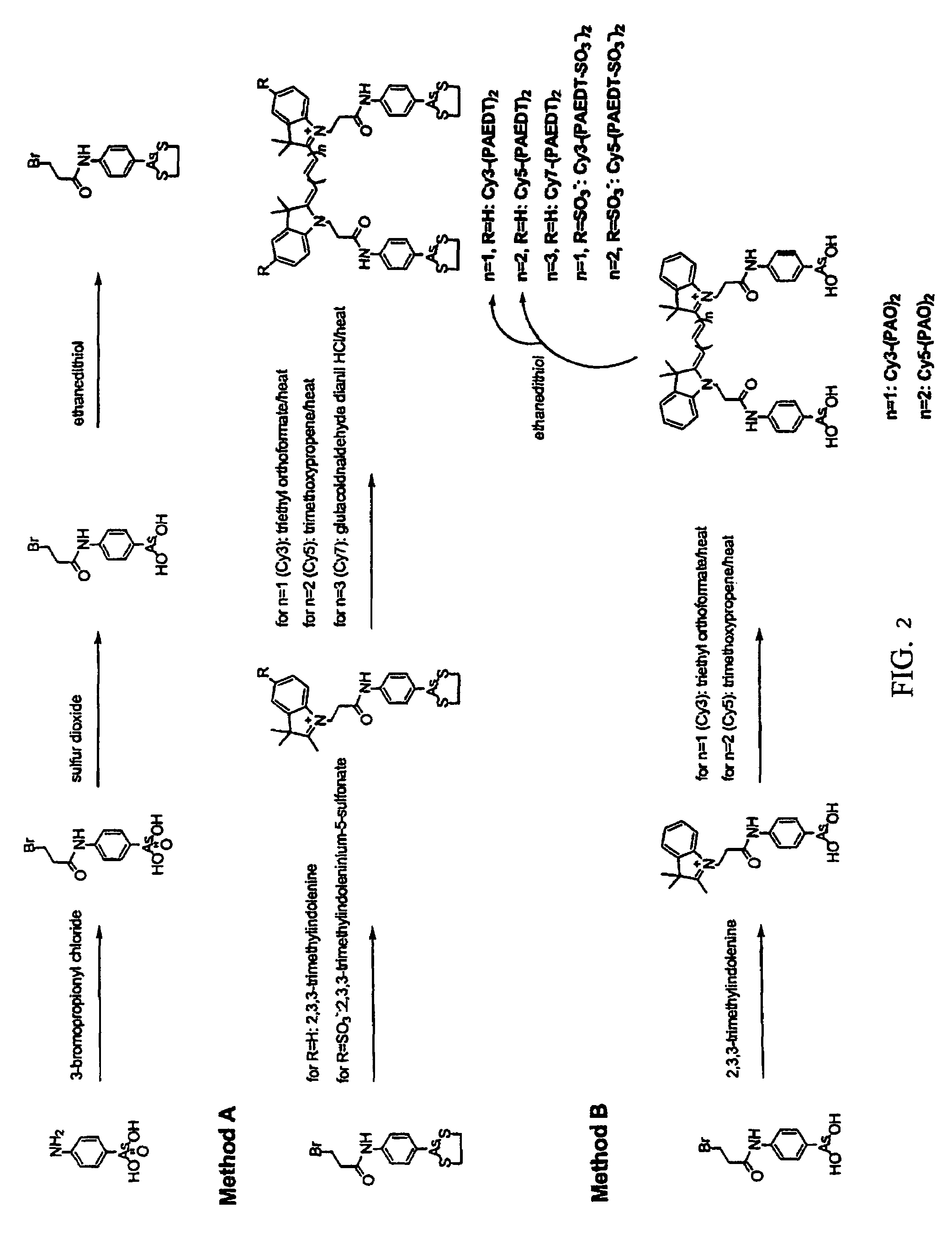
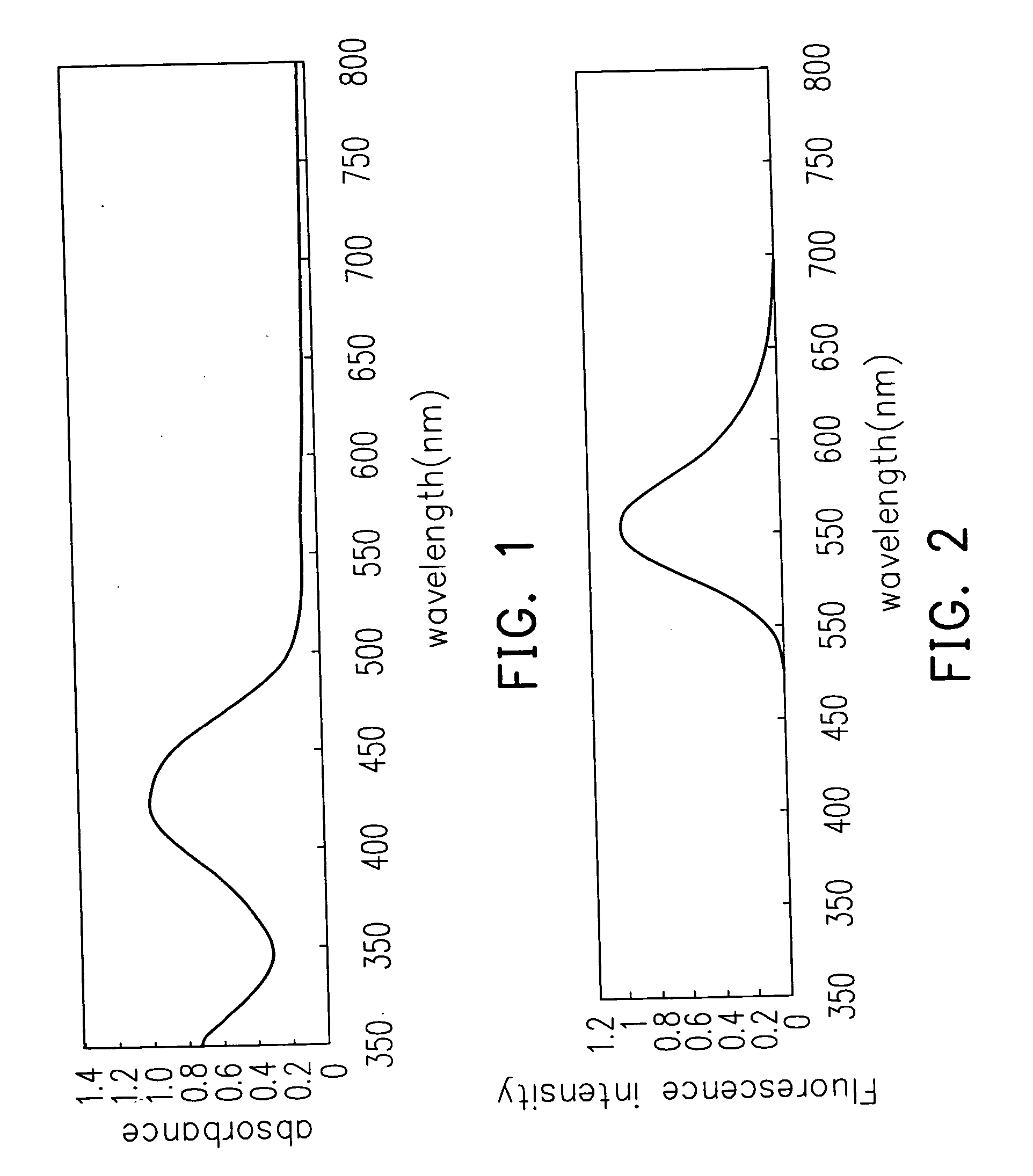
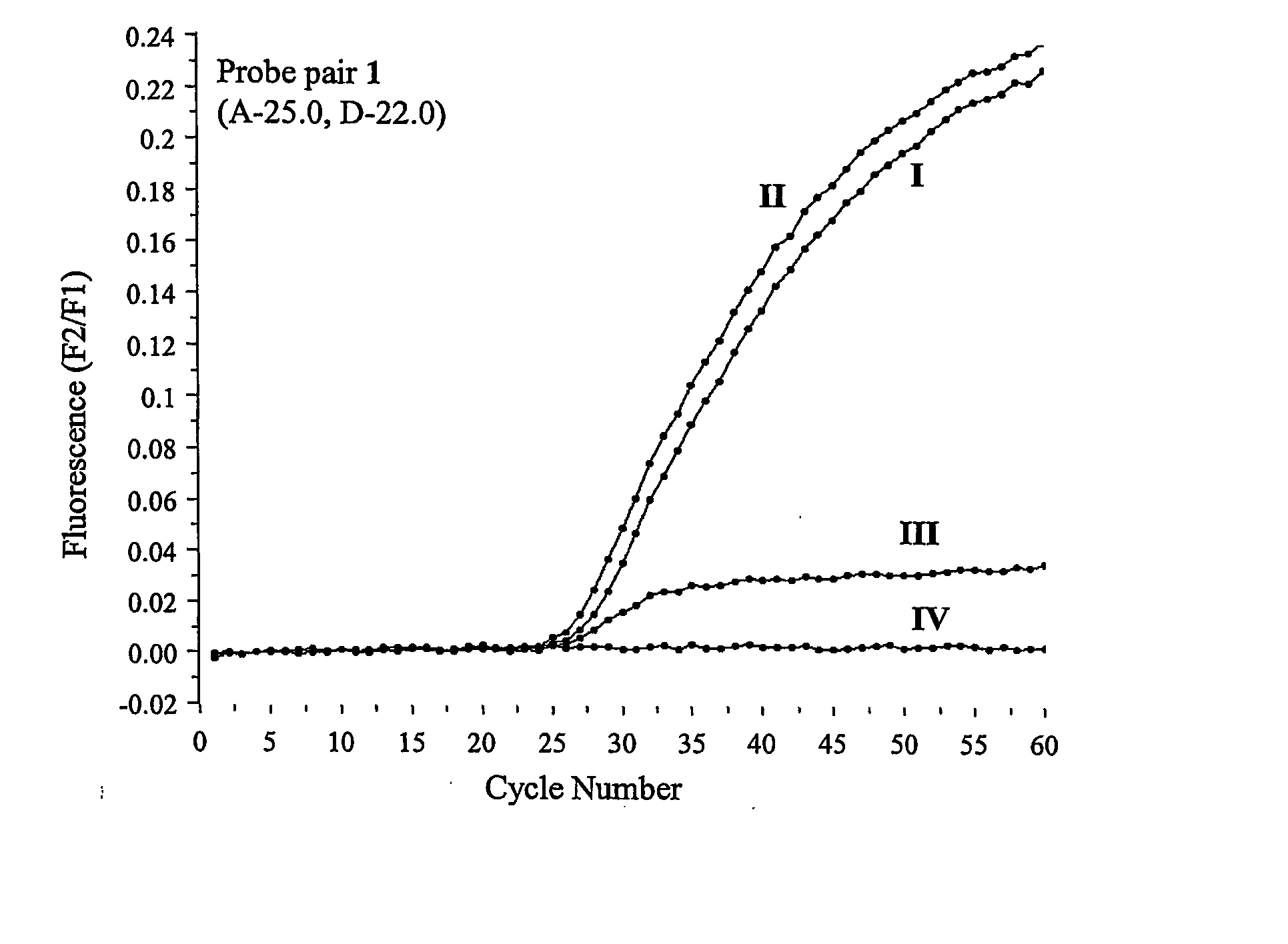
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Epicocconone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
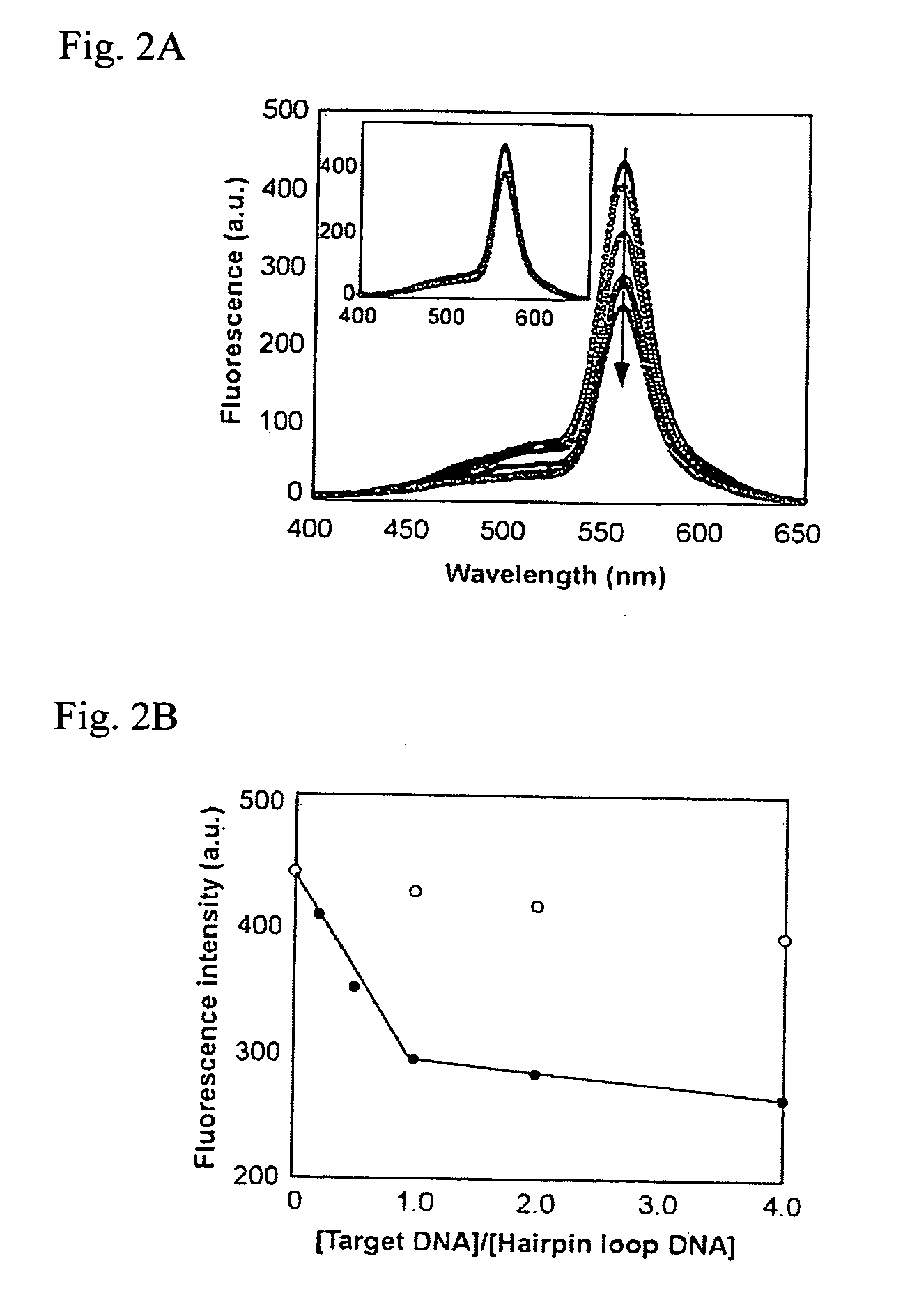
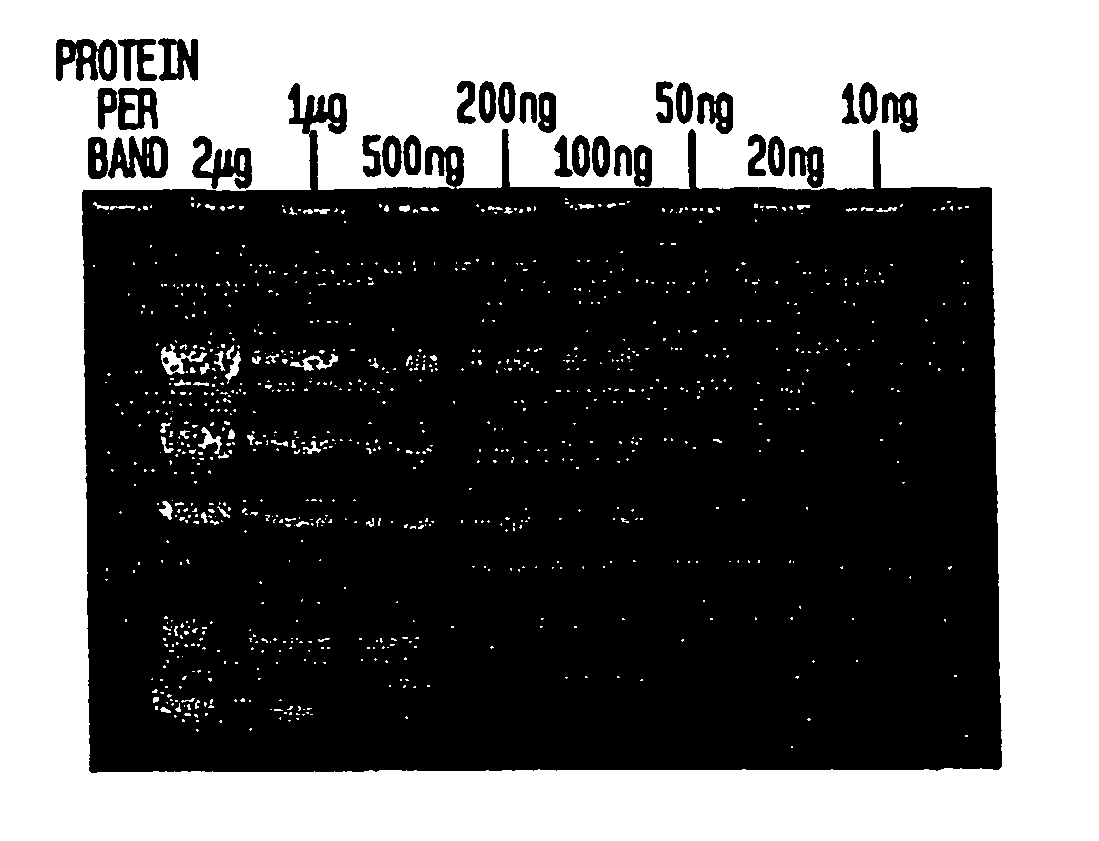
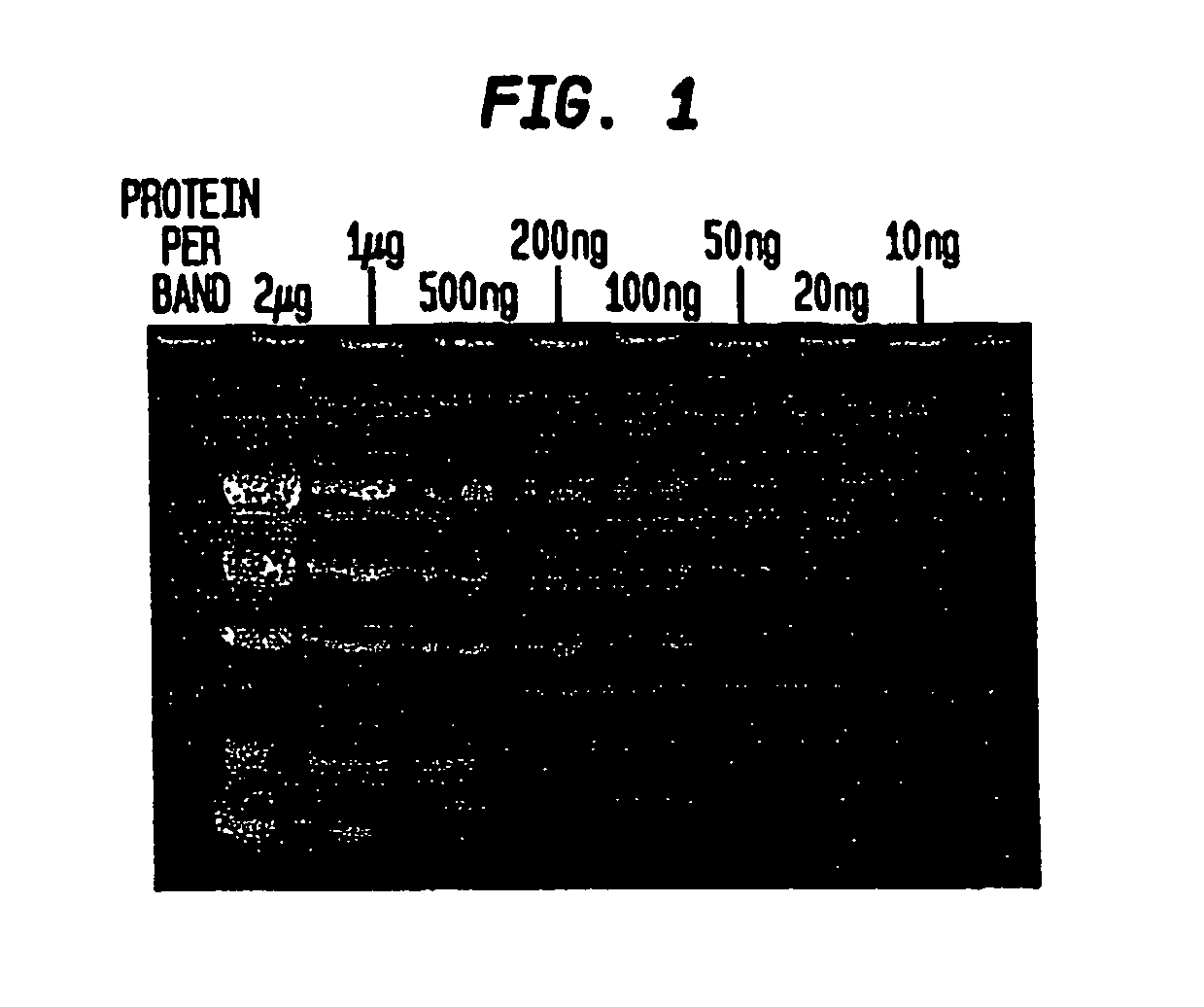
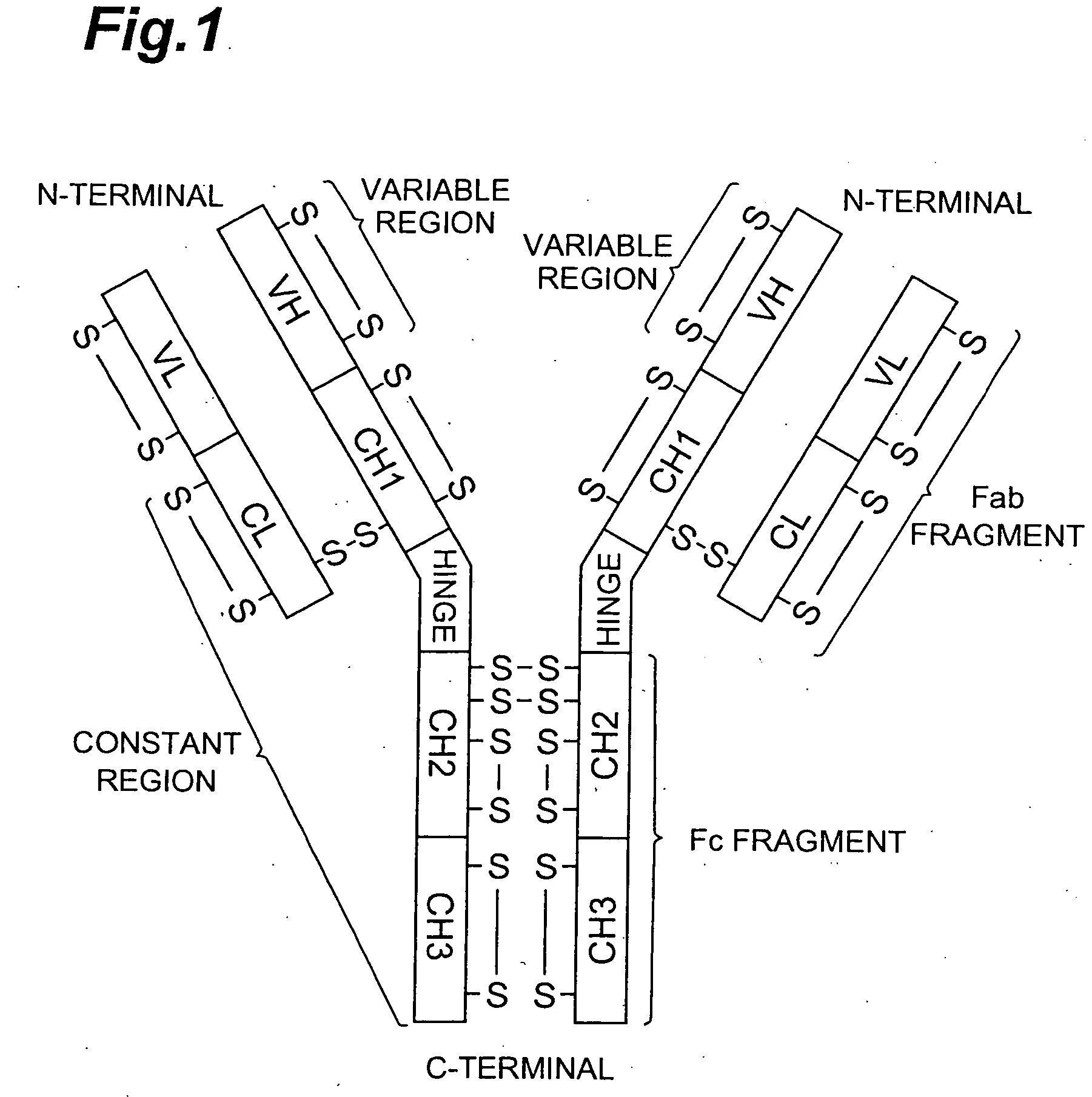
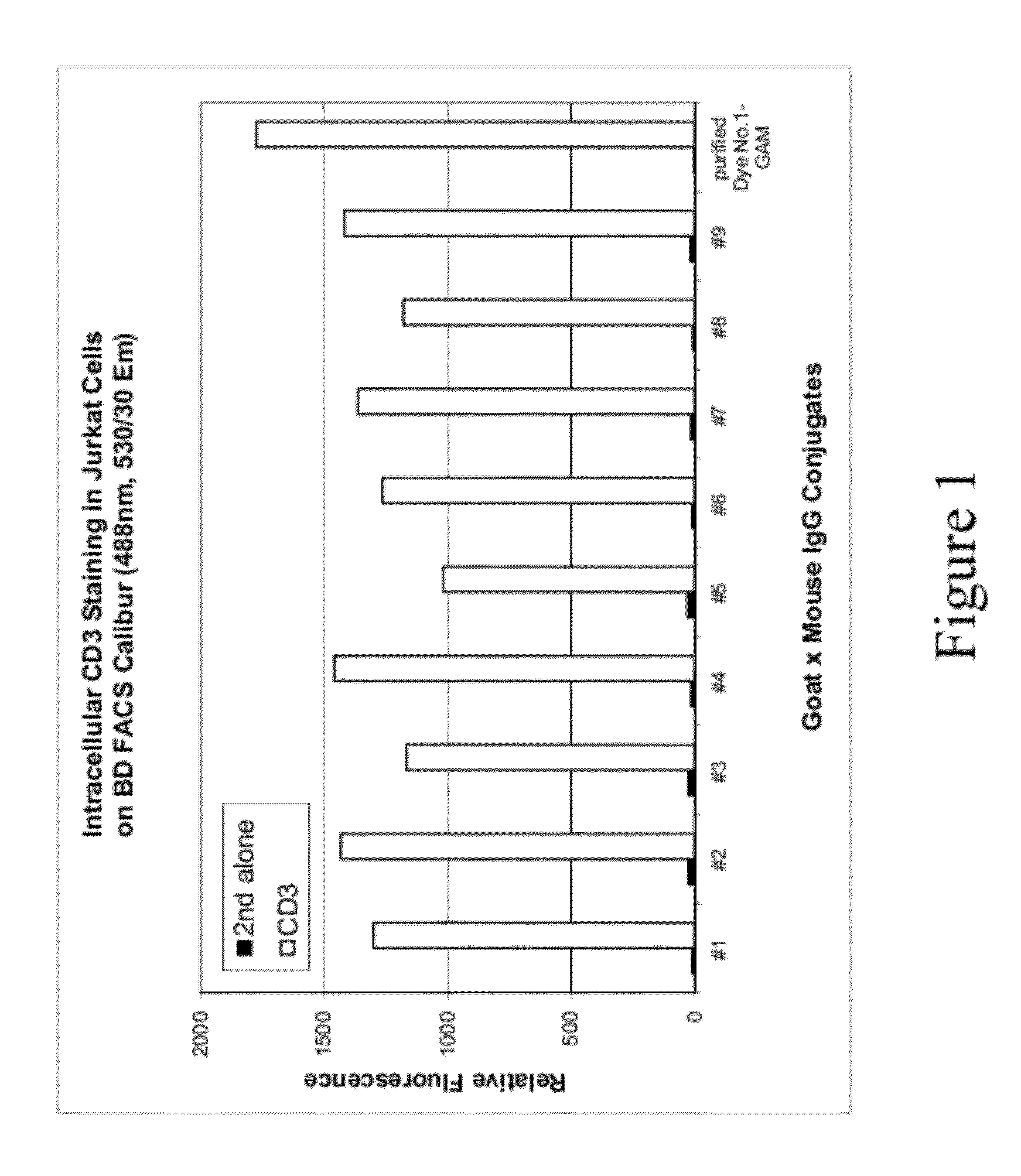
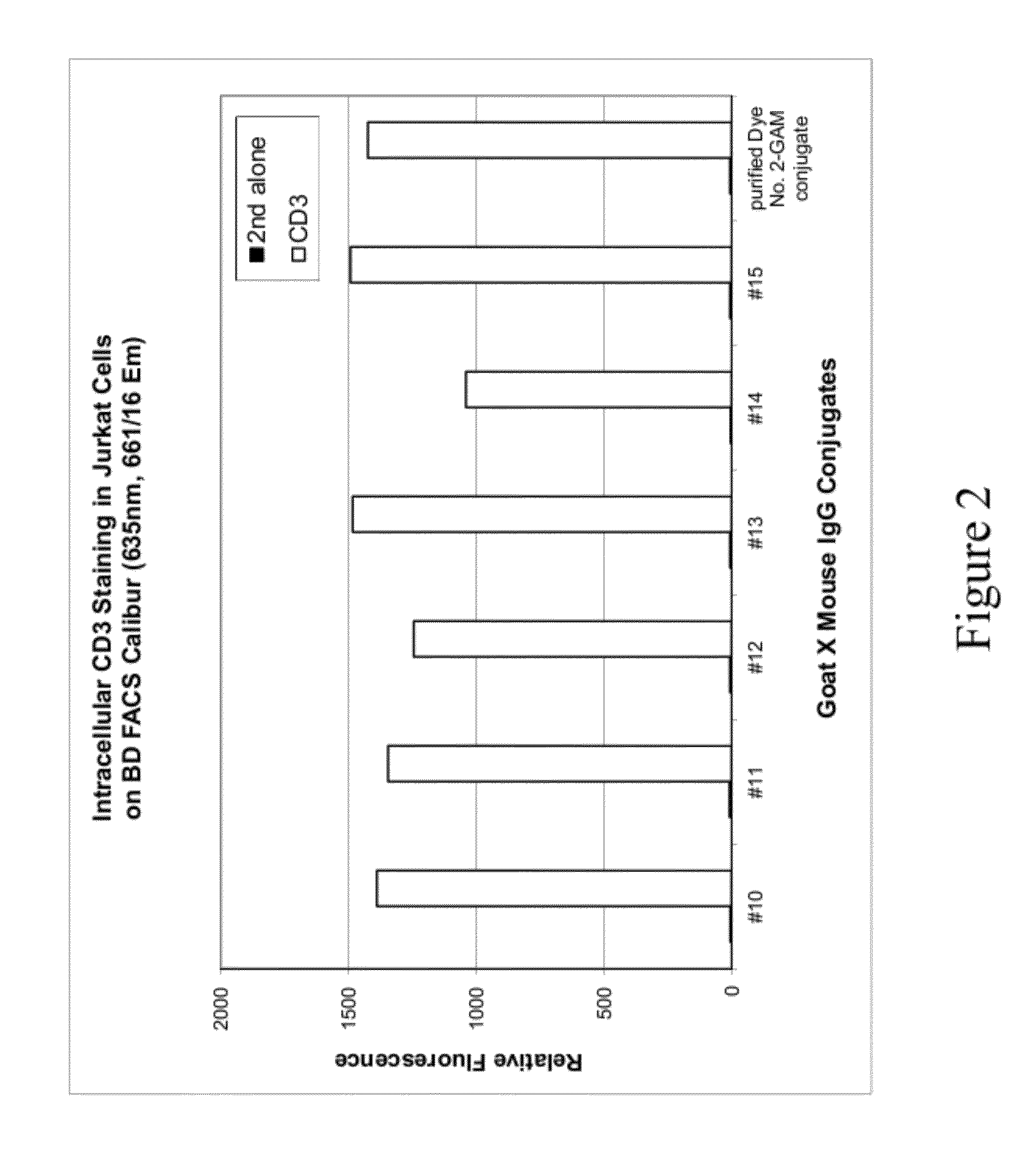
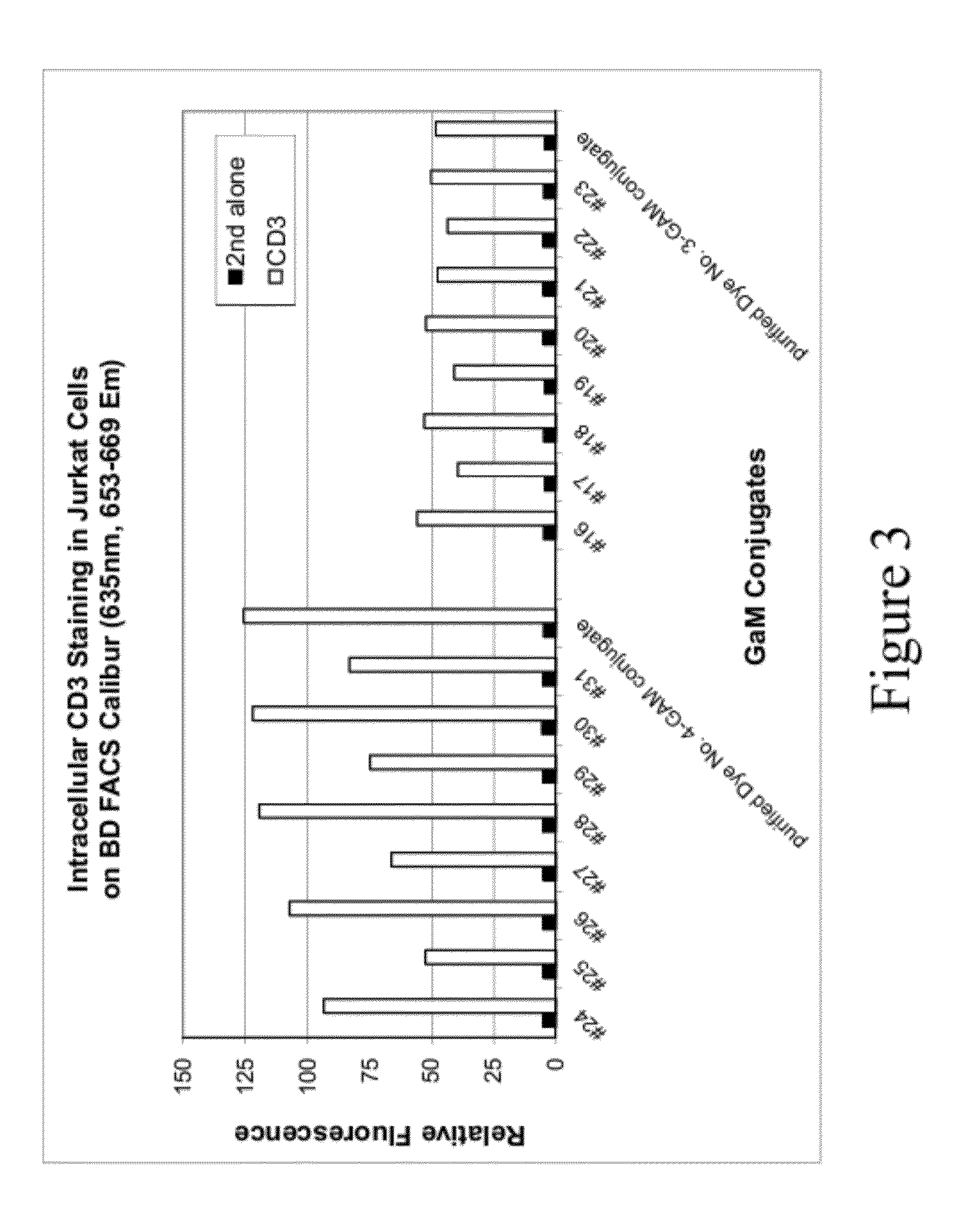
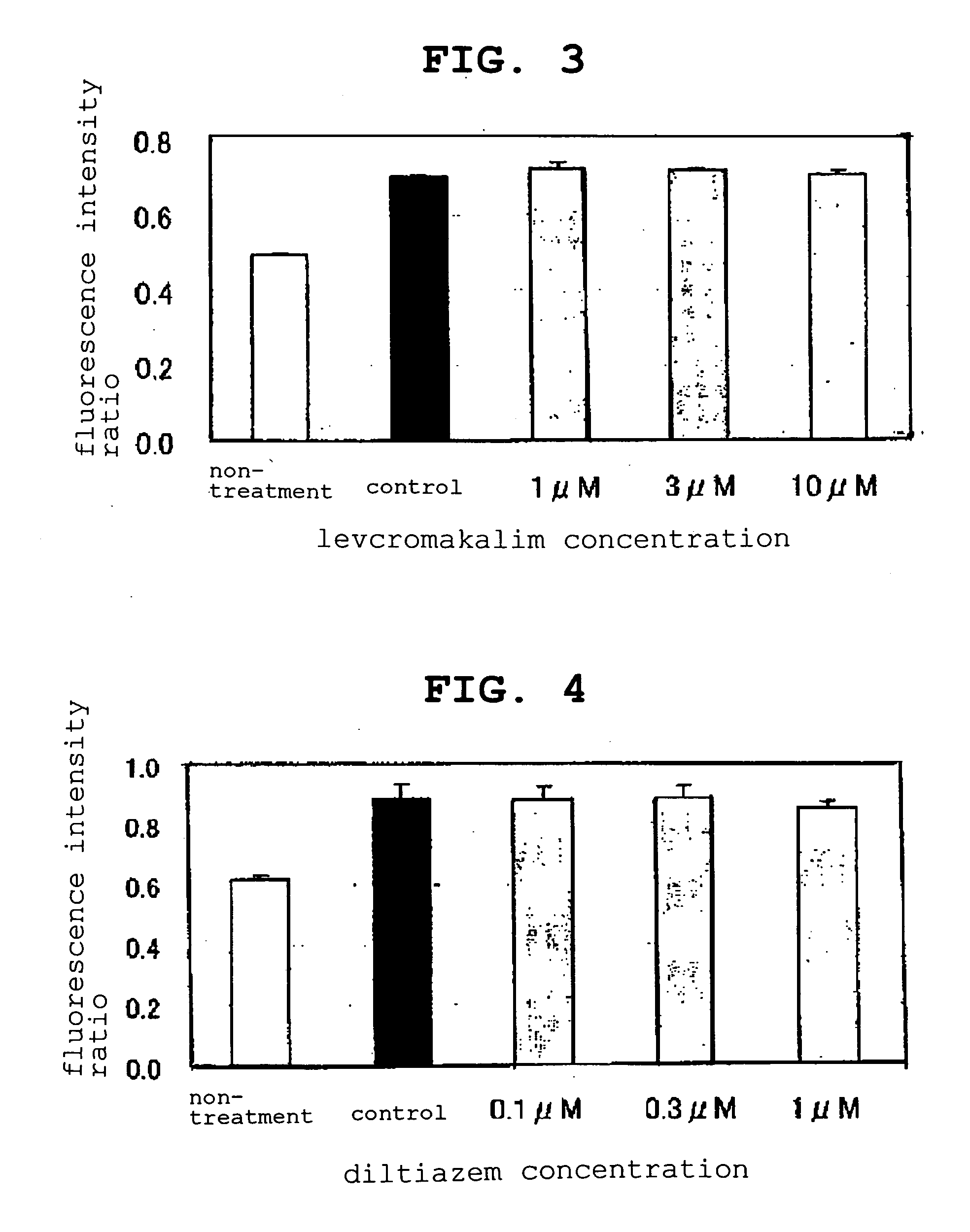
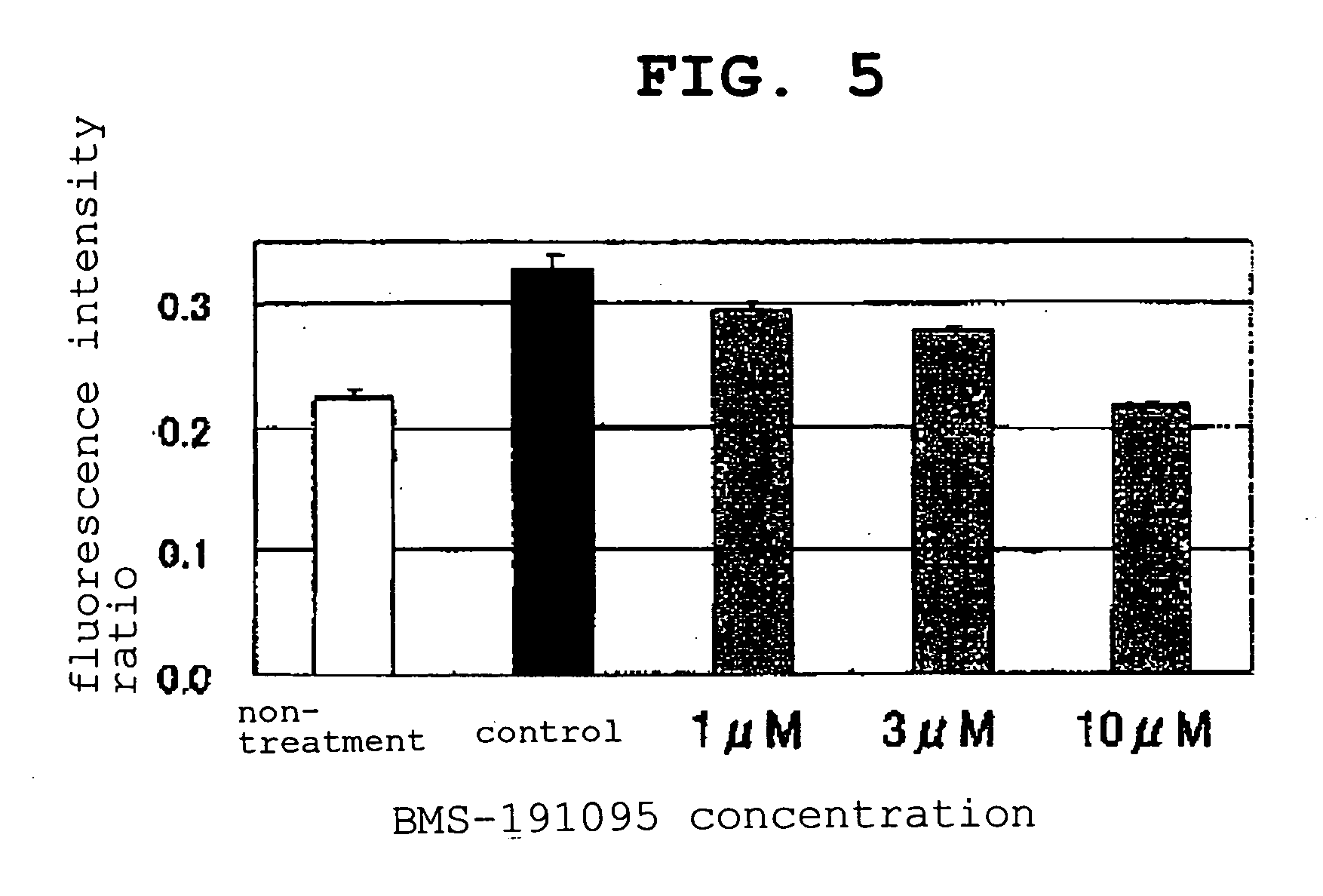
Epicocconone is long Stokes' shift fluorescent dye found in the fungus Epicoccum nigrum. Though weakly fluorescent in water (green emission, 520 nm) it reacts reversibly with proteins to yield a product with a strong orange-red emission (610 nm). This dye can be used as a sensitive total protein stain for 1D and 2D electrophoresis, quantitative determination of protein concentration, making it a powerful loading control for Western blots.
Microparticles with multiple fluorescent signals and methods of using same
This invention provides a novel fluorescent particle including a core or carrier particle having on its surface a plurality of smaller polymeric particles or nanoparticles, which are stained with different fluorescent dyes. When excited by a light source they are capable of giving off multiple fluorescent emissions simultaneously, which is useful for multiplexed analysis of a plurality of analytes in a sample. The coupled complex particles carrying on their surface fluorescent nanoparticles, methods of preparing such polymer particles, and various applications and methods of using such particles are claimed.
Owner:LUMINEX
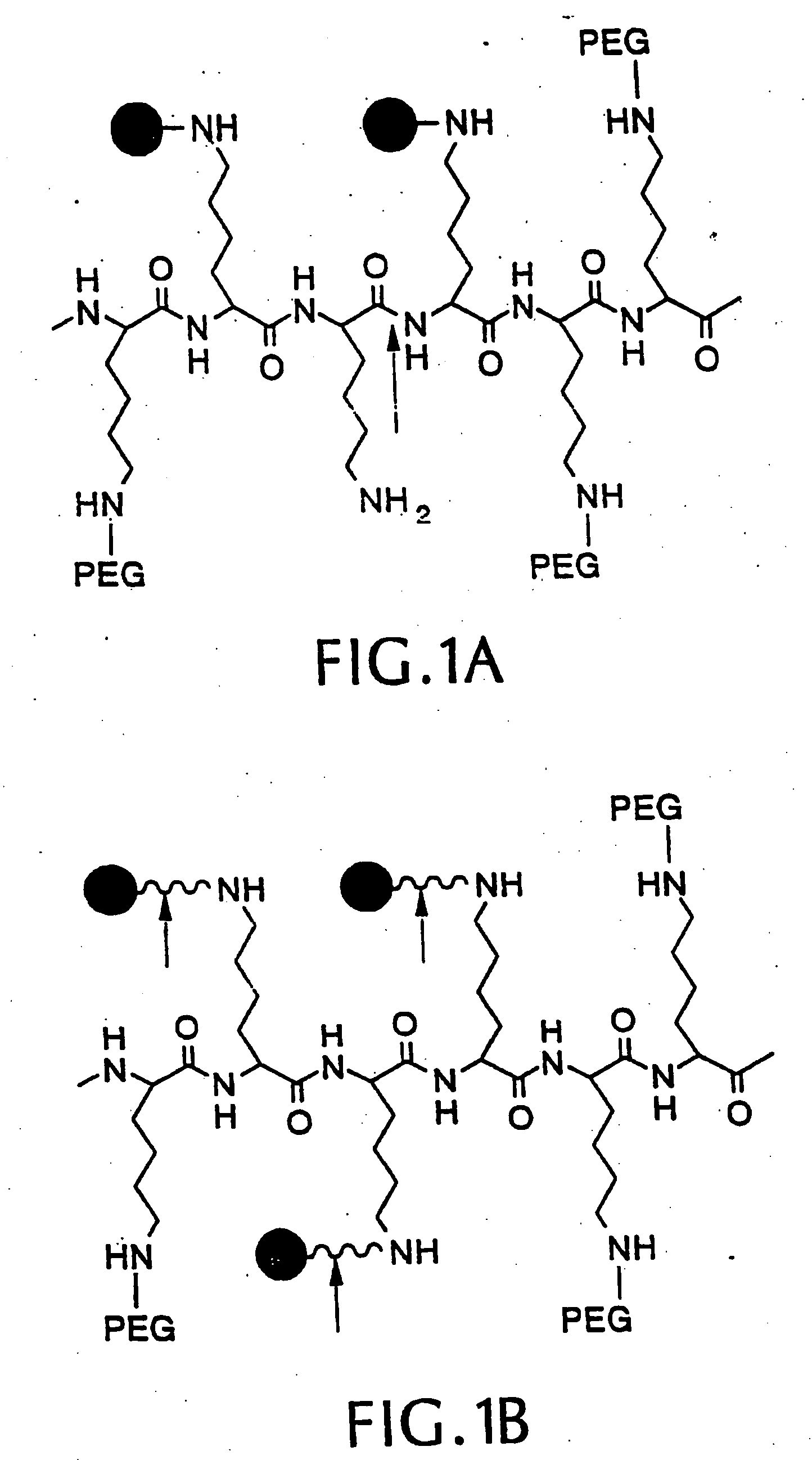
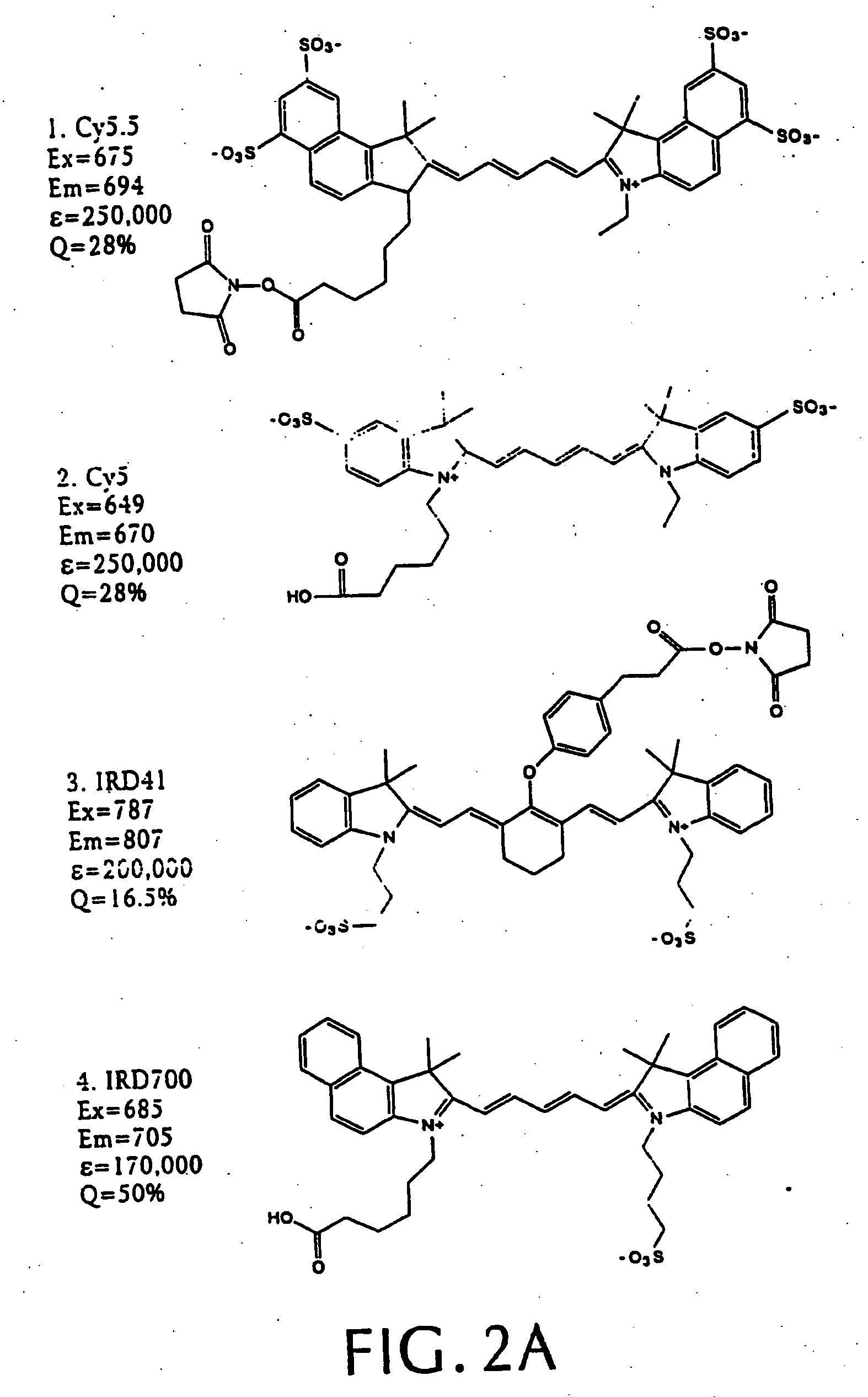
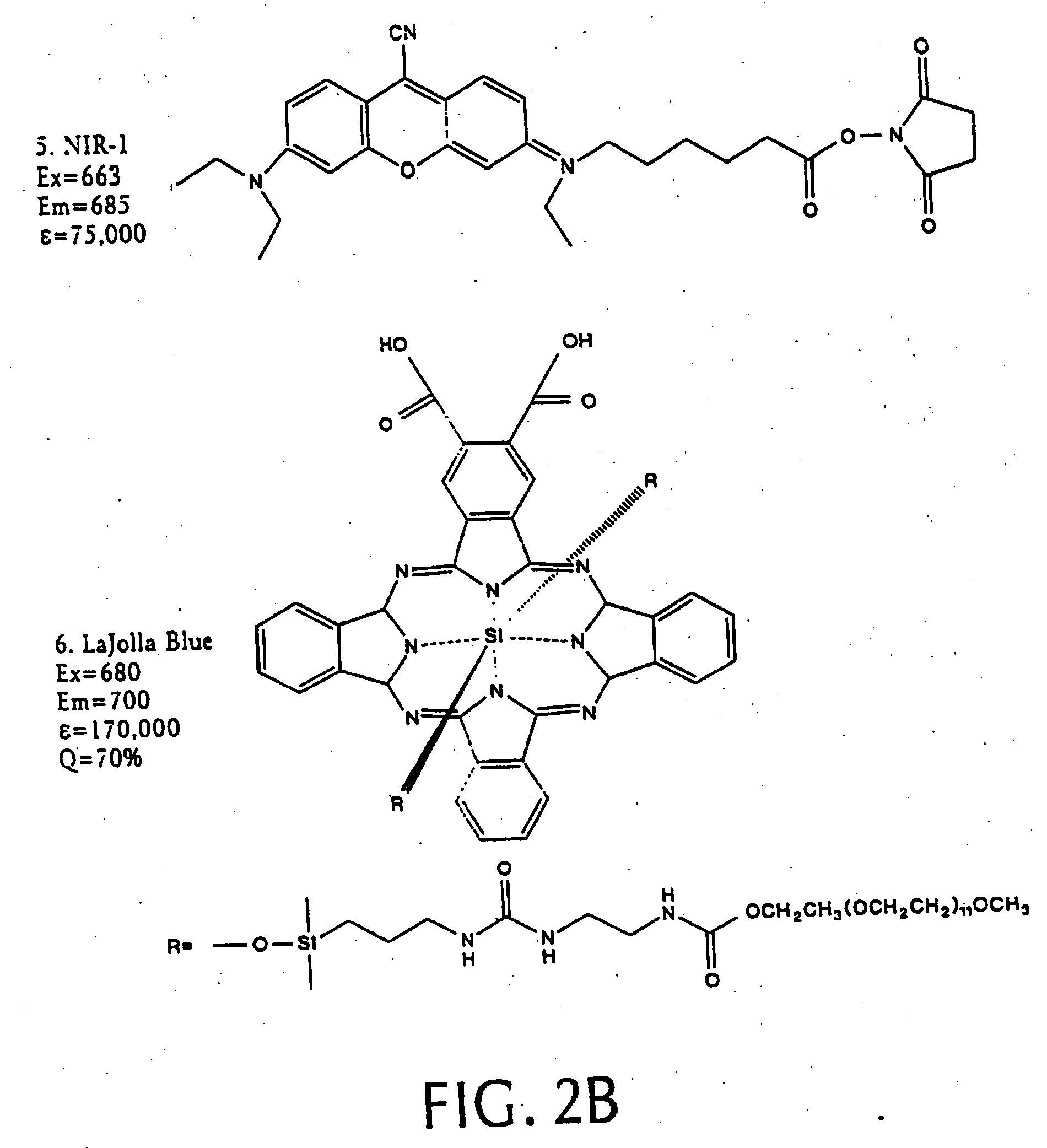
Intramolecularly-quenched near infrared fluorescent probes
InactiveUS20060275775A1Increases target/background ratioRaise the ratioUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryEpicoccononeIn vivo
An intramolecularly-quenched, near infrared fluorescence probe that emits substantial fluorescence only after interaction with a target tissue (i.e., activation) is disclosed. The probe includes a polymeric backbone and a plurality of near infrared fluorochromes covalently linked to the backbone at fluorescence-quenching interaction-permissive positions separable by enzymatic cleavage at fluorescence activation sites. The probe optionally includes protective chains or fluorochrome spacers, or both. Also disclosed are methods of using the intramolecularly-quenched, near infrared fluorescence probes for in vivo optical imaging.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
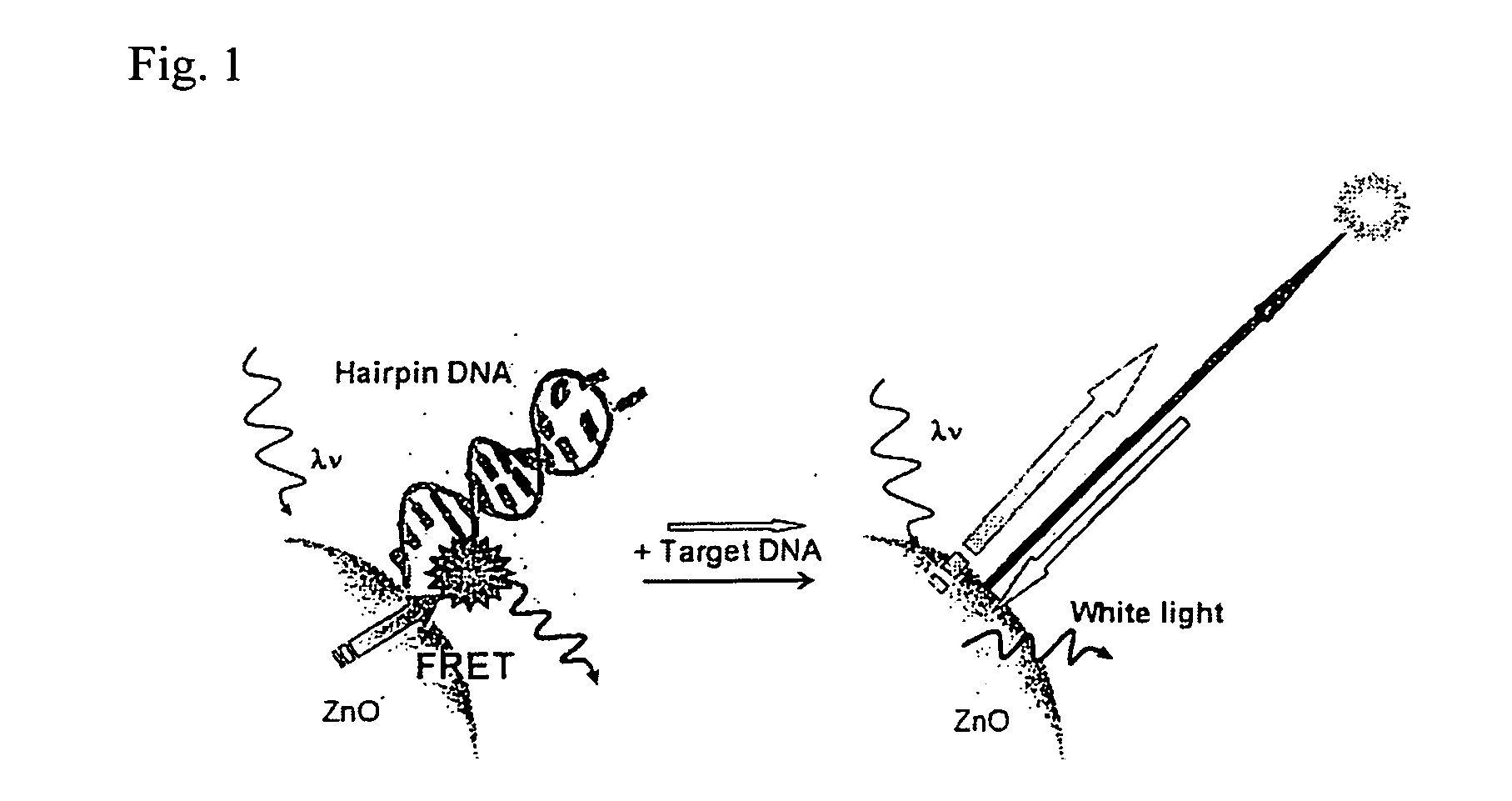
Fluorescent probe and fluorescence detecting method
InactiveUS20070105139A1Easy to separateSensitivity loss can be avoidedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferNanoparticle
A fluorescent probe having a base sequence complementary to a specific sequence in a target nucleic acid, wherein the fluorescent probe has one end labeled with a nano particle fluorescent material, and the other end labeled with a fluorescent dye capable of fluorescence resonance energy transfer from the nano particle fluorescent material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Automated sample analysis
ActiveUS20050003554A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEpicoccononePhotomultiplier
Samples of materials used in industrial processes are analyzed to determine the concentration of certain materials of interest. The quantitative analysis of samples for these materials is provided without the need for manual methods such as titration. Indicators such as fluorescent dyes for which the intensity of fluorescence is indicative of the concentration of a material of interest are used. The dyes are made to fluoresce by means of a light source, and a photomultiplier or other detector capable of measuring light intensity detects the resulting fluorescence. The intensity of fluorescence in the sample is compared to the intensities of fluorescence produced by samples with known concentrations of the material of interest to determine the concentration of the material of interest of the sample.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Ultra-high specificity fluorescent labeling
InactiveUS20060141531A1Reduce undesirable background noiseAccurate measurementGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsEnergy transferFluorescence
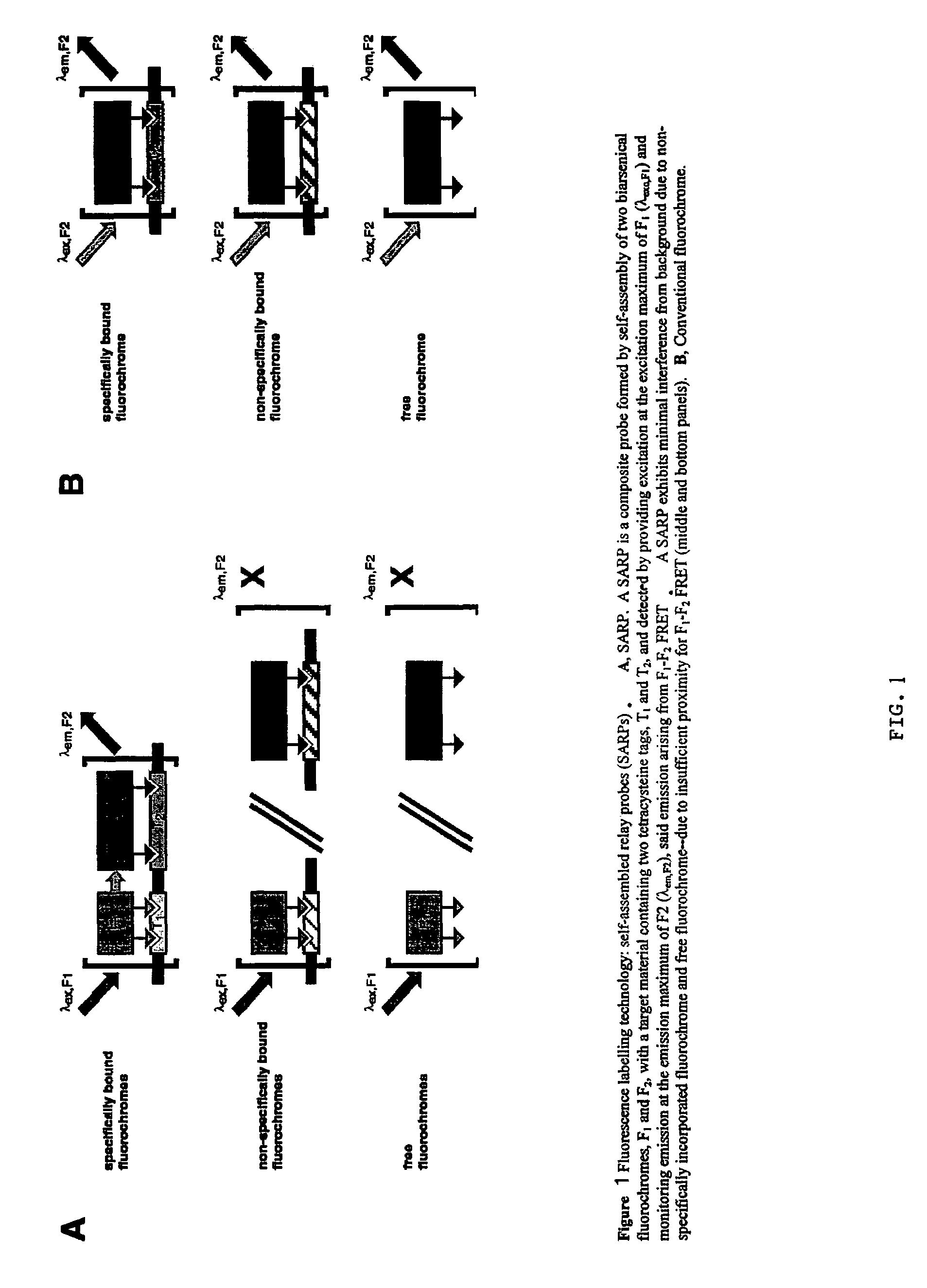
A self-assembled relay probe for detecting a target material is provided including: a first peptide tag bound to the target material; and a first fluorescent conjugate including a first fluorochrome and a first tag binding group; wherein the first fluorescent conjugate selectively associates with the first tag. The probe further includes a second peptide tag bound to the target material; and a second fluorescent conjugate including a second fluorochrome having a longer wavelength and distinct excitation and emission maxima from the first fluorochrome and a second tag binding group. Upon exposure to the target material, the first and second fluorescent conjugates independently associate with the first and second peptide tags, respectively, so as to be a distance apart represented by about 0.1 times R0 to about 2 times R0, such that upon excitation of the first fluorescent conjugate, fluorescence resonance energy transfer results in excitation of the second fluorescent conjugate, yielding detectable emission from the second fluorescent conjugate.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Azulene dimer-quenched, near-infrared fluorescent probes
InactiveUS20060147378A1Reduced background fluorescenceFeasibility of simultaneous multiple probe useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesEpicoccononeIn vivo
An intramolecularly-quenched, near-infrared fluorescence probe that emits substantial fluorescence only after interaction with a target tissue (i.e., activation) is disclosed. The probe includes a polymeric backbone and a plurality of near-infrared fluorochromes covalently linked to the backbone at fluorescence-quenching interaction-permissive positions separable by enzymatic cleavage at fluorescence activation sites. The probe optionally includes protective chains or fluorochrome spacers, or bothours. Also disclosed are methods of using the intramolecularly-quenched, near-infrared fluorescence probes for in vivo optical imaging.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
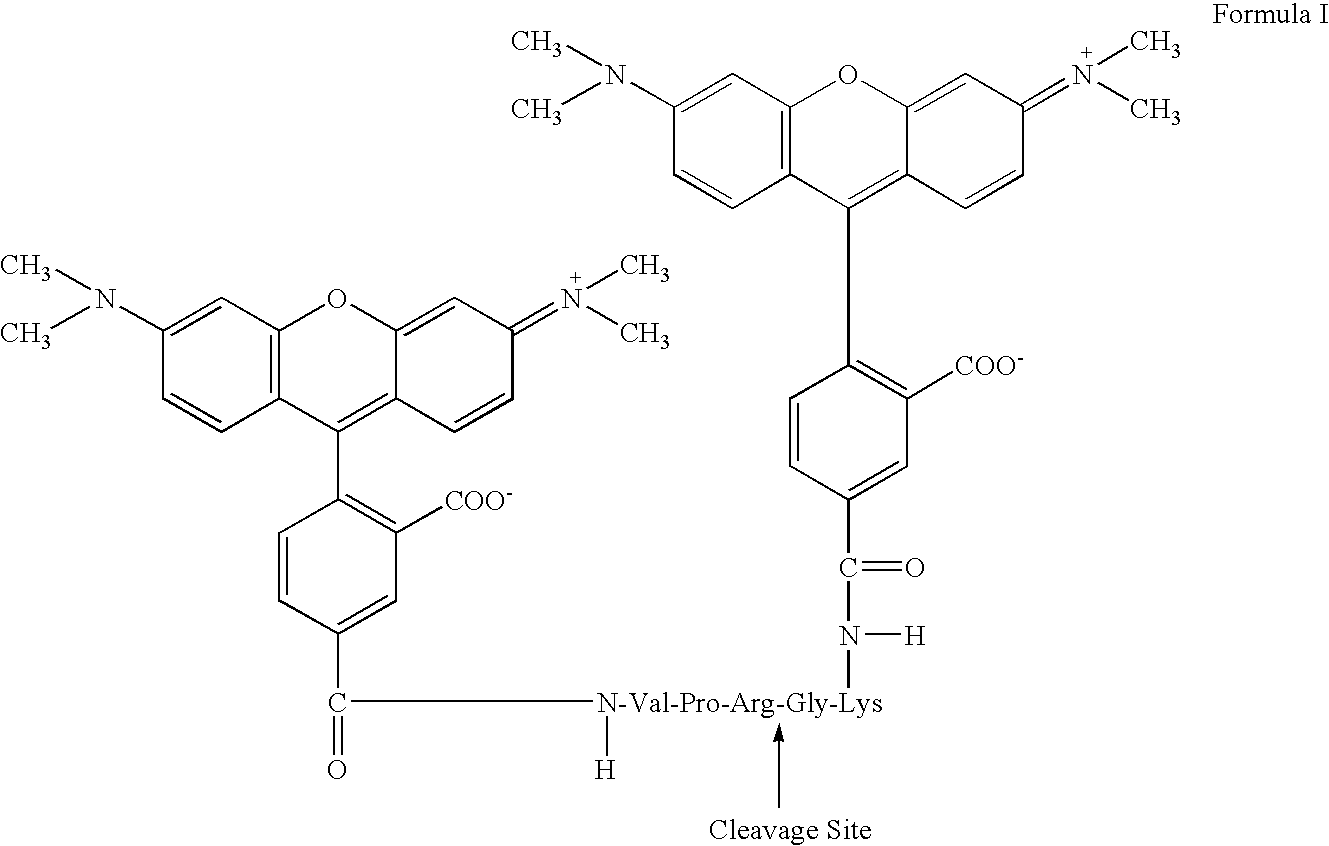
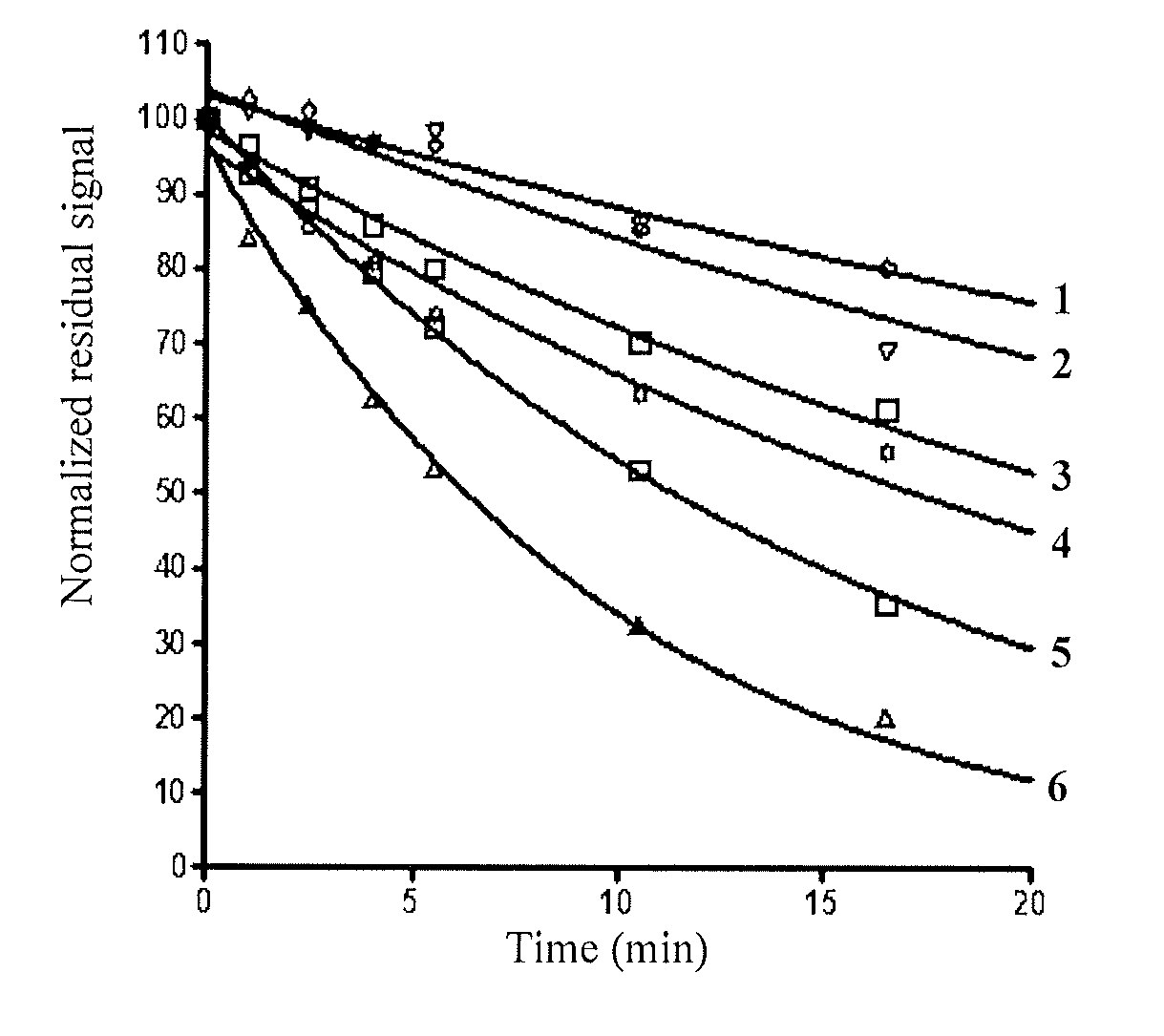
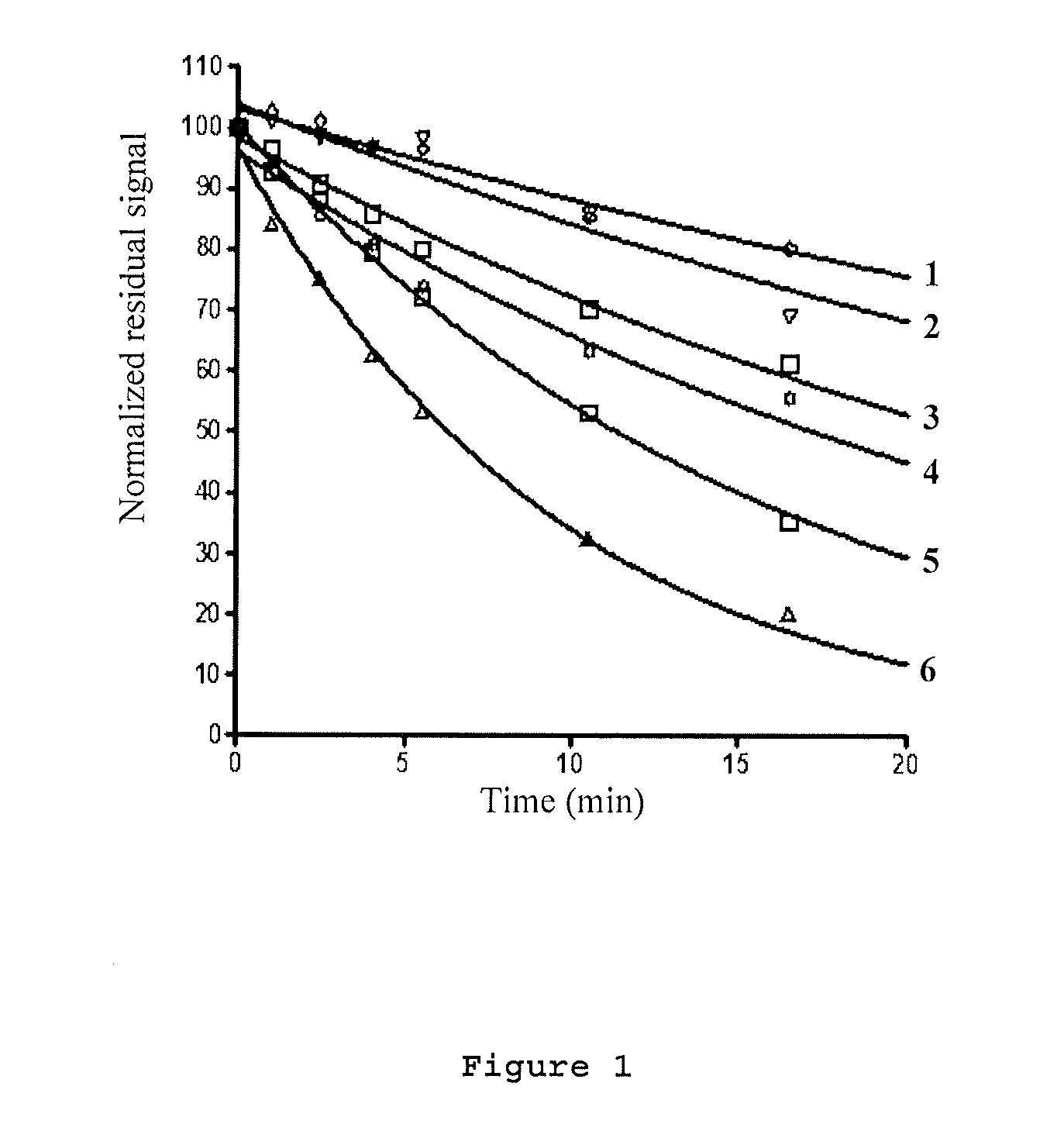
Fluorogenic ph sensitive dyes and their method of use
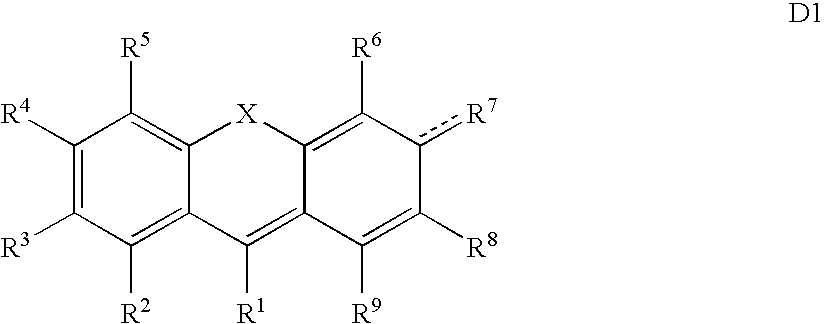
A new class of pH sensitive fluorescent dyes and assays relating thereto are described. The dyes and assays are particularly suited for biological applications including phagocytosis and monitoring intracellular processes. The pH sensitive fluorescent dyes of the present invention include compounds of Formula I:wherein the variables are described throughout the application.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Visible wavelength fluorescent calcium indicators that are (i) leakage resistant and (ii) operate near membranes
InactiveUS20050233467A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistryPropanoic acidFluorescence
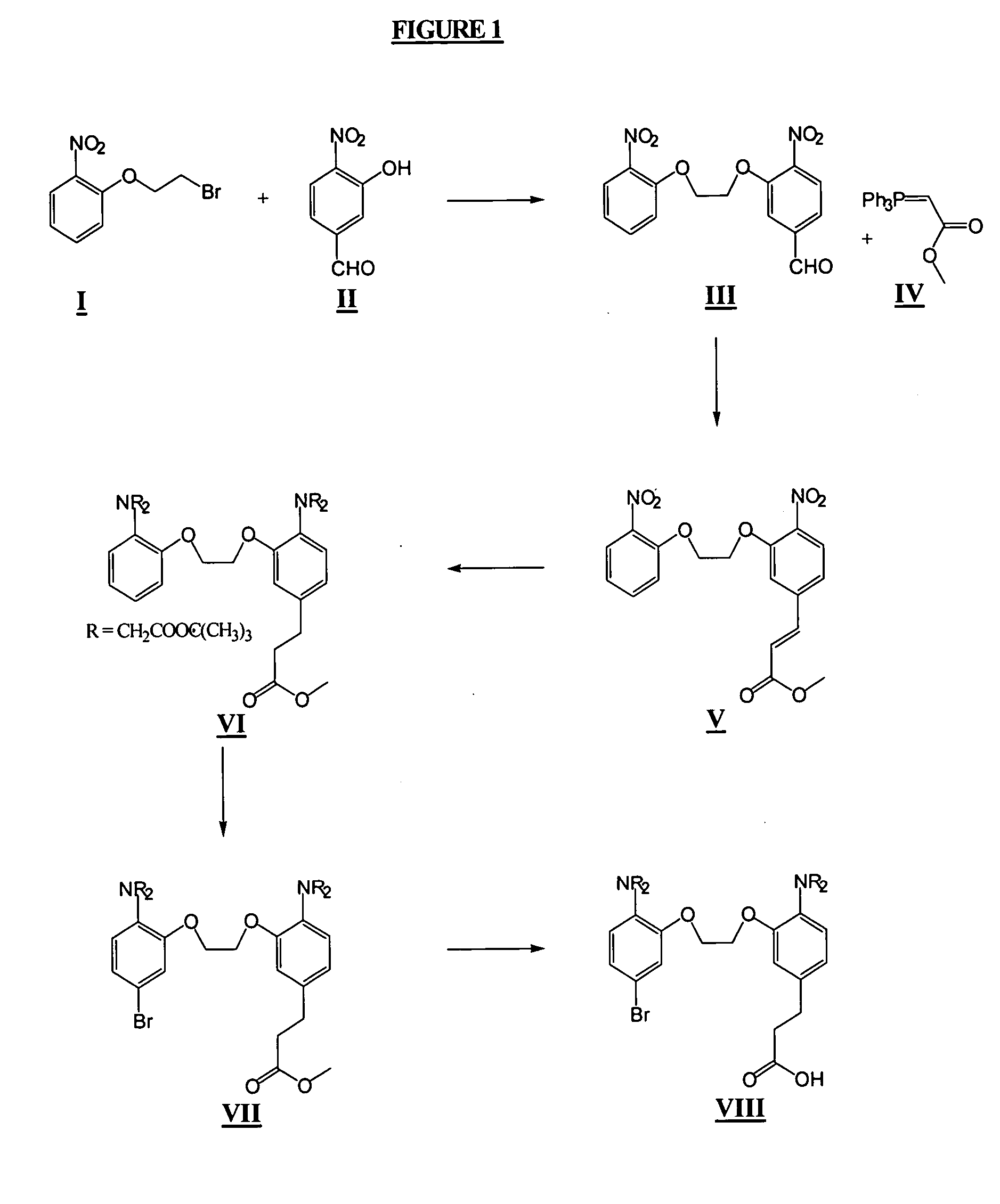
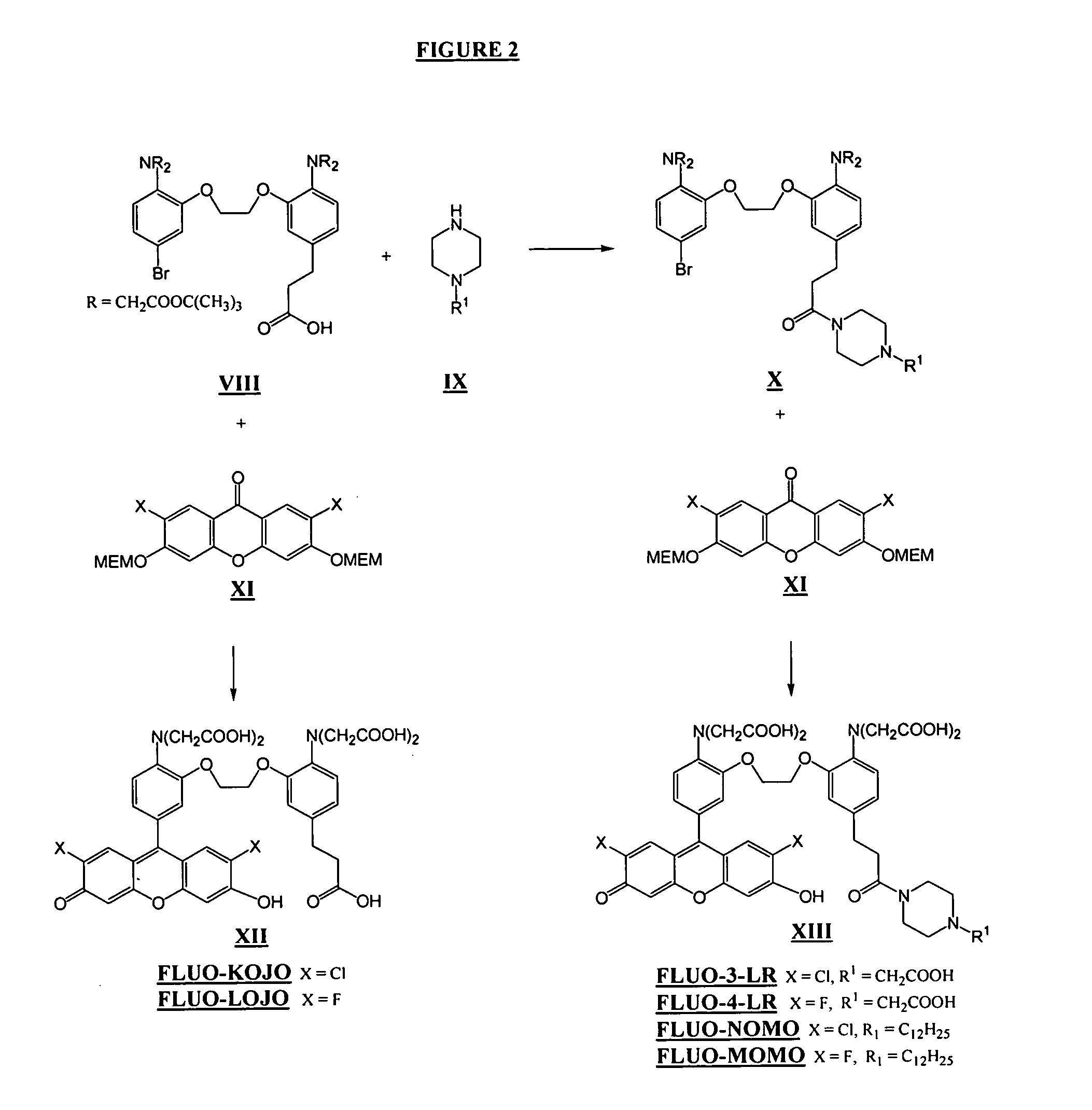
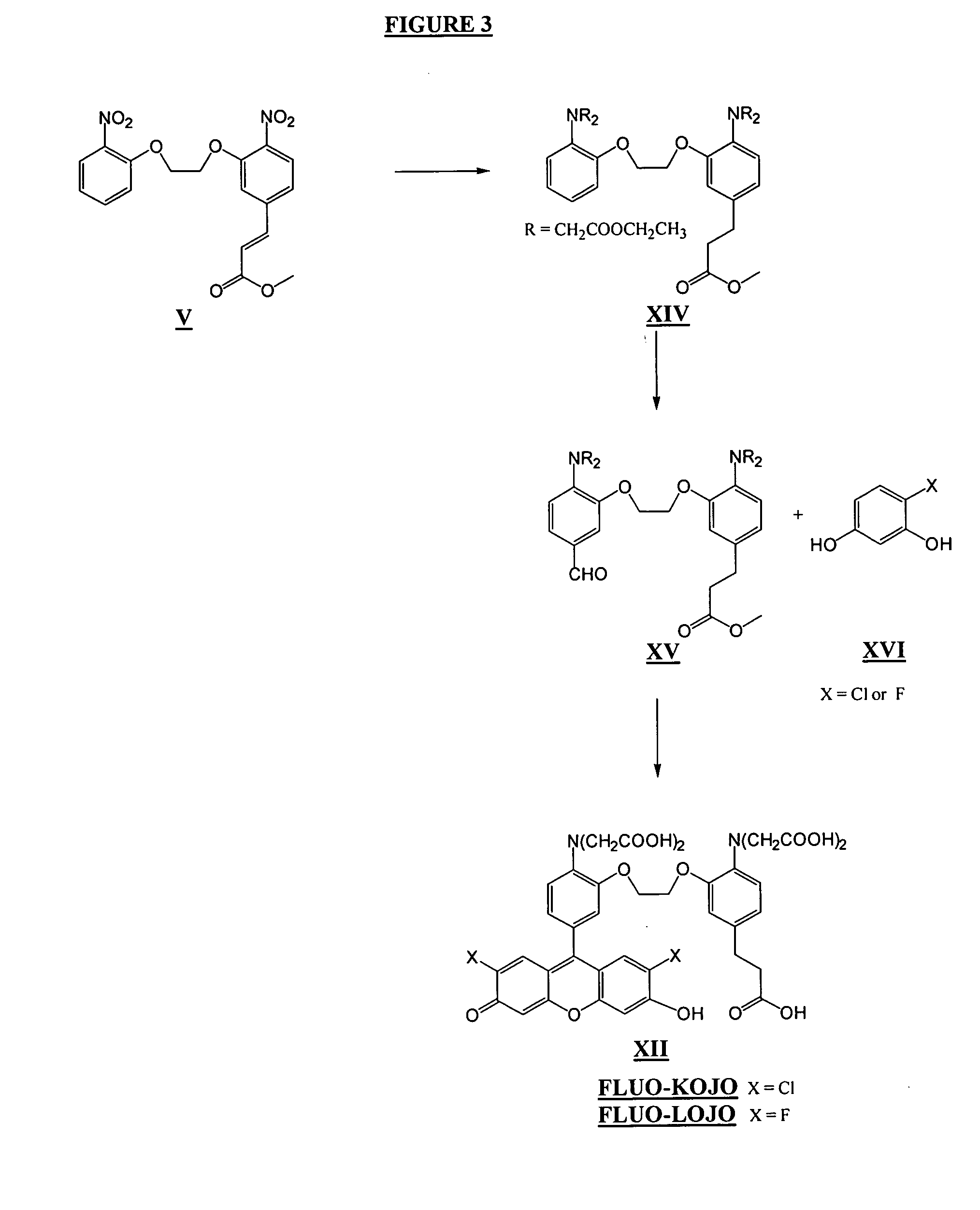
A new class of visible wavelength fluorescent calcium indicators with the BAPTA-like portion rendered zwitterionic by introduction of amine and carboxylic groups. “Fluo” compounds generally function with no extra ionized groups. The modified BAPTA moiety confers new properties while retaining ion selectivity and pH insensitivity. The dyes demonstrate reduced cell leakage and improved ability to study calcium near the cell membrane and preserve the fluorescent properties of “fluo” dyes. The modifications include (a) piperazinoacetic acid XIII for the leakage resistance (FLUO-LR), (b) dodecylpiperazine XIII for a near membrane indicator (FLUO-MOMO, FLUO-NOMO amphipathic “fluo” indicators which bind to cellular membranes and respond to calcium near the membrane), and (c) a propionic acid XII for general leakage resistance -FLUO-LOJO, FLUO-KOJO “fluo” indicators with an extra charge that enables them to resist leakage).
Owner:INVITROGEN
Methods for isolation and purification of fluorochrome-antibody conjugates
InactiveUS20060160998A1Low backgroundEnhanced signalHybrid immunoglobulinsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesStationary phaseFluorescence
The invention provides methods for isolating a fluorochrome-antibody conjugate from an aqueous mixture of the conjugate and unconjugated fluorochrome. The method involves contacting the mixture with a water insoluble stationary phase having a metal ion chelated thereto and binding the conjugate to the stationary phase. The phase containing bound conjugate is then washed to remove unbound fluorochrome. Thereafter the conjugate is eluted from the stationary phase and recovered in a form substantially free of the unconjugated fluorochrome.
Owner:SUK ROELF JOHAN
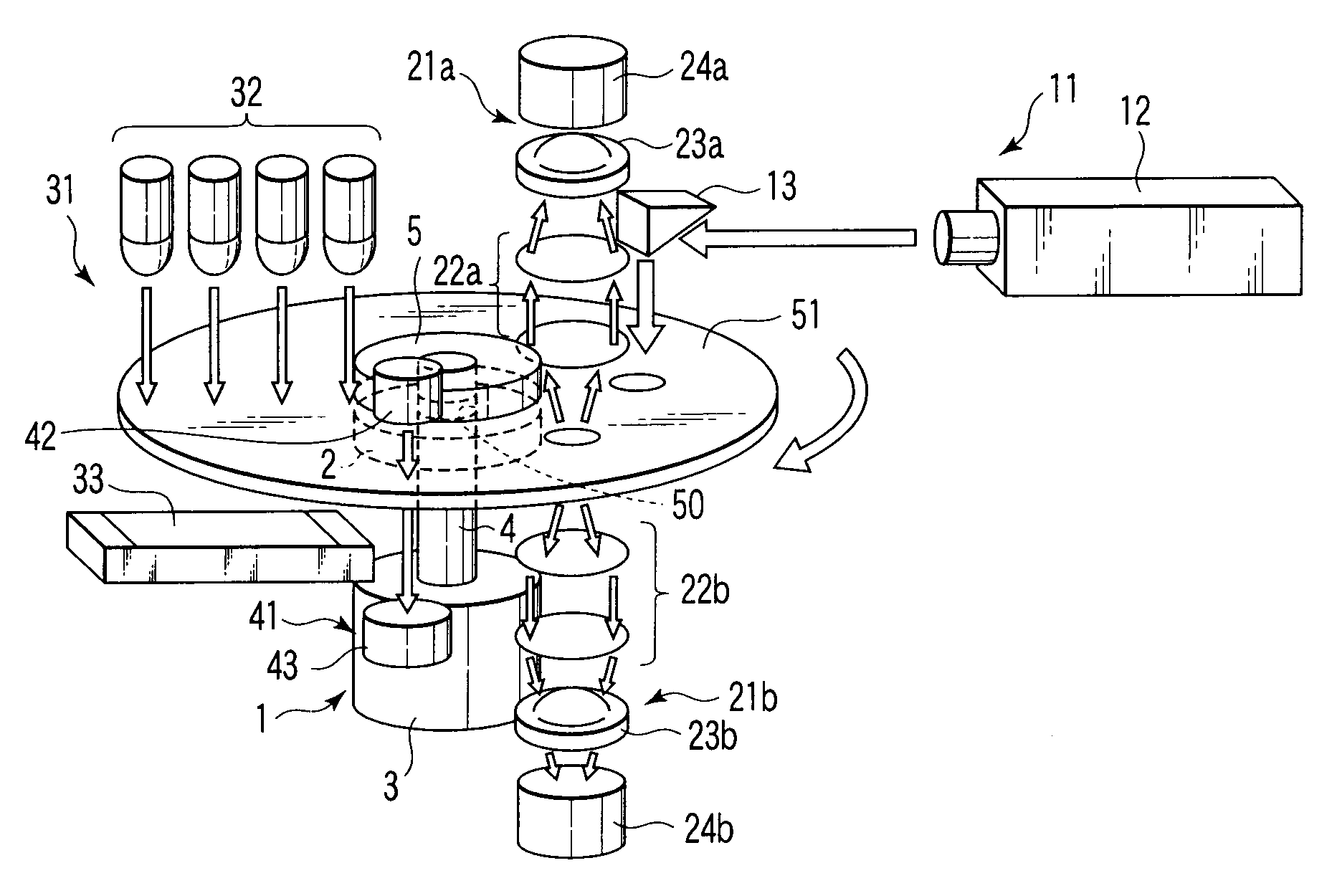
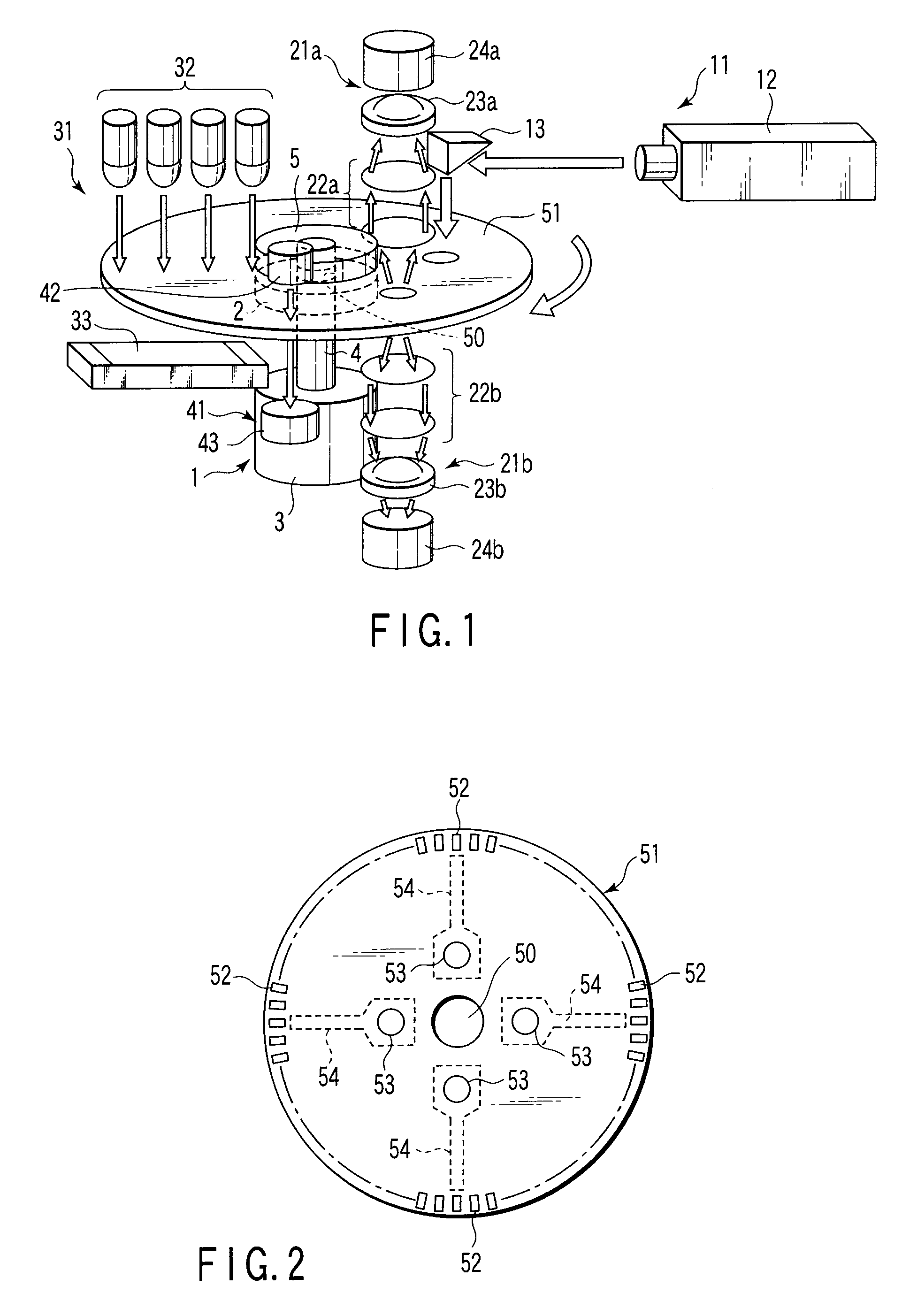
Fluorometric apparatus, fluorometric method, container for fluorometry, and method of manufacturing container for fluorometry
InactiveUS20080003668A1Easy to operateImprove space utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryProtein targetEngineering
A fluorometric apparatus capable of configuring to have a small size and operability requiring a simple and easy operation of centrifuging a specimen in a container a rotation center of which is detachably supported by a rotation axis (not shown), exciting the specimen by means of an N2 laser apparatus and an excitation light irradiator for guiding the laser light emitted from the N2 laser apparatus, and receiving fluorescence having two types of wavelengths emitted from antibodies labeled with fluorescent dyes in the specimen in a region separate from the region in which the excitation light is radiated by a predetermined angle by using a photomultiplier tube, obtaining a ratio of light intensity for each wavelength, comparing the obtained ratio with a standard value, and estimating a target protein concentration.
Owner:SANKO JUNYAKU CO LTD +1
Application of flow cytometry method to vaccine production real-time monitoring
ActiveCN104198357ASave operating timeObvious superiorityIndividual particle analysisBiotechnologyVaccine Production
The invention discloses the application of a flow cytometry method to vaccine production real-time monitoring. The application is to apply the flow cytometry method to the vaccine production process, and monitor the viable bacteria count in real time during the vaccine production process. The application comprises the steps of dyeing bacterial cell through fluorescent dye, detecting the change of bacteria fluorescence signals through a flow cytometer, and obtaining an FCM diagram with at least two types of the following parameters by measuring the change of the bacteria fluorescence signals: viable bacteria count, dead bacteria count and total bacteria count, obtaining the ratio of the viable bacteria count according to the FCM diagram, obtaining the concentration of target bacteria solution through an absolute counting method, and obtaining the viable bacteria amount and the dead bacteria amount of target bacteria according to the ratio of the viable bacteria count and the concentration of the target bacteria solution. The invention provides a convenient, rapid and reliable bacterial activity monitoring method for the vaccine production process and is convenient and easy, the operation time is only 30 minutes, and the quality of the vaccine production process can be accurately controlled.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HEALTH GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Fluorescent labeling reagents with multiple donors and acceptors
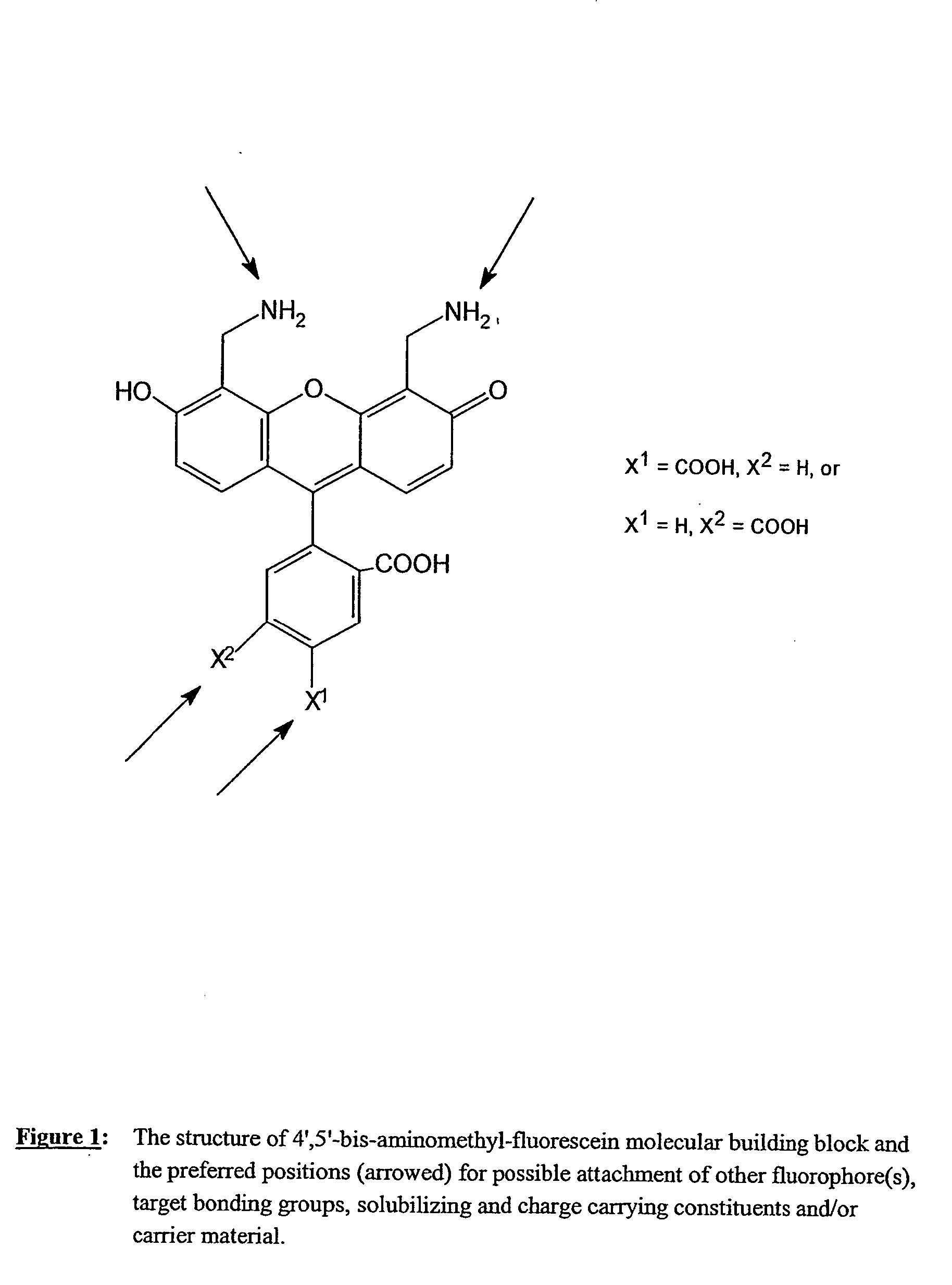
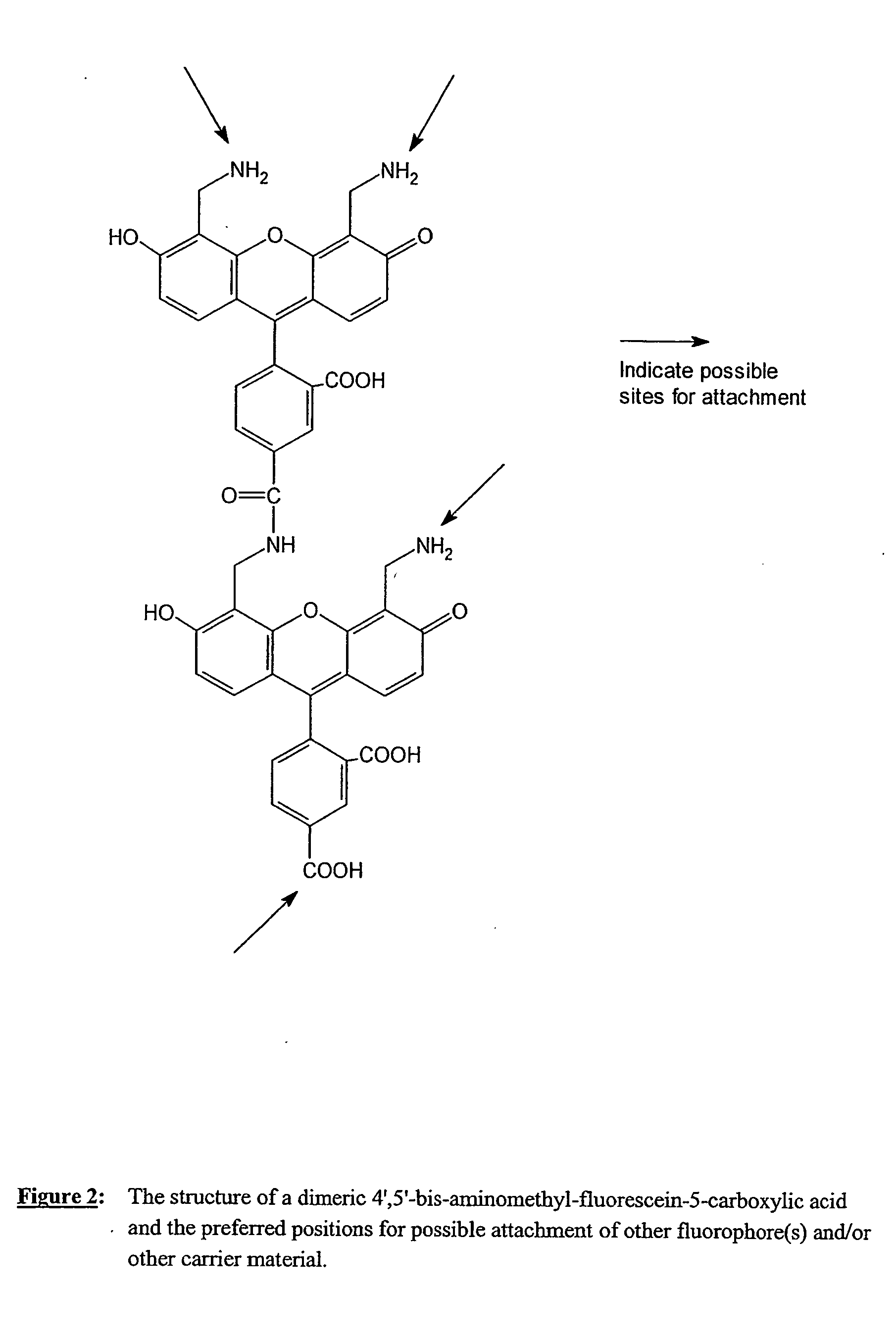
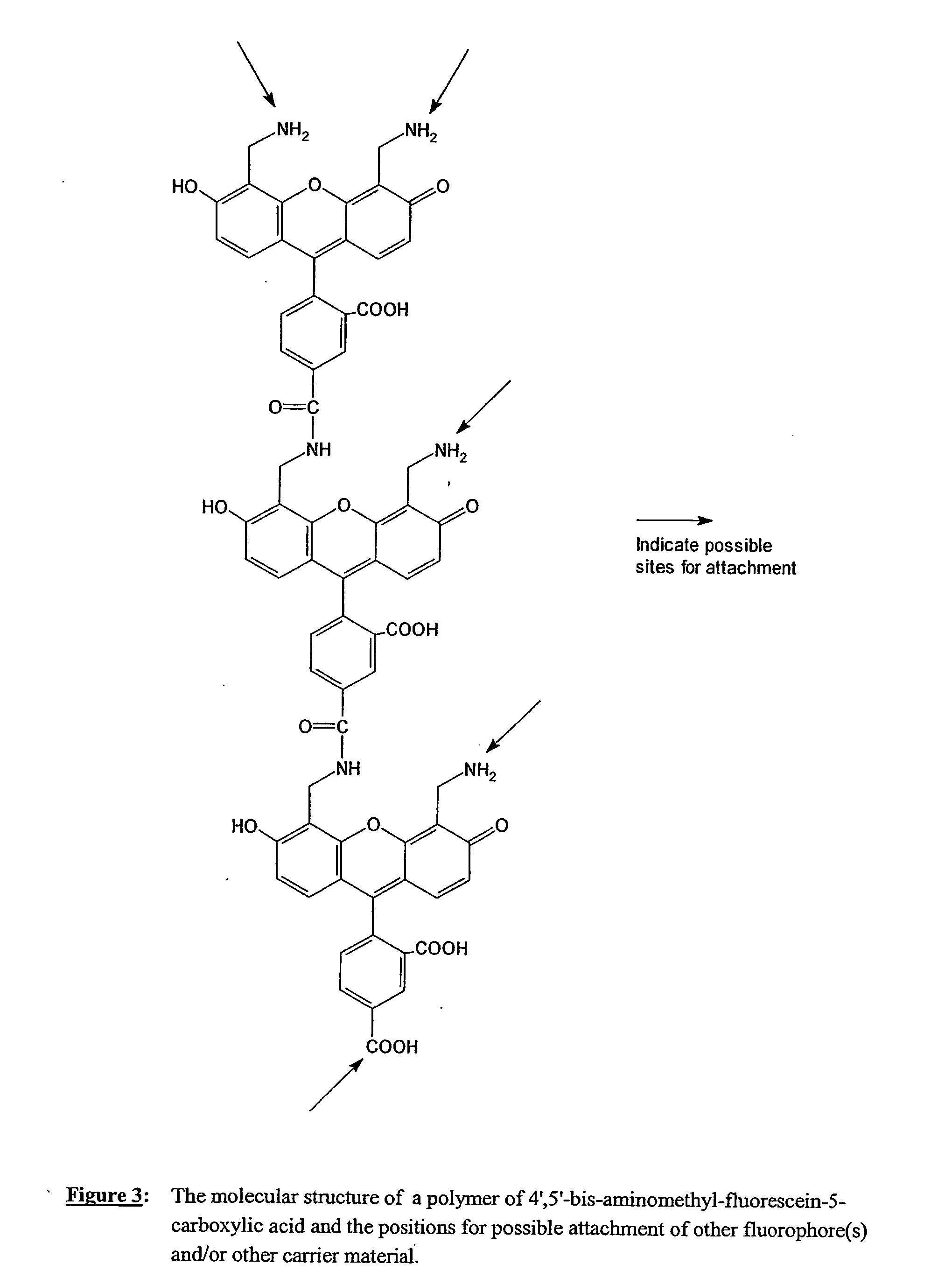
Disclosed is a novel class of fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET) labelling reagents, based on and synthesised from easily prepared dye building blocks. The labelling reagents are in the form of “cassettes” which enable their attachment to a wide variety of biological and other materials. A labelling reagent comprises at least two fluorescent dye moieties covalently linked via a linker group and optionally having a target bonding group for attaching the reagent to a target. The energy transfer labelling reagents may be bound to target materials through covalent or non-covalent attachment. The dyes are selected so that the emission spectrum of a first (or donor) dye overlaps the absorption spectrum of a second dye, thereby allowing energy transfer to occur between the dyes. The dye building blocks are 4′, 5′-bis-aminomethyl-fluorescein and / or its 5(6)-carboxylic acid and having the structure (1). In addition to the embodiment of the invention which includes a single donor and a single acceptor fluorochrome, the fluorescent energy transfer labelling reagents according to the invention may further comprise one or more third fluorochromes each having third absorption and emission spectra covalently attached to said first or second fluorochromes.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Evanescent wave excited fluorescence detection method
InactiveUS20060154303A1Reduce background noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid layerFluorescence
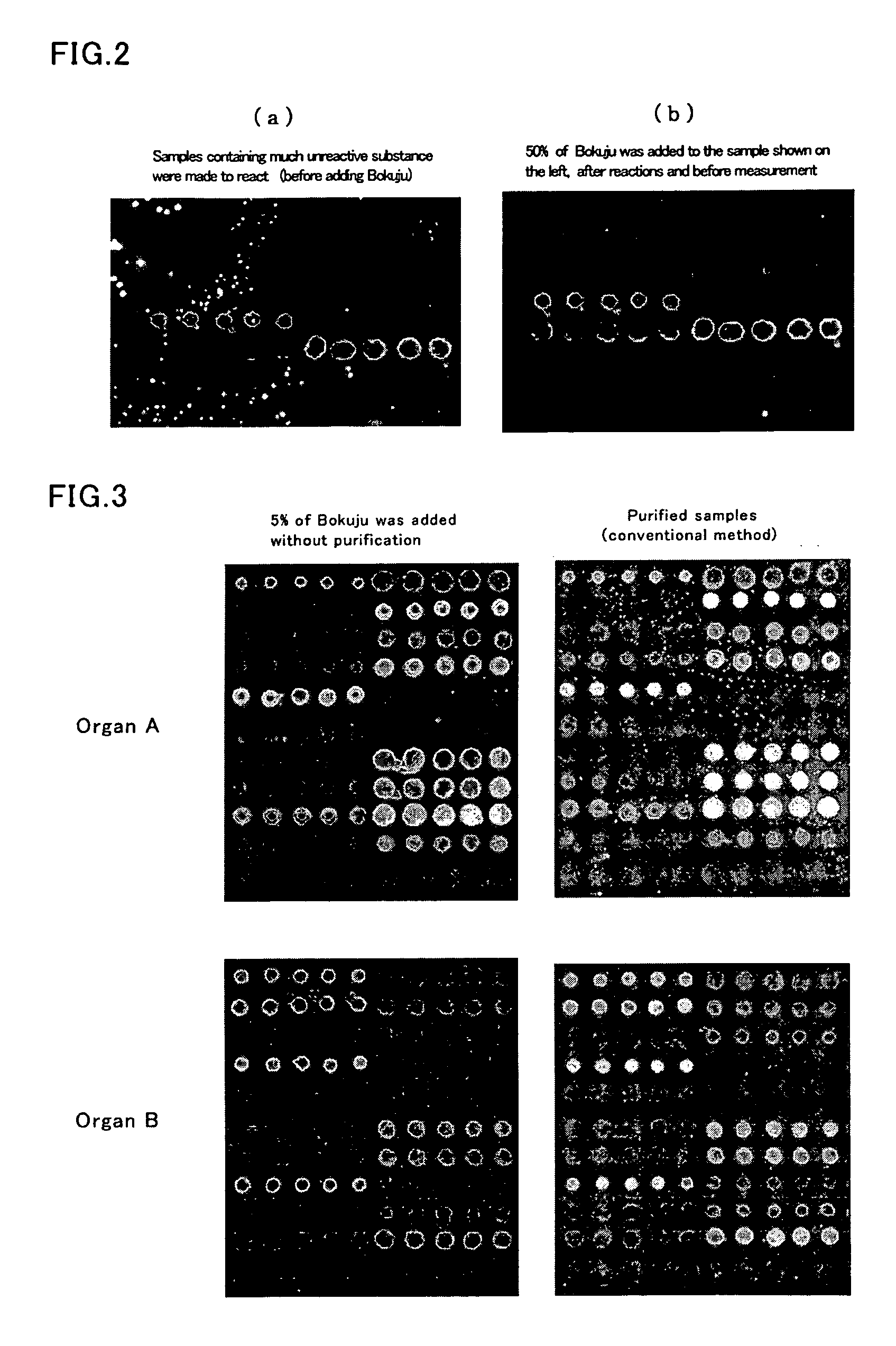
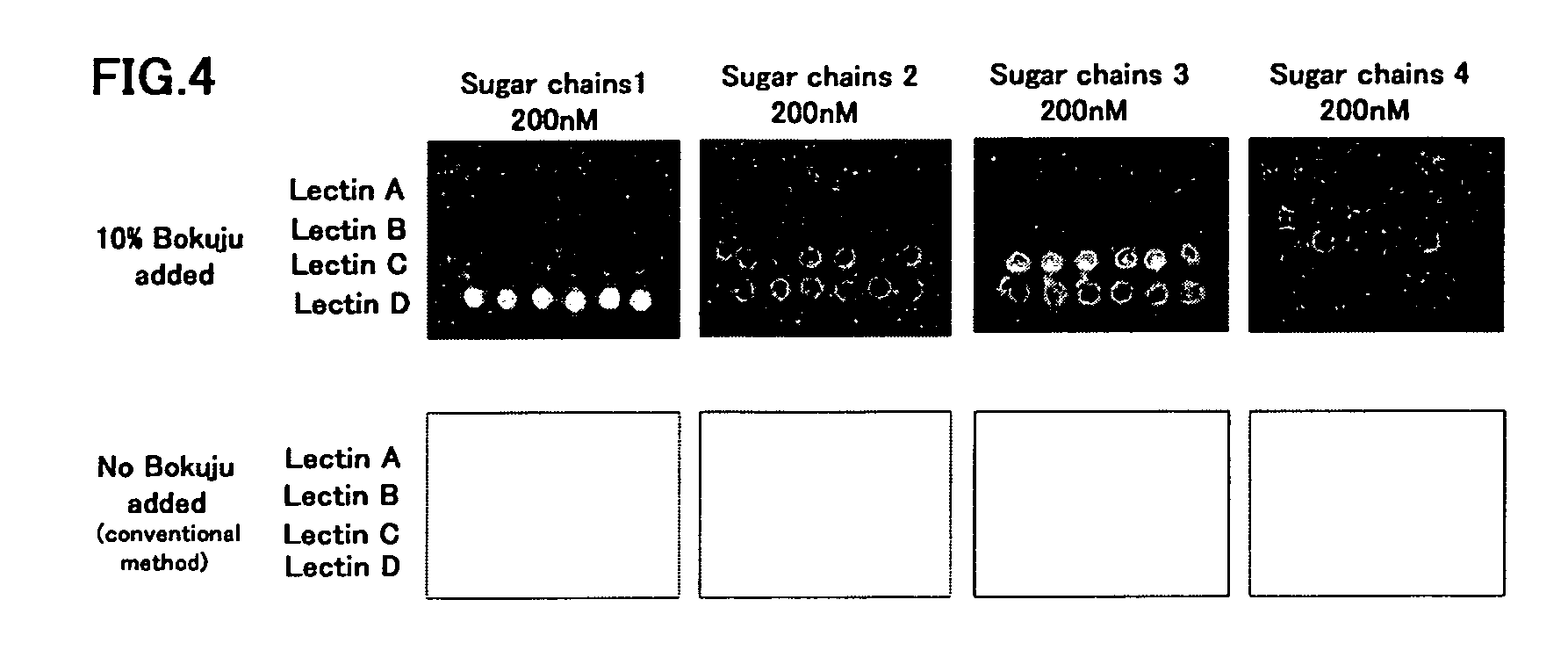
In the case where many interactional substances are immobilized on the front surface side of a light transmitting plate capable of generating evanescent waves on the front surface, and where the fluorescence levels in the interactions between the interactional substances and a fluorescence labeled test substance are detected in a liquid layer according to a conventional method, the detection sensitivity and S / N ratio are low due to the background noise. Furthermore, it is necessary to perform a gel filtration purification step for the purpose of removing an excessive amount of the fluorescence dye used for labeling a test substance before the interactions between the fluorescence labeled test substance and the interactional substances are performed. To solve these problems, this invention proposes the above-mentioned method for detecting the evanescent wave excited fluorescence comprising the step of adding a black colorant, for example, a pigment based colorant mainly containing fine particles such as Bokuju.
Owner:MORITEX CORP +1
Polymer composition for photobioreactors
InactiveUS20120184027A1Modified absorptionModified transmission characteristicBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyUltravioletFluorescent light
Owner:GEORG FISCHER DEKA
In-gel fluorescent protein staining technique
InactiveUS20060144708A1Reduces post-electrophoretic process timeManipulation can be minimizedElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementStaining techniqueGlycine
An “in-gel” staining technique for detecting and / or separating proteins during electrophoresis, illustratively as a modification of the standard Laemmli procedure. A fluorescent dye, such as Nile red or Phosphine, is included in the running buffer (mobile phase) which may be a standard Laemmli Tris-Glycine SDS buffer that has been modified to reduce the concentration of detergent (SDS) to less than the typical concentration (0.10% v / v). The fluorescent dye stains proteins during electrophoretic separation. The post-electrophoretic operations are, therefor, reduced and the separated, stained fractions are recoverable for further processing, purifying or analysis.
Owner:KITZLER JEFFREY +2
Method for quantitatively detecting antigen
InactiveUS20050239215A1Improve accuracyHigh precision analysisAnimal cellsSugar derivativesFluorescenceImmune complex deposition
A method for quantitatively detecting an antigen which comprises (1) a first step of providing an Fab′ antibody having a uniform isoelectric point, said antibody forming an immune complex with an antigen in an analytical sample and being modified by adding an amino acid sequence comprising a charged amino acid residue and by being labeled with a fluorescent dye, (2) a second step of mixing the Fab′ antibody having a uniform isoelectric point with the analytical sample containing the antigen to obtain a mixture comprising the immune complex, (3) a third step of separating the mixture by performing electrophoresis in a carrier, (4) a fourth step of irradiating an excitation light which excites the fluorescent dye to the mixture separated in the third step to cause fluorescence in the immune complex, and (5) a fifth step of detecting the fluorescence.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
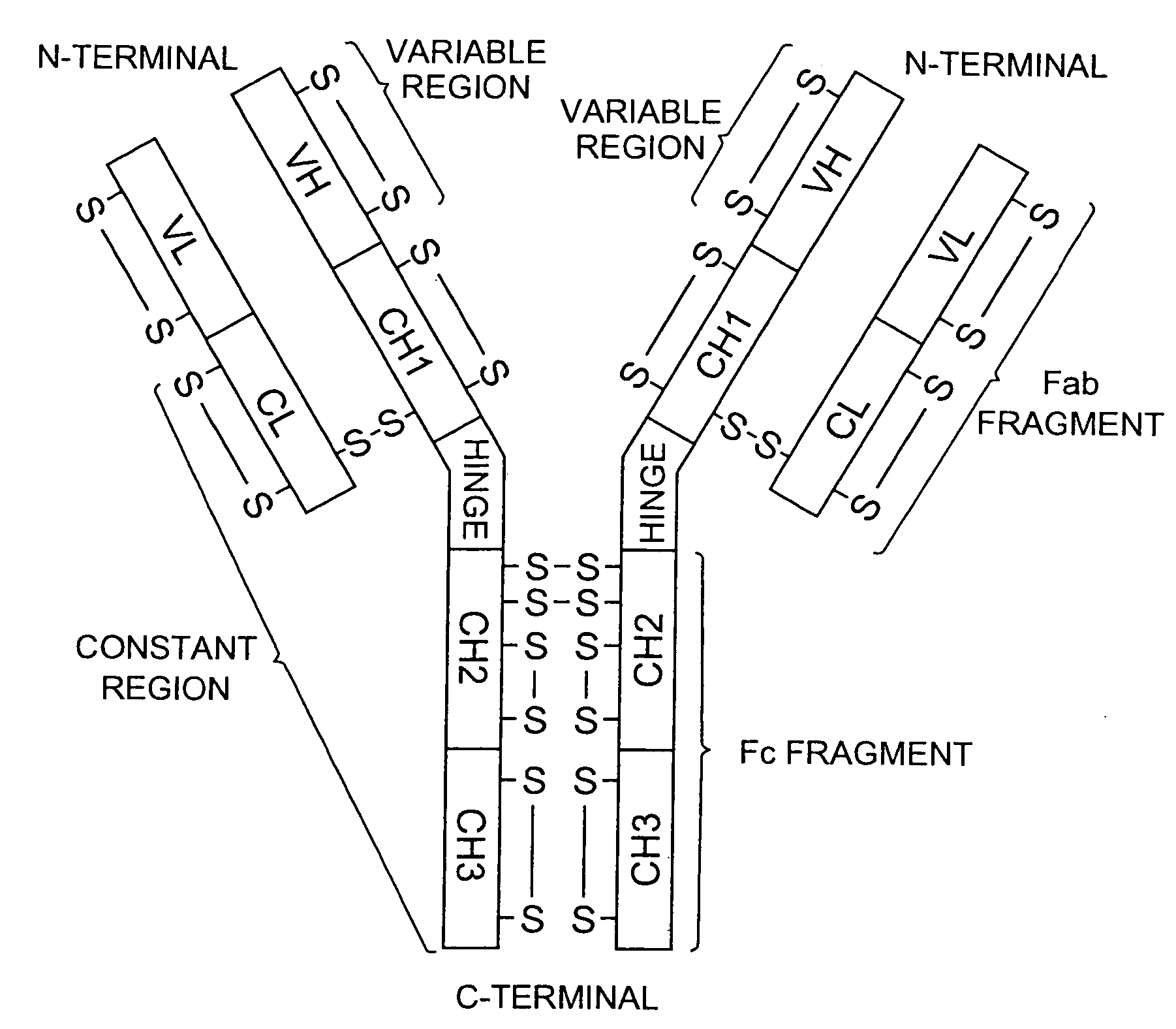
Novel Fluorescent Dyes and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20110014599A1Narrow bandwidthLarge Stokes shiftPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAnalyteFluorescein
The present invention provides fluorescent dyes that are based on firefly luciferin structure. These dyes are optimally excited at shorter wavelengths and have Stokes shift of at least 50 nm. The fluorescent dyes of the invention are useful for preparation of dye-conjugates, which can be used in detection of an analyte in a sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
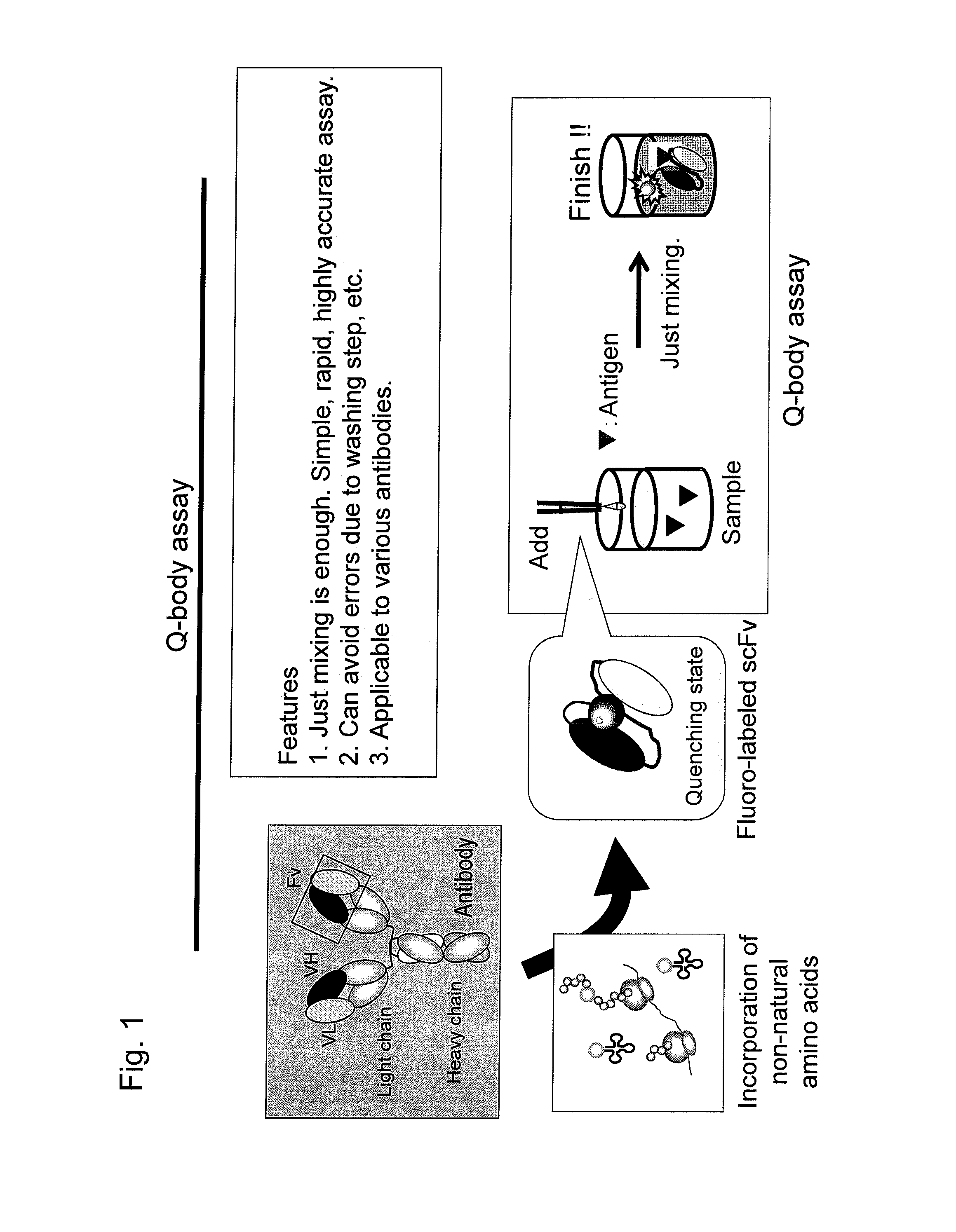
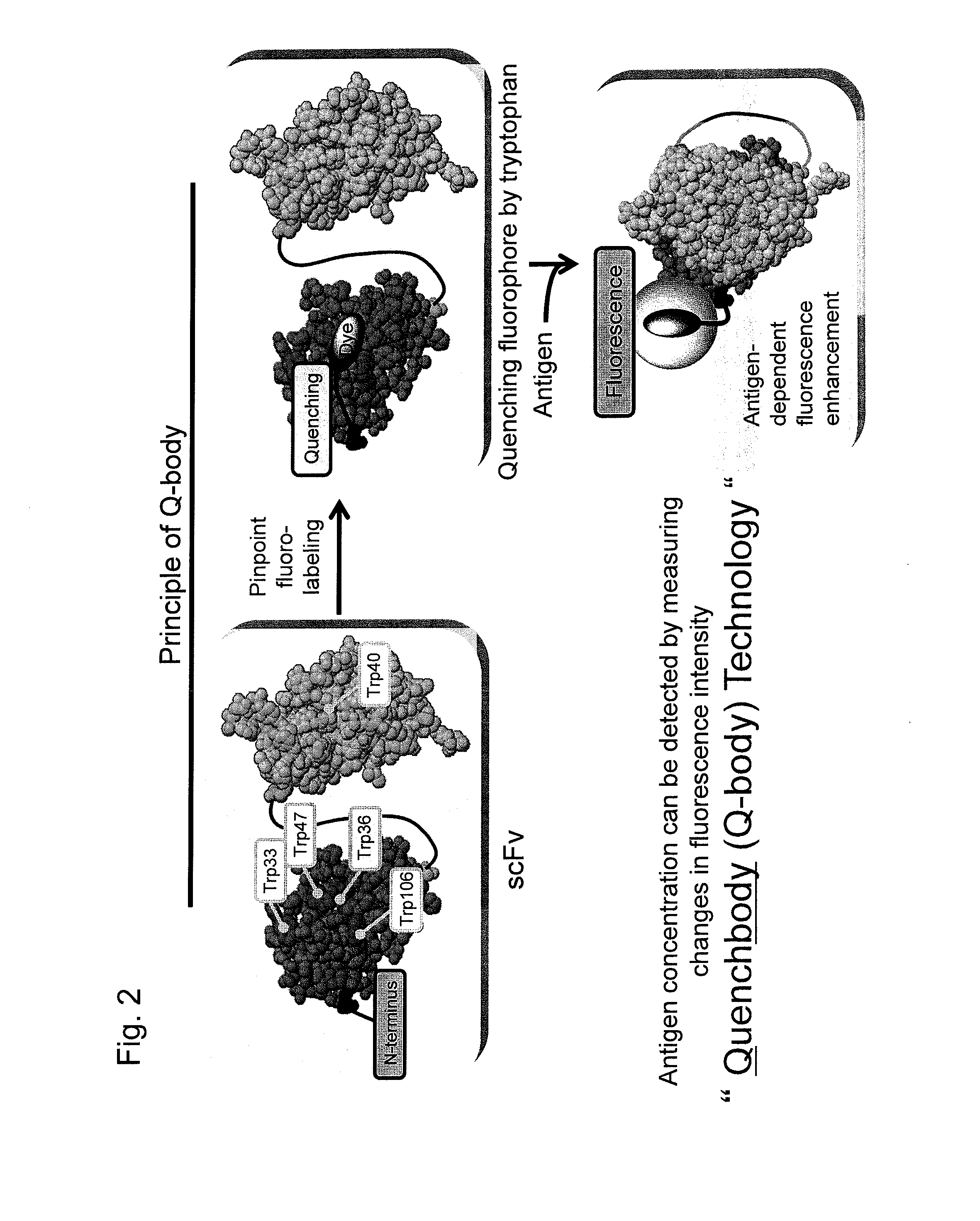
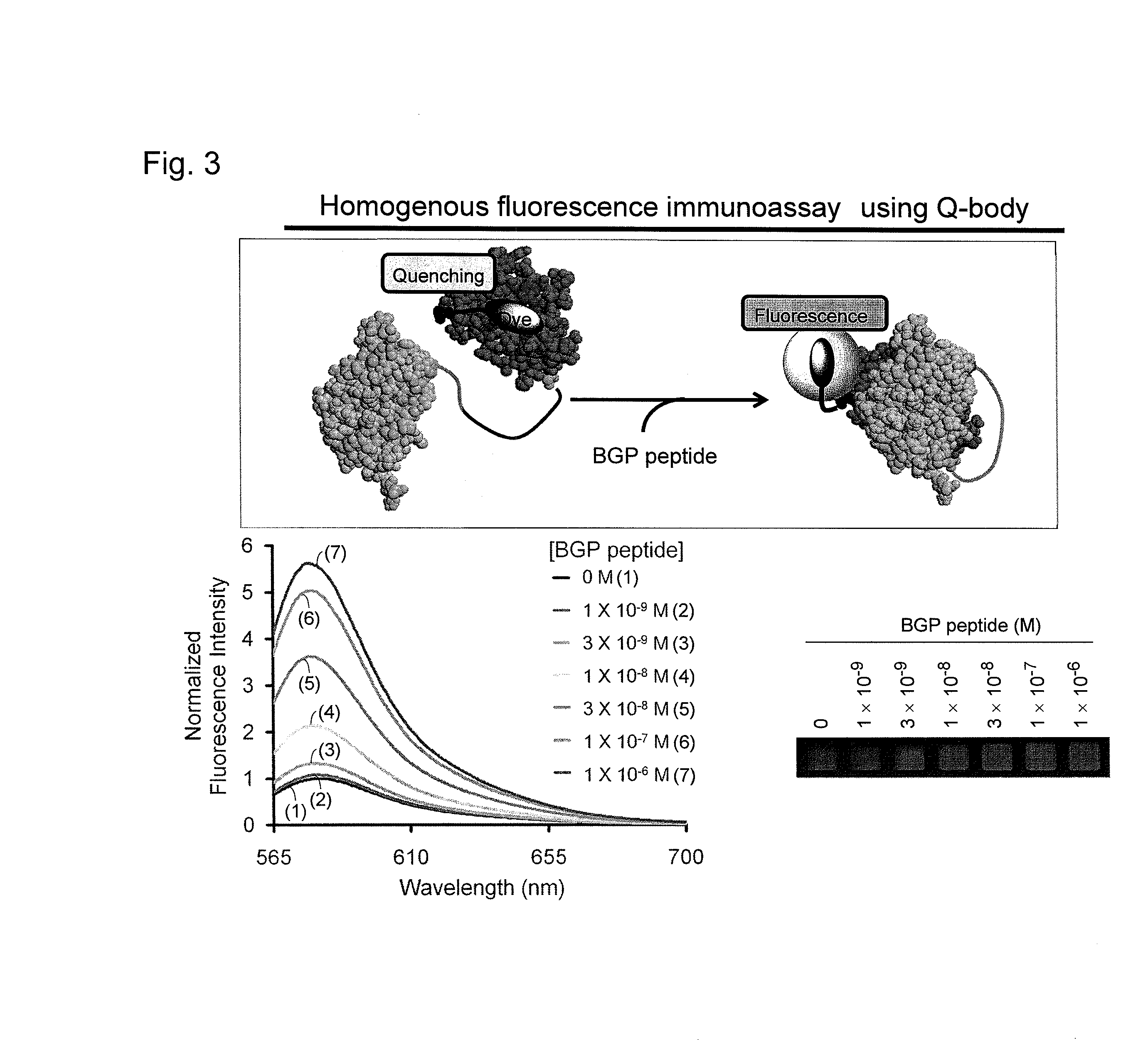
Fluorescence immunoassay using polypeptide complex containing fluoro-labeled antibody variable region
InactiveUS20140329228A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescence immunoassayHeavy chain
An object of the present invention is to provide an immunoassay that enables the rapid and convenient quantitative measurement with high detection sensitivity of a target substance in a liquid phase without the need of immobilization and washing steps and enables the visualization of an antigen. The present invention achieves the object by performing sequentially the steps of:(a) bringing, in a liquid phase, a complex comprising a polypeptide containing an antibody light-chain variable region and a polypeptide containing an antibody heavy-chain variable region into contact with an antigen in a specimen for measurement, wherein either or both the polypeptides are labeled with a fluorescent dye(s);(b) detecting the fluorescence of the fluorescent dye(s) or measuring the fluorescence intensity; and(c) calculating the amount of the antigen contained in the sample or visualizing the antigen using the positive correlation between the antigen concentration and the fluorescence intensity of the fluorescent dye(s) as an indicator, thereby measuring the concentration of the target antigen existing in the test substance.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Security element formed from at least two materials present in partially or fully overlapping areas, articles carrying the security element, and authentication methods
ActiveUS20190126659A1Strong authenticationEasy to measurePaper-money testing devicesPattern printingEpicoccononeRadiation exposure
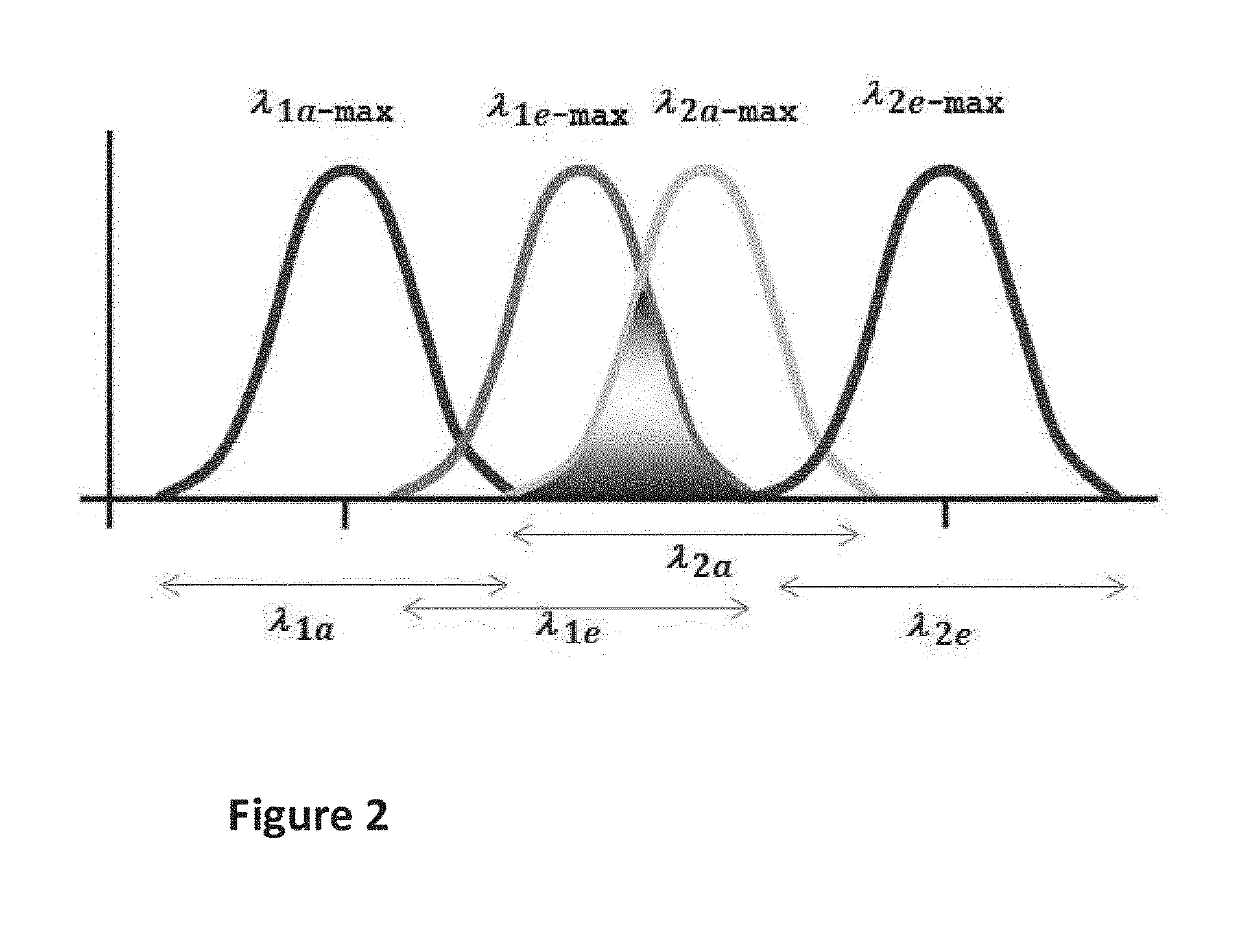
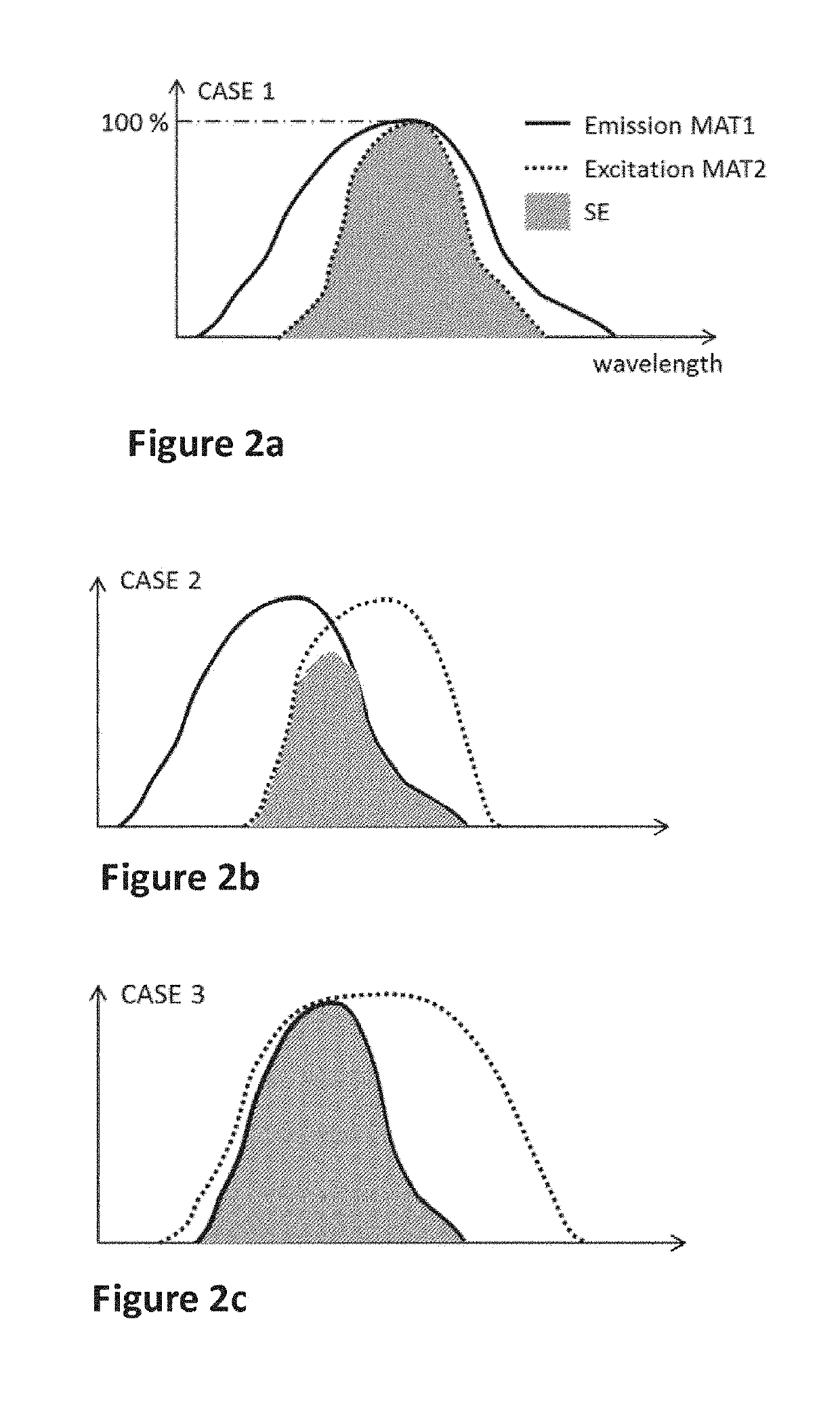
Security element comprising a first material MAT1 and a second material MAT2 formed in or on a substrate, in such a manner that areas occupied by MAT1 and MAT2 overlap partially or fully,the first material MAT1 comprising a phosphorescent pigment (donor), the second material MAT2 comprising a fluorescent dye or pigment (acceptor),wherein the phosphorescent pigment present in MAT1 is capable of emitting phosphorescence radiation in at least one first phosphorescence emission wavelength range λ1e upon excitation by electromagnetic radiation falling within a phosphorescence excitation wavelength range λ1a, andthe fluorescent dye or pigment present in MAT2 is capable of emitting fluorescence radiation in at least one second fluorescence emission wavelength range λ2e upon excitation by electromagnetic radiation falling within an fluorescence excitation wavelength range λ2a of the fluorescent dye or pigment, andsaid first phosphorescence emission wavelength range λ1e of the phosphorescent pigment present in MAT1 overlaps with the excitation wavelength range λ2a of the fluorescent dye or pigment present in MAT2, so that after irradiation of the security element with electromagnetic radiation within the phosphorescence excitation wavelength range λ1a the emission of fluorescence radiation in the emission wavelength range λ2e is observable.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
Ultra-high specificity fluorescent labeling
InactiveUS7282373B2Reduce undesirable background noiseAccurate measurementGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsEnergy transferResonance
A self-assembled relay probe for detecting a target material is provided including: a first peptide tag bound to the target material; and a first fluorescent conjugate including a first fluorochrome and a first tag binding group; wherein the first fluorescent conjugate selectively associates with the first tag. The probe further includes a second peptide tag bound to the target material; and a second fluorescent conjugate including a second fluorochrome having a longer wavelength and distinct excitation and emission maxima from the first fluorochrome and a second tag binding group. Upon exposure to the target material, the first and second fluorescent conjugates independently associate with the first and second peptide tags, respectively, so as to be a distance apart represented by about 0.1 times R0 to about 2 times R0, such that upon excitation of the first fluorescent conjugate, fluorescence resonance energy transfer results in excitation of the second fluorescent conjugate, yielding detectable emission from the second fluorescent conjugate.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
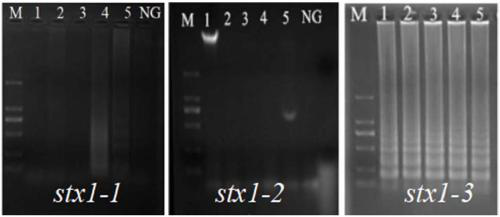
Primers, kit and method for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by PSR (polymerase spiral reaction)
ActiveCN109355408AReduce sensitivityGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliFluorescence
The invention discloses primers, kit and method for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by PSR (polymerase spiral reaction). The primers for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I are designedaccording to specific target sequence stx1 of Shiga toxin I and include detection primer Ft and detection primer Bt, as well as acceleration primer IF and acceleration primer IB, and their nucleotidesequences are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 to 4. The invention also provides a kit for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by PSR; the kit includes the above primers, Bst DNA polymerase, and a mixed solution of calcein and manganese chloride, is suitable for detecting Escherichia coli Shiga toxin I by polymerase spiral reaction; after developing with a fluorescent dye, the results can be judged witheyes. The kit is simple and quick to operate, low in detection cost and suitable for field detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Fluorescent dyes, energy transfer couples and methods
Fluorescent dyes, fluorescence energy transfer dye couples, multi-color dye sets, can be employed in art-recognized assays and certain novel methods, such as in proximity assays.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting vibrio quantity in seawater
InactiveCN101988083ALow operating environment requirementsSimple resultMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerFluorescence
In the invention, vibrio quantity in aquaculture water is rapidly detected by fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. A specific primer for vibrio bacteria is designed by taking a ribosome 16S rRNA gene as a target gene; a fluorescent quantitative standard curve is constructed in a mode of recombinant plasmid; a 20 mu L reaction system, which comprises 10 mu L of SYBR Green I fluorescent premixed reagent, 0.4 mu L of forward primer, 0.4 mu L of reverse primer, 1.6 mu L of DNA template and 7.6 mu L of deionized water, is established by a Premix Ex TaqTM reagent. The fluorescent quantitative PCR method has intuitive result, high specificity and high sensitivity, is rapid to detect the vibrio quantity, solves the problem of an inaccurate result caused by mold breeding in the conventional detection method, overcomes the defect of low specificity of a thiosulfate citrate bile salts sucrose agar (TCBS) culture medium for a vibrio quantitative detection method, and has long-term market development and economic investment potential.
Owner:LIAONING OCEAN & FISHERIES SCI RES INST
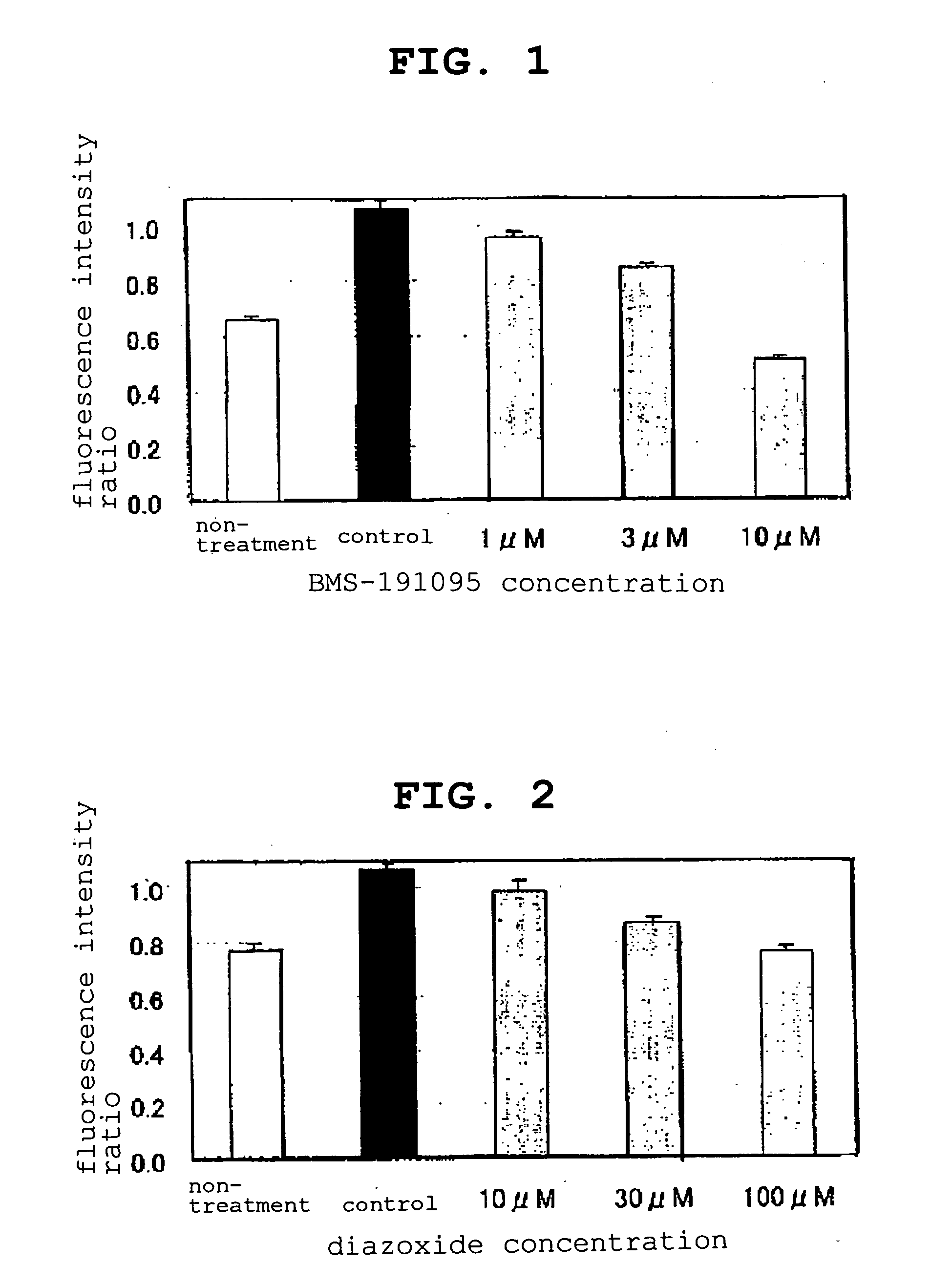
Method Of Assaying Substance Capable Of Changing Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
InactiveUS20070202486A1Improve accuracyEase of evaluationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementCell membraneCell culture media
The present invention aims to provide a convenient and high precision evaluation method of a pharmaceutical agent that changes the mitochondrial membrane potential, using a mitochondrial membrane potential of a cultured cell as an index. The present invention provides a method for evaluating the ability of a test substance to change the mitochondrial membrane potential by using, as an index, the change in the mitochondrial membrane potential, which is produced by the addition of an ion permeability regulator on a cellular membrane to a cell culture medium, wherein the change is measured as variation in the fluorescent intensity of a fluorescent dye.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
Fluorogenic protease substrates based on dye-dimerization
InactiveUS20050089946A1Rapid and convenient homogeneous approachImprove accuracyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme assayQuenching
A method of biological assay comprises the steps of providing an enzyme substrate comprising two fluorescence dye groups bound to a flexible peptide, the dye groups being of proximity sufficiently close so as to allow free energy attractions to draw the dyes together to essentially self-quench fluorescence of the dye groups, wherein self quenching of fluorescence of the dye groups is effected by dye dimerization or stacking, and enzymatically cleaving the peptide to release the fluorescence dye groups from dye dimerization or stacking, thereby producing an increase in fluorescence intensity. A protease substrate for use in the method of the invention is also disclosed. This invention finds use in detection and identification of microorganisms, sterilization assurance, pharmaceutical discovery, enzyme assays, immunoassays, and other biological assays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
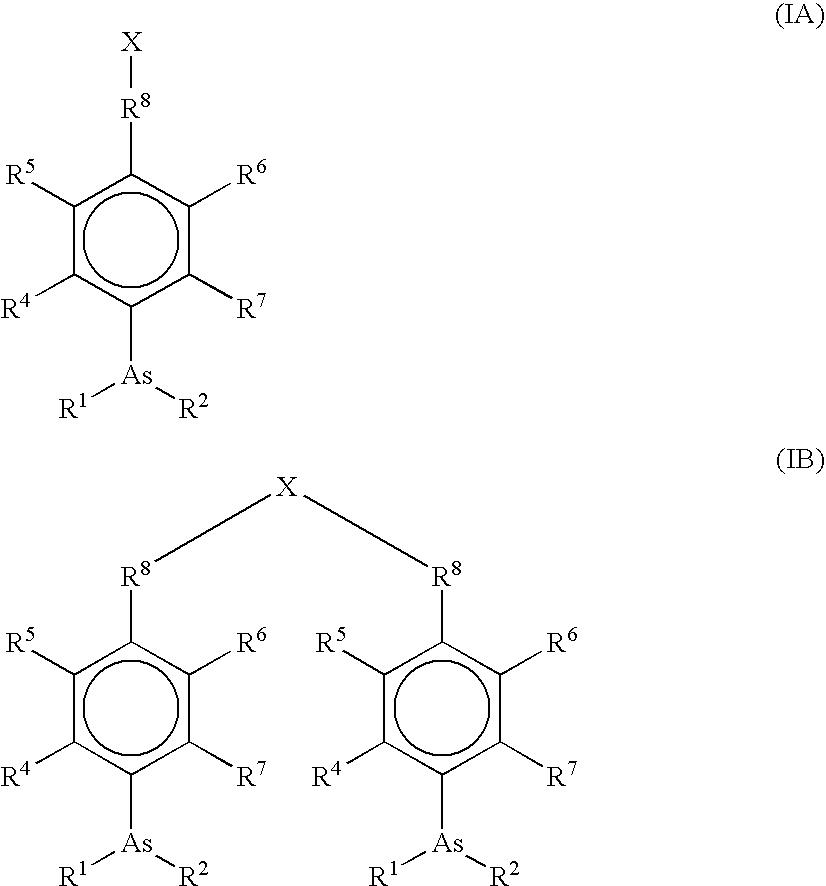
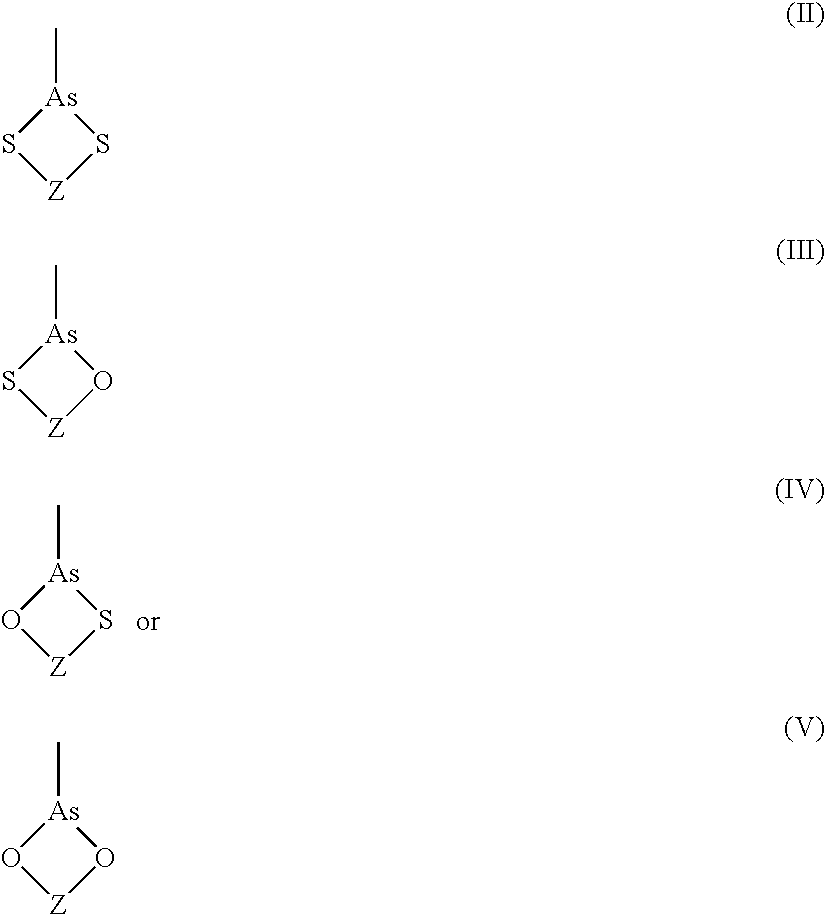
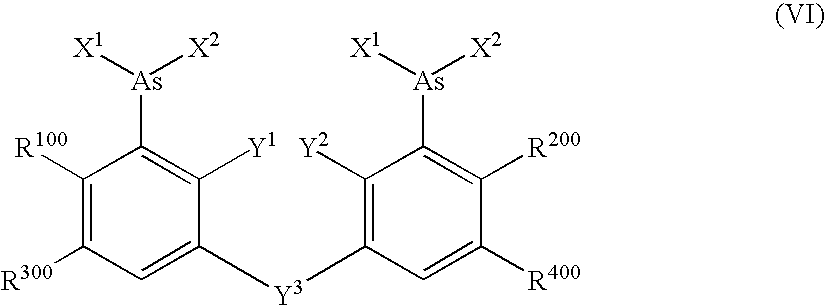
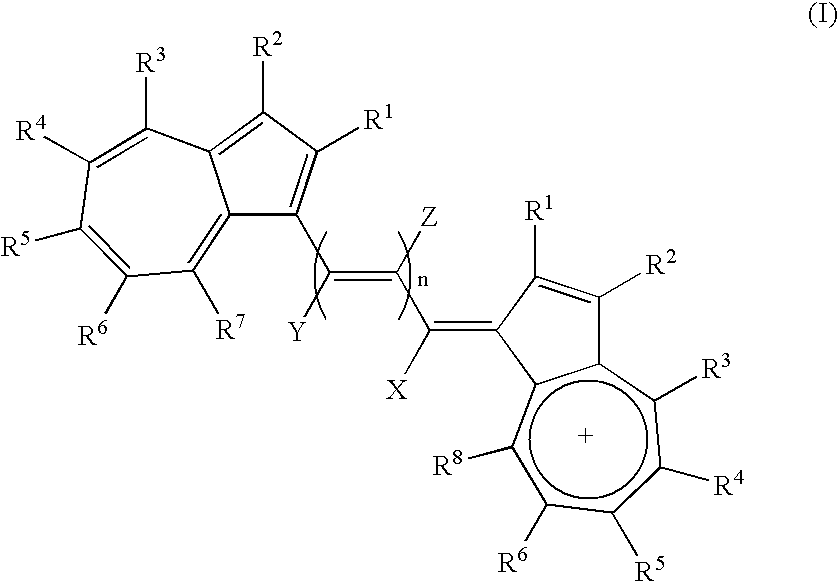
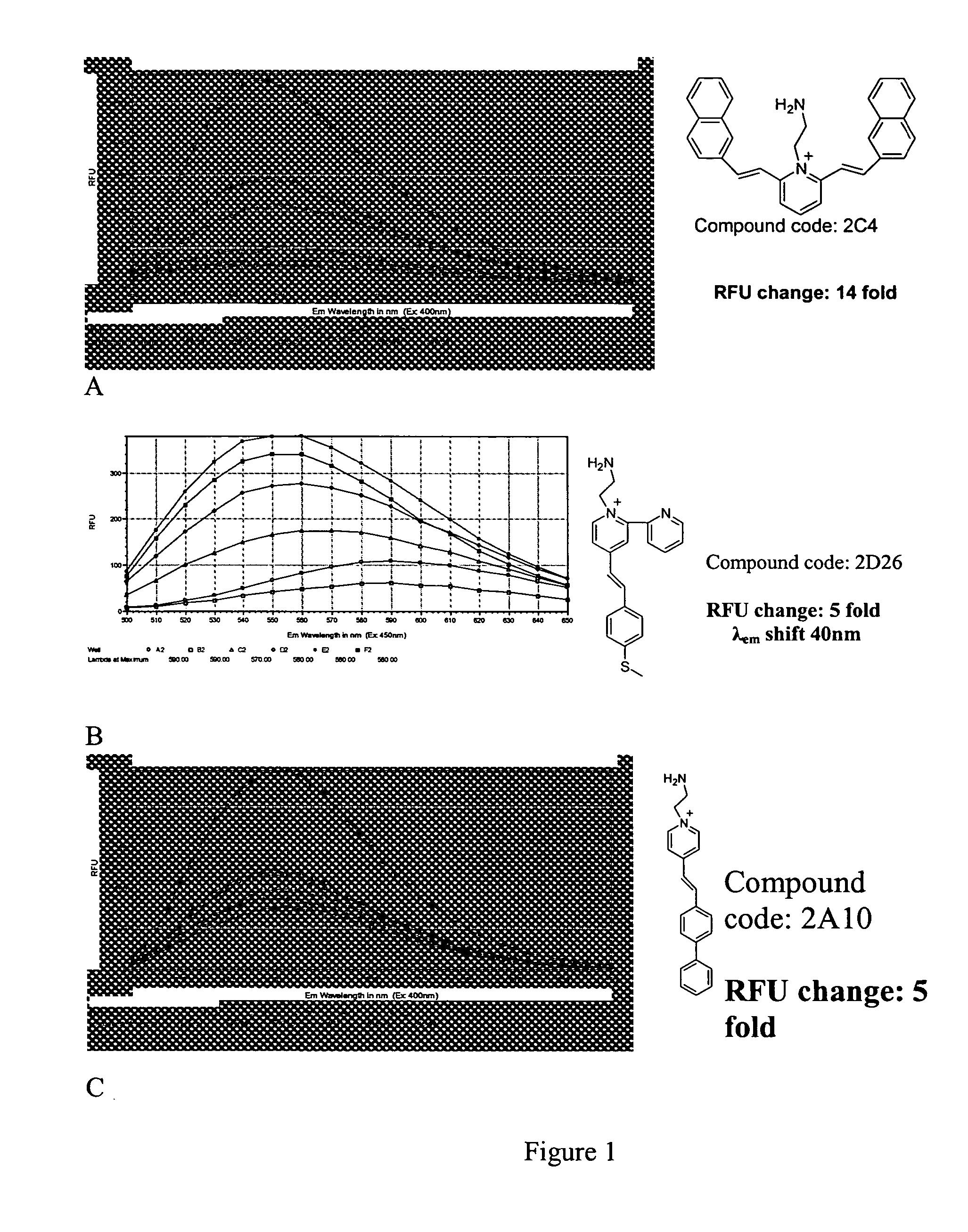
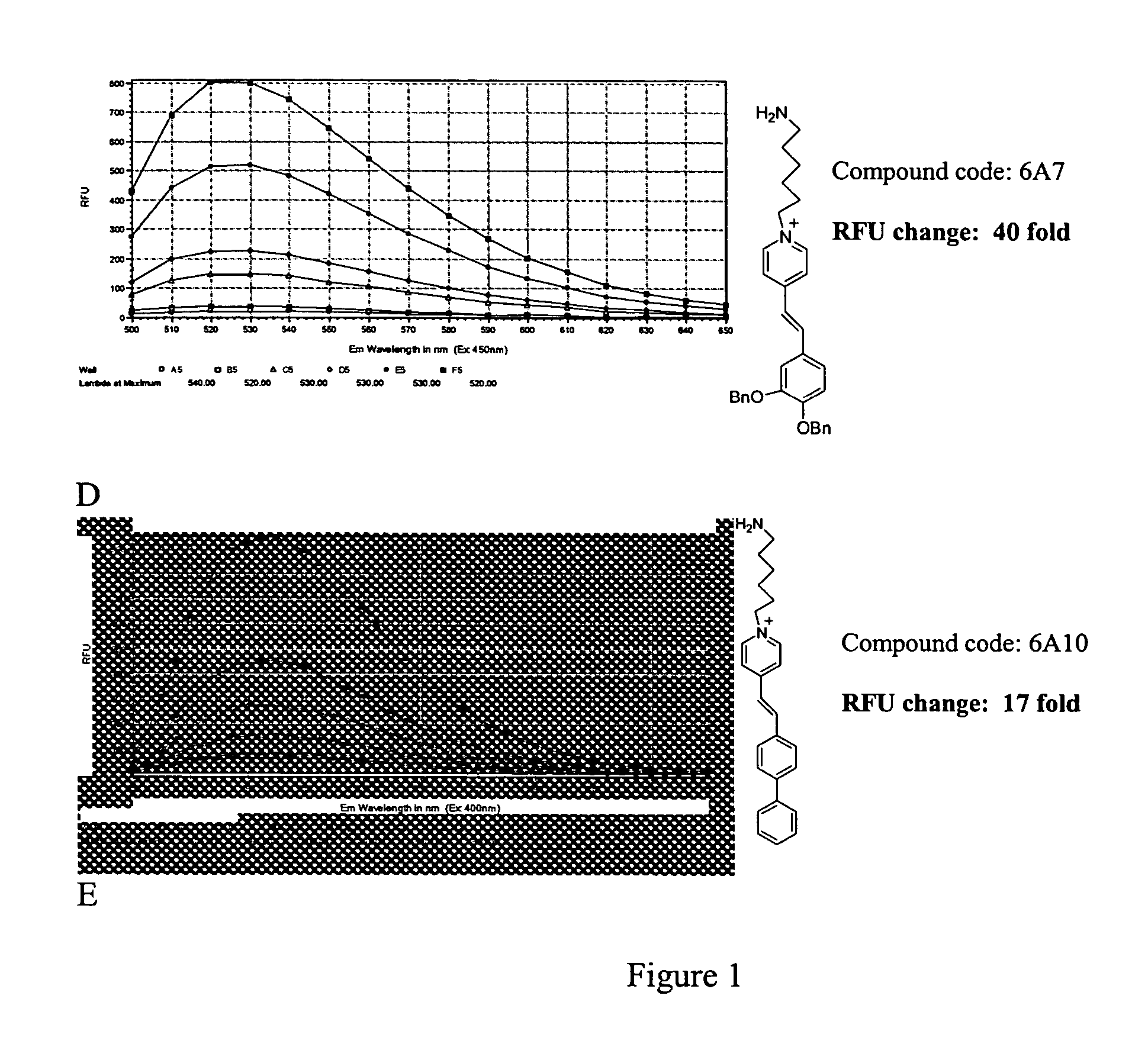
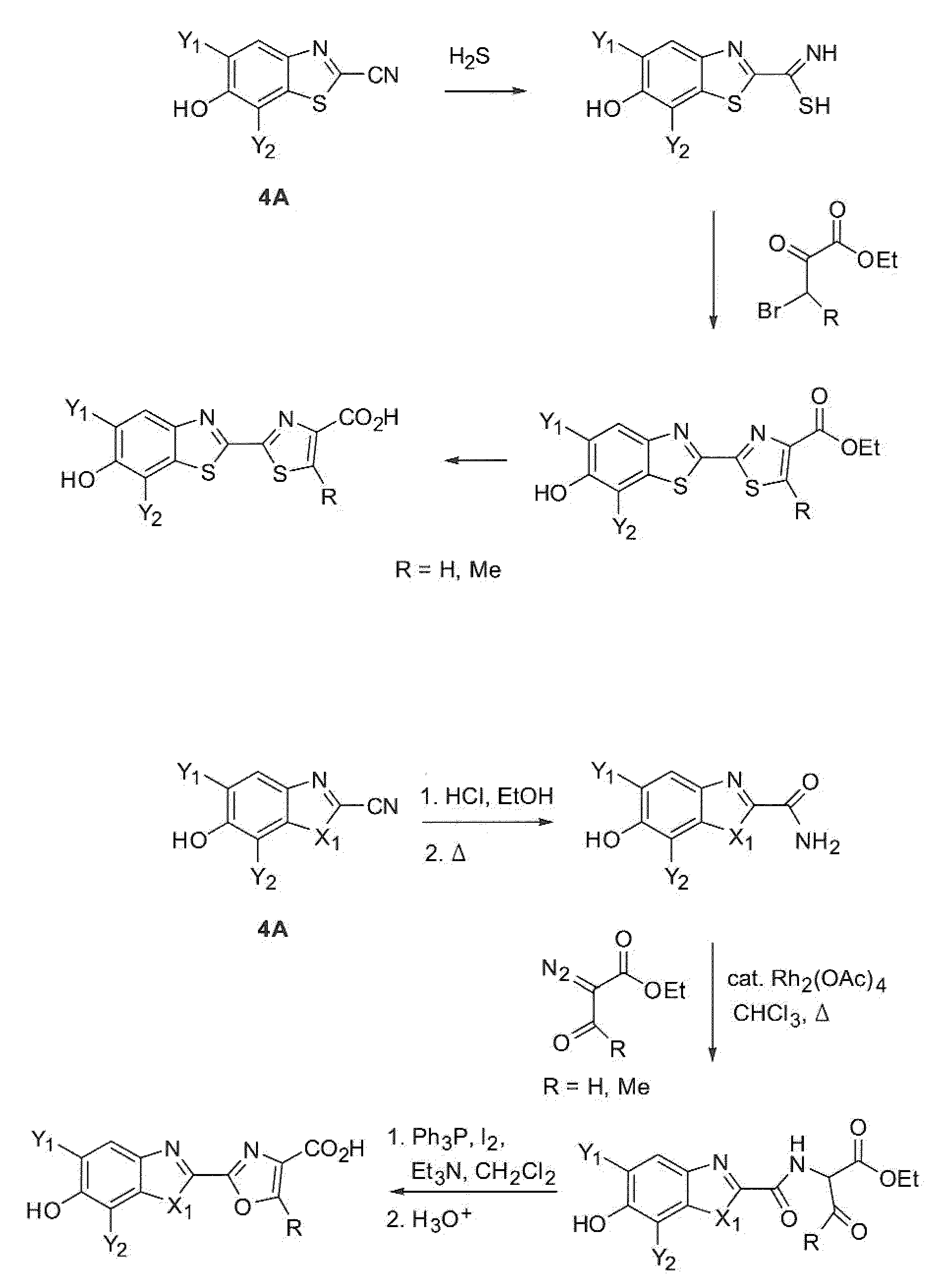
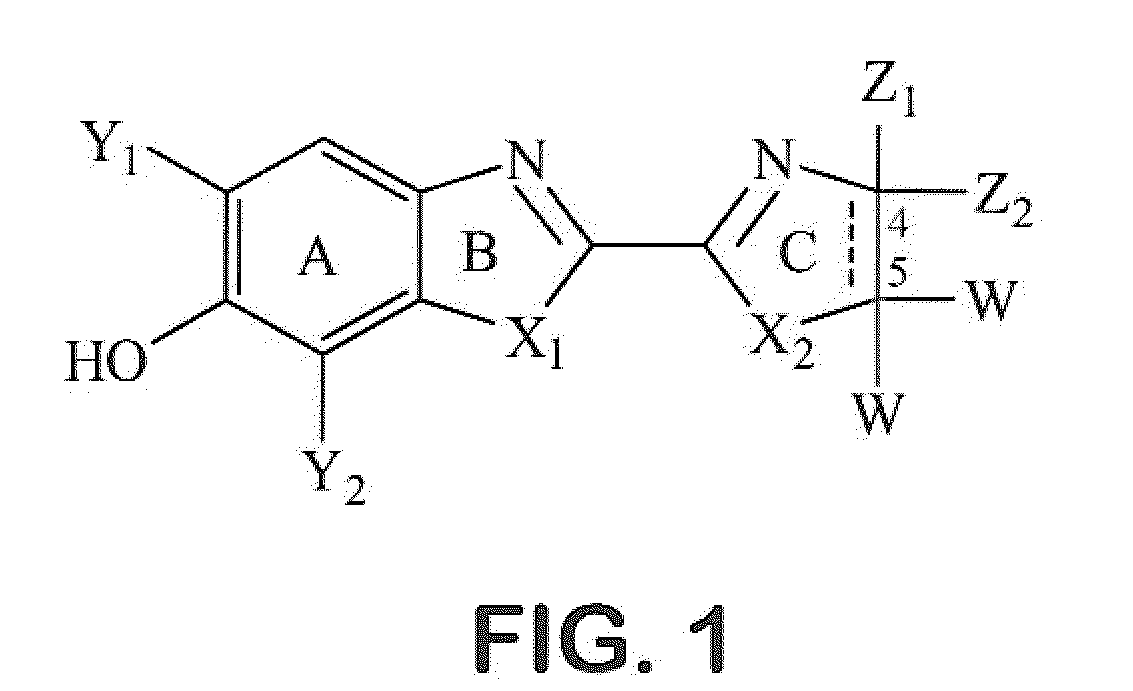
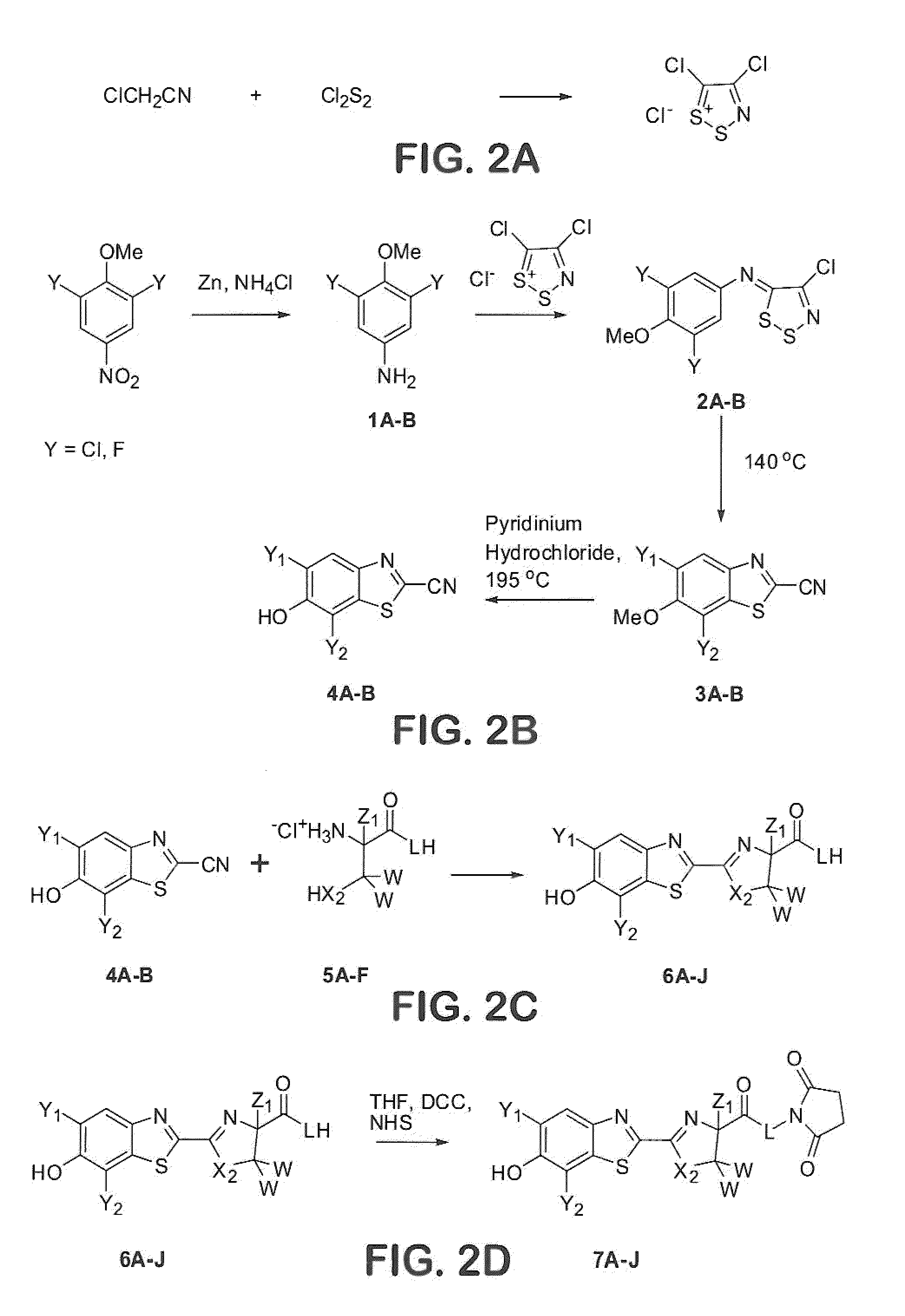
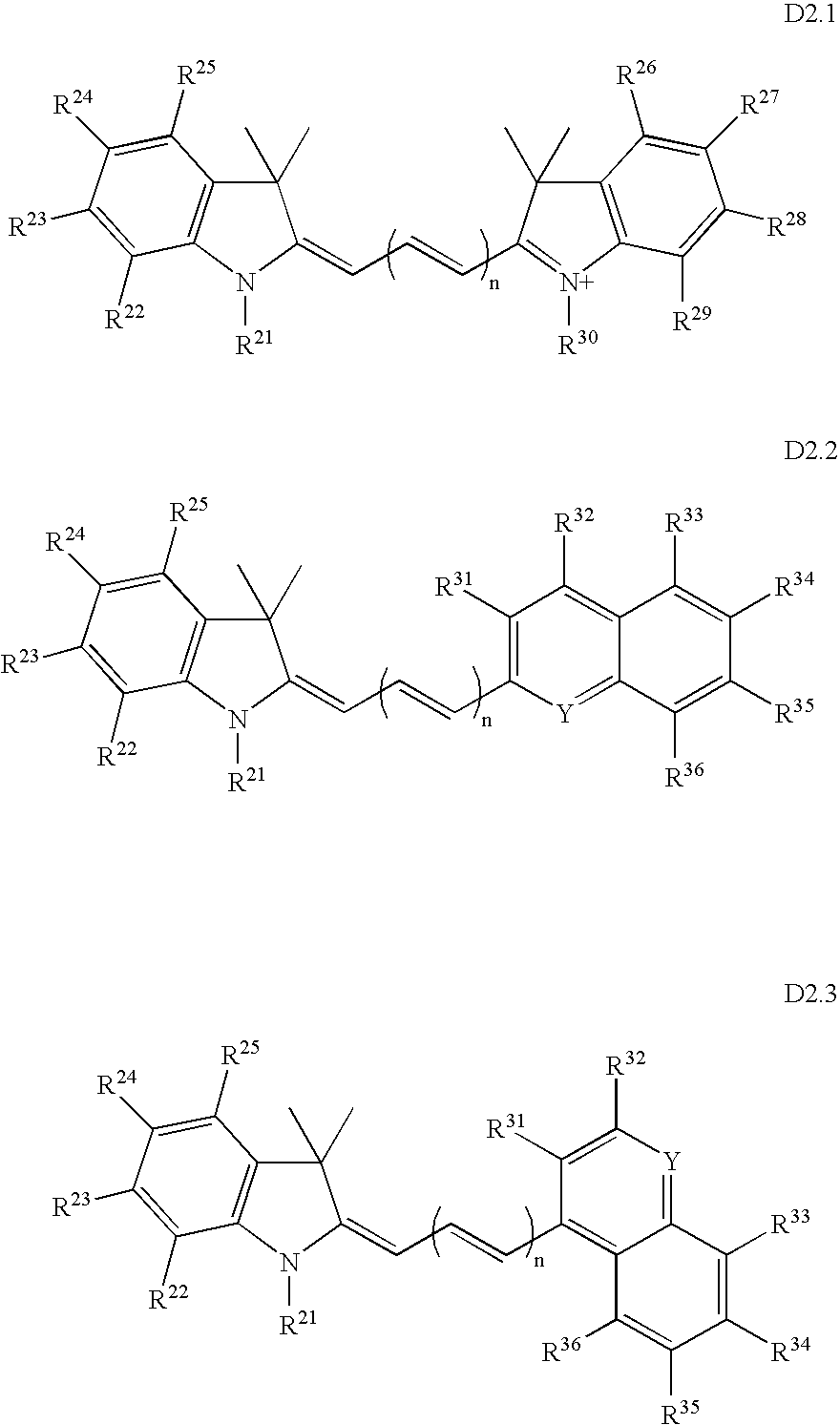
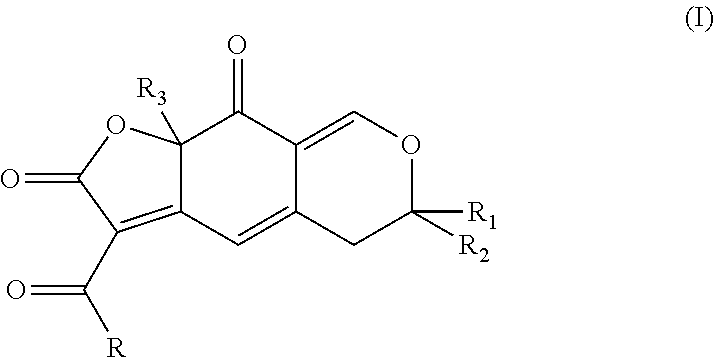
Process for synthesizing epicconone analogs
InactiveUS20120214194A1Organic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMedicinal chemistryTotal synthesis
The present invention relates to a process for the total synthesis of epicocconone analogs of formula (I):The invention also relates to novel epicocconone analogs.
Owner:UNIV DE ROUEN (FR) +3
Fluorescent dye and structure and manufacturing method of fluorescent storage media using thereof
InactiveUS20070134594A1Avoid radiationEasy to separateMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryChemical structureFluorescence
A fluorescent dye, a structure of a fluorescent storage media and method using thereof, are disclosed. The fluorescent dye of the present invention comprises an organic violet fluorescent compound having a chemical structure (I) is suitable for using a short wavelength laser having a wavelength less than 500 nm as an excitation source. When a short wavelength laser is used for exciting the organic violet fluorescent compound (I), a fluorescence having an emission wavelength larger than 500 nm is induced, and a reading signal can be provided by detecting the intensity of the fluorescence radiation.
Owner:LEE MING CHIA +8
Fluorogenic Nucleic Acid Probes Including Lna for Methods to Detect and/or Quantify Nucleic Acid Analytes
The present invention relates to novel methods for detecting or quantifying nucleic acid analytes through their interactions with a nucleic acid probe or a pair of nucleic acid probes, wherein the probe or the pair of probes is comprised of at least one monomeric LNA moiety and two or more dyes, wherein at least one of said dyes is fluorescent. Preferably the probe or the pair of probes is comprised of a combination of two dyes, wherein either both are fluorescent dyes that coactively function as the donor dye and the acceptor dye of a FRET system, or wherein one of said dyes is a fluorescent dye and the other is a corresponding non-fluorescent quencher dye. Included in the present invention are novel nucleic acid probes for use in the detection and quantification of analytes according to the methods of this invention. The novel nucleic acid probes of the invention are comprised of an n-meric nucleic acid comprising any number of 1 to n monomeric locked nucleic acid (LNA) moieties that may be located in any position(s) of the nucleic acid sequence. The nucleic acid probes are further characterized in that they are derivatized with one or more dyes, wherein said dyes are independently selected from fluorescent dyes or non-fluorescent quencher dyes. The methods provided by the invention are based on the change of fluorescence resulting from the hybridization of the inventive nucleic acid probes or pairs of nucleic acid probes with nucleic acid analytes.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com