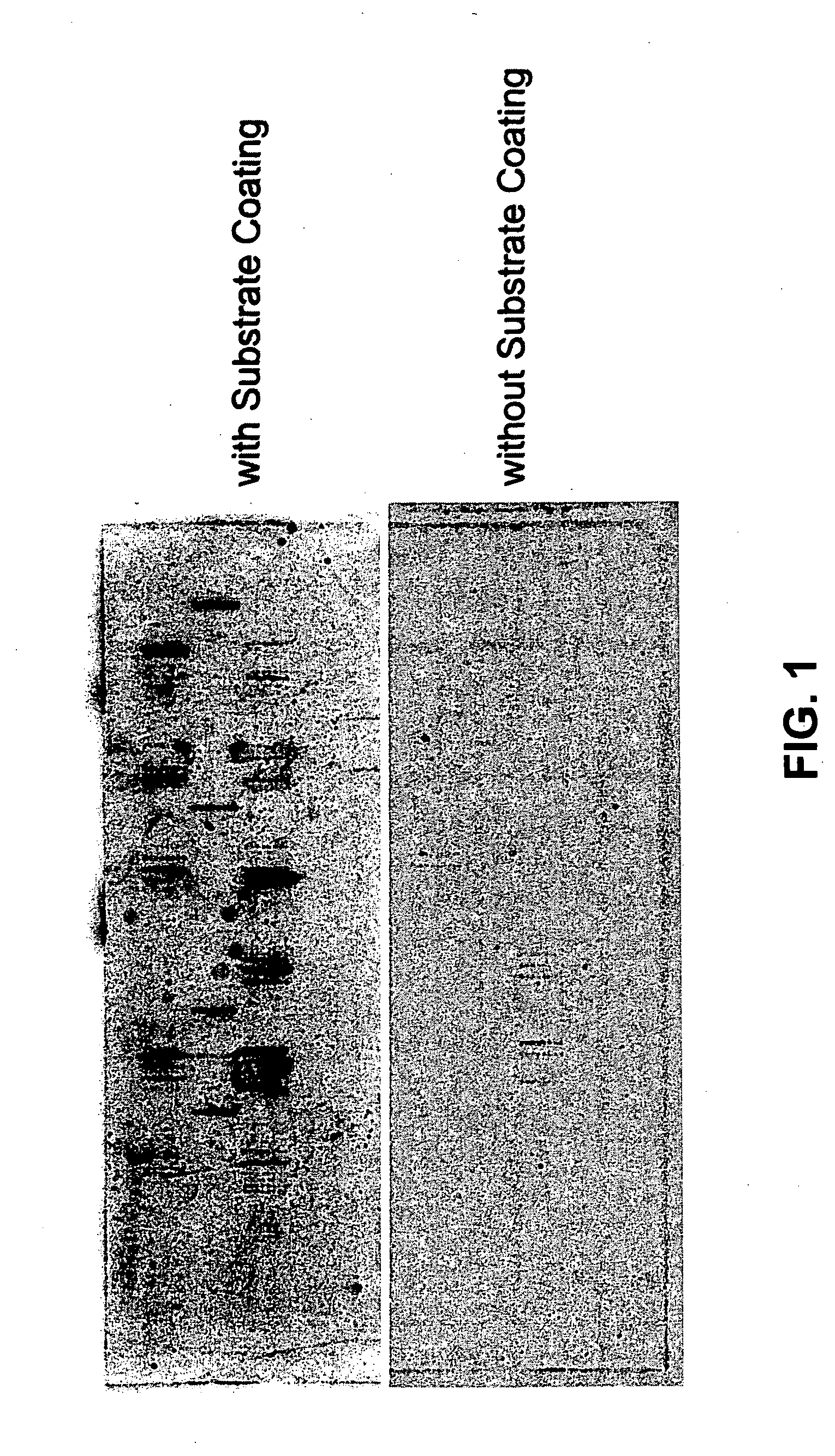
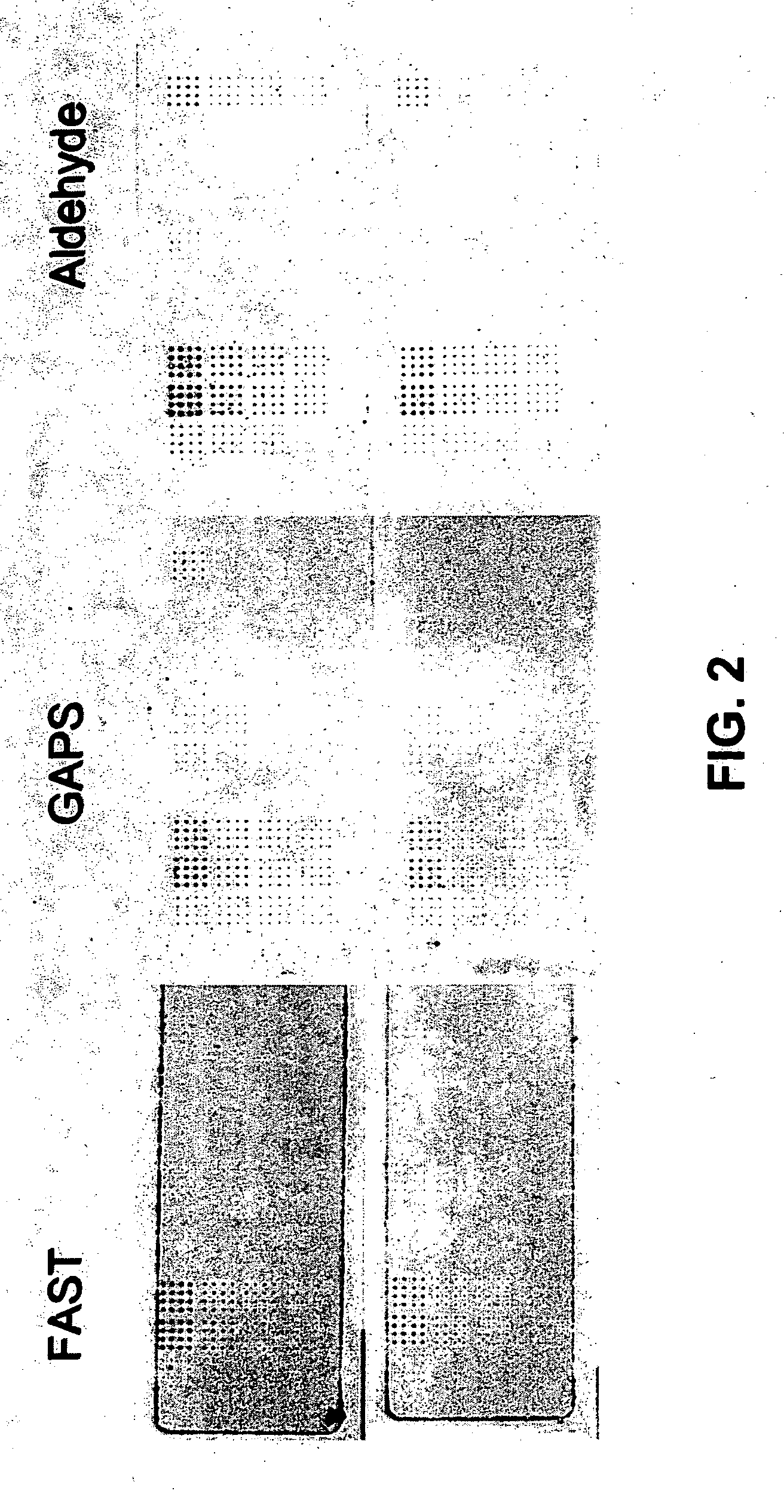
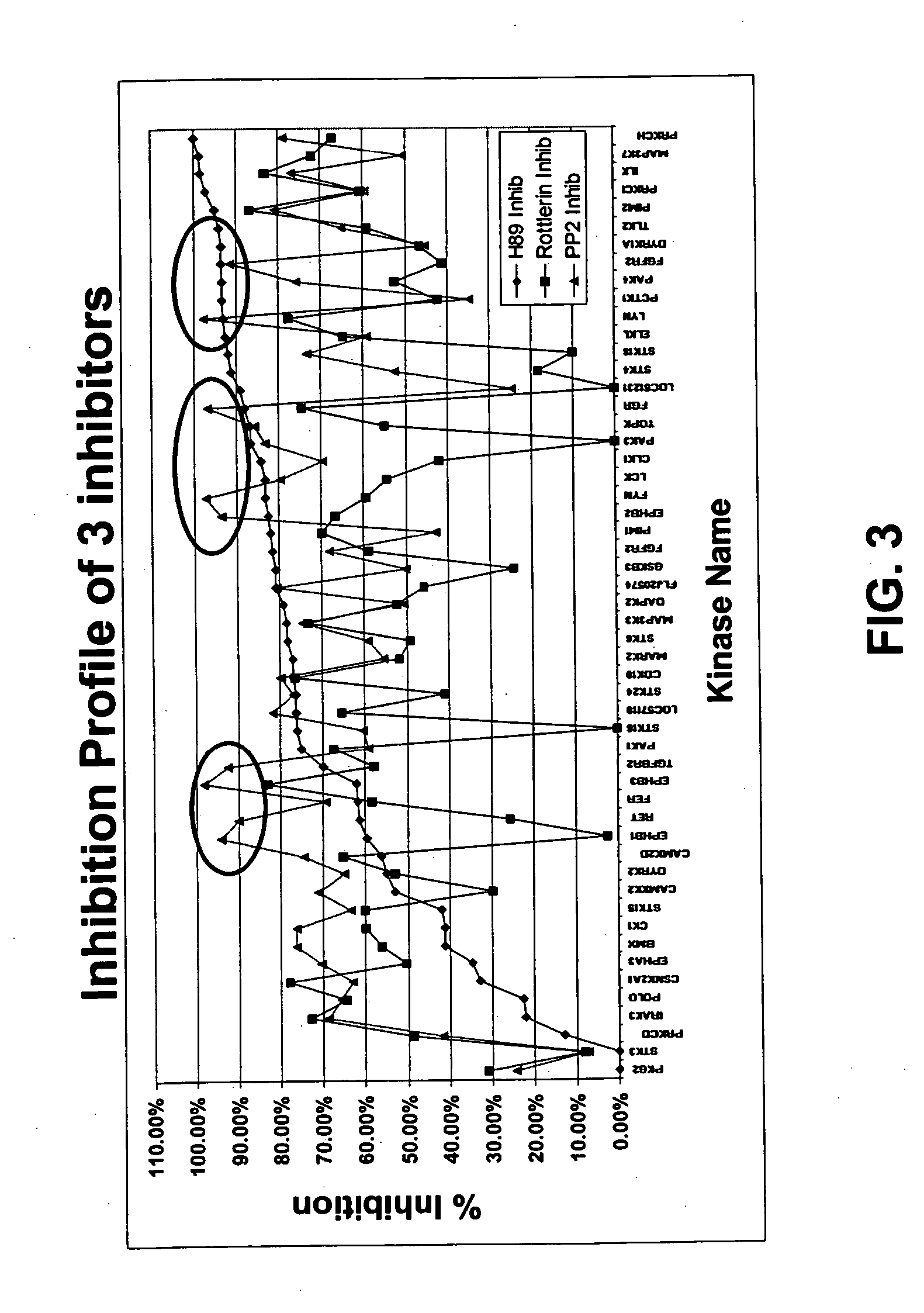
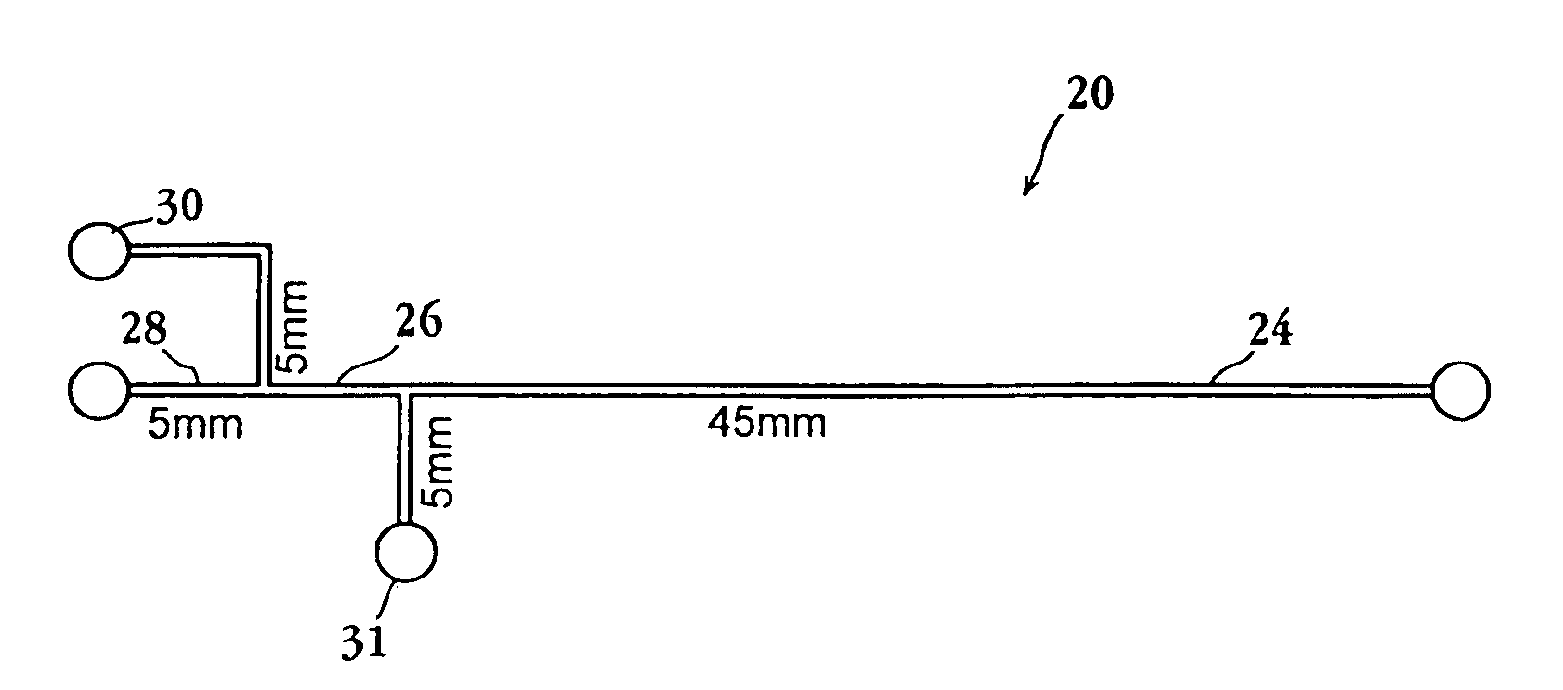
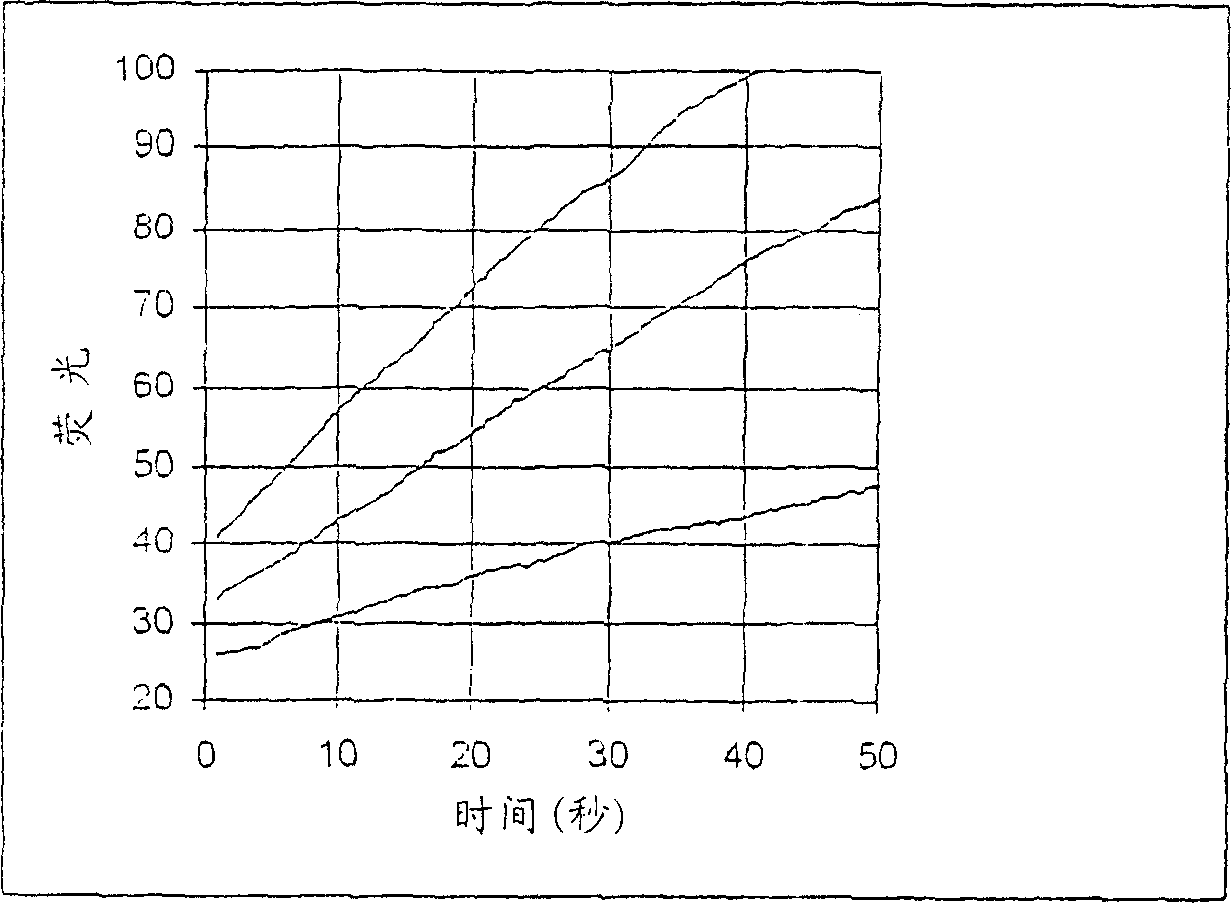
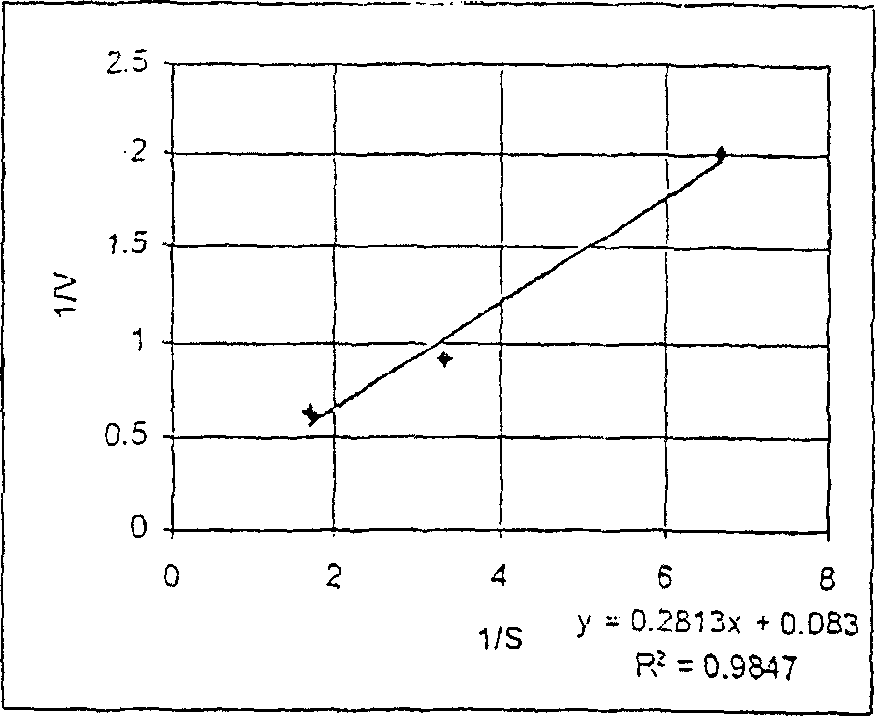
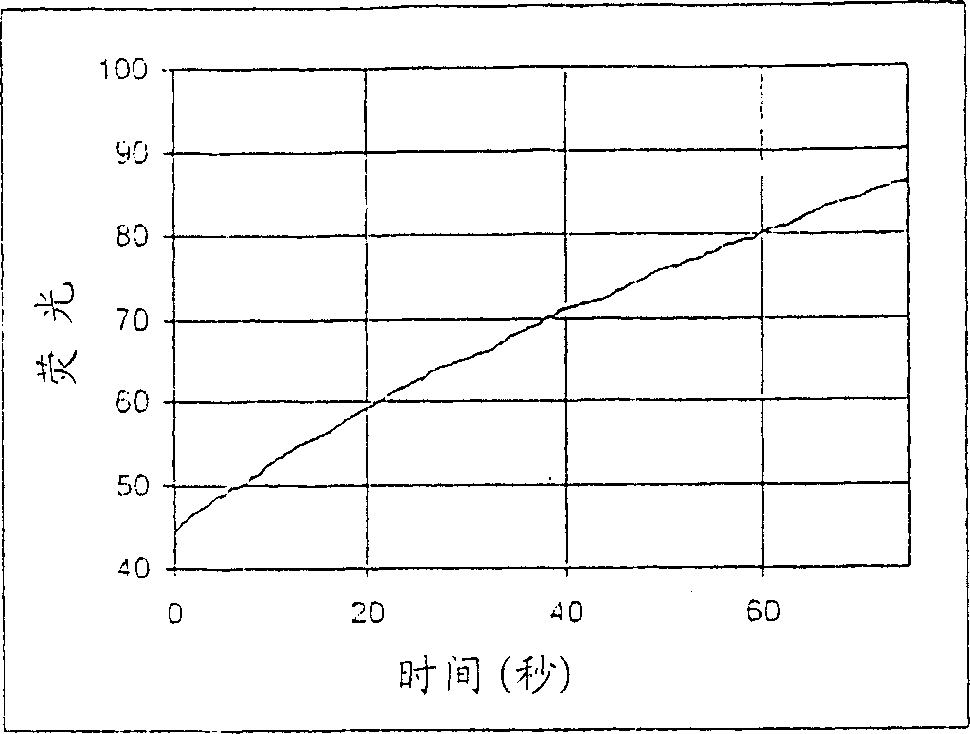
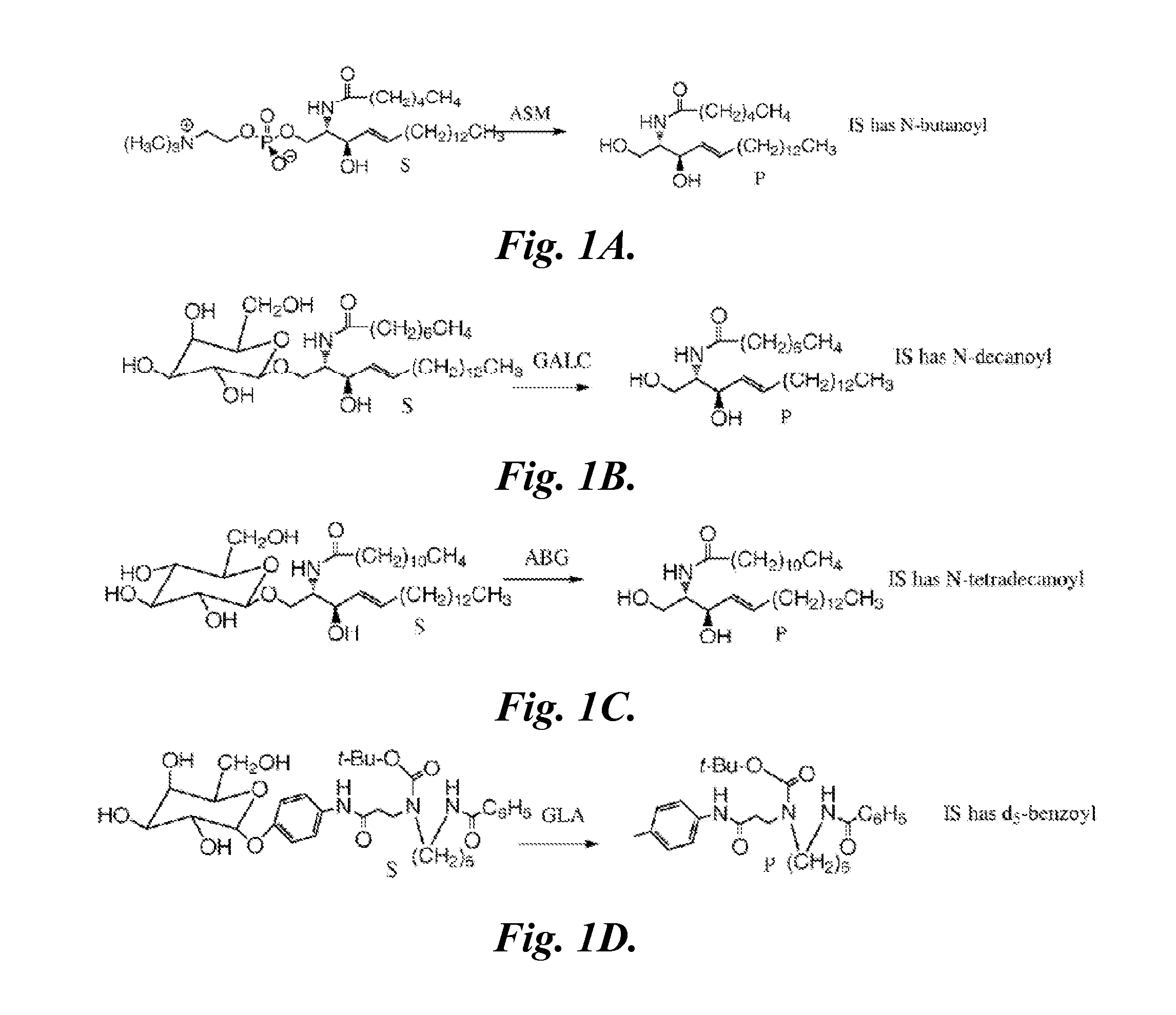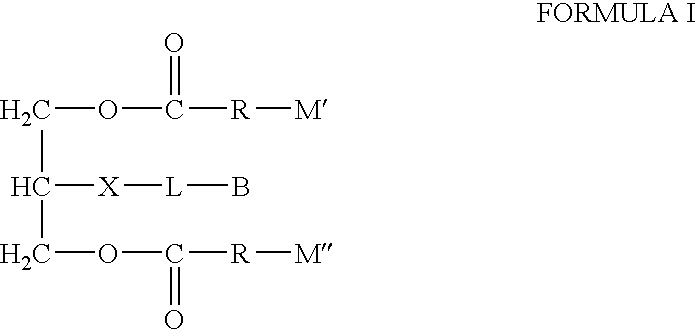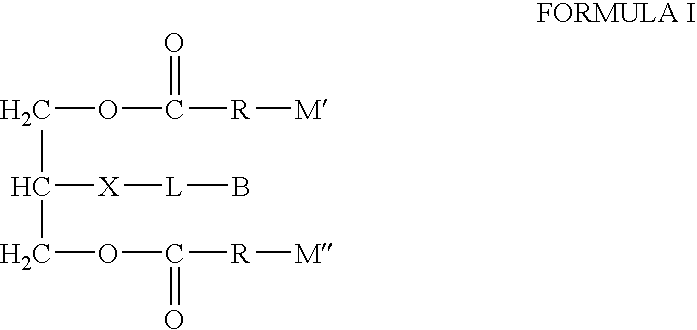Patents
Literature
142 results about "Enzyme assay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods for measuring enzymatic activity. They are vital for the study of enzyme kinetics and enzyme inhibition.
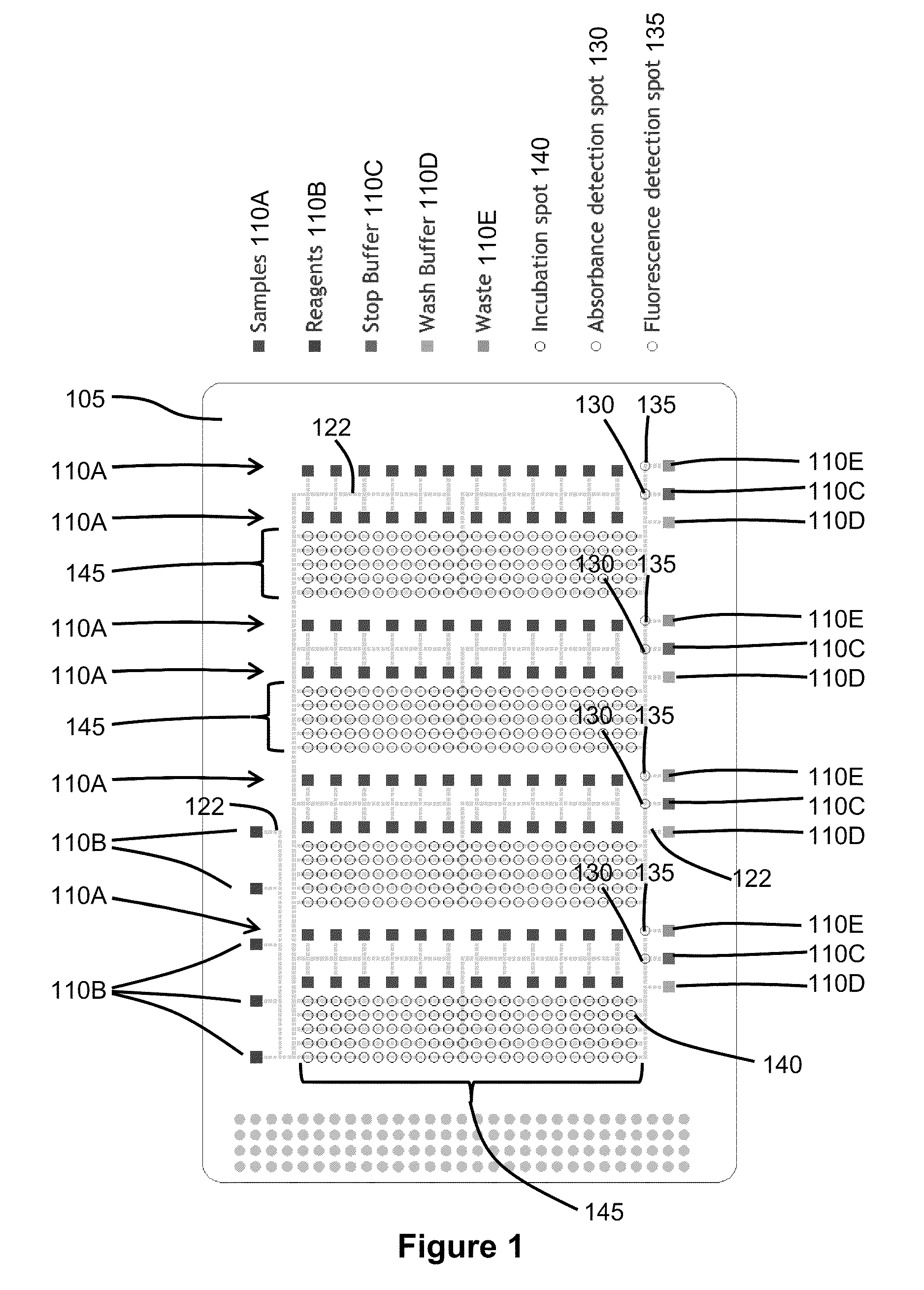
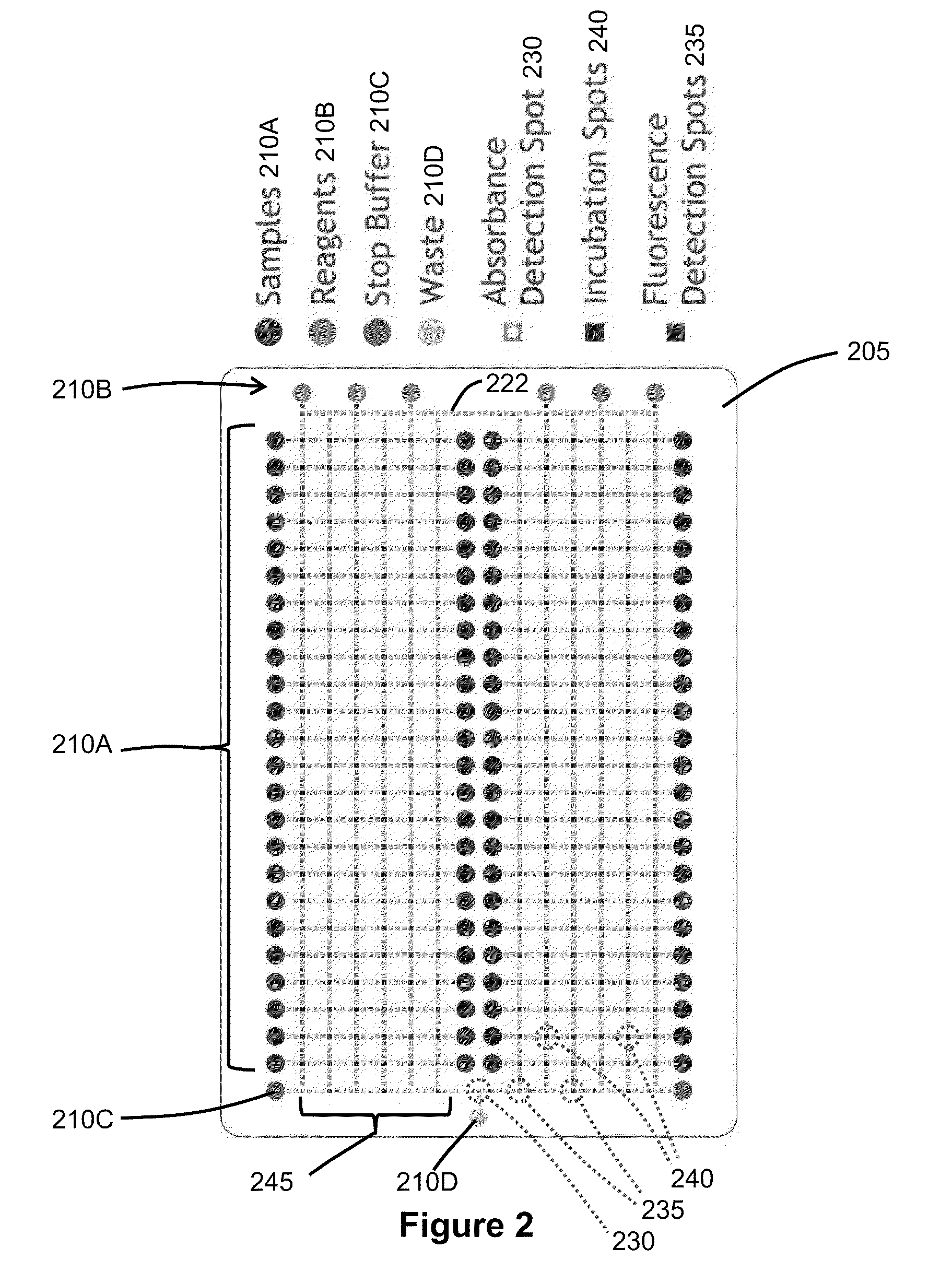
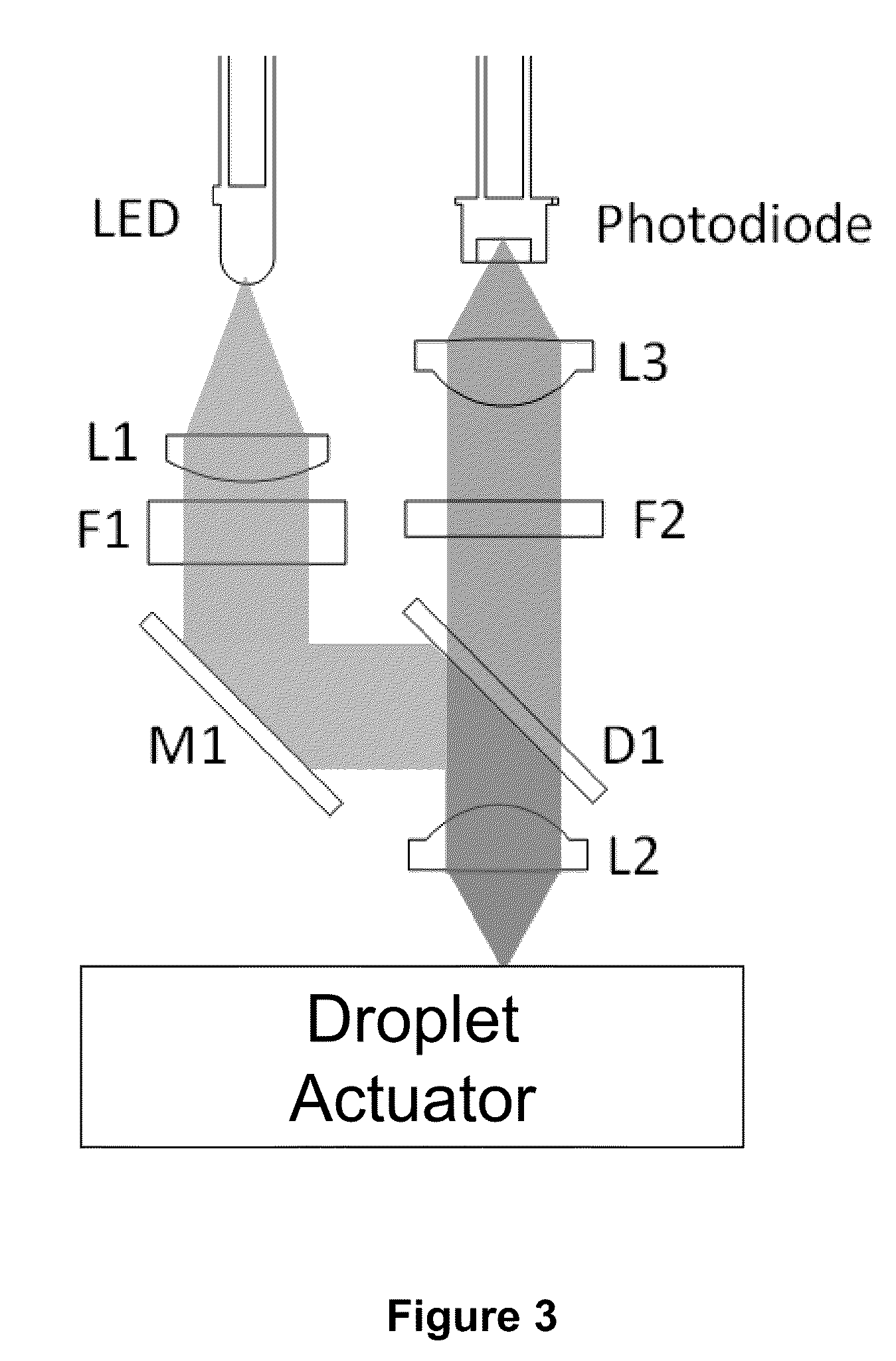
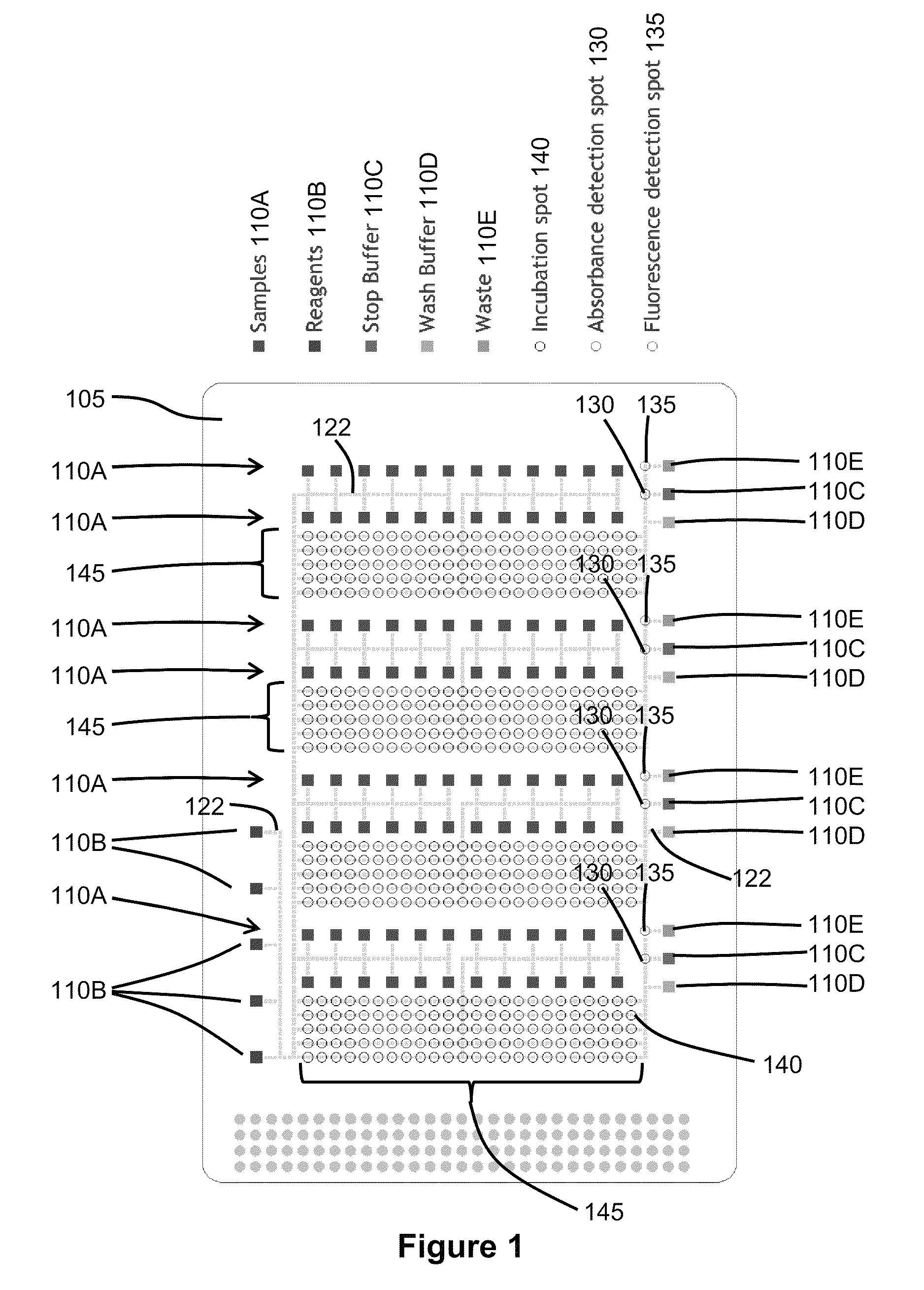
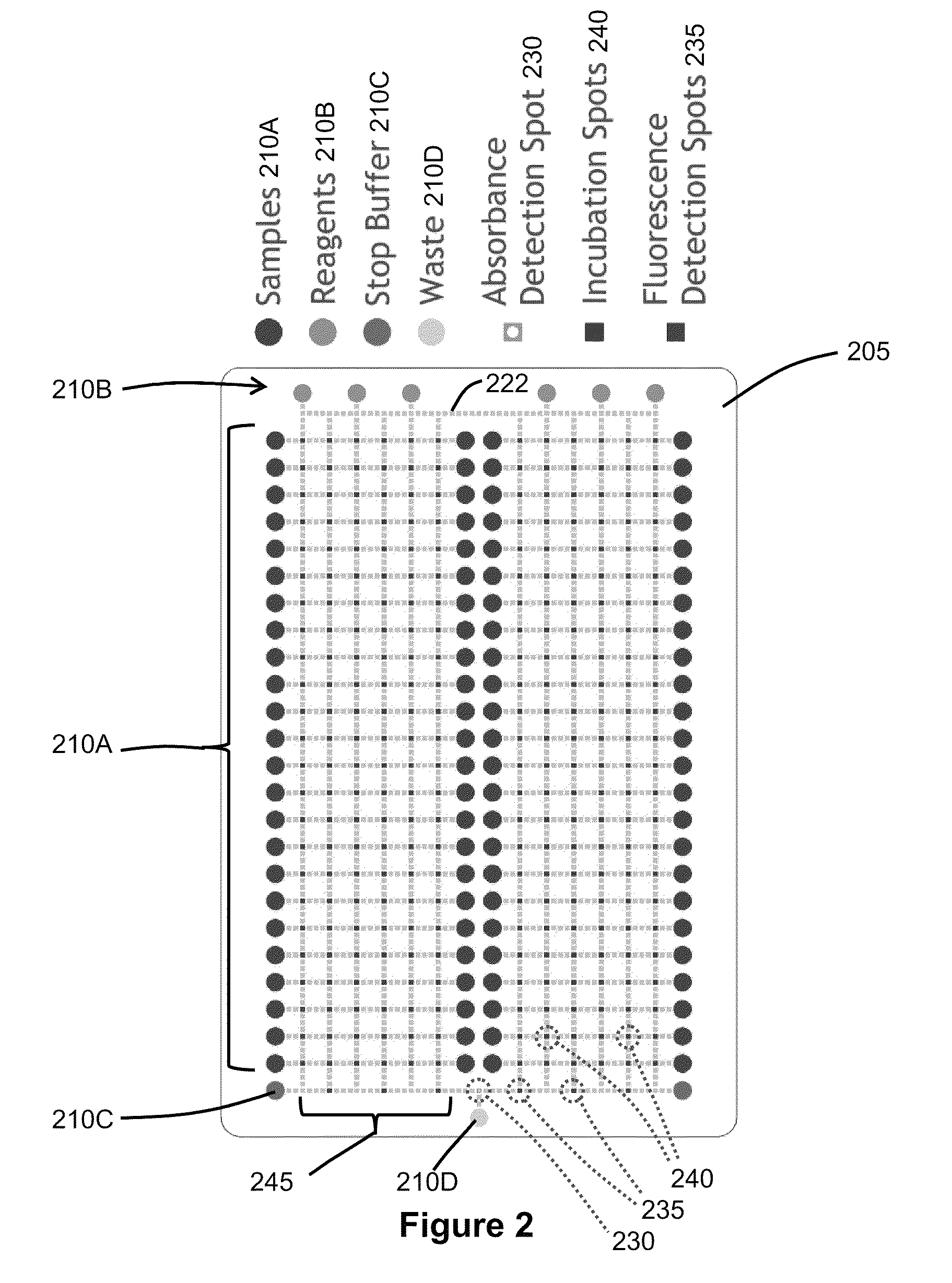
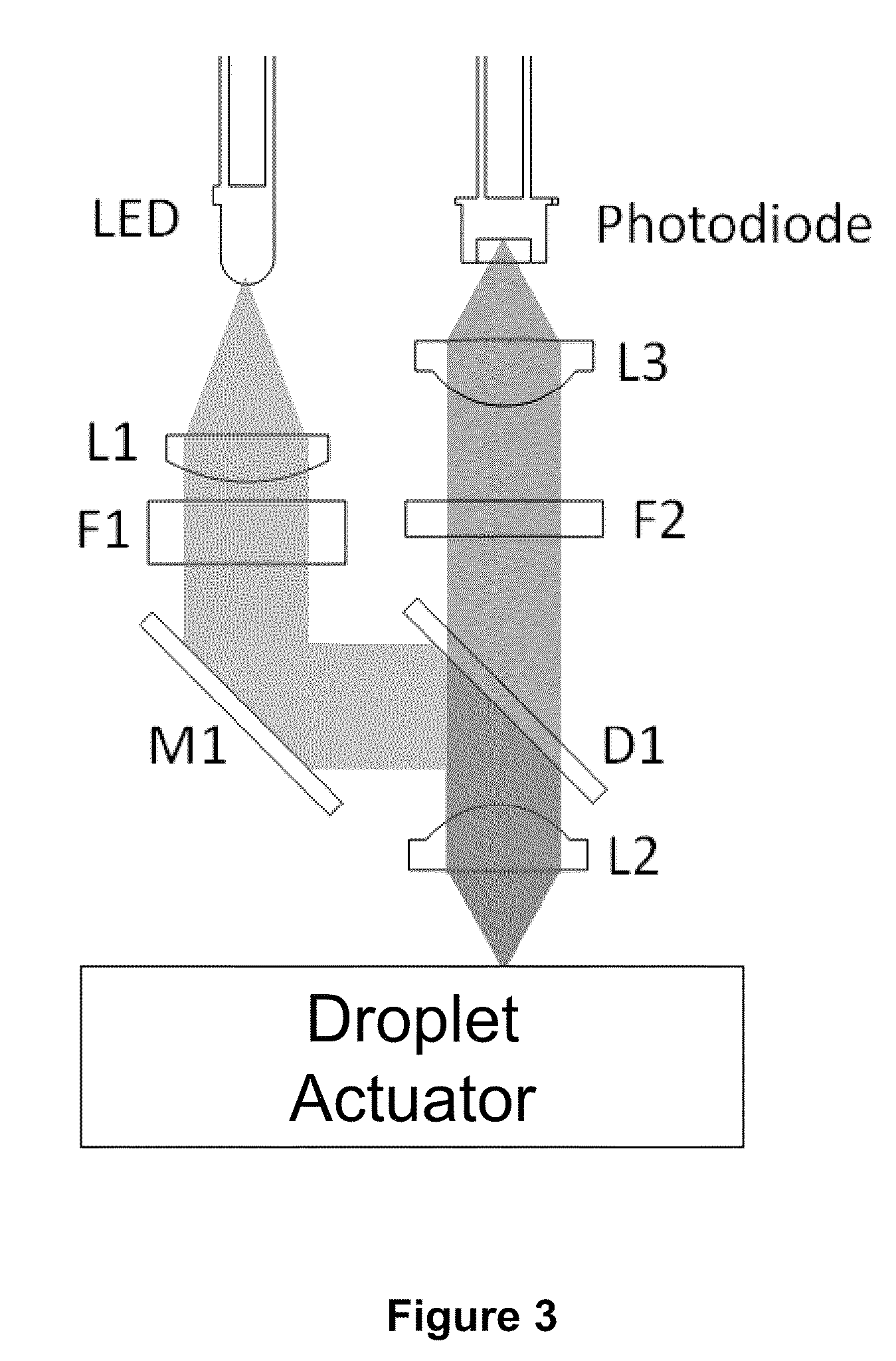
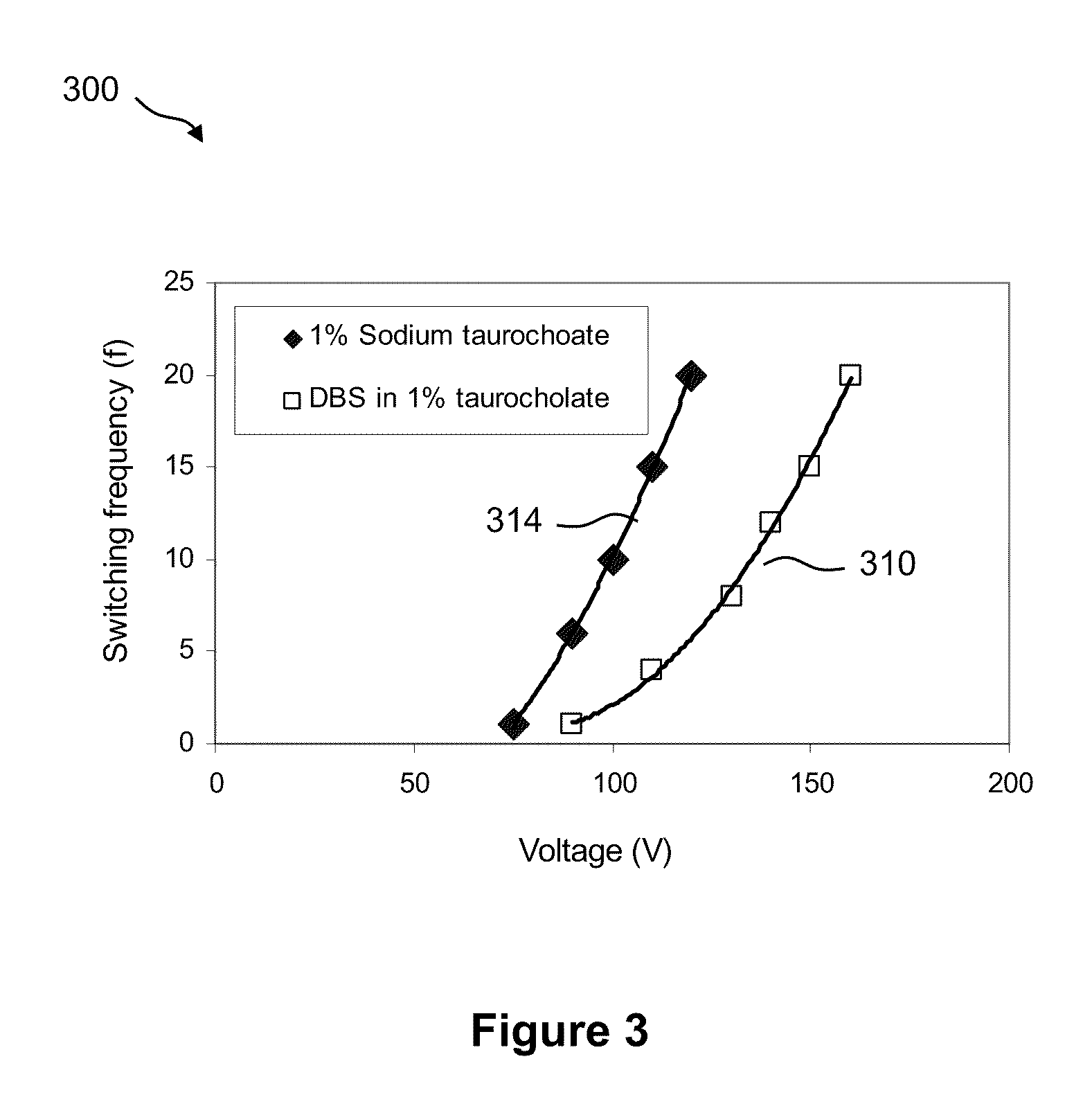
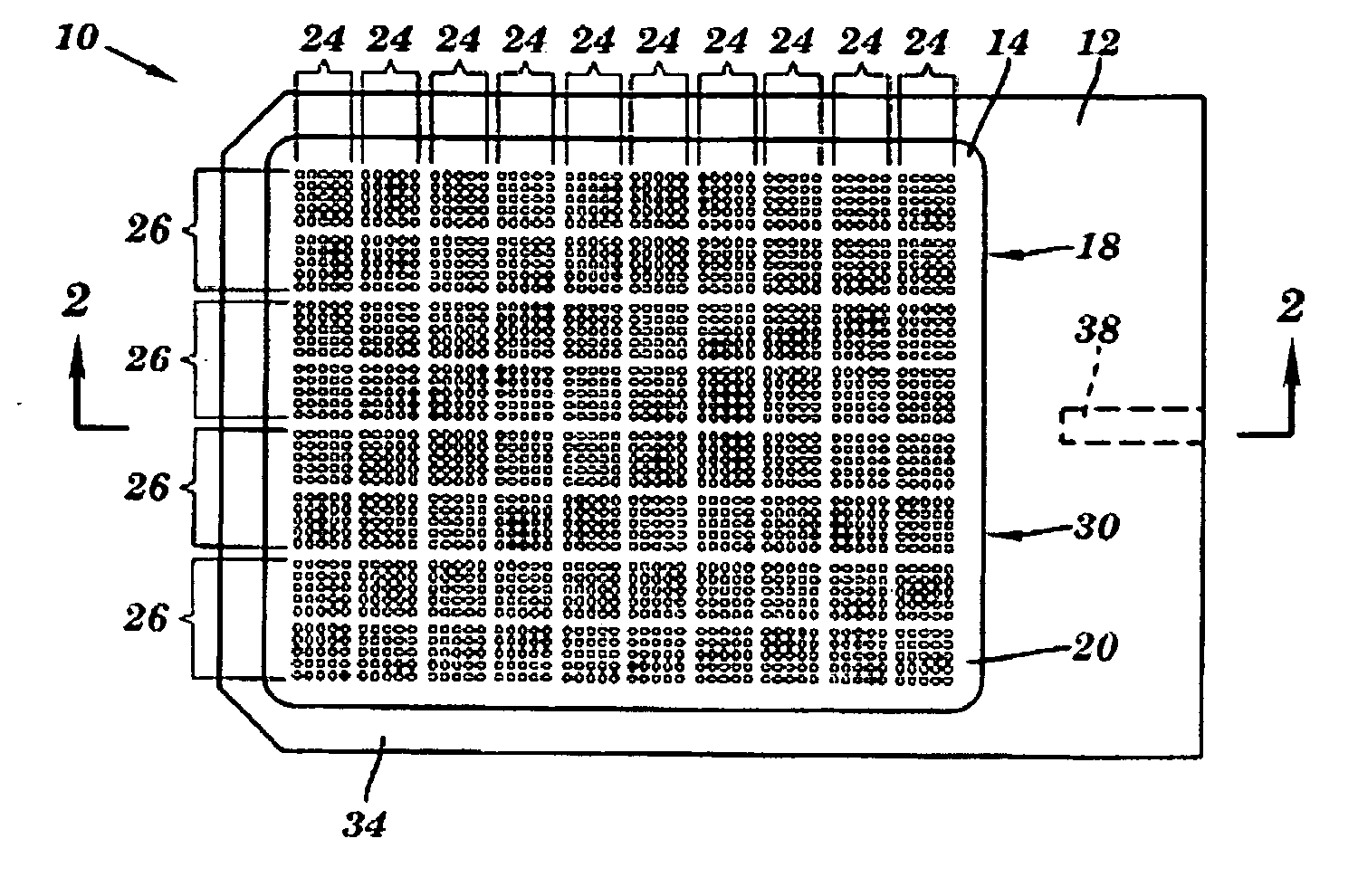
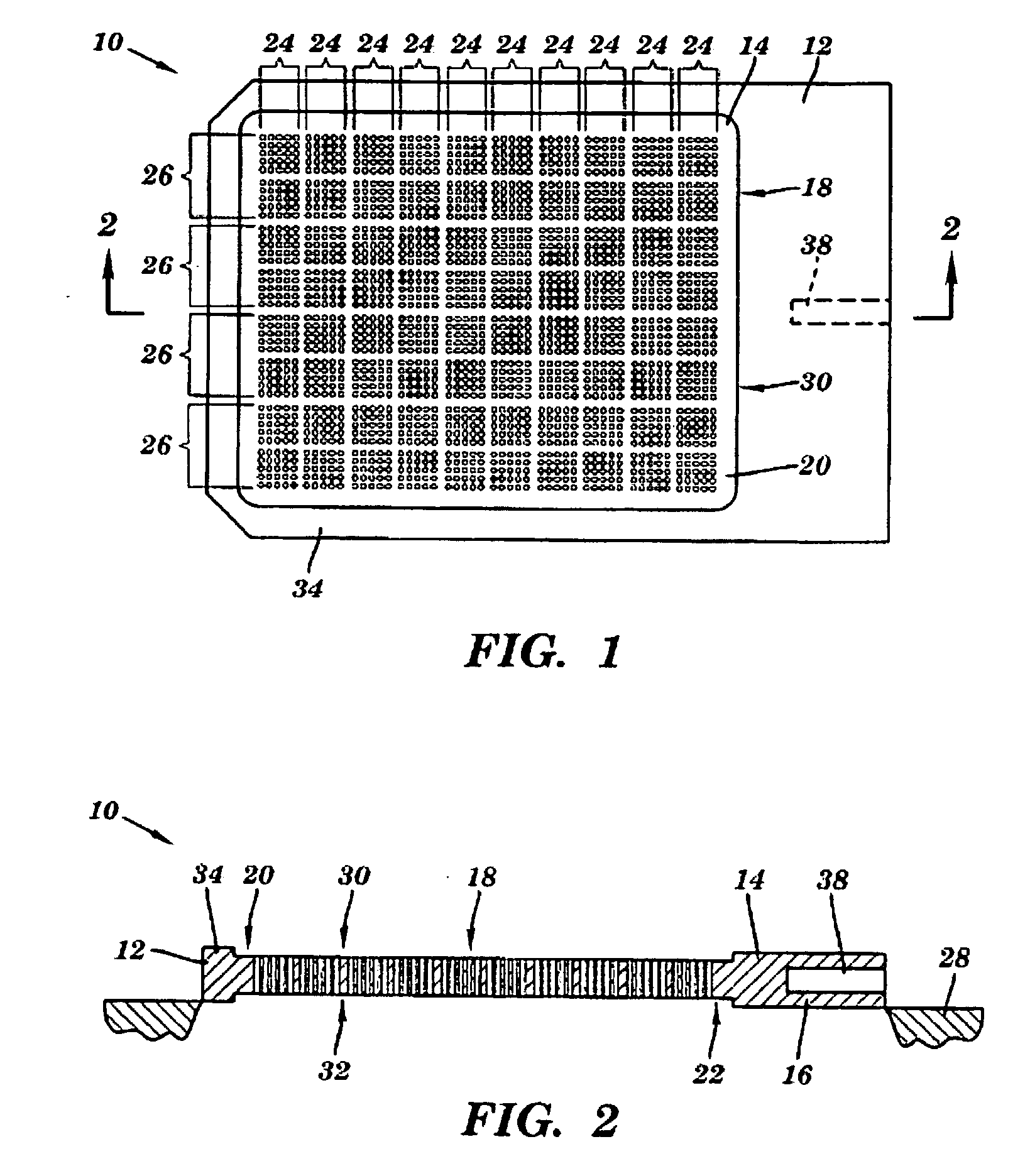
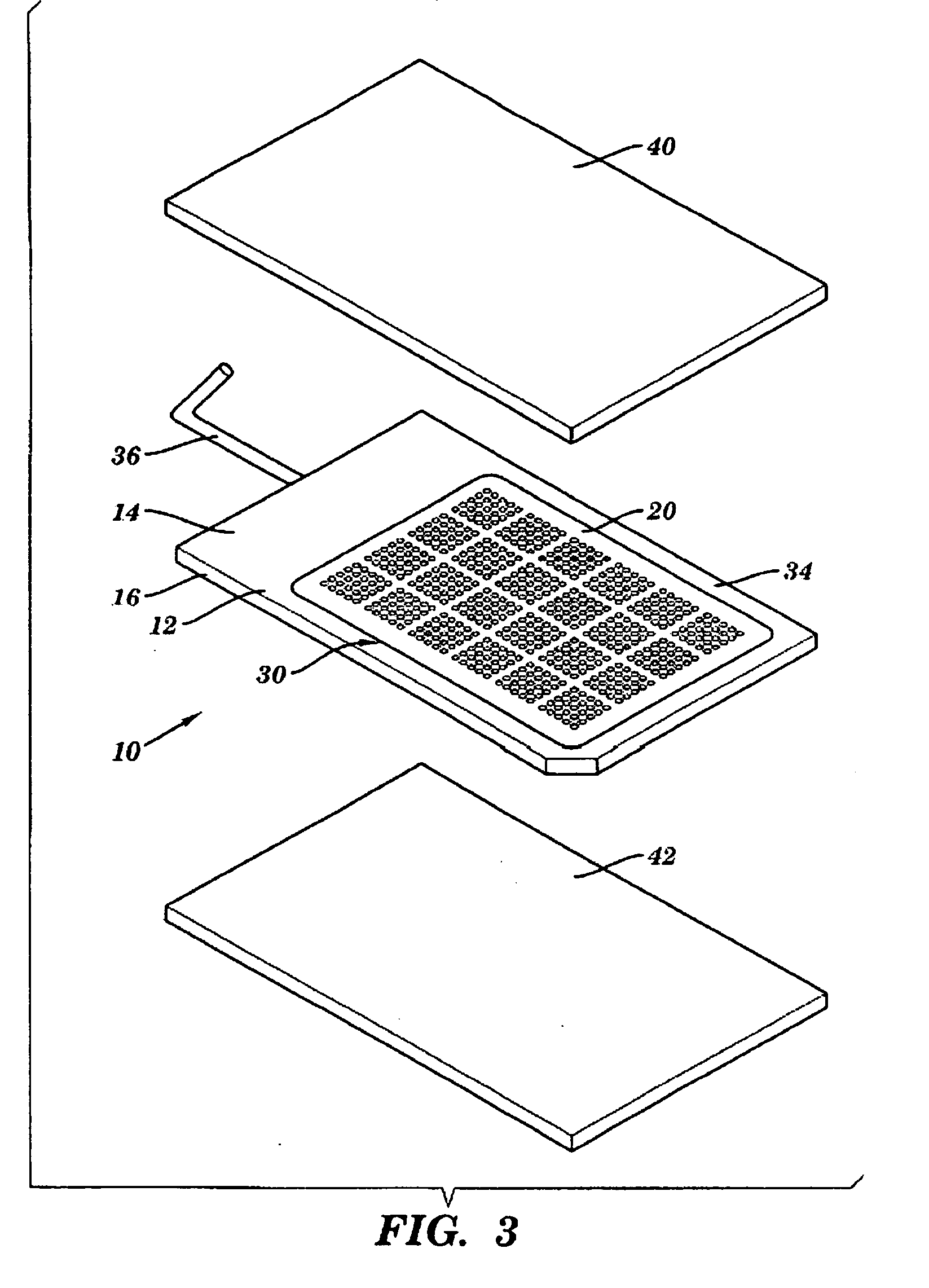
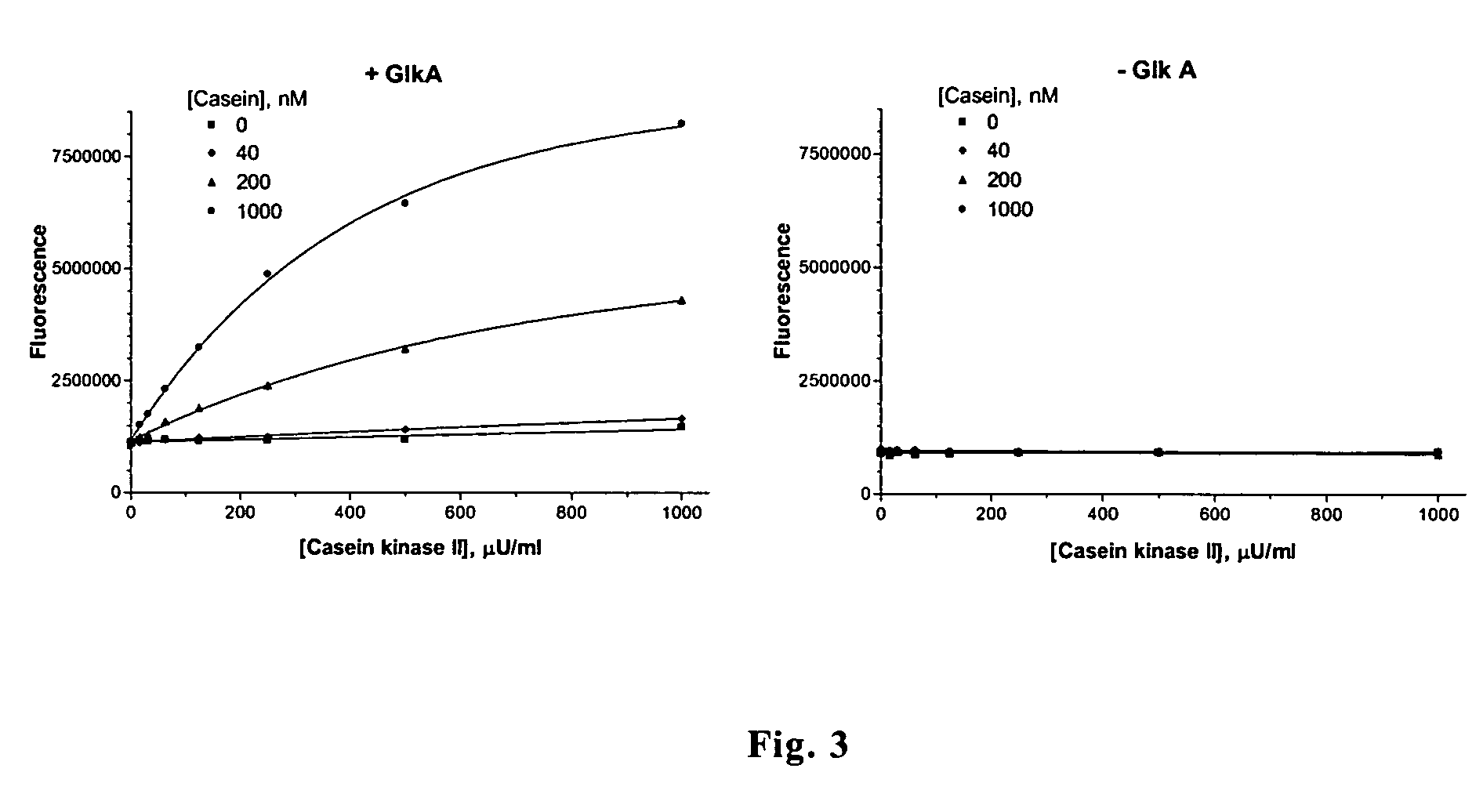
Enzyme Assays for a Droplet Actuator
ActiveUS20100041086A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertyTransportation and packagingMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme assayActuator
The invention relates to a microfluidic platform and methods of using the platform for conducting enzyme assays using a droplet actuator. The enzyme assays of the invention are useful for, among other things, identifying and / or characterizing disorders resulting from conditions in which enzymes are defective or are produced in inappropriate amounts. Enzyme assays of the invention may, for example, be used to detect altered activity of a particular enzyme in a sample, which may serve as an indicator of a particular disease. Altered activity may, for example, be caused by conditions which result in the increased or reduced production of a certain enzyme or its substrate and / or conditions which result in defective enzymes and / or substrates exhibiting increased or decreased effectiveness relative to corresponding normal enzymes and / or substrates.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Enzyme assays for a droplet actuator
ActiveUS8202686B2Easy to useFacilitates of propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransportation and packagingEnzyme assayActuator
The invention relates to a microfluidic platform and methods of using the platform for conducting enzyme assays using a droplet actuator. The enzyme assays of the invention are useful for, among other things, identifying and / or characterizing disorders resulting from conditions in which enzymes are defective or are produced in inappropriate amounts. Enzyme assays of the invention may, for example, be used to detect altered activity of a particular enzyme in a sample, which may serve as an indicator of a particular disease. Altered activity may, for example, be caused by conditions which result in the increased or reduced production of a certain enzyme or its substrate and / or conditions which result in defective enzymes and / or substrates exhibiting increased or decreased effectiveness relative to corresponding normal enzymes and / or substrates.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Enzymatic Assays for a Droplet Actuator
ActiveUS20100151439A1Extension of timeReduce resultSugar derivativesTransportation and packagingChemistryEnzymatic Assays
A method of conducting a droplet-based enzymatic assay is provided. The method generally makes use of a droplet actuator. A droplet comprising an enzyme of interest is provided on the droplet actuator along with a droplet comprising a substrate which is potentially modified in the presence of the enzyme. The method involves executing droplet operations on the droplet actuator to combine the droplets, thereby yielding an assay droplet, and detecting modification of the substrate by the enzyme in the assay droplet on the droplet actuator. The enzyme of interest may, for example, be a potentially mutated or improperly folded enzyme exhibiting altered enzyme activity as compared to a corresponding normal enzyme.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Methods for conducting assays for enzyme activity on protein microarrays
The present invention relates to methods of conducting assays for enzymatic activity on microarrays useful for the large-scale study of protein function, screening assays, and high-throughput analysis of enzymatic reactions. The invention relates to methods of using protein chips to assay the presence, amount, activity and / or function of enzymes present in a protein sample on a protein chip. In particular, the methods of the invention relate to conducting enzymatic assays using a microarray wherein a protein and a substance are immobilized on the surface of a solid support and wherein the protein and the substance are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the substance and the protein. The invention also relates to microarrays that have an enzyme and a substrate immobilized on their surface wherein the enzyme and the substrate are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the enzyme and the substrate.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
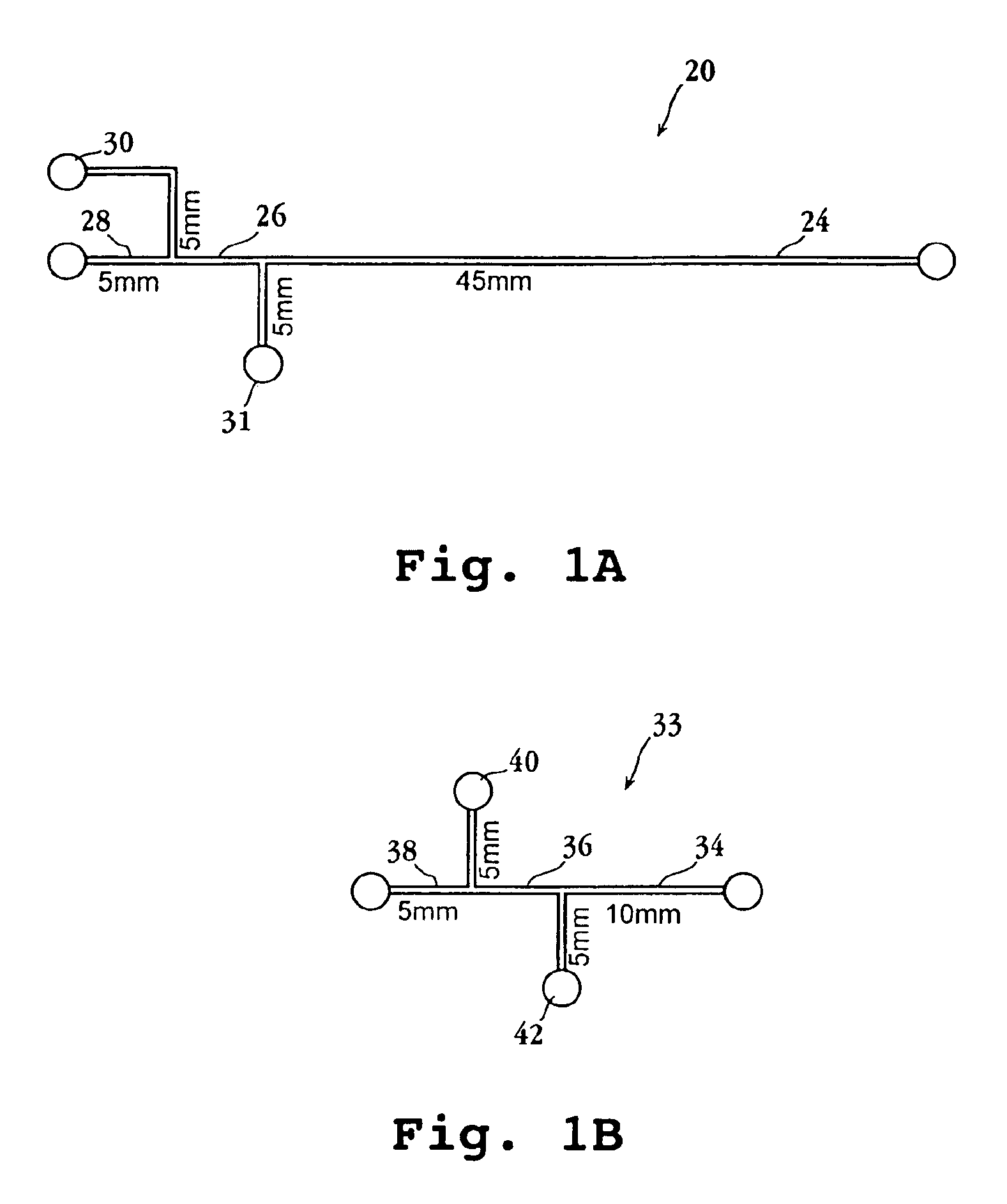
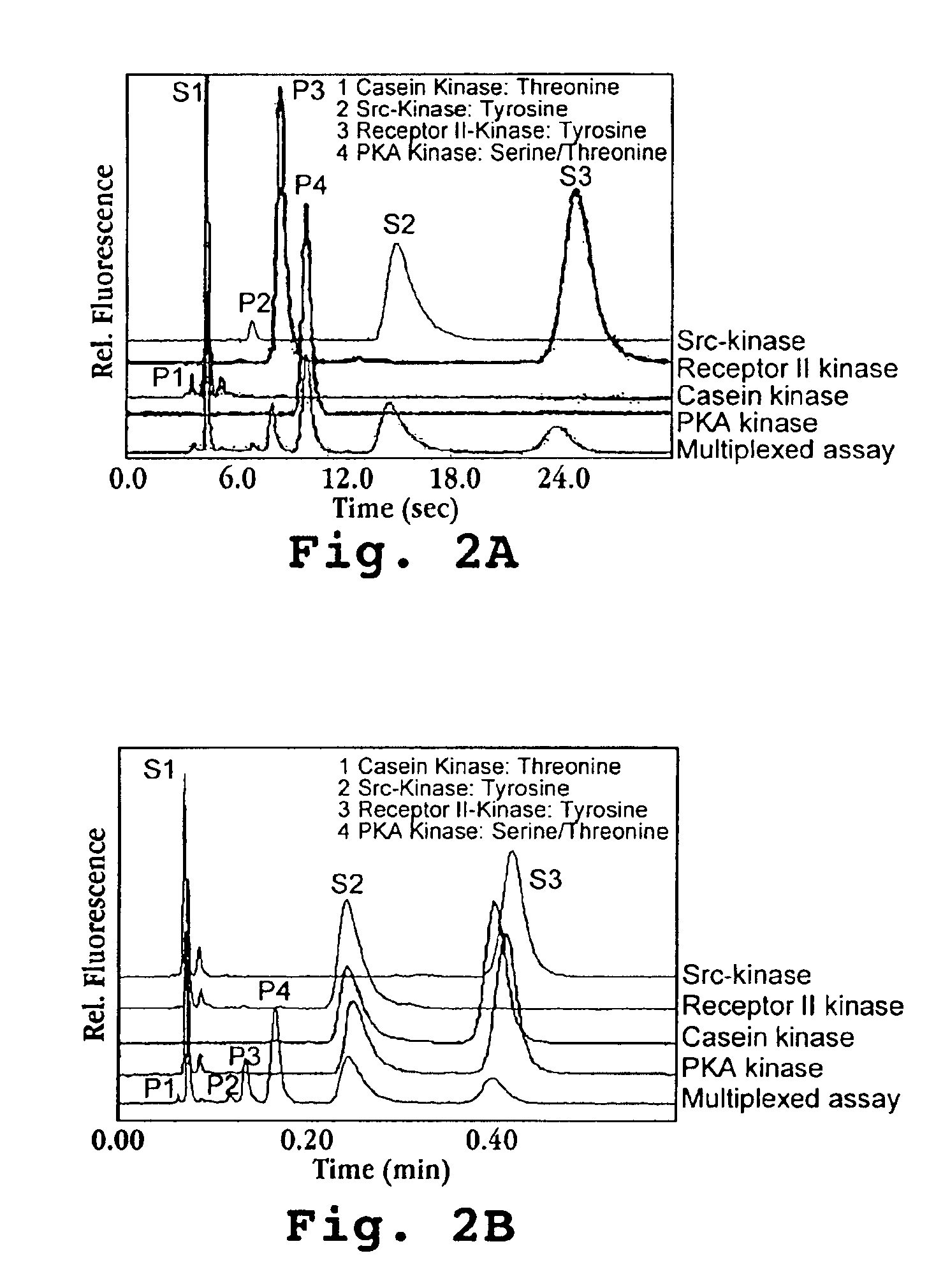
Multiplexed enzymatic assays
A mutiplexed enzyme assay method and substrate set for performing the method are disclosed. The method includes performing a plurality of enzyme reactions in the presence of a plurality of enzymes substrates, under conditions effective to convert an enzyme substrate to a corresponding product, where the product of each substrate and the substrate have different separation characteristics from each other and from the other substrates and their corresponding products. After performing the reactions, which may be carried out in separate or combined reactions, the substrates and products in said reactions are separated in a single separation medium. For each separated product and substrate, a separation characteristic effective to identify that product and substrate and a signal related to the amount of the product and substrate is detected. From this, one can determine the amount of substrate converted to the corresponding product in each of the reactions.
Owner:VIROLOGIC INCORPORATED
Monoclonal antibody specific for the extracellular domain of prostate specific membrane antigen
InactiveUS7476513B2VirusesIn-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoenzymatic assayProstate specific membrane
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies that bind to the extracellular domain of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), hybridoma cell lines producing the antibodies, and methods of using such antibodies for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. In particular, thirty-five monoclonal antibodies reactive with PSMA expressed on the cell surface are exemplified. Additionally, the present invention relates to a novel protein variant (PSM′) of PSMA detected by a number of the antibodies of the invention. The hydrolase activity of PSMA and PSM′ allows the use of an immunoenzymatic assay for their detection.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
High-throughput screening with multi-through hole testing plate
InactiveUS20060183171A1Simplify the test procedureEasy constructionSequential/parallel process reactionsLaboratory glasswaresAnalyteHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Monoclonal antibodies specific for the extracellular domain of prostate-specific membrane antigen
InactiveUS7381407B1In-vivo radioactive preparationsVirusesImmunoenzymatic assayProstate specific membrane
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Novel microarray techniques for nucleic acid expression analyses
ActiveUS20060078925A1Eliminate biasConvenient experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMiRNA GeneExonuclease I
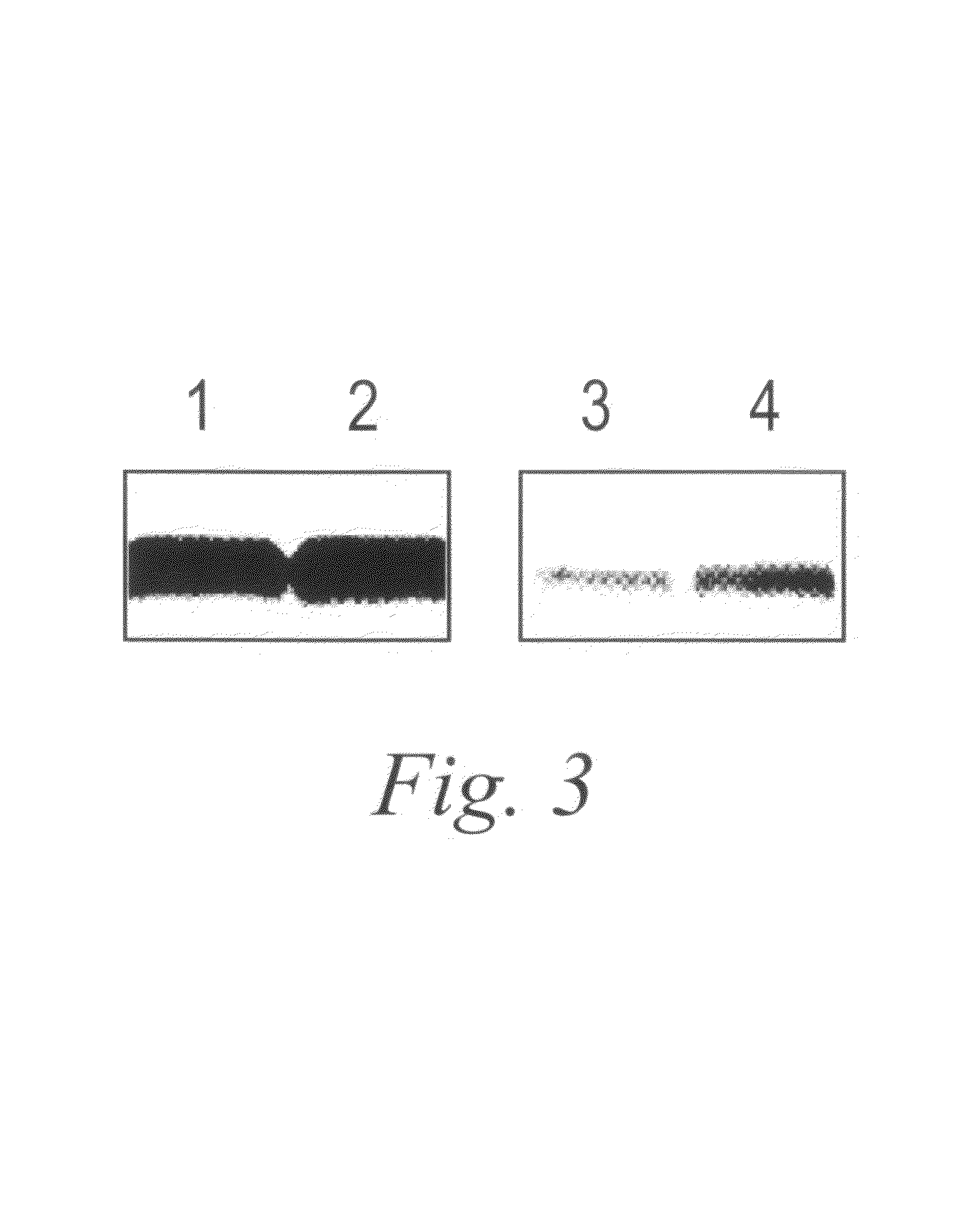
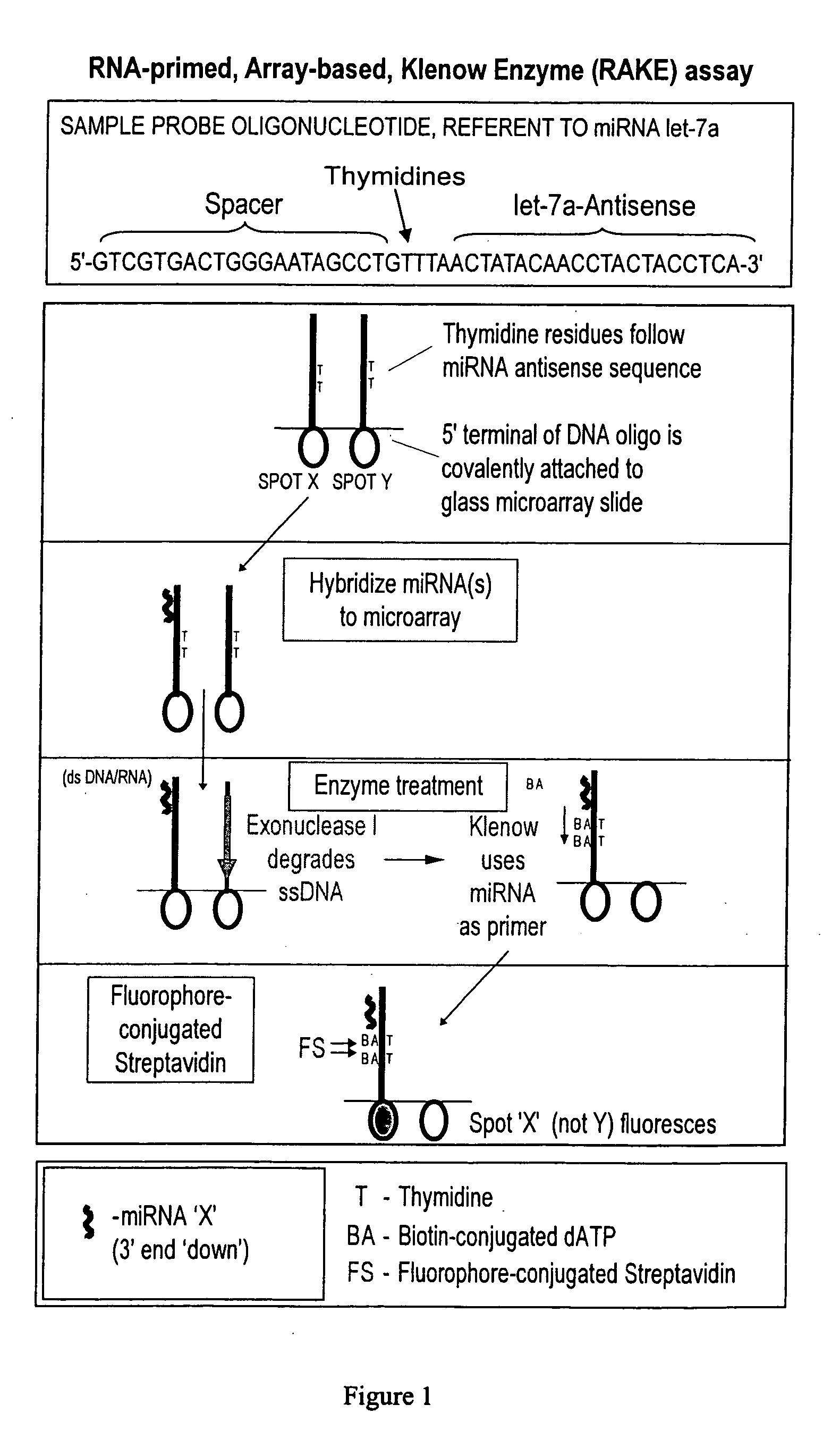
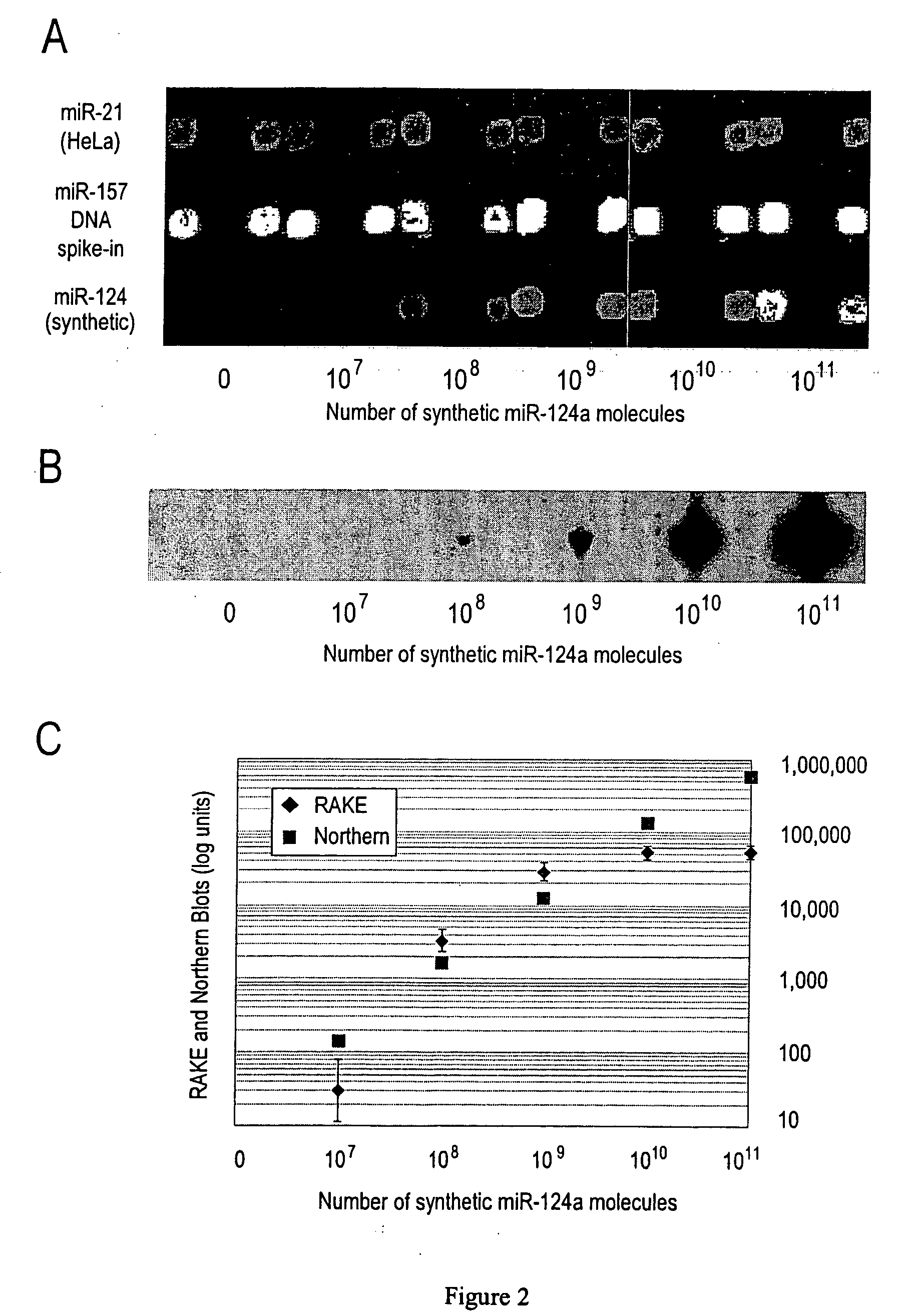
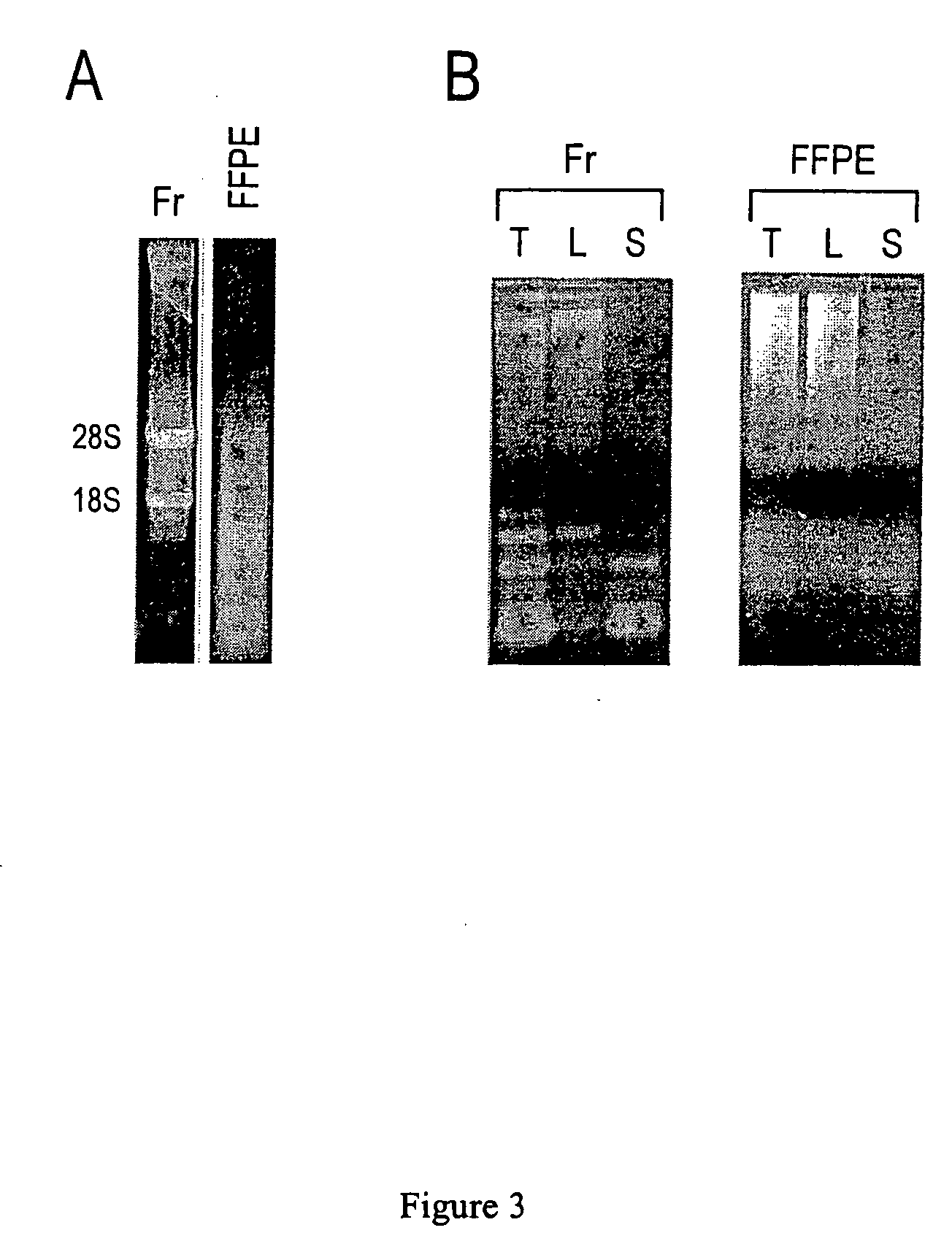
Provided are DNA microarray techniques that allow hybridization without RNA amplification, without using cDNA, and without labeling the nucleic acid prior to hybridization. Referred to as the Double-stranded Exonuclease Protection (DEP) assay, the technique permits the sample RNA to be used directly for hybridization, without manipulation in any way. Further provided is a microarray technique for high-throughput miRNA gene expression analyses, termed the RNA-primed, Array-based, Klenow Enzyme (RAKE) assay. The RAKE assay is a sensitive and specific technique for assessing single-stranded DNA and RNA targets, and offers specific advantages over Northern blots.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for conducting assays for enzyme activity on protein microarrays
The present invention relates to methods of conducting assays for enzymatic activity on microarrays useful for the large-scale study of protein function, screening assays, and high-throughput analysis of enzymatic reactions. The invention relates to methods of using protein chips to assay the presence, amount, activity and / or function of enzymes present in a protein sample on a protein chip. In particular, the methods of the invention relate to conducting enzymatic assays using a microarray wherein a protein and a substance are immobilized on the surface of a solid support and wherein the protein and the substance are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the substance and the protein. The invention also relates to microarrays that have an enzyme and a substrate immobilized on their surface wherein the enzyme and the substrate are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the enzyme and the substrate.
Owner:PROTOMETRIX
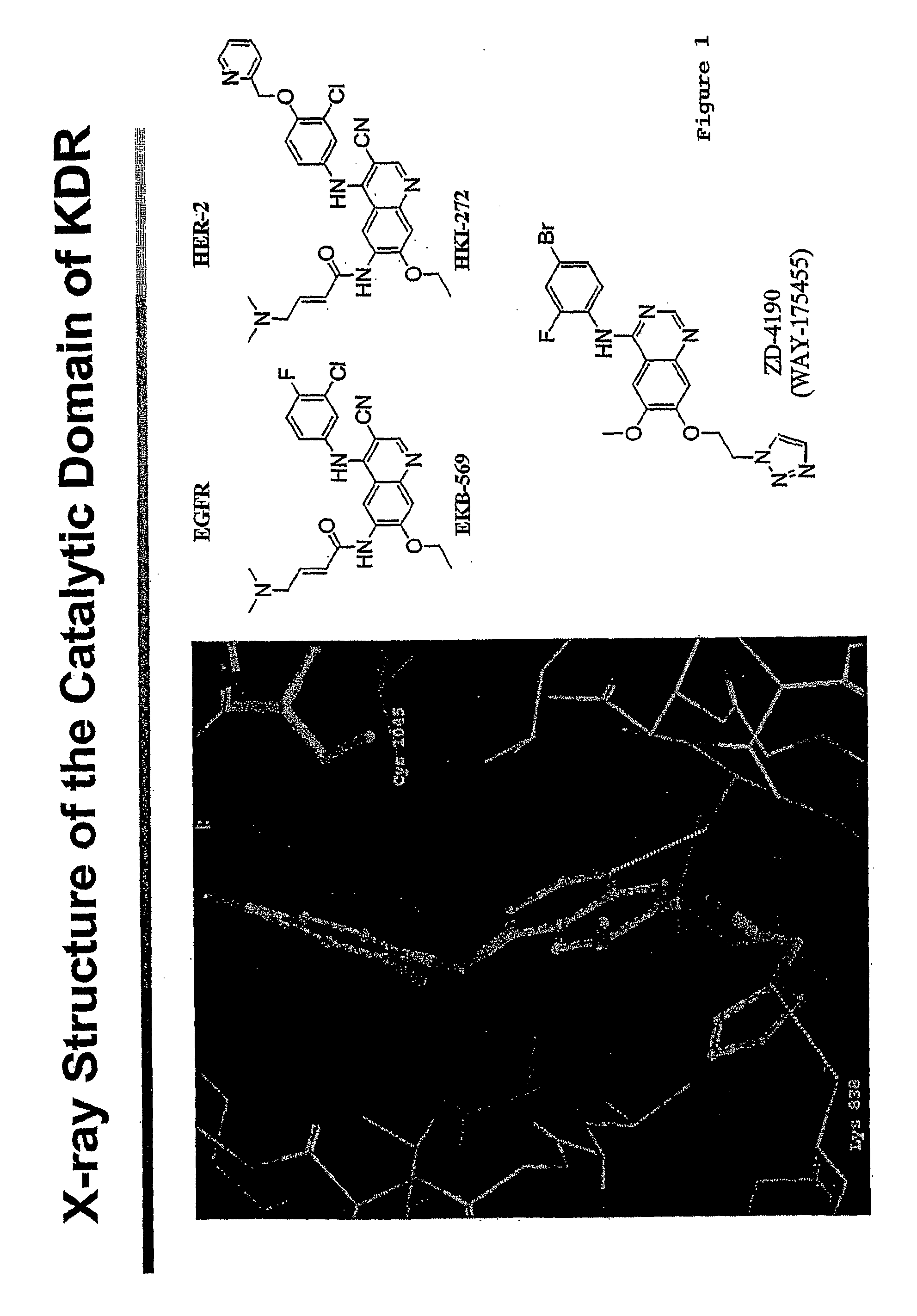
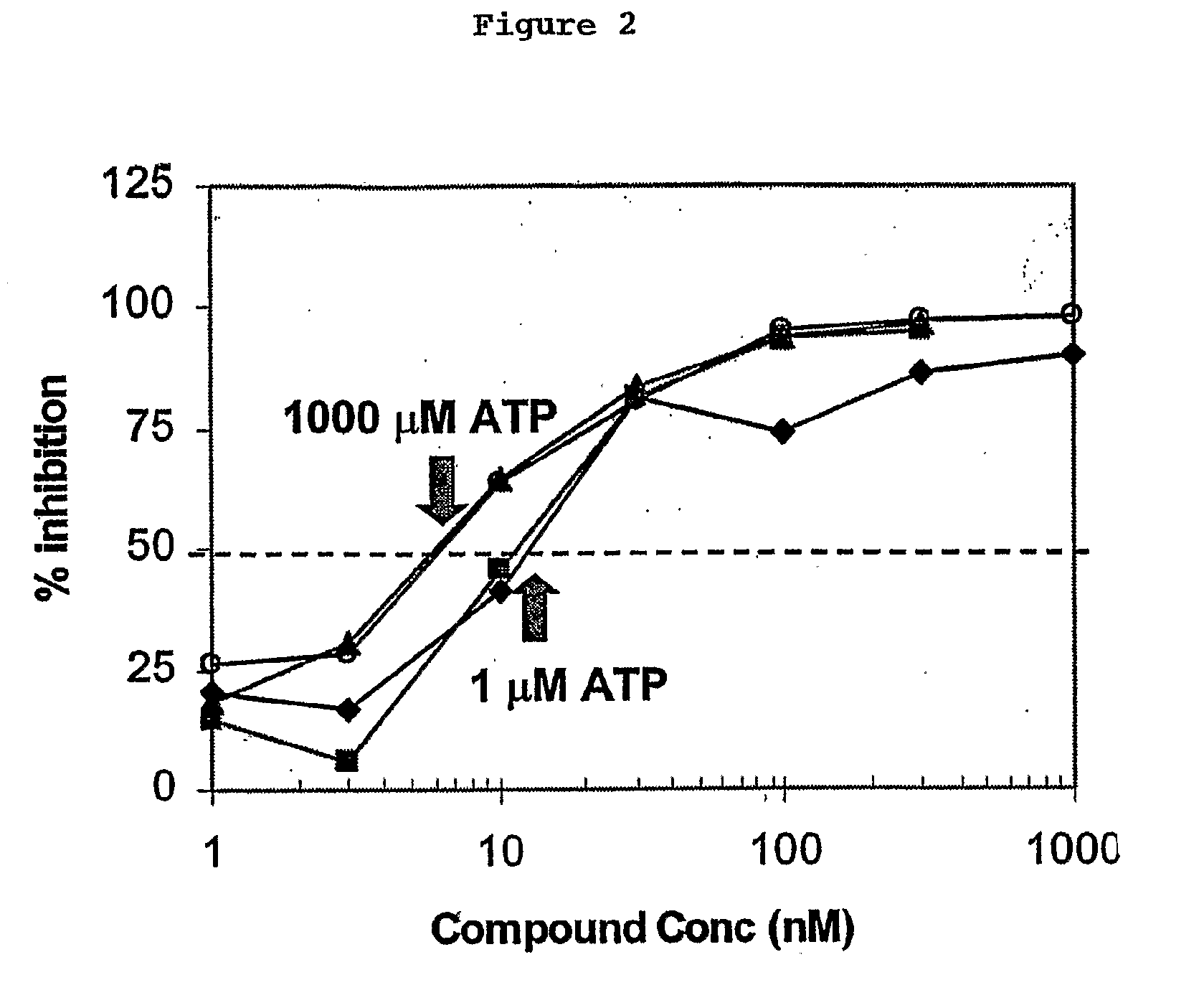
Assays to Identify Irreversibly Binding Inhibitors of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention relates to a method of identifying an inhibitor of a receptor tyrosine kinase that irreversibly binds to the kinase. Specifically, the method comprises using a variety of assays, either alone or in combination, to identify compounds that irreversibly bind to tyrosine kinases. More specifically, there are four assays, which are novel variations of a basic enzyme assay and identify irreversible binding inhibitors.
Owner:WYETH LLC
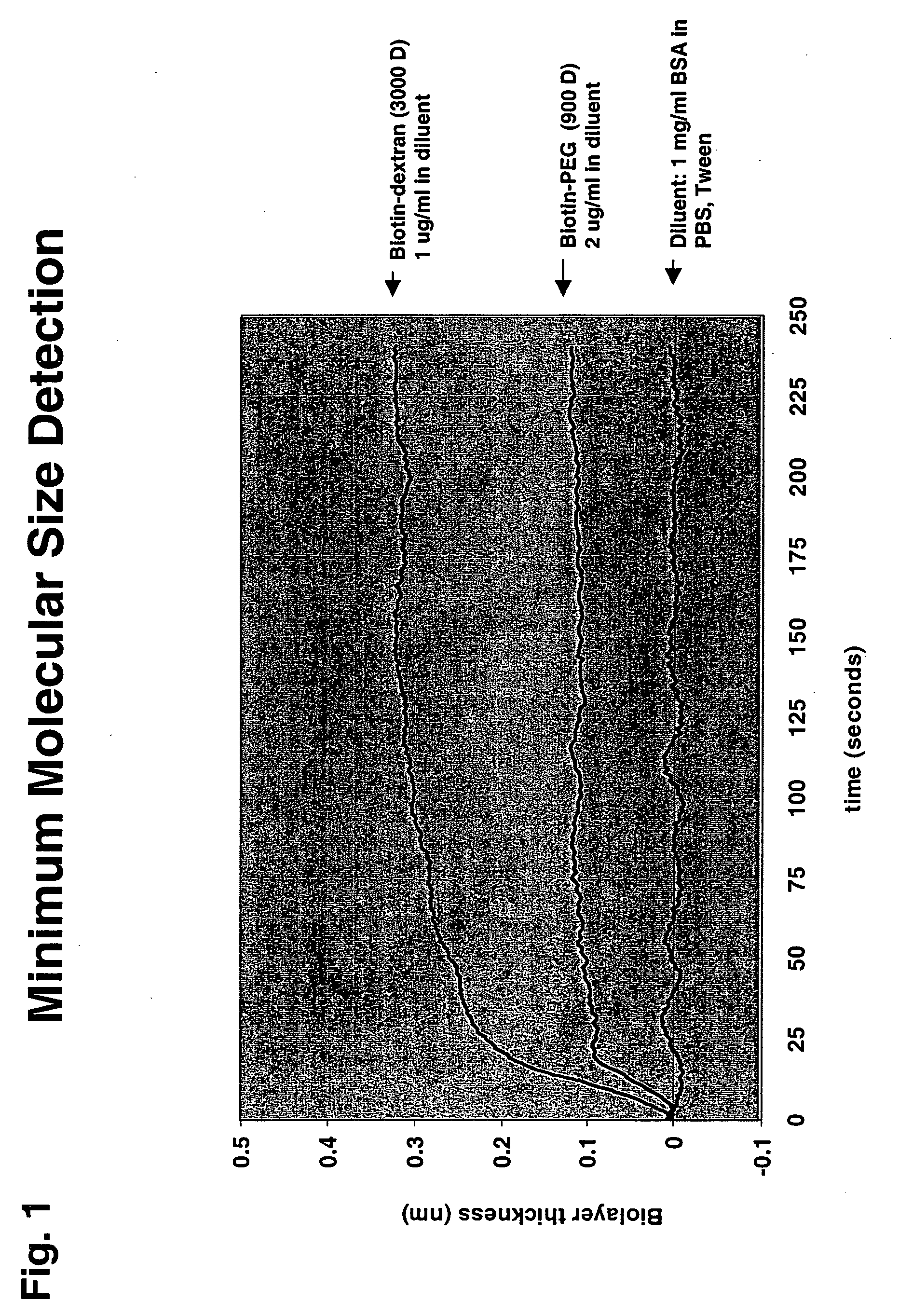
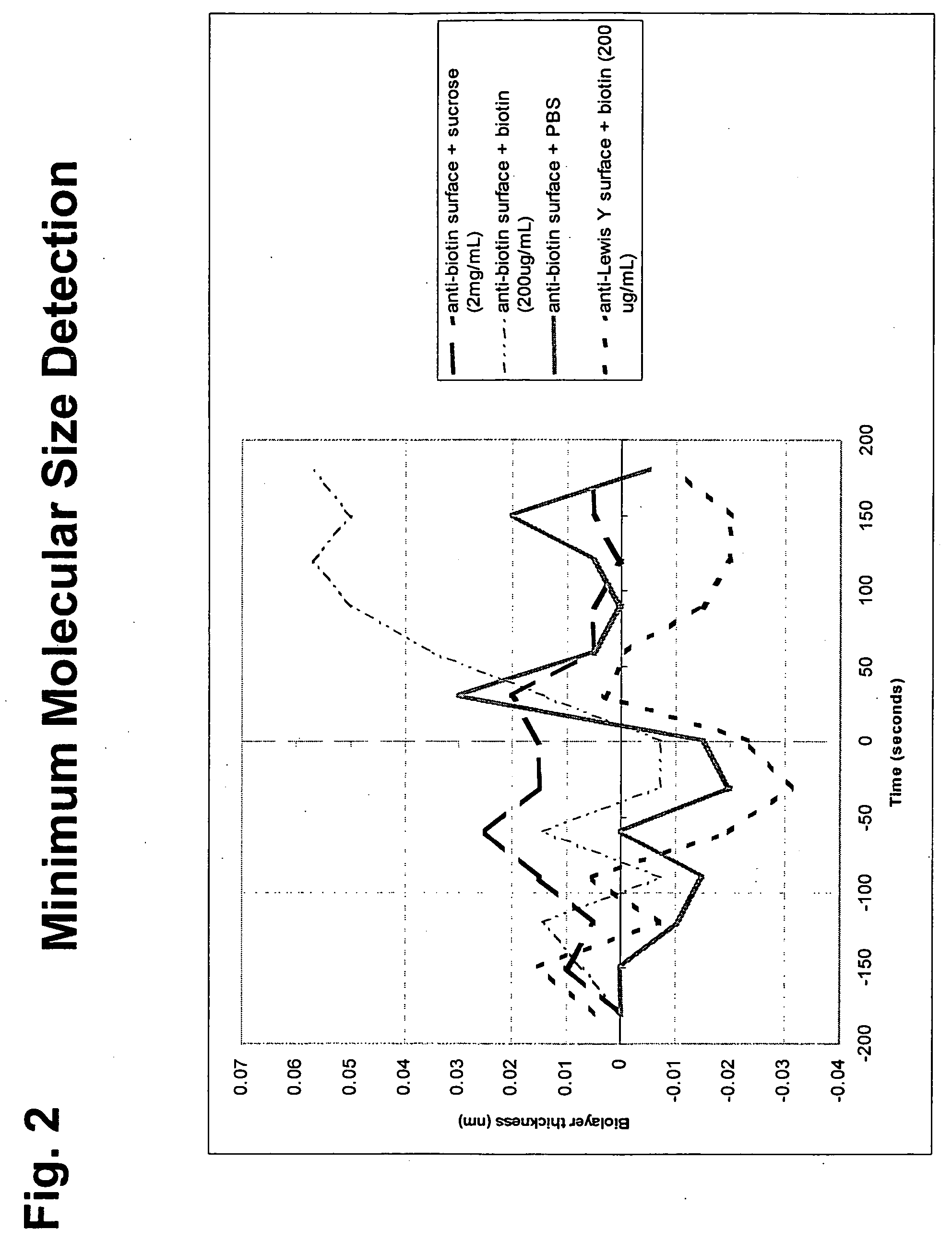
Enzyme activity measurement using bio-layer interferometry
ActiveUS20060154320A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingActivity measurementsEnzyme assay
Disclosed are enzyme assays using biolayer interferometry. Assays may be carried out using immobilized substrate or with a substrate capture format. In certain embodiments, the assays are carried out using unlabeled substrates. The methods are broadly applicable to enzyme assay measurements, can be carried out in vivo or in vitro, and are easily multiplexed.
Owner:SARTORIUS BIOANALYTICAL INSTR INC
Personalized protease assay to measure protease activity in neoplasms
Disclosed herein, the invention pertains to methods and compositions that find use in diagnostic, prognostic and characterization of neoplasia samples based on the ability of a neoplasia sample to cleave a MTS molecule of the present invention. In some embodiments, a MTS molecule disclosed herein has the formula (A-X-B-C), wherein A is a peptide with a sequence comprising 5 to 9 consecutive acidic amino acids, wherein the amino acids are selected from: aspartates and glutamates; B is a peptide with a sequence comprising 5 to 20 consecutive basic amino acids; X is a linker; and C is a detectable moiety.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
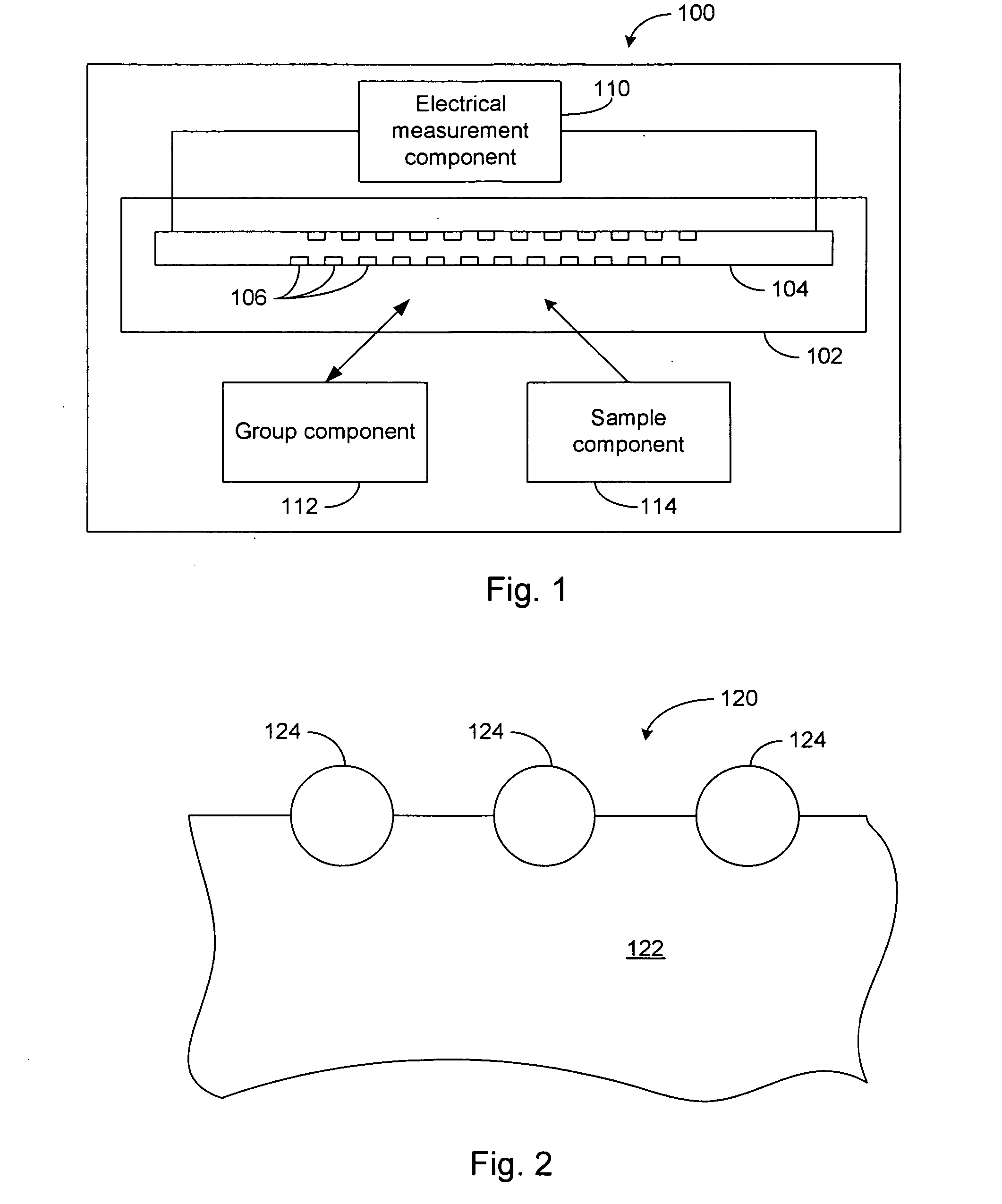
Microfluidic assays and microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20070134739A1Increase freedomEasy to useBiological testingImmune complex depositionEnzymatic Assays
The invention is a method for determining in the amount of an analyte (An) in a sample. The method comprises competitive immunoassays and enzymatic assays in which a soluble product (immune complex and enzymatic product, respectively) is formed. The product is subsequently measured in a measuring zone of a microchannel structure of a microfluidic device.
Owner:GYROS
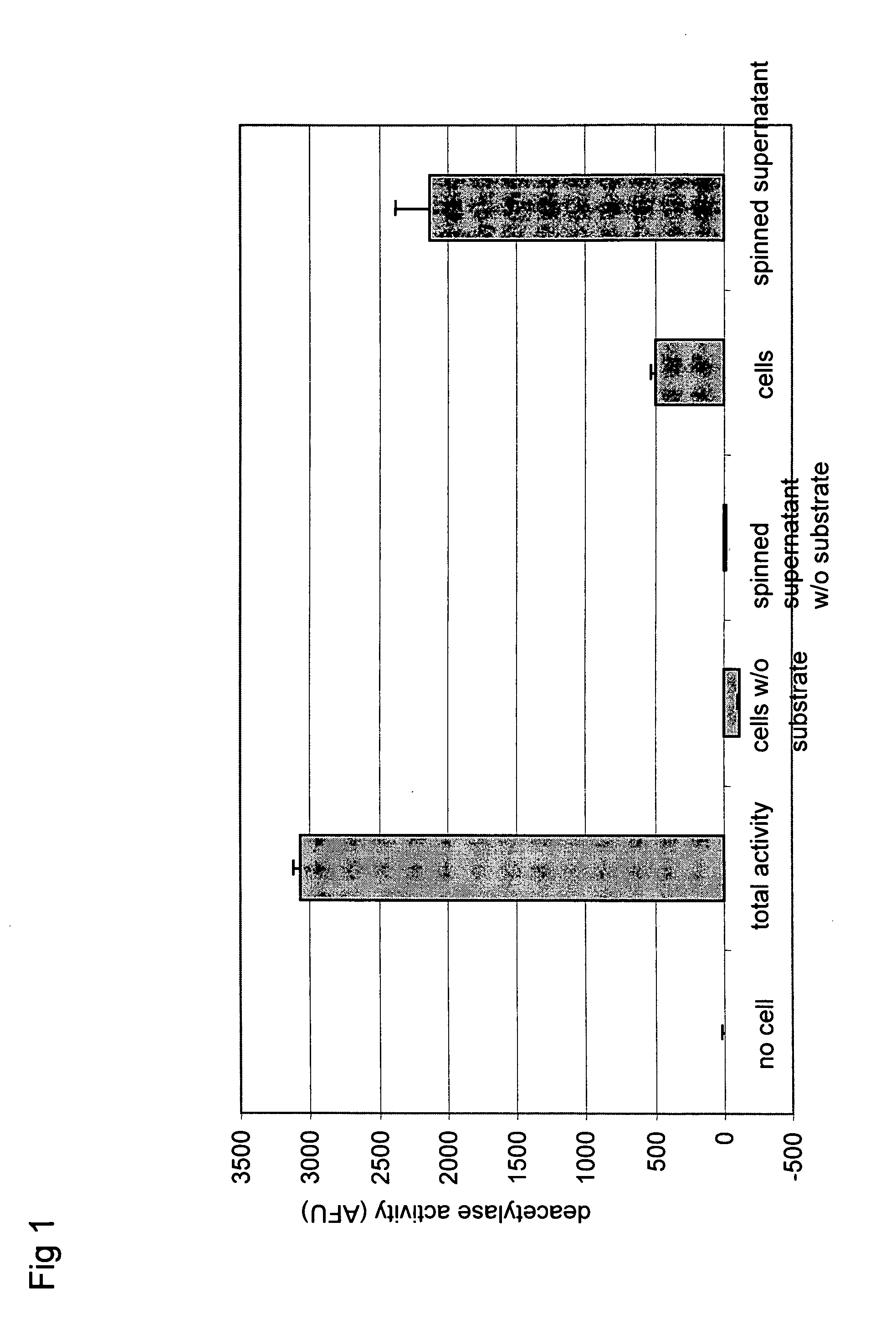
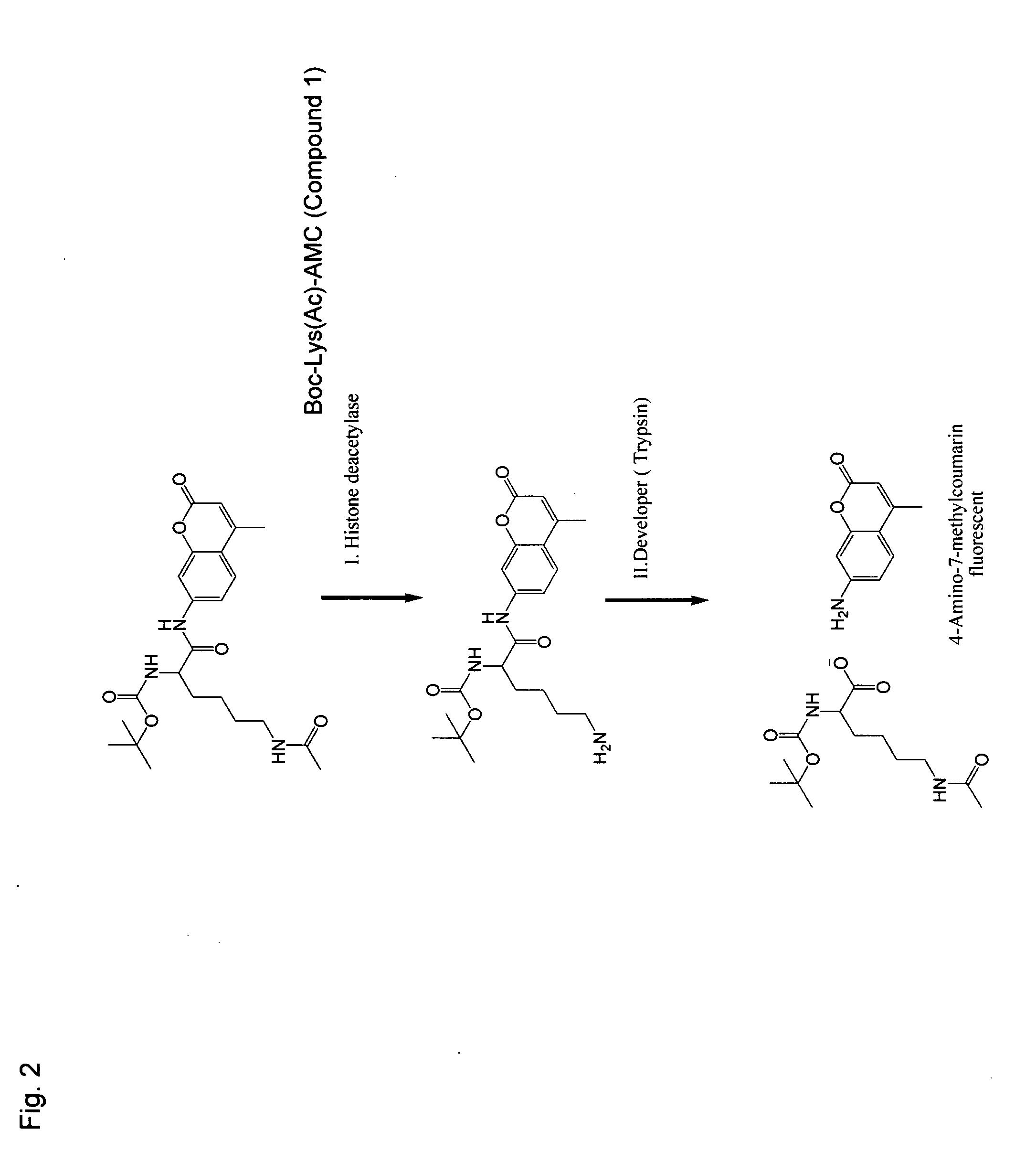
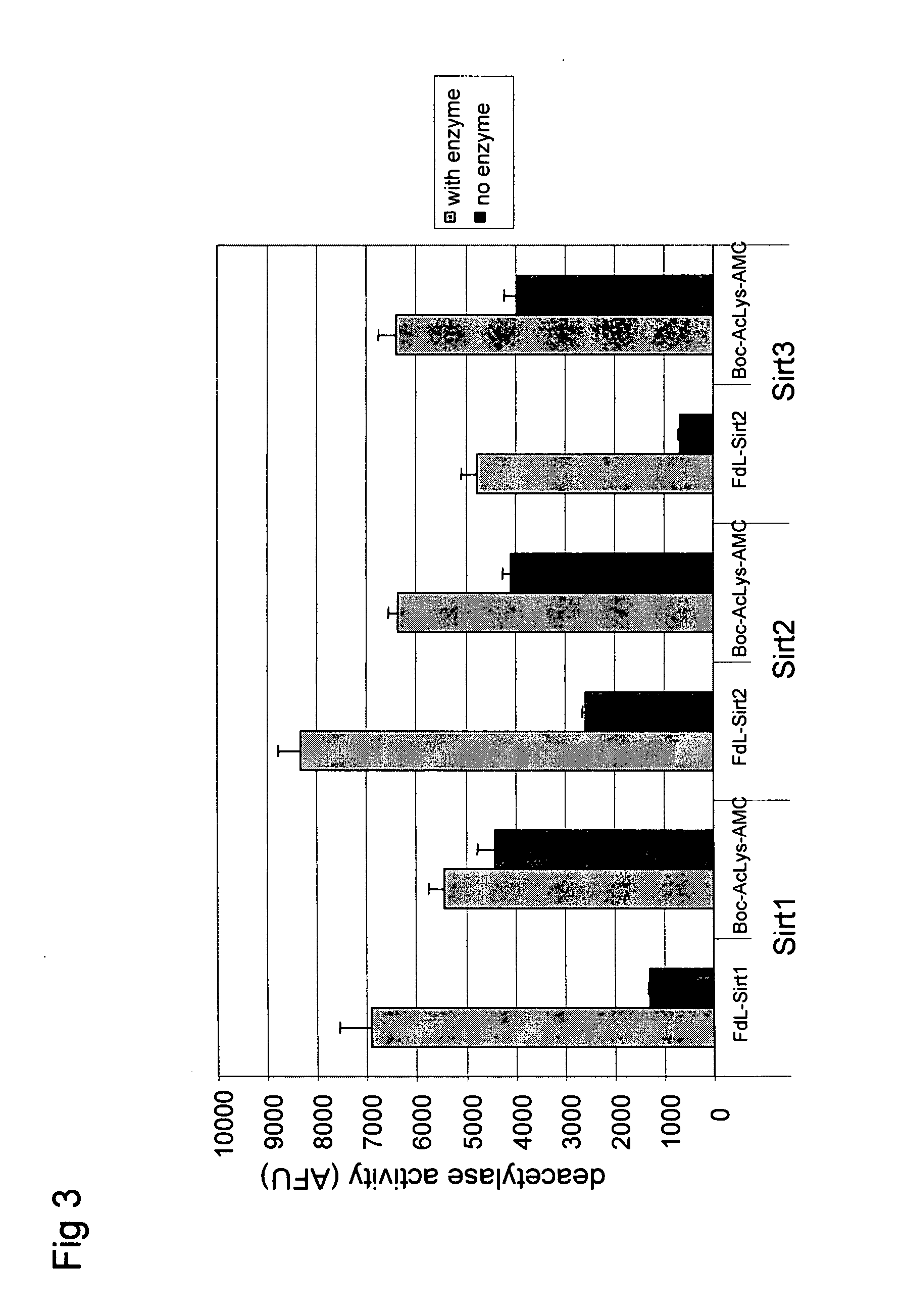
Histone deacetylase whole cell enzyme assay
InactiveUS20060063210A1Reduce in quantityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein insertionMammal
The invention relates to enzymatic assays for protein deacetylases. More particularly, the invention relates to such assays utilizing whole cells. The invention provides assays which allow assessment of the level of a protein deacetylase activity in whole cells taken directly from the body of the mammal.
Owner:METHYLGENE
Enzyme assay with nanowire sensor
InactiveUS20060084128A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanowireEnzyme assay
Systems and methods for enzyme assay using nanowire sensor are disclosed. In some embodiments, a substrate and a group suitable for assaying a target enzyme are identified. The selected substrate is immobilized to a nanowire. The target enzyme introduced to the immobilized substrate modifies the substrate to facilitate addition or removal of the selected group to or from the substrate by formation or breaking of a covalent bond between the group and the substrate. The activity of the target enzyme can be determined by measuring a change in an electrical property of the nanowire due to the addition or removal of the group to or from the immobilized substrate. Kinase and phosphatase are two example reactions that can be assayed by such a method.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Fluorogenic kinase assays and substrates
InactiveUS20050245726A1Facilitate in fluorescence of fluorescentPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme assayKinase
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
HEMOGLOBIN A1c MEASUREMENT METHOD AND MEASUREMENT KIT
ActiveUS20160251695A1Performed rapidly and simply and accurately and satisfactorilyHigh measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementHemoglobin hbEnzyme assay
This invention provides an amadoriase that acts on the β-chain of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and generates hydrogen peroxide, a method for measurement of HbA1c using such amadoriase, and a reagent kit for measurement of HbA1c using such amadoriase. The method for measurement of HbA1c involves the use of an amadoriase that has specific activity of 0.1 U / mg or greater to αF6P and oxidizes the HbA1c β-chain amino terminus so as to generate hydrogen peroxide, and the reagent kit for measurement of HbA1c comprises such amadoriase. The method and the kit for measurement of HbA1c enable quantification of HbA1c to be performed rapidly, simply, and accurately.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Fluorescent enzyme assay methods and compositions
Owner:阿普尔拉股份有限公司
ADMA (Asymmetric Dimethylarginine) immunoassay reagent and detection method
InactiveCN106290903AStrong immunogen specificityStrong specificityBiological testingSpecific antibodyReaction system
The invention relates to a method and reagent for immunological detection of a homogeneous enzyme determination technology, and is used for determination of the ADMA (N<G>,N<G>,dimethyl-L-arginine, asymmetric dimethylarginine, ADMA) content in a detected sample. According to the invention, anti-ADMA specific antibodies and enzyme-ADMA complexes are used, the immunological reaction of the enzyme-ADMA complexes and the anti-ADMA specific antibodies is utilized, after antigen antibody complexes are formed, the activity of the enzyme-ADMA complexes is inhibited, the changes of enzymatic activity in a reaction system is determined to obtain the number of combined enzyme markers, so as to obtain the content of ADMA in the detected sample. The method has the advantage of capability of realizing immunoassay as the common biochemical enzyme method, so as to simultaneously determine multiple samples on a full-automatic biochemical analyzer.
Owner:北京德奥平生物技术有限公司
Fluorogenic protease substrates based on dye-dimerization
InactiveUS7256012B2High fluorescence intensityEasy to observePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismImmuno assay
A method of biological assay comprises the steps of providing an enzyme substrate comprising two fluorescence dye groups bound to a flexible peptide, the dye groups being of proximity sufficiently close so as to allow free energy attractions to draw the dyes together to essentially self-quench fluorescence of the dye groups, wherein self quenching of fluorescence of the dye groups is effected by dye dimerization or stacking, and enzymatically cleaving the peptide to release the fluorescence dye groups from dye dimerization or stacking, thereby producing an increase in fluorescence intensity. A protease substrate for use in the method of the invention is also disclosed. This invention finds use in detection and identification of microorganisms, sterilization assurance, pharmaceutical discovery, enzyme assays, immunoassays, and other biological assays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
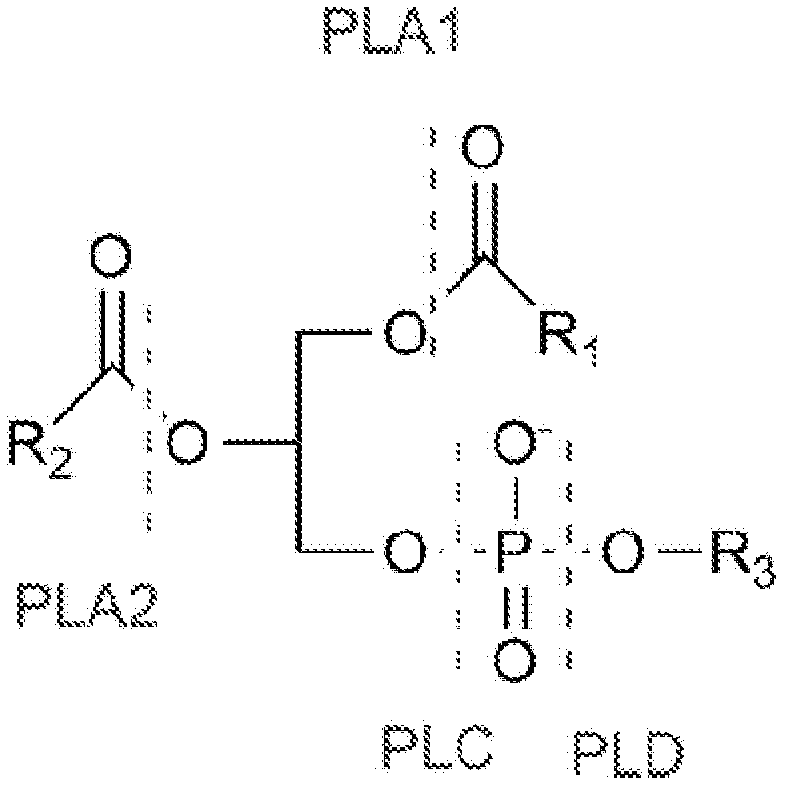
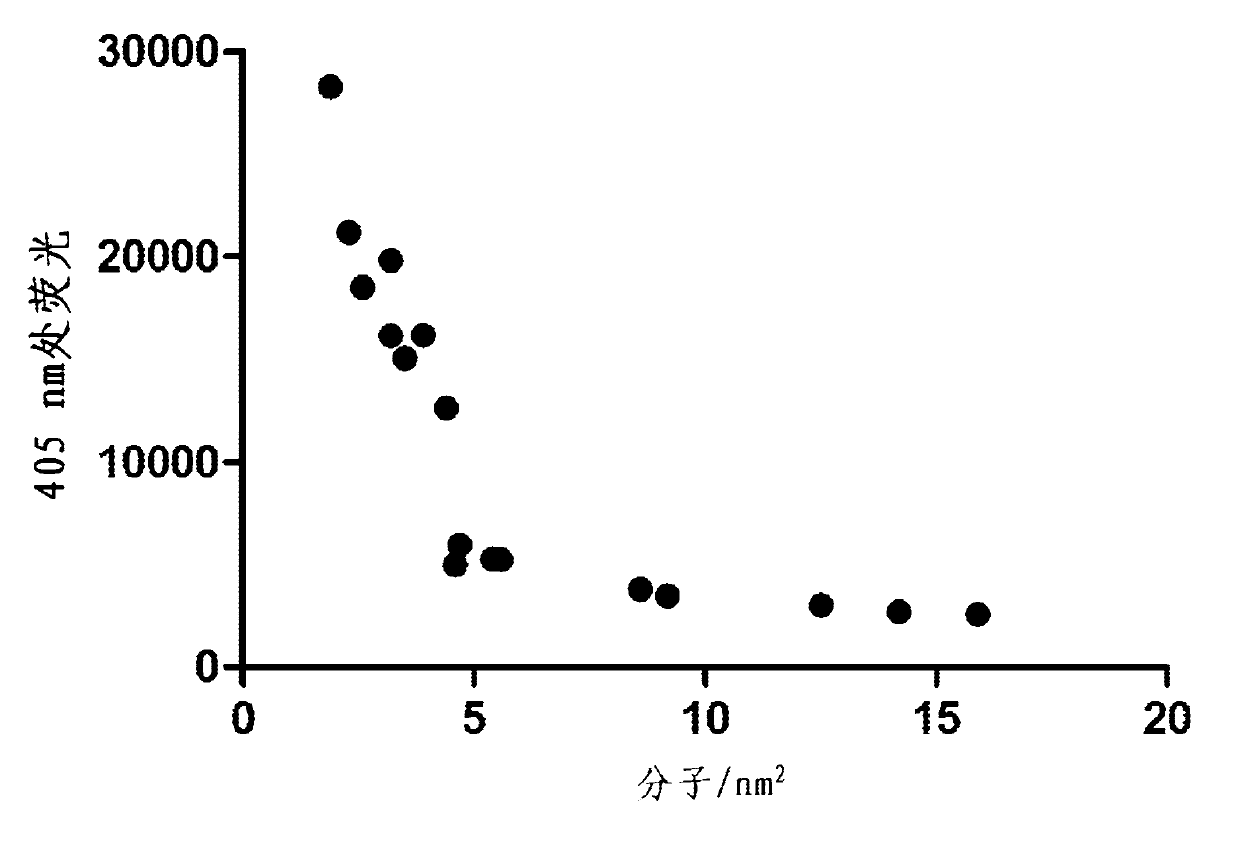
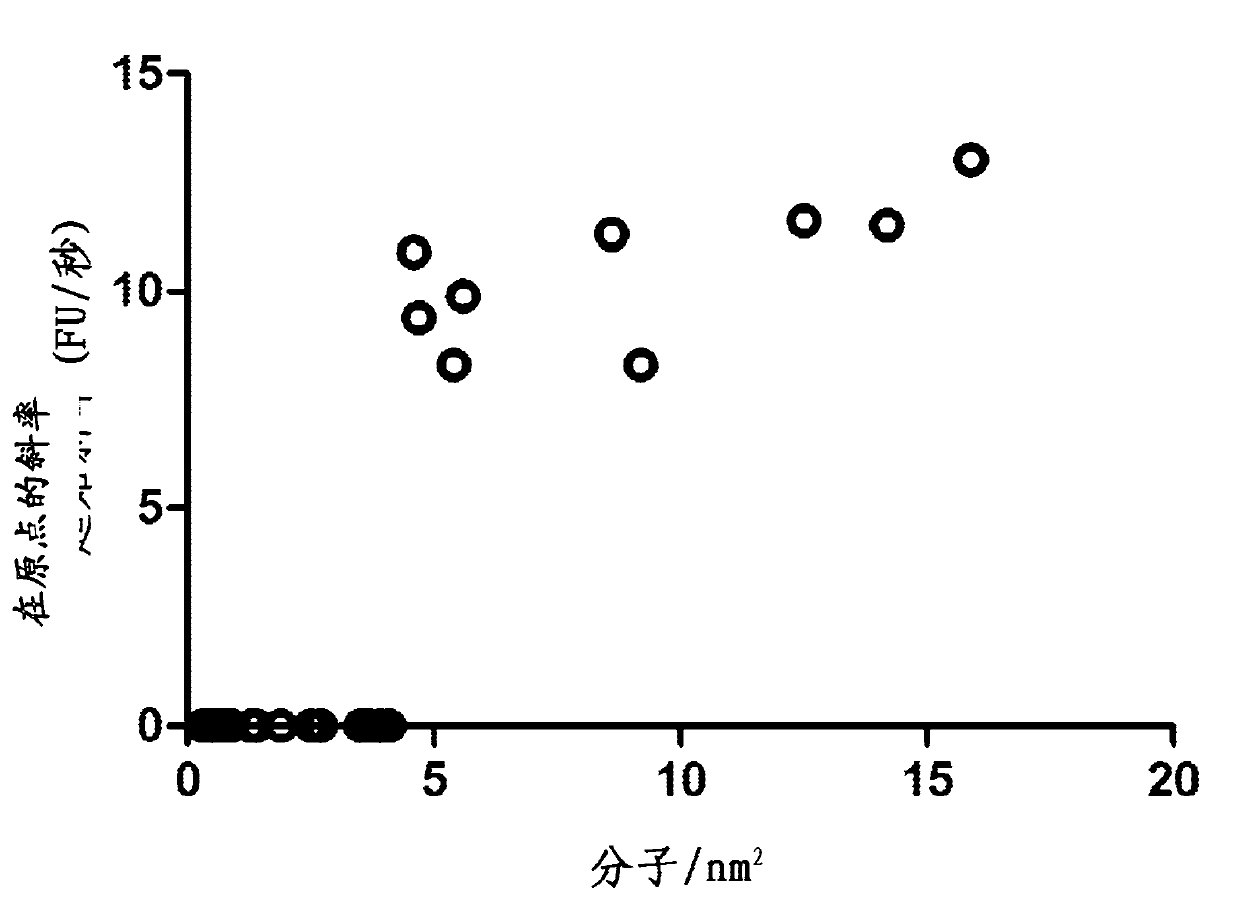
Enzymatic assay for the quantitative determination of phospholipase A1 or A2 activity in a sample
InactiveCN102388311ASensitivity advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisQuantitative determinationFluorescence
The invention relates to a new method for measuring phospholipase A1 or A2 activity in a sample, using a solid phase coated with a fluorochrome-labelled phospholipase A1 or A2 substrate, wherein the molecular coverage is in the range from 8 to 30 fluorochrome-labelled phospholipase A1 or A2 substrate molecules / nm2, and kit for carrying out said method.
Owner:ATEROVAX
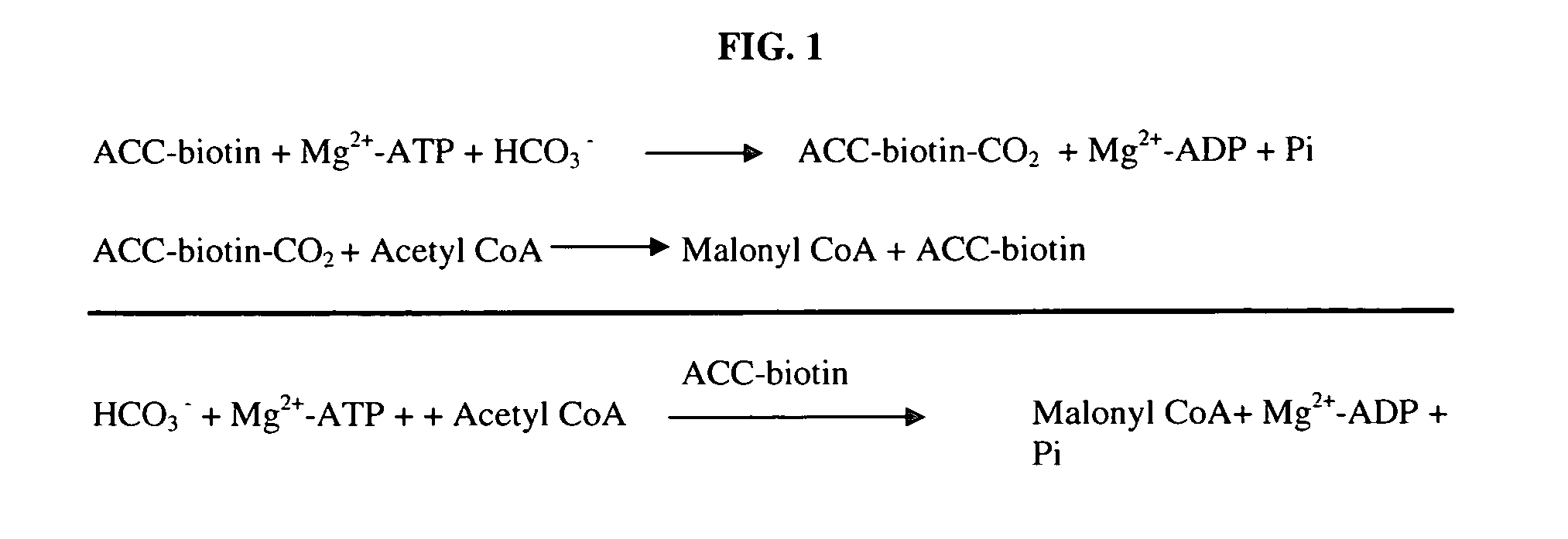
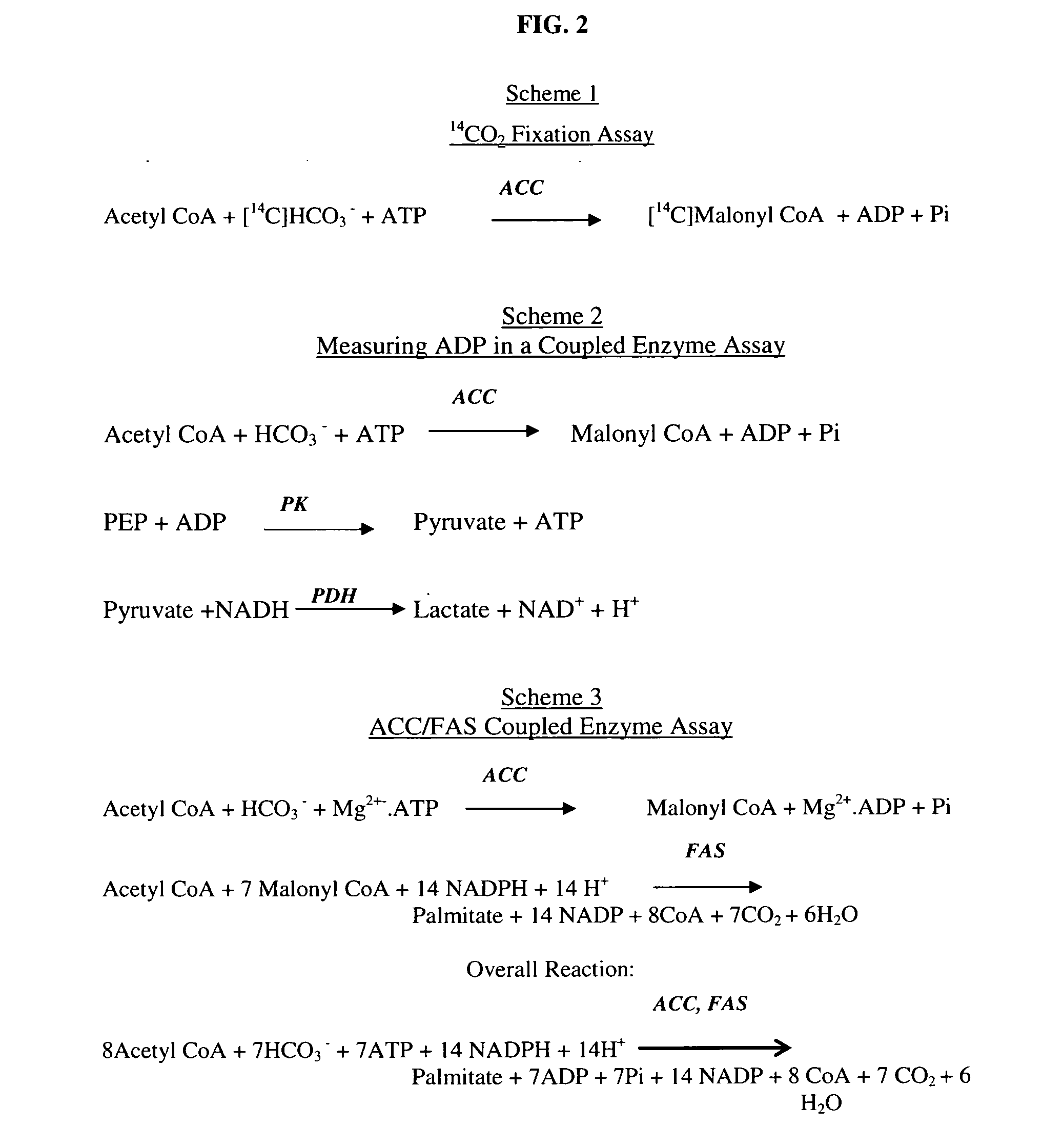
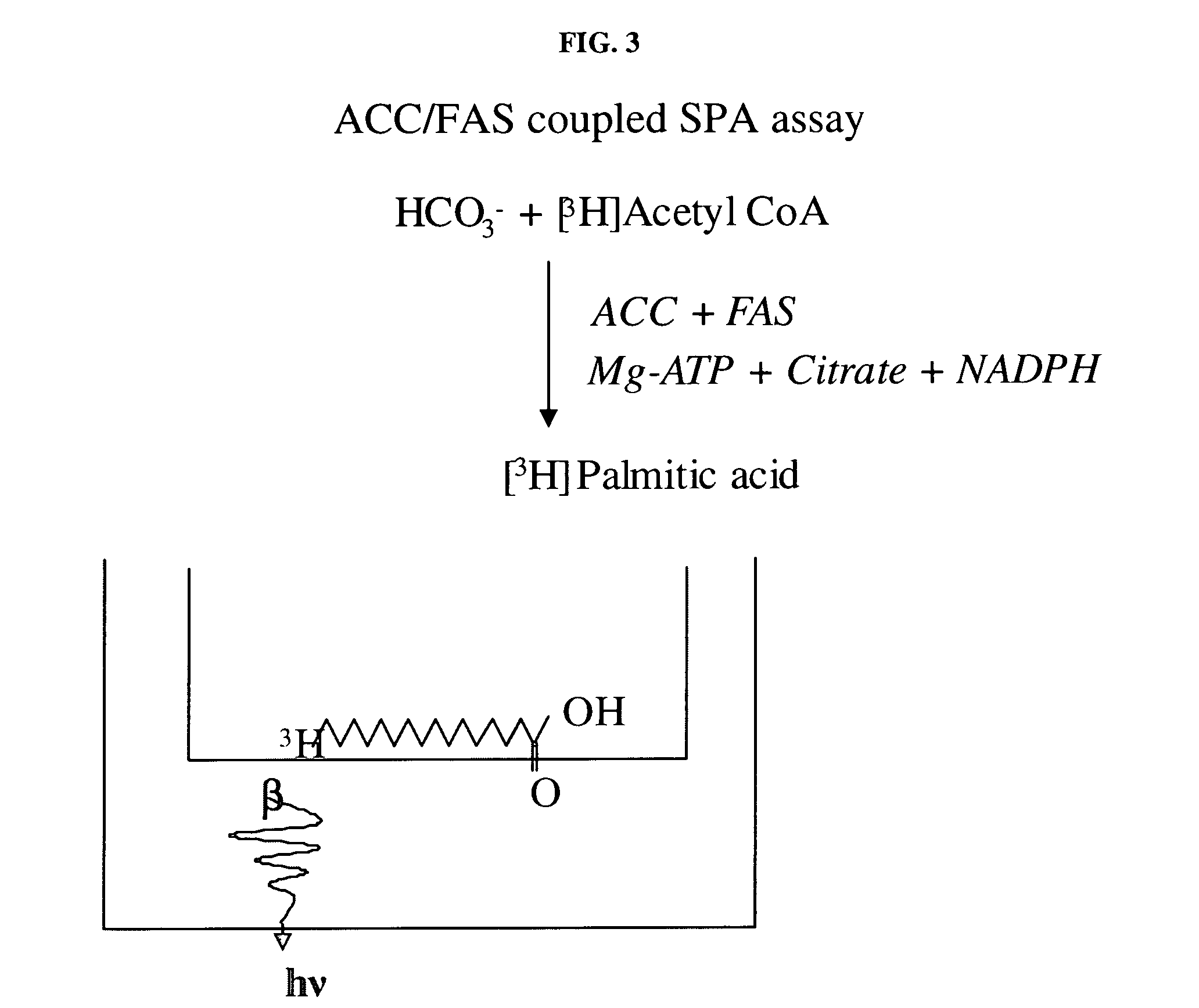
Scintillation proximity assay method of measuring acetyl CoA carboxylase enzyme activity
InactiveUS20050221410A1High activityCatalytic rate was not increasedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAssay
The present invention relates generally to enzyme assays and more particularly to a rapid, sensitive, reliable and robust homogeneous assay for acetyl CoA carboxylase activity comprising a coupled enzyme assay in a scintillation proximity format suitable for high-throughput screening. In one aspect, the assay couples ACC and FAS and the product, palmitic acid is then detected by scintillation counting. The invention also relates to the identification of modulators of ACC activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
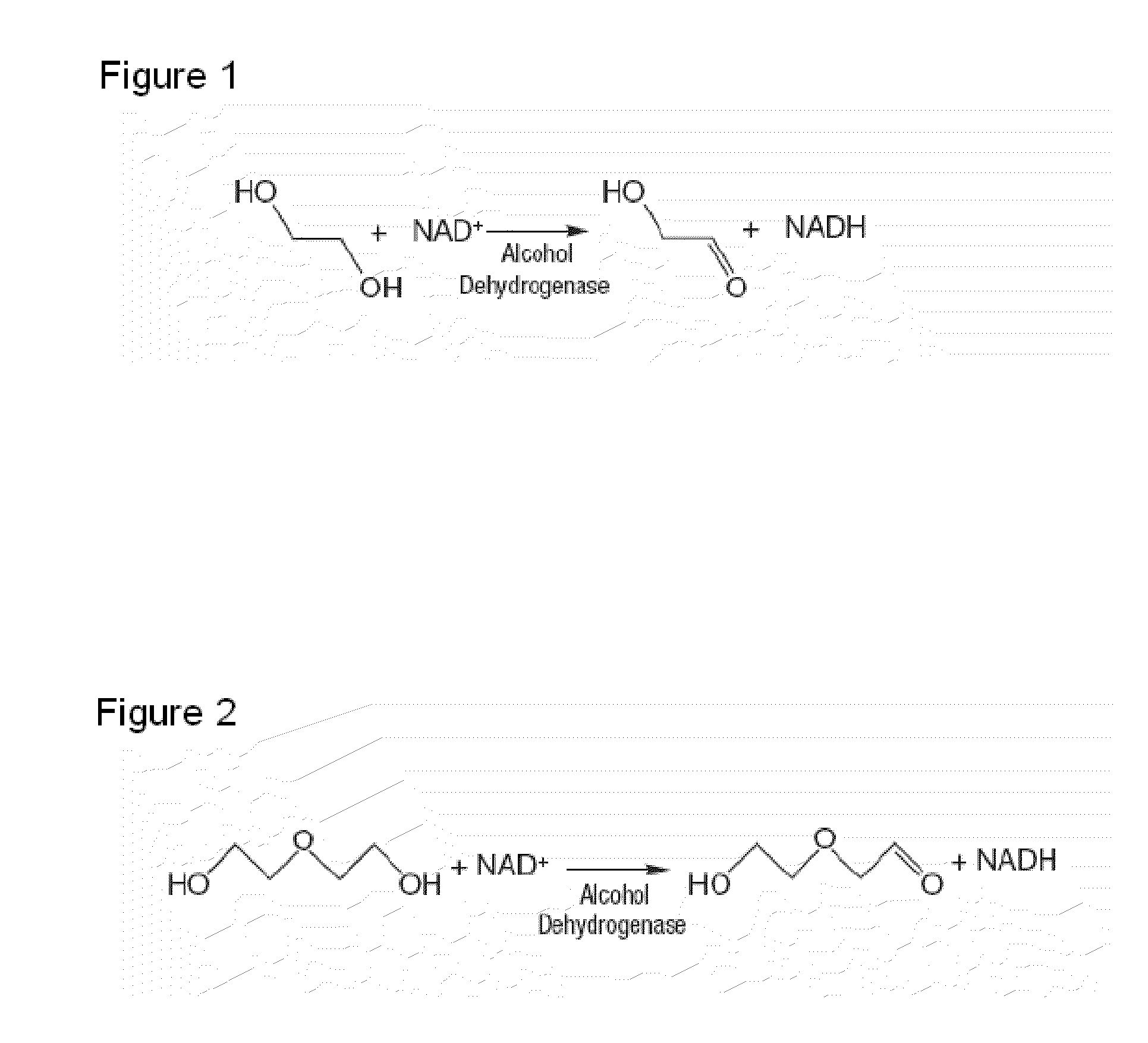
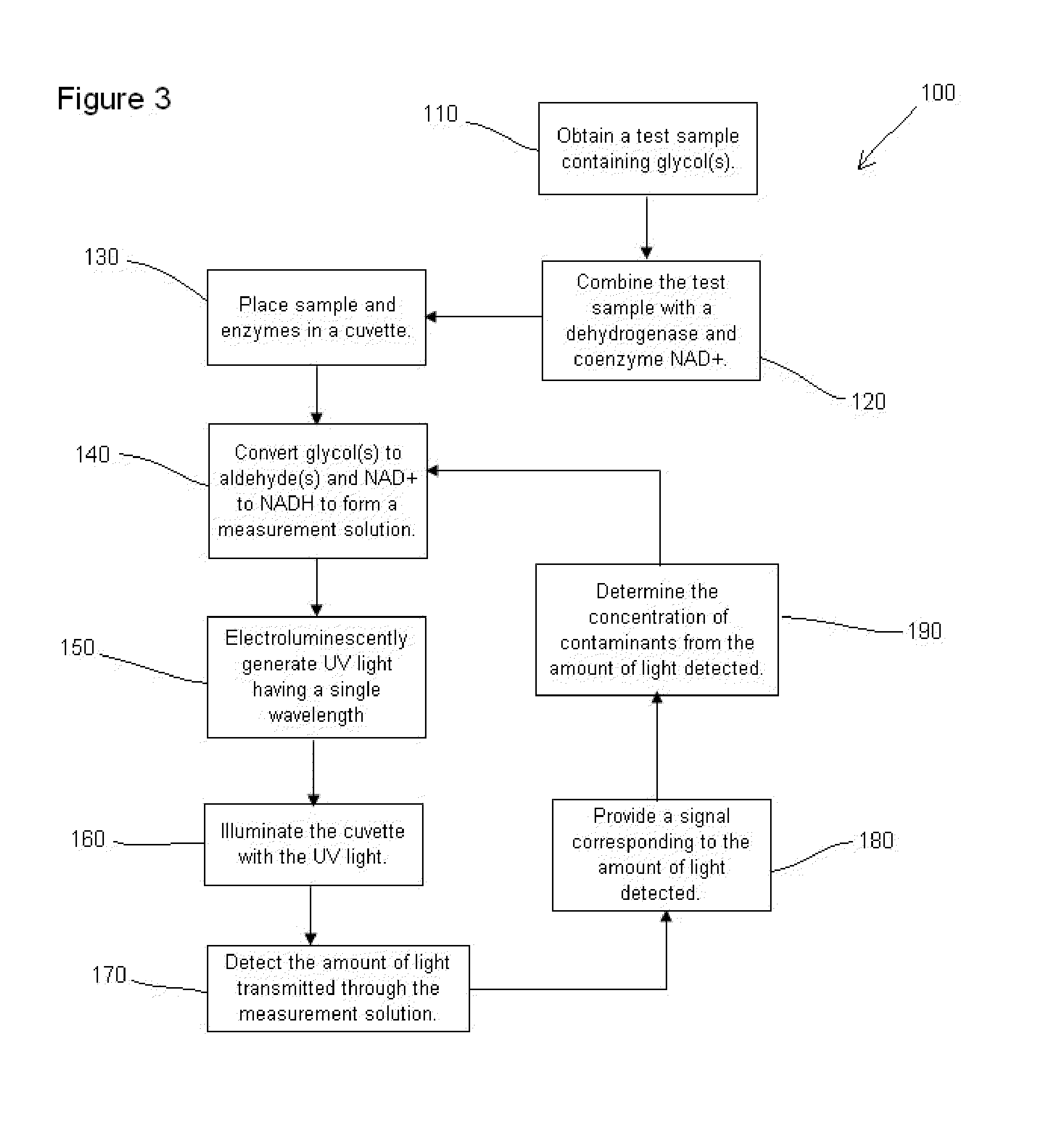
Apparatus and method for detecting glycol
InactiveUS20130157350A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceDiethylene glycol
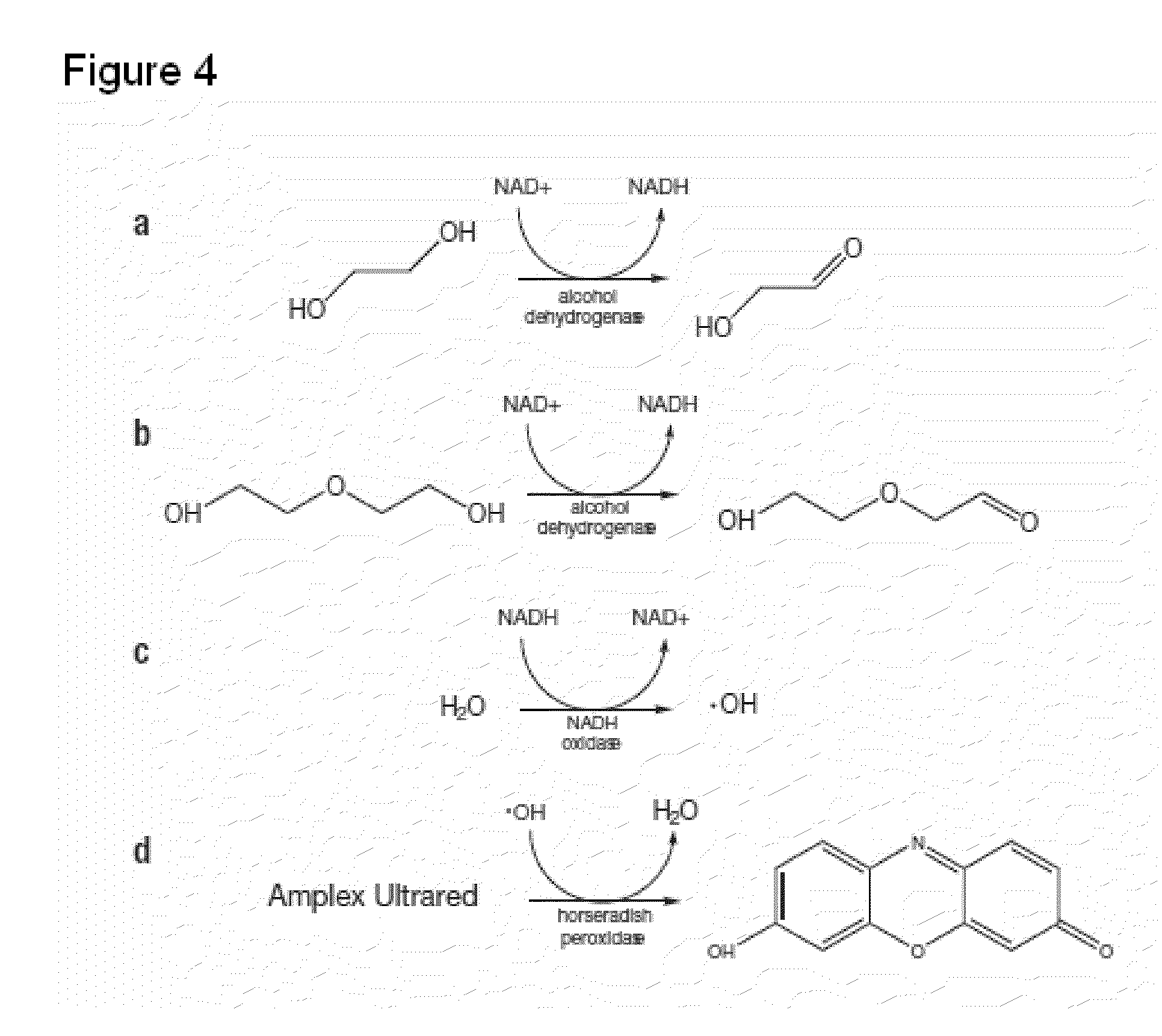
A method and apparatus are provided for detecting contaminants, such as ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol, in various materials, including household products, and medicines. The contaminants can be detected using enzyme assays that produce measurable changes in light absorption and / or light fluorescence.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
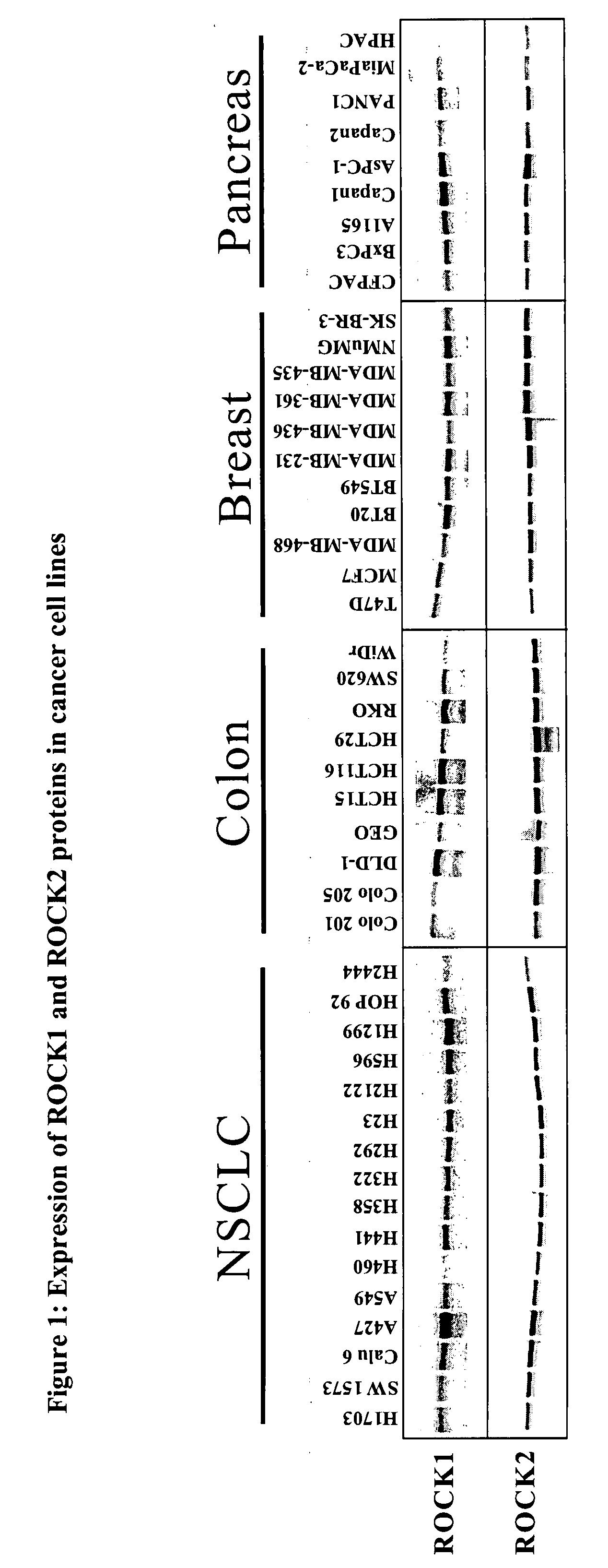
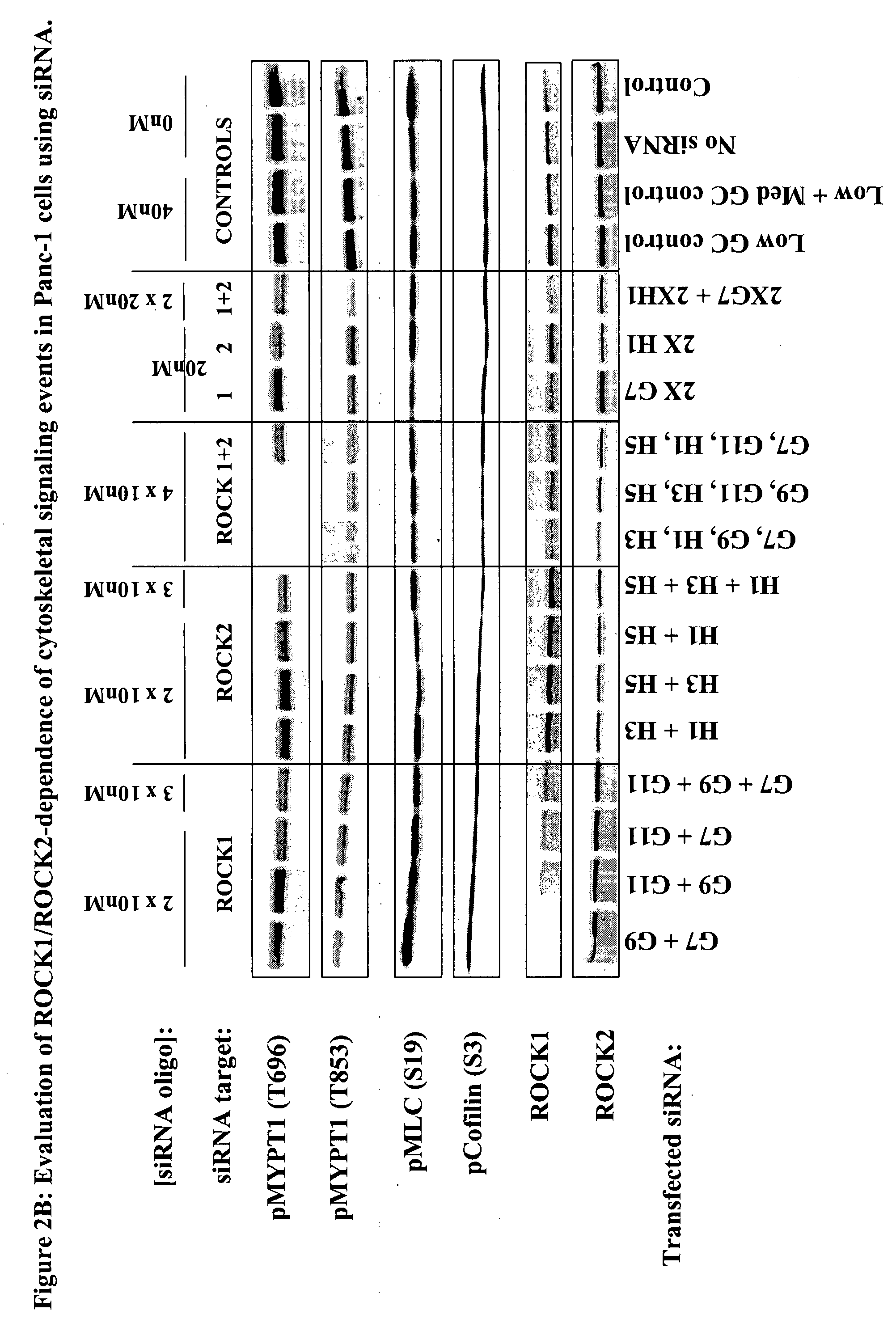
Method for the assay of rock kinase activity in cells
The present invention provides a method for determining the intracellular activity of ROCK kinase comprising, providing a sample of cells to be tested for ROCK kinase activity, determining the level of phosphorylation of MYPT1 in the sample, and determining the intracellular activity of ROCK kinase in the sample of cells, wherein the level of MYPT1 phosphorylation directly correlates with the level of intracellular ROCK kinase activity. The invention further provides a method for identifying an agent that inhibits the intracellular activity of ROCK kinase comprising, providing a sample of cells having ROCK kinase activity, determining the degree of reduction of phosphorylation of MYPT1 in the sample by contacting the sample of cells with a test agent and comparing the MYPT1 phosphorylation level with the phosphorylation level of MYPT1 in an identical control sample of cells that was not contacted with the test agent, determining the degree of inhibition of intracellular activity of ROCK kinase in the sample of cells contacted with the agent, wherein the level of MYPT1 phosphorylation directly correlates with the level of intracellular ROCK kinase activity, and thus determining whether the test agent is an agent that inhibits the intracellular activity of ROCK kinase. The test agent may for example be a compound not known to have ROCK kinase inhibitory activity, or a compound identified by an in vitro ROCK kinase assay as having inhibitory activity.
Owner:OSI PHARMA INC
Biotin-peg-substrate for a lipase assay
InactiveUS20040014133A1Microbiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAssayChemical compound
Disclosed is a compound of Formula (I), wherein: L is a linking agent; B is a binding agent; X is an atom or group suitable for attaching L to the glycerol chain; and R is a straight chain saturated or unsaturated alkyl group having from 8 to 30 carbon atoms, substituted with M' or M" wherein at least one of M' and / or M" is a detectable label. The compound can be used as a lipase substrate in a solid phase-based assay system, such as a scintillation proximity assay, to detect lipase enzyme activity.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
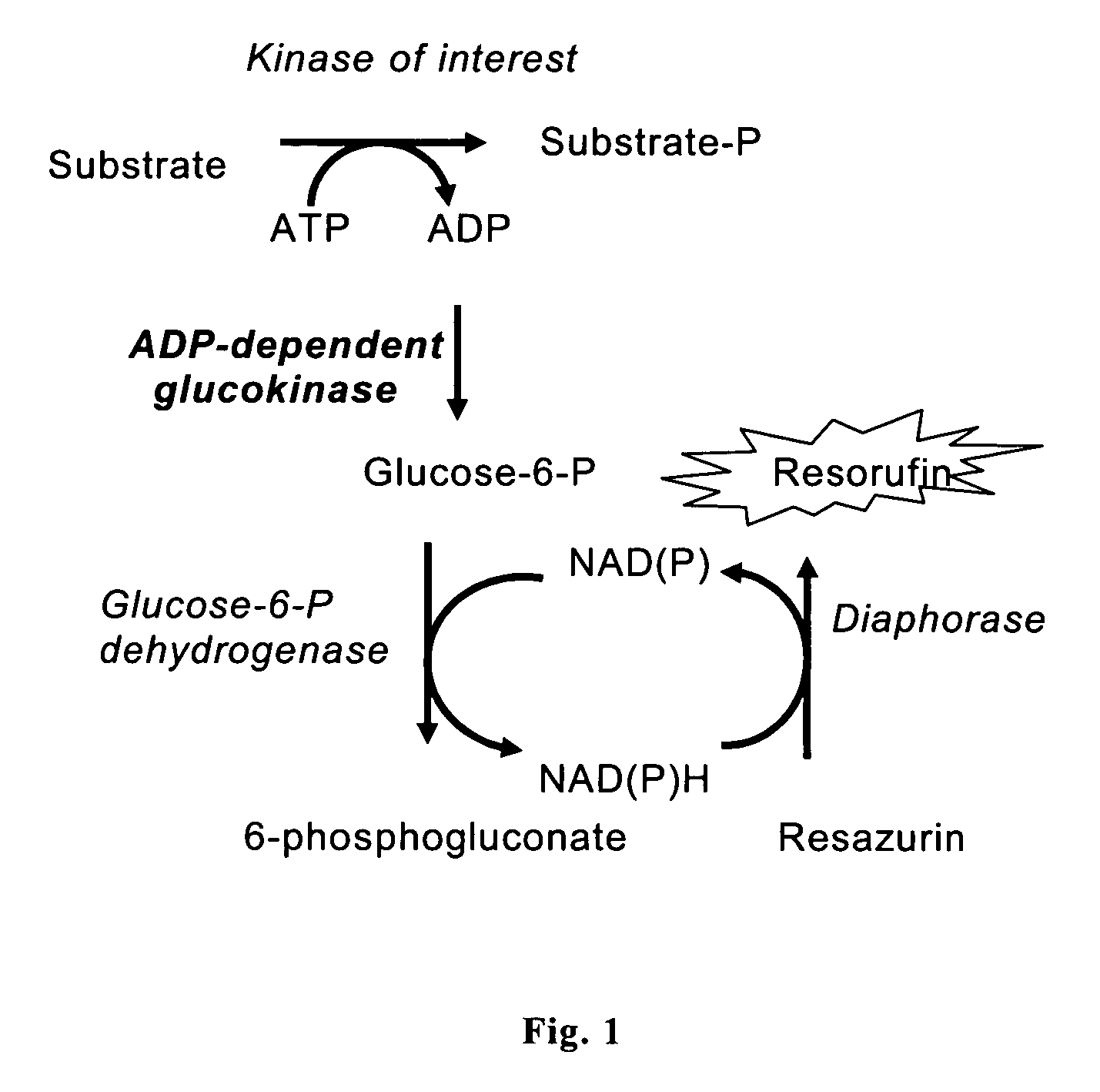
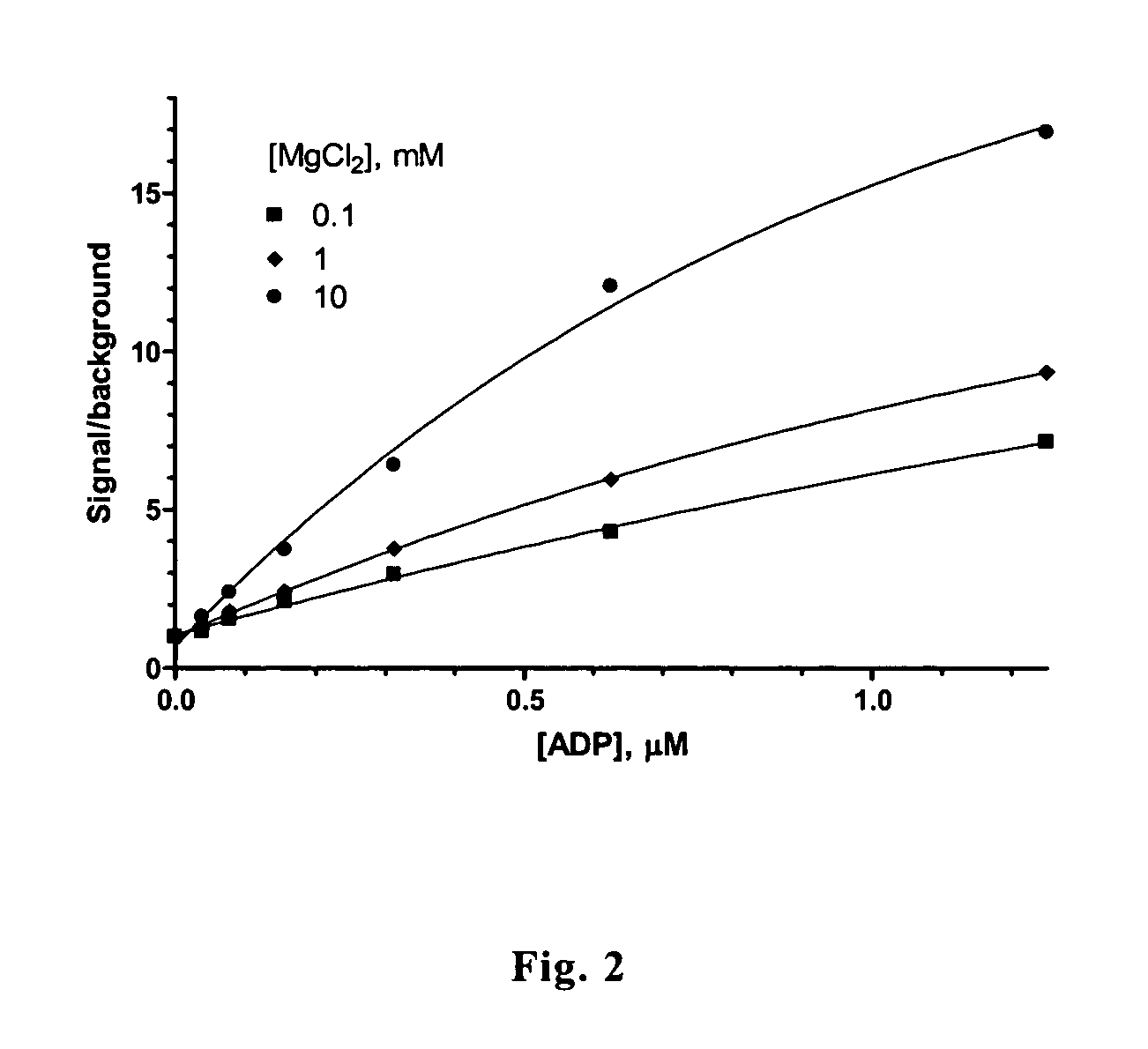
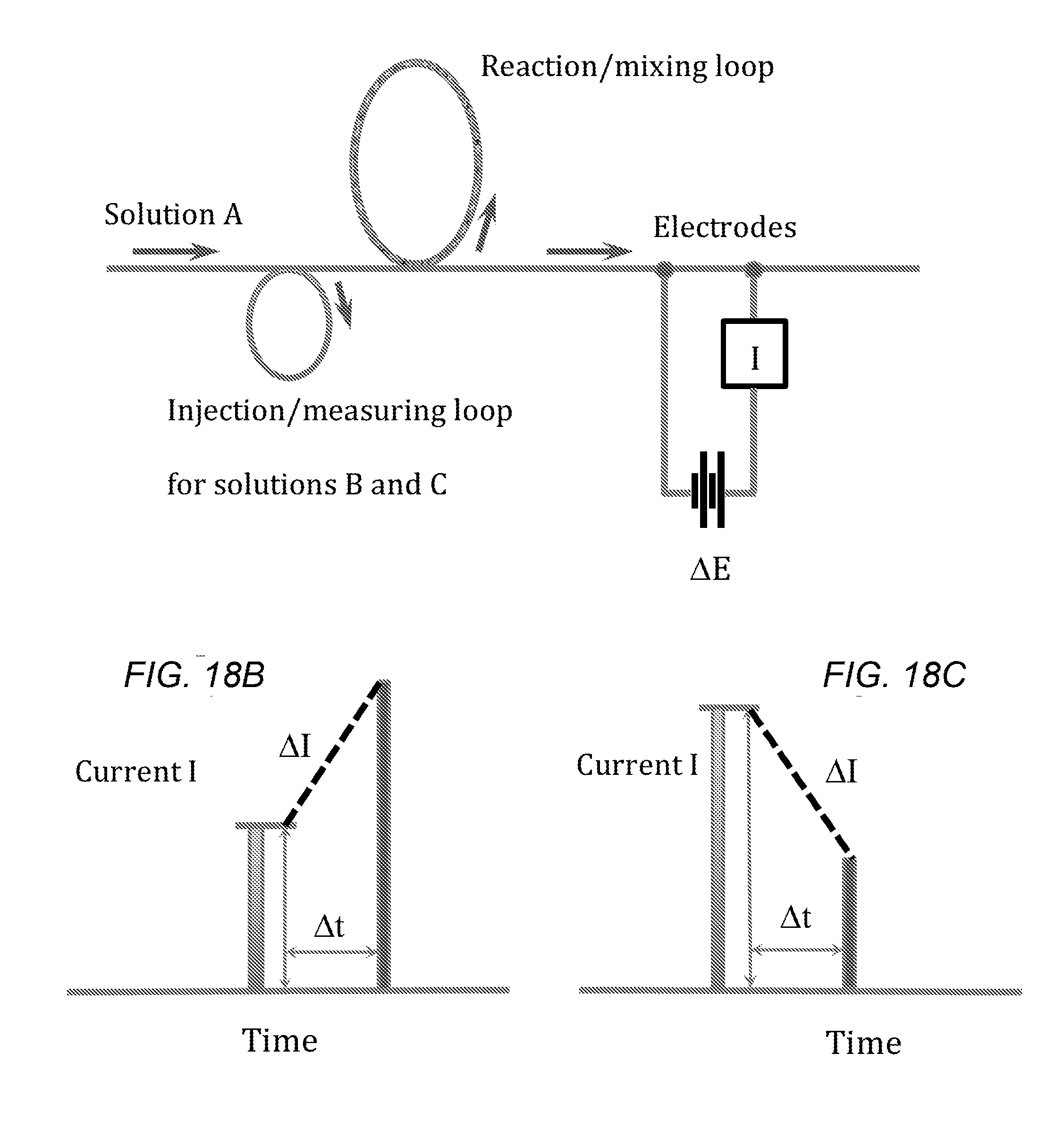
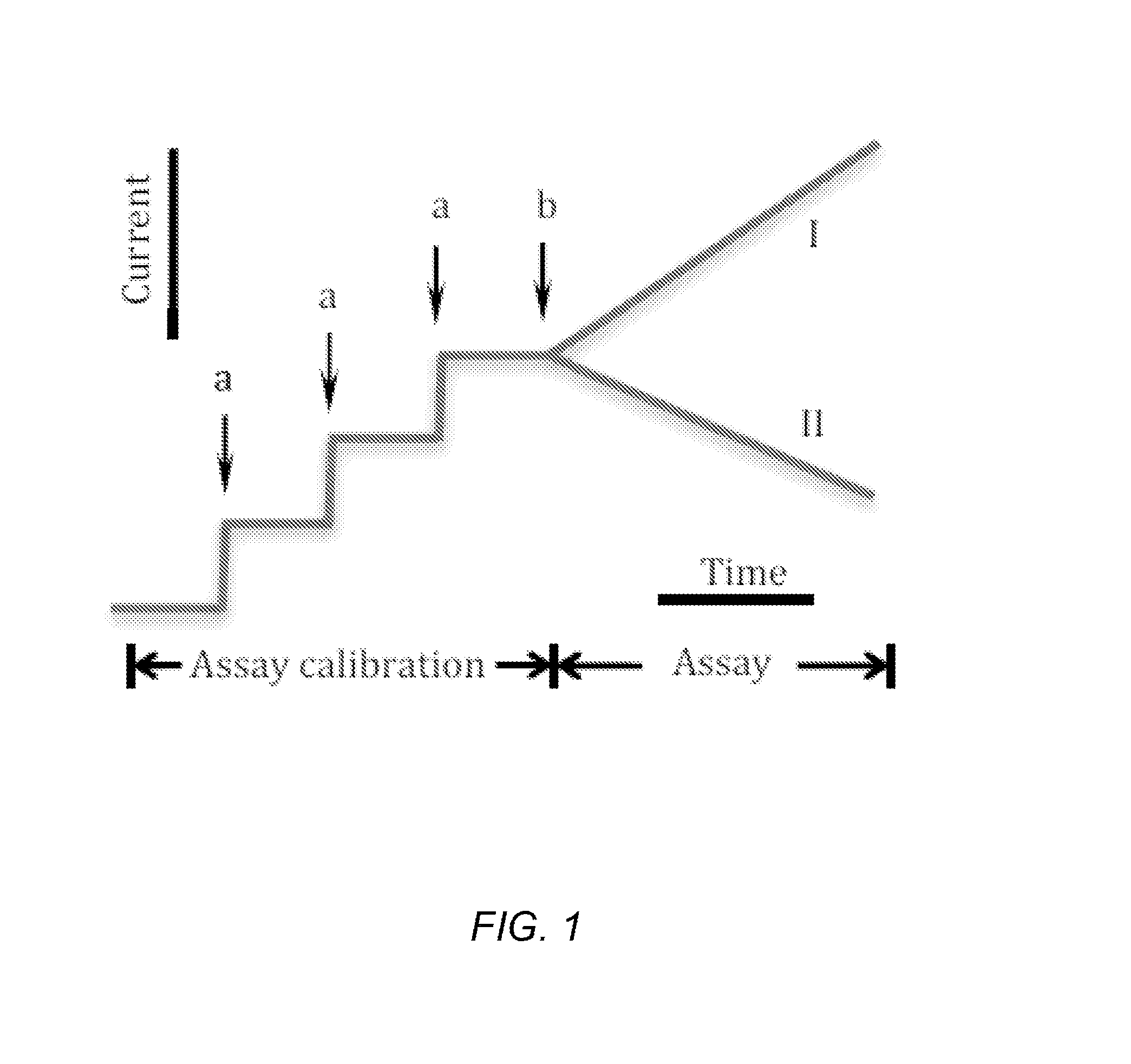
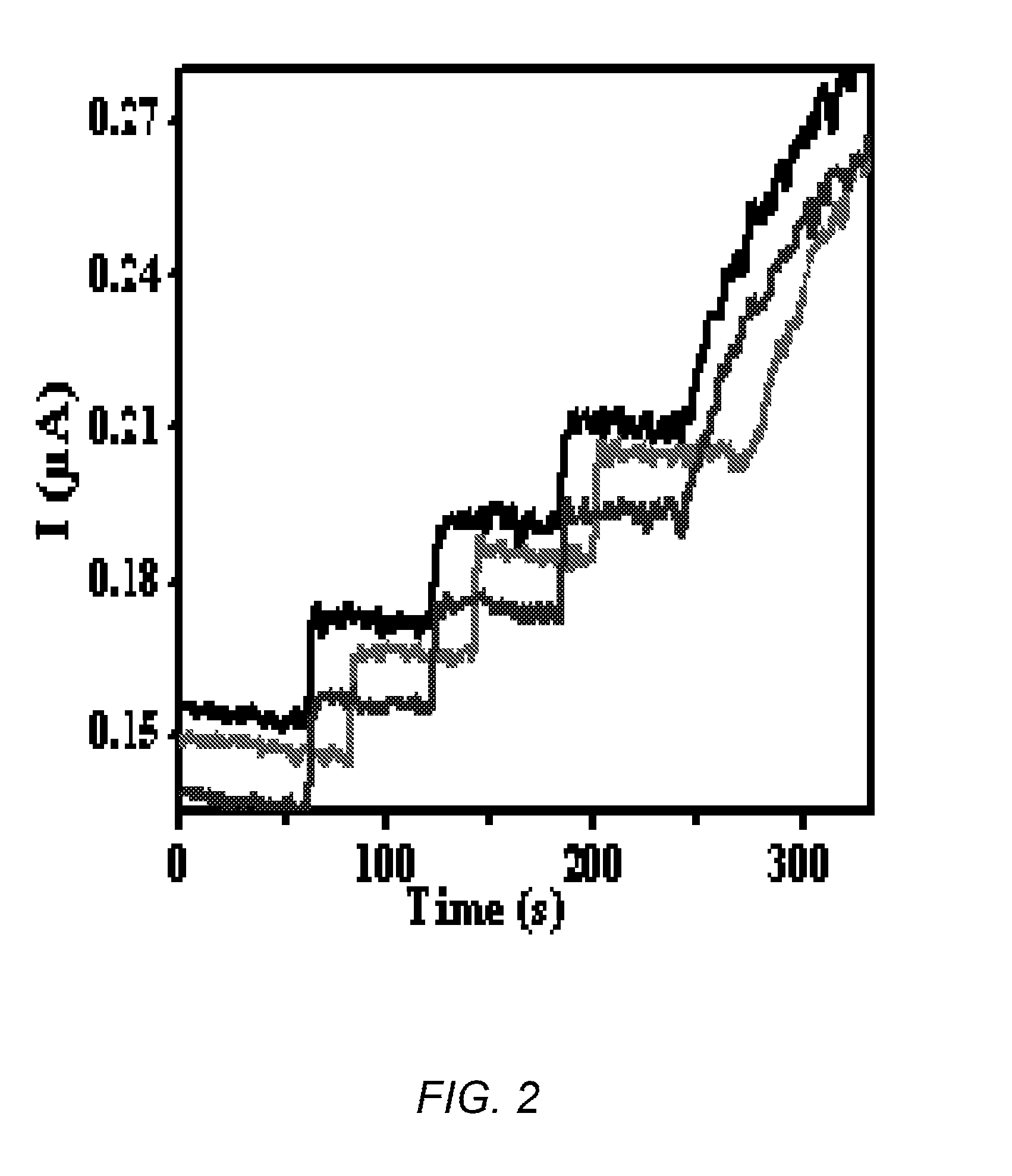
Fast quantification of enzyme activity by electroanalysis
The internally calibrated electrochemical continuous enzyme assay (ICECEA) was developed for the fast determination of enzyme activity unit. The assay uses integration of enzyme-free pre-assay calibration with the actual enzyme assay in one continuous experiment. Such integration results in a uniquely shaped amperometric trace that allows for the selective and sensitive determination of enzymes.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Micro-screening apparatus, process, and products
Microcavity arrays and methods for quantitative biochemical and biophysical analysis of populations of biological variants. Examples include high-throughput analysis of cells and protein products usea range of fluorescent assays, including binding-affinity measurement and time-resolved enzyme assays. Laser-based extraction of microcavity contents. In one aspect, the disclosure is directed to a system including an array comprising a plurality of distinct cavities comprising open first ends and open second ends, an electromagnetic radiation absorbing material associated with cavities, and a pulsed diode laser configured to deliver electromagnetic radiation to the electromagnetic radiation absorbing material. In various embodiment's of the system, the cavities may be fused capillaries.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com