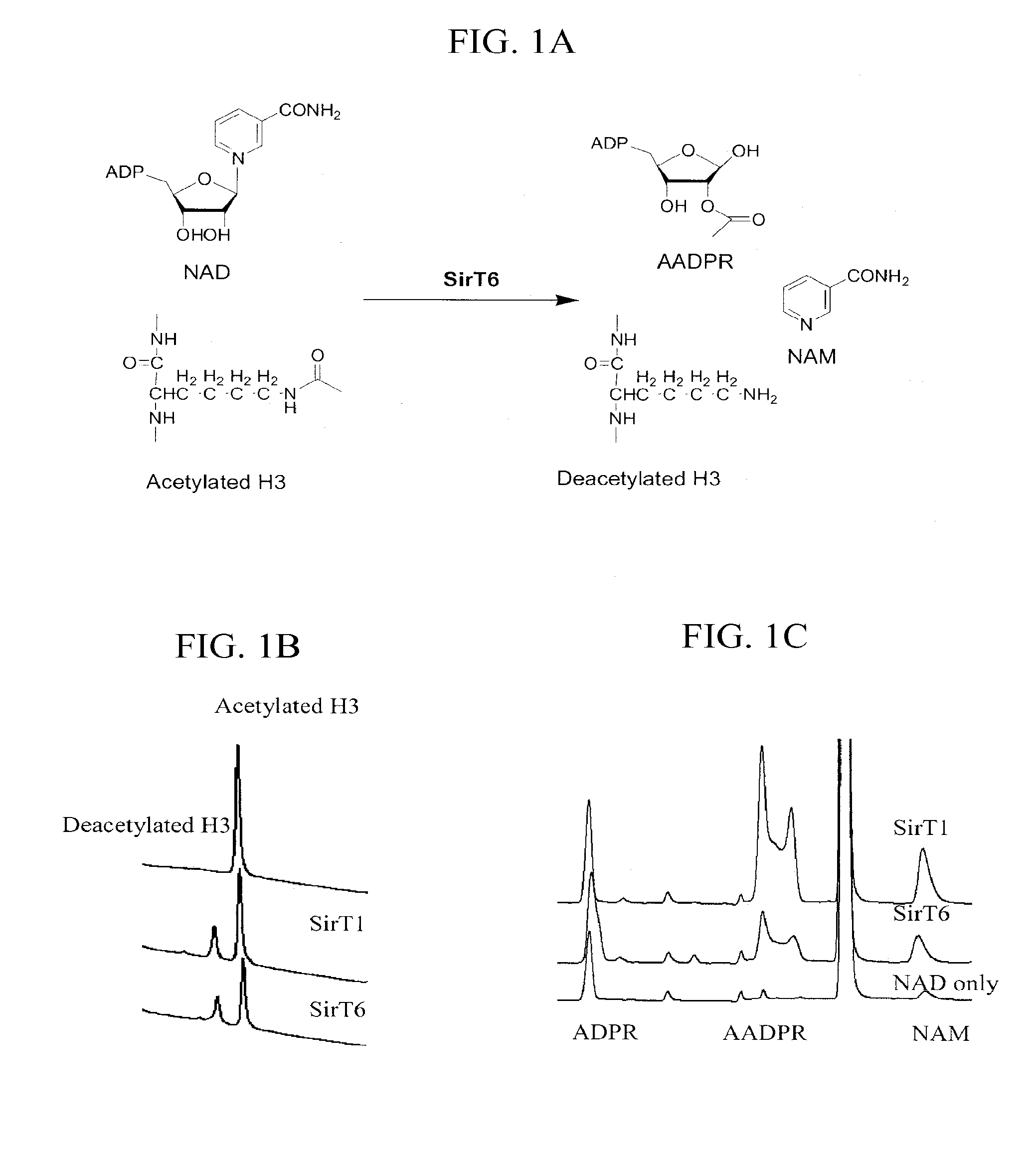
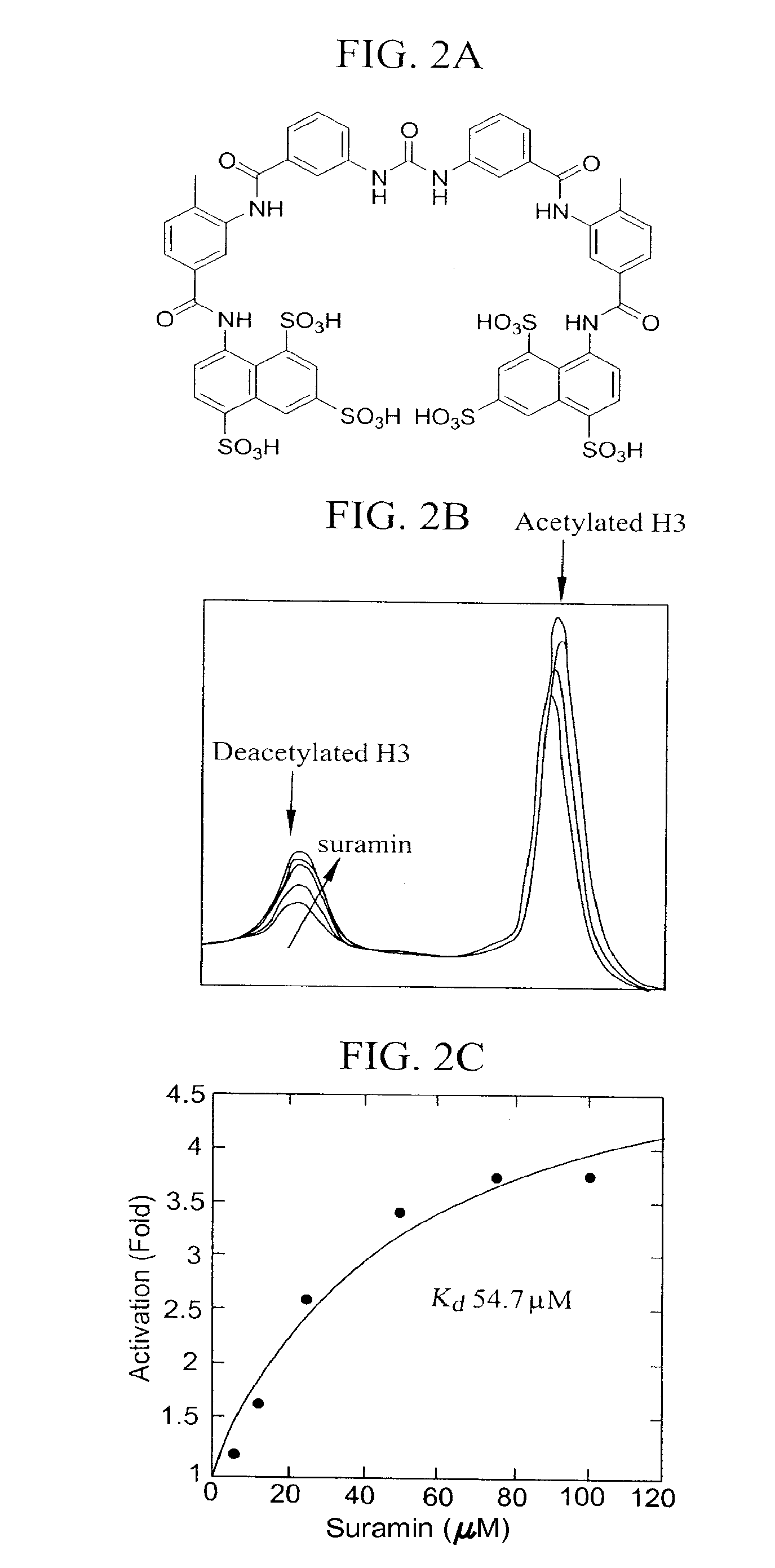
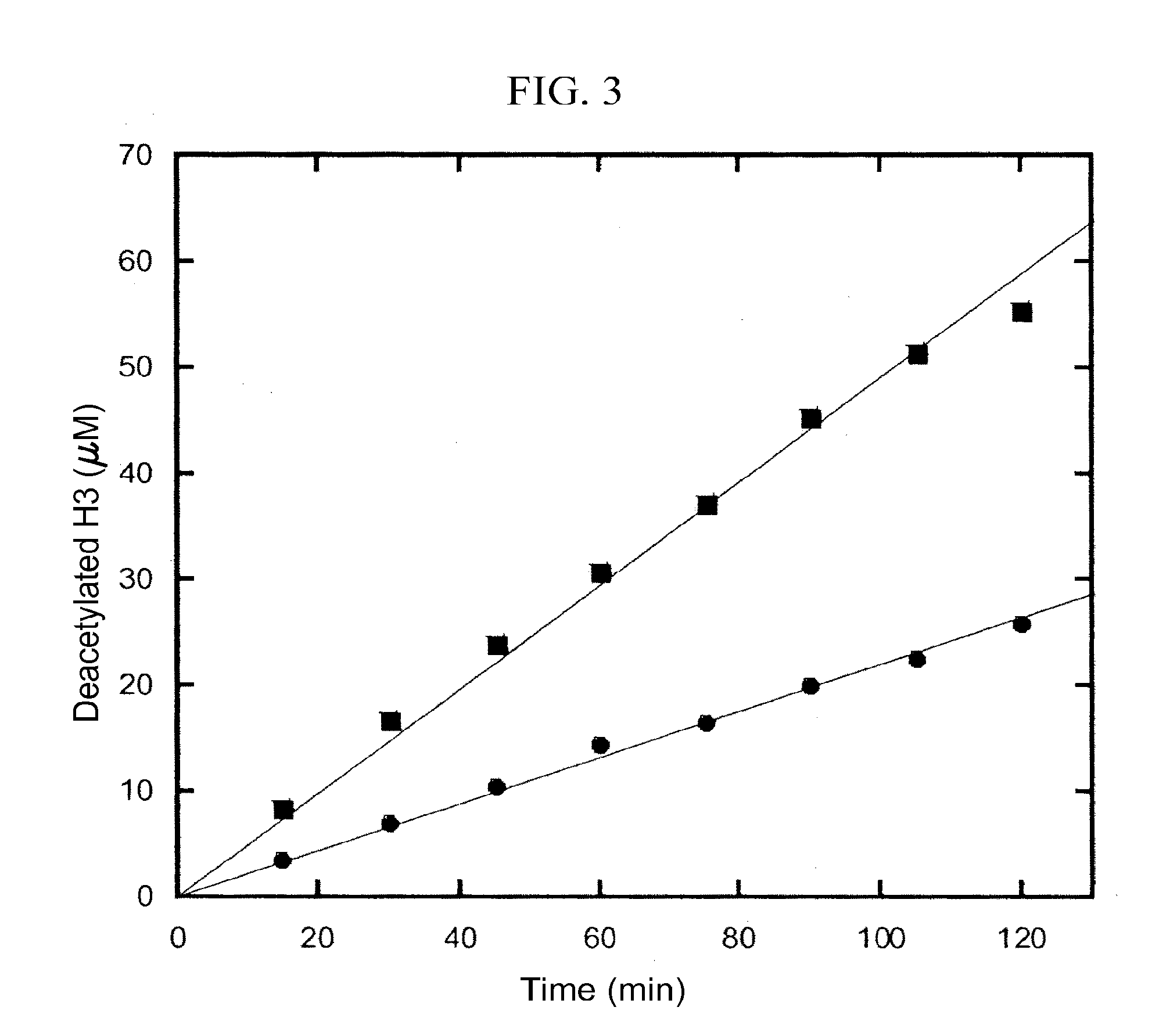
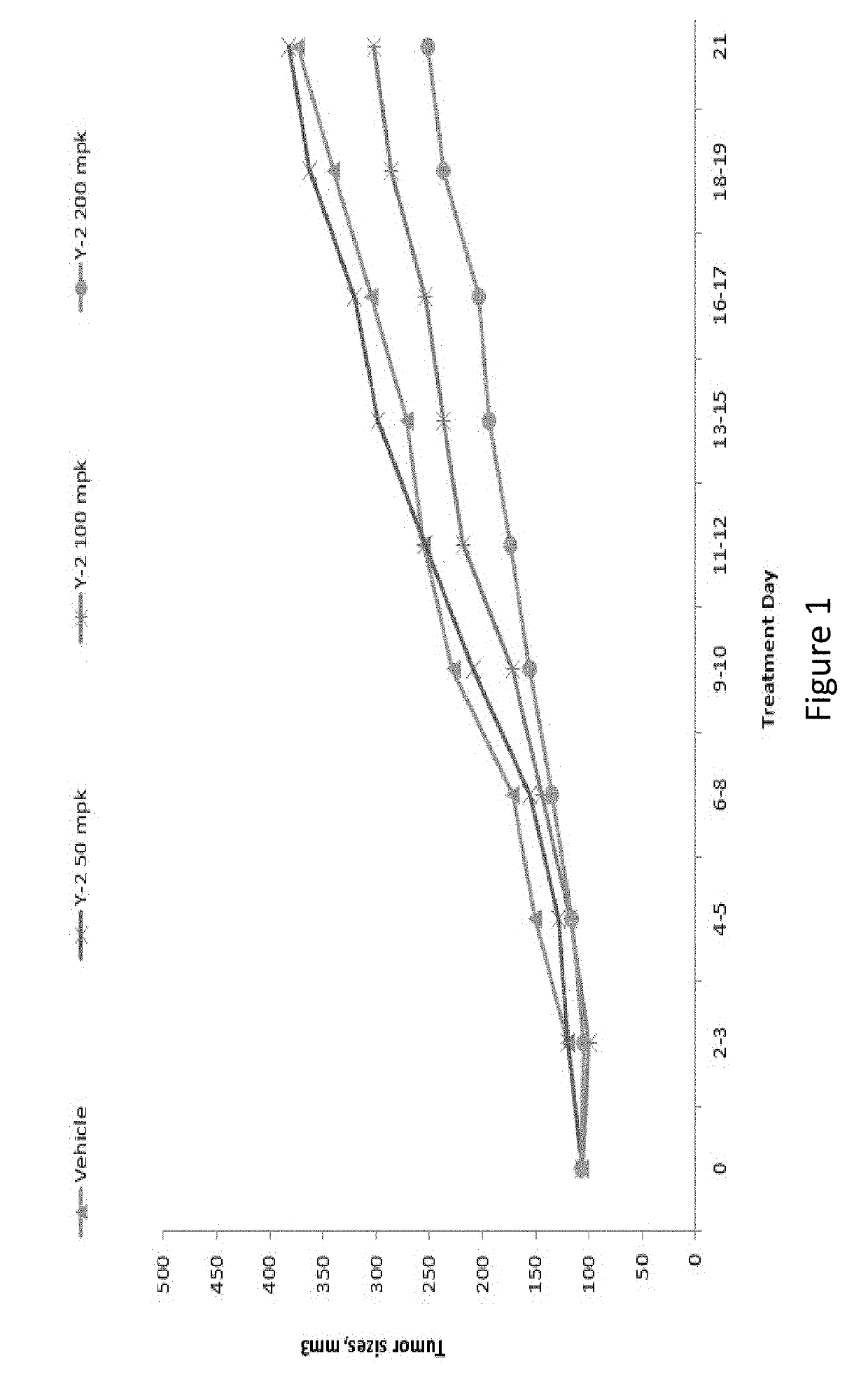
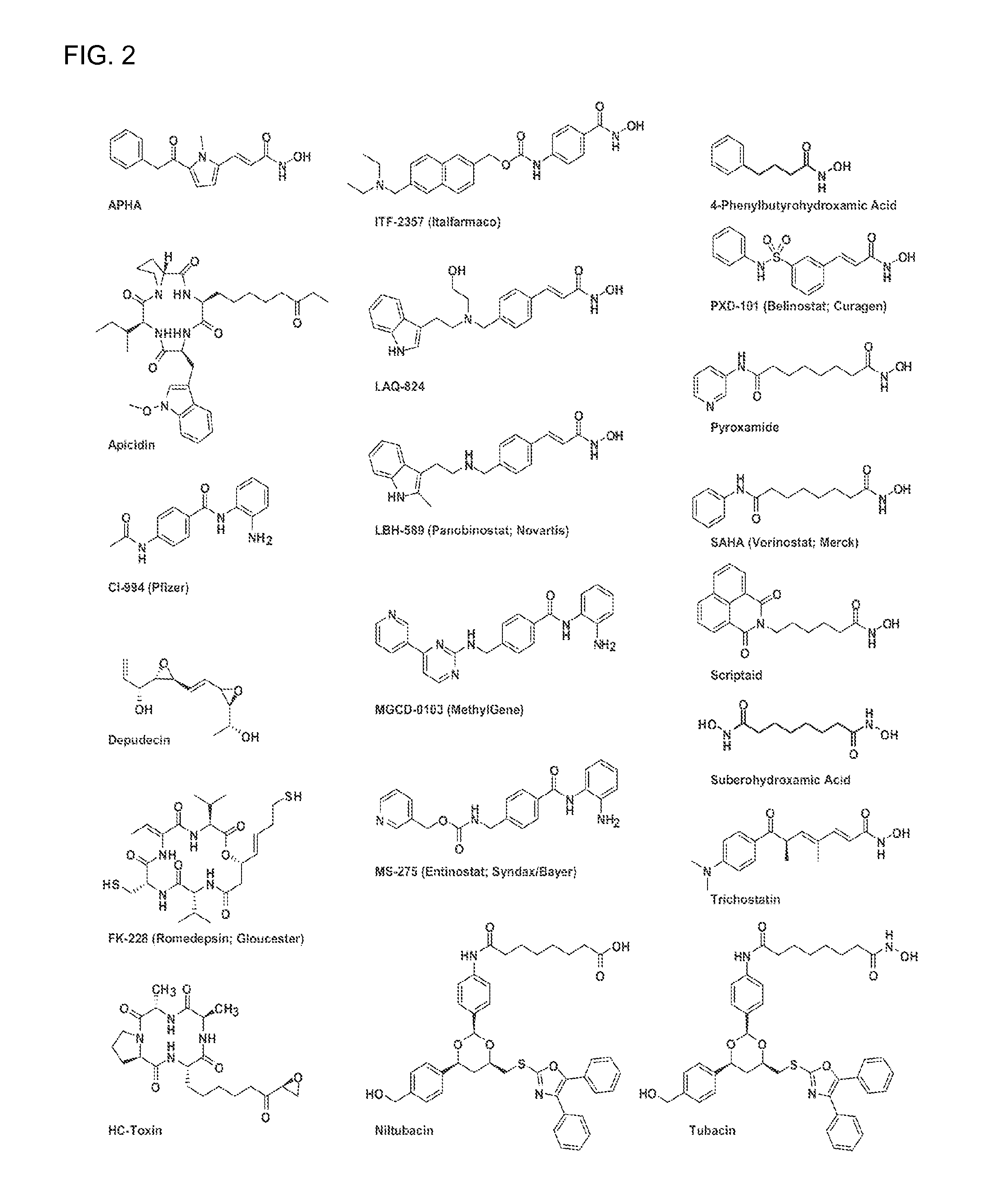
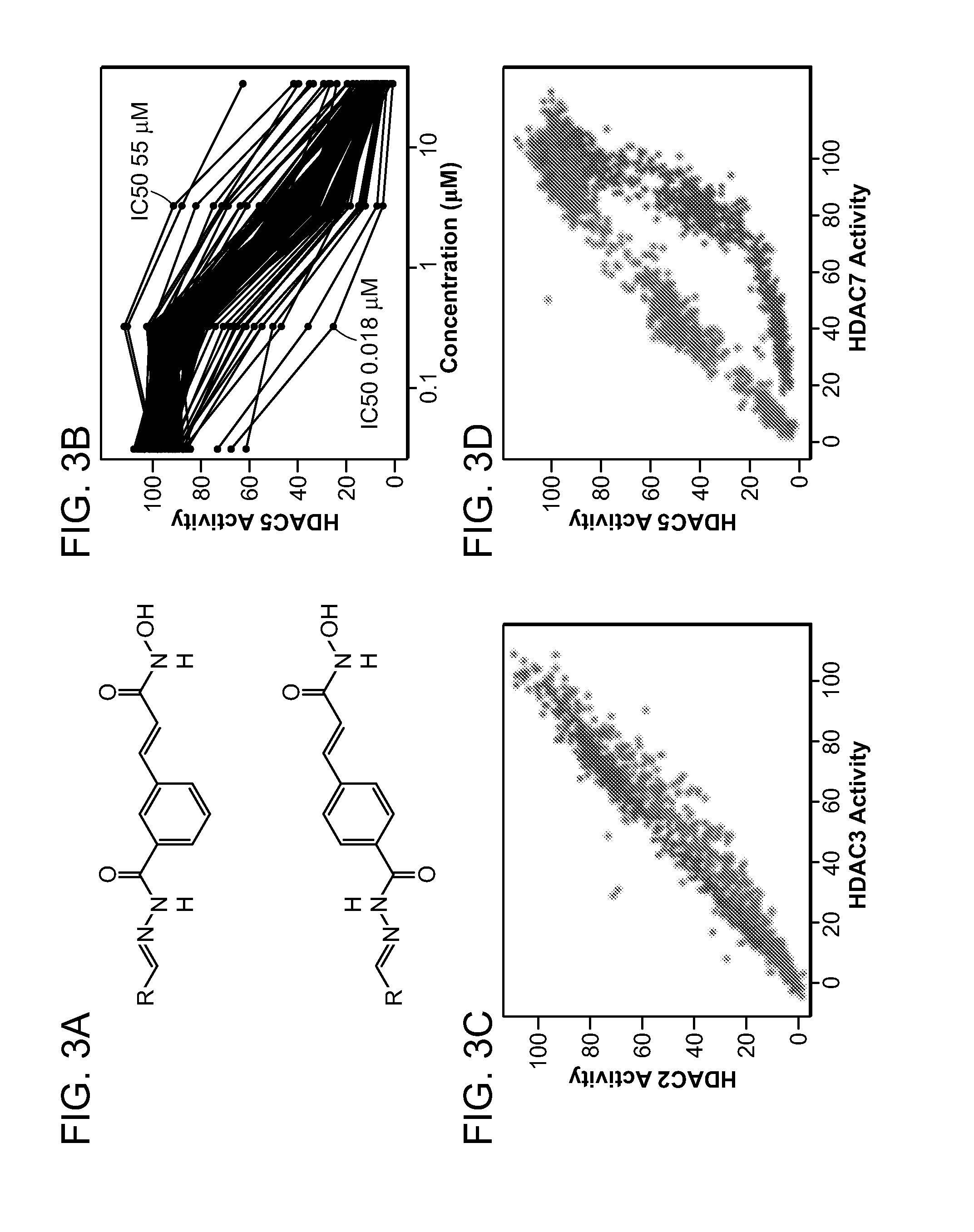
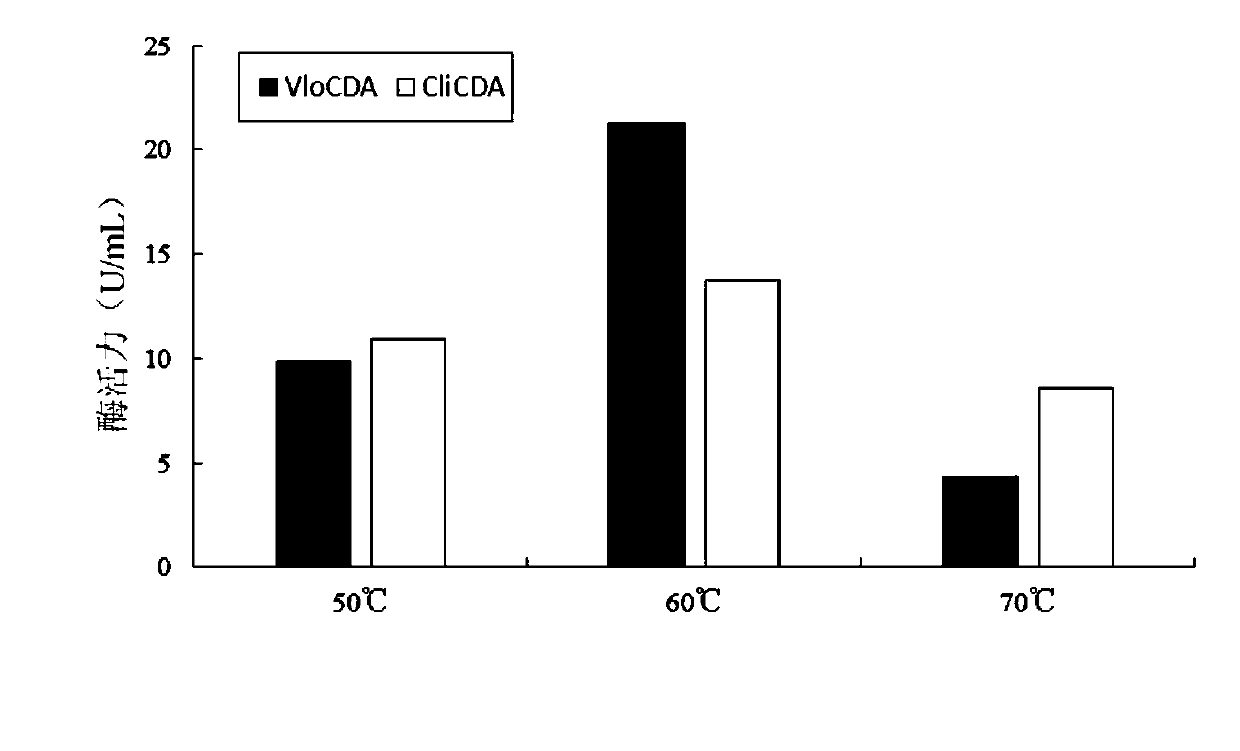
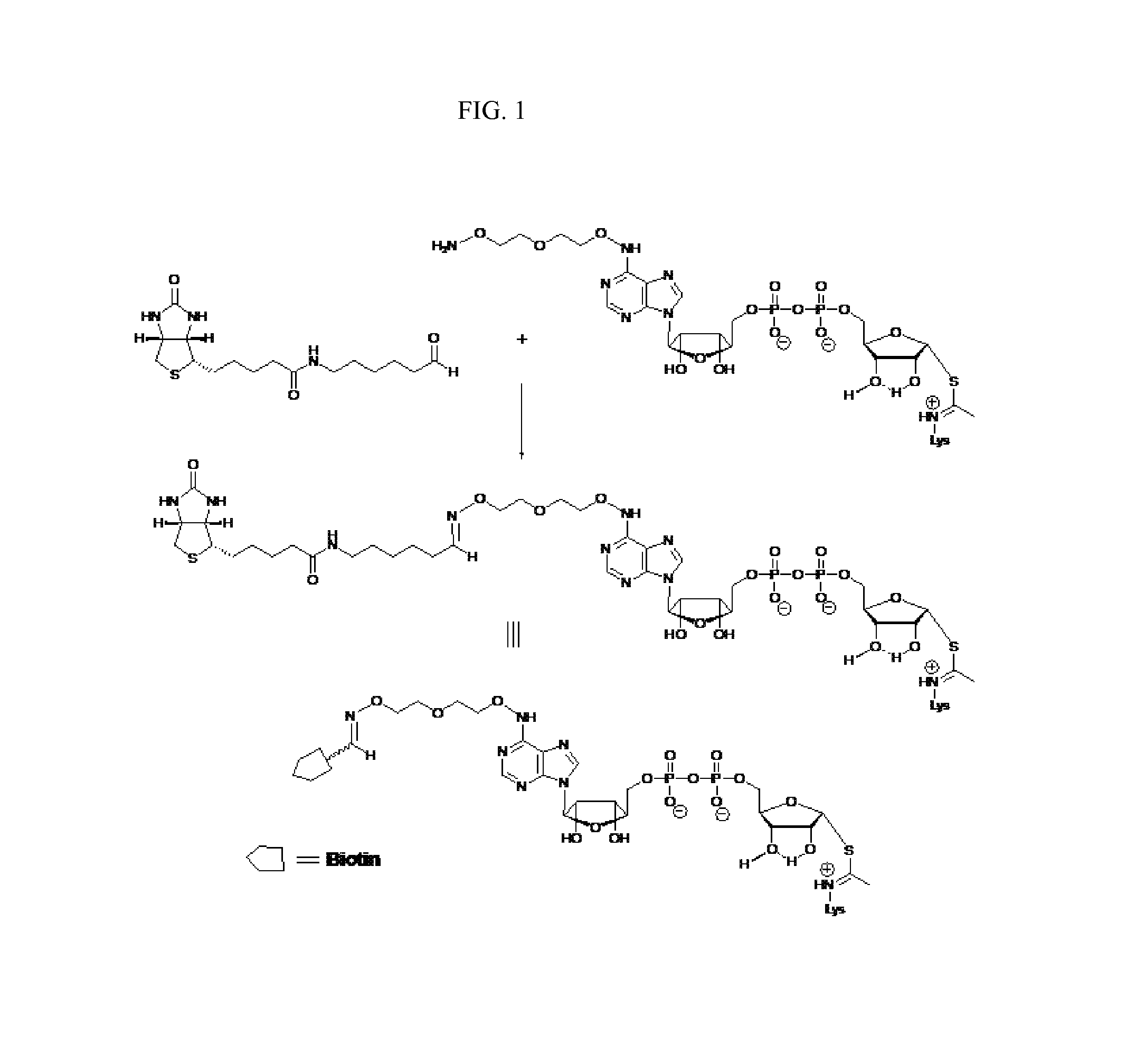
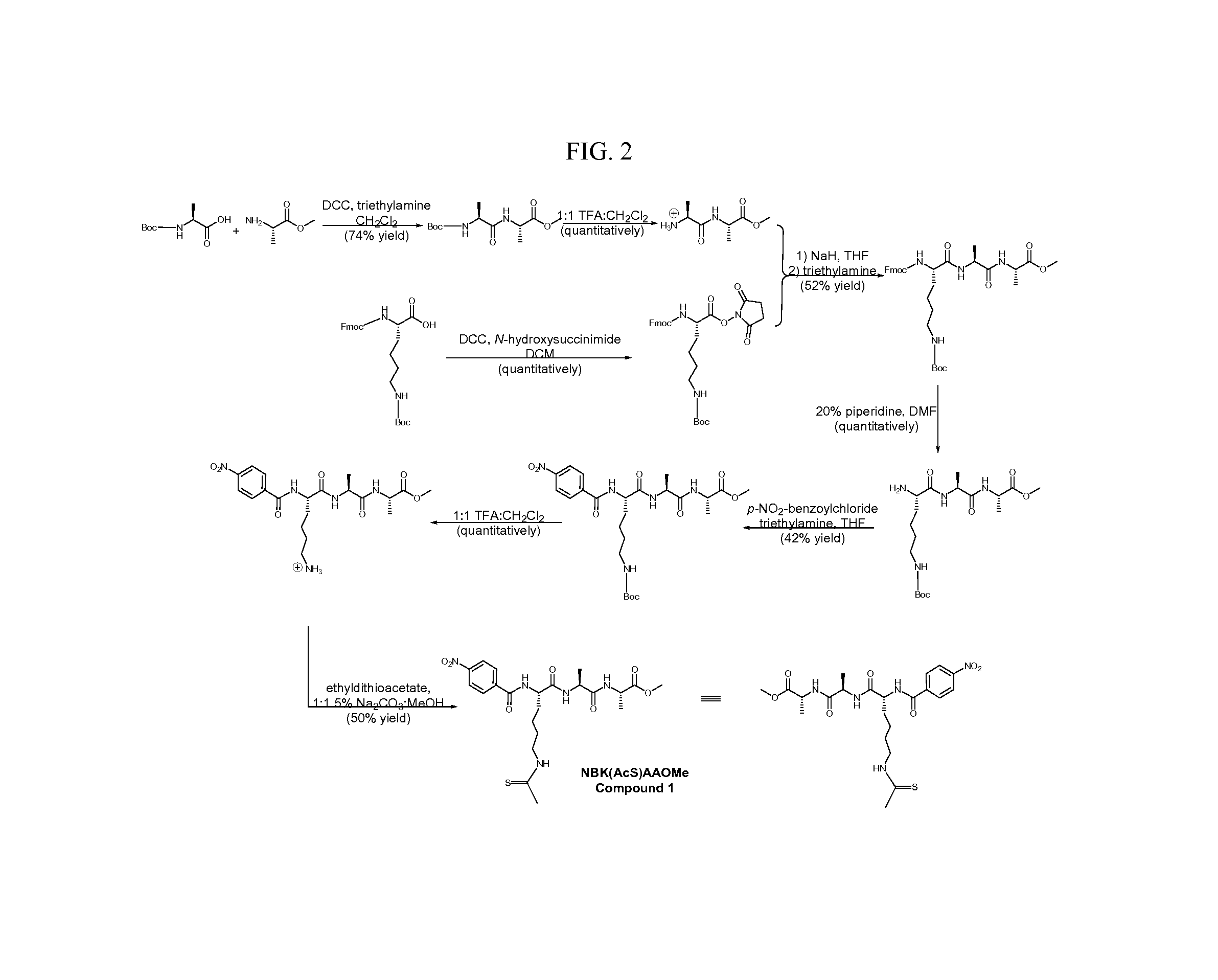
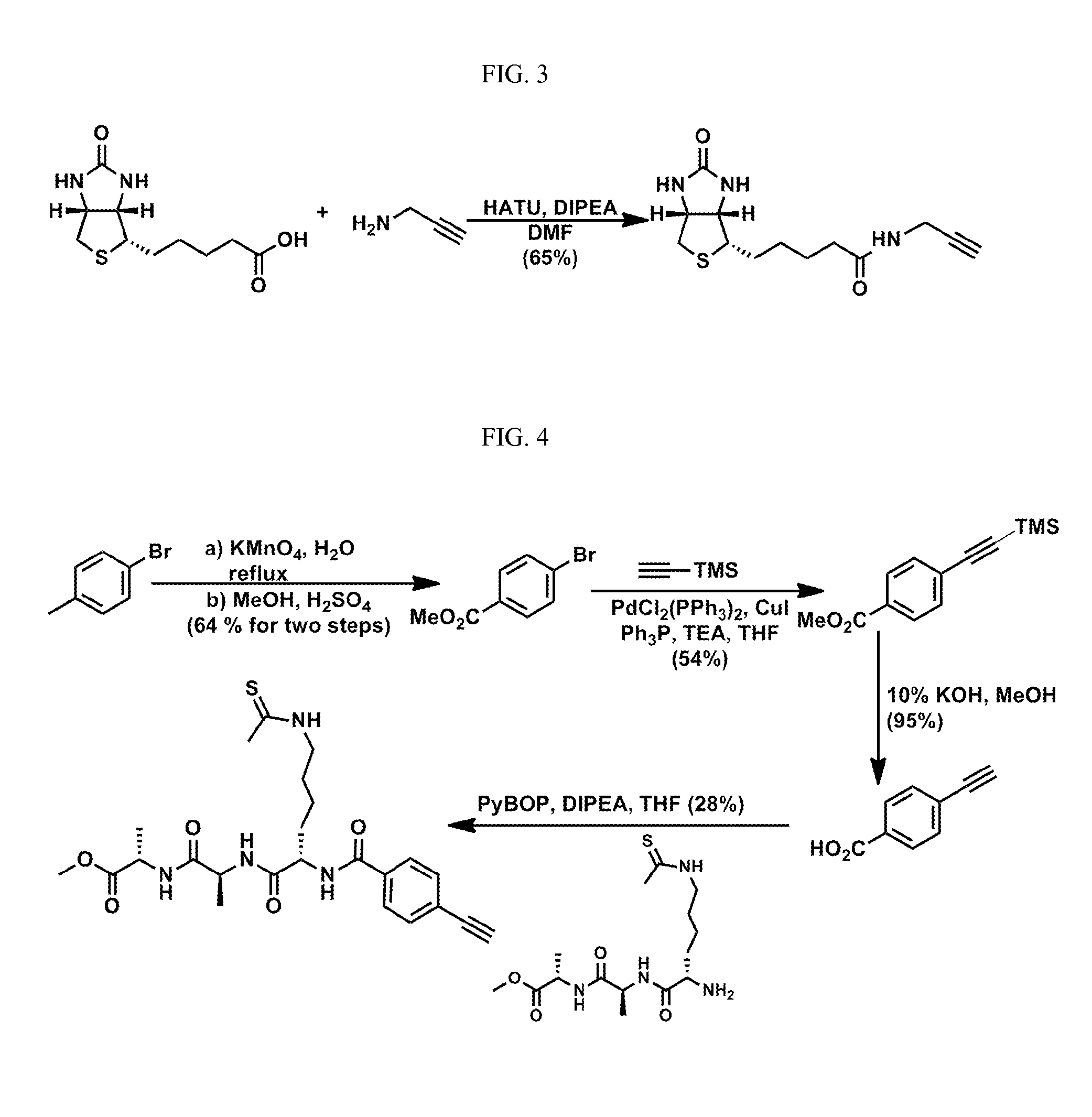
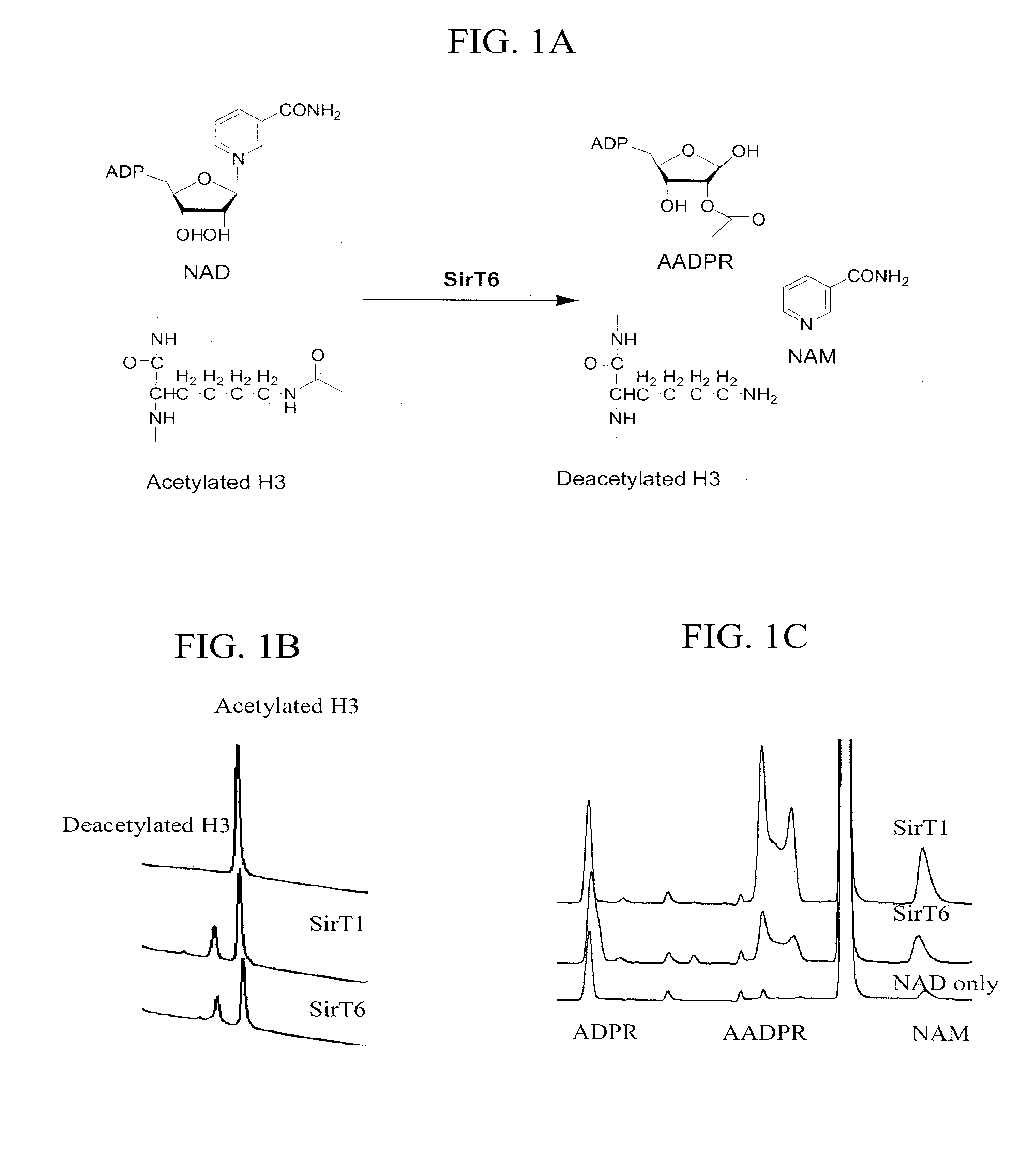
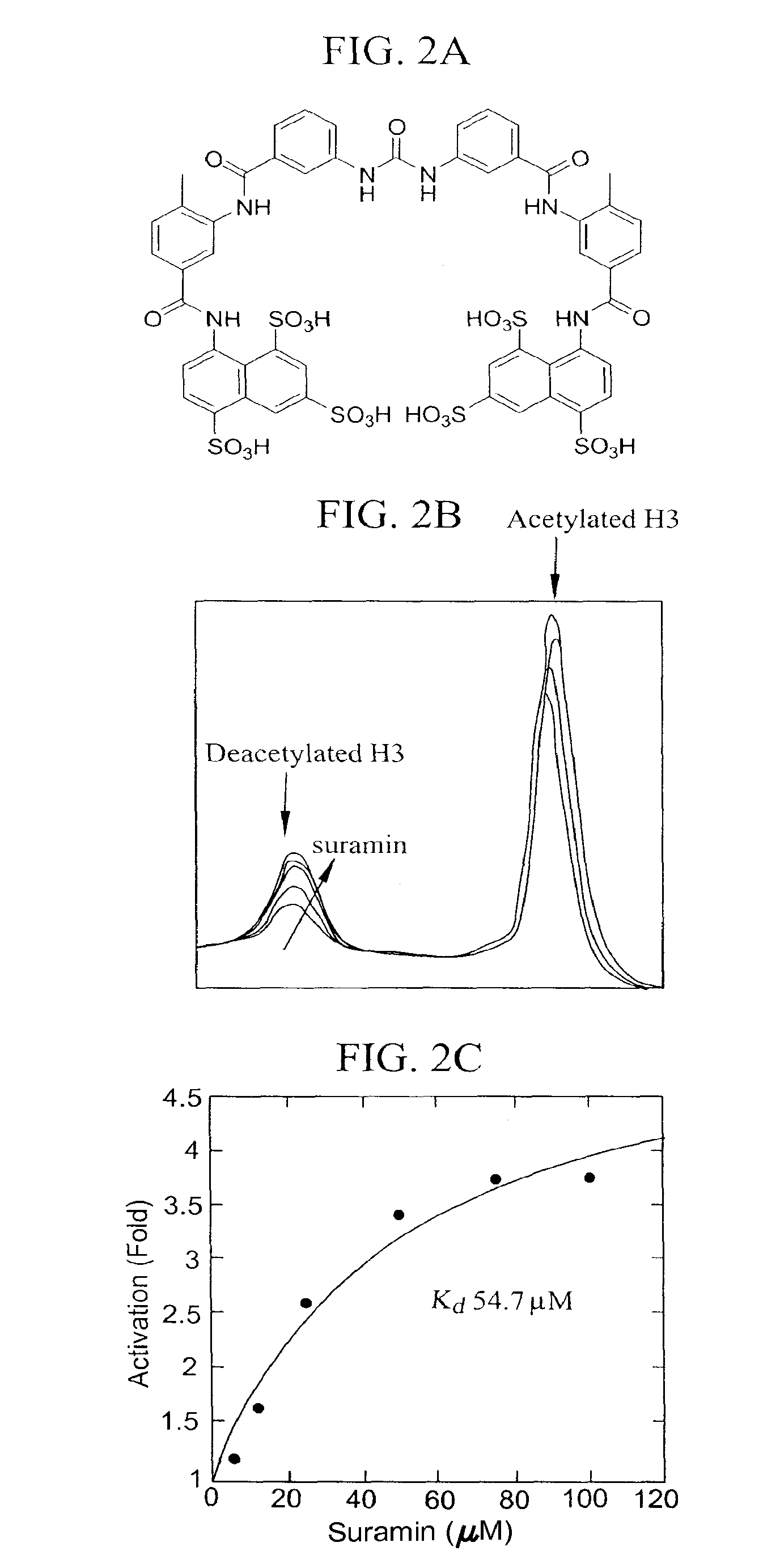
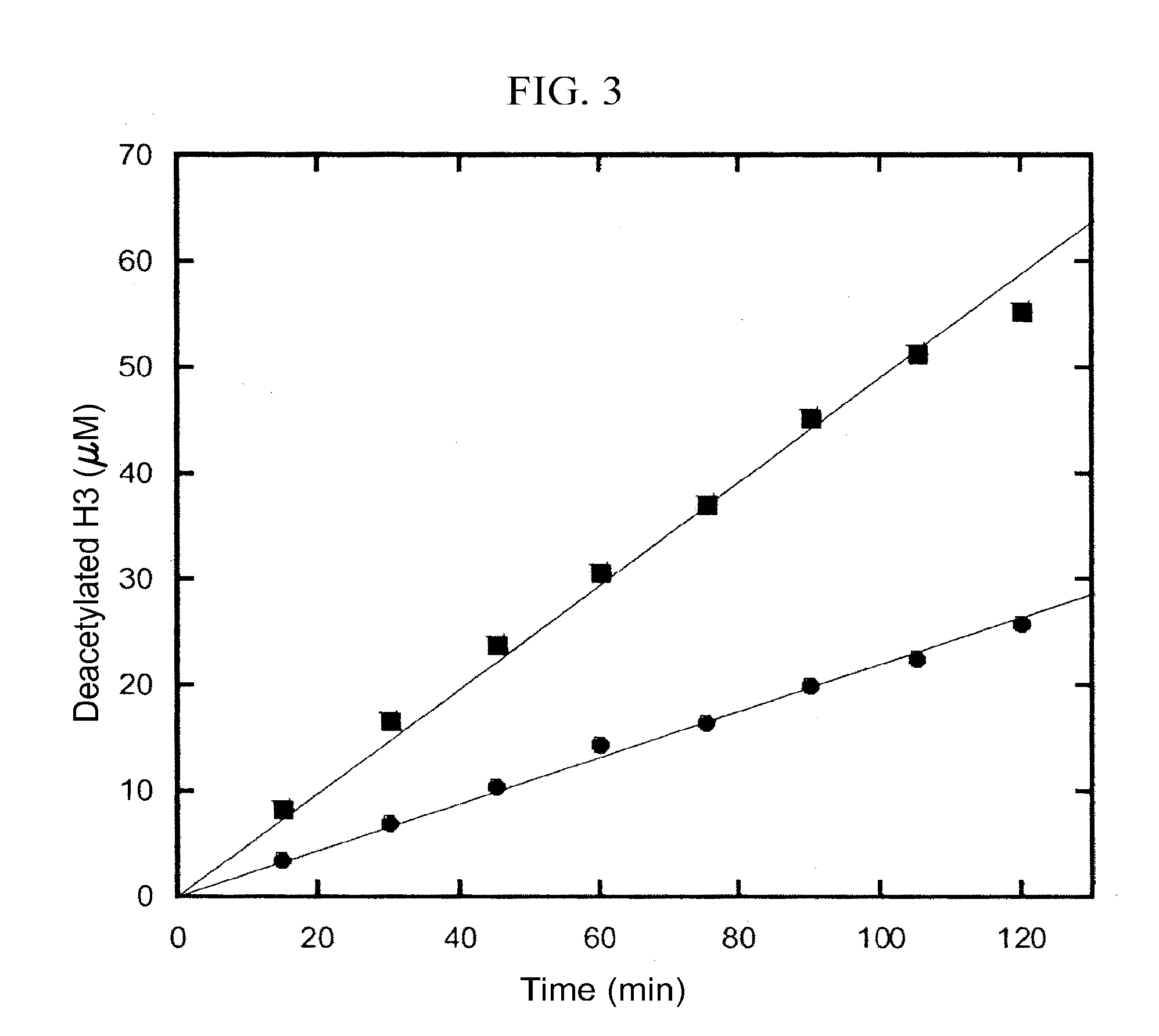
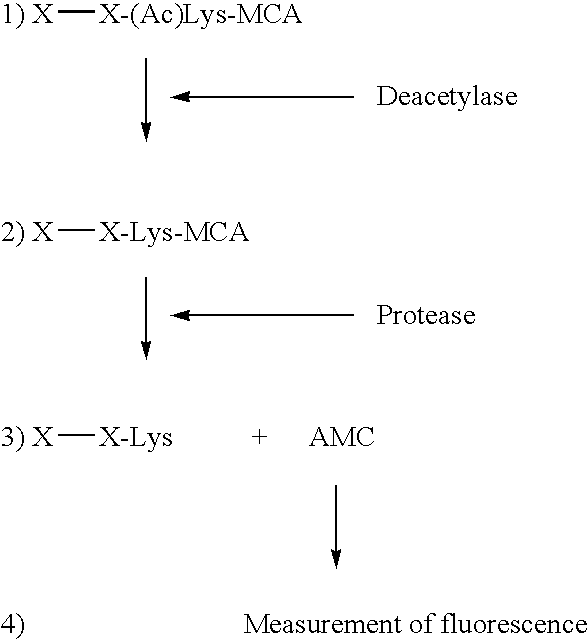
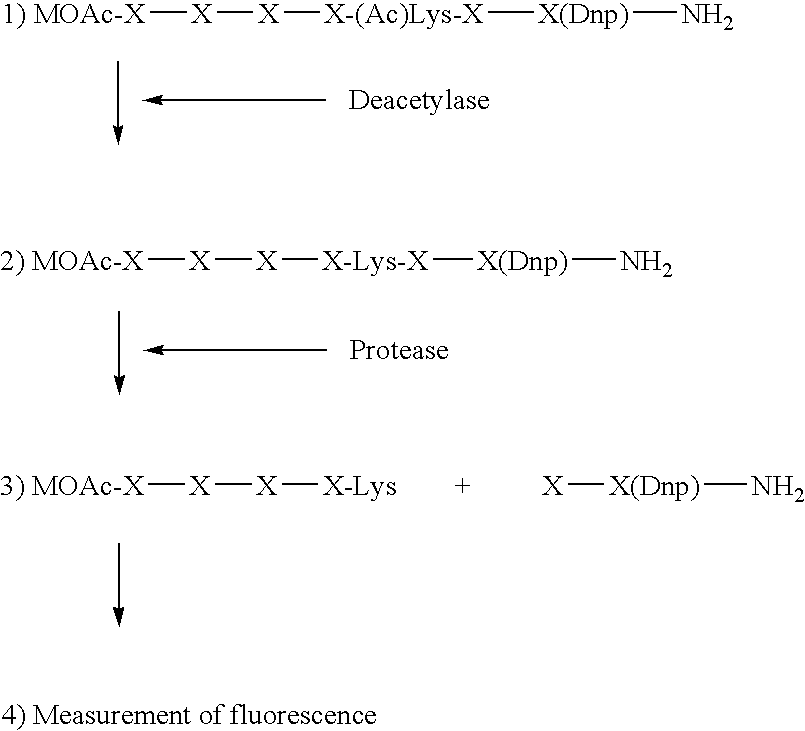
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Deacetylase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of an acetyl group or groups from a substrate molecule. [GOC:jl]
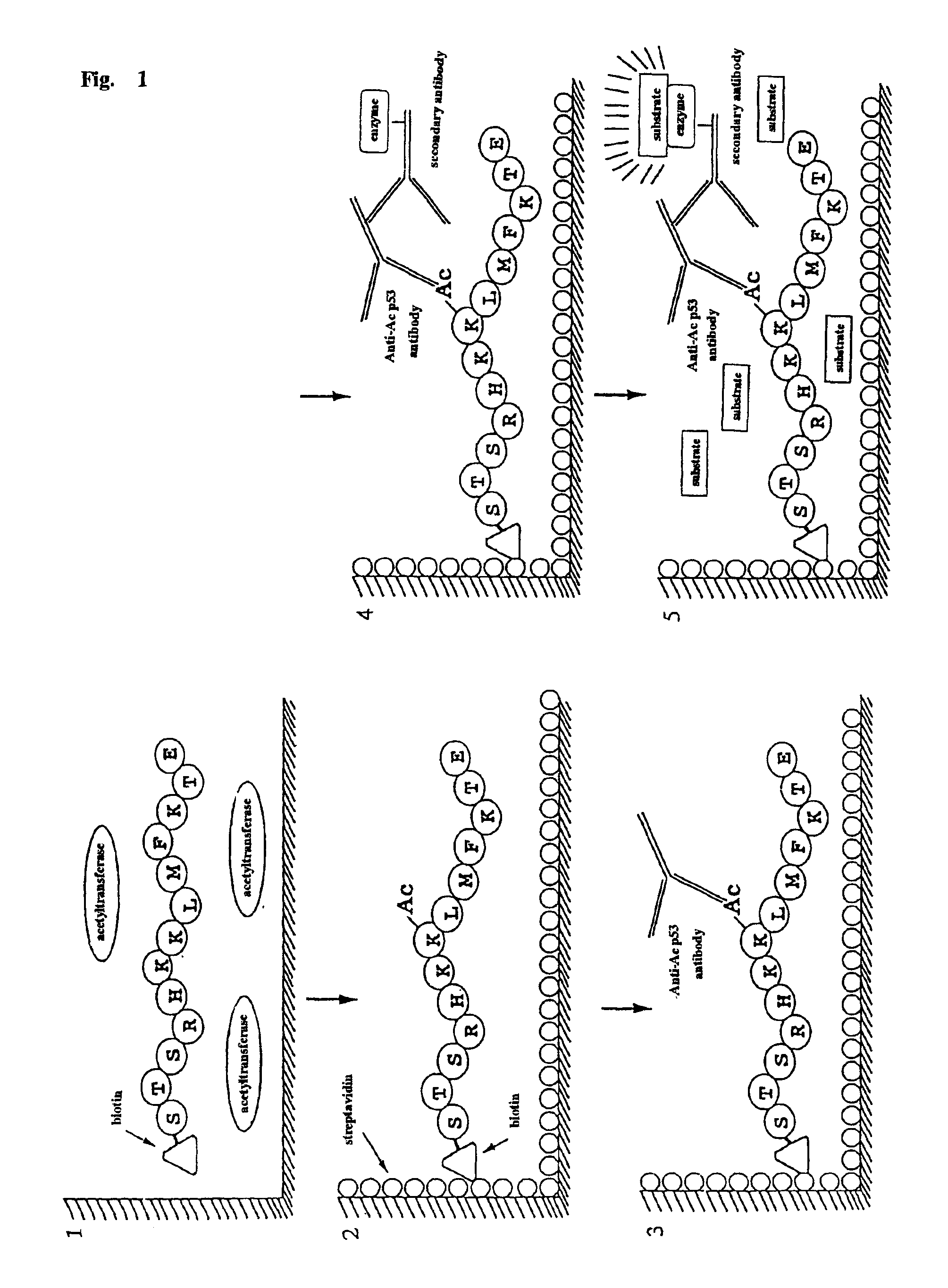
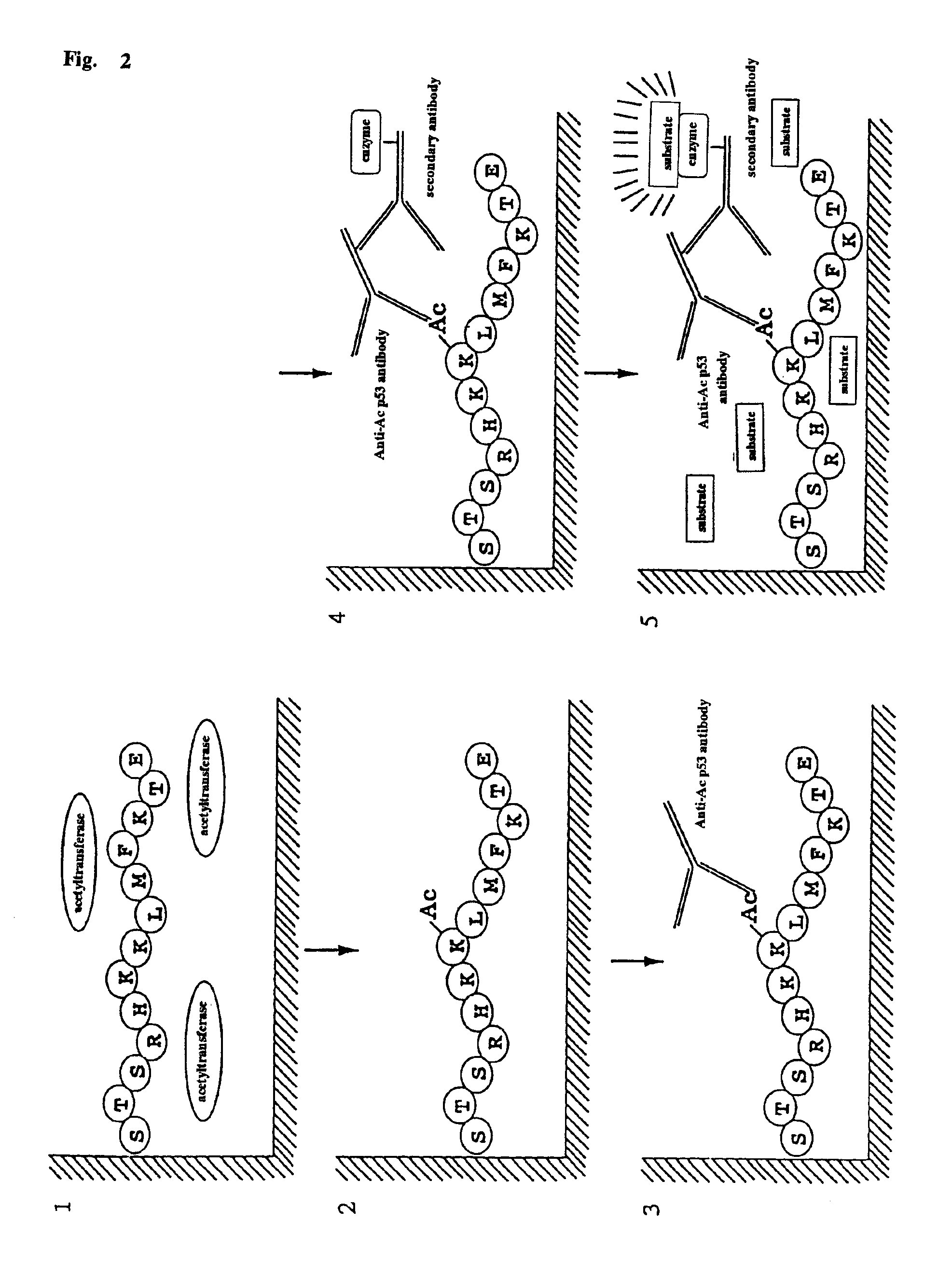
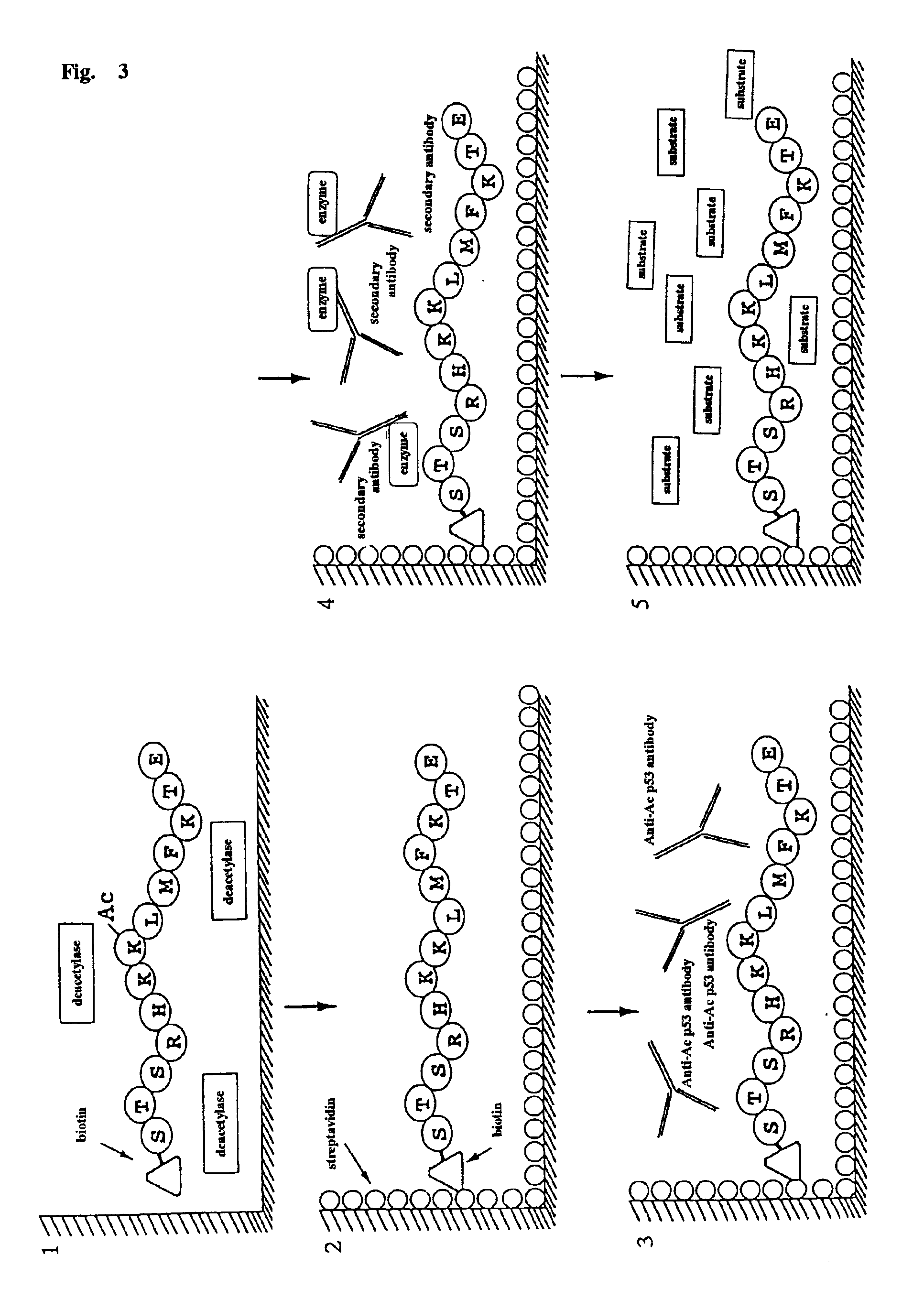
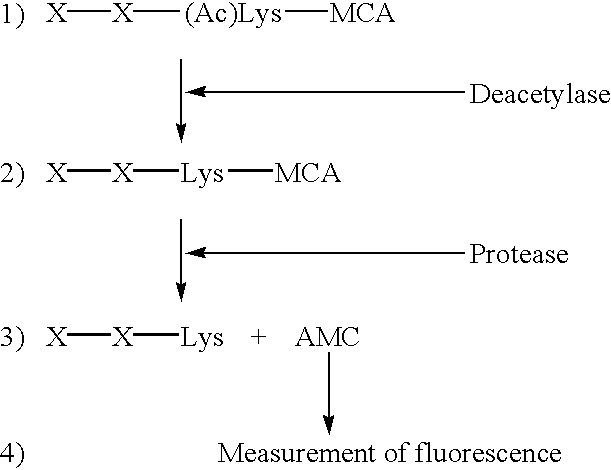
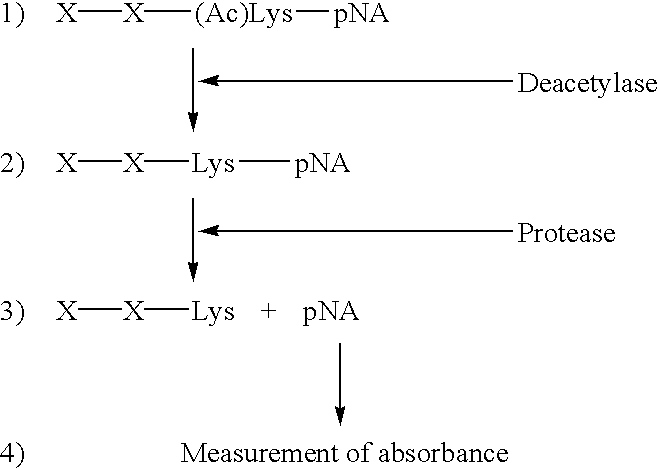
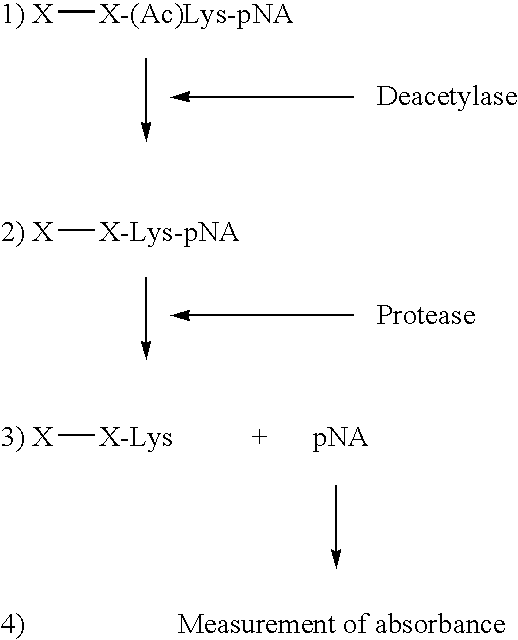
Method for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities and method for screening inhibitors or enhancers of these enzymes
InactiveUS6884597B1Easy to detectConducive to screeningCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPeptide substrateAcetyltransferase
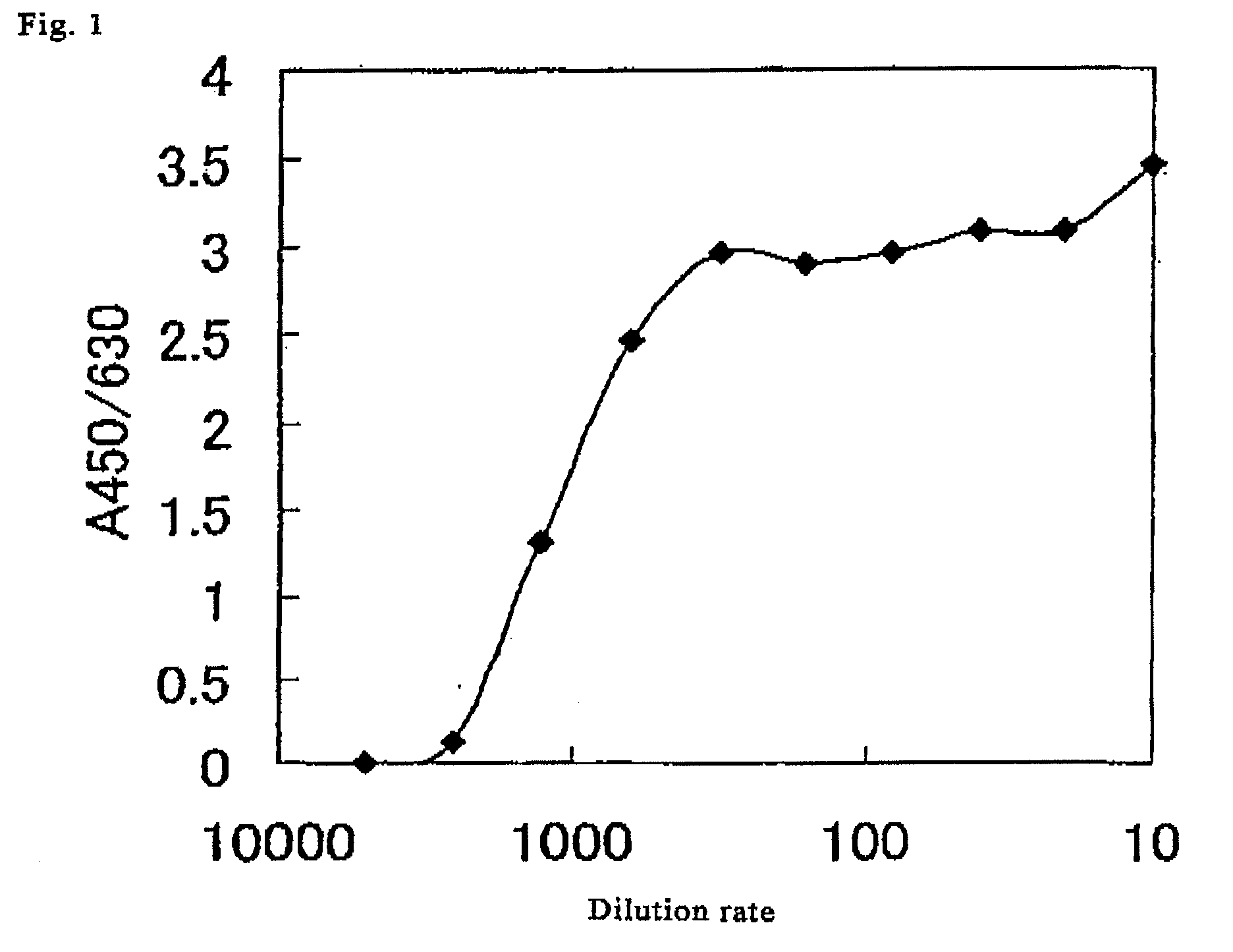
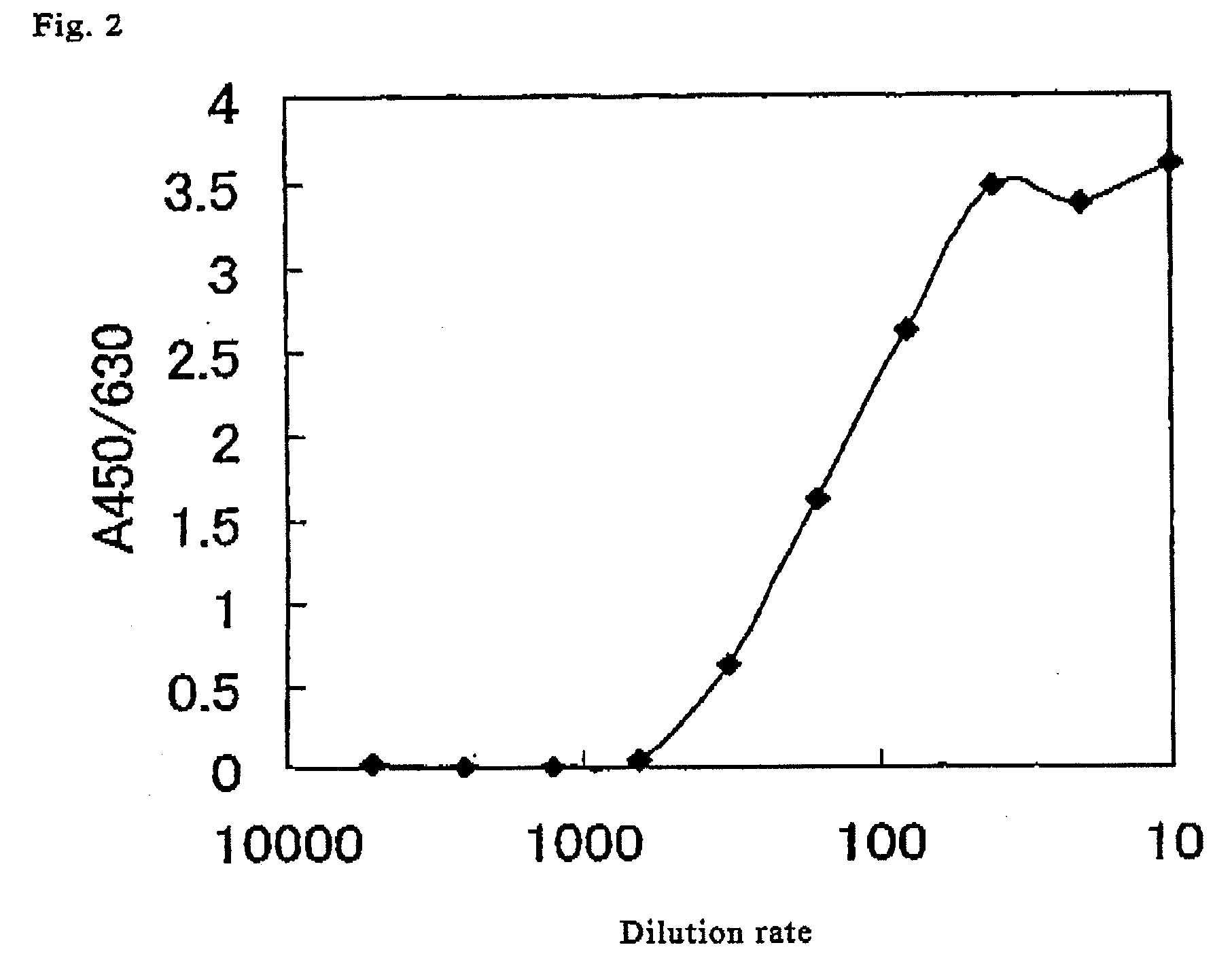
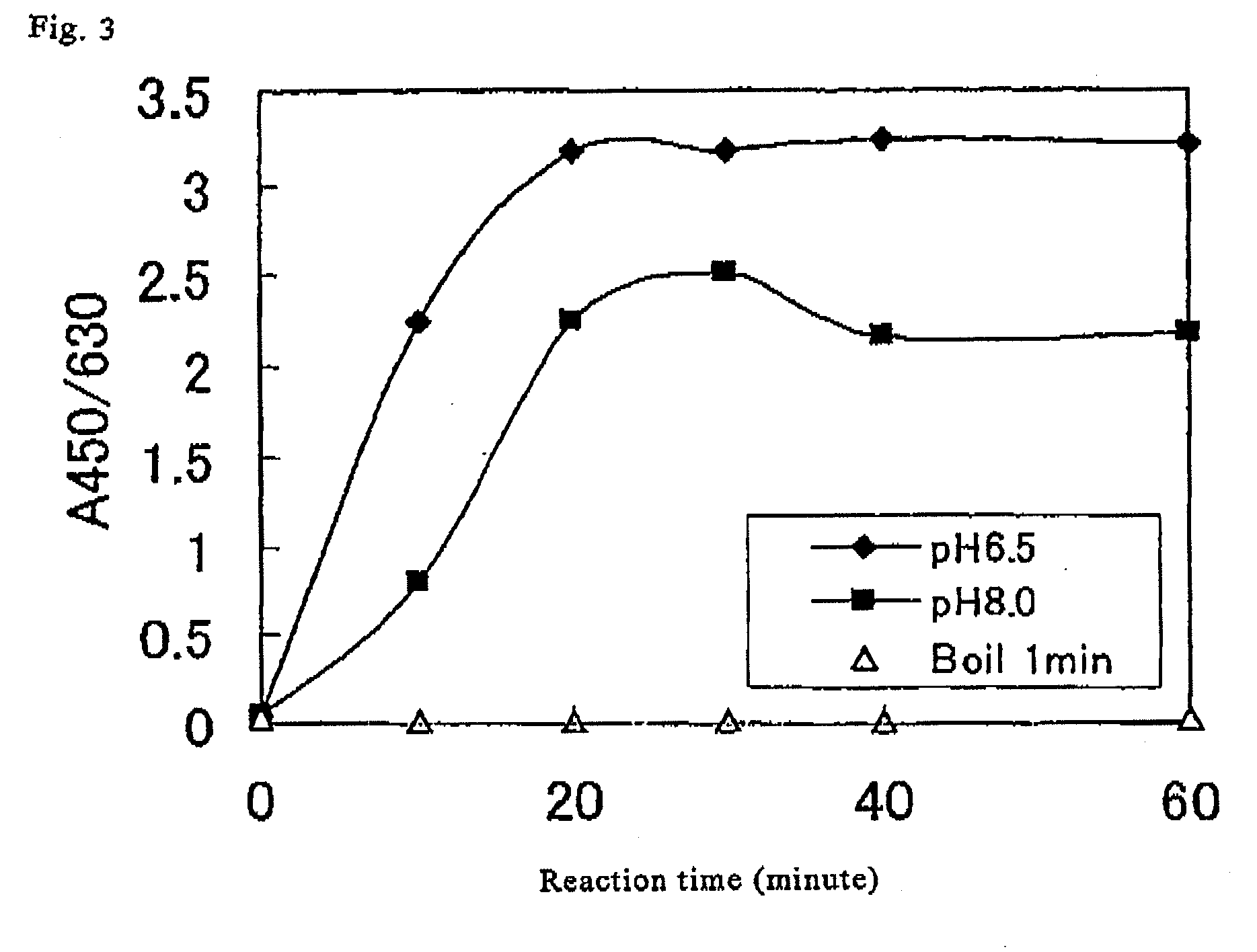
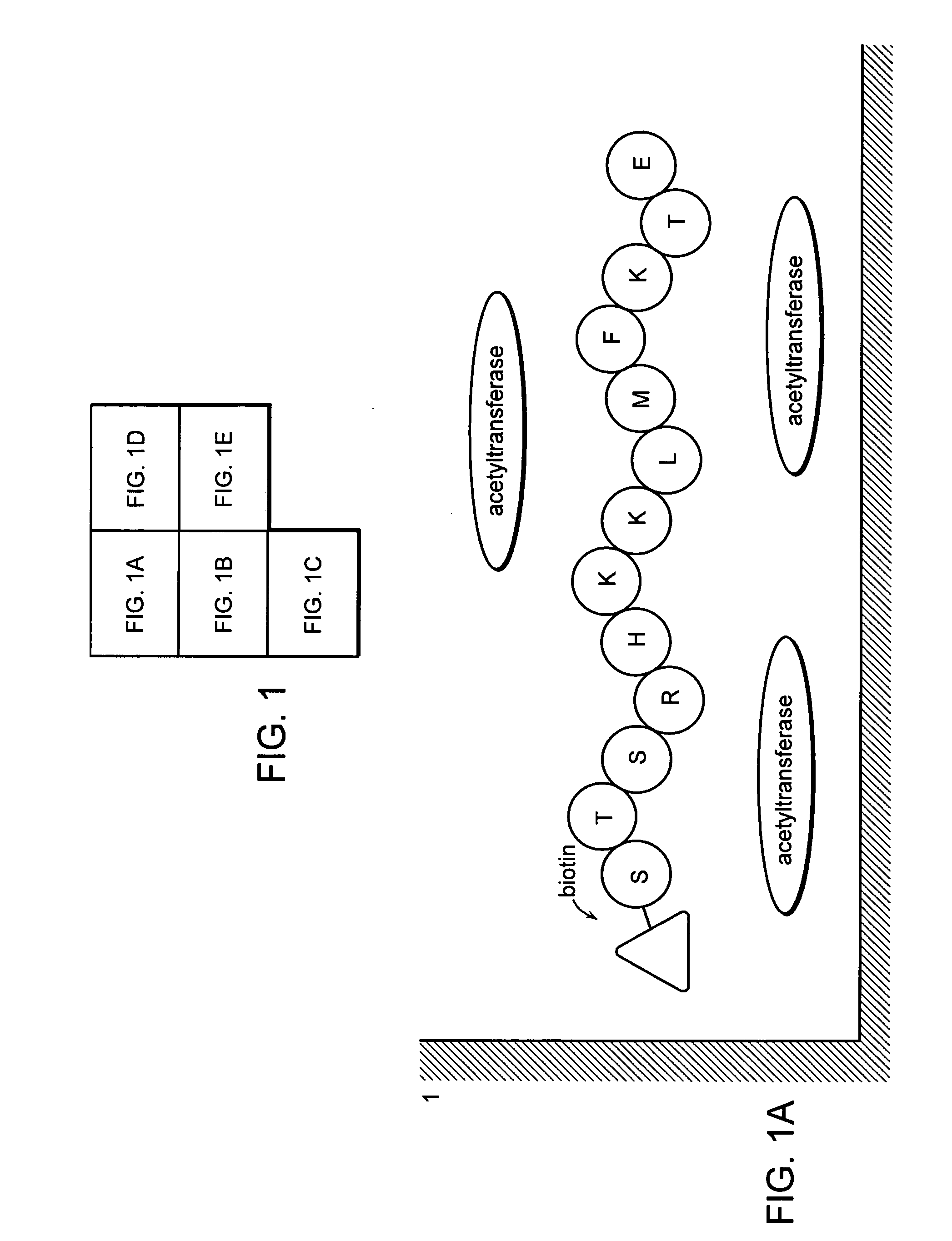
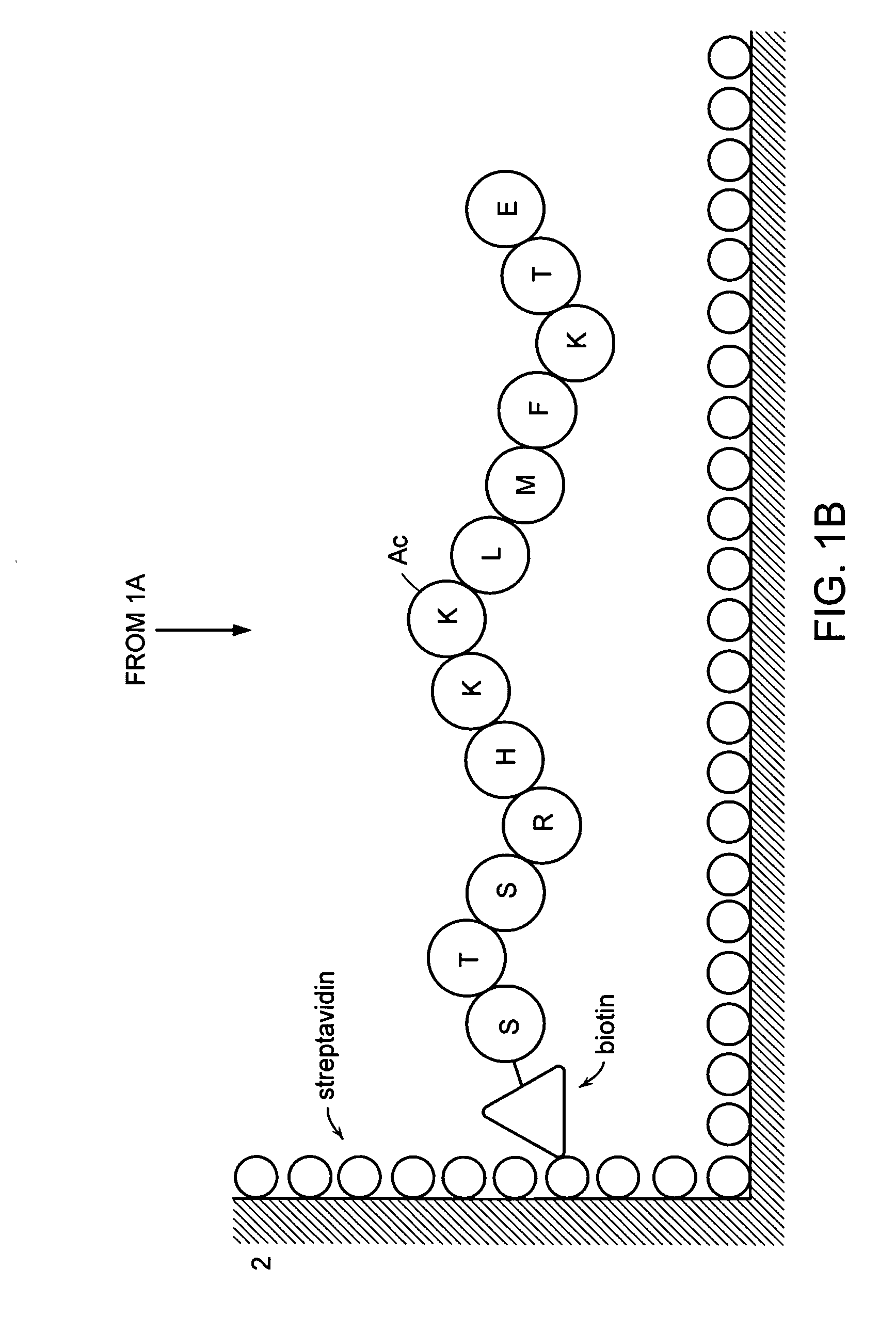
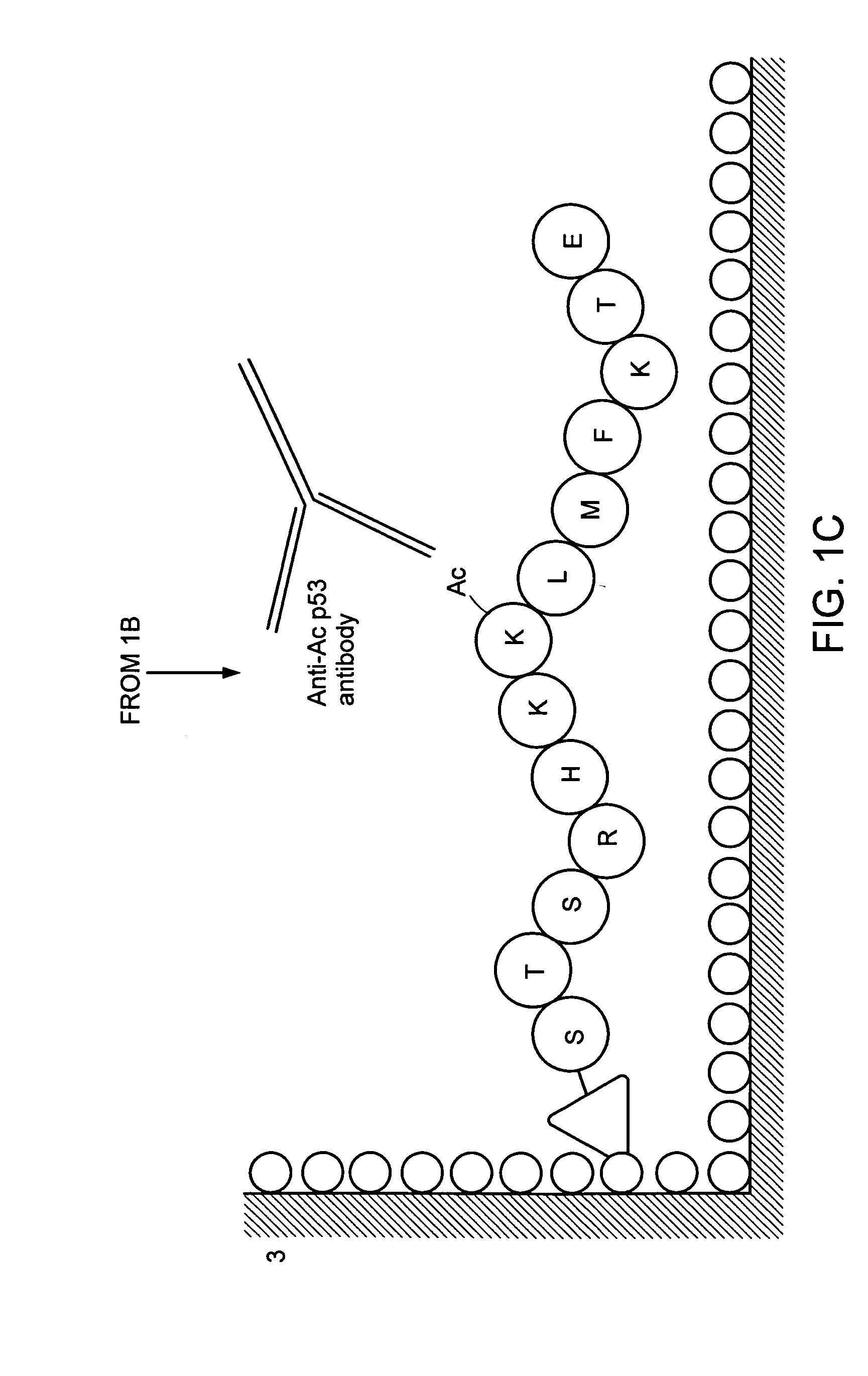
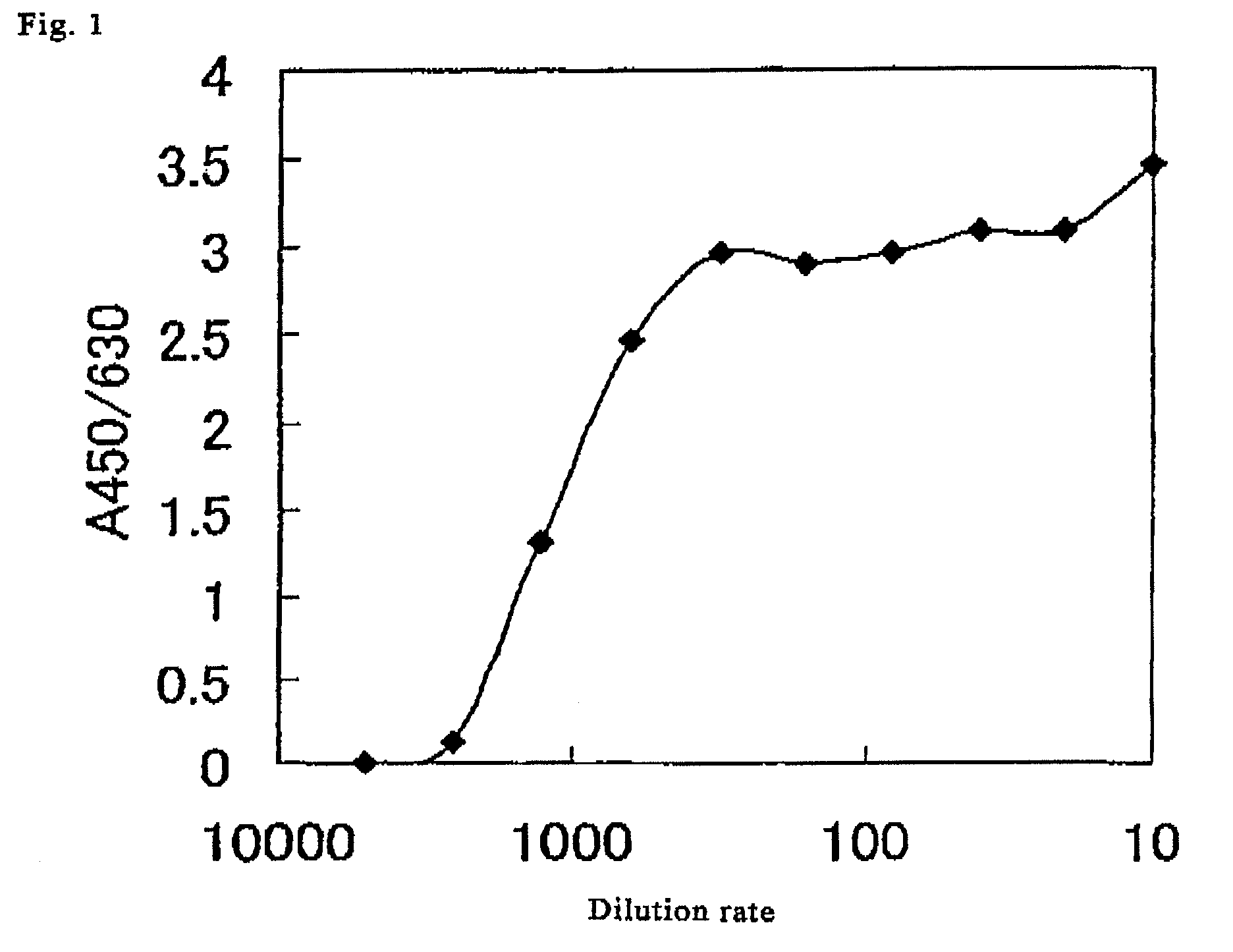
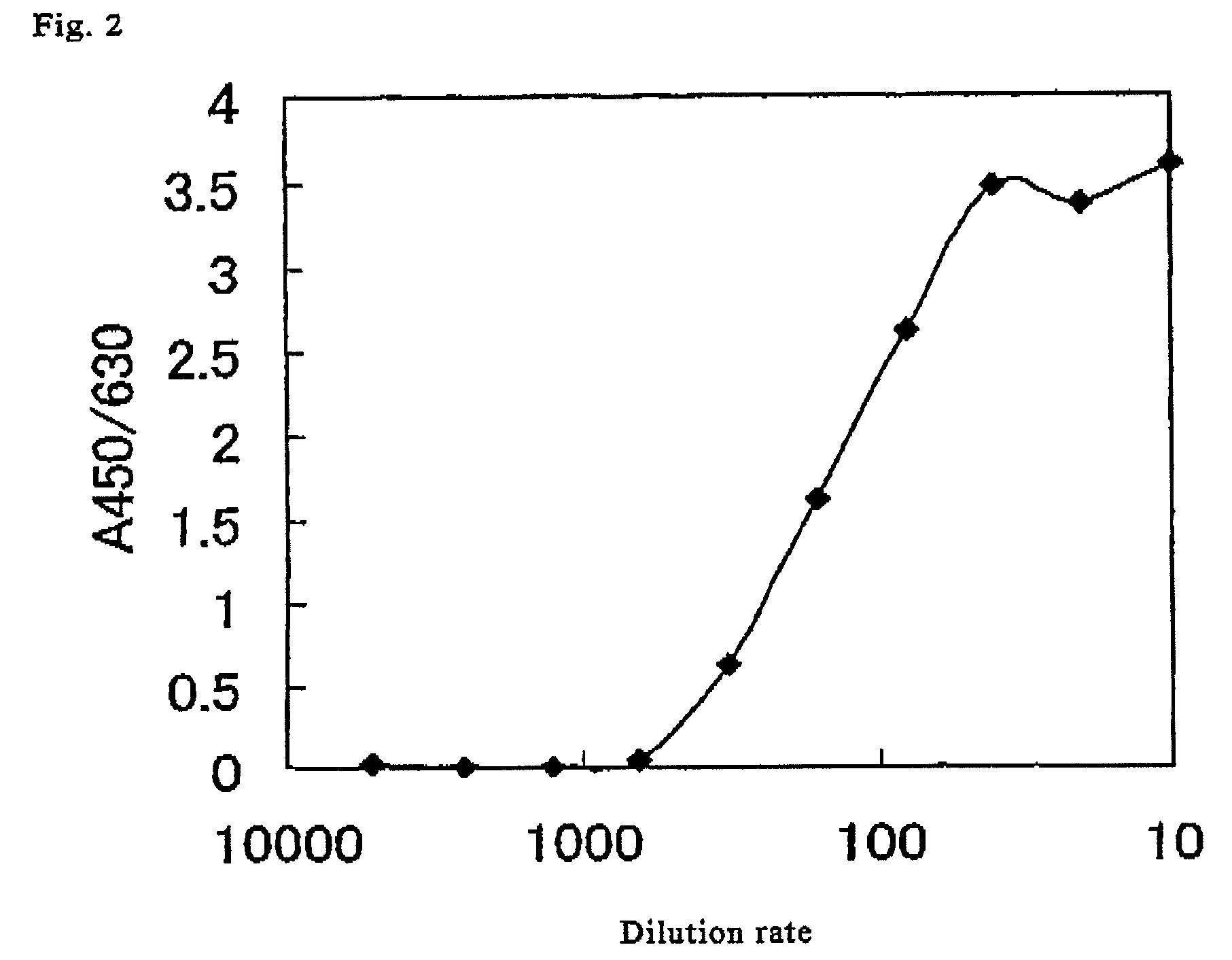
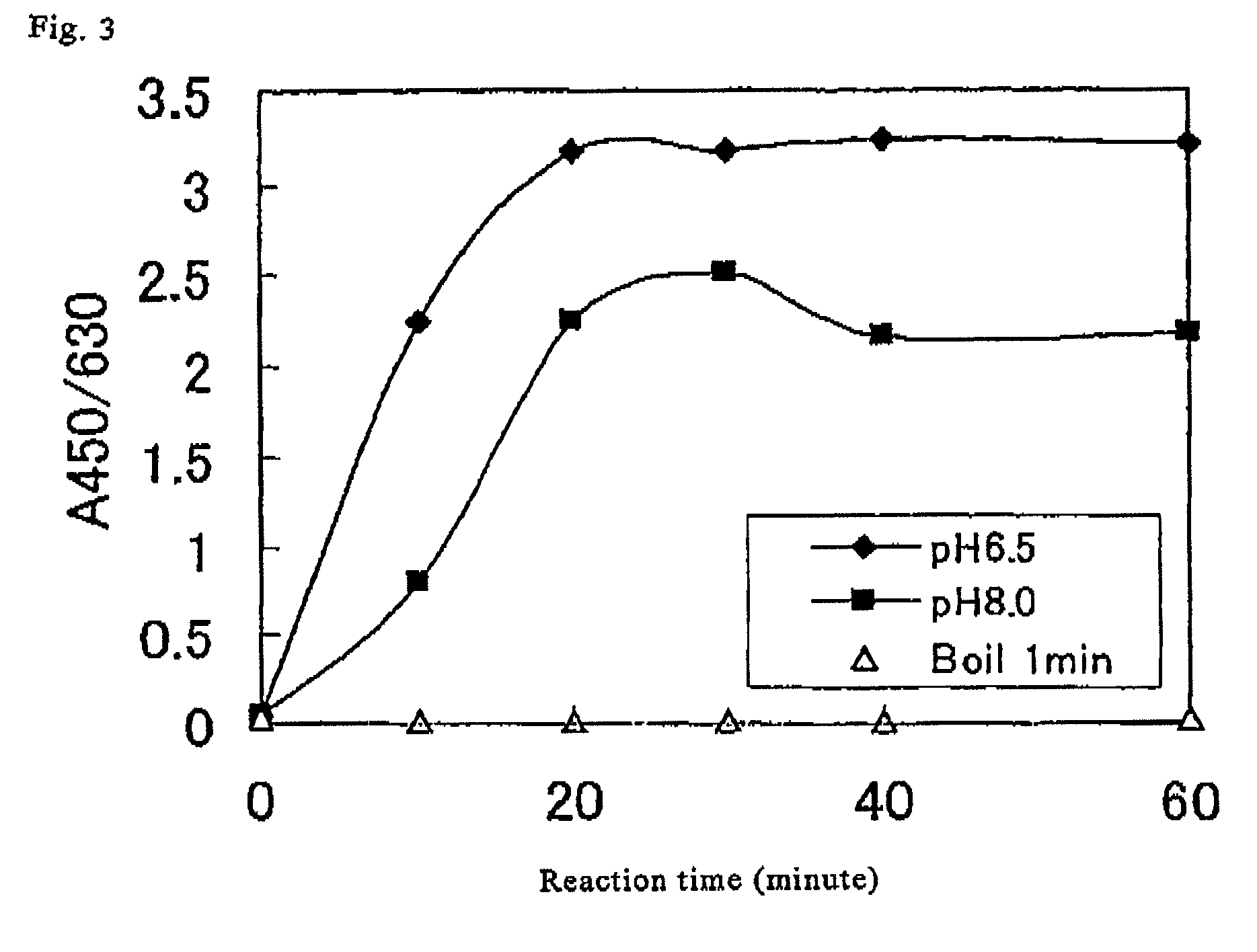
A method for simply and conveniently detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities of proteins by executing an acetylation reaction of a peptide substrate with an acetyltransferase, or a deacetylation reaction of an acetylated peptide substrate with a deacetylase, and after the completion of these reactions, detecting the acetyl group bound to the peptide substrate by using an anti-acetylated peptide antibody. This system for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities using the anti-acetylated peptide antibody enables screening inhibitors or enhancers of acetyltransferase and deacetylase. A system for screening deacetylase inhibitors or acetyltransferase enhancers using cultured cells is also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
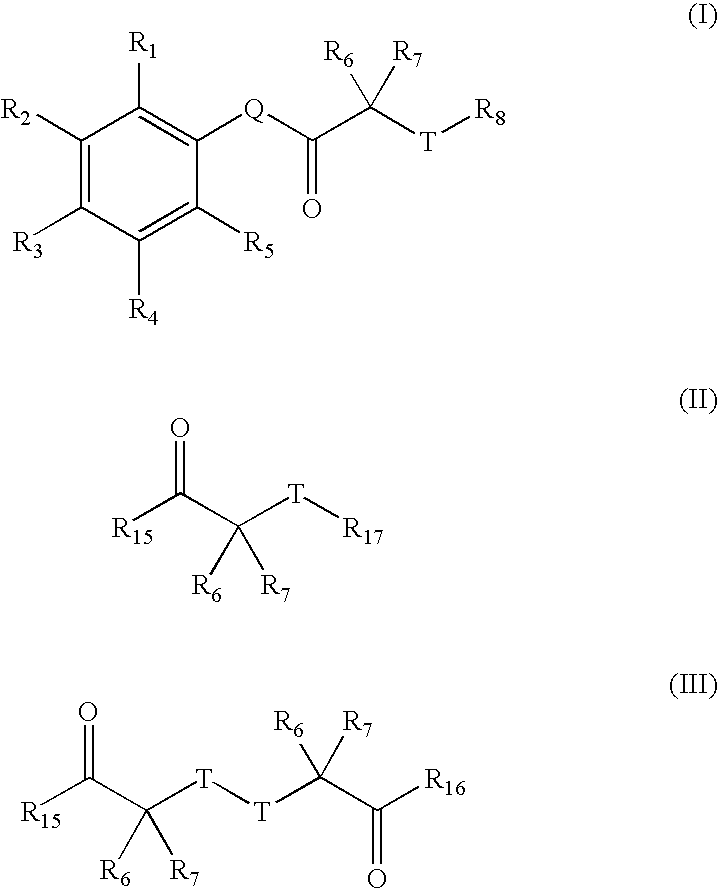
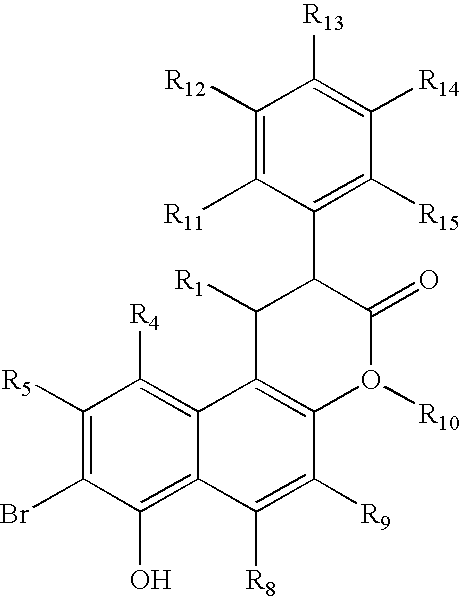
Carbonyl compounds as inhibitors of histone deacetylase for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20050026907A1Inhibition of catalytic activityBiocideOrganic chemistryAutoimmune conditionHistone deacetylase
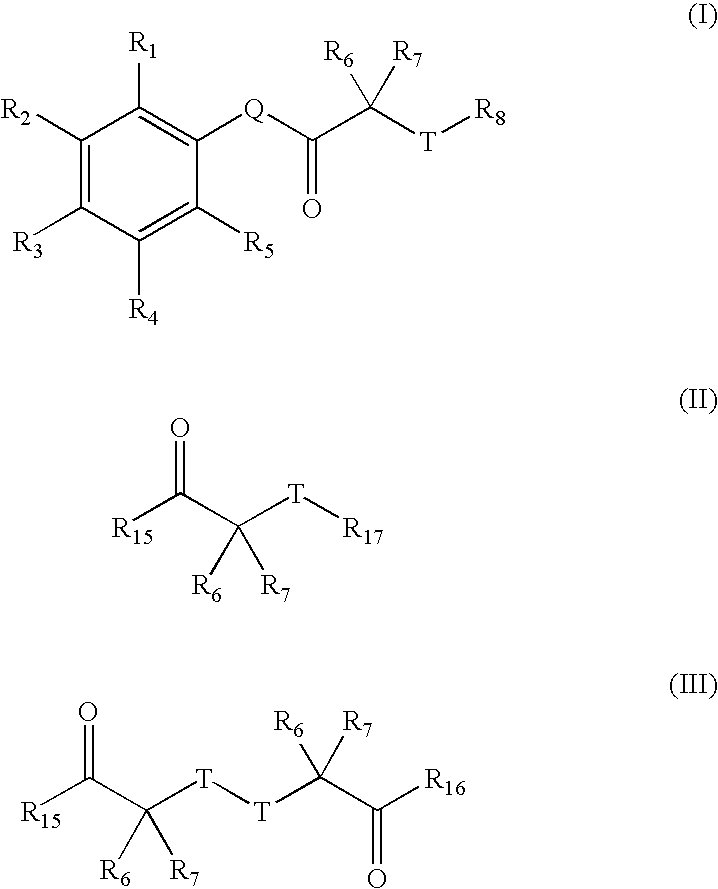
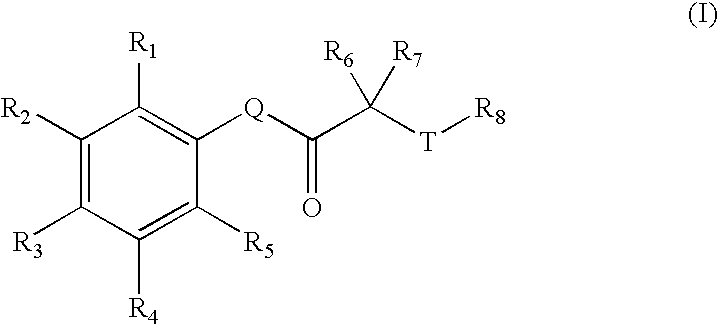
Disclosed herein are carbonyl compounds of Formula I, II, or III, and others as described herein. Also disclosed are methods of treating disease, such as cancer, neurological disorders, including polyglutamine-repeat disorders, anemias, thalassemias, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune diseases and cardiovascular conditions, using the compounds of the invention. In addition, methods of modulating the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) are also disclosed.
Owner:KALYPSYS INC
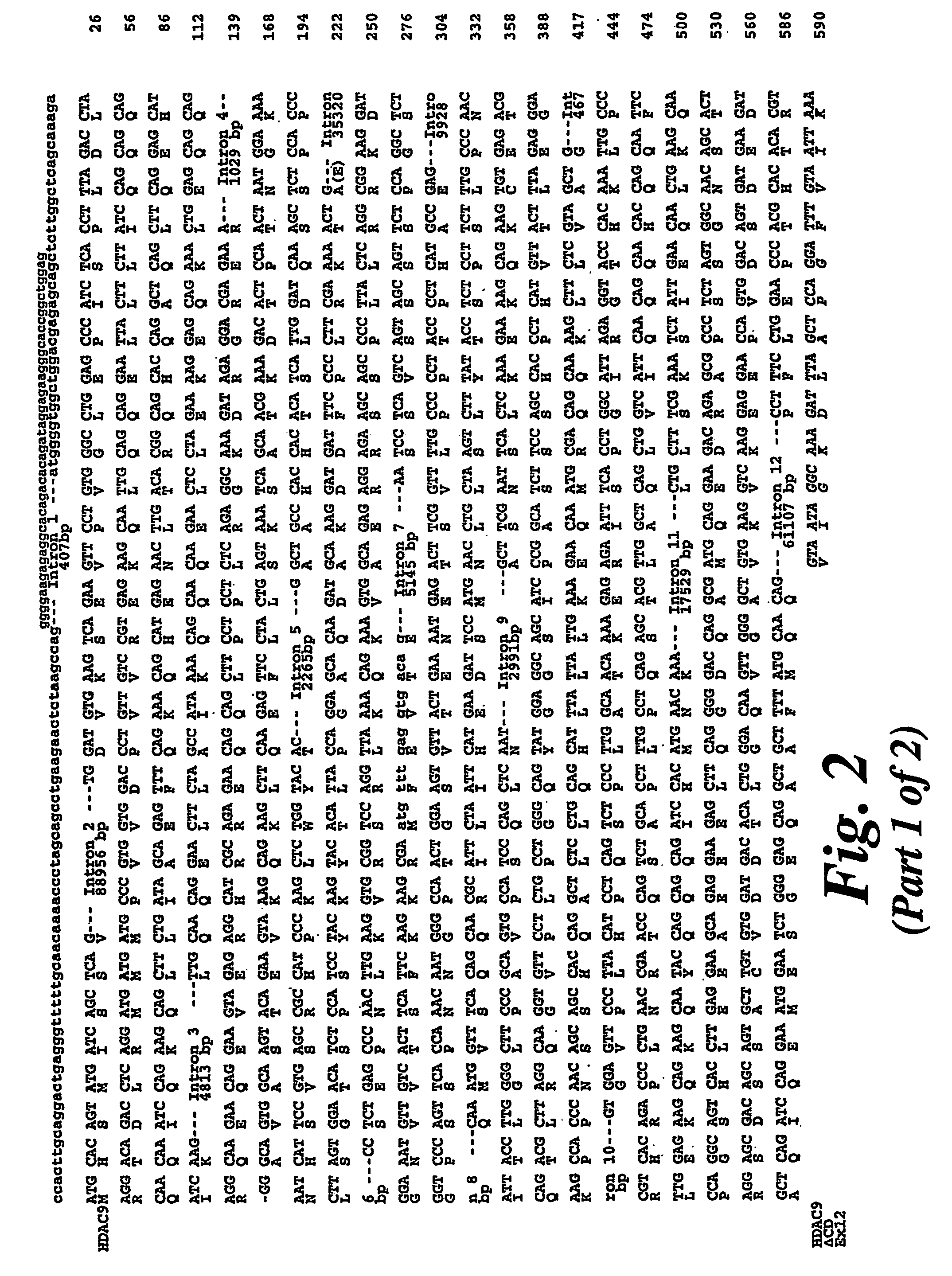
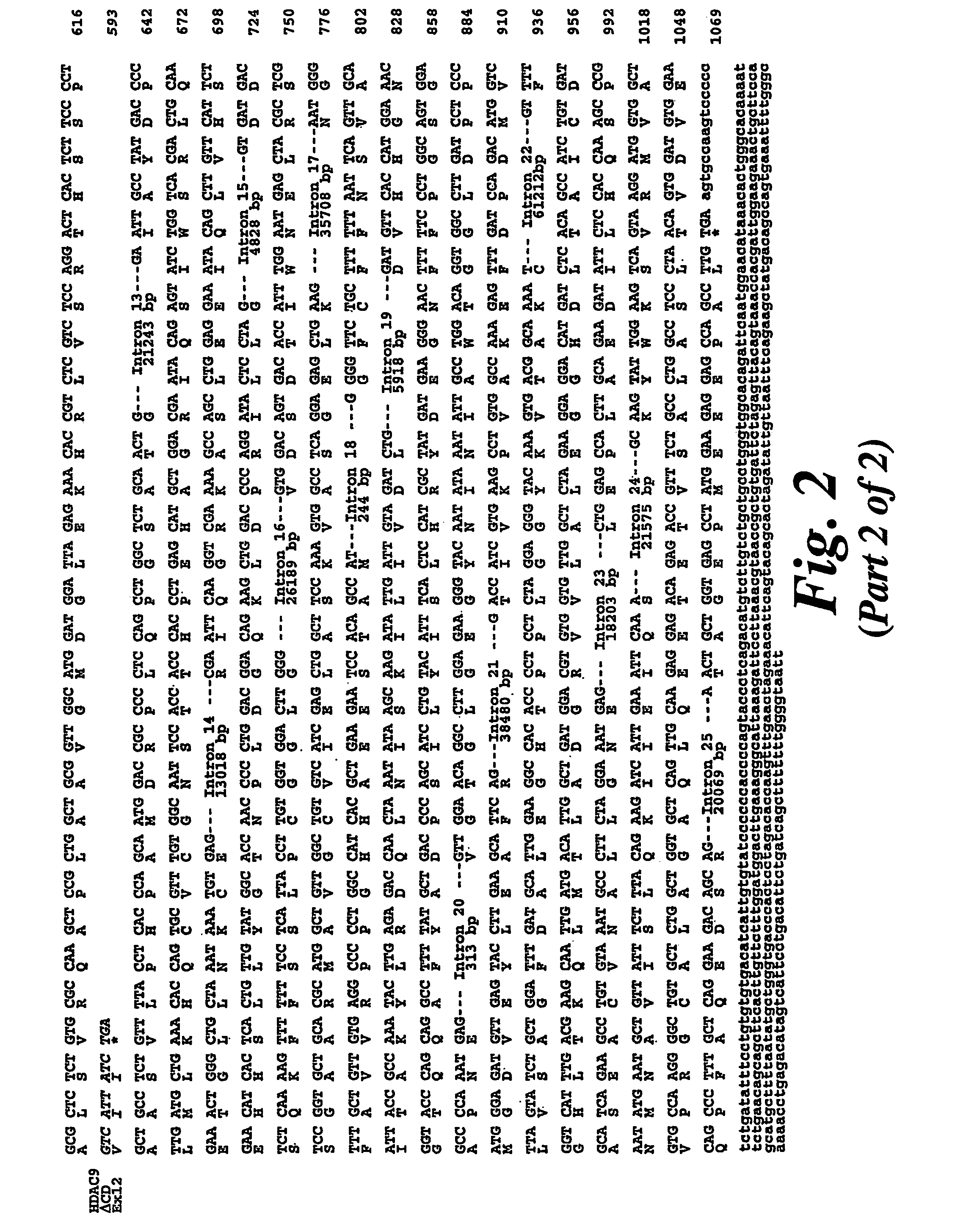
Histone deacetylase 9
The identification and cloning of histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9) is disclosed, and in particular full length HCAC9 polypeptides and HDAC9 polypeptides which have deacetylase activity, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these polypeptides. The uses of these polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules are disclosed, for example for screening for compounds that are capable of modulating HDAC9 biological activity.
Owner:THE INST OF CANCER RES
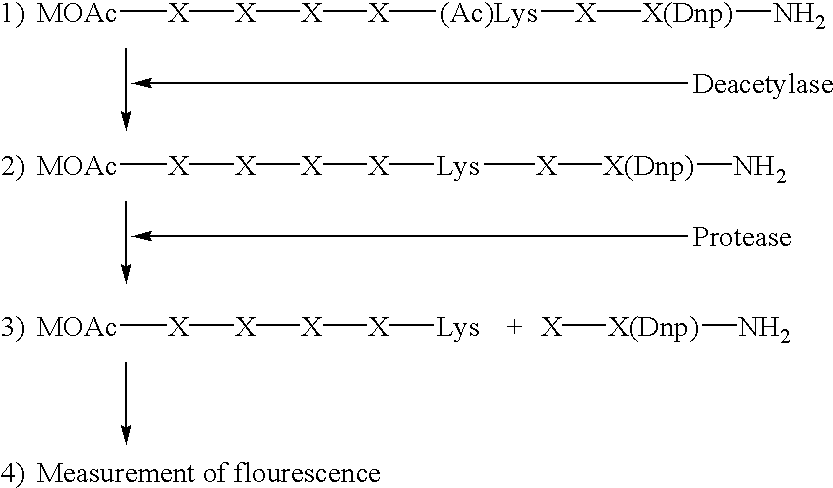
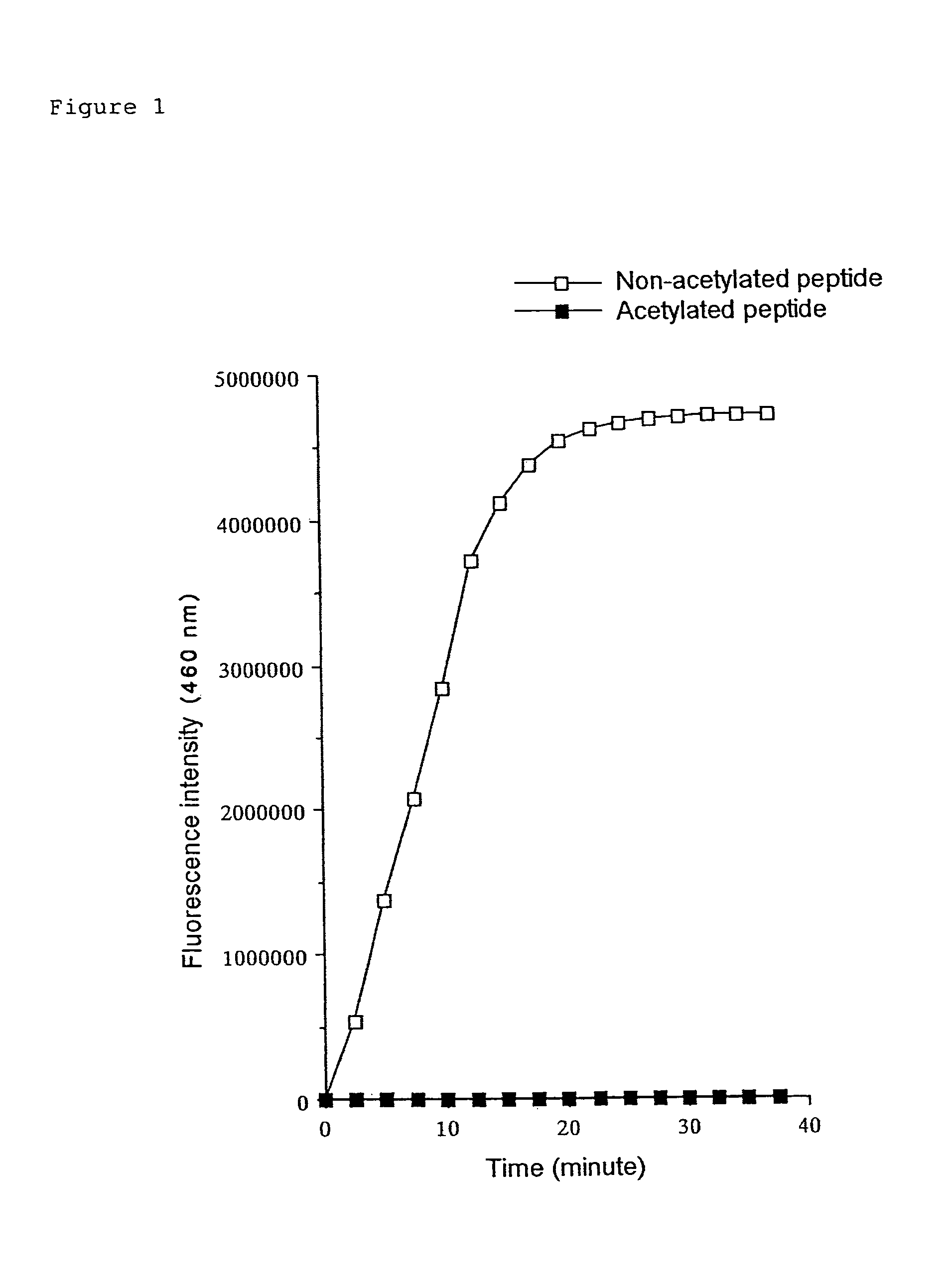
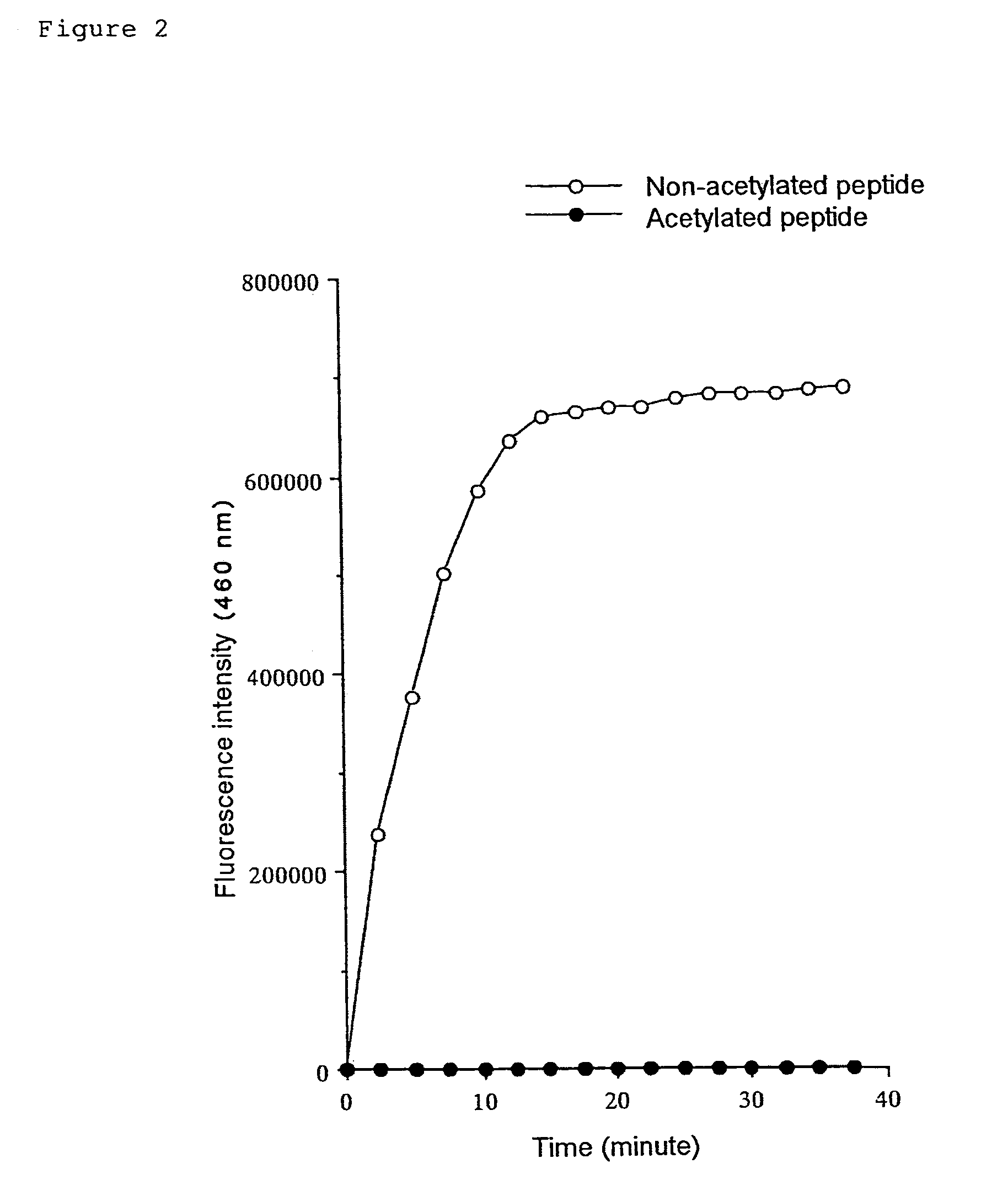
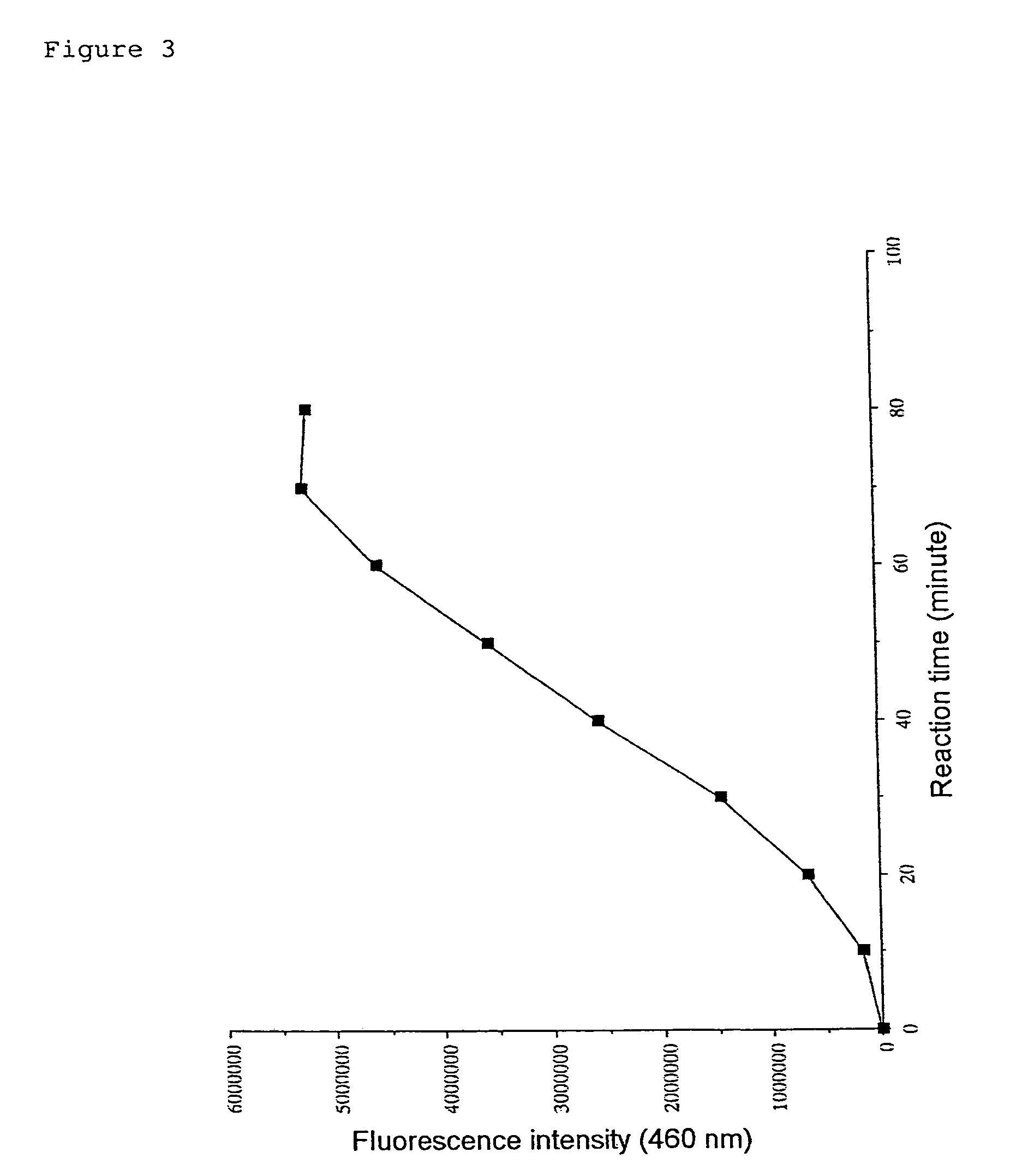
Methods for determining the acetylation level of a peptide based on sensitivity of the peptide to peptidase
InactiveUS7033778B2Simple methodReduced activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAcetylationEnzyme
Owner:CYLEX
Kit for determining the acetylation level of a peptide based on sensitivity of the peptide to peptidase
InactiveUS7256013B2Simple methodReduced activityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical treatment enzyme inactivationAcetylationEnzyme
The acetylation level of a peptide is determined utilizing the fact that the changes in the acetylation level are reflected in the sensitivity of the substrate peptide to a peptidase. This method can be used for measuring activities of deacetylase and acetylase, and also enables screening for substances that influence the activity of these enzymes. The deacetylase activity can be measured by a simple procedure according to the present invention.
Owner:CYLEX
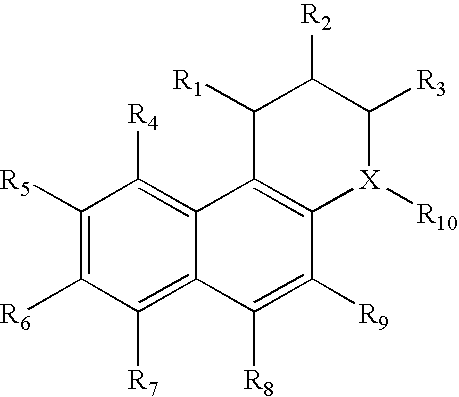
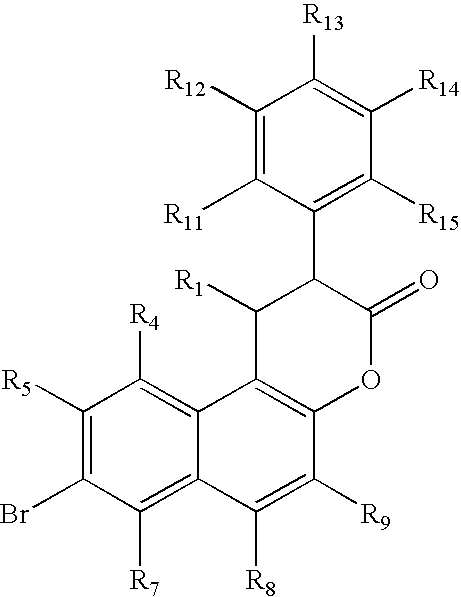
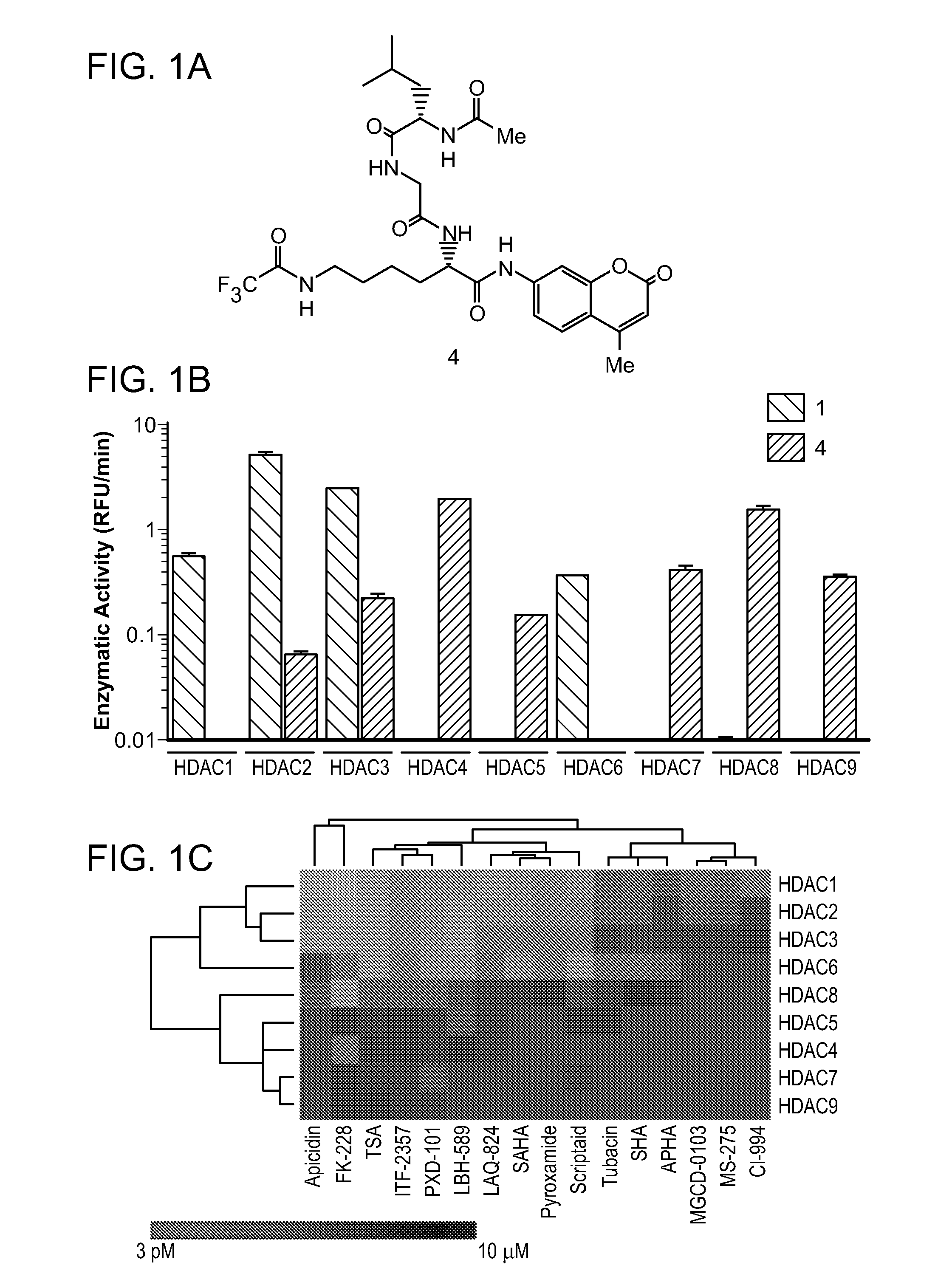
Class- and isoform-specific HDAC inhibitors and uses thereof
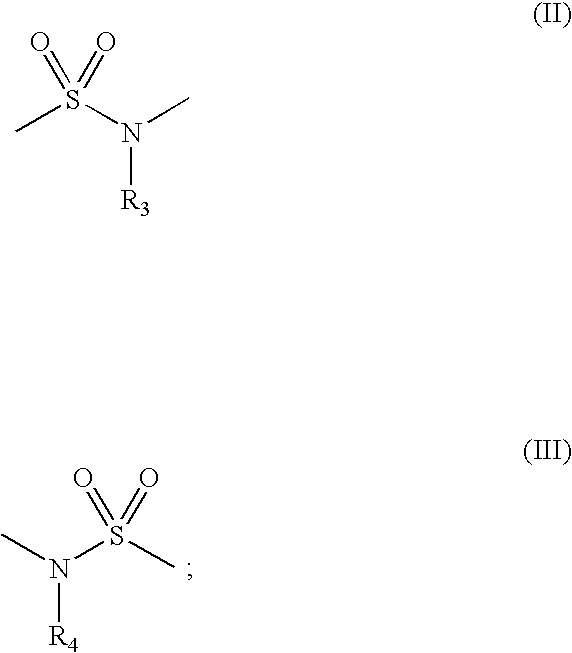
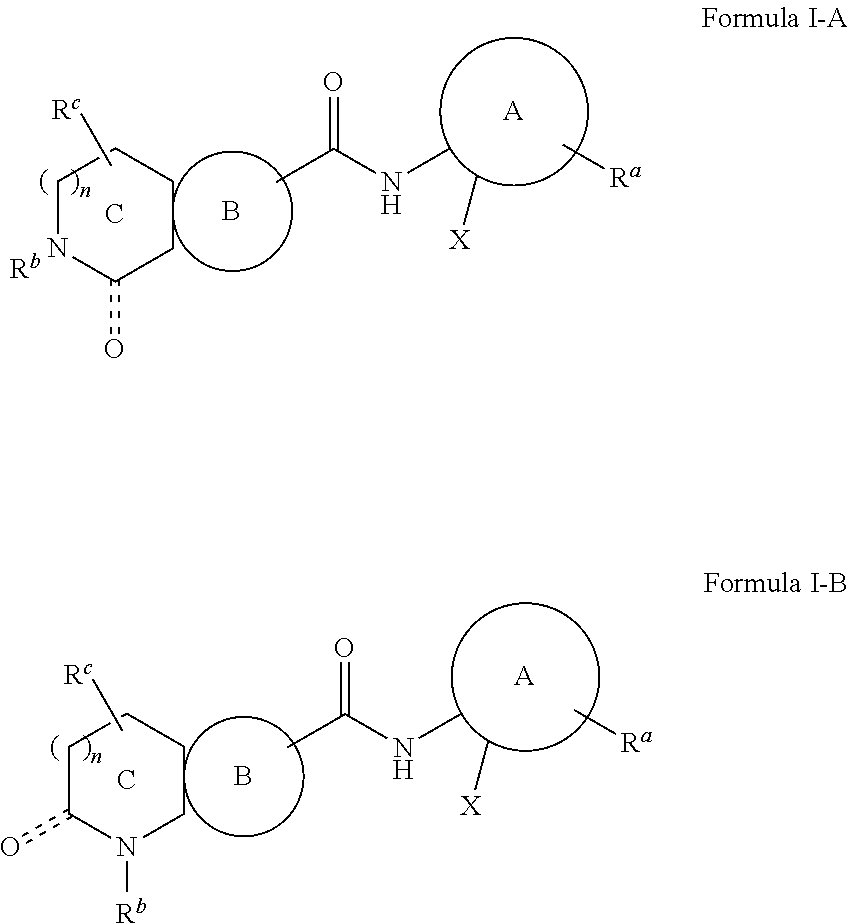
HDAC inhibitors of the general formula (I) and (II) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as described herein, are useful as inhibitors of histone deacetylases or other deacetylases, and thus are useful for the treatment of various diseases and disorders associated with acetylase / deacetylase activity as described herein (e.g., cancer). In certain embodiments, the compounds of the invention selectively target either a class or isoform of the HDAC family. Another aspect of the invention provides an assay for determining the inhibitory effect of a test compound on an HDAC protein comprising: incubating the HDAC protein with a substrate of general formula (IIIc) in the presence of a test compound; and determining the activity of the HDAC protein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Inhibitors of histone deacetylase for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20070135438A1Inhibition of catalytic activityInhibiting cellular functionBiocideOrganic chemistryAutoimmune conditionHistone deacetylase
Disclosed herein are carbonyl compounds of having the structural formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, or prodrug thereof, Methods and compositions are disclosed for treating disease states including, but not limited to cancers, autoimmune diseases, tissue damage, central nervous system disorders, neurodegenerative disorders, fibrosis, bone disorders, polyglutamine-repeat disorders, anemias, thalassemias, inflammatory conditions, cardiovascular conditions, and disorders in which angiogenesis play a role in pathogenesis, using the compounds of the invention. In addition, methods of modulating the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) are also disclosed.
Owner:KALYPSYS INC
Compositions and methods for modulating sirtuin activity
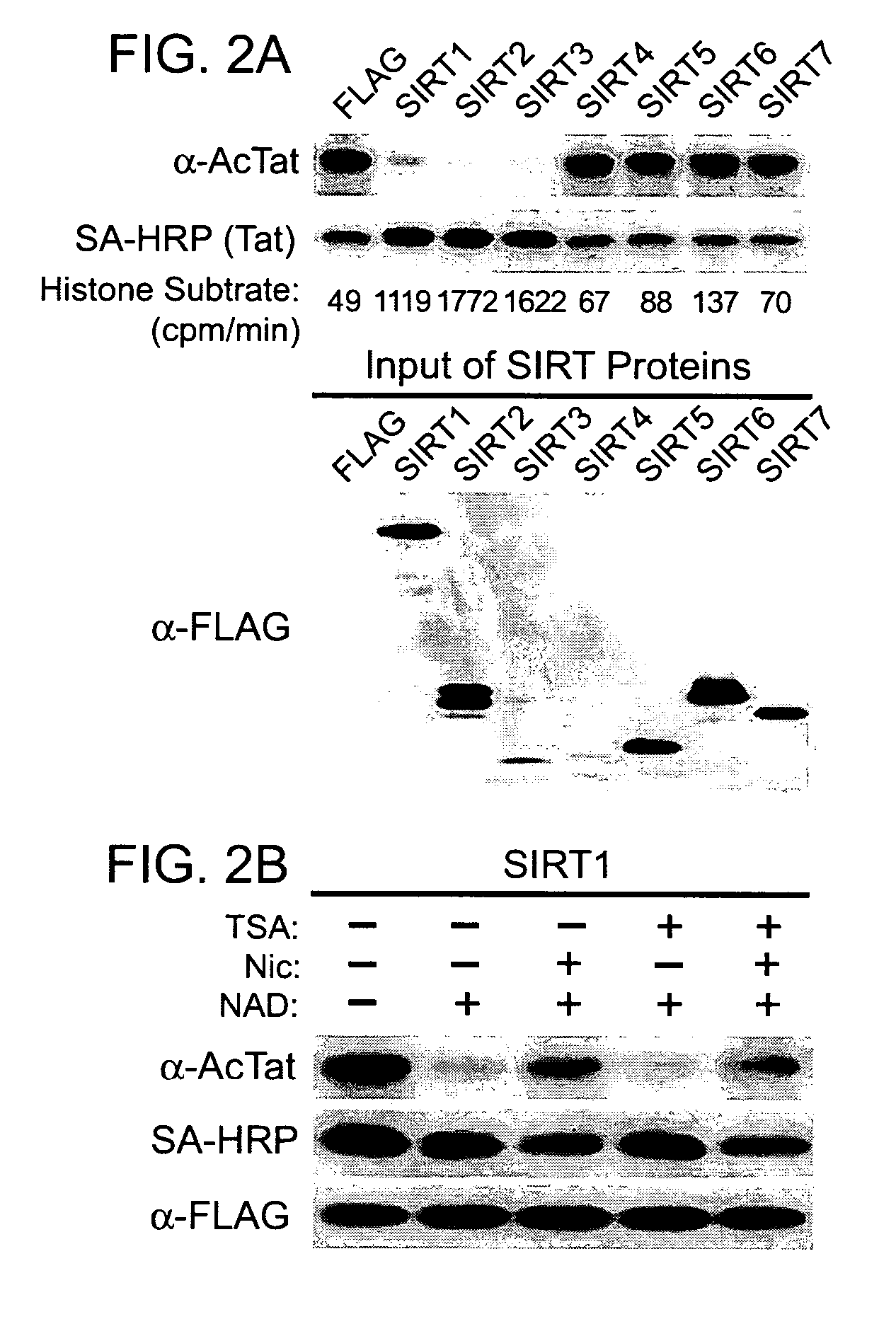
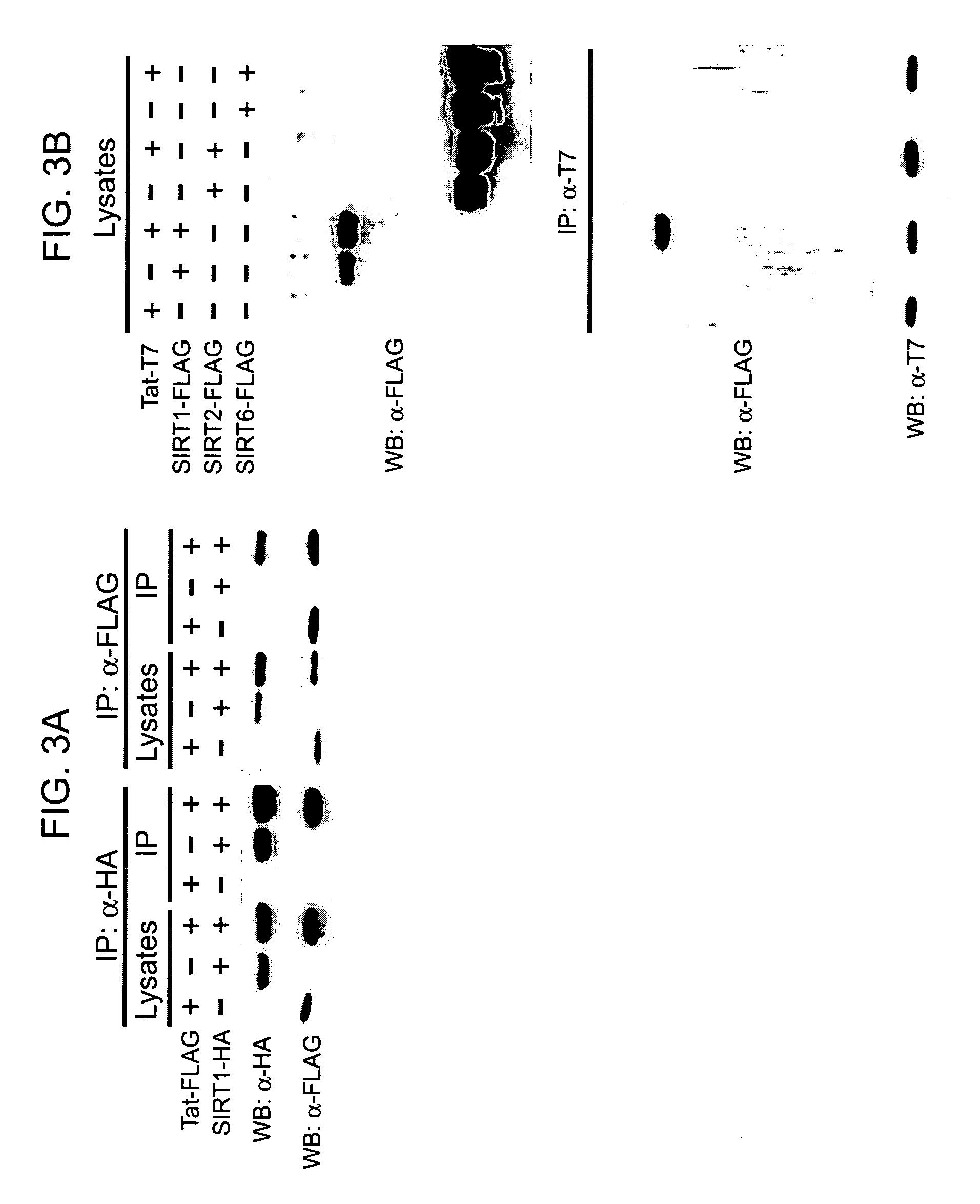
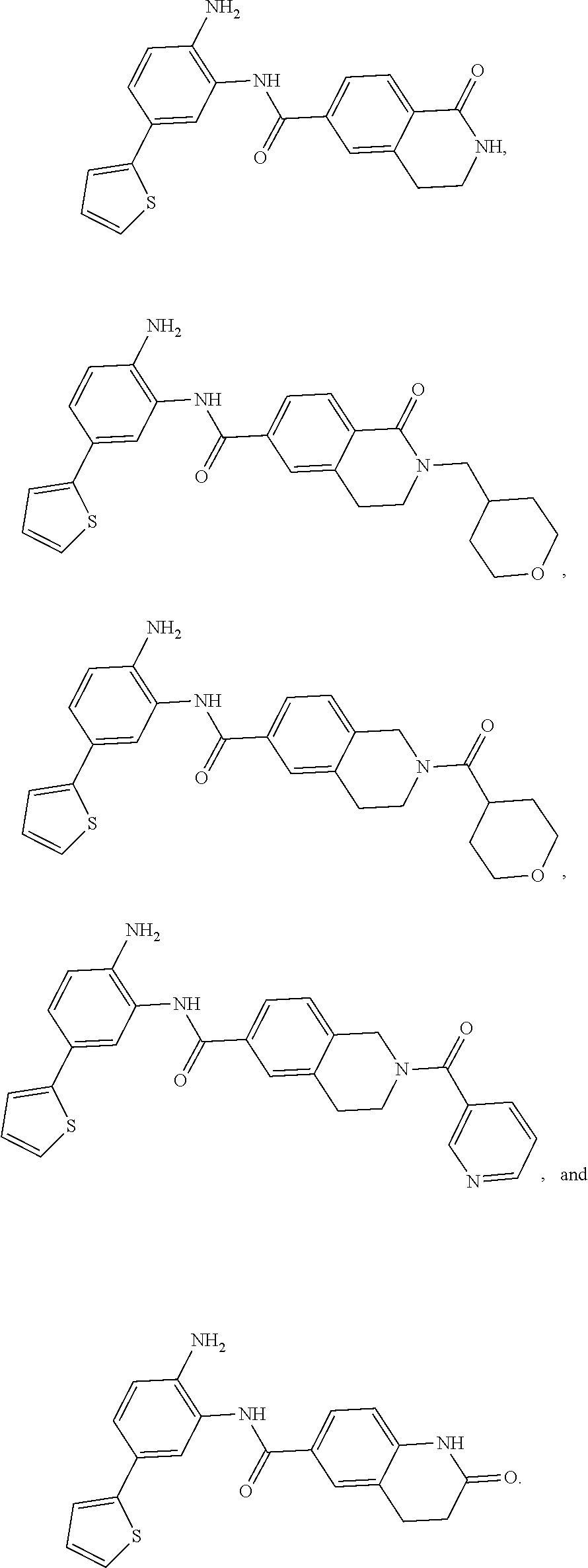
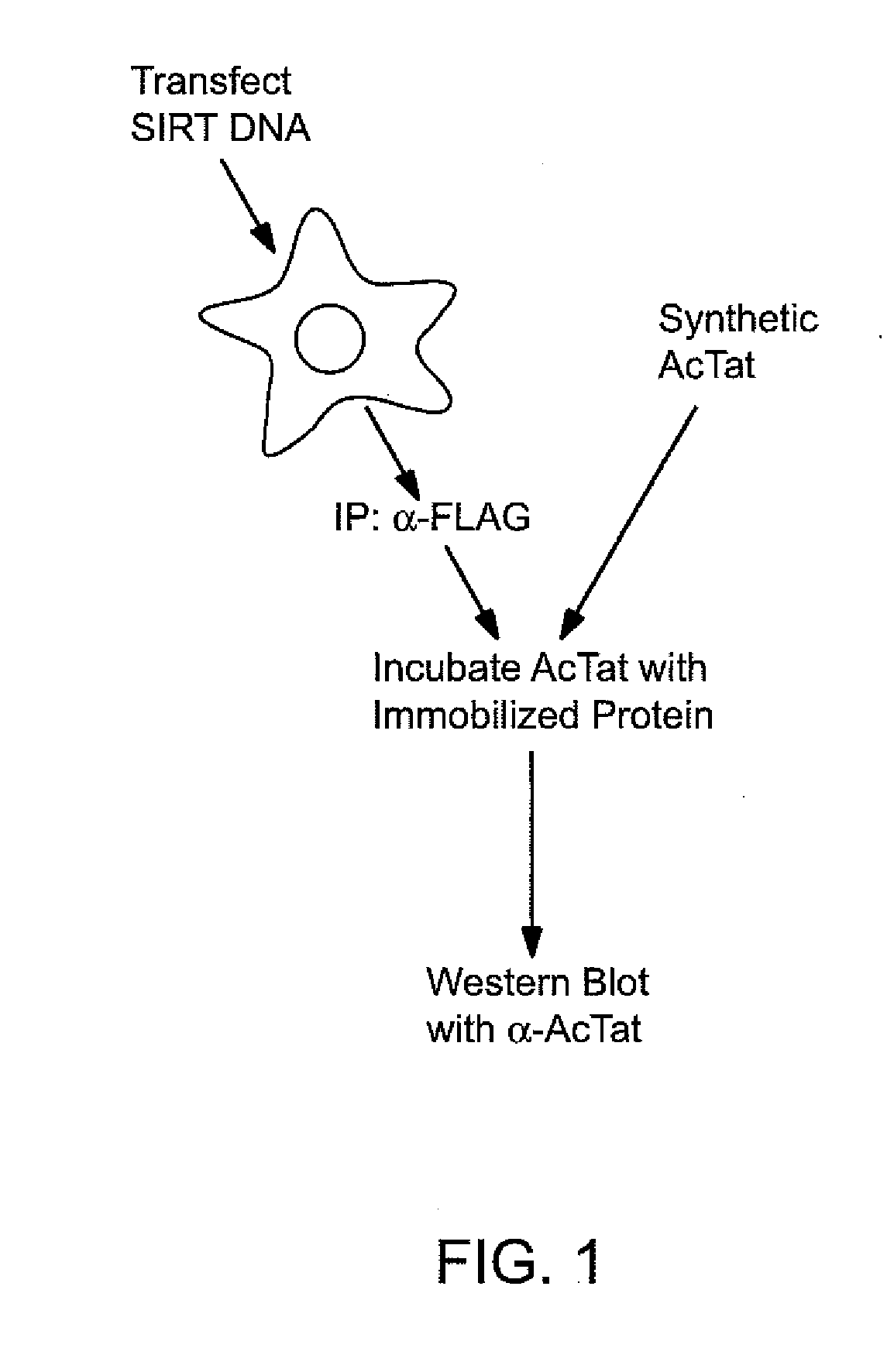
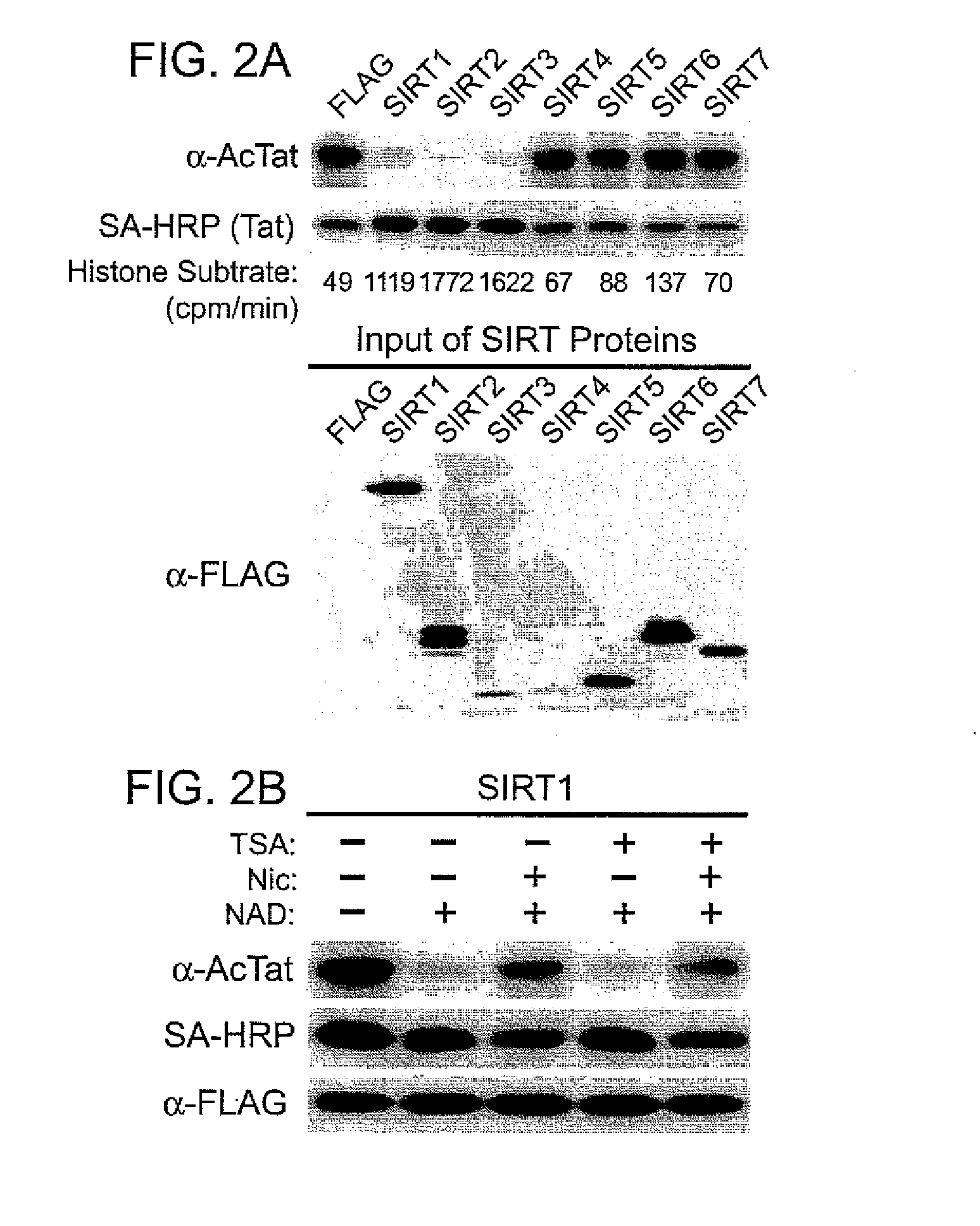
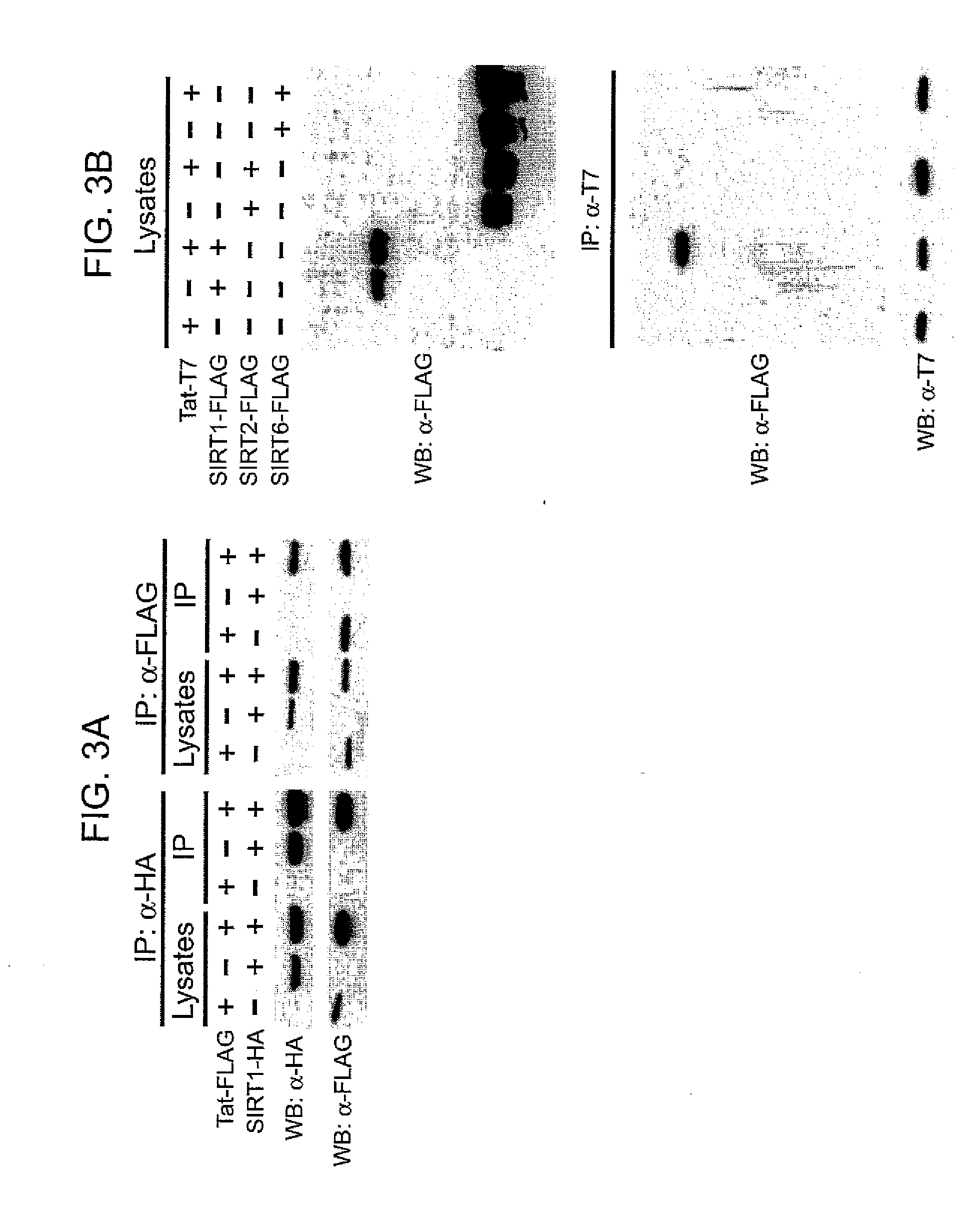
The present invention provides treatment methods involving modulating a sirtuin activity and / or a sirtuin mRNA and / or a sirtuin polypeptide level. In some embodiments, the present invention provides treatment methods involving modulating SIRT1 activity and / or SIRT mRNA and / or polypeptide level. The present invention provides methods of inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity. Methods of inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity are useful for treating immunodeficiency virus infections, particularly human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Thus, the present invention provides methods of treating an immunodeficiency virus infection, generally involving inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity. The present invention further provides methods of identifying agents that modulate sirtuin activity (e.g., SIRT1 activity), particularly ability of sirtuins to interact with (e.g., bind and / or deacetylate) a substrate, e.g., a viral substrate such as a Tat polypeptide. The present invention further provides active agents that modulate sirtuin activity or expression; and compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the active agents.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Small molecule compound combination and method for preparing vascular endothelial cells by using small molecule compound combination to induce differentiated cells
PendingCN108070549ASmall sample sizeEasy to collectArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsVascular endotheliumBeta-catenin
The invention discloses a small molecule compound combination and a method for preparing vascular endothelial cells by using the small molecule compound combination to induce differentiated cells. According to the method, differentiated cells are subjected to targeted induction so as to finally obtain vascular endothelial cells, wherein the targeted induction comprises: inhibiting the activity oflysine deacetylase activity, inhibiting the signaling pathway of TGF-beta, inhibiting the activity of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT), activating the signaling pathway of WNT / beta-catenin, and activatingthe signaling pathway of cAMP. According to the present invention, through the induction with the small molecule compound combination, the differentiated cells can be transdifferentiated into the vascular endothelial cells, each step can be subjected to precise quality control, and the standardized operation and the large-scale production can be conveniently achieved; and the donor source of themethod is wide, the patient himself can be served as the donor, and the vascular endothelial cells required by basic research, clinical treatment or tissue engineering production can be obtained within a short time.
Owner:深圳臻德济慈药品研发有限公司
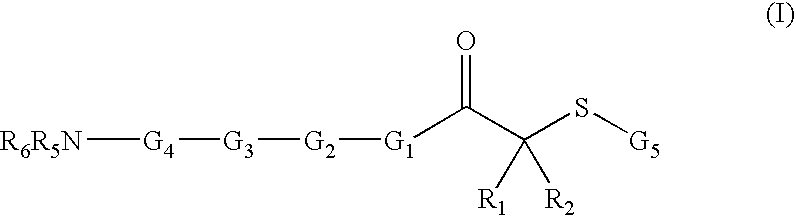
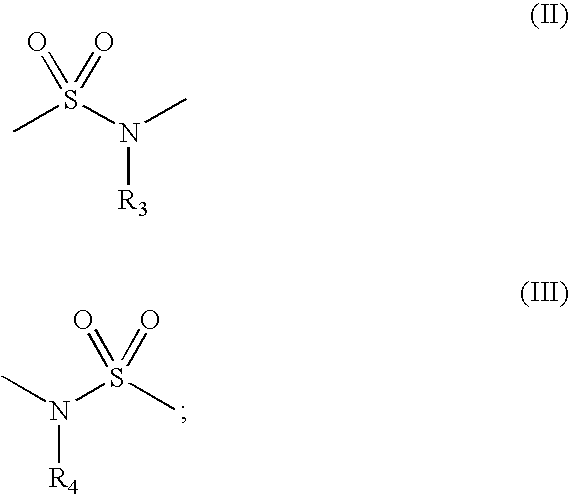
Novel sulfonamides as inhibitors of histone deacetylase for the treatment of disease
Disclosed herein are carbonyl compounds of having the structural formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, amide, ester, or prodrug thereof, Methods and compositions are disclosed for treating disease states including, but not limited to cancers, autoimmune diseases, tissue damage, central nervous system disorders, neurodegenerative disorders, fibrosis, bone disorders, polyglutamine-repeat disorders, anemias, thalassemias, inflammatory conditions, cardiovascular conditions, and disorders in which angiogenesis play a role in pathogenesis, using the compounds of the invention. In addition, methods of modulating the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) are also disclosed.
Owner:KALYPSYS INC
Screening methods for the identification of agents that inhibit SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity
The present invention provides treatment methods involving modulating a sirtuin activity and / or a sirtuin mRNA and / or a sirtuin polypeptide level. In some embodiments, the present invention provides treatment methods involving modulating SIRT1 activity and / or SIRT mRNA and / or polypeptide level. The present invention provides methods of inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity. Methods of inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity are useful for treating immunodeficiency virus infections, particularly human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Thus, the present invention provides methods of treating an immunodeficiency virus infection, generally involving inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity. The present invention further provides methods of identifying agents that modulate sirtuin activity (e.g., SIRT1 activity), particularly ability of sirtuins to interact with (e.g., bind and / or deacetylate) a substrate, e.g., a viral substrate such as a Tat polypeptide. The present invention further provides active agents that modulate sirtuin activity or expression; and compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the active agents.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Method for determination of enzymatic activity
ActiveUS20090104627A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSulfotransferase activityPolysaccharide
A novel modified polysaccharide, a solid phase to which the polysaccharide is adhered, methods for detecting N-deacetylase activity, N-sulfotransferase activity and N-deacetylase / N-sulfotransferase activity in a sample which utilizes said solid phase, and detection kits thereof.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Activation and activators of SIRT6
ActiveUS20130029930A1High activityIncreasing deacetylase activityBiocideCompound screeningBiological activationDeacetylase activity
The invention provides a method of increasing a deacetylated activity of SIRT6 by contacting SIRT6 with an agent that binds SIRT6 and reduces the Km of SIRT6 for a substrate, thereby increasing the deacetylase activity of SIRT6. The invention also provides compounds of the formulas (II) and (III).
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Quinoline and Isoquinoline Based HDAC Inhibitors and Methods of Use Thereof
The present invention relates to methods of modulating activity of histone deacetylases (HDACs). The present invention also relates to methods of treating HDAC-associated diseases including, but not limited to, cancers, inflammatory disorders, and neurodegenerative disorders. The present invention also provides novel compounds and compositions thereof and methods of preparation of the same. The present invention also includes methods of inhibiting HDACs, and methods of treating HDAC-associated diseases using the compounds of the invention.
Owner:REACTION BIOLOGY
Compositions and methods for modulating sirtuin activity
The present invention provides treatment methods involving modulating a sirtuin activity and / or a sirtuin mRNA and / or a sirtuin polypeptide level. In some embodiments, the present invention provides treatment methods involving modulating SIRT1 activity and / or SIRT mRNA and / or polypeptide level. The present invention provides methods of inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity. Methods of inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity are useful for treating immunodeficiency virus infections, particularly human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Thus, the present invention provides methods of treating an immunodeficiency virus infection, generally involving inhibiting SIRT1 Tat deacetylase activity. The present invention further provides methods of identifying agents that modulate sirtuin activity (e.g., SIRT1 activity), particularly ability of sirtuins to interact with (e.g., bind and / or deacetylate) a substrate, e.g., a viral substrate such as a Tat polypeptide. The present invention further provides active agents that modulate sirtuin activity or expression; and compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the active agents.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Histone deacetylase 9
The identification and cloning of histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9) is disclosed, and in particular full length HCAC9 polypeptides and HDAC9 polypeptides which have deacetylase activity, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these polypeptides. The uses of these polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules are disclosed, for example for screening for compounds that are capable of modulating HDAC9 biological activity.
Owner:THE INST OF CANCER RES
Class- and isoform-specific HDAC inhibitors and uses thereof
HDAC inhibitors of the general formula (I) and (II) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as described herein, are useful as inhibitors of histone deacetylases or other deacetylases, and thus are useful for the treatment of various diseases and disorders associated with acetylase / deacetylase activity as described herein (e.g., cancer). In certain embodiments, the compounds of the invention selectively target either a class or isoform of the HDAC family. Another aspect of the invention provides an assay for determining the inhibitory effect of a test compound on an HDAC protein comprising: incubating the HDAC protein with a substrate of general formula (IIIc) in the presence of a test compound; and determining the activity of the HDAC protein.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Chitin deacetylase and application thereof
ActiveCN109609485ALow requirements for production conditionsReduce pollutionBacteriaHydrolasesBiologyChitin deacetylase
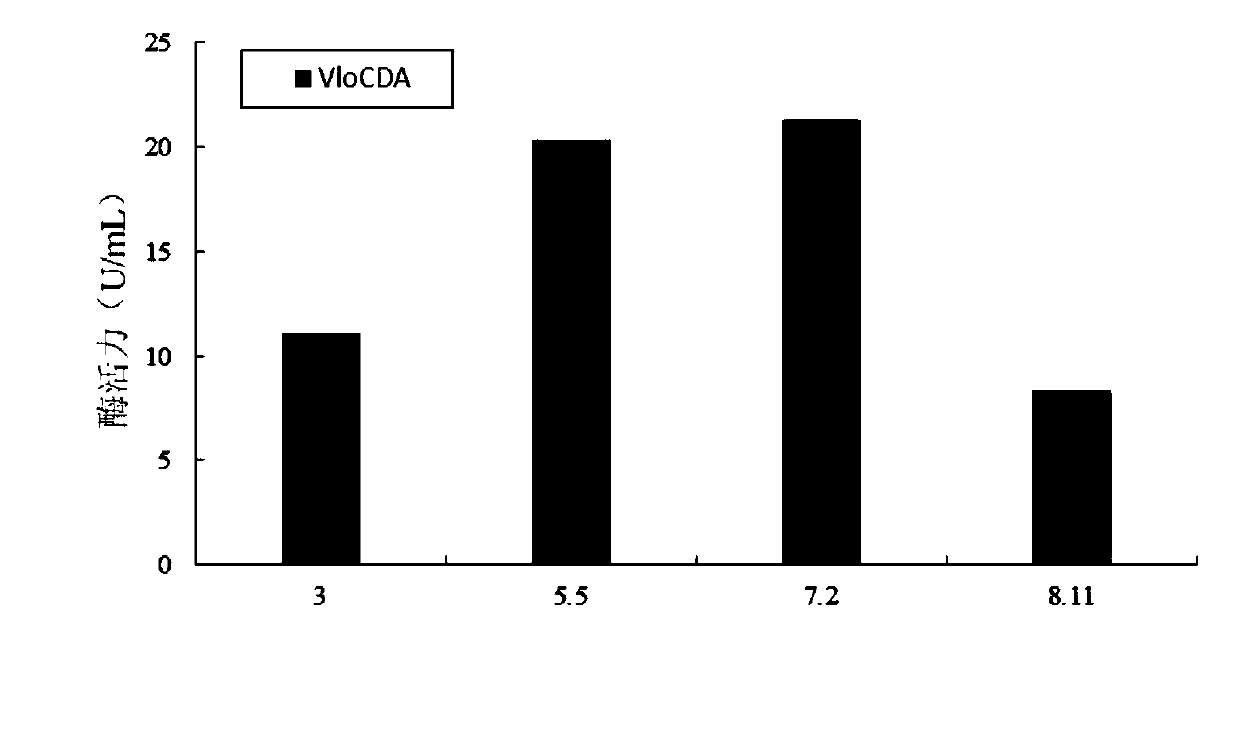
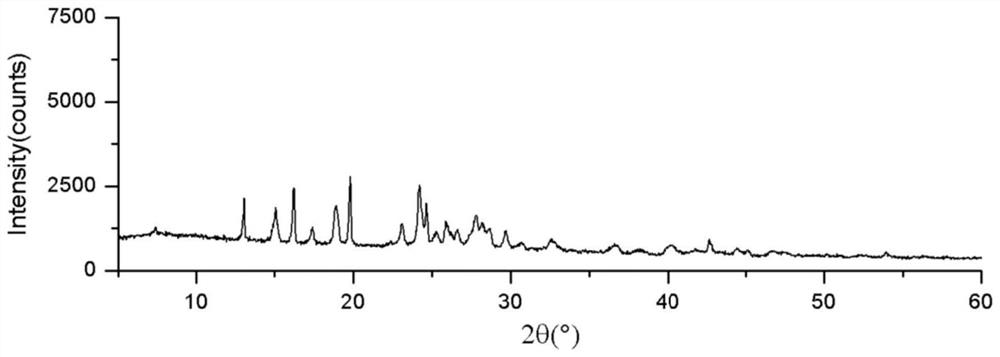
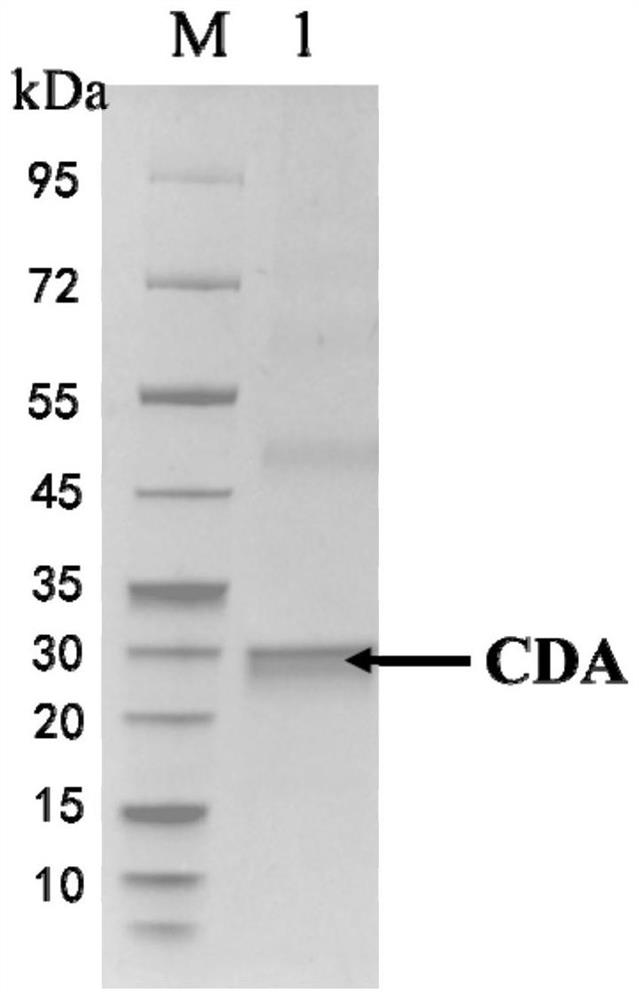
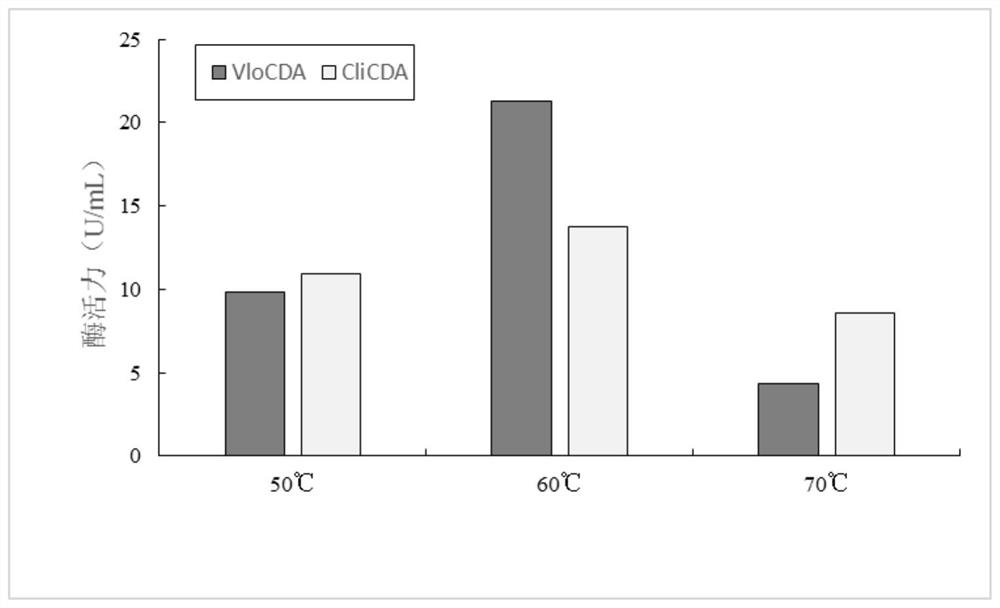
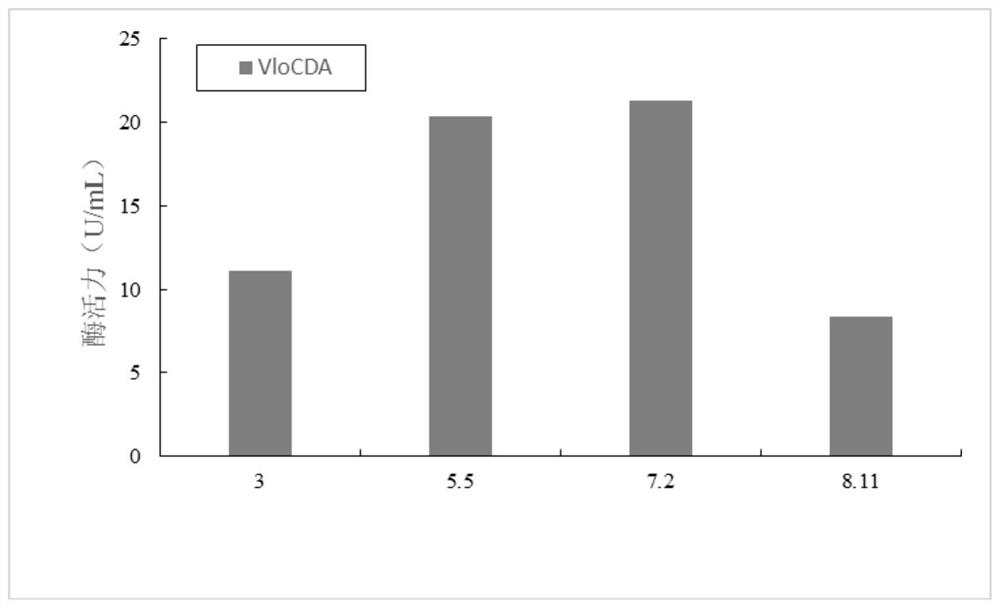
By analyzing and studying different genomic sequences of different species, several unknown proteins are screened out, and chitin deacetylase with excellent deacetylase activity is further identified.More specifically, the invention relates to a chitin deacetylase derived from verticillium longisporum Vlo. Compared with the reported chitin deacetylase, the chitin deacetylase has lower requirements for production conditions, has higher biosafety, and has characteristics more suitable for industrial applications, and shows wide application potential.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM +2
Method for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities and method for screening inhibitors or enhancers of these enzymes
InactiveUS20060035296A1Easy to detectConducive to screeningBiocideCompound screeningPeptide substrateAcetyltransferases
A method for simply and conveniently detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities of proteins by executing an acetylation reaction of a peptide substrate with an acetyltransferase, or a deacetylation reaction of an acetylated peptide substrate with a deacetylase, and after the completion of these reactions, detecting the acetyl group bound to the peptide substrate by using an anti-acetylated peptide antibody. This system for detecting acetyltransferase and deacetylase activities using the anti-acetylated peptide antibody enables screening inhibitors or enhancers of acetyltransferase and deacetylase. A system for screening deacetylase inhibitors or acetyltransferase enhancers using cultured cells is also provided.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
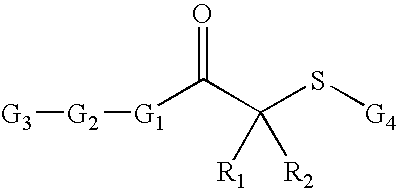
Reagents and methods for sirtuin capture
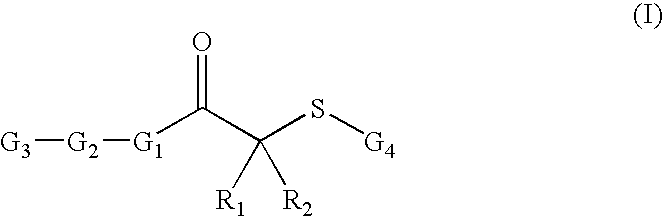
The invention provides a method of preparing a sirtuin complex, a method for detecting a sirtuin in a sample, and a method of screening for compounds which inhibit the deacetylase activity of a sirtuin. The method includes (a) providing a sirtuin substrate having the formula:(b) providing NAD+ or an NAD+ analog having the formula:and (c) providing a sirtuin, wherein R1-R4, A1, A2, and n are as defined herein.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Activation and activators of SirT6
The invention provides a method of increasing a deacetylated activity of SIRT6 by contacting SIRT6 with an agent that binds SIRT6 and reduces the Km of SIRT6 for a substrate, thereby increasing the deacetylase activity of SIRT6. The invention also provides compounds of the formulas (II) and (III).
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Kit for determining the acetylation level of a peptide based on sensitivity of the peptide to peptidase
InactiveUS20060040336A1Simple methodReduced activityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical treatment enzyme inactivationAcetylase activityDeacetylase activity
The acetylation level of a peptide is determined utilizing the fact that the changes in the acetylation level are reflected in the sensitivity of the substrate peptide to a peptidase. This method can be used for measuring activities of deacetylase and acetylase, and also enables screening for substances that influence the activity of these enzymes. The deacetylase activity can be measured by a simple procedure according to the present invention.
Owner:CYLEX
Acetyl glucosaminyl inositol deacetylase, a mycothiol biosynthetic enzyme, and methods of use
InactiveUS20050124021A1Growth inhibitionReduced activityBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsMammal
The present invention provides a family of bacterial acetyl glucosaminyl inositol deacetylases (MshB) with deacetylase activity against acyl glucosaminyl inositol and which play a key role in mycothiol biosynthesis. The invention deacetylases are characterized by a conserved 100 amino acid N-terminal region and three highly conserved histidine-containing regions and by having deacetylase activity as well as amide hydrolase activity. The invention further provides methods for using the invention deacetylases in drug screening assays to determine compounds that inhibit activity. The invention provides for treatment of actino-mycete infections in mammals using antibiotics that inhibit production or activity of MshB and thereby reduce the production of mycothiol and the virulence of the infecting bacteria.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
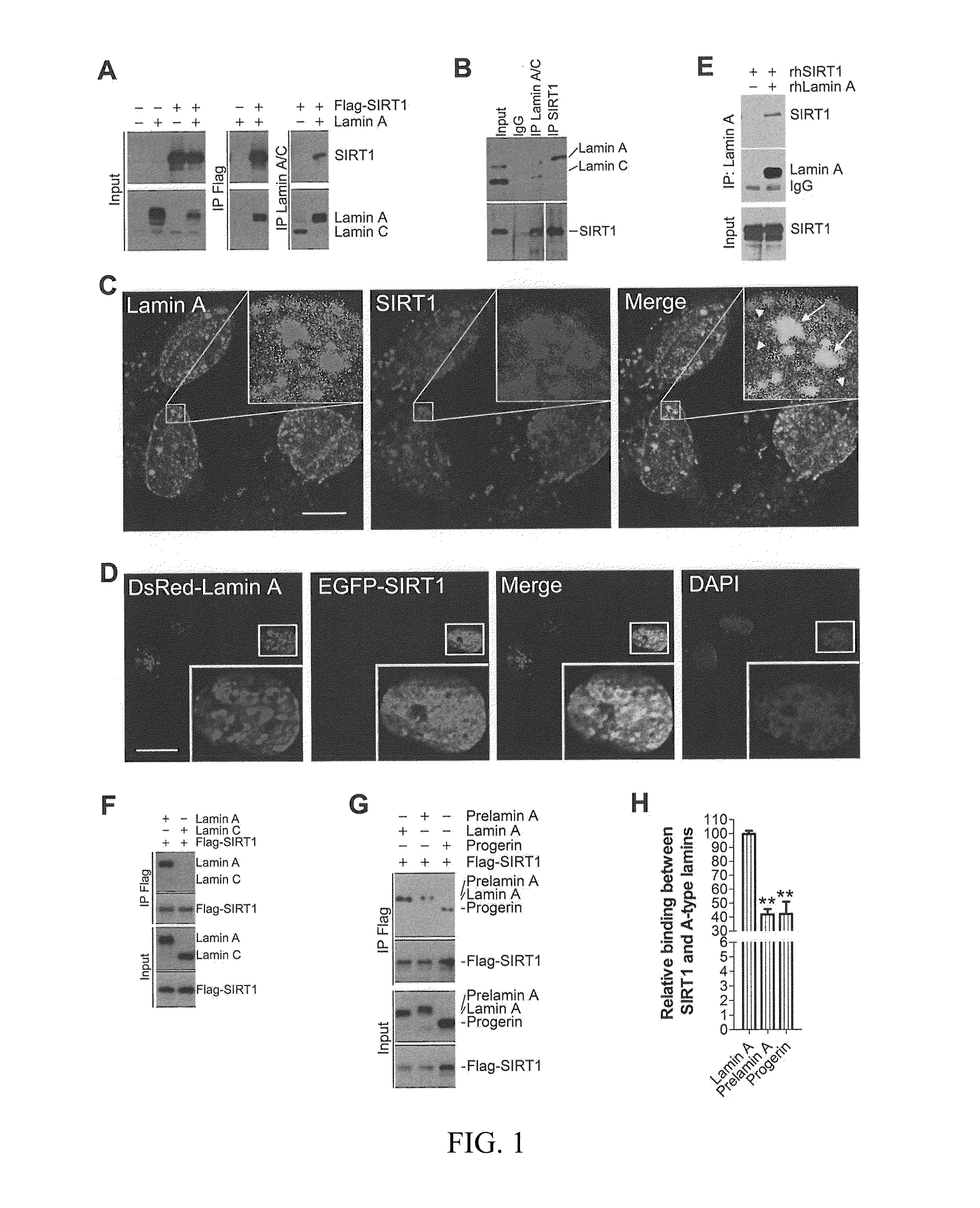
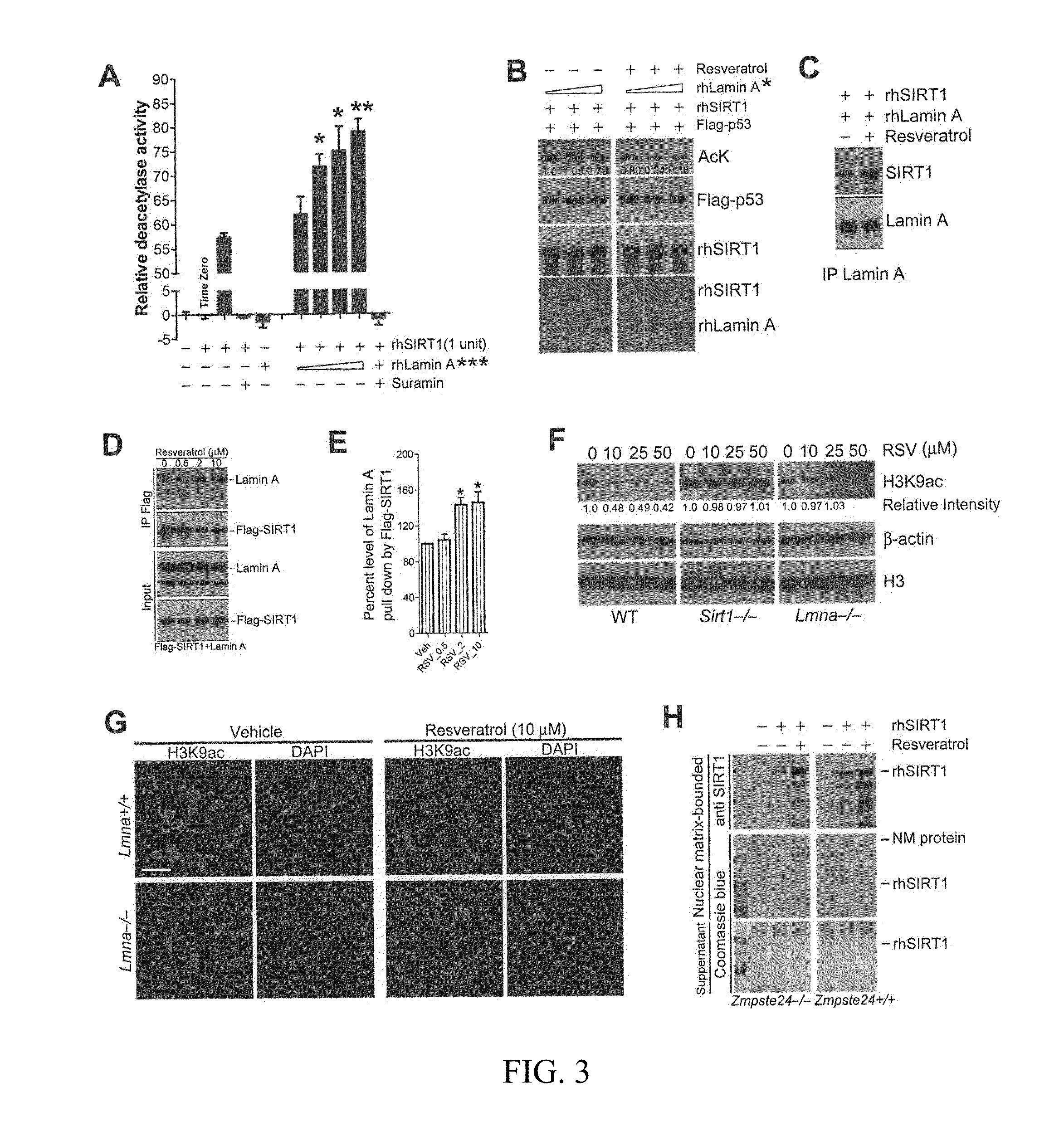
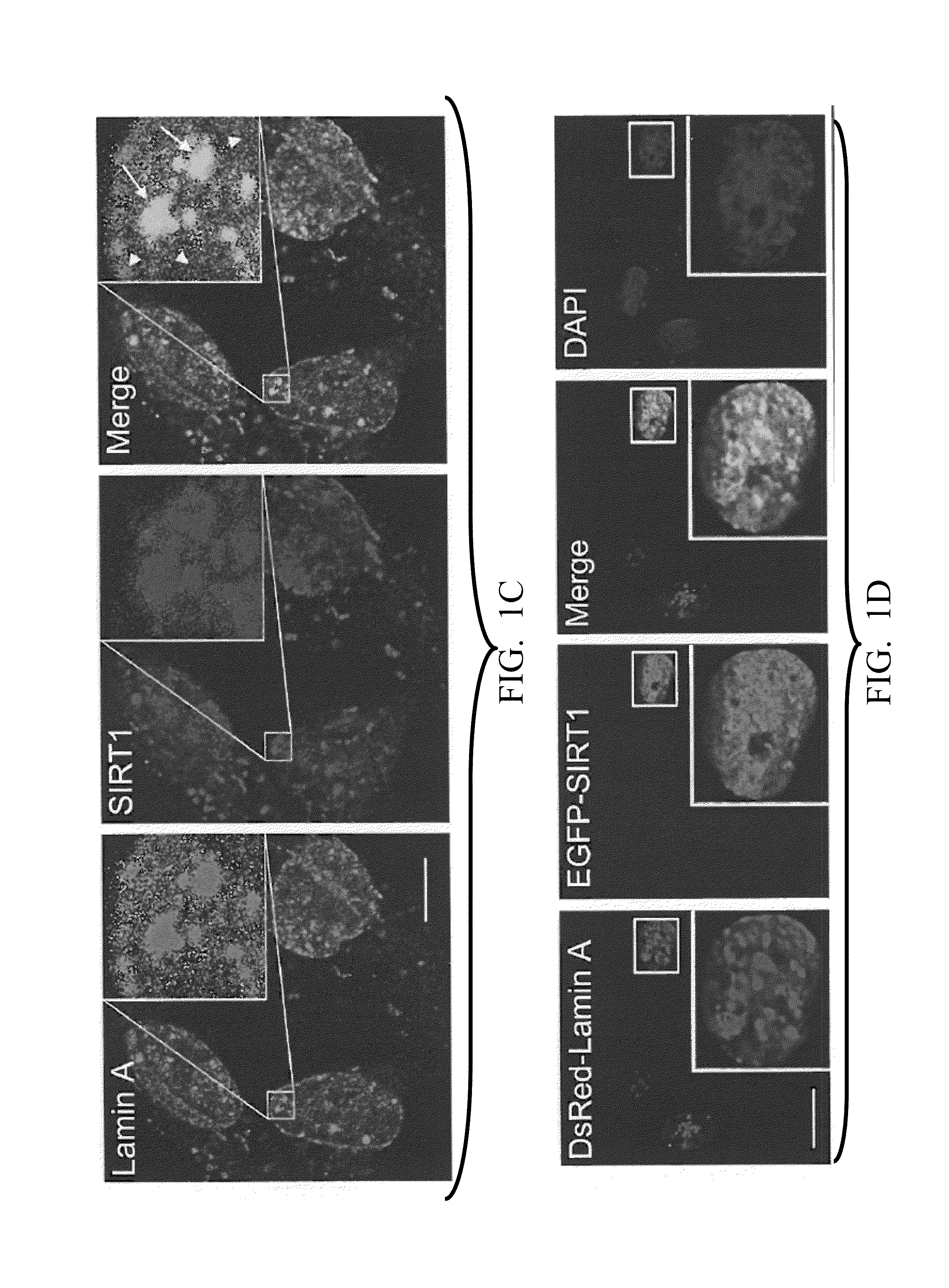
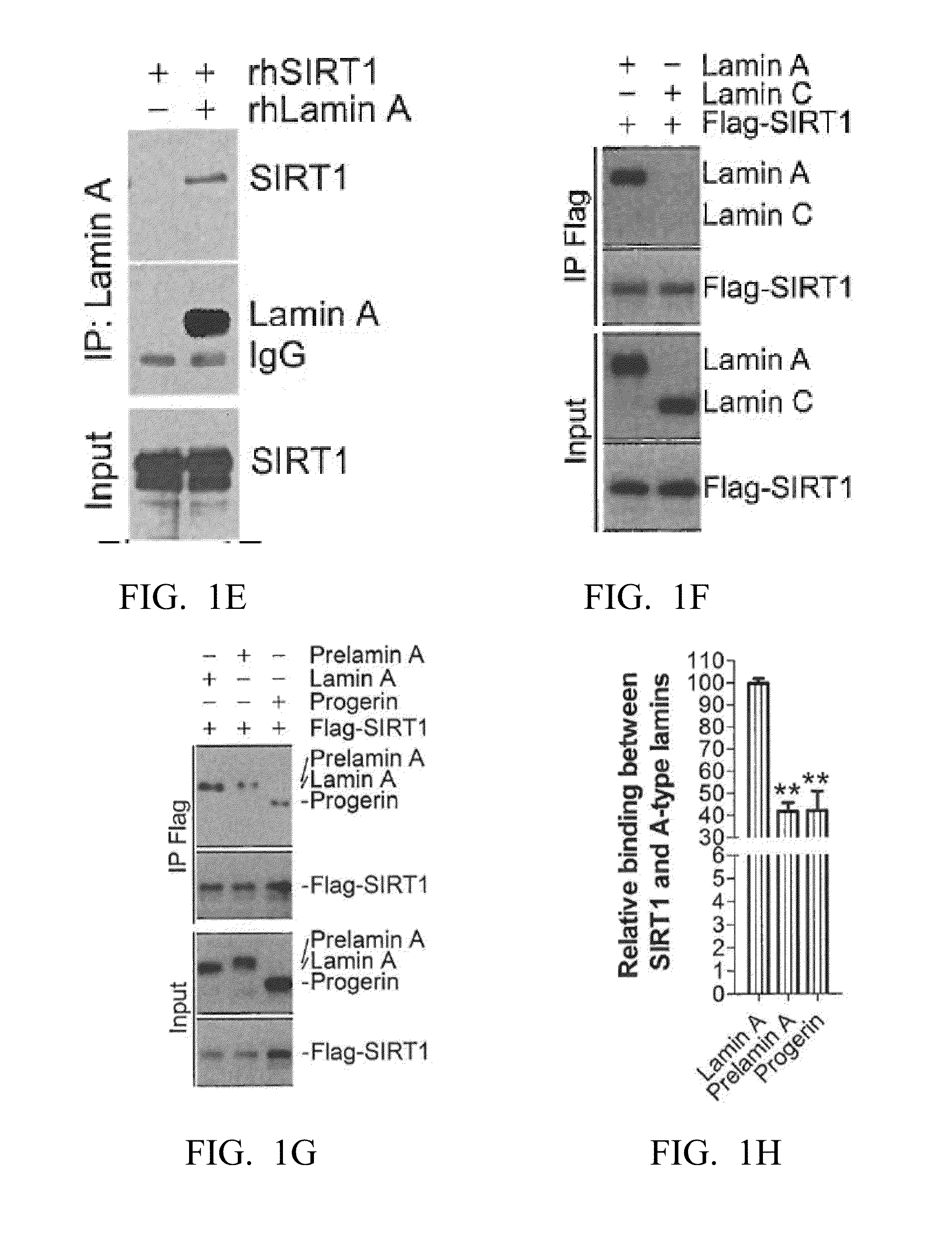
Lamin A, An Activator of Longevity/Anti-Aging SIRT1 Protein
InactiveUS20140135271A1High binding capacityDeacetylase activity can be increasedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMalignancyAnti ageing
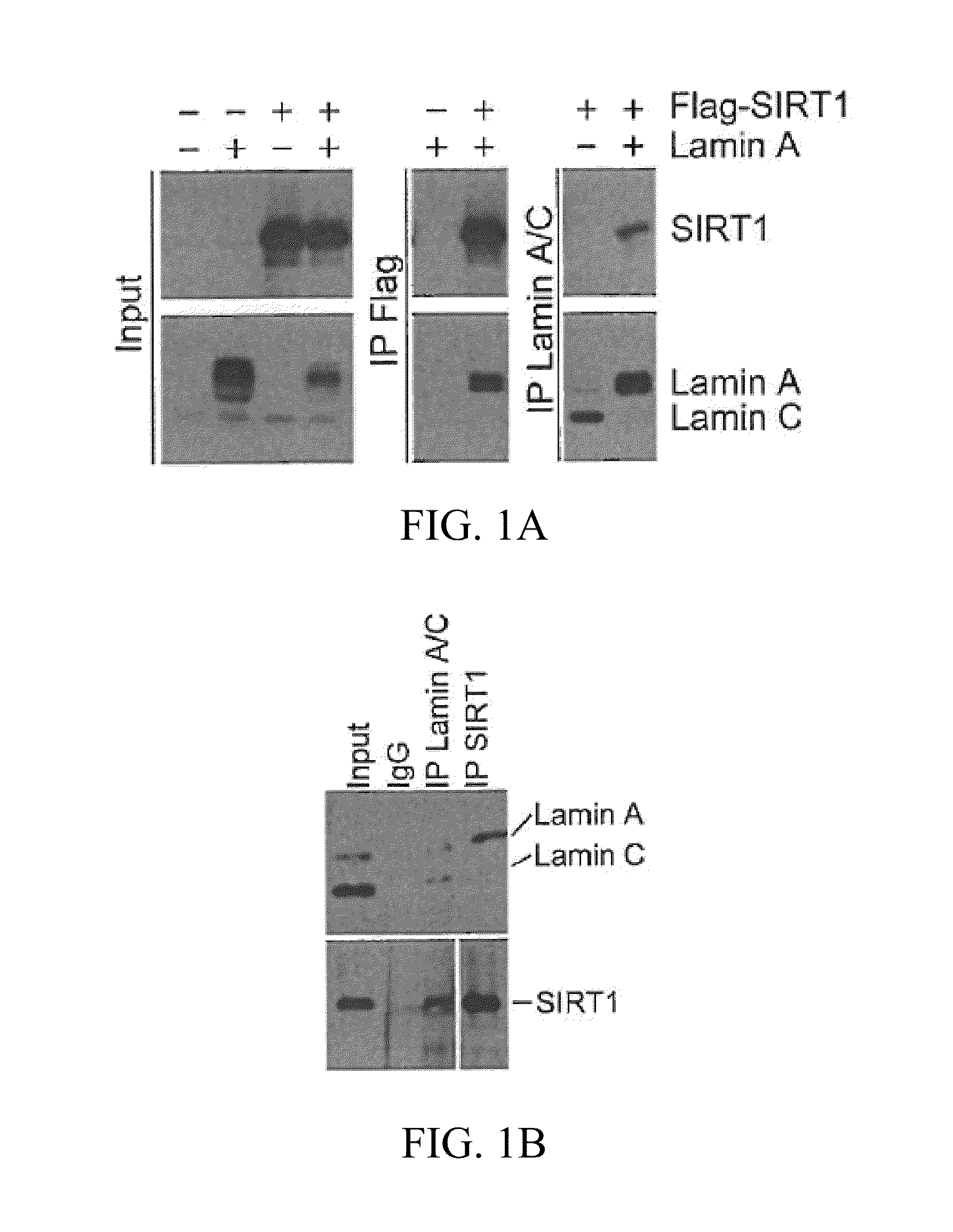
In one embodiment, the present invention provides methods of modulating the deacetylase activity of SIRT1 in one or more cell by modifying the binding affinity of lamin A to SIRT1 via one or more interaction modifying compound. In another embodiment, the present invention provides methods of screening SIRT1-activating / inhibiting compounds based on the interaction between lamin A and SIRT1 proteins and SIRT1-activating property of lamin A. In another embodiment, the present invention provides uses of SIRT1-activating compounds to treat patient(s) suffering from metabolic and / or aging-related degenerative diseases, and uses of SIRT1-inhibiting compounds to treat human malignancies.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
A kind of genetically engineered bacterial strain producing L-citrulline and its application
ActiveCN112280728BIncrease production intensityStable fermentationBacteriaHydrolasesPurineSuccinic acid
The present invention provides a genetically engineered strain CIT 4 for efficient and stable production of L-citrulline. The strain uses Escherichia coli as a host. First, the host lacks the activity of argininosuccinate synthase to block the degradation of L-citrulline. It is arginine succinate; the gene argG encoding Escherichia coli argininosuccinate synthase is also integrated on the host genome, and is controlled by the tryptophan promoter P trp Regulate expression; also make the host lack of acetylornithine deacetylase activity; also integrate the gene argJ of Corynebacterium glutamicum encoding glutamate acetyltransferase on the host genome, so as to strengthen the synthesis of glutamate Metabolic flux in the process of acetylglutamate; also integrated on the host genome the genes pyrAA and pyrAB encoding the two subunits of carbamoyl phosphate synthase in the Bacillus subtilis mutant strain A260 to release arginine for carbamoyl phosphate Feedback inhibition of synthetases increases the supply of the precursor carbamoyl phosphate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determination of N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase activity
InactiveUS9150902B2High sensitivityImprove accuracyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSulfotransferase activityPolysaccharide
A novel modified polysaccharide, a solid phase to which the polysaccharide is adhered, methods for detecting N-deacetylase activity, N-sulfotransferase activity and N-deacetylase / N-sulfotransferase activity in a sample which utilizes said solid phase, and detection kits thereof.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Lamin A, An Activator of Longevity/Anti-Aging SIRT1 Protein
ActiveUS20160067305A1Decreasing and inhibiting deacetylase activityReduced activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMalignancyAnti ageing
In one embodiment, the present invention provides methods of modulating the deacetylase activity of SIRT1 in one or more cell by modifying the binding affinity of lamin A to SIRT1 via one or more interaction modifying compound. In another embodiment, the present invention provides methods of screening SIRT1-activating / inhibiting compounds based on the interaction between lamin A and SIRT1 proteins and SIRT1-activating property of lamin A. In another embodiment, the present invention provides uses of SIRT1-activating compounds to treat patient(s) suffering from metabolic and / or aging-related degenerative diseases, and uses of SIRT1-inhibiting compounds to treat human malignancies.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
3-aryl coumarin derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113121485AHigh affinityUpregulation of sirtuin activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAcetic anhydrideAntidiabetics drug
The invention discloses a 3-aryl coumarin derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out tandem condensation-lactonization reaction on substituted phenylacetic acid and substituted 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde as raw materials in the presence of triethylamine and acetic anhydride, and after the reaction is finished, respectively and independently carrying out three post-treatment methods to obtain the 3-aryl coumarin derivative. The 3-aryl coumarin derivative provided by the invention has good affinity to SIRT3 protein, can up-regulate the deacetylase activity of the SIRT3 protein and reverse ISO (isoprenaline) stimulated and induced cardiac hypertrophy, and can be used for preparing anti-cardiovascular disease or anti-diabetes drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A kind of chitin deacetylase and its application
ActiveCN109609485BBiosafetyLow requirements for production conditionsBacteriaHydrolasesBiochemistryChitin deacetylase
The present invention screens out several unknown proteins by analyzing and researching different genome sequences of different species, and further identifies a chitin deacetylase with excellent deacetylase activity. More specifically, the present invention relates to a A chitin deacetylase derived from Verticillium longisporum Vlo. Compared with the reported chitin deacetylase, the chitin deacetylase requires less production conditions and has higher biosafety properties, and has characteristics more suitable for industrial applications, showing a wide range of application potential.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM +2
Nucleic acid molecules coding for a protein with deacetylase activity, said protein, and method for the production of chitosan
The invention relates to nucleic acid molecules selected from the group comprising: a) nucleic acid molecules that code for a form of the polypeptide with the derived amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID No. 3, said polypeptide having a deacetylase activity; b) nucleic acid molecules that comprise the nucleotide sequence according to SEQ ID No. 1 or SEQ ID No. 2 and that code for one form of said polypeptide; c) nucleic acid molecules that code for a fragment or a derivative of a polypeptide that is coded by a nucleic acid molecule according to a) or b), wherein one or more amino acid groups are conservatively substituted in said derivative as compared to said polypeptide, and wherein said fragment or derivative has a deacetylase activity; d) nucleic acid molecules that have a sequence identity of at least 95% with a nucleic acid molecule according to a) to c), and that code for a polypeptide with deacetylase activity; e) nucleic acid molecules that have a sequence identity of at least 70% with a nucleic acid molecule according to a) to c) and that code for a polypeptide with deacetylase activity; f) or the complementary string of a nucleic acid molecule according to a) to e).
Owner:WESTFAELISCHE WILHEMS UNIV MUENSTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com