Patents
Literature
753 results about "Sequence identity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Identity in sequence alignment is the number of characters that match exactly between two different sequences. Hence, gaps do not count when assessing identity. The measurement is considered to be relational to the shorter sequence among the two sequences.
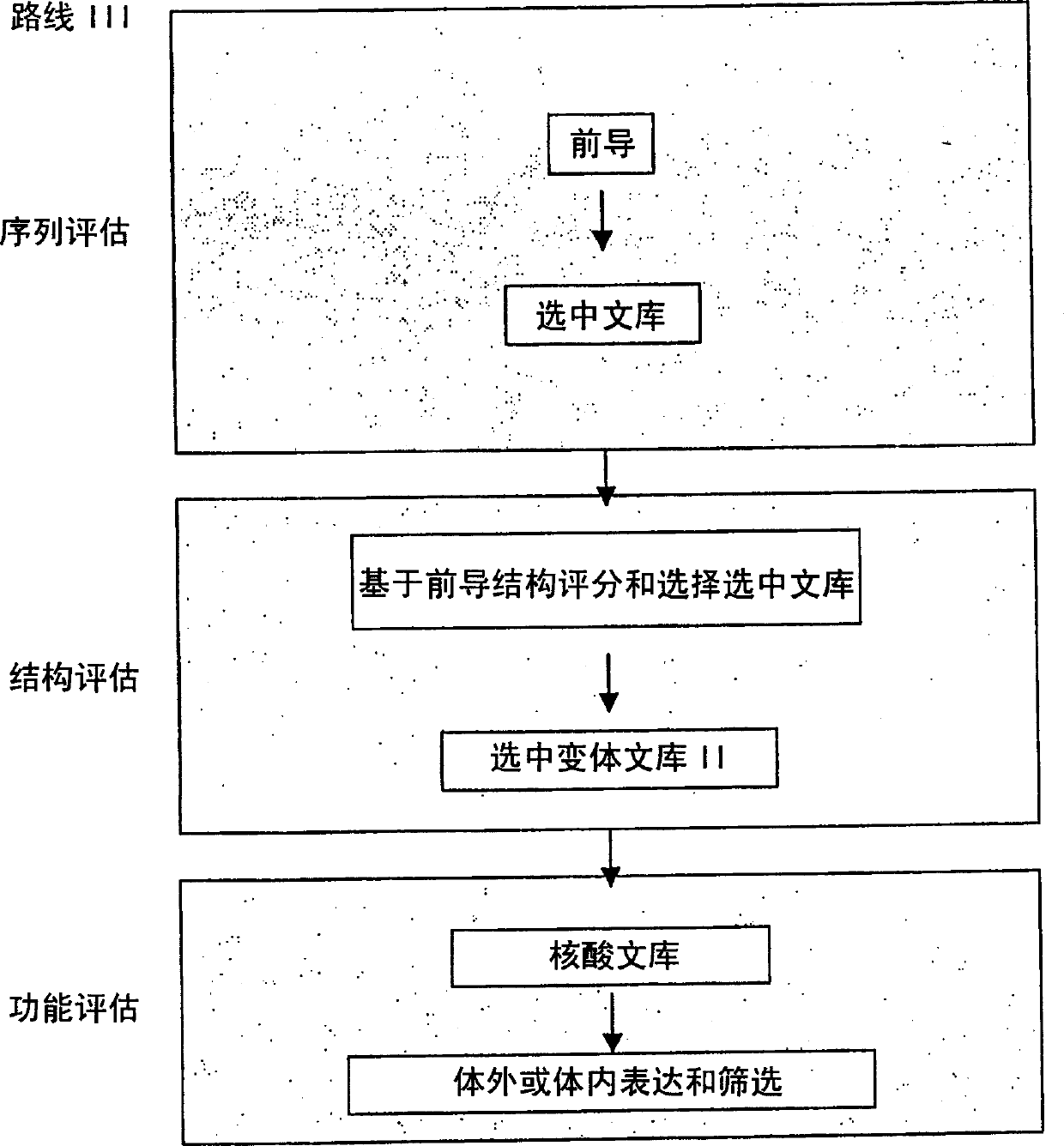
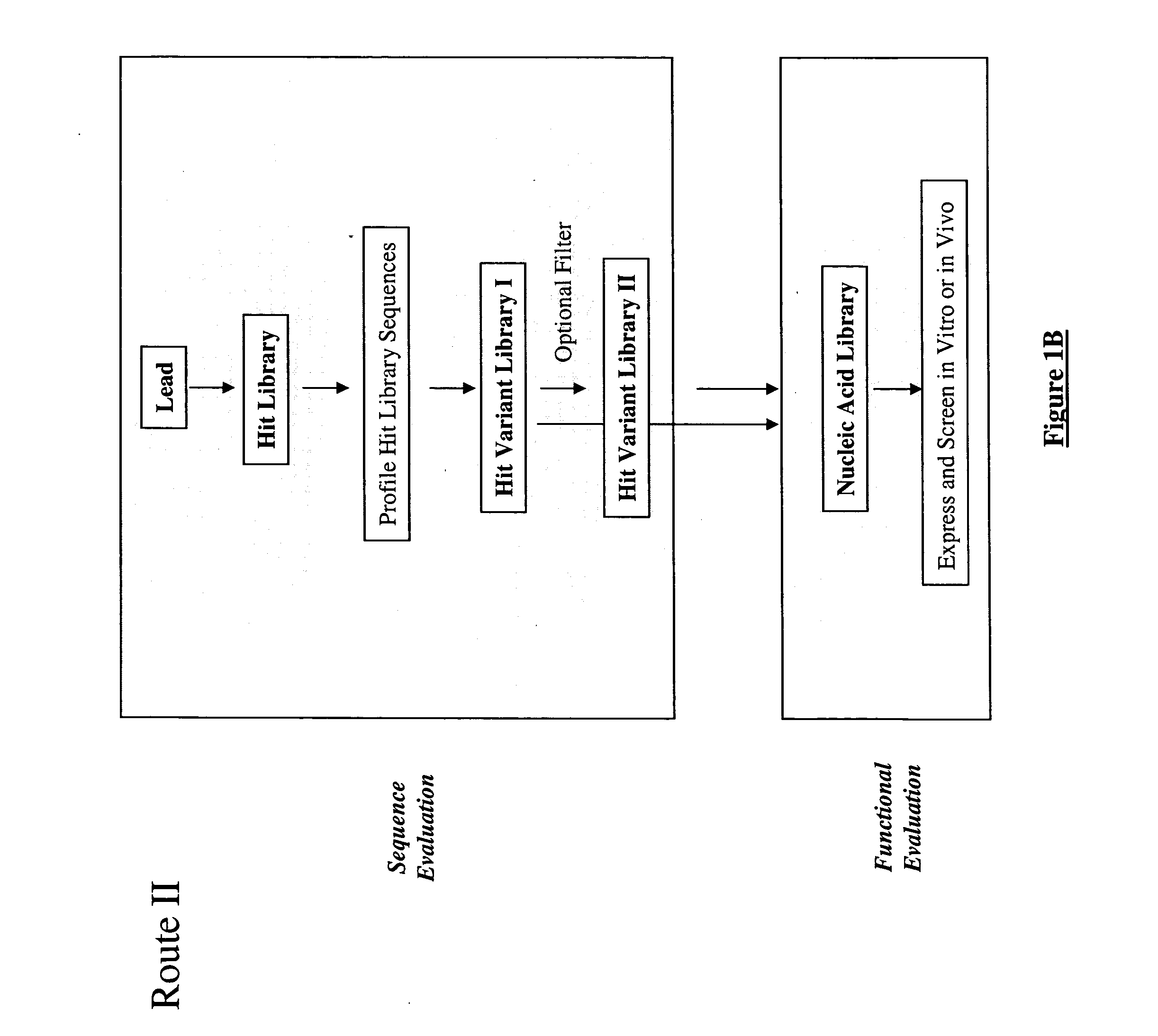
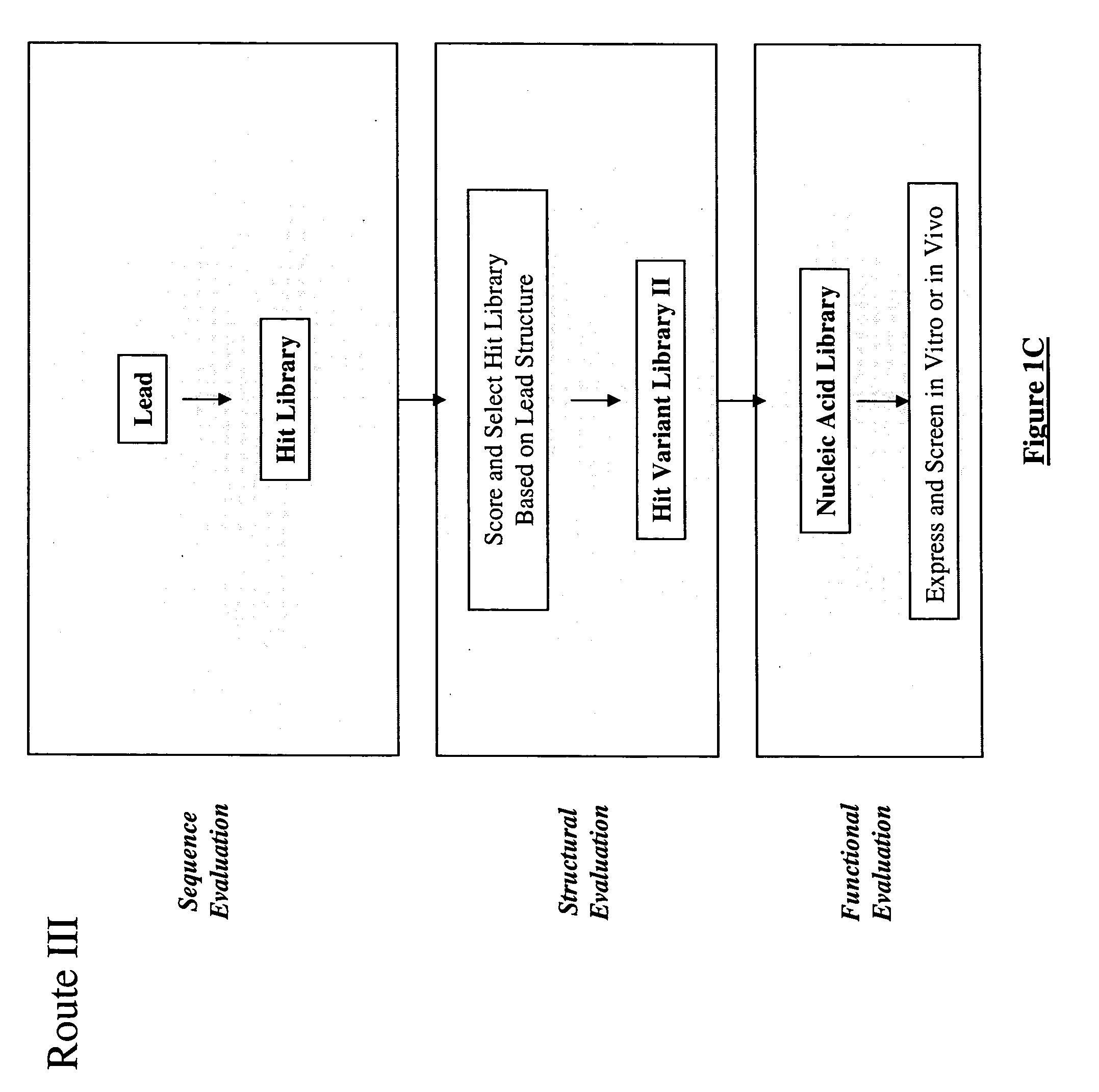
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
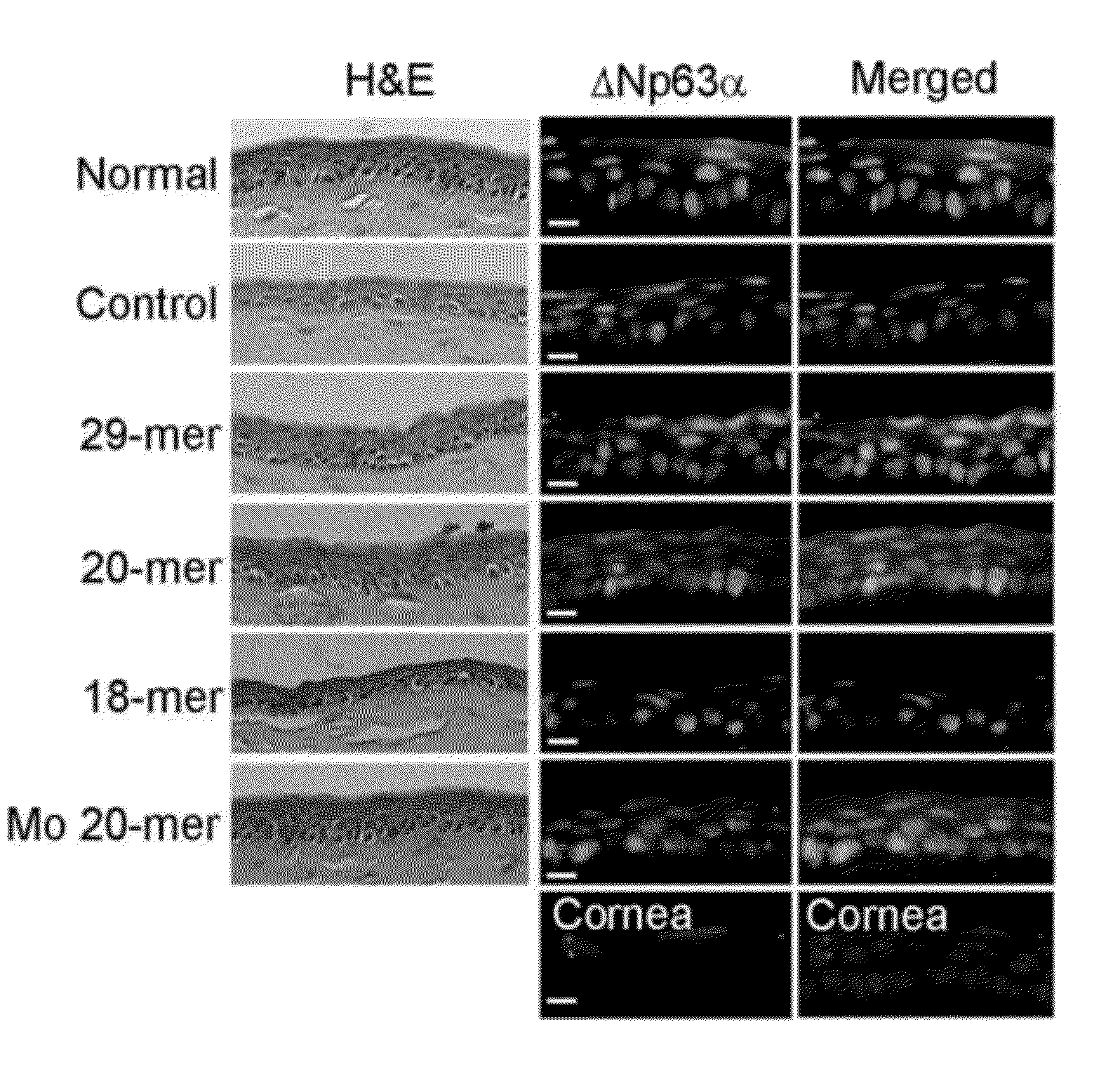
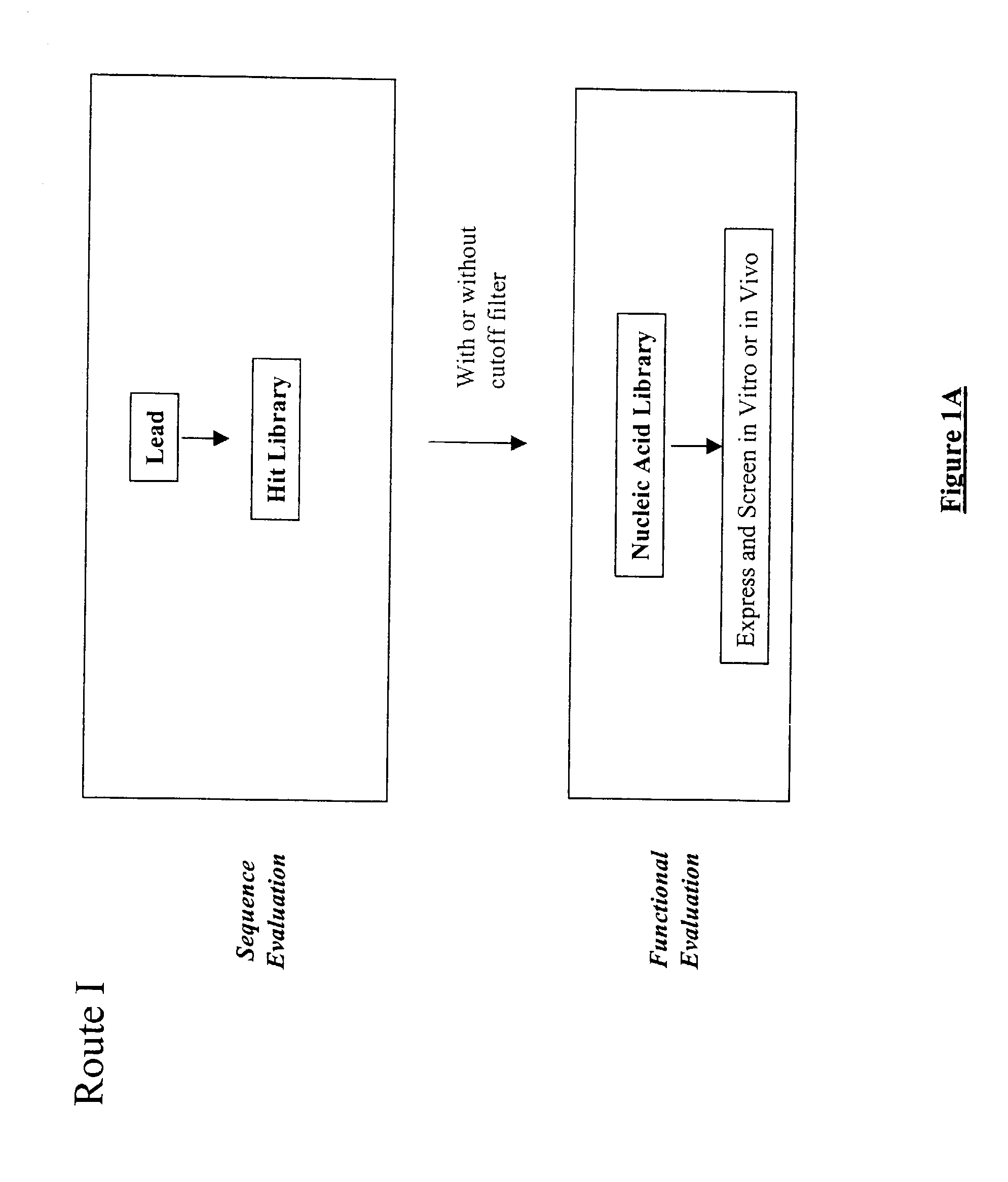
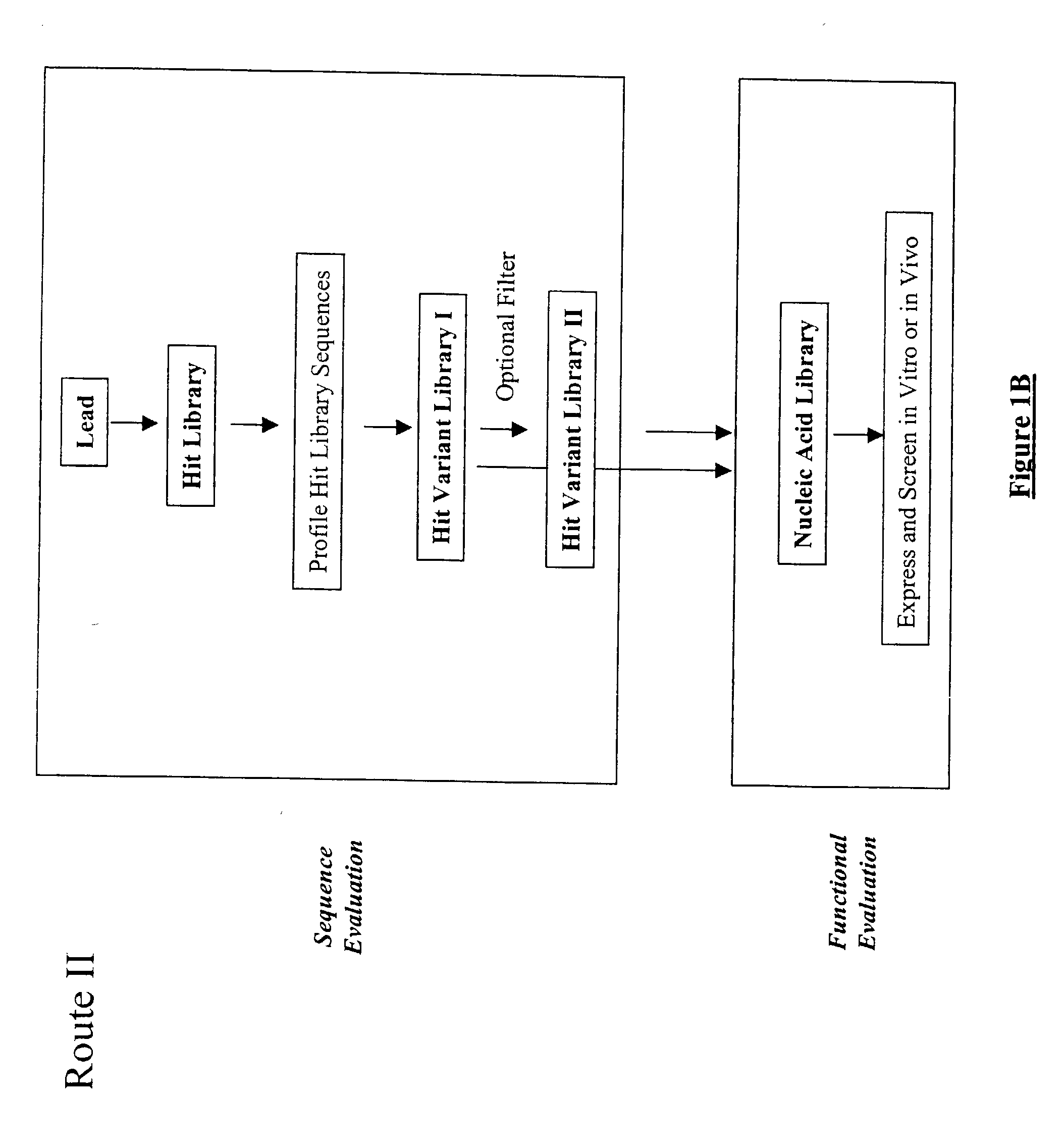
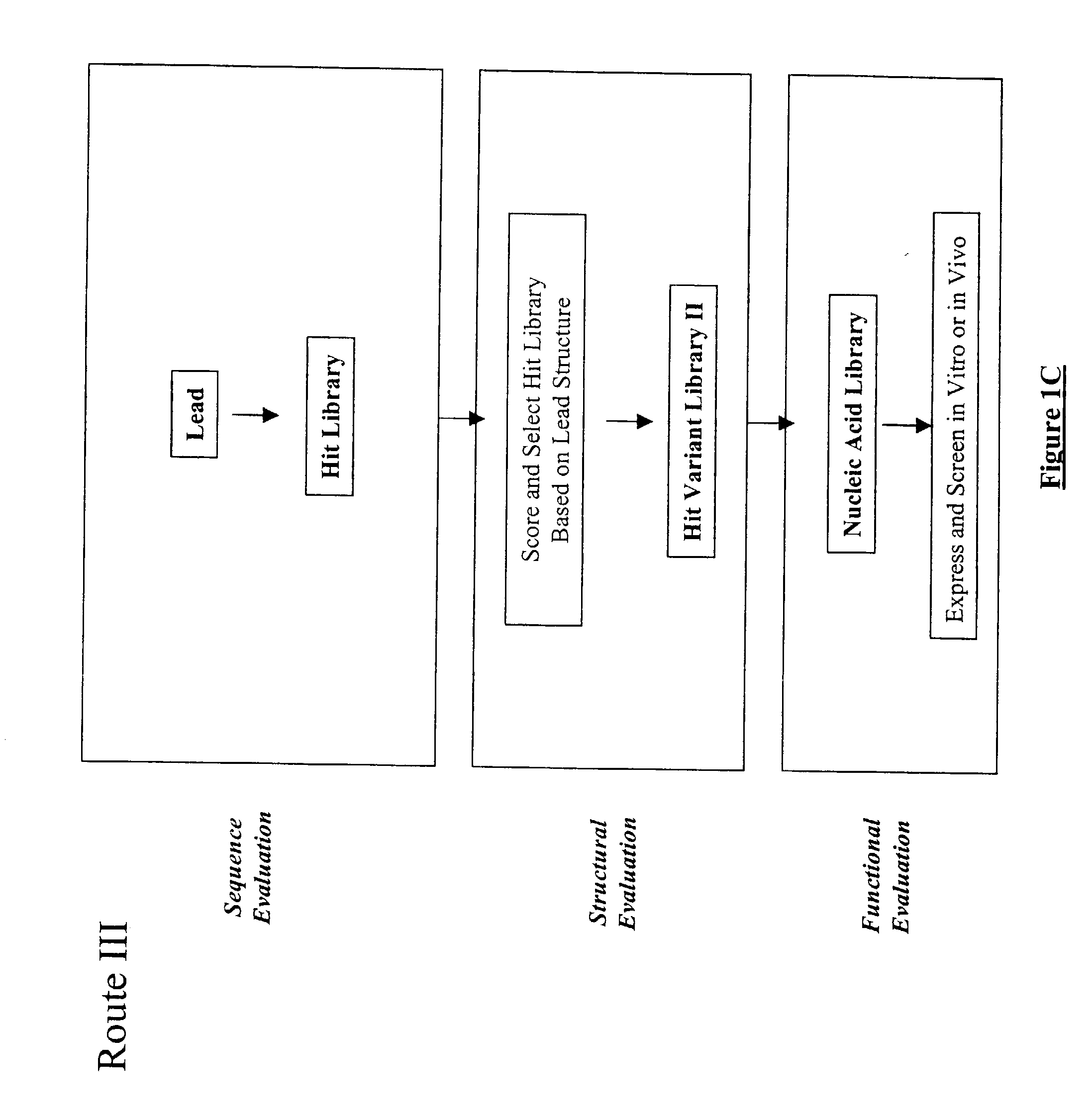
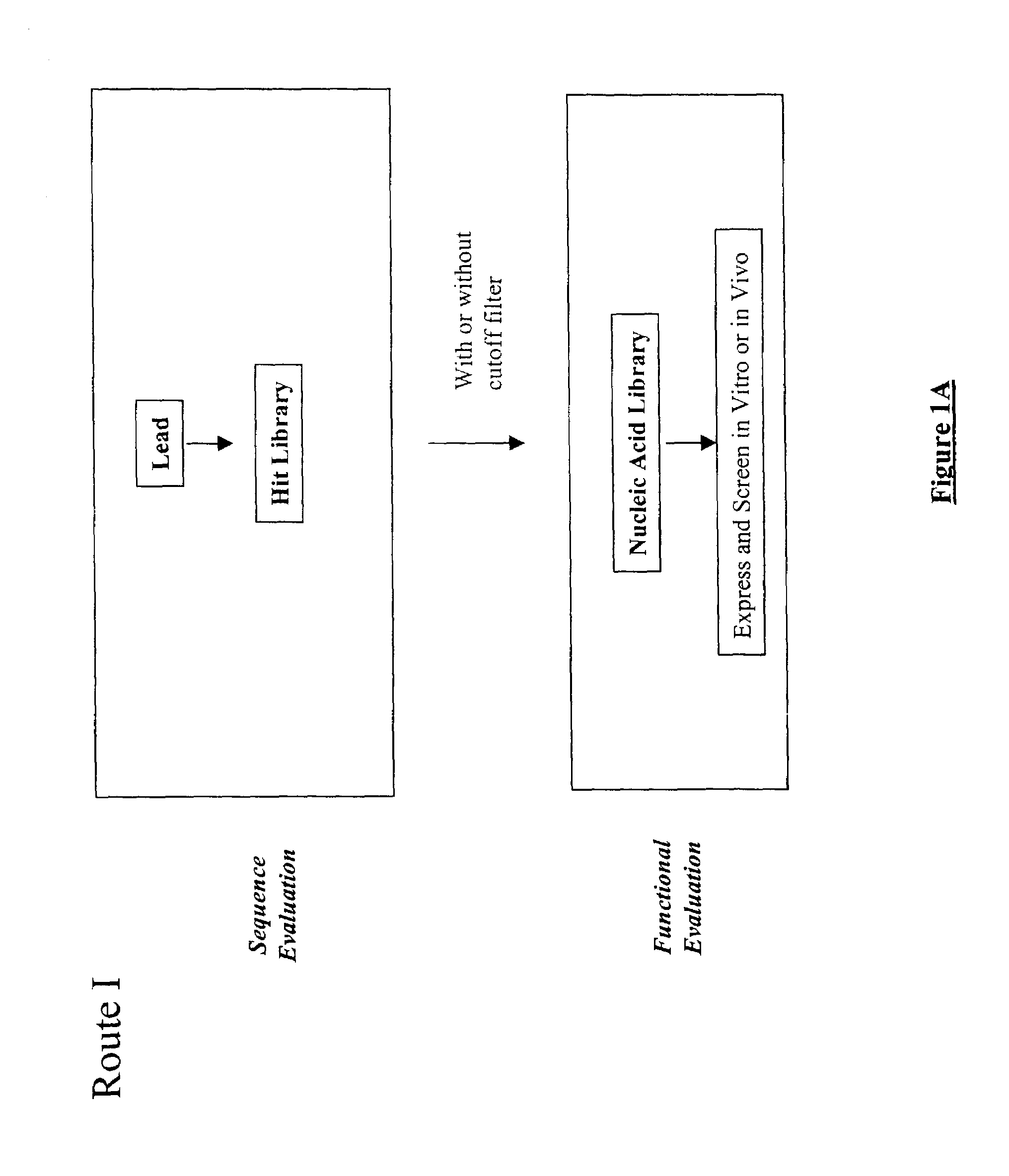
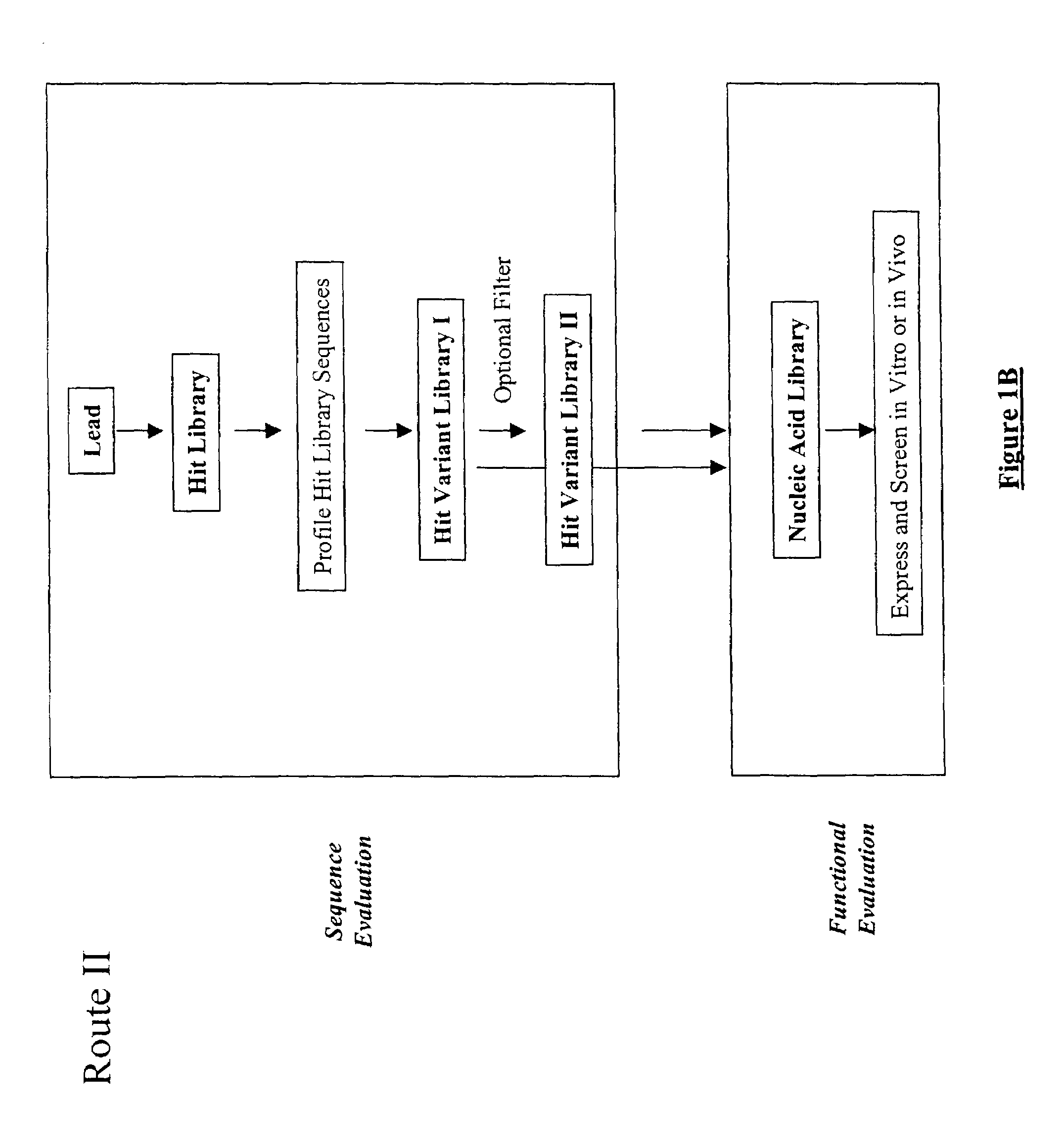
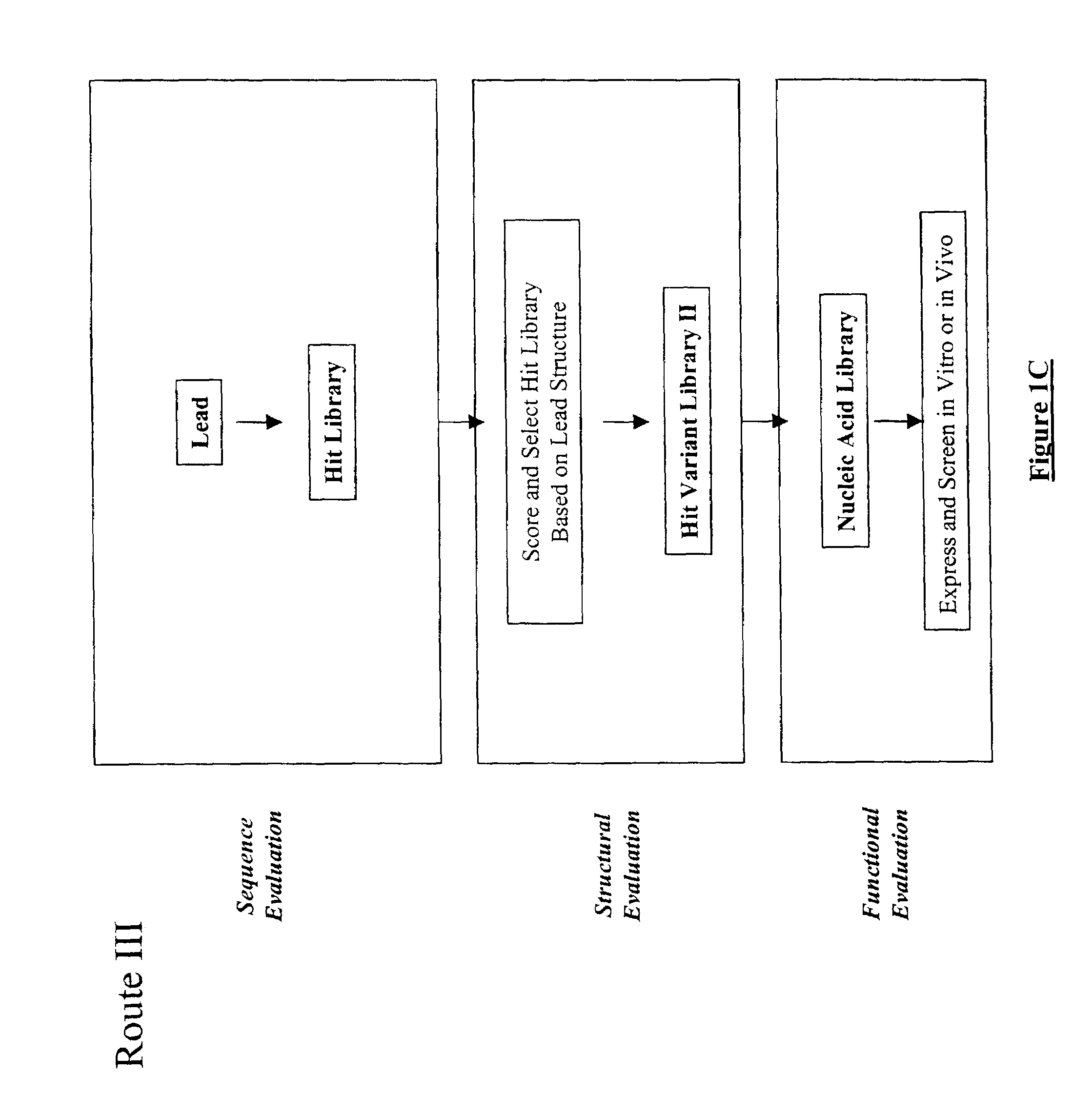
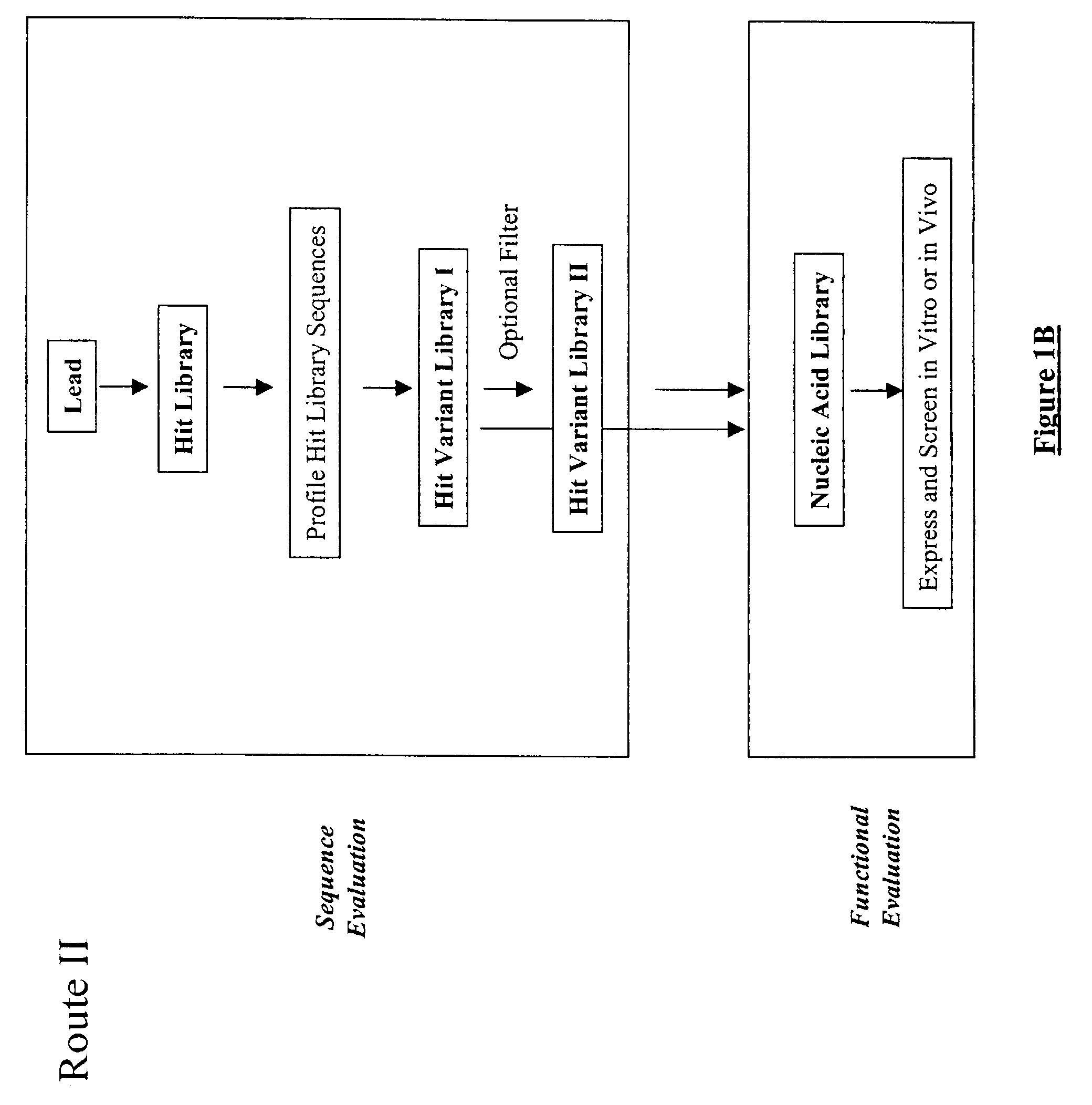
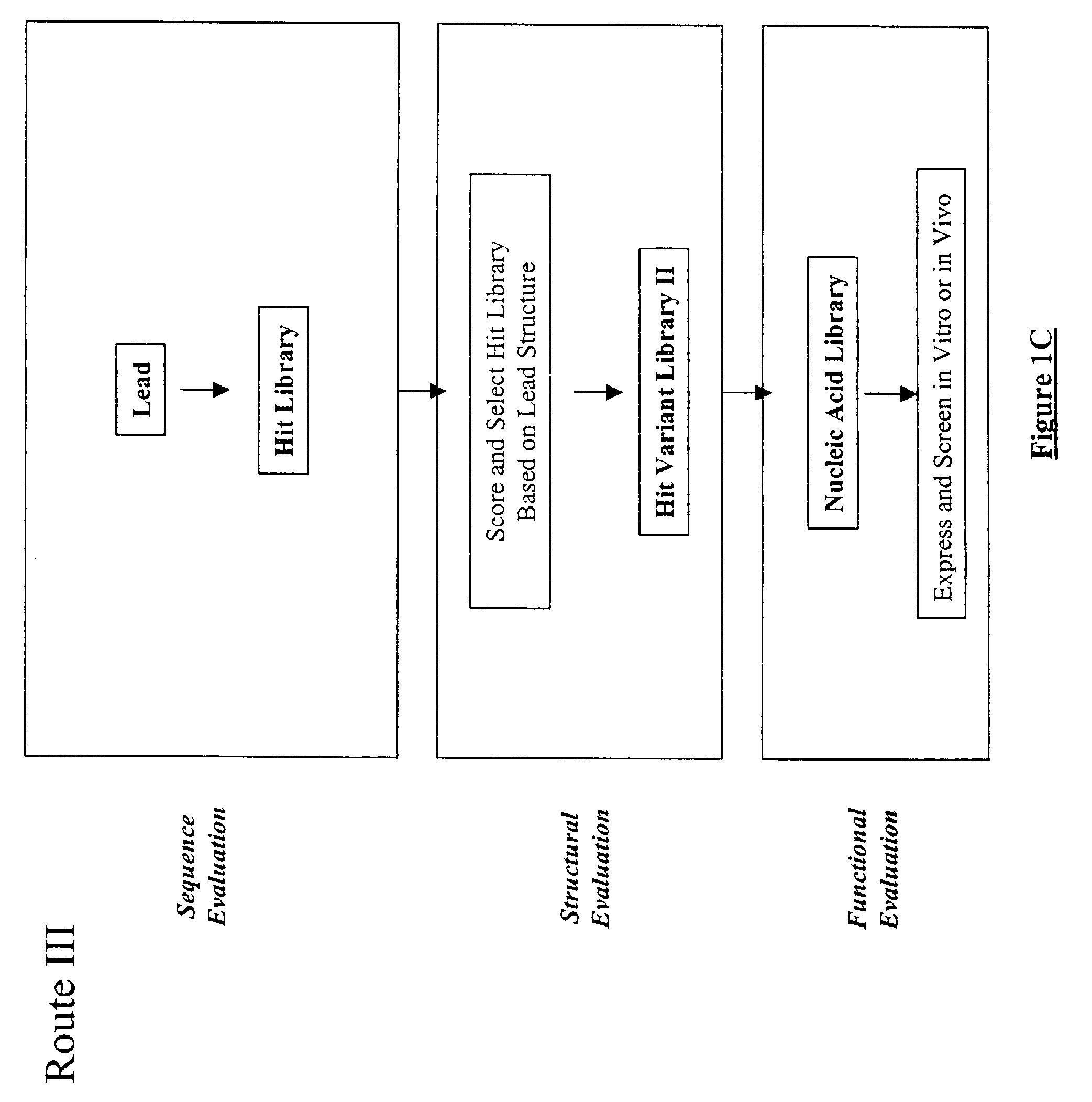
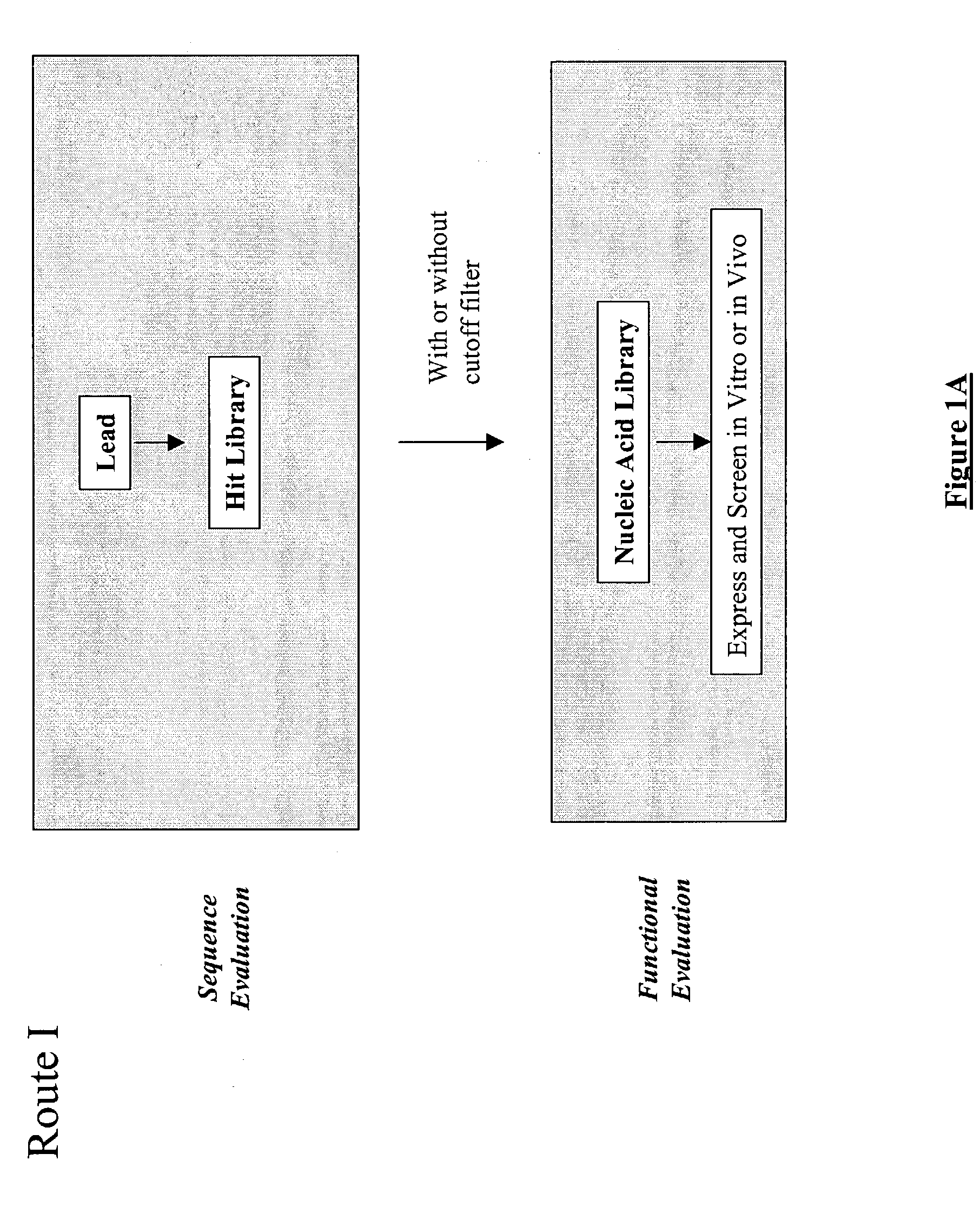
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
InactiveUS7117096B2High affinityImprove throughputPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein insertionIn vivo
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
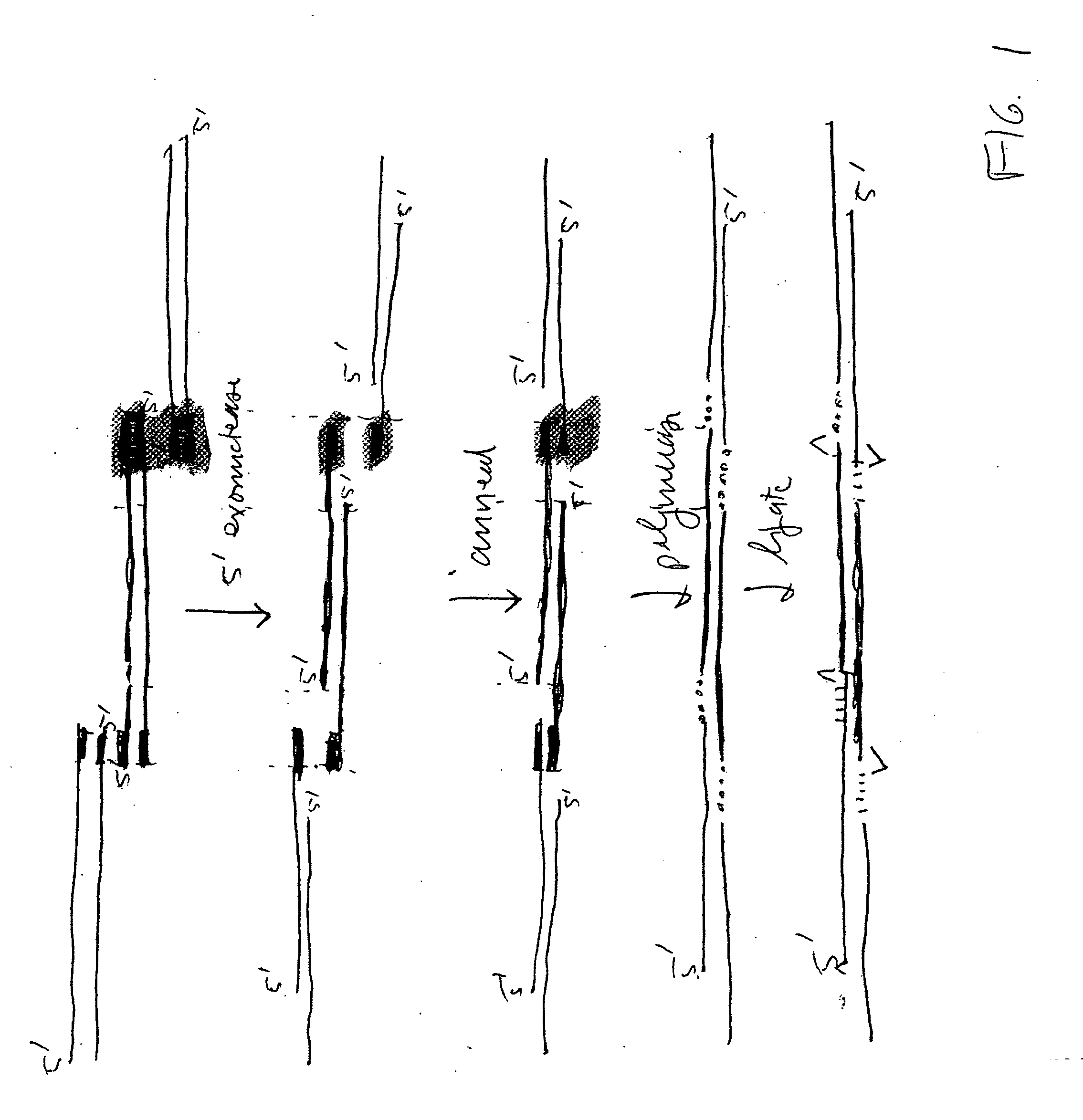
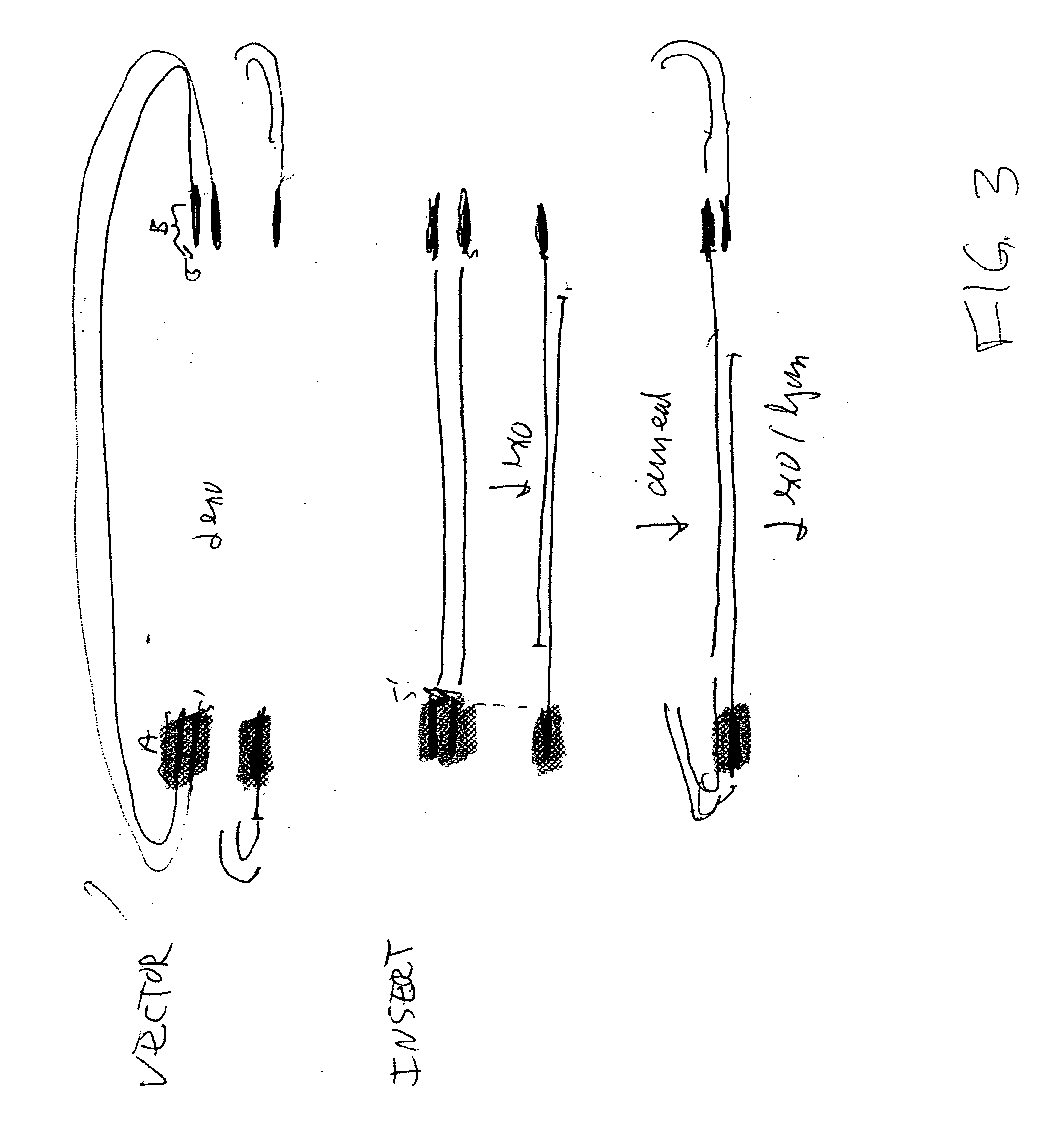
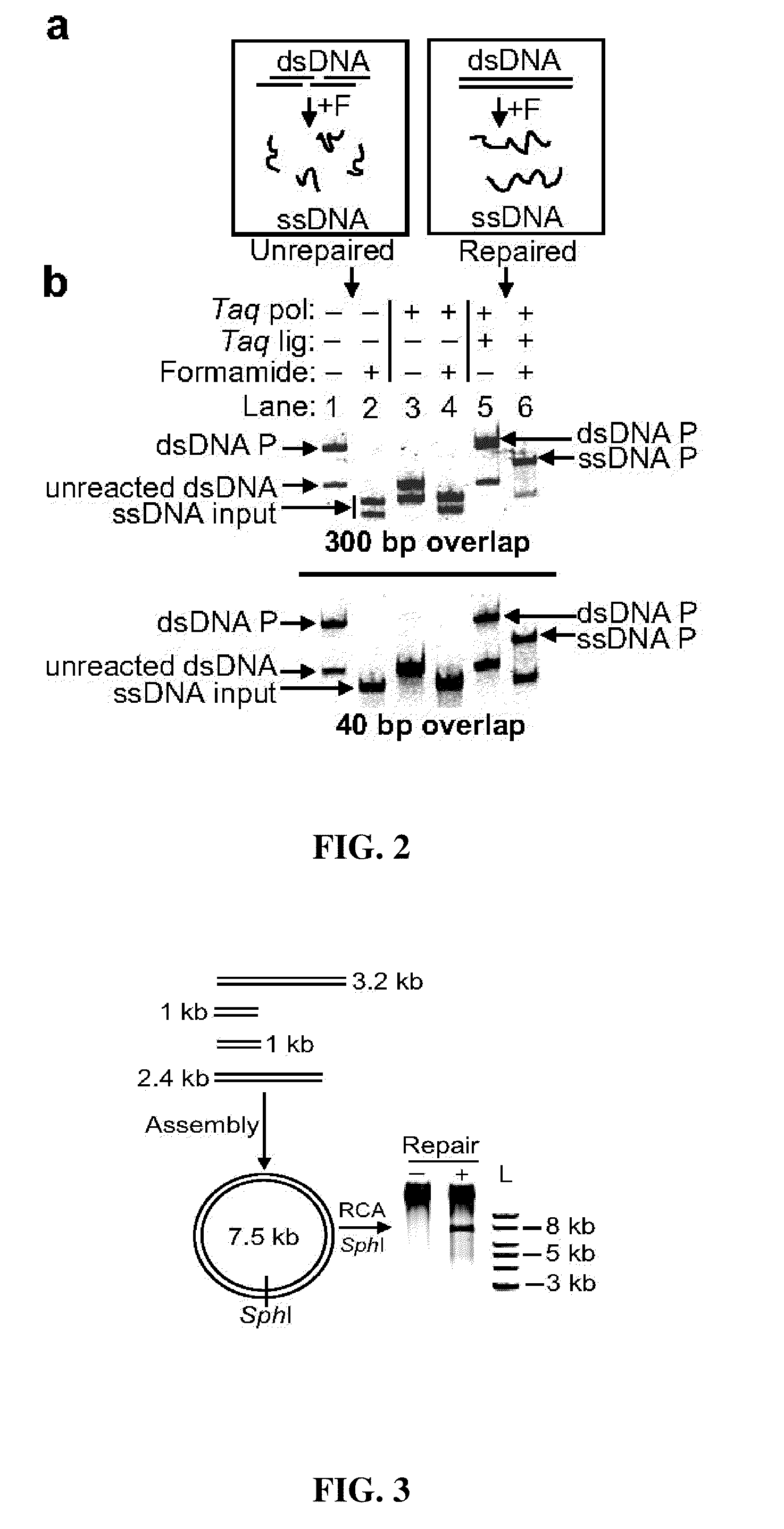
In vitro recombination method
ActiveUS20070037197A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand DNA-binding proteinSequence identity
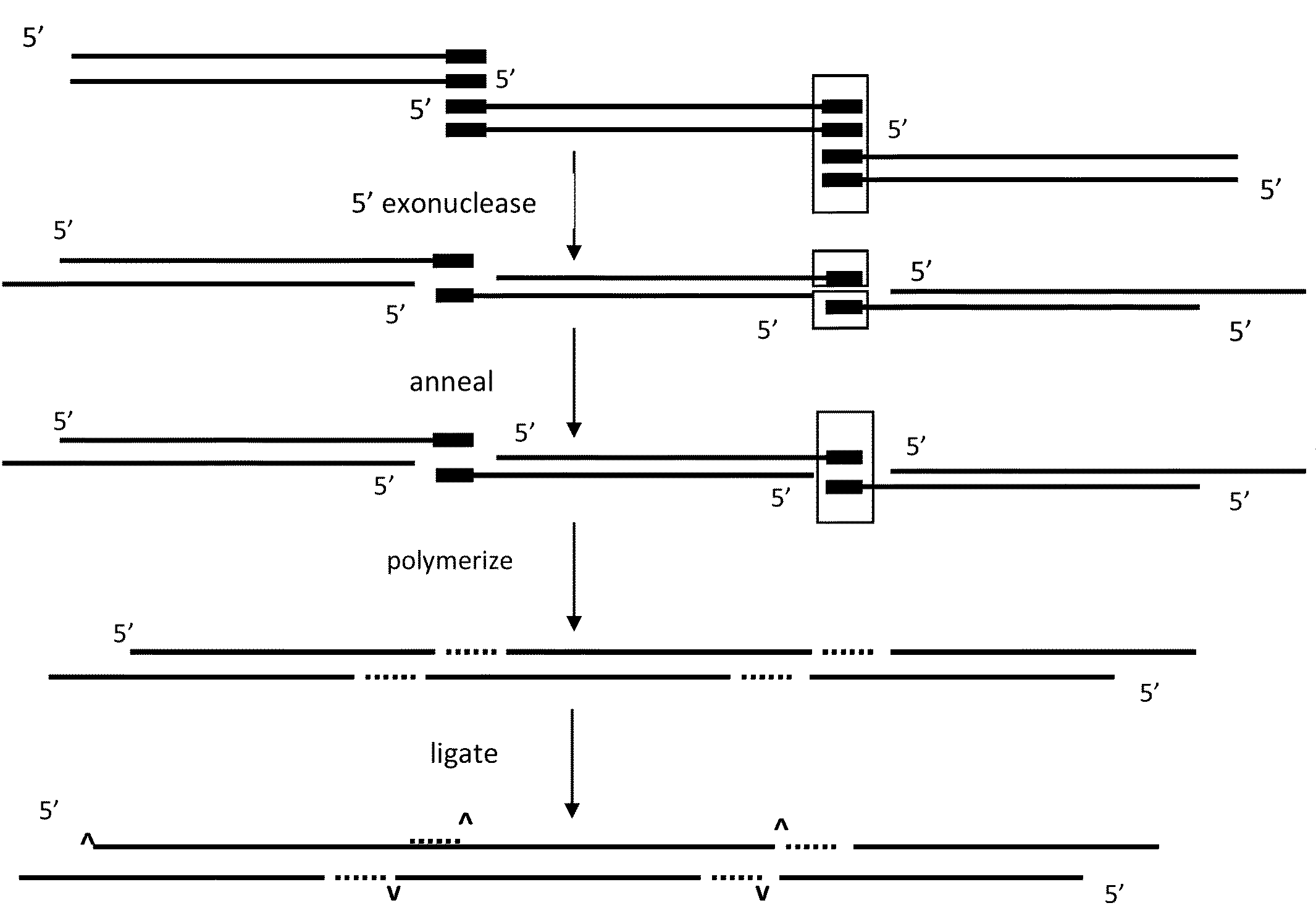
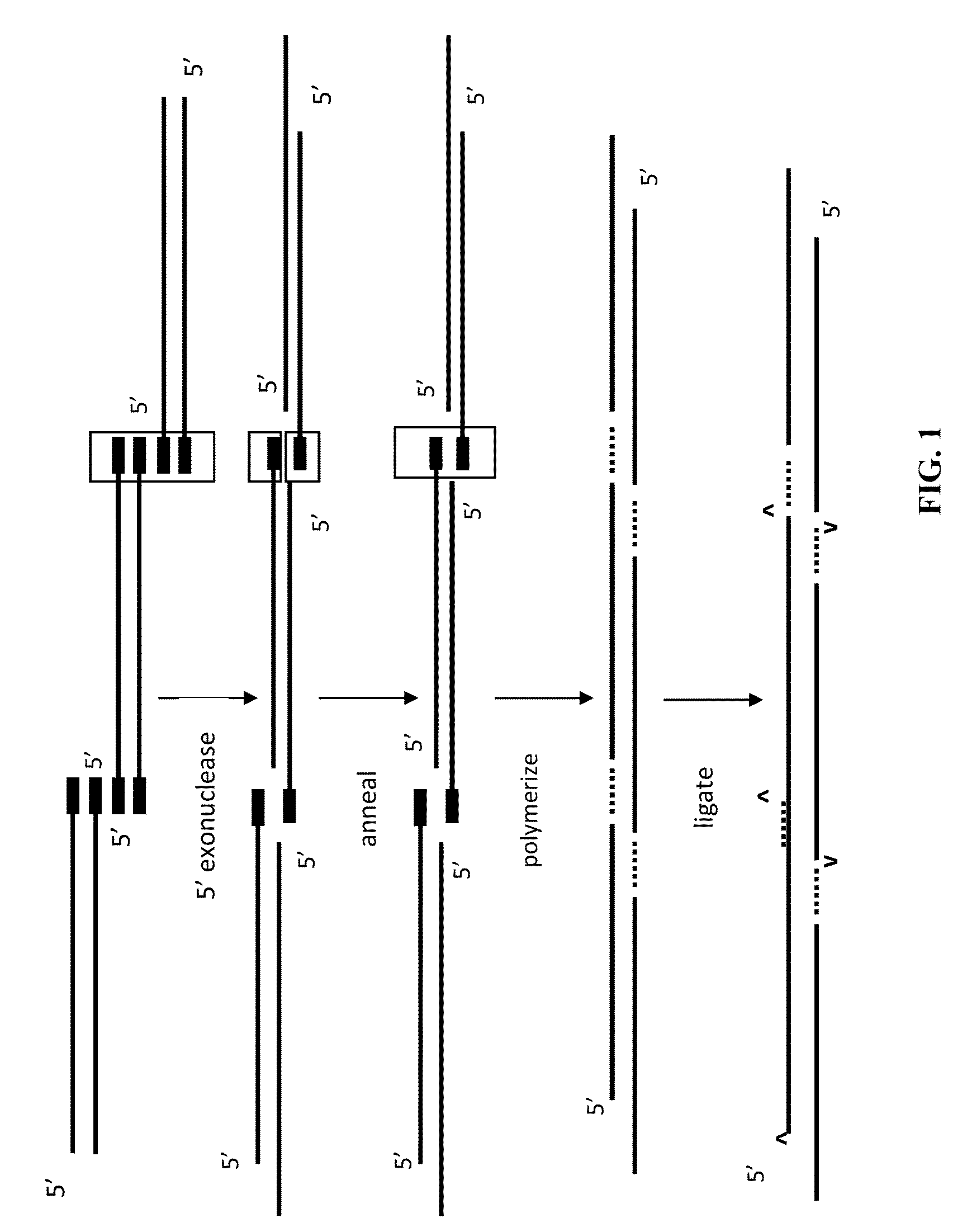
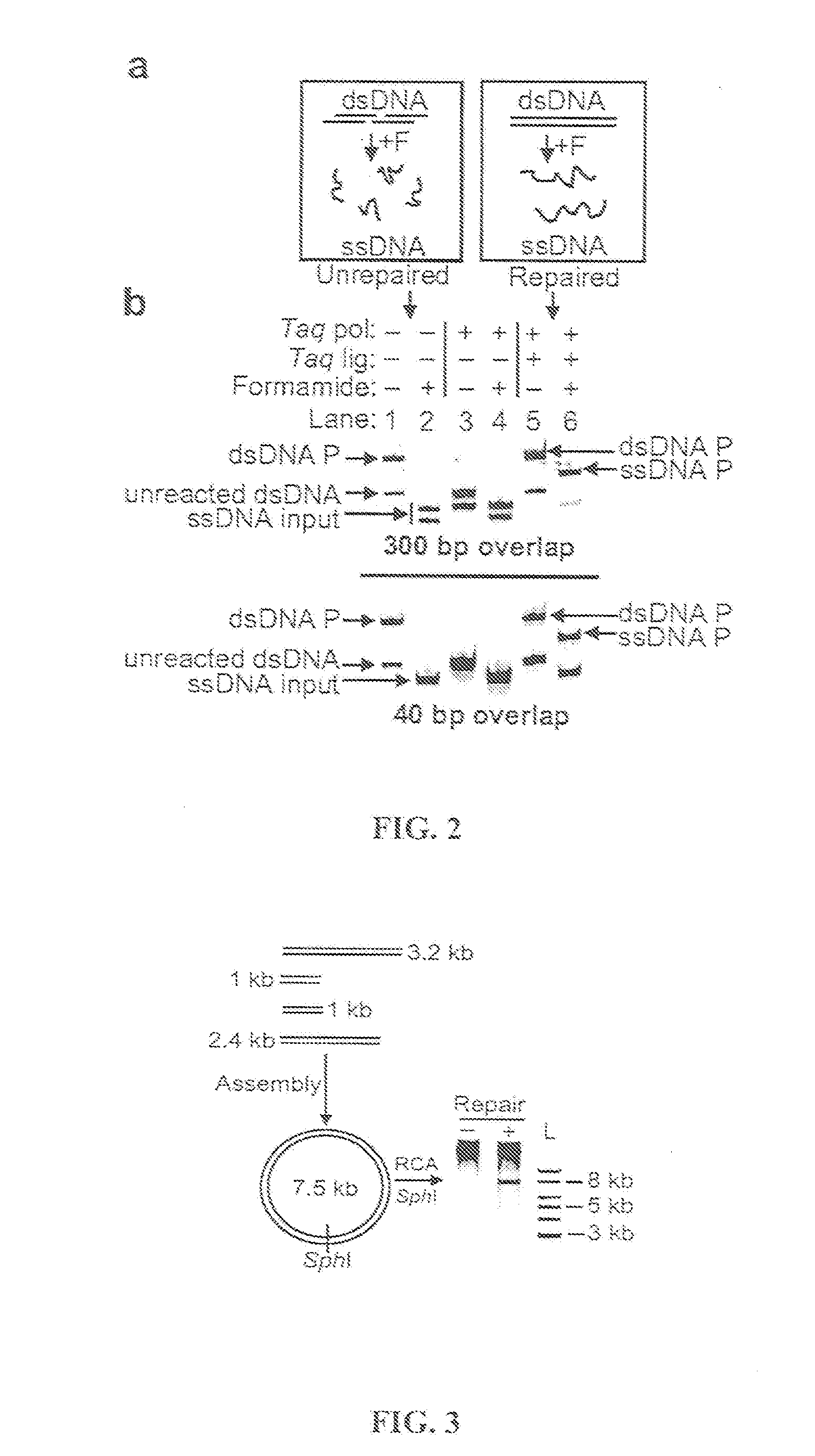
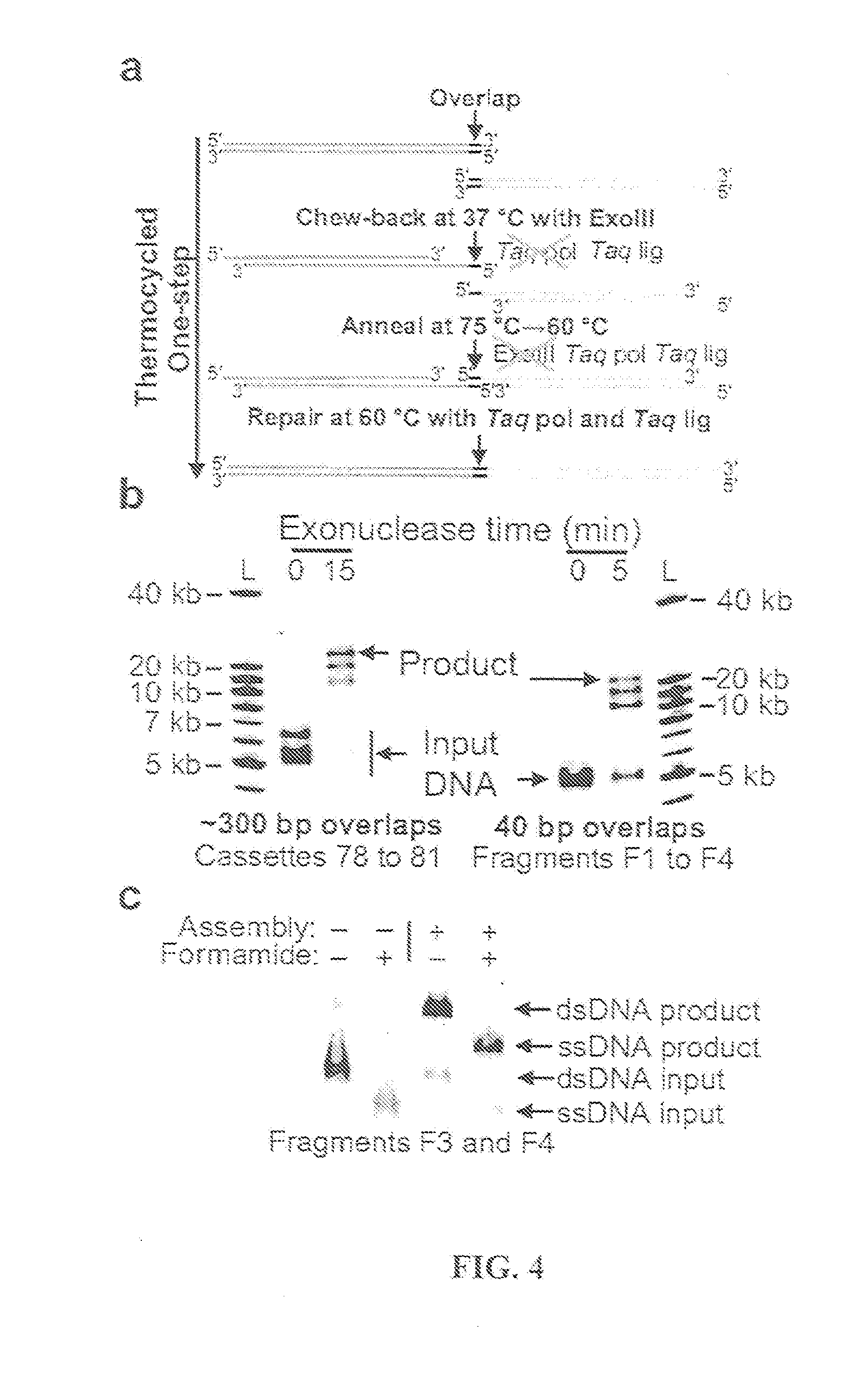
The present invention relates, e.g., to in vitro method, using isolated protein reagents, for joining two double stranded (ds) DNA molecules of interest, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule share a region of sequence identity, comprising contacting the two DNA molecules in a reaction mixture with (a) a non-processive 5′ exonculease; (b) a single stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) which accelerates nucleic acid annealing; (c) a non strand-displacing DNA polymerase; and (d) a ligase, under conditions effective to join the two DNA molecules to form an intact double stranded DNA molecule, in which a single copy of the region of sequence identity is retained. The method allows the joining of a number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Promoter BgIosP587, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a promoter, in particular to a promoter for monocotyledons such as rice, and a preparation method and application thereof. The promoter of the invention has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, or has a variant which has the functions of the promoter and is selected from the following sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence hybridized with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 under the condition of advanced tightness; 2) a nucleotide sequence carrying out substitution, loss, modification and addition of one or more basic groups on the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; and 3) a nucleotide sequence having at least 90 percent of sequence identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. In addition, the invention also relates to a method for preparing the promoter and the application of the promoter in adjusting and controlling the target gene expression in the monocotyledons.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
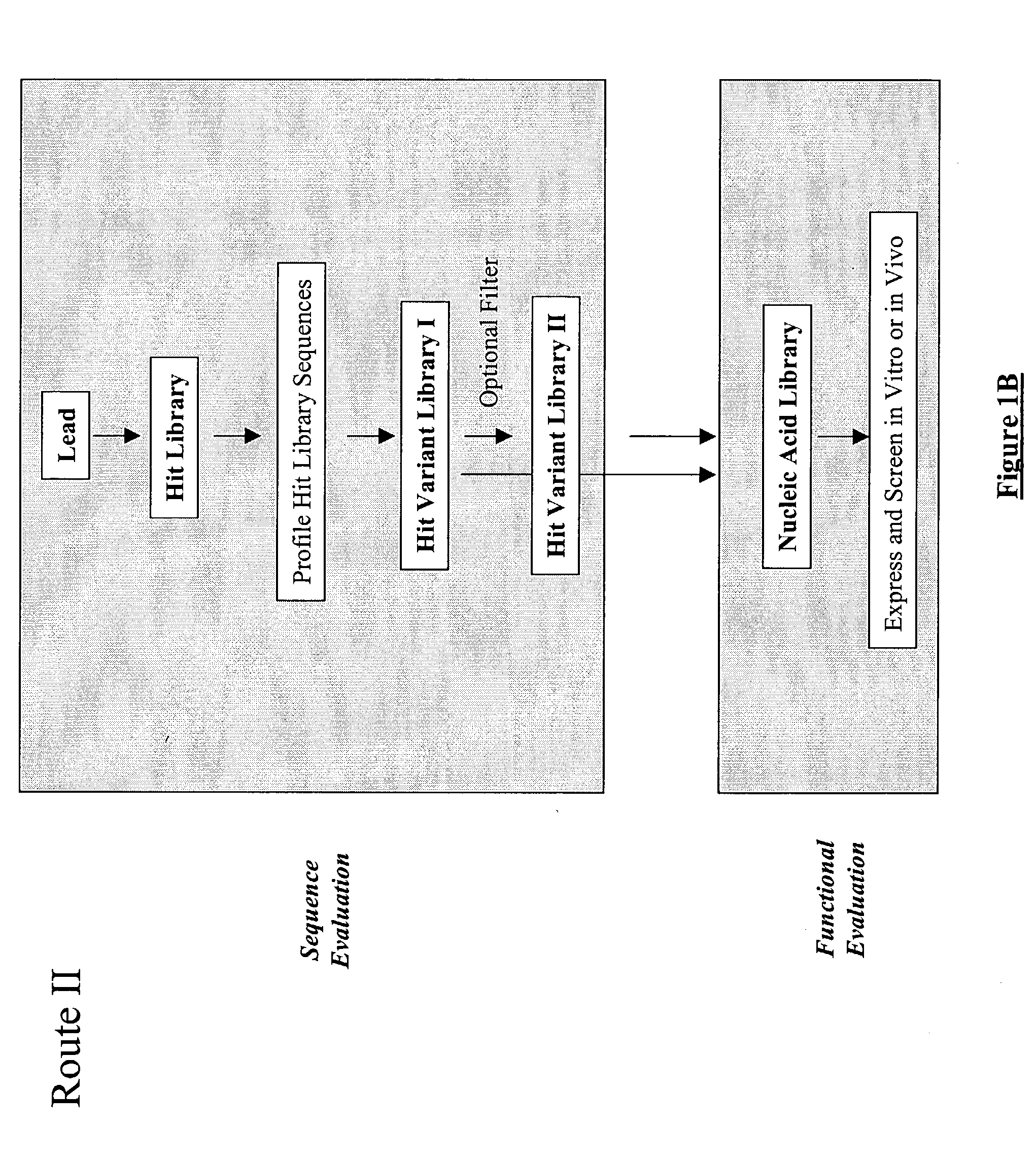
Generation and affinity maturation of antibody library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on the amino acid sequence of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library. The hit library of antibody sequences can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Antibodies and methods for making and using them
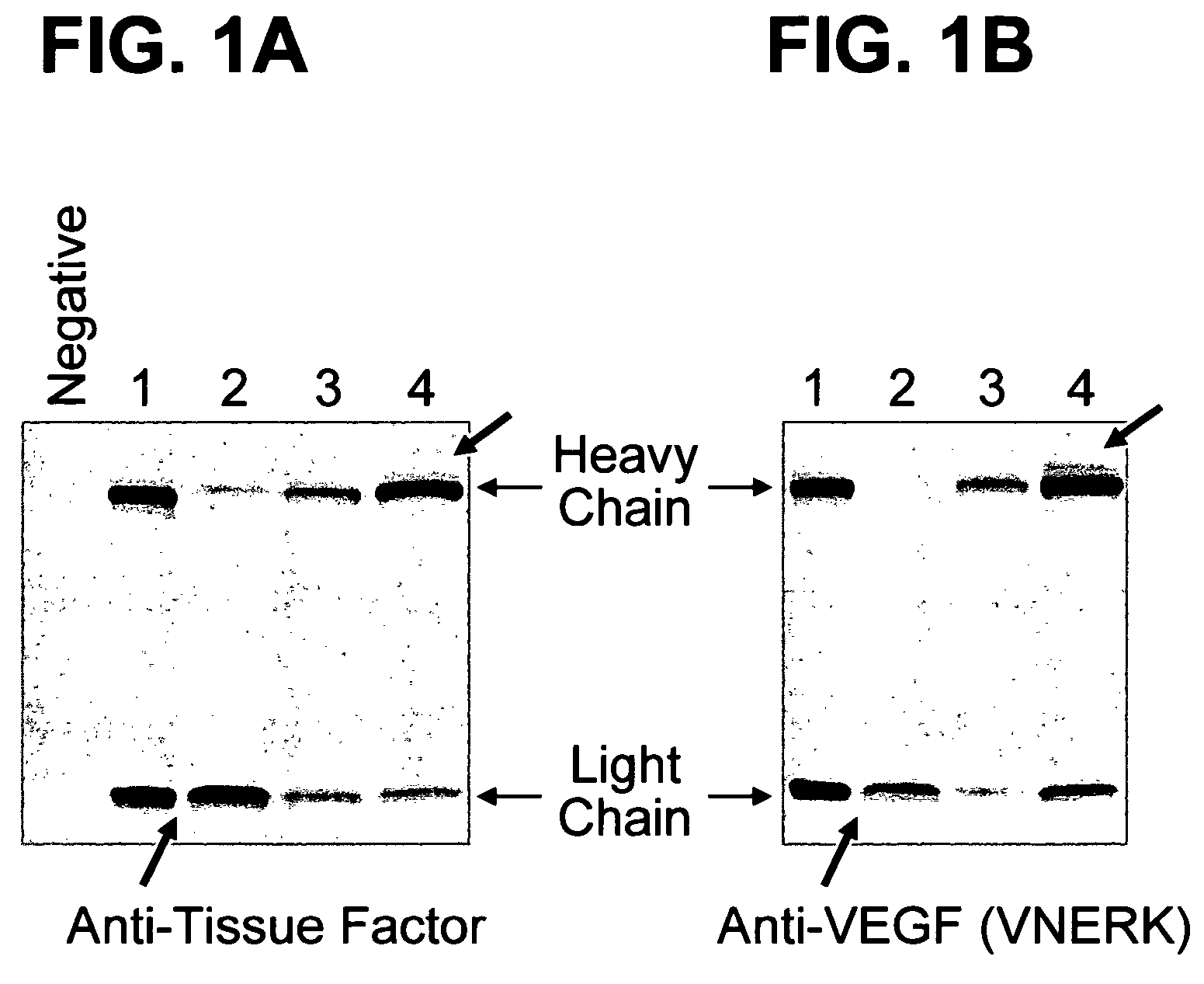
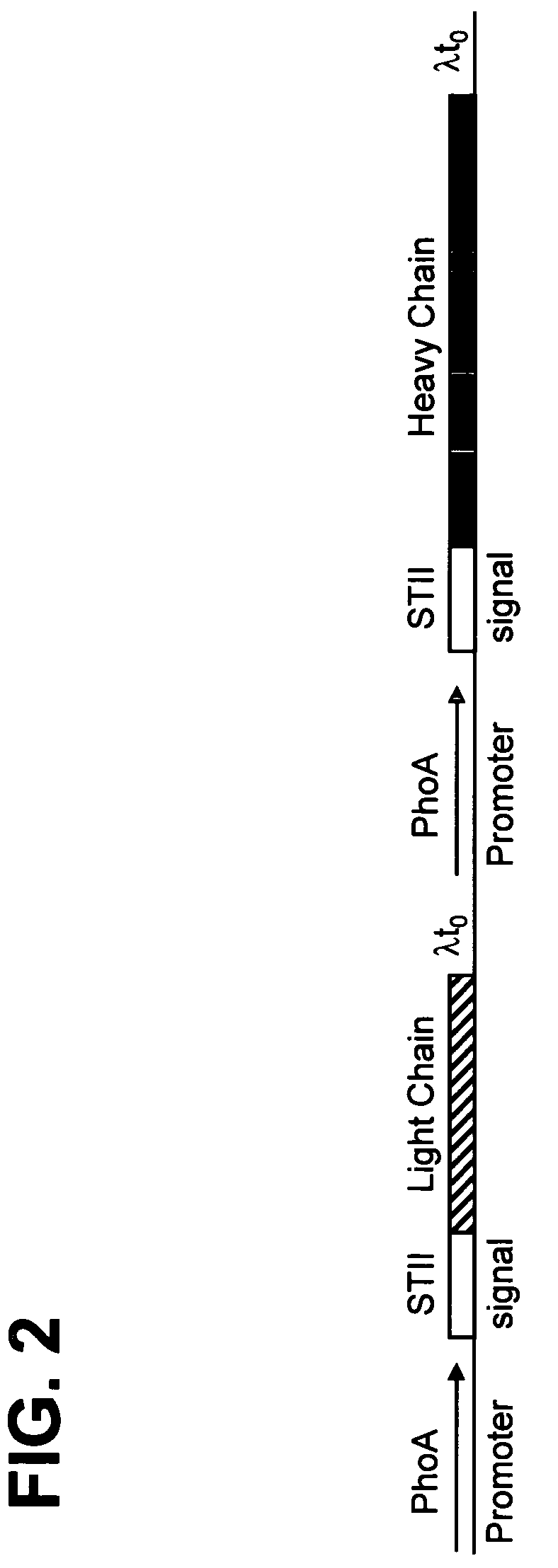
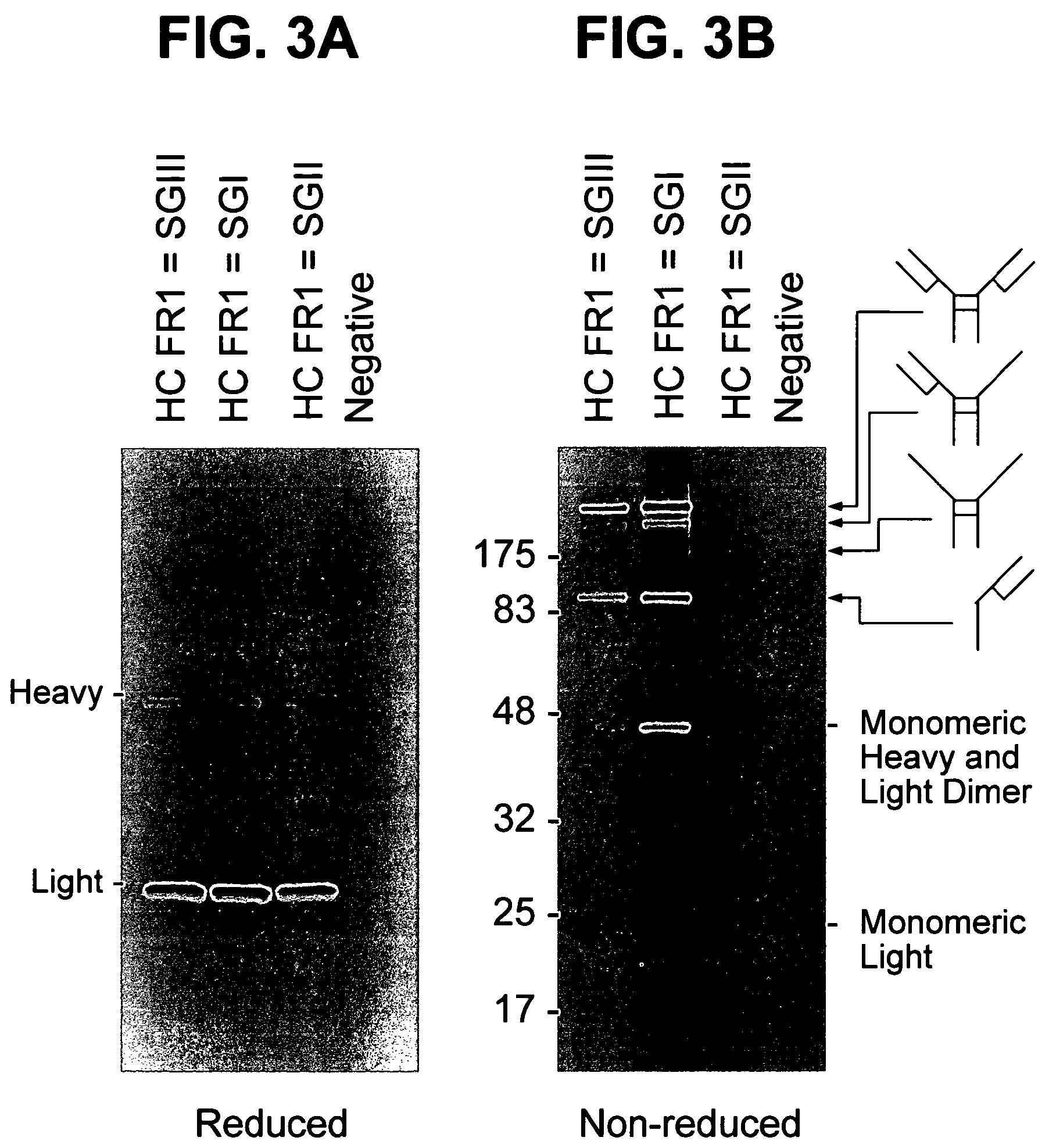
InactiveUS20080187966A1Speed up the processIncrease productionImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyDisulfide bondingAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides methods for producing humanized antibodies and increasing the yield of antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments when produced in cell culture. In one aspect of the invention, at least one framework region amino acid residue of the variable domain is substituted by a corresponding amino acid from a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain. In another aspect, an amino acid is placed at a position proximal to a cys residue that participates in an intrachain variable domain disulfide bond that corresponds to an amino acid found at that position in a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
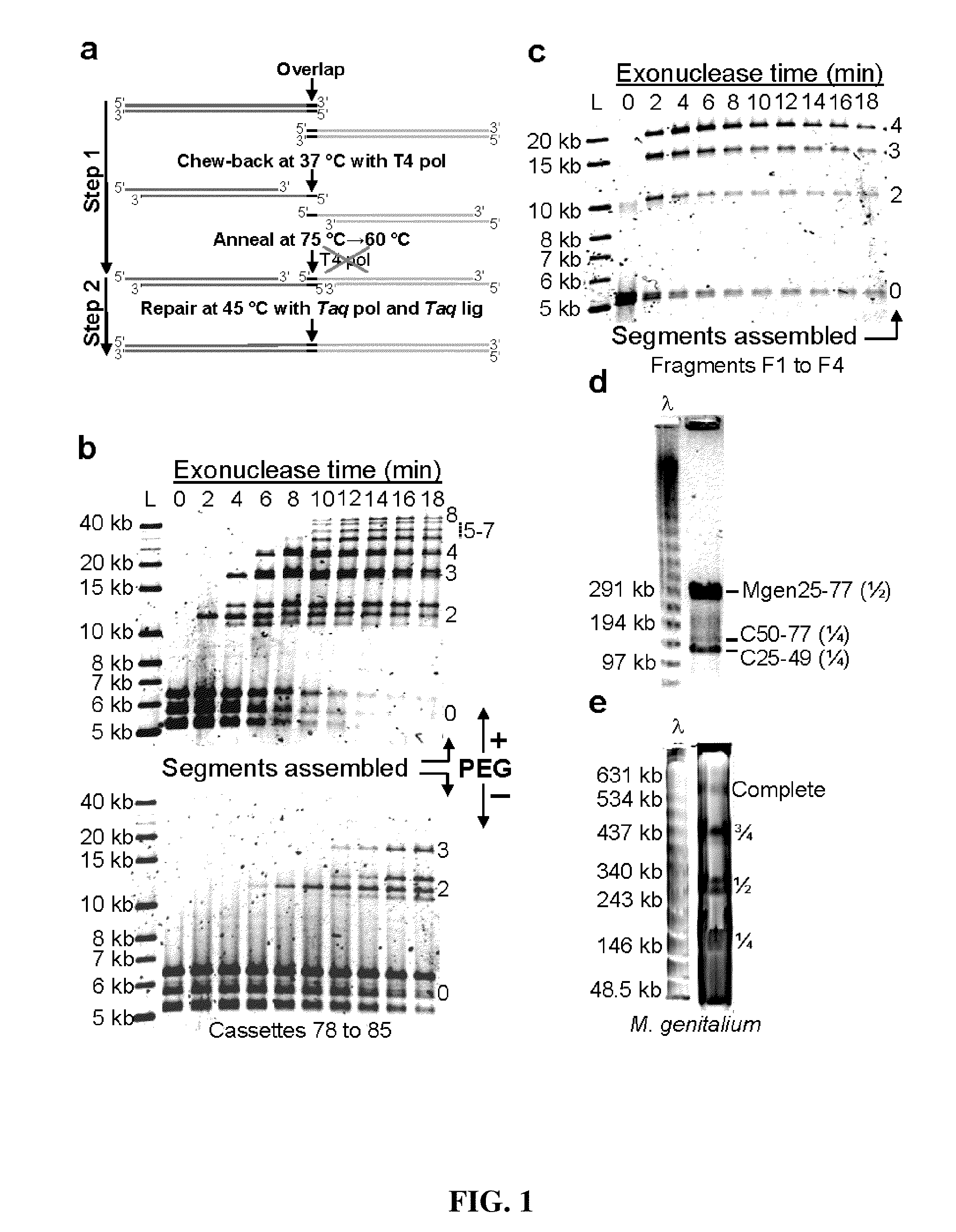
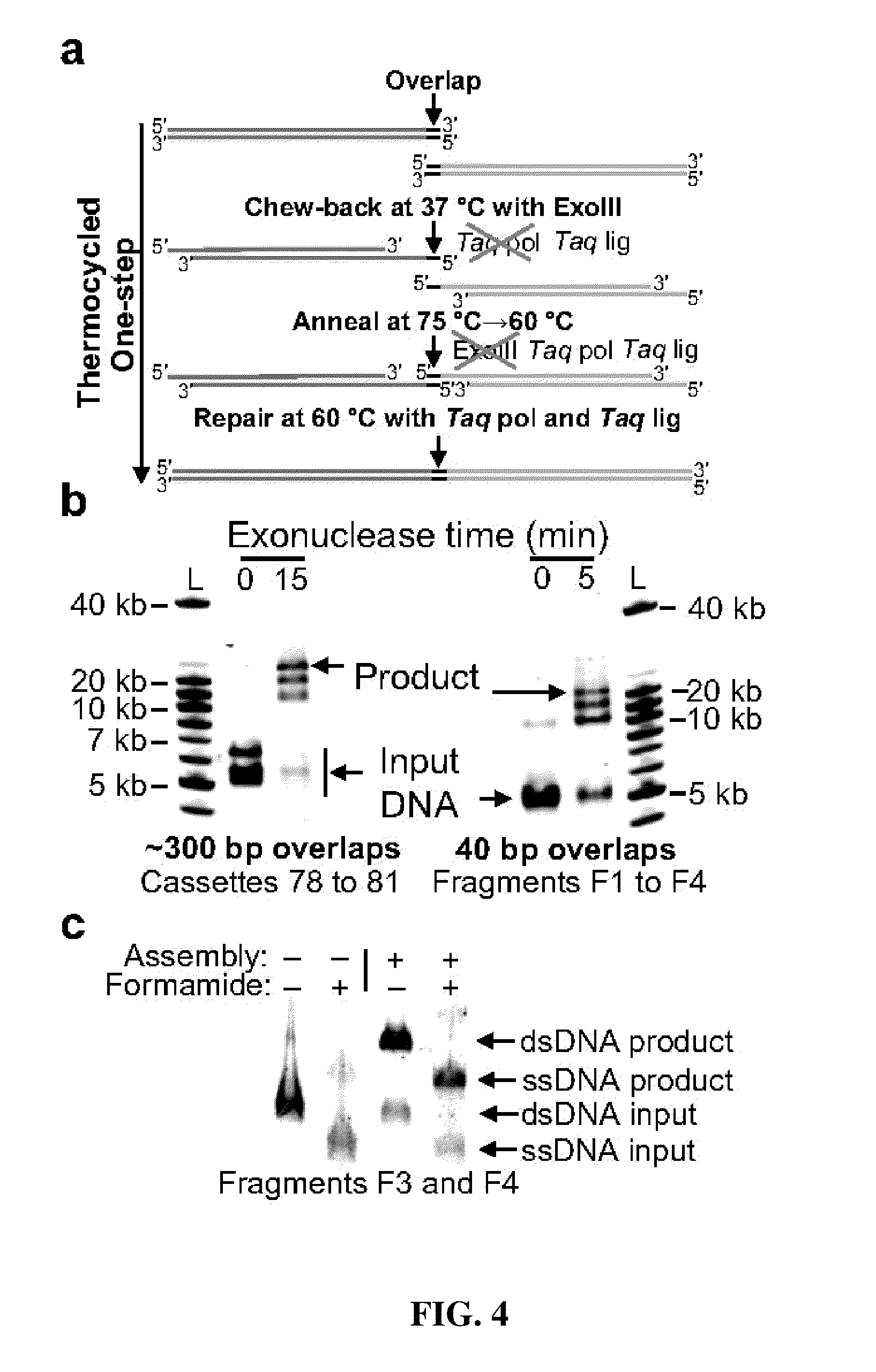
Methods for in vitro joining and combinatorial assembly of nucleic acid molecules
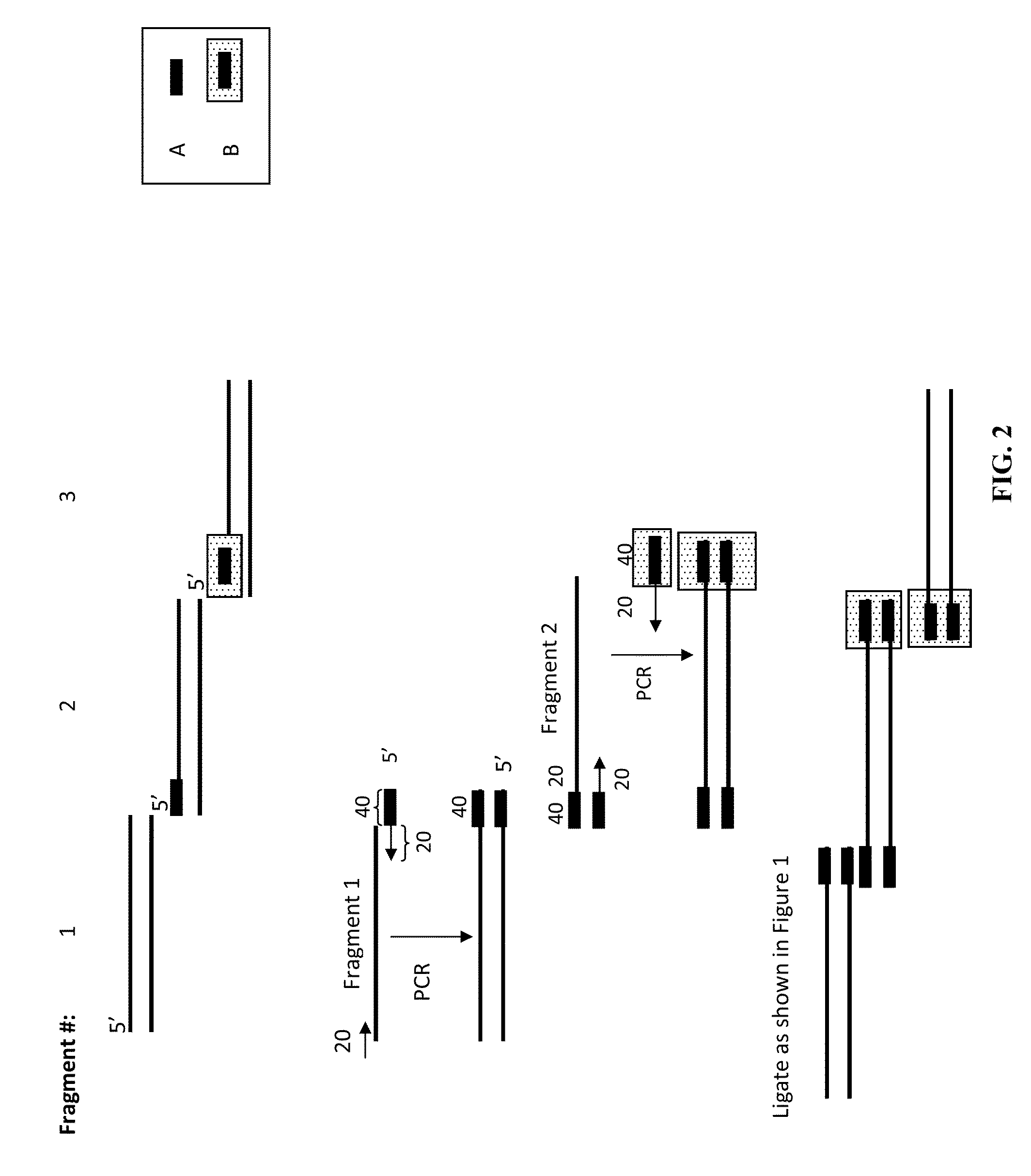
The present invention relates to methods of joining two or more double-stranded (ds) or single-stranded (ss) DNA molecules of interest in vitro, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule of each pair share a region of sequence identity. The method allows the joining of a large number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes. It can be used, e.g., to join synthetically produced sub-fragments of a gene or genome of interest. Kits for performing the method are also disclosed. The methods of joining DNA molecules may be used to generate combinatorial libraries useful to generate, for example, optimal protein expression through codon optimization, gene optimization, and pathway optimization.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
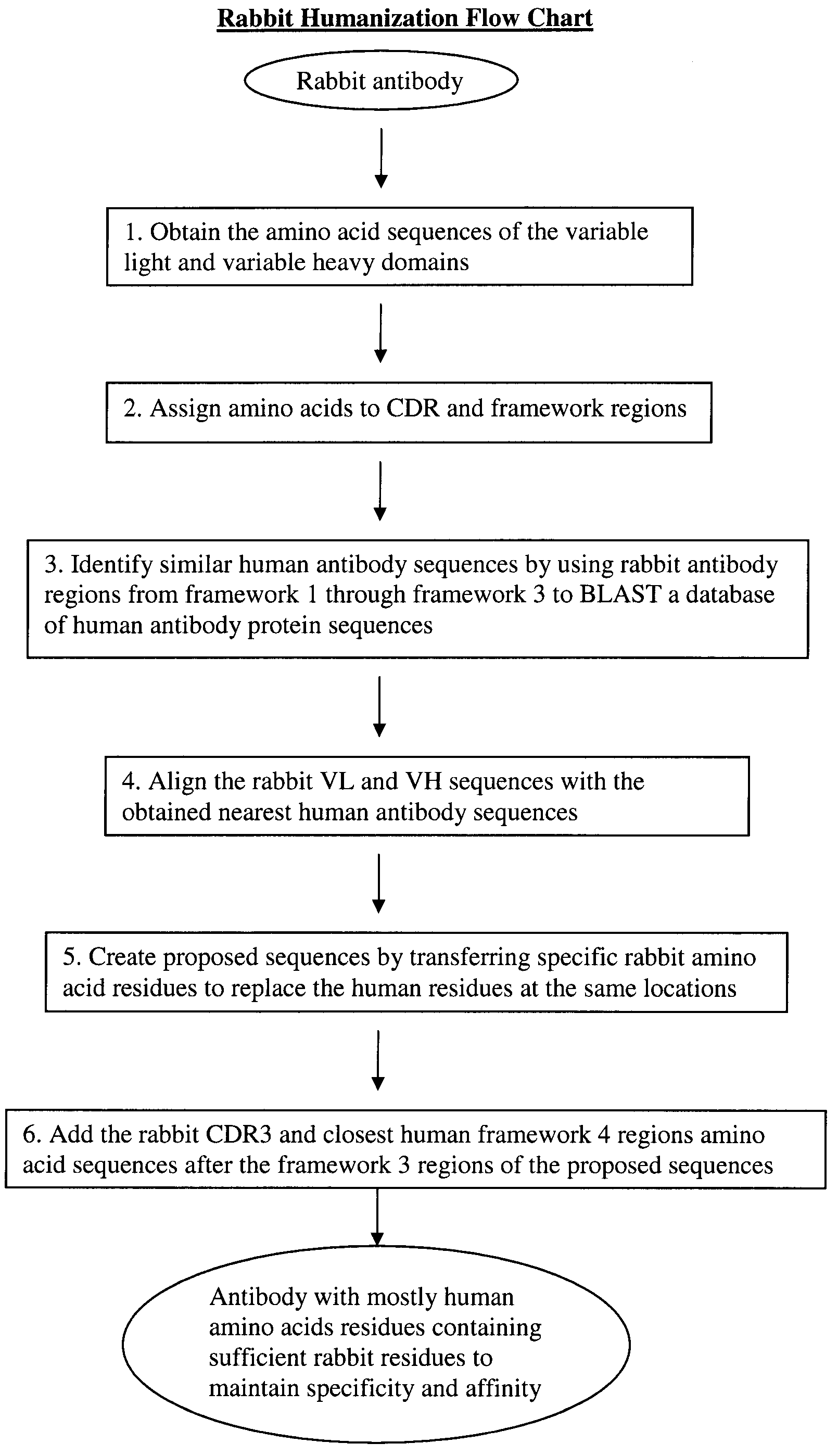
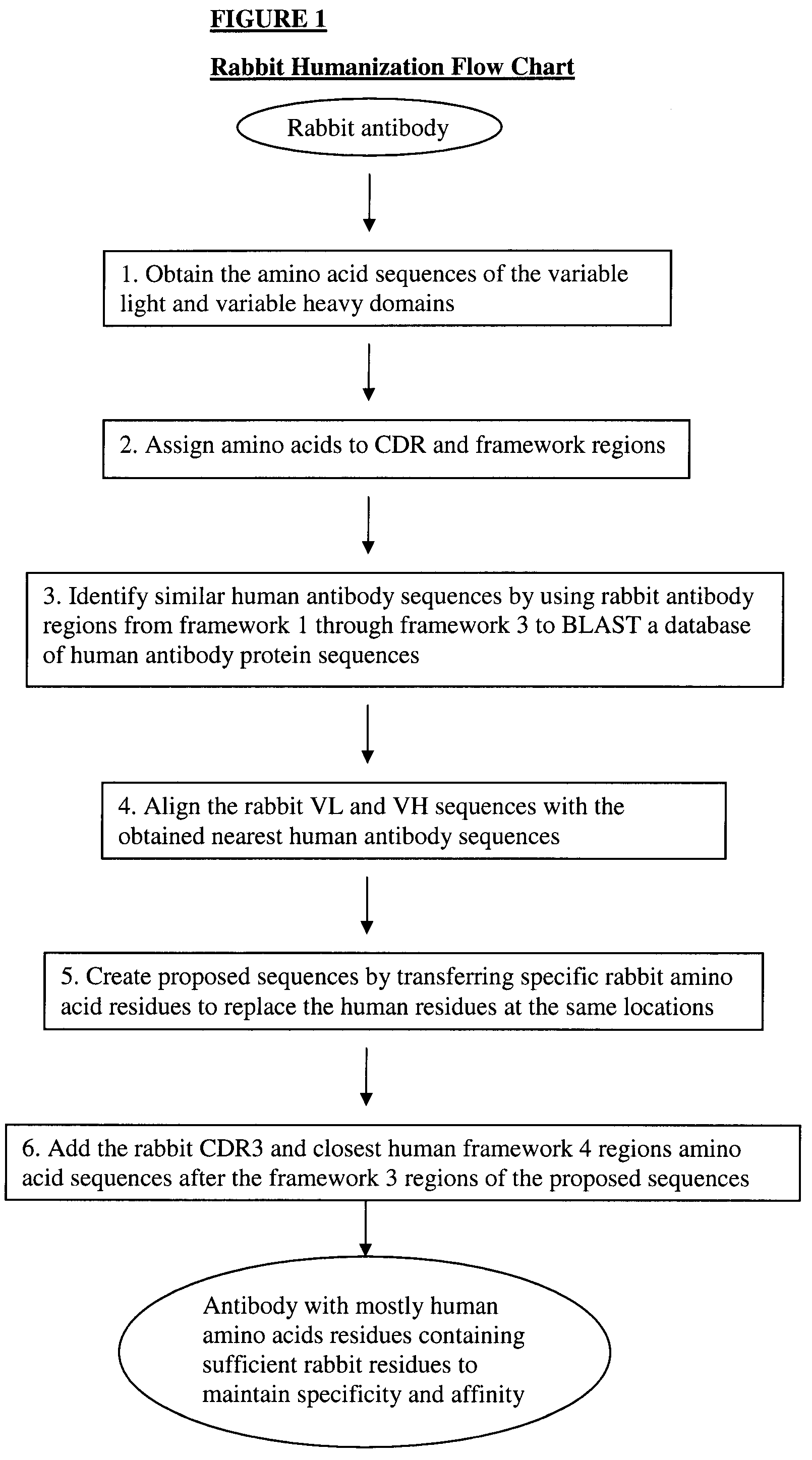
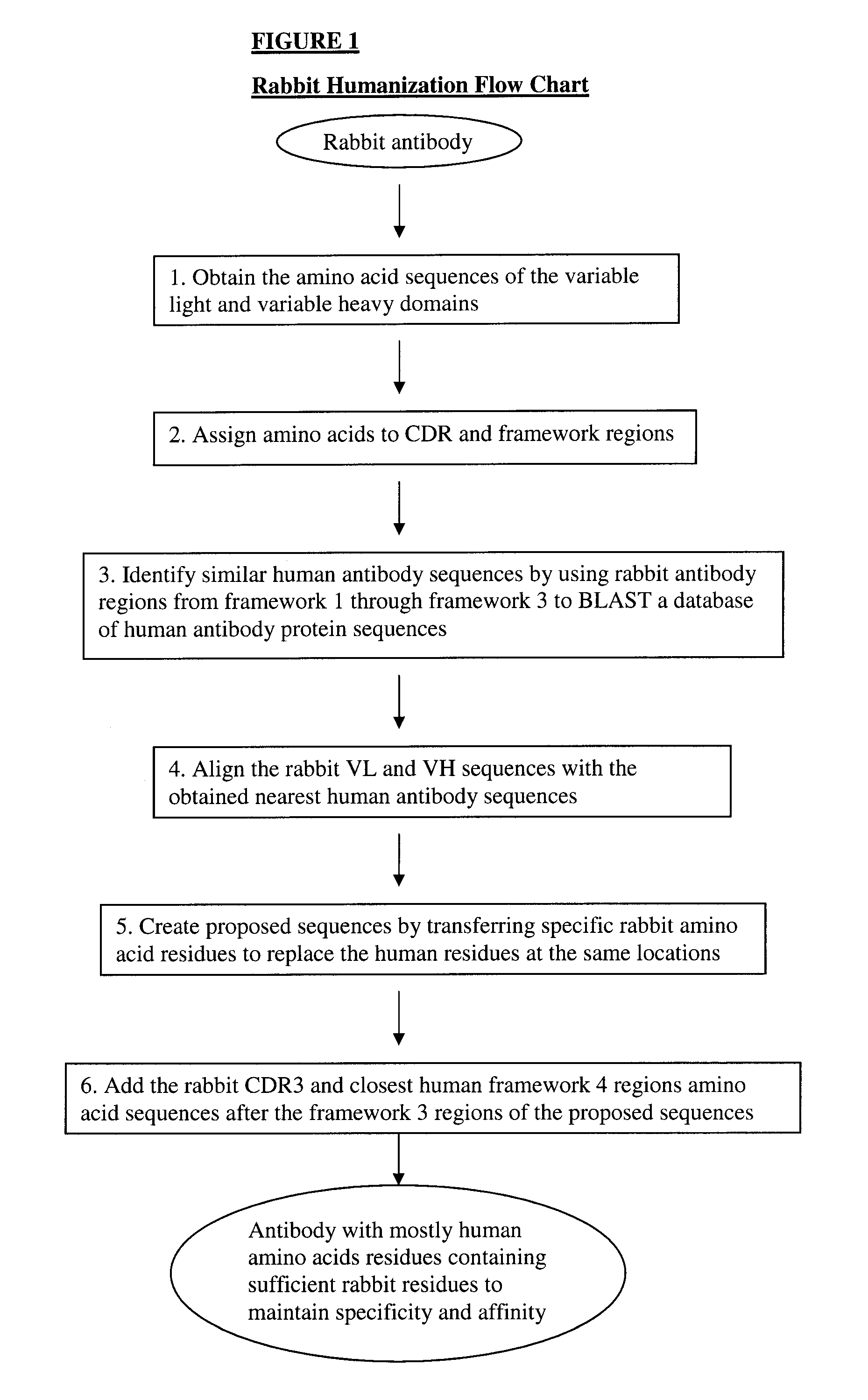
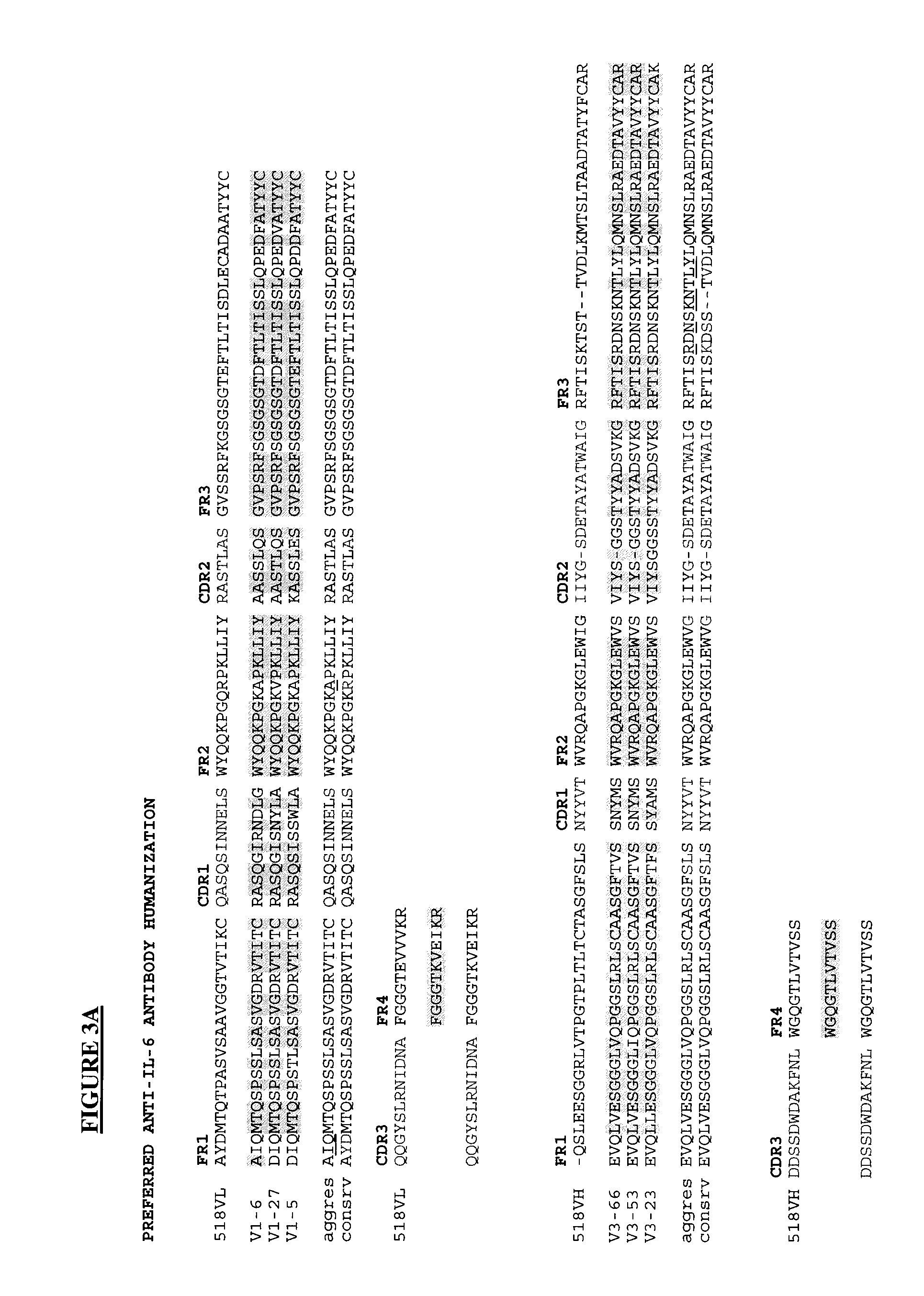
Novel Rabbit Antibody Humanization Methods and Humanized Rabbit Antibodies
The present invention is directed to novel and improved methods for humanizing rabbit heavy and light variable regions. The resulting humanized rabbit heavy and light chains and antibodies and antibody fragments containing are well suited for use in immunotherapy and immunodiagnosis as they retain the antigen binding affinity of the parent antibody and based on their very high level of sequence identity to human antibody sequences should be essentially non-immunogenic in humans. The invention exemplifies the protocol for the manufacture of therapeutic humanized anti-human TNF-alpha and anti-human IL-6 antibodies.
Owner:ALDERBIO HLDG LLC
Novel rabbit antibody humanization methods and humanized rabbit antibodies
The present invention is directed to novel and improved methods for humanizing rabbit heavy and light variable regions. The resulting humanized rabbit heavy and light chains and antibodies and antibody fragments containing are well suited for use in immunotherapy and immunodiagnosis as they retain the antigen binding affinity of the parent antibody and based on their very high level of sequence identity to human antibody sequences should be essentially non-immunogenic in humans. The invention exemplifies the protocol for the manufacture of therapeutic humanized anti-human TNF-alpha and anti-human IL-6 antibodies.
Owner:ALDERBIO HLDG LLC
In vitro recombination method
The present invention relates, e.g., to in vitro method, using isolated protein reagents, for joining two double stranded (ds) DNA molecules of interest, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule share a region of sequence identity, comprising contacting the two DNA molecules in a reaction mixture with (a) a non-processive 5′ exonculease; (b) a single stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) which accelerates nucleic acid annealing; (c) a non strand-displacing DNA polymerase; and (d) a ligase, under conditions effective to join the two DNA molecules to form an intact double stranded DNA molecule, in which a single copy of the region of sequence identity is retained. The method allows the joining of a number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Chimeric antigen receptor with stable antigen binding units, method for preparing chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN104829733APeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor targetAntigen receptors
The invention relates to a chimeric antigen receptor with stable antigen binding units. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises the extracellular antigen binding units, trans-membrane domains and intracellular co-stimulation signal domains. The antigen binding units can be stably expressed as compared with specific tumor targets and comprise heavy chains and light chains which are connected with one another by hinges of SEQ ID NO.2 (sequence identity number.2) amino acid sequence codes. The invention further relates to cells for expressing the receptor and application of the receptor.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BIO GENE TECH CO LTD
Methods and compositions for using argonaute to modify a single stranded target nucleic acid
The present disclosure provides compositions, kits, genetically modified cells, non-human transgenic organisms, and methods for binding and / or cleaving a single stranded target nucleic acid. A method of cleaving includes contacting a single stranded target nucleic acid with (e.g., introducing into a cell) a subject argonaute (Ago) polypeptide and a guide RNA (e.g., having a 5′-OH). In some embodiments, a subject Ago polypeptide includes an amino acid sequence having 70% or more sequence identity with amino acids 282-430 and / or 431-639 of the Marinitoga piezophila argonaute (MpAgo) protein set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1. The present disclosure provides variant Ago polypeptides; and methods of use of same.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
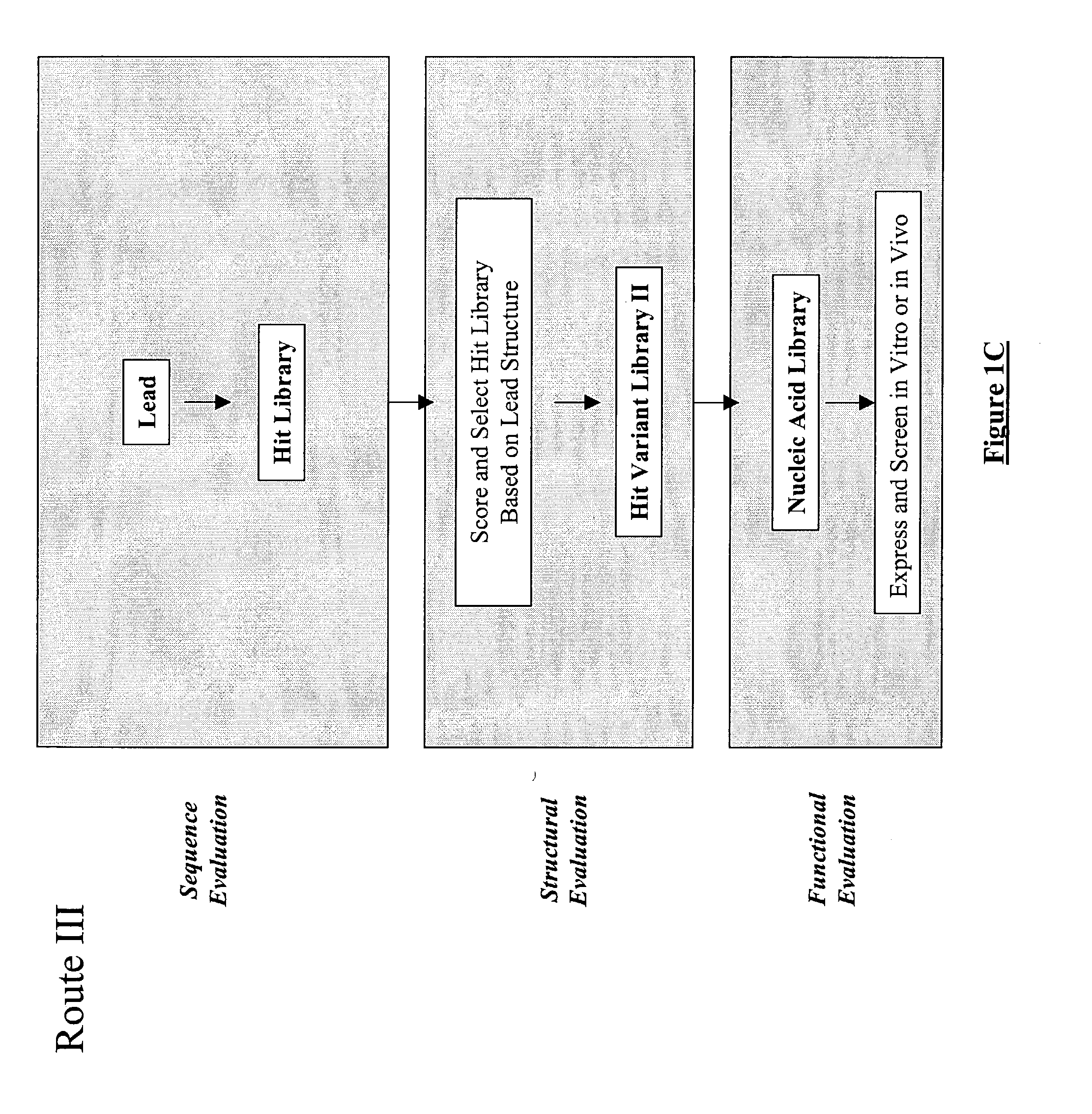
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method for constructing a library of designed proteins, comprising the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, the amino acid sequence being designated as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; and forming a library of designed proteins by substituting the lead sequence with the hit library. The library of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant proteins that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead protein, such as an antibody against therapeutically important target.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Methods for in vitro joining and combinatorial assembly of nucleic acid molecules
The present invention relates to methods of joining two or more double-stranded (ds) or single-stranded (ss) DNA molecules of interest in vitro, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule of each pair share a region of sequence identity. The method allows the joining of a large number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes. It can be used, e.g., to join synthetically produced sub-fragments of a gene or genome of interest. Kits for performing the method are also disclosed. The methods of joining DNA molecules may be used to generate combinatorial libraries useful to generate, for example, optimal protein expression through codon optimization, gene optimization, and pathway optimization.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides methods for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimal proteins with desired biological functions, such as improved binding affinity for biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The method is performed in silico in a high-throughput fashion by mining the ever-expanding database of protein sequences in all living things, especially humans. In one embodiment, a method of constructing a designer protein library comprises the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, referred to as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of test protein sequences; Select at least two peptide fragments having at least 15% sequence identity with the leader sequence from each test protein sequence, and the selected peptide fragments form a selection library; a library of designed proteins is formed by replacing the leader sequence with the selection library. Libraries of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to generate libraries of recombinant proteins that can be screened for new or improved functions relative to lead proteins, such as antibodies against a therapeutically important target.
Owner:埃博马可西斯公司
Immunity-inducing agent
ActiveUS20110123492A1Shrinkage or regression of existing cancerTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideIn vivo
The invention relates to an immunity-inducing agent comprising, as an active ingredient, at least one polypeptide having immunity-inducing activity that is selected from among polypeptides (a), (b), and (c): (a) a polypeptide of at least seven contiguous amino acids of the amino acid sequence shown by any even SEQ ID number selected from SEQ ID NOs: 2 to 30 listed in the Sequence Listing; (b) a polypeptide of at least seven amino acids having 90% or more sequence identity with the polypeptide (a); and (c) a polypeptide comprising the polypeptide (a) or (b) as a partial sequence thereof, or a recombinant vector comprising a polynucleotide encoding said polypeptide and capable of expressing said polypeptide in vivo.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
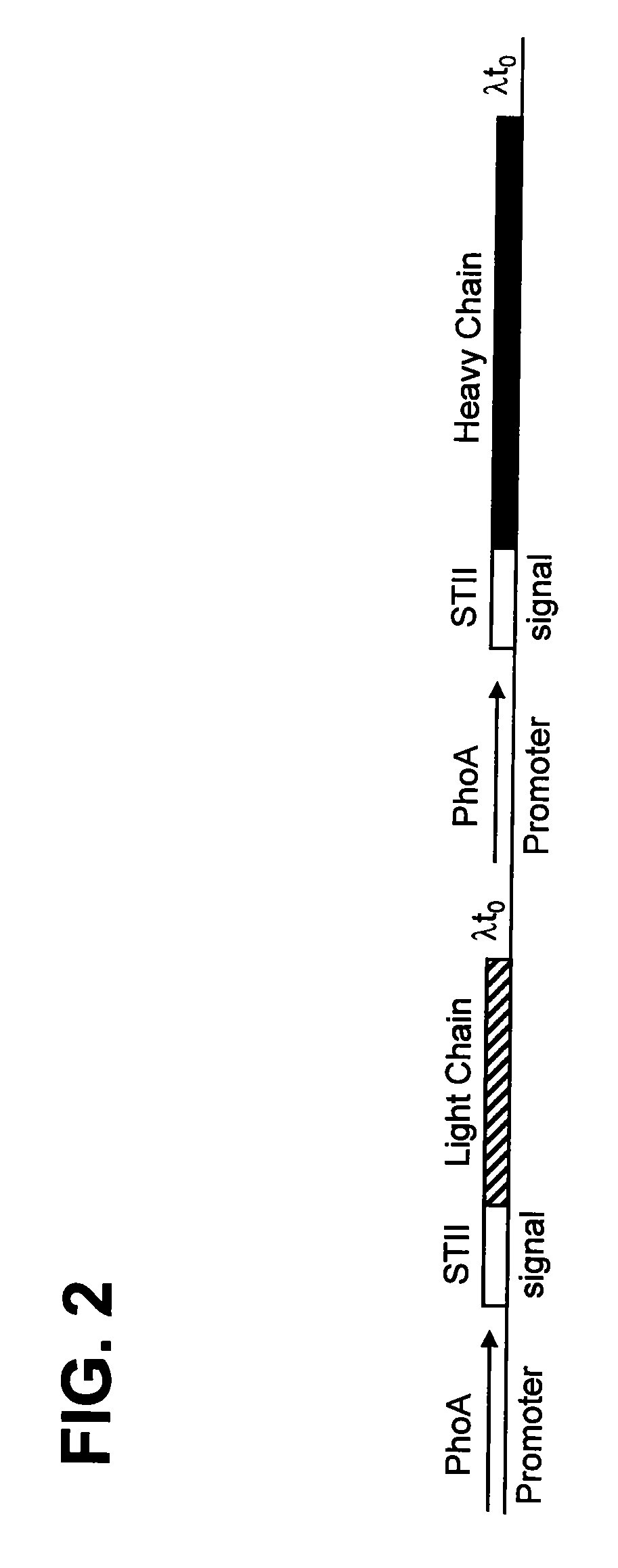
Methods for producing humanized antibodies and improving yield of antibodies or antigen binding fragments in cell culture
ActiveUS7575893B2Speed up the processIncrease productionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntigen Binding FragmentAmino acid substitution
The present invention provides methods for producing humanized antibodies and increasing the yield of antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments when produced in cell culture. In one aspect of the invention, at least one framework region amino acid residue of the variable domain is substituted by a corresponding amino acid from a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain. In another aspect, an amino acid is placed at a position proximal to a cys residue that participates in an intrachain variable domain disulfide bond that corresponds to an amino acid found at that position in a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequenc of the variable domain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Herbicide resistance protein and encoding genes thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to herbicide resistance protein, encoding genes of the herbicide resistance protein and application of the herbicide resistance protein. The herbicide resistance protein comprises protein (a) which is composed of an amino acid sequence shown in a second sequence generator (SEQ) ID, or protein (b) which is derived by protein (a) and provided with herbicide resistance activity through replacement and / or deficiency and / or addition of one or more amino acids of the amino acid sequence in the protein (a), or protein (c) which is composed of an amino acid sequence which has at least 90 percent of sequence identity with the second SEQ ID. The herbicide resistance protein is particularly suitable for expression in plants, wide in herbicide resistance, and particularly used in phenoxy auxin herbicide.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Novel fiber-preferential promoter in cotton
The present application discloses an isolated nucleic acid sequence comprising (a) at least 700 consecutive nucleotides of SEQ ID NO: 1; (b) a nucleotide sequence with at least 80% sequence identity to the nucleotide sequence of (a); (c) a nucleotide sequence hybridizing under stringent conditions to the nucleotide sequence of (a) or (b); and (d) a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence of any one of (a) to (c). Further disclosed herein is a chimeric gene comprising the isolated nucleic acid described herein operably linked to a nucleic acid coding for an expression product of interest, and a transcription termination and polyadenylation sequence. Also disclosed herein are a vector, a transgenic plant cell, a transgenic plant and a seed as characterized in the claims. Methods disclosed herein relate to the production of a transgenic plant, growing cotton, producing a seed, effecting fiber-preferential expression of a product in cotton and of altering fiber properties in a cotton plant as characterized in the claims.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC +1
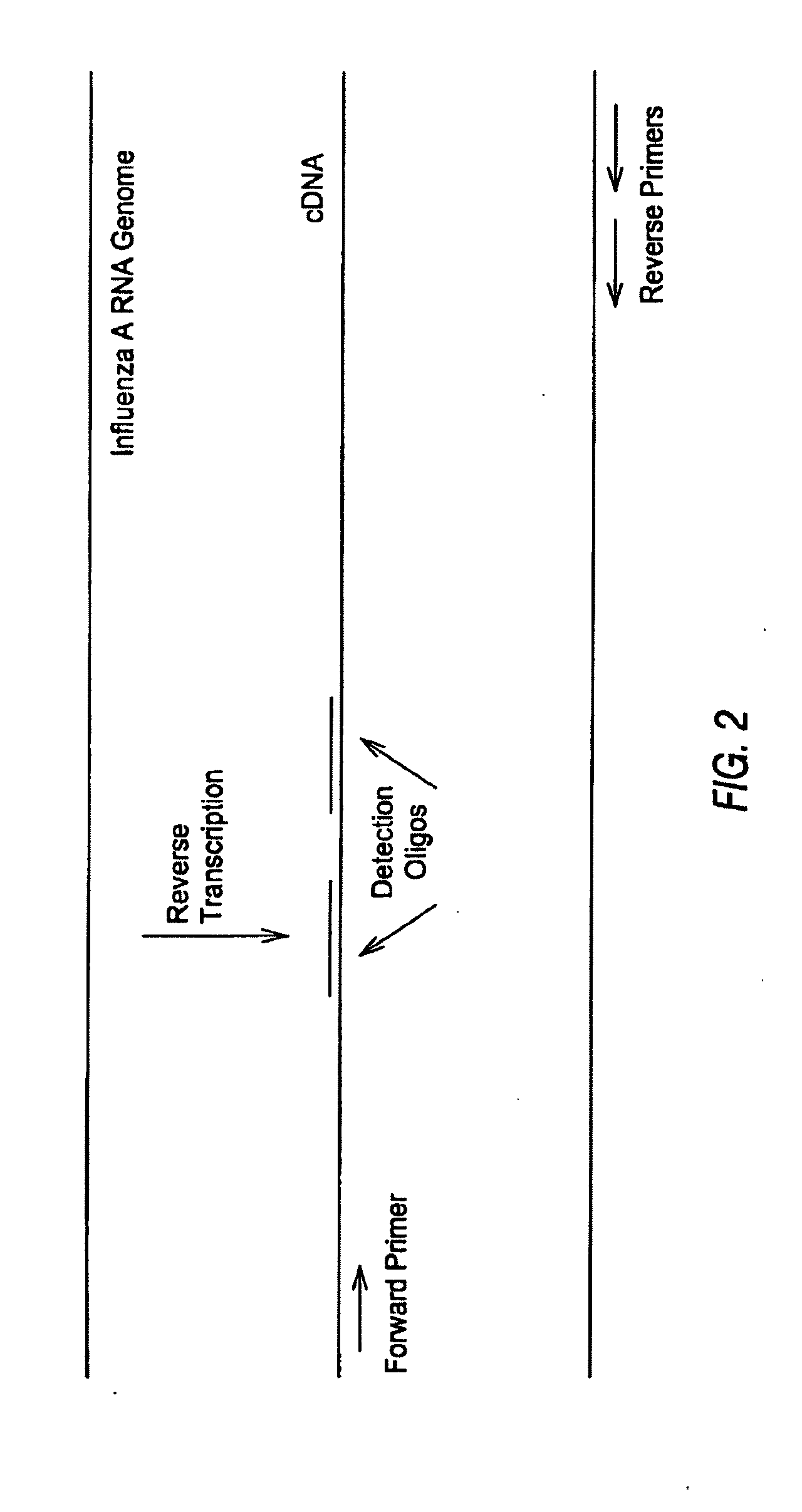
100% sequence identity detection methods for variable genomes
The present disclosure provides methods, reagents and kits for the detection of all known human variants of influenza A virus and at least 90% of avian and swine variants of influenza A virus in a biological sample, based on amplification primers and detection probes that are specific to a highly conserved region of the influenza A matrix gene.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI INC
Protease-deficient cells
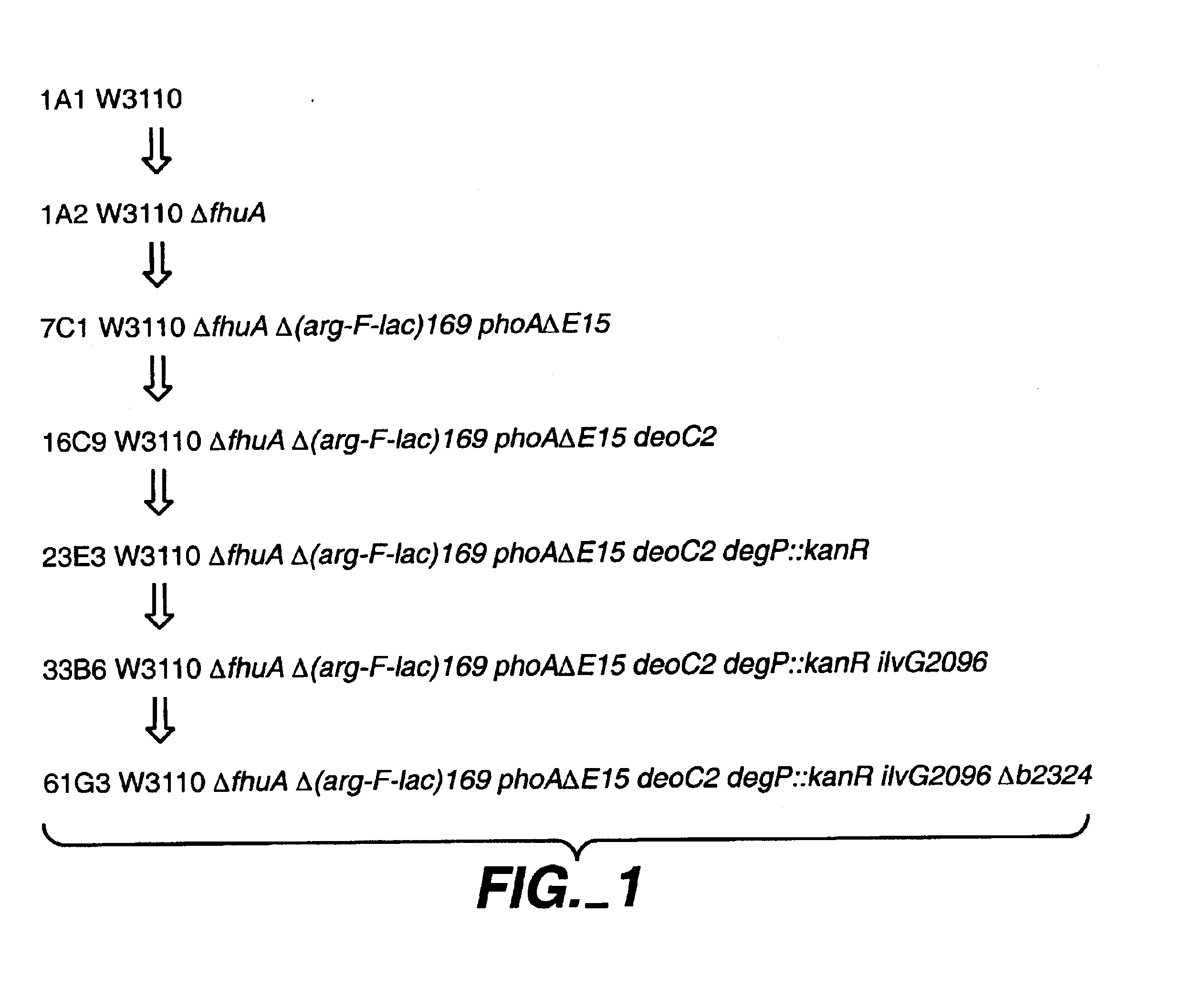
A gram-negative bacterial cell is described that is deficient in a chromosomal gene present in a wild-type such cell which gene shares at least 80% sequence identity with the native sequence of the yfcK gene and encodes an aminopeptidase. Alternatively, a gram-negative bacterial cell is deficient in a chromosomal gene present in a wild-type such cell which gene encodes an aminopeptidase that shares at least 80% sequence identity with the native sequence of aminopeptidase b2324. Either of these types of cells, when comprising a nucleic acid encoding a heterologous polypeptide, produces an N-terminal unclipped polypeptide when it is cultured and the polypeptide recovered, with virtually no N-terminal clipped polypeptide produced as an impurity. Conversely, a method is provided for cleaving an N-terminal amino acid from a polypeptide comprising contacting the polypeptide with an aminopeptidase sharing at least 80% sequence identity with the native sequence of aminopeptidase b2324.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Use of pedf-derived polypeptides for promoting stem cells proliferation and wound healing
ActiveUS20120245097A1Well formedSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTORWound healing
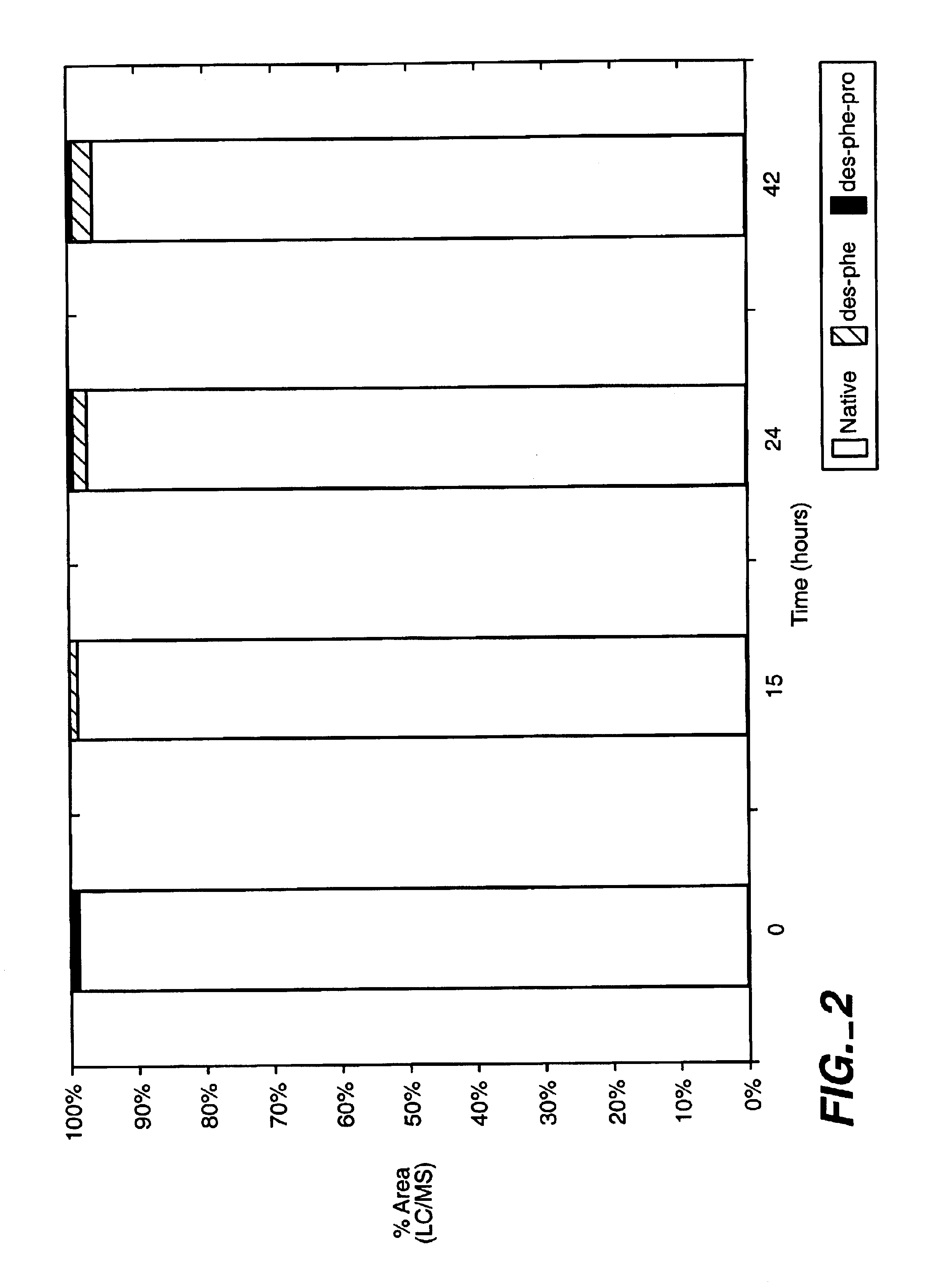
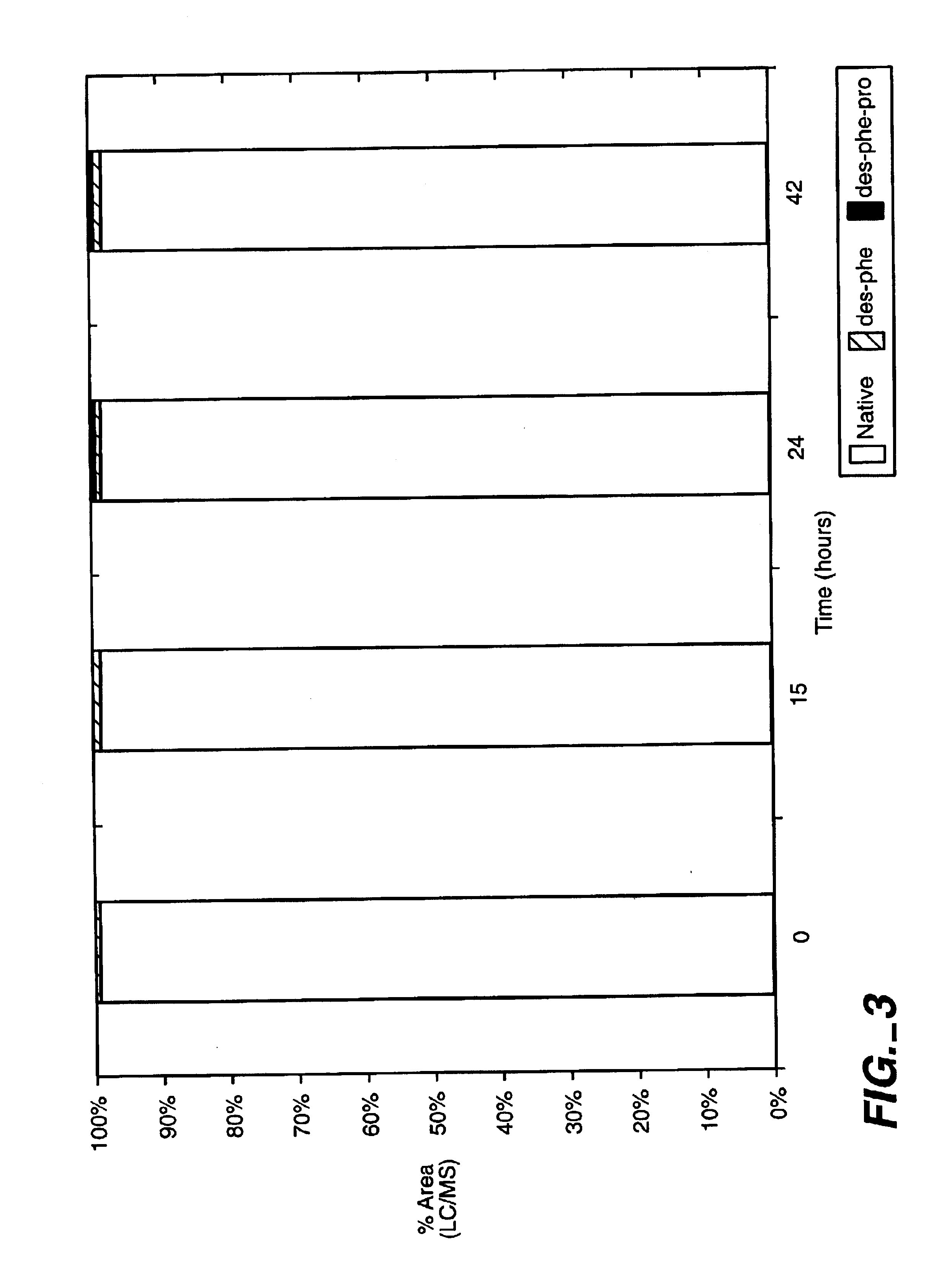
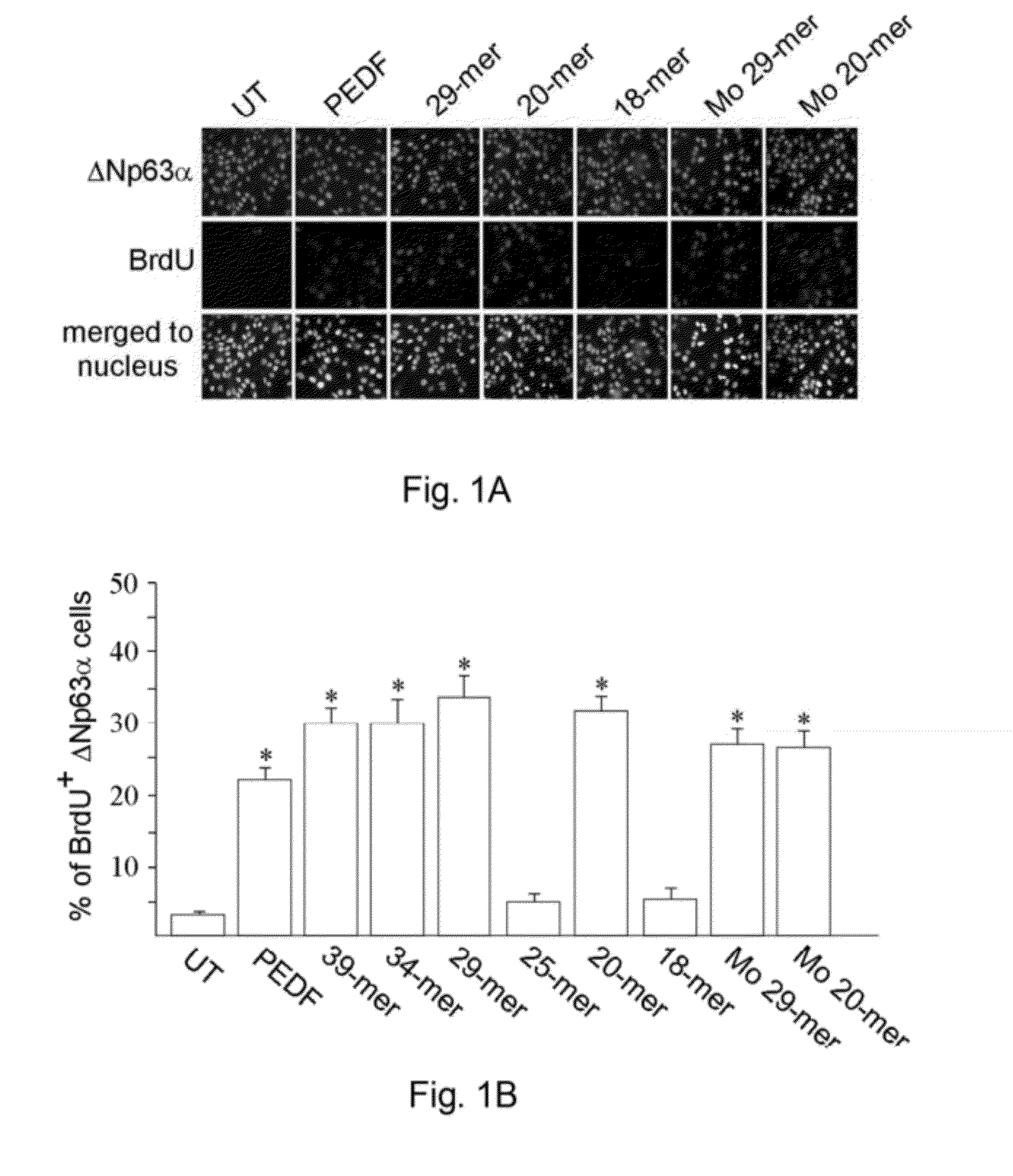
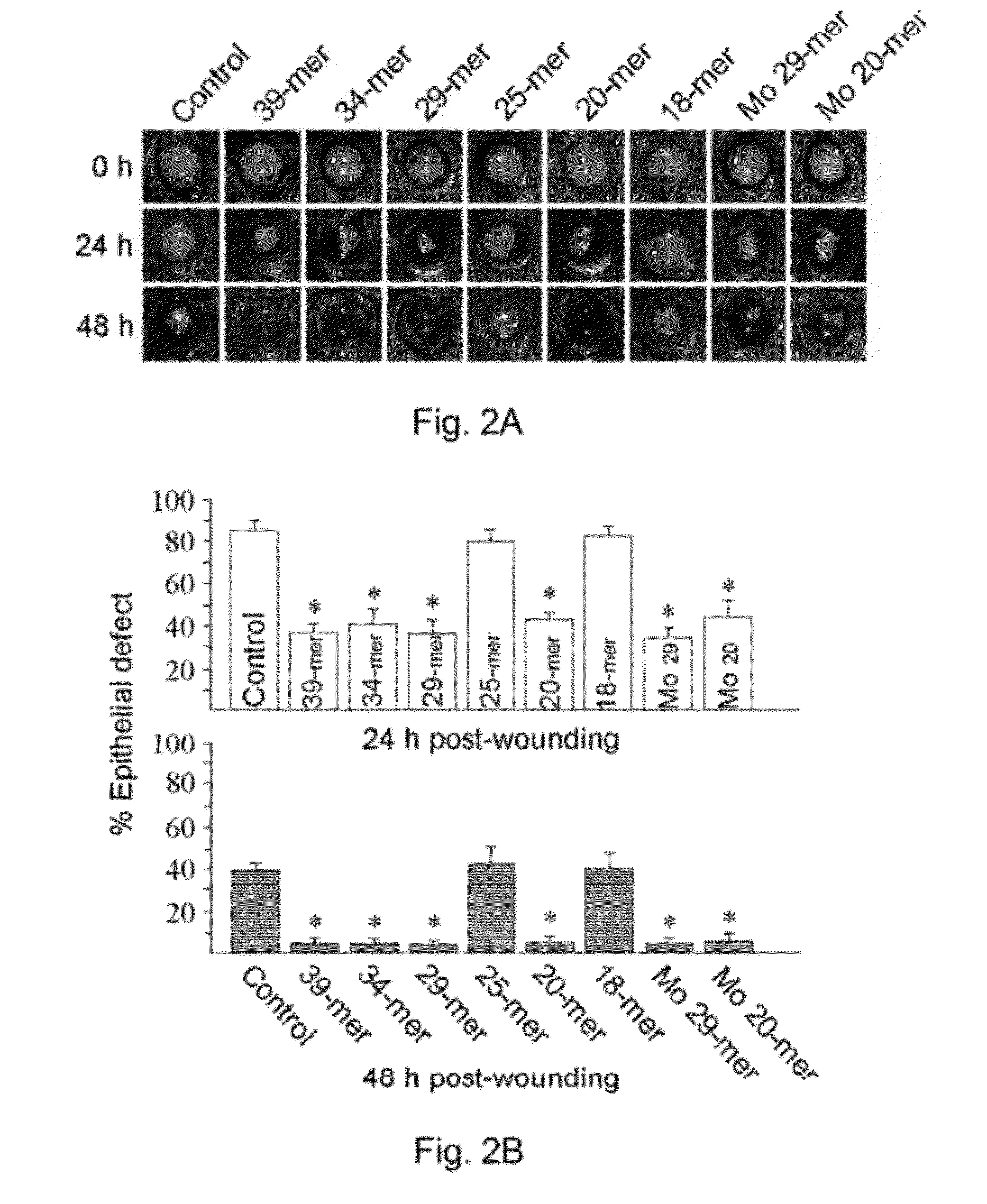
Disclosed herein is a synthetic peptide, which has an amino acid sequence that has 20-39 amino acid residues. The synthetic peptide has at least 80% amino acid sequence identity to SEQ ID NO: 1, and includes at least 20 consecutive residues that has at least 90% amino acid sequence identity to residues 11-30 of SEQ ID NO: 1. Also disclosed herein are compositions containing the synthetic peptide and applications thereof. According to various embodiments of the present disclosure, the synthetic peptide is useful in promoting stem cells proliferation or wound healing.
Owner:MACKAY MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid Hybridization for Organism Identification
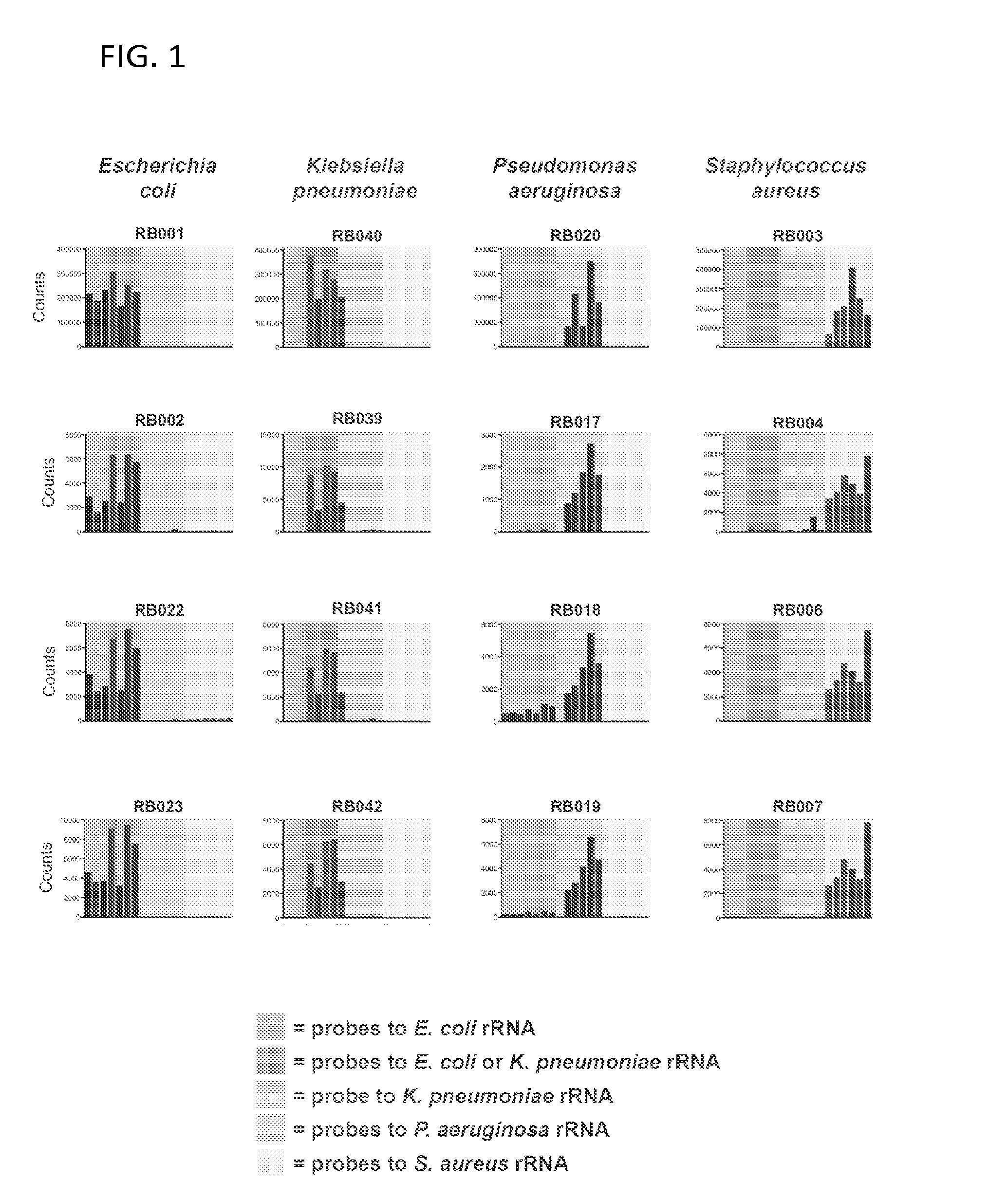
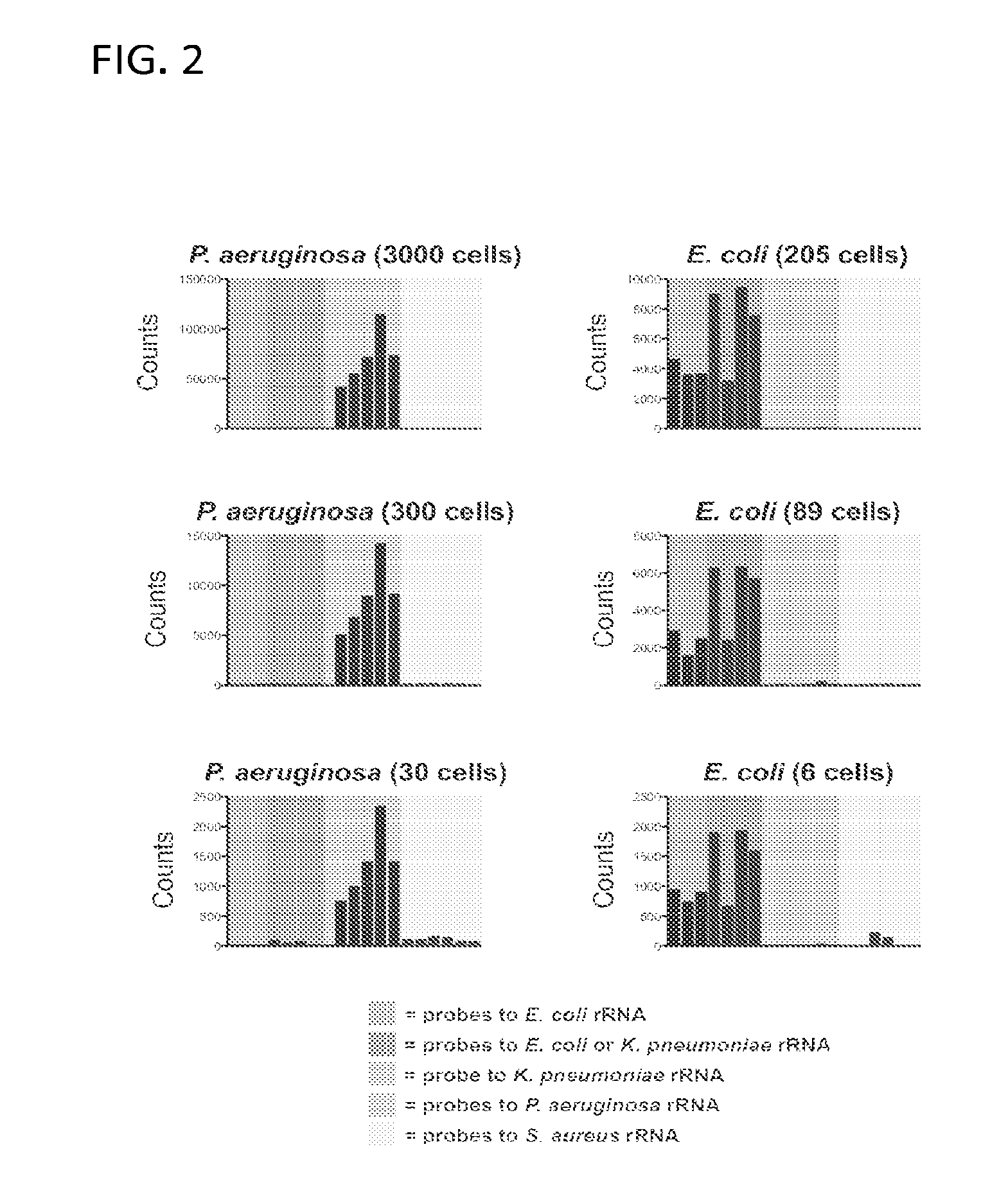
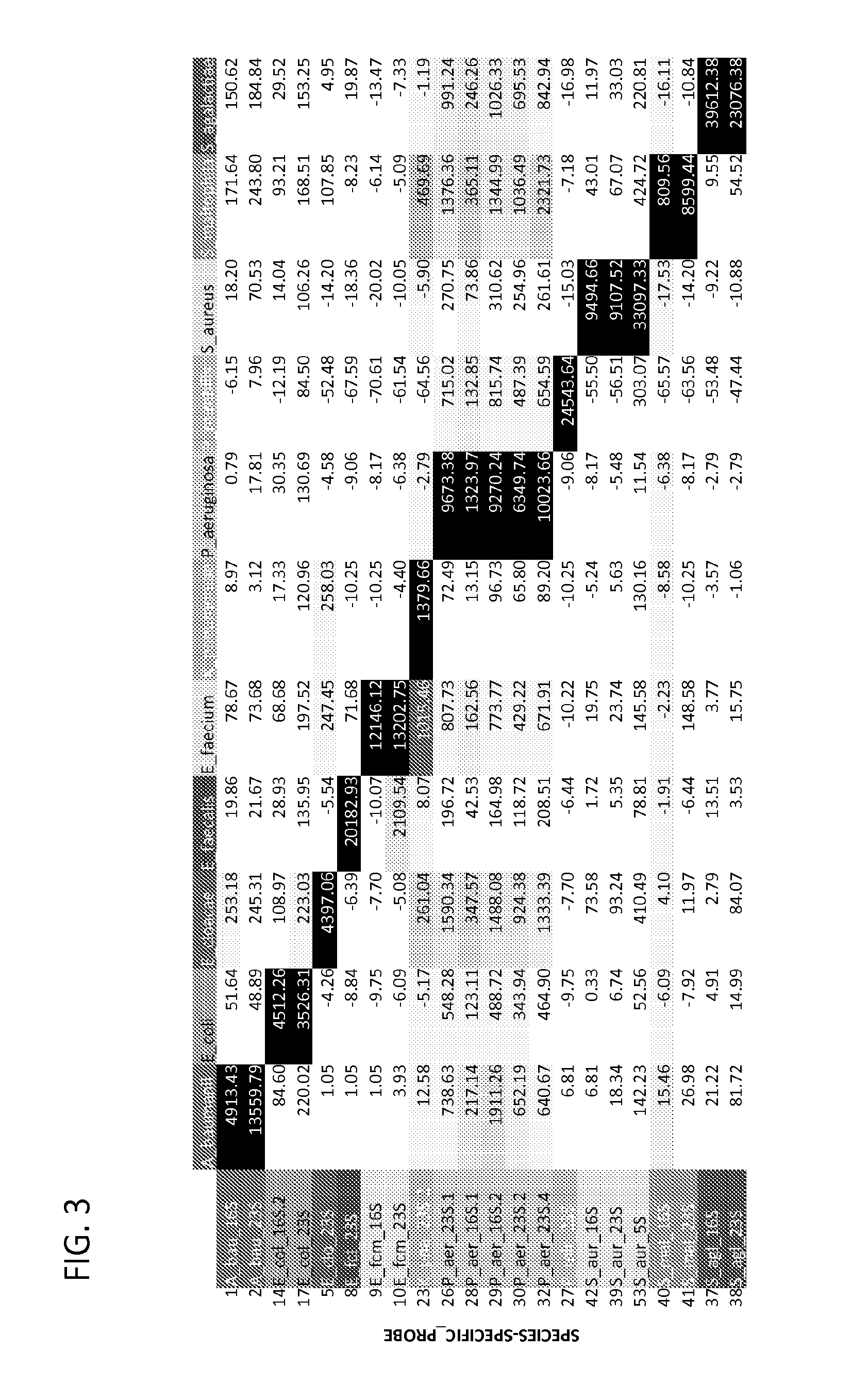
The present disclosure relates to method of distinguishing between two or more species of one or more organisms in a sample, by contacting a biological sample comprising ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) with a set of antisense probes, wherein the set of probes contains at least one detectable probe that is specific for a target rRNA sequence of each species to be tested, and wherein the individual probes specific for each species comprises less than about 85% sequence identity; and, detecting hybridization between one or more of the probes and the rRNA, thereby distinguishing between two or more species in a sample.
Owner:NANOSTRING TECH INC +2
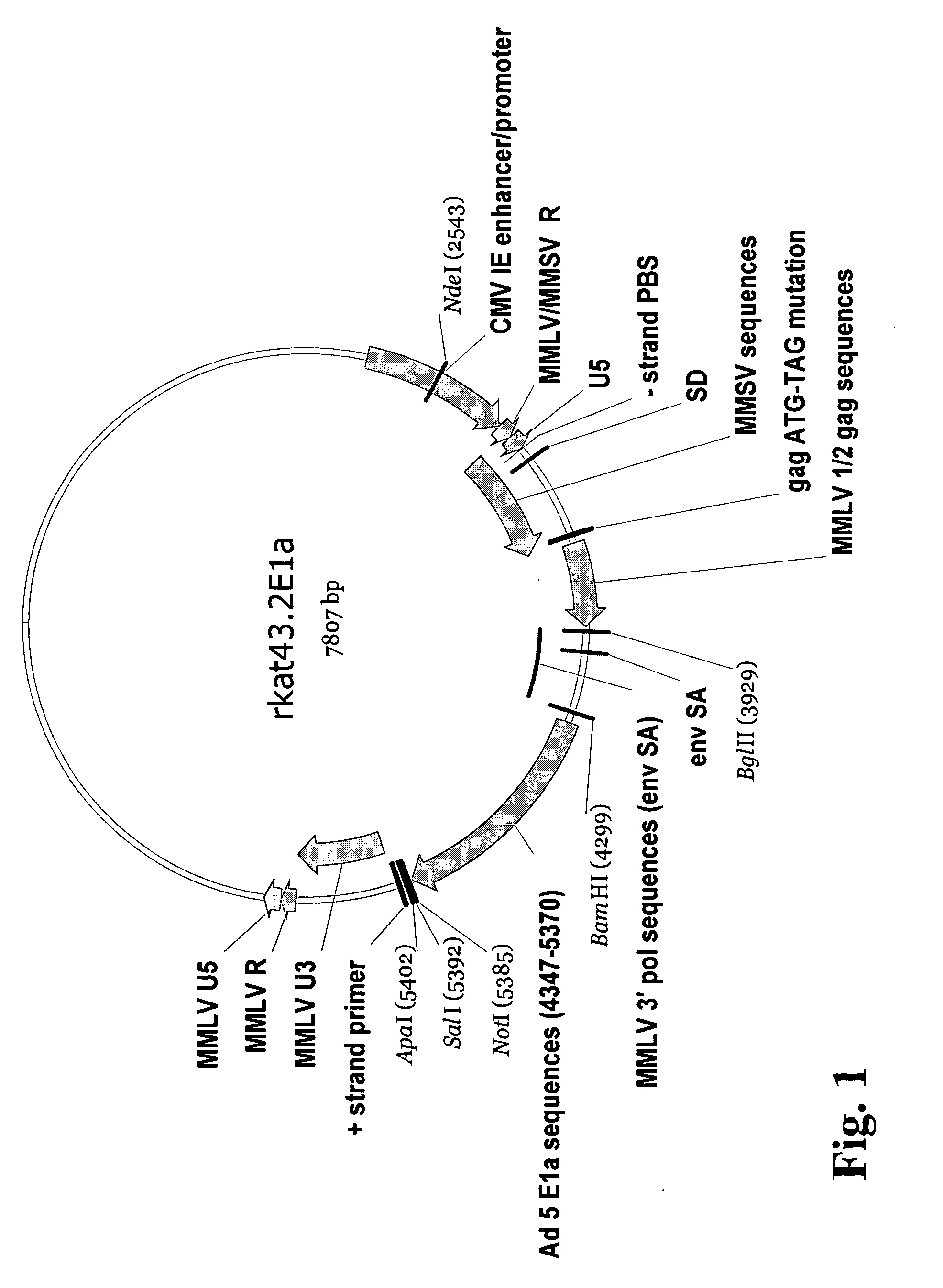
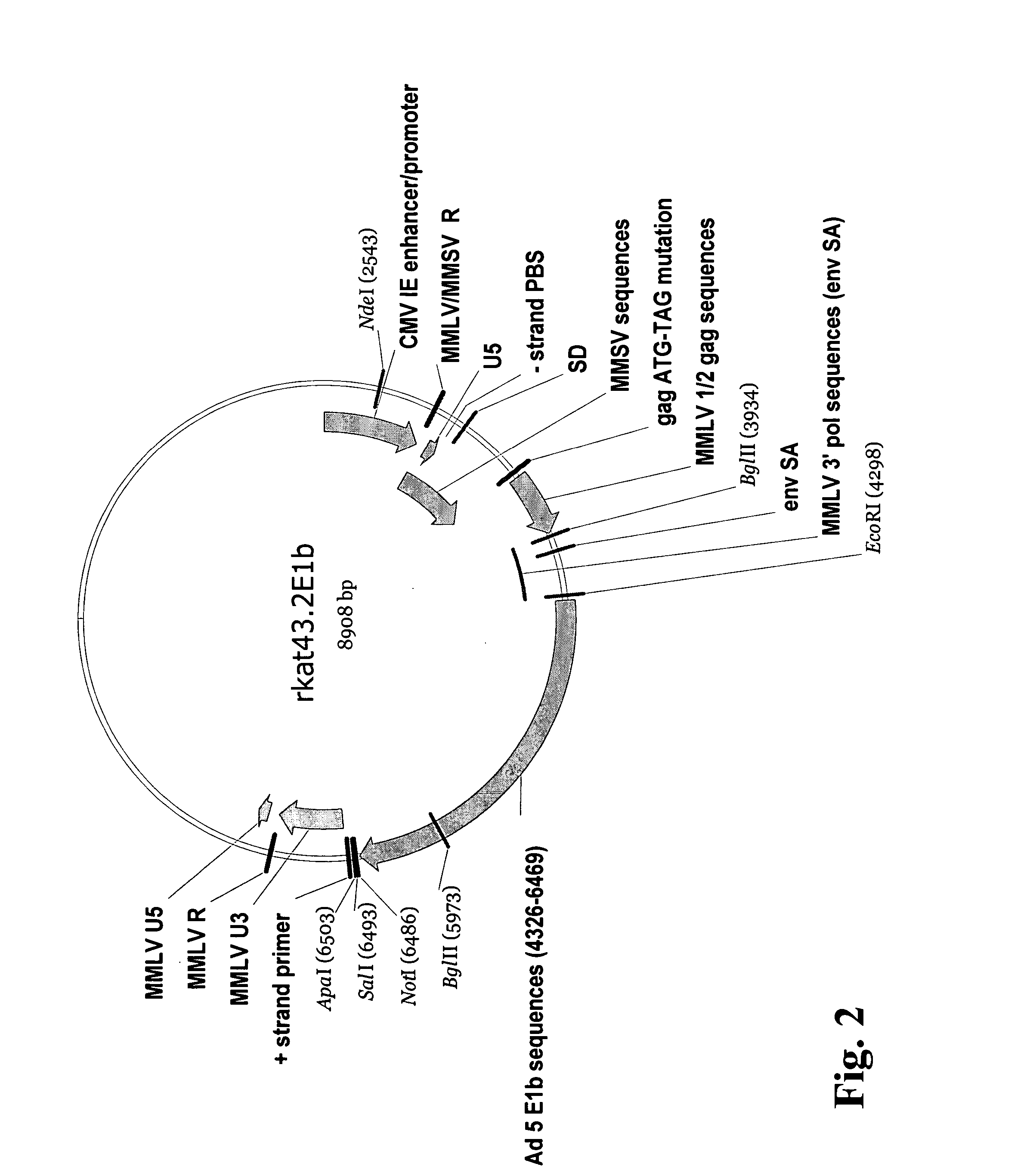
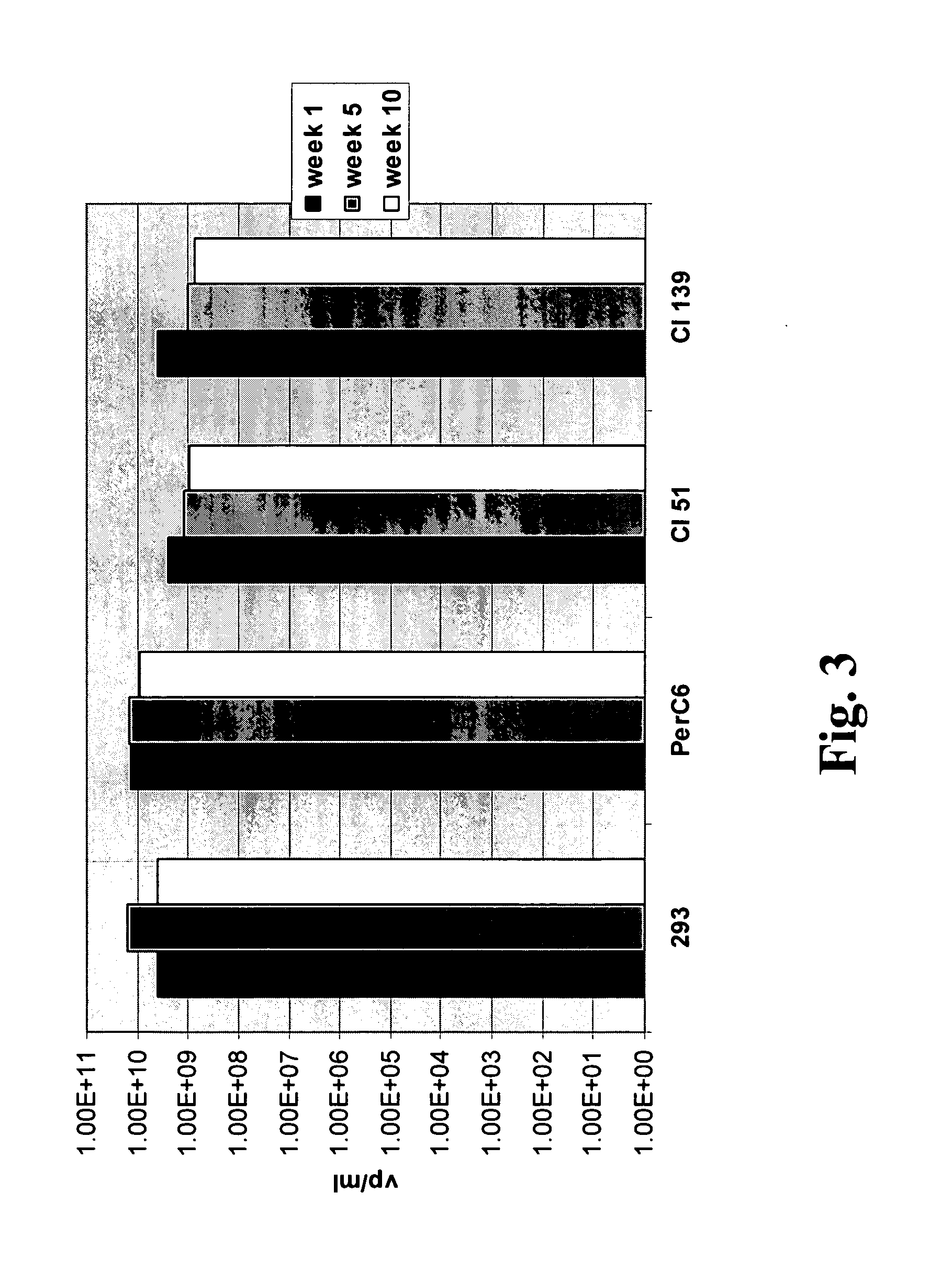
Adenoviral E1A/E1B complementing cell line
Owner:CELLS GENESYS INC
Hydrocarbon-producing genes and methods of their use
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids and isolated polypeptides involved in the synthesis of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon intermediates. Homologs of, conservative variants of, and sequences having at least about 35% sequence identity with nucleic acids involved in the synthesis of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon intermediates are also provided. The invention further provides methods for producing an aliphatic ketone or a hydrocarbon, as well as a method for identifying an enzyme useful for the production of hydrocarbons.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
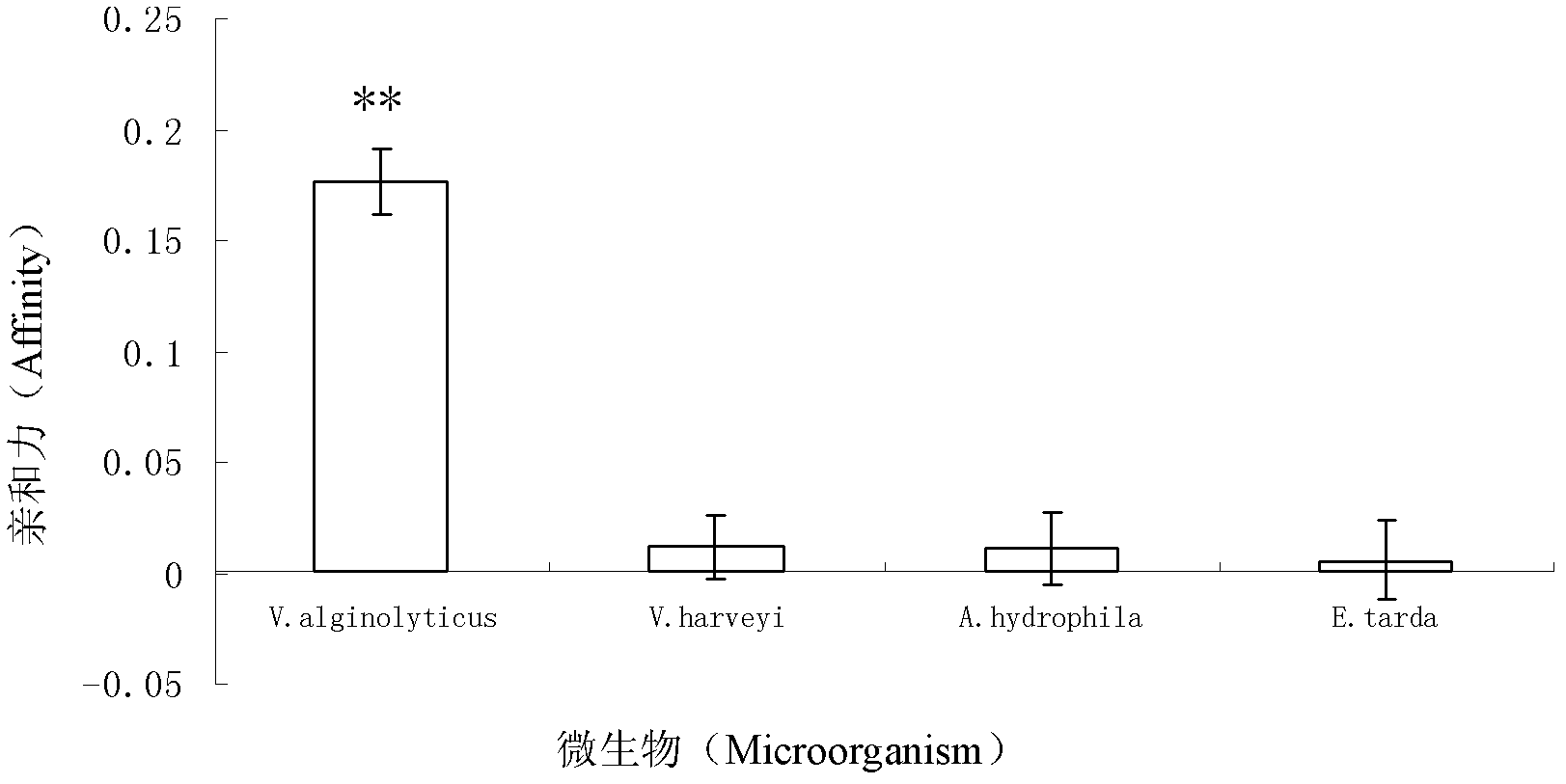
Three oligonucleotide sequences for identification and detection of vibrio alginolyticus as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102329862AImprove stabilityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSingle strandOligonucleotide
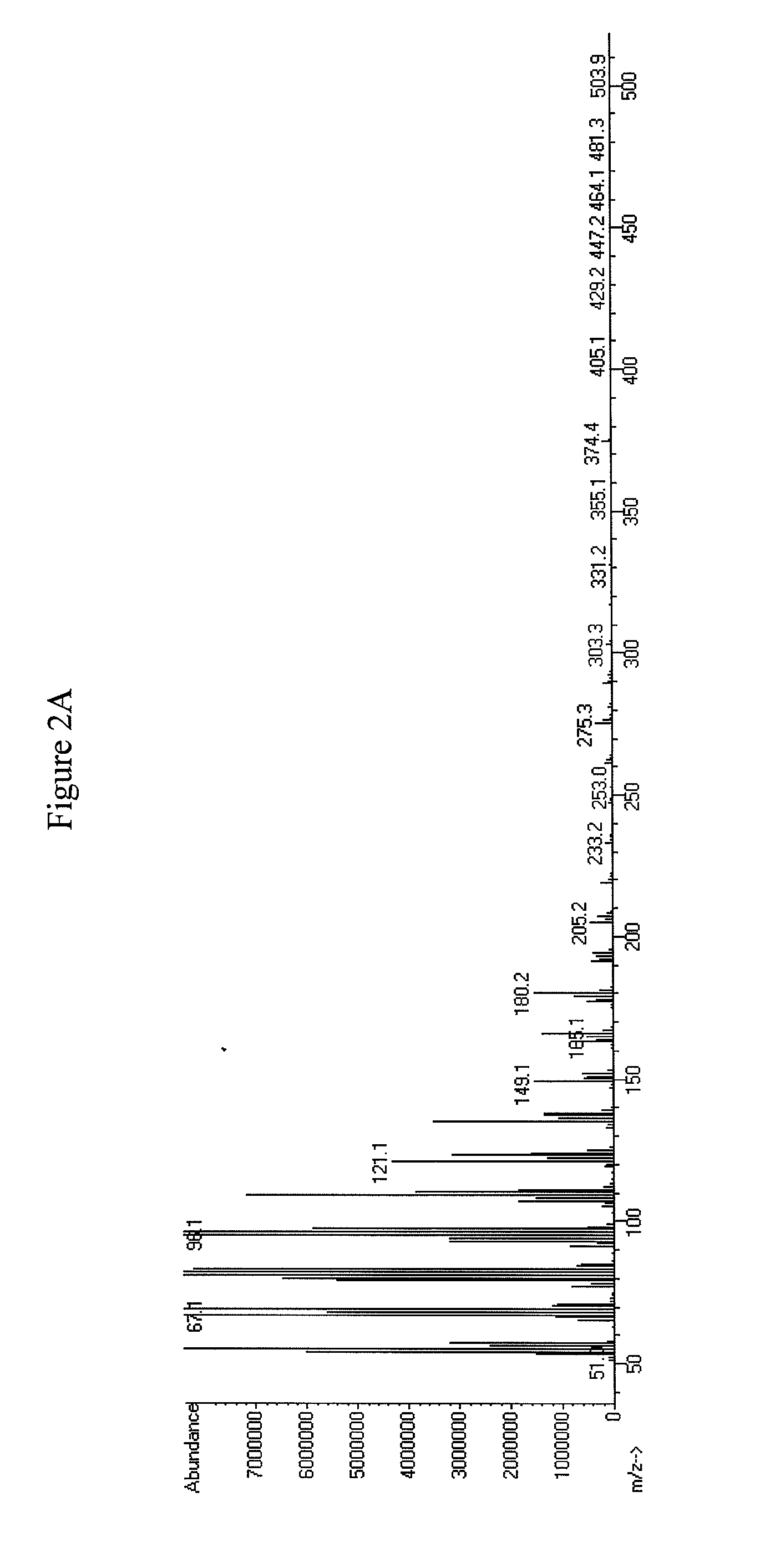
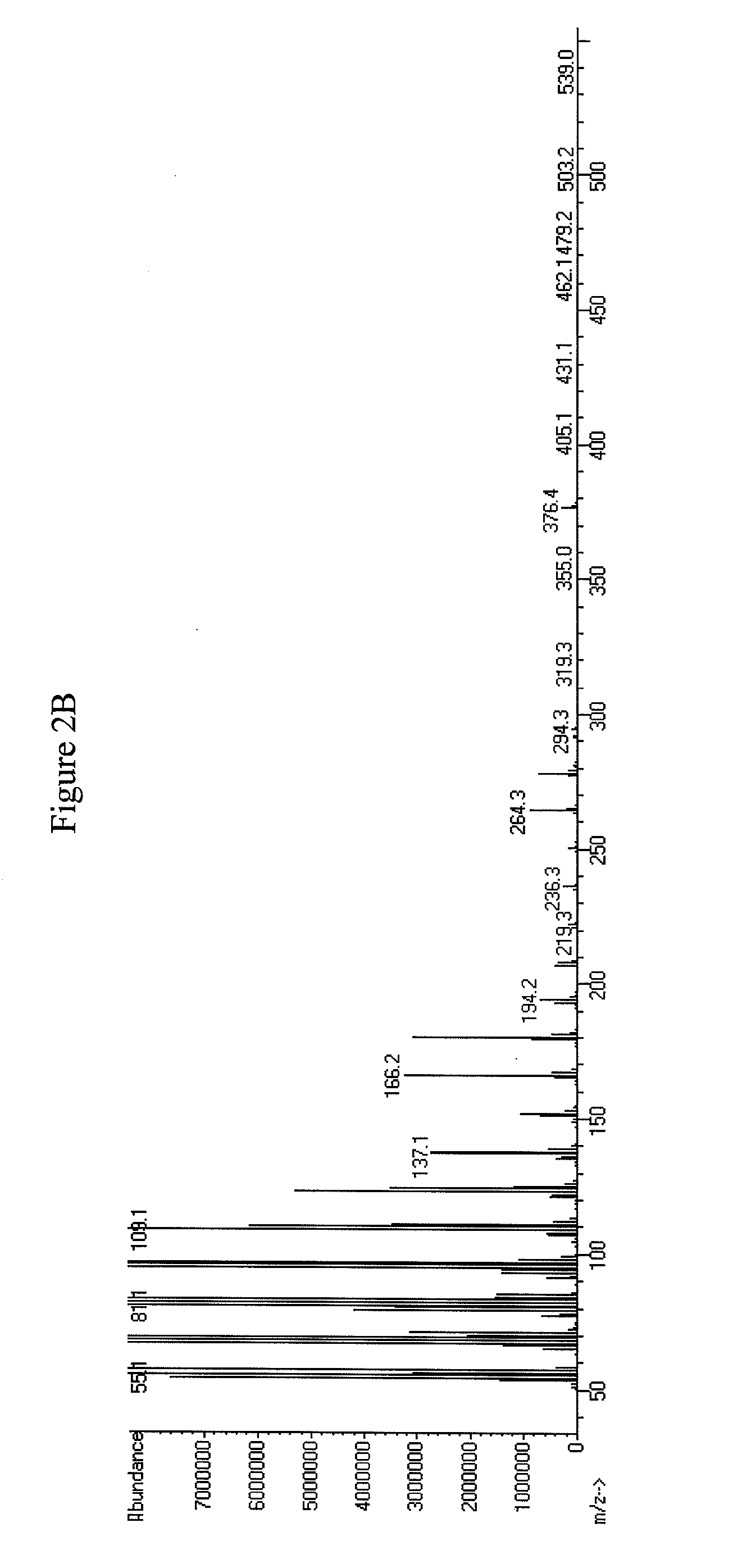
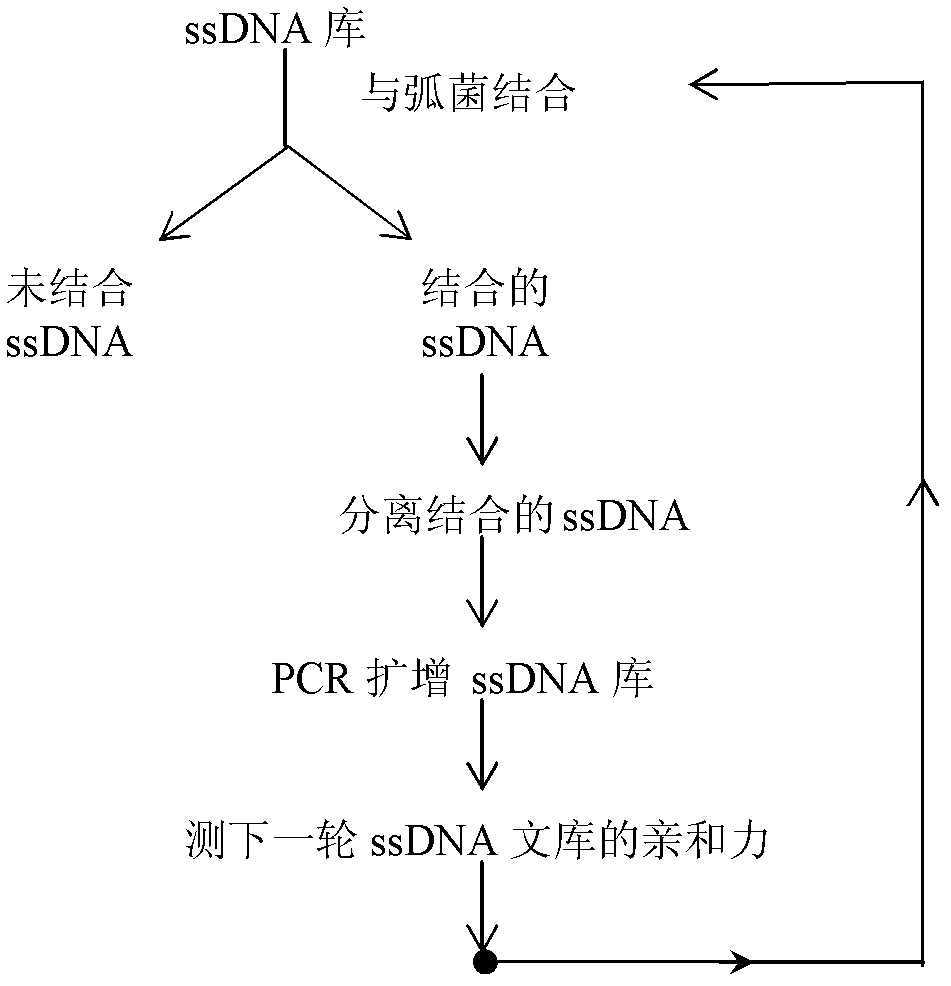
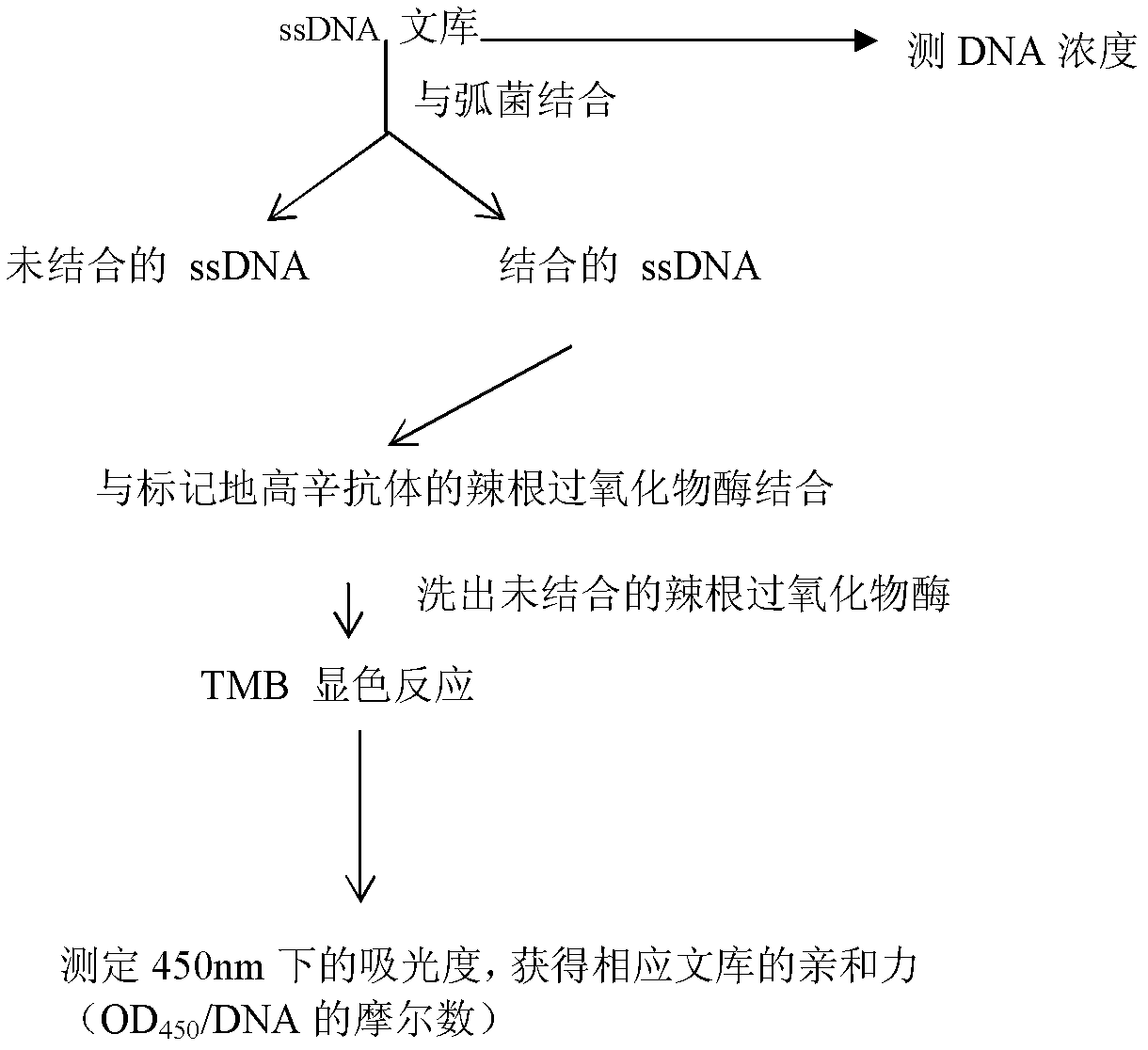
The invention discloses three oligonucleotide sequences for identification and detection of vibrio alginolyticus as well as a preparation method and an application thereof and relates to identification and detection of vibrio alginolyticus. The oligonucleotide sequences comprise SEQ ID No. 1-3 (sequence identity number 1-3). The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an ssDNA (single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) oligonucleotide library (5'-TCA GTC GCT TCG CCG TCT CCT TC----N35----GCA CAA GAG GGA GAC CCC AGA GGG-3') for screening; mixing the oligonucleotide library with the vibrio alginolyticus and then performing SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) screening; performing cloning and sequencing on an aptamer-enhanced library after completing the SELEX screening; performing interception in different lengths on high-copy ssDNA emerged in the sequencing result so as to get a series of new sequences, and further constructing complementary sequences of the new sequences; and performing affinity and specificity verification on the obtained new sequences and the complementary sequences thereof so as to get corresponding aptamers.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
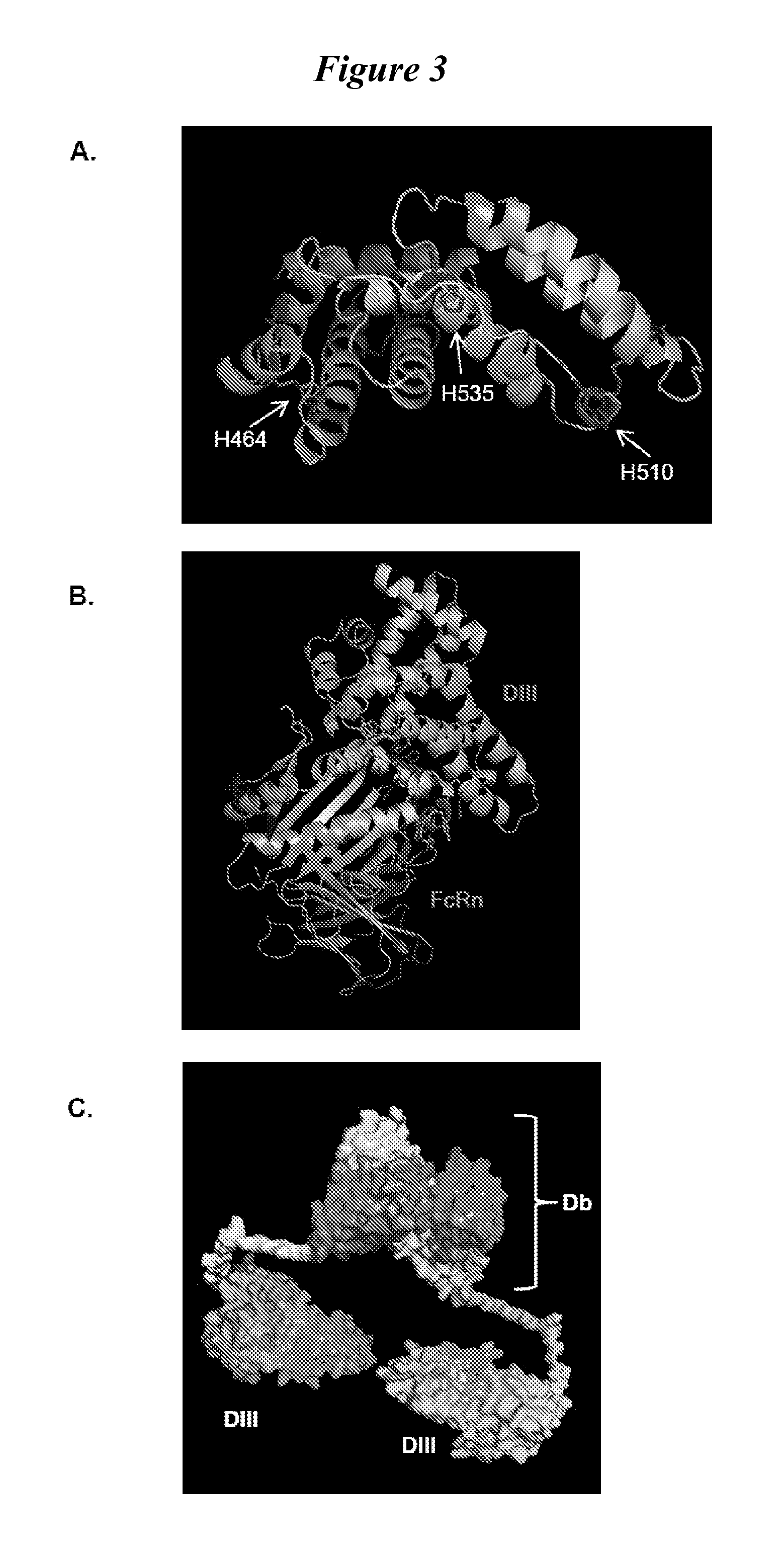
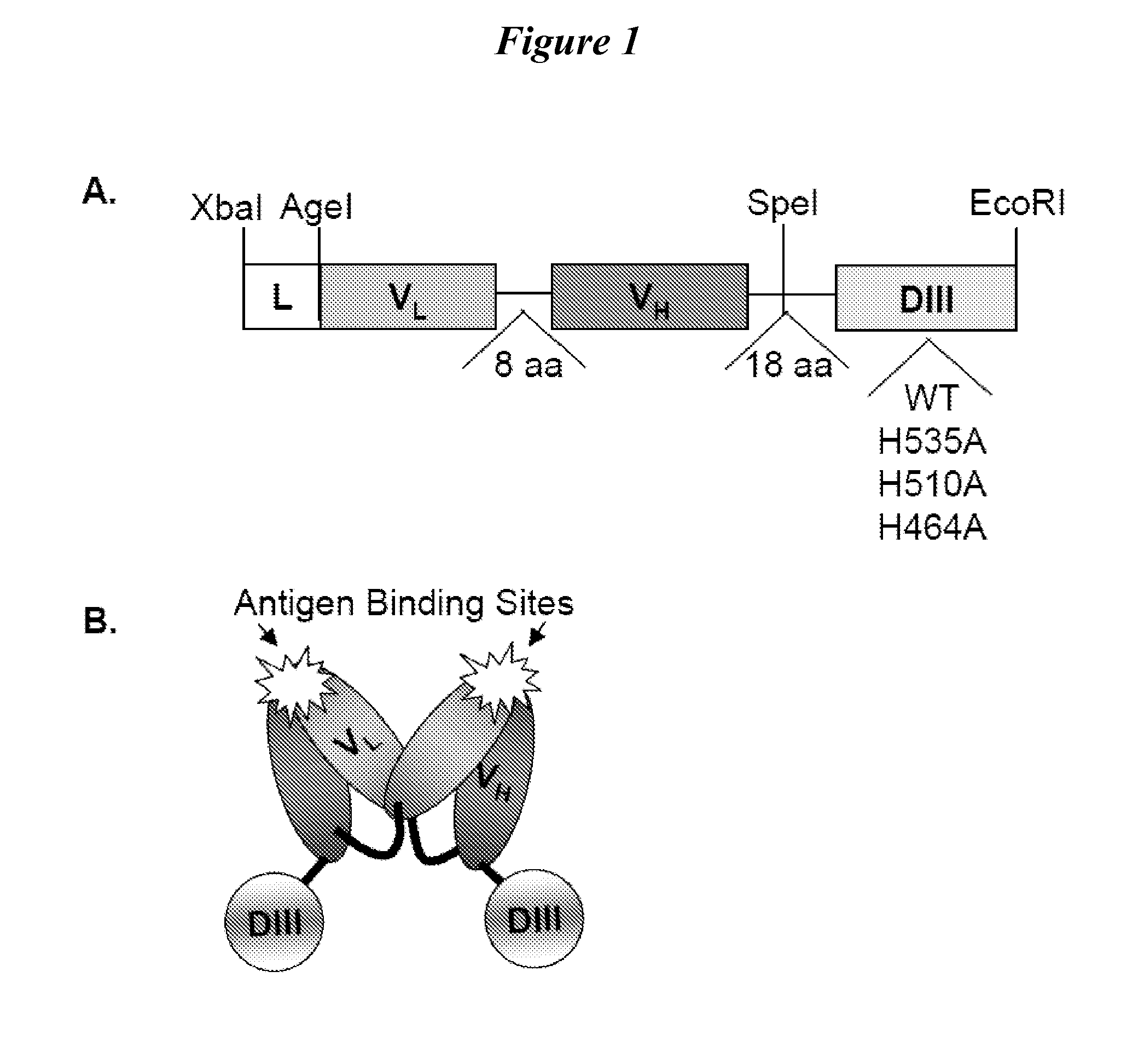
Human protein scaffold with controlled serum pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20120076728A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman proteinsSequence identity
This invention provides constructs comprising a protein scaffold, wherein the scaffold comprises Domain III, Domain IIIa, or Domain IIIb of human serum albumin or a polypeptide having substantial sequence identity to the Domain III, the Domain IIIa, or the Domain IIIb; and a targeting moiety in covalent linkage to the protein scaffold; and a therapeutic moiety and / or an imaging moiety in covalent linkage to the protein scaffold. The scaffold can be modified to tune the serum pharmacokinetics of the construct. In addition to methods of making the constructs, therapeutic, imaging and diagnostic uses of the constructs are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
InactiveUS20070037214A1High affinityImprove throughputPeptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIn vivoOrganism
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method for constructing a library of designed proteins, comprising the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, the amino acid sequence being designated as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; and forming a library of designed proteins by substituting the lead sequence with the hit library. The library of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant proteins that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead protein, such as an antibody against therapeutically important target.
Owner:LUO PEIZHI +5
Weed controller metabolism proteins, genes thereof and use of the same
InactiveUS20050084859A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTransport systemElectron donor
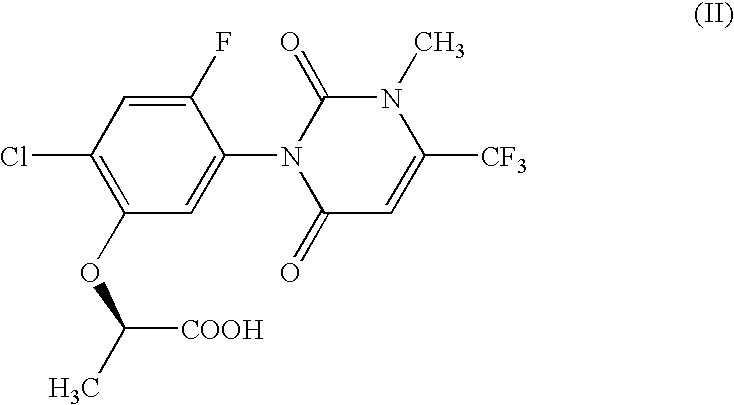
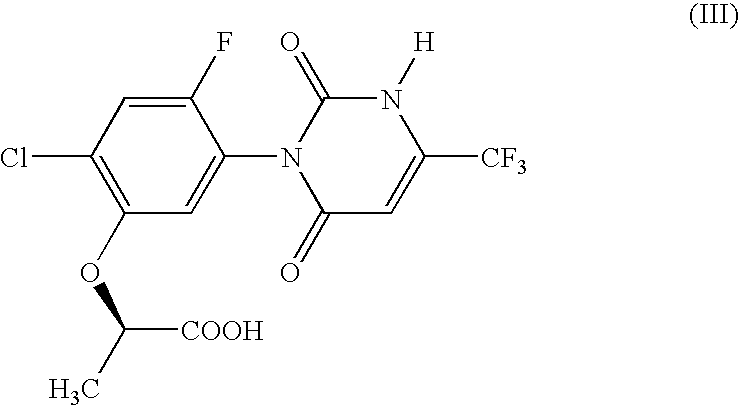
The present invention provides, for example, DNA encoding a herbicide metabolizing protein selected from the protein group below. Such DNA may, for example, be employed to produce herbicidally resistant plants. <protein group>a protein comprising the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3, 108, 159, 160, 136, 137, 138, 215, 216, 217, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223 or 224, a protein having an ability to convert in the presence of an electron transport system containing an electron donor, a compound of formula (II): to a compound of formula (III): and comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 80% sequence identity with an amino acid sequence shown in any one of SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3, 108, 159, 136, 137, 138, 215, 216, 217, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223 or 224 or an amino acid sequence having at least 90% sequence identity with an amino acid sequence shown in any one of SEQ ID NO: 160, 215, 216, 218, 222 or 224.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION FOR TREATING BONE DISEASES WHICH COMPRISES PROTEIN COMPRISING Frizzled1, Frizzled2 OR Frizzled7 EXTRACELLULAR CYSTEINE-RICH DOMAIN
InactiveUS20110237514A1High densityAdd additional massOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBone densityMammal
This invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of a bone disease comprising, as an active ingredient, a protein comprising an extracellular cysteine-rich domain, which is from the Frizzled receptor selected from the group consisting of mammalian animal-derived Frizzled 1, Frizzled 2, and Frizzled 7 and has activity of increasing bone mass, bone density, and / or bone strength, or a mutant of such domain having sequence identity of 85% or higher to the amino acid sequence of the domain and having activity of increasing bone mass, bone density, and / or bone strength, or a vector comprising a nucleic acid encoding the protein.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com