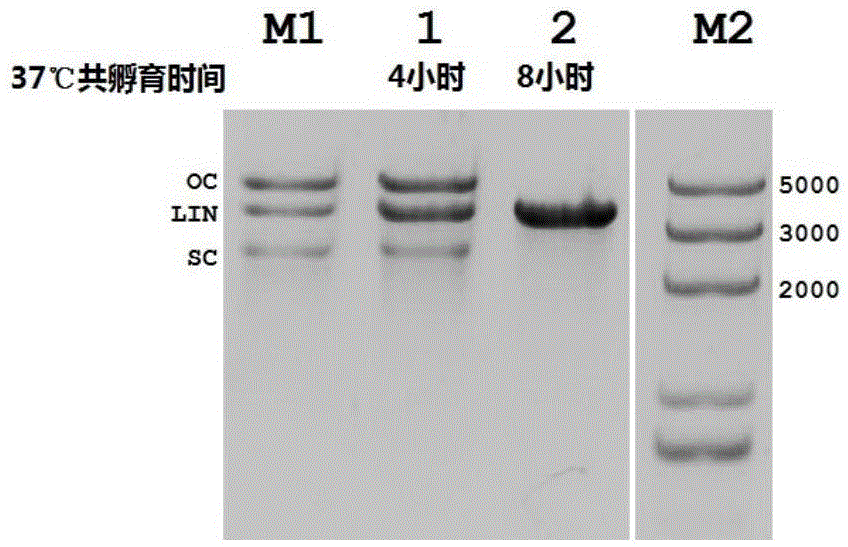
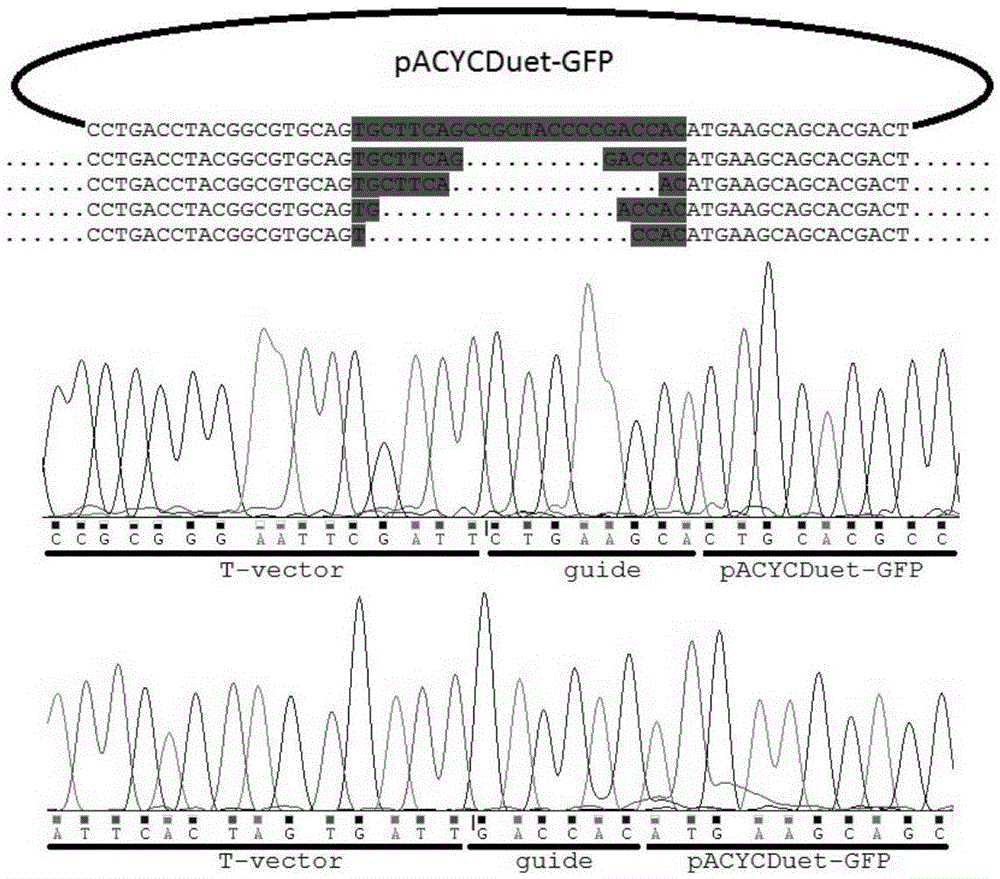
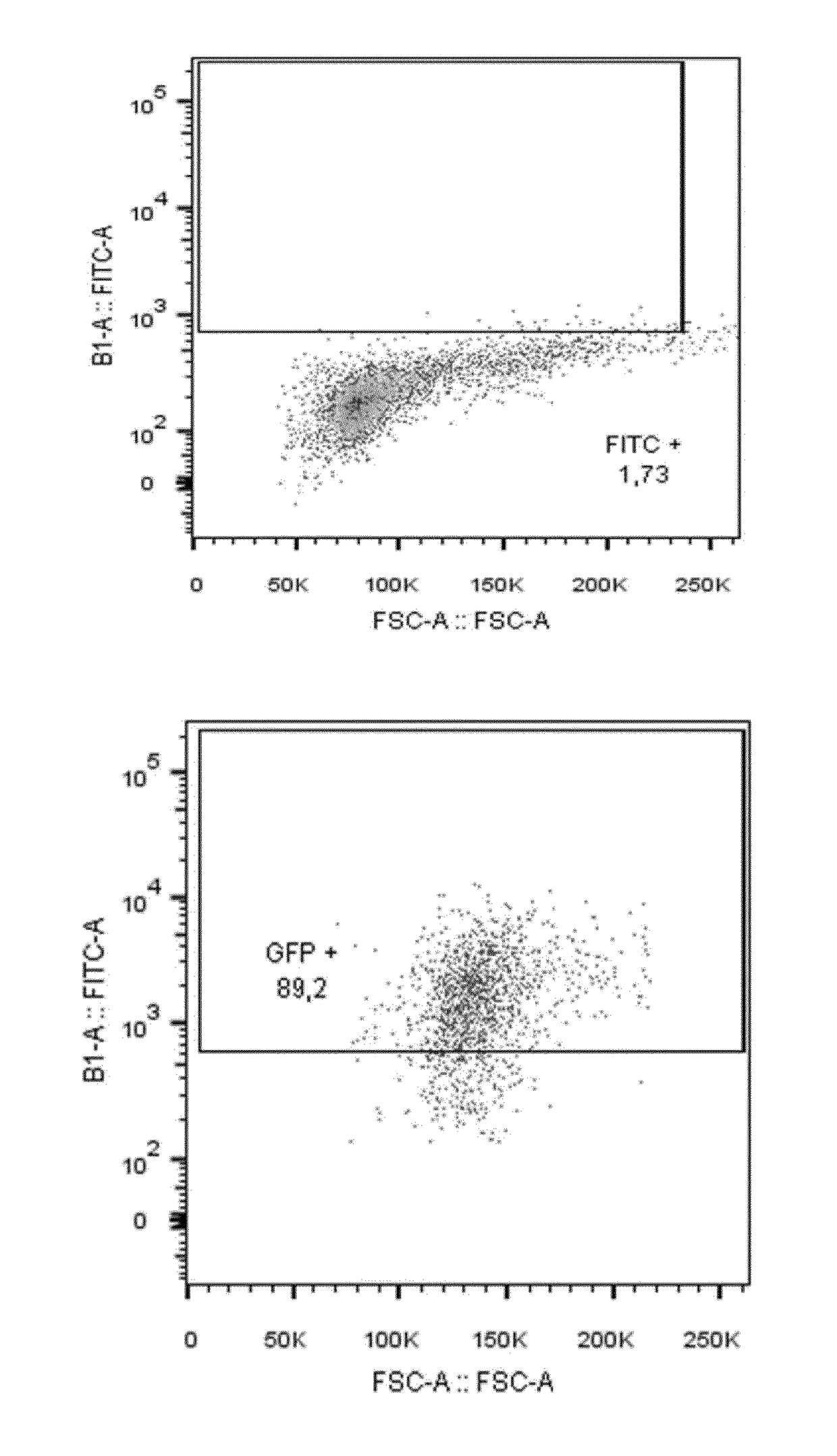
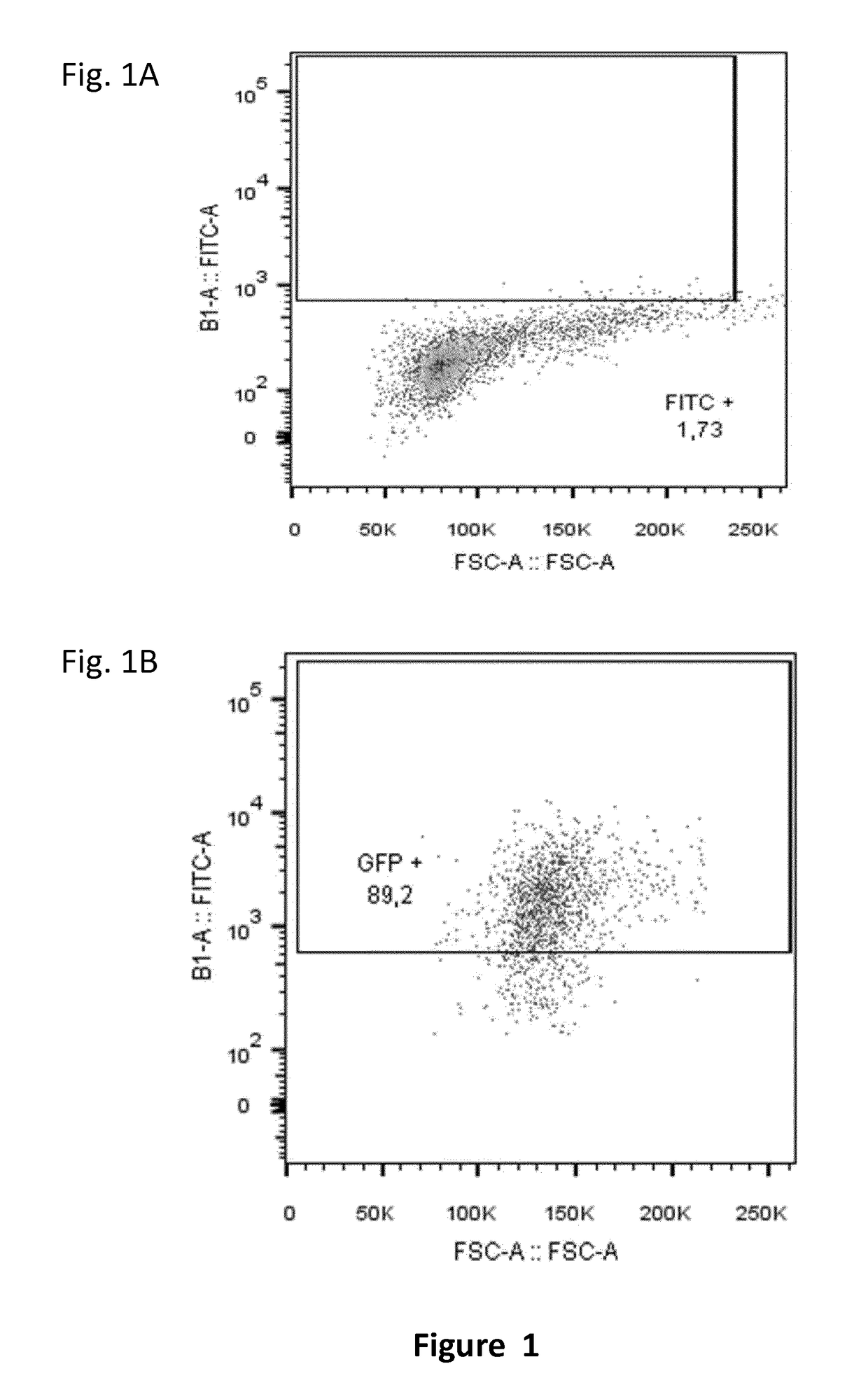
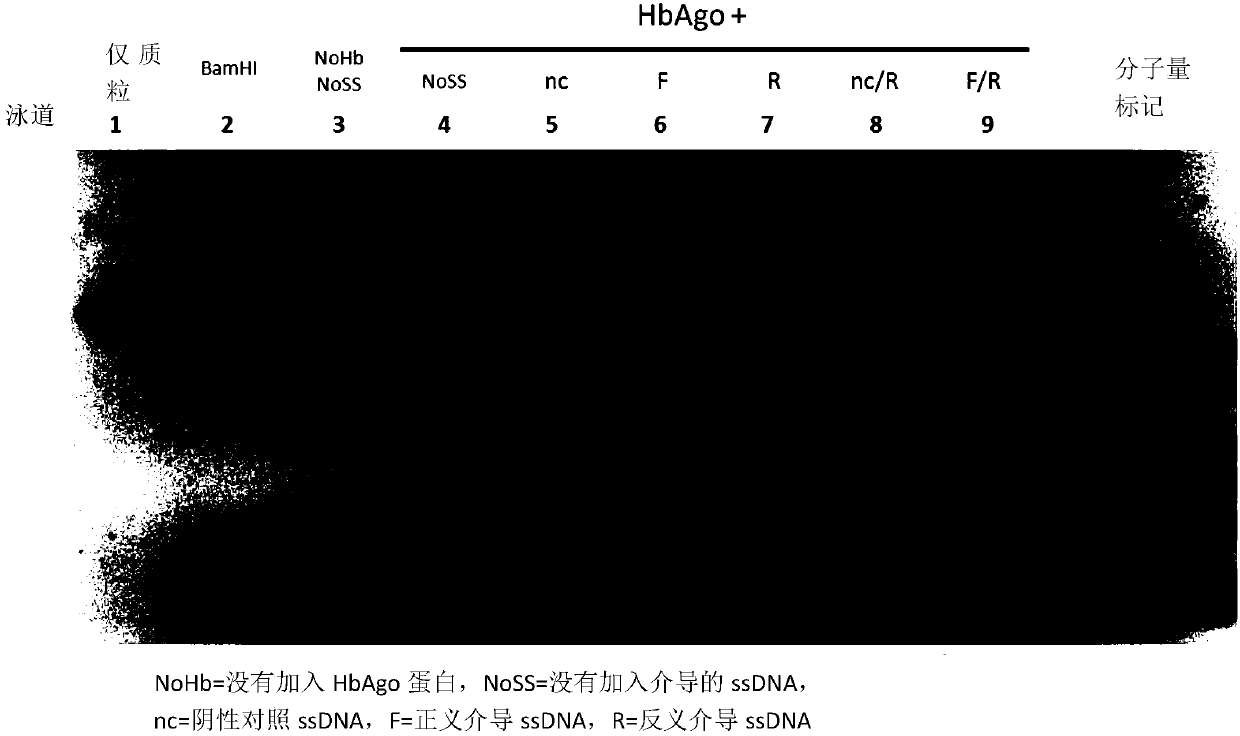
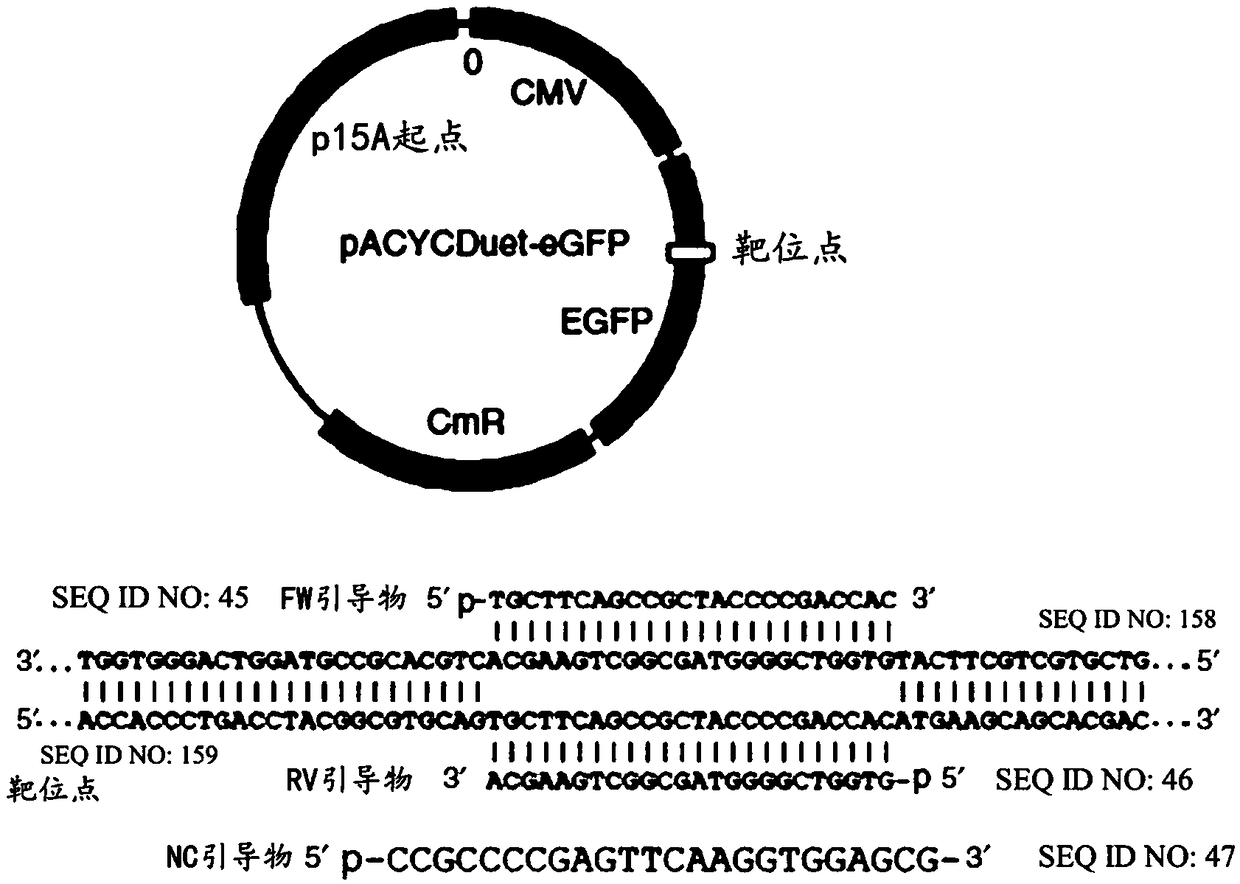
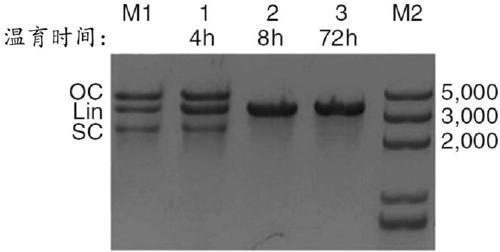
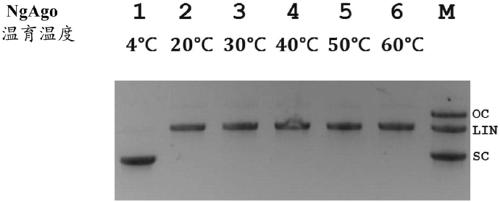
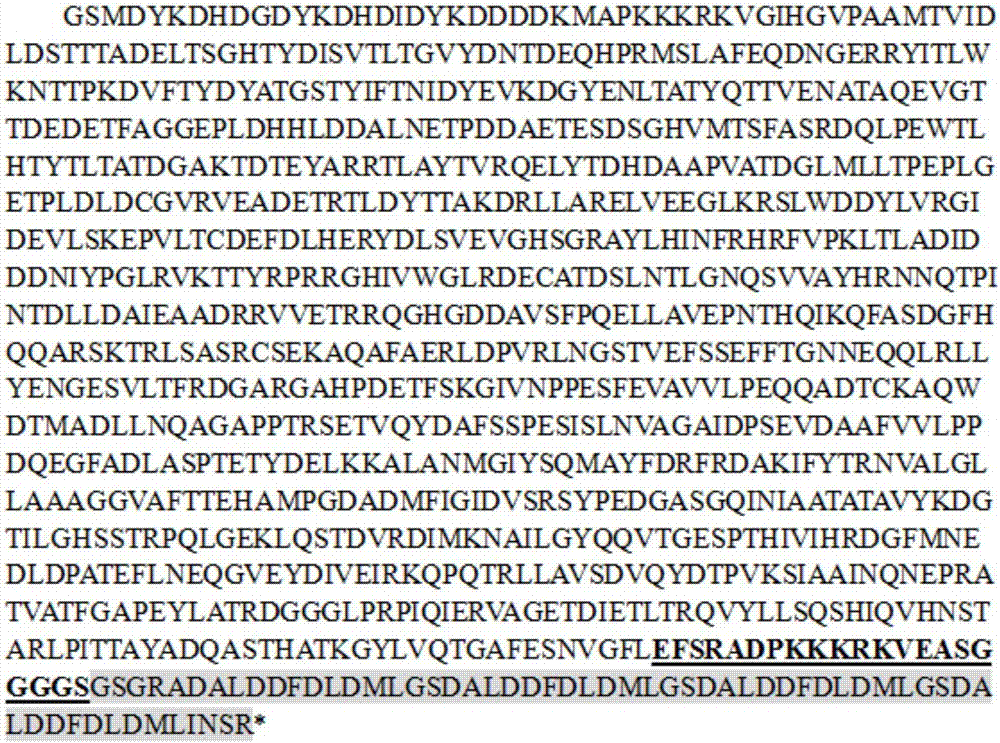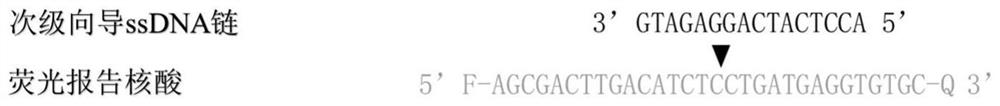Patents
Literature
47 results about "Argonaute" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
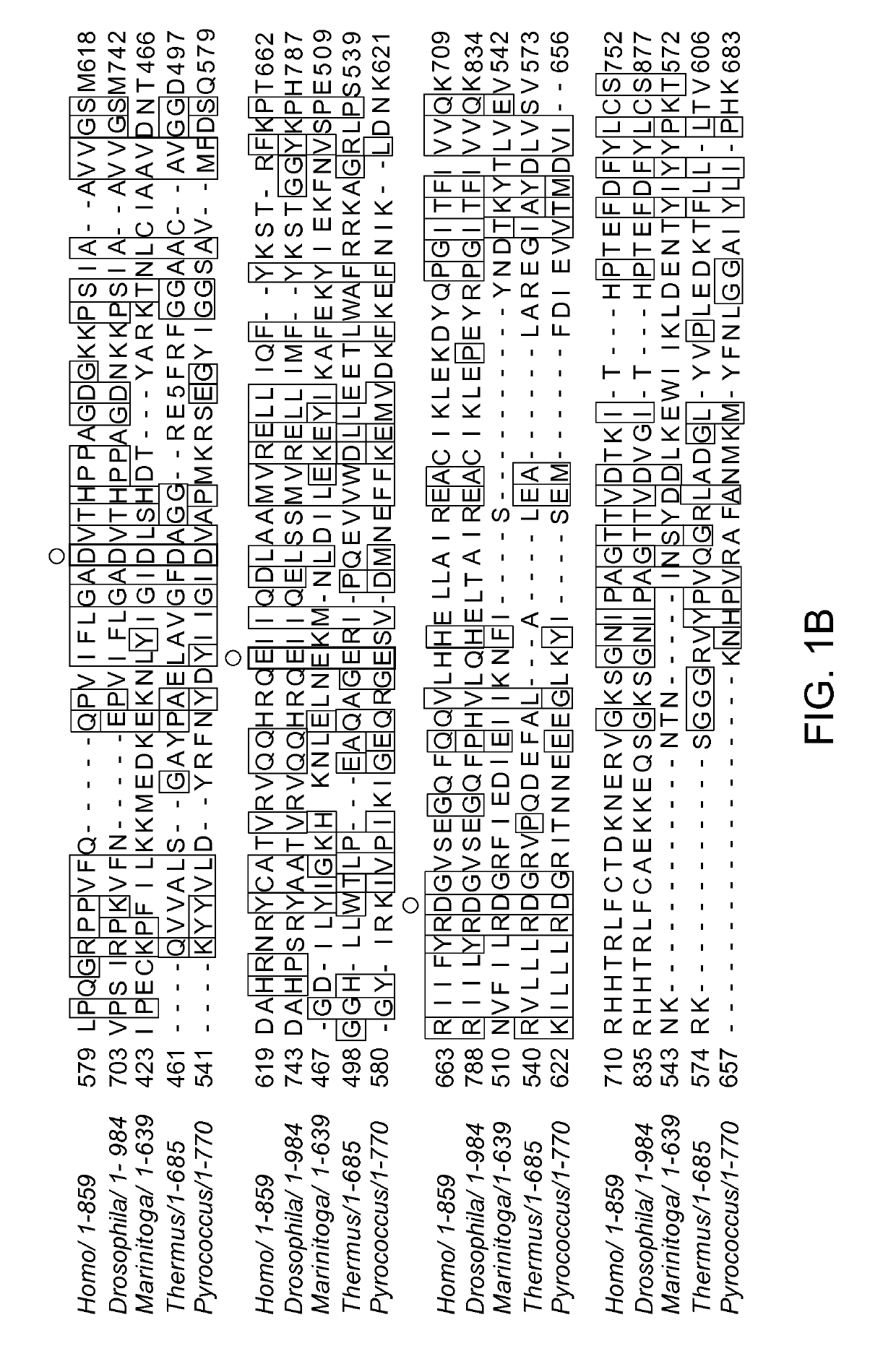
The Argonaute protein family plays a central role in RNA silencing processes, as essential components of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC is responsible for the gene silencing phenomenon known as RNA interference (RNAi). Argonaute proteins bind different classes of small non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). Small RNAs guide Argonaute proteins to their specific targets through sequence complementarity (base pairing), which then leads to mRNA cleavage or translation inhibition.
Methods and compositions for using argonaute to modify a single stranded target nucleic acid
The present disclosure provides compositions, kits, genetically modified cells, non-human transgenic organisms, and methods for binding and / or cleaving a single stranded target nucleic acid. A method of cleaving includes contacting a single stranded target nucleic acid with (e.g., introducing into a cell) a subject argonaute (Ago) polypeptide and a guide RNA (e.g., having a 5′-OH). In some embodiments, a subject Ago polypeptide includes an amino acid sequence having 70% or more sequence identity with amino acids 282-430 and / or 431-639 of the Marinitoga piezophila argonaute (MpAgo) protein set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1. The present disclosure provides variant Ago polypeptides; and methods of use of same.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
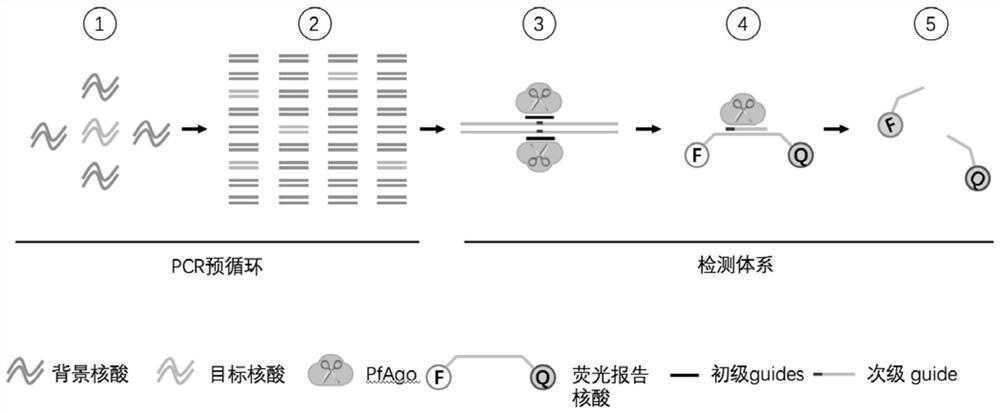
Nucleic acid testing method based on prokaryotic Argonaute protein and application of nucleic acid testing method
ActiveCN108796036AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMedical diagnosis
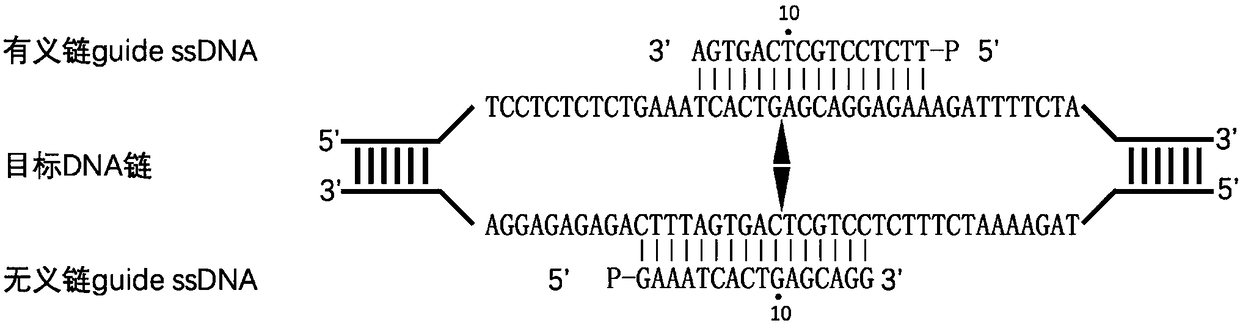
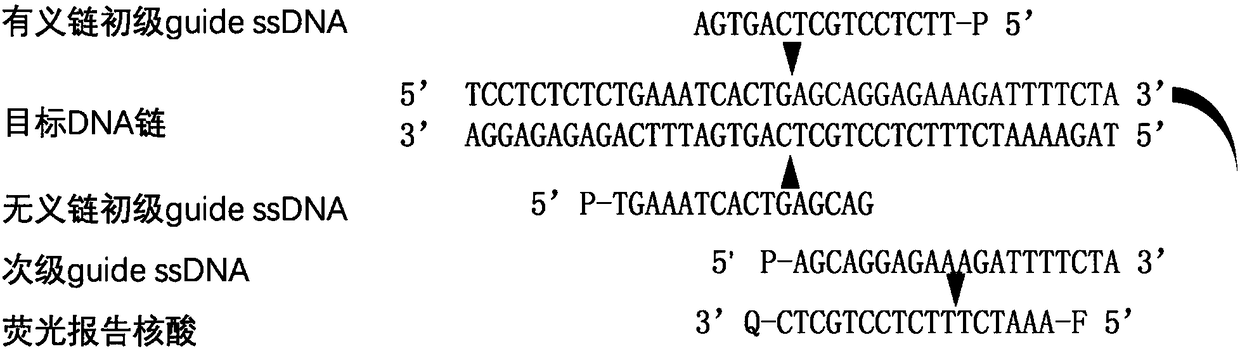
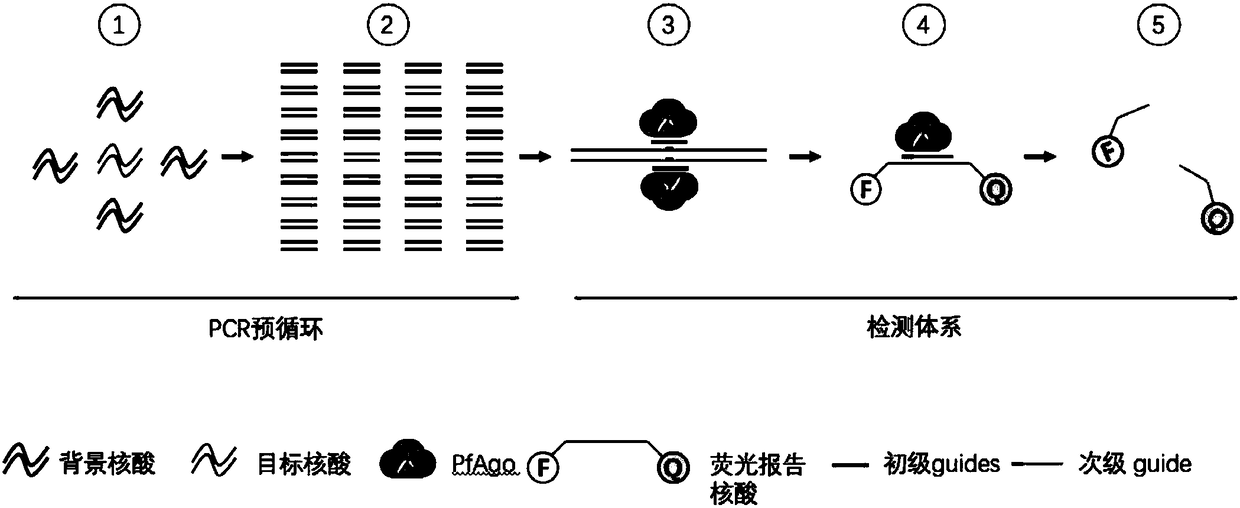
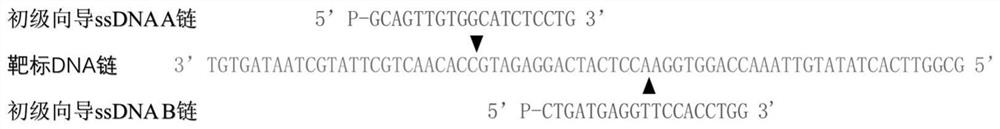
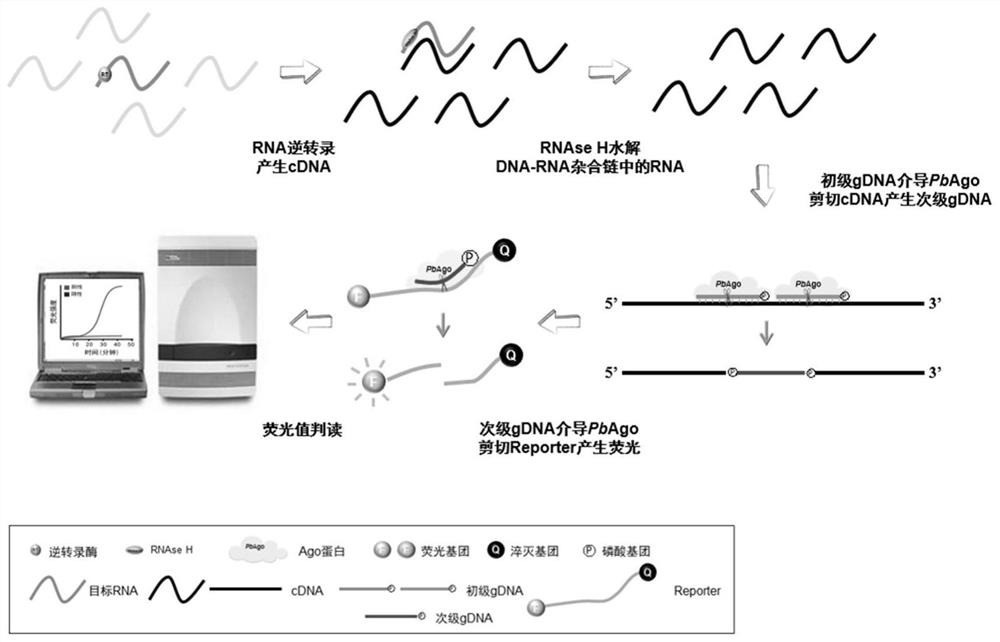
The invention provides a nucleic acid testing method based on a prokaryotic Argonaute protein and an application of the nucleic acid testing method, and particularly provides a system for detecting atarget nucleic acid molecule. The system comprises guide ssDNAs, gene editing enzyme Pyrococcus furiosus Argonaute (PfAgo) and a fluorescence reporter nucleic acid. The nucleic acid testing method ishigh in sensitivity, good in specificity and high in flux and can be widely applied to the fields of molecular medical diagnosis, food safety testing, environmental monitoring and the like.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
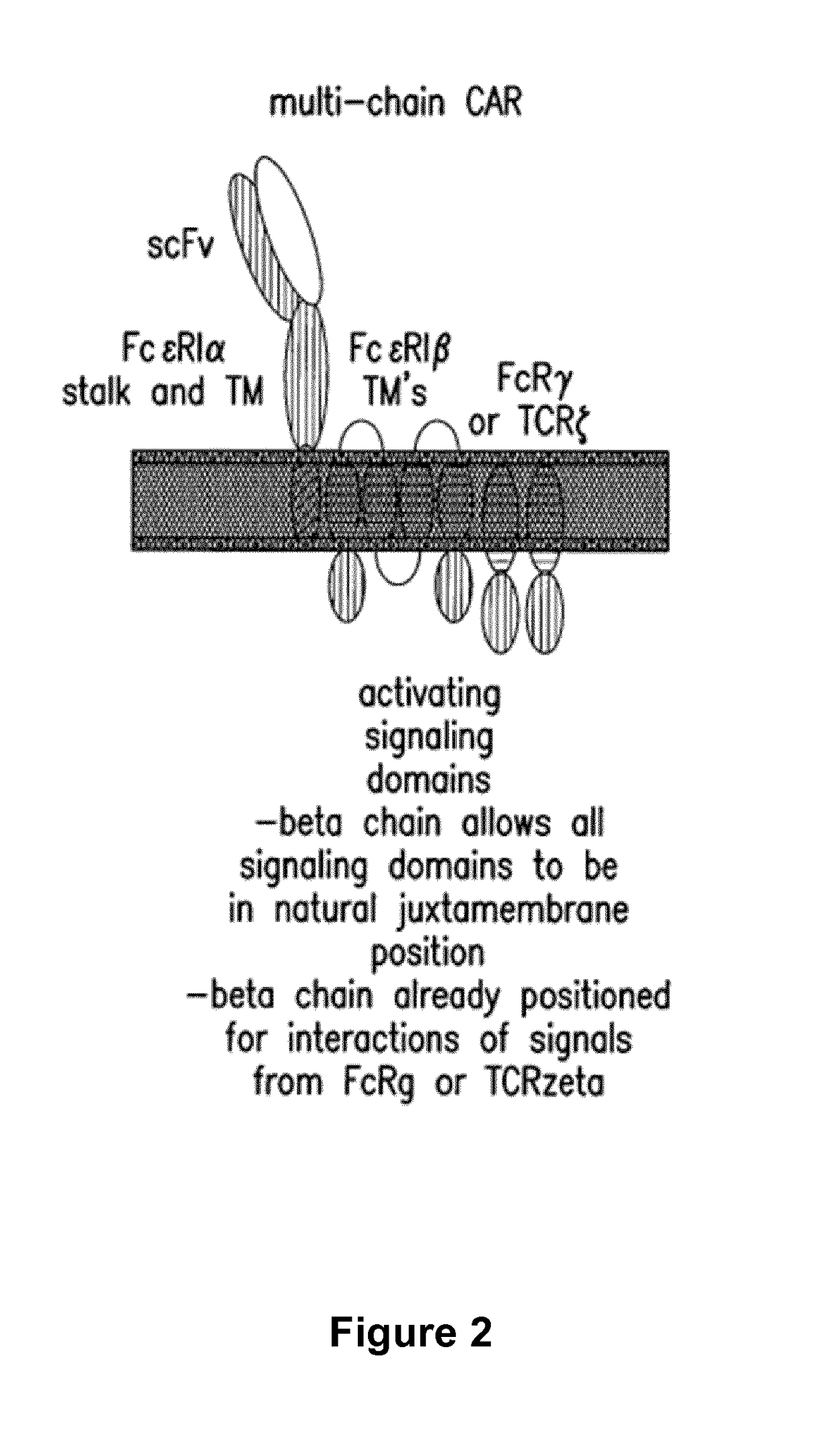
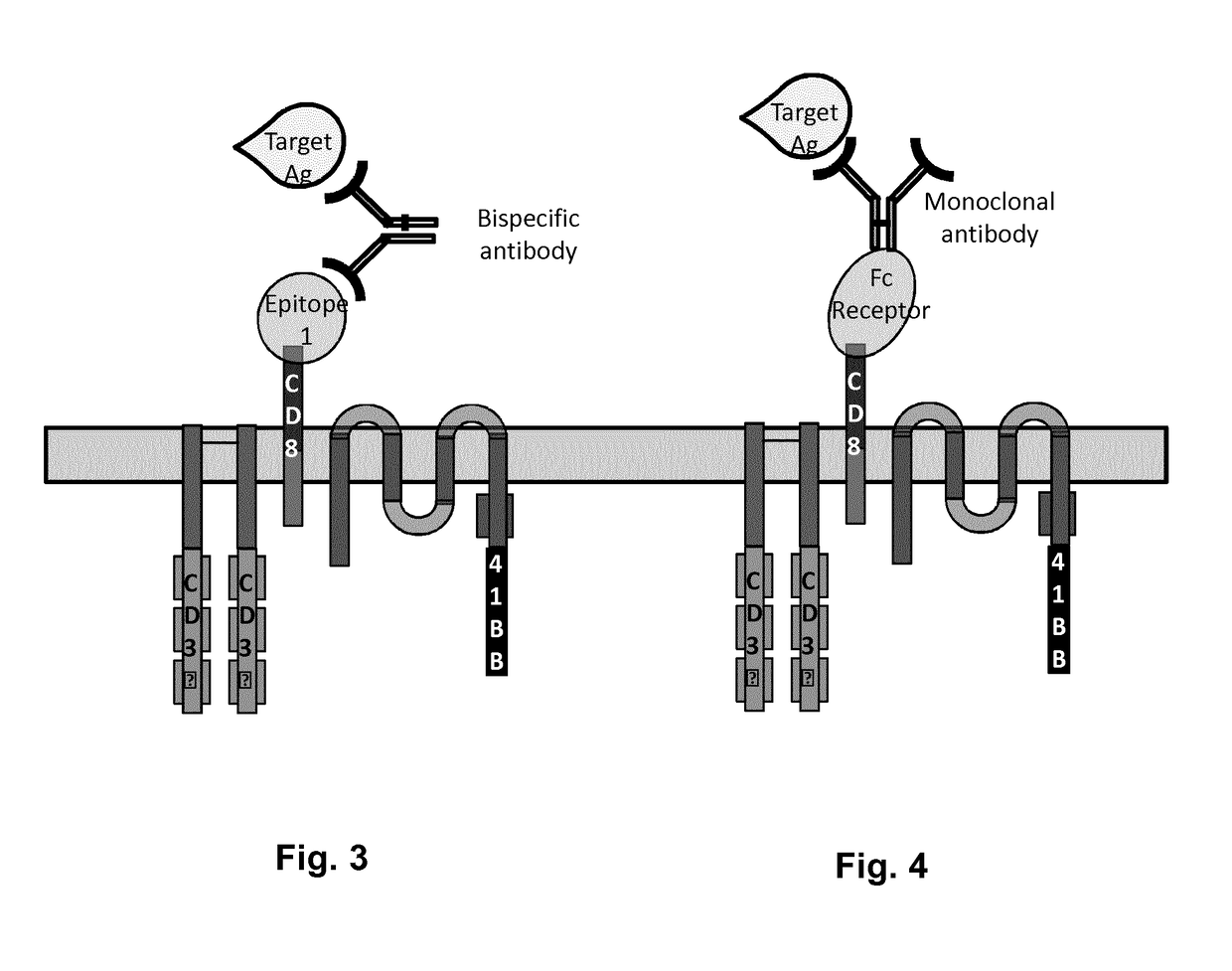
Cells for immunotherapy engineered for targeting antigen present both on immune cells and pathological cells
ActiveUS20180201901A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsAntigens present
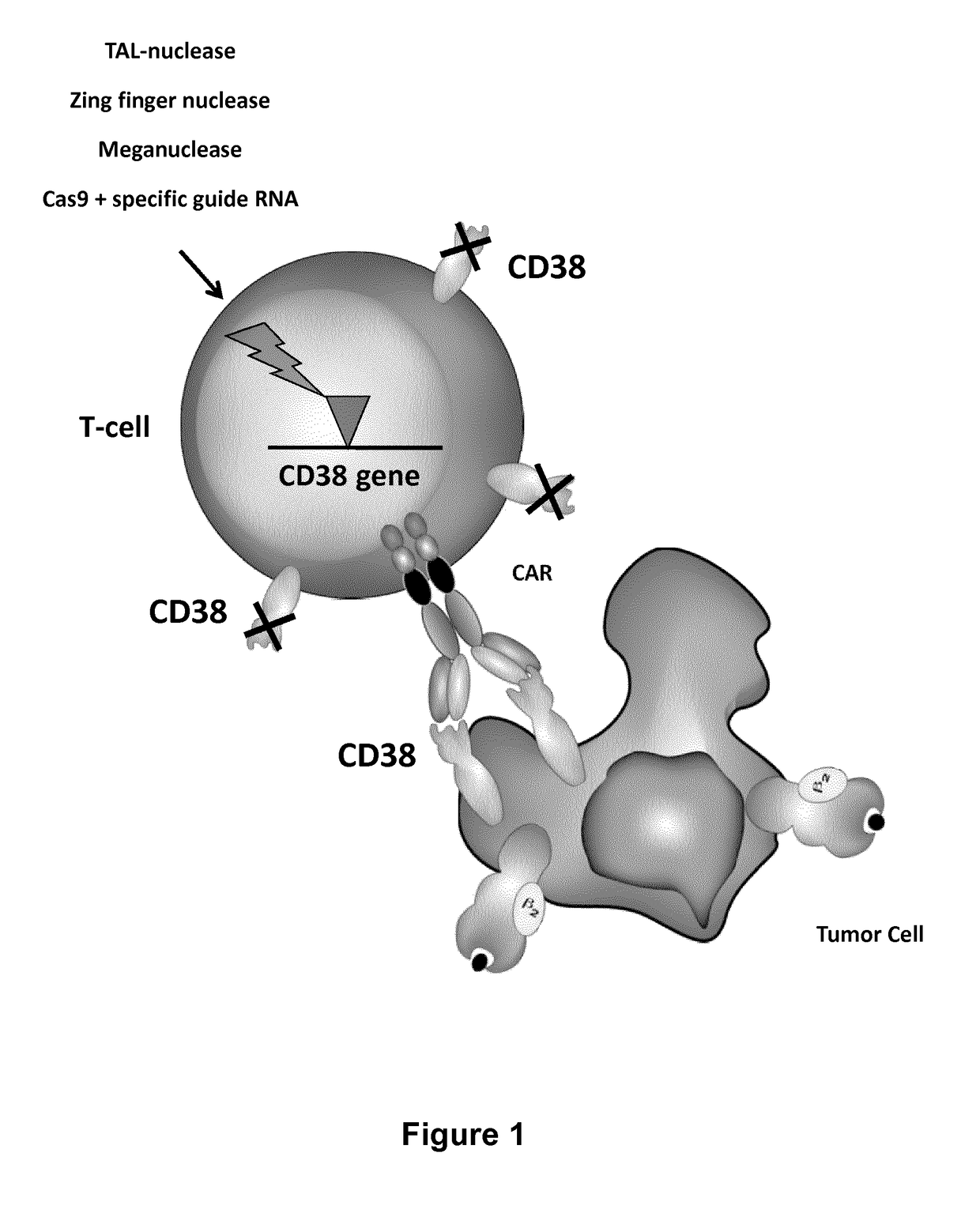
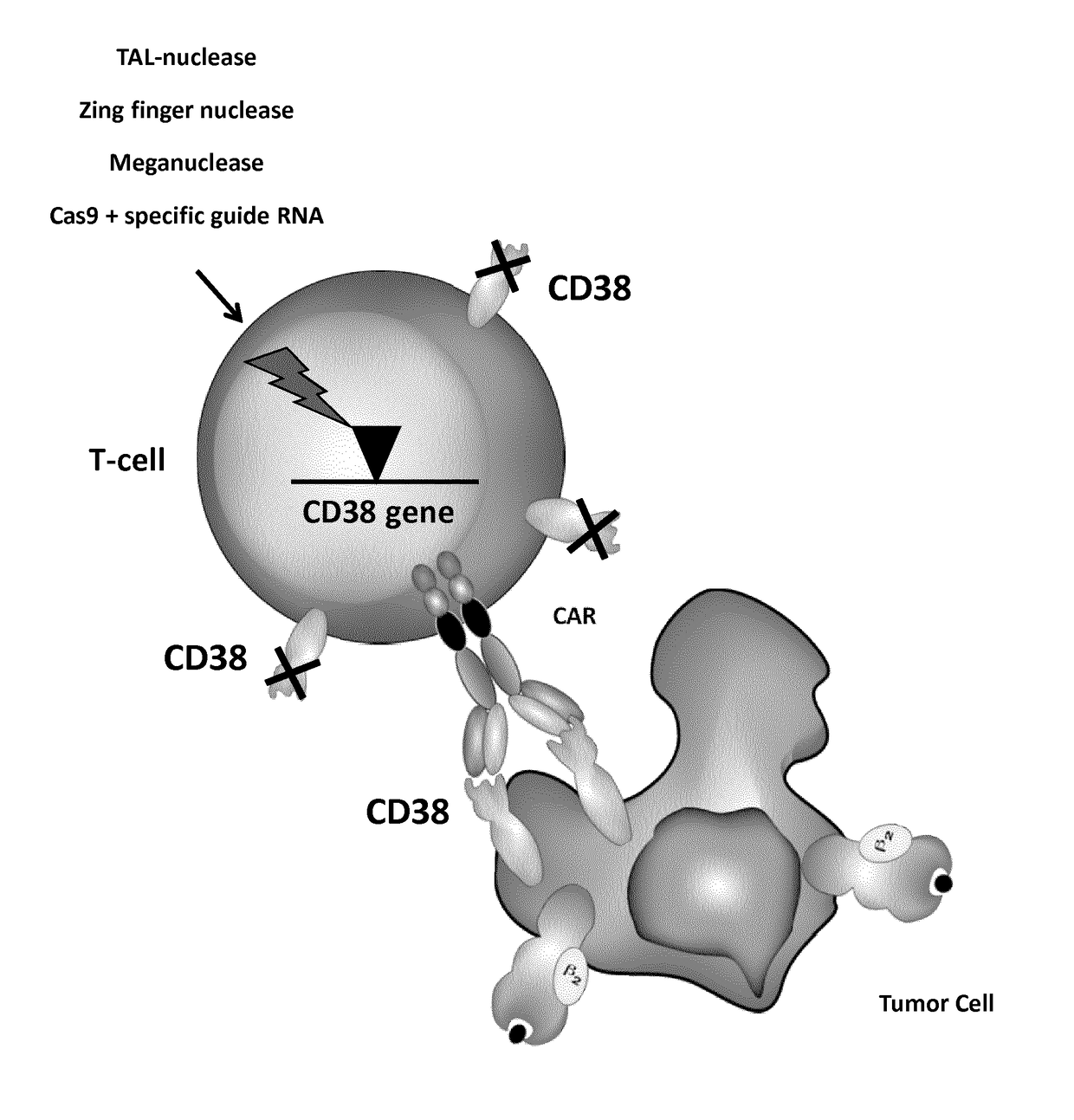
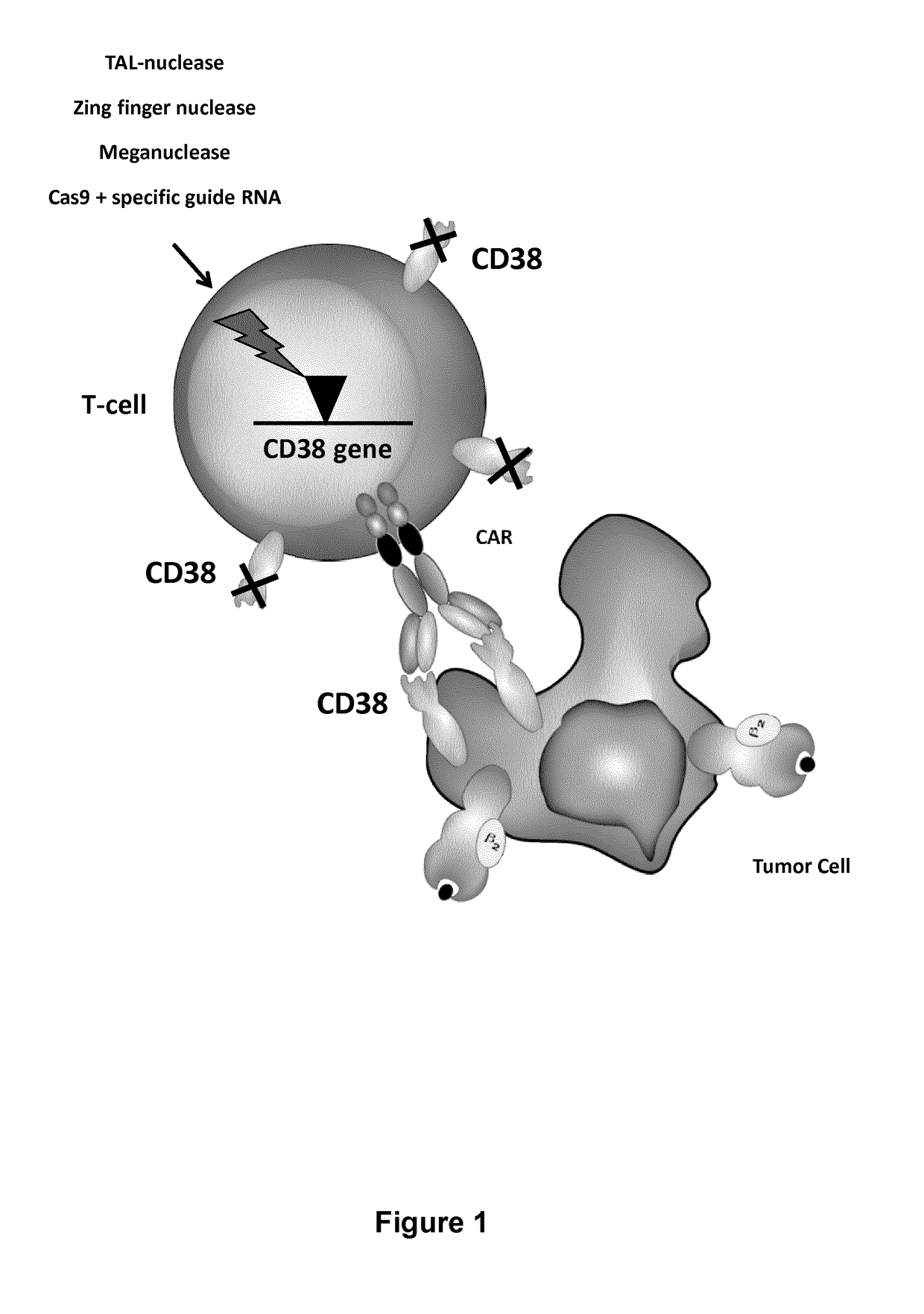
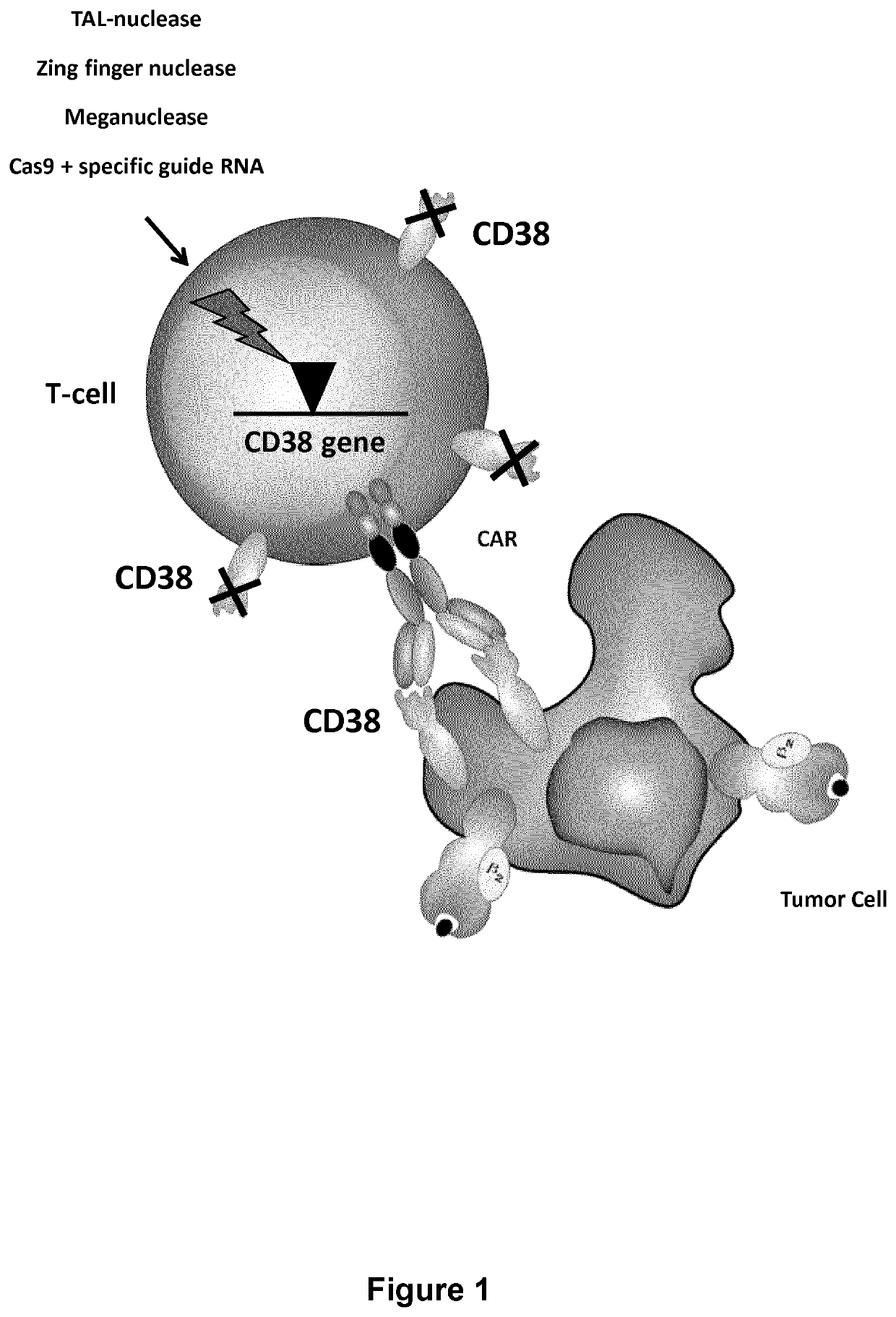
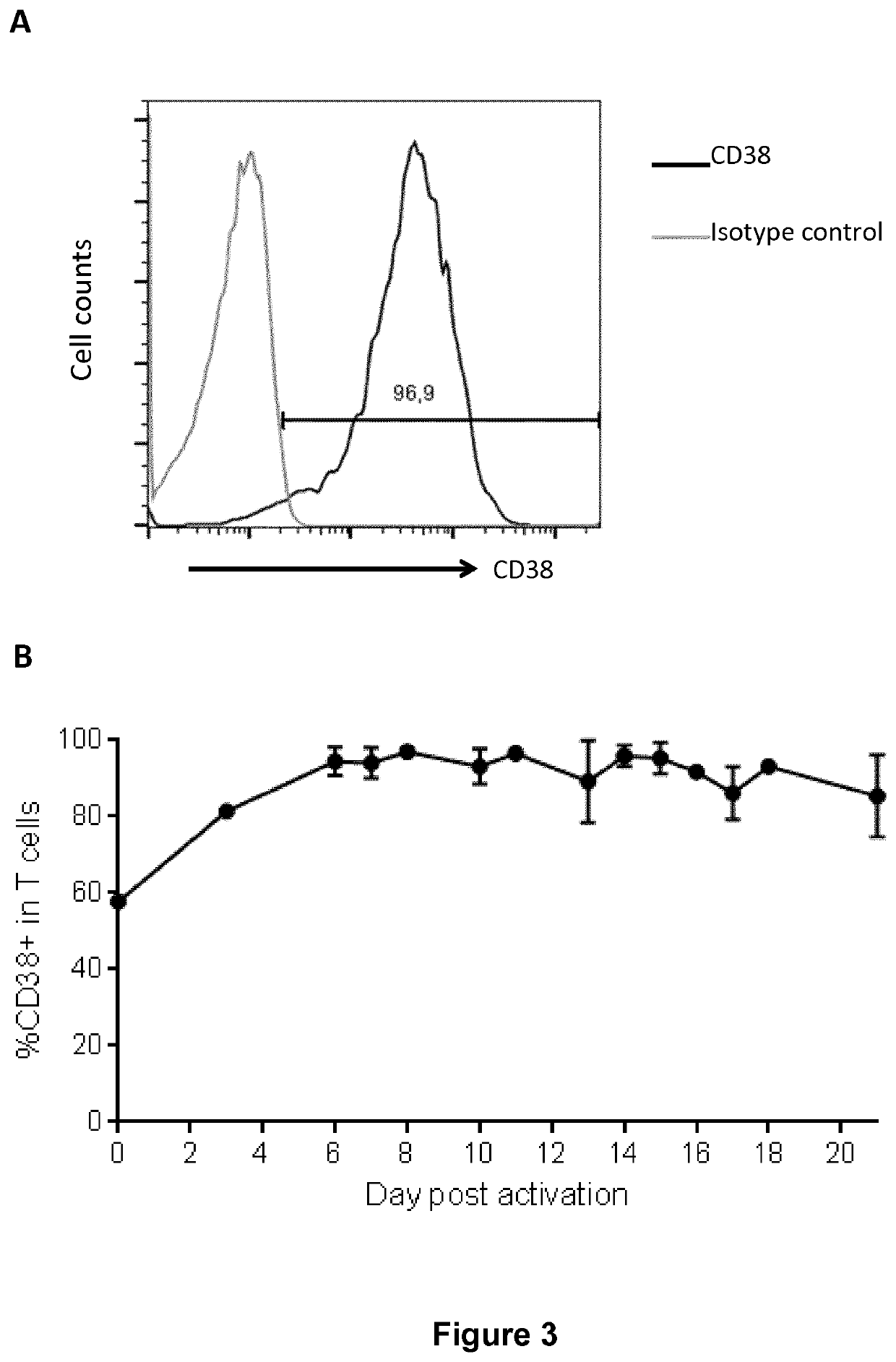
Methods of developing genetically engineered immune cells for immunotherapy, which can be endowed with Chimeric Antigen Receptors targeting an antigen marker that is common to both the pathological cells and said immune cells (ex: CD38, CS1 or CD70) by the fact that the genes encoding said markers are inactivated in said immune cells by a rare cutting endonuclease such as TALEN, Cas9 or argonaute.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Gene editing technique taking Argonaute nuclease as core
InactiveCN105483118ASimple designThe dosage is easy to controlDNA preparationGenome editing3-deoxyribose
The invention discloses a gene editing technique taking Argonaute nuclease as a core. In the presence of guide DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), Argonaute endonuclease can cut any locus of a targeted DNA sequence, including a genome of a mammal to cause breakage of DNA double chains, thereby fulfilling an editing aim. Editing means include incision, deletion, mutagenesis induction, exogenous sequence insertion, fragment substitution and the like. Editing effects include gene inactivation, gene mutation, exogenous gene induction and the like. The protein can serve as an important tool for genome editing. A gene editing tool taking the protein as the core has the characteristics of easiness in operation, high efficiency, low target missing rate and high fidelity. Moreover, almost any genome locus can be effectively targeted and cut by the Argonaute nuclease. By using the technique, high-specificity and high-efficiency genome targeted editing is helpfully realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Methods for improving functionality in nk cell by gene inactivation using specific endonuclease
PendingUS20180171298A1Efficient and durable responseFunction increasePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCytotoxicityNuclease
The present invention relates to methods for improving therapeutic activity of NK cell, such as their cytotoxic / cytolytic activity, to be used in immunotherapy, by gene editing. In particular, these methods comprise a step of reduction or inactivation of gene expression using specific endonuclease such as TAL-nuclease, CRISPR or Argonaute. An additional genetic modification can be performed by (over)expressing at least one gene involved in N K function. The present invention encompasses also engineered NK cell, pharmaceutical composition containing the same.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Nucleobase editors comprising nucleic acid programmable DNA binding proteins
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome ofa cell or subject, e. g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of nucleic acid programmable DNA binding proteins (napDNAbp), e. g., Cpf 1 or variants thereof, and nucleic acid editing proteins or protein domains, e. g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e. g., fusion proteins of a napDNAbp (e. g., CasX, CasY, Cpfl, C2cl, C2c2, C2C3, and Argonaute) and nucleic acid editing proteins or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Argonaute protein mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110229799APromote enrichmentReduce lossesFusion with RNA-binding domainNucleotide librariesTernary complexMutant
The present invention relates to an Argonaute protein mutant which lacks DNA cleavage activity, but has DNA binding activity. The mutation of the mutant is located in a PIWI domain. The invention alsorelates to application of the protein mutant particularly in the enrichment of target DNA and in the construction of a sequencing library. Therefore, the present invention also relates to a method for enriching the target DNA. The method comprises the steps of: (a) designing a leader sequence for a specific sequence in the target DNA; (b) combining the mutant, the leader sequence and the target DNA according to the present invention to obtain a mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex; (c) capturing the mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex through a capture medium; and (d) isolating the target DNA from the captured mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex to obtain enriched target DNA.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Use of argonaute endonucleases for eukaryotic genome engineering
InactiveUS20170367280A1Low costHigh inherent stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyEndonuclease
The present invention relates to the use of Argonaute systems in plants for genome engineering, and compositions used in such methods.
Owner:KWS SAAT SE
Methods of using oligonucleotide-guided argonaute proteins
InactiveUS20160289734A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSpecific detectionNucleic Acid Probes
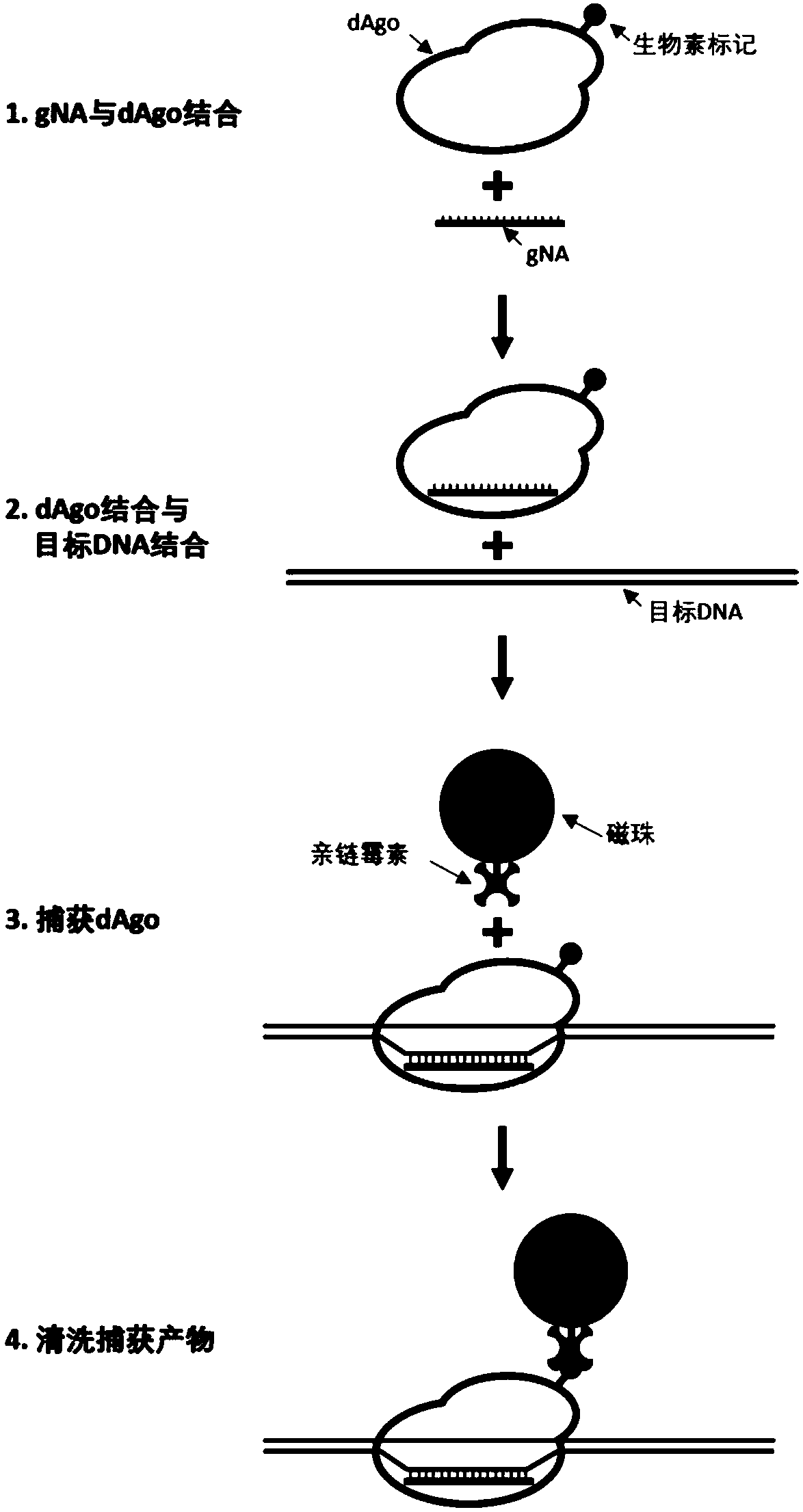
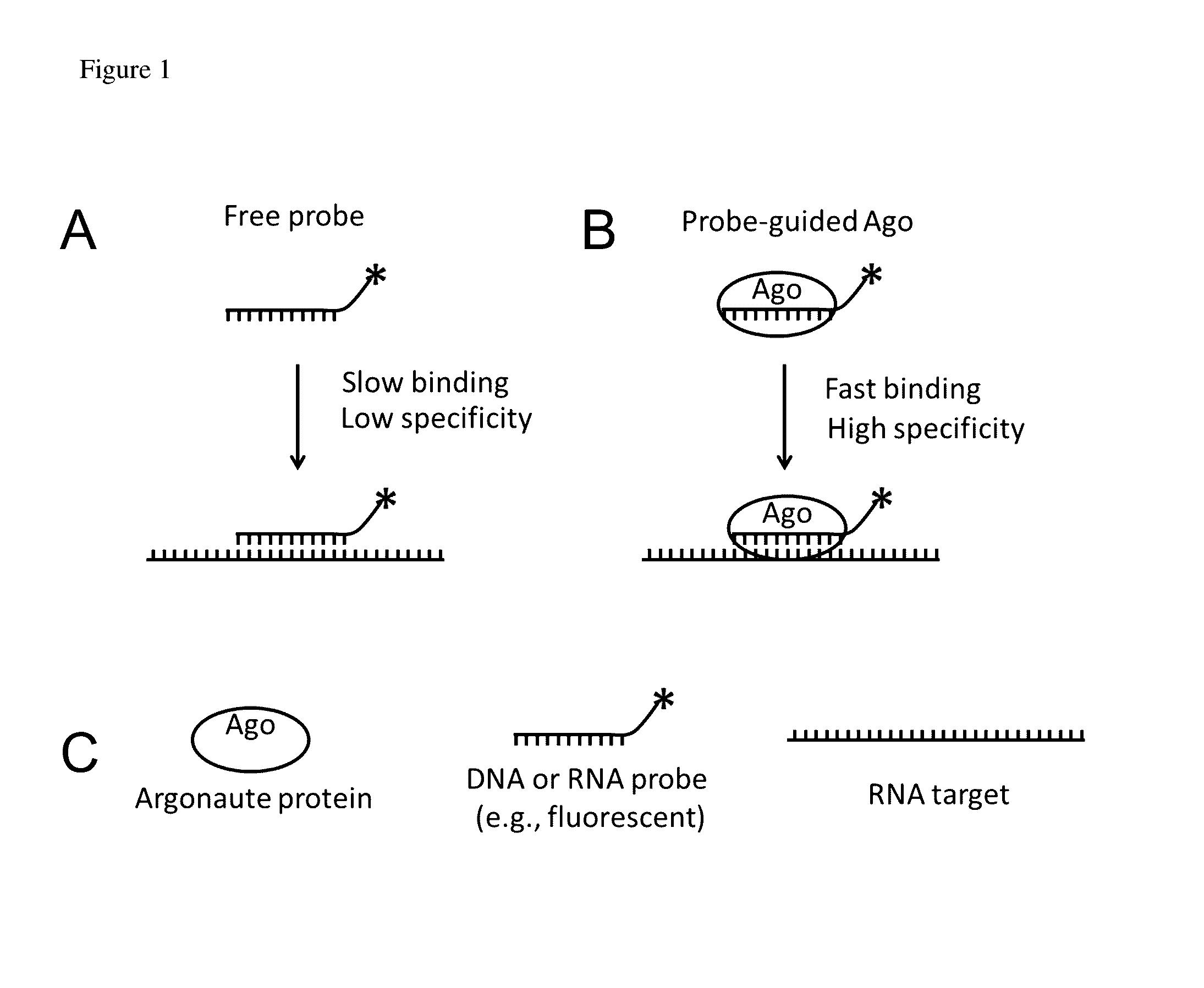
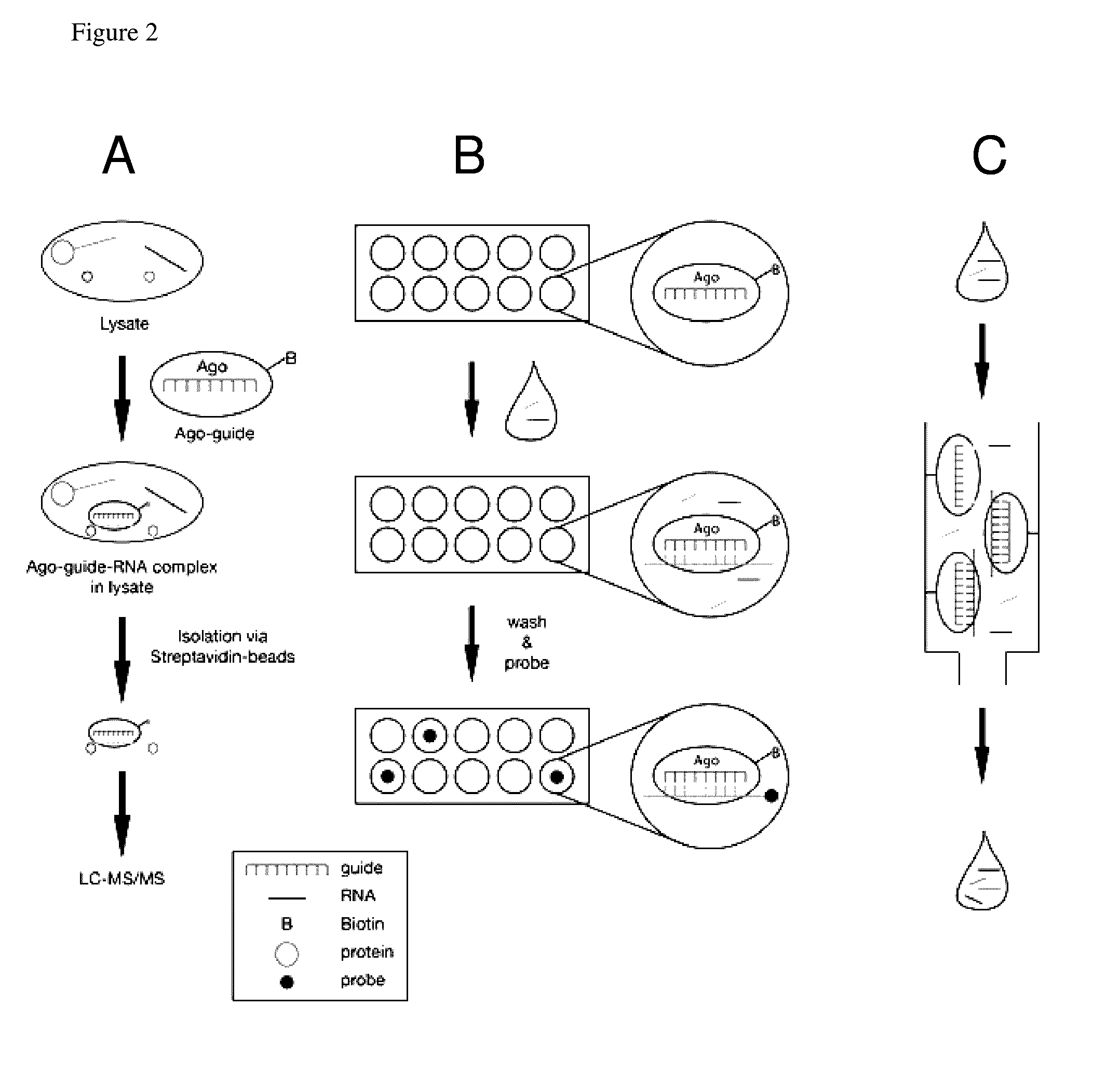
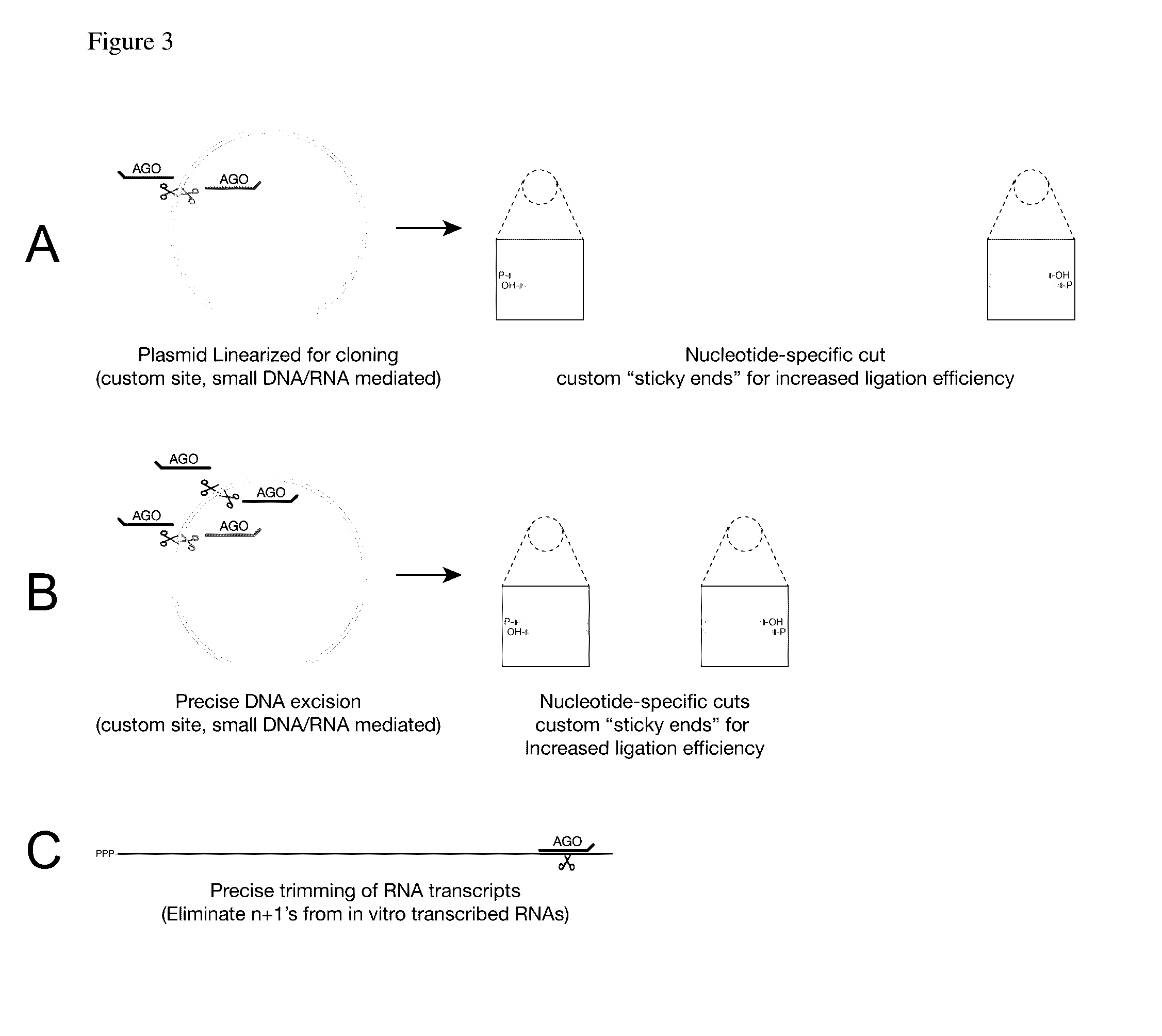
The invention relates to the use of Argonaute polypeptide:guide molecule complexes as fast and specific nucleic acid probes, as specific, nucleic acid-guided restriction enzymes for DNA and RNA substrates, and as a means to detect RNA-protein interactions, RNA detection, DNA detection, and RNA depletion. Using such Argonaute polypeptide:guide molecule complexes enables fast and specific detection, purification, and enzymatic activity.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Cells for immunotherapy engineered for targeting cd38 antigen and for cd38 gene inactivation
ActiveUS20180236053A1Reduce riskSpecific targetingPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAntigen receptors
Methods of developing genetically engineered immune cells for immunotherapy, which can be endowed with Chimeric Antigen Receptors targeting an antigen marker that is common to both the pathological cells and said CD38 immune by the fact that the genes encoding said markers are inactivated in said immune cells by a rare cutting endonuclease such as TALEN, Cas9 or argonaute.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Prokaryote-derived argonaute protein and application thereof
ActiveCN112538470AShort synthesis cycleLow priceHydrolasesFermentationProkaryote organismsGene Modification
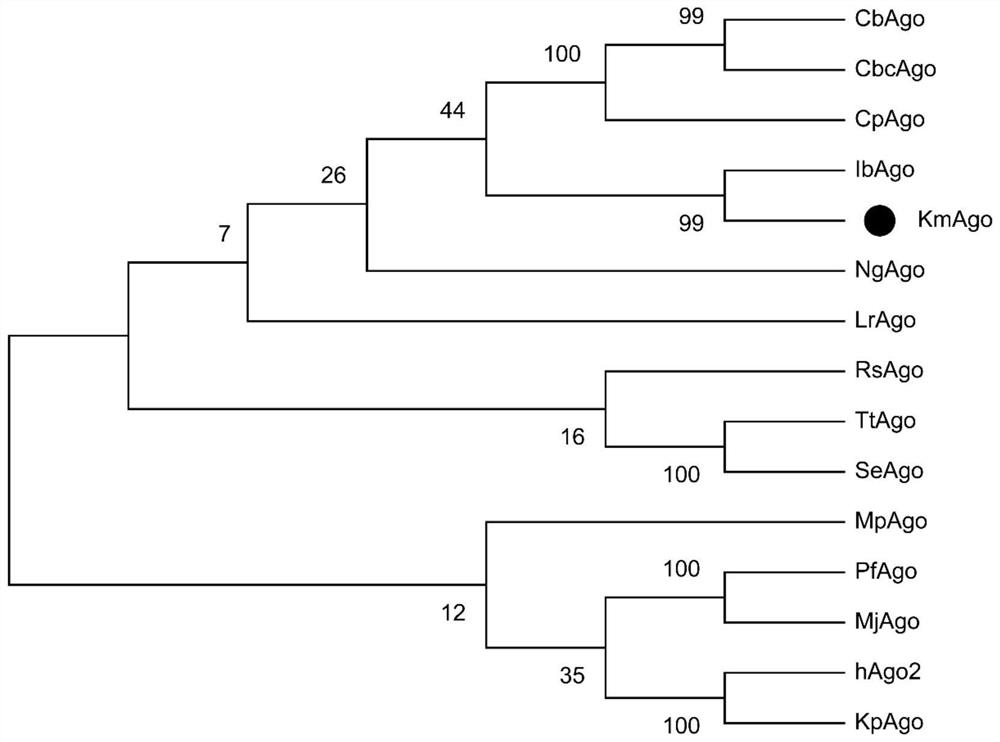
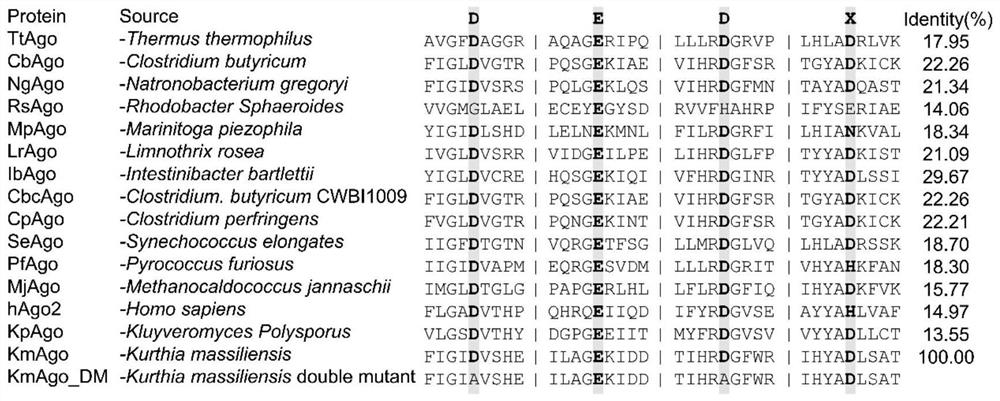
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and discloses prokaryote-derived argonaute protein and application thereof. The prokaryote-derived argonaute protein is derived frommedium-temperature prokaryote kurthia masiliensis, and the prokaryote-derived argonaute protein is named as KmAgo. According to the protein and the application, polypeptide, nucleic acid, an expression vector, a composition, a kit and a method can perform site-specific modification on intracellular and extracellular genetic substances so that the protein can be effectively applied to many fields of biotechnology, such as nucleic acid detection, gene editing and gene modification, and a new tool is provided for gene editing, modification and molecular detection of the prokaryote-derived Argonaute polypeptide.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Argonaute-nucleic acid sequence component system used for sequence control, method and composition thereof
InactiveCN107805634AEasy to synthesizeThe dosage is easy to adjustOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesSequence controlNucleotide
The present invention relates to Argonaute-nucleic acid sequence component systems, methods and compositions for sequence manipulation. Specifically, the present invention relates to Argonaute, Argonaute-nucleic acid sequence component composition, Argonaute-nucleic acid sequence component sequence manipulation system capable of cleaving target nucleotide sequences with the help of nucleic acid strands, and the use of said Argonaute, Argonaute-nucleic acid Sequence Component Compositions and Argonaute-Nucleic Acid Sequence Component Sequence Manipulation System Methods for Manipulating Sequences. The Argonaute of the present invention can cut target nucleotide sequences with the help of nucleic acid chains at normal temperature, the cutting efficiency is not lower than 20%, and the optimal salt concentration is 100-200 mmol / L.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Compositions and methods for gene editing
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Ngago-based gene-editing method and the uses thereof
PendingUS20190284547A1Reduced random DNA cleaving abilityMore flexibleHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorPhosphorylationMutant
This invention relates to a method to produce gene alterations in the genomes of a eukaryotic and prokaryotic host cell. The method comprises utilizing Argonaute from Natronobacterium gregoryi (NgAgo) or a mutant thereof, and complementary 5′ phosphorylated single-stranded DNA that target the enzyme to cleave specific regions of the chromosome. Additionally, N-terminal truncations (deletion of the repA domain; N-del), or its mutants including N-del / E598A, N-del / D601P, and N-del / E602P reduces random cleavage and can be used for targeted gene editing with a guide DNA. An expression system or a host cell and method of creating thereof are also in the scope of this application.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Characterization and application of novel high-temperature Argonaute protein
ActiveCN113106087AShear preferenceHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid cleavageEndonuclease
The invention provides characterization and application of a novel high-temperature Argonaute protein. Specifically, the invention provides a nucleic acid cleavage system, which is characterized in that the nucleic acid cleavage system comprises: (a) guide DNA (gDNA); (b) a programmable endonuclease Argonaute (Ago); and (c) optionally a reporter nucleic acid wherein if the reporter nucleic acid is cleaved, the cleavage can be detected. In addition, the invention also provides a system and a method for enriching and detecting low-abundance target nucleic acid based on the programmable endonuclease Ago provided by the invention. The detection system and method provided by the invention can specifically and effectively enrich and efficiently detect low-abundance nucleic acid, and the programmable endonuclease Ago provided by the invention has strong gene manipulation potential.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
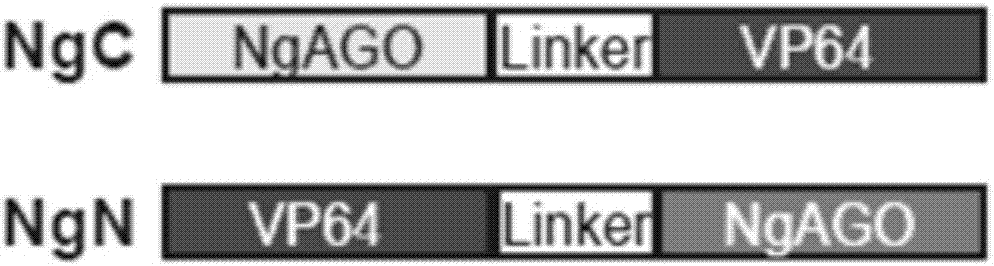
Method for targetedly activating gene transcription on basis of natronobacterium gregoryi Argonaute
The invention discloses a NgAGO-VP64 fusion protein, a guided DNA (gDNA) and a method for targetedly activating gene transcription on the basis of natronobacterium gregoryi Argonaute (NgAGO). The sequence of the NgAGO-VP64 fusion protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2. The guided DNA is any one or more of mixtures among sequence segment shown as SEQ ID NO.3-12. By utilizing the NgAGO-VP64 fusion protein, the guided DNA and transfection reagent to cotransfect cells, endogenous gene transcription can be targetedly activated. The invention proves that NgAGO has the capability of combining with the guided DNA and identifying target genome DNA. The invention discovers for the first time that the fusion protein constructed from NgAGO and VP64 has the capability of activating endogenous gene in cells. The invention solves the problem that people doubt the application of NgAGO recently, and provides support for the development of target genome editing tools and other tools.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Eukaryote-derived Argonaute protein and application thereof
ActiveCN114606215AProposed application potentialHas the activity of cleaving RNAHydrolasesFermentationExtracellularIntracellular
The invention discloses an Argonaute protein derived from eukaryotes and application of the Argonaute protein. The amino acid sequence of the Argonaute protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or the amino acid sequence of the Argonaute protein has at least 50% of sequence consistency with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; according to the invention, the specific cleavage activity of the eukaryotic Argonaute protein on DNA is proved for the first time, and experimental proof is provided for research on interaction between the eukaryotic Argonaute and DNA; meanwhile, the polypeptide, the nucleic acid, the expression vector, the composition, the kit and the method used in the invention can perform site-specific operation on intracellular and extracellular genetic materials, can be effectively applied to many fields of biotechnology, and provide a new tool for gene editing, modification and molecular detection based on the Argonaute polypeptide derived from eukaryotes.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Gene editing application of prokaryotic Argonaute protein
The invention discloses a gene editing application of a prokaryotic Argonaute protein, which comprises the following steps: constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the Argonaute protein derived from bacteria, detecting the degradation of the expression vector and a co-transformation vector of the Argonaute protein after transforming a host cell, and detecting genome sites. It is found that the gene has the ability of being activated by a specific transcript and targeting a specific DNA target sequence, and gene editing with the inDel frequency of 3% is carried out on a genome target sequence under the participation of guide RNA transcribed in eukaryotic cells. Experimental results show that the prokaryotic Argonaute protein can be used for developing intracellular gene editing tools.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Cells for immunotherapy engineered for targeting CD38 antigen and for CD38 gene inactivation
ActiveUS10709775B2Reduce riskSpecific targetingPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAntigen receptors
Methods of developing genetically engineered immune cells for immunotherapy, which can be endowed with Chimeric Antigen Receptors targeting an antigen marker that is common to both the pathological cells and said CD38 immune by the fact that the genes encoding said markers are inactivated in said immune cells by a rare cutting endonuclease such as TALEN, Cas9 or argonaute.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Prokaryotic Argonaute Proteins and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20190292537A1Effective “ locking-in ”Improve reliabilityHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering tools, methods and techniques for nucleic acid, gene or genome editing. Specifically, the invention concerns prokaryotic Argonaute (pAgo) polypeptides having nuclease activity against target DNA when pAgo is complexed with a DNA guide. The invention also provides expression vectors comprising nucleic acids encoding said polypeptides as well as compositions and kits for, and methods of cleaving and editing target nucleic acids in a sequence-specific manner. The polypeptides, nucleic acids, expression vectors, compositions, kits and methods of the invention allow site-specific modifications of genetic material, whether isolated from cells in vitro, or within cells in situ and as such may usefully find application in many fields of biotechnology, including, for example, synthetic biology, gene therapy and agricultural or microbial biotechnology.
Owner:WAGENINGEN UNIV
MicroRNA detection system and method based on exponential amplification reaction and Argonaute nuclease
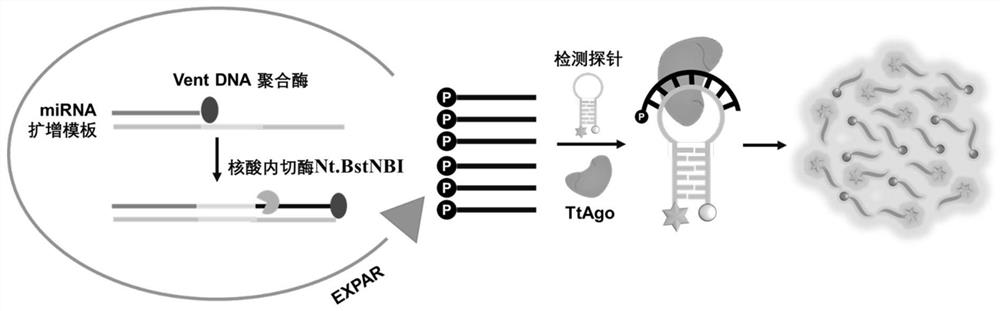
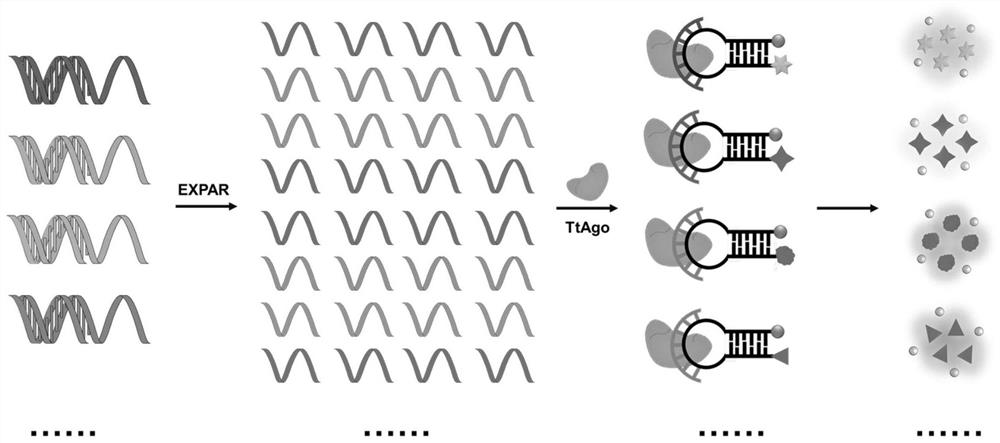
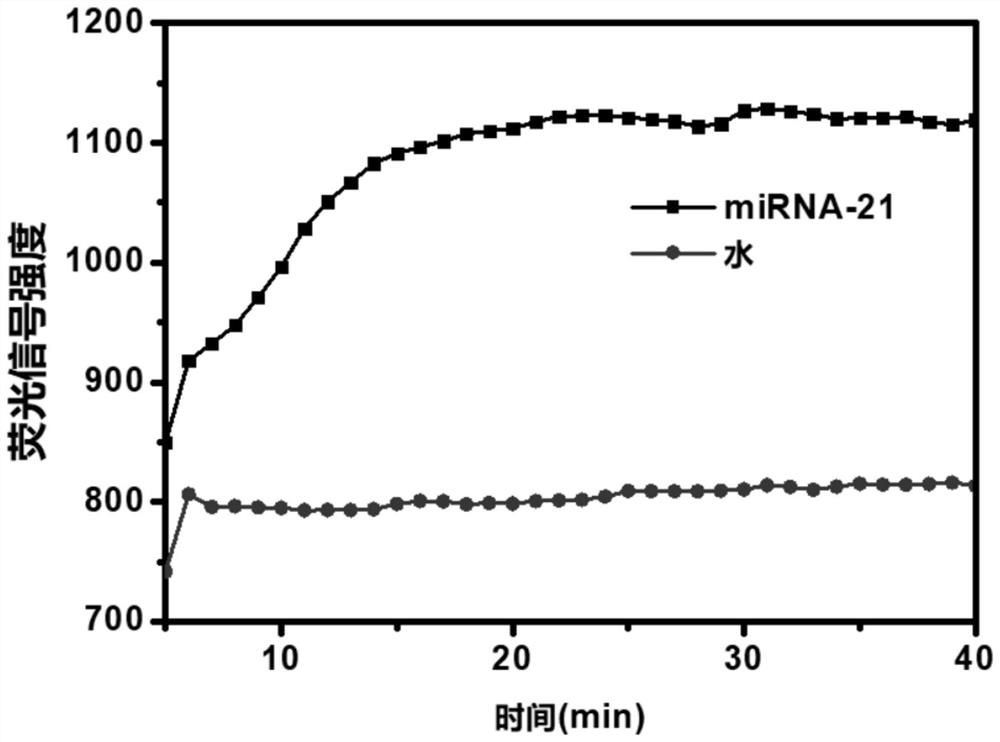
PendingCN114250276AOvercoming the problem of false positivesHighly specific detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JFluorophore
The invention discloses a microRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) detection system and a microRNA detection method based on an exponential amplification reaction and Argonaute nuclease. The invention provides a microRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) detection system based on exponential amplification reaction and Argonaute nuclease, and the microRNA detection system comprises: (a) guide DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), which is an amplification product obtained by amplifying a target object microRNA by adopting an exponential amplification reaction system; (b) an Argonaute nuclease, and a method for preparing the same; (c) the detection probe is provided with a fluorophore and a quenching group, and the detection probe comprises a region complementary to an amplification product obtained by amplifying the target microRNA by adopting the index amplification reaction system. According to the microRNA detection system provided by the invention, miRNA detection with single base specificity and high sensitivity as well as multiple miRNA detection and miRNA typing analysis are realized.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
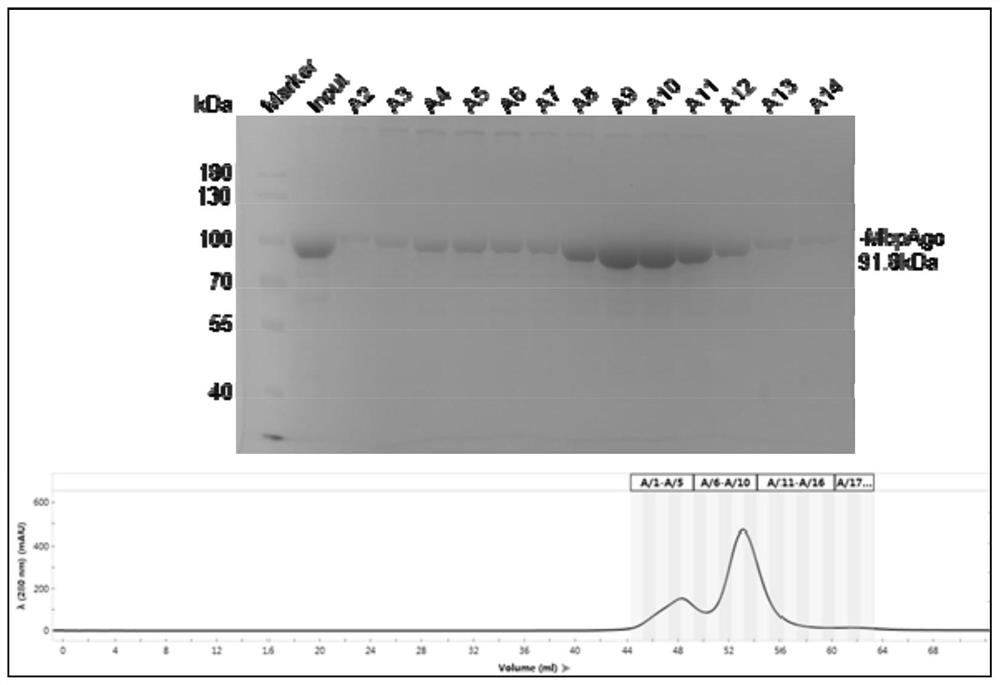
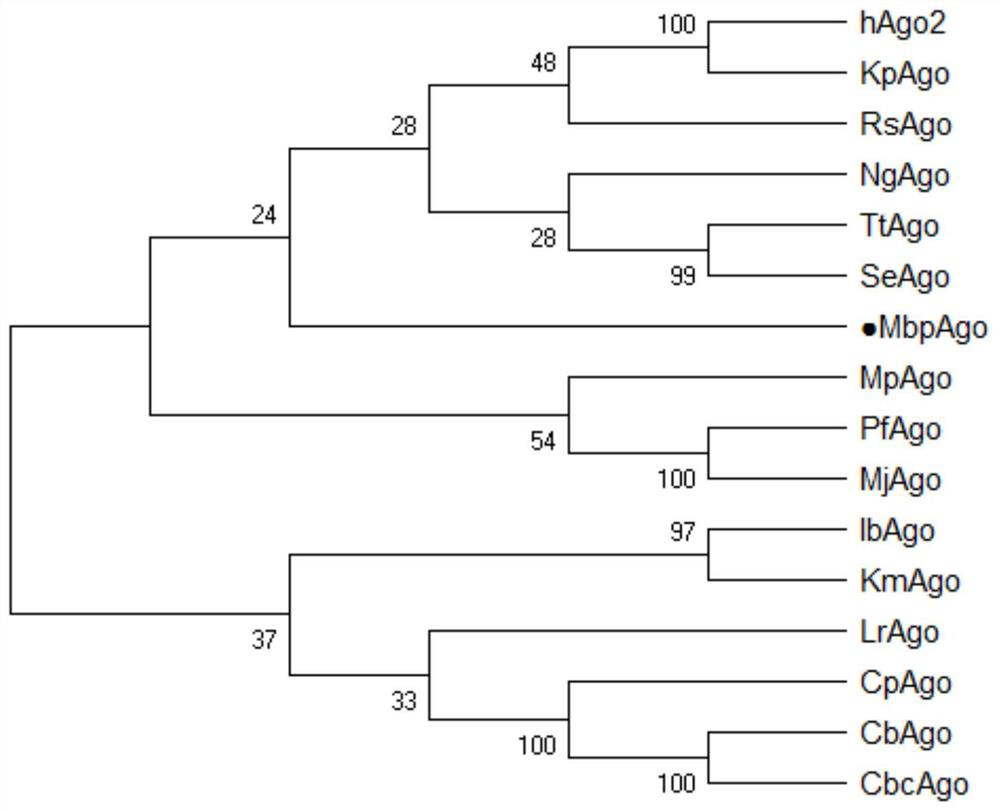
Prokaryote-derived Mbp_Argonaute protein and application thereof
ActiveCN113373129AHave binding activityHas nuclease activityHydrolasesFermentationProkaryote organismsPlant cell
The invention discloses a prokaryote-derived Mbp_Argonaute protein and application thereof. The Mbp_Argonaute protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or as shown in a sequence which has at least 50% or at least 80% of homology with SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the invention, an Argonaute protein gene derived from a cold-resistant prokaryotic organism Mucilaginibacter paaluis is synthesized, the protein is named as MbpAgo, and researches find that the MbpAgo has binding activity to single-stranded guide DNA and has nuclease activity to target RNA and / or target DNA complementarily paired with the single-stranded guide DNA, therefore, the MbpAgo can be used for targeted RNA editing in vivo and in vitro, and then specific site modification of genetic material. The MbpAgo not only can modify RNA with a high-grade structure, but also does not influence an endogenous RNAi pathway of animal and plant cells, provides a brand new powerful tool for RNA editing, and is high in cutting activity and good in specificity.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
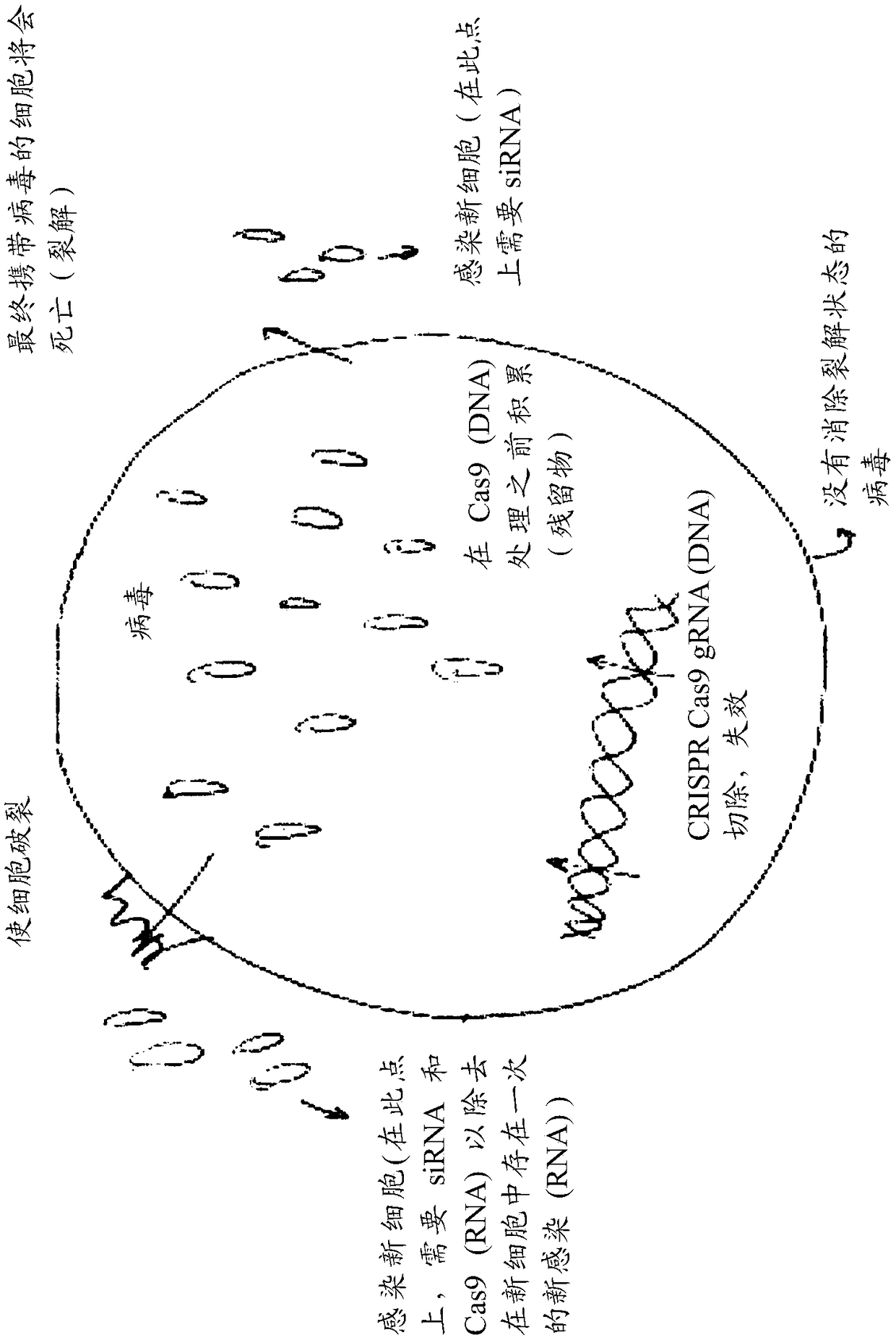
Compositions and methods of treatment for lytic and lysogenic viruses
Owner:EXCISION BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for using argonaute to modify a single stranded target nucleic acid
The present disclosure provides compositions, kits, genetically modified cells, non-human transgenic organisms, and methods for binding and / or cleaving a single stranded target nucleic acid. A method of cleaving includes contacting a single stranded target nucleic acid with (e.g., introducing into a cell) a subject argonaute (Ago) polypeptide and a guide RNA (e.g., having a 5′-OH). In some embodiments, a subject Ago polypeptide includes an amino acid sequence having 70% or more sequence identity with amino acids 282-430 and / or 431-639 of the Marinitoga piezophila argonaute (MpAgo) protein set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1. The present disclosure provides variant Ago polypeptides; and methods of use of same.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nucleic acid detection method based on normal-temperature prokaryotic Argonaute protein and application thereof
PendingCN114277109AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid detectionPathogenic bacteria
The invention provides a nucleic acid detection method based on normal-temperature prokaryotic Argonaute protein and application of the nucleic acid detection method. Specifically, the invention provides a detection system for detecting a target nucleic acid molecule, and the system comprises (a) a guide ssDNA pair; (b) a normal-temperature Argonaute protein (Ago enzyme), wherein the normal-temperature Argonaute protein (Ago enzyme) is a normal-temperature Argonaute protein (Ago enzyme) which is used for guiding the shearing of a target DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) by taking the DNA as a guide; (c) fluorescence report nucleic acid, wherein the fluorescence report nucleic acid carries a fluorophore and a quenching group; wherein the target nucleic acid molecule is a target RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The method is simple, convenient and good in compatibility, and can be widely applied to the fields of detection of infectious diseases such as major infectious diseases and pathogen infectious diseases (viruses and pathogenic bacteria) and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Compositions and methods for gene editing
InactiveUS20200040334A1Free from pollutionBacteria peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionSingle strandMammalian cell
(57) Abstract: The present application provides methods, compositions, delivery systems, ami kits for modifying a target nucleic acid using an Argonaute (Ago) and a single-stranded guide DNA. In some embodiments, methods of gene editing in a cell, such as a mammalian cell, arc provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
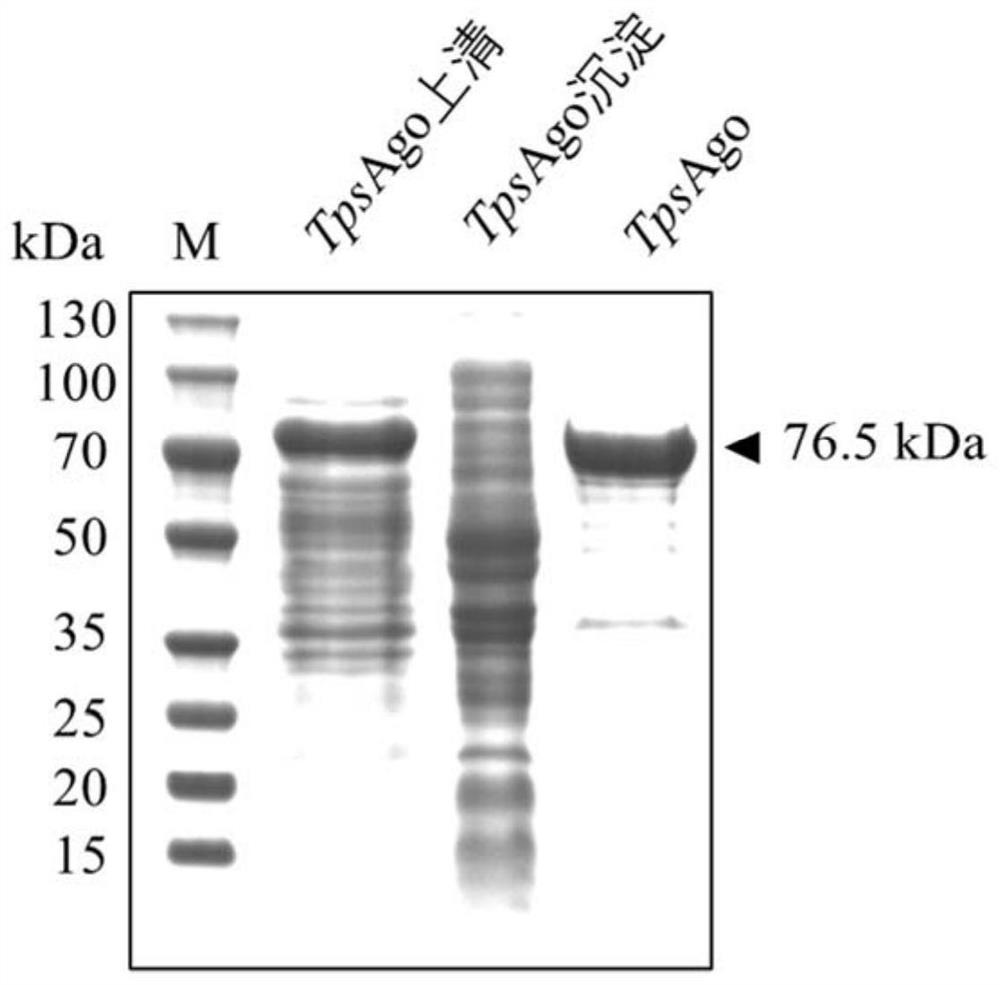
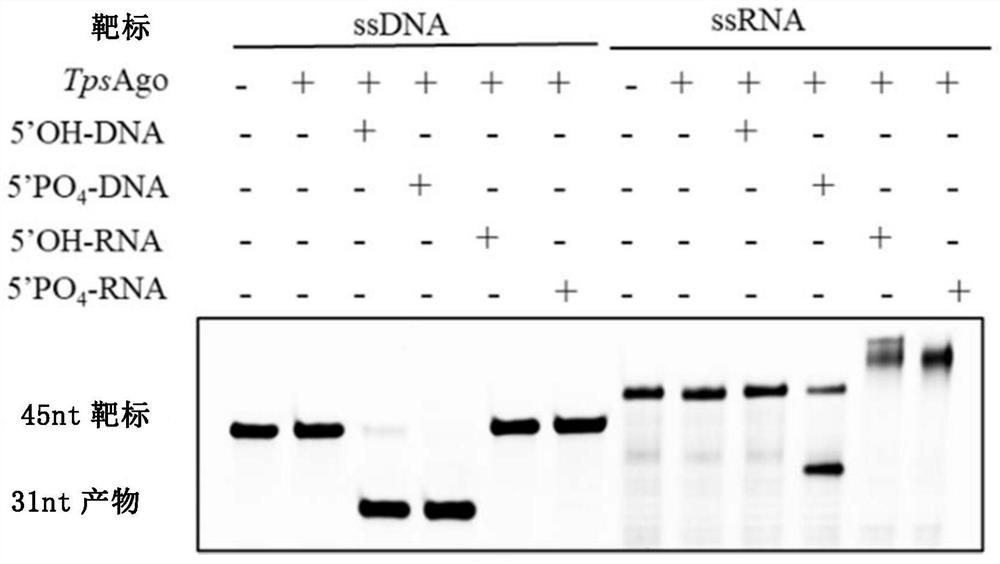
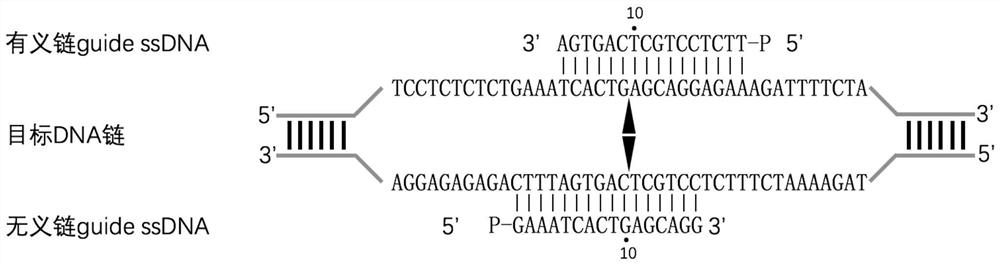
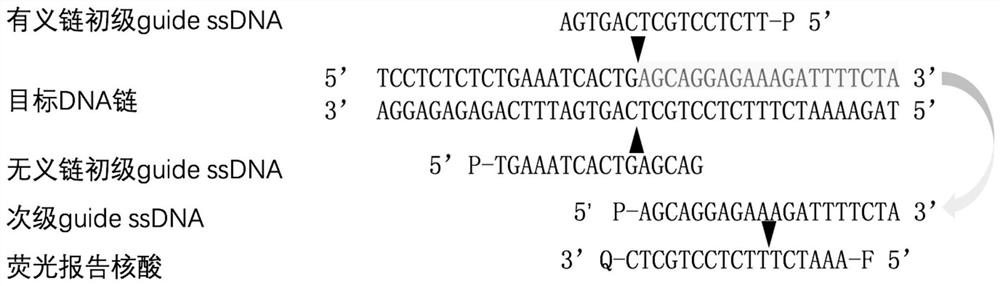
Characterization and application of Novel high-temperature Argonaute protein TpsAgo
ActiveCN113201578AShear preferenceHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid cleavageEndonuclease
The invention provides characterization and application of a novel high-temperature Argonaute protein. Specifically, the invention provides a nucleic acid cleavage system, which is characterized in that the nucleic acid cleavage system comprises: (a) guide DNA (gDNA); (b) a programmable endonuclease Argonaute (Ago); and (c) optionally a reporter nucleic acid, wherein if the reporter nucleic acid is cleaved, the cleavage can be detected. In addition, the invention also provides a system and a method for enriching and detecting low-abundance target nucleic acid based on the programmable endonuclease TpsAgo provided by the invention. The detection system and method provided by the invention can specifically and effectively enrich and efficiently detect low-abundance nucleic acid, and the programmable endonuclease TpsAgo provided by the invention has strong gene manipulation potential.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and kit for down-regulating eukaryotic gene expression
ActiveCN106566844AStable and efficient down-regulationFast and efficient entryMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionSequence designEukaryotic gene
The invention discloses a method and kit for down-regulating the eukaryotic gene expression. The gene expression is down-regulated through combining 5'-phosphorylated single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide (5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo) and Argonaute mRNA. The method comprises the following steps: reconstructing NgAgo gene, constructing an expression plasmid, carrying out linearization, in vitro transcription and recovery on the expression plasmid to obtain the Argonaute mRNA, designing and synthesizing the 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo according to a target gene sequence, and introducing the Argonaute mRNA and the 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo to a target cell. The NgAgo gene constructed in the method can rapidly and highly-efficiently enter a nucleus in the target cell; the 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo sequence designed according to the target gene has good specificity on target sequence identification; a 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo / NgAgo system can stably and highly-efficiently down-regulate the target gene expression through the inhibition effect on an eukaryotic cell in the DNA level; the 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo has good stability, and well plays a role in the cells; and no endogenous 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo exists in the eukaryotic cell under natural conditions, so the 5'-p-ss-DNA Oligo has high specificity.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid detection method based on prokaryotic argonaute protein and its application
ActiveCN108796036BMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNucleic acid detectionFood safety
The invention provides a prokaryotic Argonaute protein-based nucleic acid detection method and application thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides a detection system for detecting target nucleic acid molecules, the system comprising guide ssDNAs, gene editing enzyme Pyrococcus furiosus Argonaute (PfAgo) and fluorescent reporter nucleic acid. The nucleic acid detection method of the invention has high sensitivity, good specificity, and high throughput, and can be widely used in many fields such as molecular medical diagnosis, food safety detection, and environmental monitoring.
Owner:JIAOHONG BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com