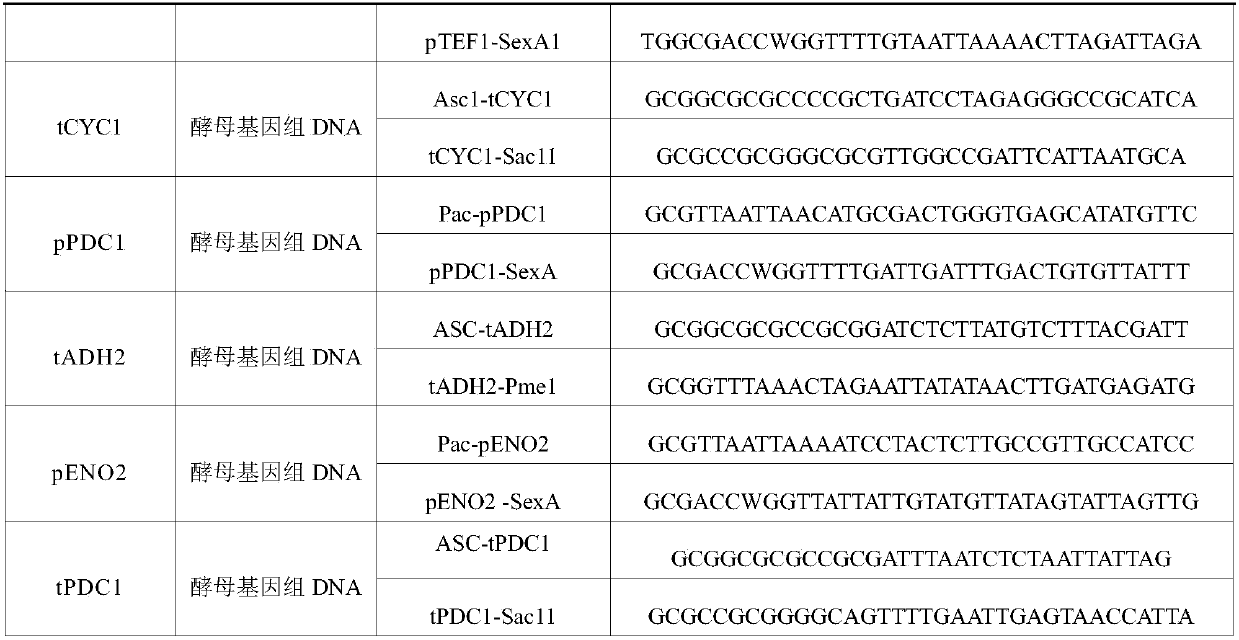
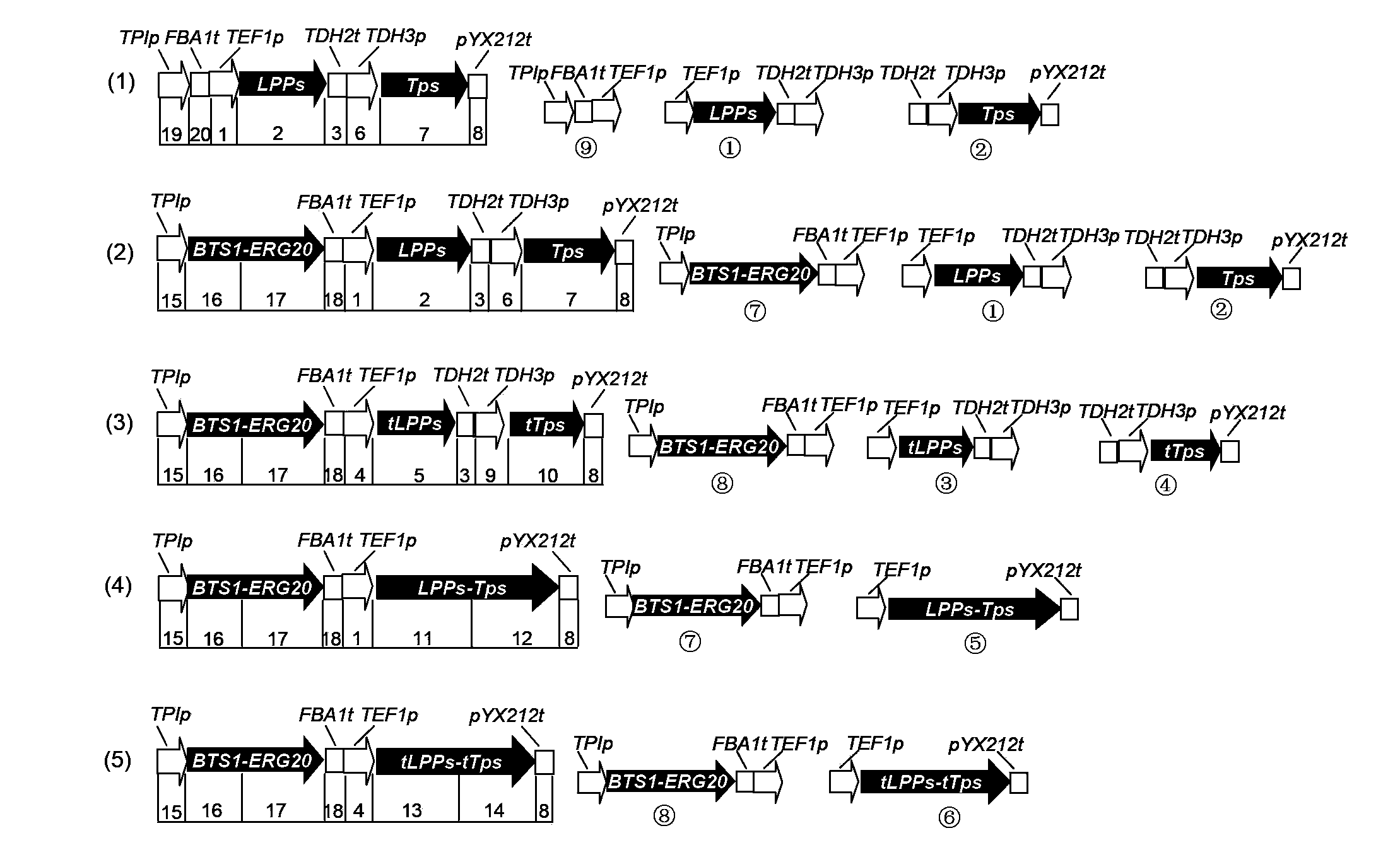
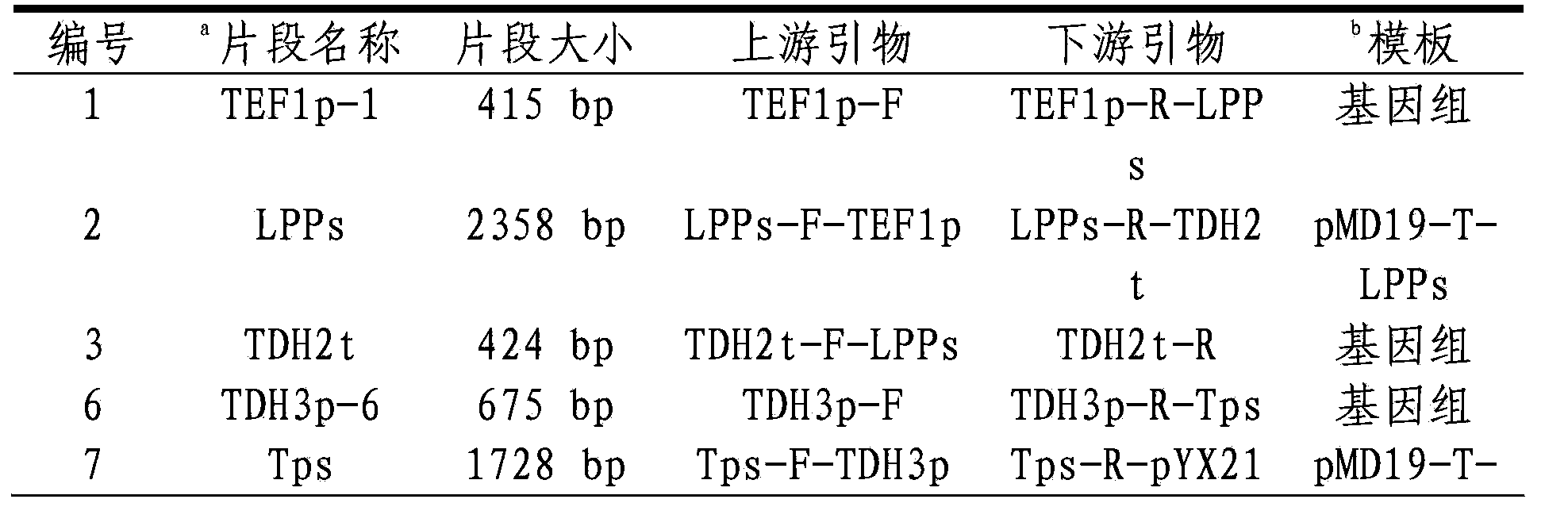
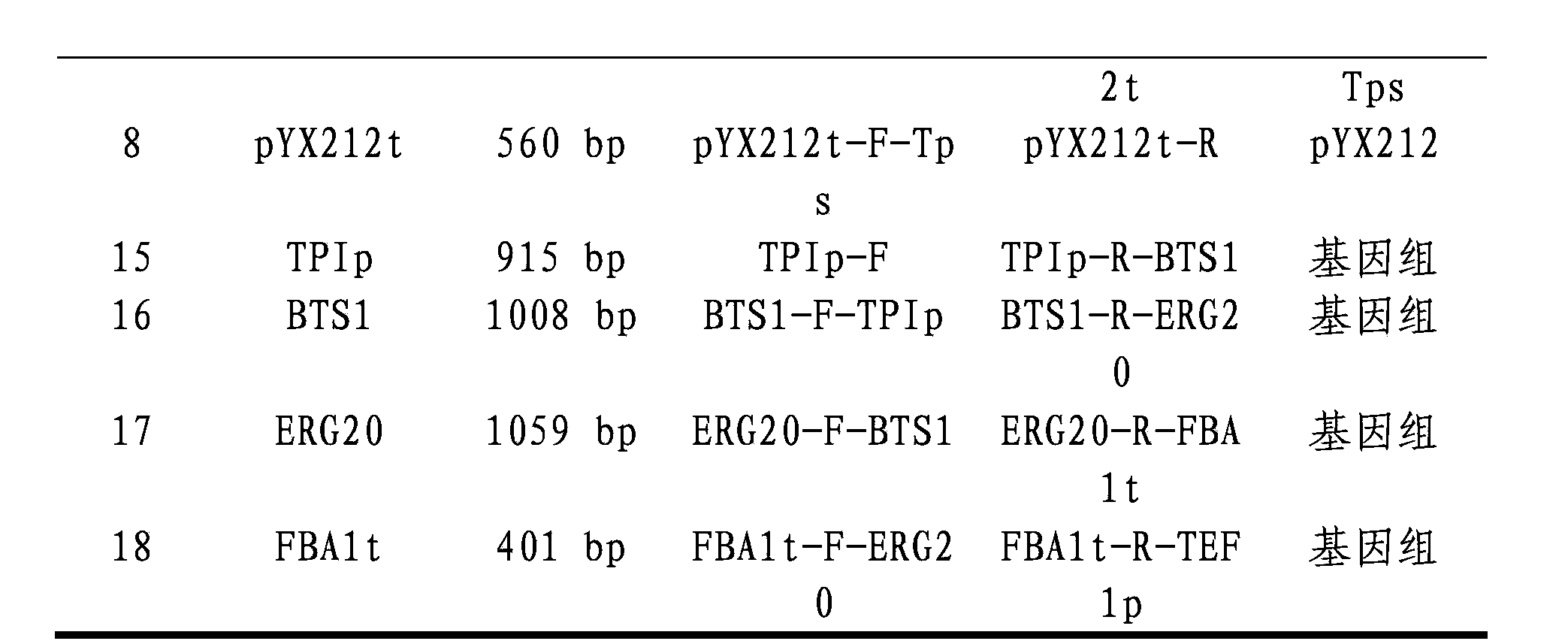
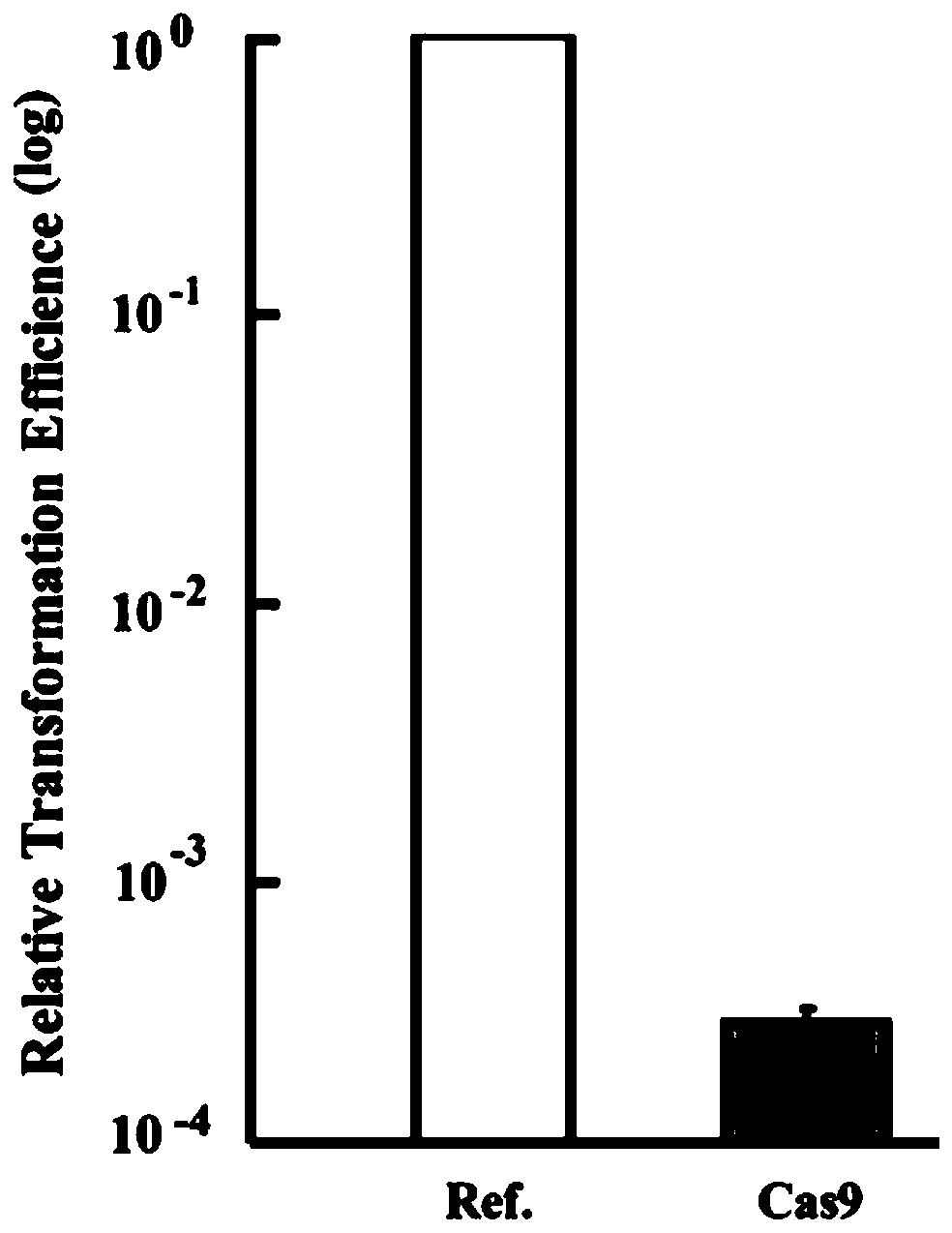
Patents
Literature
307 results about "Synthetic biology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is an interdisciplinary branch of biology and engineering. Decreasing costs of DNA synthesis and recent advances in technology have fueled the success of synthetic biology companies in recent years, and now comprises one of the fastest growing and most funded areas of commercial biotechnology.
Nucleic acid constructs and methods of use
ActiveUS9085798B2Minimization requirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic biologyMutation screening
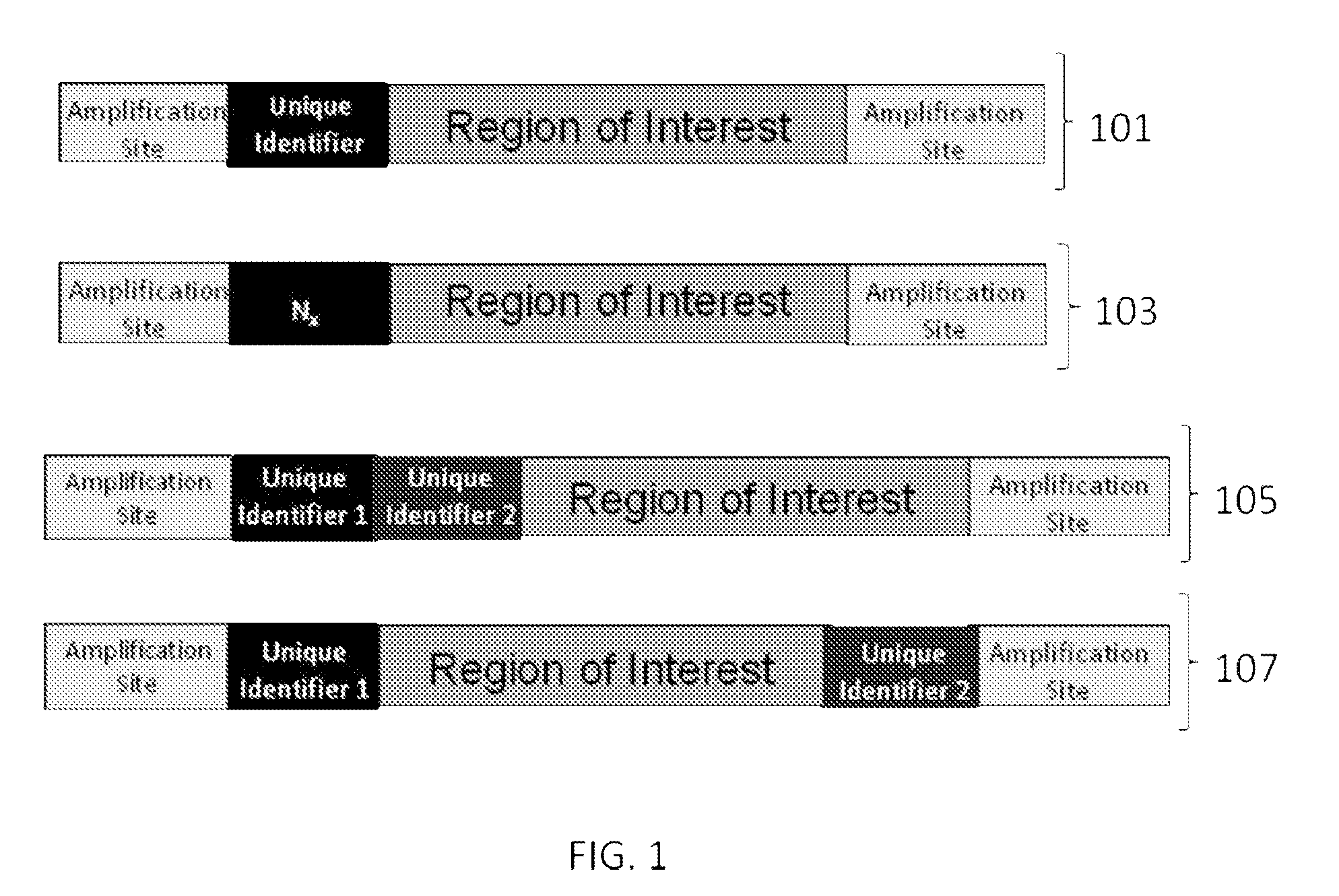
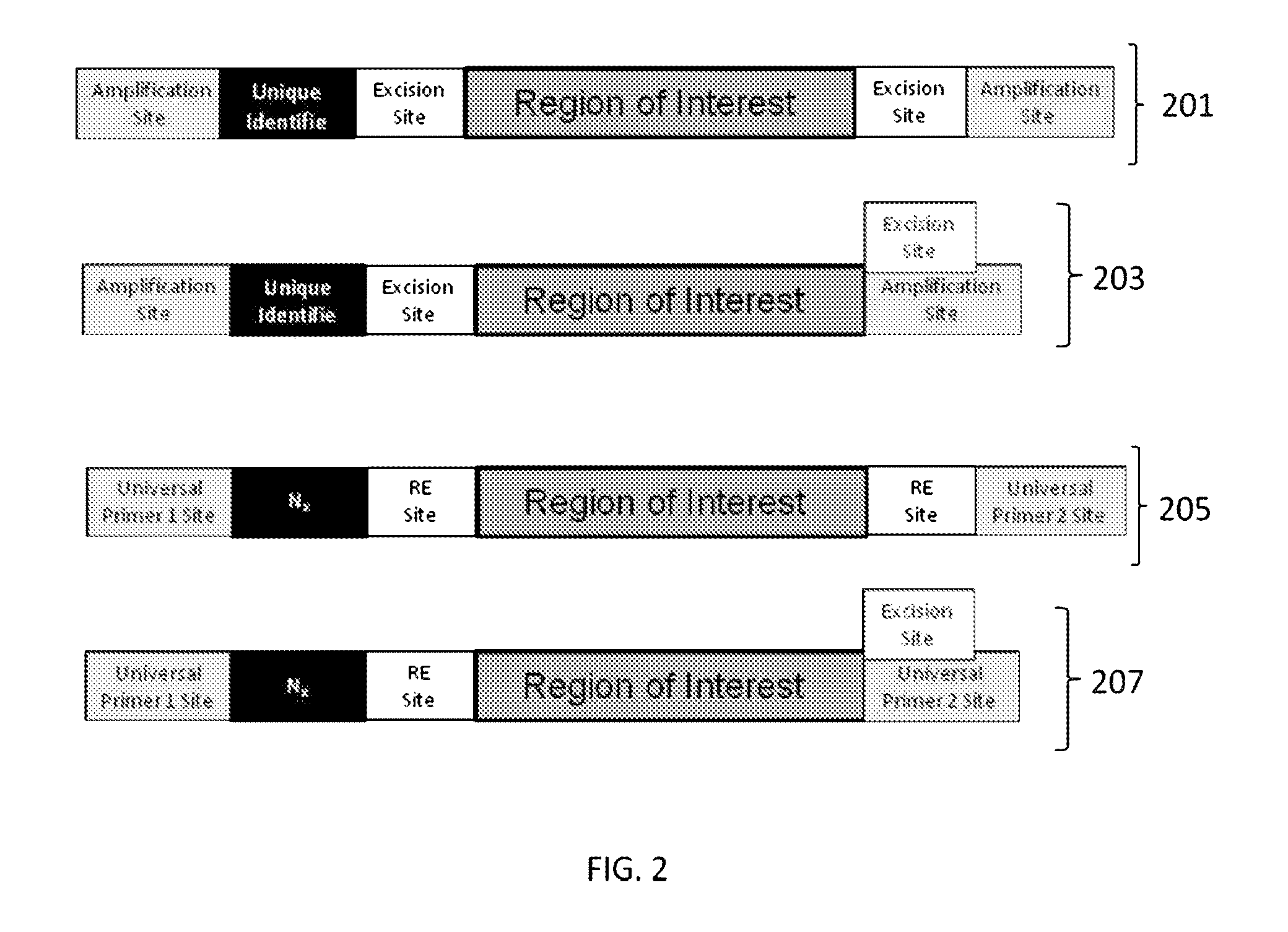
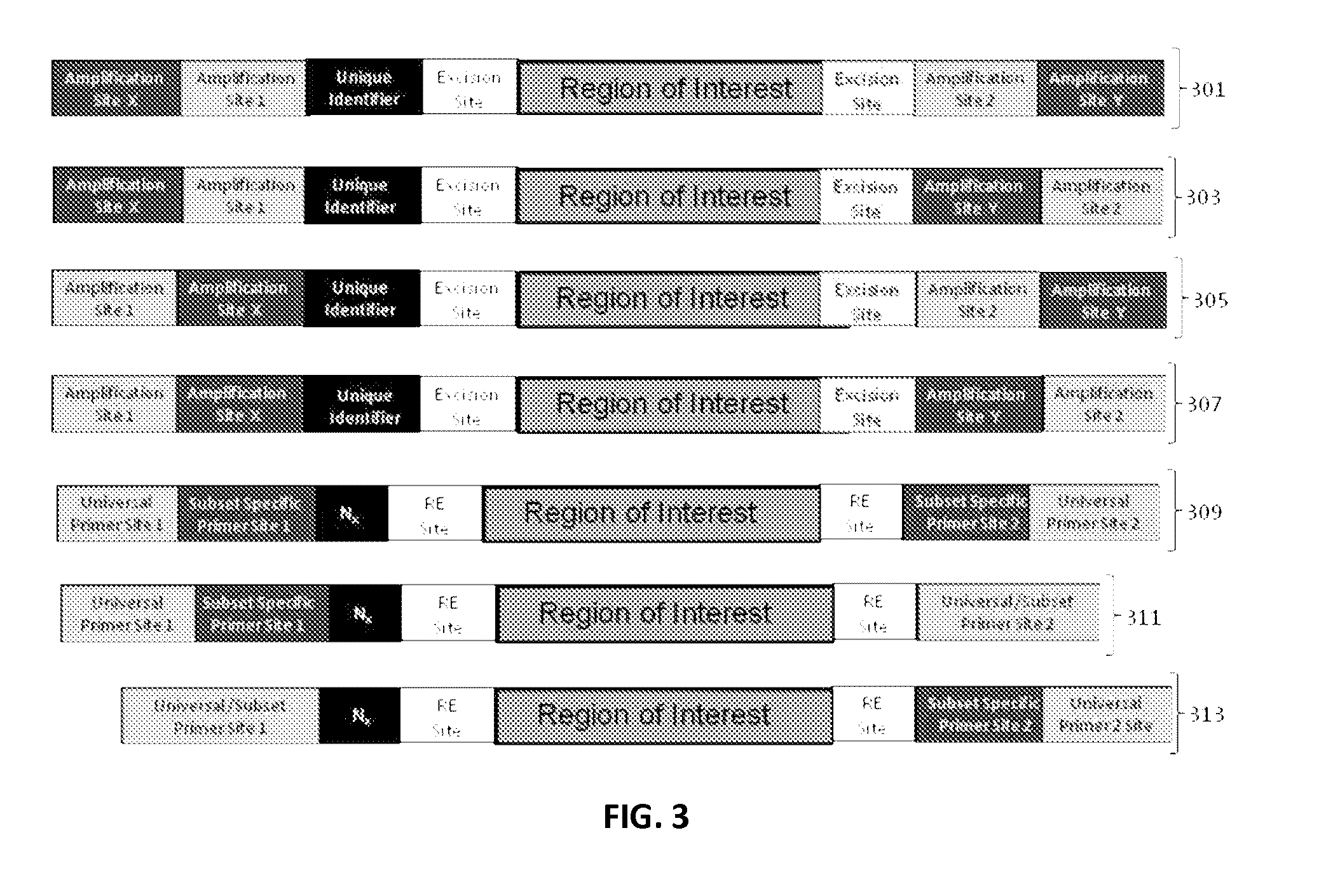
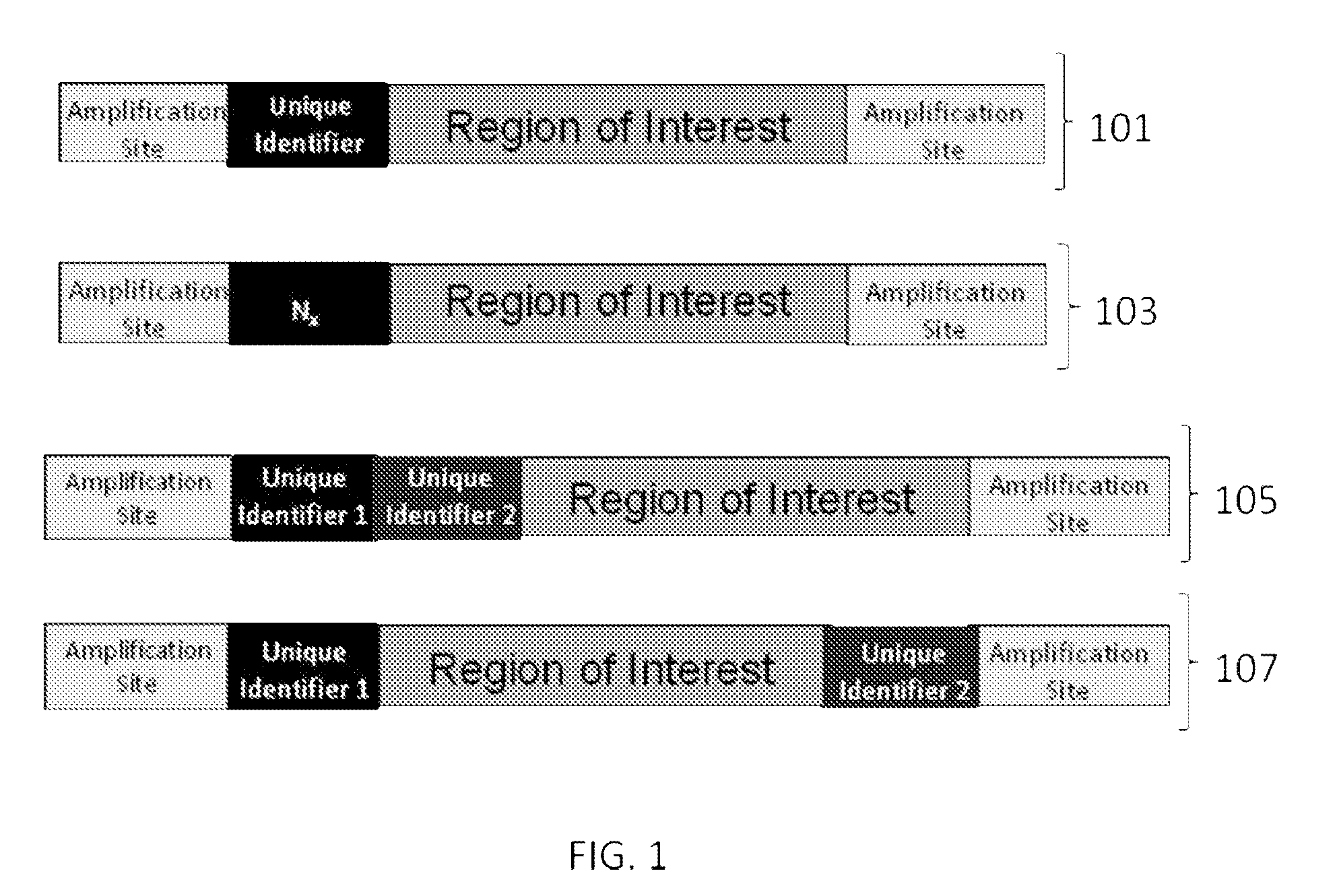
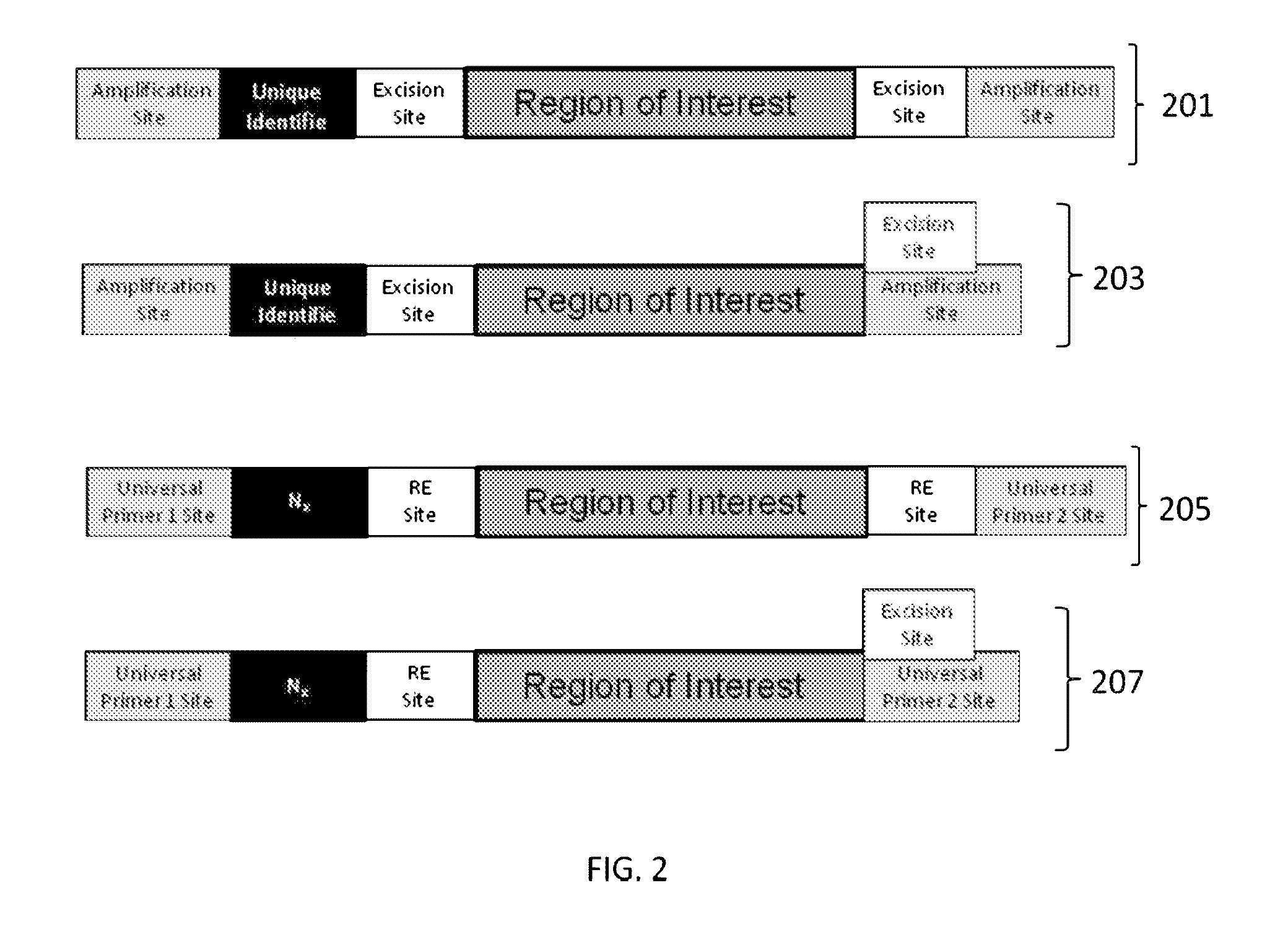
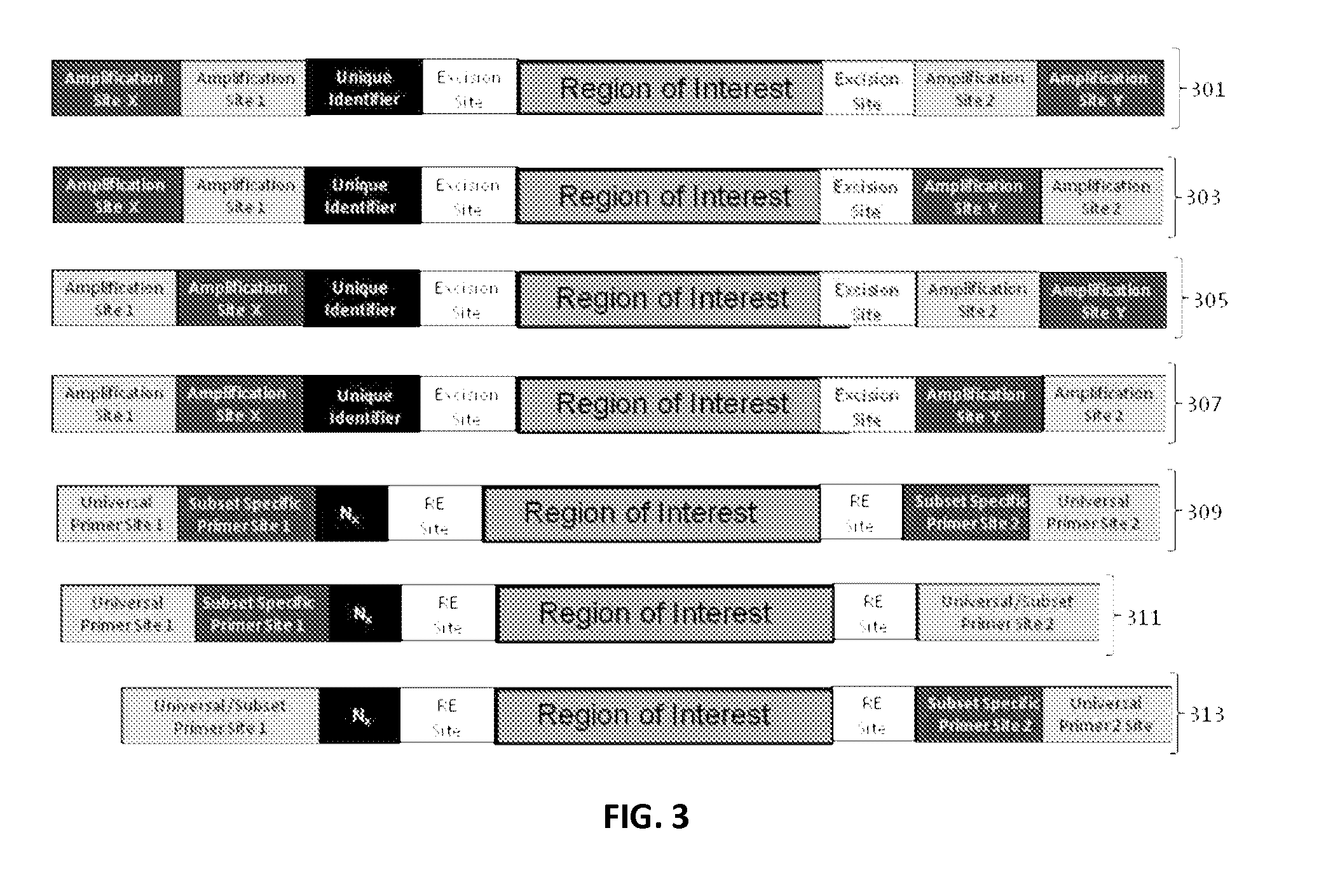
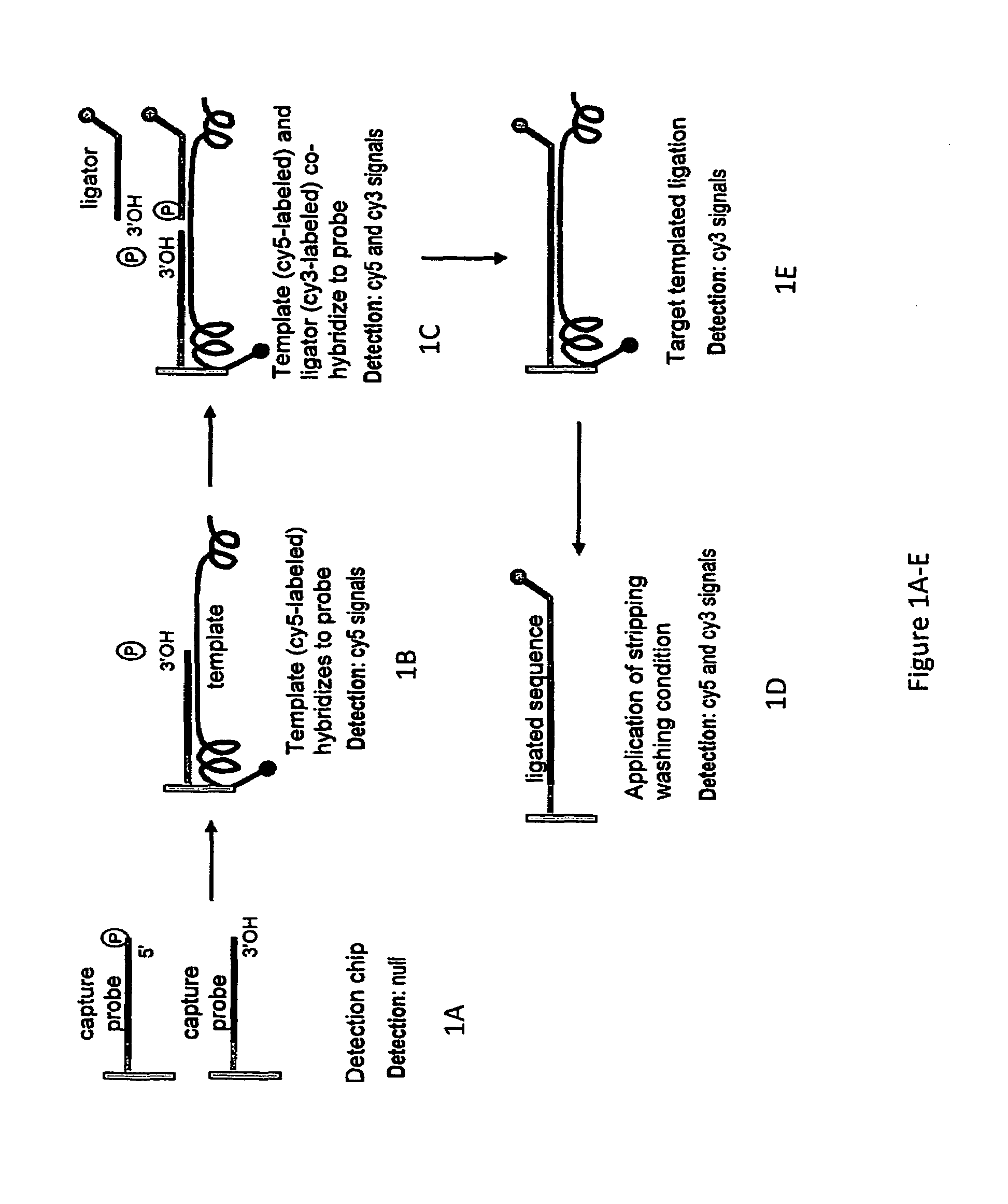
The present invention provides oligonucleotide constructs, sets of such oligonucleotide constructs, and methods of using such oligonucleotide constructs to provide validated sequences or sets of validated sequences corresponding to desired ROIs. Such validated ROIs and constructs containing these have a wide variety of uses, including in synthetic biology, quantitative nucleic acid analysis, polymorphism and / or mutation screening, and the like.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Nucleic acid constructs and methods of use
ActiveUS20120065081A1Minimization requirementsNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic biologyMutation screening
The present invention provides oligonucleotide constructs, sets of such oligonucleotide constructs, and methods of using such oligonucleotide constructs to provide validated sequences or sets of validated sequences corresponding to desired ROIs. Such validated ROIs and constructs containing these have a wide variety of uses, including in synthetic biology, quantitative nucleic acid analysis, polymorphism and / or mutation screening, and the like.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for producing solvents
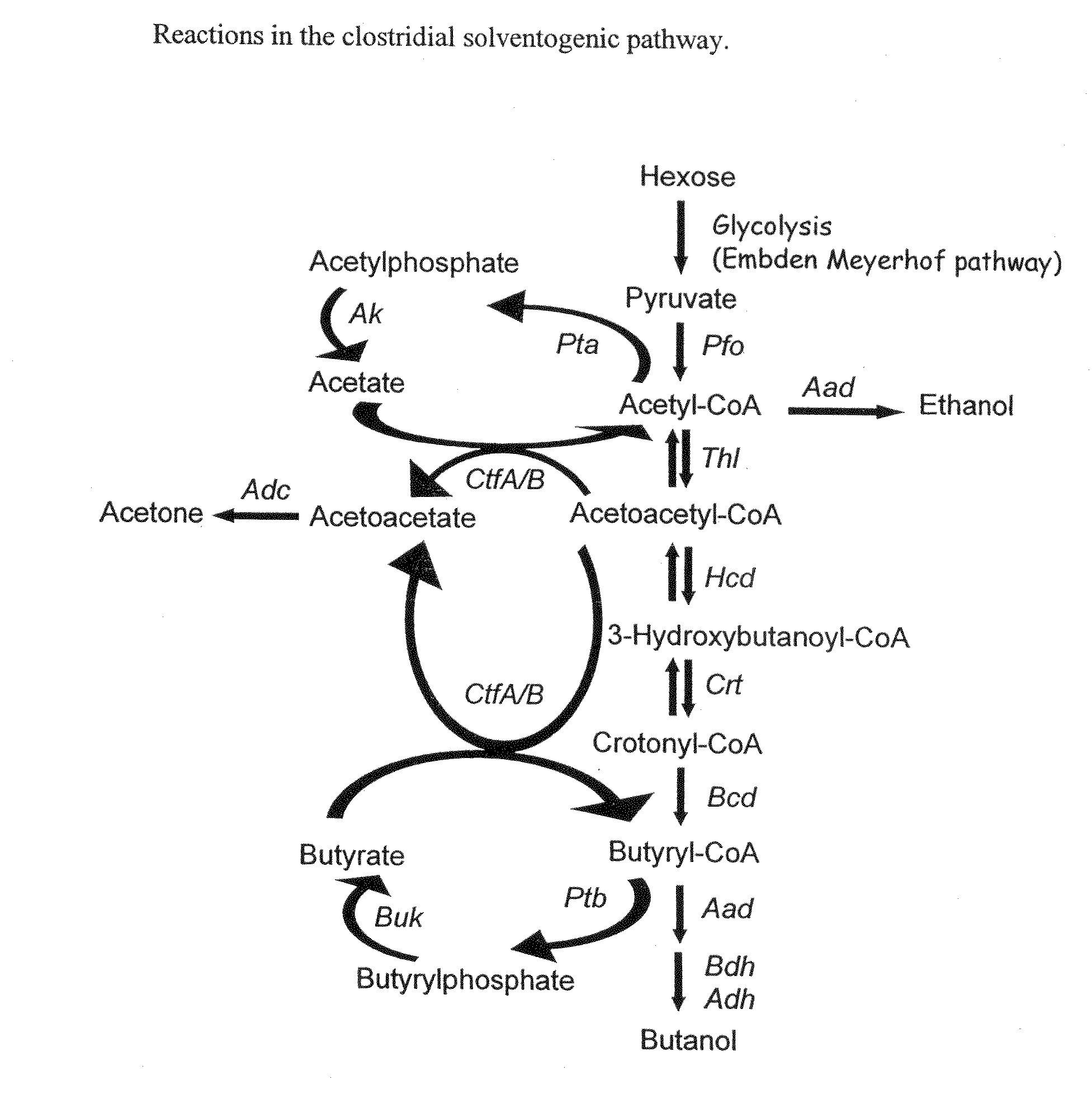
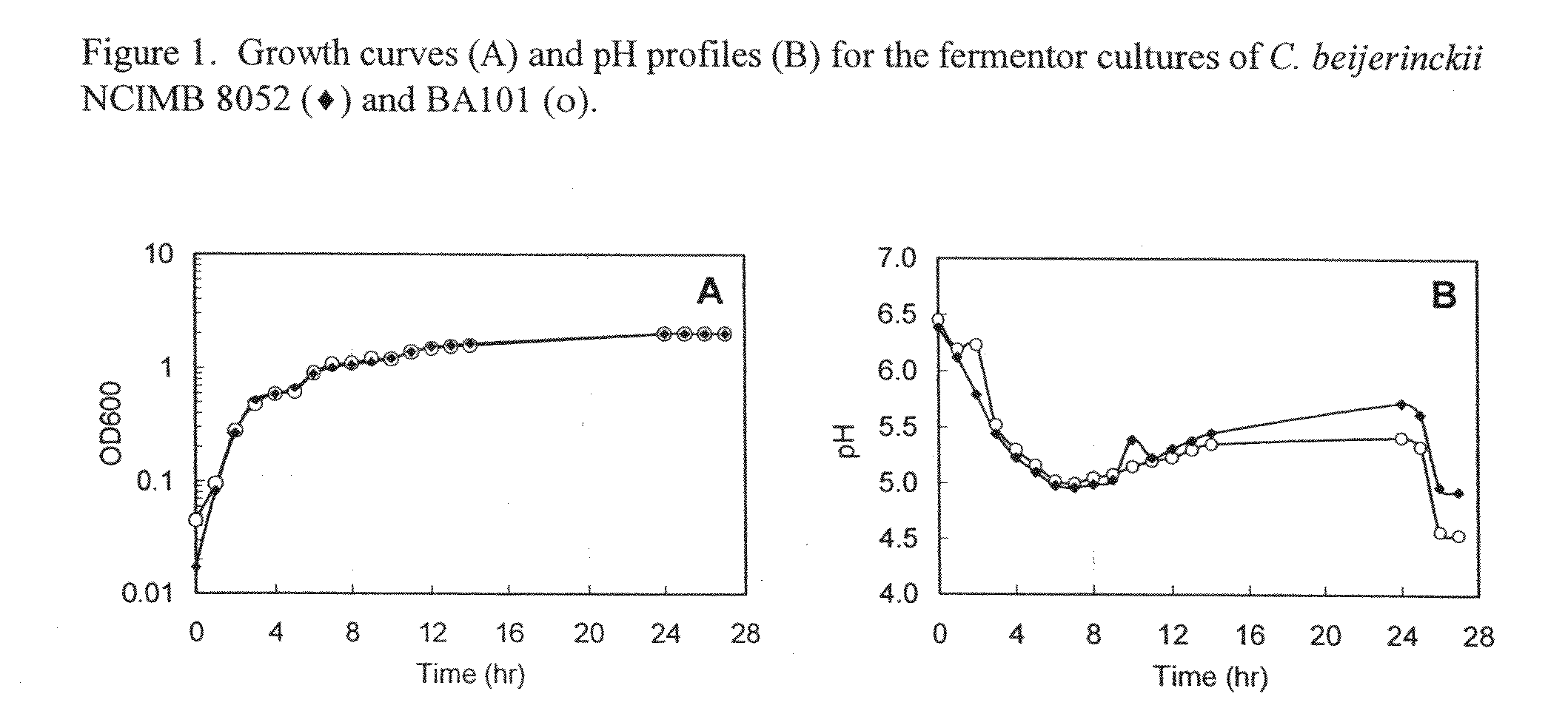
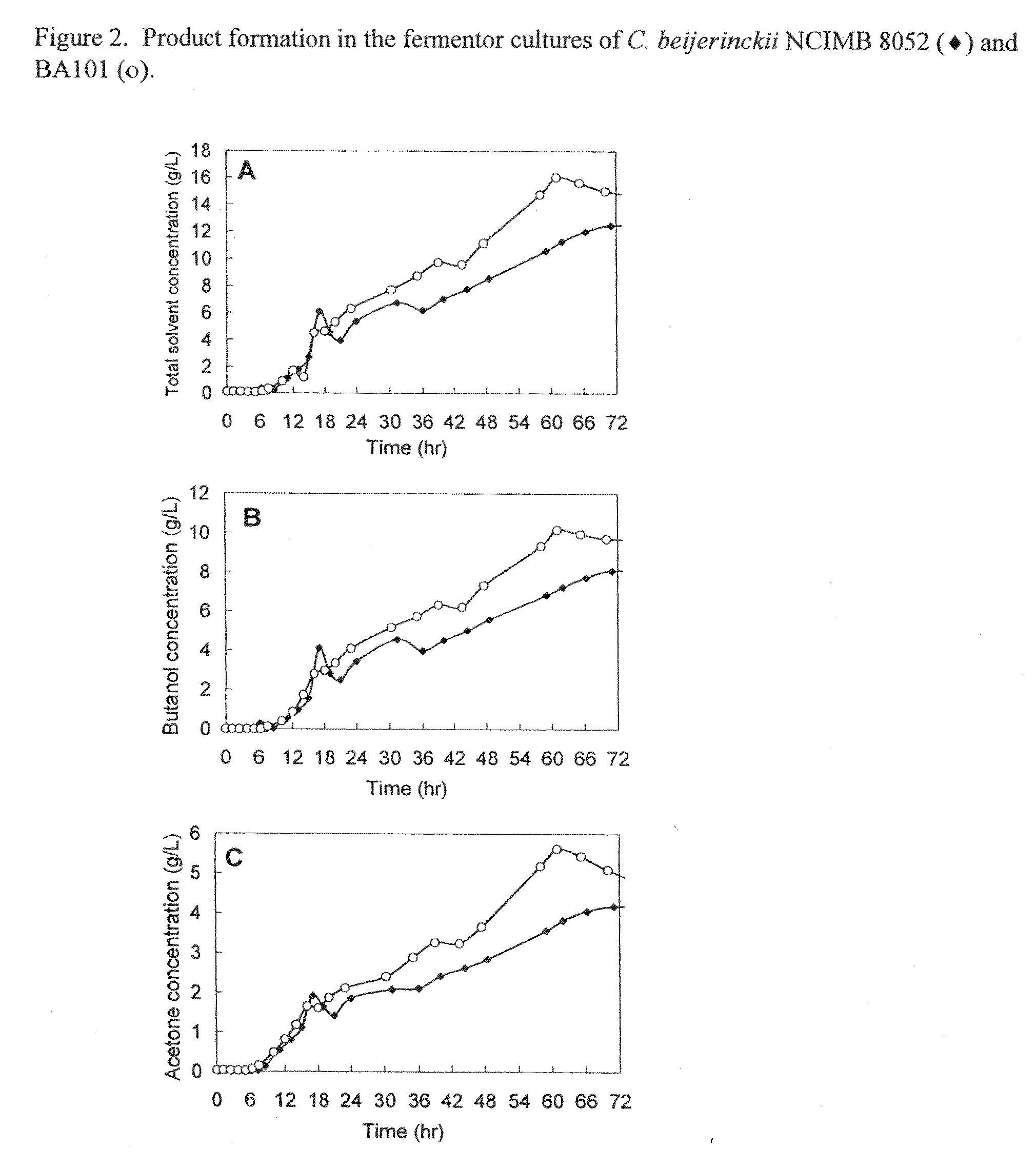
Described herein are methods, compositions and synthetic biology approaches for solvent production, including but not limited to butanol production. Described herein are recombinant bacteria and yeast strains which may be used in production of a solvent, including but not limited to butanol, from lignocellulosic and other plant-based feedstocks. Described herein are methods of producing solvents, including but not limited to butanol, using bacteria and yeast strains. Described herein are methods of producing organisms that display highly efficient butanol production.
Owner:EASTMAN RENEWABLE MATERIALS LLC +1
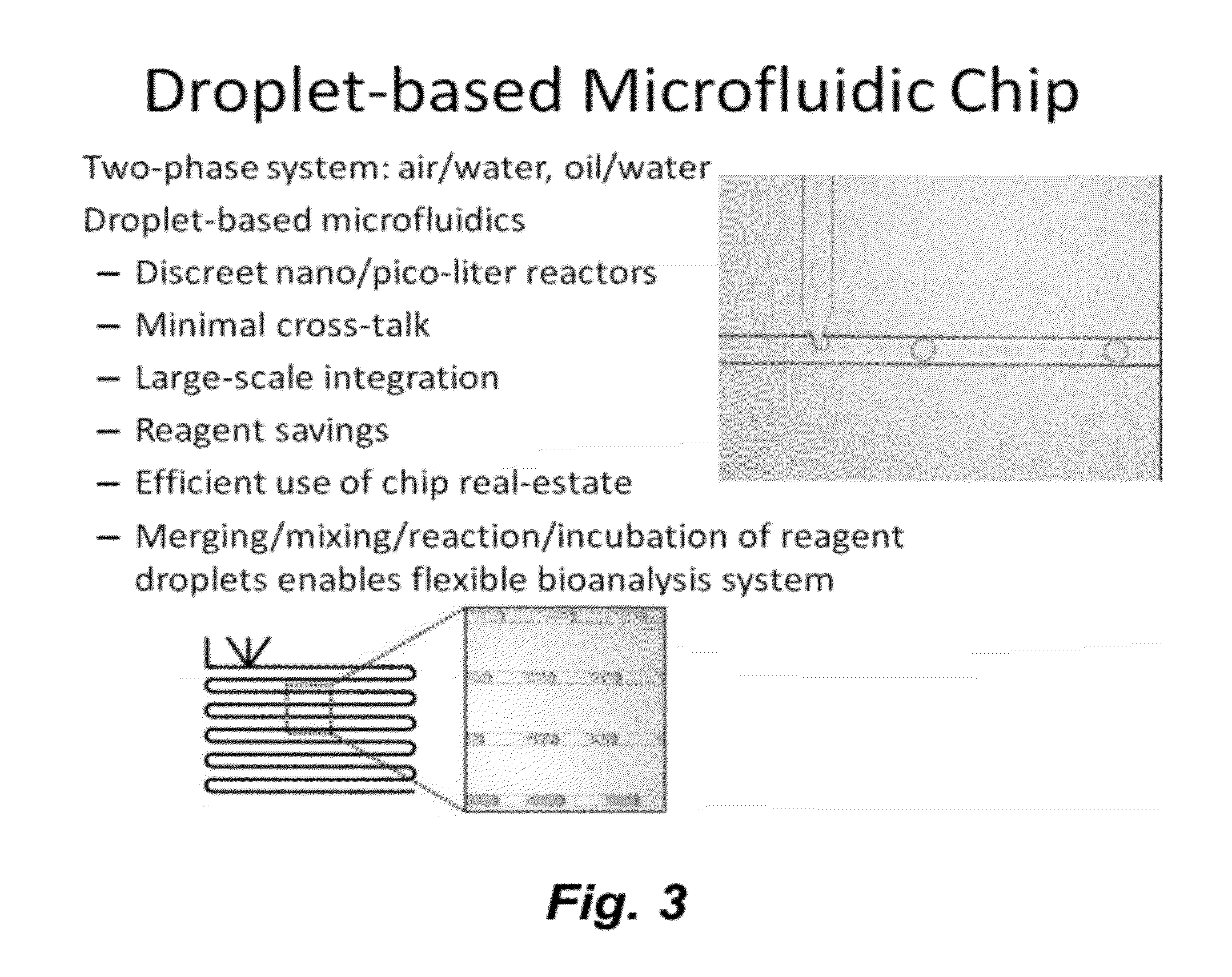
Microfluidic platform for synthetic biology applications
ActiveUS20120258487A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologySynthetic biology
This invention provides methods and compositions for assembling biological constructs (e.g., plasmids, transformed cells, etc.). In certain embodiments the methods involve encapsulating separate components of said biological construct each in a fluid droplet confined in a fluid channel; optionally mixing droplets from different fluid channels to for a sequenced order of droplets carrying different components of said biological construct in a channel or chamber; and optionally combining two or more droplets each containing different components of said biological construct to permit said components to react with each other in one or more reactions contributing to the assembly of said biological construct.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Bacterial strain for producing farnesene and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103243065AIncrease productionRational experimentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainCulture mediums
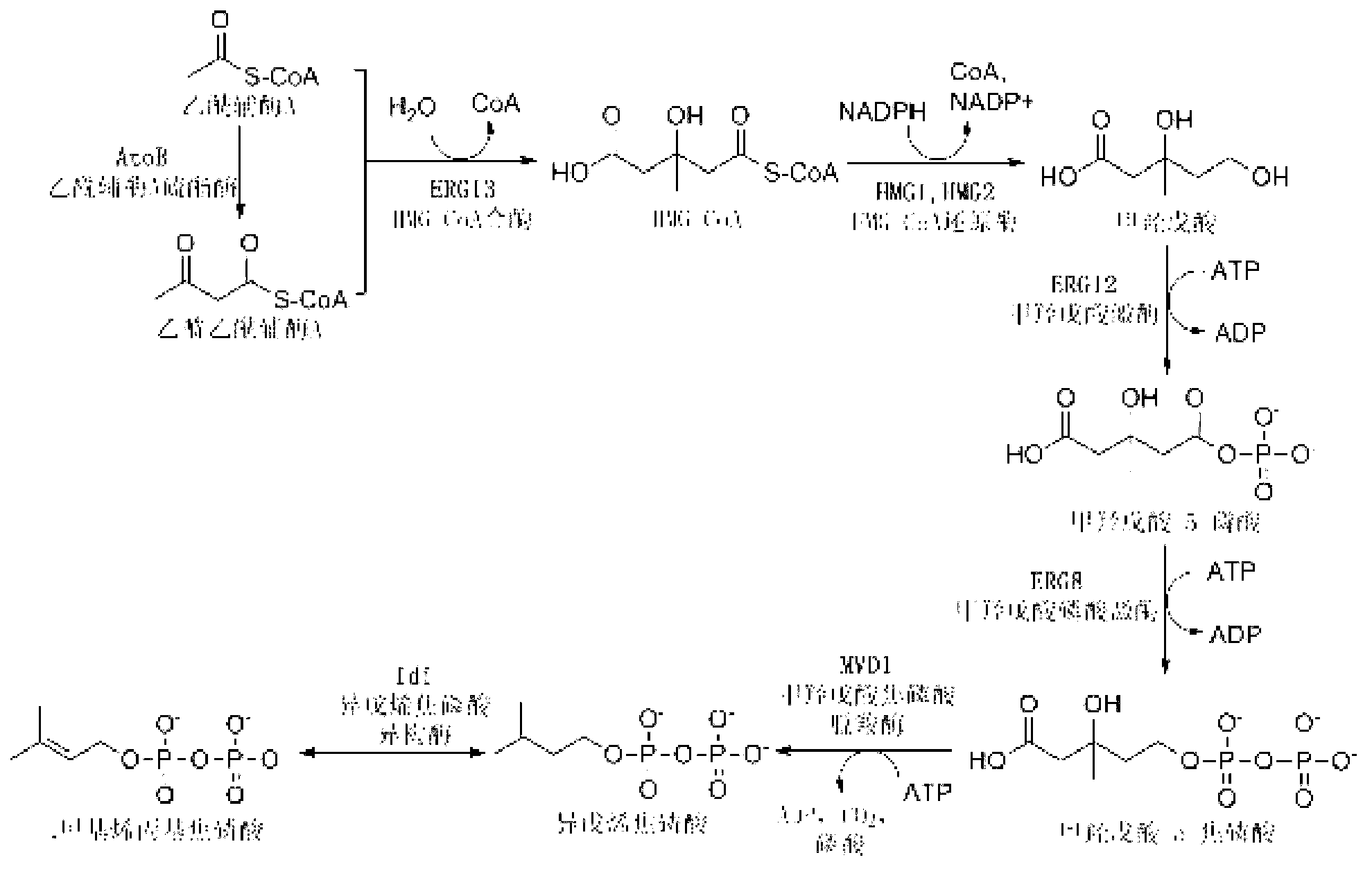
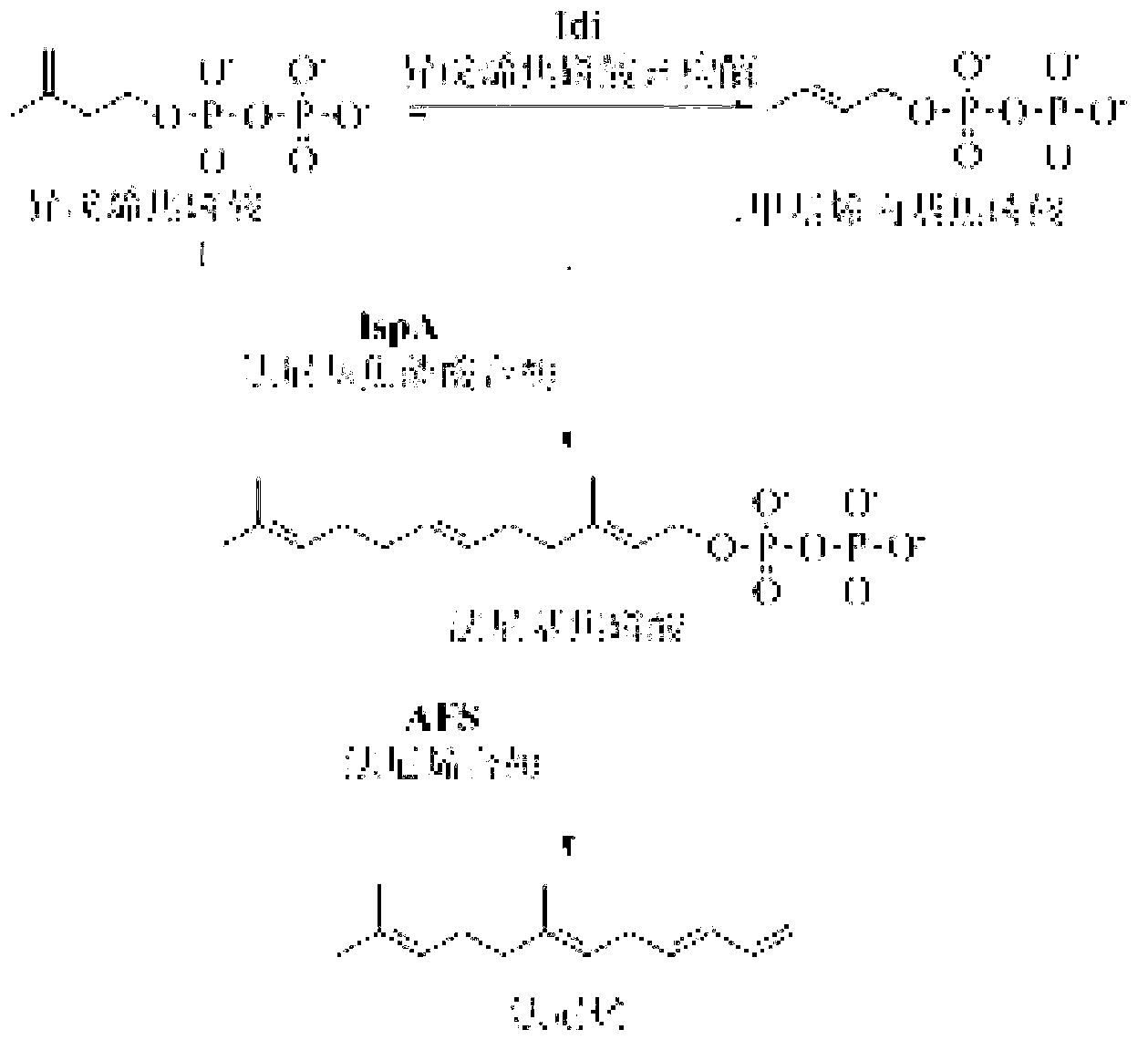
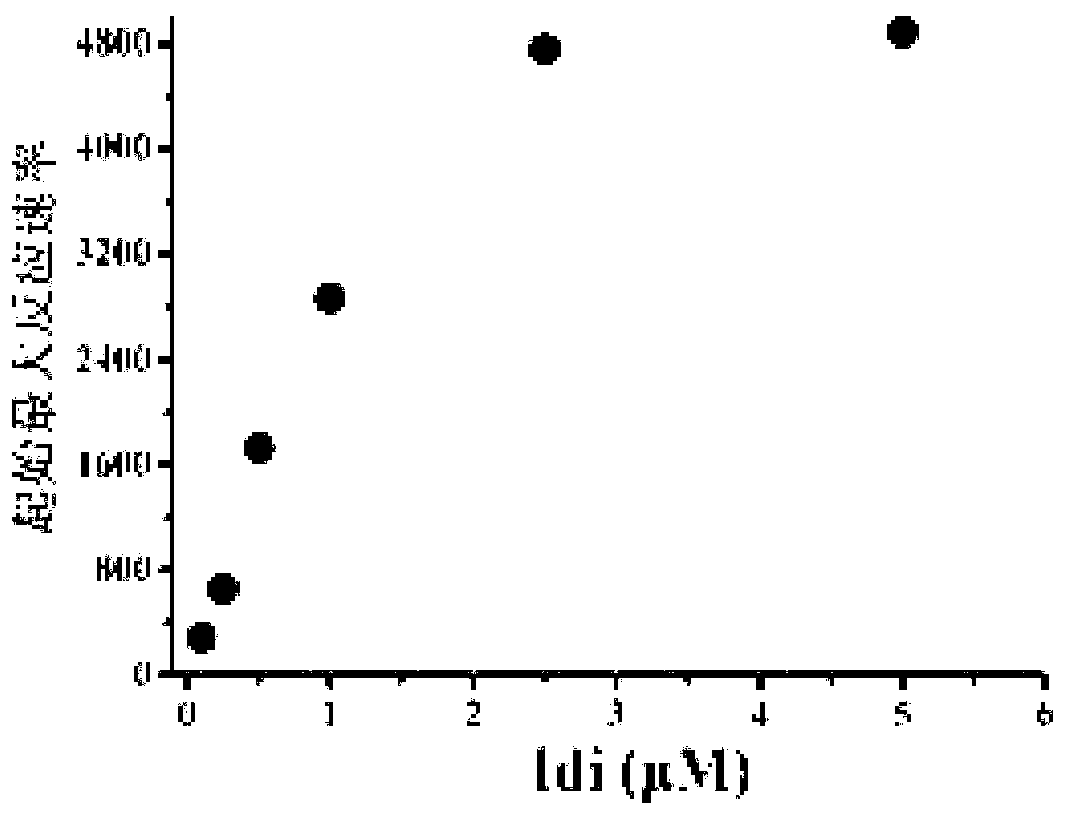
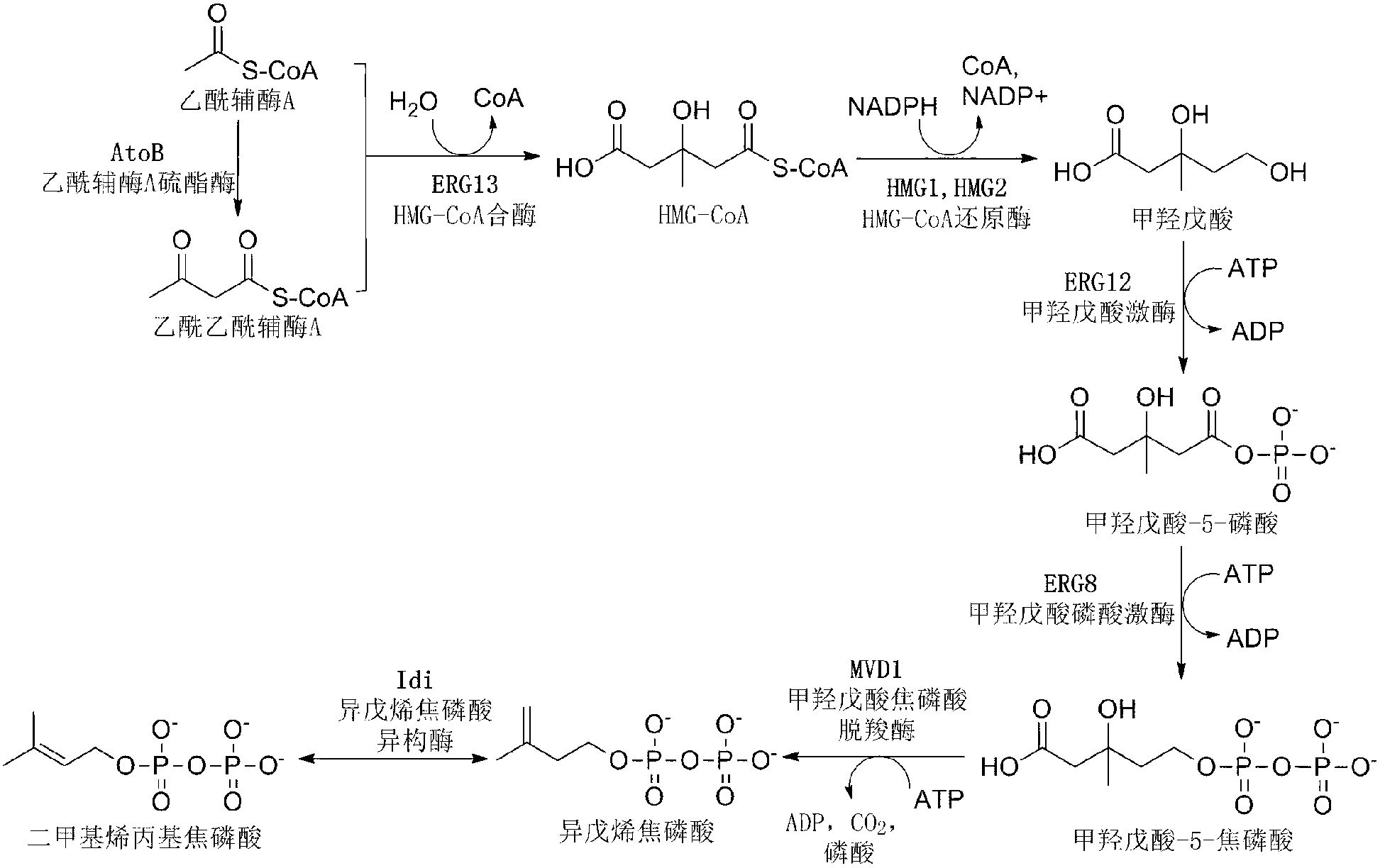
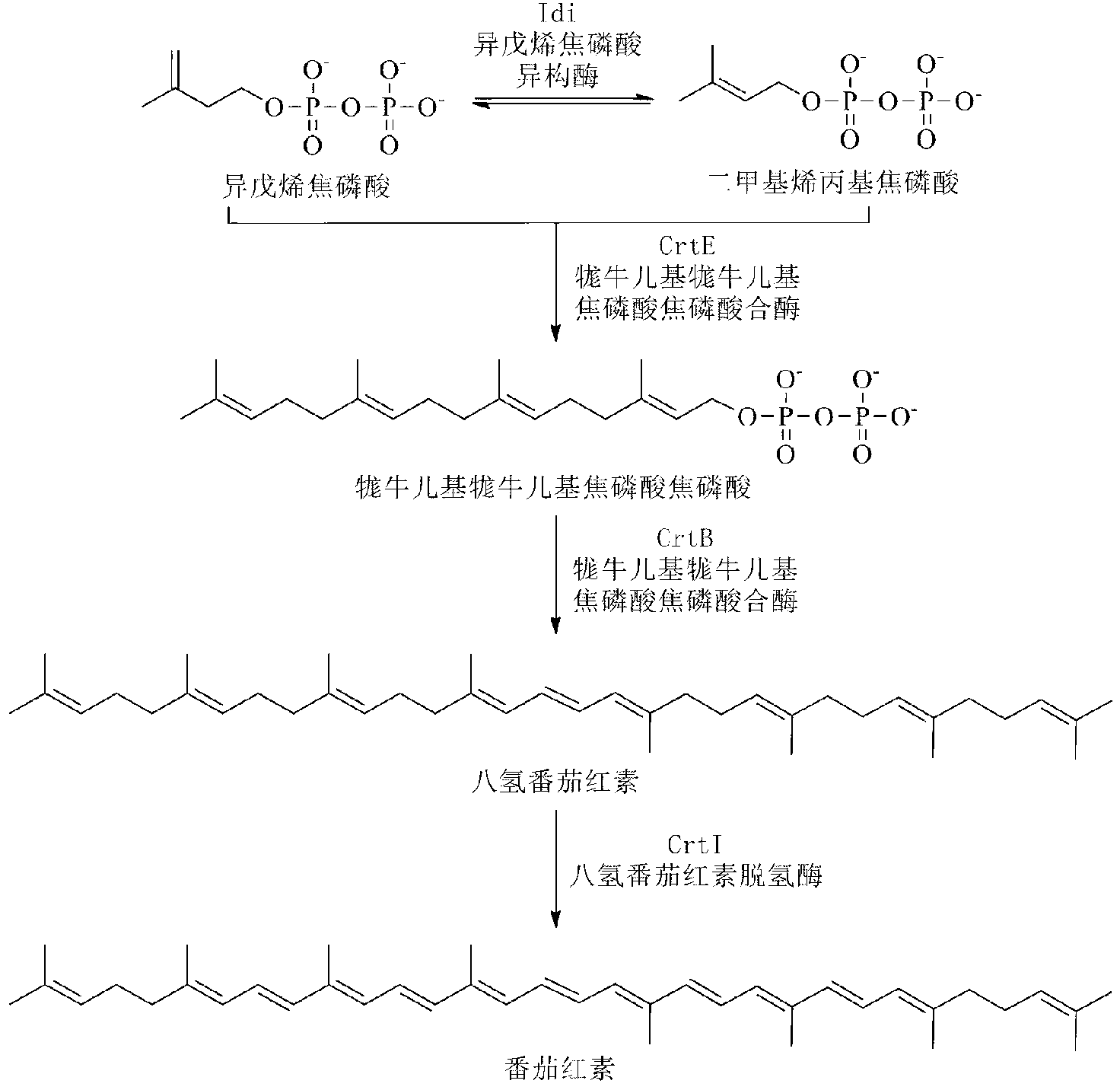
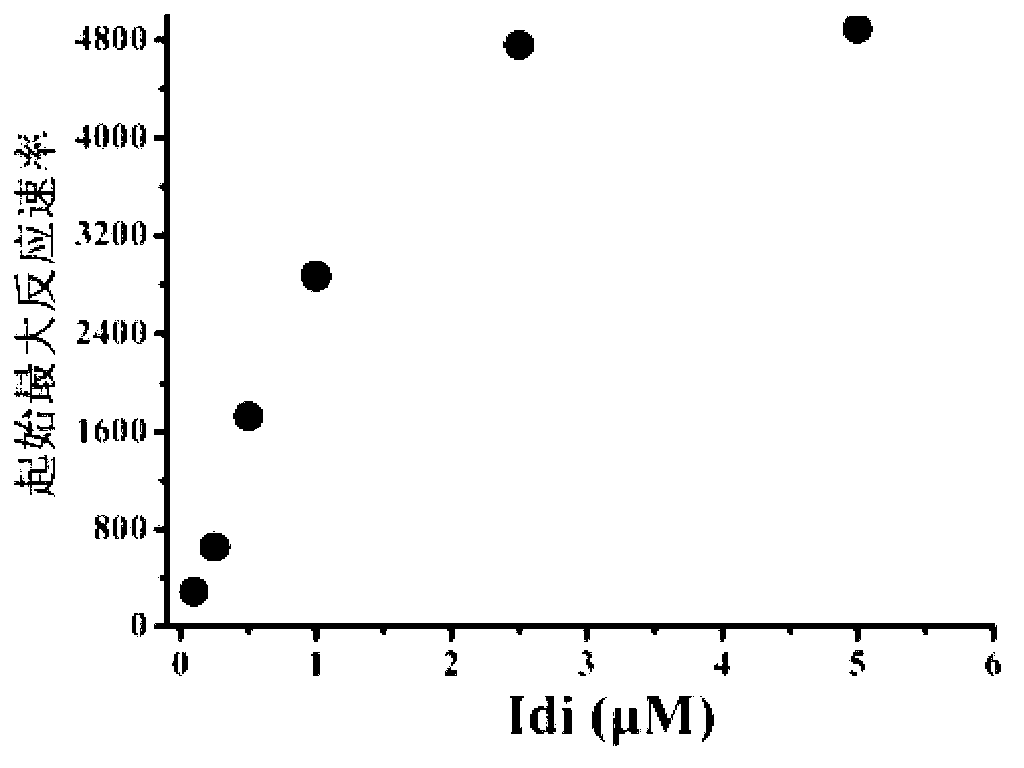
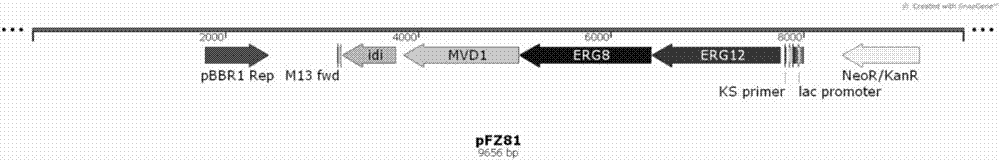
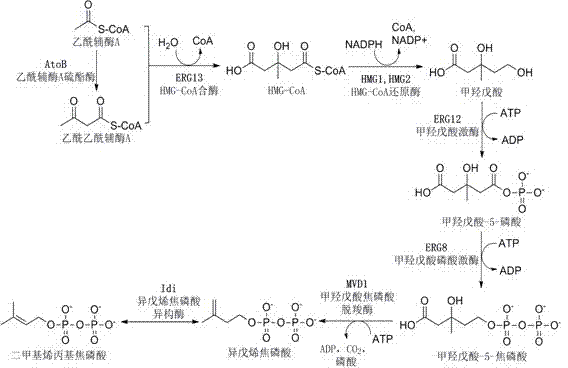
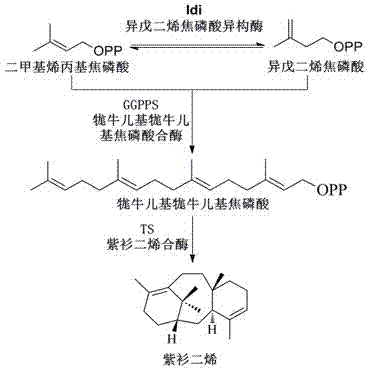
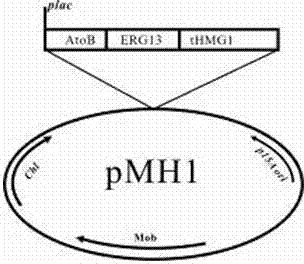
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing farnesene and an application of the bacterial strain, belonging to the field of synthetic biology. The bacterial strain for producing the farnesene contains related genes for synthesizing the farnesene through a mevalonic acid pathway and codon optimization; and the sequence of a farnesene synthetic gene afs optimized by codons is as shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The bacterial strain can be used for producing the farnesene, and a seed solution of the bacterial strain is inoculated into a culture medium containing a carbon source to carry out prokaryotic expression to obtain the farnesene. The gene for synthesizing the farnesene is subjected to codon optimization or the farnesene is synthesized by using the mevalonic acid pathway to ensure that each protein is closer to a ratio of AtoB:ERG13:tHMG1:ERG12:ERG8:MVD1:Idi:IspA:AFS=1:10:2:5:5:2:5:2:2, so that the production of the farnesene can be further promoted. By adopting the bacterial strain, the output of the farnesene is greatly improved to be more than 1g / L.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACTION TECH CO LTD
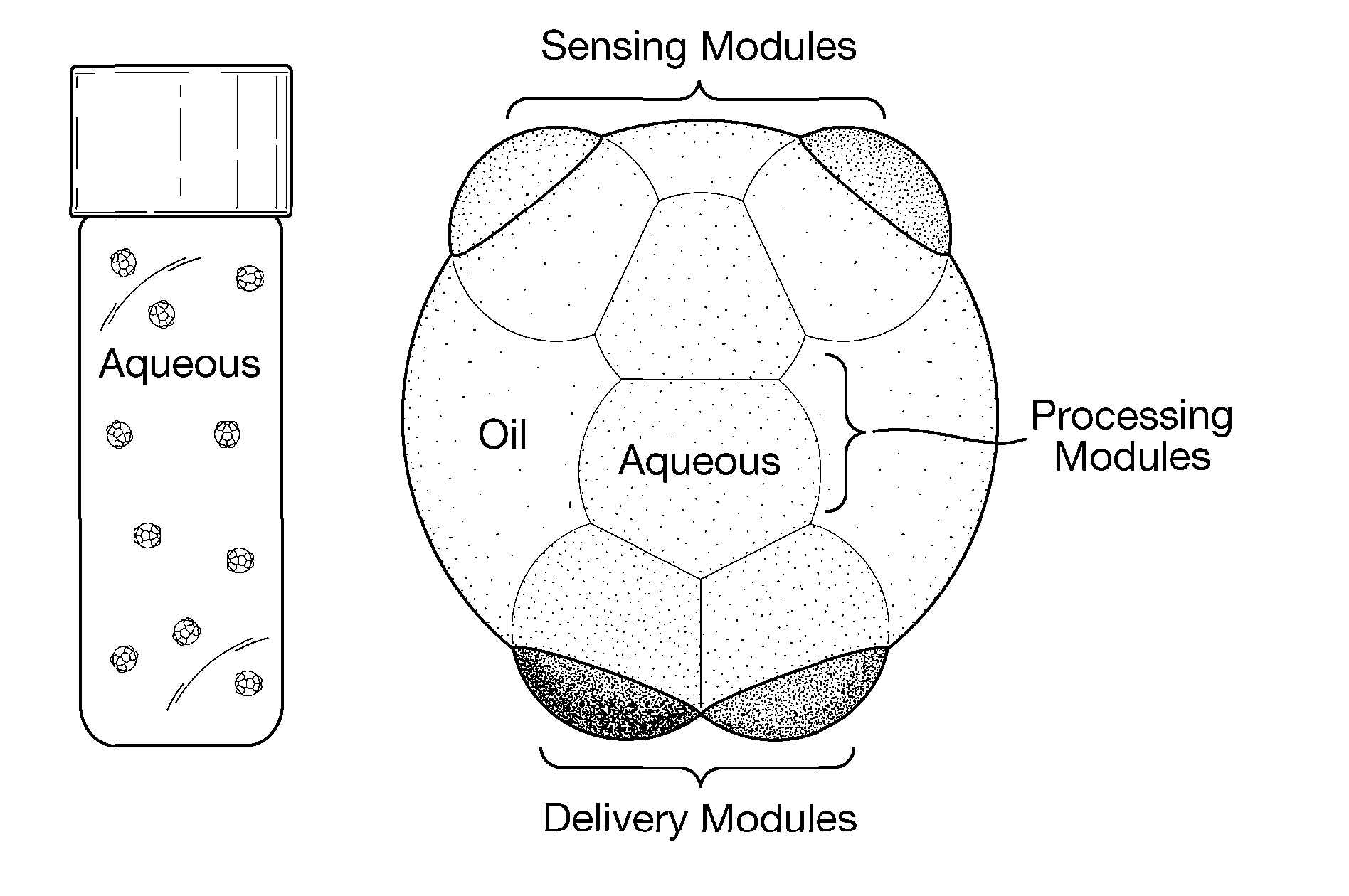
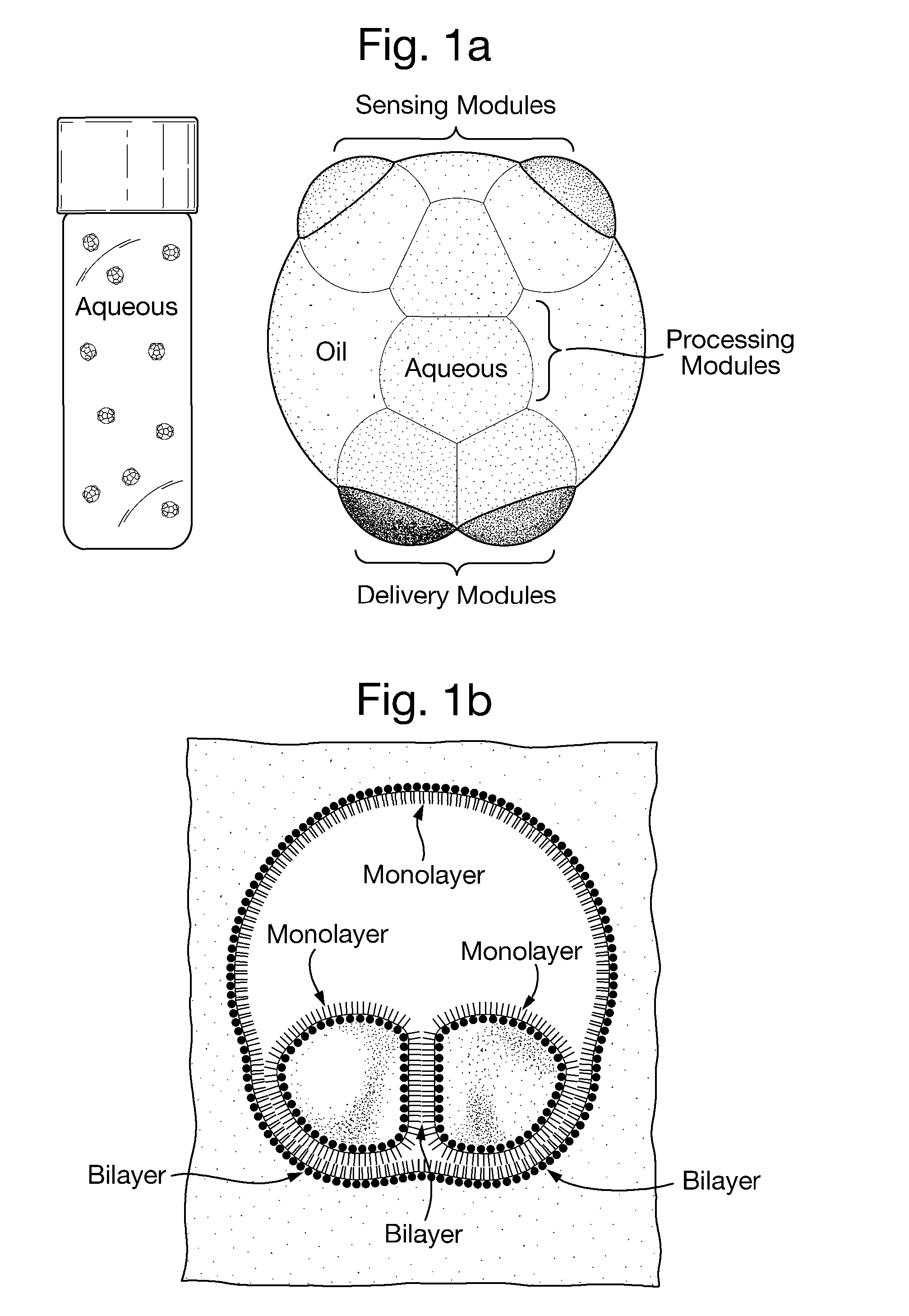
Multisomes: Encapsulated Droplet Networks
ActiveUS20140356289A1Drug being deliveredMethod can be usedOrganic active ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsSynthetic biologyMedicine
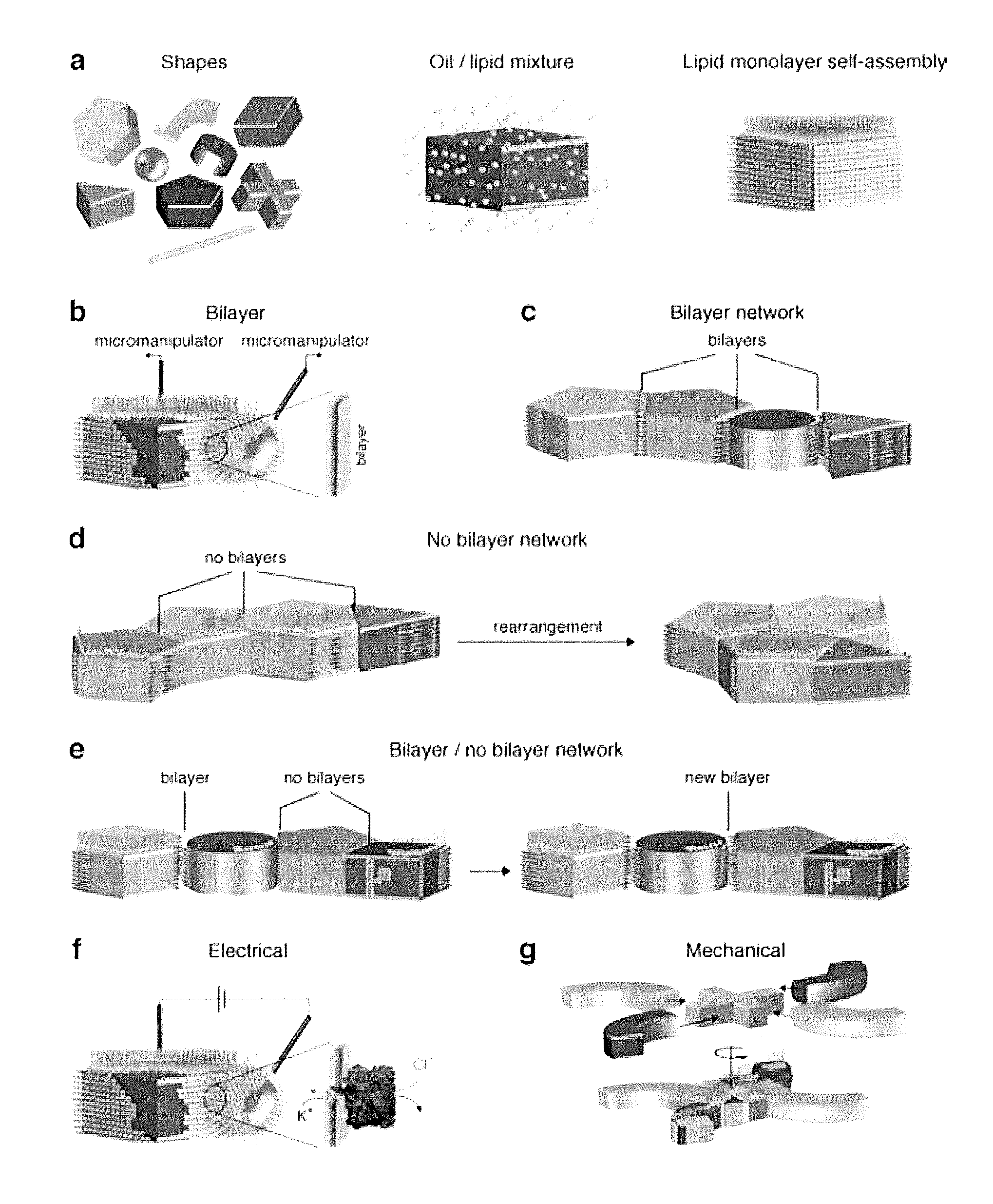
The invention provides a droplet encapsulate comprising: a drop of a hydrophobic medium; a peripheral layer of non-polymeric amphipathic molecules around the surface of the drop; and an aqueous droplet within the peripheral layer, the aqueous droplet comprising: (a) an aqueous medium and (b) an outer layer of non-polymeric amphipathic molecules around the surface of the aqueous medium. The invention also provides processes for preparing the droplet encapsulates. Various uses of the droplet encapsulates are also described, including their use as drug delivery vehicles, in synthetic biology, and in the study of membrane proteins.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
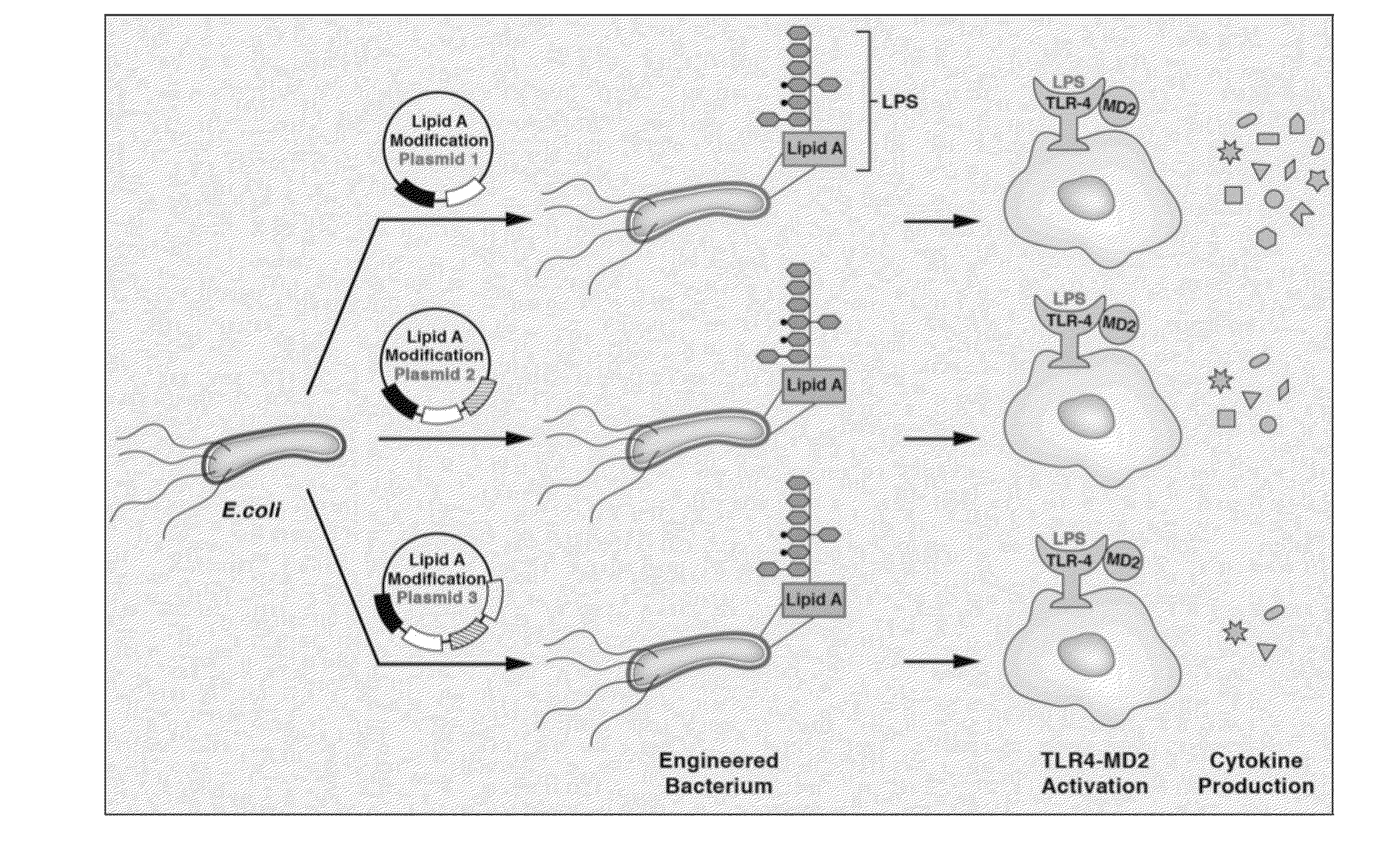
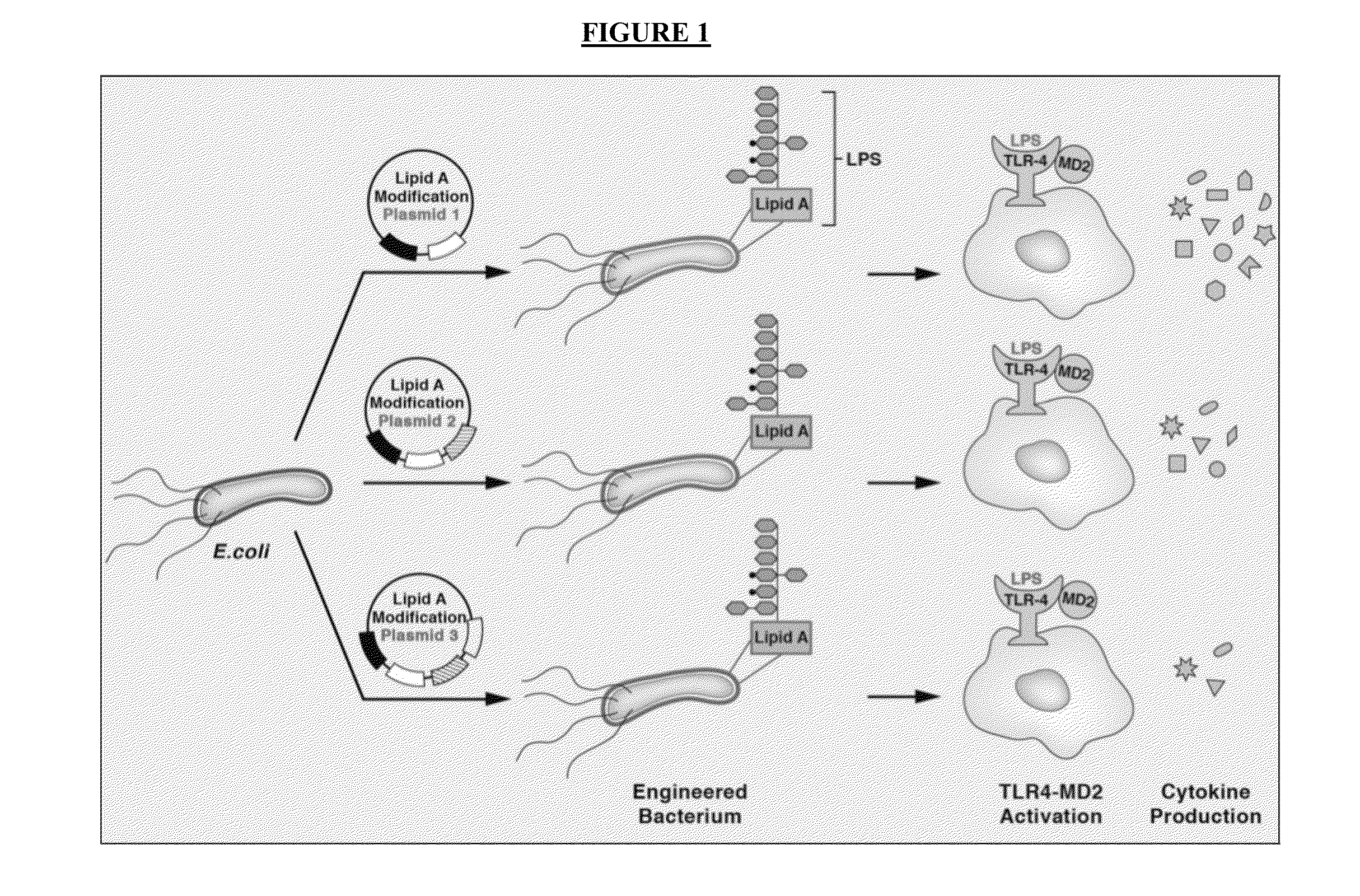
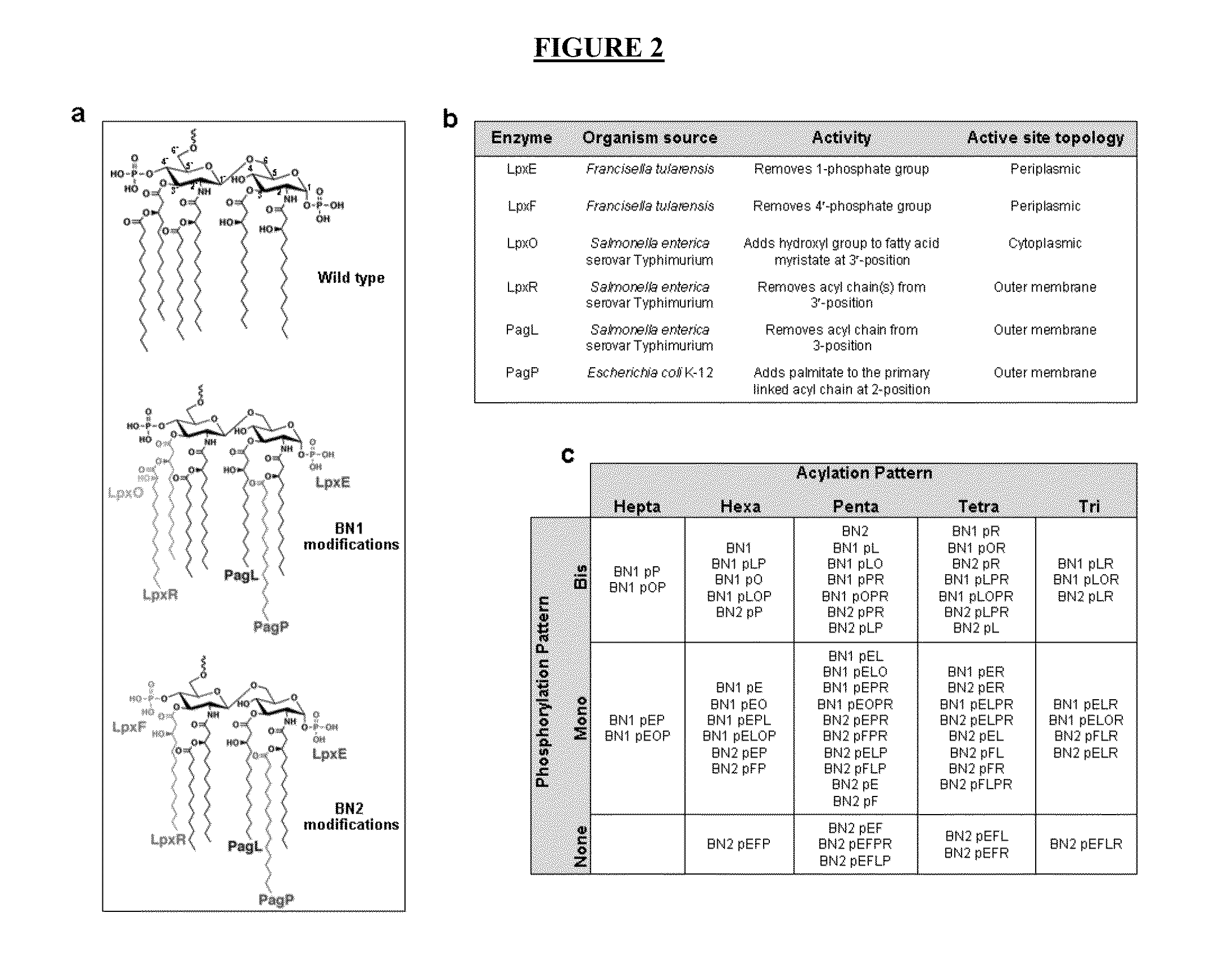
Synthetic lipid biology for combinatorial engineering of endotoxin
The present disclosure generally relates to genetic engineering of bacteria. More particularly, the present disclosure relates to genetic engineering of Gram-negative bacteria expressing different species of lipid A on their surface. In one embodiment, the present disclosure provides for an engineered strain of E. coli according to Table 1. In another embodiment, the present disclosure provides for a lipopolysaccharide purified from an engineered strain of E. coli according to Table 1.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
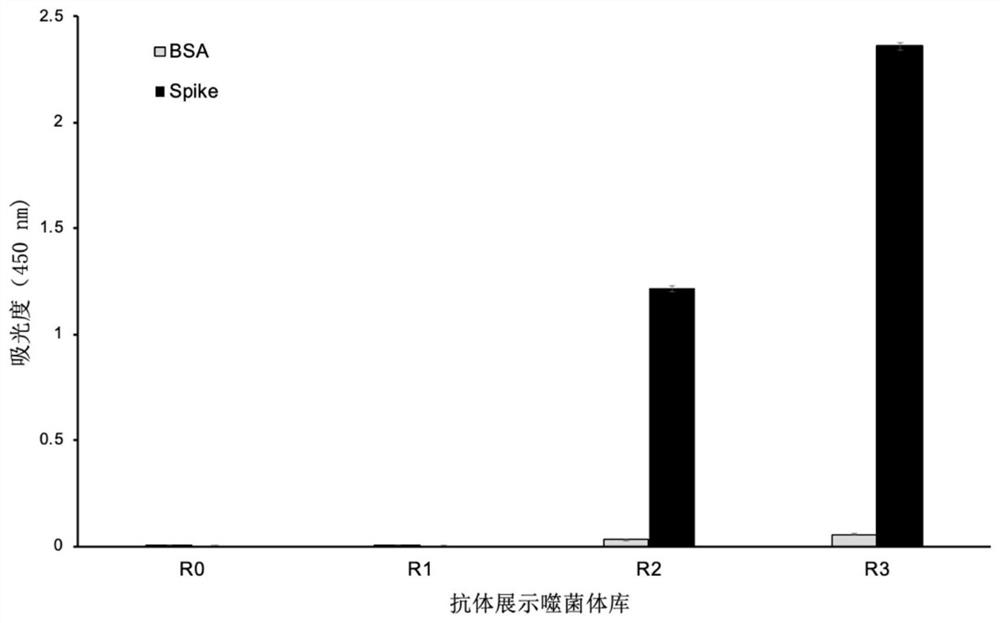
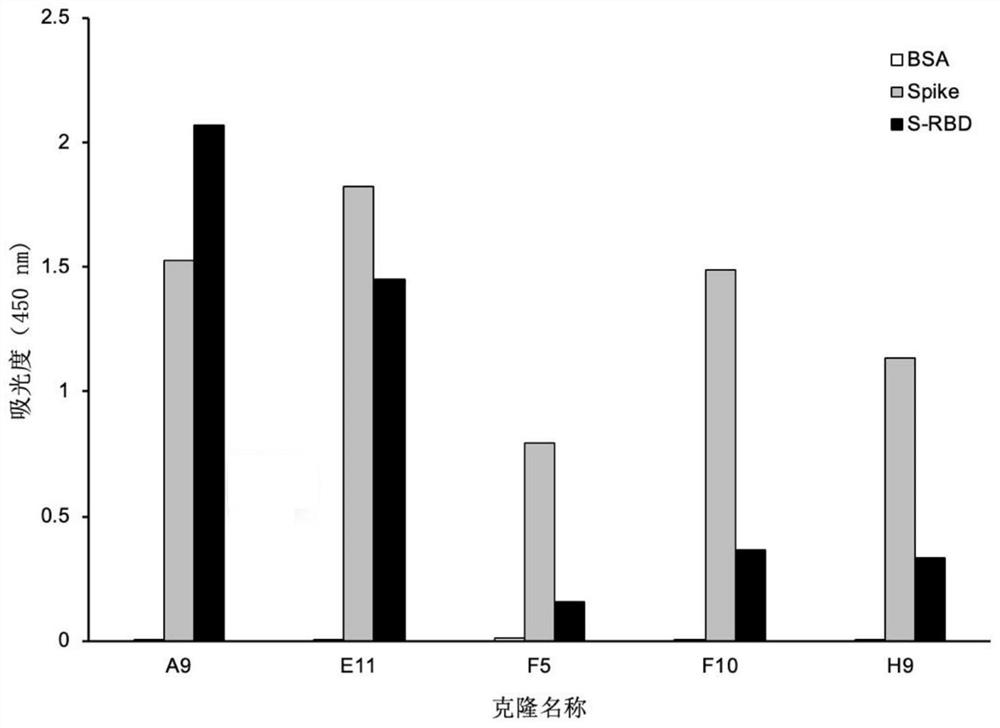
Phage display antibody library and monoclonal antibodies aiming at novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and obtained by panning based on same
ActiveCN111778218ANeutralizes contagionMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against virusesEscherichia coliMonoclonal antibody agent
The invention discloses a phage display antibody library and five strains of screened antibodies capable of being combined with S protein of novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Mutation is introduced into an ultra-variable region of an antibody variable region based on synthetic biology and a phage display technology, and a gene is transferred into escherichia coli, so that a synthetic antibody librarycontaining 108 kinds of antibodies is constructed; the phage display antibody library provided by the invention can perform screening to obtain the antibody with the specificity and the detection function, so that powerful resources of biological research and medical diagnosis are expanded; and the five strains of antibodies capable of being combined with the S protein of the novel coronavirus arefurther screened out and can be used for detecting the virus, part of the antibodies can block combination of the virus and cells, and the antibodies have the capacity of neutralizing novel coronavirus infectivity, can be used for preparing a novel coronavirus detection product, preparing a drug for inhibiting the novel coronavirus and preparing a pharmaceutical preparation for preventing or treating diseases caused by the novel coronavirus, and have a wide application prospect.
Owner:山东宽和正生物医药有限公司
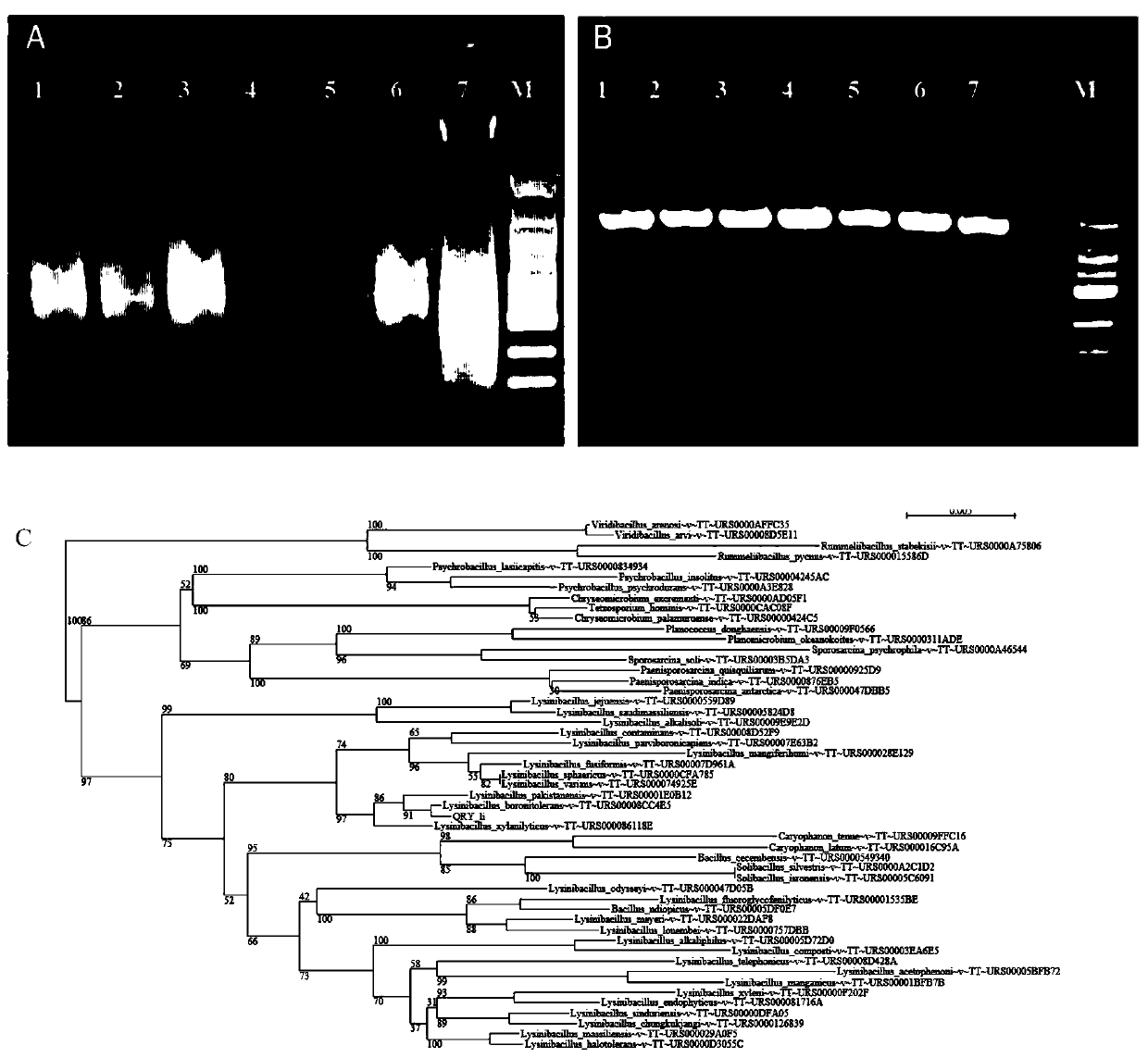
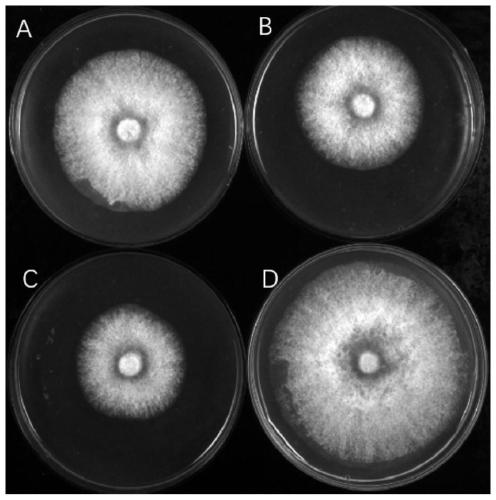
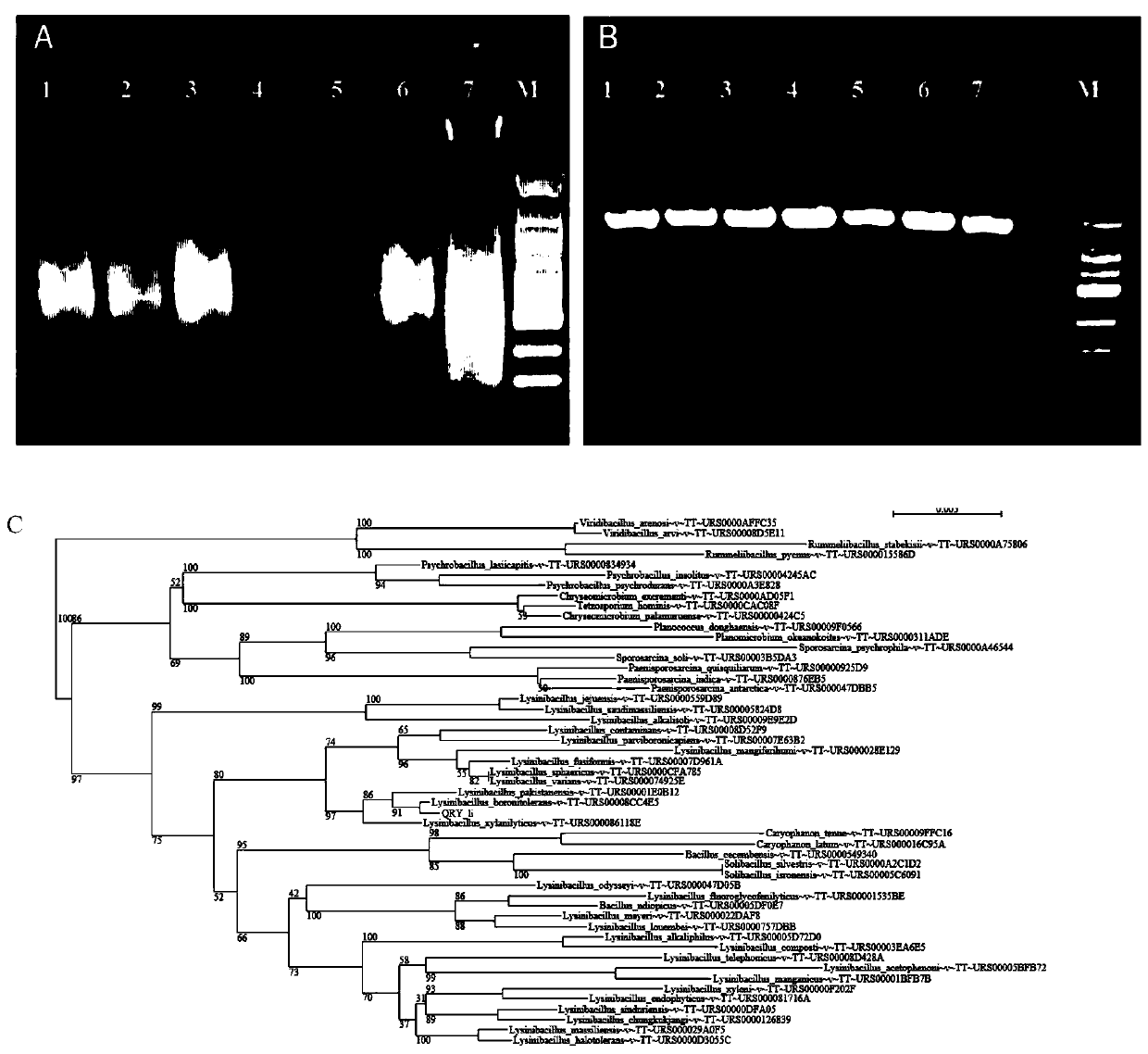
Rice blast bactericide prepared by taking lysinibacillus boronitolerans as chassis cell
The invention relates to application of lysinibacillus boronitolerans in inhibiting growth of magnaporthe oryzea. The lysinibacillus boronitolerans not only can reduce the occurrence and hazard of therice blast to a great extent, but also has no influence on the ecological environment, is expected to serve as a high-quality chassis microorganism for synthetic biology researches, and brings a newdirection for control over the rice blast.
Owner:海南果云农业科技有限公司
Nuclease-mediated genome editing
ActiveUS20180282713A1Reduce advantageImprove fidelityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesSynthetic biologyGenome editing
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering tools, methods and techniques for gene or genome editing. Specifically, the invention concerns isolated polypeptides having nuclease activity, host cells and expression vectors comprising nucleic acids encoding said polypeptides as well as methods of cleaving and editing target nucleic acids in a sequence-specific manner. The polypeptides, nucleic acids, expression vectors, host cells and methods of the present invention have application in many fields of biotechnology, including, for example, synthetic biology and gene therapy.
Owner:WAGENINGEN UNIV
Bacterial strain for producing lycopene and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103243066AImprove the ability to produce lycopeneIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLycopene synthesisBacterial strain
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing lycopene and an application of the bacterial strain, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The bacterial strain for producing lycopene contains a mevalonate pathway and a related gene which is synthetized by the lycopene optimized by a codon; and the synthetic gene sequence of the lycopene optimized by the codon is shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. The bacterial strain can be used for producing the lycopene; and a seed solution of the bacterial strain is inoculated into a culture medium containing a carbon source to carry out prokaryotic expression, so as to obtain the lycopene. The gene synthetized by the lycopene is optimized by the codon or each protein of the mevalonate pathway is closer to A to B:ERG13:tHMG1:ERG12:ERG8:MVD1:Idi=1:10:2:5:5:2:5; and production of the lycopene can be further promoted. By adopting the bacterial strain, the yield of the lycopene can be greatly improved to over 1g / L; and the fermentation cycle is shortened by over 50%.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Making nucleic acid sequences in parallel and use
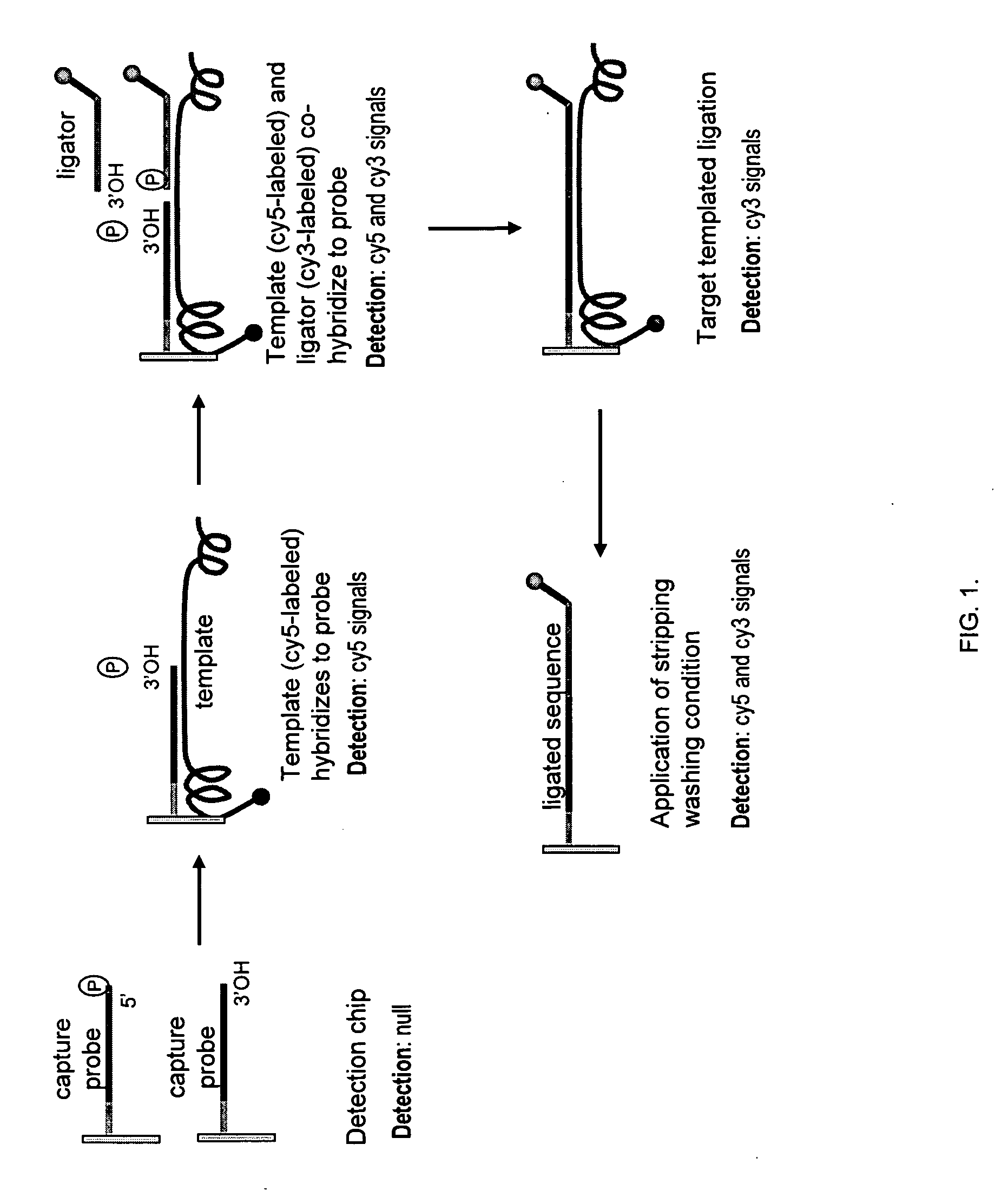
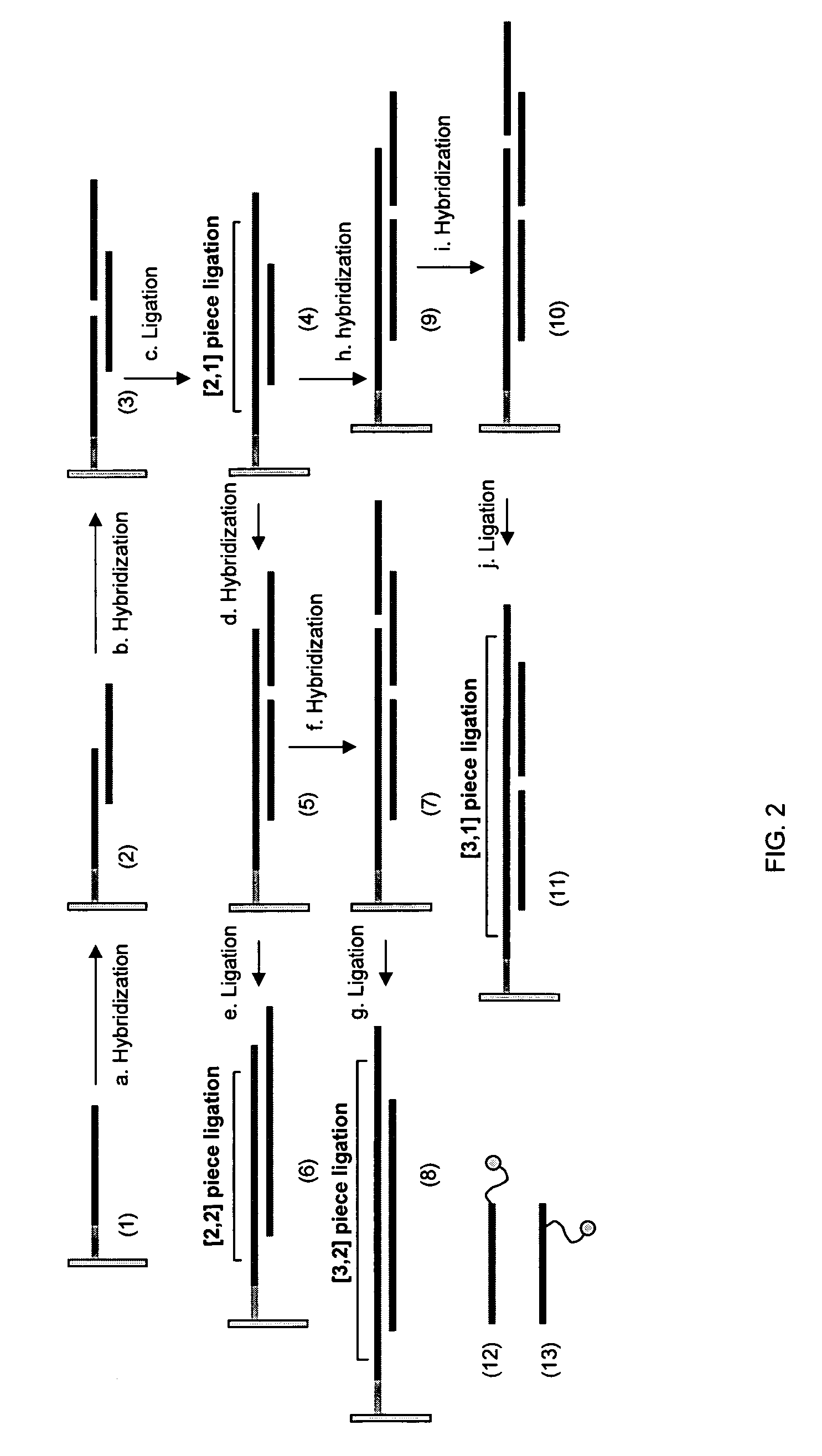
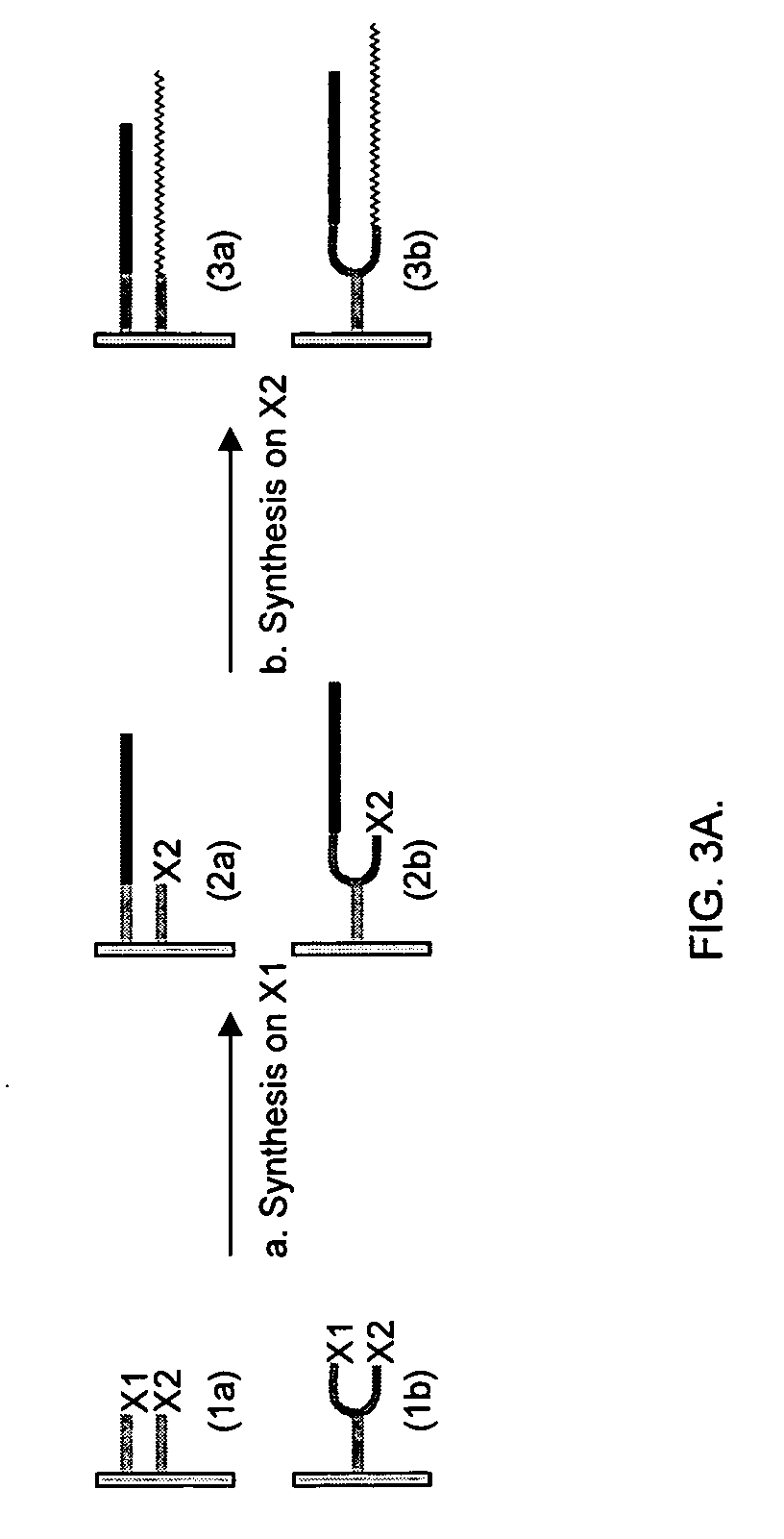
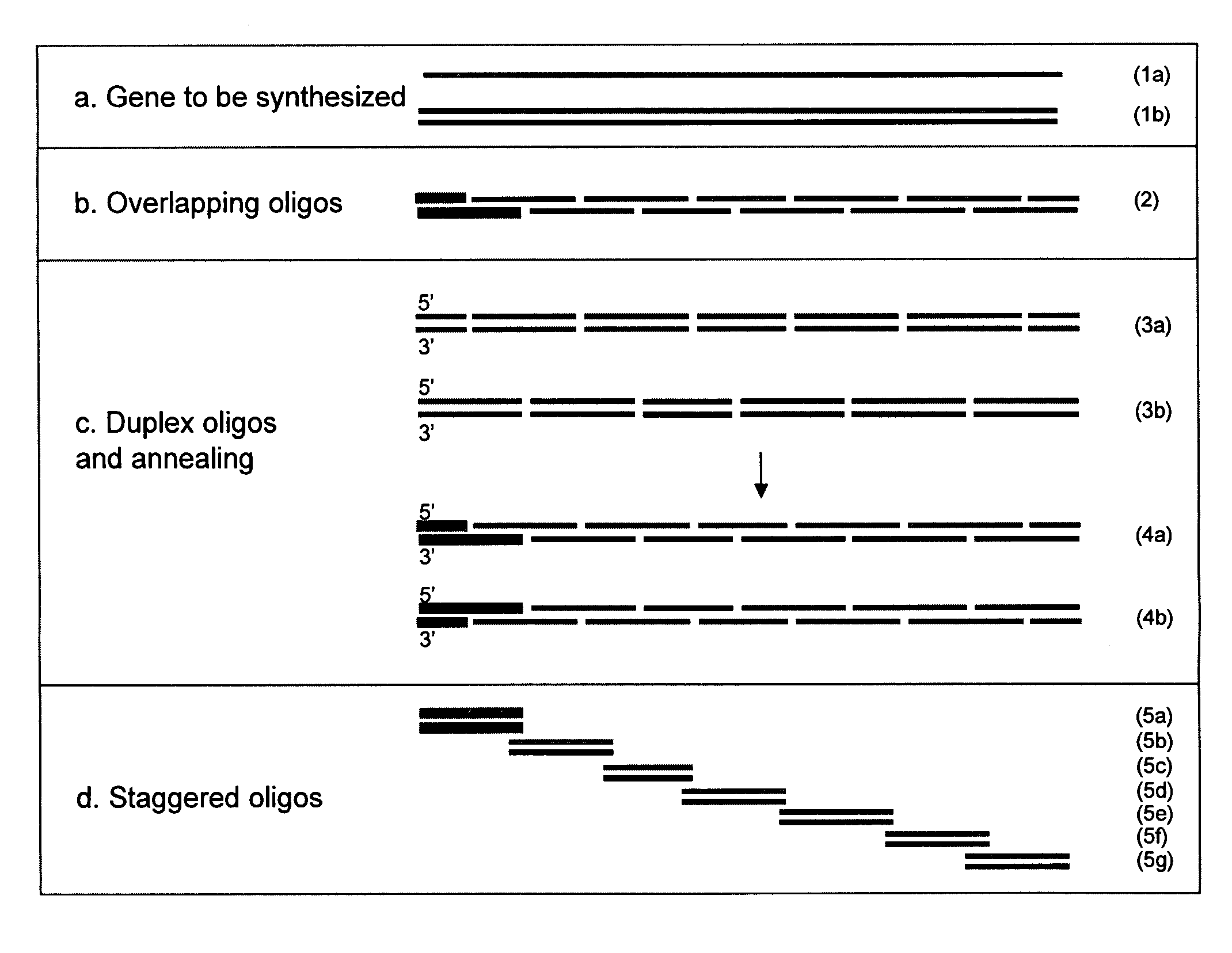
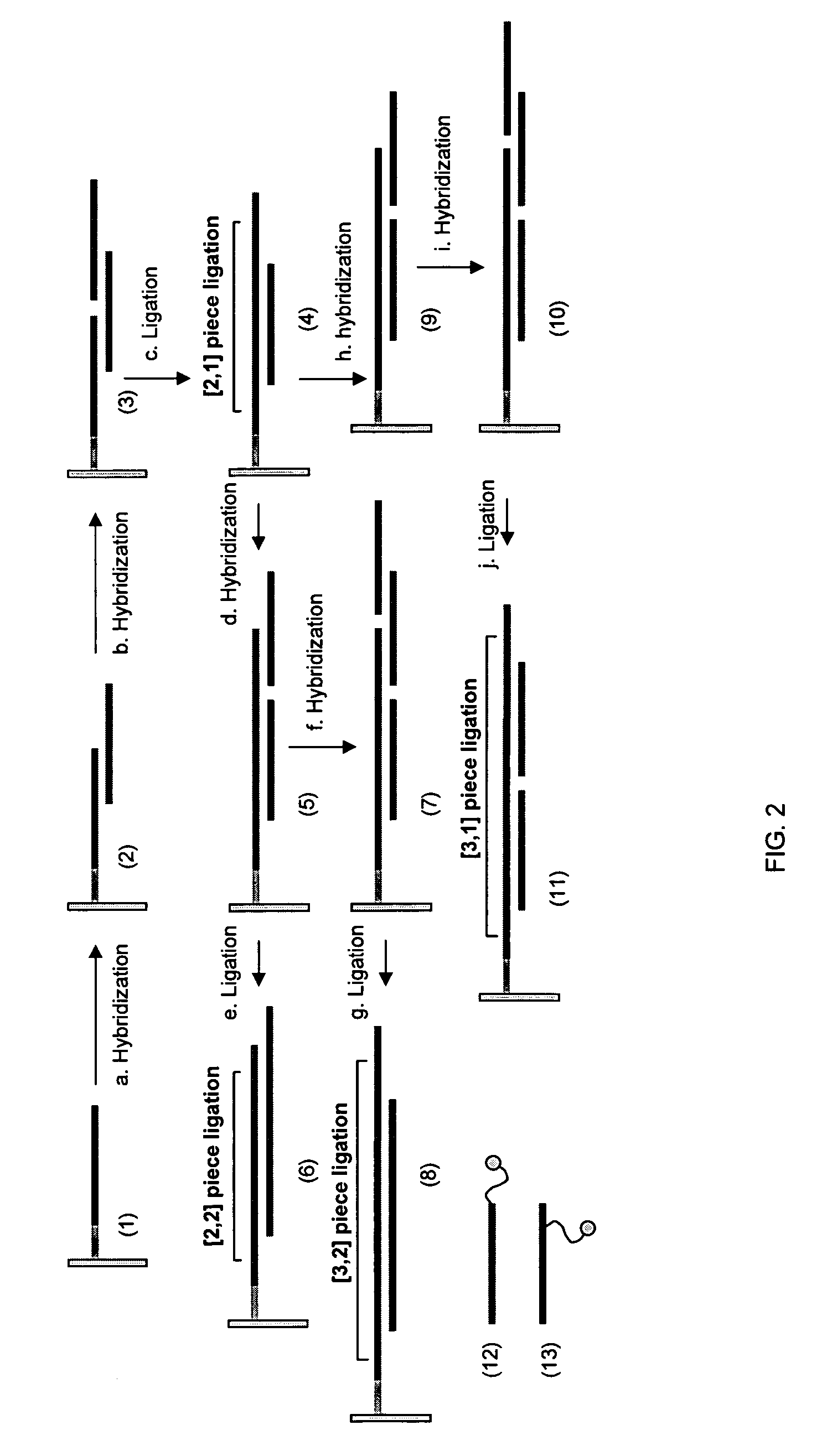
ActiveUS20070031942A1Strong hybridization specificityImprove fidelitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsSynthetic biology
The present invention relates generally to the fields of genomics, synthetic biology and genetic engineering. More particularly, the present invention concerns the methods that enable parallel multiplex ligation and amplification on surface for making assemblies of nucleic acids of various biological applications and for analysis of biological samples such as DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Owner:LC SCI LC
Applications of glycosyltransferase and related materials thereof in construction of engineering bacteria for producing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1
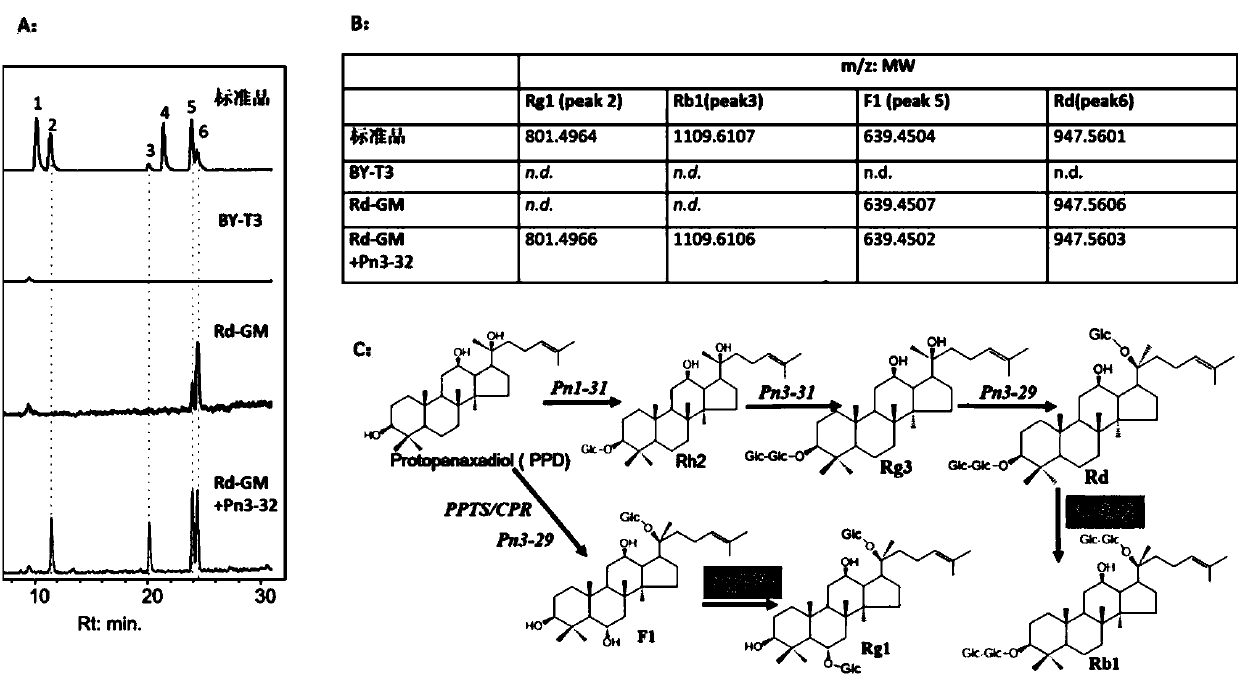
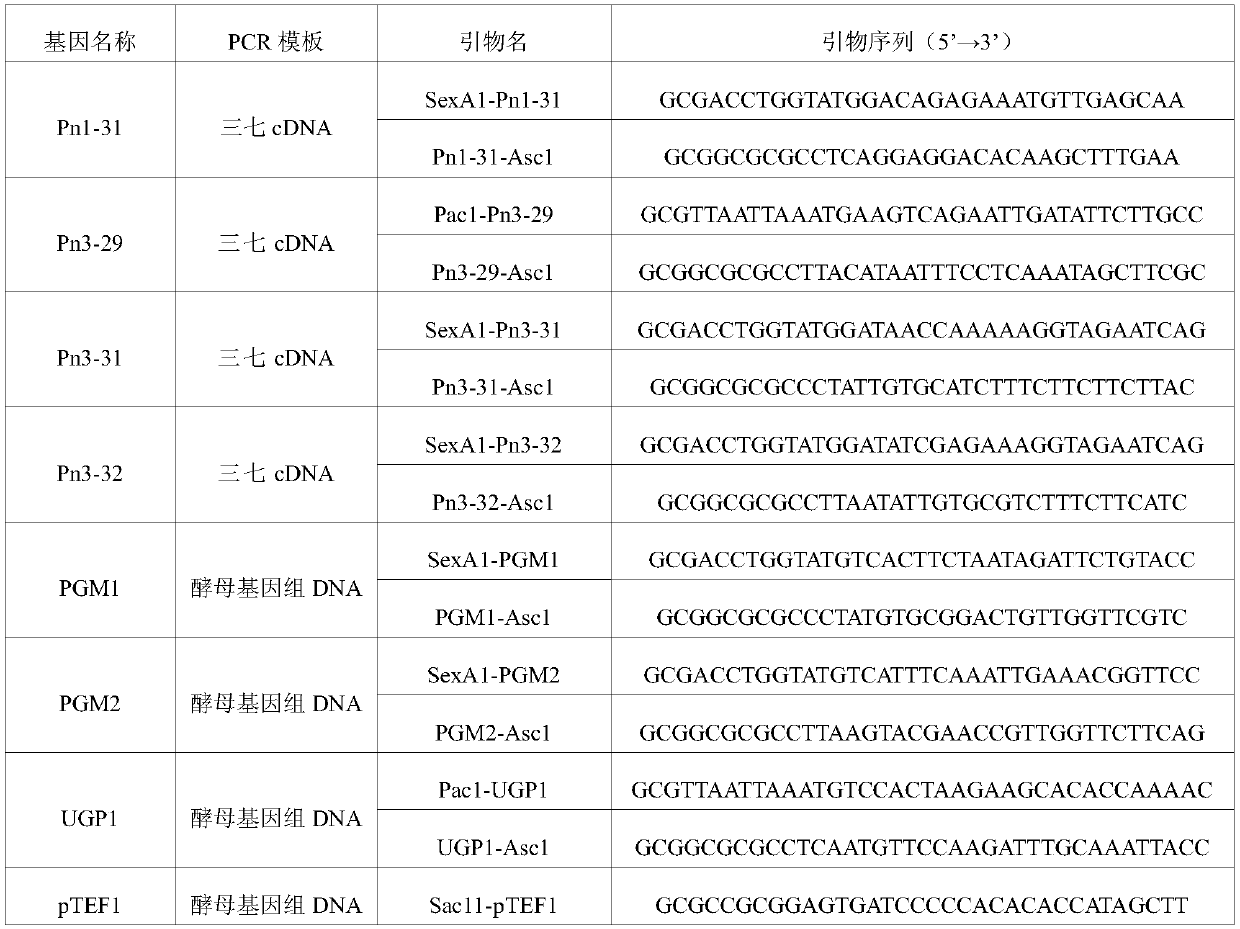
The invention discloses applications of glycosyltransferase and related materials thereof in the construction of engineering bacteria for producing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1. A glycosyltransferase genePn3-32 which can catalyze ginsenoside Rd to generate ginsenoside Rb1 can be successfully identified through a synthetic biological method; and the gene can simultaneously catalyze ginsenoside F1 to generate ginsenoside Rg1 and construct recombinant yeast producing the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1. Through experiments, the constructed recombinant yeast producing the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1 can simultaneously generate the ginsenoside Rb1 and the ginsenoside Rg1. Pn1-31, Pn-3-29, Pn3-31 and Pn3-32 glycosyltransferase genes in medicinal plant radix notoginseng are firstly utilized to continuously catalyze protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol to synthetize the ginsenoside Rb1, the ginsenoside Rg1 and corresponding intermediates, so that novel cases can be provided formicrobial strains to produce natural products.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Areca nut root rot fungicide taking lysinibacillus boronitolerans as base cells
ActiveCN111100806AGuaranteed outputEffectively prevent production loss and even deathBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention relates to an application of lysinibacillus boronitolerans in inhibiting growth of cerrena unicolor. The lysinobacterium boronitrotolarans not only can reduce occurrence of areca nut root rot to a great extent, but also has no threat to the ecological environment, is expected to be used as a high-quality base microorganism for synthetic biology research, and thus brings a new direction to prevention and treatment of areca nut root rot.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Hydrogel network
ActiveUS20150248949A1Inhibited DiffusionEfficient interfaceInsulated cablesRecord information storageSynthetic biologyElectrochemistry
The invention provides a hydrogel network comprising a plurality of hydrogel objects, wherein each of said hydrogel objects comprises: a hydrogel body, and an outer layer of amphipathic molecules, on at least part of the surface of the hydrogel body, wherein each of said hydrogel objects contacts another of said hydrogel objects to form an interface between the contacting hydrogel objects. A process for producing the hydrogel networks is also provided. The invention also provides an electrochemical circuit and hydrogel component for mechanical devices comprising a hydrogel network. Various uses of the hydrogel network are also described, including their use in synthetic biology and as components in electrochemical circuits and mechanical devices.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
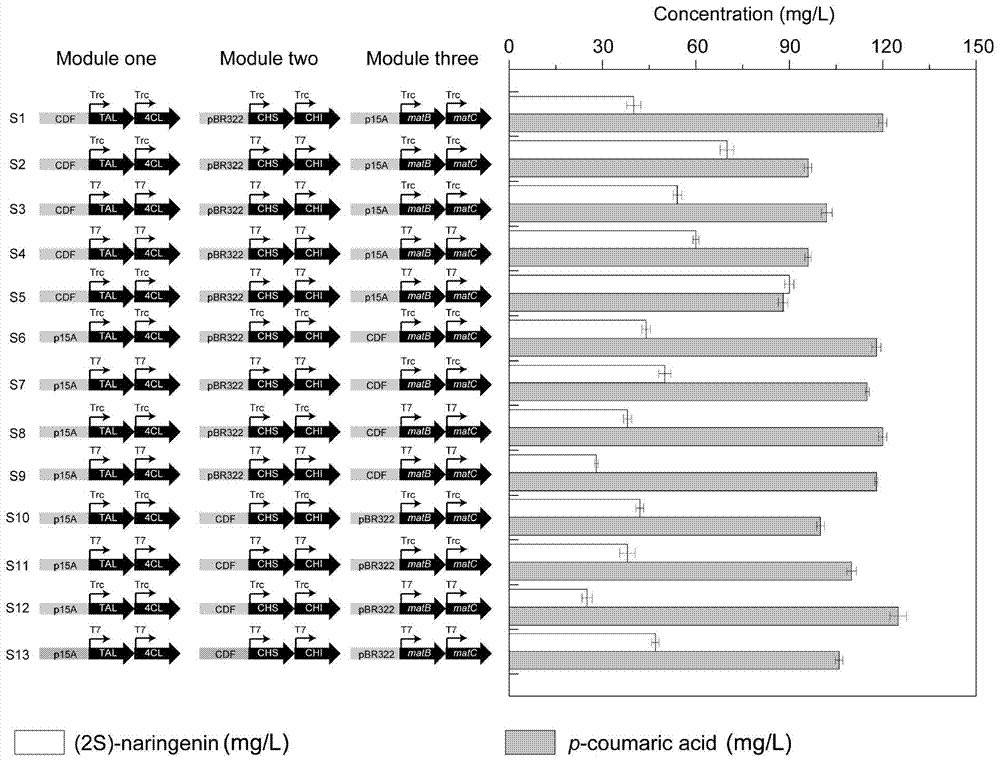
Genetic engineering strain taking tyrosine as substrate to synthesize naringenin and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a genetic engineering stain taking tyrosine as a substrate to synthesize naringenin and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of synthetic biology or metabolic engineering. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, a synthesis route constituted by six genes, namely a gene matB encoding a malonic acid transporting enzyme, a gene matC encoding a malonic acid absorption route, a gene encoding a tyrosine ammonialyase (TAL), the gene encoding a 4-cinnamic acid: coenzyme A ligase (4CL), the gene encoding a chalcone synthase (CHS) and the gene encoding a chalcone isomerase (CHI) is introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 to obtain a recombinant strain capable of taking the tyrosine as the substrate to synthesize the naringenin, the synthesis route is further optimized through a modular transformation theory, the strain is finally fermented in a shaking flask for 72 hours by taking the tyrosine as the substrate, and the yield of the naringenin achieves 90mg / L. A strategy adopted by the construction method disclosed by the invention provides certain reference significance for future production of natural small molecular substances by a microbiological method.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
Screening, identification and application of SmAP2/ERF82 transcription factor for regulating tanshinone biosynthesis
ActiveCN107699576APromote biosynthesisReduce contentPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideControl line
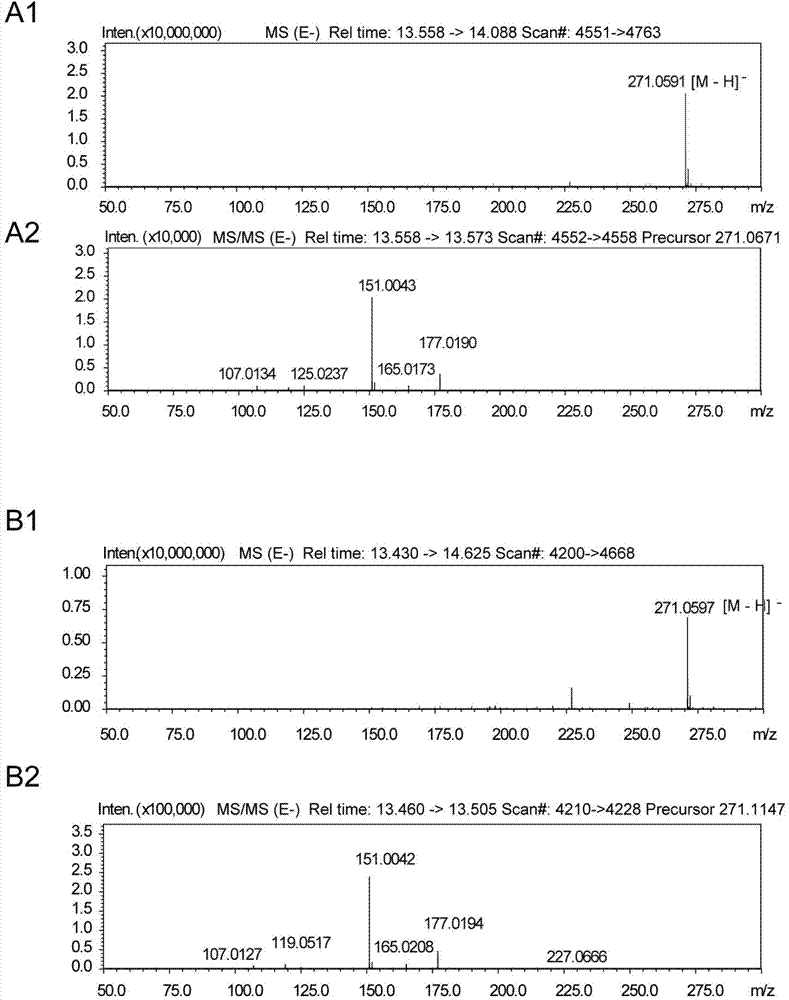
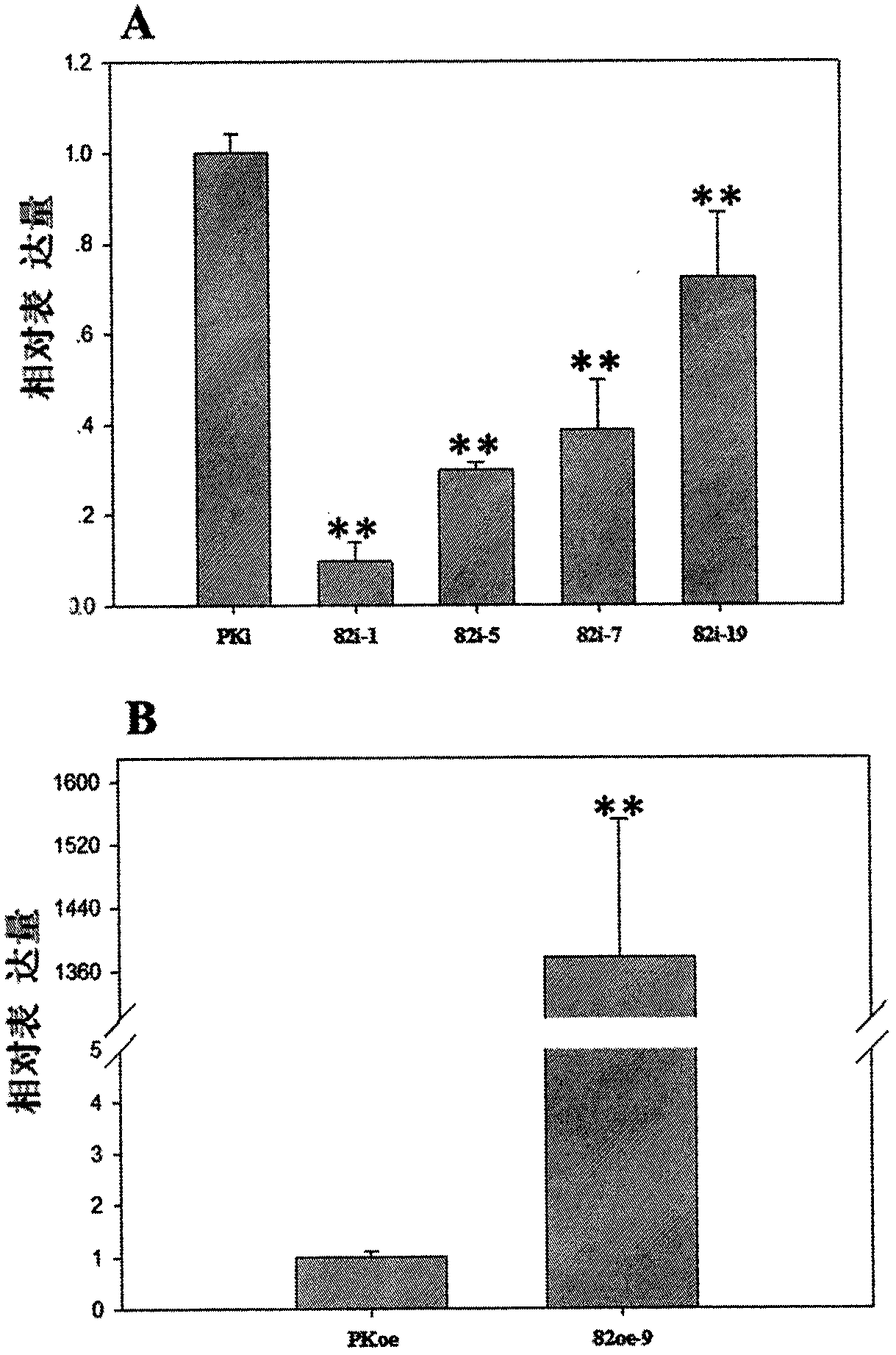
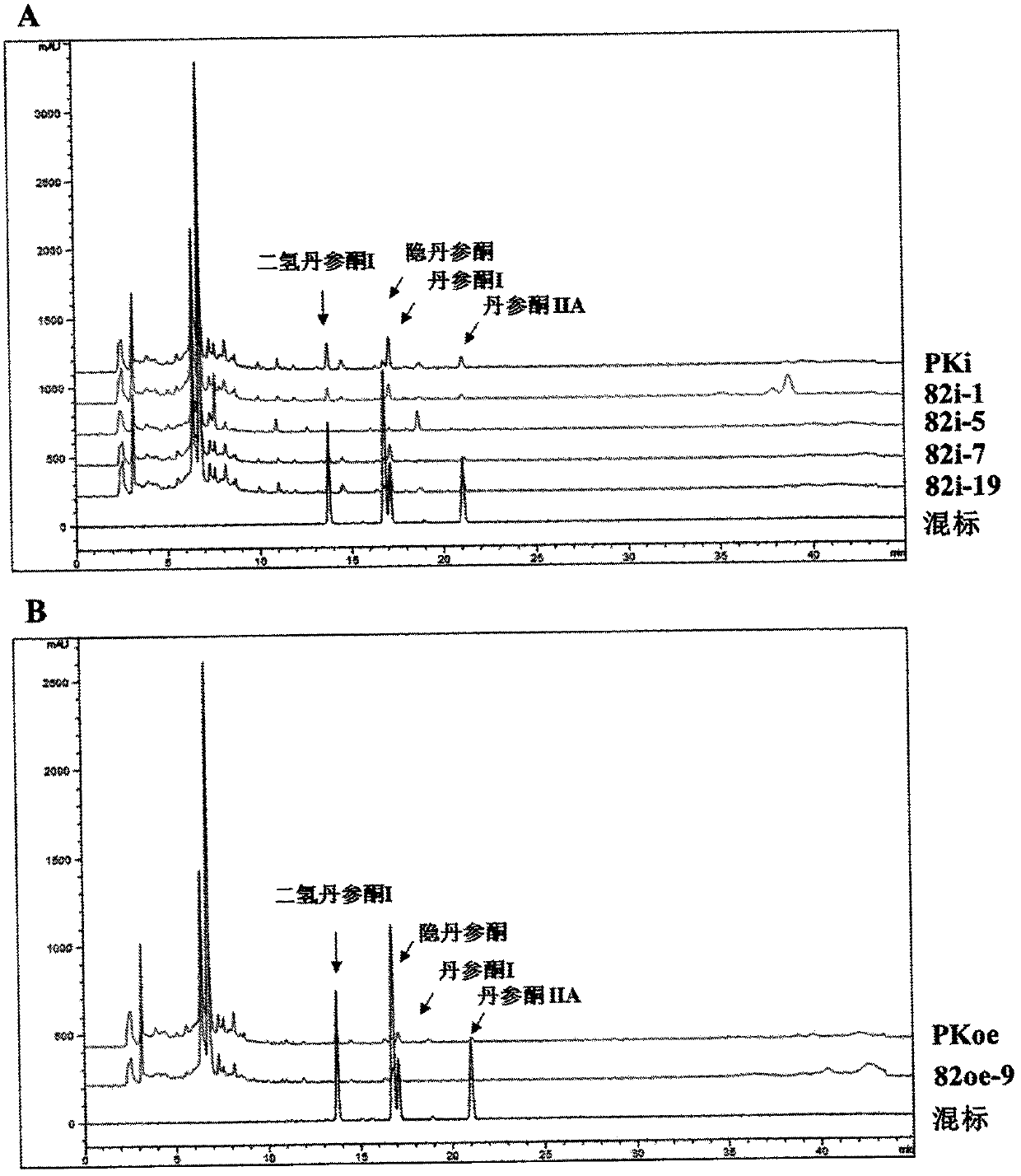
The invention discloses a coding gene sequence of an AP2 / ERF transcription factor SmAP2 / ERF82 for regulating tanshinone synthesis. The SmAP2 / ERF82 gene provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence as shown in the SEQ ID No.1. The gene encoded protein has an amino acid sequence as shown in the SEQ ID No.2. A SmAP2 / ERF82-RNAi vector and a SmAP2 / ERF82-overexpression vector are constructed in the invention. Through a genetic transformation method for transformation of red sage root, transgenic hairy roots are obtained. In comparison with a control line, contents of dihydrotanshinone I, cryptotanshinone, tanshinone I and tanshinone II A in the SmAP2 / ERF82-RNAi line are remarkably reduced, and contents of dihydrotanshinone I and cryptotanshinone in the SmAP2 / ERF82-overexpression line areremarkably raised. The SmAP2 / ERF82 provided by the invention has the function of positive regulation of tanshinone compound biosynthesis. The compounds have remarkable efficacy of treating cardiovascular diseases. The invention brings forth new ideas for the research on molecular mechanism for tanshinone synthesis regulation and lays a foundation for the biological research on synthesis of tanshinone.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
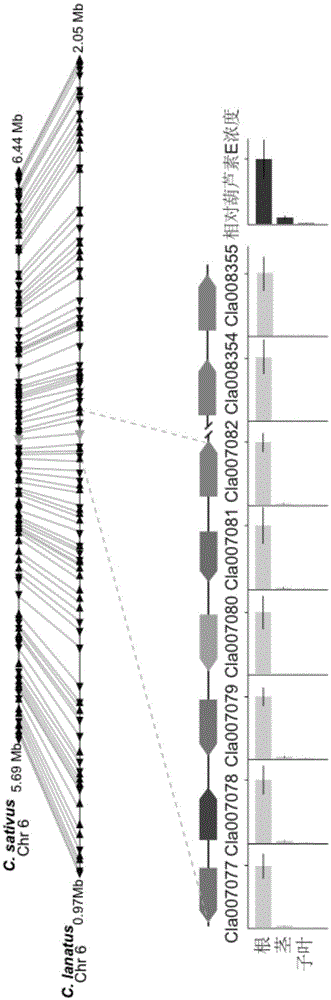
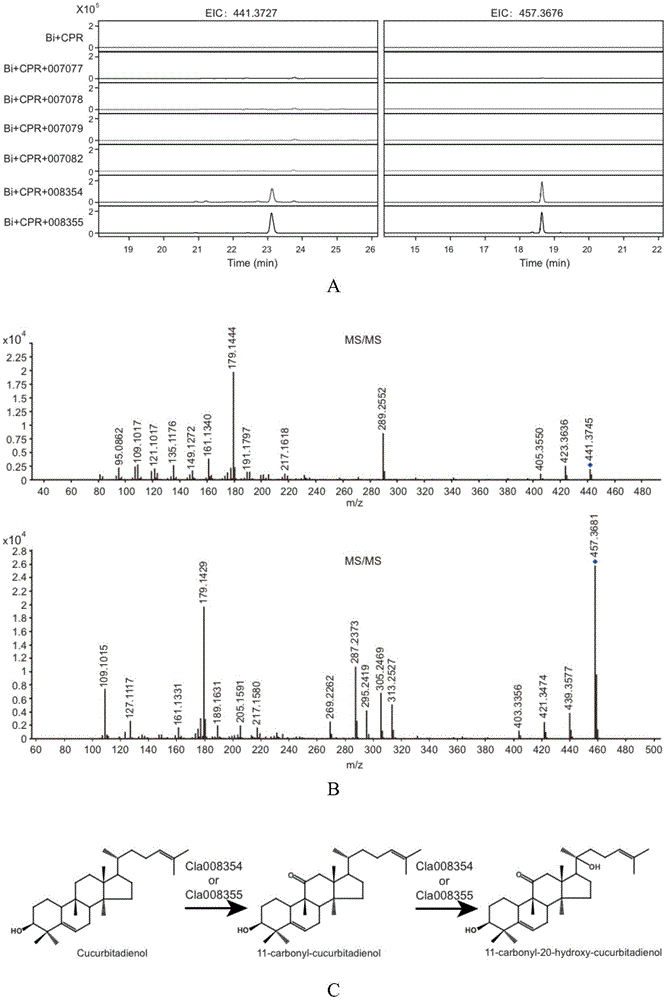
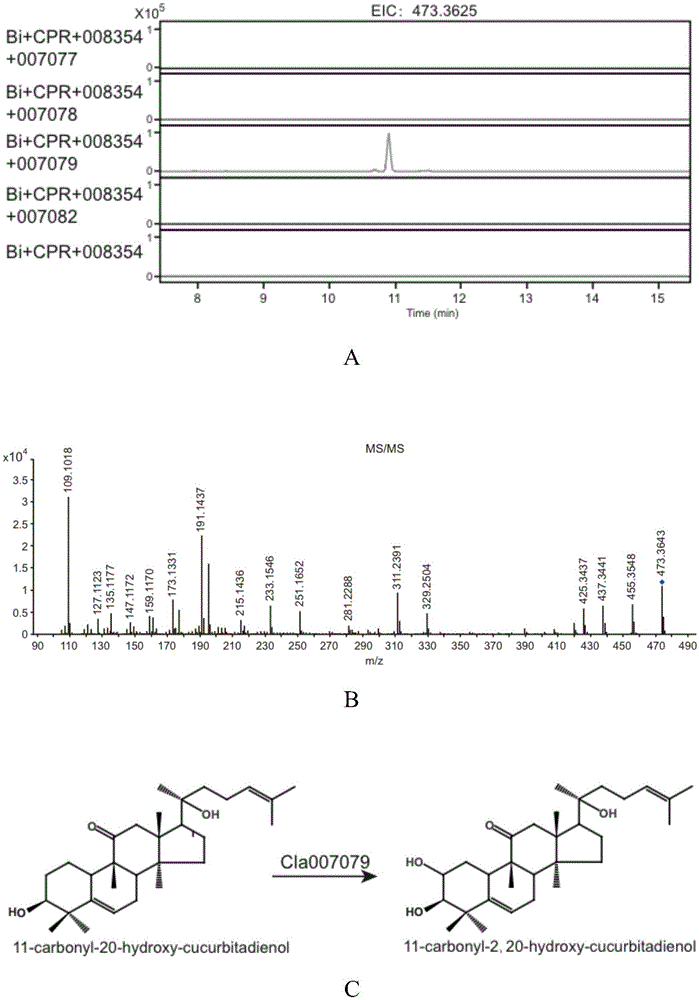
Gene cluster participating in synthesis of cucurbitacin E of watermelon and application of gene cluster
InactiveCN105039274ASpeed up the breeding processAchieve in vitro synthesisFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention relates to a gene cluster participating in synthesis of cucurbitacin E of watermelon and an application of the gene cluster. According to the invention, the gene cluster participating in synthesis of cucurbitacin E is found in the watermelon genome for the first time, the gene cluster comprises eight genes, wherein six of the eight genes are positioned within the range of the No.6 chromosome 57kb. A yeast system is adopted for analyzing the reaction from the step 1 to the step 4 of the synthesis of cucurbitacin E. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism for forming the bitter taste of the watermelon, so that a theoretical basis and a molecule assistant breeding objective are provided for the breeding of the watermelon without the bitter taste, and valuable experiences are provided for heterologous biosynthesis and development and utilization of cucurbitacine. The technology provided by the invention can replace the traditional method for extracting bitter principle from a plant material, so that synthesis of the bitter principle in vitro is realized by utilizing synthetic biology.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
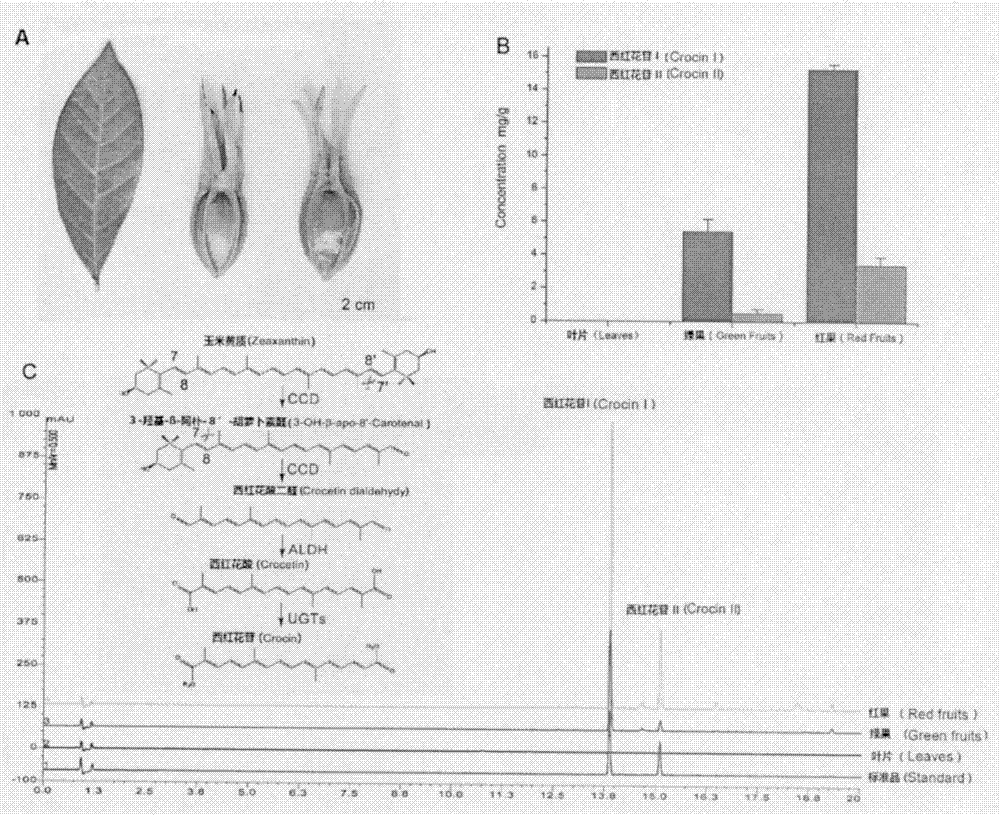
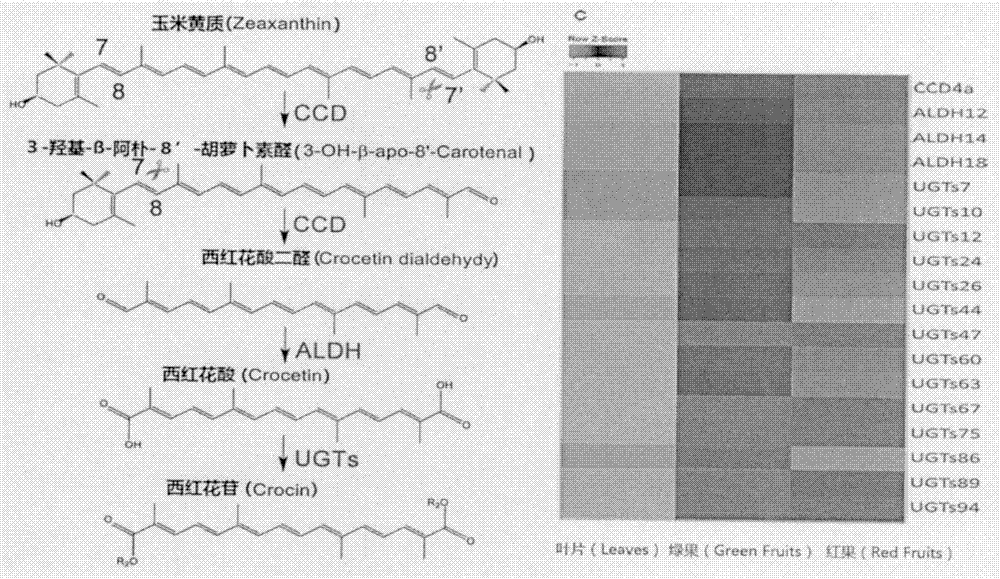
Screening and function verification of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase encoding gene participating in synthesis of gardenia jasminoides ellis crocin
InactiveCN107502614ASignificant application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesOpen reading frameAmino acid
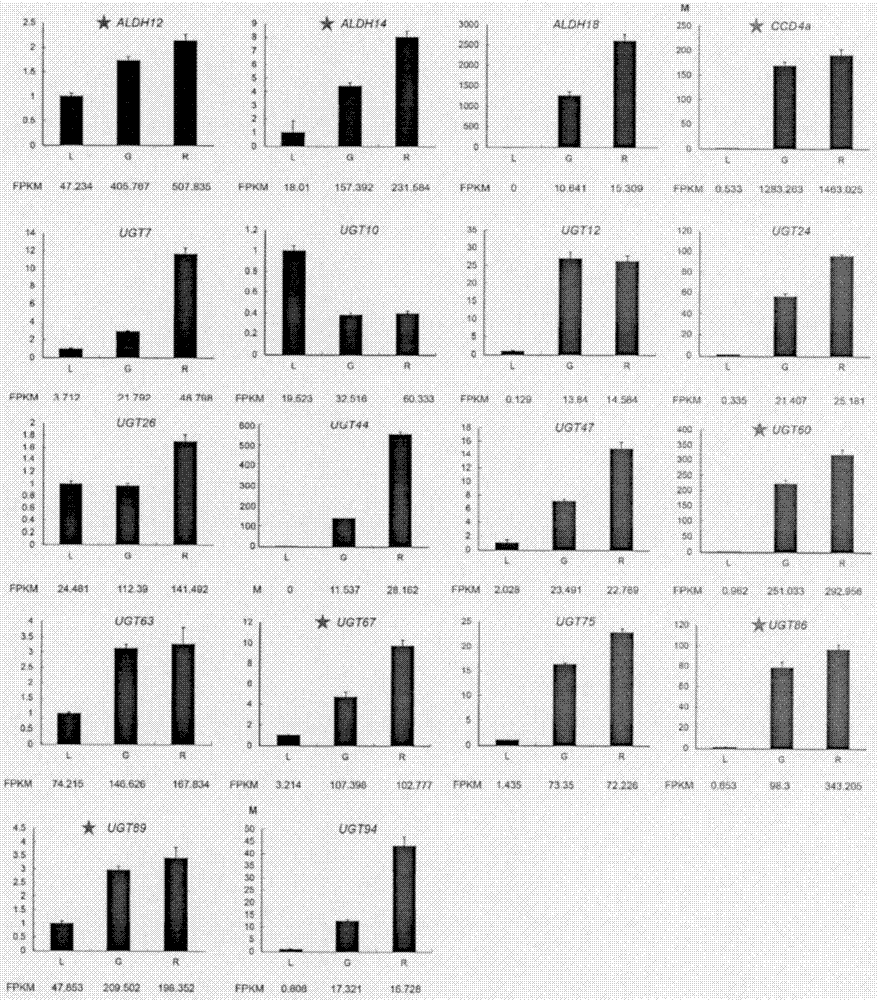
The present invention relates to a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD4a involved in the synthesis of gardenia jasminoides ellis crocin, an encoding gene and functions thereof, belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses the open reading frame sequence of a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD4a gene and the amino acid sequence encoded by the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD4a gene. According to the present invention, the CCD4a gene is screened based on transcriptomics, the functions of CCD4a are verified in vitro by using zeaxanthin as the substrate and constructing the pET28a-CCD4a prokaryotic expression vector, and the results prove that CCD4a has the functions of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase so as to establish the foundation for the analysis and biosynthetic research of the crocin source pathway.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Pseudomonas putida gene knockout and genome simplification system
ActiveCN106086056AAvoid reorganizationIncreased probability of correct mutationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSynthetic biology
The invention discloses a pseudomonas putida gene knockout and genome simplification system, and belongs to the field of microbial gene engineering. According to the pseudomonas putida gene knockout and genome simplification system disclosed by the invention, a suicide plasmid knockout system and a site specific recombination system are skillfully combined, so that the correction rate of two turns of screening is greatly improved to be higher than 90%, and the correction rate is still higher than 90% when a gene cluster, which is 69 genes long, is knocked out. The system disclosed by the invention achieves the continuous knockout of the gene cluster, simple and convenient to operate, efficient, high in correction rate and low in cost. The system disclosed by the invention lays a molecular basis for the simplification and the optimization of a pseudomonas putida genome; therefore, the system is conducive to the implementation of efficient construction of chassis cells of synthetic biology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
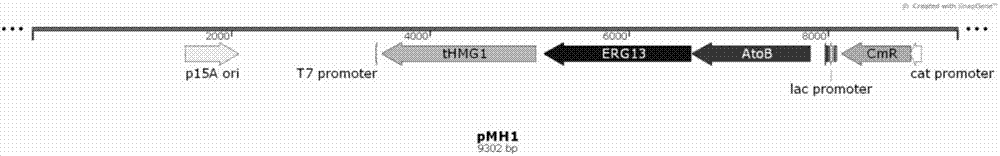
Construction method for high-yield sclareol strain
InactiveCN103387944AEfficient productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for constructing a high-yield sclareol engineering strain by a synthetic biology methdo, and an application thereof. The construction method for the strain relates to express plant sourced key enzymes for synthesizing sclareol, wherein the key enzymes comprise a pyrophosphoric acid ladanum enediol ester synthase and a sclareol synthase; and overexpress a combination of one or more yeast endogenous enzyme-based genes, wherein the enzyme-based genes comprise a key enzyme of a mevalonic acid approach-(hydroxymethyl) coenzyme A reductase, and two enzymes of an isopentenylpyrophosphate approach-a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase and a geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. The method can efficiently produce sclareol, with a shake flask fermentation level reaches 9 mg / l, and has industrial application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
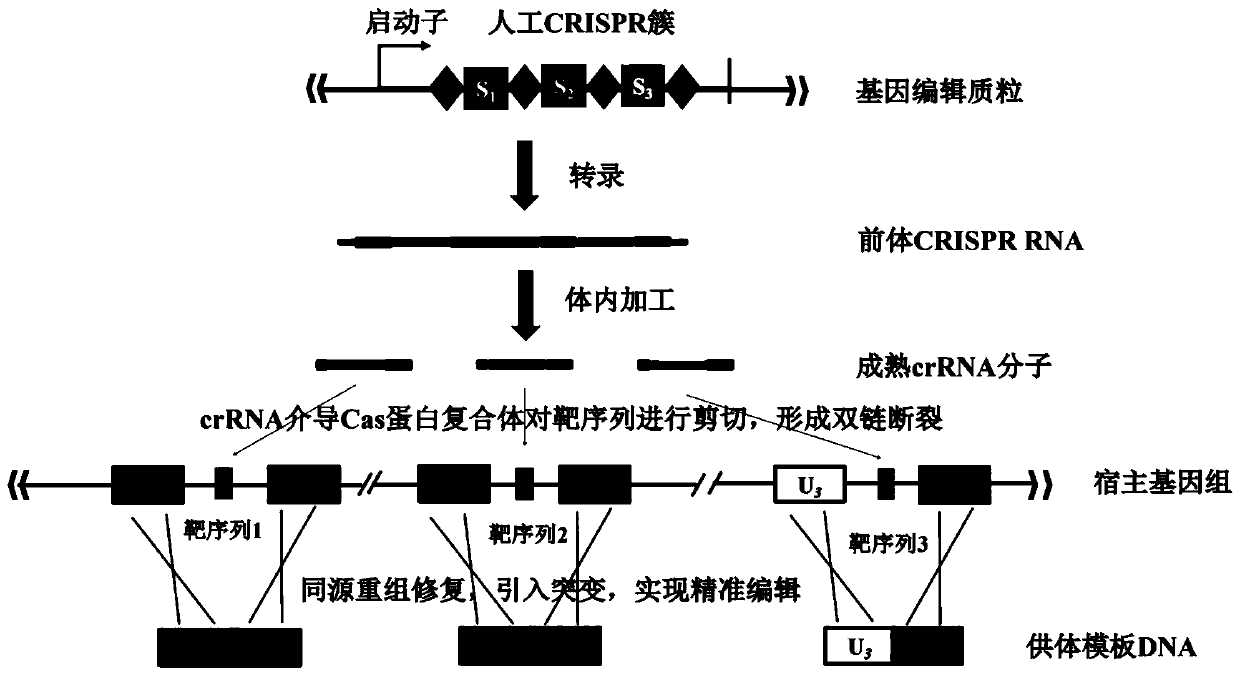
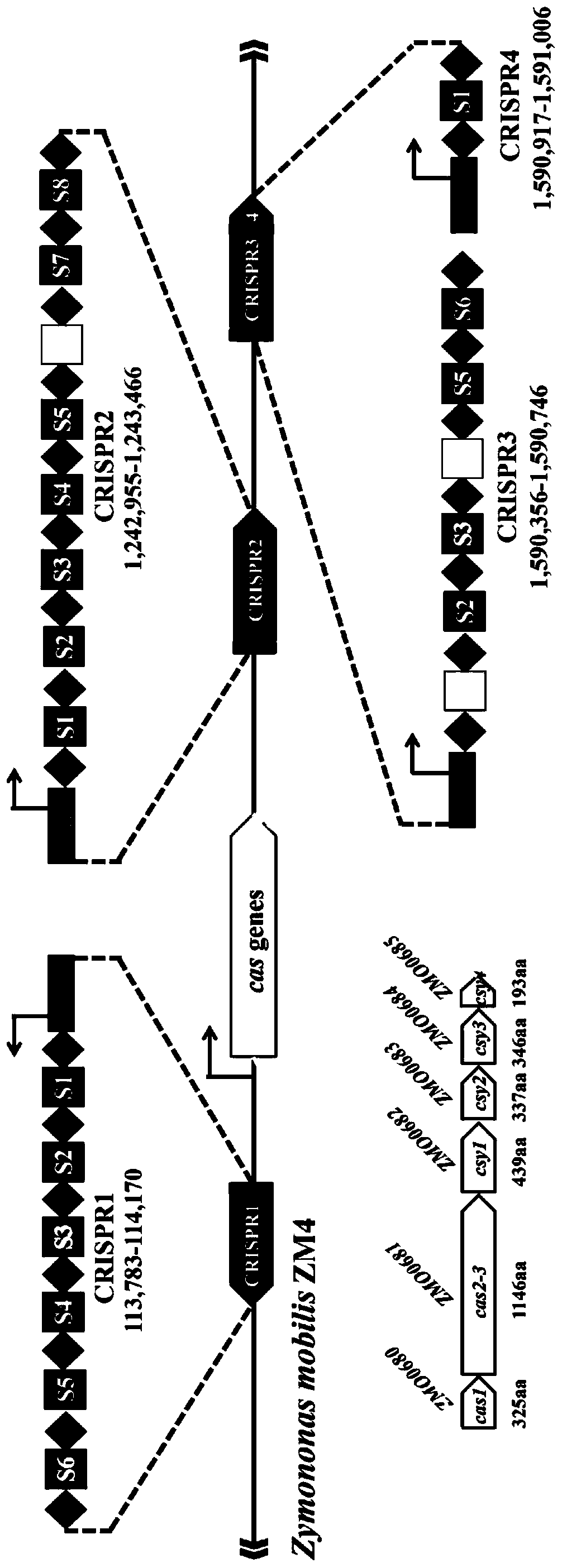
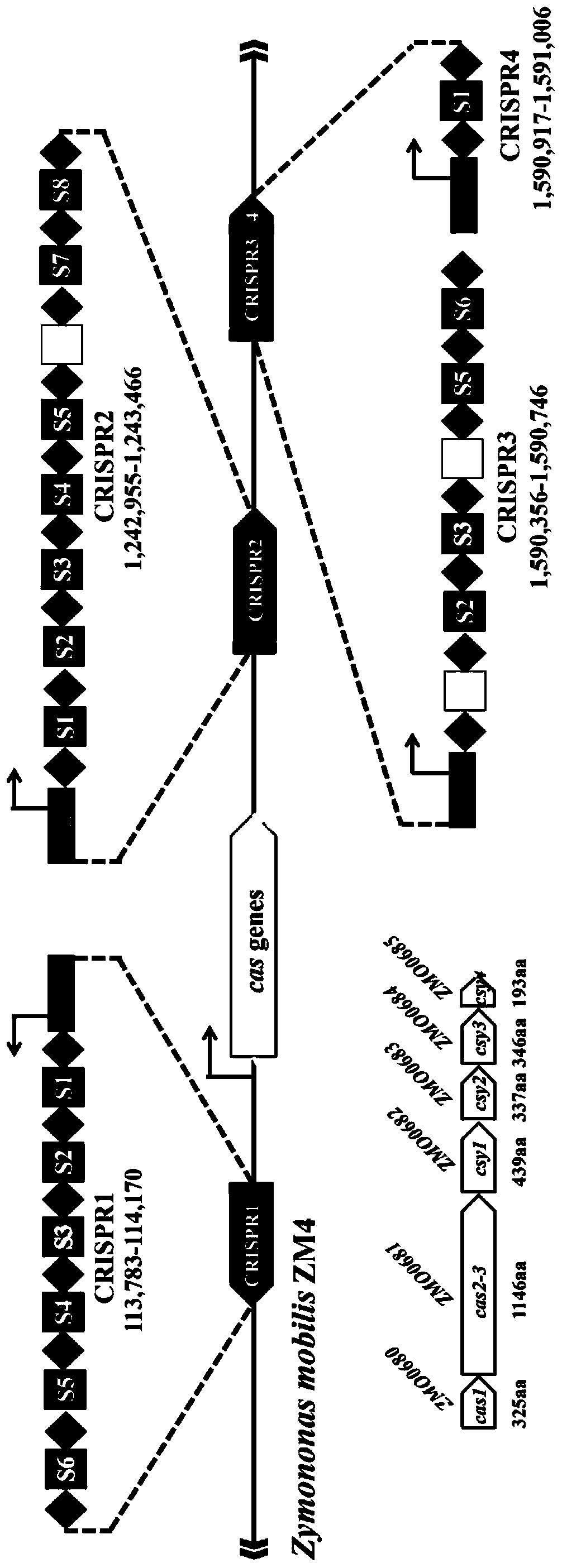
Multi-gene locus simultaneous editing method based on endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a multi-gene locus simultaneous editing method based on an endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis and application thereof. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: constructing a plasmid containing an artificial CRISPR expression unit; selecting a plurality of target editing target loci, and designing a gRNA sequence; connecting a plurality of gRNA sequences in series, and constructing the gRNA sequences on the plasmid containing the artificial CRISPR expression unit; constructing a donor DNA sequence on a vector to obtain an edited plasmid; and transforming the edited plasmid into competent cells for editing. The method constructs a gene editing platform by utilizing theendogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis, breaks the limitation of low efficiency of exogenous CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in the strain, realizes rapid and efficient knockout of multiple genes in the strain, and promotes the development of metabolic engineering, systemic biology and synthetic biology.
Owner:武汉睿嘉康生物科技有限公司
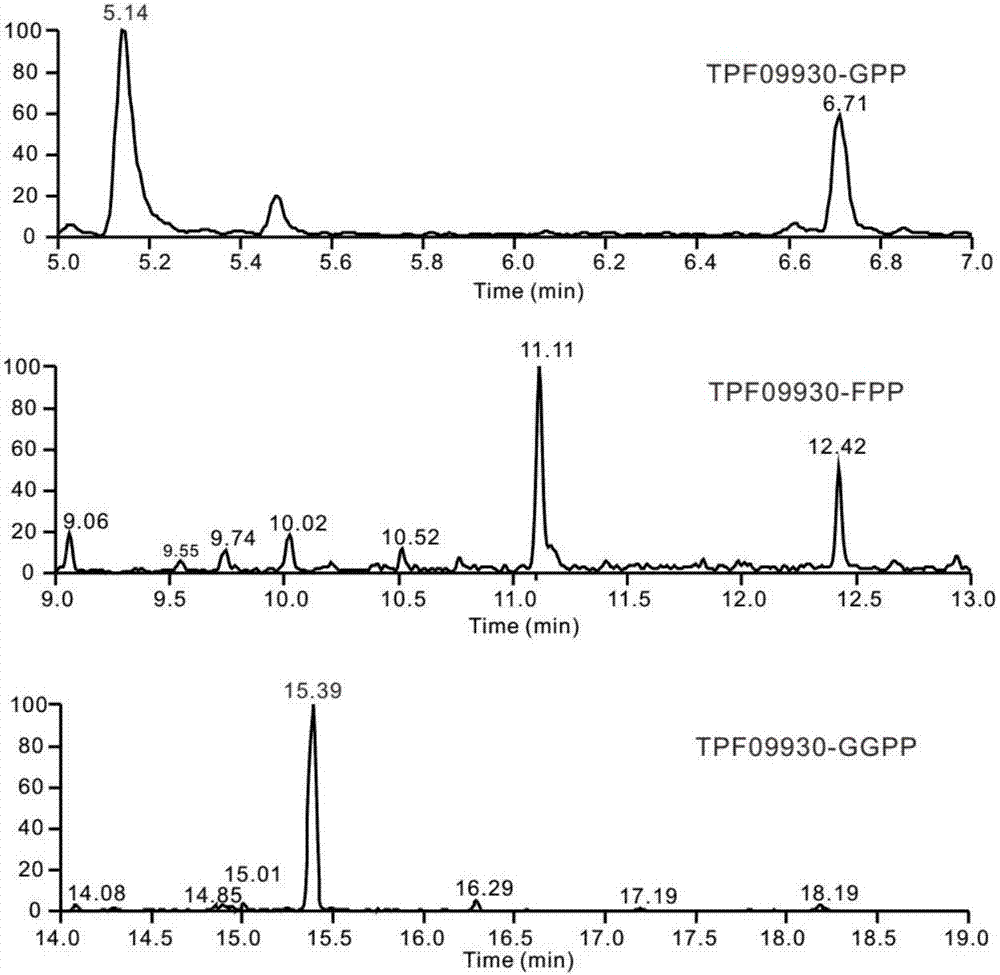
Terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof
ActiveCN106906201ASpecificEfficientBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSynthetic biology
The invention discloses a terpenoid synthase for producing nerolidol and application thereof, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. Terpene synthase TPF09930 for producing the nerolidol is provided, a nucleotide sequence of the terpene synthase TPF09930 is as shown in SEQIDNO:2, the terpene synthase TPF09930 is combined with mevalonic acid pathway related genes to construct a strain for producing the nerolidol. By overexpression of Escherichia coli XL1 blue-derived atoB gene or idi gene of mevalonic acid pathway, catalytic substrate Farnesyl pyrophosphate can be synthesized in large scale, and producing of the nerolidol can be further promoted. The terpene synthase has specificity and high efficiency, can improve the nerolidol yield, greatly overcomes the defects of a large amount of raw materials and a low nerolidol yield, reduces study cost, and ensures greenness and environmental friendliness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Recombinant bacillus subtilis of high-yield pullulanase and construction method thereof
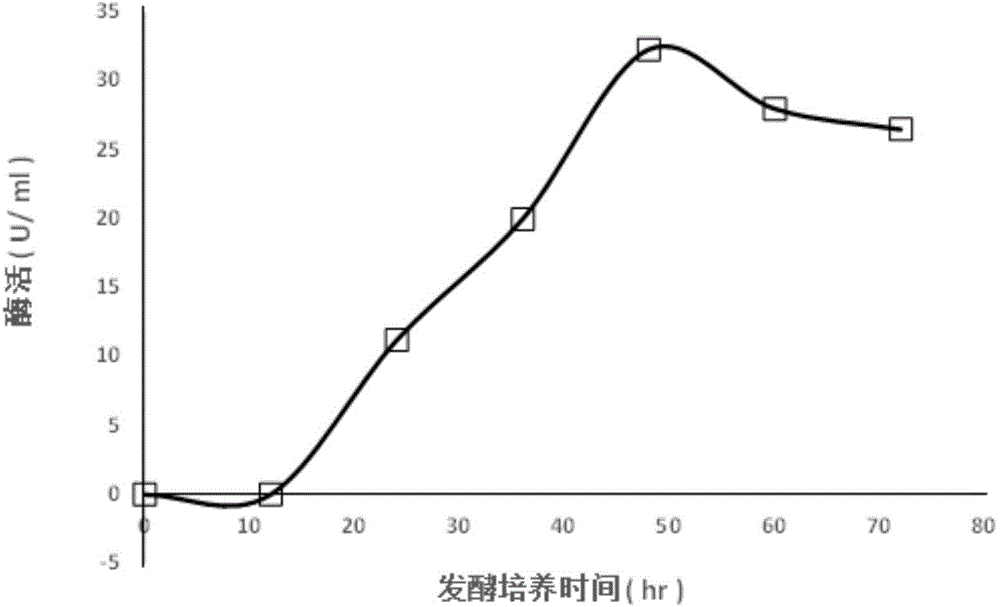
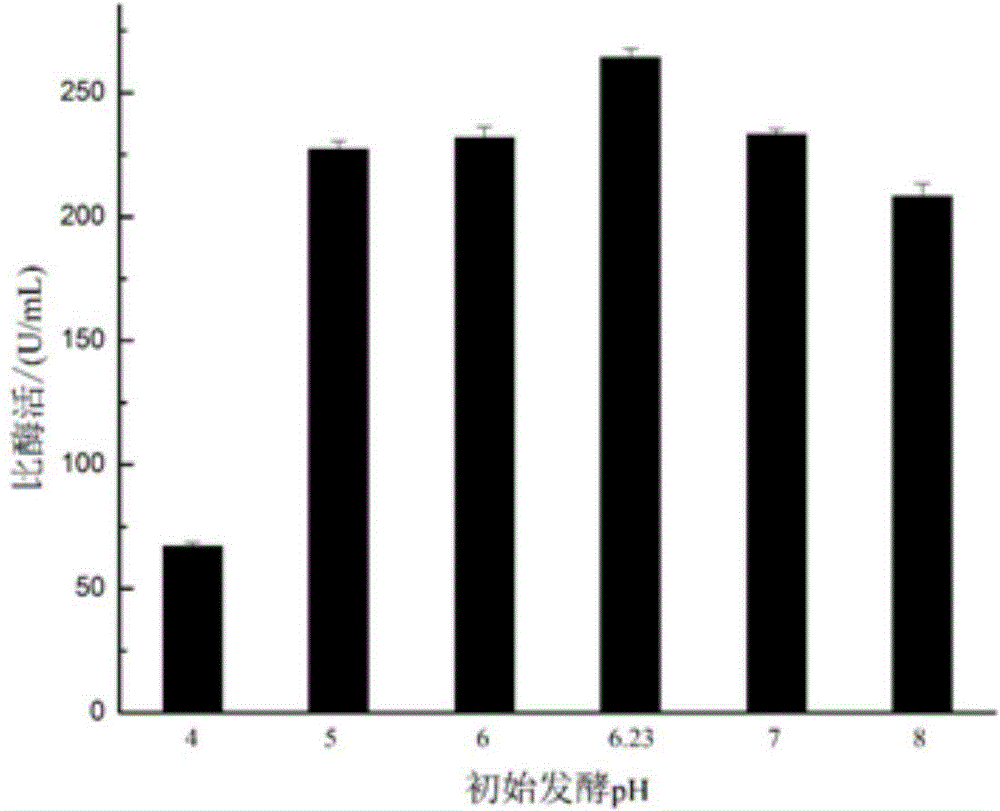
ActiveCN104694452AIncreased gene transcription levelsImprove translation efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynthetic biologyCompetent cell
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus subtilis of high-yield pullulanase and a construction method thereof. The construction method of the recombinant bacillus subtilis of the high-yield comprises the following steps that an artificial operon BPB used for expressing the pullulanase is used for constructing a recombinant plasmid pGE-BPB; the nucleotide sequence of the artificial operon BPB is shown in the graph SEQ ID NO.4; the constructed recombinant plasmid pGE-BPB is converted into a bacillus subtilis competent cell, and through secondary recombination, a neutral protease gene nprE in the bacillus subtilis competent cell is replaced by the artificial operon BPB in situ. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis of the high-yield pullulanase and the construction method thereof, firstly, the acidproof and heatproof pullulanase gene of an original bacterial strain is optimized, based on the synthetic biology method, a plurality of molecular elements capable of improving the gene transcriptional level are assembled into the artificial operon, and the recombinant bacillus subtilis can be obtained through construction. The recombinant bacterial strain can ferment to generate the high-yield pullulanase, and the enzyme activity each unit can reach or exceed 300 U / ml.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genome editing method based on zymomonas mobilis endogenous CRISPR-Cas system and application thereof
ActiveCN110358768AAvoid cytotoxicityRealize simultaneous editingBacteriaStable introduction of DNABasic researchZymomonas mobilis
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, particularly relates to a genome editing method based on a zymomonas mobilis endogenous CRISPR-Cas system and application thereof and aims at taking Z.mobilis 4 as a type strain and utilizing the I-F type CRISPR-Cas system coded by its genome to establish a genome editing platform. A powerful tool is provided for basic research and application research in the strain and similar cells, and the development of metabolic engineering, system biology and synthetic biology is promoted. According to the technical scheme, the genome editing method is characterized by comprising the steps of constructing a plasmid containing an artificial CRISPR expression unit; selecting a guide RNA sequence aiming at a target site; constructing aguide RNA primer sequence on the plasmid containing the artificial CRISPR expression unit; constructing a donor DNA sequence on a vector to obtain an editing plasmid; transforming the editing plasmidinto competent cells for editing.
Owner:武汉睿嘉康生物科技有限公司
Multiscale platform for coordinating cellular activity using synthetic biology
ActiveUS20150133339A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSynthetic biologyMacro level
This invention provides a multiscale platform for coordinating behavior using synthetic biology. The platform reduces the impact of underlying noise, making outputs more coherent and reliable at the macroscopic level.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Making nucleic acid sequences in parallel and use
ActiveUS7544793B2Strong specificityImprove fidelitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsSynthetic biology
The present invention relates generally to the fields of genomics, synthetic biology and genetic engineering. More particularly, the present invention concerns the methods that enable parallel multiplex ligation and amplification on surface for making assemblies of nucleic acids of various biological applications and for analysis of biological samples such as DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Owner:LC SCI LC
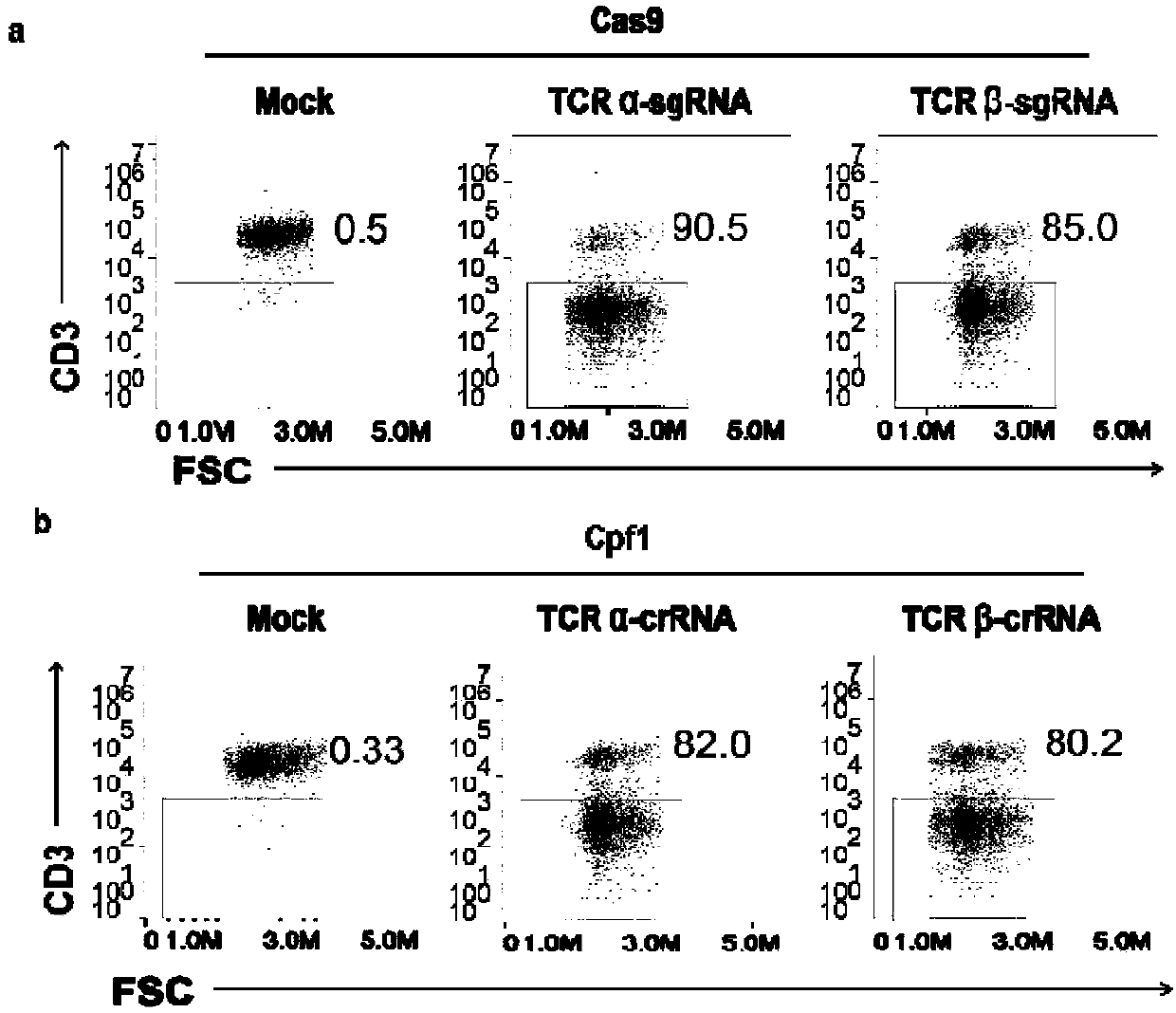
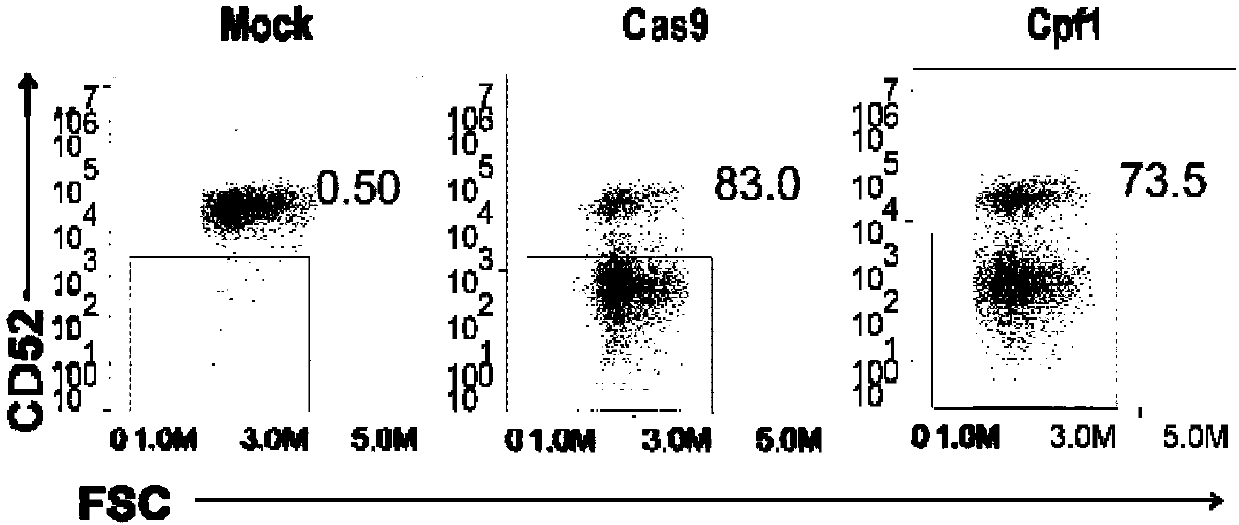
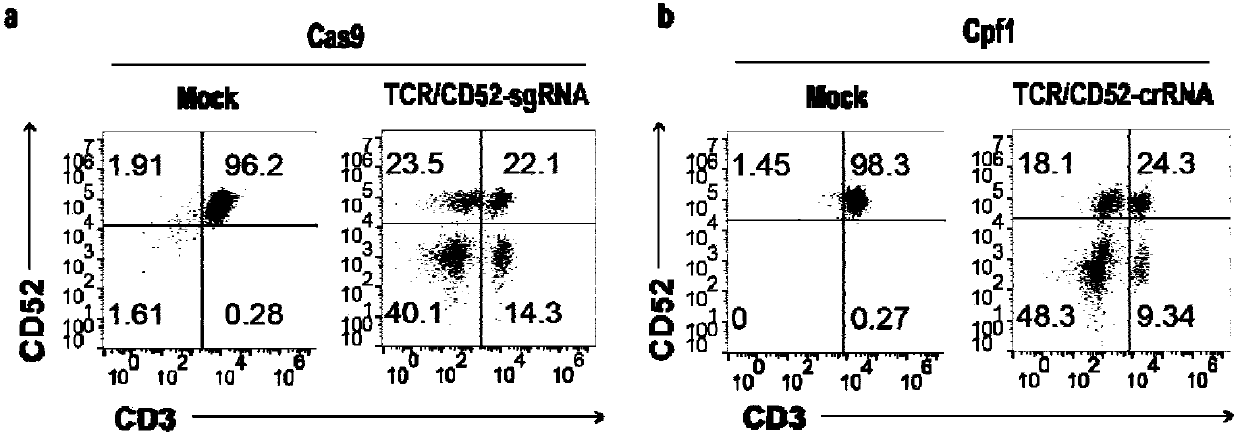
General type CART/TCRT cells with antibody drug resistance as well as construction method of general type CART/TCRT cells
ActiveCN107828730APreserve targetingAvoid exclusionImmunoglobulin superfamilyMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenAntigen receptors
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and synthetic biology, and in particular relates to general type CART / TCRT cells with antibody drug resistance as well as a construction method of the general type CART / TCRT cells. The general type CART / TCRT cells are allogeneic T cells having chimeric antigen receptors and T cell receptors, and alpha and beta chains and CD52 molecules ofthe T cell receptors are knocked out; a technology for knocking out the alpha and beta chains and the CD52 molecules of the T cell receptors is a CRISPR technology; the general type CART / TCRT cells not only retain the targeting of tumor specific antigen, but also eliminate the problems of GvHD and rejection, and weaken the sensitivity to an antibody drug Alemtuzumab; the general type CART / TCRT cells can be used as a general type simple, low-cost and high-activity CART / TCRT cell preparation.
Owner:NANJING BIOHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
System and microorganism for producing taxadiene, and application of system or microorganism
The invention discloses a system and microorganism for producing taxadiene, and application of the system or the microorganism, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology. The system for producing the taxadiene comprises mevalonate pathway related genes or functional equivalents thereof, and taxadiene synthetized related genes or functional equivalents thereof. The mevalonate pathway related genes are selected from atoB and idi of escherichia coli BL21, and erg13, thmg1, erg12, erg8, and mvd1 of brewer's yeast INVSC1; gene nucleotide sequences of the taxadiene synthetized related genes ggpps are shown by SEQID No.1 and SEQID No.2. The microorganism for producing the taxadiene is the microorganism containing the system for producing the taxadiene, by applying the system into the microorganism, the microorganism for producing the taxadiene is obtained. The microorganism produced in the invention can produce culture for the taxadiene stably, lays a foundation for further using the microorganism to produce paclitaxel, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
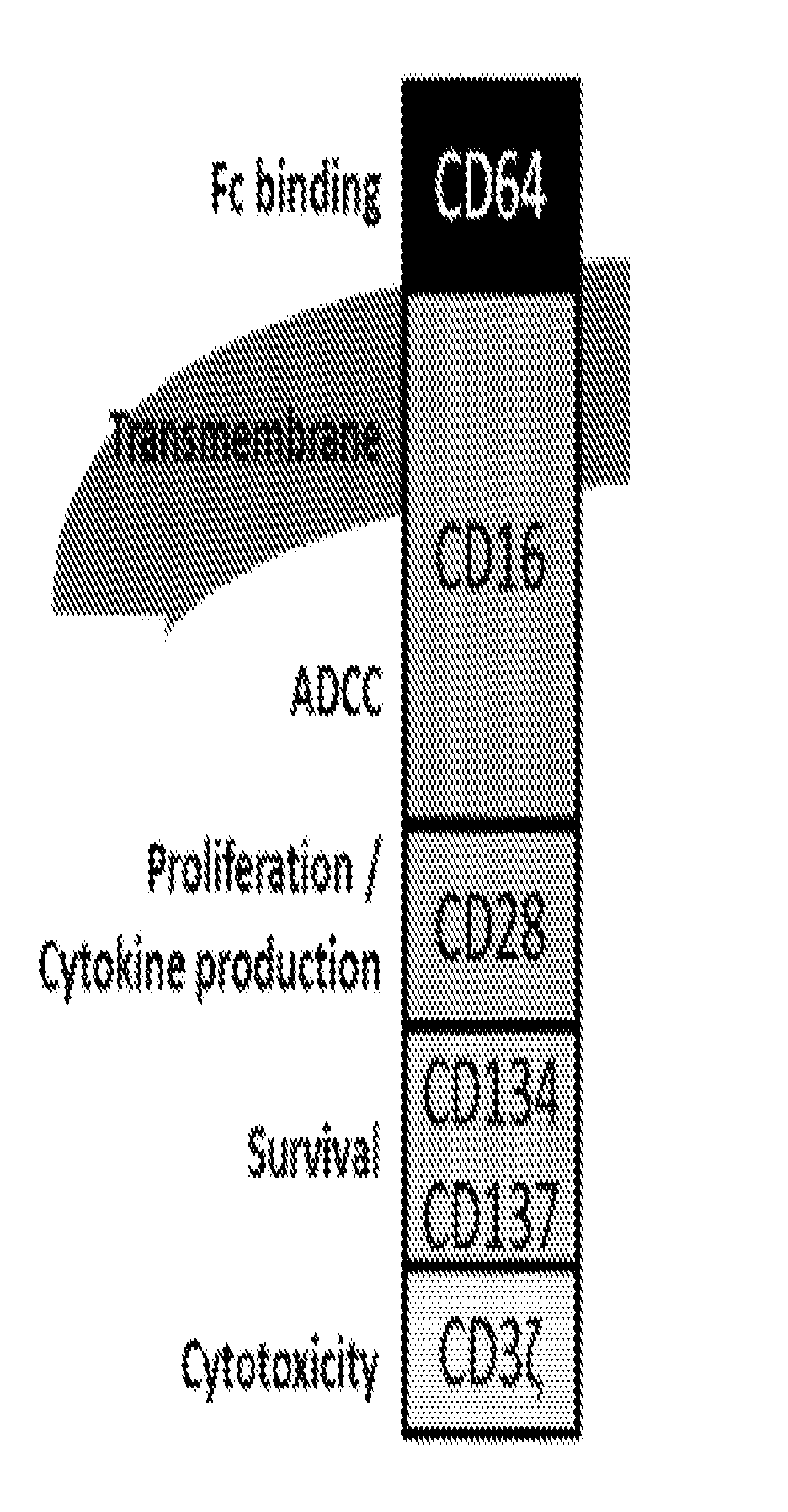
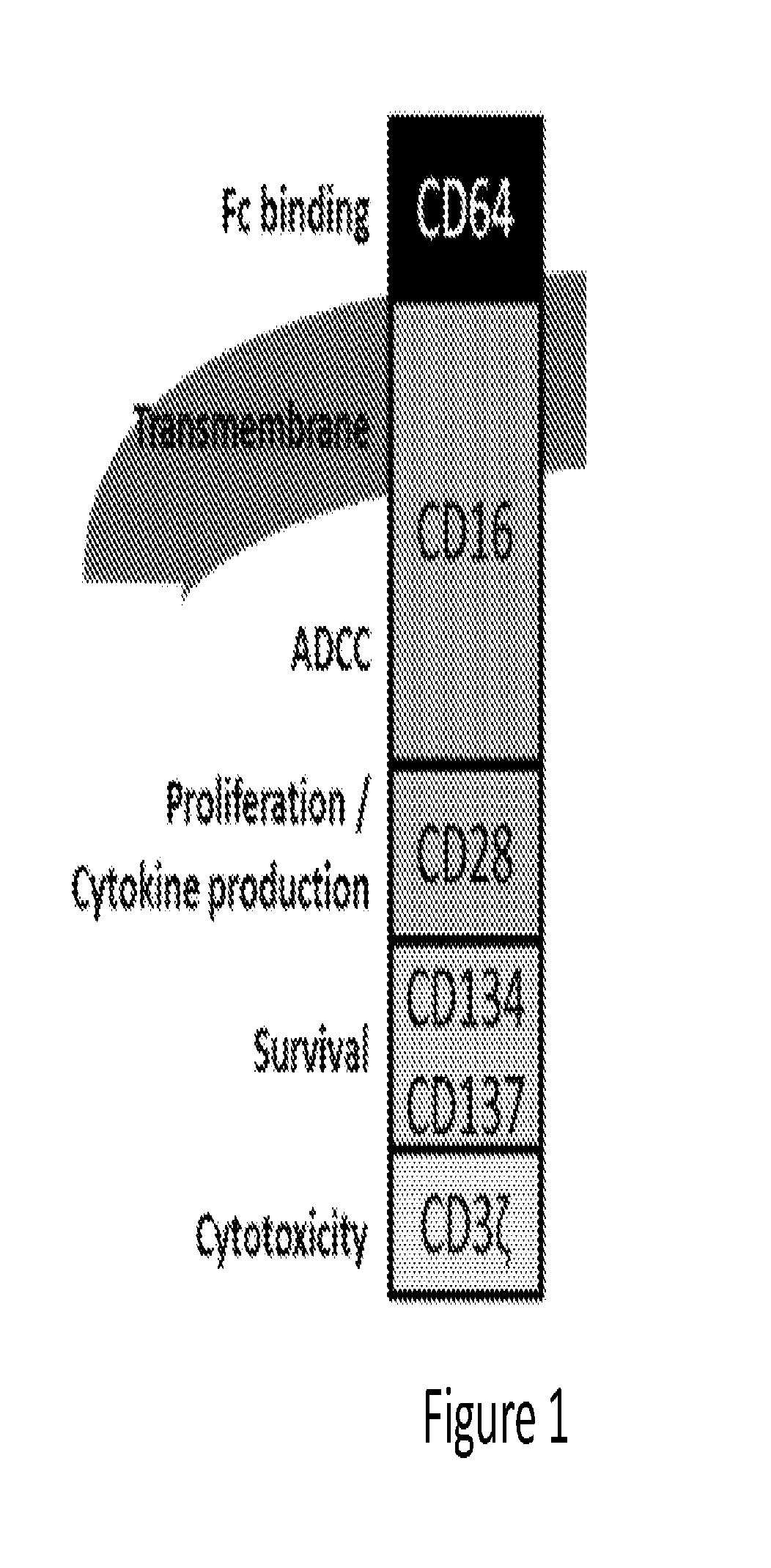
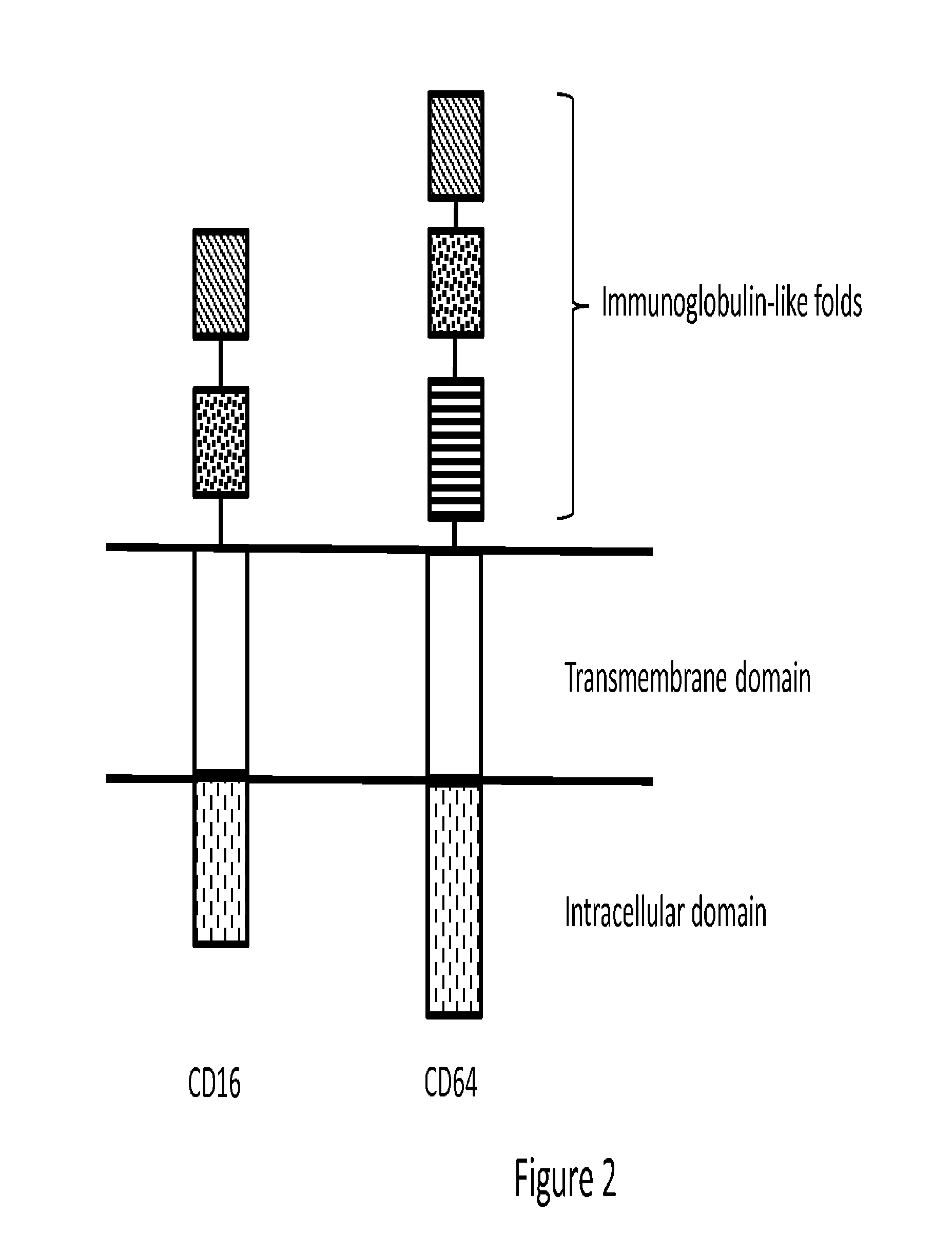
Novel Synthetic Biology-Based ADCC Technology
ActiveUS20160355566A1Improve defenseHigh detection sensitivityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSynthetic biologyAutoimmune disease
A novel synthetic biology-based ADCC technology is provided that enhances or enables ADCC response. The novel ADCC technology can be used to prevent or treat cancers, infectious, inflammatory or autoimmune diseases, and other diseases where elimination of diseased cells is desirable.
Owner:1GLOBE BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com