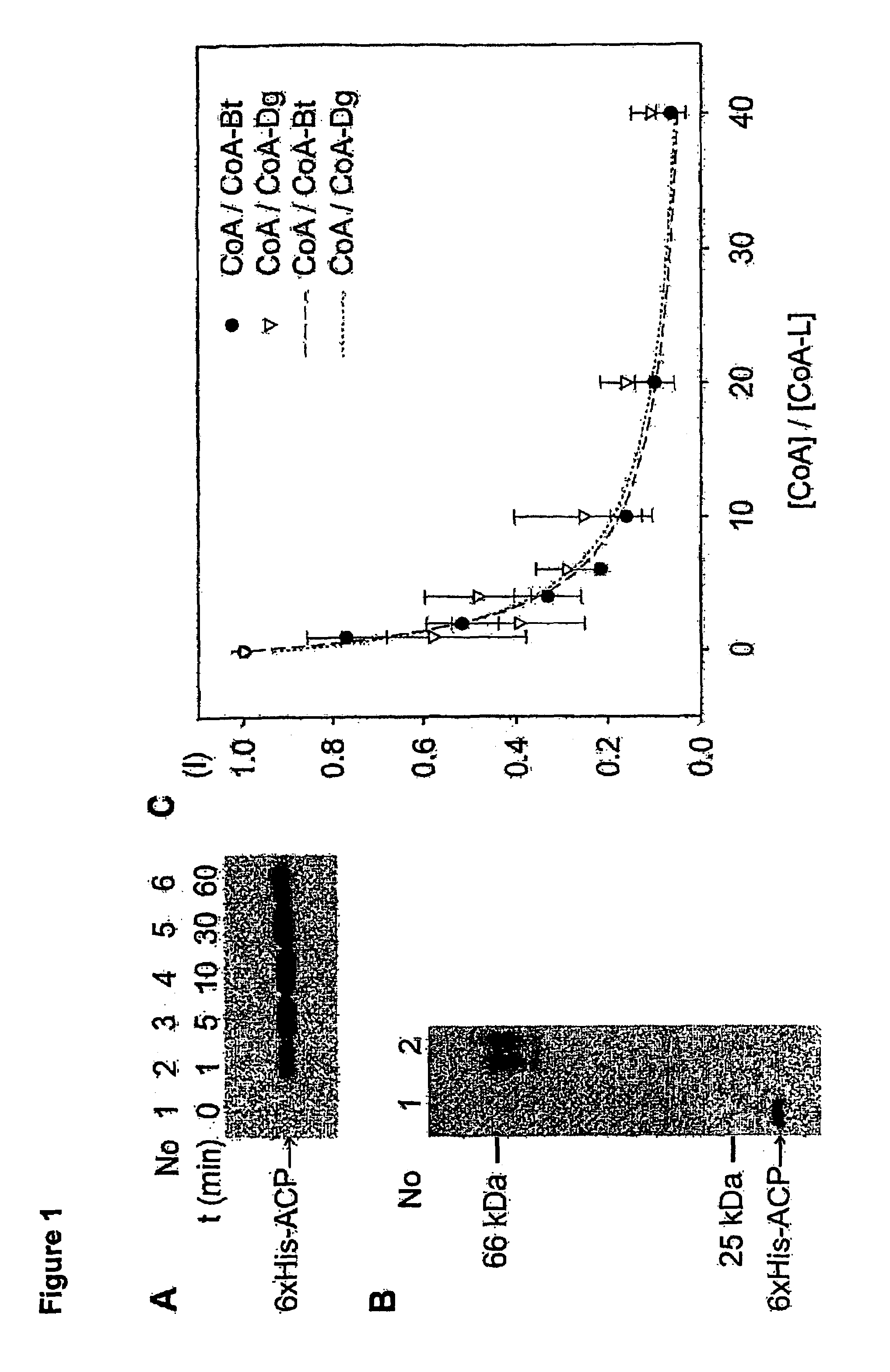
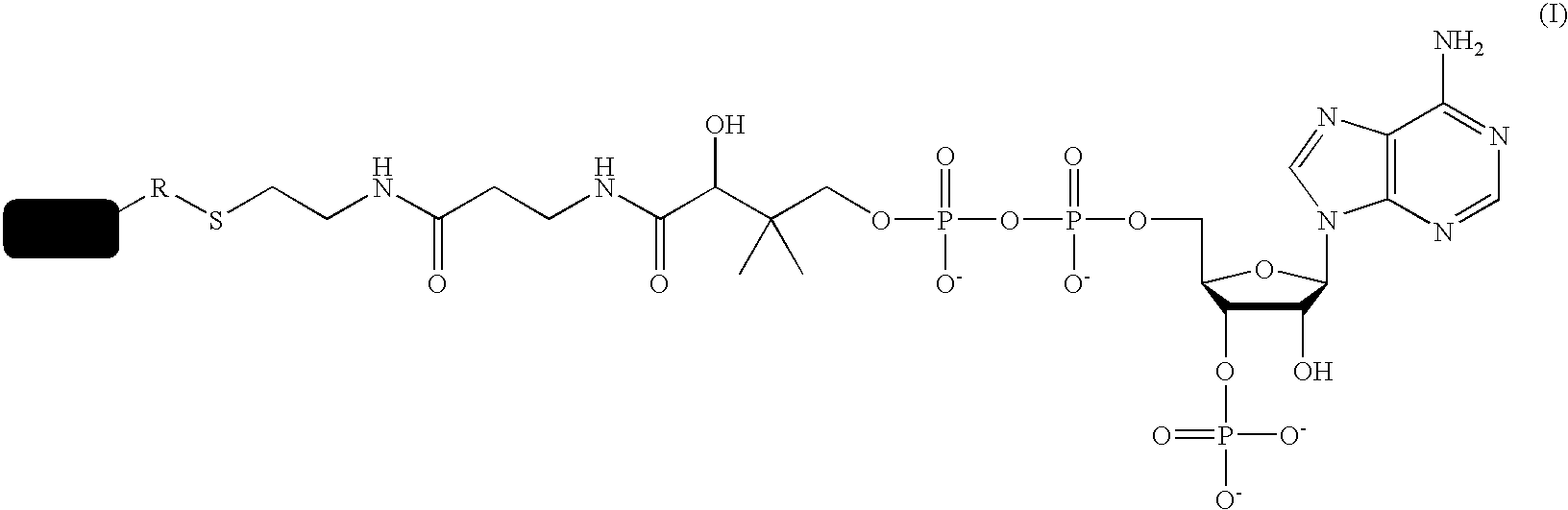
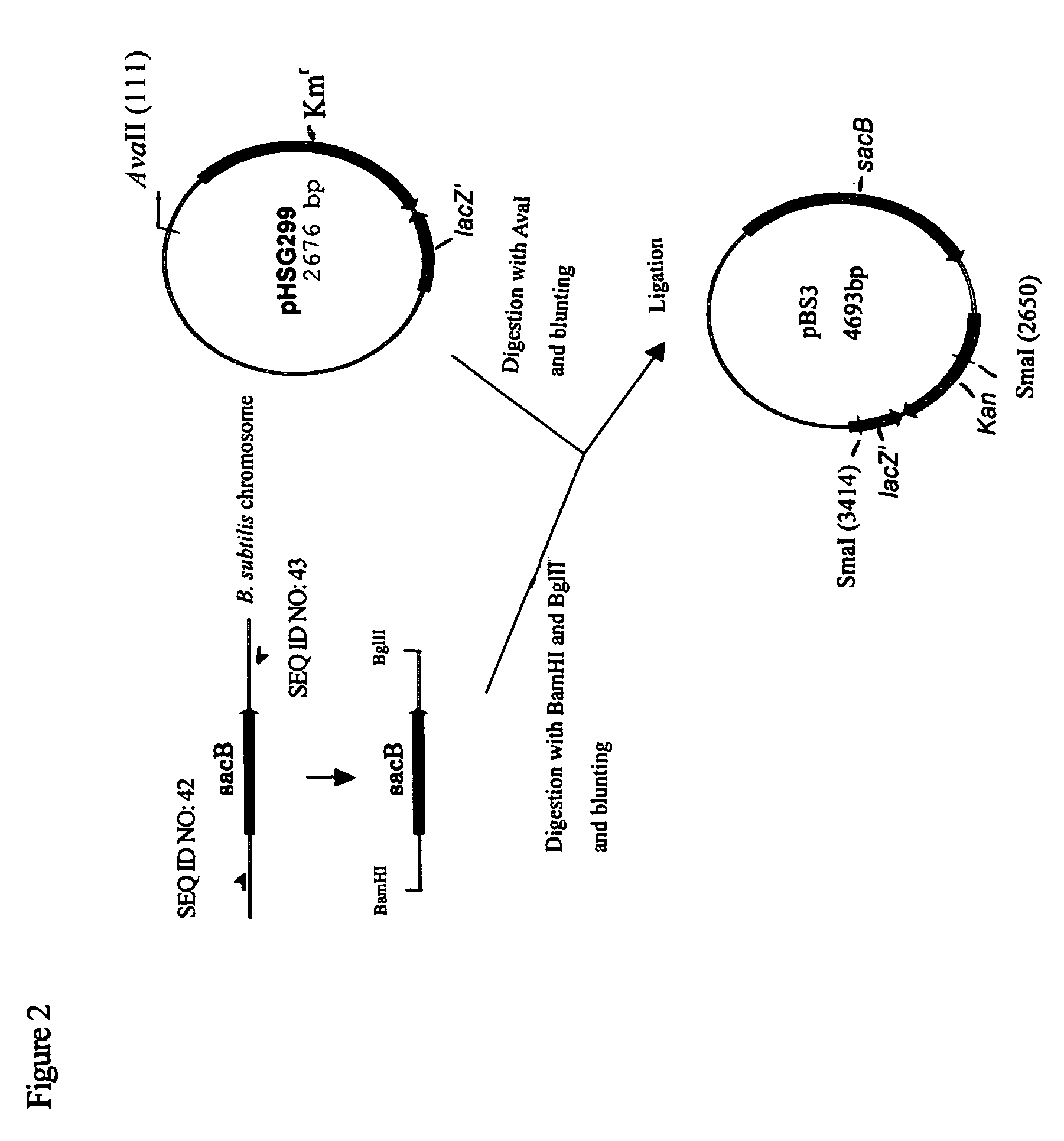
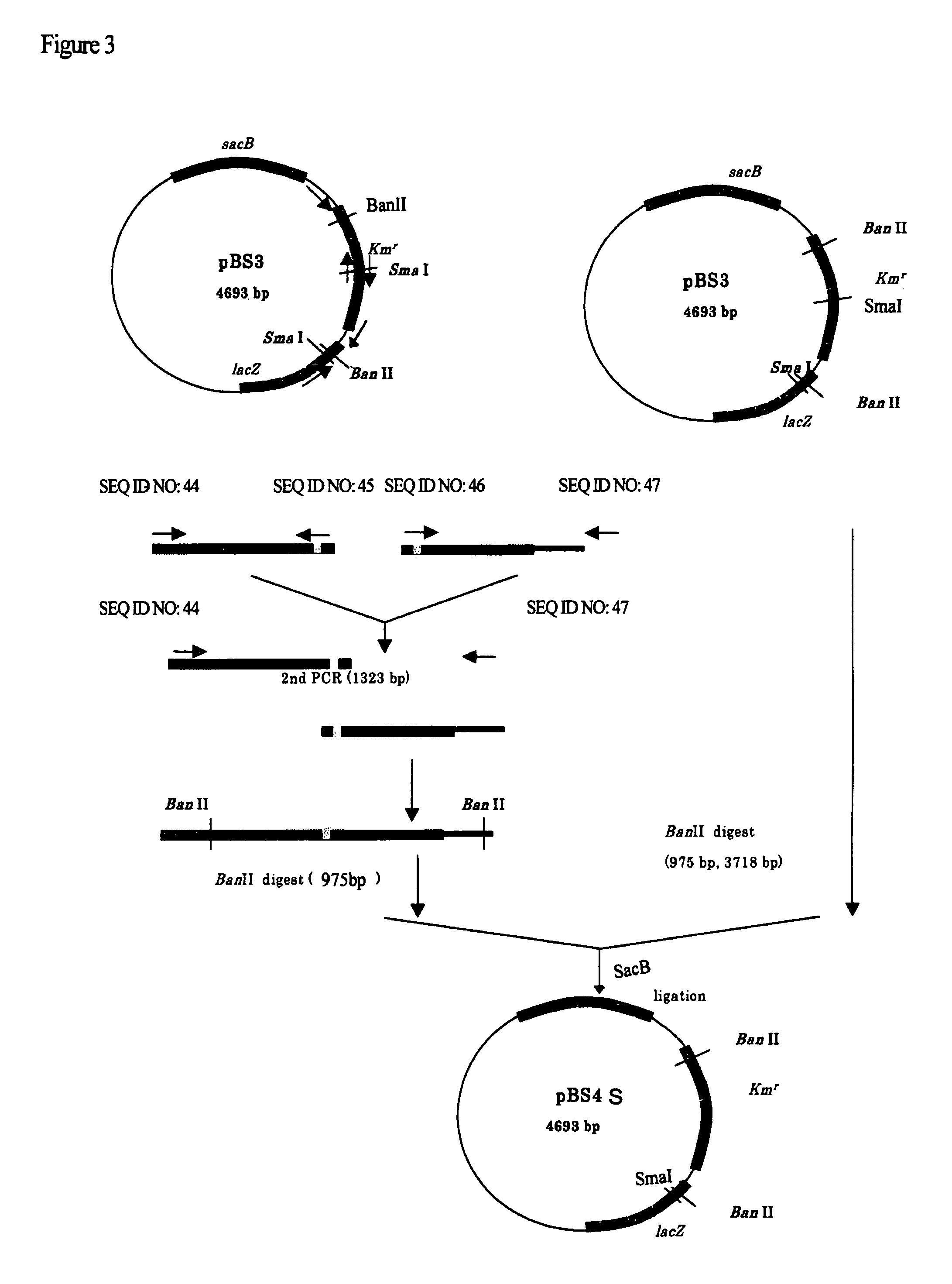
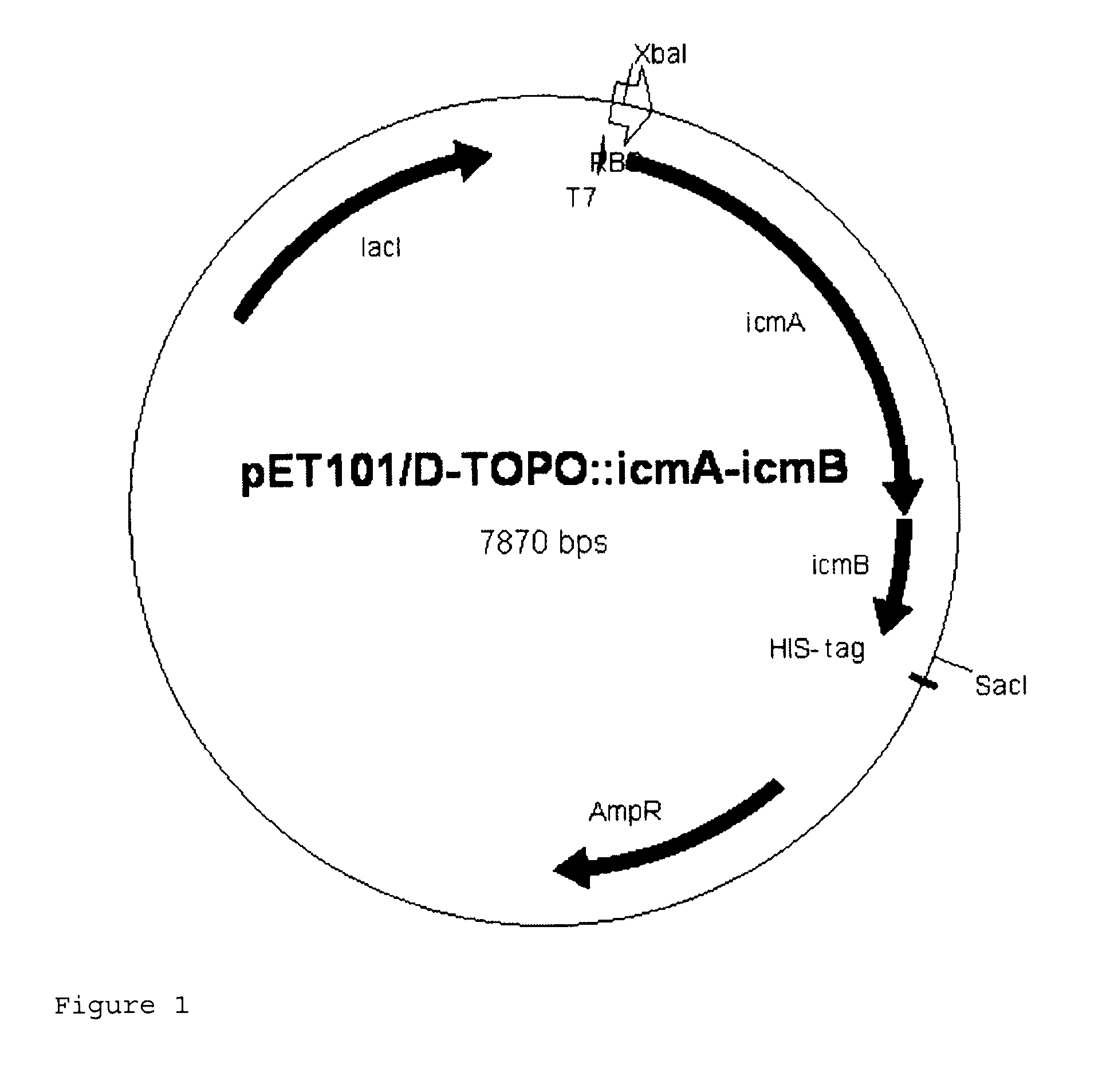
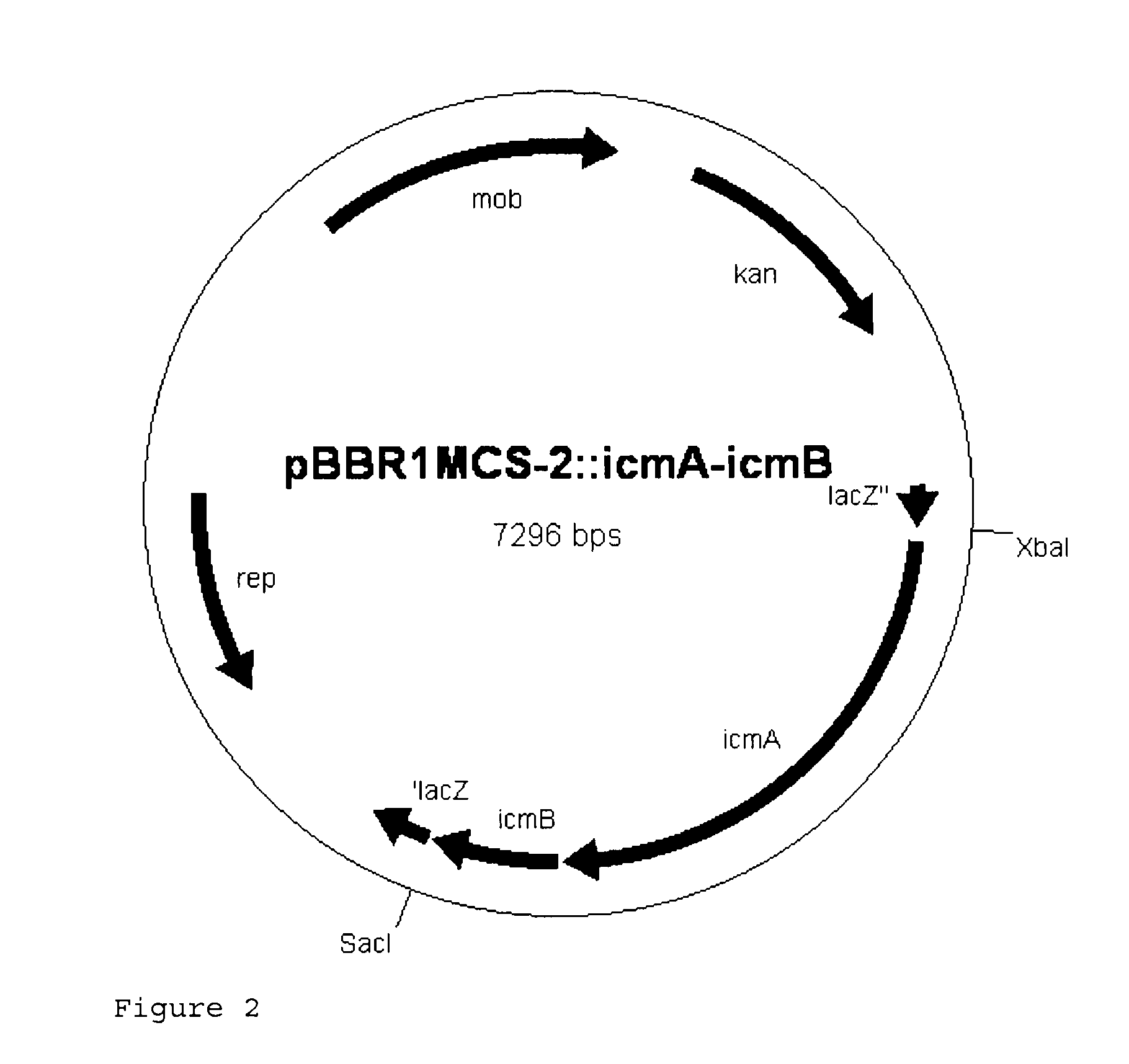
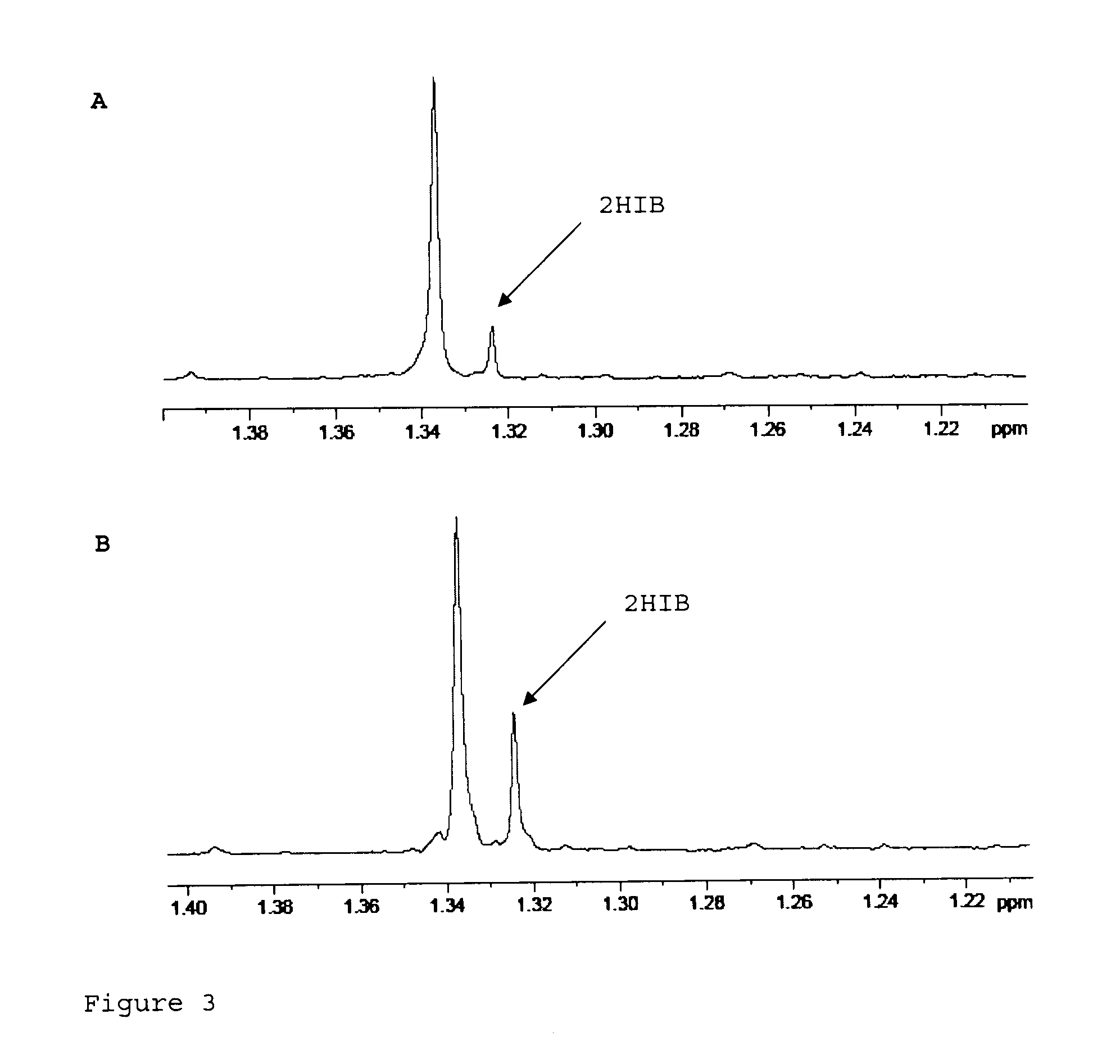
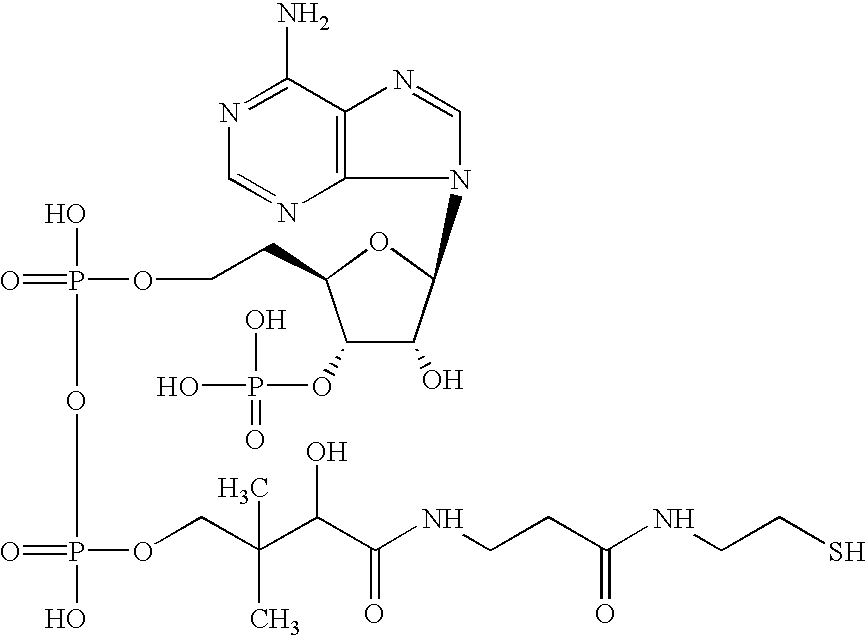
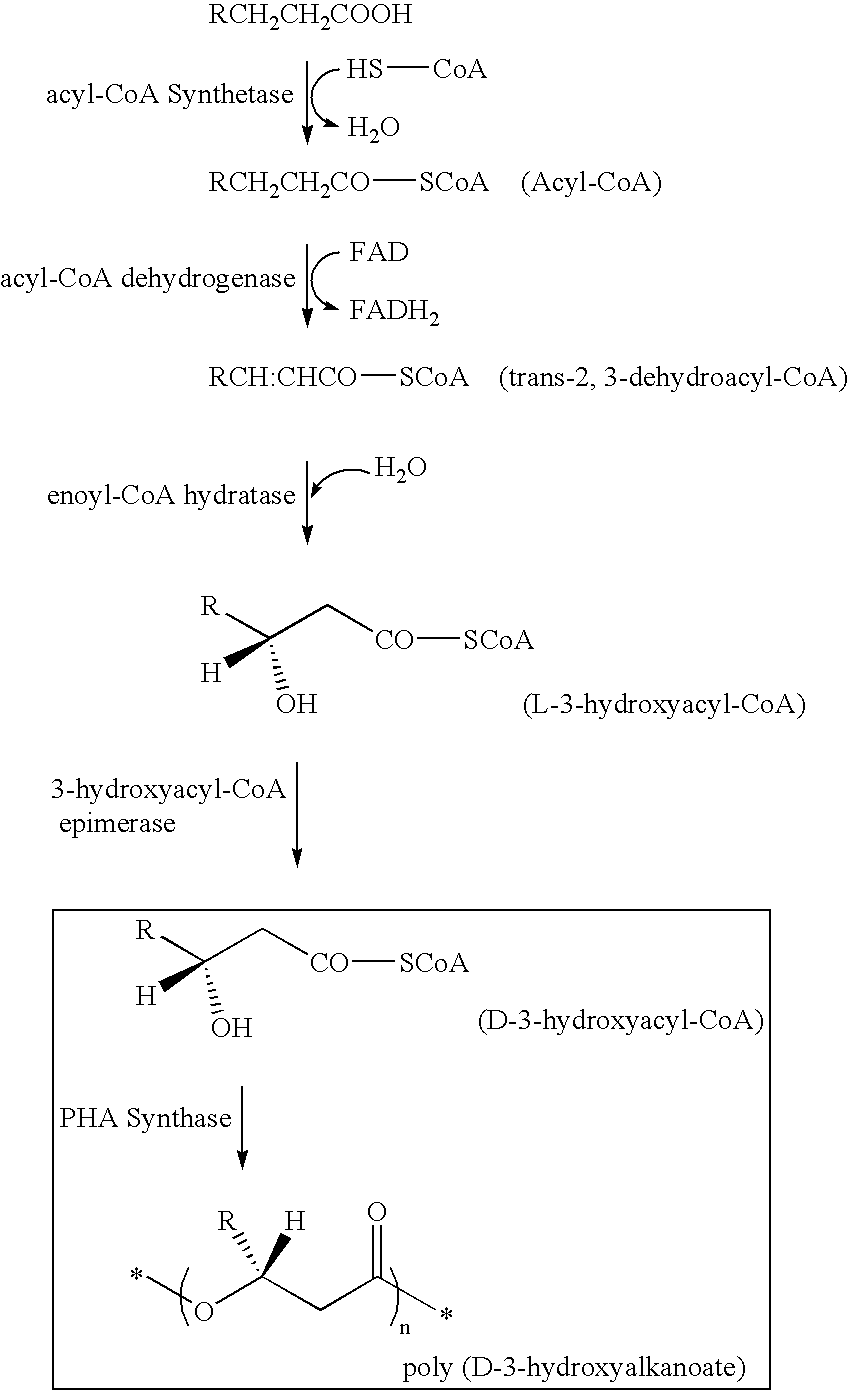
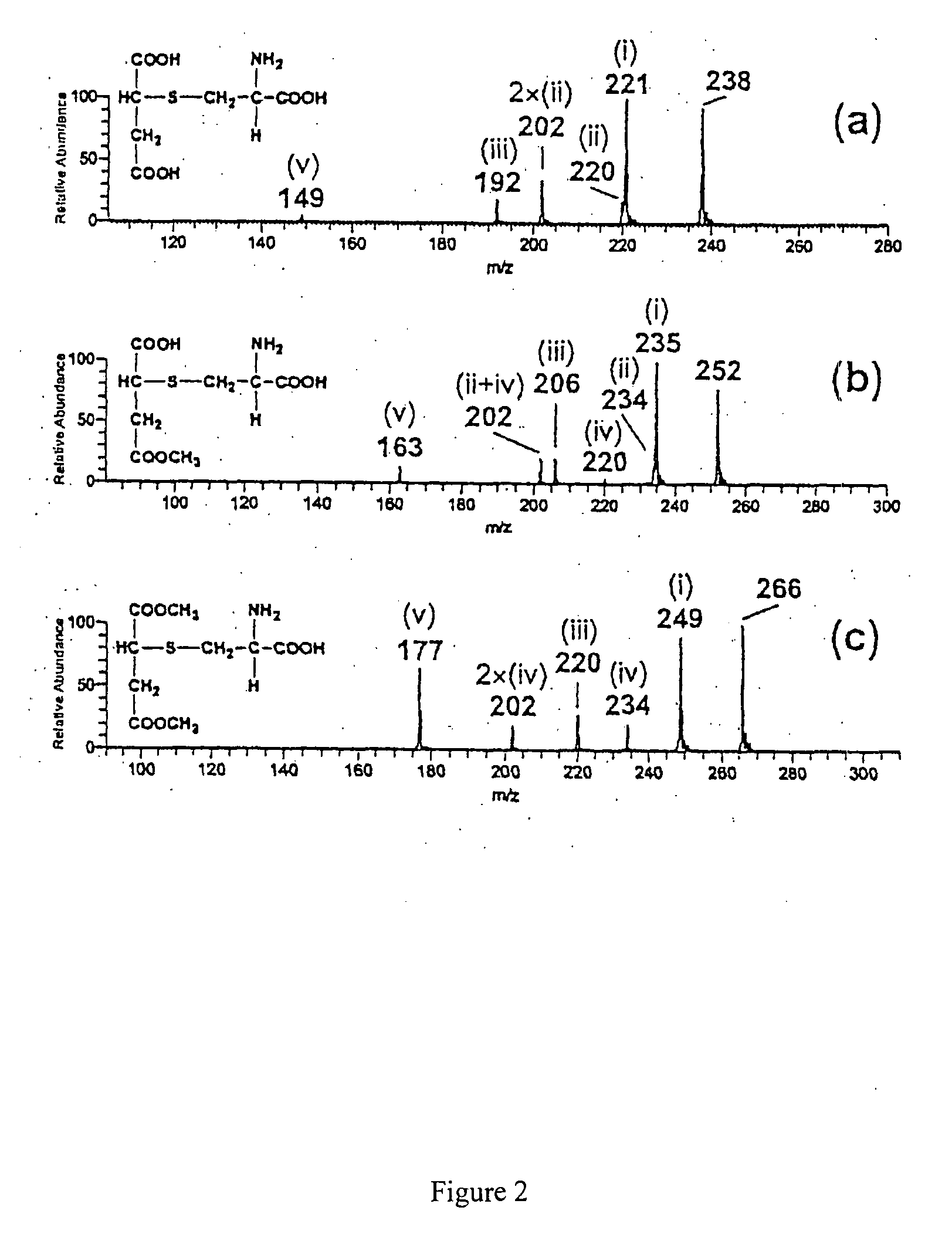
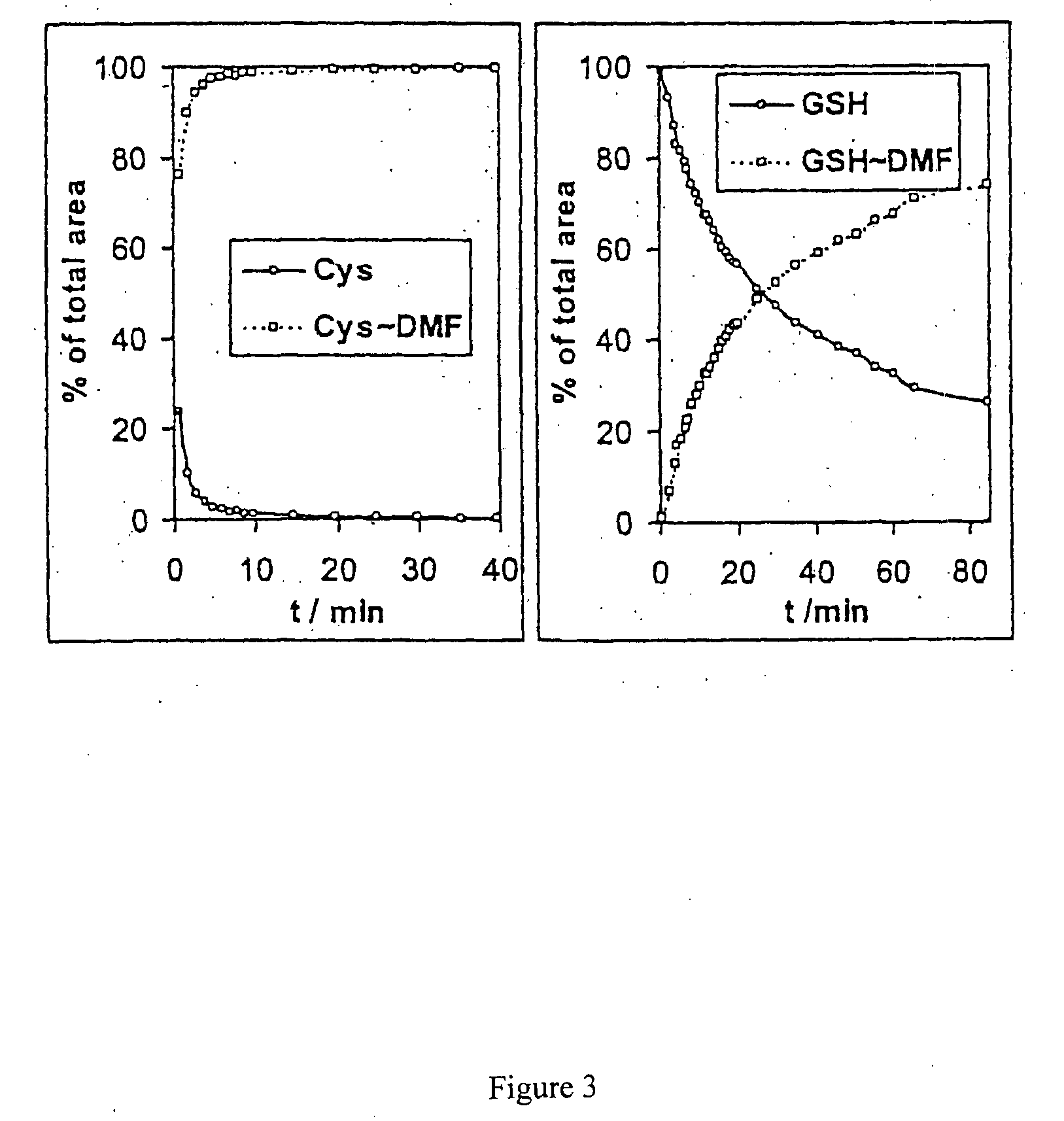
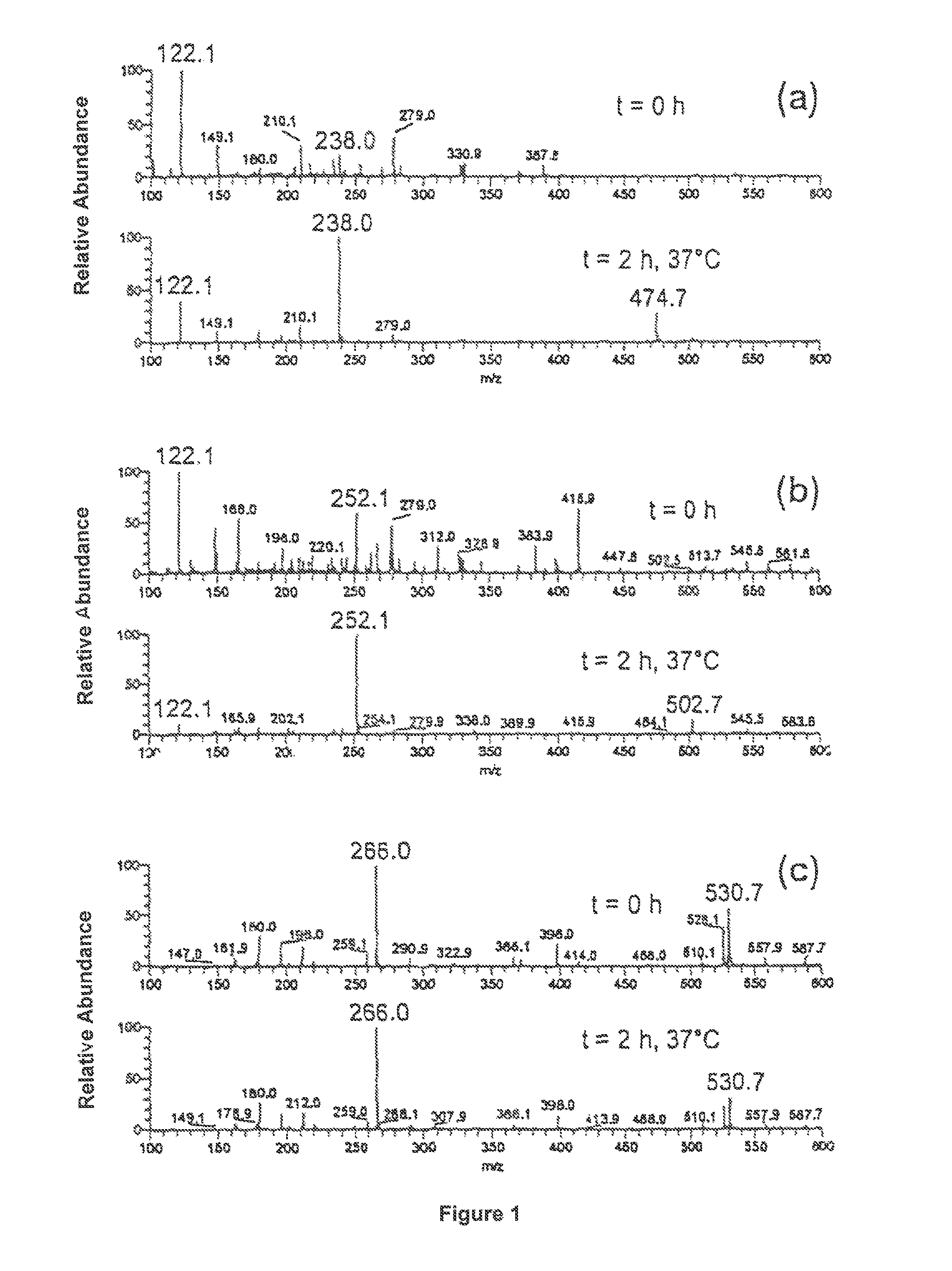
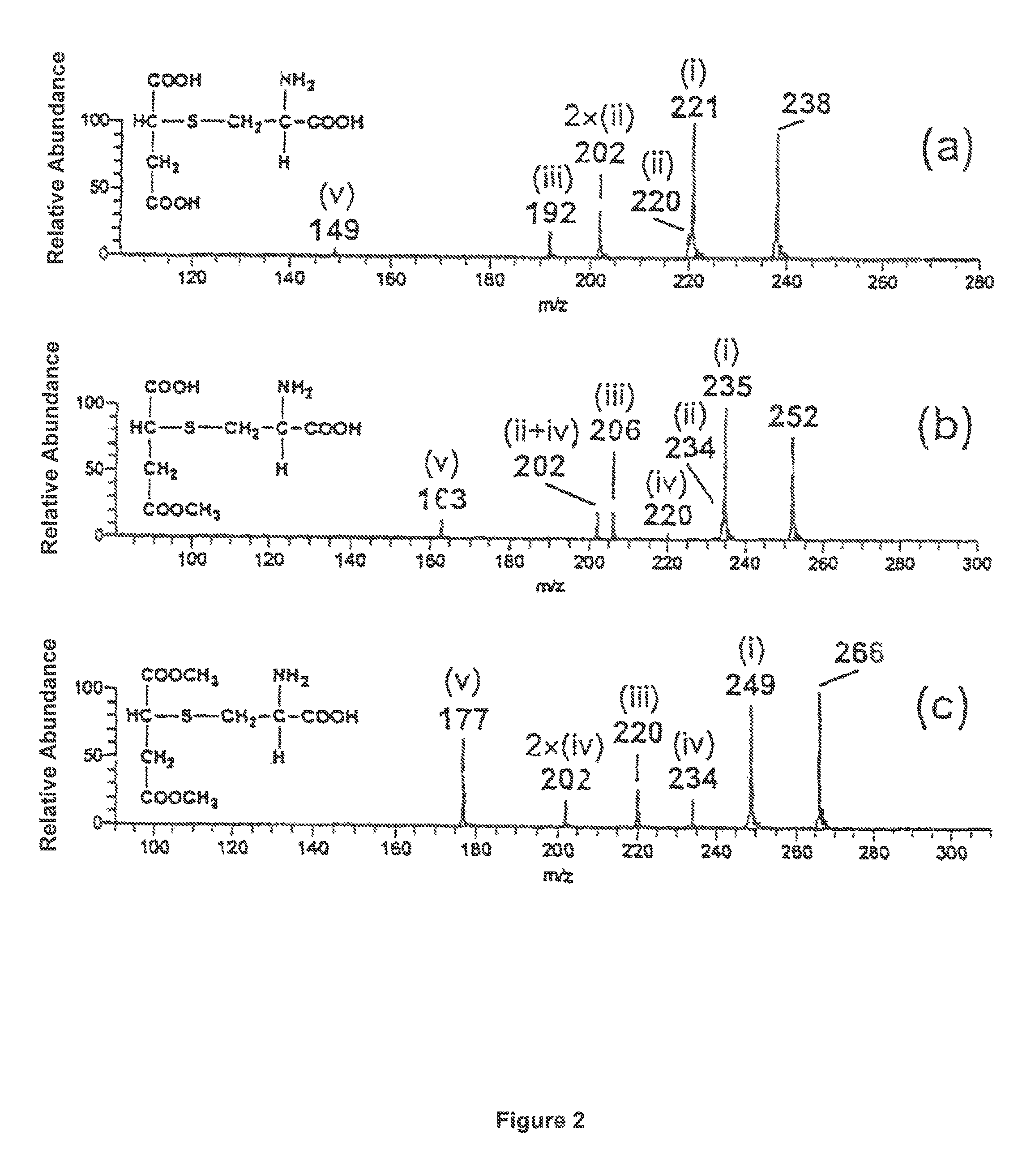
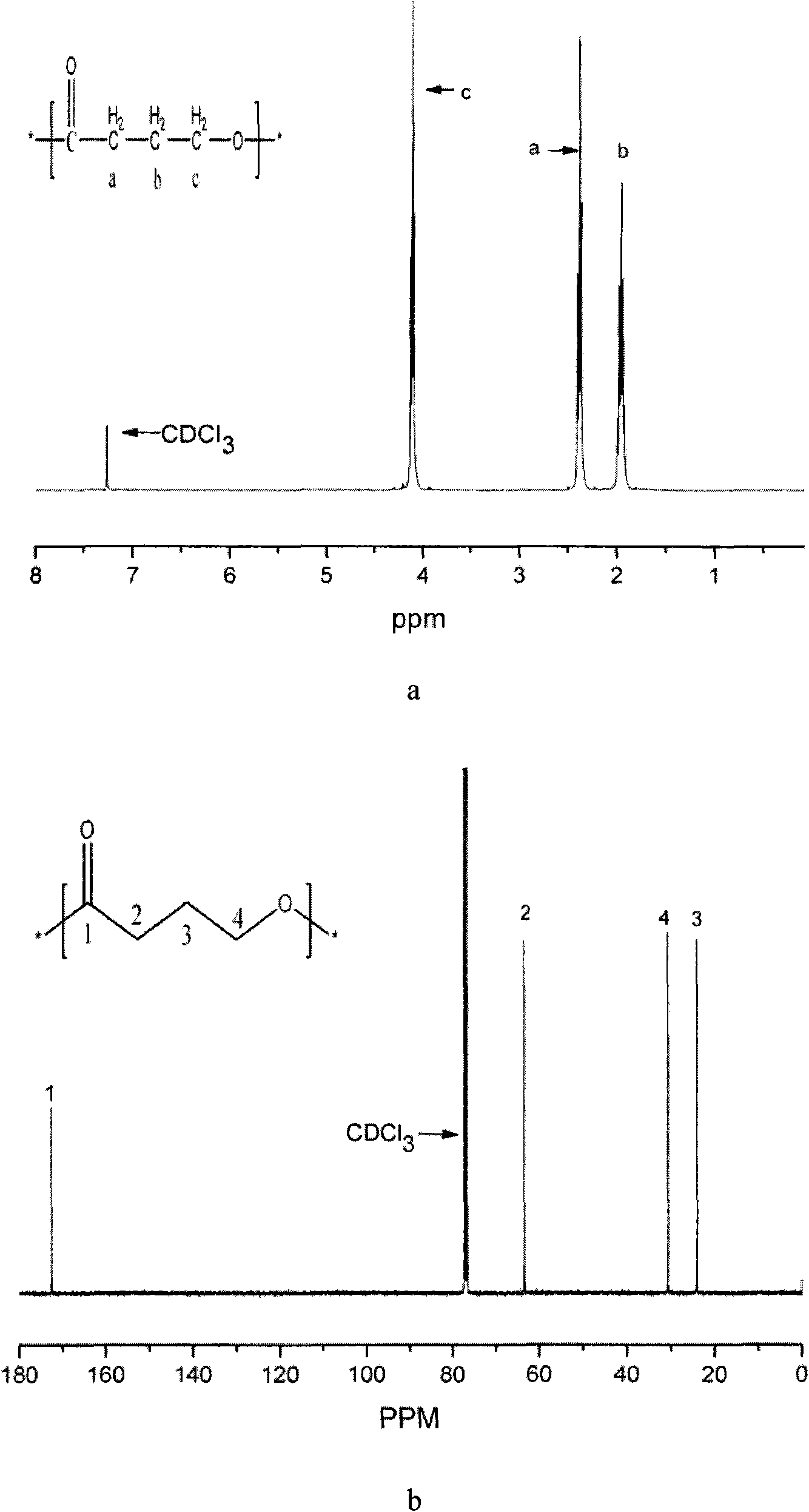
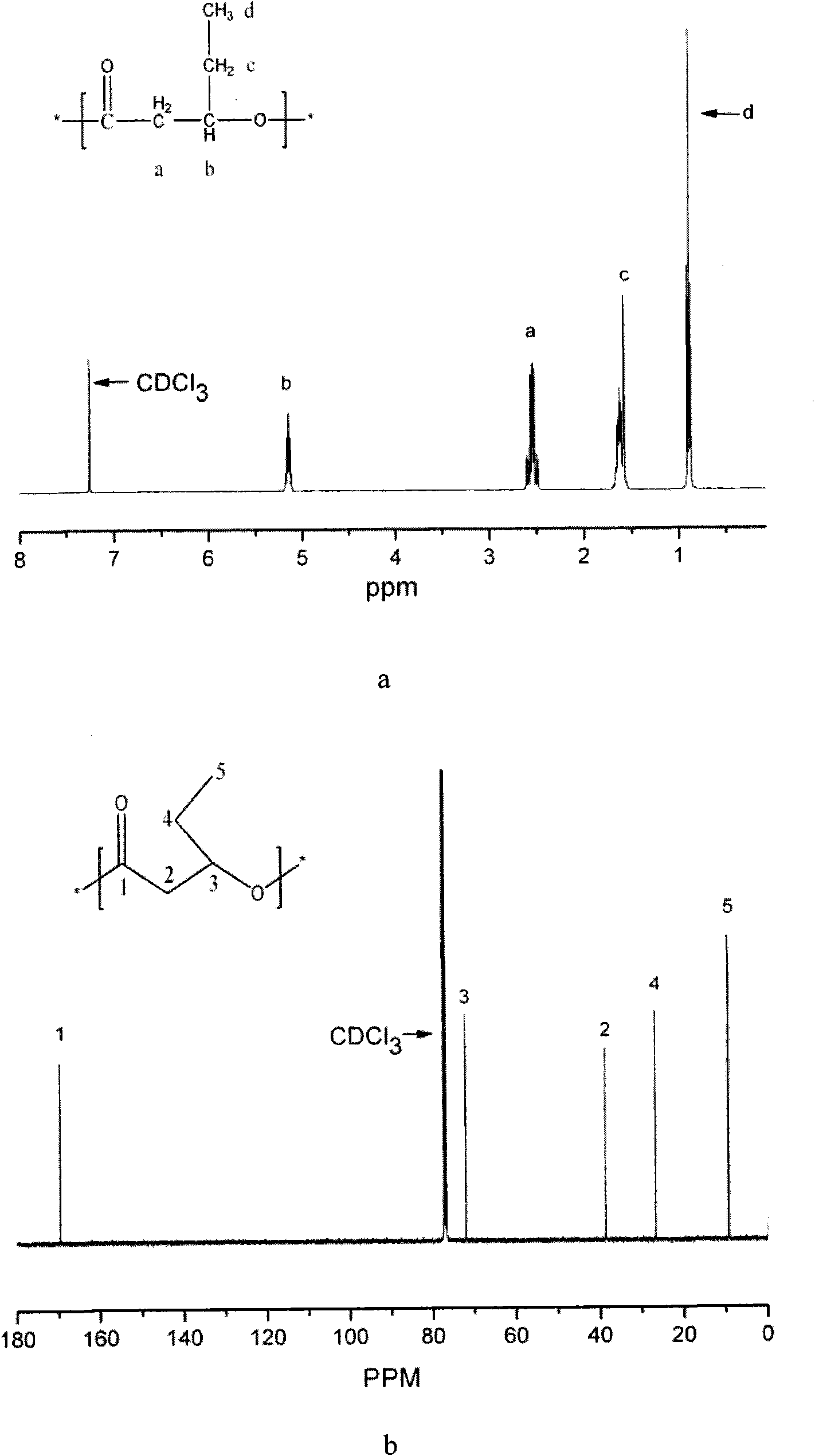
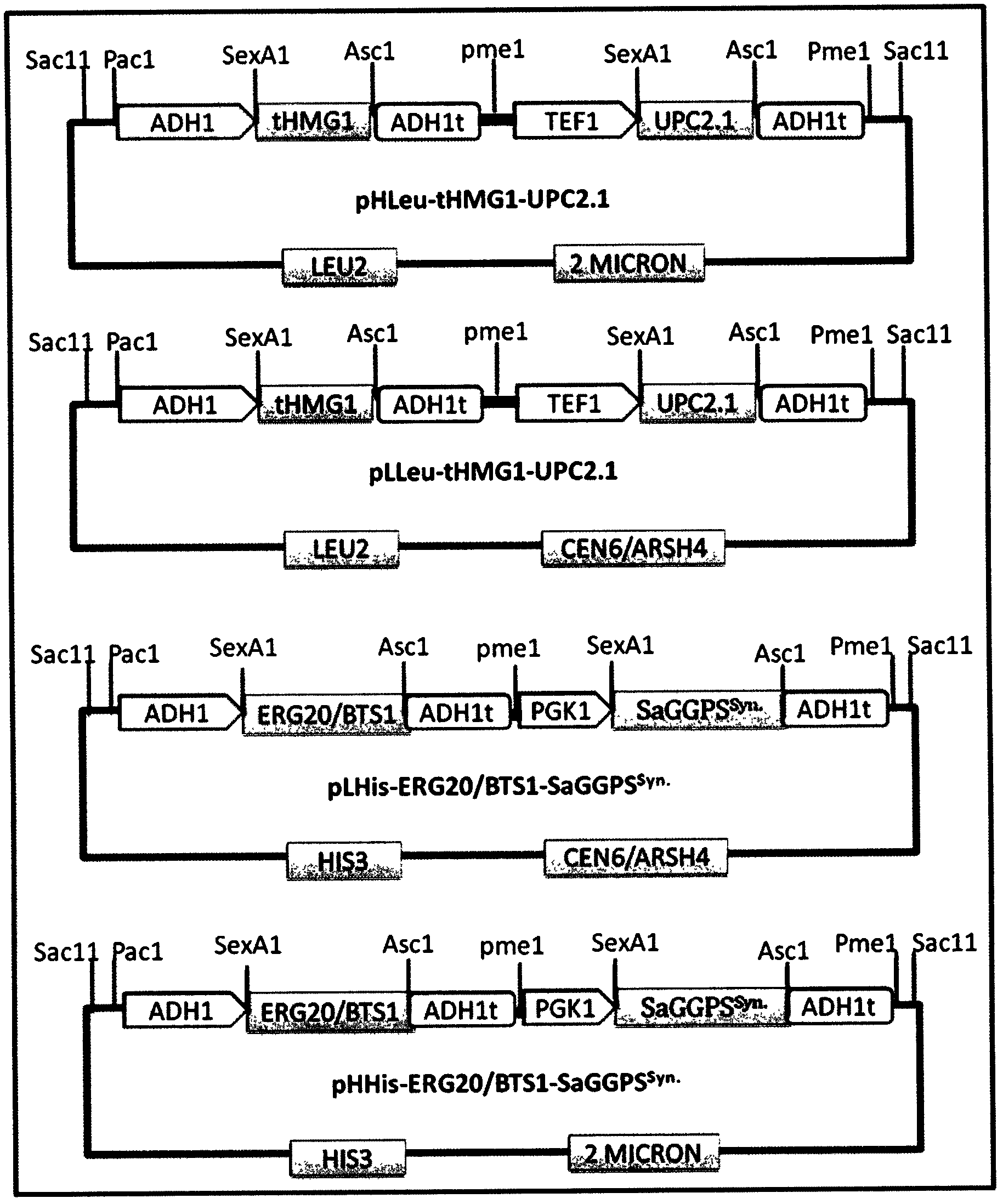
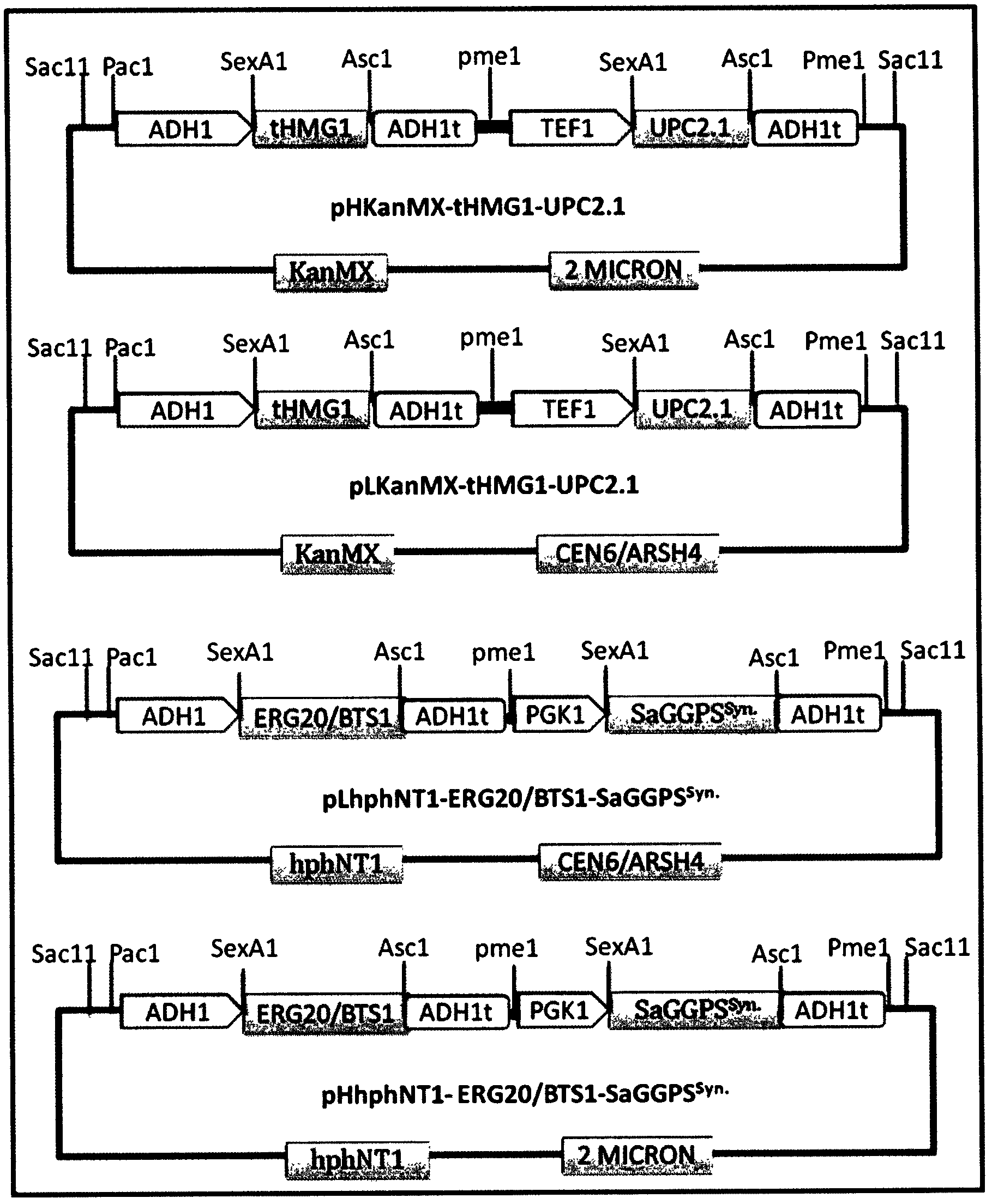
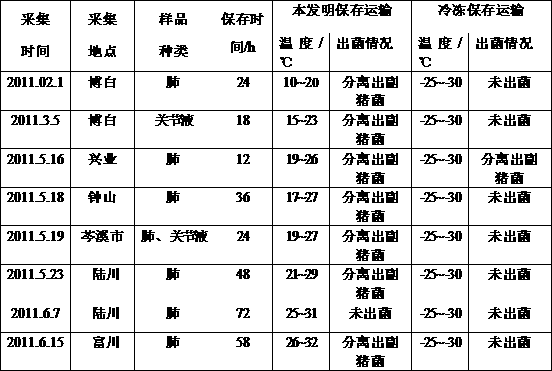
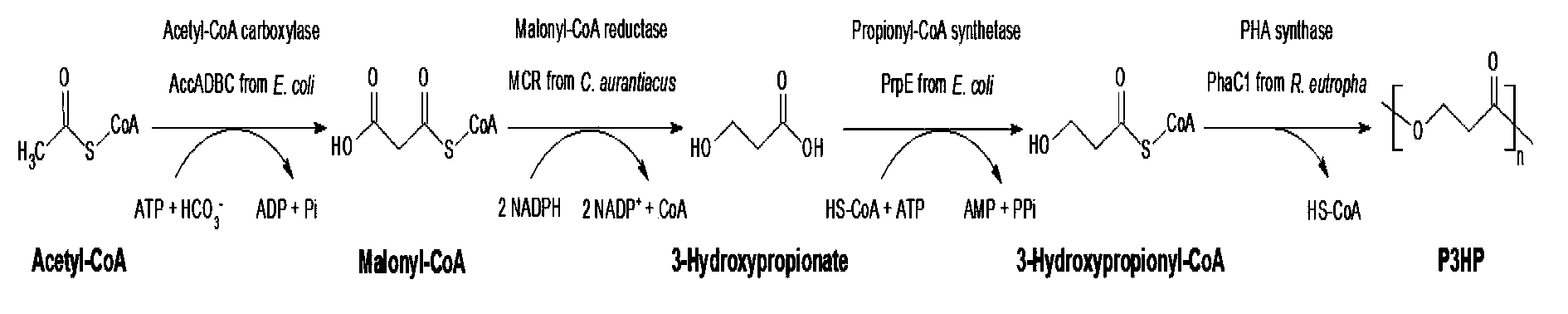
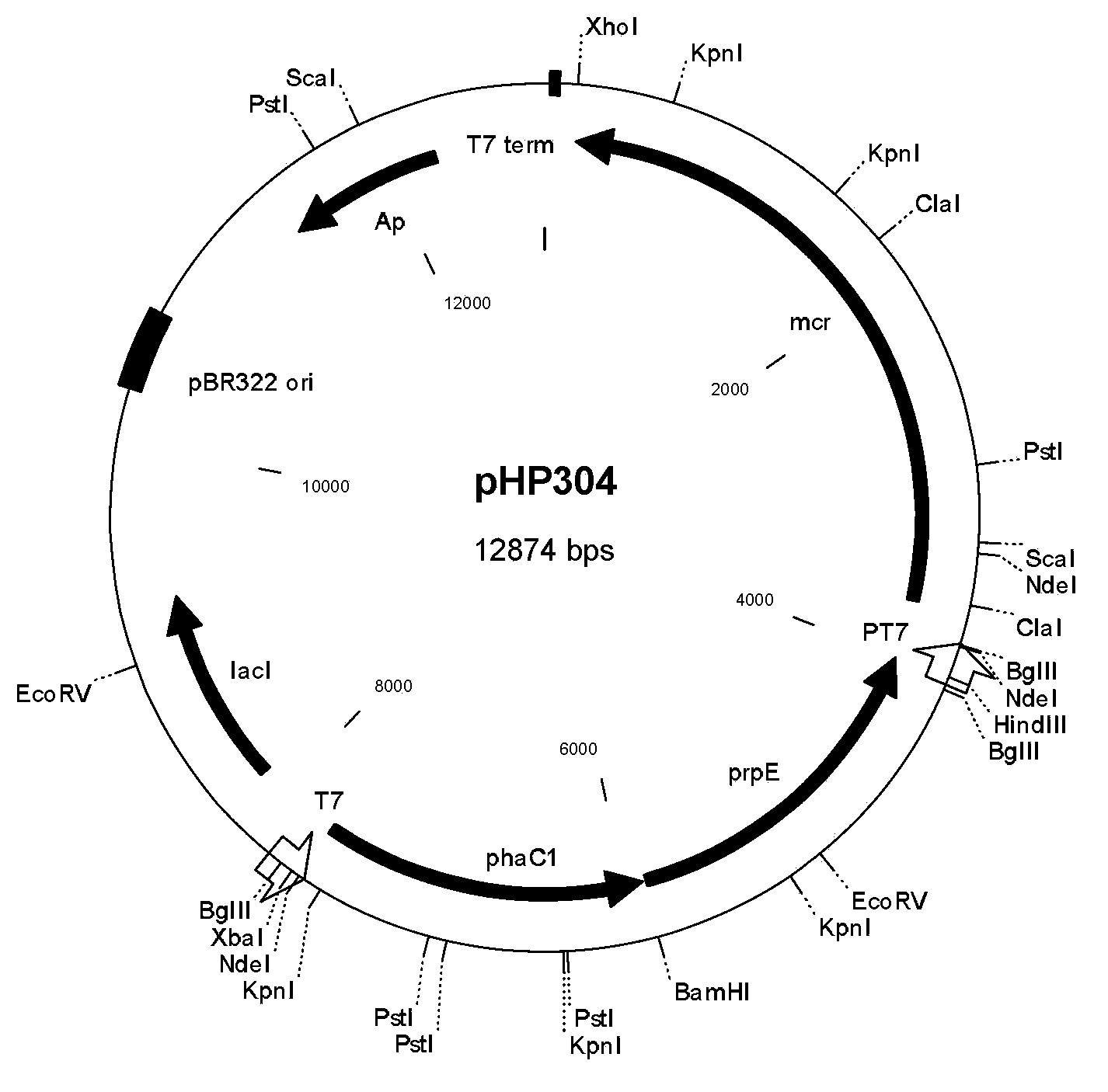
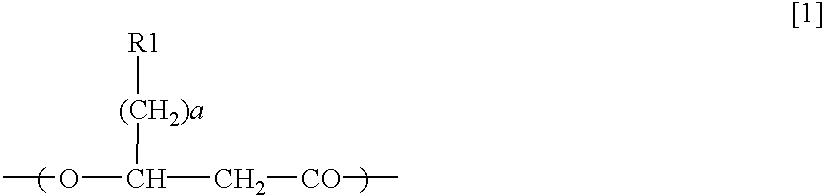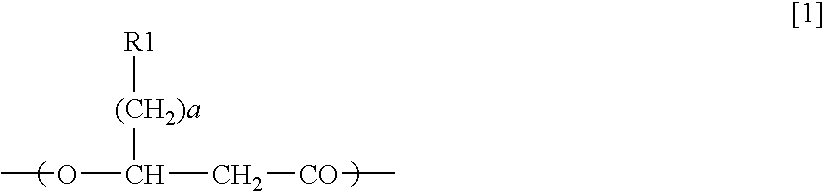Patents
Literature
409 results about "Coenzyme A biosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
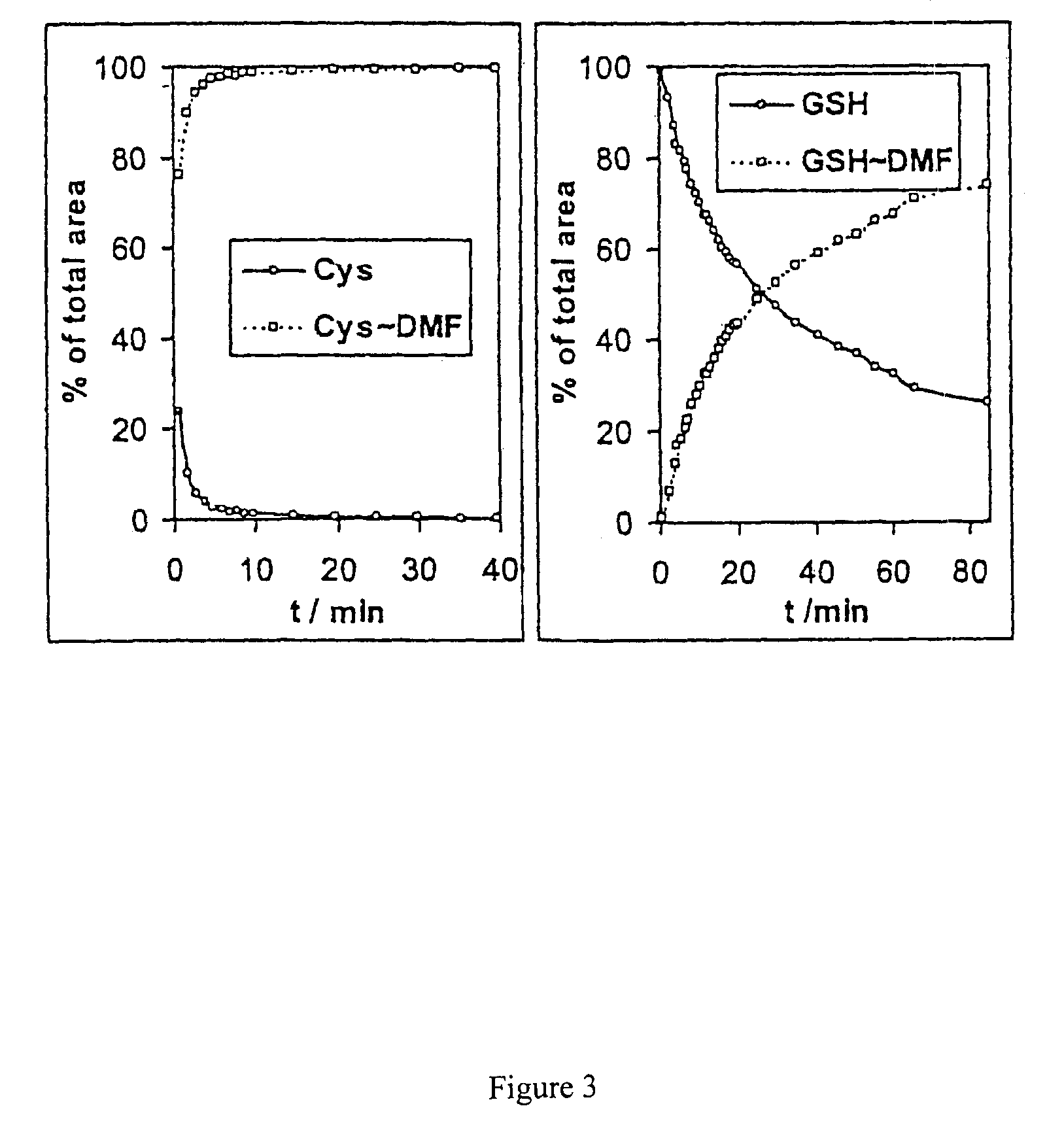
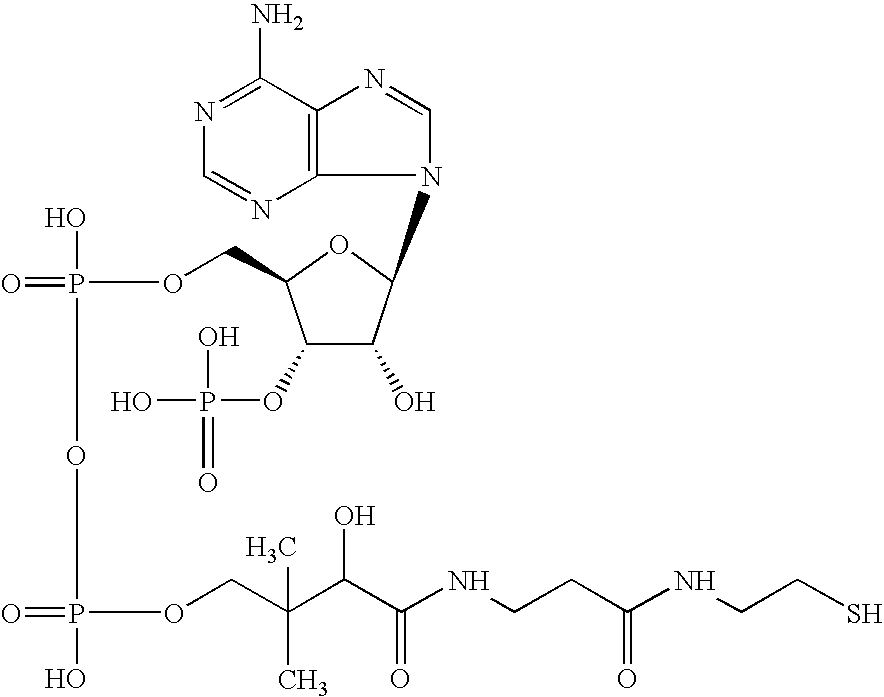
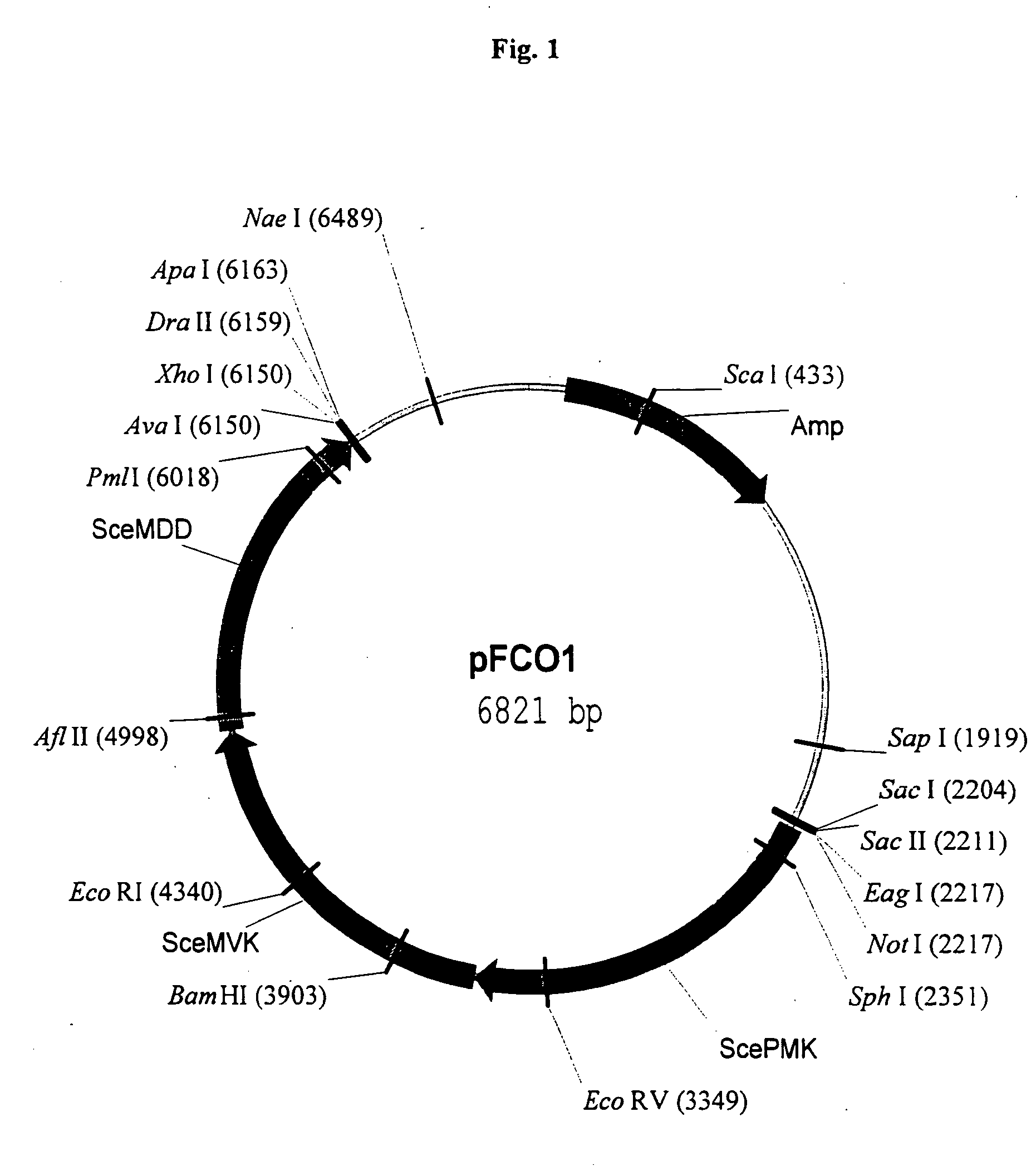
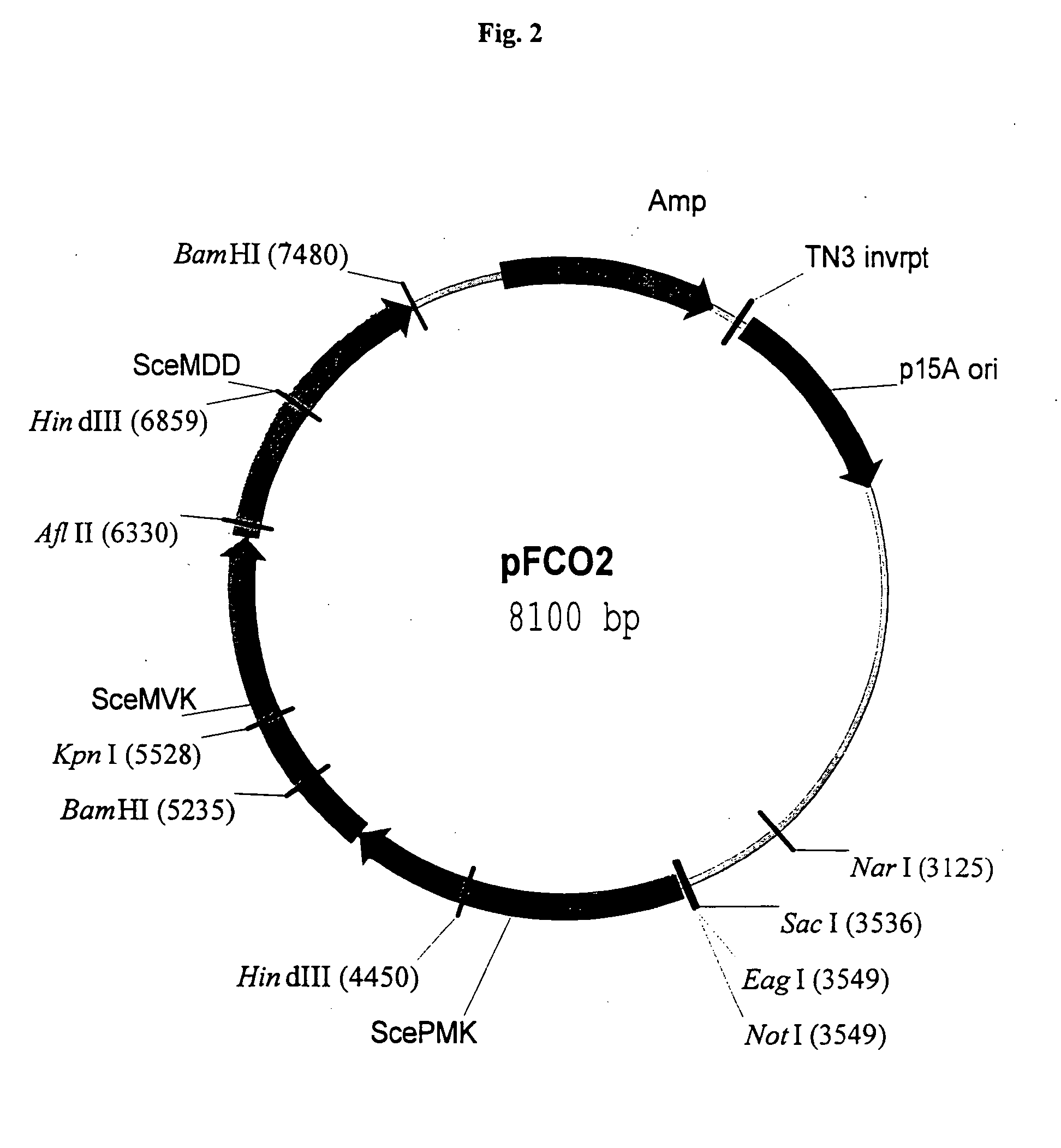
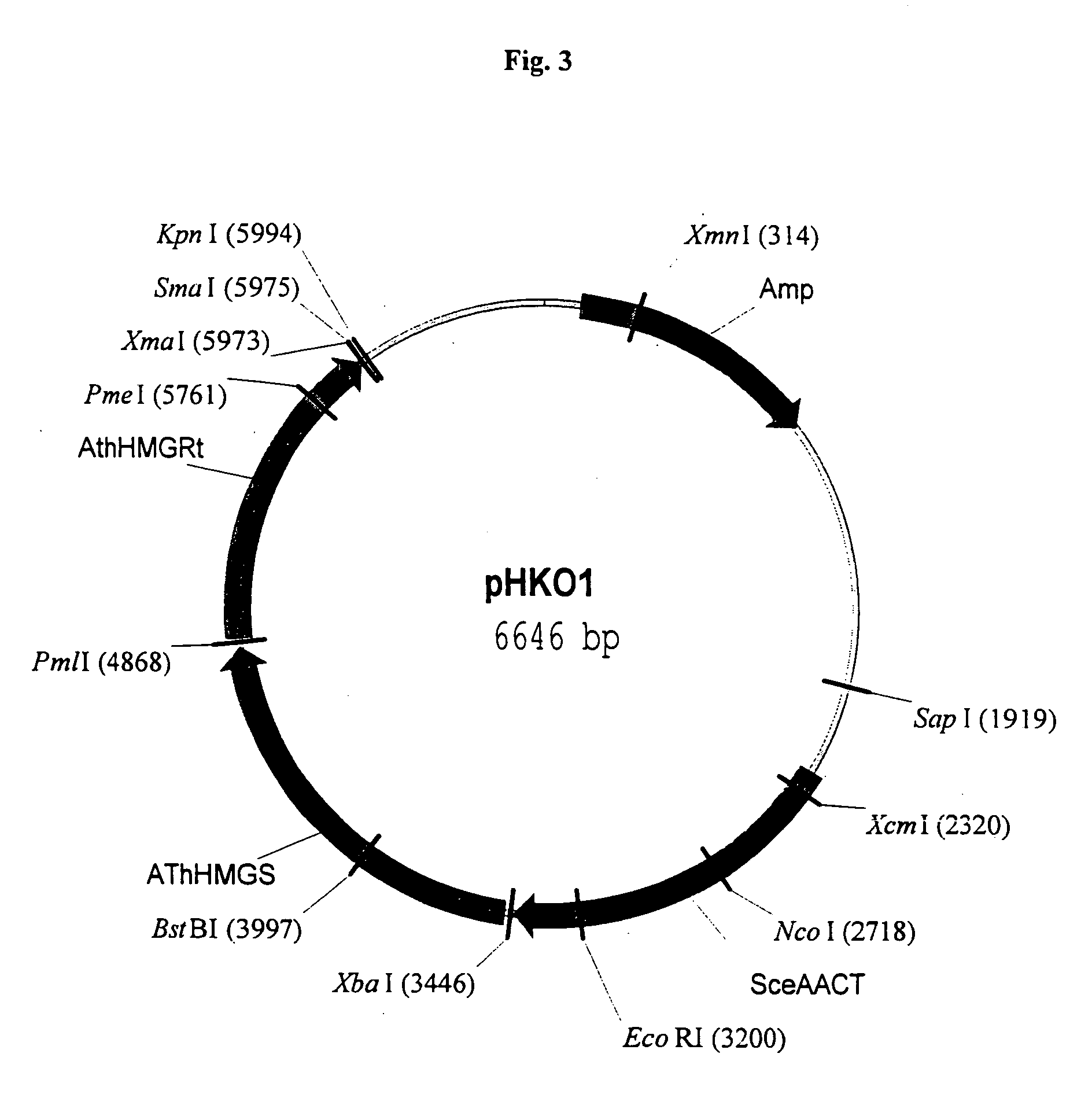
Coenzyme A, three ADP, one monophosphate, and one diphosphate are harvested from biosynthesis. New research shows that coenzyme A can be synthesized through alternate routes when intracellular coenzyme A level are reduced and the de novo pathway is impaired.
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
InactiveUS7666612B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCarrier protein
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Recombinant cell producing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid
ActiveUS20110171702A1Less stressfulFew stepsMicroorganismsFermentationAcetoacetyl coenzyme AWild type
The invention relates to a cell which has been genetically modified so as to be capable of producing more 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid or more polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid monomer units than its wild type, characterized in that 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid or polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid monomer units are produced via acetoacetyl-coenzyme A as intermediate and 3-hydroxybutyryl-coenzyme A as precursor.
Owner:ROHM GMBH
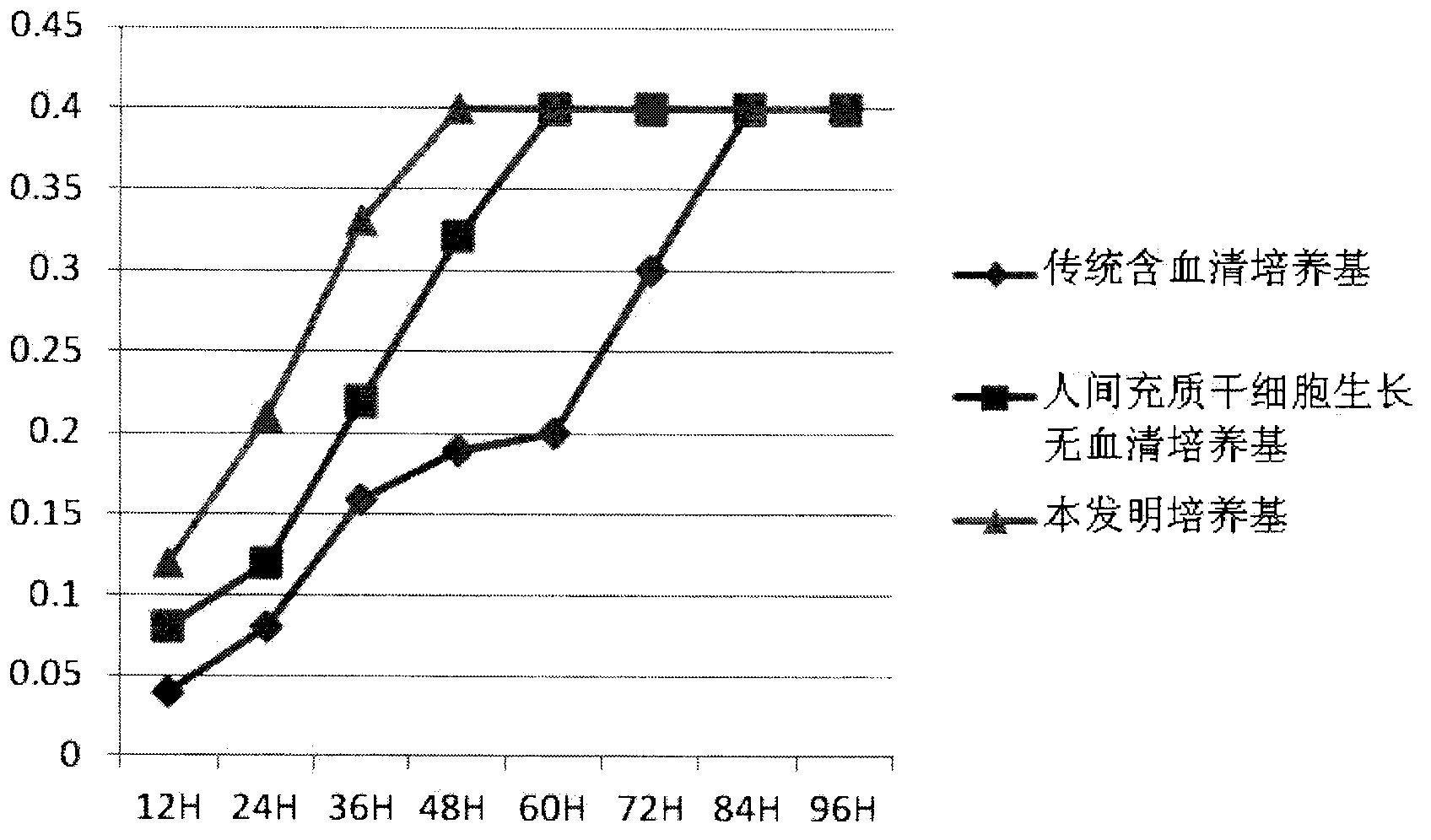
Clinical-grade human mesenchymal stem cell serum-free complete medium
ActiveCN103243071APromote growthLow toxicitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin-like growth factorCuticle
The invention relates to a human mesenchymal stem cell culture medium. According to the culture medium, the basal culture medium comprises the following components based on the final concentration: 1-2g / L of human serum albumin, 5-10mg / L of transferring, 2-8mg / L of fibronectin, 1-4mg / L of laminin, 50g / L of Fe(NO3)3.9H2O, 417g / L of FeSO4.7H2O, 1-3mu g / L of estradiol, 2-5mu g / L of testosterone, 1-3mu g / L of progesterone, 39.25-117.74 mu g / L of dexamethasone, 5-10mg / L of insulin, 376.36mg / L of riboflavin, 80.96-242.87mg / L of coenzyme A, 4.41-6.17mg / L of butanediamine, 1-2mg / L of taurine, 0.61-1.85mg / L of aminoethanol, 8.81-26.42mg / L of pyruvic acid, 3.78-7.56mu g / L of sodium selenate, 292.3-584.6mg / L of L-glutamine, 2-8mu g / L of vascular endothelial growth factor, 4-10mu g / L of epidermal growth factor, 4-10mu g / L of basic fibroblast growth factor, 1-5mu g / L of leukaemia inhibitory factor, 1-5mu g / L of insulin-like growth factor-I and 2-8mu g / L of stem cell factor. The culture medium does not contain the animal serum, the potential animal endogenous endotoxin or virus of the animal serum is eliminated, and the culture medium is conveniently applied to clinics.
Owner:QINGDAO RESTORE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
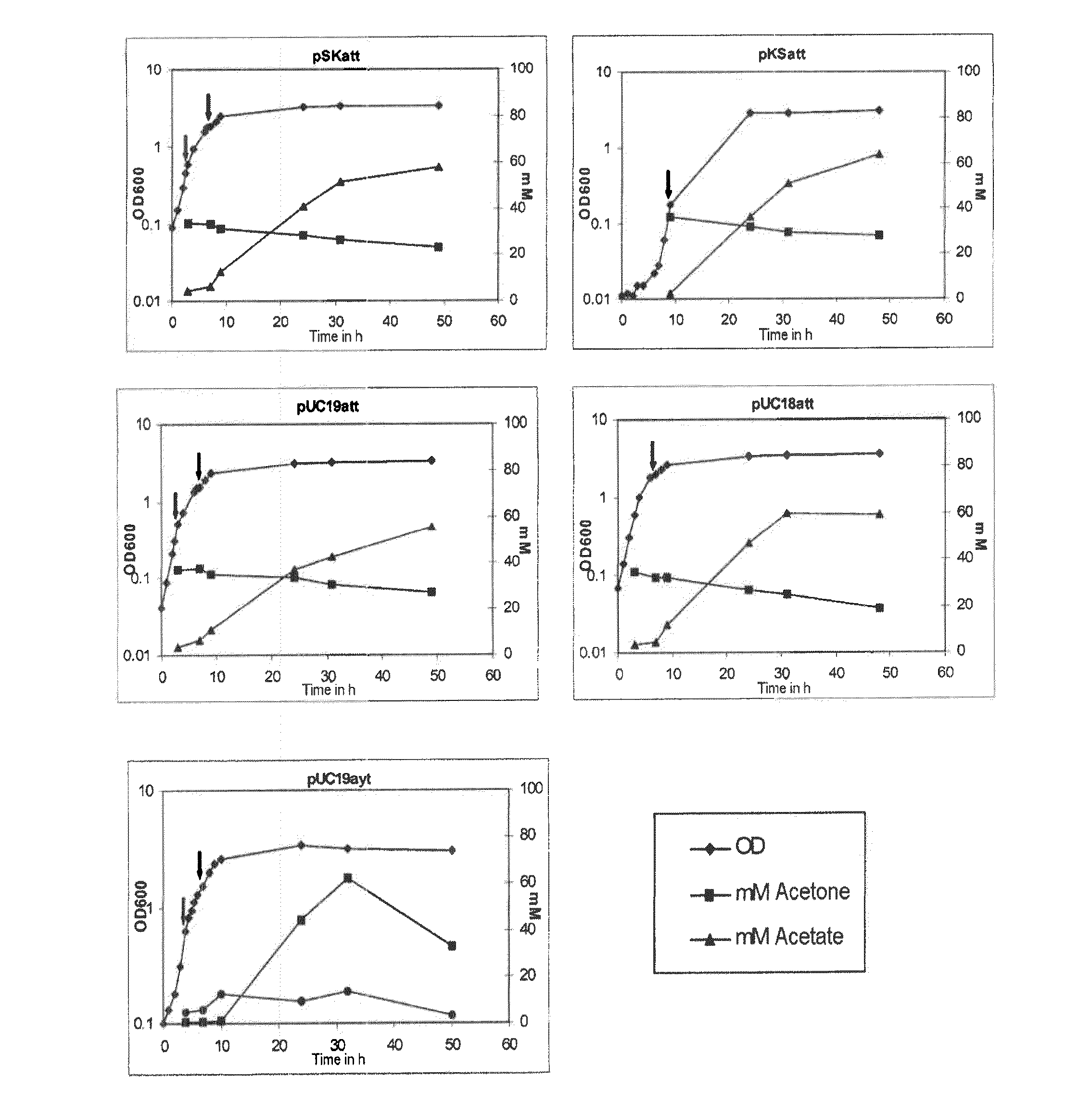
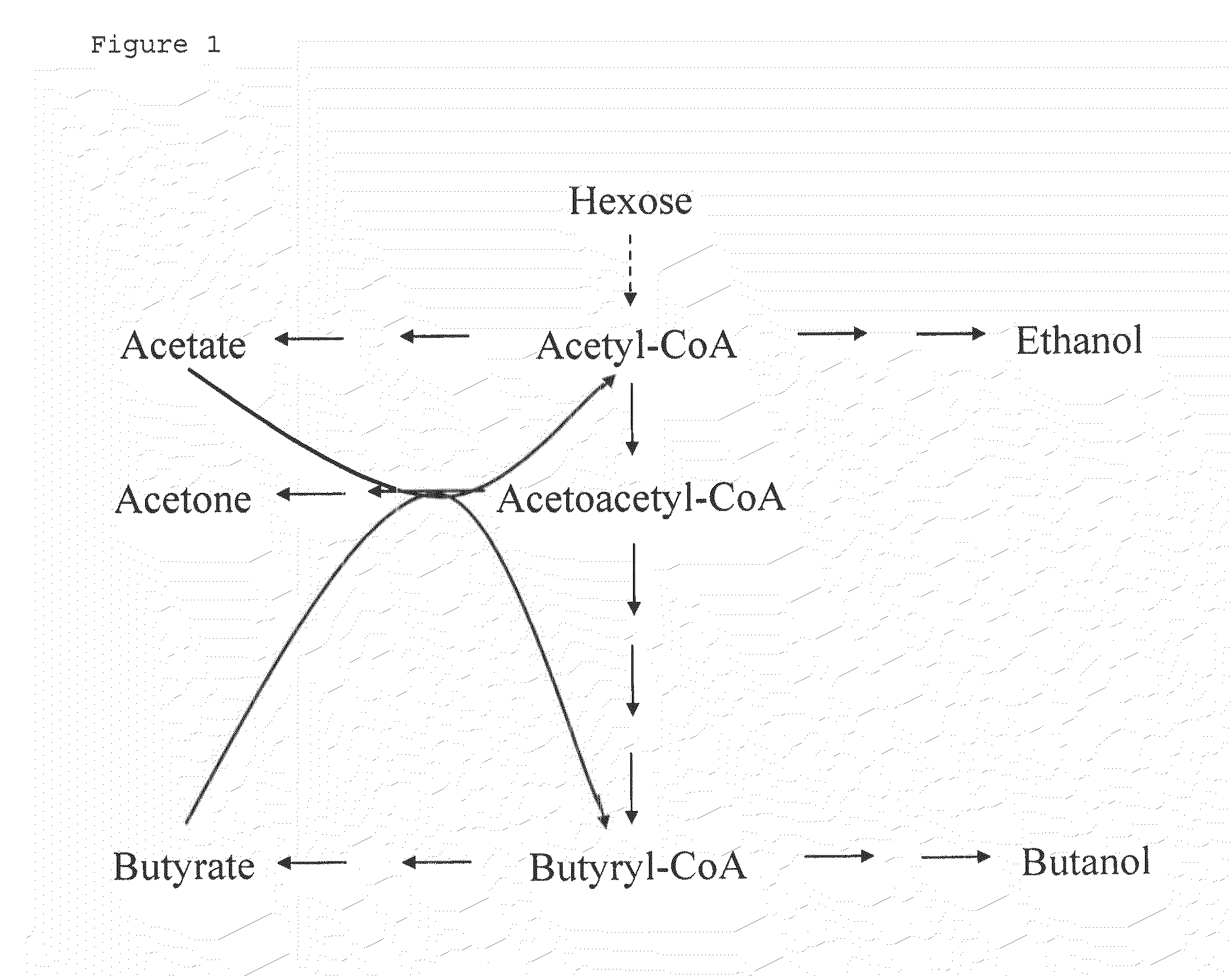
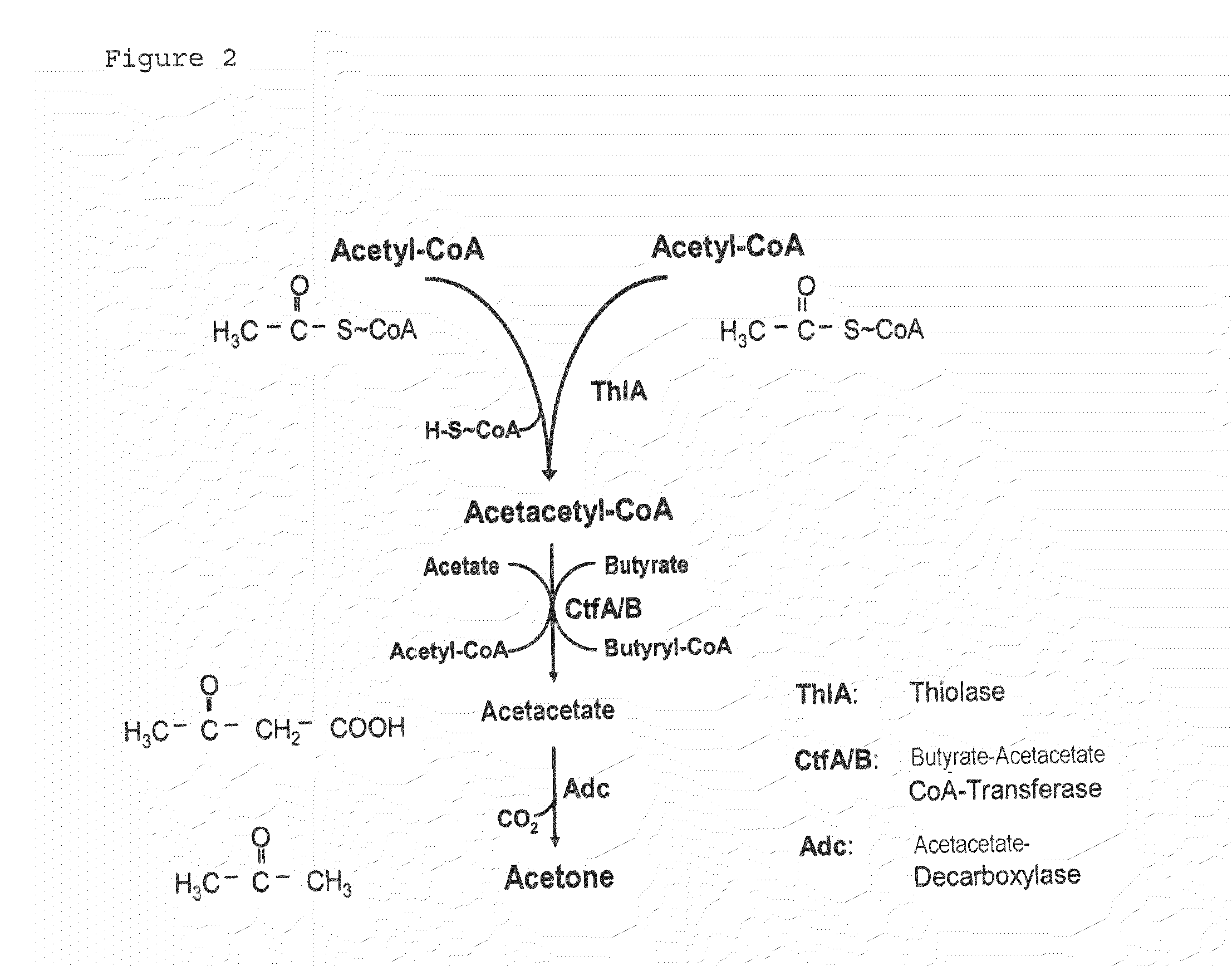
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
InactiveUSRE36520E1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsBiochemistry3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A
Novel 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors are useful as antihypercholesterolemic agents and are represented by the following general structural formula (II):
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6951745B2Effectively immobilize a PHA synthaseImmobilised enzymesBacteriaCoenzyme A biosynthesisAmino acid
A method for manufacturing polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with polyhydroxyalkanoate, the method comprises the steps of immobilizing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase on the base material surface, synthesizing, on the base material surface, polyhydroxyalkanoate using a 3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A to become the substrate of the synthase and the synthase and coating at least a part of the base material surface with the synthesized polyhydroxyalkanoate, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material. A polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with a polyhydroxyalkanoate, comprises the base material, a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase immobilized on the base material surface, and the polyhydroxyalkanoate with which at least a part of the base material surface is coated, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material.
Owner:CANON KK
Thiosuccinic Acid Derivatives and the Use Thereof
ActiveUS20090011986A1Similar effectEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsBiocideThio-Autoimmune disease
The present invention relates to compounds of the Formula (I), wherein X1 and X2 independently represent O, NH or S; R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of a C1-C30 hydrocarbyl group, an amino acid bonded via an amide bond or a peptide bonded via an amide bond each having up to 200 amino acids, the conjugated residue X1 or X2 in this case being NH, and hydrogen, both radicals R1 and R2 preferably not being H; and R3 is a residue selected from group consisting of —S—R6, wherein R6 is a C1-C30 hydrocarbyl group, at least one of R1 and R2 not being H when X1 and X2 are oxygen, —S—CH2—CH(NH2)(COOH) (cysteine-S-yl), a homologue or derivative (e.g. N-acetyl cysteine-S-yl) thereof, a peptide having up to 200 amino acids which contains at least one amino acid radical with a thiol group, preferably a cysteine radical, and is bonded via the thio sulfur, preferably via the cysteine sulfur (peptide-S-yl), coenzyme A which is bonded via a thiol group or fragments thereof, acyl carrier protein bonded via a thiol group, and dihydrolipoic acid bonded via a thiol group; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The present invention also relates to the use of these compounds for preparing a drug, drugs containing the same and their use for the therapy of diseases such as autoimmune disease, NF-kappaB mediated diseases, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, neurodermitis, enteris regionalis Crohn, cardiac insufficiency, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and asthma and in transplantation medicine.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
Thiosuccinic acid derivatives and the use thereof
ActiveUS8067467B2Easy to prepareImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideThio-Coenzyme A biosynthesis
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula (I) wherein X1 and X2 independently represent O, NH or S, R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of a C1-C30 hydrocarbyl group, an amino acid bonded via an amide bond or a peptide bonded via an amide bond each having up to 200 amino acids, the conjugated residue X1 or X2 in this case being NH, and hydrogen, both radicals R1 and R2 preferably not being H, wherein R3 is a residue selected from group consisting of —S—R6, wherein R6 is a C1-C30 hydrocarbyl group, at least one of R1 and R2 not being H when X1 and X2 are oxygen, —S—CH2—CH(NH2)(COOH) (cysteine-S-yl), a homologue or derivative (e.g. N-acetyl cysteine-S-yl) thereof, a peptide having up to 200 amino acids which contains at least one amino acid radical with a thiol group, preferably a cysteine radical, and is bonded via the thio sulfur, preferably via the cysteine sulfur (peptide-S-yl), coenzyme A which is bonded via a thiol group or fragments thereof, acyl carrier protein bonded via a thiol group, and dihydrolipoic acid bonded via a thiol group, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The present invention also relates to the use of these compounds for preparing a drug and drugs containing the same.
Owner:BIOGEN INT
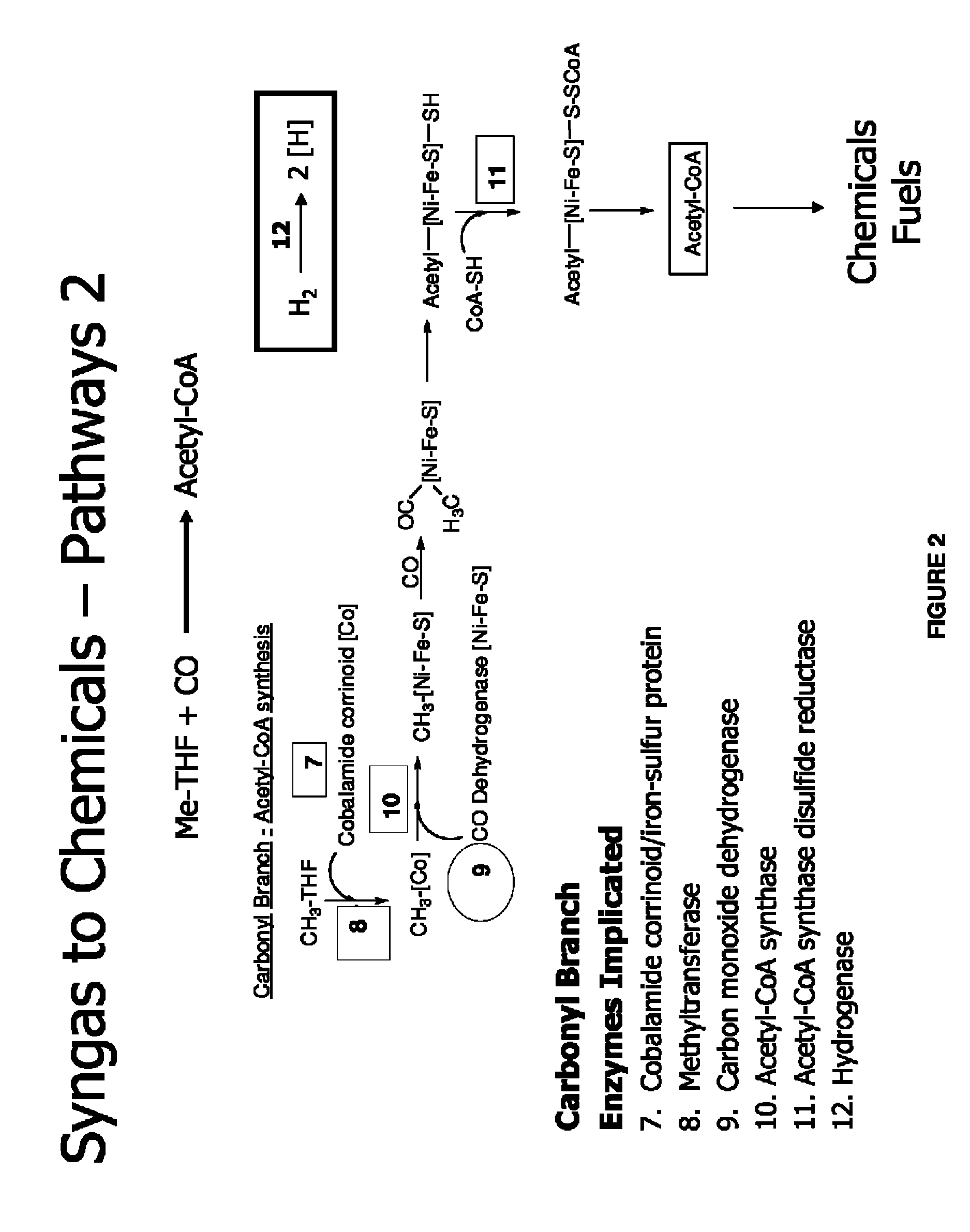
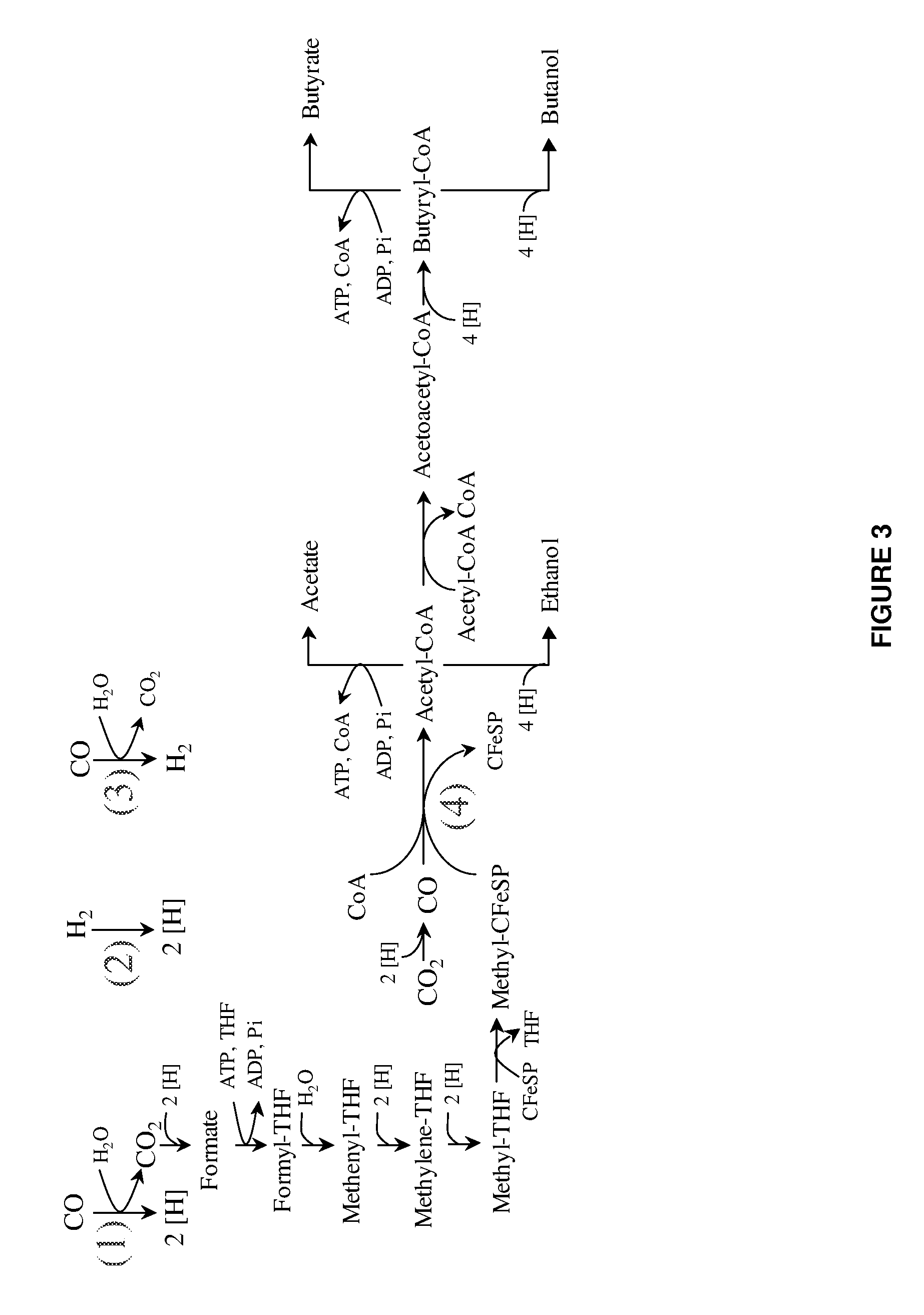
Methods and organisms for utilizing synthesis gas or other gaseous carbon sources and methanol
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microbial organism having an acetyl-CoA pathway and the capability of utilizing syngas or syngas and methanol. In one embodiment, the invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism, comprising one or more exogenous proteins conferring to the microorganism a pathway to convert CO, CO2 and / or H2 to acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), methyl tetrahydrofolate (methyl-THF) or other desired products, wherein the microorganism lacks the ability to convert CO or CO2 and H2 to acetyl-CoA or methyl-THF in the absence of the one or more exogenous proteins. For example, the microbial organism can contain at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an enzyme or protein in an acetyl-CoA pathway. The microbial organism is capable of utilizing synthesis gases comprising CO, CO2 and / or H2, alone or in combination with methanol, to produce acetyl-CoA. The invention additionally provides a method for producing acetyl-CoA, for example, by culturing an acetyl-CoA producing microbial organism, where the microbial organism expresses at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acetyl-CoA pathway enzyme or protein in a sufficient amount to produce acetyl-CoA, under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce acetyl-CoA.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
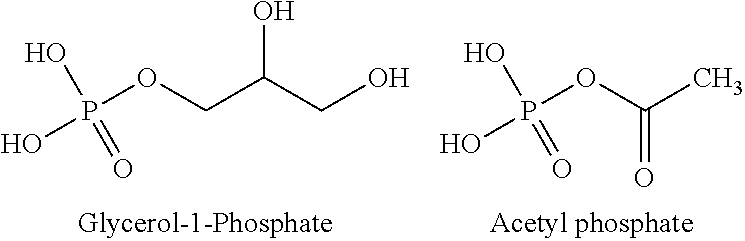
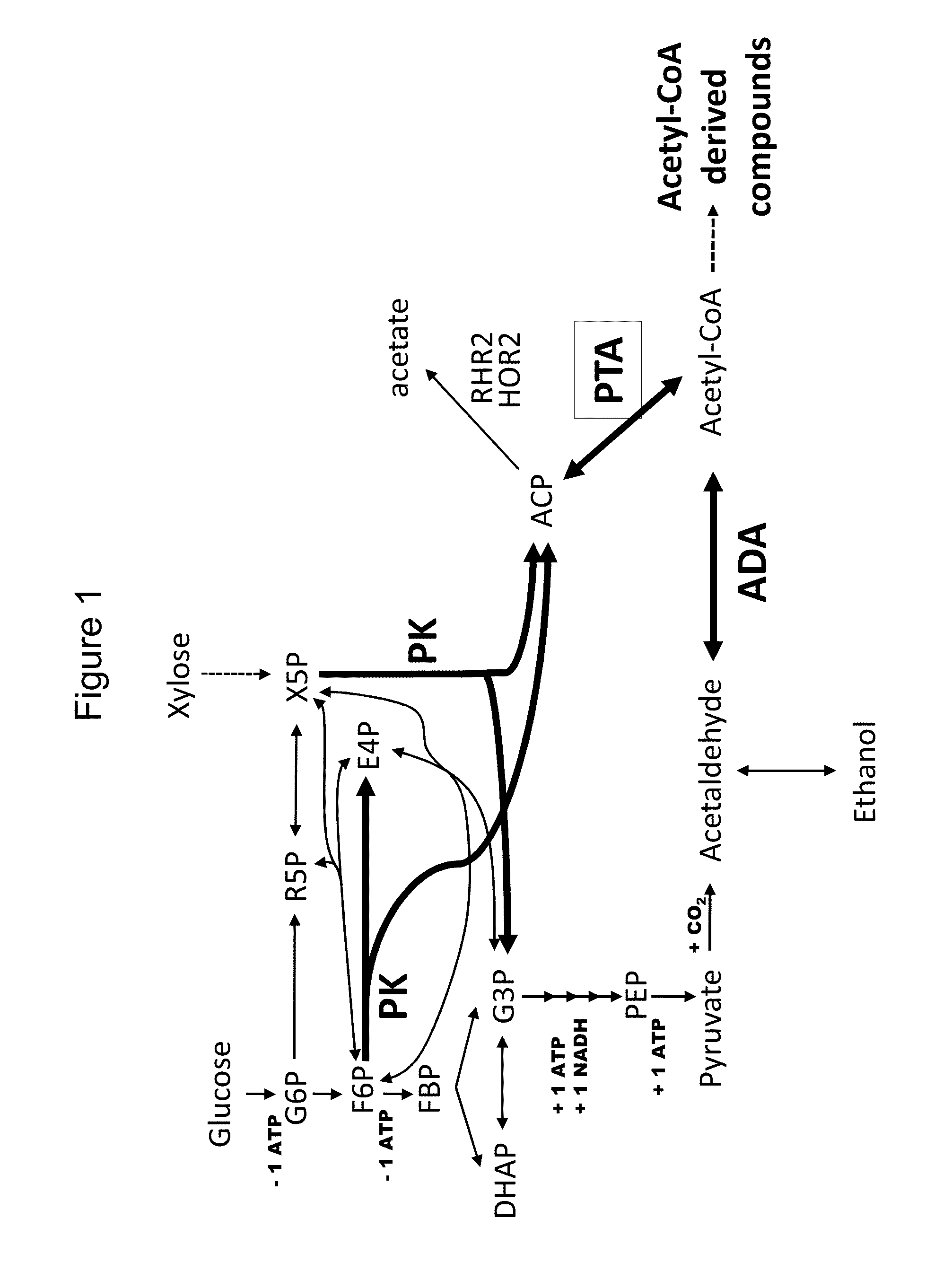
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Methods for stabilizing production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
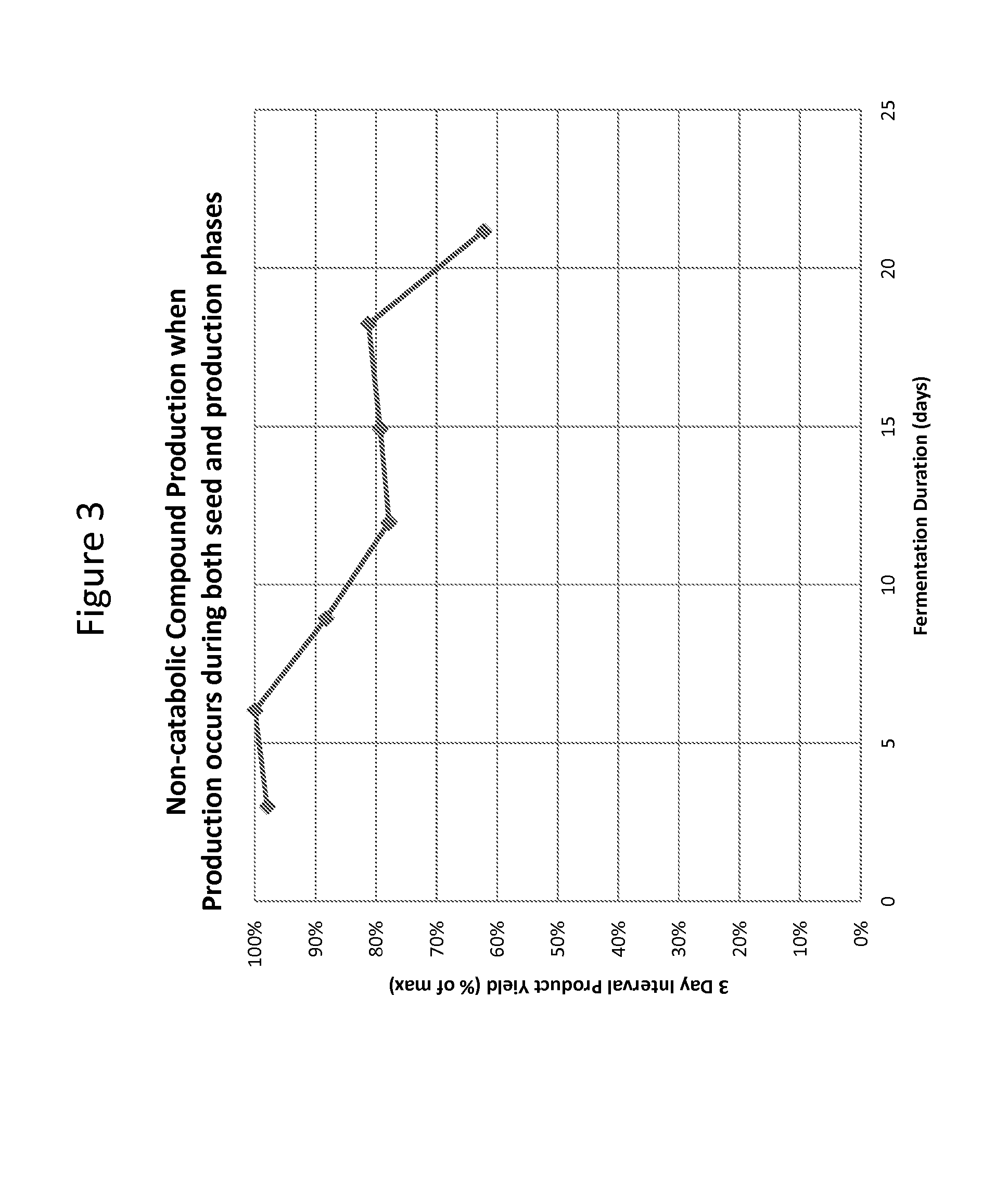
ActiveUS20160177341A1Increase probabilityLonger sustained non-catabolic compound productionFungiBacteriaMicroorganismHeterologous
The present disclosure relates to the use of a switch for the production of heterologous non-catabolic compounds in microbial host cells. In one aspect, provided herein are genetically modified microorganisms that produce non-catabolic compounds more stably when serially cultured under aerobic conditions followed by microaerobic conditions, and methods of producing non-catabolic compounds by culturing the genetically modified microbes under such culture conditions. In another aspect, provided herein are genetically modified microorganisms that produce non-catabolic compounds more stably when serially cultured in the presence of maltose followed by the reduction or absence of maltose, and methods of producing non-catabolic compounds by culturing the genetically modified microbes under such culture conditions.
Owner:AMYRIS INC +1
Polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050208635A1Effectively immobilize a PHA synthaseImmobilised enzymesDuplicating/marking methodsCoenzyme A biosynthesisPolyhydroxyalkanoate synthase
A method for manufacturing polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with polyhydroxyalkanoate, the method comprises the steps of immobilizing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase on the base material surface, synthesizing, on the base material surface, polyhydroxyalkanoate using a 3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A to become the substrate of the synthase and the synthase and coating at least a part of the base material surface with the synthesized polyhydroxyalkanoate, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material. A polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with a polyhydroxyalkanoate, comprises the base material, a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase immobilized on the base material surface, and the polyhydroxyalkanoate with which at least a part of the base material surface is coated, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material.
Owner:CANON KK
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
Novel 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors are useful as antihypercholesterolemic agents and are represented by the following general structural formulae (I) and (II):
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
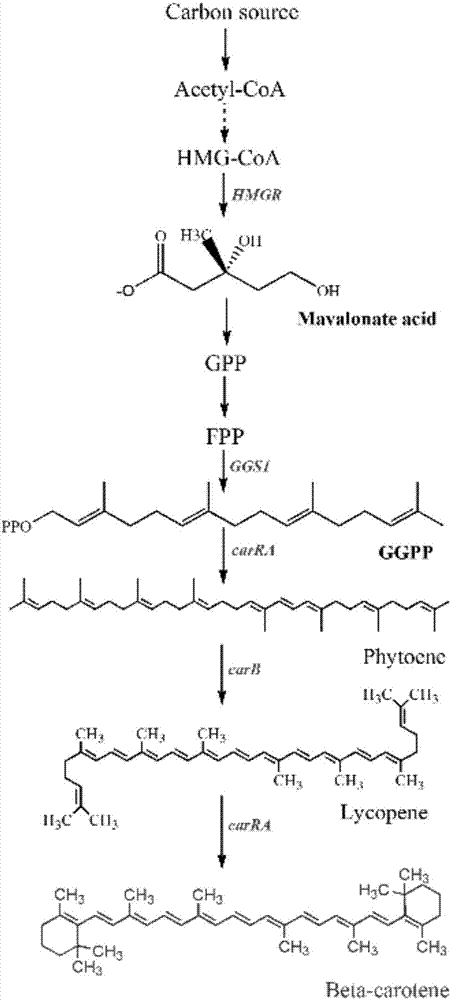
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
InactiveUS20070082336A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesProtein markersProtein labeling
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Composition with efficacies of whitening, moisturizing, repairing and caring skin, as well as preparation method and applications of composition
InactiveCN107411982AIncrease brightnessFirming and Lifting ContourCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsArginineCuticle
The invention relates to a composition with the efficacies of whitening, moisturizing, repairing and caring the skin, as well as a preparation method and applications of the composition. The skin care composition is prepared from the following raw materials: water, sodium hyaluronate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, potassium chloride, sodium hydroxide, calcium chloride, glutamine, benzalkonium chloride, magnesium sulfate, aminobutyric acid, sodium ascorbate, alanine, arginine, lysine hydrochloride, valine, histidine, leucine, taurine, coenzyme A, alcohol, polysorbate 80, thiamine, disodium diphosphate, recombinant human epidermal cell growth factors and the like. The skin care composition disclosed by the invention can permeate the muscle bottom for replenishing water for the skin from the deep layer, so that the skin is full of elasticity, the color of the skin is brightened, the fine wrinkles are reduced, the skin is clean and watery, the balance of water and oil is regulated, the pores are shrunk, meanwhile, the brightness of the face can be increased, the injured epidermal layer is effectively repaired, the activity of tyrosinase is inhibited, the generation of skin melanin is reduced, so that the skin is healthy, natural and white.
Owner:刘毅
Manipulation of genes of the mevalonate and isoprenoid pathways to create novel traits in transgenic organisms
InactiveUS20050241017A1Other foreign material introduction processesIsomerasesOpen reading frameNucleotide
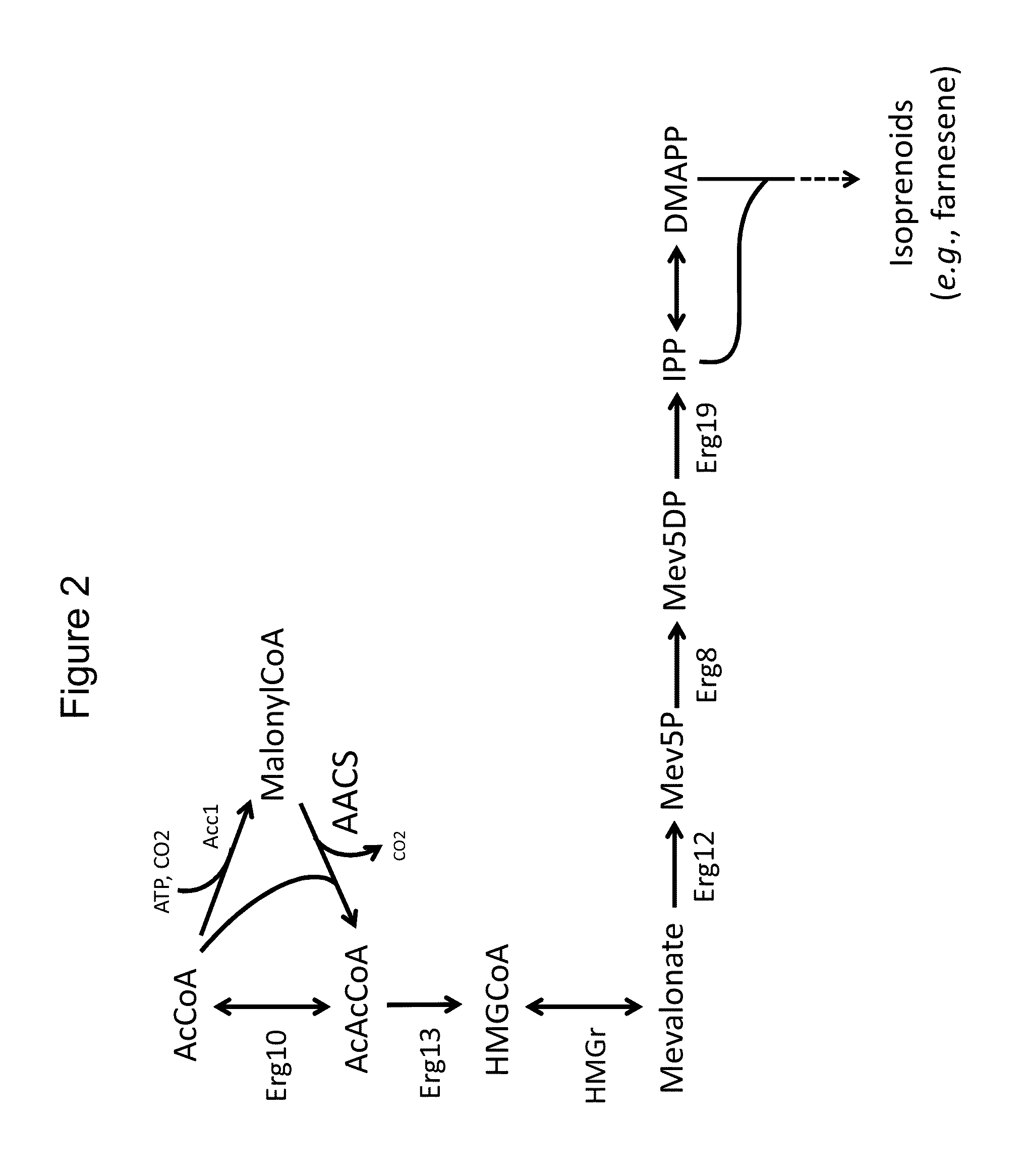
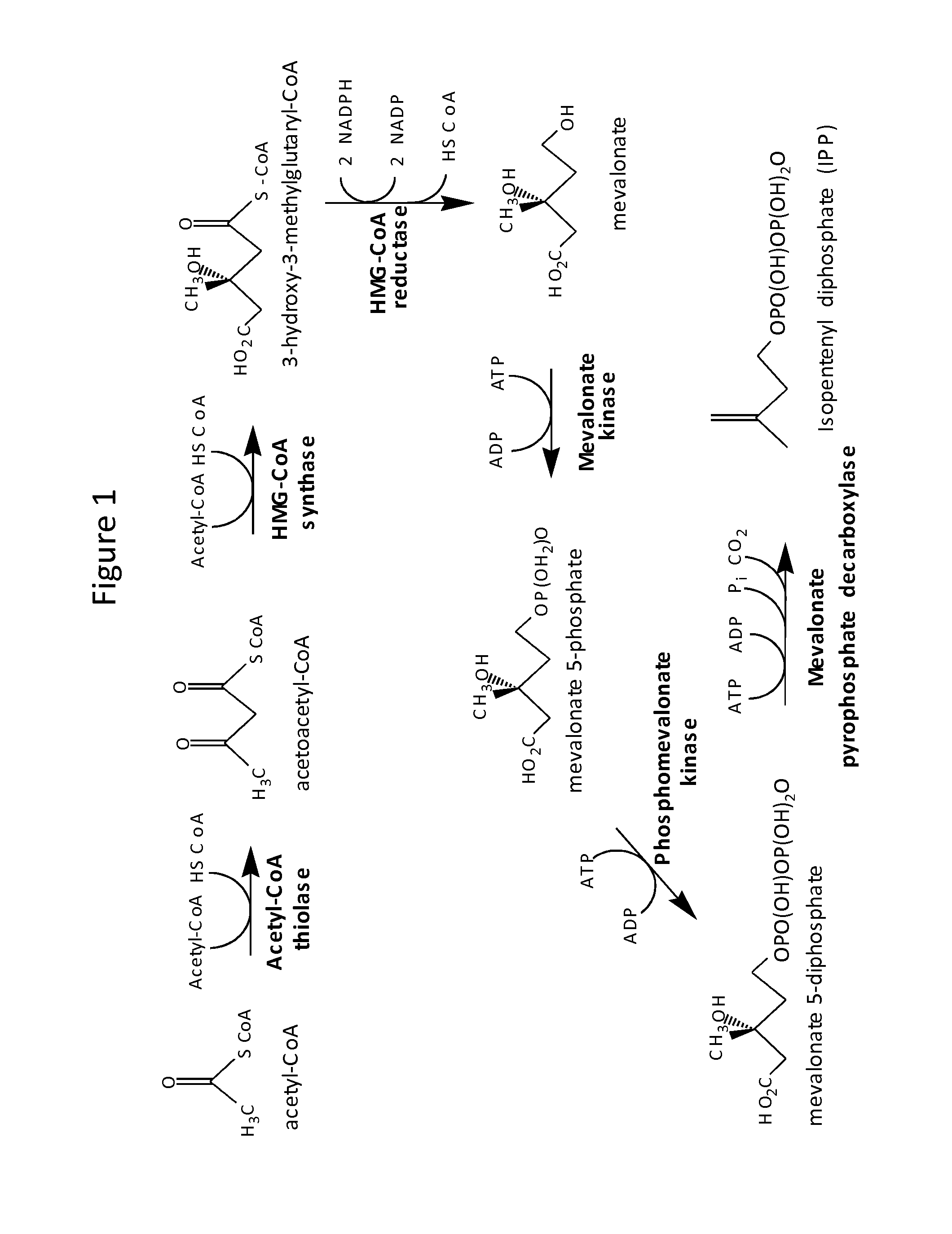
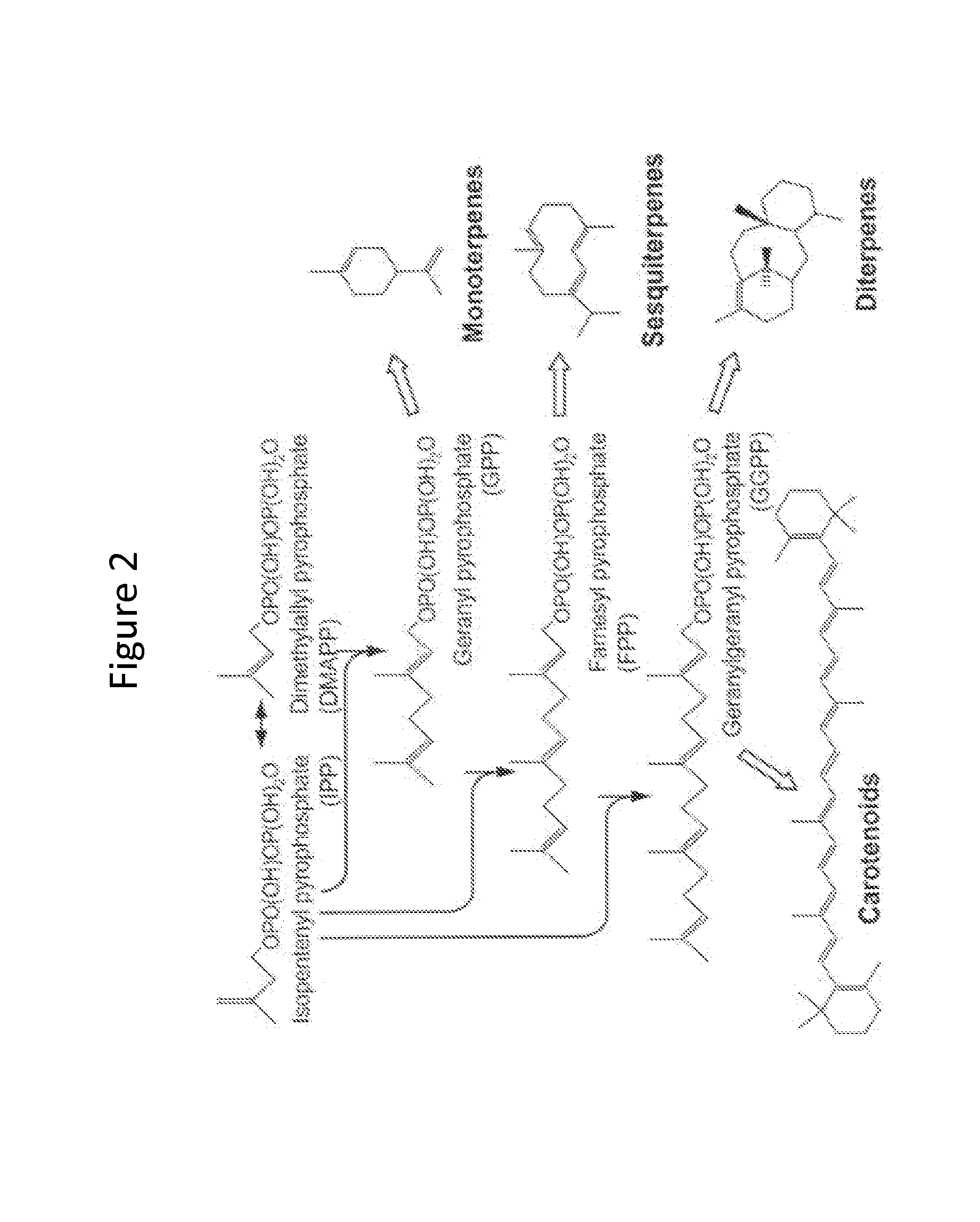
Disclosed are the uses of specific genes of the mevalonate and isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways, and of inactive gene sites (the pseudogene) to (1) enhance biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate, dimethylallyl diphosphate and isoprenoid pathway derived products in the plastids of transgenic plants and microalgae, (2) create novel antibiotic resistant transgenic plants and microalgae, and (3) create a novel selection system and / or targeting sites for mediating the insertion of genetic material into plant and microalgae plastids. The specific polynucleotides to be used, solely or in any combination thereof, are publicly available from GeneBank and contain open reading frames having sequences that upon expression will produce active proteins with the following enzyme activities: (a) acetoacetyl CoA thiolase (EC 2.3.1.9), (b) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) synthase (EC 4.1.3.5), (c) HMG-CoA reductase (EC 1.1.1.34), (d) mevalonate kinase (EC 2.7.1.36), (e) phosphomevalonate kinase (EC 2.7.4.2), (f) mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.33), (g) isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.2), and (h) phytoene synthase (EC 2.5.1.32).
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +1
Methods for treatment of a sarcoma using an epimetabolic shifter (coenzyme q10)
Methods and formulations for treating a sarcoma in humans using an epimetabolic shifter, such as Coenzyme Q10, a building block of CoQ10, a derivative of CoQ10, an analog of CoQ10, a metabolite of CoQ10, or an intermediate of the coenzyme biosynthesis pathway, are described. Methods for assessing the efficacy of treatment of, diagnosing, and prognosing sarcoma are also provided.
Owner:BERG
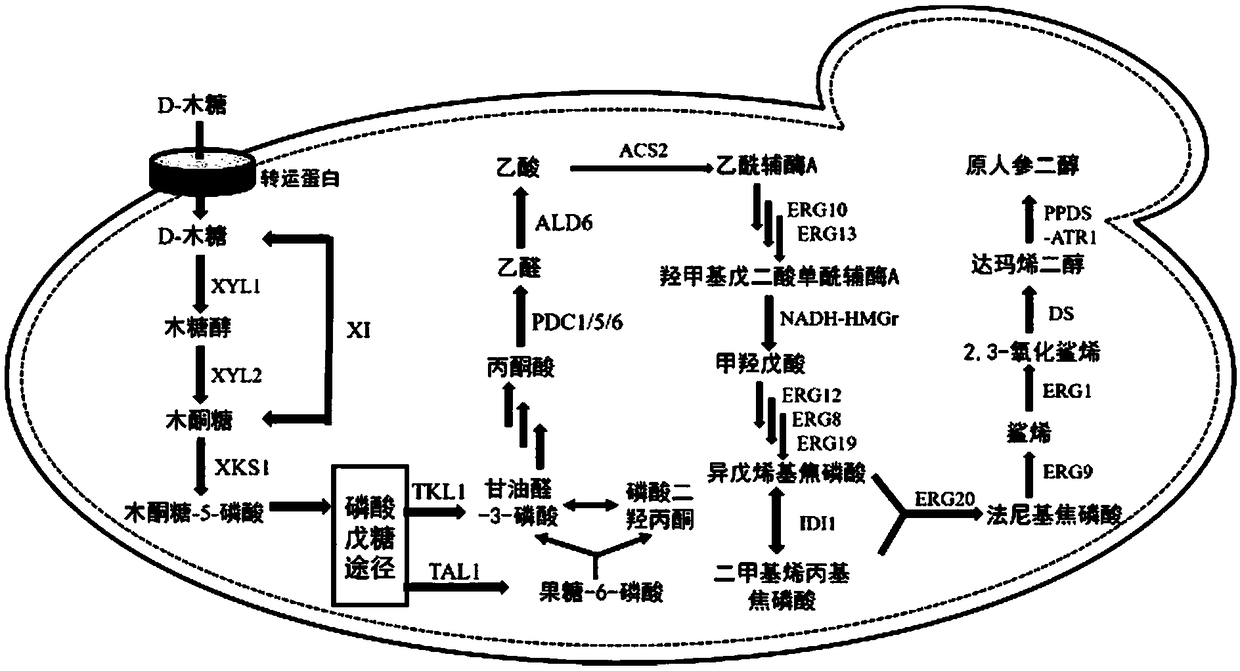
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
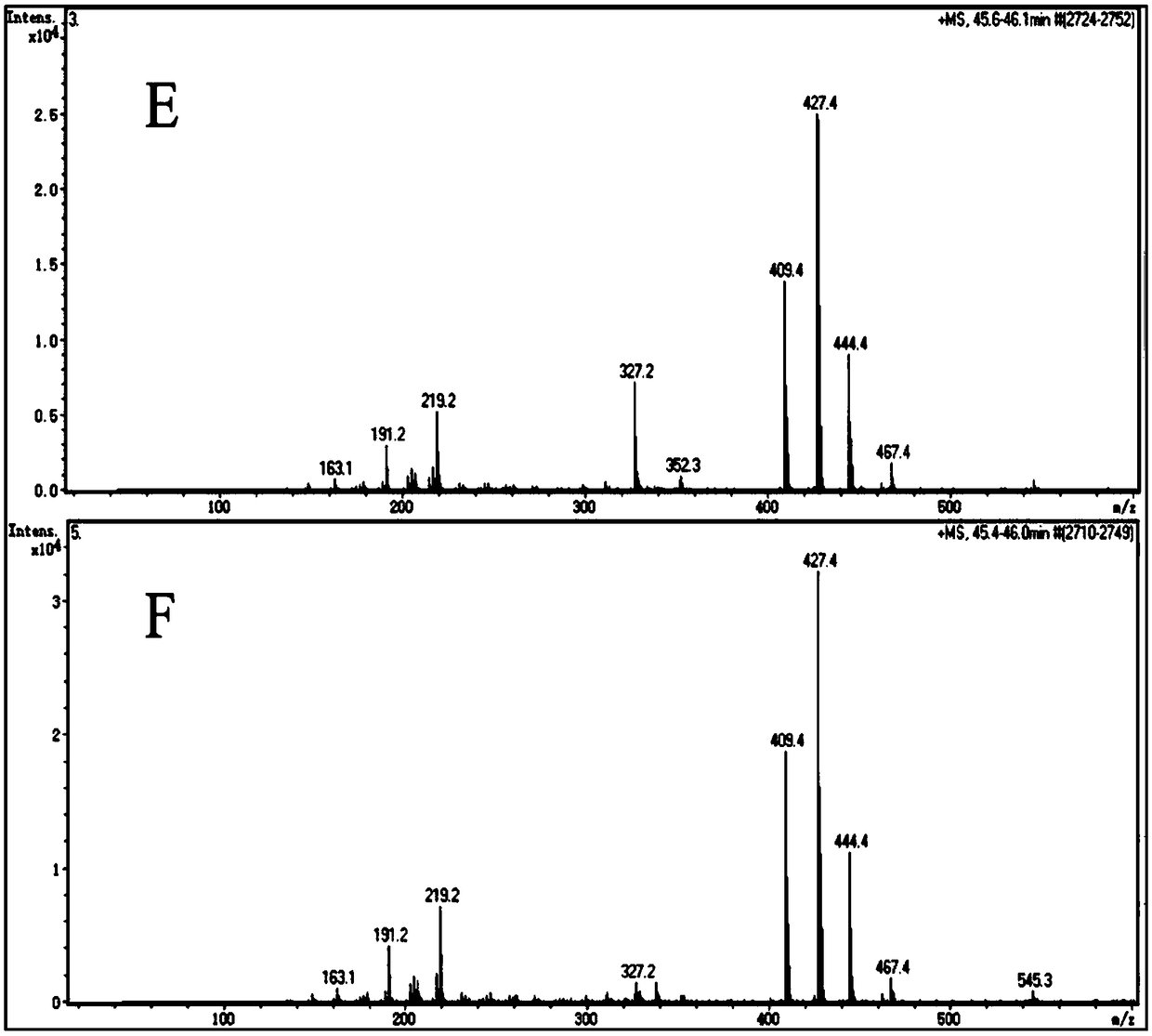
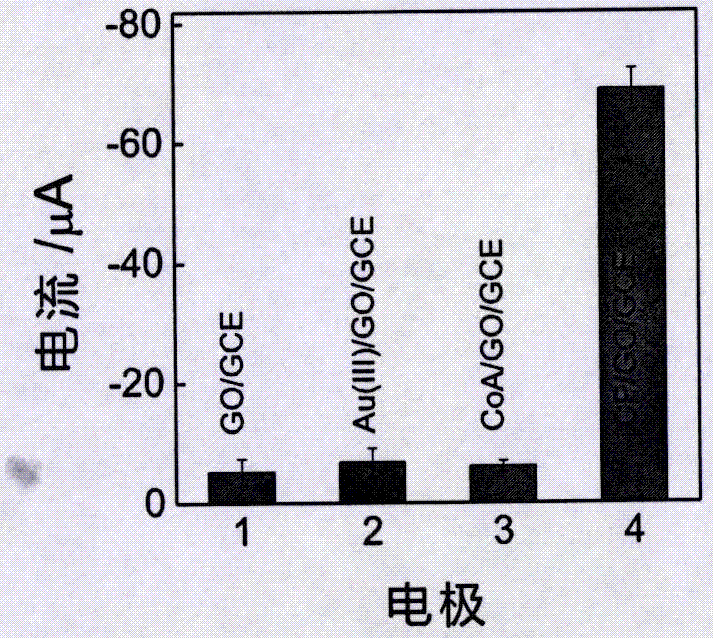
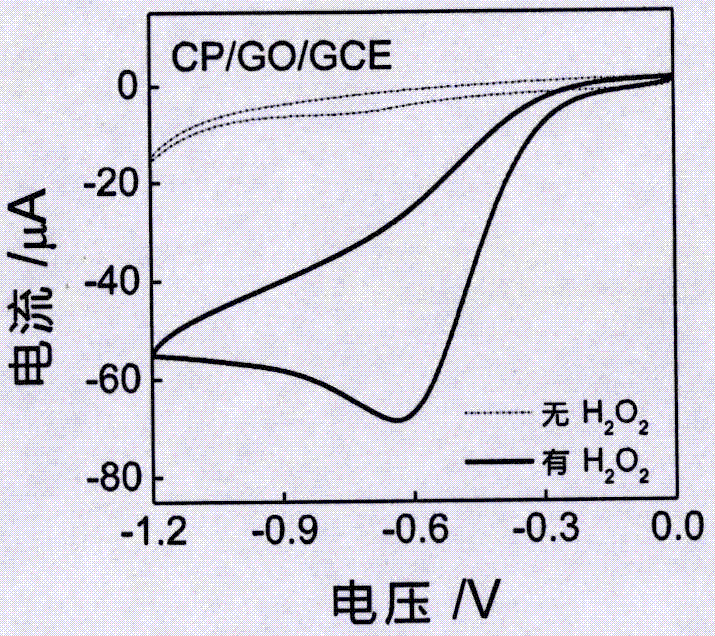
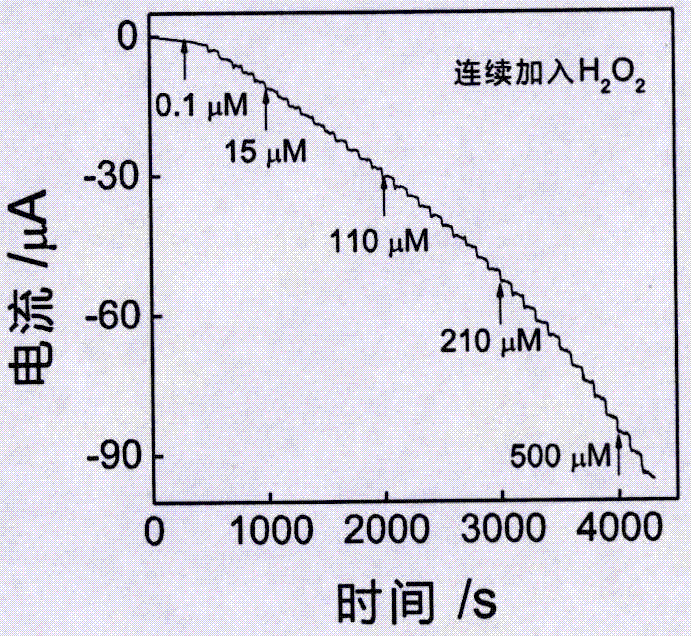
Preparation method and application of electrochemical biosensor based on coenzyme A-Au(I) coordination polymer
ActiveCN107064259AEasy to passHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorPeroxidase
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an electrochemical biosensor based on a nucleic acid-like CoA-Au(I) coordination polymer capable of simulating peroxidase character. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: (1) dissolving graphene into an acetic acid buffer solution and ultrasonically dispersing in an ultrasonic cleaner to obtain graphene dispersion liquid; (2) evenly mixing coenzyme A, chloroauric acid and a phosphoric acid buffer solution in a PCR pipe, continuously oscillating to enable gold ions to be reduced and obtaining a CoA-Au(I) coordination polymer in room temperature; (3) electrolytically depositing graphene on a bare glassy carbon electrode and then dropwise adding a CoA-Au(I) coordination polymer solution to be used for detecting hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen peroxide concentration in a biological sample. The electrochemical biosensor has the advantages of good specificity, high flexibility, quick detection speed, accurate and reliable result and low cost.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for enhancing adipic acid yield in Escherichia coli
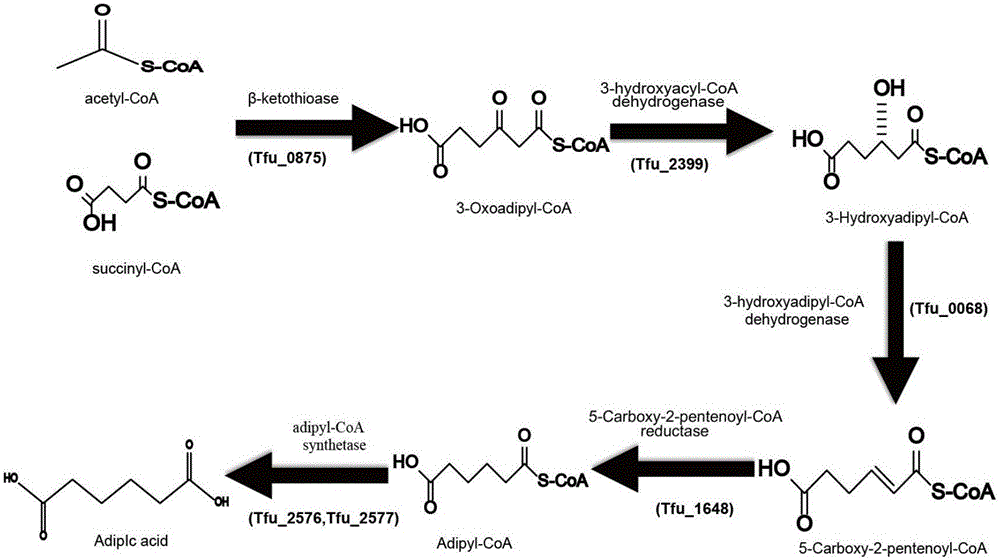
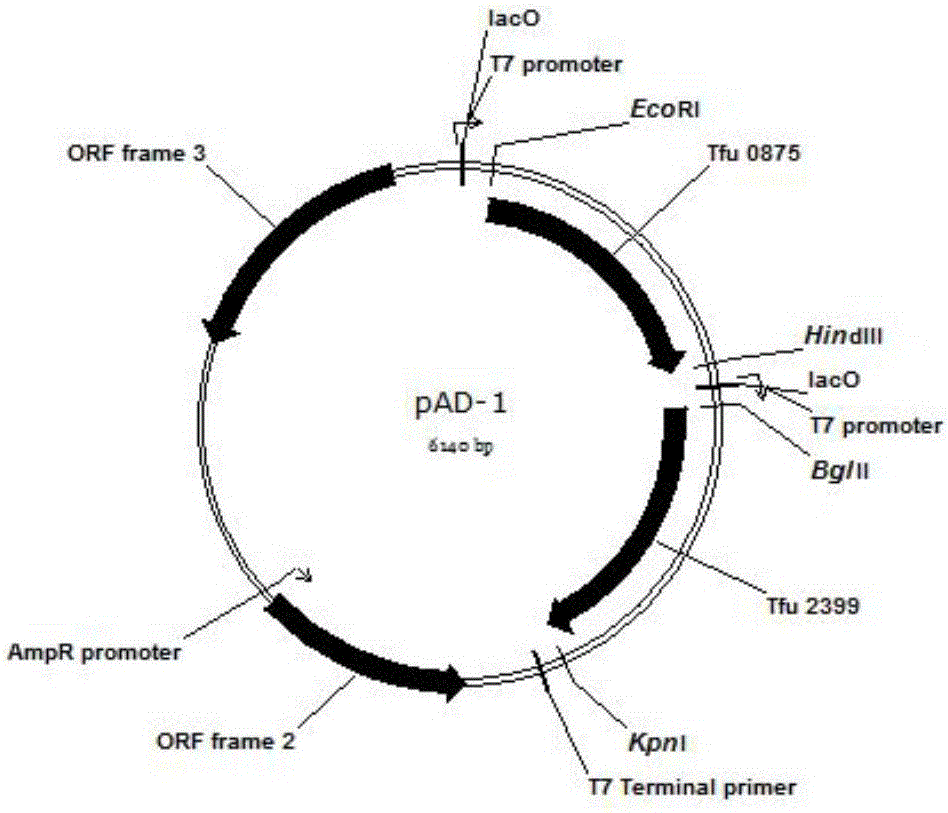
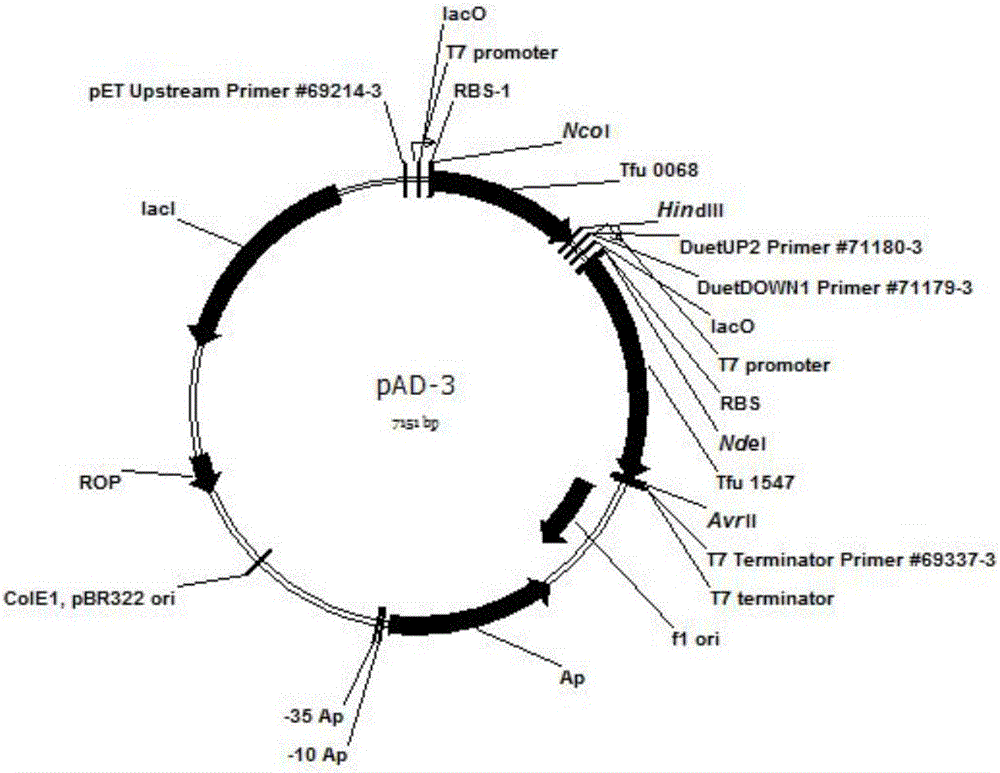
ActiveCN106834200AReduce pollutionEasy to recycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBeta-ketothiolase
The invention discloses a method for enhancing adipic acid yield in Escherichia coli, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The method is implemented by overexpressing beta-ketothiolase gene, 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene, 3-hydroxyadipyl dehydrogenase gene, 5-carboxyl-2-pentene acylcoenzymea A reductase gene and adipyl coenzyme A in different modules by using atoB-gene-knock-out Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) as a host; and the adipic acid yield can reach 25.57 g / L. The recombinant bacterium can also perform cyclic fermentation; and after ten cycles, the adipic acid accumulated yield is up to 18.94 g / L. The method has important functions on industrial continuous mass production, can shorten the thallus growth time, and has the advantages of time saving, high speed and cost saving since the cyclic thallus fermentation is directly utilized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
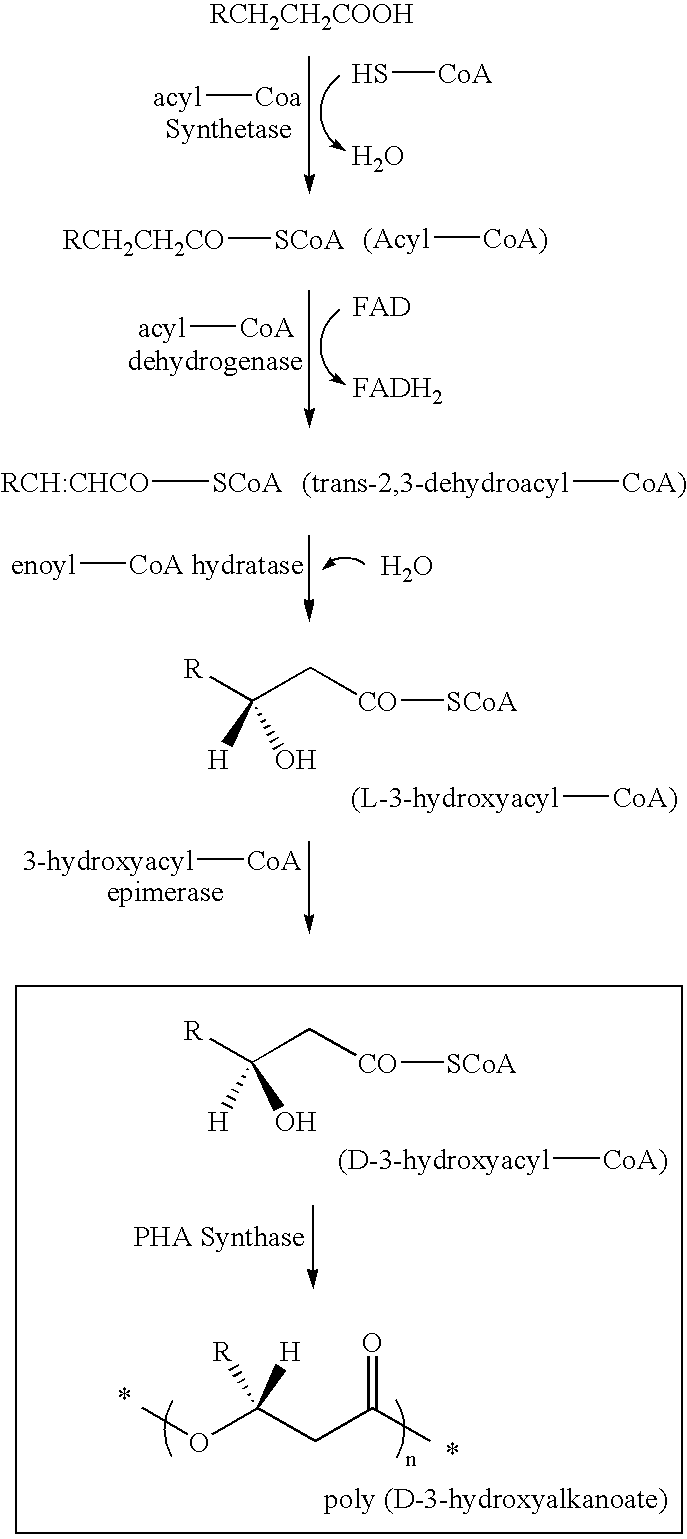
Method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof
ActiveCN101845414AHigh purityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas putidaCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer and special bacteria thereof. Recombinant pseudomonas putida is prepared by the method comprising the following steps of: depriving coding functions of 3-hydroxyfatty acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase coding gene and 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase coding gene in pseudomonas putida to obtain recombinant pseudomonas putida, and recording the recombinant pseudomonas putida as recombinant pseudomonas putida I. Experiments prove that the hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer, particularly medium and long-chain hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer (C4-C14), can be obtained by using the recombinant bacteria organism to synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate. The obtained hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer has high purity and high yield. The method of the invention can synthesize the medium and long-chain hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer with random length, and overcomes the defect that only one 3-hydroxybutyrate (HB) homopolymer can be obtained by biosynthesis in the prior art. Therefore, the method of the invention has broad application prospect in the biosynthesis field of the hydroxyalkanoate homopolymer.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
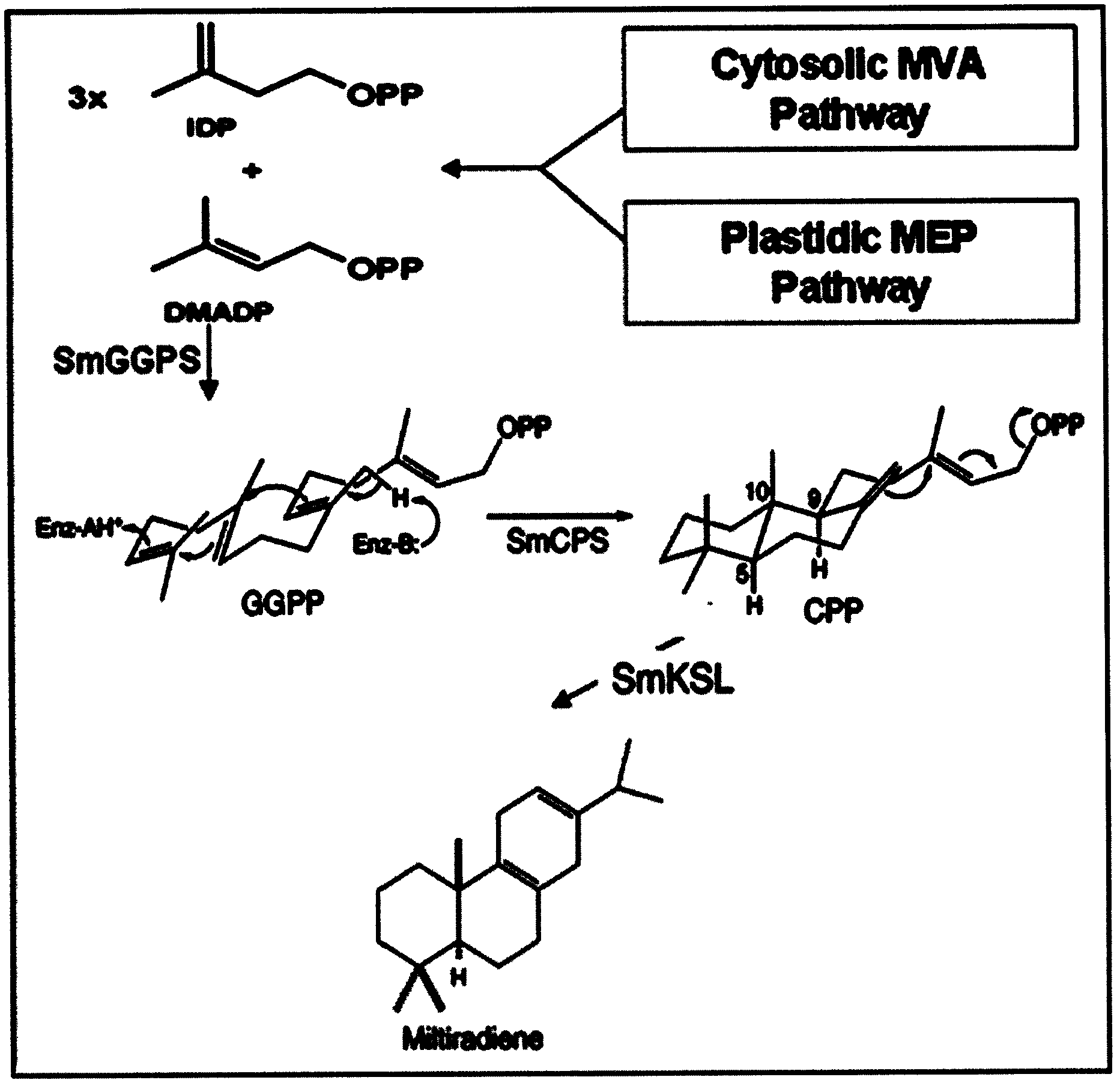
Brewer yeast gene engineering strains for producing miltiradiene, and construction method and application of brewer yeast gene engineering strains
The invention discloses a brewer yeast gene engineering strains for producing miltiradiene, and a construction method and application of the brewer yeast gene engineering strains. The construction method for the gene engineering strains comprises the following steps of introducing exogenous SmCPS (salvia miltiorrhiza copalyl pyrophosphate synthase) and SmKSL (salvia miltiorrhiza kaunene synthase like) into original brewer yeast to obtain recombinant brewer yeasts for producing the miltiradiene, wherein the recombinant brewer yeasts are recorded as ZD-T-000 and ZD-T-010; improving the activity of one or more proteins in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase, a terpene control element protein UPC2, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase and farnesyl phosphate synthase on such a basis to construct 24 high-miltiradiene yield recombinant brewer yeast strains (ZD-T-001 to ZD-T-008, ZD-T-011 to ZD-T-018 and ZD-T-021 to ZD-T-028). The brewer yeast ZD-Tans-001 can be used for producing 487.91mg / L miltiradiene after being fermented for 6 days under an aerobic condition.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Haemophilus parasuis culture medium
ActiveCN103215208AMaintain integrityIncrease success rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSerum igeHaemophilus
The invention discloses a haemophilus parasuis culture medium. A preparation method of the haemophilus parasuis culture medium comprises the steps of preparing a basic culture solution, treating coenzyme A, and perfecting a culture medium, wherein the basic culture solution comprises peptone, tryptone, sodium chloride, dextrose, yeast extract, glycerin and distilled water, and the basic culture solution, the coenzyme A and fetal bovine serum are uniformly mixed so as to obtain the haemophilus parasuis culture medium. The haemophilus parasuis culture medium provided by the invention can keep haemophilus parasuis, thereby facilitating the transportation of suspicious haemophilus parasuis samples; and the death of haemophilus parasuis is not caused in the process of transportation, thereby increasing the separation probability of the haemophilus parasuis.
Owner:广西悦牧生物科技有限公司
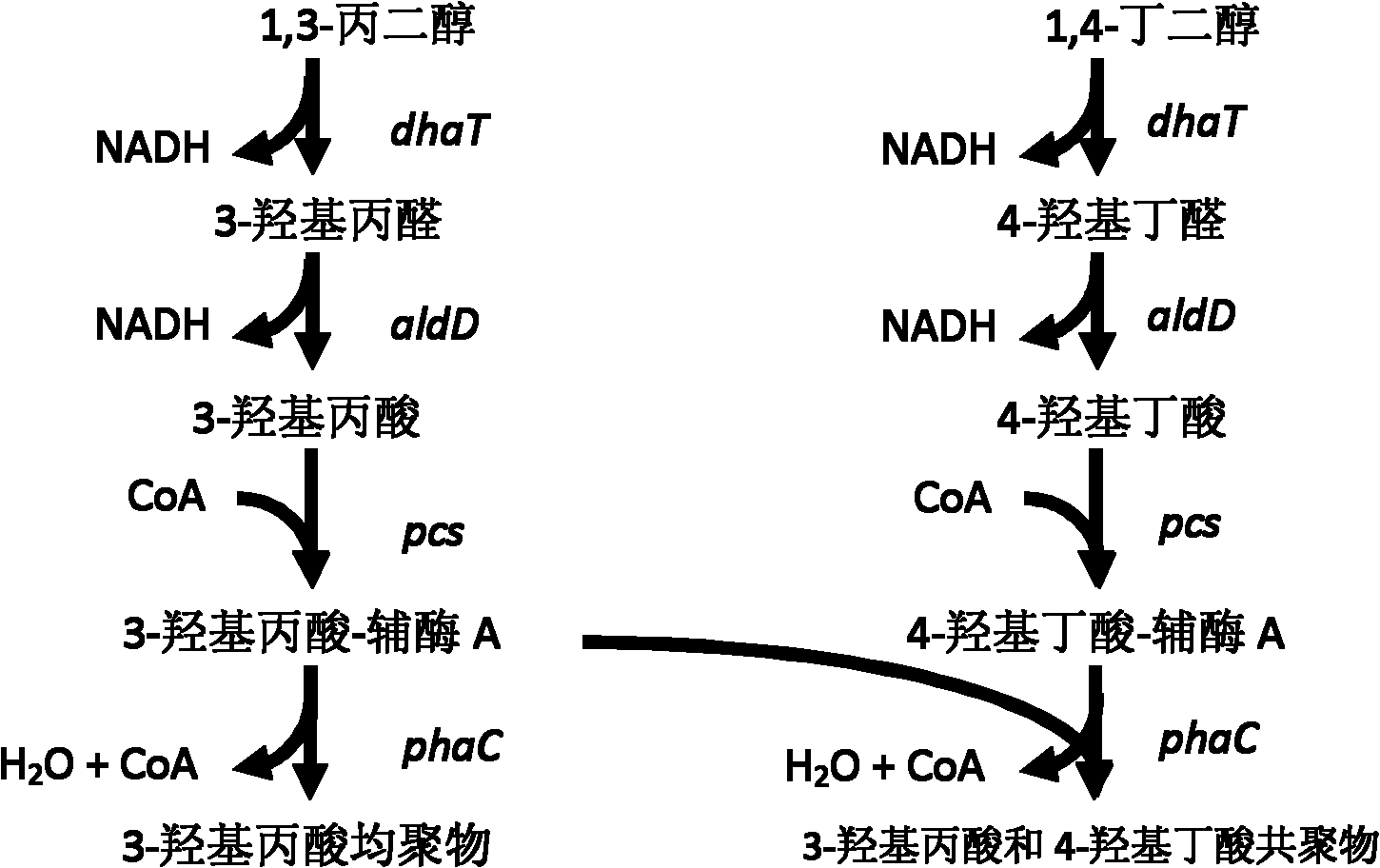
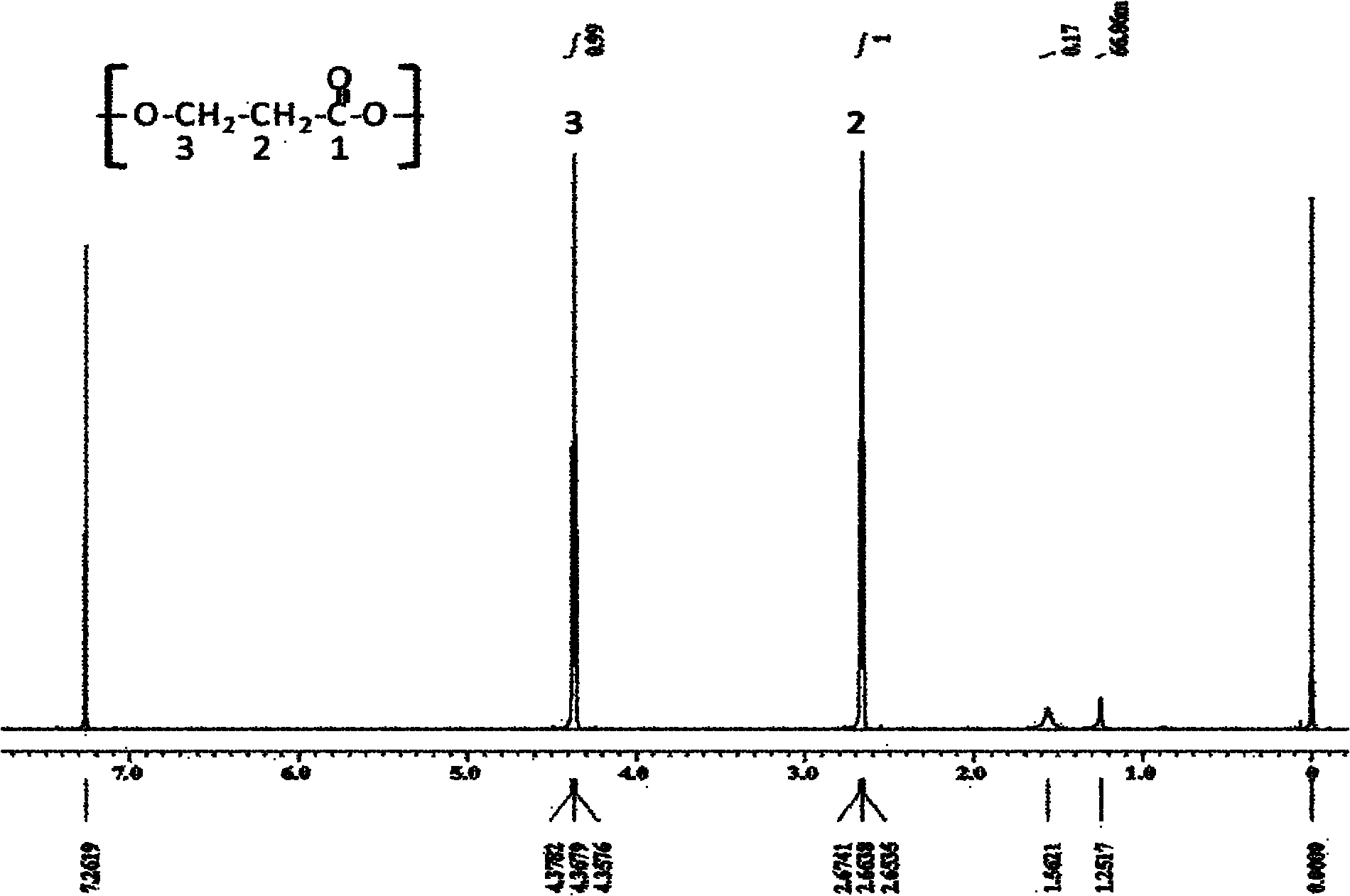
Method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid
InactiveCN103898034AWide variety of sourcesSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli strain, a preparation method of the recombinant escherichia coli strain and a method for biologically synthesizing poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid from acetyl coenzyme A. The method comprises the following steps: with glucose or glycerin and the like as carbon sources, commonly over-expressing endogenous or exogenous acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes (acc) and propionyl coenzyme A synthetase genes (prpE) as well as exogenous malony coenzyme A reductase genes (mcr) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase genes (phaC) in proper host cells (such as escherichia coli), and degrading intermediate products by virtue of glucose so as to biologically synthesize the poly-3-hydroxypropionic acid, wherein acetyl coenzyme A is finally obtained from simple starting materials such as the glucose and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Reduction or prevention of alcohol reaction with dietary supplements
InactiveUS20140256760A1Improve the level ofReduce average peak blood level of acetaldehydeBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsAlcoholDietary supplement
The present invention is directed to compositions for preventing or reducing the flush and other unpleasant symptoms that sometimes accompany the consumption of alcoholic beverages, and methods for use of said compositions. The compositions comprise an agent, or combinations of various agents, such as an agent capable of increasing intracellular or intramitochondrial concentration of NAD in the subject; an agent capable of increasing glutathione concentration in the subject; an anti-oxidant; alpha-lipoic acid or a precursor to alpha-lipoic acid; and / or an agent capable of increasing the level of Coenzyme A in the subject; where the agent or agents are present or administered in amounts effective to prevent or reduce the alcohol reaction in a subject who has consumed one or more alcoholic beverages.
Owner:NOGLO
Multiple-effect instillation liquid for trees and use method thereof
ActiveCN102718595ASolve the problem that cannot be directly absorbed by plantsEffective moisture balanceFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsVitamin CInjury mouth
The invention relates to the technical field of landscaping plantation and especially relates to a multiple-effect instillation liquid for trees and a use method thereof. The multiple-effect instillation liquid for trees comprises: coconut, radix astragali and ephedra, Chinese ephedra root, dextrose, coenzyme A, triphosadenine, vitamin B1, vitamin C, dexamethasone sodium phosphate, cytex, brassin, potassium sorbate, boric acid, manganese sulfate, zinc sulfate, an auxin and an antiseptic. The multiple-effect instillation liquid for trees can realize the one-time supply of nutrients to a nursery stock, balancing of moisture of a nursery stock, resistance of water evaporation, fast healing of wounds of a wounded root system, promotion of early rooting, and prevention of infection.
Owner:LINGNAN LANDSCAPE
Lymphocyte cultivation liquid and method and application
ActiveCN101037668AIncrease multipleHigh value-addedBlood/immune system cellsSodium bicarbonateLymphocyte culture
The invention discloses a lymphocyte culture fluid and culture method thereof and application therefor, the culture fluid is adding ATP and coenzyme A in completely culture fluid containing basic culture fluid RPMI-1640, albumin, L-glutamine, glucose, baking soda and HEPES. The culture method includes steps: (1) preparing culture fluid; (2) suspending cell in culture fluid prepared by step (1); (3) activating cell; (4) washing activated cell by the culture fluid prepared by step (1); (5) collecting cell. The culture fluid of the invention cultures cell with higher amplification times and longer generation time.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF CHANGZHOU
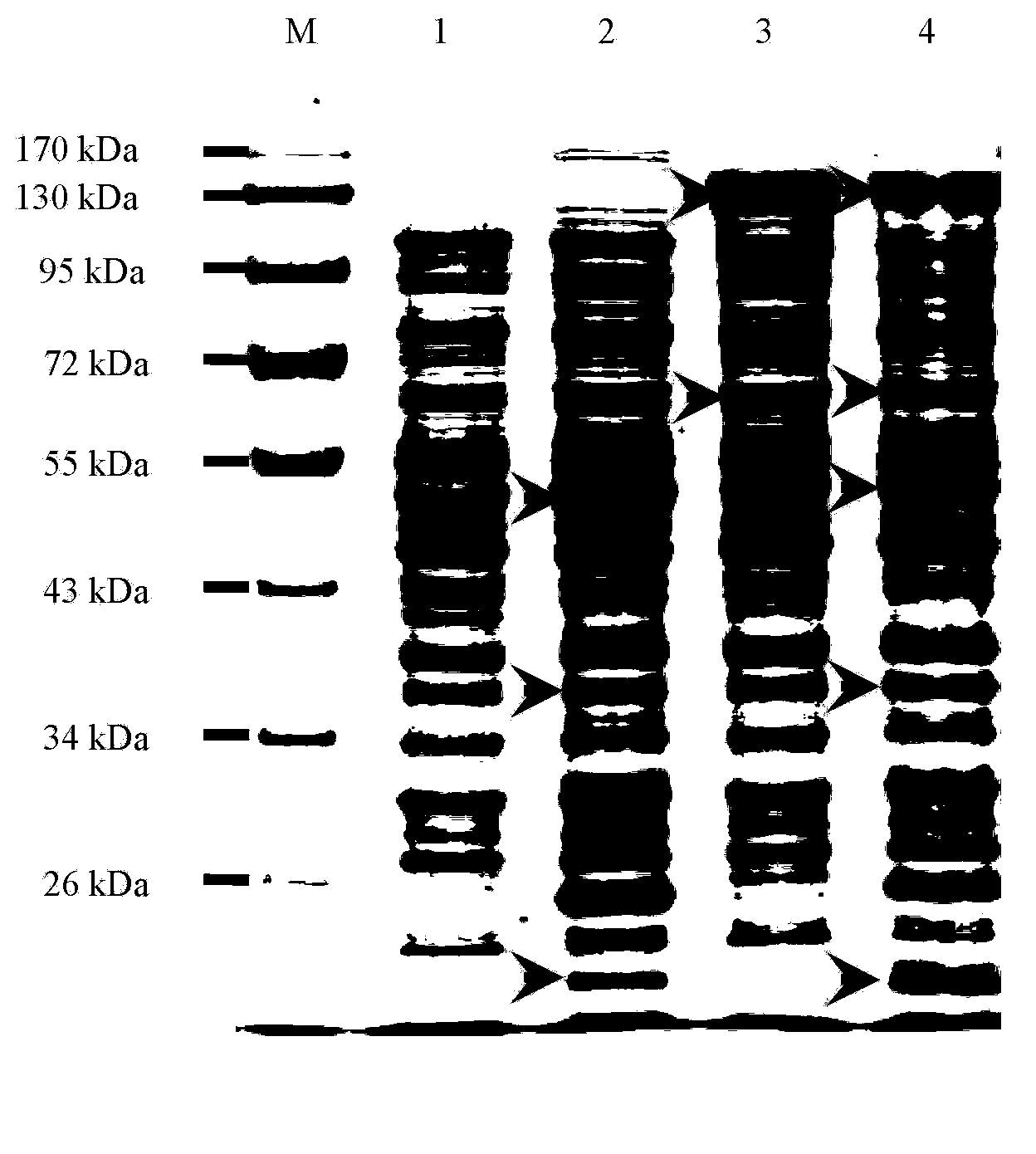
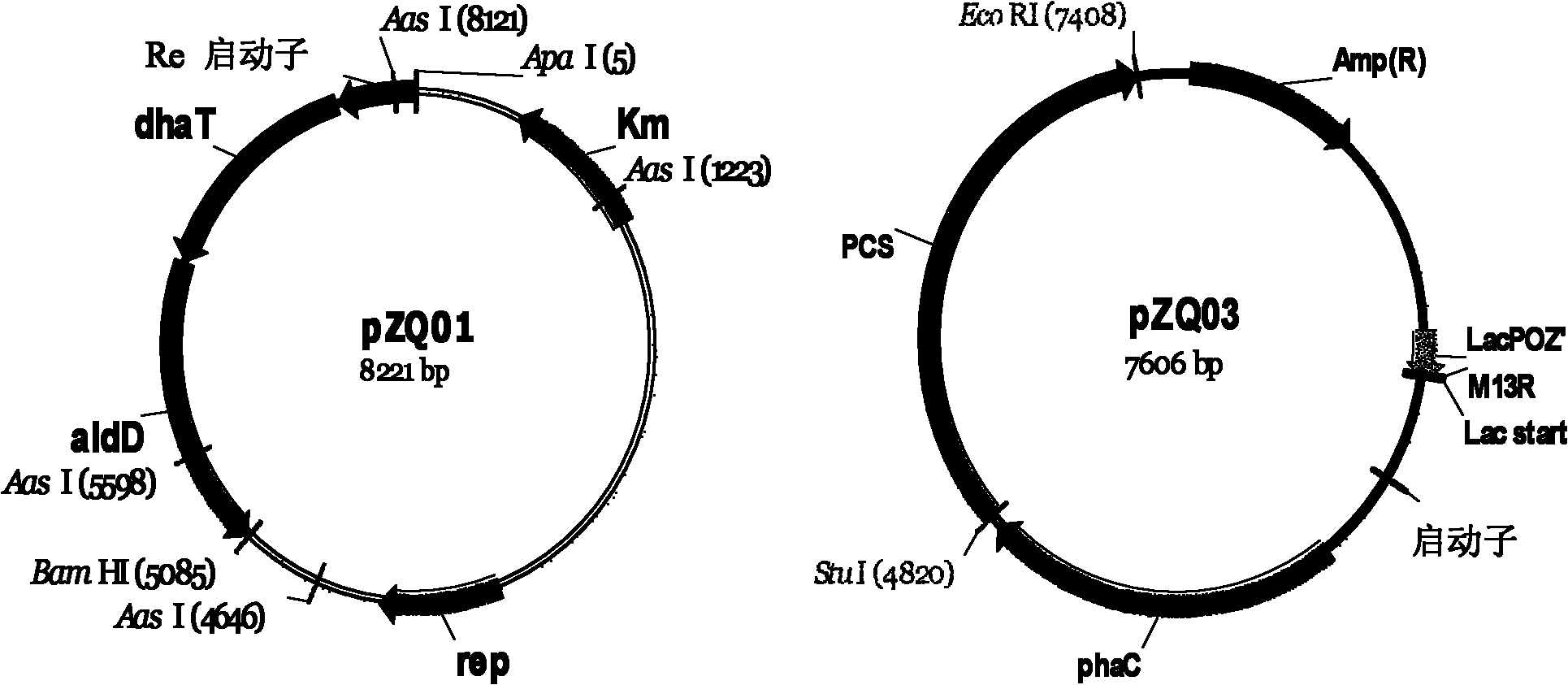
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542AImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPolymerase L
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com