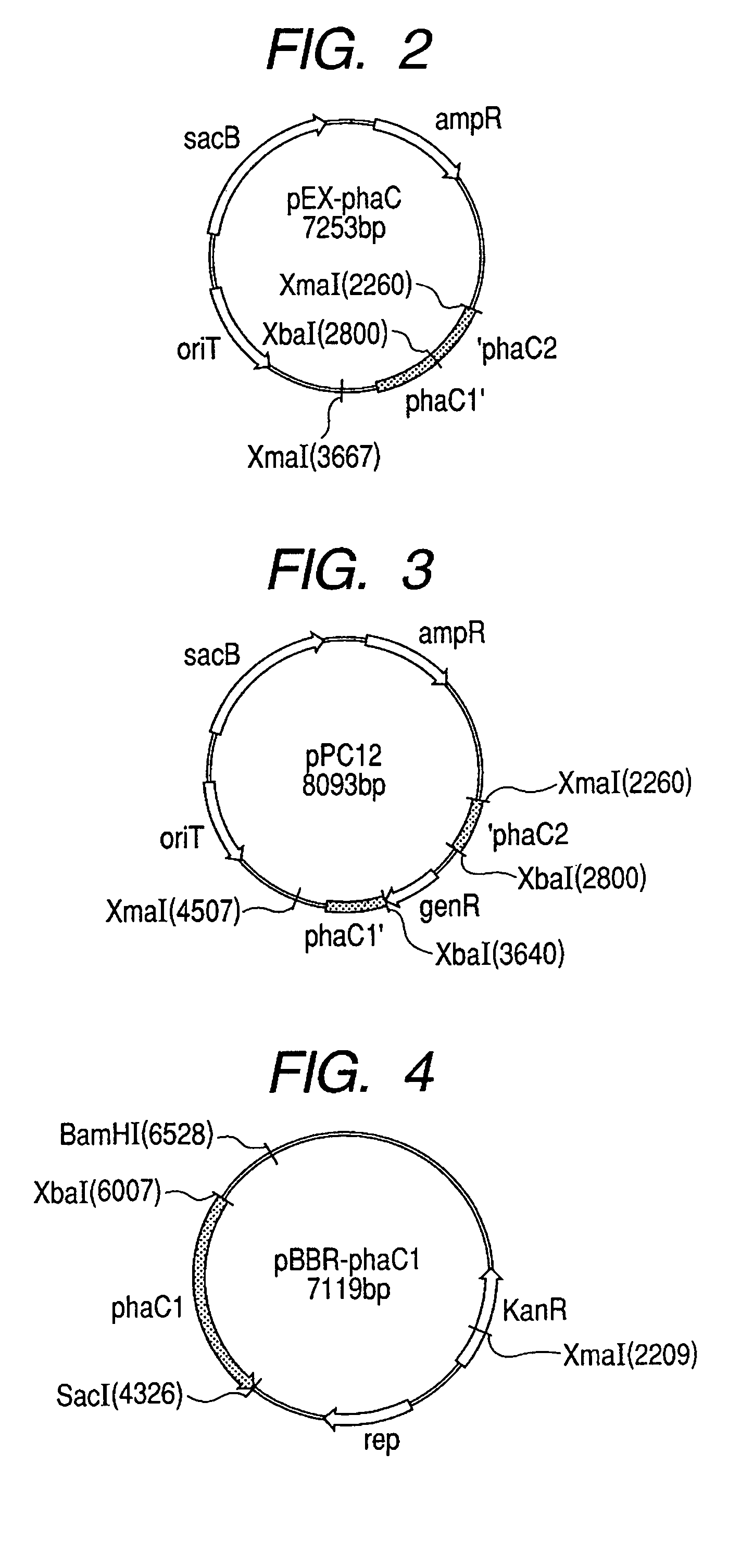
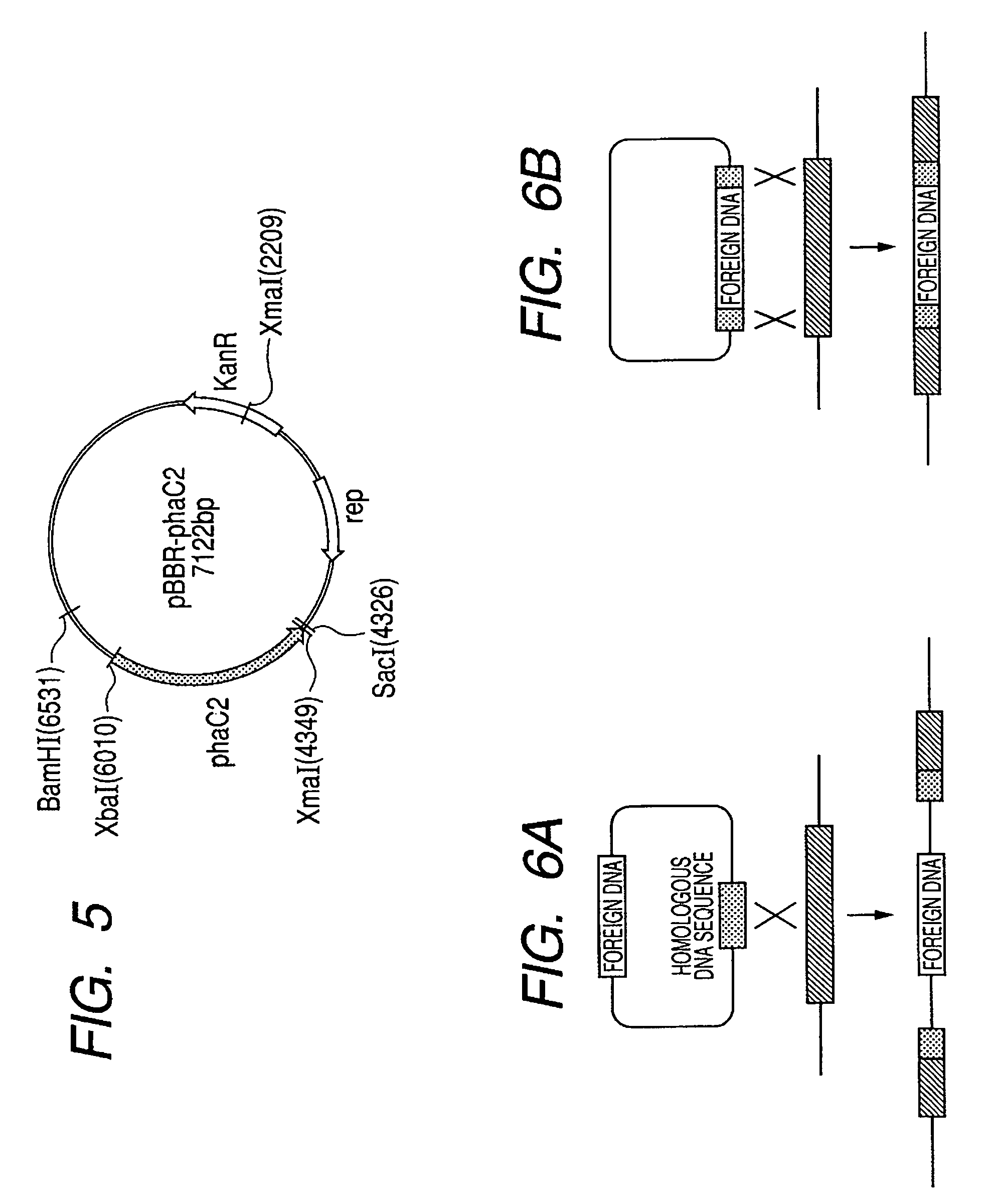
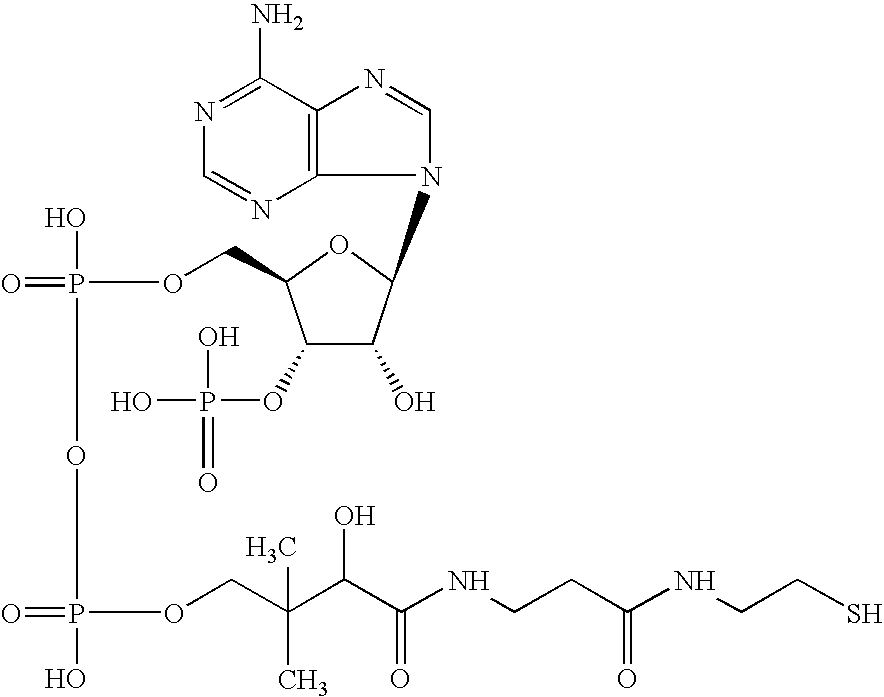
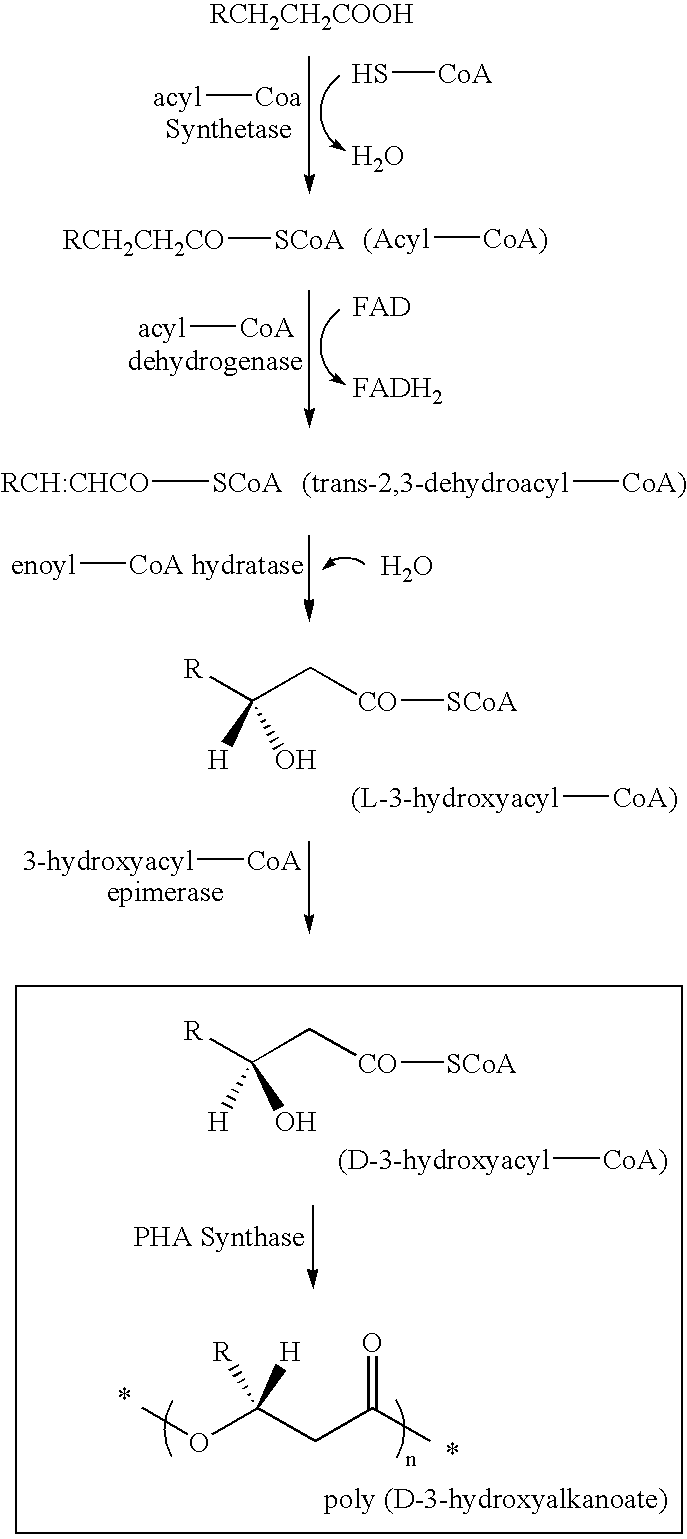
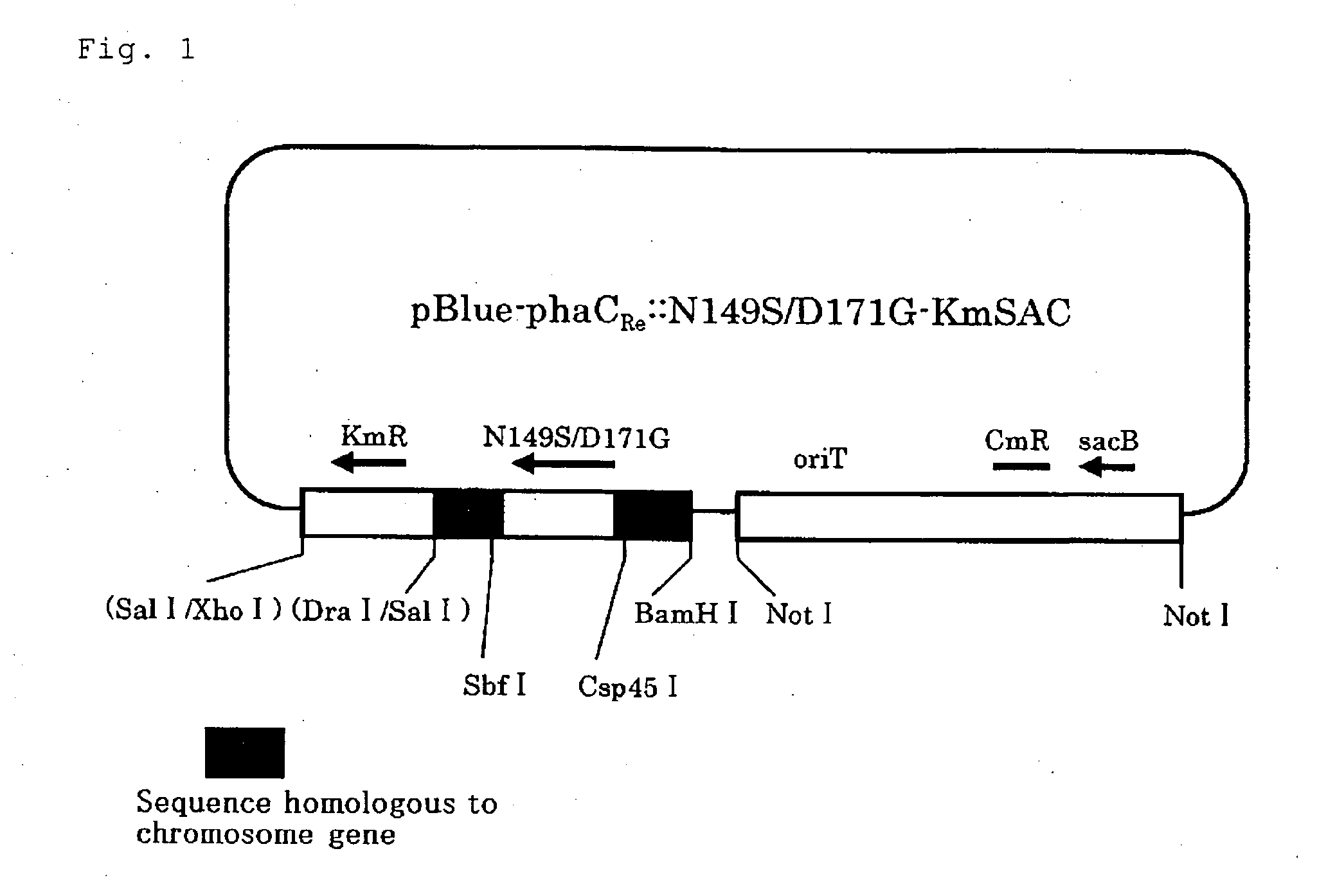
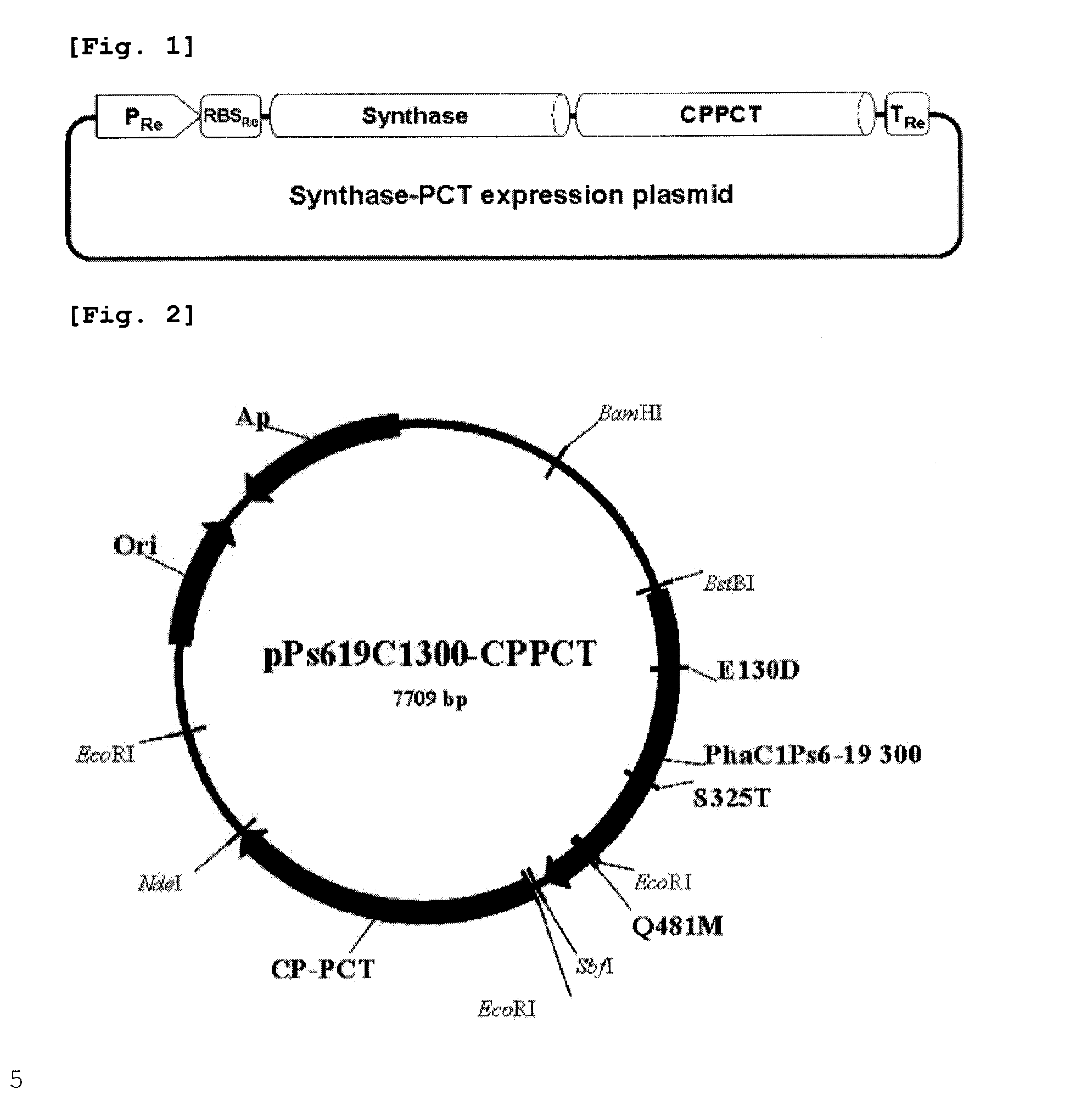
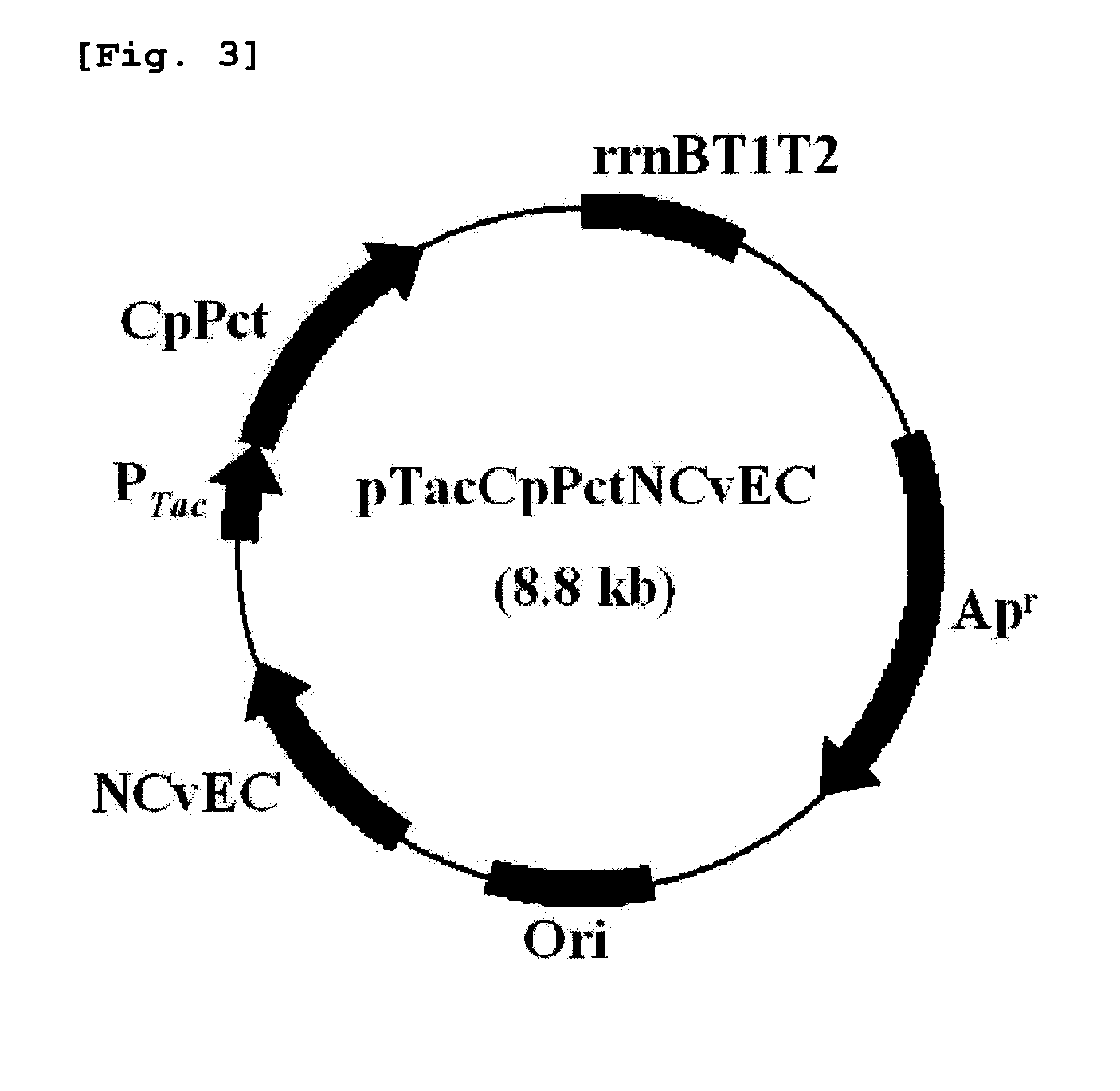
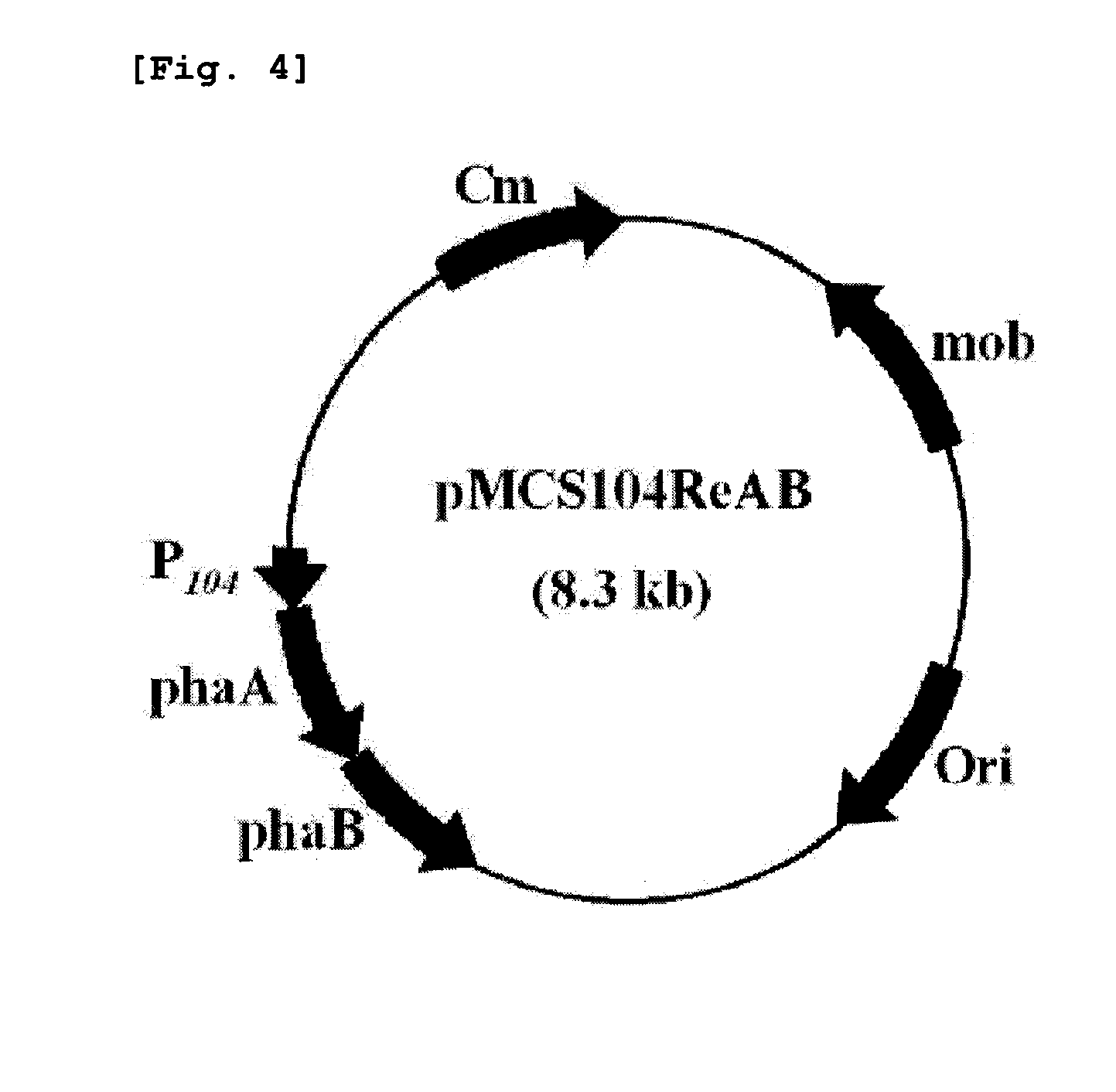
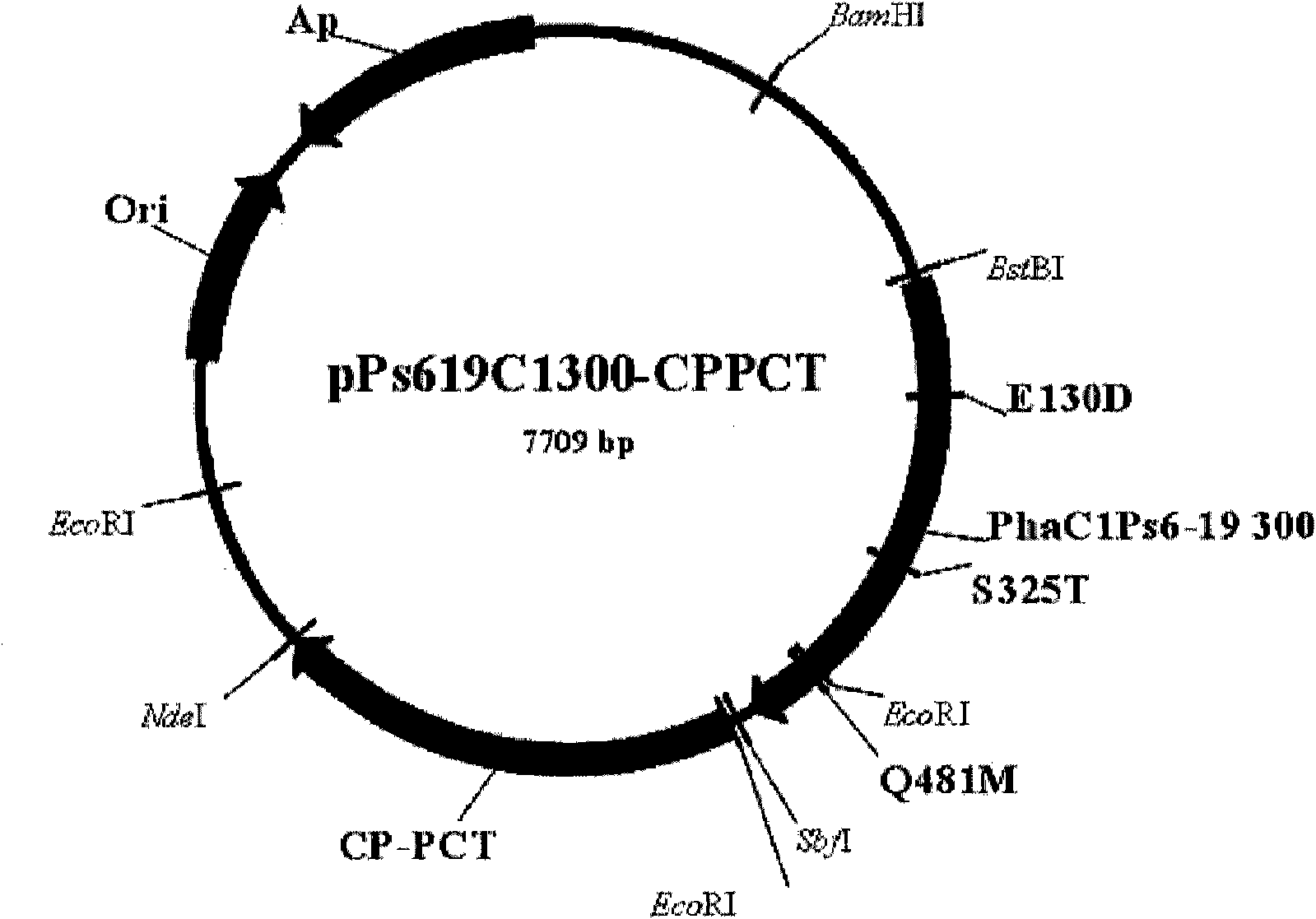
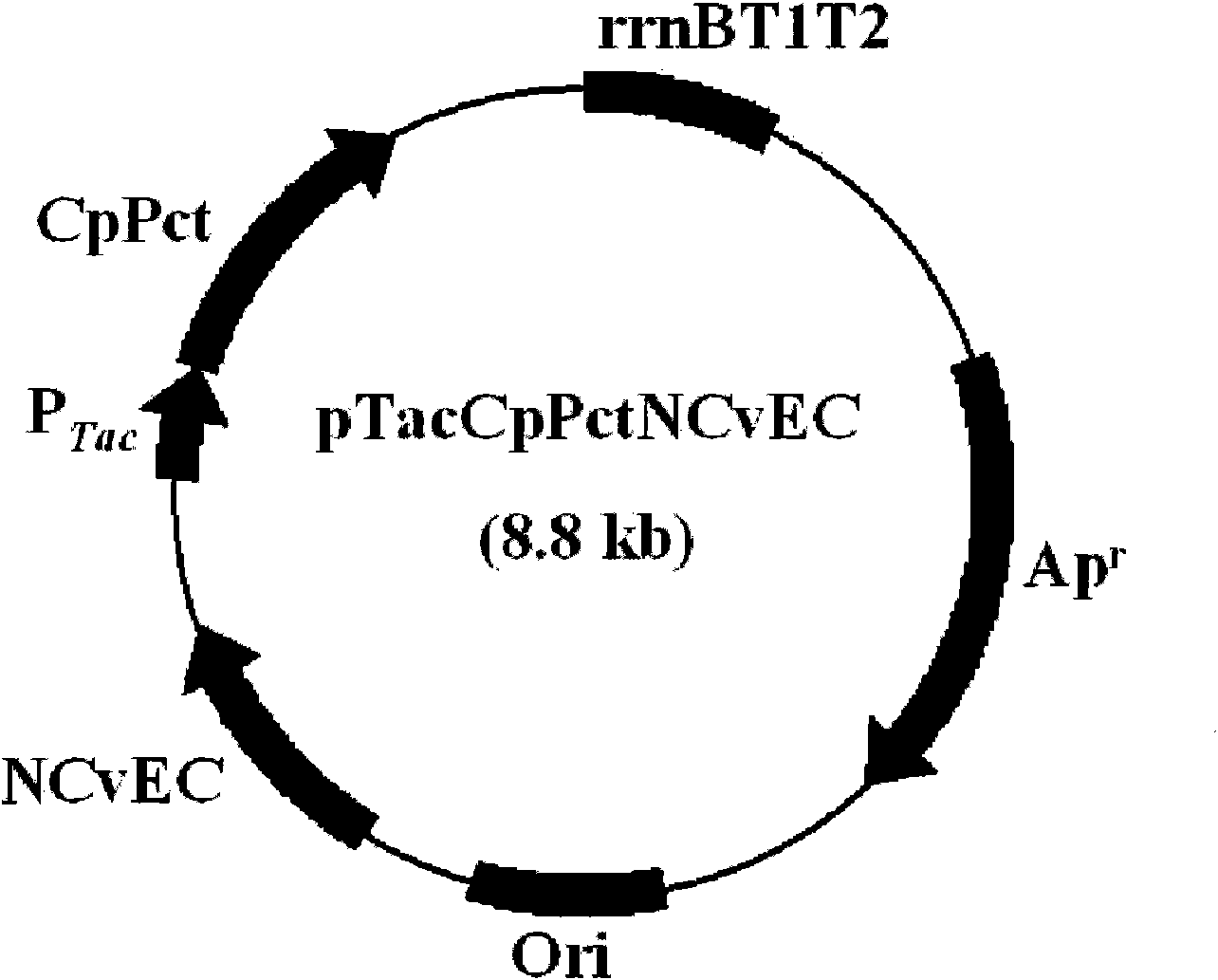
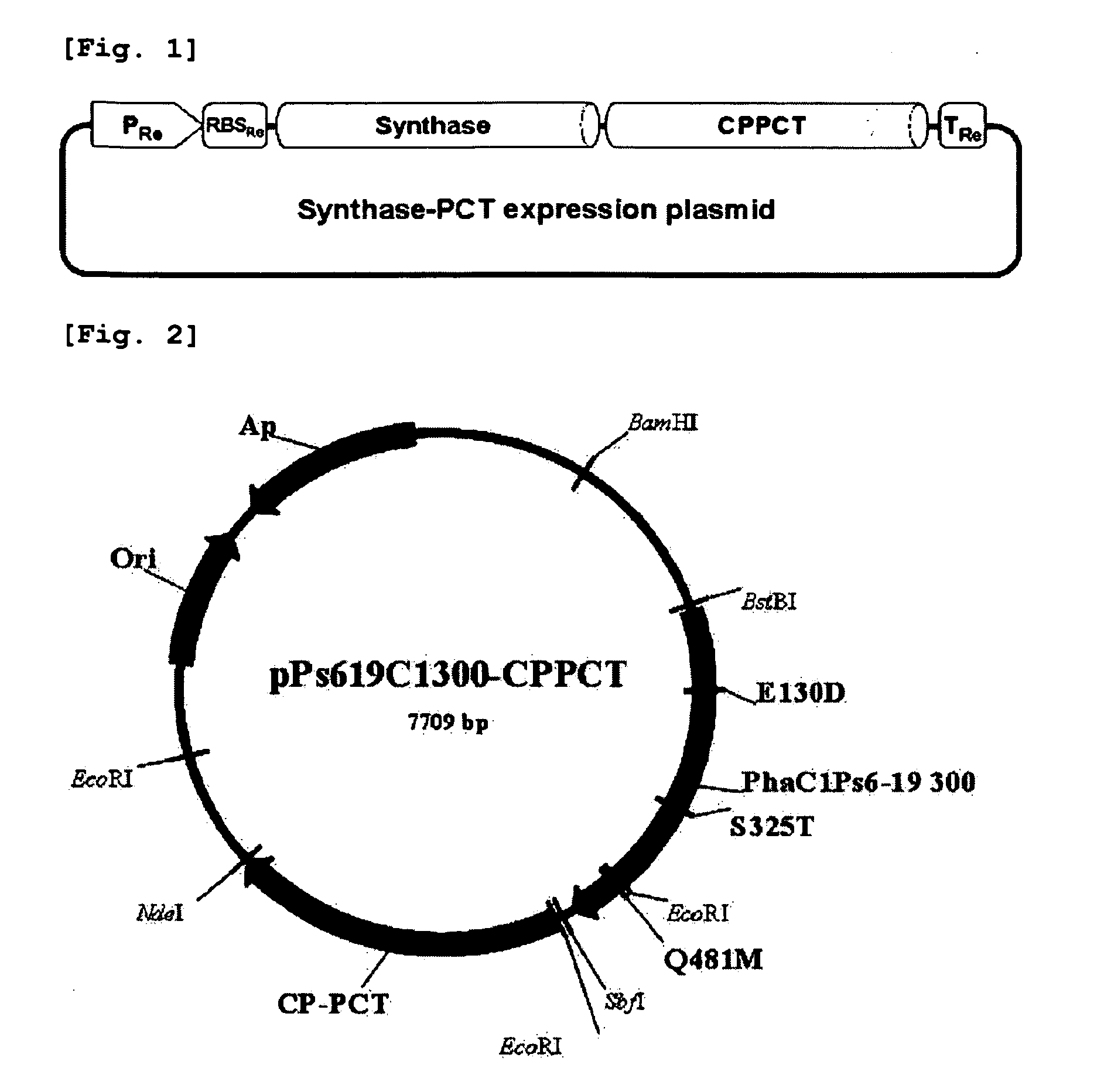
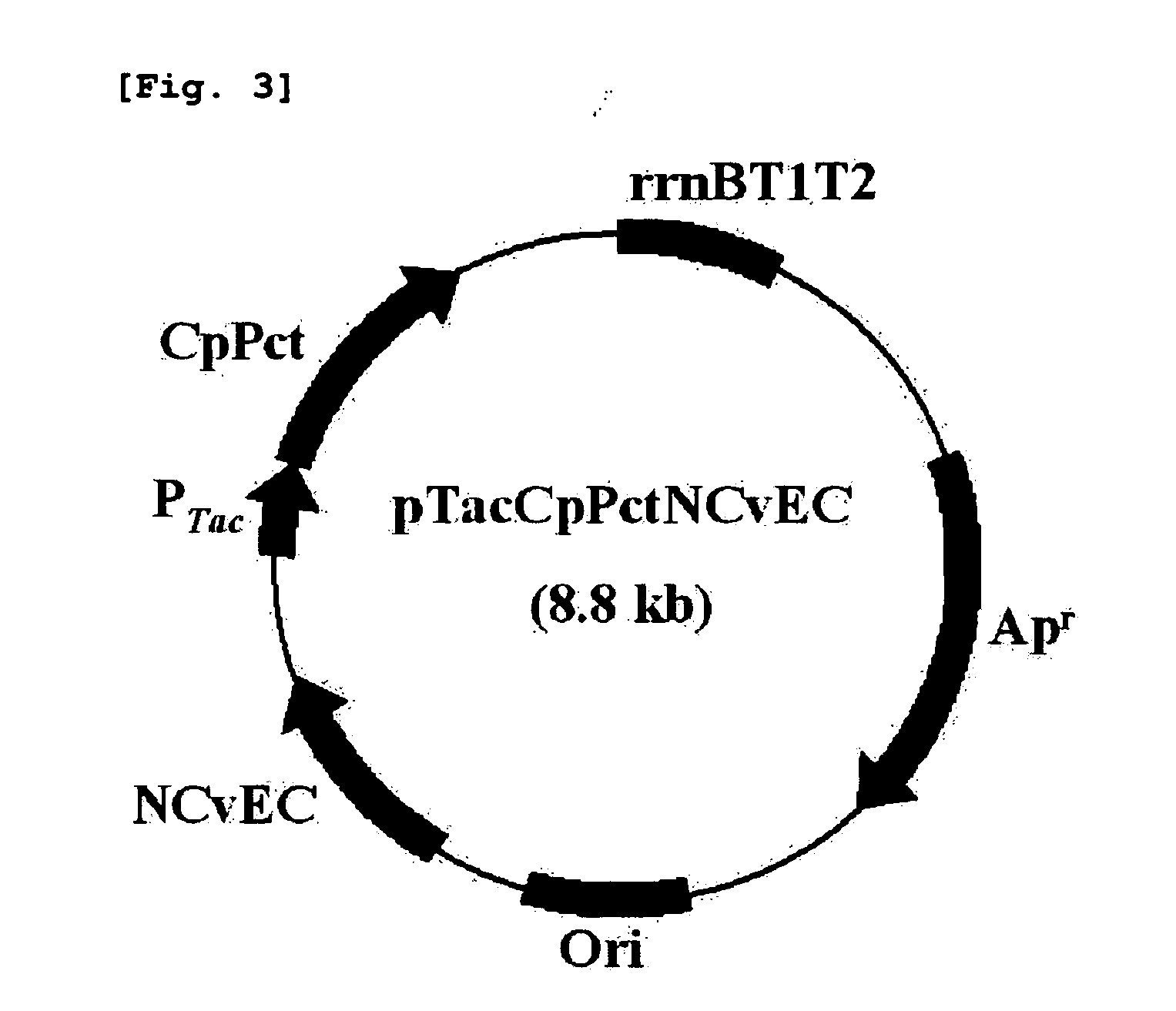
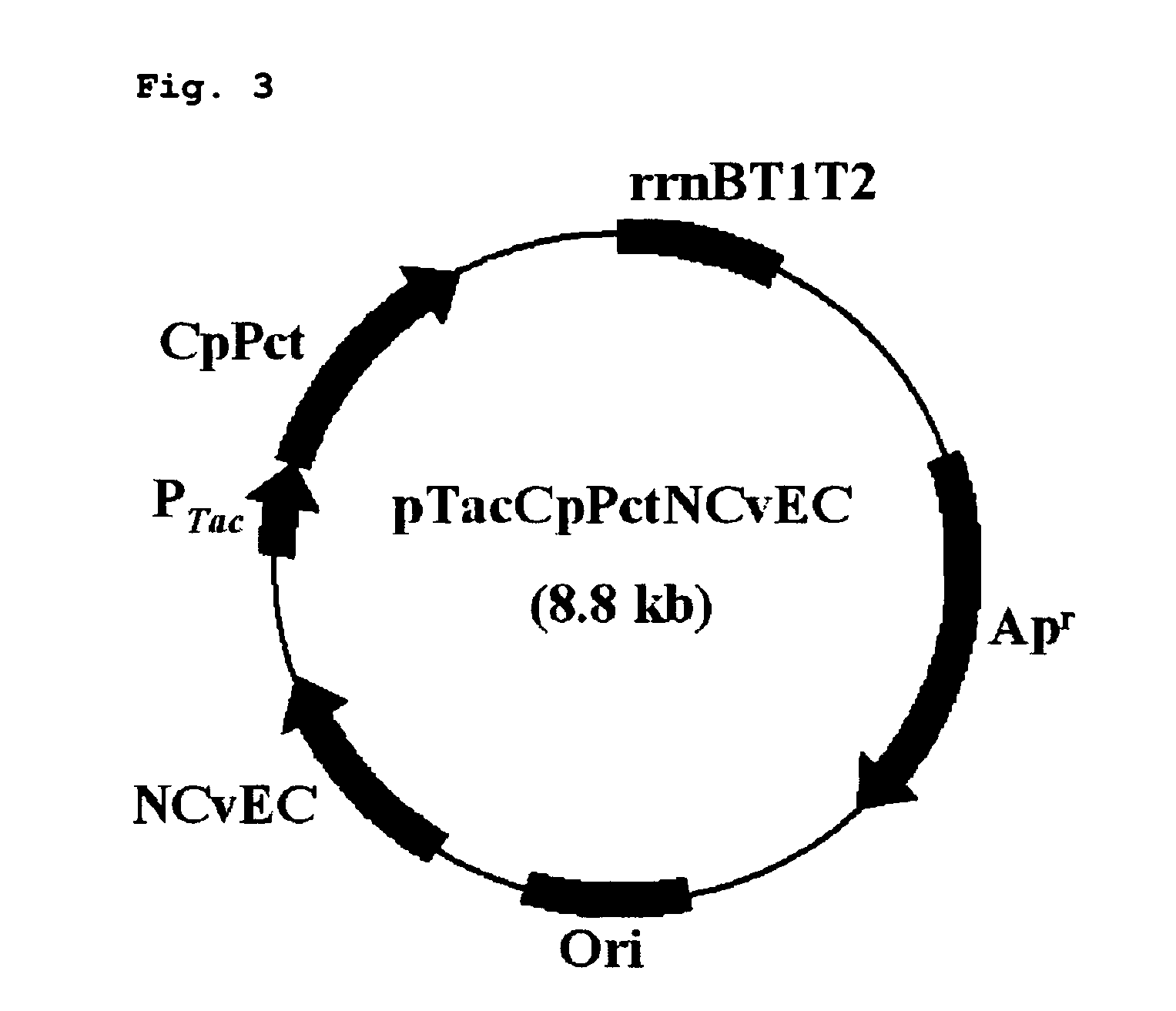
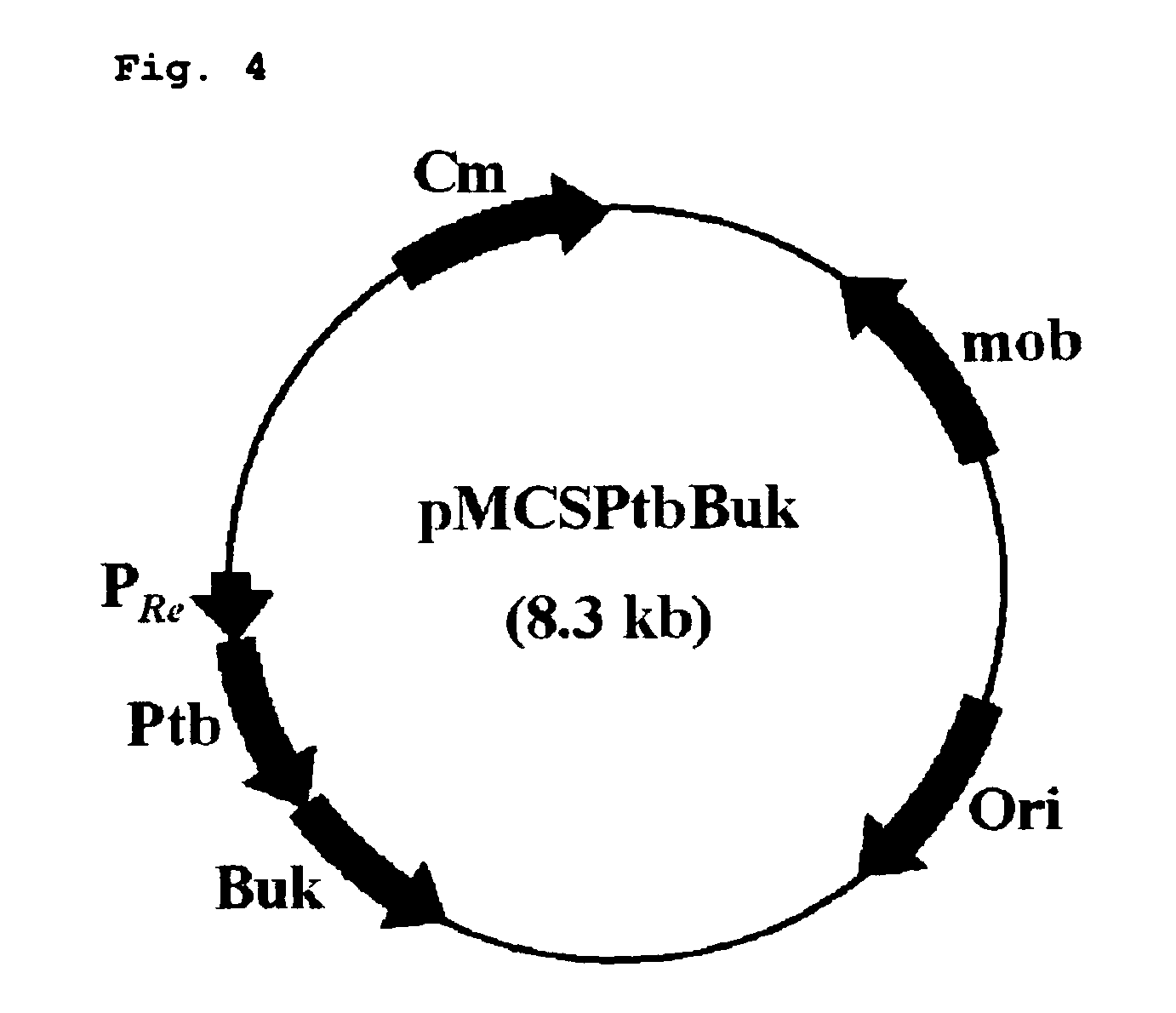
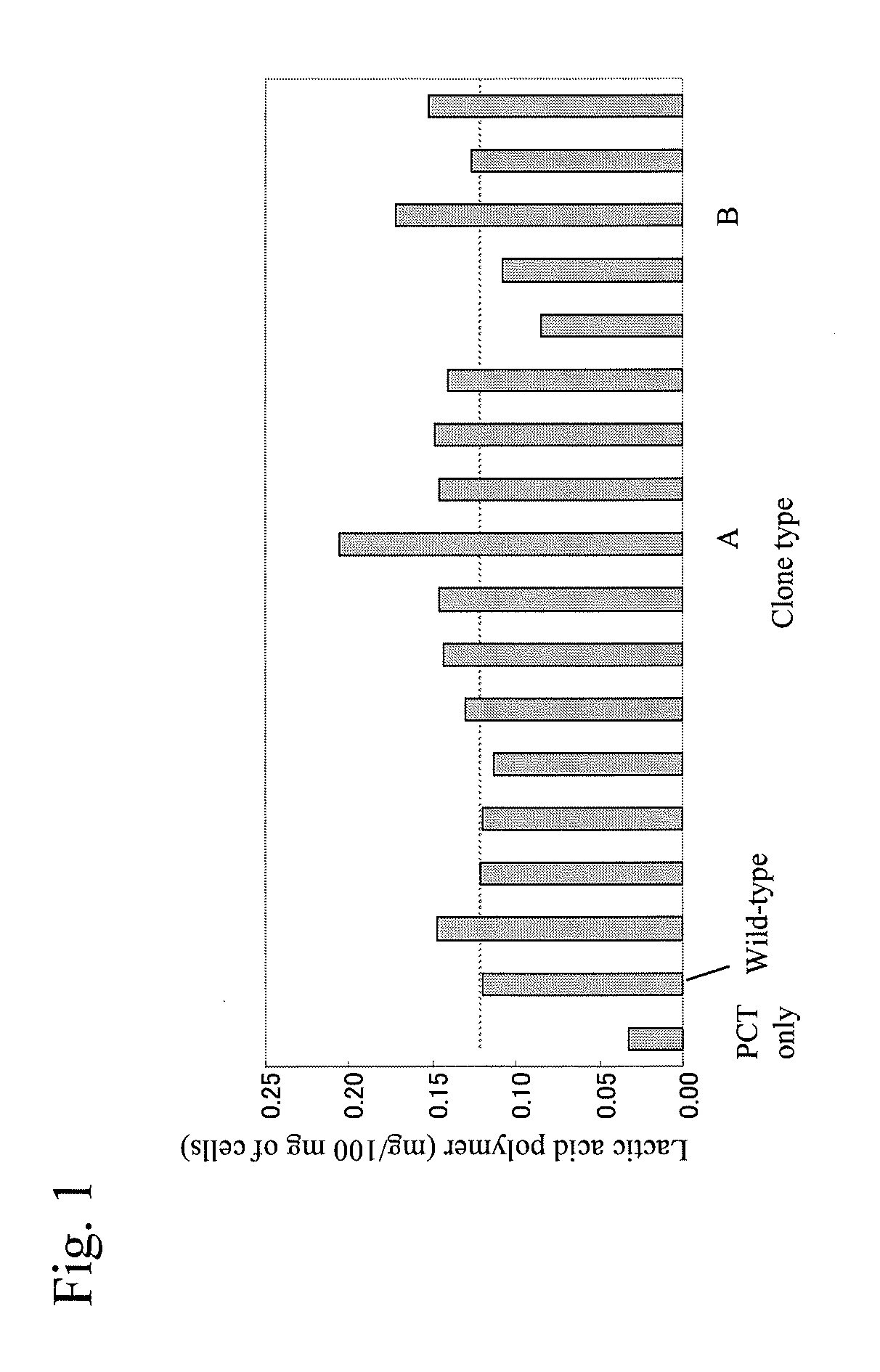
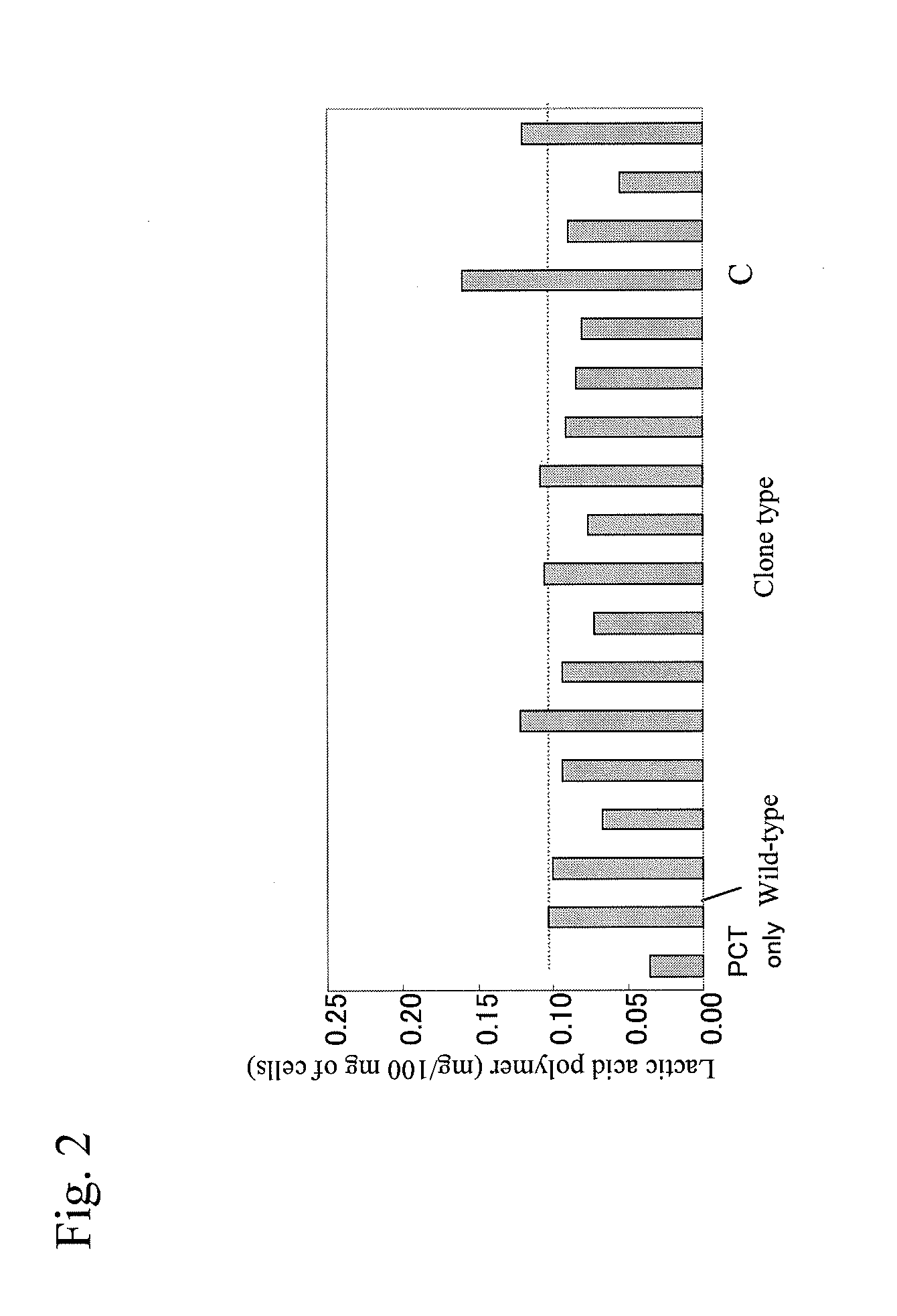
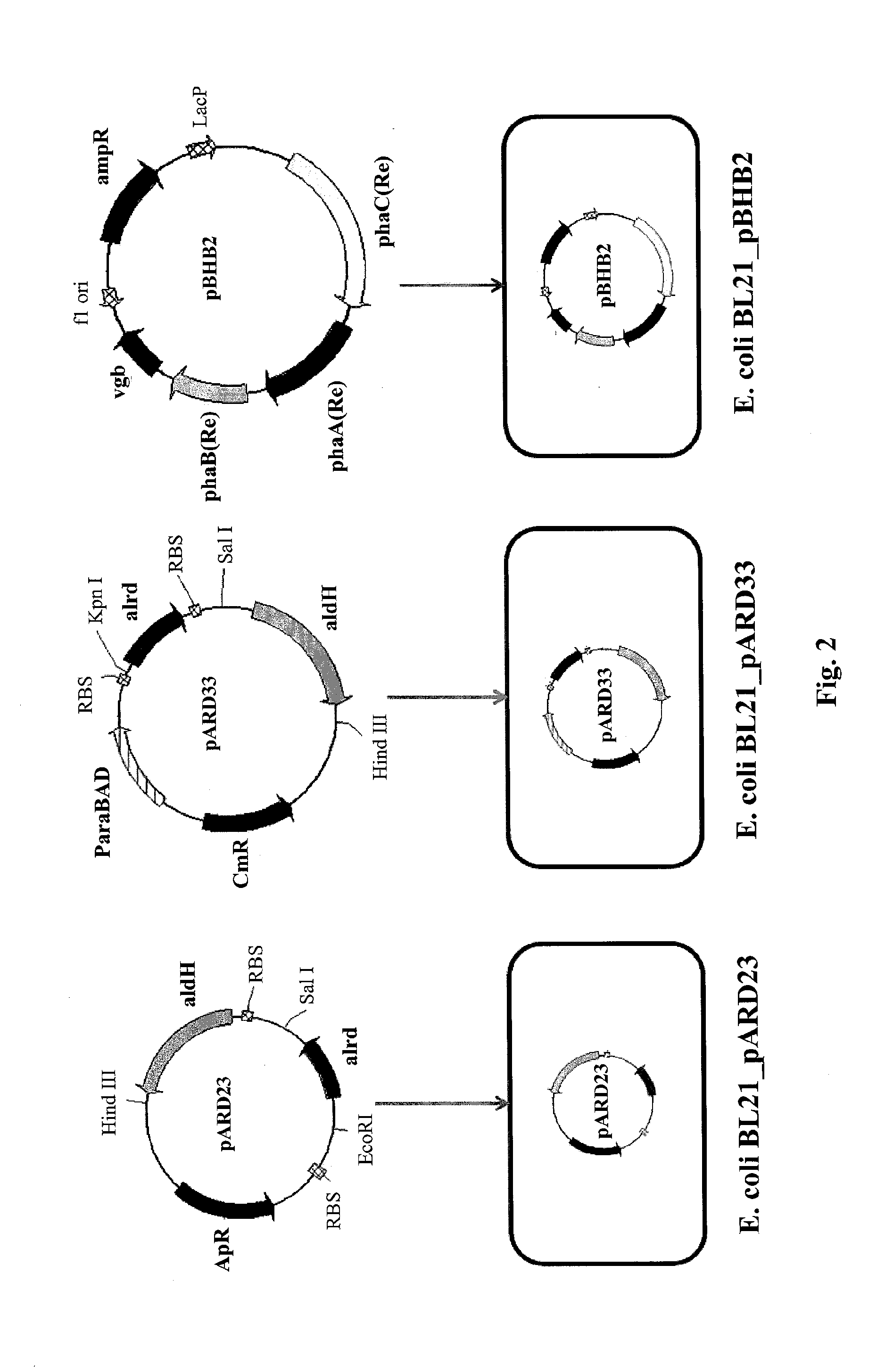
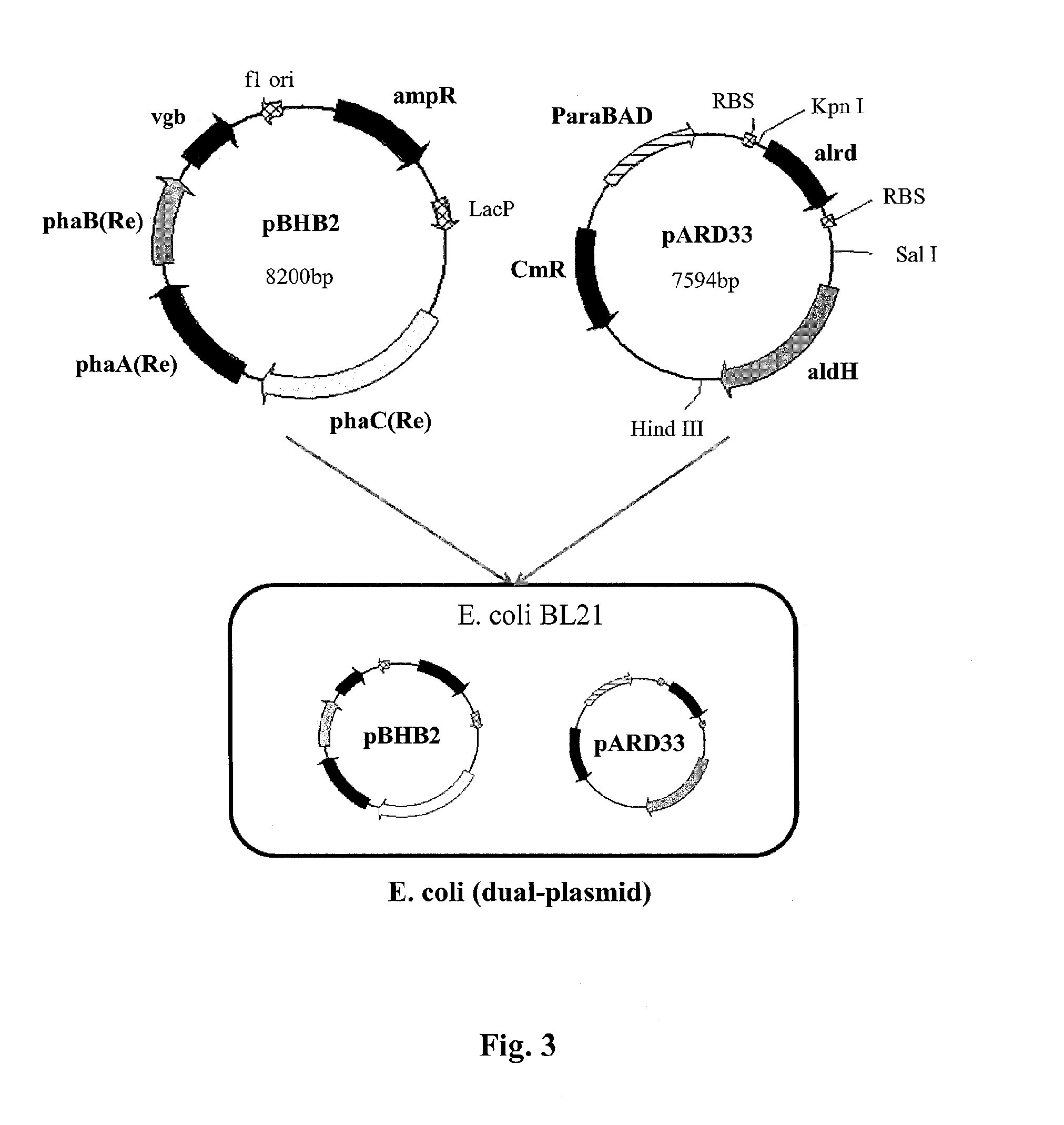
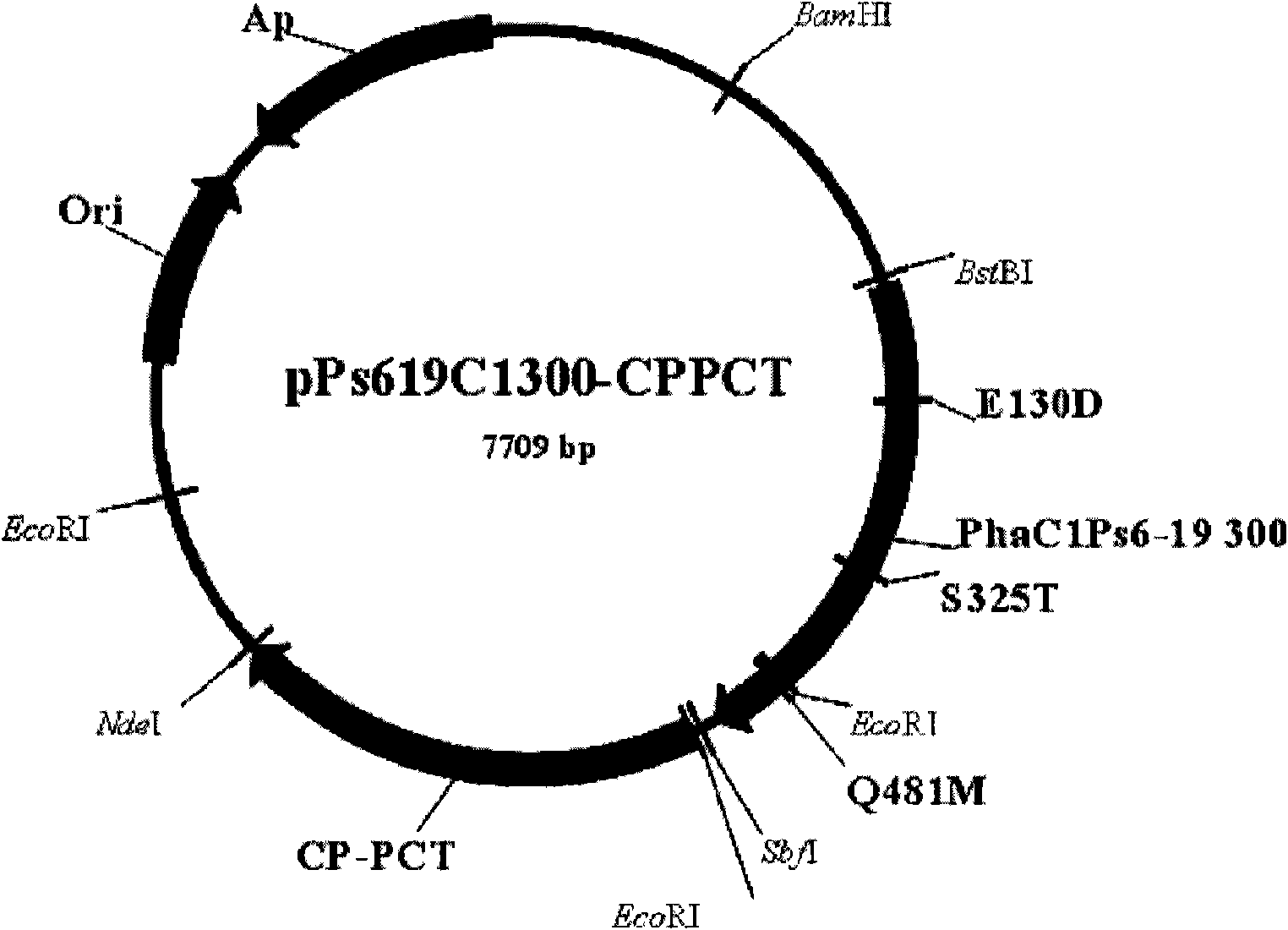
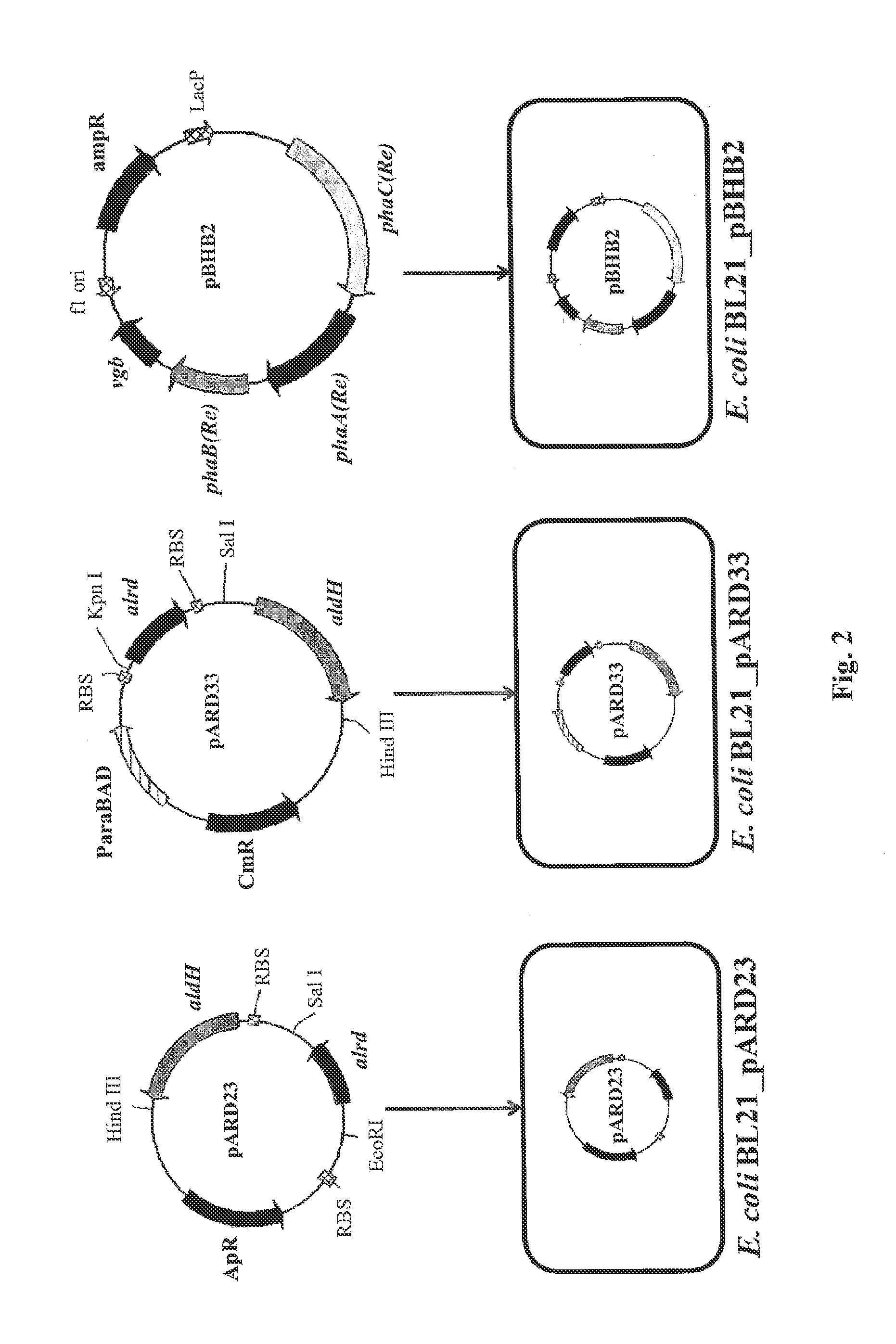
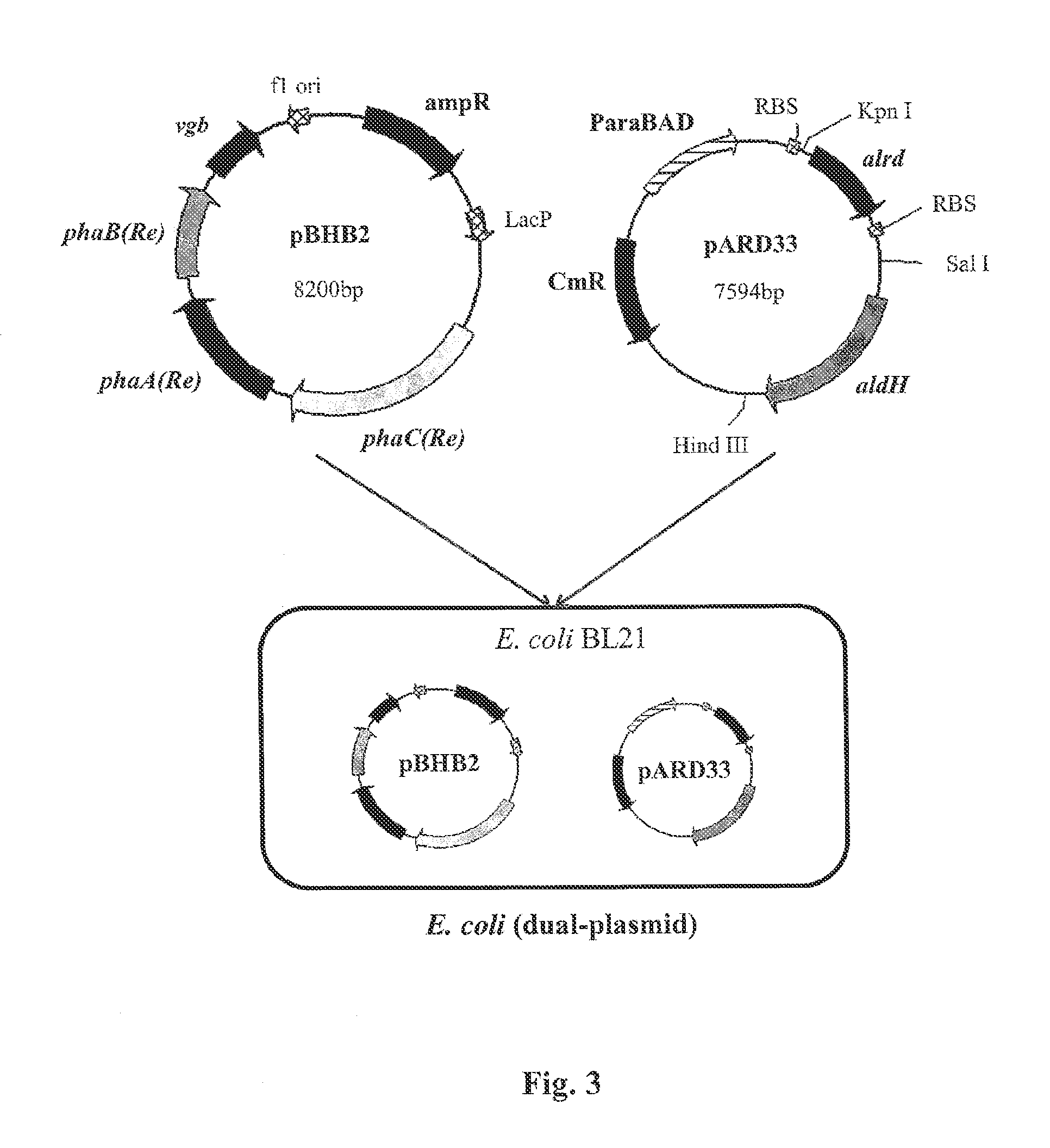
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biological systems for manufacture of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers containing 4-hydroxyacids
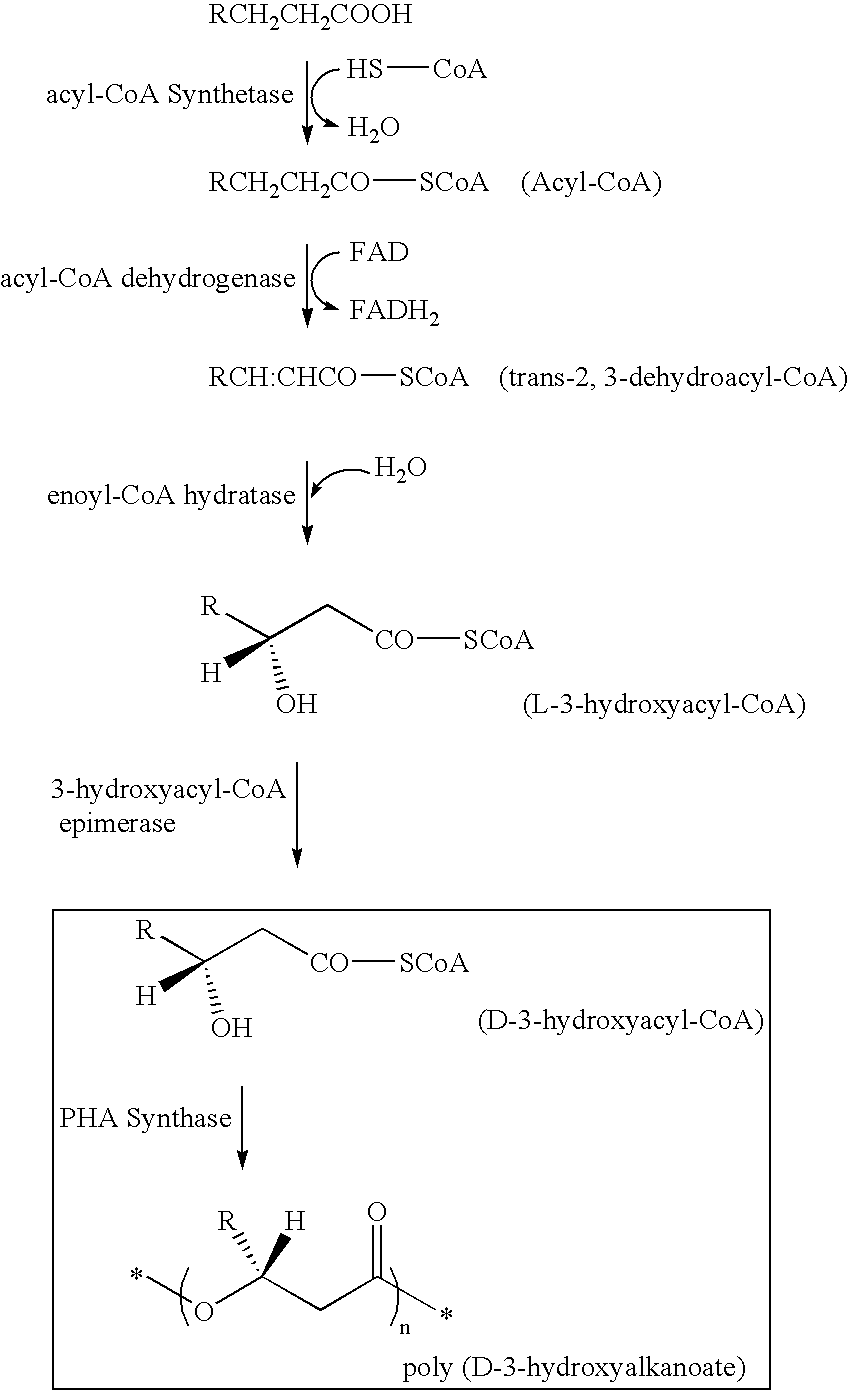
The gene encoding a 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA transferase has been isolated from bacteria and integrated into the genome of bacteria also expressing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, to yield an improved production process for 4HB-containing polyhydroxyalkanoates using transgenic organisms, including both bacteria and plants. The new pathways provide means for producing 4HB containing PHAs from cheap carbon sources such as sugars and fatty acids, in high yields, which are stable. Useful strains are obtaining by screening strains having integrated into their genomes a gene encoding a 4HB-CoA transferase and / or PHA synthase, for polymer production. Processes for polymer production use recombinant systems that can utilize cheap substrates. Systems are provided which can utilize amino acid degradation pathways, α-ketoglutarate, or succinate as substrate.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
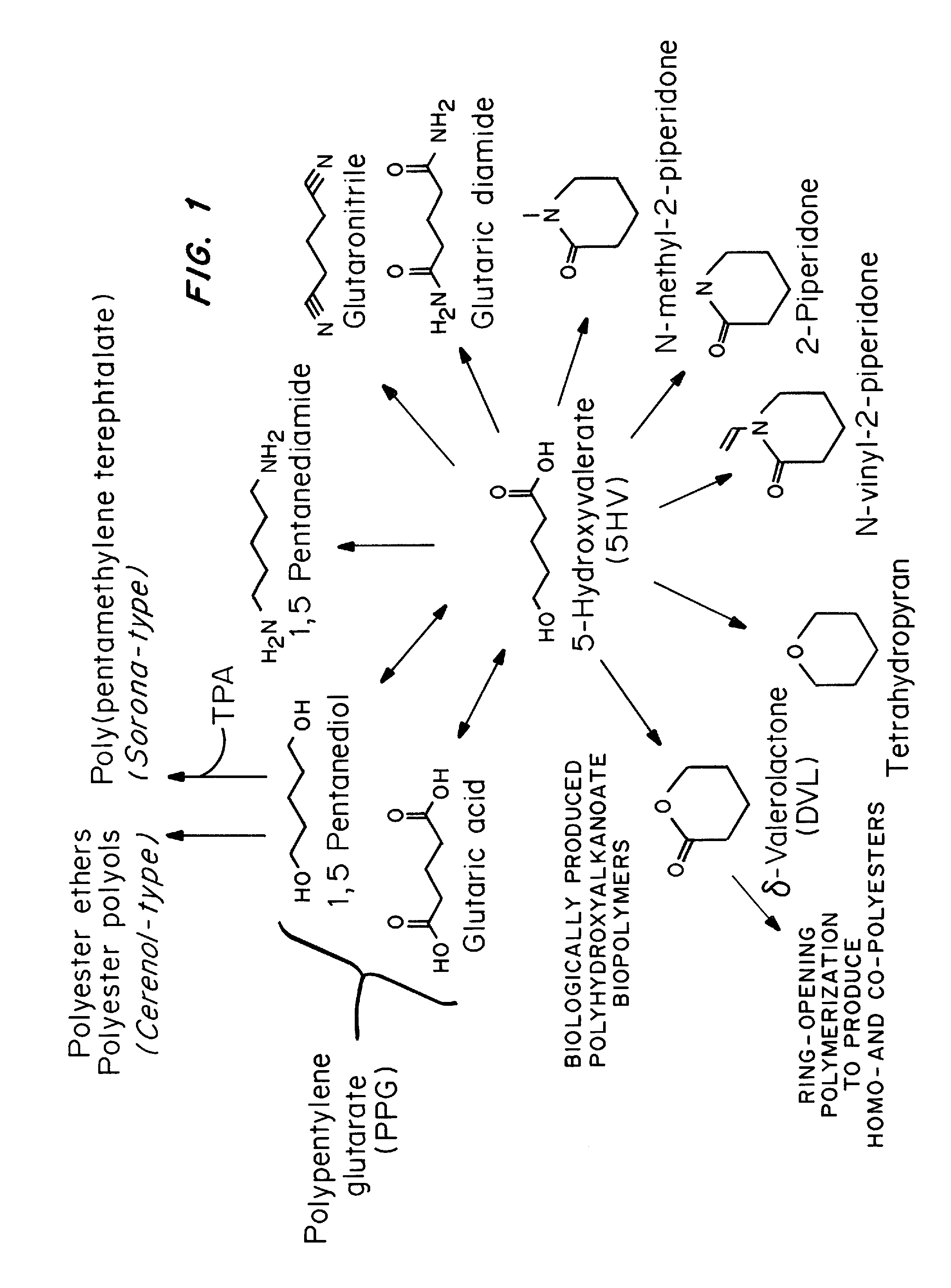
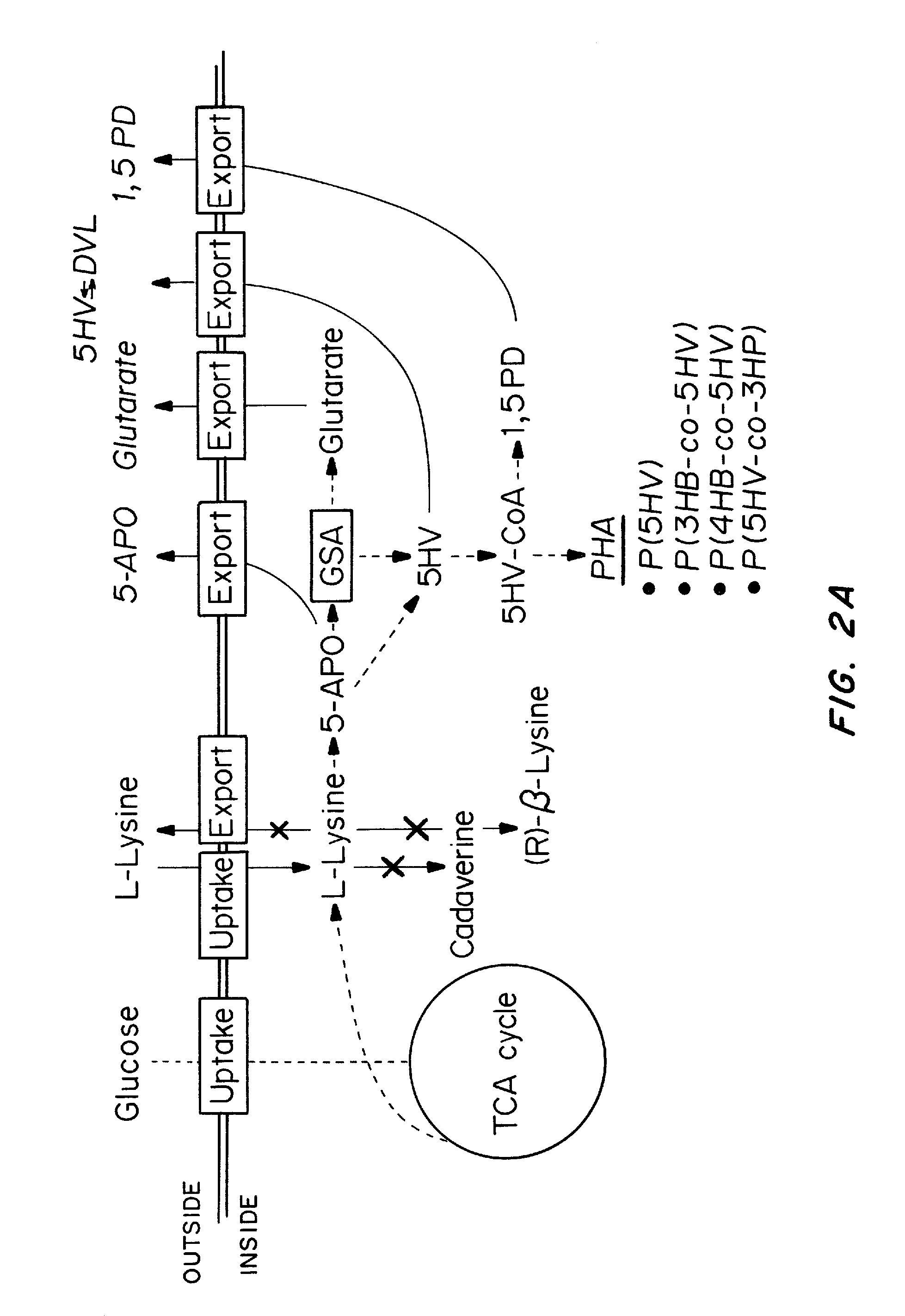
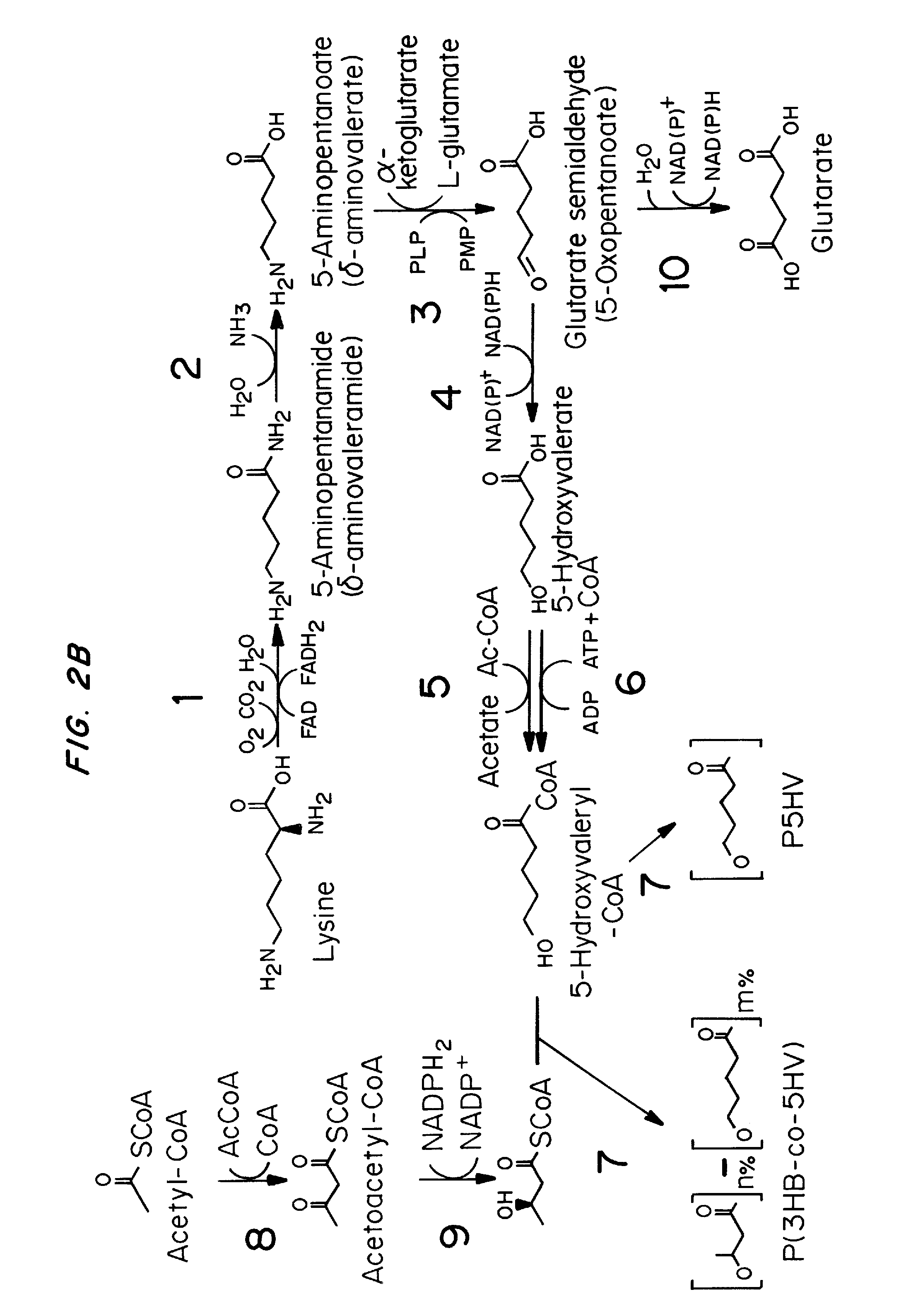
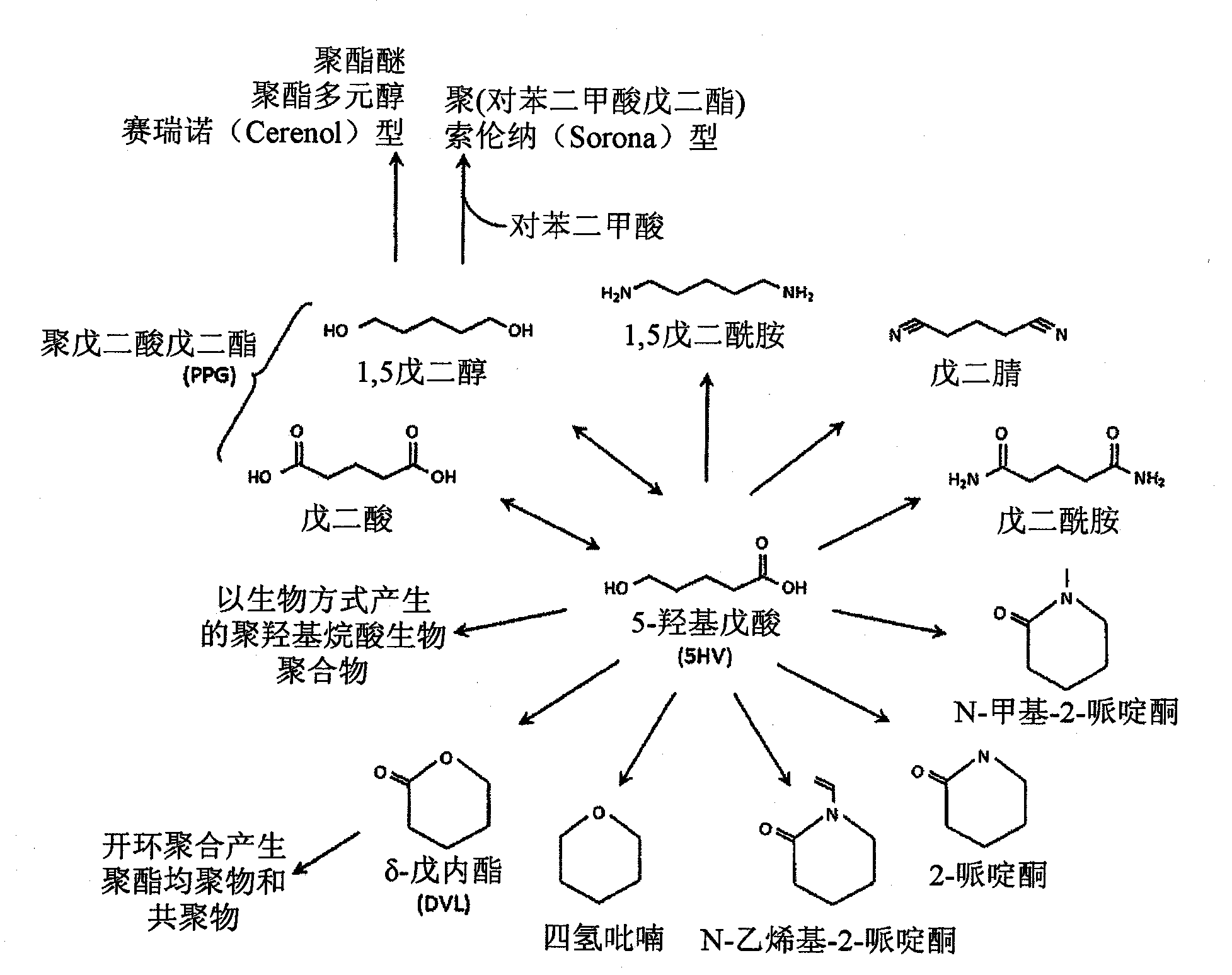
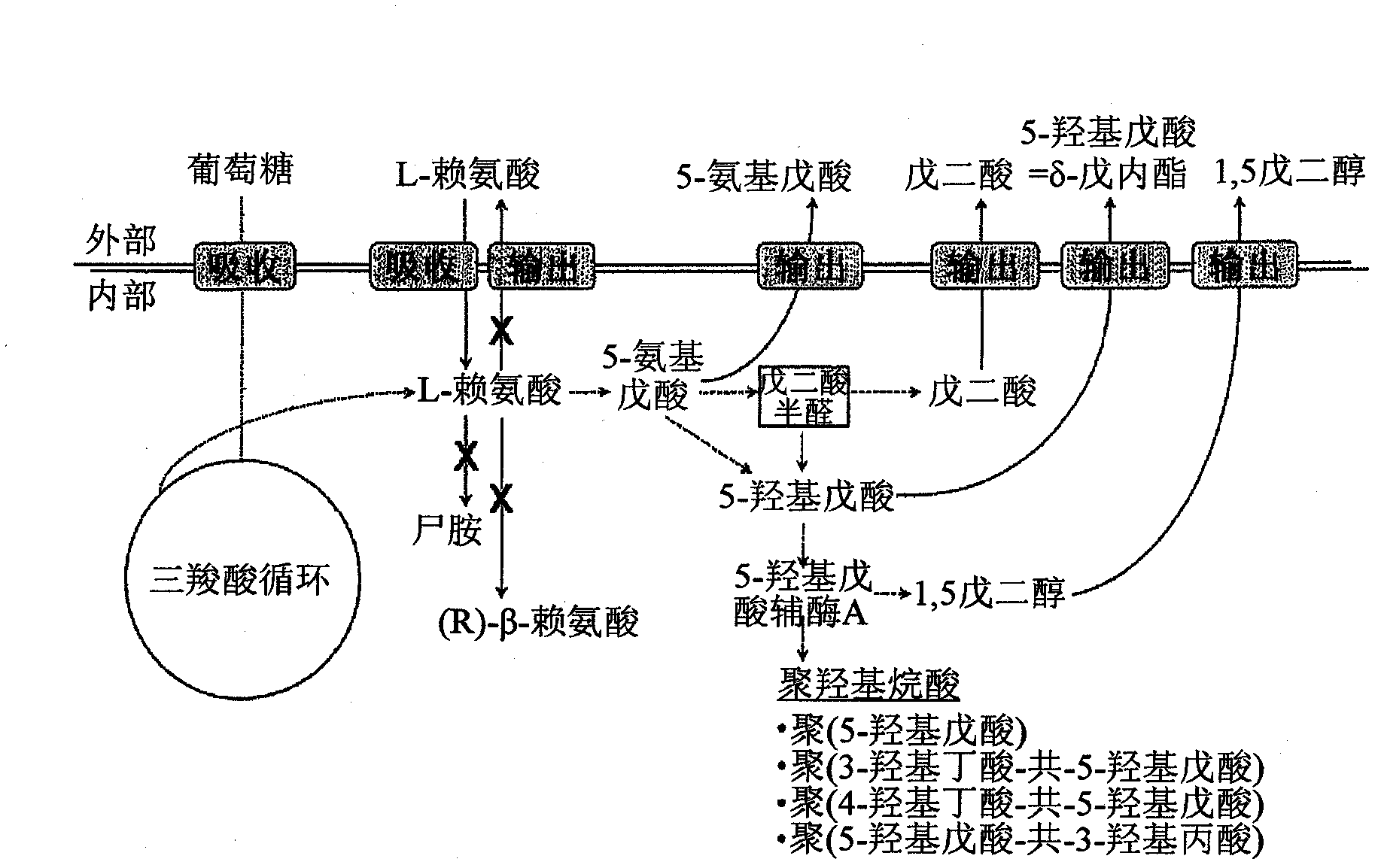
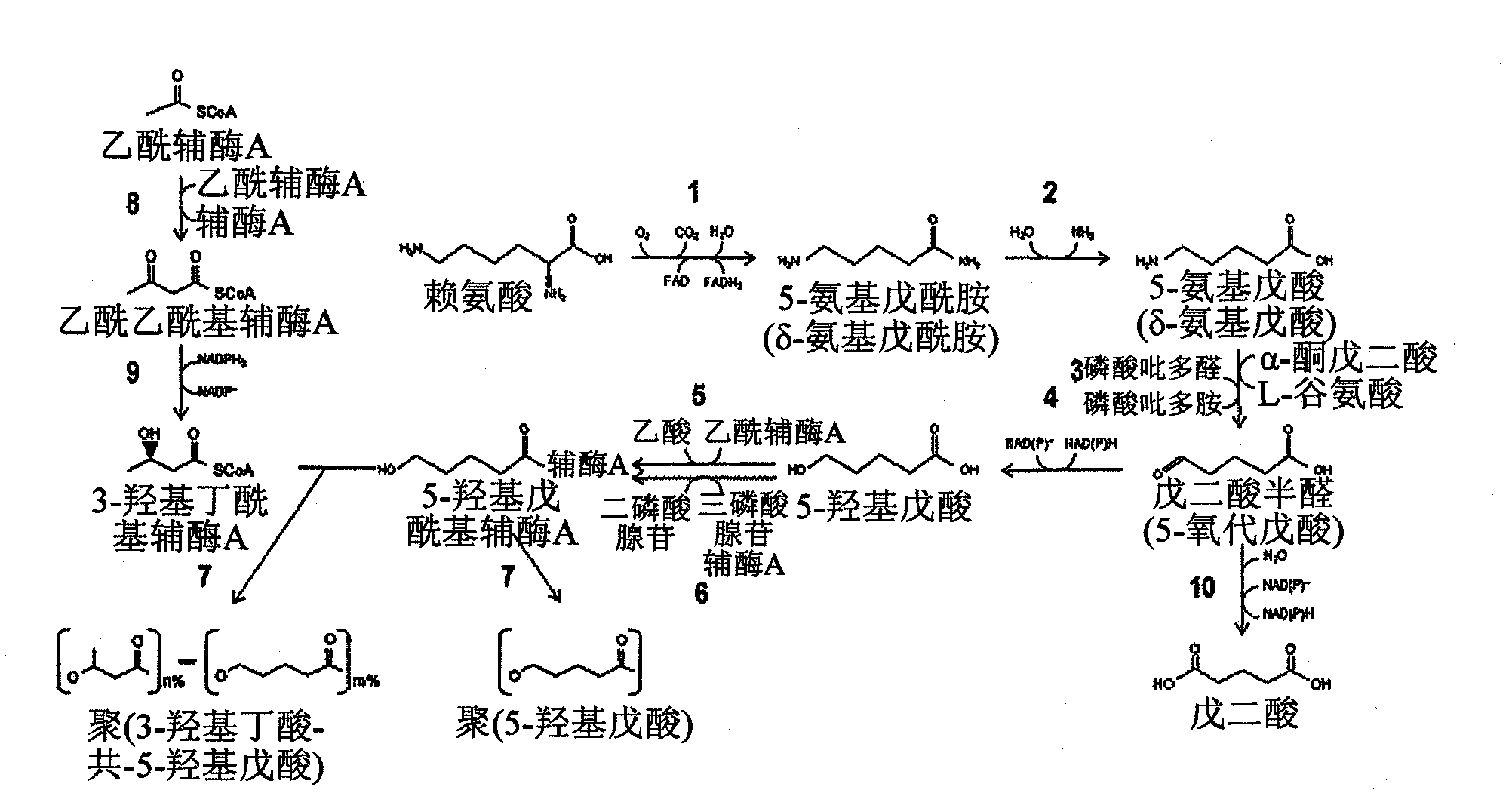
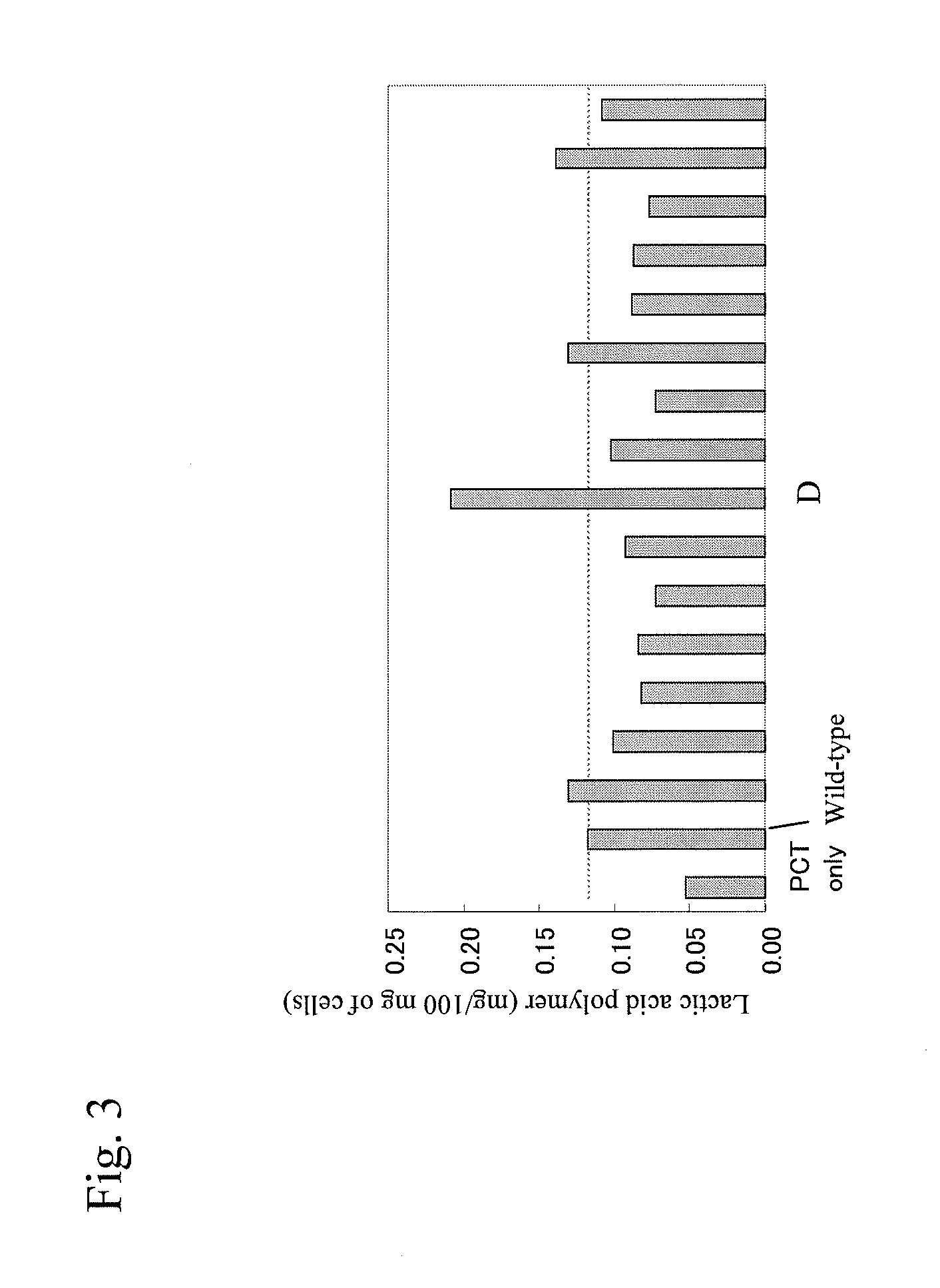
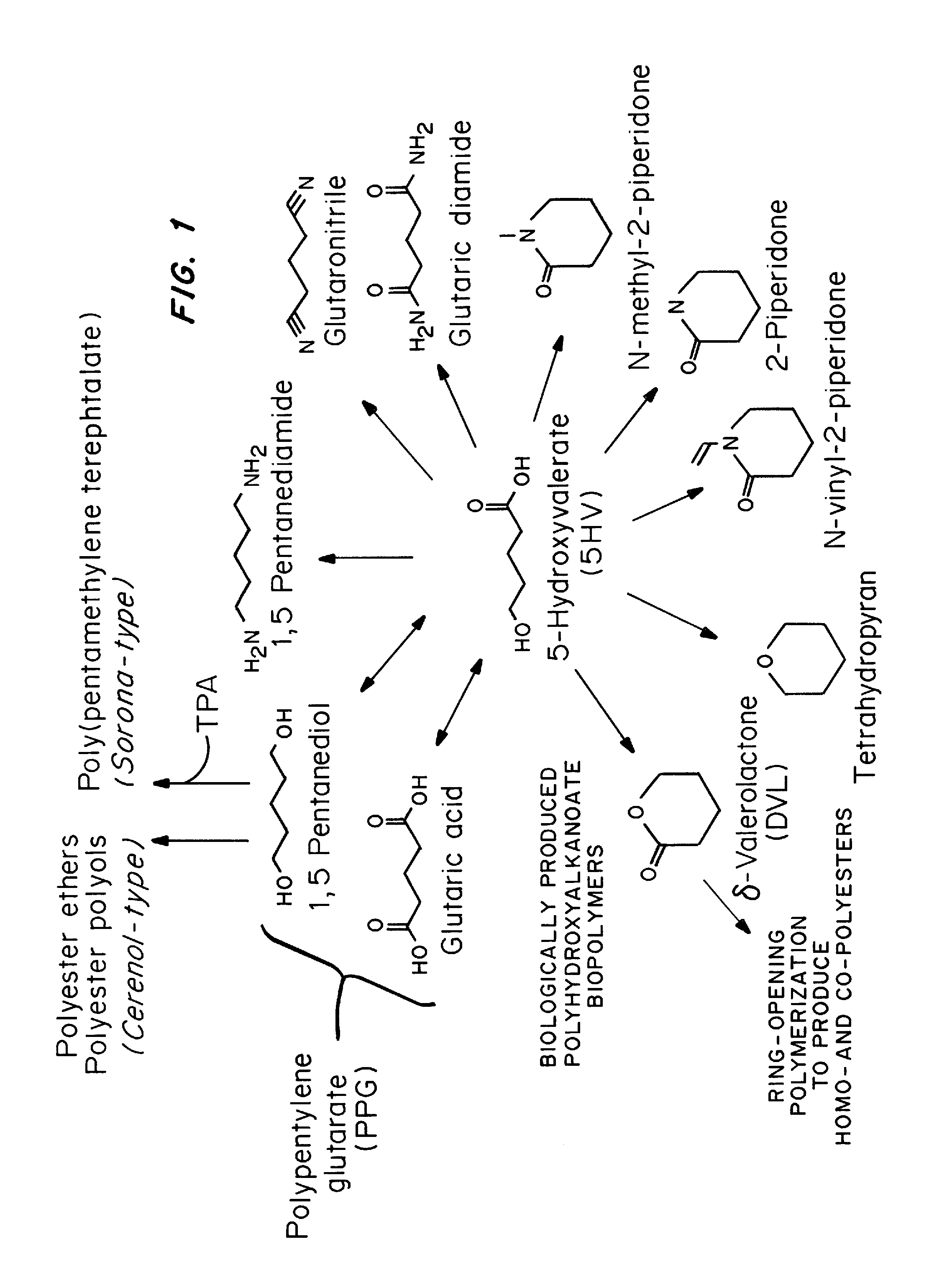
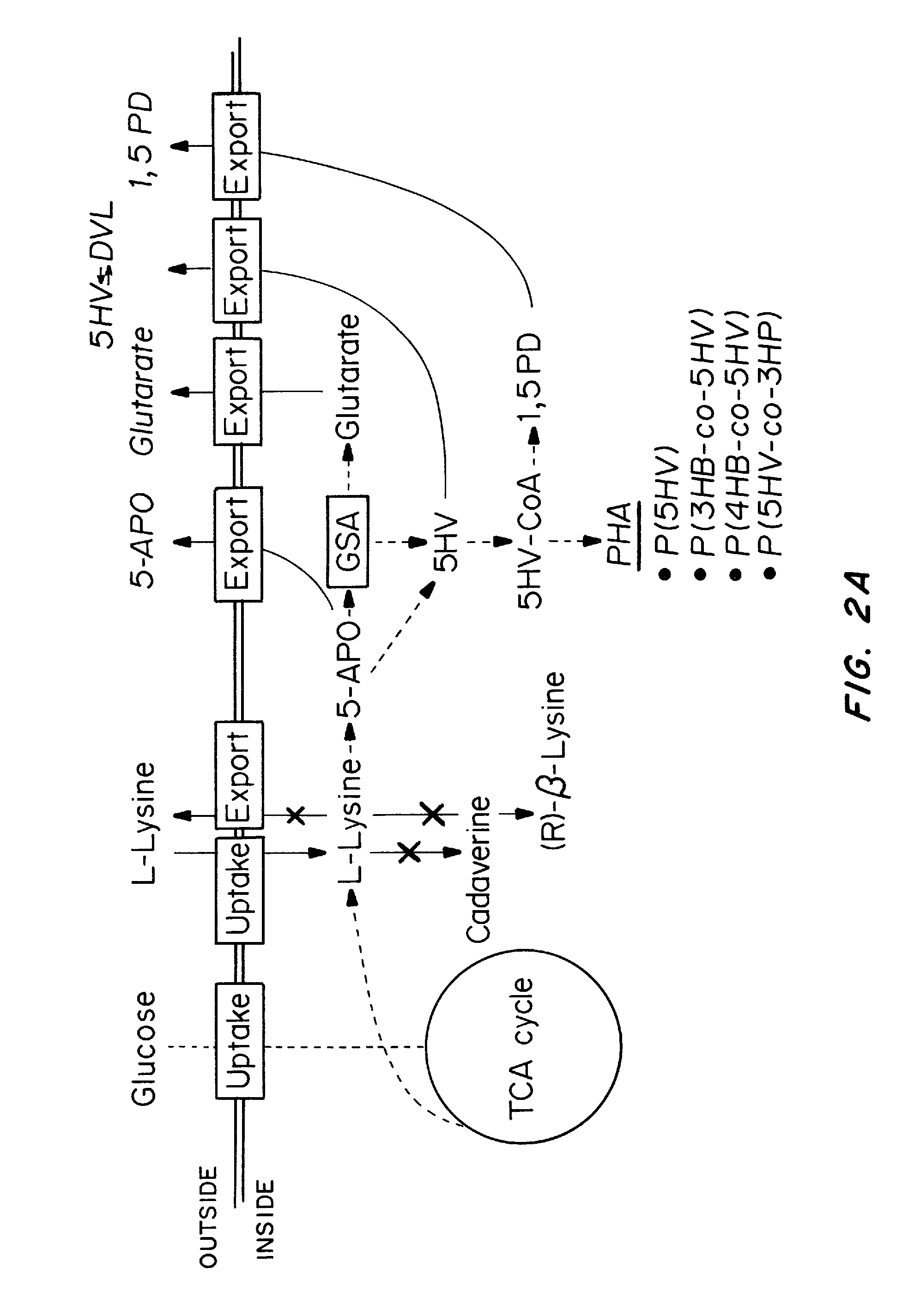
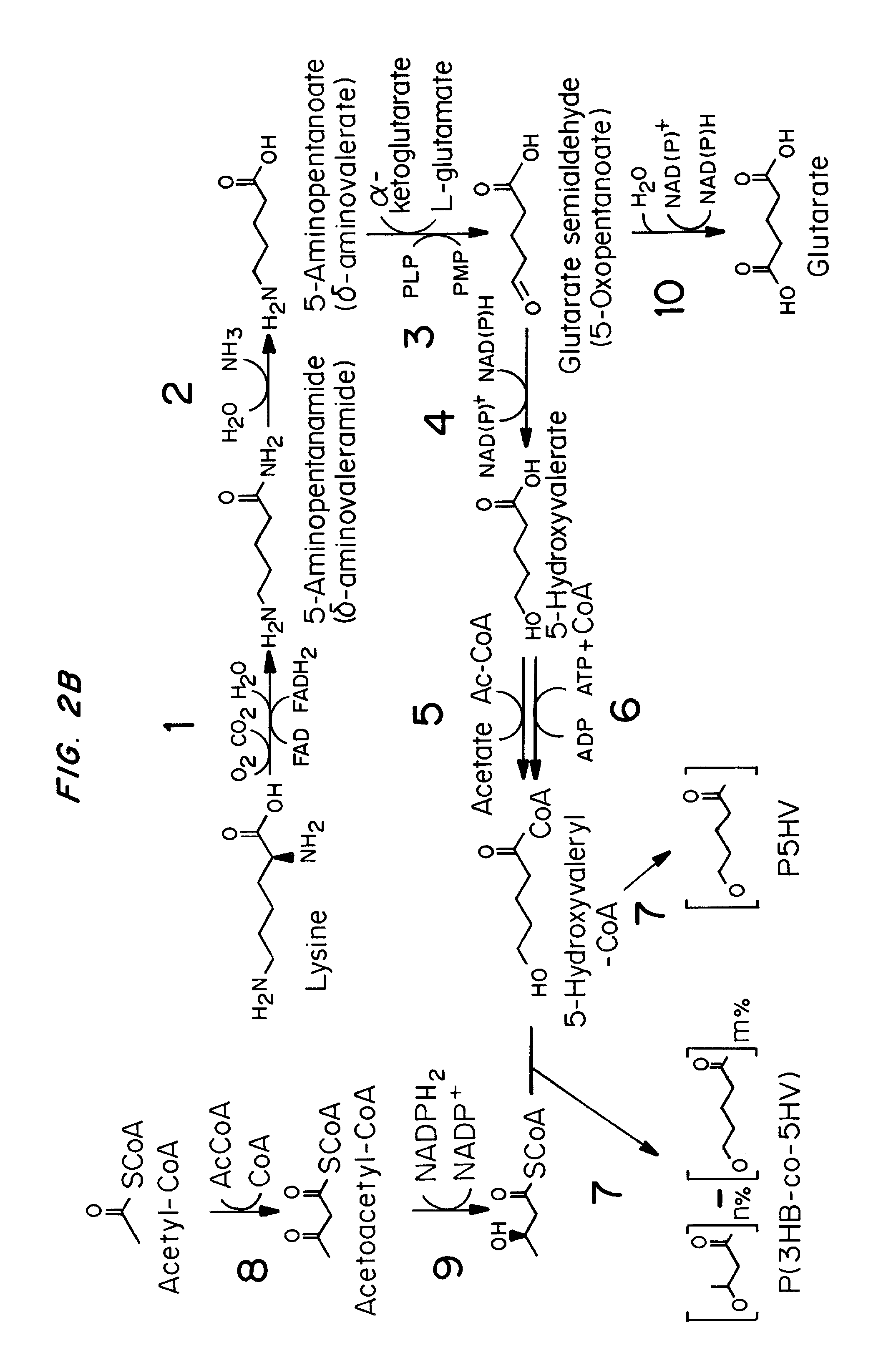
Green process and compositions for producing poly(5HV) and 5 carbon chemicals
Recombinant hosts for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates and methods of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable carbon substrates are provided. Certain recombinant hosts that produce 5 carbon chemicals such as 5-aminopentanoate (5AP), 5-hydroxyvalerate (5HV), glutarate, and 1,5 pentanediol (PDO) are also provided. One embodiment provides a recombinant host expressing a gene encoding a heterologous enzyme selected from the group consisting of a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5-hydroxyvalerate-CoA (5HV-CoA) transferase, wherein the host produces a polymer containing 5-hydroxyvalerate. Preferably, the host expresses both a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5HV-CoA transferase. The host can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. A preferred prokaryotic host is E. coli. The polymers produced by the recombinant hosts can be homopolymers or copolymers of 5-hydroxyvalerate. A preferred copolymer is poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-5-hydroxyvalerate).
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Biological systems for manufacture of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers containing 4-hydroxyacids
InactiveUS20060084155A1Increase productionHigh activitySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyDegradation pathway
The gene encoding a 4-hydroxybutyryl-Co A transferase has been isolated from bacteria and integrated into the genome of bacteria also expressing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, to yield an improved production process for 4HB-containing polyhydroxyalkanoates using transgenic organisms, including both bacteria and plants. The new pathways provide means for producing 4HB containing PHAs from cheap carbon sources such as sugars and fatty acids, in high yields, which are stable. Useful strains are obtaining by screening strains having integrated into their genomes a gene encoding a 4HB-CoA transferase and / or PHA synthase, for polymer production. Processes for polymer production use recombinant systems that can utilize cheap substrates. Systems are provided which can utilize amino acid degradation pathways, α-ketoglutarate, or succinate as substrate.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6951745B2Effectively immobilize a PHA synthaseImmobilised enzymesBacteriaCoenzyme A biosynthesisAmino acid
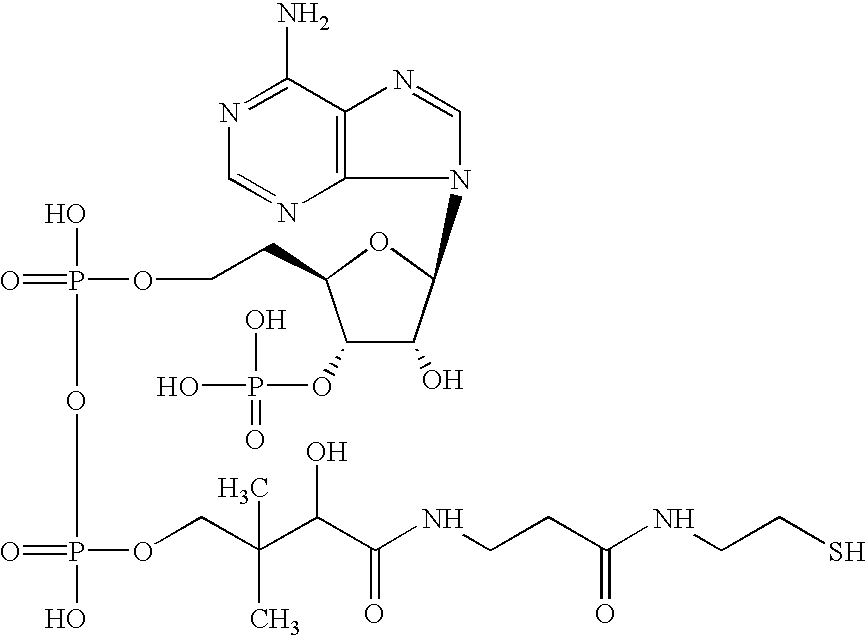
A method for manufacturing polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with polyhydroxyalkanoate, the method comprises the steps of immobilizing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase on the base material surface, synthesizing, on the base material surface, polyhydroxyalkanoate using a 3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A to become the substrate of the synthase and the synthase and coating at least a part of the base material surface with the synthesized polyhydroxyalkanoate, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material. A polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with a polyhydroxyalkanoate, comprises the base material, a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase immobilized on the base material surface, and the polyhydroxyalkanoate with which at least a part of the base material surface is coated, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material.
Owner:CANON KK
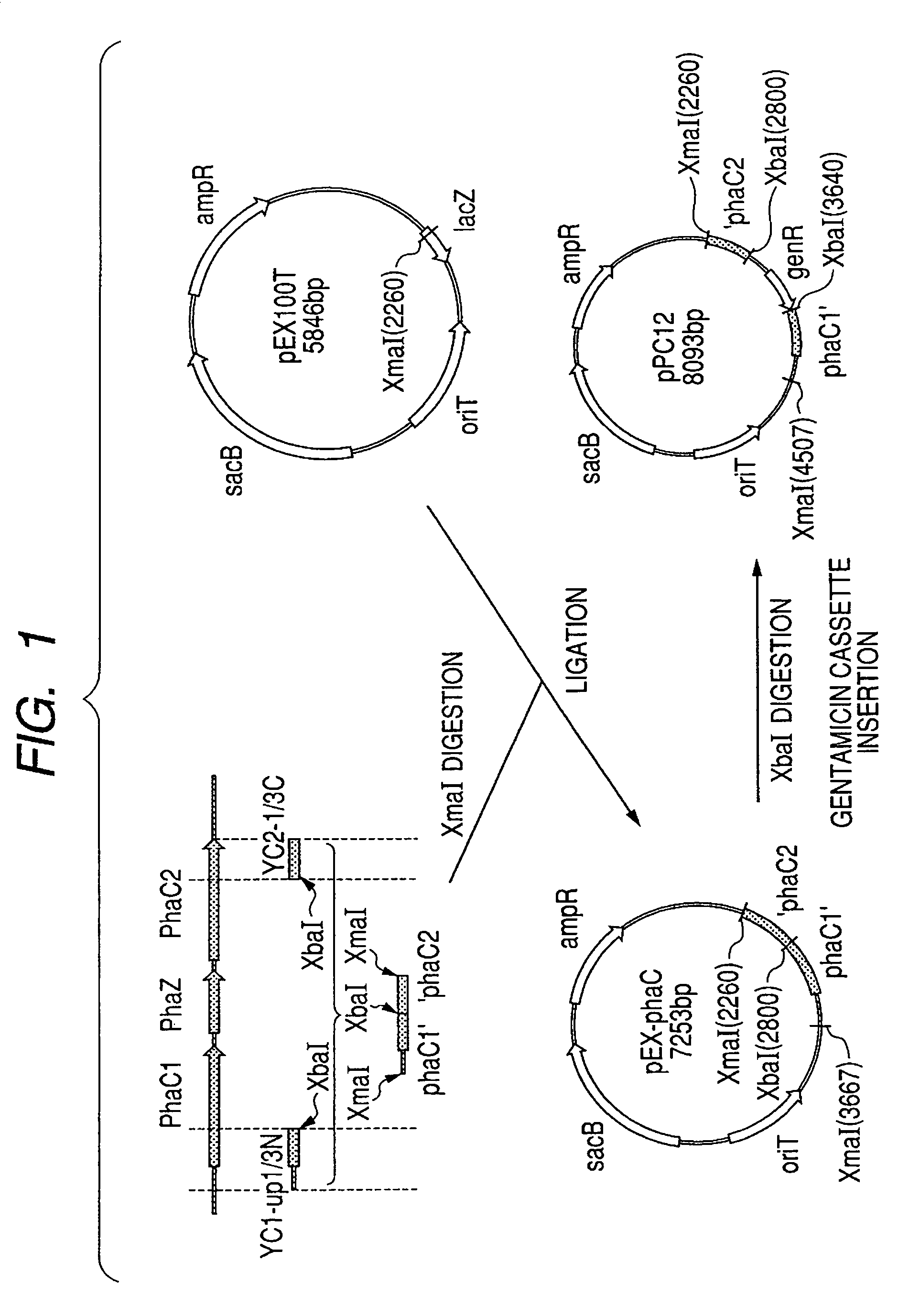
Isogenic strain line of bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate in which polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene is disrupted and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using the same
A host-vector system which is equipped with a substrate supply system enzyme for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and which is suitable for evolutionary engineering modification of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. An isogenic strain line is produced by disrupting a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene of a bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate.
Owner:CANON KK
Polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050208635A1Effectively immobilize a PHA synthaseImmobilised enzymesDuplicating/marking methodsCoenzyme A biosynthesisPolyhydroxyalkanoate synthase
A method for manufacturing polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with polyhydroxyalkanoate, the method comprises the steps of immobilizing a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase on the base material surface, synthesizing, on the base material surface, polyhydroxyalkanoate using a 3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A to become the substrate of the synthase and the synthase and coating at least a part of the base material surface with the synthesized polyhydroxyalkanoate, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material. A polyhydroxyalkanoate-containing structure, at least a part of a base material surface of the structure being coated with a polyhydroxyalkanoate, comprises the base material, a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase immobilized on the base material surface, and the polyhydroxyalkanoate with which at least a part of the base material surface is coated, wherein the synthase contains an amino acid sequence capable of binding to the base material.
Owner:CANON KK
Isogenic strain line of bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate in which polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene is disrupted and method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using the same
InactiveUS20060172398A1Change in amountEasy to getBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyVector system
A host-vector system which is equipped with a substrate supply system enzyme for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and which is suitable for evolutionary engineering modification of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. An isogenic strain line is produced by disrupting a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene of a bacterium for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate.
Owner:CANON KK
Novel Transformant and Process for Producing Polyester Using the Same
The present invention provides a process for producing yeast excellent in cell productivity and gene manipulation of which is easy, being added with nutritional requirement by disrupting only a specific gene, and a transformant thereof. Moreover, the present invention also provides a process for producing a gene expression product, particularly a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid.In the present invention, yeast in which a plurality of genes is disrupted is produced using the homologous recombination. Moreover, a transformant is obtained by introducing a plurality of enzyme genes involved with polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthesis such as a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase gene and an acetoacetyl CoA reductase gene into said gene-disrupted yeast. Furthermore, said transformant is cultured, copolyesters comprising a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid are efficiently accumulated within the cells, and a polymer is harvested from the cultured product.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Microorganism capable of producing improved polyhydroxyalkanoate and method of producing polyhydroxyalkanoate by using the same
InactiveUS20110091948A1Good flexibilityEfficient fermentation productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesMicroorganismEnzyme Gene
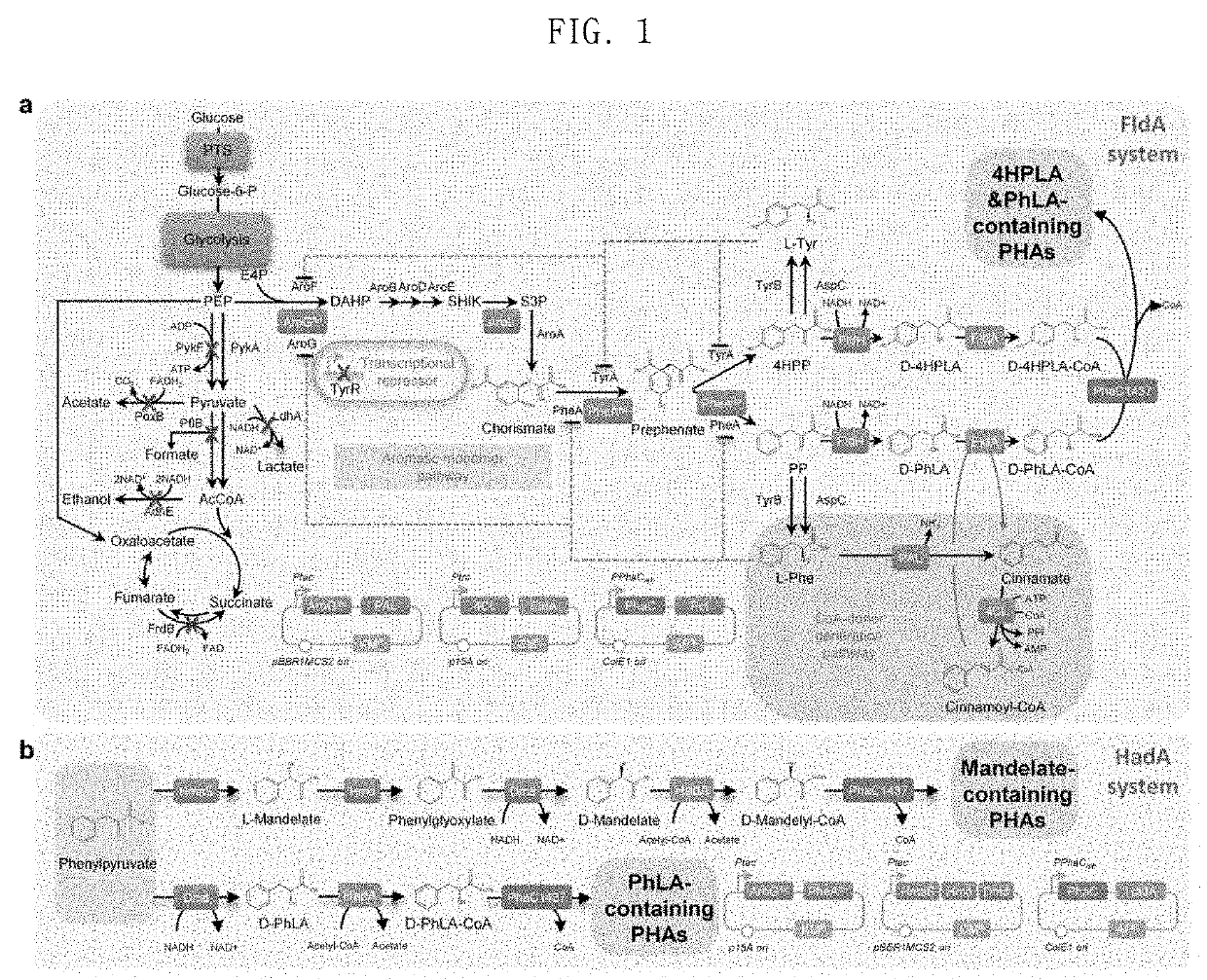
The present invention relates to a microorganism which is capable of producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) and satisfies the requirements: (1) expression of a phbA gene is repressed or a catalytic activity of an enzyme encoded by the gene is repressed; (2) expression of a bktB gene is enhanced or a catalytic activity of an enzyme encoded by the gene is increased; and (3) a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene and a crotonyl-CoA reductase gene are introduced thereinto. Culture of this microorganism enables efficient production of P(3HB-co-3HH), which is a PHA having excellent flexibility and being applied to a variety of applications, with an inexpensive carbon source.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for constructing genetic engineering bacteria and enhancing stress resistance of 1,3-propanediol producing strain
InactiveCN101381696AImprove stress resistanceIncrease added valueBacteriaBiofuelsHigh concentrationGlycerol
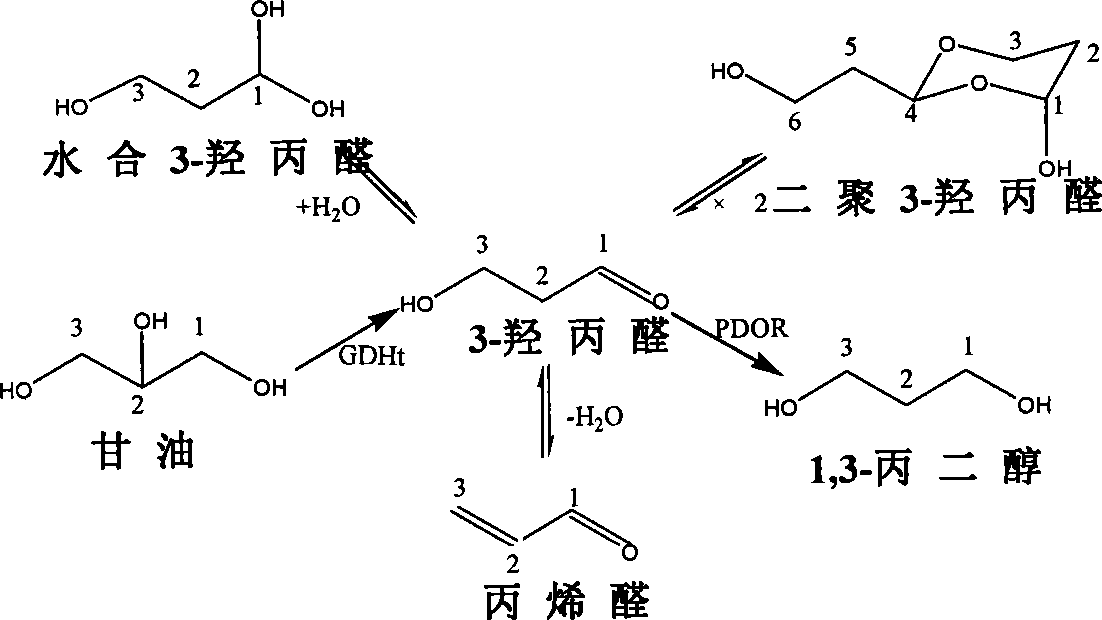
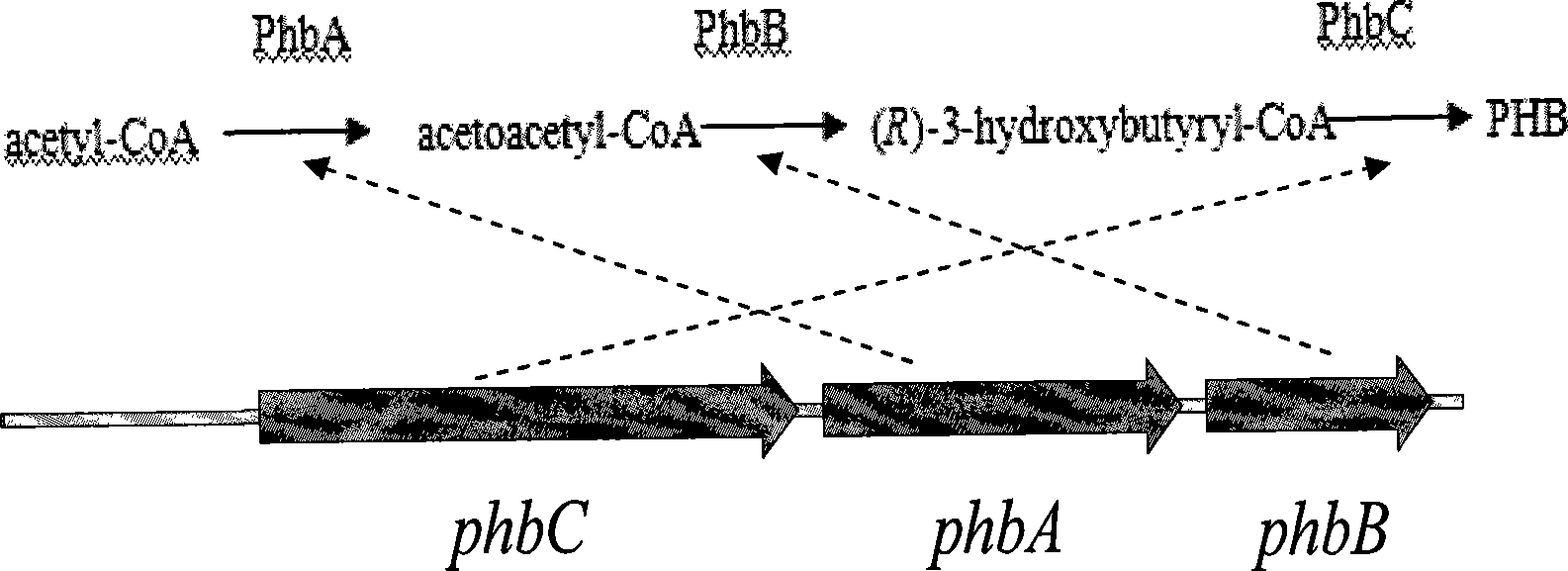
The invention provides a method for constructing a gene engineering strain to enhance the resistance of a 1, 3-propanediol (PDO) production strain, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering and comprises the step of: introducing Beta-ketothiolase PhbA, NADPH-dependent acetoacetyl CoA, PhbB and polyhydroxyalkanoates synthases, PhbC gene to a wild bacteria which can produce PDO to accumulate high concentration of PHB while the bacterial strain produces PDO so as obviously improve the tolerance of the bacterial strain to glycerol and 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde; the method can also be used to co-produce PHB and PDO. The method has the advantages that the constructed gene engineering strain improves the resistance of the bacterial strain to the high concentration of glycedrol and the intermediate product 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde and reduces the abnormal fermentation in industrial production; in addition, high concentration of PHB can be accumulated while PDO is produced, and PHB can be used as a separated product, thereby promoting the added valve of products and the utilization rate of materials and reducing the production cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
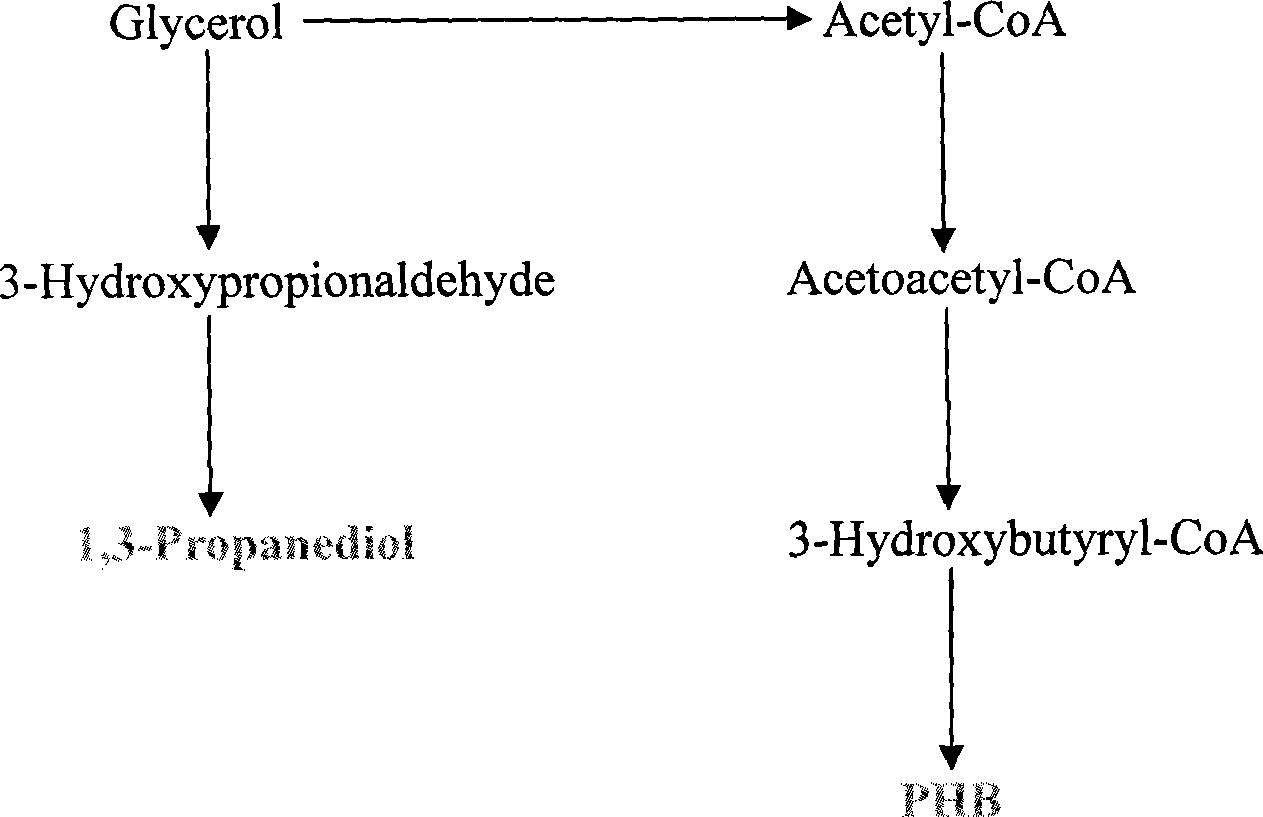
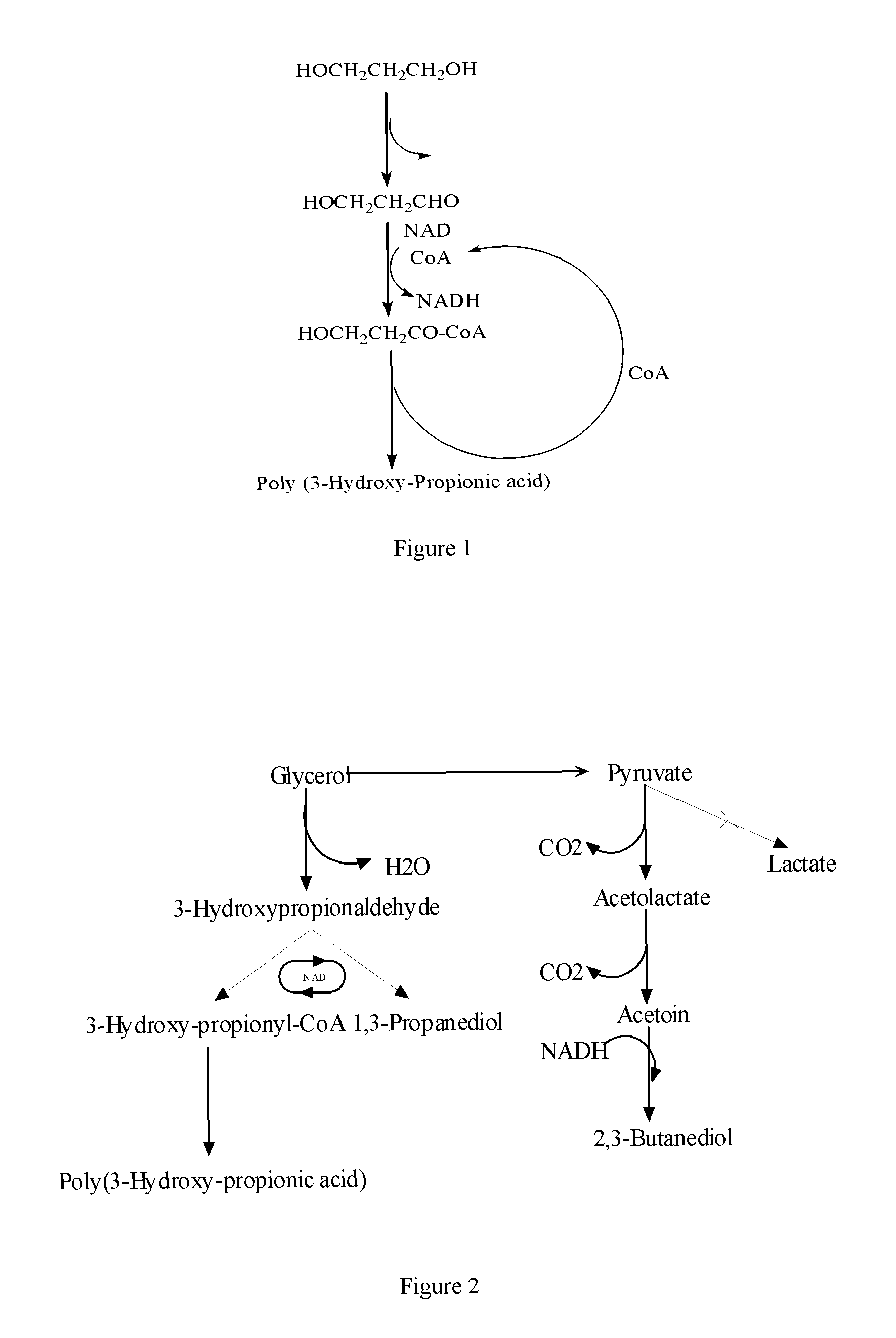
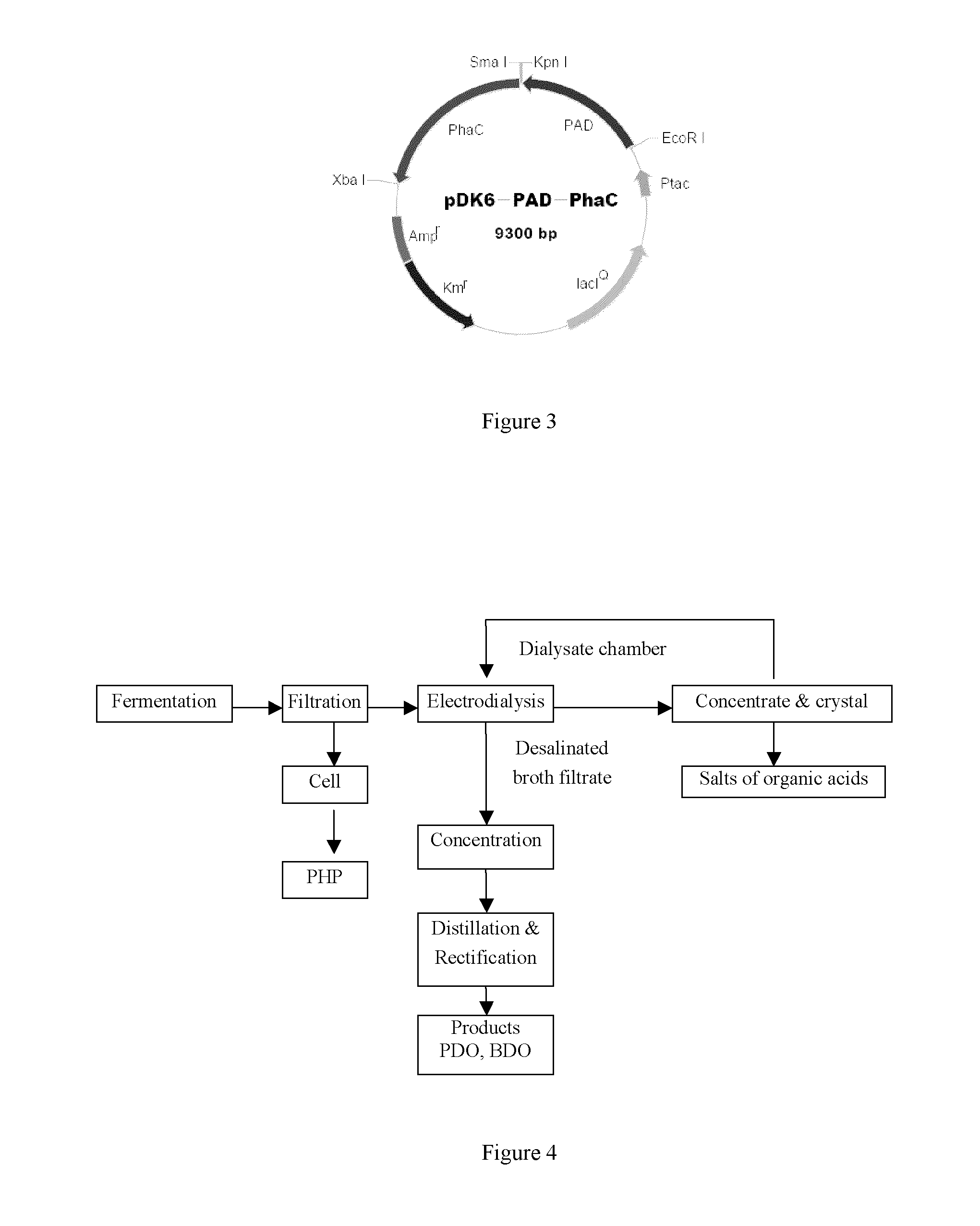
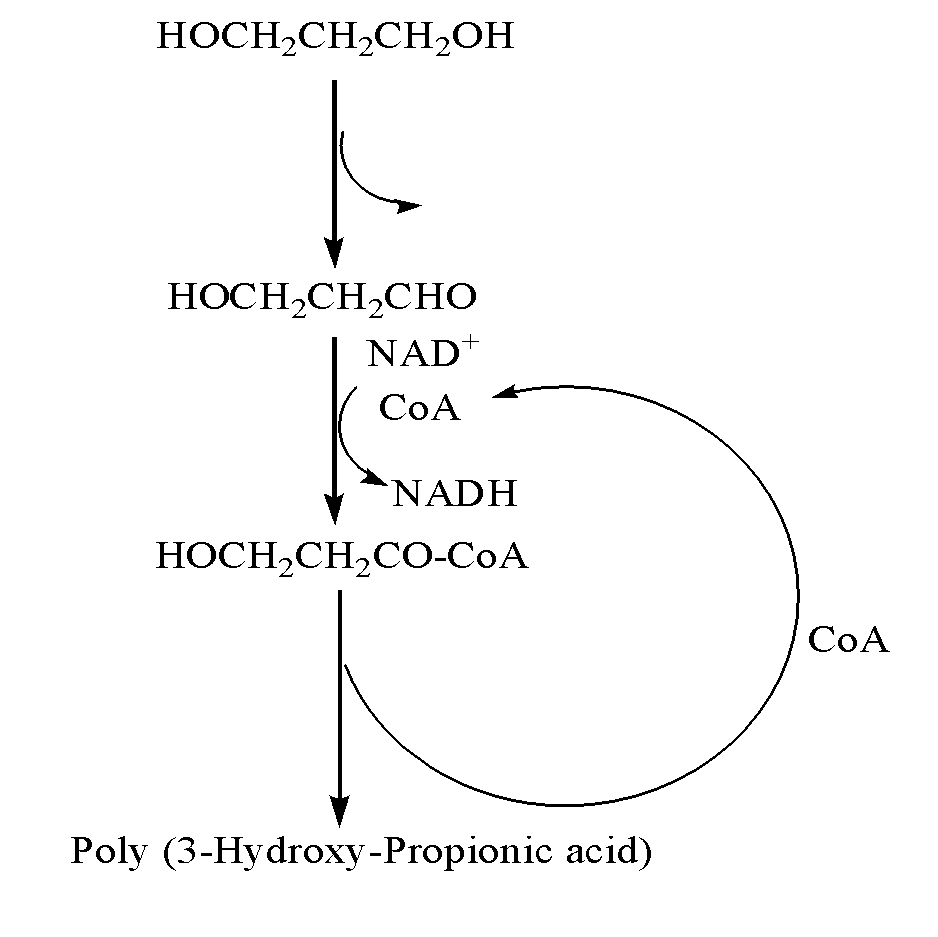
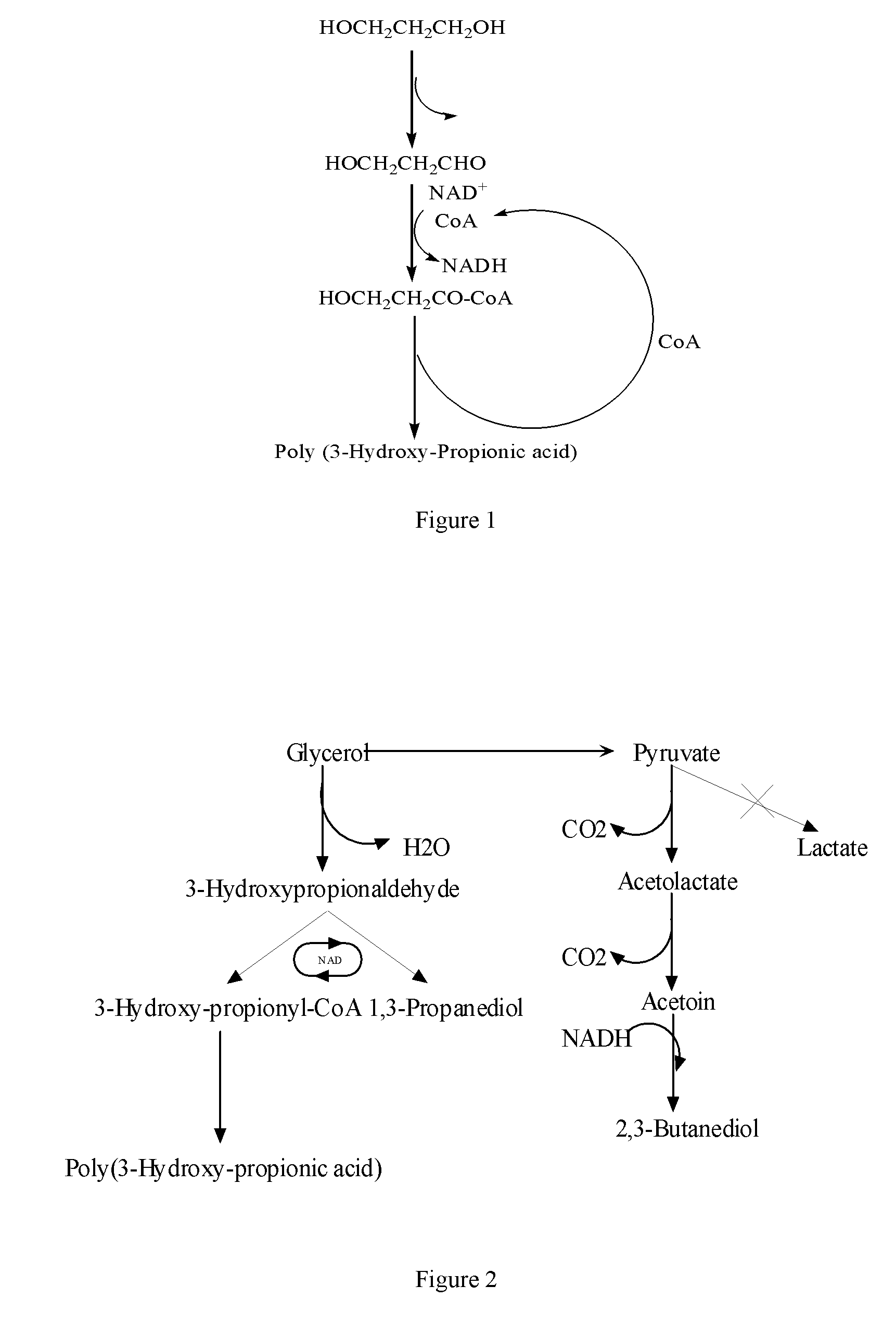
Methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation
The present invention relates to genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of 1,3-propanediol (PDO), 2,3-butanediol (BDO), and polyhydroxypropionic acid (PHP) by fermentation. In particular, the invention relates to a genetically engineered micro-organism suitable for combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation, characterized in that: compared with corresponding wild-type starting micro-organism, the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene in the genetically engineered micro-organism is deleted or functionally inactivated, and the genetically engineered micro-organism comprises a heterogenous polynucleotide encoding the Coenzyme A-dependent Aldehyde dehydrogenase and a heterogenous polynucleotide encoding the Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Methods for the construction of such micro-organisms, and methods for combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation of a genetically engineered bacterium are also taught.
Owner:HUNAN RIVERS BIOTECH +1
Methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of pdo, bdo and php by fermentation
ActiveUS20110117617A1Less producedImprove isolationBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The present invention relates to methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of PDO, BDO, and PHP by fermentation. The micro-organism is characterized in that its D-lactate dehydrogenase gene has been deleted or functionally inactivated, and it comprises heterogenous polynucleotides encoding the Coenzyme A-dependent Aldehyde dehydrogenase and the Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Methods for the construction of such micro-organisms are also disclosed
Owner:HUNAN RIVERS BIOTECH +1
Gene-substituted microorganisms, and production method of polyesters using the same
The present invention has for its object to provide a recombinant microbial strain capable of stably producing a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid (PHA) at a high production rate in an industrial fermentation process.The present invention relates to a recombinant microbial strain prepared by substituting an exogenous polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase gene for a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase gene on the chromosome of the microorganism.
Owner:DANIMER IPCO LLC +1
Copolymer containing 3-hydroxyalkanoate unit and lactate unit, and its manufacturing method
The present invention relates to a copolymer comprising 3-hydroxyalkanoate monomer unit and lactate monomer unit, or their preparing method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a copolymer comprising lactate monomer and 3-hydroxyalkanoate monomer, wherein the method comprises culturing a cell or plant comprising the gene of enzyme converting lactate and 3-hydroxyalkanoate into lactyl-CoA and 3-hydroxyalkanoyl-CoA, respectively, and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene together, and the copolymer made by the method. The copolymer of the present invention is a biodegradable polymer being able to be usefully used instead of conventional synthetic plastic, and the copolymer can be used also for medical use.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Green process and compositions for producing poly(5HV) and 5 carbon chemicals
Recombinant hosts for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates and methods of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable carbon substrates are provided. Certain recombinant hosts that produce 5 carbon chemicals such as 5-amino?entanoate (5AP), 5 -hydroxy valerate (5HV), glutarate, and 1,5 pentanediol (PDO) are also provided. One embodiment provides a recombinant host expressing a gene encoding a heterologous enzyme selected from the group consisting of a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5-hydroxyvalerate-CoA (5HV-CoA) transferase, wherein the host produces a polymer containing 5-hydroxyvalerate. Preferably, the host expresses both a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5HV-CoA transferase. The host can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. A preferred prokaryotic host is E. coli. The polymers produced by the recombinant hosts can be homopolymers or copolymers of 5-hydroxyvalerate.; A preferred copolymer is poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-5-hydroxyvalerate).
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Copolymer containing 3-hydroxyalkanoate unit and lactate unit, and its manufacturing method
The present invention relates to a copolymer comprising 3-hydroxyalkanoate monomer unit and lactate monomer unit, or their preparing method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a copolymer comprising lactate monomer and 3-hydroxyalkanoate monomer, wherein the method comprises culturing a cell or plant comprising the gene of enzyme converting lactate and 3-hydroxyalkanoate into lactyl-CoA and 3-hydroxyalkanoyl-CoA, respectively, and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene together, and the copolymer made by the method. The copolymer of the present invention is a biodegradable polymer being able to be usefully used instead of conventional synthetic plastic, and the copolymer can be used also for medical use.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Copolymer comprising 4-hydroxybutyrate unit and lactate unit and its manufacturing method
The present invention relates to a copolymer comprising 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer unit and lactate monomer unit, a copolymer 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer unit, lactate monomer unit and 3-hydroxyalkanoate, or their preparing method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a copolymer comprising lactate monomer; 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer; and optionally 3-hydroxyalkanoate, wherein the method comprises culturing a cell or plant comprising the gene of enzyme converting lactate and 3-hydroxyalkanoate into lactyl-CoA and 3-hydroxyalkanoyl-CoA, respectively, phosphotransbutylase gene, butyrate kinase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene together, and the copolymer made by the method. The copolymer of the present invention is a biodegradable polymer being able to be usefully used instead of conventional synthetic plastic, and the copolymer can be used for medical use.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
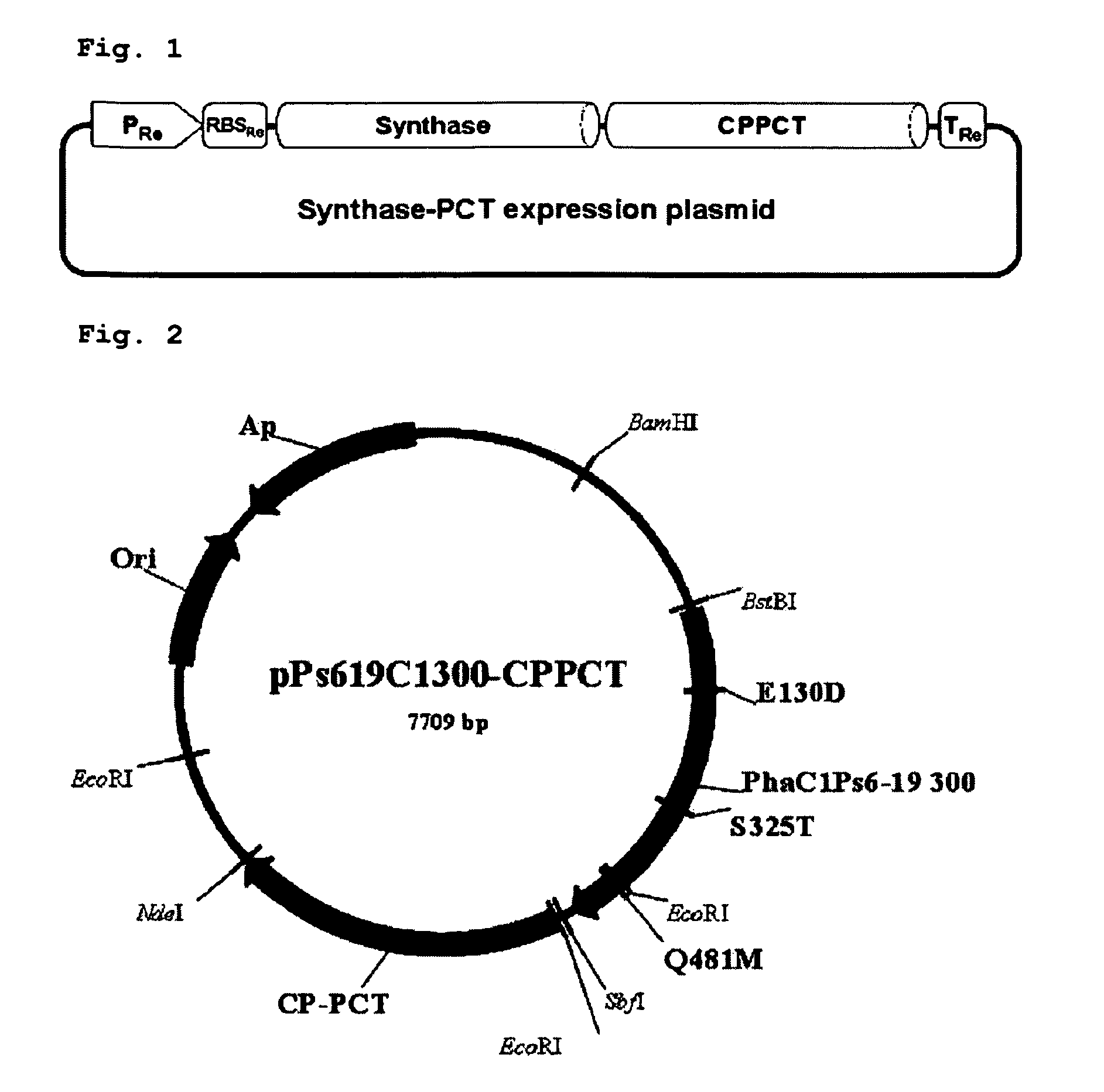
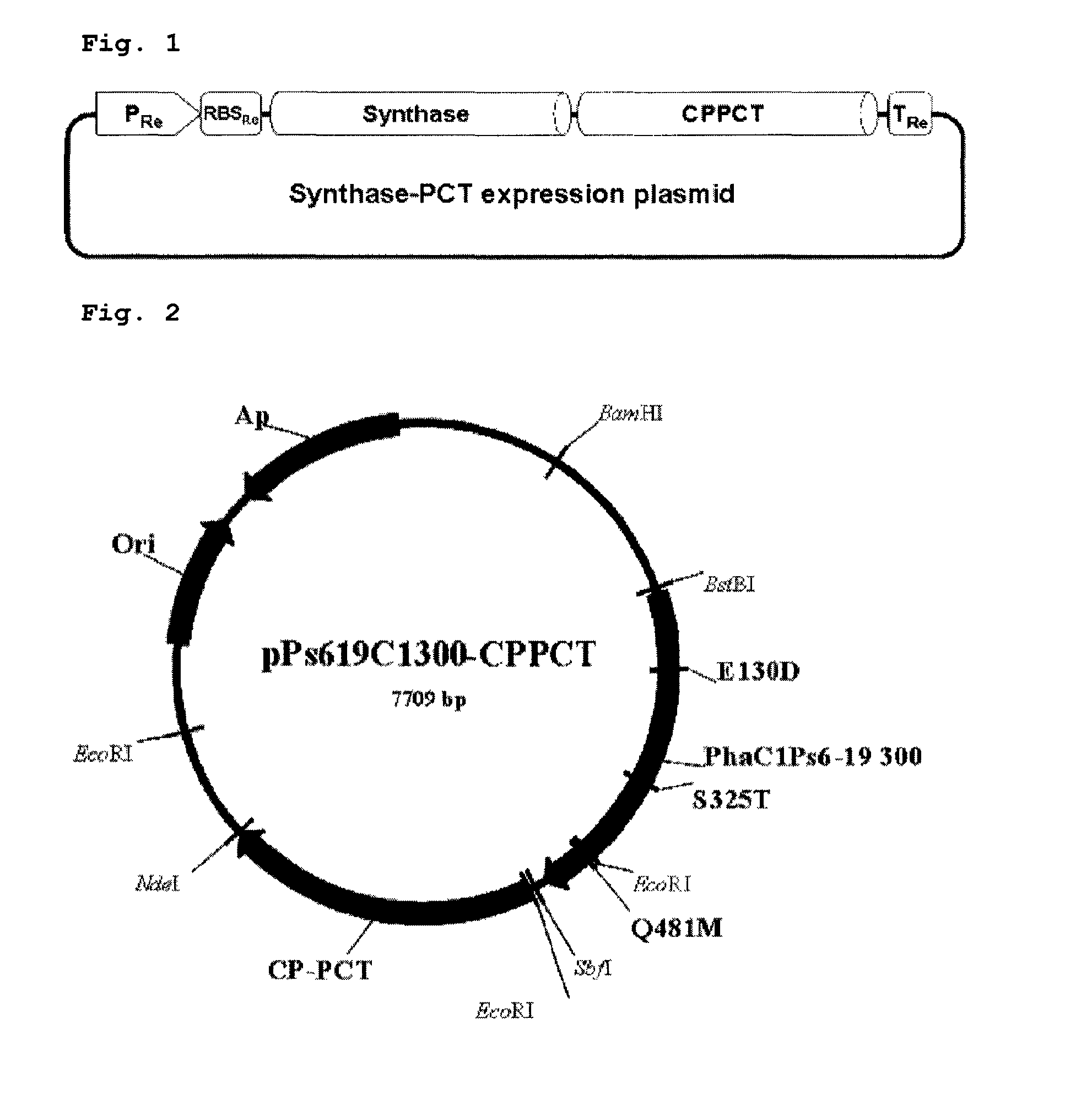
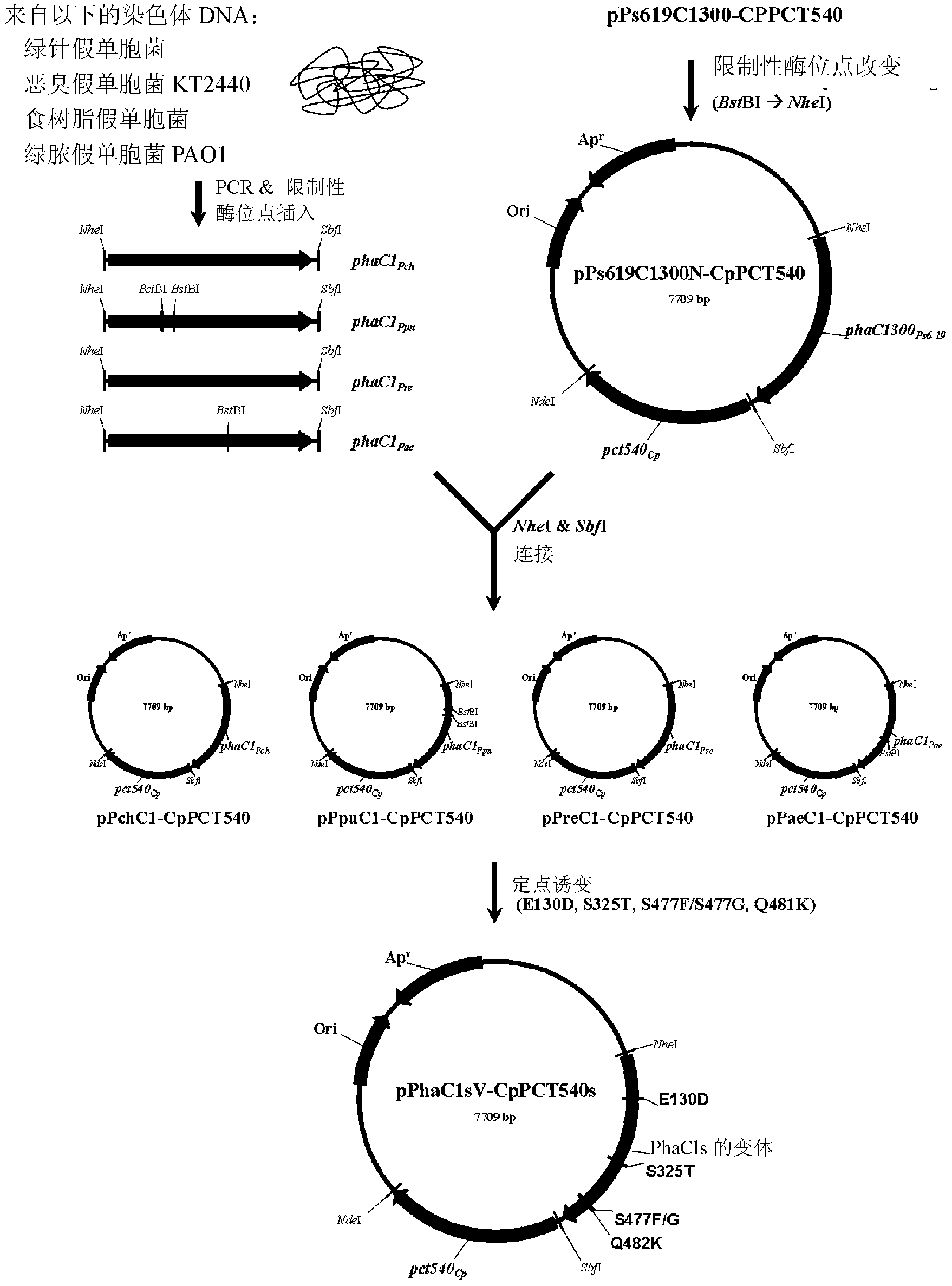
Mutants of pha synthase from pseudomonas sp. 6-19 and method for preparing lactate homopolymer or copolymer using the same
ActiveUS20100050298A1Easy to transformEasy to useSugar derivativesBacteriaMutantPolyhydroxyalkanoate synthase
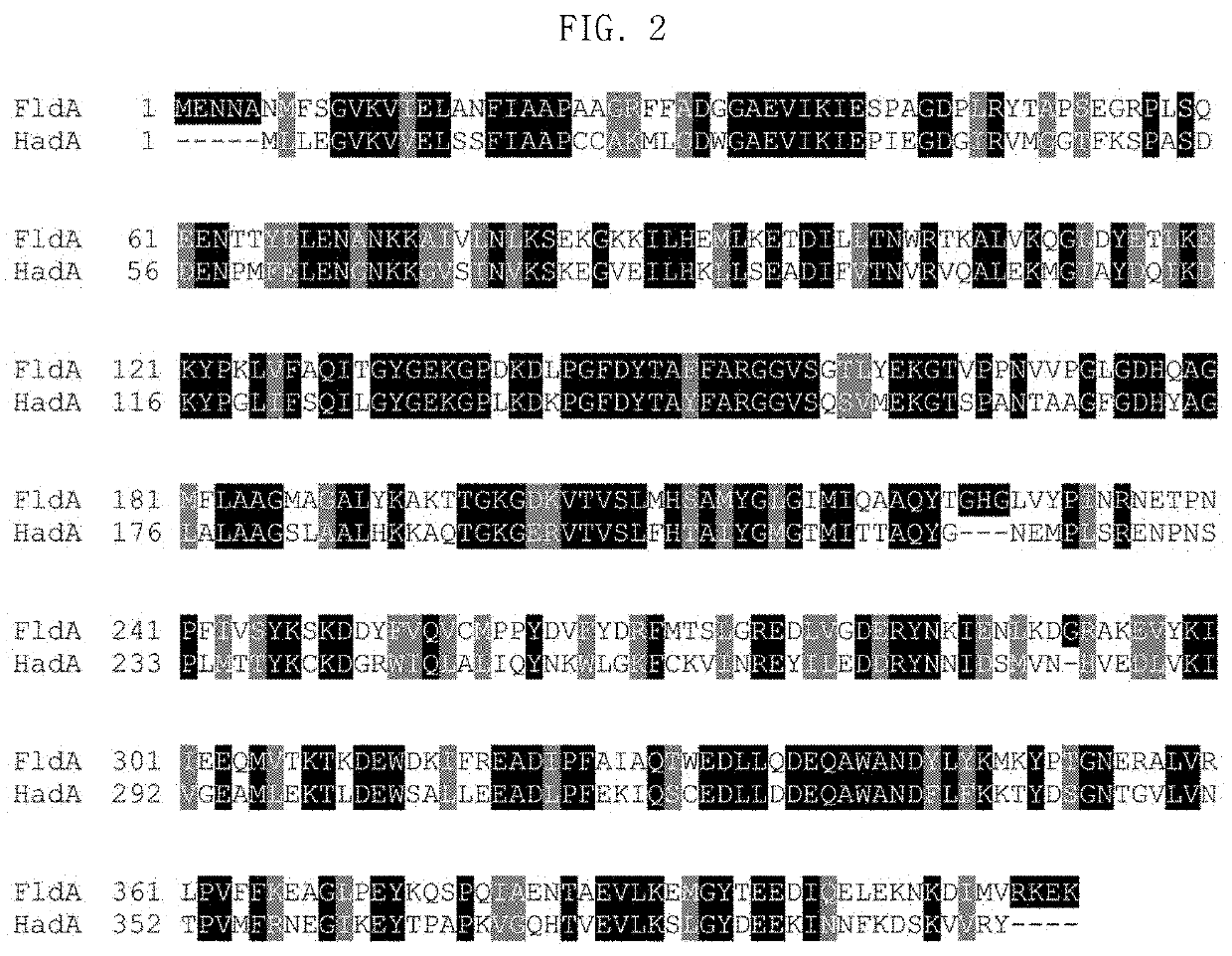
The present invention relates to polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase (PHA synthase) mutant originated from Pseudomonas sp. 6-19 (KCTC 11027BP) which can prepare lactate polymer and / or copolymer by using lactyl-CoA as a substrate. The present invention relates to a method for preparing lactate polymer and / or copolymer with the synthase mutant. The polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase mutants of the present invention originated from Pseudomonas sp. 6-19 can efficiently prepare lactate polymer and / or copolymer by using as a substrate lactyl-CoA which is difficult to be used as a substrate by conventional polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Microorganism capable of producing polyhydroxyalkanoate, polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, and gene encoding the same
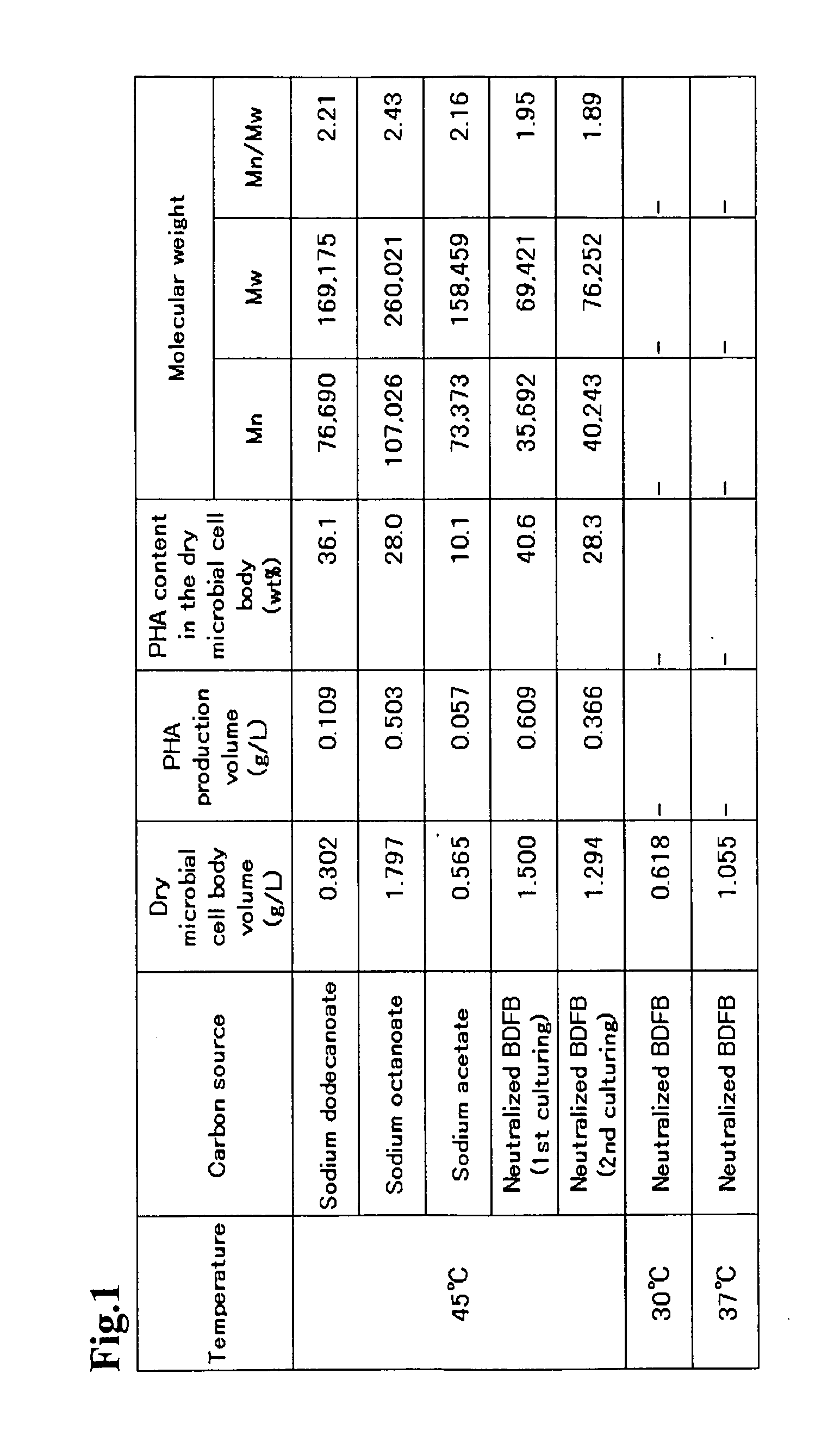
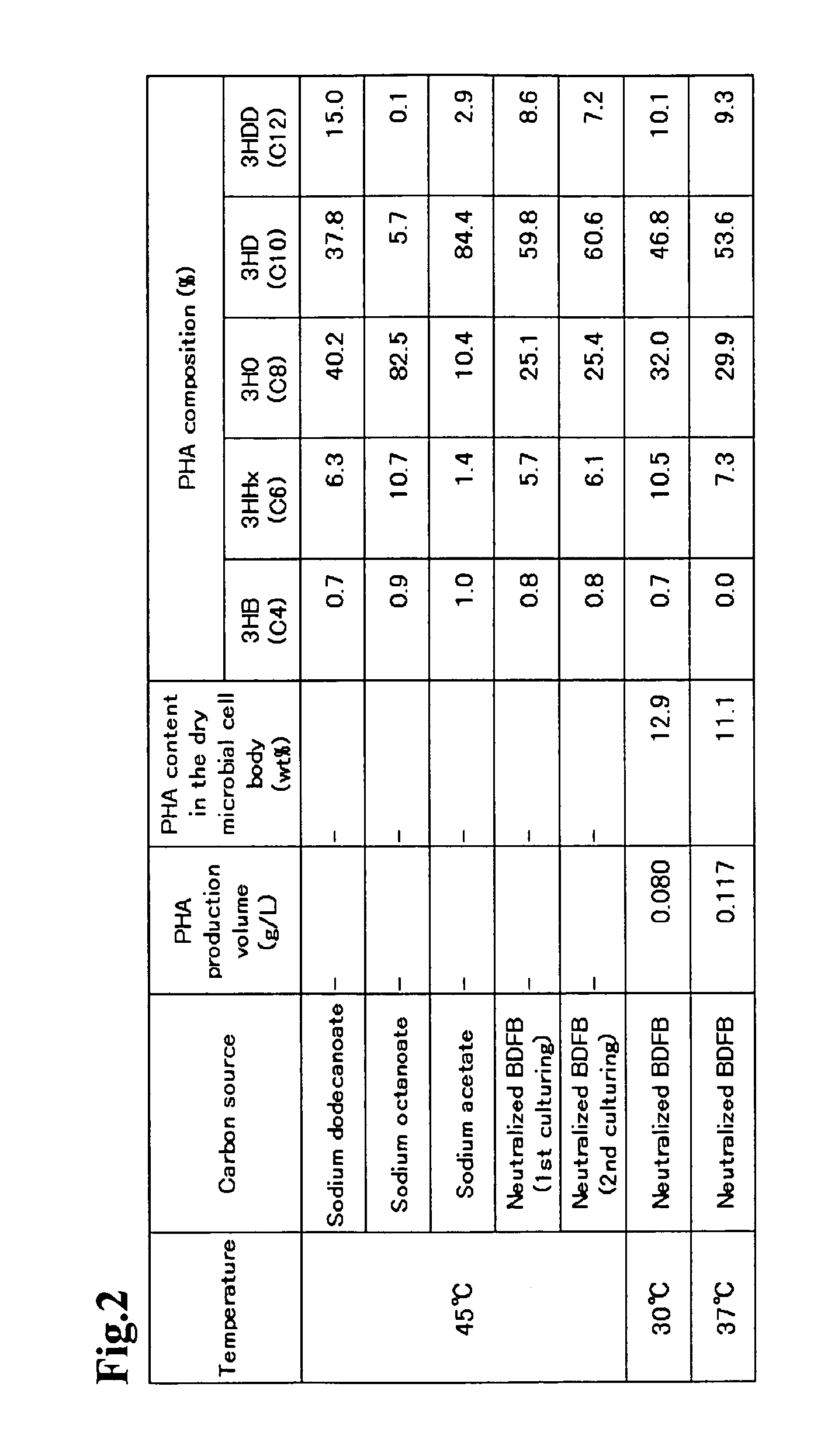
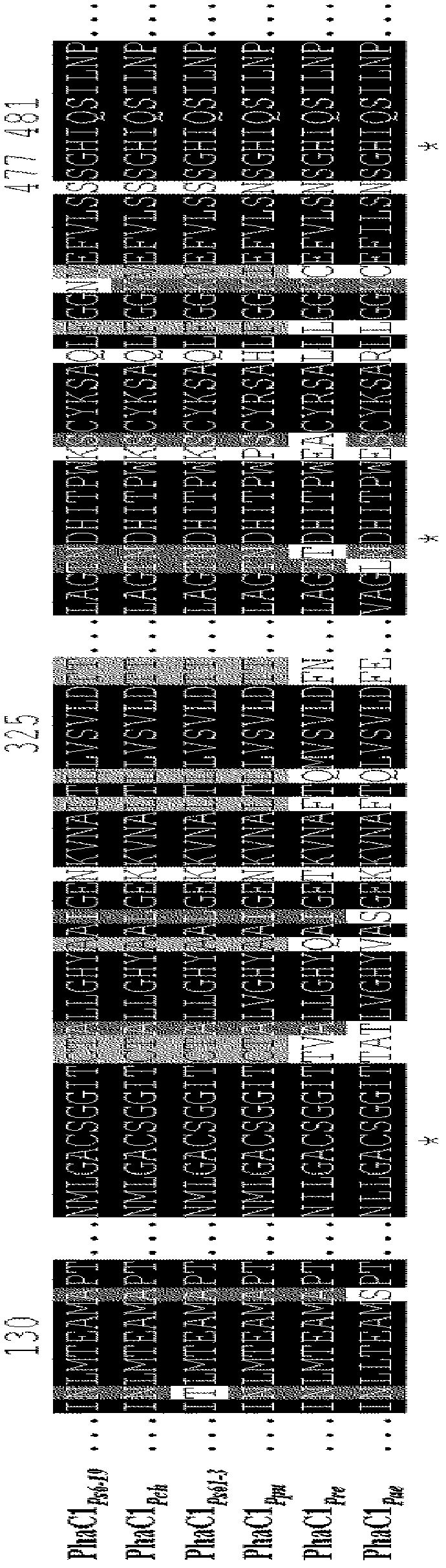
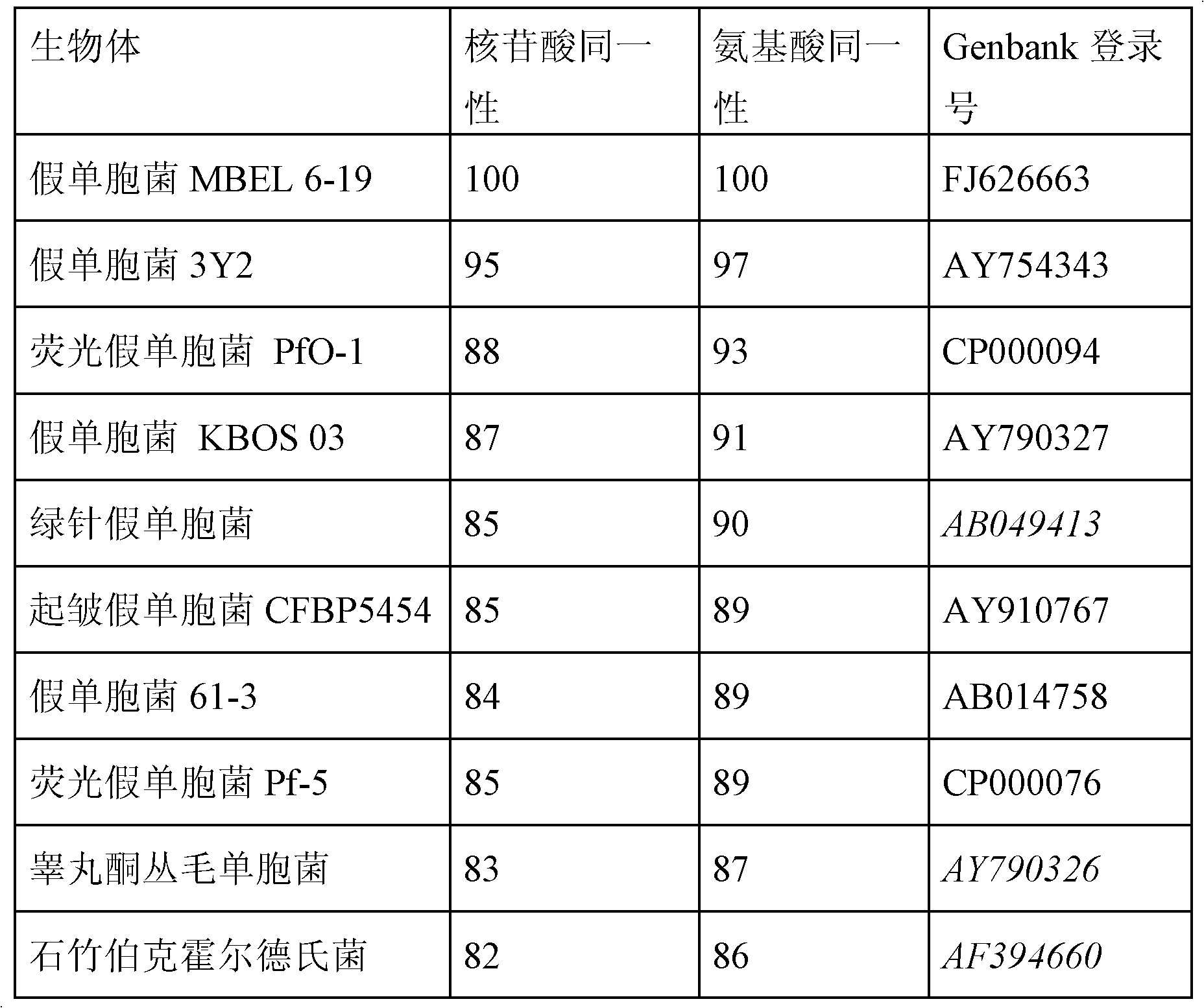
Problem to be Solved: To provide a new microorganism capable of producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a PHA synthase gene, an expression cassette including the gene, a vector including the expression cassette, a transformant transformed by the vector, a polypeptide having PHA synthase activity, a method for producing a PHA synthase and a method for producing a PHA.Solution: The new microorganism is capable of producing a polyhydroxyalkanoate comprising a 16S rRNA gene whose polynucleotide sequence shows 99% or more homology to a polynucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No: 1, having an optimum temperature of an activity temperature range for the growth and PHA production of the microorganism of at least 45° C. and being capable of growing at a pH range from 6 to 10.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Copolymer comprising 4-hydroxybutyrate unit and lactate unit and its manufacturing method
The present invention relates to a copolymer comprising 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer unit and lactate monomer unit, a copolymer 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer unit, lactate monomer unit and 3-hydroxyalkanoate, or their preparing method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a copolymer comprising lactate monomer; 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer; and optionally 3-hydroxyalkanoate, wherein the method comprises culturing a cell or plant comprising the gene of enzyme converting lactate and 3-hydroxyalkanoate into lactyl-CoA and 3-hydroxyalkanoyl-CoA, respectively, phosphotransbutylase gene, butyrate kinase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene together, and the copolymer made by the method. The copolymer of the present invention is a biodegradable polymer being able to be usefully used instead of conventional synthetic plastic, and the copolymer can be used for medical use.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Mutant polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase gene and method for producing aliphatic polyester using the same
InactiveUS20130157327A1High polymerization activityImprove productivitySugar derivativesBacteriaPolyester1-aminohydantoin
A substitution mutation that improves polymerization activity of a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase is identified. At least 1 amino acid residue selected from the group consisting of a histidine residue at position 17, a proline residue at position 71, a valine residue at position 131, a methionine residue at position 205, a leucine residue at position 230, and a proline residue at position 239 of a polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase derived from Alcanivorax borkumensis is subjected to substitution mutation with another amino acid.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Green process and compositions for producing poly(5HV) and 5 carbon chemicals
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Copolymer containing 3-hydroxyalkanoate unit and lactate unit, and its manufacturing method
The present invention relates to a copolymer comprising 3-hydroxyalkanoate monomer unit and lactate monomer unit, or their preparing method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a copolymer comprising lactate monomer and 3-hydroxyalkanoate monomer, wherein the method comprises culturing a cell or plant comprising the gene of enzyme converting lactate and 3-hydroxyalkanoate into lactyl-CoA and 3-hydroxyalkanoyl-CoA, respectively, and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene together, and the copolymer made by the method. The copolymer of the present invention is a biodegradable polymer being able to be usefully used instead of conventional synthetic plastic, and the copolymer can be used also for medical use.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Method for producing biodegradable polymer and biomass fuel converted from carbon source by recombinant microorganisms
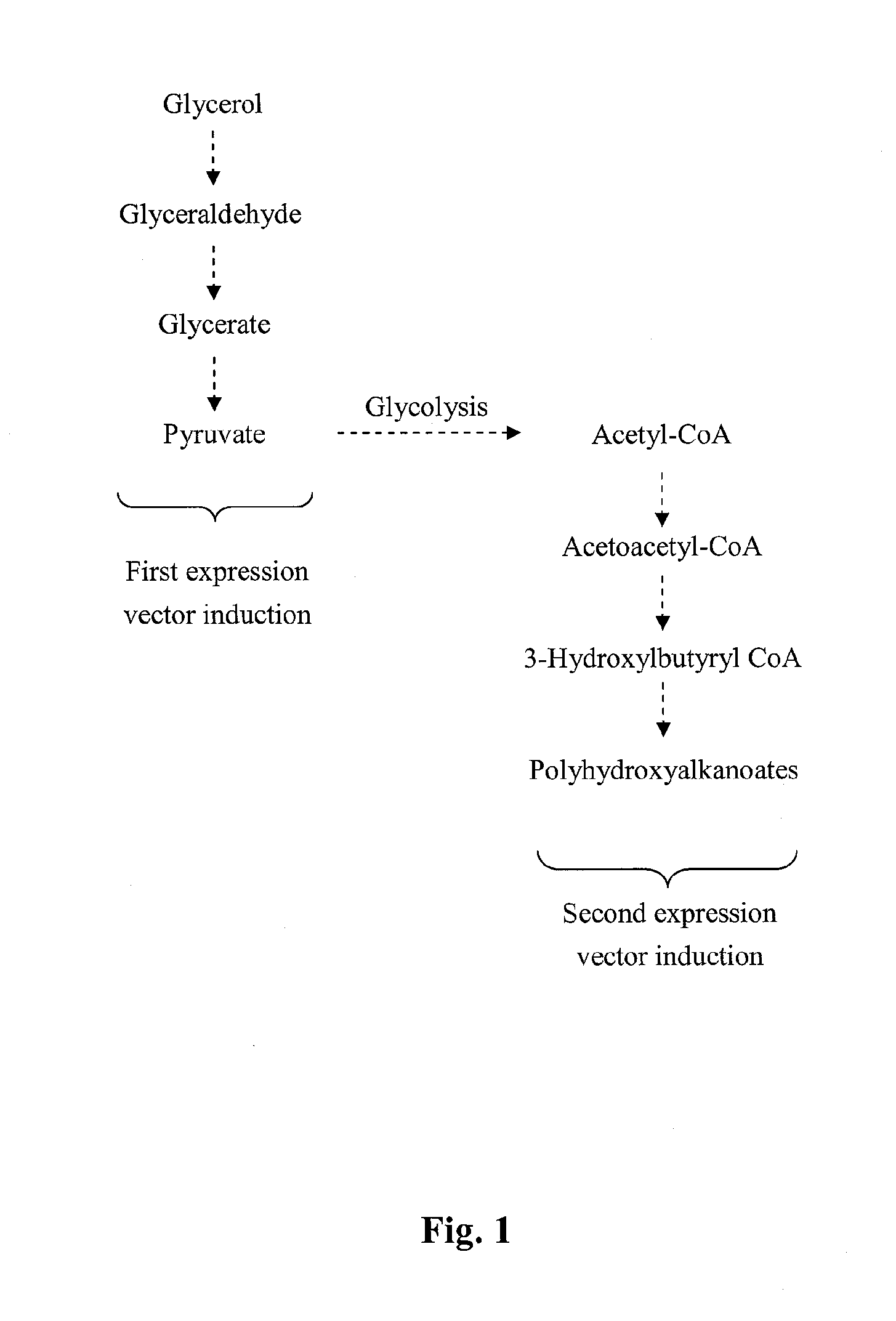
InactiveUS20130302867A1Improve defectsProne to environmental pollutionBiofuelsOxidoreductasesGlycerolBiodegradable polymer
Disclosed is a method for producing biodegradable polymer and biomass fuel converted from carbon source by using recombinant microorganisms, comprising the steps of: (A) providing recombinant microorganisms transformed with plasmids containing at least a gene encoding for glycerol utilizing enzyme and a gene encoding for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase; (B) culturing the recombinant microorganisms in a medium containing glycerol; (C) inducing expression of the genes of step (A), thereby obtaining polyhydroxyalkanoate and ethanol; and (D) recovering the polyhydroxyalkanoate and the ethanol; wherein the recombinant microorganisms have a glycerol utilization rate more than 90% (w / w), and have polyhydroxyalkanoate accumulated therein to a biomass content thereof at least 30% (w / w).
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Copolymer comprising 4-hydroxybutyrate unit and lactate unit and its manufacturing method
The present invention relates to a copolymer comprising 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer unit and lactate monomer unit, a copolymer 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer unit, lactate monomer unit and 3-hydroxyalkanoate, or their preparing method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a copolymer comprising lactate monomer; 4-hydroxybutyrate monomer; and optionally 3-hydroxyalkanoate, wherein the method comprises culturing a cell or plant comprising the gene of enzyme converting lactate and 3-hydroxyalkanoate into lactyl-CoA and 3-hydroxyalkanoyl-CoA, respectively, phosphotransbutylase gene, butyrate kinase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene together, and the copolymer made by the method. The copolymer of the present invention is a biodegradable polymer being able to be usefully used instead of conventional synthetic plastic, and the copolymer can be used for medical use.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
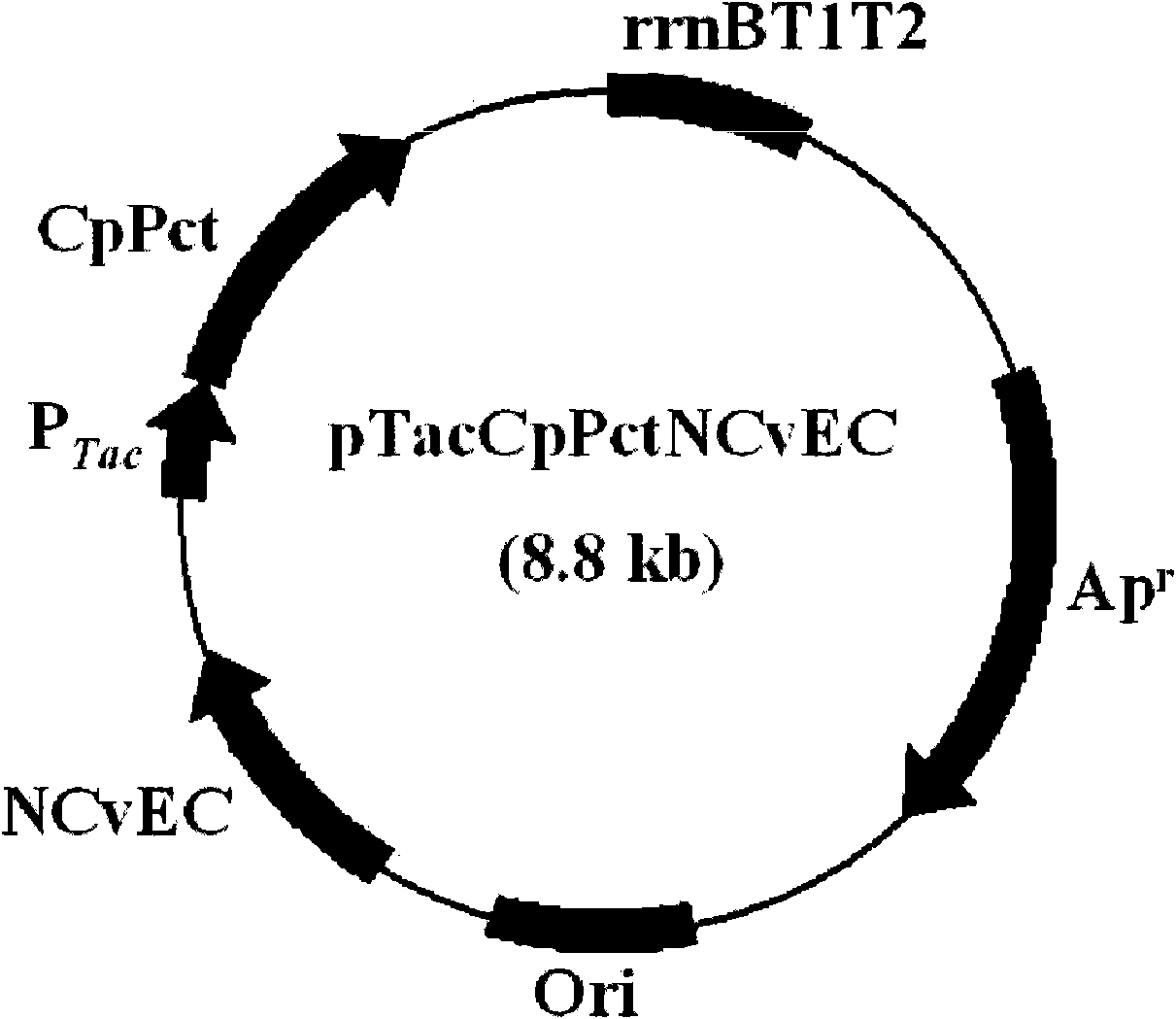
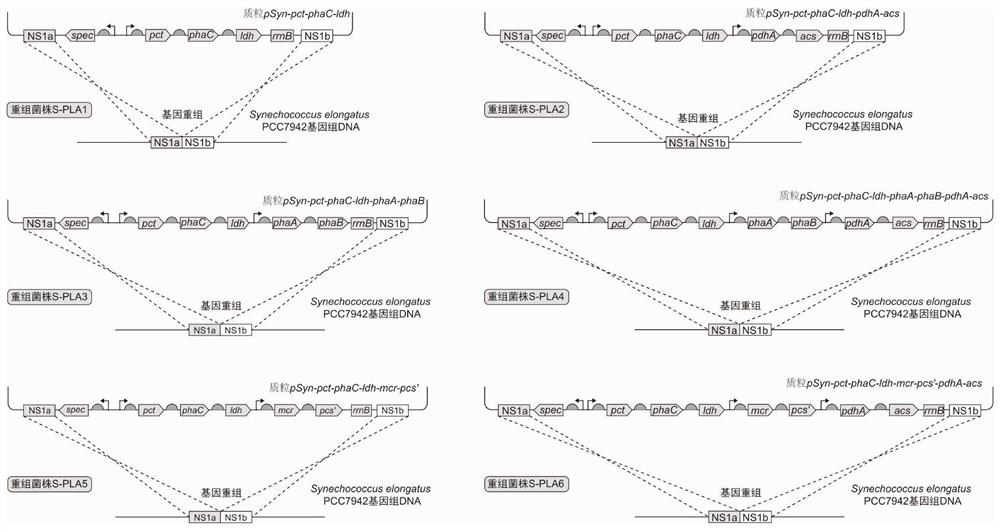
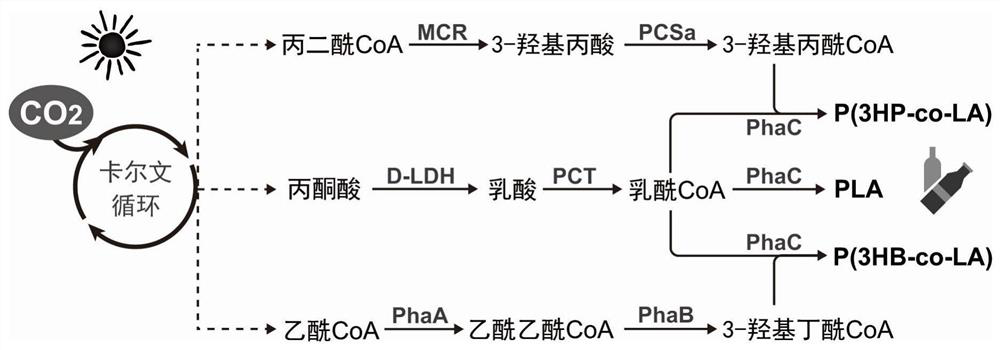
Photosynthetic microorganism as well as application and plasmid thereof
ActiveCN114703067AAvoid consumptionLow costUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCyanobacteria
The invention discloses a photosynthetic microorganism and application and plasmid thereof, the photosynthetic microorganism contains a plurality of exogenous genes, and the exogenous genes comprise a coding gene of propionyl-coenzyme A transferase, a coding gene of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a coding gene of d-lactic dehydrogenase. The genetic engineering blue algae provided by the invention can be used for efficiently producing polylactic acid (PLA) and lactic acid copolymers by directly utilizing greenhouse gas CO2 through photosynthesis, so that the consumption of carbohydrates and expensive precursors and the use of inducers are avoided. The invention also provides application of the genetic engineering cyanobacteria, especially application of the genetic engineering cyanobacteria in production of PLA and copolymers, a new technology is developed for production of degradable plastics, the production cost is reduced, and the genetic engineering cyanobacteria has an important application prospect.
Owner:上海光玥生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of lactate polymers and lactate copolymers using polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase mutants
The present invention relates to diverse polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase (PHA synthase) mutants capable of synthesizing lactate polymers (PLAs) and lactate copolymers (PLA copolymers), and a preparation method of the lactate polymers and copolymers using the PHA synthase mutants. More specifically, the present invention relates to polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase mutants having SEQ. ID. NO: 2, 4, 6 or 8; and a preparation method of PLA polymers and PLA copolymers using the synthase mutants. According to the present invention, polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase mutants having SEQ. ID. NO: 2, 4, 6 or 8 can have PLA polymer and copolymer synthase activity by the variation in amino acid sequence that affects the PLA polymer synthase activity. Further, the use of such synthase mutants makes it possible to prepare PLA polymers and copolymers having different properties from each other.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate using 2-hydroxyisocaproate-coa transferase
The present invention relates to a recombinant microorganism to which a gene coding for 2-hydroxyisocaproate-CoA transferase and a gene coding for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase are introduced and which has a potential of producing polyhydroxyalkanoate bearing an aromatic monomer or a long-chain 2-HA monomer and a method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate bearing an aromatic monomer or a long-chain 2-HA monomer, using the recombinant microorganism. According to the present invention, a biodegradable polymer bearing an aromatic monomer or a long-chain 2-HA monomer can be produced.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of lactate polymers and lactate copolymers using polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase mutants
InactiveUS20120171737A1High of amino acid sequenceImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesMutantCopolymer
Mutants of various polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthases capable of synthesizing a lactate polymer (PLA) and a lactate copolymer (PLA copolymer), and a method of preparing a lactate polymer and a lactate copolymer using the same are provided. More specifically, a mutant of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, or 8, and a method of preparing lactate polymer and lactate copolymer using the mutant of synthase are provided. The polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, or 8 can have an activity of synthesizing a lactate polymer and a lactate copolymer by an amino acid sequence mutation affecting an activity of synthesizing a lactate polymer, and can produce a lactate polymer and a copolymer that have different features, respectively, by using the mutants of the synthase.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com