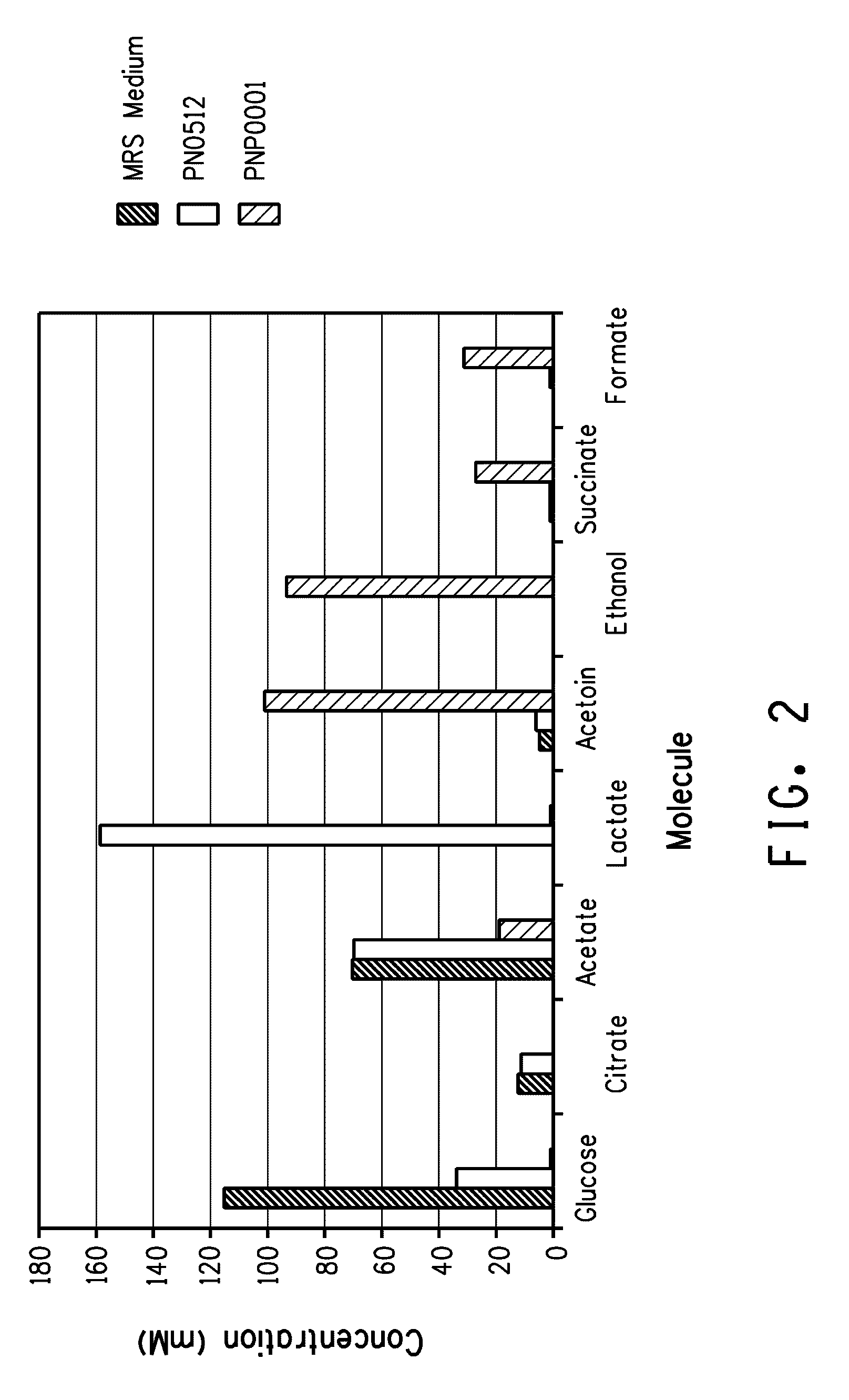
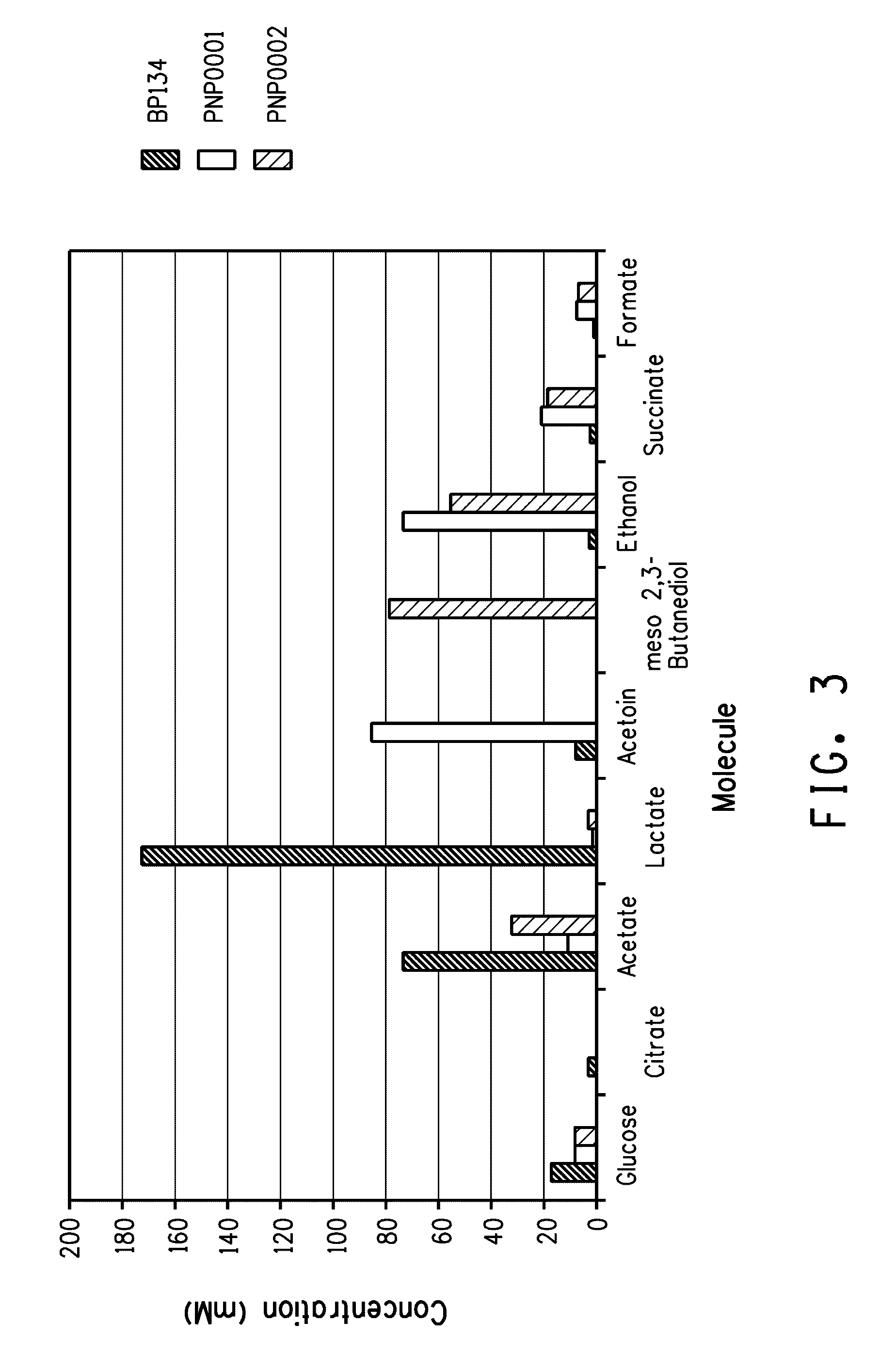
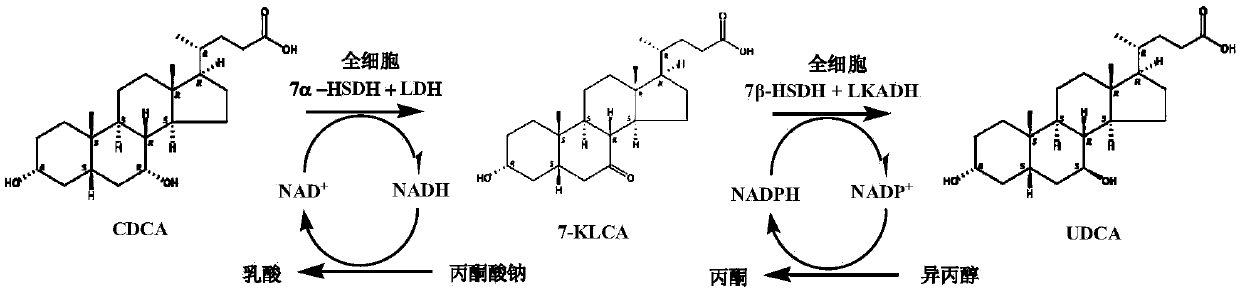
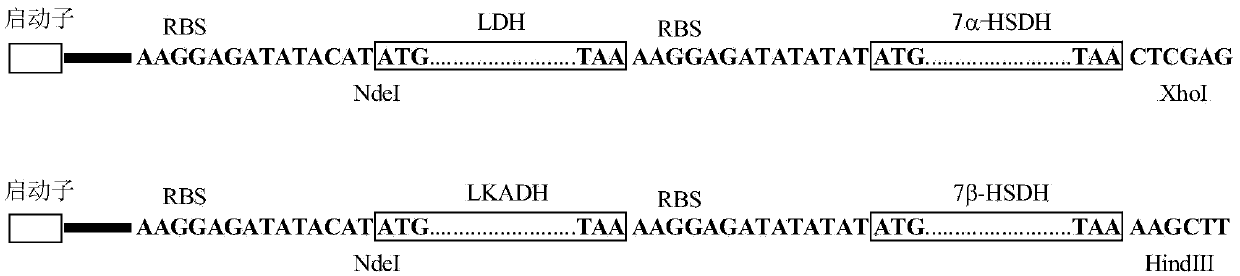
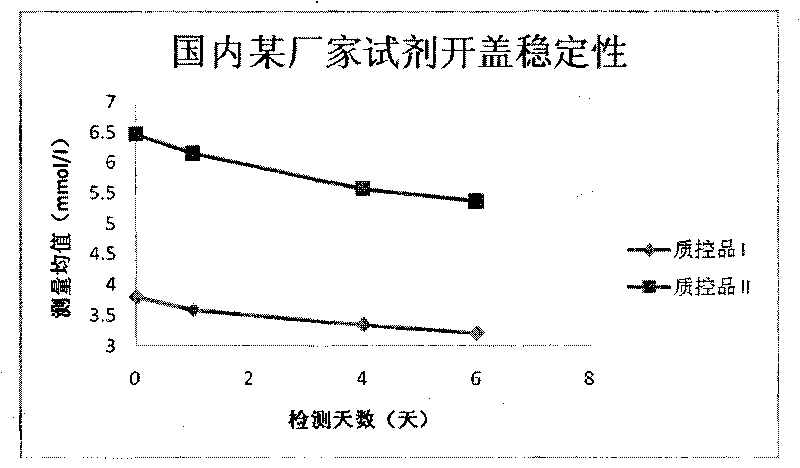
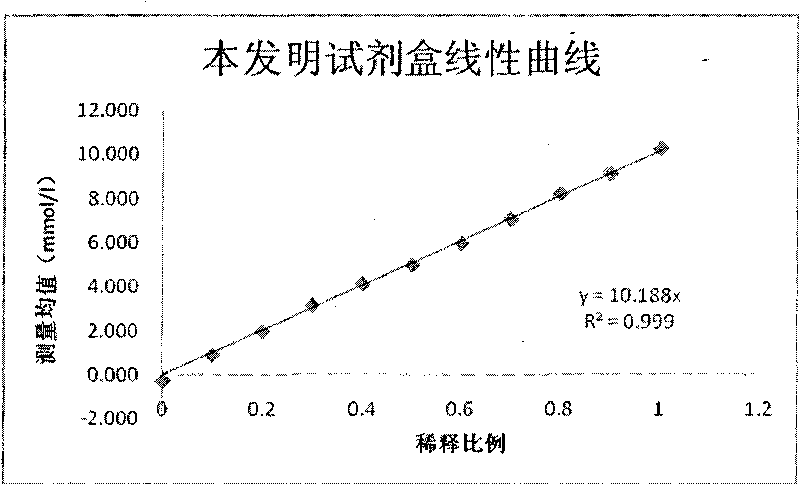
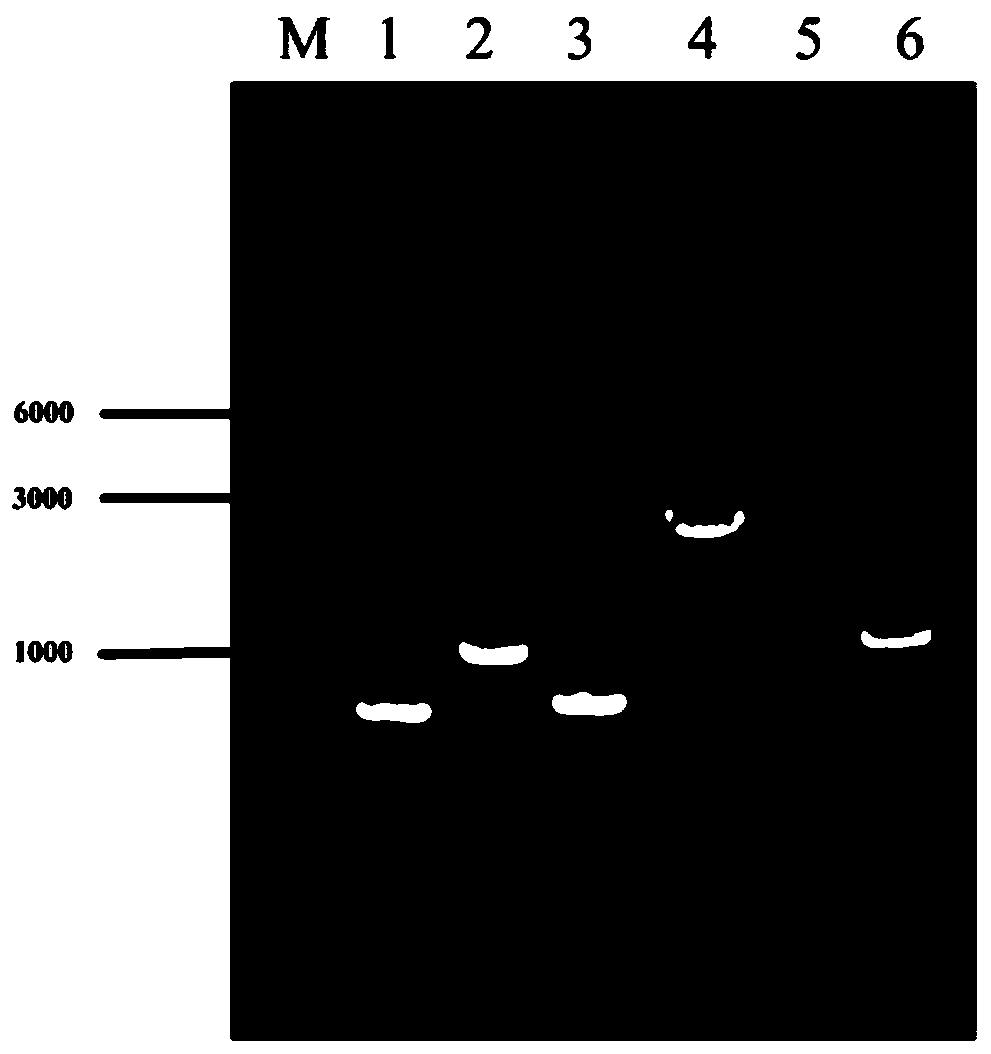
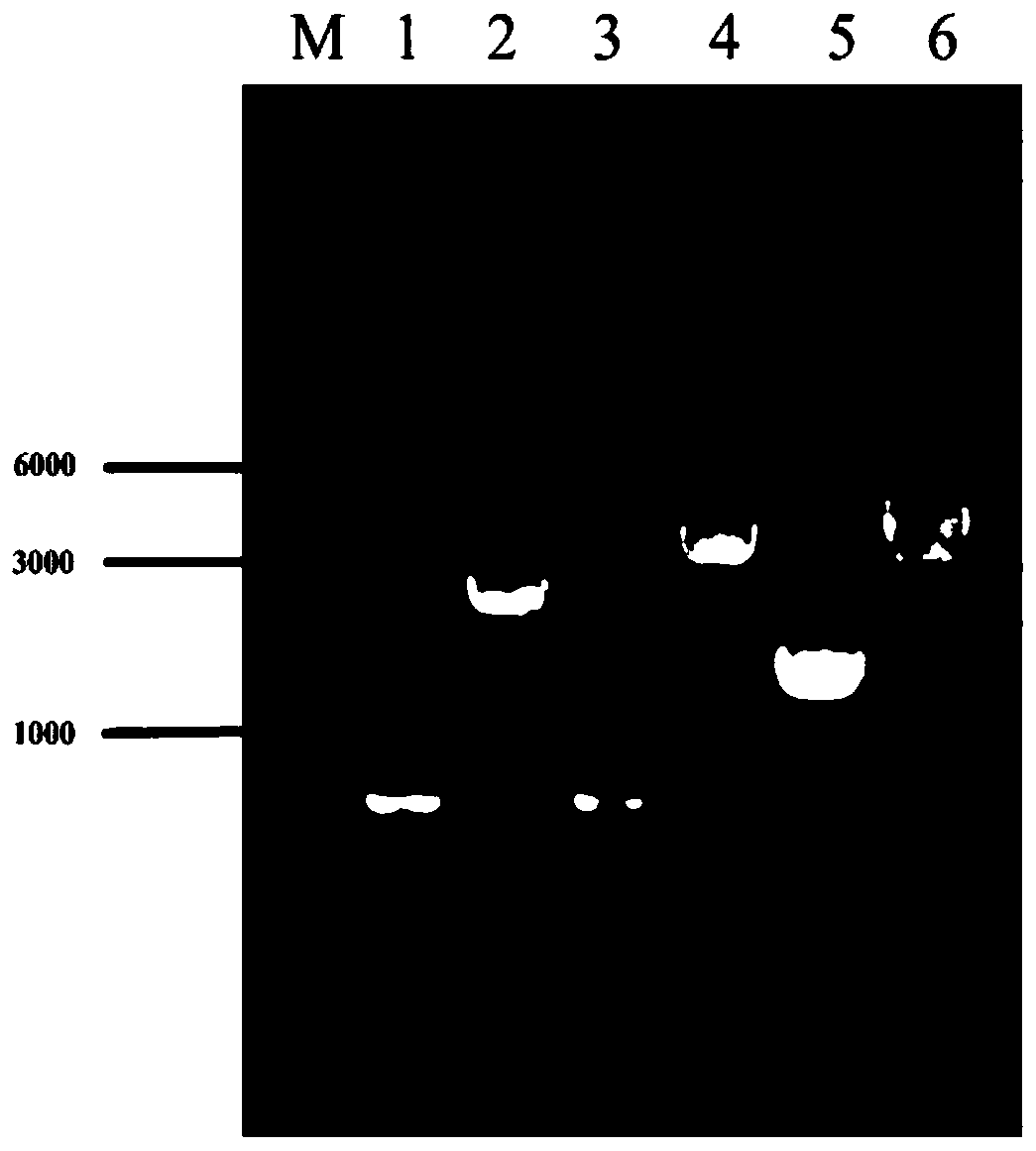
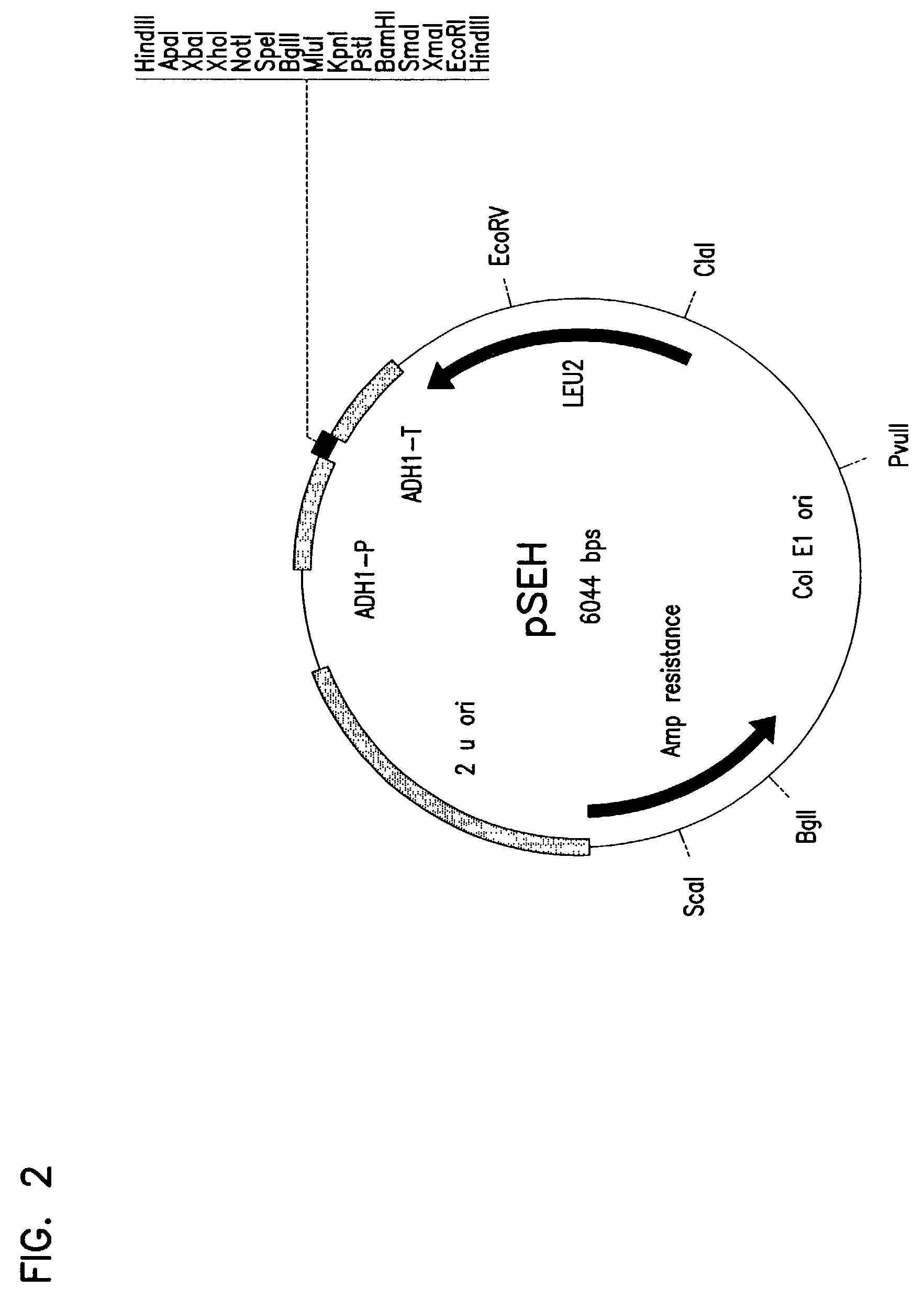
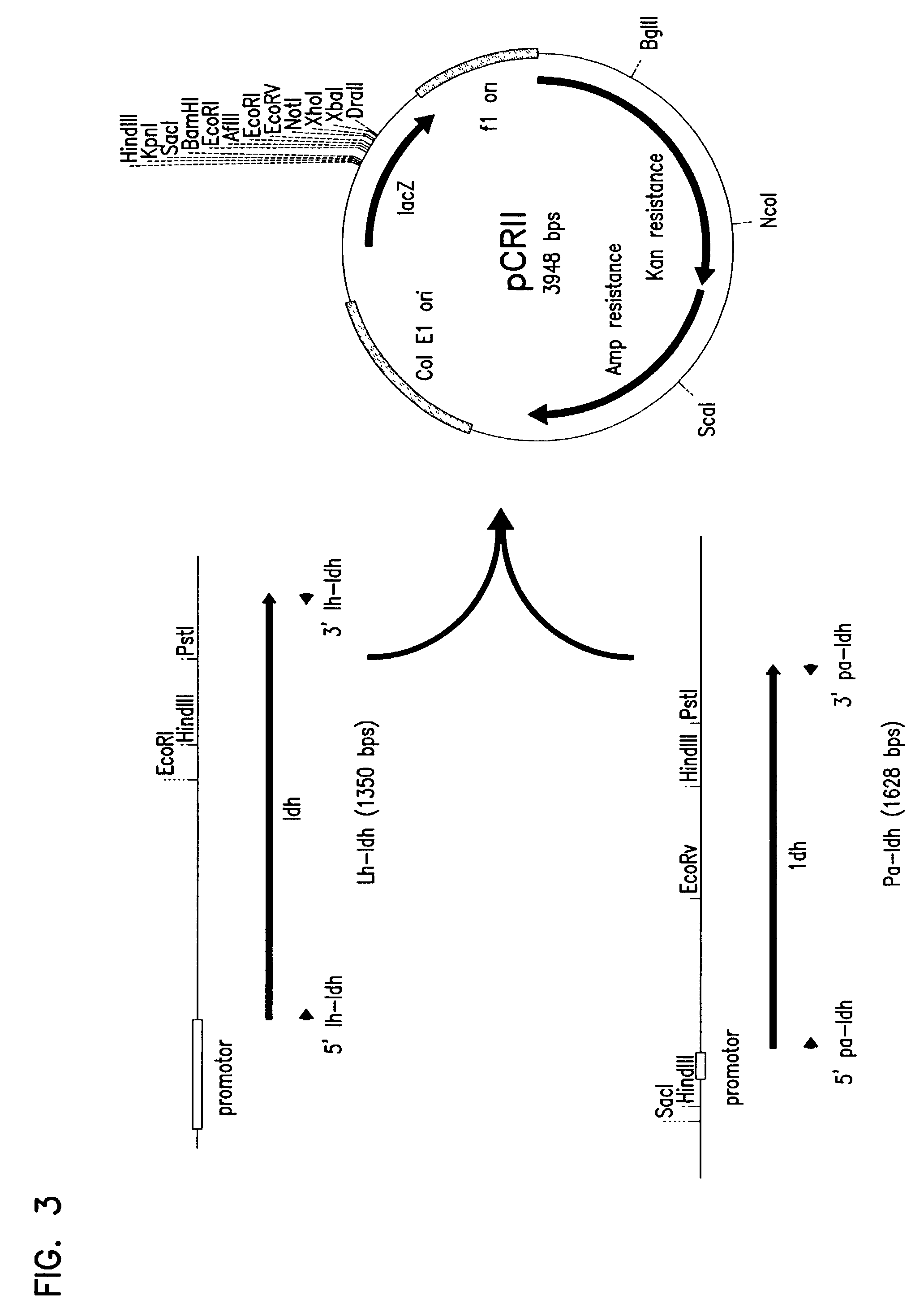
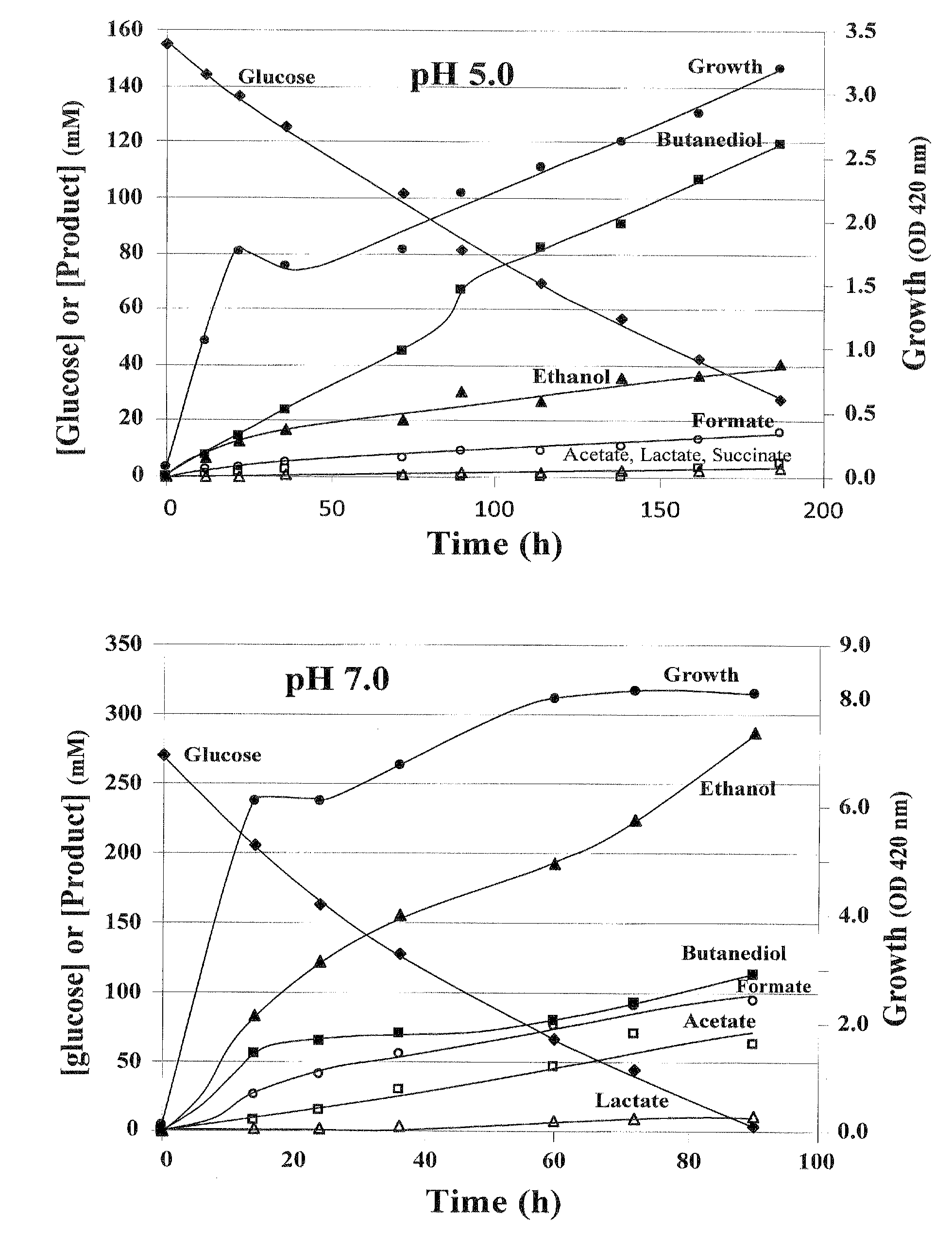
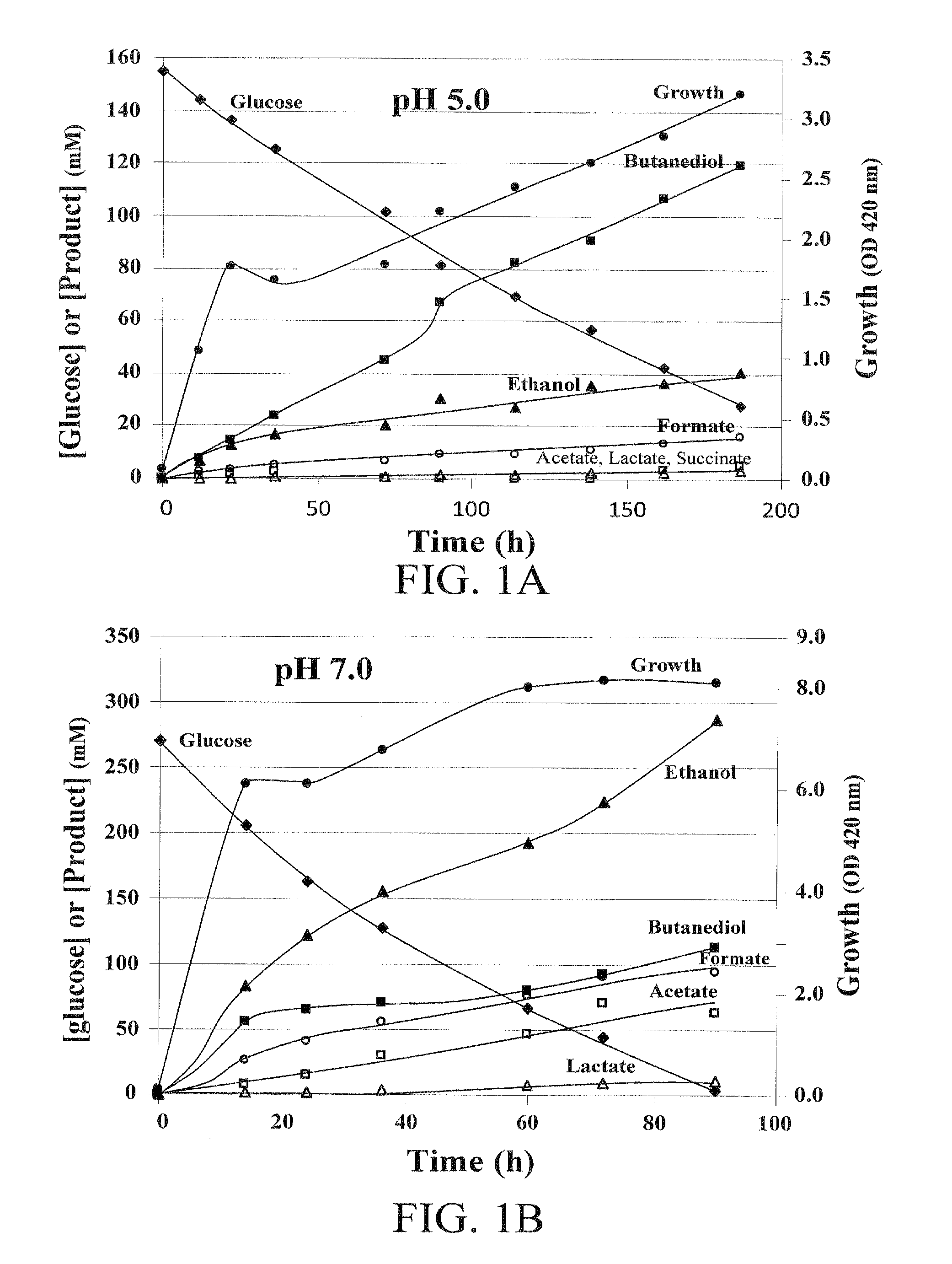
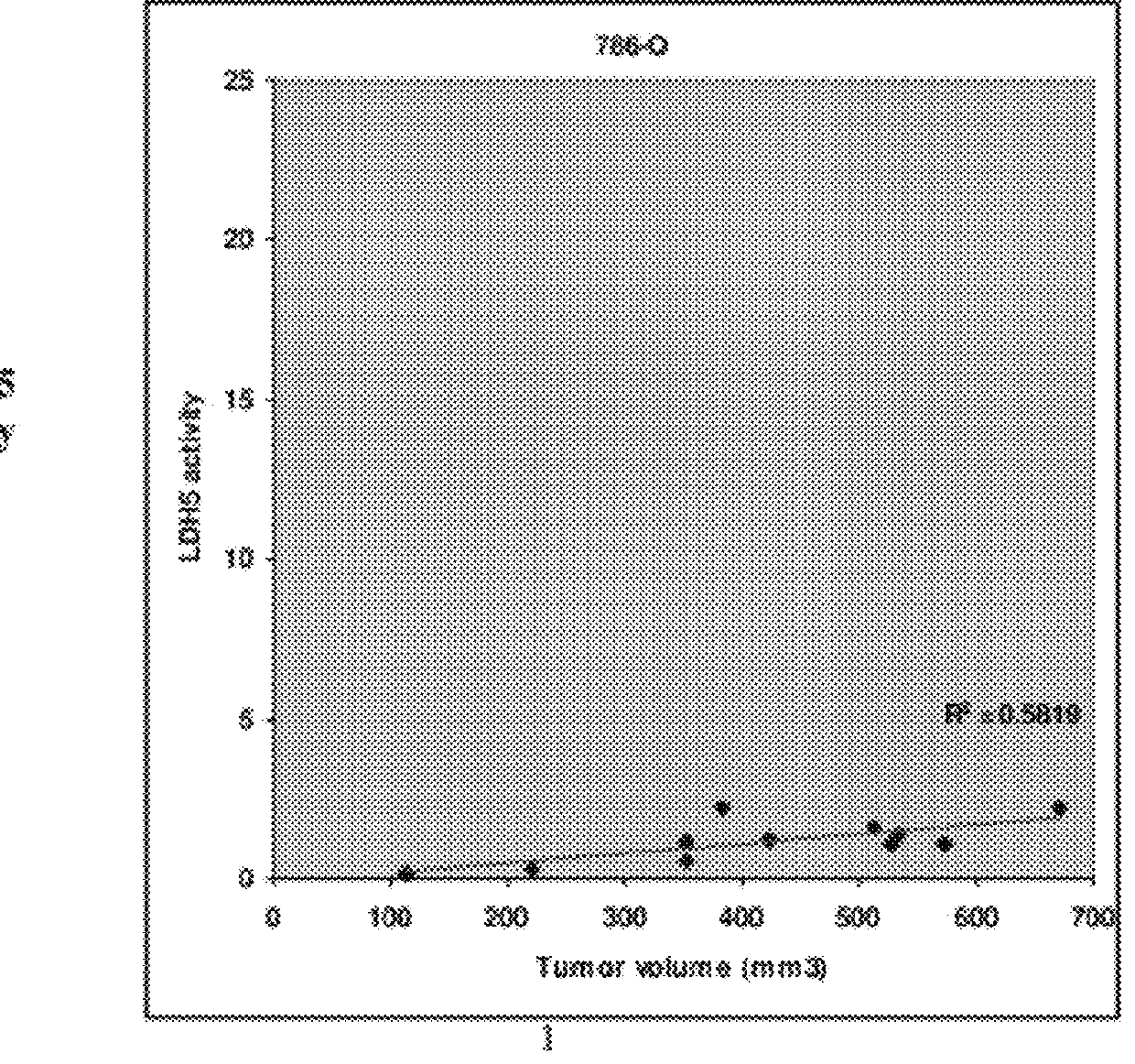
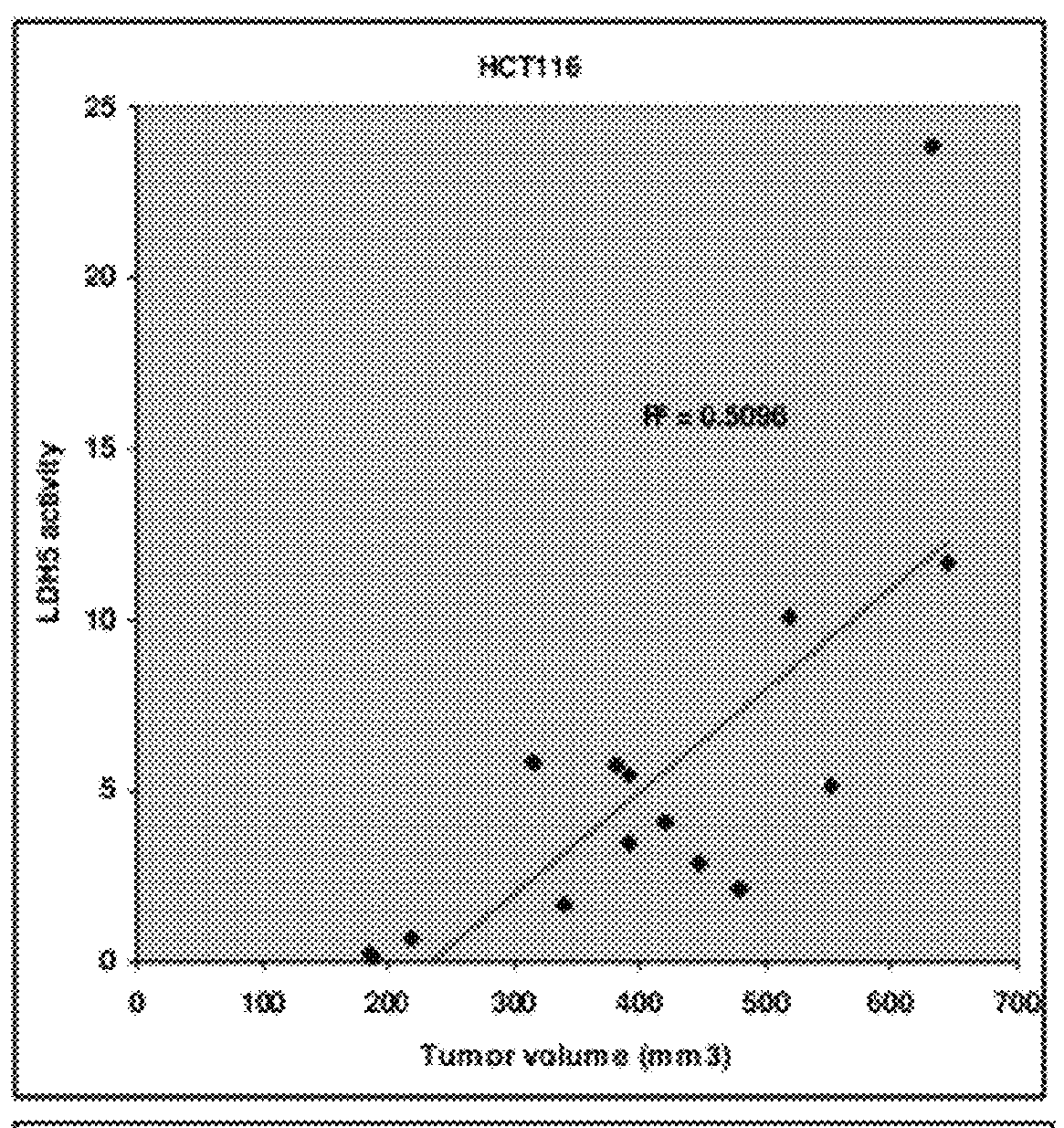
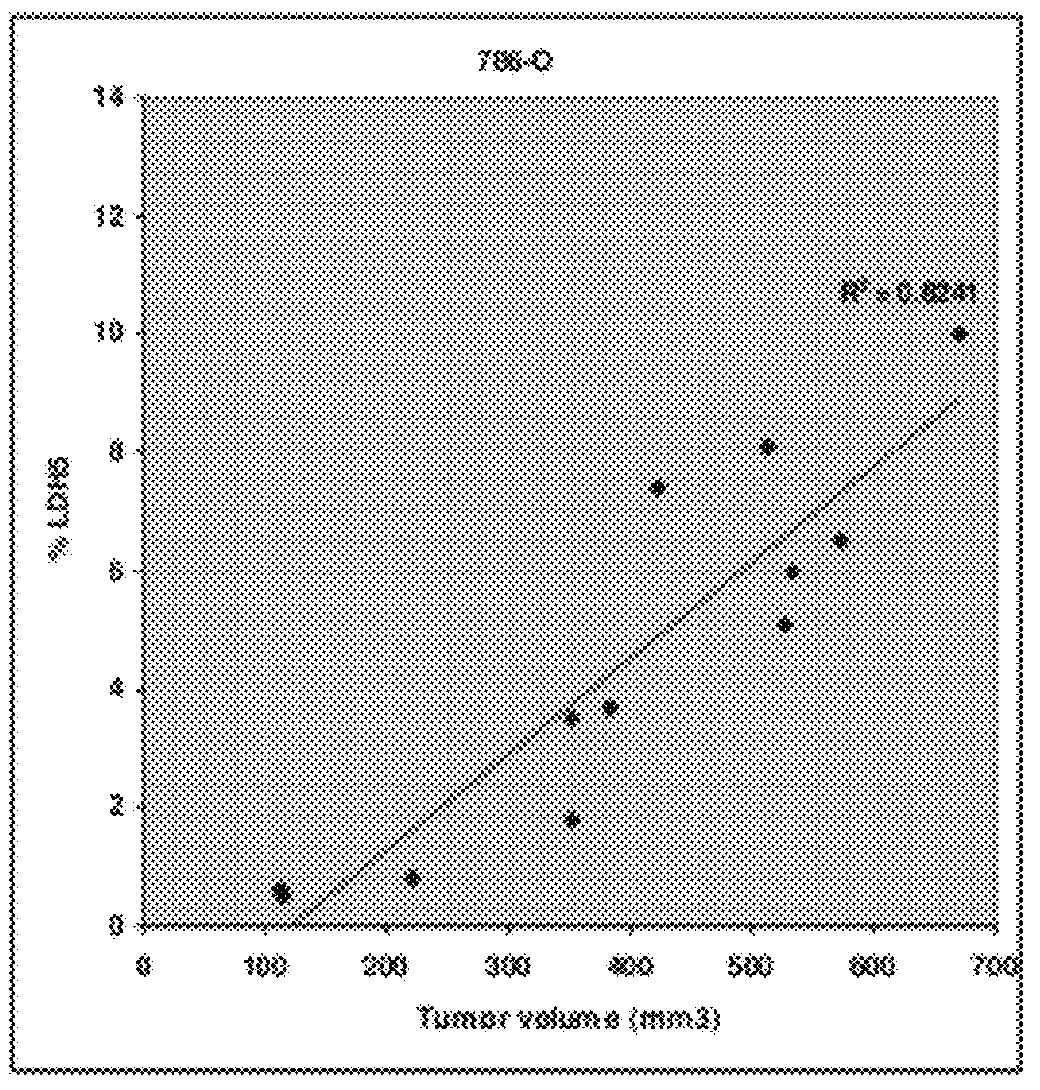
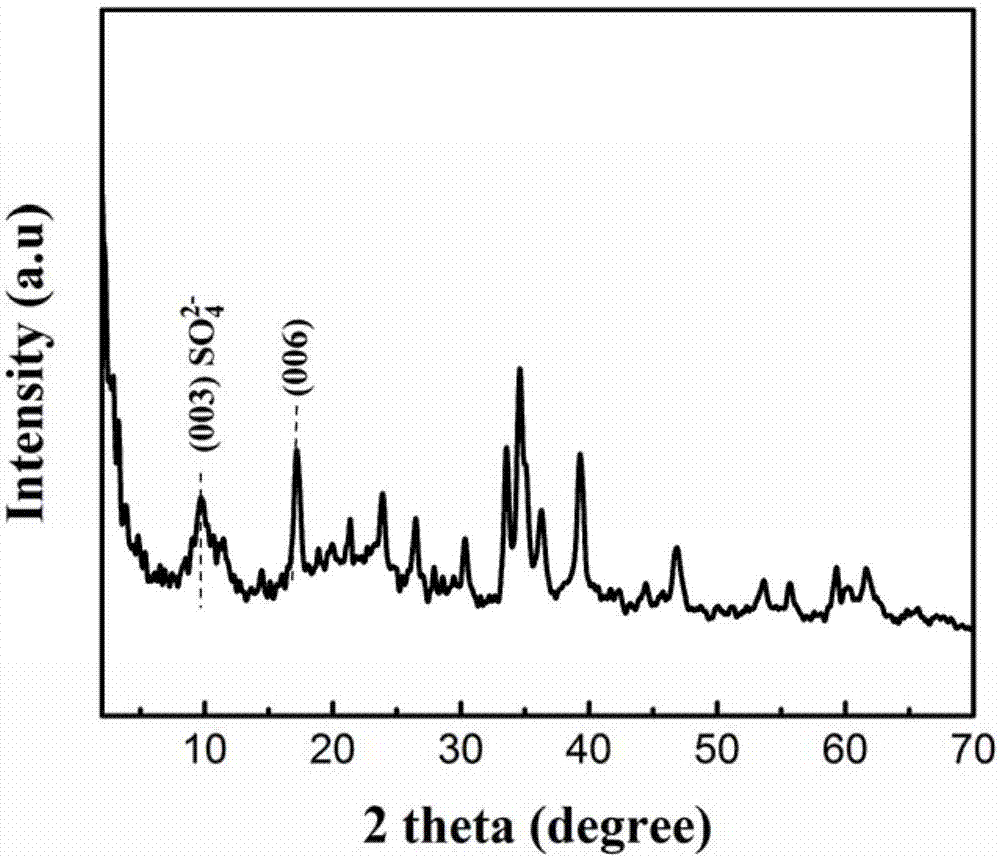
Patents
Literature
295 results about "Lactate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
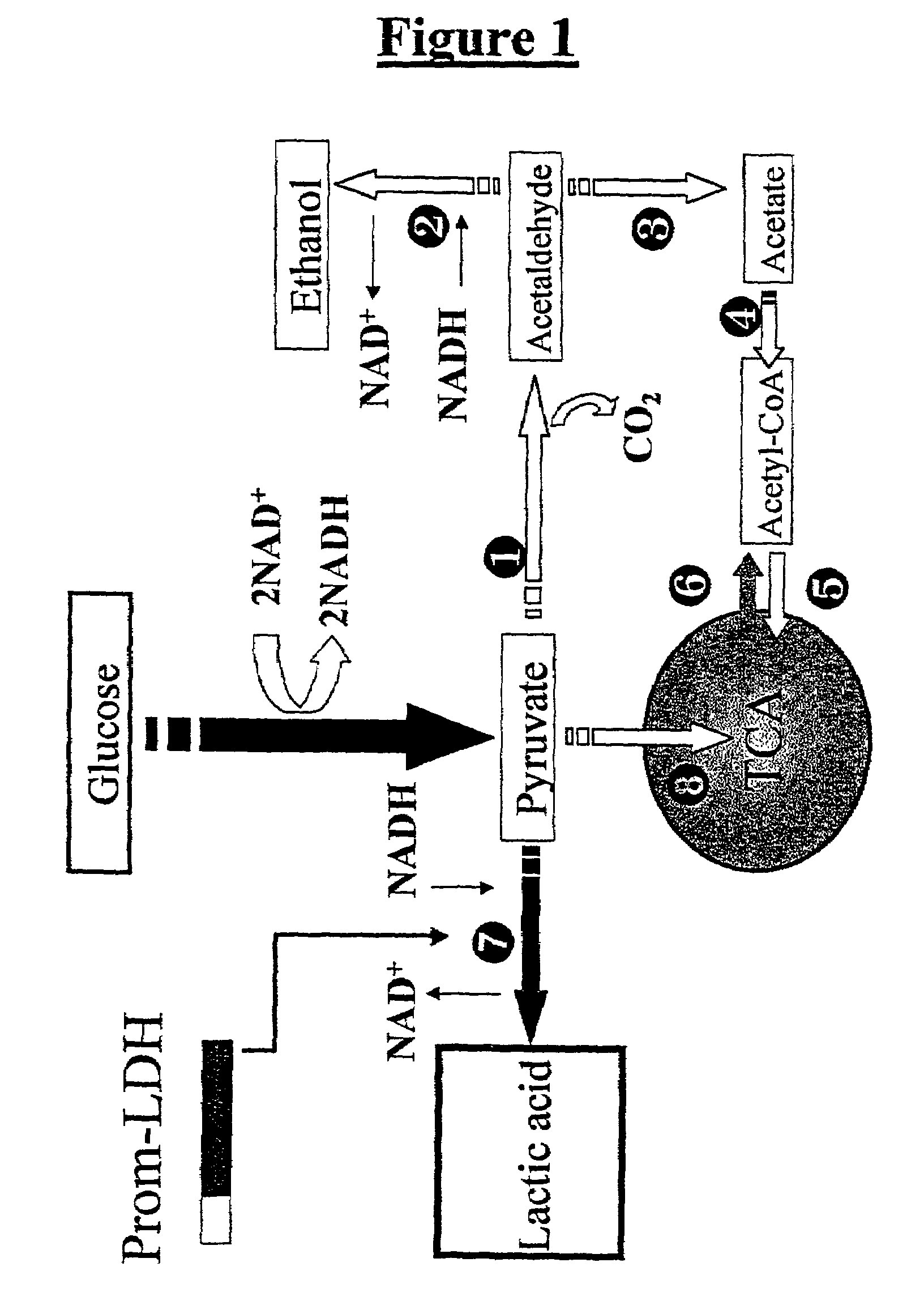
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH or LD) is an enzyme found in nearly all living cells (animals, plants, and prokaryotes). LDH catalyzes the conversion of lactate to pyruvate and back, as it converts NAD⁺ to NADH and back. A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that transfers a hydride from one molecule to another.
Methods and materials for the synthesis of organic products
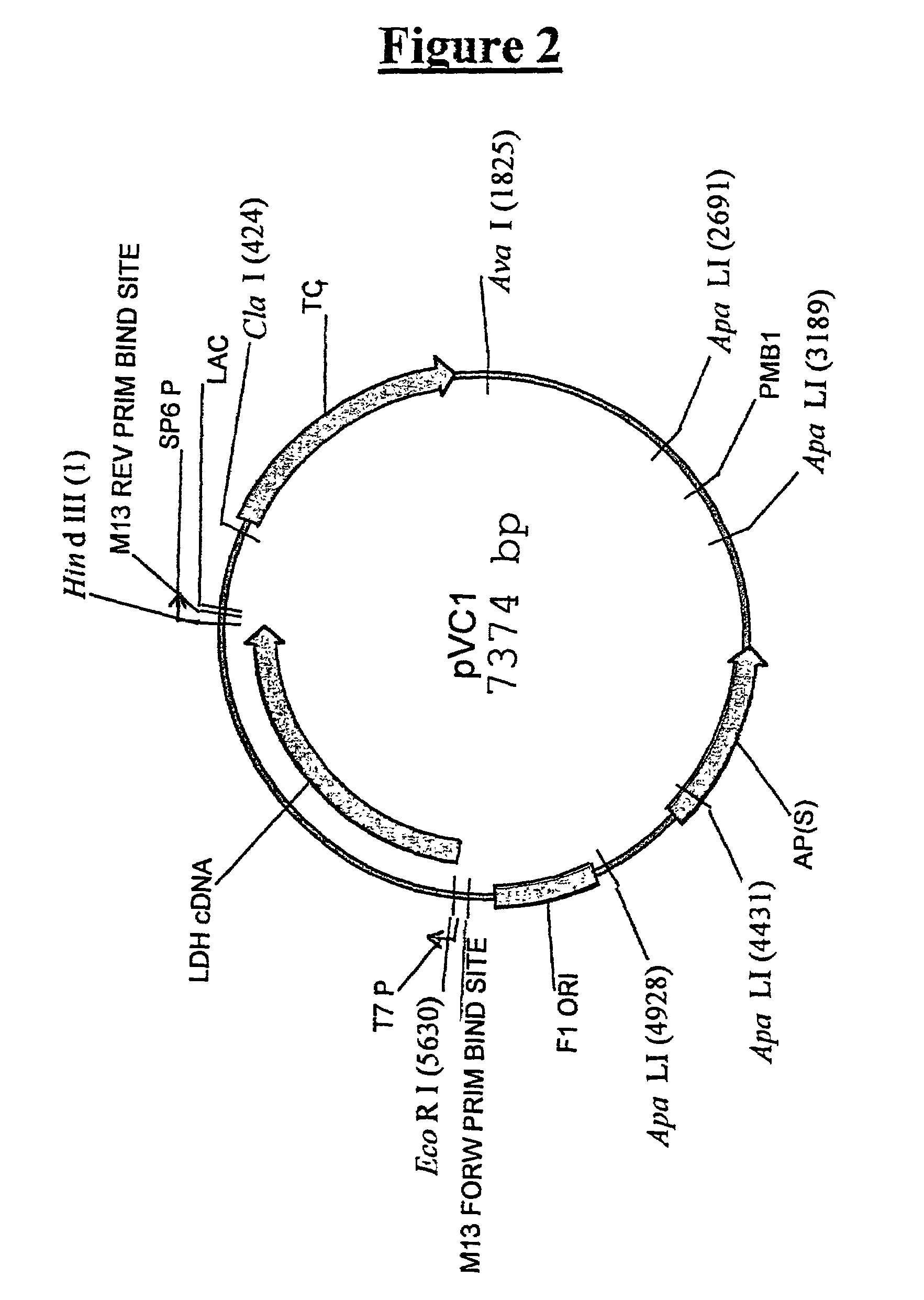
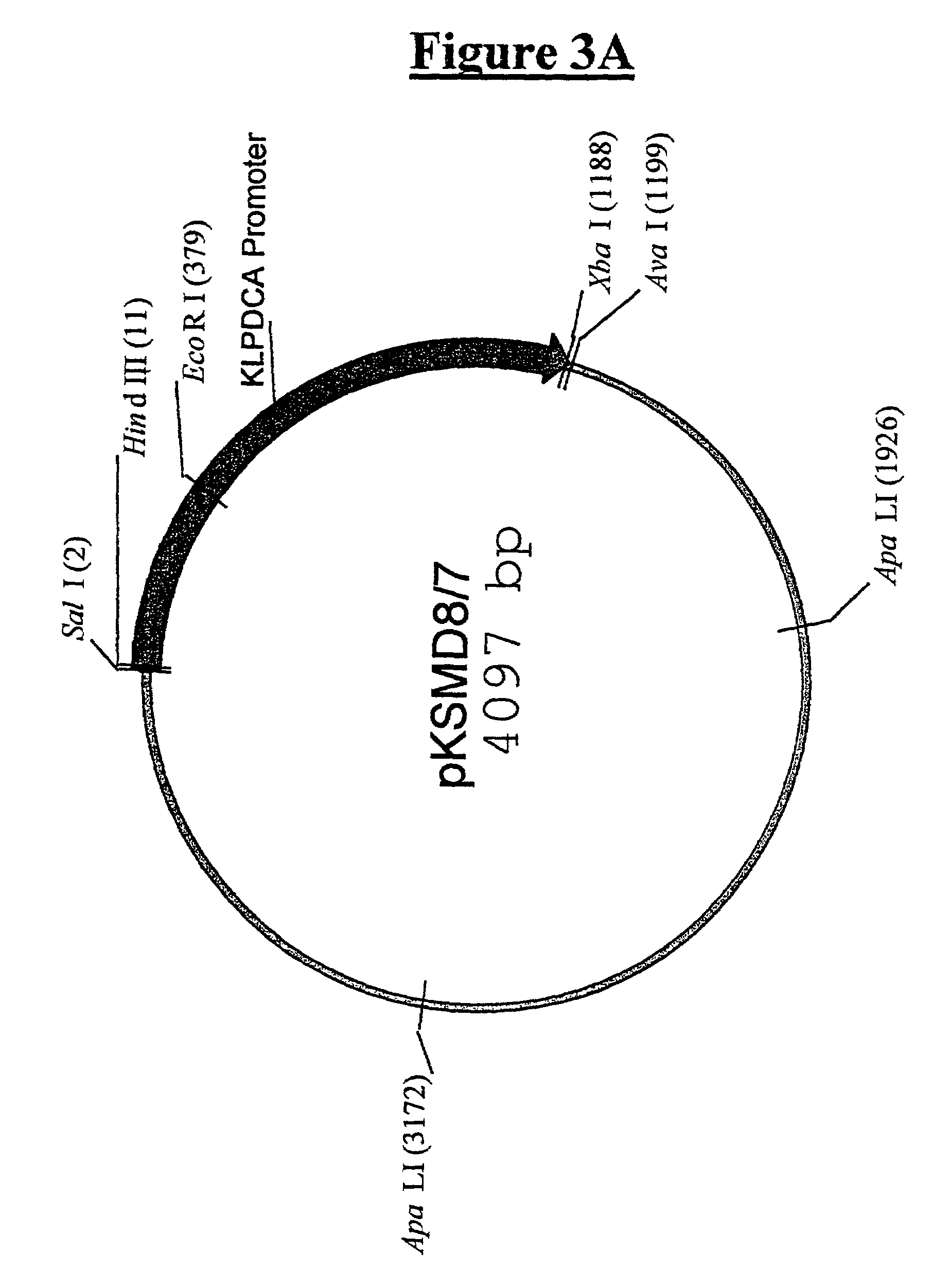
This invention provides biocatalysts that are recombinant yeast cells comprising recombinant expression vectors encoding heterologous lactate dehydrogenase genes for producing lactate.
Owner:RAJGARHIA VINEET +4
Mutant E. coli strain with increased succinic acid production
InactiveUSRE37393E1Cheap productionIncrease biomassBacteriaUnicellular algaeLactate dehydrogenaseBiological body
A method for isolating succinic acid producing bacteria is provided comprising increasing the biomass of an organism which lacks the ability to catabolize pyruvate, and then subjecting the biomass to glucose-rich medium in an anaerobic environment to enable pyruvate-catabolizing mutants to grow.The invention also provides for a mutant that produces high amounts of succinic acid, which has been derived from a parent which lacked the genes for pyruvate formate lyase and lactate dehydrogenase, and which belongs to the E.coli Group of Bacteria.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Production of D-lactic acid with yeast
InactiveUS20070031950A1Increase productivityHigh yieldFungiOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyLactate dehydrogenase
A yeast strain, wherein the yeast strain is transformed with at least one copy of a gene coding for <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactate dehydrogenase functionally linked to a promoter sequence allowing the expression of the gene in the yeast strain and the yeast strain has undergone disruption of one or more pyruvate decarboxylase genes or pyruvate dehydrogenase genes. Also, a method of producing <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactic acid including culturing such a yeast strain in a medium and recovering <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactic acid.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
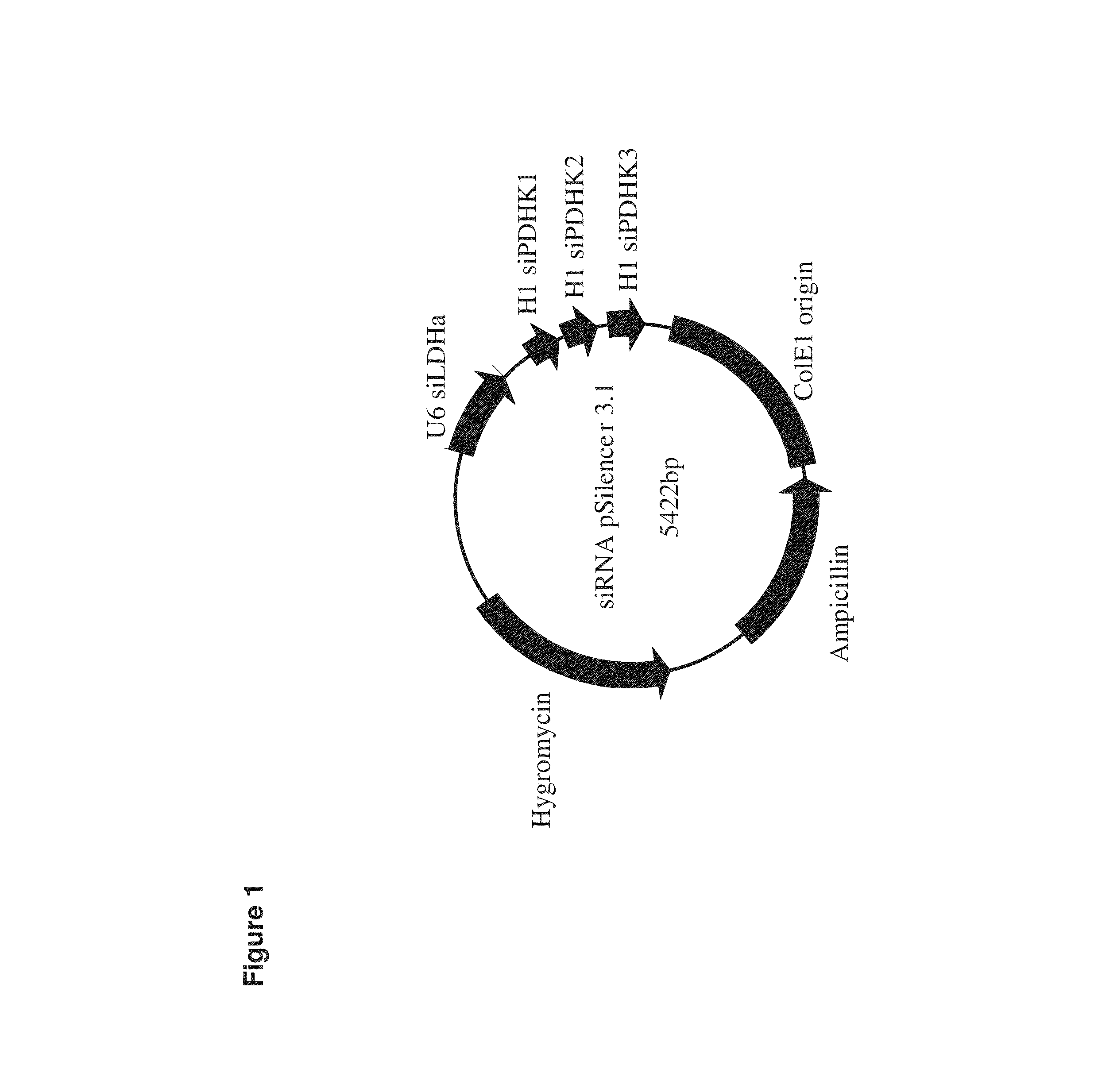
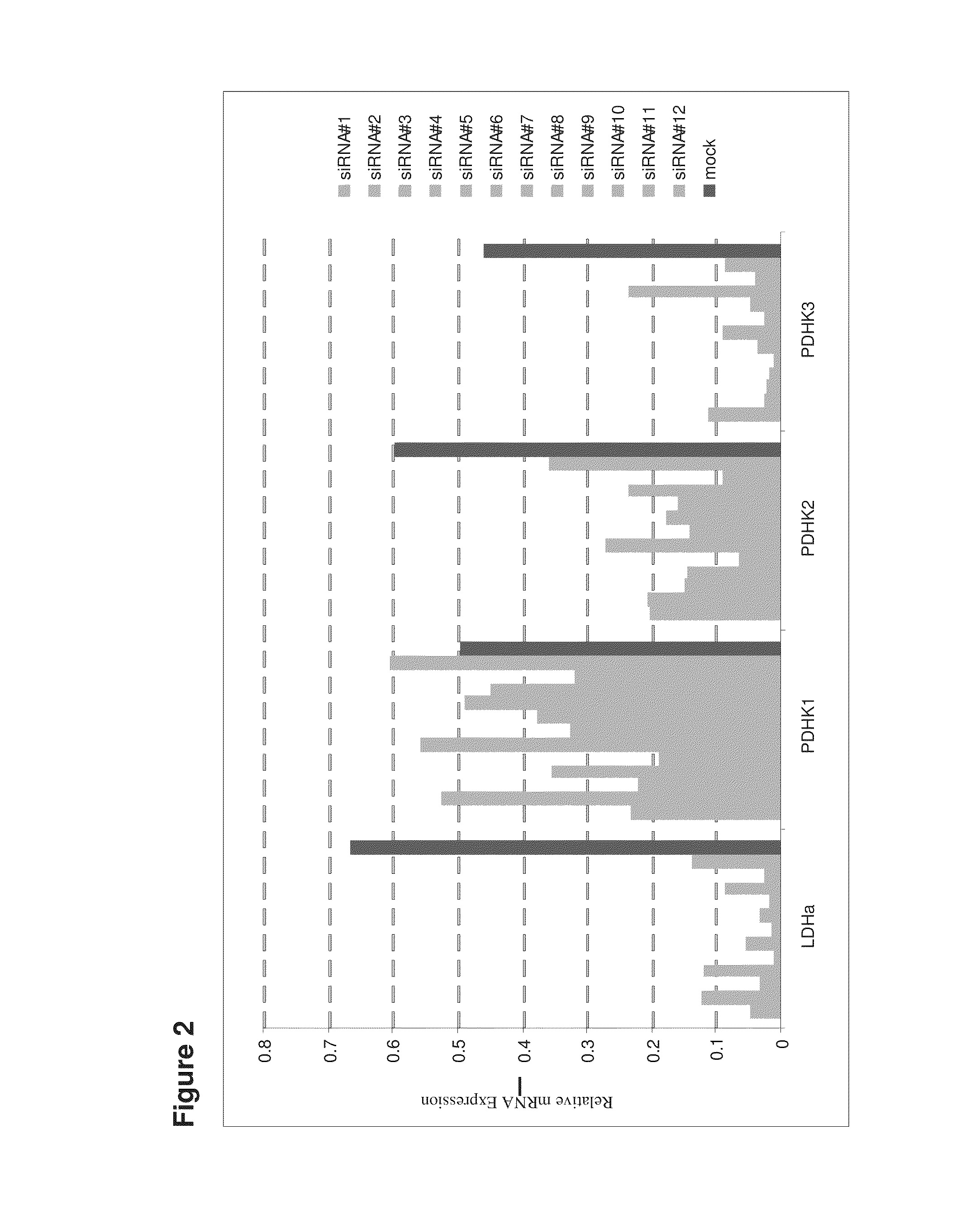
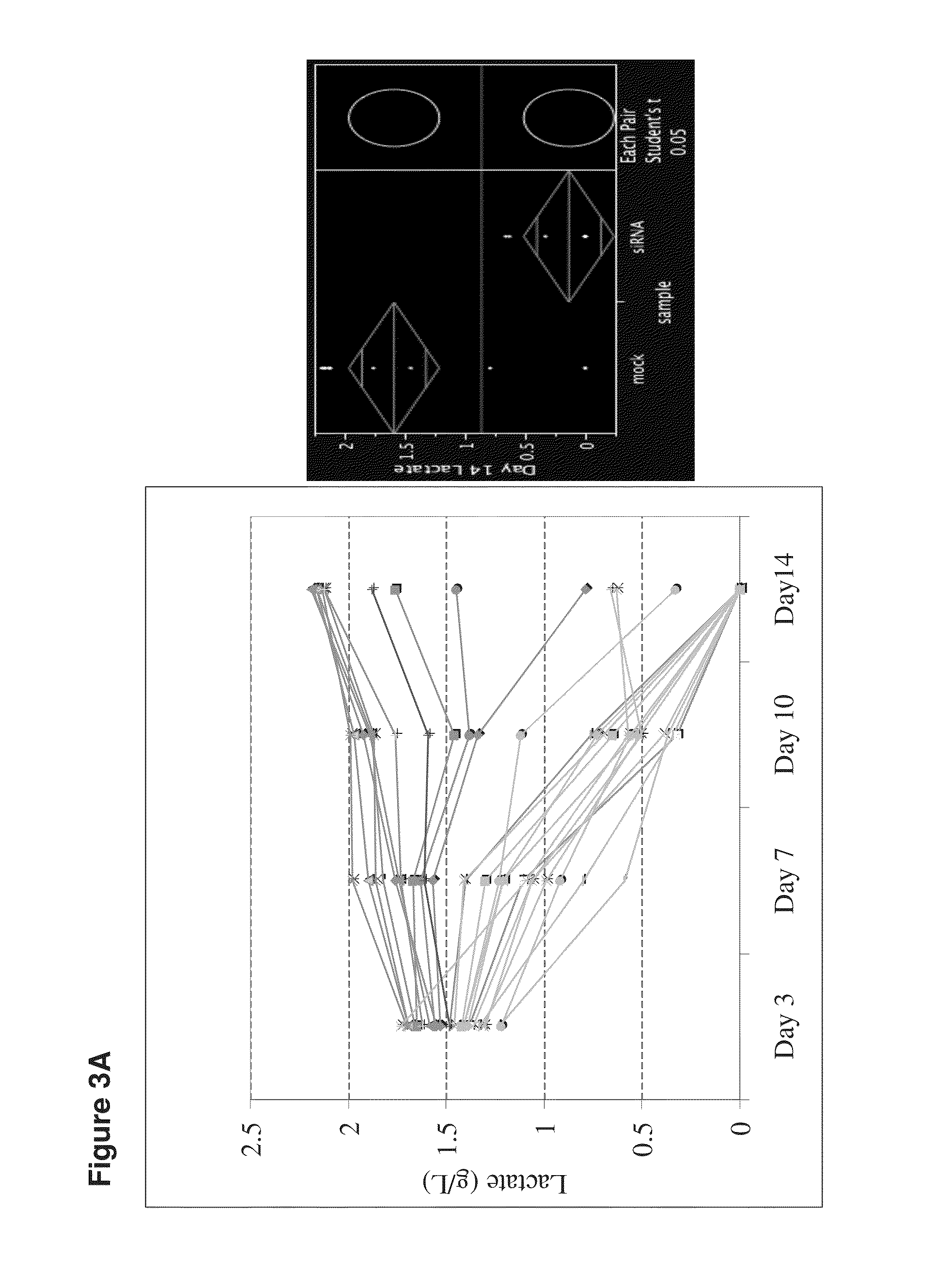
Decreasing lactate level and increasing polypeptide production by downregulating the expression of lactate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase
ActiveUS20130084605A1Reducing lactate productionIncreasing polypeptide productionAnimal cellsFused cellsLactate dehydrogenaseCulture cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for reducing lactate production and increasing polypeptide production in cultured cells. In one aspect, the invention provides a method comprising culturing cells expressing a) a small interfering RNA (siRNA) specific for a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and b) an siRNA specific for a pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDHK). In another aspect, the invention provides cultured cells or vectors comprising an siRNA specific for a LDH and an siRNA specific for a PDHK.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Enhanced pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol conversion in lactic acid bacteria
A high flux of metabolites from pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol in Lactobacillus plantarum was achieved through genetic engineering. Substantial elimination of lactate dehydrogenase activity in the presence of heterologously expressed butanediol dehydrogenase activity led to 2,3 butanediol production that was at least 49% of the total of major pyruvate-derived products.
Owner:GEVO INC
Method for catalyzing chenodeoxycholic acids to compound ursodesoxycholic acids through efficient whole-cells
ActiveCN105368828AFermentation methods are cheap and readily availableSuitable for industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisLactate dehydrogenase
The invention provides a method for catalyzing chenodeoxycholic acids to compound ursodesoxycholic acids through efficient whole-cells. A 7a-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7a-HSDH) and a lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) for regeneration of coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) are efficiently co-expressed in escherichia coli, escherichia coli whole cells are used to catalyze chenodeoxycholic acids (CDCA) to generate 3 alpha (Alpha)-hydroxyl-7-oxo-5bata (Beta)- cholanic acids (7-KLCA), and a reaction liquid which is obtained by catalyzing the chenodeoxycholic acids through whole cells is adjusted to be 7-KLCA crude products. Reconstitution cells can be easily obtained in low cost through a fermentation process, are better than a chemical synthesis method in production cost and product quality, and are suitable for commercial process.
Owner:苏州天绿生物制药有限公司
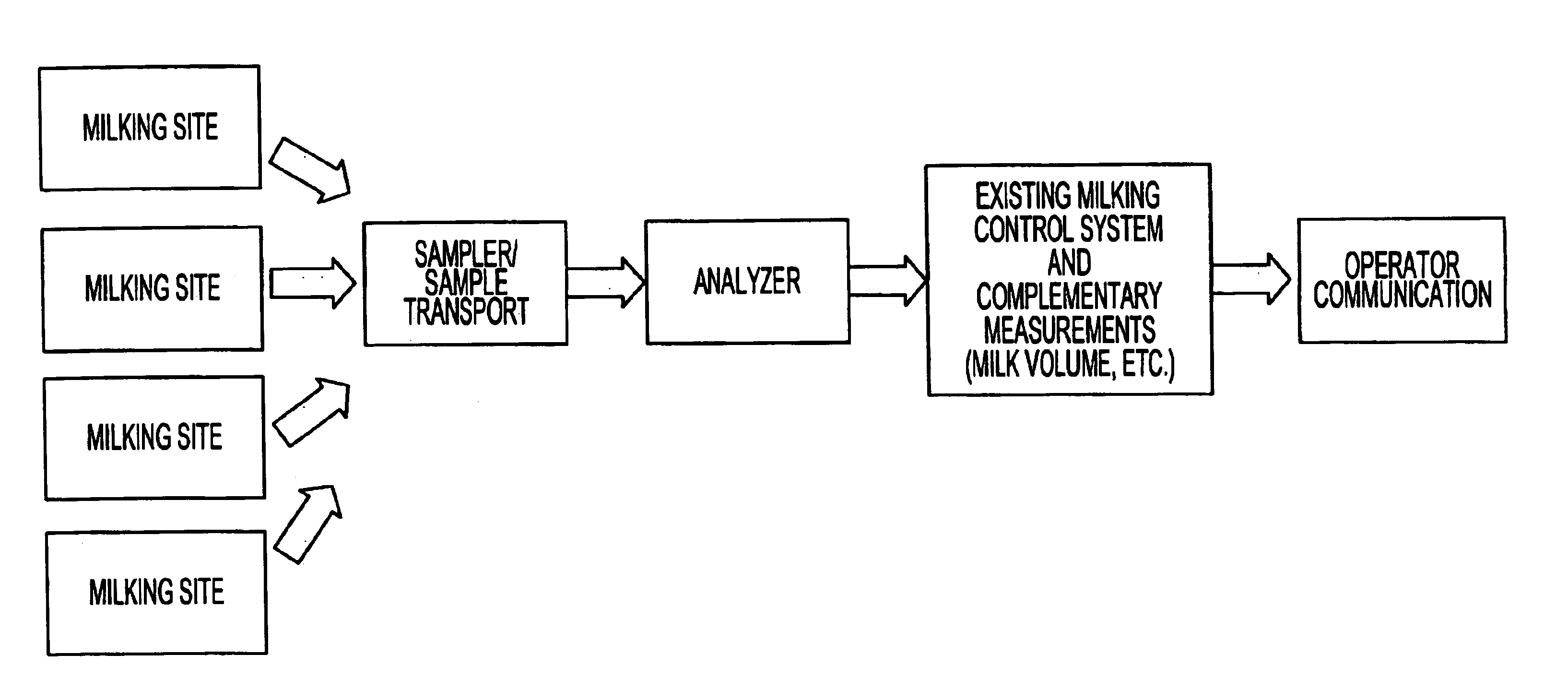
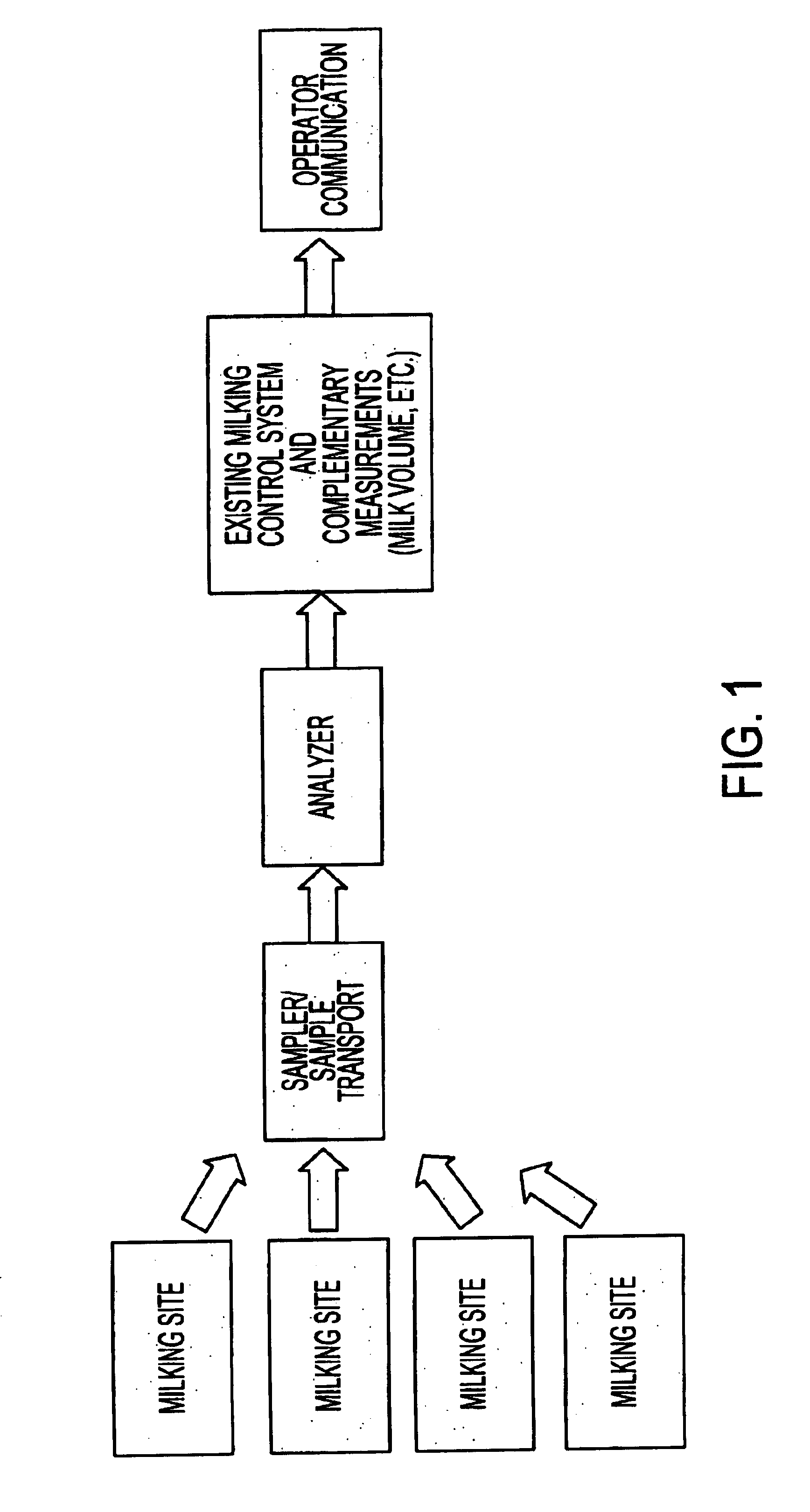
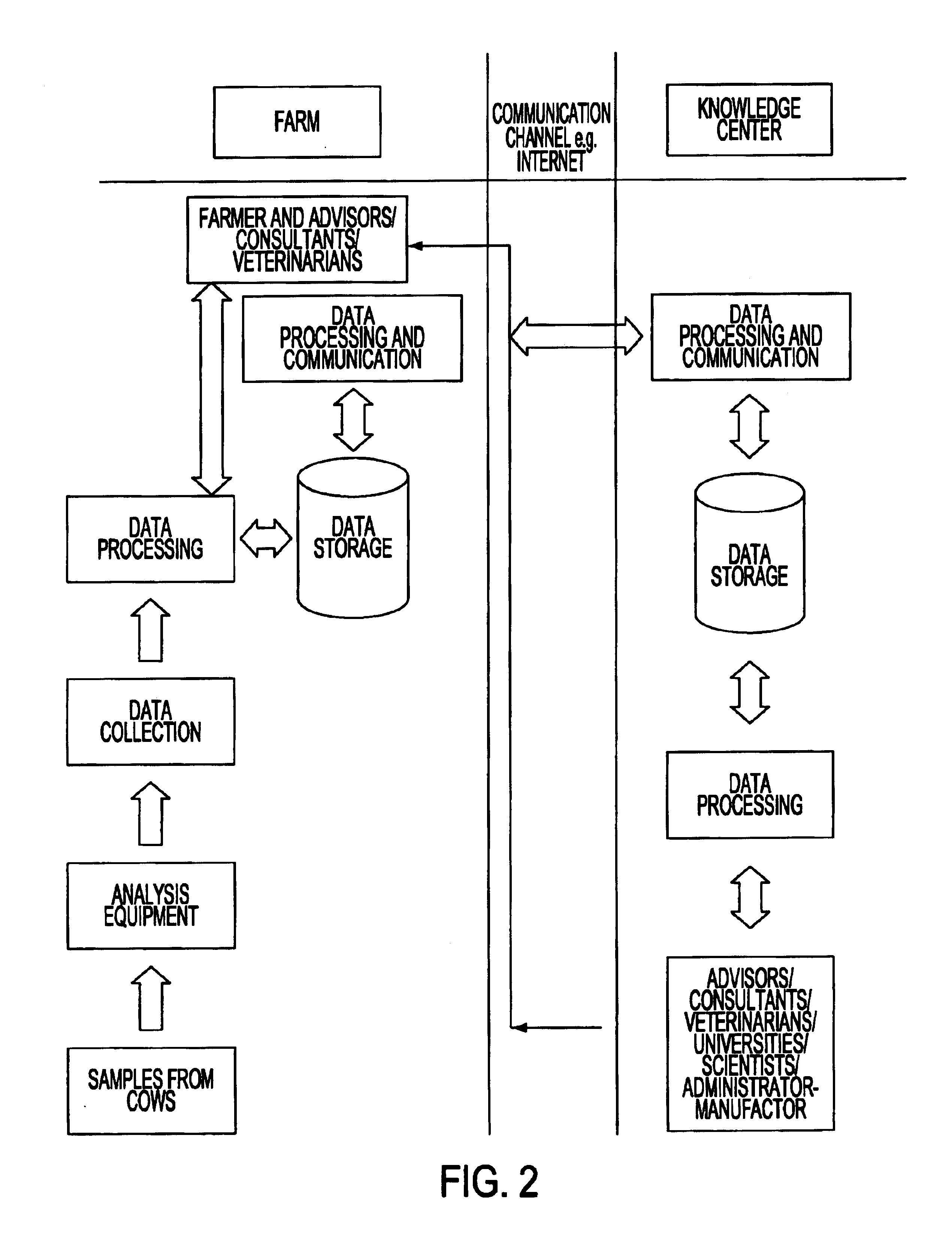
System for optimizing the production performance of a milk producing animal herd
InactiveUS6814025B2Increase productivityIncrease profitabilitySamplingCathetersLactate dehydrogenaseAgricultural science
Owner:LATTEC
Enhanced pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol conversion in lactic acid bacteria
A high flux of metabolites from pyruvate to 2,3-butanediol in Lactobacillus plantarum was achieved through genetic engineering. Substantial elimination of lactate dehydrogenase activity in the presence of heterologously expressed butanediol dehydrogenase activity led to 2,3 butanediol production that was at least 49% of the total of major pyruvate-derived products.
Owner:GEVO INC
Processes for producing lactic acid using yeast transformed with a gene encoding lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Testing system for determining hypoxia induced cellular damage
InactiveUS20130052675A1Quick testEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLactate dehydrogenaseCell damage
The present invention relates to a testing system for assessing hypoxia induced cellular damage in a mammal including human, comprising a disposable device having a sample inlet and a collection chamber separated by a separation device wherein the collection chamber is connected to at least two, a first and a second, visible detection compartments, whereof at least one is arranged with chemical means for direct visual detection, said first detection compartment being arranged to determine whether level of hemoglobin (Hb) in a sample of body fluid taken from said mammal exceeds a predetermined threshold value, and said second detection compartment being arranged to evaluate level of total amount of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in said sample.
Owner:CALMARK SWEDEN AB
Process for producing succinic acid
ActiveUS20060205048A1Improve productivityProducing succinicBacteriaSugar derivativesPyruvate carboxylaseLactate dehydrogenase
Succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance fumarate reductase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. More preferably, succinic acid is produced by allowing a bacterium modified to enhance activities of fumarate reductase and pyruvate carboxylase and decrease lactate dehydrogenase activity or cell preparation thereof to react with an organic raw material in a reaction solution containing one of a carbonate ion, a bicarbonate ion, and carbon dioxide gas to generate succinic acid. Succinic acid is obtained by collecting the produced succinic acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Blood ammonia content determination method and blood ammonia diagnosis kit
InactiveCN1769481AStrong specificityLess susceptible to interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseMedical testing
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of blood ammonia, and also the reagent kit for blood ammonia diagnosis. The reagent kit comprises cushioning solution, adenosine triphosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate phosphatase, deacidized type coenzyme, ammonia kinase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, and stabilizer. By mixing sample and reagent of a predetermiend volumetric ratio, generating coupling reaction between them, subjecting the final reactant to biochemiscal analyser, the main wavelength absorbancy variance ratio (speed) can be detected, and the blood ammonia content can thus be measured. The method of the invention can be used to obtain the needed measurement result purely through biochemical analytic instruments, and advantages of the method include higher sensibility, better accuracy, less susceptibility to contamination of internal or external materials, and easy application.
Owner:王尔中
Liquid double reagent diagnostic reagent kit for determining content of potassium ions in serum and blood plasma
ActiveCN101717814AFast measurementImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsLactate dehydrogenasePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a liquid double reagent diagnostic reagent kit for determining the content of potassium ions in serum and blood plasma. By using the reaction principle that phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP) can be catalyzed by K+dependency pyruvate kinase (PK) to be converted into pyruvic acid and taking lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) as indicator enzyme by means of NADH, the reagent kit detects the reduction amount of the NADH at 340 nm and obtains the result that the change of the absorbance every minute (delta / min) is directly proportional to the content of K+, thereby establishing an enzyme coupling method for continuously determining the potassium ions. In addition, enzyme and a primer system required by slowly generating reduction type nicotinoyl coenzyme are added in a system andan enzyme-primer-coenzyme slow reaction system is formed in a reagent, so that the coenzyme can be slowly and circularly supplemented and the reagent can be stabilized when the concentration reaches a certain balance. The liquid double reagent diagnostic reagent kit is convenient and concise to use, carries out rapid detection on a common ultraviolet / visible light analyzer or a semiautomatic / fully-automatic chemical analyzer, needs no special or extra instrument and has low cost.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine and method for producing L-valine by fermentation
ActiveCN110607268AEasy to synthesizeReduce synthesisBacteriaHydrolasesLactate dehydrogenaseSaccharic acid
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine. A construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium comprises the steps that starting from an escherichia coli W3110, an acetolactate synthase gene alsS of a bacillus subtilis is integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; an escherichia coli ppGpp 3'-pyrophosphoric acid hydrolytic enzyme mutant R290E / K292D gene spoT is integrated on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; genes of frdA, frdB, frdC and frdD of four subunits of a lactic dehydrogenase gene ldhA, a pyruvate formate lyase I gene pflB and fumaric reductase on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 are knocked out; a branched chain amino acid transaminasegene ilvE of the escherichia coli is replaced with leucine dehydrogenase gene bcd of the bacillus subtilis; and an acetyl-hydroxyl acid isomerized reductase gene ilvC of the escherichia coli is replaced with an encoding gene of a mutant L67E / R68F / K75E. According to the genetically engineered bacterium for the high-yielding L-valine, an L-valine fermentation method is further modified. Double-phasedissolved oxygen control is adopted, and the L-valine yield and the saccharic acid conversion rate are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetic modification for production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid
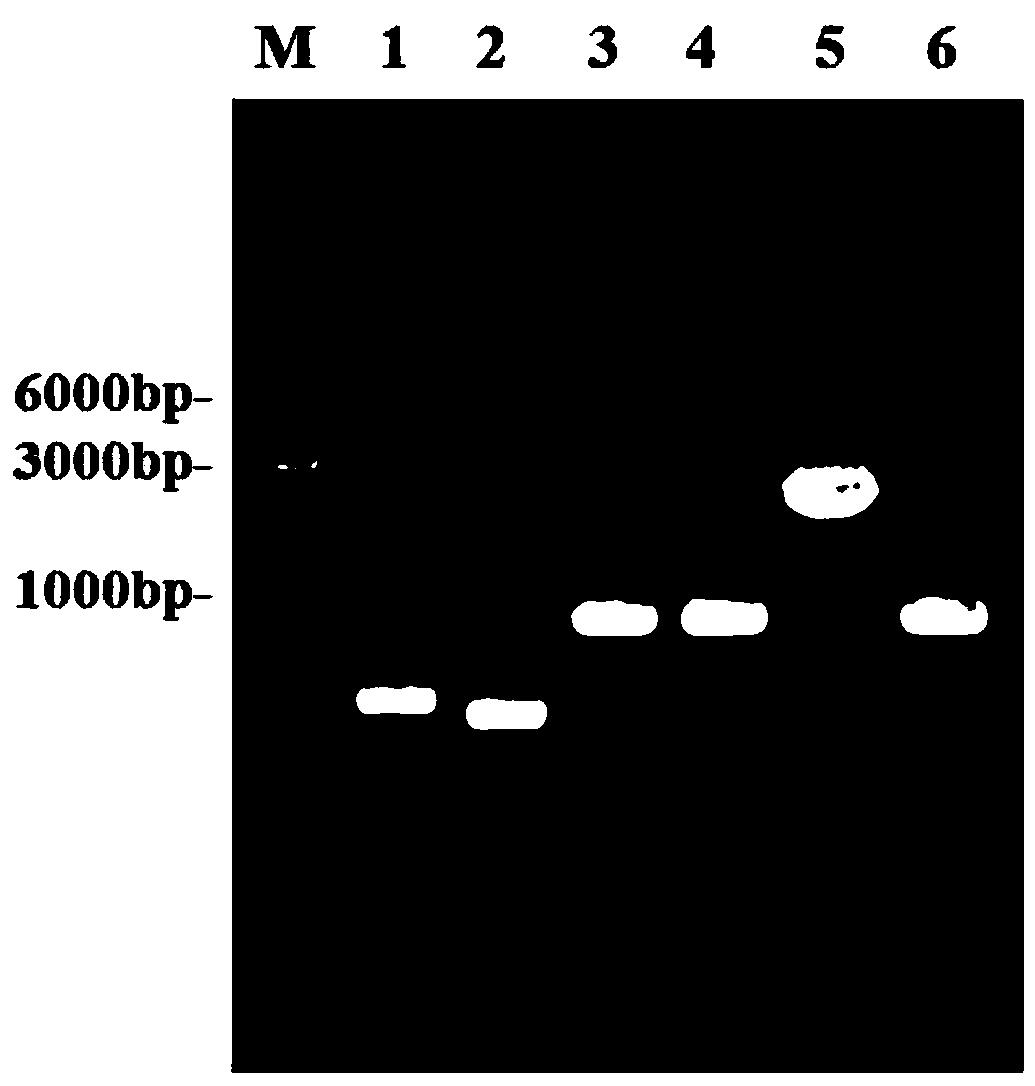
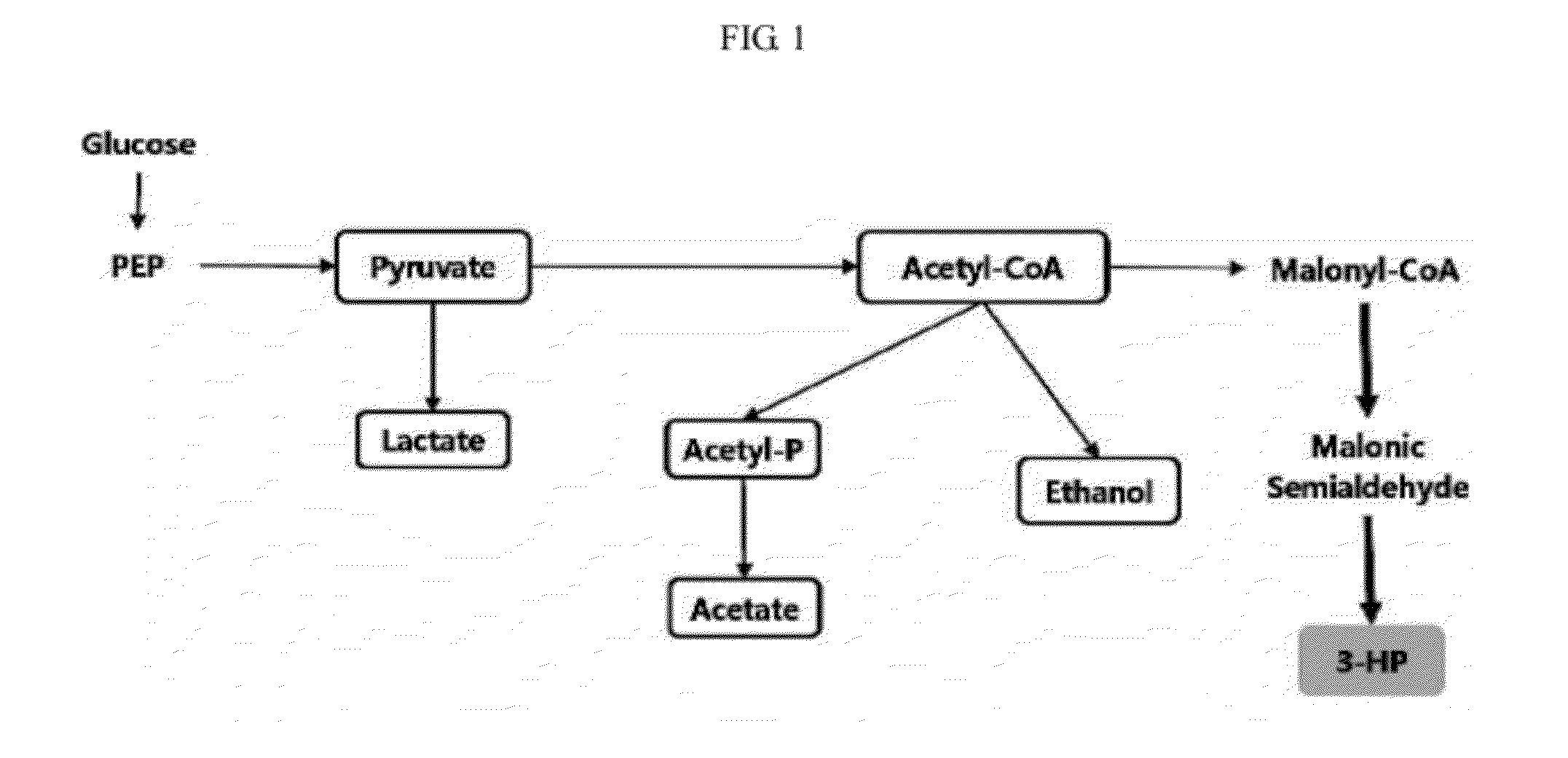
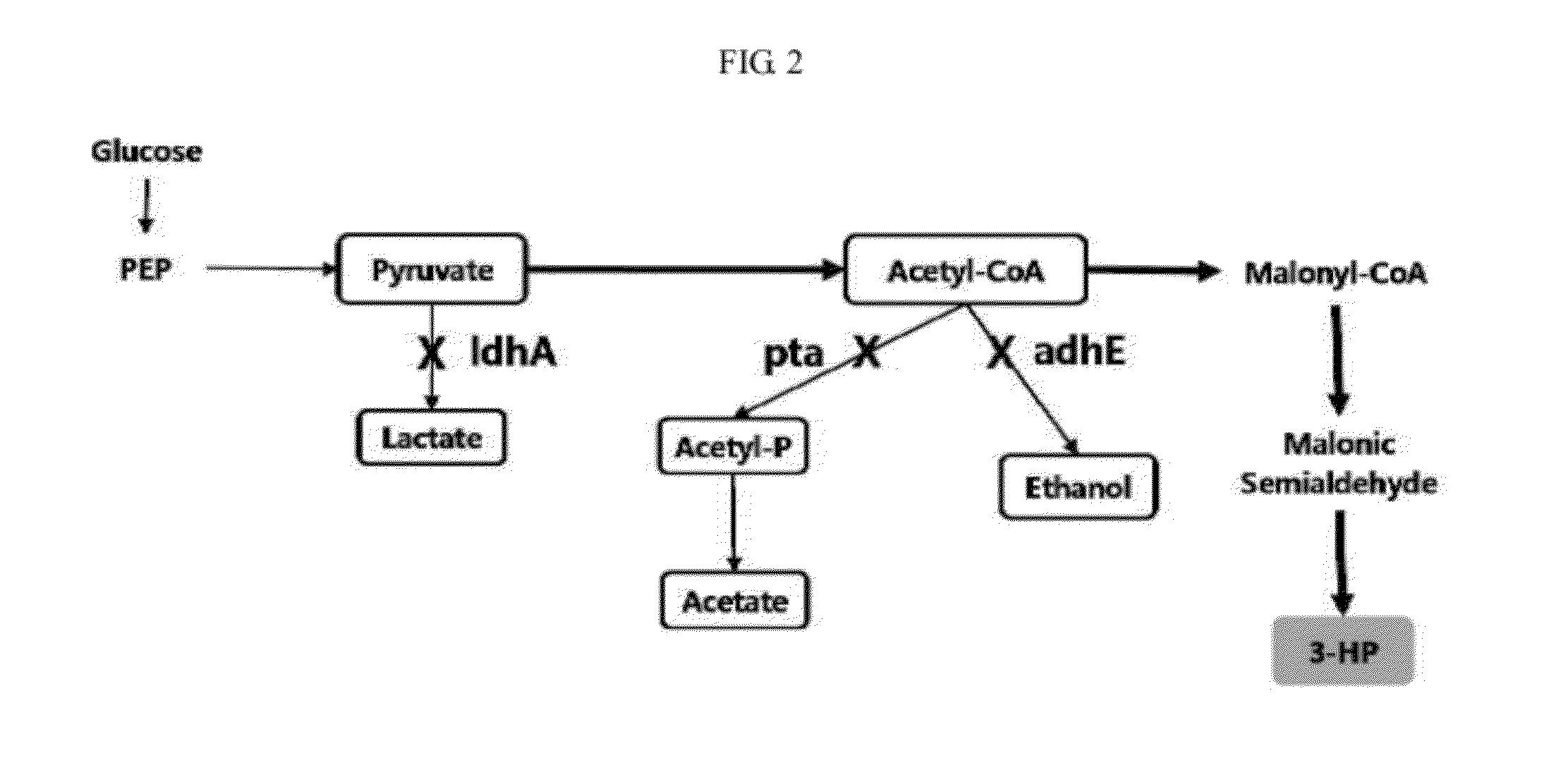
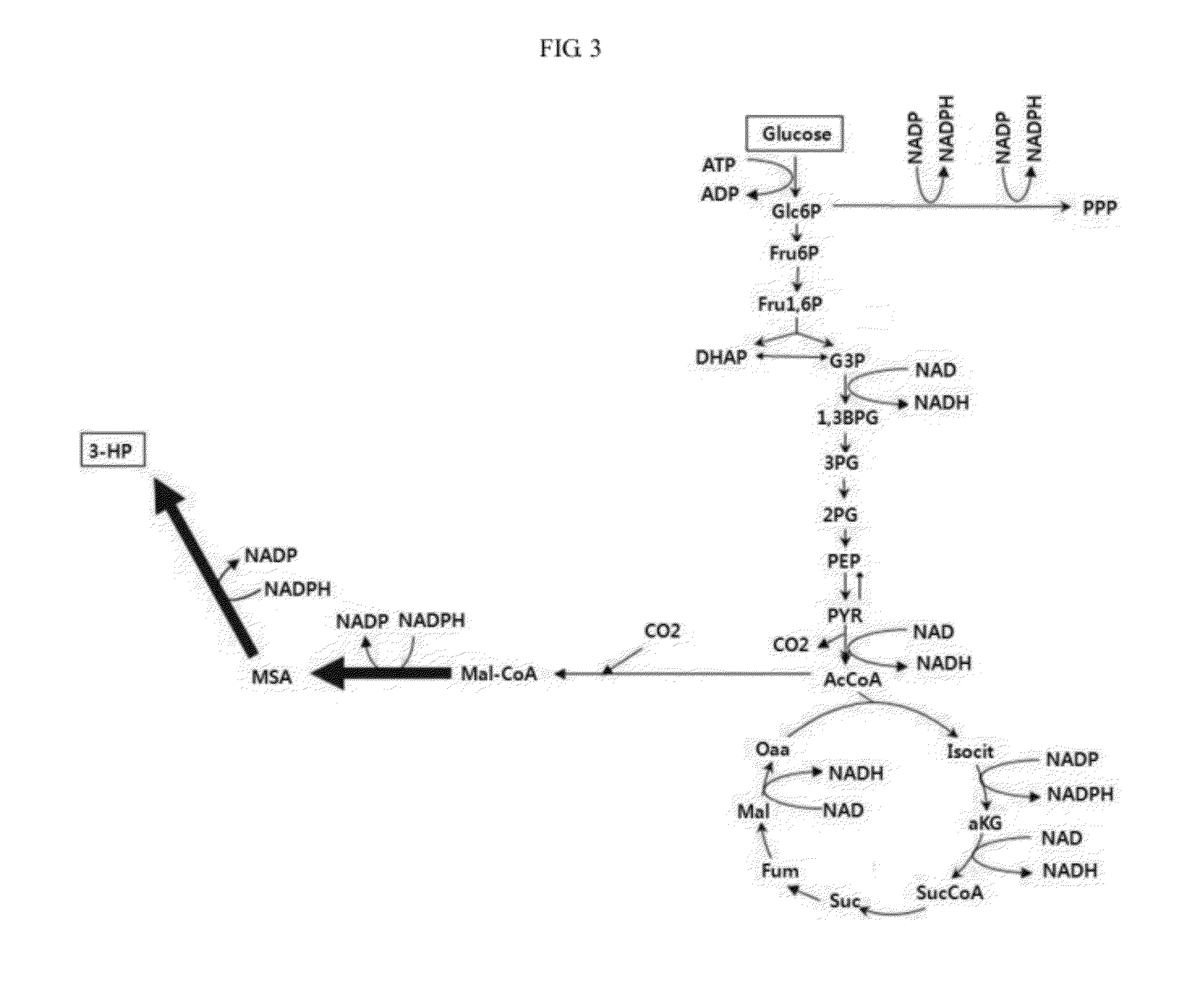
InactiveUS20120329110A1Improve production yield and producibilityIncrease productivityFungiBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseMetabolite
A method of increasing 3-HP production efficiency by inhibiting expression of a lactate dehydrogenase, a phosphotransacetylase, and an alcohol dehydrogenase in production of 3-HP using a malonic semialdehyde reduction pathway to prevent metabolite leak and increase a malonyl-CoA pool is disclosed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
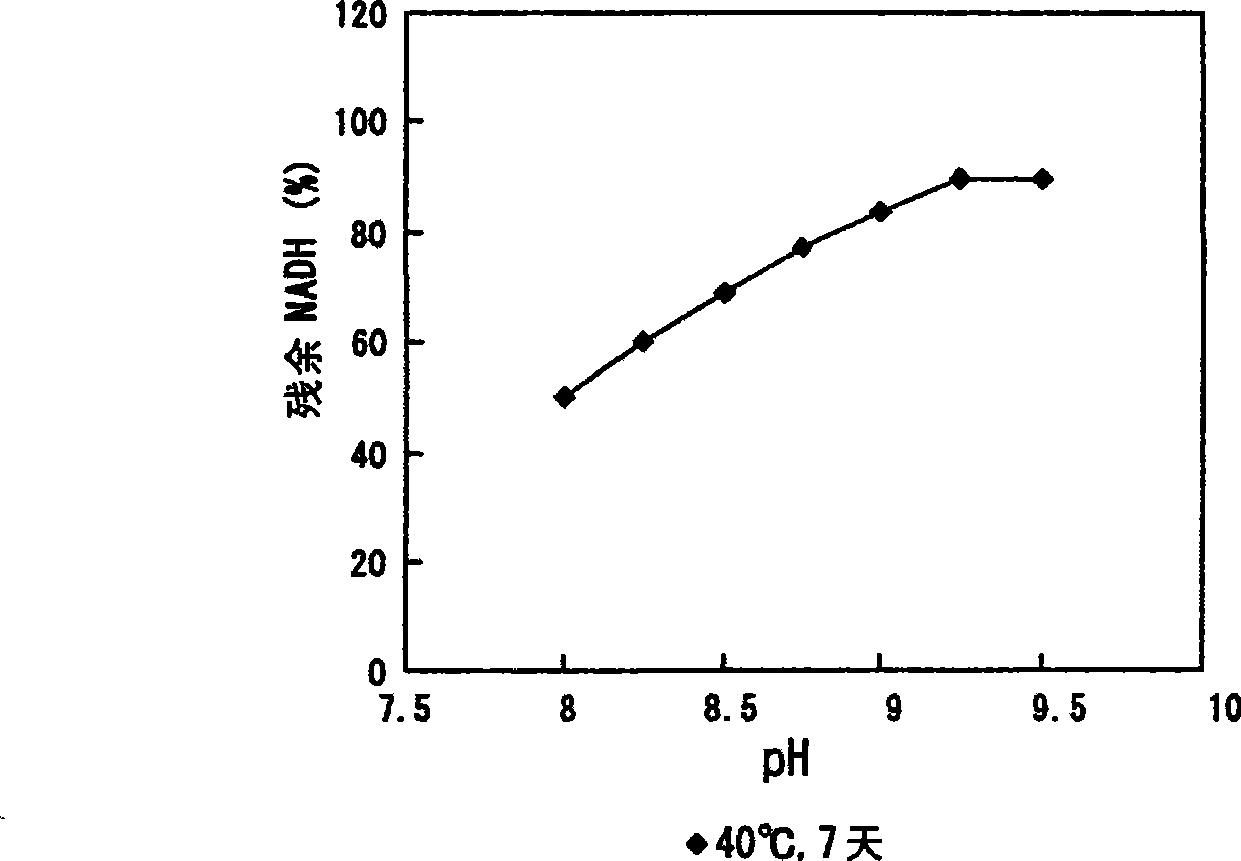
Stable composition containing NAD+ or NADH
InactiveCN102863495AImprove stabilitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLactate dehydrogenaseAlanine aminotransferase
The invention provides a stable composition containing NAD+ or NADH. Bioactivity of NAD+ or NADH can be stably maintained for a long time. By the use of a stabilizer which contains trehalose, glycerol, a buffer solution and a surfactant, stability of NAD+ and NADH dissolved state is raised. The invention also provides a method for stabilizing NAD+ or NADH, and also provides an application of a composition composed of trehalose, glycerol, the buffer solution, the surfactant and a pH regulator in increasing stability of NAD+ or NADH. The composition can be used for a lactate dehydrogenase reagent, an alanine aminotransferase reagent, an aspartate aminotransferase reagent, a urea kid and the like, and is widely applied.
Owner:上海执诚生物科技有限公司
Enzyme combining stabilizer
ActiveCN1986785APlay a role in quality stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationLactate dehydrogenaseCreatinine rise
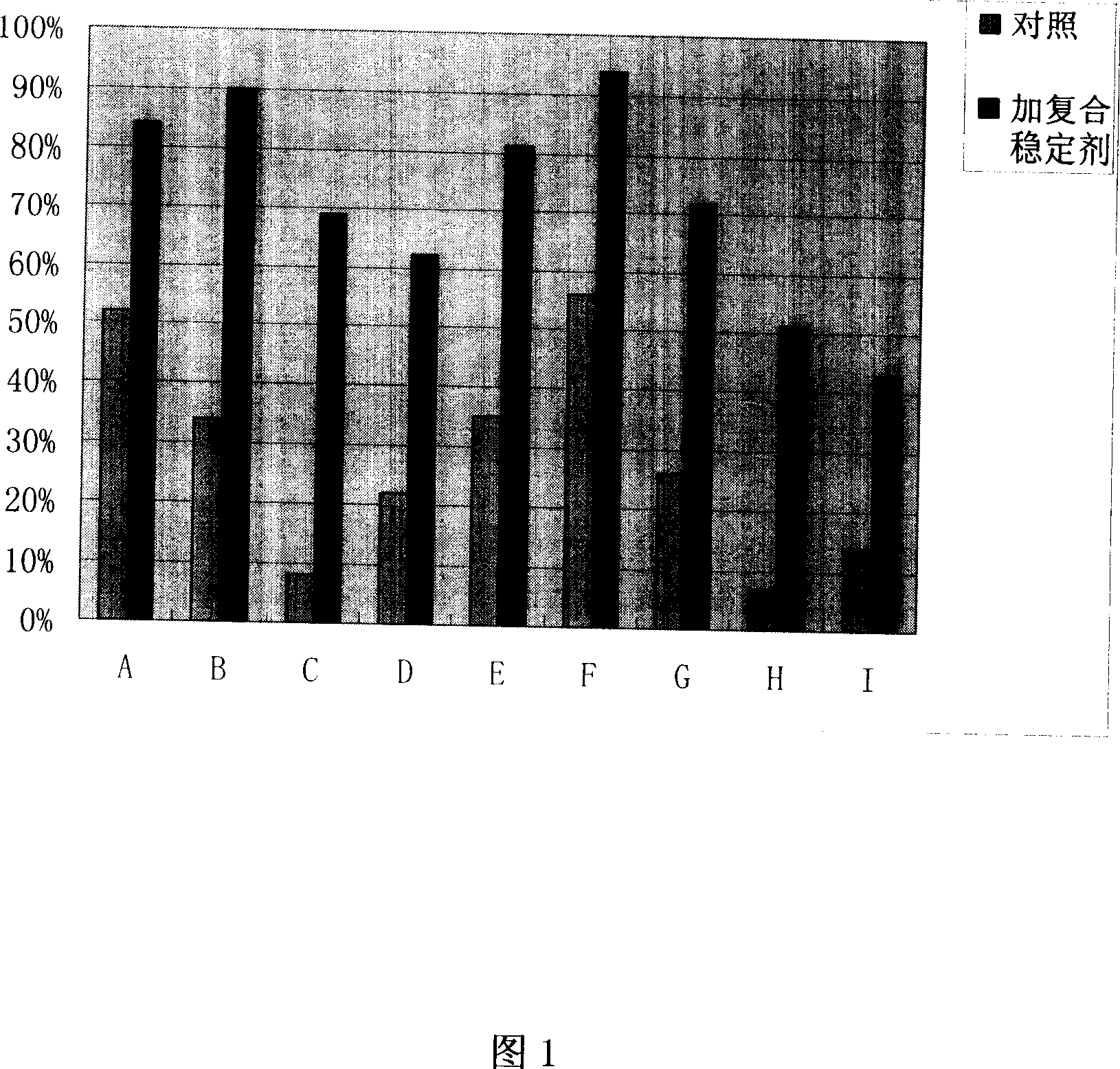
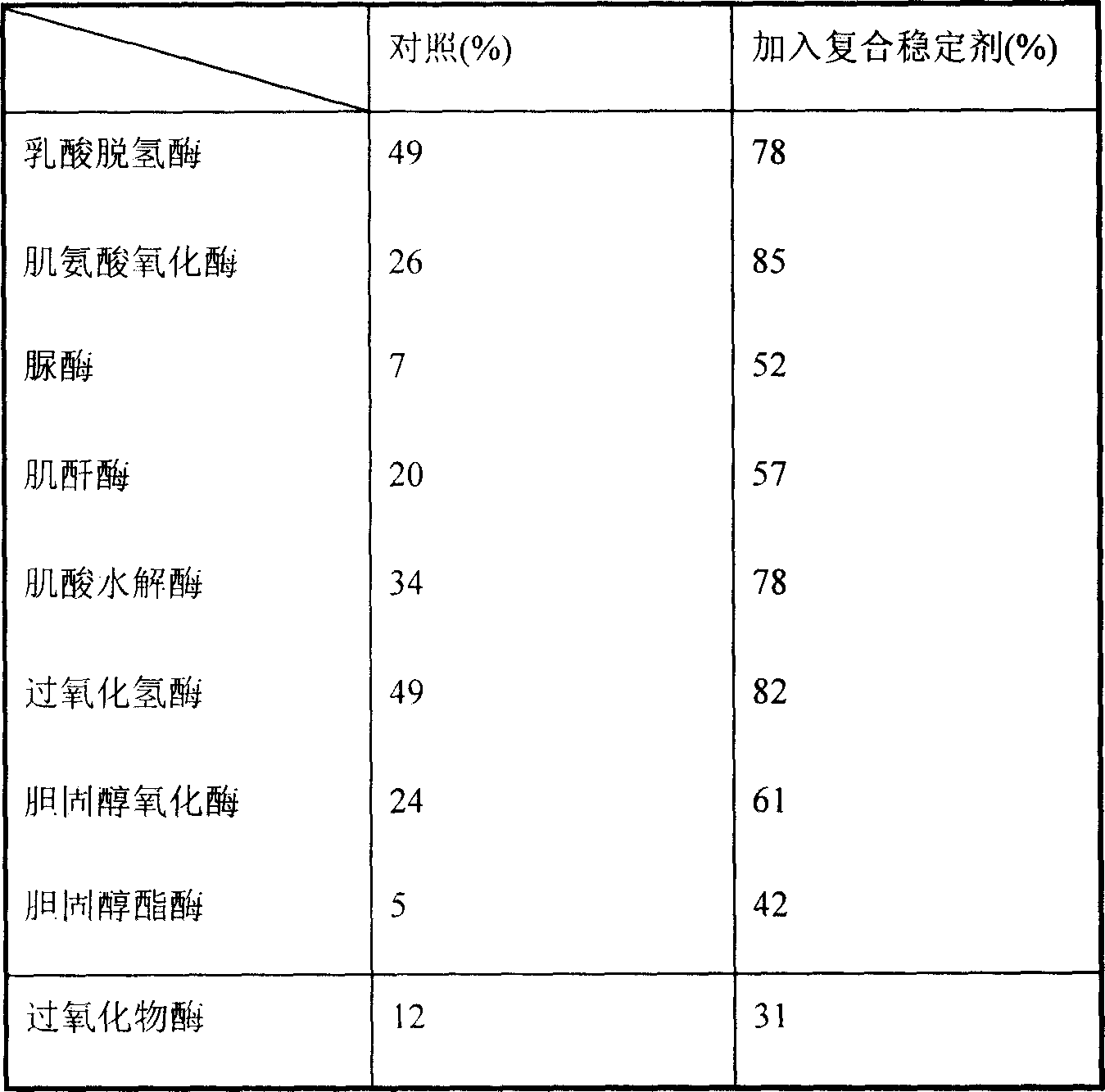
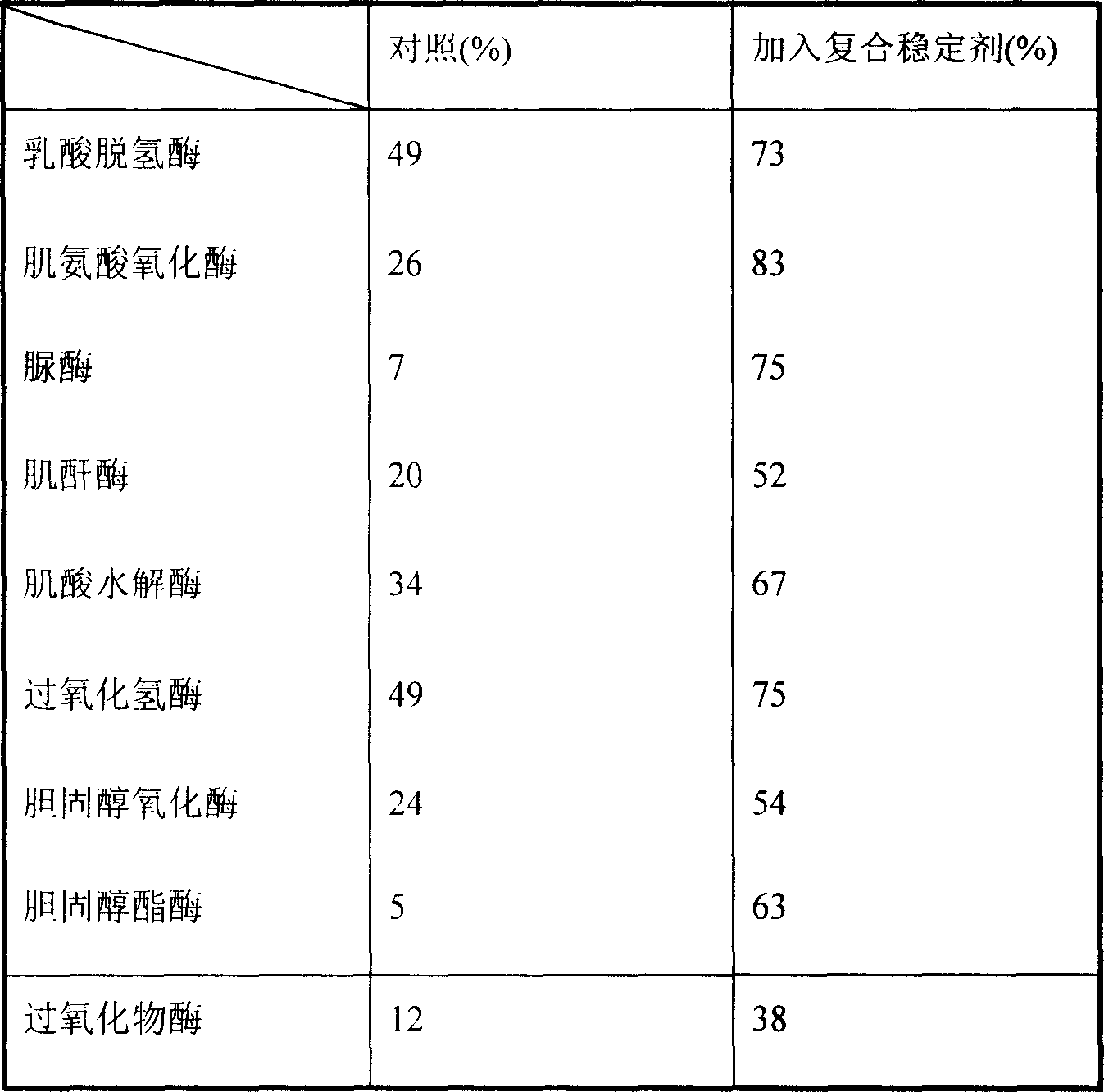
The present invention provides a kind of efficient enzyme combining stabilizer with high stabilizing effect on enzymes for clinical diagnosis reagent. The enzyme combining stabilizer consists of bovine serum albumin, EGTA, 1, 2-dithio threitol, potassium gluconate, sodium chloride, proclin300, magnesium acetate, etc. It has powerful stabilizing effect on lactate dehydrogenase, sarcosie oxidase, urease, creatinine enzyme, creatine hydrolase, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI FOSUN LONG MARCH MEDICAL SCI CO LTD +1
Methods and materials for the synthesis of organic products
InactiveUS7109010B2Considerable purificationLess costlyFungiSugar derivativesLactate dehydrogenaseBiotechnology
Owner:CARGILL INC
Immunity-chromatography kit for rapid diagnosis of malaria and its pathogen species and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102103141AThe detection method is simpleObservation is quick and intuitiveTissue cultureImmunoglobulins against enzymesOperating instructionCellulose
The invention discloses an immunity-chromatography kit for the rapid diagnosis of malaria and its pathogen species and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a colloidal gold immunity-chromatography test strip, a matching cell-free lysate, a sample cup, a blood taking needle, and an operating instruction. The colloidal gold immunity-chromatography test strip comprises a sample pad, a colloidal-gold pad, a cellulose membrane, and a water-absorbing pad, wherein the colloidal-gold pad contains colloidal gold labelled antibodies; a detection line and a quality control line are disposed on the cellulose membrane; and the colloidal gold labelled antibody and the detection line are composed of monoclonal antibodies which can specifically bind the lactate dehydrogenase of plasmodia. The immunity-chromatography kit for the rapid diagnosis of malaria and its pathogen of the invention can distinguish falciparum malaria from vivax malaria, has the advantages of simplicity, sensitivity, specificity, and rapidity, and is suitable for clinical and field applications.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEW JIEER CLEANING PRODS
Pyruvate producing yeast strain
InactiveUS7405068B2Improve the level ofIncrease concentrationFungiFungi based processesLactate dehydrogenaseBiotechnology
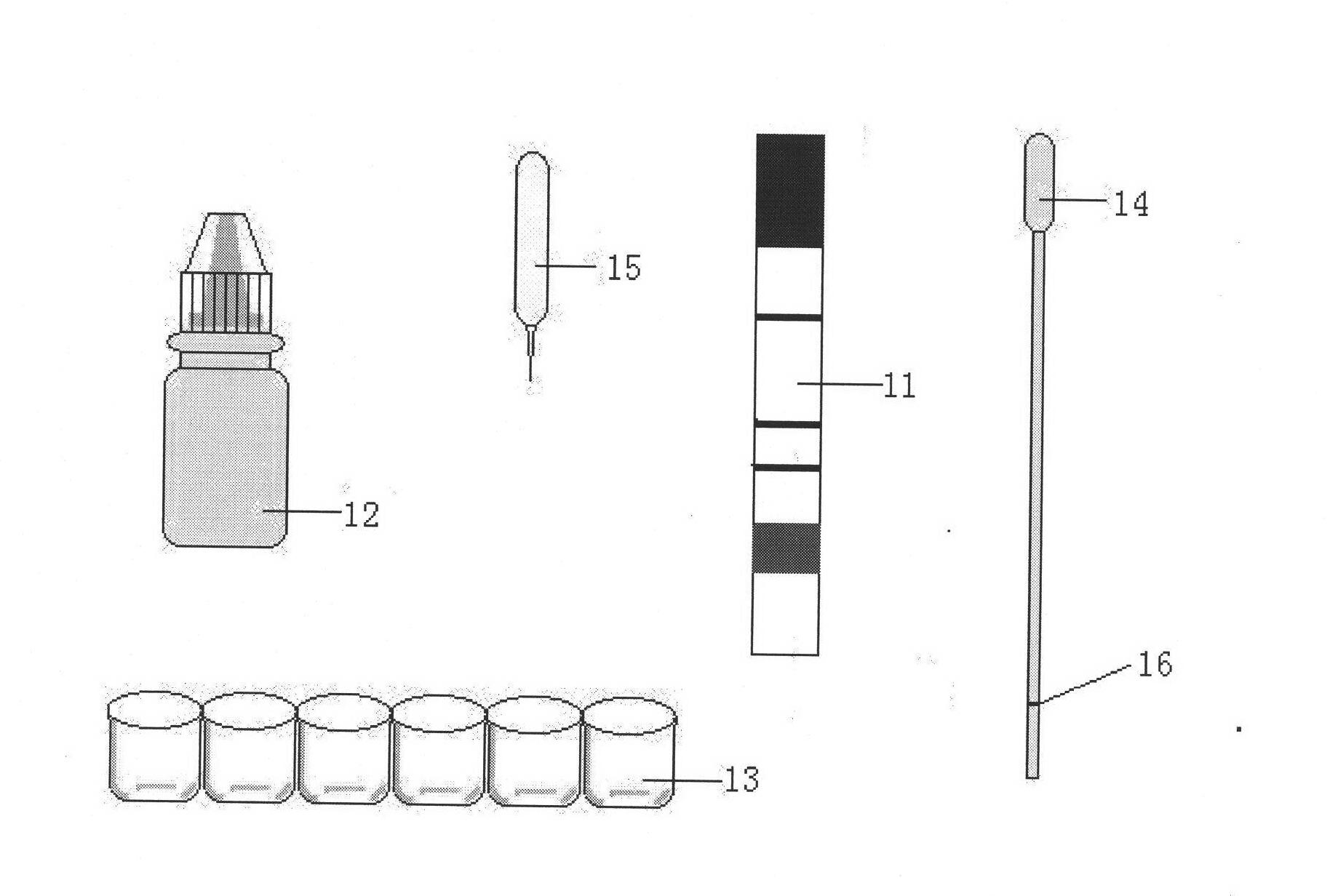
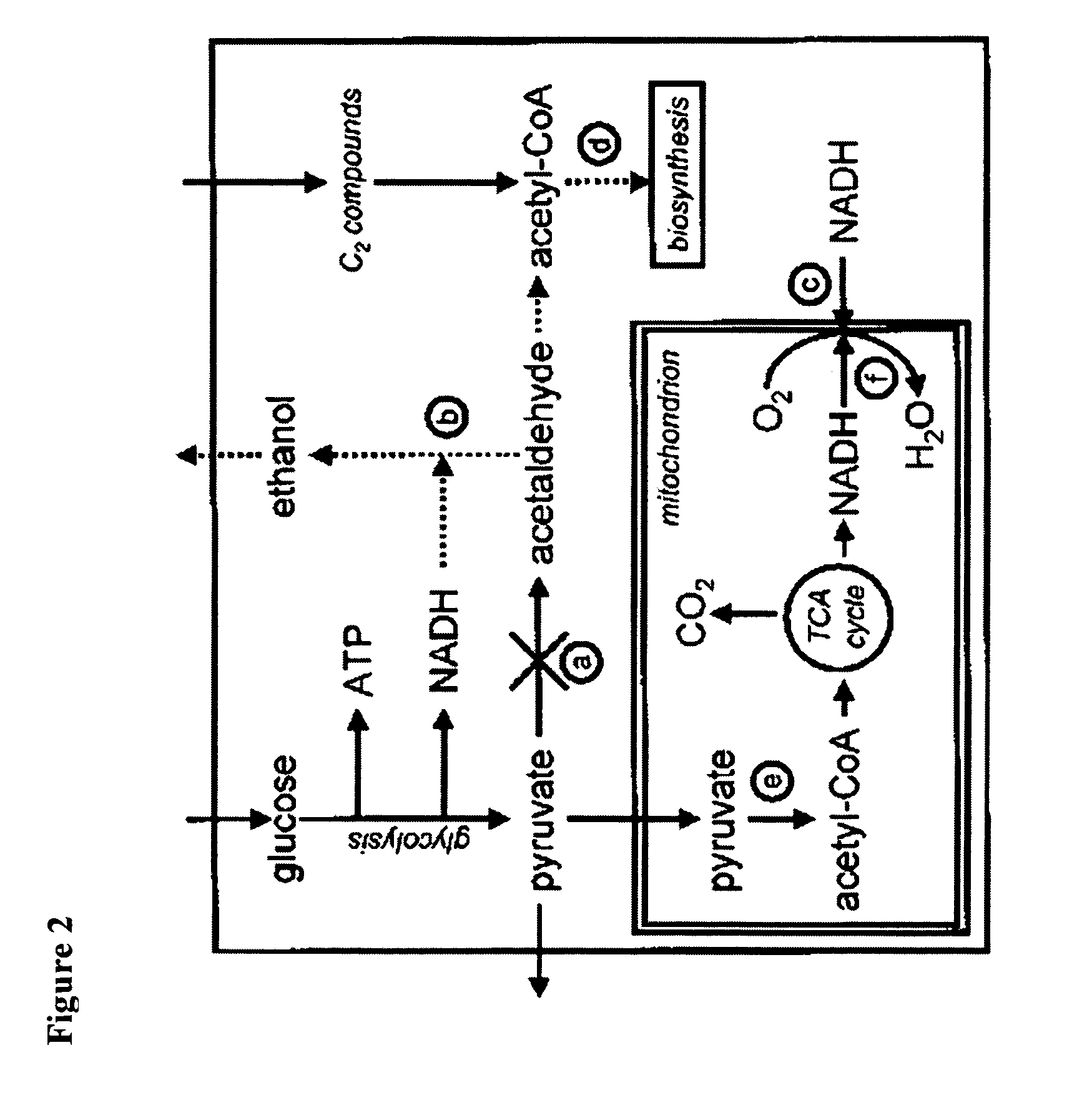
Disclosed herein are glucose tolerant C2 carbon source-independent (GCSI) yeast strains having no detectable amount of pyruvate decarboxylase activity, wherein wild type yeast strains for the glucose tolerant C2 carbon source-independent yeast strains are Crabtree positive. Also disclosed are methods of selecting glucose tolerant C2 carbon source-dependent yeast strains, and methods of producing pyruvic acid or salts thereof using glucose tolerant C2 carbon source-independent yeast strain. Further disclosed herein are GCSI yeast strains having a genome that comprises an exogenous lactate dehydrogenase gene.
Owner:DELFT ENTERPRISES BV
Transformant and process for production thereof, and process for production of lactic acid
The present invention relates to a transformant, containing a lactate dehydrogenase gene which is introduced into Schizosaccharomyces pombe as a host, in which a part of a gene cluster encoding a pyruvate decarboxylase in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe host is deleted or inactivated.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
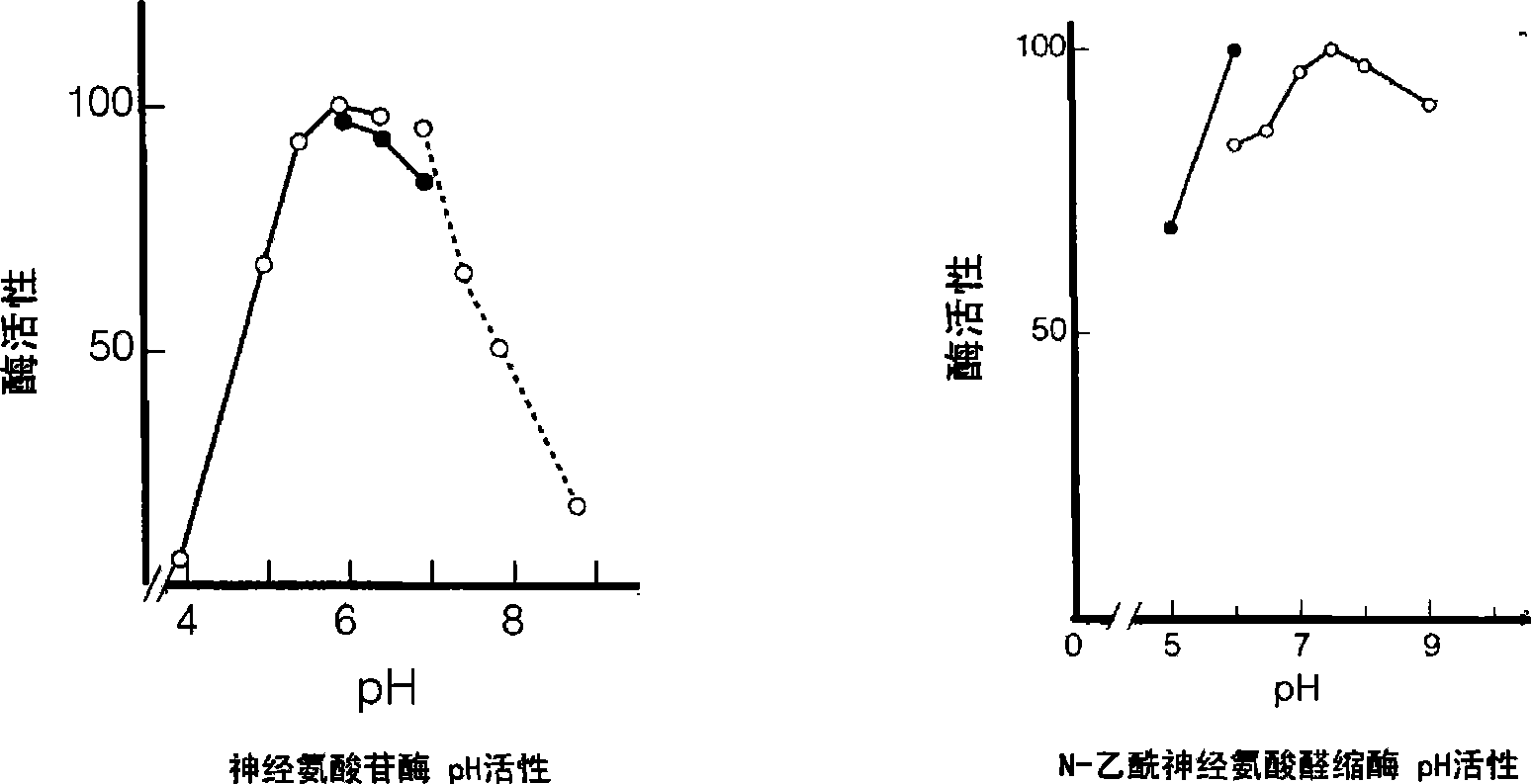
Double reagent for detecting sialic acid liquid by stable enzyme method and use thereof
ActiveCN101469344AEasy to useLittle difference between bottlesMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseNeuraminidase
The invention relates to a double reagent, in particular to a liquid double reagent for determining sialic acid by an enzyme method and application thereof. The technical proposal of the liquid double reagent comprises: the steady liquid double reagent for determining the sialic acid by the enzyme method consists of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises 0.01 to 50KU / L of neuraminidase, 0.1 to 50KU / L of lactate dehydrogenase, and 25 to 100mmol / L of buffer liquid; and the reagent 2 comprises 0.1 to 50KU / L of N-acetyleuraminic acid aldolase, 0.05 to 5mmol / L of reducing coenzyme NADH, 0.1 to 10000U / L of glucose dehydrogenase, 0.1 to 500mmol / L of glucose, and 5 to 100mmol / L of the buffer liquid. The liquid double reagent has the advantages that the liquid double reagent has convenient use, does not need a dissolving solution to redissolve, has small difference among bottles, ensures that the packaging of the liquid double reagent can adapt to various automatic biochemical analyzers, can avoid secondary pollution, and simplify a production technology method.
Owner:上海微鸿企业管理有限公司
Methods for the synthesis of lactic acid using crabtree-negative yeast transformed with the lactate dehydrogenase gene
InactiveUS7229805B2Considerable purificationSimpler and less-costlyFungiBiofuelsLactate dehydrogenaseTrichosporon
The invention provides methods and materials related to the production of lactic acid. Specifically, the invention provides methods for producing lactic acid using a crabtree-negative yeast, such as of the Kluyveromyces, Pichia, Candida, Trichosporon and Yamadazmya genera, which have been transformed with a lactate dehydrogenase gene.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Engineering of thermotolerant bacillus coagulans for production of d(-)-lactic acid
Genetically modified microorganisms having the ability to produce D(−)-lactic acid at temperatures between 30° C. and 55° C. are provided. In various embodiments, the microorganisms may have the chromosomal lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene and / or the chromosomal acetolactate synthase (alsS) gene inactivated. Exemplary microorganisms for use in the disclosed methods are Bacillus spp., such as Bacillus coagulans.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Modified Microorganisms with Inactivated Lactate Dehydrogenase Gene
InactiveUS20090197314A1Increased ethanol productionBiocideBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseMicroorganism
Modified microorganisms are prepared by inactivation of the endogenous lactate dehydrogenase gene. The microorganisms are deposited under NCIMB Accession Nos. 41277, 41278, 41279, 41280 or 41281.
Owner:TMO RENEWABLES LTD
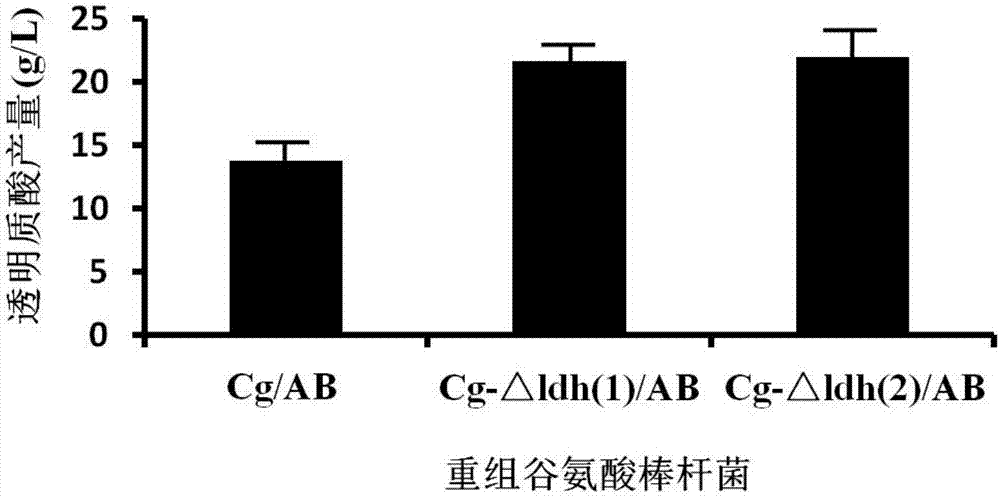
Gene engineering bacterium for high-yield hyaluronic acid and construction method and application of gene engineering bacteria
PendingCN107354119AIncrease productionNon-pathogenicBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLactate dehydrogenaseGene engineering
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterium for high-yield hyaluronic acid and a construction method and application of the gene engineering bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and biochemical engineering. The gene engineering bacterium for high-yield hyaluronic acid is constructed through the steps that a lactate dehydrogenase gene in corynebacterium glutamicum is inactivated, and then a hyaluronan synthase gene is transferred into the corynebacterium glutamicum. According to the gene engineering bacterium for high-yield hyaluronic acid, a corynebacterium glutamicum host has no pathogenicity to both humans and animals and is a food-grade safe microorganism; and the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for high-yield hyaluronic acid is high in hyaluronic acid yield which is up to 22g / L or above and three times the level of existing industrial production, and a new bacterial strain has good industrialization application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Thermophilic Microorganisms with Inactivated Lactate Dehydrogenase Gene (LDH) for Ethanol Production
A mutated thermophilic microorganism is prepared, with a modification to inactivate the lactate dehydrogenase gene of a wild-type microorganism. The mutated microorganism is used in the production of ethanol, utilising C3, C5 or C6 sugars as the substrate.
Owner:TMO RENEWABLES LTD
Preselection of subjects for therapeutic treatment based on hypoxic status
InactiveUS20120128665A1Reduce medical costsBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseCancer cell
The present invention provides methods for the preselection of a subject for therapeutic treatment with an agent based on modulated levels of hypoxia in cancerous cells in the subject. In one embodiment, the invention provides methods for the preselection of a subject for therapeutic treatment with an agent based on modulated levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in a cell, e.g., a cancerous cell. The invention also provides methods for treating cancer in a subject by administering an effective amount of an agent to the subject, wherein the subject has been selected based on a modulated level of hypoxia. The invention further provides kits to practice the methods of the invention.
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
Method for growing laminated double-metal hydroxide on surface of any substrate
The invention discloses a method for growing laminated double-metal hydroxides on the surface of any substrate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving dopamine and polyethyleneimine in a buffer solution, soaking a substrate into the solution, and performing oscillation deposition so as to obtain a dopamine / polyethyleneimine modified substrate; and (2) soaking the surface modified substrate obtained in the step (1) into a solution of soluble divalent metal salts, soluble trivalent metal salts and alkali substances, and performing a hydrothermal reaction for 1-24 hours at 90-120 DEG C, thereby obtaining a composite material that laminated double-metal hydroxides are uniformly grown on the surface of the substrate. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient to operate and wide in application, and the preparation time of an LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) functional device is effectively shortened; and in addition, as no organic solvent or surfactant is used, the cost is relatively low, and the environment is not polluted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
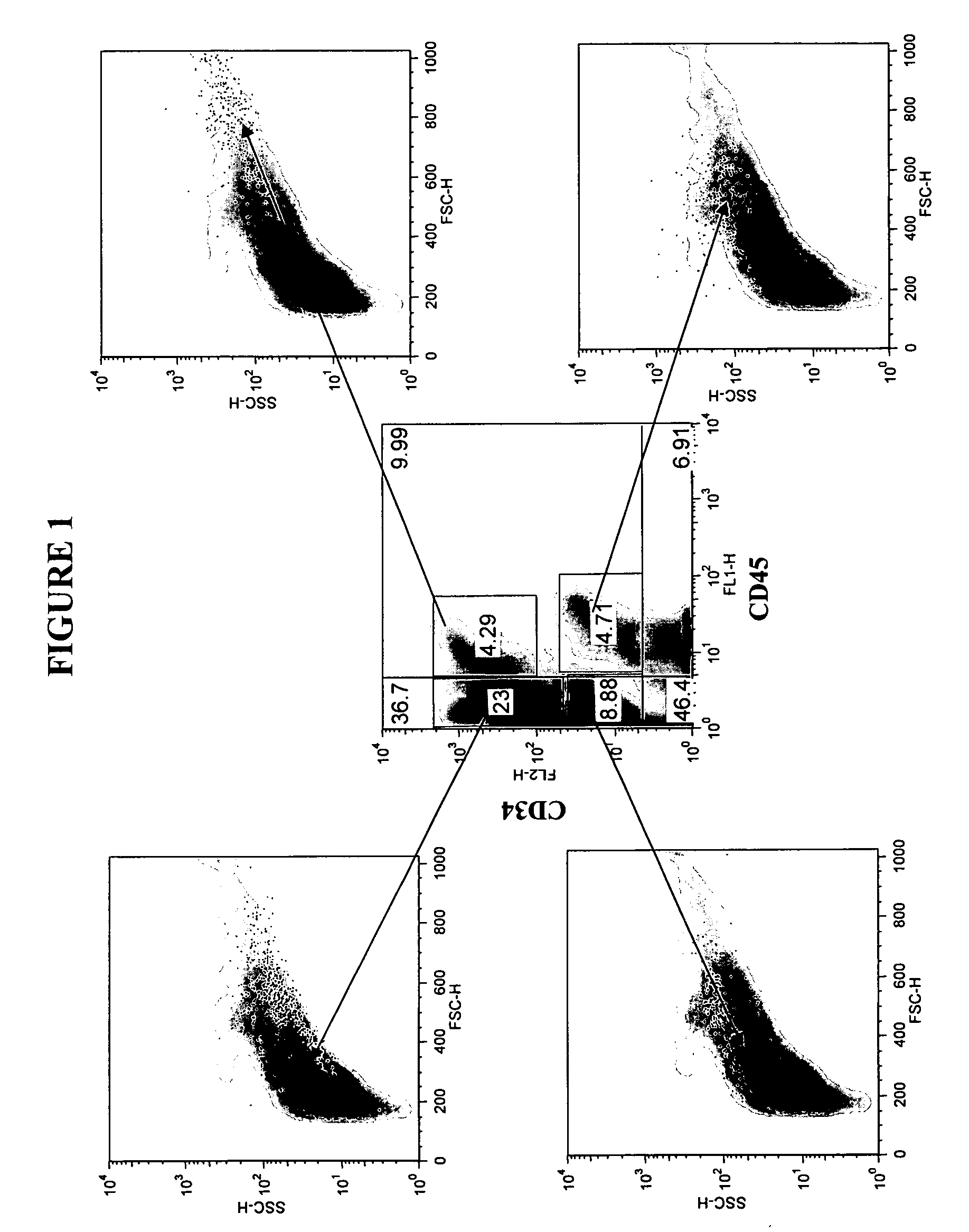
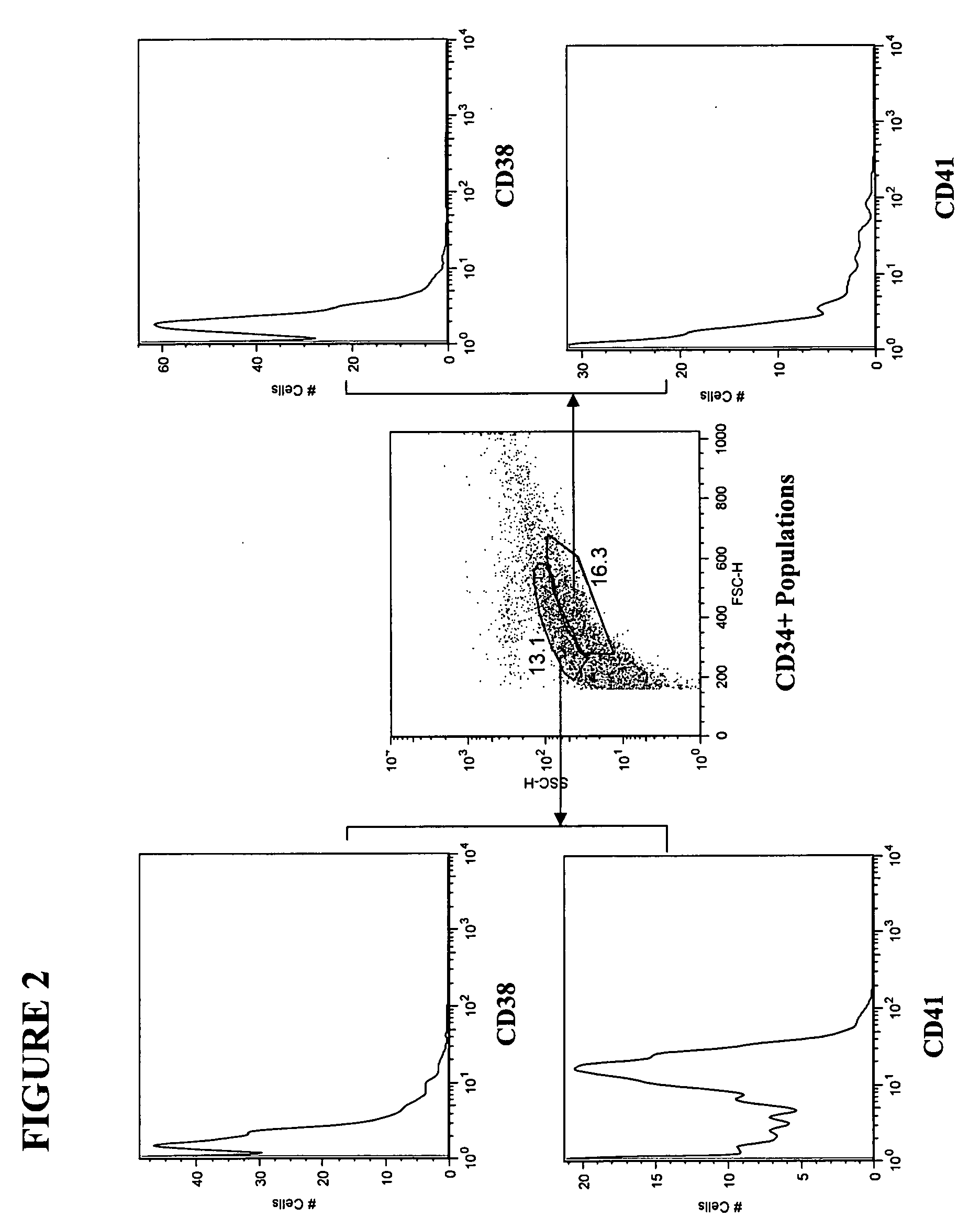
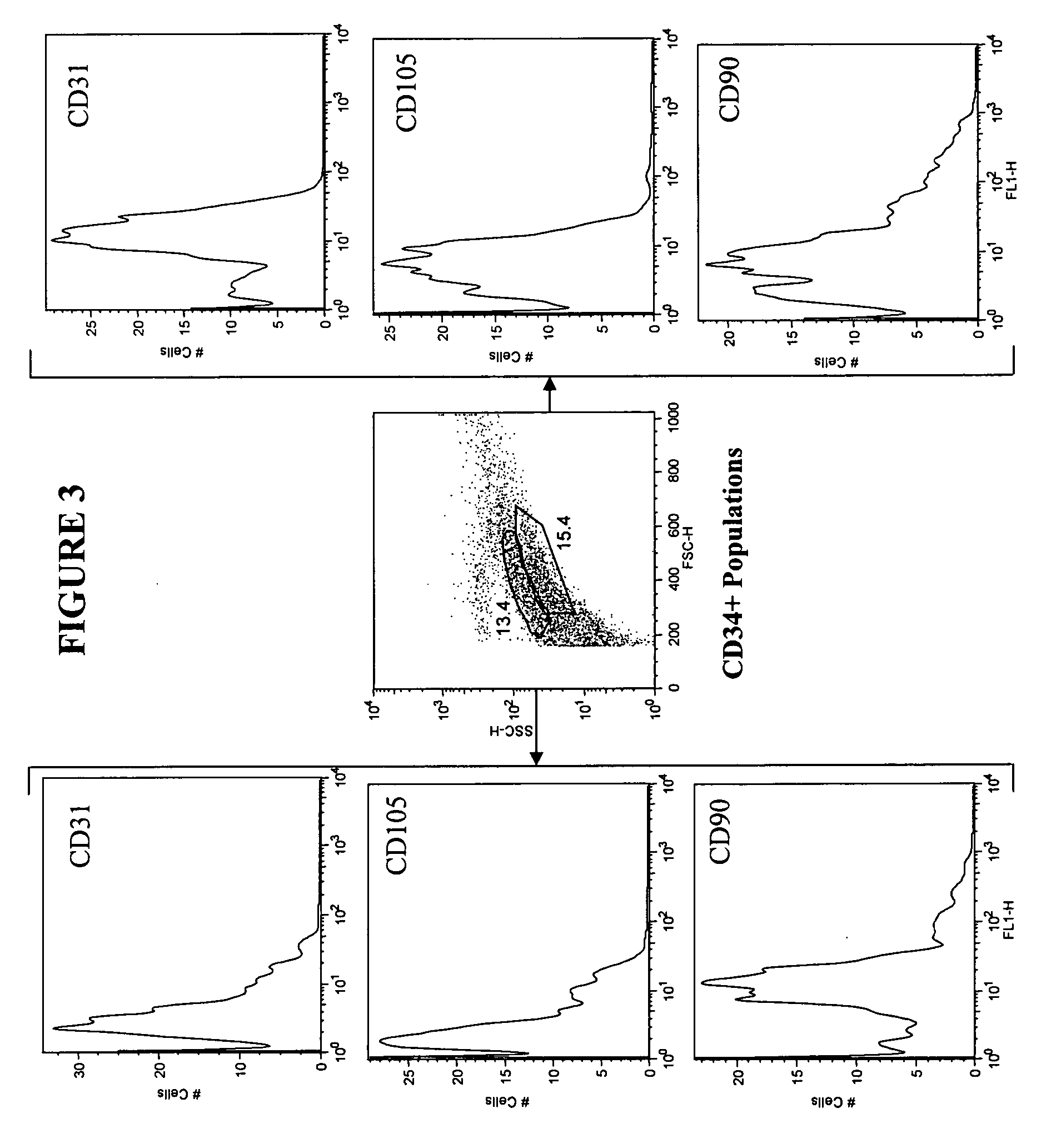
Isolation and purification of hematopoietic stem cells from post-liposuction lipoaspirates
The present invention relates to a method of isolating hematopoietic stem cells from adipose tissue. The method yields a notably high number of CD34+, ALDHbr and / or ABCG2-expressing cells, comprising hematopoietic stem cells, permitting the use of the cells with no or minimal expansion.
Owner:COGNATE BIOSERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com