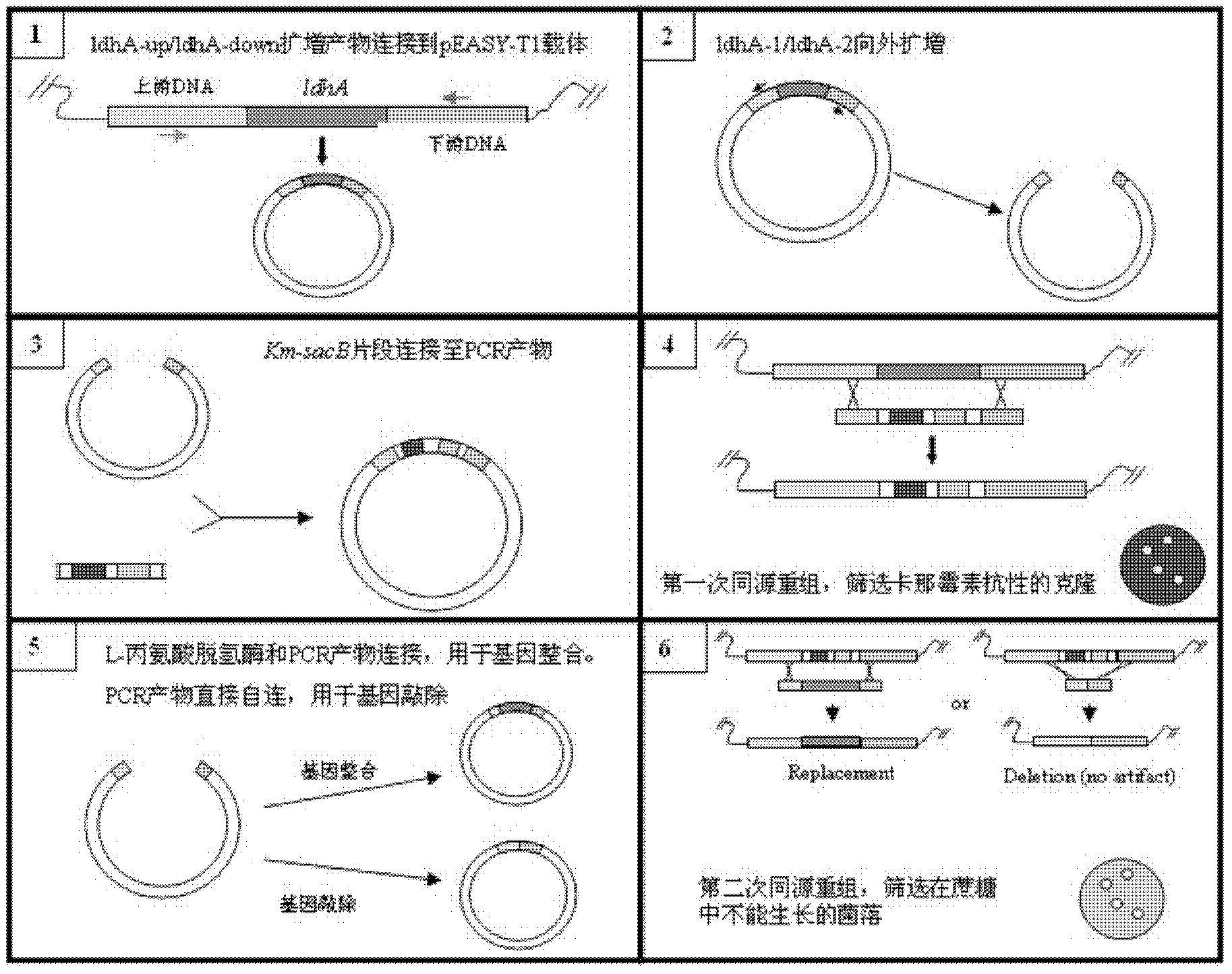
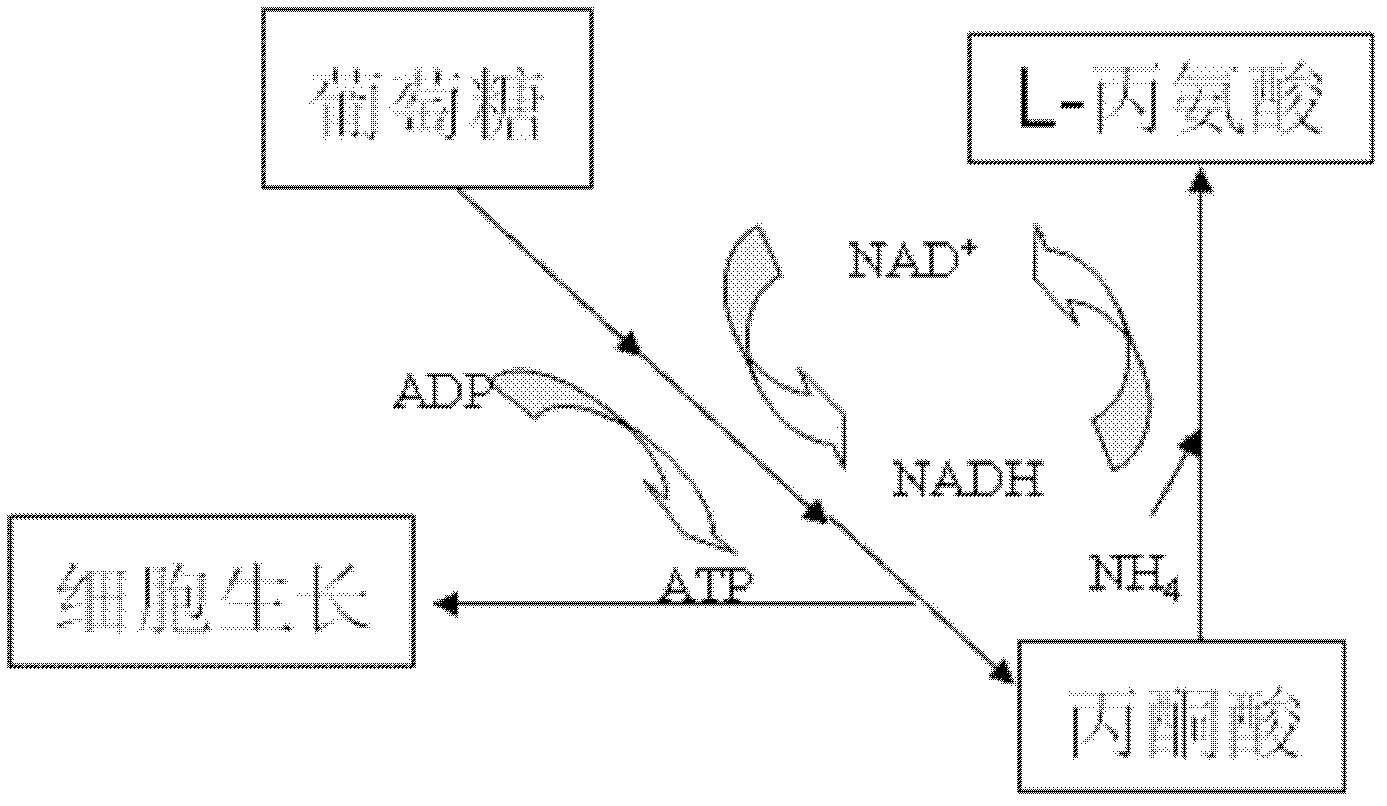
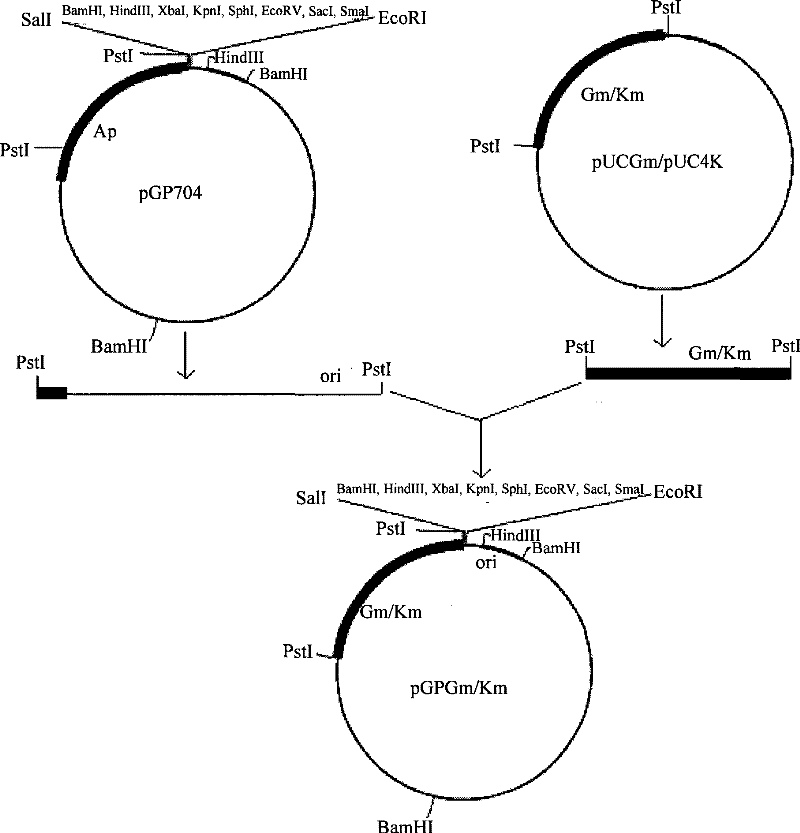
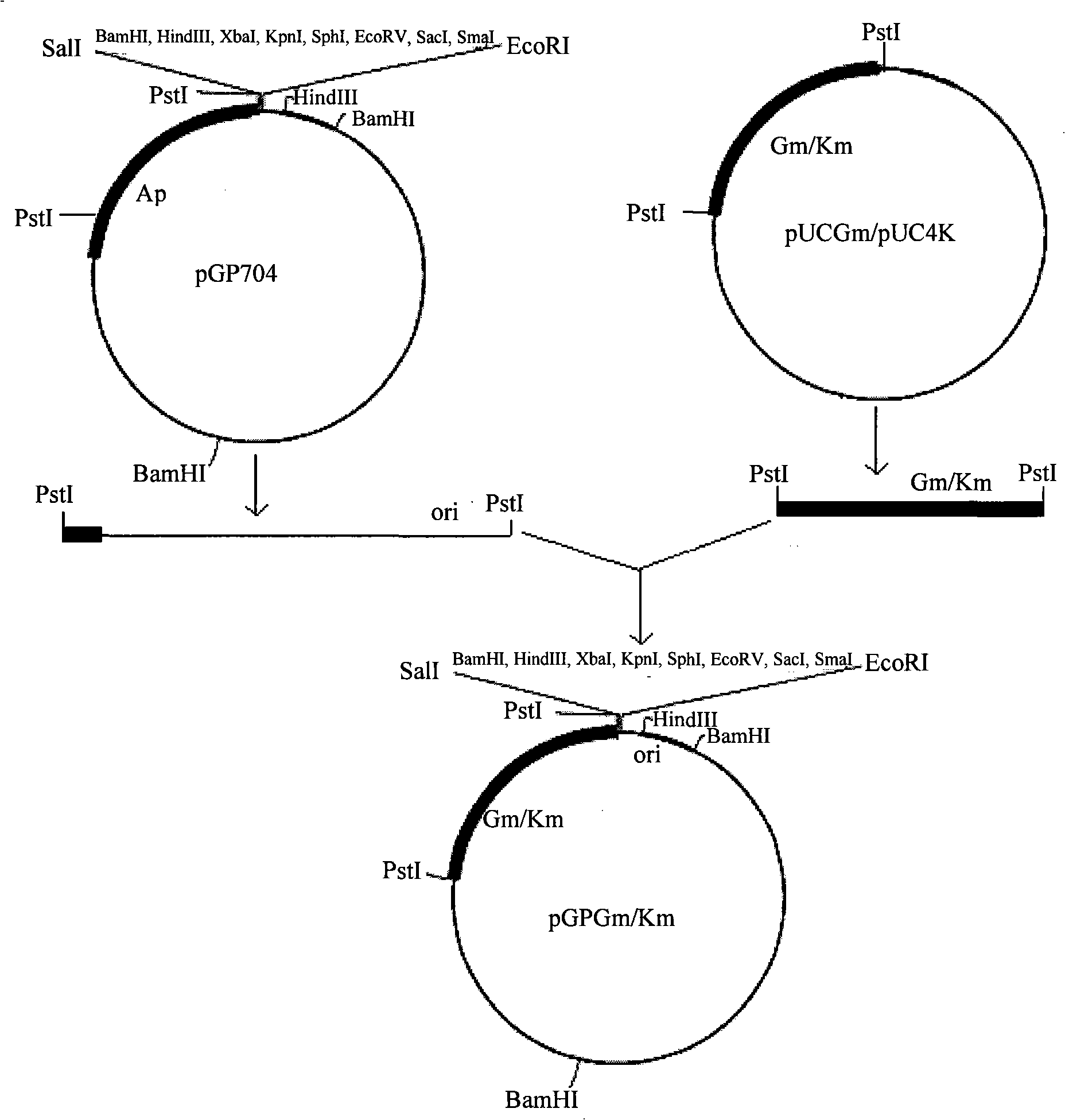
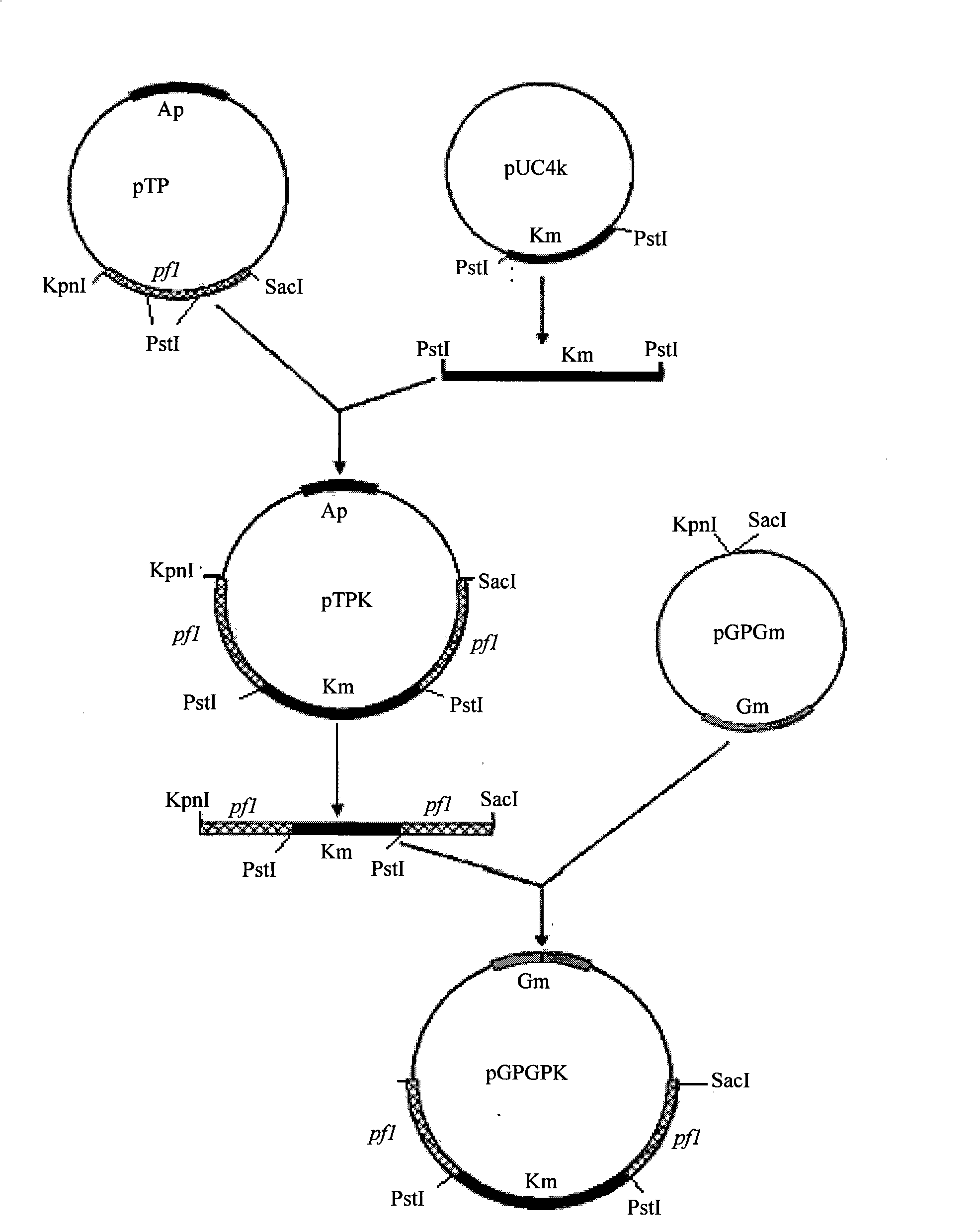
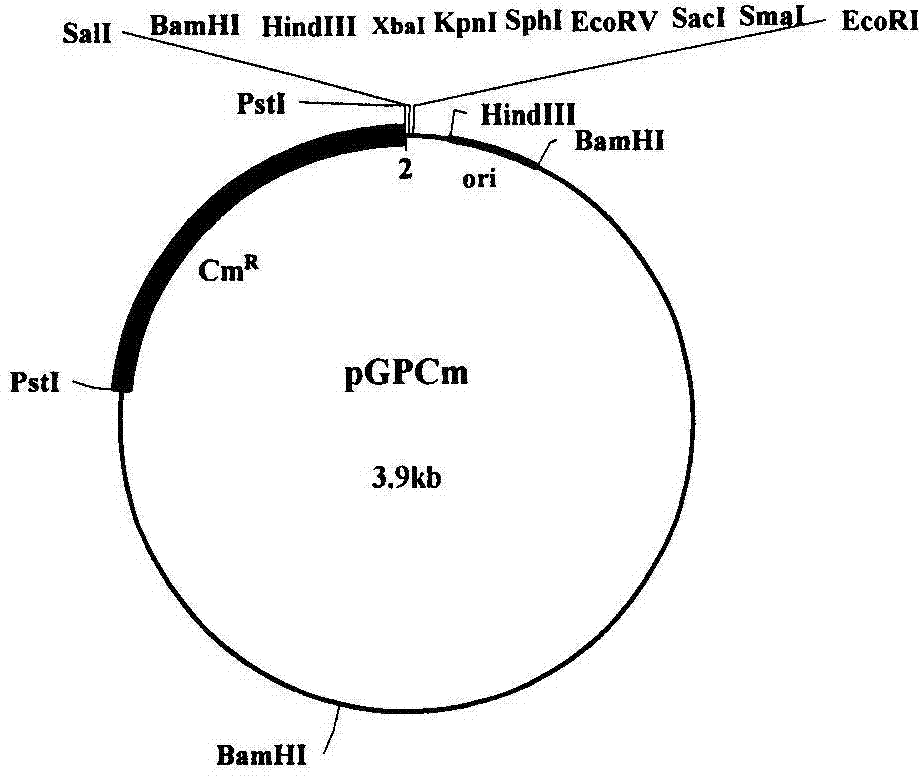
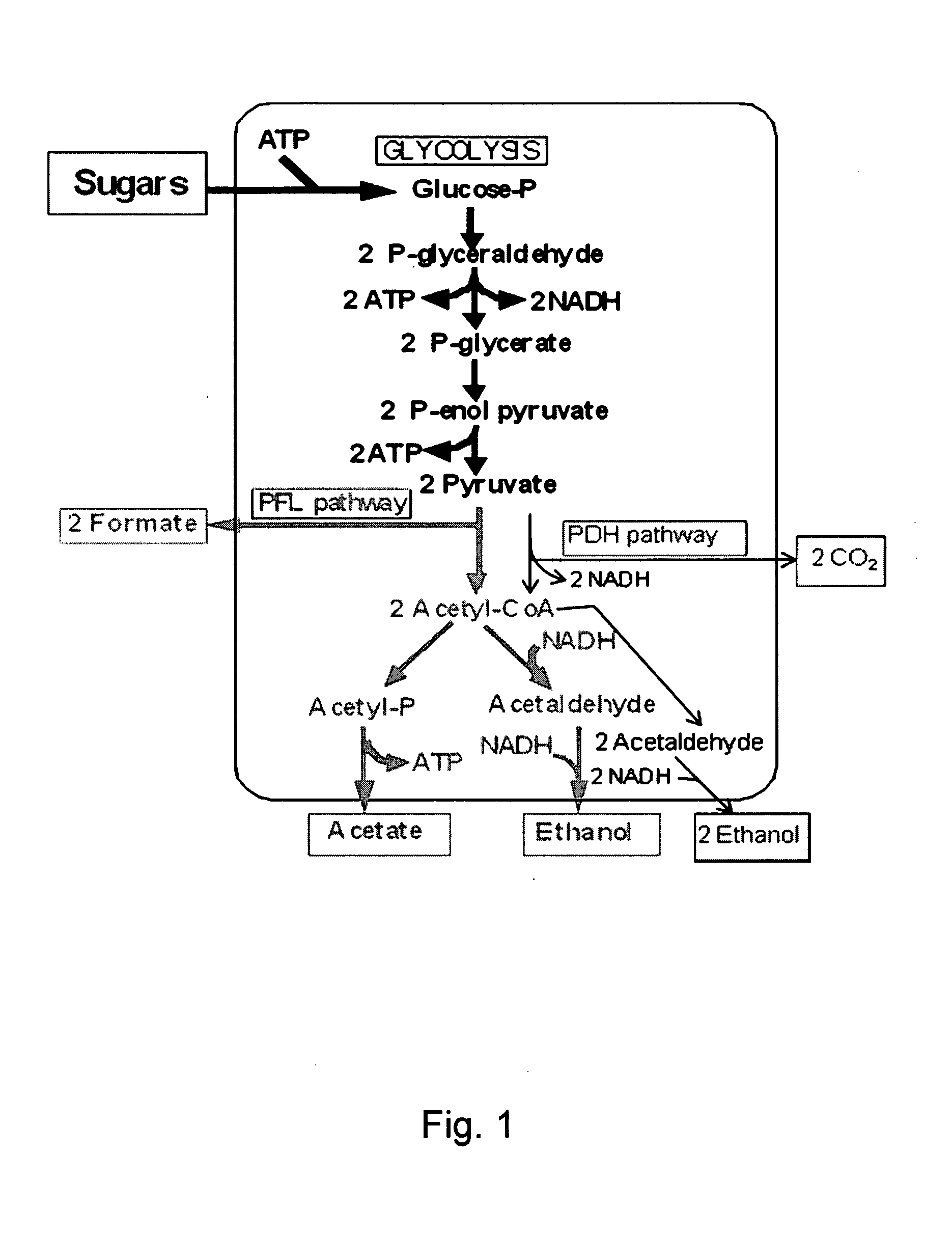
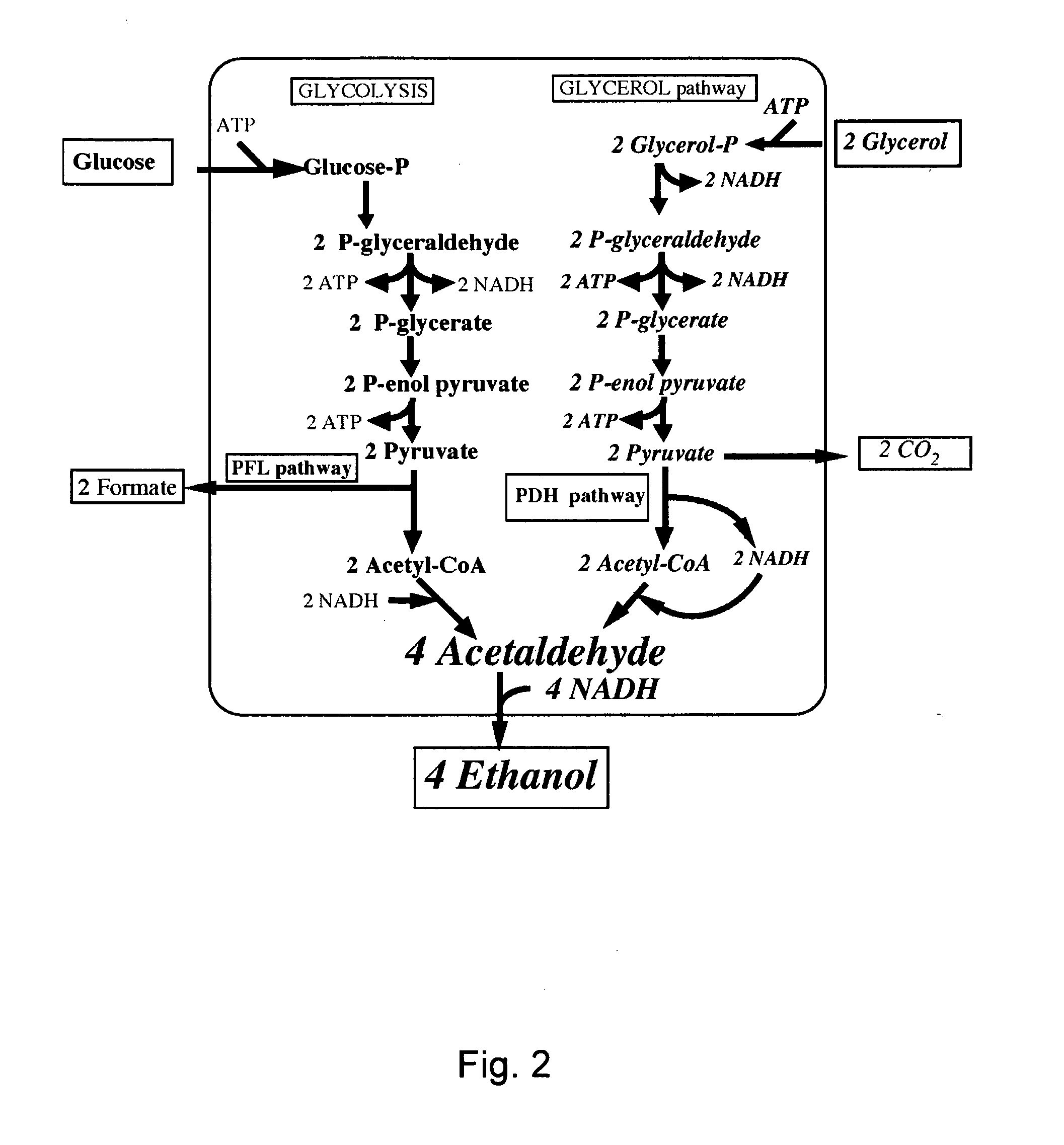
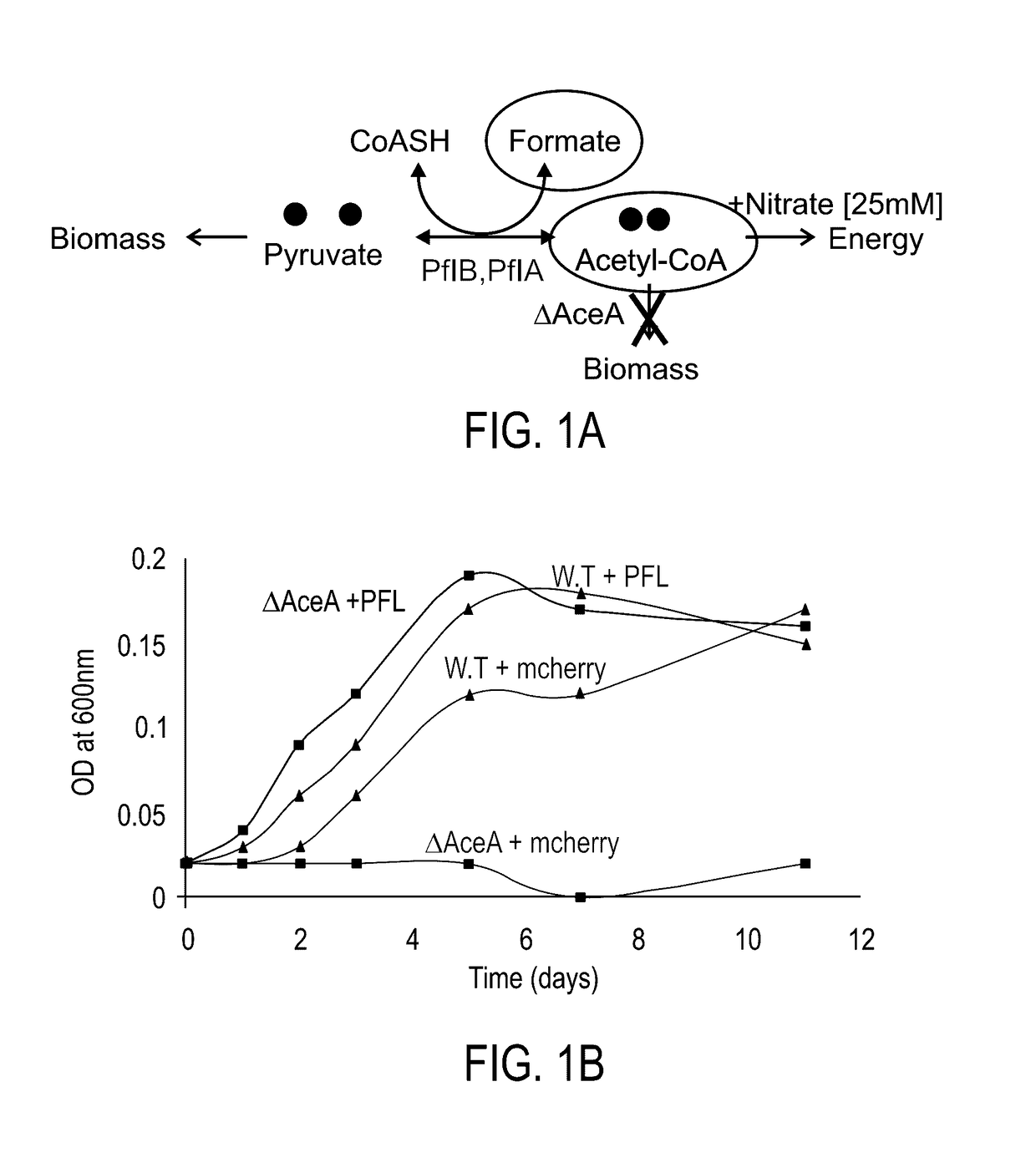
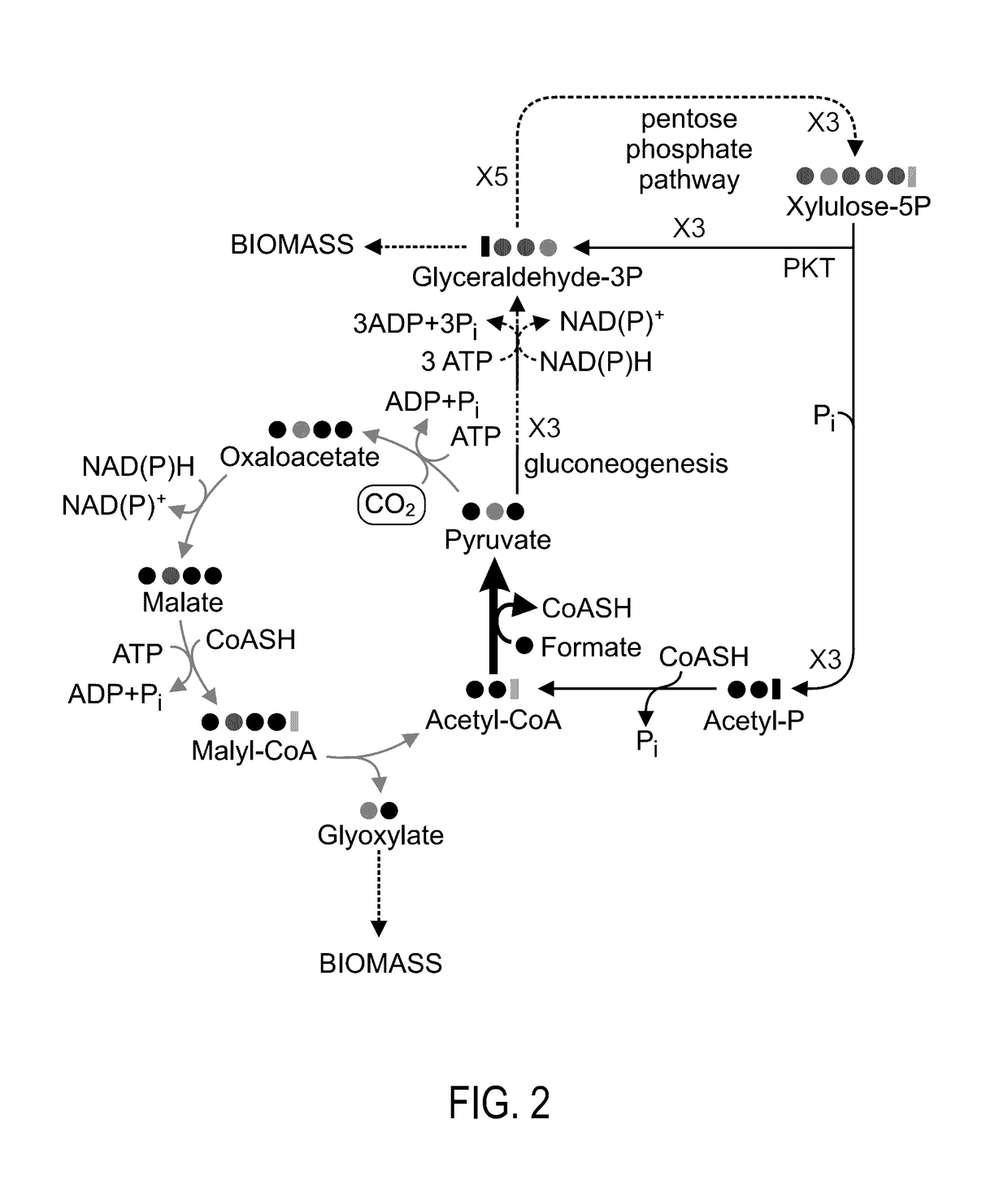
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Pyruvate formate lyase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
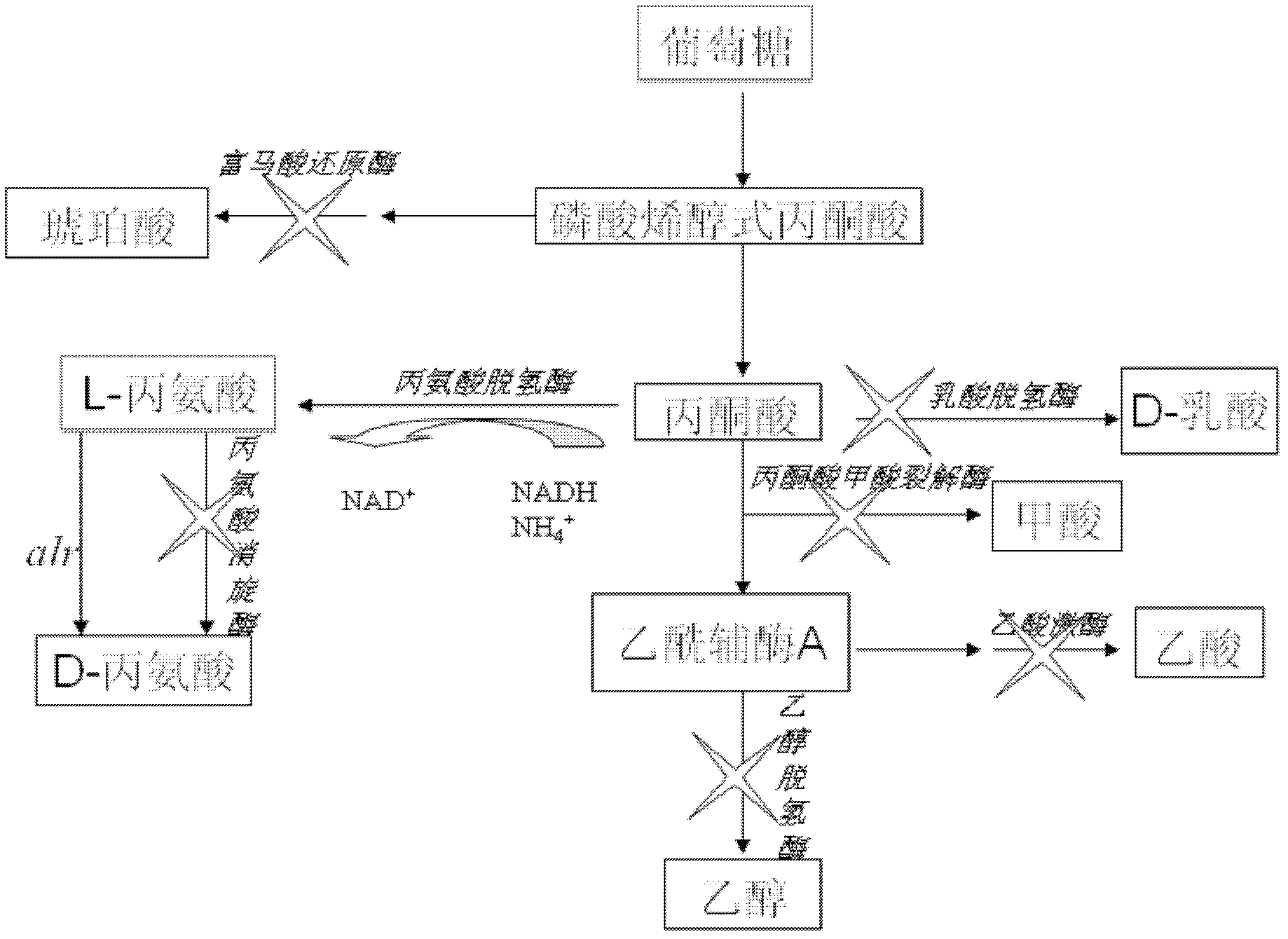
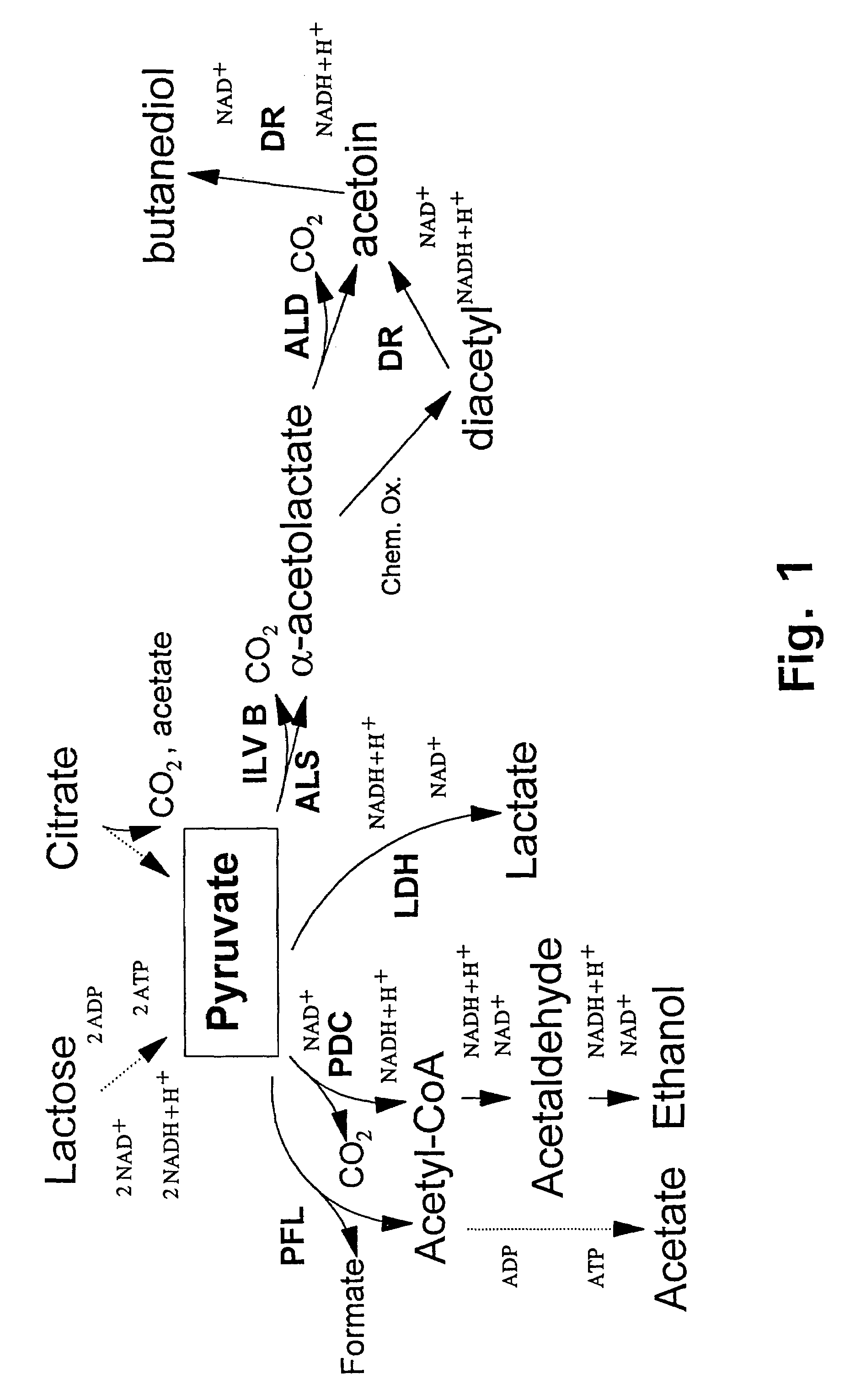
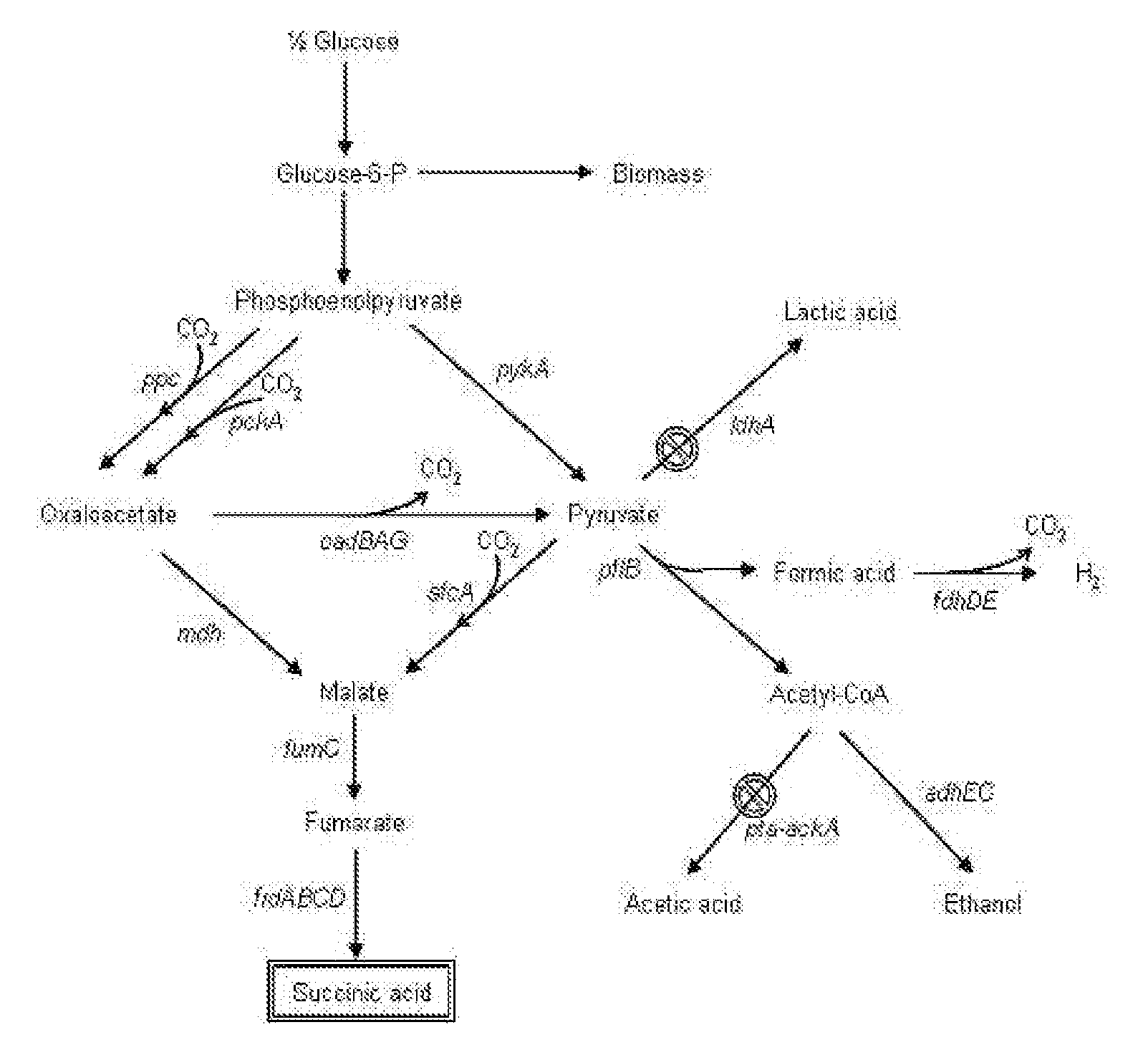
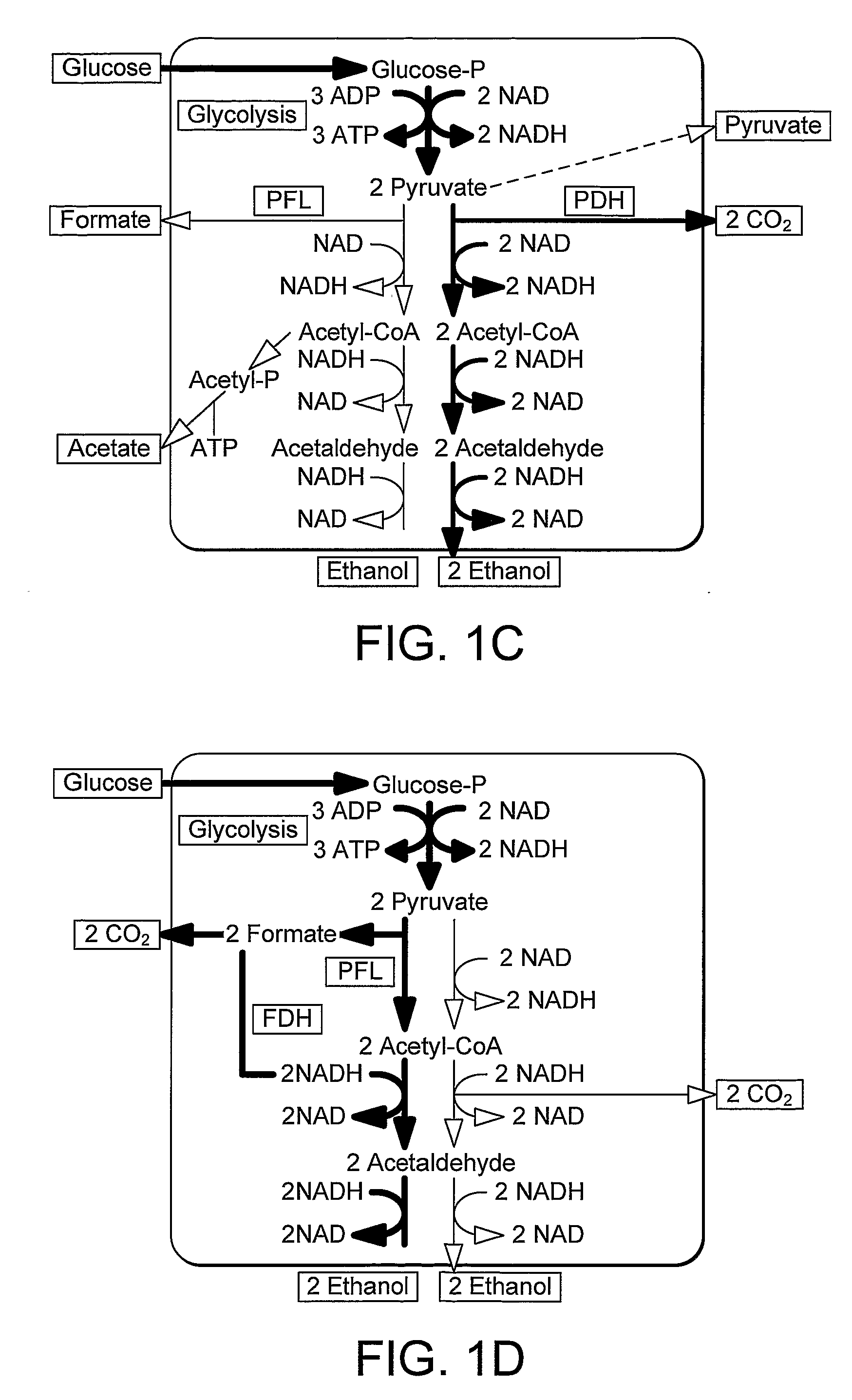
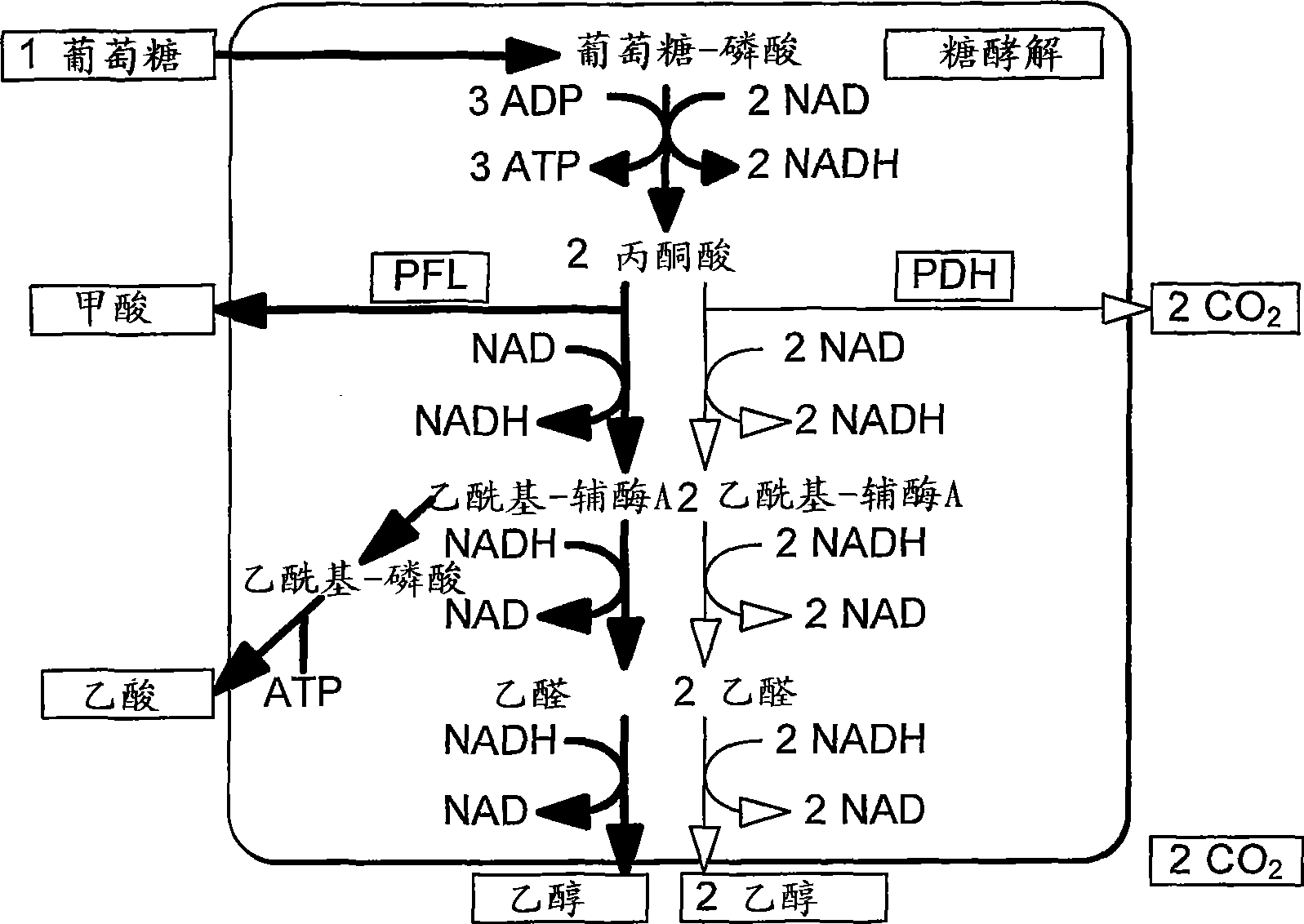
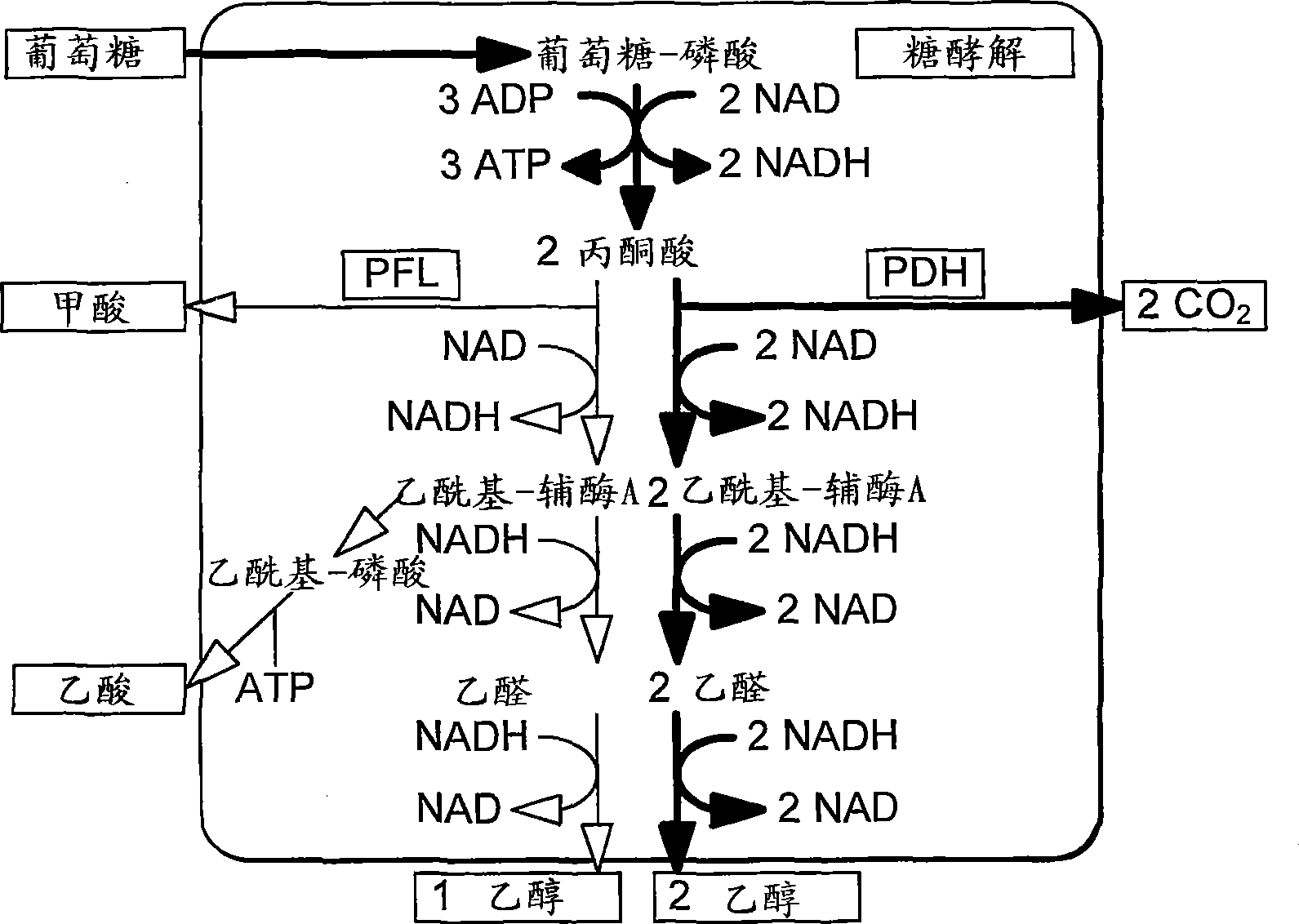
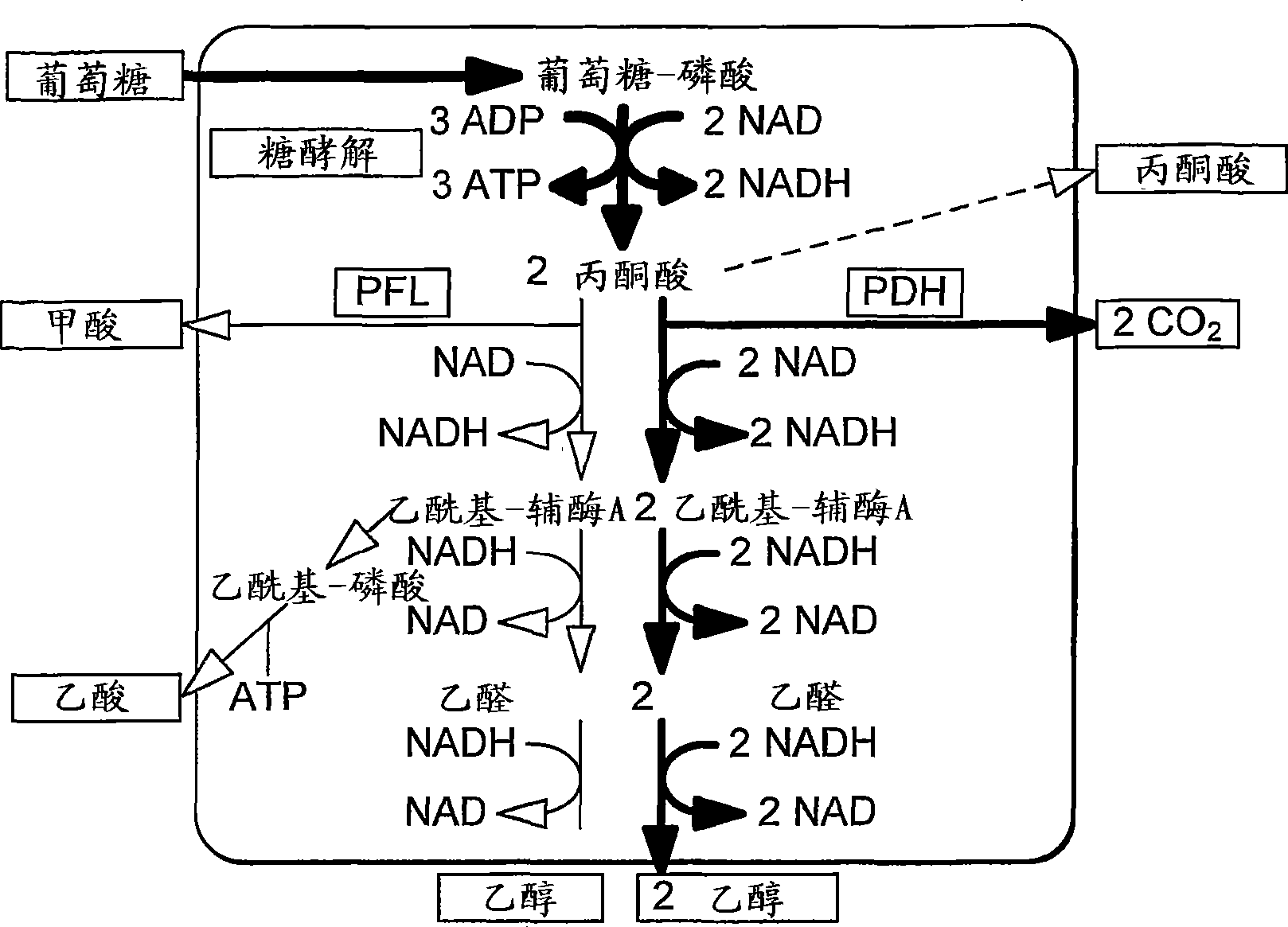
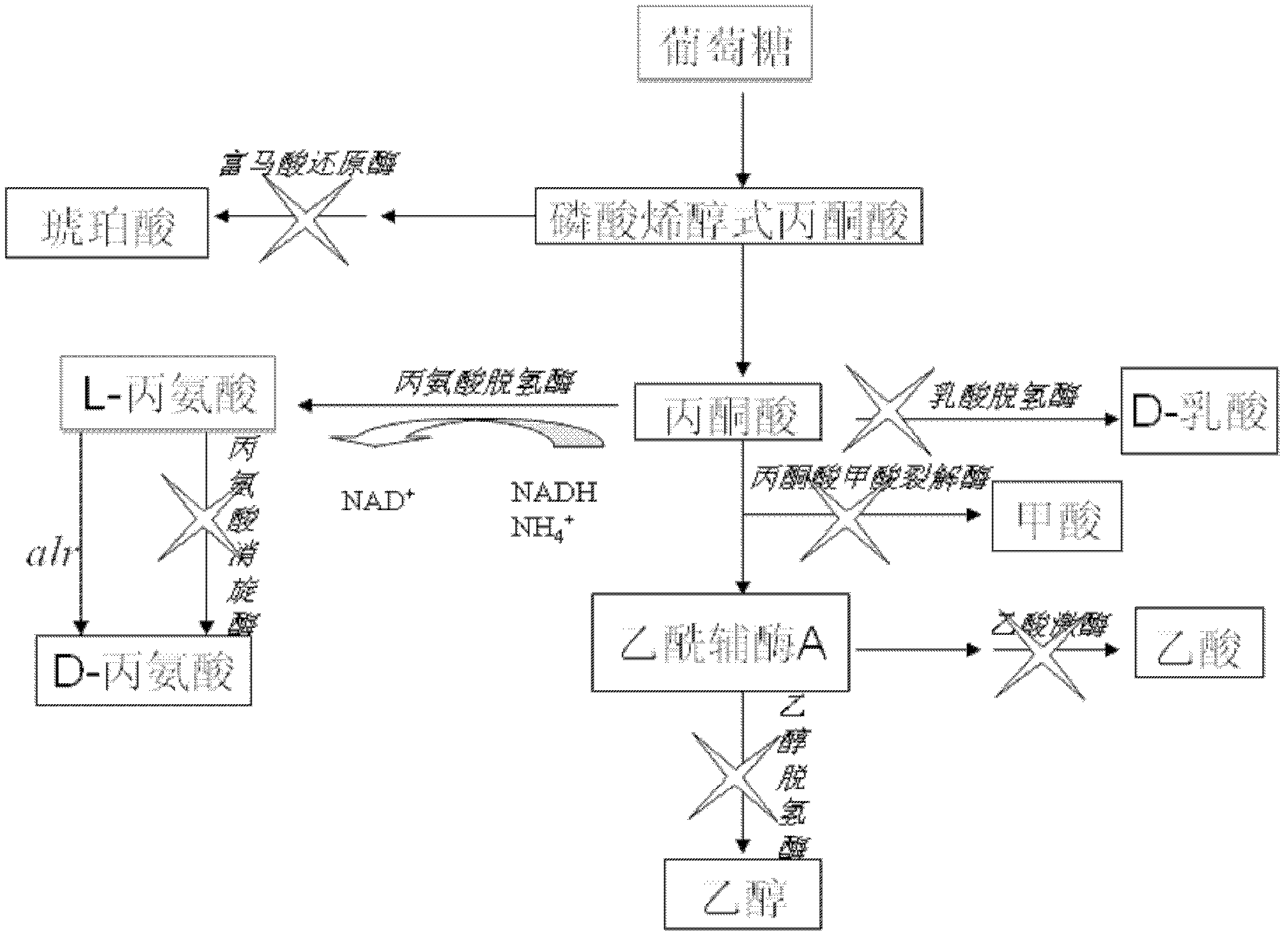
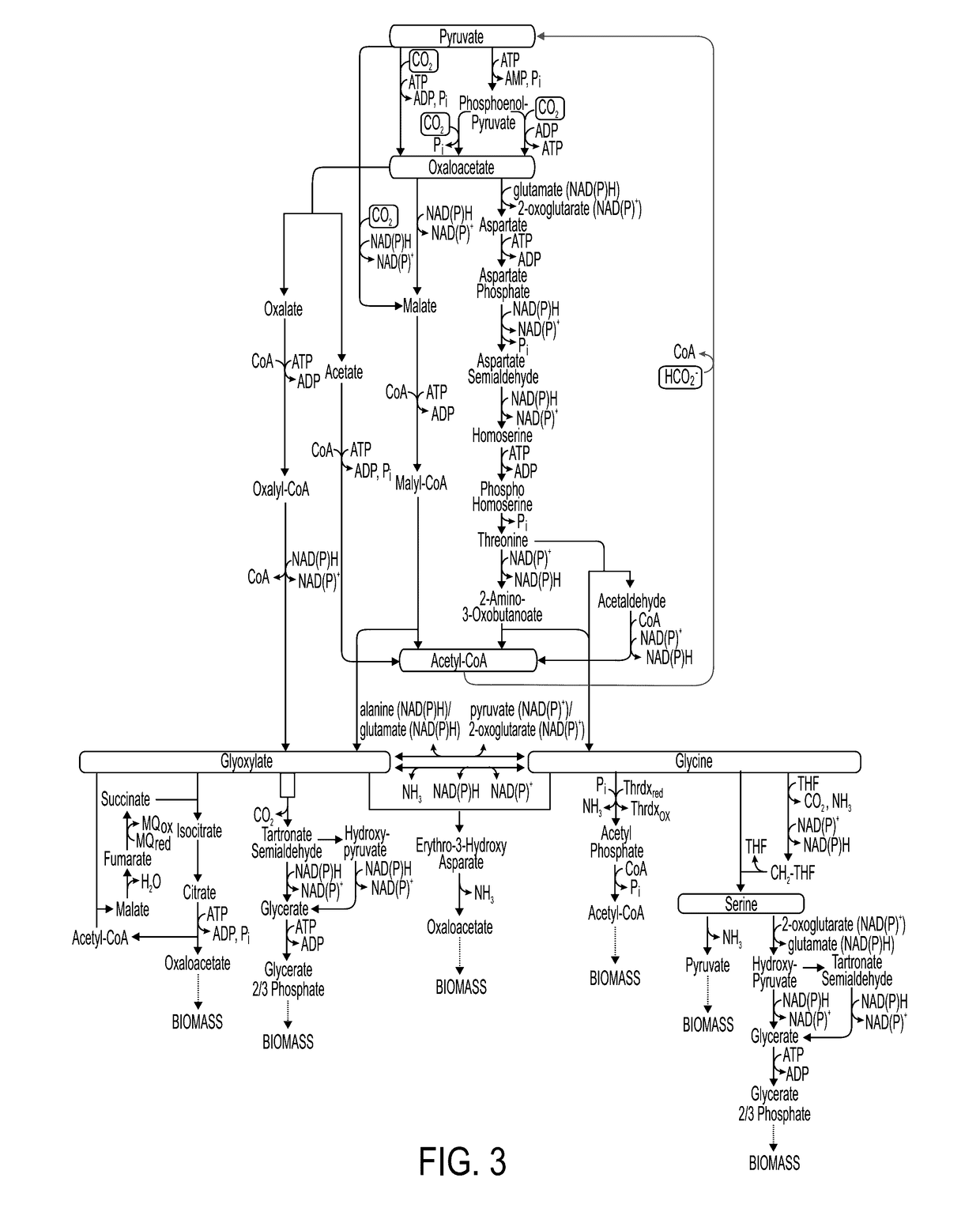
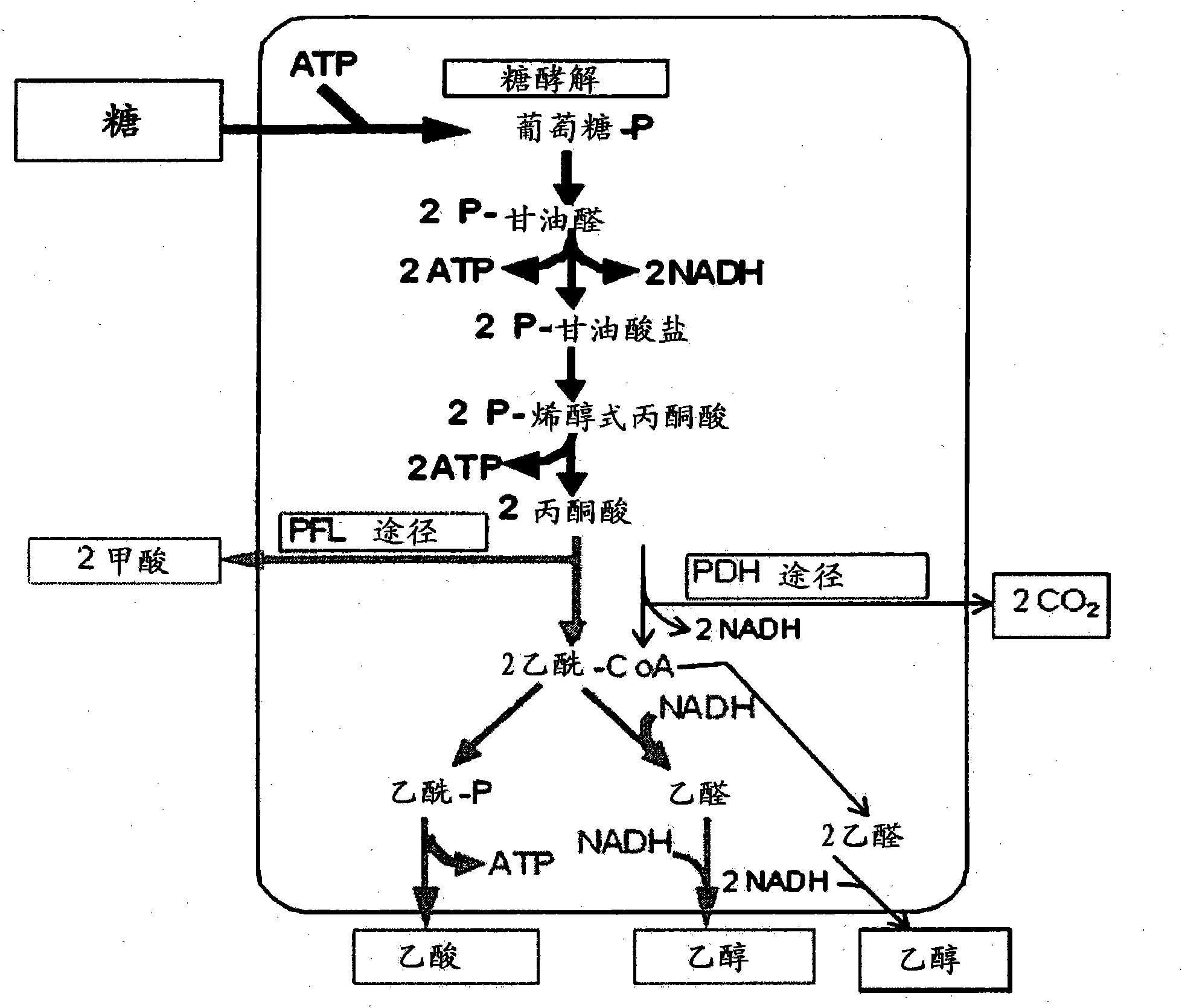
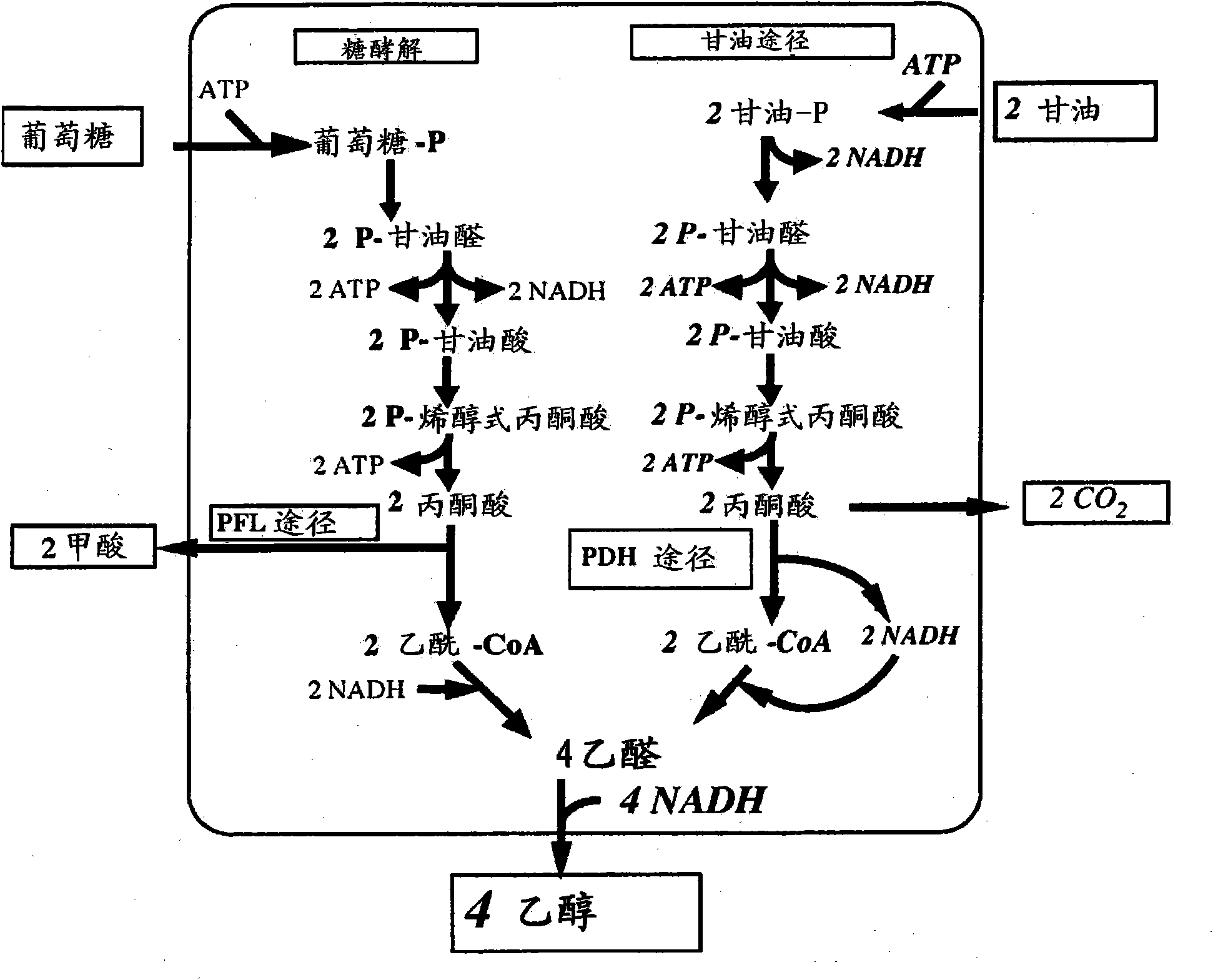
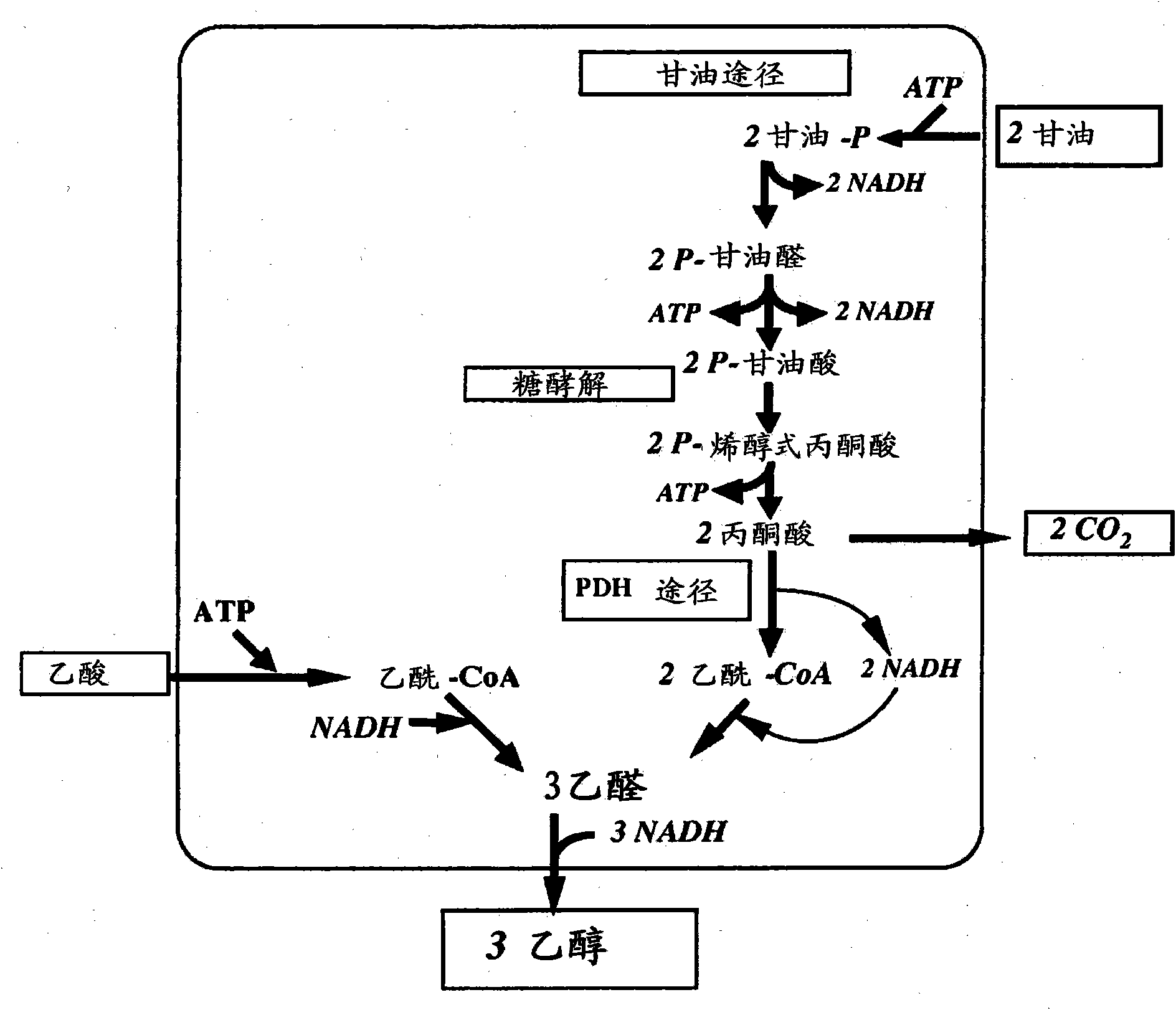
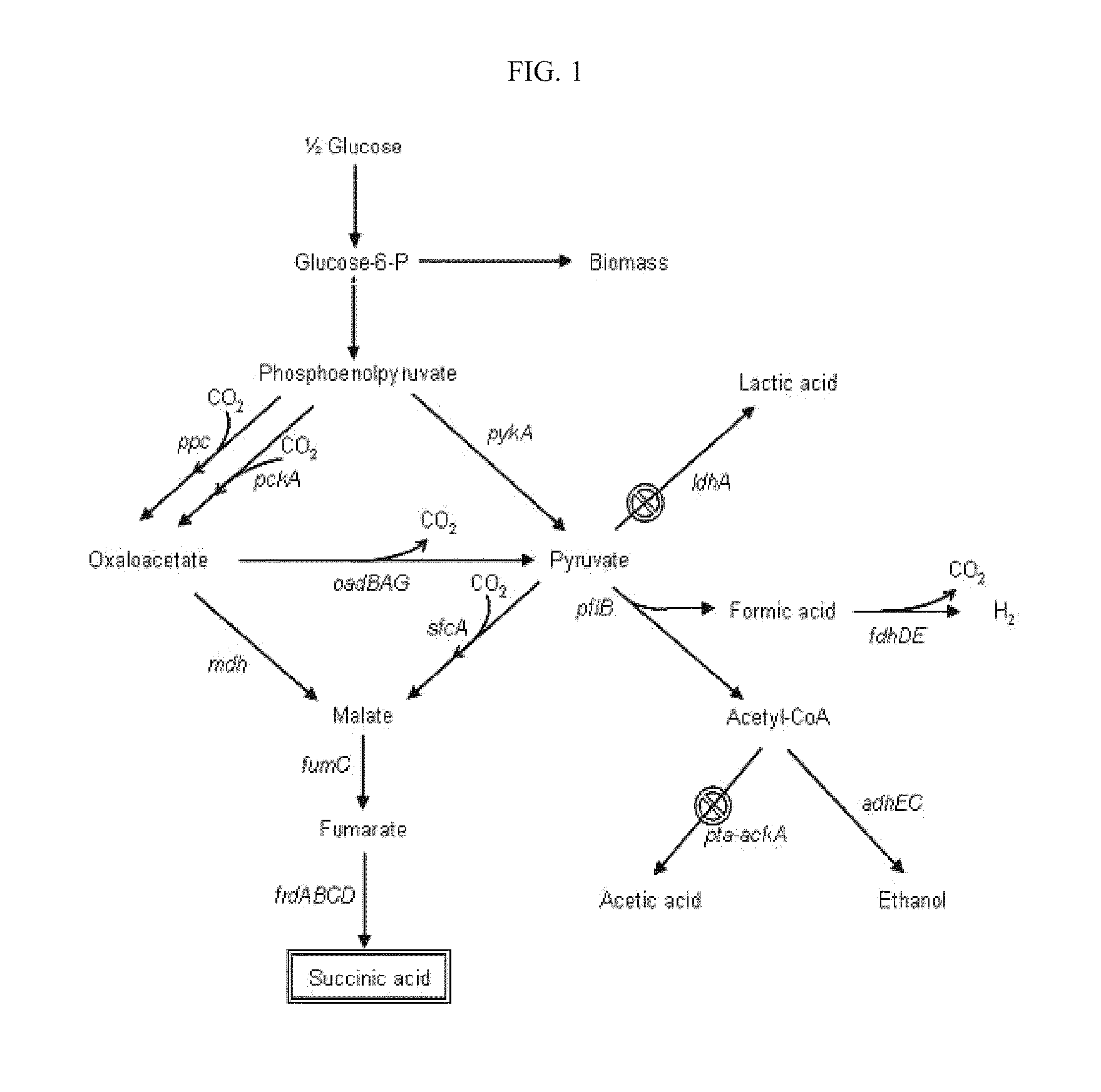
In enzymology, formate C-acetyltransferase (pyruvate formate lyase) (EC 2.3.1.54) is an enzyme. Pyruvate formate lyase is found in Escherichia coli and other organisms. It helps regulate anaerobic glucose metabolism. Using radical non-redox chemistry, it catalyzes the reversible conversion of pyruvate and coenzyme-A into formate and acetyl-CoA.
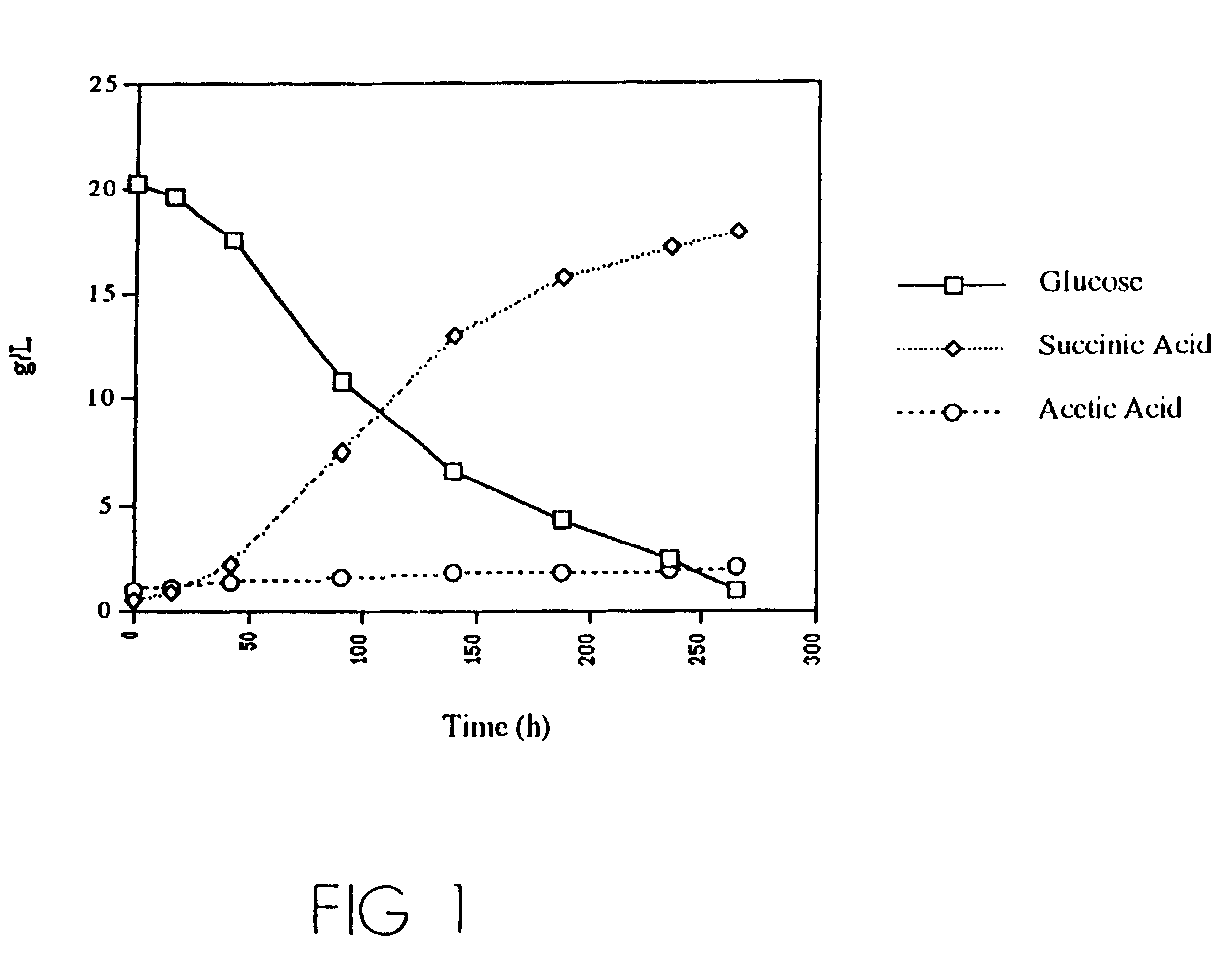
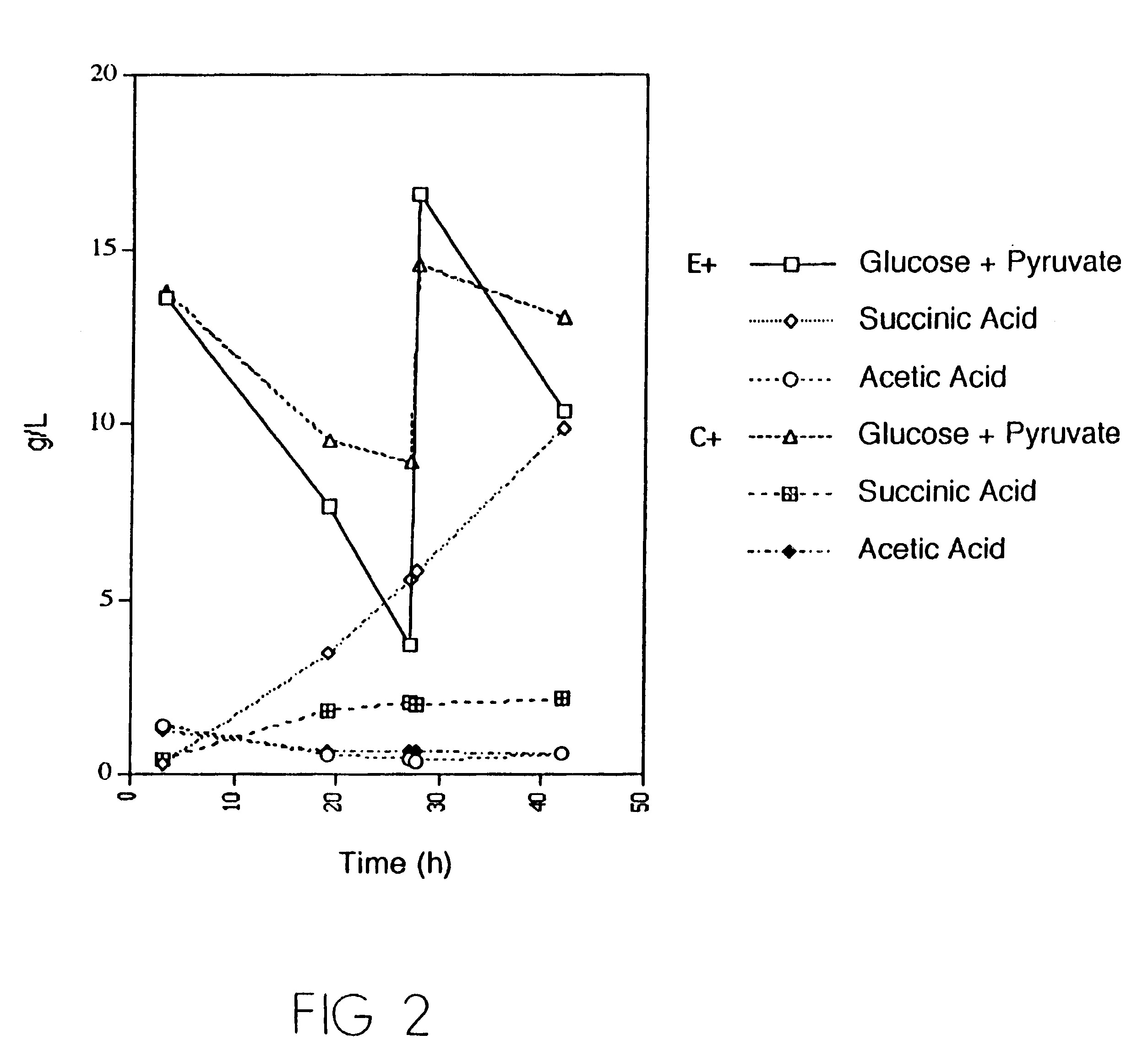
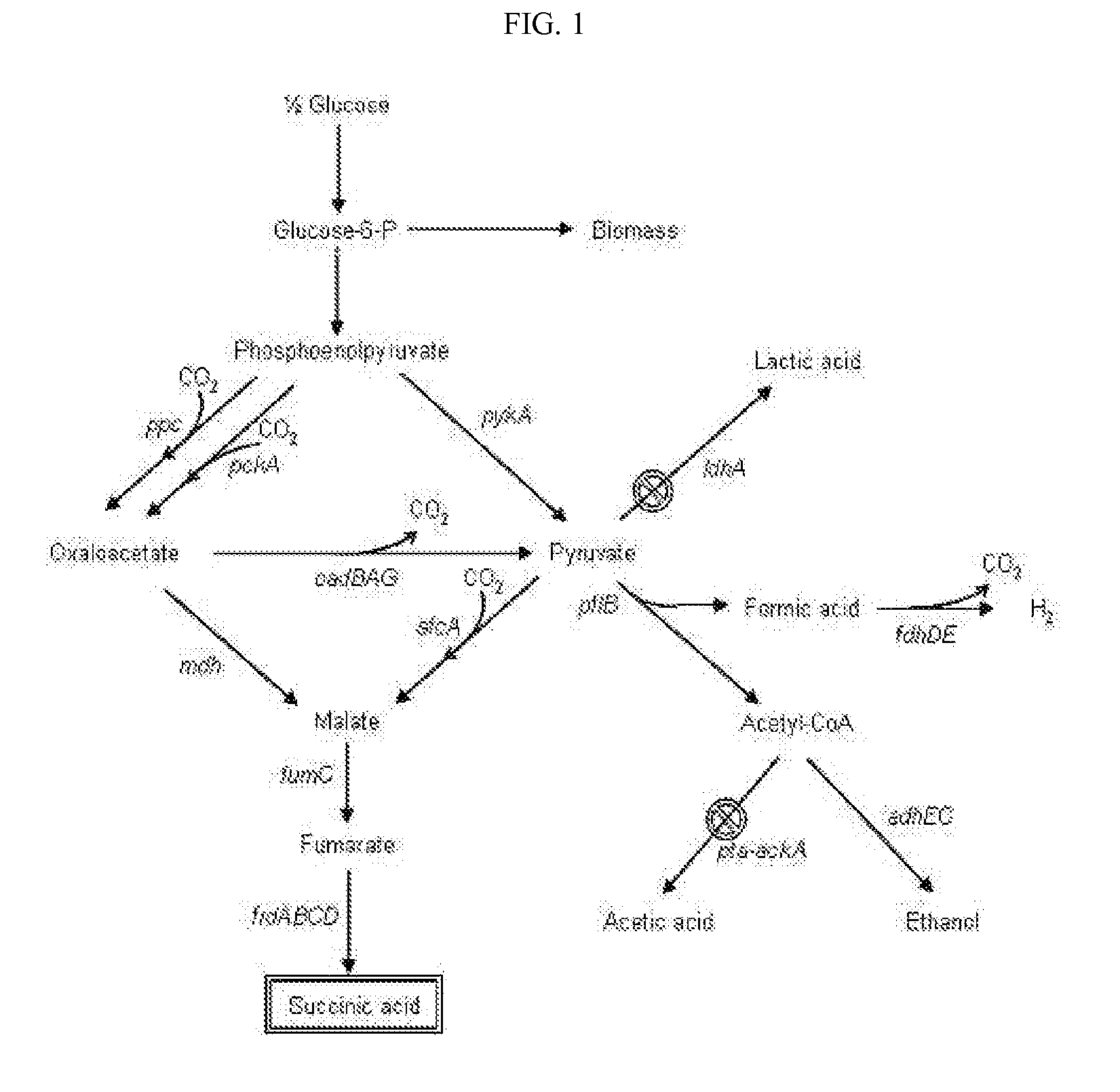
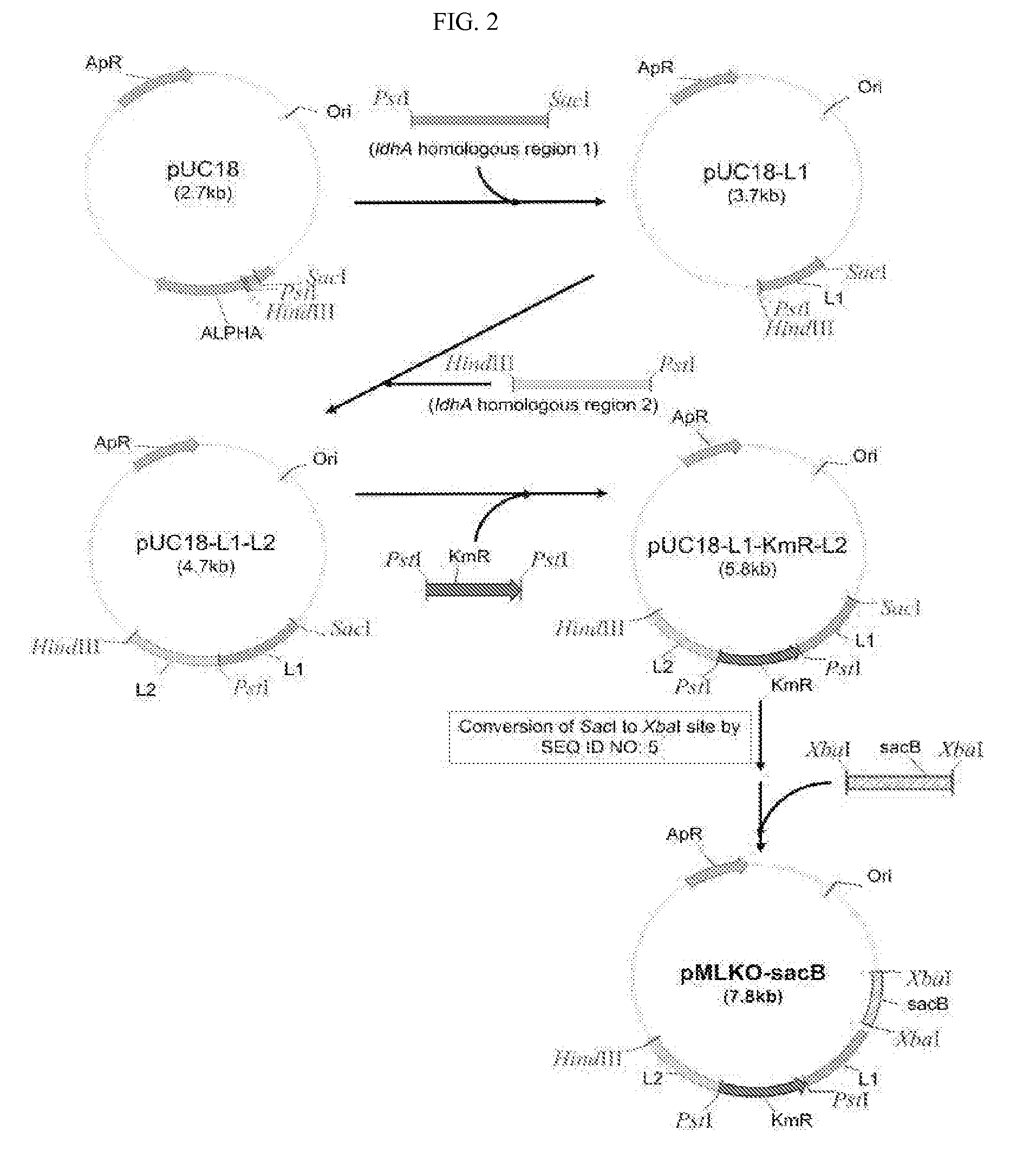
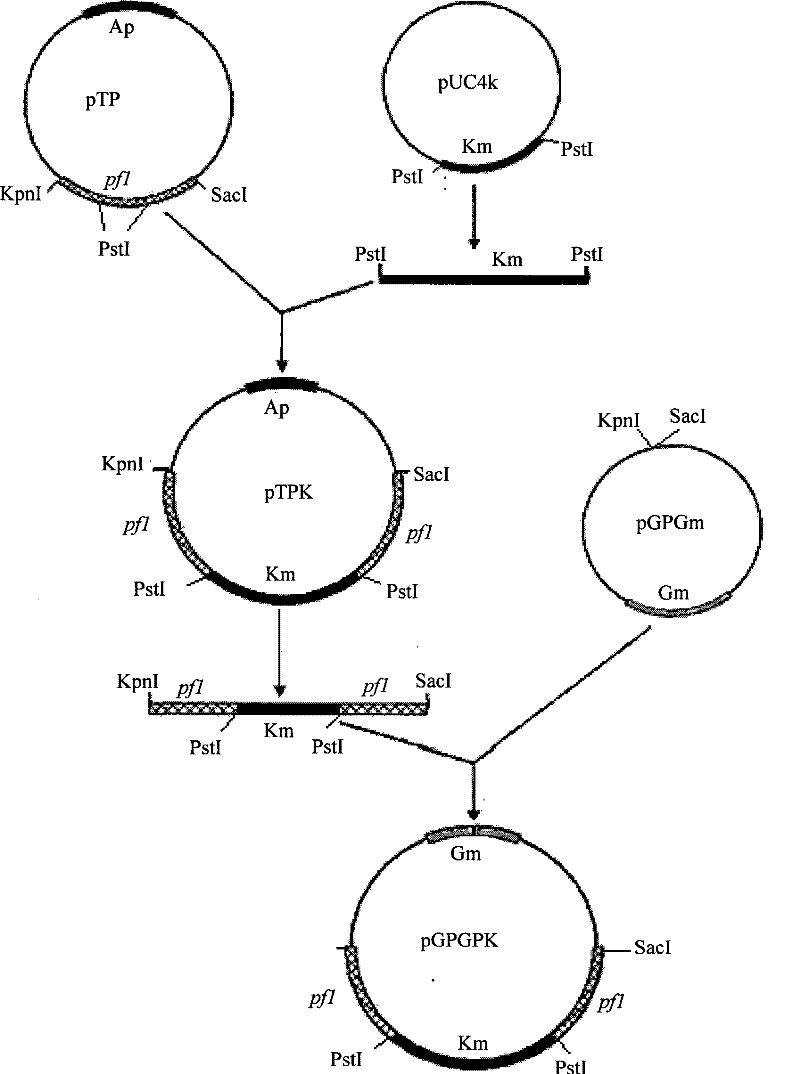
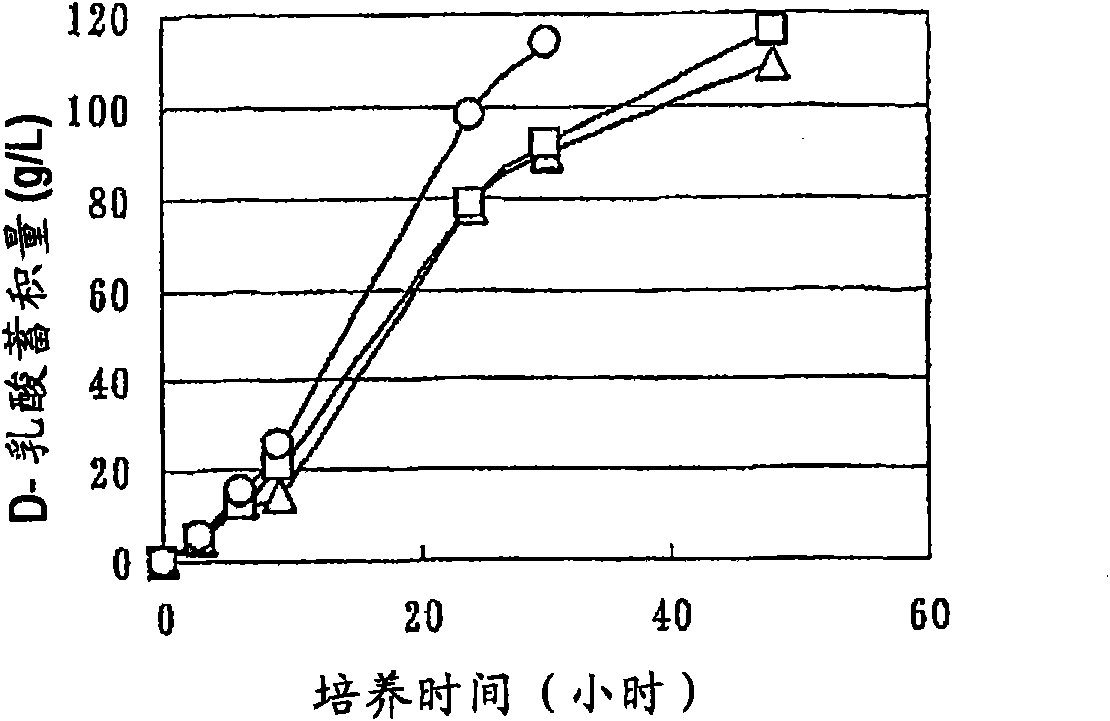
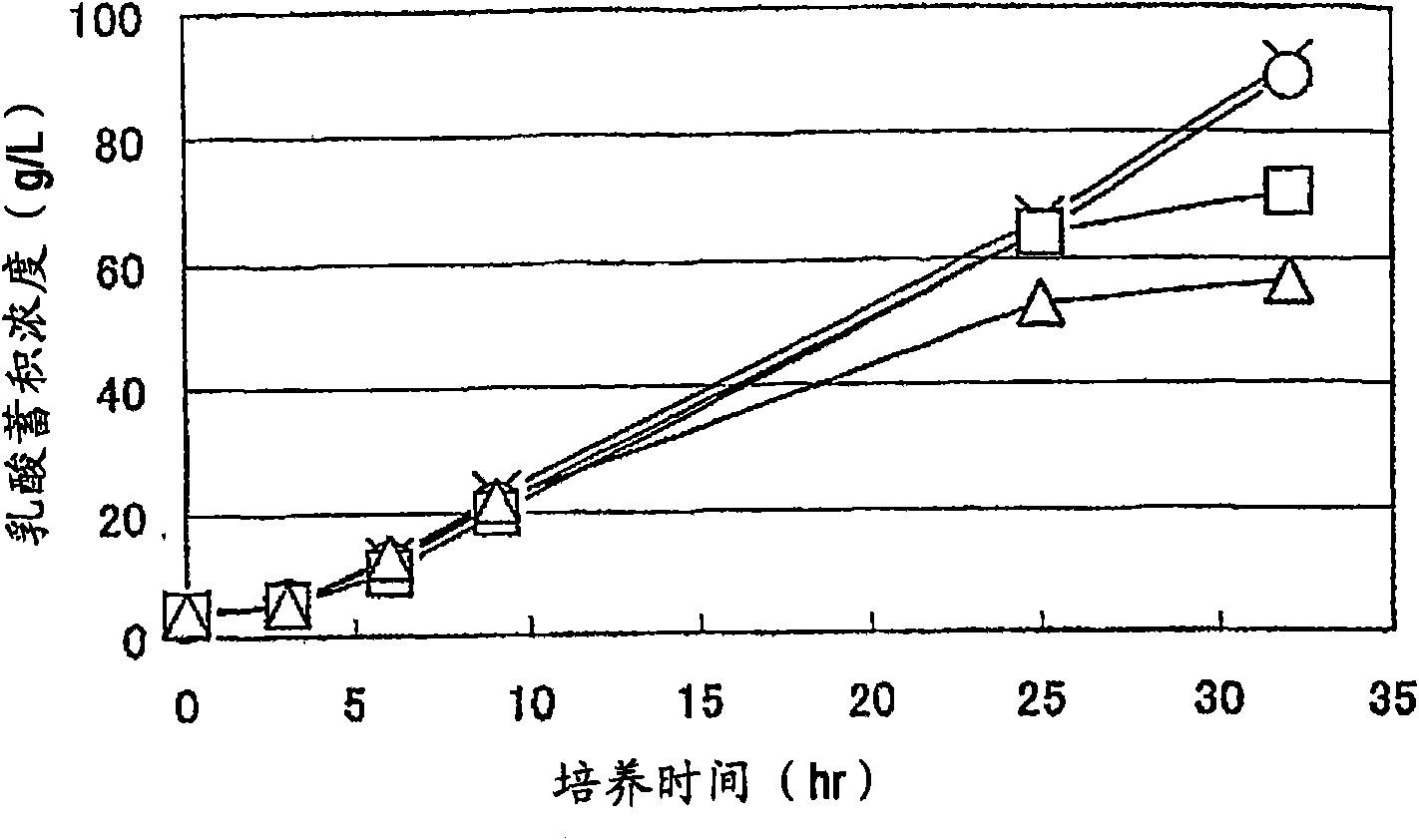
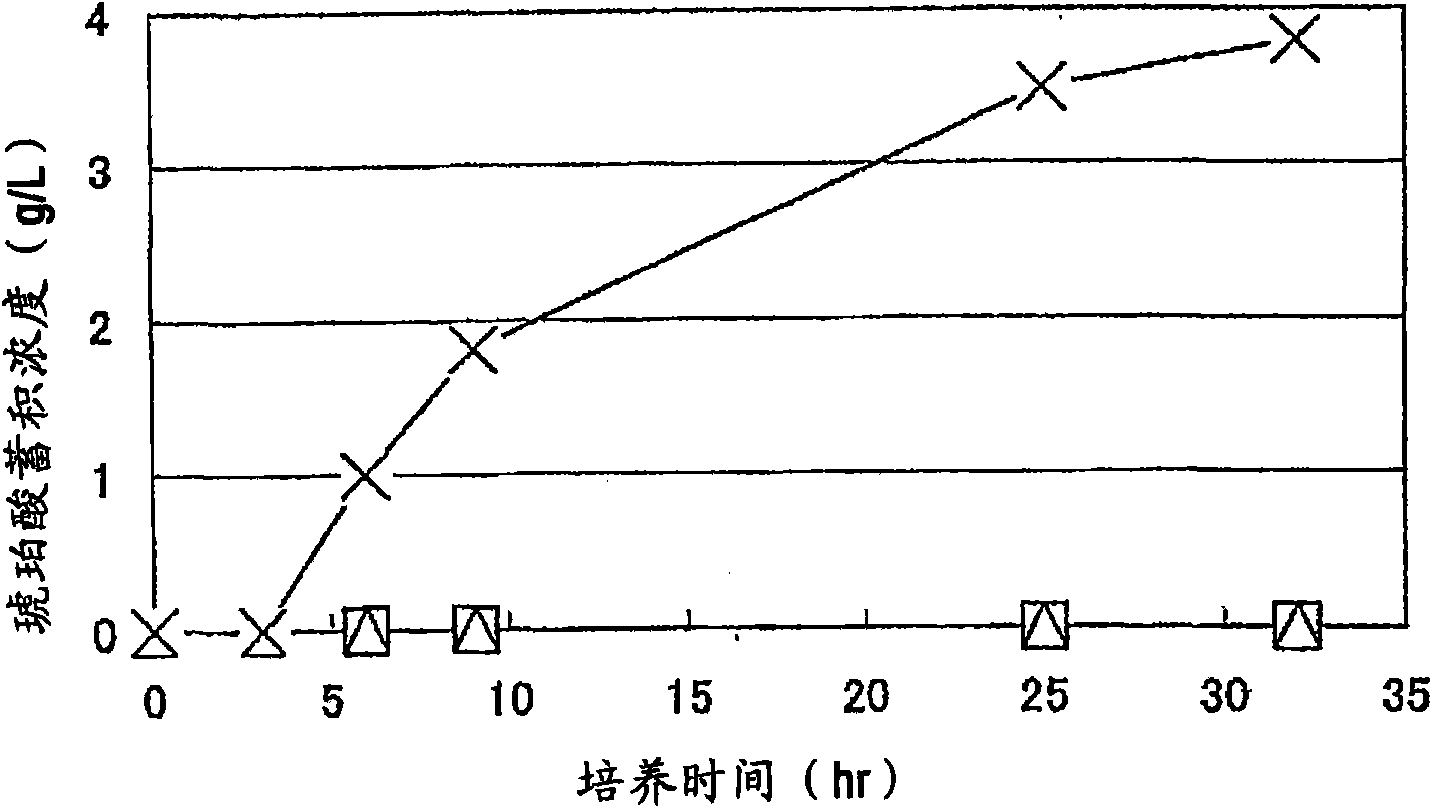
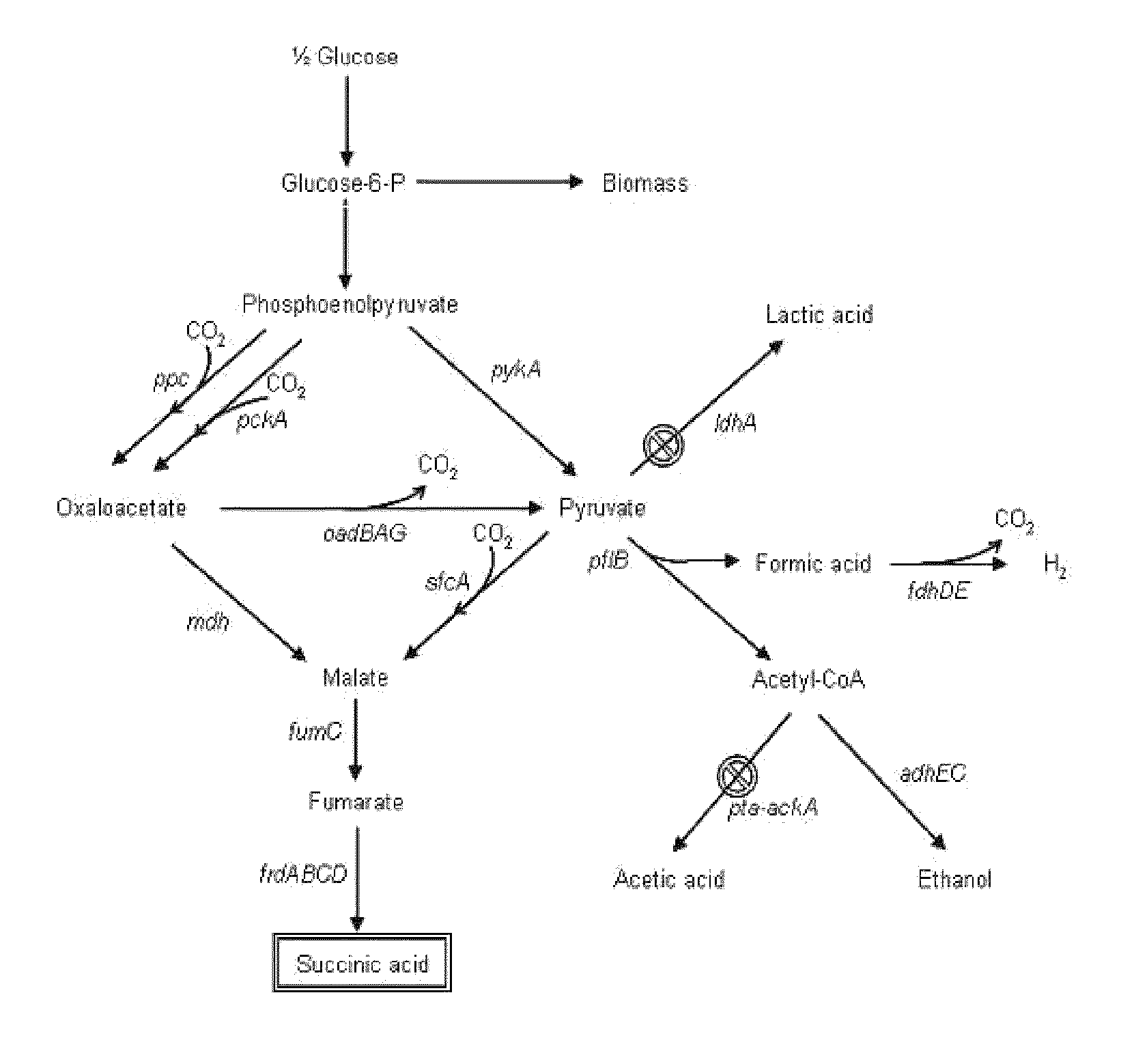
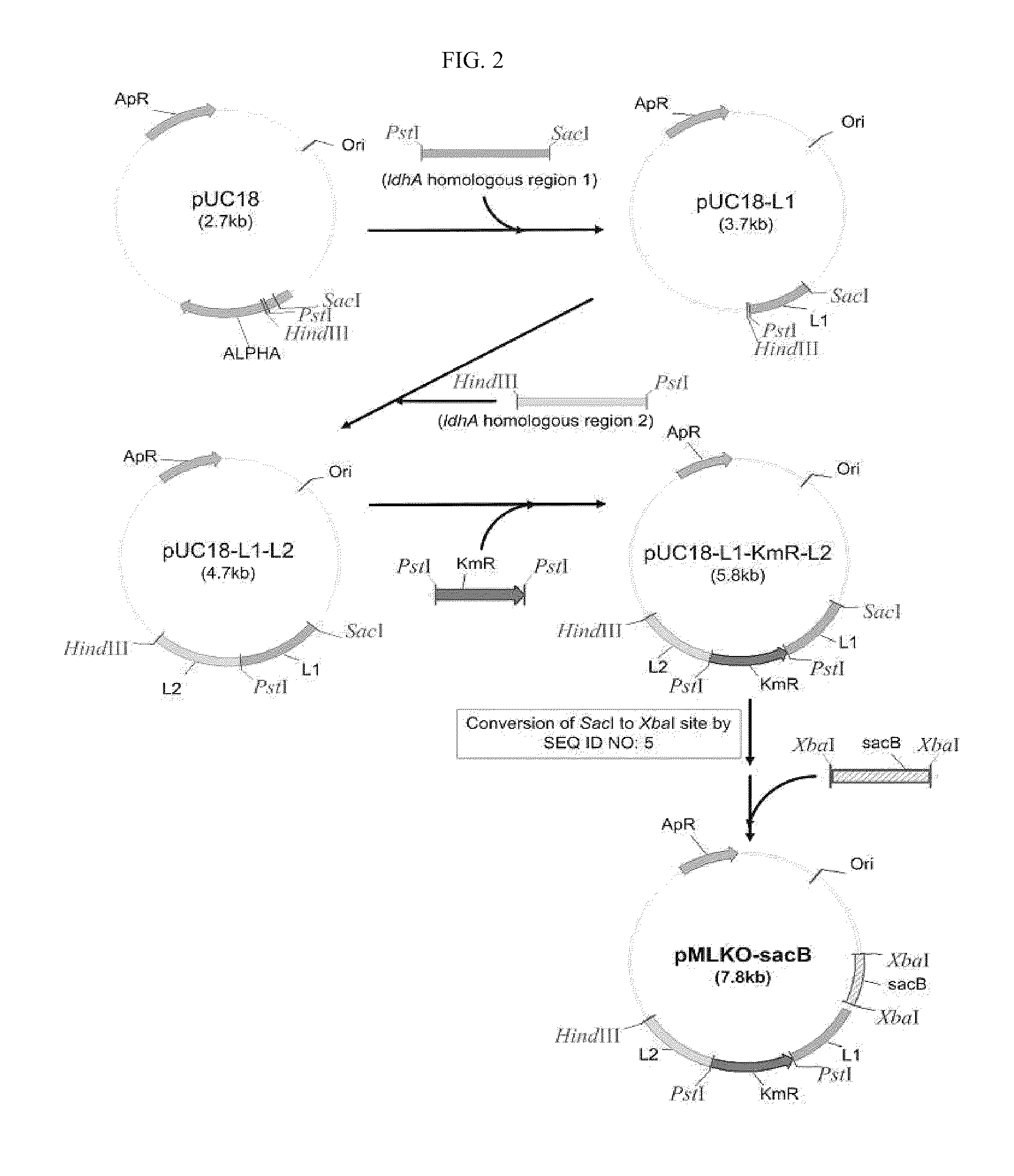
Mutant E. coli strain with increased succinic acid production
InactiveUSRE37393E1Cheap productionIncrease biomassBacteriaUnicellular algaeLactate dehydrogenaseBiological body
A method for isolating succinic acid producing bacteria is provided comprising increasing the biomass of an organism which lacks the ability to catabolize pyruvate, and then subjecting the biomass to glucose-rich medium in an anaerobic environment to enable pyruvate-catabolizing mutants to grow.The invention also provides for a mutant that produces high amounts of succinic acid, which has been derived from a parent which lacked the genes for pyruvate formate lyase and lactate dehydrogenase, and which belongs to the E.coli Group of Bacteria.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
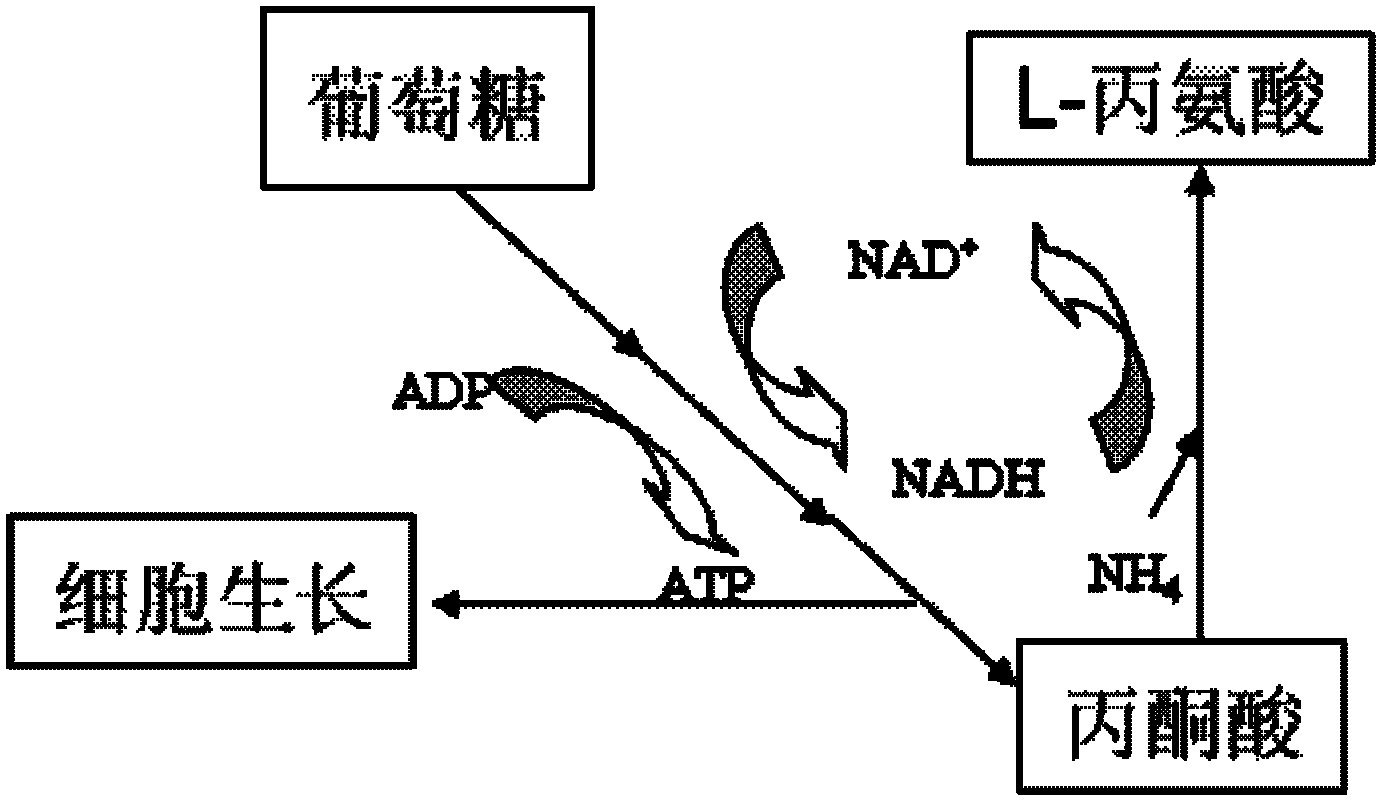
XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield as well as construction method and application of XZ-A26 bacterial strain
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine and method for producing L-valine by fermentation
ActiveCN110607268AEasy to synthesizeReduce synthesisBacteriaHydrolasesLactate dehydrogenaseSaccharic acid
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yielding L-valine. A construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium comprises the steps that starting from an escherichia coli W3110, an acetolactate synthase gene alsS of a bacillus subtilis is integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; an escherichia coli ppGpp 3'-pyrophosphoric acid hydrolytic enzyme mutant R290E / K292D gene spoT is integrated on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 and subjected to high expression; genes of frdA, frdB, frdC and frdD of four subunits of a lactic dehydrogenase gene ldhA, a pyruvate formate lyase I gene pflB and fumaric reductase on the genome of the escherichia coli W3110 are knocked out; a branched chain amino acid transaminasegene ilvE of the escherichia coli is replaced with leucine dehydrogenase gene bcd of the bacillus subtilis; and an acetyl-hydroxyl acid isomerized reductase gene ilvC of the escherichia coli is replaced with an encoding gene of a mutant L67E / R68F / K75E. According to the genetically engineered bacterium for the high-yielding L-valine, an L-valine fermentation method is further modified. Double-phasedissolved oxygen control is adopted, and the L-valine yield and the saccharic acid conversion rate are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
ActiveUS20070054387A1High yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesHigh concentrationPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
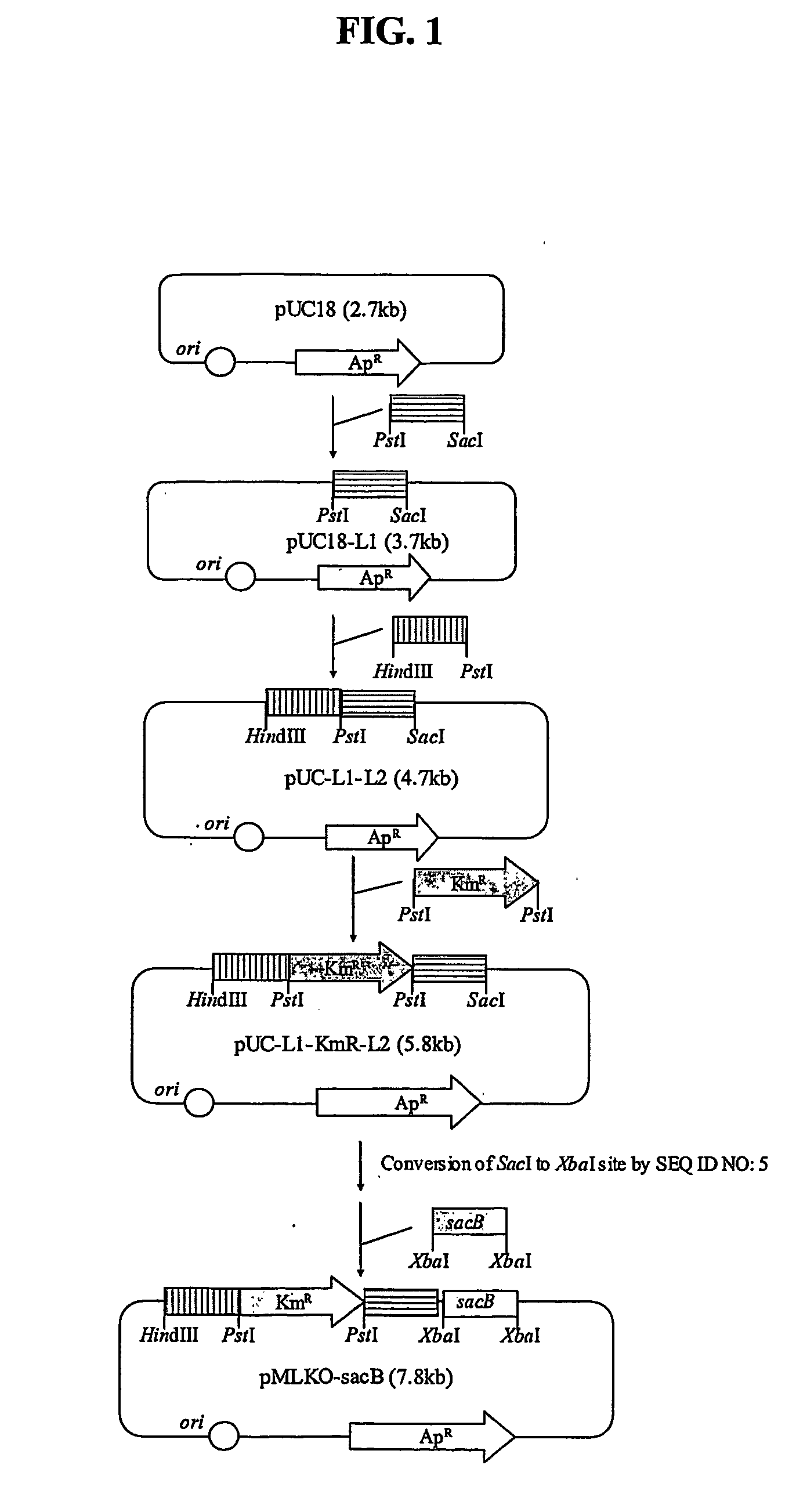
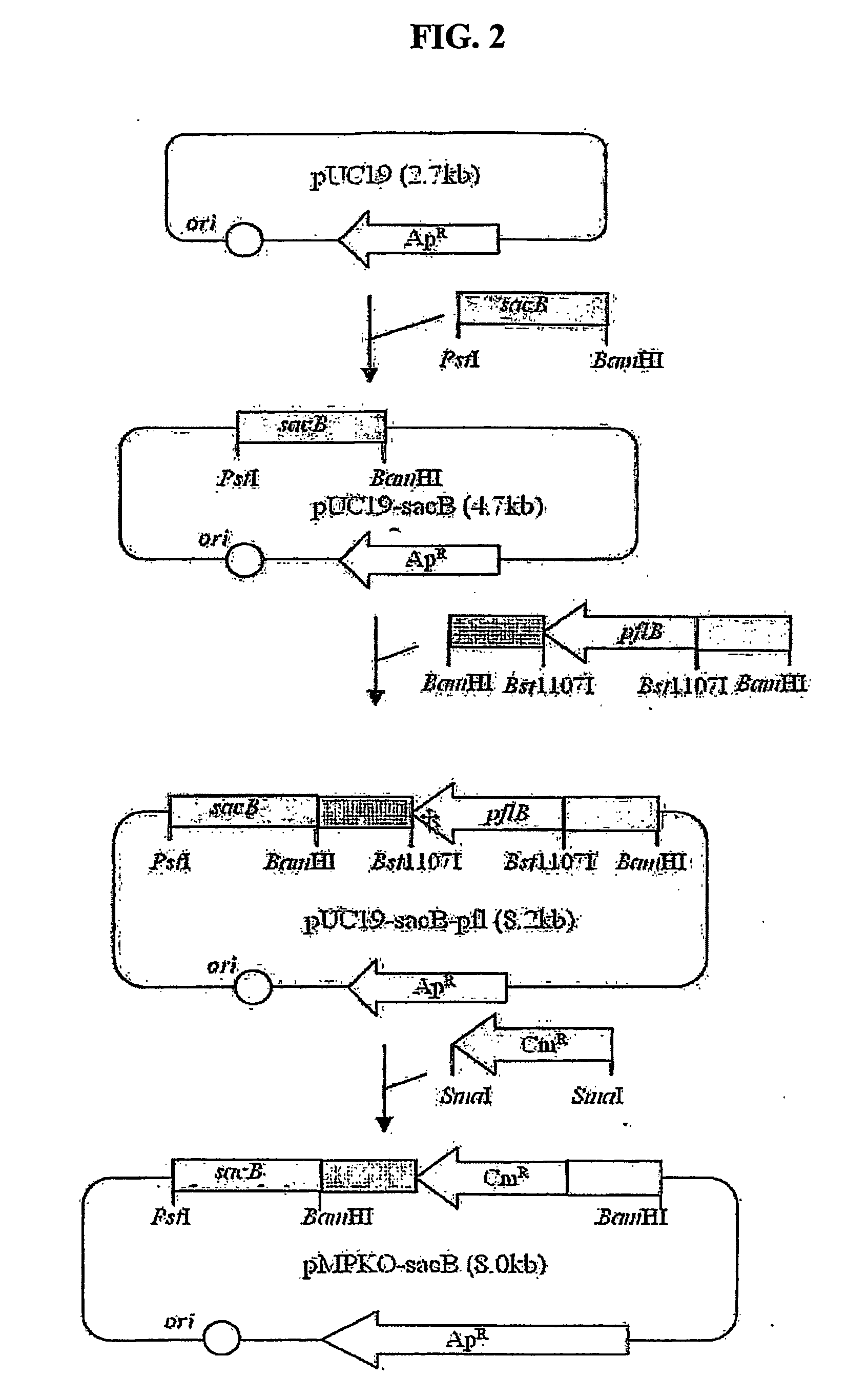
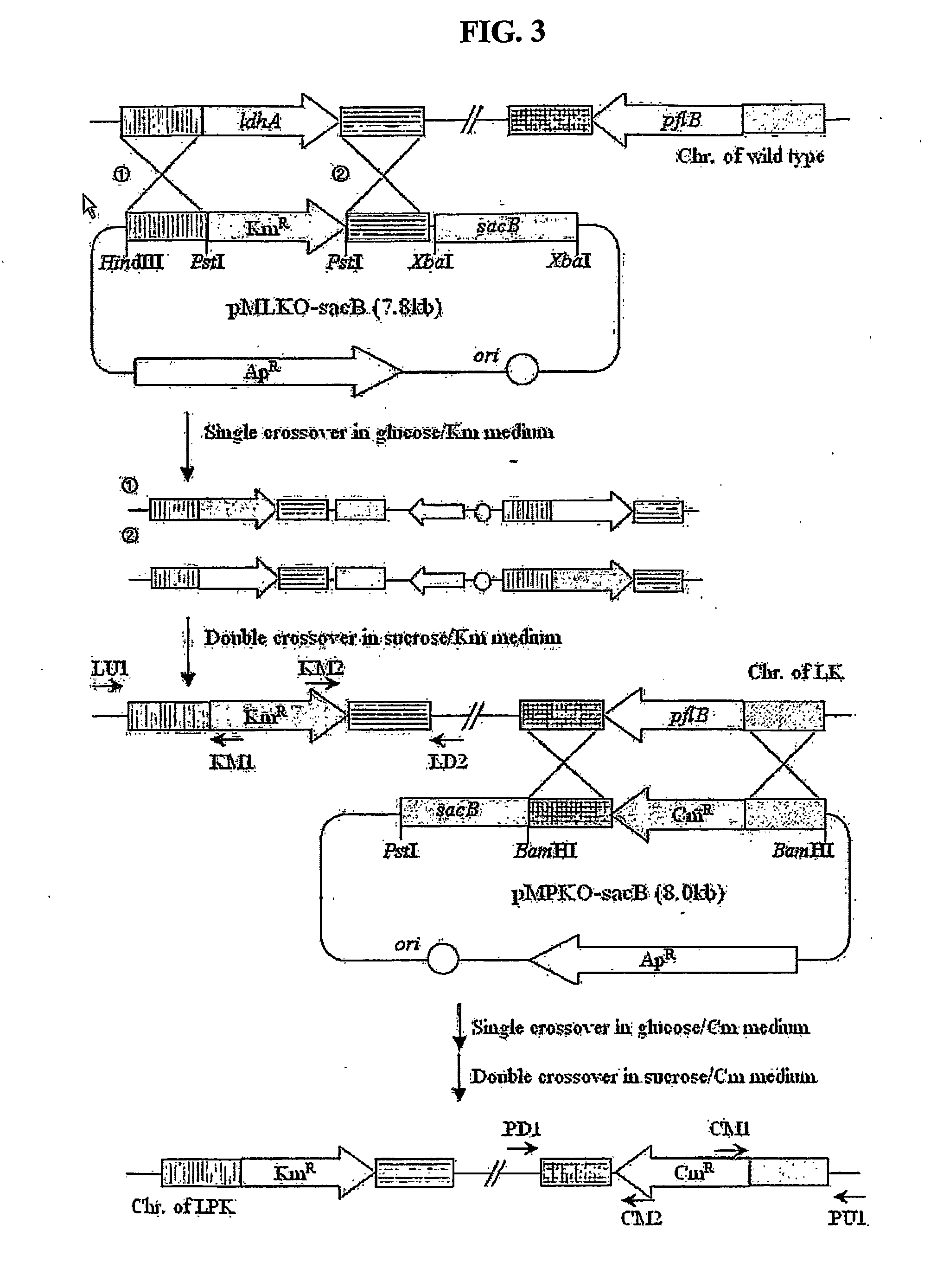
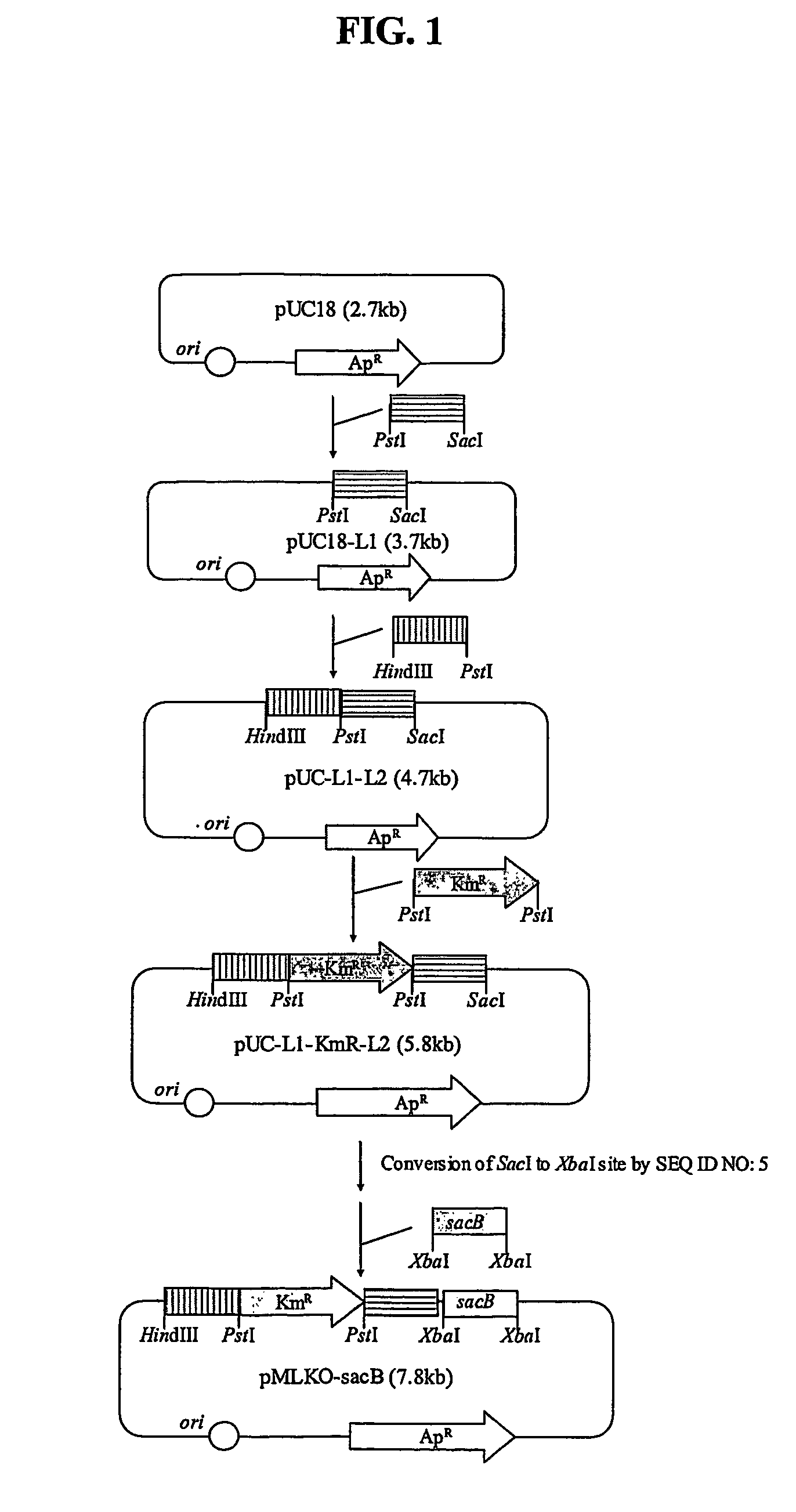
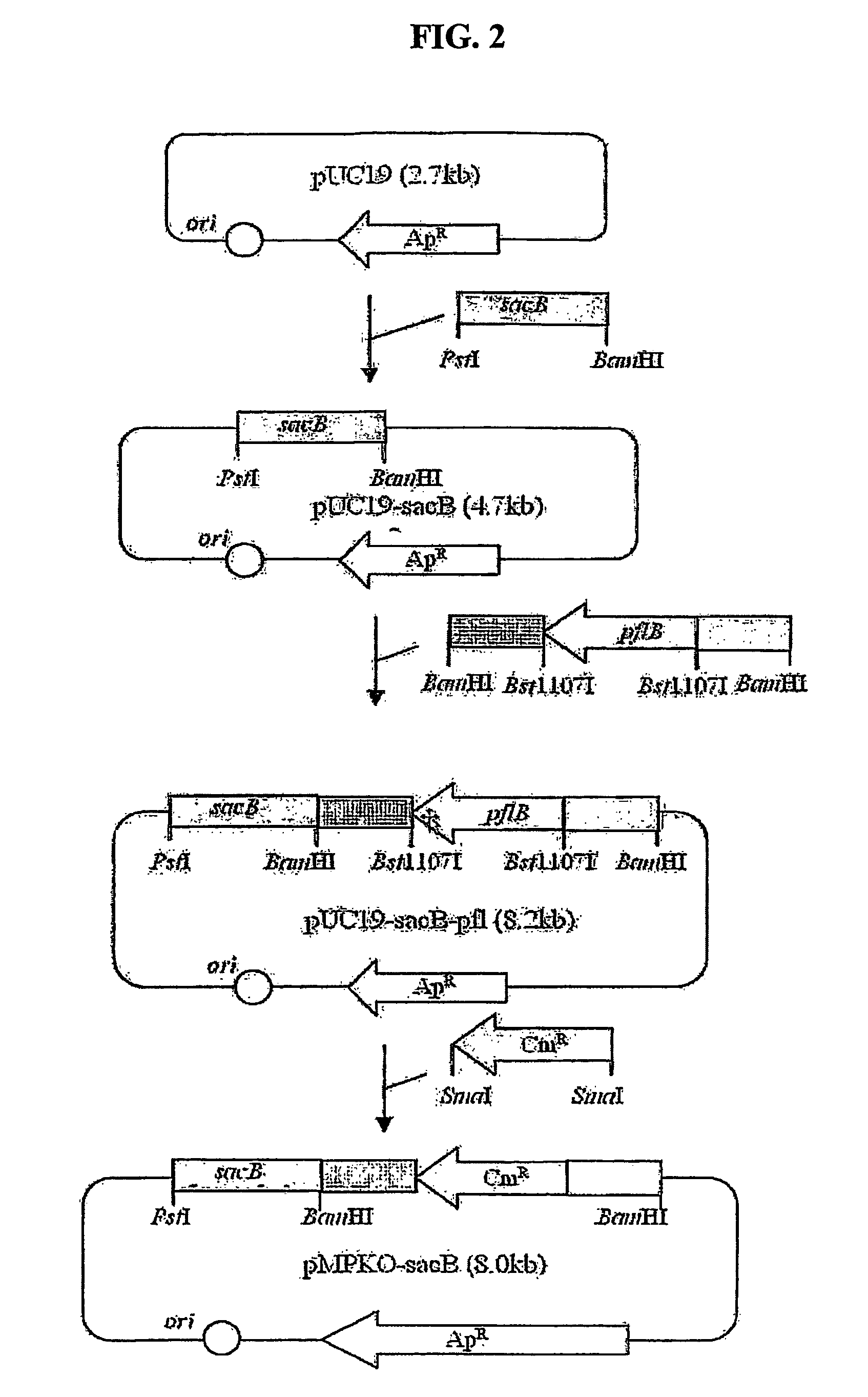
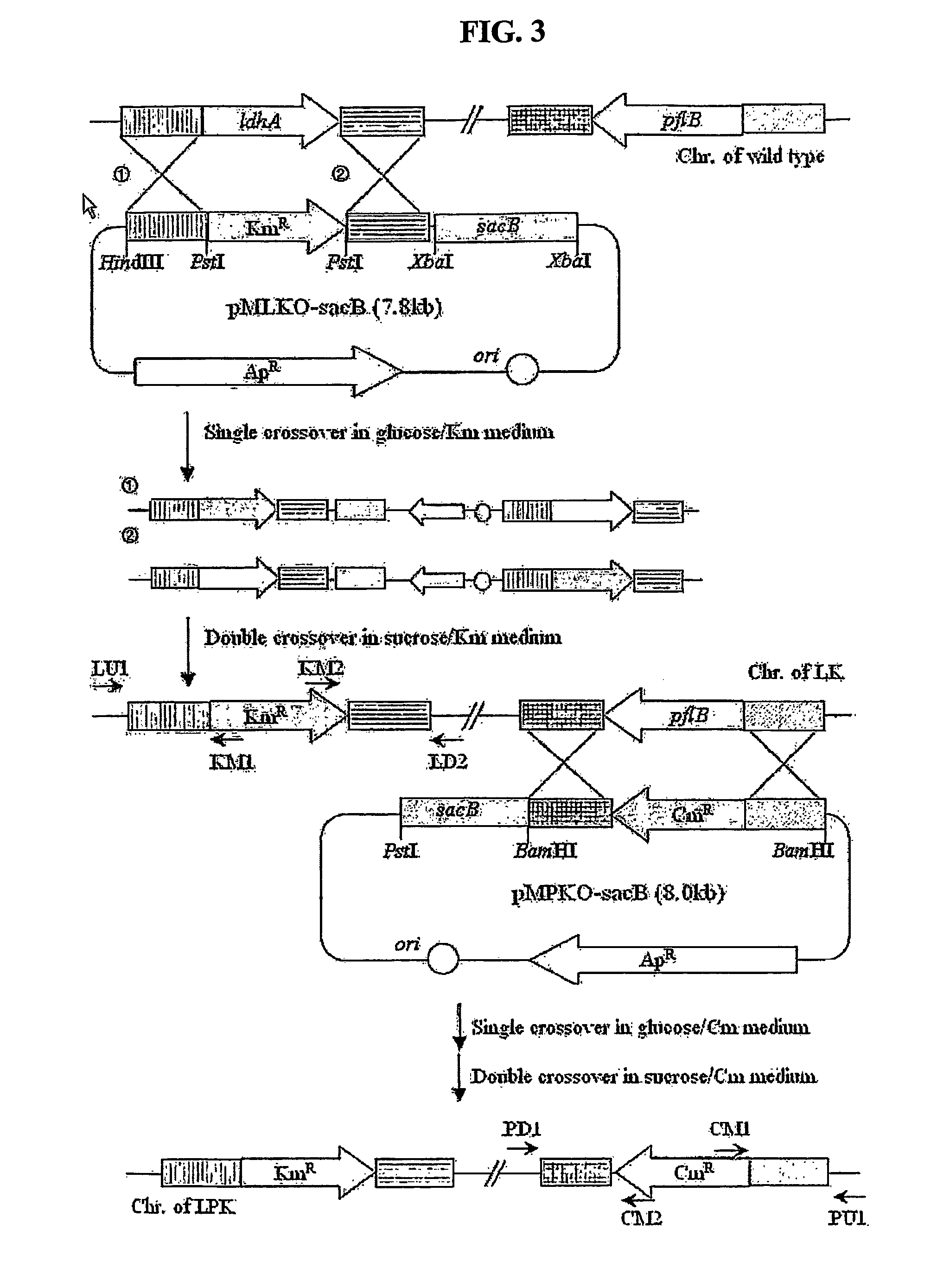
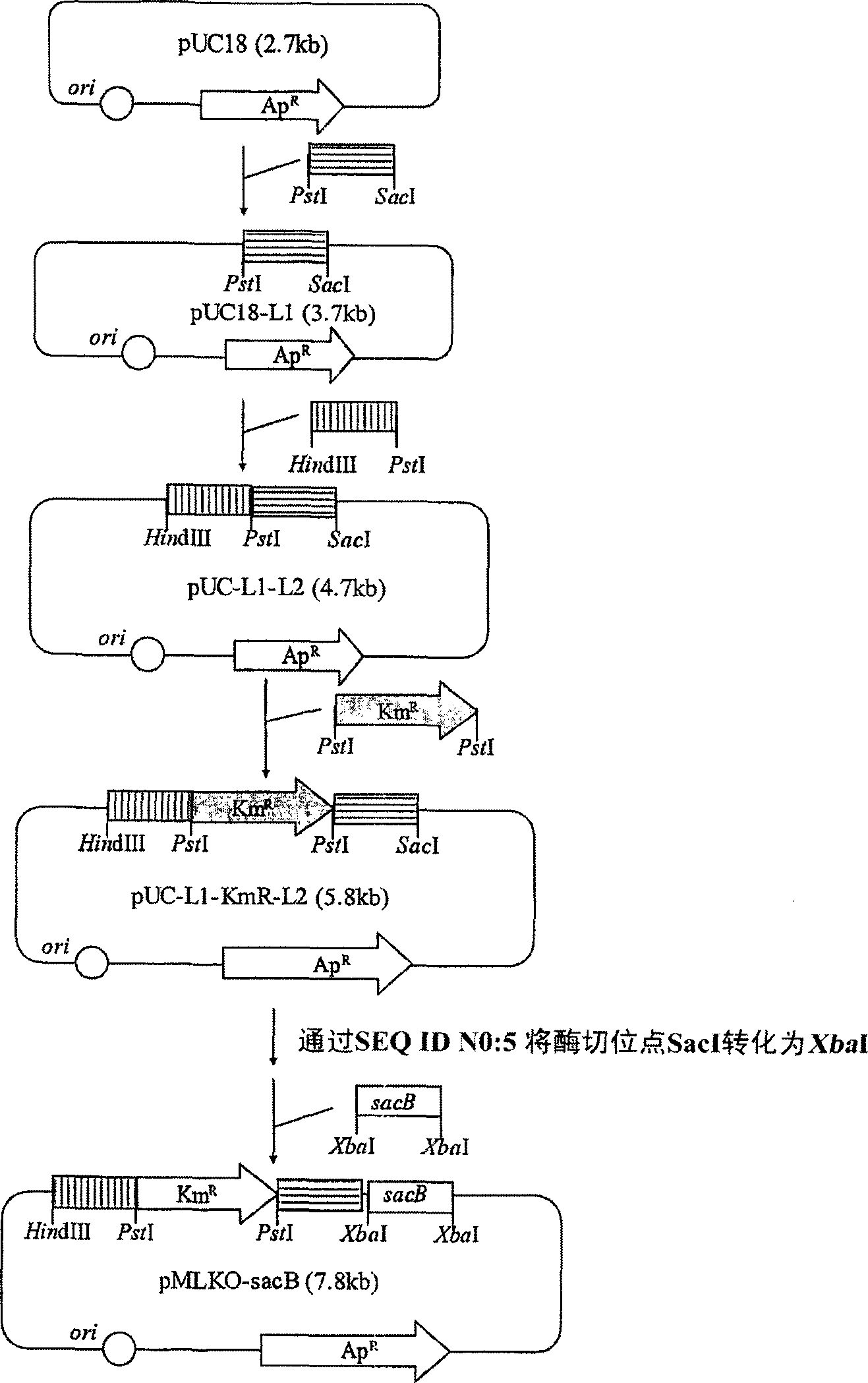
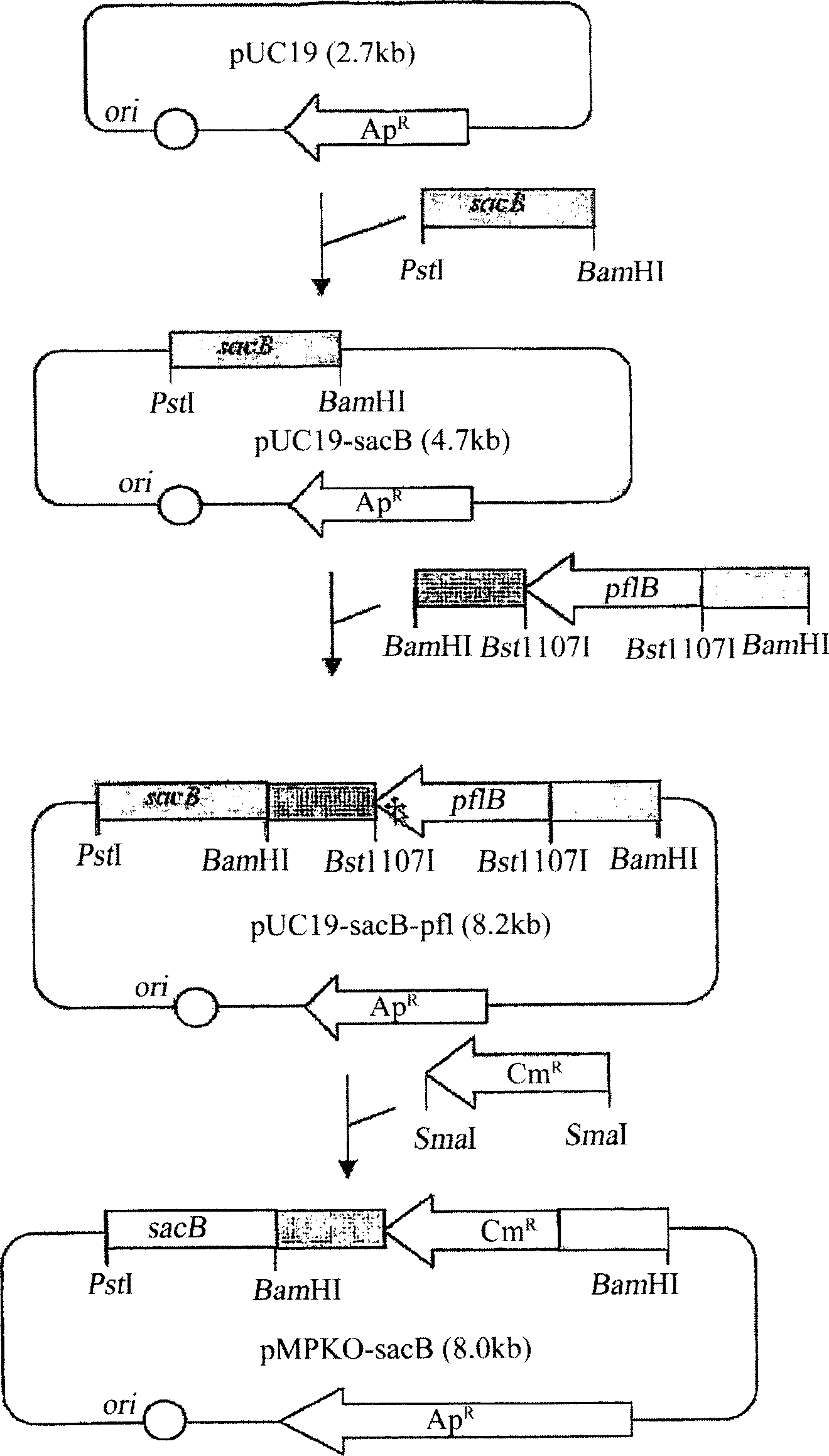
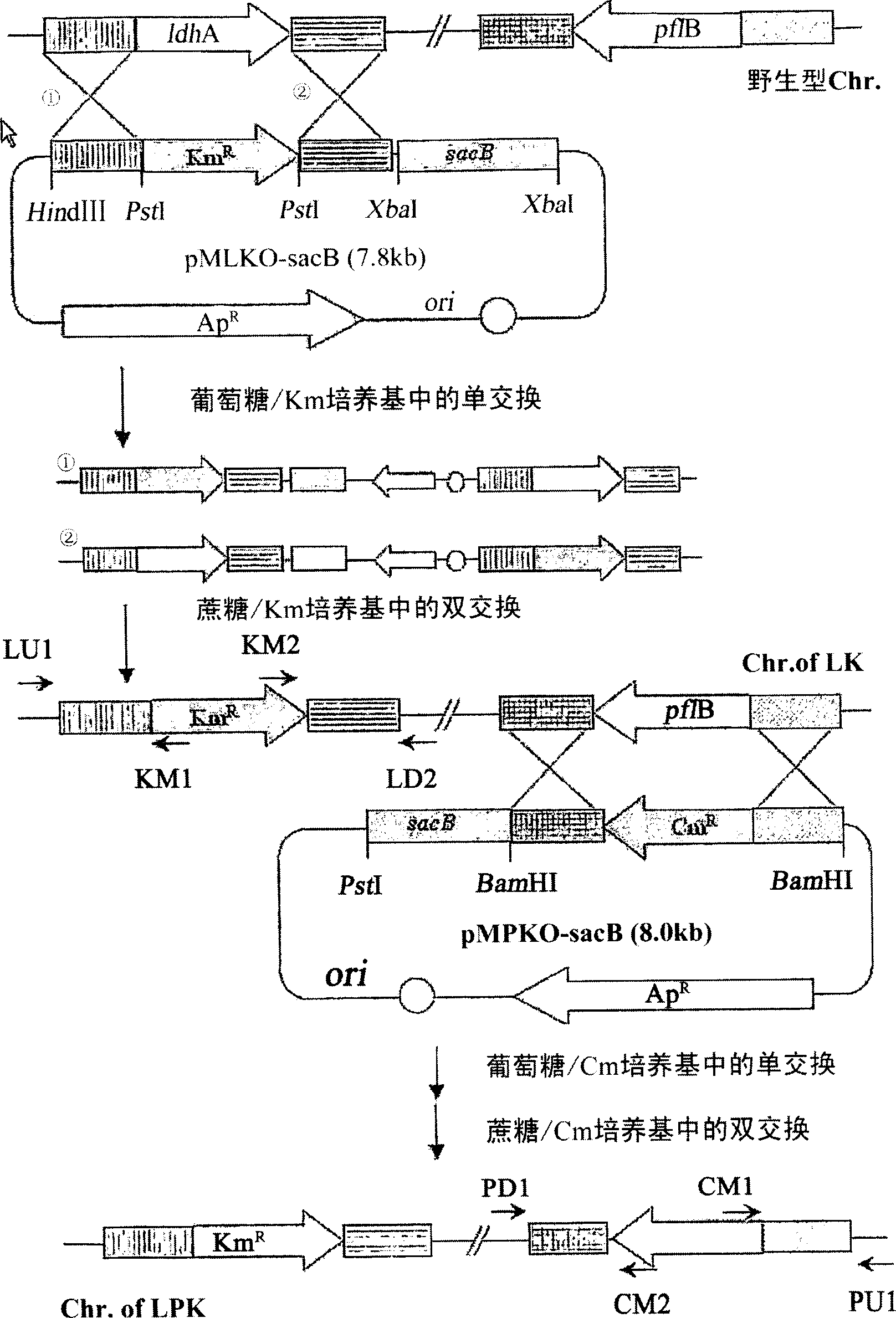
The present invention relates to novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) (which are involved in the production of lactic acid, formic acid and acetic acid) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl), a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by the culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The inventive bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the inventive bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
ActiveUS7470530B2High yieldSugar derivativesBacteriaHigh concentrationPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
Provided are novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a ldhA, a pfl,a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a ldhA, a pfl, and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, characterized by culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Engineering bacteria producing DL-alanine and method of producing DL-alanine by using engineering bacteria
ActiveCN103045528AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEthanol dehydrogenaseAlanine racemase
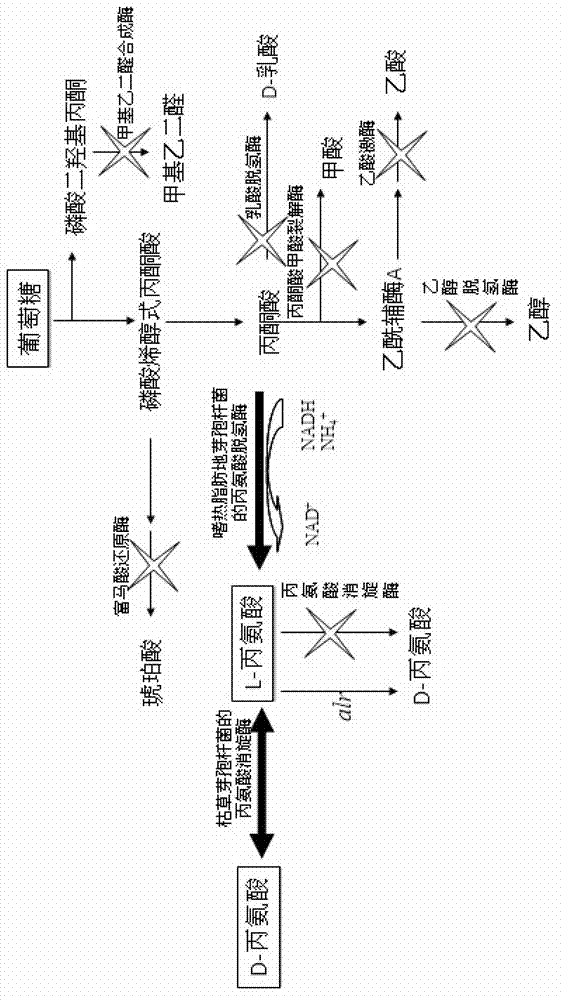
The invention discloses a strain of engineering bacteria producing DL-alanine. Lactic dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, alcohol dehydrogenase, acetic acid kinase, fumaric acid reductase, alanine racemase and methyl glyoxal synthetase of the strain of engineering bacteria producing the DL-alanine are inactivated; and exogenous L-alanine dehydrogenase gene and alanine racemase gene are integrated on the chromosome of the engineering bacteria. According to the invention, pyroracemic acid, an intermediate product of the glycolysis is converted to L-alanine by integrating the exogenous L-alanine dehydrogenase gene into the chromosome of the engineering bacteria; and an exogenous alanine racemase gene is further integrated into the chromosome, and part of the L-alanine is converted into D-alanine. Then producing the DL-alanine from raw material sugar in one step is realized, the production period of the DL-alanine is decreased and the productivity of the DL-alanine is enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Method of improving the efficacy of lactic acid bacterial starter cultures and improved starter culture compositions
InactiveUS20020081712A1Enhancement of acid productionIncreased biomass productionMilk preparationBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseBacteroides
Methods of enhancing the growth rate and / or controlling the metabolic activity of lactic acid bacteria and of improving the shelf life and / or the quality of an edible product using lactic acid bacterial organisms which are defective in their pyruvate metabolism. There is also provided starter culture compositions comprising such defective lactic acid bacteria as helper organisms and lactic acid bacterial starter culture strains. Useful helper organisms are Lactococcus strains which are defective with respect to pyruvate formate lyase (Pfl) and / or lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh) activity. The helper organisms may overexpress a gene coding for an NAD+ regenerating enzyme such as NADH oxidase encoded by nox gene.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Metabolically engineered lactic acid bacteria and their use
InactiveUS7465575B2Reduced growth rateReduce probabilityBiocideBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseLactic bacteria
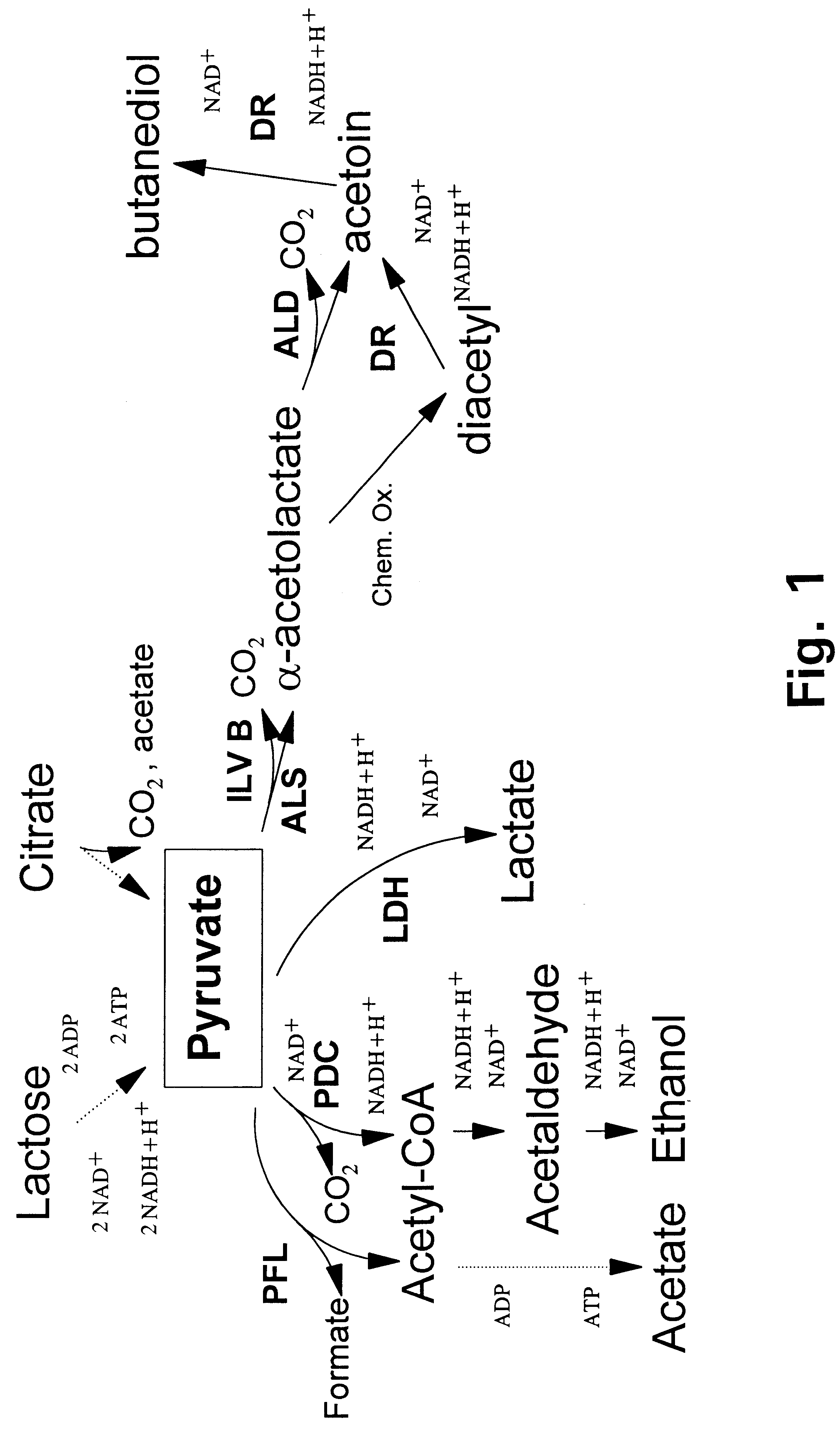
Mutants of lactic acid bacteria including Lactococcus lactis which are defective in pyruvate formate-lyase production and / or in their lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh) production and methods of isolating such mutants or variants are provided. The mutants are useful in the production of food products or in the manufacturing of compounds such as diacetyl, acetoin and acetaldehyde and as components of food starter cultures.
Owner:NILSSON DAN
Ethanol fermentation engineering bacteria capable of reducing fermentation byproduct
InactiveCN101875912AReduce accumulationReduce contentBacteriaMutant preparationLactate dehydrogenaseEscherichia coli
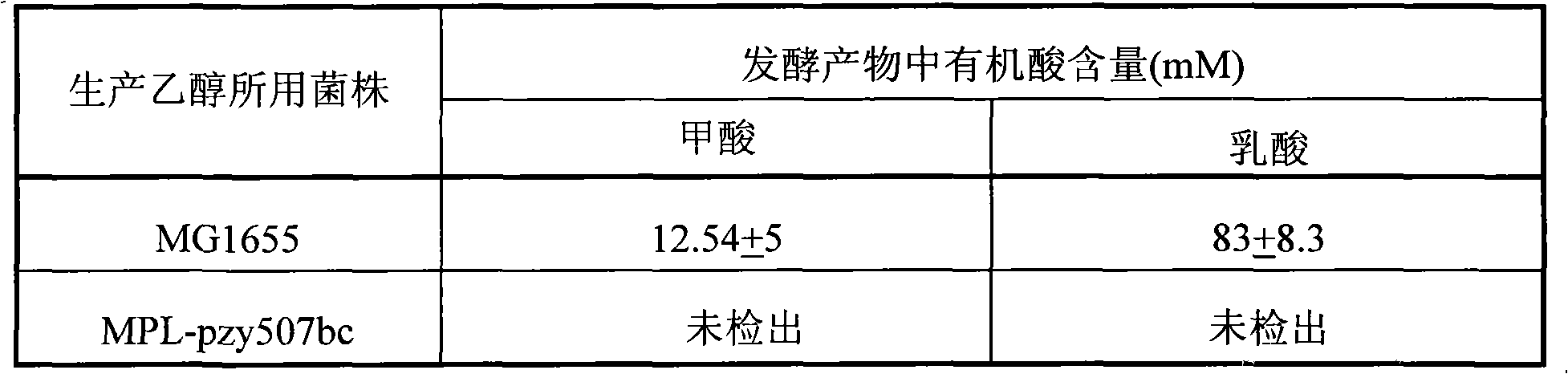
The invention relates to an ethanol fermentation engineering bacteria capable of reducing a fermentation byproduct. The ethanol fermentation engineering bacteria is characterized in that a pyruvate formate-lyase gene and a lactate dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli are inactivated; and a Zymomonas mobilis gene is transferred into the Escherichia coli. When ethanol is produced by fermenting hexose and pentose with the engineering bacteria, lactic acid and formic acid are not produced and the byproduct is reduced, so that the ethanol productivity is improved.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Biocatalyst for production of d-lactic acid (as amended)
ActiveUS20070065930A1Increase productivityHigh selectivityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliD-lactate dehydrogenase
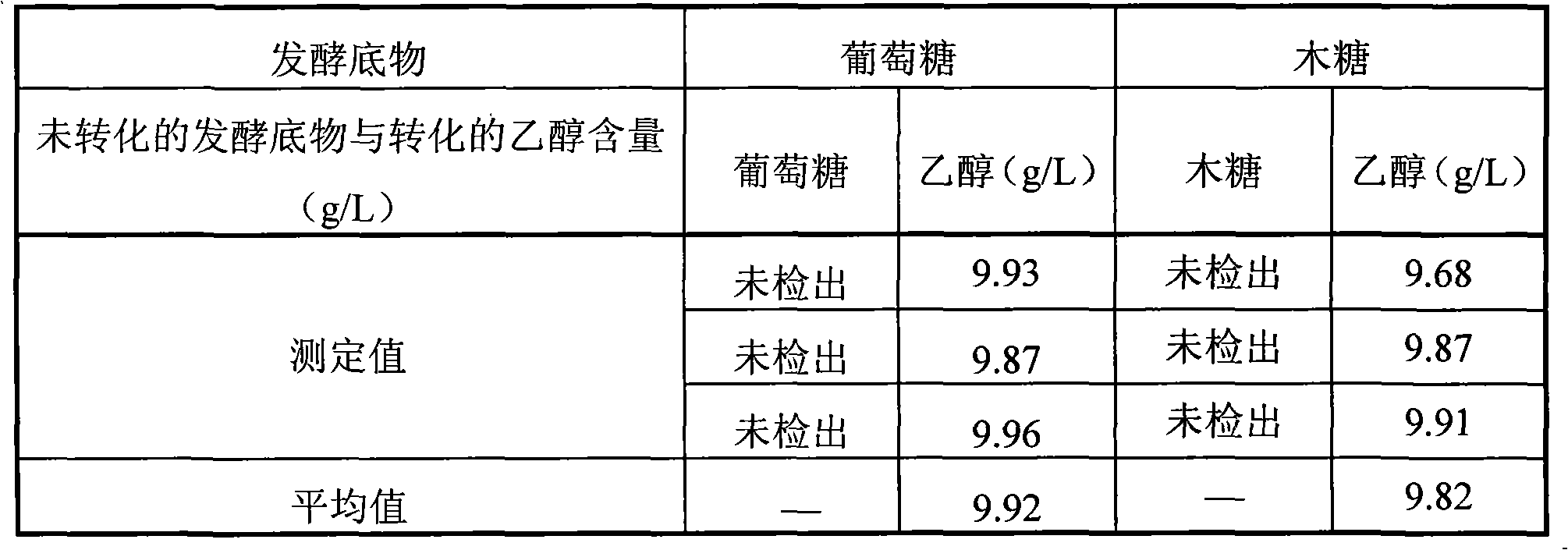
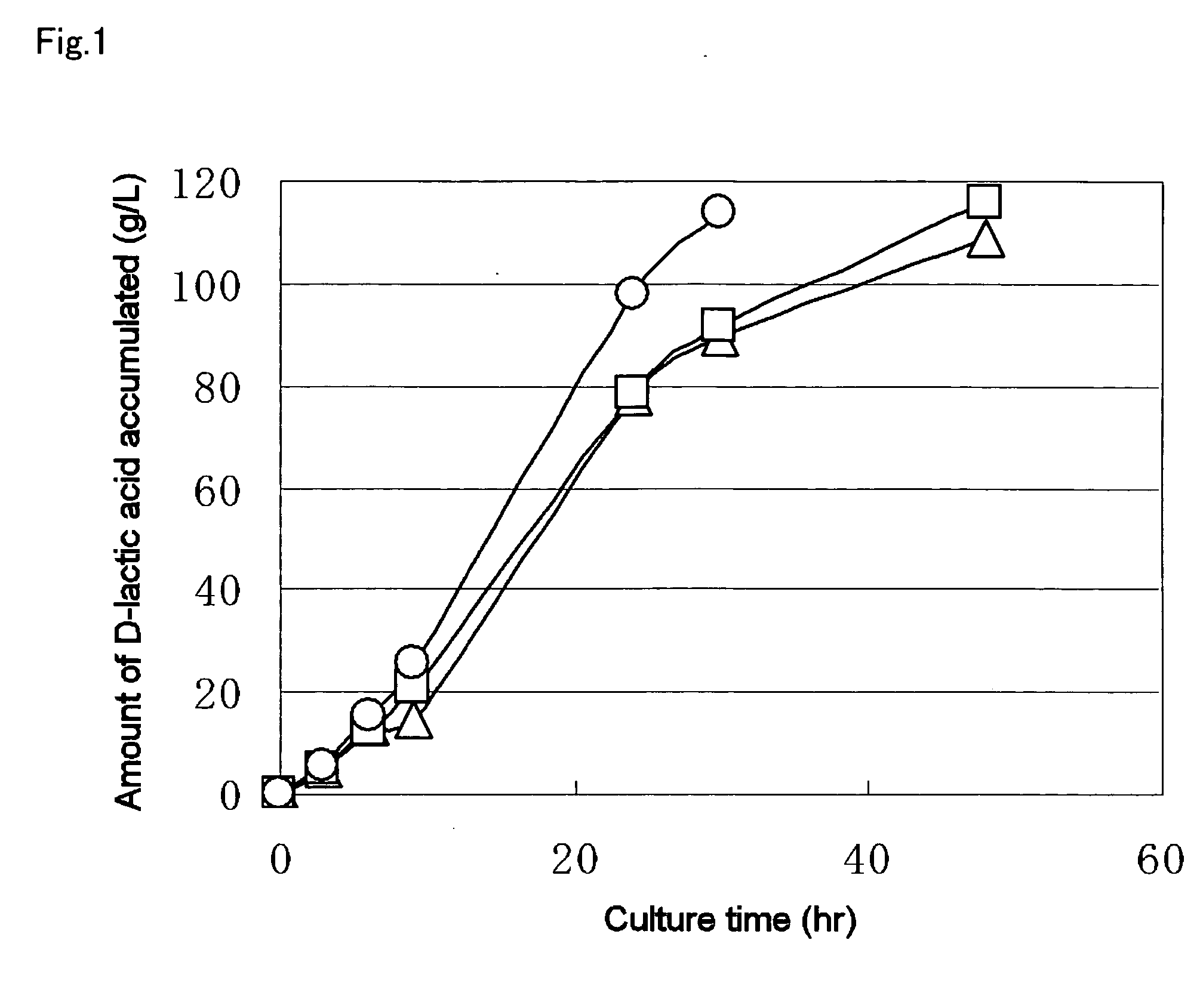
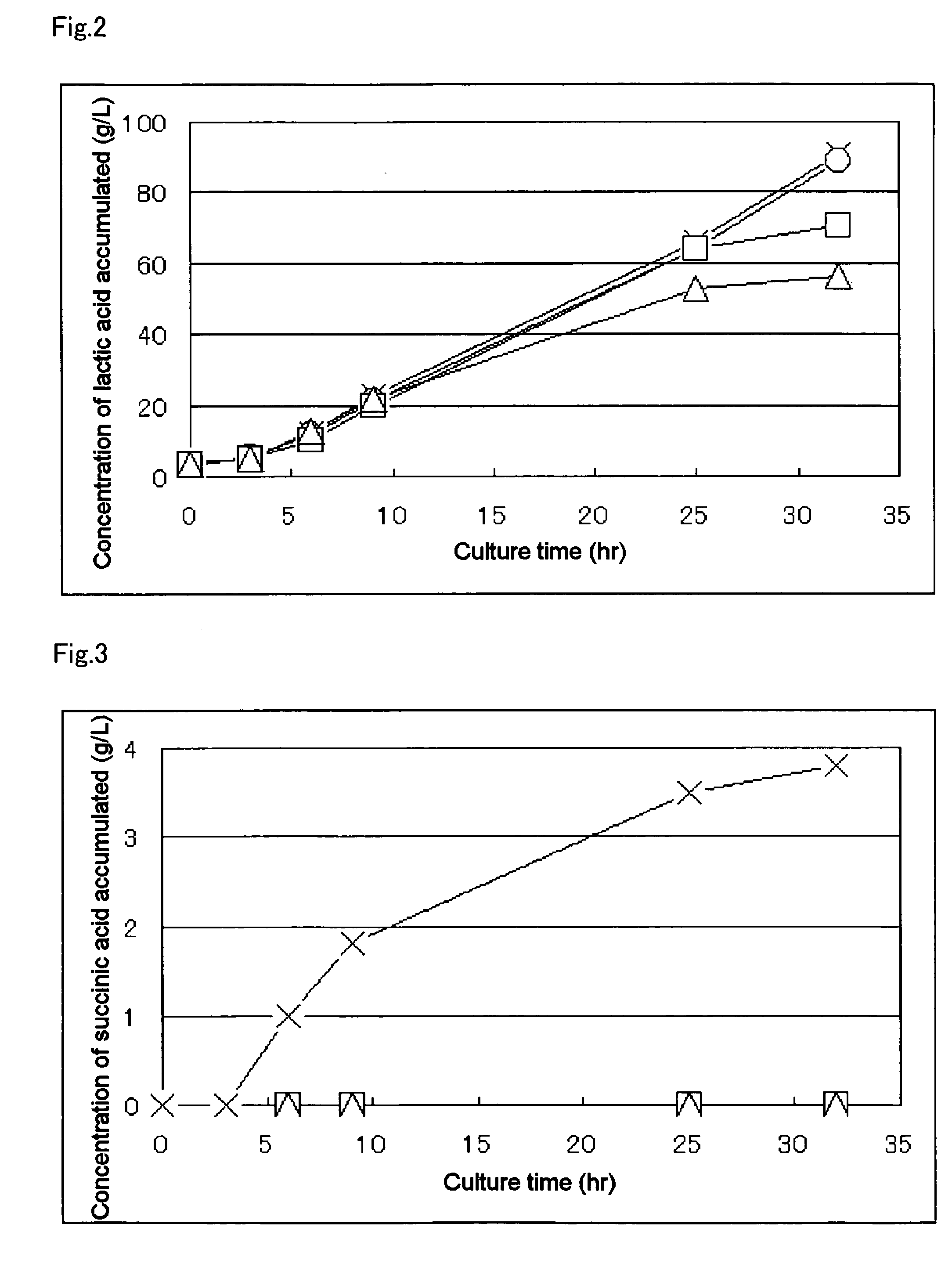
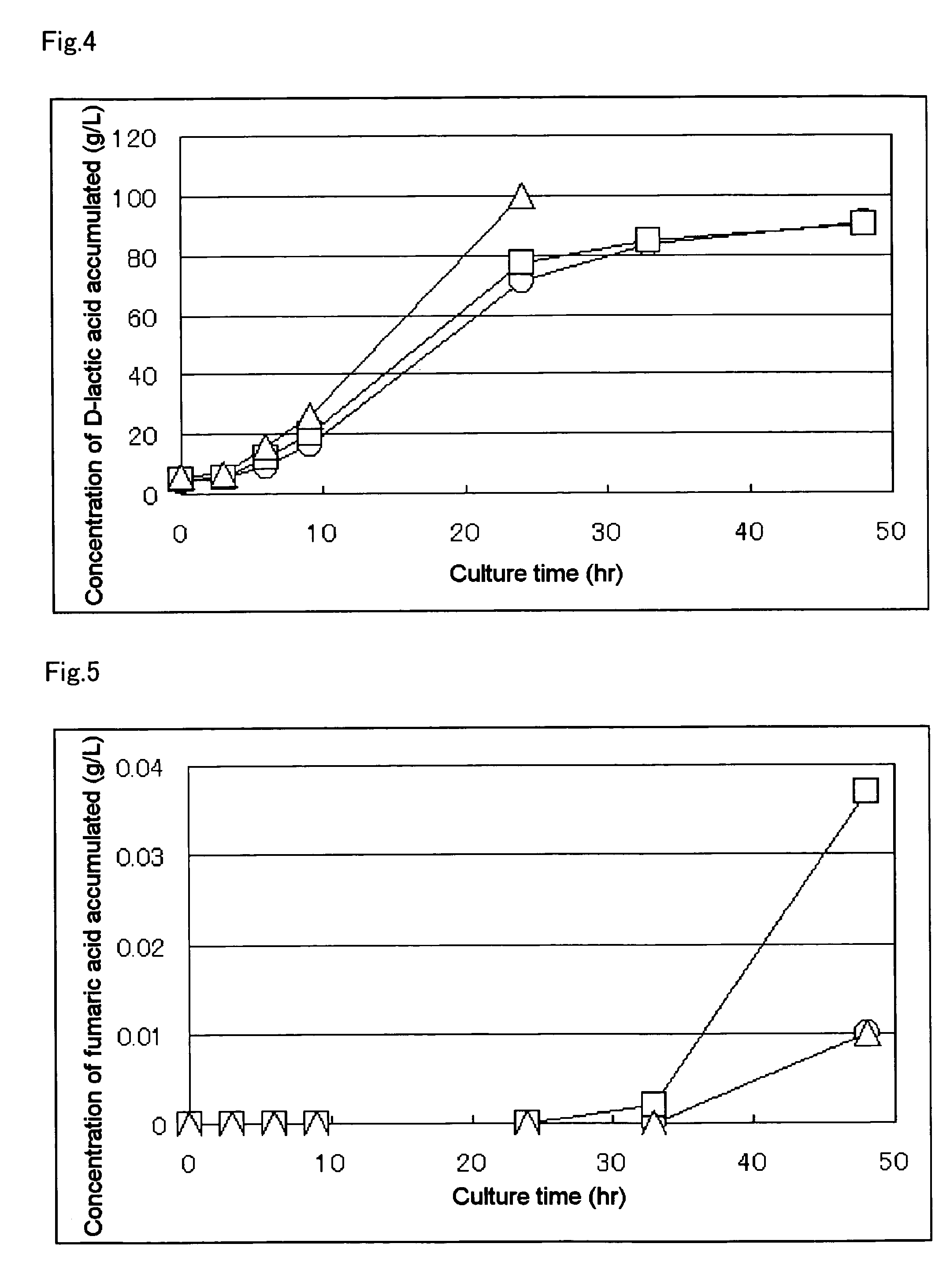
A method for producing D-lactic acid in high yield, and to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid with high selectivity, in which optical purity is high and a by-product organic acid is small. In one aspect, a microorganism, wherein activity of pyruvate formate-lyase (pfl) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of Escherichia coli-derived NADH-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA) is enhanced, is cultured to efficiently produce D-lactic acid. With regard to a method for enhancing ldhA activity, by linking, on a genome, a gene encoding ldhA with a promoter of a gene which controls expression of a protein involved in a glycolytic pathway, a nucleic acid biosynthesis pathway or an amino acid biosynthesis pathway, suitable results are obtained compared to the method for enhancing expression of the gene using an expression vector. A microorganism in which a dld gene is substantially inactivated or decreased is cultured to produce high quality D-lactic acid with reduced concentration of pyruvic acid.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Novel rumen bacteria variants and process for preparing succinic acid employing the same
The present invention relates to novel rumen bacterial mutants resulted from the disruption of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA) and a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) (which are involved in the production of lactic acid, formic acid and acetic acid) from rumen bacteria; a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK7) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl), a phosphotransacetylase gene (pta), and a acetate kinase gene (ackA); a novel bacterial mutant (Mannheimia sp. LPK4) having disruptions of a lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldhA), a pyruvate formate-lyase gene (pfl) and a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene (ppc) involved in the immobilization of CO2 in a metabolic pathway of producing succinic acid; and a method for producing succinic acid, which is characterized by the culture of the above mutants in anaerobic conditions. The inventive bacterial mutants have the property of producing succinic acid at high concentration while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior wild-type strains of producing various organic acids. Thus, the inventive bacterial mutants are useful as strains for the industrial production of succinic acid.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Novel engineered microorganism producing homo-succinic acid and method for preparing succinic acid using the same
ActiveUS20090203095A1High yieldIncrease productivityBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesHigh concentrationMannheimia
The present invention relates to a mutant microorganism, which is selected from the group consisting of genus Mannheimia, genus Actinobacillus and genus Anaerobiospirillum, producing homo-succinic acid and a method for producing homo-succinic acid using the same, and more particularly to a mutant microorganism producing succinic acid at a high concentration while producing little or no other organic acids in anaerobic conditions, which is obtained by disrupting a gene encoding lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA), a gene encoding phosphotransacetylase (pta), and a gene encoding acetate kinase (ackA), without disrupting a gene encoding pyruvate formate lyase (pfl), as well as a method for producing succinic acid using the same. The inventive mutant microorganism has the property of having a high growth rate and succinic acid productivity while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior strains producing succinic acid. Thus, the inventive mutant microorganism is useful to produce succinic acid for industrial use.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Enhancement of Microbial Ethanol Production
InactiveUS20090226992A1Easy to transformEfficient fermentationSugar derivativesBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseDNA construct
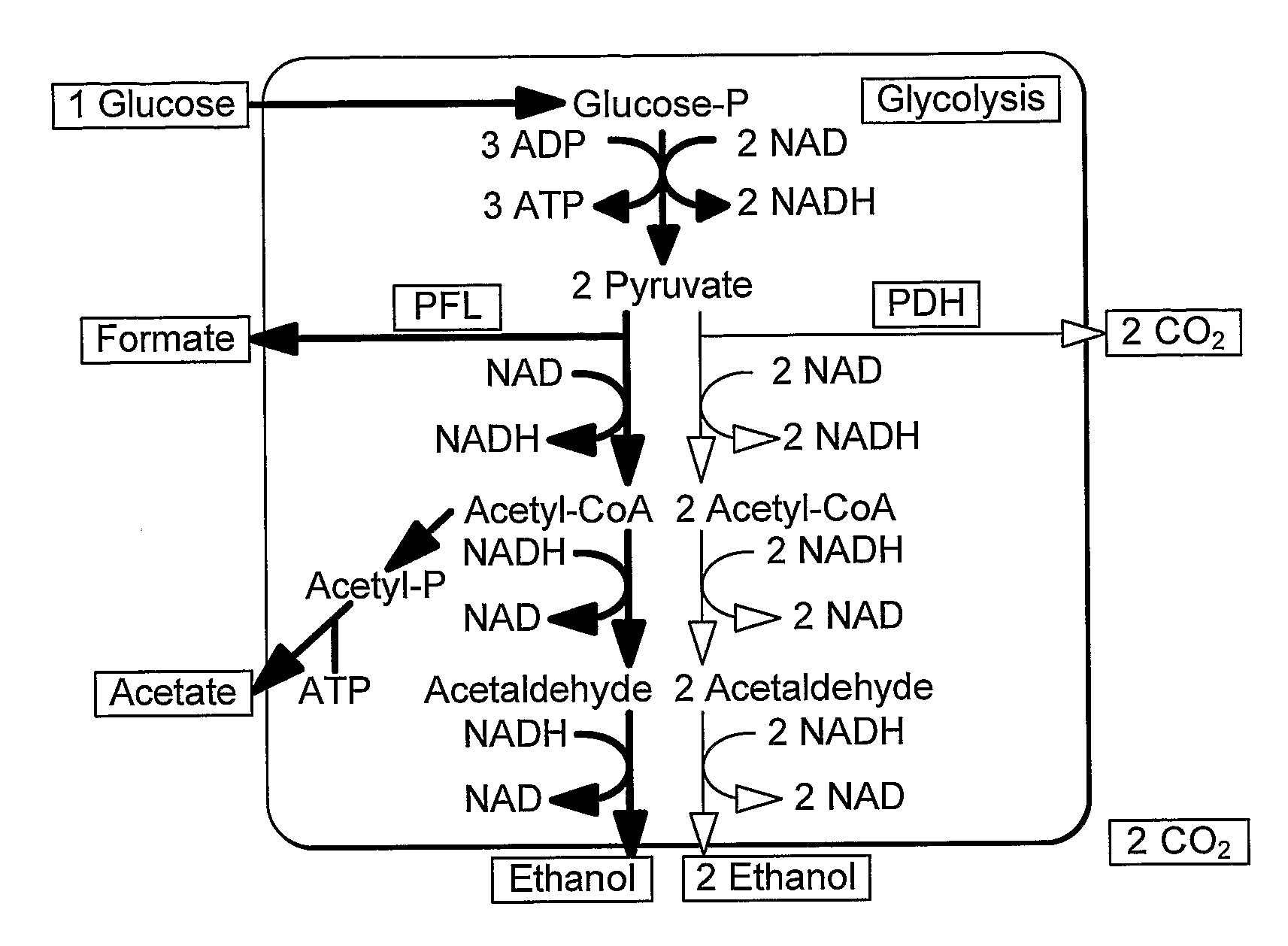
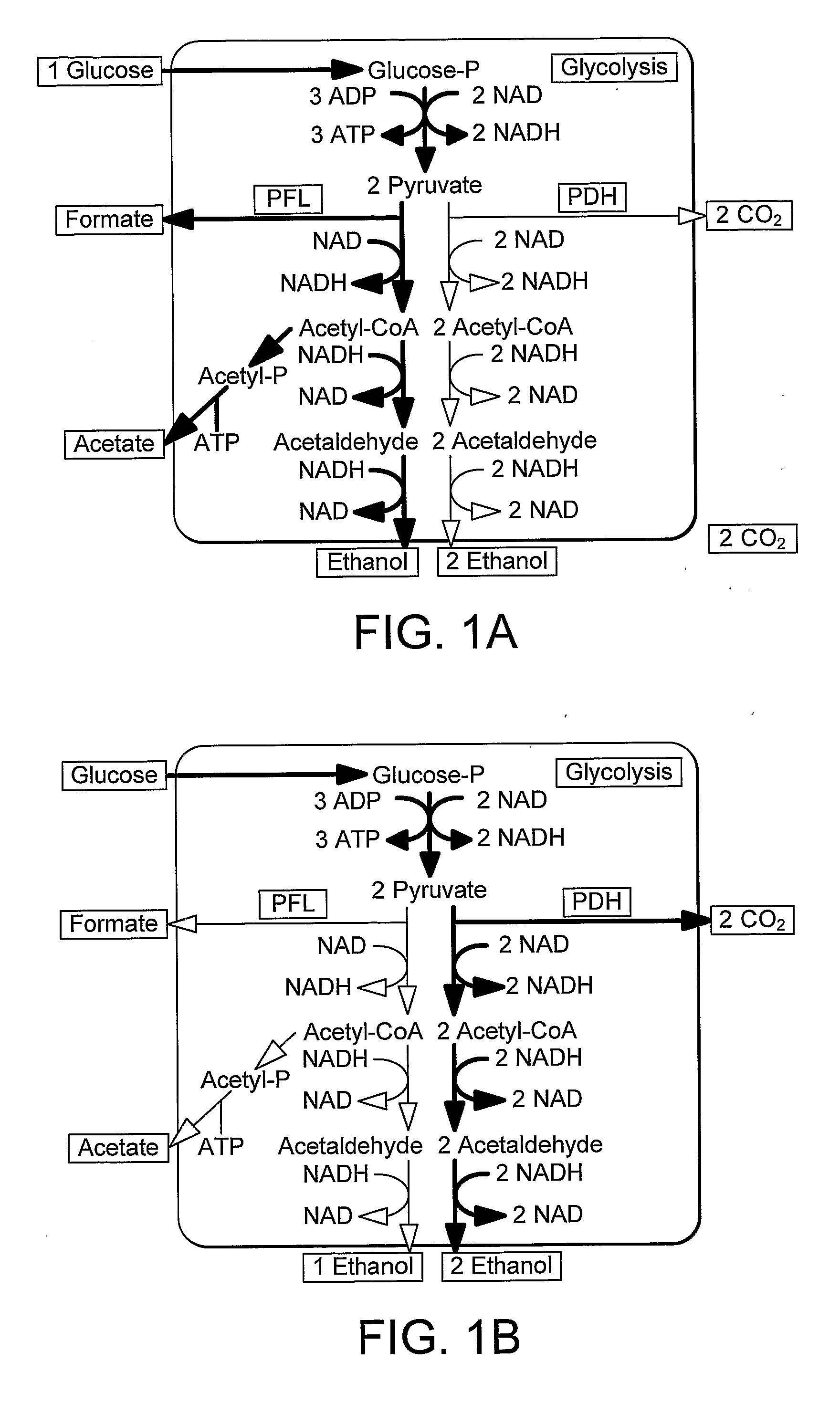
A thermophilic microorganism lacks lactate dehydrogenase activity and preferably contains an active pyruvate formate lyase pathway. The thermophilic microorganism contains a gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase. The gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase is preferably a codon optimised version of the gene encoding a thermostable NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase. DNA constructs allow stable expression of the gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase in the thermophilic microorganism. The DNA constructs are based upon use of an insertion sequence to achieve stable expression or recombination to insert the gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase into the lactate dehydrogenase gene, thus achieving gene knockout and new functionality in a single step. The microorganisms are useful in fermentation of sugars to produce ethanol.
Owner:BIOCONVERSION TECH LTD
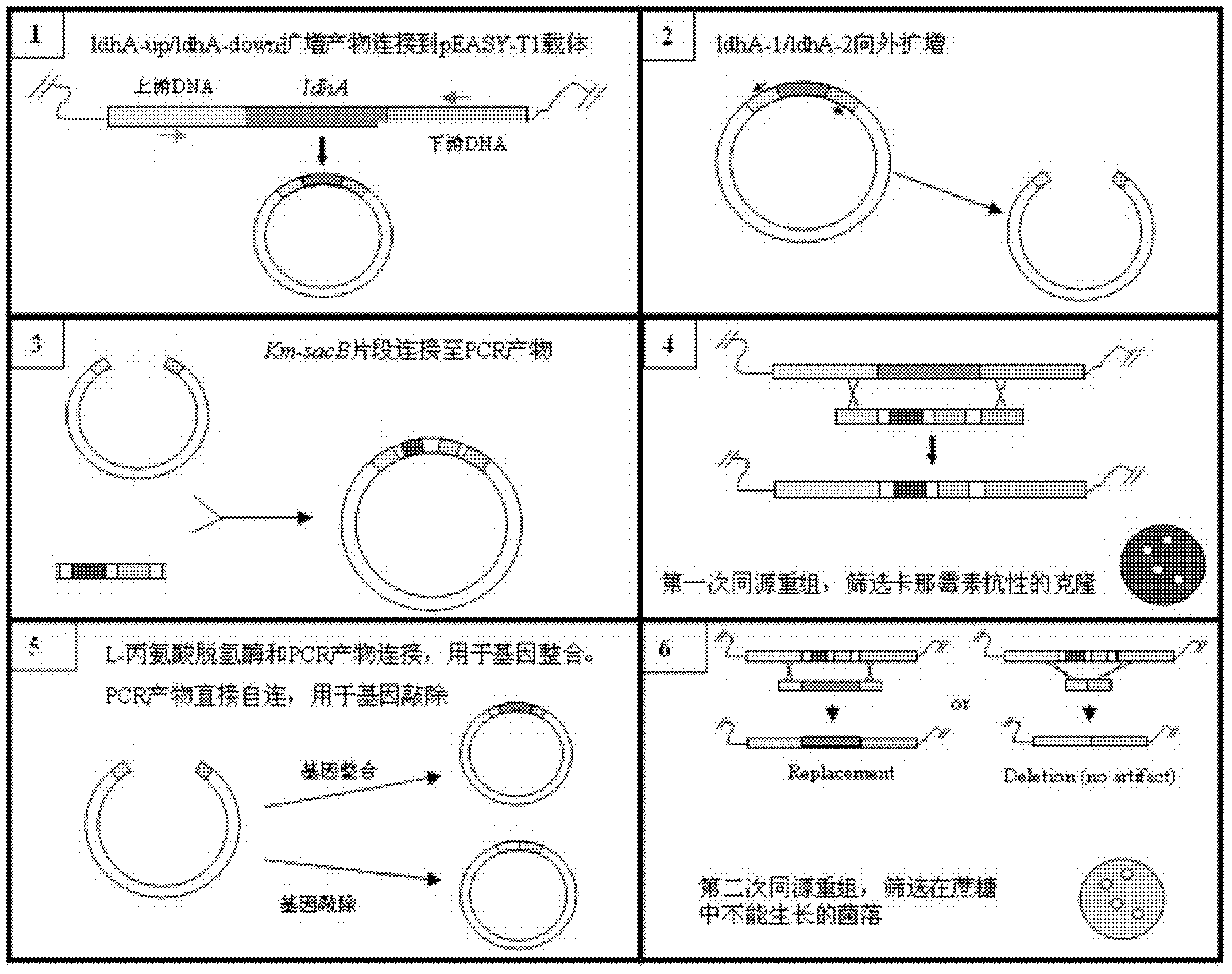
Genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and acidogenic fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102533626AOvercomes the inability to utilize glucoseBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biology engineering technology, and relates to a genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and an acidogenic fermentation method of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose is named as Escherichia coli BA205 and the preservation number is registered as CCTCC No.M2011447. In the construction process, Escherichia coli which is short of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) gene and Pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) gene activity is mainly used as an original strain; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) gene is removed by utilizing a homologous recombination technology; and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase are excessively co-expressed; therefore the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly increased. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation manner is adopted, the biomass is improved in an aerobic stage and the acidogenic fermentation is carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering bacterium for synthesizing pyruvic acid and D-alanine as well as construction method and application thereof
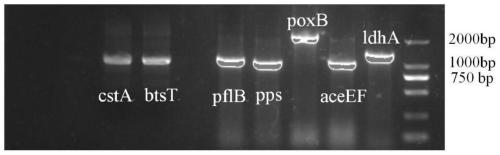
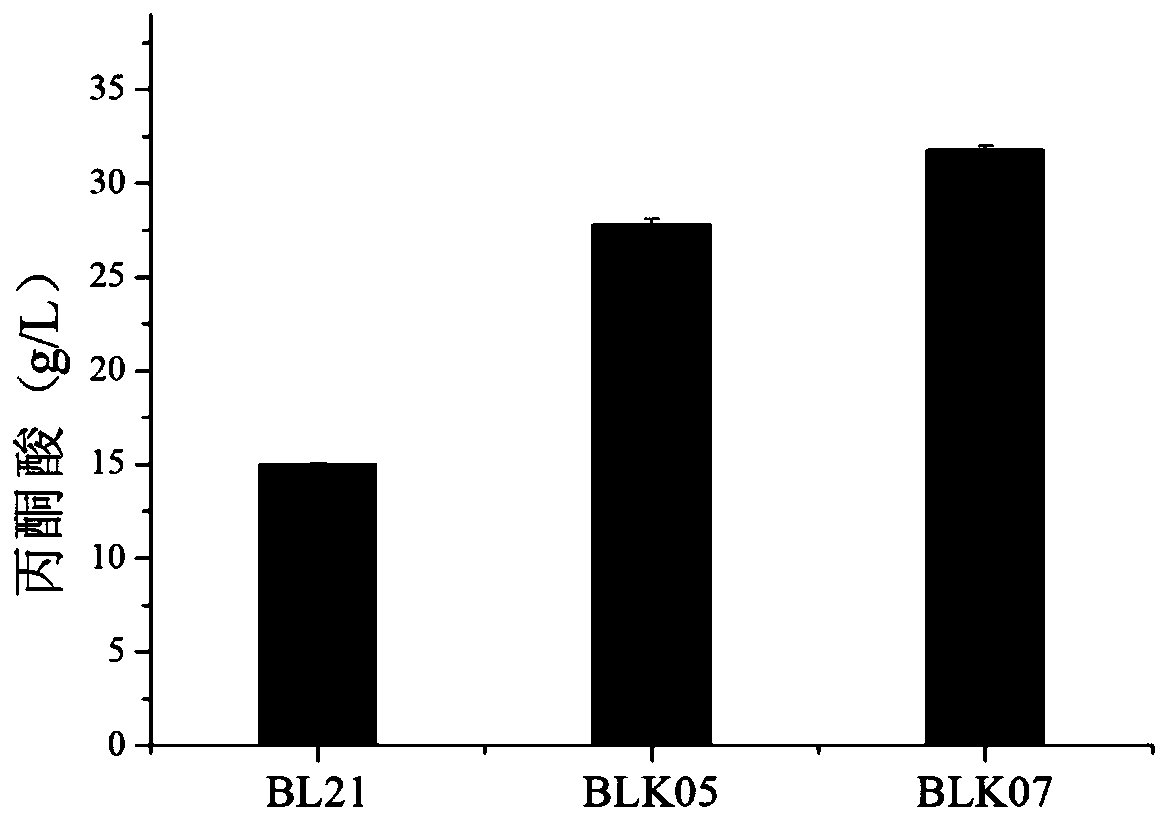
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterium for synthesizing pyruvic acid and D-alanine as well as a construction method and application thereof. Recombinant escherichia coli of the invention is obtained by knocking out apyruvate dehydrogenase complex achEF gene, a pyruvate lyase pflB gene, a pyruvate oxidase poxB gene, a phosphoenolpyruvate synthase pps gene and a lactic dehydrogenaseldhA gene in escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), blocking a key pathway of further metabolism of pyruvic acid and knocking out genes btsT and cstA for encoding a pyruvic acid transport protein. For the genetic engineering bacterium disclosed by the invention, L-amino acid deaminase pm1 is utilized to catalyze D, L-alanine, so that L-alanine can be converted to the pyruvic acid and can be separated to obtain D-alanine at the same time, and a new idea and method is provided to chiral separation of the D, L-alanine; and the recombinant escherichia coli capable of efficiently synthesizing the pyruvic acid and the D-alanine is obtained through modification, the yield of the pyruvic acid reaches 32.0g / L, the conversion rate of the L-alanine reaches up to 80 percent, and the separation rate of the D / L-alanine reaches up to 80 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microbial succinic acid producers and purification of succinic acid
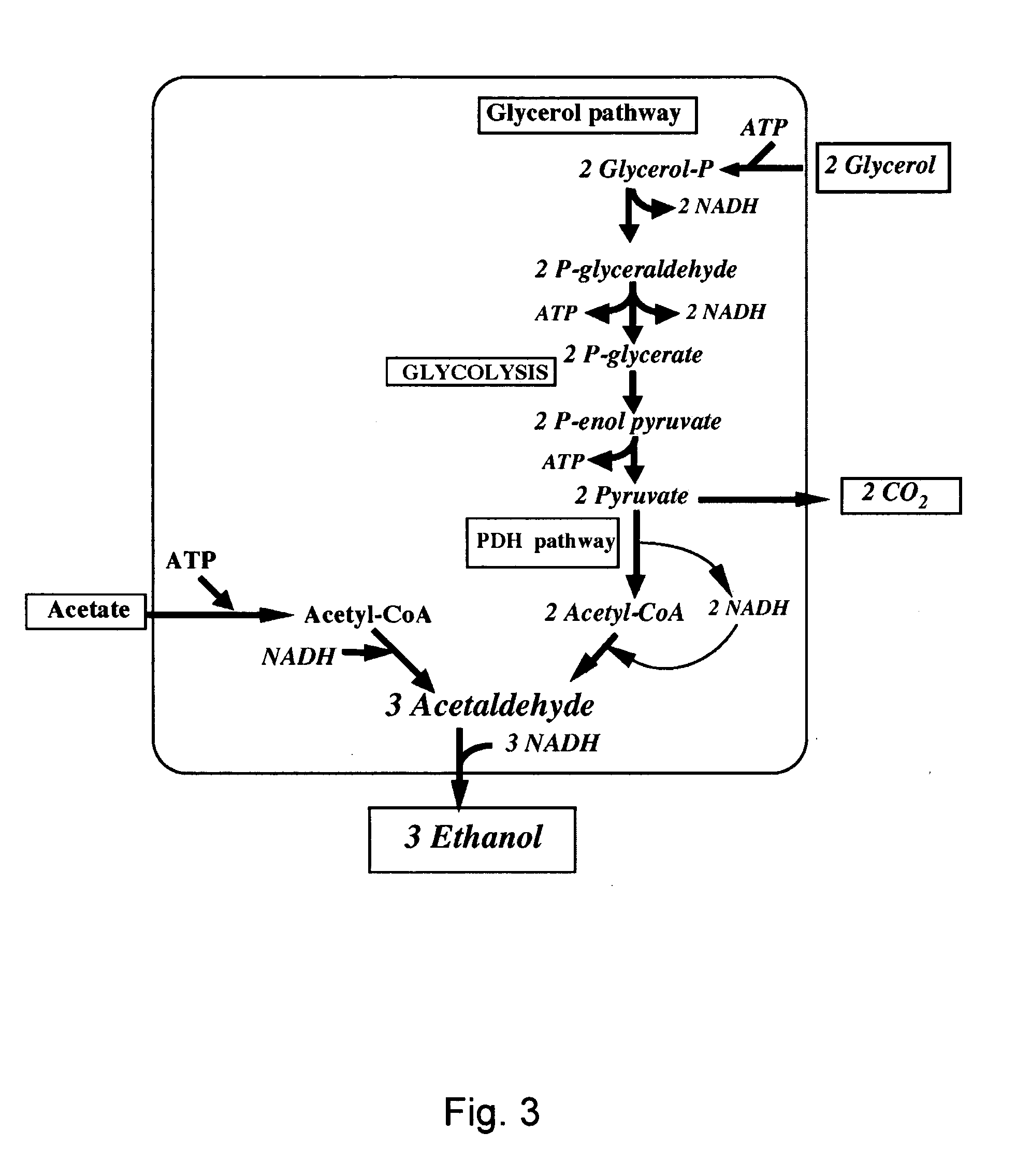
The present invention relates to bacterial strains, capable of utilizing glycerol as a carbon source for the fermentative production of succinic acid, wherein said strains are genetically modified so that they comprise a deregulation of their endogenous pyruvate-formate-lyase enzyme activity, as well as to methods of producing organic acids, in particular succinic acid, by making use of such microorganism. The present invention also relates to the downstream processing of the produced organic acids by cation exchange chromatography.
Owner:BASF SE
Enhancement of microbial ethanol production
Owner:BIOCONVERSION TECH INC
XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield as well as construction method and application of XZ-A26 bacterial strain
The invention discloses an XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC No.4036. The XZ-A26 bacterial strain has the ability of fermenting to produce high-concentration L-alanine and is genetic engineering bacteria prepared by integrating the L-alanine dehydrogenase gene on Escherichia Coli chromosome of a lipase gene from Geobacillus Stearothermophilus at the lactic dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 chromosome, then sequentially removing a pyruvate formate-lyase gene, an ethanol dehydrogenase gene, an acetokinase gene, a fumarate reductase gene and an alanine racemase gene of the escherichia coli chromosome and then continuously subculturing in a fermentation tank. The invention also relates to a construction method of the bacterial strain and the application of the bacterial strain in preparing the L-alanine. According to the metabolic engineering method, the escherichia coli CGMCC No.4036 capable of fermenting to produce the high-concentration L-alanineis constructed, and the yield of the L-alanine produced by fermenting the bacterial strain is as high as 115g / L. The invention is suitable for the industrial production of L-alanine.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Enterobacteria recombinant strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101348775BLess quantityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyKlebsiella oxytoca
The invention discloses a recombination strain for an enterobacterium and application of the recombination strain for the enterobacterium. The recombination strain provided by the invention is a recombination strain obtained after deactivation of a pyruvate formate-lyase gene in the enterobacterium. As shown by experiments, the amount of by-product CO2 produced during the fermentation process of the recombination strain is obviously reduced and the amount of target products is obviously improved compared with the control. For example, the amount of lactic acid, the amount of succinic acid and the amount of 2, 3-butanediol produced by fermentation of klebsiella oxytoca are respectively improved by 30 percent, 9 percent and 23 percent compared with the control, and the amount of the CO2 produced is only 8.04 percent compared with the control. The recombination strain helps to release the pressure of the greenhouse effect, has important function in the actual industrial production,not only can greatly reduce the yield of the CO2, but also can improve the conversion rate of converting substrates into products, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Biocatalyst for production of d-lactic acid
ActiveCN101654666AImprove productivityHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSuccinic acid
The subject of the present invention is to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid in high yield, and to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid with high selectivity, in which optical purity is high and a by-product organic acid is small. A microorganism, wherein activity of pyruvate formate-lyase (pfl-) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of Escherichia coli-derived NADH-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA) is enhanced, is cultured to produce a remarkable amount of D-lactic acid in a short time. With regard to a method for enhancing ldhA activity, by linking, on agenome, a gene encoding 1dhA with a promoter of a gene which controls expression of a protein involved in a glycolytic pathway, a nucleic acid biosynthesis pathway or an amino acid biosynthesis pathway, suitable results are obtained compared to the method for enhancing expression of the gene using an expression vector. In addition, a microorganism in which a did gene is substantially inactivatedor decreased is cultured to produce high quality D-lactic acid with reduced concentration of pyruvic acid. Furthermore, it is possible to suppress by-production of succinic acid and fumaric acid whilemaintaining high D-lactic acid productivity by using the above-mentioned microorganism having a TCA cycle, wherein activity of malate dehydrogenase (mdh) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of aspartate ammonia-lyase (aspA) is inactivated or decreased.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Enterobacteria recombinant strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101348775ALess quantityImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesKlebsiella oxytocaEnterobacter
The invention discloses a recombination strain for an enterobacterium and application of the recombination strain for the enterobacterium. The recombination strain provided by the invention is a recombination strain obtained after deactivation of a pyruvate formate-lyase gene in the enterobacterium. As shown by experiments, the amount of by-product CO2 produced during the fermentation process of the recombination strain is obviously reduced and the amount of target products is obviously improved compared with the prior art. For example, the amount of lactic acid, the amount of succinic acid and the amount of 2, 3-butanediol produced by fermentation of klebsiella oxytoca are respectively improved by 30 percent, 9 percent and 23 percent compared with the prior art, and the amount of the CO2 produced is only 8.04 percent compared with the prior art. The recombination strain helps to release the pressure of the greenhouse effect, has important function in the actual industrial production, not only can greatly reduce the yield of the CO2 but also can improve the conversion rate of converting substrates into products, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Engineering bacteria for knocking out pyruvate formate-lyase genes and application of engineering bacteria
ActiveCN104498523AReduce metabolic shunt effectReduce synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processes1,3-PropanediolPropanediol
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for knocking out pyruvate formate-lyase genes and an application of the engineering bacteria. The pyruvate formate-lyase (flpB) genes in a wild-type strain for producing 1,3-propanediol are knocked out by utilizing a gene homologous recombination and gene insertional inactivation method, so that the gene engineering bacteria with blocked metabolic pathways of methanoic acid can be obtained. The engineering bacteria are used for fermenting production of 1,3-propanediol, and the synthesis of the byproduct methanoic acid is greatly reduced, so that the toxicity effect of the methanoic acid for cells can be reduced, and the concentration, production intensity and substrate conversion rate of the 1,3-propanediol can be improved. The experiment shows that when the engineering bacteria are fermented for 32h in a conventional method, the synthesis amount of the methanoic acid is reduced by more than 90 percent, and the concentration of the 1, 3-propanediol can reach more than 72g / L. By adopting the engineering bacteria, the progress of the technology for producing the 1,3-propanediol in the microorganism fermentation method can be promoted, and the application value can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Increased ethanol production by bacterial cells
InactiveUS20110020890A1Improve the level ofMaximize productionBacteriaMutant preparationLactate dehydrogenaseHydrolysate
Fermentation processes for production of ethanol include supplying a thermophilic microorganism lacking lactate dehydrogenase activity with sugars under conditions in which they metabolise them predominantly by the pyruvate-formate lyase pathway. Importantly, the processes also include supplying sufficient glycerol to convert all of the sugars to ethanol. A further embodiment of the invention includes supplying additional glycerol sufficient to convert the exogenous acetate present in biomass hydrolysates into ethanol. Any type of fermentation system can be used for these processes, but a preferred embodiment includes continuous cultures at high temperatures in which ethanol is removed continuously by vacuum evaporation.
Owner:ENSUS
Metabolically engineered lactic acid bacteria and their use
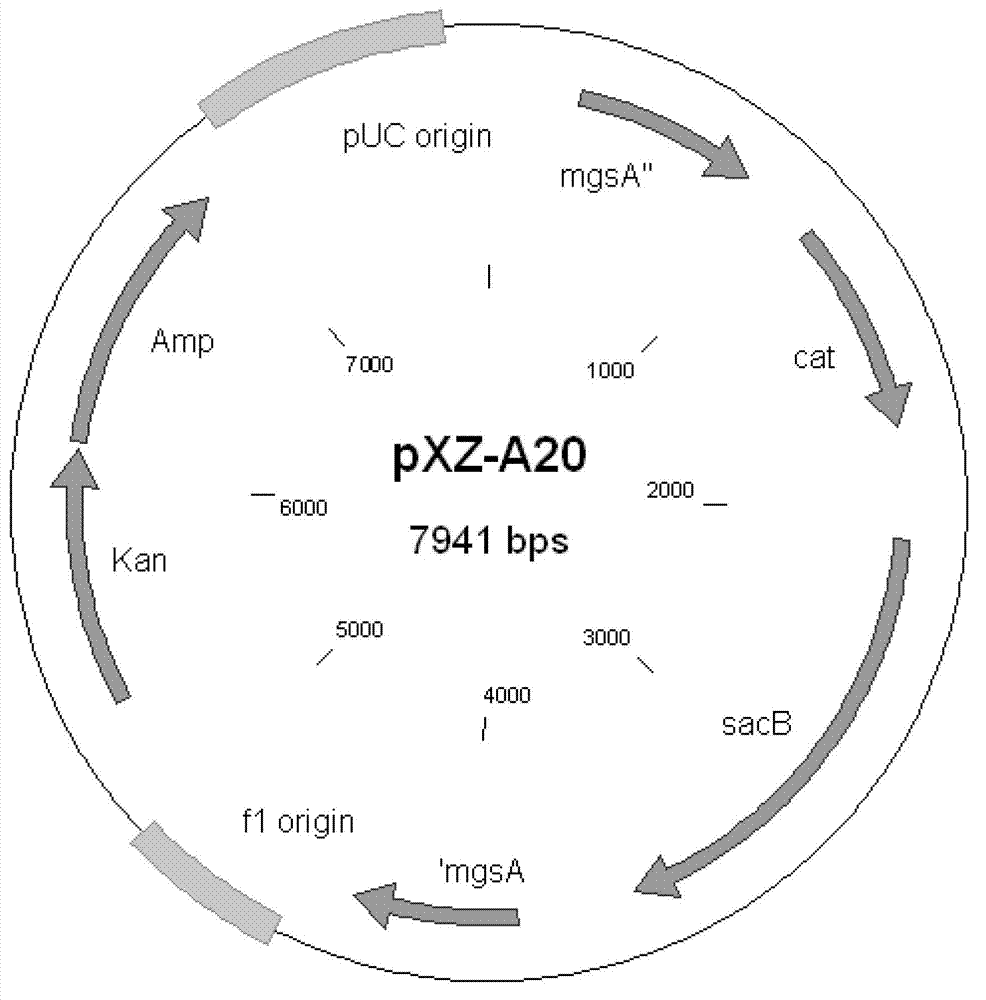
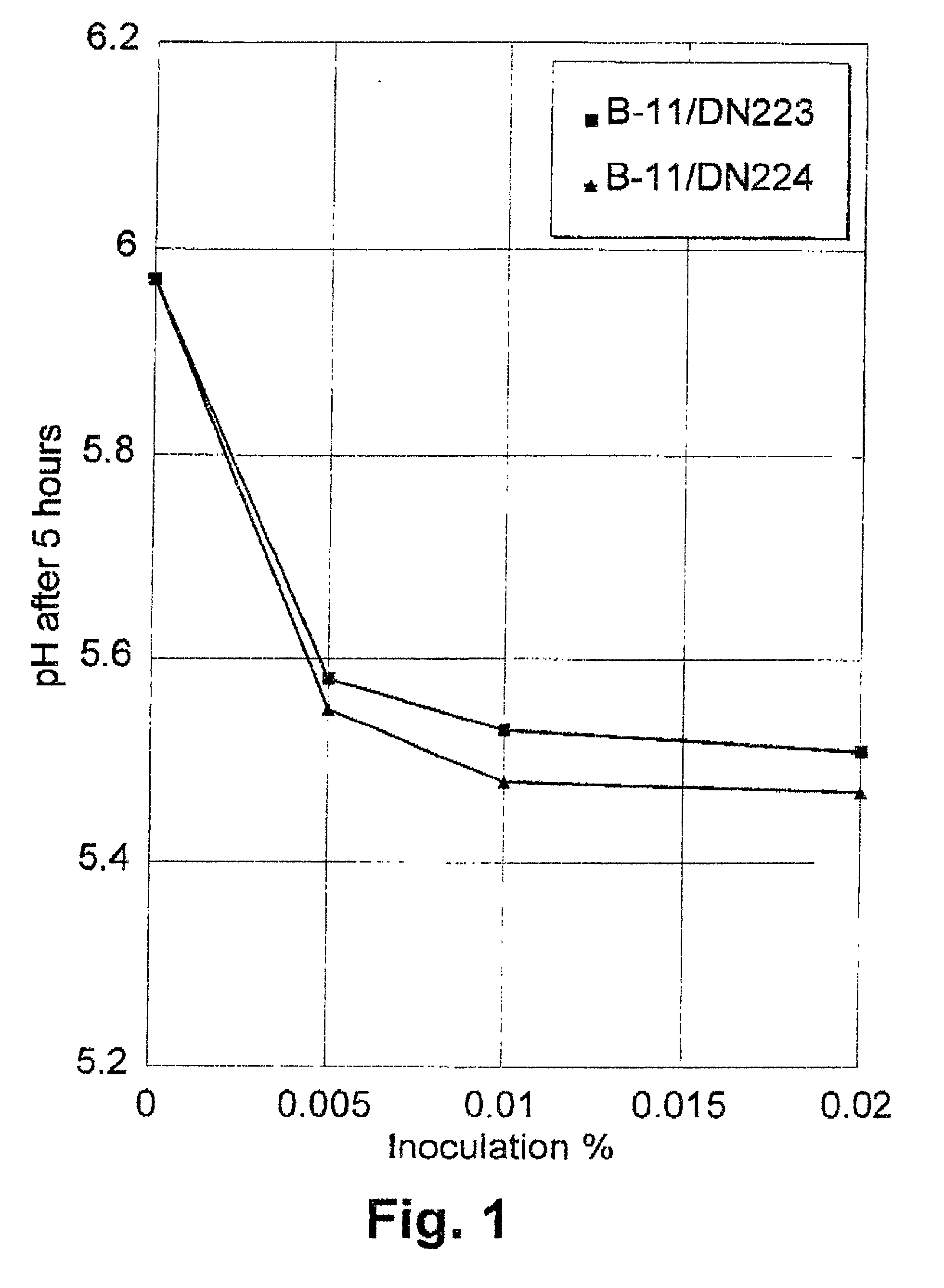
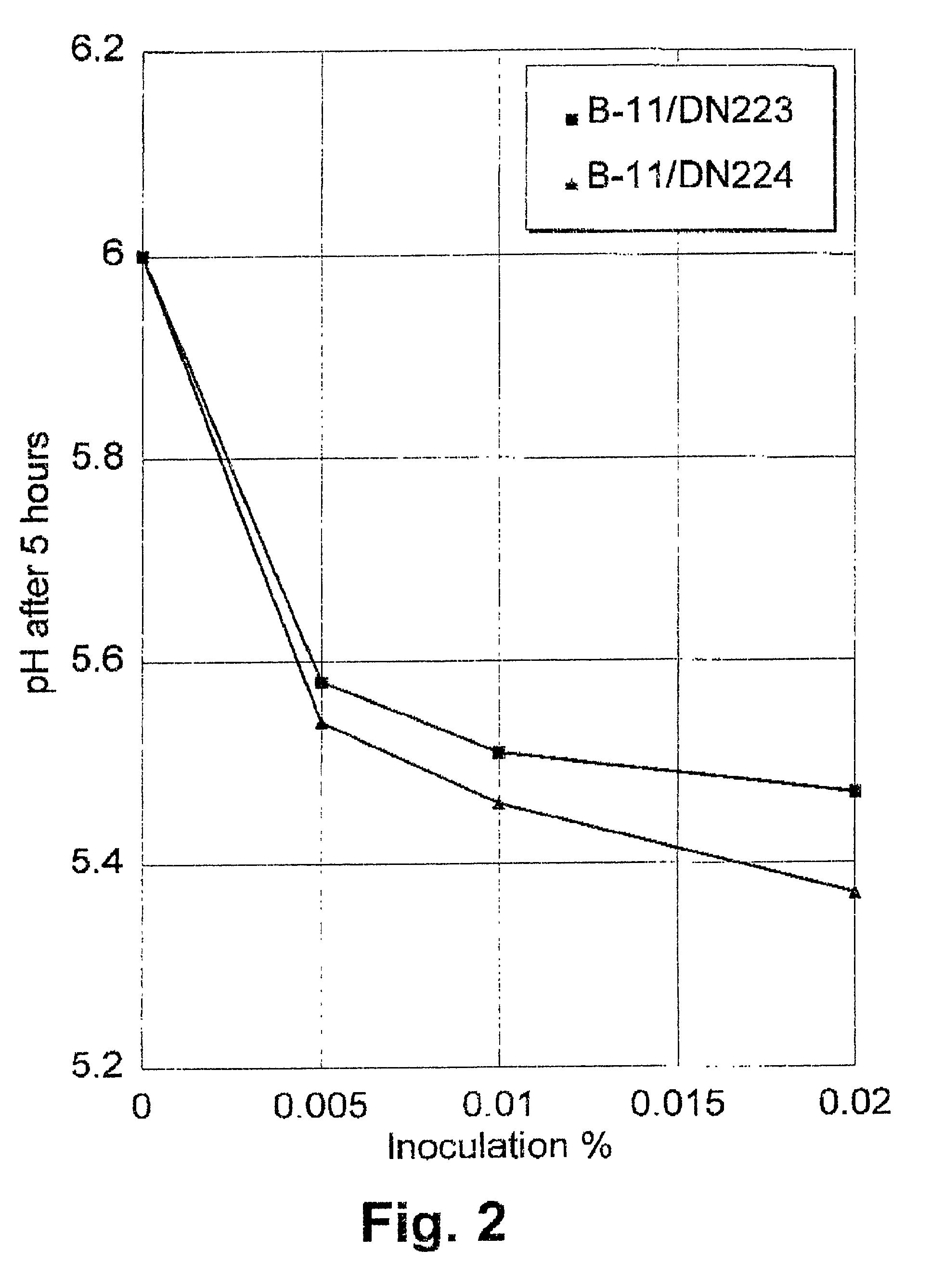
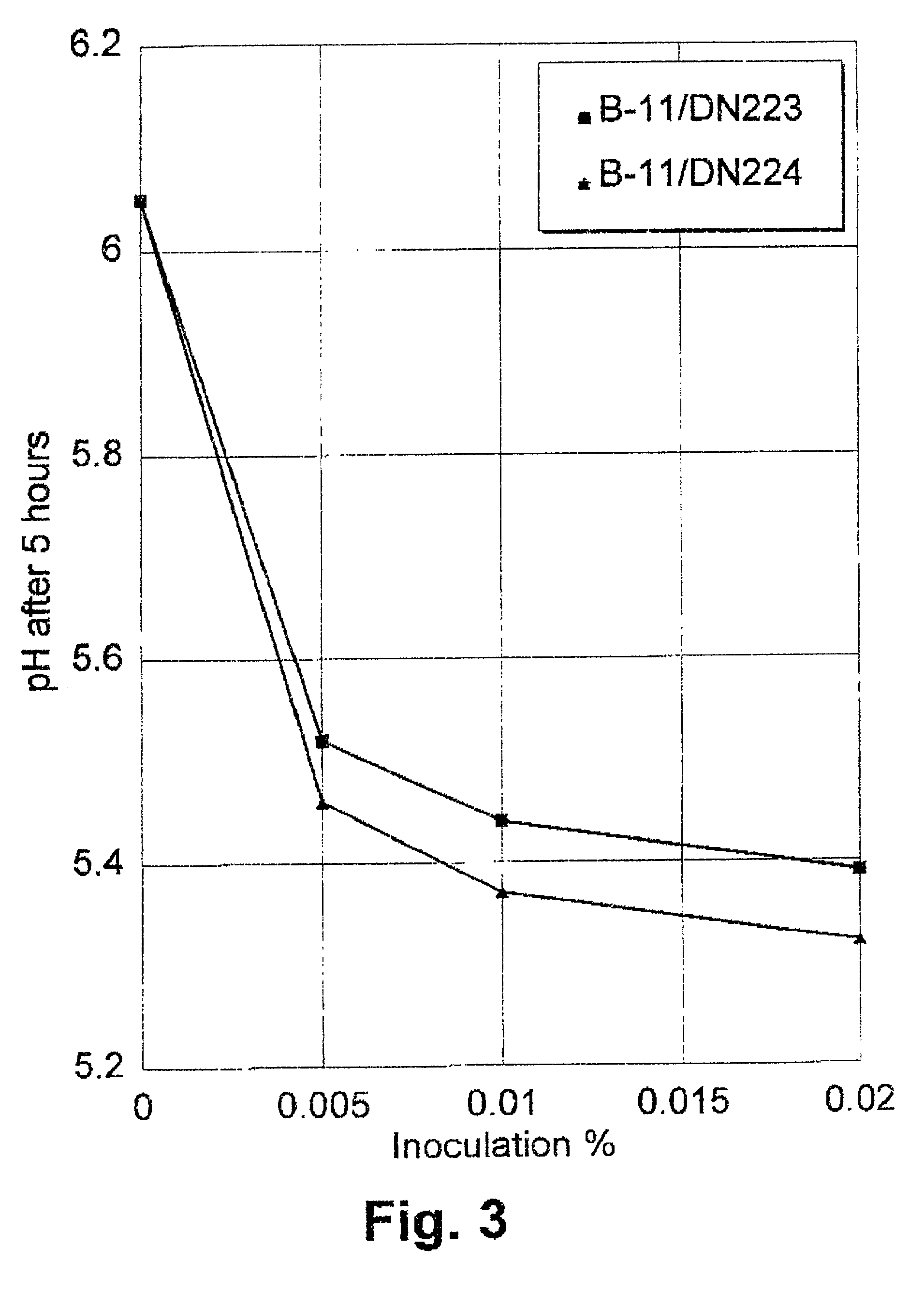
Mutants of lactic acid bacteria including Lactococcus lactis which are defective in pyruvate formate-lyase production and / or in their lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh) production and methods of isolating such mutants or variants are provided. The mutants are useful in the production of food products or in the manufacturing of compounds such as diacetyl, acetoin and acetaldehyde and as components of food starter cultures. In particular, Lactococcus lactis DN223 deposited under the accession No. DSM 11036.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Microorganisms that co-consume glucose with non-glucose carbohydrates and methods of use
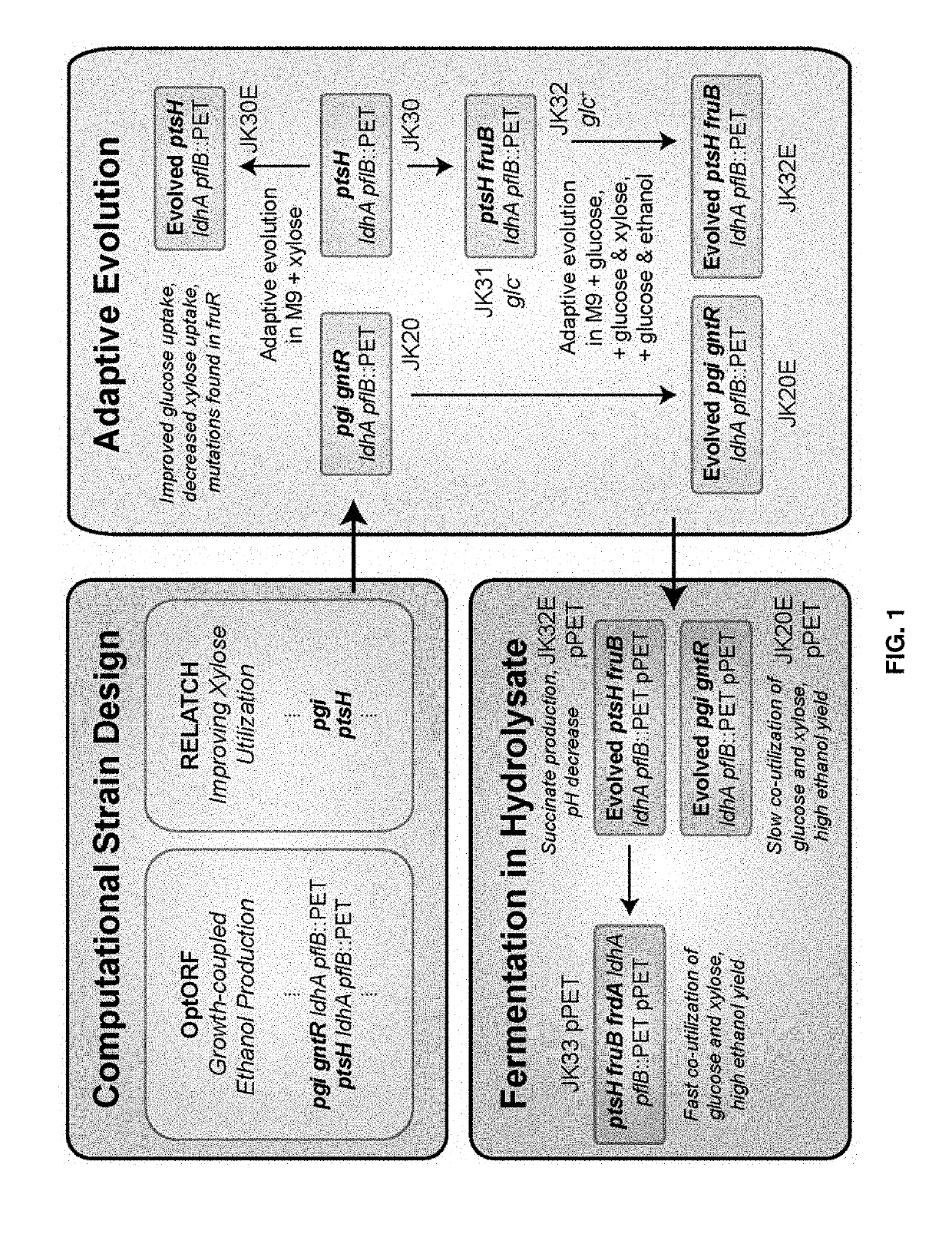
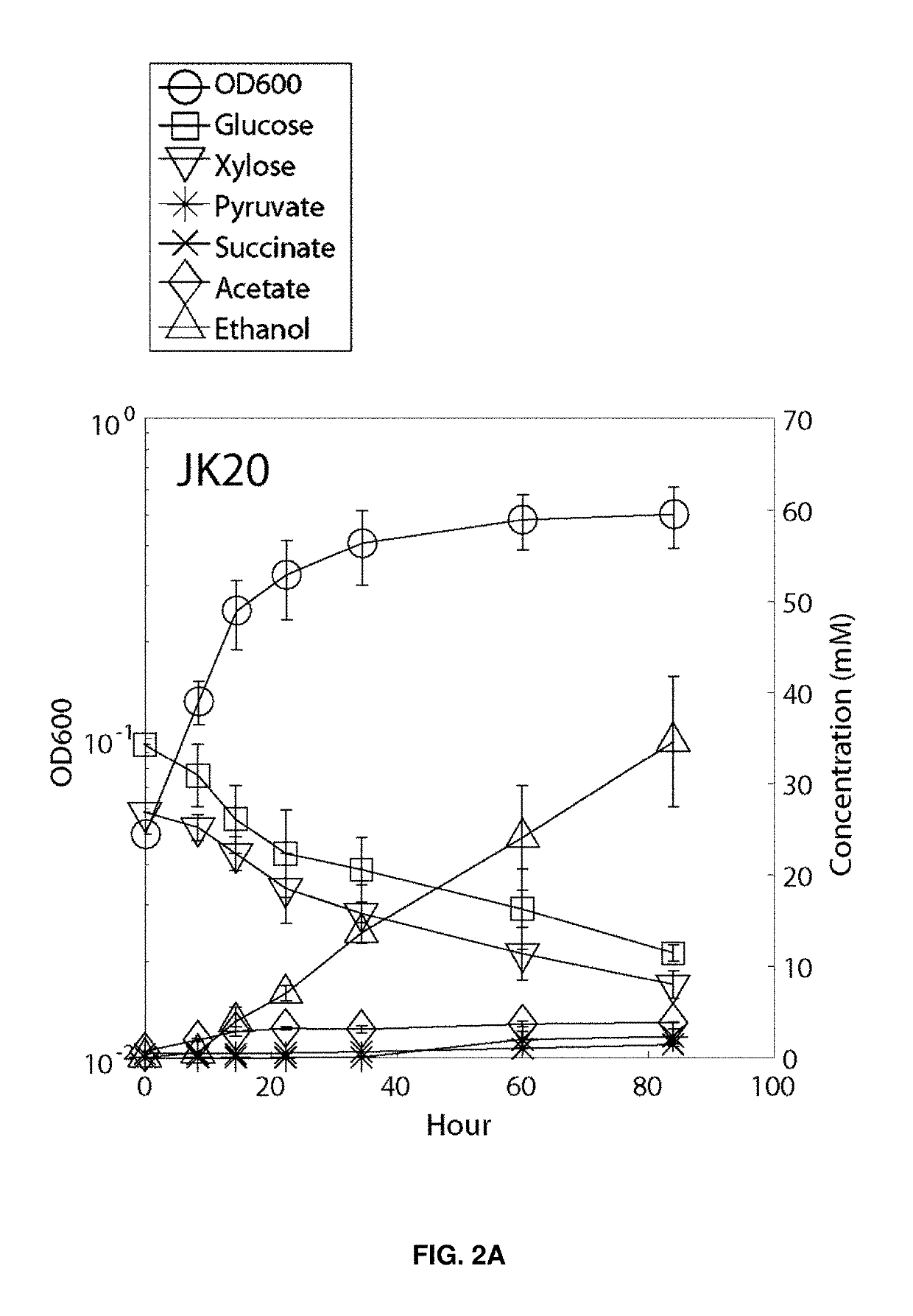
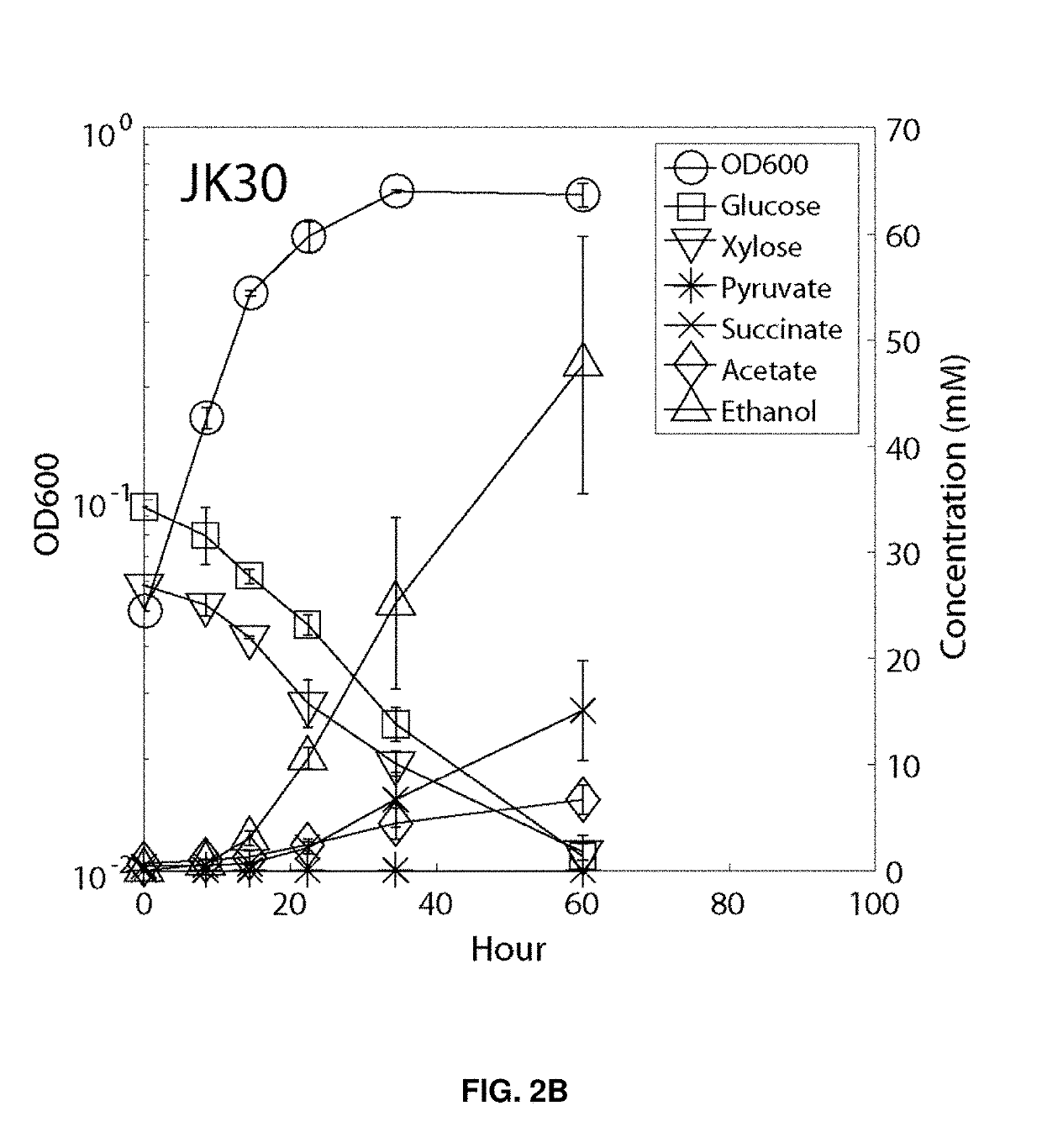
Microorganisms that co-consume glucose with non-glucose carbohydrates, such as xylose, and methods of using same. The microorganisms comprise modifications that reduce or ablate the activity of a phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP):carbohydrate phosphotransferase system (PTS) protein or modifications that reduce or ablate the activity of a phosphoglucose isomerase and a GntR. The PTS protein may be selected from an enzyme I (EI), an HPr, an FPr, and an enzyme IIGlc (EIIGlc). Additional modifications include reduction or ablation of the activity of a pyruvate formate lyase, a lactate dehydrogenase, and a fumarate reductase and inclusion of recombinant pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase genes. The microorganisms are particularly suited to co-consuming glucose and xylose in media containing these substrates and producing ethanol therefrom.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Engineering strain capable of producing succinic acid at low pH value and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation
InactiveCN104232553APromote progressBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain capable of producing succinic acid at a low pH value. The classification name of the genetic engineering strain is Escherichia coli BA601, and the collection number is CCTCCNO: M2014210. The invention further discloses a method for producing succinic acid by using the strain. According to the strain disclosed by the invention, an Escherichia coli AFP111 which is lack of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) genes and has activity of pyruvate formate lyase (PFL) genes and ptsG spontaneous mutation of a phosphotransferase system is taken as a starting strain for over-expression of acid-resistant genes gadBC. The method of enabling the Escherichia coli AFP111 which can not grow under low-pH (pH 5.6) conditions originally and can not produce acid by fermentation to efficiently utilize glucose to produce succinic acid through a biological and microbial acclimation means is not disclosed before, and the application can greatly promote the progress and development of the succinic acid industry.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Use of enzymes which catalyze pyruvate synthesis from formate and acetyl-coa and bacteria expressing same
An isolated microorganism is disclosed being genetically modified to express pyruvate formate lyase (PFL) or 2-ketobutyrate formate lyase, wherein acetyl-CoA of the microorganism is converted to pyruvate in the presence of formate in a single step reaction, wherein the net flux of the reaction is in the direction of pyruvate synthesis.Uses of the microorganism and products comprising same are also disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Increased ethanol production by bacterial cells
InactiveCN101952450AHigh purityEasy to separateBacteriaMutant preparationLactate dehydrogenaseHydrolysate
Owner:BIOCONVERSION TECH INC
Escherichia coli for producing isobutanol and ethanol and preparation method of escherichia coli
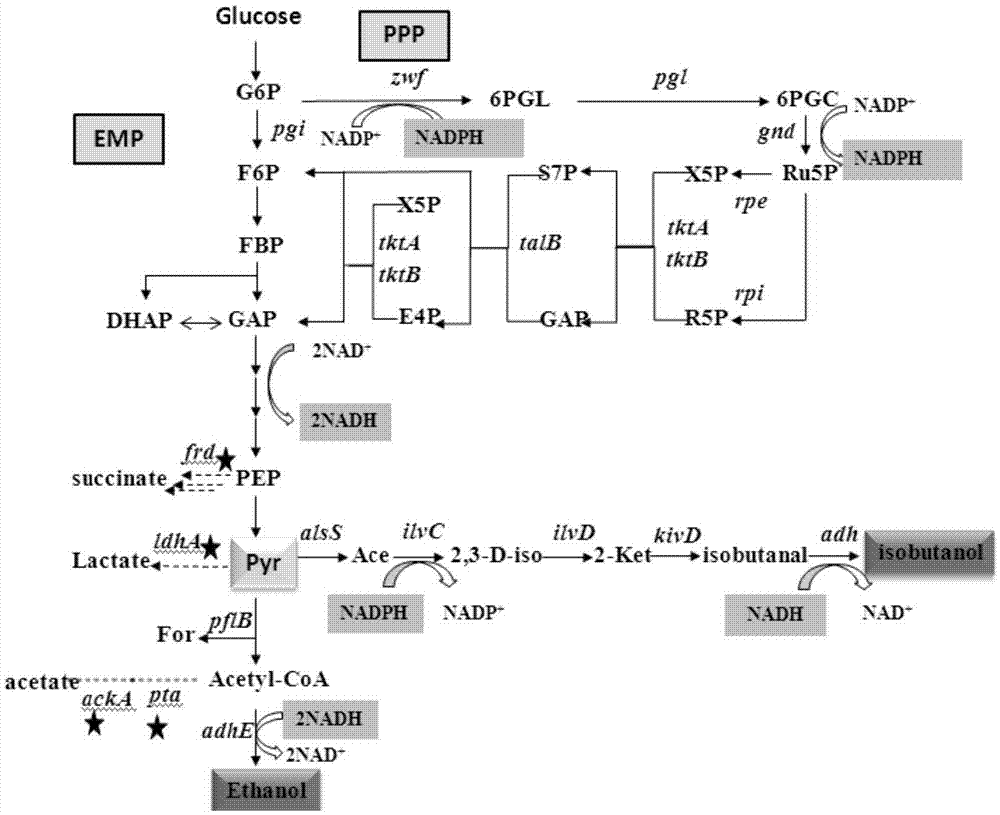
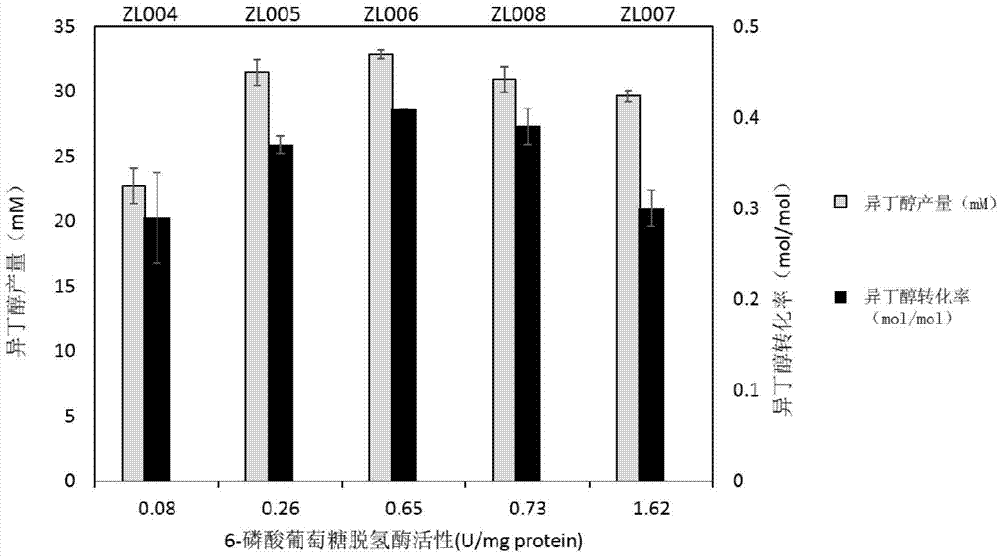
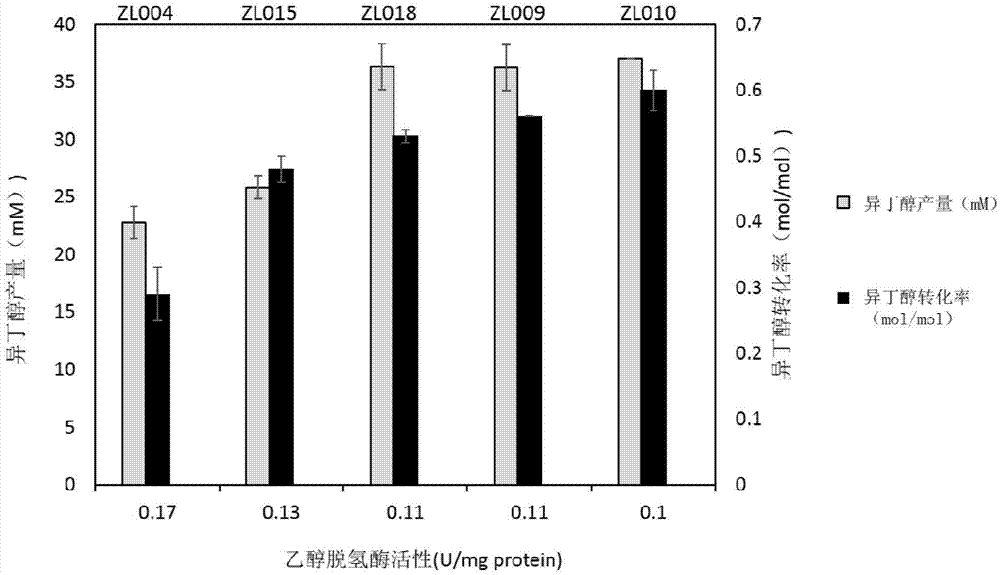
The invention discloses escherichia coli for producing isobutanol and ethanol and a preparation method of the escherichia coli. The invention provides a method for constructing recombinant bacteria for producing isobutanol and / or ethanol, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1) expressing an ethanol dehydrogenase adhE and a pyruvate formate-lyase coding gene pflB in the escherichia coli AS108, so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium which is named as A; and 2) reducing enzymatic activity of ethanol dehydrogenase in the recombinant bacterium which is named as A and / or improving enzymatic activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the recombinant bacterium which is named as A, so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium which is named as B. Experiments prove that excessive NADH can be consumed through a mode of introducing ethanol production in the AS108 strain based upon researches, so that toxicity to cells due to accumulation of the NADH is relieved; and meanwhile, NADPH supply can be promoted by activating a pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), so that an isobutanol production capacity is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Engineered microorganism producing homo-succinic acid and method for preparing succinic acid using the same
ActiveUS9217138B2Increase productivityHigh rateBacteriaStable introduction of DNAHigh concentrationMannheimia
The present invention relates to a mutant microorganism, which is selected from the group consisting of genus Mannheimia, genus Actinobacillus and genus Anaerobiospirillum, producing homo-succinic acid and a method for producing homo-succinic acid using the same, and more particularly to a mutant microorganism producing succinic acid at a high concentration while producing little or no other organic acids in anaerobic conditions, which is obtained by disrupting a gene encoding lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA), a gene encoding phosphotransacetylase (pta), and a gene encoding acetate kinase (ackA), without disrupting a gene encoding pyruvate formate lyase (pfl), as well as a method for producing succinic acid using the same. The inventive mutant microorganism has the property of having a high growth rate and succinic acid productivity while producing little or no organic acids, as compared to the prior strains producing succinic acid. Thus, the inventive mutant microorganism is useful to produce succinic acid for industrial use.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com