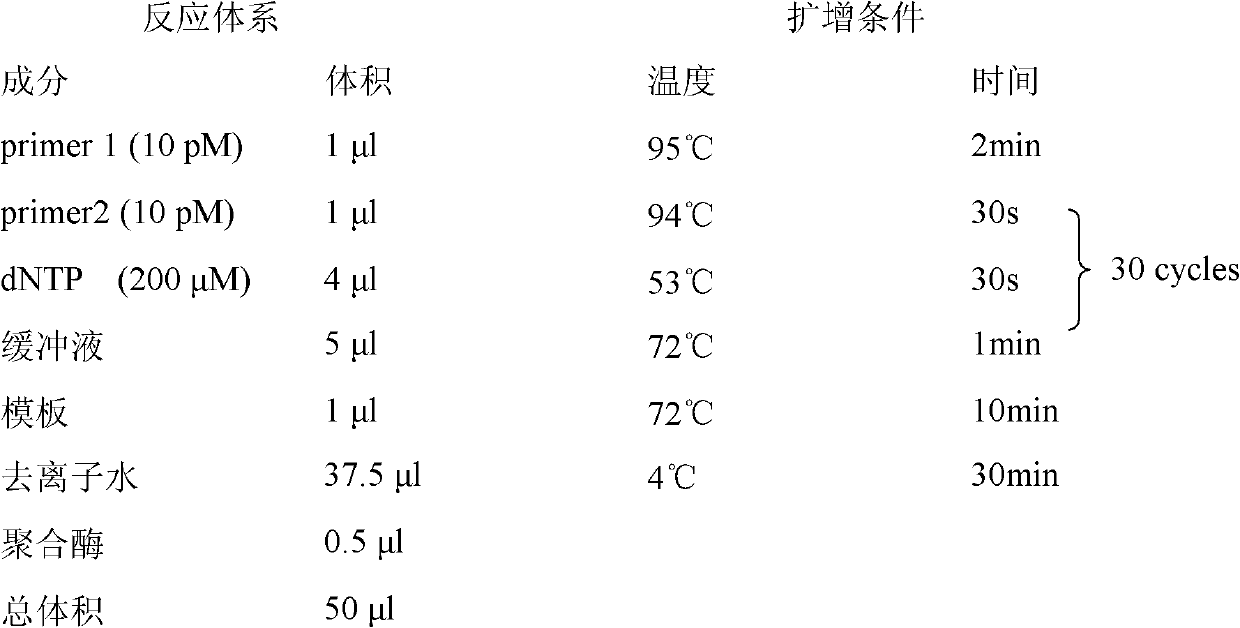
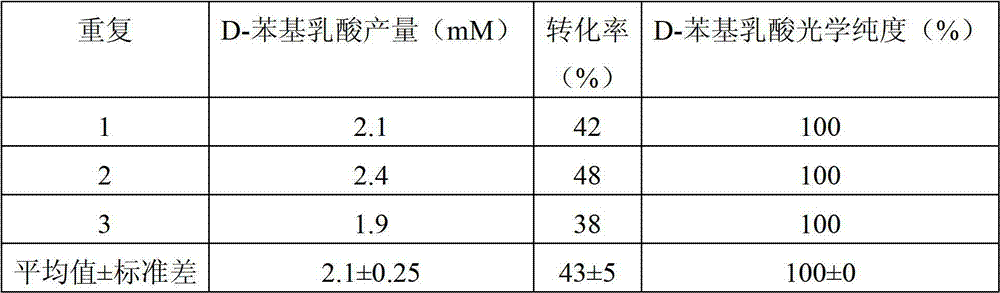
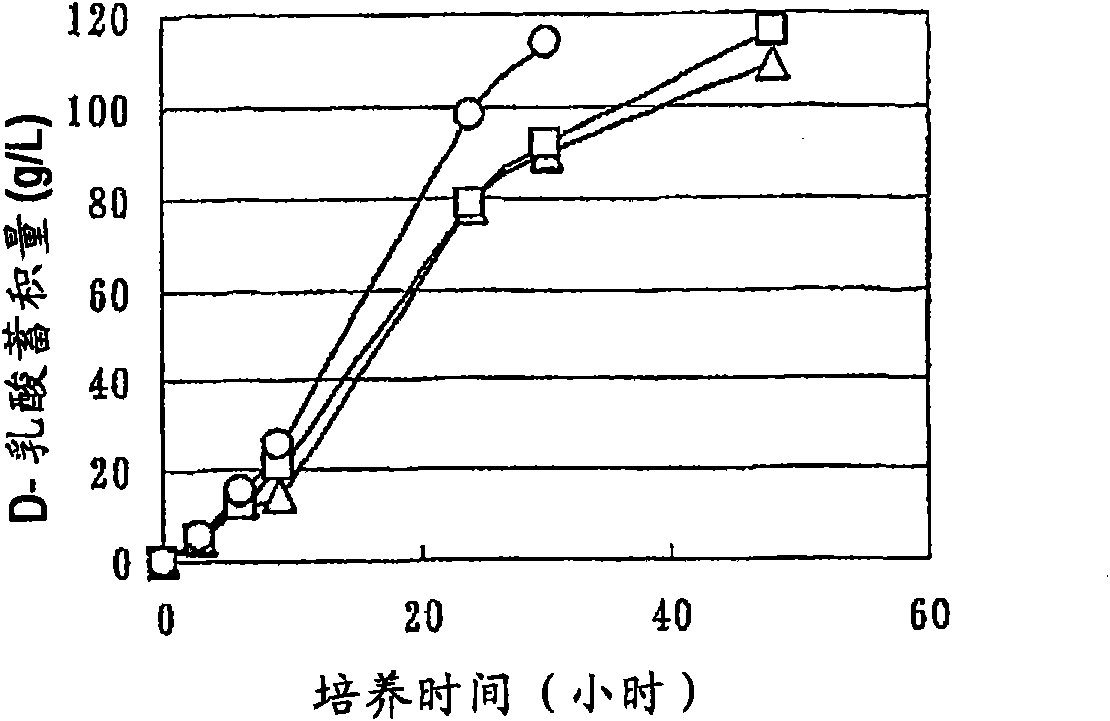
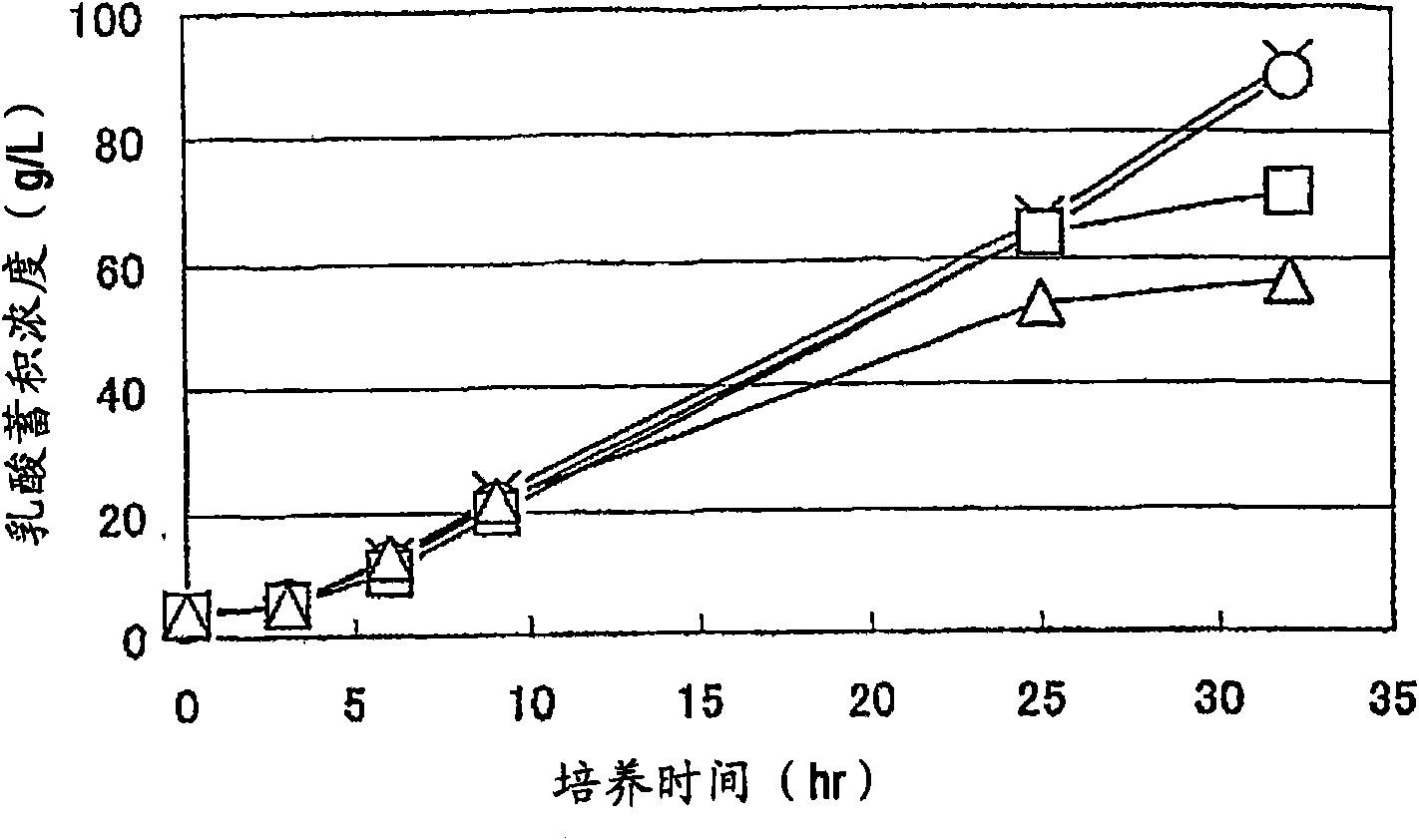
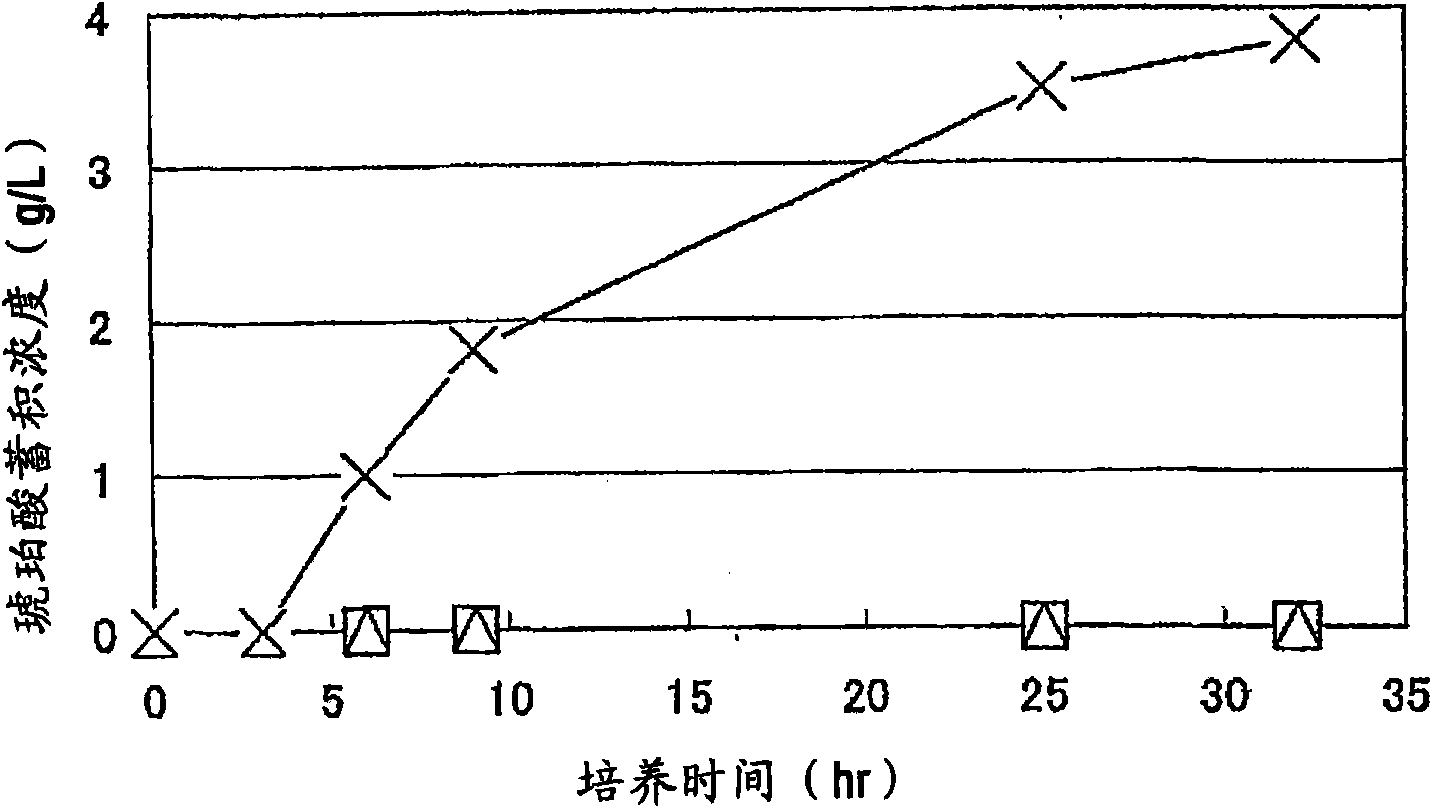
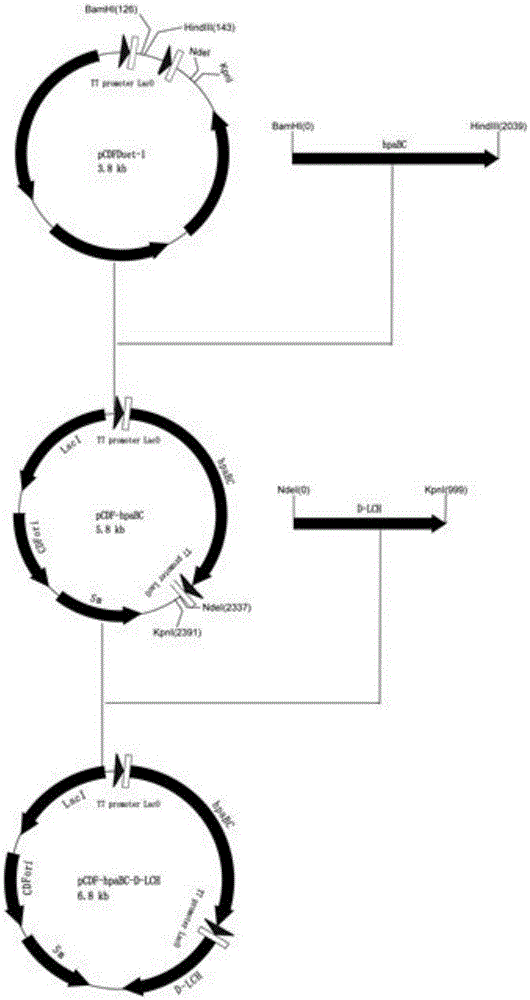
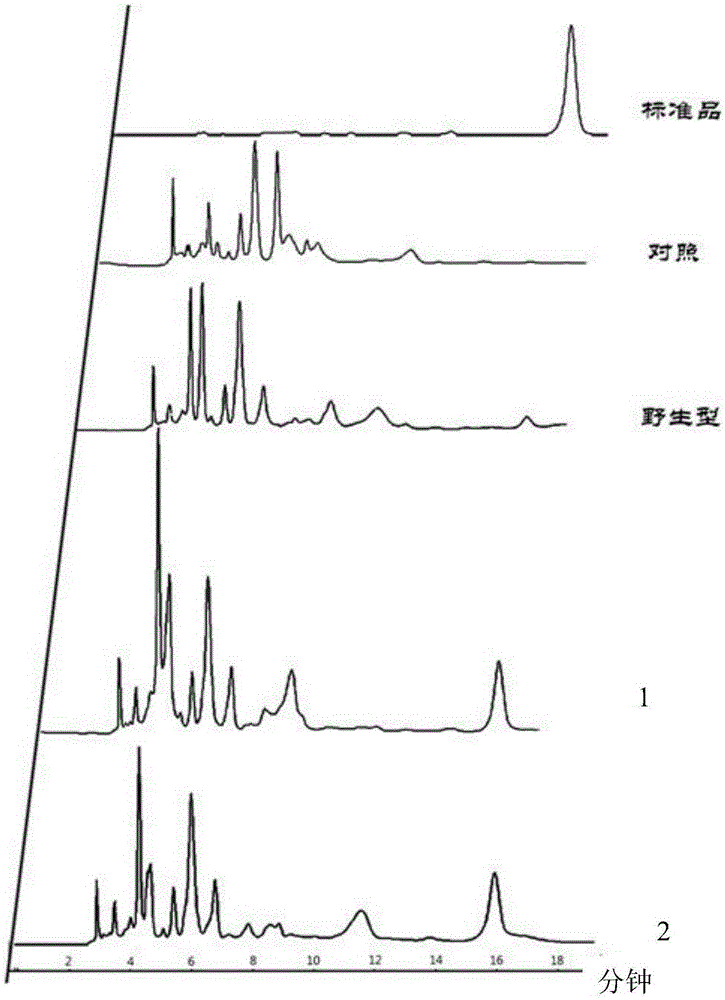
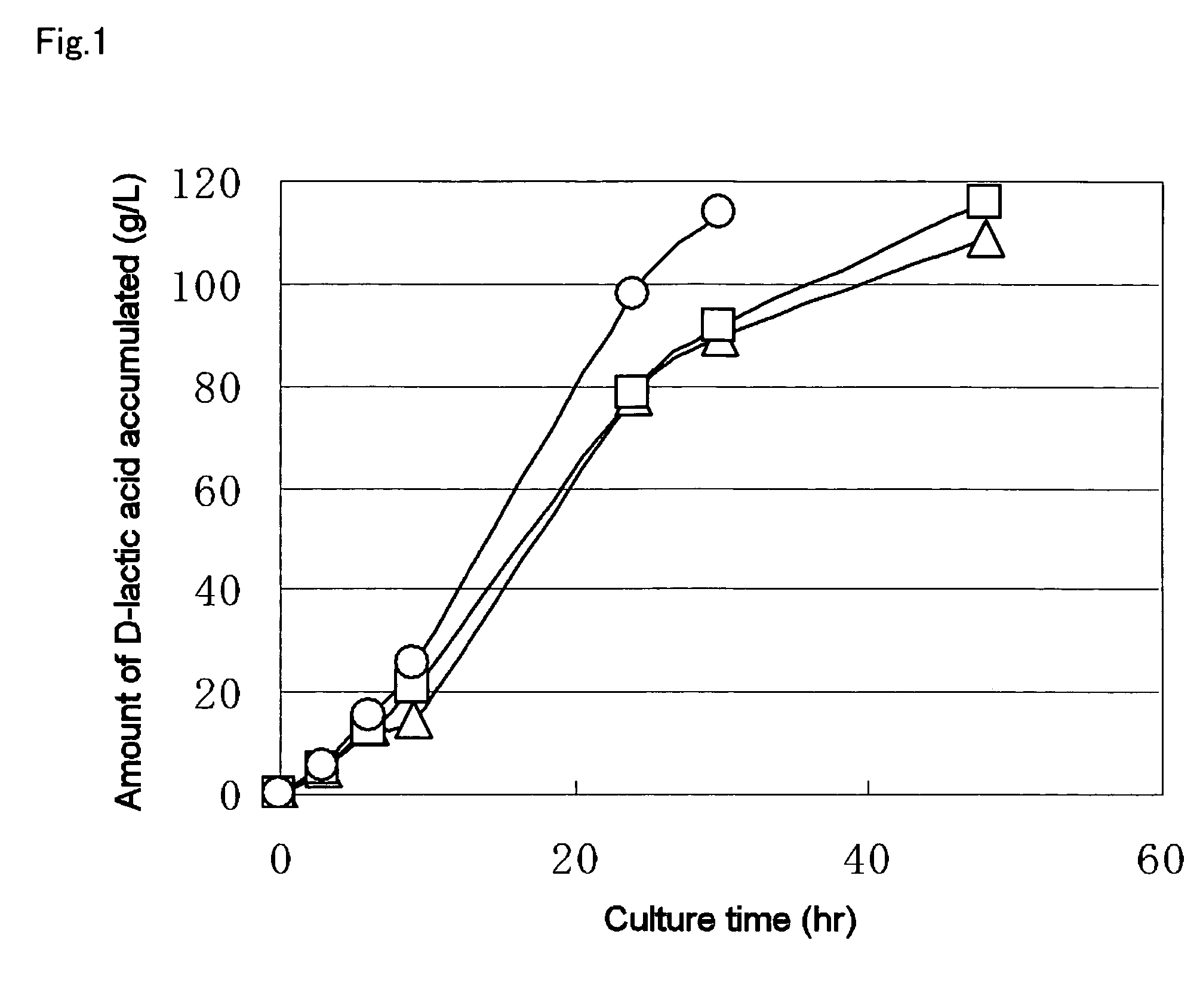
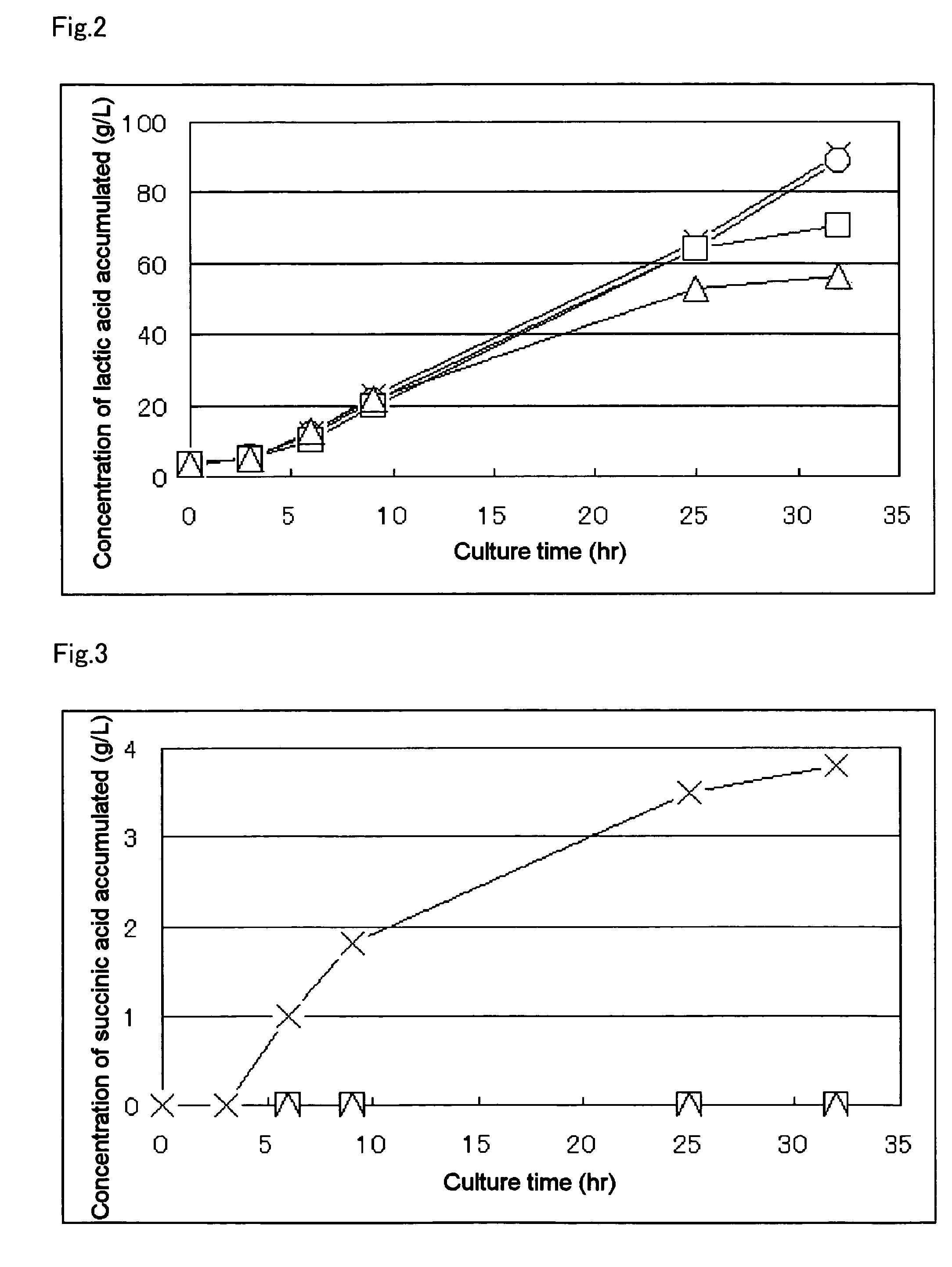
Patents
Literature
41 results about "D-lactate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
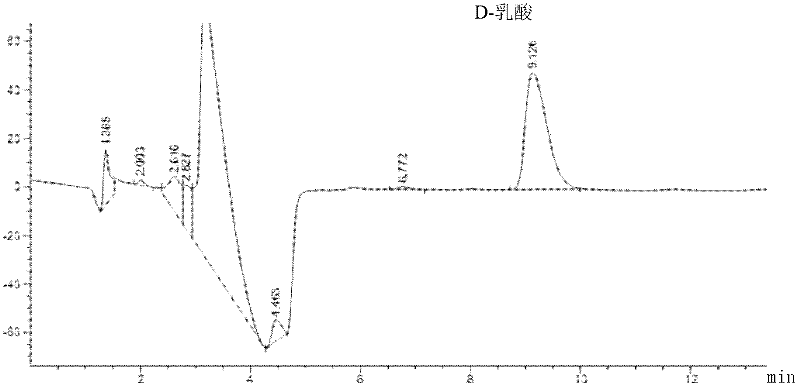
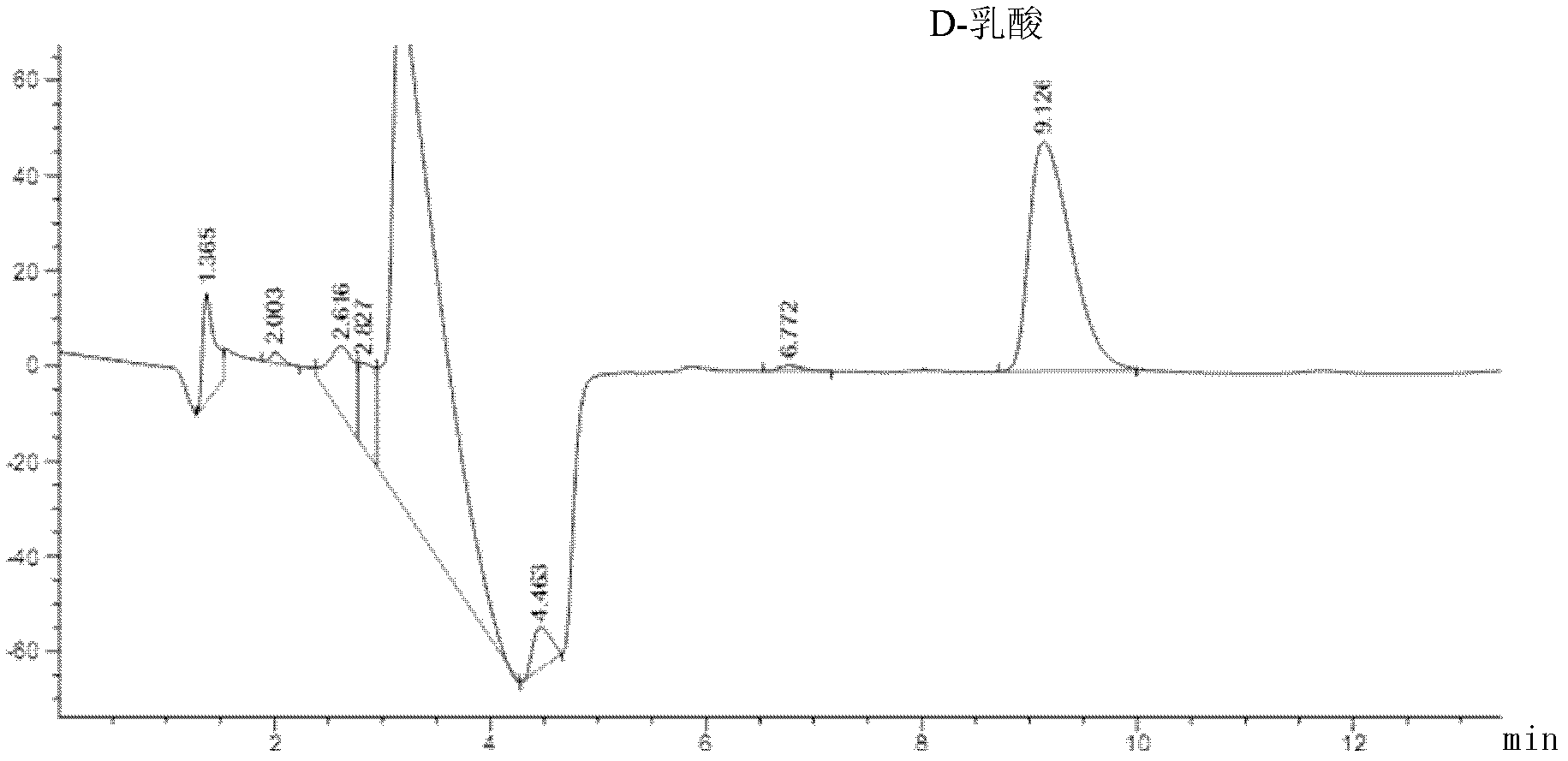
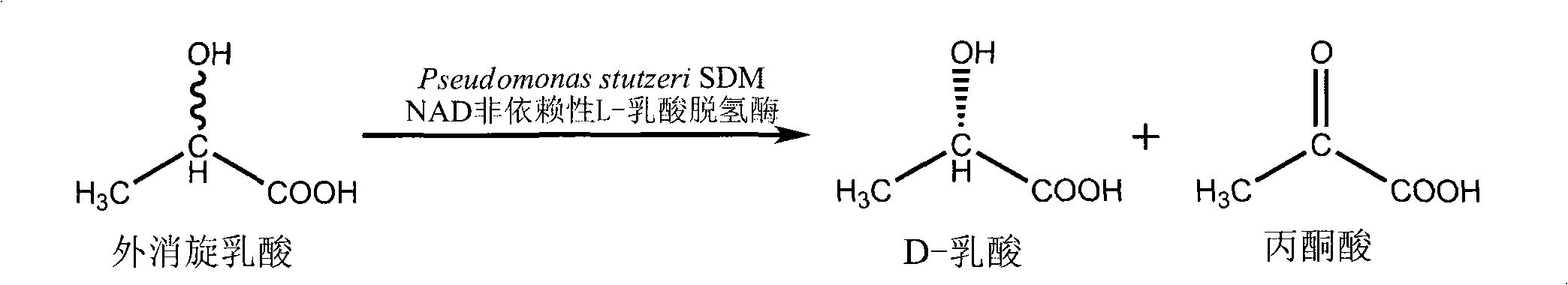
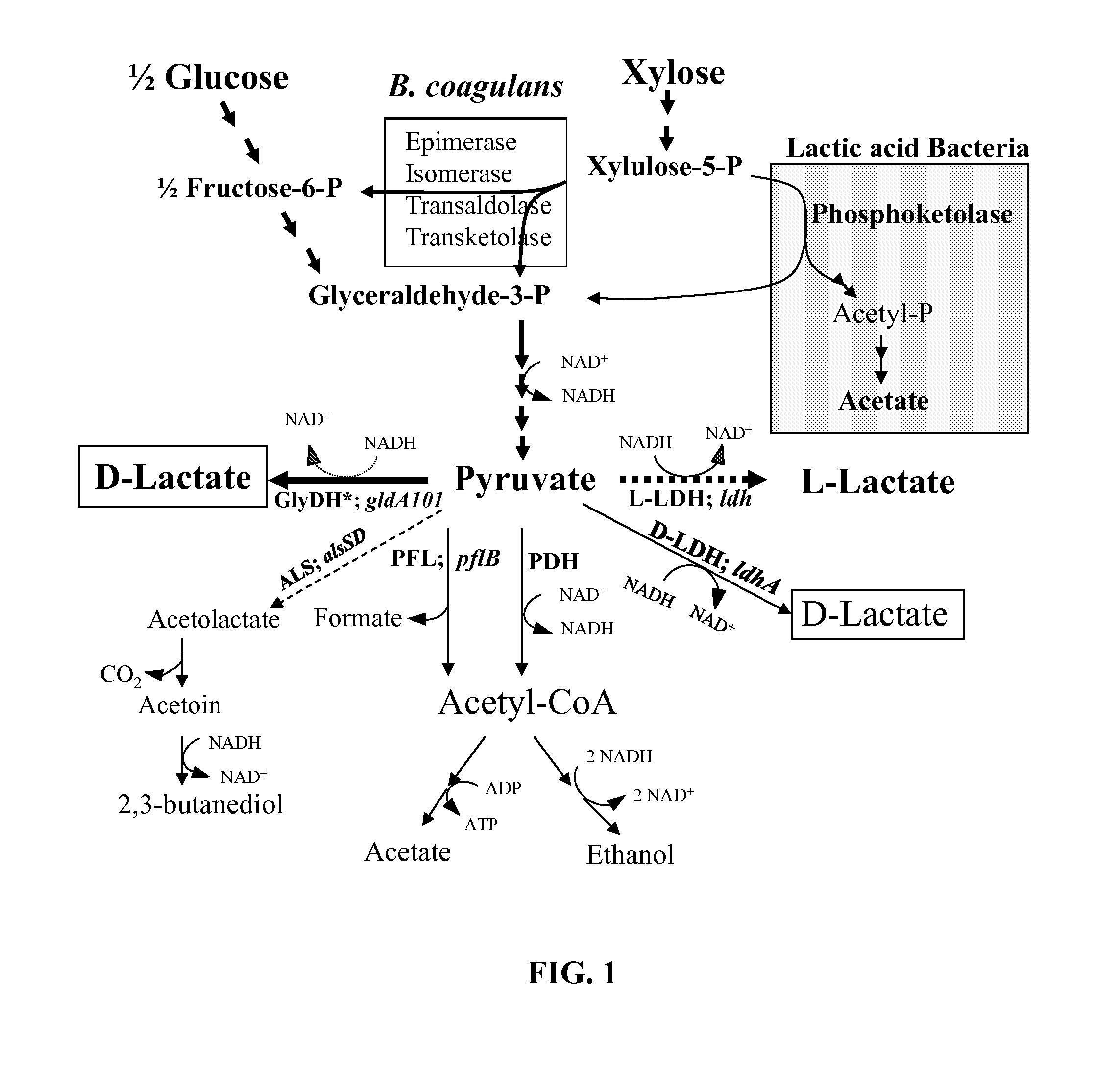
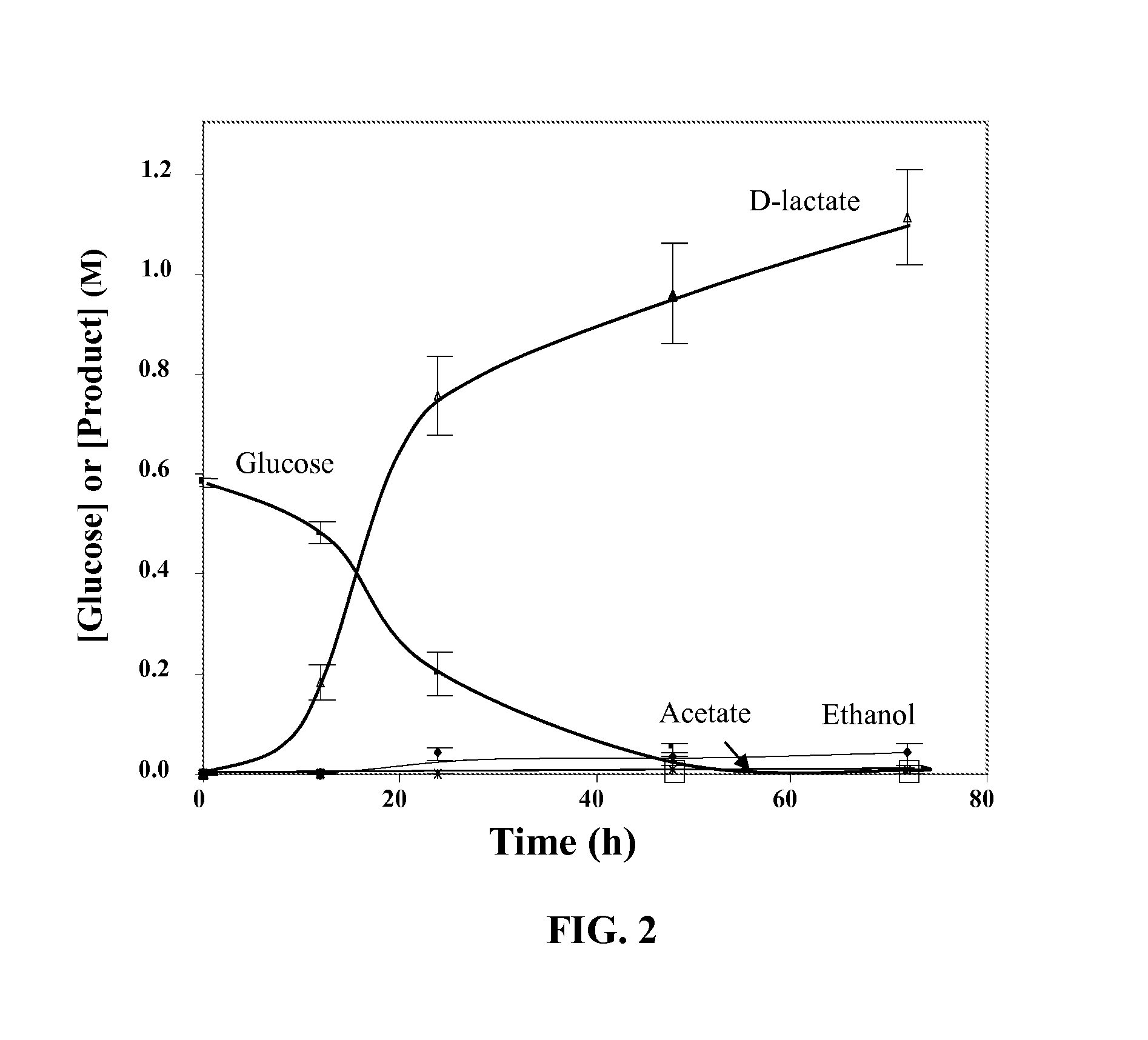
D-lactate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.28, lactic acid dehydrogenase, lactic acid dehydrogenase, D-specific lactic dehydrogenase, D-(-)-lactate dehydrogenase (NAD+), D-lactic acid dehydrogenase, D-lactic dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name (R)-lactate:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction (R)-lactate + NAD⁺ ⇌ pyruvate + NADH + H⁺
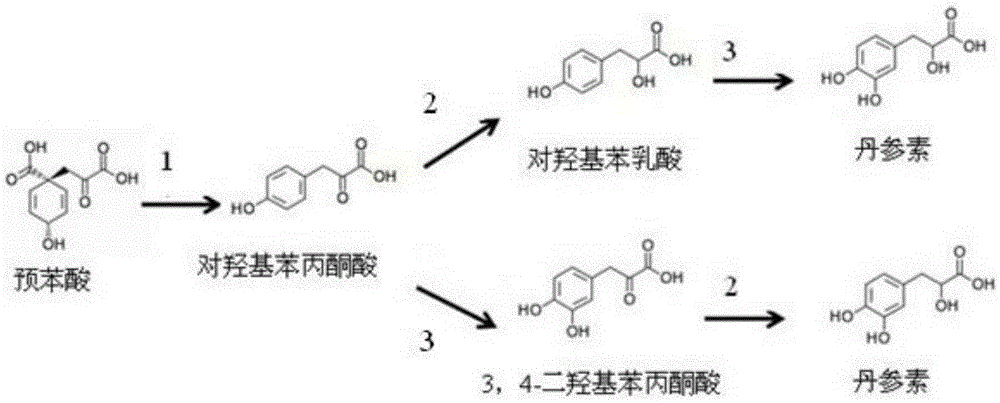
Biological production method of tanshinol
ActiveCN103667371ADe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalvia miltiorrhizaEscherichia coli
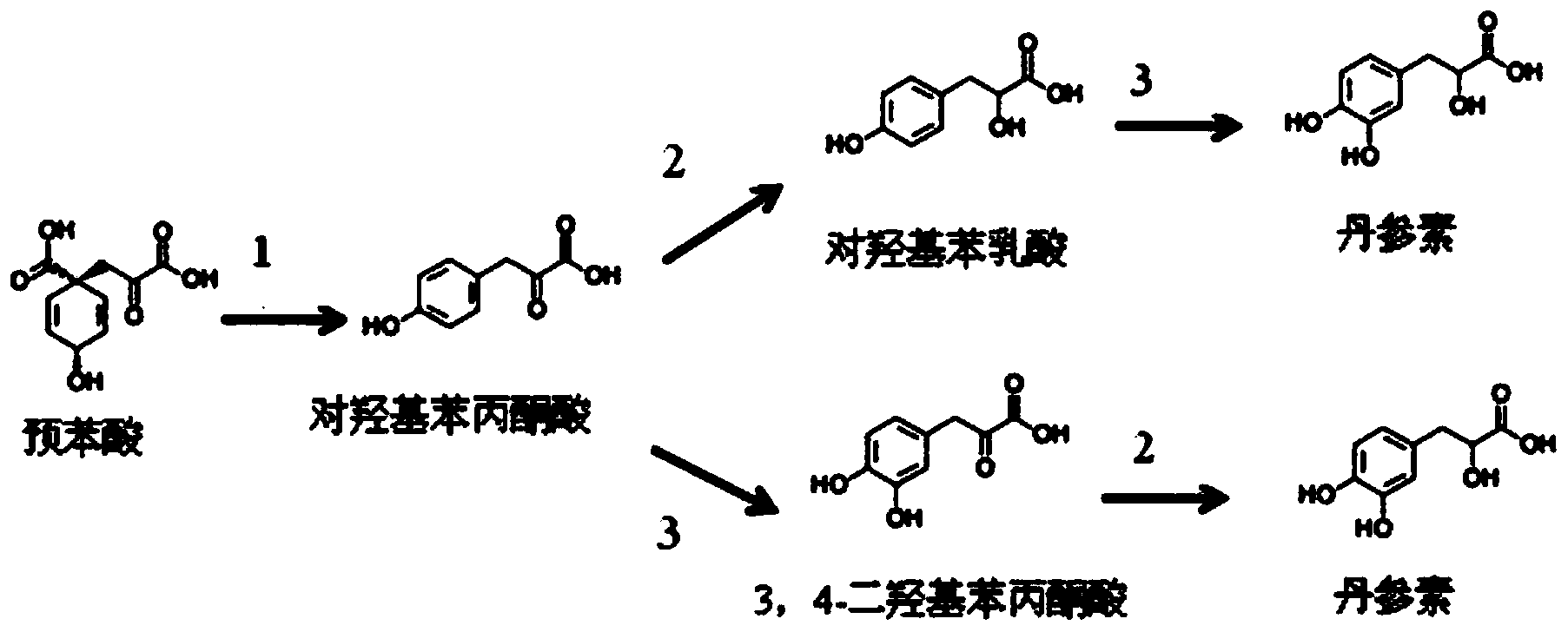
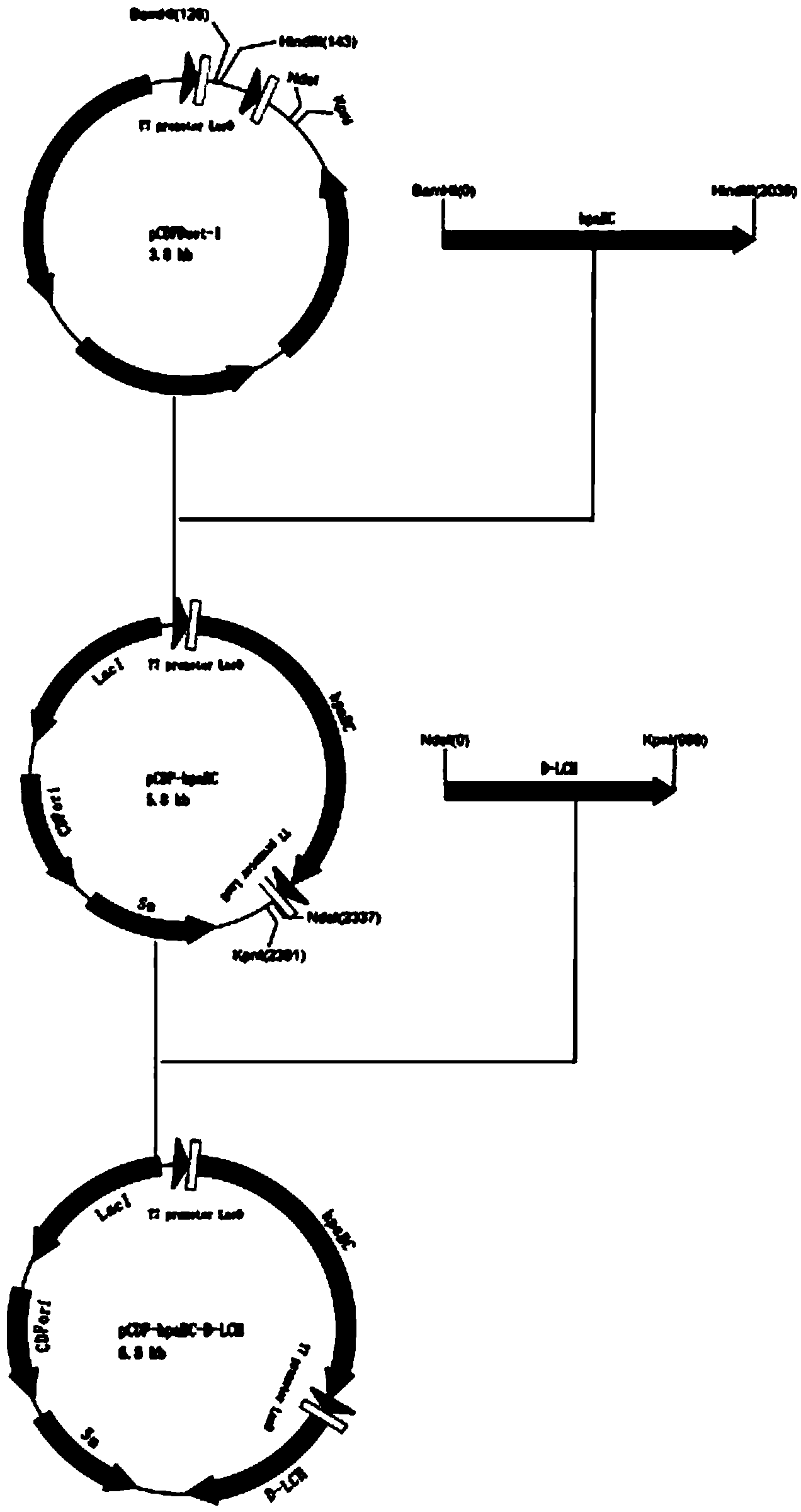
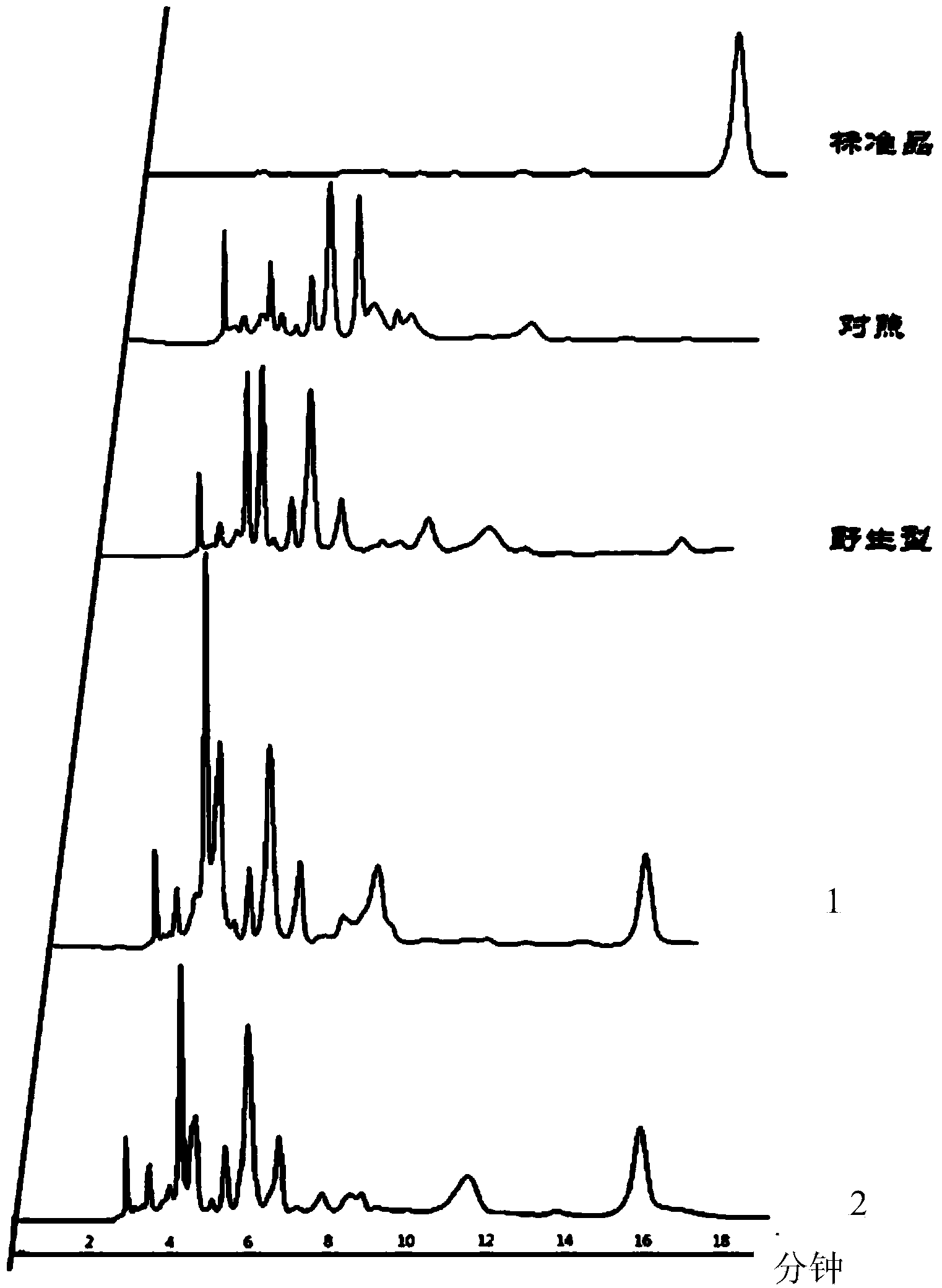
The invention discloses a biological production method of tanshinol, which comprises the following steps: synthesizing p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid into 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpyruvic acid under the catalytic action of a p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid meta-position hydroxylation enzyme, and then, synthesizing to obtain the tanshinol under the catalytic action of a D-lactate dehydrogenase; or synthesizing p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid into p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid under the catalytic action of a D-lactate dehydrogenase, and then, synthesizing to obtain the tanshinol under the catalytic action of a p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid meta-position hydroxylation enzyme. According to the invention, gene engineering glutamic acid corynebacteria and Escherichia coli are used to produce the tanshinol through fermentation, and the tanshinol can be synthesized without adding a substrate, thereby realizing de novo synthesis of the tanshinol and solving the problem on the source of the tanshinol; and meanwhile, the production cost is lowered to the greatest extent. Thus, the biological production method is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
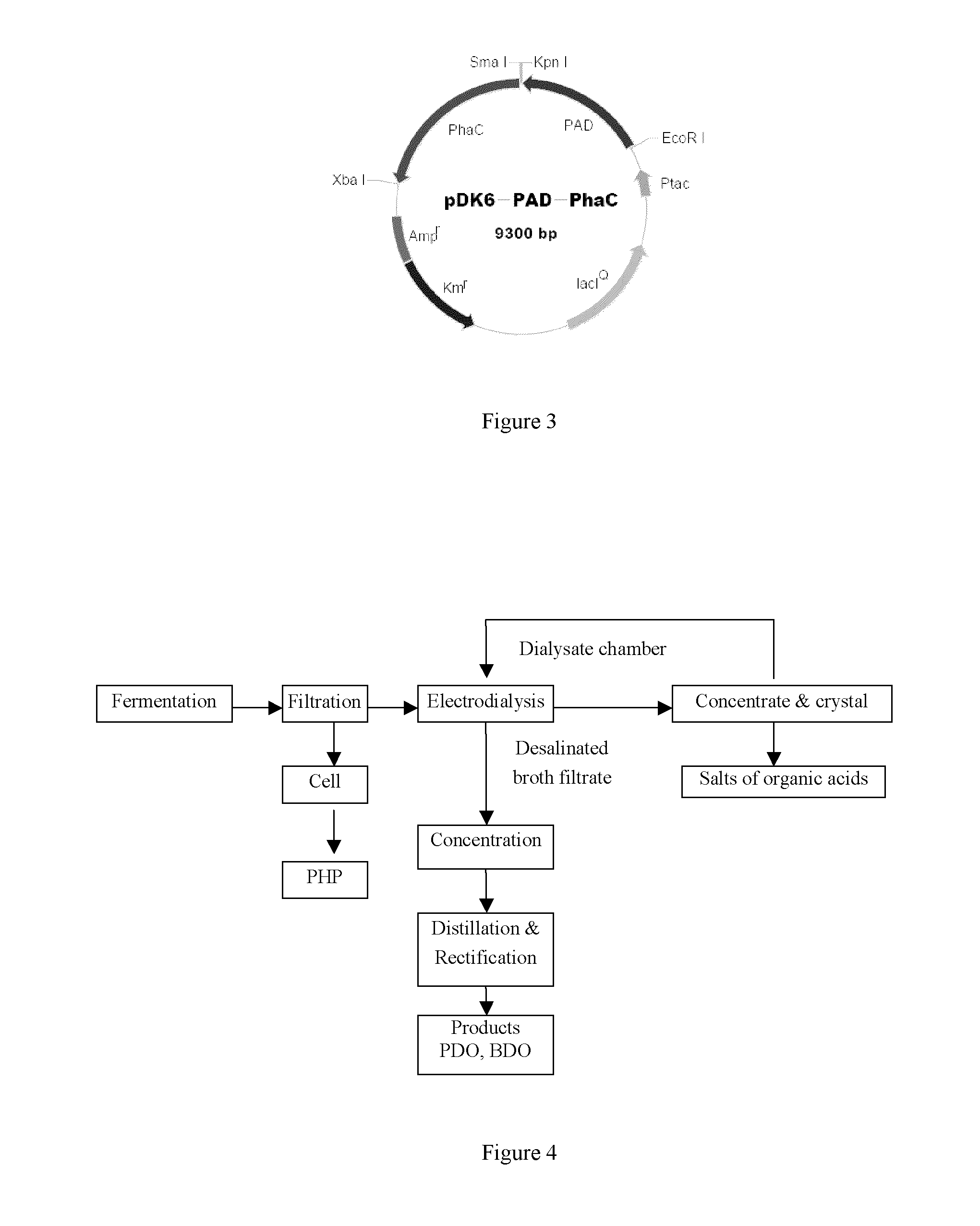
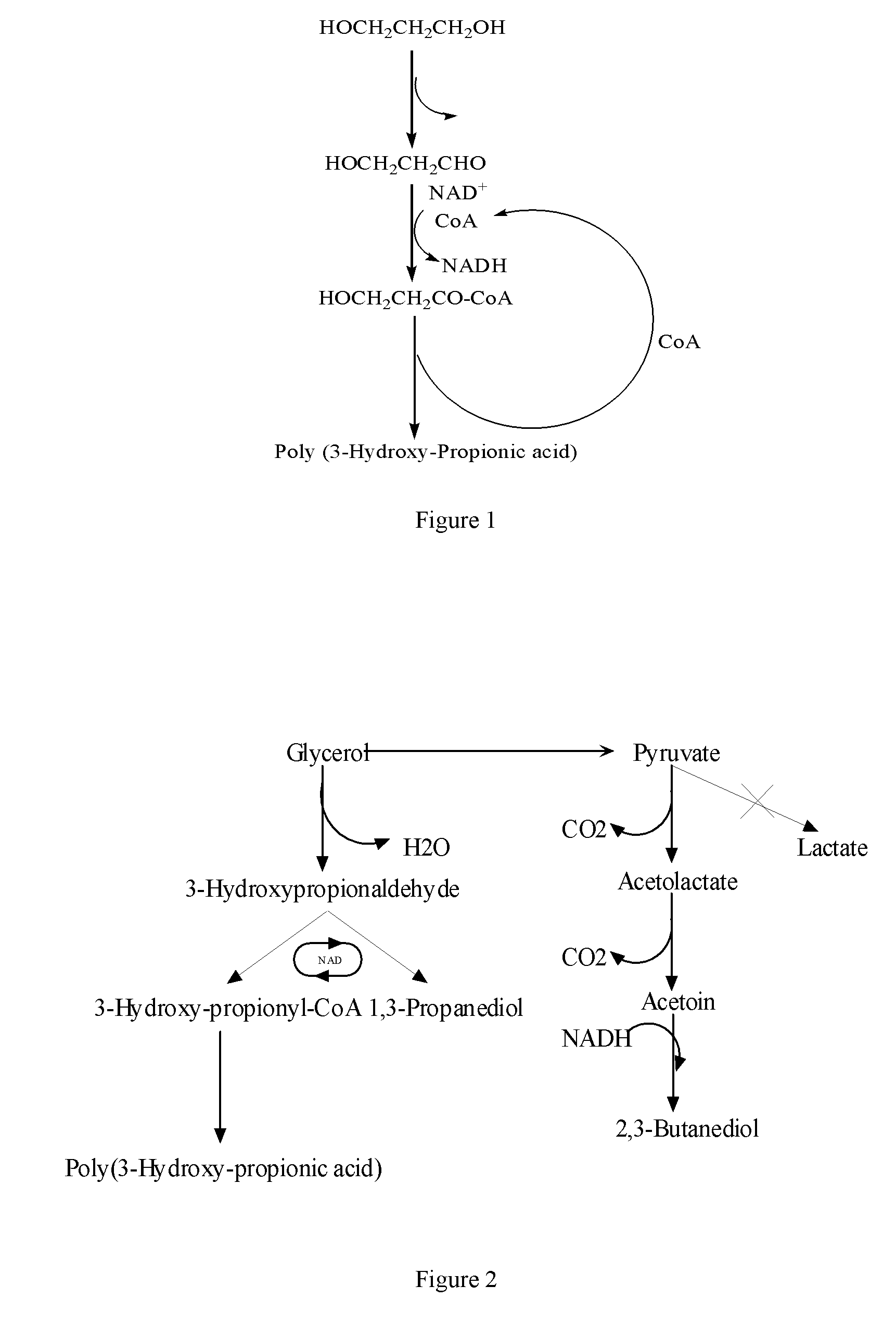
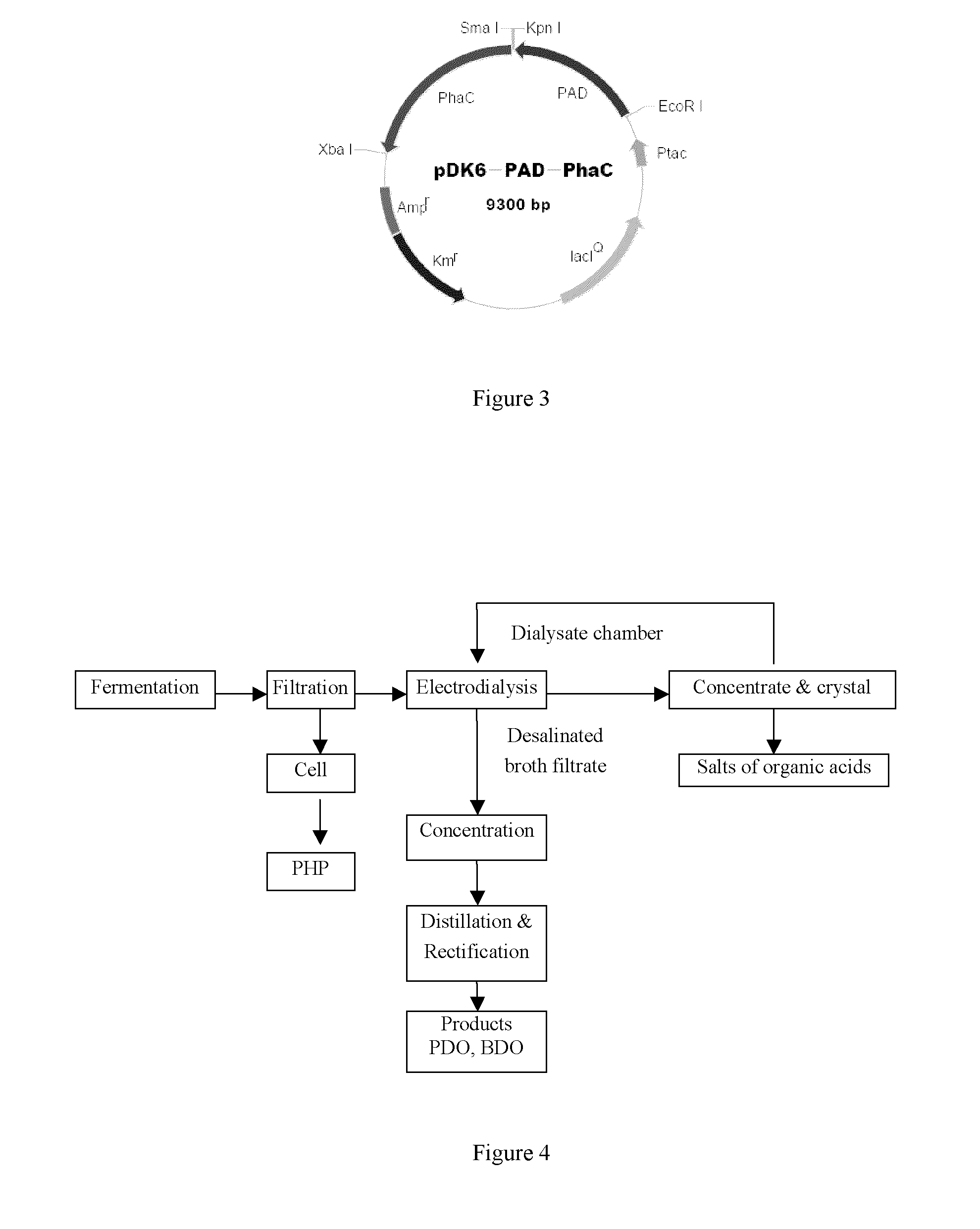
Methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation
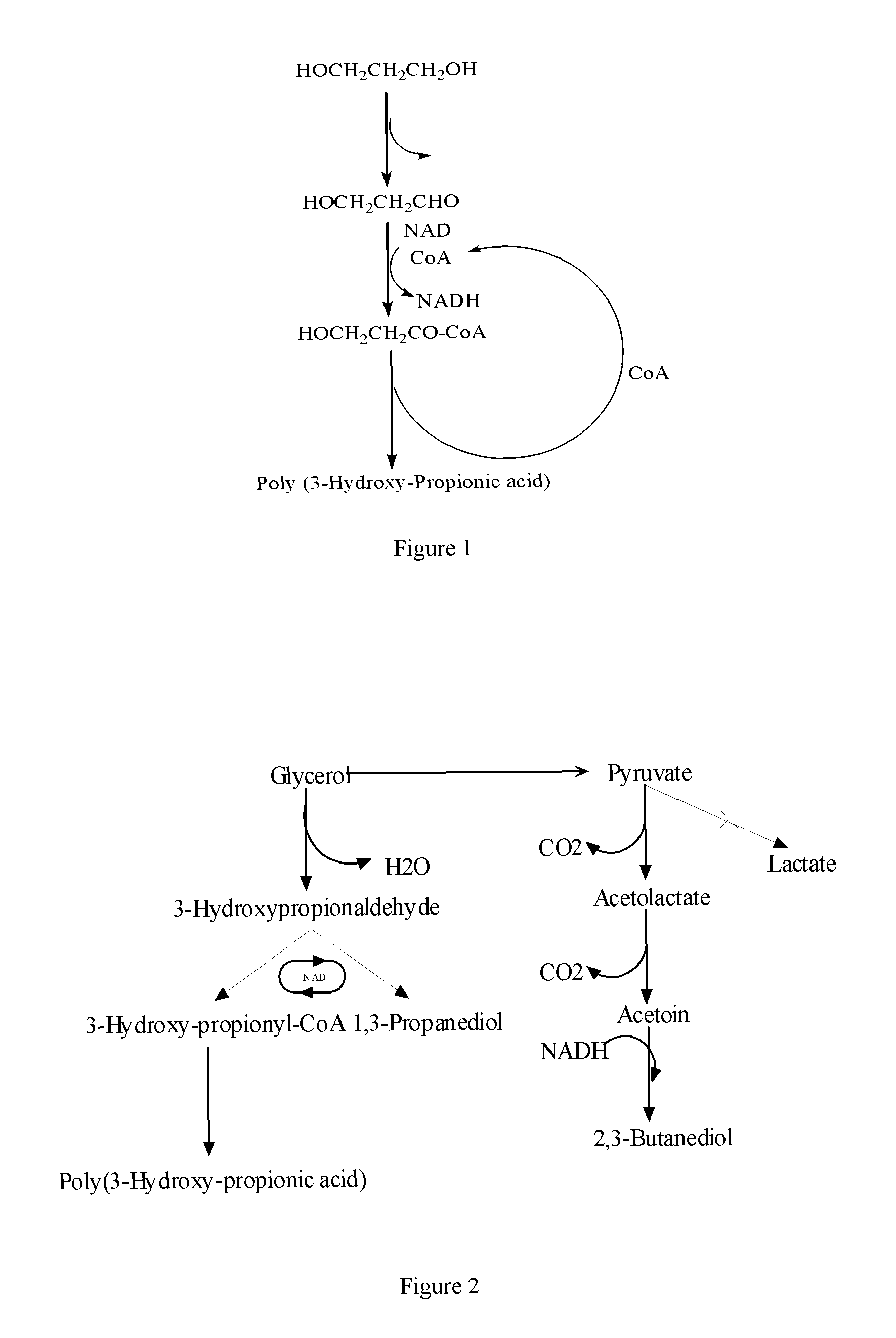
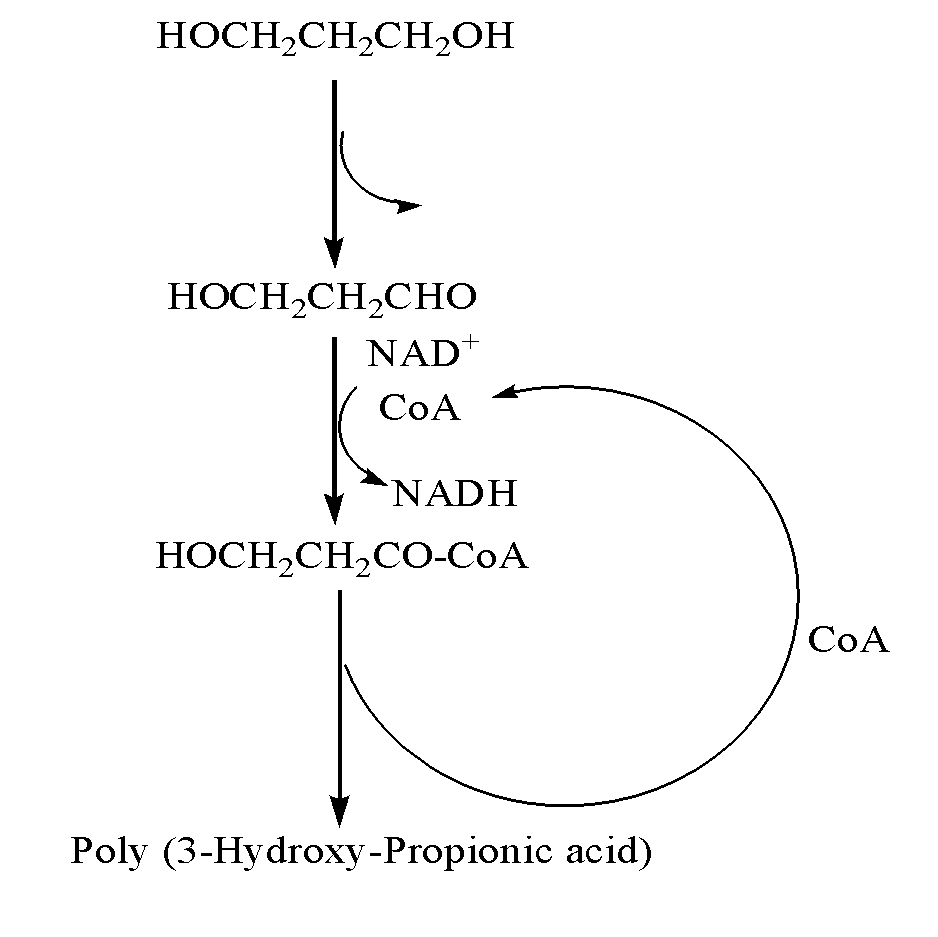
The present invention relates to genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of 1,3-propanediol (PDO), 2,3-butanediol (BDO), and polyhydroxypropionic acid (PHP) by fermentation. In particular, the invention relates to a genetically engineered micro-organism suitable for combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation, characterized in that: compared with corresponding wild-type starting micro-organism, the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene in the genetically engineered micro-organism is deleted or functionally inactivated, and the genetically engineered micro-organism comprises a heterogenous polynucleotide encoding the Coenzyme A-dependent Aldehyde dehydrogenase and a heterogenous polynucleotide encoding the Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Methods for the construction of such micro-organisms, and methods for combined production of PDO, BDO and PHP by fermentation of a genetically engineered bacterium are also taught.
Owner:HUNAN RIVERS BIOTECH +1
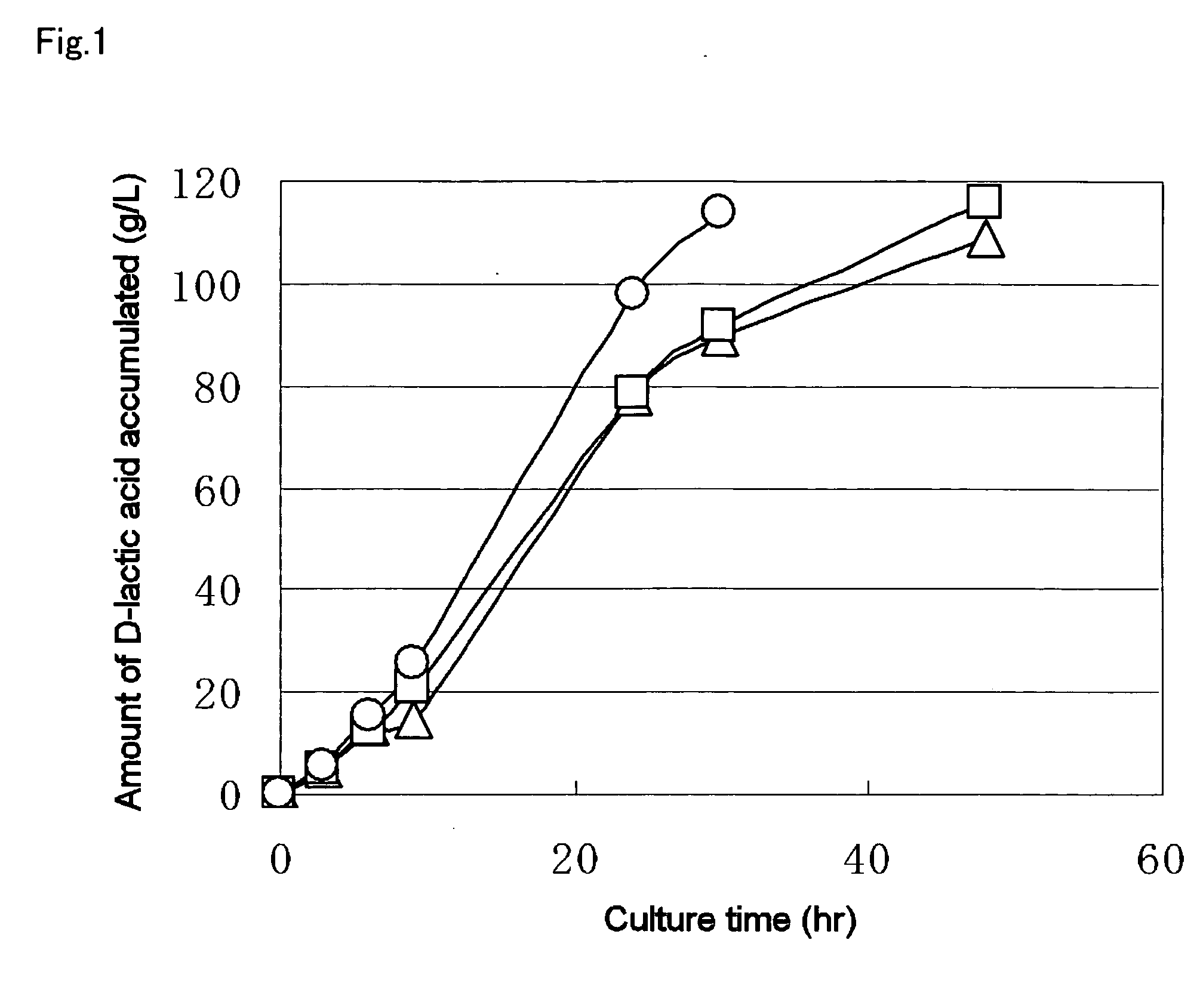
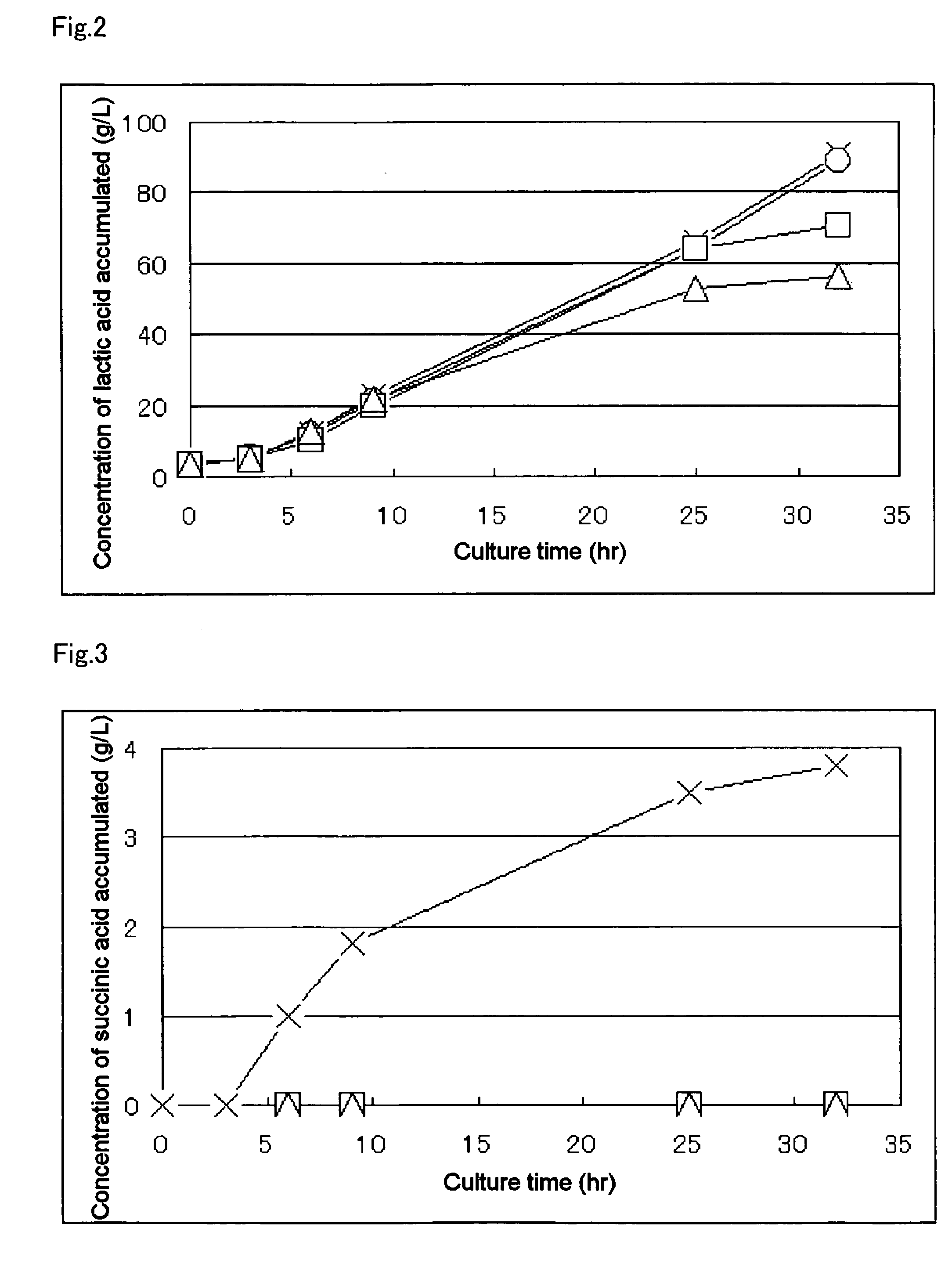
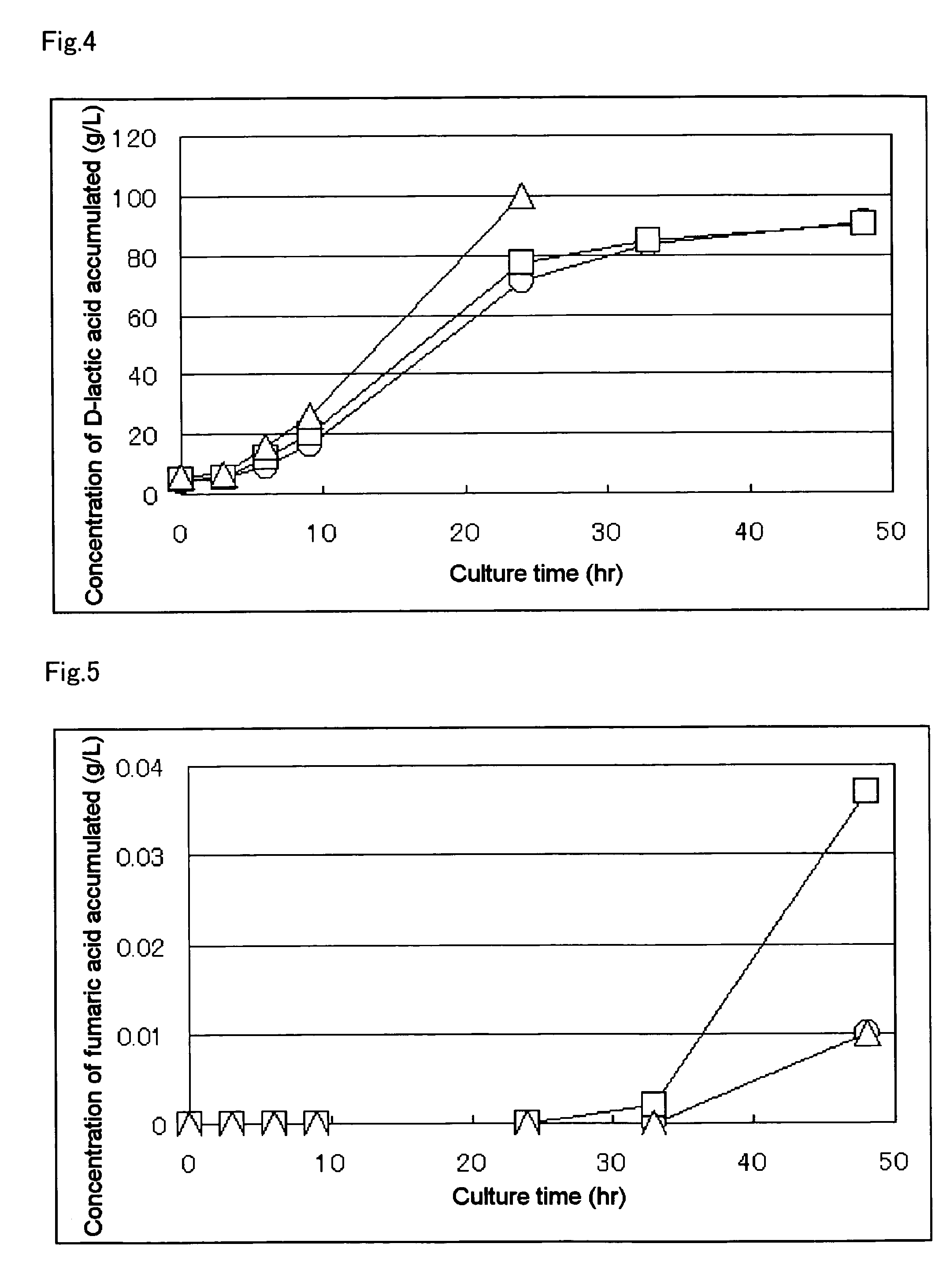
Biocatalyst for production of d-lactic acid (as amended)
ActiveUS20070065930A1Increase productivityHigh selectivityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliD-lactate dehydrogenase
A method for producing D-lactic acid in high yield, and to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid with high selectivity, in which optical purity is high and a by-product organic acid is small. In one aspect, a microorganism, wherein activity of pyruvate formate-lyase (pfl) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of Escherichia coli-derived NADH-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA) is enhanced, is cultured to efficiently produce D-lactic acid. With regard to a method for enhancing ldhA activity, by linking, on a genome, a gene encoding ldhA with a promoter of a gene which controls expression of a protein involved in a glycolytic pathway, a nucleic acid biosynthesis pathway or an amino acid biosynthesis pathway, suitable results are obtained compared to the method for enhancing expression of the gene using an expression vector. A microorganism in which a dld gene is substantially inactivated or decreased is cultured to produce high quality D-lactic acid with reduced concentration of pyruvic acid.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
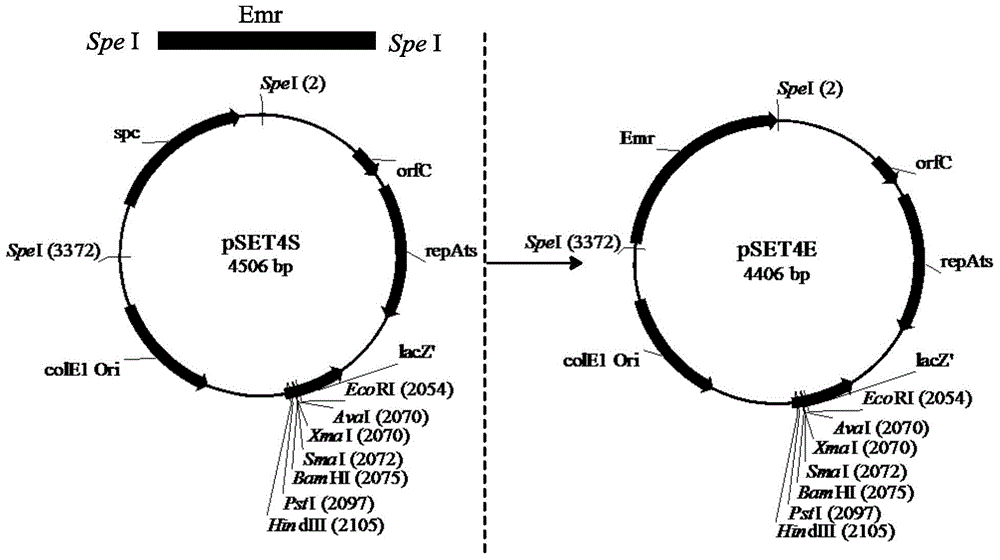
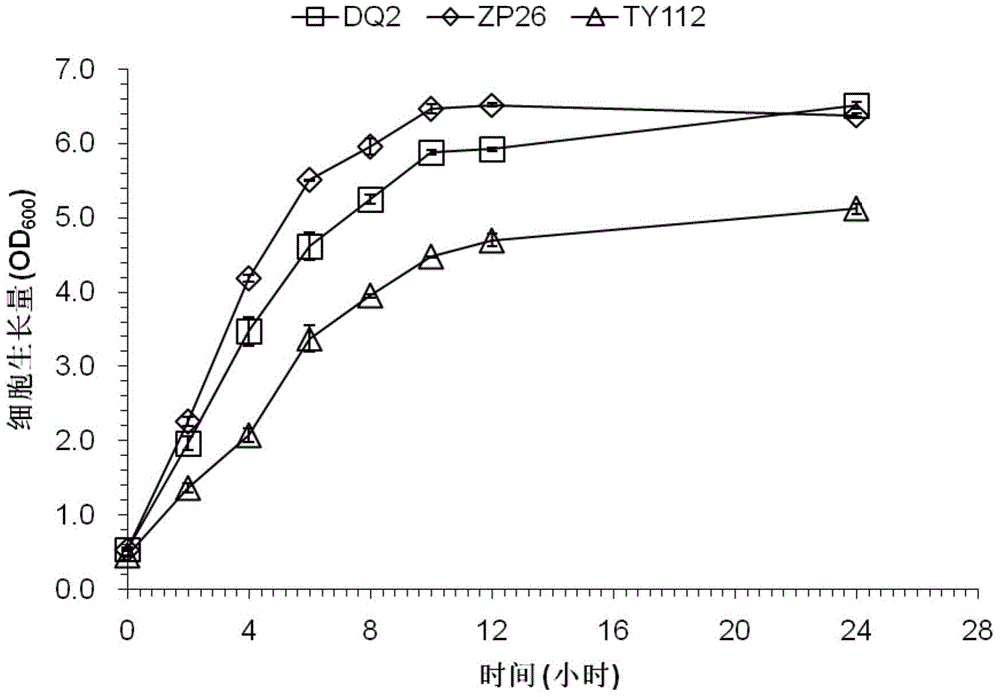
Unmarked gene knock-out method of pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 based on homologous recombination
InactiveCN105821071ARapid knockoutStable knockoutBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBacterial strain
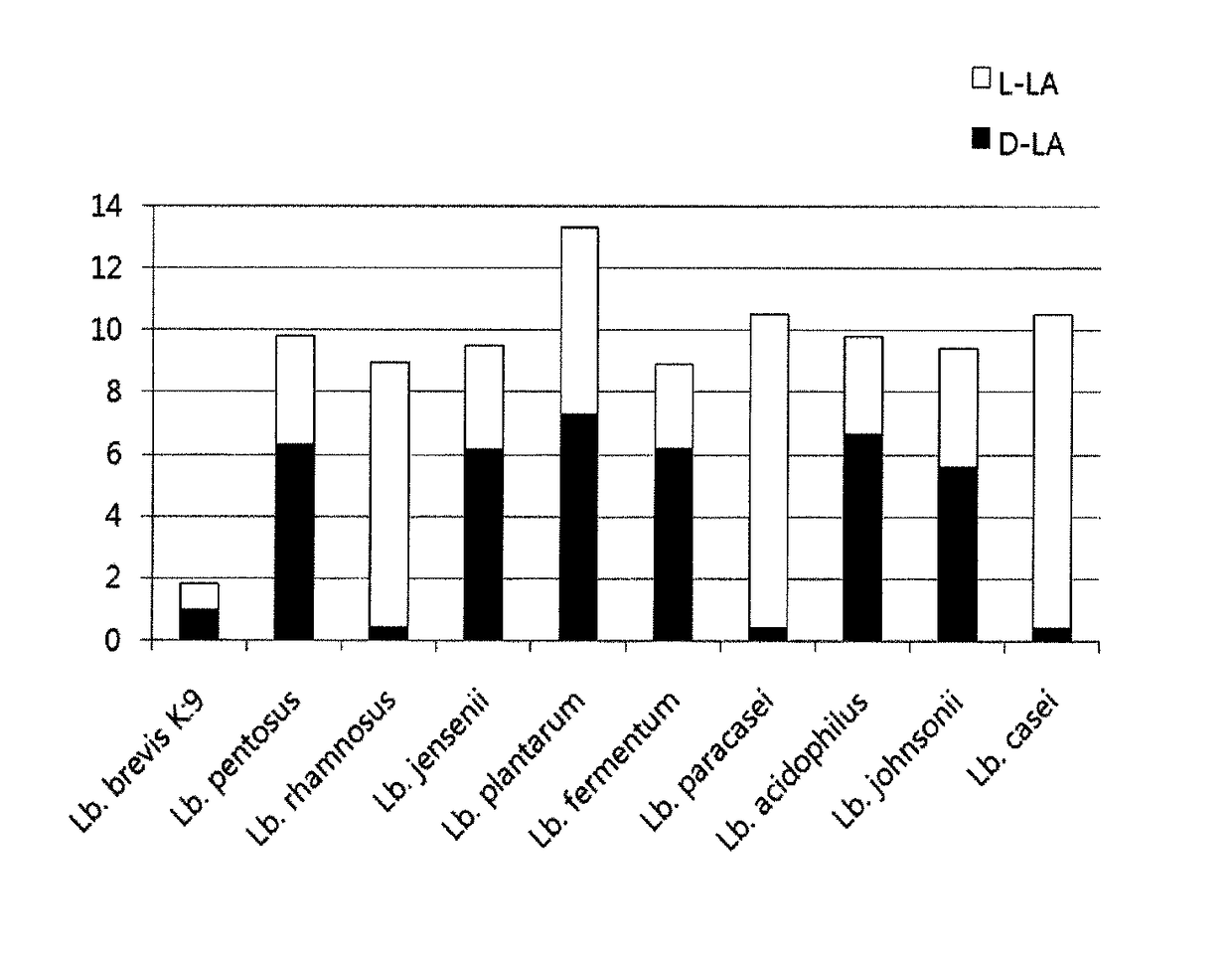
The invention relates to an unmarked gene knock-out method of pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 based on homologous recombination. The method comprises the following steps: temperature sensitive-type shuttle plasmid pSET4E and knock-out plasmid containing homologous fragments at upstream and downstream parts of target genes to be knocked out are constructed, the knock-out plasmid is subjected to electrotransformation into pediococcus acidilactici, and single commutators generating homologous recombination for the first time and double-exchange mutant strains generating homologous recombination for the second time are screened and identified. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the unmarked gene knock-out of pediococcus acidilactici for the first time, the obtained knock-out bacterial strain does not carry any resistant gene, can be taken as a original strain for subsequent and reconstruction, and also can be used for large-scale industrial production in a safe mode. The method is used for respective knock-out of L-lactate dehydrogenase gene and d-lactate dehydrogenase gene of the pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 (a preservation number is CGMCC NO.7471), the obtained knock-out bacterial strains are respectively named as pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 and TY112, the preservation numbers are CGMCC NO.8665 and CGMCC NO.8664 respectively, and optically pure D-lactic acid and L-lactic acid are respectively generated.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of pdo, bdo and php by fermentation
ActiveUS20110117617A1Less producedImprove isolationBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The present invention relates to methods and genetically engineered micro-organisms for the combined production of PDO, BDO, and PHP by fermentation. The micro-organism is characterized in that its D-lactate dehydrogenase gene has been deleted or functionally inactivated, and it comprises heterogenous polynucleotides encoding the Coenzyme A-dependent Aldehyde dehydrogenase and the Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Methods for the construction of such micro-organisms are also disclosed
Owner:HUNAN RIVERS BIOTECH +1
Dna encoding a protein having d-lactate dehydrogenase activity and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070105202A1Large capacityPositively affect production of D-lacticFungiSugar derivativesNucleotideDna encoding
This invention provides a polynucleotide that encodes a protein having lactate dehydrogenase activity and such protein that can be used for producing D-lactic acid. This polynucleotide has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (a), and it hybridizes under stringent conditions with a probe comprising all or part of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary strand thereof and encodes a protein having D-lactate dehydrogenase activity (b).
Owner:TEIJIN LTD +1
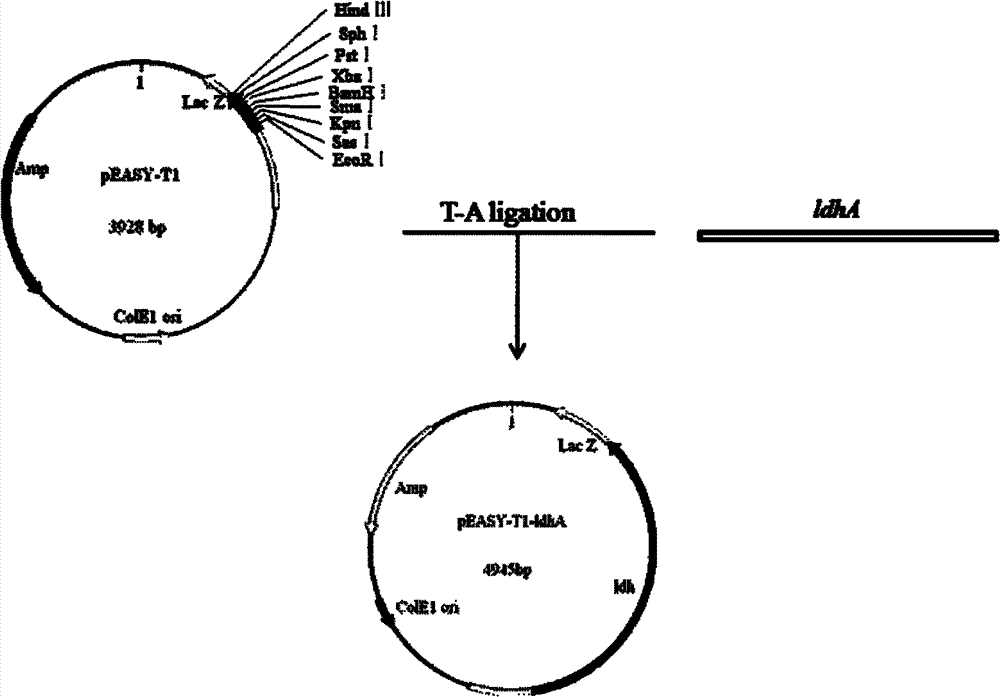
Genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and constructon method and application thereof
InactiveCN101993850AHigh optical purityIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseMicroorganism
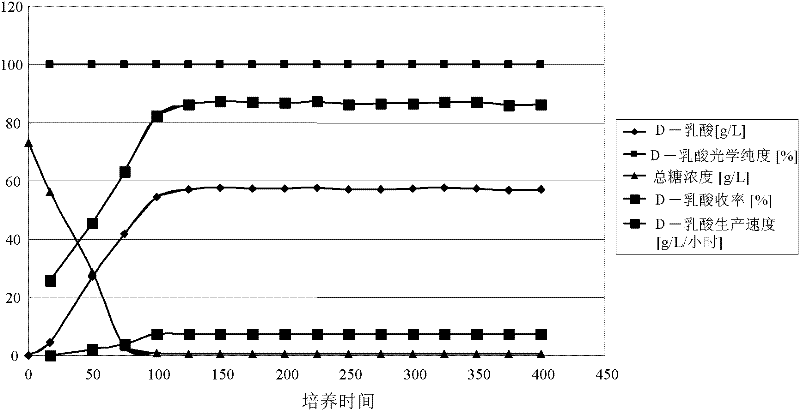
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and a construction method and application thereof. The strain of C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh deleted in L-lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldh) is used as a starting strain to over express exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene so as to obtain C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh / ldhA. The genetic engineering bacteria are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preserving registration number of CGMCC No.4041. By utilizing the genetic engineering means, the expression of the exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene is realized in the corynebacterium glutamicum deleted in L-lactic acid metabolic pathway, and the genetic engineering bacteria producing high optical purity D-lactic acid are successfully constructed. When the engineering bacteria are used for producing lactic acid through fermentation, the yield of the D-lactic acid is over 40g / L, and the purity is over 99 percent. The invention has important significance for the industrial production of the D-lactic acid, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
Engineering bacterium capable of producing D-lactate by aid of pentose and hexose synchronously by means of fermentation, and fabrication and application of engineering bacterium
InactiveCN105062938AHigh purityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention discloses fabrication and application of an engineering bacterium capable of producing D-lactate with high optical purity by the aid of pentose and hexose synchronously by means of fermentation, and belongs to the field of genetic fermentation engineering. Escherichia coli capable of producing alcohol by the aid of the pentose by means of fermentation is used as an original strain, alcohol dehydrogenase genes (adhE) are replaced by D-lactate dehydrogenase genes (idhA) by means of homologous recombination, and encoding genes (ptsG) of enzymes IICB <Glc> of glucose transfer endocytosis are knocked out, so that the engineering bacterium capable of producing the D-lactate with the high optical purity by the aid of the pentose and the hexose synchronously by means of fermentation can be obtained. The fabrication and the application of the engineering bacterium have the advantages that mixed carbon sources are used for lactate fermentation production, accordingly, glucose effects can be reduced, the pentose and the hexose can be synchronously utilized, and the utilization efficiency of the carbon sources in unit time can be improved; carbon metabolic flux is redistributed, accordingly, accumulation of a large quantity of D-lactate which is a target product can be promoted, generation of other byproducts such as acetic acid can be basically prevented, the D-lactate is high in optical purity, and the optical purity of the D-lactate can reach 99.8% at least.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
D-Lactate Dehydrogenase, Engineered Strain Containing D-Lactate Dehydrogenase and Construction Method and Use of Engineered Strain
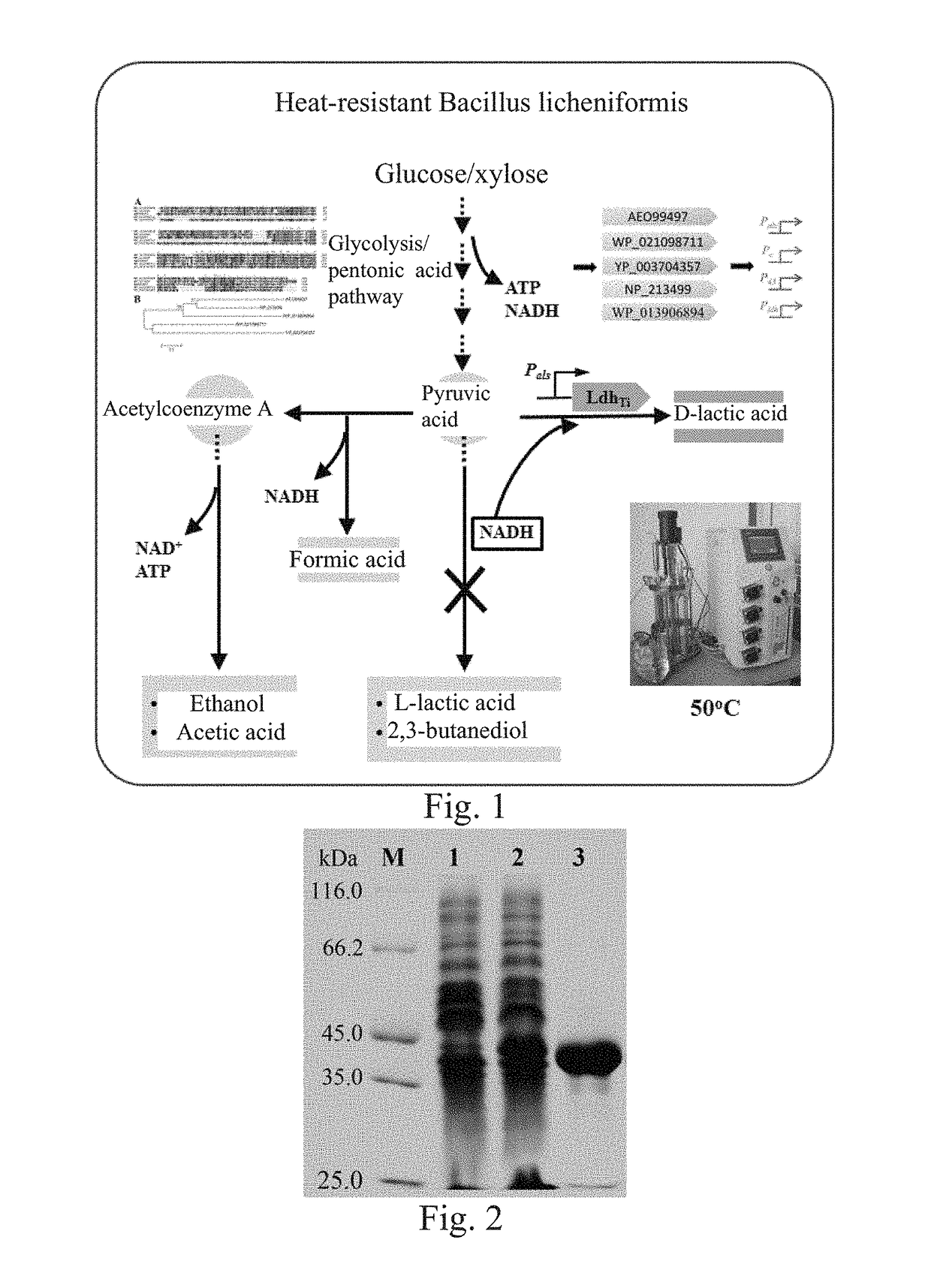
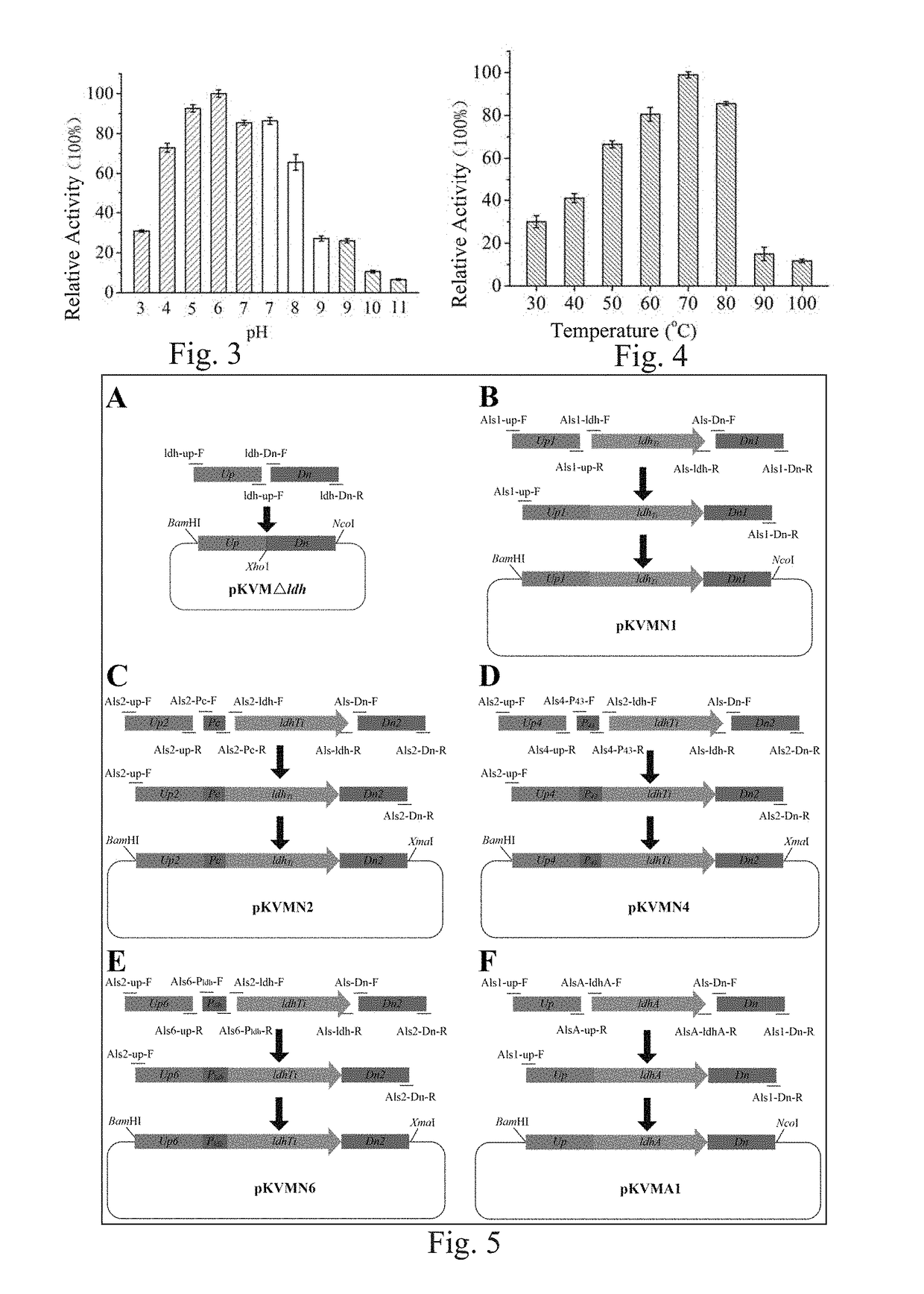
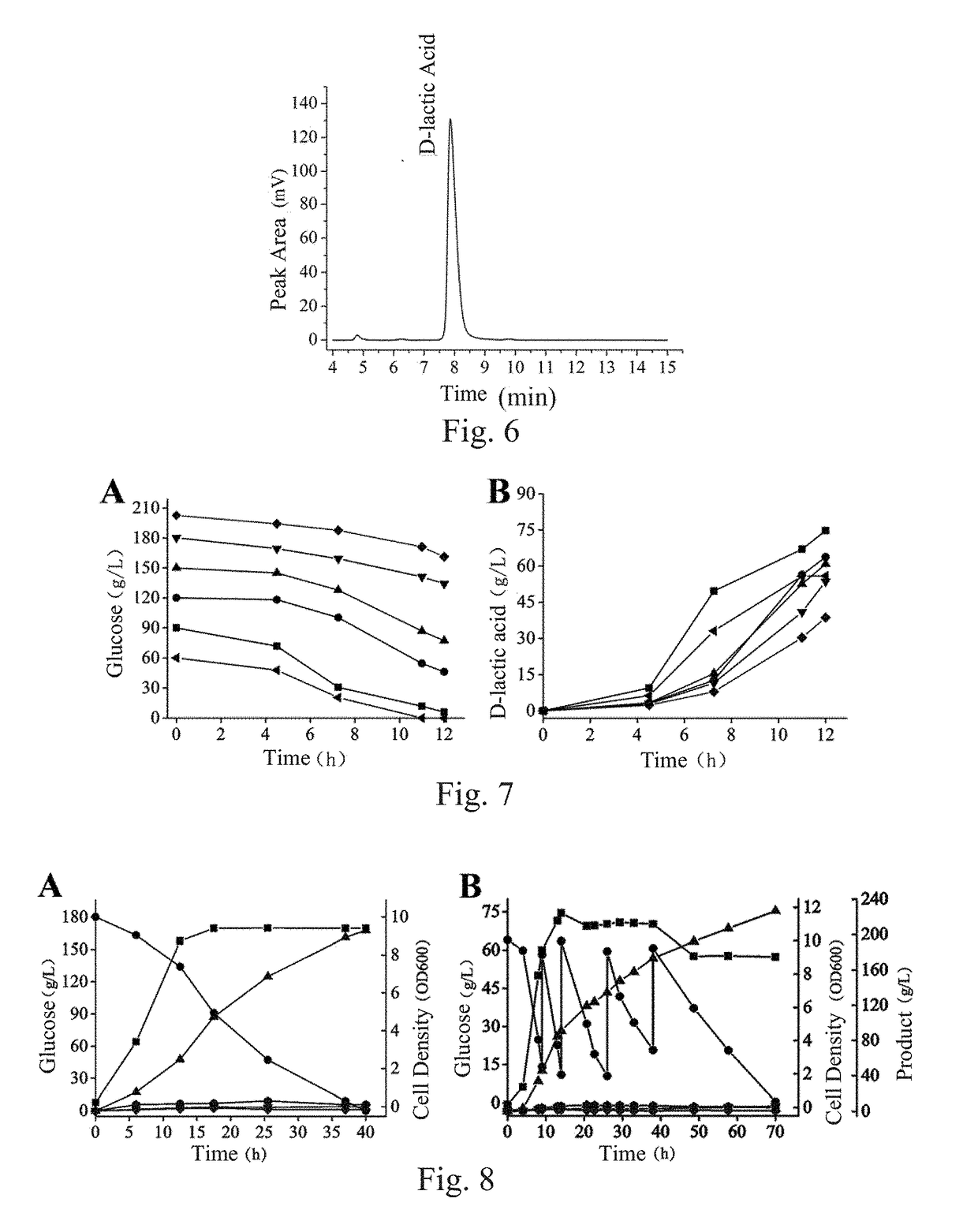
ActiveUS20190040425A1Good thermophily and heat stabilityHigh yieldTransferasesOxidoreductasesBacillus licheniformis2,3-Butanediol
Provided herein is D-lactate dehydrogenase, an engineered strain containing the D-lactate dehydrogenase, and a construction method and use of the engineered strain. The D-lactate dehydrogenase has unique properties and is from Thermodesulfatator indicus, and the D-lactate dehydrogenase has good thermophily and heat stability. By using the D-lactate dehydrogenase and said gene engineering reconstruction method, a fermentation product of the reconstructed Bacillus licheniformis can be redirected to optically-pure D-lactic acid with a high yield from naturally produced 2,3-butanediol, and the optical purity of the produced D-lactic acid reaches 99.9%; and raw materials for fermentation are low-cost, and a fermentation state is between an anaerobic fermentation state and a microaerobic fermentation state. By using the method for producing D-lactic acid through fermentation at high temperature, the production cost can be reduced, the production efficiency can be improved and there is a wide industrial application prospect for the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
DNA Encoding a Protein Having a D-Lactate Dehydrogenase Activity and Uses Thereof
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC +1
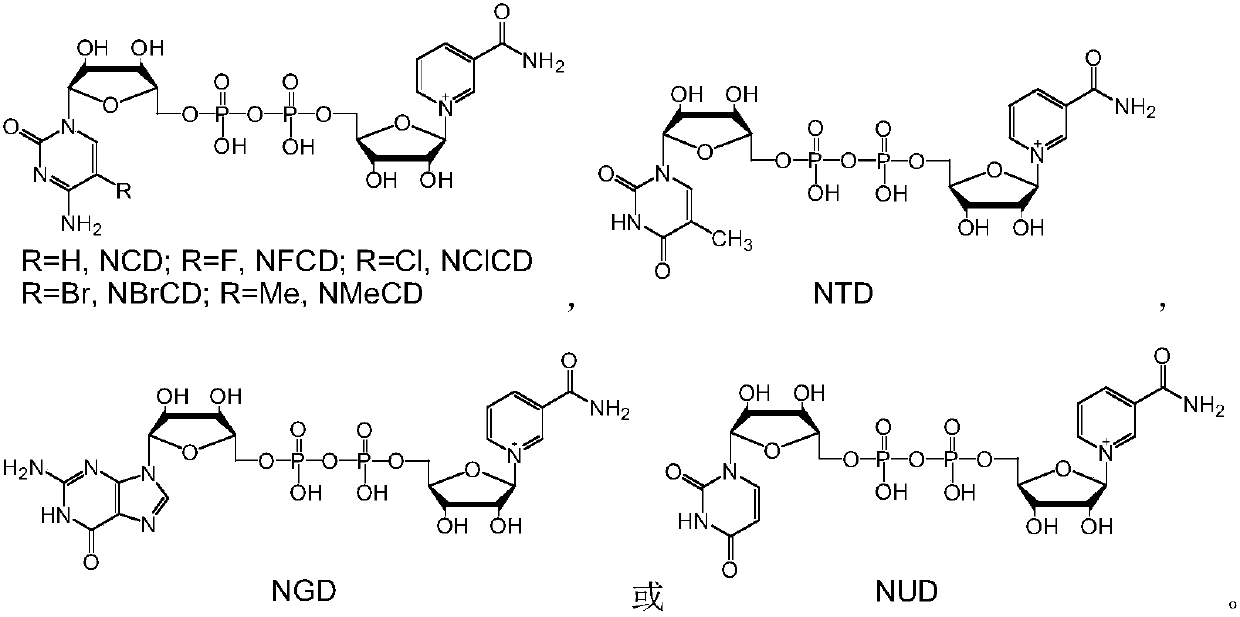
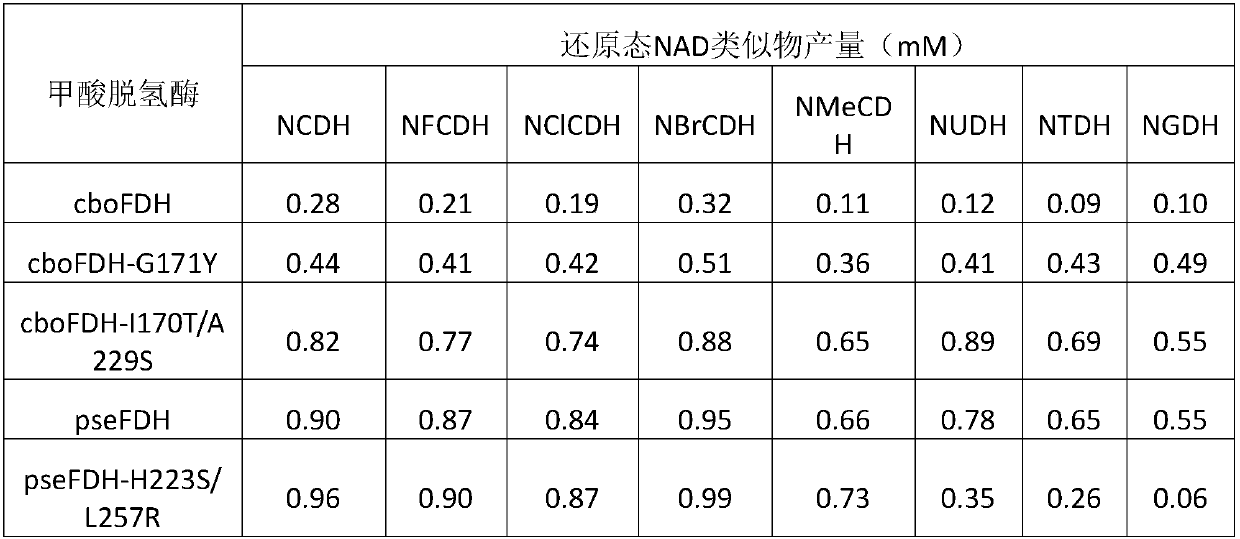
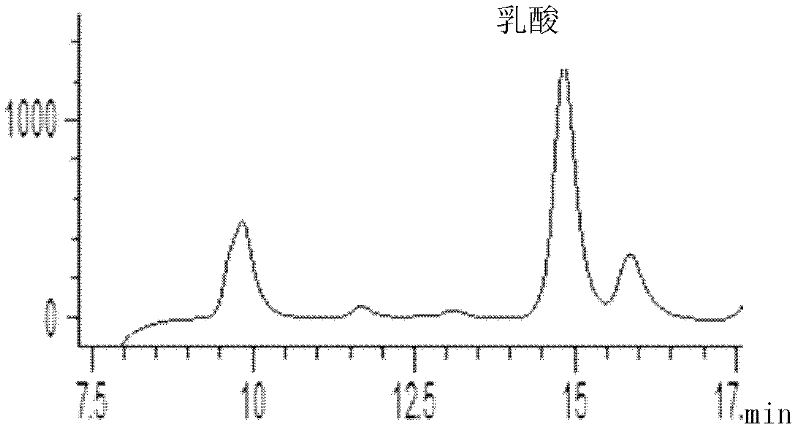
Reduction method of NAD analog
The invention discloses a reduction method of a NAD analog and an application of the reduction method. According to the method, a reducing agent is a formic acid compound, a catalyst is hydrogenlyasewhich can use the formic acid compound, and when the hydrogenlyase is used for oxidating the formic acid compound, the NAD analog is converted into a reducing state. The method can be used for producing the reducing state NAD analog or a deuterated reducing state analog, and can also be used for providing reducing power for an enzyme reaction consuming the reducing state NAD analog, and the reducing state NAD analog can also be used as coenzyme to be used for a reduction reaction of enzyme catalysis of malic enzyme ME-L310R / Q401C, D-lactate dehydrogenase DLDH-V152R, saccharomyces cerevisiae alcohol dehydrogenase and the like. Wide application of the NAD analog is facilitated. According to the reducing method of the NAD analog, under the mild condition, the regenerated reducing state NAD analog can be used for preparing malic acid or lactic acid, and can also be used as oxidation-reduction power for adjusting and controlling the metabolism intensity of the malic acid or the lactic acidin microorganisms.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombination blue-green alga for producing lactic acid as well as preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN102517303AAchieve productionEasy genetic manipulationBacteriaEnergy inputGenetics manipulationD-lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a recombination blue-green alga for producing a lactic acid as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: modifying a metabolic pathway, and importing a coding gene of D-lactic dehydrogenase into a genome of the blue-green alga to obtain the recombination blue-green alga for producing an optical pure D-lactic acid. An amino acid sequence of the D-lactic dehydrogenase is a sequence 3 in a sequence table. Proved by experiments, the recombination blue-green alga disclosed by the invention is constructed through a metabolic engineering modification method, and carbon dioxide (CO2) can be directly converted into organic matter by utilizing solar energy by utilizing the characteristic that the blue-green alga is photoautotrophic; and the recombination blue-green alga can be directly synthetized into the optical pure D-lactic acid by utilizing the solar energy and the CO2 by utilizing the characteristic that the blue-green alga can grow in seawater and sewage and the advantage that genetic manipulation can be easily performed on the blue-green alga.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genes of D-lactic dehydrogenase from serratia marcescens and research of cloning and expressing recombinant strains and recombinant enzymes
The invention relates to genes of D-lactic dehydrogenase from serratia marcescens and the research of cloning and expressing recombinant strains and recombinant enzymes, in particular provides new D-lactic dehydrogenase ('D-LDH protein' for short), polynucleotide for encoding the D-LDH protein and a method for generating the D-LDH protein through recombination technology. The invention also discloses application of the polynucleotide for encoding the D-LDH protein. The D-LDH protein has the function of catalyzing pyruvic acid to form D-lactic acid, and can be used for producing the D-lactic acid of which the price is 8 to 10 times higher than that of L-lactic acid efficiently, so the D-LDH protein has huge application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
D-lactic acid dehydrogenase of Sporolactobacillus inulinus, coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a D-lactic acid dehydrogenase derived from Sporolactobacillus inulinus, a coding gene and application thereof. The D-lactate acid dehydrogenase provided by the invention is (a) or (b) as below: (a) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 1 in the sequence table; and (b) a sequence 1 derived protein, with D-lactate acid dehydrogenase activity, obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 1. The D-lactate acid dehydrogenase provided by the invention can use NADH or NADPH as a coenzyme to catalyze pyruvic acid for generation of D-lactic acid, and can also use NADH as a coenzyme to catalyze phenyl pyruvic acid for generation of D-phenyl lactic acid; and a generated product has optical purity reaching 100% (without L-product generation). Therefore, the invention has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biocatalyst for production of d-lactic acid
ActiveCN101654666AImprove productivityHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSuccinic acid
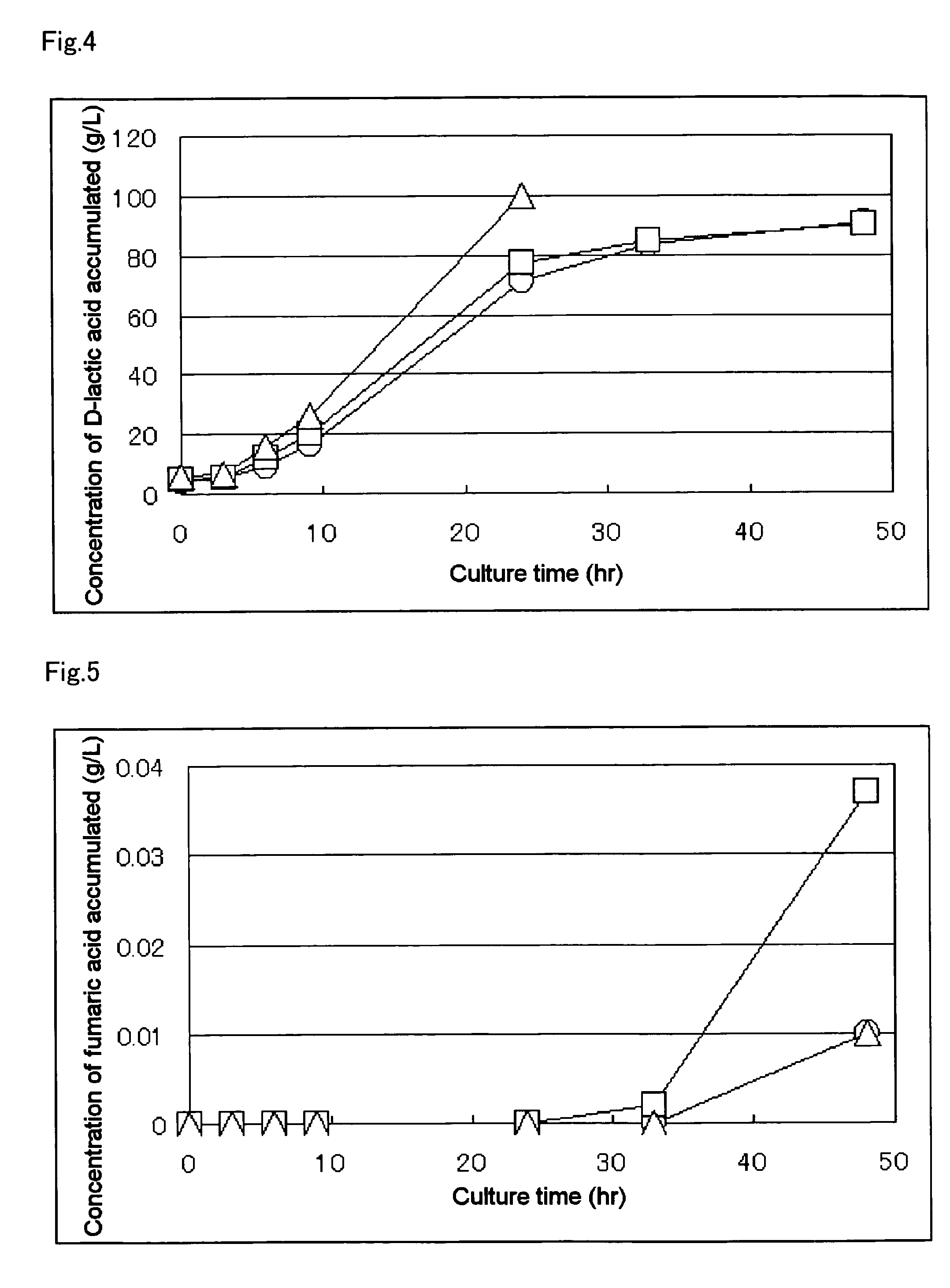
The subject of the present invention is to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid in high yield, and to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid with high selectivity, in which optical purity is high and a by-product organic acid is small. A microorganism, wherein activity of pyruvate formate-lyase (pfl-) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of Escherichia coli-derived NADH-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA) is enhanced, is cultured to produce a remarkable amount of D-lactic acid in a short time. With regard to a method for enhancing ldhA activity, by linking, on agenome, a gene encoding 1dhA with a promoter of a gene which controls expression of a protein involved in a glycolytic pathway, a nucleic acid biosynthesis pathway or an amino acid biosynthesis pathway, suitable results are obtained compared to the method for enhancing expression of the gene using an expression vector. In addition, a microorganism in which a did gene is substantially inactivatedor decreased is cultured to produce high quality D-lactic acid with reduced concentration of pyruvic acid. Furthermore, it is possible to suppress by-production of succinic acid and fumaric acid whilemaintaining high D-lactic acid productivity by using the above-mentioned microorganism having a TCA cycle, wherein activity of malate dehydrogenase (mdh) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of aspartate ammonia-lyase (aspA) is inactivated or decreased.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
D-lactic acid diagnosis/determination reagent kit and method for determining D-lactic acid concentration
InactiveCN101324561AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFerricytochrome cPeroxidase
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating D-lactic acid by utilizing the technologies of the enzymatic cycling amplification method, the enzymic colorimetric method and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on the specificity of the D-lactic acid. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the D-lactic acid, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, 2-ferricytochrome-c, ammonia ions, D-lactate dehydrogenase, alanine dehydrogenase, glycine oxidase, peroxidase, a reduced chromogen combination and a stabilizer. Through a series of enzymatic reactions, the colorless reduced chromogen combination is finally oxidized into colored dyes, thereby mensurating the content of the dyes at 400nm-700nm of the wavelength by utilizing a visible light analyzer and further reflecting the concentration of the D-lactic acid directly.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
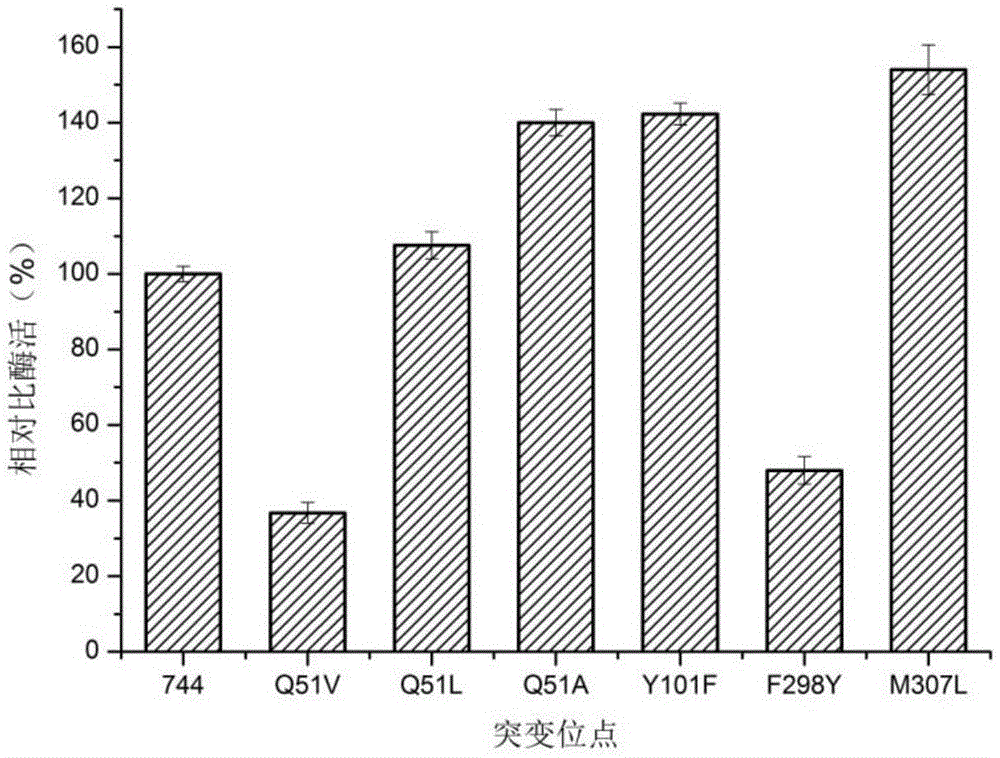
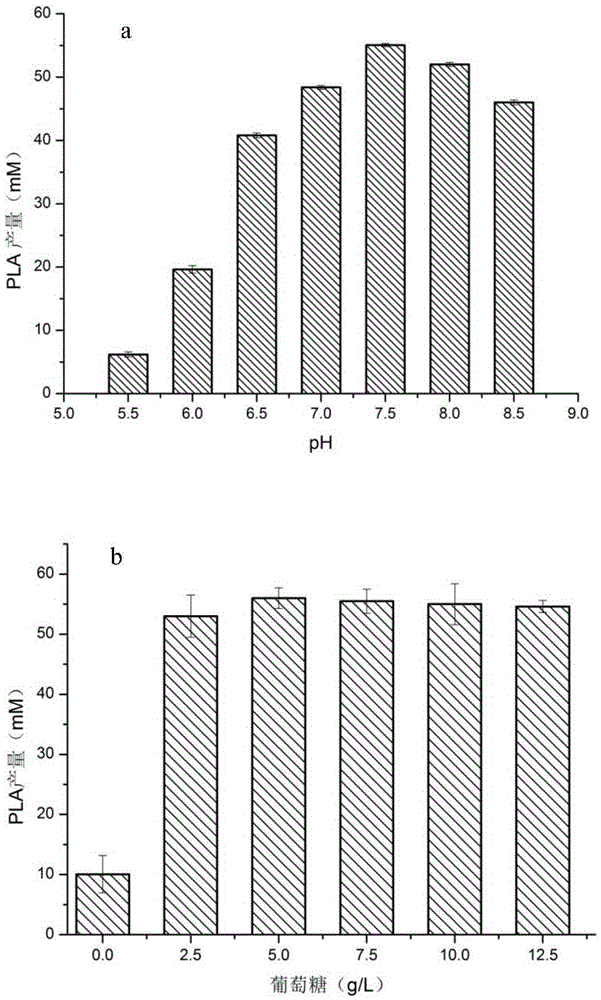
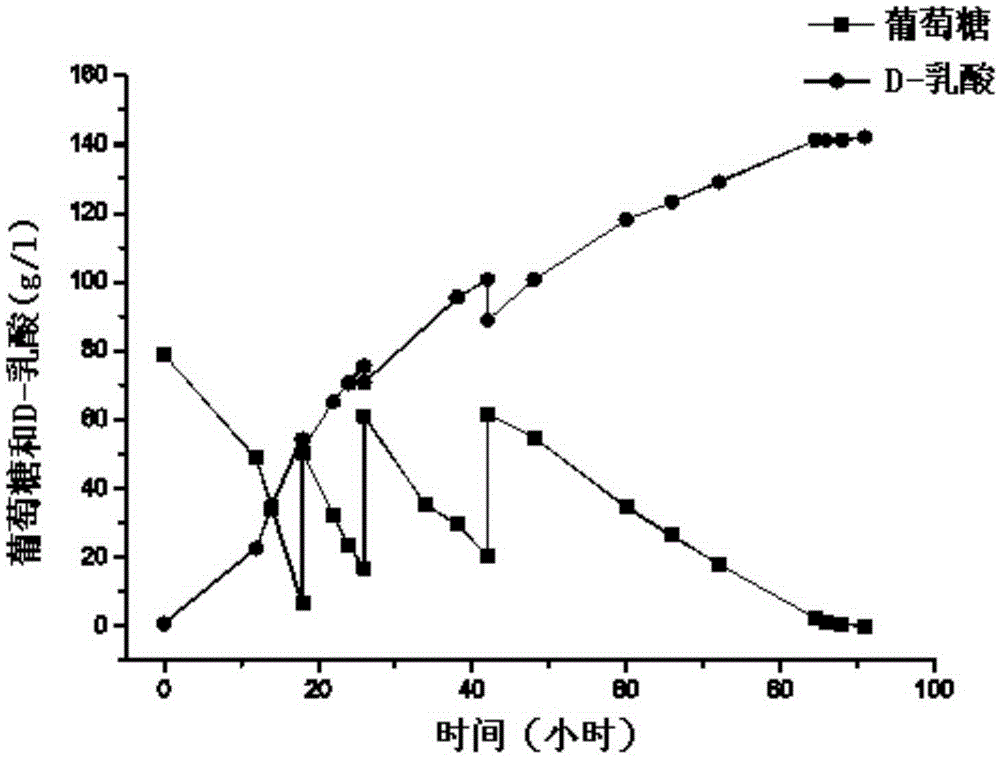
D-lactic dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN105586323AHigh D-lactate dehydrogenase activityIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringWAS PROTEINAgricultural science
The invention discloses a D-lactic dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. Protein is protein shown in the sequence A or is protein which has the same function, is derived from the sequence A and is formed by substituting, and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues to the protein shown in the sequence A; the sequence A is a sequence obtained by mutating Met at the <307>th bit into Leu in the sequence 2. It is proved through experiments that D-LDH 744 form Sporolactobacillus inulinus is selected and mutated to obtain the D-lactic dehydrogenase mutant M307L. The mutant has high D-lactic dehydrogenase activity, and compared with D-lactic dehydrogenase without mutation, and enzyme activity of D-LDH with PPA (phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride) as a substrate is improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
D-lactic acid diagnosis/determination reagent kit and method for determining D-lactic acid concentration
InactiveCN101324560AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFerricytochrome cAlanine dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating D-lactic acid by utilizing the technologies of the enzymatic cycling amplification method, the enzymic colorimetric method and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on the specificity of the D-lactic acid. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the D-lactic acid, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, 2-ferricytochrome-c, ammonia ions, D-lactate dehydrogenase, alanine dehydrogenase, glycine oxidase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby mensurating the concentration of the D-lactic acid.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Recombined bacillus alcalophilus, preparing method and application thereof, and method for preparing D-lactic acid
ActiveCN106884001AHigh optical purityReduce pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBacillus alcalophilus
The invention discloses a method for preparing recombined bacillus alcalophilus. According to the method, bacillus alcalophilus for producing L-lactic acid is used as original strain, and by means of genetic engineering operation, the original strain is made not to express L-lactic dehydrogenase but to express D-lactic dehydrogenase. The invention further discloses recombined bacillus alcalophilus prepared with the method, application of the recombined bacillus alcalophilus, and a method for preparing D-lactic acid. When the recombined bacillus alcalophilus prepared with the method for preparing the recombined bacillus alcalophilus is applied to preparation of D-lactic acid, the optical purity of the obtained D-lactic acid is higher than 99.8%, the conversion rate is 94% or more, and the yield can reach 142 g / L.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
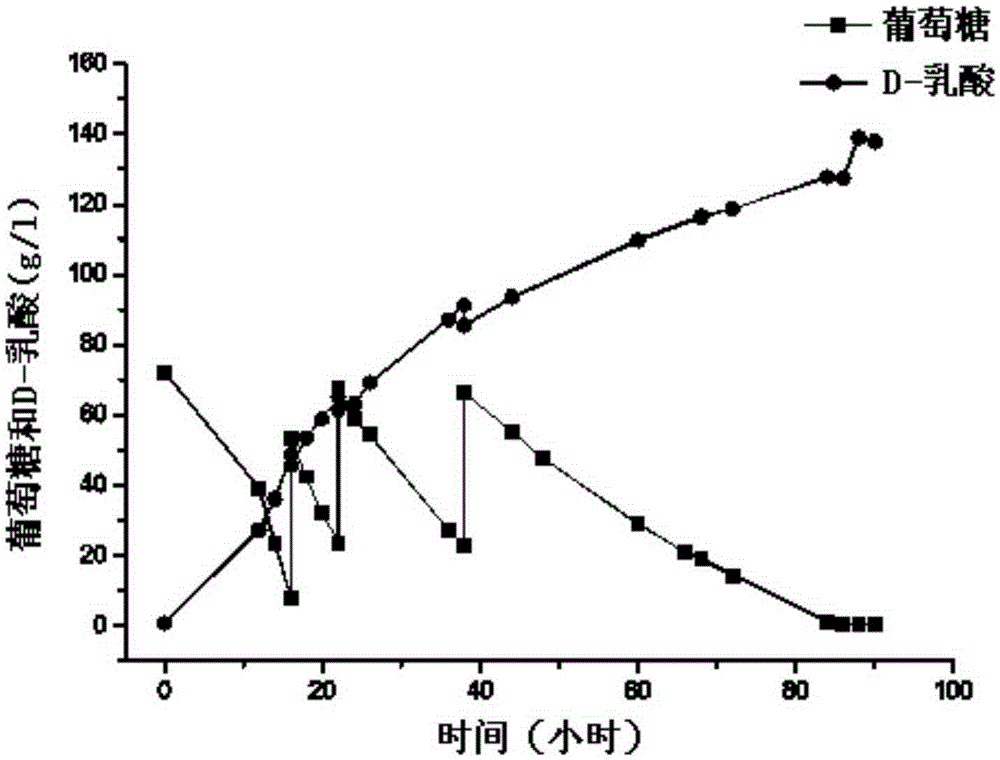
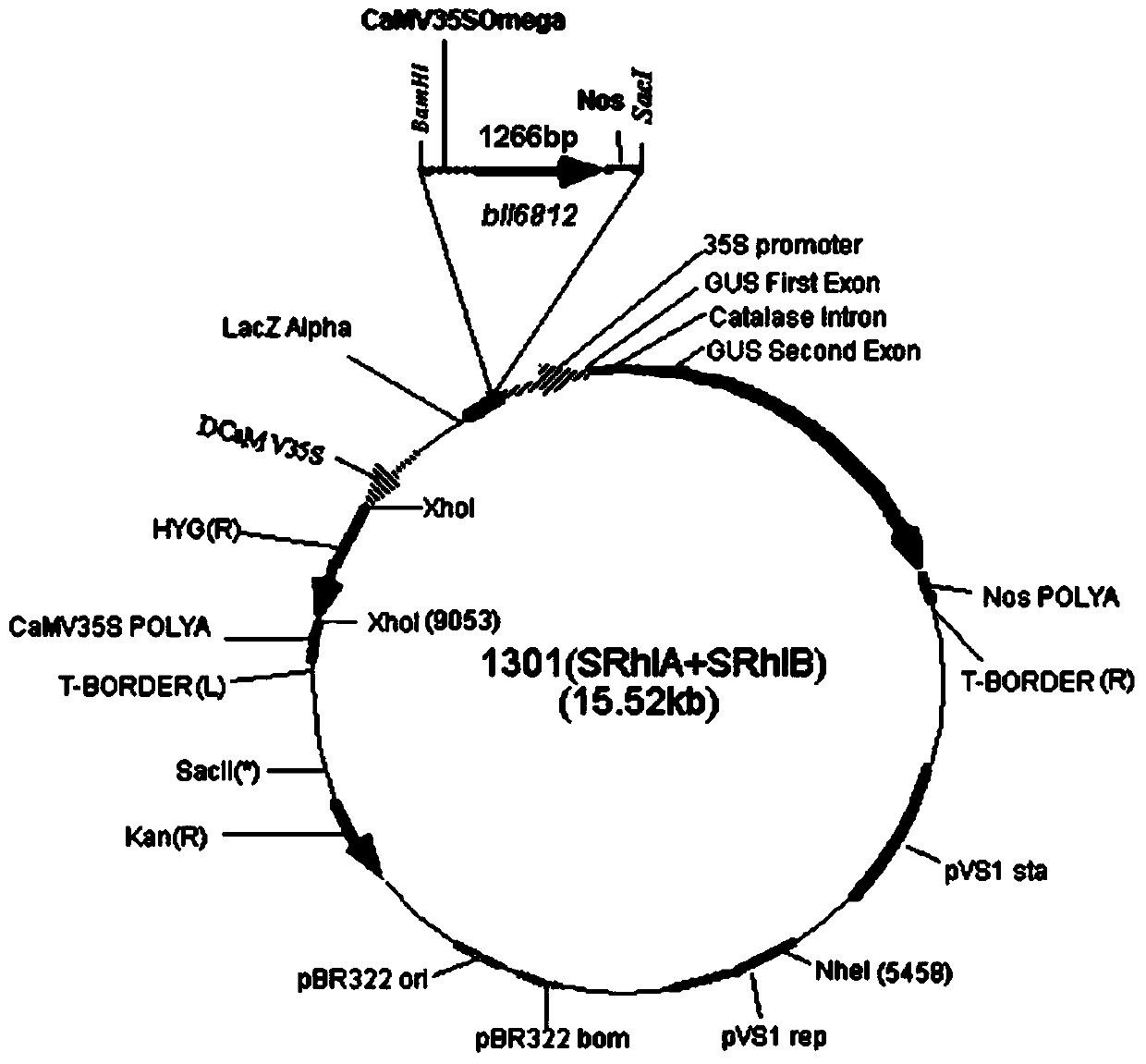
D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103740737AObvious resistance to glyphosateImproved resistance to glyphosateMicroorganism based processesFermentationNucleotideGlyphosate
The invention discloses a D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S derived from a high-efficiency nitrogen fixation bradyrhizobium japonicum as well as a preparation method and application of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S. A nucleotide sequence of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and an amino acid sequence coded by the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is prepared by reconstructing a D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812 derived from the high-efficiency nitrogen fixation bradyrhizobium japonicum according to a plant preferred codon and by using a gene synthesis method. The D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is converted into arabidopsis thaliana to obtain a transgenosis arabidopsis thaliana, and the performance of the transgenosis arabidopsis thaliana resisting glyphosate is remarkably superior to that of wild type arabidopsis thaliana, and can be applied to glyphosate-resisting crop breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
D-lactic acid diagnosis/determination reagent kit and method for determining D-lactic acid concentration
InactiveCN101324555AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzyme catalysisAbsorbance
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / mensurating D-lactic acid by utilizing the technology of the enzymic colorimetric method based on the specificity of the D-lactic acid. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for mensurating the concentration of the D-lactic acid, and belongs to the technology field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, D-lactate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby mensurating the concentration of the D-lactic acid.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and constructon method and application thereof
InactiveCN101993850BHigh optical purityIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and a construction method and application thereof. The strain of C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh deleted in L-lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldh) is used as a starting strain to over express exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene so as to obtain C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh / ldhA. The genetic engineering bacteria are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preserving registration number of CGMCC No.4041. By utilizing the genetic engineering means, the expression of the exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene is realized in the corynebacterium glutamicum deleted in L-lactic acid metabolic pathway, and the genetic engineering bacteria producing high optical purity D-lactic acid are successfully constructed. When the engineering bacteria are used for producing lactic acid through fermentation, the yield of the D-lactic acid is over 40g / L, and the purity is over 99 percent. The invention has important significance for the industrial production of the D-lactic acid, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
High-D-lactic acid-yield recombinant bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN106520644AEfficient synthesisHigh optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a high-D-lactic acid-yield recombinant bacterium and application thereof, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The recombinant bacterium provided by the invention is recombinant Klebsiella pneumoniae obtained by overexpressing D-lactate dehydrogenase gene ldhA in Klebsiella pneumoniae. According to the production method of D-lactic acid, progressive amplification culture is carried out after the recombinant bacterium is activated, thereby implementing pilot-scale production on the 500L fermentation tank level. The production method of D-lactic acid is simple and easy to implement, and implements high-efficiency synthesis of D-lactic acid on the pilot-scale level; the yield reaches 210 g / L, the D-lactic acid is free of L-lactic acid; and the recombinant bacterium has the characteristics of high yield and lower production cost, and has favorable market prospects and economic benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombination blue-green alga for producing lactic acid as well as preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN102517303BAchieve productionEasy genetic manipulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenetics manipulationD-lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing D-lactic acid by enzyme resolution of D,L-lactic Acid
InactiveCN101333554BShorten the growth cycleLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationD-lactic acid dehydrogenaseSubstrate concentration
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
D-lactic acid-producing strain and use thereof
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a D-lactic acid-producing strain modified to inhibit L-lactate dehydrogenase (L-LDH) activity and to introduce D-lactate dehydrogenase (D-LDH) activity in an L-lactic acid-producing strain, a mutated D-lactic acid-producing strain prepared by the above method, and a method for producing D-lactic acid including the steps of culturing the strain and recovering D-lactic acid from the culture media.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Polypeptide having d-lactate dehydrogenase activity, polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide, and process for production of d-lactic acid
Disclosed is a transformant which is produced by introducing, into a host cell, a polynucleotide encoding any one polypeptide selected from polypeptides (A) to (C) each having a higher D-lactate dehydrogenase activity than those of conventional polypeptides so that the polypeptide can be expressed in the host cell, and which can achieve D-lactic acid fermentation with high productivity. (A) A polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2. (B) A polypeptide which comprises an amino acid sequence produced by substituting, deleting, inserting and / or adding one or several amino acid residues in the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2, and which has a D-lactate dehydrogenase activity. (C) A polypeptide which comprises an amino acid sequence having at least 80% sequence identity to the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2, and which has a D-lactate dehydrogenase activity.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Variants of glycerol dehydrogenase having d-lactate dehydrogenase activity and uses thereof
The present invention provides methods of designing and generating glycerol dehydrogenase (GlyDH) variants that have altered function as compared to a parent polypeptide. The present invention further provides nucleic acids encoding GlyDH polypeptide variants having altered function as compared to the parent polypeptide. Host cells comprising polynucleotides encoding GlyDH variants and methods of producing lactic acids are also provided in various aspects of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
A kind of biological production method of danshensu
ActiveCN103667371BDe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliP-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Biocatalyst for production of D-lactic acid
ActiveUS8669093B2High selectivityHigh optical puritySugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliD-lactate dehydrogenase
A method for producing D-lactic acid in high yield, and to provide a method for producing D-lactic acid with high selectivity, in which optical purity is high and a by-product organic acid is small. In one aspect, a microorganism, wherein activity of pyruvate formate-lyase (pfl) is inactivated or decreased, and further activity of Escherichia coli-derived NADH-dependent D-lactate dehydrogenase (ldhA) is enhanced, is cultured to efficiently produce D-lactic acid. With regard to a method for enhancing ldhA activity, by linking, on a genome, a gene encoding ldhA with a promoter of a gene which controls expression of a protein involved in a glycolytic pathway, a nucleic acid biosynthesis pathway or an amino acid biosynthesis pathway, suitable results are obtained compared to the method for enhancing expression of the gene using an expression vector. A microorganism in which a dld gene is substantially inactivated or decreased is cultured to produce high quality D-lactic acid with reduced concentration of pyruvic acid.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com