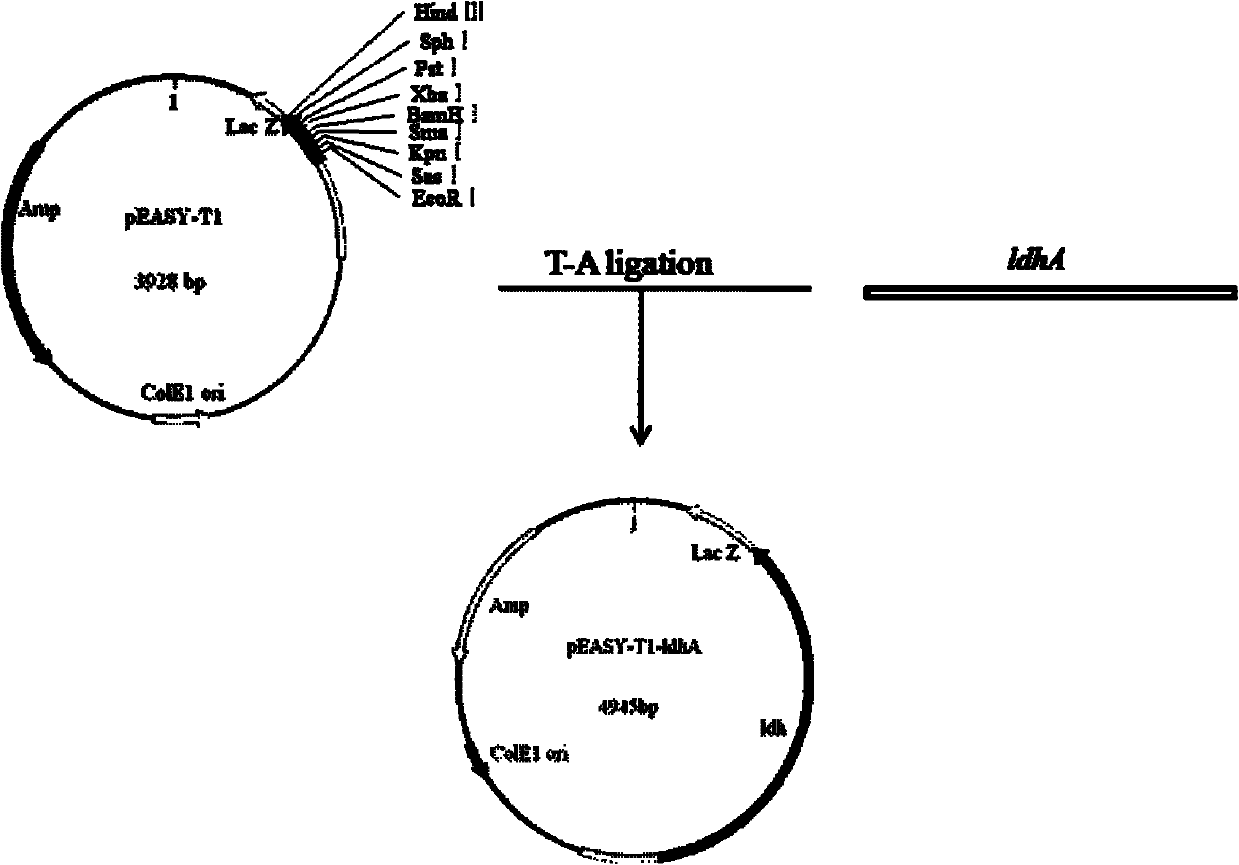
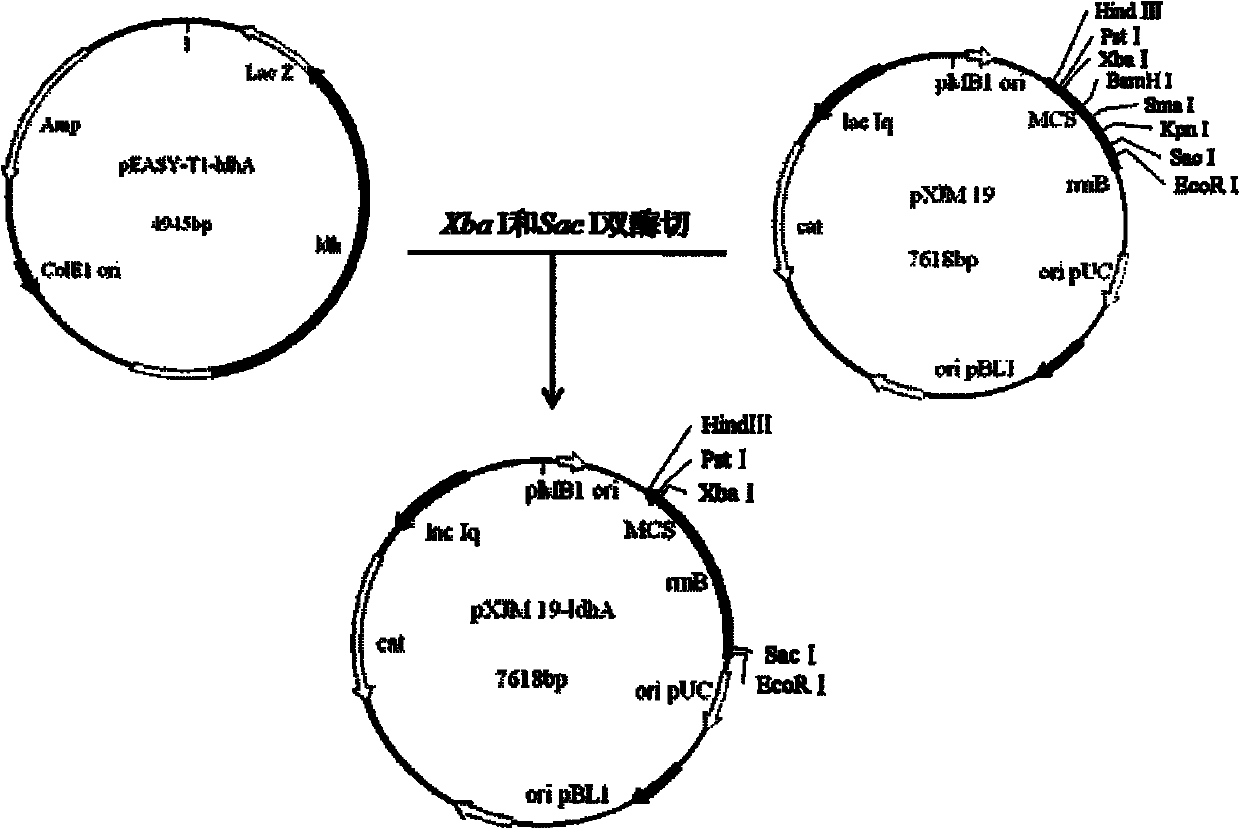
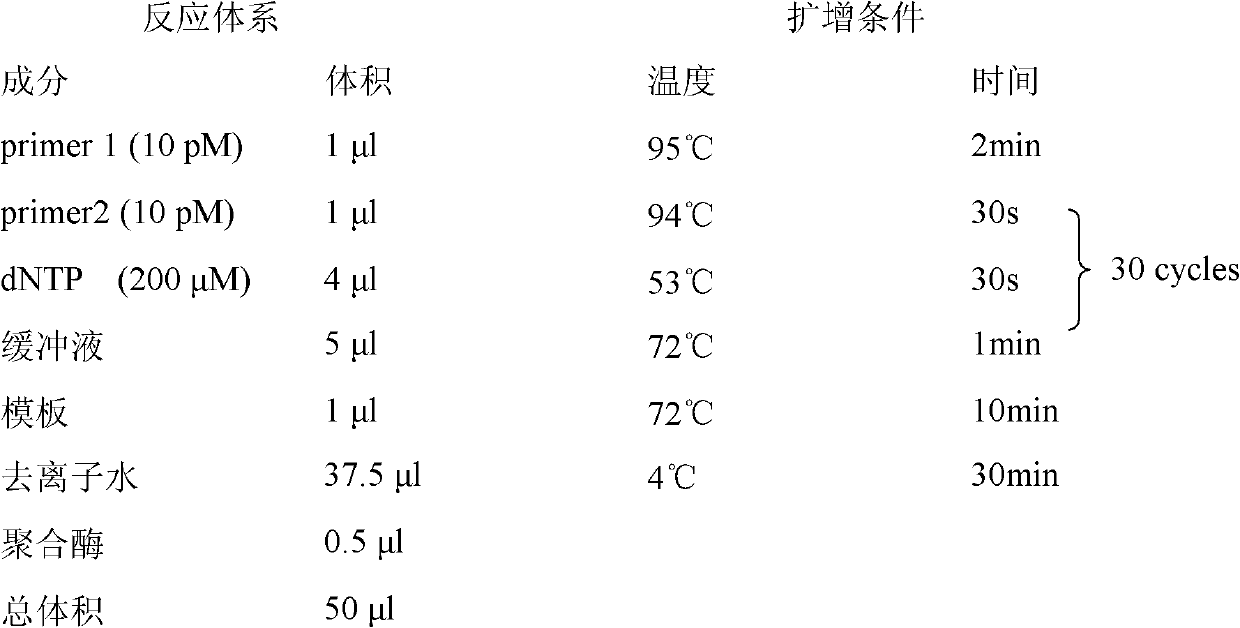
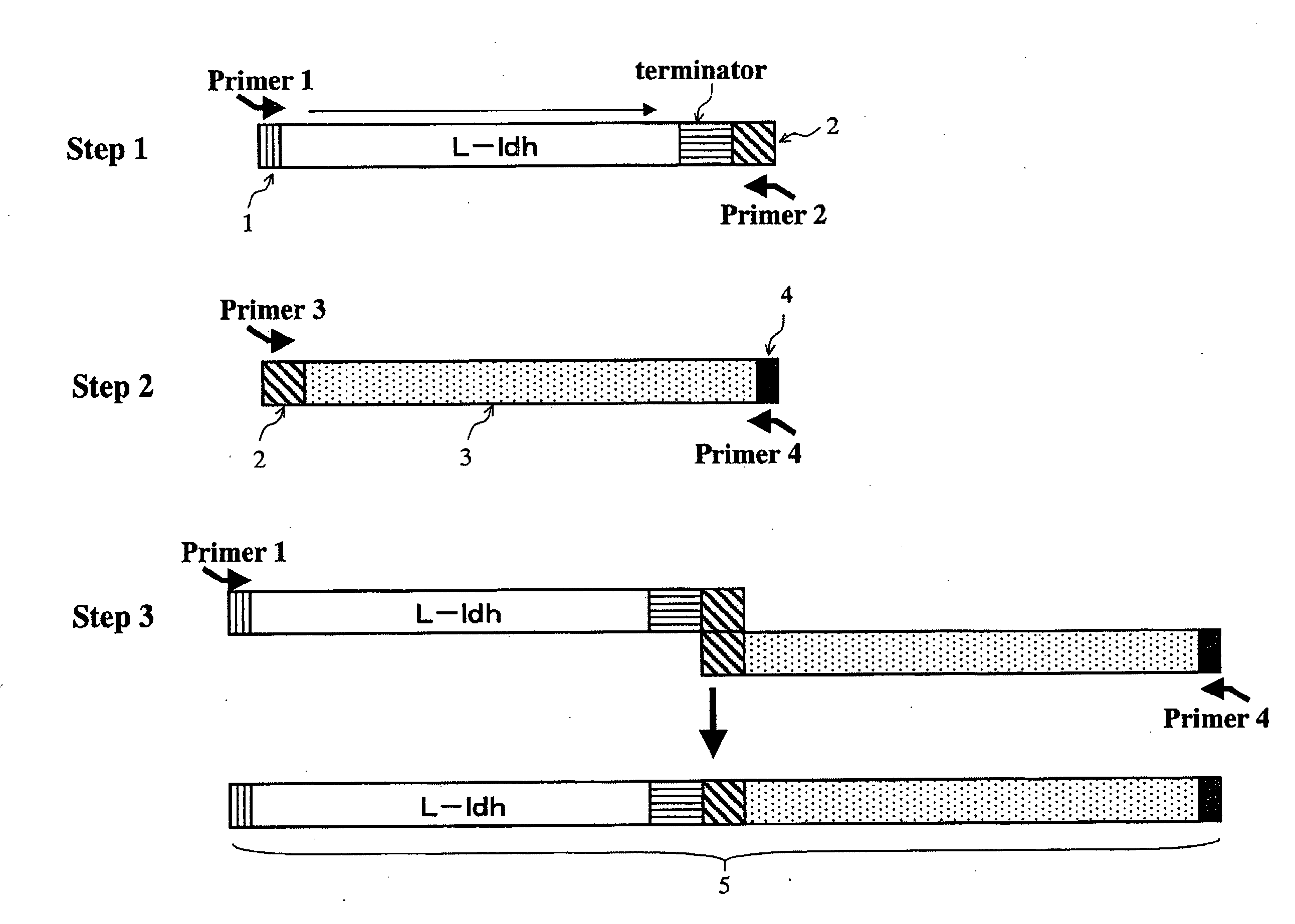
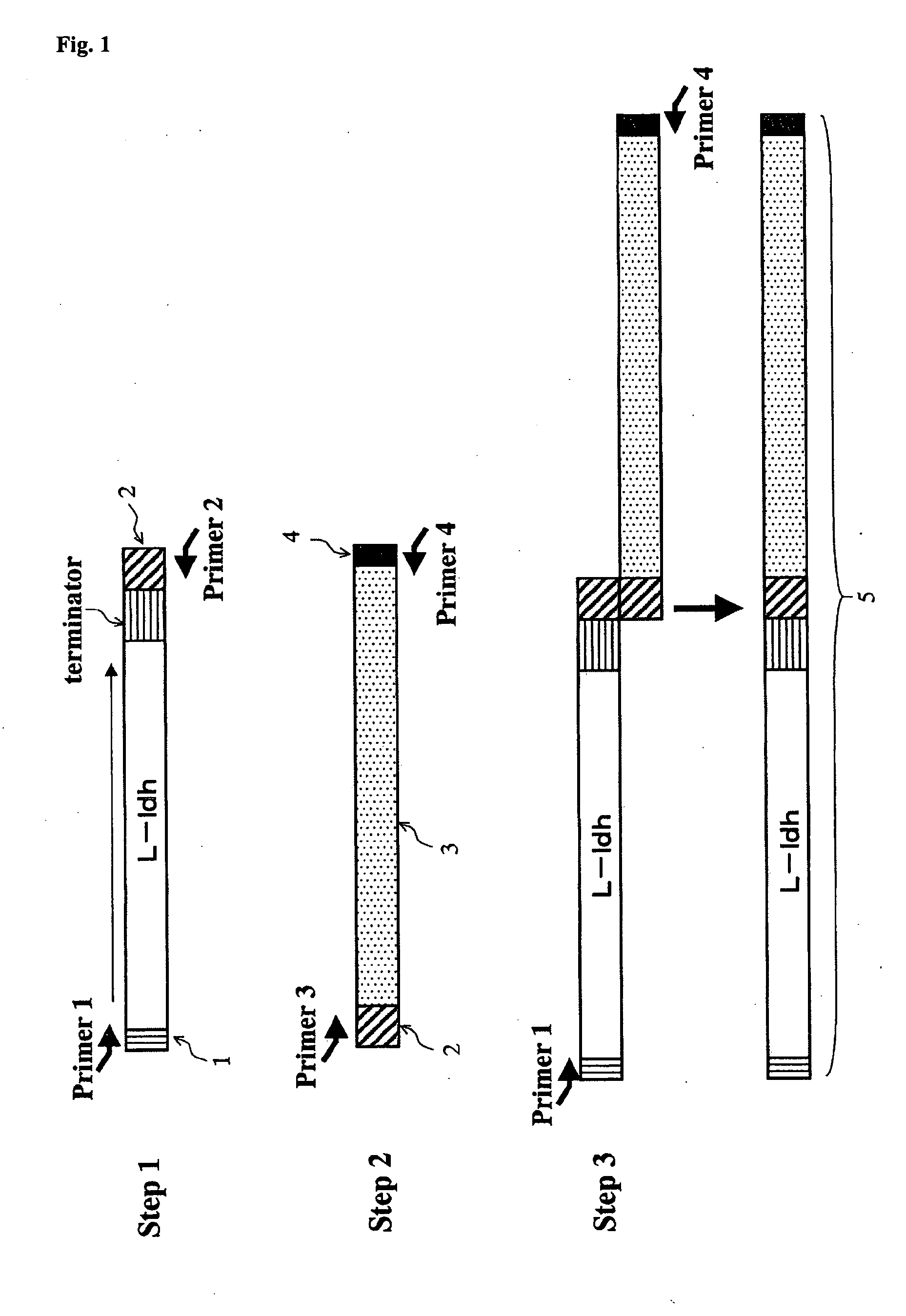
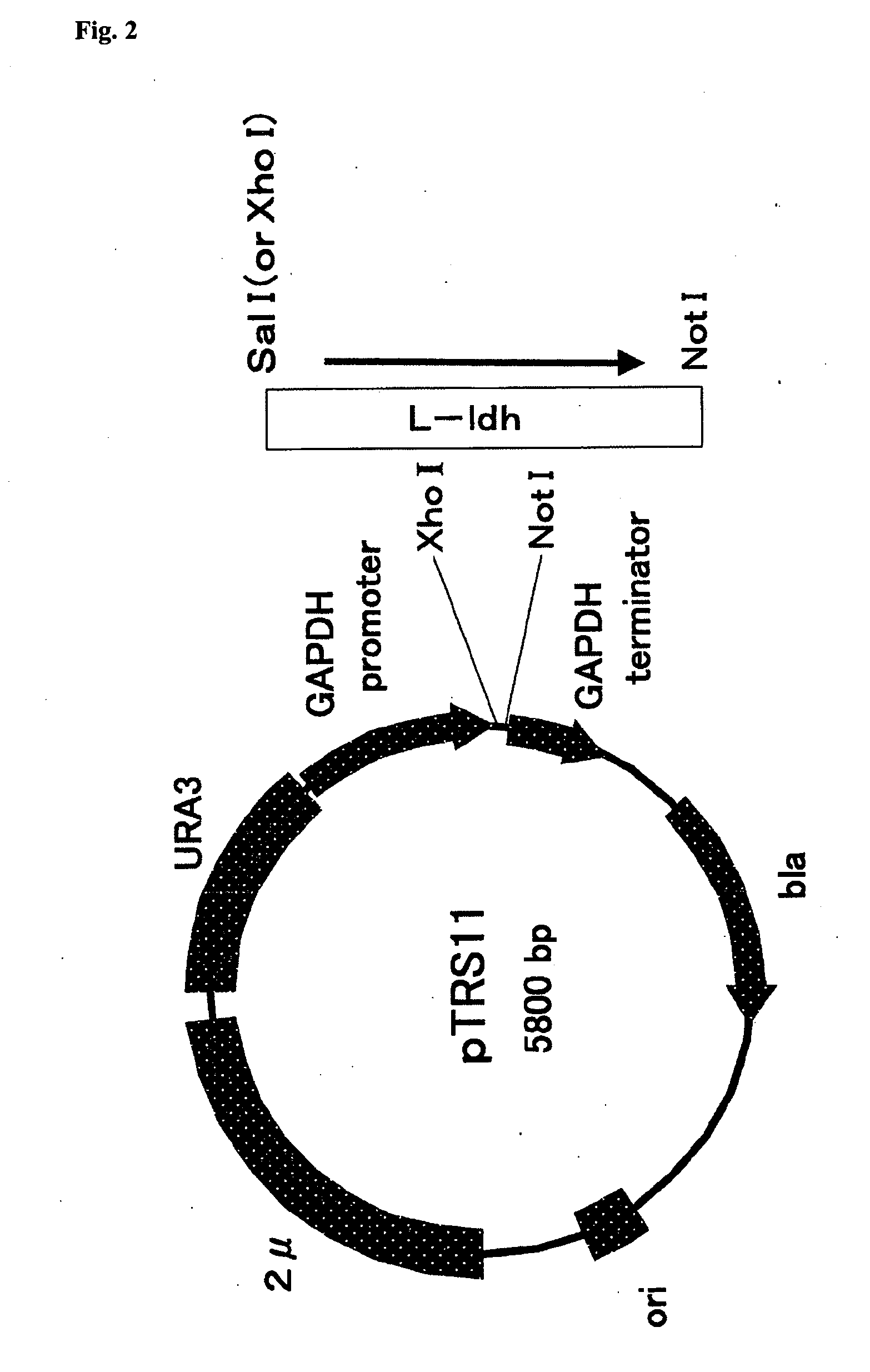
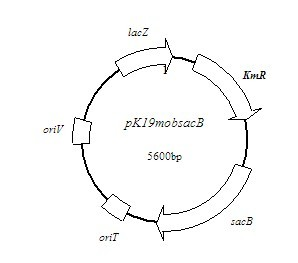
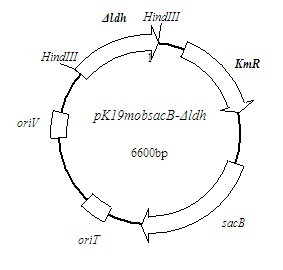
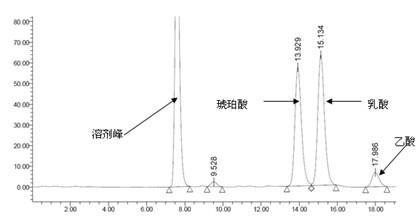
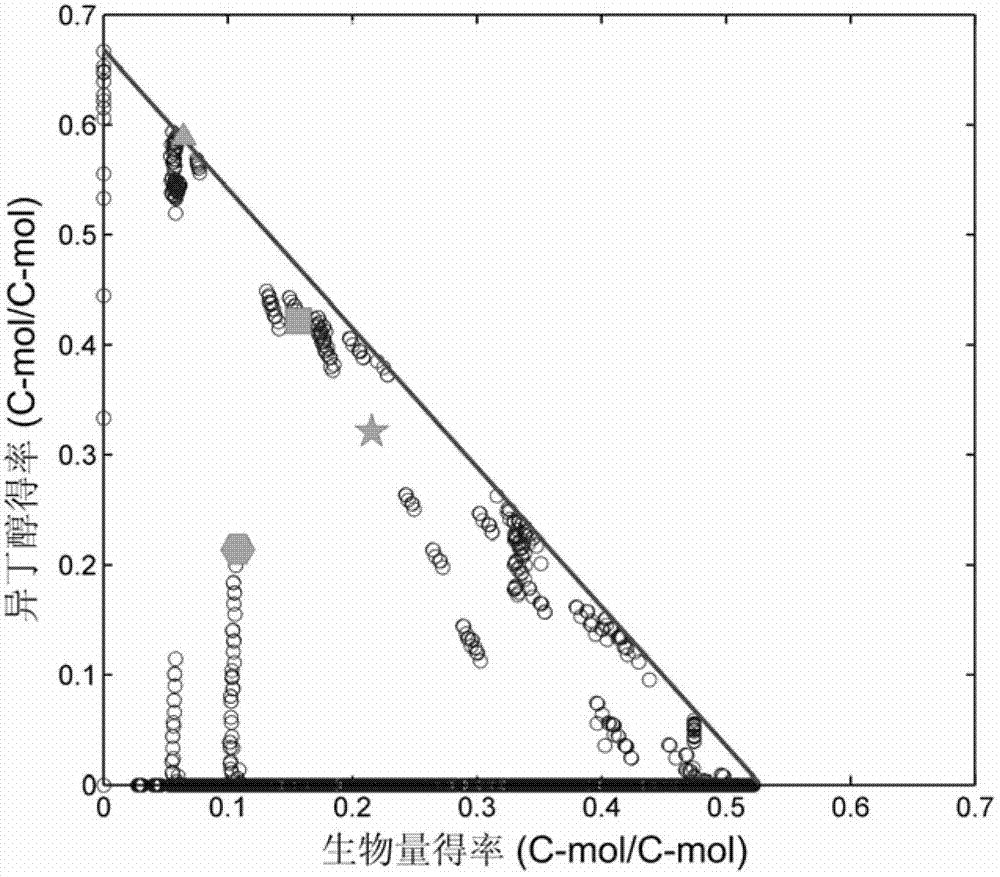
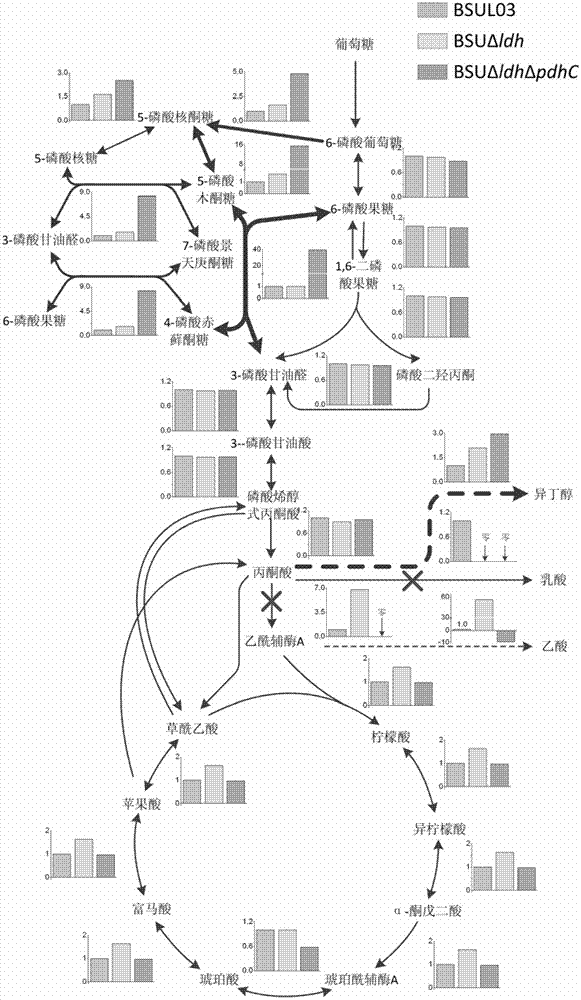
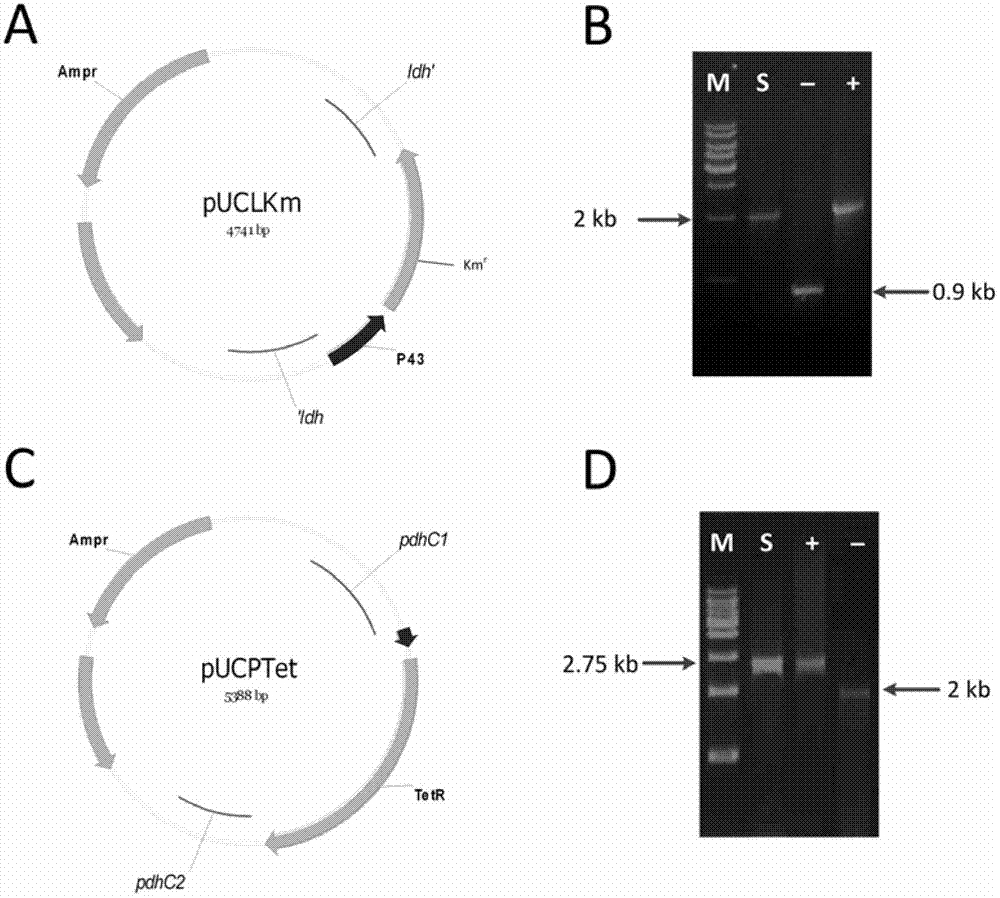
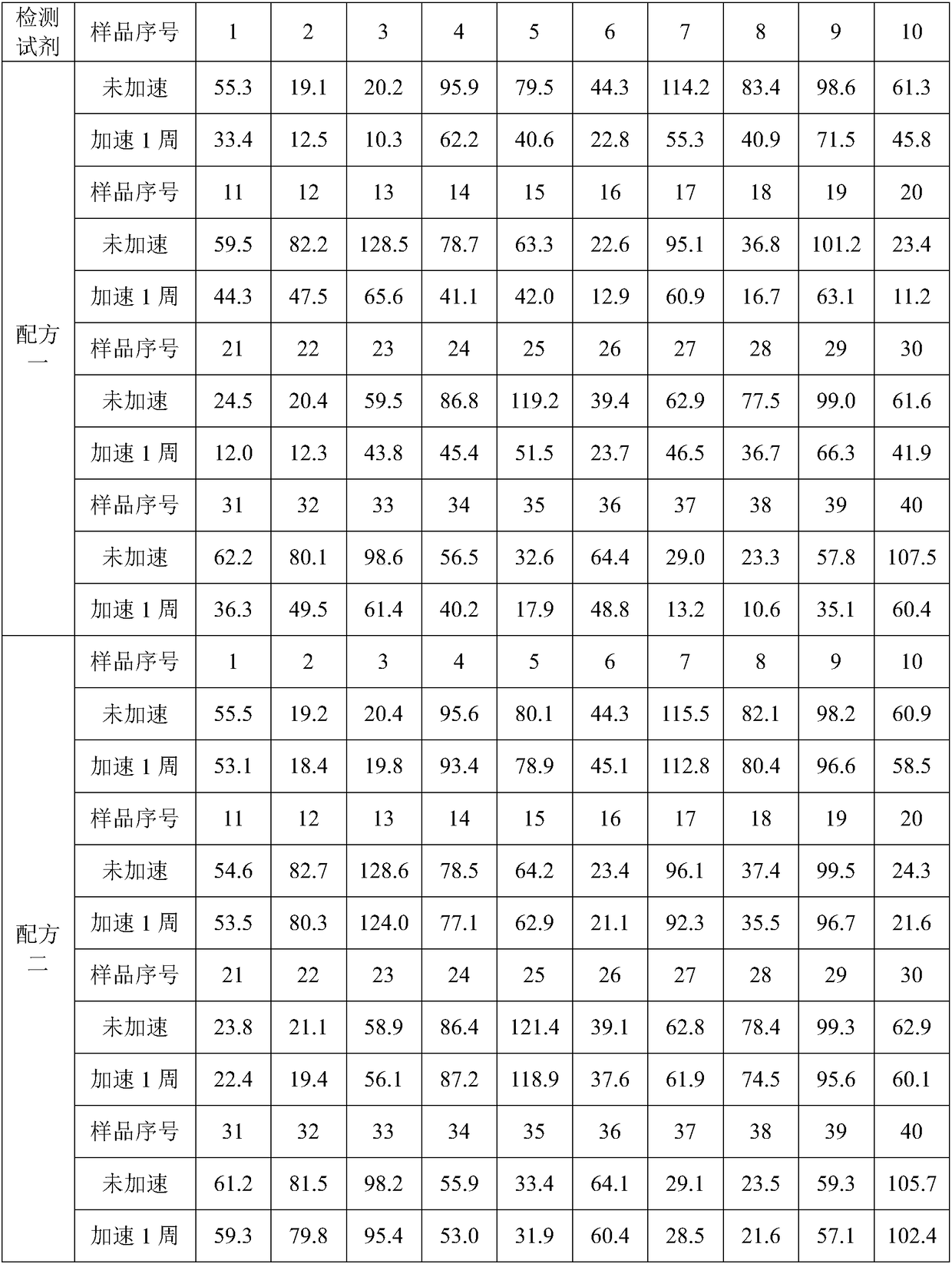
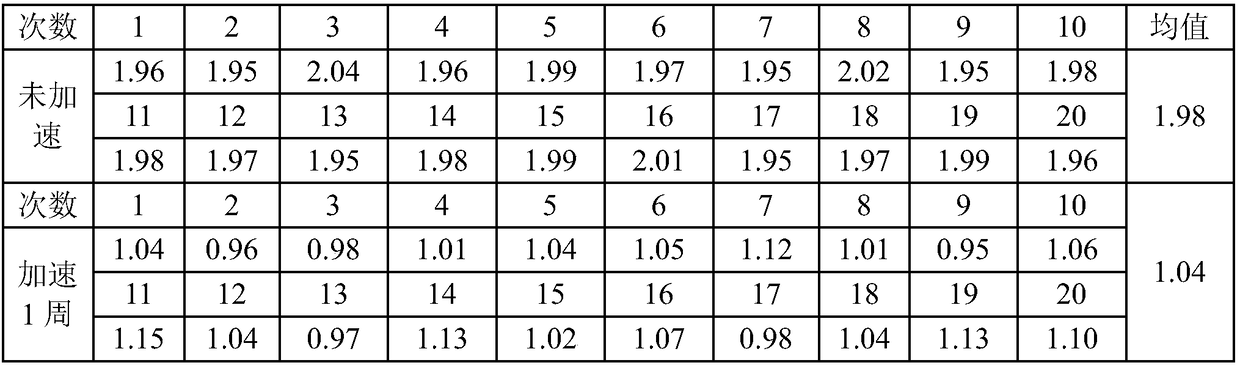
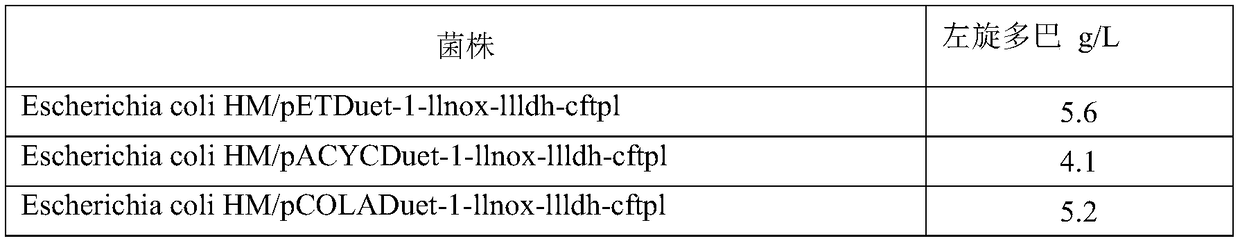
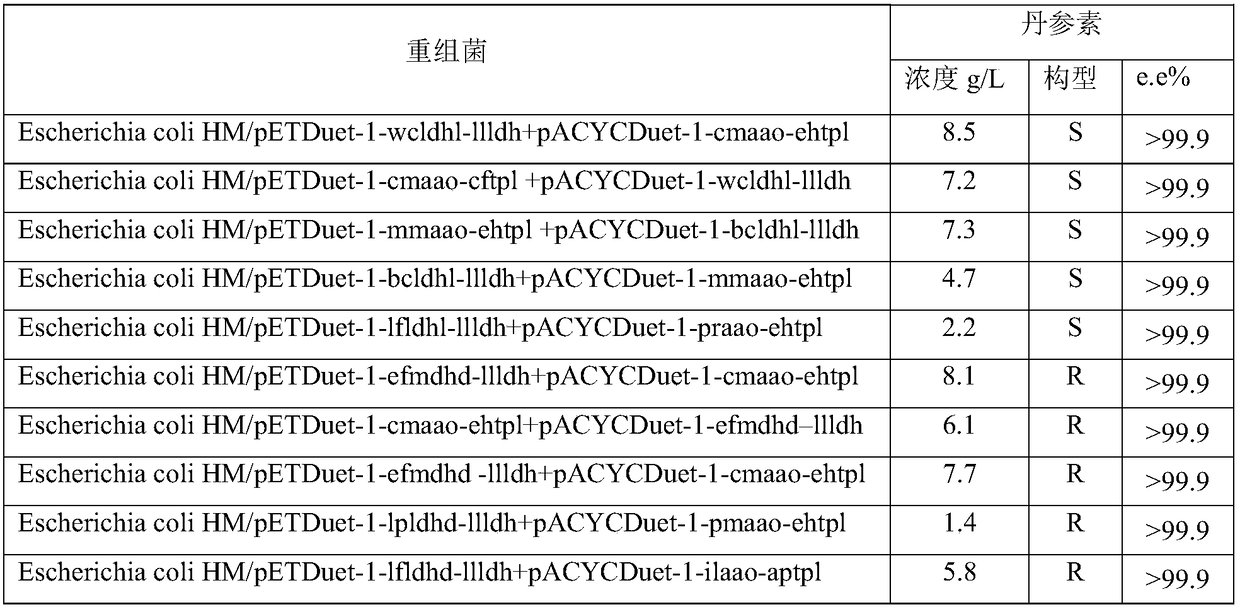
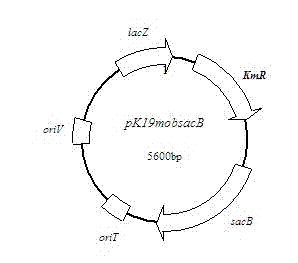
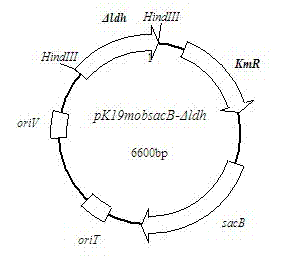
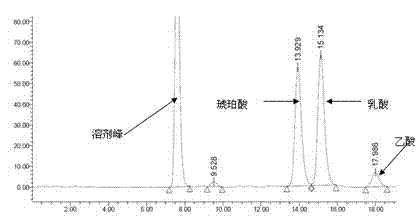
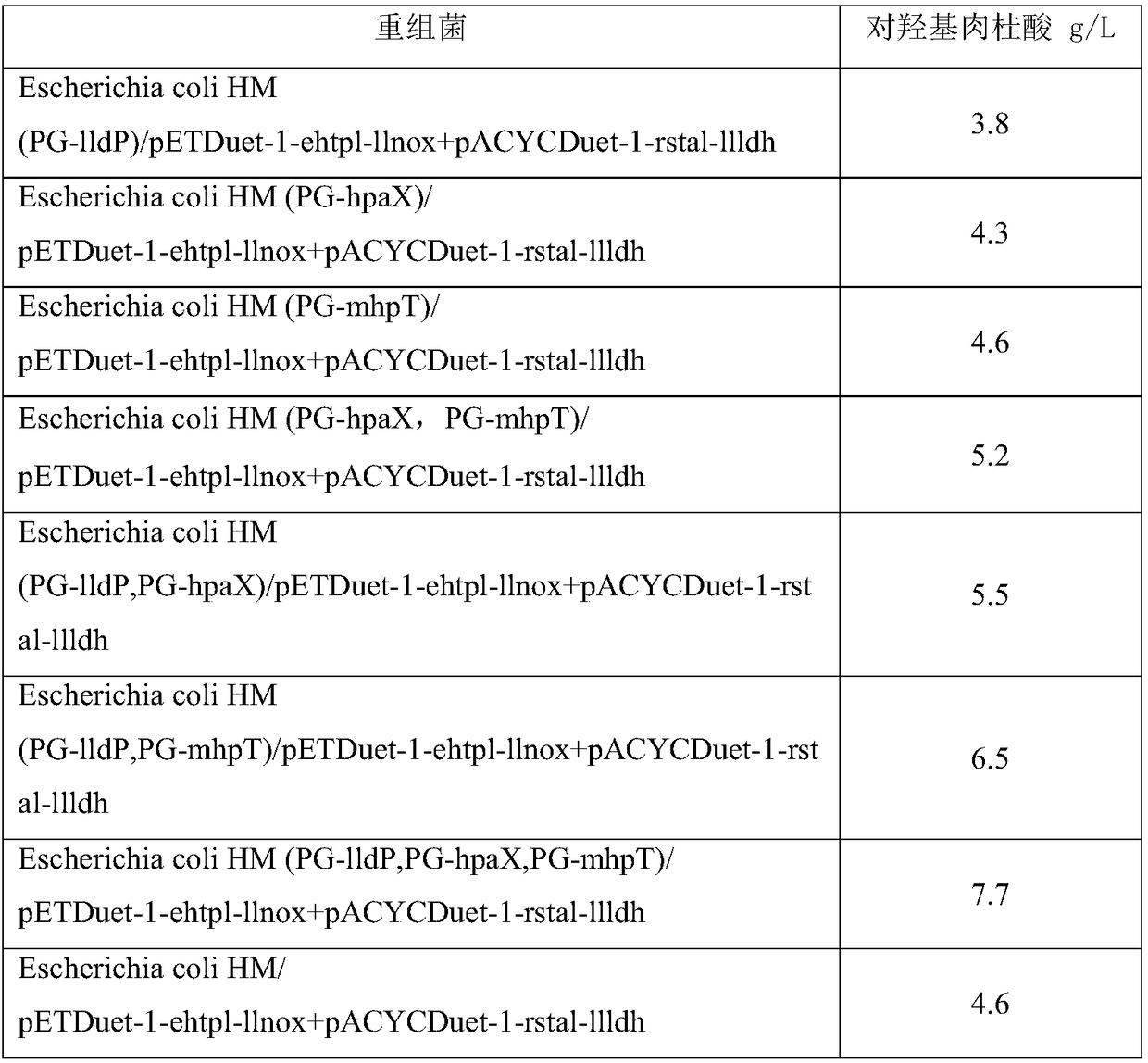
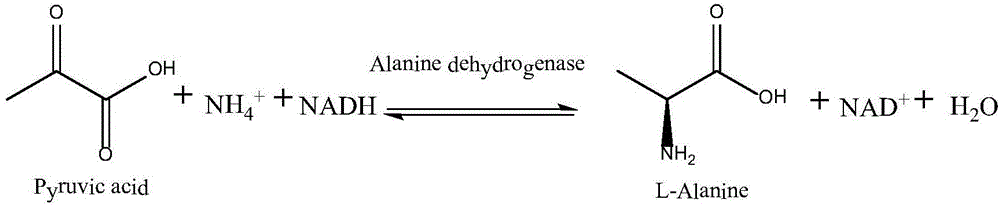Patents
Literature
30 results about "L-Lactate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
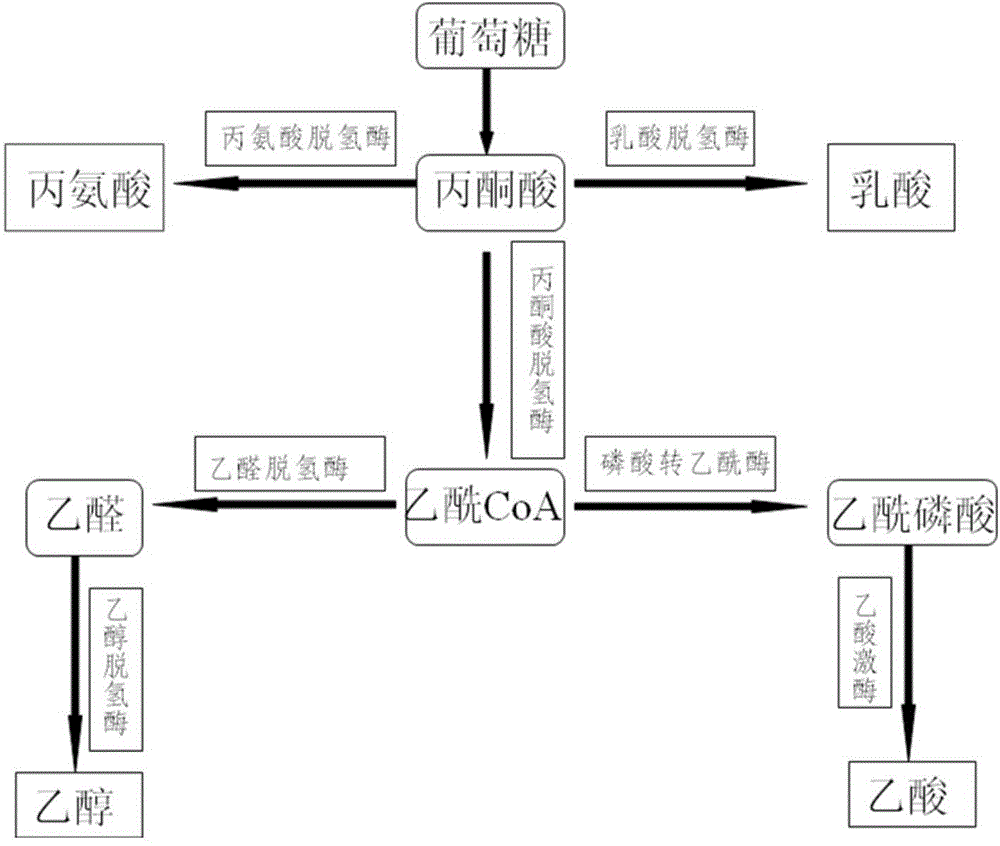
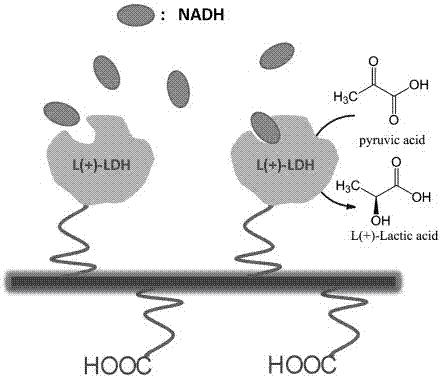
L-lactate dehydrogenase (L-LDH) catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and NADH+ to L-lactate and NAD+. H-lactate dehydrogenase (H-LDH) catalyzes the interconversion of D-lactate and ferricytochrome c to pyruvate and ferrocytochrome c. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is an important enzyme in humans.
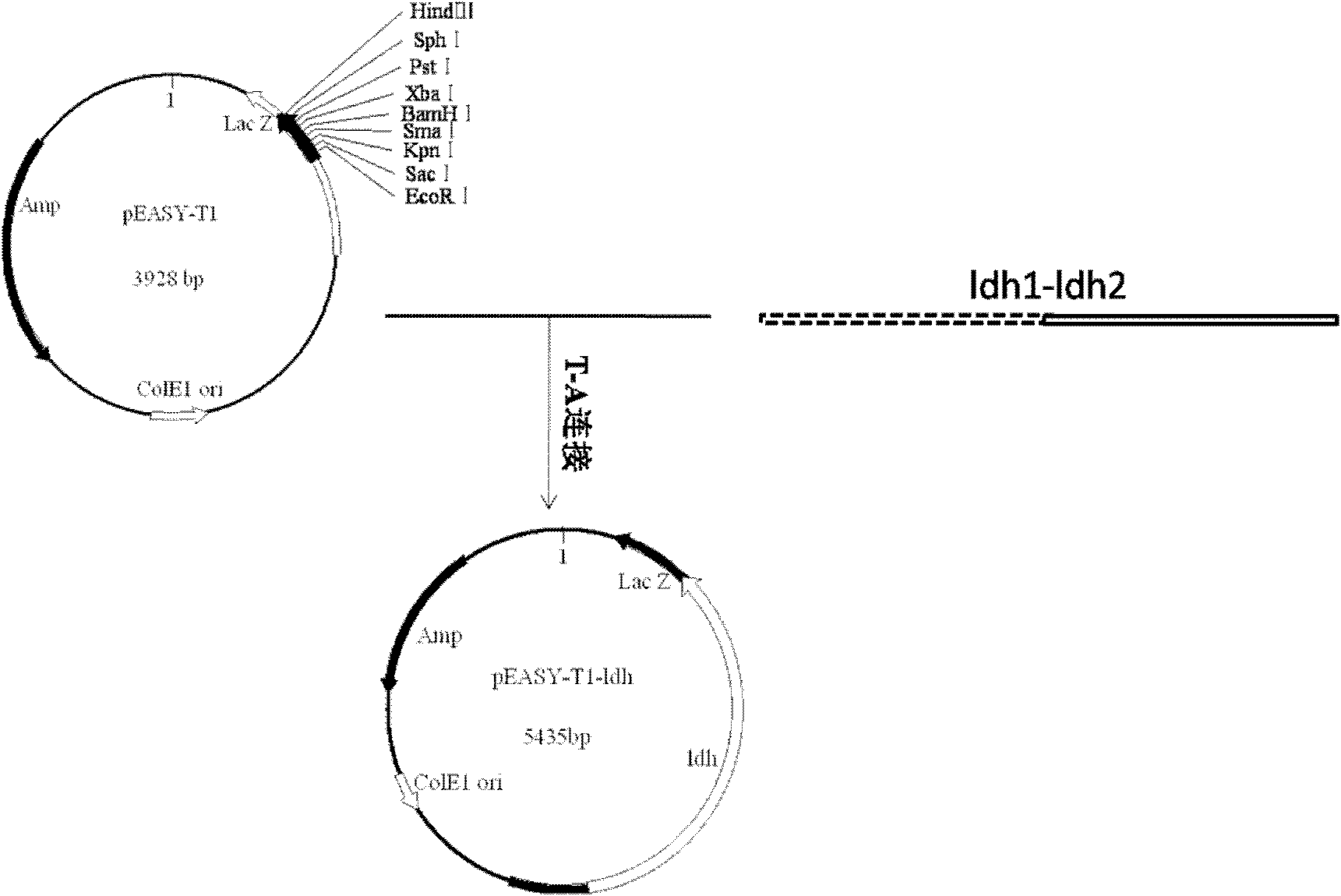
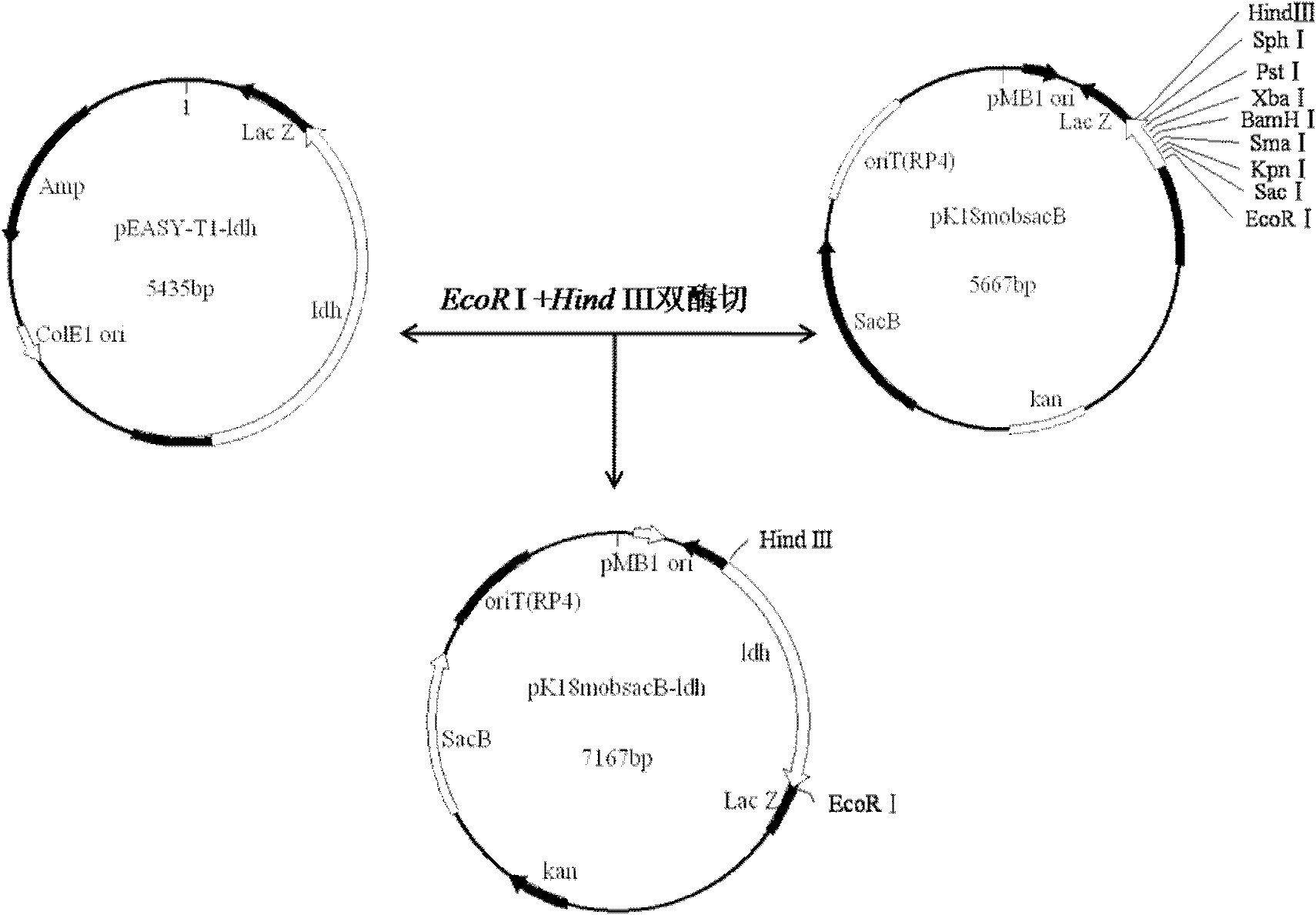
L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deleted engineering bacterium and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102102086ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseLactic acid fermentation
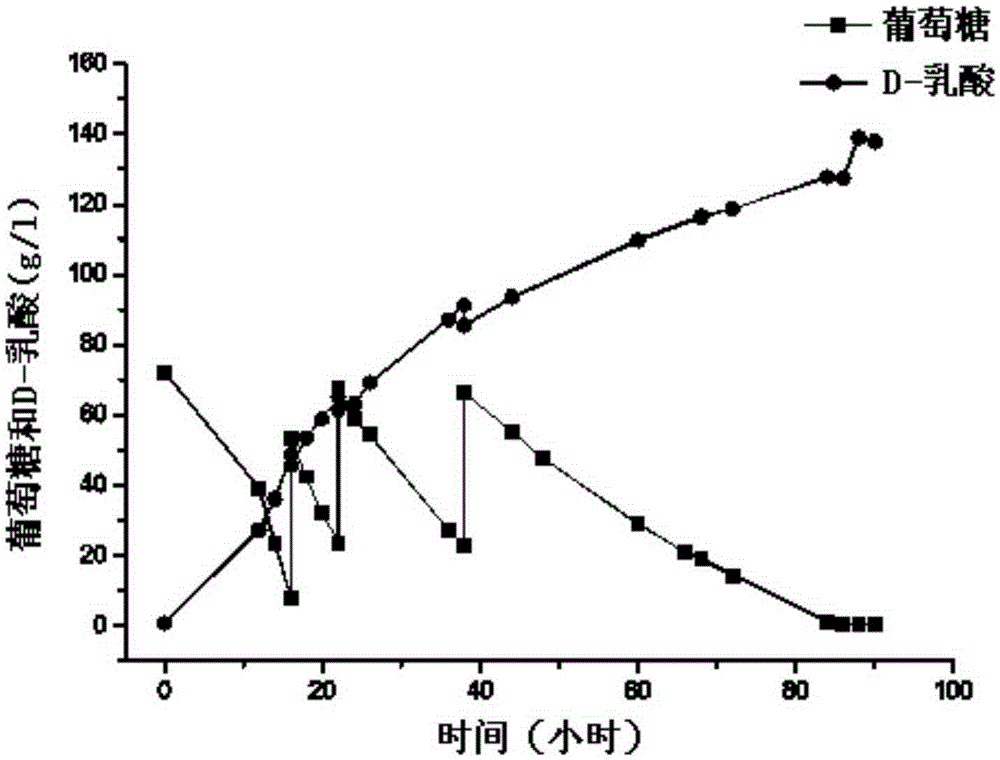
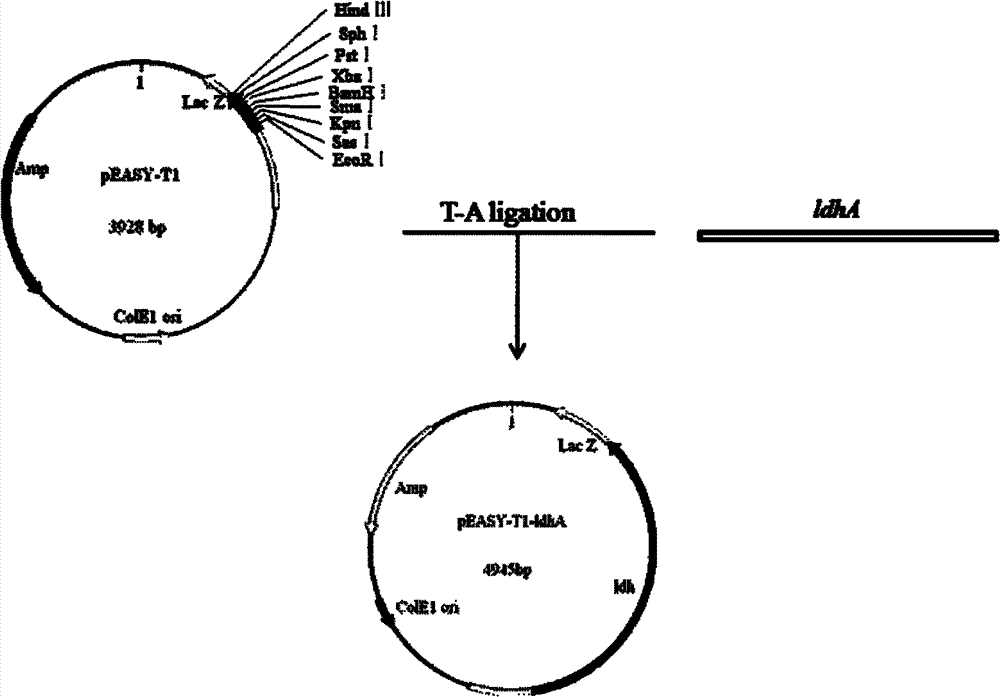
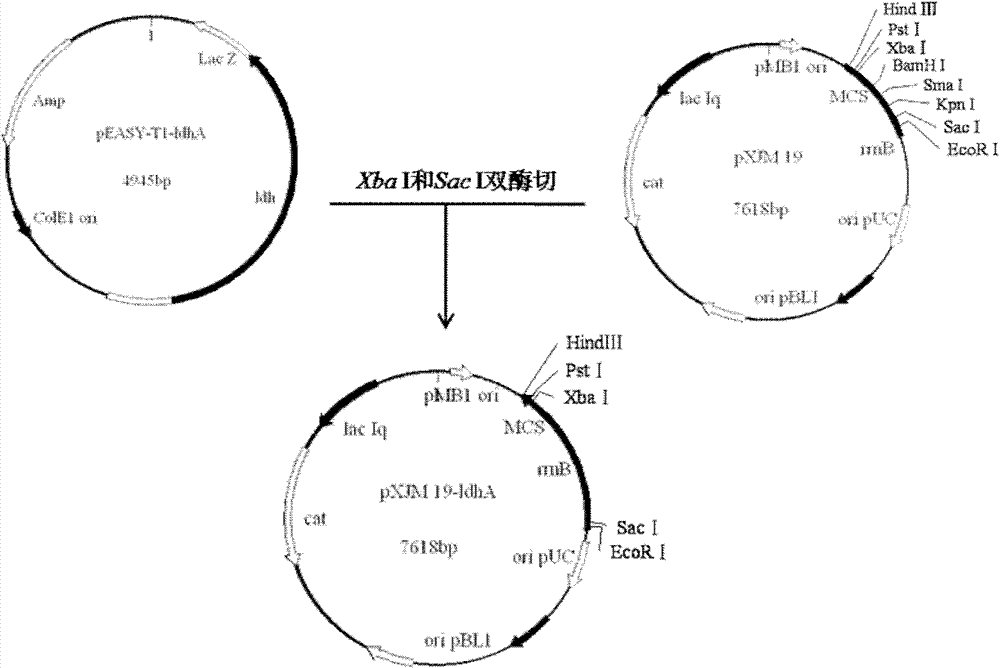
The invention relates to an L-lactate dehydrogenase gene-deleted engineering bacterium and a construction method and application thereof. Upstream and downstream sequences of ldh1 and ldh2 of L-lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) gene are subjected to polymerase chain reaction amplification, cloned segments are connected to a gene knock-out vector, the constructed knock-out vector is inoculated into corynebacterium glutamicum, and the gene engineering bacterium C.glutamicum Res167 delta ldh is obtained by silencing and screening L-lactate dehydrogenase (ldh) genes in the strain through a homologous recombination method. By the homologous recombination method, the L-lactate dehydrogenase genes in the corynebacterium glutamicum are silenced, so that the gene engineering bacterium for producing pureD-lactic acid is obtained. When the engineering bacterium is used for lactic acid fermentation production, the yield of the D-lactic acid is more than 20g / L, and the purity is over 99 percent. The invention has important significance for industrial production of the D-lactic acid and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
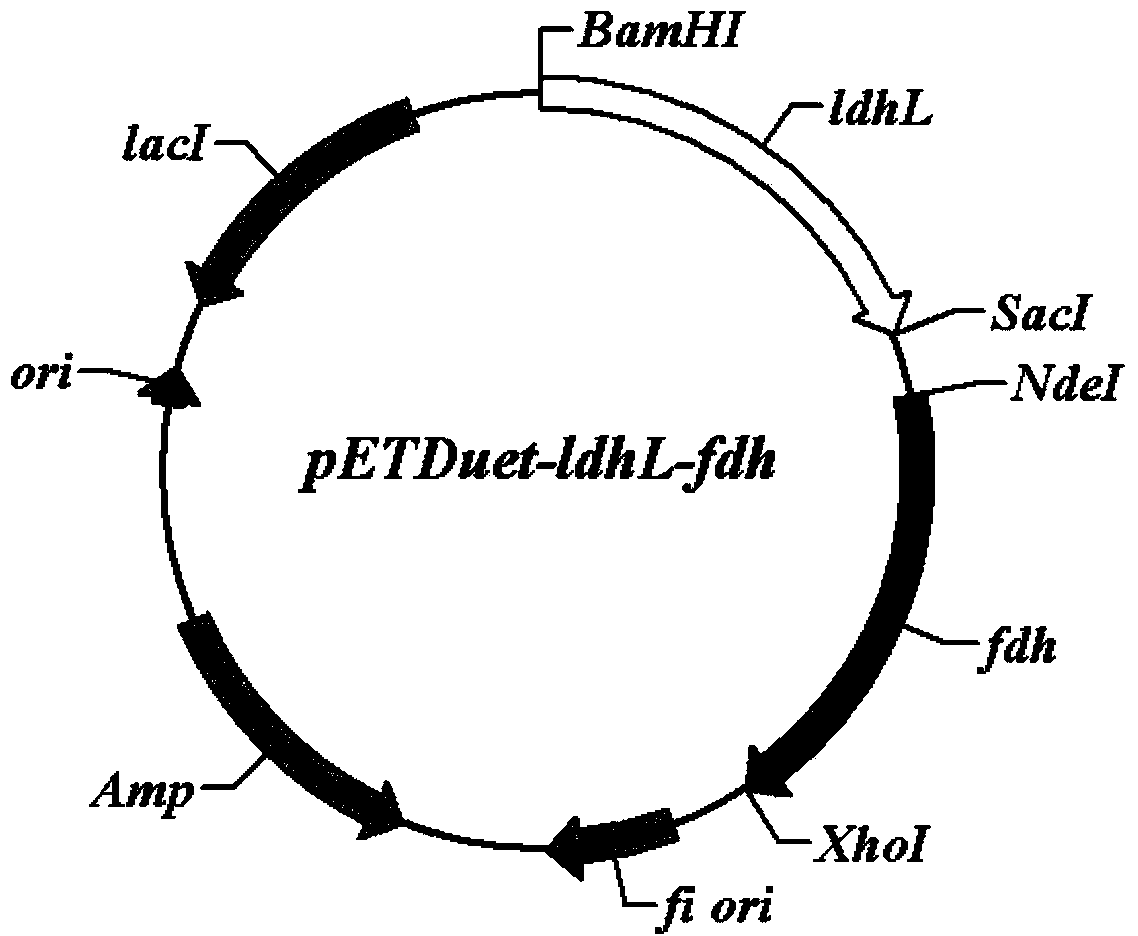
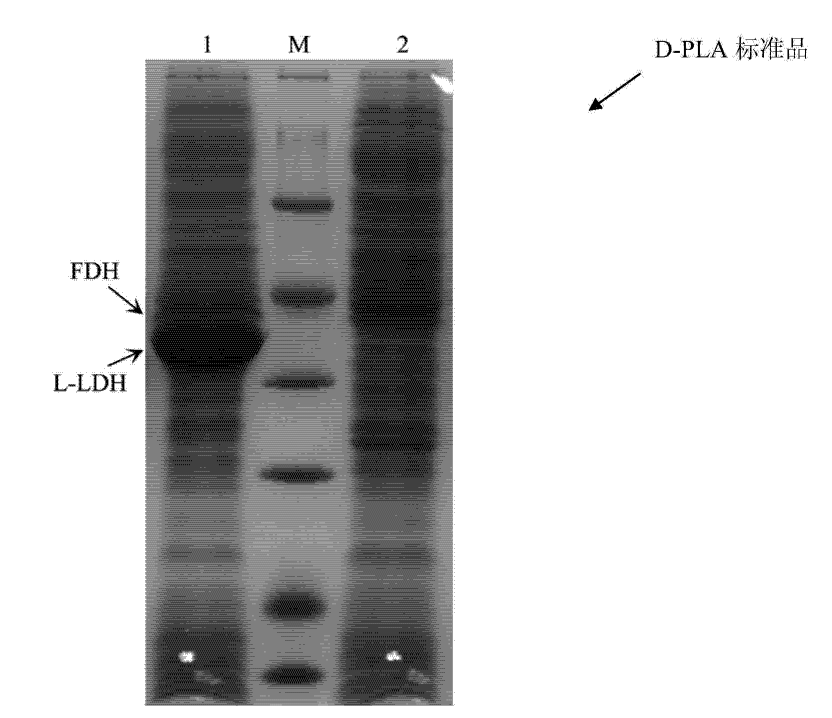
Escherichia coli with coexpression of L-lactate dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase as well as construction method and application of escherichia coli
ActiveCN104130967ANotable featuresRemarkable effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses escherichia coli with coexpression of L-lactate dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase. The escherichia coli is characterized in that L-lactate dehydrogenase genes ldhL from bacillus coagulans and formate dehydrogenase genes fdh from candida boidinii are introduced into the escherichia coli, wherein the register number of GenBank of nucleotide sequences of the L-lactate dehydrogenase genes ldhL is KF386111; the register number of GenBank of nucleotide sequences of the formate dehydrogenase genes fdh is AJ011046. The invention further discloses a construction method and an application of the reconstructed escherichia coli. The method has the characteristics of being simple to operate, low in cost, high in product synthesis efficiency and high in optical purity. Thus, an effective way for biosynthesis of L-phenyllactic acid is provided.
Owner:深圳市华利康纤生物科技有限公司
Unmarked gene knock-out method of pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 based on homologous recombination
InactiveCN105821071ARapid knockoutStable knockoutBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBacterial strain
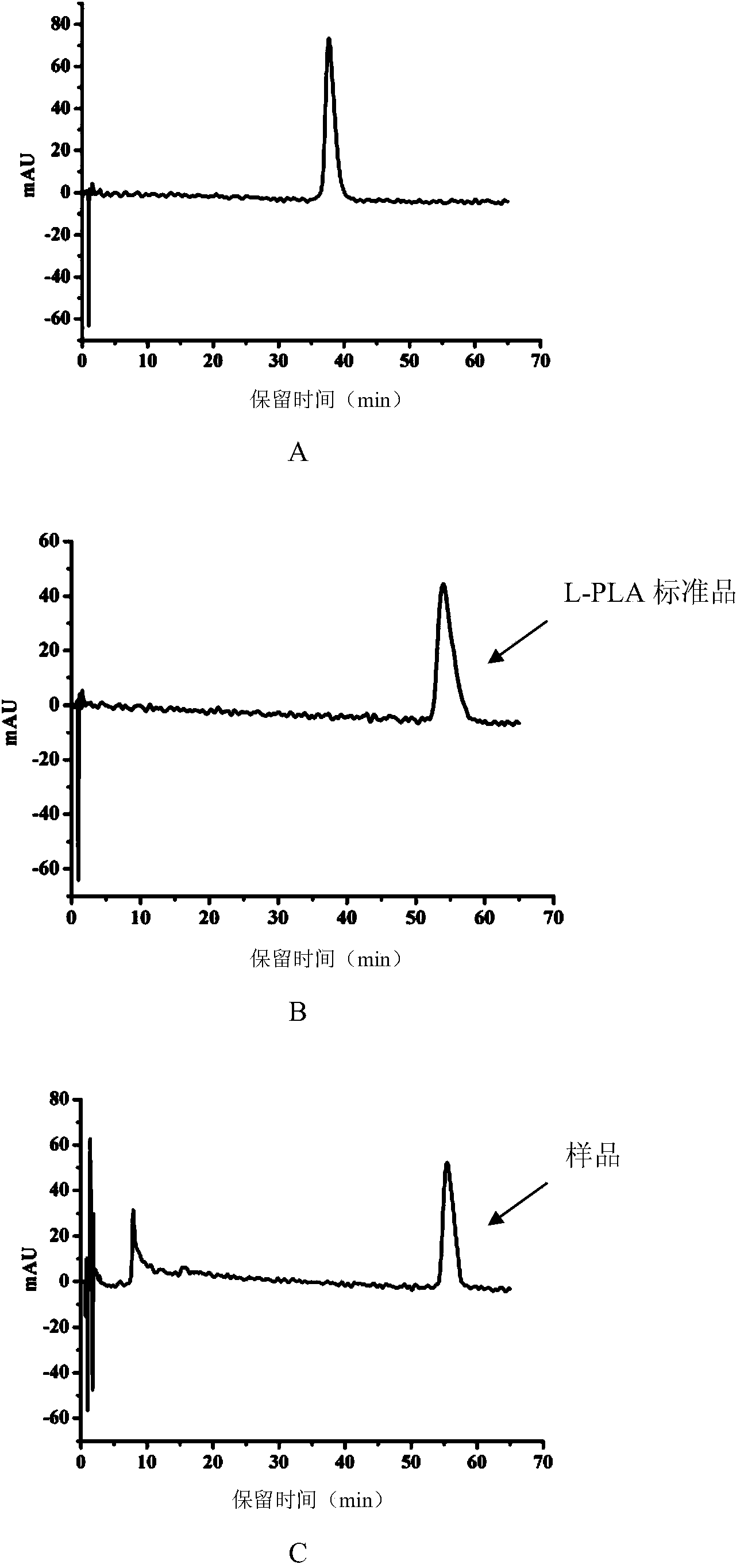
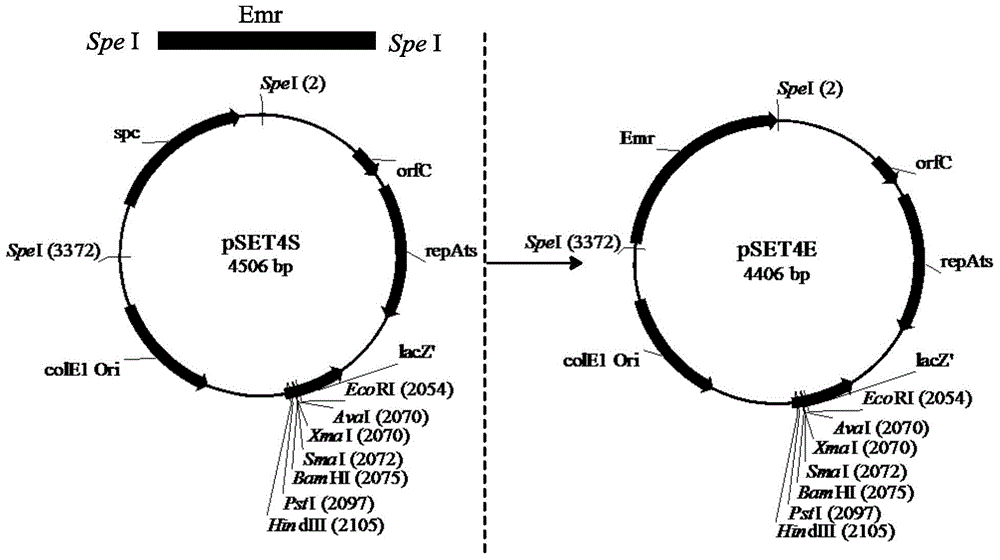
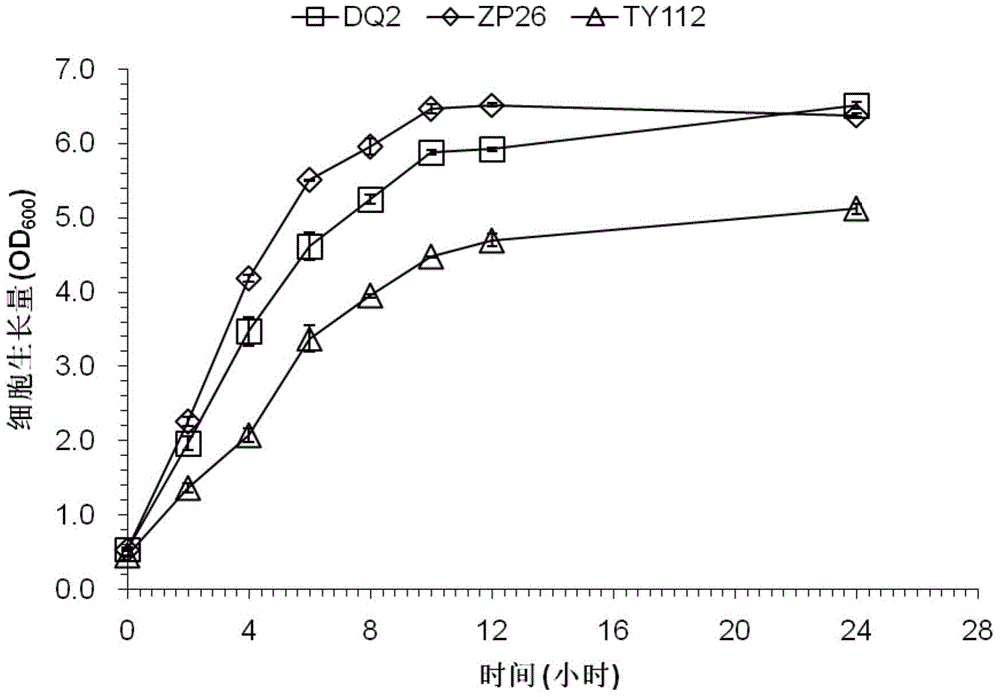
The invention relates to an unmarked gene knock-out method of pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 based on homologous recombination. The method comprises the following steps: temperature sensitive-type shuttle plasmid pSET4E and knock-out plasmid containing homologous fragments at upstream and downstream parts of target genes to be knocked out are constructed, the knock-out plasmid is subjected to electrotransformation into pediococcus acidilactici, and single commutators generating homologous recombination for the first time and double-exchange mutant strains generating homologous recombination for the second time are screened and identified. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the unmarked gene knock-out of pediococcus acidilactici for the first time, the obtained knock-out bacterial strain does not carry any resistant gene, can be taken as a original strain for subsequent and reconstruction, and also can be used for large-scale industrial production in a safe mode. The method is used for respective knock-out of L-lactate dehydrogenase gene and d-lactate dehydrogenase gene of the pediococcus acidilactici DQ2 (a preservation number is CGMCC NO.7471), the obtained knock-out bacterial strains are respectively named as pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 and TY112, the preservation numbers are CGMCC NO.8665 and CGMCC NO.8664 respectively, and optically pure D-lactic acid and L-lactic acid are respectively generated.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and constructon method and application thereof
InactiveCN101993850AHigh optical purityIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and a construction method and application thereof. The strain of C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh deleted in L-lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldh) is used as a starting strain to over express exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene so as to obtain C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh / ldhA. The genetic engineering bacteria are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preserving registration number of CGMCC No.4041. By utilizing the genetic engineering means, the expression of the exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene is realized in the corynebacterium glutamicum deleted in L-lactic acid metabolic pathway, and the genetic engineering bacteria producing high optical purity D-lactic acid are successfully constructed. When the engineering bacteria are used for producing lactic acid through fermentation, the yield of the D-lactic acid is over 40g / L, and the purity is over 99 percent. The invention has important significance for the industrial production of the D-lactic acid, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
Yeast and Method of Producing L-Lactic Acid
Yeast includes an introduced gene coding a Homo sapiens- or frog-derived L-lactate dehydrogenase.It is possible to produce lactic acid, which has a variety of applications, efficiently and more cost-effectively by using the yeast and the method of producing lactic acid by using the yeast.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Corynebacterium acetoacidophilum strain and method for producing succinic acid therefrom
ActiveCN102634474AIncrease concentrationFood safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSodium bicarbonateL-Lactate dehydrogenase
A corynebacterium acetoacidophilum strain and a method for producing succinic acid therefrom belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention discloses a corynebacterium acetoacidophilum strain YF / delta ldh and a method for producing succinic acid therefrom. The corynebacterium acetoacidophilum strain is an ldh (L-lactate dehydrogenase) missing bacterium built by gene knockout technology, is preserved in china center for type culture collection on February 29th, 2012, and encoded as CCTCC NO.M2012041. The strain is high in acid yield, highly resistant to sodions and high in foodsafety, can accumulate succinic acid more than 95g / L by being culture for 48 hours in the anaerobic environment using glucose as substrate and sodium bicarbonate as carbon dioxide donor, and can accumulate succinic acid 136g / L by being cultured for 94 hours.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and molecular modification method
InactiveCN102768713ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseIsobutanol synthesis
The invention relates to an isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and a molecular modification method. According to the method, the necessary path for the thallus growth and the isobutanol synthesis is calculated by a network module, the metabolic network model is subjected to the element mode analysis, the standard deviation coefficient of each gene is calculated, and the isobutanol biosynthesis yield of different genes is determined; the two key genes including an L-lactate dehydrogenase gene 1dh and a pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2 subunit coding gene pdhC which are most important to the isobutanol biosynthesis are predicted according to a principle that the standard deviation coefficient is smaller than 0.35, the standard deviation coefficients of the two genes are respectively 2.5 to 3 and 1.5 to 2; and through the determination of the two genes, the isobutanol yield can be improved, and 0.5-0.6C-mol / C-mol glucose can be reached. The key genes which are most important to the isobutanol biosynthesis are obtained through utilizing the relative flux value and are used as modification target spots, the molecular modification of the isobutanol synthetic bacterium is guided, and the isobutanol yield is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Vector for knocking out L-lactic dehydrogenase 1 gene and construction method of vector
InactiveCN104673819AUse lessAvoid joiningMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
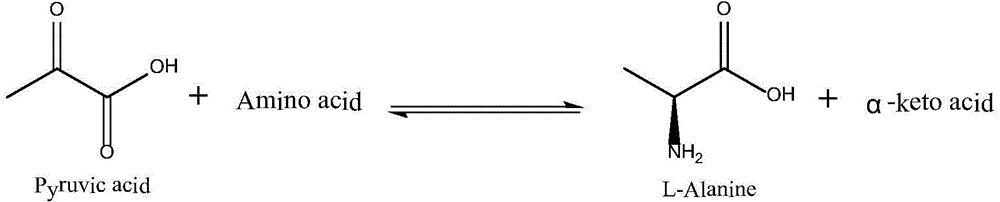
Production of alpha-hydroxy-carboxylic acids using a coupled enzyme system
InactiveUS20040053382A1High yieldUseful and cost-effectiveOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementL-Lactate dehydrogenaseElectron donor
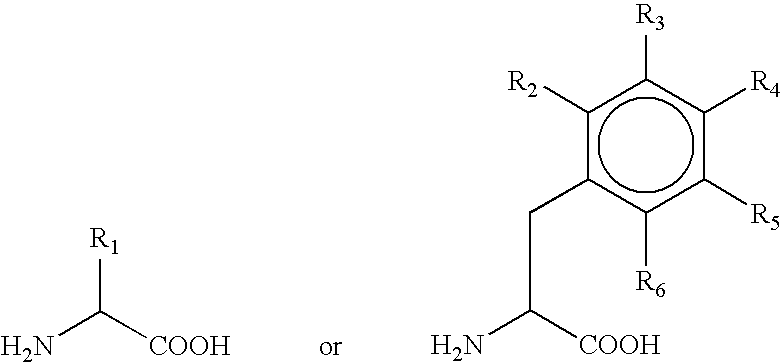
An economical and expedient method is disclosed for the preparation of alpha-hydroxy-carboxylic acids or salts thereof in very high enantiomeric purity which comprises oxidizing a corresponding alpha-amino-carboxylic acid or salt thereof using an amino acid deaminase followed by reducing the corresponding alpha-keto-carboxylic acid or salt produced using a D- or L-lactate dehydrogenase in the combination with an electron donor and an enzyme / substrate system for recycling the electron donor. The resulting alpha-hydroxy-carboxylic acids, hydrates, and salts thereof are valuable components and intermediates in the preparation of chiral compounds, especially pharmaceuticals. This invention also relates to the use of alpha-amino-carboxylic acids, hydrates, and salts thereof and a coupled enzyme system in the production of alpha-hydroxy-carboxylic acids, hydrates, and salts thereof.
Owner:EXCELSYN MOLECULAR DEV
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of caffeic acid
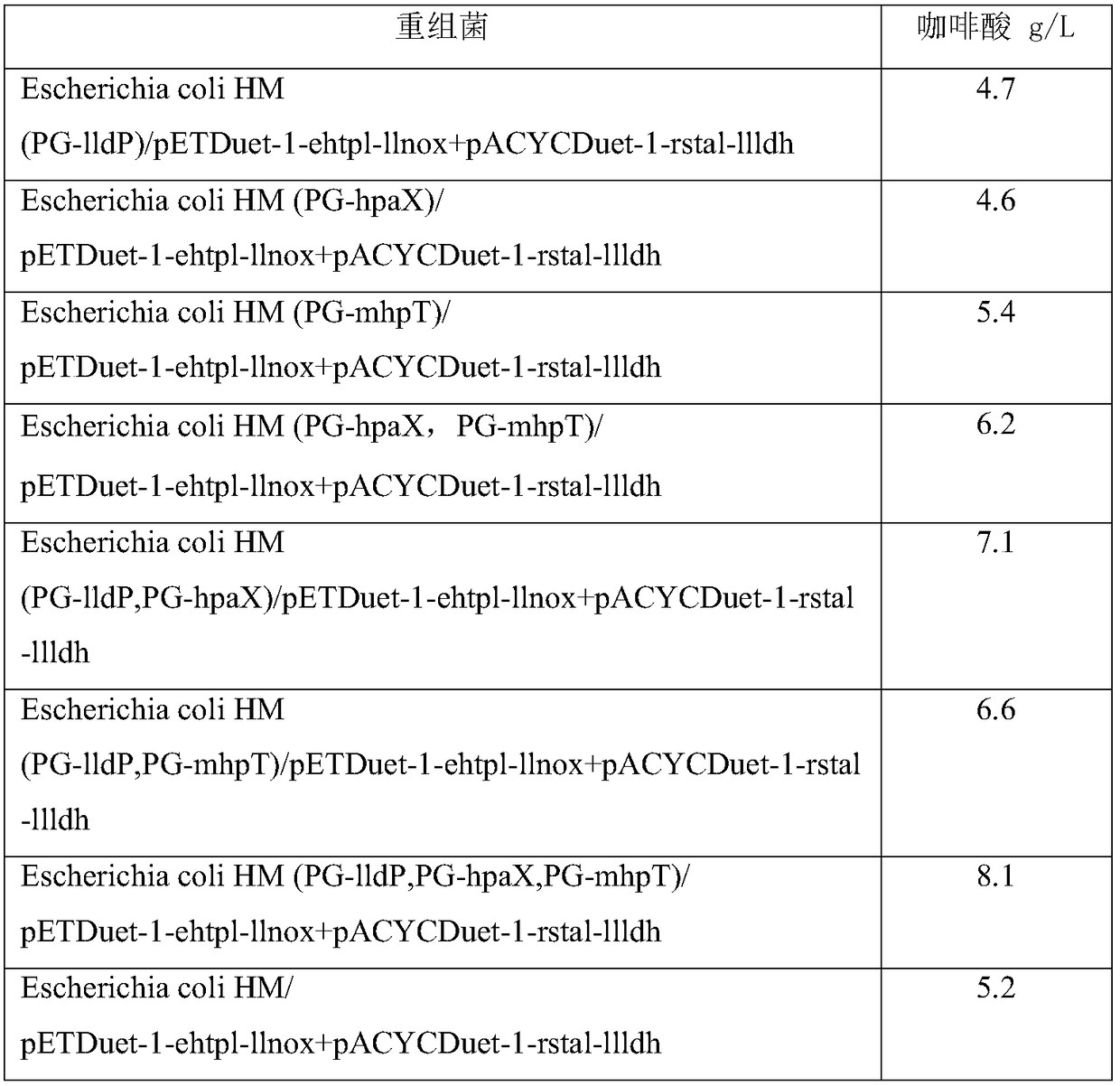
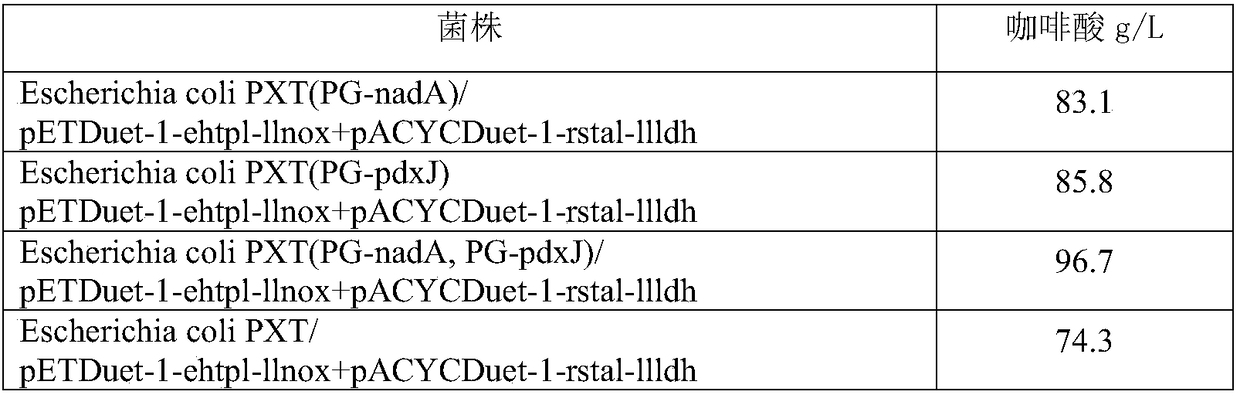
ActiveCN108949652AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseCaffeic acid
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of caffeic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium providedby the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing caffeic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages of realization of the efficient production ofcaffeic acid, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Sialic acid assay kit and assay method thereof
InactiveCN108866153AImprove measurement accuracyImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisL-Lactate dehydrogenaseSucrose
The invention provides a sialic acid assay kit, comprising a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 is prepared from the following components with corresponding concentrations: 8-20g / L tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane, 5-15ml / L HCL, 0.5-5KU / L neuraminidase, 0.5-5KU / L lactate dehydrogenase and 0.1-2mmol / L NADH; the reagent R2 is prepared from the following components with correspondingconcentrations: 8-20g / L tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane, 5-15ml / L HCL, 0.5-5KU / L N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase, 25-100g / L sucrose and 0.6-1.2 ml / L triethanolamine. The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The sialic acid assay kit provided by the invention significantly enhances the anti-interference ability while improving the stability, can significantly reducethe interference of bilirubin, hemoglobin, triglyceride and the like, and is good in accuracy when being used for the determination of sialic acid.
Owner:广州市伊川生物科技有限公司
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of levodopa
ActiveCN108949649ANot easy to decomposeHigh NAD contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of levodopa, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium is a recombinant Escherichia coli capable of producing pure levodopa at low cost; the recombinant Escherichia coli simultaneously expresses exogenous L-lactate dehydrogenase, NADH oxidase and tyrosine phenol lyase, and is obtained by knocking out an aromatic compound-degrading gene from host Escherichia coli; and the recombinant Escherichia coli can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, an ammonia ion transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene, an NAD synthesis gene and a pyridoxal phosphate synthesis gene. A bacterium can be applied to the production of levodopa, and a method for producing the levodopa has the advantages of simple production process, few impurities, easily available raw materials and good industrial application prospect.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of Danshensu by using cheap substrate
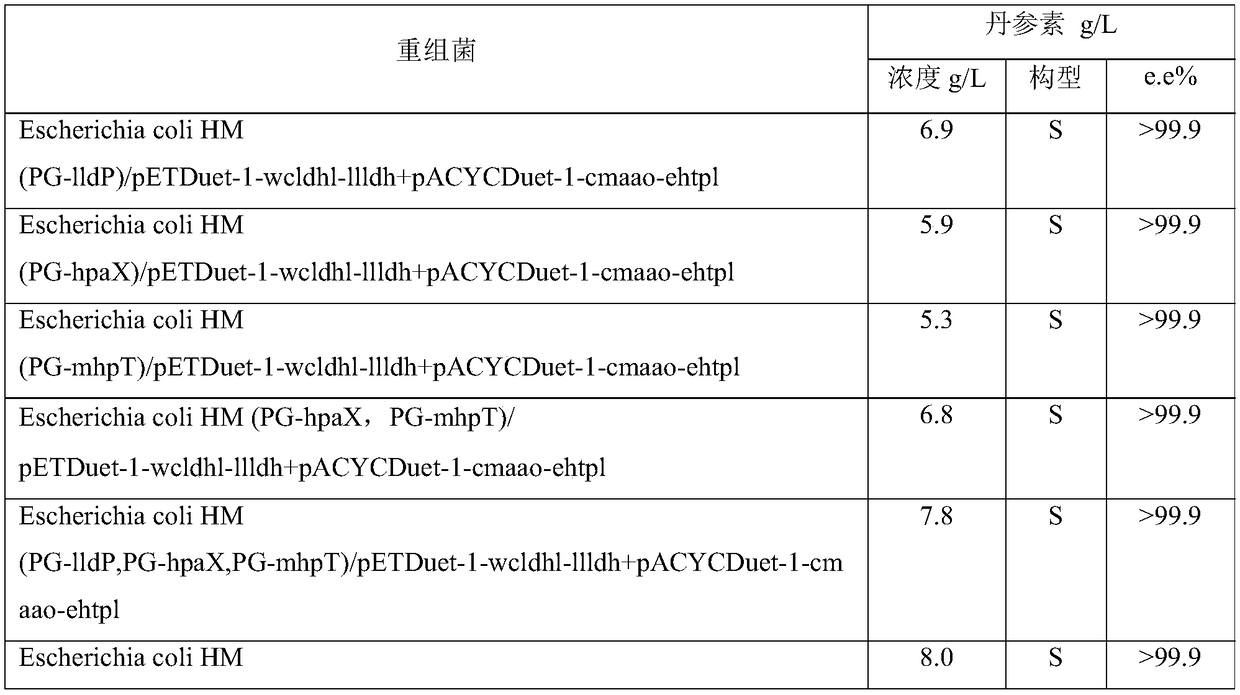
ActiveCN108949648APoor substrate specificityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseL-amino-acid oxidase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of Danshensu by using a cheap substrate, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing Danshensu at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosinephenol lyase, L-amino acid oxidase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages ofrealization of the efficient production of Danshensu, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:HONGTAOSIM RES INST OF ANALYCAL SCI & TECH LTD CO
Yeast and method of producing l-lactic acid
A yeast having a human- or frog-origin gene encoding L-lactate dehydrogenase transferred thereinto. By producing lactic acid by using the above-described gene and a method of producing lactic acid with the use of the enzyme, it is possible to efficiently produce lactic acid which is widely usable. As a result, lactic acid can be provided at a lower cost.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Engineering bacteria for expressing L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution and application thereof
ActiveCN102559570BIncrease vitalityAchieve preparationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for expressing L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution, which is engineering escherichia coli capable of heterologously expressing NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) independent L-lactate dehydrogenase subjected to orthogenetic evolution. The engineering bacteria can highly express corresponding mutant protein on the basis of commercial escherichia coli C43 (DE3) and through transporting an expression vector pETDuet-1-mlldD containing the mutant NAD independent L-lactate dehydrogenase, and has the S-mandelic acid degrading activity. The invention also discloses an application of the engineering bacteria in the resolution of racemic mandelic acid. The racemic mandelic acid is conducted through taking intact cells of the constructed engineering bacteria as a catalyst, and meanwhile, homochiral R-mandelic acid and benzoyl formic acid are produced. The engineering bacteria has the advantages of high substrate utilization rate, high product concentration, high optical purity, simplicity and convenience in future extraction, and the like.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of pyruvic acid
ActiveCN108949656ANot easy to decomposeHigh NAD contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of pyruvic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium simultaneously expresses exogenous L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase, is obtained by knocking out a pyruvic acid absorption gene from host Escherichia coli, and can achieve enhanced expression of a lactic acid transporter gene, a pyruvic acid transporter gene and an NAD synthesis gene. The double-enzyme co-expression engineering bacterium is constructed on the basis of reconstructing Escherichia coli transportation and a coenzyme synthesis system in order to realize efficient production of pyruvic acid and reduce the generation of impurities.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
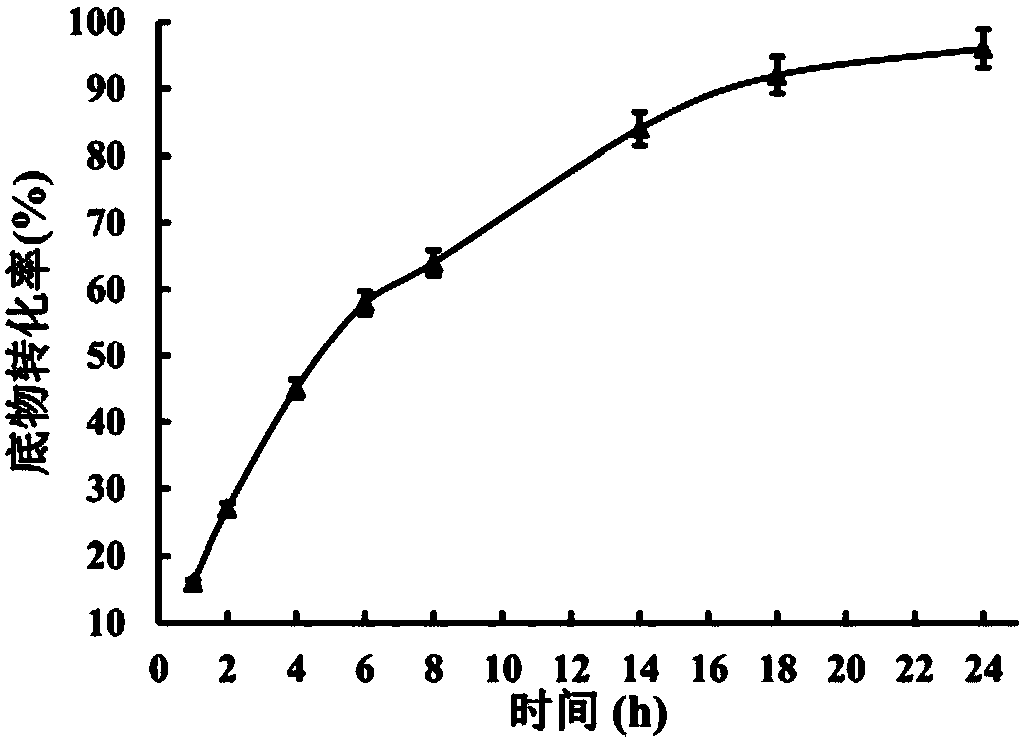
Recombined bacillus alcalophilus, preparing method and application thereof, and method for preparing D-lactic acid
ActiveCN106884001AHigh optical purityReduce pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBacillus alcalophilus
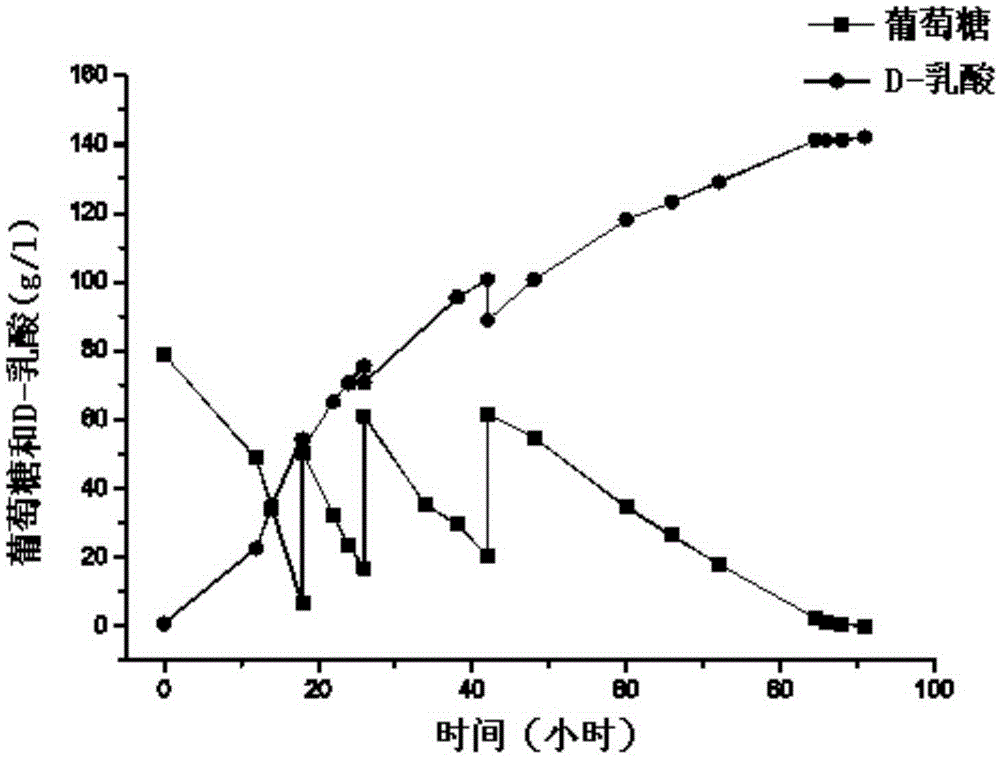
The invention discloses a method for preparing recombined bacillus alcalophilus. According to the method, bacillus alcalophilus for producing L-lactic acid is used as original strain, and by means of genetic engineering operation, the original strain is made not to express L-lactic dehydrogenase but to express D-lactic dehydrogenase. The invention further discloses recombined bacillus alcalophilus prepared with the method, application of the recombined bacillus alcalophilus, and a method for preparing D-lactic acid. When the recombined bacillus alcalophilus prepared with the method for preparing the recombined bacillus alcalophilus is applied to preparation of D-lactic acid, the optical purity of the obtained D-lactic acid is higher than 99.8%, the conversion rate is 94% or more, and the yield can reach 142 g / L.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and constructon method and application thereof
InactiveCN101993850BHigh optical purityIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to genetic engineering bacteria for producing D-lactic acid and a construction method and application thereof. The strain of C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh deleted in L-lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldh) is used as a starting strain to over express exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene so as to obtain C.glutamicum Res 167 delta ldh / ldhA. The genetic engineering bacteria are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preserving registration number of CGMCC No.4041. By utilizing the genetic engineering means, the expression of the exogenous D-lactate dehydrogenase gene is realized in the corynebacterium glutamicum deleted in L-lactic acid metabolic pathway, and the genetic engineering bacteria producing high optical purity D-lactic acid are successfully constructed. When the engineering bacteria are used for producing lactic acid through fermentation, the yield of the D-lactic acid is over 40g / L, and the purity is over 99 percent. The invention has important significance for the industrial production of the D-lactic acid, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
Construction method of bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria for high yielding of alanine
InactiveCN104593405AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseGene mutation
The invention discloses a preparation method of bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria for high yielding of alanine, wherein the method comprises that alanine-synthesized branched metabolism genes L-lactate dehydrogenase gene ldh and acetate kinase gene ackA on a B.subtilis 168 chromosome are knocked out by using a homologous recombination method, and a mutant strain is obtained. The single-gene mutant strain has the preservation number of IBL23-ldh, the construction of the mutant strain is achieved by knocking out a part of the lactate dehydrogenase gene of bacillus subtilis; a double-gene mutant strain is obtained by again knocking out the acetate kinase gene based on the single-gene mutant strain and has the number for IBL23-ldh / ackA.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
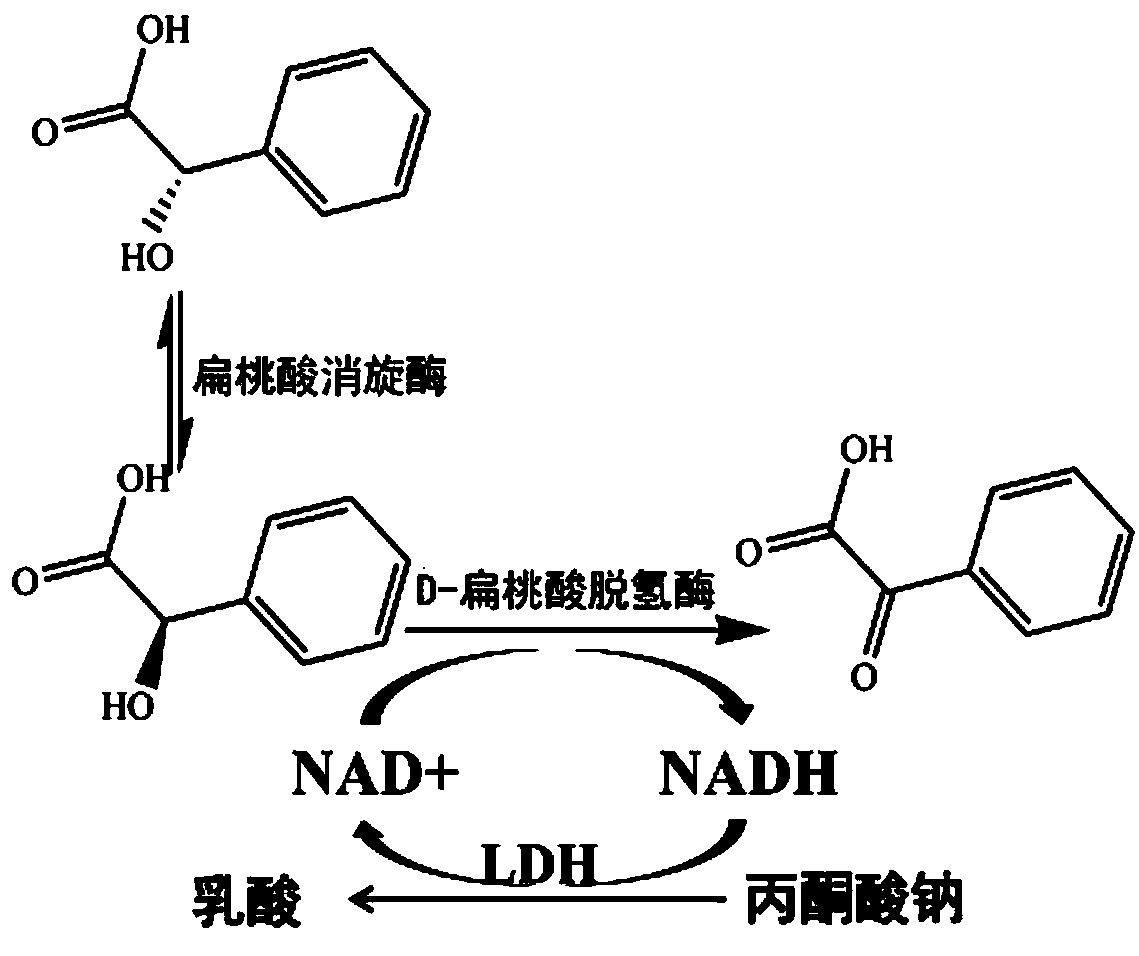
Genetic engineering compound bacteria and application thereof in biosynthesis of PGA (phenylglyoxylic acid)
The invention discloses genetic engineering compound bacteria and an application thereof in biosynthesis of PGA (phenylglyoxylic acid). The genetic engineering compound bacteria contain a novel L-lactate dehydrogenase gene LhLDH, an existing D-mandelate dehydrogenase gene and encoded genes thereof as well as a novel mandelate racemase gene HrMR, the genetic engineering compound bacteria are utilized for production and application of PGA synthesized through whole-cell catalysis of racemic mandelic acid, the production process is simple, the conditions are mild, the efficiency is high and the cost is low. The genetic engineering compound bacteria have the benefits as follows: the constructed genetic engineering compound bacteria can realize high yield of D-mandelate dehydrogenase, L-lactatedehydrogenase and mandelate racemase; on the basis of whole-cell catalysis, the genetic engineering compound bacteria can efficiently oxidize racemic mandelic acid for production of PGA without addition of coenzymes. Through the genetic engineering compound bacteria, the conversion rate of racemic mandelic acid can be 96% or above, the purity of PGA can be 99% or above, and the genetic engineeringcompound bacteria have good industrial prospects.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
L-lactate dehydrogenase mutant with improved catalysis efficiency and building method thereof
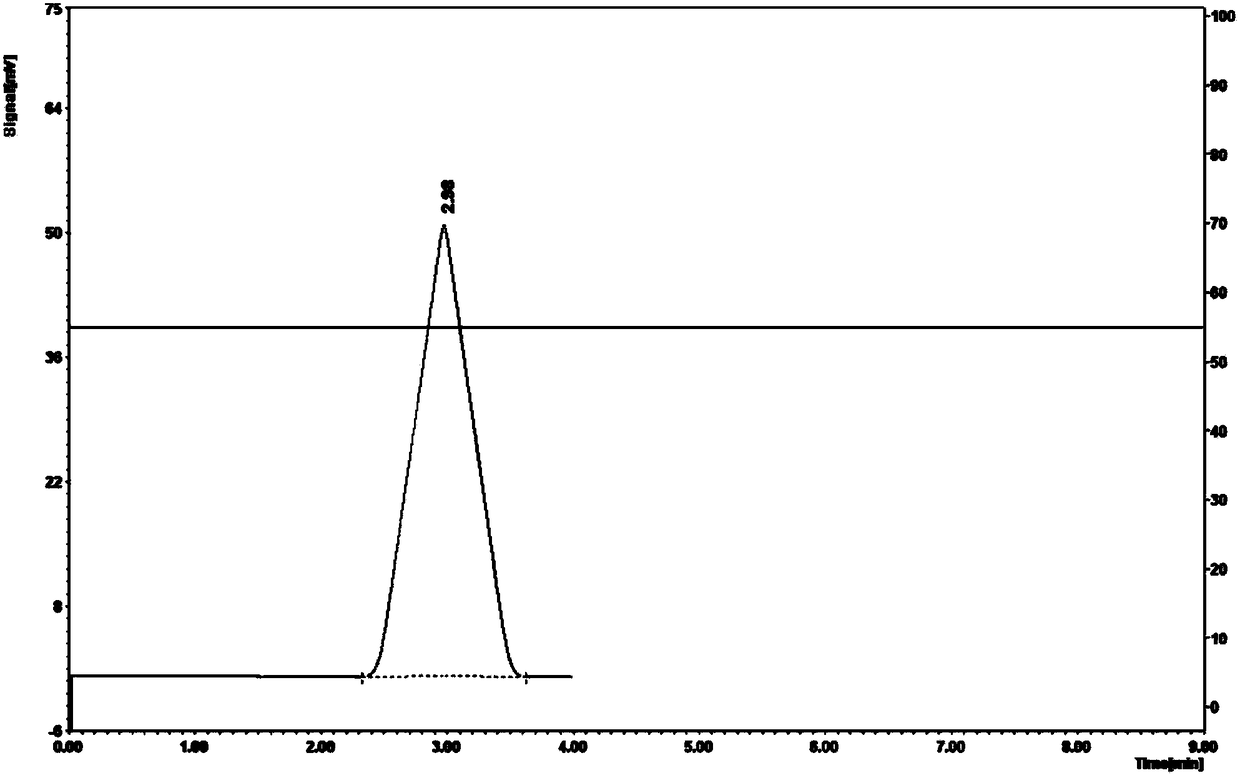
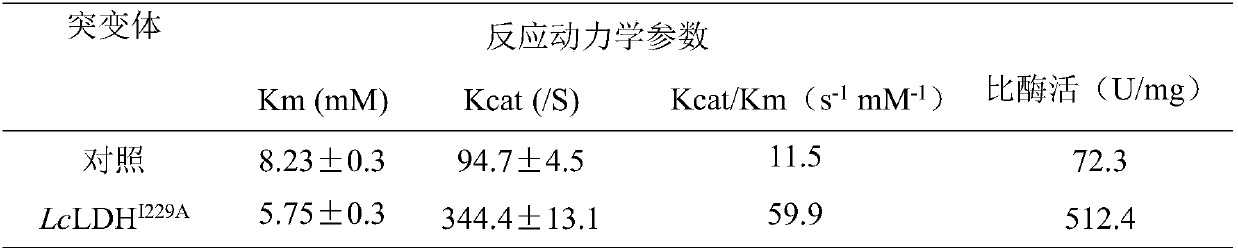
ActiveCN108034644ASolve the limiting problem of low catalytic activityThe specific enzyme activity of the mutant enzyme is increasedBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsL-Lactate dehydrogenaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an L-lactate dehydrogenase mutant with the improved catalysis efficiency and a building method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. On the basisof L-lactate dehydrogenase, the L-lactate dehydrogenase molecular structures are modified through a site-specific mutagenesis biological technology; one strain of L-lactate dehydrogenase escherichia coli engineering bacterium is obtained; the mutant enzyme specific enzyme activity is improved by 6.1 times; the catalytic activity is improved by 4.2 times. The limitation problem of low catalysis activity of the L-lactate dehydrogenase is solved; a novel idea is provided for the L-lactate dehydrogenase molecular modification.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-lactate dehydrogenase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and application thereof
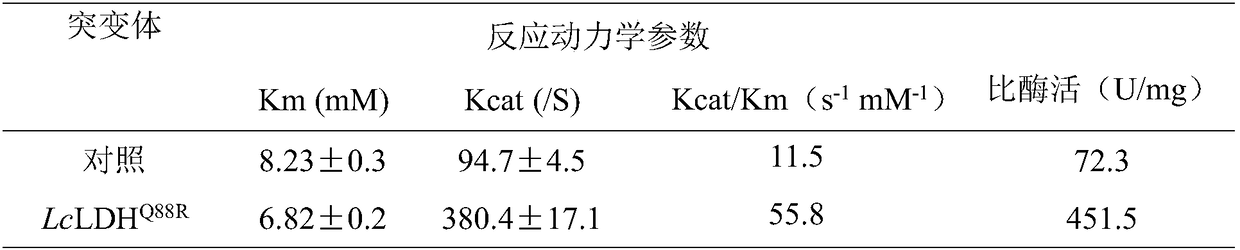
ActiveCN108559734ASolve the limiting problem of low catalytic activityHigh catalytic activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an L-lactate dehydrogenase mutant with improved catalytic efficiency and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. On the basis of L-lactate dehydrogenase, the molecular structure of L-lactate dehydrogenase is transformed through a site-directed mutagenesis biotechnology to obtain engineered L-lactate dehydrogenase escherichia coli, thespecific activity of mutant enzymes is increased by 5.2 times, and the catalytic activity is increased by 3.8 times. The L-lactate dehydrogenase mutant solves the limitation problem of low catalyticactivity of L-lactate dehydrogenase and provides a new idea for the molecular transformation of L-lactate dehydrogenase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium acetoacidophilum strain and method for producing succinic acid therefrom
ActiveCN102634474BIncrease concentrationFood safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseSodium bicarbonate
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
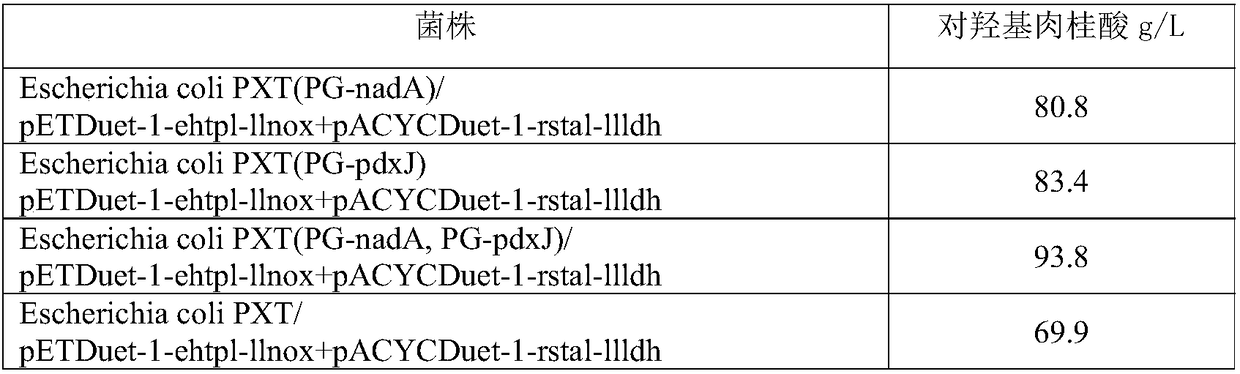
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid
ActiveCN108949840AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseBio engineering
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing p-hydroxycinnamic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a phenol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium can realize the efficient production of p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and a method for producing the p-hydroxycinnamic acid has the advantages of simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
D-lactic acid-producing strain and use thereof
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a D-lactic acid-producing strain modified to inhibit L-lactate dehydrogenase (L-LDH) activity and to introduce D-lactate dehydrogenase (D-LDH) activity in an L-lactic acid-producing strain, a mutated D-lactic acid-producing strain prepared by the above method, and a method for producing D-lactic acid including the steps of culturing the strain and recovering D-lactic acid from the culture media.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
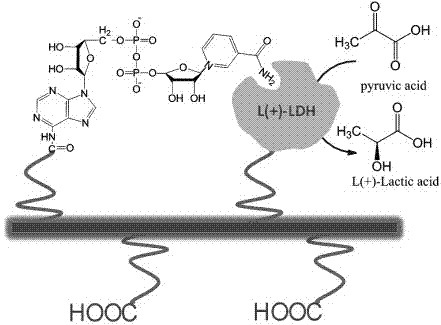
P-carboxypropanamide phenyl silica, its co-immobilized l-lactate dehydrogenase complex and its preparation method
InactiveCN104311589BGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationL-Lactate dehydrogenaseSpace environment
The invention relates to p-carboxyl propionamidophenyl silicon oxide, a co-immobilized L-lactic dehydrogenase compound and a preparation method thereof. The compound is formed by using p-carboxyl propionamidophenyl silicon oxide with regularly-arranged carboxyl groups as a skeleton, and grafting L-lactic dehydrogenase and cofactor NADH. The novel organic / inorganic composite two-dimension lamellar compound overcomes the disadvantages that conventional montmorillonite and hydrotalcite lamellar materials are difficult to control a layer space environment; an application scope of functional enzyme is greatly broadened by developing and synthesizing the organic / inorganic composite lamellar compound with the functional enzyme; and a series of novel biological functional composite materials with various performances are developed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
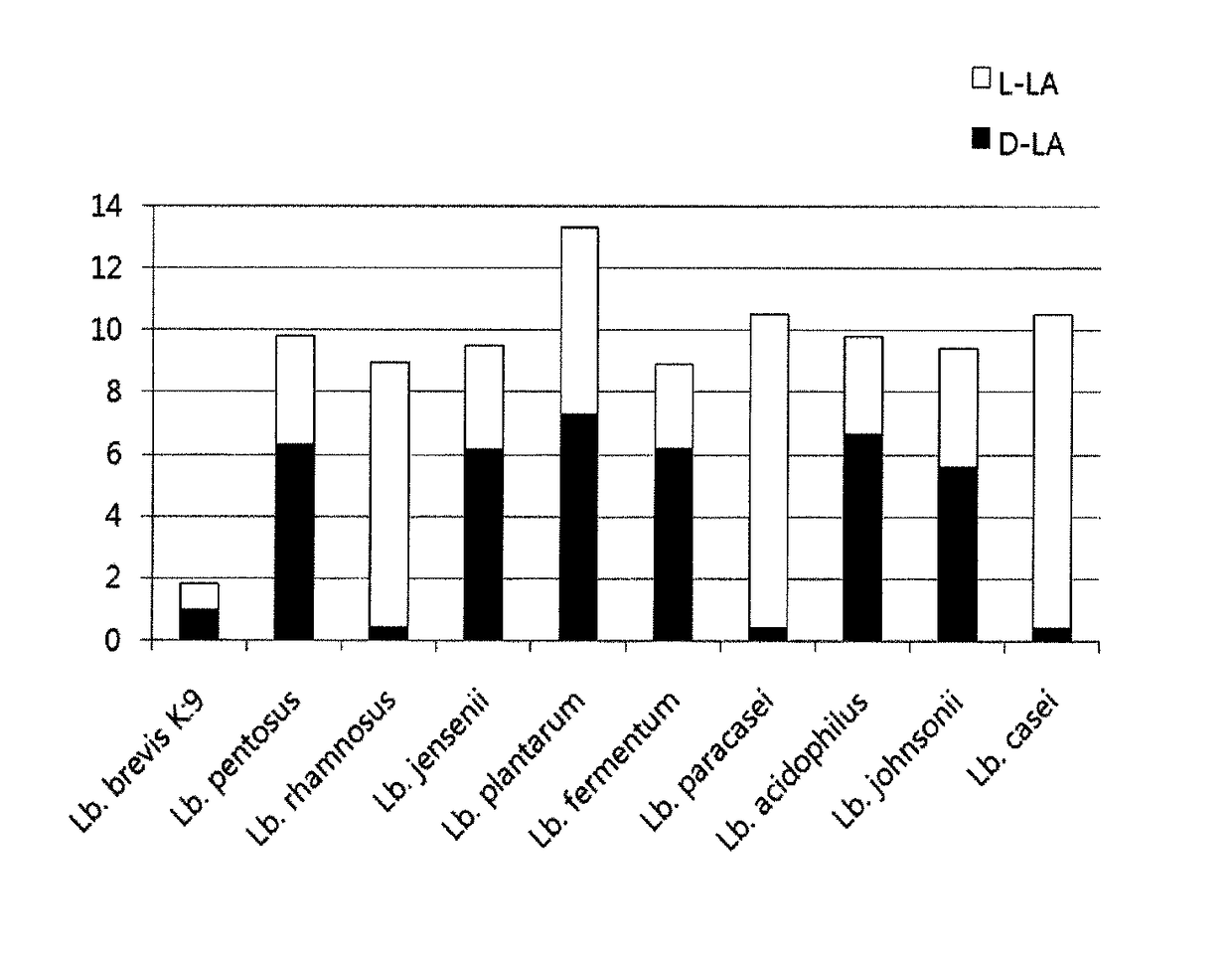
Method for quickly distinguishing lactic acid bacterium strains
InactiveCN105567787AAccurate distinctionQuick distinctionMicrobiological testing/measurementL-Lactate dehydrogenaseLactobacillus
The invention provides a method for quickly distinguishing lactic acid bacterium strains. The method includes the steps that firstly, a culture solution of lactic acid bacterium strains to be detected is centrifuged, and supernate is taken and diluted by 20-25 folds; secondly, the supernate, water, a glycylglycine buffer solution, NAD+ and D-GPT are mixed for 2-4 min before D or L-lactic dehydrogenase is added according to the table 1, a light-absorbing value A1 is read, then D-or L-LDA is added for reacting for 4-6 min, and a light-absorbing value A2 is read; thirdly, a light-absorbing value change value (A2-A1) of samples is subtracted by a contrasted light-absorbing value change value (A2-A1) to obtain deltaAD-lactic acid or deltaAL-lactic acid, the deltaAD-lactic acid or deltaAL-lactic acid is substituted into the following formula to calculate the concentration of D-lactic acid or L-lactic acid of the lactic acid bacterium strains to be detected, and please see the formula in the description. The lactic acid bacterium strains to be detected are distinguished according to the concentration ratio of D-lactic acid and L-lactic acid of the lactic acid bacterium strains to be detected.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD CO LTD
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid by using cheap substrate
ActiveCN108949651APoor substrate specificityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid by using a cheap substrate, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium constructed in the invention can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, L-amino acid oxidase, alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid oxidase and L-lactate dehydrogenase respectively. The knockout or enhanced expression of a related gene on the genome of the Escherichia coli can promote the transportation of the substrate and reduce the decomposition of the product. The method for producing the p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid has the advantages of simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Homocysteine determination kit, preparation method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN109358017BHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsL-Lactate dehydrogenasePhosphoric acid
The present invention relates to a homocysteine assay kit and its preparation method and detection method. The homocysteine assay kit includes reagent R1 and reagent R2. Reagent R1 is prepared from the following components: Aqueous solution: phosphate buffer, 1.8~2.2mL / L Triton X‑100, 0.11~0.16g / L L‑serine, 805~815KU / L lactate dehydrogenase, 0.5~0.75g / L NADH and 0.8-1.2mL / L ProcLin300; reagent R2 is an aqueous solution prepared from the following components: phosphate buffer, 1.8-2.2mL / L Triton X-100, 0.05-0.10g / EDTA dihydrate disodium salt in L, ProcLin300 in 0.8-1.2mL / L, cystathionine-β-synthase in 20.0-22.0KU / L and cystathionine-β-synthase in 10.0-14.0KU / L ‑Decomposing enzymes. The homocysteine determination kit forms a reagent R1 and a reagent R2 by screening each component containing a specific ratio, and has a low detection limit, high sensitivity, wide linear range as a whole, and good stability.
Owner:WUHAN CHANGXINSHENG BIOTECH
Method for preparing L-alanine by using lactic acid and strain
ActiveCN110305823AHigh NAD contentEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-Lactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an engineering bacteria and an application in preparation of L-alanine, which belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The recombinant Escherichia coli of the presentinvention simultaneously express exogenous L-lactate dehydrogenase and L-alanine dehydrogenase, and enhances the expression of a lactate transporter gene and a NAD synthase gene on the basis of the host Escherichia coli. The method constructs the double-enzyme co-expressed engineering bacteria on the basis of engineering Escherichia coli transport and coenzyme synthesis system, and realizes efficient preparation of L-alanine by using cheap raw materials.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com