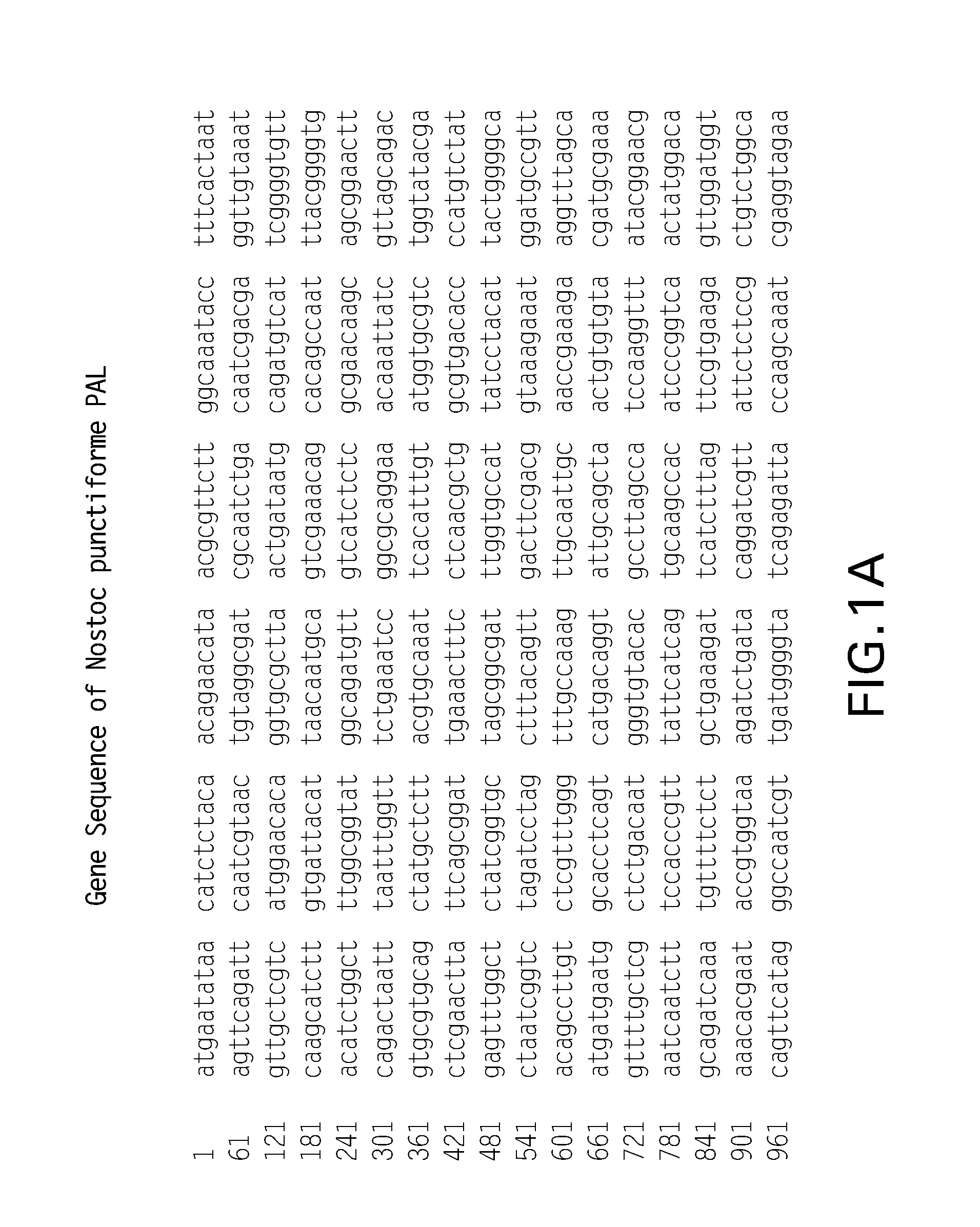
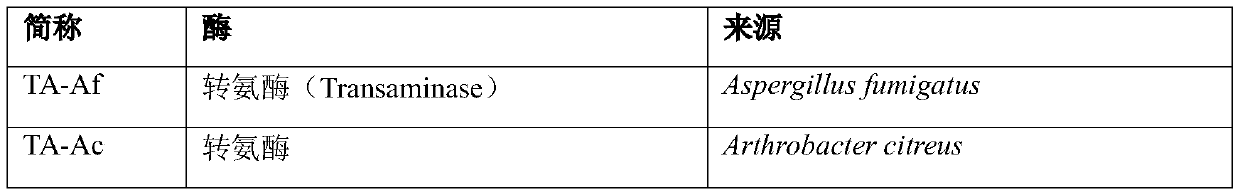
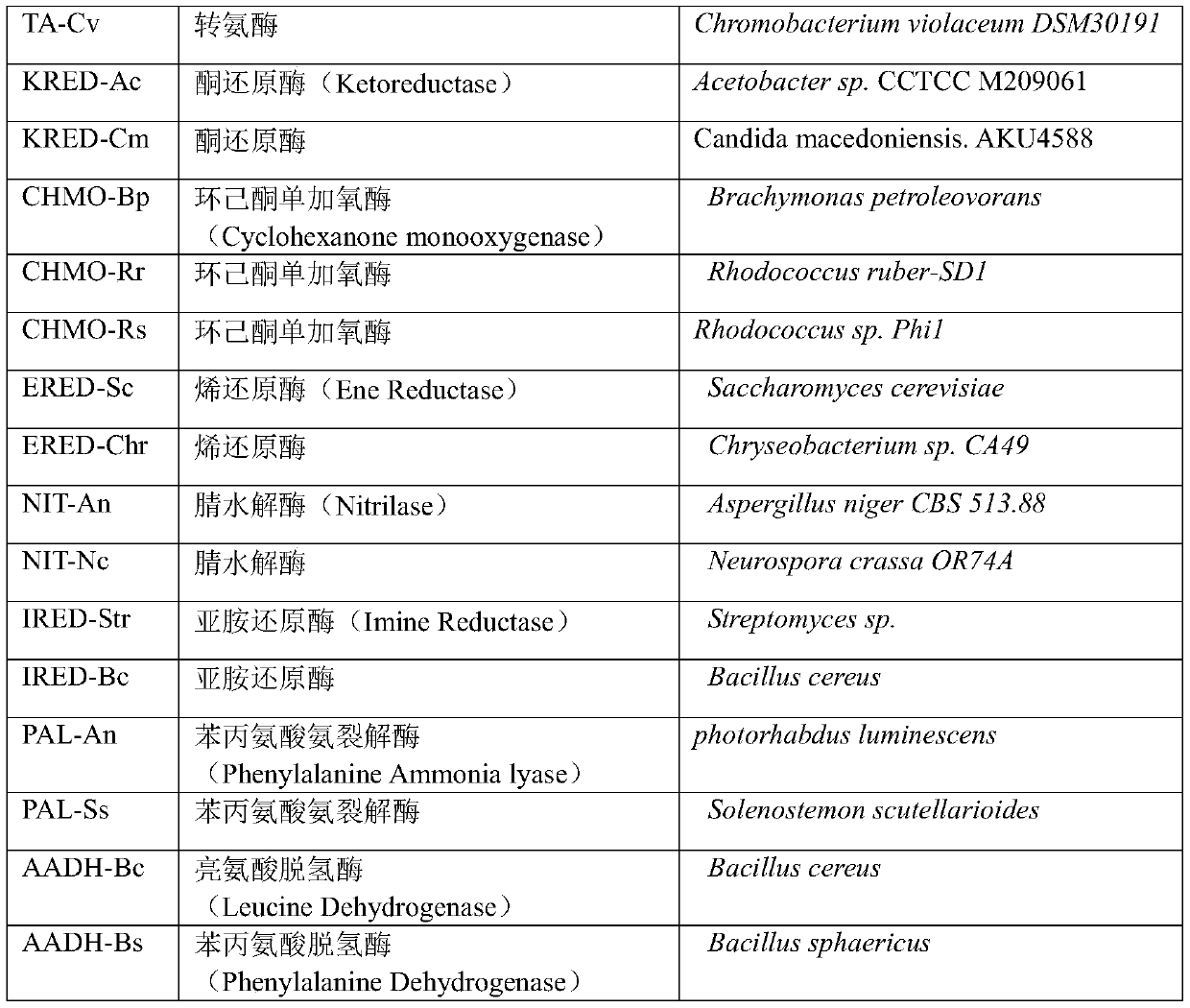
Patents
Literature
275results about "Carbon-nitrogen lyases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of using compositions thereof
ActiveUS7531341B1Extended half-lifeLow immunogenicityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typePAL
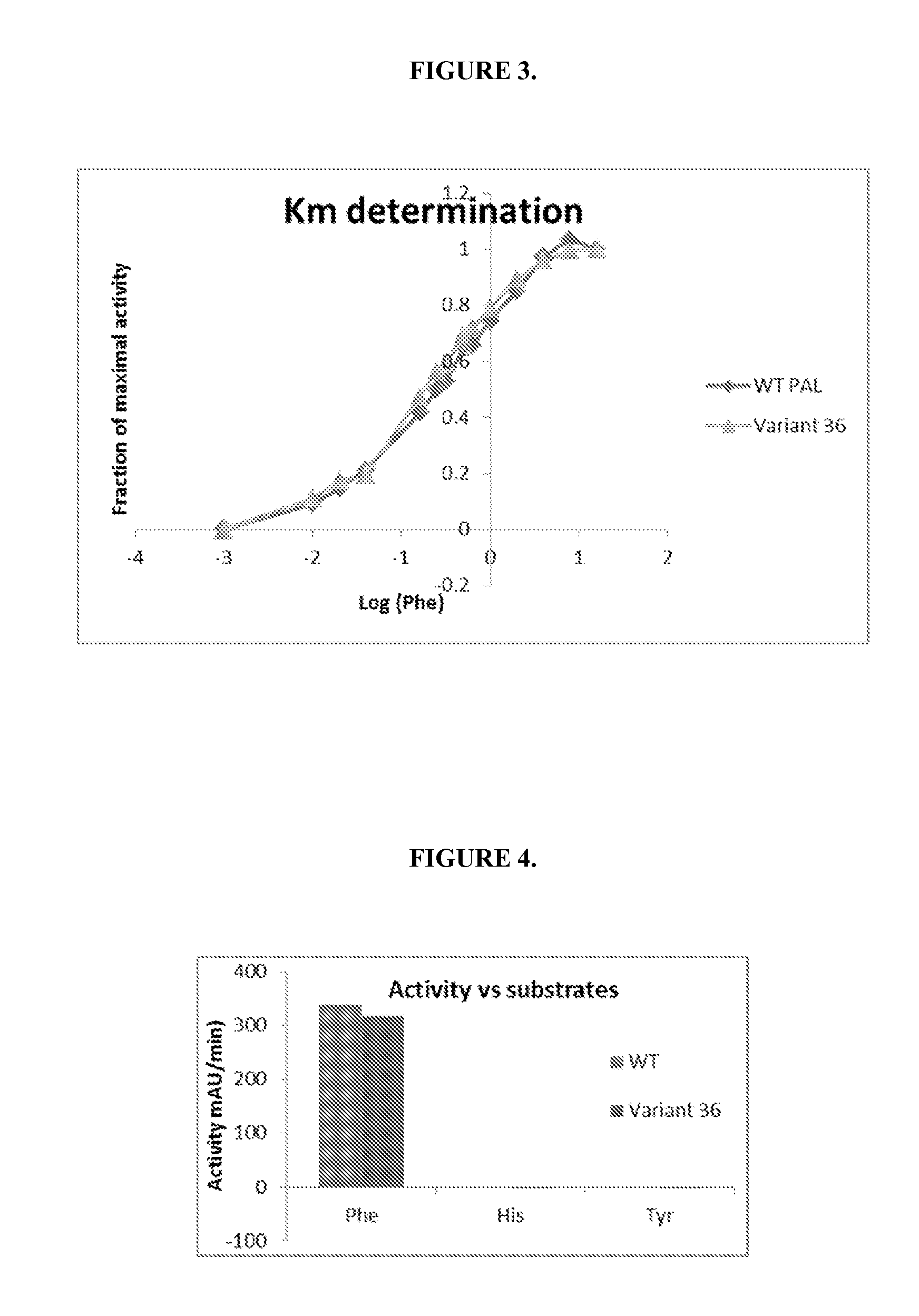
The present invention is directed to phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL wherein the PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity as compared to a wild-type PAL. The invention thus provides compositions of bacterial PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants and analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, and use of such compositions for therapeutic and industrial purposes.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase variants and methods of using compositions thereof
InactiveUS20130039898A1Effective treatmentImprove propertiesCarbon-nitrogen lyasesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeImmunogenicity
Provided herein are phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) variants produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. Further provided are compositions of prokaryotic PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants or analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, formulation, and use of such compositions for industrial and therapeutic purposes, e.g., treating hyperphenylalaninemia, including phenylketonuria, and other disorders, including cancer.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Use of bacterial phage-associated lysing proteins for preventing and treating bacterial infections in humans, animals and fowl
InactiveUS20060292135A1Change propertiesImprove purification effectCarbon-nitrogen lyasesPeptide/protein ingredientsFowlLyase
A composition and method for treating bacterial infections by the use of an effective amount of at least one lytic specific for the bacteria causing specific. The lytic enzyme is genetically coded for by a bacteriophage which may be specific for said bacteria. The enzyme may be at least one lytic protein or peptides in a natural or modified form.
Owner:NEW HORIZONS DIAGNOSTICS
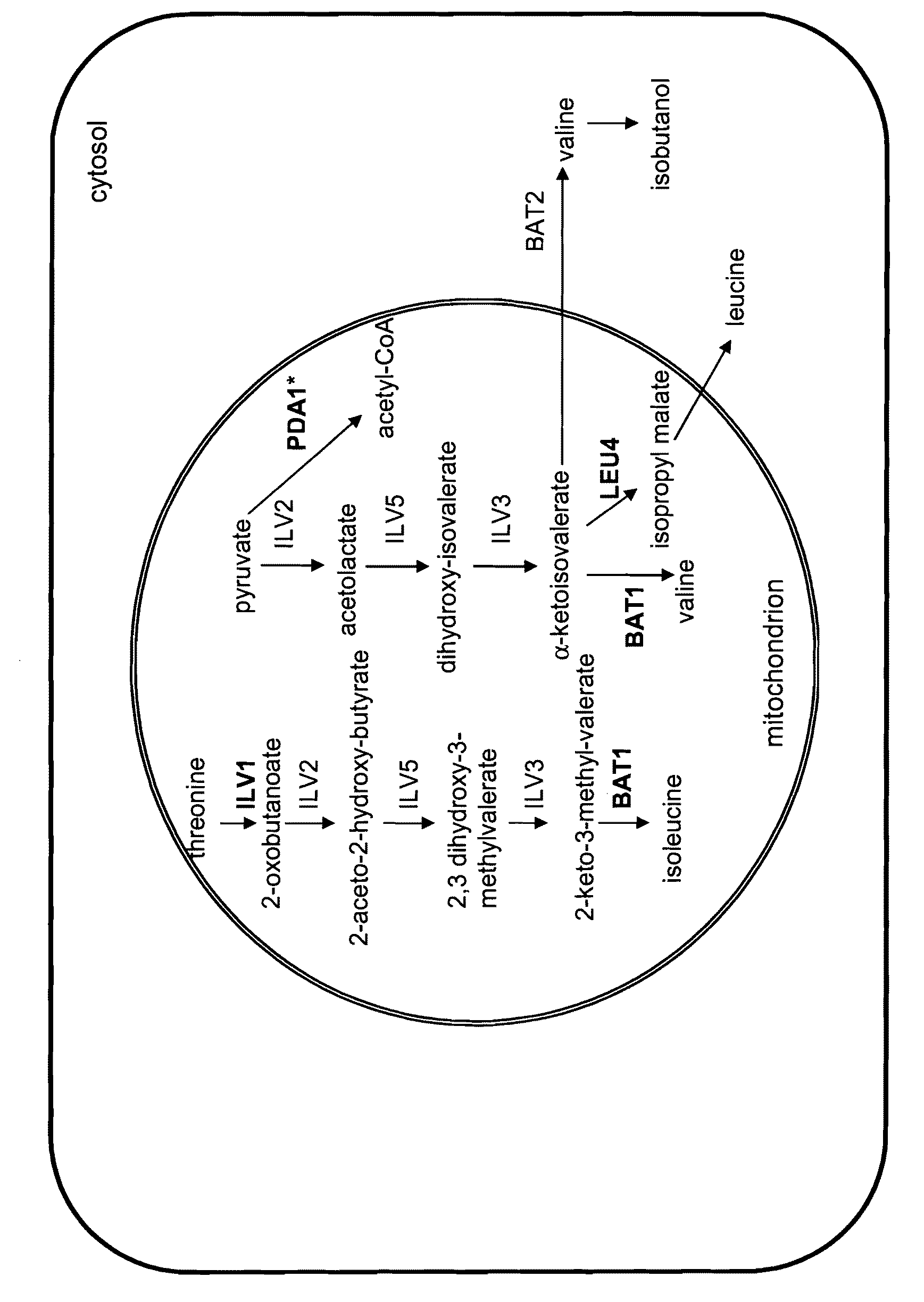
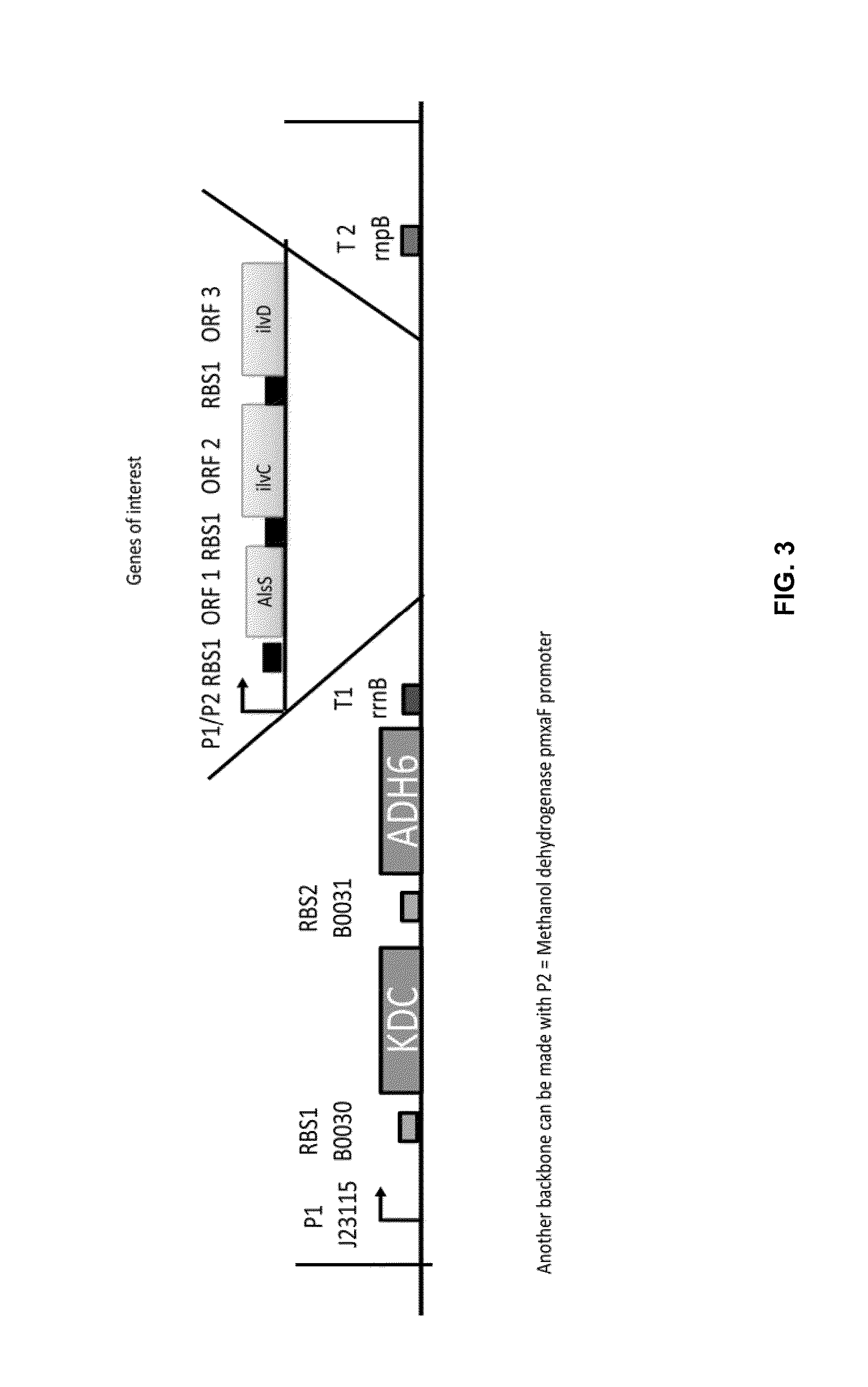
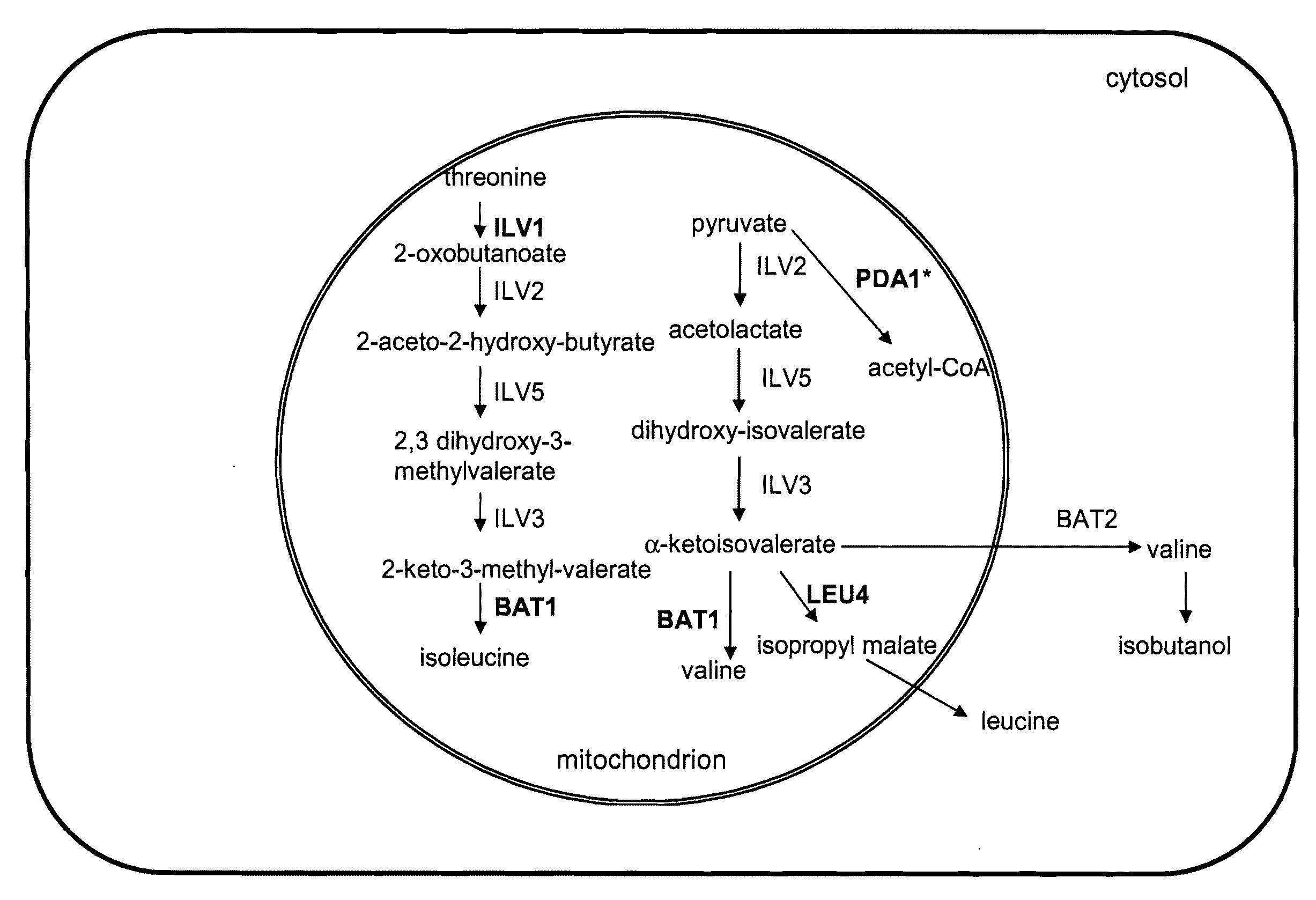
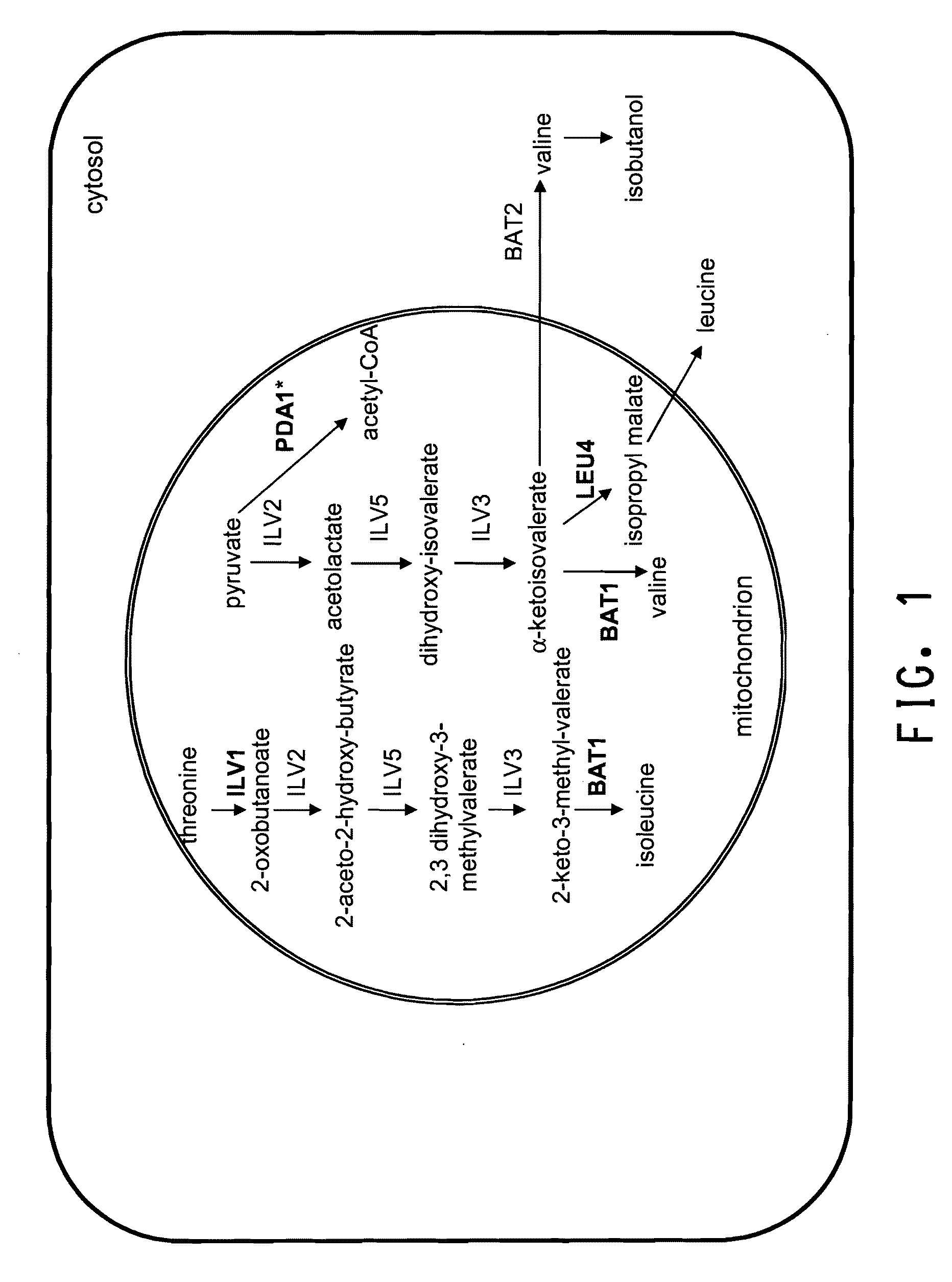
Increased production of isobutanol in yeast with reduced mitochondrial amino acid biosynthesis
ActiveUS8465964B2Reduced activityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesMicroorganismsIsobutanolBranched-chain-amino-acid transaminase
Owner:GEVO INC
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
ActiveUS7445911B2Efficient and high yieldImprove bioavailabilityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesOxidoreductasesLyaseKeto acid
Conversion in vitro of X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly or X—NH2 (X being a peptide or any other compound having a carbonyl group capable of forming a covalent bond with glycine) is accomplished enzymatically in the presence of keto acids, or salts or esters thereof, to provide a good yield without the necessity of catalase or similar enzymatic reaction enhancers. Peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) is a preferred enzyme for catalyzing the conversion. Alternatively, peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) is utilized to convert X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly which may be recovered, or optionally may be simultaneously or sequentially converted to an amide by either a Lewis base or action of the enzyme peptidyl α-hydroxyglycine α-amidating lyase (PAL). Both PHM and PAL are functional domains of PAM.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Biological Conversion of Multi-Carbon Compounds from Methane
Multi-carbon compounds such as ethanol, n-butanol, sec-butanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, fatty (or aliphatic long chain) alcohols, fatty acid methyl esters, 2,3-butanediol and the like, are important industrial commodity chemicals with a variety of applications. The present invention provides metabolically engineered host microorganisms which metabolize methane (CH4) as their sole carbon source to produce multi-carbon compounds for use in fuels (e.g., bio-fuel, bio-diesel) and bio-based chemicals. Furthermore, use of the metabolically engineered host microorganisms of the invention (which utilize methane as the sole carbon source) mitigate current industry practices and methods of producing multi-carbon compounds from petroleum or petroleum-derived feedstocks, and ameliorate much of the ongoing depletion of arable food source “farmland” currently being diverted to grow bio-fuel feedstocks, and as such, improve the environmental footprint of future bio-fuel, bio-diesel and bio-based chemical compositions.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Increased production of isobutanol in yeast with reduced mitochondrial amino acid biosynthesis
ActiveUS20100129887A1Reduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityReduced activityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiThreonineYeast form
Yeast cells with reduced activity of certain enzymes involved in branched chain amino acid biosynthesis in yeast mitochondria are described. Target enzymes include threonine deaminase, isopropylmalate synthase, and optionally branched chain amino acid transaminase.
Owner:GEVO INC
Corynebacterium glutamicum and application
InactiveCN106190921AIncrease productionSignificant progressCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaMicrobiologyEnzyme
The invention provides corynebacterium glutamicum and application. The corynebacterium glutamicum is compared with a genomic sequence of a corynebacterium glutamicum standard strain ATCC 13032, and multiple base mutations exist in an amino acid sequence of an enzyme related to valine synthesis. The preservation number of the corynebacterium glutamicum is CGMCC No.12152, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has an important application value in the aspect of preparing valine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
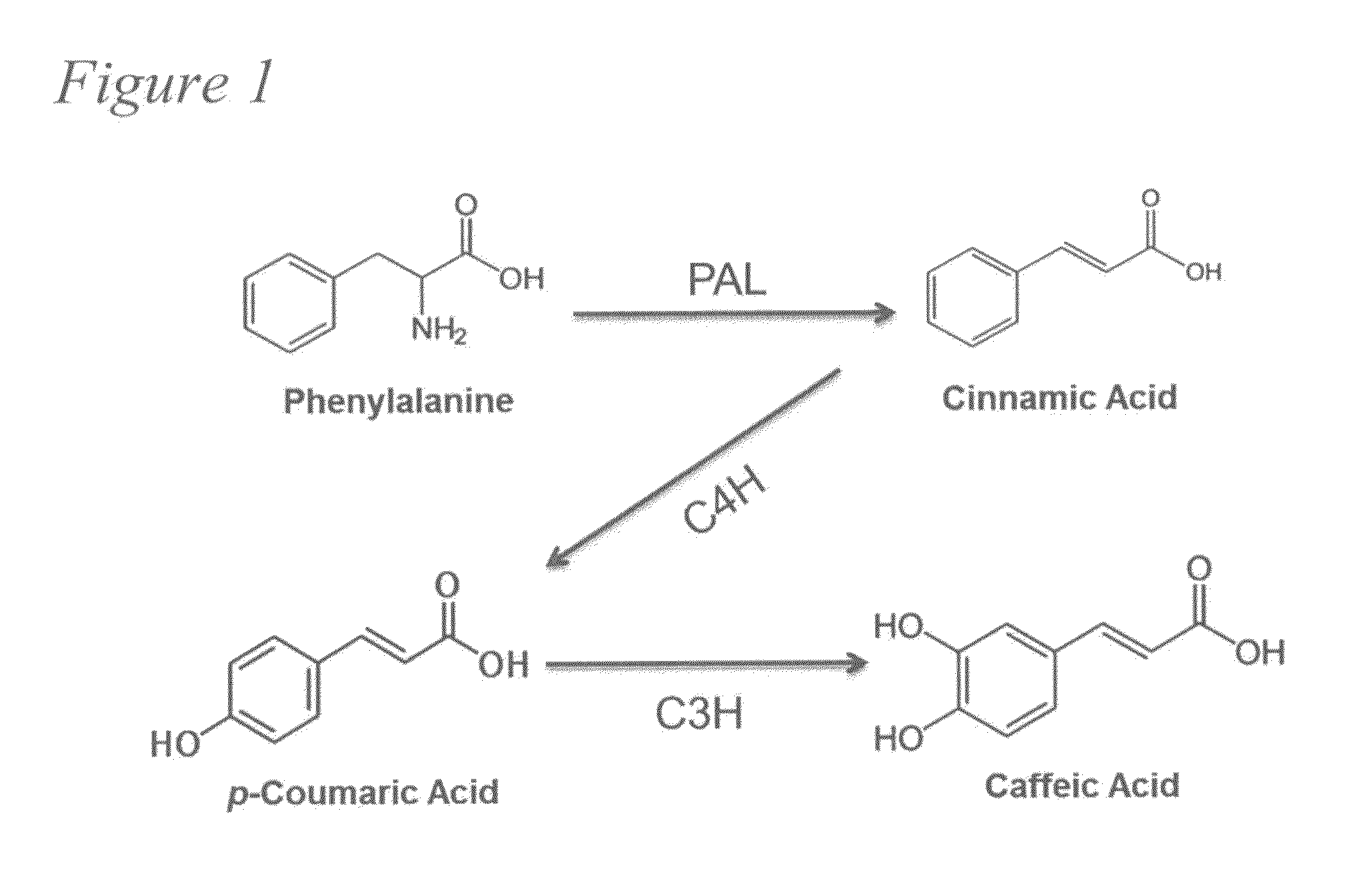
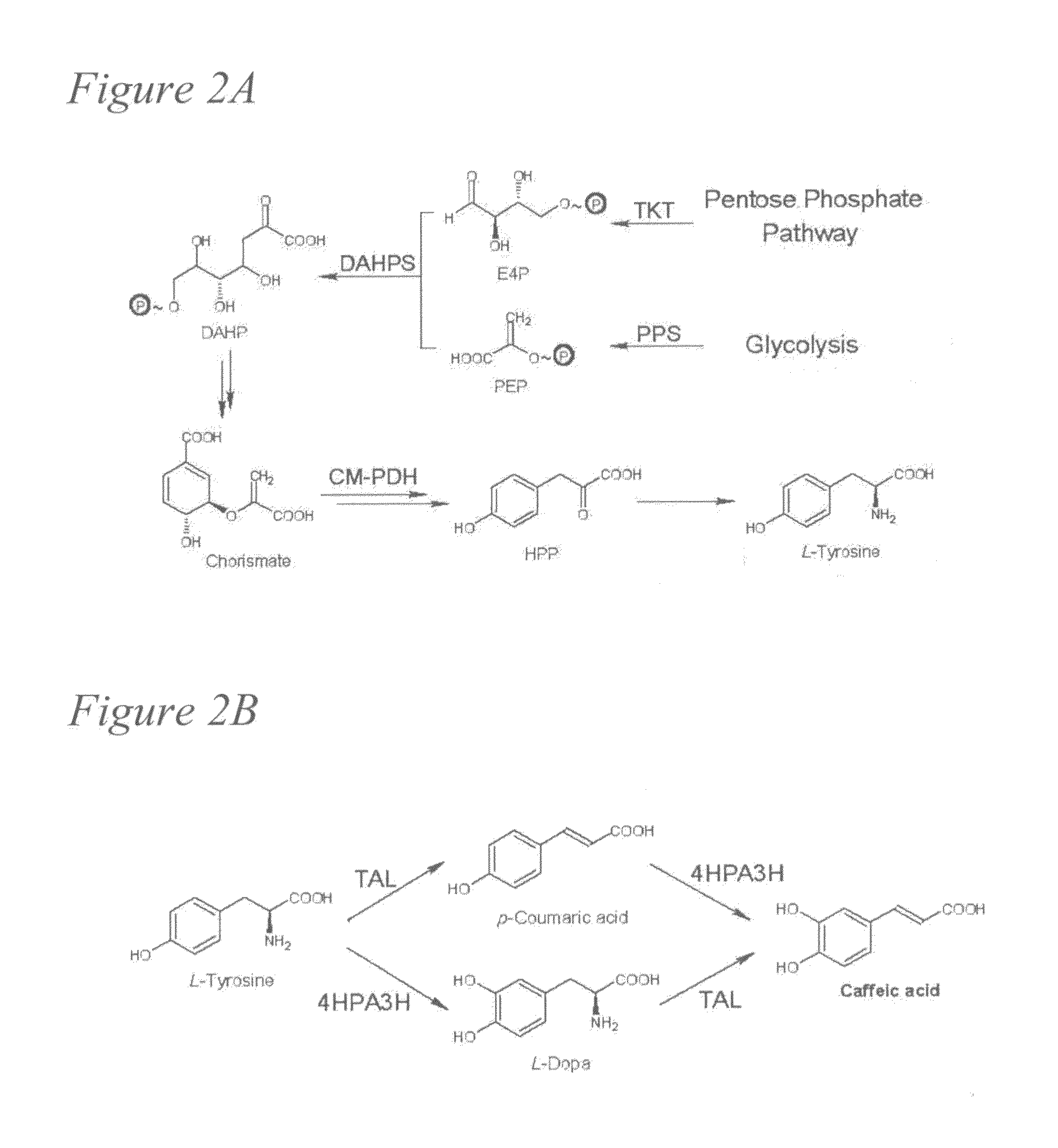
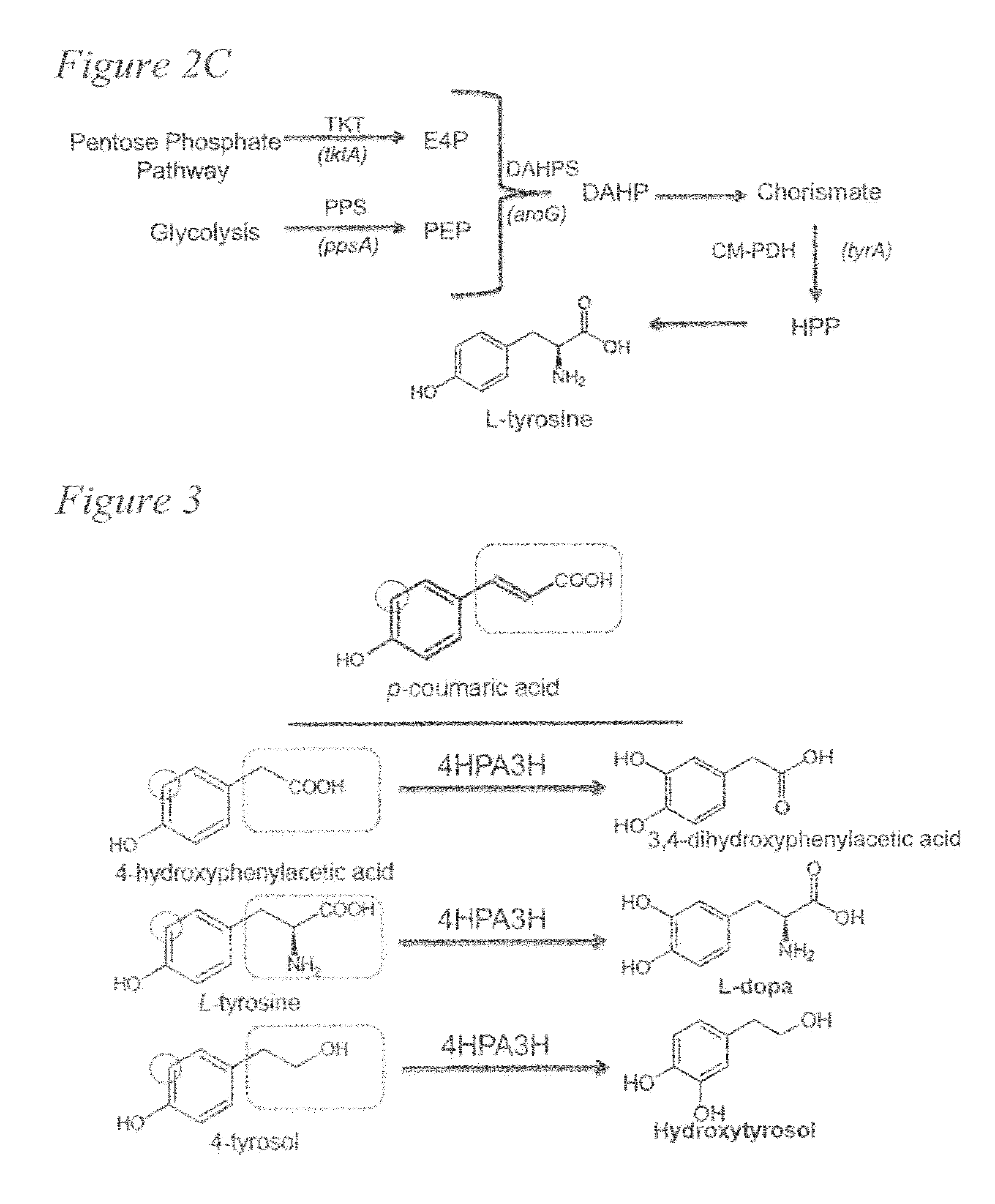
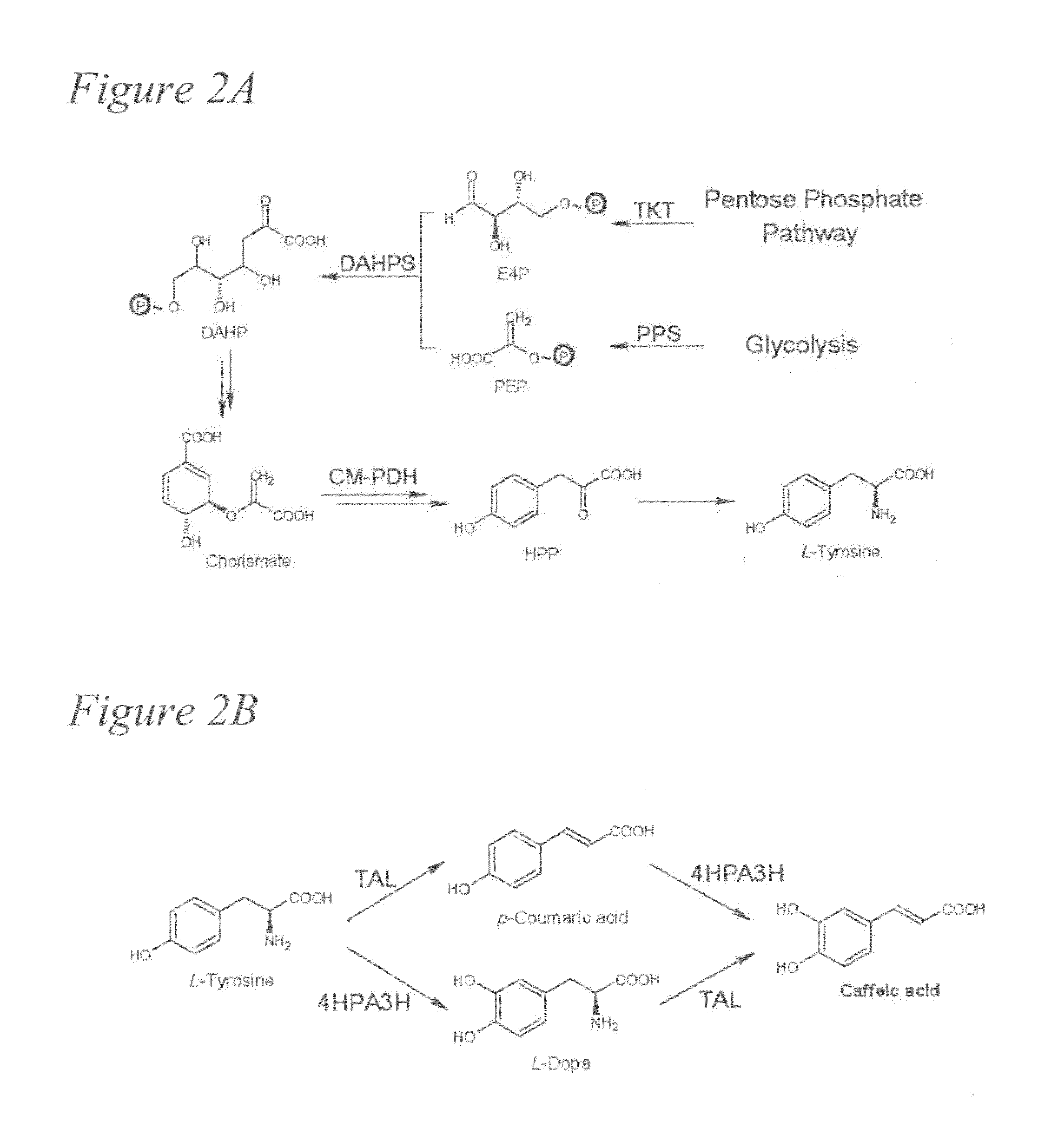
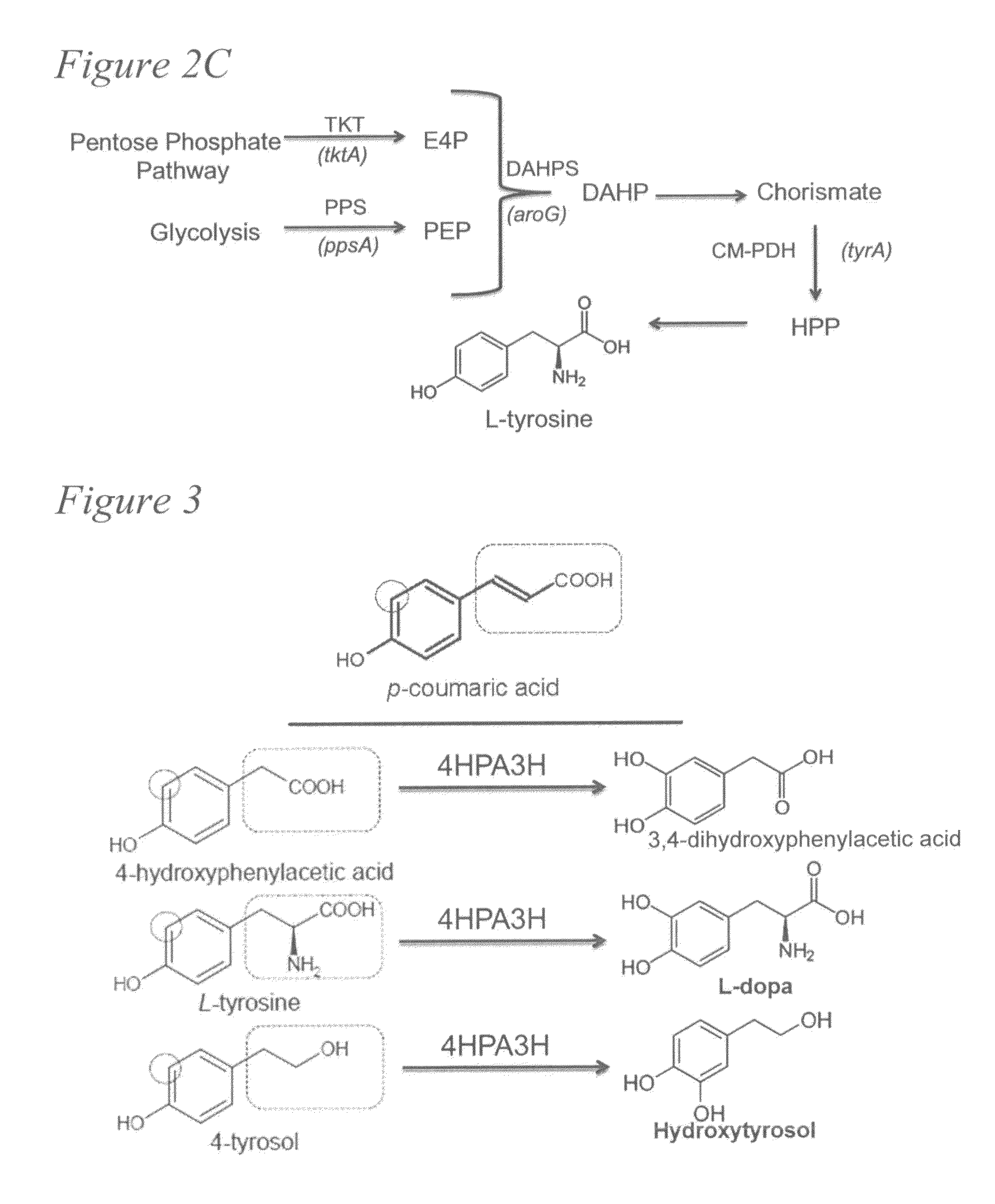
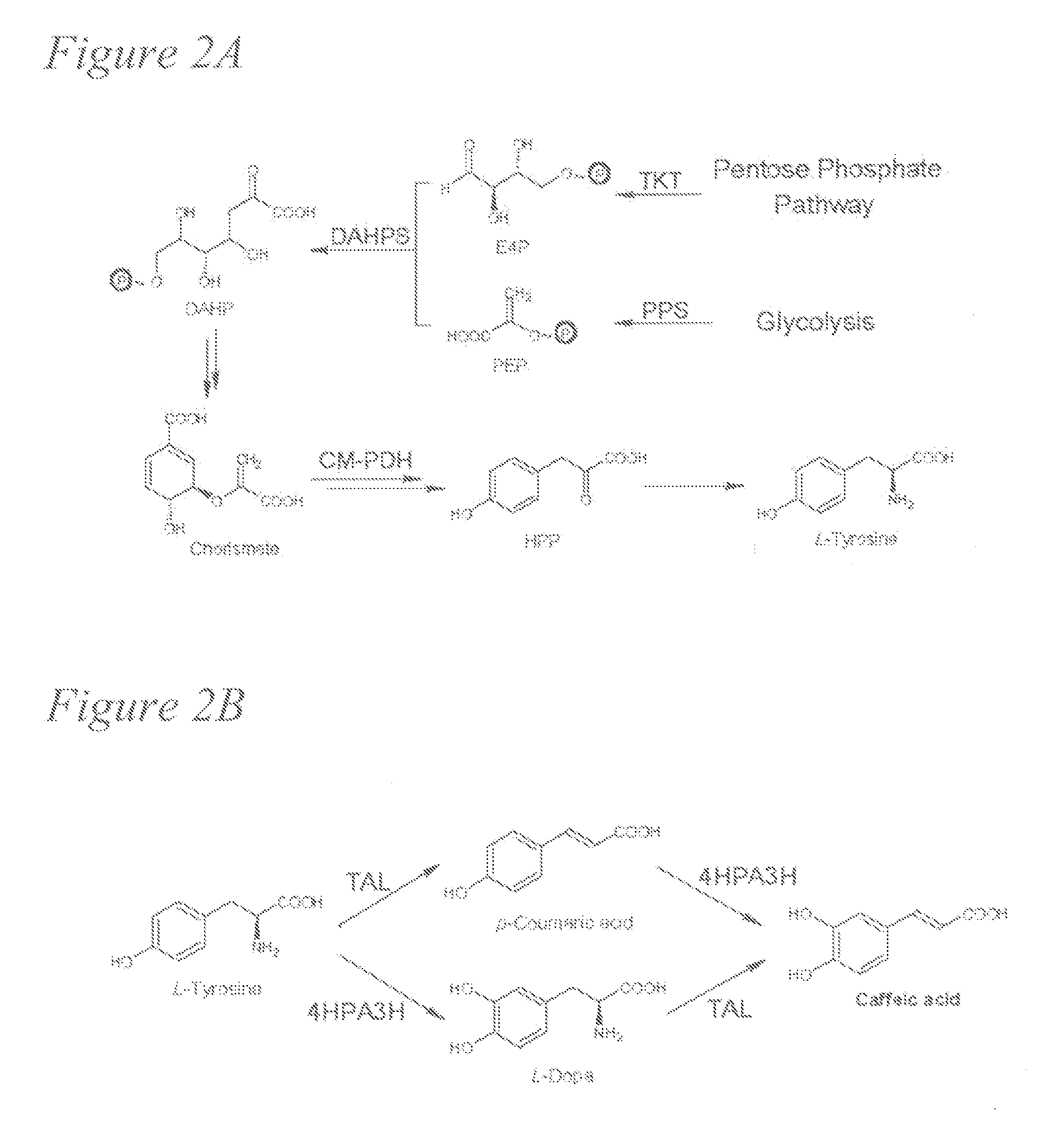
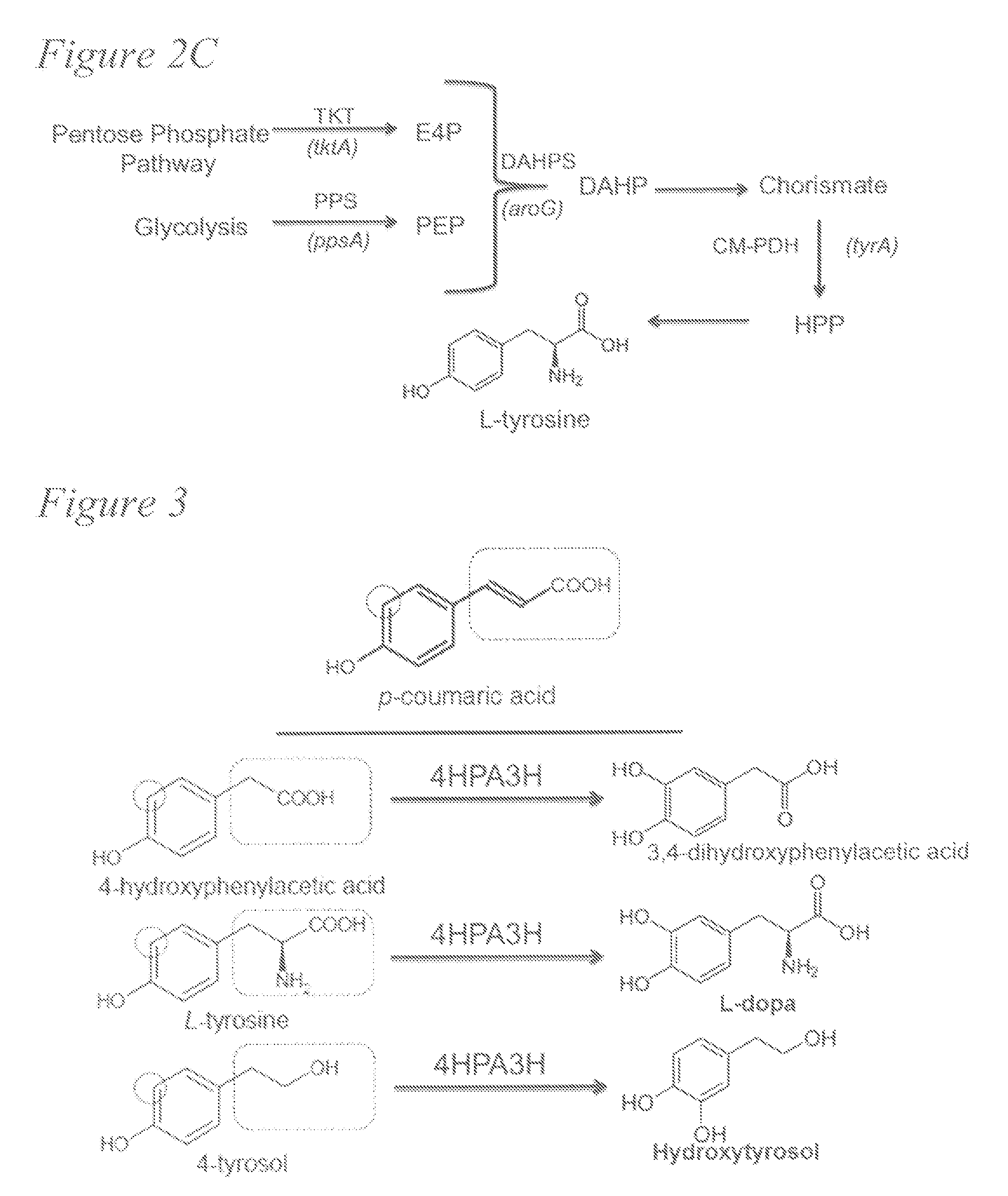
Biosynthesis of caffeic acid and caffeic acid derivatives by recombinant microorganisms
Microorganisms are genetically engineered to synthesize caffeic acid from simple carbon sources via a tyrosine intermediate by means of a dual pathway that utilizes both endogenous and engineered enzymatic activities.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
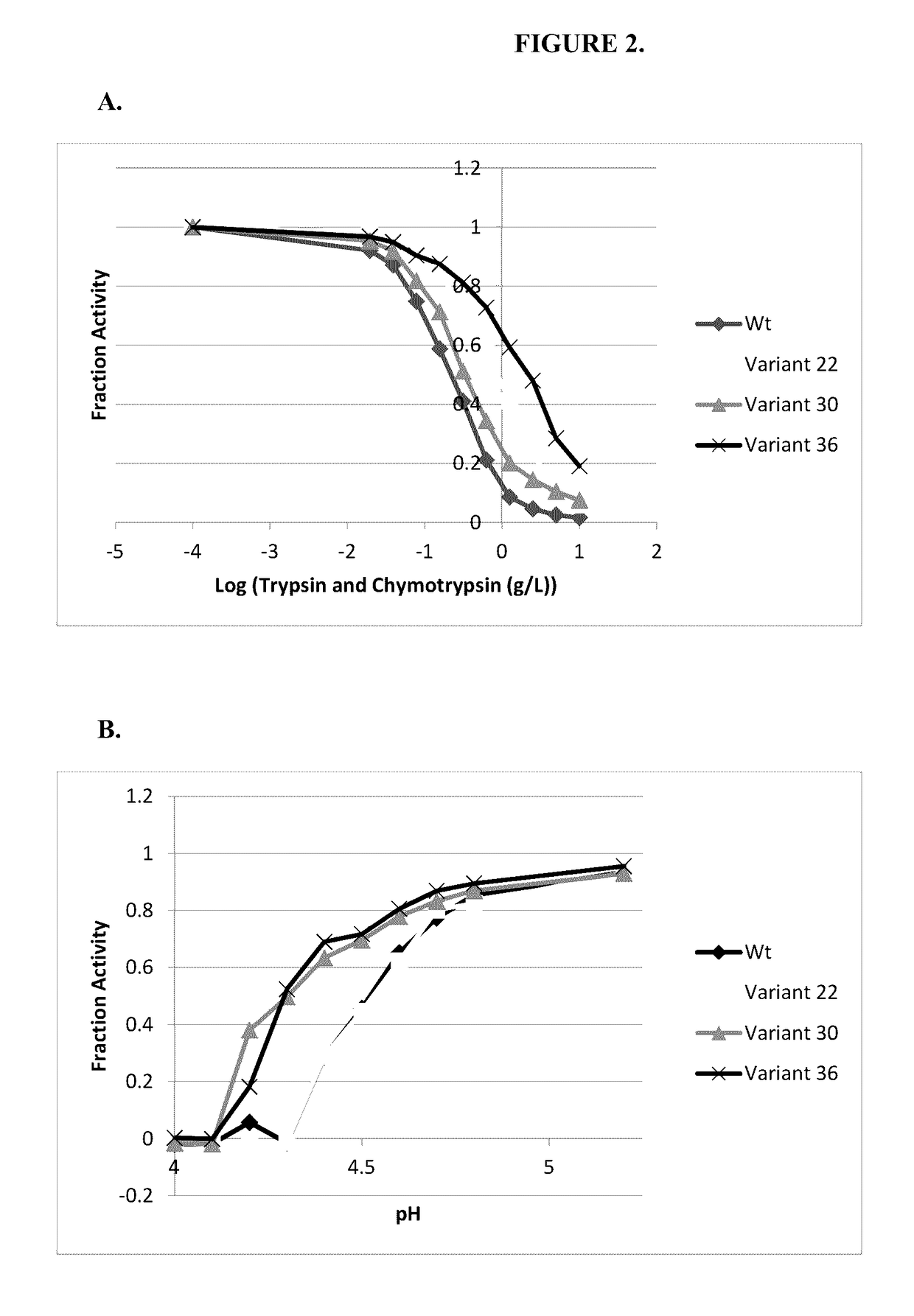
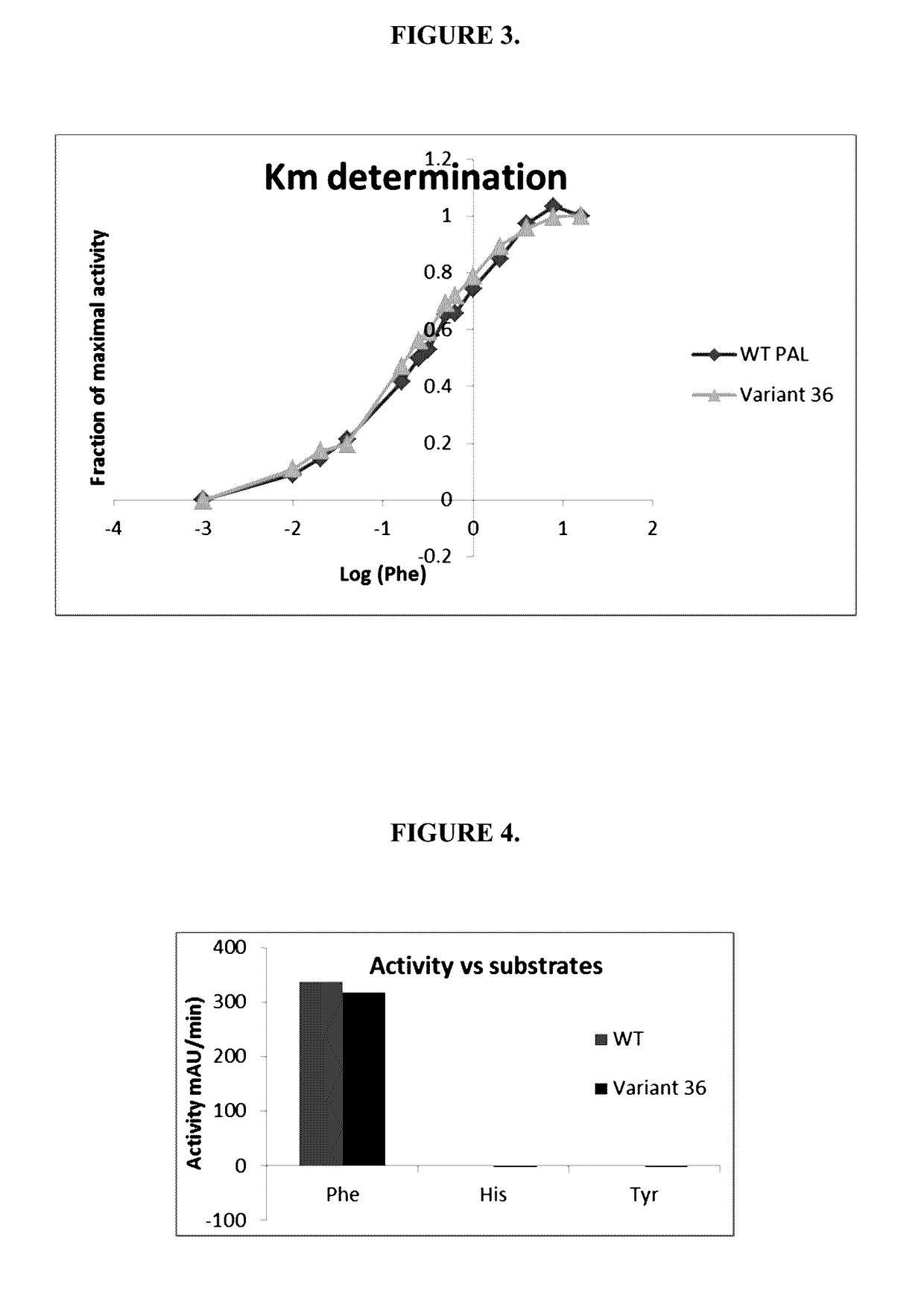
Engineered phenylalanine ammonia lyase polypeptides
ActiveUS9611468B2Improve toleranceReduce sensitivityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesNervous disorderLyasePolynucleotide
The present invention provides engineered phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) polypeptides and compositions thereof, as well as polynucleotides encoding the engineered phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) polypeptides.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
High yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a high yield L-leucine engineering bacterium and an application of the bacterium.The invention provides a method for preparing a recombinant bacterium. The method comprises the following step of importing an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant encoding gene into a target bacterium to form the recombinant bacterium, wherein an alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase mutant is enzyme obtained by mutating 494th arginine of alpha-isopropylmolic acid synthetase into histidine, 497th glycine into aspartic acid and 499th leucine into valine.The high yield L- leucine engineering bacterium, particularly corynebacterium glutamicum MD0032, has higher L-leucine yield than bacterial strains produced at home at present, has a unique identification label and is a L-leucine production strain with a high production and application value.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV +1
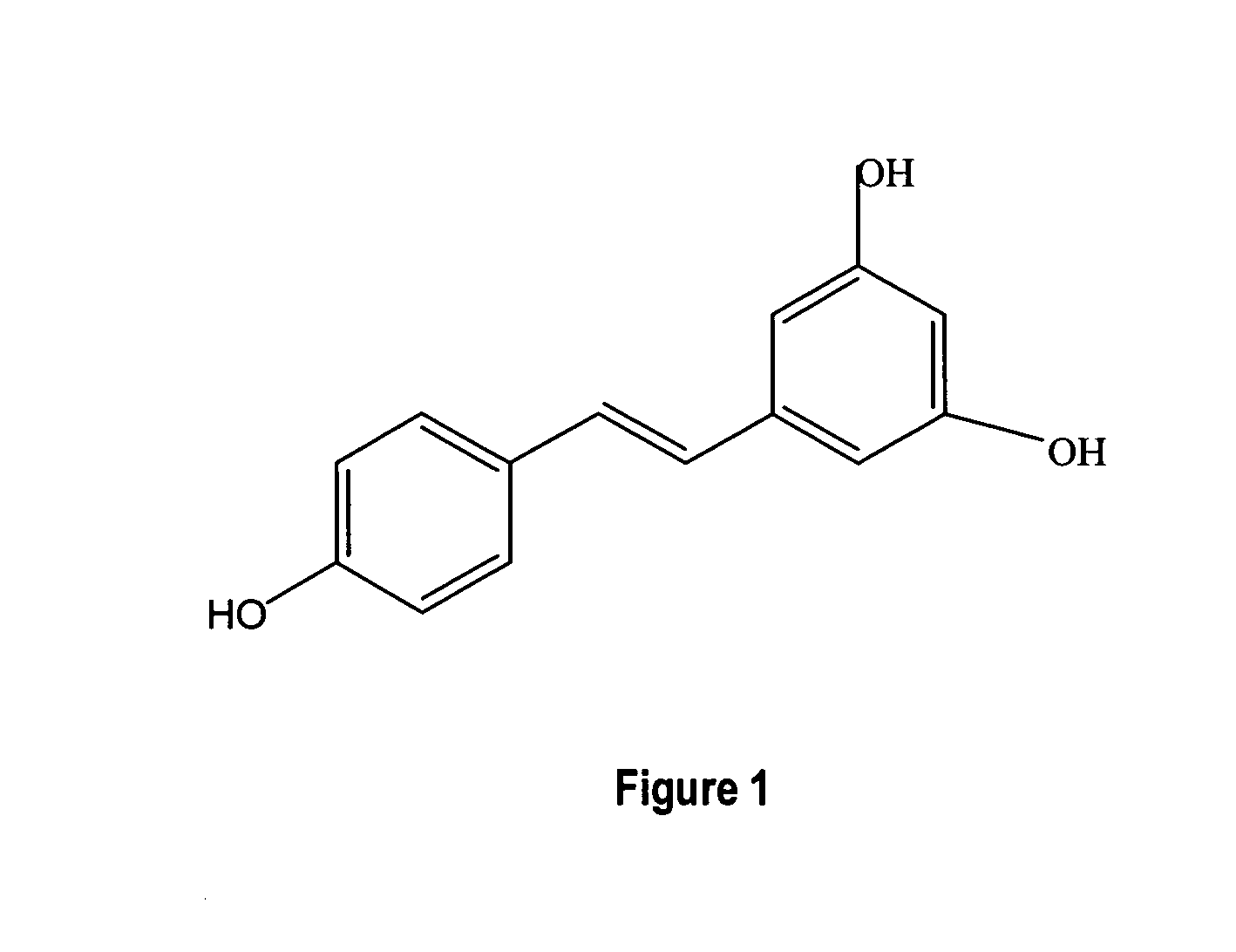
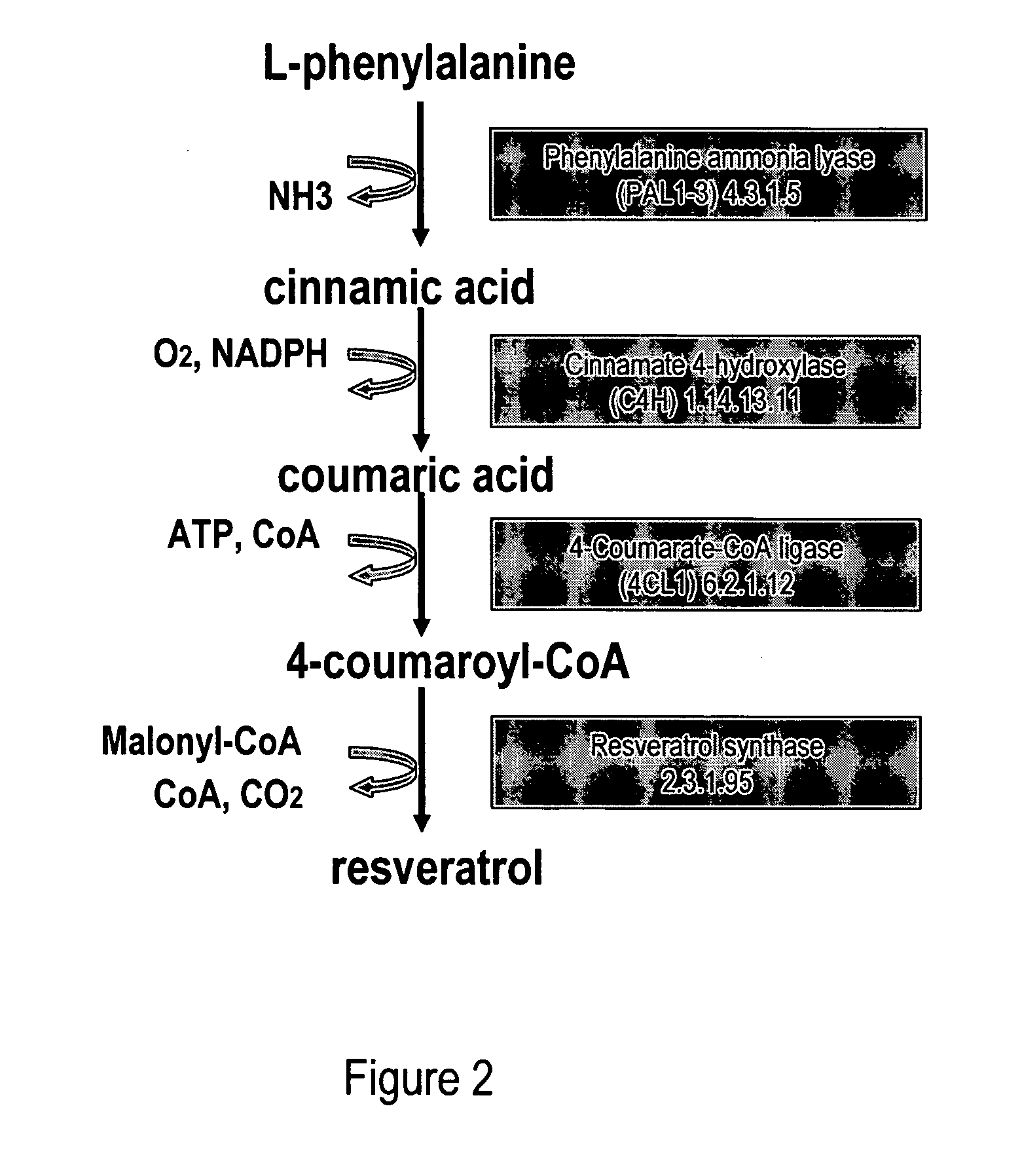
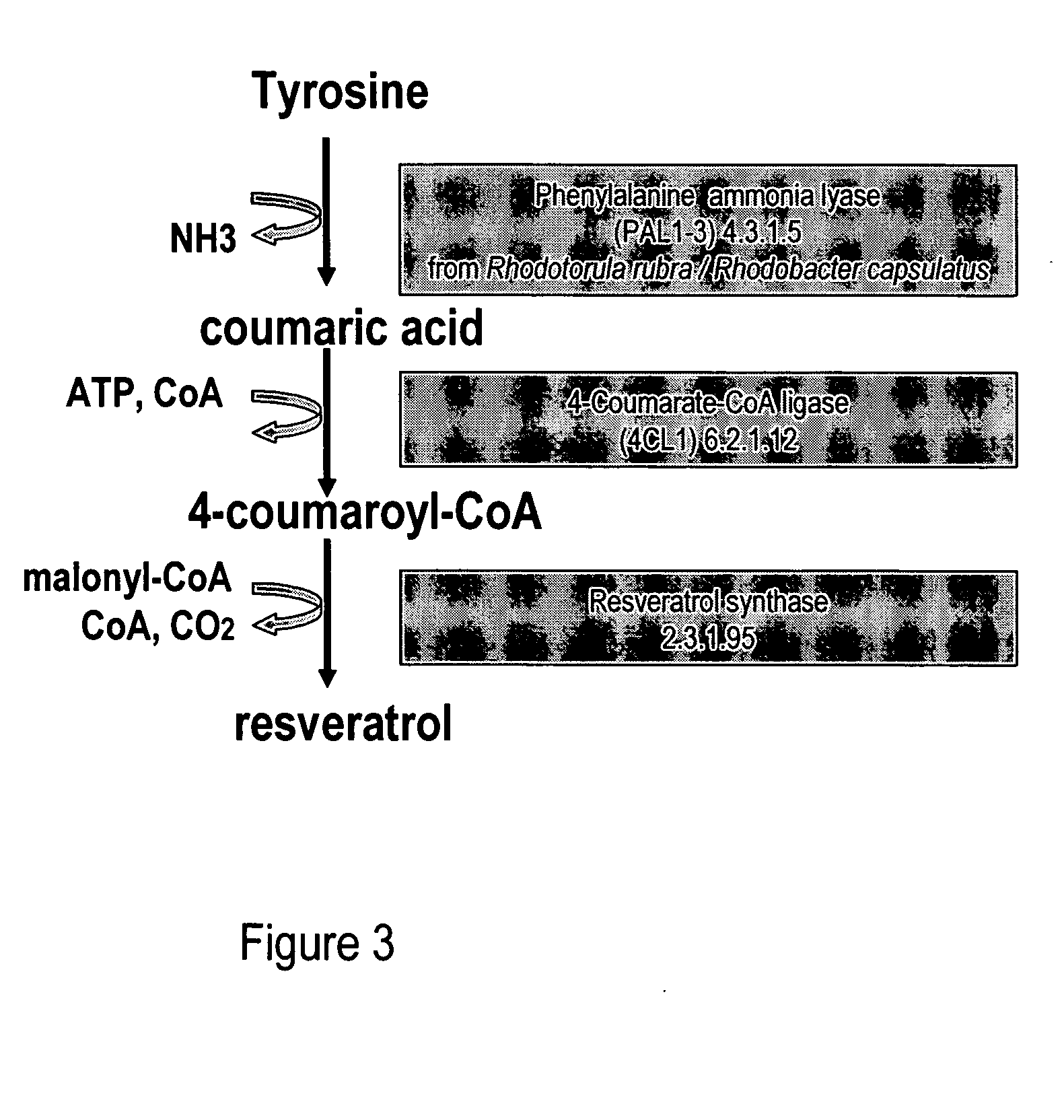
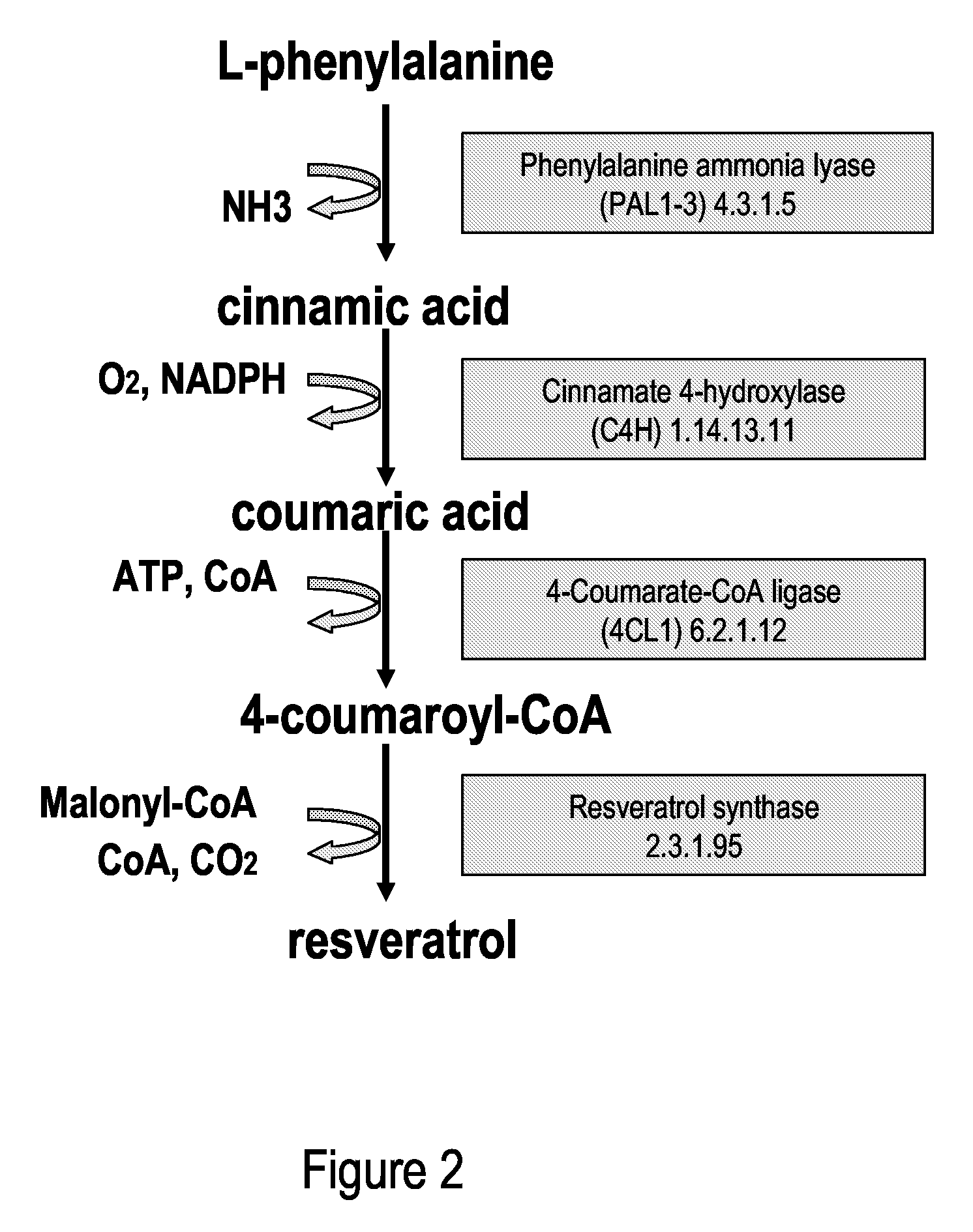
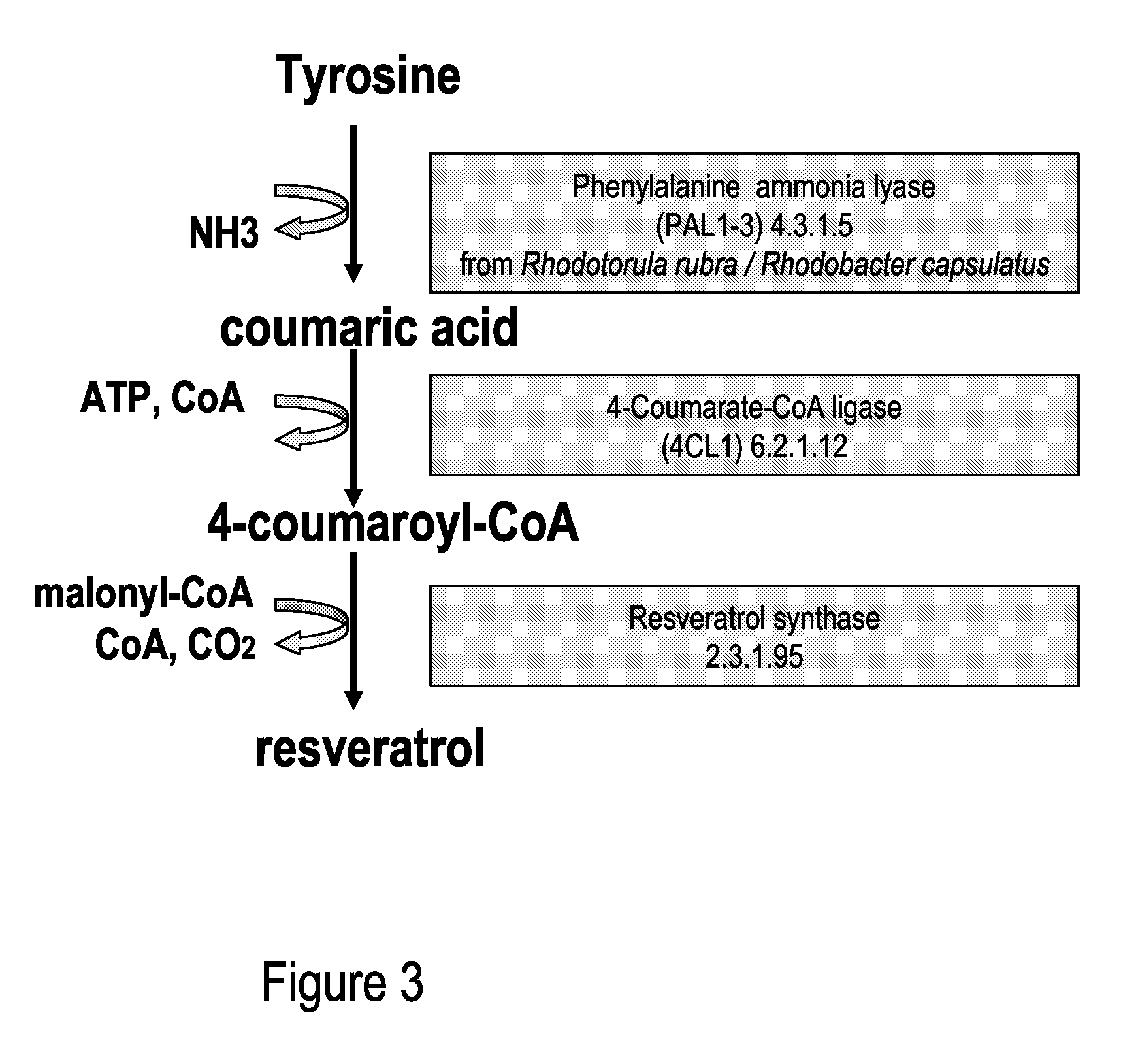
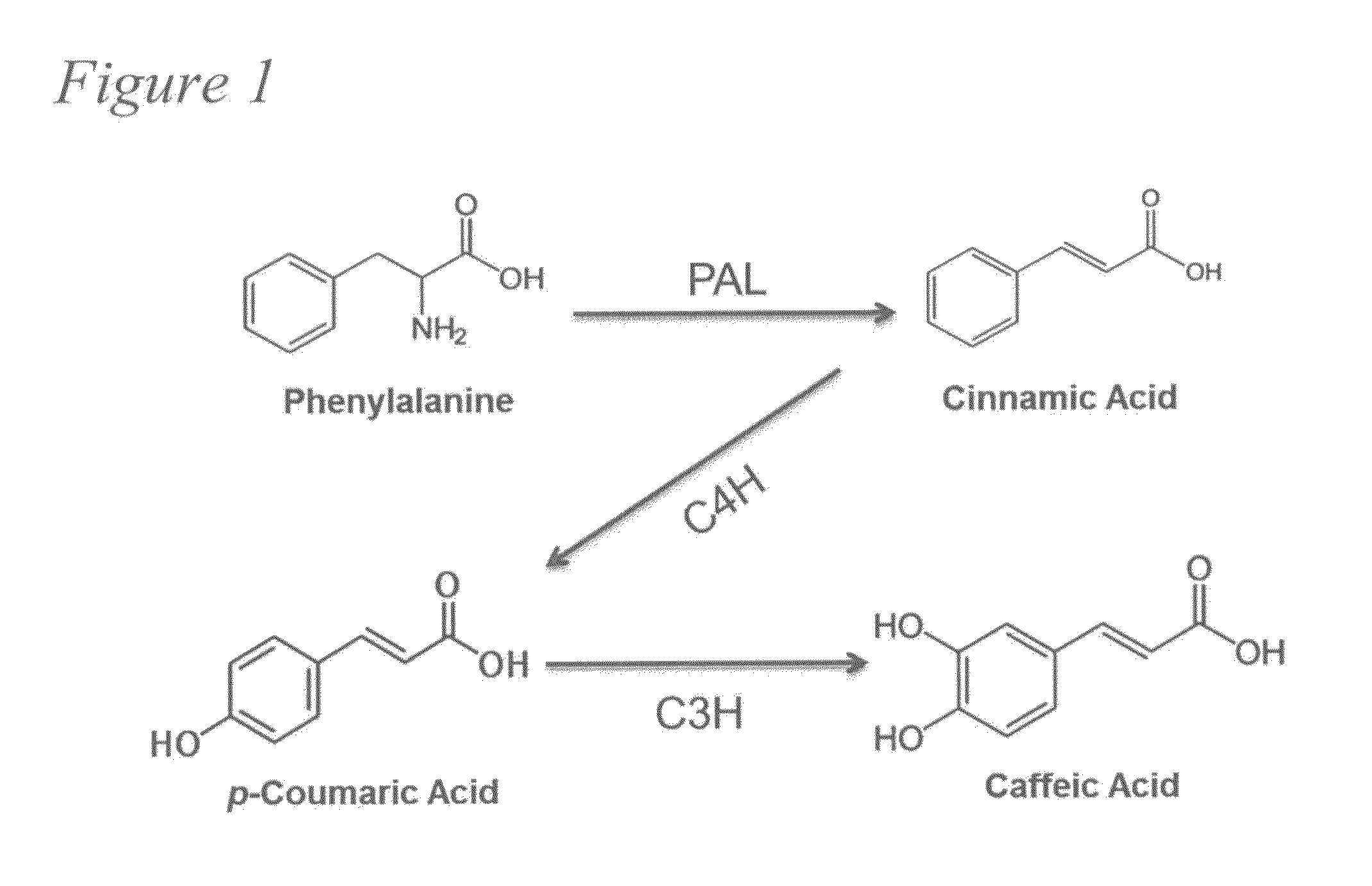
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of resveratrol or an oligomeric or glycosidically-bound derivative thereof
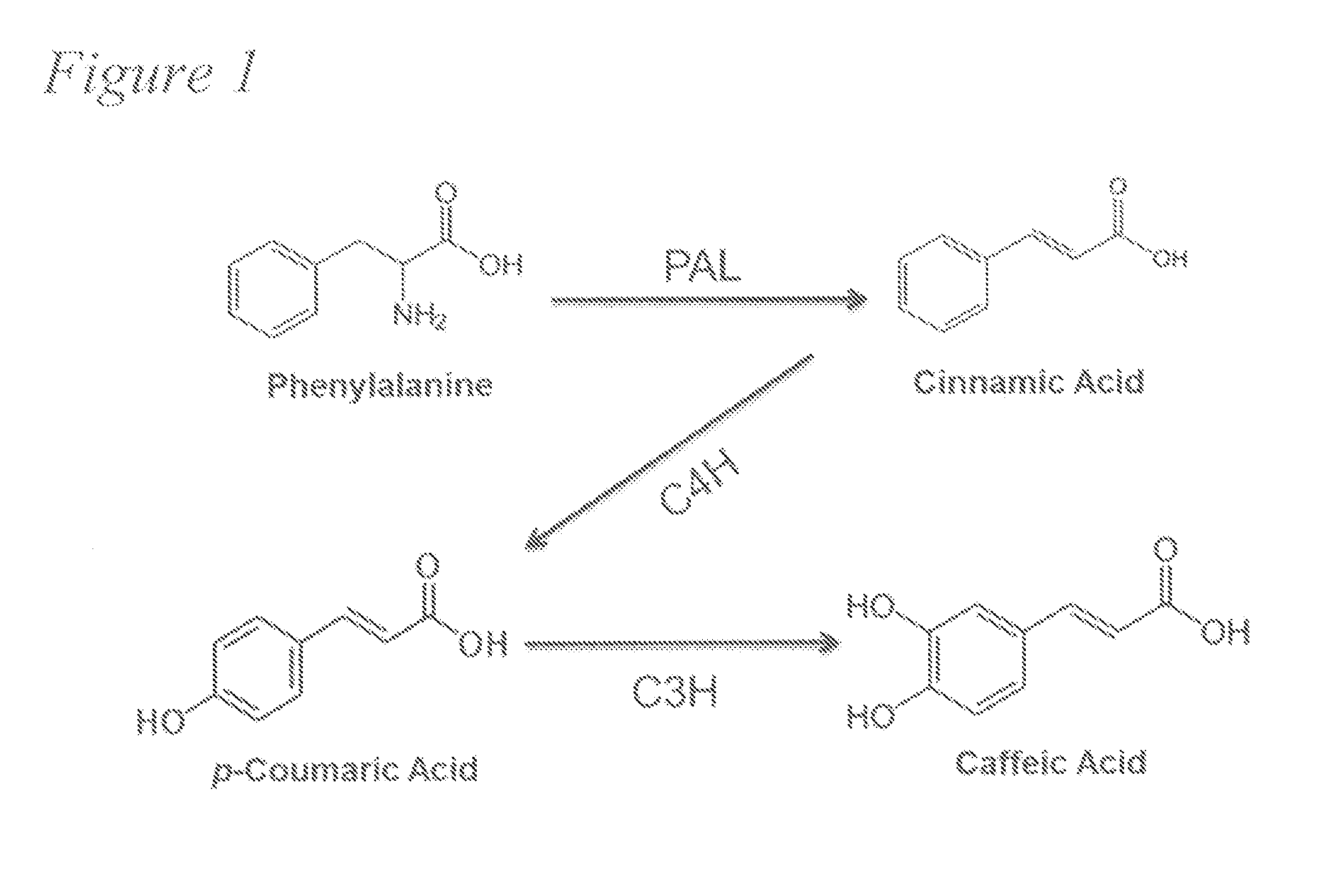
A recombinant micro-organism producing resveratrol by a pathway in which phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produces trans-cinnamic acid from phenylalanine, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) produces 4-coumaric acid from said trans-cinnamic acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA, or in which L-phenylalanine- or tyrosine-ammonia lyase (PAL / TAL) produces 4-coumaric acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA. The micro-organism may be a yeast, fungus or bacterium including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, Lactococcus lactis, Aspergillus niger, or Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
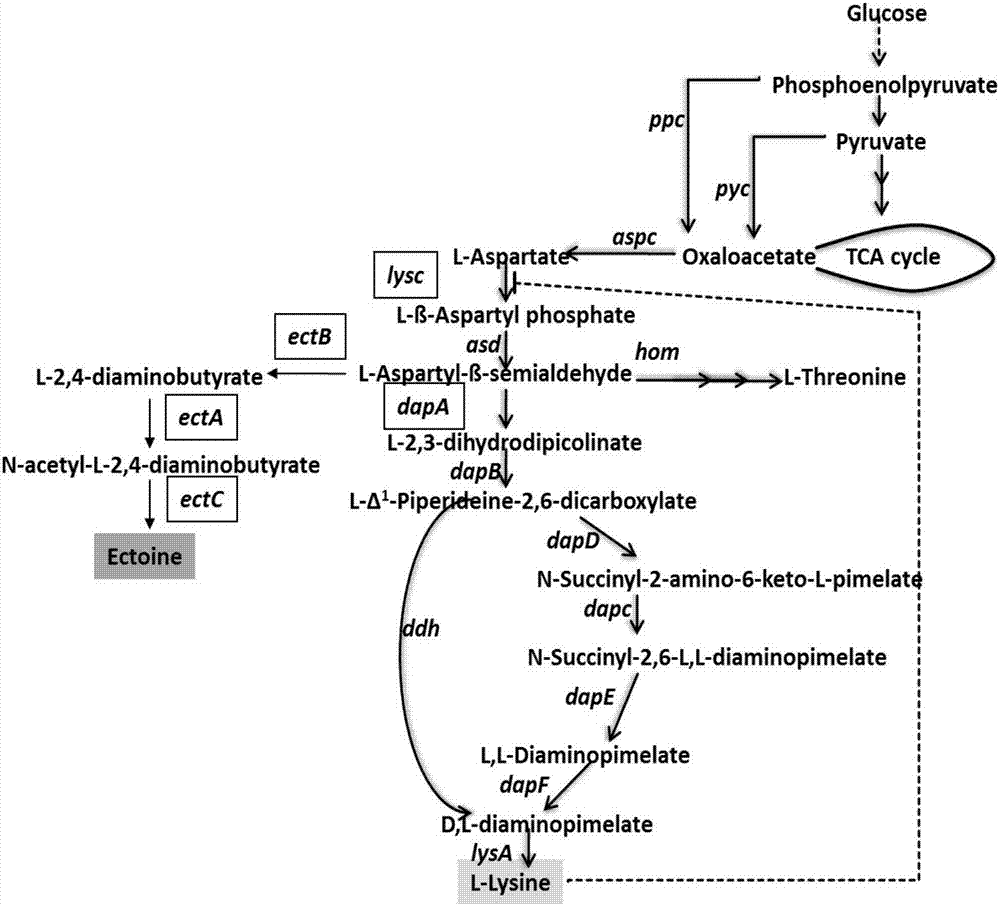
Method of producing tetrahydropyrimidine by fermenting recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum
ActiveCN107142234ALow costAddressing Biosecurity IssuesCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaBacterosiraFermentation
The invention provides a method of producing tetrahydropyrimidine by fermenting recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by the steps of performing overexpression in corynebacterium glutamicum to relieve an aspartokinase gene lysC of feedback inhibition; then replacing a promoter of a dihydropyrimidine dicarboxylic acid synthetase in the recombinant bacteria to weaken the activity of the dihydropyrimidine dicarboxylic acid synthetase; and then transferring tetrahydropyrimidine synthetic path related gene ectABC into the recombinant bacteria to obtain the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum provided by the invention can use different cheap raw materials to produce tetrahydropyrimidine by fermentation under a low salt condition, and cheap corn slurry can be also used as a nutritional component which replaces expensive yeast powder, so that the cost of the raw materials is further lowered. Meanwhile, the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum provided by the invention solves the problem of biosafety, simplifies the post-extraction process and has a good market application prospect.
Owner:北京绿色康成生物技术有限公司
Bifidobacterial gene sequences and their use
This invention provides nucleic acids and proteins involved in oligosaccharide modification in the species Bifidobacteria. The invention provides methods for utilizing the proteins of the invention to generate human milk oligosaccharides or oligosaccharide mimics. The invention also provides compositions containing the human milk oligosaccharides or oligosaccharide mimics and methods for use.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of resveratrol or an oligomeric or glycosidically-bound derivative thereof
A recombinant micro-organism producing resveratrol by a pathway in which phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produces trans-cinnamic acid from phenylalanine, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) produces 4-coumaric acid from said trans-cinnamic acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA, or in which L-phenylalanine- or tyrosine-ammonia lyase (PAL / TAL) produces 4-coumaric acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA. The micro-organism may be a yeast, fungus or bacterium including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, Lactococcus lactis, Aspergillus niger, or Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
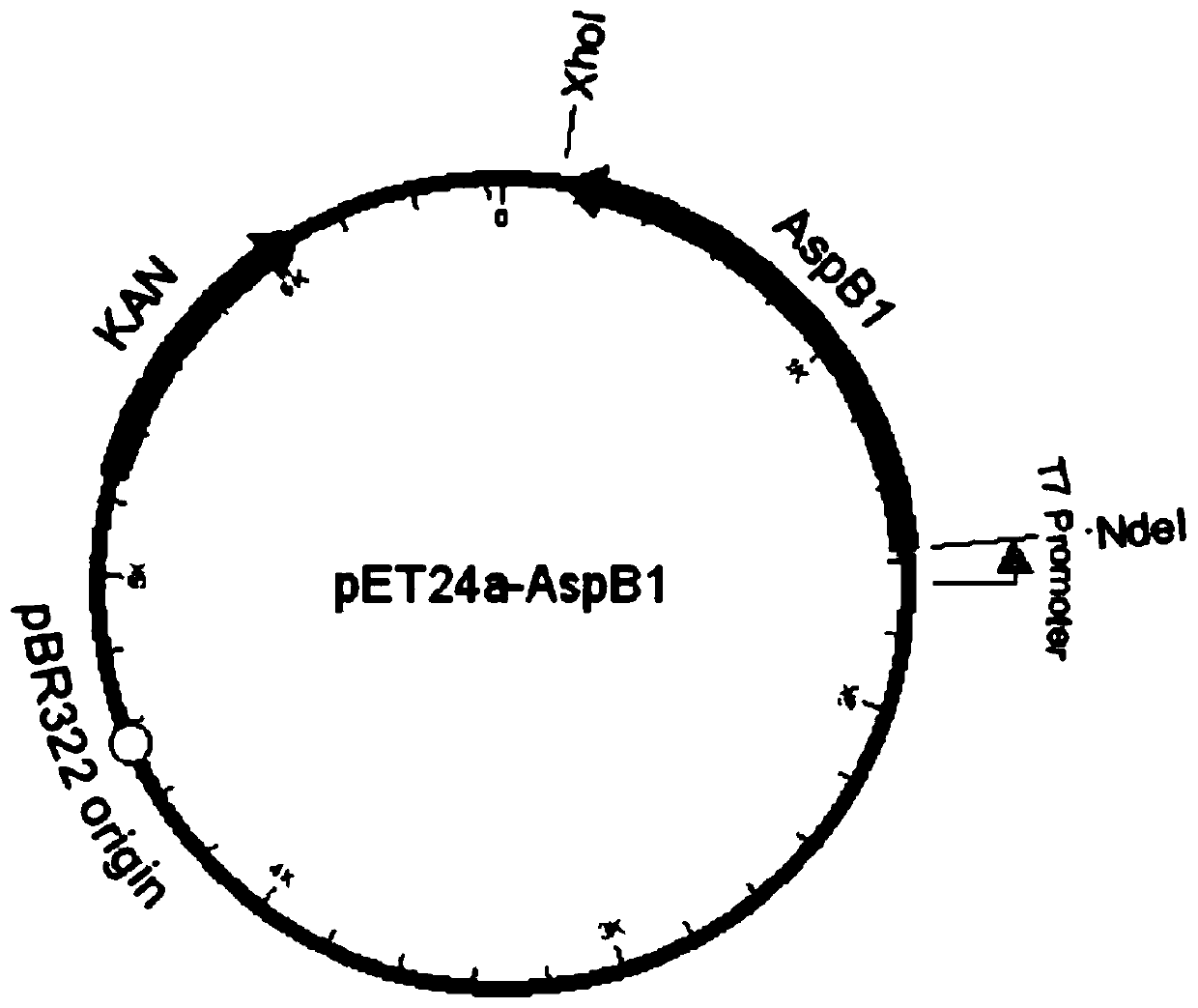
Aspartate ammonia lyase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110791493AIncrease enzyme activityWith industrial developmentCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaOrganic chemistryEnzyme
The amino acid sequence of an aspartate ammonia lyase mutant, an amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO: 3, and compared with an initial aspartate ammonia lyase AspB, the enzyme activity of catalyzing acrylic acid to generate beta-alanine is remarkably improved. When the whole cell expressing the aspartate ammonia lyase mutant is used for catalyzing a 120g / L acrylic acid substrate to react to generate beta-alanine, the conversion rate exceeds 95%, and the aspartate ammonia lyase mutant has an industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
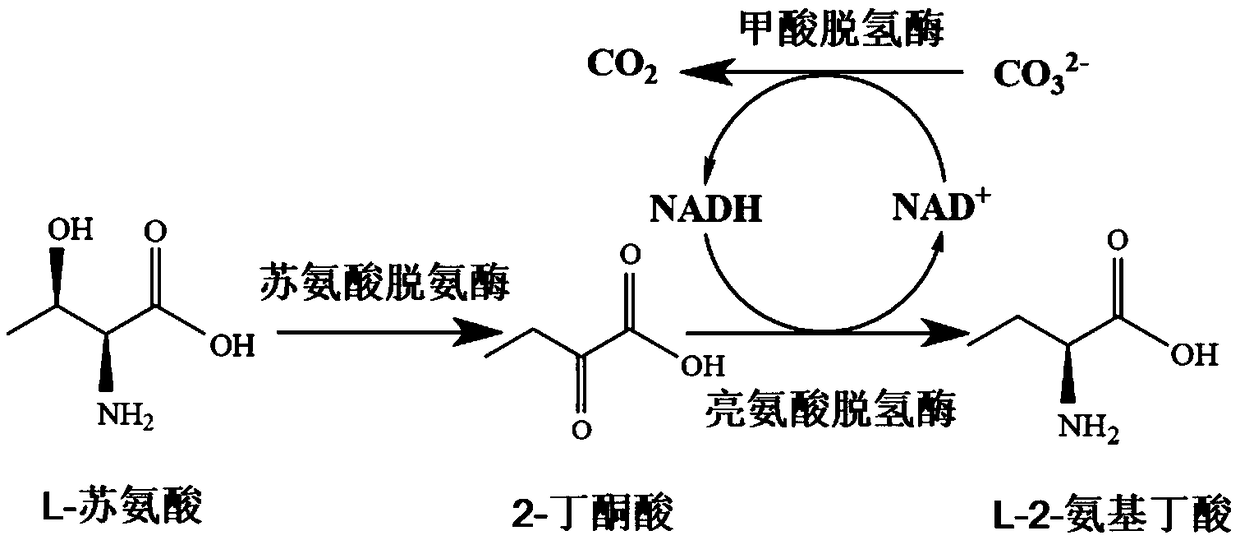
Construction and application of recombinant strain converting L-threonine to L-2-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN109266595ALow costEasy to scale up industrial productionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-threonineSal ammoniac
The invention discloses a construction and application of a recombinant strain converting L-threonine to L-2-aminobutyric acid, belonging to the field of bioengineering technology. The production method of the invention utilizes a recombinant bacterium expressing two plasmids to simultaneously realize the high-efficient expression of three enzymes, and comprises the steps of: conversion of L-threonine to L-2-aminobutyric acid, coupled with a coenzyme regeneration system, converts NAD+ into NADH, so that the concentration of NADH in the system is relatively stable, and the conversion can be carried out efficiently. Furthermore, the CO<2> converted from ammonium formate can be dissolved in ammonia water, which has little environmental pollution and industrial application value. The method has the advantages of mild conversion condition, strong specificity, low cost and short conversion time. The L-2-aminobutyric acid is prepared adopting the method, 40g / L L-threonine is added, The concentration of the obtained product L-2-aminobutyric acid is 43.3 g / L, and the conversion ratio was over 99.9%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Aspartase mutant and applications thereof
ActiveCN111041019AImprove conversion rateHigh stereoselectivityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaButyrateMutant
The invention discloses an aspartase mutant, which comprises the following mutations M321V, K324T and N326S on an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.2, and has high enzymatic activity compared with wild-type aspartase in catalysis of (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)2-butenoic acid. The invention also discloses applications of the aspartase mutant in preparation of (R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-butyric acid. According to the invention, with the application of the aspartase mutant in an enzyme catalytic reaction to prepare a sitagliptin chiral intermediate (R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-butyric acid, the conversion rate is high, the stereoselectivity is high, the yield is high, the production cost is low, the environment is friendly, and industrial large-scale production is facilitated.
Owner:ABIOCHEM BIOTECH CO LTD
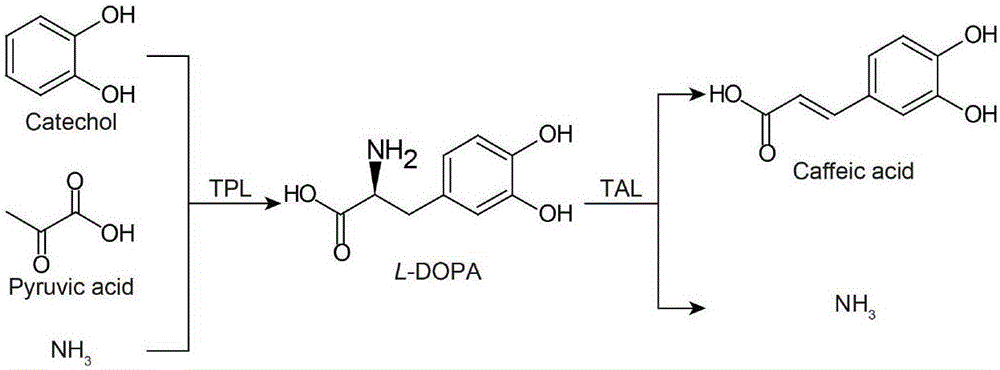
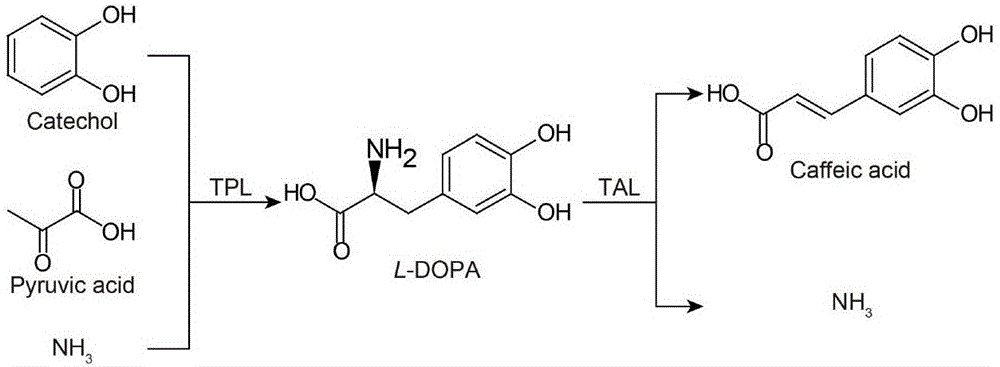
High efficiency biosynthesis method of caffeic acid with catechol as substrate
InactiveCN106701843AEase of mass productionEfficient synthesisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaChemical synthesisCaffeic acid
Belonging to the field of biochemical engineering, the invention discloses a high efficiency biosynthesis method of caffeic acid with catechol as the substrate. According to the invention, tyrosine phenol-lyase takes catechol, pyruvic acid and ammonia as the substrate to synthesize levodopa, tyrosine ammonia-lyase converts levodopa into trans-caffeic acid and NH3. Catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride are relatively cheap compounds, therefore the caffeic acid biosynthesis method provided by the invention has large potential. Compared with the previous conversion methods taking L-tyrosine as the substrate, the substrate used by the method are cheaper and easier for large-scale production. Compared with chemical synthesis methods, the product of the method provided by the invention is single trans-caffeic acid, and further separation of an isomer is unnecessary.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Biosynthesis of caffeic acid and caffeic acid derivatives by recombinant microorganisms
Microorganisms are genetically engineered to synthesize caffeic acid from simple carbon sources via a tyrosine intermediate by means of a dual pathway that utilizes both endogenous and engineered enzymatic activities.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Engineered phenylalanine ammonia lyase polypeptides
ActiveUS20140314843A1High catalytic activityReduced sensitivity to proteolysisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesNervous disorderPolynucleotidePhenylalanine ammonia-lyase
The present invention provides engineered phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) polypeptides and compositions thereof, as well as polynucleotides encoding the engineered phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) polypeptides.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
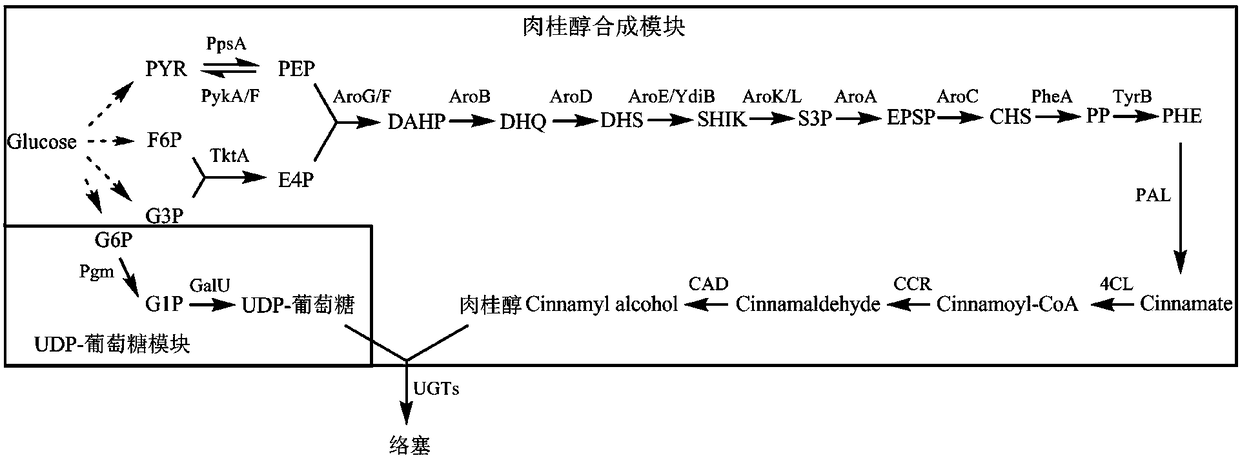
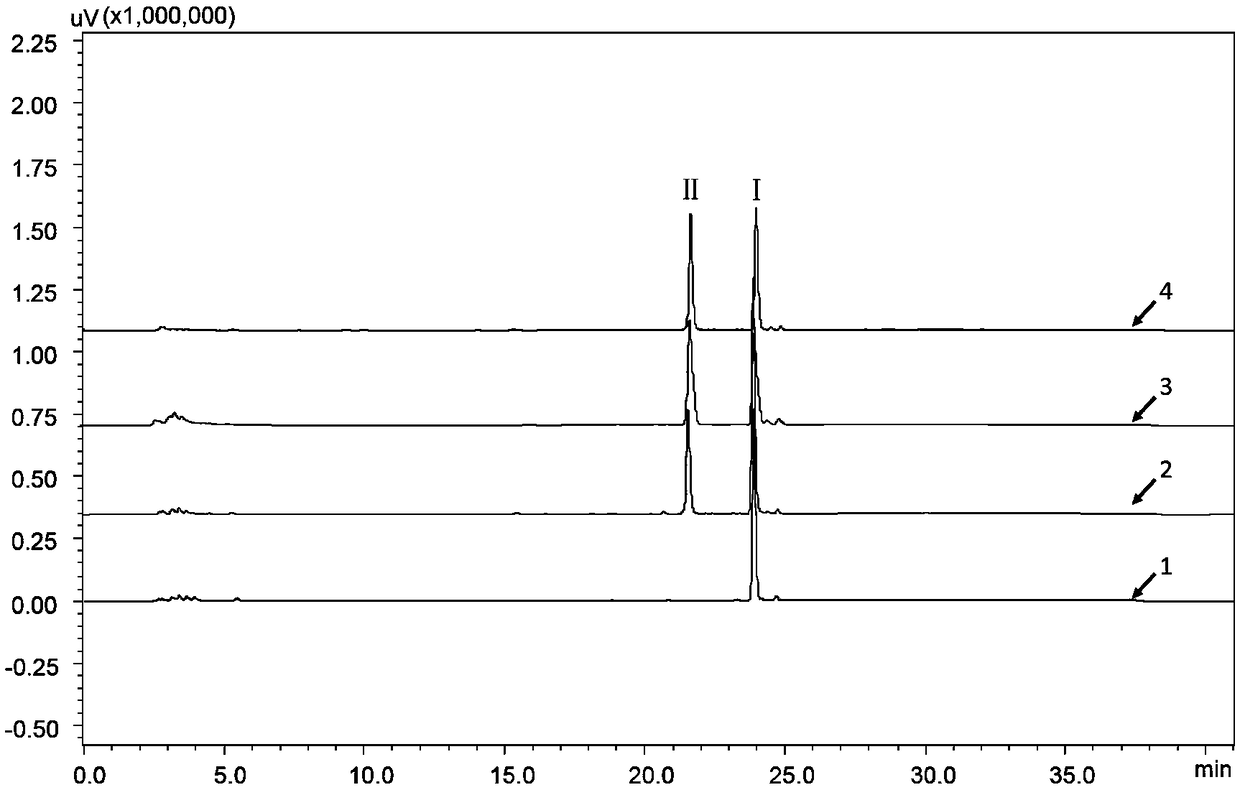
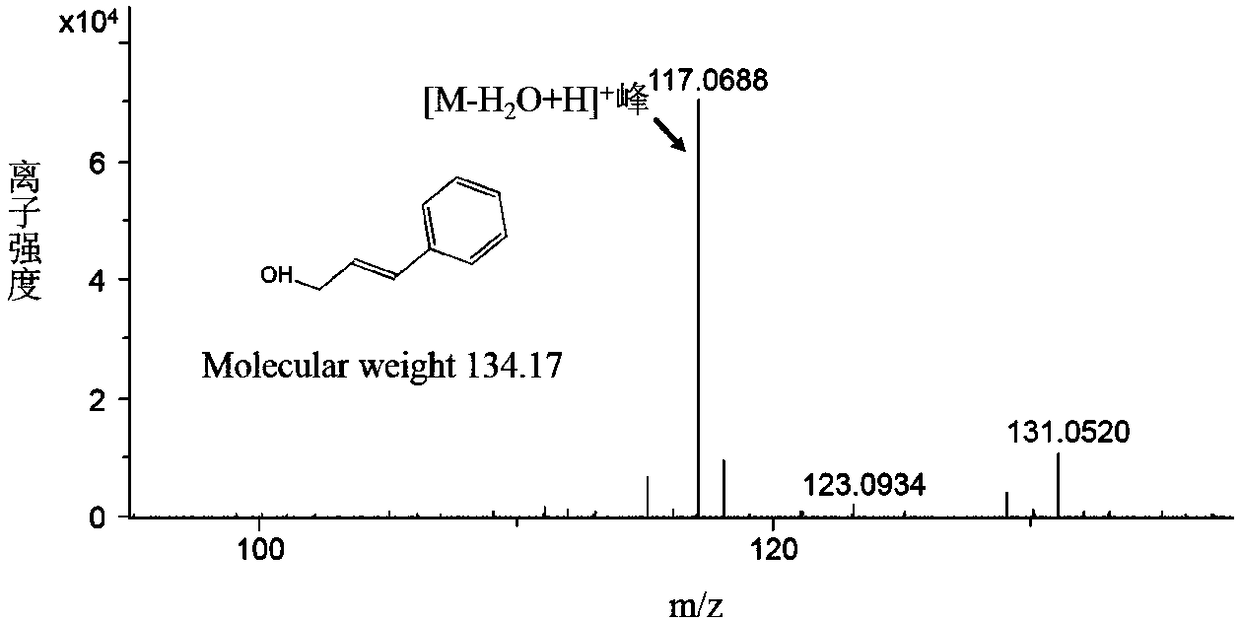
Recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin, and construction method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108203713AClear backgroundGrow fastCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin, and a construction method and applications thereof. The construction method comprises followingsteps: phenylalnine ammonialyase PAL, p-hydroxycinnamic acid coenzyme A ligase 4CL, and cinnamamide coenzyme A reductase CCR are introduced into Escherichia coli so as to obtain the recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol. In the construction method, Escherichia coli is taken as a model organism, the background is clear, growth speed is high, large scale fermentation culture is convenient to realize, and cost is low. The recombinant escherichia coli capable of producing cinnamic alcohol and rosin is obtained via construction of a cinnamic alcohol synthesis pathway, the cinnamic alcohol yield is 300mg / L; UDP glucosyltransferase is introduced into Escherichia coli further, so that organic combination of biological synthesis pathways of rosin and cinnamic alcohol isrealized, the highest rosin yield is 280mg / L. The construction method is capable of providing large scale industrialized production of cinnamic alcohol and / or rosin with foundation.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacteria and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111849794AOne-step synthesisFull synthesisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiCaffeic acidRate limiting enzyme
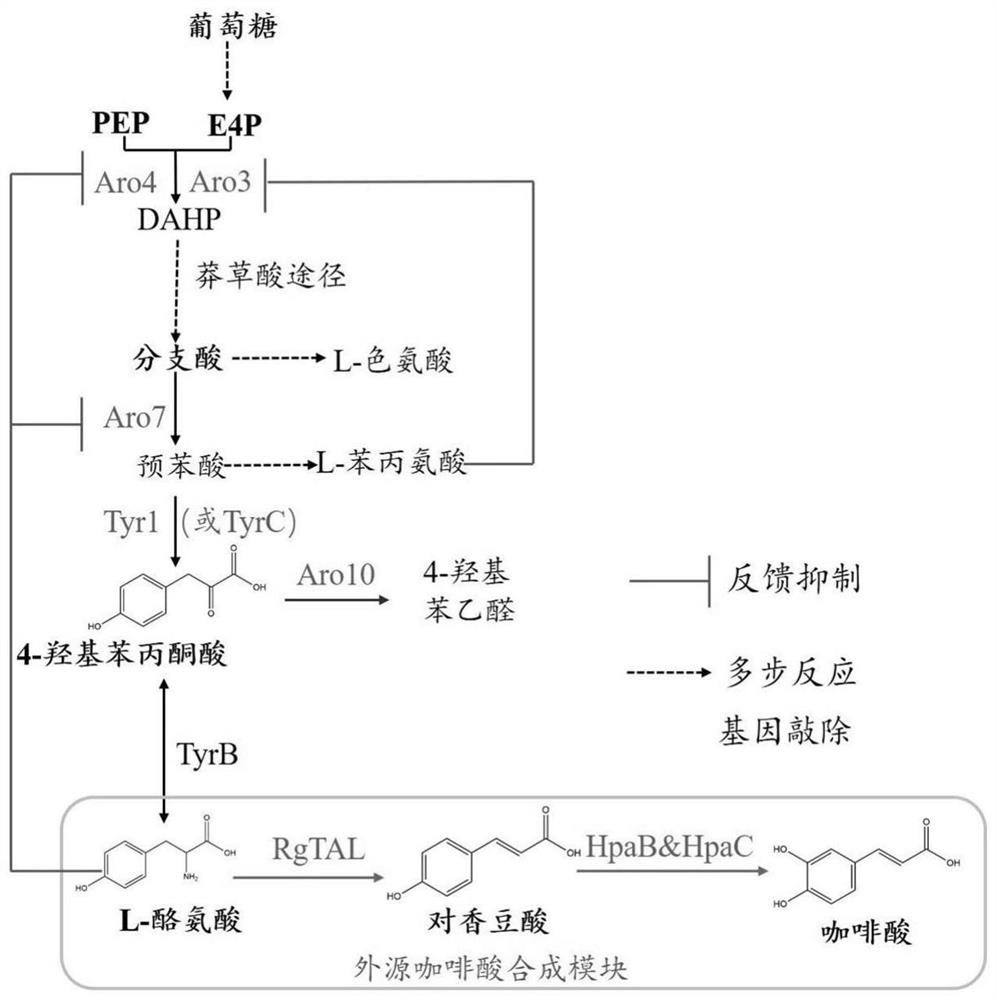
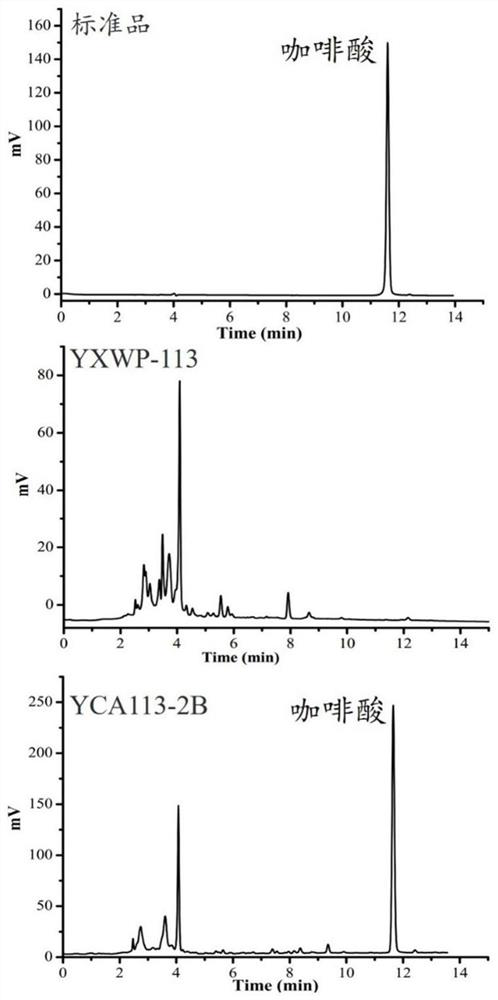
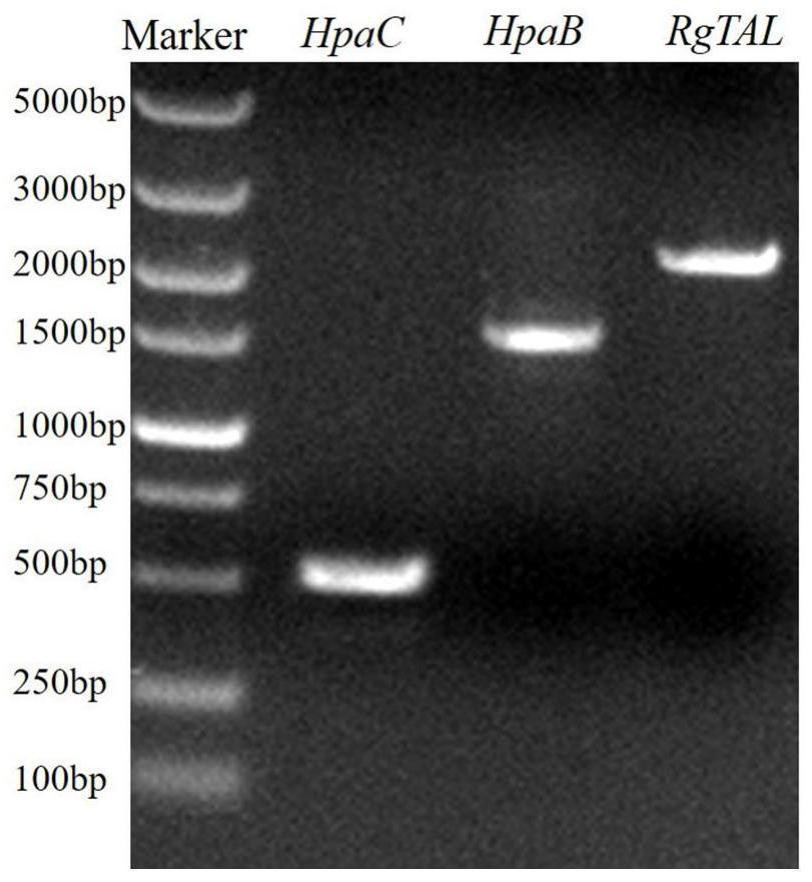
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium. According to the saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium, an RgTAL gene, an HpaB gene and an HpaC gene are integrated in a genome. The invention further discloses a construction method and application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacteria. The invention finally discloses a production method of caffeic acid. According to the invention, three exogenous genes required by caffeic acid synthesis are integrated into saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes; total synthesis from glucose to caffeic acid is achieved through knockout of competitive pathway genes, elimination of feedback inhibition steps and overexpression of rate-limiting enzymes, the shake flask yield reaches about 760 mg / L, the shake flaskyield is the highest level of the yeast yield reported at present, and a new method is provided for industrial production of caffeic acid.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Biosynthesis of caffeic acid and caffeic acid derivatives by recombinant microorganisms
Microorganisms are genetically engineered to synthesize caffeic acid from simple carbon sources via a tyrosine intermediate by means of a dual pathway that utilizes both endogenous and engineered enzymatic activities.
Owner:GENEDARTEC INC
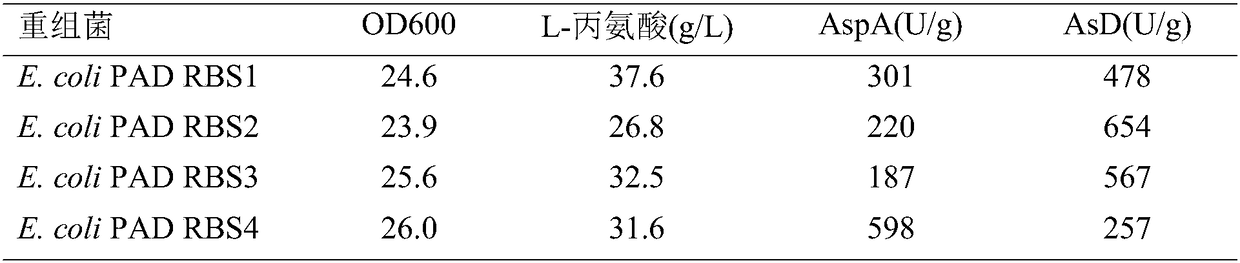
Escherichia coli capable of producing L-alanine through fermentation and application of escherichia coli
ActiveCN108060114AImprove transportation capacityClear genetic backgroundCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaSaccharic acidEscherichia coli
The invention discloses escherichia coli capable of producing L-alanine through fermentation and application of the escherichia coli and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the escherichia coli, aspartase AspA and L-aspartic acid-beta-decarboxylase AsD are introduced into the escherichia coli capable of producing fumaric acid through the fermentation; furthermore, a YgaW gene is over-expressed to strengthen the transport ability of the L-alanine in recombinant bacteria, so that a novel strain capable of fermenting glucose to produce the L-alanine is constructed; when the recombinant strain is fermented in a fermentation tank for 45h, the yield of the L-alanine reaches 147g / L and the saccharic acid conversion rate is 79.0 percent.
Owner:金华利家园生物工程有限公司 +1
Method for efficient synthesis of caffeic acid with catechol as substrate
Belonging to the field of biochemical engineering, the invention discloses a method for efficient synthesis of caffeic acid with catechol as the substrate. A recombinant strain constructed by the invention employs catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride to synthesize caffeic acid, the caffeic acid yield can reach 1.51g / L, and catechol, sodium pyruvate and ammonium chloride are all relatively cheap compounds, therefore the method provided by the invention is a caffeic acid biosynthesis method with great potential. Compared with the previous bioconversion method using L-tyrosine as the substrate, the method provided by the invention significantly improves the caffeic acid yield. Compared with the chemical synthesis method, the product of the method is a single trans-caffeic acid, and further separation of an isomer is not needed.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
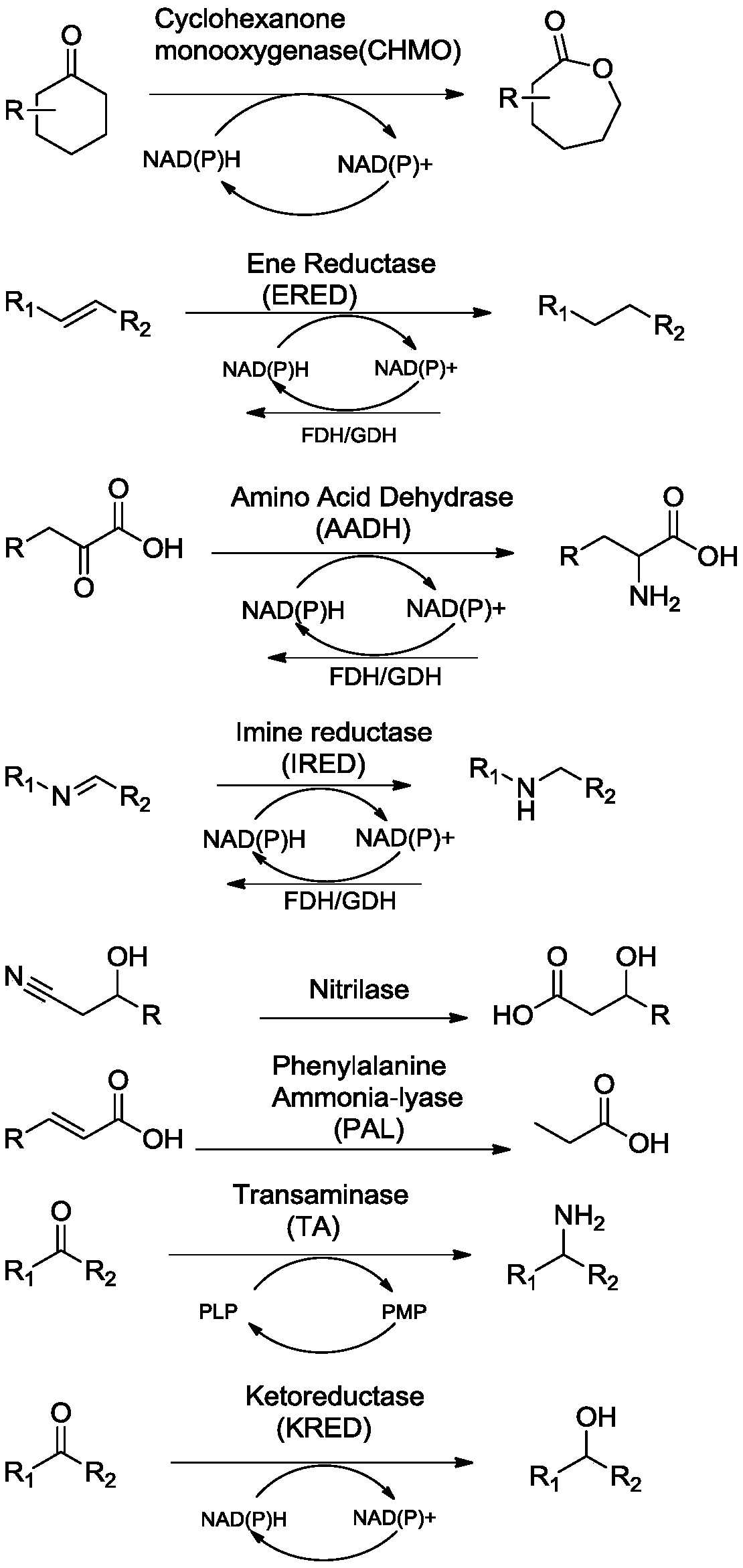
Immobilized enzyme as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110964710AEasy to fixImprove recycling efficiencyCarbon-nitrogen lyasesHydrolasesLyaseCross linker
The invention provides an immobilized enzyme as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The immobilized enzyme comprises an enzyme and an amino resin carrier for immobilizing the enzyme, the enzyme is selected from any one of transaminase, ketoreductase, monooxygenase, ammonia lyase, alkene reductase, imine reductase, amino acid dehydrogenase and nitrilase, the amino resin carrieris the cross-linking agent modified amino resin carrier, and a cross-linking agent is a cross-linking agent treated by a high polymer. The amino resin carrier is modified by adopting the cross-linking agent treated by the high polymer, so that enzymes immobilized on the amino resin carrier can form netted cross-linking, the immobilization effect of the enzymes is more stable, and the cyclic utilization efficiency of the enzymes is improved.
Owner:JILIN ASYMCHEM LAB CO LTD
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-isoleucine and application thereof
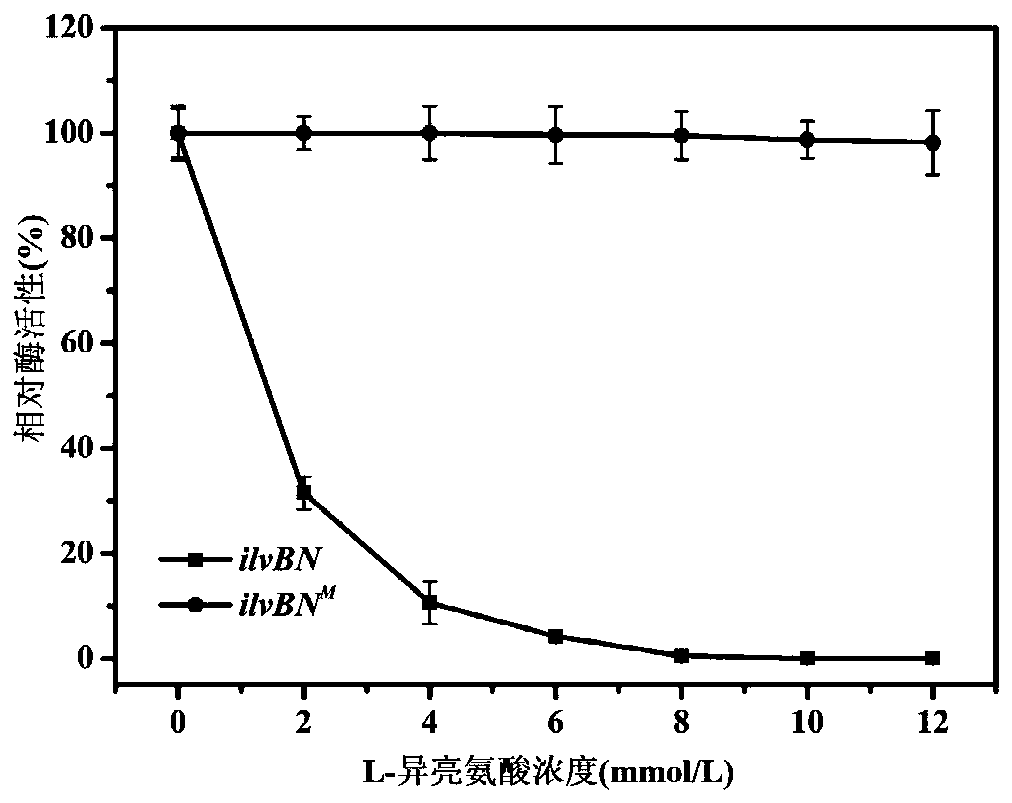
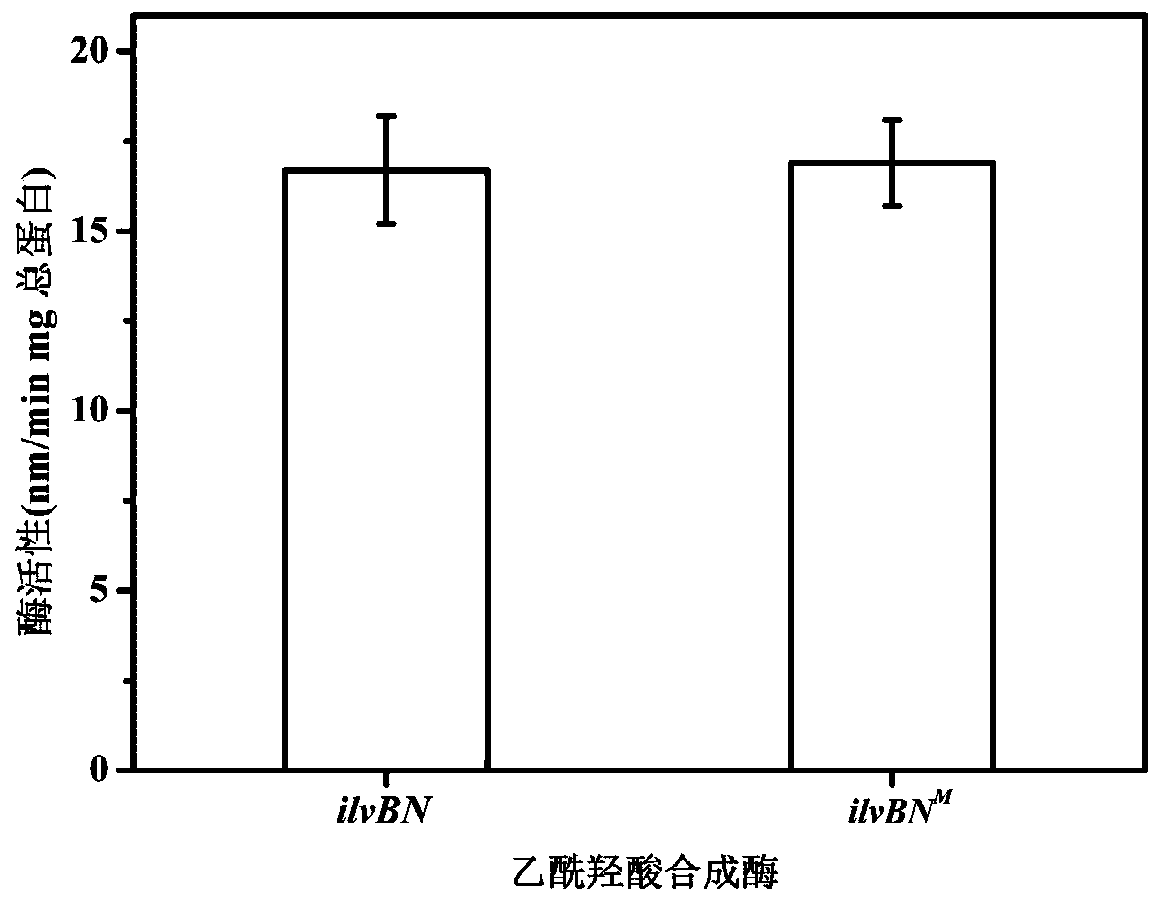
ActiveCN110305829AReduced activityNo nutritional deficienciesCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaAcetohydroxy Acid SynthetaseNutritional deficiency
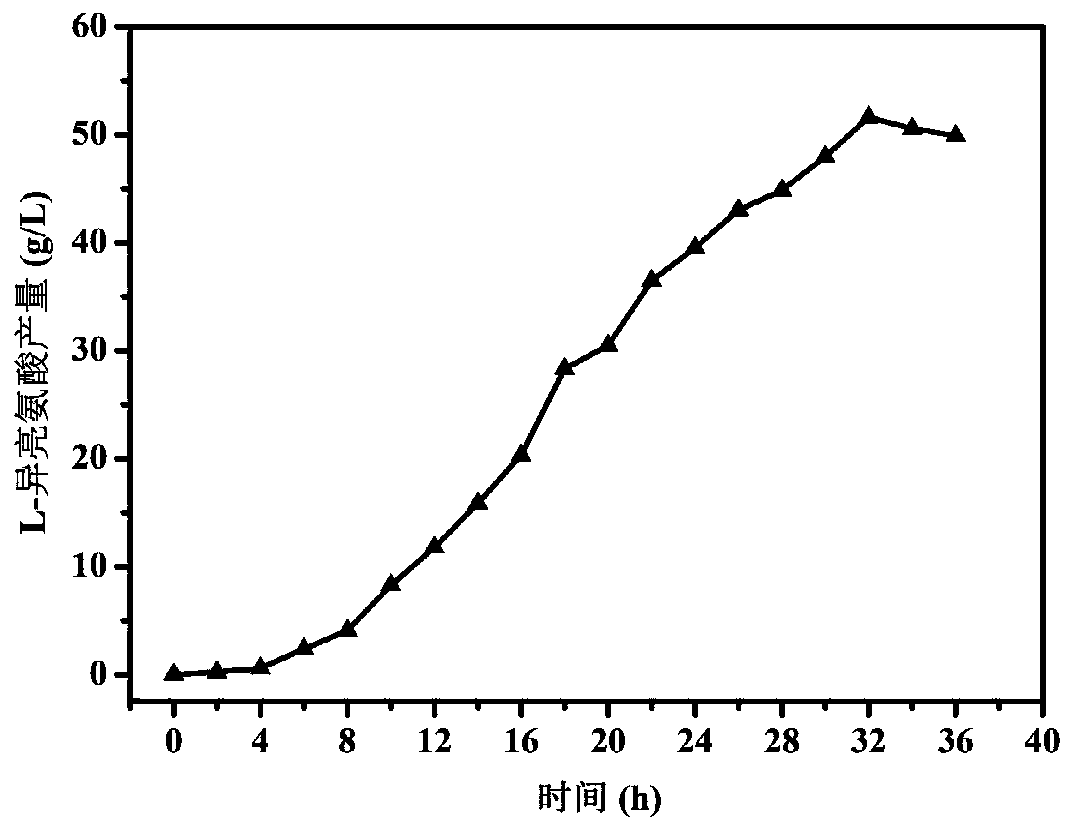
The invention relates to a genetic engineering bacterium for producing L-isoleucine and an application thereof, which belong to the field of metabolic engineering. The genetic engineering bacterium isobtained by overexpressing an acetohydroxyacidsynthase encoding gene ilvBN<M>, a threonine dehydratase encoding gene ilvA, and a threonine operon thrABC releasing feedback inhibition of L-isoleucine,the acetohydroxyacidsynthase encoded by ilvBN<M> releases the feedback inhibition of L-isoleucine, and its activity is not significantly lower than that of the wild-type ilvBN-encoded acetohydroxyacidsynthase; The L-isoleucine genetic engineering bacterium of the invention has no nutritional deficiency, rapid growth, short fermentation cycle, high yield and high conversion rate, and after 26-36hfermentation, the concentration of L-isoleucine in a fermentation broth reaches 42.5-51.6g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation
ActiveCN106434510AGet Rid of Reliance on Petroleum-Based Fumaric AcidCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliDry weight
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation. The classification naming of the genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli CM-AS-115, and the preservation number of the genetically engineered bacterium is CCTCC NO: M 2016457. The bacterial strain relates to inactivation of multiple genes, evolution, metabolism and domestication are simultaneously carried out on the bacterial strain which knockouts the multiple genes, and a mutant strain, namely, CM-AS-105, which has a lower respiratory quotient under the aerobic condition and of which the highest dry cell weight is 60-70% of dry weight of an original strain W1485 is obtained; meanwhile, the bacterial strain further relates to over expressions of two genes, wherein the two genes comprise an enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene (ppc) and an aspartase encoding gene (aspA), and the obtained bacterial strain is CM-AS-115. The genetically engineered bacterium for directly producing L-aspartic acid through fermentation achieves a way of completely adopting renewable biomass resources such as starch and cellulose as raw materials to ferment and prepare the L-aspartic acid, and the way is green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:CHANGMAO BIOCHEMICAL ENG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com