Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of caffeic acid
A technology of caffeic acid and recombinant bacteria, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of high cost, easy decomposition, low yield of caffeic acid, etc., and achieve the effects of simple production process, easy availability of raw materials, and good prospects for industrial application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] According to the method described in the literature Large scale validation of an efficient CRISPR / Cas-based multigene editing protocol in Escherichia coli. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1): 68, hpaD and mhpB on Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) were singled out or double knockout. Among them, the gene knockout plasmid used in the present invention is pCasRed and pCRISPR-gDNA (hpaD sgRNA) and the homology arm (hpaDdonor) are introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and Cas9 / sgRNA induces the host to generate double strands at the hpaD gene locus Break, the recombinase Red integrates the hpaD donor into the hpaD gene to achieve gene knockout, and sequence verification. hpaD sgRNA, hpaD donor, mhpB sgRNA, and mhpB donor are respectively shown in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO:10, SEQ ID NO:11, SEQ ID NO:12, and SEQ ID NO:13. mhpB was knocked out in the same way.
[0066] Prepare a solution with a pH of 8, catechol or caffeic acid 2g / L, wet bacterial mass 100g / L, and m...
Embodiment 2
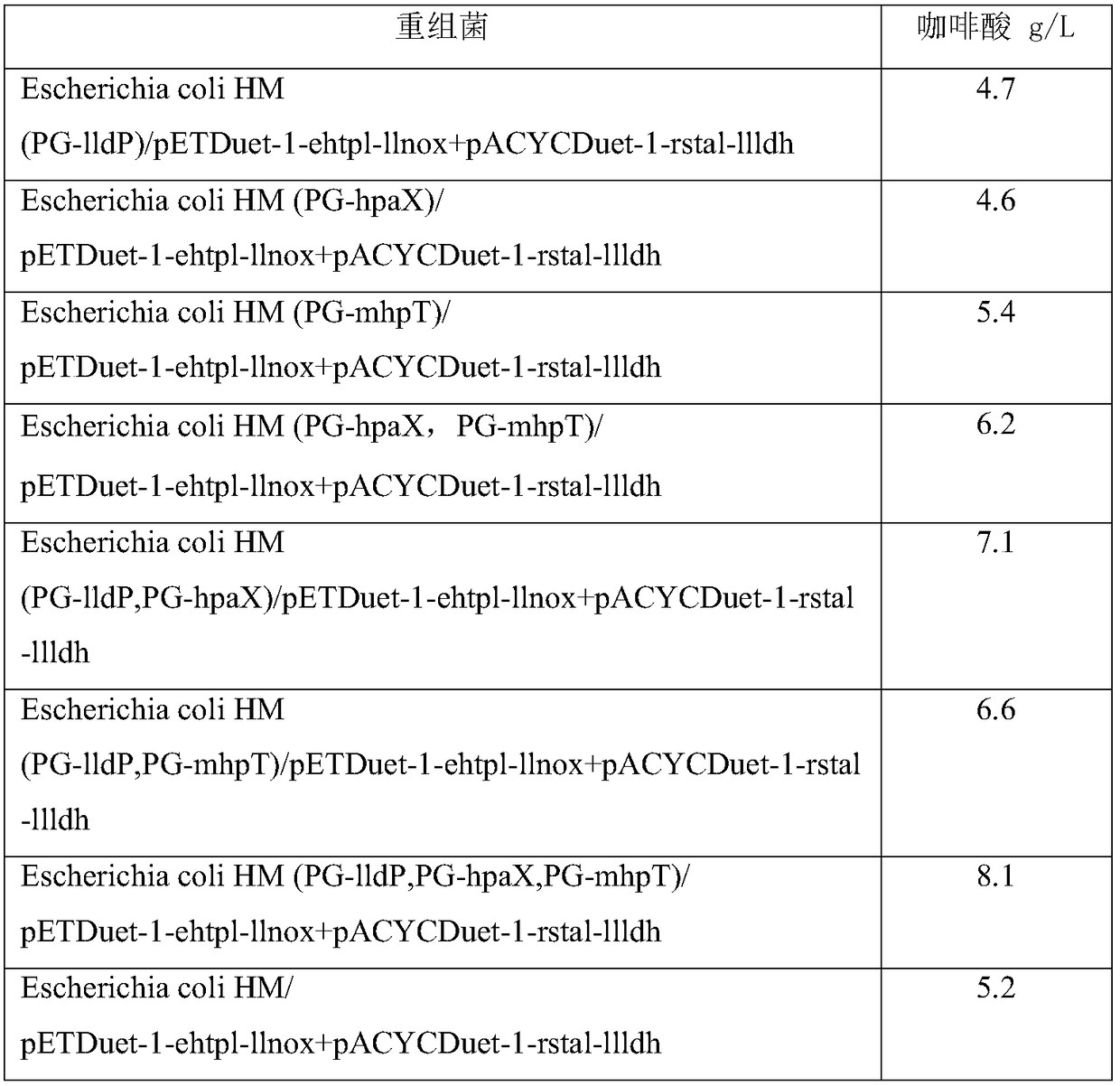
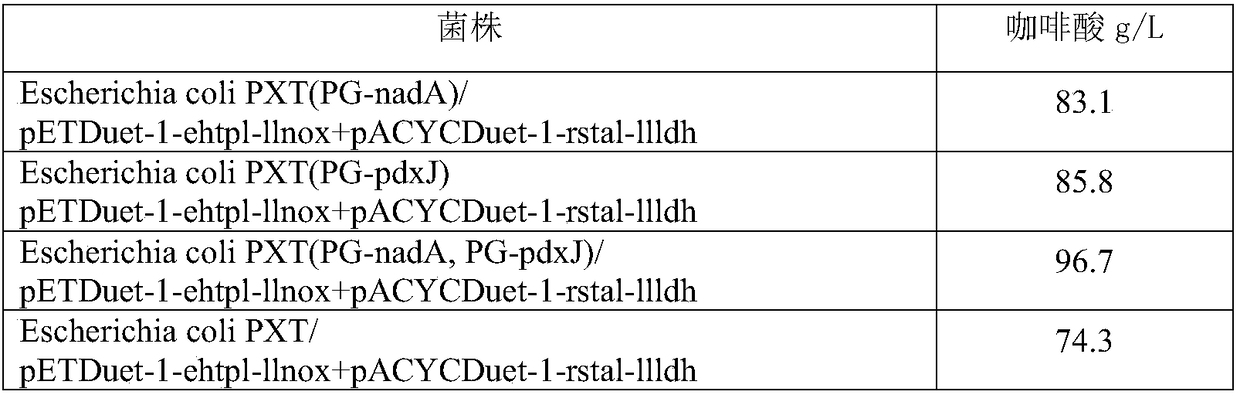
[0071] Recombinant Escherichia coli construction: Firstly, the genes encoding tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, NADH oxidase and L-lactate dehydrogenase were connected to pETDuet-1 or pACYCDuet-1 plasmid respectively. Two kinds of double-gene co-expression recombinant plasmids were obtained, and the two plasmids were transformed into Escherichia coli HM, and positive transformants were obtained by screening with chloramphenicol and ampicillin plates, that is, recombinant Escherichia coli was obtained.
[0072] Induced expression method: the recombinant Escherichia coli is transferred to LB fermentation medium (peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L) in the amount of 2% by volume ratio, when the cell OD 600 After reaching 0.6-0.8, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.4mM, induce expression and culture at 20°C for 8h. After induction of expression, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 20° C., 8000 rpm, and 20 minutes.
[0073] After the induction...
Embodiment 3
[0077]Using the method described in the literature Large scale validation of an efficient CRISPR / Cas-based multigene editing protocol in Escherichia coli.Microbial Cell Factories, 2017,16(1):68, the corresponding gene on the Escherichia coli HM genome was increased before the Escherichia coli The moderate expression strength constitutive promoter (PG) in front of the 3-phosphate glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase gene (gpdA), the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:9.
[0078] When enhancing the expression of the gene lldP, use the Escherichia coli HM genome as a template, and use the primers lldP-FF / lldP-FR, lldP-gpdA-F / lldP-gpdA-R, lldP-RF / lldP-RR to amplify the upstream, promoter sub, downstream sequences, and lldP-FF and lldP-RR primers were fused into an expression cassette containing the gpdA promoter. Then, after the plasmid pCasRed and pCRISPR-gDNA (including lldP sgRNA) were transferred into Escherichia coli HM, Cas9 / sgRNA induced the host to undergo a double-strand break at t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com